Patents
Literature
371 results about "Power analysis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
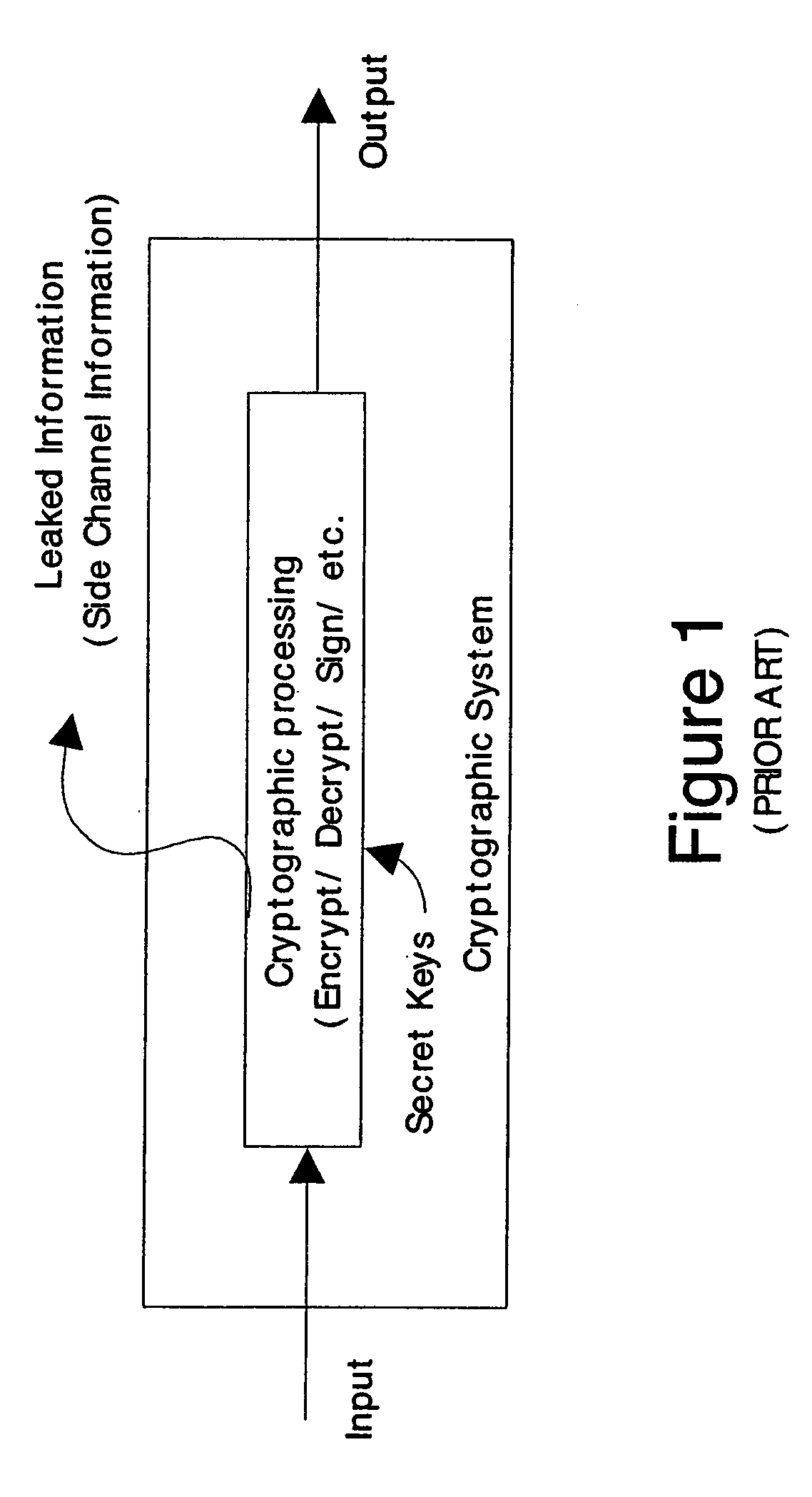
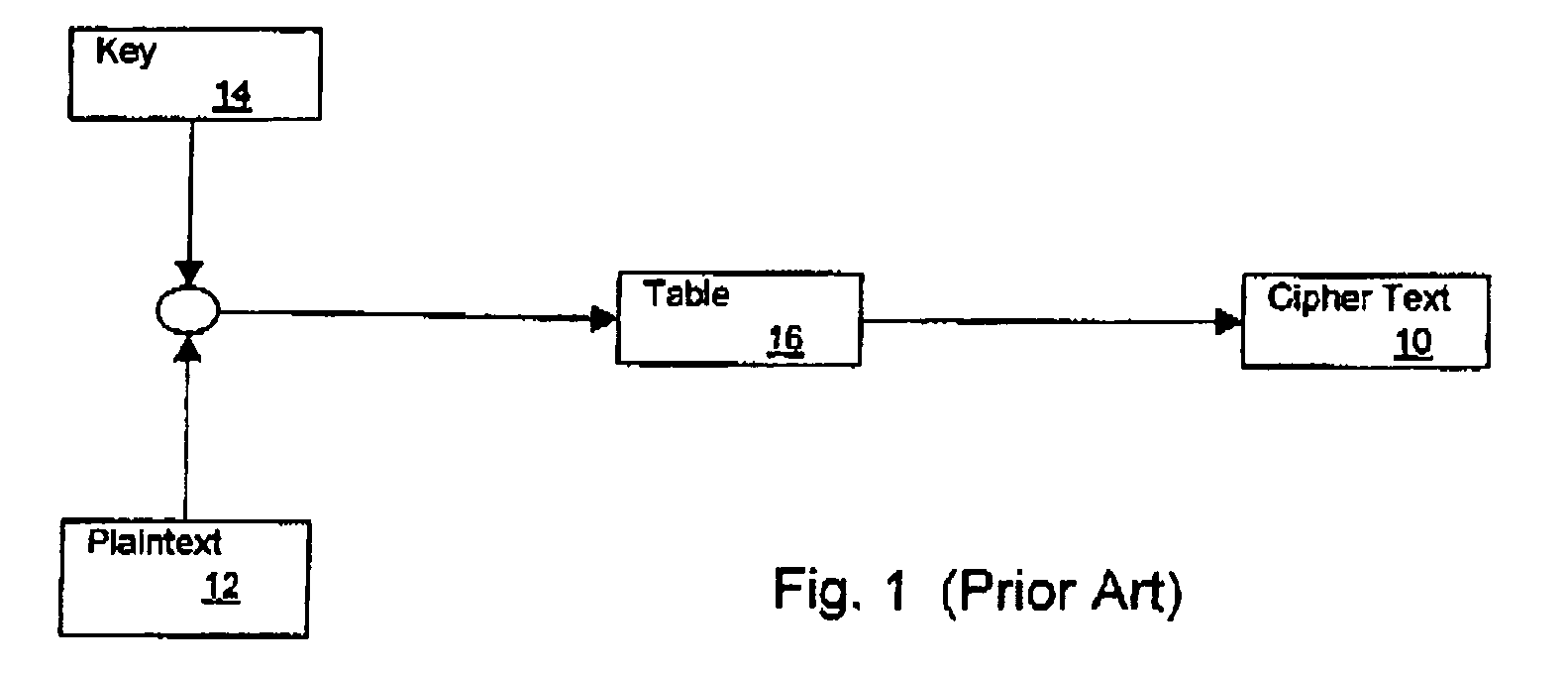
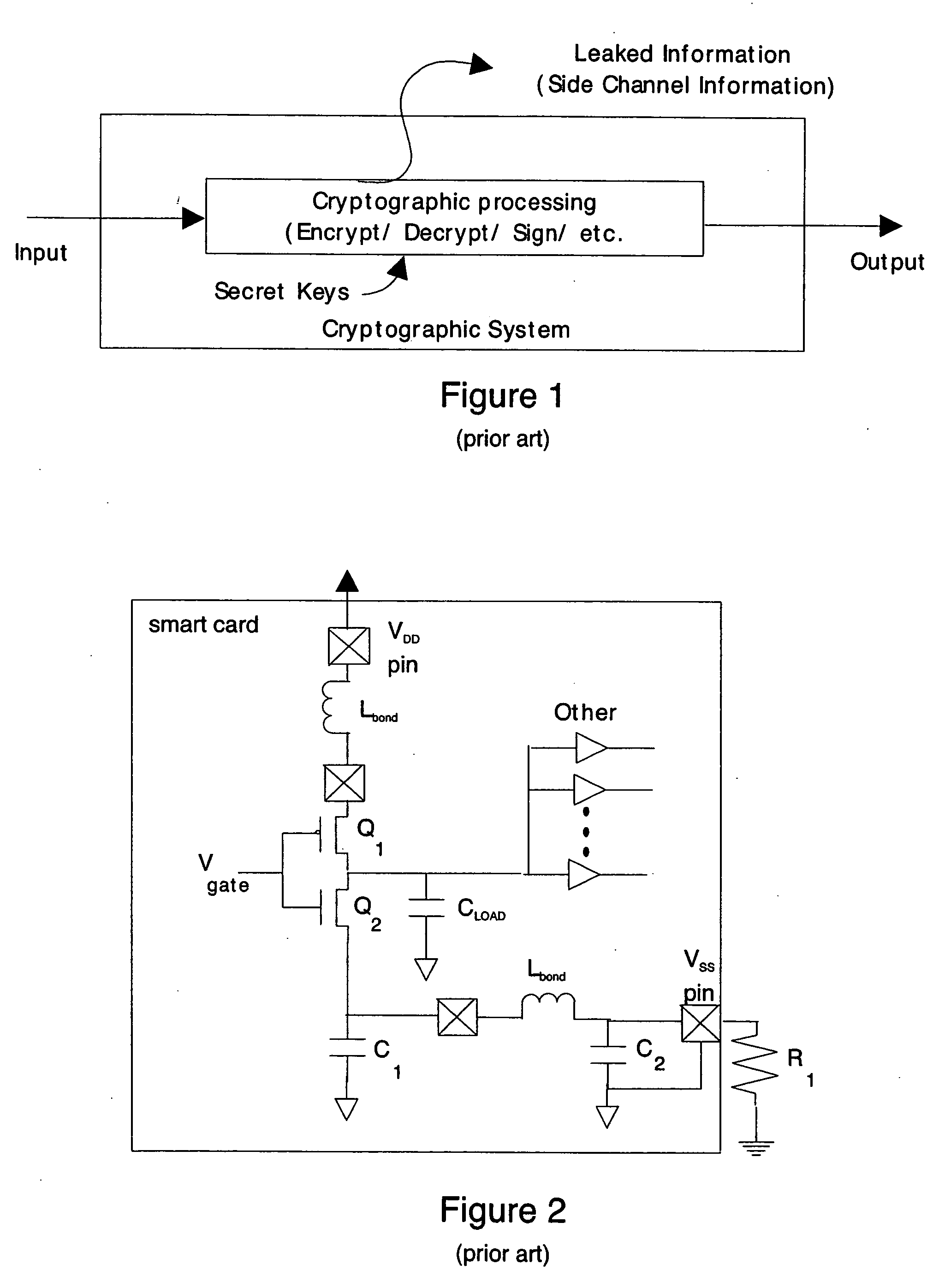
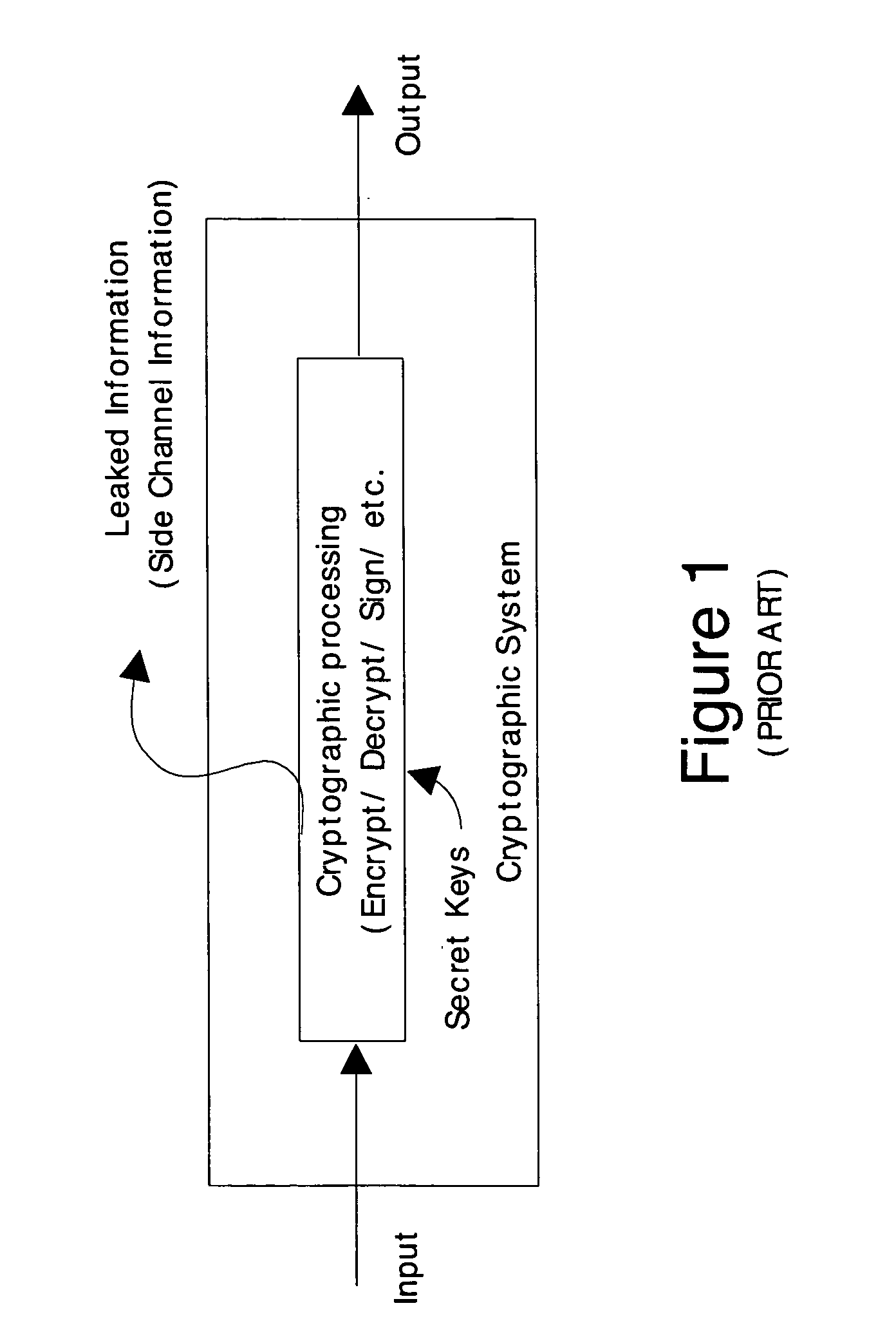
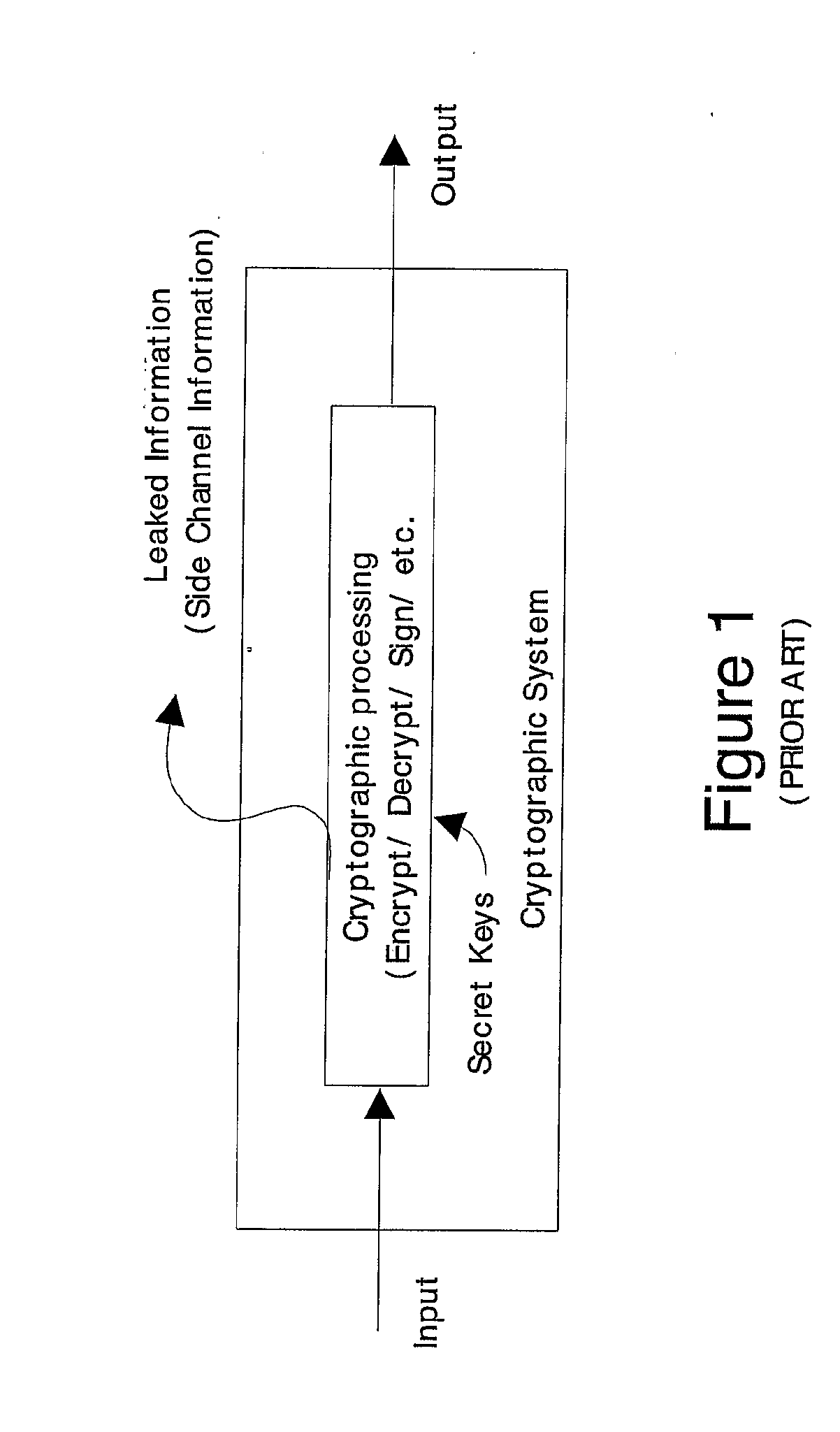
In cryptography, power analysis is a form of side channel attack in which the attacker studies the power consumption of a cryptographic hardware device (such as a smart card, tamper-resistant "black box", or integrated circuit). The attack can non-invasively extract cryptographic keys and other secret information from the device.
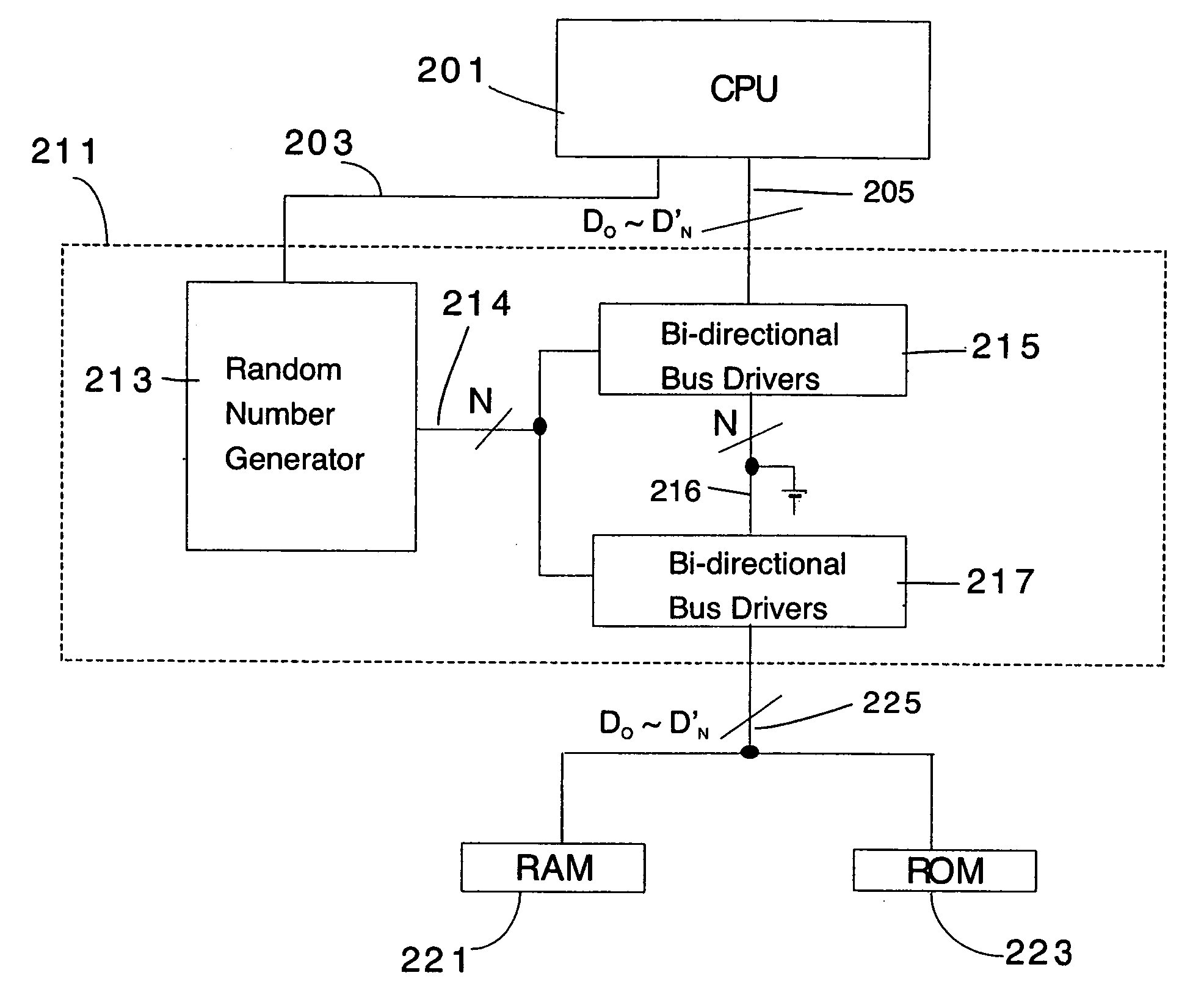
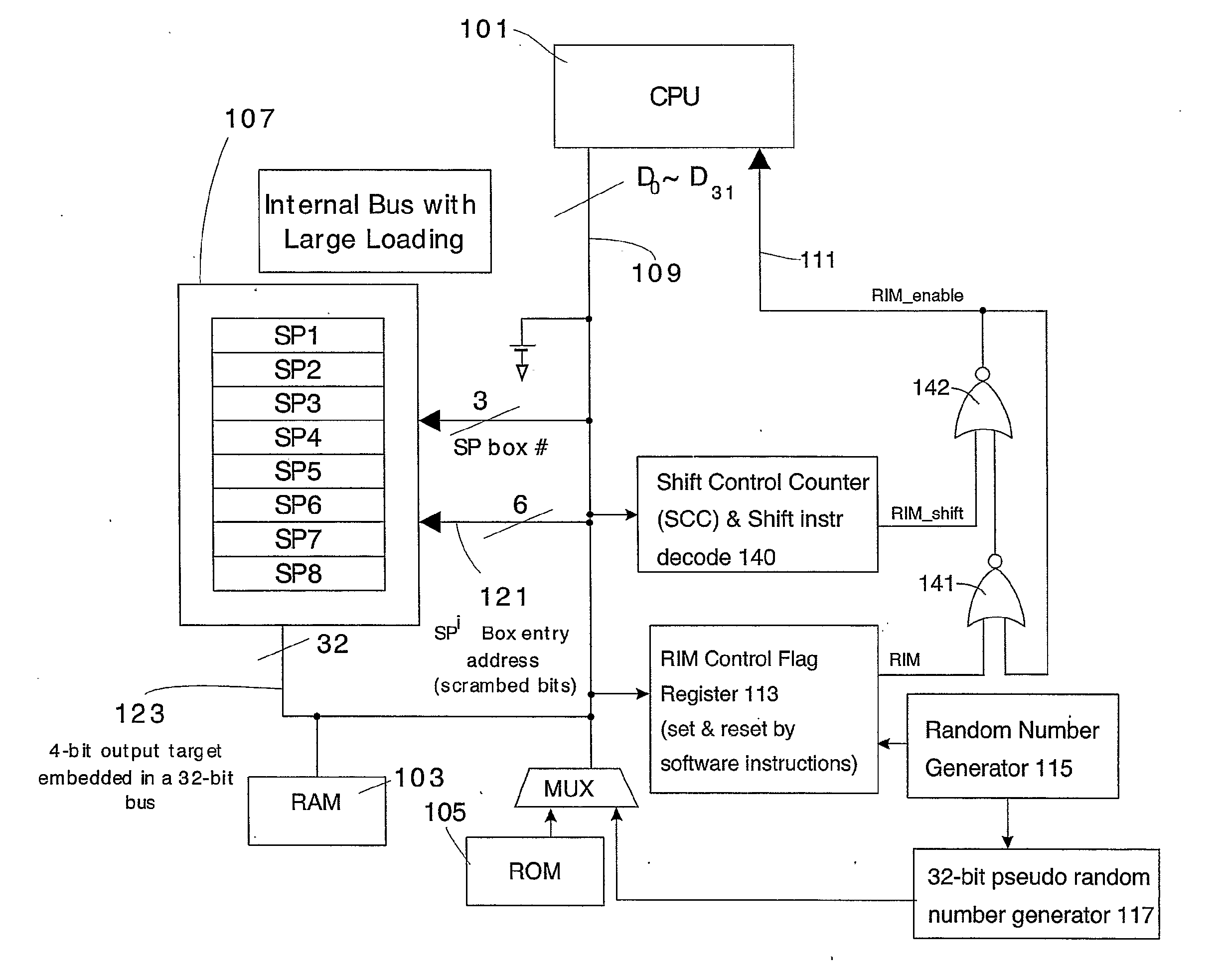
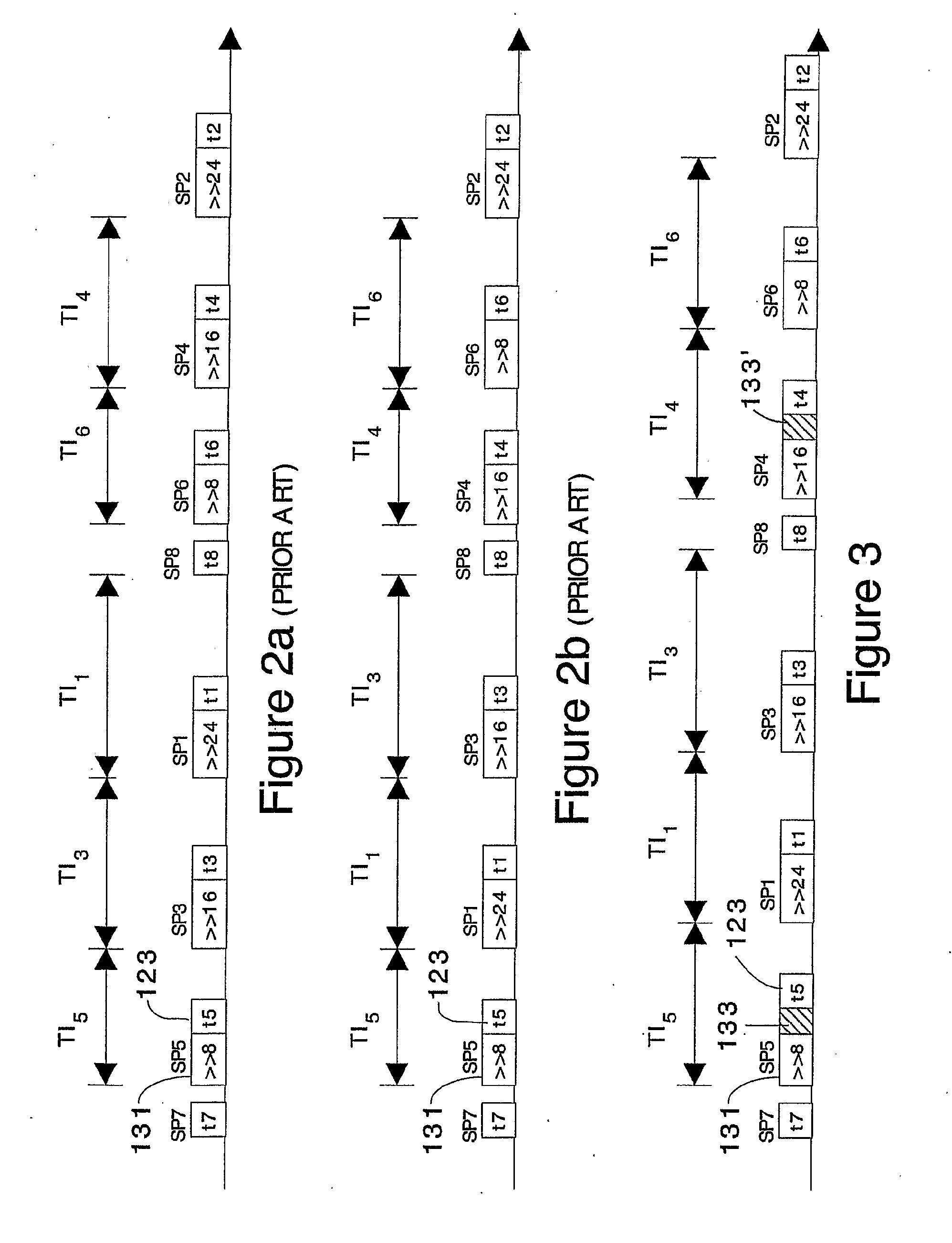
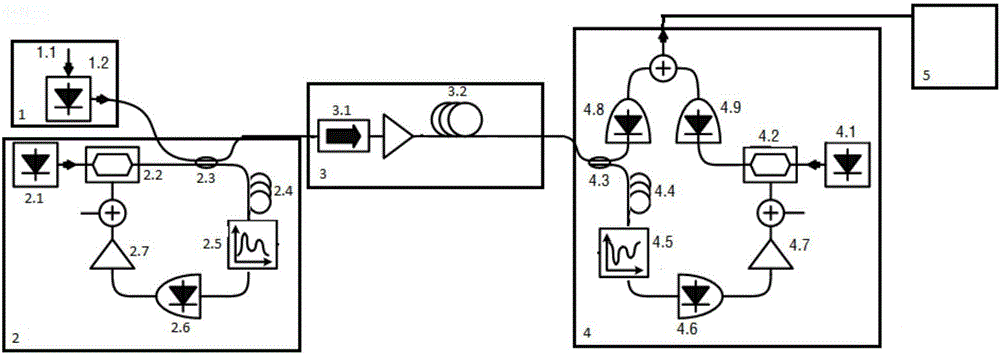
Method for Protecting IC Cards Against Power Analysis Attacks
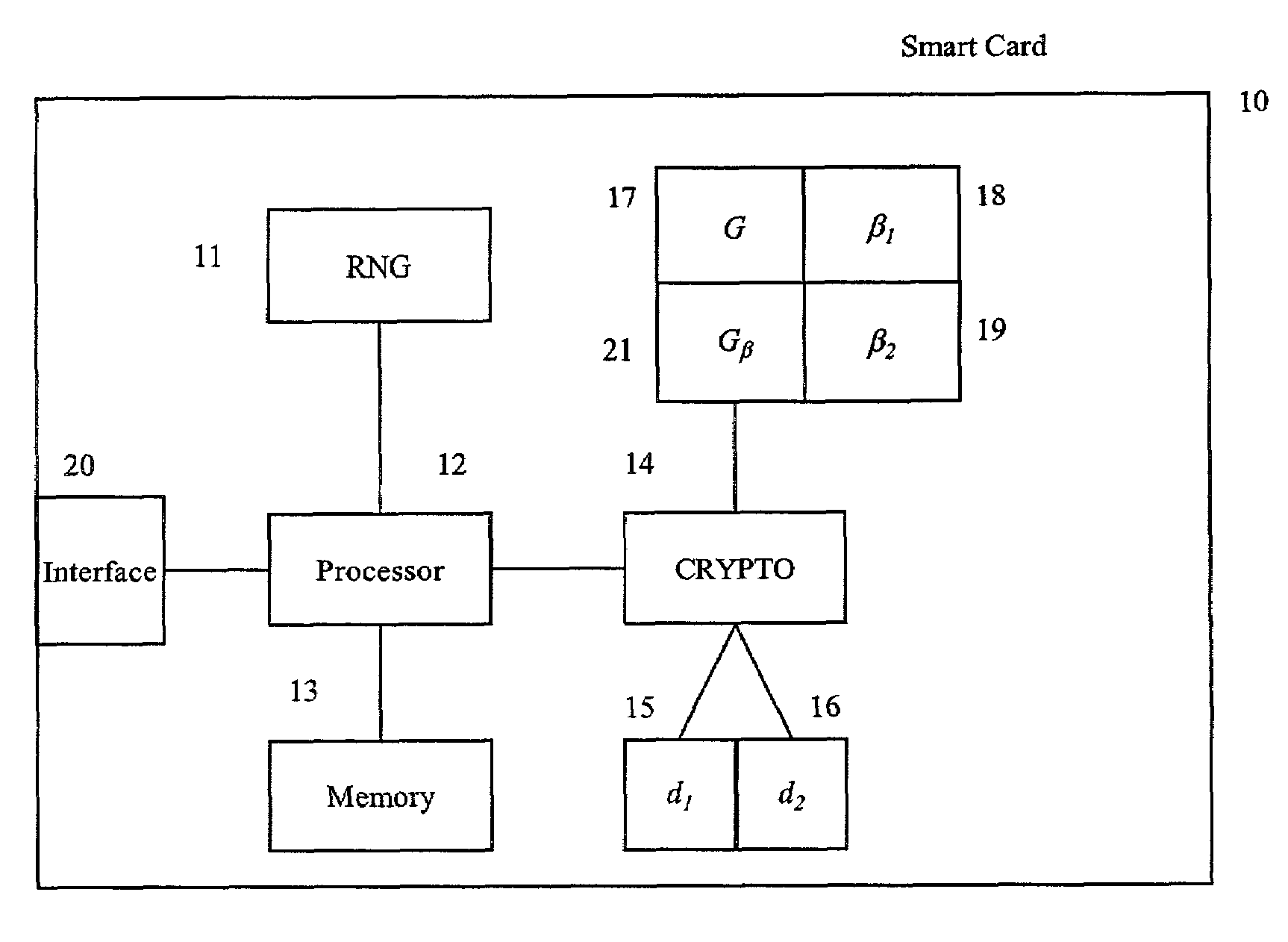
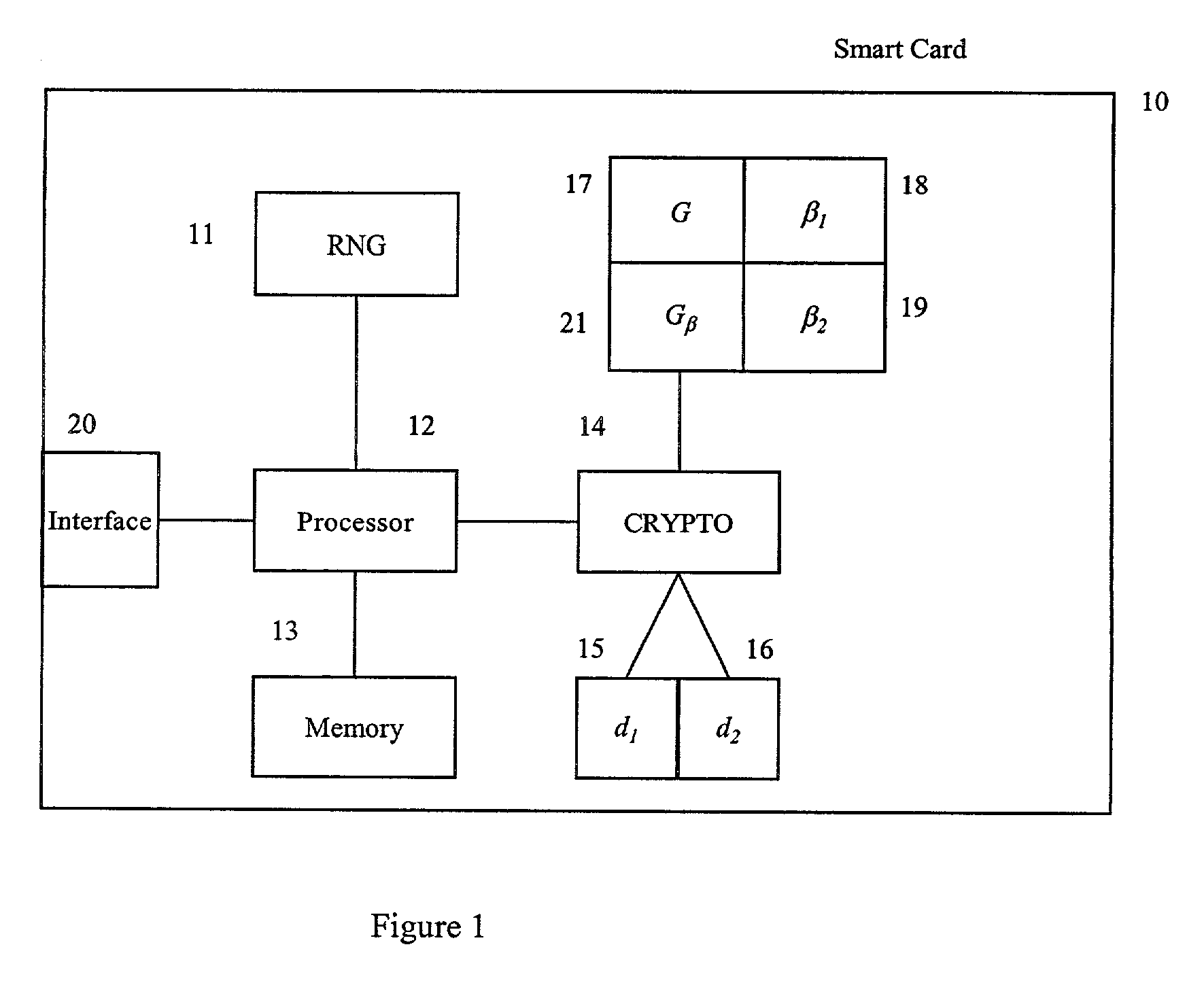
ActiveUS20080019507A1Prevent power analysis attackImprove automationInternal/peripheral component protectionSecret communicationComputer hardwarePower analysis
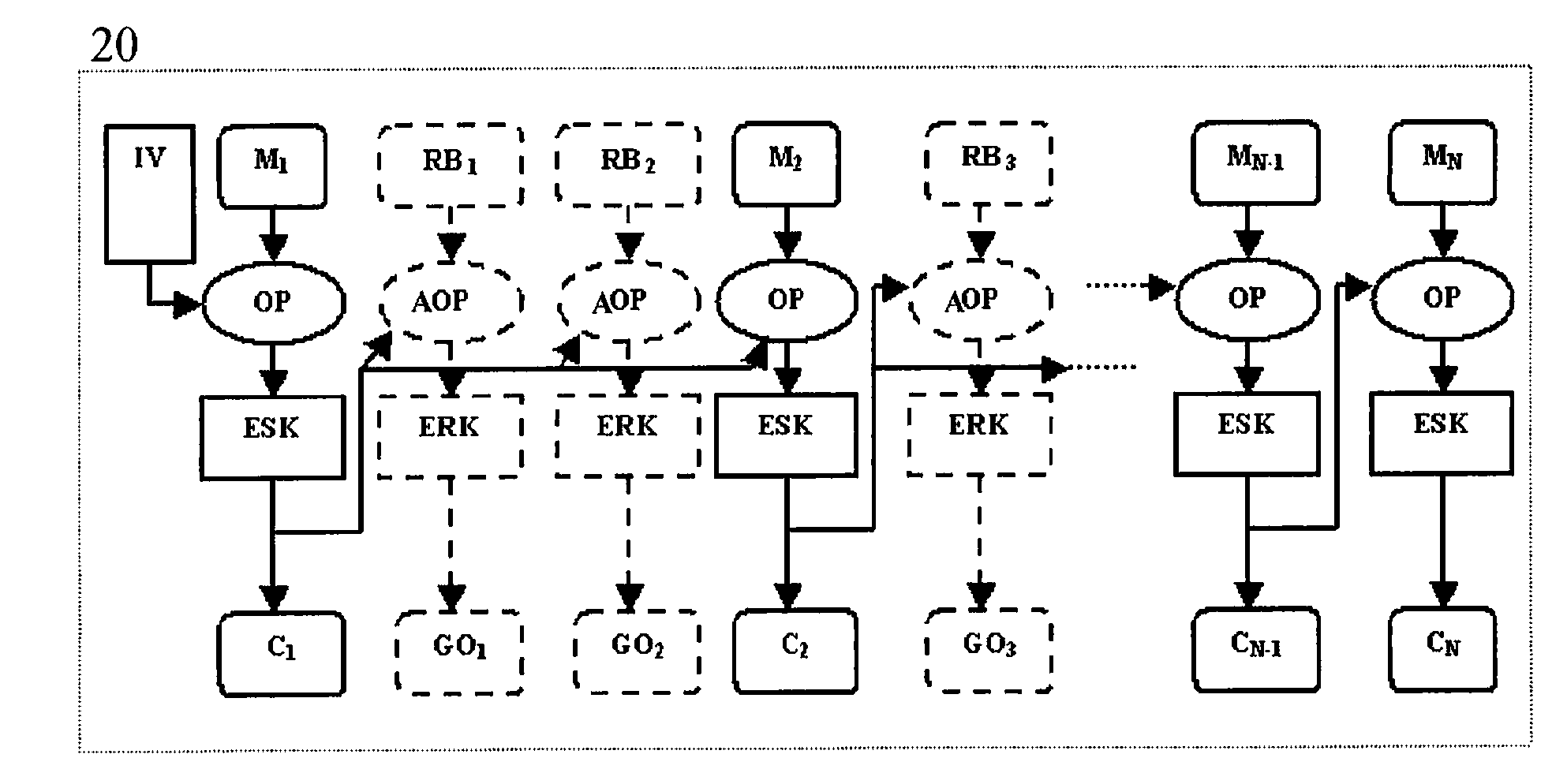
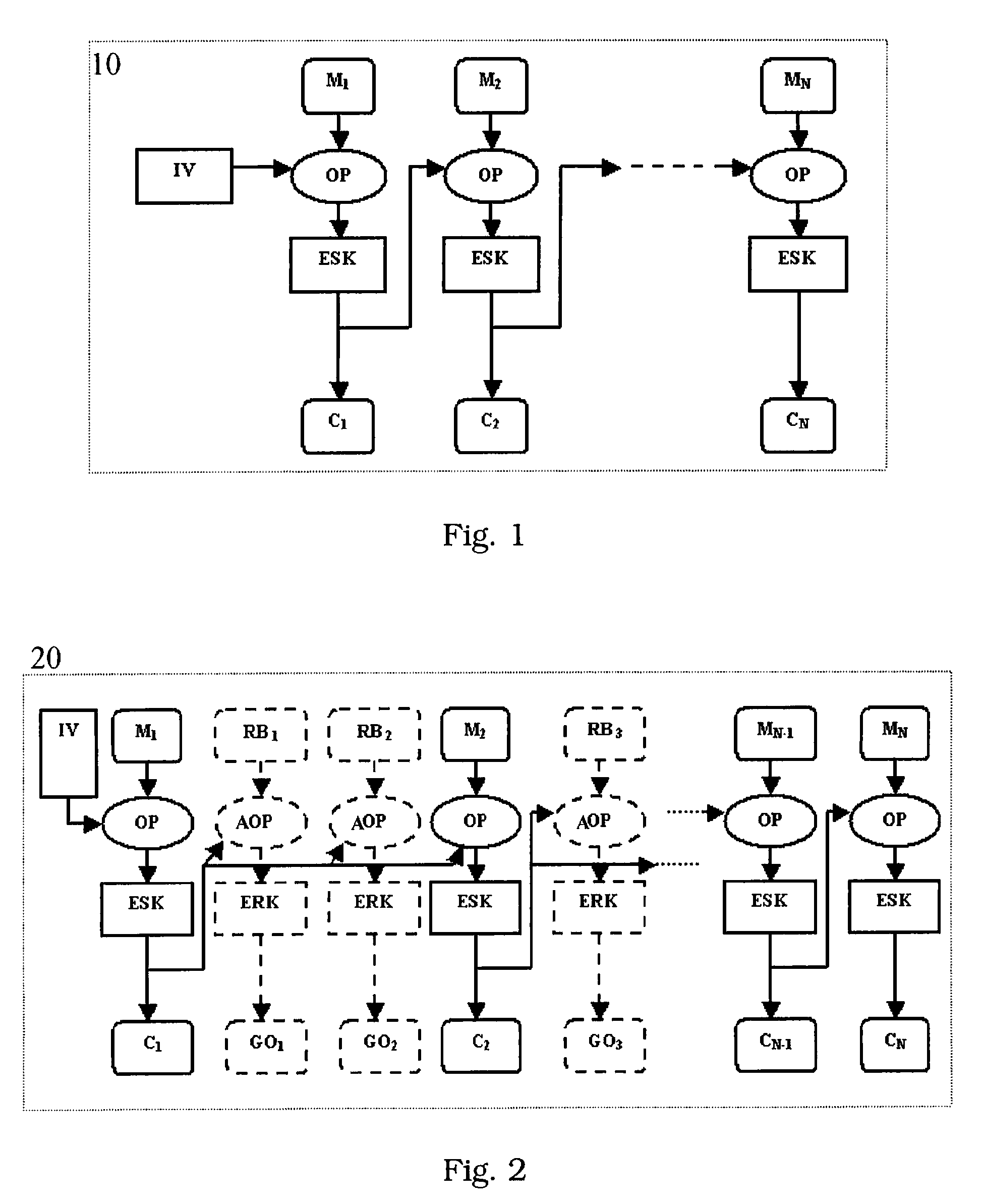
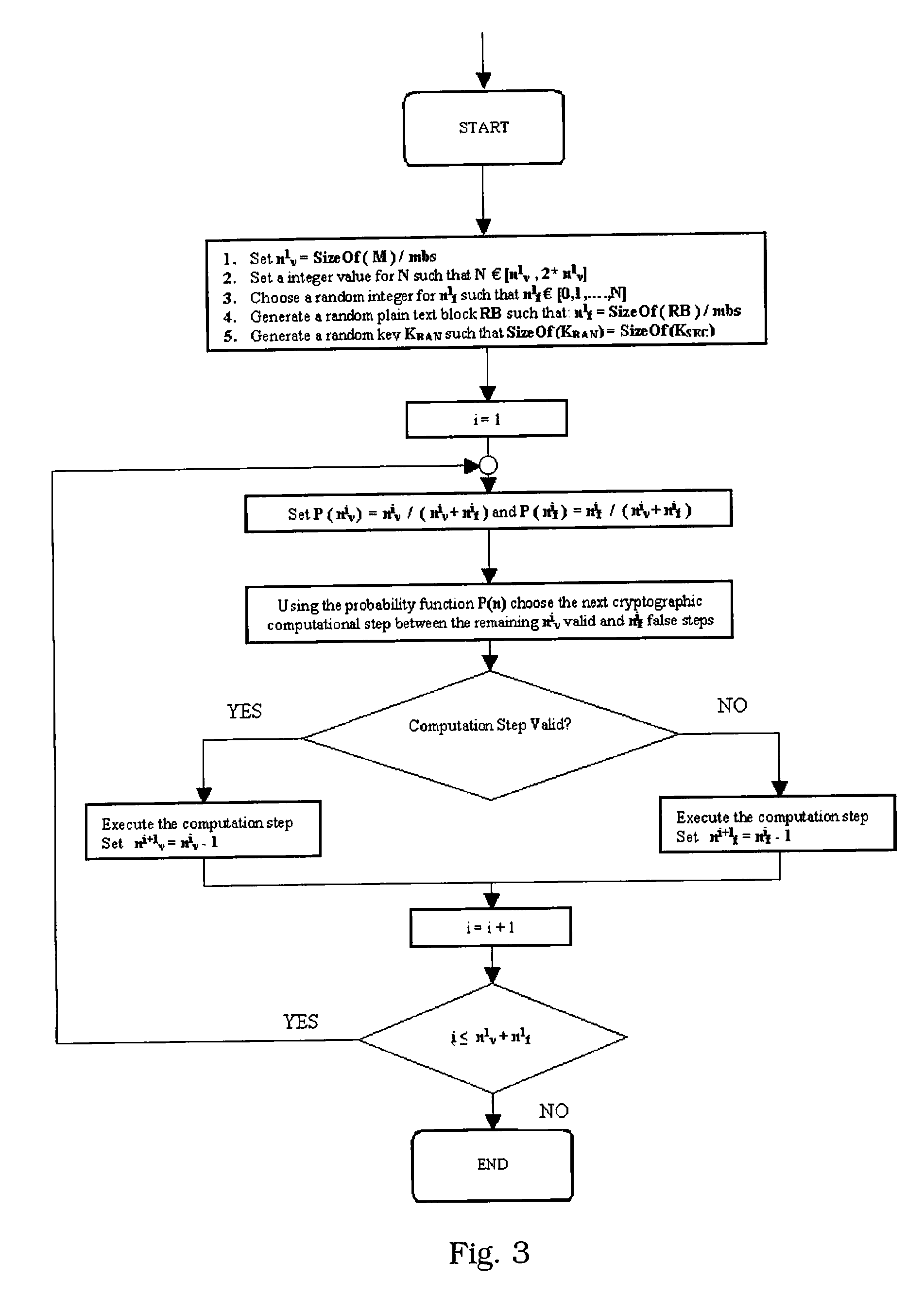
A method for protecting data against power analysis attacks includes at least a first phase of executing a cryptographic operation for ciphering data in corresponding enciphered data through a secret key. The method includes at least a second phase of executing an additional cryptographic operation for ciphering additional data in corresponding enciphered additional data. An execution of the first and second phases is undistinguishable by the data power analysis attacks. Secret parameters are randomly generated and processed by the at least one second phase. The secret parameters include an additional secret key ERK for ciphering the additional data in the corresponding enciphered additional data.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS INT NV
Techniques for power analysis
ActiveUS20110016342A1Enhanced thermal profileComponent can be removedHardware monitoringPower supply for data processingPower analysisData center
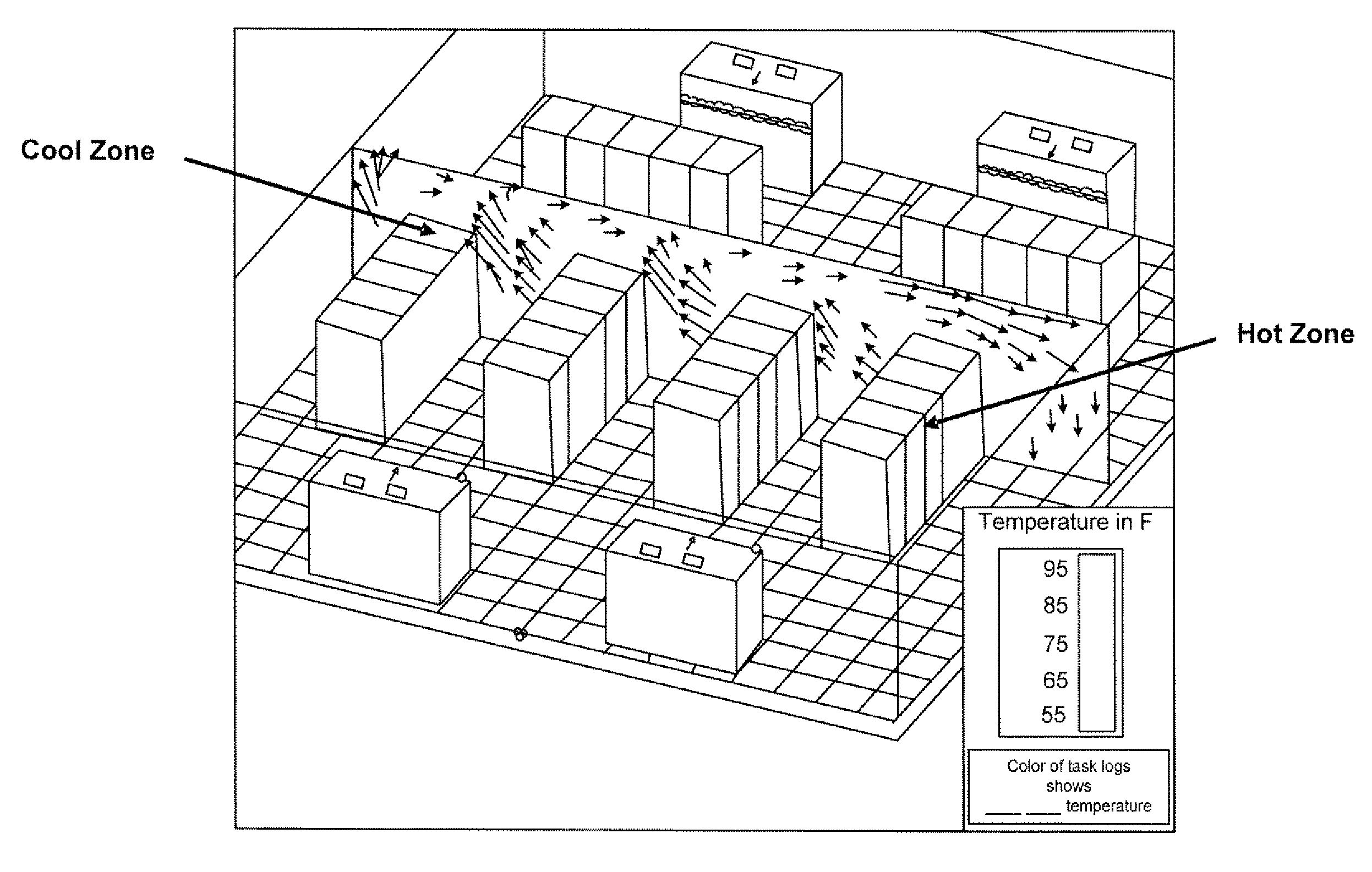
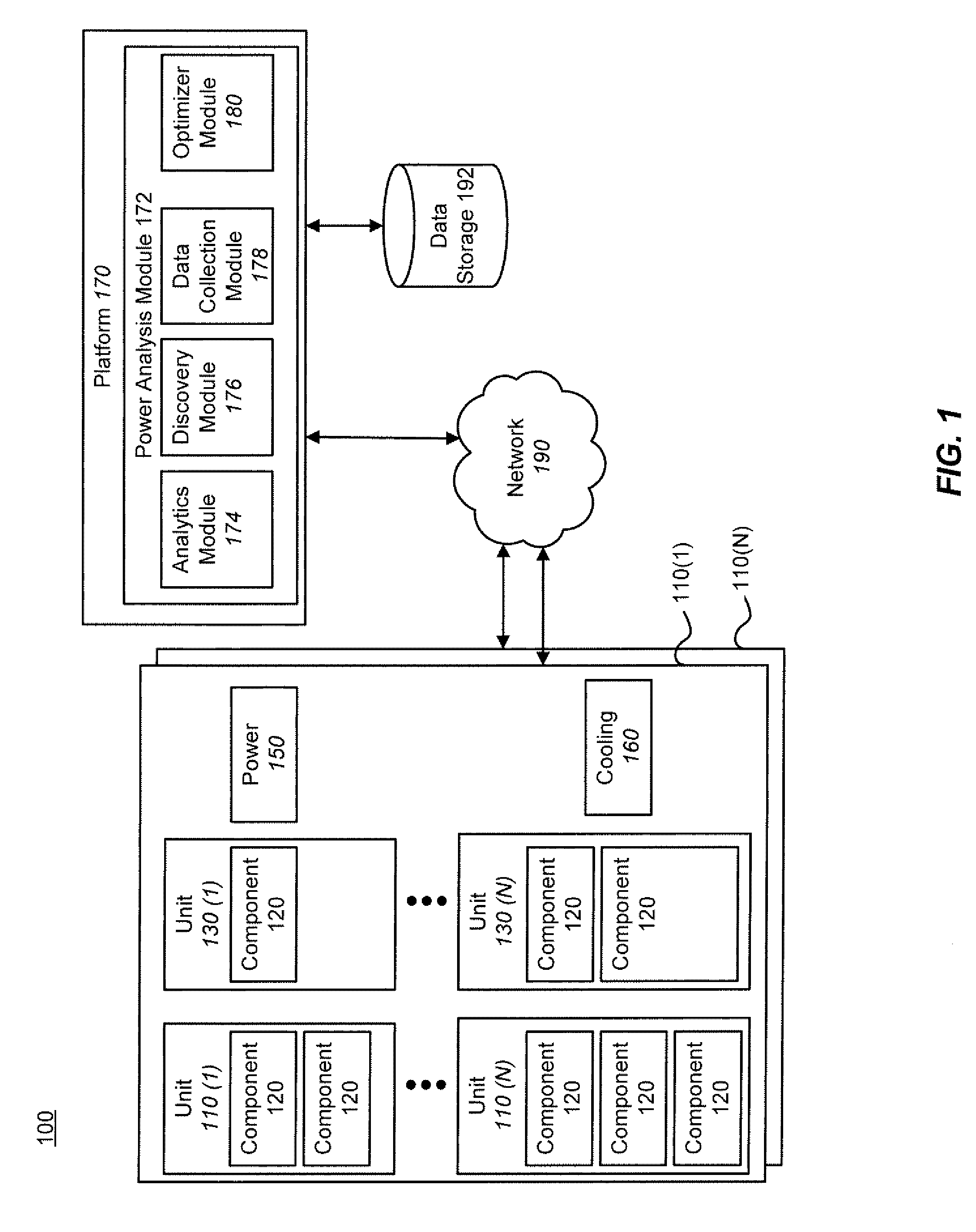
Techniques for power analysis for data centers are disclosed. In one particular exemplary embodiment, the techniques may be realized as a method for power analysis for a plurality of computing platform components comprising receiving information associated with a component, retrieving, using a computer processor, electronically stored data associated with the component, estimating power usage of the component based at least in part on the stored data, and outputting an indicator of power usage.
Owner:SCHNEIDER ELECTRIC IT CORP
Processing apparatus, program, or system of secret information
InactiveUS6873706B1Reduce correlationTotal current dropKey distribution for secure communicationPublic key for secure communicationComputer hardwarePower analysis
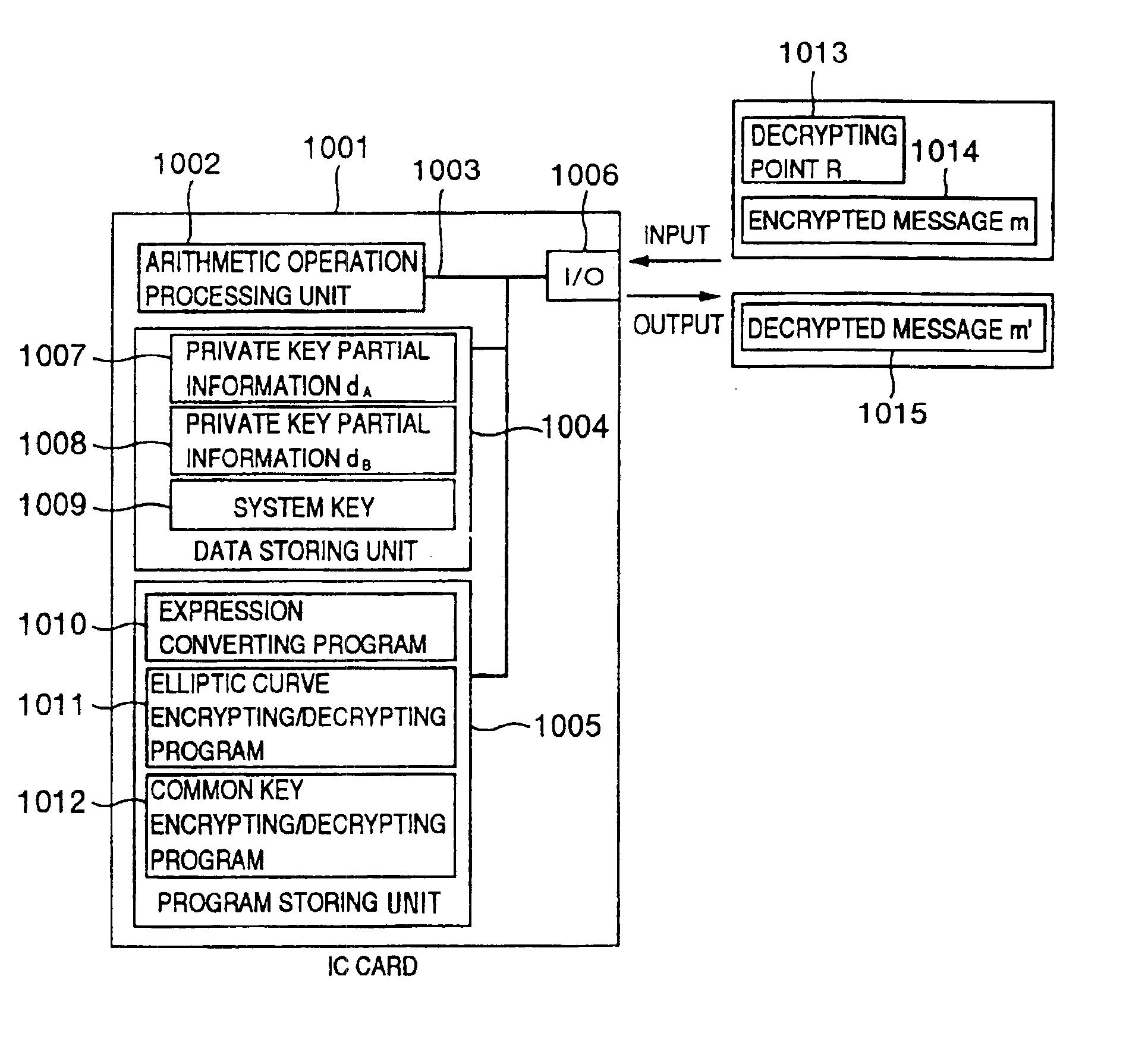
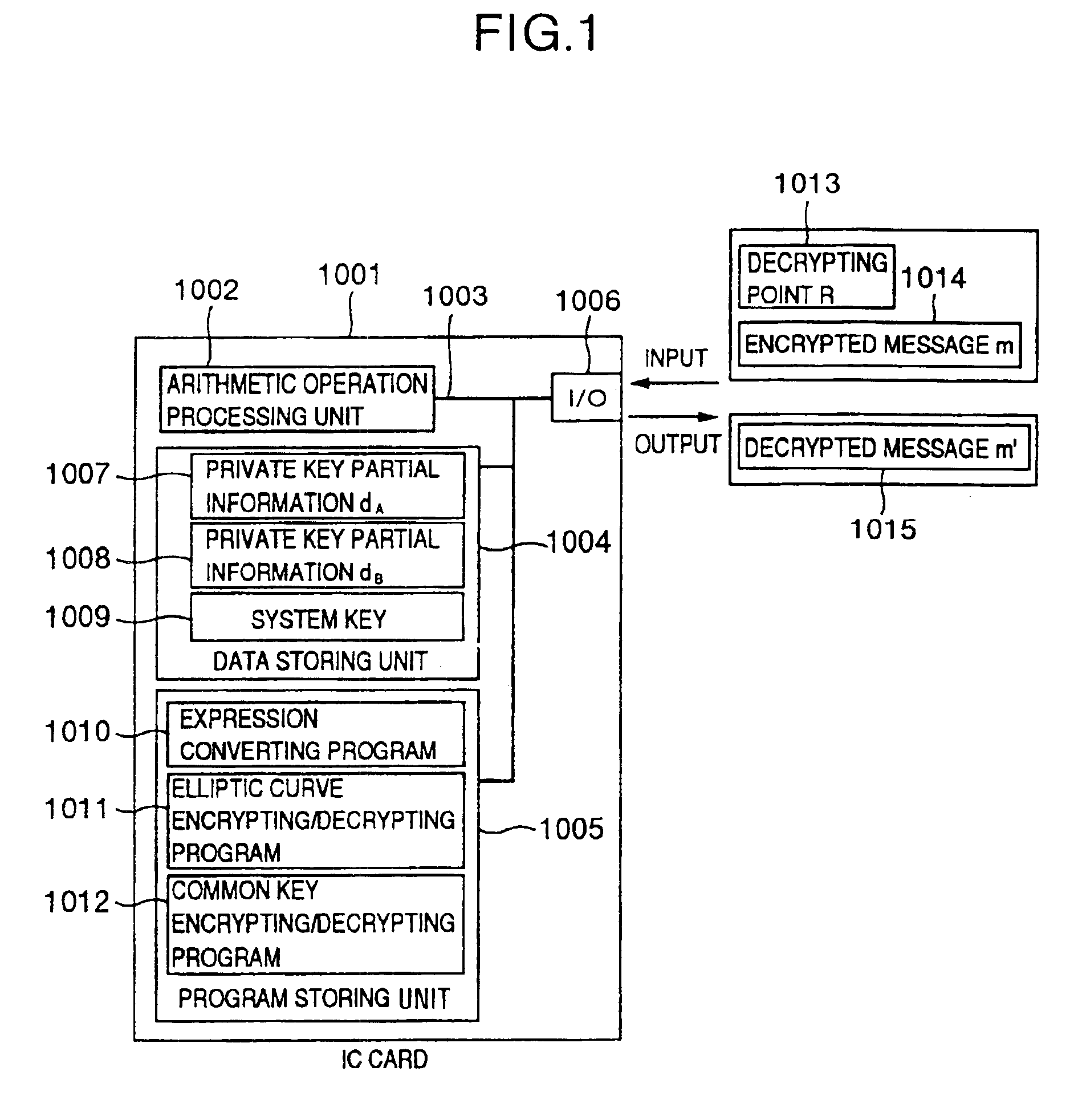
To provide a secure cryptographic device such as an IC card which can endure TA (Timing Attack), DPA (Differential Power Analysis), SPA (Simple Power Analysis), or the like as an attaching method of presuming secret information held therein, when the secret information held in the card or another information which is used in the secret information or an arithmetic operation using such secret information when such an arithmetic operation is performed is shown by a plurality of expressing methods and the arithmetic operation is performed, thereby making an arithmetic operation processing method different each time the arithmetic operation is performed and making each of an arithmetic operation time, an intensity of a generated electromagnetic wave, and a current consumption different.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
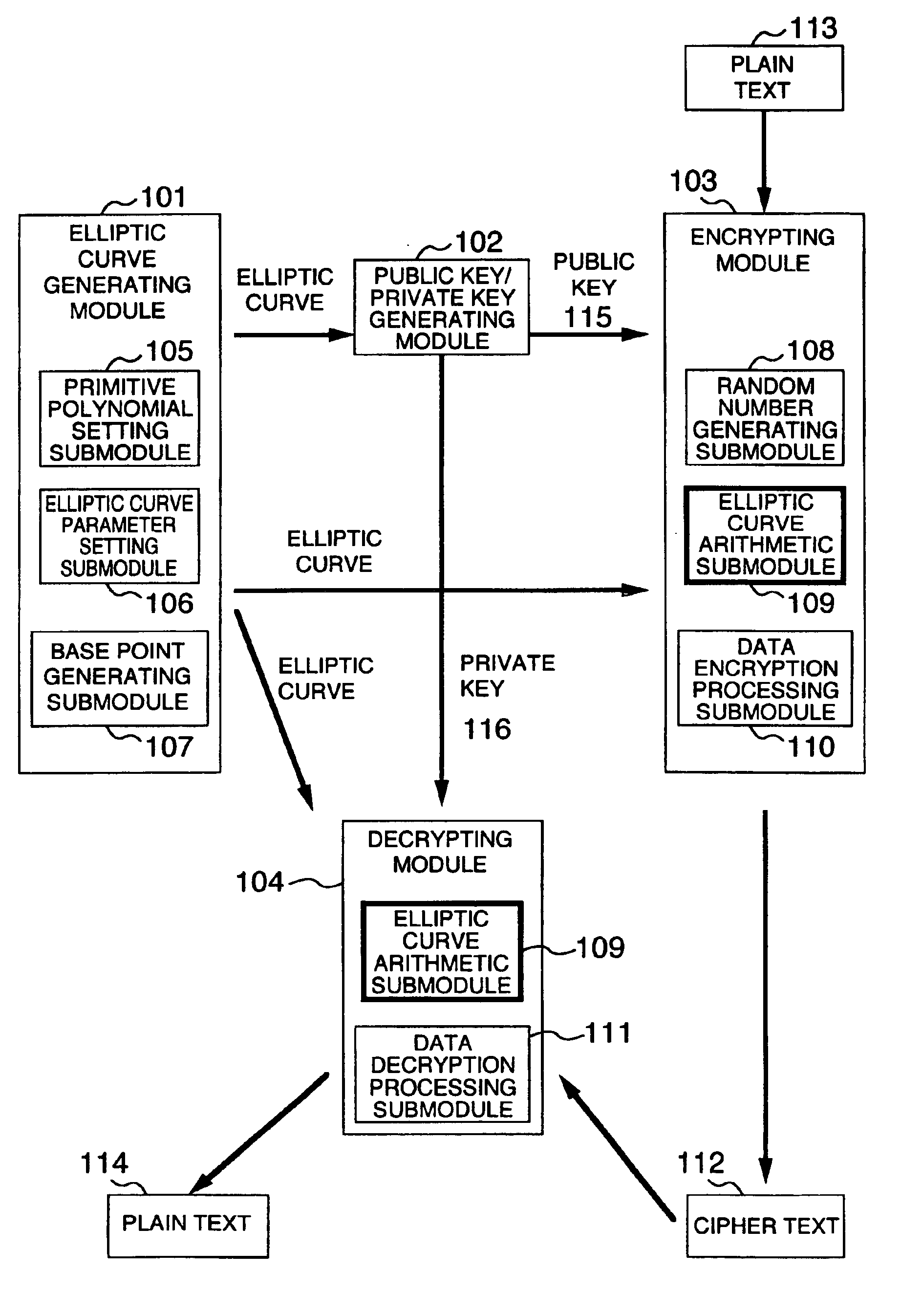
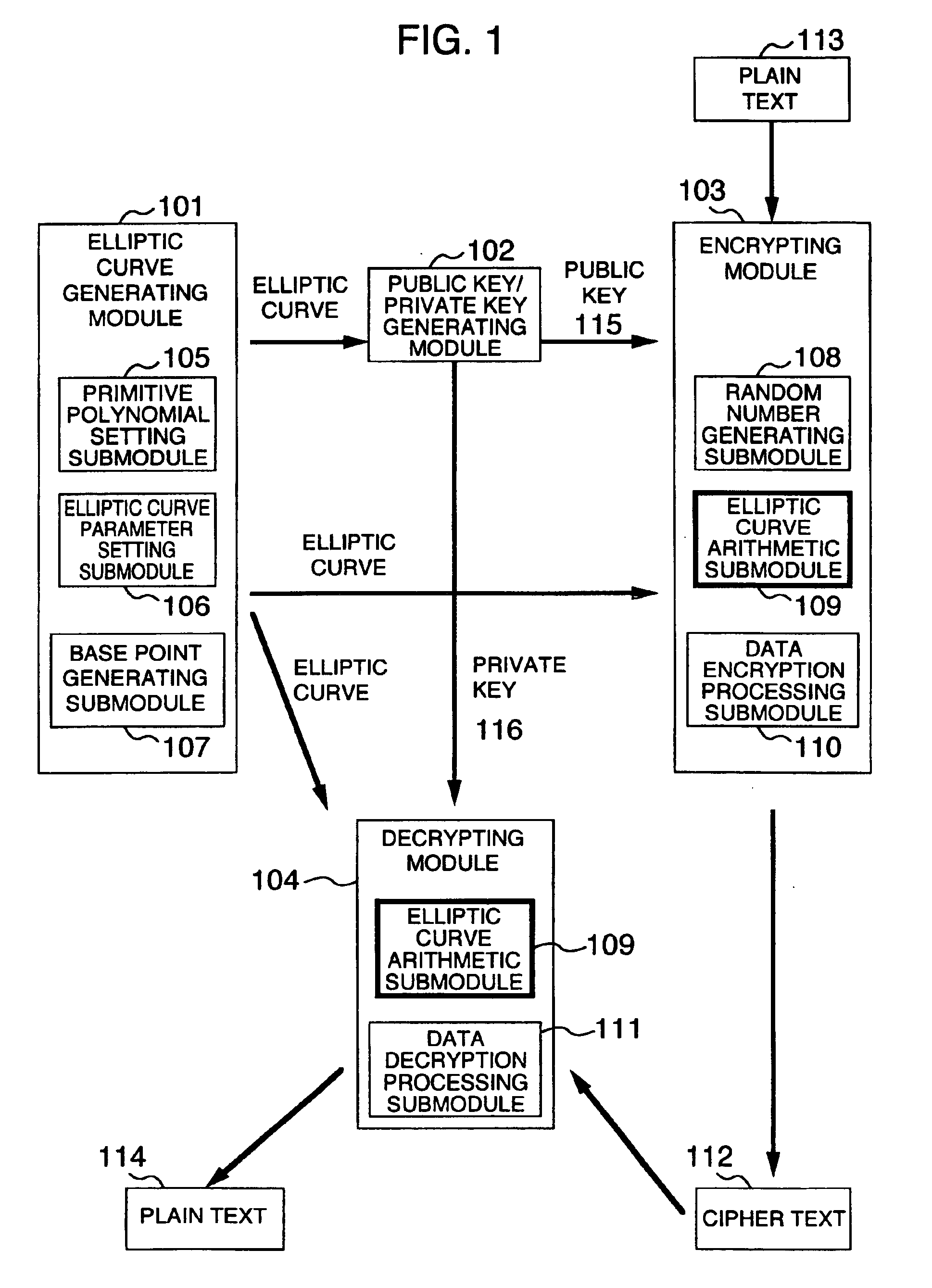
Method and apparatus for elliptic curve cryptography and recording medium therefore
InactiveUS6876745B1Prevent leakageRandom number generatorsPublic key for secure communicationComputer hardwarePower analysis
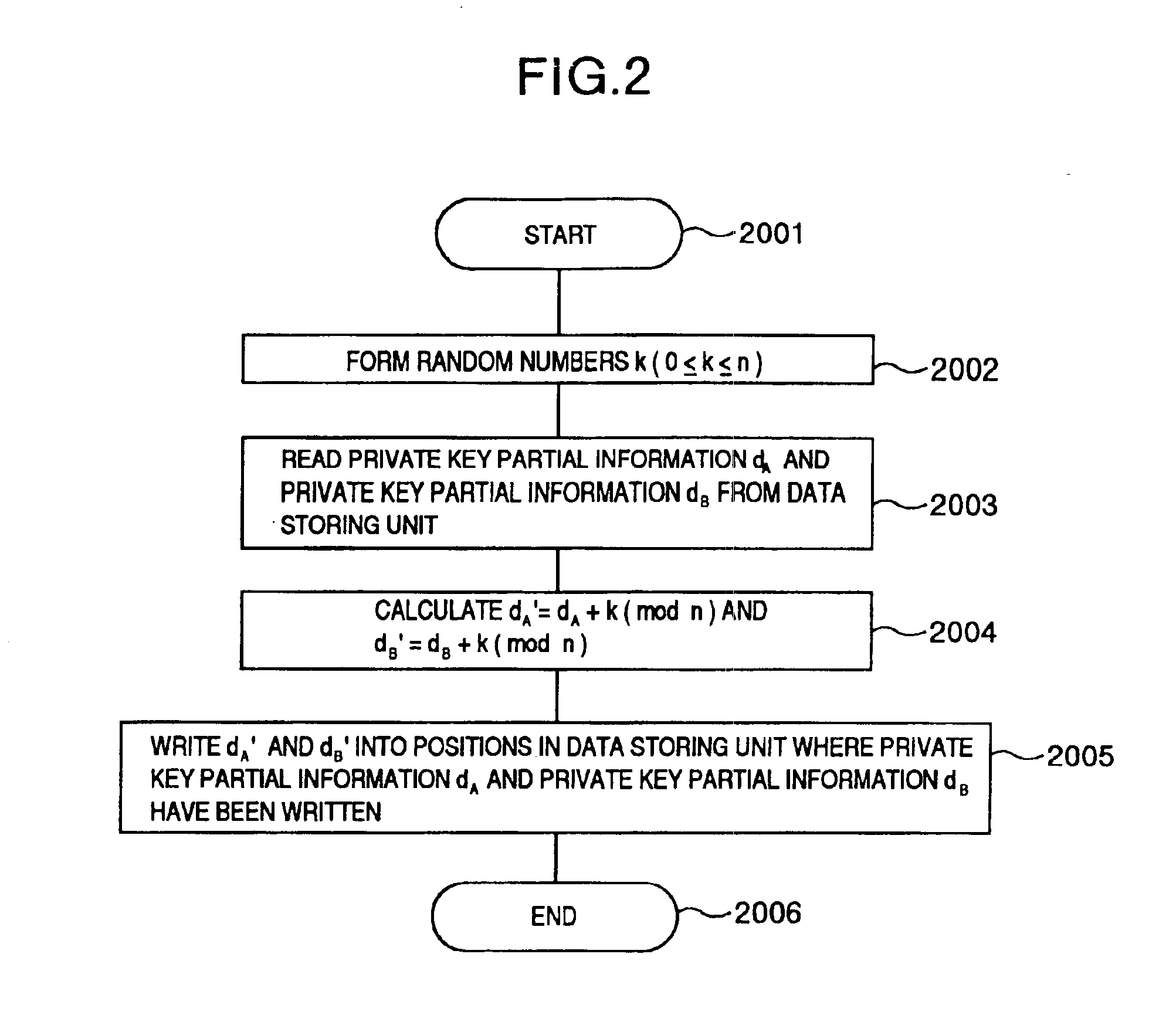
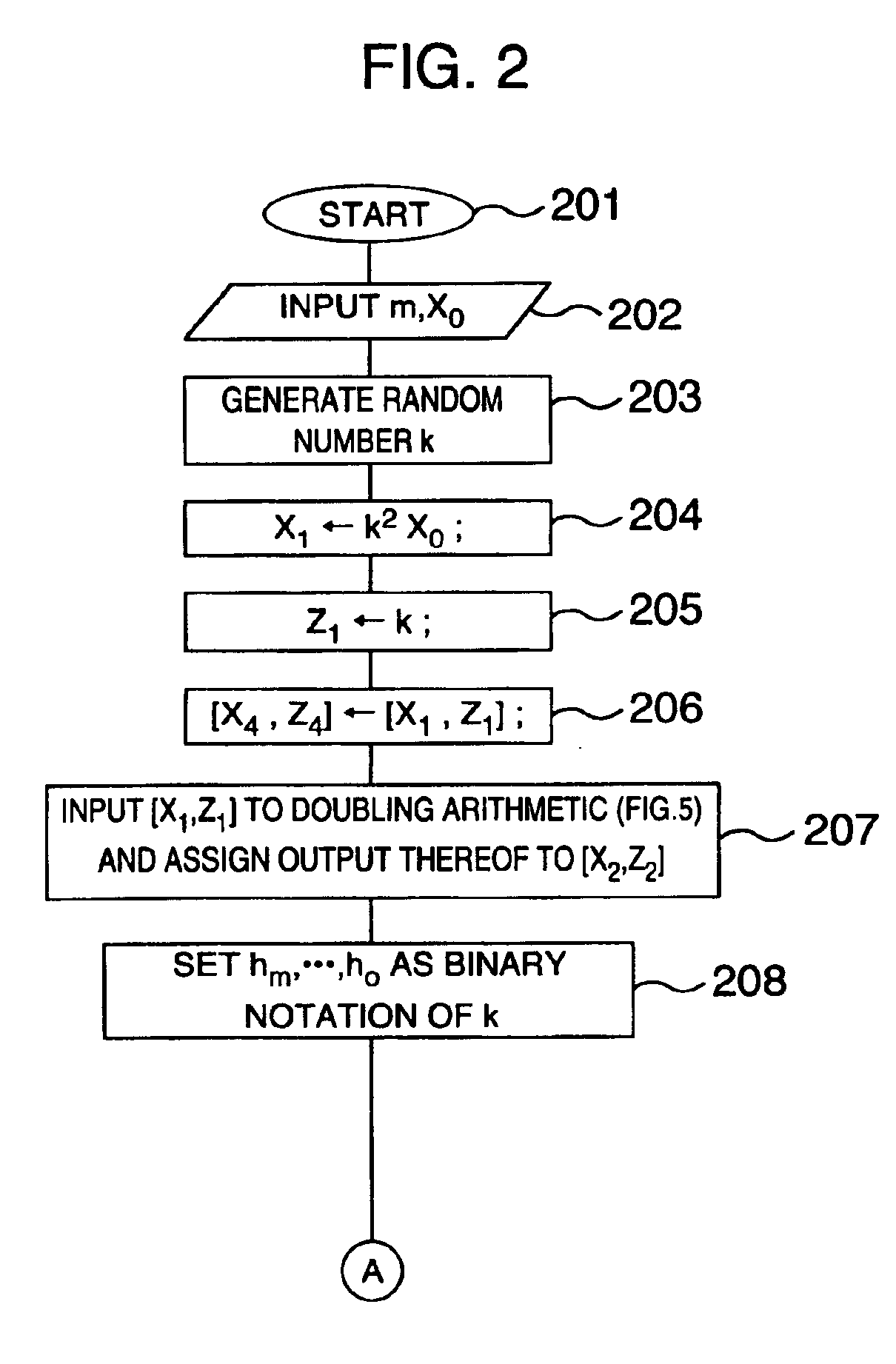
A method and an apparatus capable of realizing at a high speed an elliptic curve cryptography in a finite field of characteristic 2, in which the elliptic curve is given by y2+xy=x3+ax2+b (b≠0) and an elliptic curve cryptography method which can protect private key information against leaking from deviation information of processing time to thereby defend a cipher text against a timing attack and a differential power analysis attack are provided. To this end, an arithmetic process for executing scalar multiplication arithmetic d(x, y) a constant number of times per bit of the private key d is adopted. Further, for the scalar multiplication d(x, y), a random number k is generated upon transformation of the affine coordinates (x, y) to the projective coordinates for thereby effectuating the transformation (x, y)→[kx, ky, k] or alternatively (x, y)→[k2x, k3y, k]. Thus, object for the arithmetic is varied by the random number (k).
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Cryptographic architecture with random instruction masking to thwart differential power analysis
ActiveUS20050271202A1Memory loss protectionEncryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesComputer hardwarePower analysis
An apparatus and method for preventing information leakage attacks that utilize timeline alignment. The apparatus and method inserts a random number of instructions into an encryption algorithm such that the leaked information can not be aligned in time to allow an attacker to break the encryption.
Owner:HRL LAB
Security countermeasures for power analysis attacks
ActiveUS20050232430A1High performance cryptographic implementationControl overheadKey distribution for secure communicationEncryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesPower analysisCountermeasure
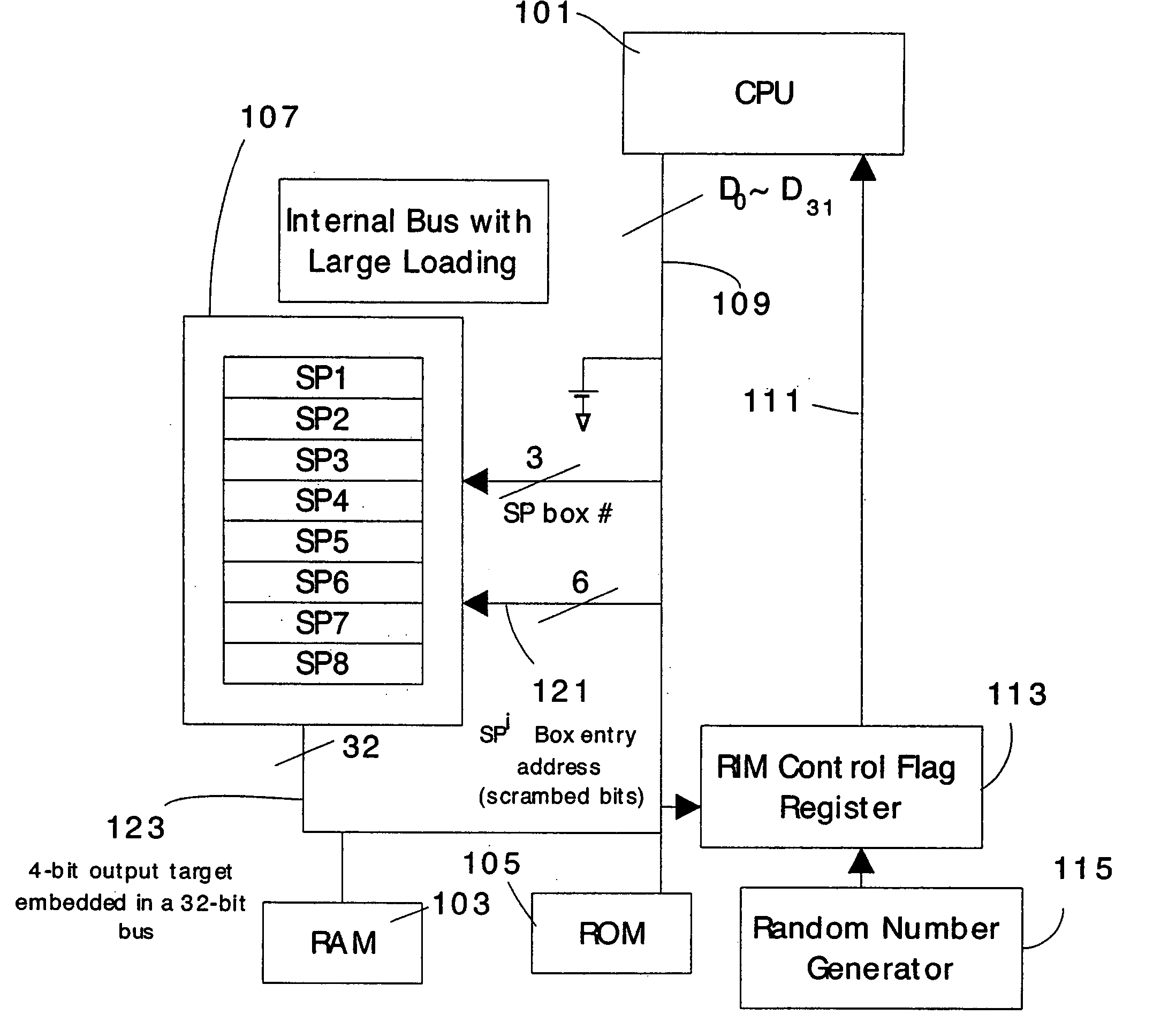
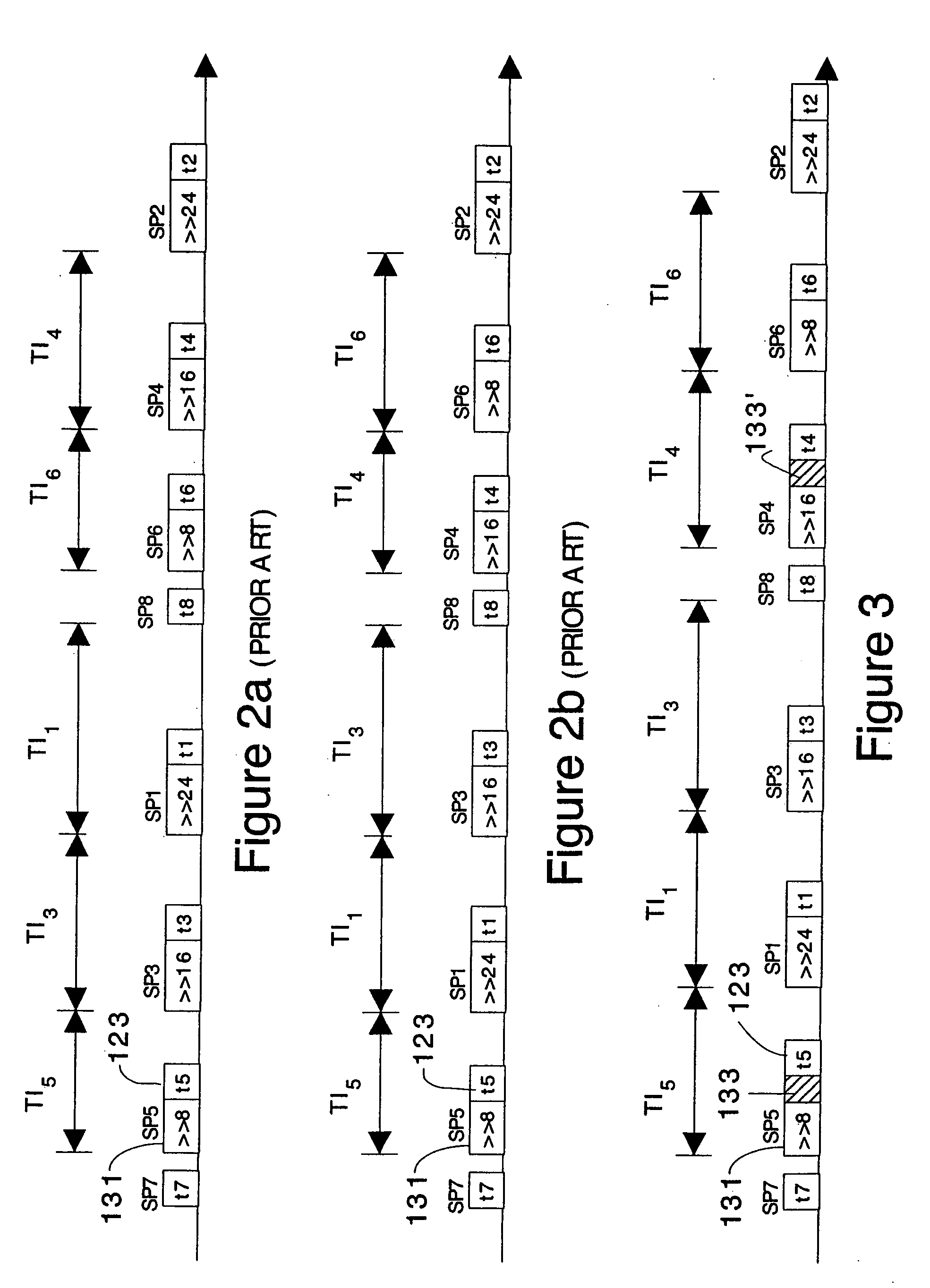
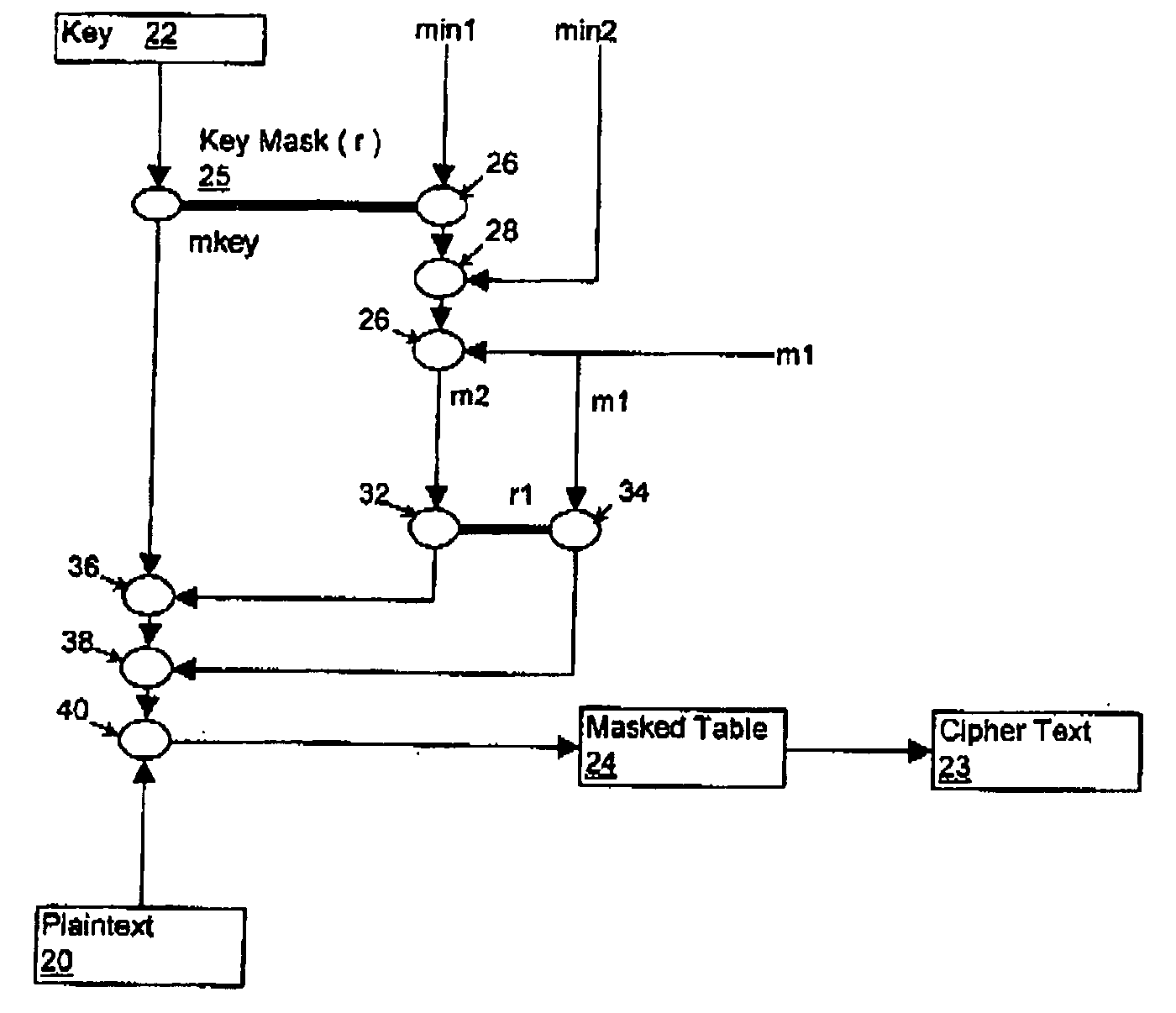
A countermeasure for differential power analysis attacks on computing devices. The countermeasure includes the definition of a set of split mask values. The split mask values are applied to a key value used in conjunction with a masked table defined with reference to a table mask value. The set of n split mask values are defined by randomly generating n−1 split mask values and defining an nth split mask value by exclusive or'ing the table mask value with the n−1 randomly generated split mask values.
Owner:MALIKIE INNOVATIONS LTD
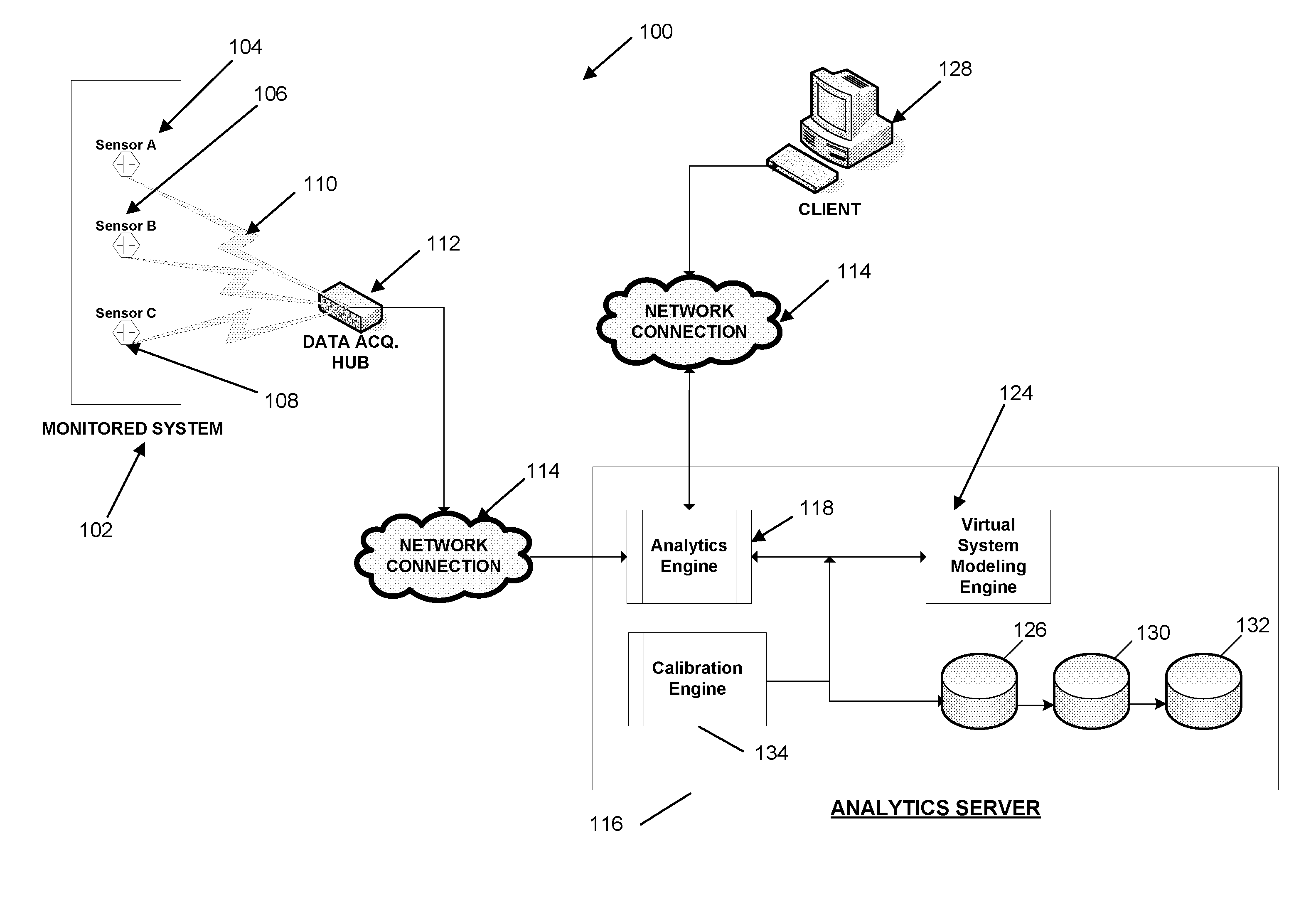
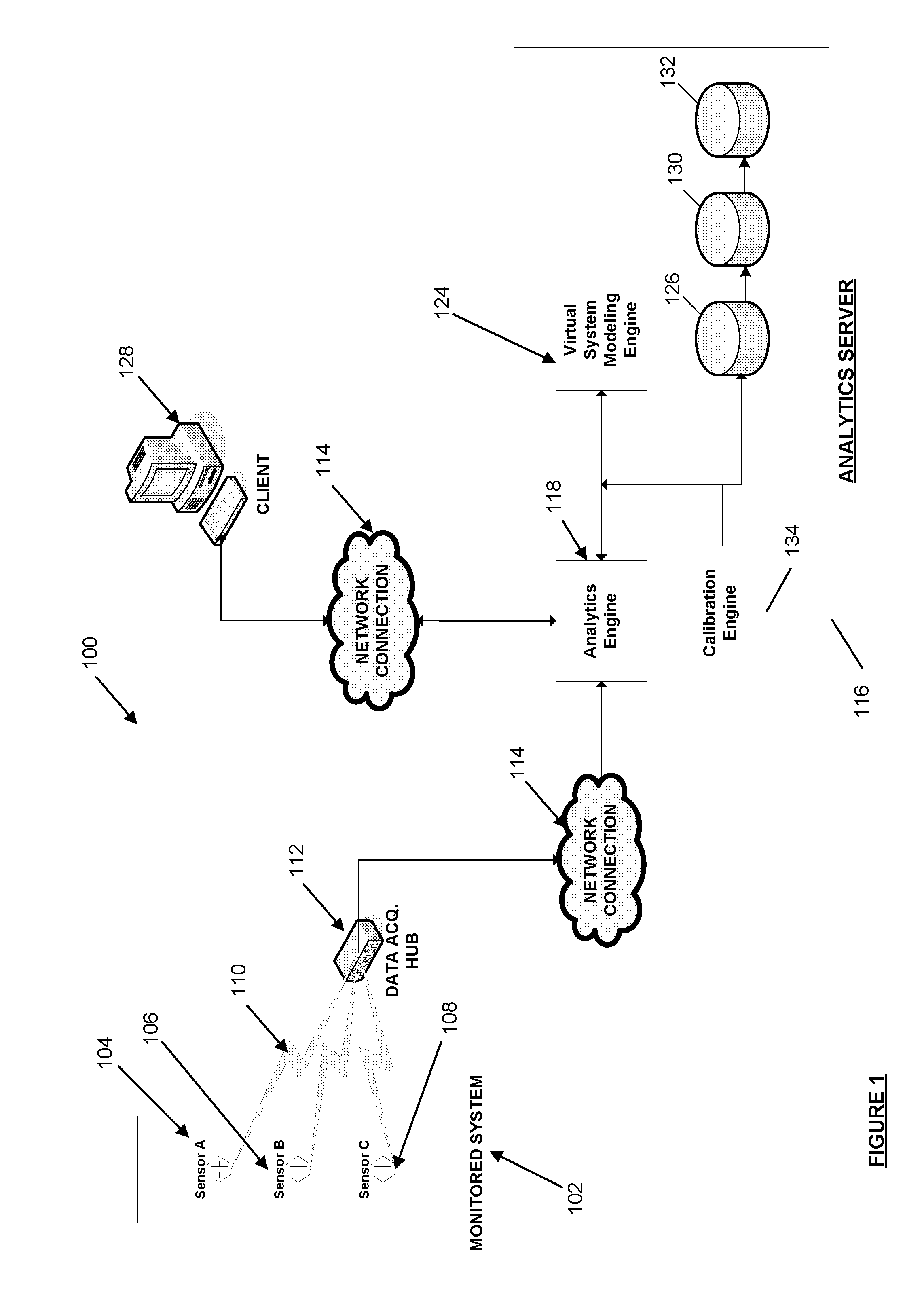
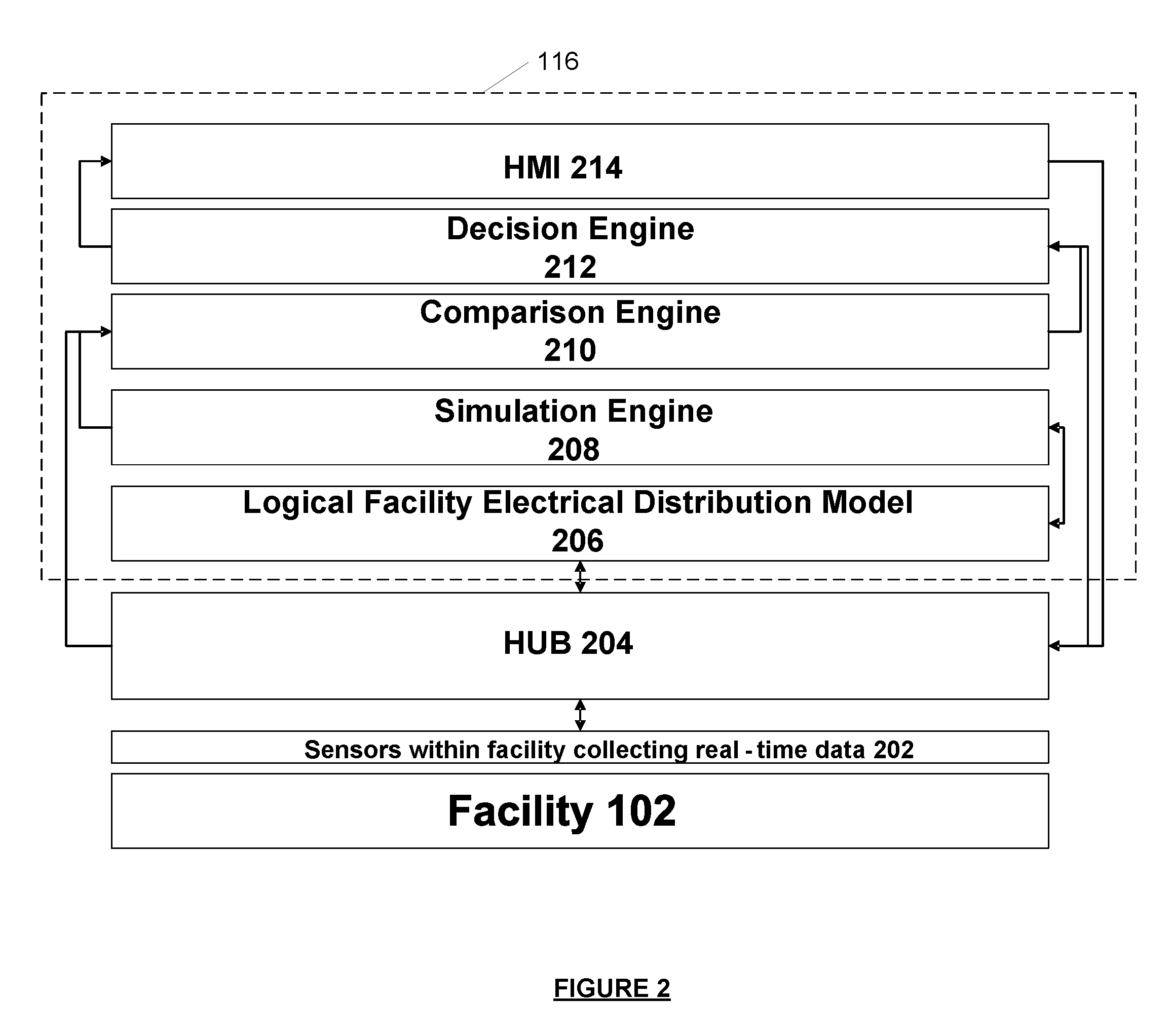
Systems and methods for alarm filtering and management within a real-time data acquisition and monitoring environment
A system for filtering and interpreting real-time sensory data from an electrical system is disclosed. The system includes a data acquisition component, a power analytics server and a client terminal. The data acquisition component acquires real-time data output from the electrical system. The power analytics sewer is comprised of a virtual system modeling engine, an analytics engine, and a decision engine. The virtual system modeling engine generates predicted data output for the electrical system. The analytics engine monitors real-lime data output and predicted data output of the electrical system. The decision engine compares the real-time data output against the predicted data output to filter out and interpret indicia of electrical system health and performance. The client terminal is communicatively connected to the power analytics server and configured to display the filtered and interpreted indicia
Owner:POWER ANALYTICS CORP
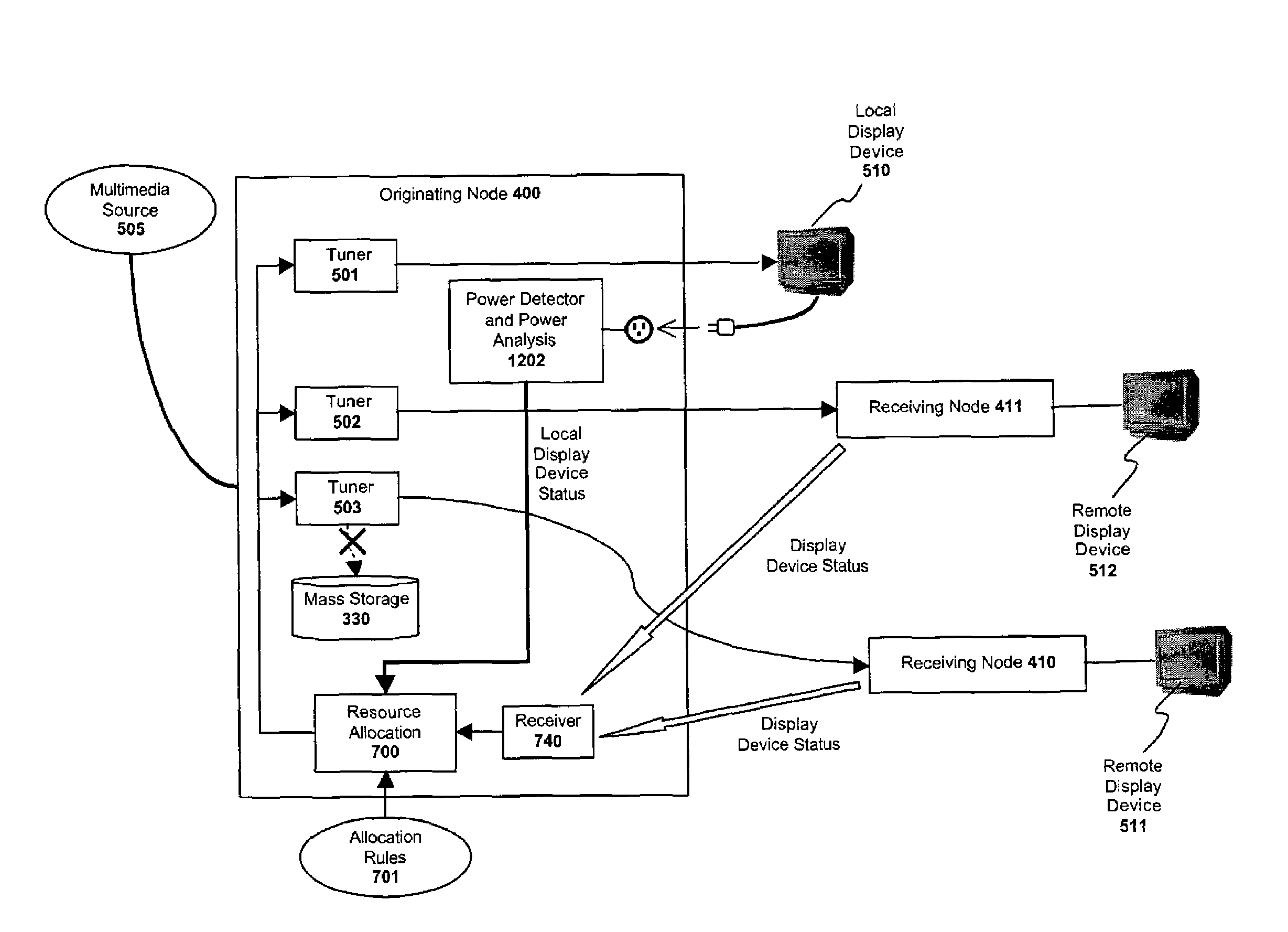
System and method for automatically sensing the state of a video display device
Owner:ARRIS ENTERPRISES LLC
Cryptographic bus architecture for the prevention of differential power analysis
InactiveUS20050273630A1Encryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesDigital data processing detailsComputer hardwarePower analysis
An apparatus and method for preventing information leakage attacks through a polarized cryptographic bus architecture. The polarized cryptographic bus architecture randomly changes the polarity of the target bit such that the leaked information cannot be consistently averaged to yield statistical key material. Further, to increase the prevention of information leakage attacks, a set of dual rails is used to write data to a given register bit.
Owner:HRL LAB
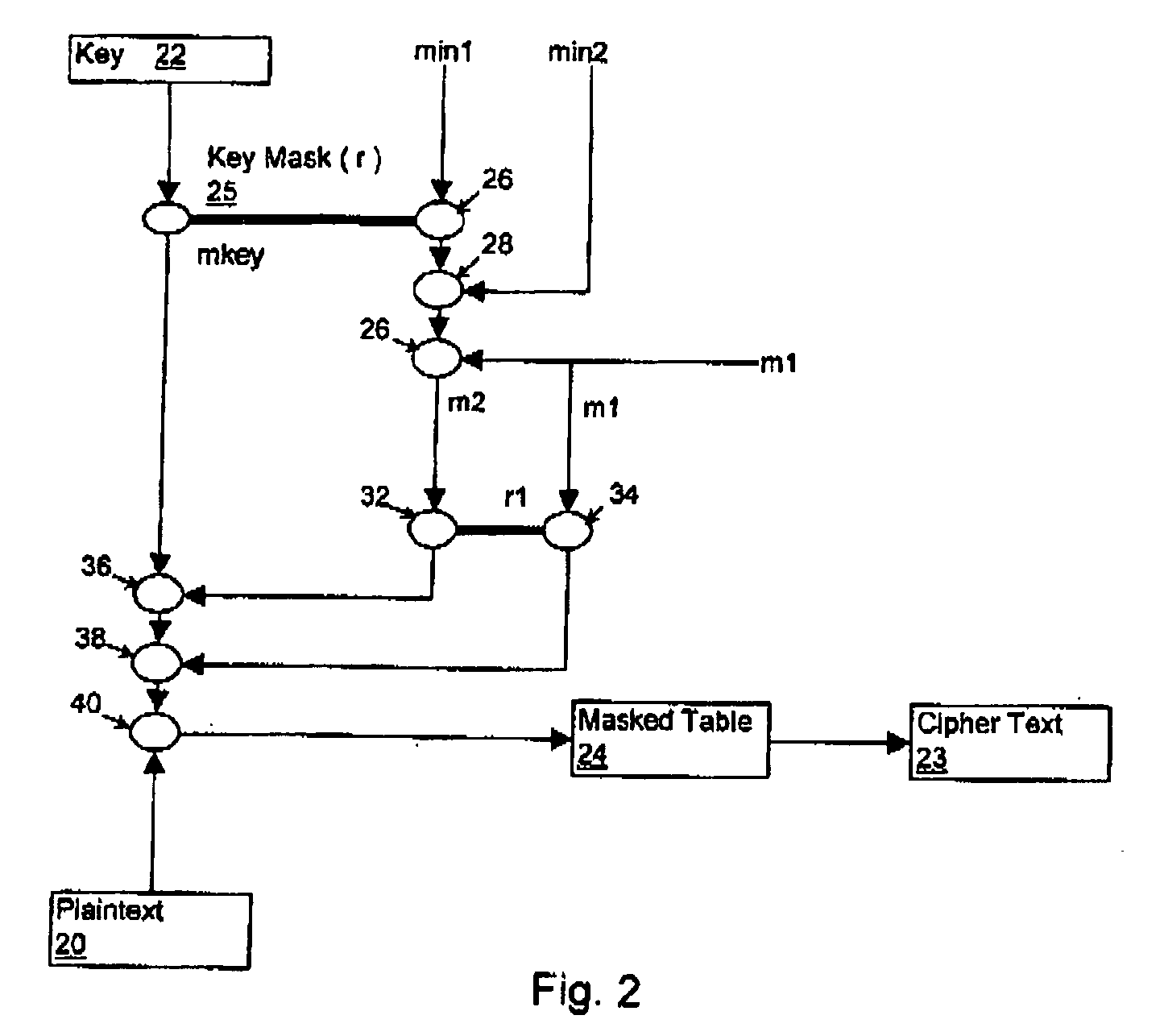
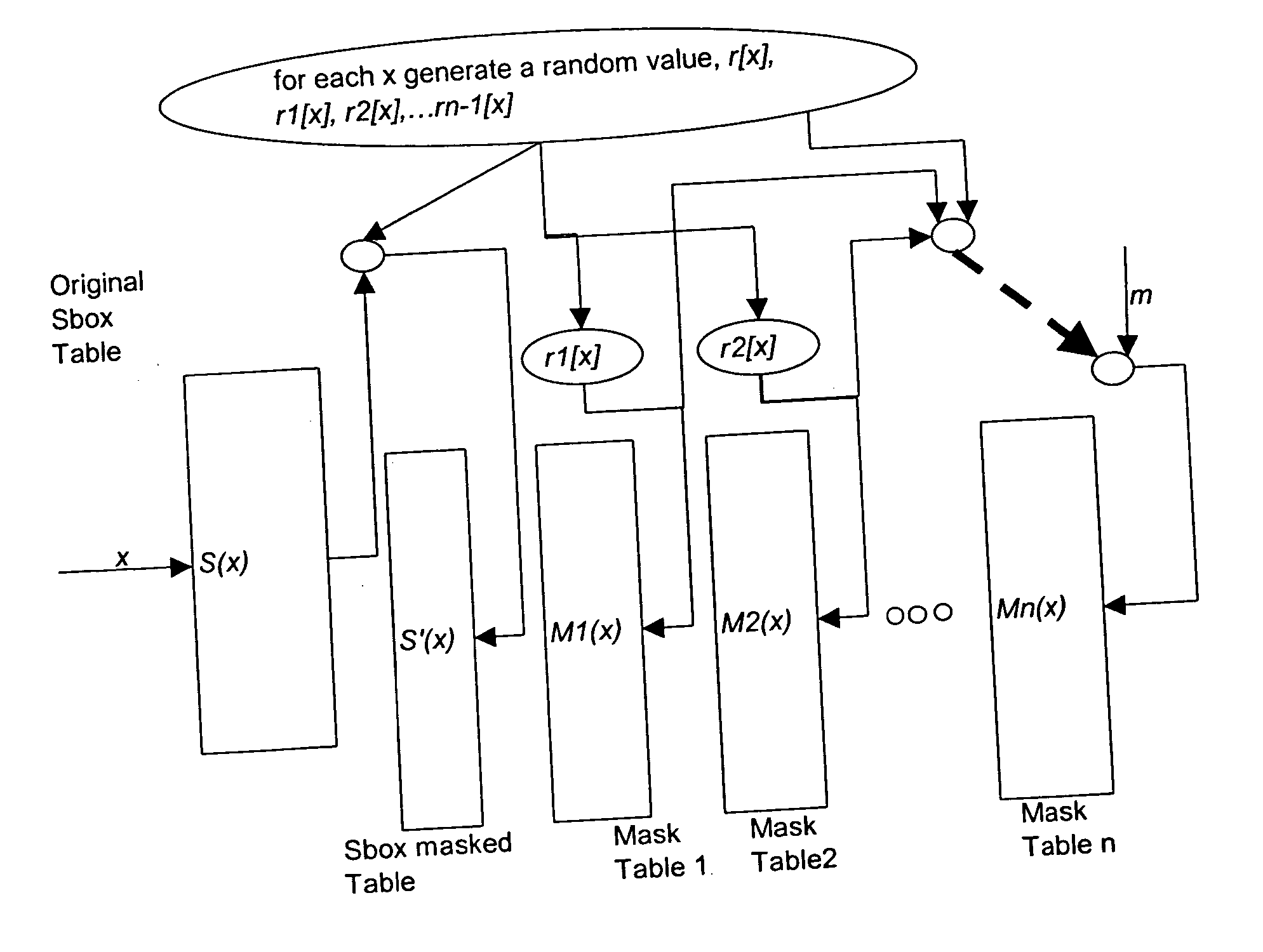
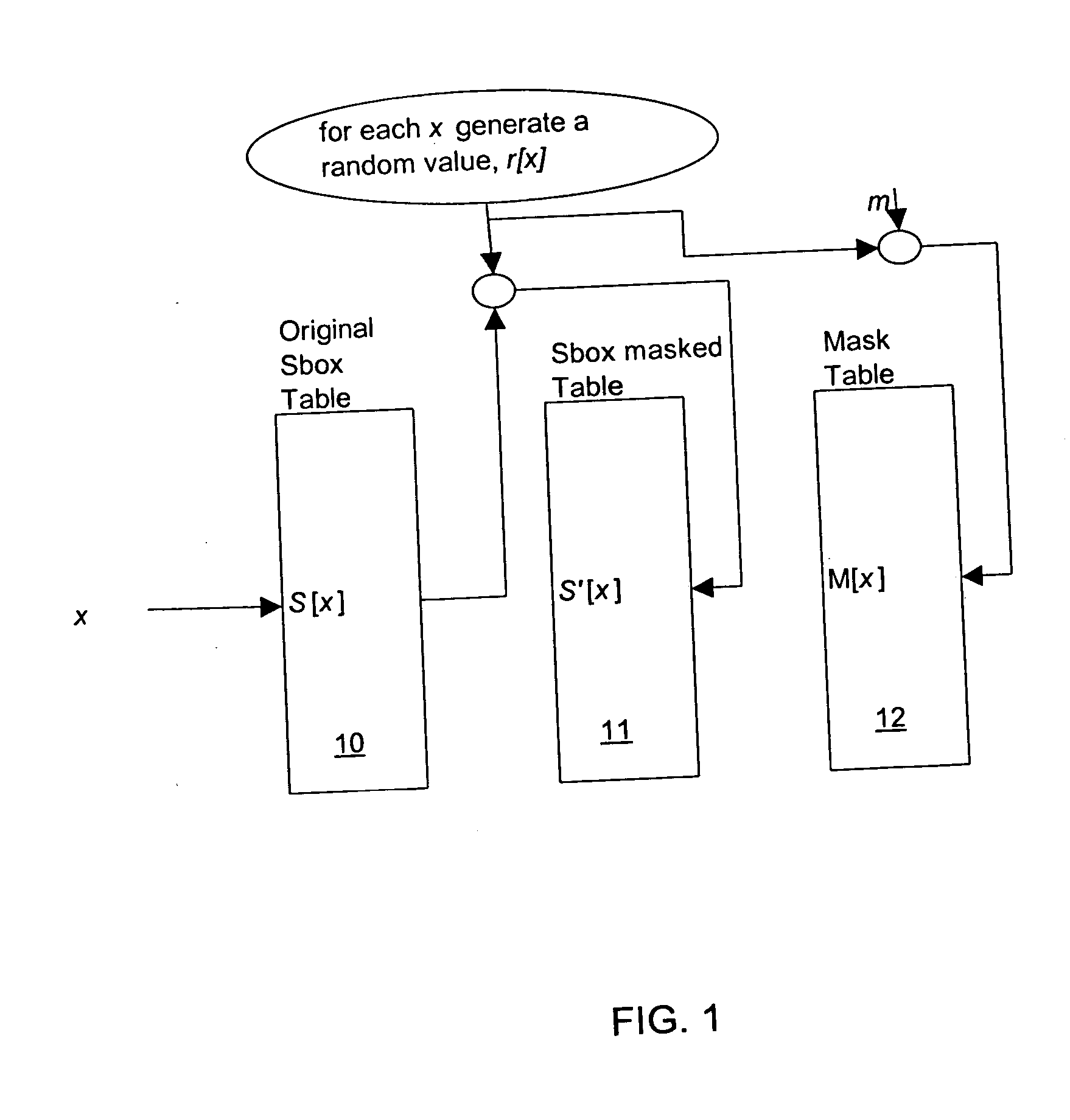
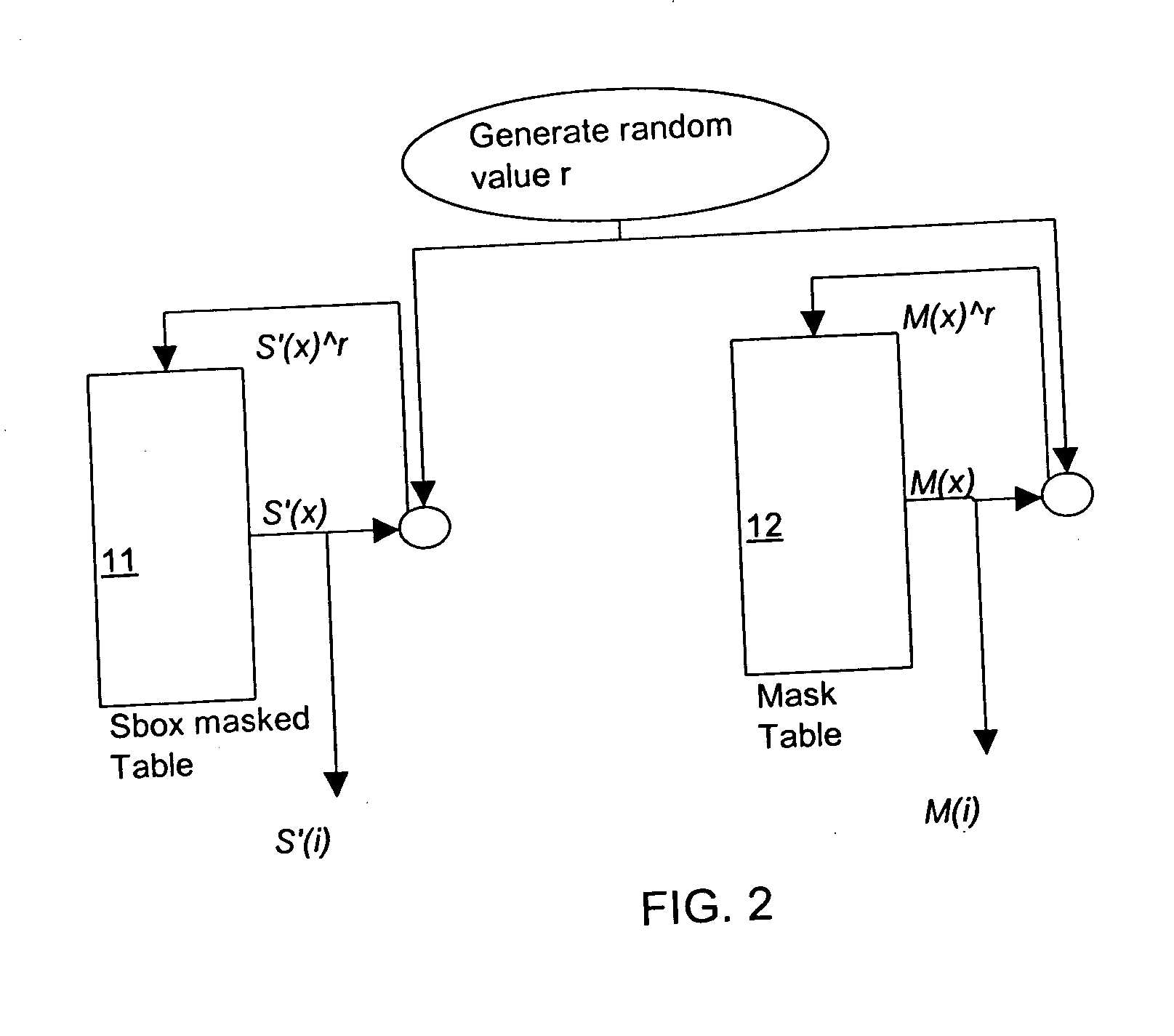
Table masking for resistance to power analysis attacks
ActiveUS20050259814A1Enhanced countermeasureEncryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesUser identity/authority verificationPower analysisComputer hardware
Tables are defined to permit output masking for table look-ups to be carried out to resist power analysis attacks on cryptographic operations. A set of individually defined random values is used to mask each entry in a substitution table, defining a masked substitution table. A mask table is also defined such that the values of each entry, masked with the corresponding random value, is the value of a fixed mask. The masked substitution tables and the mask tables may be used in cryptographic operations to permit the output of table look-ups to be masked, without directly using the fixed mask value in the computations of the cryptographic operations.
Owner:BLACKBERRY LTD
Cryptographic CPU architecture with random instruction masking to thwart differential power analysis
InactiveUS20050273631A1Memory loss protectionEncryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesComputer hardwarePower analysis
An apparatus and method for preventing information leakage attacks that utilize timeline alignment. The apparatus and method inserts a random number of instructions into an encryption algorithm such that the leaked information can not be aligned in time to allow an attacker to break the encryption.
Owner:HRL LAB
System and apparatus for vehicle electrical power analysis
InactiveUS20070103284A1Comprehensive informationVehicle testingRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesPower analysisAlternator
Apparatus for monitoring an electrical power supply system of a vehicle, the vehicle having a battery and internal combustion engine, an alternator, and a starter. The apparatus has a filter for determining the battery terminal voltage when the vehicle ignition is turned on. There is also a voltage gradient detector for detecting phase and gradient change of the battery terminal voltage when the vehicle ignition is on. A waveform detector is used for detecting and separating different waveforms when the vehicle ignition is on, and an engine-rotating sensor is used to sense a speed of the internal combustion engine when the vehicle ignition is on. Also included is a processor for processing at least one of the battery terminal voltage, the phase and gradient change, the different waveforms, and the speed of the internal combustion engine. An output is provided that is indicative of a condition of the electrical power supply system. A system for monitoring an electrical power supply system of a vehicle is also disclosed.
Owner:VEPAC TECH PTE
Cryptographic architecture with instruction masking and other techniques for thwarting differential power analysis
ActiveUS20070180541A1Encryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesVolume/mass flow measurementComputer hardwarePower analysis
Owner:HRL LAB
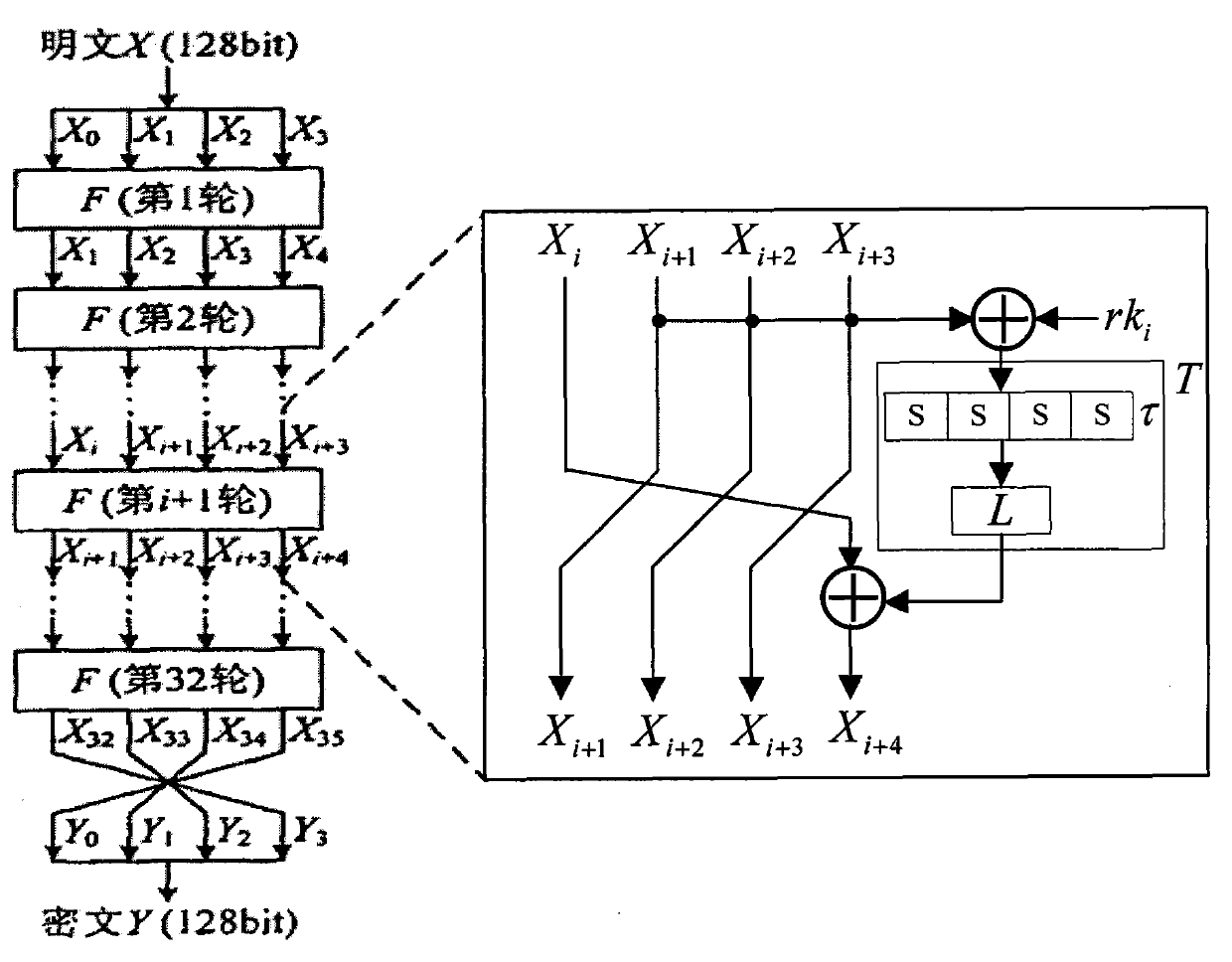
Application method of Hamming distance model on SM4 cryptographic algorithm lateral information channel energy analysis and based on S box input
ActiveCN103138917AExtended Side Channel Energy Analysis MethodEfficient analysisEncryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesPower analysisS-box
The invention discloses an application method of a Hamming distance model on SM4 cryptographic algorithm lateral information channel energy analysis and based on S box input. The application method is characterized in that the Hamming distance model is established by selecting an S box or a round function as an attacking point in the process that the SM4 cryptographic algorithm lateral information channel energy analysis is carried out, the input of the S box is used as an initial state v1 of the Hamming distance model, the output of the S box is used as subsequent state v2 of the Hamming distance (HD (v1, v2)) model when the S box is attacked, and the output / input of the round function is used as the subsequent state v2 of the Hamming distance (HD (v1, v2)) model when the round function is attacked. The method can be applied to CPA / DPA lateral information channel energy analysis of the SM4 cryptographic algorithm. Correlation between a correct guess secret key and energy information is improved, and validity and success rate of the analysis are enhanced.
Owner:国家密码管理局商用密码检测中心
Post-wavelet analysis treating method and device for electric power transient signal
InactiveCN1847867AMeet the requirements of high transmission rateFault locationElectric power transmissionPower quality
The present invention discloses post-wavelet analysis treating method and device for electric power transient signal. The treating method for electric power transient signal after wavelet analysis and before feeding to the electric power monitoring center includes the following treatment on wavelet coefficient: the extraction of module maximum and the detection of irregularity; the statistics and cluster analysis of wavelet coefficient; neural network classification; energy analysis; and wavelet entropy calculation. The present invention can extract the characteristic of electric power transient signal for the application in traveling wave ranging, fault recognition, electric energy quality analysis and equipment fault diagnosis in the transmission line of power system.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
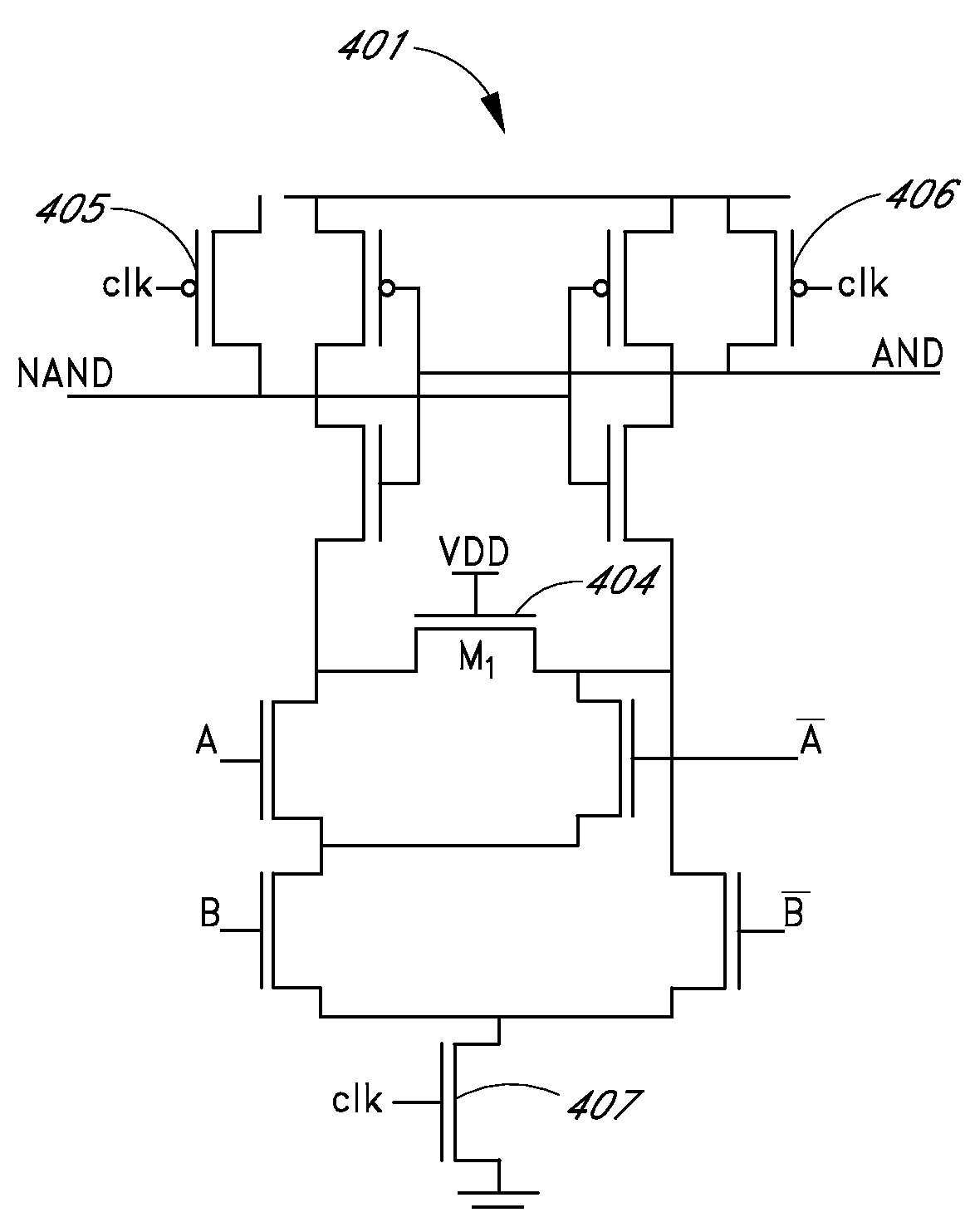
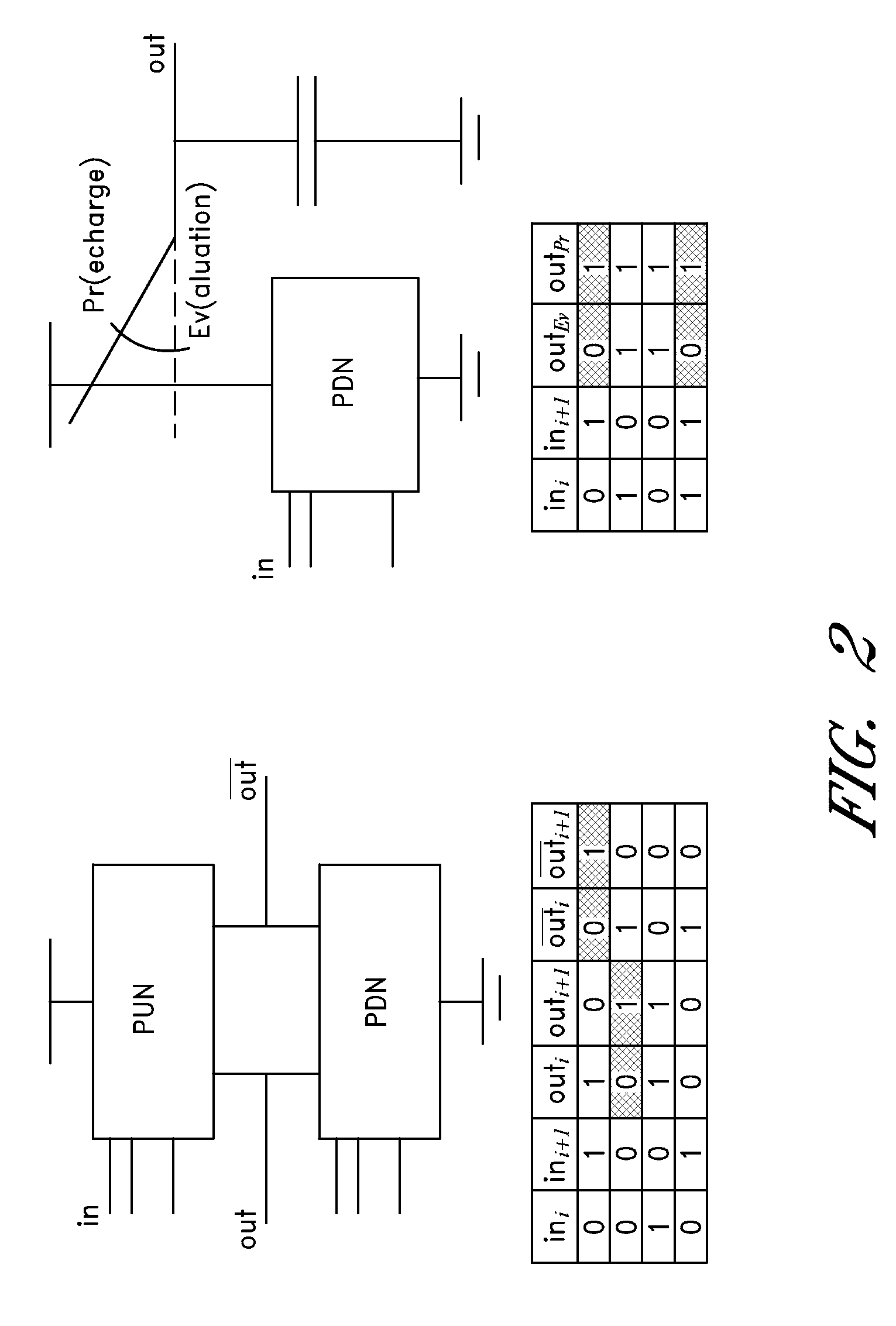
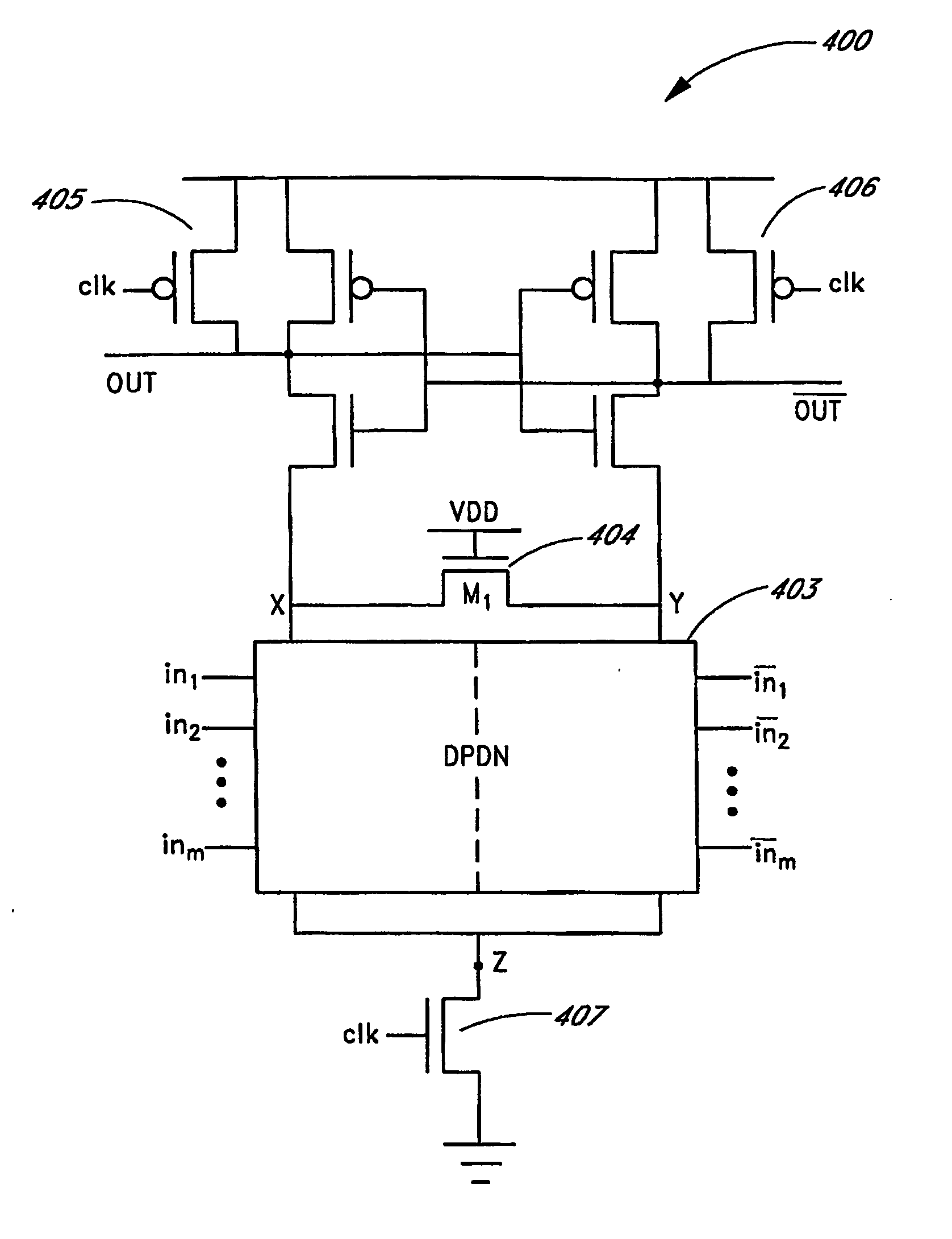
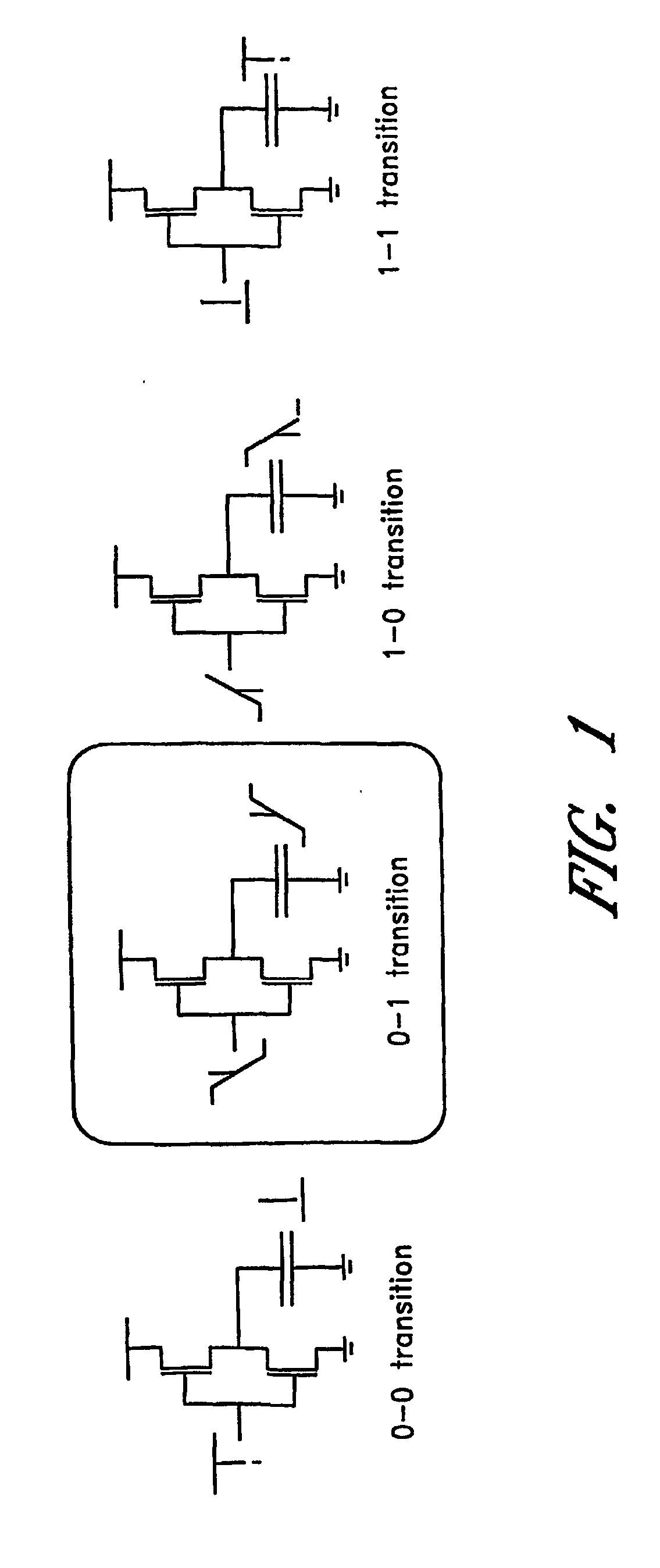
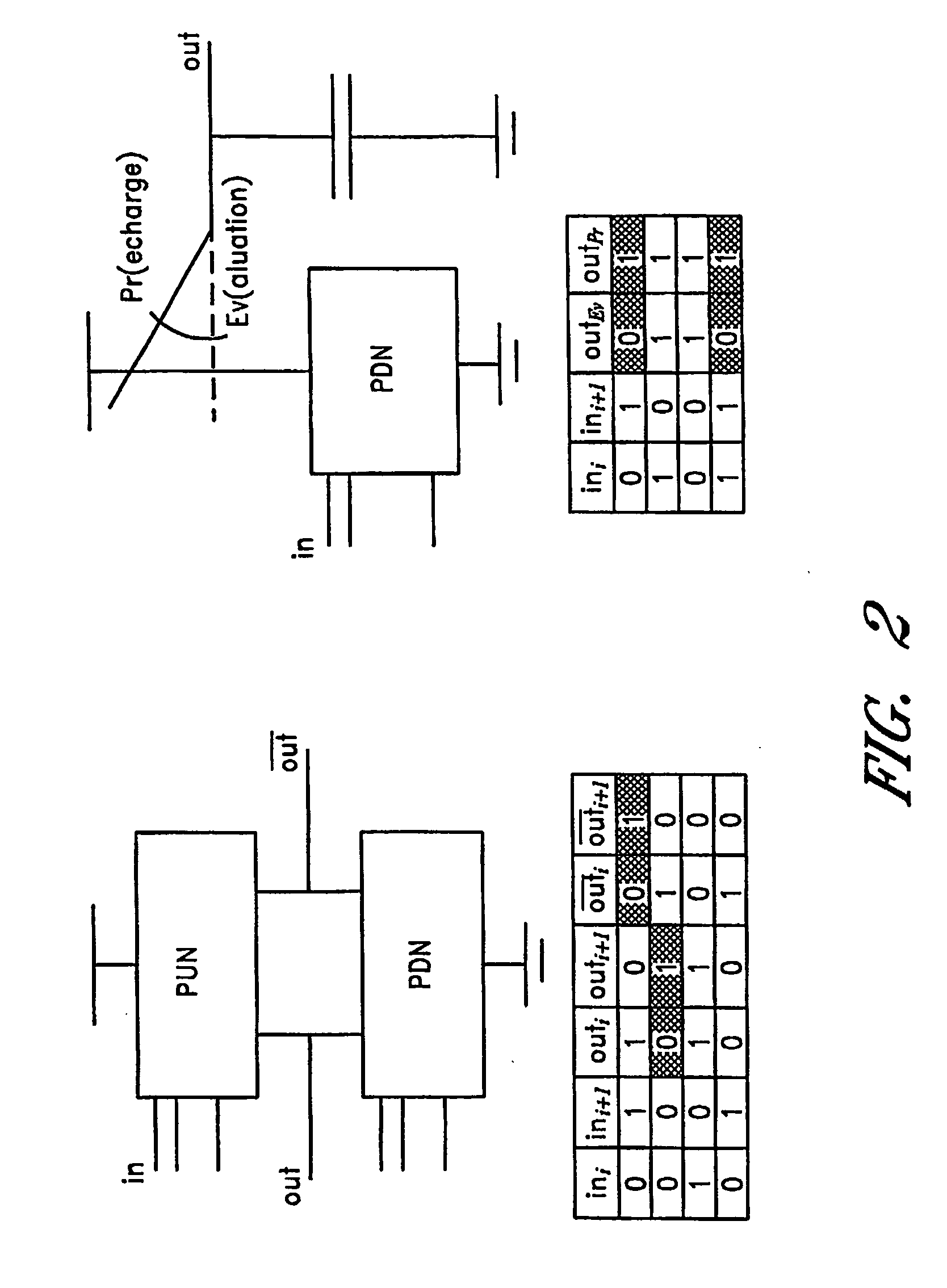
Dynamic and differential CMOS logic with signal-independent power consumption to withstand differential power analysis
InactiveUS7417468B2Logic circuits characterised by logic functionCurrent/voltage measurementPower analysisCapacitance
A dynamic and differential CMOS logic style is disclosed in which a gate uses a fixed amount of energy per evaluation event. The gate switches its output at every event and loads a constant capacitance. The logic style is a Dynamic and Differential Logic (DDL) style. The DDL style logic typically has one charging event per clock cycle and the charging event does not depend on the input signals. The differential feature masks the in-put value because a precharged output nodes is discharged during the evaluation phase. The dynamic feature breaks the input sequence: the discharged node is charged during the subsequent precharge phase.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Cryptographic computation using masking to prevent differential power analysis and other attacks
InactiveUS7668310B2Easy to convertInhibition of informationEncryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesComputer security arrangementsPlaintextPower analysis
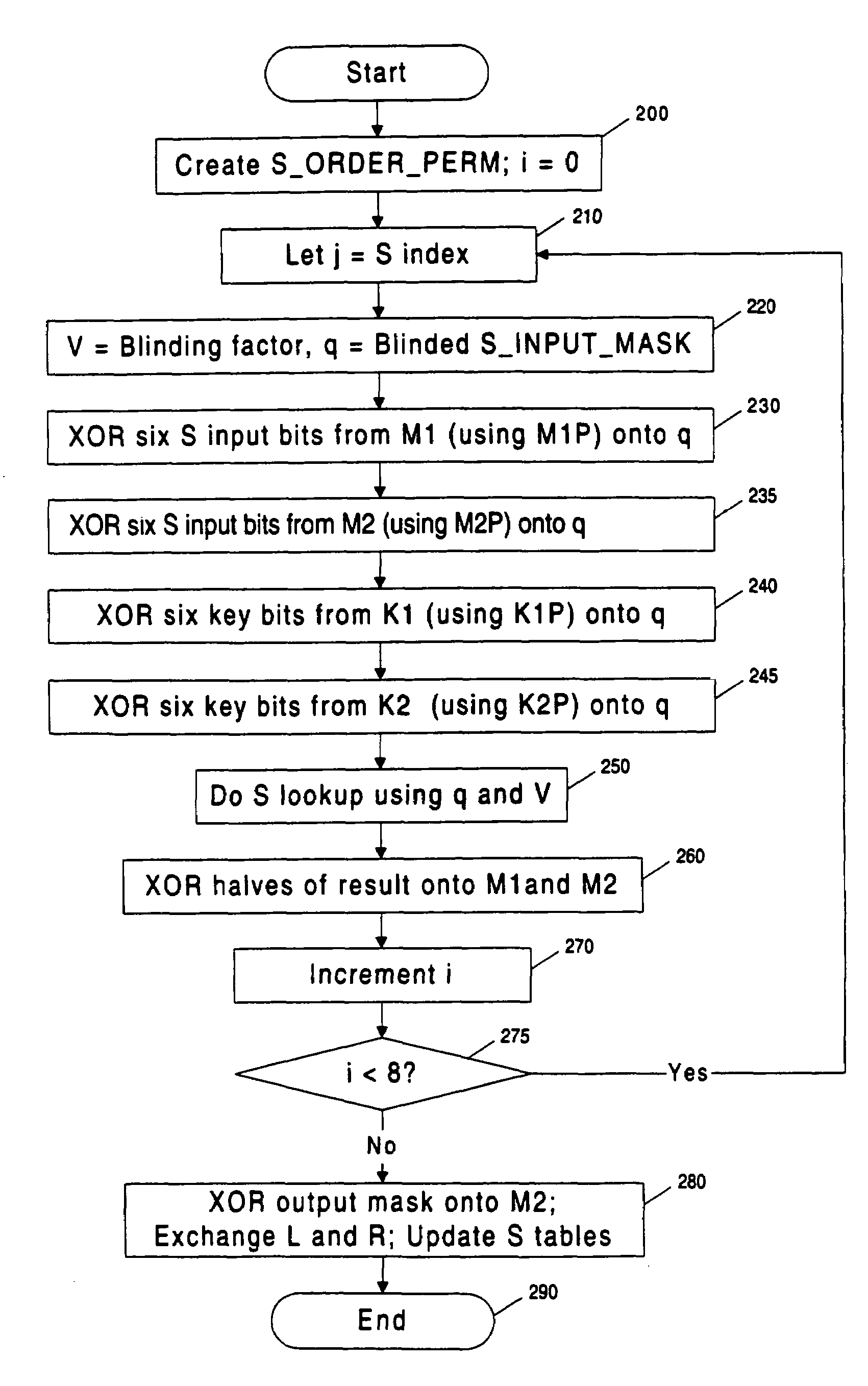
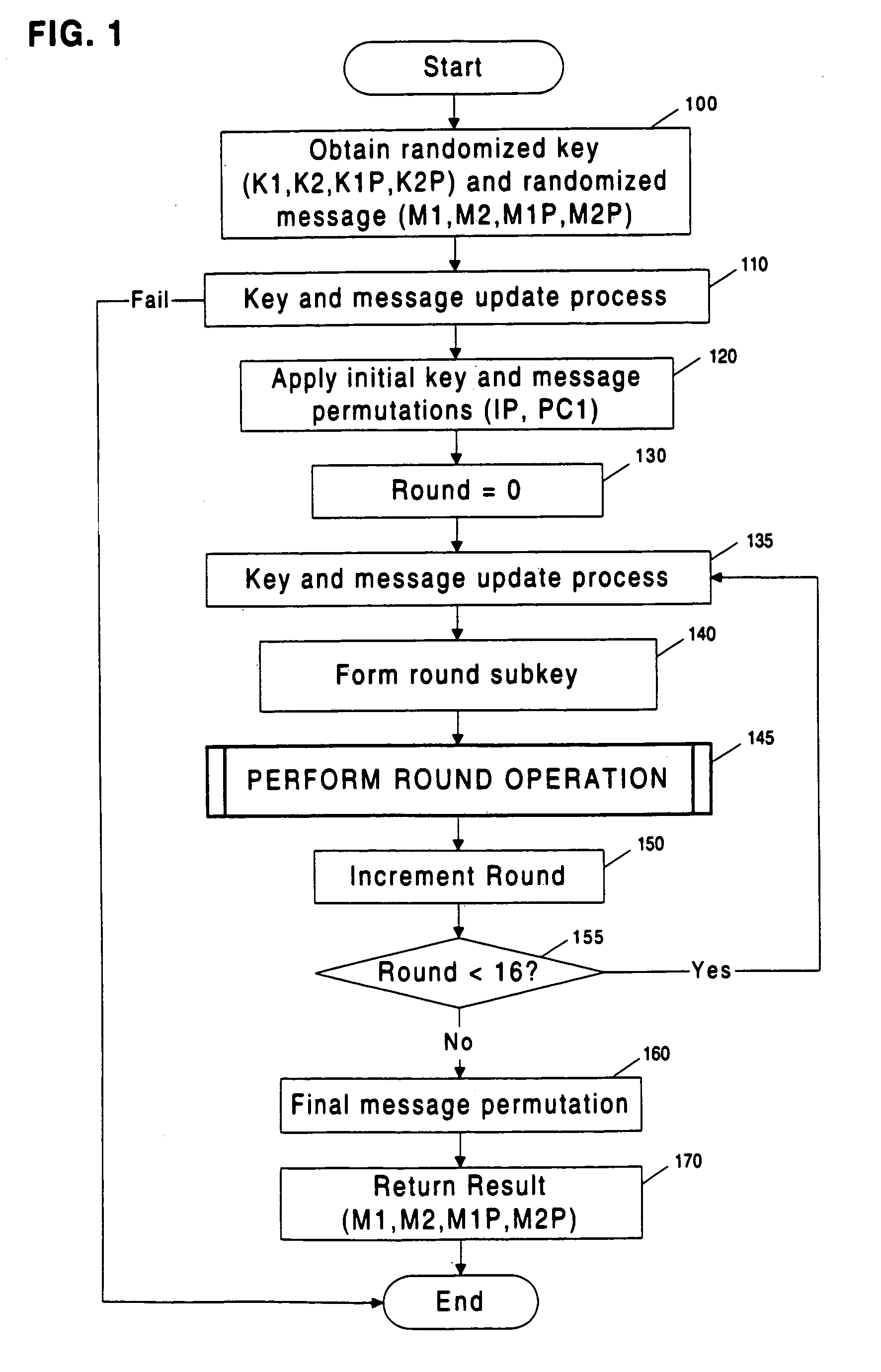
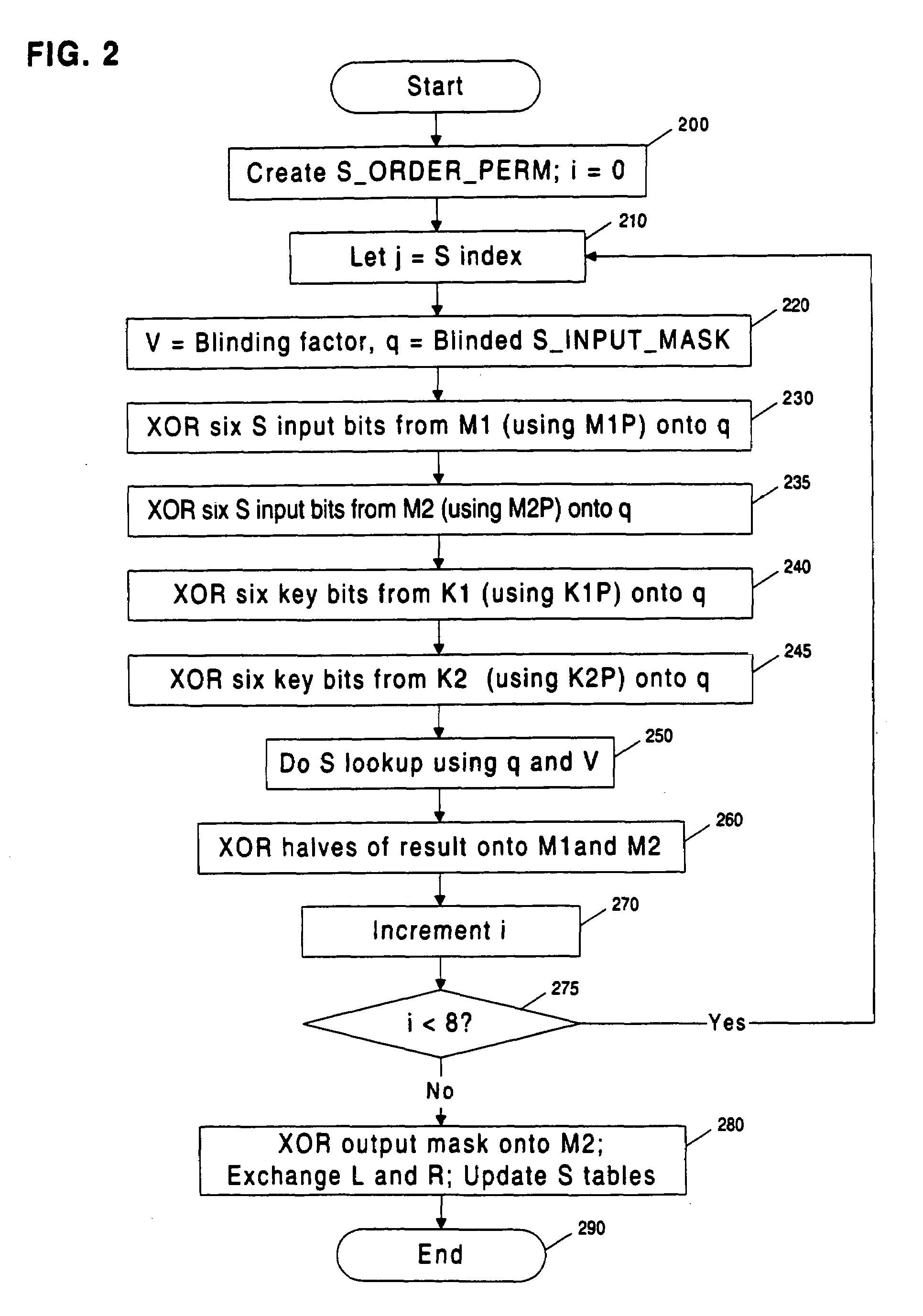
Methods and apparatuses are disclosed for improving DES and other cryptographic protocols against external monitoring attacks by reducing the amount (and signal-to-noise ratio) of useful information leaked during processing. An improved DES implementation of the invention instead uses two 56-bit keys (K1 and K2) and two 64-bit plaintext messages (M1 and M2), each associated with a permutation (i.e., K1P, K2P and M1P, M2P) such that K1P{K1} XOR K2P {K2} equals the “standard” DES key K, and M1P{M1} XOR M2P{M2} equals the “standard” message. During operation of the device, the tables are preferably periodically updated, by introducing fresh entropy into the tables faster than information leaks out, so that attackers will not be able to obtain the table contents by analysis of measurements. The technique is implementable in cryptographic smartcards, tamper resistant chips, and secure processing systems of all kinds.
Owner:CRYPTOGRAPHY RESEARCH
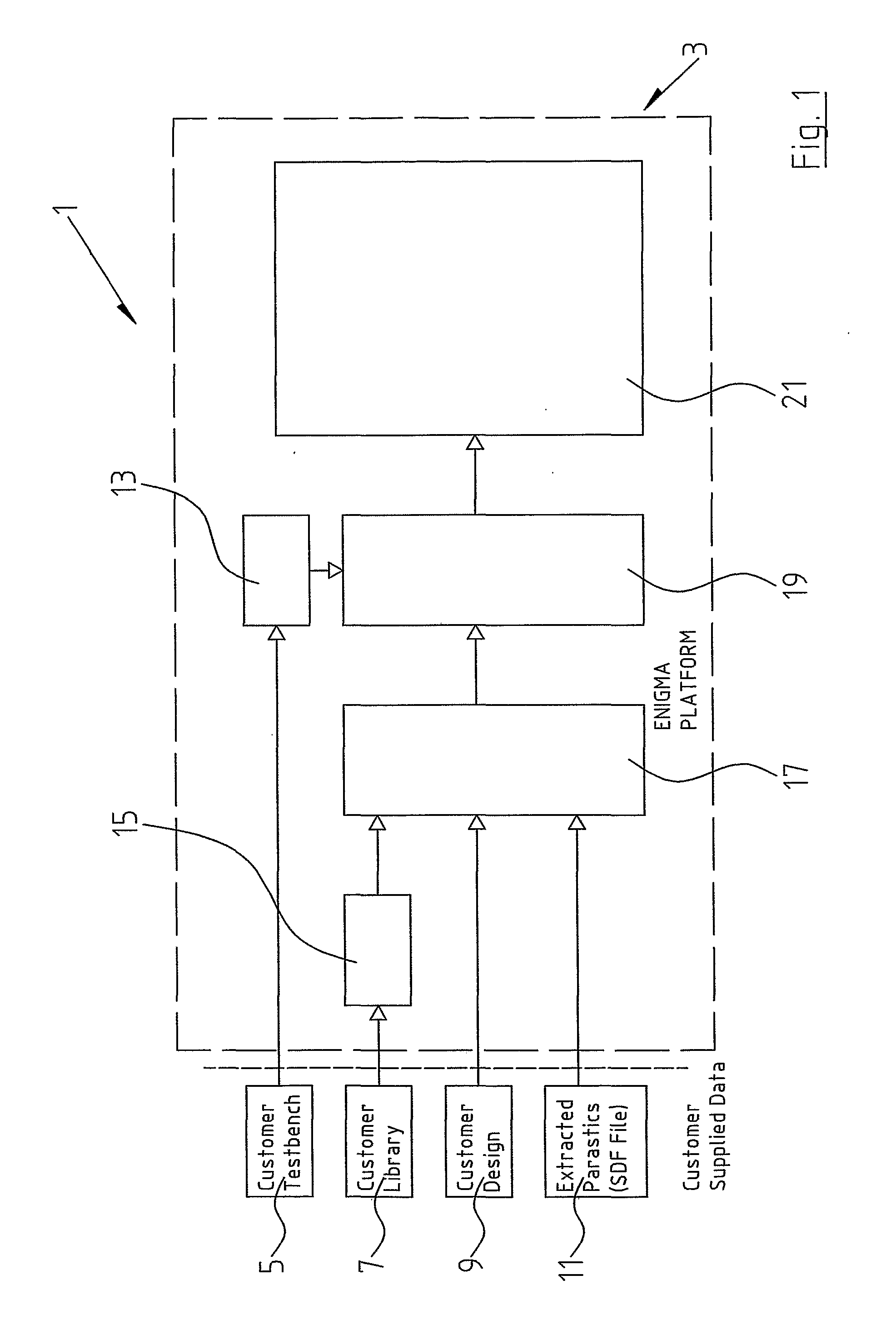
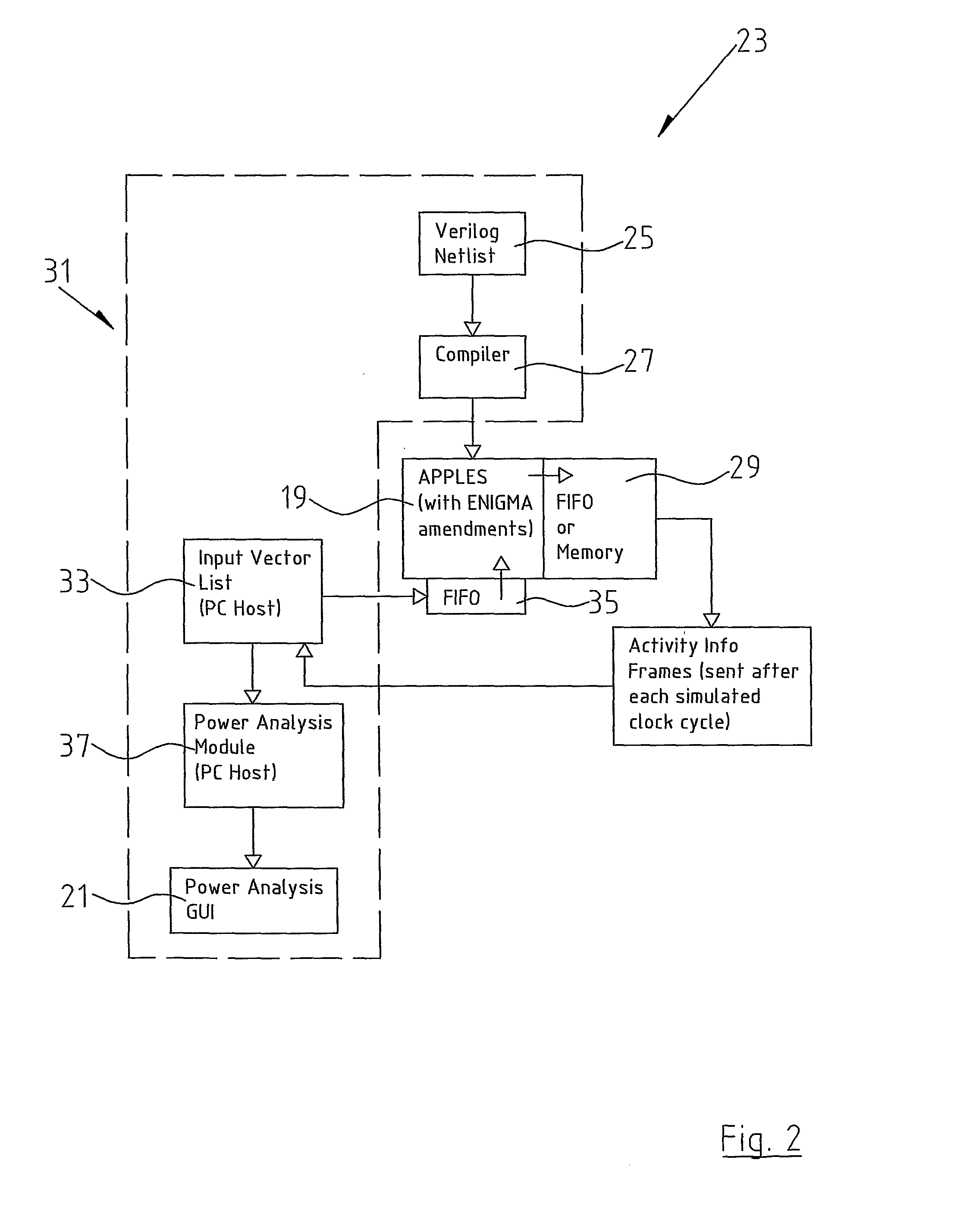
Method and Processor for Power Analysis in Digital Circuits
InactiveUS20080092092A1Accurate analysisSimple calculationCAD circuit designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationPower analysisProcessor register
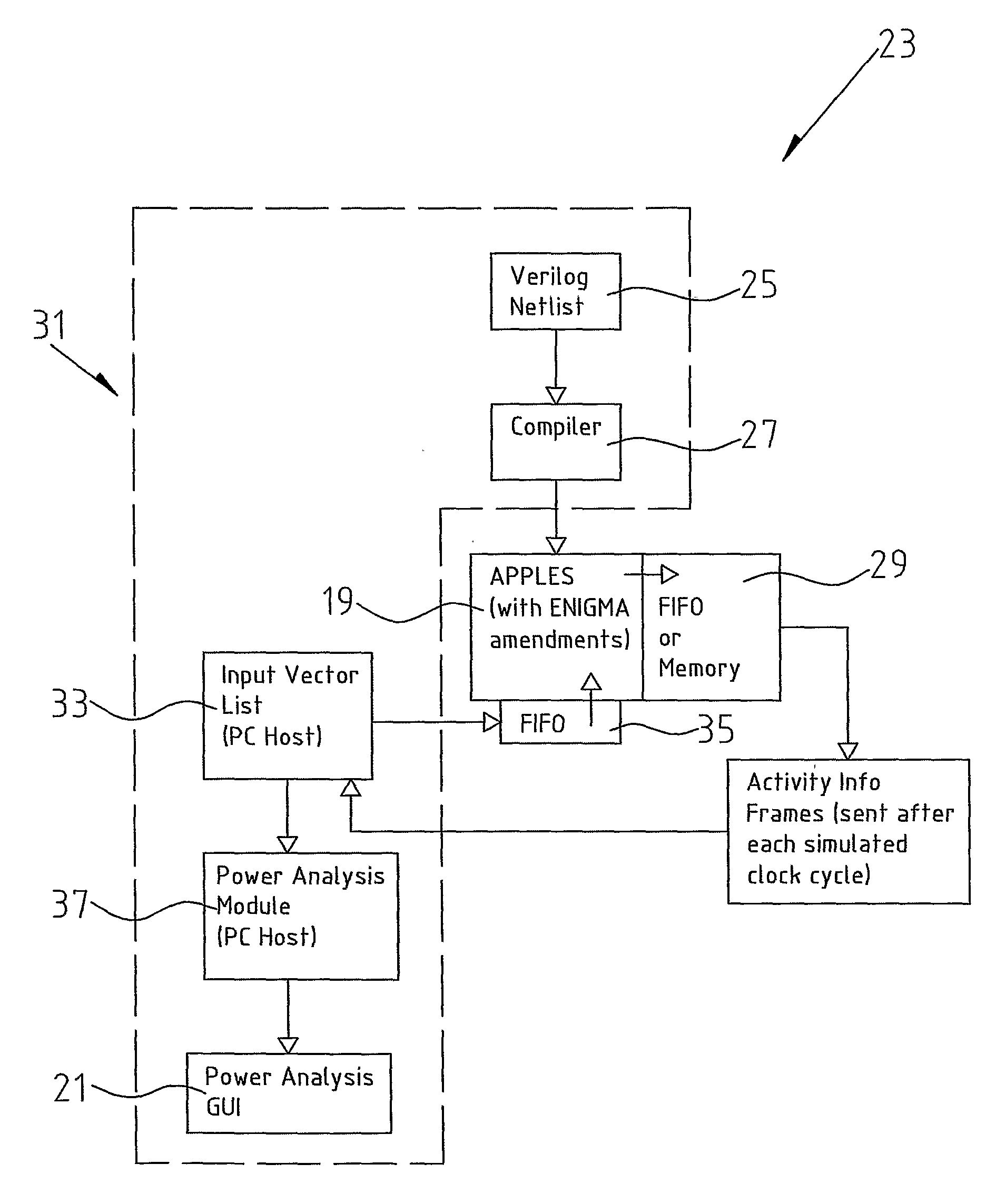
This invention relates to a method and processor (19) for power analysis in digital circuits. The method incorporates a main processor (19) and an associative memory mechanism (101a, 101b, 102, 104, 105, 106), the associative memory mechanism comprising a plurality of associative arrays (101a, 101b), an input value register (102), at least one result register (104) and a memory block area (29). A circuit design is transformed into a functionally equivalent model format suitable for processing in the associative array and thereafter input vectors are applied to the circuit and a record is kept of the inputs and or the outputs on each of the gates in the circuit over a specified time period. In this way, it is possible to calculate the leakage power dissipation as well as both the toggle dynamic power and the transition dynamic power.
Owner:UNIV COLLEGE DUBLIN NAT UNIV OF IRELAND DUBLIN
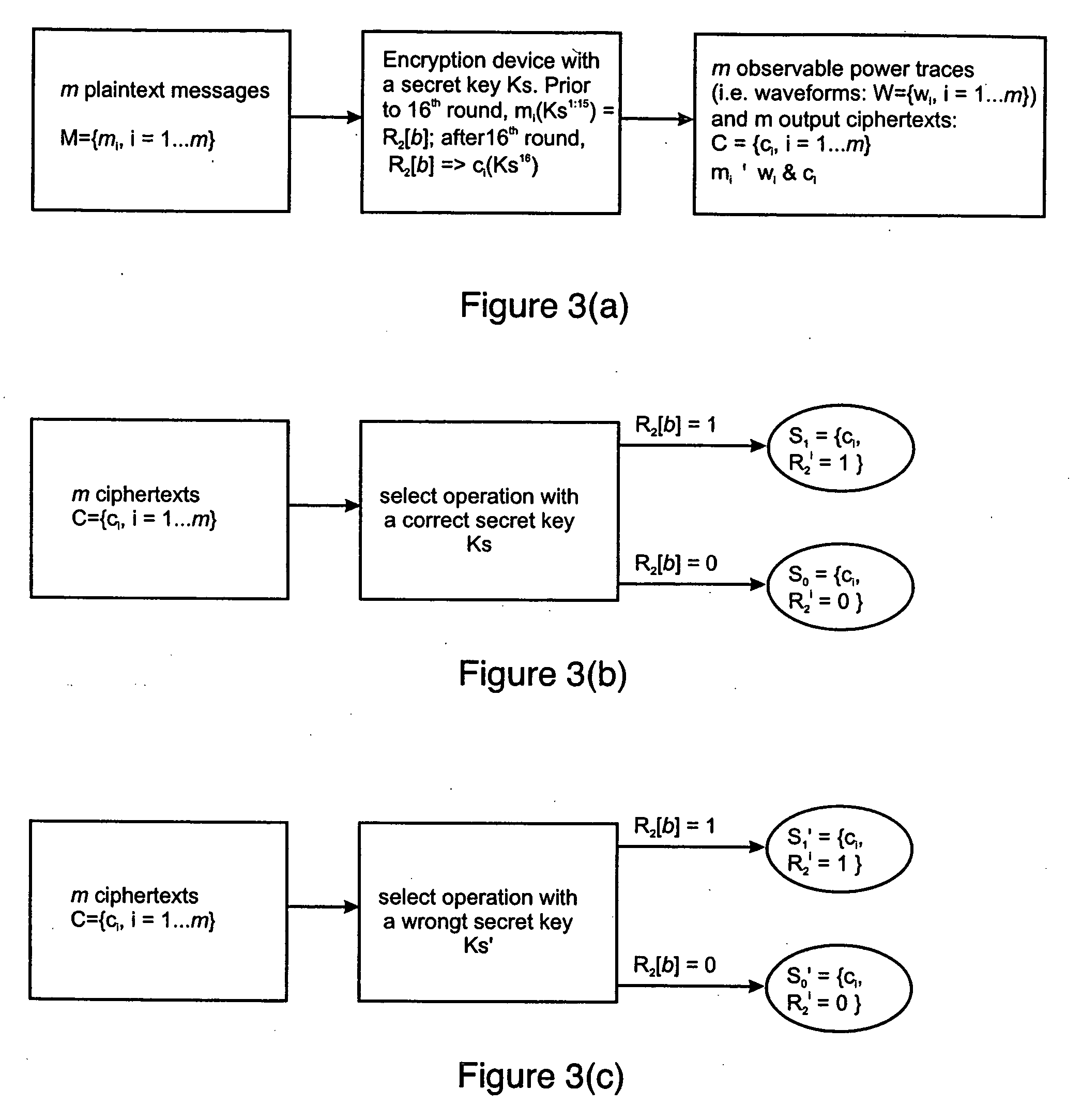
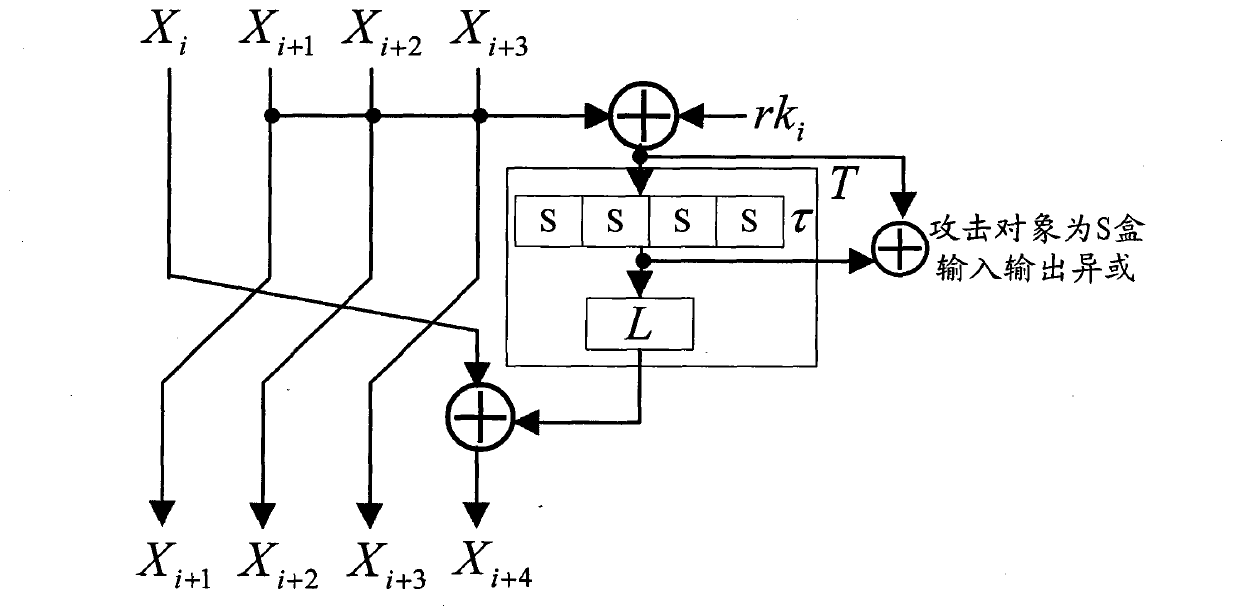
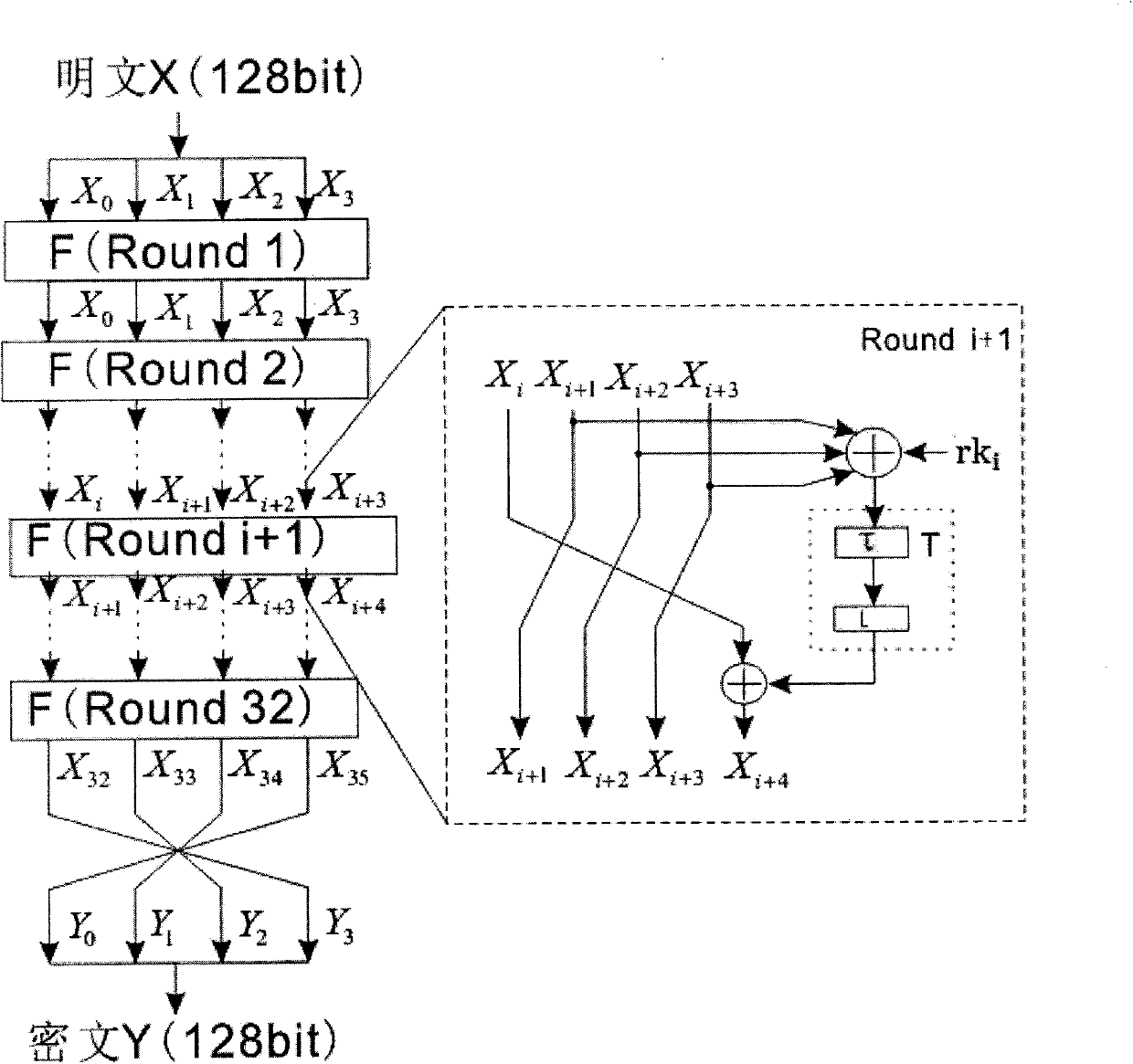
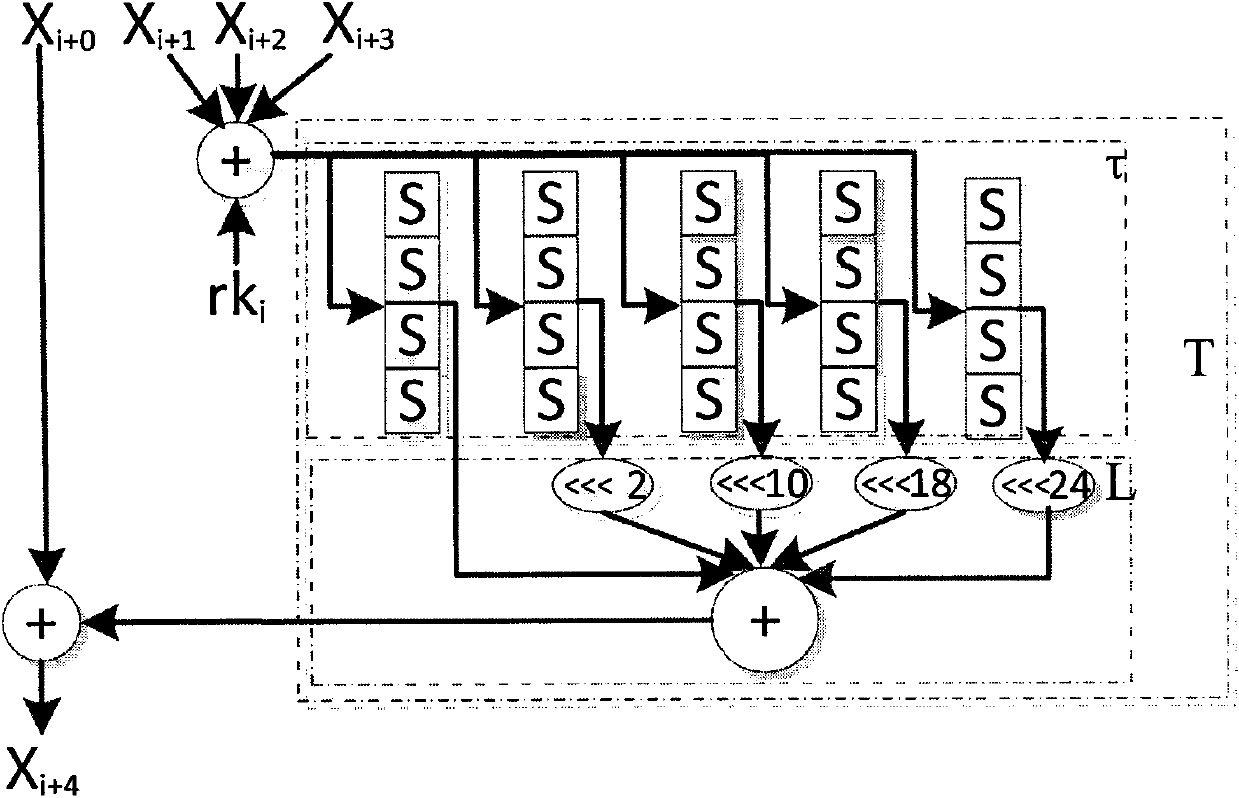
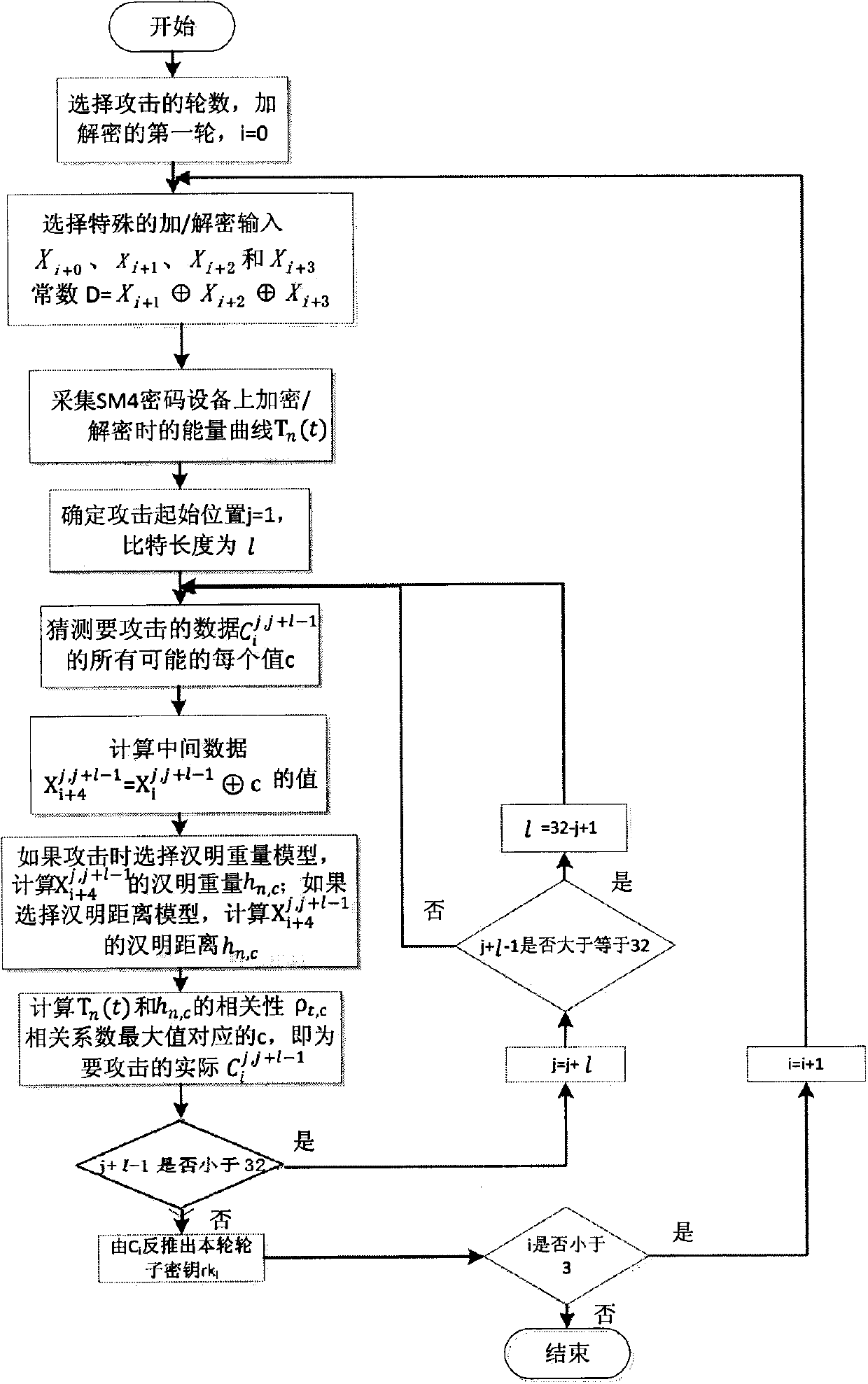
Plaintext or ciphertext selection based side channel power analysis attack method on round function output of SM4 cipher algorithm
InactiveCN104202145APractical applicabilityIncrease flexibilityEncryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesComputer hardwarePlaintext
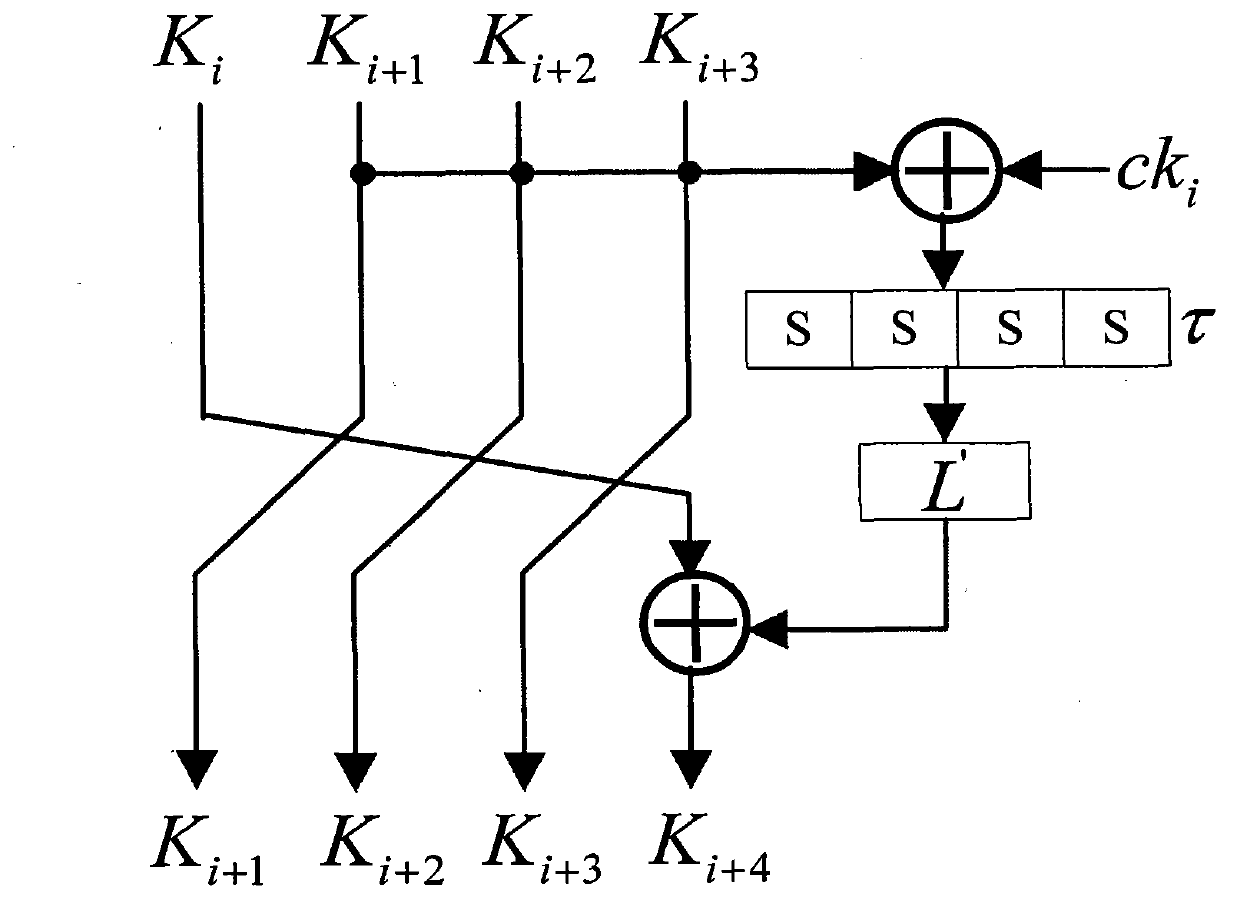
The invention discloses a plaintext or ciphertext selection based side channel power analysis attack method on round function output of the SM4 cipher algorithm. The method includes the steps of S1, selecting plaintext or ciphertext to input X<i+0>, X<i+1>, X<i+2> and X<i+3> on the condition of allowing the exclusive OR result of the X<i+1>, X<i+2> and X<i+3> to be a constant value and guaranteeing randomness of the X<i+0>, utilizing side channel power attack processes to attack the output C of linear transform L of each round of the first four round functions, and deducing inversely to acquire the round key rk of the first four round functions in encryption or decryption according to the output C; S2, according to the round keys rk<0>, rk<1>, rk<2> and rk<3> of the first four found functions, inversely calculating the initial key by a key expansion algorithm. The method can realize power analysis attack by means of multiple attacks and can attack with selection of proper-length bits according to actual computing capacity, thus flexibility, effectiveness and success rate of analysis are improved.
Owner:CHENGDU UNIV OF INFORMATION TECH +2
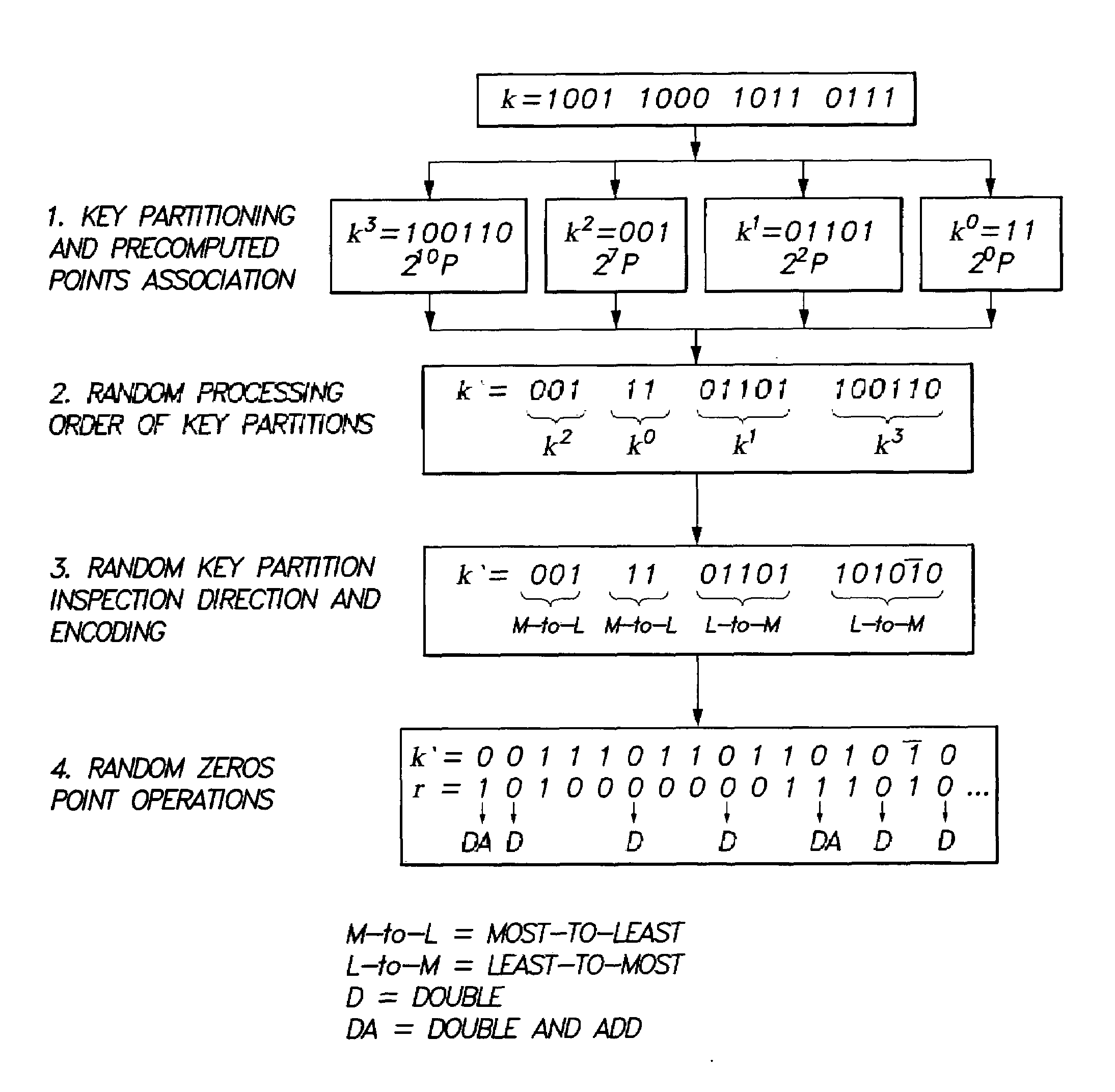
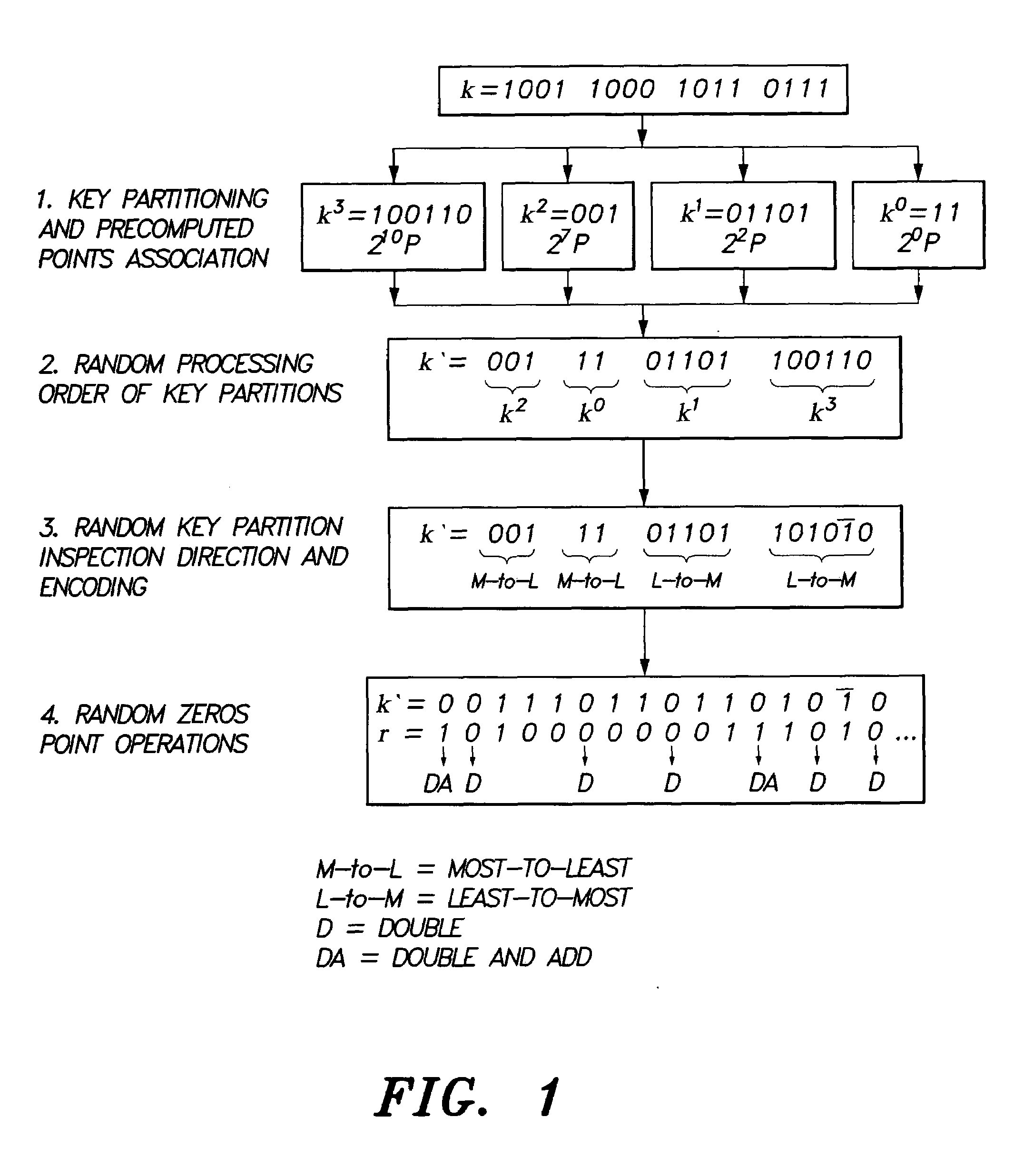
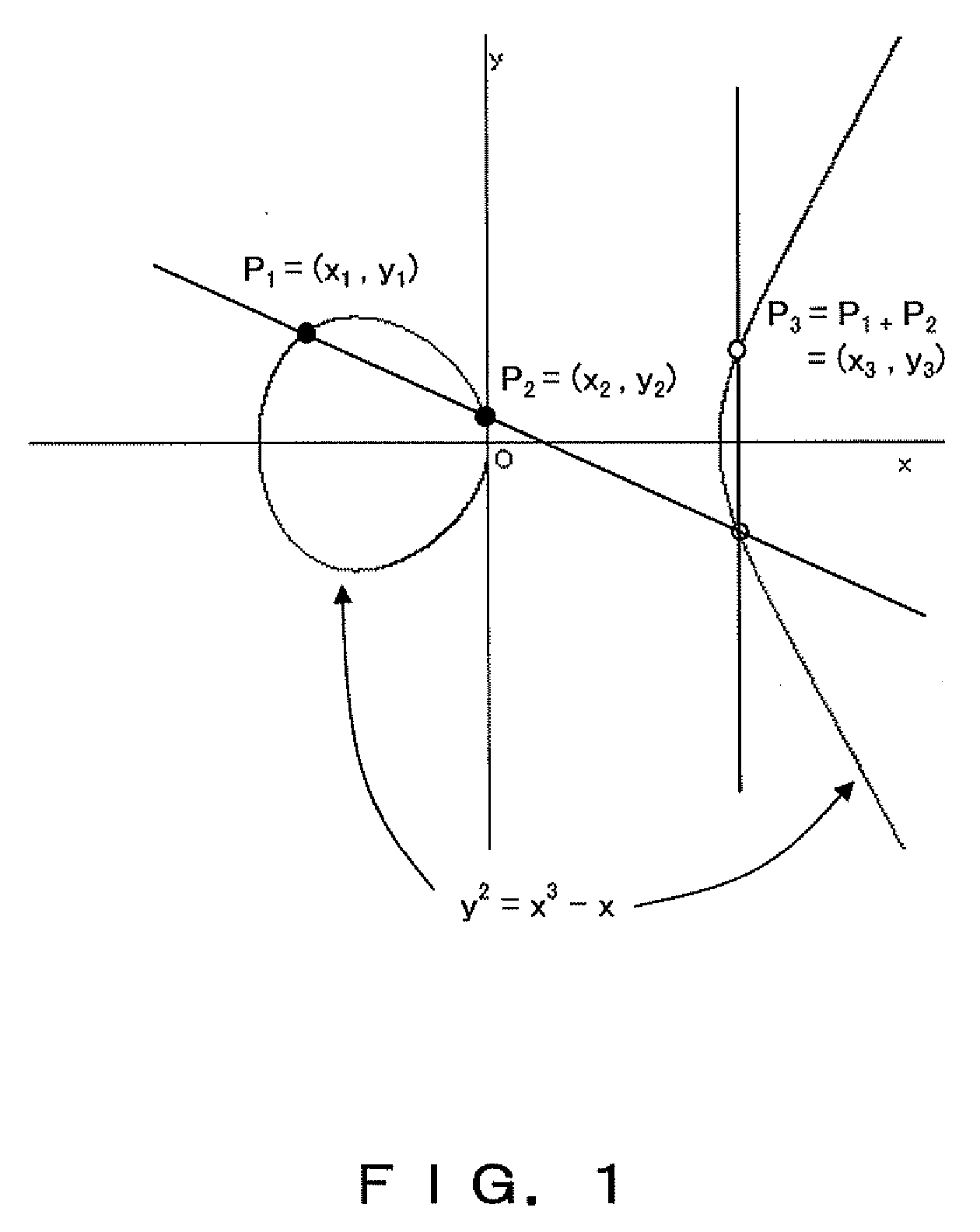
Method for elliptic curve scalar multiplication
InactiveUS20090214023A1Improve the immunityImprove securityDigital data processing detailsSecret communicationPower analysisCountermeasure
The method for elliptic curve scalar multiplication may provide several countermeasures to protect scalar multiplication of a private key k by a point P to produce the product kP from power analysis attacks. First, the private key, k, is partitioned into a plurality of key partitions, which are processed in a random order, the resulting points being accumulated to produce the scalar product kP. Second, in each partition, the encoding is randomly selected to occur in binary form or in Non-Adjacent Form (NAF), with the direction of bit inspection being randomly assigned between most-to-least and least-to-most. Third, in each partition, each zero in the key may randomly perform a dummy point addition operation in addition to the doubling operation. The method may be implemented in software, smart cards, circuits, processors, or application specific integrated circuits (ASICs) designed to carry out the method.
Owner:KING FAHD UNIVERSITY OF PETROLEUM AND MINERALS
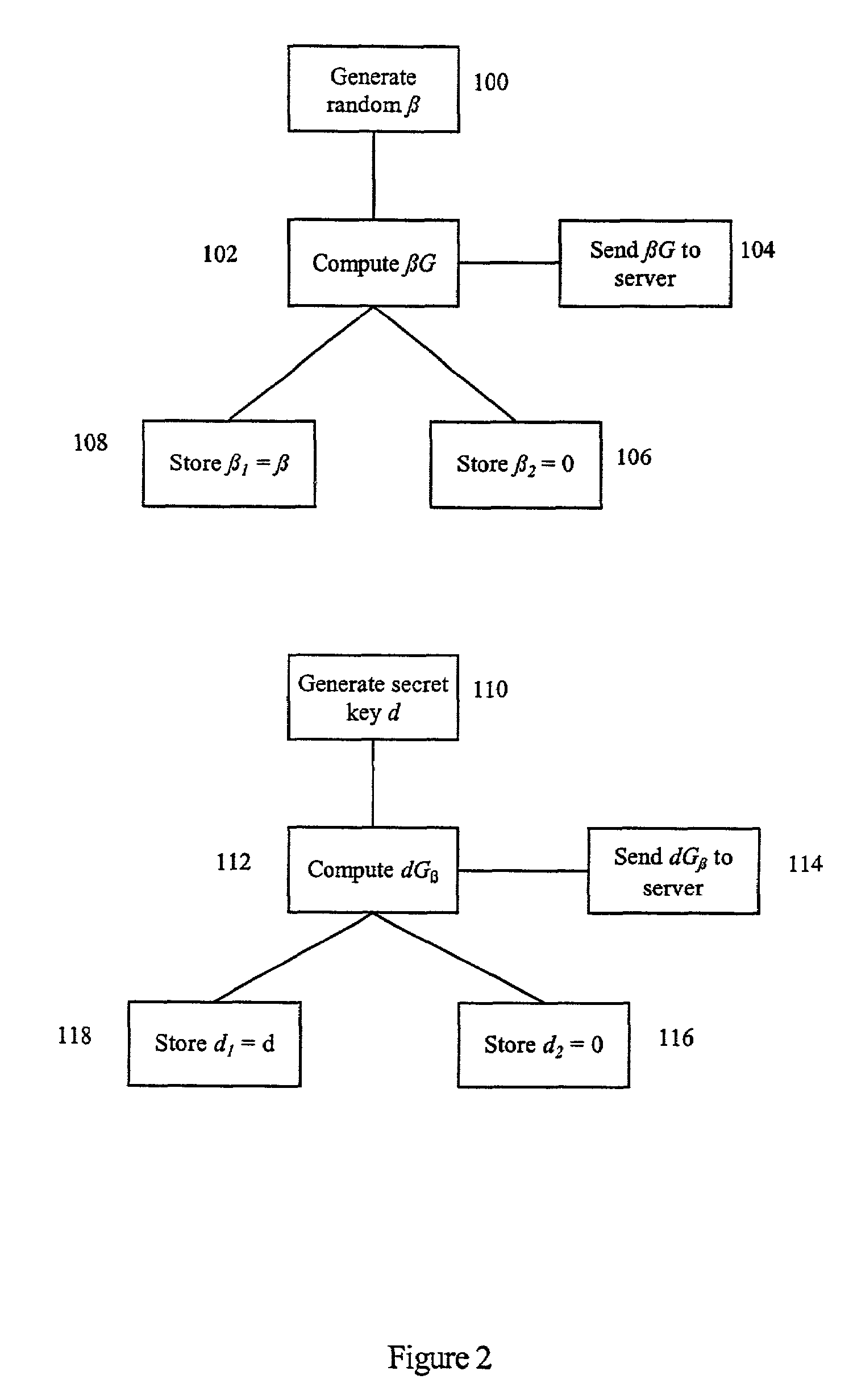
Method for strengthening the implementation of ECDSA against power analysis
InactiveUS7599491B2Convenient introductionProtection attackPublic key for secure communicationError detection/correctionPower analysisComputer security
A method of inhibiting the disclosure of confidential information through power analysis attacks on processors in cryptographic systems. The method masks a cryptographic operation using a generator G. A secret value, which may be combined with the generator G to form a secret generator is generated. The secret value is divided into a plurality of parts. A random value is generated for association with the plurality of parts. Each of the plurality of parts is combined with the random value to derive a plurality of new values such that the new values when combined are equivalent to the secret value. Each of the new values is used in the cryptographic operation, thereby using the secret generator in place of the generator G in the cryptographic operation. The introduction of randomness facilitates the introduction of noise into algorithms used by cryptographic systems so as to mask the secret value and provide protection against power analysis attacks.
Owner:MALIKIE INNOVATIONS LTD
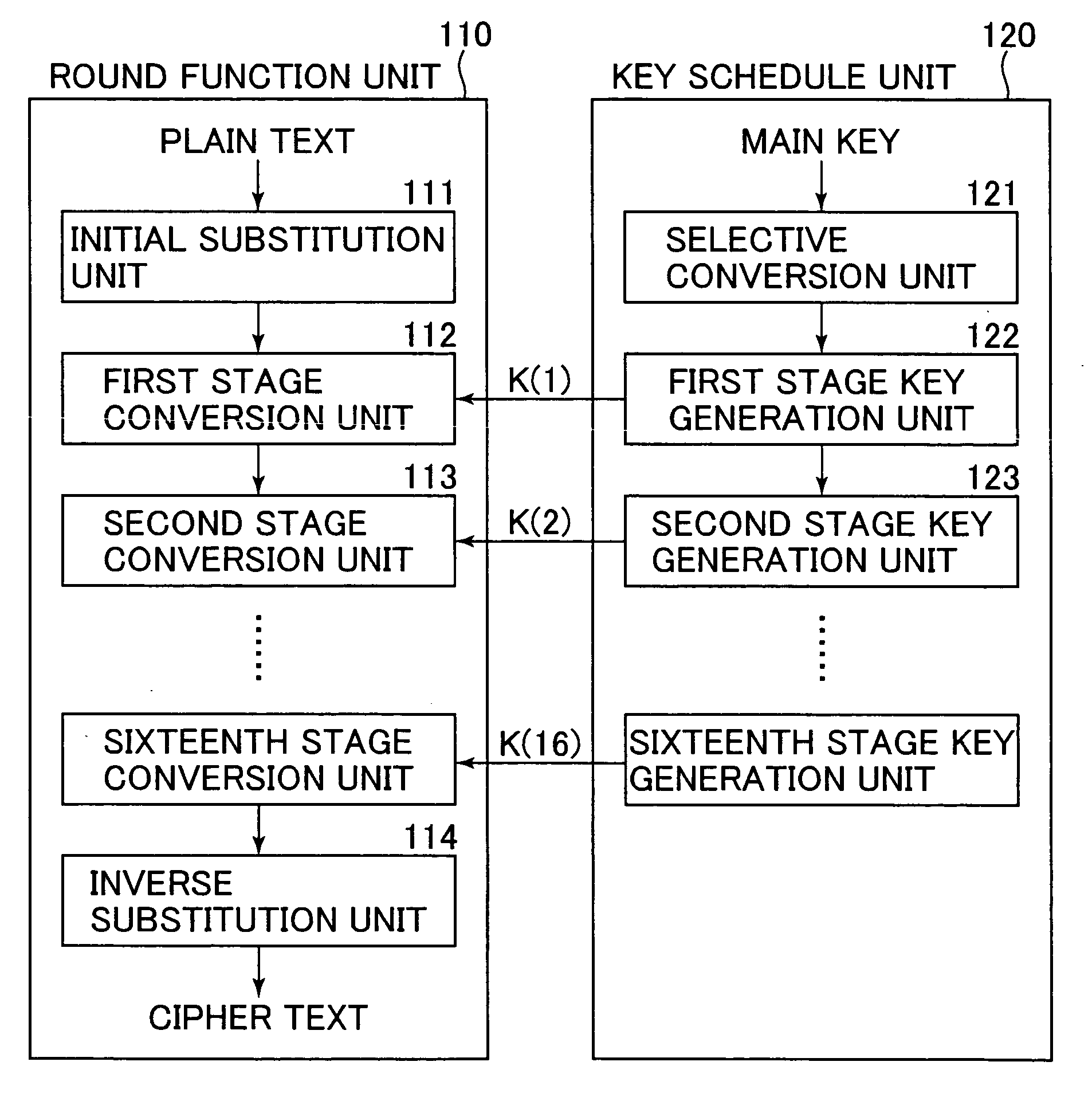
Cryptographic processing apparatus, cryptographic processing method and computer program
InactiveUS20050055596A1Increase the difficultyWithout process algorithmEncryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesDigital data processing detailsPower analysisInformation analysis
According to the configuration of the present invention, the modulation clock signal is generated in accordance with a signal based on a random number, and a data processing timing is determined in accordance with the modulation clock signal to execute data processing. Accordingly, secret information analysis of an encryption key, a decryption key and the like through measurements of consumption powers in terms of a lapse time of a cryptographic processing apparatus for encrypting and decrypting data, i.e., cryptanalysis based on the power analysis, can be made difficult to thereby realize a cryptographic processing apparatus and method having a high security level.
Owner:SONY CORP
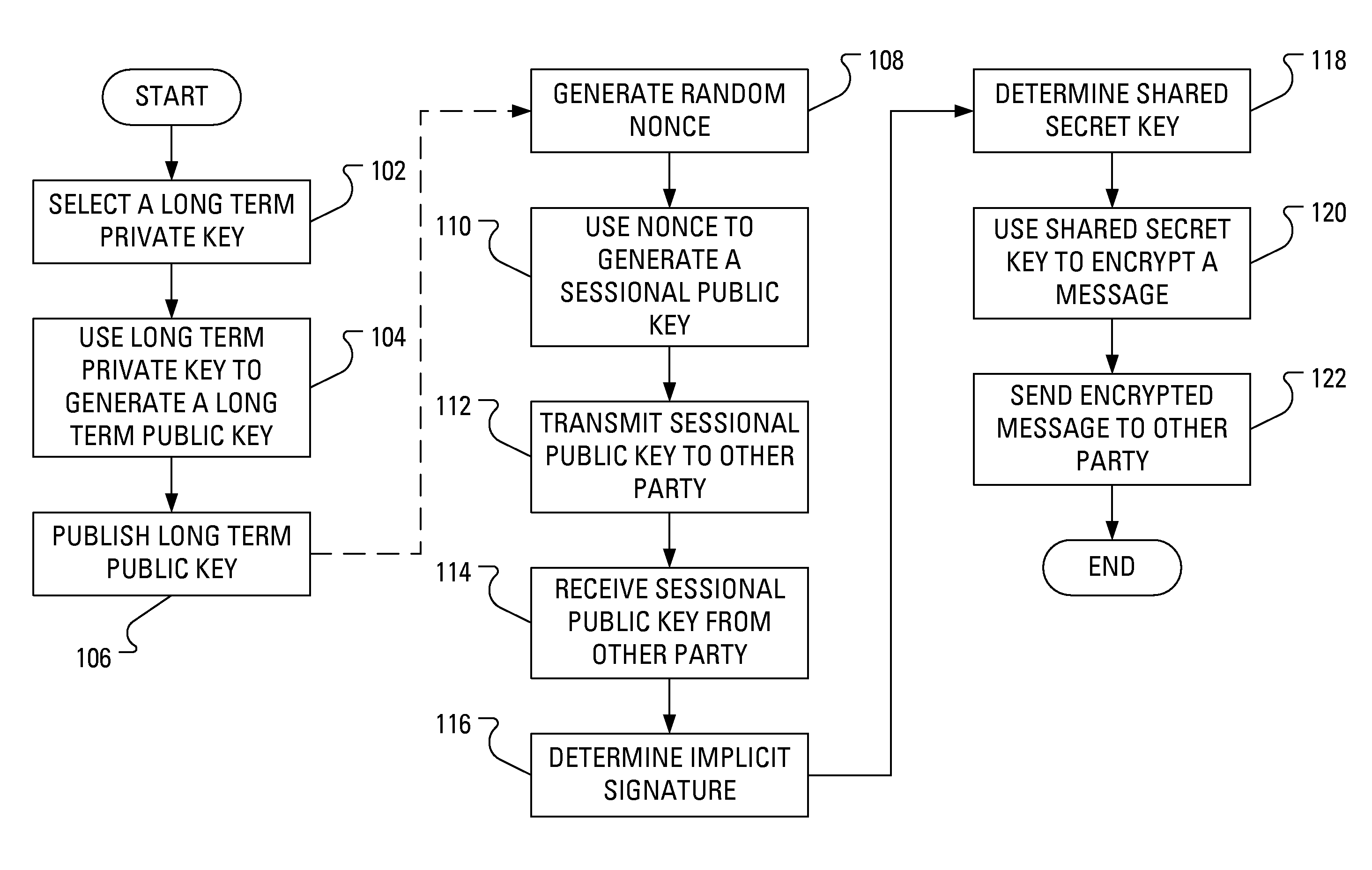
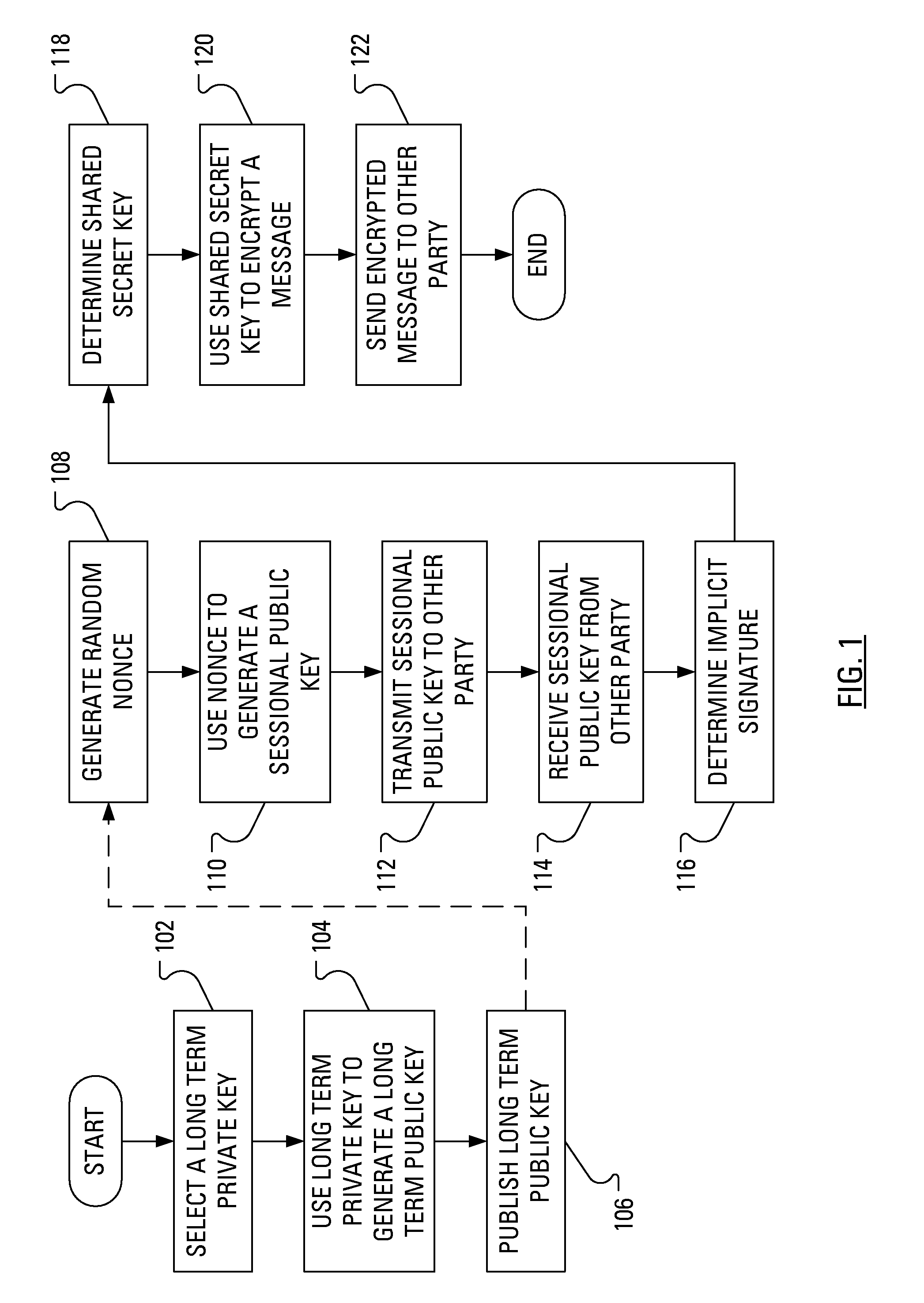
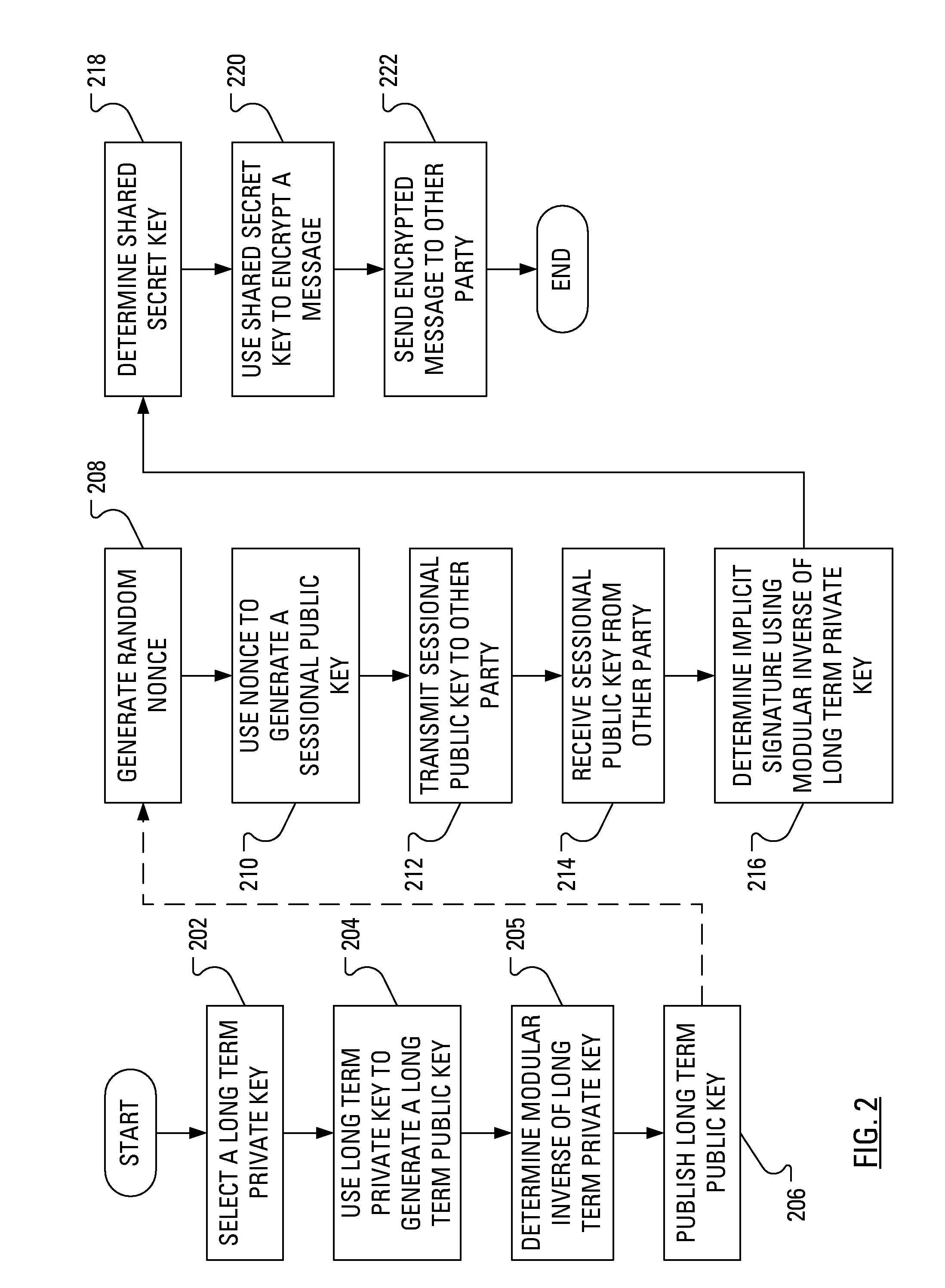
Power Analysis Countermeasure for the ECMQV Key Agreement Algorithm
ActiveUS20080301459A1Encryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesUser identity/authority verificationPower analysisComputer hardware
Execution of the ECMQV key agreement algorithm requires determination of an implicit signature, which determination involves arithmetic operations. Some of the arithmetic operations employ a long-term cryptographic key. It is the execution of these arithmetic operations that can make the execution of the ECMQV key agreement algorithm vulnerable to a power analysis attack. In particular, an attacker using a power analysis attack may determine the long-term cryptographic key. By modifying the sequence of operations involved in the determination of the implicit signature and the inputs to those operations, power analysis attacks may no longer be applied to determine the long-term cryptographic key.
Owner:BLACKBERRY LTD
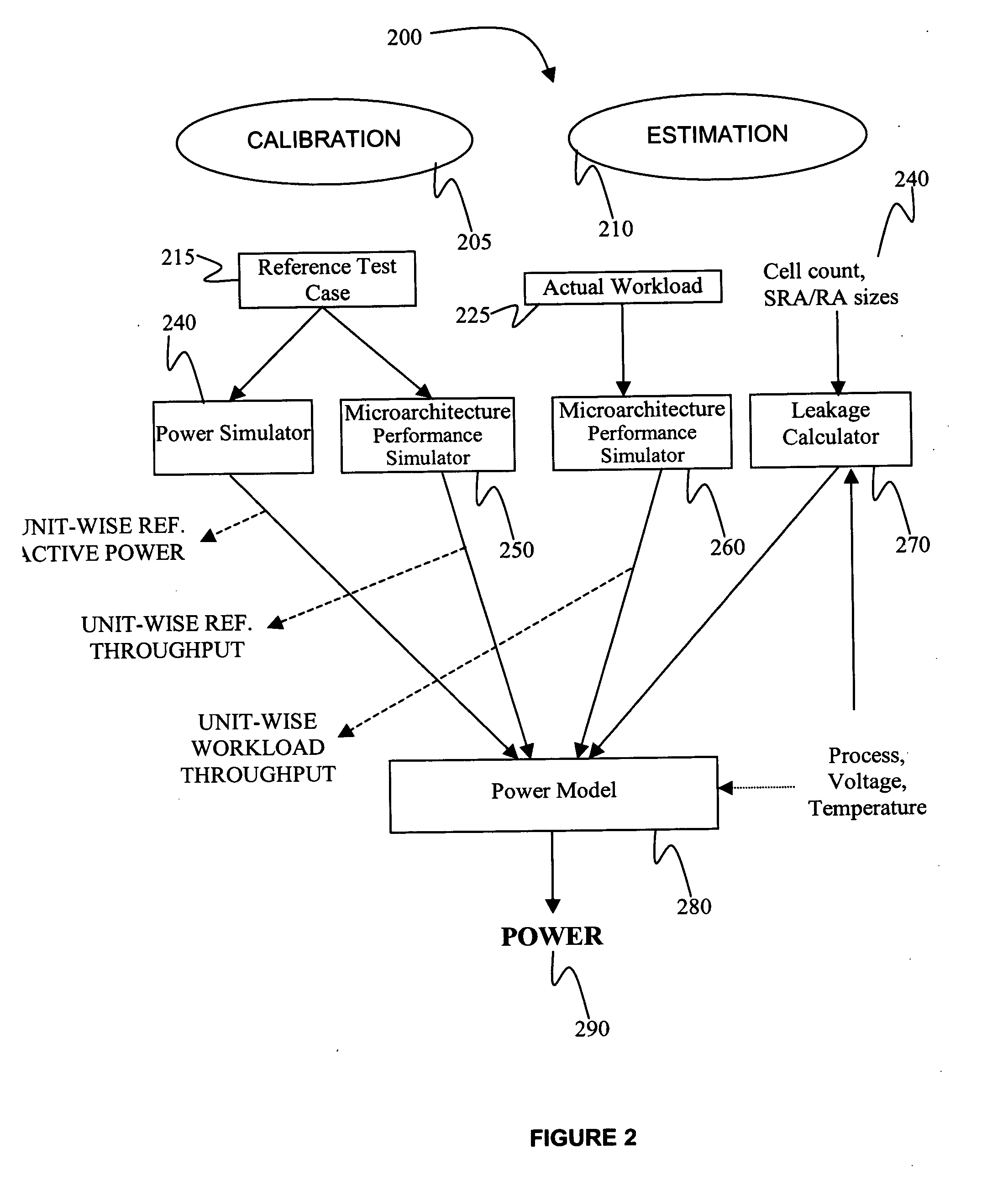
Architectural level throughput based power modeling methodology and apparatus for pervasively clock-gated processor cores
InactiveUS20060080625A1Improve performanceAnalogue computers for nuclear physicsCAD circuit designPower analysisReference test
A method, system, and apparatus for estimating the power dissipated by a processor core processing a workload, where the method includes analyzing a reference test case to generate a reference workload characteristic. Analyzing an actual workload to generate an actual workload characteristic. Performing a power analysis for the reference test case to establish a reference power dissipation value. Estimating an actual workload power dissipation value responsive to the actual and reference workload characteristics and the reference power dissipation value
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Dynamic and differential cmos logic with signal-independent power consumption to withstand differential power analysis
InactiveUS20070057698A1Logic circuits characterised by logic functionCurrent/voltage measurementCapacitancePower analysis
A dynamic and differential CMOS logic style is disclosed in which a gate uses a fixed amount of energy per evaluation event. The gate switches its output at every event and loads a constant capacitance. The logic style is a Dynamic and Differential Logic (DDL) style. The DDL style logic typically has one charging event per clock cycle and the charging event does not depend on the input signals. The differential feature masks the in-put value because a precharged output nodes is discharged during the evaluation phase. The dynamic feature breaks the input sequence: the discharged node is charged during the subsequent precharge phase.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
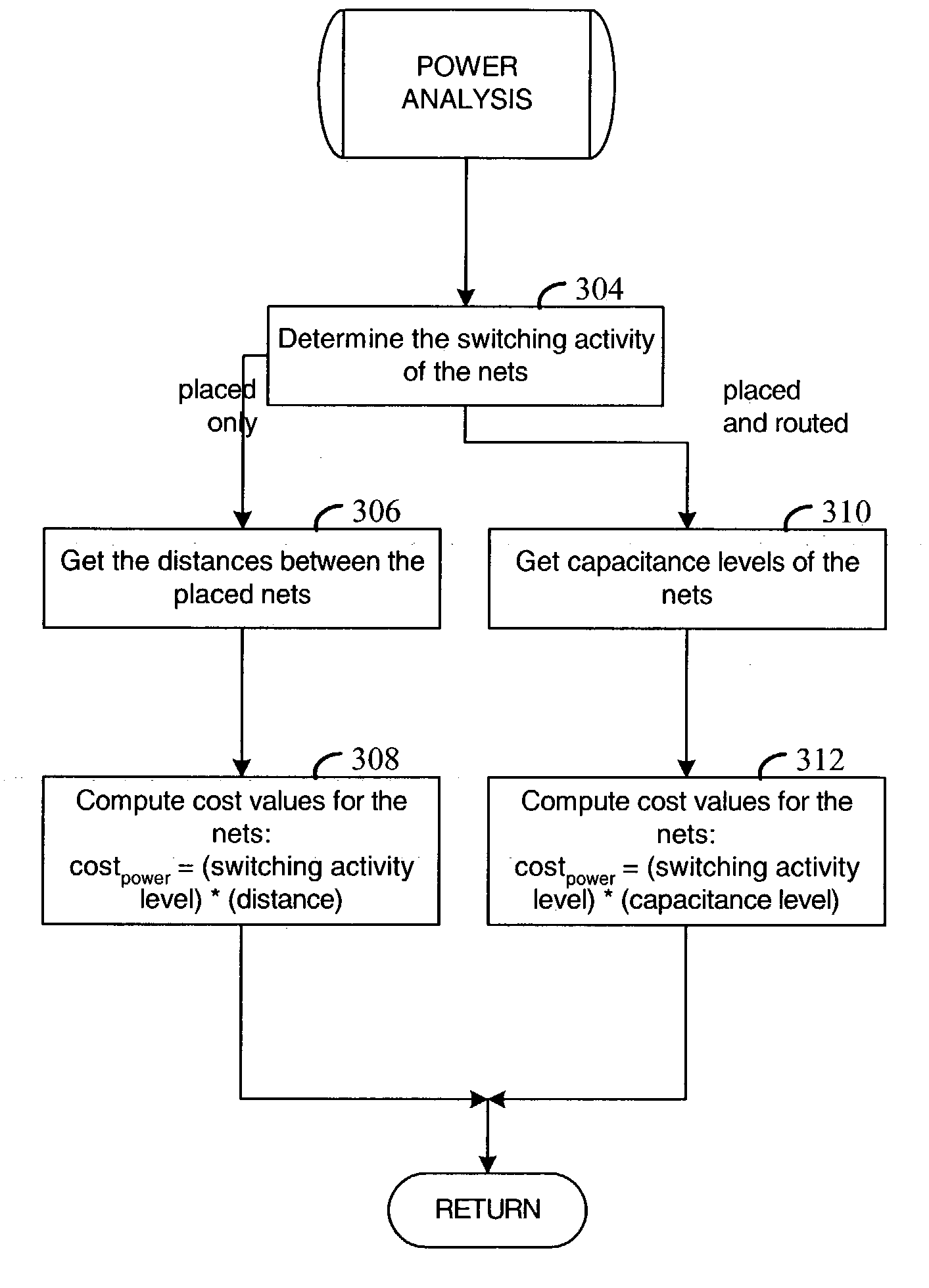
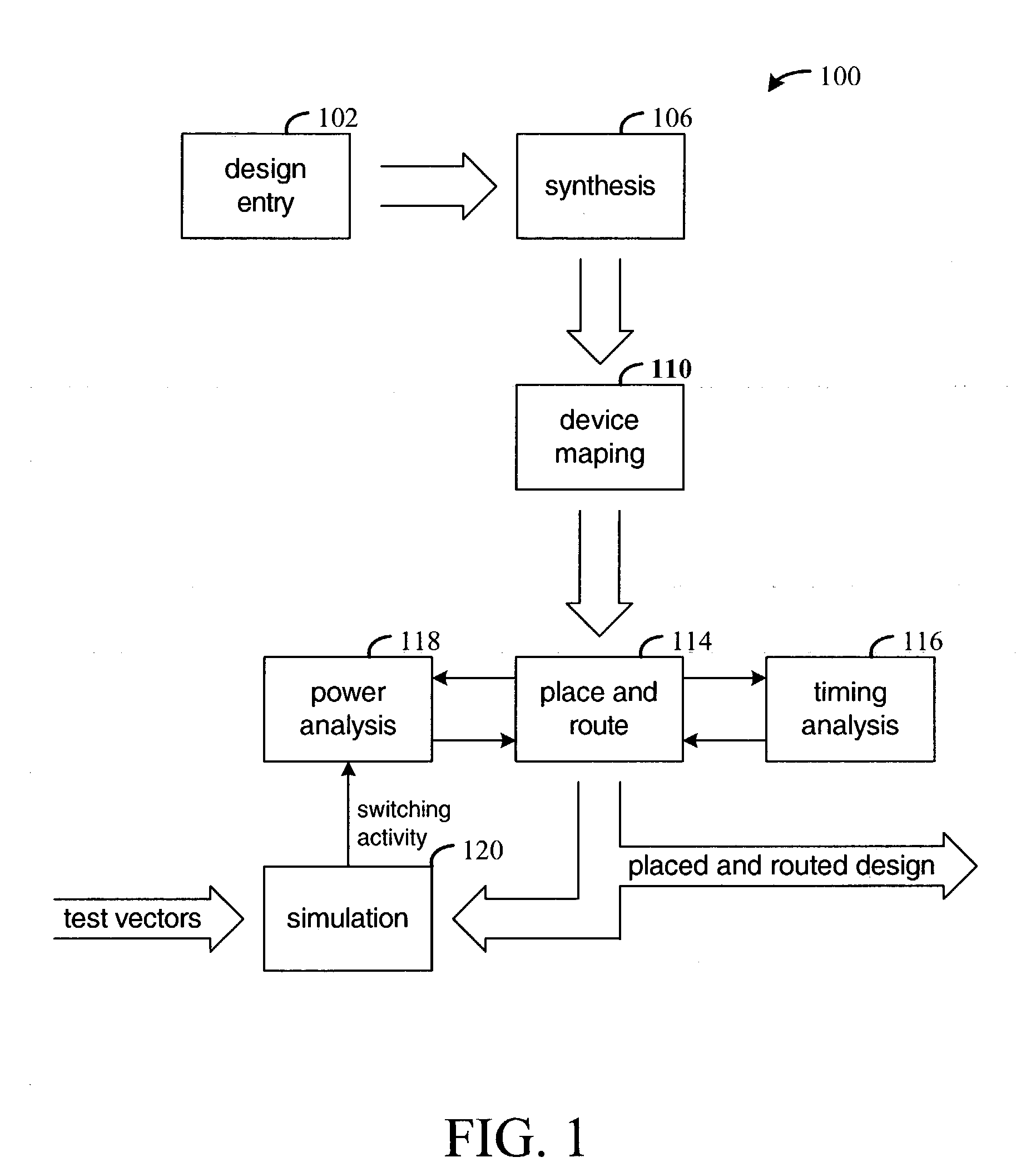
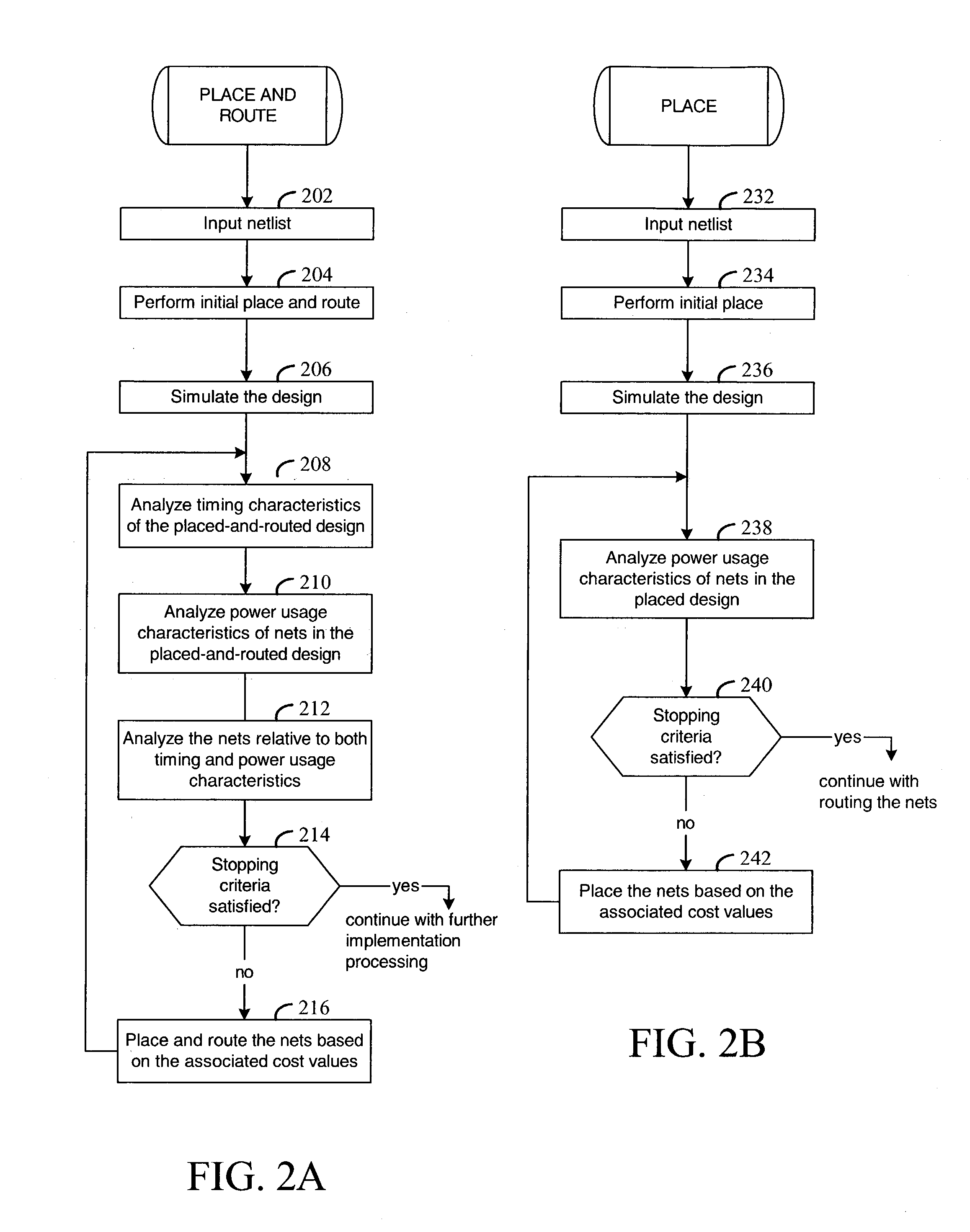
Place-and-route with power analysis
InactiveUS6950998B1Reduce power consumptionTime requiredComputer aided designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationPower analysisEngineering
Method and apparatus for placing and routing an electronic circuit design. Various embodiments are disclosed for analyzing placed and / or routed designs for power consumption characteristics and timing characteristics. New designs are iteratively generated in order to reduce power consumption and satisfy timing requirements of the design.
Owner:XILINX INC
Cryptographic device having tamper resistance to power analysis attack
InactiveUS20080025500A1Improve securityIncrease the difficultyRandom number generatorsPublic key for secure communicationPower analysisTamper resistance
A randomly selected point on an elliptic curve is set as the initial value of a variable and calculation including a random point value is performed in an algorithm for calculating arbitrary scalar multiple operation on an elliptic curve when scalar multiplication and addition on an elliptic curve are defined, then a calculation value obtained as a result of including a random point is subtracted from the calculation result, whereby an intended scalar multiple operation value on an elliptic curve is determined.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
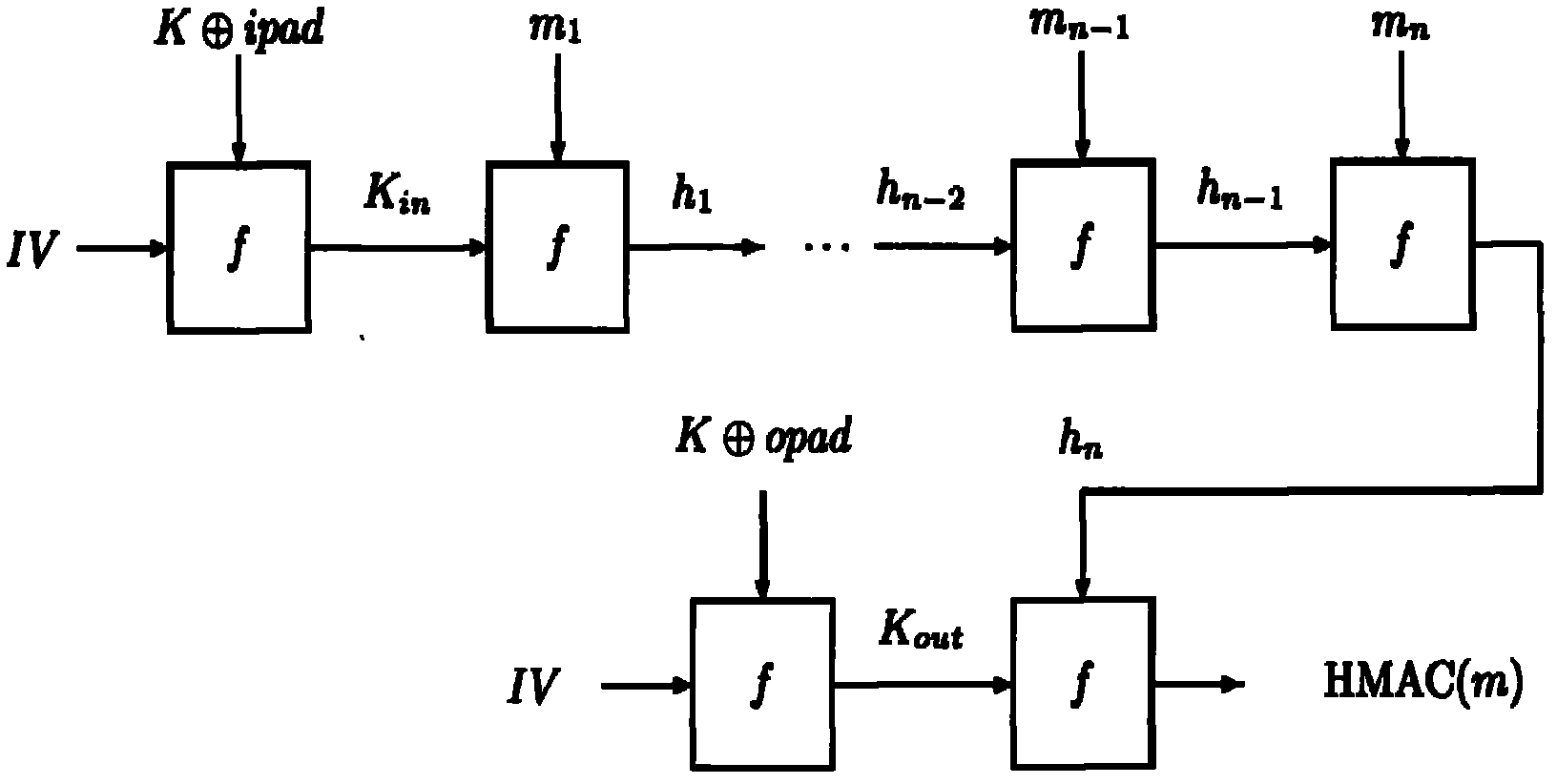
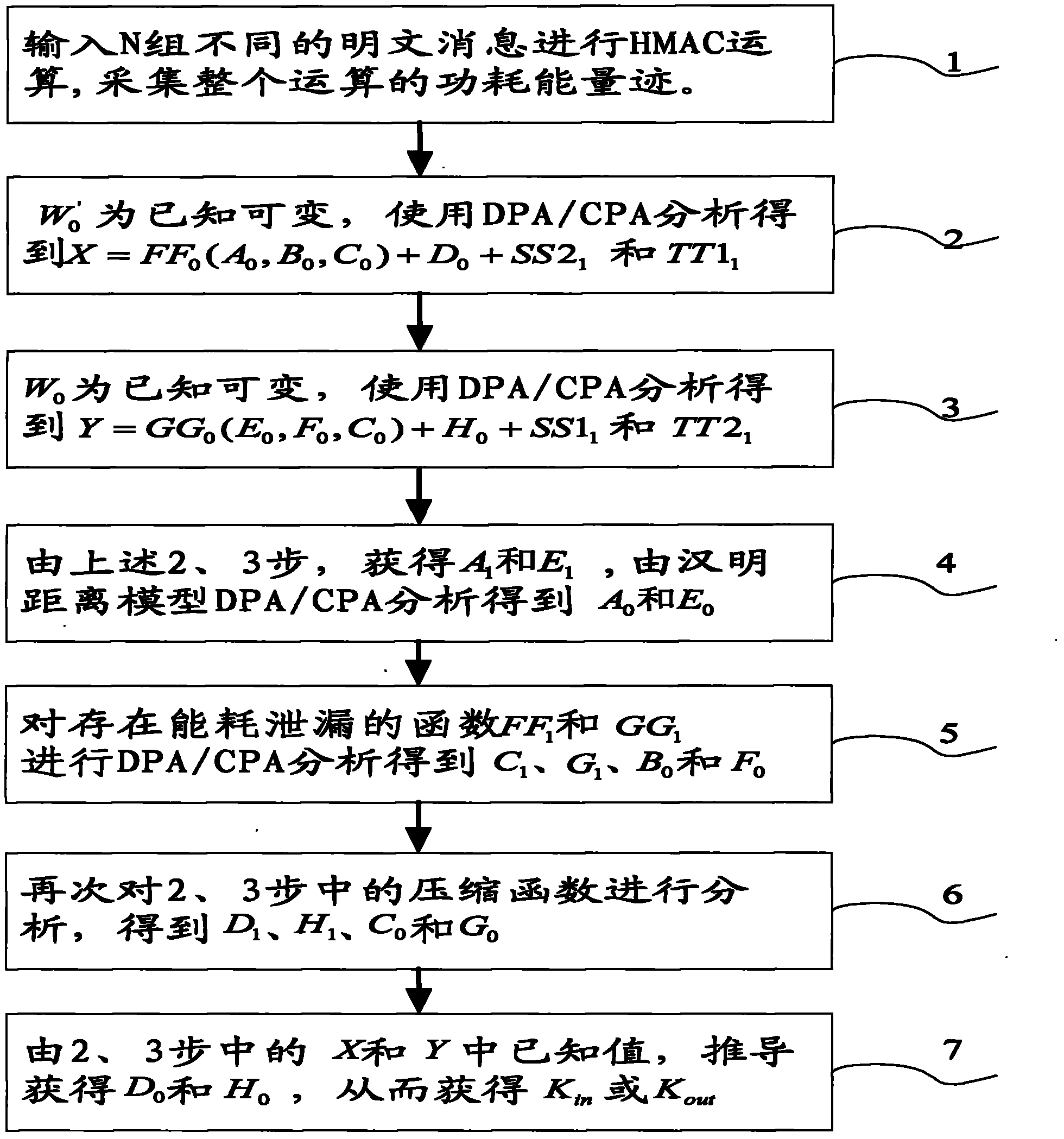
Side channel energy analysis method for SM3 cryptographic algorithm HMAC mode
ActiveCN103457719AEncryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesComputer security arrangementsPower analysisChannel analysis
The invention discloses a side channel energy analysis method for an SM3 cryptographic algorithm HMAC mode. The method performs analyses on implementation characteristics of a SM3 cryptographic algorithm and the HMAC mode of the SM3 cryptographic algorithm. Based on a DPA attack method and a CPA attach method, the SM3 cryptographic algorithm HMAC mode is successfully cracked in combination with the characteristics of the SM3 cryptographic algorithm HMAC mode and energy consumption leakage points, and output summaries can be freely fabricated. According to the technical scheme, the method includes the steps that 1, energy traces of HMACs are collected; 2, a K[in] is obtained through analyses and the K[in] is an intermediate state value in a first hash algorithm; 3, a K[out] is obtained through analyses and the K[out] is an intermediate state value in a second hash algorithm. The method in the step 3 is the same as that in the step 2. According to the technical scheme, the method provides a solution for side channel analysis implementation of the SM3 cryptographic algorithm.
Owner:国家密码管理局商用密码检测中心
Secondary chaotic encryption optical communication system based on phase transformation
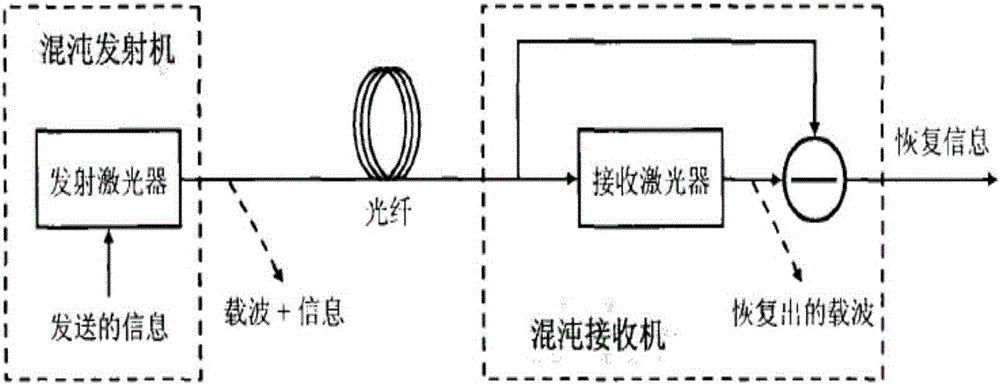
InactiveCN106330428AEasy to adjustThere are many adjustable parameters for encryptionSecuring communication by chaotic signalsElectromagnetic receiversConfidentialityOptical communication
The invention discloses a secondary chaotic encryption optical communication system based on phase transformation. The system comprises an optical signal transmitting device, a chaotic combined phase transformation encryption device, a transmission fiber, a chaotic combined phase transformation decryption device and a signal receiving device. The signal encryption part is a chaotic encryption module added with a phase transformation decryption device in a feedback loop, and the signal decryption device is an open-loop chaotic laser receiving module comprising a phase transformation decryption device. The system overcomes the defect that encryption variables of a chaotic encryption system are few; by combining phase transformation decryption with chaotic encryption, an eavesdropper is difficult in analyzing and attacking the energy; high-speed signals can be supported, and 10 Gb / s high-speed signals can be directly encrypted; a light emitting source of an existing WDM (Wavelength Division Multiplexing) system can be directly used for encrypting, and a special ultra-short pulse light source is not needed; and decryption can be implemented by using the same phase transformation modules at the receiving end as at the transmitting end, so that the adjusting difficulty is reduced without changing the confidentiality.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
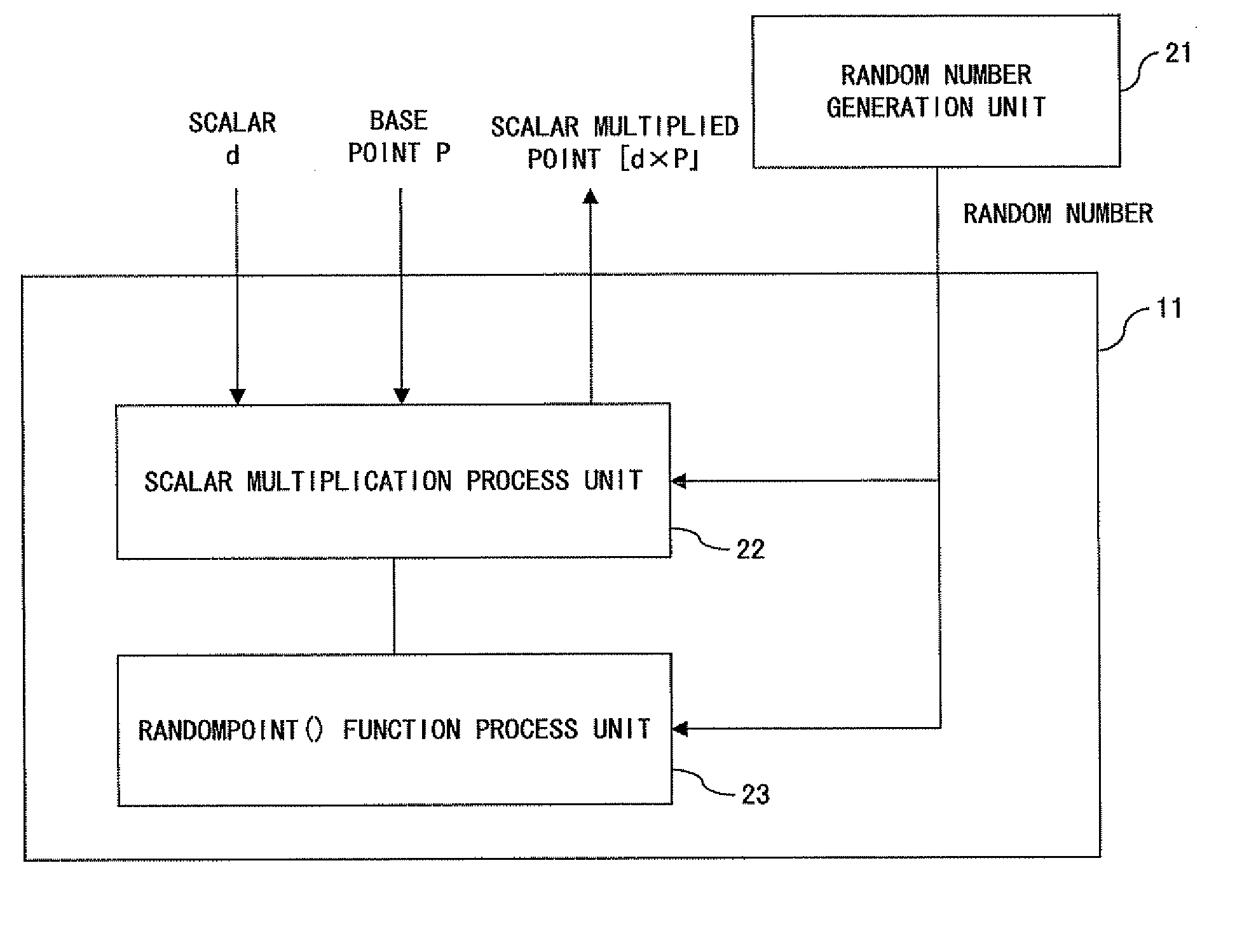
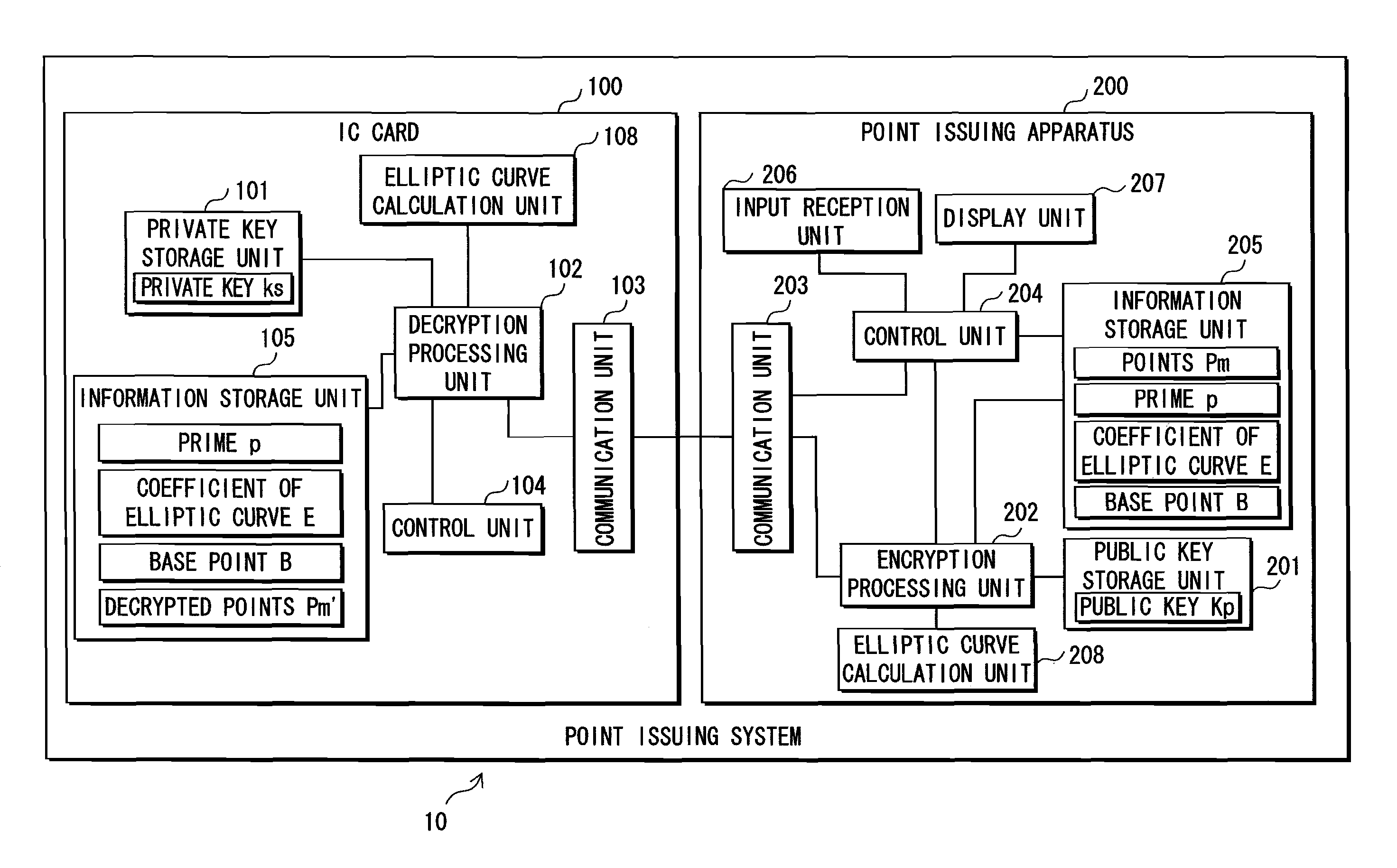
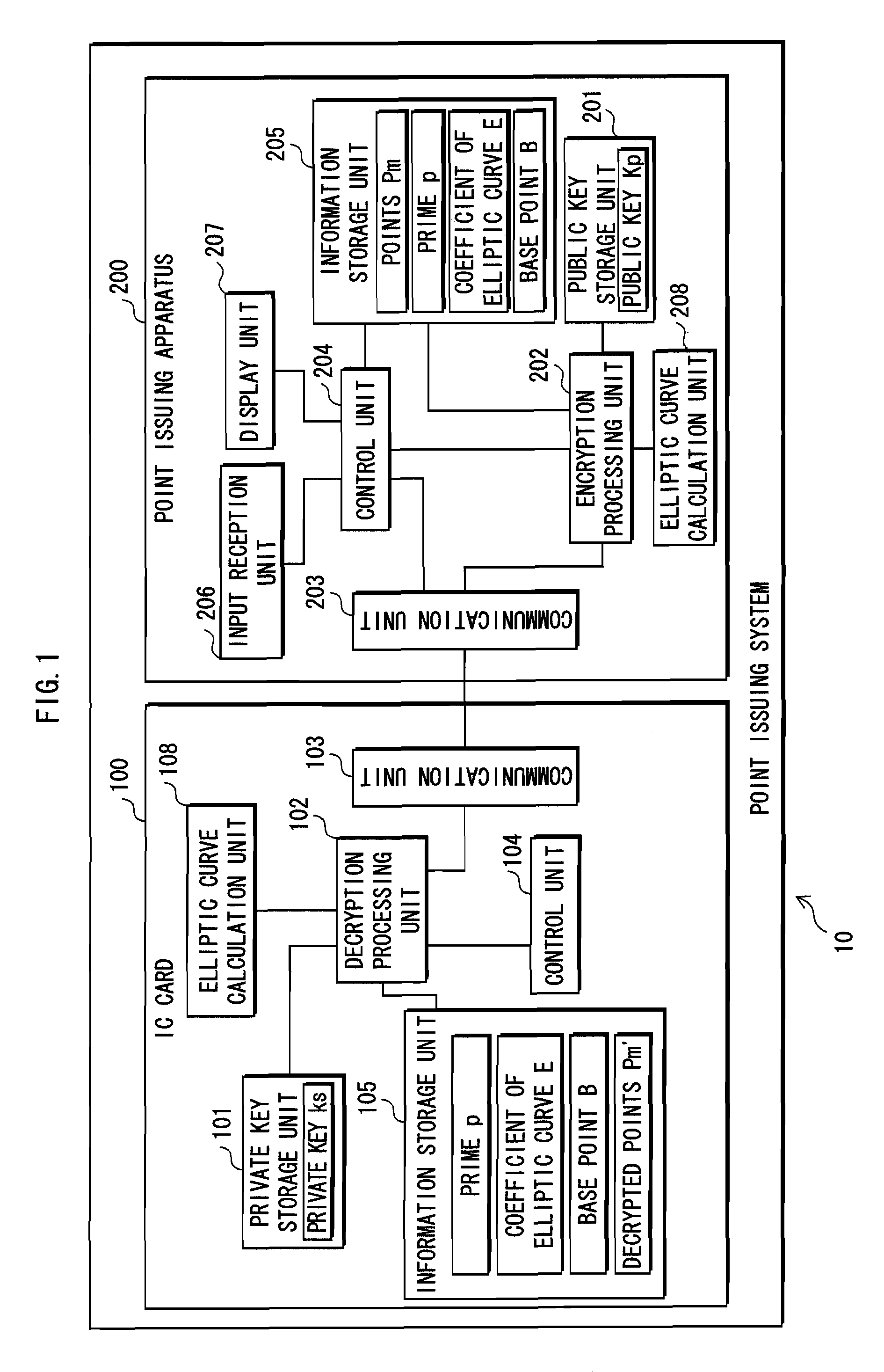
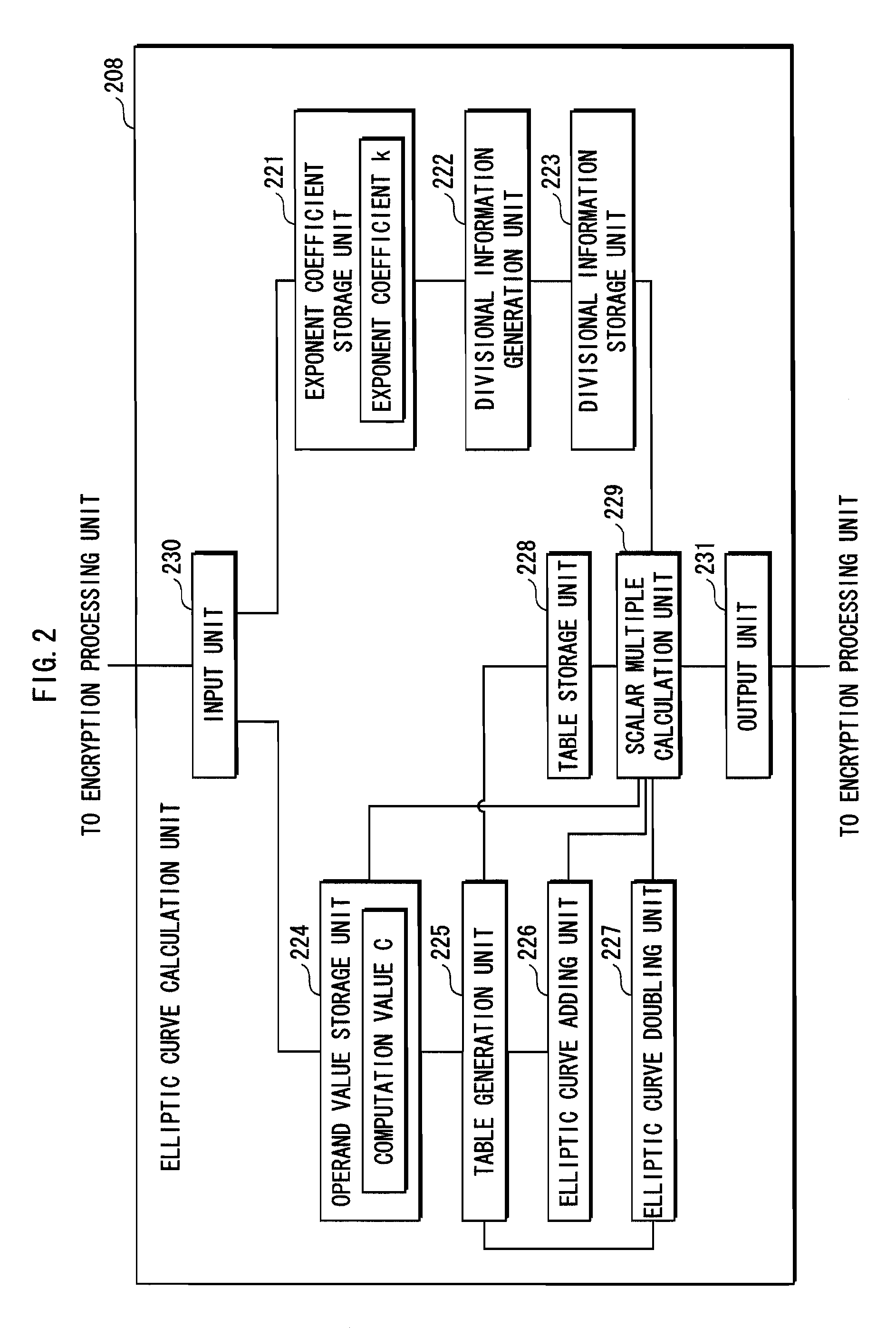
Information security device and elliptic curve operating device
InactiveUS7940927B2Reduce in quantityReduce the numberRandom number generatorsSecret communicationComputer hardwarePower analysis
Resistance against simple power analysis is maintained while a smaller table is used. An IC card 100 decrypts encrypted information using elliptic curve calculation for calculating a point k*C by multiplying a point C on an elliptic curve E with a coefficient k that is a positive integer less that a prime p. The calculation of the point k*C is performed by adding a multiplication result obtained by multiplying a digit position (window) value w of the acquired coefficient k with the point C in a position corresponding to the digit position, and is performed with respect to all digit positions. When a non-negative integer t exists that fulfills a condition that the acquired digit value w_can be divided by 2t and cannot be divided by 2t+1, the multiplication includes adding a point obtained by multiplying a point Q with w / 2t.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com