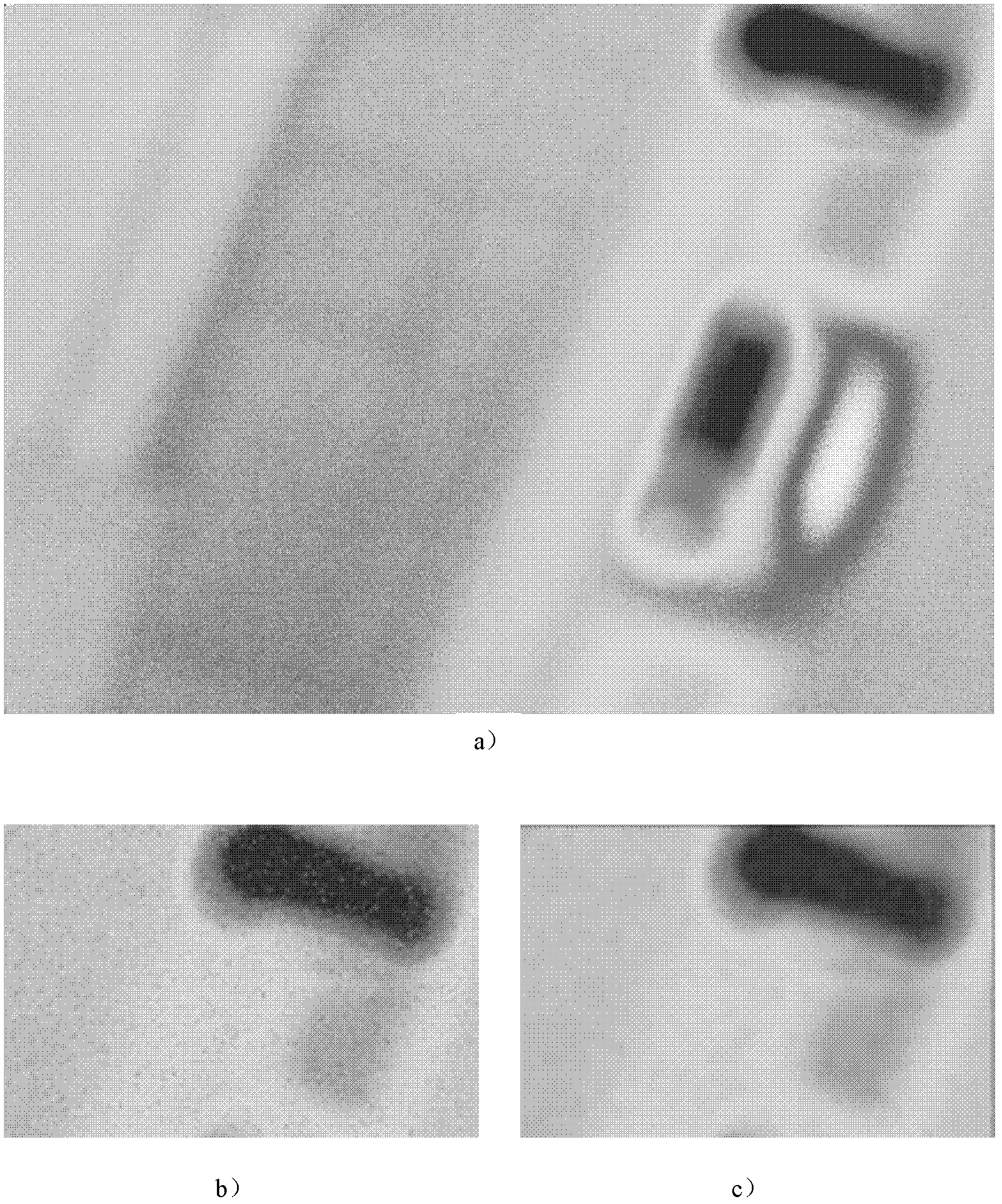Patents
Literature
400 results about "Leakage power" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
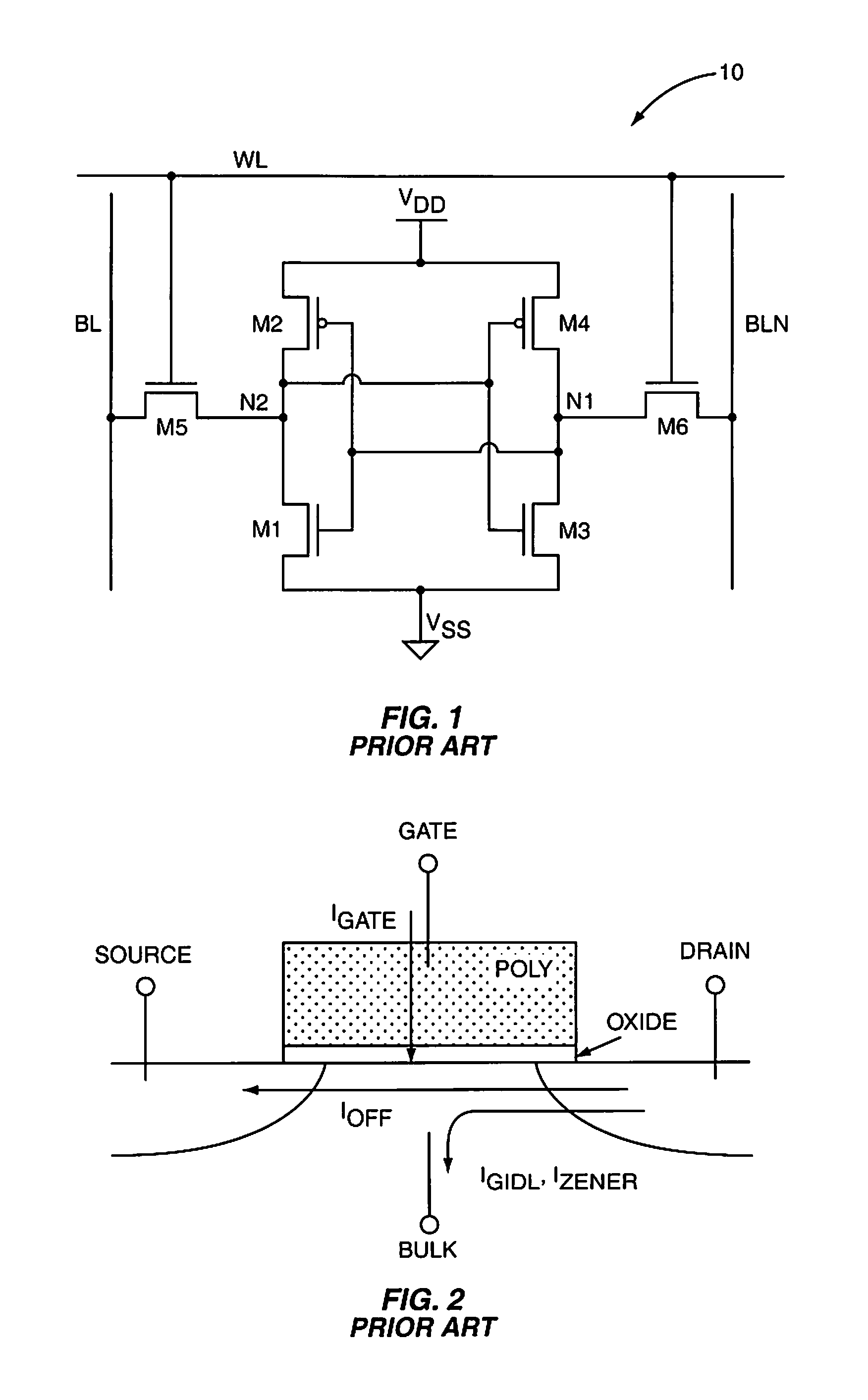
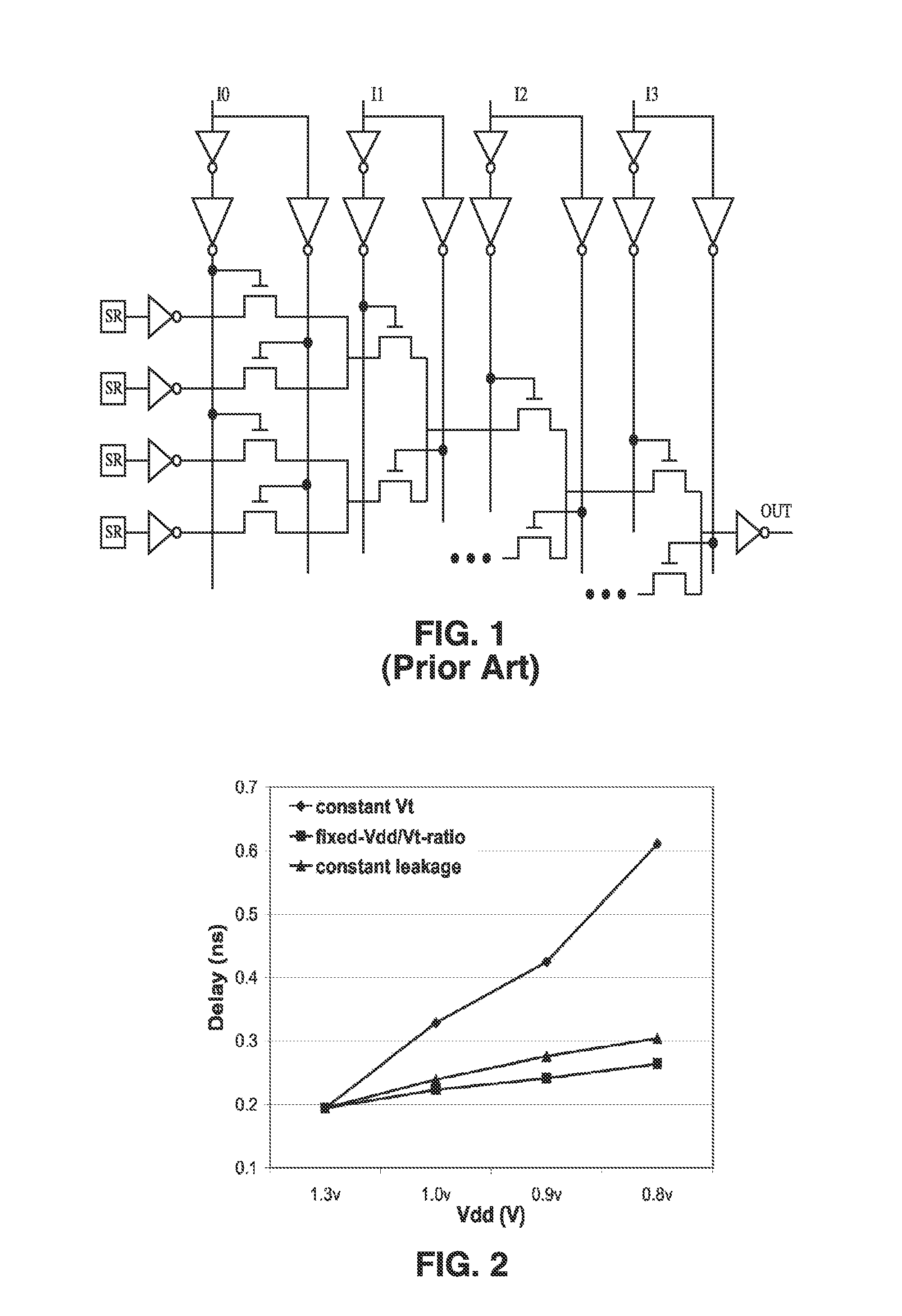
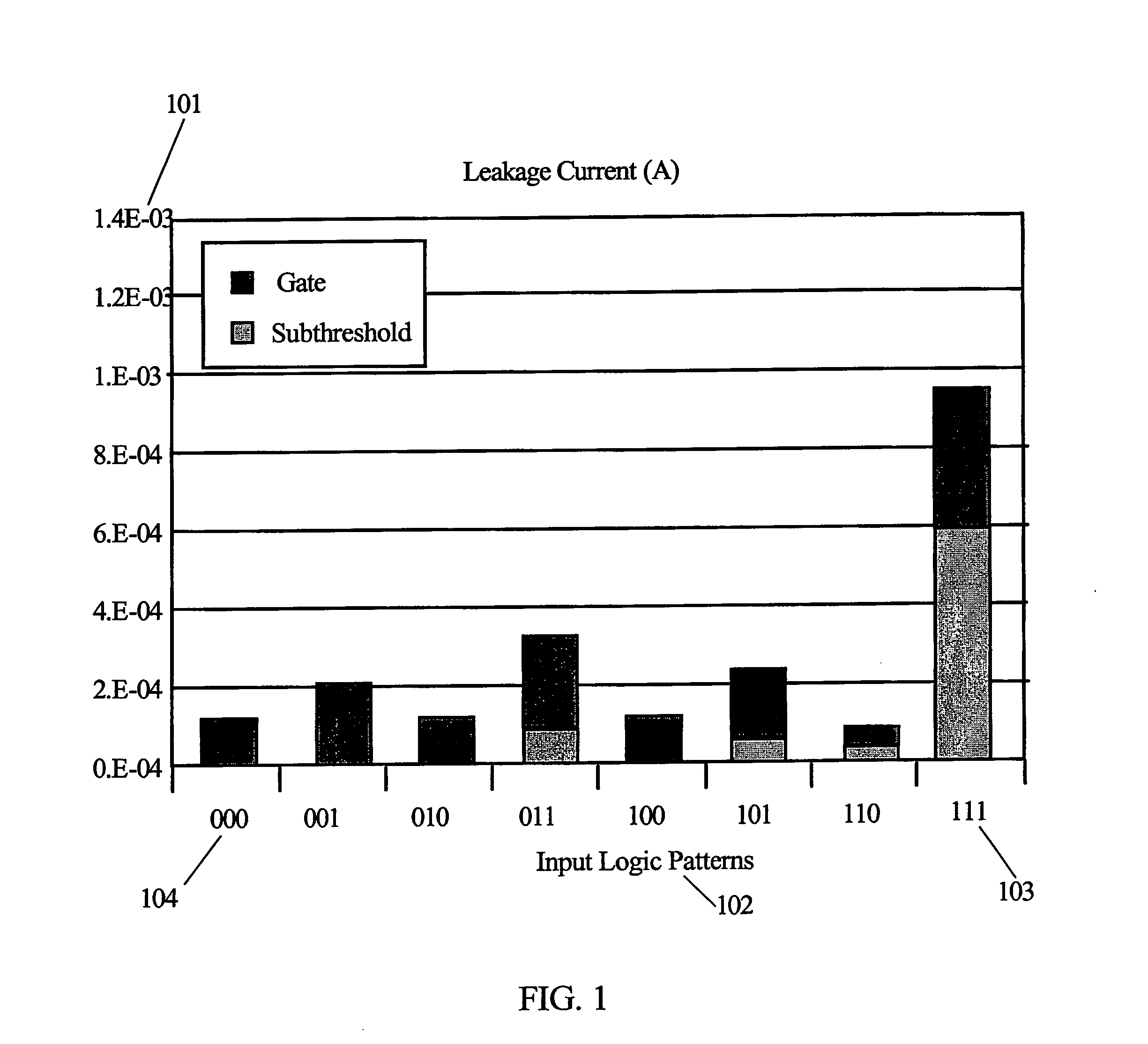
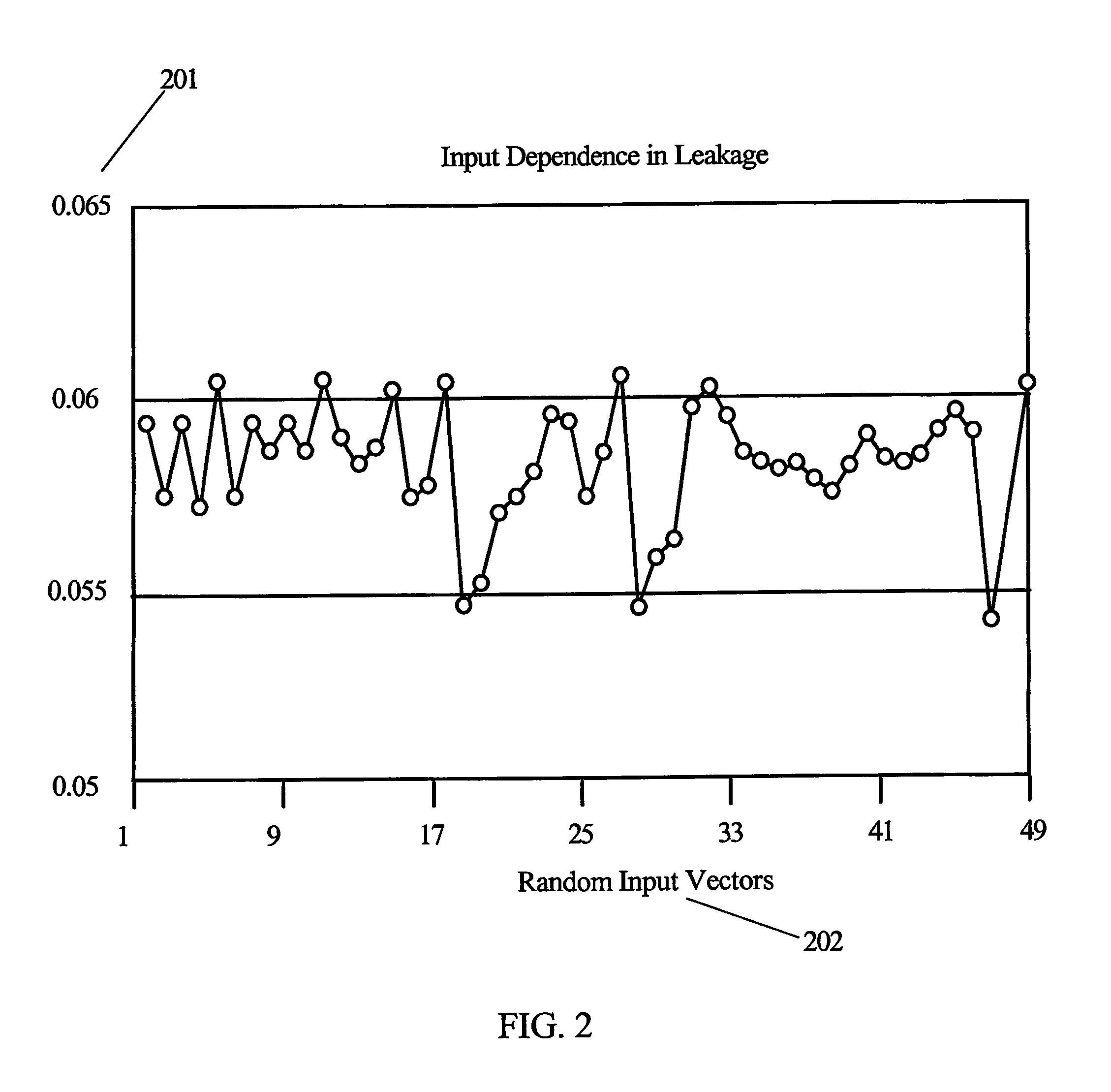
Leakage Power. The power consumed by the sub threshold currents and by reverse biased diodes in a CMOS transistor is considered as leakage power. The leakage power of a CMOS logic gate does not depend on input transition or load capacitance and hence it remains constant for a logic cell.
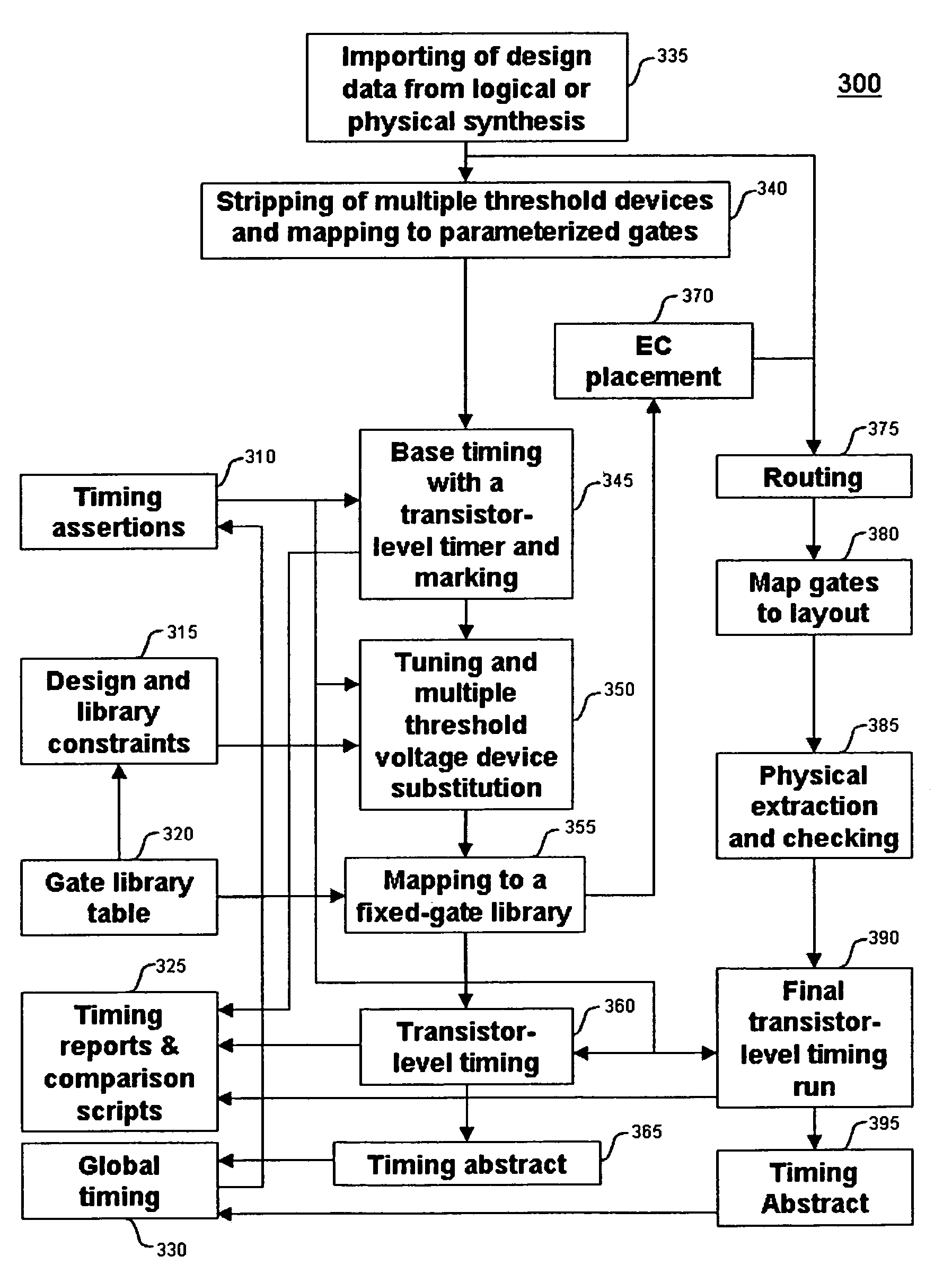
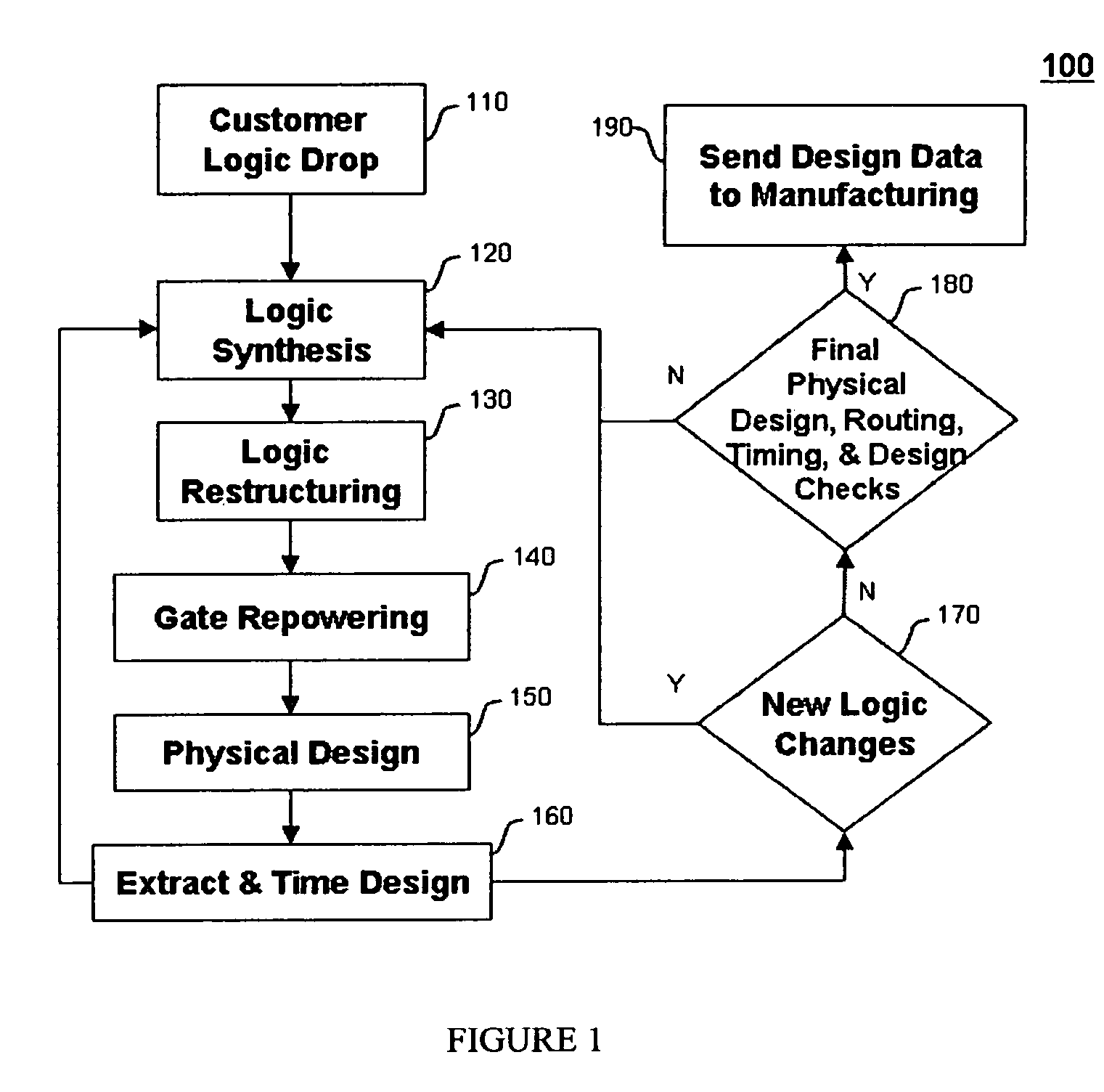
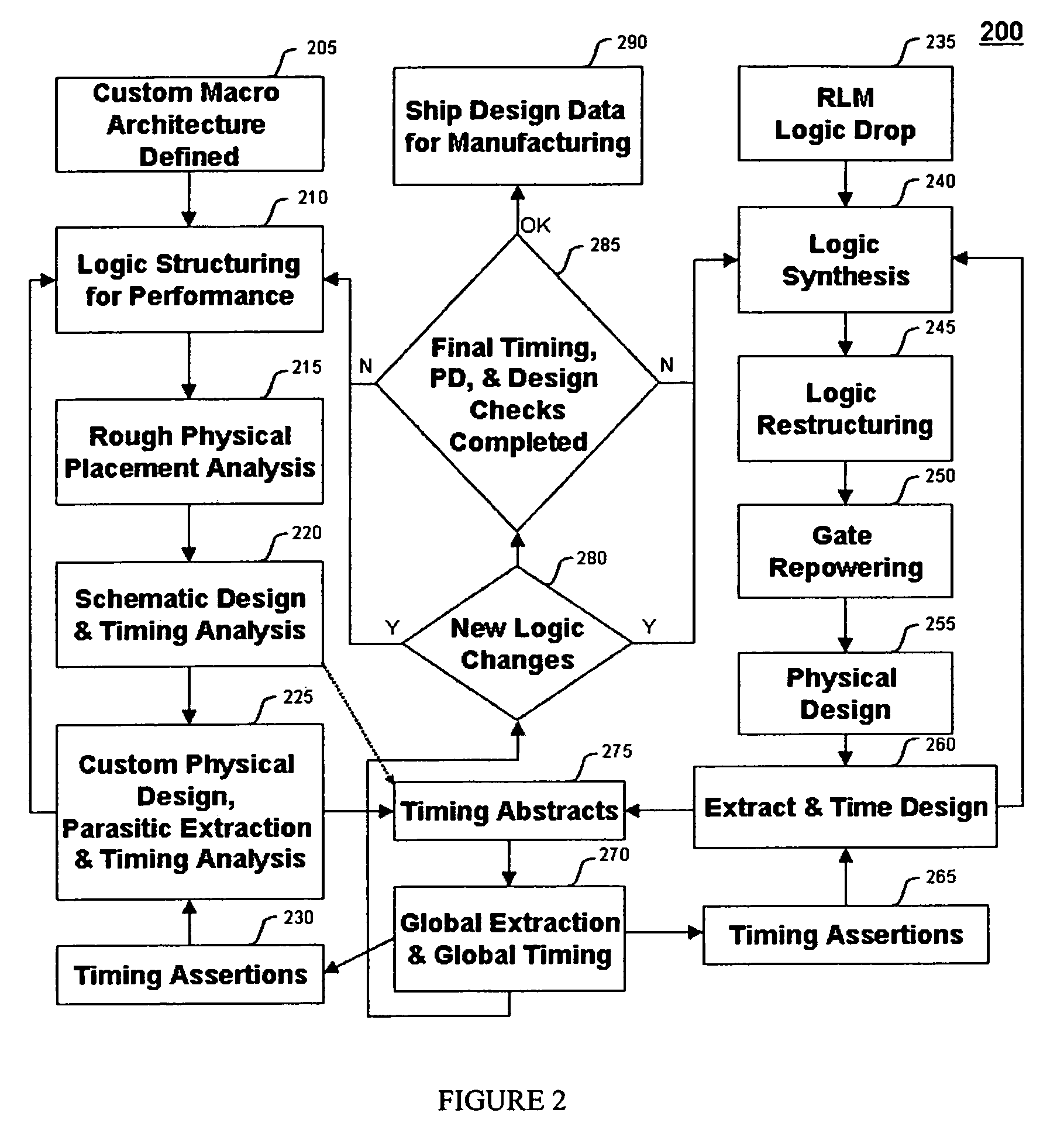
Method for tuning a digital design for synthesized random logic circuit macros in a continuous design space with optional insertion of multiple threshold voltage devices
InactiveUS7093208B2Efficient and effective methodologyError minimizationDigital storageComputer aided designContinuous designCritical section
A Digital Design Method which may be automated is for obtaining timing closure in the design of large, complex, high-performance digital integrated circuits. The methodincludes the use of a tuner on random logic macros that adjusts transistor sizes in a continuous domain. To accommodate this tuning, logic gates are mapped to parameterized cells for the tuning and then back to fixed gates after the tuning. Tuning is constrained in such a way as to minimize “binning errors” when the design is mapped back to fixed cells. Further, the critical sections of the circuit are marked in order to make the optimization more effective and to fit within the problem-size constraints of the tuner. A specially formulated objective function is employed during the tuning to promote faster global timing convergence, despite possibly incorrect initial timing budgets. The specially formulated objective function targets all paths that are failing timing, with appropriate weighting, rather than just targeting the most critical path. Finally, the addition of multiple threshold voltage gates allows for increased performance while limiting leakage power.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
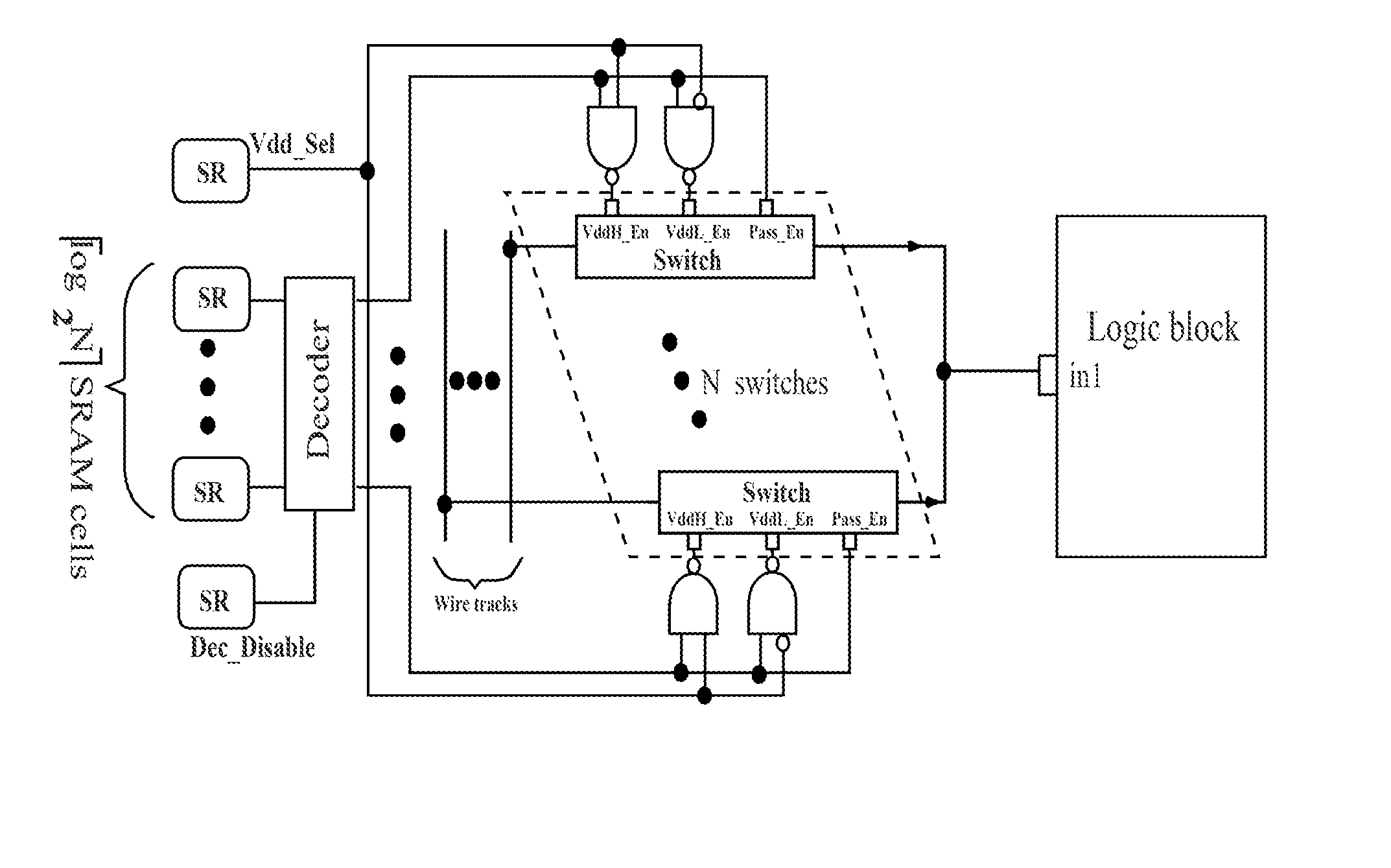
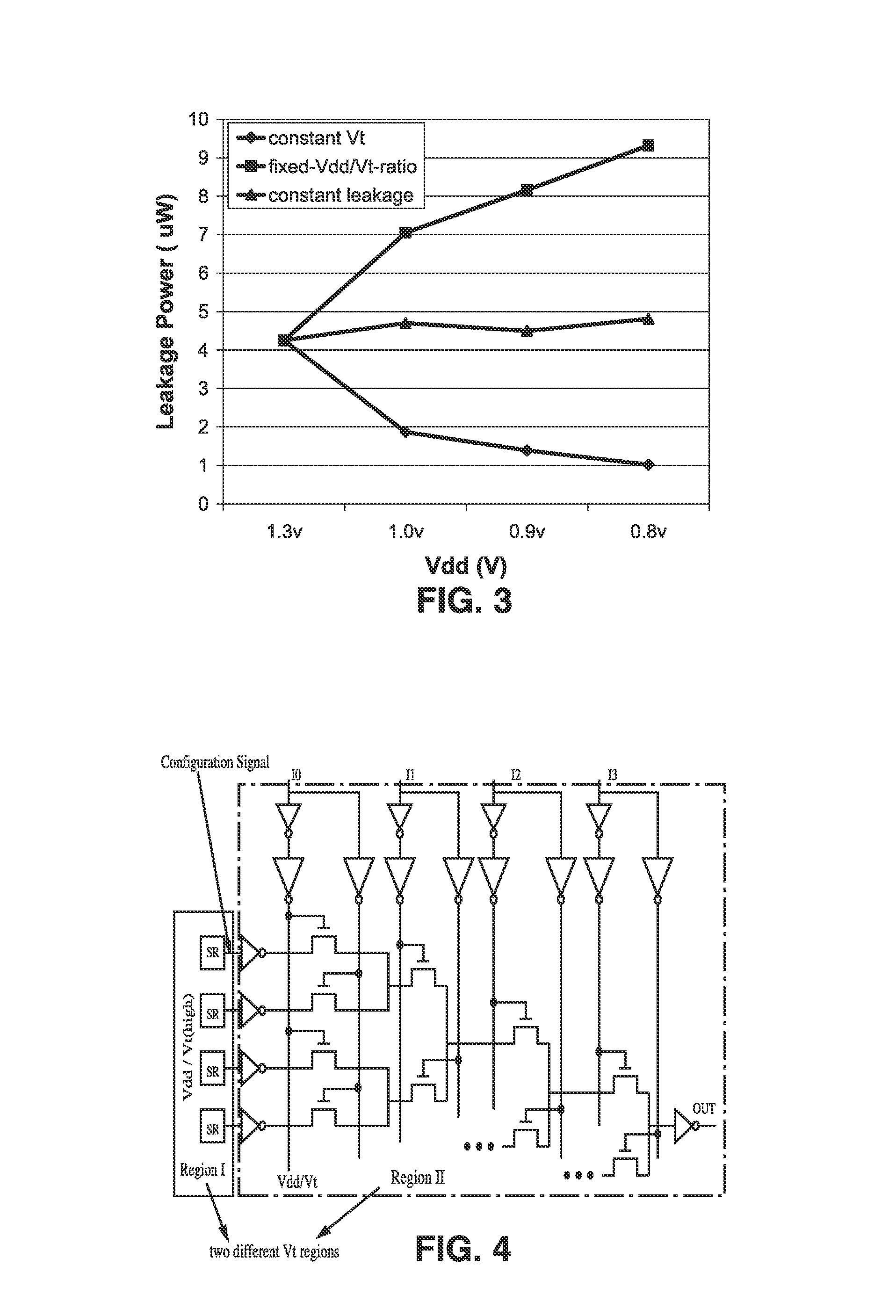
Low-power FPGA circuits and methods
InactiveUS20070164785A1Increase profitReduce needSolid-state devicesCAD circuit designEngineeringLeakage power
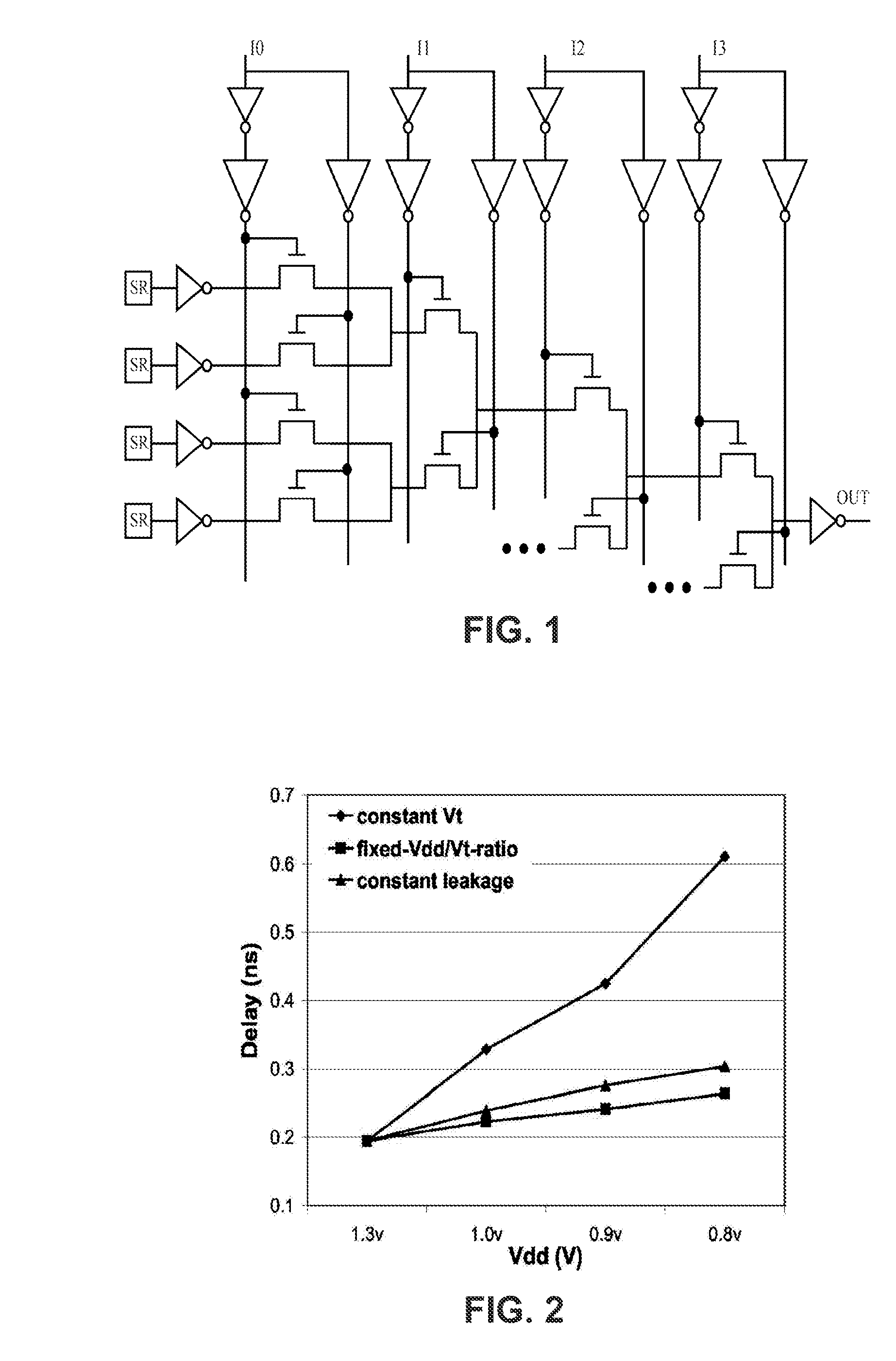
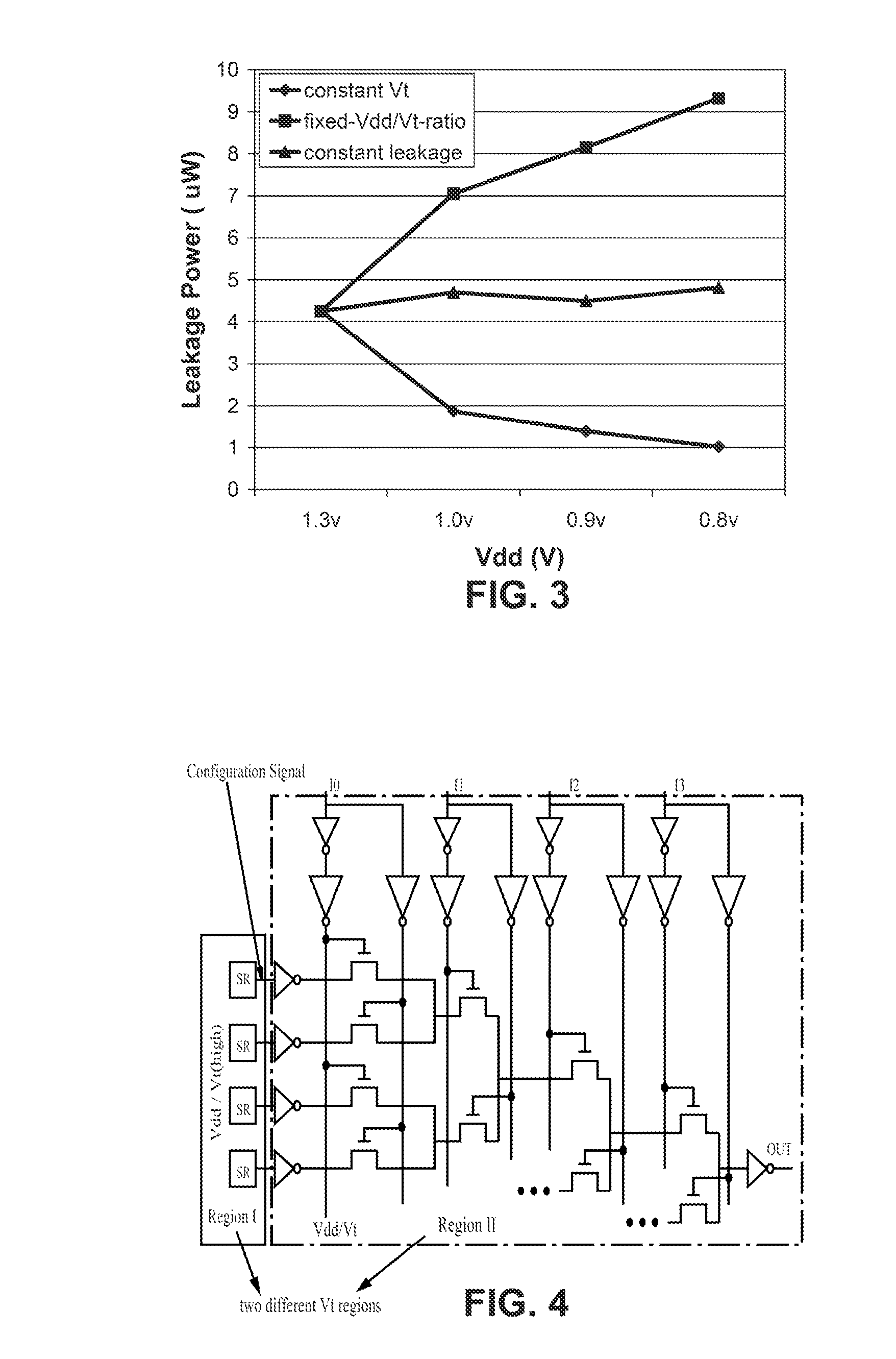
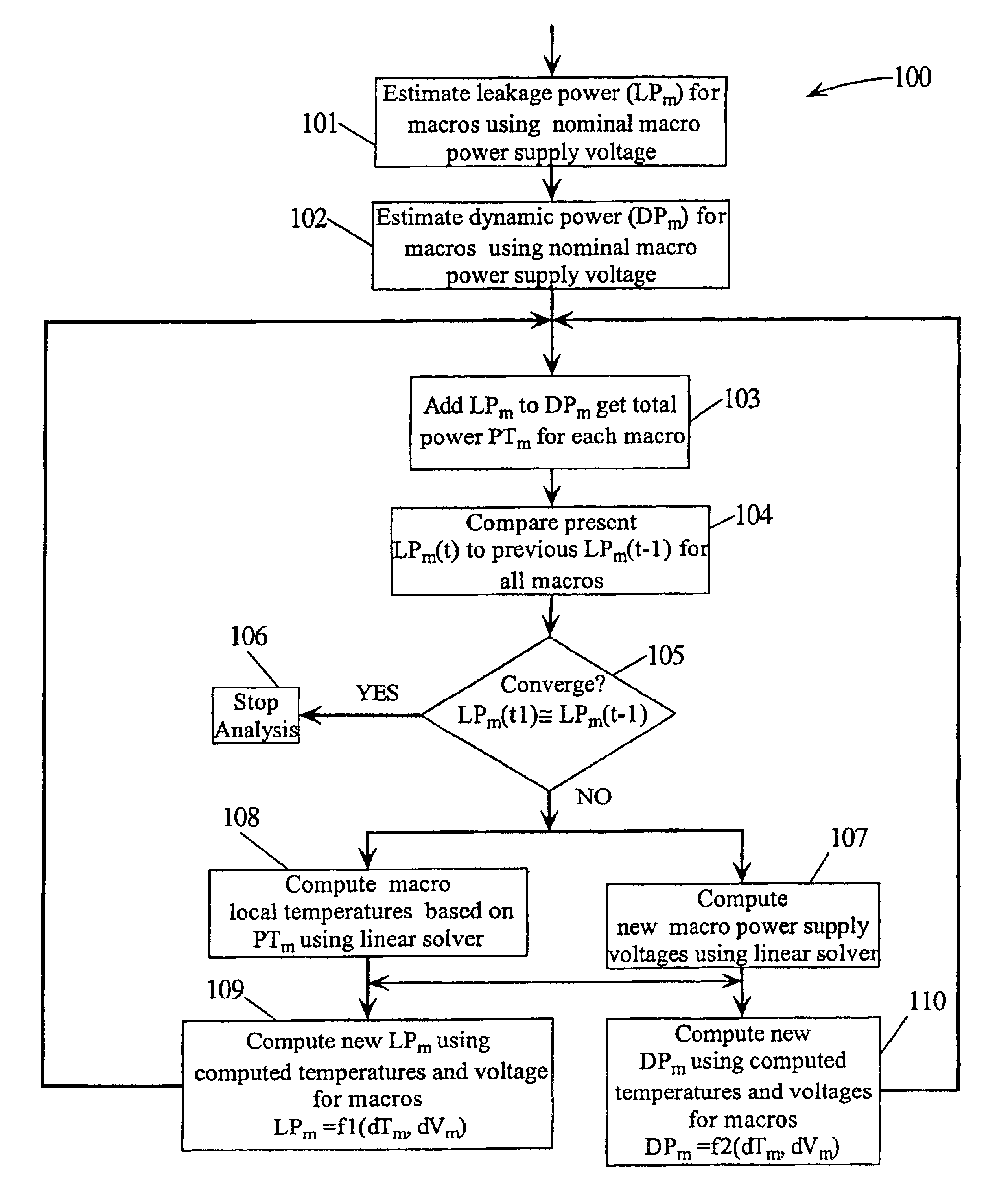
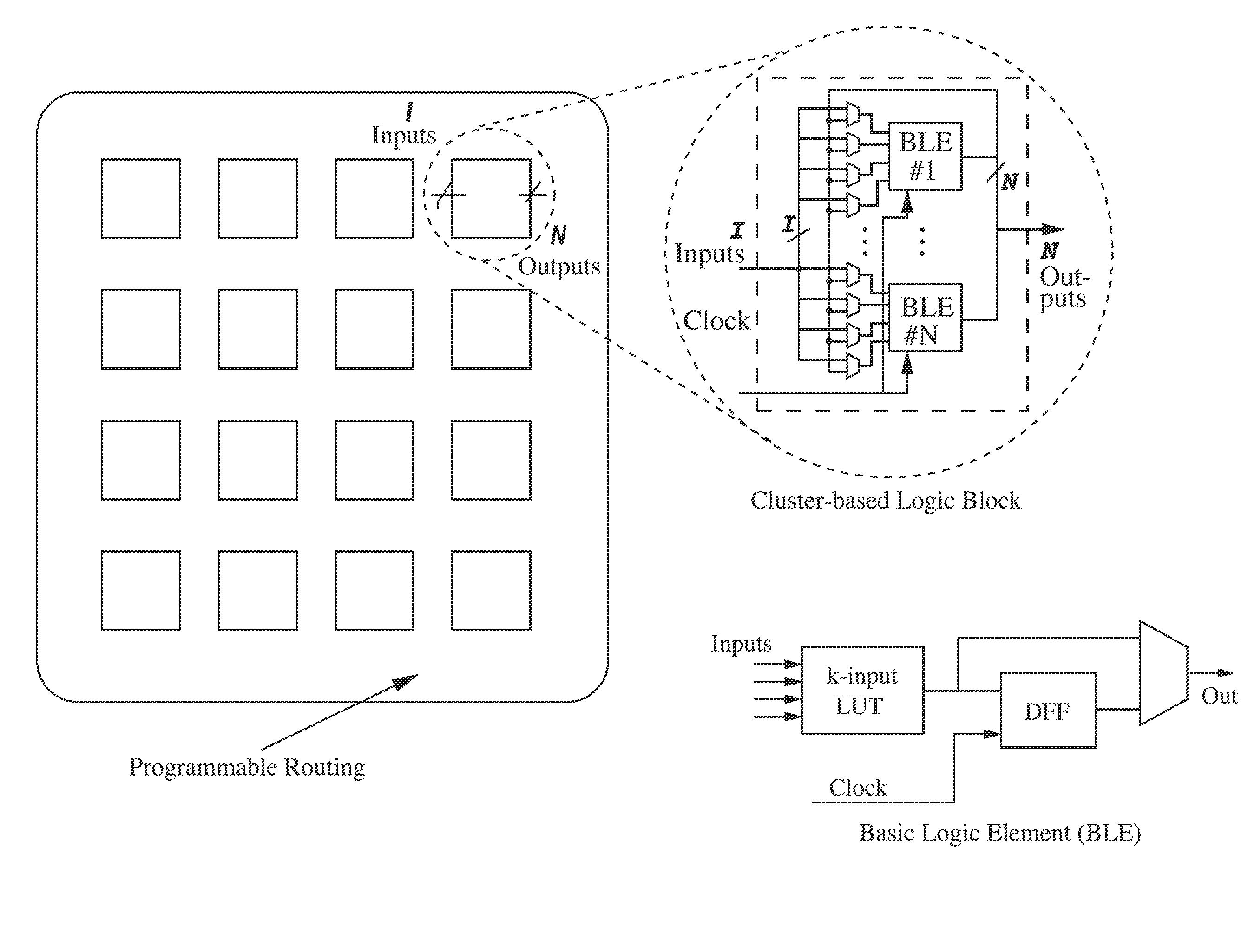
Field Programmable Logic Arrays (FPGAs) are described which utilize multiple power supply voltages to reduce both dynamic power and leakage power without sacrificing speed or substantially increasing device area. Power reduction mechanisms are described for numerous portions of the FPGA, including logic blocks, routing circuits, connection blocks, switch blocks, configuration memory cells, and so forth. Embodiments describe circuits and methods for implementing multiple supplies as sources of Vdd, multiple voltage thresholding Vt, signal level translators, and power gating of circuitry to deactivate portions of the circuit which are inactive. The supply voltage levels can be fixed, or programmable. Methods are described for performing circuit CAD in the routing and assignment process on FPGAs, in particular for optimizing FPGA use having the power reduction circuits taught. Routing methods describe utilizing slack timing, power sensitivity, trace-based simulations, and other techniques to optimize circuit utilization on a multi Vdd FPGA.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Method for determining the leakage power for an integrated circuit
InactiveUS6842714B1Electric devicesCurrent/voltage measurementElectrical resistance and conductanceElectric distribution network
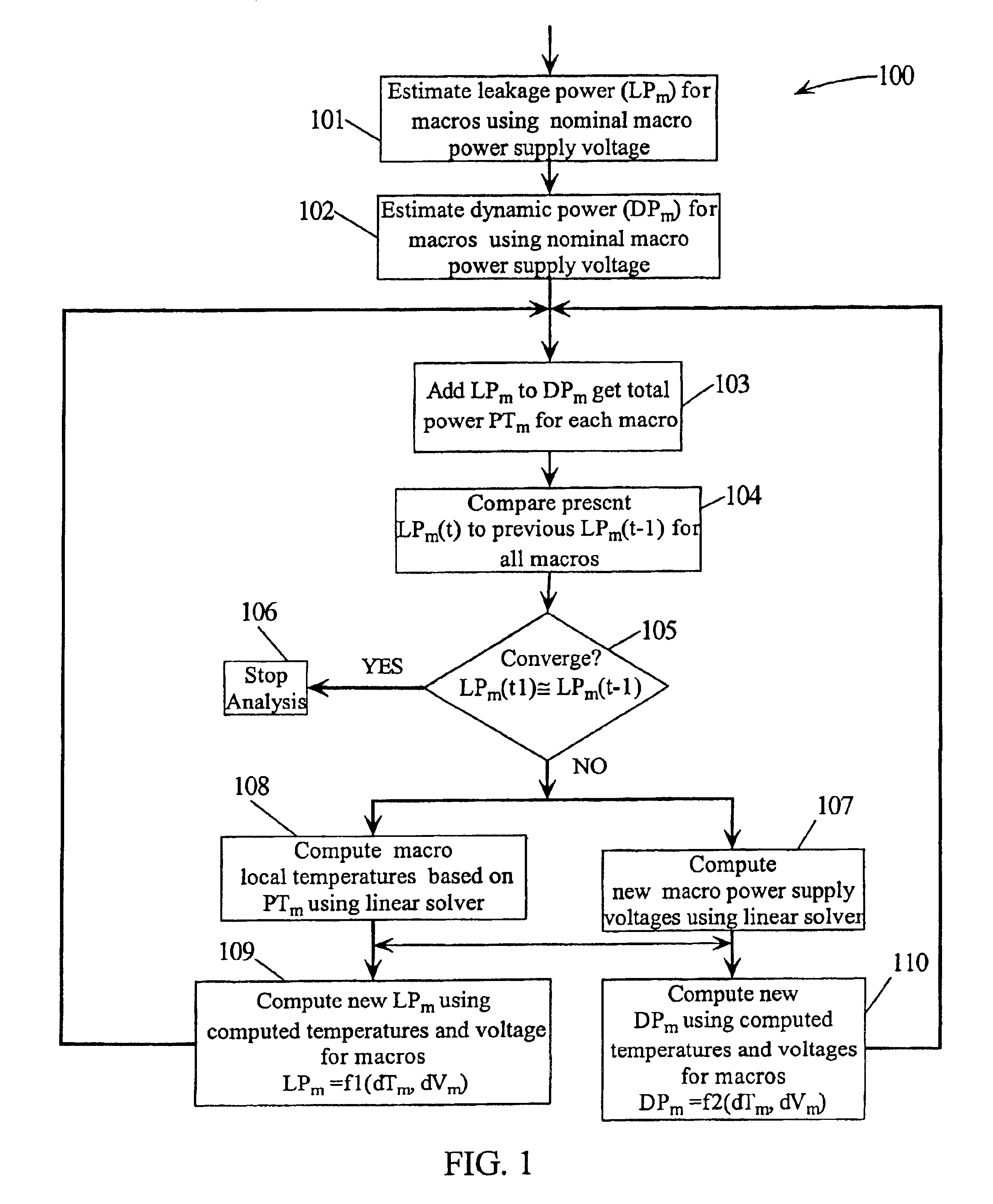
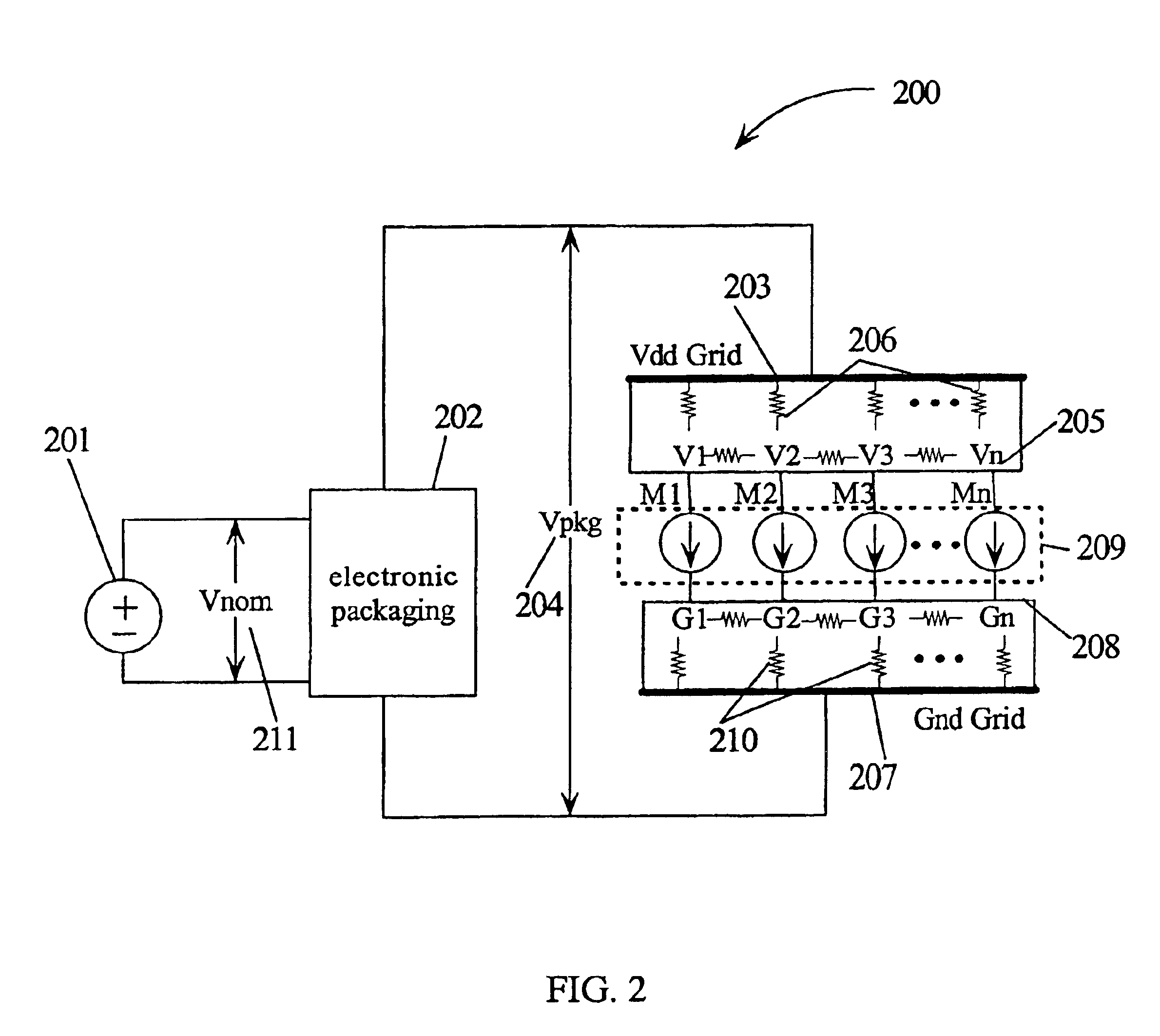
A method for determining full chip leakage power first estimates leakage power and dynamic power for each circuit macro. The power supply voltage to each macro is first assumed to be nominal. The power dissipation for each macro is modeled as a current source whose value is the estimated power divided by the nominal power supply voltage. The power distribution network is modeled as a resistive grids. The thermal environment of the IC and its electronic package are modeled as multi dimensional grids of thermal elements. Algebraic multi-grid (AMG) methods are used to calculate updated circuit macro voltages and temperatures. The macro voltages and temperatures are updated and updated leakage and dynamic power dissipation are calculated. Iterations are continued until leakage power converges to a final value.
Owner:IBM CORP
Low-power FPGA circuits and methods
InactiveUS20100281448A1Improve utilizationEasy to controlCAD circuit designMulti-objective optimisationComputer architectureMemory cell
Field Programmable Logic Arrays (FPGAs) are described which utilize multiple power supply voltages to reduce both dynamic power and leakage power without sacrificing speed or substantially increasing device area. Power reduction mechanisms are described for numerous portions of the FPGA, including logic blocks, routing circuits, connection blocks, switch blocks, configuration memory cells, and so forth. Embodiments describe circuits and methods for implementing multiple supplies as sources of Vdd, multiple voltage thresholding Vt, signal level translators, and power gating of circuitry to deactivate portions of the circuit which are inactive. The supply voltage levels can be fixed, or programmable. Methods are described for performing circuit CAD in the routing and assignment process on FPGAs, in particular for optimizing FPGA use having the power reduction circuits taught. Routing methods describe utilizing slack timing, power sensitivity, trace-based simulations, and other techniques to optimize circuit utilization on a multi Vdd FPGA.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
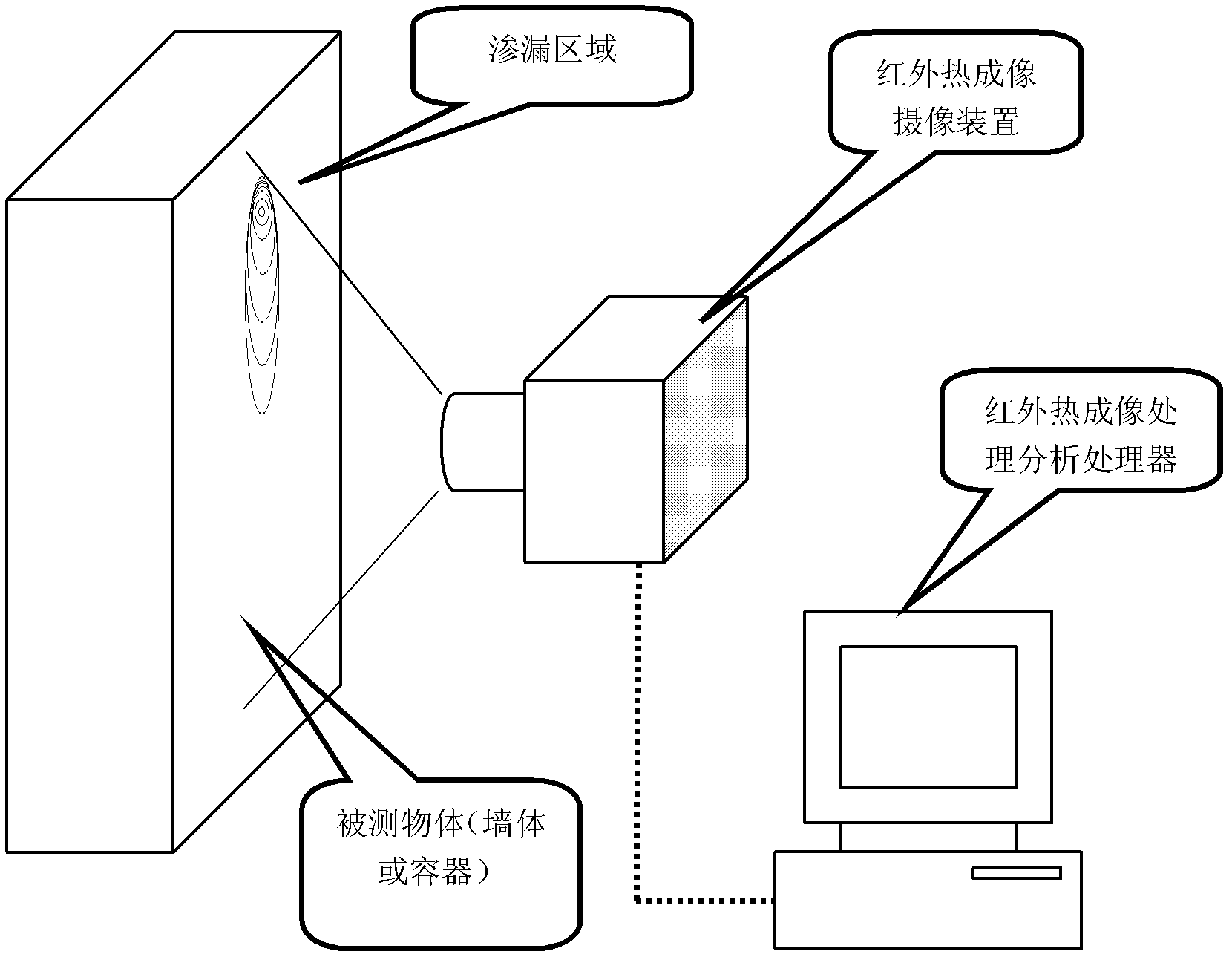
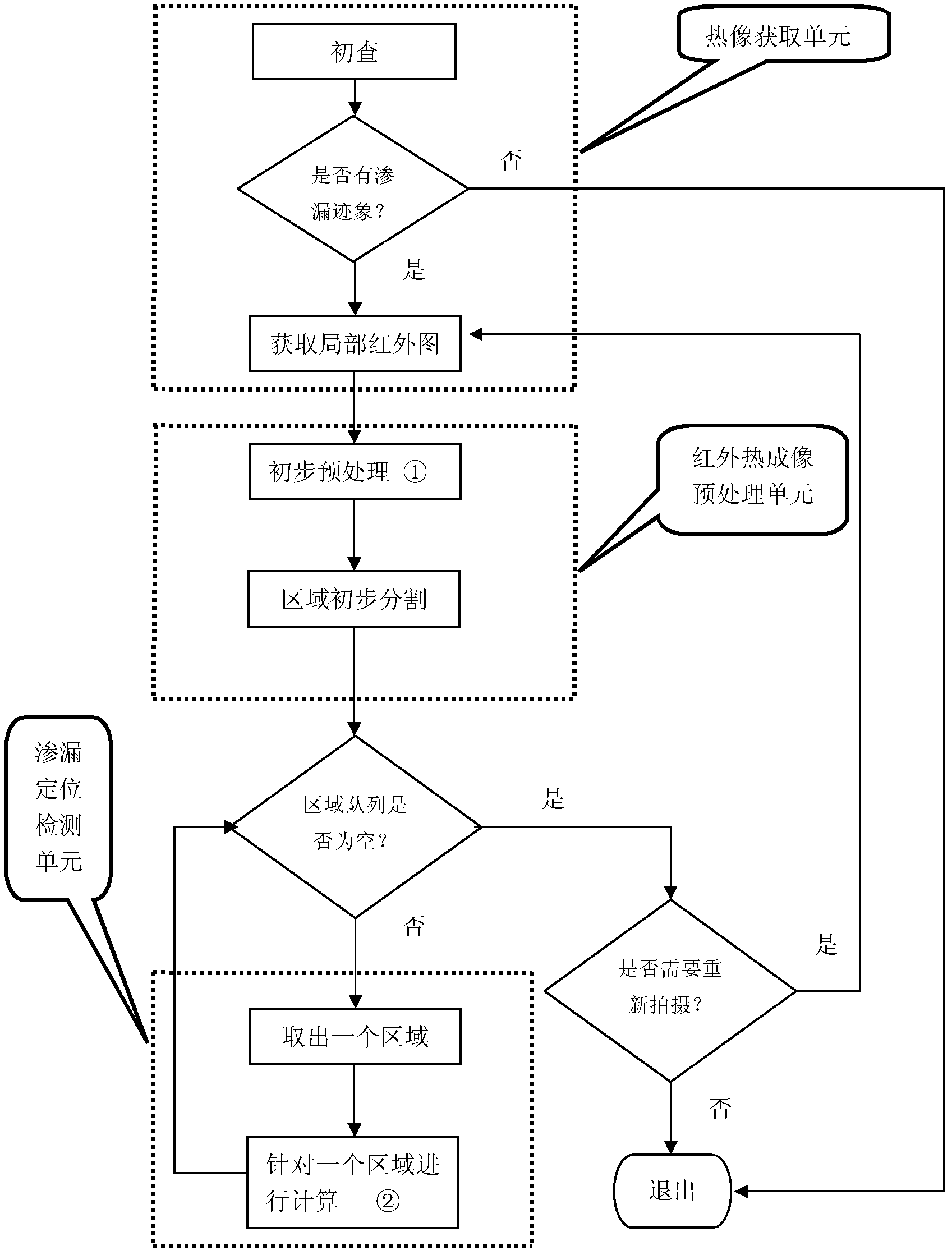
Leakage source detecting device based on infrared thermal imaging processing
ActiveCN102636313ASolve the problem of difficult detection and positioningIncrease lossDetection of fluid at leakage pointEngineeringLeakage power
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
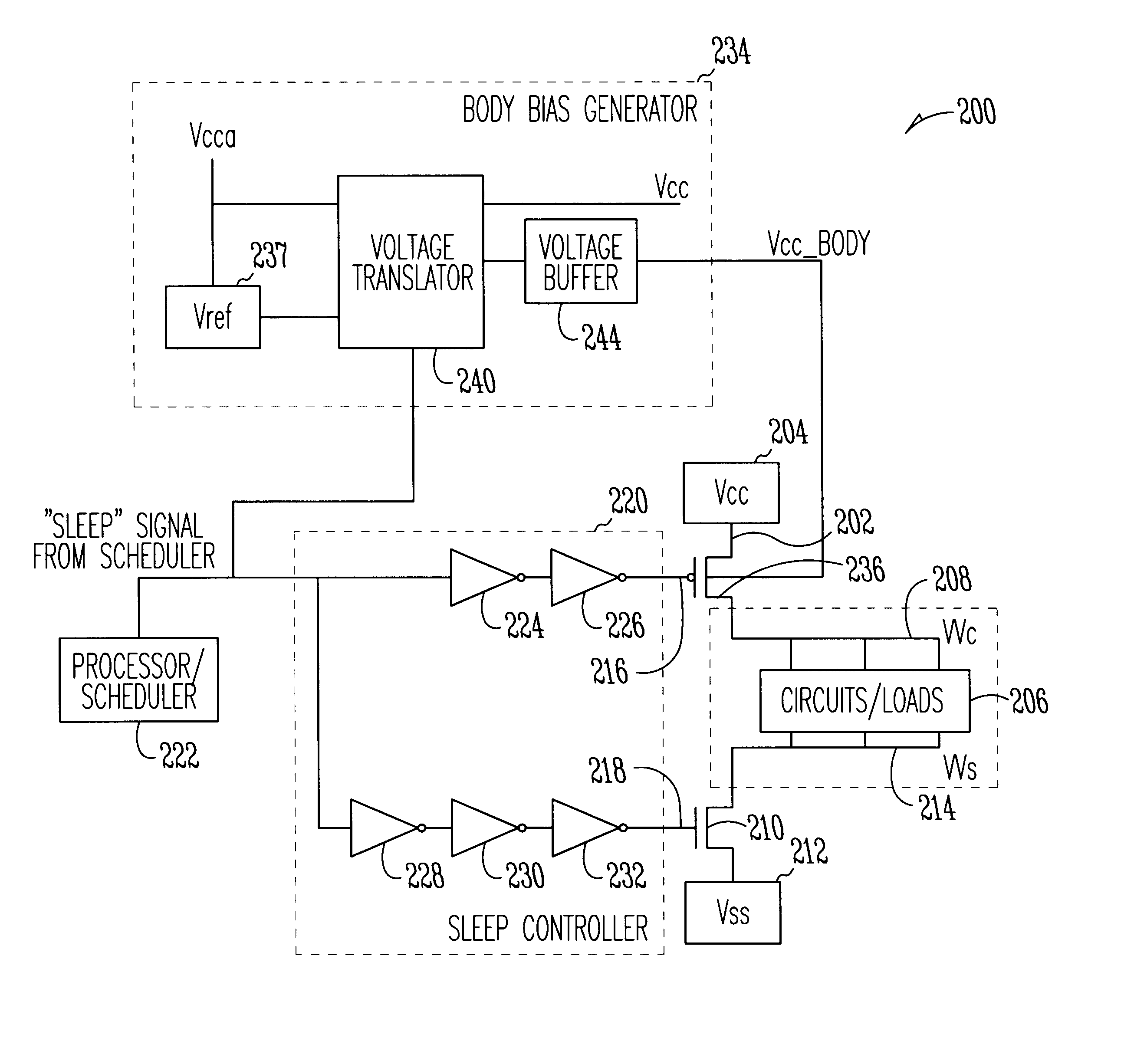
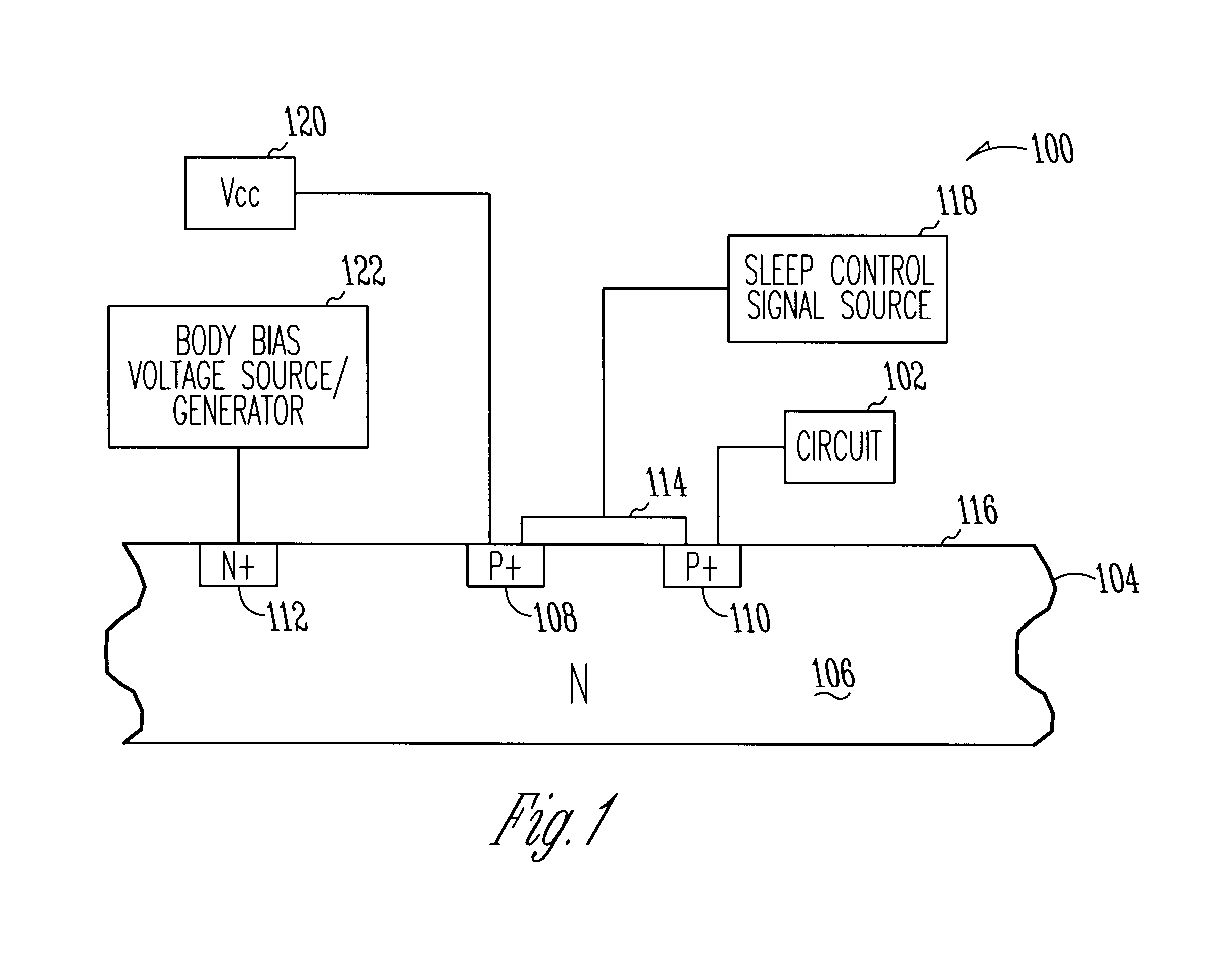
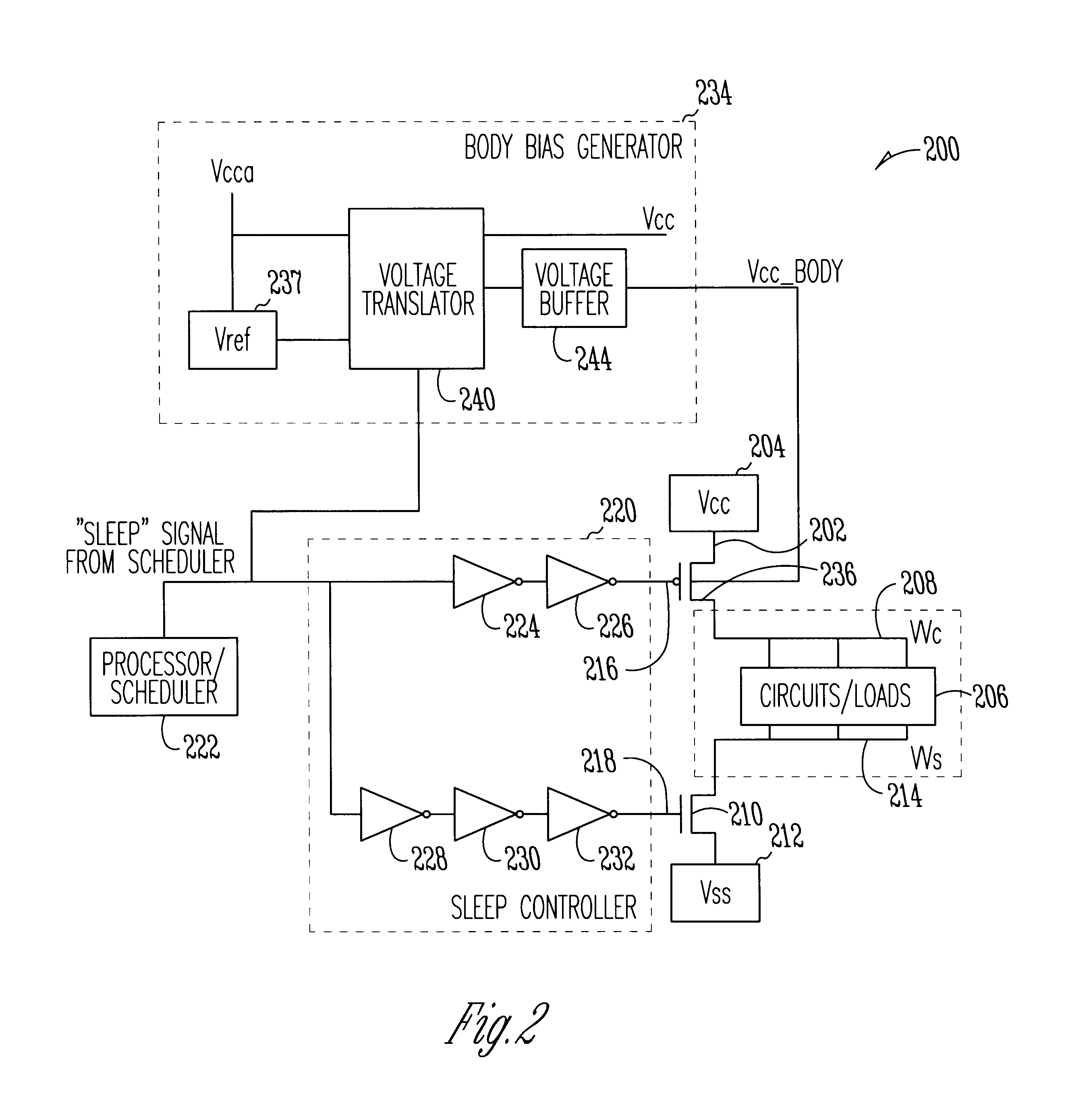
System using body-biased sleep transistors to reduce leakage power while minimizing performance penalties and noise
InactiveUS6744301B1Electric pulse generator detailsElectric variable regulationSleep controlVoltage generator
A system and method to reduce leakage power while minimizing performance penalties and noise is disclosed. In accordance with one embodiment of the invention, the system includes at least one sleep transistor operatively coupleable between a system power supply and at least one circuit powered by the system power supply to control the application of power to the circuit. The sleep transistor is also operatively coupleable to receive a sleep control signal to turn the sleep transistor on and off. A body bias voltage generator is operatively coupleable to a body of the at least one sleep transistor to substantially reduce leakage current when the sleep transistor is non-operational or idle and to improve the operational characteristics of the sleep transistor when the transistor is operational by reducing the performance penalty of the sleep transistor and by reducing impact of noise on the circuit and other devices.
Owner:INTEL CORP
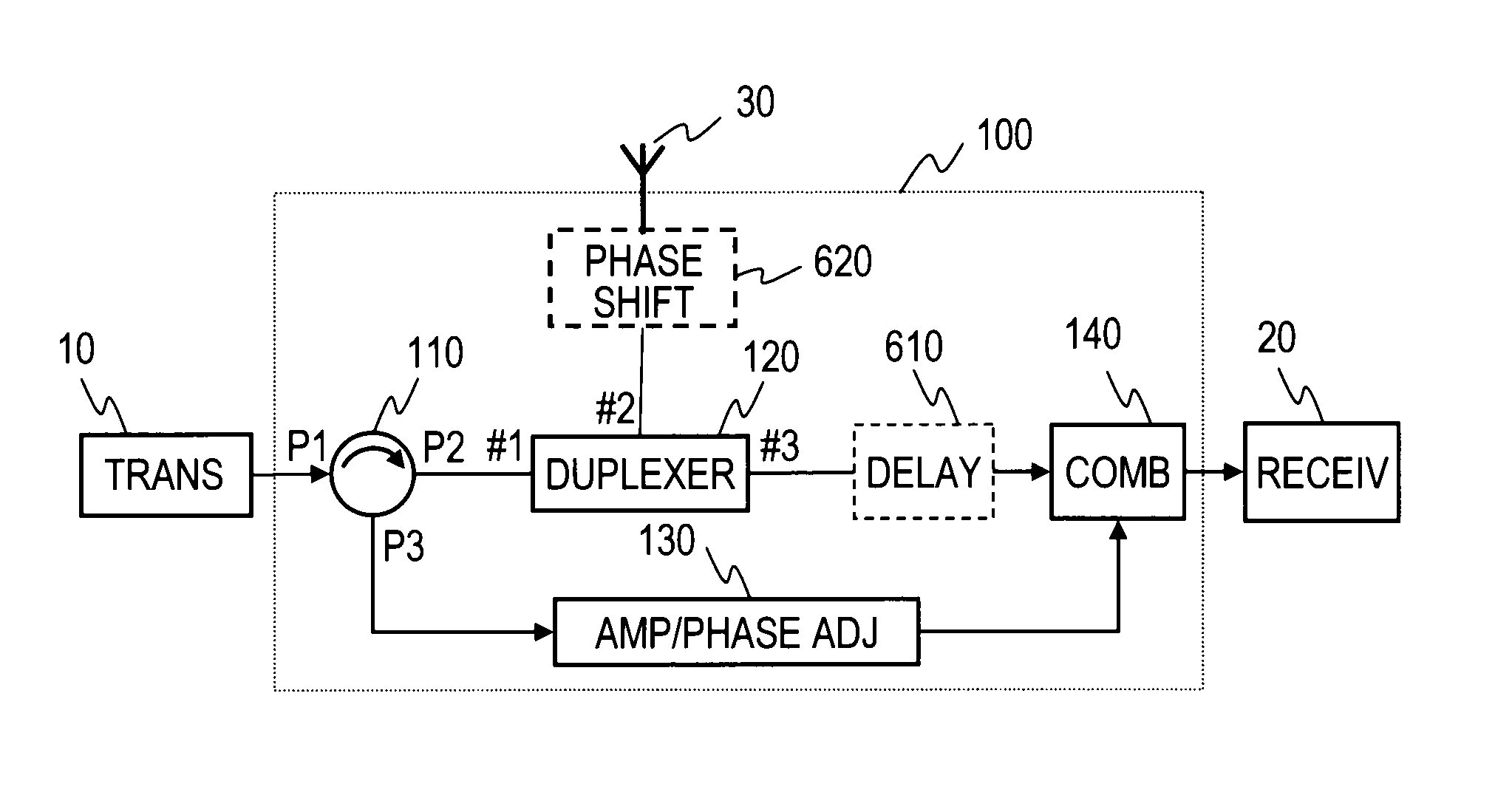
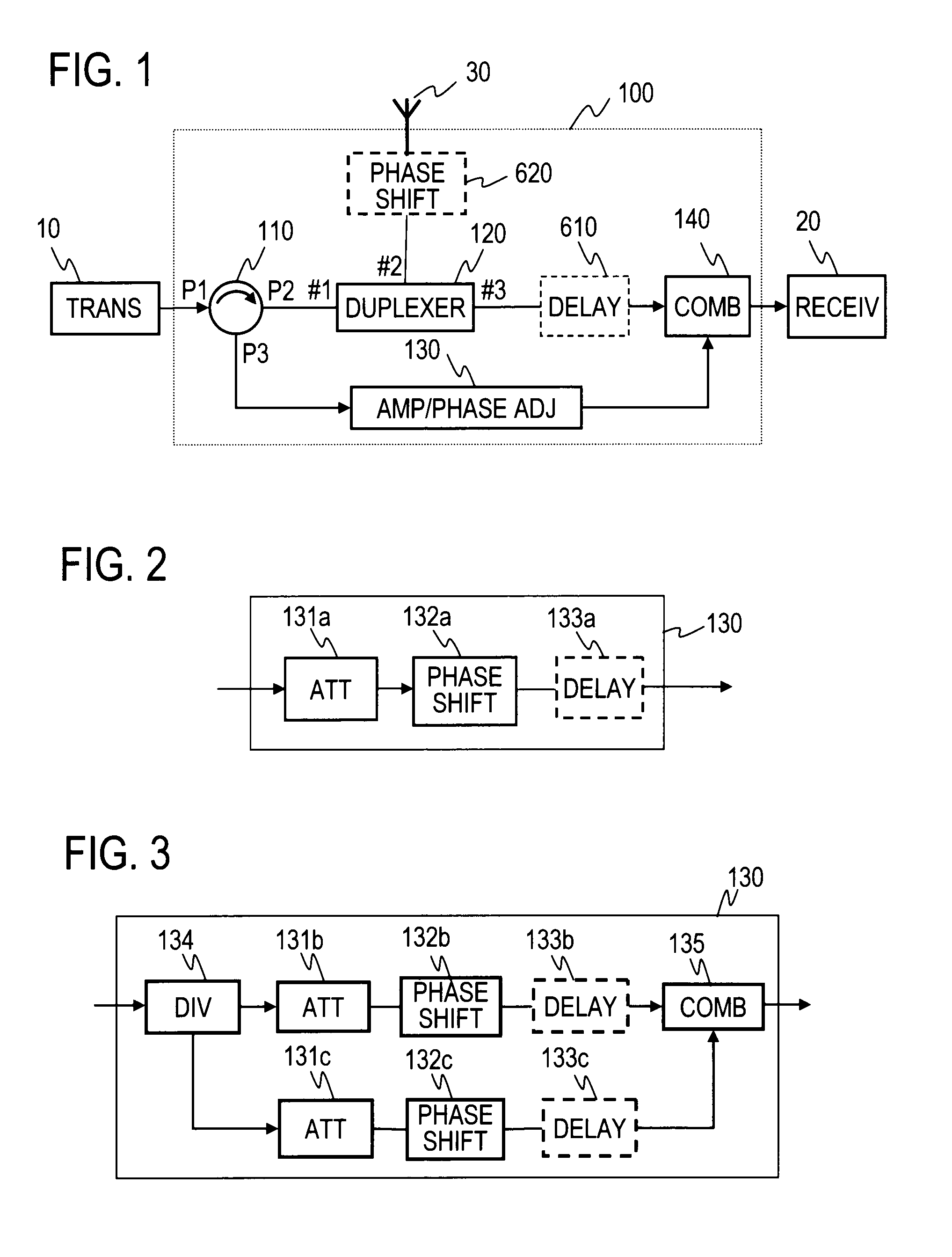
Leakage power reduction apparatus
InactiveUS8086191B2Suppress leakageWithout lowering power utilization efficiencyTransmission control/equalisingEngineeringLeakage power
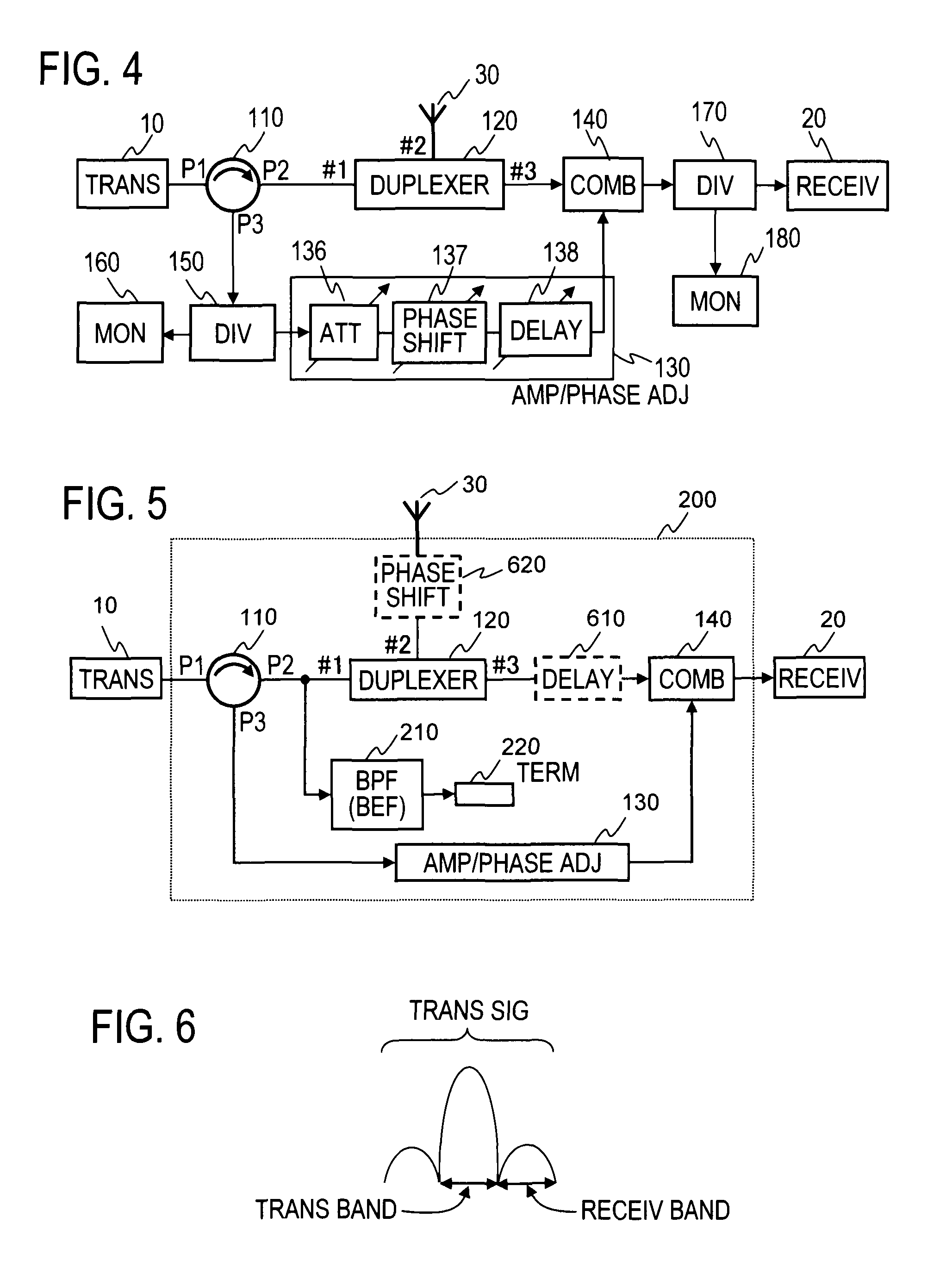
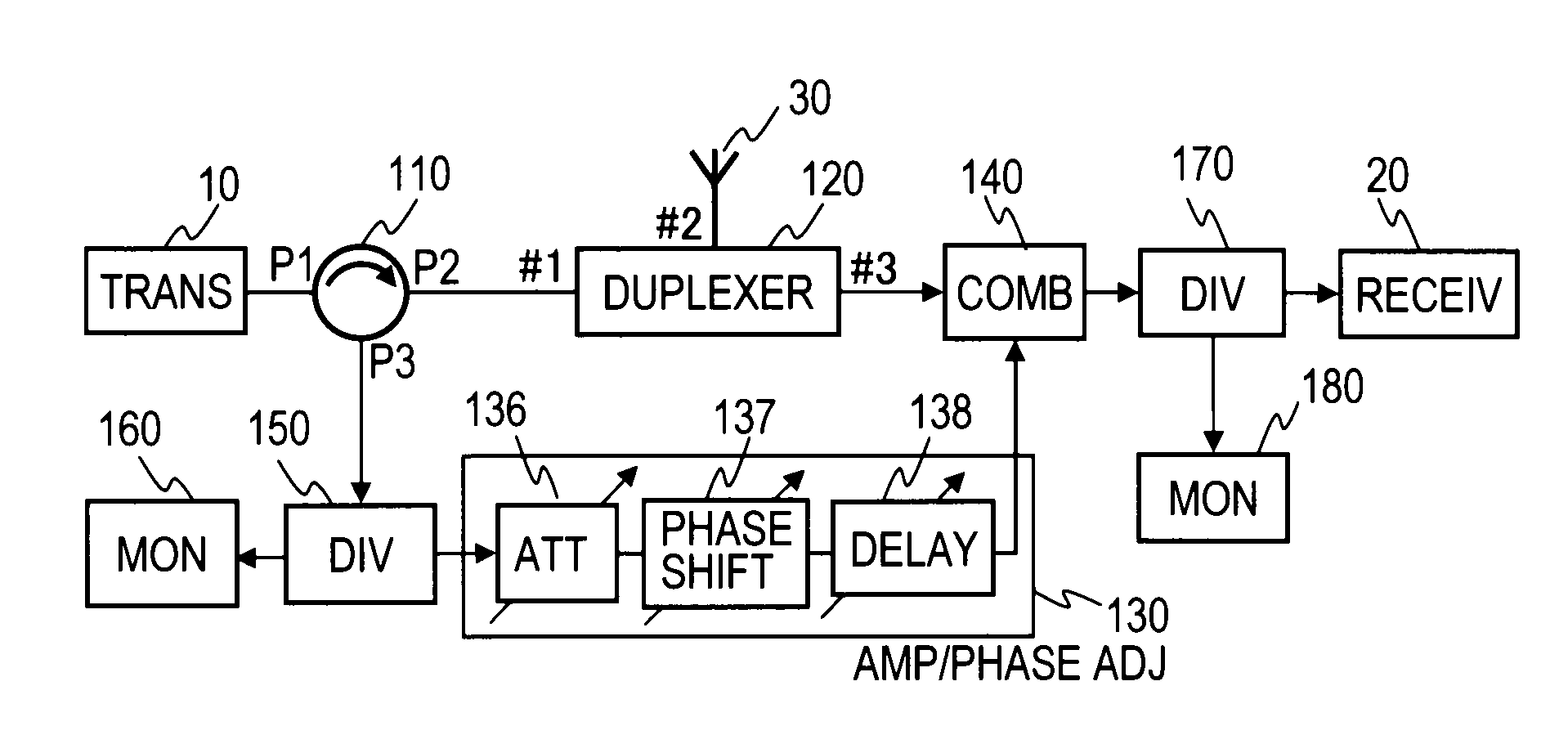
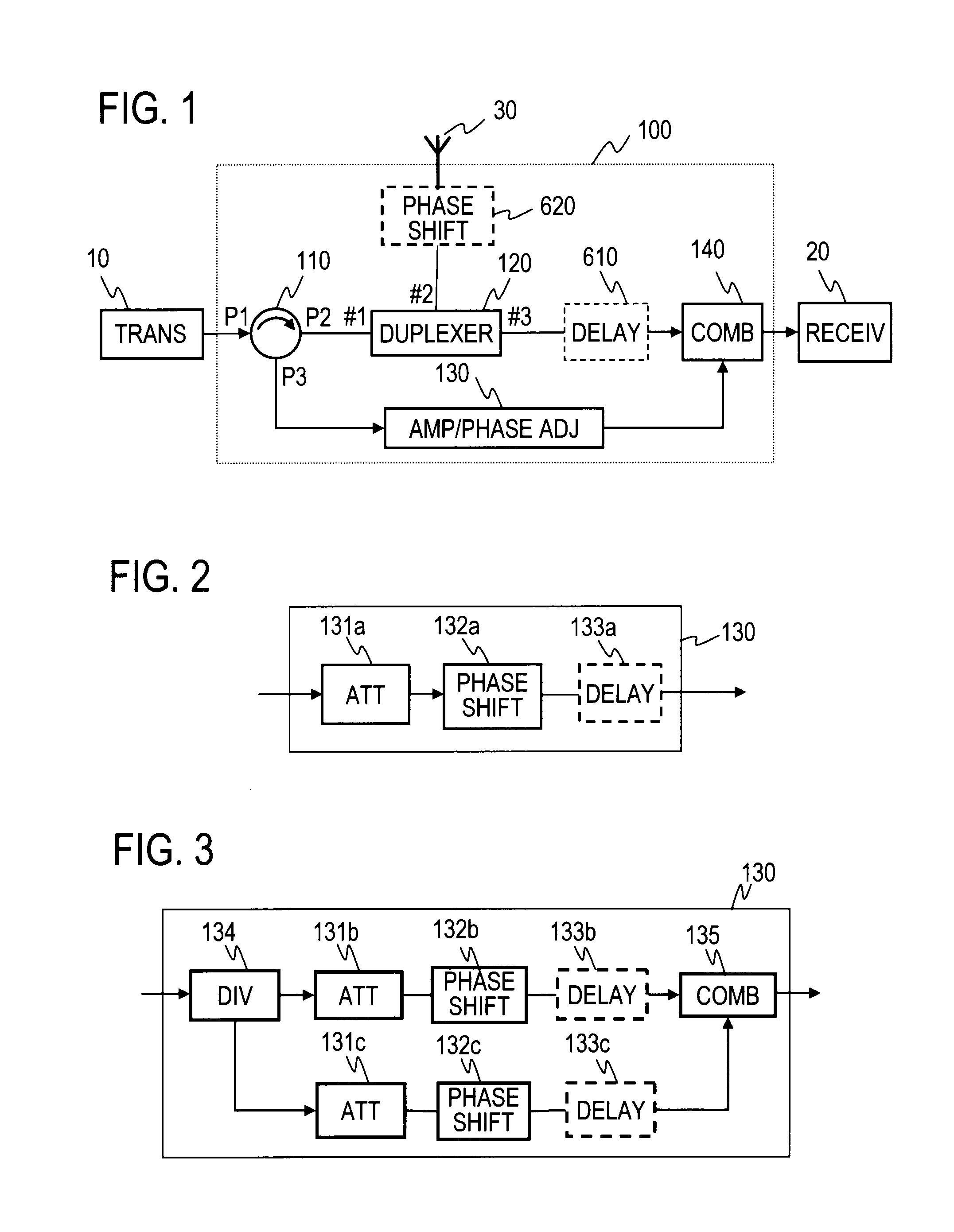
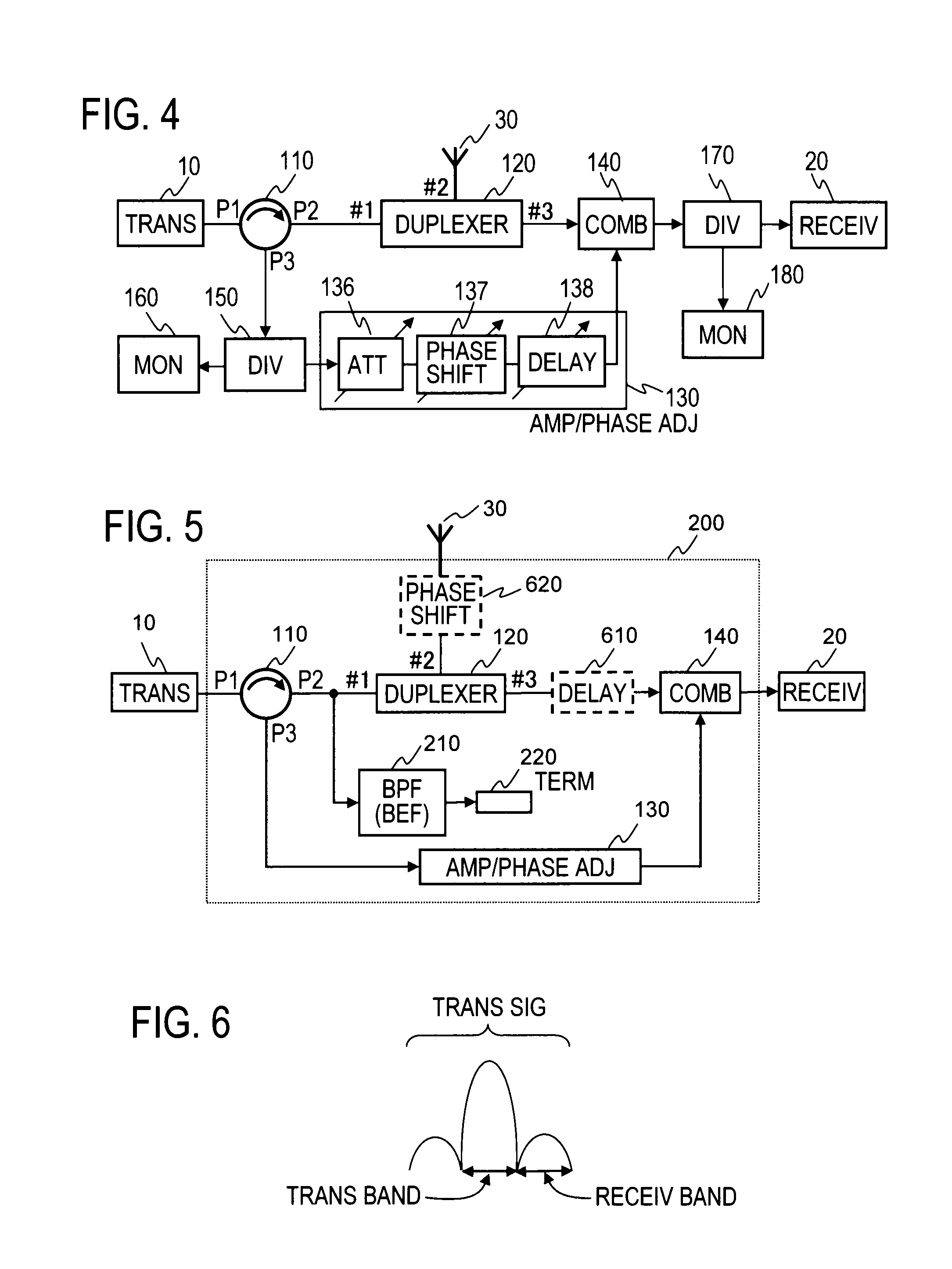
A circulator extracts a transmission signal sent from a transmitter to antenna via the circulator and a duplexer, reflected by an antenna, and returned via the duplexer to the transmitter side. The amplitude and phase of the extracted signal are adjusted by an amplitude-and-phase adjuster to generate an offset signal having the same amplitude and the opposite phase with respect to a leaking transmission signal included in a signal output from a third terminal of the duplexer when combined by a combiner. The offset signal is combined in the combiner with the leaking transmission signal included in the signal output from the third terminal of the duplexer to suppress the leaking transmission signal.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
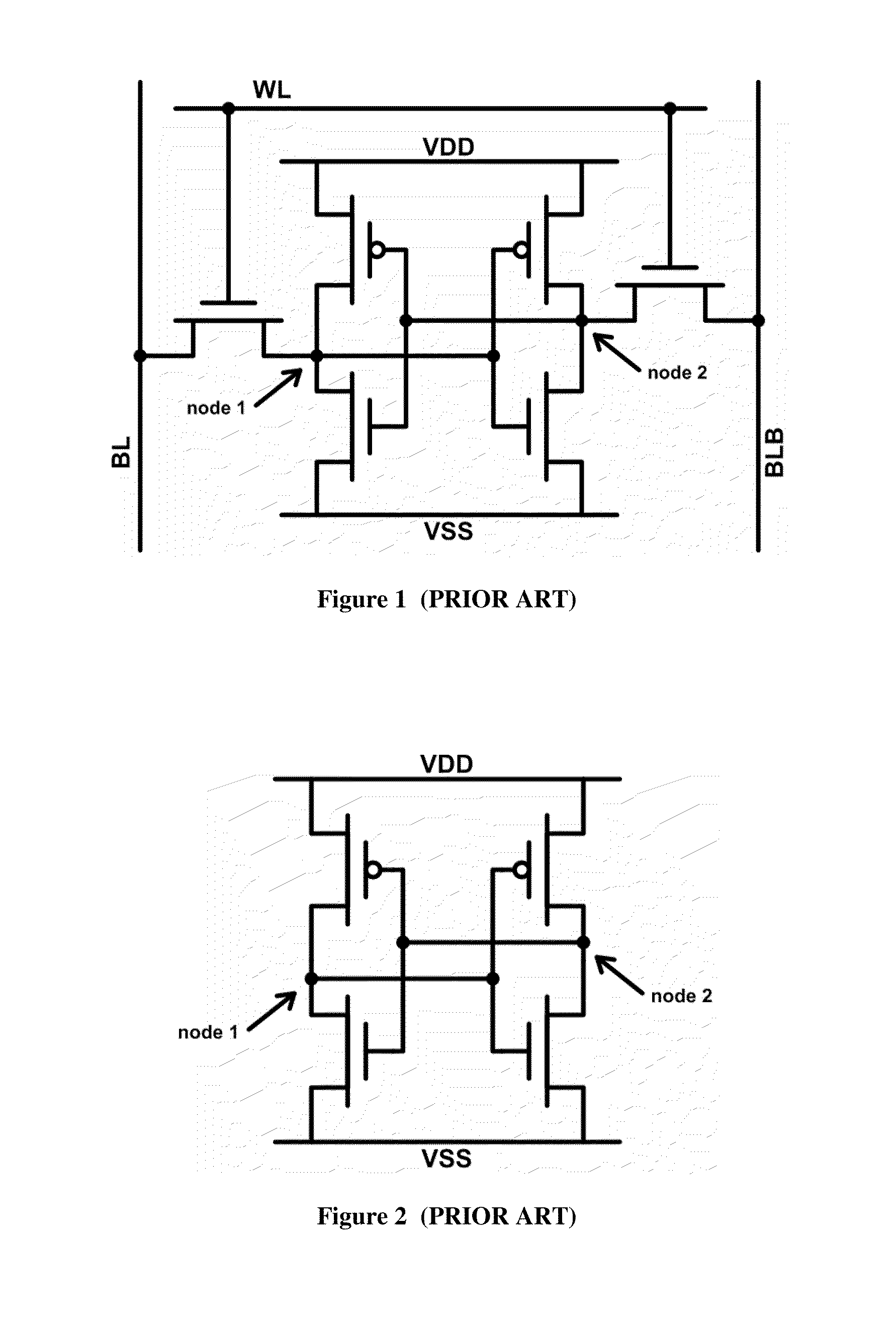
SRAM cell with intrinsically high stability and low leakage
InactiveUS7920409B1Improve stabilityReduce leakageDigital storageStatic random-access memoryControl signal
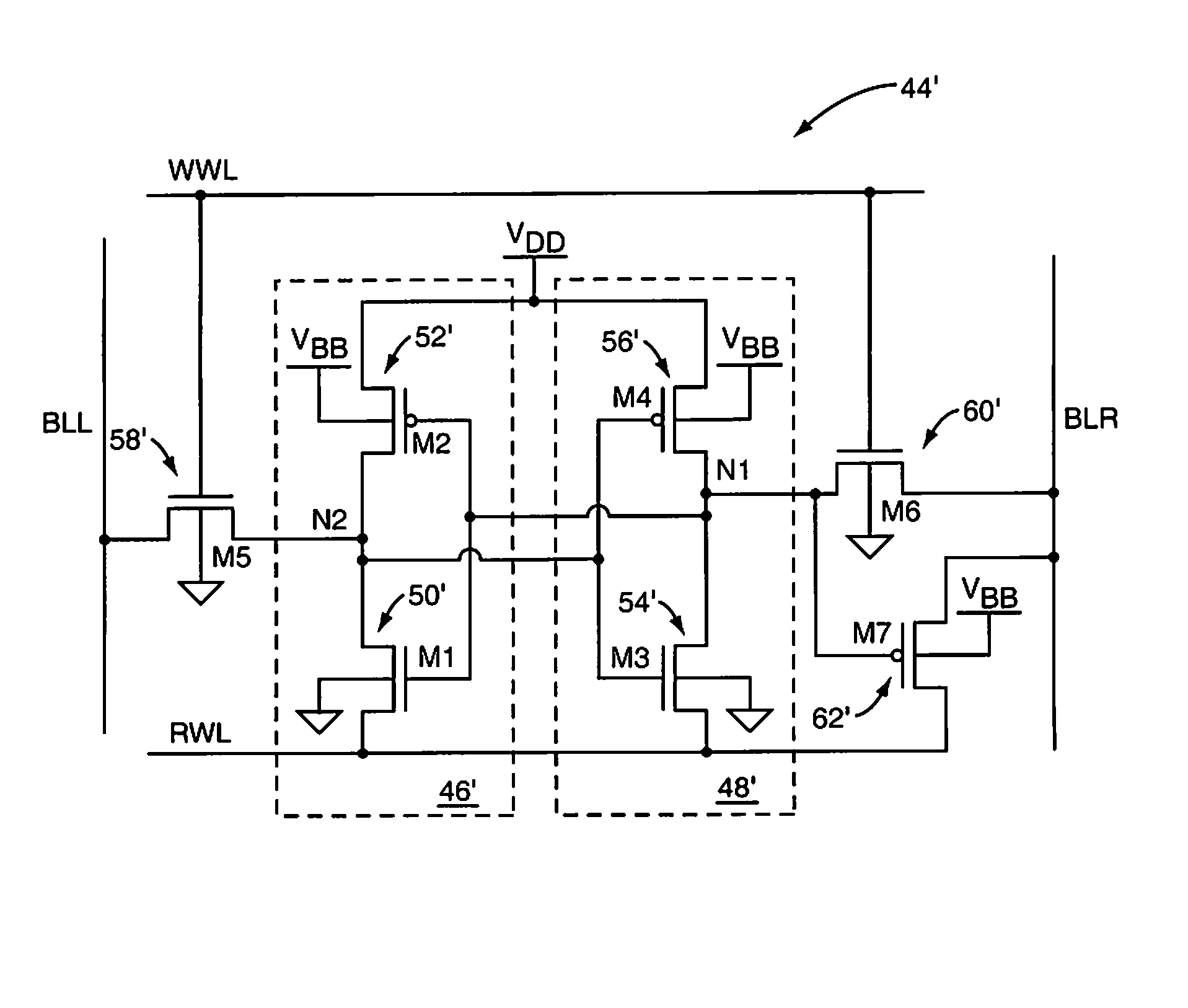
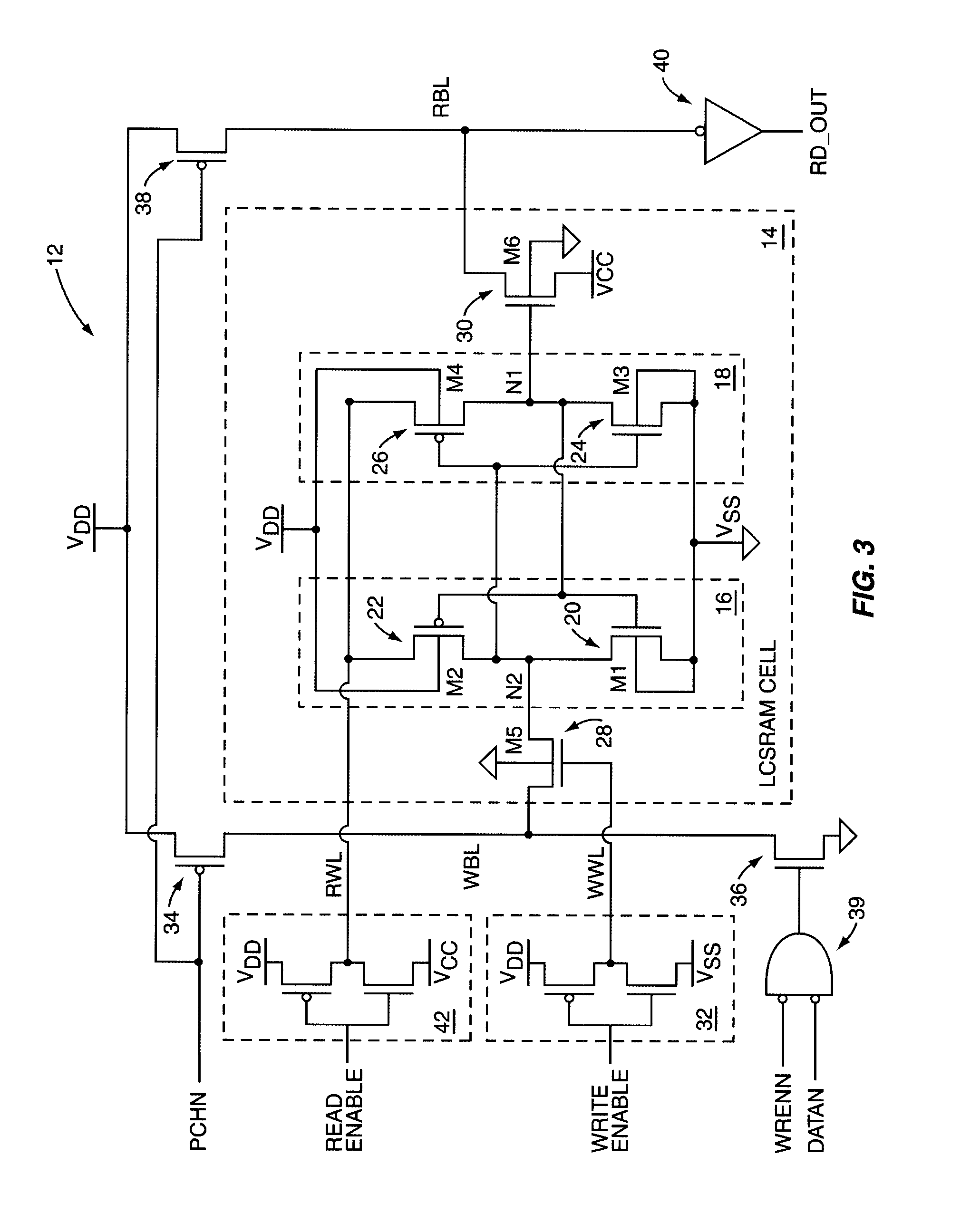
A Static Random Access Memory (SRAM) cell having high stability and low leakage is provided. The SRAM cell includes a pair of cross-coupled inverters providing differential storage of a data bit. Power to the SRAM cell is provided by a read word line (RWL) signal, which is also referred to herein as a read control signal. During read operations, the RWL signal is pulled to a voltage level that forces the SRAM cell to a full-voltage state. During standby, the RWL signal is pulled to a voltage level that forces the SRAM cell to a voltage collapsed state in order to reduce leakage current, or leakage power, of the SRAM cell. A read-transistor providing access to the bit stored by the SRAM cell is coupled to the SRAM cell via a gate of the read transistor, thereby decoupling the stability of the SRAM cell from the read operation.
Owner:ARIZONA STATE UNIVERSITY
Modeling behavior of an electrical circuit
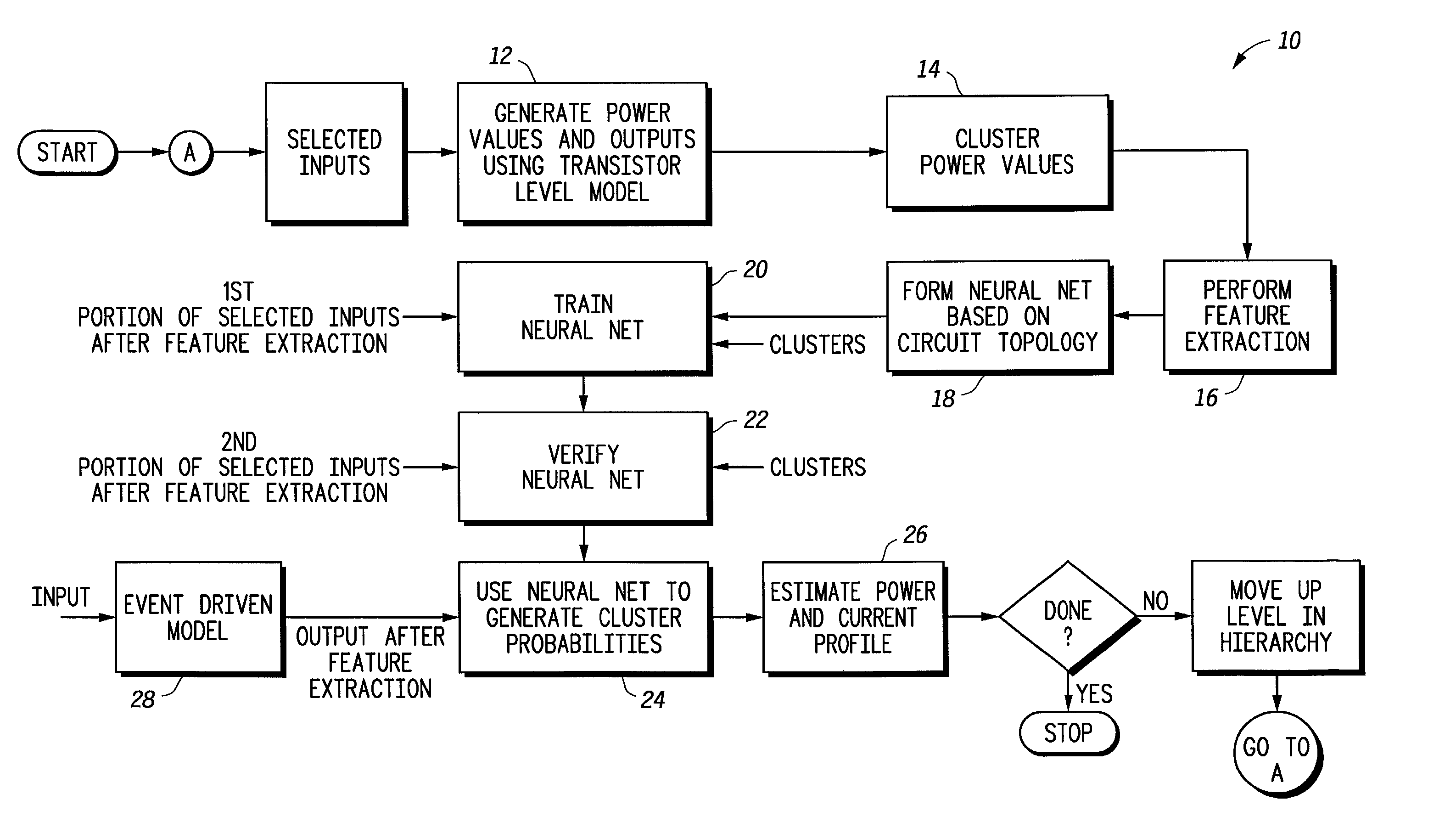
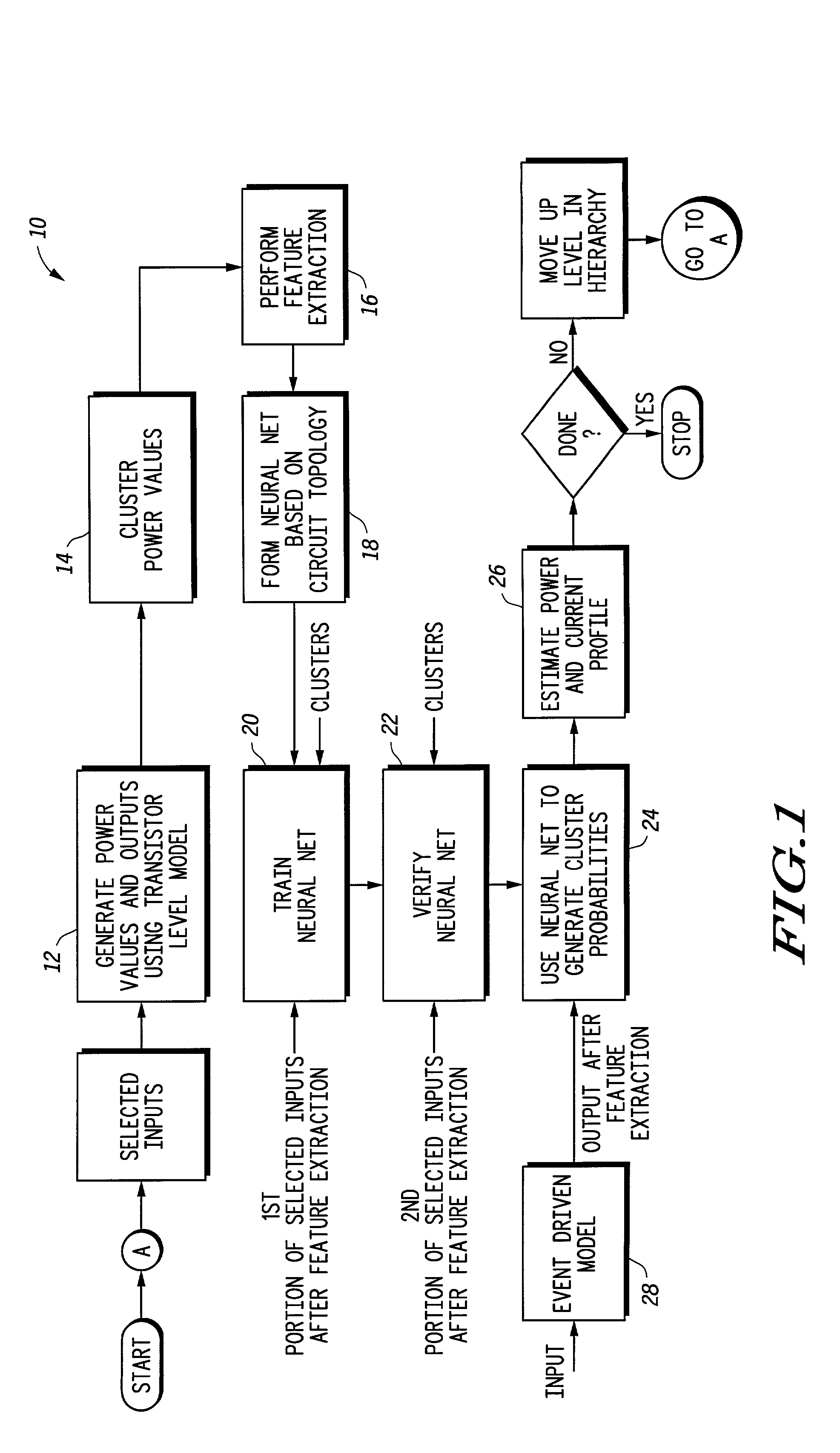
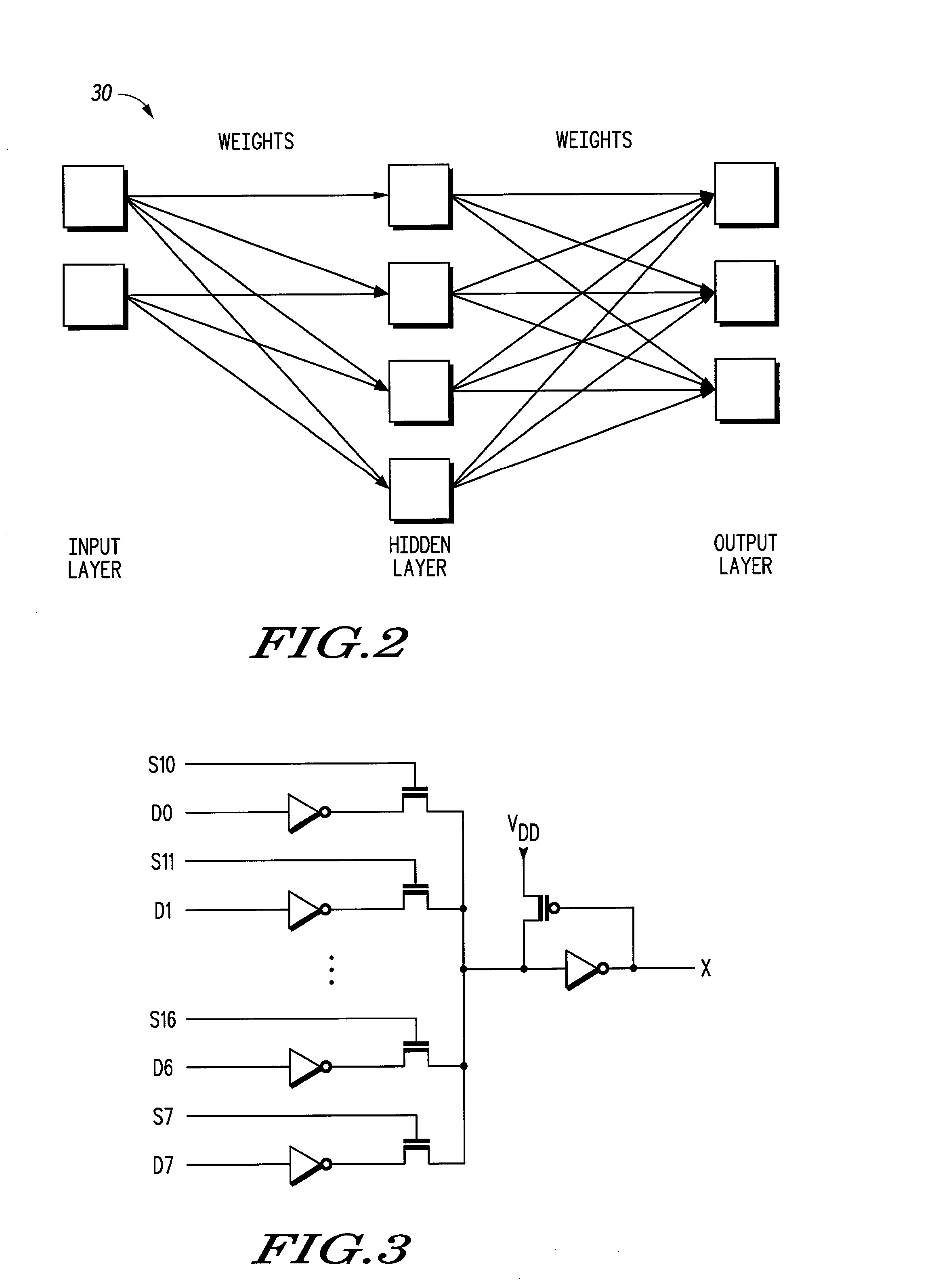
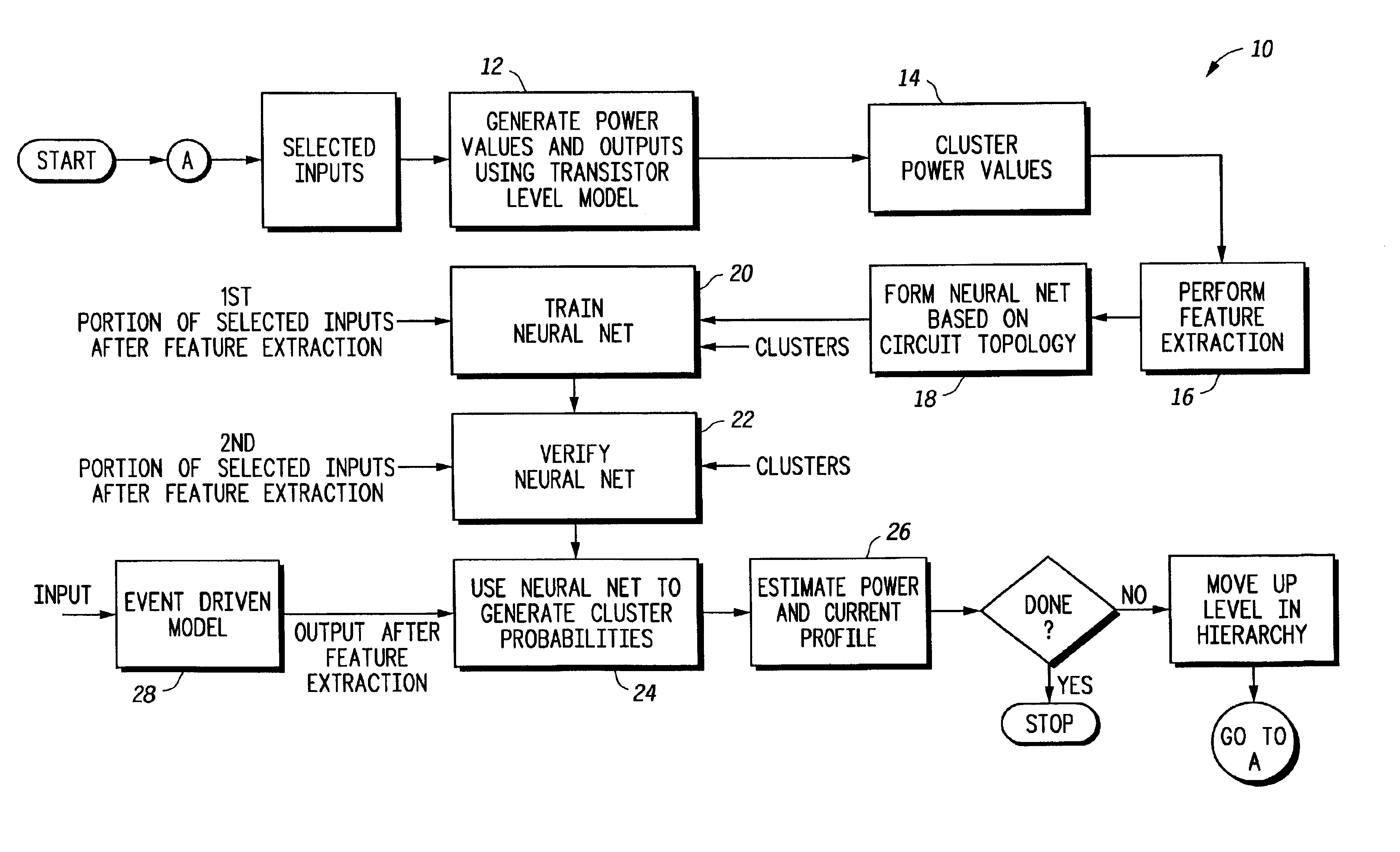
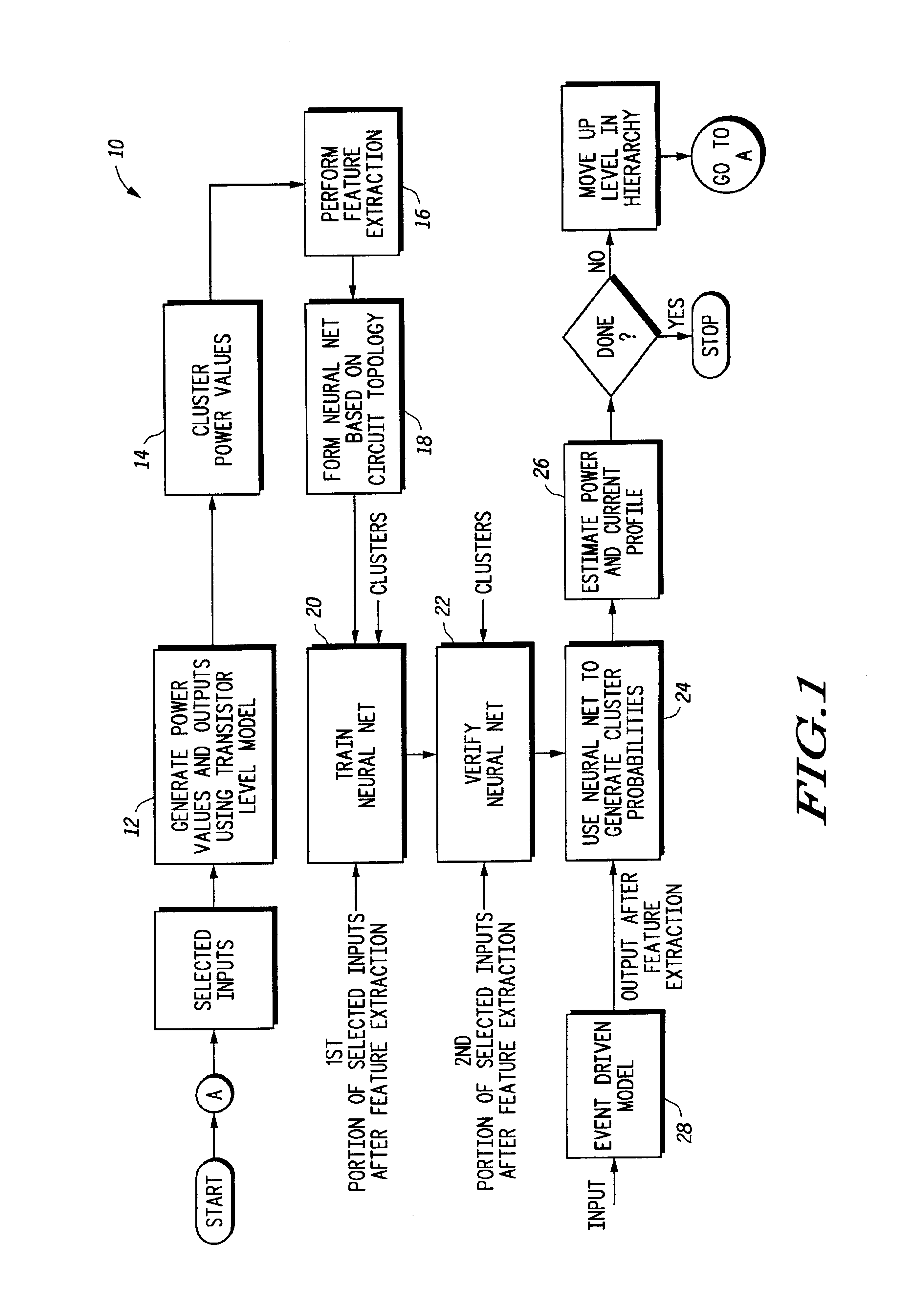
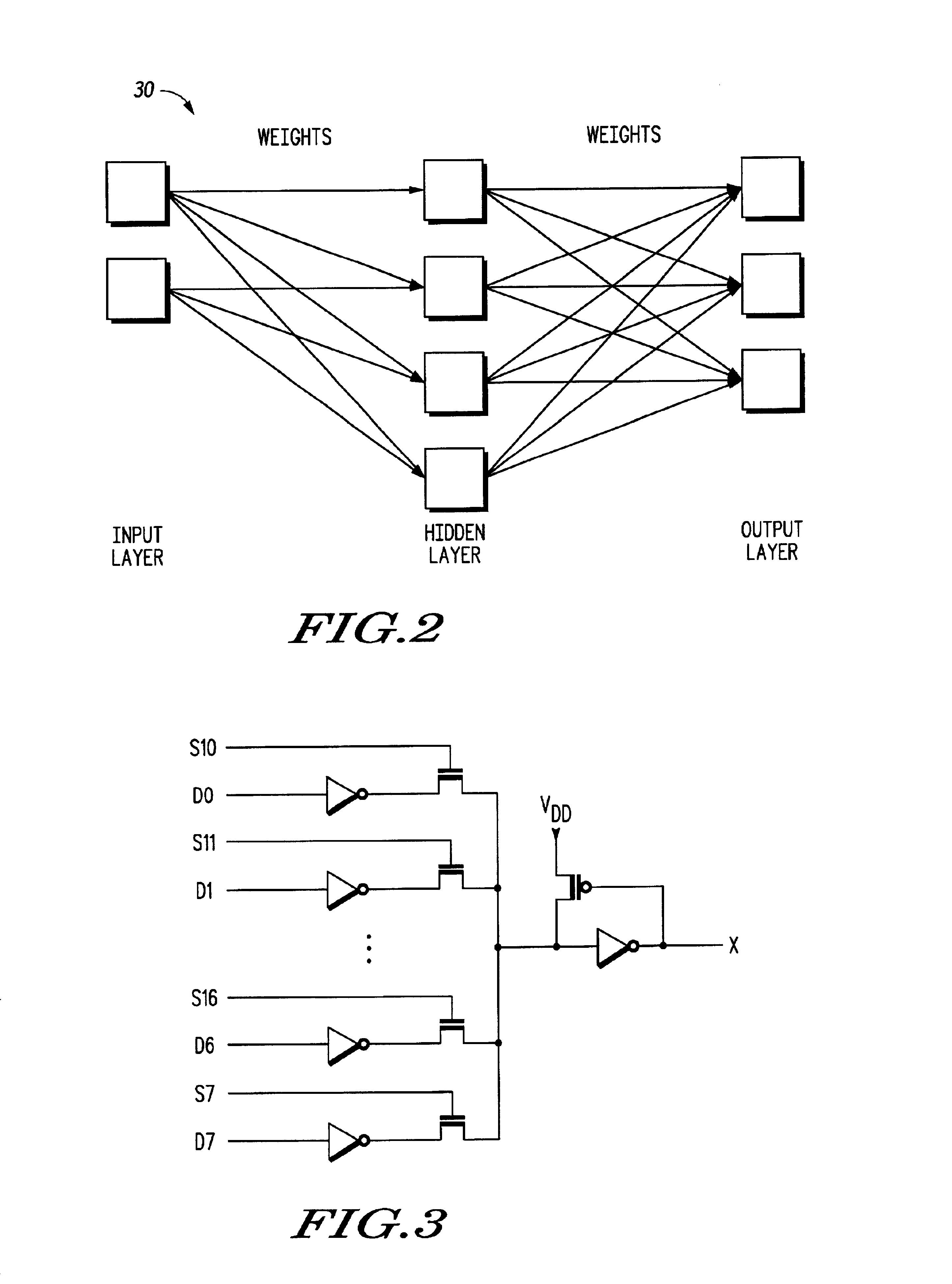
Behavior of an electrical circuit can be modeled using a trained neural network. For example, using one or more neural networks, power consumption, including leakage power and switching energy, can be estimated. Also, a profile of current versus time can be generated for the electrical circuit. A hierarchy of neural networks may be used to model the circuit at different levels. In one embodiment, a circuit behavior is modeled using one or more neural networks, cluster values, and cluster probabilities.
Owner:APPLE INC
Low-power FPGA circuits and methods
InactiveUS7714610B2Increase profitEasy to controlSolid-state devicesCAD circuit designEngineeringLevel converter
Field Programmable Logic Arrays (FPGAs) are described which utilize multiple power supply voltages to reduce both dynamic power and leakage power without sacrificing speed or substantially increasing device area. Power reduction mechanisms are described for numerous portions of the FPGA, including logic blocks, routing circuits, connection blocks, switch blocks, configuration memory cells, and so forth. Embodiments describe circuits and methods for implementing multiple supplies as sources of Vdd, multiple voltage thresholding Vt, signal level translators, and power gating of circuitry to deactivate portions of the circuit which are inactive. The supply voltage levels can be fixed, or programmable. Methods are described for performing circuit CAD in the routing and assignment process on FPGAs, in particular for optimizing FPGA use having the power reduction circuits taught. Routing methods describe utilizing slack timing, power sensitivity, trace-based simulations, and other techniques to optimize circuit utilization on a multi Vdd FPGA.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
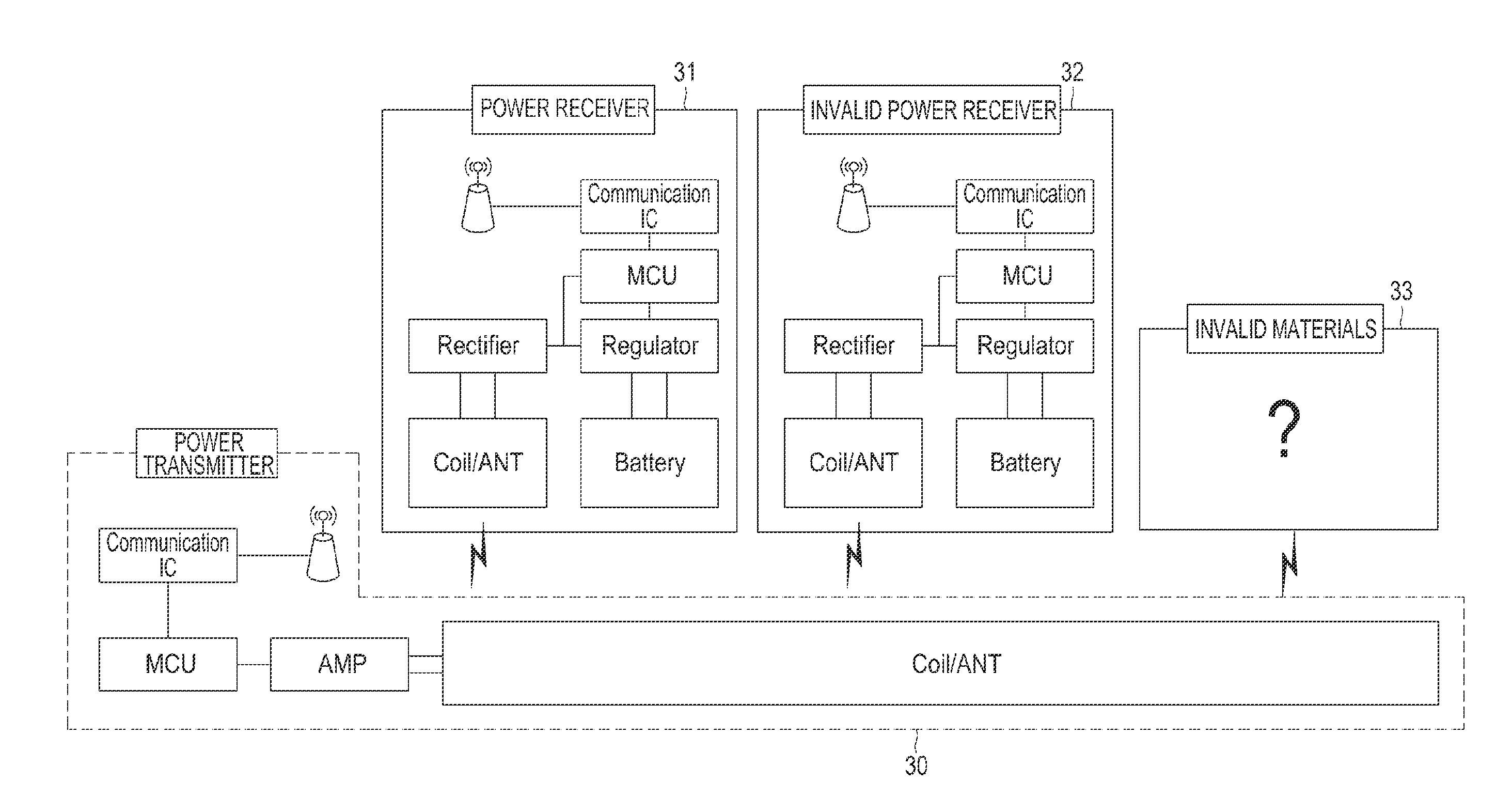
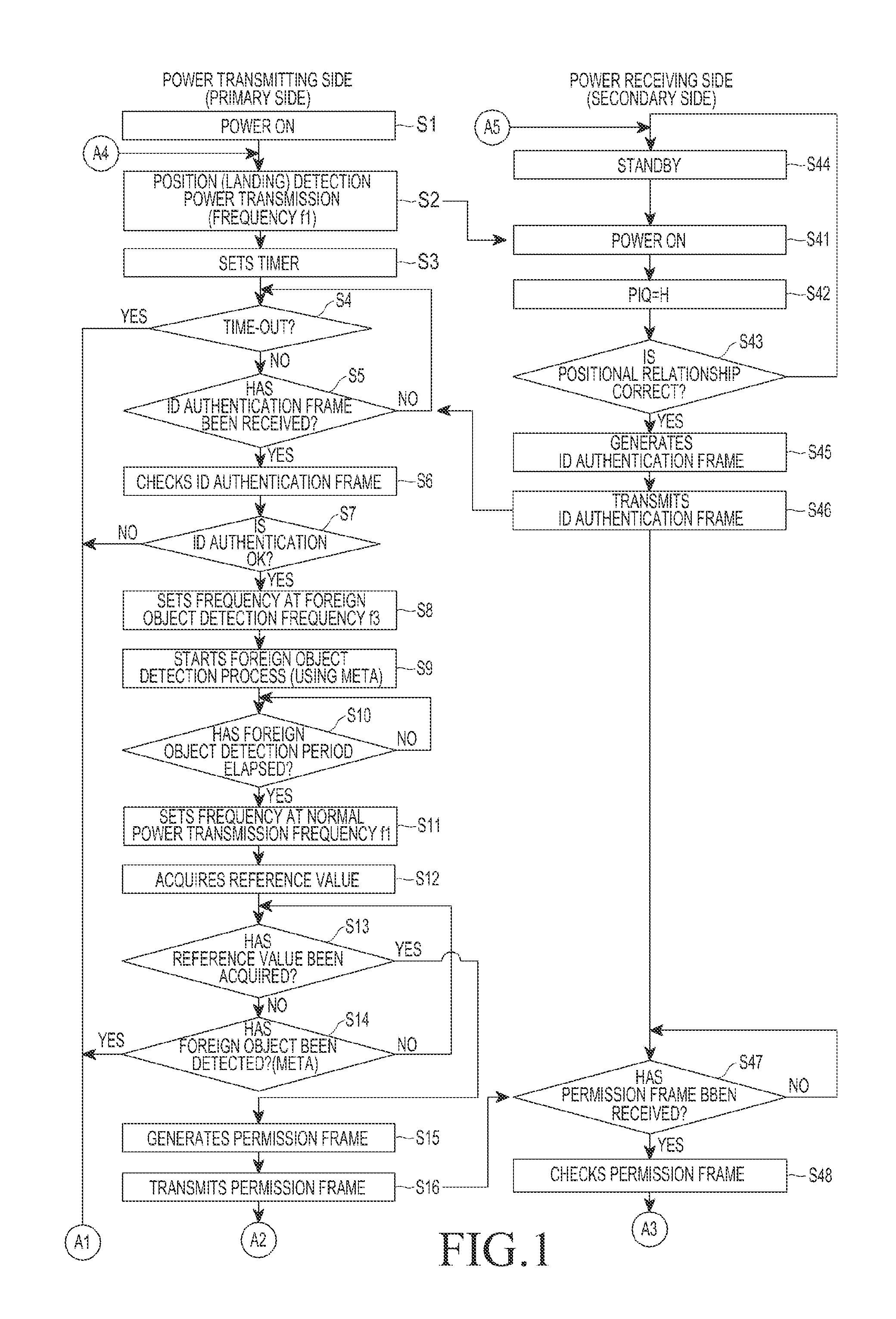
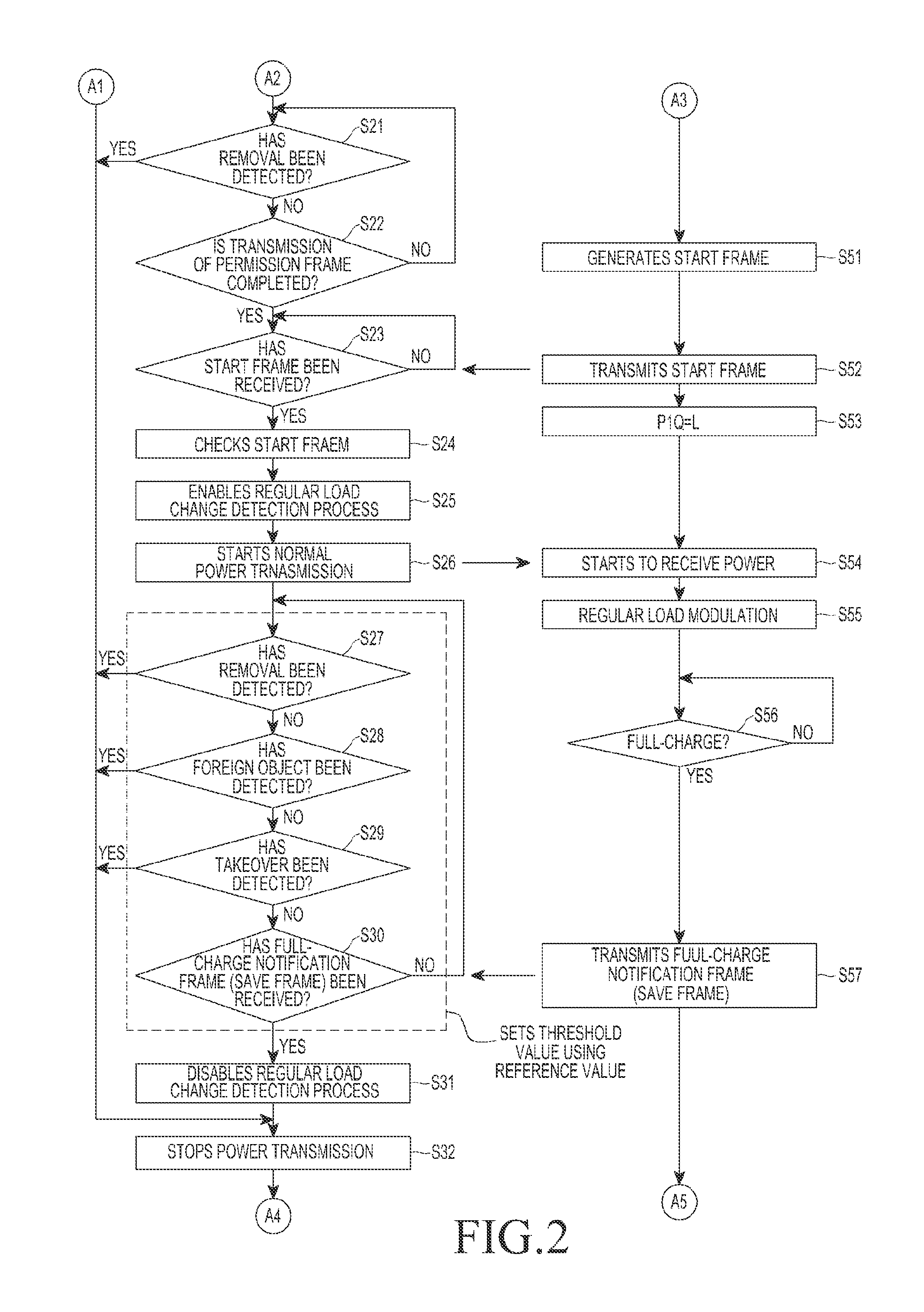
Power transmitter and method for detecting non-intended object of power reception
ActiveUS20130293028A1Efficient detectionTransformersTransformers/inductances circuitsElectric power transmissionTime segment
Methods and apparatus are provided for detecting a non-intended object of power reception by a power transmitter. Power transmission for communication is performed, when the load change is sensed that has a value greater than or equal to a predetermined threshold. It is determined whether a subscription request, for subscribing to a network is received within a predetermined time period. The power transmission for communication is stopped when the subscription request is not received within the predetermined time period. Power is transmitted to a power receiver that has transmitted the subscription request, when the subscription request is received within the predetermined time period. It is determined whether a leakage power value exceeds an allowable range, when the power state report is received from the power receiver. The transmission of the power to the power receiver is stopped, when the leakage power value exceeds the allowable range.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
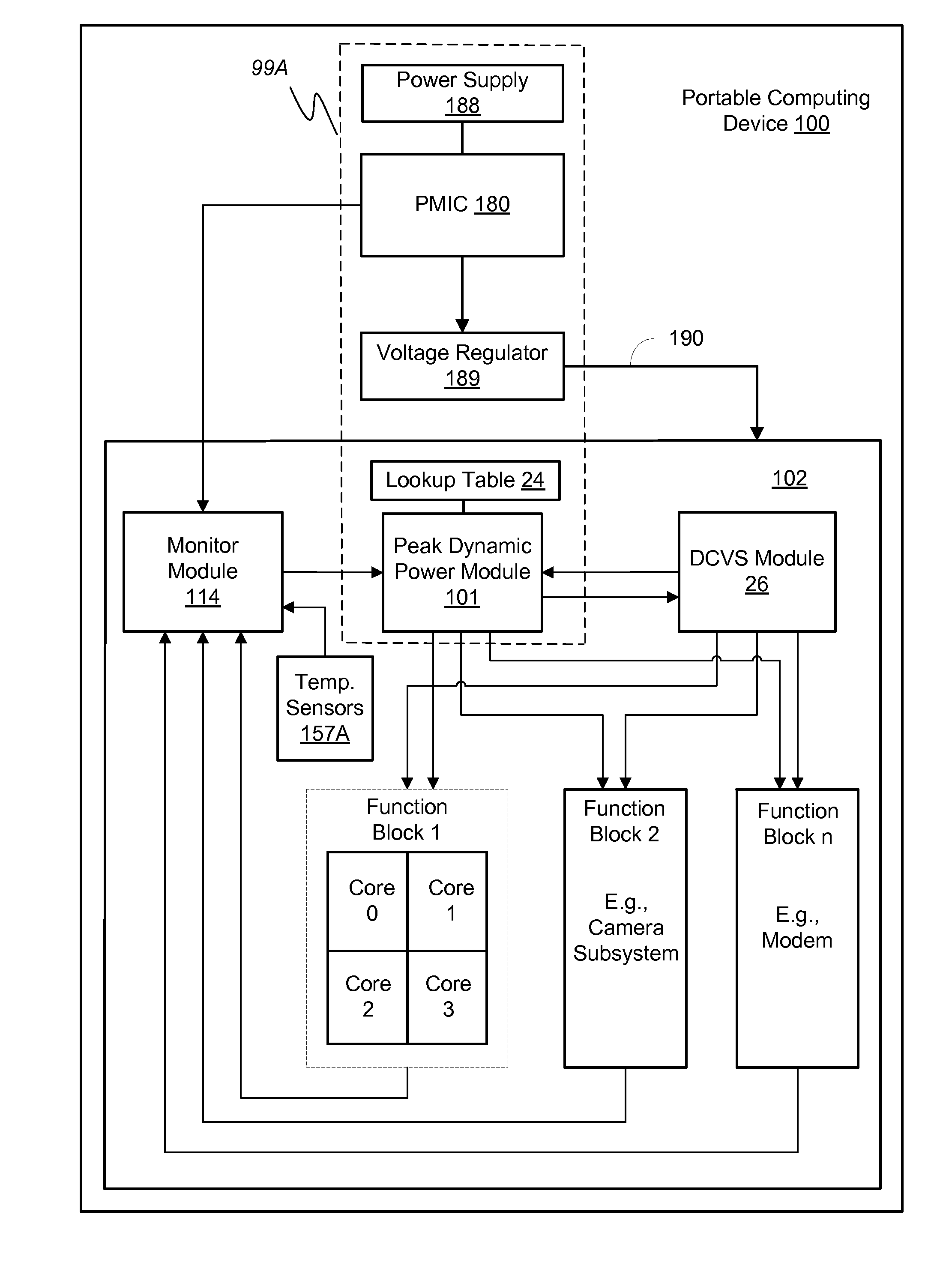
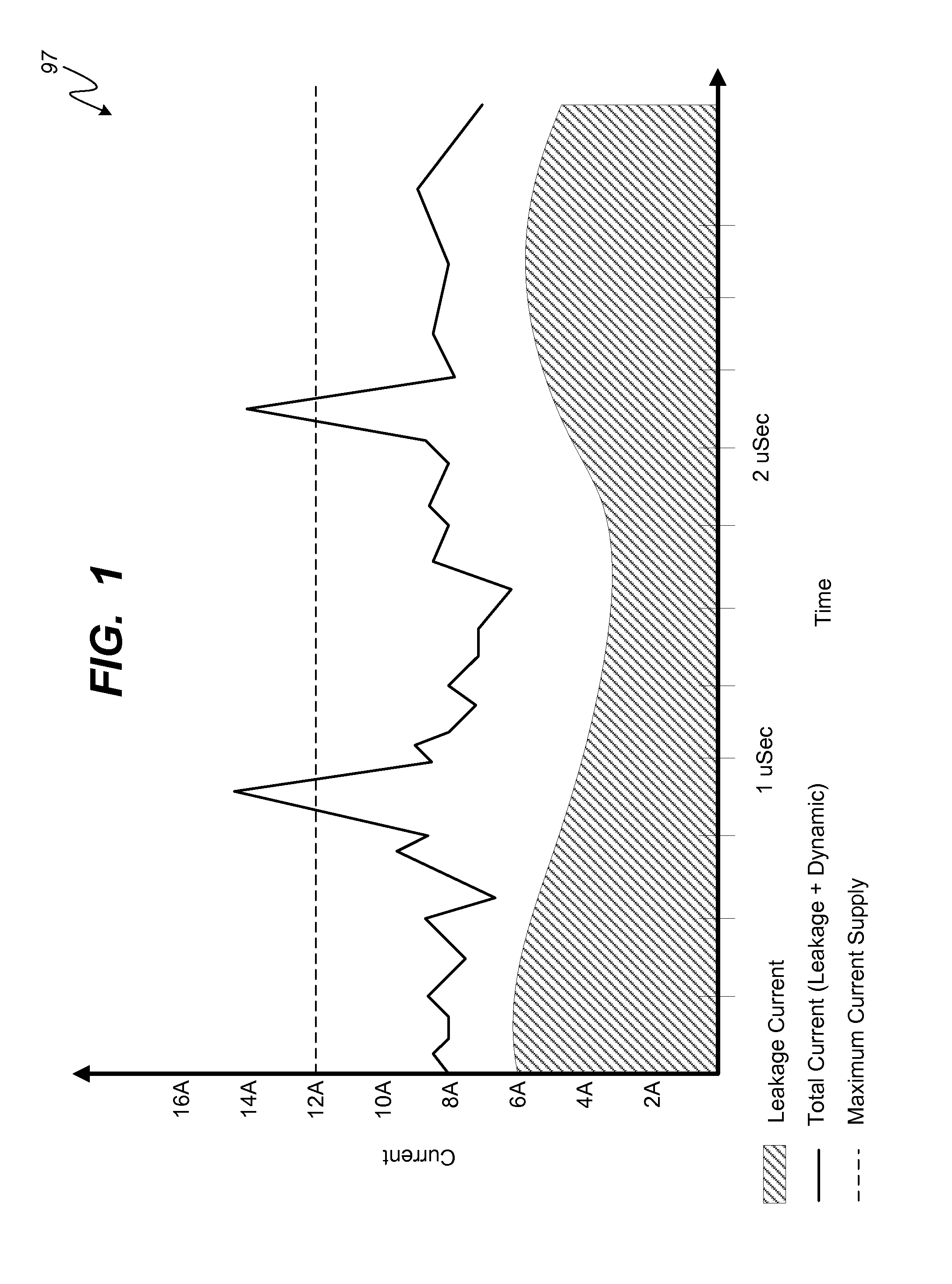
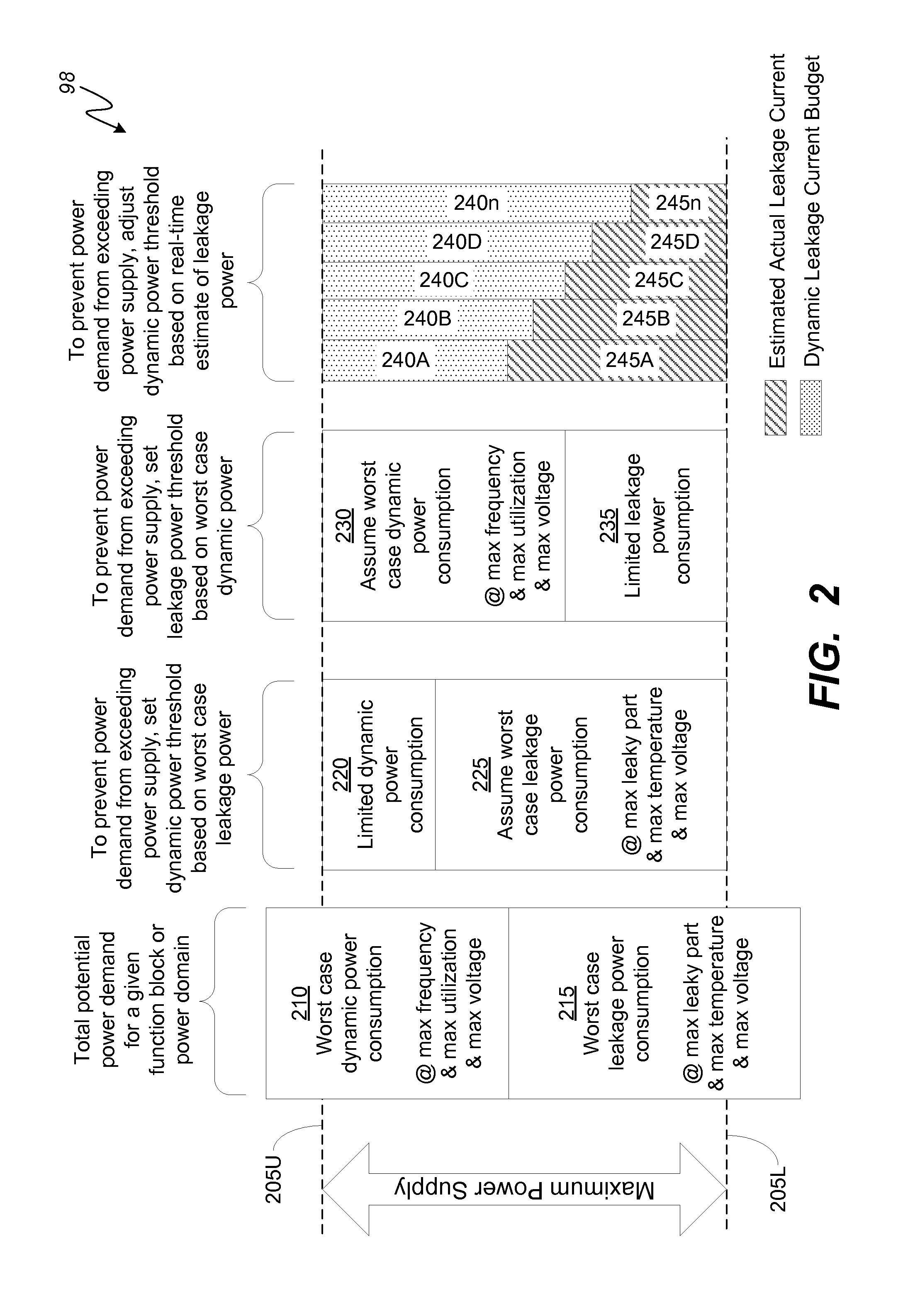
System and method for peak dynamic power management in a portable computing device
ActiveUS20160179164A1A large amountHardware monitoringPower supply for data processingQuality of serviceElectricity
Various embodiments of methods and systems for dynamically adjusting a peak dynamic power threshold are disclosed. Advantageously, embodiments of the solution for peak dynamic power management optimize a peak dynamic power threshold based on estimations of real-time leakage current levels and / or actual power supply levels to a power domain of a system on a chip (“SoC”). In this way, embodiments of the solution ensure that a maximum amount of available power supply is allocated to dynamic power consumption for processing workloads at an optimum performance or quality of service (“QoS”) level without risking that the total power consumption (leakage power consumption+dynamic power consumption) for the power domain exceeds the power supply capacity.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
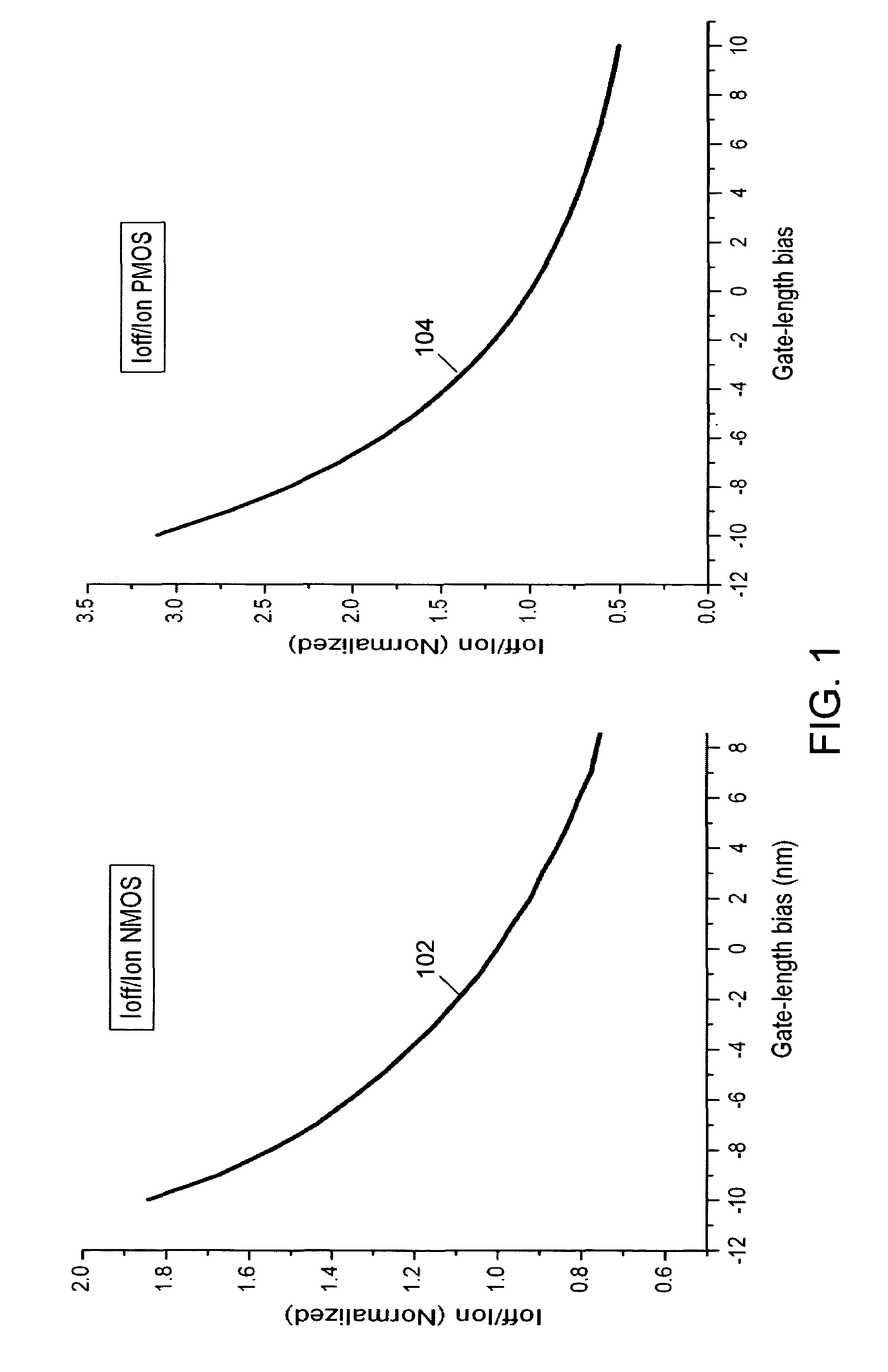
Method for determining and using leakage current sensitivities to optimize the design of an integrated circuit
InactiveUS7137080B2Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCAD circuit designTime criticalEngineering
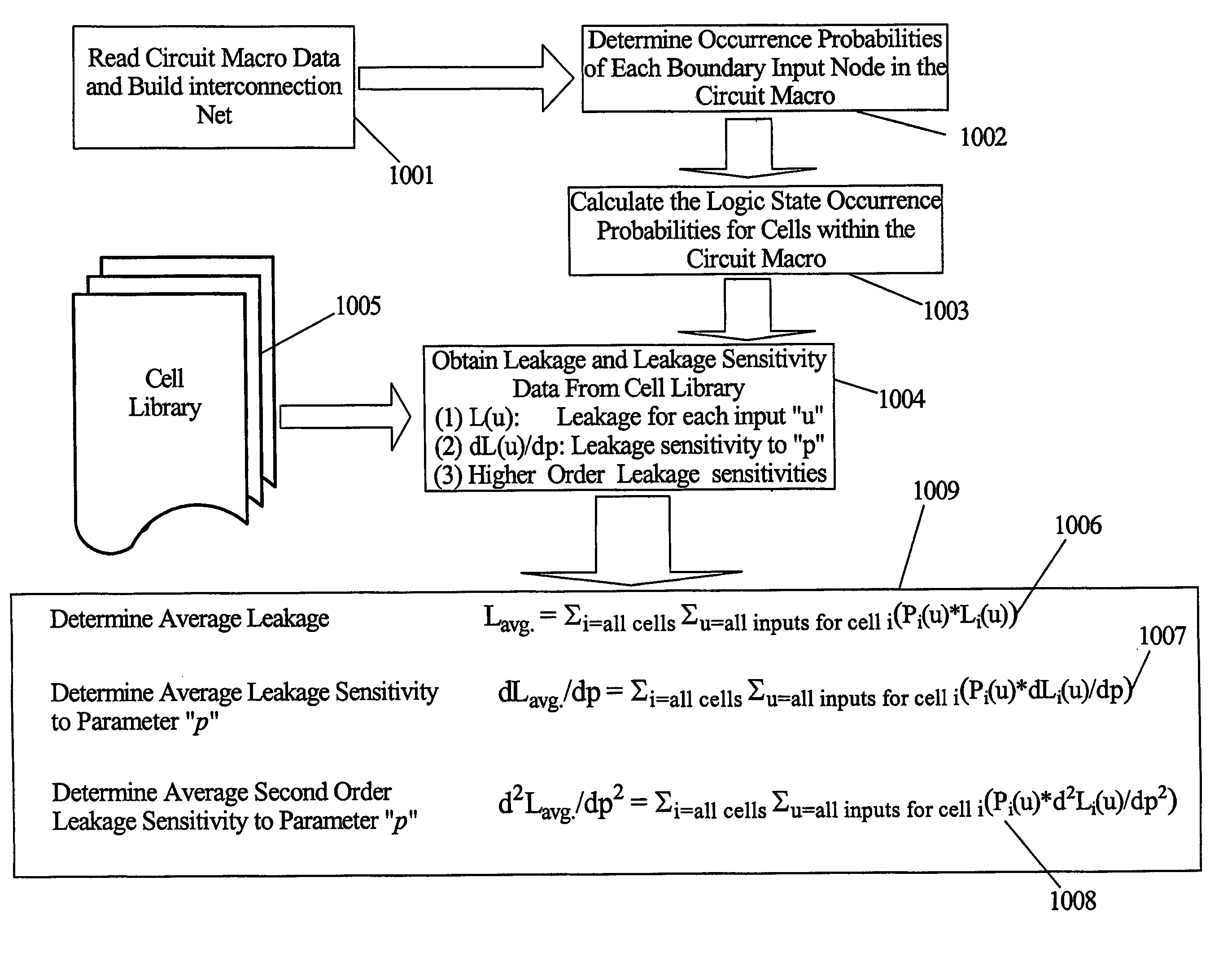
An integrated circuit design has circuit macros made up of device cells. The cells are characterized by determining the leakage current dependency on various process, environmental and voltage parameters. When circuit macros are designed their leakage power is calculated using this data and multi-dimensional models for power and temperature distribution. Circuit macros are identified as timing-critical and timing-noncritical macros. Statistical methods are used to determine the average leakage sensitivities for the specific circuit macros designed. The designer uses the sensitivity data to determine how to redesign selected circuit macros to reduce leakage power. Reducing leakage power in these selected circuits may be used to reduce overall IC power or the improved power margins may be used in timing-critical circuits to increase performance while keeping power dissipation unchanged.
Owner:IBM CORP
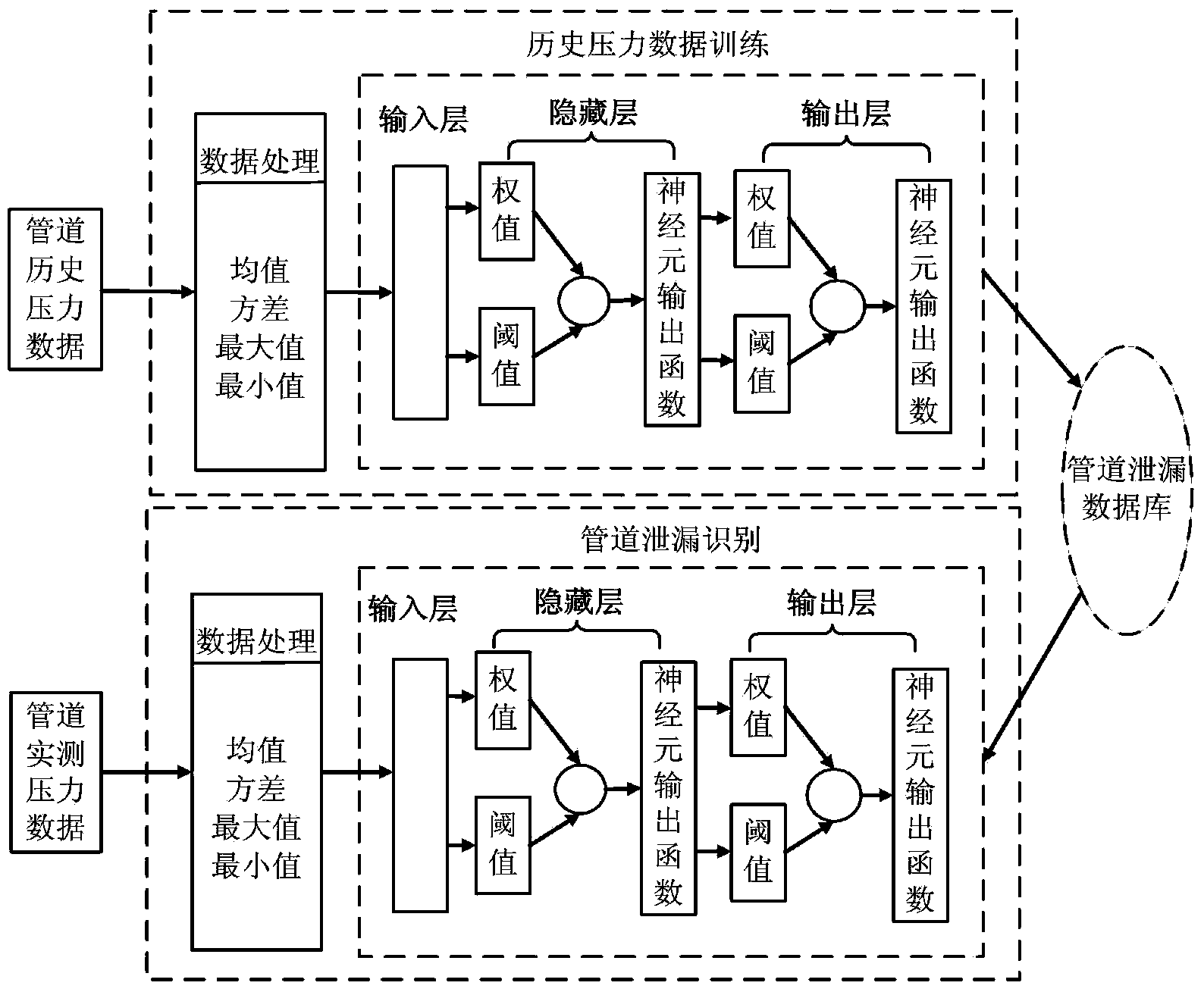
Pipeline leakage detection method based on neural network
InactiveCN104061445ASimple and fast operationImprove forecast accuracyPipeline systemsEngineeringNetwork model
The invention provides a pipeline leakage detection method based on a neural network. The pipeline leakage detection method based on a neural network comprises the steps of collecting pressure data of the whole pipe through a pressure collection device under leakage conditions and non-leakage conditions, and marking the collected data into a leakage type and a non-leakage type to serve as training samples; performing normalization processing on the training samples, and respectively computing a maximum value, a minimum value, an average value and a variance; establishing a BP neural network model to perform training; collecting the pressure data in a real-time mode, and inputting the processed data into the trained neural network to obtain pipeline leakage results. The pipeline leakage detection method based on the neural network is suitable for all working conditions of the pipeline and has good detection accuracy.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
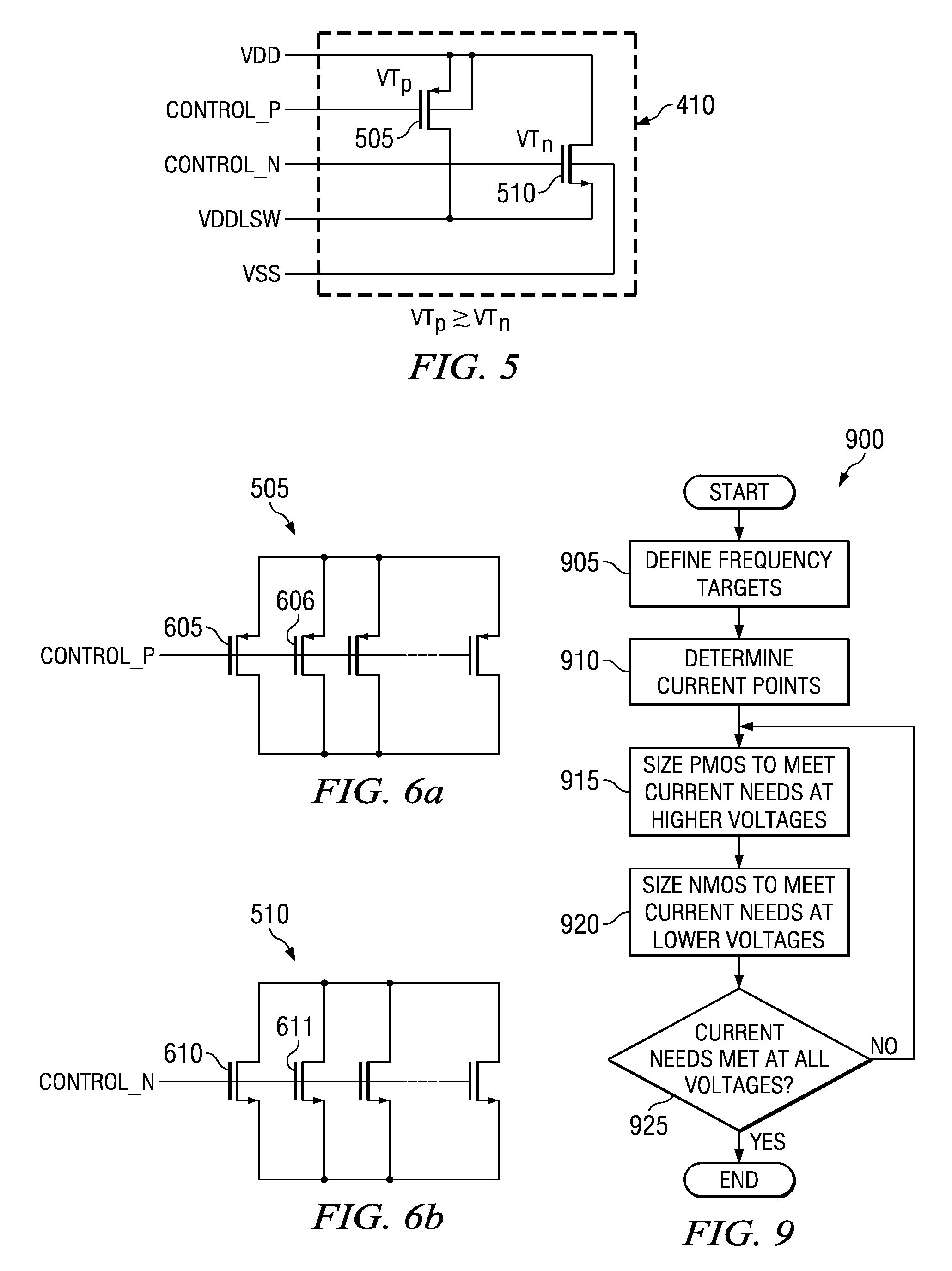
Integrated header switch with low-leakage PMOS and high-leakage NMOS transistors
ActiveUS7164291B2High currentLower unit costPower reduction in field effect transistorsElectronic switchingControl signalLow voltage
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
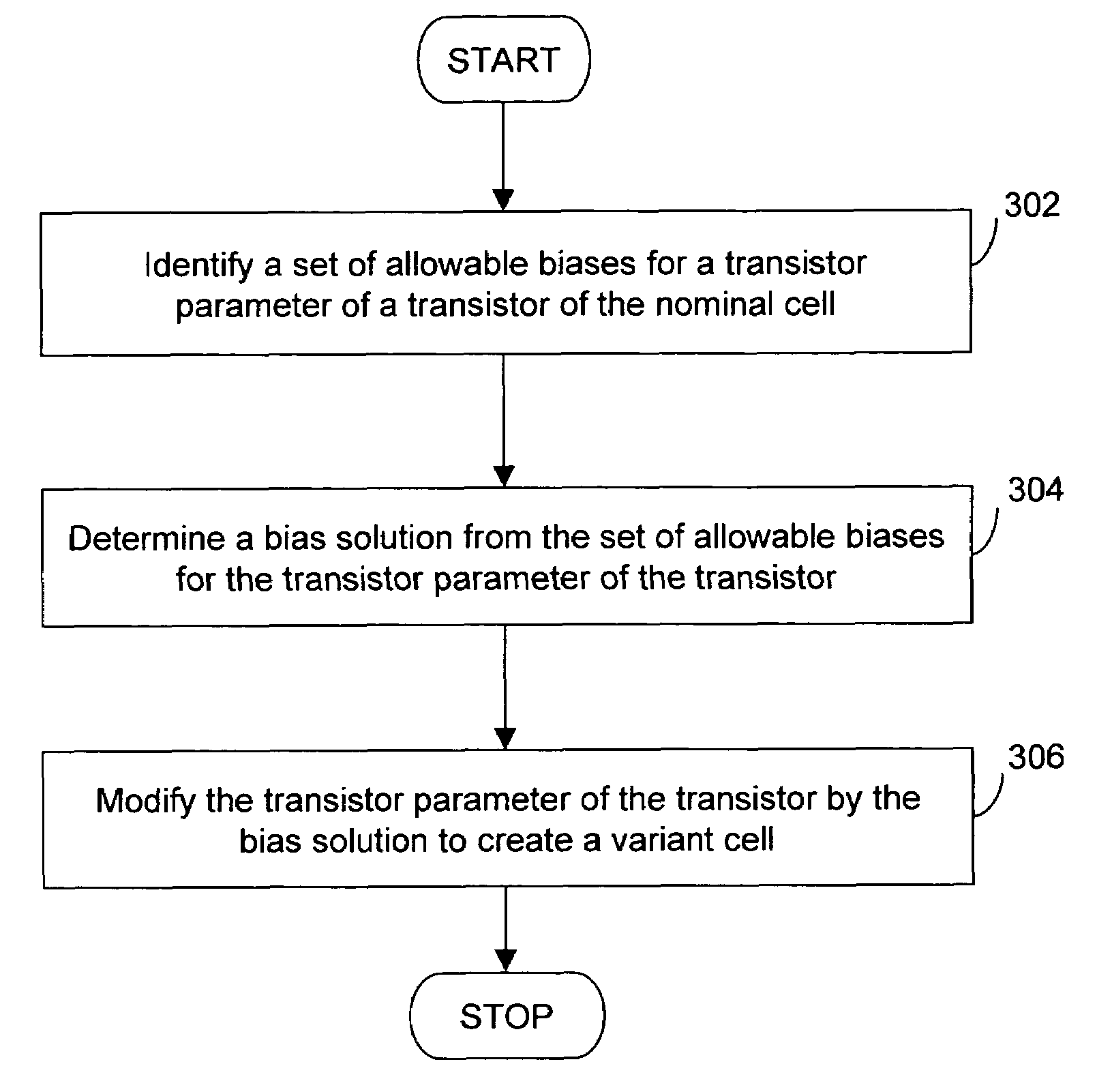
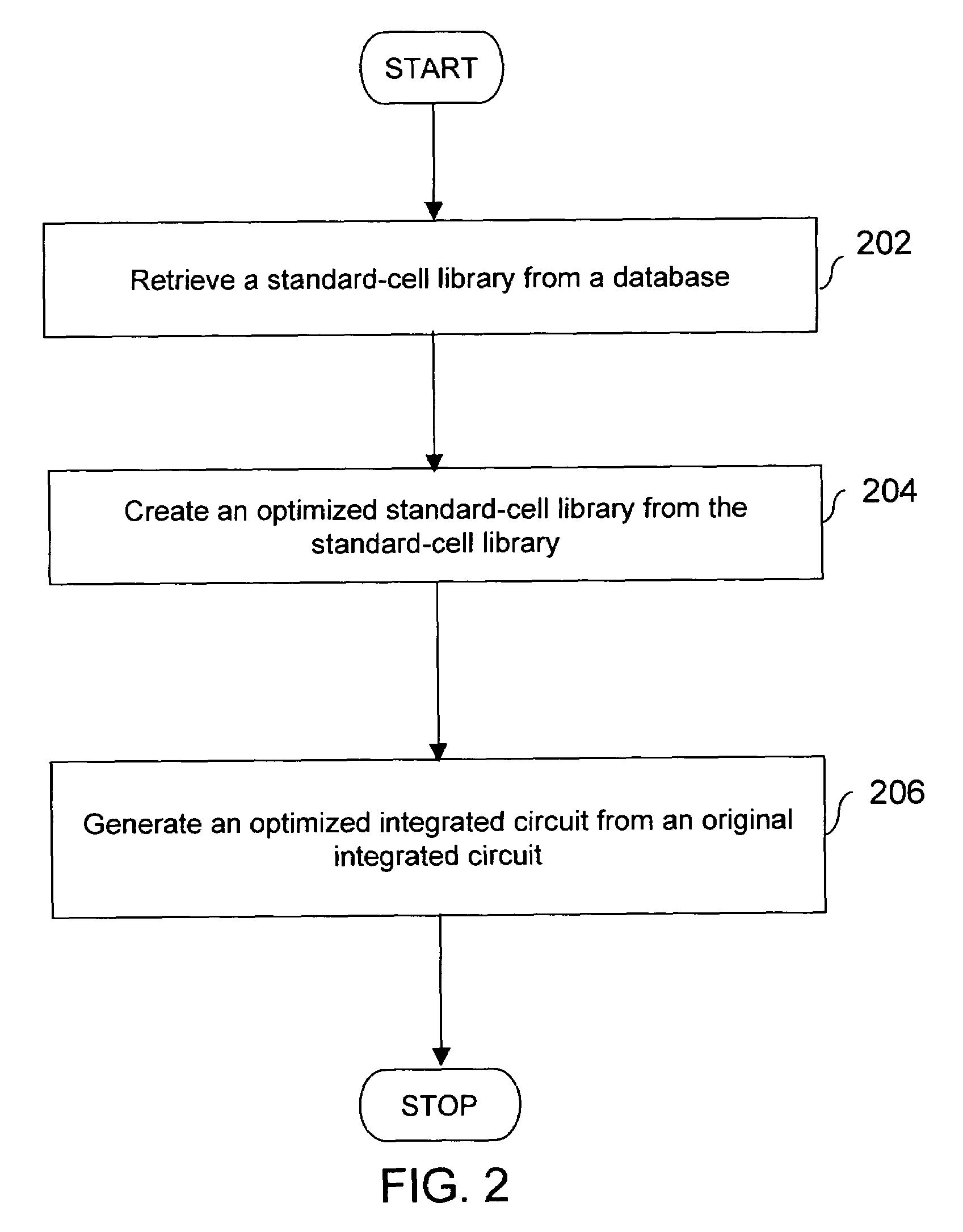
Method and system for integrated circuit optimization by using an optimized standard-cell library
InactiveUS7716612B1Improved leakage power consumptionImprove performanceCAD circuit designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationEngineeringLeakage power
A method and system for integrated circuit optimization to improve performance and to reduce leakage power consumption of an integrated circuit (IC). The original IC includes a plurality of nominal cells, and each of the nominal cells includes a plurality of transistors. The method creates an optimized standard-cell library from a standard-cell library. The standard-cell library includes a plurality of nominal cells, and each of the nominal cells includes a plurality of transistors. Further, an optimized IC is generated by using the optimized standard-cell library from the original IC. The optimized IC has an improved performance and reduced leakage power characteristics, as compared to the original IC.
Owner:RPX CORP
Modeling behavior of an electrical circuit
InactiveUS6910025B2Digital computer detailsBiological neural network modelsNerve networkLeakage power
Behavior of an electrical circuit can be modeled using a trained neural network. For example, using one or more neural networks, power consumption, including leakage power and switching energy, can be estimated. Also, a profile of current versus time can be generated for the electrical circuit. A hierarchy of neural networks may be used to model the circuit at different levels. In one embodiment, a circuit behavior is modeled using one or more neural networks, cluster values, and cluster probabilities.
Owner:APPLE INC
Distortion compensation device
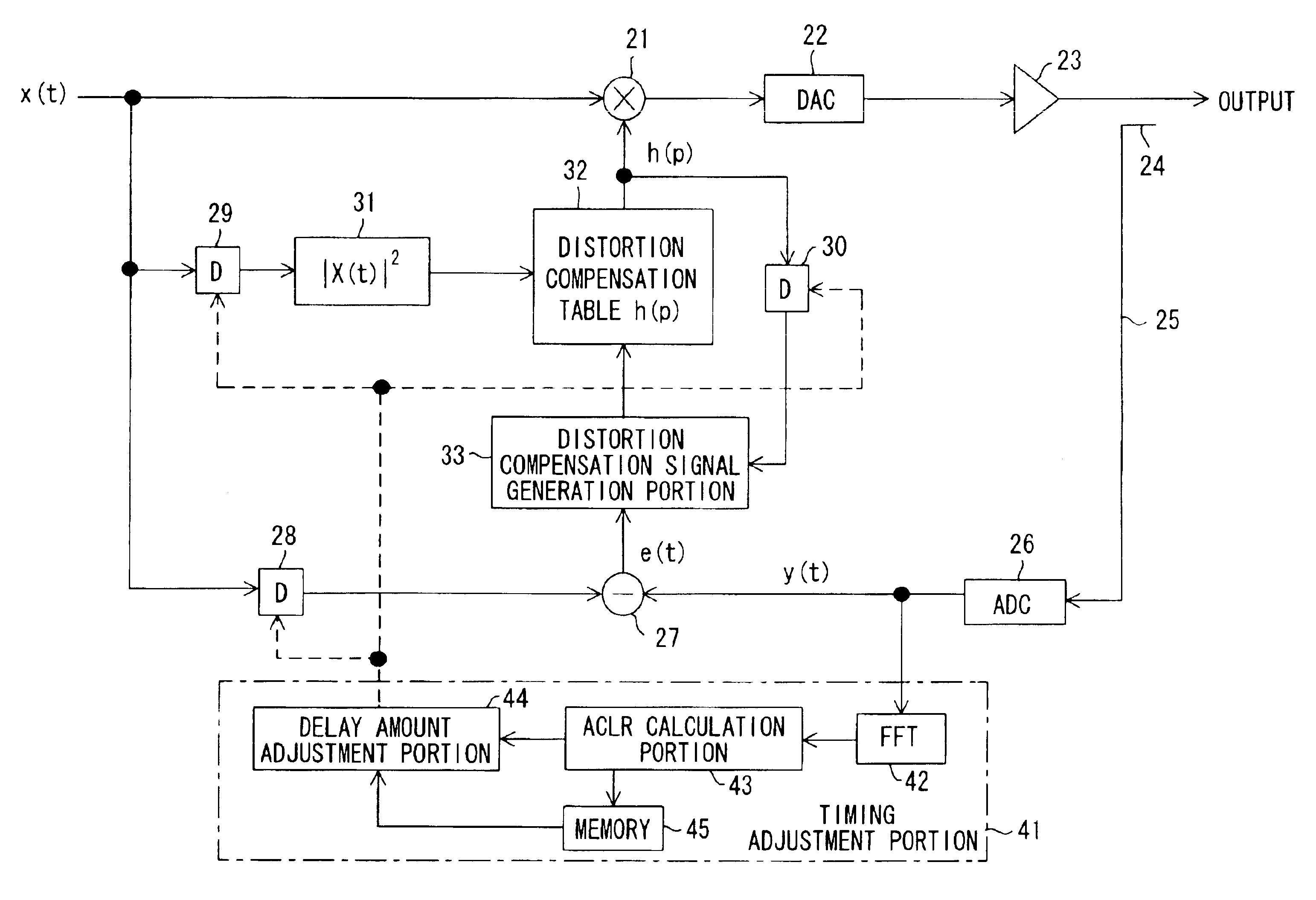
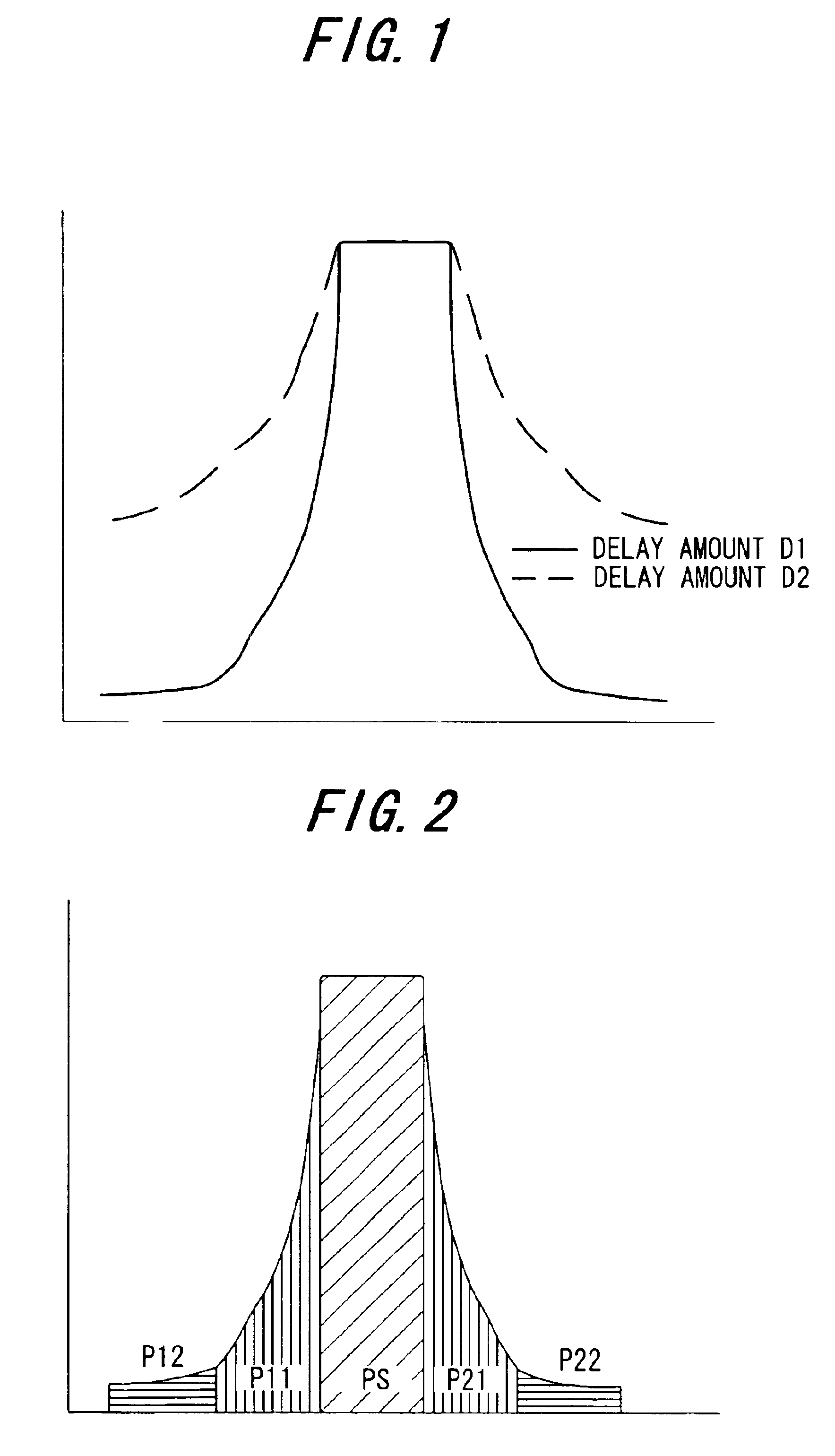
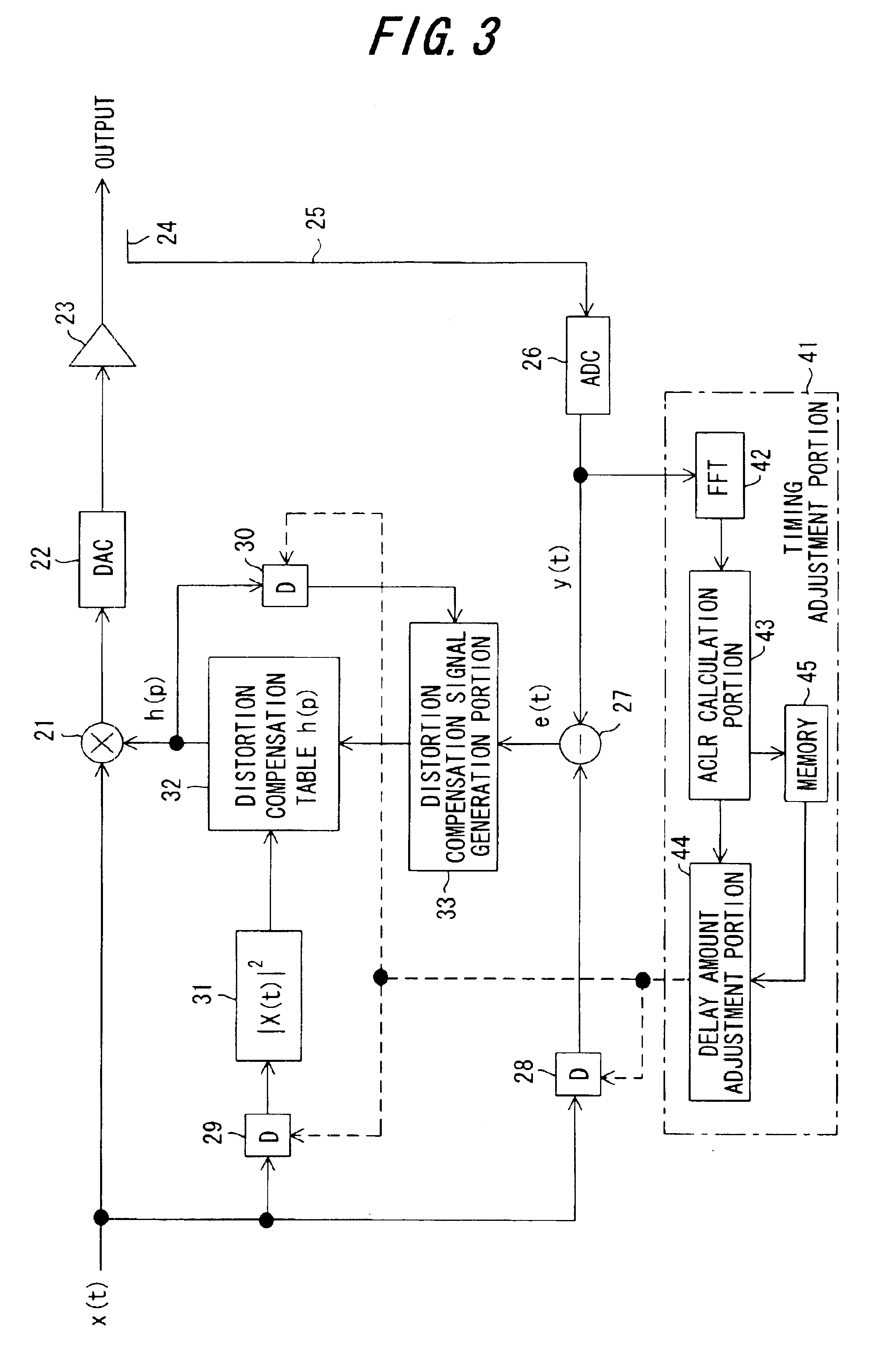
InactiveUS6864745B2Guaranteed uptimeHigh precisionAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceFast Fourier transformSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
In a distortion compensation device which uses distortion compensation coefficients to subject distortion compensation processing to an input signal and supply the result of the distortion compensation processing to a distorting device, calculates the distortion compensation coefficients based on the input signal before distortion compensation and the feedback signal fed back from the output side of the distorting device, and stores the calculated distortion compensation coefficients in association with the input signal, (1) the feedback signal is AD-converted; (2) the AD-converted output is subjected to fast Fourier transform (FFT) processing; (3) the FFT calculation result is used to calculate the value of either the signal-to-noise ratio SNR, or the adjacent channel leakage power ratio ACLR, or the noise level; (4) the delay time occurring in the distorting device and feedback loop is adjusted such that the difference between the above calculated value at the current time and the above calculated value at the immediately preceding time is either zero, or is equal to or less than a threshold value; and, (5) this adjustment processing is repeated to determine the accurate delay time, and based on this delay time the timing of each of the portions of the distortion compensation device is adjusted.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Integrated circuit with leakage control and method for leakage control
InactiveUS20050149799A1Improved leakage power controlReduce leakage powerPower reduction by control/clock signalDigital circuit testingPower modeState variable
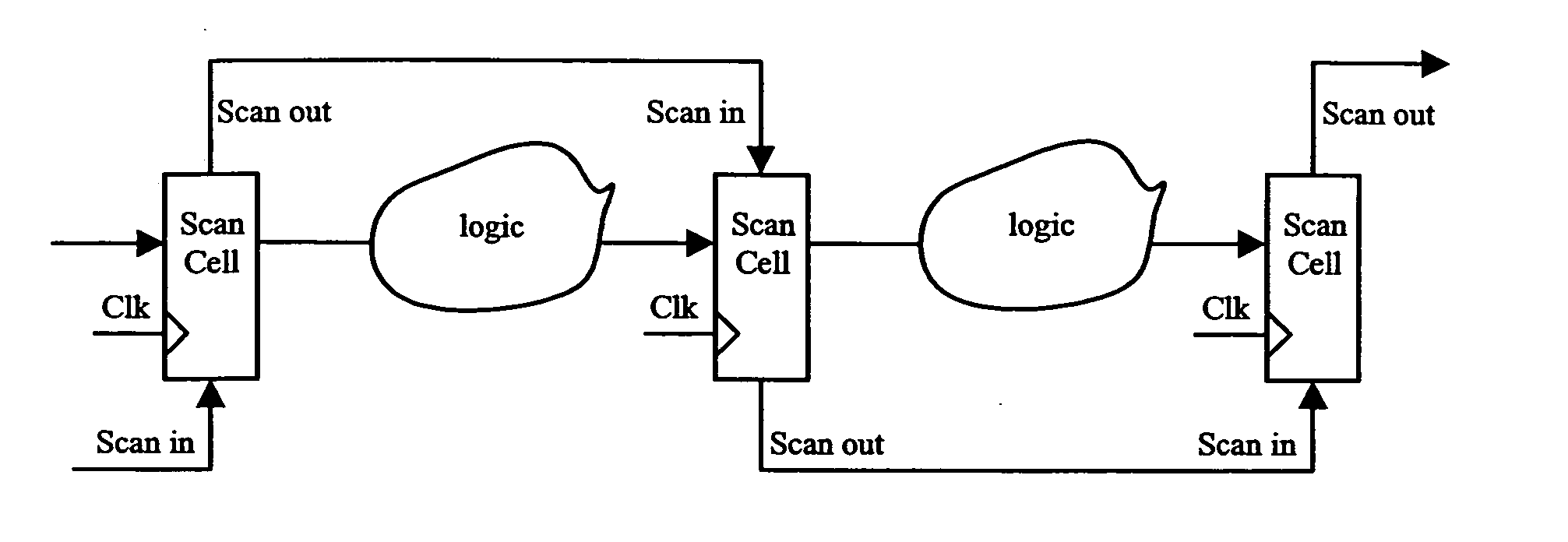
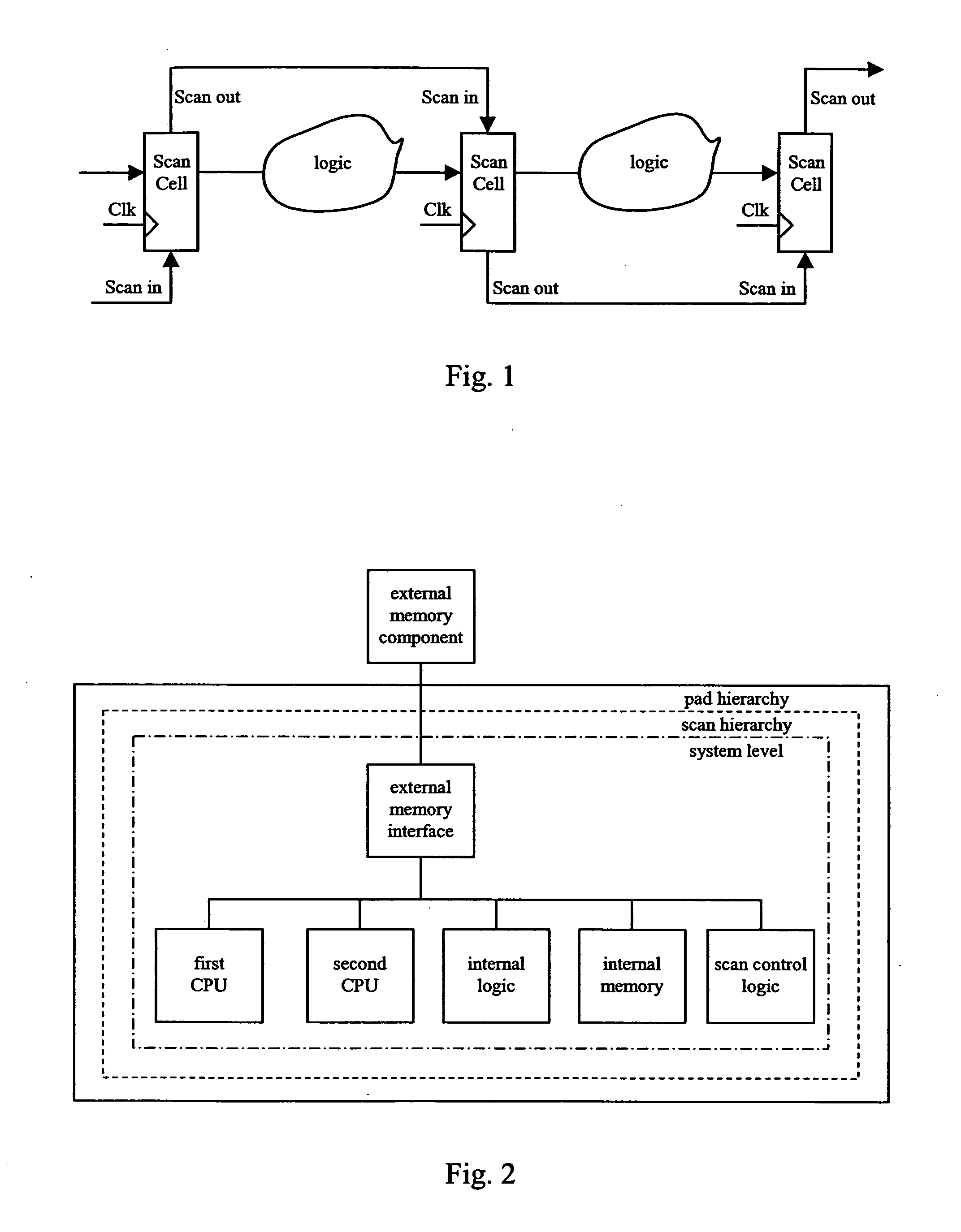
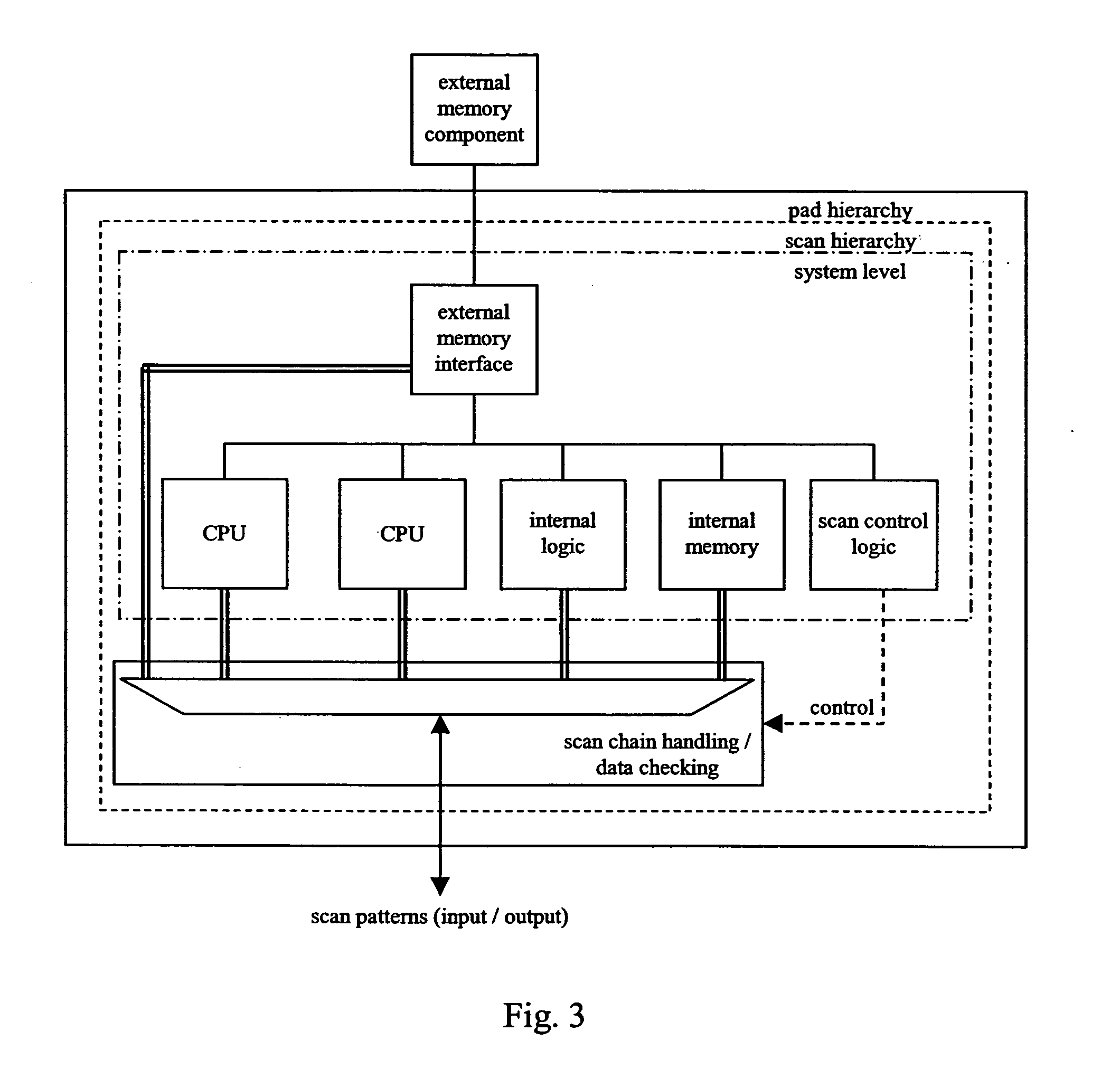
The present invention relates to integrated circuit with reduced leakage power and in particular to a methodology for retaining an operational state of at least a part of the integrated circuit while the part is in standby / low power mode. In detail, the inventive methodology is based on the use of scan chains being implemented in the integrated circuit for production testing purposes. Via the scan chains circuit-internal state-variable memory element content is read out and / or written in such that the operational state of for instance a specific part (power domain) of the integrated circuit may be captured on the basis of the circuit internal contents, retained in an adequately provided data storage and afterwards scanned into the specific part of the integrated circuit to restore the operational state thereof.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
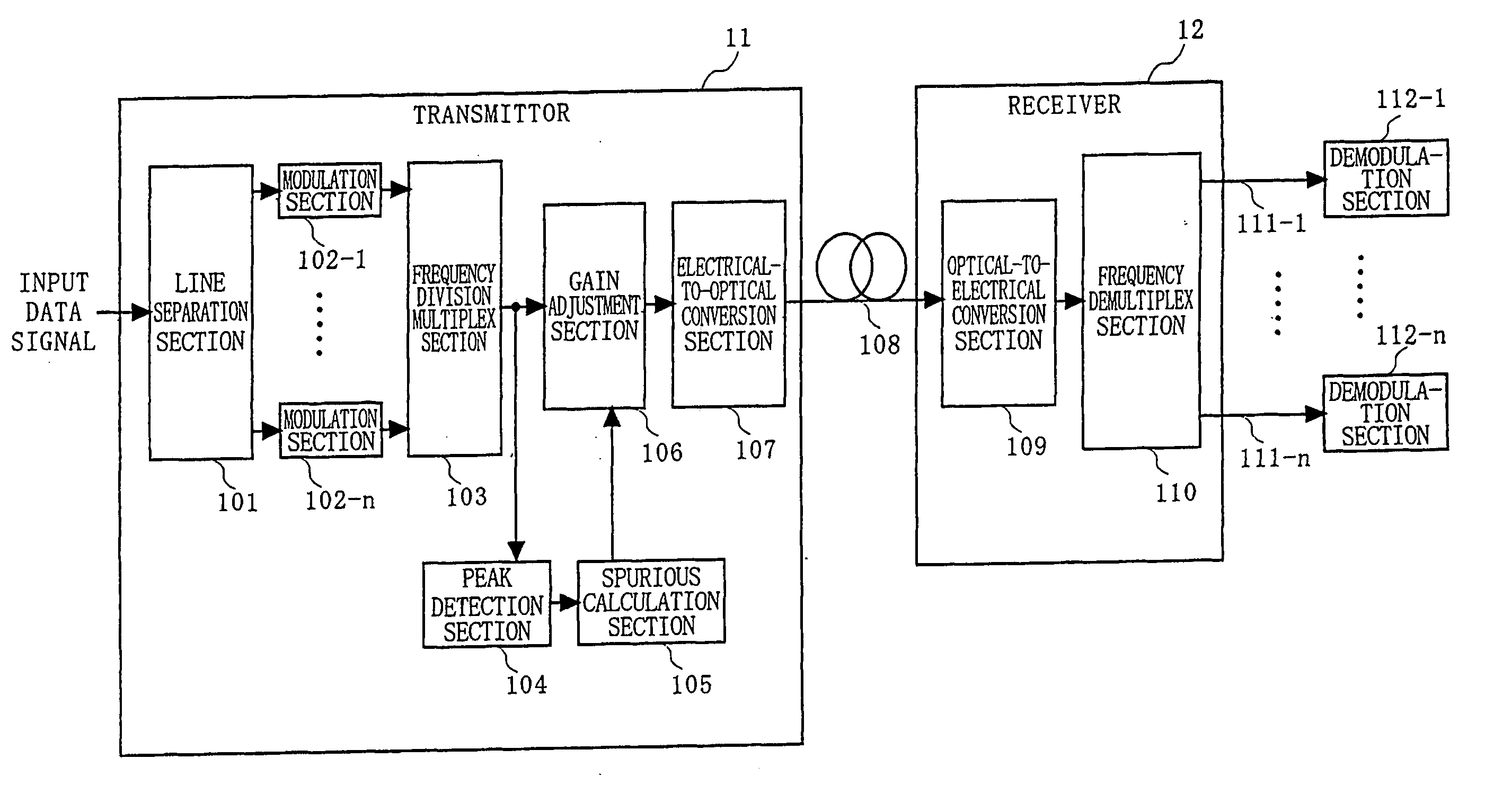
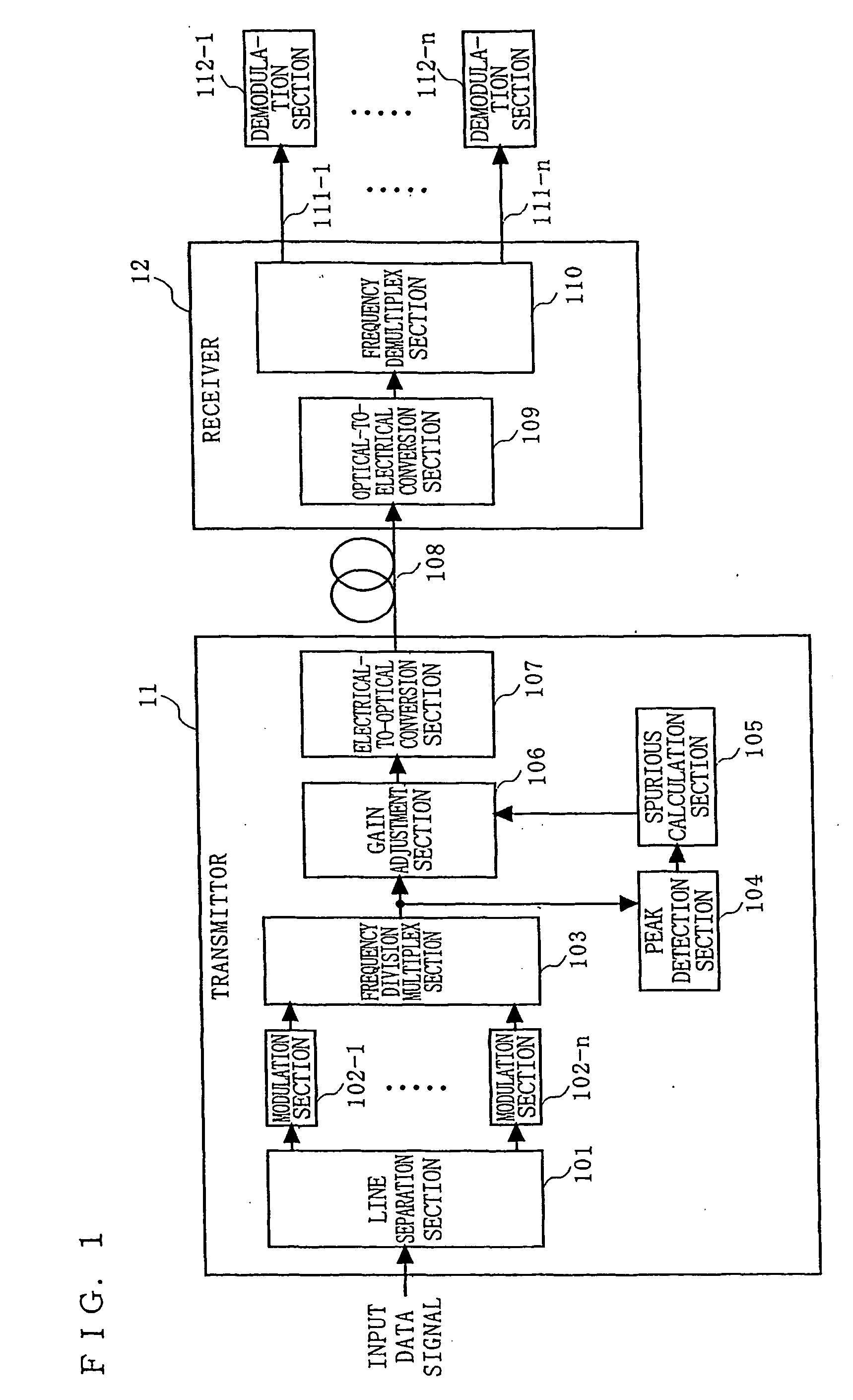
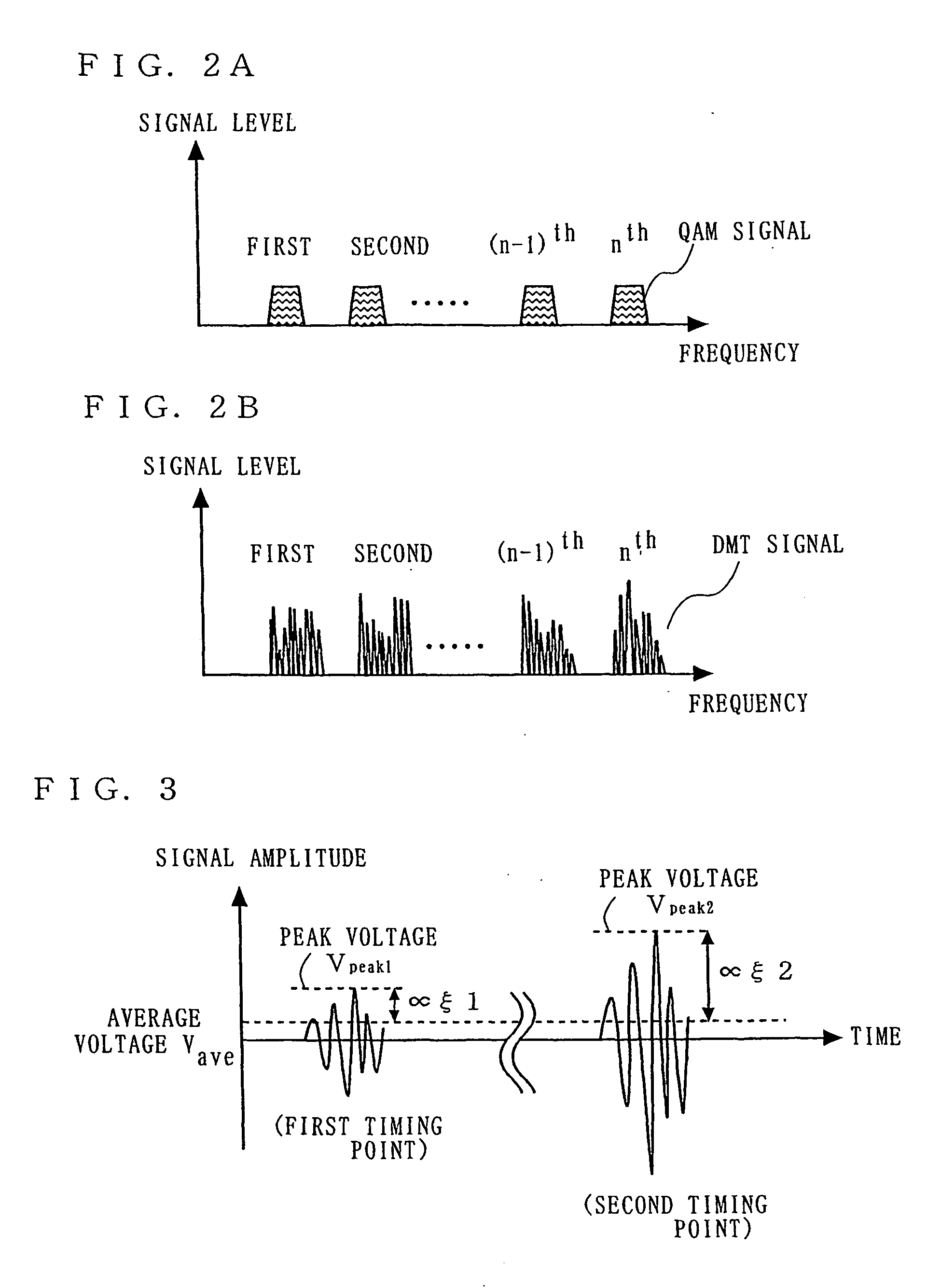
Optical transmission system, and trasmitter, receiver and signal level adjustment method for use therein
InactiveUS20050265730A1Reduce componentsMaintain qualityWavelength-division multiplex systemsDistortion/dispersion eliminationTransport systemPeak value
In a transmitter (11), a peak detection section (104) detects a peak factor of a frequency division multiplexed signal which is output from a frequency division multiplex section (103). A spurious calculation section (105) instructs a gain adjustment section (106) to adjust the signal level of the frequency division multiplexed signal so that the level of spurious components (e.g., adjacent channel leakage power ratio (ACLR)) is equal to or less than a predetermined level, based on the peak factor.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
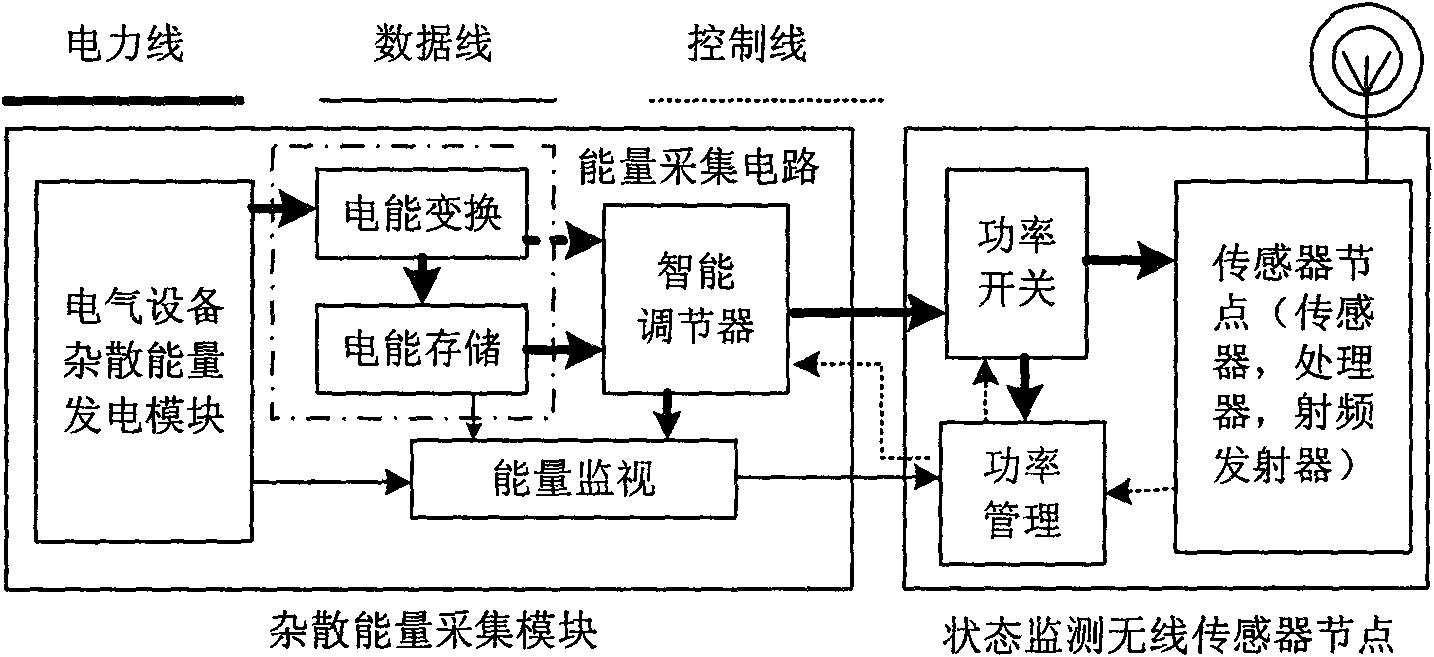
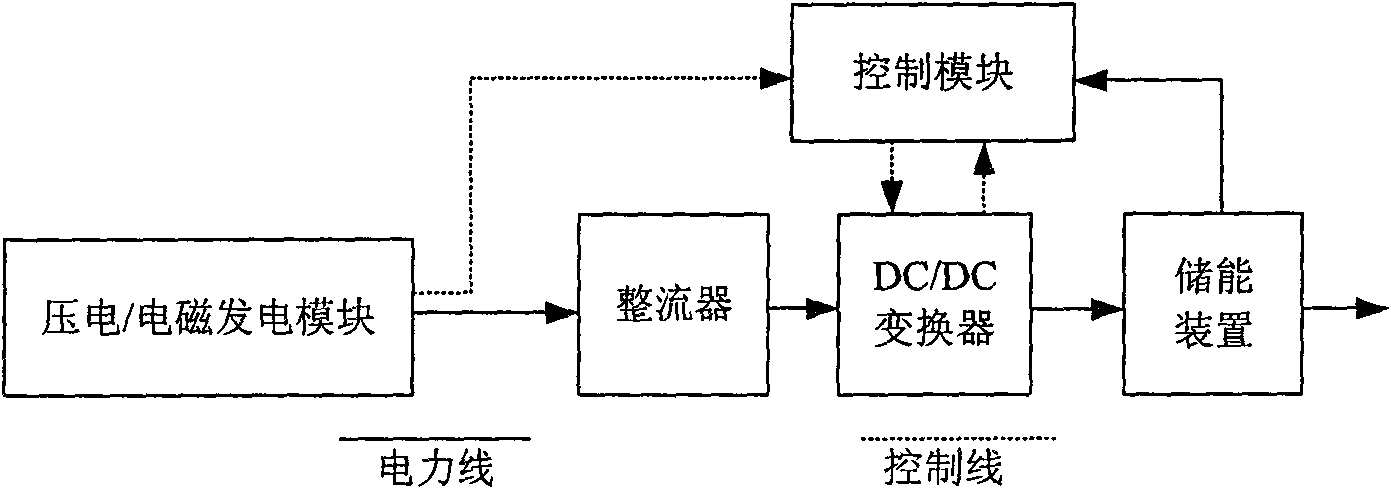
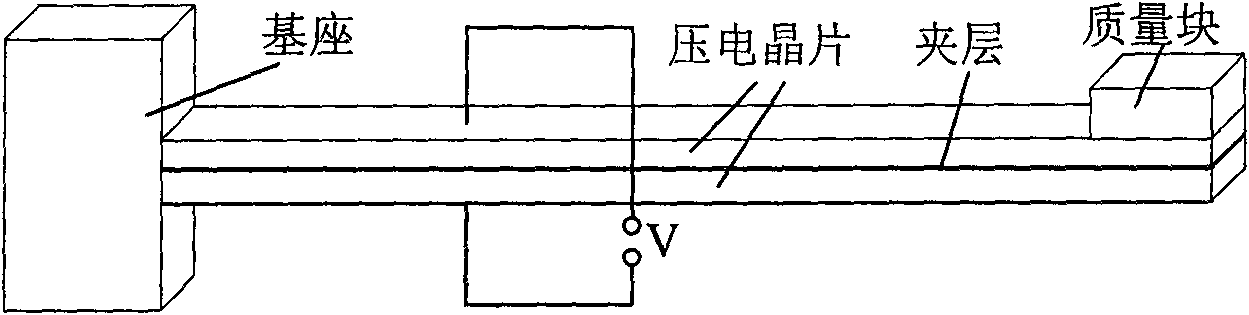
Stray energy power supplying method of electrical equipment status monitoring wireless sensing system and device thereof
InactiveCN101656492ASolve power problemsMeet the requirements of energy saving and environmental protectionBatteries circuit arrangementsPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesElectrical devicesEngineering
The invention relates to a stray energy power supplying method of an electrical equipment status monitoring wireless sensing system; a vibration power-generating device, or a temperature difference power-generating device or a flux leakage power-generating deice is adopted to lead mechanical vibration energy or heat energy or flux leakage energy which is generated in the operating process of the electrical equipment to be converted into electrical energy, and the electrical energy is transformed and adjusted by a transformation module, and the transformed electrical energy is stored in an energy storage device such as a rechargeable battery, a capacitor and the like, so as to supply power for the node of the electrical equipment status monitoring wireless sensor. A device applied to the stray energy power supplying method comprises a stray energy power-generating module such as vibration power generation, temperature difference power generation or flux leakage power generation, an electrical energy conversion module and an electrical energy storage module which are arranged on the electrical equipment. The invention can effectively utilize stray energy generated in the operating process of the electrical equipment to supply power for the node of the wireless sensor.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRICAL ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
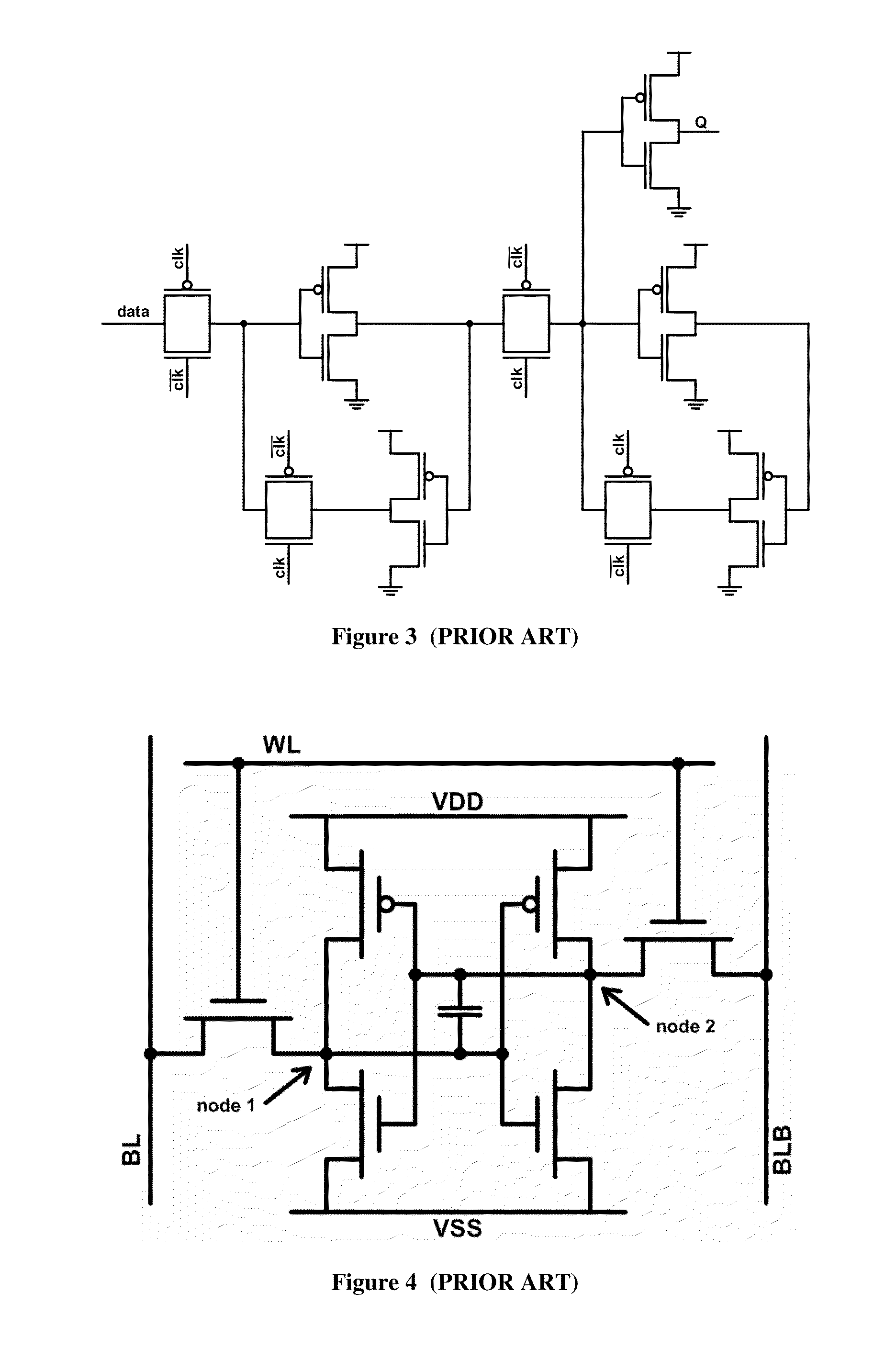
Eight transistor soft error robust storage cell
Owner:NYTELL SOFTWARE LLC
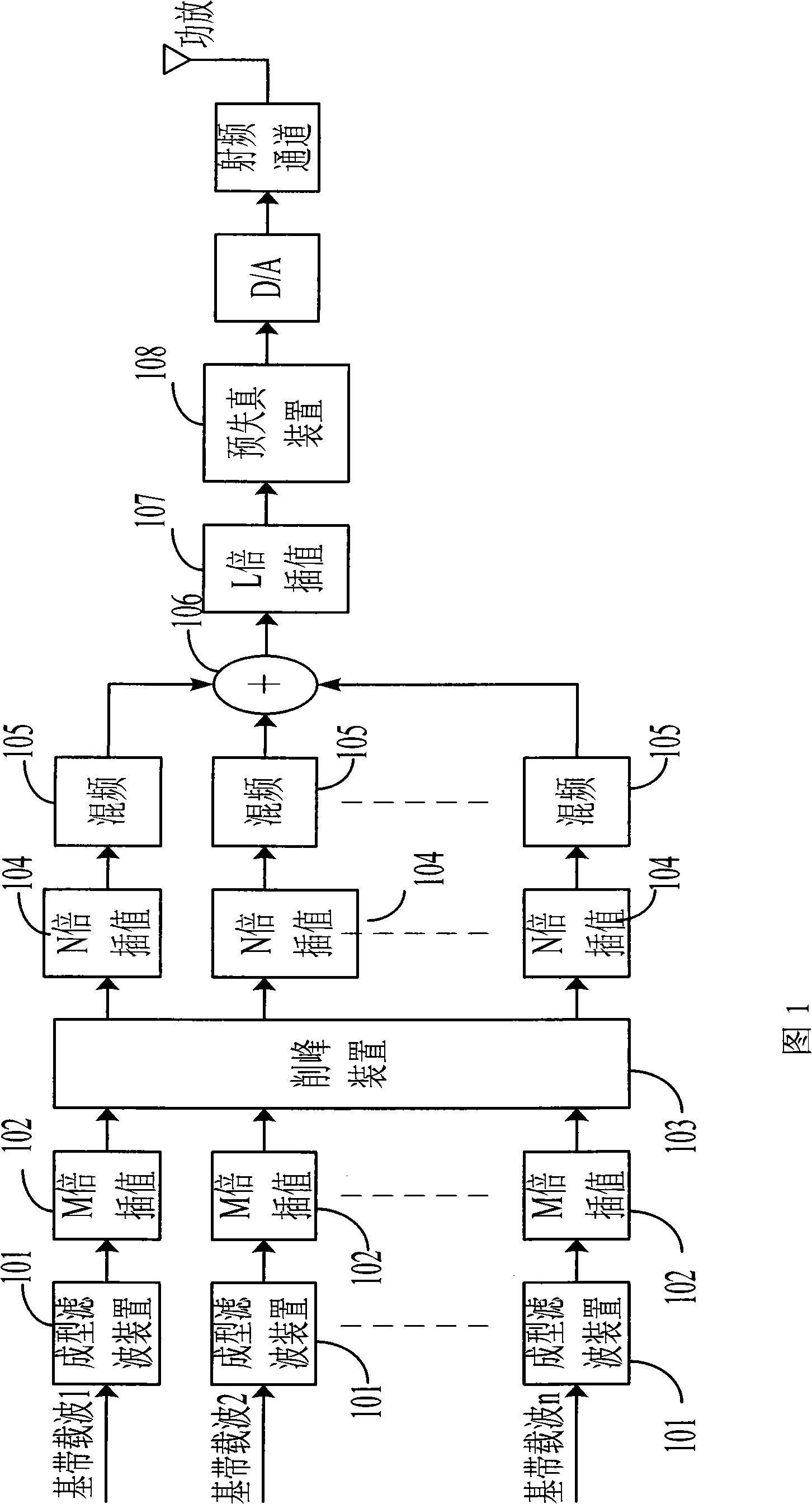
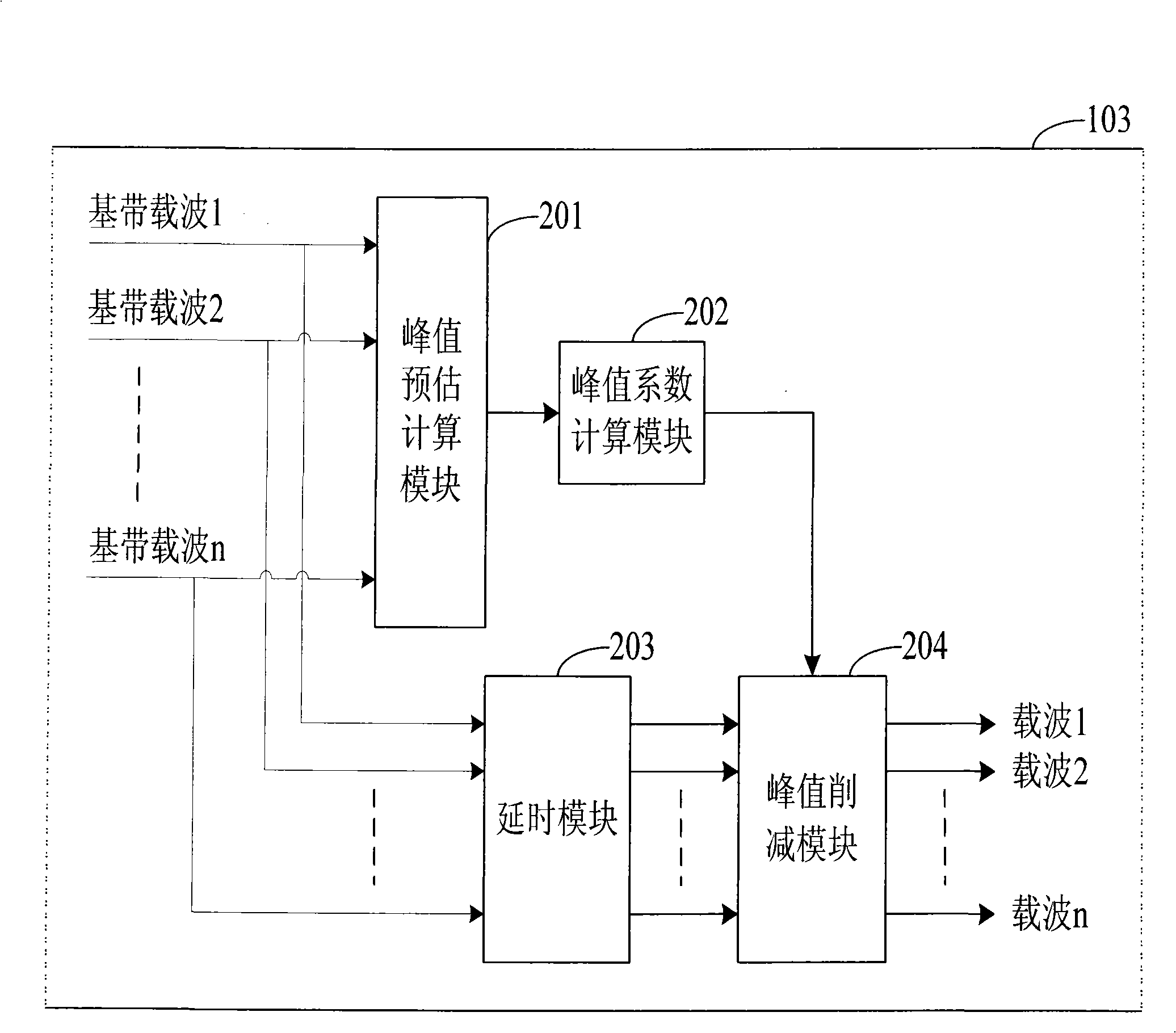
System and method for cutting peak of preprocess discontinuousness allocating multiple carrier waves
InactiveCN101257481AAchieve individual peak clippingArbitrary configurationMulti-frequency code systemsTransmitter/receiver shaping networksIntermediate frequencyLow data rate
The invention provides a peak clipping system for pretreating discontinuous arrangement multicarrier and a method thereof. The system includes a figure up-conversion device having multilevel interpolation filter and a peak clipping device, wherein the peak clipping device is arranged between arbitrary two-stage interpolation filter. The method includes carrying through the medium frequency process on the baseband carrier, and processing peak clipping between arbitrary two stages with multilevel interpolation. The project of the invention realizes the single peak clipping on each baseband carrier, thereby the carrier frequency point can be arranged arbitrarily in a certain frequency range when mixing; the peak clipping device is in the middle of the up-conversion channel, with low data rate, wide signal bandwidth, easy design, which can preferably restrain the noise out of the signal range and ensure the near channel leakage power ration of the transmitter without great change.
Owner:XUZHOU MASTER MECHANICAL TECH CO LTD
Leakage power reduction apparatus
InactiveUS20080279122A1Suppress leakageWithout lowering power utilization efficiencyTransmission control/equalisingDuplex signal operationEngineeringLeakage power
A circulator extracts a transmission signal sent from a transmitter to antenna via the circulator and a duplexer, reflected by an antenna, and returned via the duplexer to the transmitter side. The amplitude and phase of the extracted signal are adjusted by an amplitude-and-phase adjuster to generate an offset signal having the same amplitude and the opposite phase with respect to a leaking transmission signal included in a signal output from a third terminal of the duplexer when combined by a combiner. The offset signal is combined in the combiner with the leaking transmission signal included in the signal output from the third terminal of the duplexer to suppress the leaking transmission signal.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
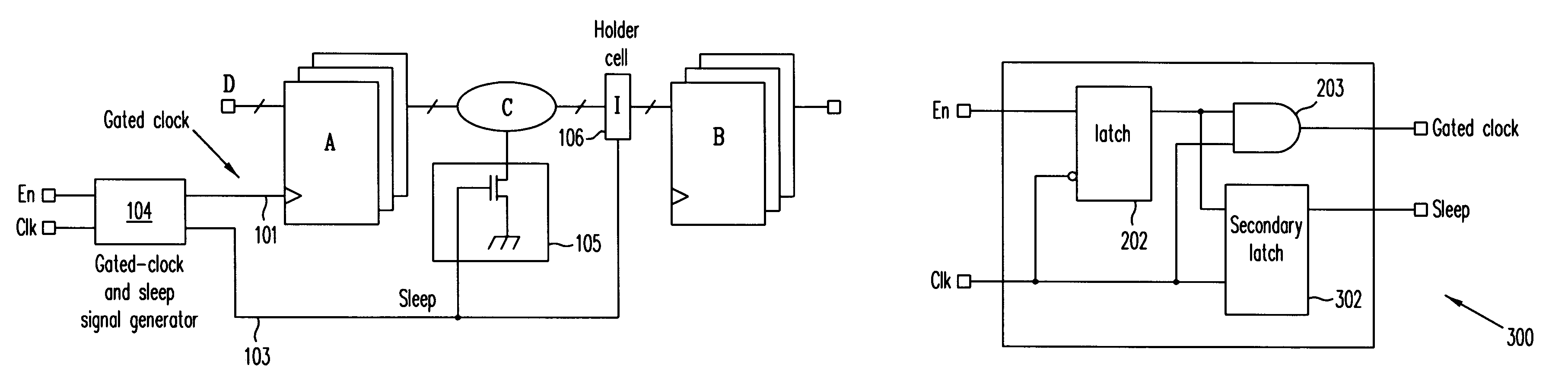
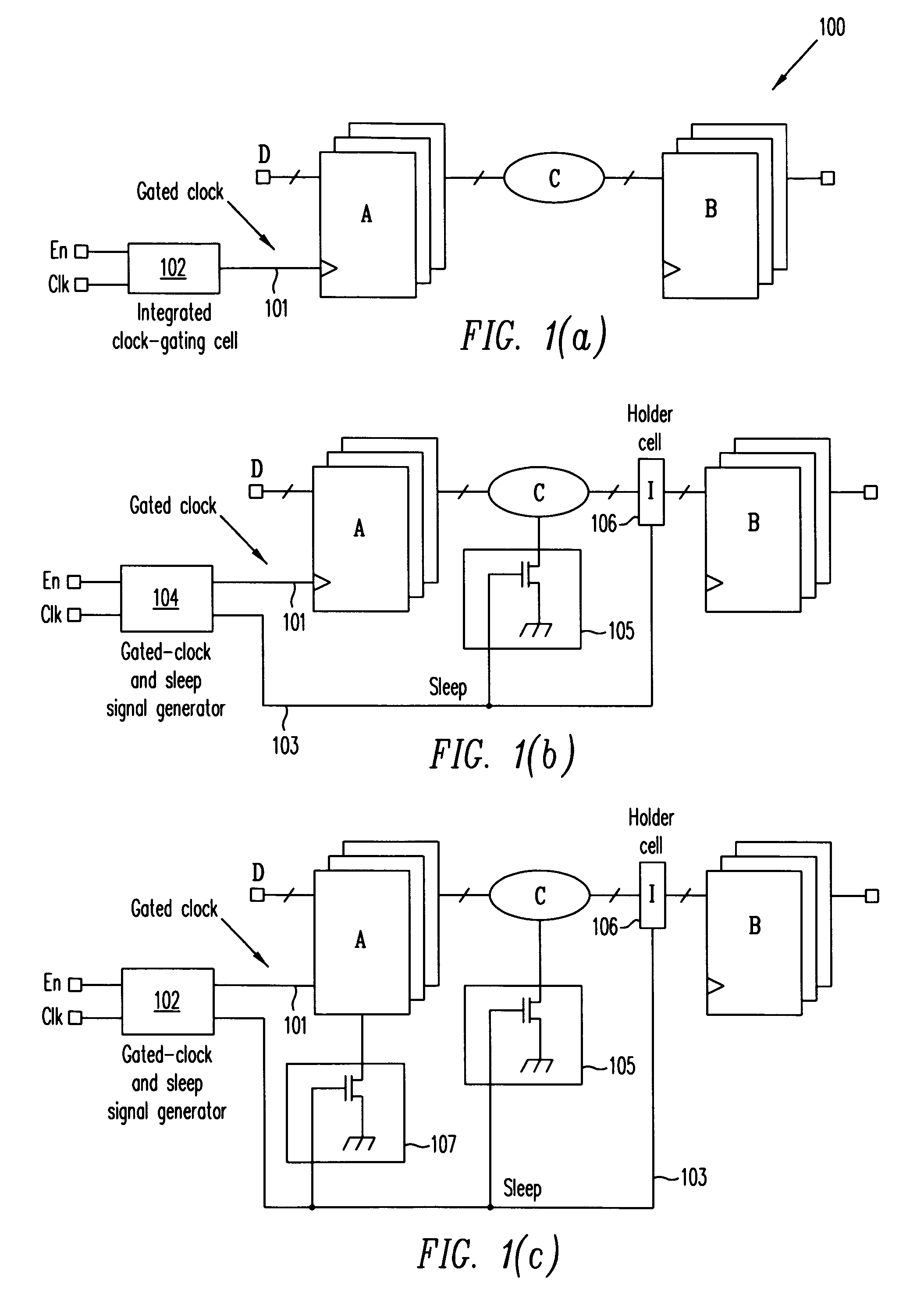
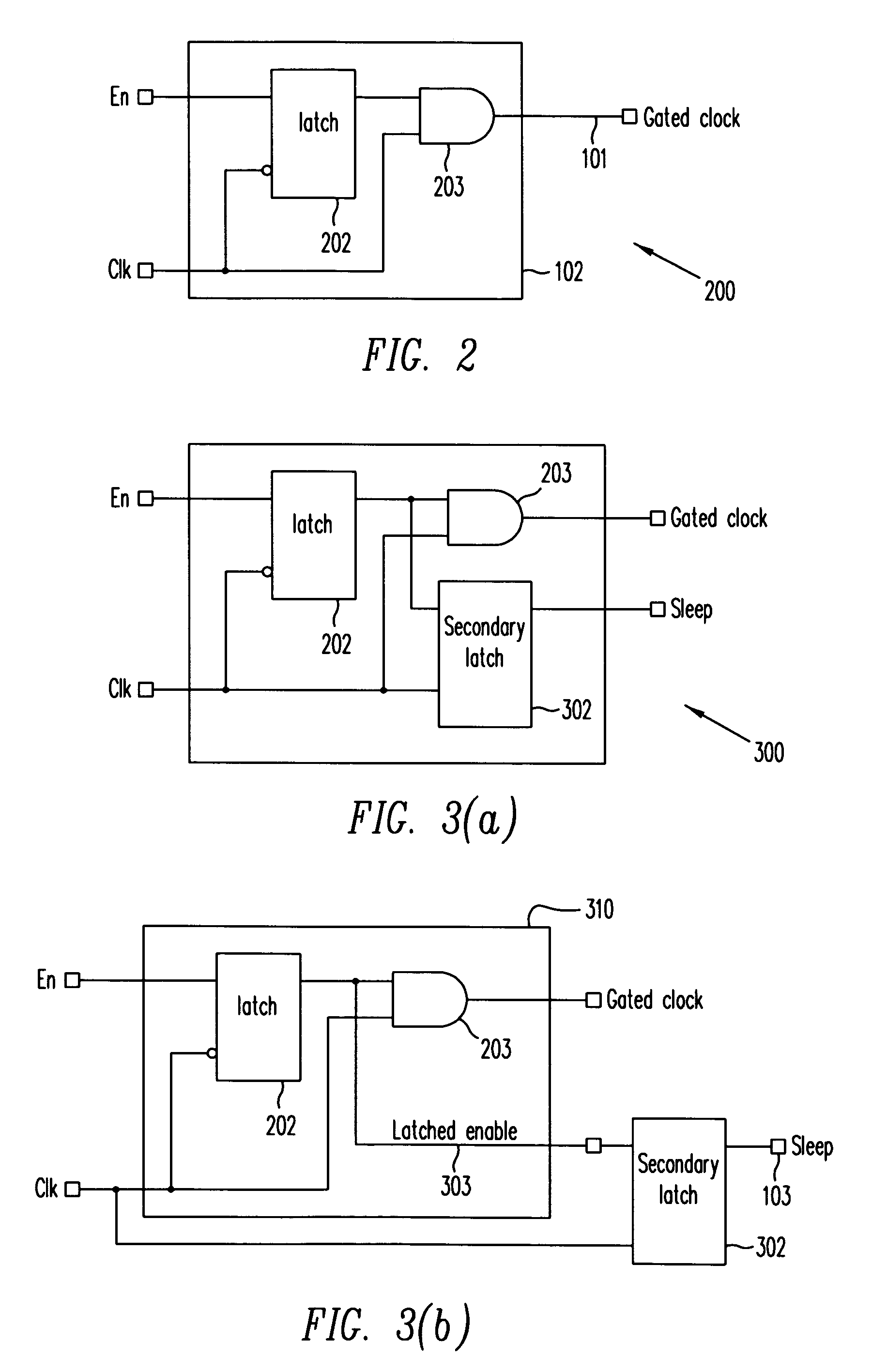
Automatic extension of clock gating technique to fine-grained power gating
A method extends a clock-gating technique to provide a sleep signal for controlling switch circuits that reduce active leakage power. Using this extension of the clock-gating technique, fine-grained power-gating is achieved. The method automatically identifies, at an RTL or a gate level, the logic circuits that can be power-gated. The method of the present invention derives a sleep signal for fine-grained power-gating that may be applicable to both time-critical and non-time-critical designs.
Owner:ANSYS
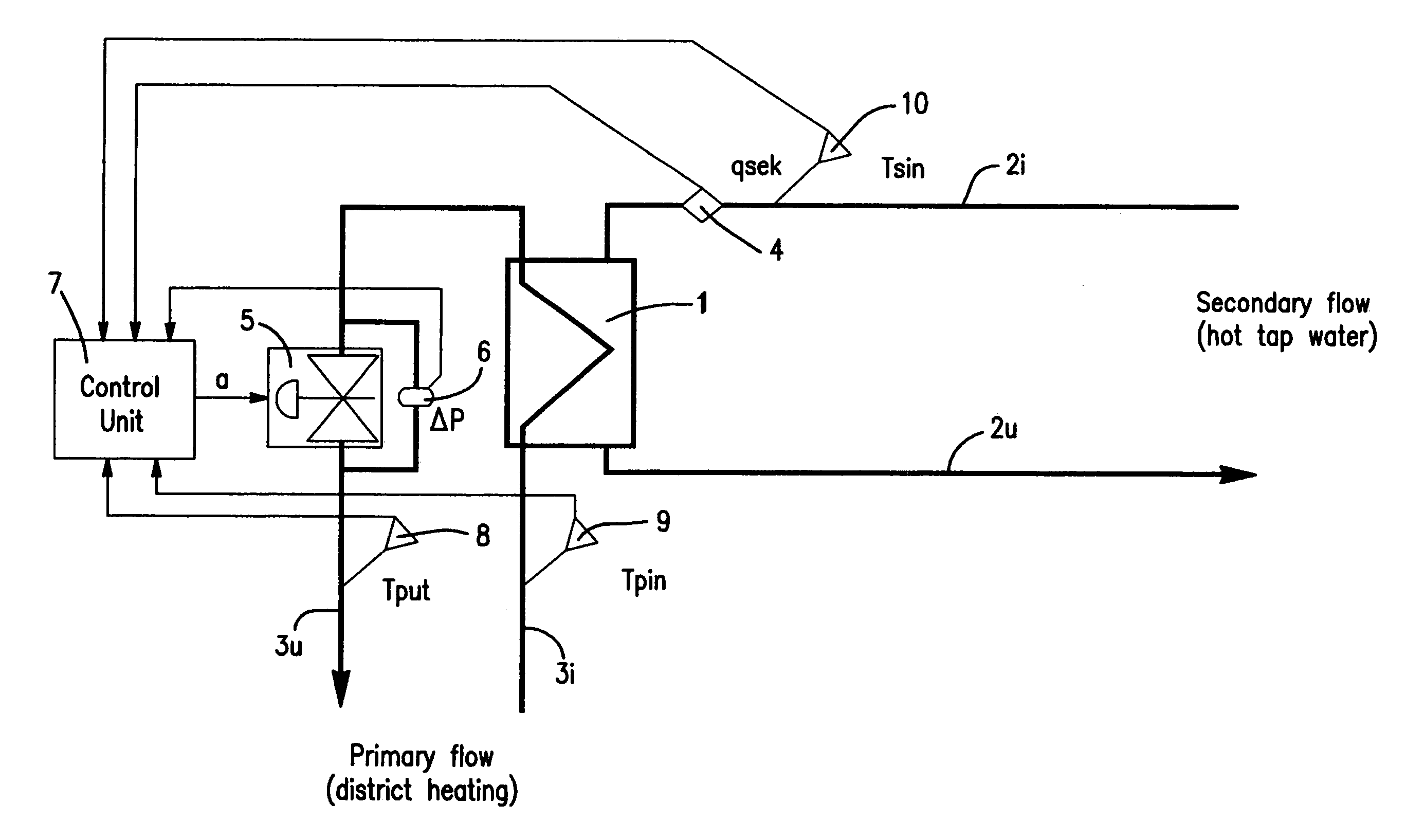
Method and arrangement for controlling the temperature of the outstream flow from a heat exchanger and measuring produced heat
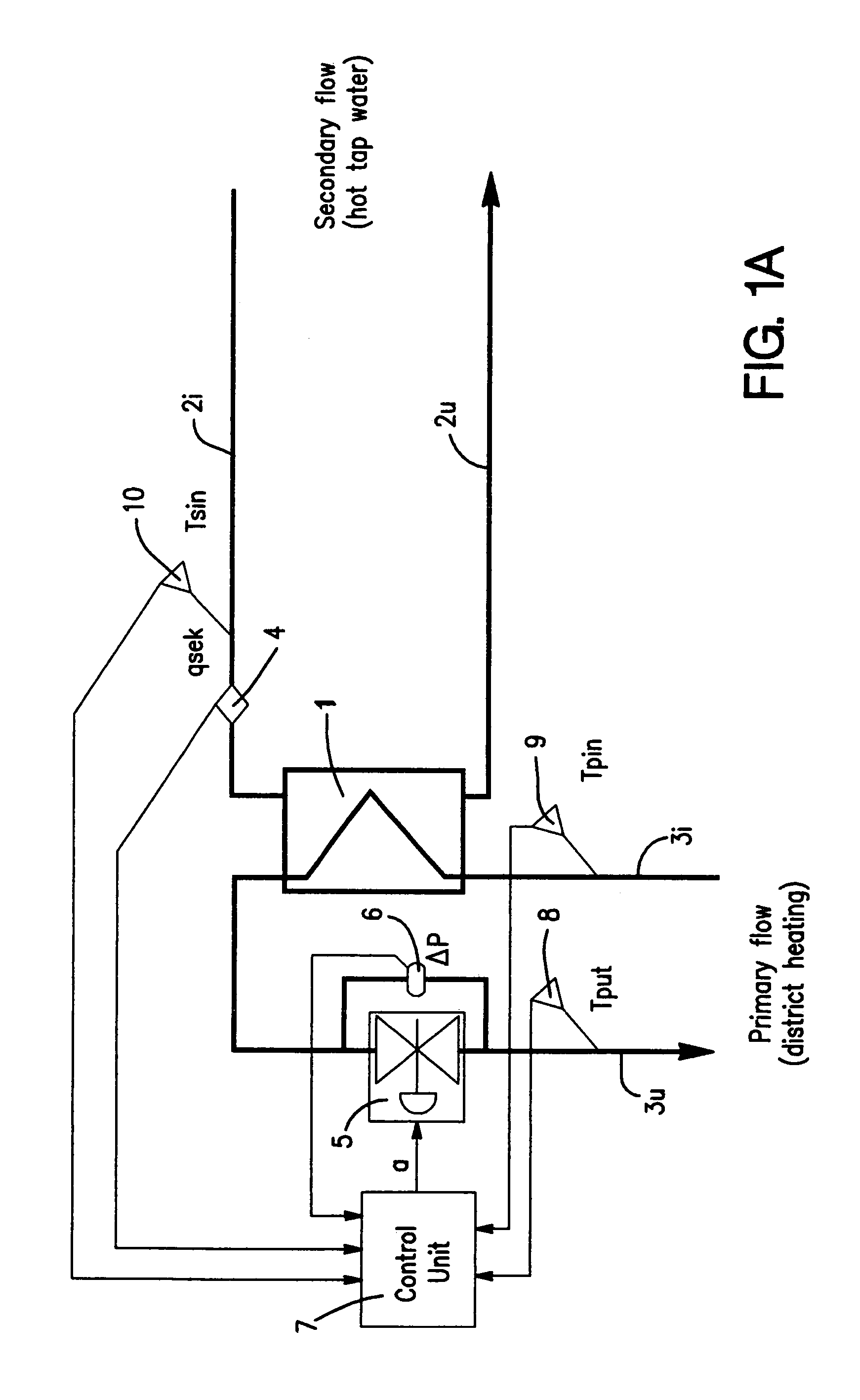
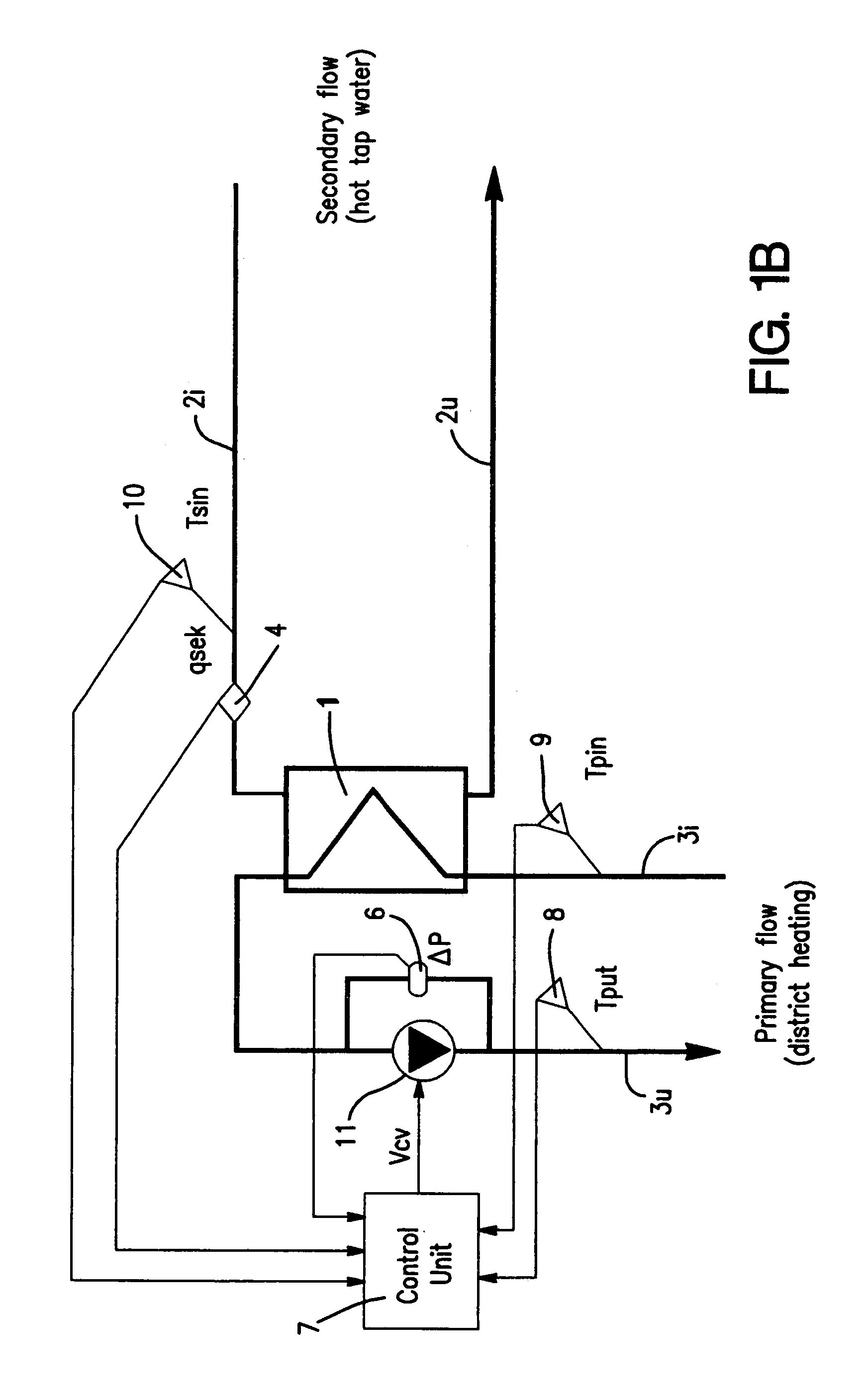
InactiveUS7069976B2Improve adaptabilityReduce riskDistrict heating systemAir-treating devicesEngineeringSecondary circuit
Owner:LINDGREN
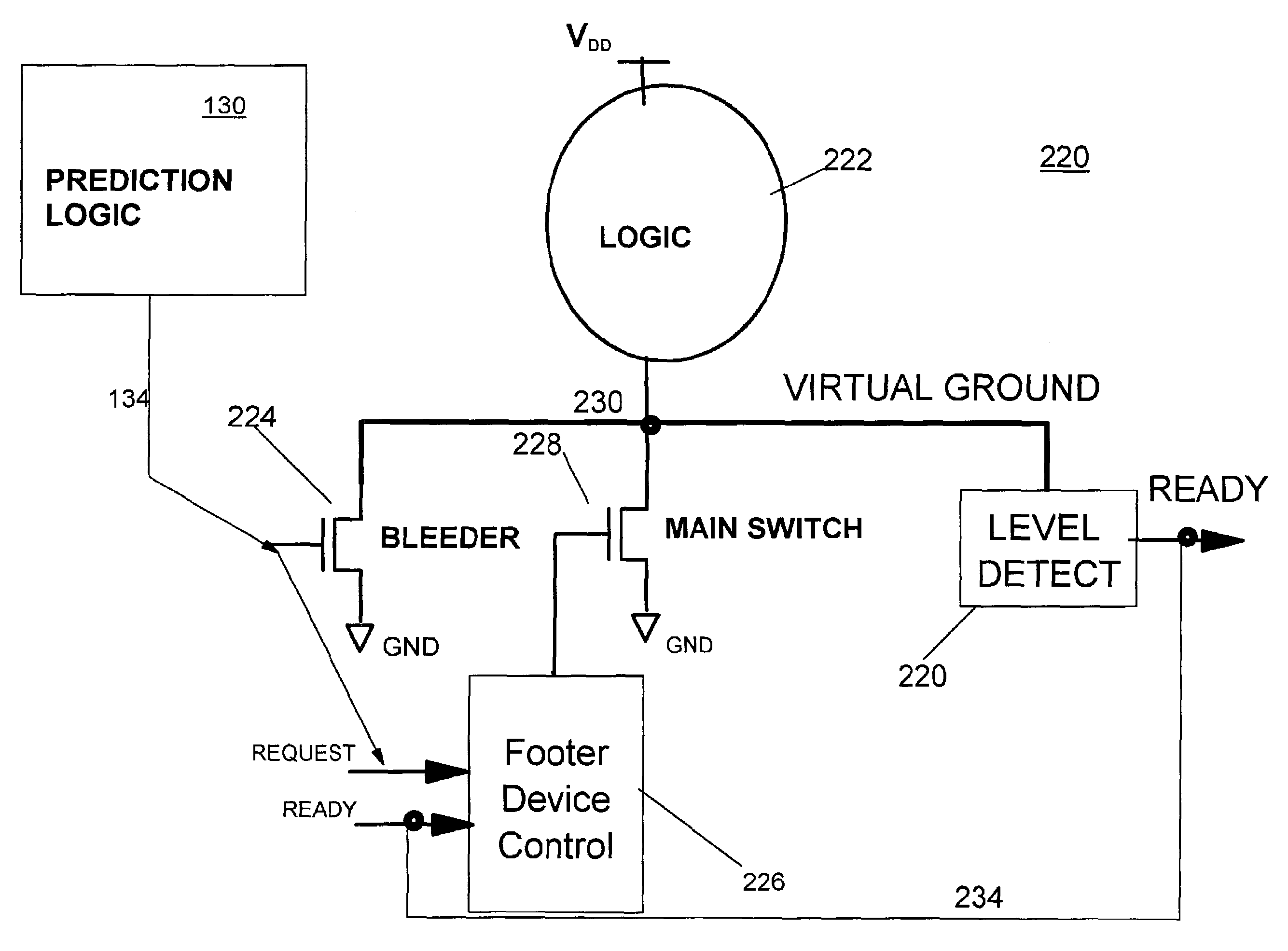
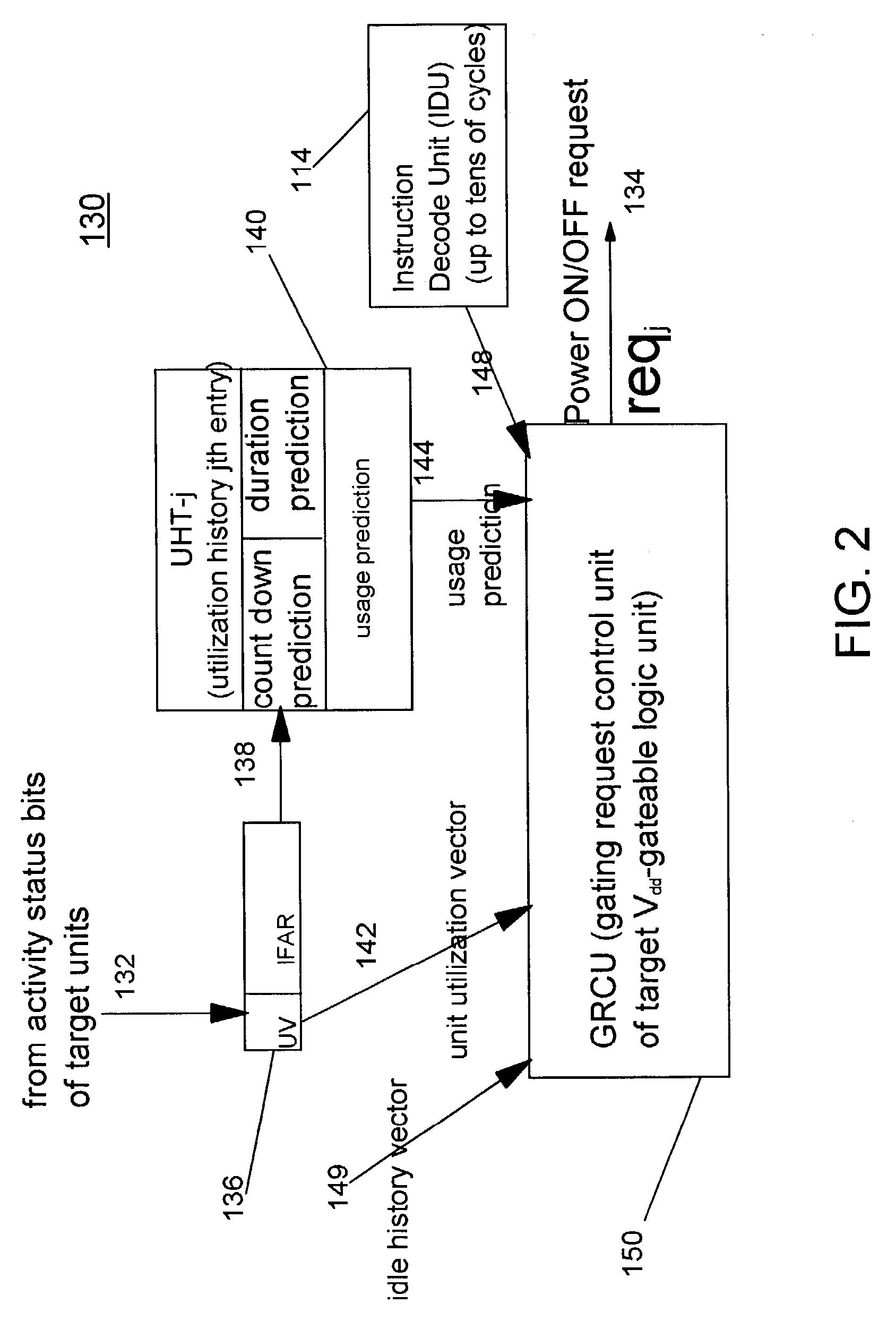
Processor with low overhead predictive supply voltage gating for leakage power reduction
ActiveUS7134028B2Decreasing processor power consumptionNo performance lossEnergy efficient ICTVolume/mass flow measurementTurn on timeLeakage power
An integrated circuit (IC) including unit power control, leakage reduction circuit for controllably reducing leakage power with reduced LdI / dt noise in the IC and, an activity prediction unit invoking active / dormant states in IC units. The prediction unit determines turn on and turn off times for each IC unit. The prediction unit controls a supply voltage select circuit selectively passing a supply voltage to a separate supply line at the predicted turn on time and selectively blocking the supply voltage at the predicted turn off time.
Owner:IBM CORP
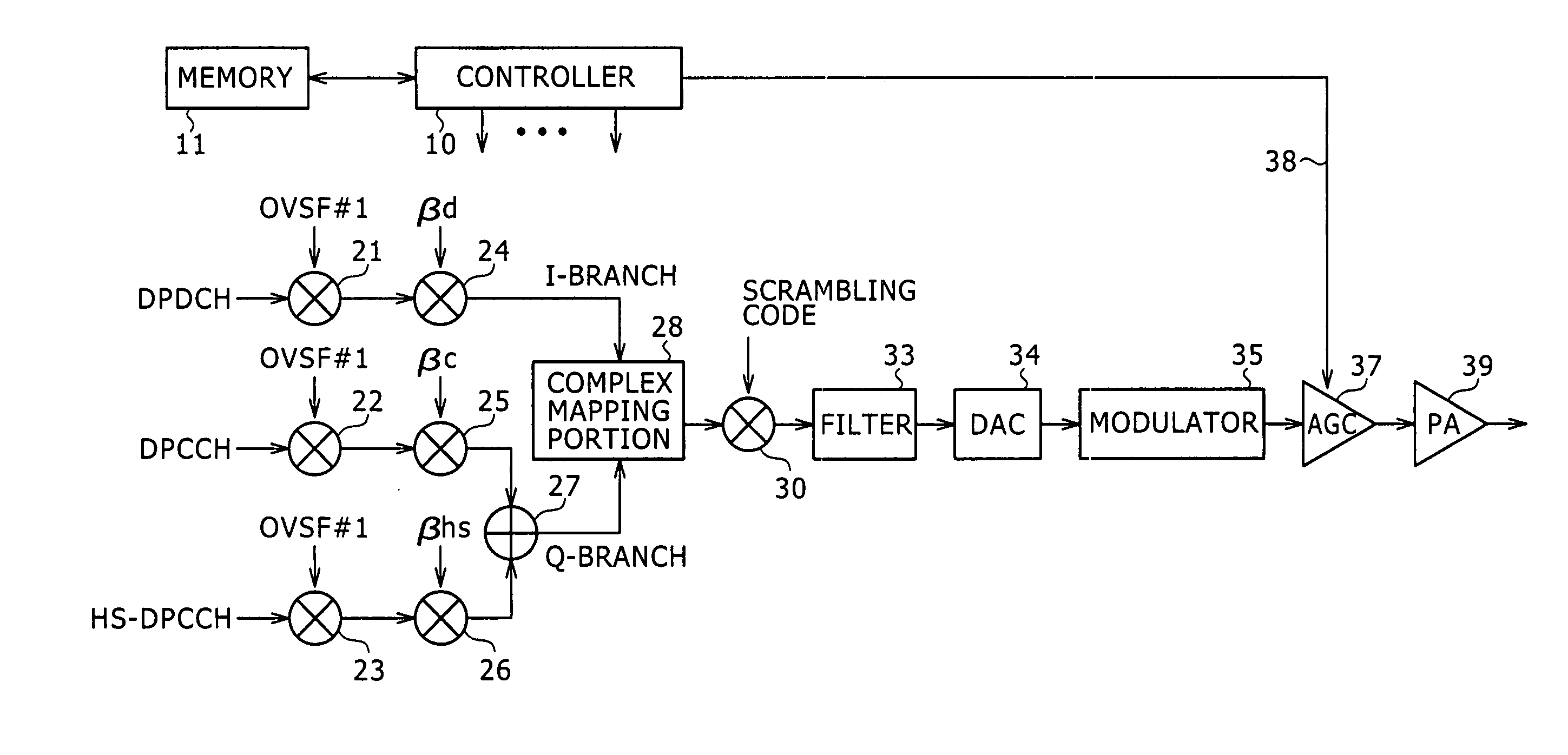
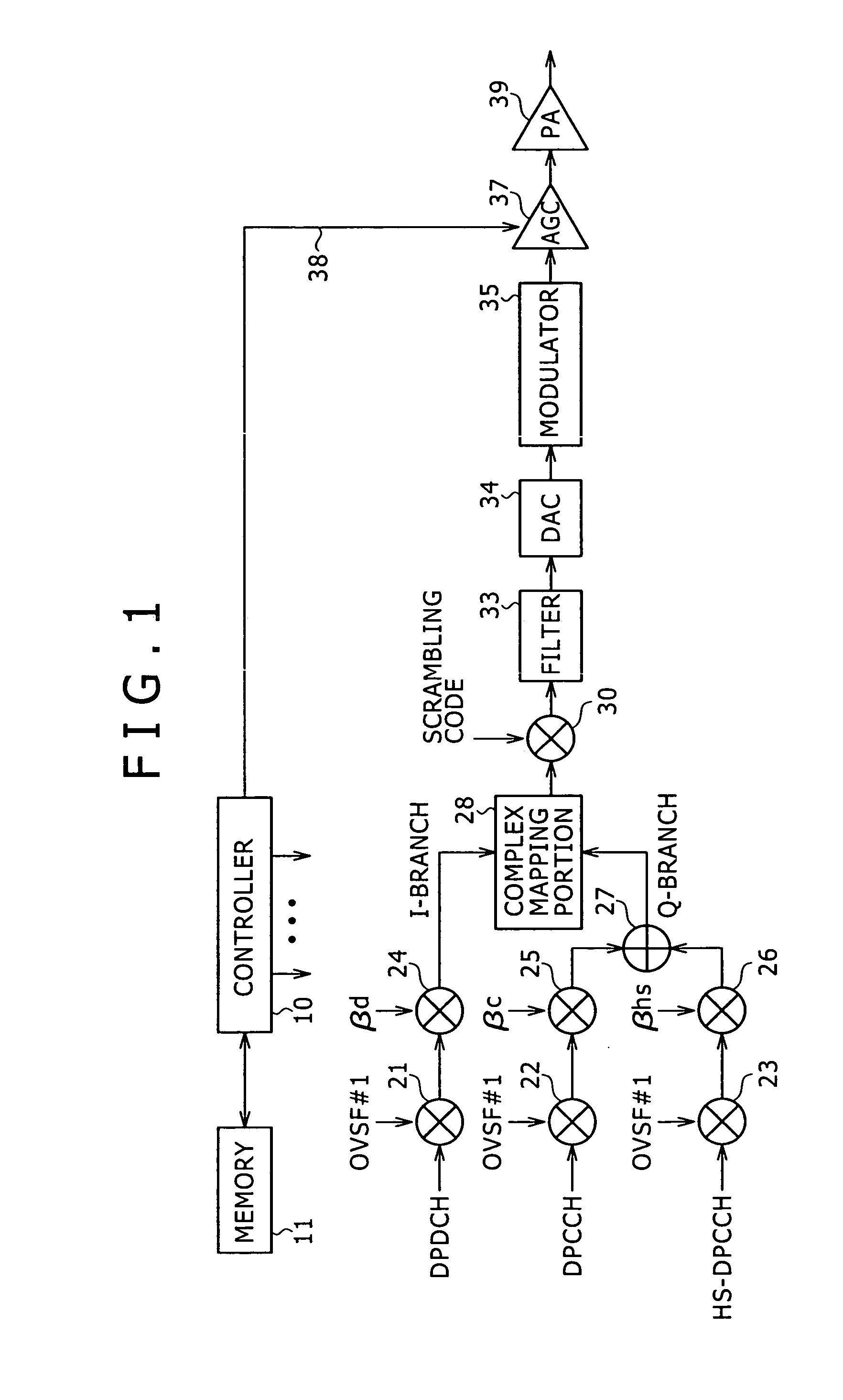
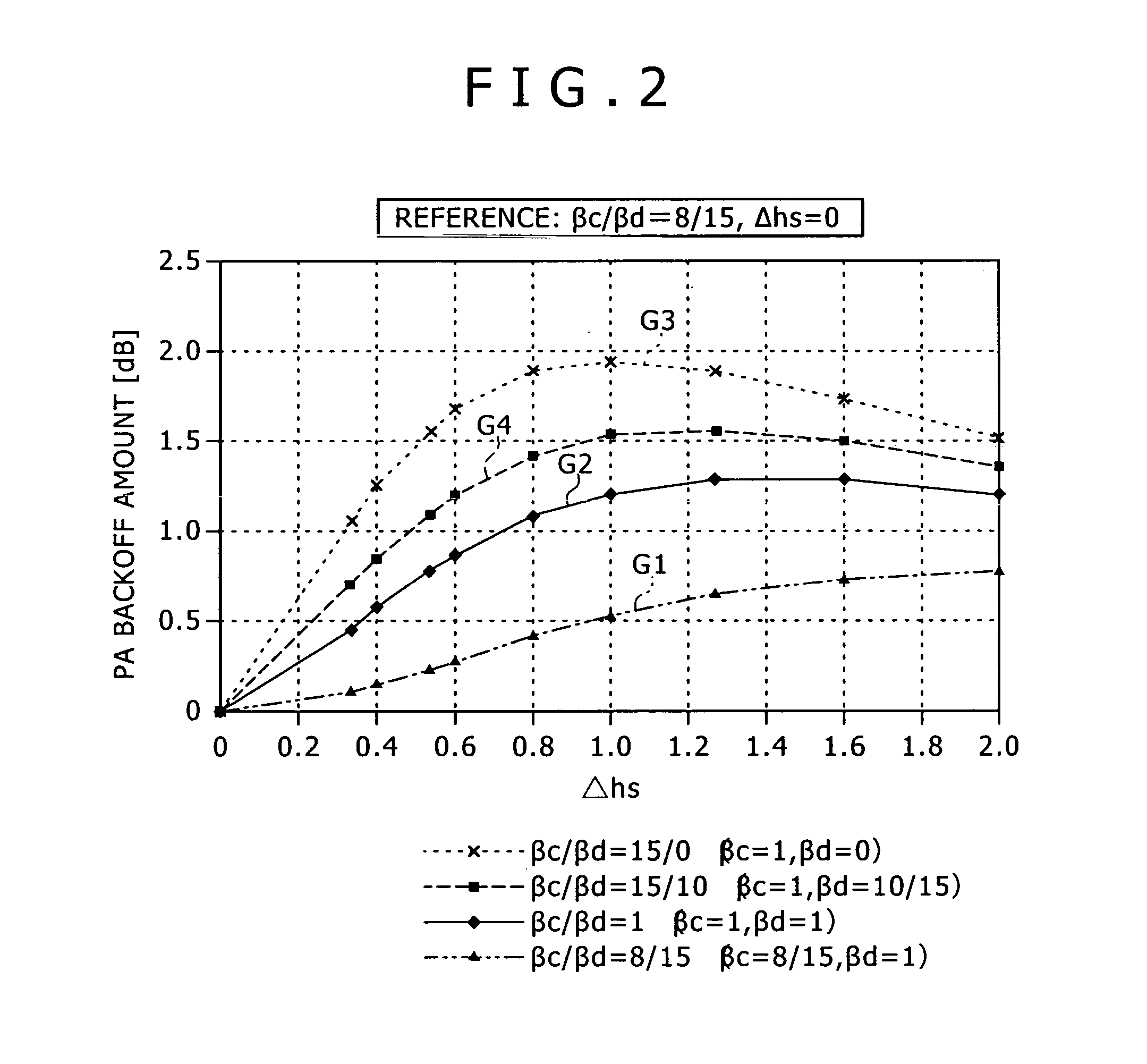
Transmission power control method and device
ActiveUS7324828B2Solve the power is smallAppropriate amountEnergy efficient ICTPower managementMultiplexingEngineering
Disclosed is a method and an apparatus for controlling transmission electric power capable of minimizing a decrease in the amount of maximum transmission electric power without degrading an adjacent channel leakage power ratio when code-multiplexing additional control information with data and main control information. A mobile device checks values of gain factors βd and βc when performing code multiplexing to transmit signals from channels DPDCH to transmit data, DPCCH to transmit main control information, and HS-DPCCH to transmit additional control information. A maximum transmission electric power is decreased at a plurality of levels based on the check result and a ratio (Δhs) between the gain factors βc and βhs. It may be preferable to check the presence or absence of transmission data instead of the gain factor βd. In this case, when no transmission data is available, the maximum transmission electric power is decreased at a plurality of levels based on Δhs. When transmission data is available, the maximum transmission electric power is decreased at a plurality of levels based on the gain factor βc and Δhs.
Owner:SONY CORP
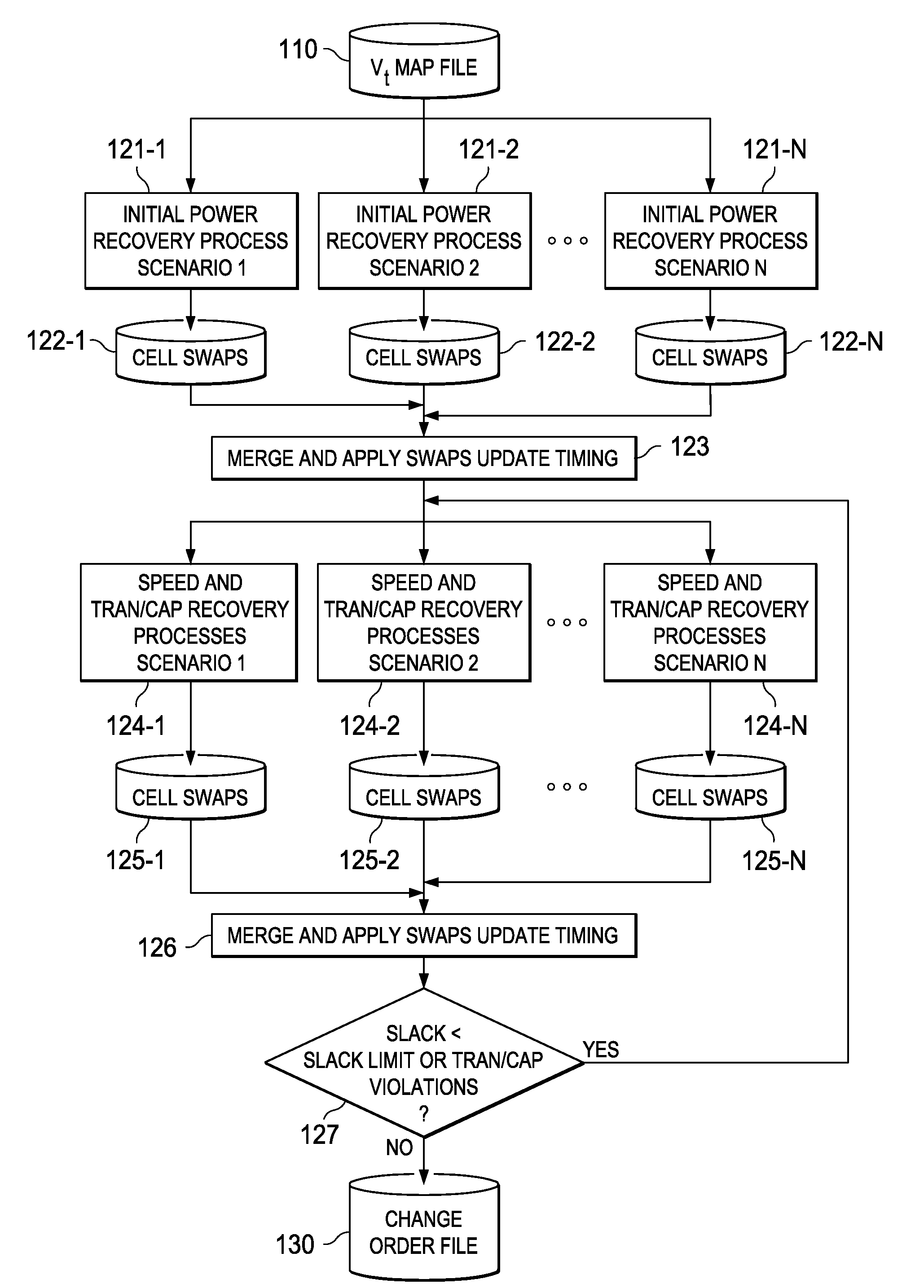
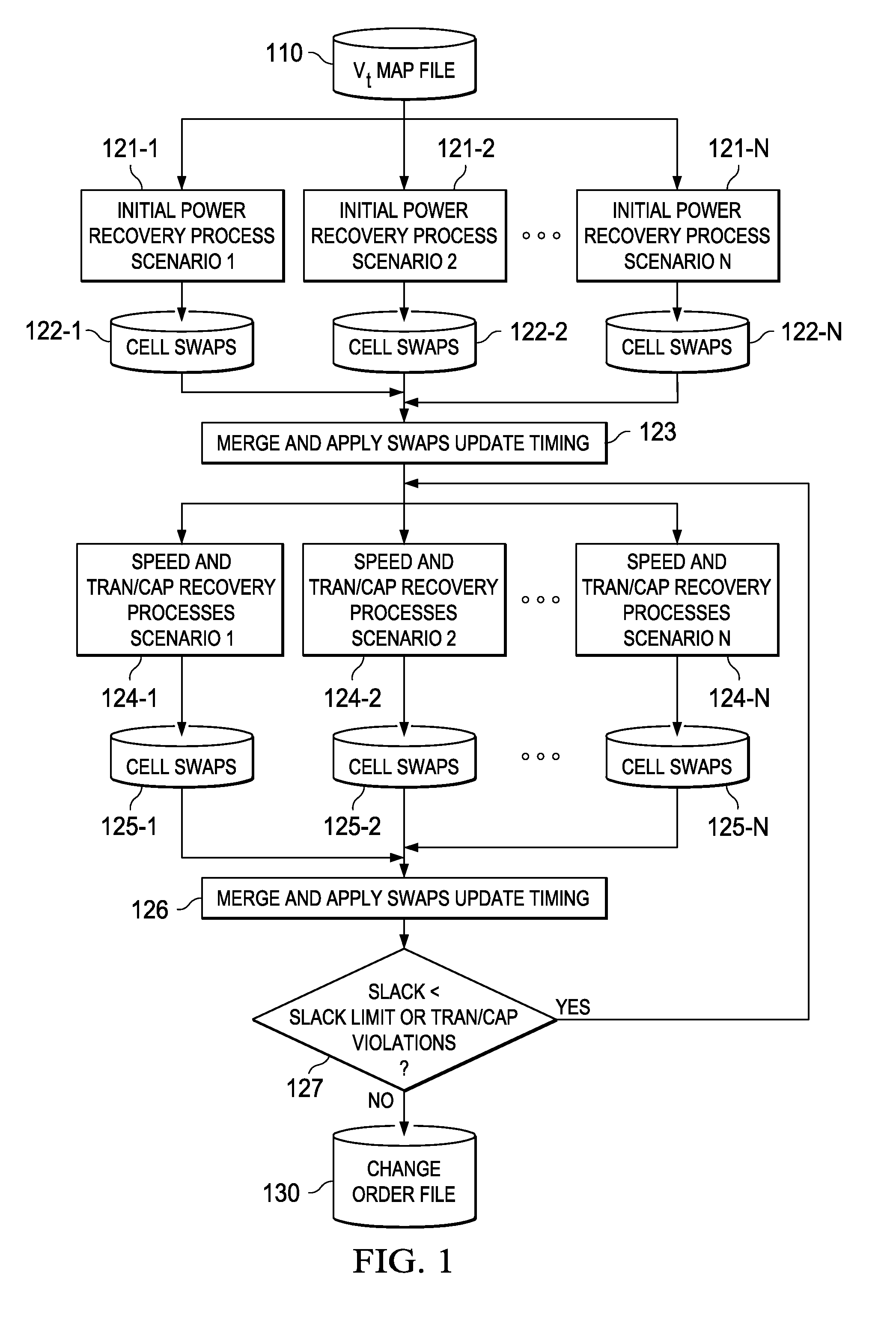
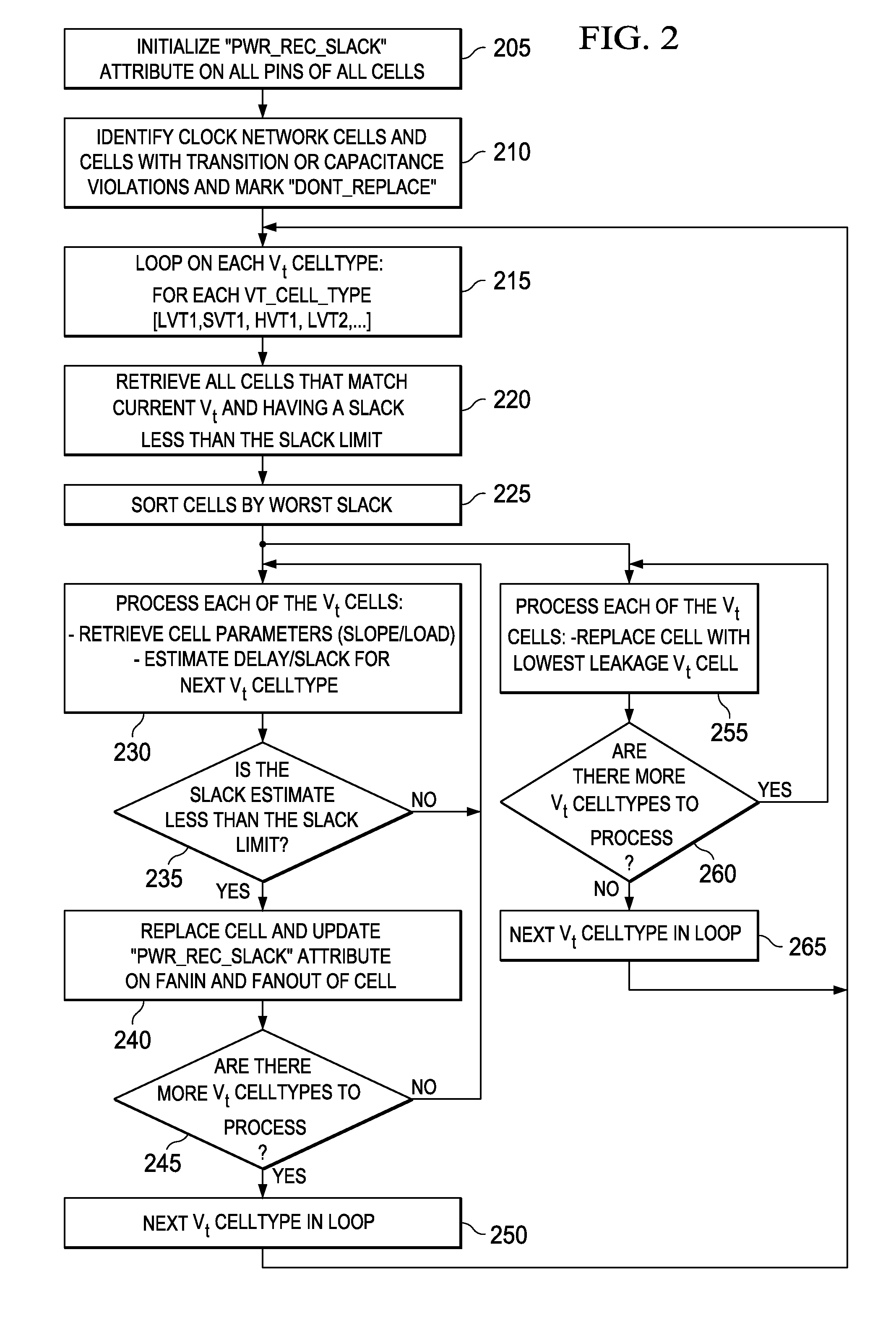
System and method for employing signoff-quality timing analysis information concurrently in multiple scenarios to reduce leakage power in an electronic circuit and electronic design automation tool incorporating the same
InactiveUS20100153897A1CAD circuit designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationLow leakageLeakage power
A leakage power recovery system and method, and a electronic design automation (EDA) tool incorporating either or both of the system and the method. In one embodiment, the timing signoff tool includes: (1) a power recovery module configured to carry out an instance of an initial power recovery process in each of multiple scenarios concurrently, the initial power recovery process including making first conditional replacements of cells in at least one path in a circuit design with lower leakage cells and estimating a delay and a slack of the at least one path based on the first conditional replacements and (2) a speed recovery module associated with the power recovery module and configured to carry out a speed recovery process in each of the multiple scenarios concurrently, the speed recovery process including determining whether the first conditional replacements cause a timing violation with respect to the at least one path and making second conditional replacements with higher leakage cells until the timing violation is removed.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
High-performance low leakage power consumption master-slave type D flip-flop
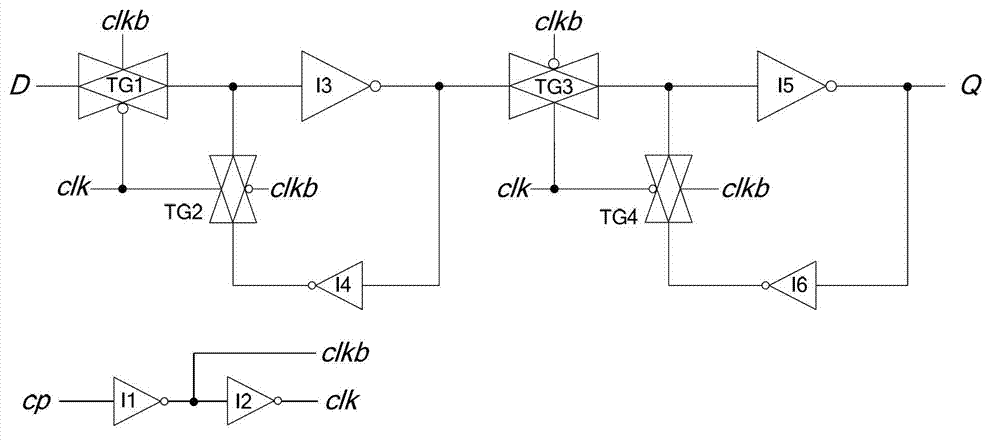
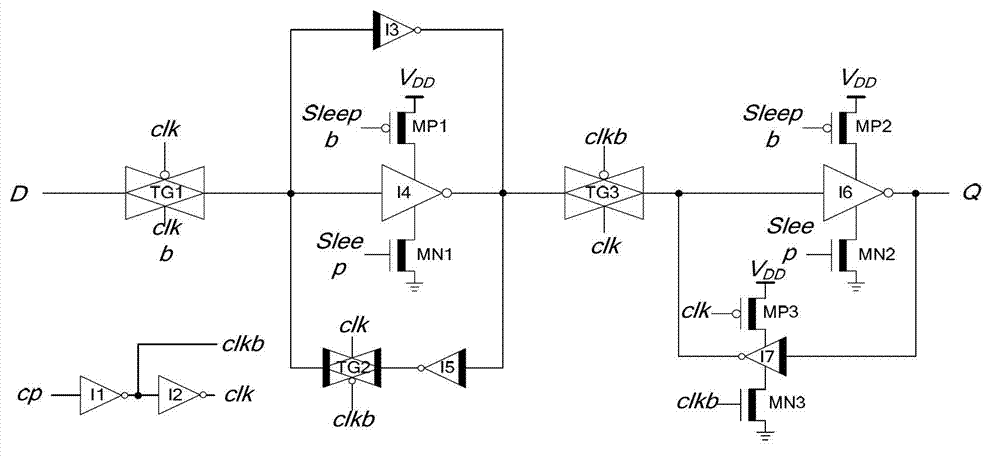
InactiveCN103199823ASimple structureLow transistor countElectric pulse generatorLow leakageEngineering
The invention discloses a high-performance low leakage power consumption master-slave type D flip-flop. The high-performance low leakage power consumption master-slave type D flip-flop is characterized by comprising a clock signal inverter circuit, a master latch circuit, a slave latch circuit, an N-channel metal oxide semiconductor (NMOS) pipe power control switch, a P-channel Metal Oxide Semiconductor (PMOS) pipe power control switch and a maintaining inverter. The clock signal inverter circuit is connected with the master latch circuit, the clock signal inverter circuit is connected with the slave latch circuit, the master latch circuit is connected with the slave latch circuit, the slave latch circuit is connected with the maintaining inverter, the maintaining inverter is connected with the PMOS pipe power control switch, the clock signal inverter circuit, the master latch circuit and the slave latch circuit are all connected with the NMOS pipe power control switch, and the maintaining inverter is connected with the PMOS pipe power control switch. The high-performance low leakage power consumption master-slave type D flip-flop has the advantages of being simple in circuit structure, small in the number of transistors, simple in timing sequence switching of a normal working state and a sleep mode, good in working performance, low in dynamic power consumption and leakage power consumption, and suitable for being used as a standard cell of a digital circuit to be applicable to the design of a low power consumption integrated circuit in deep submicron complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor transistor (CMOS) process.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com