Patents
Literature
132 results about "Transistor sizing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
They vary in size from 4 microns (.004 mm) to 100 microns (.1 mm) in diameter. Their length varies from a fraction of an inch to several feet. Transistors on currently manufactured CPUs are at the 14nm node, while GPUs and memory are often on slightly older processes (22 or 32nm).
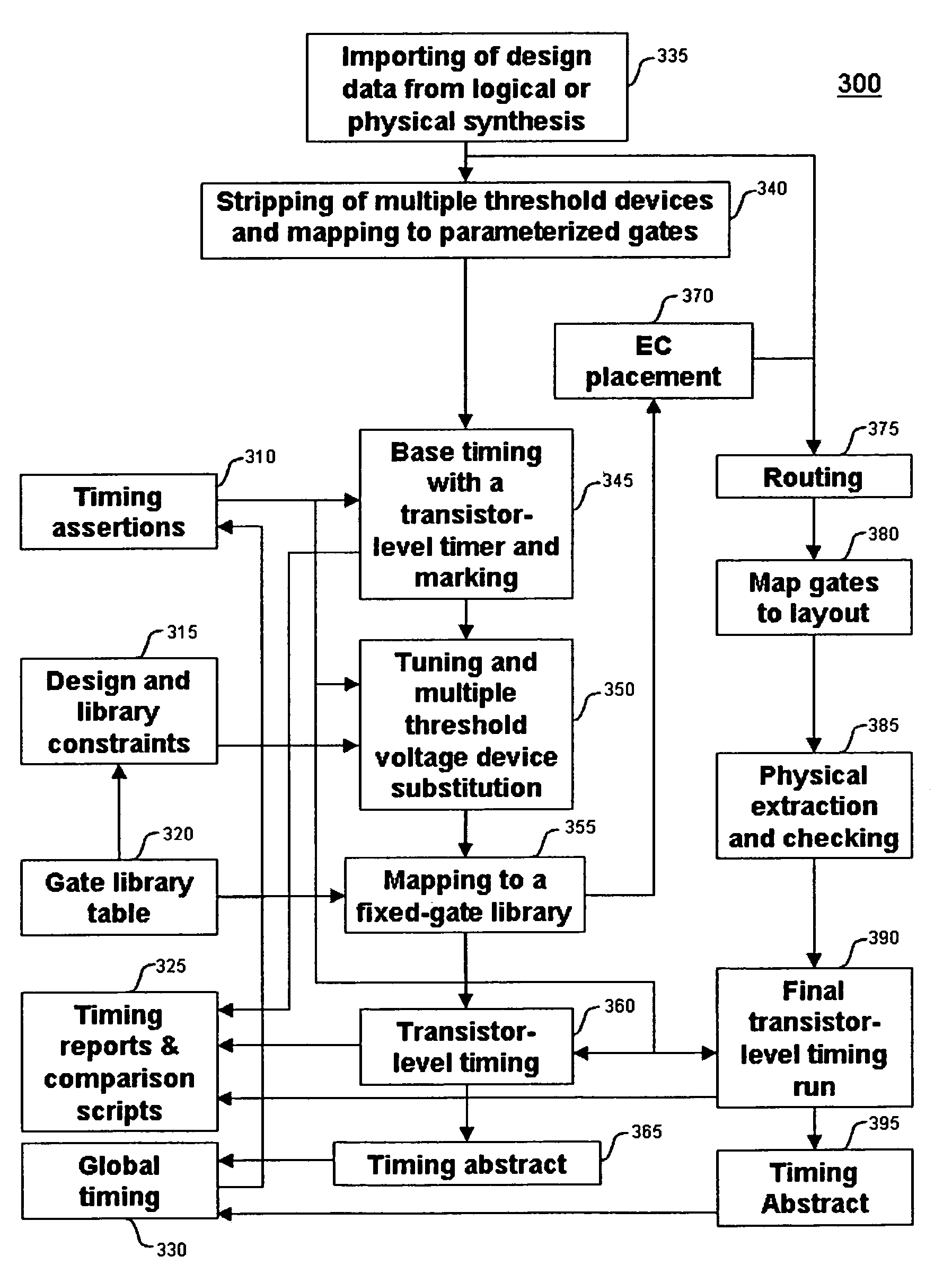
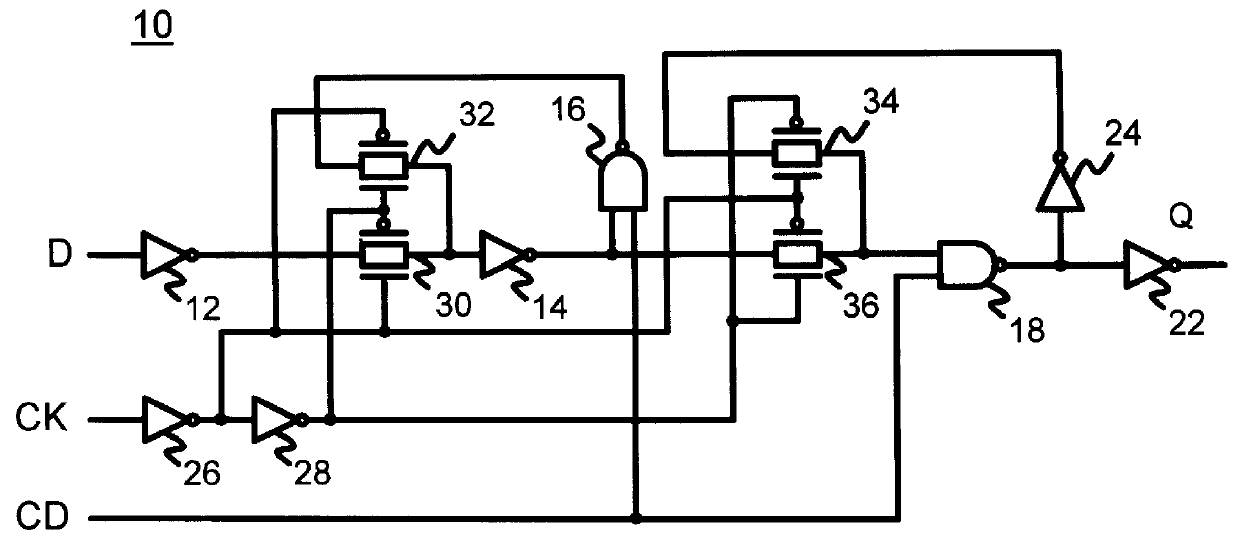
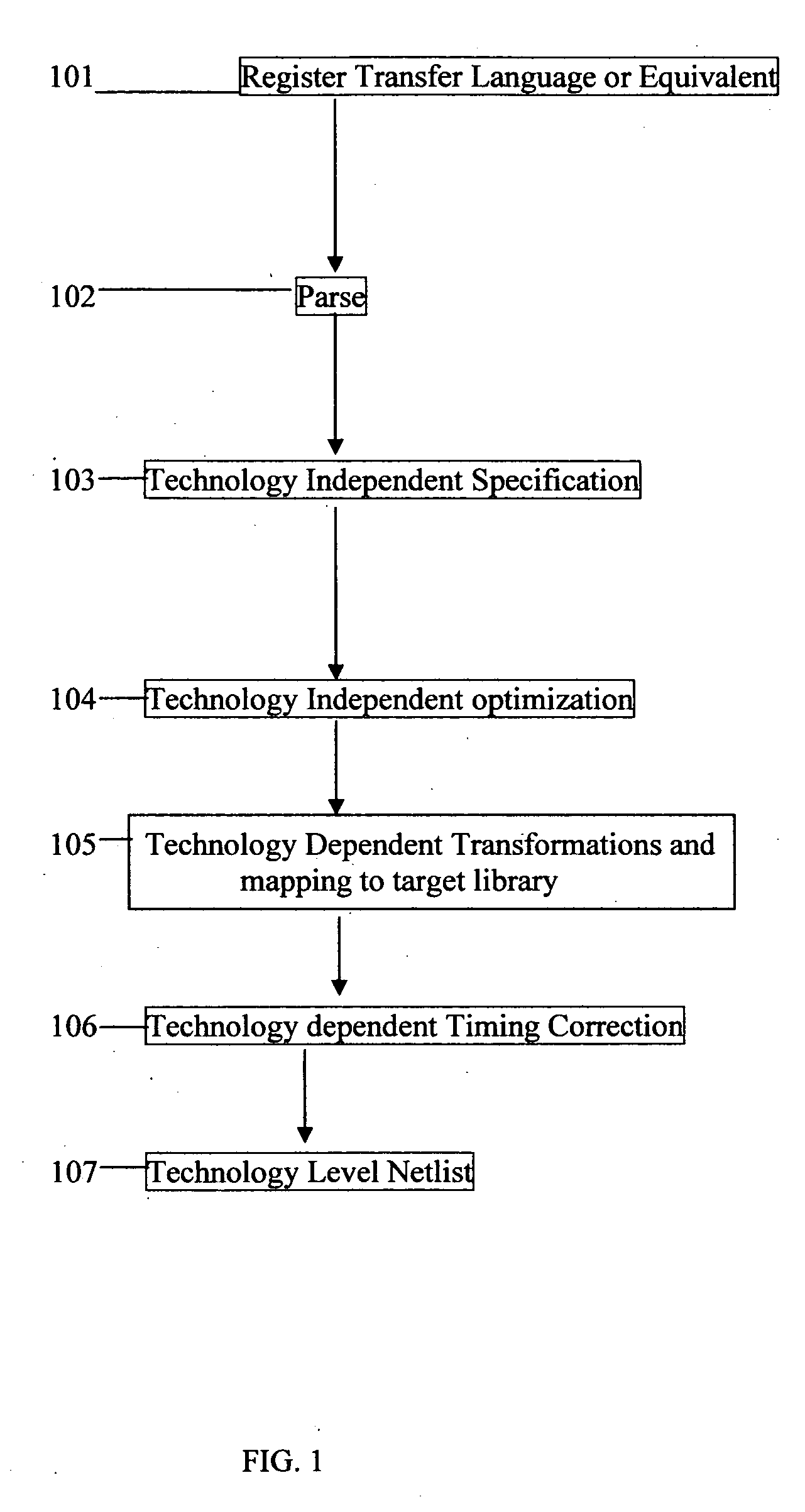
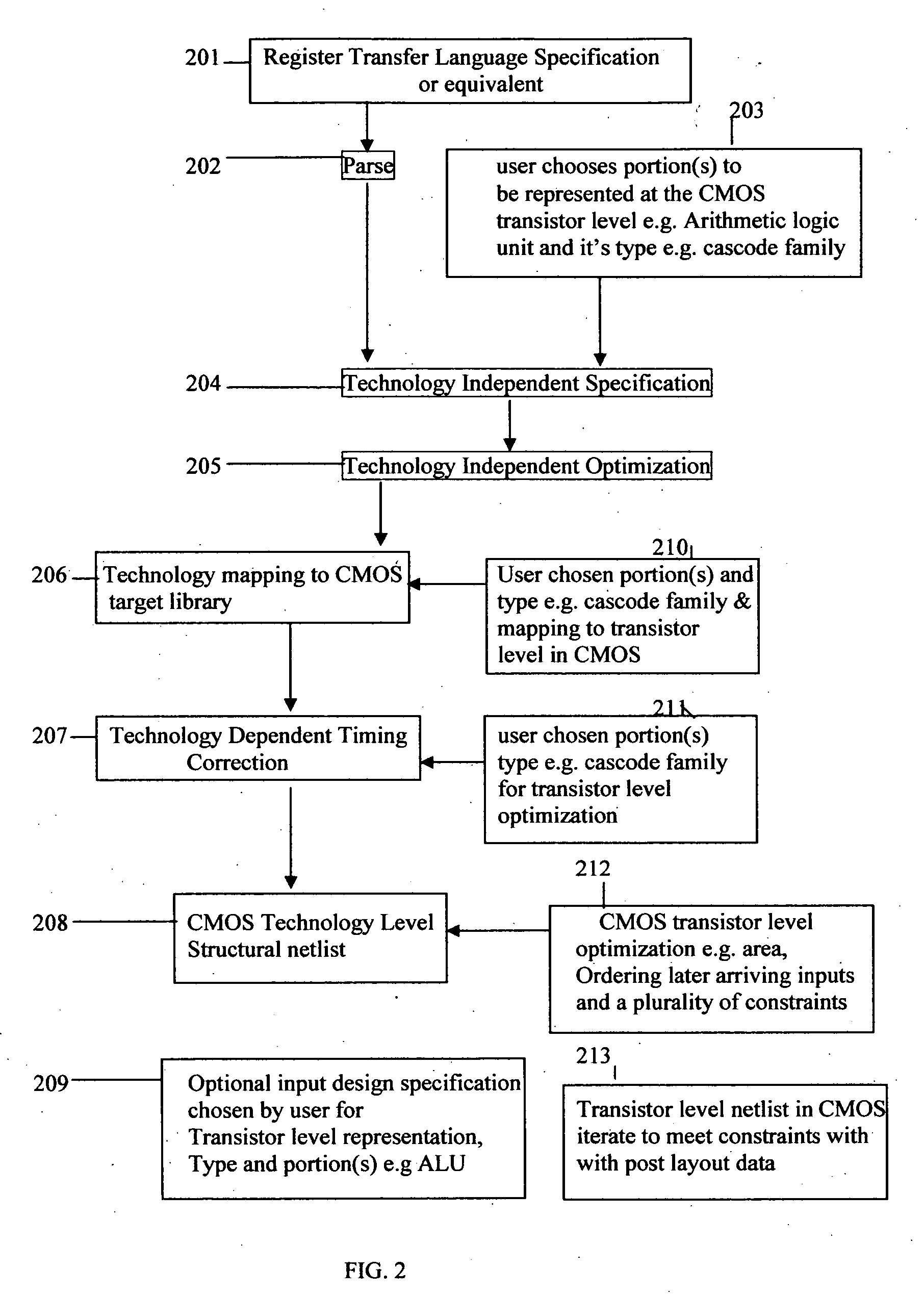
Method for tuning a digital design for synthesized random logic circuit macros in a continuous design space with optional insertion of multiple threshold voltage devices
InactiveUS7093208B2Efficient and effective methodologyError minimizationDigital storageComputer aided designContinuous designCritical section
A Digital Design Method which may be automated is for obtaining timing closure in the design of large, complex, high-performance digital integrated circuits. The methodincludes the use of a tuner on random logic macros that adjusts transistor sizes in a continuous domain. To accommodate this tuning, logic gates are mapped to parameterized cells for the tuning and then back to fixed gates after the tuning. Tuning is constrained in such a way as to minimize “binning errors” when the design is mapped back to fixed cells. Further, the critical sections of the circuit are marked in order to make the optimization more effective and to fit within the problem-size constraints of the tuner. A specially formulated objective function is employed during the tuning to promote faster global timing convergence, despite possibly incorrect initial timing budgets. The specially formulated objective function targets all paths that are failing timing, with appropriate weighting, rather than just targeting the most critical path. Finally, the addition of multiple threshold voltage gates allows for increased performance while limiting leakage power.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
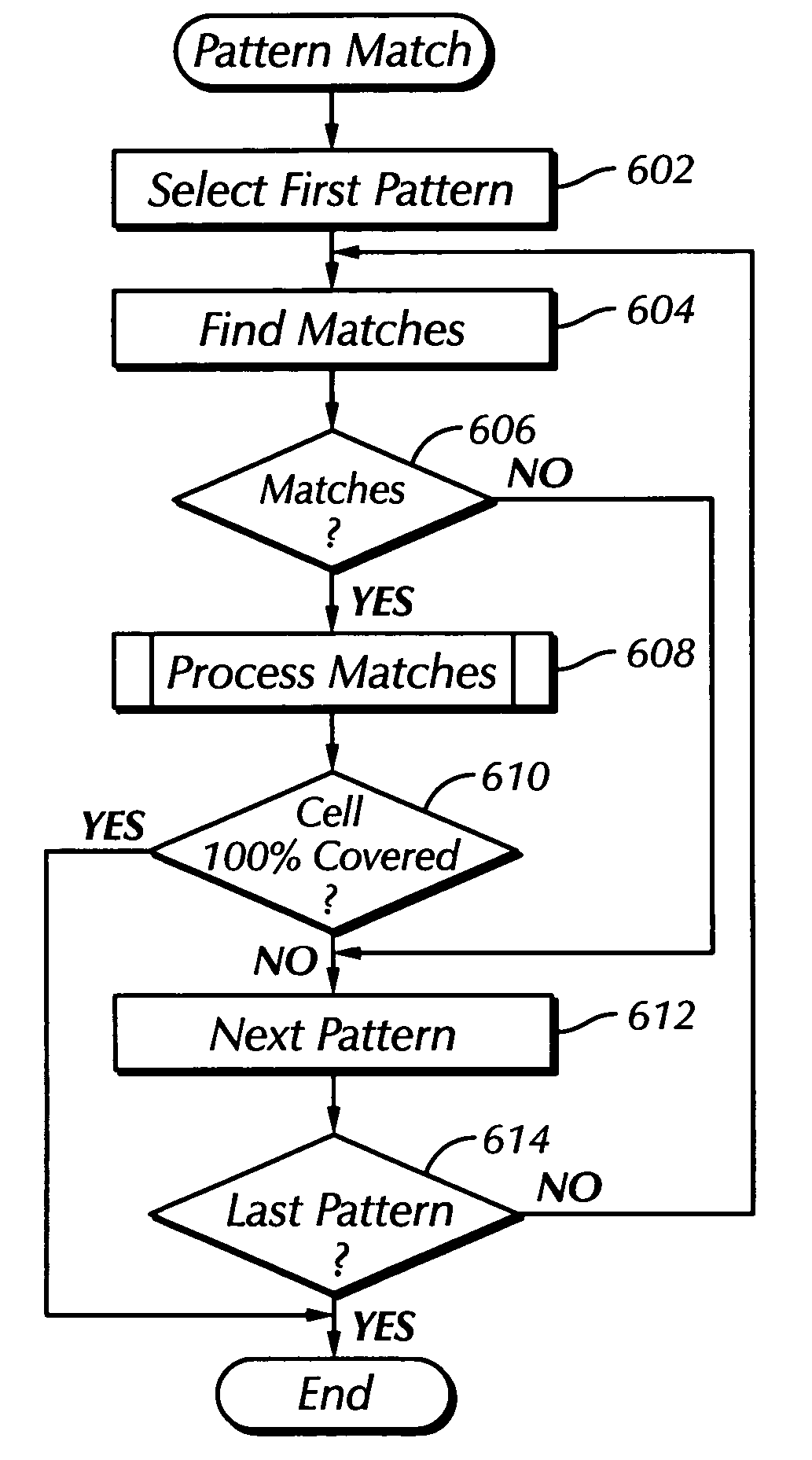
Physical realization of dynamic logic using parameterized tile partitioning
The matching algorithm of the layout synthesis method and apparatus disclosed locates transistor pattern matches in a design, links a parameterized tile to each identified match, and adjusts certain variable parameters of the linked parameterized tile to meet the physical design requirements of each located match. Each transistor pattern corresponds to a parameterized tile, which is an actual physical representation of the corresponding pattern and includes variable parameters, which may include transistor size. The matching algorithm locates matches in the design for an ordered list of patterns, names each located match, links the proper parameterized tile to each named match, and adjusts the tile's variable parameters as required. Transistors in the design are included in one and only one named located match.
Owner:APPLE INC
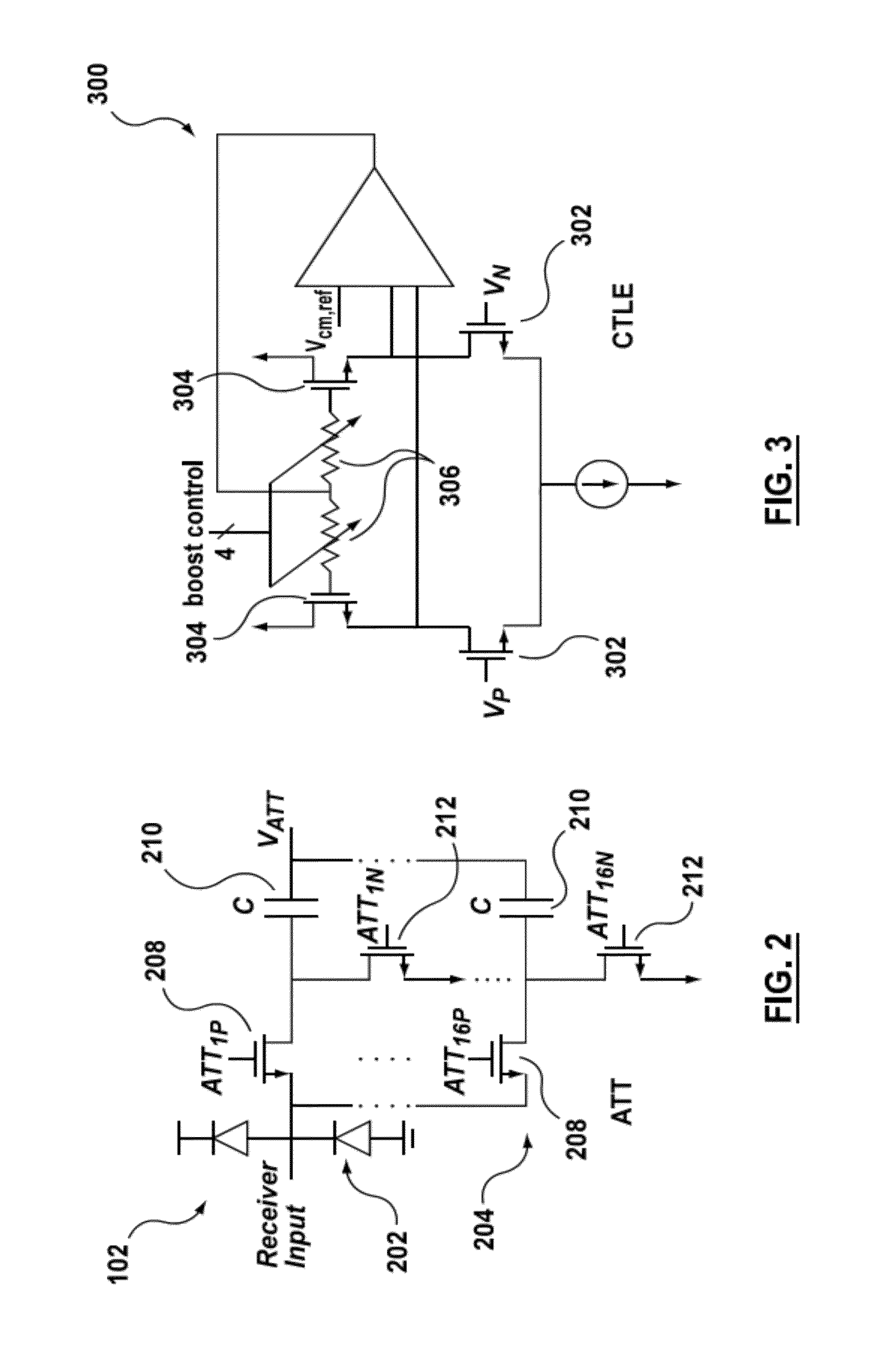
Decision feedback equalizer and transceiver
A decision feedback equalizer, transceiver, and method are provided, the equalizer having at least one comparator, the at least one comparator comprising a first stage, comprising a main branch having two track switches with a resistive load, an offset cancellation branch, a plurality of tap branches with transistor sizes smaller than the main branch, in which previous decisions of the equalizer are mixed with the tap weights using current-mode switching, and a cross coupled latch branch; and a second stage, comprising a comparator module for making decisions based on the outputs of the first stage and a clock input, and a plurality of flip-flops for storing the output of the comparator module.
Owner:RAMBUS INC
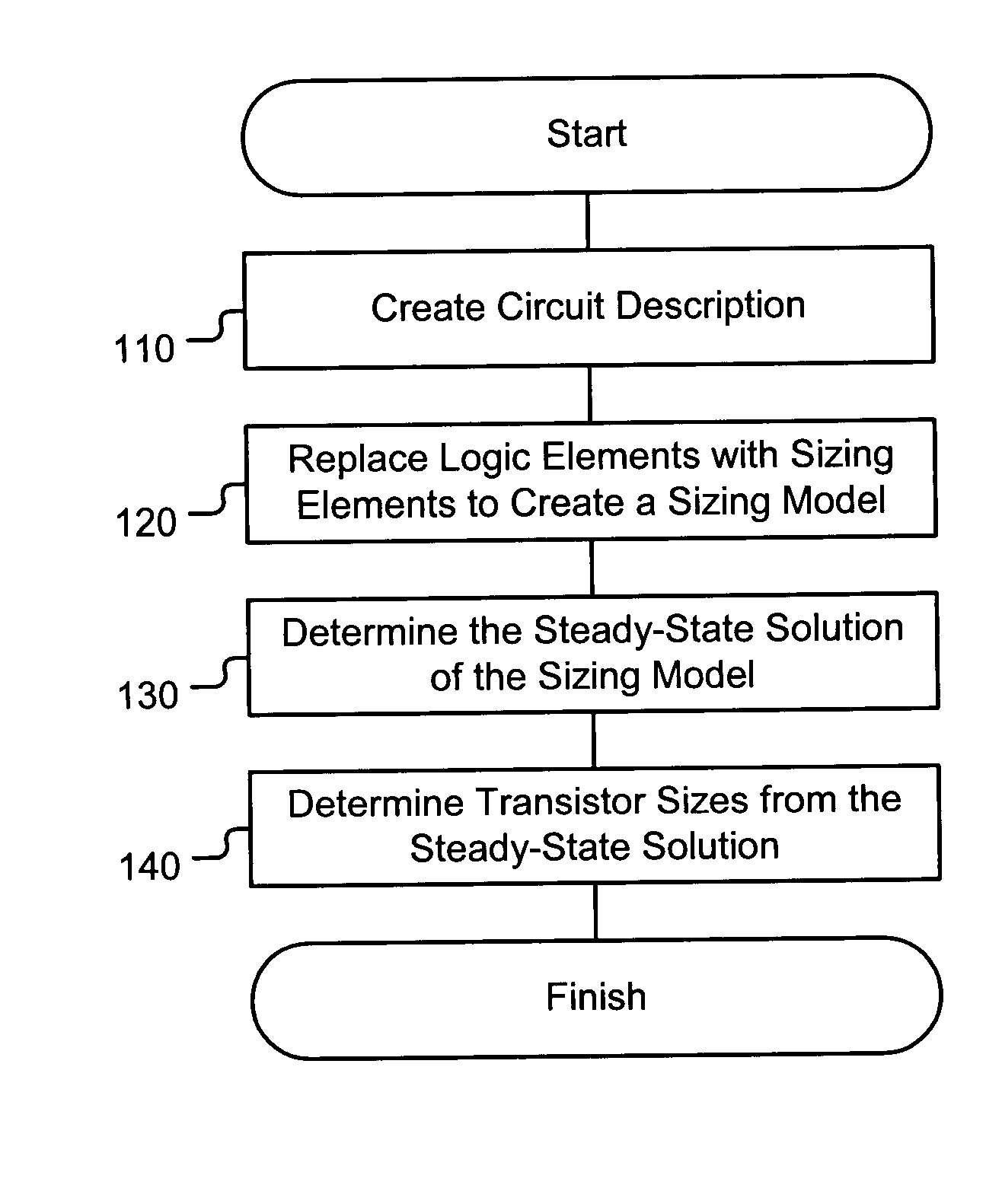
Method and apparatus for determining transistor sizes
A method of determining at least one ratio of transistor sizes. The method includes creating a sizing model by replacing at least one logic element in a circuit description with a sizing element that includes a piece-wise-linear current source. The method also includes determining a steady state solution to the sizing mode and determining at least one ratio of transistor sizes from the steady state solution. The method may also include determining at least one dimension of a transistor based at least in part upon the ratio of transistor sizes.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
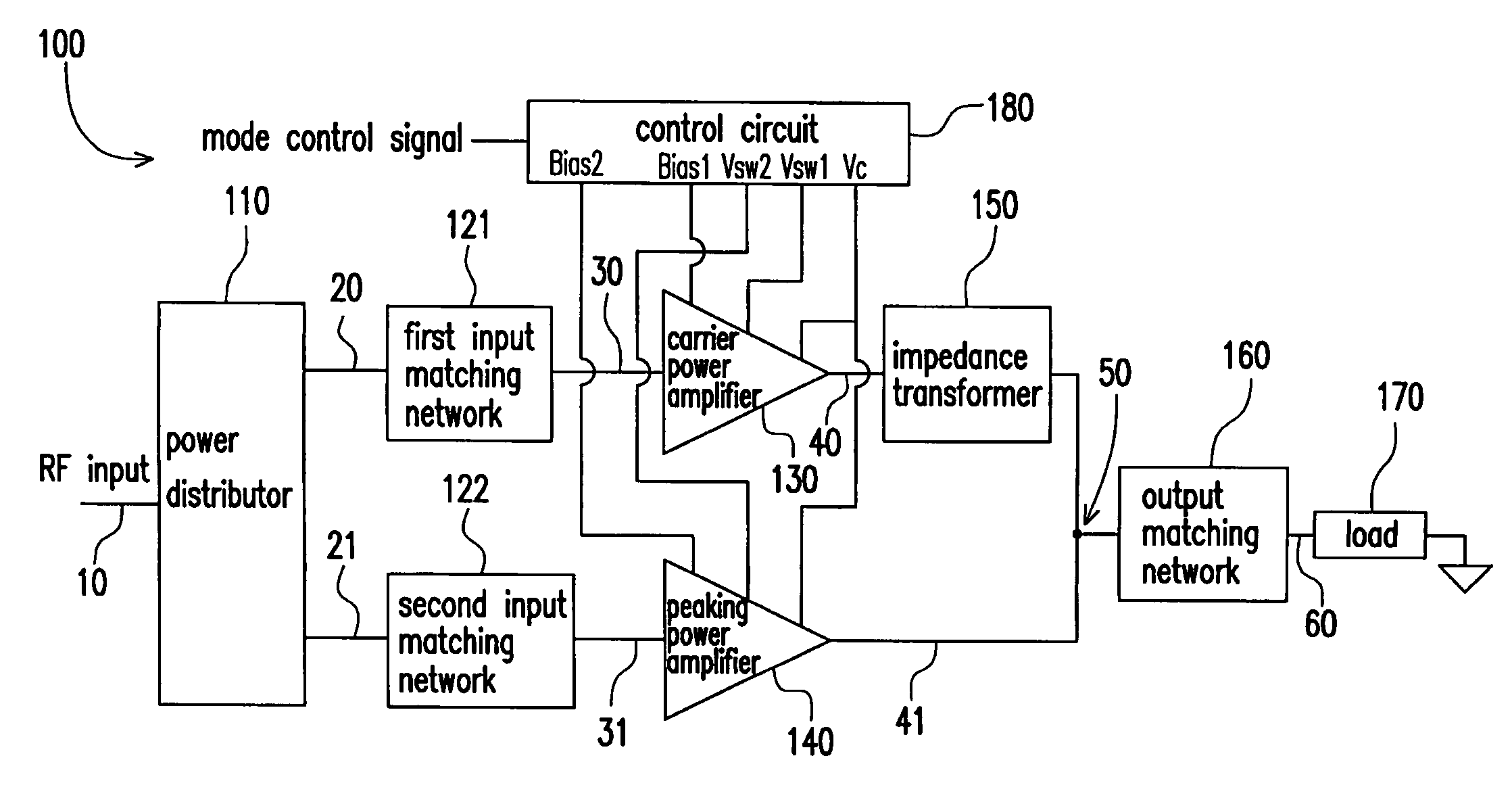
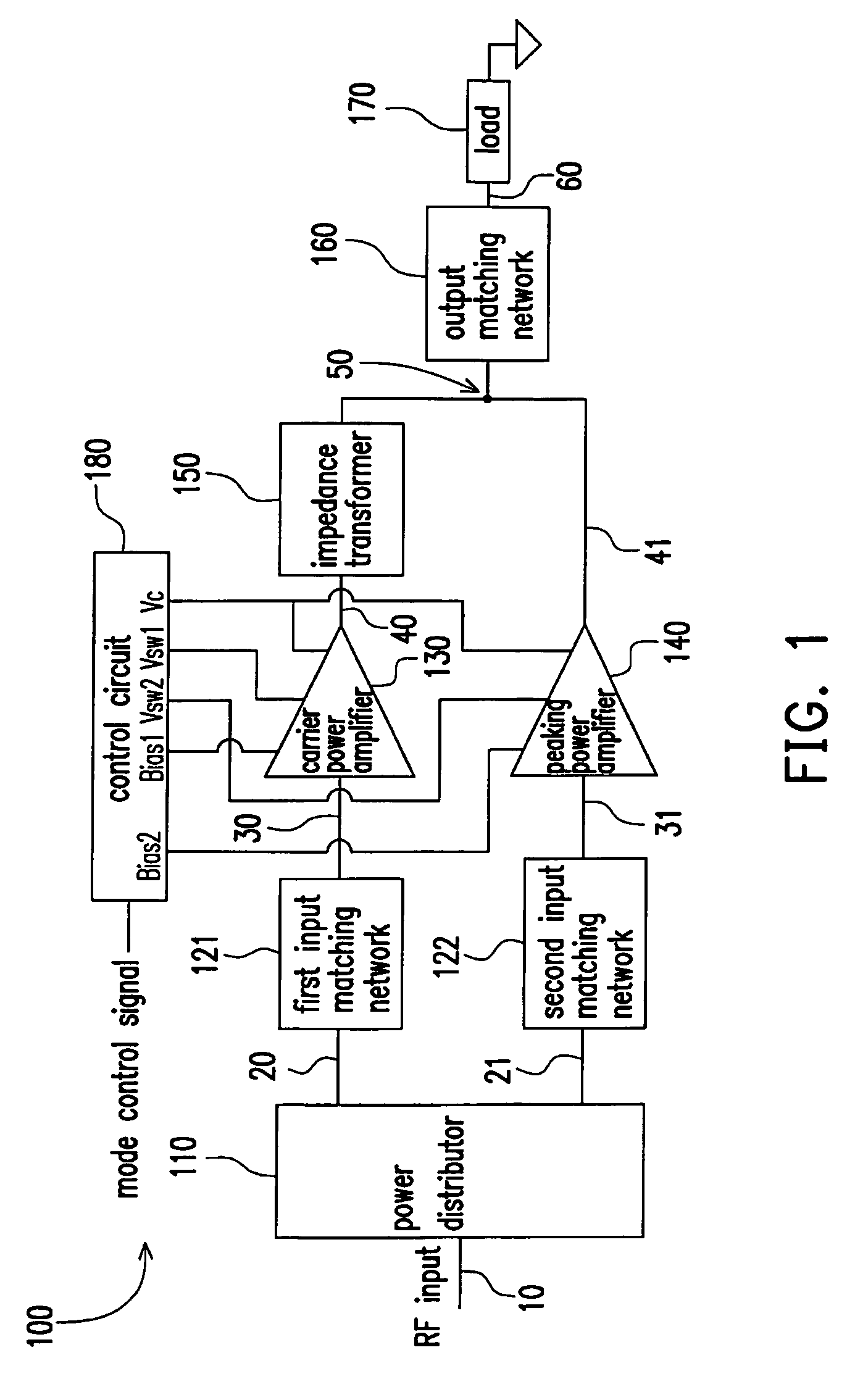
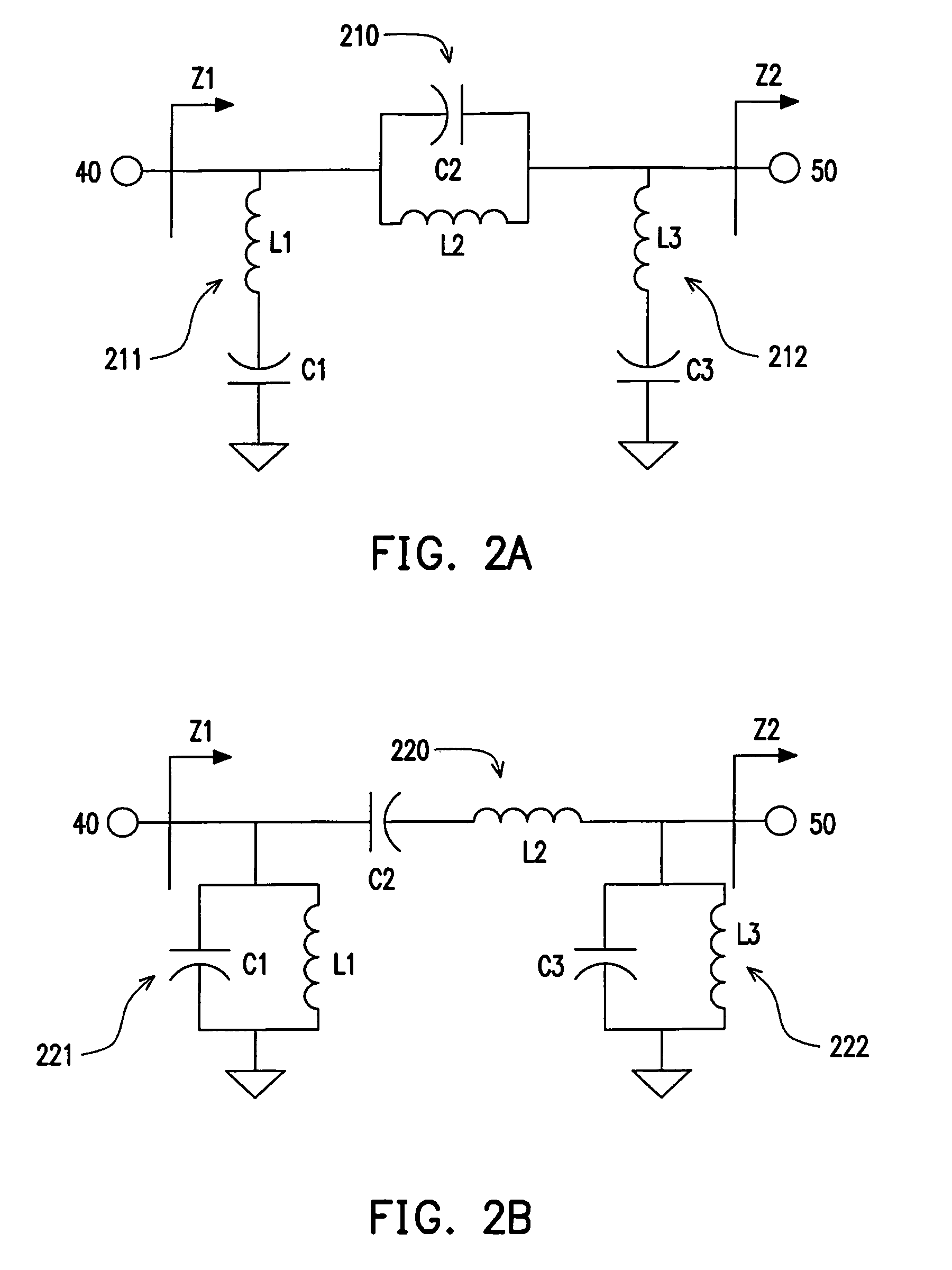
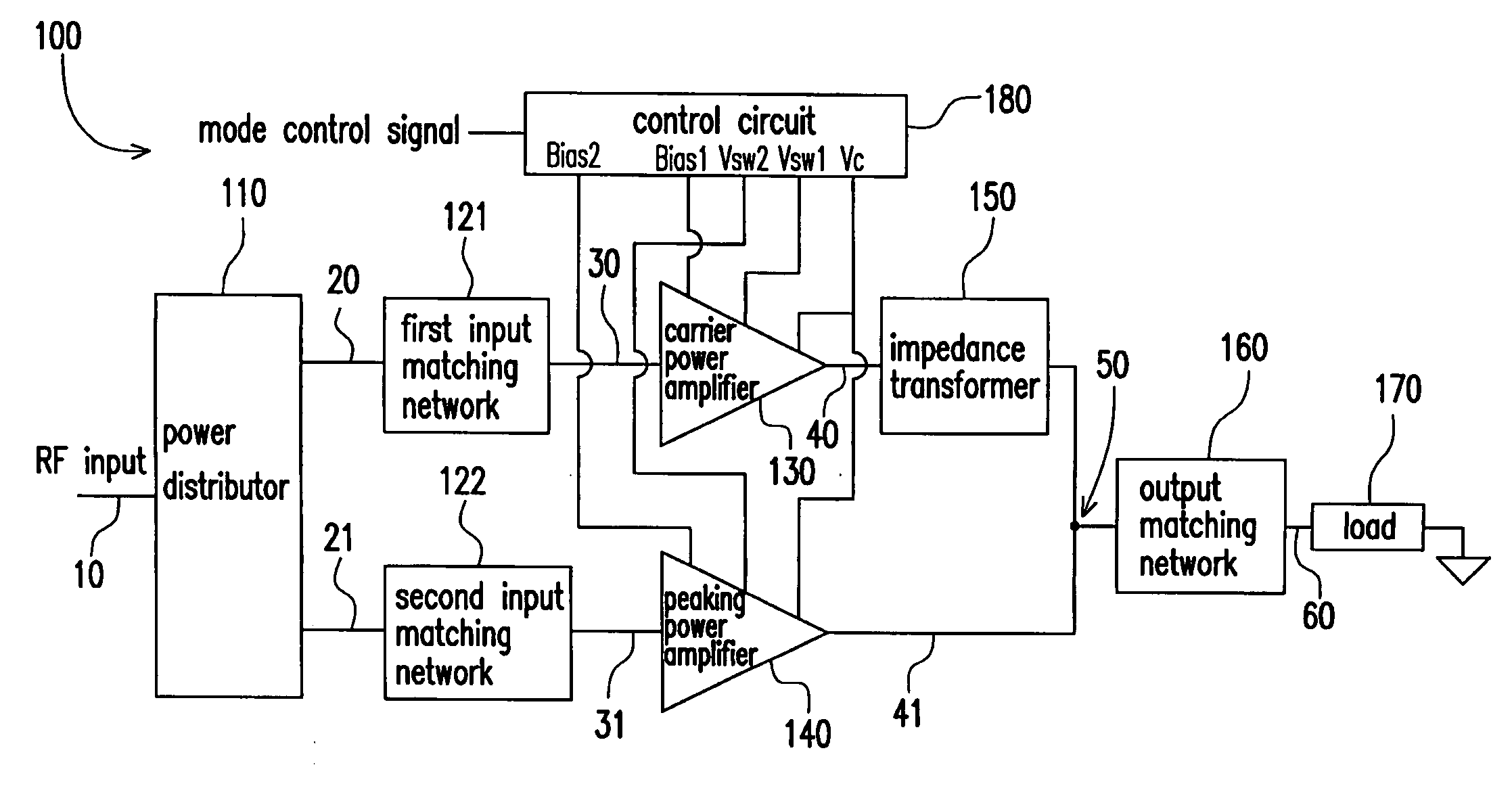
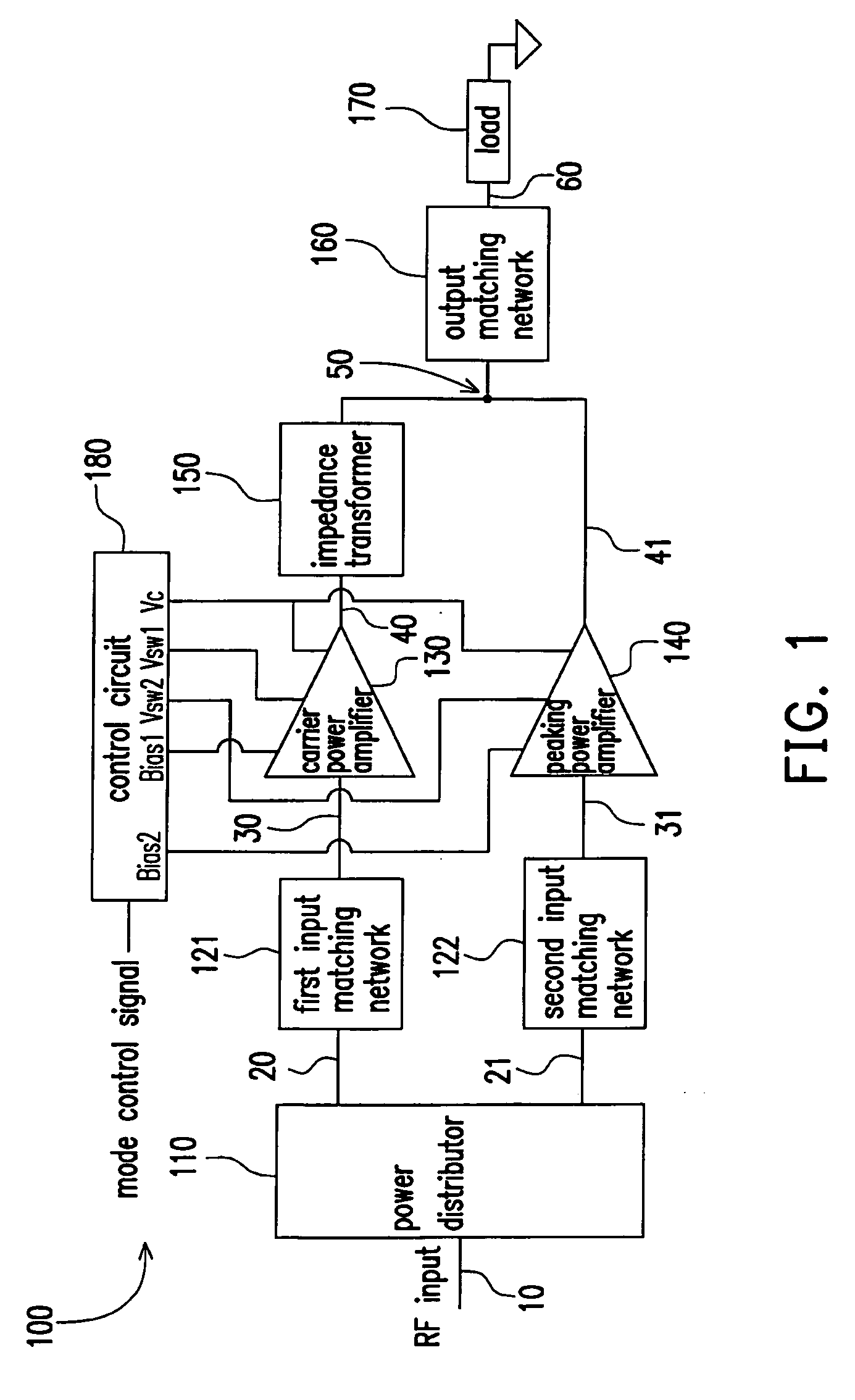
Power amplifier circuit for multi-frequencies and multi-modes and method for operating the same
A multi-frequency and multi-mode power amplifier is provided. The amplifier has a carrier power amplifier and a peaking power amplifier. The carrier power amplifier receives a first signal and outputs a first amplified signal, in which a first transistor size adjusting unit is included to adjust an equivalent transistor size based on a mode indication signal. The peaking power amplifier receives a second signal and outputs a second amplified signal, in which a second transistor size adjusting unit is included to adjust an equivalent transistor size based on the mode indication signal.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Power amplifier circuit for multi-frequencies and multi-modes and method for operating the same
ActiveUS20090045877A1Amplifier combinationsDual/triple band amplifierAudio power amplifierEngineering
A multi-frequency and multi-mode power amplifier is provided. The amplifier has a carrier power amplifier and a peaking power amplifier. The carrier power amplifier receives a first signal and outputs a first amplified signal, in which a first transistor size adjusting unit is included to adjust an equivalent transistor size based on a mode indication signal. The peaking power amplifier receives a second signal and outputs a second amplified signal, in which a second transistor size adjusting unit is included to adjust an equivalent transistor size based on the mode indication signal.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
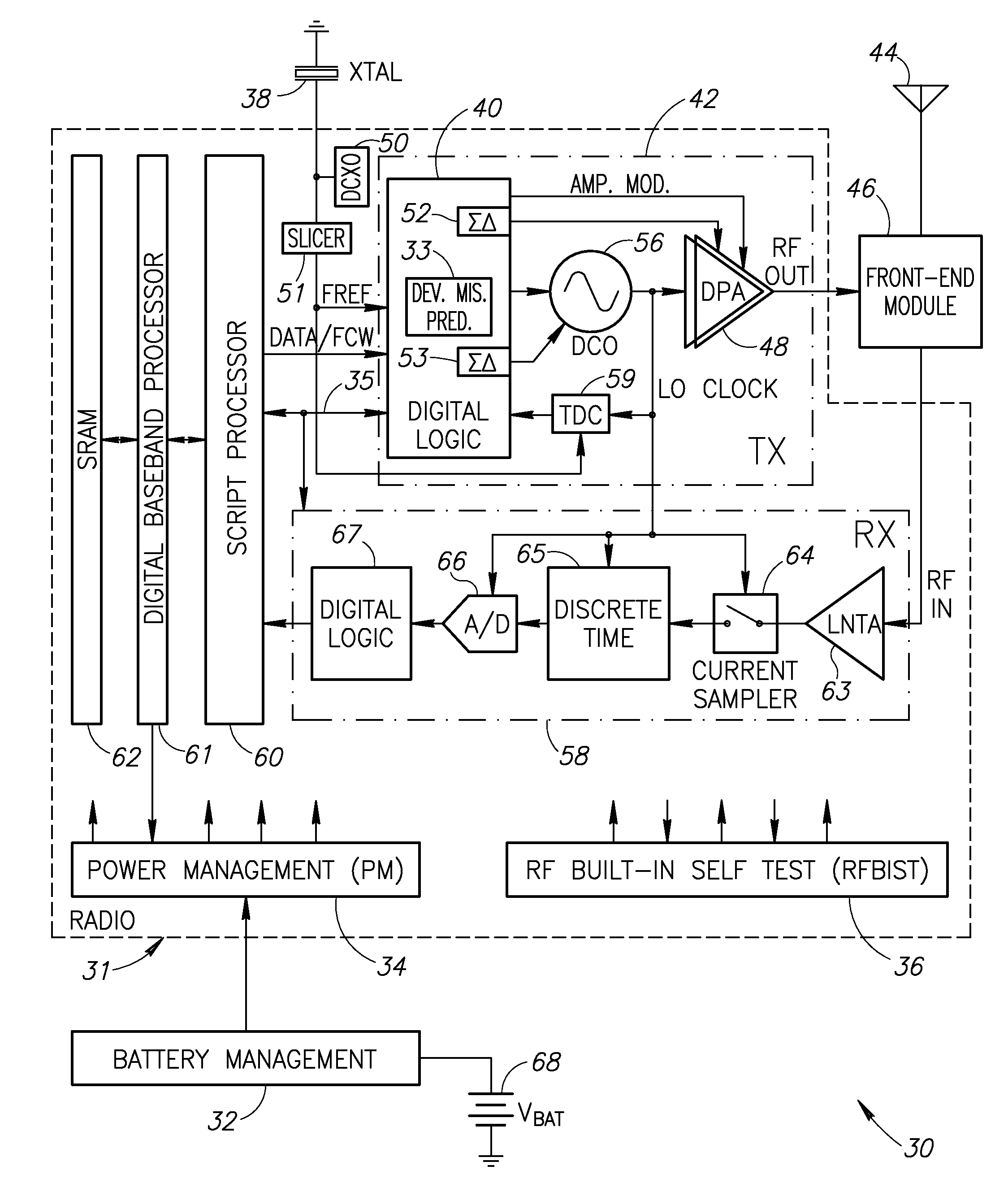
Predistortion mechanism for compensation of transistor size mismatch in a digital power amplifier
InactiveUS20100188148A1Minimal area requirementImprove performanceAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceAmplifier modifications to reduce temperature/voltage variationError vector magnitudeTransistor sizing
A novel and useful apparatus for and method of predistortion compensation of device (e.g., transistor) mismatch in a digital power amplifier (DPA). The device mismatch predistortion mechanism of the present invention addresses the problem of matching between two types of binary weighted transistors, whereby mismatched transistors cause degradation in wideband noise. The invention provides a digital predistortion mechanism which functions to pre-distort the mismatch ratio based on a data table calculated a priori enabling a polar transmitter to meet output spectrum and error vector magnitude (EVM) requirements of the particular modern wideband wireless standard, such as GSM, 3G WCDMA, etc.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Color display device
EL display elements are configured by sequentially laminating an anode, an emissive layer and a cathode, and emit light of R, G, and B. Each EL display element is supplied with a drive current from an EL element driving TFT. The transistor sizes of the EL element driving TFTs connected to the display pixels for respective colors are designated such that the size of the TFT for a green display pixel including an EL element having the highest emissive efficiency is the smallest, and the sizes of the TFTs for red and blue display pixels having sequentially decreasing emissive efficiency are made sequentially larger.
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD
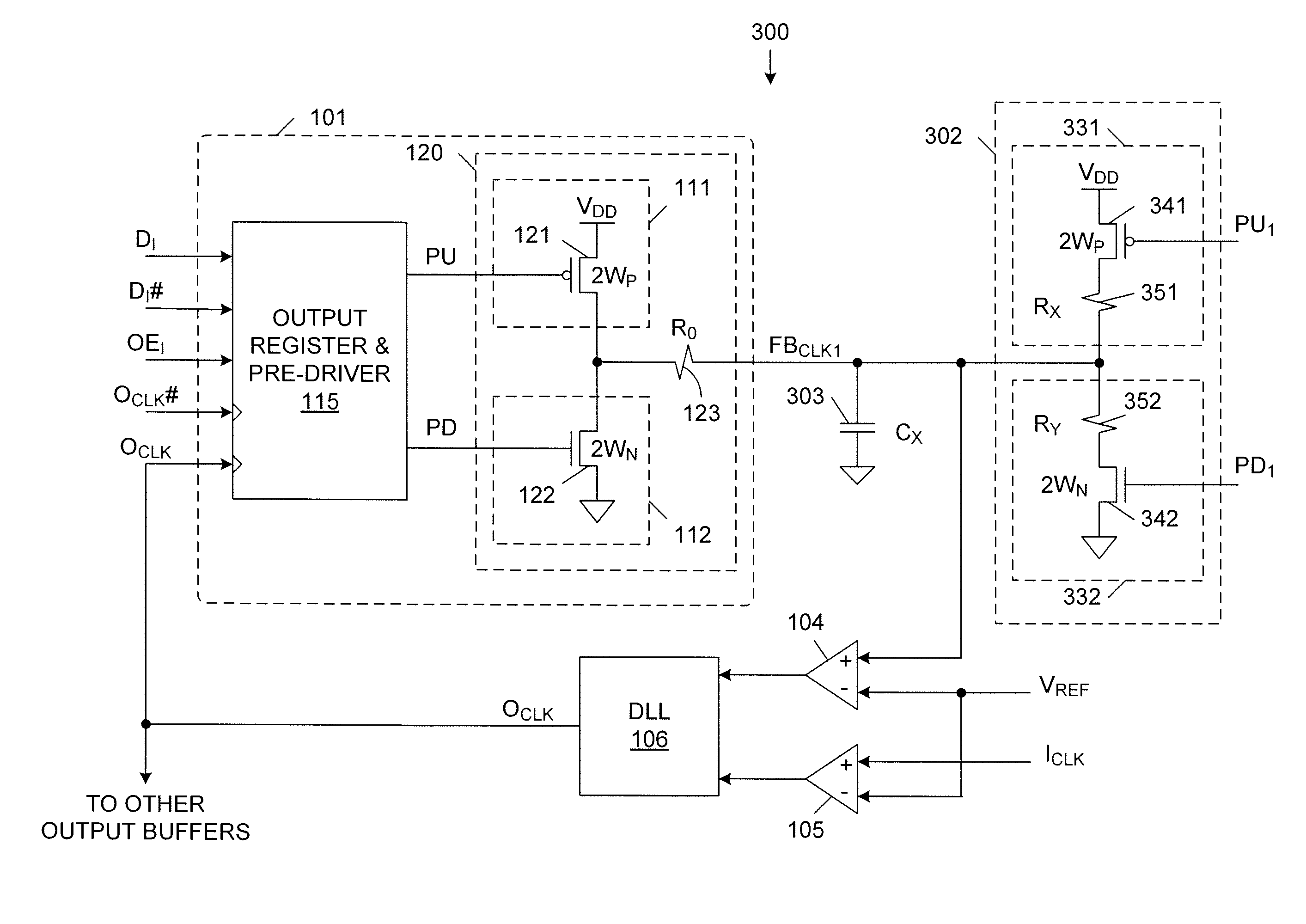
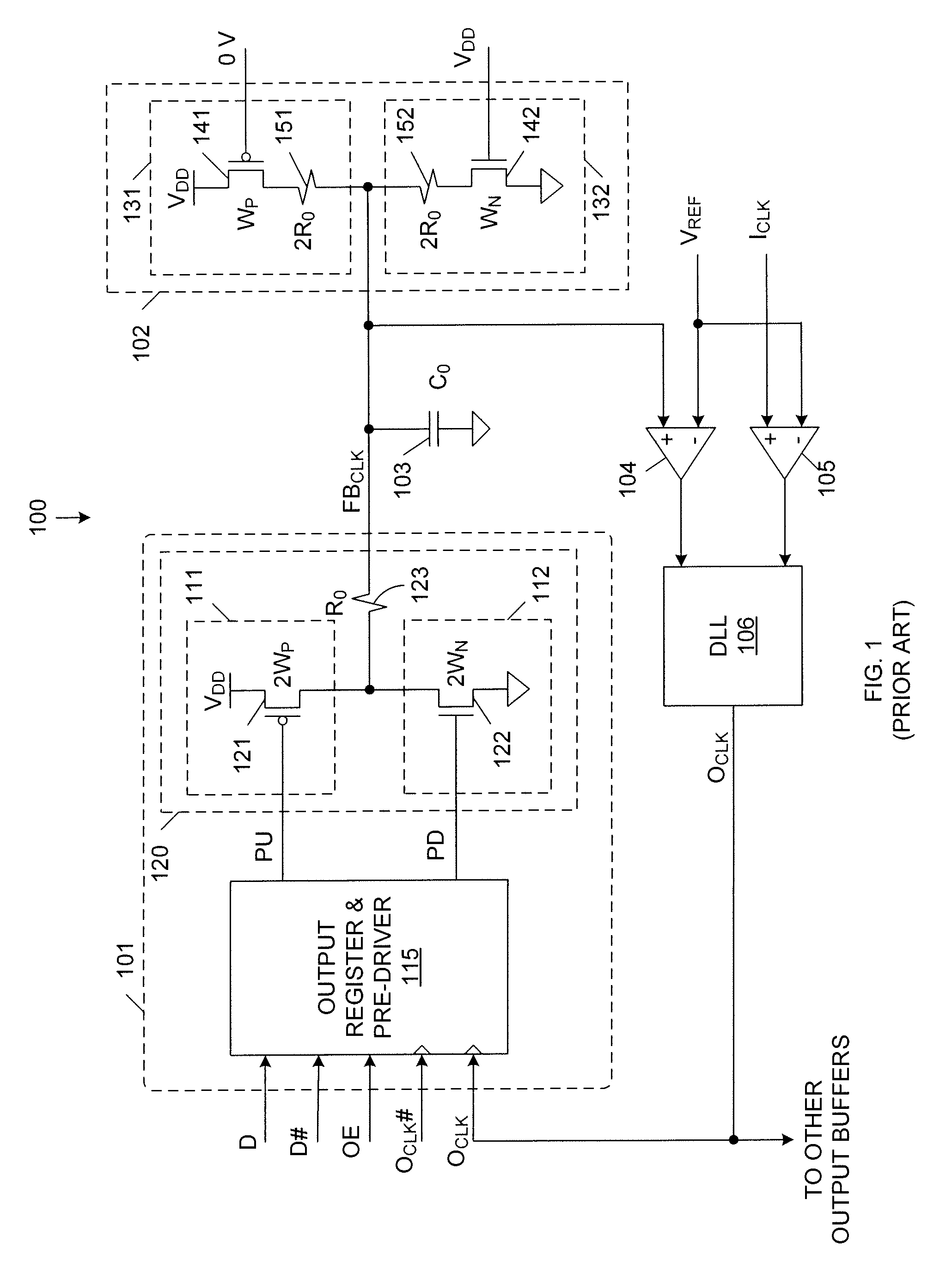
Input termination for delay locked loop feedback with impedance matching
ActiveUS7898288B2Input/output impedence modificationReliability increasing modificationsDelay-locked loopEngineering
A reference output circuit for generating an output clock signal for driving signals off of an integrated circuit chip uses a switched terminated load in combination with an output buffer to generate a feedback clock signal, which is used, in combination with a reference input clock signal, to generate the output clock signal. The switched terminated load uses transistors having the same size as transistors in the output buffer. The switched terminated load draws the same DC current as the output buffer. As a result, the switched terminated load and the output buffer have the same electro-migration performance. Pull-up and pull-down MOS impedances of the switched terminated load are easily adjusted during switching periods of the switched terminated load. The design of the switched terminated load minimizes variations in the terminated load impedance due to MOS impedance variations.
Owner:INTEGRATED DEVICE TECH INC
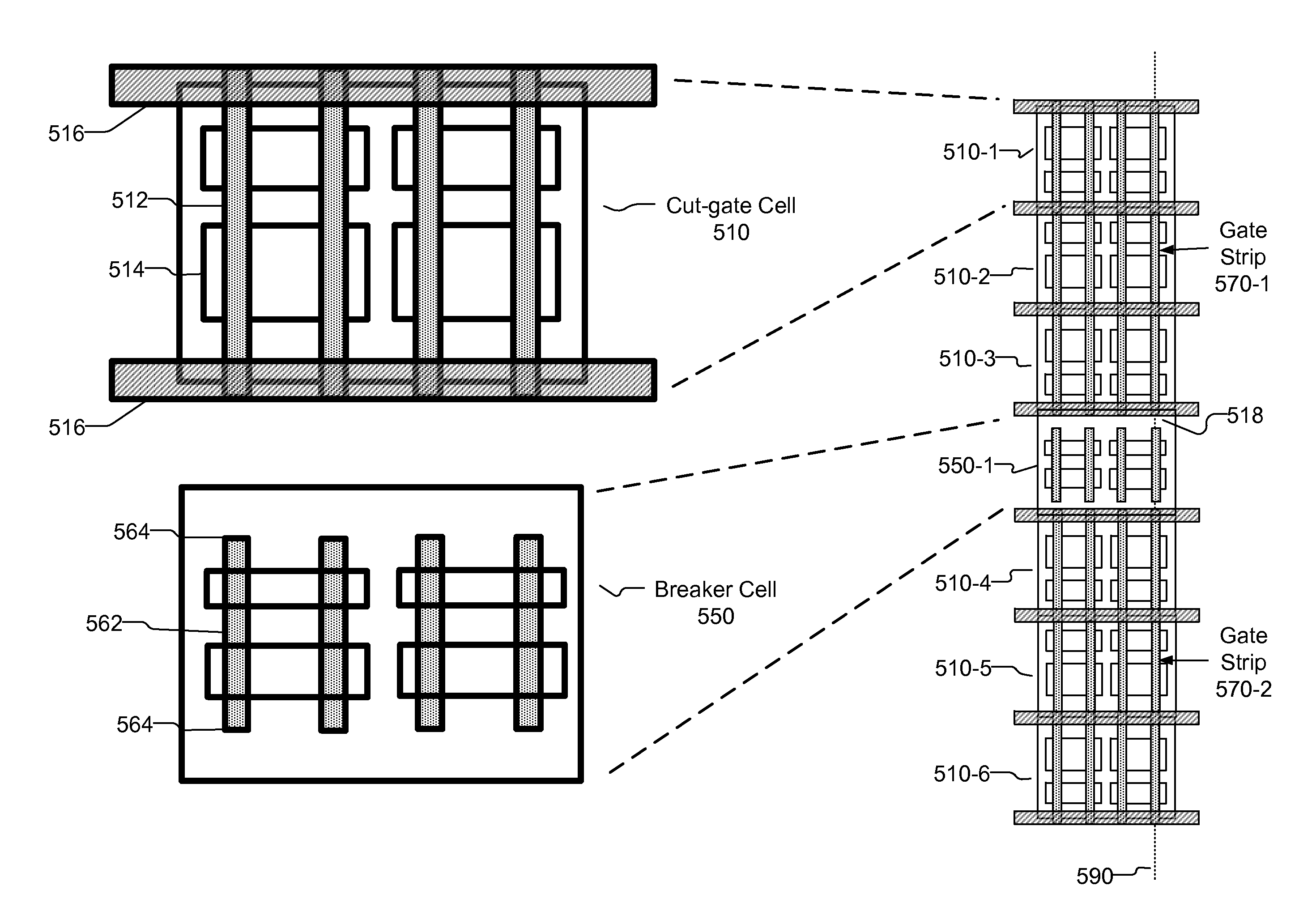
Cell Architecture for Increasing Transistor Size
ActiveUS20120254817A1Efficient layoutCAD circuit designSpecial data processing applicationsCell basedCircuit breaker
A cell-based architecture for an integrated circuit that uses at least two categories of cells: cut-gate cells and breaker cells. Cut-gate cells have gates that extend from one boundary of the cell to an opposite boundary of the cell. Cut gate features are located along the boundaries of the cell to indicate locations for cutting the gates during fabrication. Instances of the cut-gate cells are arranged in abutting rows that result in the formation of continuous gate strips during the fabrication process, which are then cut into individual gates with a cut-gate mechanism. Breaker cells have gates that do not extend to the boundaries of the breaker cell. To prevent the continuous gate strips from exceeding design rule requirements, instances of breaker cells are placed at intervals between the rows of cut-gate cell instances to restrict the size of the gate strips.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
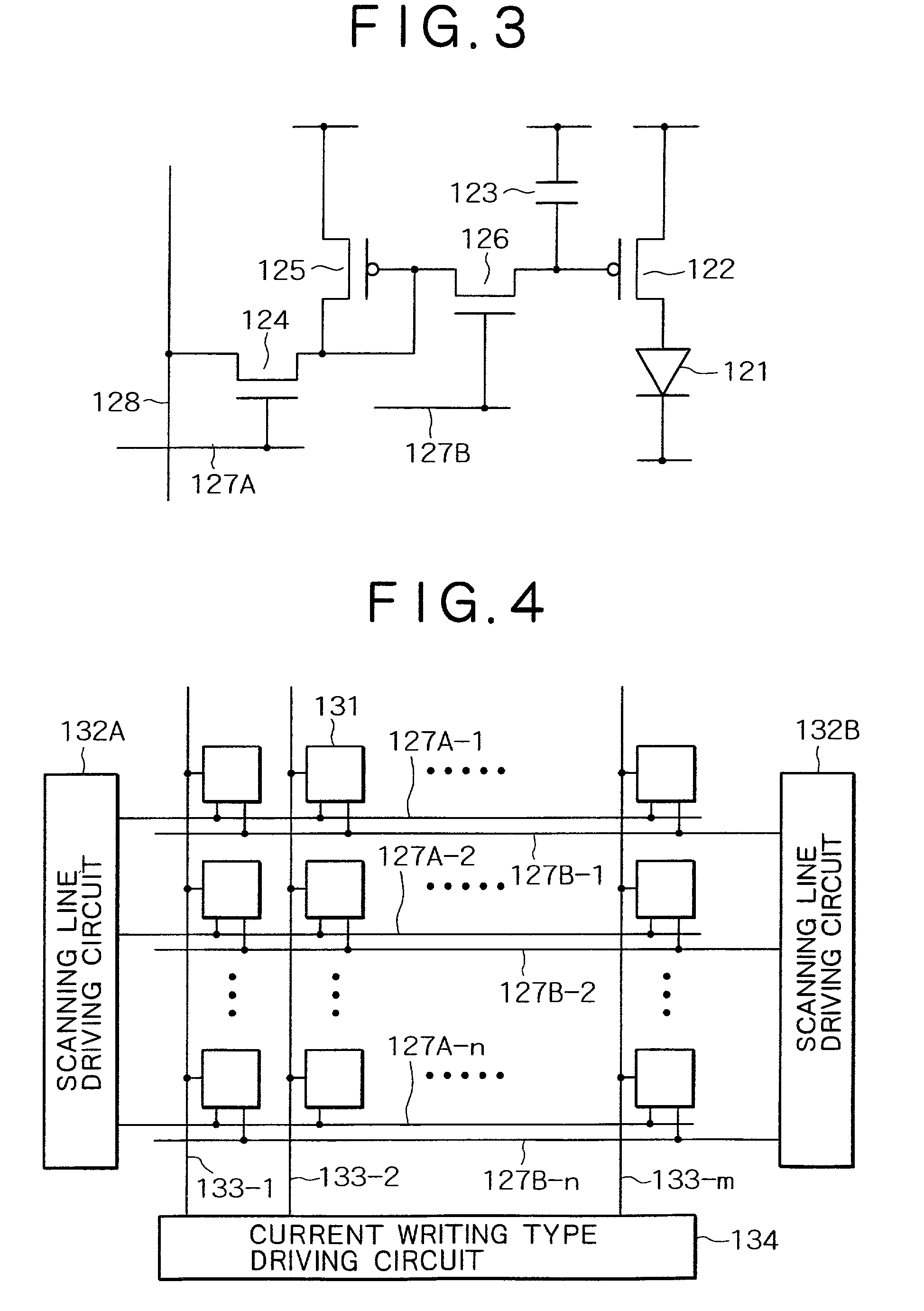
Active matrix type display apparatus, active matrix type organic electroluminescence display apparatus, and driving methods thereof
InactiveUS6975290B2Improve resolutionIncrease in sizeSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDriving currentActive matrix
An active matrix type organic EL display apparatus according to the present invention which apparatus uses current writing type pixel circuits is provided with a current control circuit for each of data lines connected to the pixel circuits. The current control circuit supplies part of a data line current to a pixel circuit as a bypass current. The current control circuit handles the bypass current of the data line current represented by (data line current=data current+bypass current). Thereby, the data line driving current can be set greater than the data current flowing through TFTs provided in the pixel circuit, thus reducing luminance data writing time. Also, when the writing time is set unchanged, transistor size of the TFTs provided in the pixel circuit can be reduced.
Owner:SONY CORP
Silicon carbide gate transistor
InactiveUS6936849B1Low magnitudeEase in downward scalingSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingTransistor sizingPolycrystalline silicon
A field-effect transistor (FET) device and method of fabrication uses an electrically interconnected polycrystalline or microcrystalline silicon carbide (SiC) gate having a lower electron affinity and higher work function than a polysilicon gate FET. The smaller threshold voltage magnitude of the SiC gate FET allows reduced power supply voltages (lowering power consumption and facilitating downward scaling of transistor dimensions), and enables higher switching speeds and improved performance. The smaller threshold voltage magnitudes are obtained without ion-implantation, which is particularly useful for SOI and thin film transistor devices. Threshold voltage magnitudes are stable in spite of subsequent thermal processing steps. N-channel threshold voltages are optimized for enhancement mode.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
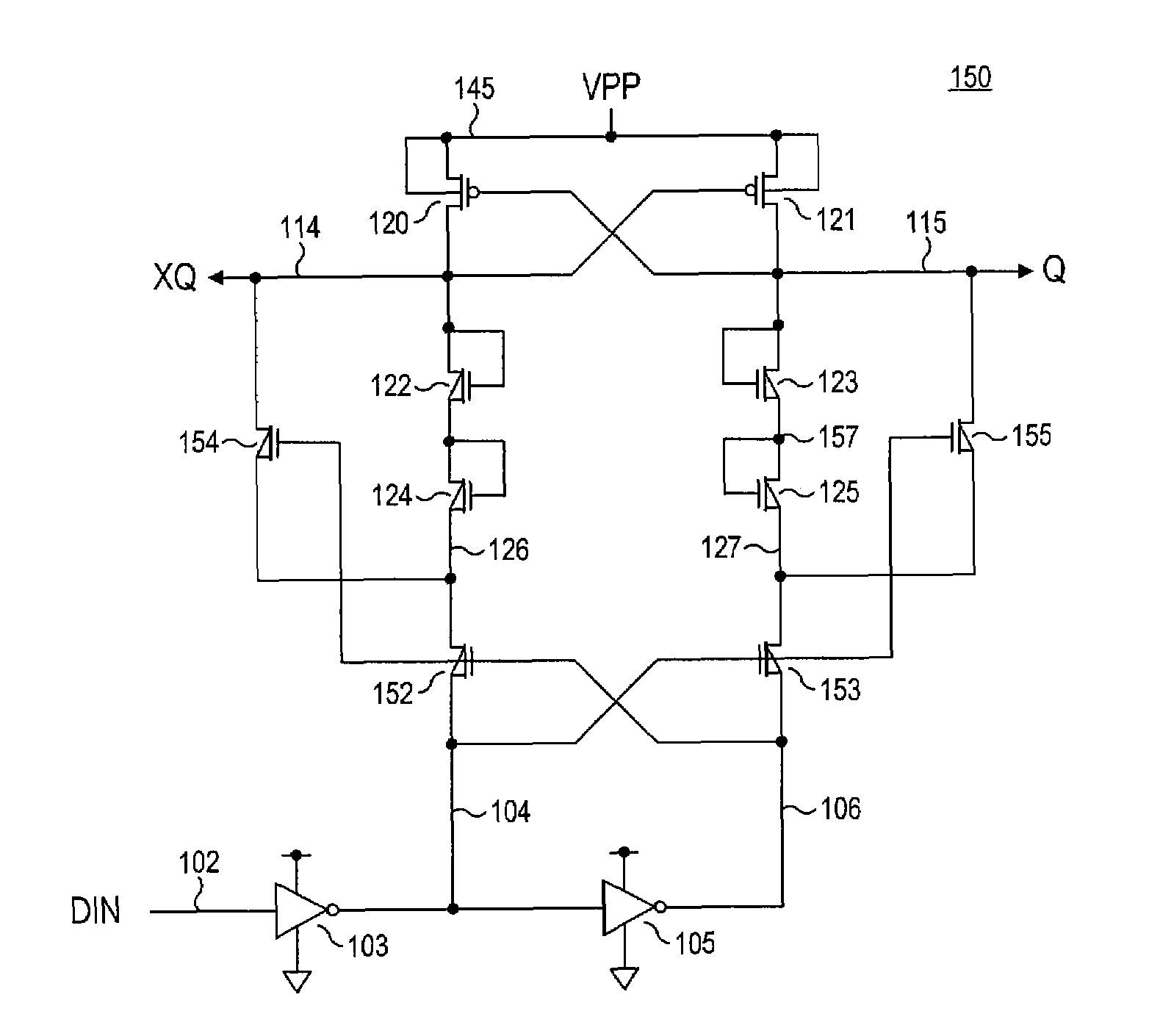
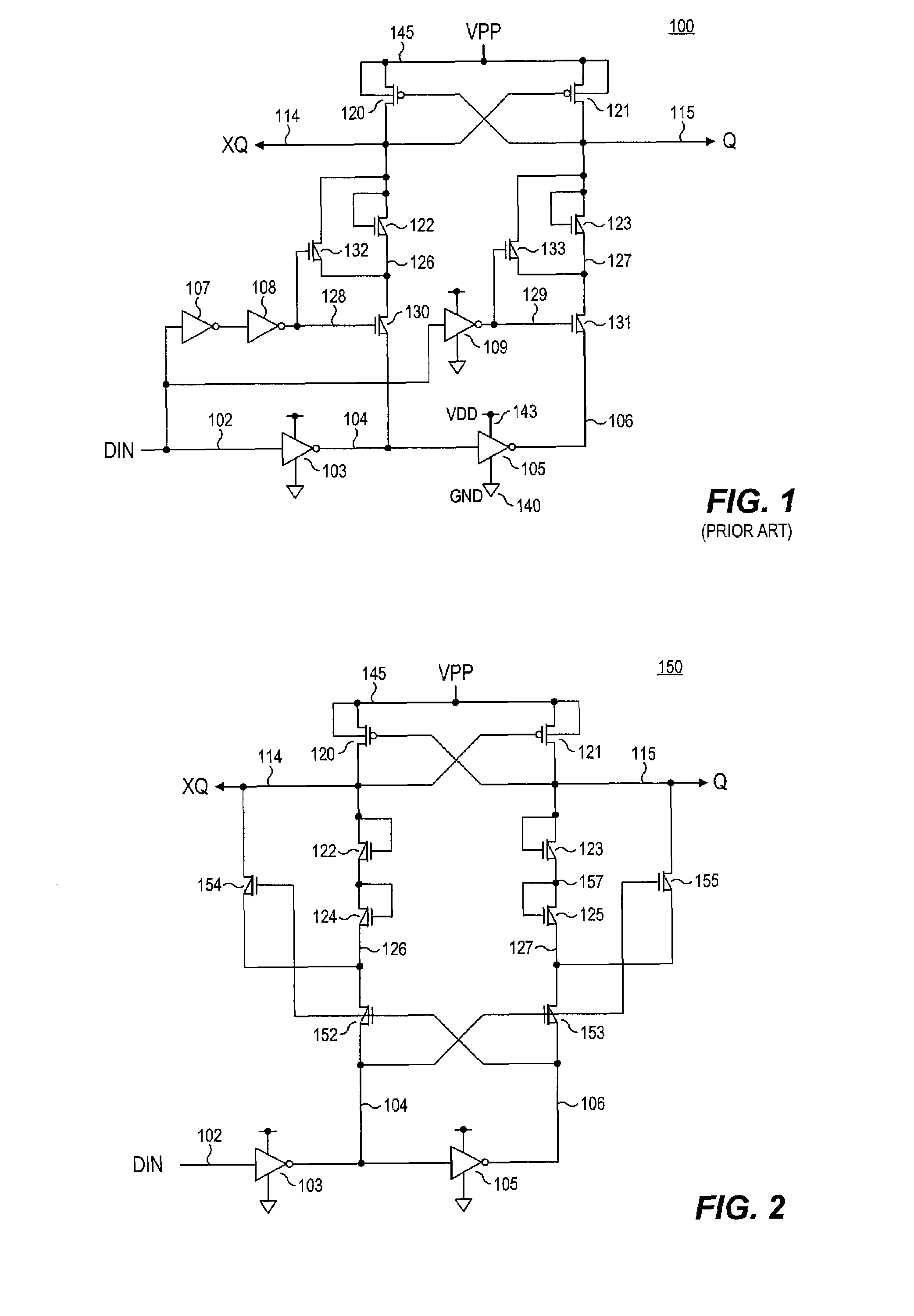
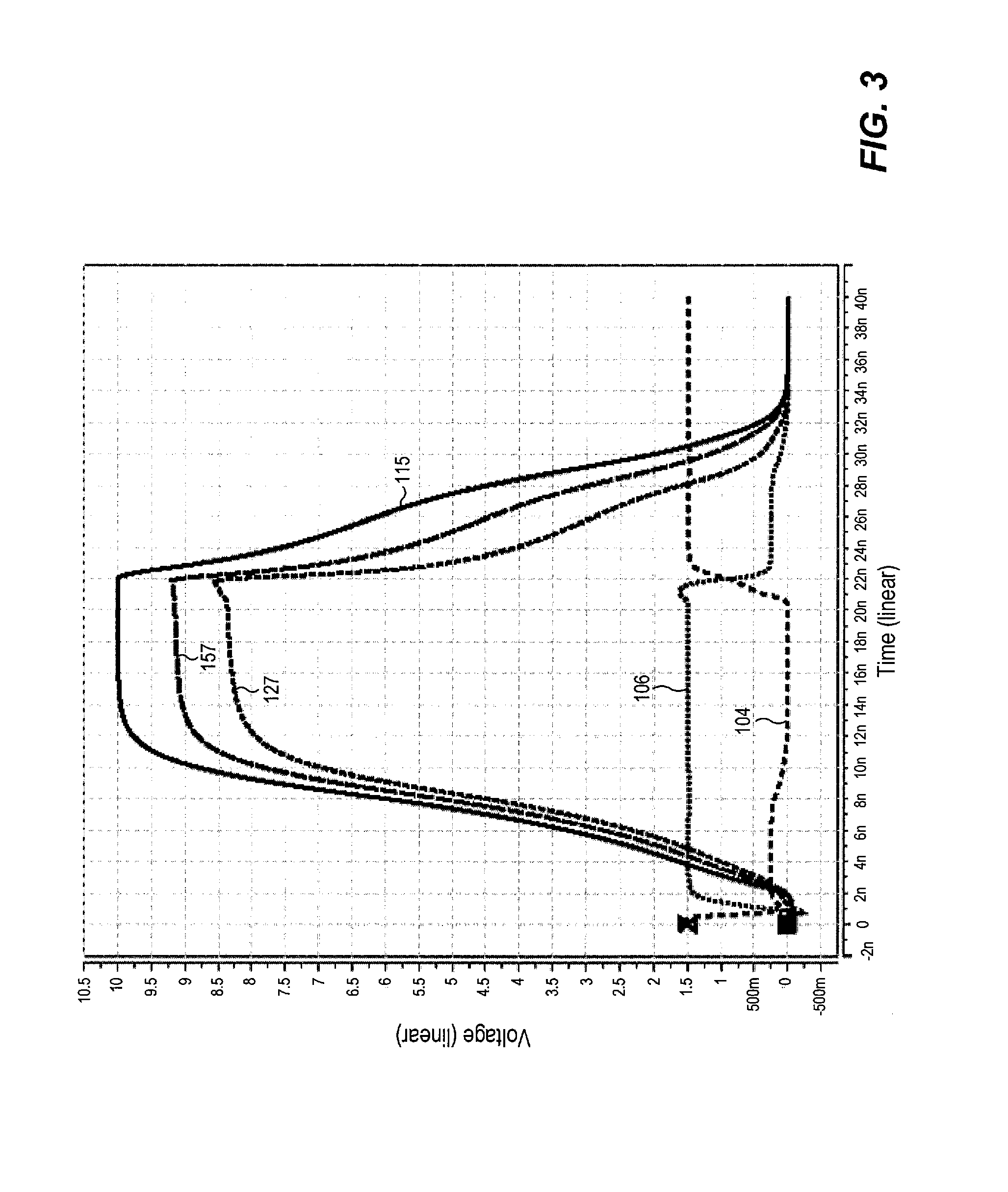
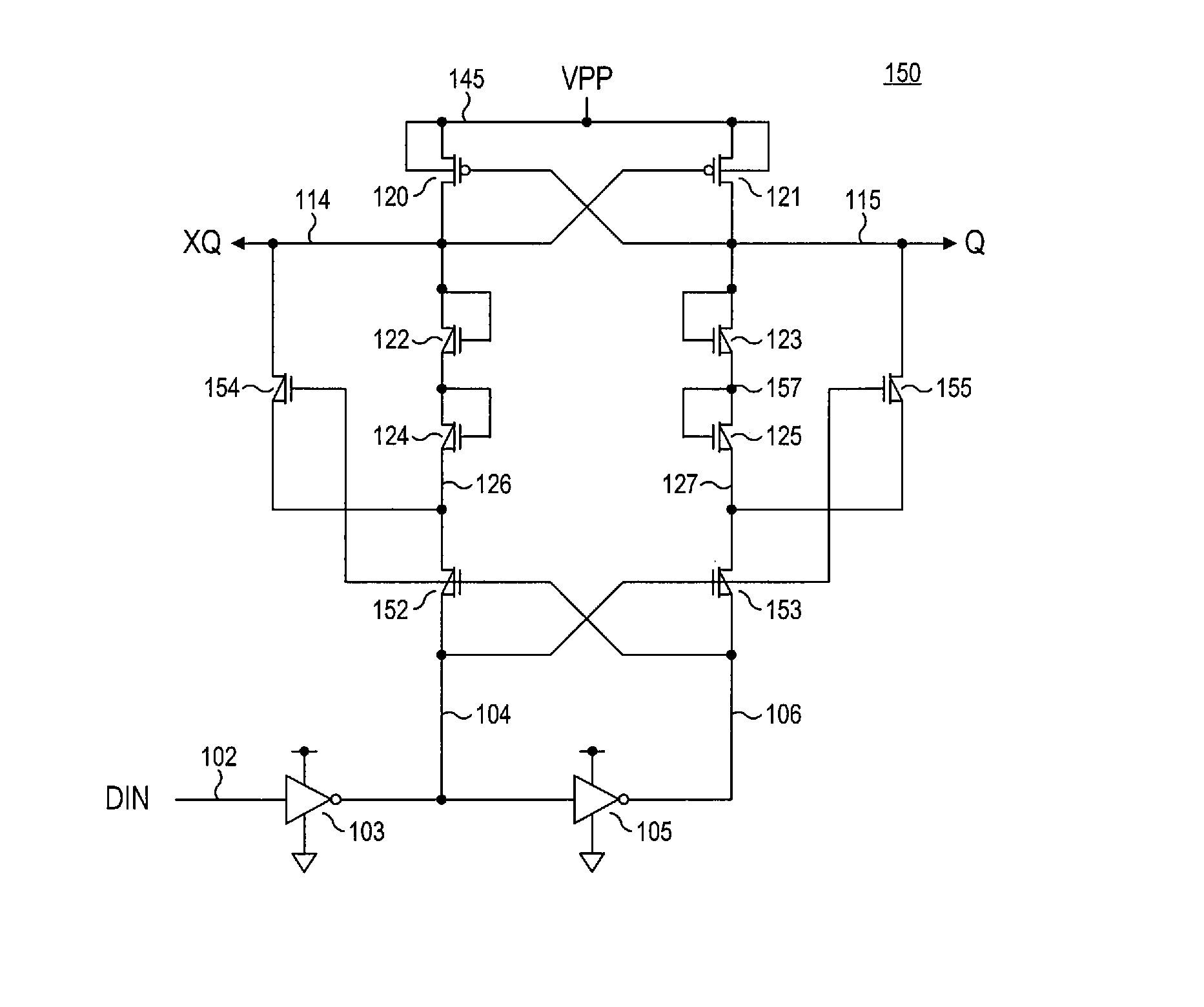
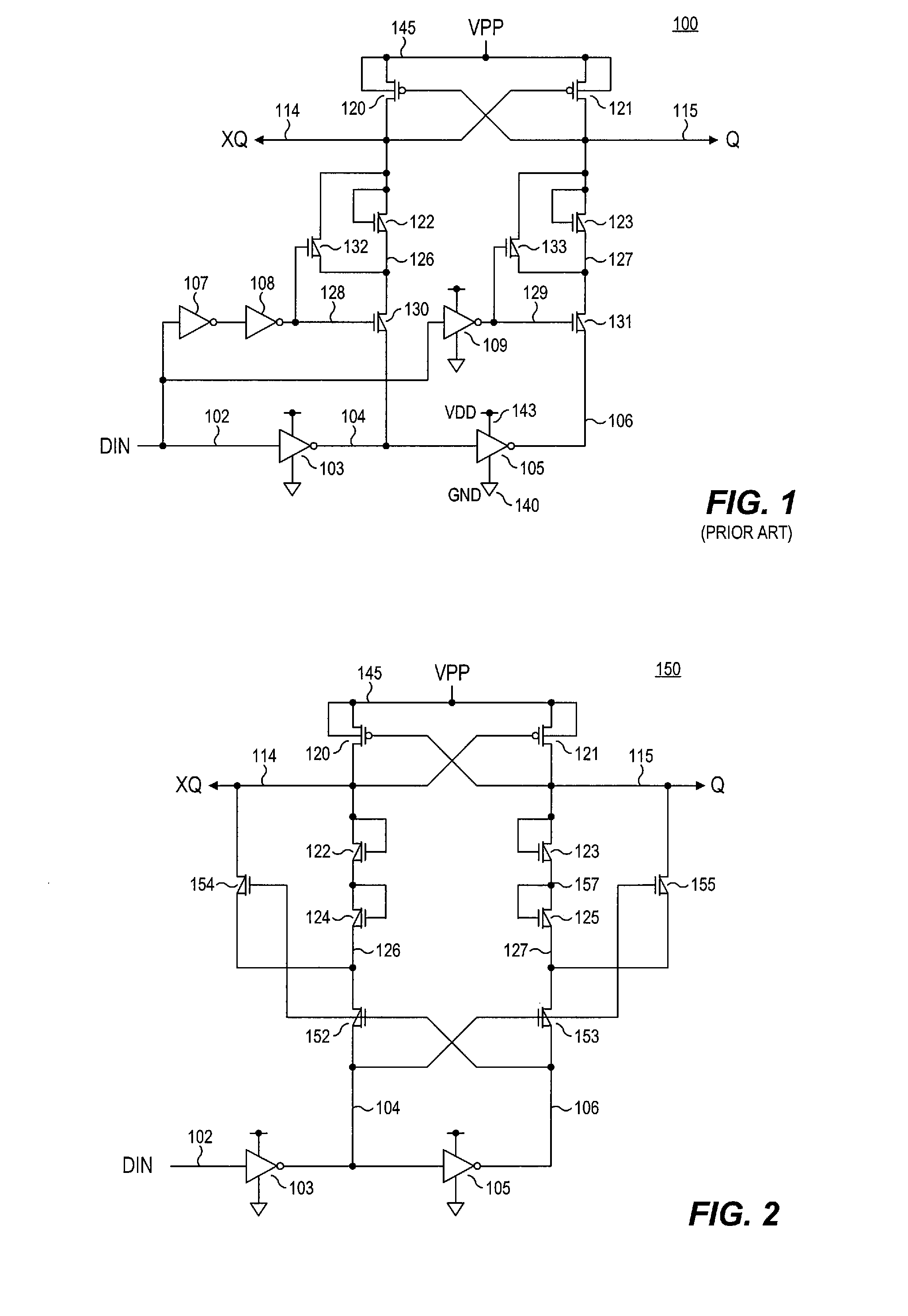
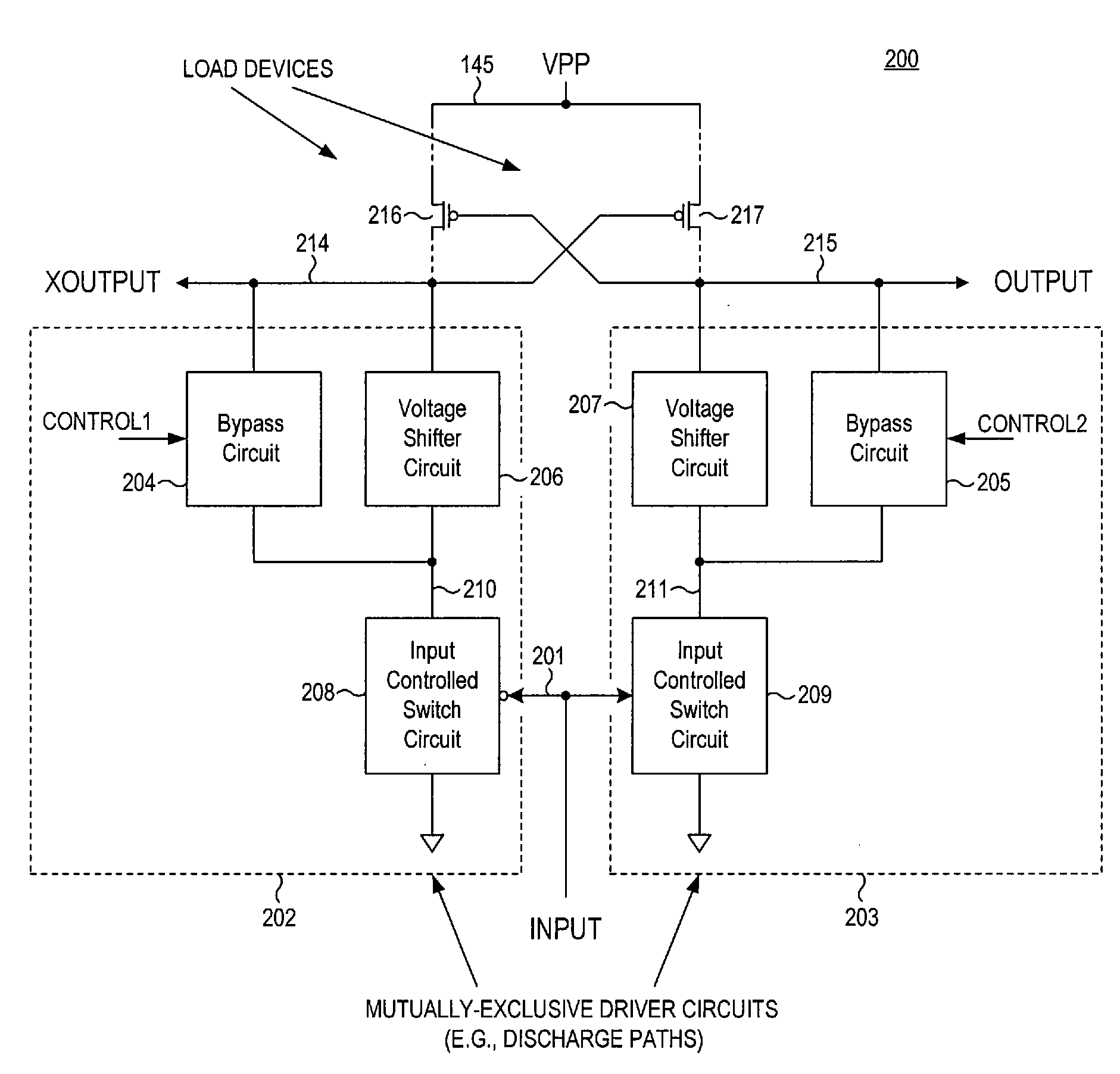
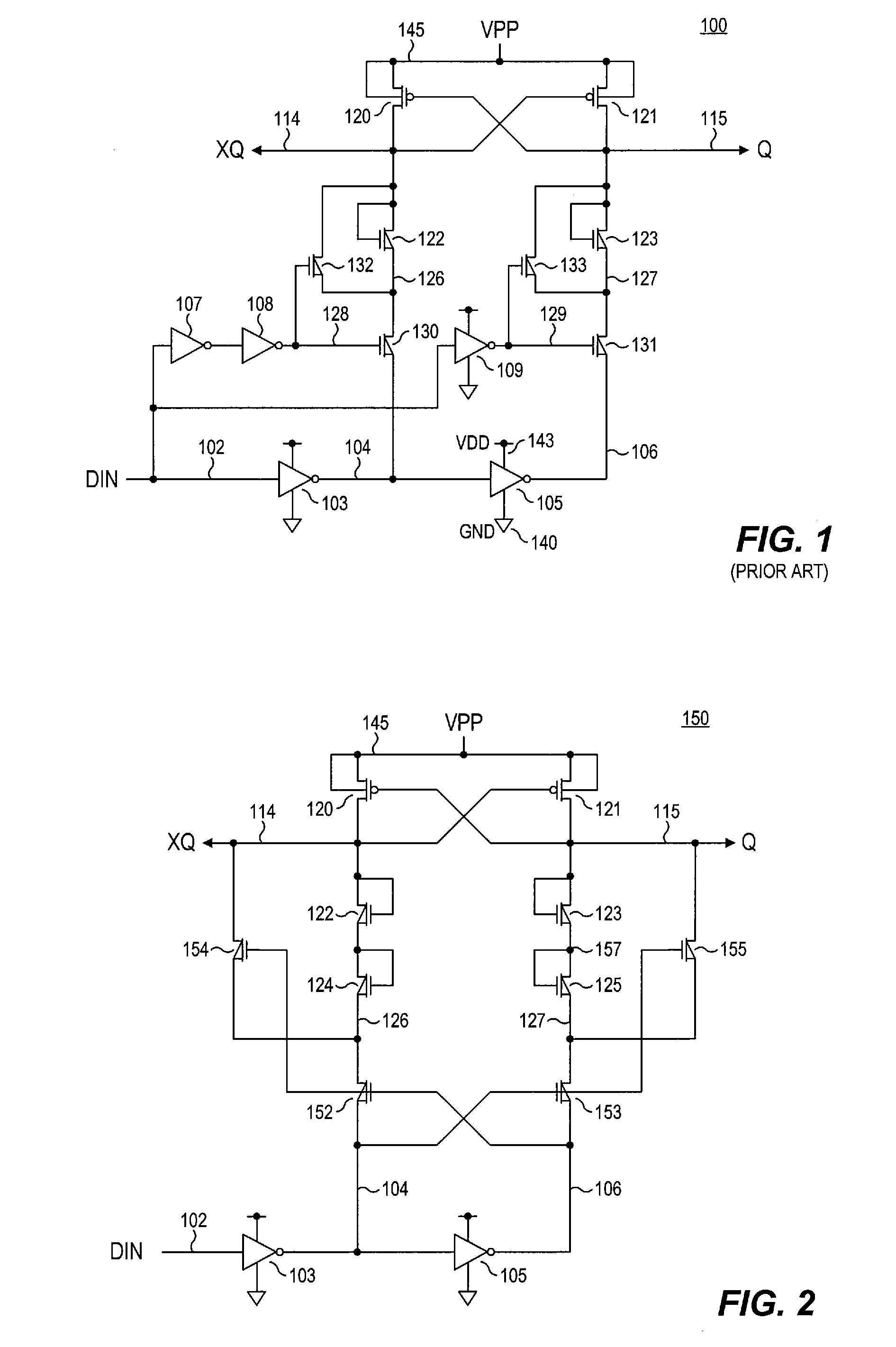
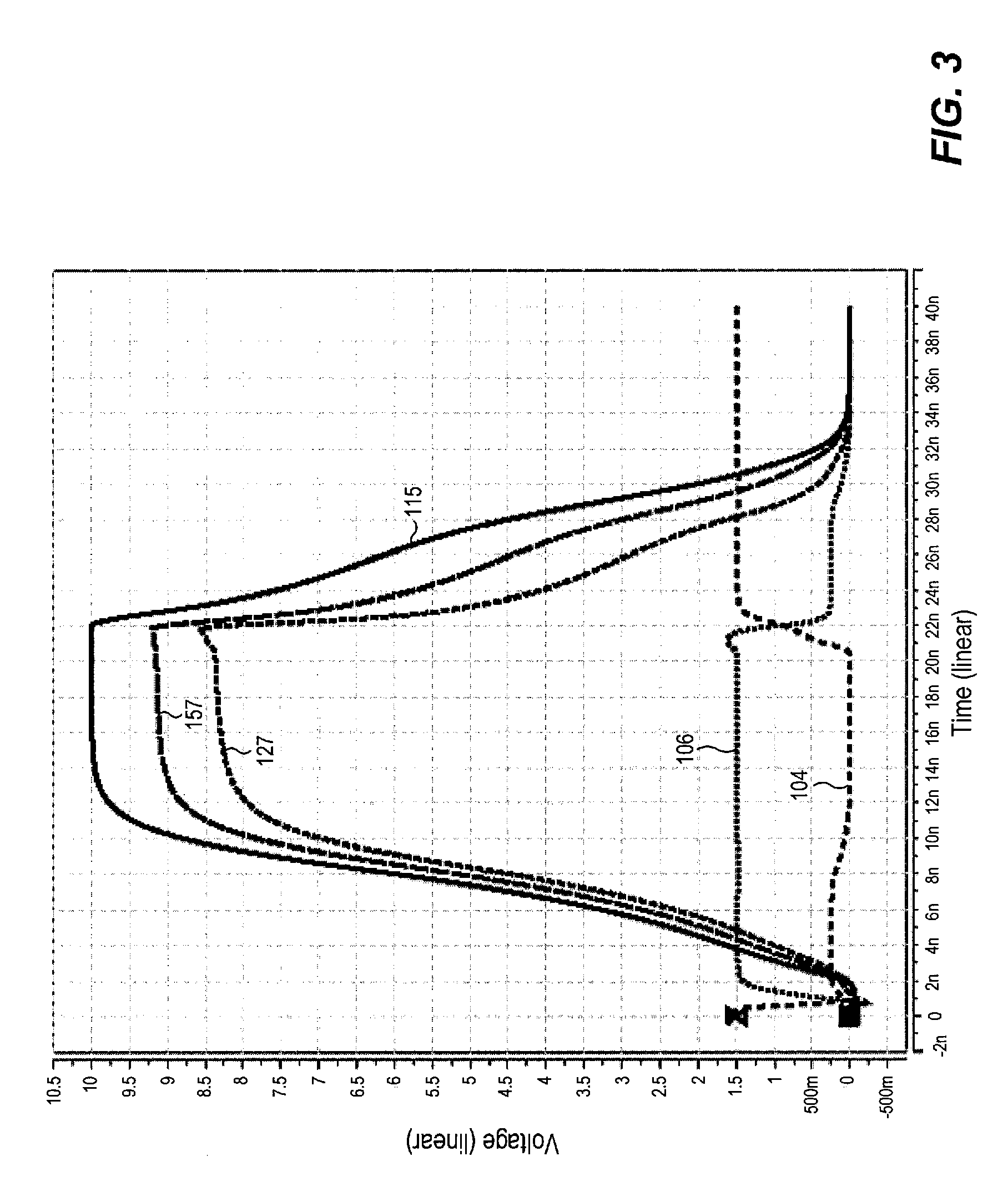
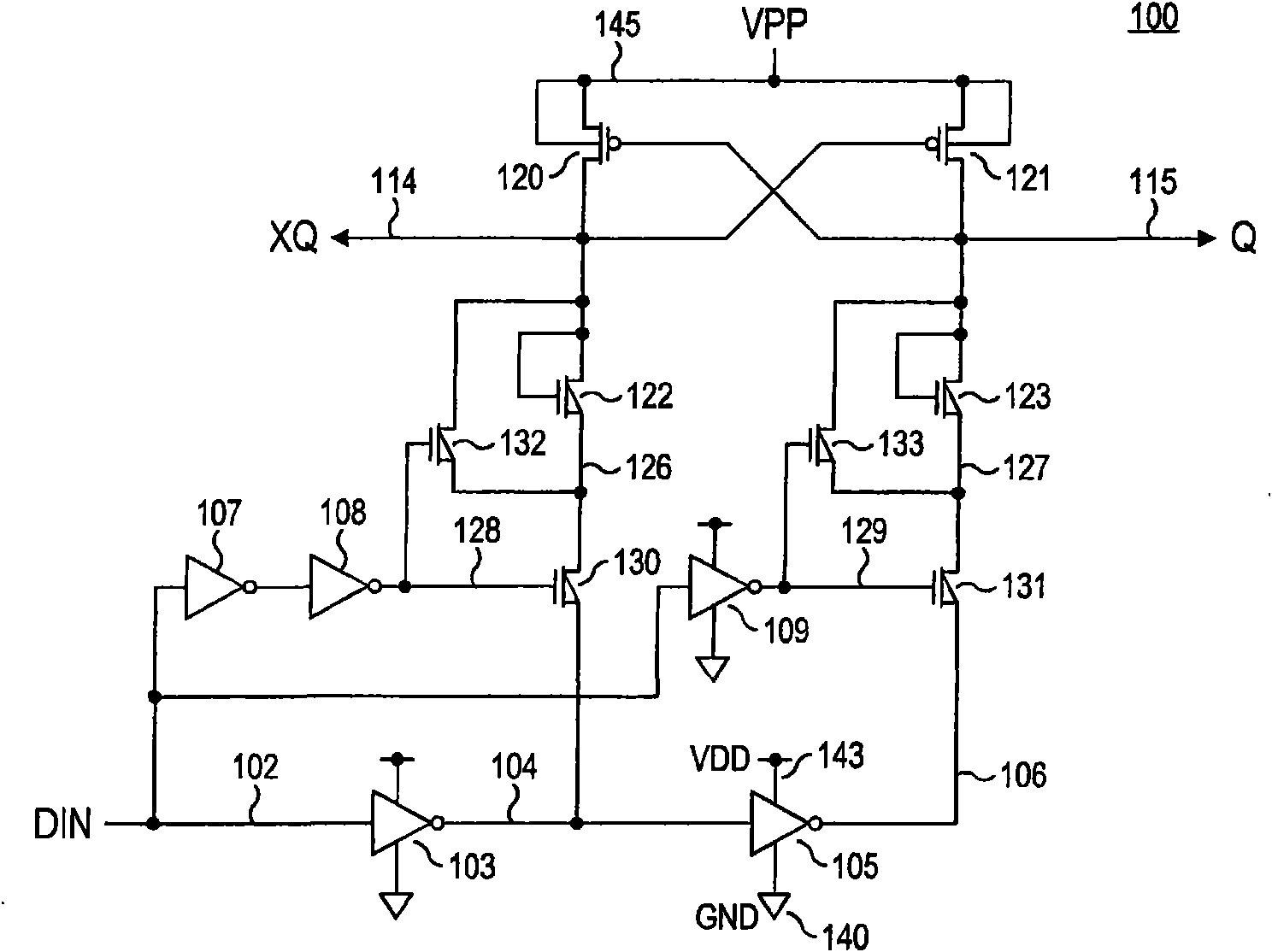
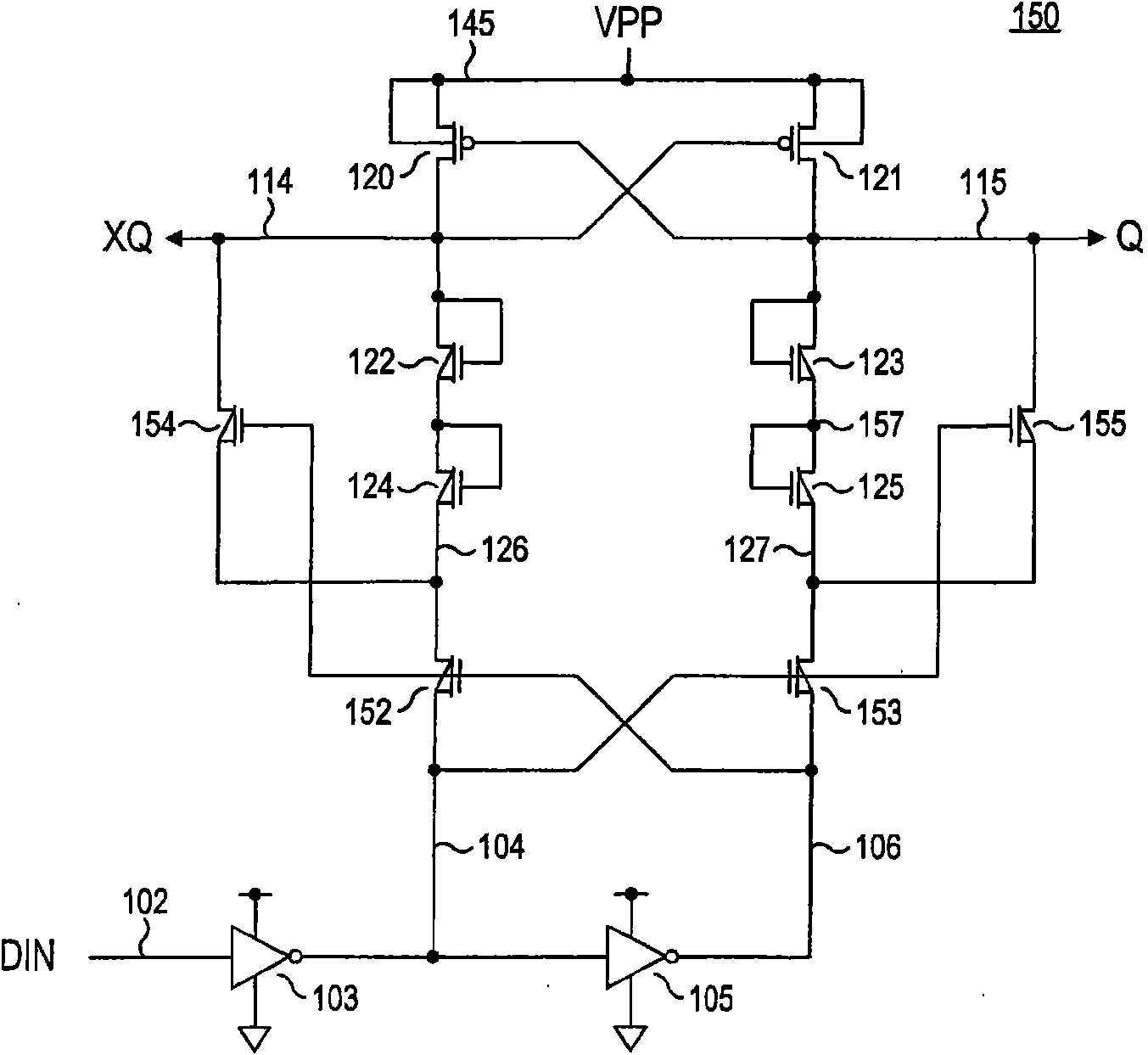
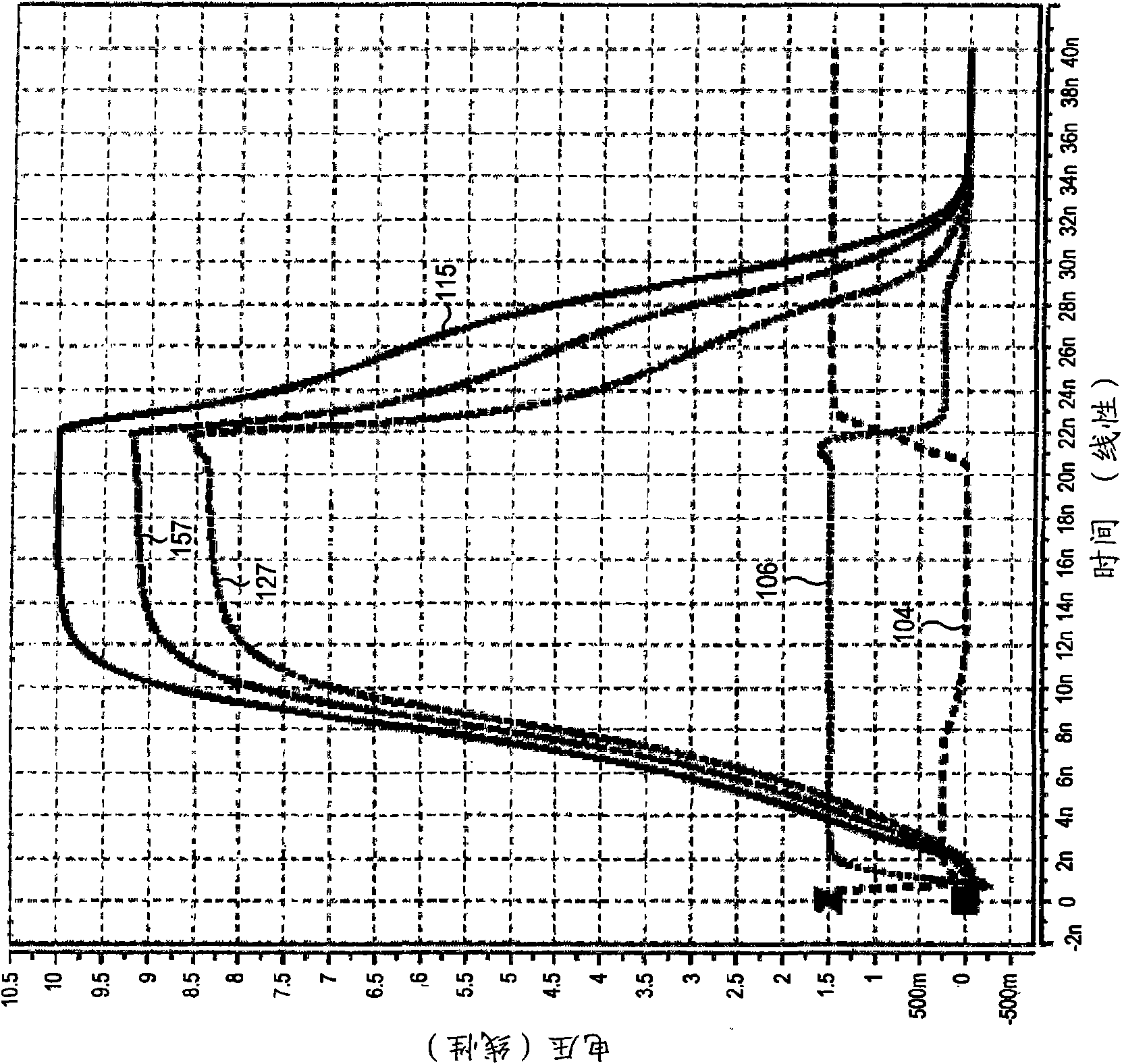
Level shifter circuit incorporating transistor snap-back protection
ActiveUS7696805B2Limit voltagePulse automatic controlElectric pulse generatorCapacitanceLevel shifting
Level shift circuits are disclosed for level shifting an input signal corresponding to a first voltage domain, to generate a pair of complementary output signals corresponding to a second, higher-voltage domain. Snap-back sensitive devices in a discharge circuit for a high voltage output node are protected, irrespective of the loading on the output node, and without requiring precise transistor sizing as a function of the output loading. The snap-back sensitive devices are protected by a voltage shifter circuit in series with the sensitive devices, to limit the voltage across the sensitive devices, even for a high capacitance output node at its highest output voltage. The voltage shifter circuit is then bypassed to provide for an output low level that fully reaches the lower power supply rail.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
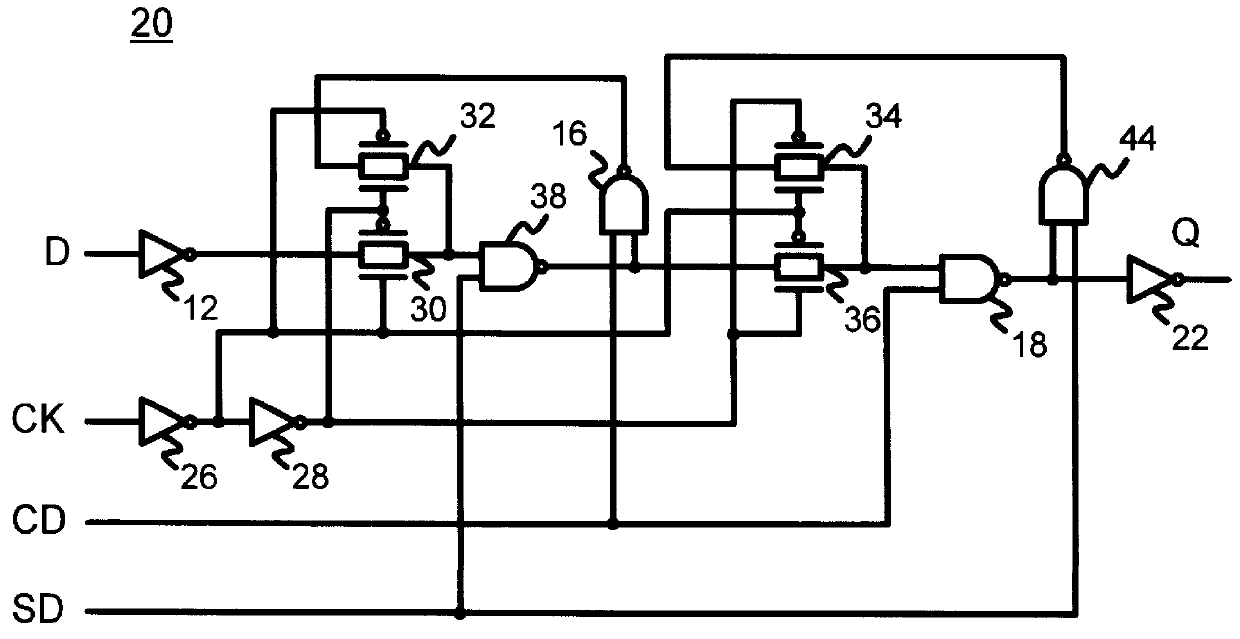
Versatile gate-array cell with interstitial transistors for compact flip-flops with set or clear
InactiveUS6144241AEasy to eliminateReduce in quantitySolid-state devicesElectric pulse generatorTransmission gateDirect feedback
A gate-array cell uses smaller and larger transistors. Four larger transistors are provided: two n-channel and two p-channel. A small p-channel transistor is placed between the contact tabs of the polysilicon lines of the two larger p-channel transistors, and between the p-channel transistors and a N-well tap. A small n-channel transistor is similarly placed between the contact tabs of polysilicon lines of the two larger n-channel transistors, and between the n-channel transistors and a P-well tap. The cell is slightly expanded in height to accommodate the two smaller transistors. The smaller transistors enable a reduction in the number of transistors required for latches and flip-flops. The smaller transistors allow a feedback inverter to directly connect to an input, since the input can easily over-power the feedback current. This is not possible for standard gate array cells having only one transistor size. Transmission gates are eliminated when direct feedback is feasible. Thus, the smaller transistors enable a reduction in transistor count as well as being smaller in size. Clear and set are provided by larger pull-down or pull-up transistors rather than NAND gates, since the larger pull-down and pull-up transistors can easily over-power the feedback inverters.
Owner:DIODES INC
Level shifter circuit incorporating transistor snap-back protection
ActiveUS20080238523A1Limit voltagePulse automatic controlElectric pulse generatorCapacitanceLevel shifting
Level shift circuits are disclosed for level shifting an input signal corresponding to a first voltage domain, to generate a pair of complementary output signals corresponding to a second, higher-voltage domain. Snap-back sensitive devices in a discharge circuit for a high voltage output node are protected, irrespective of the loading on the output node, and without requiring precise transistor sizing as a function of the output loading. The snap-back sensitive devices are protected by a voltage shifter circuit in series with the sensitive devices, to limit the voltage across the sensitive devices, even for a high capacitance output node at its highest output voltage. The voltage shifter circuit is then bypassed to provide for an output low level that fully reaches the lower power supply rail.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Shift register circuit
ActiveUS20070071158A1Reduce decreaseReduced circuit layout areaDigital storageShift registerLiquid-crystal display
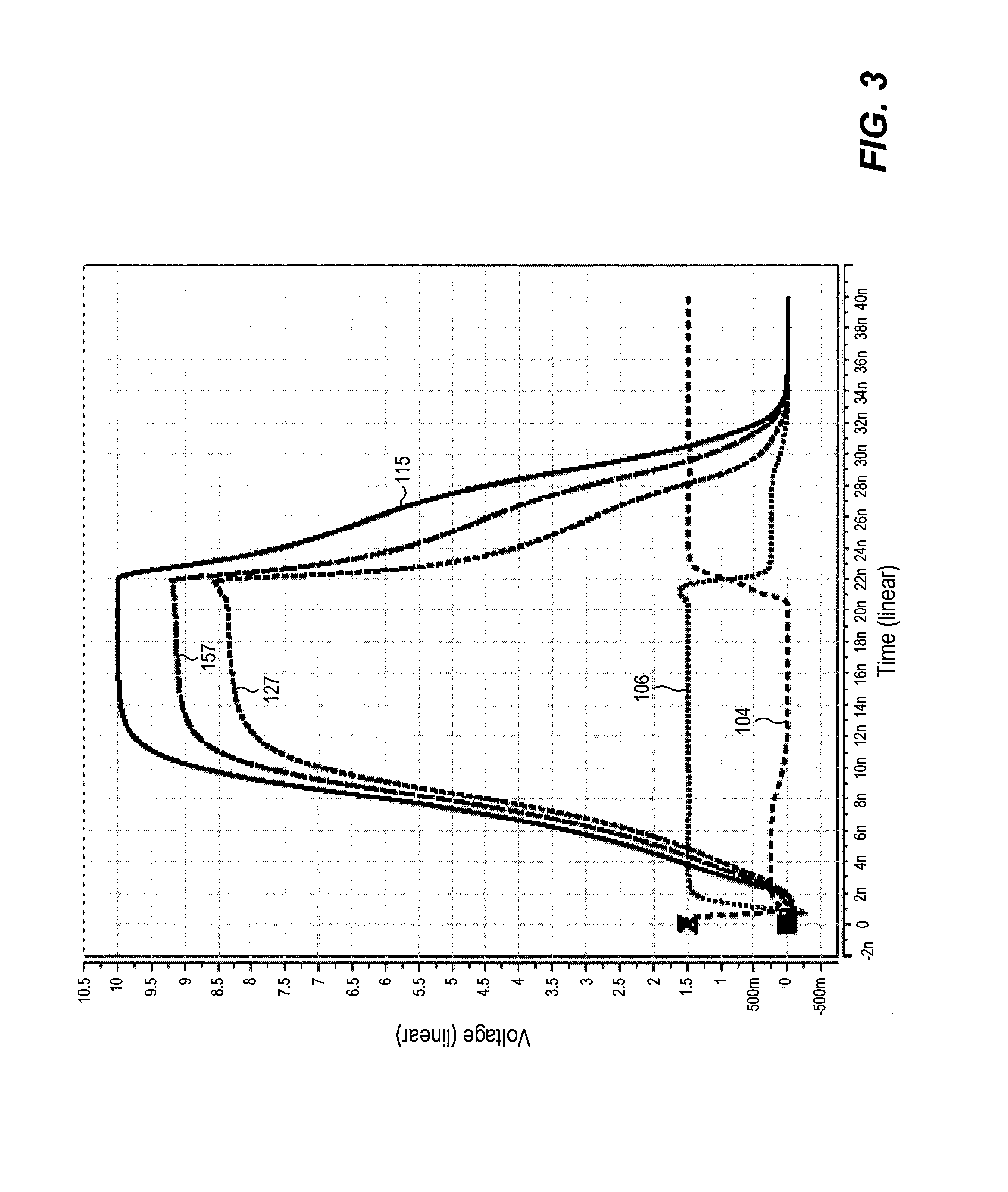
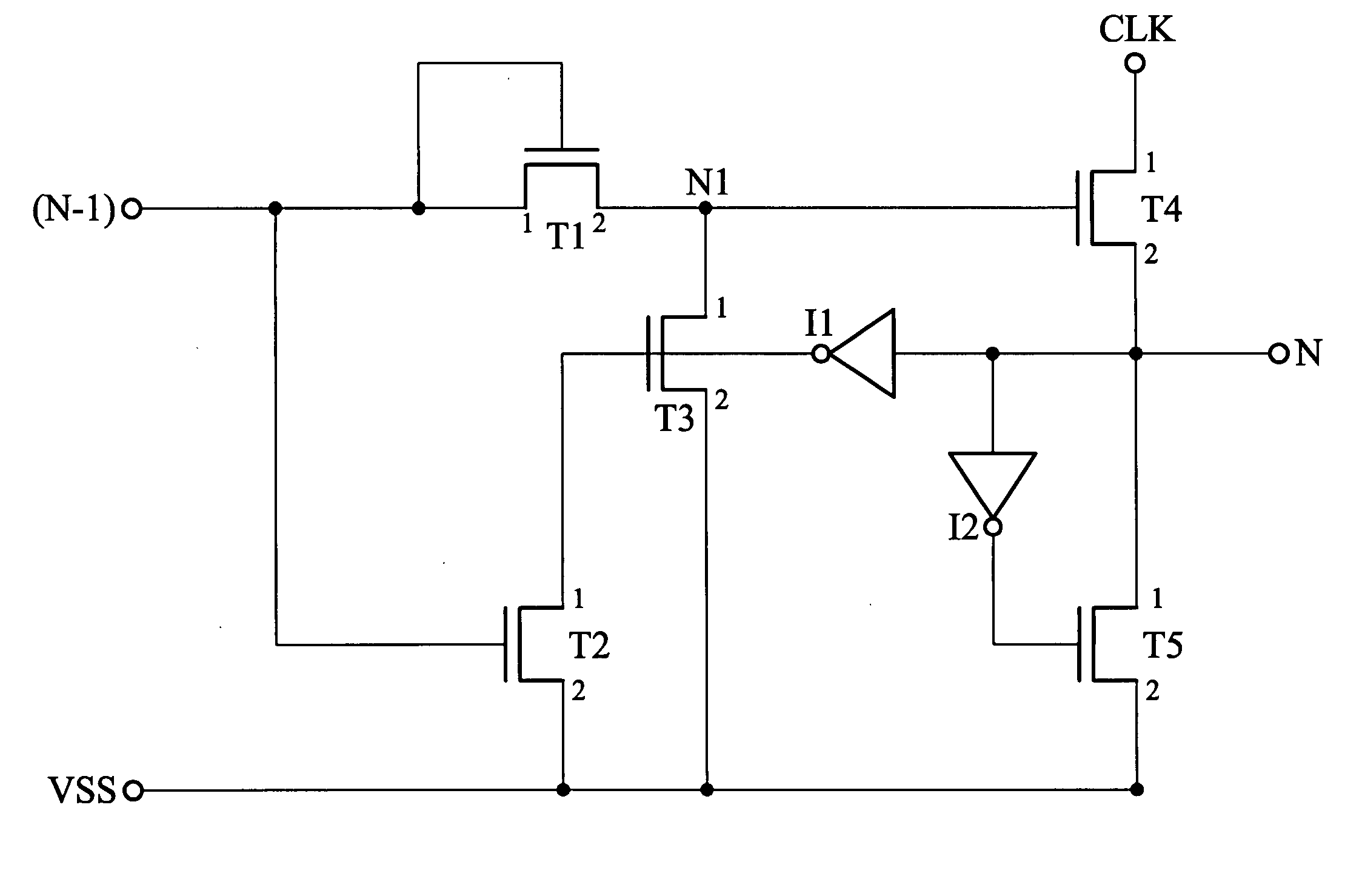
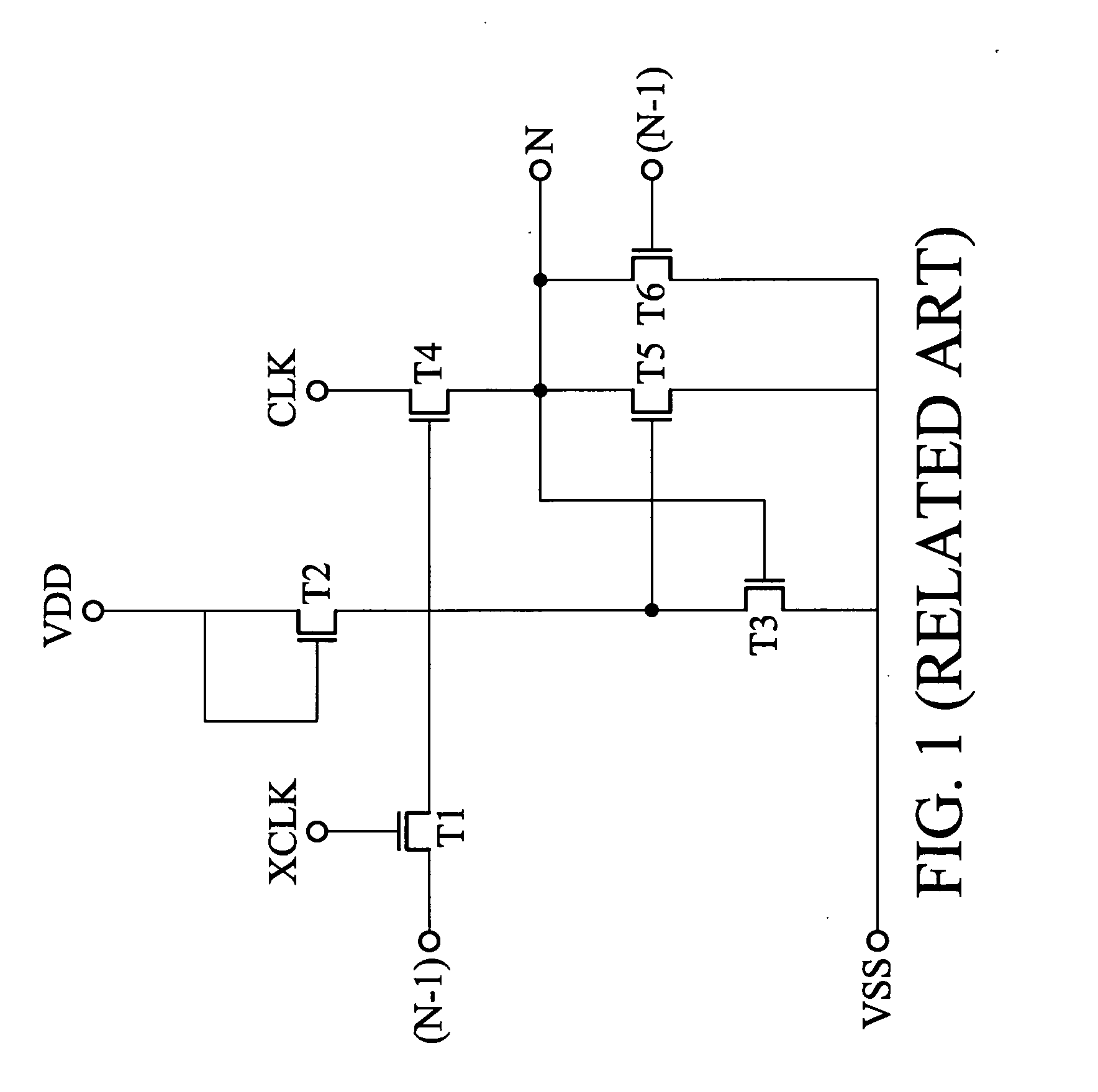
A shift register without a feedback signal of a post-stage shift register utilizing a latch mechanism and a clock signal to control the voltage of an output of the shift register is provided. The shift register reduces the transistor size and the circuit layout area. The shift register also improves the issue the overlapping between two adjacent shift registers to reduce the after-image of a liquid crystal display.
Owner:AU OPTRONICS CORP
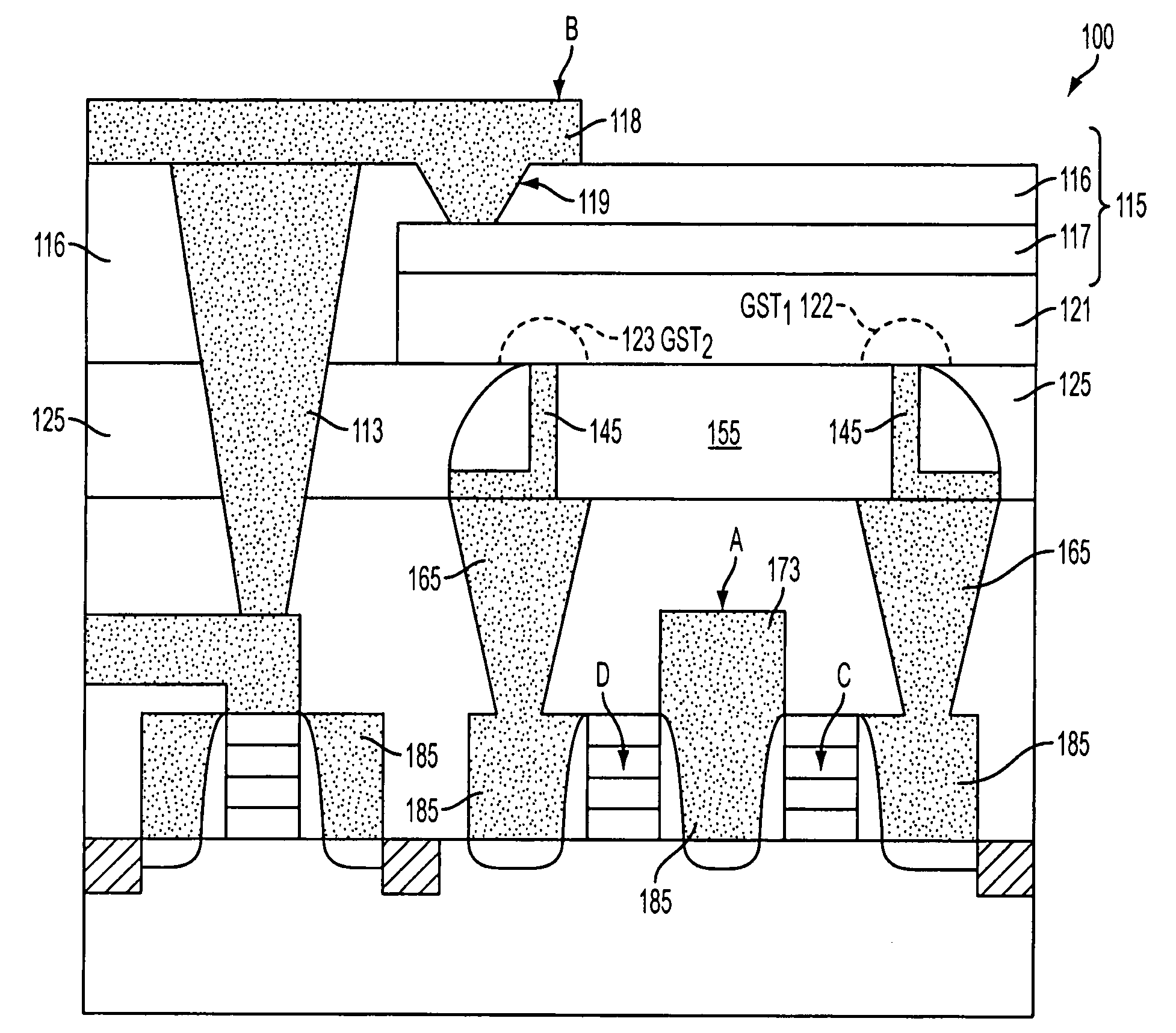
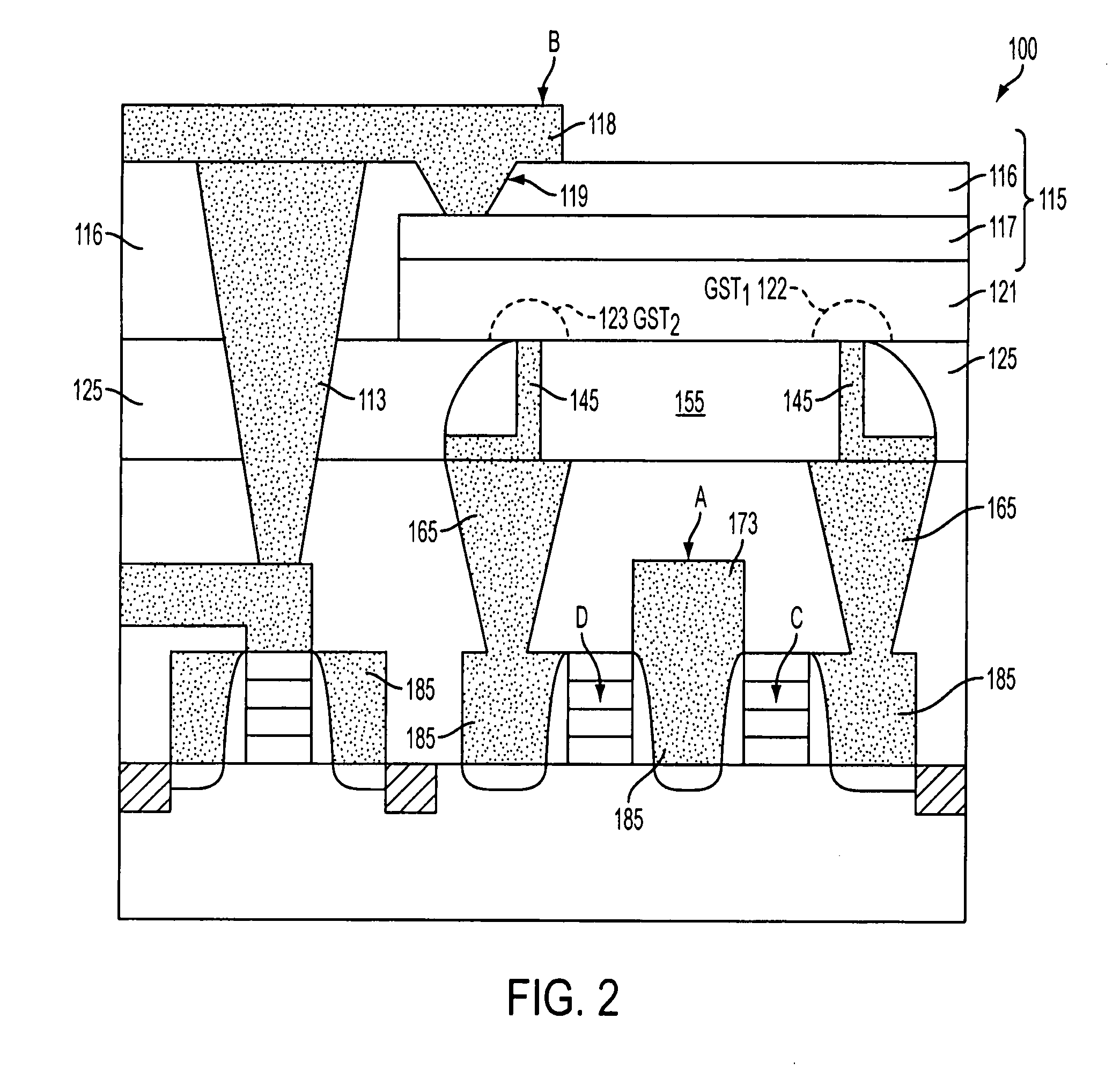
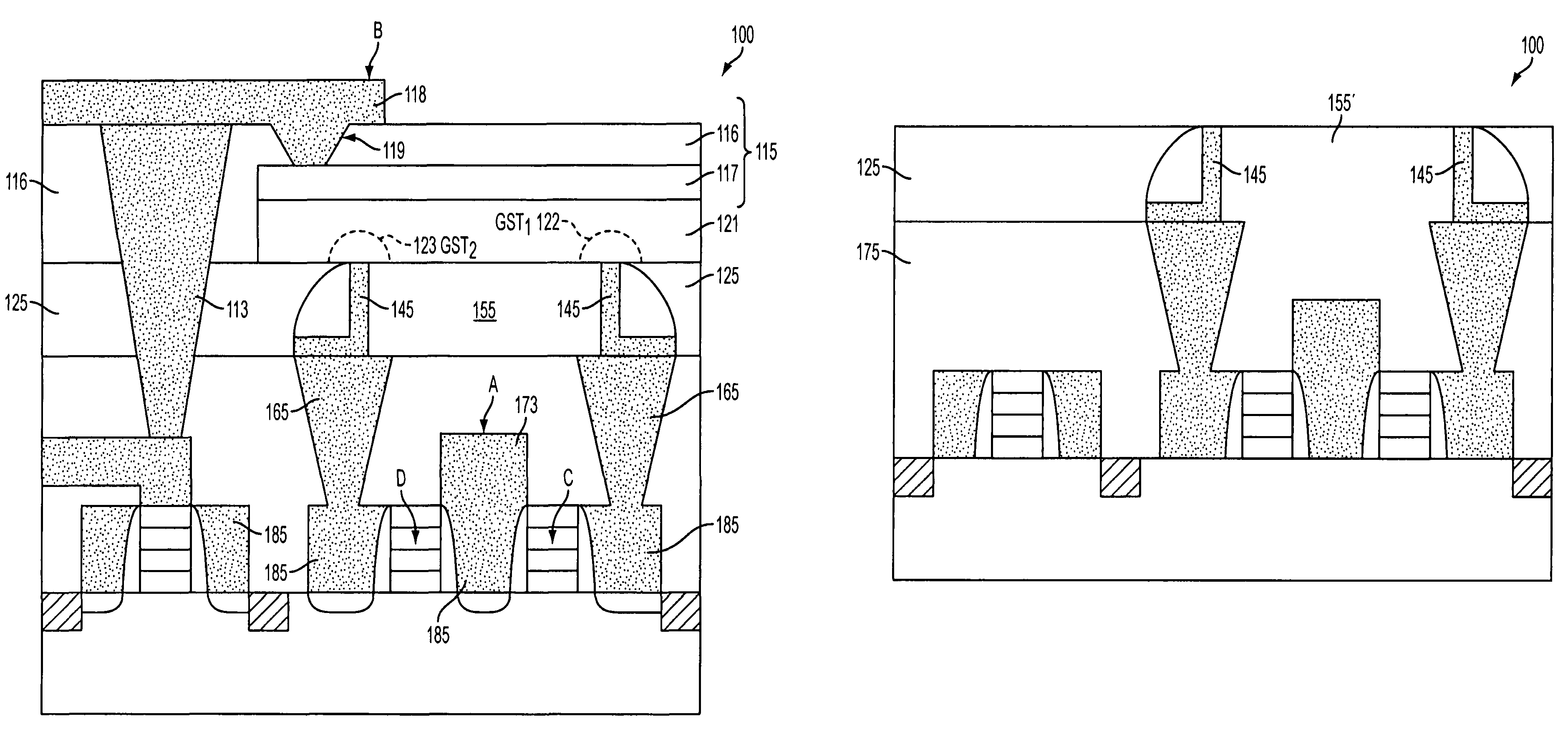
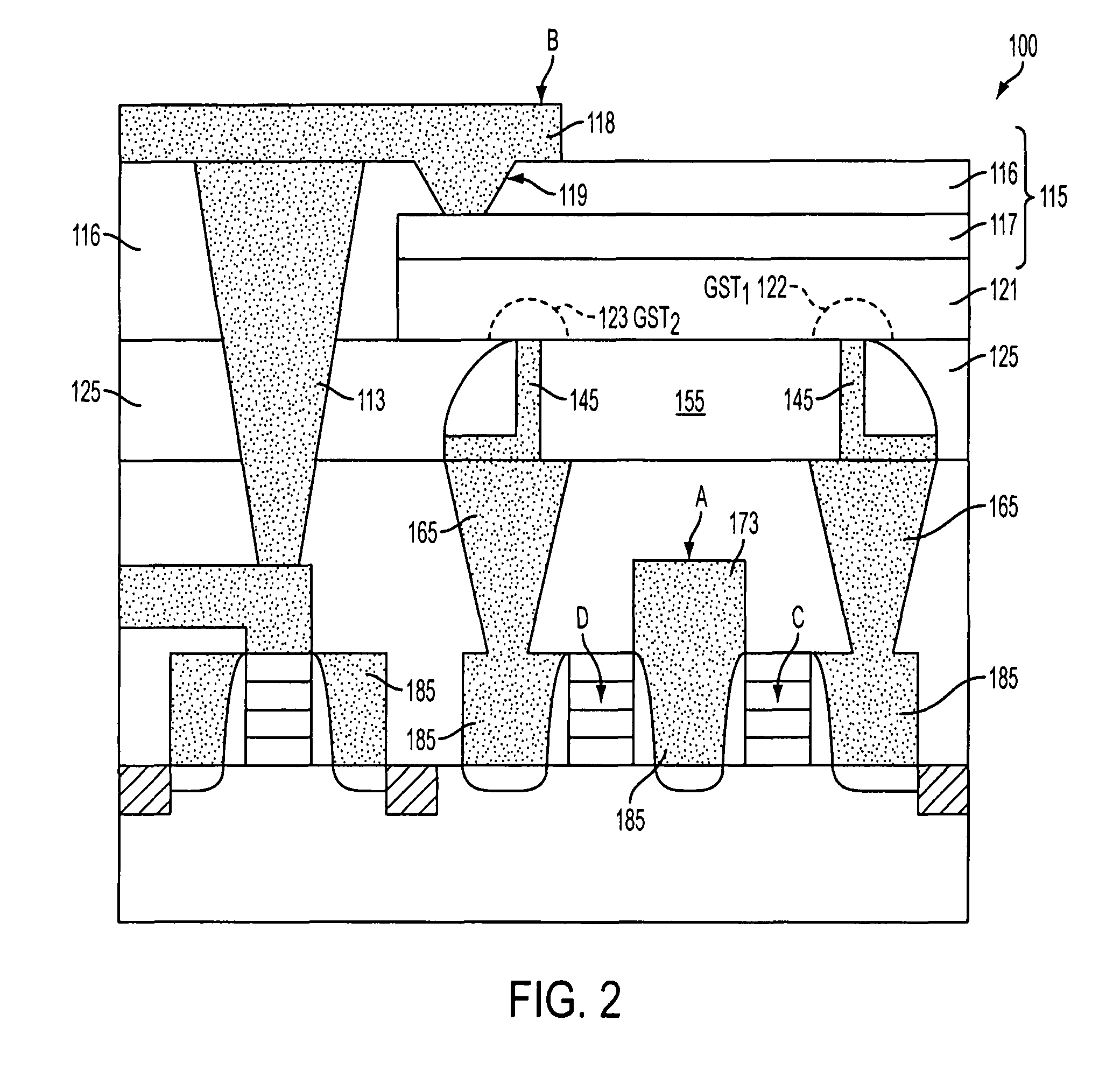
Variable resistance memory device having reduced bottom contact area and method of forming the same
ActiveUS20080283815A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectrical resistance and conductanceElectrode Contact
A variable resistance memory element and method of forming the same. The memory element includes a substrate supporting a bottom electrode having a small bottom contact area. A variable resistance material is formed over the bottom electrodes such that the variable resistance material has a surface that is in electrical communication with the bottom electrode and a top electrode is formed over the variable resistance material. The small bottom electrode contact area reduces the reset current requirement which in turn reduces the write transistor size for each bit.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
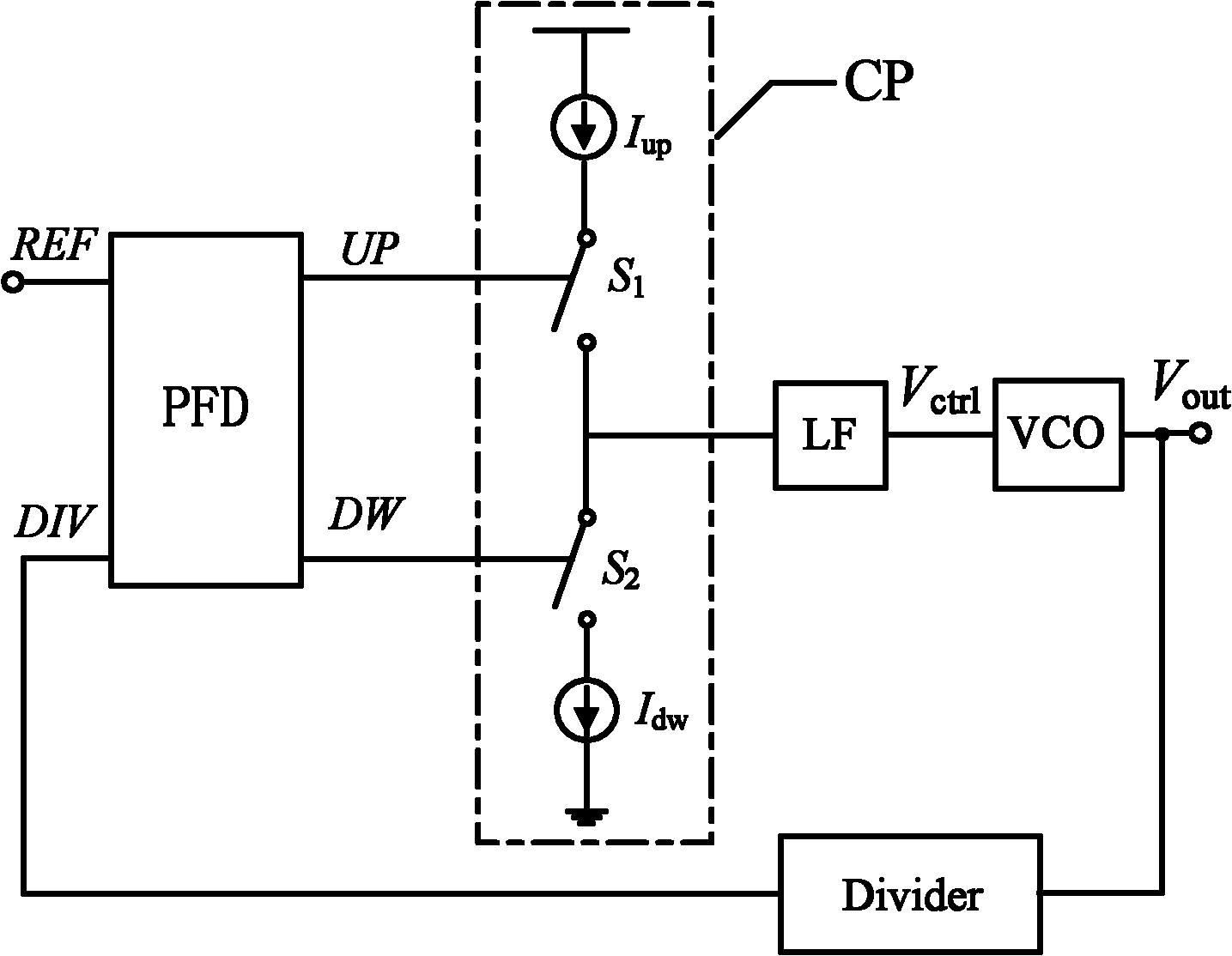
Charge pump circuit in charge pump phase-locking loop
InactiveCN102158075AIncrease charging currentReduced settling timePulse automatic controlApparatus without intermediate ac conversionReference currentEngineering
The invention relates to a charge pump circuit in a charge pump phase-locking loop, which is provided with an automatic bias current mirror circuit, a charging and discharging circuit, a copy circuit, a precharging bias circuit and a rail-to-rail operational amplification circuit. The automatic bias current mirror circuit is provided with a resistor R, three MOS (Metal Oxide Semiconductor) pipes and a reference current source. The charging and discharging circuit is provided with a charging and discharging current source consisting of a charging and discharging switch pipe and four MOS (MetalOxide Semiconductor) pipes. The copy circuit is copied from a charging and discharging circuit structure, and corresponding transistor sizes are correspondingly equal. The precharging bias circuit isprovided with five MOS pipes, the input end of the rail-to-rail operational amplification circuit is bridged between the charging and discharging circuit and the copy circuit, and the output end is connected with a charge pump charging current source.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
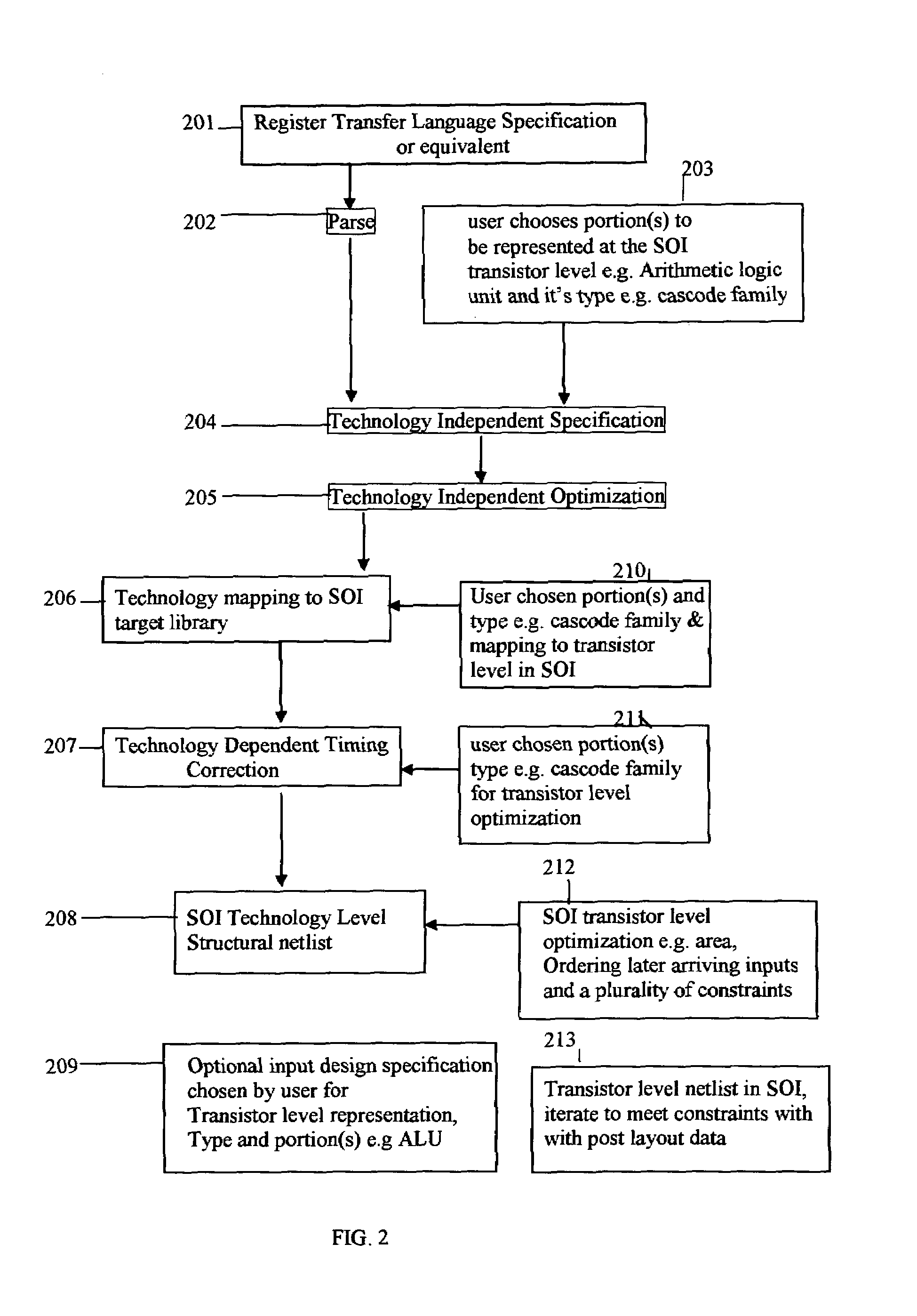
Technology dependent transformations for Silicon-On-Insulator in digital design synthesis
InactiveUS7039882B2Reduce needImprove approachCAD circuit designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationFloating body effectTechnology dependent
The present invention pertains to automated technology dependent transformations for Silicon-On-Insulator (SOI) in the digital design synthesis, the transformations include the steps of receiving input design specification in the form of technology independent specification or interconnected library of standard-cells; performing the technology dependent transformations in the digital design synthesis, resulting in interconnected SOI standard-cells from a SOI target library accounting for floating body effects, including floating body effects affecting delays over long periods of simulation time or testing over long times on fabricated SOI library cells, or SOI transistor level representations, transistor sizing and evaluating the standard-cell mapping and transistor-level representation for all or portion of the input design specification iteratively to meet delay and power constraints for SOI.
Owner:RANA AMAR PAL SINGH +1
Method for incorporating transistor snap-back protection in a level shifter circuit
ActiveUS20080238522A1Limit voltagePulse automatic controlElectric pulse generatorCapacitanceLevel shifting
Level shift circuits are disclosed for level shifting an input signal corresponding to a first voltage domain, to generate a pair of complementary output signals corresponding to a second, higher-voltage domain. Snap-back sensitive devices in a discharge circuit for a high voltage output node are protected, irrespective of the loading on the output node, and without requiring precise transistor sizing as a function of the output loading. The snap-back sensitive devices are protected by a voltage shifter circuit in series with the sensitive devices, to limit the voltage across the sensitive devices, even for a high capacitance output node at its highest output voltage. The voltage shifter circuit is then bypassed to provide for an output low level that fully reaches the lower power supply rail.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
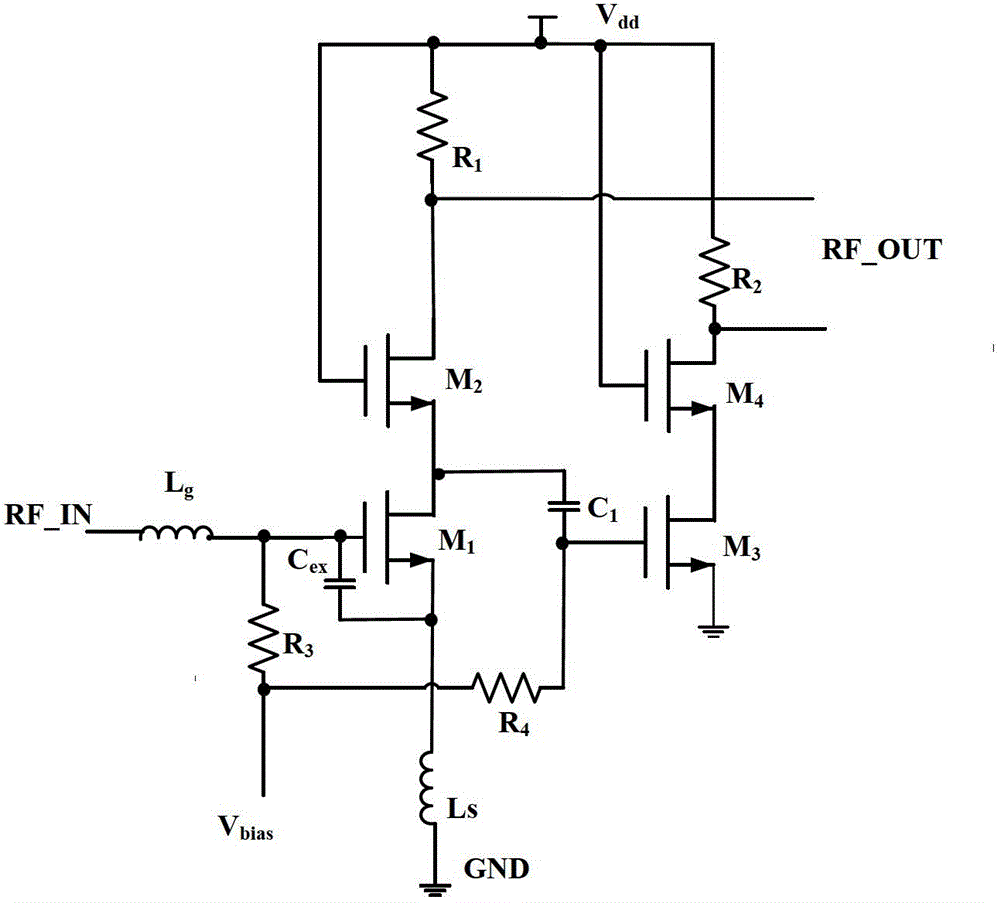
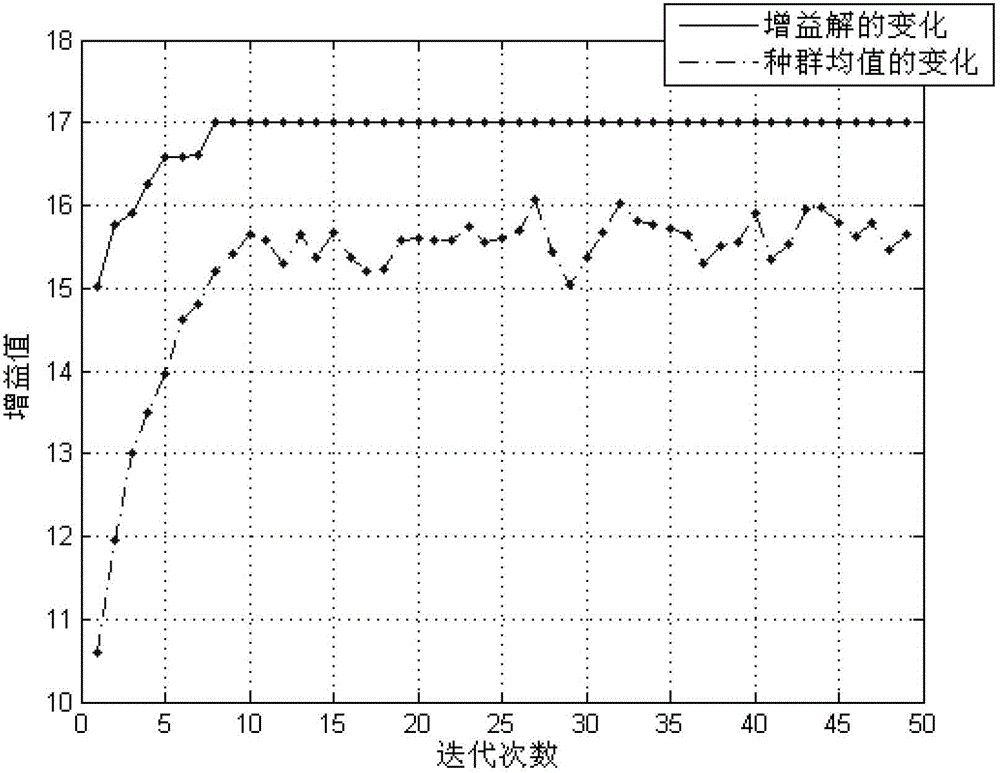
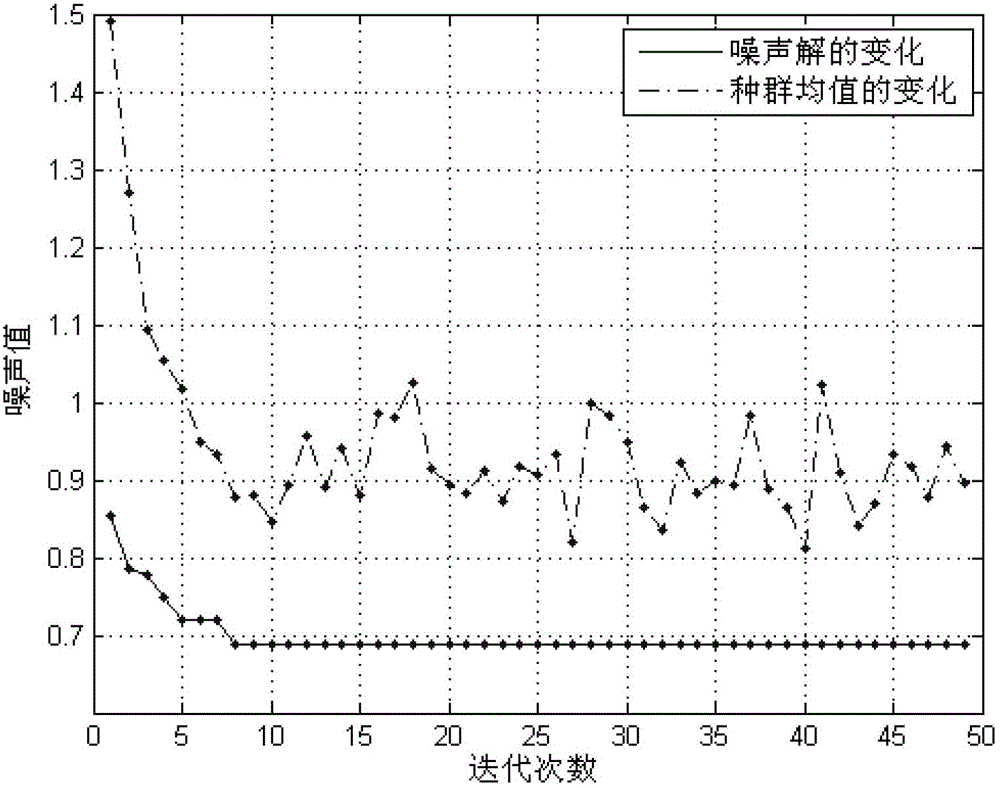
Optimization design method of low-noise amplifier based on genetic algorithm
ActiveCN103150459ASave time and costSolve the problem of large amount of calculation and time-consumingSpecial data processing applicationsAviationImpedance matching
The invention discloses an optimization design method of a low-noise amplifier (LNA) based on a genetic algorithm, and solves the problem of multi-objective optimization in LNA design. Circuit parameters in the LNA such as transistor sizes and passive device values are used as variable quantities, impedance matching of the LNA and a current equation of transistors are used as constraint conditions, a circuit performance evaluation technology based on the equation is used as a circuit performance evaluation method, a parallel genetic algorithm with elitist strategy is used as a global search algorithm, and the gain, noise coefficient and power consumption of the LNA are optimized simultaneously. Through the optimization method, the optimization result of the circuit can be quickly obtained, and the method is extremely suitable for circuit design with particular restriction, performance and function. The method can be used for deep sub-micron radio frequency CMOS (Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor) integrated circuit, and is widely applied to electronic systems in the aviation and aerospace fields.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
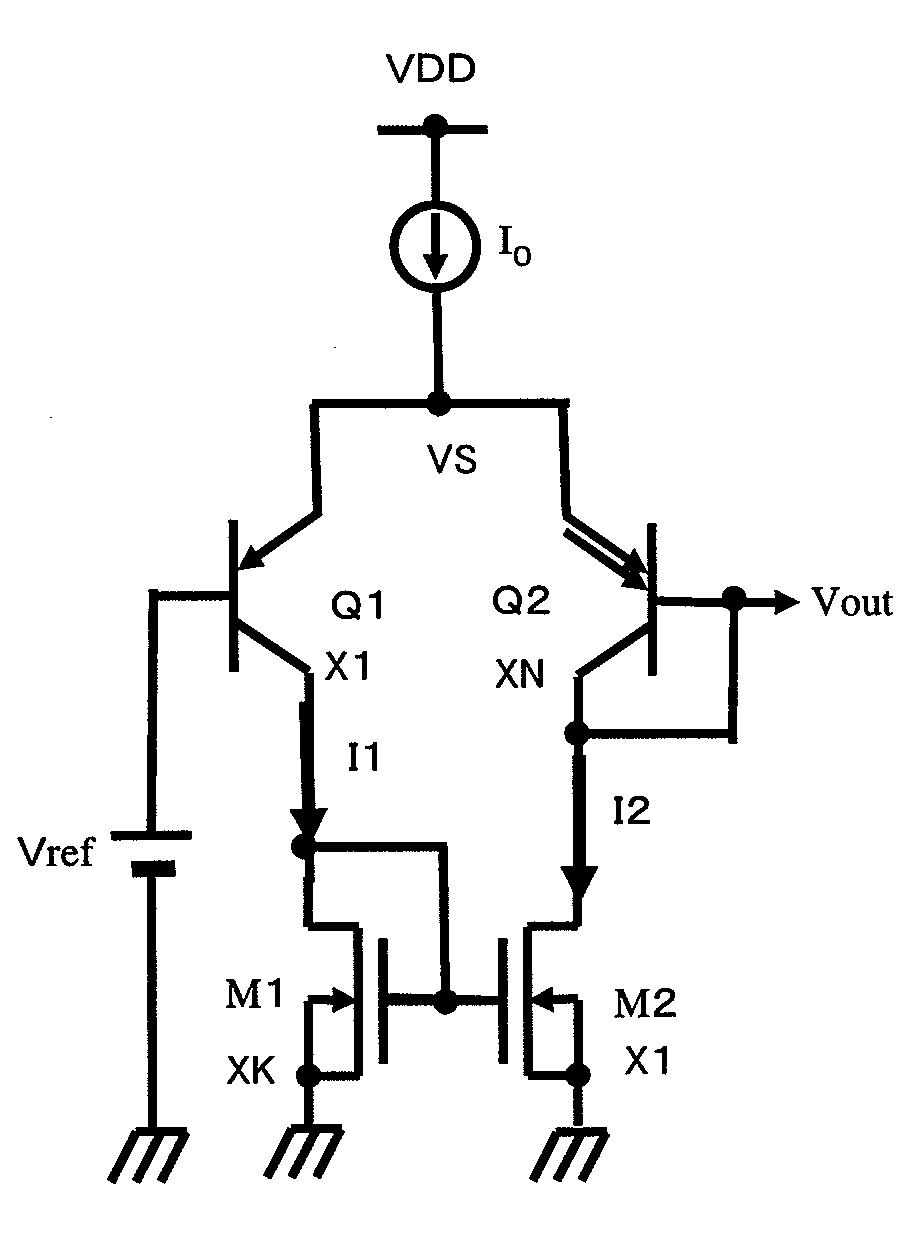
Temperature sensor circuit
InactiveUS20090146725A1Easy to makeIncrease temperatureThermometer detailsThermometers using electric/magnetic elementsVoltage referenceEngineering
Disclosed is a temperature sensor circuit including a bipolar differential pair driven by a constant current and having an emitter area ratio of 1:N (N>1) and two MOS transistors having the transistor size ratio of K:1 (K>1) connected as an active load to the bipolar differential pair. A reference voltage is applied to one of the transistors of the bipolar differential pair. The other transistor has a base and a collector connected together. A desired voltage is output between the bases of the two transistors of the bipolar differential pair. A plural number of the temperature sensor circuits may be connected in cascade (FIG. 3).
Owner:NEC ELECTRONICS CORP
Polysilicon doped transistor using silicon-on-insulator and double silicon-on-insulator
InactiveUS6645795B2High and improved performanceExcellent characteristicsTransistorSolid-state devicesSemiconductor materialsConcentration gradient
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Field effect transistor
InactiveUS20080169472A1Transistor size to be scaledIncrease the effective channel lengthTransistorNanoinformaticsEngineeringField-effect transistor
Disclosed are embodiments of a field effect transistor that incorporates an elongated semiconductor body with a spiral-shaped center channel region wrapped one or more times around a gate and with ends that extend outward from the center region in opposite directions away from the gate. Source / drain regions are formed in the end regions by either doping the end regions or by biasing a back gate to impart a preselected Fermi potential on the end regions. This disclosed structure allows the transistor size to be scaled without decreasing the effective channel length to the point where deleterious short-channel effects are exhibited. It further allows the transistor size to be scaled while also allowing the effective channel length to be selectively increased (e.g., by increasing the number of times the channel wraps around the gate). Also, disclosed are embodiments of an associated method of forming the transistor.
Owner:IBM CORP
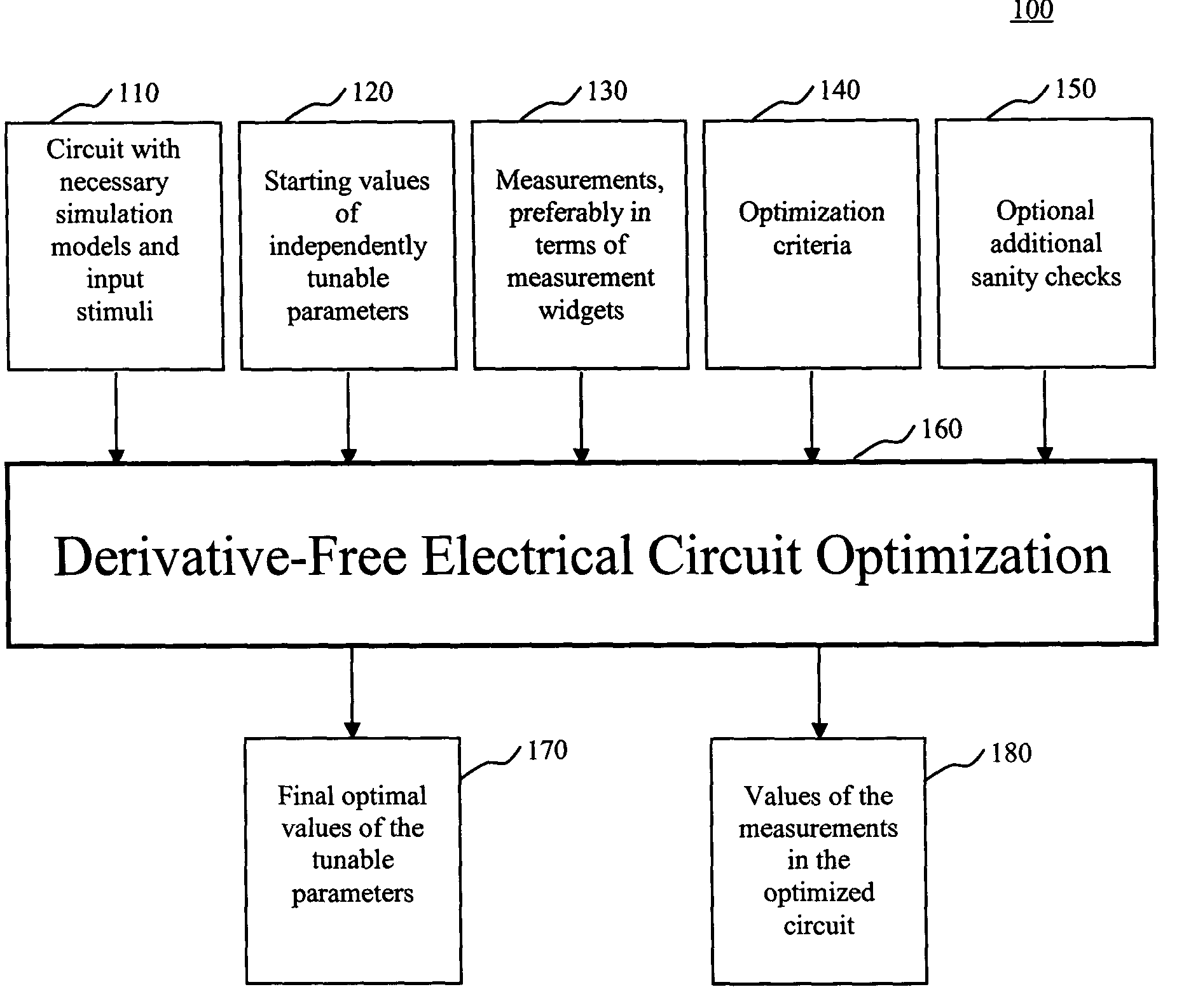
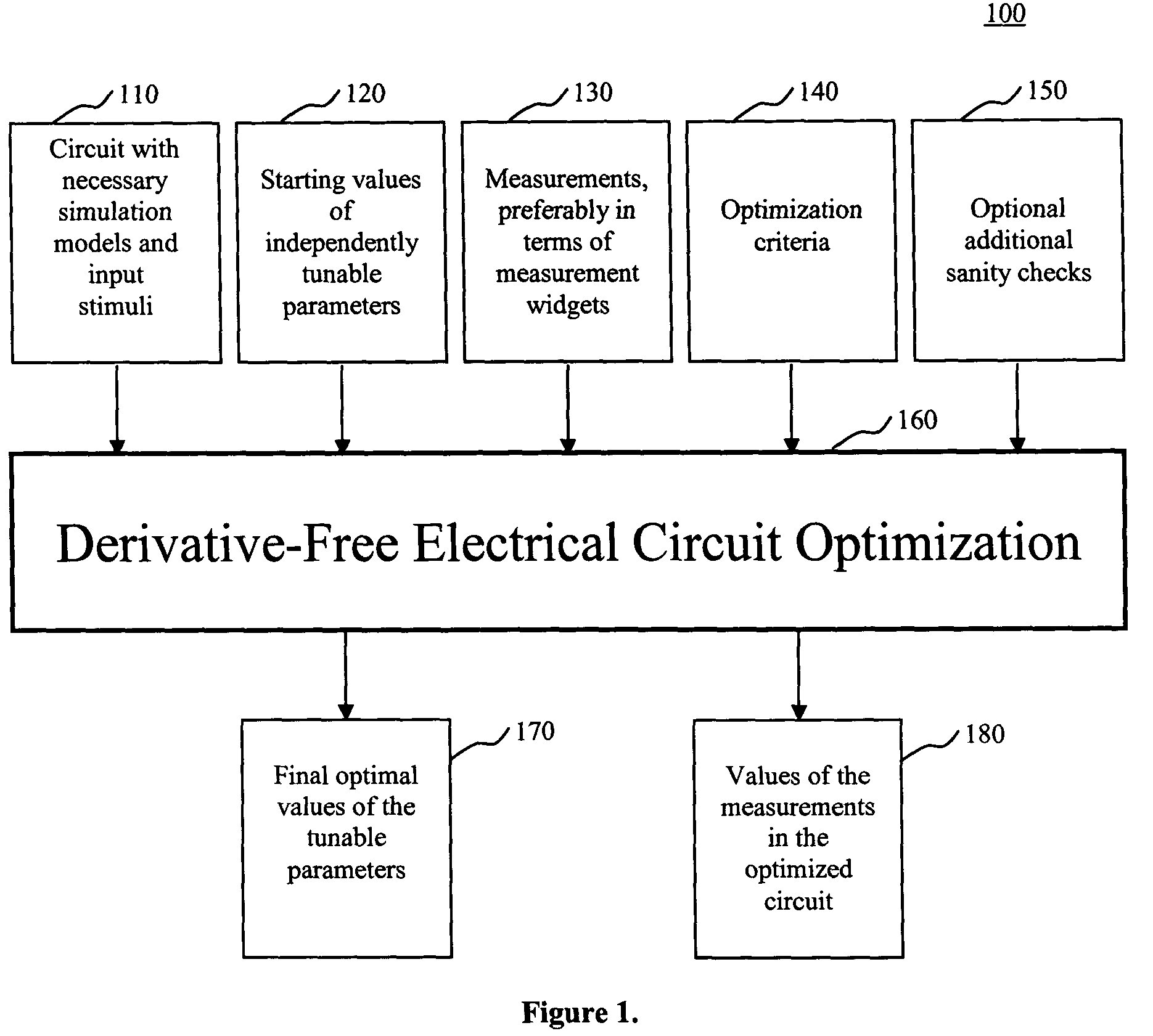
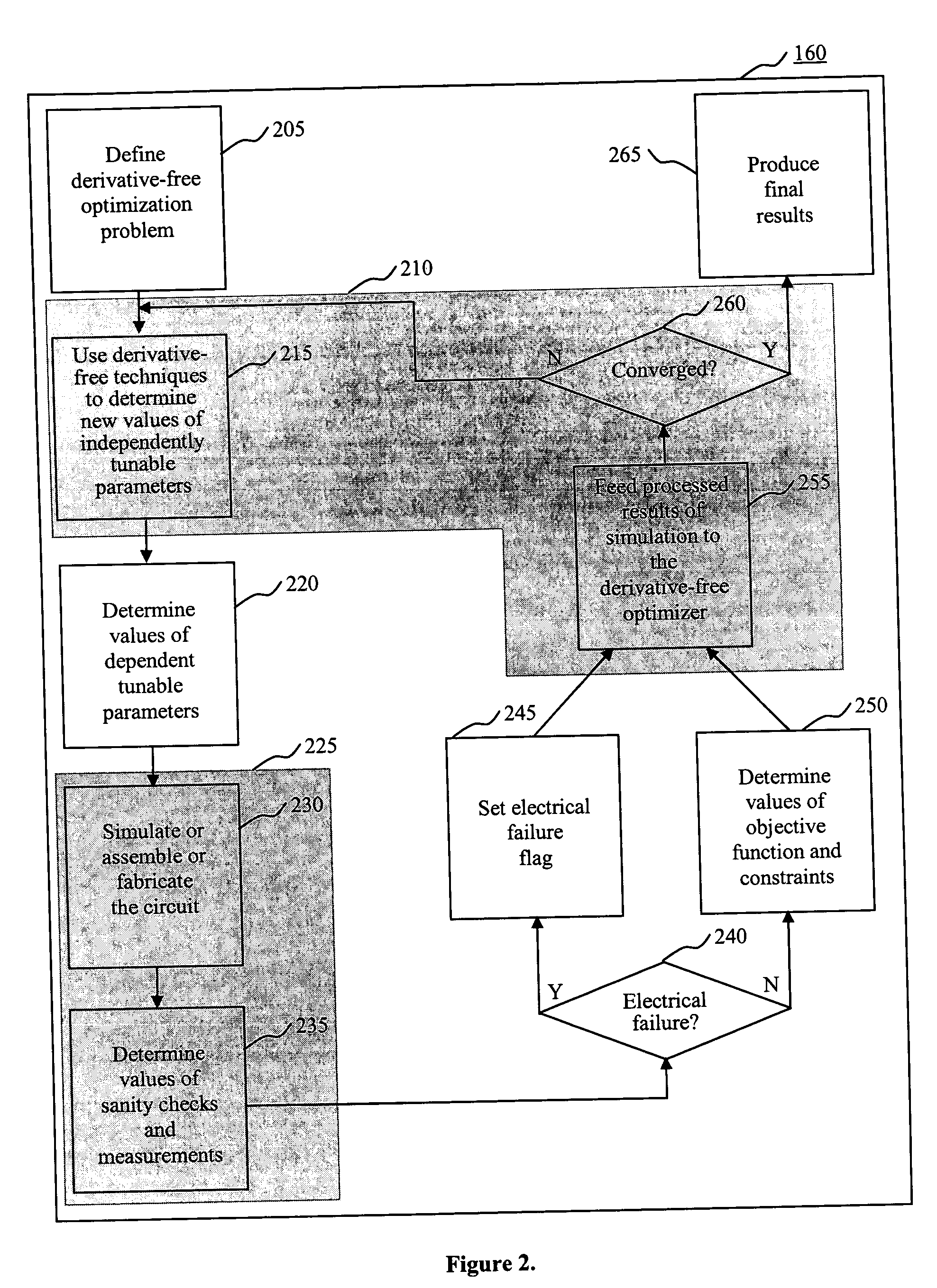
System and method for derivative-free optimization of electrical circuits
InactiveUS20050022141A1Quality improvementIncrease designer productivityCAD circuit designSpecial data processing applicationsLocal optimumElectrical Failure
The present invention is a system and method for optimizing electrical circuits by means of derivative-free optimization. Tunable parameters such as component values, transistor sizes or model parameters are automatically adjusted to obtain an optimal circuit. Any method of measuring the performance of the circuit, including computer simulation, can be incorporated into the optimization technique, with no derivative requirements. An arbitrary continuous optimization problem can be posed, including an objective function, equality and inequality constraints, and simple bounds on the tunable parameters. The optimization technique is efficient and guarantees that it will find a locally optimal solution from any starting point. Further, the procedure includes a method of automatically recovering from electrical failure to enable automatic and productive circuit optimization. A set of measurement widgets is provided to automatically introduce the checking required to recover from electrical failure. The automated circuit optimization leads to higher quality circuits, increases designer productivity, results in a better understanding of the tradeoffs inherent in the circuit and lifts the thinking of the circuit designer to a higher level.
Owner:IBM CORP
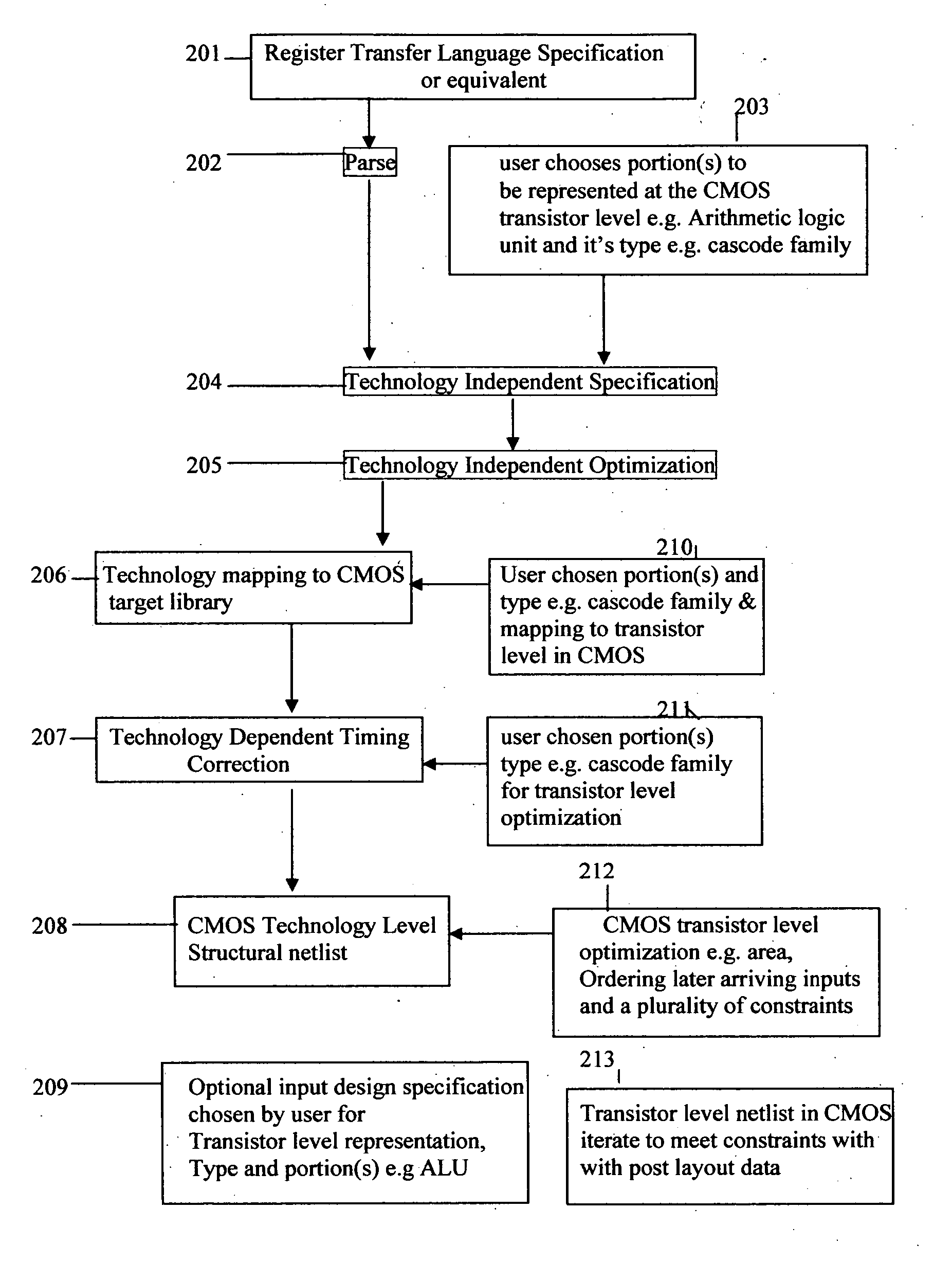
Technology dependent transformations for CMOS in digital design synthesis
InactiveUS20060075375A1CAD circuit designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationCMOSTechnology dependent
The present invention pertains to automated technology dependent transformations for CMOS digital design synthesis resulting in a combination of CMOS interconnected standard-cells from a target CMOS library being mapped and transistor-level representation for all or portion of the input design specification, the transistor level type and portion or portions to be represented at the transistor level representation being chosen by a user, transistor sizing and evaluating the combination of said transistor-level representation and standard-cell mapping iteratively to meet delay, size and power constraints for CMOS.
Owner:RANA AMAR PAL SINGH +1
Electrostatic protection circuit in a semiconductor device
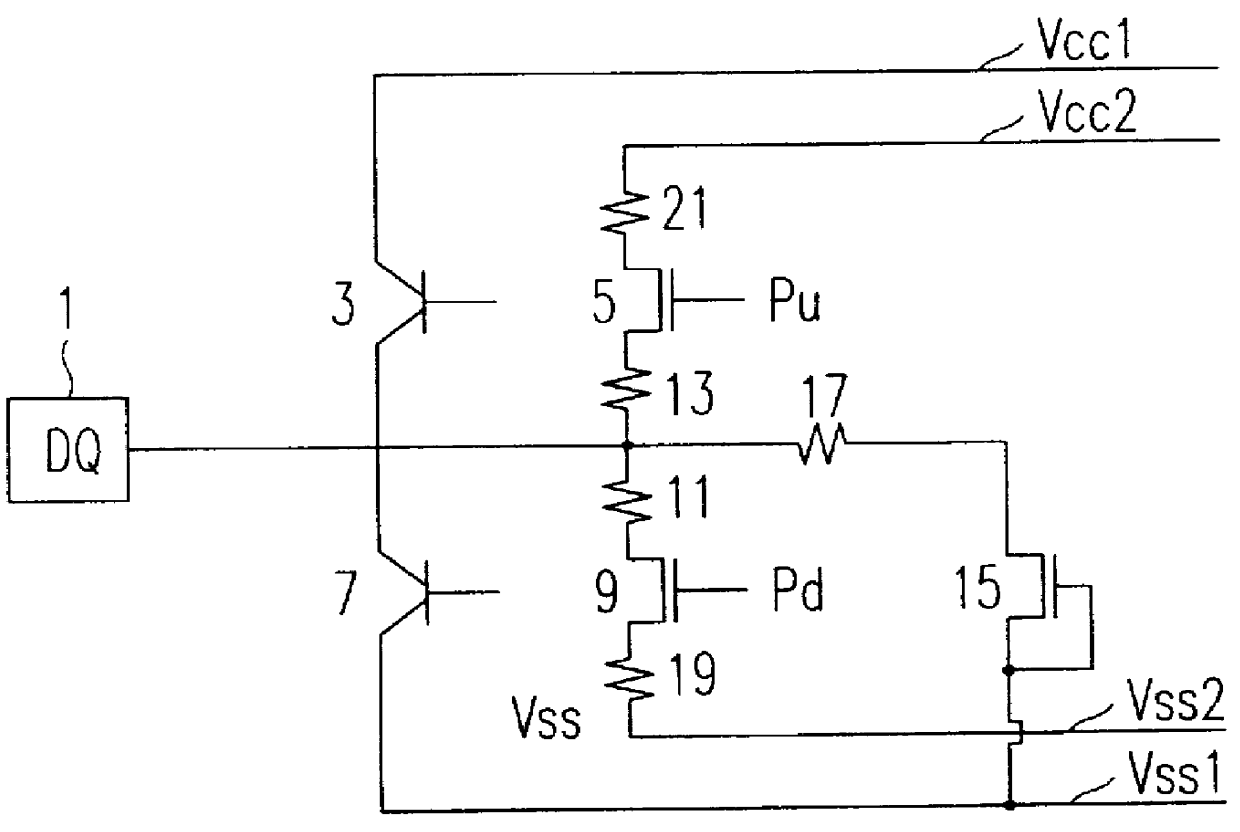
A power line and a ground line of a bipolar transistor for the electrostatic protection are isolated from a power line and a ground line of an active transistor for data input and output. Also, a resistor is coupled between a power line and a ground line of an active transistor for data input and output, and another resistor is coupled between a pad and the active transistor. Accordingly, the active transistor for data input and output is operated as an internal circuit in the electrostatic protection test since main current flows toward the bipolar transistor. An electrostatic protection circuit according to the present invention uses a bipolar transistor for the electrostatic protection and uses an active transistor for data input and output as an internal circuit in order to increase transistor size. Accordingly, a rated current of a data input and output pad is satisfied as well as the data pin capacitance is reduced since the distance between a gate and a contact in an active transistor is decreased.
Owner:HYUNDAI ELECTRONICS IND CO LTD
Level shifter circuit incorporating transistor snap-back protection
ActiveCN101682328ALogic circuits coupling/interface using field-effect transistorsElectronic switchingCapacitanceVoltage range
Level shift circuits are disclosed for level shifting an input signal corresponding to a first voltage domain, to generate a pair of complementary output signals corresponding to a second, higher-voltage domain. Snap-back sensitive devices in a discharge circuit for a high voltage output node are protected, irrespective of the loading on the output node, and without requiring precise transistor sizing as a function of the output loading. The snap-back sensitive devices are protected by a voltage shifter circuit in series with the sensitive devices, to limit the voltage across the sensitive devices, even for a high capacitance output node at its highest output voltage. The voltage shifter circuit is then bypassed to provide for an output low level that fully reaches the lower power supply rail.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Variable resistance memory device having reduced bottom contact area and method of forming the same
ActiveUS7989251B2Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectricityEngineering
A variable resistance memory element and method of forming the same. The memory element includes a substrate supporting a bottom electrode having a small bottom contact area. A variable resistance material is formed over the bottom electrodes such that the variable resistance material has a surface that is in electrical communication with the bottom electrode and a top electrode is formed over the variable resistance material. The small bottom electrode contact area reduces the reset current requirement which in turn reduces the write transistor size for each bit.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
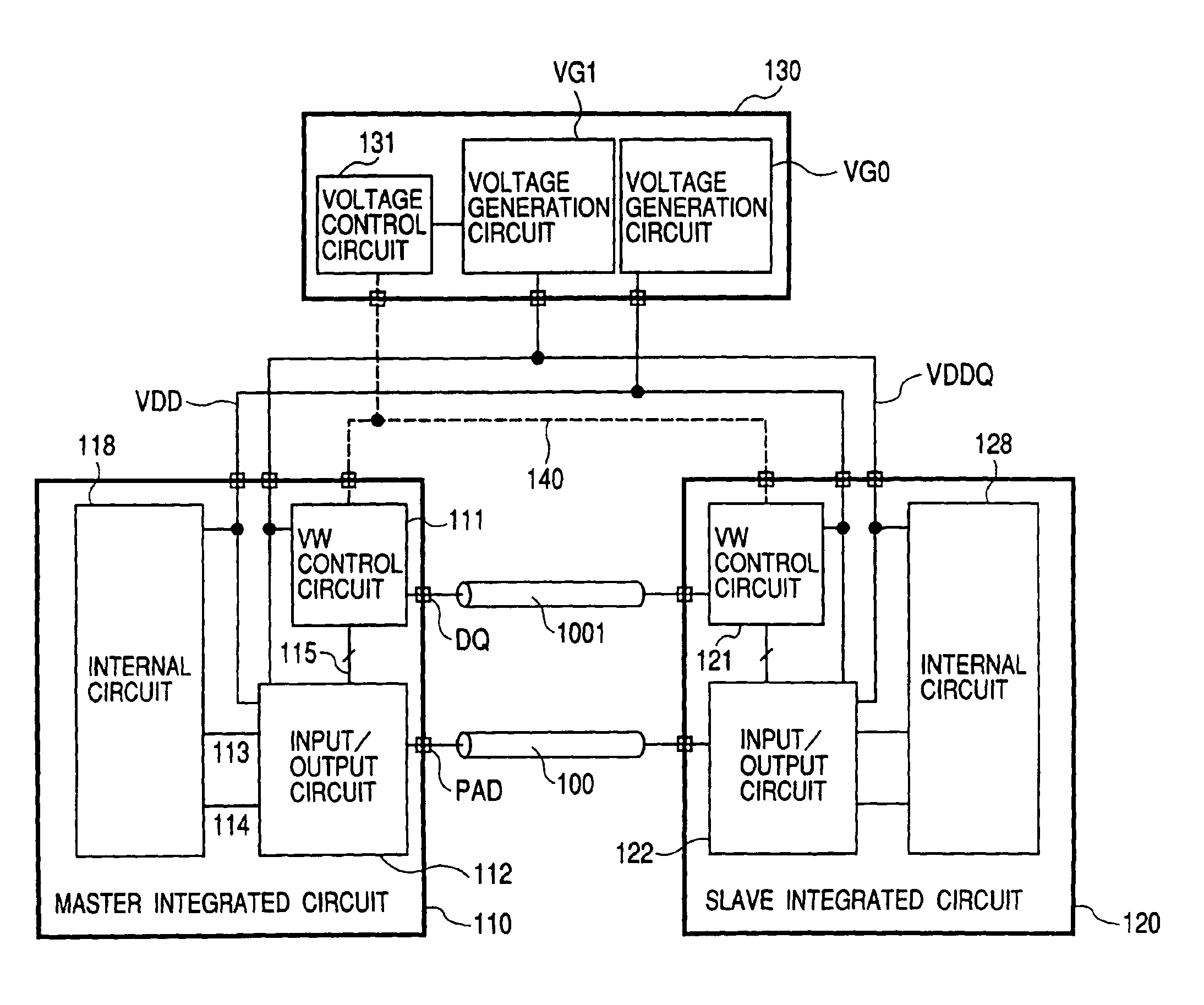
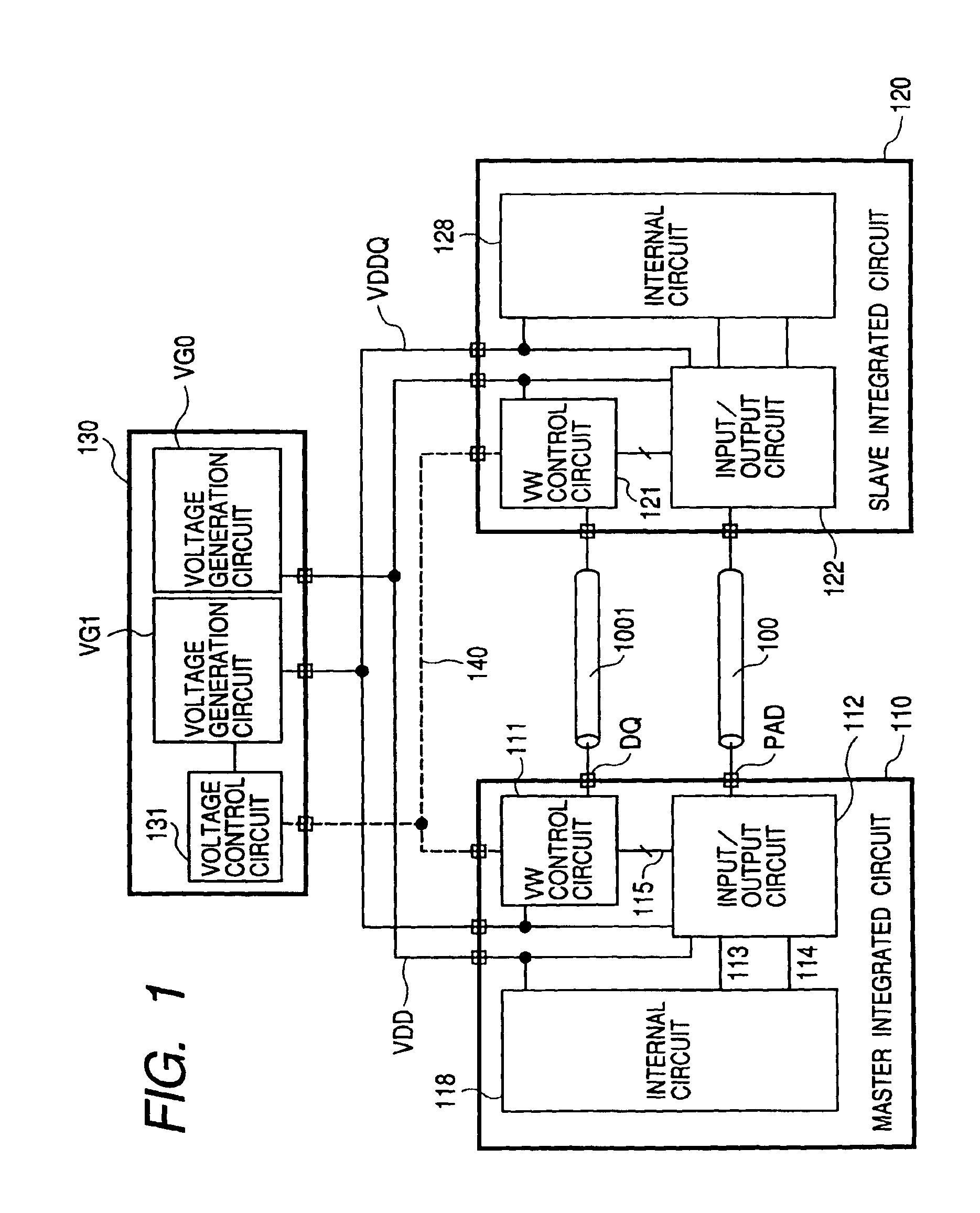
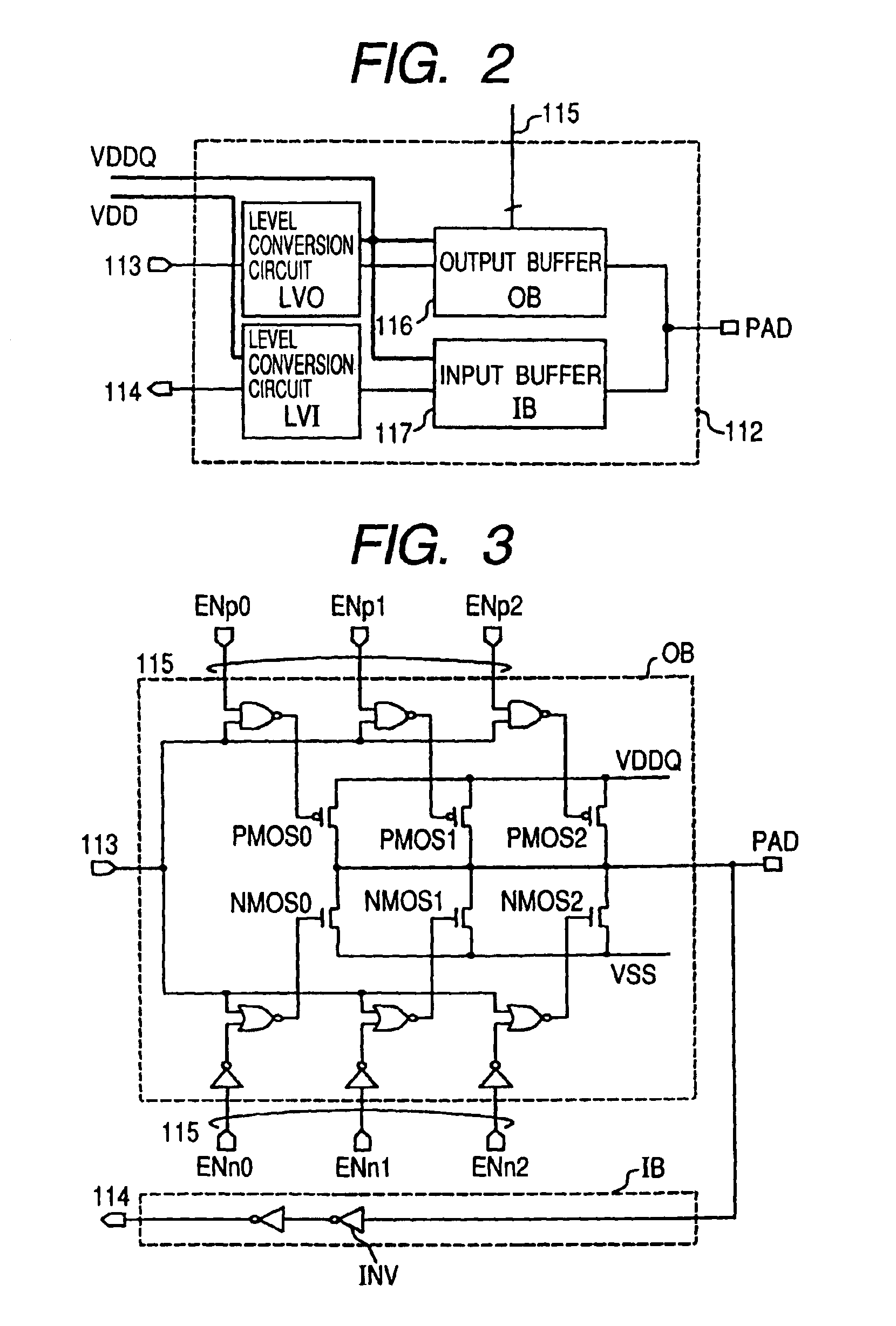
Output buffer circuit with control circuit for modifying supply voltage and transistor size
InactiveUS6937059B2Reduce power consumptionReduce total powerInput/output impedence modificationReliability increasing modificationsImpedance matchingResistor
In this invention, a control circuit (111) controls both the power supply voltage (VDDQ) and the transistor size of the external output buffer to thereby select the lowest supply voltage that achieves the impedance matching with the transmission line (100), to thereby save bus termination by a resistor, thus consequently achieving both the lowering of the power consumption and the speeding-up in the data transmission. The power consumption during the data transmission is proportional to the square of the supply voltage. If the operational supply voltage of the external output buffer is lowered, the power consumption will be reduced accordingly. If the operational supply voltage of the external output buffer is lowered, the impedance thereof will be increased apparently; and at the same time, if the transistor size of the external output buffer is increased, the increased impedance will be decreased. By bringing the output impedance (ON-resistance) of the external output buffer into conformity with the impedance of the transmission line, it becomes possible to output the signal without distortions on the waveform.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com