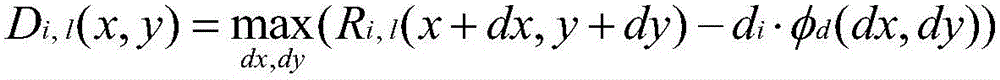Patents
Literature
93 results about "Iteration loop" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
For example, in a computer program, one form of iteration is a loop. A loop repeats code until a certain condition is met. Each time the computer runs through a loop, it is referred to as an iteration. Many computer programs and programming languages use iterations to perform specific tasks, solve problems, and present solutions.
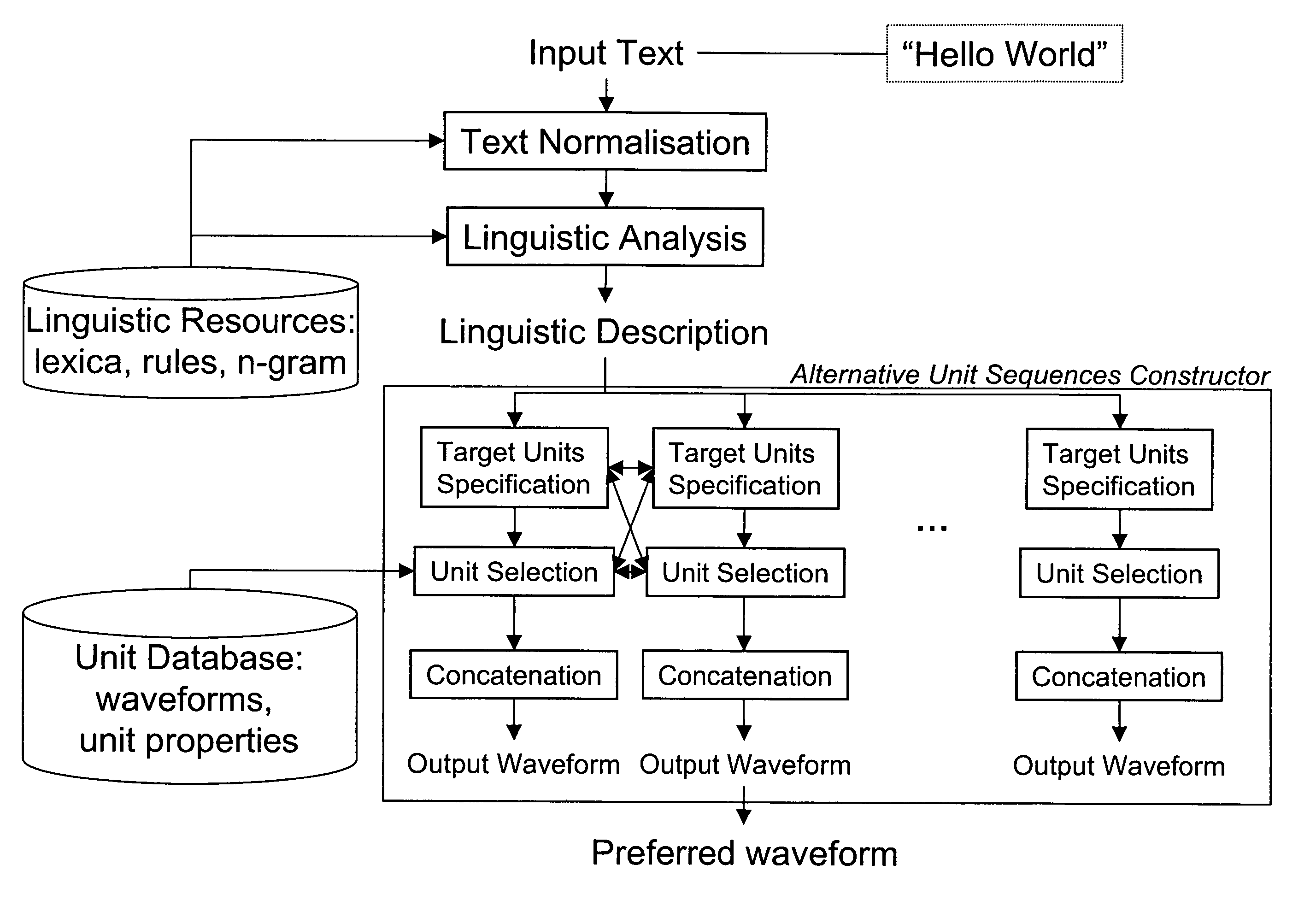
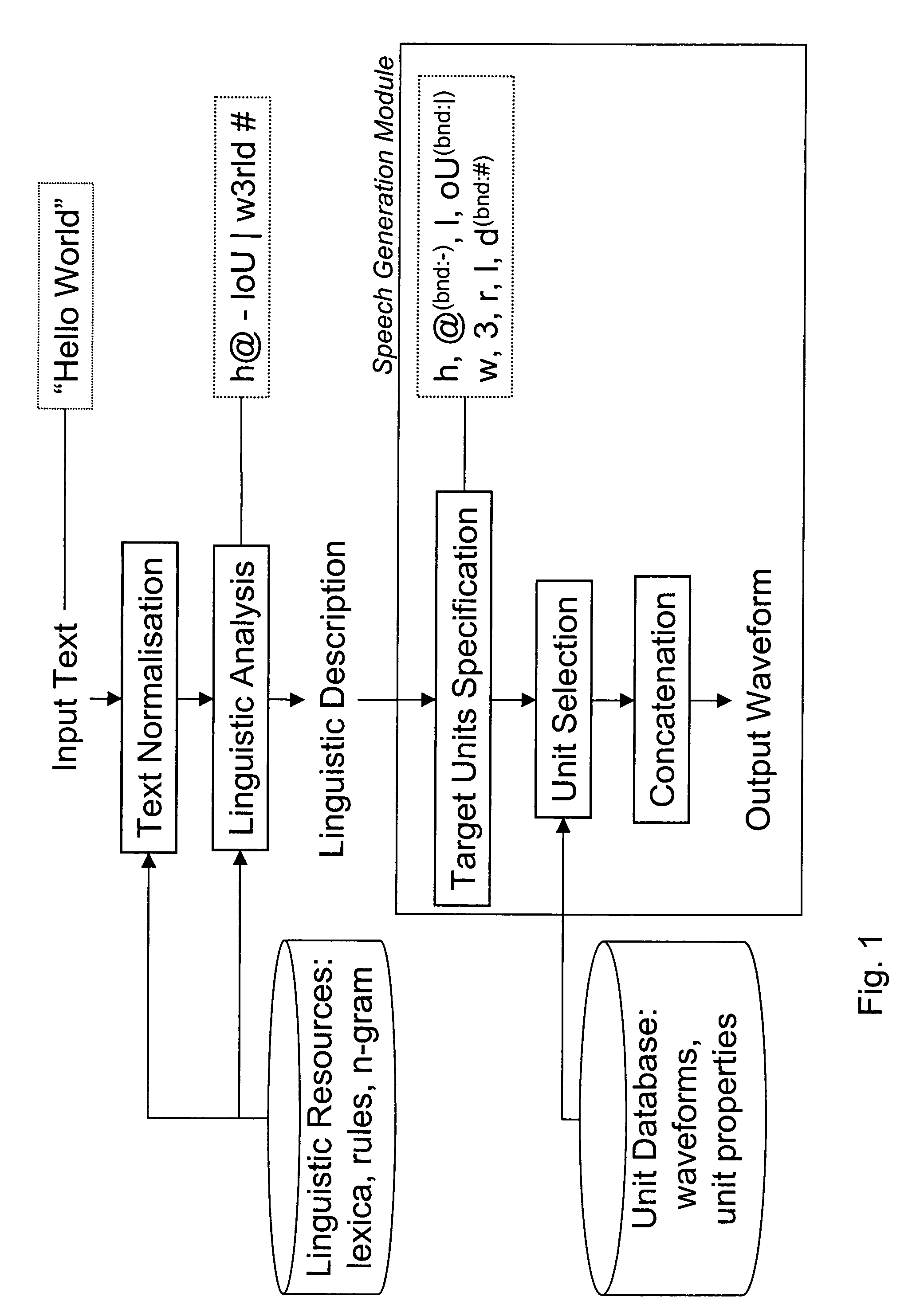
Text to speech synthesis
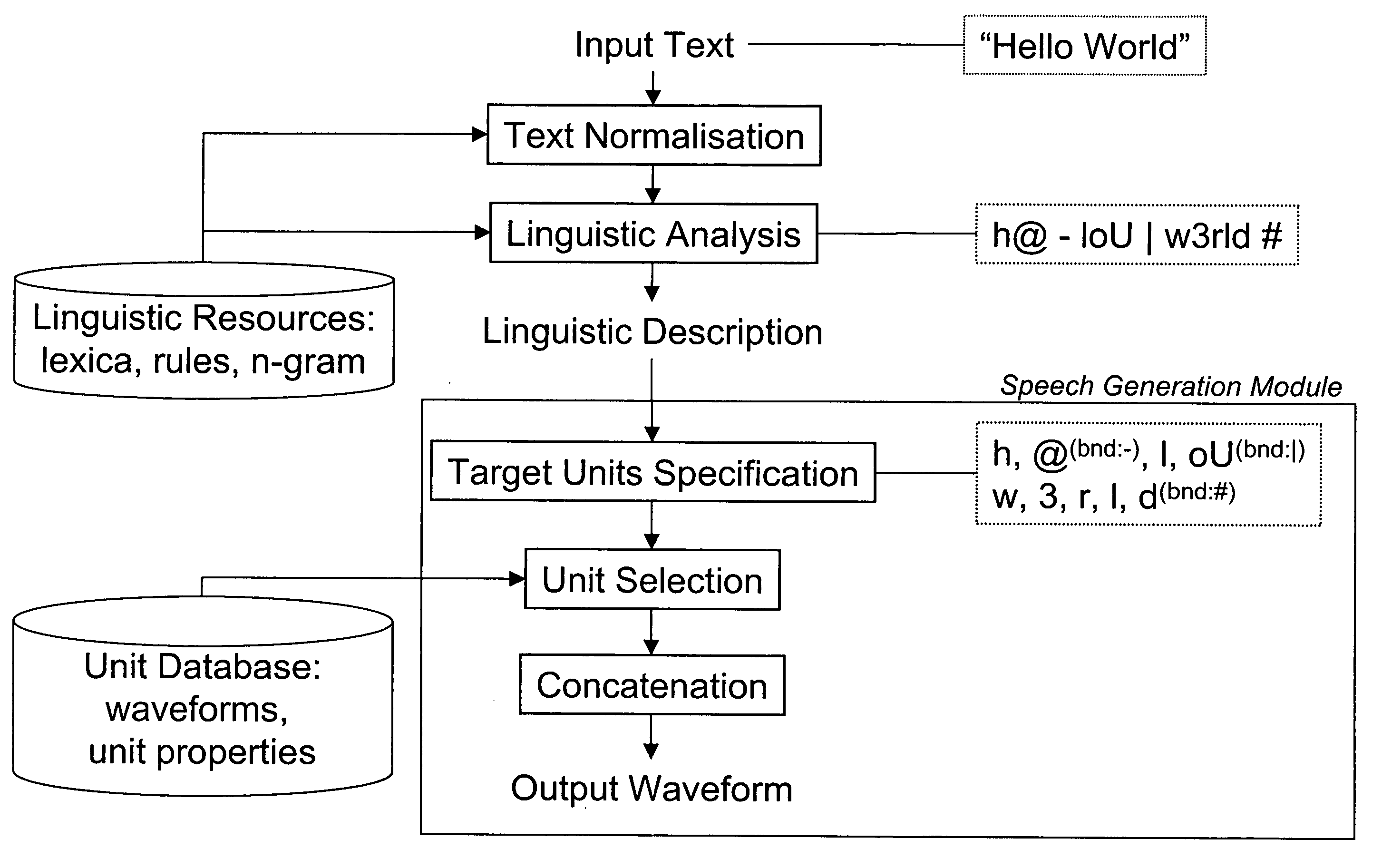
An input linguistic description is converted into a speech waveform by deriving at least one target unit sequence corresponding to the linguistic description, selecting from a waveform unit database for the target unit sequences a plurality of alternative unit sequences approximating the target unit sequences, concatenating the alternative unit sequences to alternative speech waveforms and presenting the alternative speech waveforms to an operating person and enabling the choice of one of the presented alternative speech waveforms. There are no iterative cycles of manual modification and automatic selection, which enables a fast way of working. The operator does not need knowledge of units, targets, and costs, but chooses from a set of given alternatives. The fine-tuning of TTS prompts therefore becomes accessible to non-experts.
Owner:CERENCE OPERATING CO
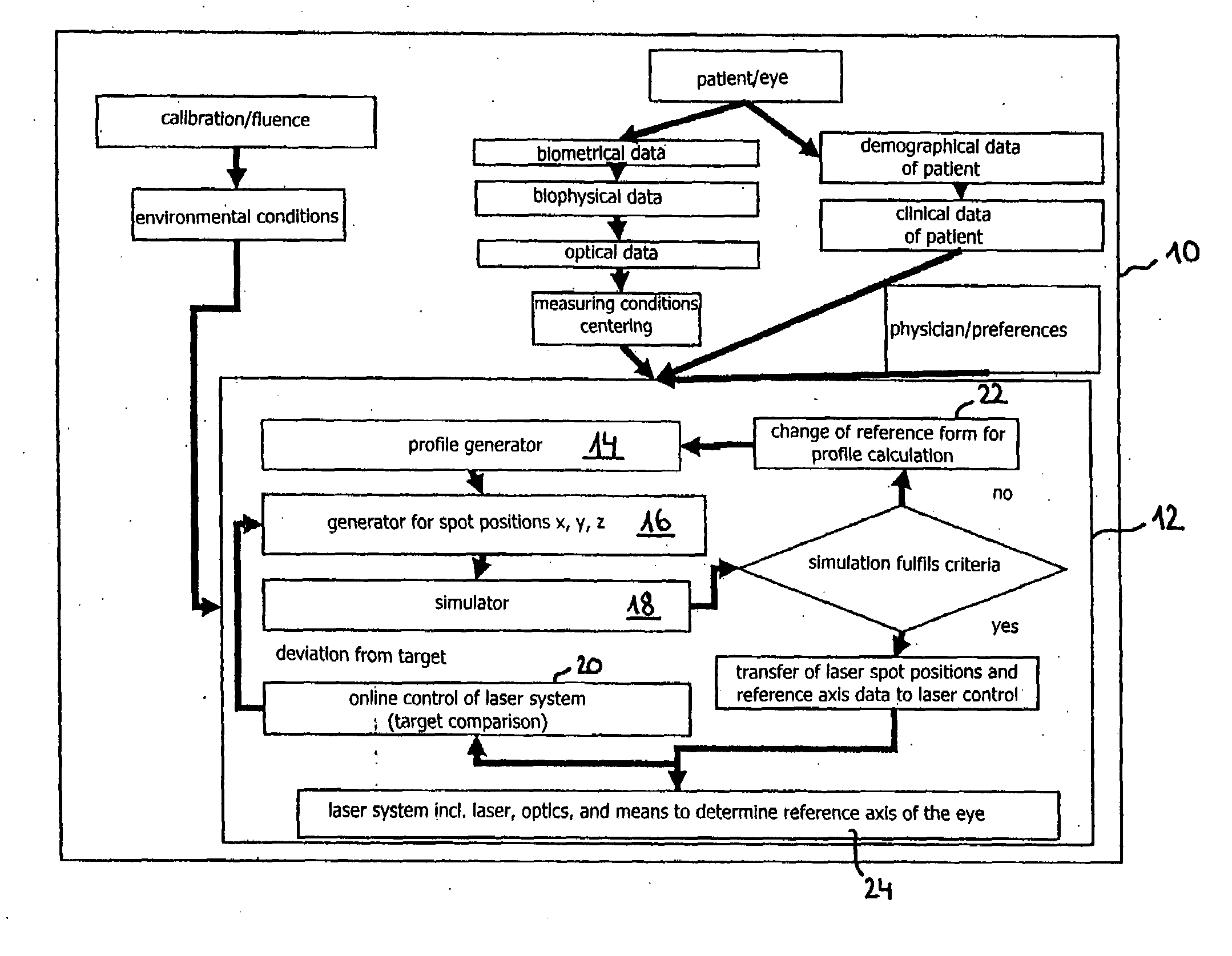
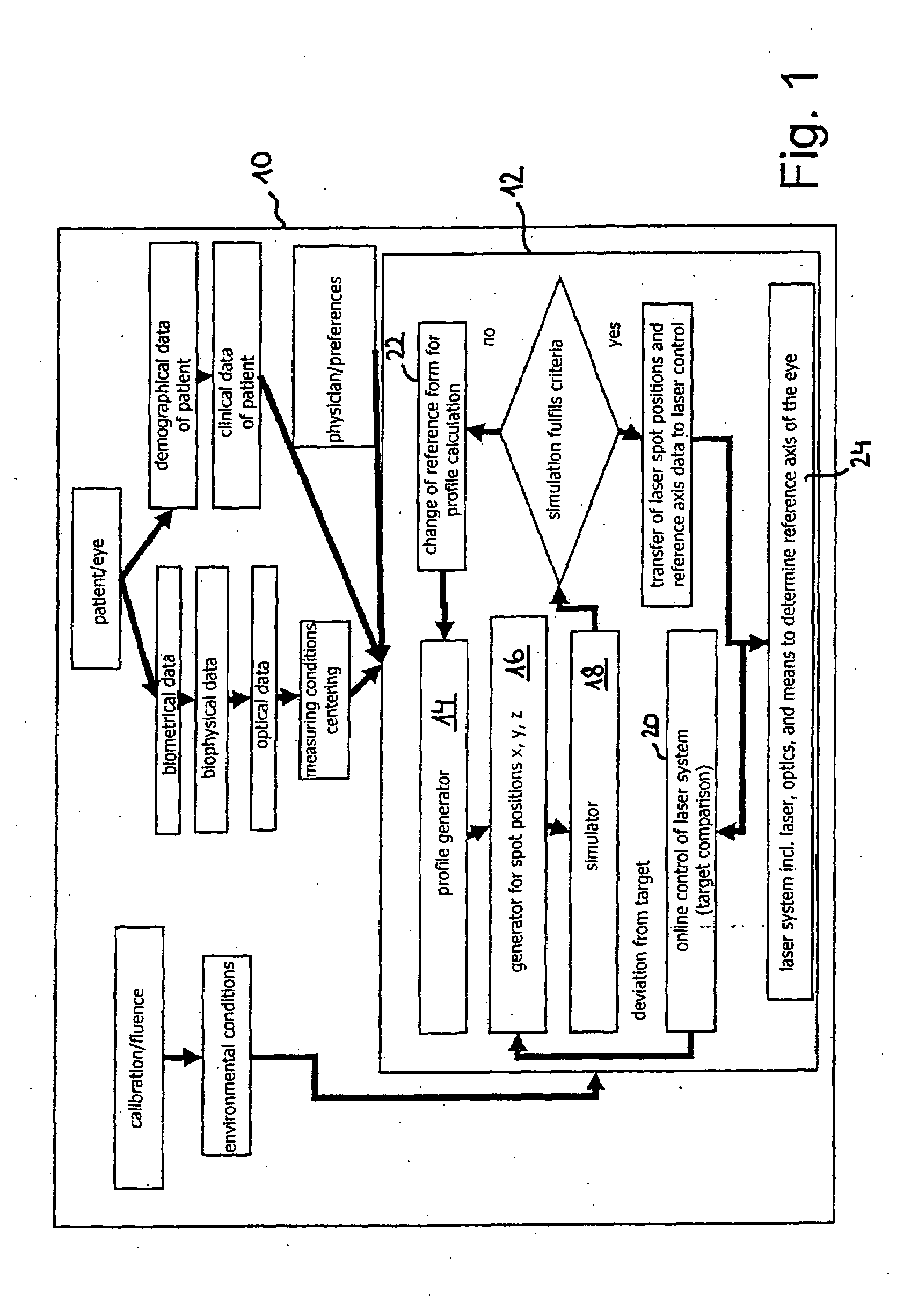
Computer program for ophthalmological surgery
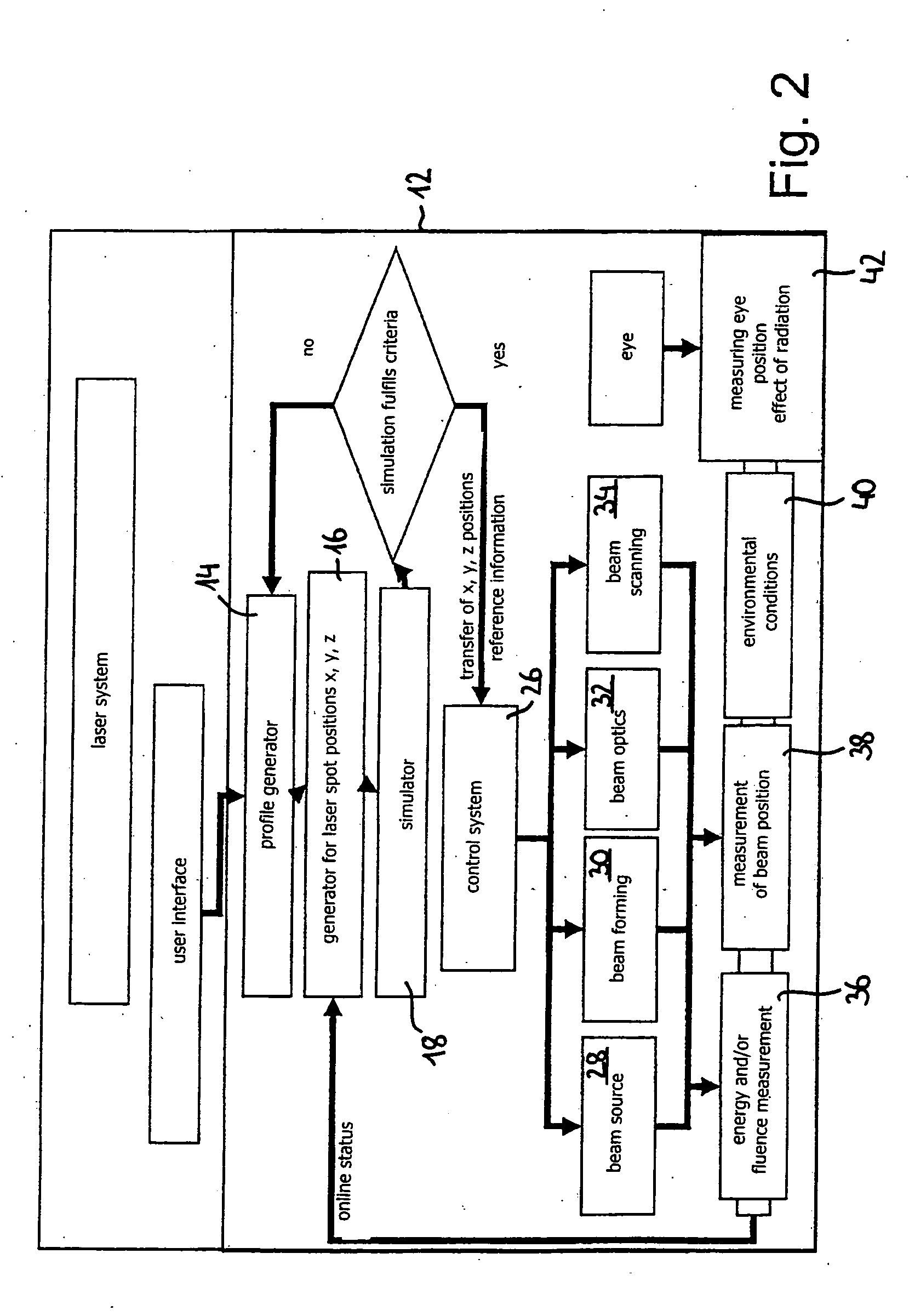
A Computer program for determining a working profile for controlling a radiation system in refractive eye surgery, said program comprising:a user interface for input of data by a user; a data receiving interface for receiving measured data regarding the eye to be corrected; a working profile generator for generating a working profile on the basis of the input data and measured data; a generator for generating control data for controlling electromagnetic radiation; a simulator for simulating a treatment result on the basis of said control data for controlling the electromagnetic radiation and the effect of said radiation on eye tissue; a judgment stage for judging said treatment results by applying pre-given criteria; an iteration loop for generating iteratively, in case of a negative judgment, another amended profile on the basis of other data or for generating iteratively other control data for controlling the electromagnetic radiation; and a transfer means for transferring control data to a control of the radiation system in case of a positive judgment in the judgment stage.
Owner:ALCON INC
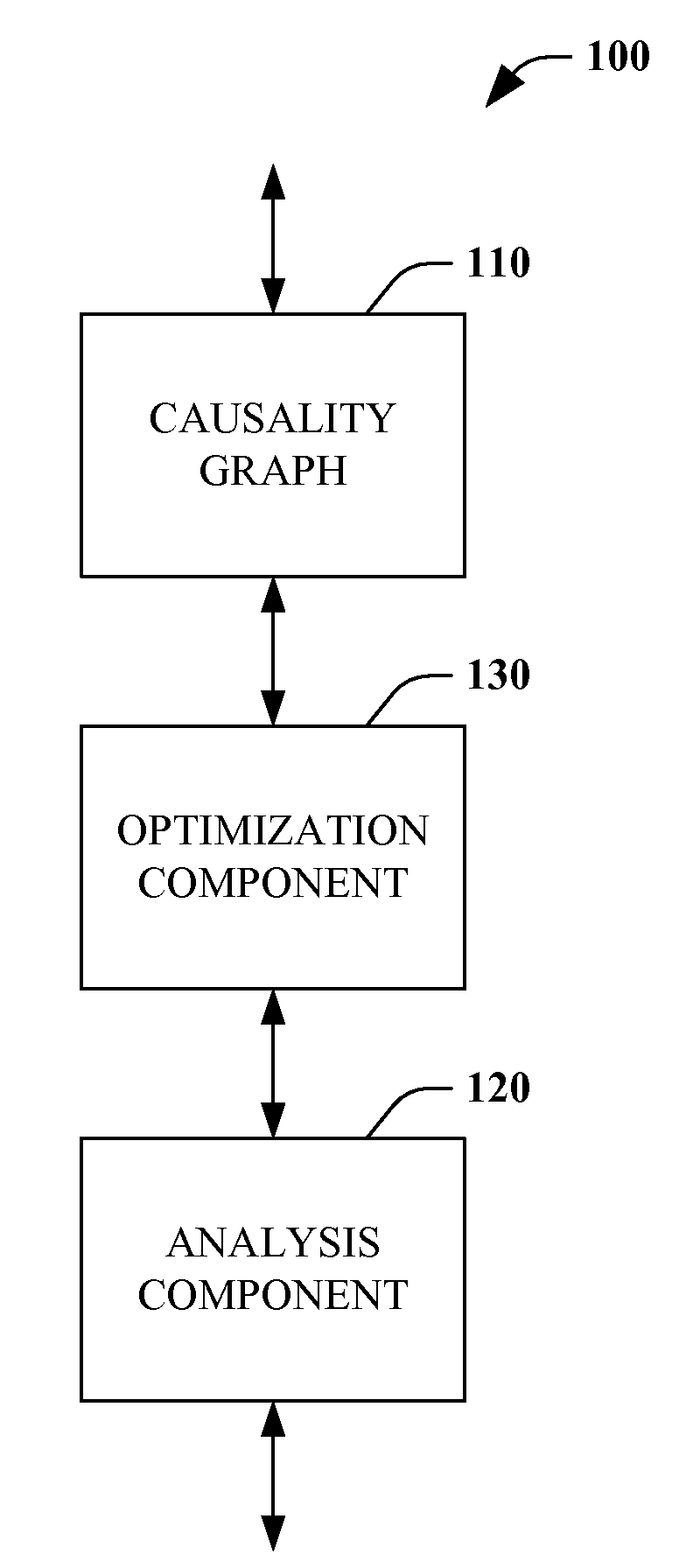
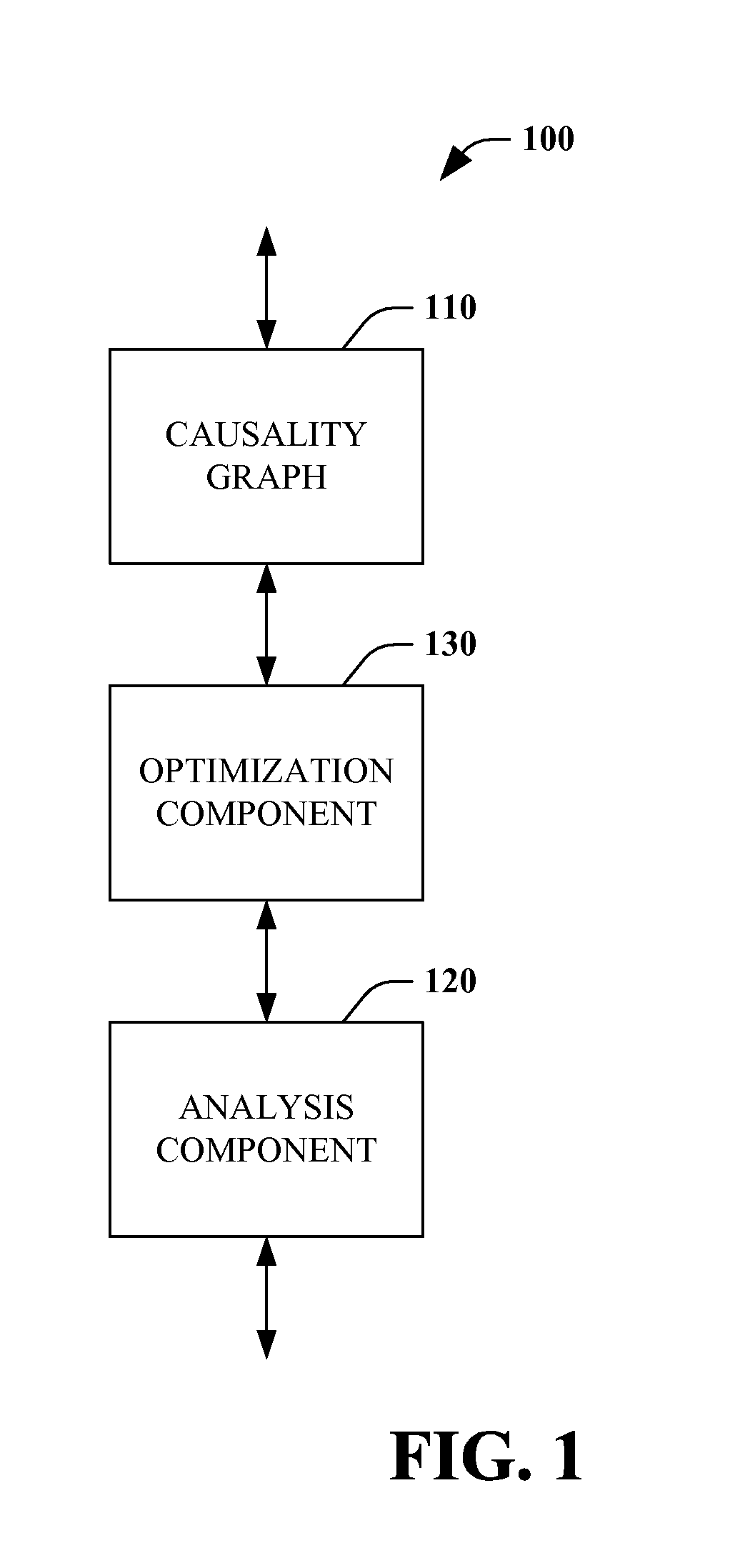
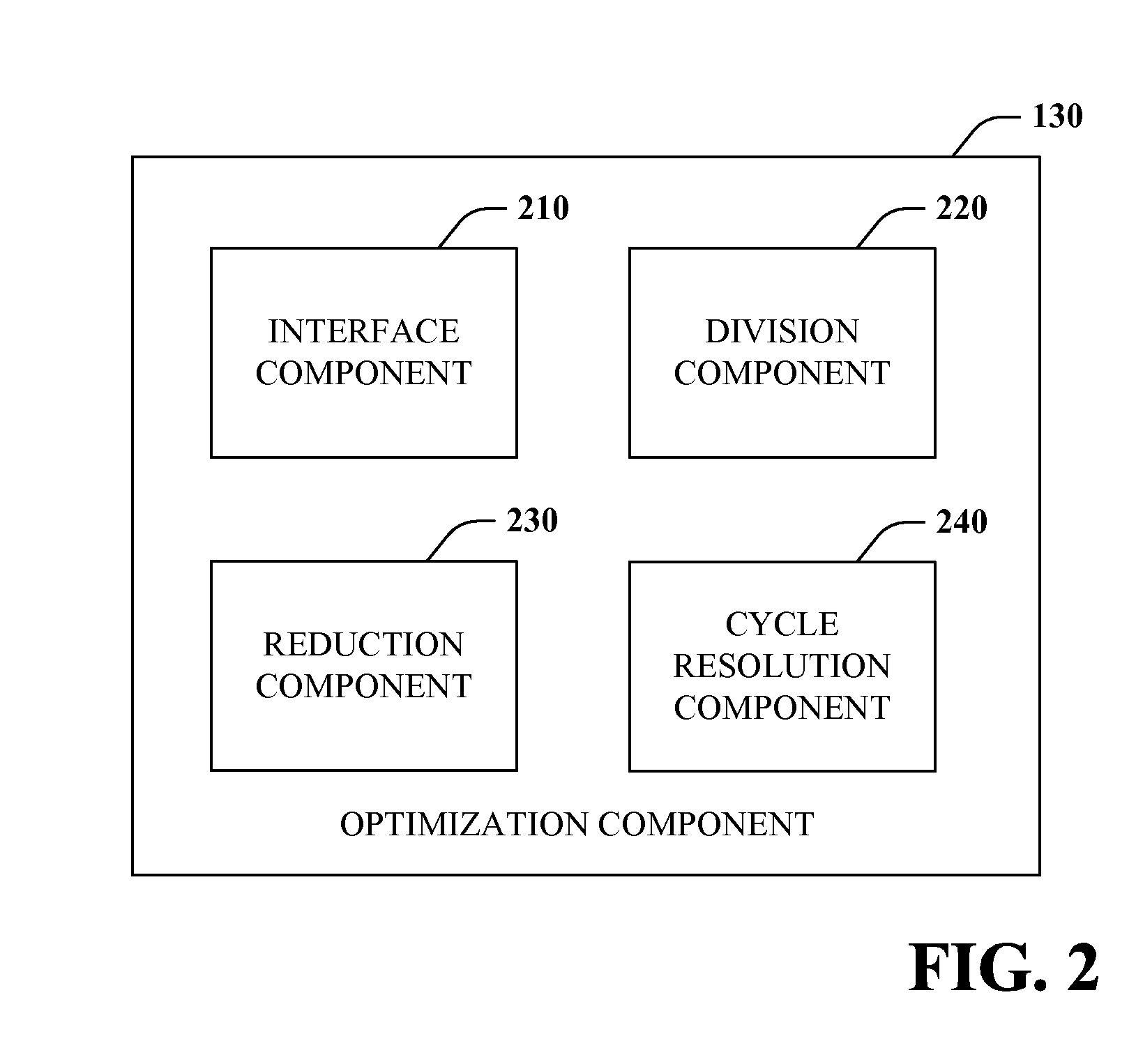
Root cause analysis optimization
InactiveUS20090327195A1Reduce in quantityEasy to operateKnowledge representationInference methodsTheoretical computer scienceRoot cause analysis
Root cause analysis is augmented by providing optimized inputs to root cause analysis systems or the like. Such optimized inputs can be generated from causality graphs by creating sub-graphs, finding and removing cycles, and reducing the complexity of the input. Optimization of inputs enables a root cause analysis system to reduce the number of iterative cycles that are required to execute probable cause analysis, among other things. In one instance, cycle removal eliminates perpetuation of errors throughout a system being analyzed.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
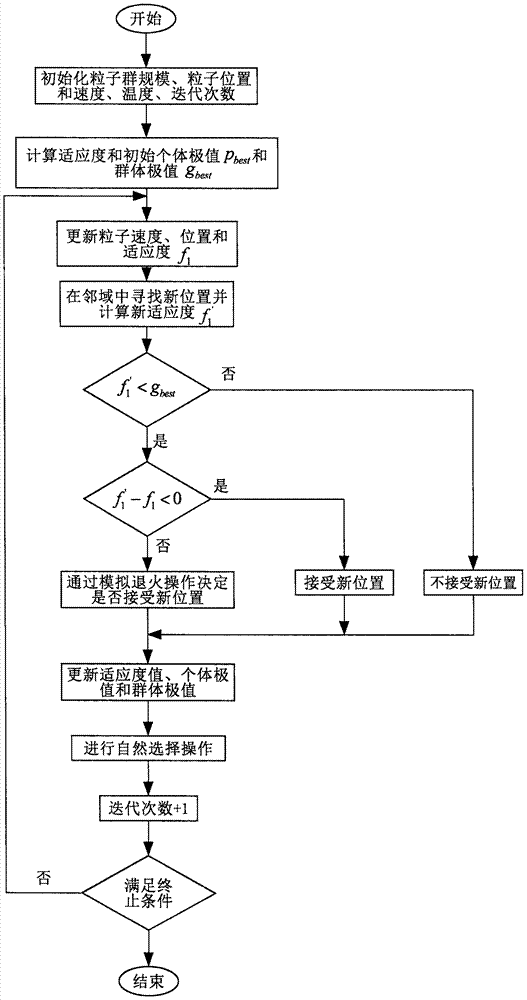
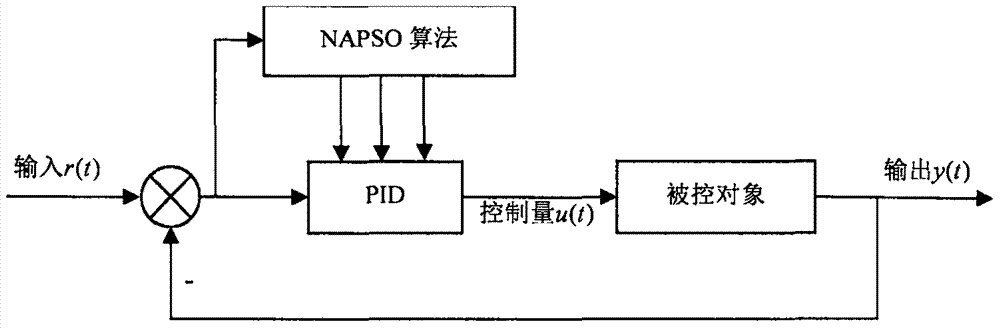
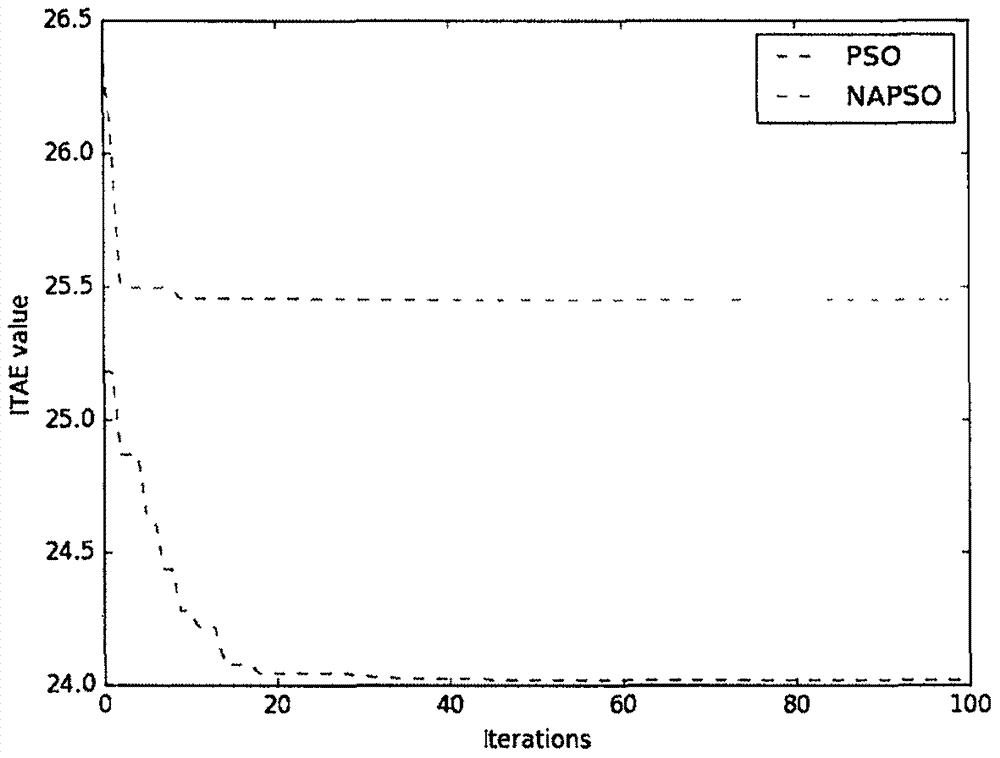
PID controller parameter setting algorithm based on improved PSO (particle swarm optimization) algorithm
InactiveCN107272403AAdaptableSlow down the rate of convergenceArtificial lifeControllers with particular characteristicsLocal optimumControl engineering
The invention discloses a PID controller parameter setting algorithm based on an improved PSO (particle swarm optimization) algorithm, and the algorithm comprises the following steps: 1, initializing the algorithm parameters; 2, switching to an iterative loop, and carrying out the updating of the position and speed of each particle; 3, randomly searching a new position in the neighborhood of a current position; 4, calculating the adaptability difference between two positions, and judging whether to accept the new position or not through a simulated annealing mechanism when the adaptability of the new position is inferior to the adaptability of an original position but is superior to the adaptability of a global optimal position; 5, updating the global optimal position of a population, carrying out the natural selection operation, carrying out the arrangement of all particles according to the adaptability values, and employing the information of a part of better particles to replace the information of the other half particles; 6, judging whether to stop the iteration or not; 7, outputting PID controller parameters or executing step 2 again. The method can achieve the automatic setting of control parameters, irons out a defect that a conventional PSO algorithm is very liable to be caught in local optimization, achieves the complementation of the simulated annealing operation and a natural selection strategy, improves the convergence precision of the algorithm under the condition that the number of convergence times of the algorithm is guaranteed, is higher in robustness and precision, and enables the PID controller to generate a more excellent control effect.
Owner:ZHEJIANG NORMAL UNIVERSITY
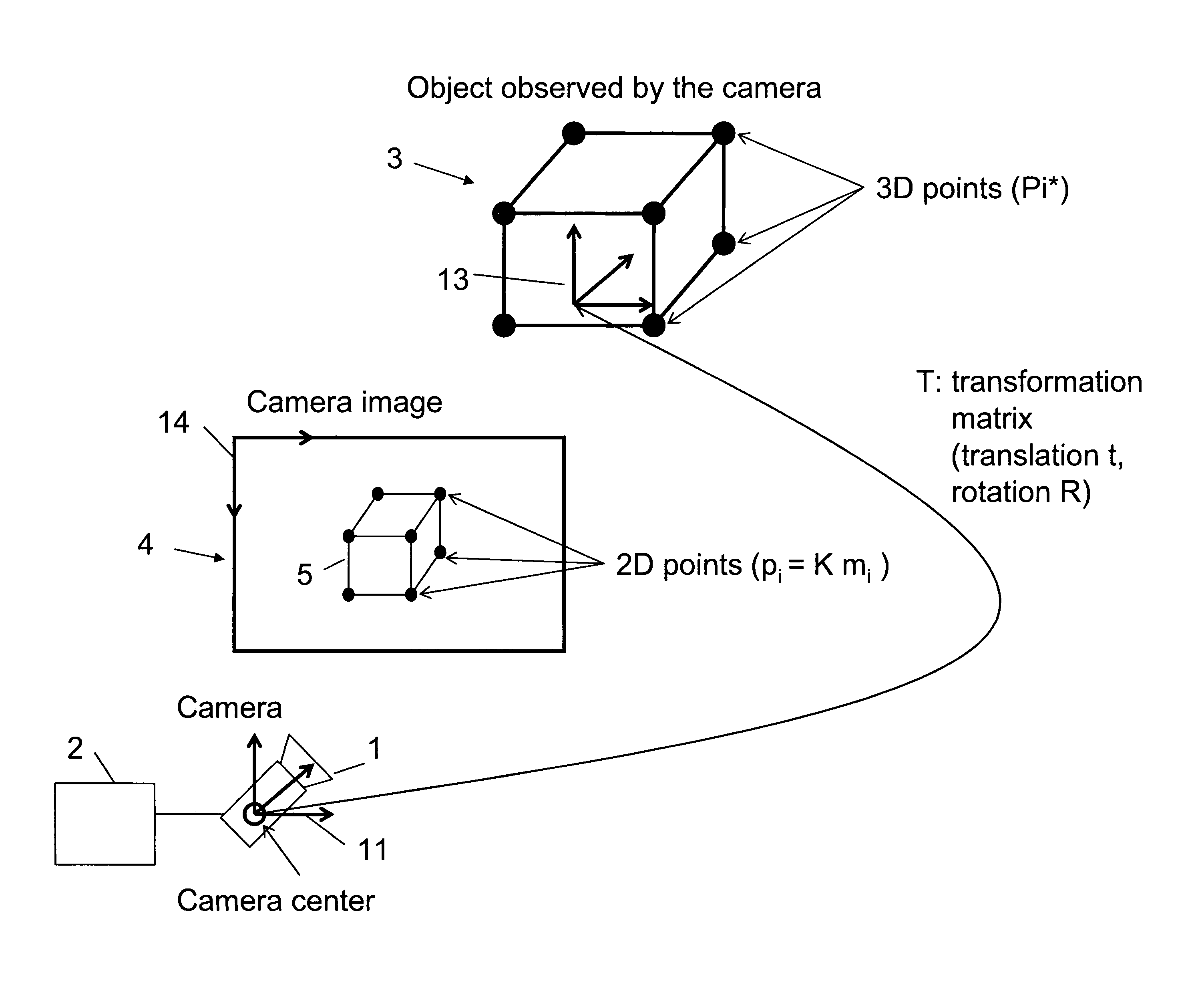
Method for determining the pose of a camera with respect to at least one real object
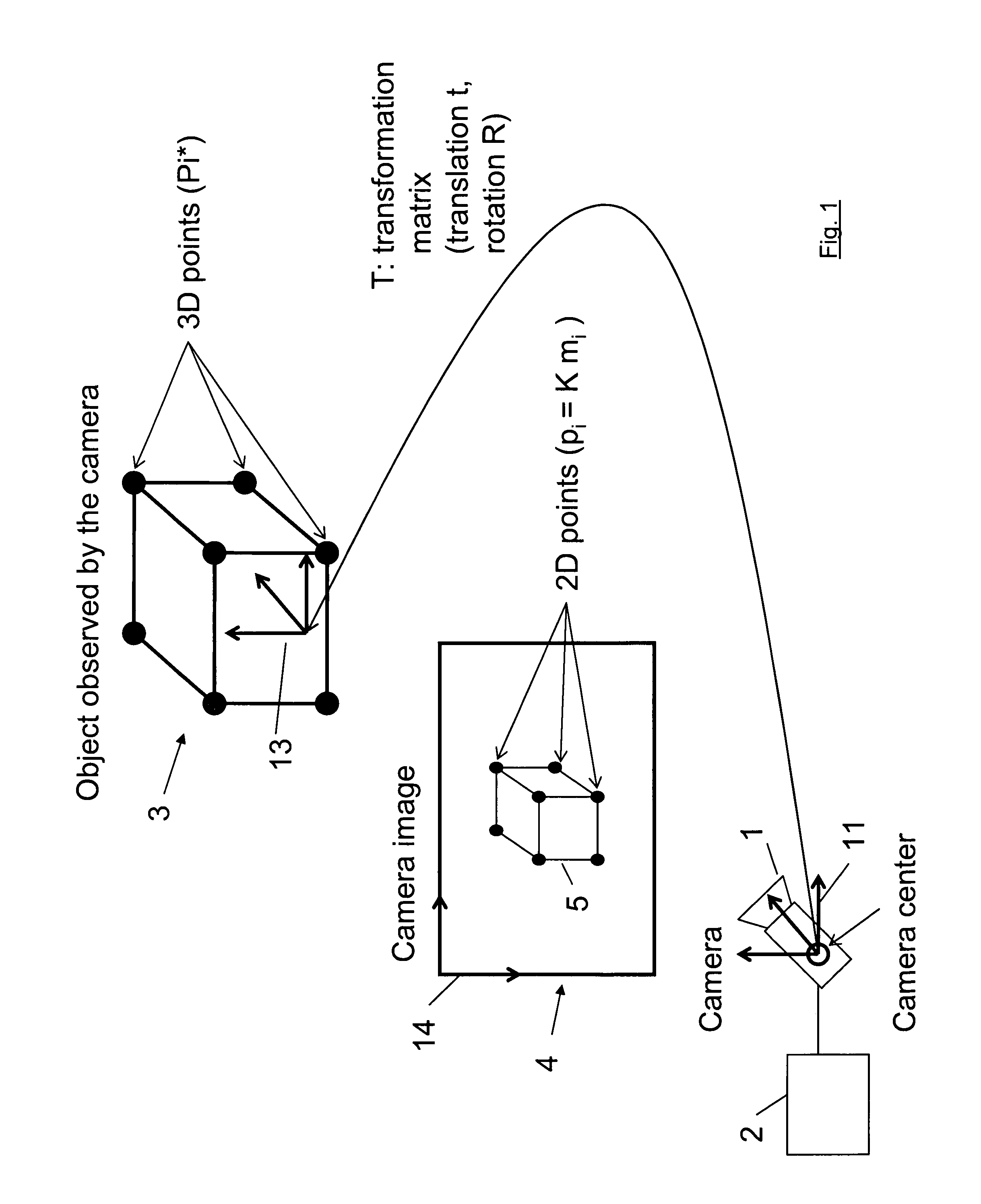
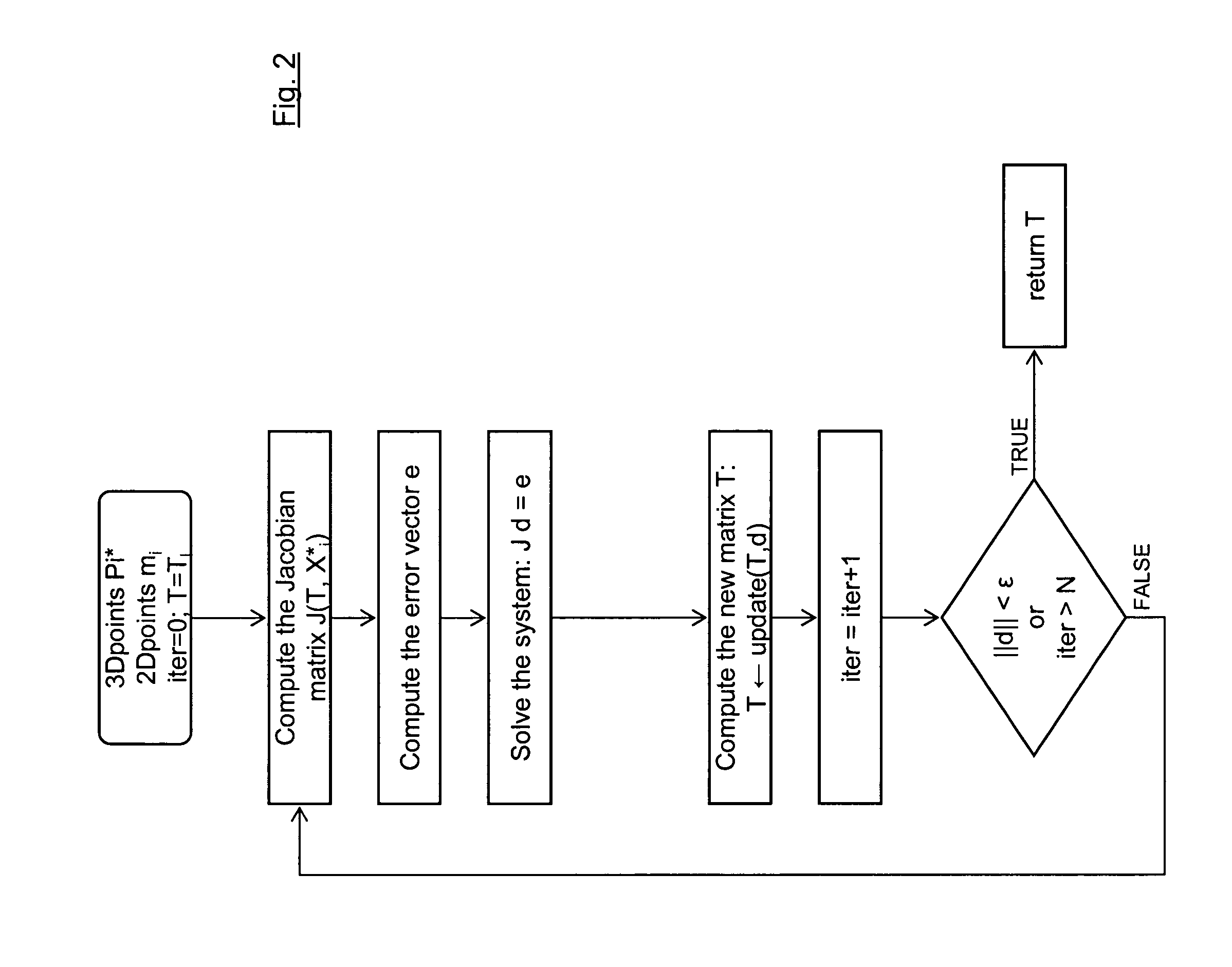
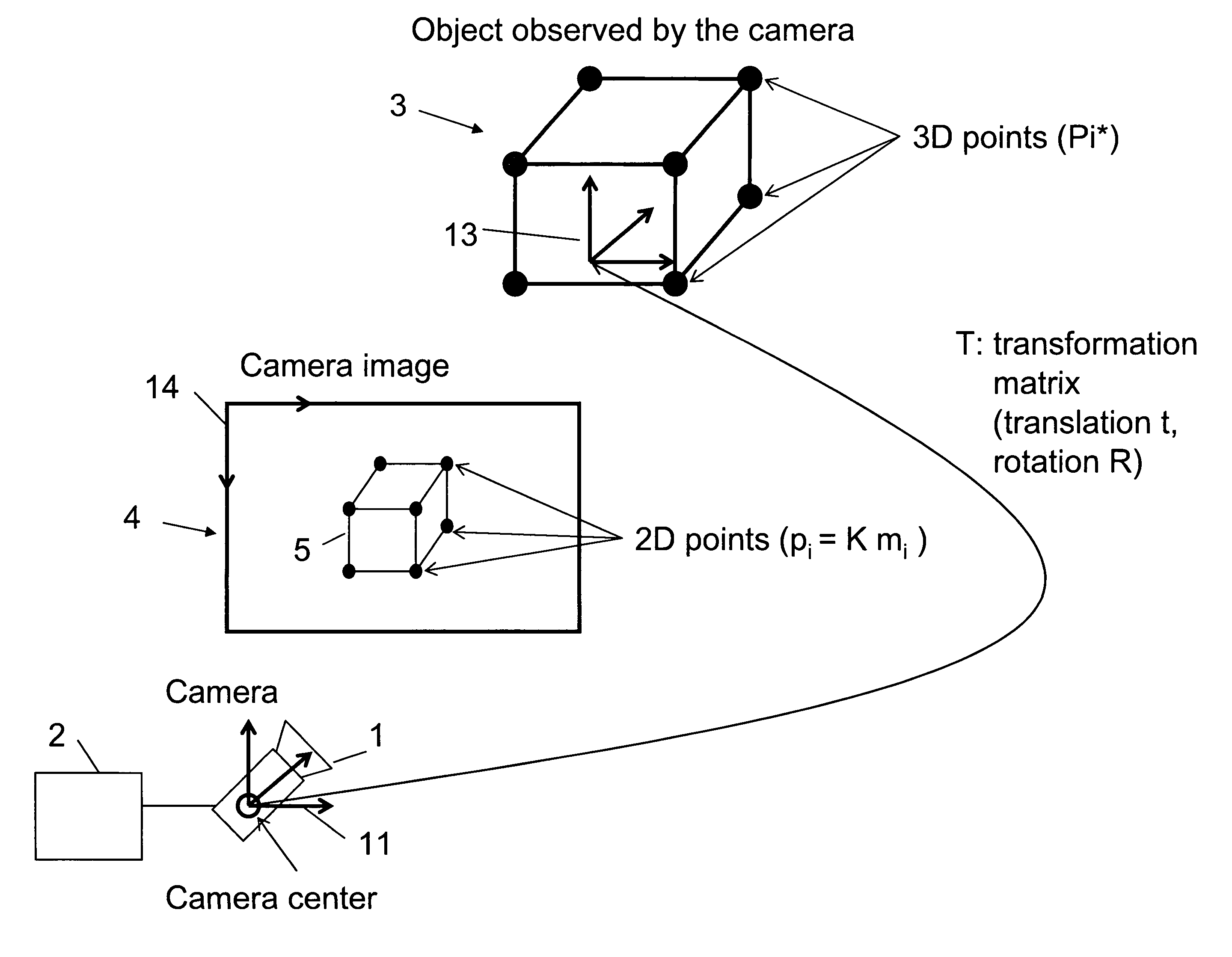
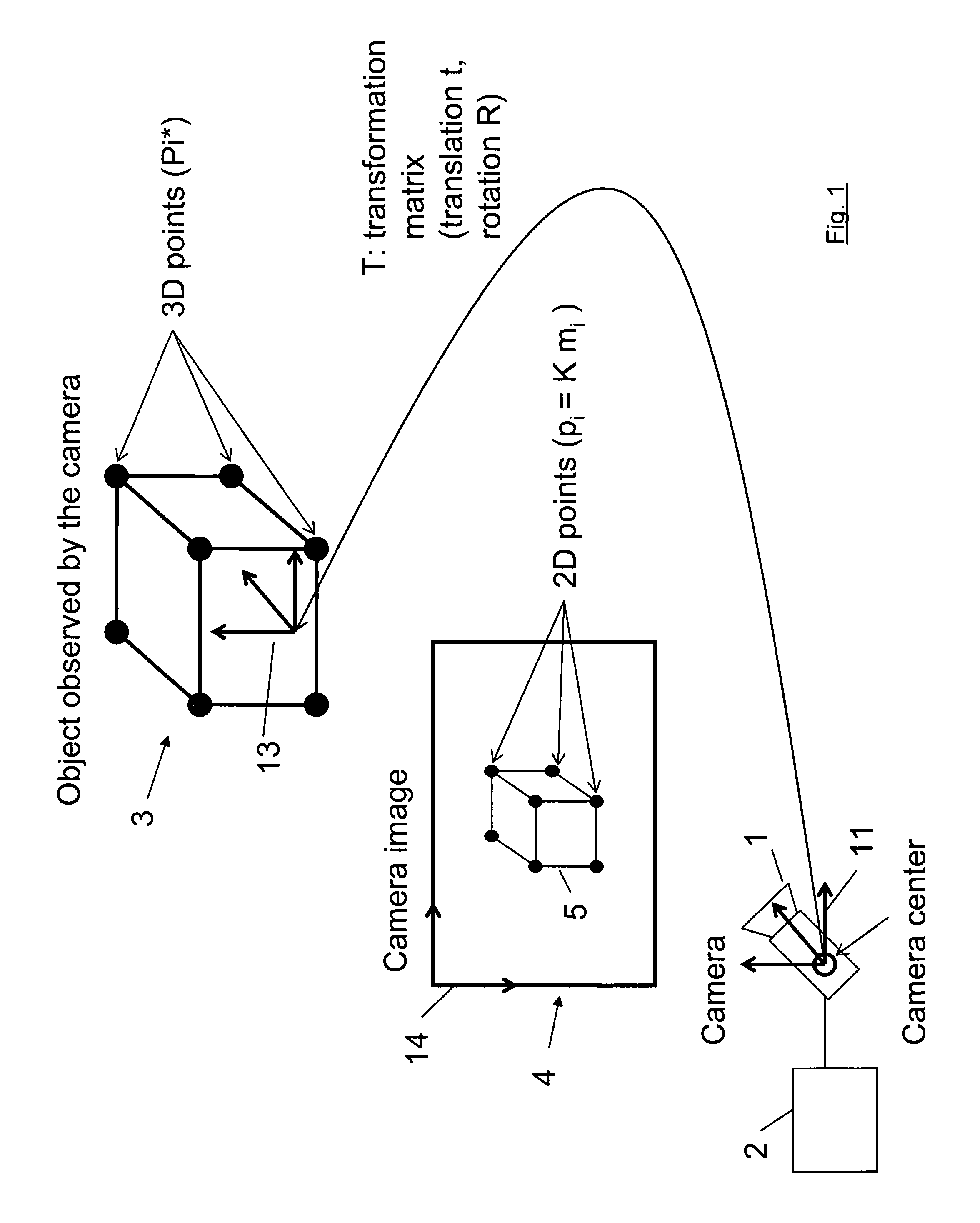
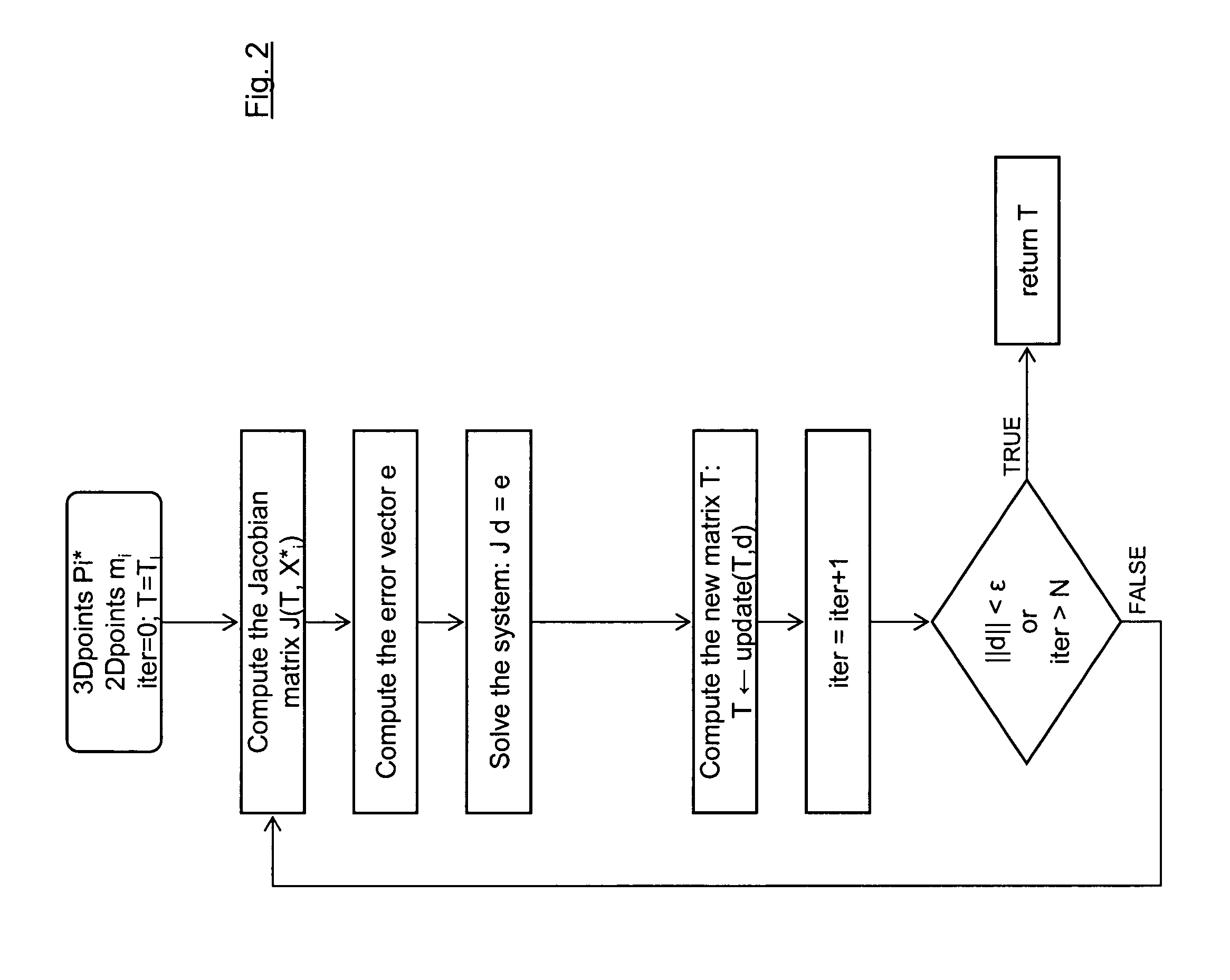
ActiveUS20120120199A1Reduce computing timeImage enhancementImage analysisIteration loopComputer vision
A method for determining the pose of a camera with respect to at least one real object, the method comprises the following steps: operating the camera (1) for capturing a 2-dimensional (or 3-dimensional) image (4) including at least a part of the real object (3), providing a transformation matrix (T) which includes information regarding a correspondence between 3-dimensional points (Pi*) associated with the real object (3) and corresponding 2-dimensional points (or 3-dimensional points) (p,) of the real object (5) as included in the 2-dimensional (or 3-dimensional) image (4), and determining an initial estimate of the transformation matrix (Tl) as an initial basis for an iterative minimization process used for iteratively refining the transformation matrix, determining a Jacobian matrix (J) which includes information regarding the initial estimate of the transformation matrix (Tl) and reference values of 3-dimensional points (Pi*) associated with the real object (3). Further, in the iterative minimization process, in each one of multiple iteration loops determining a respective updated version of the transformation matrix (T) based on a respective previous version of the transformation matrix (T) and based on the Jacobian matrix (J), wherein the Jacobian matrix is not updated during the iterative minimization process, and determining the pose of the camera (1) with respect to the real object (3) using the transformation matrix (T) determined at the end of the iterative minimization process. As a result, the camera pose can be calculated with rather low computational time.
Owner:APPLE INC
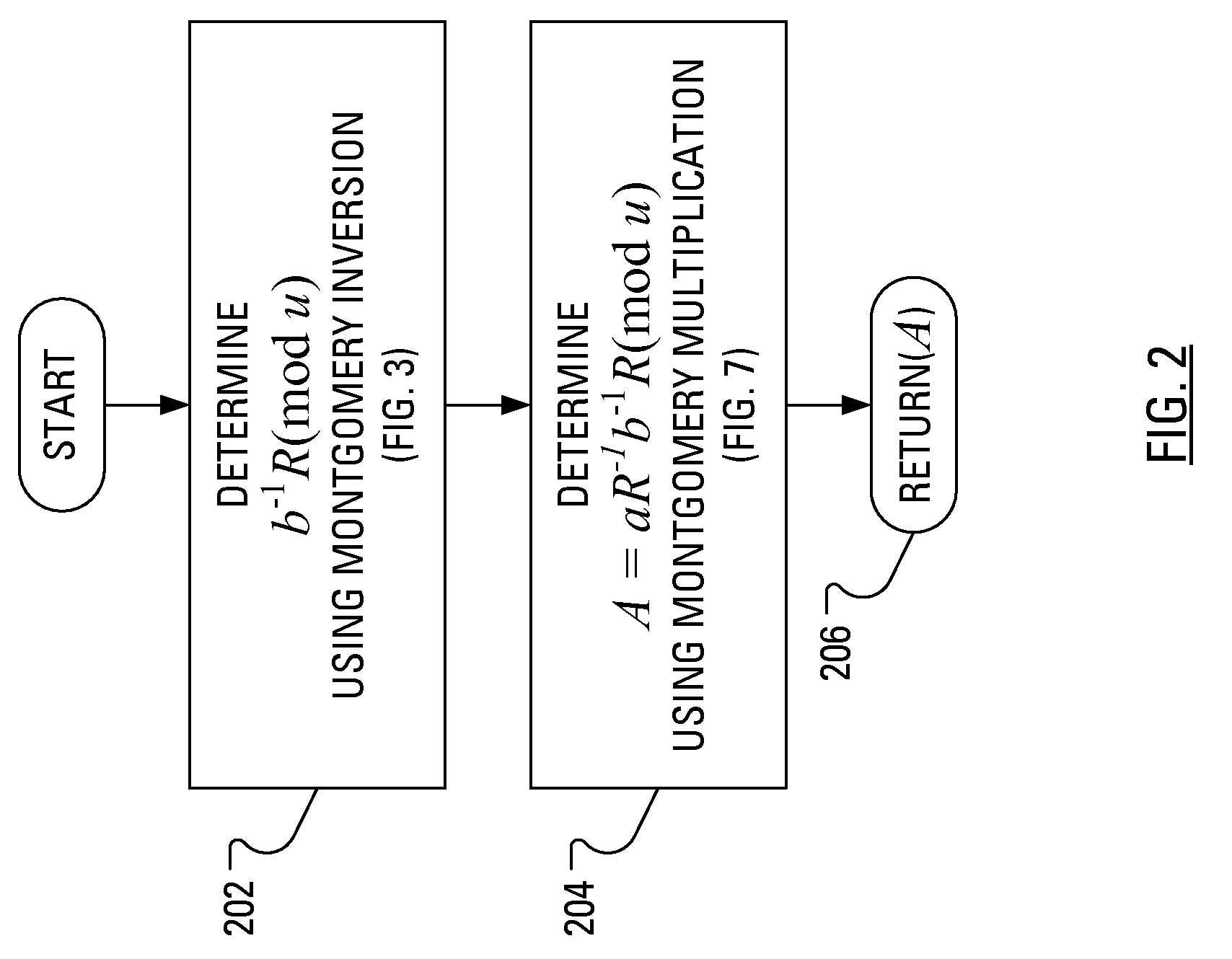
Method and Apparatus for Performing Elliptic Curve Scalar Multiplication in a Manner that Counters Power Analysis Attacks
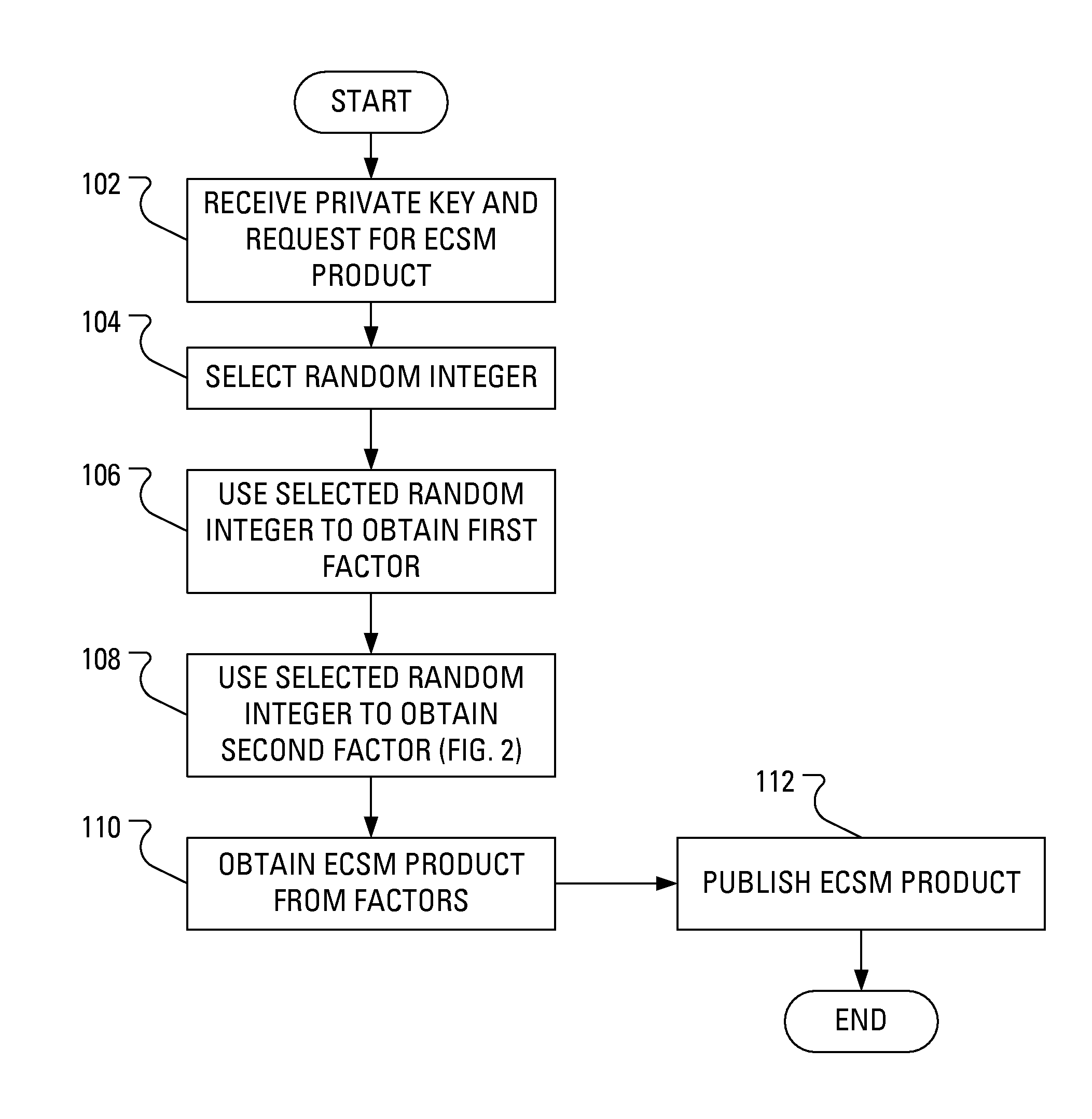
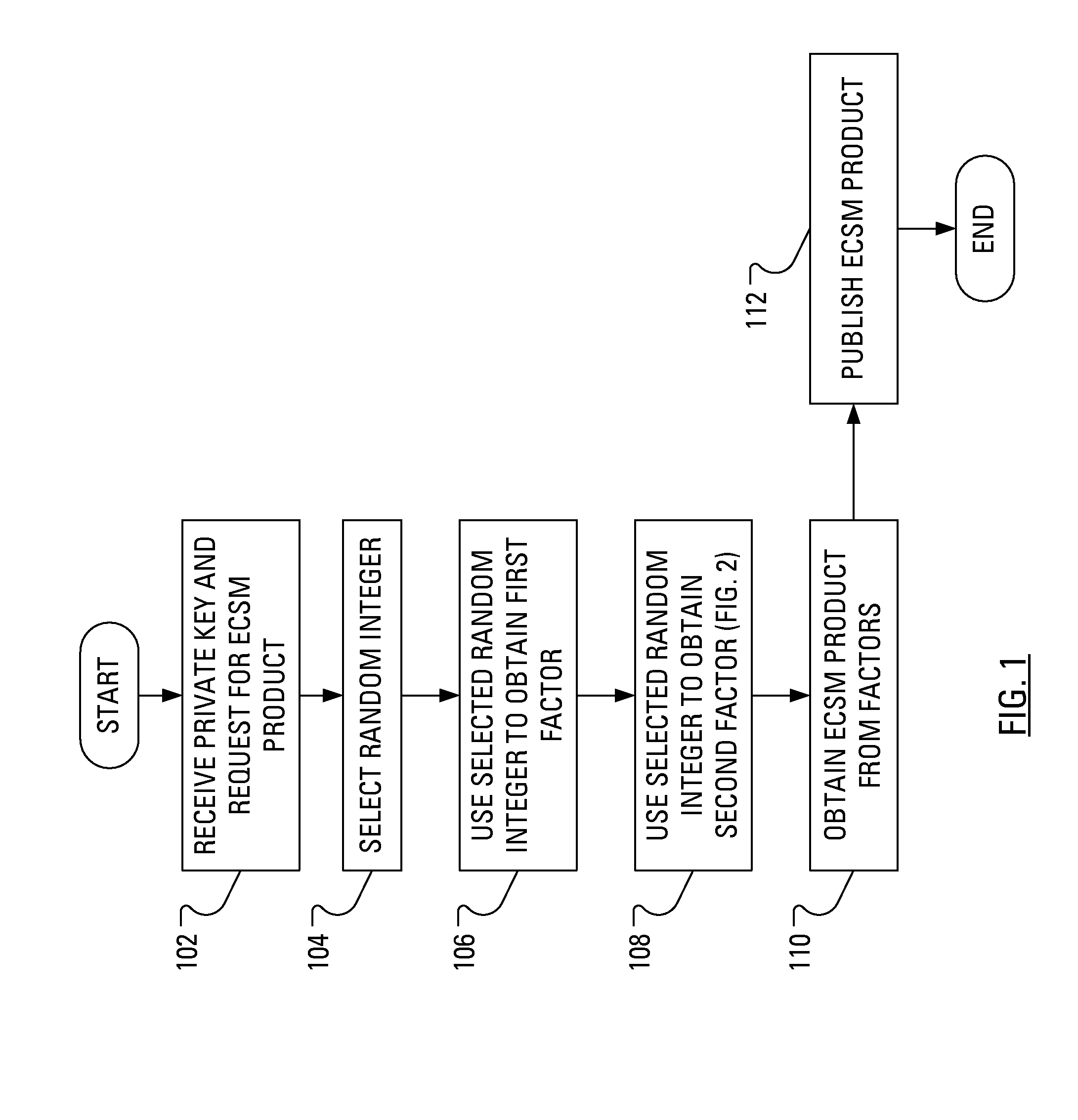
ActiveUS20080219437A1Public key for secure communicationDigital data processing detailsComputer hardwarePower analysis
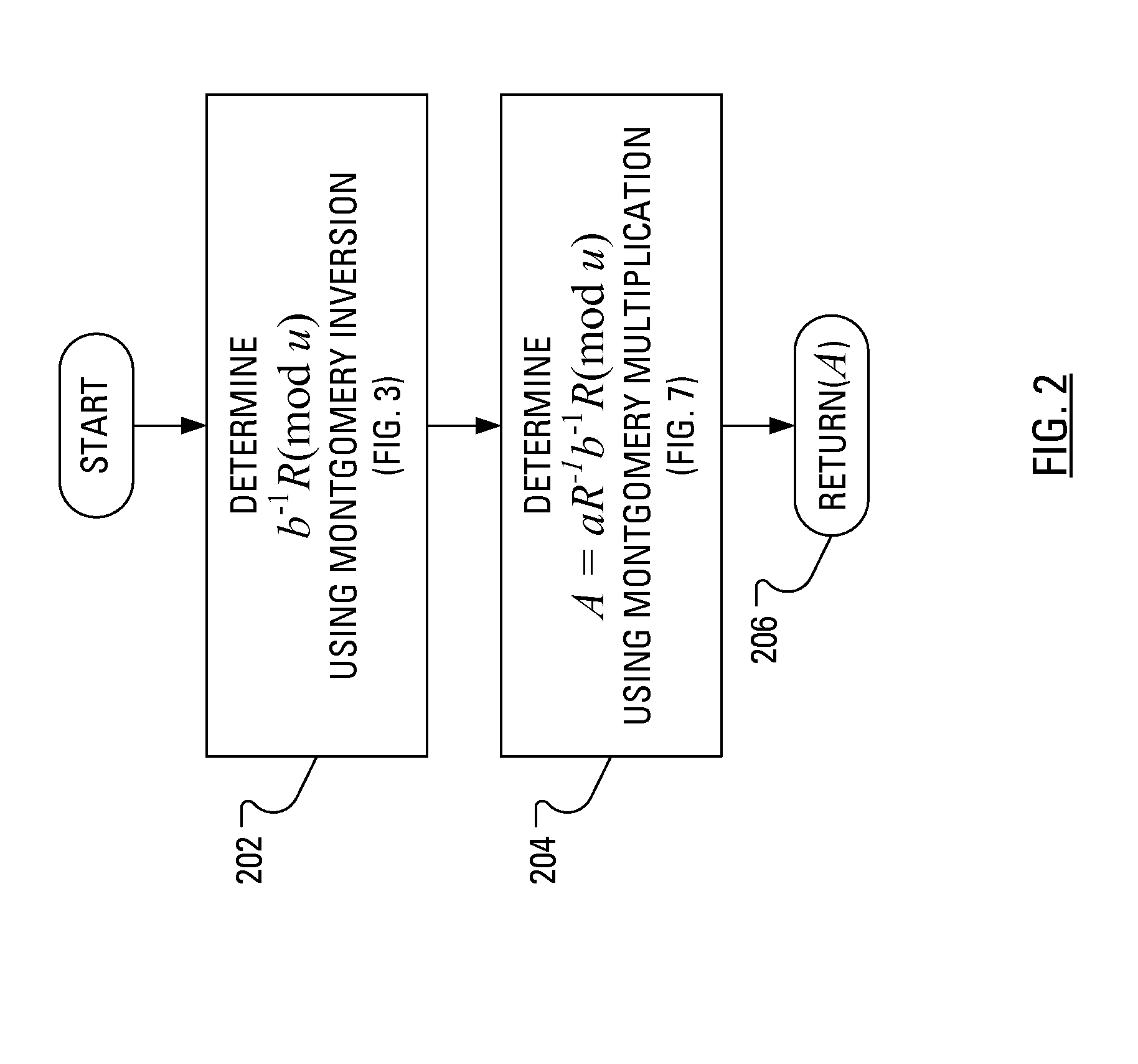
When multiplicative splitting is used to hide a scalar in an Elliptic Curve scalar Multiplication ECSM operation, the associated modular division operation employs the known Almost Montgomery Inversion algorithm. By including dummy operations in some of the branches of the main iteration loop of the Almost Montgomery Inversion algorithm, all branches of the algorithm may be viewed, from the perspective of a Power Analysis-based attack, as equivalent and, accordingly, devoid of information useful in determining the value of the scalar, which may be a cryptographic private key.
Owner:MALIKIE INNOVATIONS LTD
Game theory-based power control method of multi-antenna CDMA system
InactiveCN101321004ASolving Distributed Power Control ProblemsReduce bit error rateTransmission control/equalisingTransmitter/receiver shaping networksChannel state informationTransmitted power
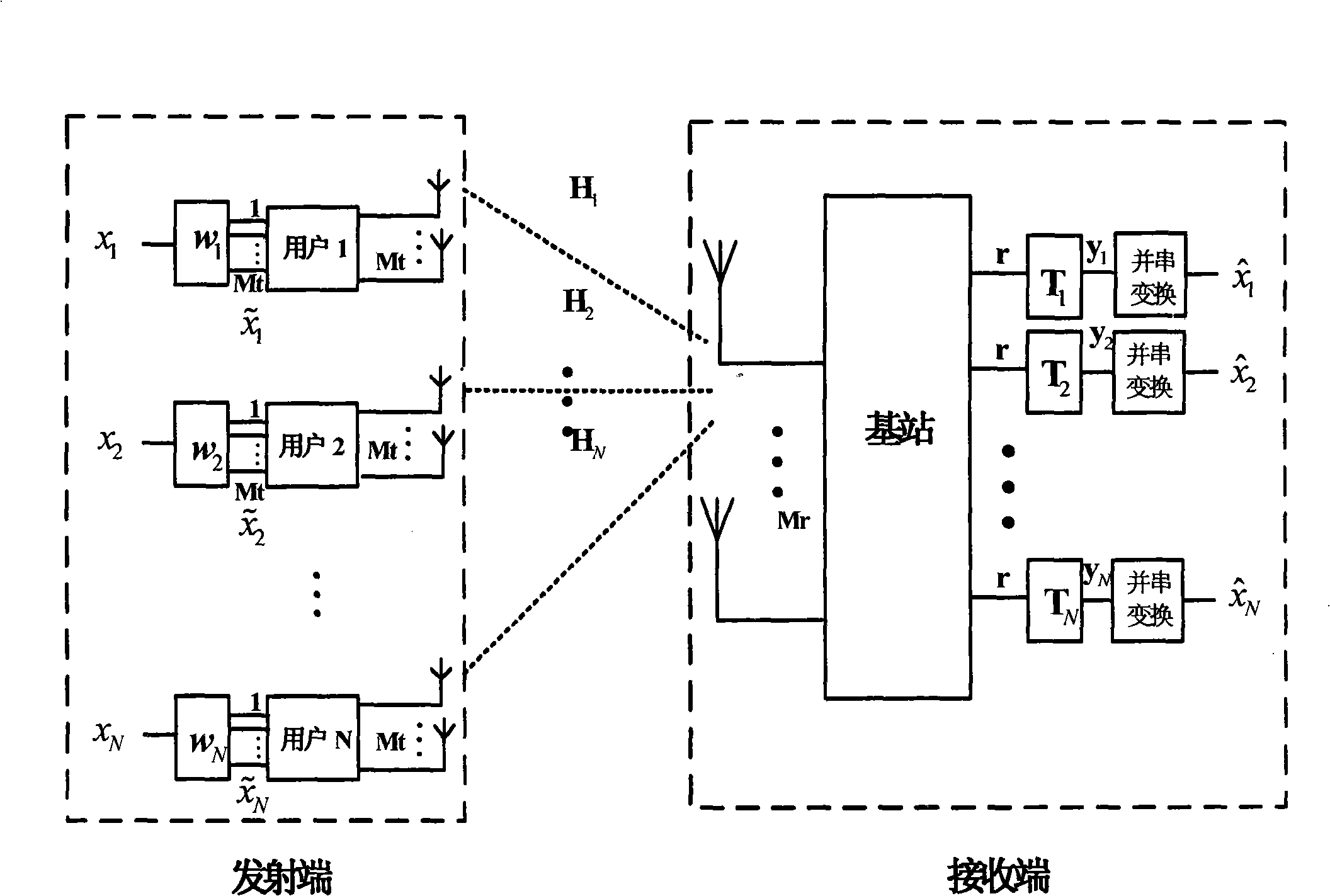
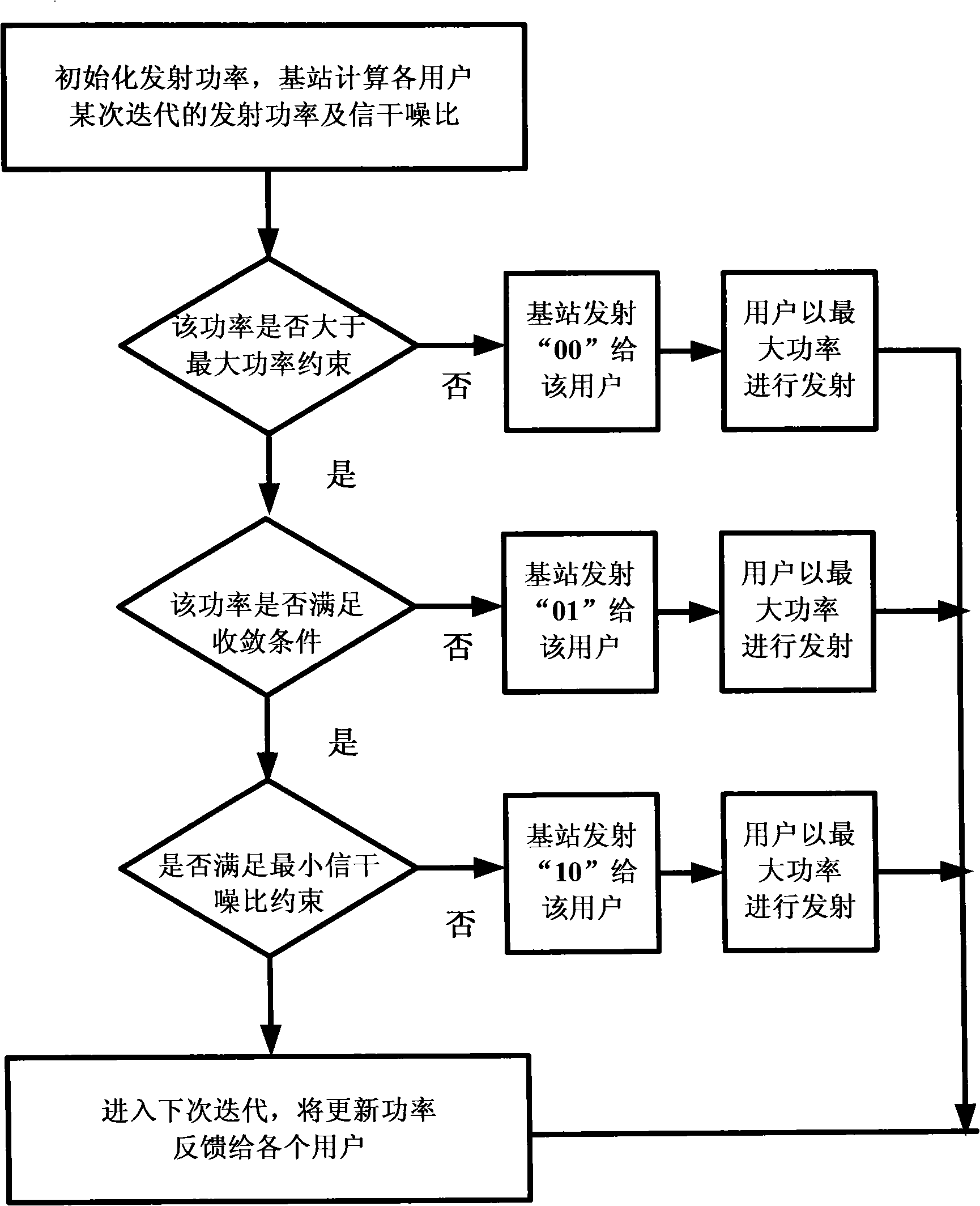
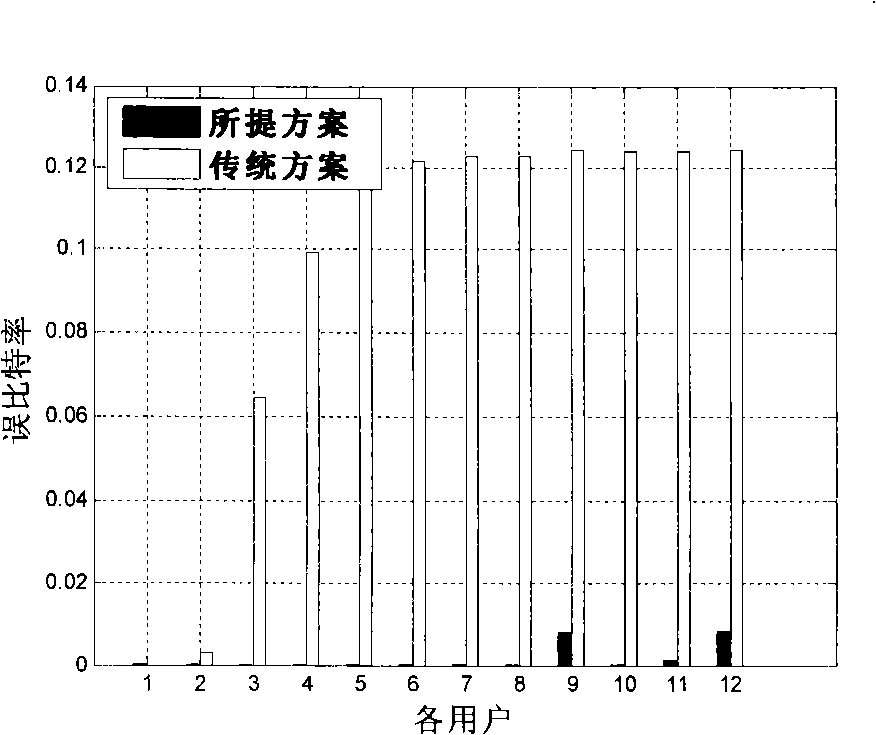
A solving method of the power control based on the game theory in the multi-antenna code division multiple access system is disclosed, wherein a game function based on the receiving end average bit error rate is designed, to realize the minimum of the user union transmitting power and the bit error rate, meanwhile, a punishment mechanism is inducted based on the link quality and the transmitting power to solve the 'far and near effect' in the CDMA system, and the punishment factor is adjusted real-time according to the different operation requirement. Each user performs the precoding treatment on the signal, divides the signal at the receiving end into N branches for processing. Each branch is multiplied by a receiving vector corresponding to the precoding vector, to cause the information update only depending on the feedback of part channel state information. The transmitting power and the signal to interference and noise ratio of each iteration by the user is computed, and the feasibility judgement is completed, till the obtained transmitting power through two times of iteration by the user satisfies that the 2-norm is smaller than the given small number after being adjusted continuously, the algorithm jumps out of the iteration cycle.
Owner:PLA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
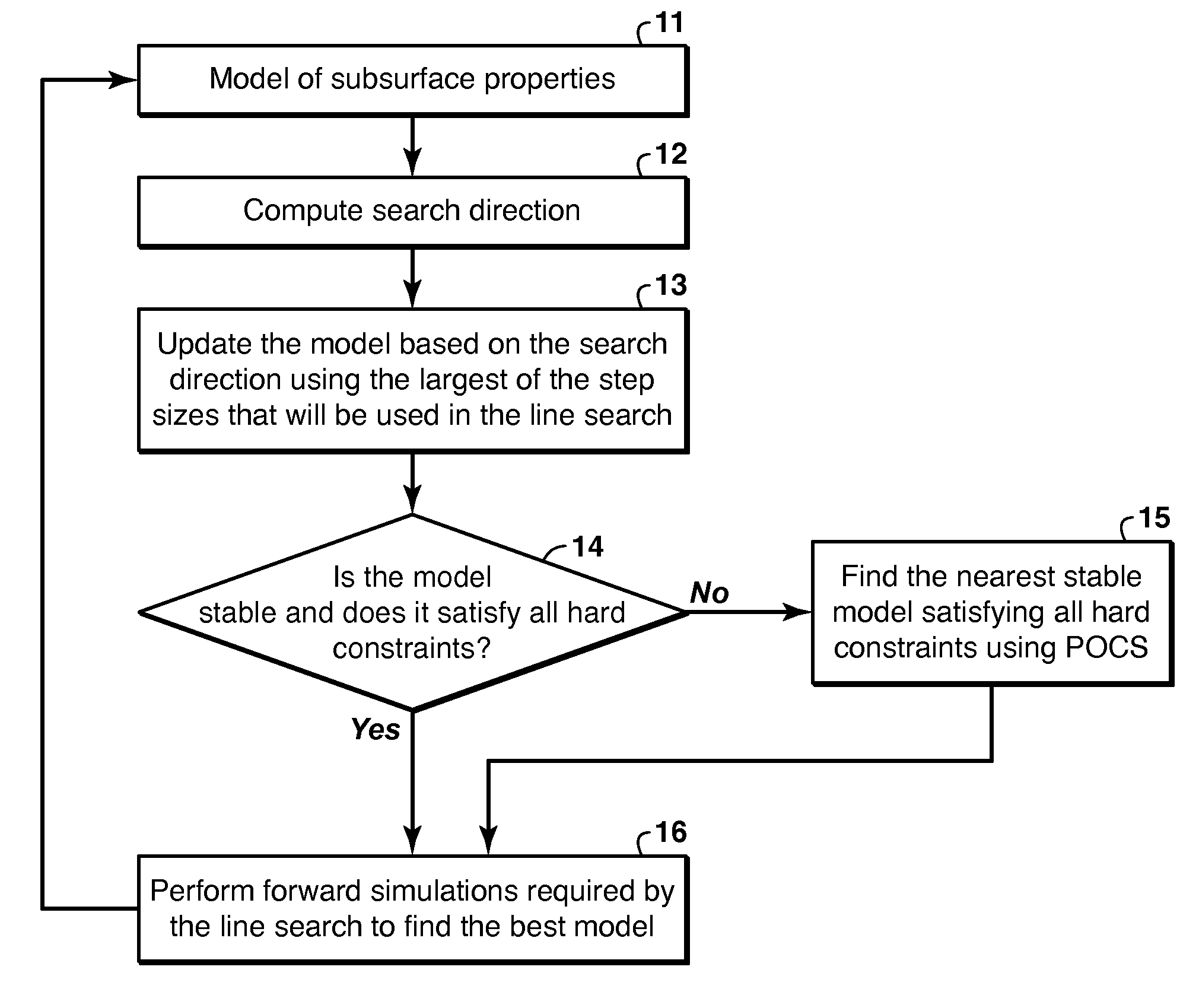
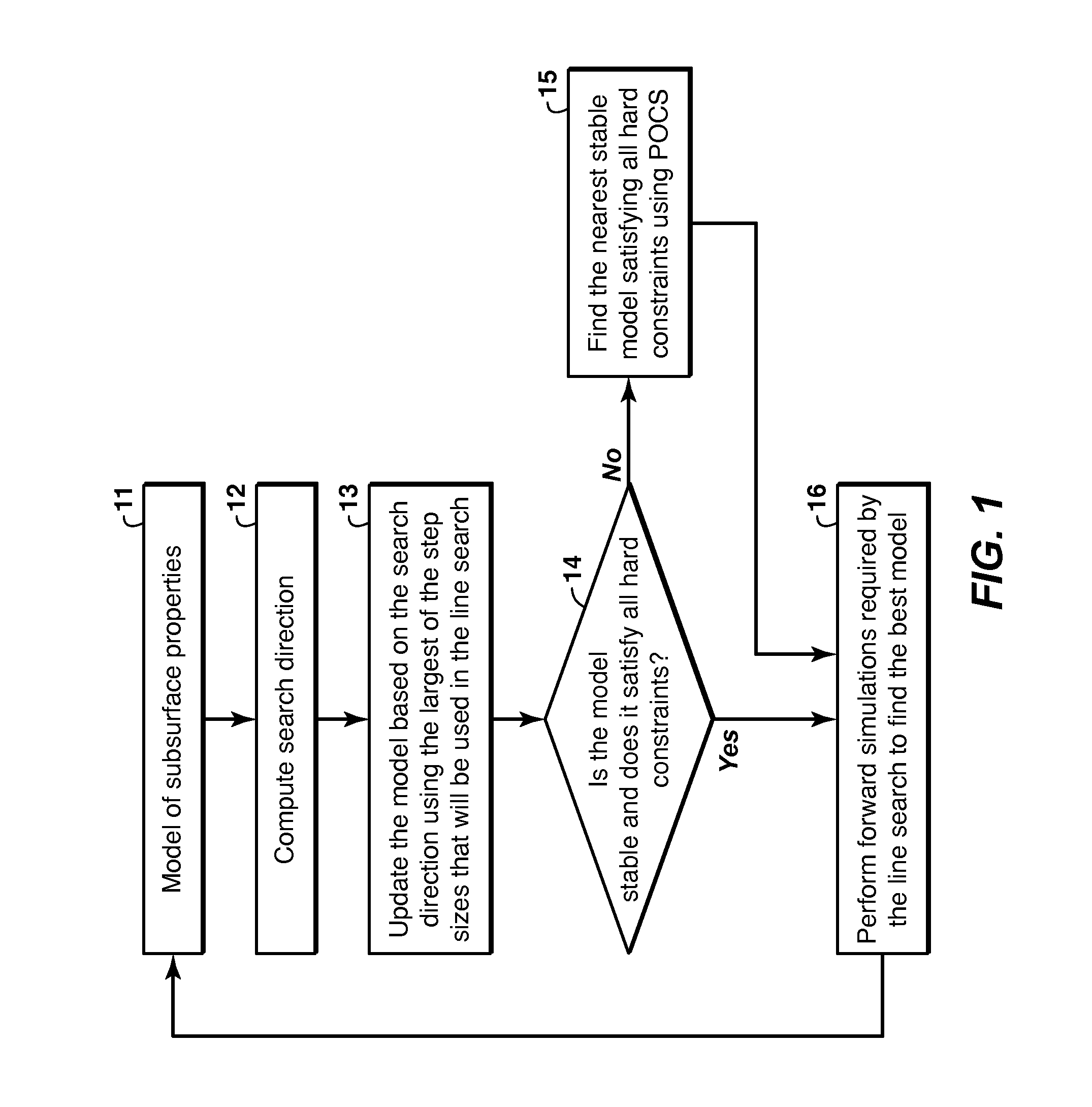
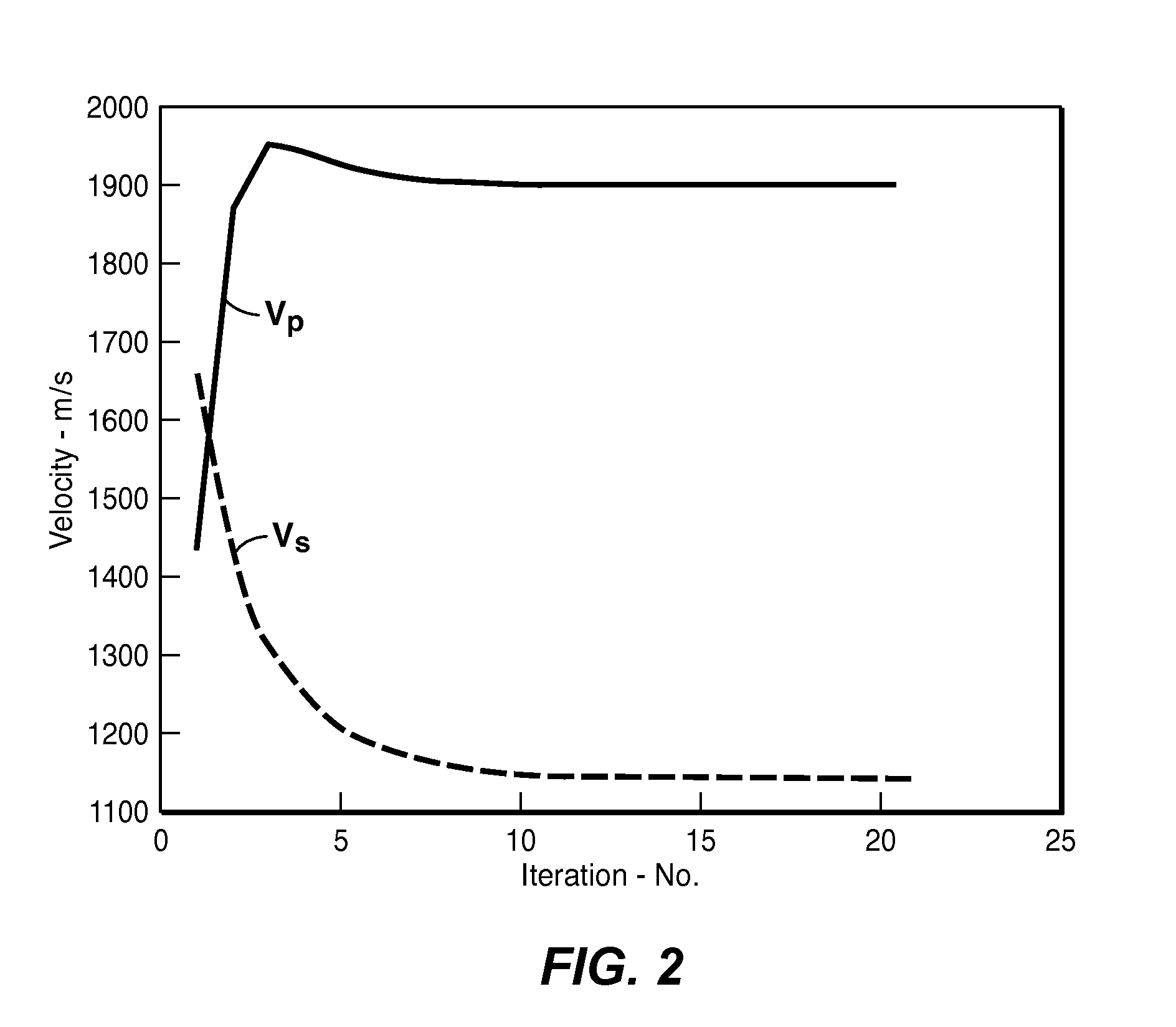
Using Projection Onto Convex Sets To Constrain Full-Wavefield Inversion
ActiveUS20130060539A1Guaranteed smooth progressComputation using non-denominational number representationSeismic signal processingProjections onto convex setsIteration loop
Method for stabilizing the updated model (13) in iterative seismic data inversion so that the model-simulated data for the next iteration does not “blow up.” A Projection Onto Convex Sets (“POCS”) operator is defined that converts the matrix corresponding to the model to a positive semi-definite matrix. The stability projection operator may be looped with physical constraint projection operators until the model converges (15). The resulting stable and constrained model is then used to simulate seismic data in the next cycle of the outer iteration loop (16).
Owner:EXXONMOBIL UPSTREAM RES CO
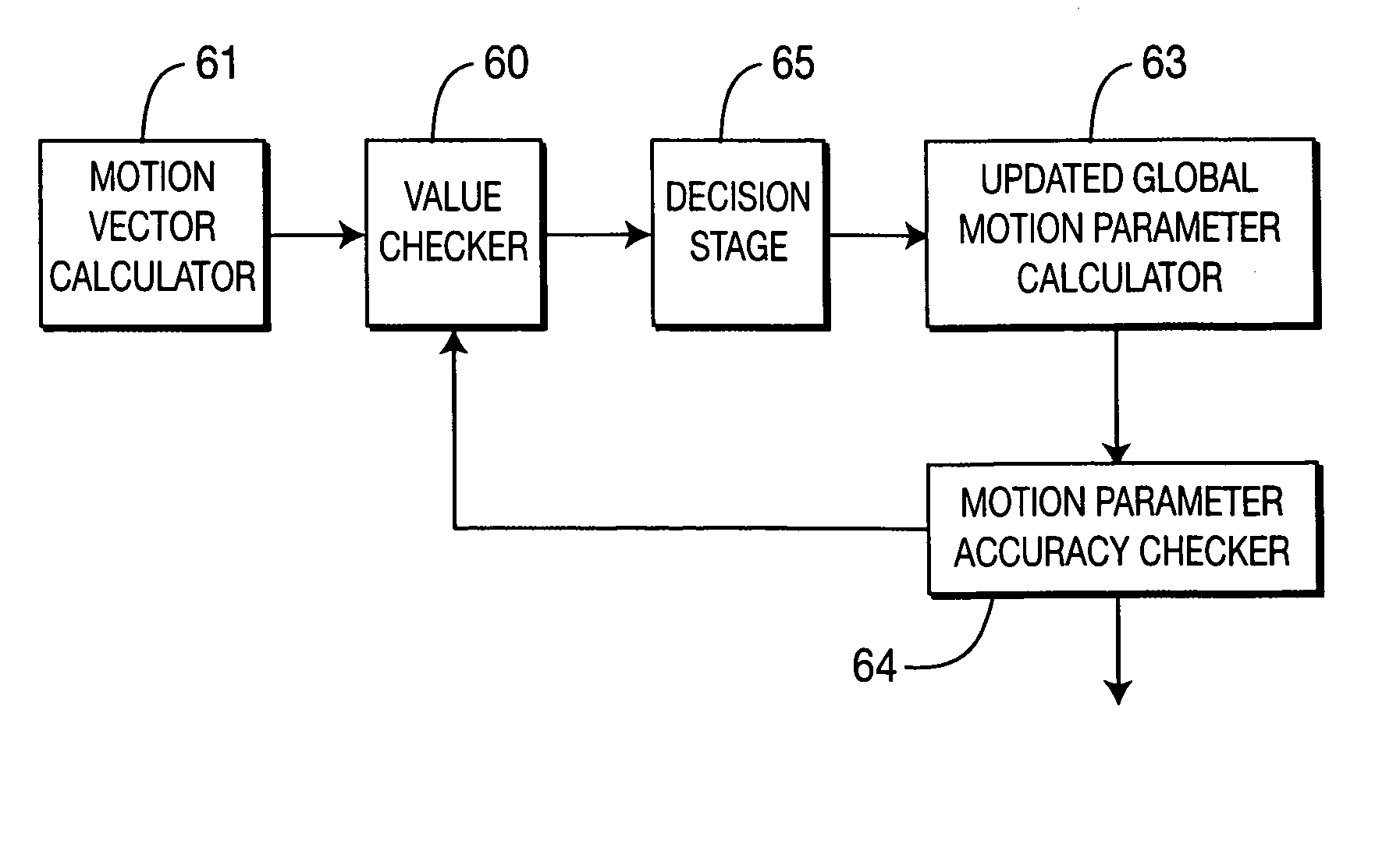
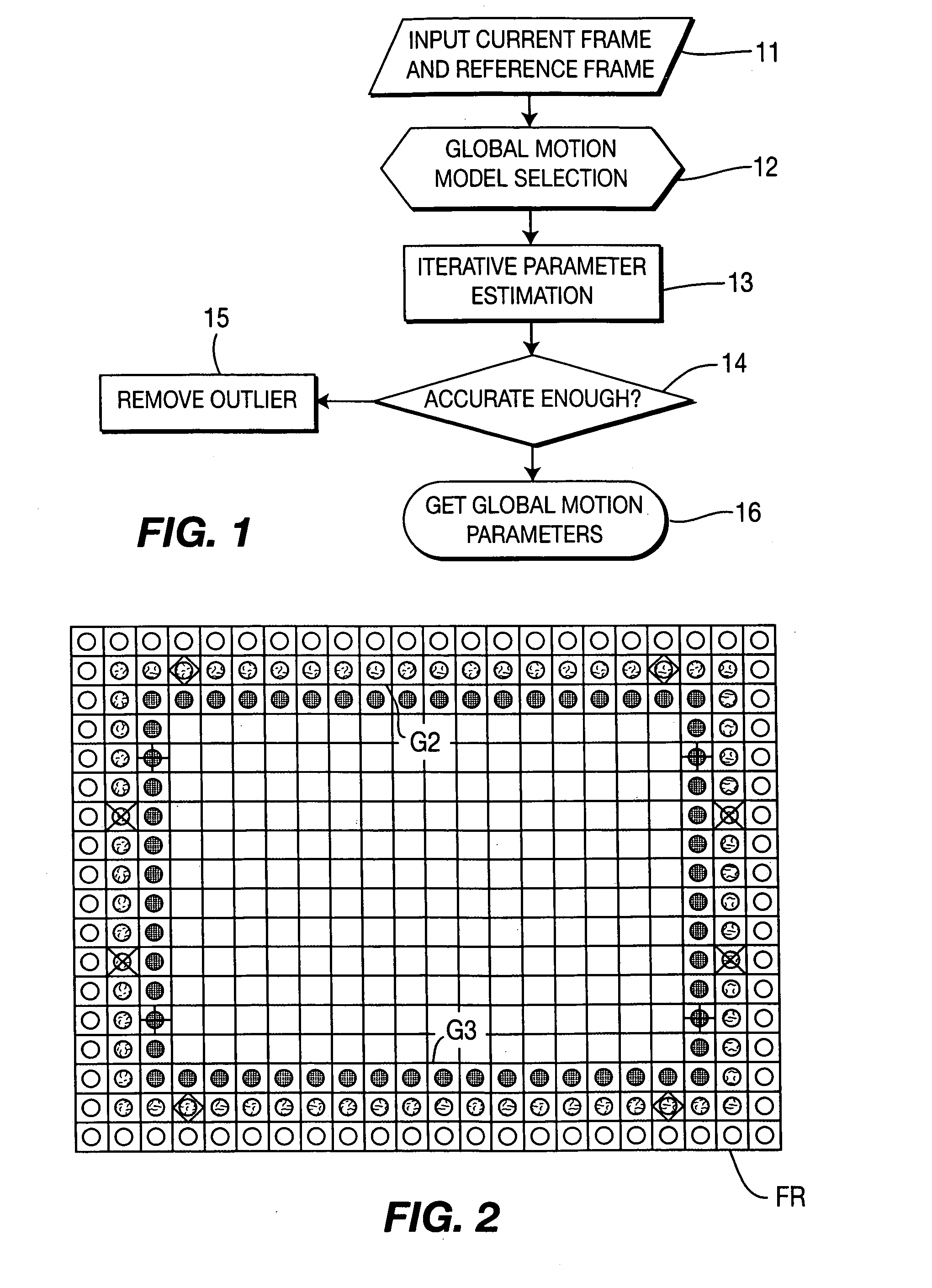
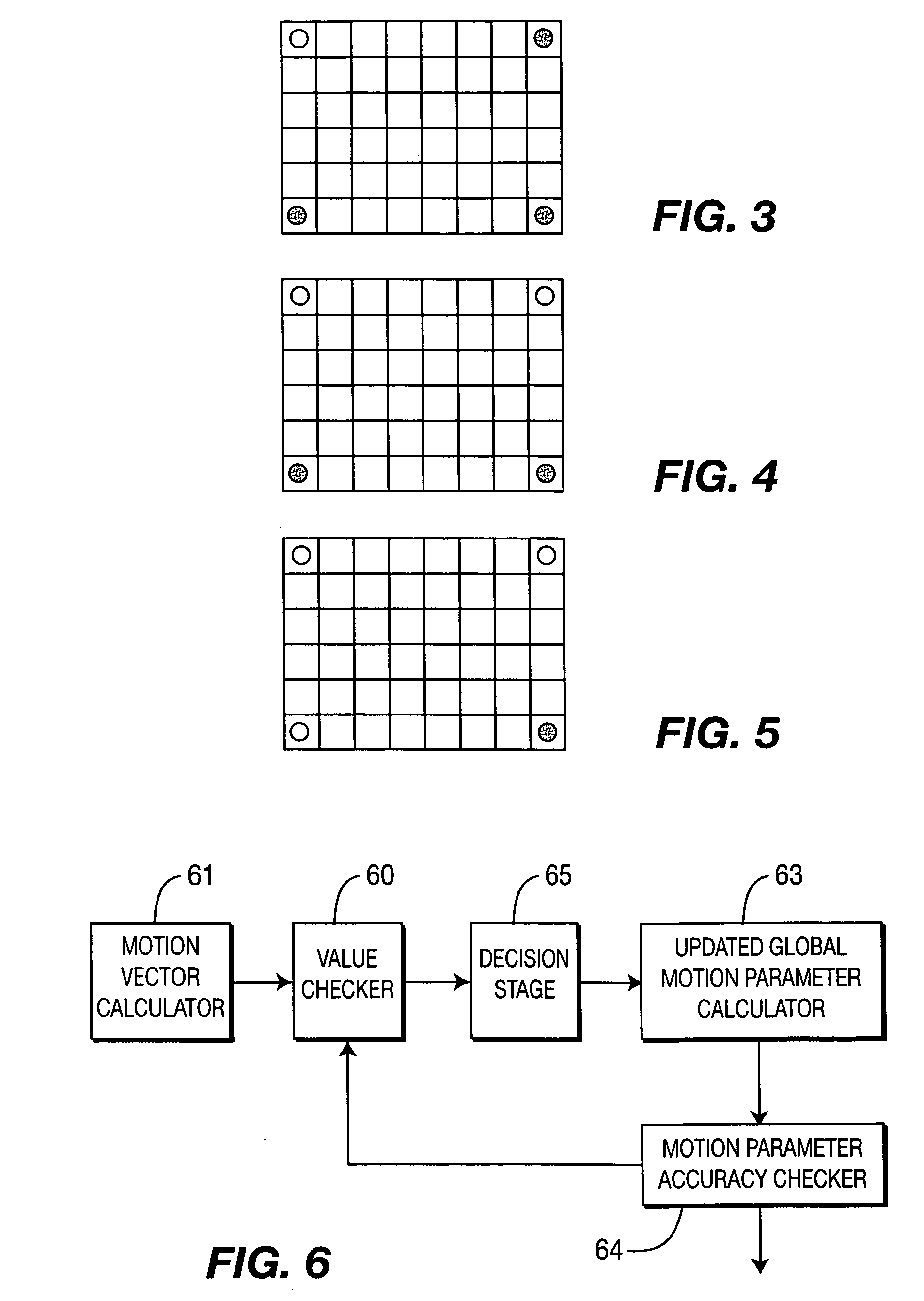
Method and apparatus for calculating interatively for a picture or a picture sequence a set of global motion parameters from motion vectors assigned to blocks into which each picture is divided
InactiveUS20070041445A1Accurate global motion parameterLow-complexity processingColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionMotion vectorMotion parameter
Global motion estimation techniques play an important role in advanced video coding. Global motion estimation is useful for increasing the coding efficiency. However, it is of high complexity due to using a multiple parameters model and an iterative processing. The invention is based on a four-parameter linear global motion estimation model. From particular block motion vectors of a frame a set of global motion parameters is calculated in an iterative process. In each iteration loop, the motion vector outliers in symmetrical motion vector blocks are processed according to a given set of rules in order to keep the symmetrical structure during the iterative process.
Owner:THOMSON LICENSING SA
Method for determining the pose of a camera with respect to at least one real object
A method for determining the pose of a camera with respect to at least one real object, the method comprises the following steps: operating the camera (1) for capturing a 2-dimensional (or 3-dimensional) image (4) including at least a part of the real object (3), providing a transformation matrix (T) which includes information regarding a correspondence between 3-dimensional points (Pi*) associated with the real object (3) and corresponding 2-dimensional points (or 3-dimensional points) (p,) of the real object (5) as included in the 2-dimensional (or 3-dimensional) image (4), and determining an initial estimate of the transformation matrix (Tl) as an initial basis for an iterative minimization process used for iteratively refining the transformation matrix, determining a Jacobian matrix (J) which includes information regarding the initial estimate of the transformation matrix (Tl) and reference values of 3-dimensional points (Pi*) associated with the real object (3). Further, in the iterative minimization process, in each one of multiple iteration loops determining a respective updated version of the transformation matrix (T) based on a respective previous version of the transformation matrix (T) and based on the Jacobian matrix (J), wherein the Jacobian matrix is not updated during the iterative minimization process, and determining the pose of the camera (1) with respect to the real object (3) using the transformation matrix (T) determined at the end of the iterative minimization process. As a result, the camera pose can be calculated with rather low computational time.
Owner:APPLE INC
Business processing method, device and system
ActiveCN104267939AImprove real-time performanceReduce processing delaySpecific program execution arrangementsData streamParallel computing
The invention discloses a business processing method. A working node acquires operators in a stream-oriented computation application model dispatched by a master node, the operators in the stream-oriented computation application model and data stream directions among the operators form at least one iteration loop, iteration times corresponding to each iteration loop is configured on an outlet operator of each iteration loop, the outlet operator is the last operator in the data stream direction of each iteration loop and receives business data, and the business data are processed according to a partial processing logic carried by each operator and are outputted from the outlet operator when the fact that the iteration times of the business data reaches that of the iteration loop with each outlet operator is determined according to the partial processing logic carried of each outlet operator. By the business processing method, data processing delay can be reduced, and data processing instantaneity is improved.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
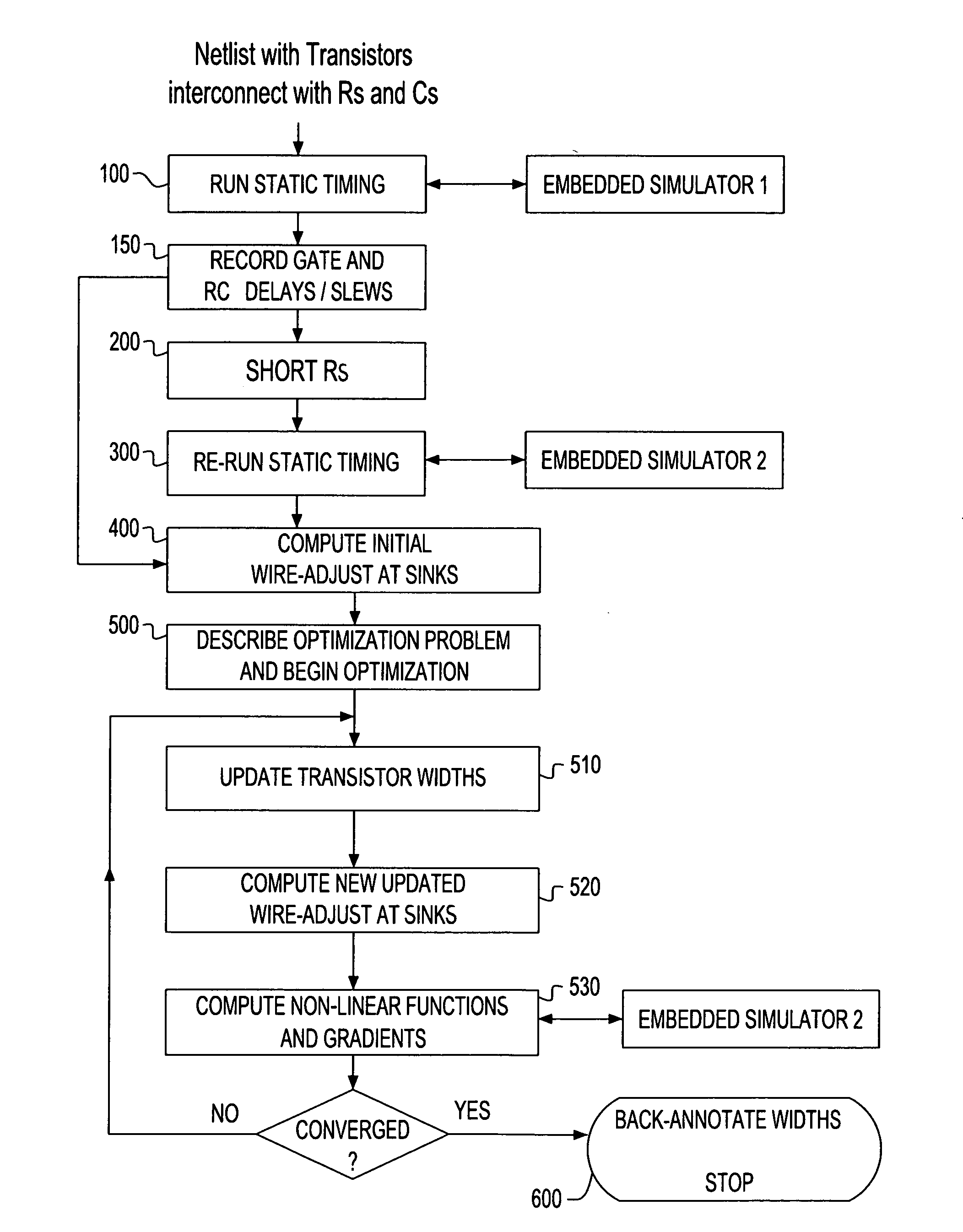
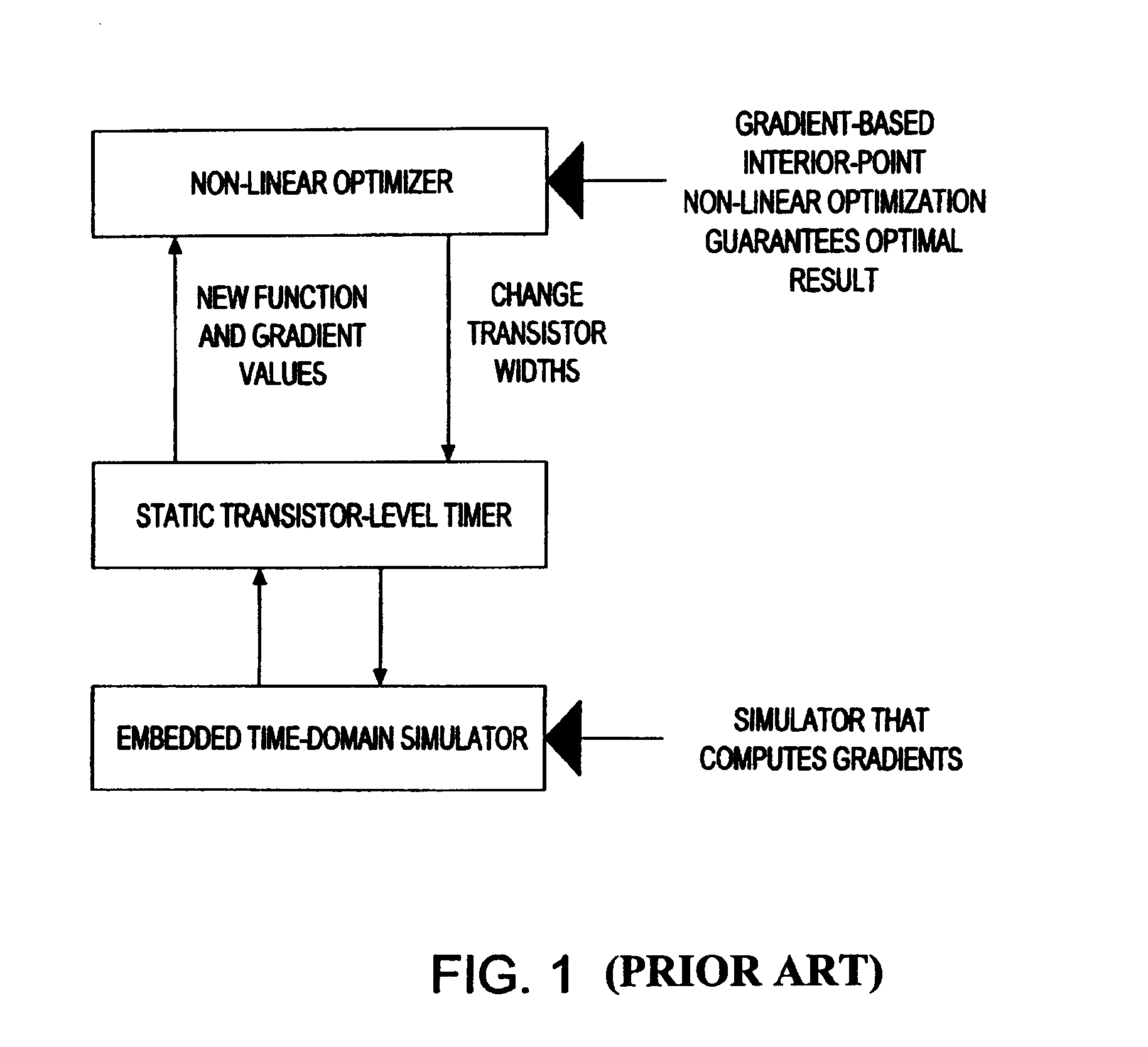
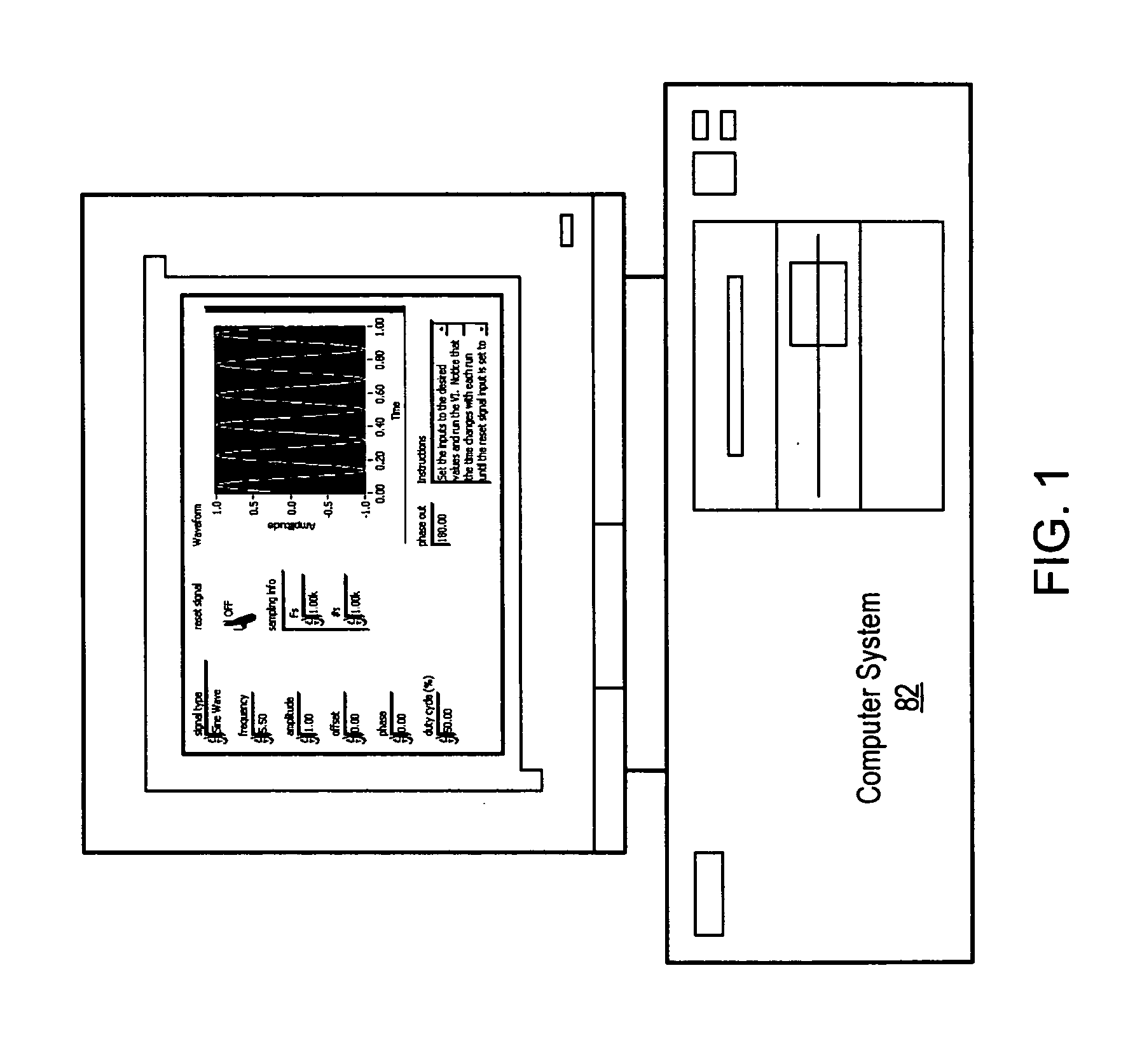
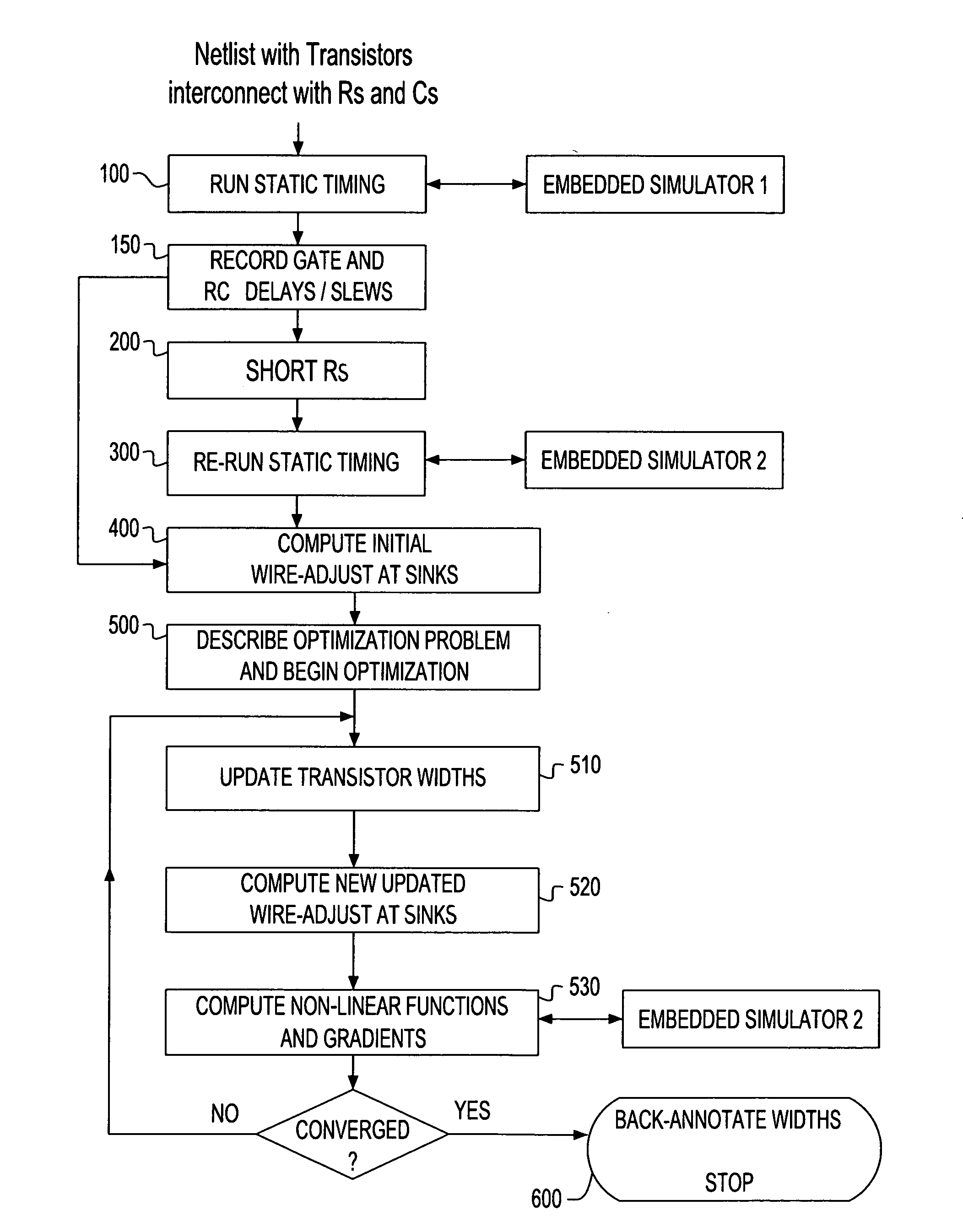
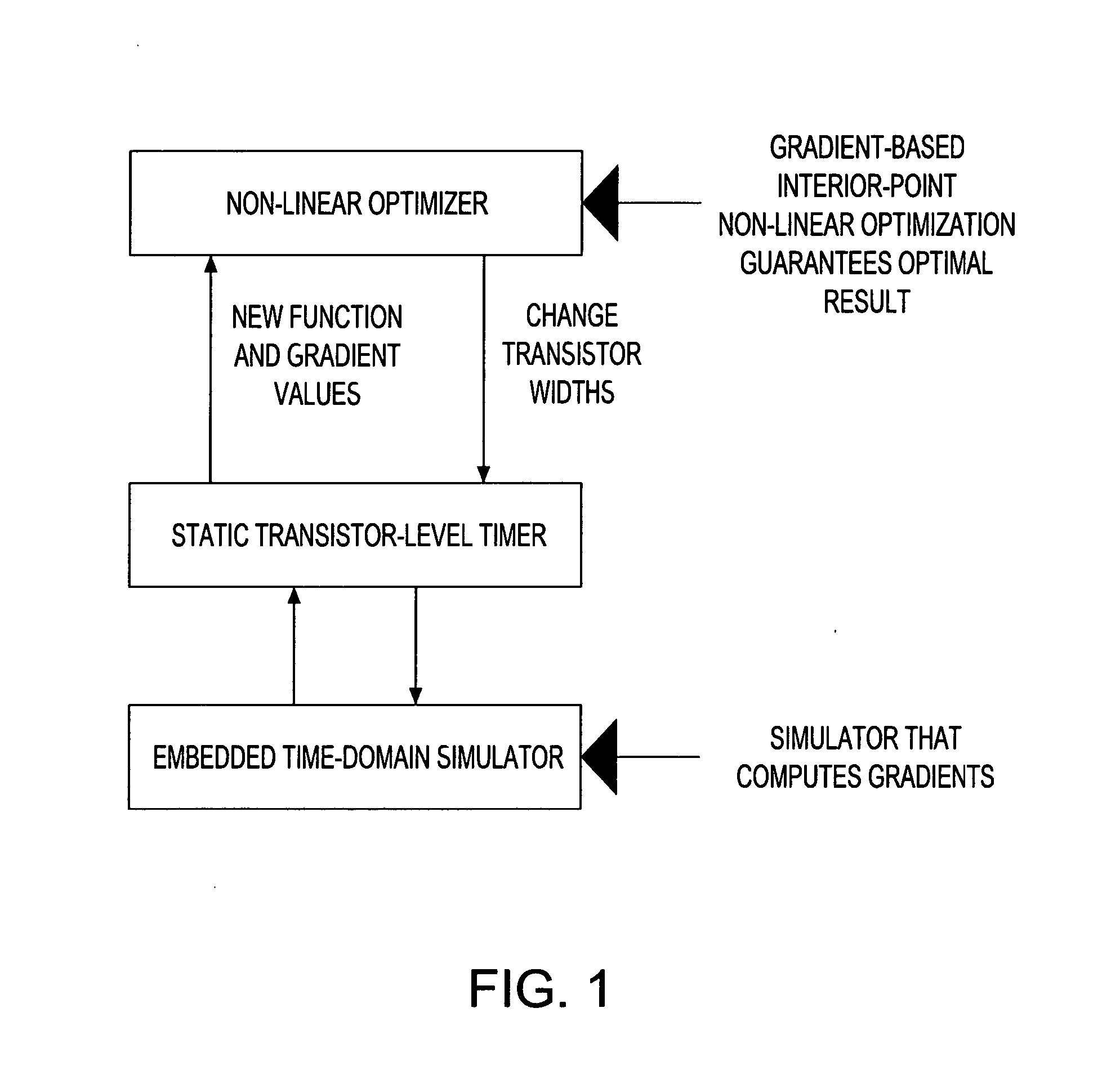
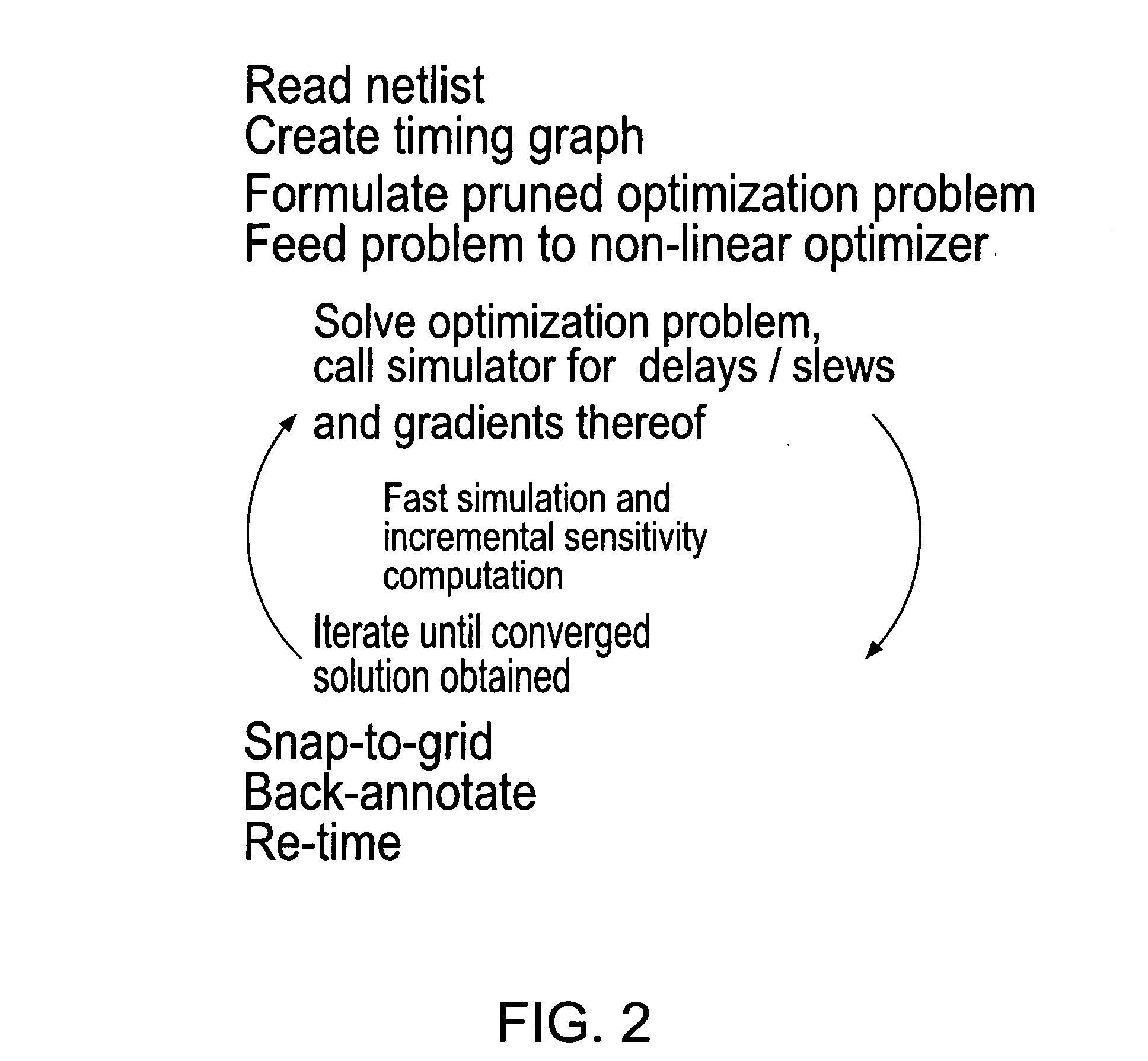
Hybrid linear wire model approach to tuning transistor widths of circuits with RC interconnect
ActiveUS7325210B2Increase widthAccount for effectCAD circuit designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationElectrical resistance and conductanceHybrid approach
A hybrid linear wire model for tuning the transistor widths of circuits linked by RC interconnects is described. The method uses two embedded simulators during the tuning process on netlists that contain resistors (Rs). A Timing oriented simulator is used only for timing purposes on the original netlist that includes all the Rs. A Gradient oriented simulator is then run only on the modified netlist with all Rs shorted and within the iterative loop of the tuner to compute gradients. The present hybrid method achieves a significant improvement in computational speed. The Timing oriented simulator is fast and accurate for only timing netlists with Rs, but cannot compute gradients efficiently. The Gradient oriented simulator computes gradients efficiently but cannot do so in the presence of Rs. To prevent “de-tuning” that typically occurs when all Rs are shorted, ‘wire-adjusts’ are provided that make the initial timing results using the Gradient oriented simulator on the shorted netlist match the timing results using Timing oriented simulator on the original netlist. This permits the optimizer sense initially the correct set of critical timing paths, and more significantly, it permits the wire-adjusts keep track of the changing transistor widths to guide the optimizer during the iterations until convergence is achieved.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES U S INC
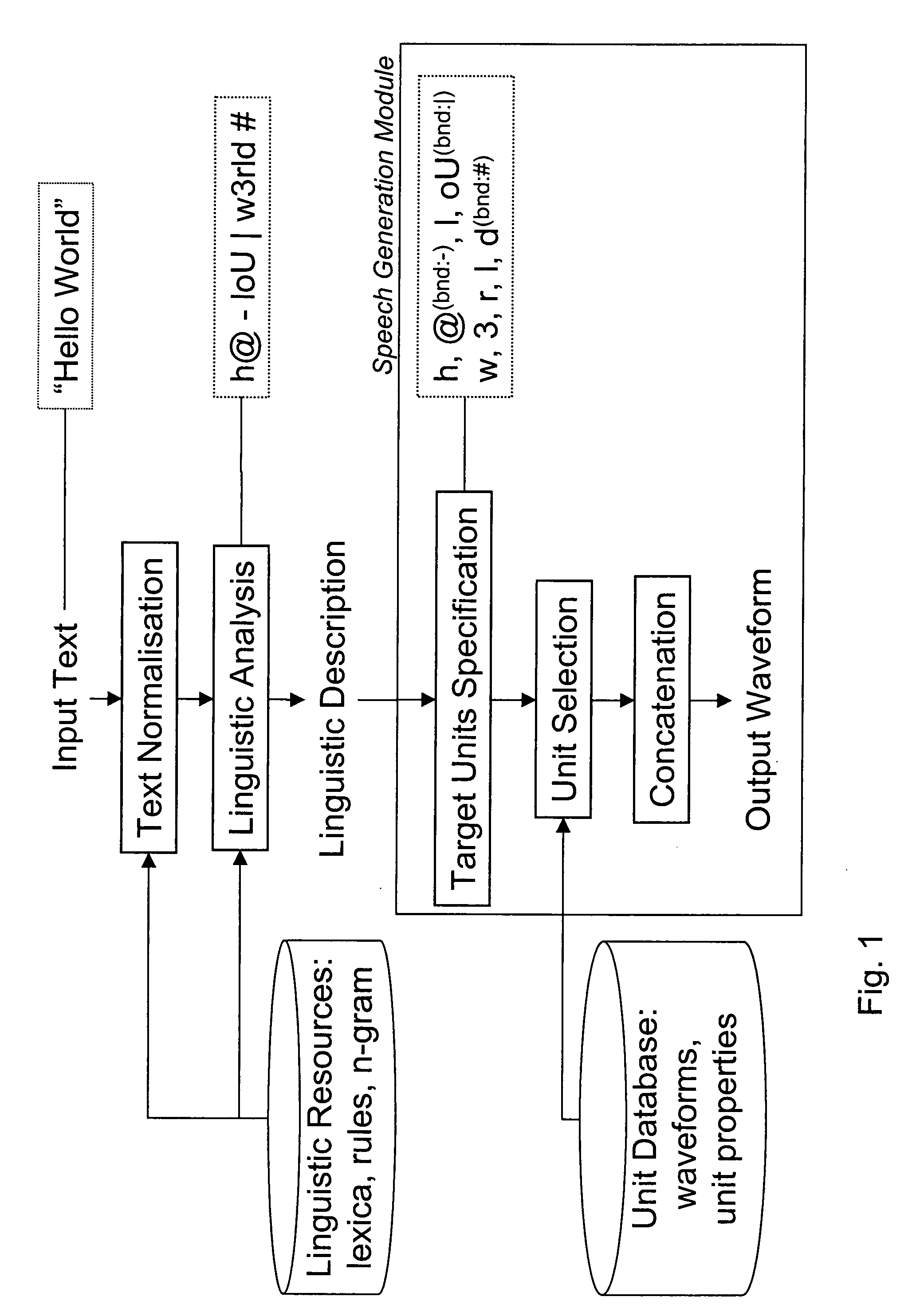
Text to speech synthesis
An input linguistic description is converted into a speech waveform by deriving at least one target unit sequence corresponding to the linguistic description, selecting from a waveform unit database for the target unit sequences a plurality of alternative unit sequences approximating the target unit sequences, concatenating the alternative unit sequences to alternative speech waveforms and presenting the alternative speech waveforms to an operating person and enabling the choice of one of the presented alternative speech waveforms. There are no iterative cycles of manual modification and automatic selection, which enables a fast way of working. The operator does not need knowledge of units, targets, and costs, but chooses from a set of given alternatives. The fine-tuning of TTS prompts therefore becomes accessible to non-experts.
Owner:CERENCE OPERATING CO
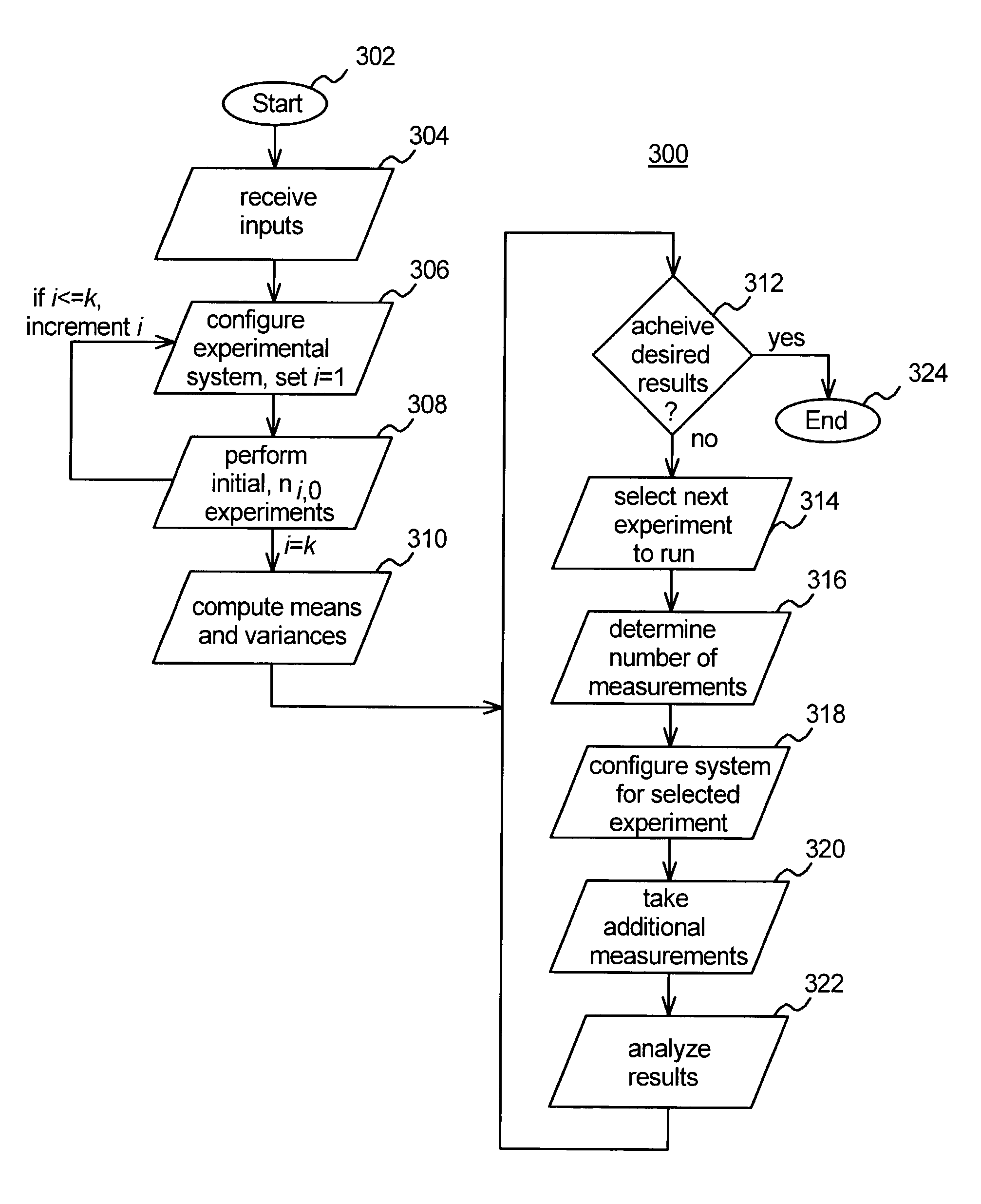
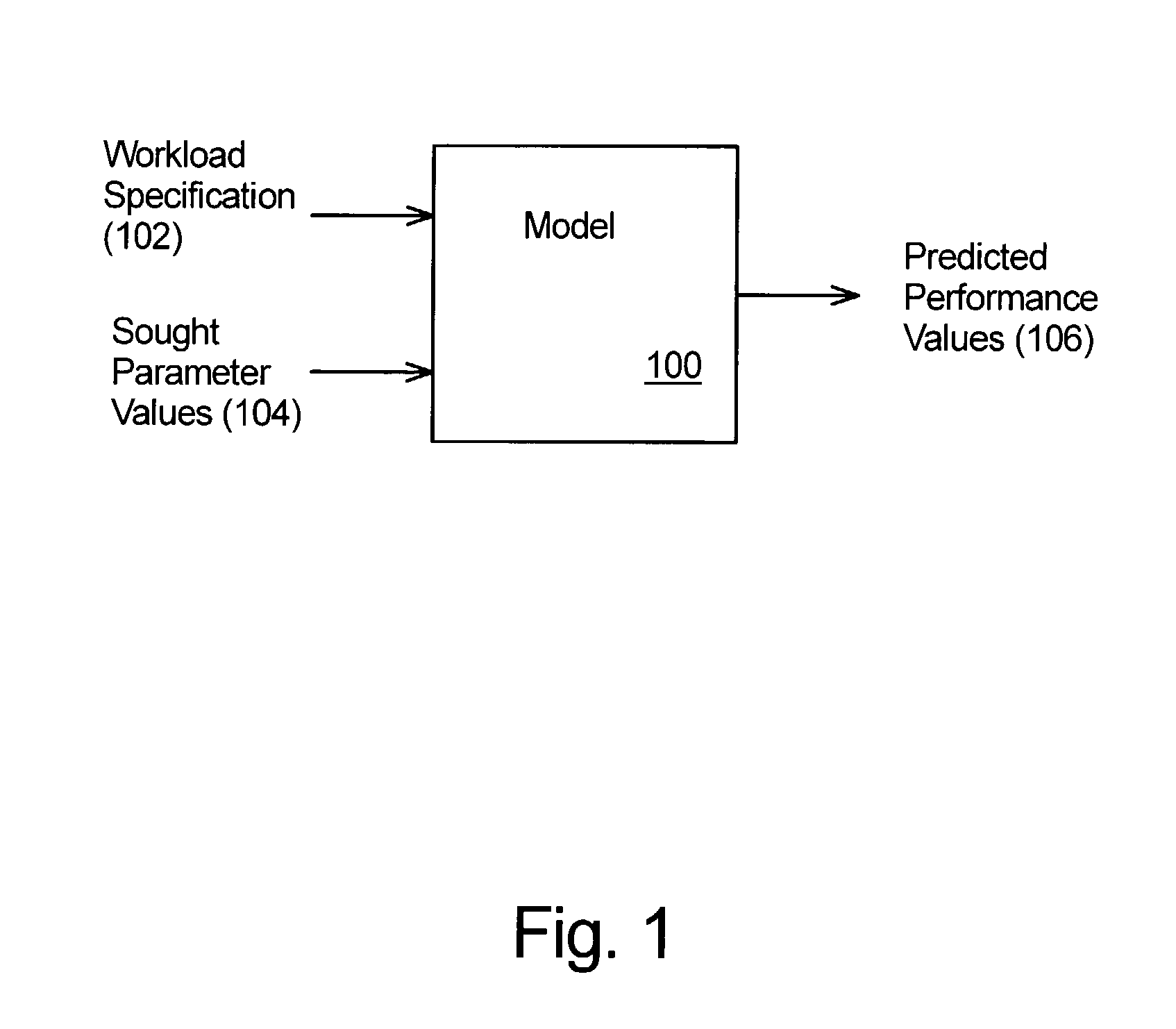
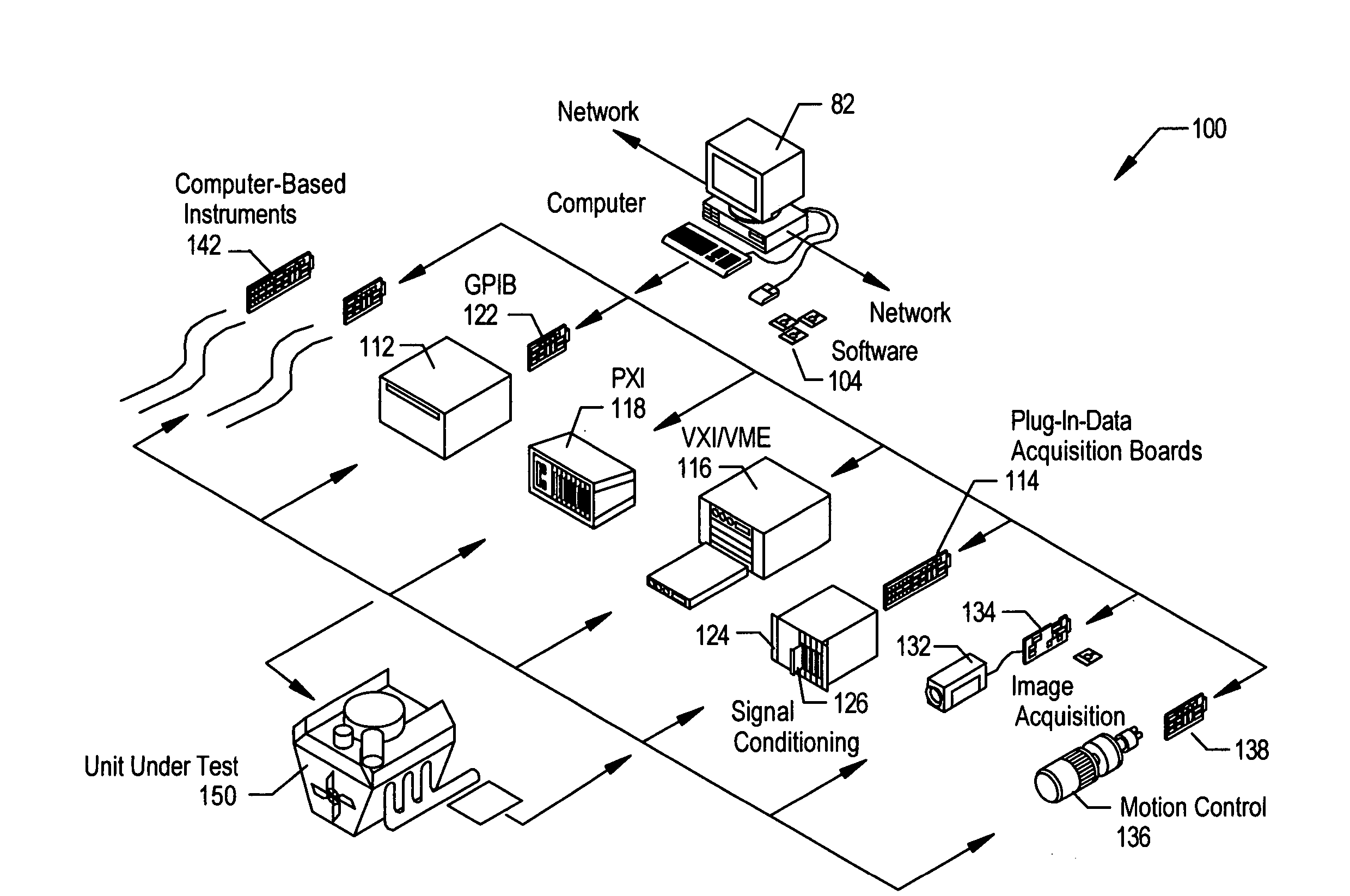
Technique for programmatically obtaining experimental measurements for model construction
InactiveUS7505886B1Simulator controlAnalogue computers for electric apparatusReal systemsIteration loop
A technique for programmatically obtaining experimental measurements for model construction. A user provides criteria for the model, such as computational algorithms which characterize behavior of the real system, specifications of experiments to be performed on the real system for collecting experimental data from the real system, an identification of sought parameters which are to be derived from results of the experiments and desired tolerance constraints on the sought parameters. From experimental data collected from the real system and from the provided criteria, the inventive method and apparatus programmatically determines in an iterative loop which additional experiments are to be performed in order to achieve the desired tolerance constraints. After one or more iterations of the loop, the values for the sought parameters are determined within the desired tolerance constraints.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Combination structure nodes for a graphical program
ActiveUS20060053408A1Visual/graphical programmingSpecific program execution arrangementsControl flowGraphics
A combination structure node is provided by a graphical programming development environment for use in a graphical program, where the combination structure node is operable to perform two or more control flow functions. For example, the combination structure node may be operable to perform two or more of: iteration, looping, conditional branching, sequencing, timed execution, event-driven execution, or other control flow functions. A user may include the combination structure node in a graphical program and associate a graphical code portion with the combination structure node. During execution of the graphical program, the combination structure node is operable to cause the associated graphical code portion to execute according to the two or more control flow functions performed by the combination structure node.
Owner:NATIONAL INSTRUMENTS
Hybrid linear wire model approach to tuning transistor widths of circuits with RC interconnect
ActiveUS20060206845A1Increase widthAccount for effectCAD circuit designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationHybrid approachEngineering
A hybrid linear wire model for tuning the transistor widths of circuits linked by RC interconnects is described. The method uses two embedded simulators during the tuning process on netlists that contain resistors (Rs). A Timing oriented simulator is used only for timing purposes on the original netlist that includes all the Rs. A Gradient oriented simulator is then run only on the modified netlist with all Rs shorted and within the iterative loop of the tuner to compute gradients. The present hybrid method achieves a significant improvement in computational speed. The Timing oriented simulator is fast and accurate for only timing netlists with Rs, but cannot compute gradients efficiently. The Gradient oriented simulator computes gradients efficiently but cannot do so in the presence of Rs. To prevent “de-tuning” that typically occurs when all Rs are shorted, ‘wire-adjusts’ are provided that make the initial timing results using the Gradient oriented simulator on the shorted netlist match the timing results using Timing oriented simulator on the original netlist. This permits the optimizer sense initially the correct set of critical timing paths, and more significantly, it permits the wire-adjusts keep track of the changing transistor widths to guide the optimizer during the iterations until convergence is achieved.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
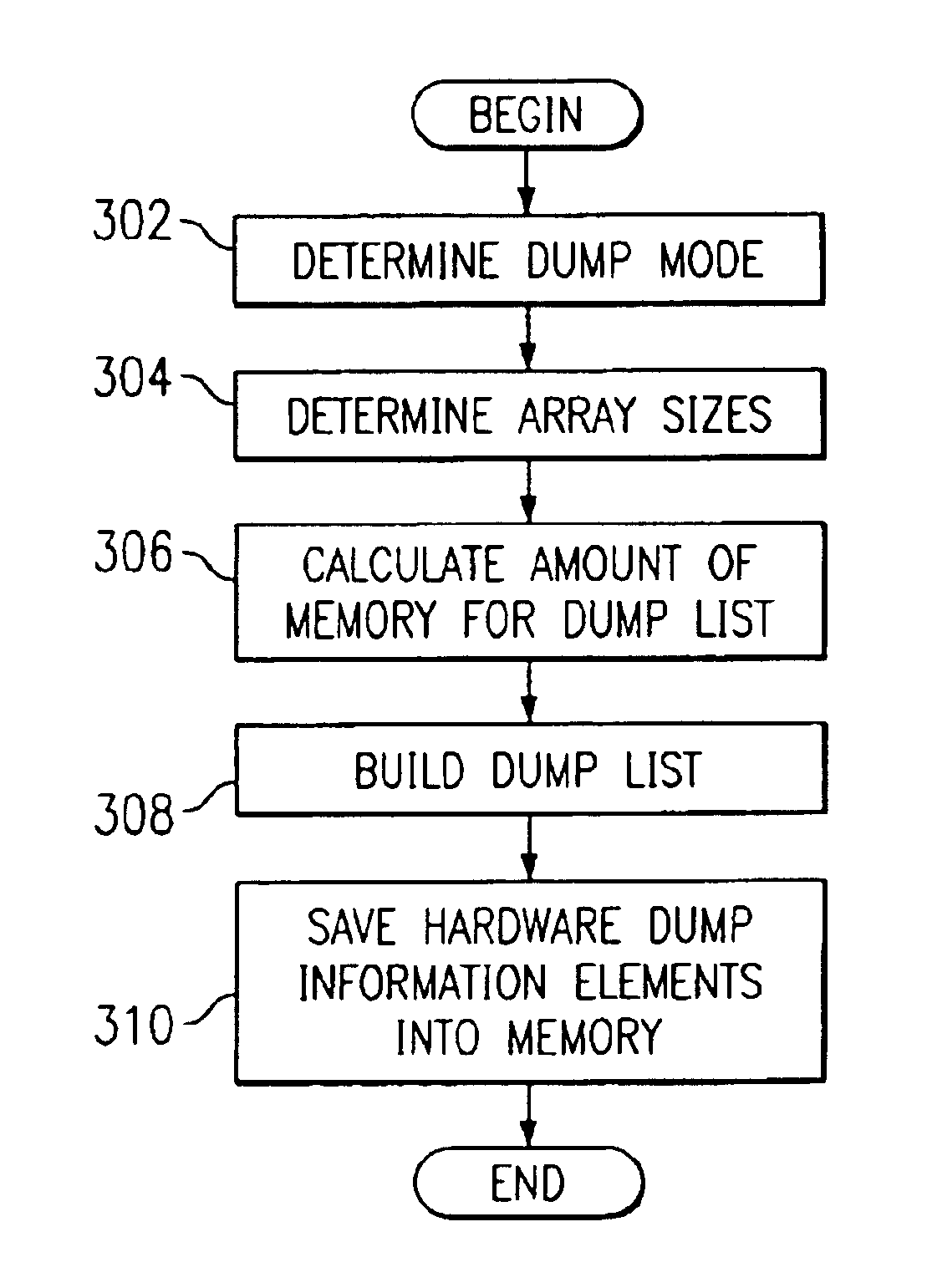
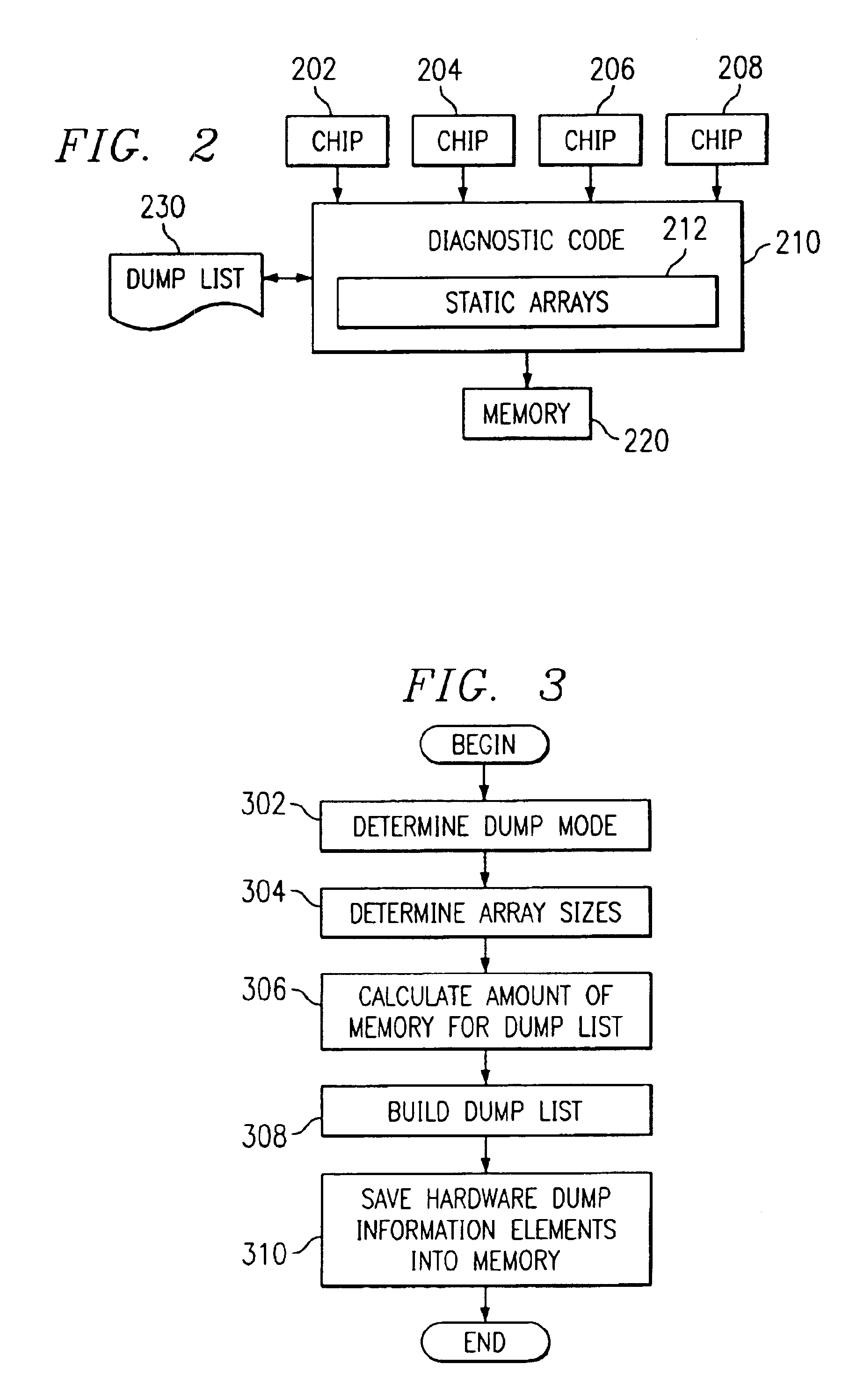
Dynamic sizing logic for dump list generation
InactiveUS6898736B2Speed up the processAccurate calculationError preventionError detection/correctionArray data structureParallel computing
An improved process for executing a dump is provided. The iteration loops are made “smart” by allowing them to determine how big the arrays are on the fly and adjust their behavior accordingly. The process uses a function to calculate the amount of memory to allocate for the dump list based on the dump mode and array sizes. Thus, if the static arrays are modified to add or delete constants or the diagnostic code is in an abbreviated dump mode, the amount of memory to be allocated will be calculated accurately.
Owner:IBM CORP
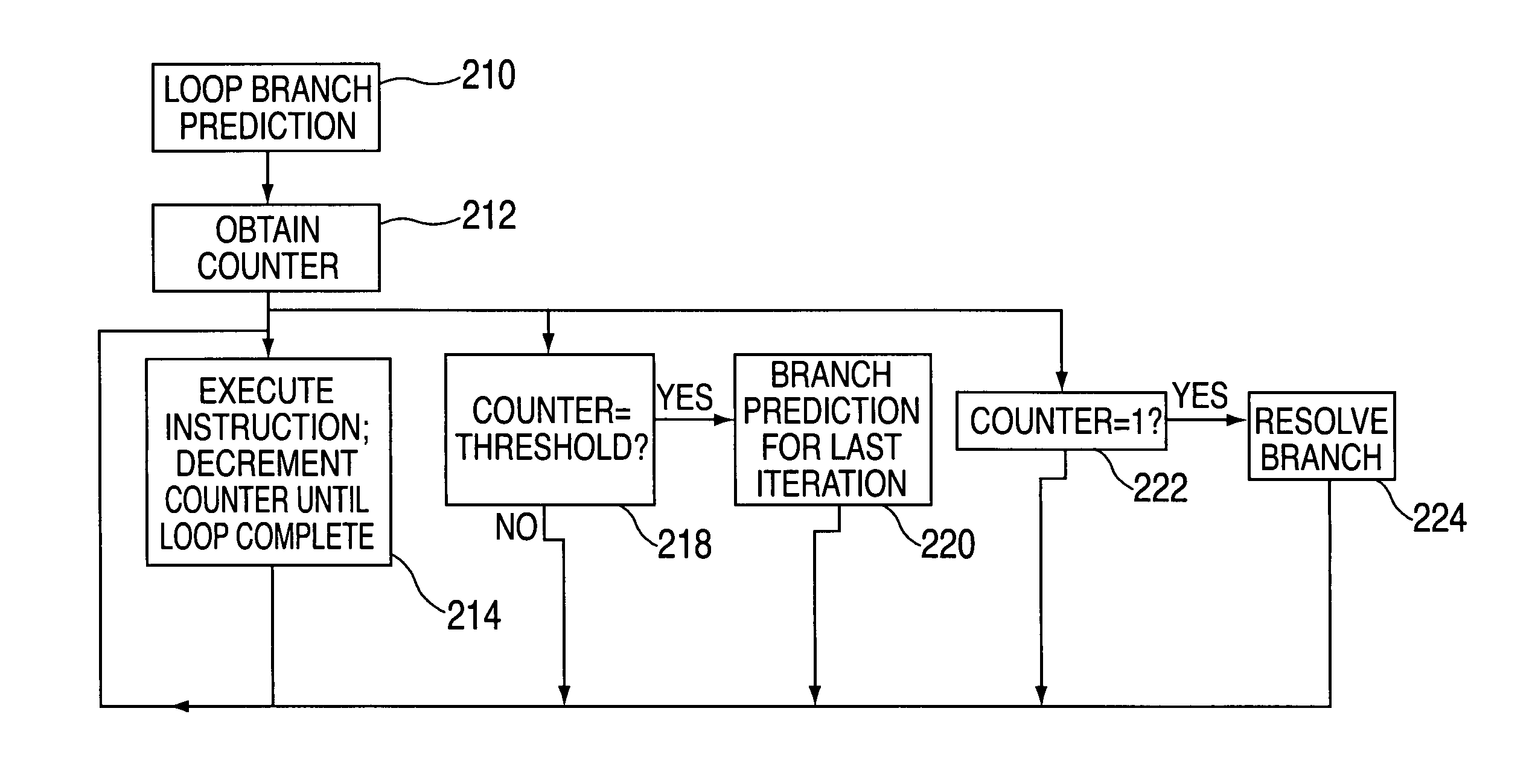
Last iteration loop branch prediction upon counter threshold and resolution upon counter one
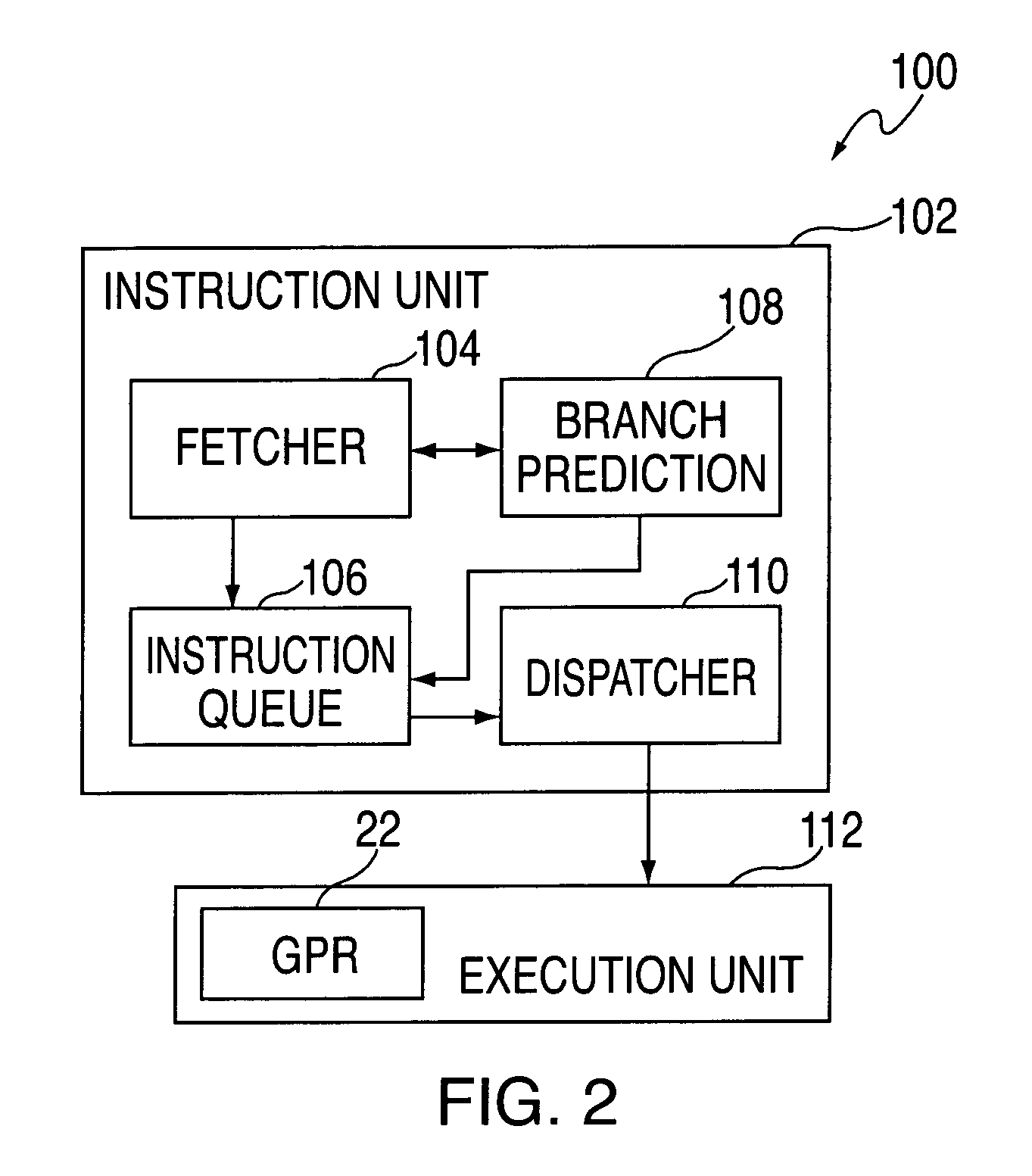
InactiveUS7010676B2Digital computer detailsNext instruction address formationInstruction unitImage resolution
An embodiment of the invention is a processor for processing loop branch instructions. The processor includes an instruction unit for fetching and decoding instructions including at least one loop branch instruction. A branch prediction unit predicts target instructions to be fetched and decoded by the instruction unit in response to the loop branch instruction. An execution unit executes instructions from the instruction unit and maintains a counter indicating an iteration of a loop. The execution unit includes detection logic for detecting when the counter equals a threshold and notifies the branch prediction unit when the counter equals the threshold.
Owner:IBM CORP
Method and computer system for determining seismic node position
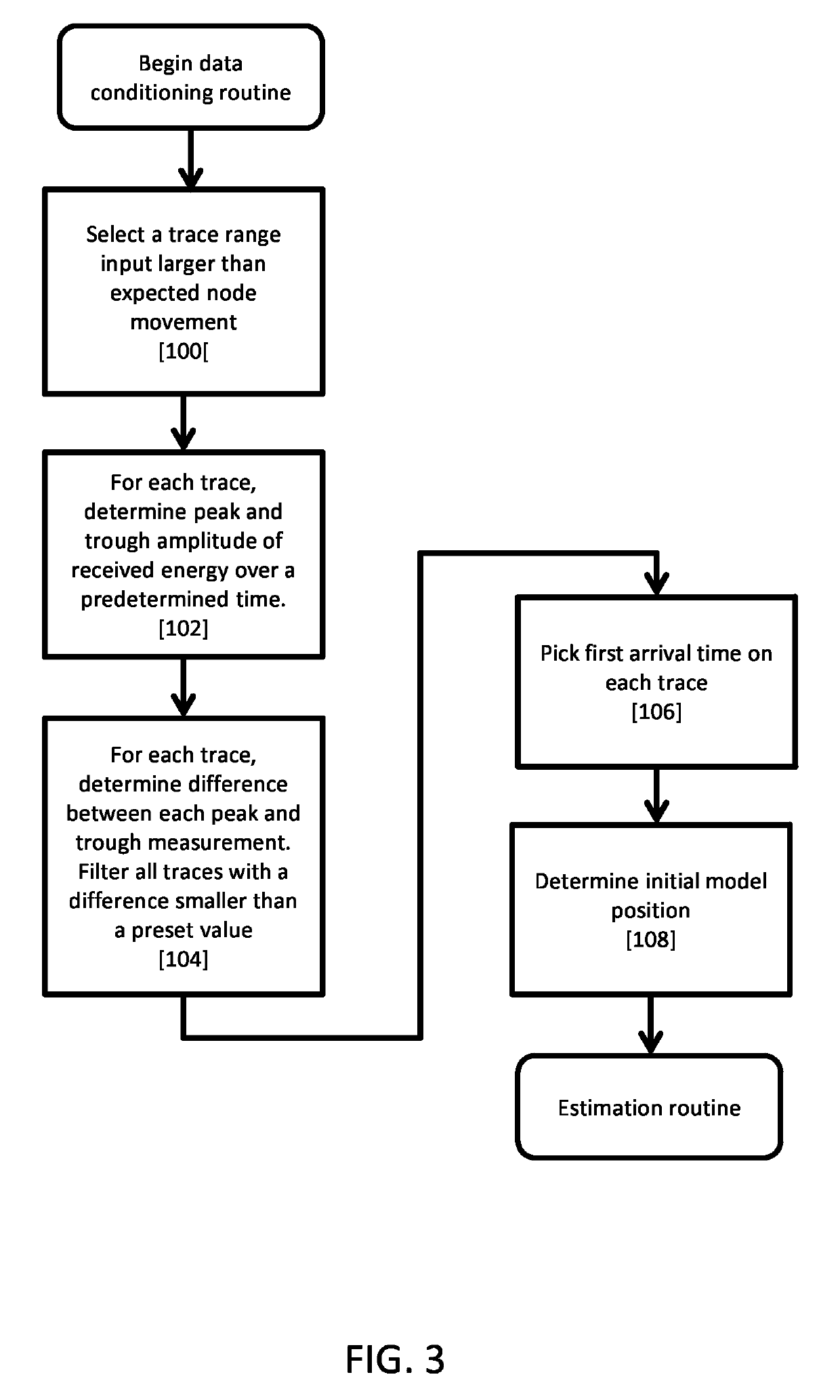
ActiveUS10379239B2Improve data qualityAccurate knowledgeSeismic signal receiversSeismic signal processingComputerized systemIteration loop
Owner:MAGSEIS FF LLC
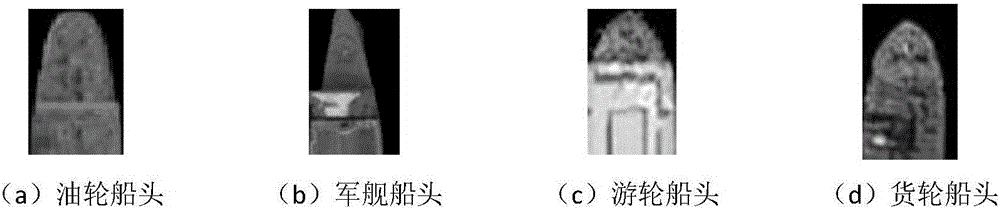
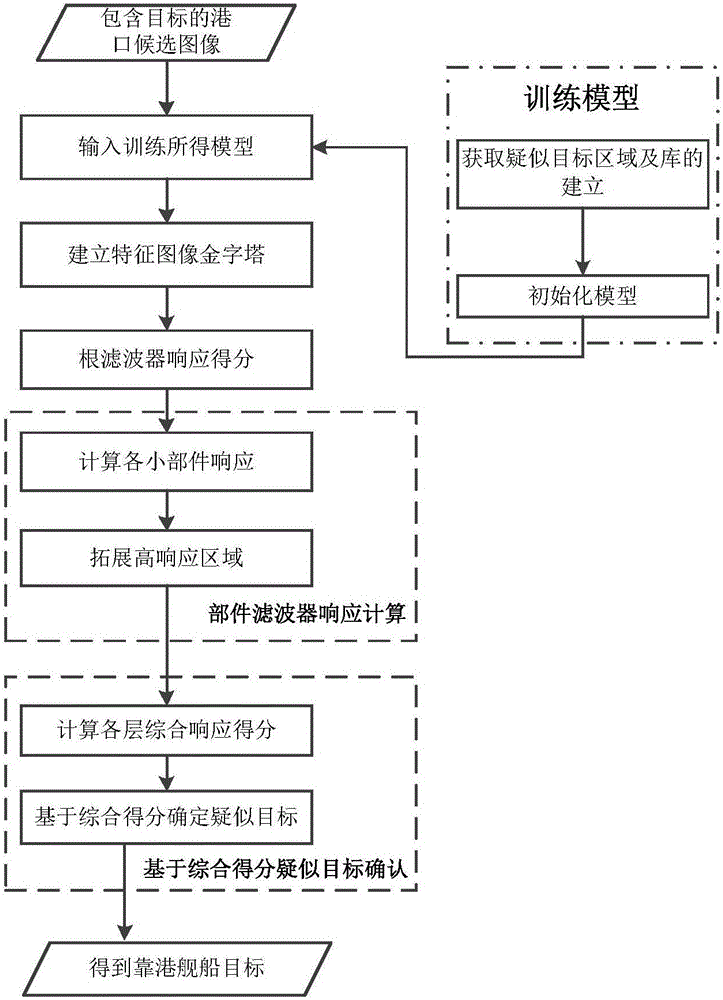
Remote sensing image anchored ship detection false alarm elimination method based on DPM algorithm
The invention provides a remote sensing image anchored ship detection false alarm elimination method based on a DPM algorithm. The effective anchored ship target false alarm elimination method is constructed for a ship target in the port in an optical remote sensing image through combination of an existing detection algorithm based on morphological property candidate areas. Firstly a ship target training database is established offline and a ship model is trained and initialized; a feature image pyramid is constructed through a HOG algorithm; then root model response scores are calculated on the images of the l-layer resolution of the feature pyramid; the feature images of twice resolution corresponding to the feature images of the l-layer are found, and part model response scores are calculated on the images and a high-score area is extended; and finally the integrated scores of all layers of the feature image pyramid are obtained according to the root model and part model scores, and the position of the ship target on the images of the candidate areas are obtained through iterative loop optimization.
Owner:NORTH CHINA UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Design techniques for analyzing integrated circuit device characteristics
InactiveUS6951002B2Reduce memory utilizationReduce processor utilizationCAD circuit designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationCapacitanceEngineering
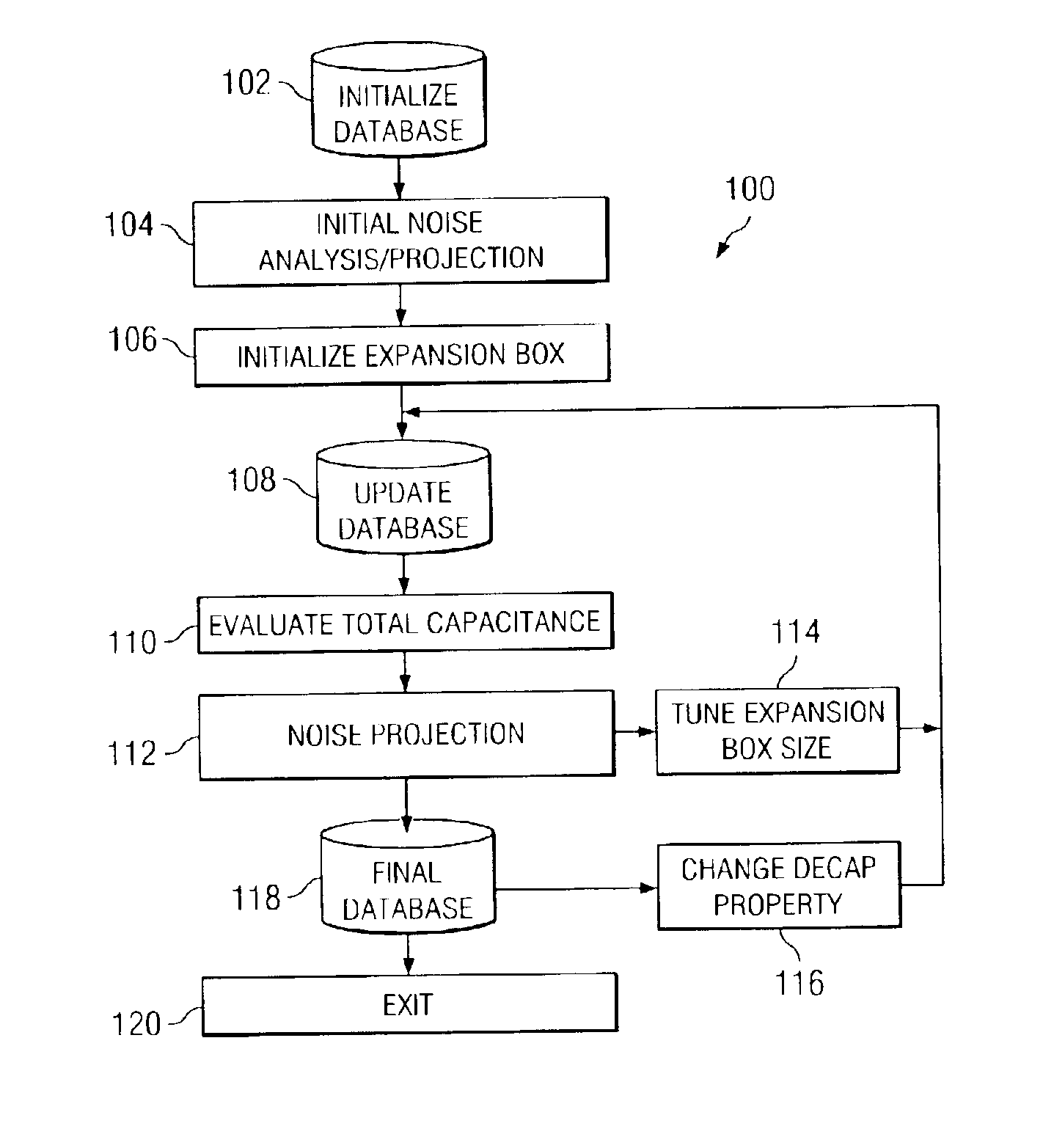
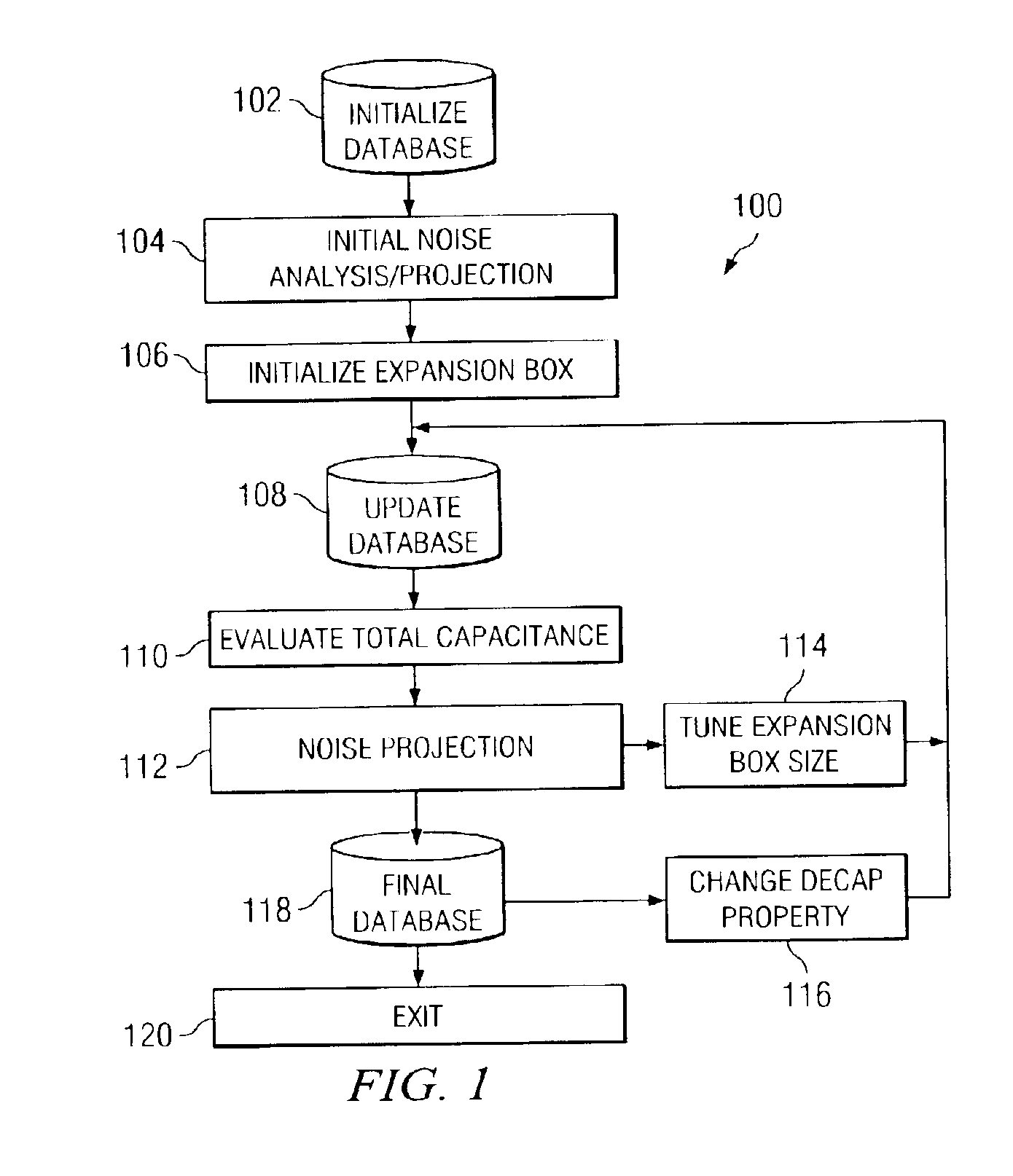
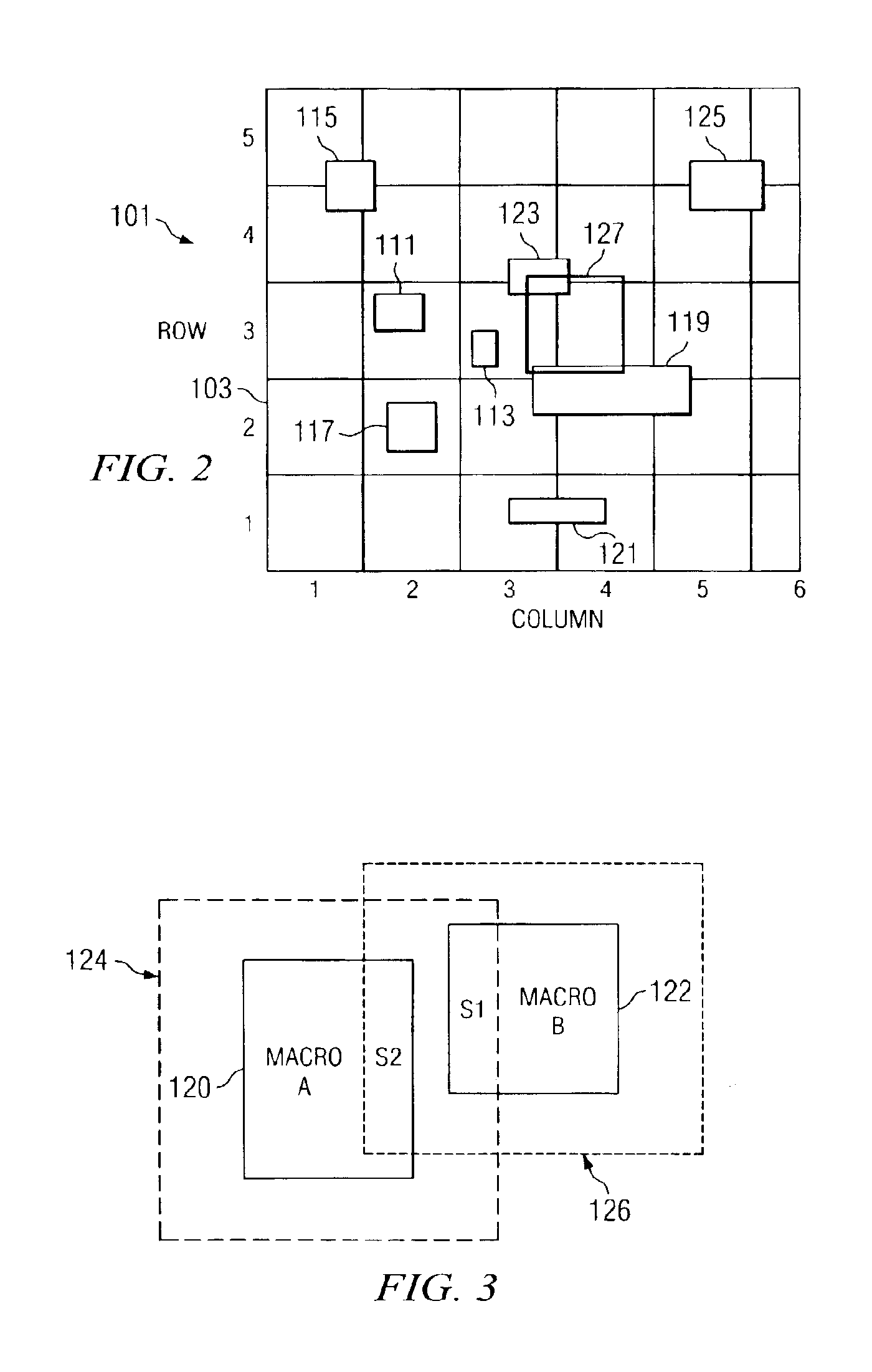
An improved method and system for integrated circuit device physical design and layout. The physical layout of the integrated circuit device is optimally stored in a database to provide improved analysis capabilities of the integrated circuit device's characteristics. The method and system evaluates local interactions between functional blocks and decoupling cells on a given floor plan of a chip using this optimized database in order to reduce memory and processor utilization. Local noise is projected by using dI / dt and capacitance estimates. Areas of highest noise concern are identified, and floor plan mitigation actions are taken by tuning the placement of neighboring decoupling cells and their properties. Upon several iterative cycles, a near optimal solution for a given floor plan of the total chip is achieved.
Owner:IBM CORP
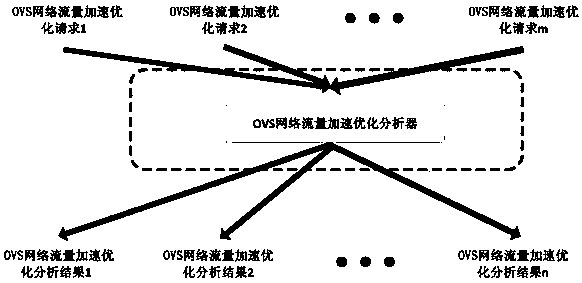
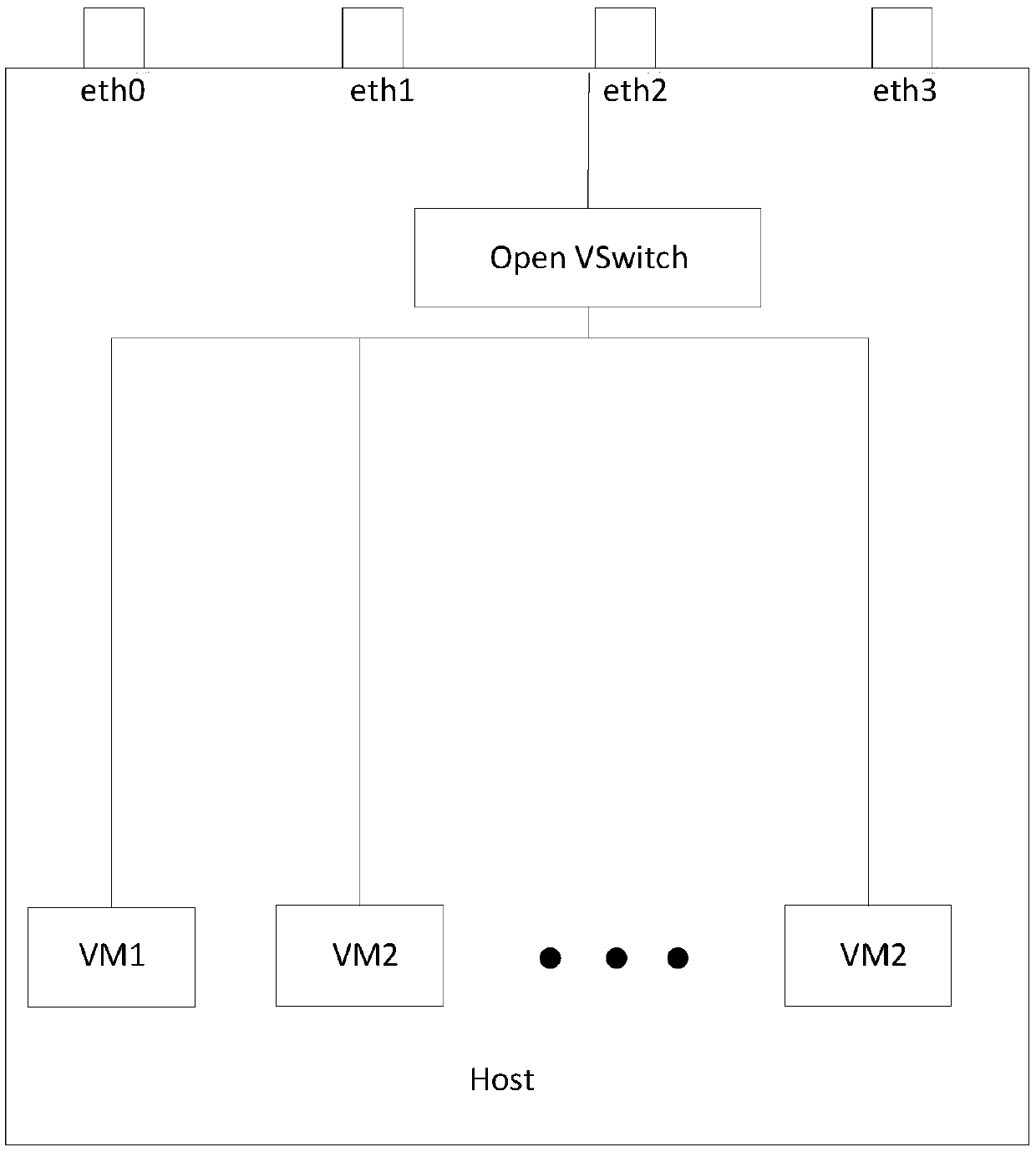
OVS network traffic accelerated optimization method and OVS network traffic accelerated optimization system
ActiveCN108023840AReduce congestionReduce data packet loss rateArtificial lifeData switching networksLoss rateIteration loop
The invention belongs to the technical field of information, and relates to an OVS network traffic accelerated optimization method and an OVS network traffic accelerated optimization system. The OVS network traffic accelerated optimization method comprises the steps of acquiring and gathering all OVS network traffic accelerated optimization request, and building an accelerated optimization model;performing accelerated optimization analysis on the OVS network traffic accelerated optimization requests, and acquiring and gathering all accelerated optimization analysis results; with the accelerated optimization analysis results as samples, performing accelerated optimization self-study to acquire optimizing vectors; determining whether an analysis result of an accelerated optimization function meets accelerated optimization analysis evaluation conditions; optimizing corresponding vectors in a module faster by using optimizing vectors in an alternate manner, iterating the above steps tillthe accelerated optimization analysis evaluation conditions are met or a maximum iteration number is reached; performing traffic forwarding according to the met accelerated optimization analysis evaluation conditions or a position at where the maximum iteration number is reached. The method and system have the advantages of light network congestion of an application system, low data loss rate, andlow consumption.
Owner:CHINA UNITED NETWORK COMM GRP CO LTD
System and method for performing over time statistics in an electronic spreadsheet environment
Owner:LINKEDIN
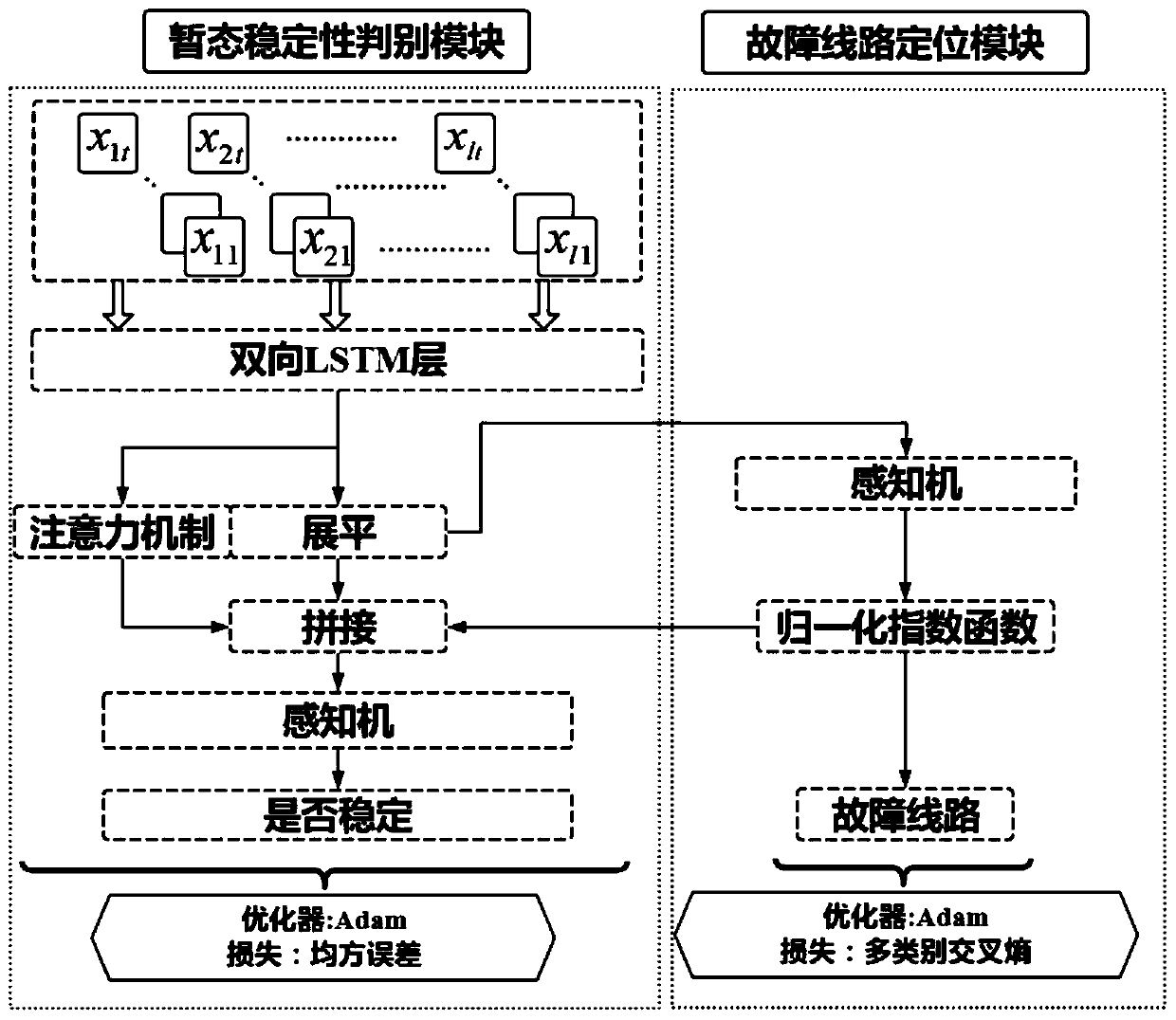
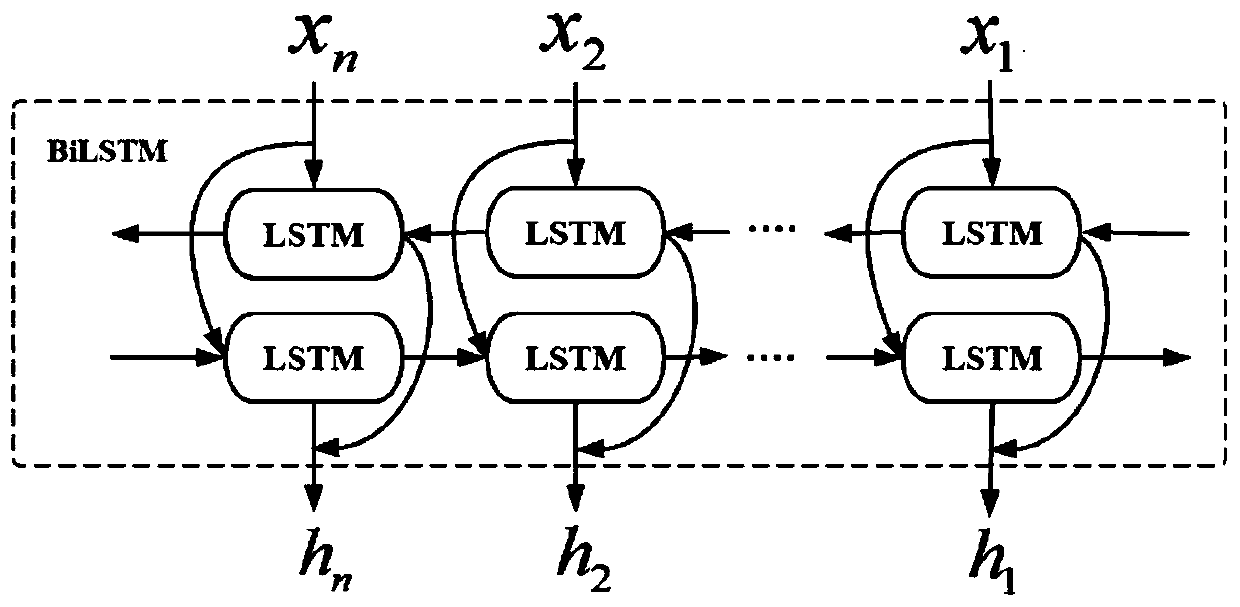
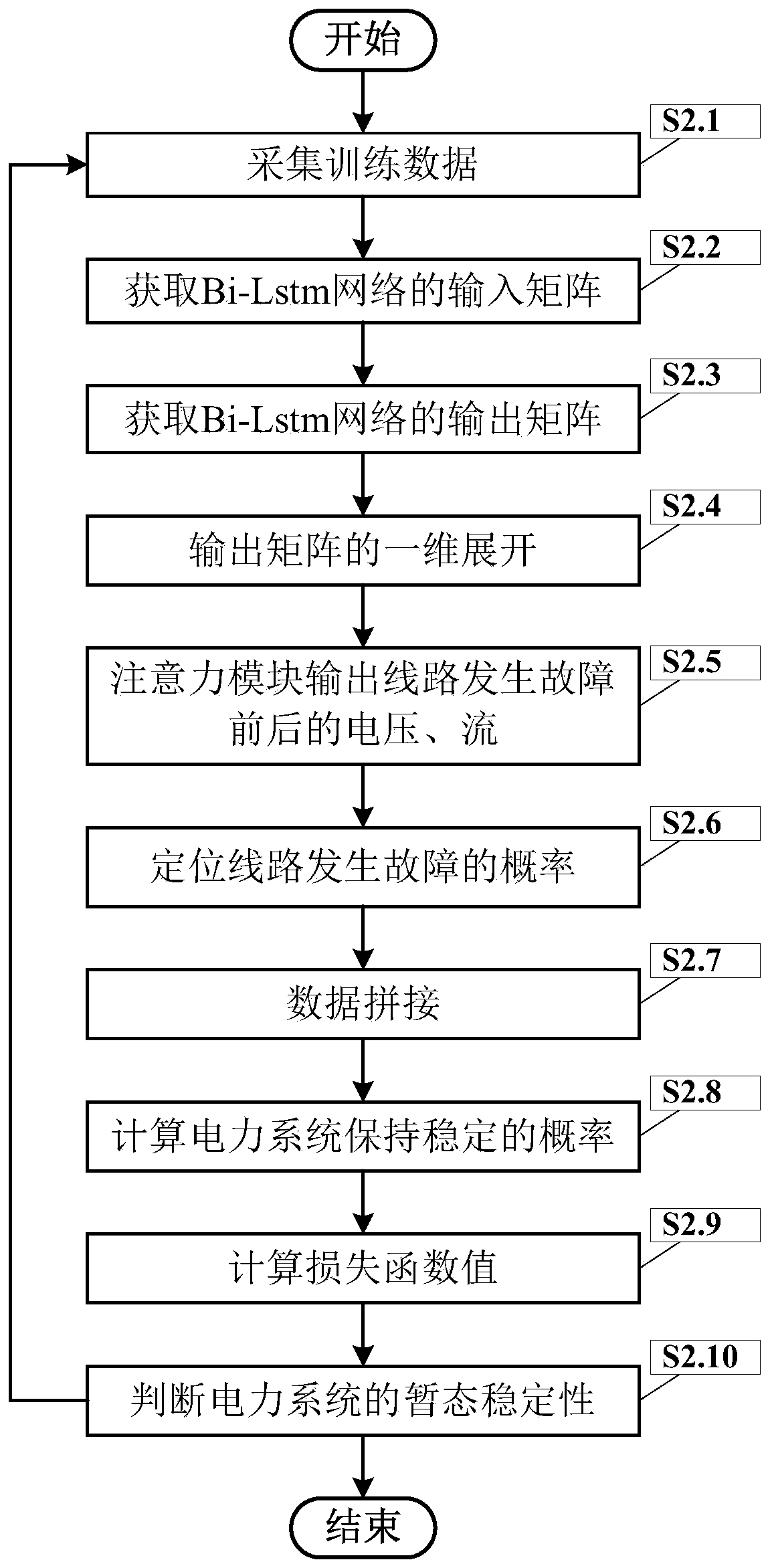
Method for predicting transient stability of power system based on LSTM double-structure model
ActiveCN110829417AEmergency protective circuit arrangementsAc network circuit arrangementsTransient stateElectric power system
The invention discloses a method for predicting the transient stability of a power system based on an LSTM double-structure model, which comprises the steps of firstly, establishing an LSTM double-structure model by utilizing an open-source framework Keras; training the LSTM double-structure model in an iterative loop mode to obtain a trained LSTM double-structure model; and finally, processing avoltage and a current to be detected into an input matrix, inputting the input matrix into the trained LSTM double-structure model, obtaining fault line position information, and judging the transientstability of the power system after a fault occurs according to the fault line position information.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
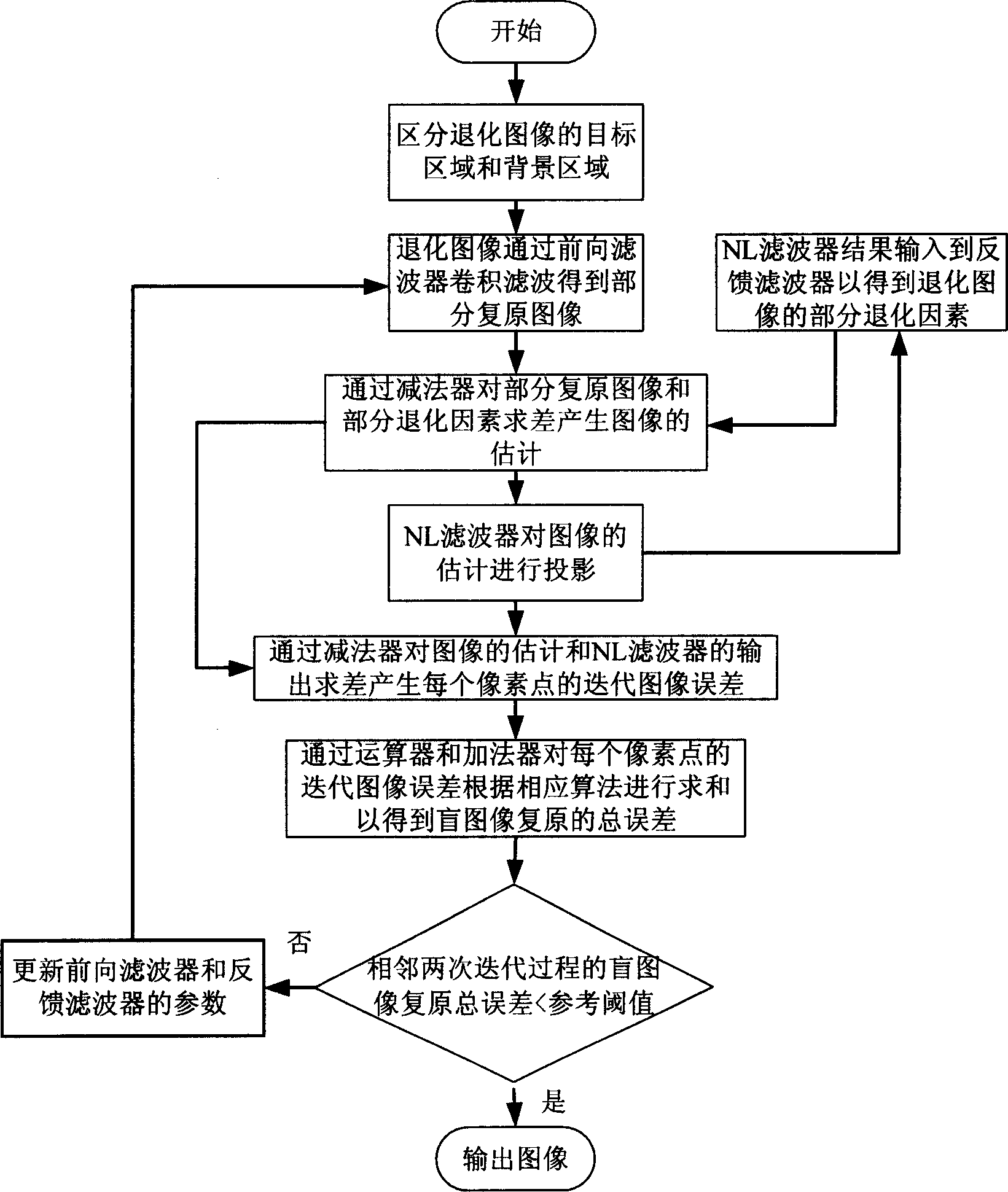
Blind image restoring method based on adaptive judgment feedback balance technique
InactiveCN1904942ASimple structureFast convergenceImage enhancementComputation complexitySignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
The invention relates to a blind image restore method based on self-adapting judgment feedback balance technology. It includes the following steps: gaining part restoring image through forward direction filter, inputting the iteration result of NL filter to feedback filter to gain part degeneration factor, taking estimation and projection, calculating the output difference of NL filter and image estimating to generate the iteration error to every pixel, and gaining total error of the blind image restoring, updating parameter of forward direction filter and feedback filter and repeating the previous process until the total error is less than the reference threshold value, and output image. The advantages of the invention are simple arithmetic structure, good astringency, low computing complex, and good image restoring effect.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
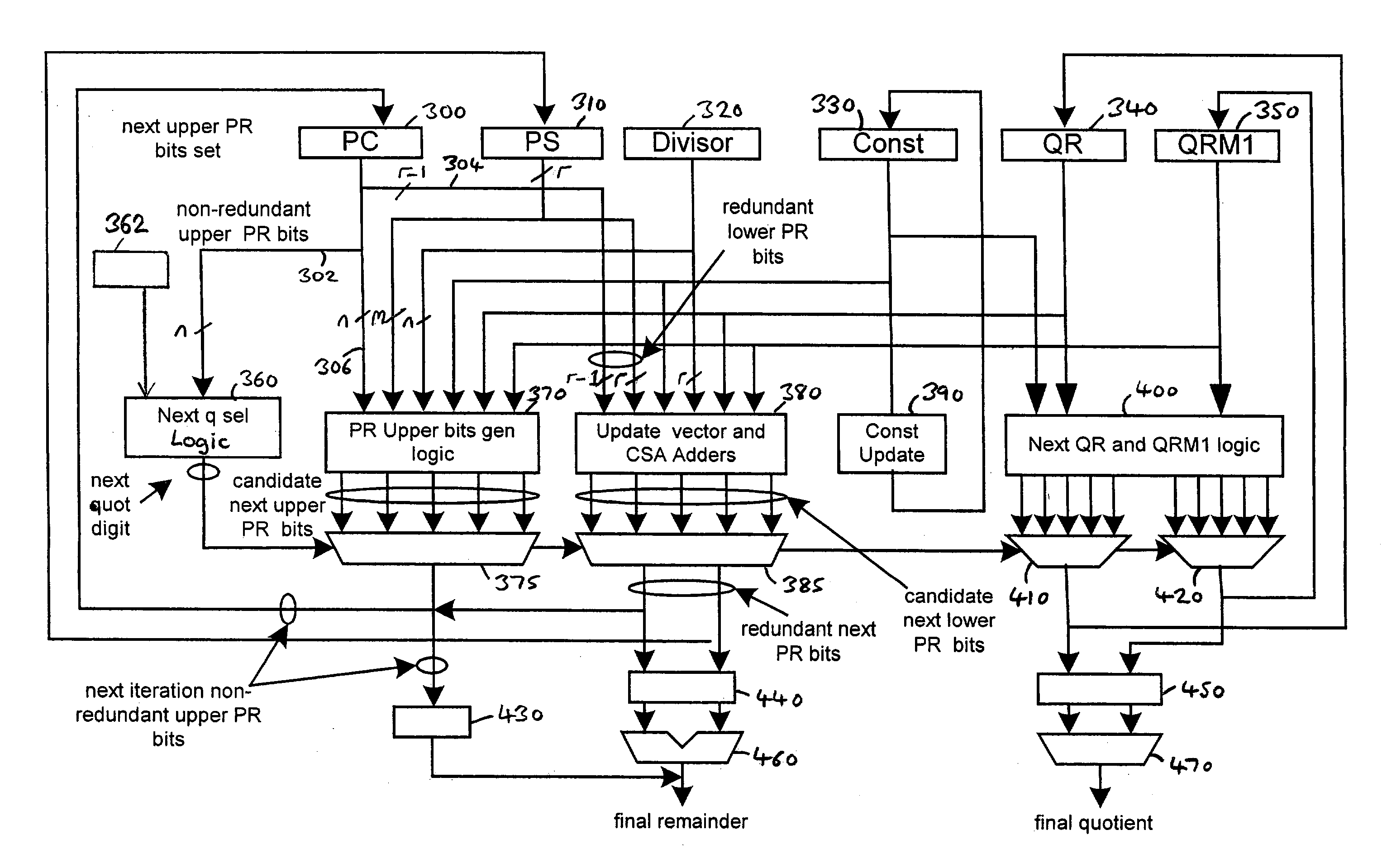
Apparatus and method for performing operations implemented by iterative execution of a recurrence equation
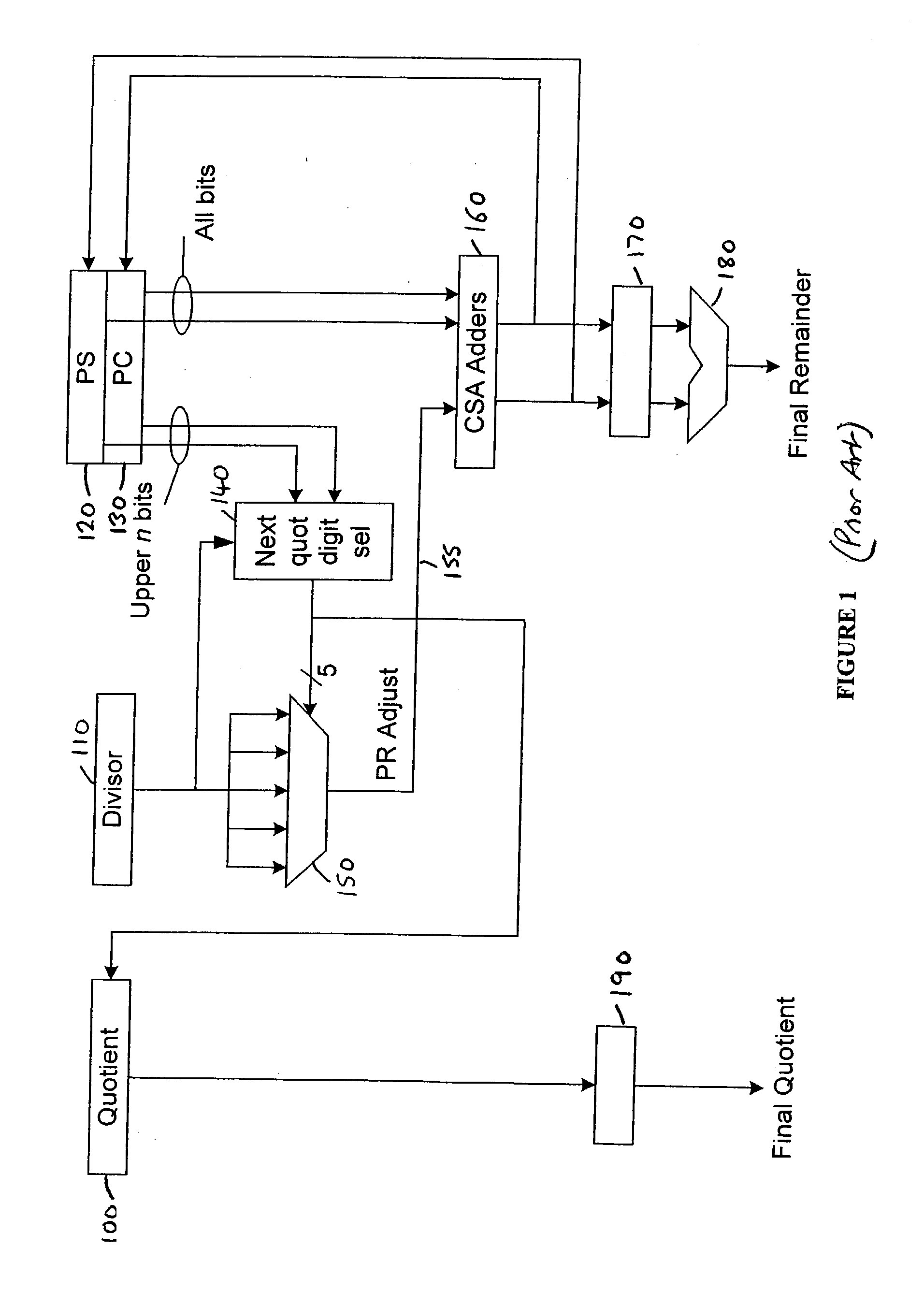
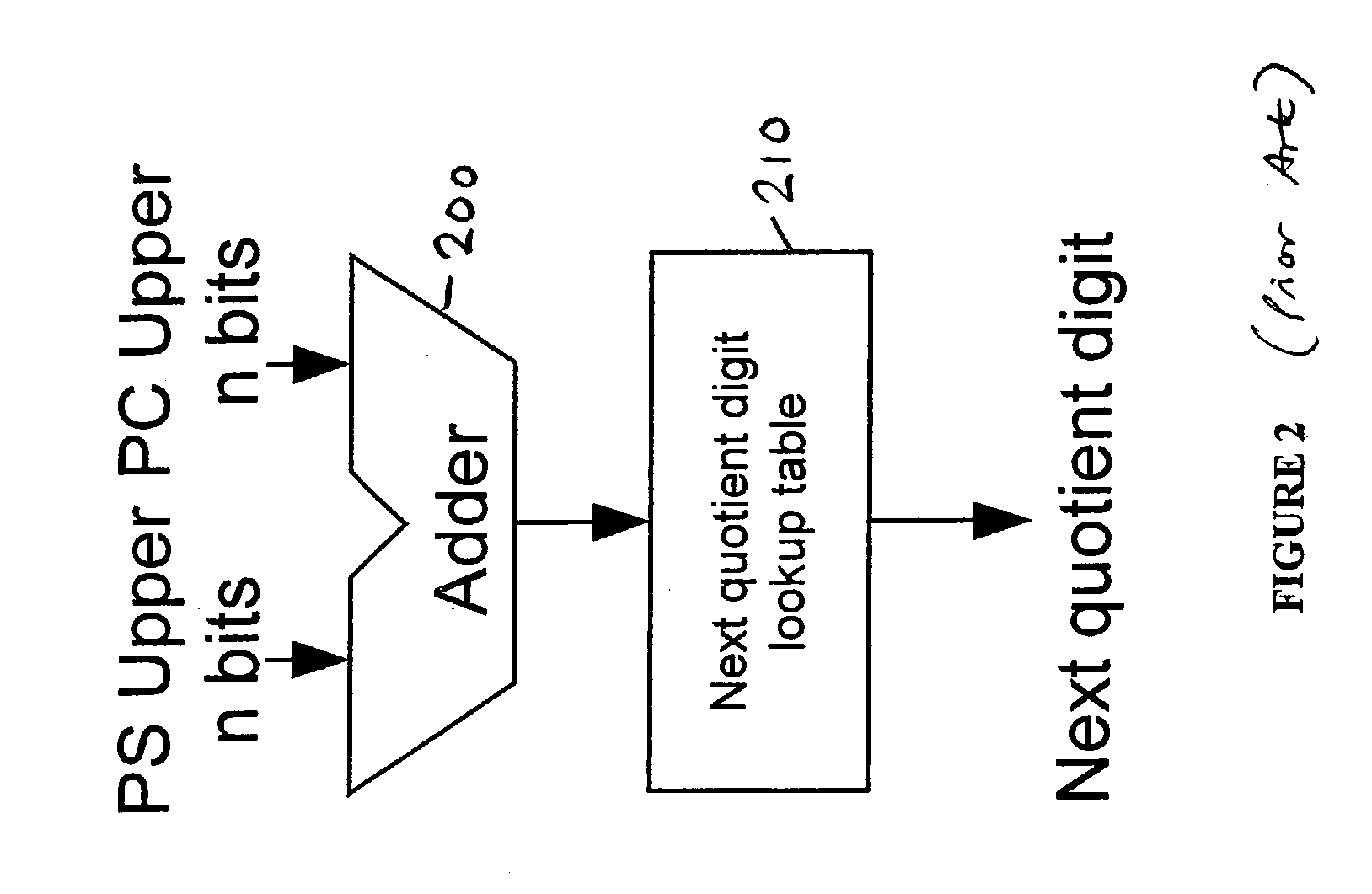
The present invention provides an apparatus and method for performing an operation on an operand or operands in order to generate a result, in which the operation is implemented by iterative execution of a recurrence equation. In each iteration, execution of the recurrence equation causes a predetermined number of bits of the result and a residual to be generated, the residual generated in a previous iteration being used as an input for the current iteration, and in the first iteration the residual comprising the operand. The apparatus comprises result digit logic operable for a current iteration to determine, having regard to a most significant n bits of the input residual, a next result digit, and residual generation logic operable for a current iteration to generate, having regard to the input residual and the next result digit, a next residual, the most significant n bits of the next residual being generated in non-redundant form and the remaining bits of the next residual being generated in redundant form. Result update logic is also provided which is operable for a current iteration to modify the result, having regard to the next result digit, to produce an updated result. Control logic is then provided to cause the iterations to continue until a predetermined condition is met, whereafter the result is indicated by the updated result and any residual existing after the final iteration. In preferred embodiments, the apparatus is used to perform division operations and / or square root operations. The apparatus enables a significant reduction in the critical path of the primary iterative cycle used to execute the recurrence equation.
Owner:ARM LTD
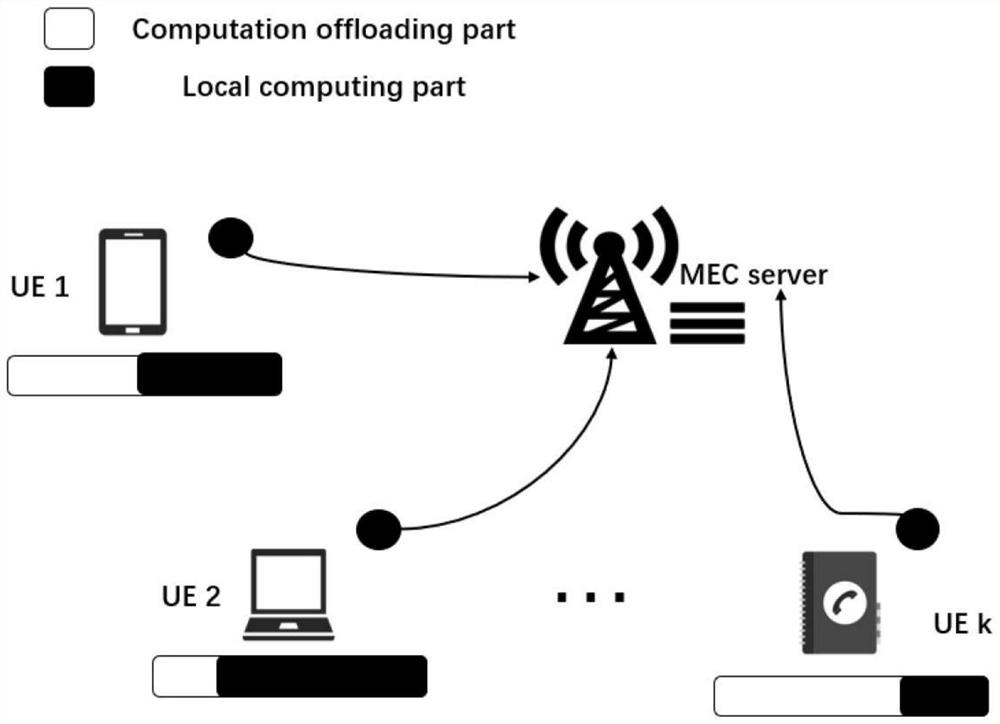
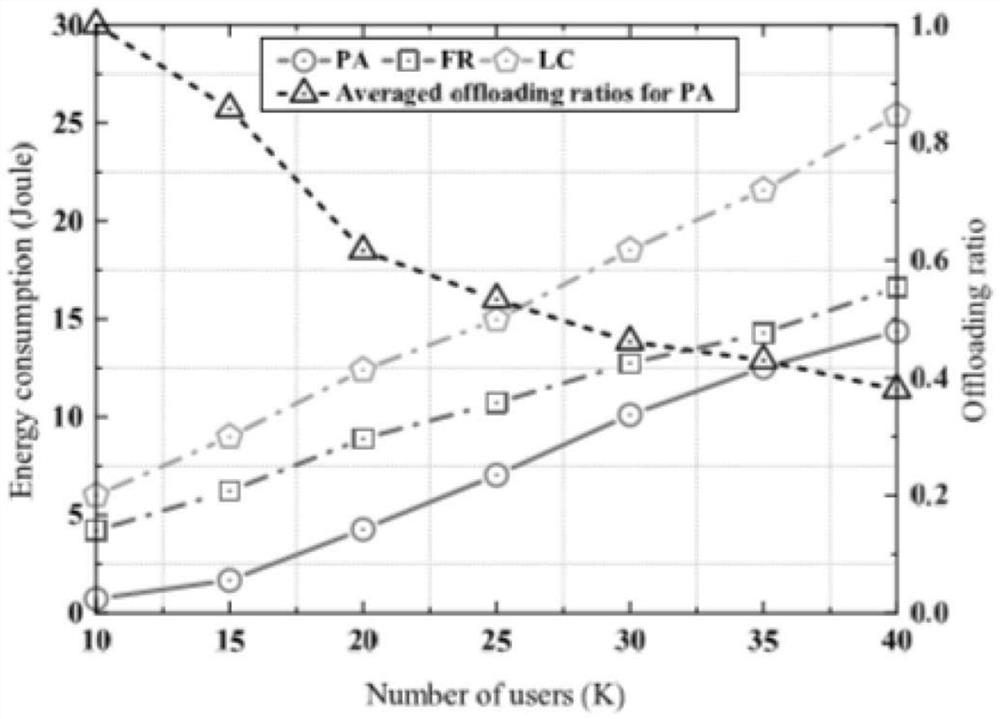
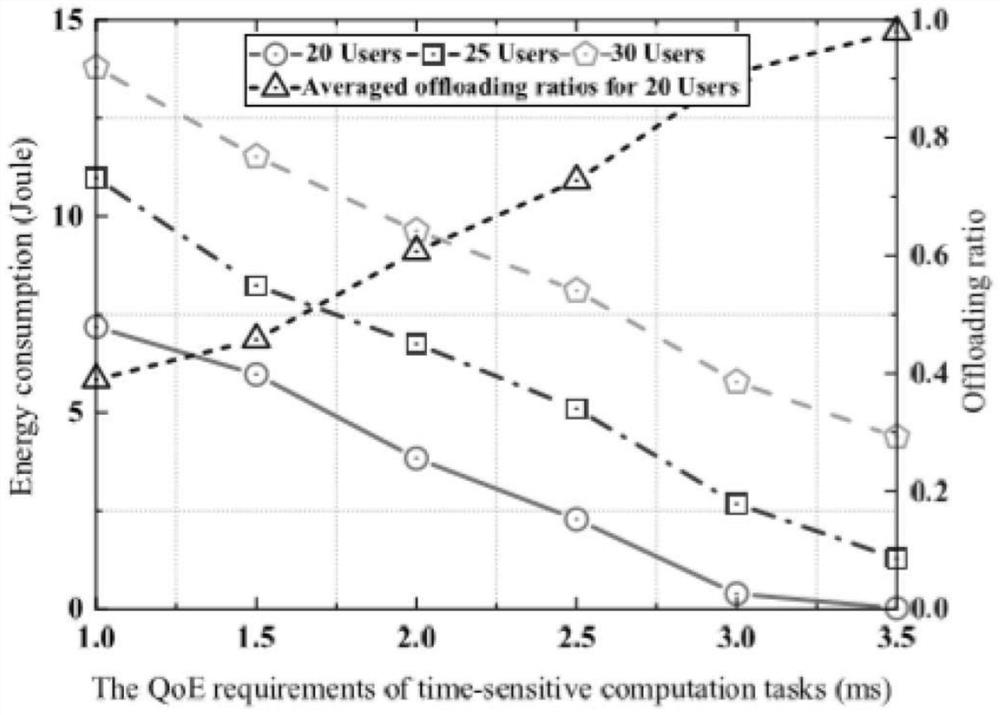
Strategy method for minimizing energy consumption of mobile edge computing network under time-sensitive condition
ActiveCN112105062AMinimize energy consumptionUnload ratio optimizationNetwork traffic/resource managementTransmissionEnergy consumption minimizationDescent algorithm
The invention relates to a strategy method for minimizing energy consumption of a mobile edge computing network under a time-sensitive condition, which is characterized by comprising the following steps of: 1, an initialization stage: acquiring basic configuration information of the network by a node in the network at the stage, and initializing related parameters; 2, establishing an energy consumption minimum system optimization model; 3, solving an initial optimal unloading ratio according to constraint conditions; 4, when the constraint condition is met, returning to the step 2, and entering the next round of iterative loop calculation according to the block coordinate descent algorithm; and 5, obtaining the optimal unloading ratio, computing resources and subcarrier allocation expressions of different computing tasks of each user node after reaching the maximum limit frequency in a circulating manner. Under the condition that the QoE requirement of a user for a timeliness calculation task is met, the total energy consumption of the whole mobile edge calculation network is minimized through three strong coupling optimization variables including decoupling optimization, unloadingratio optimization, calculation resource allocation and subcarrier allocation.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
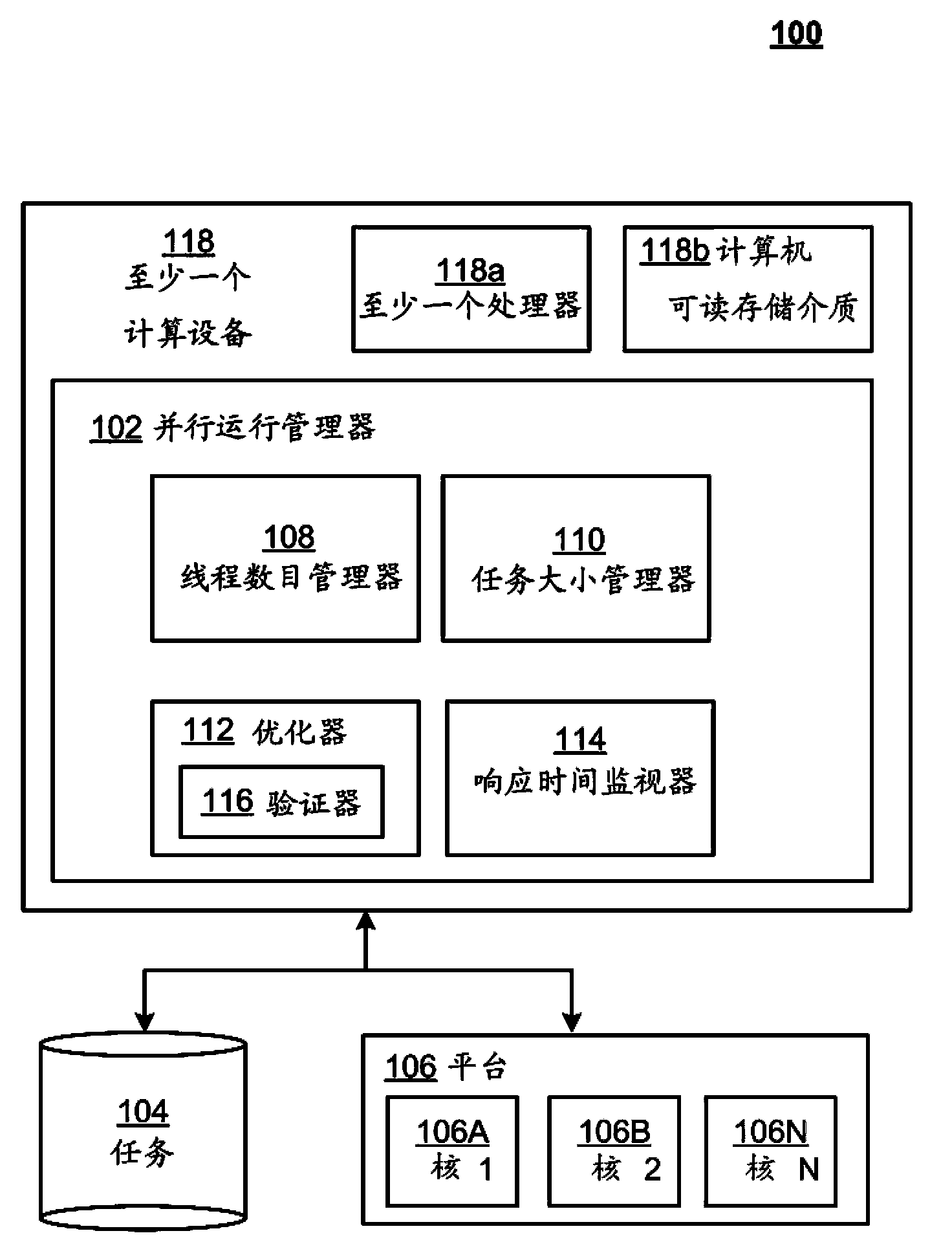
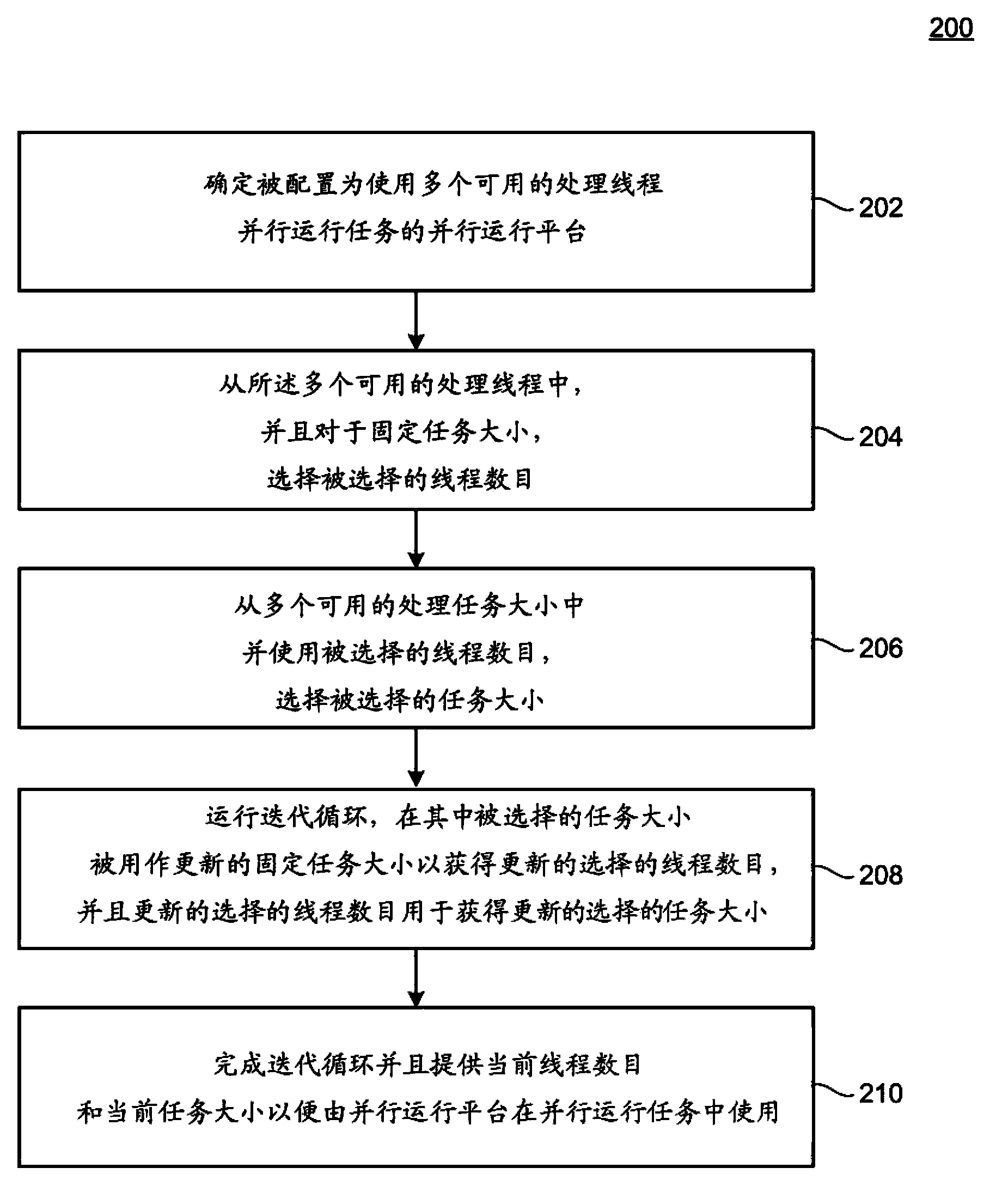
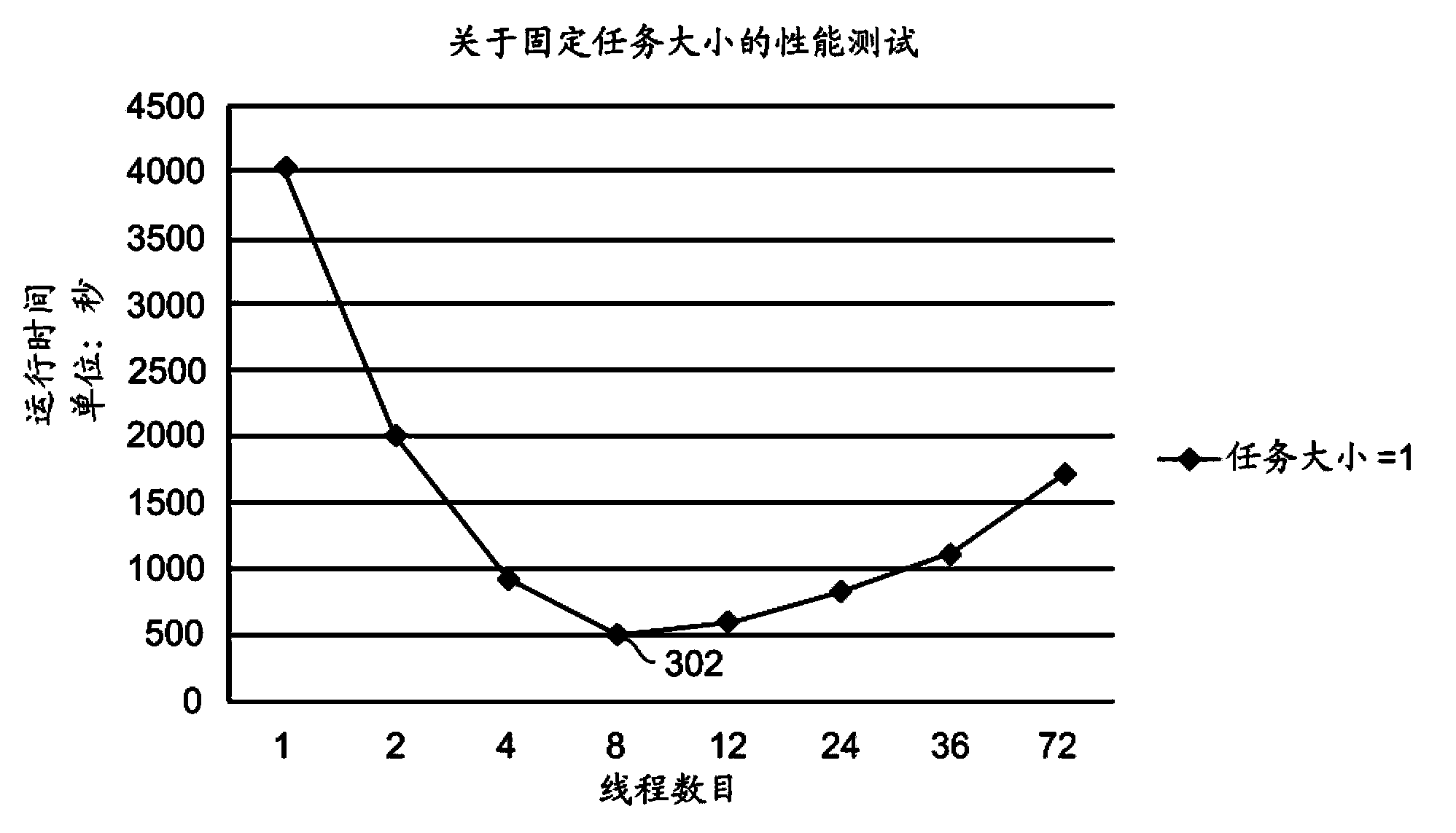
Feedback driving and adjusting system for efficient parallel running
A parallel execution manager may determine a parallel execution platform configured to execute tasks in parallel using a plurality of available processing threads. The parallel execution manager may include a thread count manager configured to select, from the plurality of available processing threads and for a fixed task size, a selected thread count, and a task size manager configured to select, from a plurality of available task sizes and using the selected thread count, a selected task size. The parallel execution manager may further include an optimizer configured to execute an iterative loop in which the selected task size is used as an updated fixed task size to obtain an updated selected thread count, and the updated selected thread count is used to obtain an updated selected task size. Accordingly, a current thread count and current task size for executing the tasks in parallel may be determined.
Owner:SAP AG
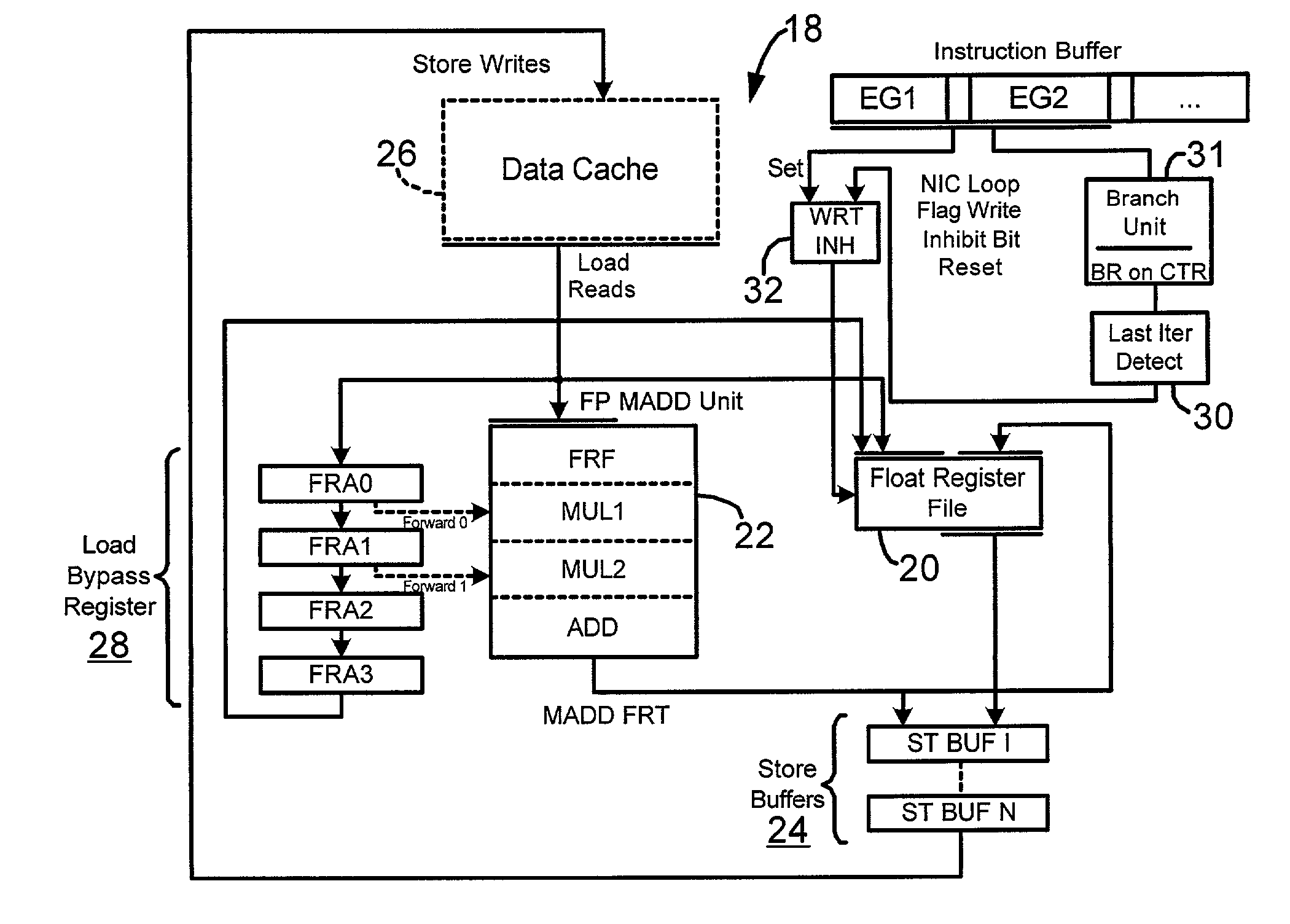
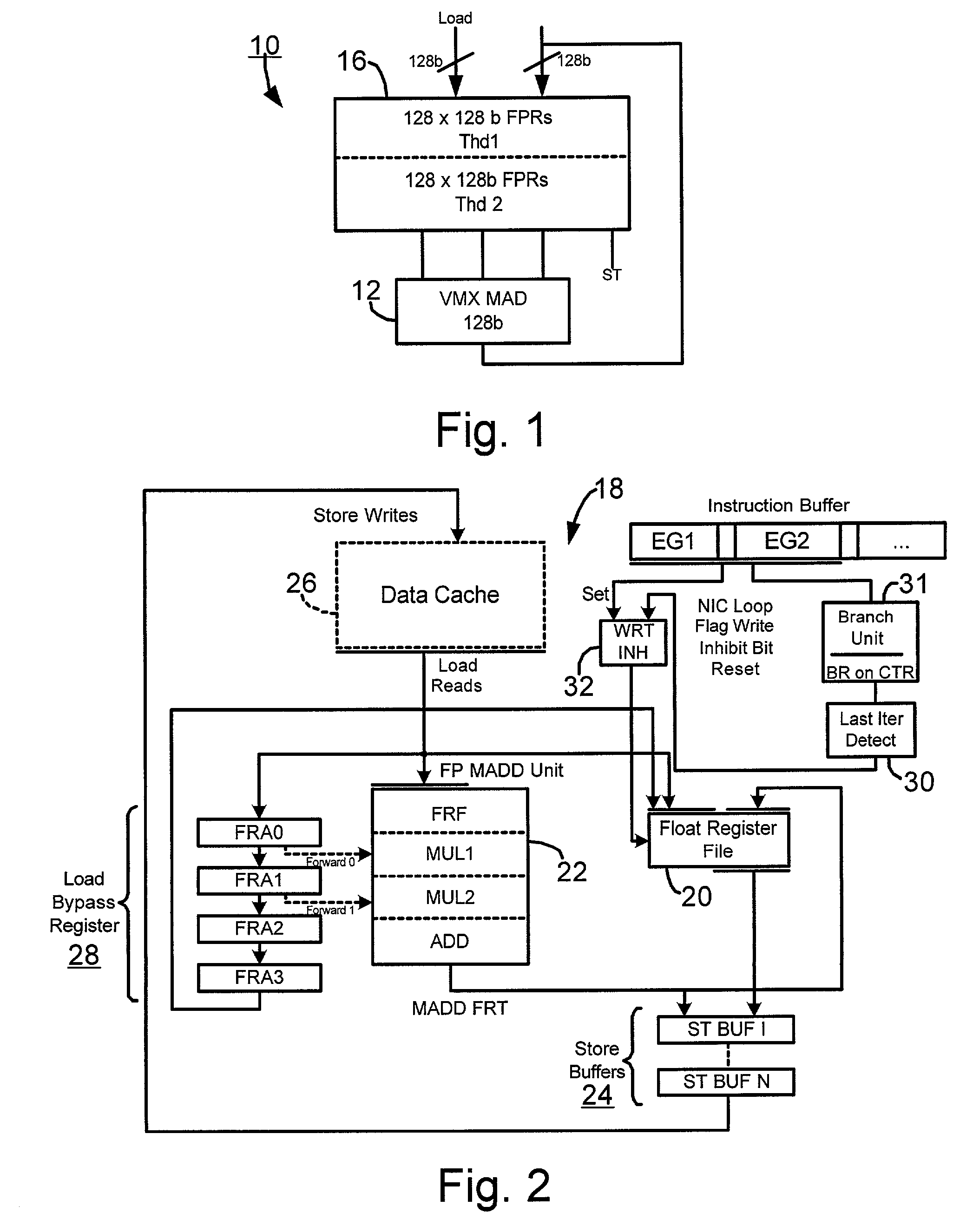
Floating point unit power reduction via inhibiting register file write during tight loop execution
InactiveUS7085940B2Reduce power consumptionMinimizes component usageVolume/mass flow measurementDigital computer detailsProcessor registerFloating-point unit
A system and method for reducing the power consumption in a floating point unit of a processor executing an iterative loop of a program by inhibiting floating point register file writes of interim values of the loop from the floating point multiply adder (FPMADD) unit. A plurality of pipeline registers is resident on the processor and holds a portion of an unrolled loop, and once the end of the loop is detected, the last value produced from the loop in the FPMADD unit is written to the floating point registers.
Owner:IBM CORP
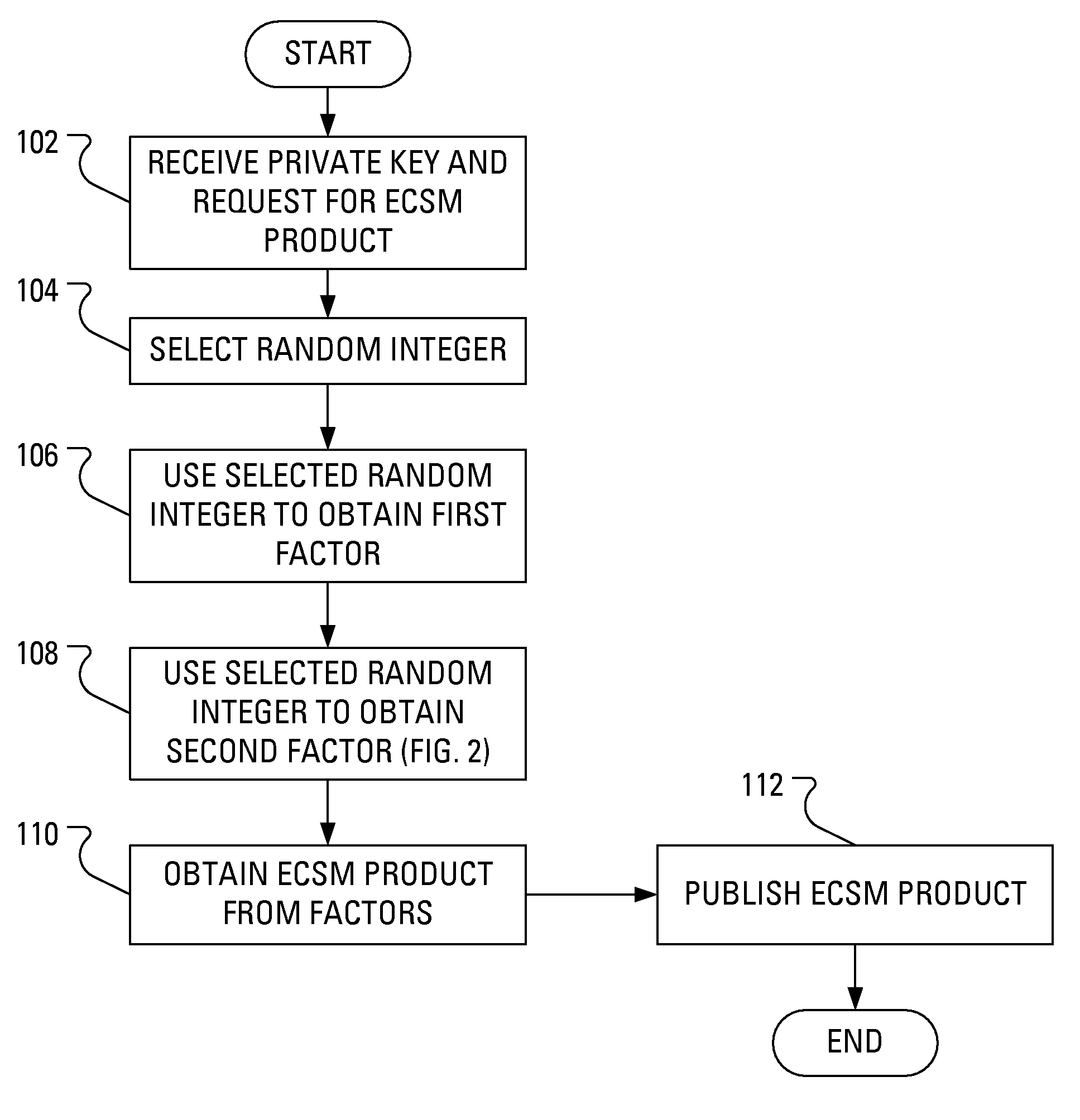
Method and apparatus for performing elliptic curve scalar multiplication in a manner that counters power analysis attacks
ActiveUS8243919B2Digital data processing detailsPublic key for secure communicationPower analysisComputer hardware
When multiplicative splitting is used to hide a scalar in an Elliptic Curve scalar Multiplication ECSM operation, the associated modular division operation employs the known Almost Montgomery Inversion algorithm. By including dummy operations in some of the branches of the main iteration loop of the Almost Montgomery Inversion algorithm, all branches of the algorithm may be viewed, from the perspective of a Power Analysis-based attack, as equivalent and, accordingly, devoid of information useful in determining the value of the scalar, which may be a cryptographic private key.
Owner:MALIKIE INNOVATIONS LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com