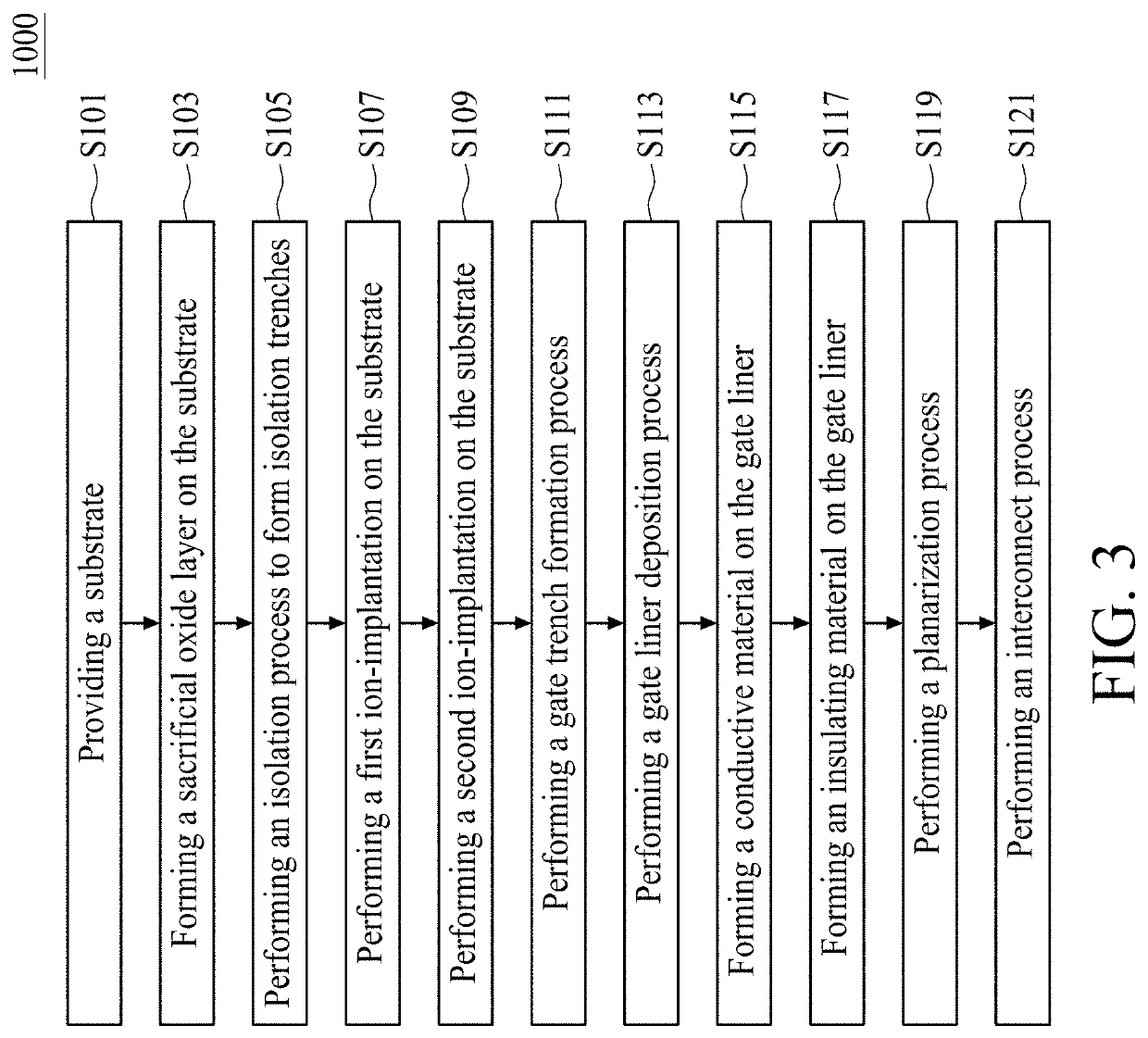
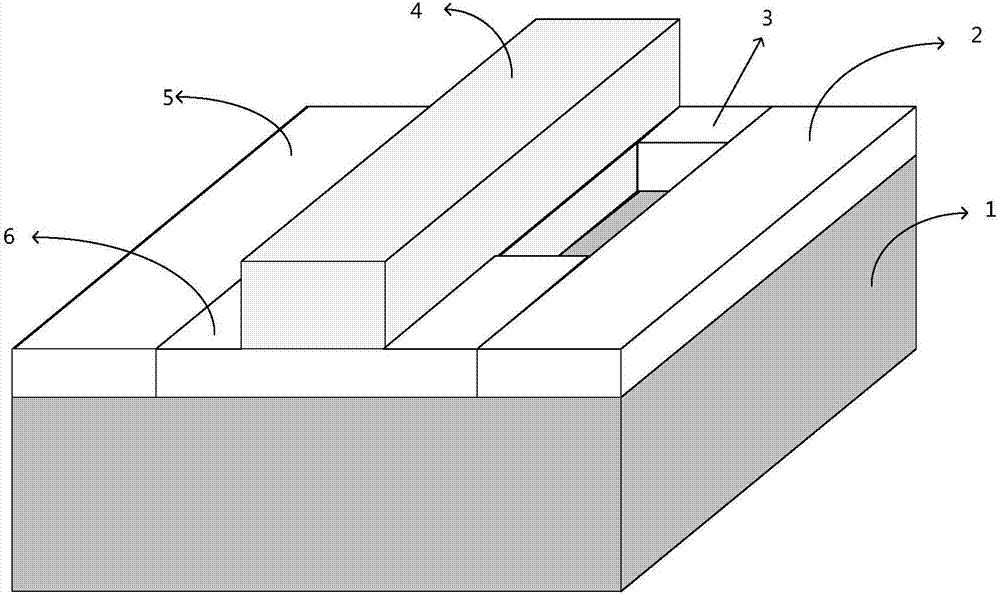
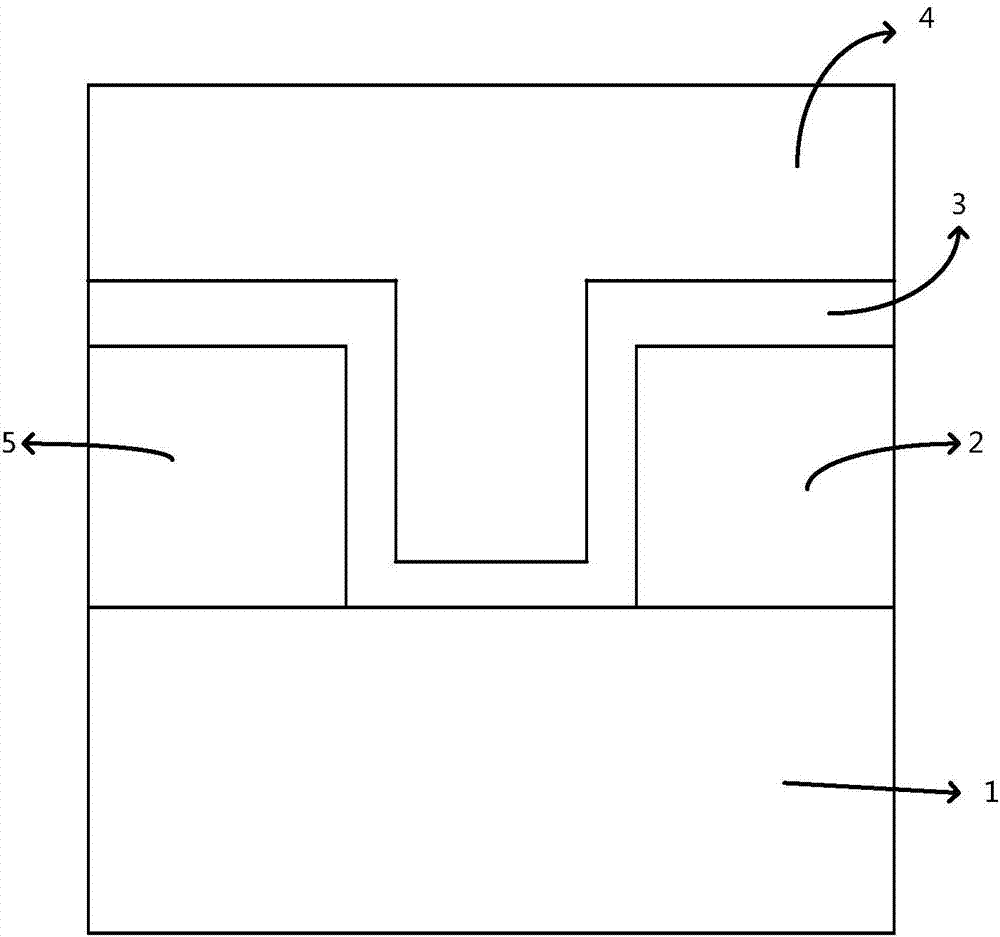
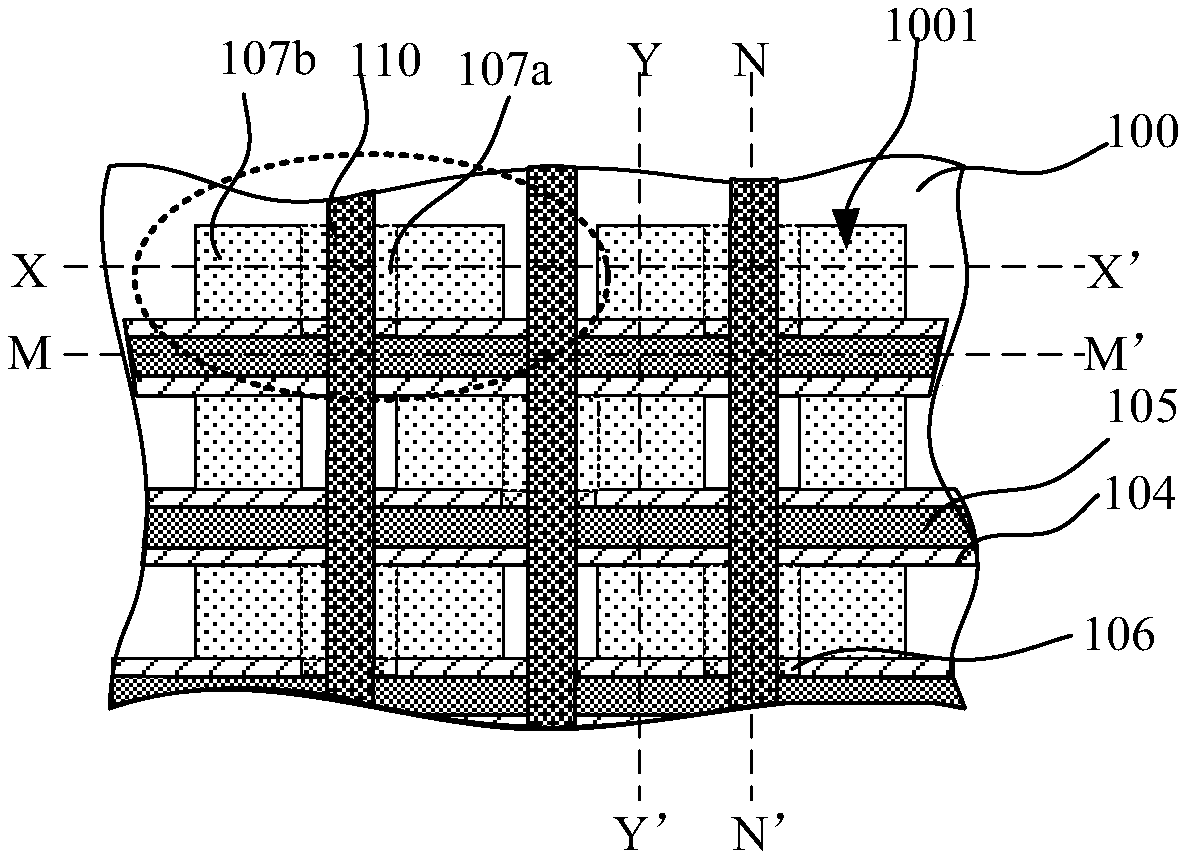
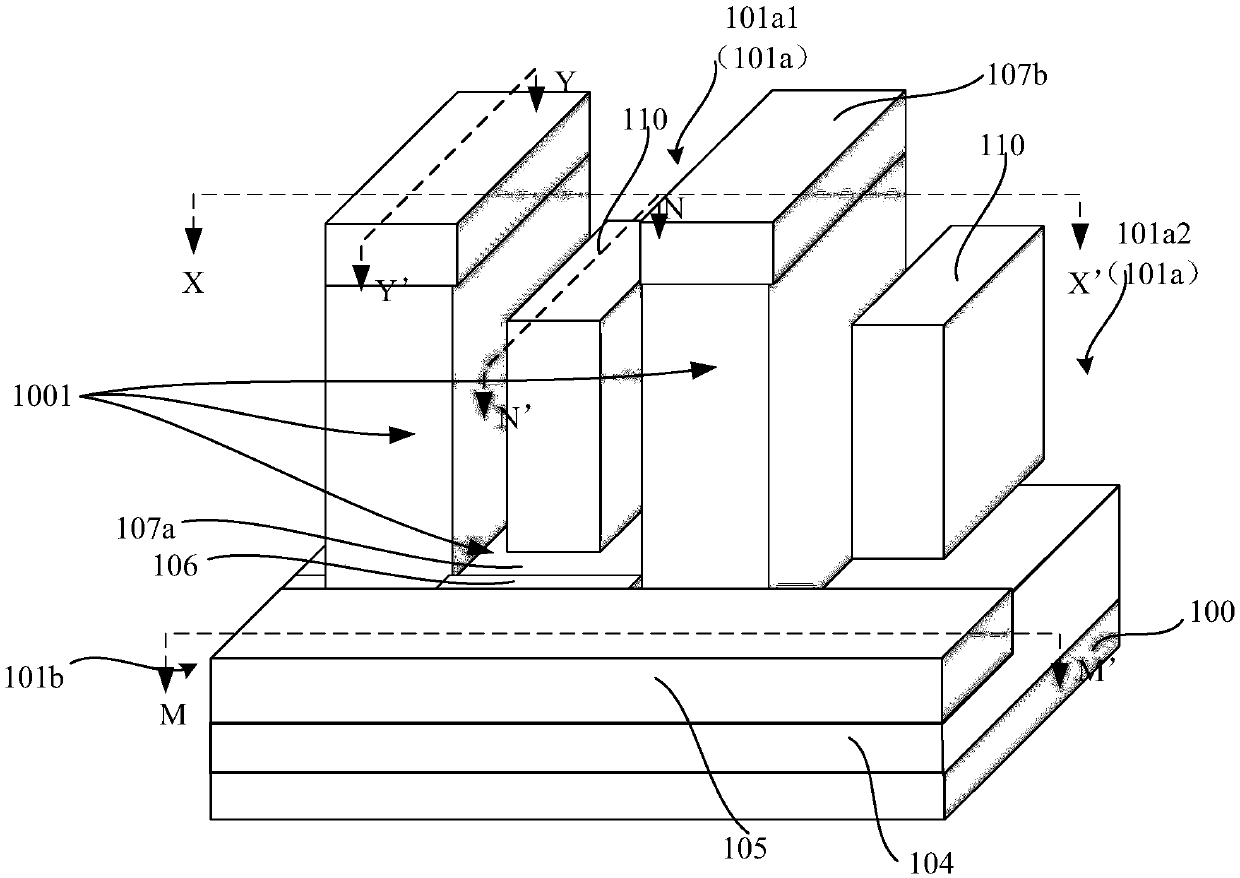
Patents
Literature
55results about How to "Increase the effective channel length" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
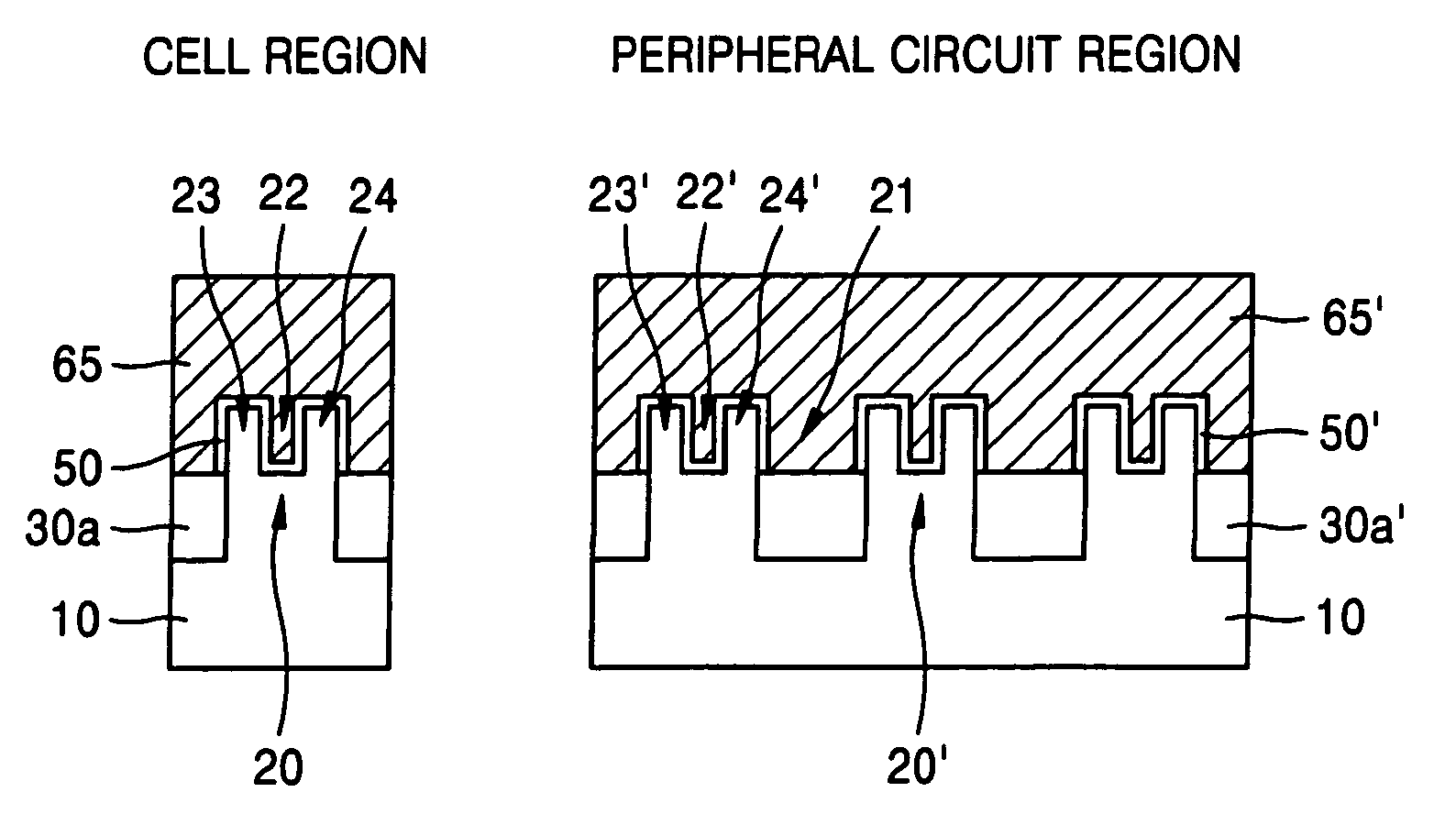
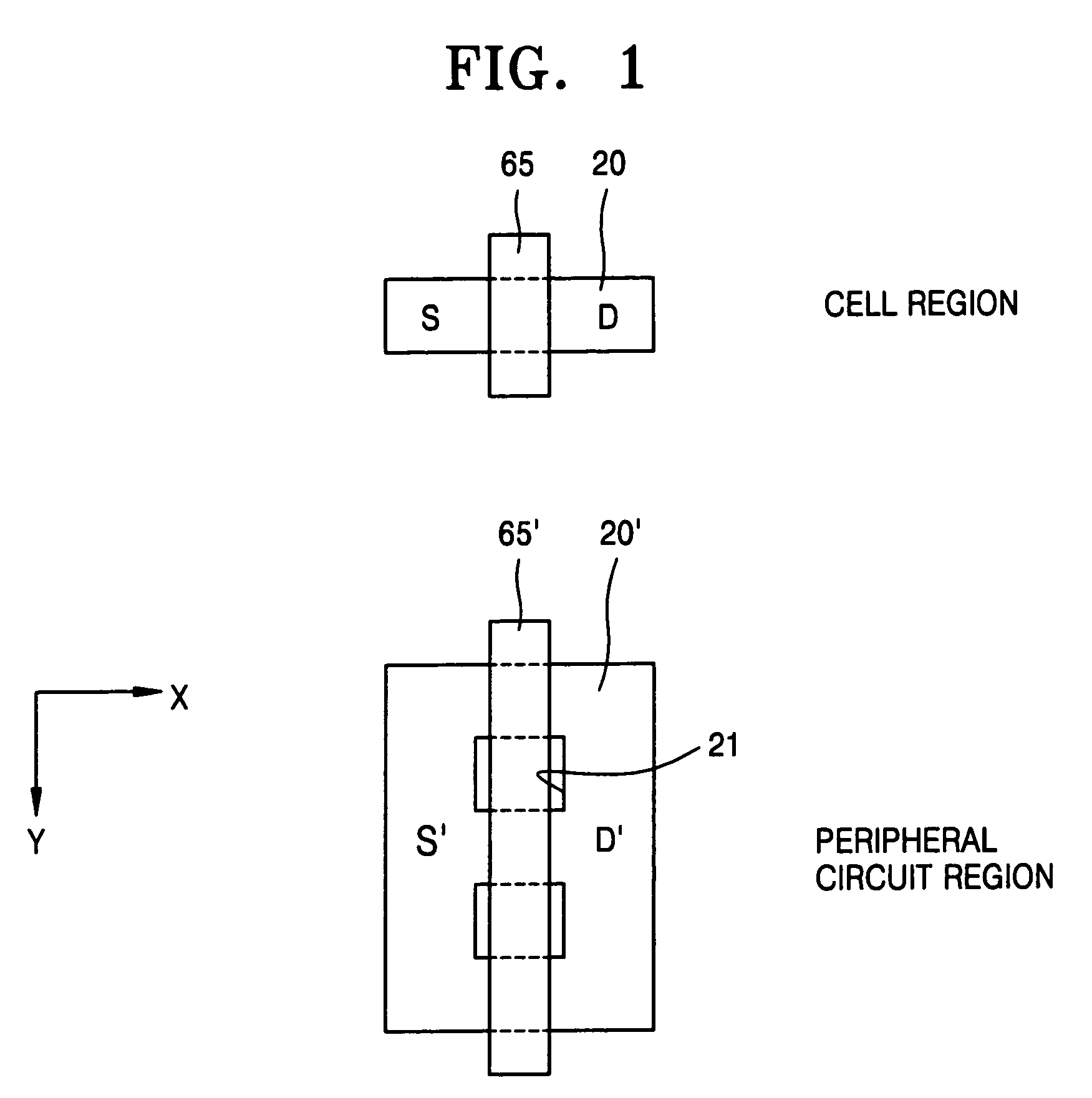
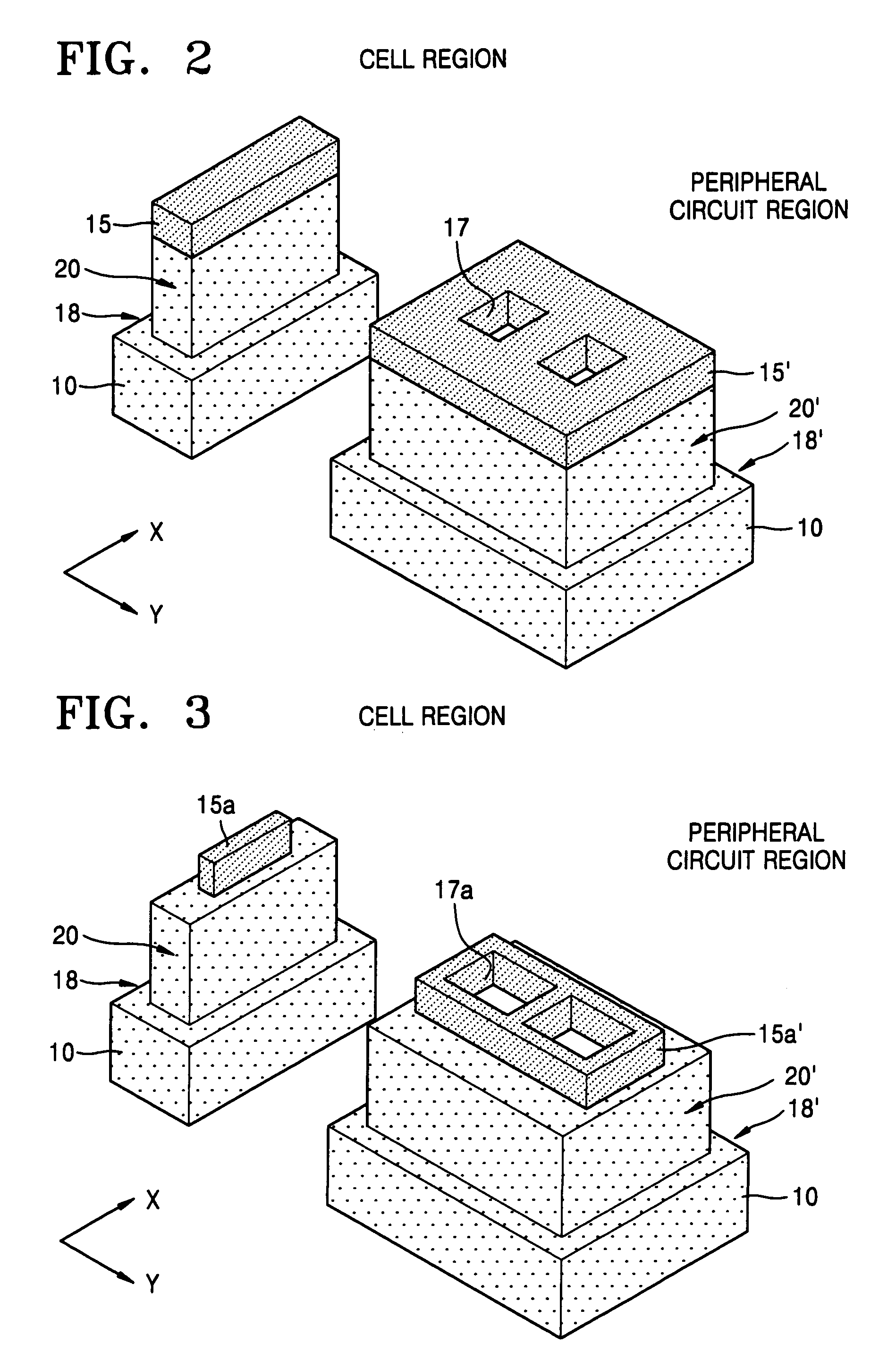
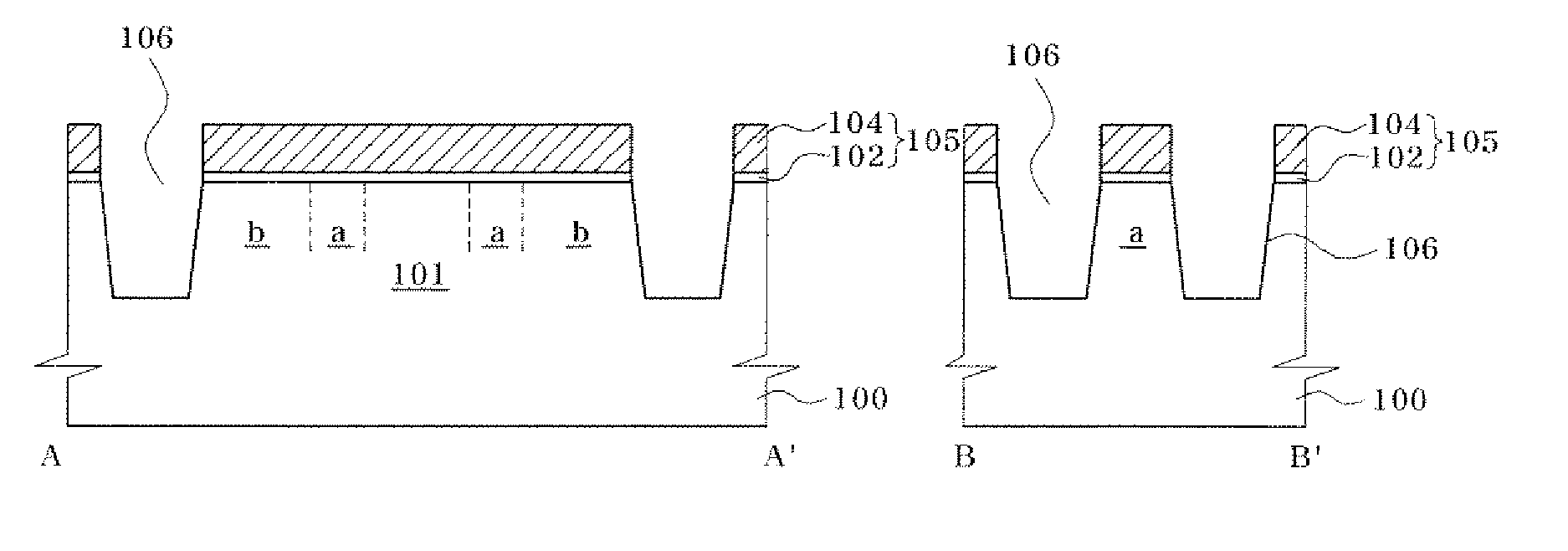
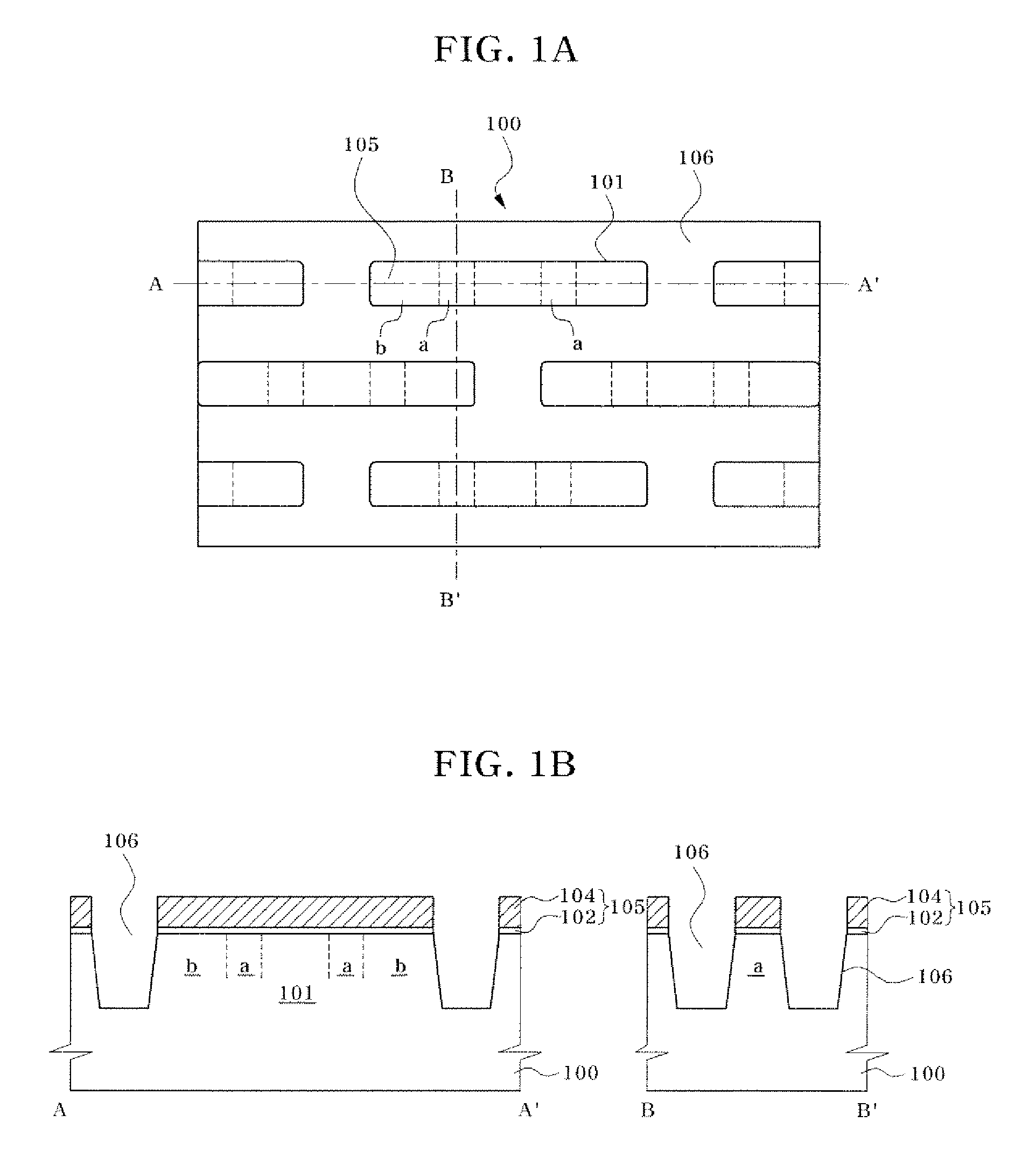
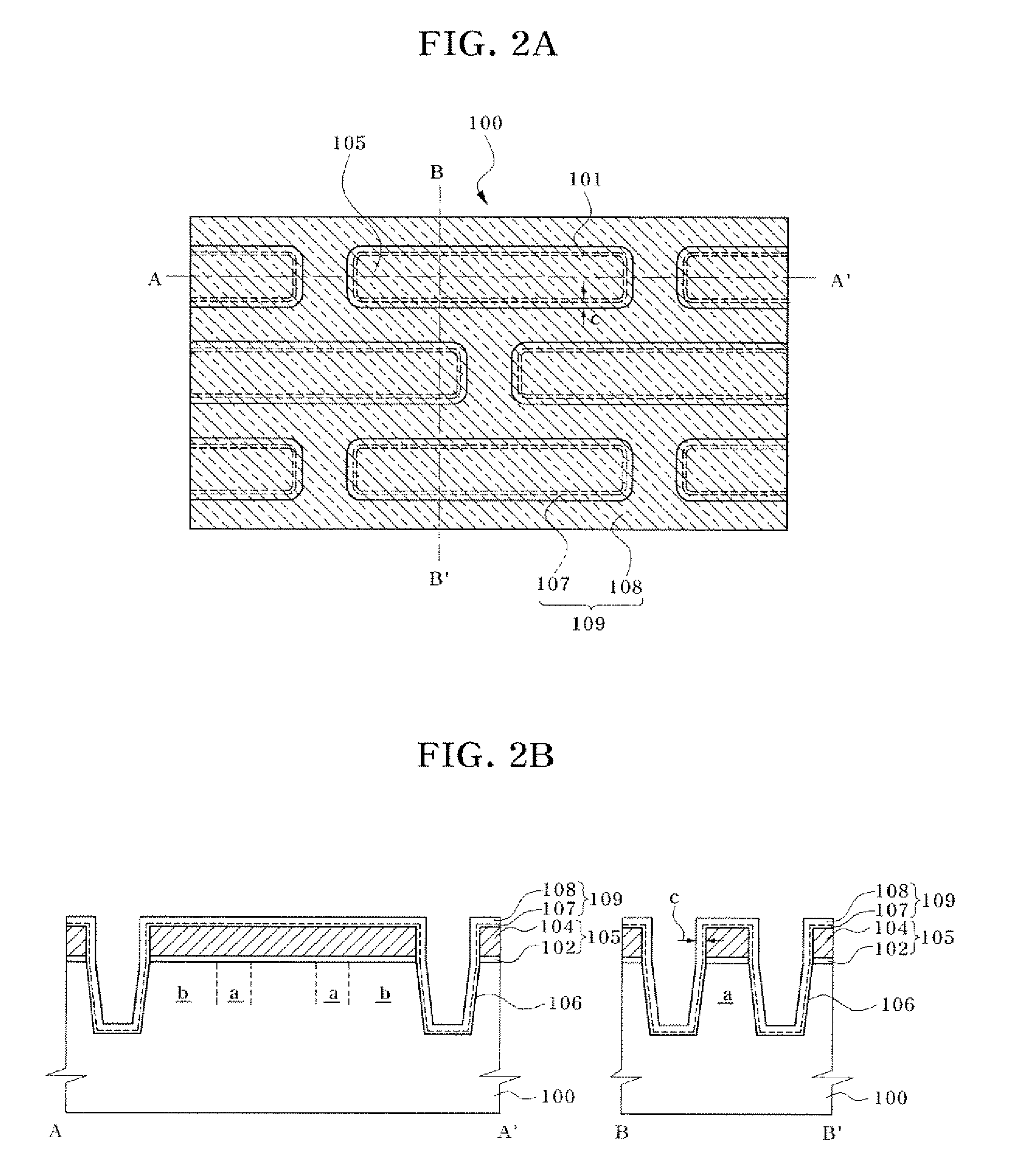
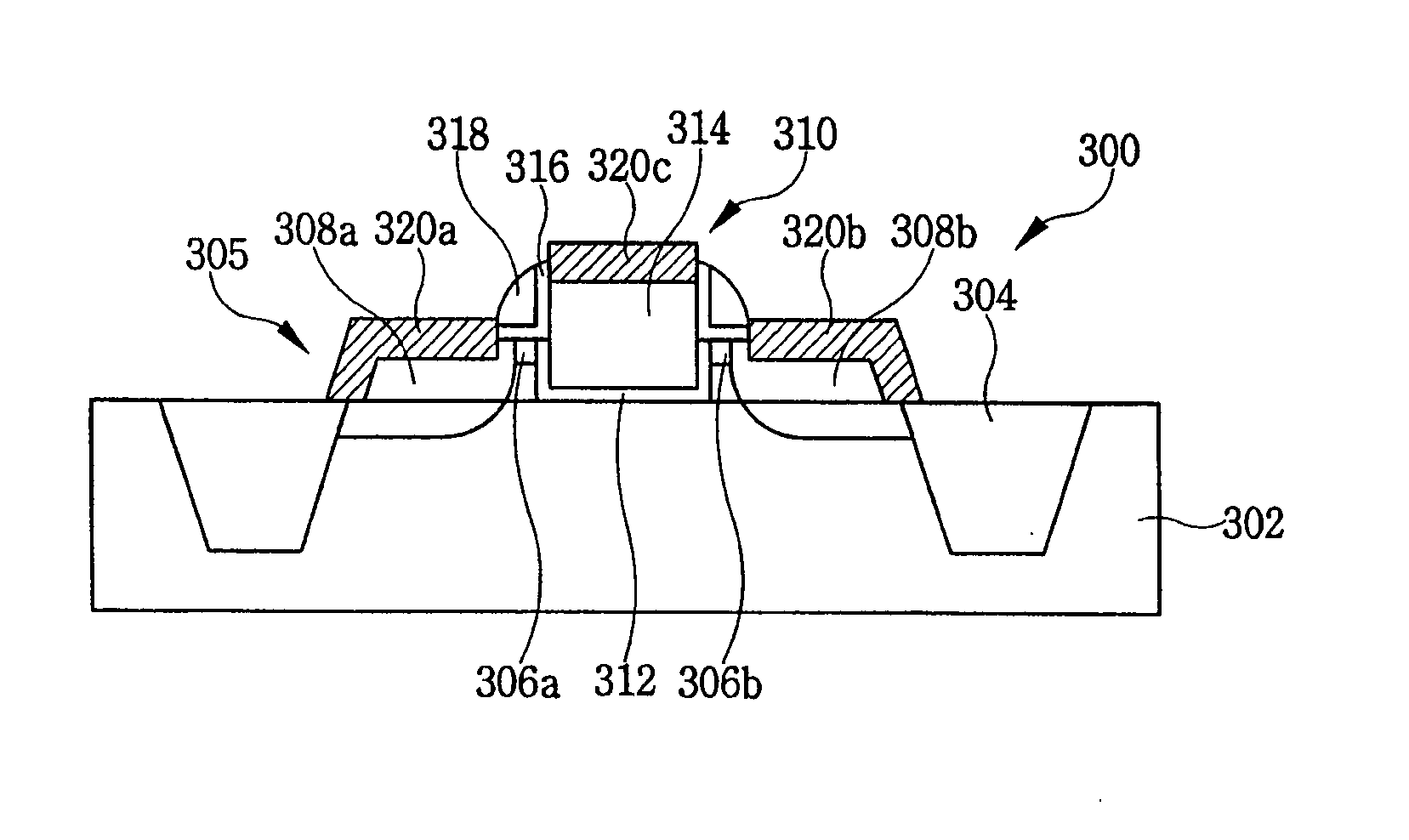
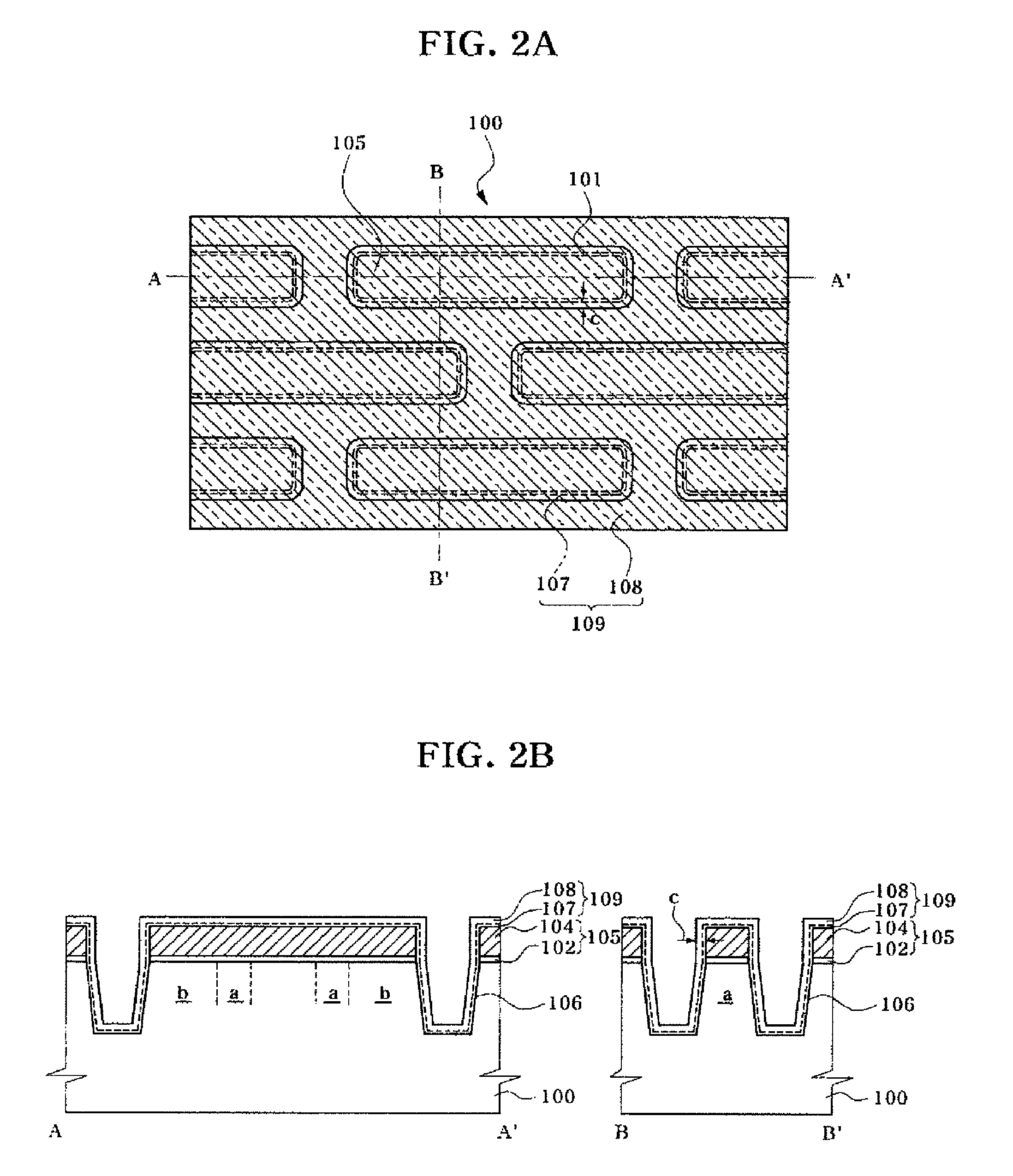
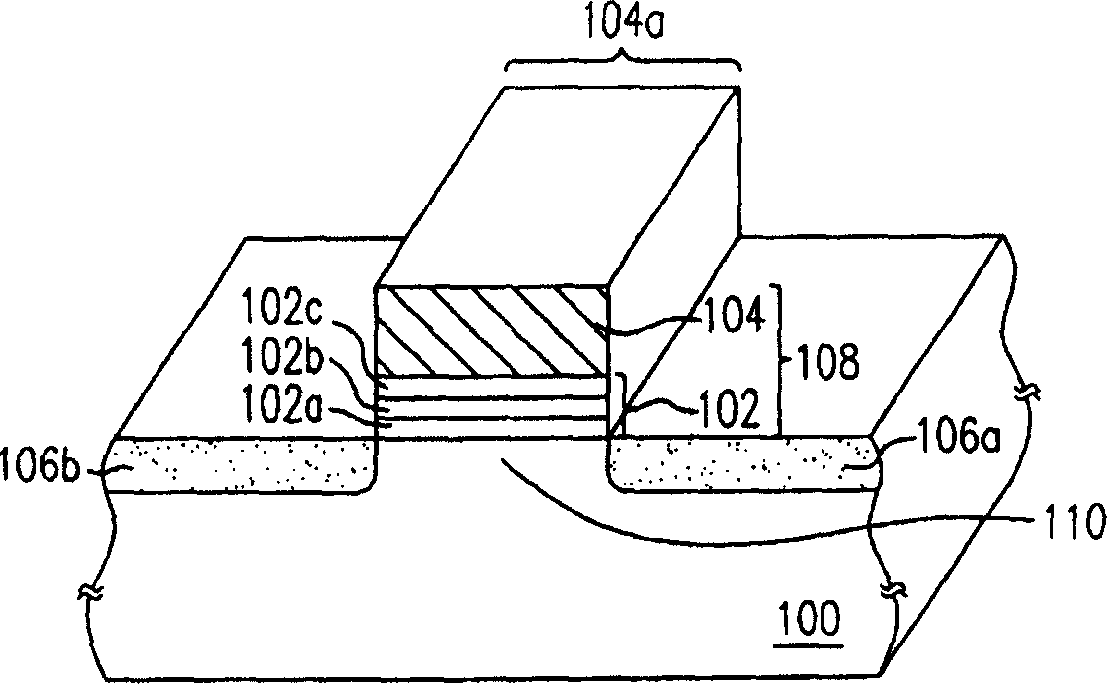
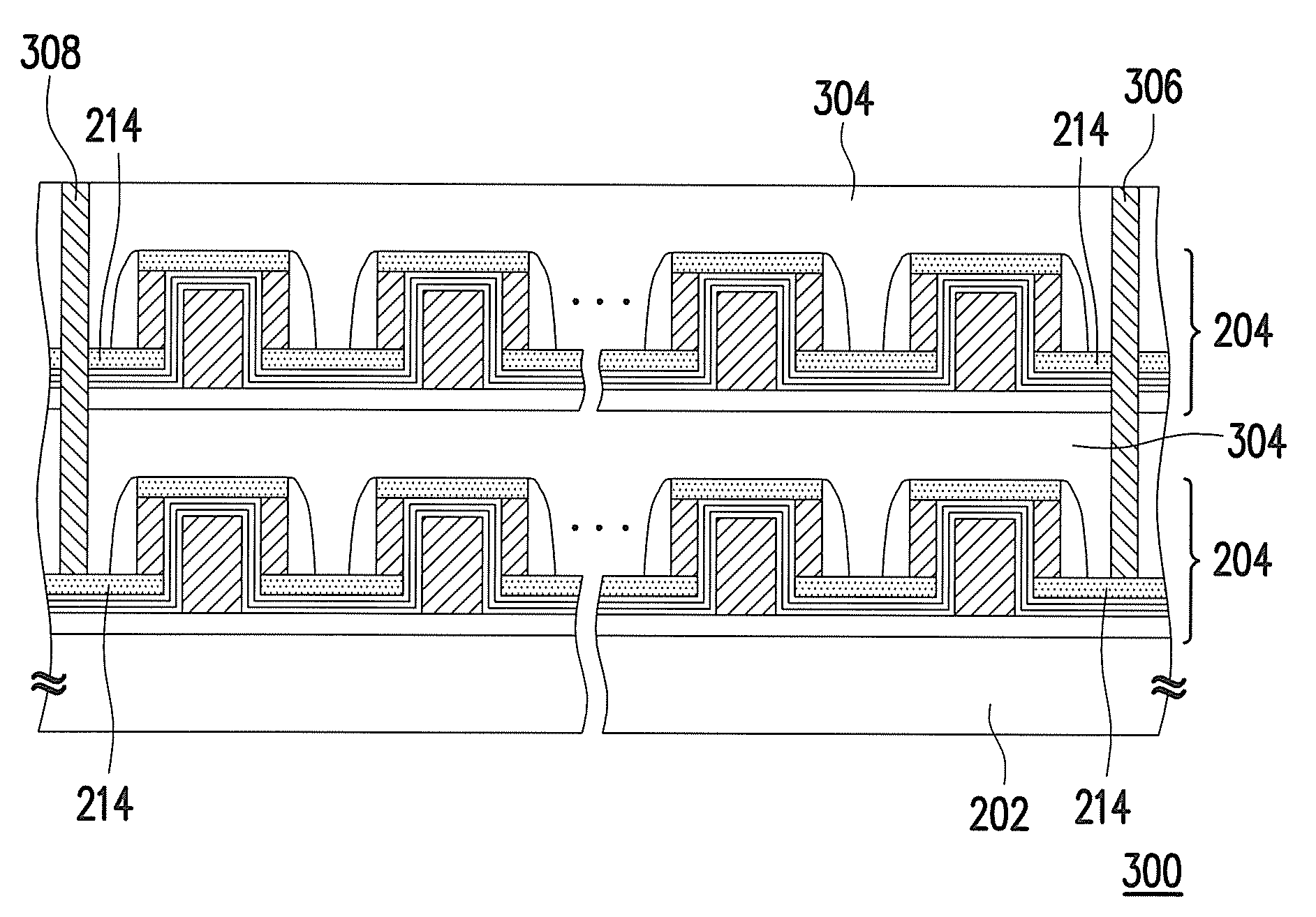
Semiconductor device including a multi-channel fin field effect transistor including protruding active portions and method of fabricating the same
ActiveUS7394116B2Increase the effective channel lengthIncrease the current levelTransistorSolid-state devicesGate dielectricDevice material
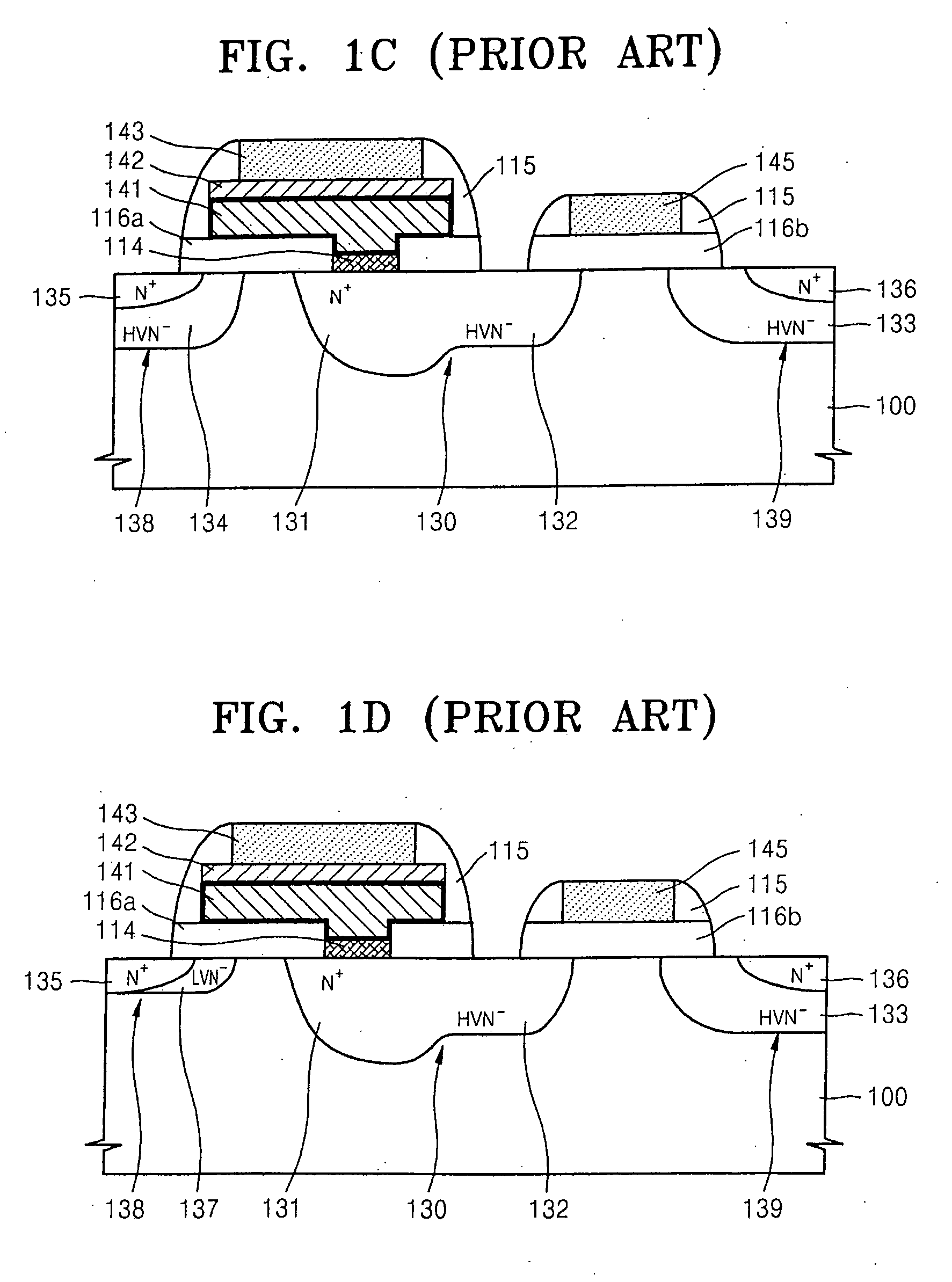
In a semiconductor device, and a method of fabricating the same, the semiconductor device includes a semiconductor substrate having a cell region and a peripheral circuit region, a portion of the semiconductor substrate in the cell region and in the peripheral circuit region including an isolation region defining an active region, a portion of the active region protruding above an upper surface of the isolation region to define at least two active channels, a gate dielectric layer formed over the active region of the semiconductor substrate including the at least two protruding active channels, a gate electrode formed over the gate dielectric layer and the isolation region of the semiconductor substrate, and a source / drain region formed in the active region of the semiconductor substrate on either side of the gate electrode.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Fabrication of a high density long channel dram gate with or without a grooved gate
InactiveUS20010003034A1Limit leakage currentIncrease channel lengthTransistorSolid-state devicesSize increaseImage enhancement
The present invention lengthens gate conductors used in memory chips to limit leakage current, while still allowing the overall size of cells to remain the same. The channel length for each gate is increased by decreasing the size of spaces between gates. Decreases in space size occurs by using photolithographic image enhancement techniques. These techniques allow the space between gate conductors to be smaller while the gate size increases. In addition, a groove may be added that additionally lengthens the effective channel length and provides an additional electrical shield to limit leakage current. These techniques lead to the same density memory cells for a given process with less leakage. Finally, if grooved gate structures are used, having a longer gate conductor allows a three sigma process to be used, which increases yields.
Owner:IBM CORP
Field effect transistor
InactiveUS20080169472A1Transistor size to be scaledIncrease the effective channel lengthTransistorNanoinformaticsEngineeringField-effect transistor
Disclosed are embodiments of a field effect transistor that incorporates an elongated semiconductor body with a spiral-shaped center channel region wrapped one or more times around a gate and with ends that extend outward from the center region in opposite directions away from the gate. Source / drain regions are formed in the end regions by either doping the end regions or by biasing a back gate to impart a preselected Fermi potential on the end regions. This disclosed structure allows the transistor size to be scaled without decreasing the effective channel length to the point where deleterious short-channel effects are exhibited. It further allows the transistor size to be scaled while also allowing the effective channel length to be selectively increased (e.g., by increasing the number of times the channel wraps around the gate). Also, disclosed are embodiments of an associated method of forming the transistor.
Owner:IBM CORP
Fabrication of a high density long channel DRAM gate with or without a grooved gate
InactiveUS6426175B2Limit leakage currentIncrease channel lengthTransistorSolid-state devicesMemory chipHigh density
The present invention lengthens gate conductors used in memory chips to limit leakage current, while still allowing the overall size of cells to remain the same. The channel length for each gate is increased by decreasing the size of spaces between gates. Decreases in space size occurs by using photolithographic image enhancement techniques. These techniques allow the space between gate conductors to be smaller while the gate size increases. In addition, a groove may be added that additionally lengthens the effective channel length and provides an additional electrical shield to limit leakage current. These techniques lead to the same density memory cells for a given process with less leakage. Finally, if grooved gate structures are used, having a longer gate conductor allows a three sigma process to be used, which increases yields.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
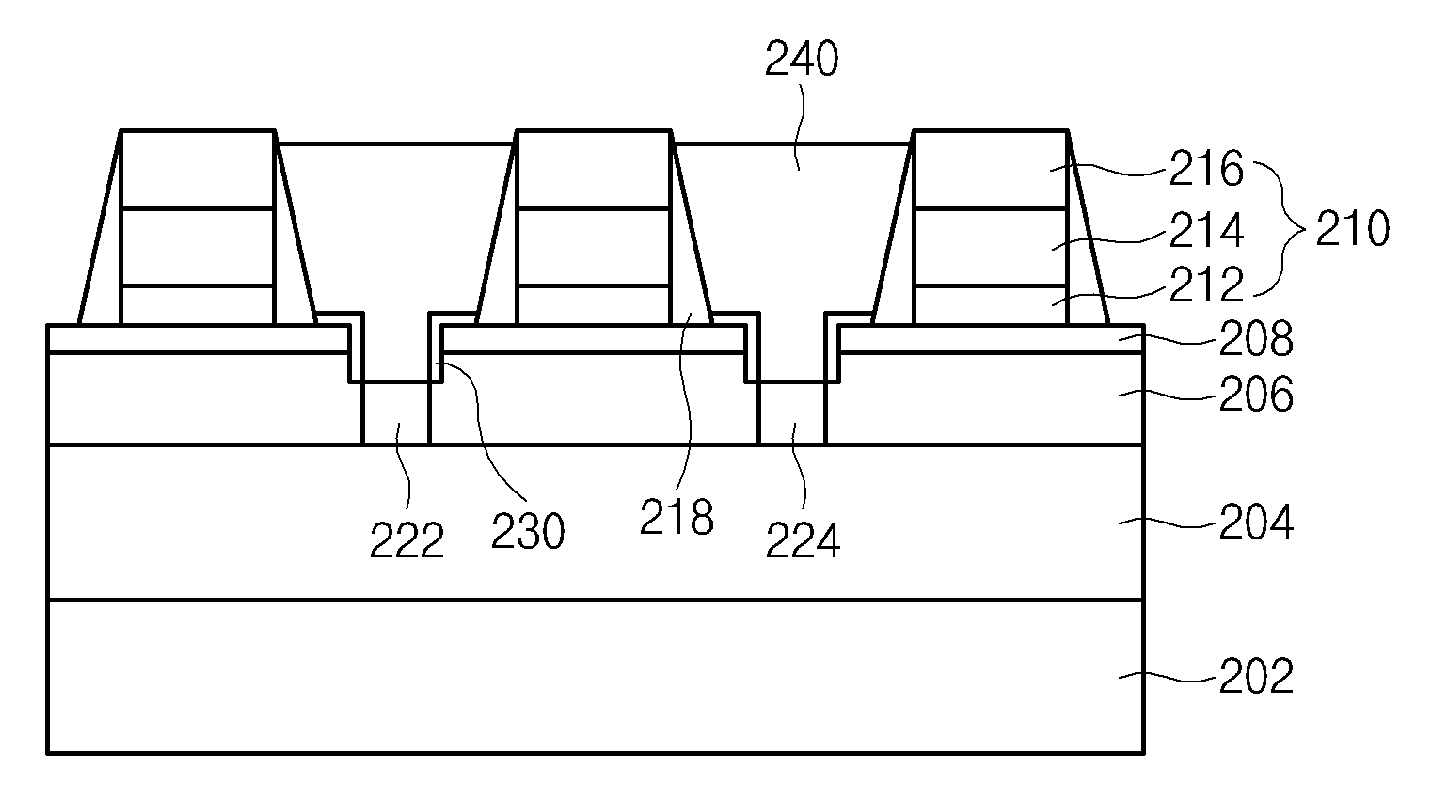
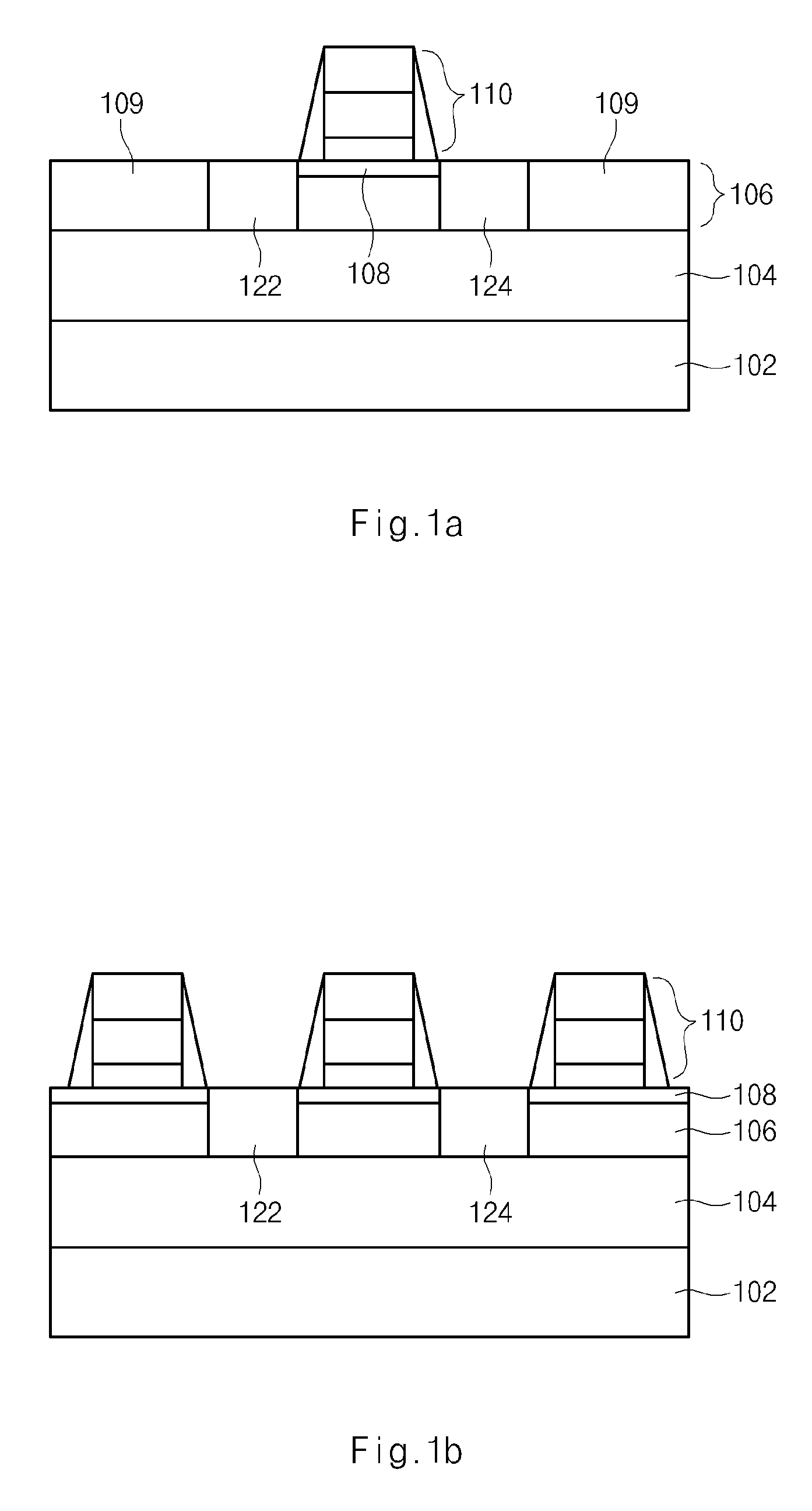
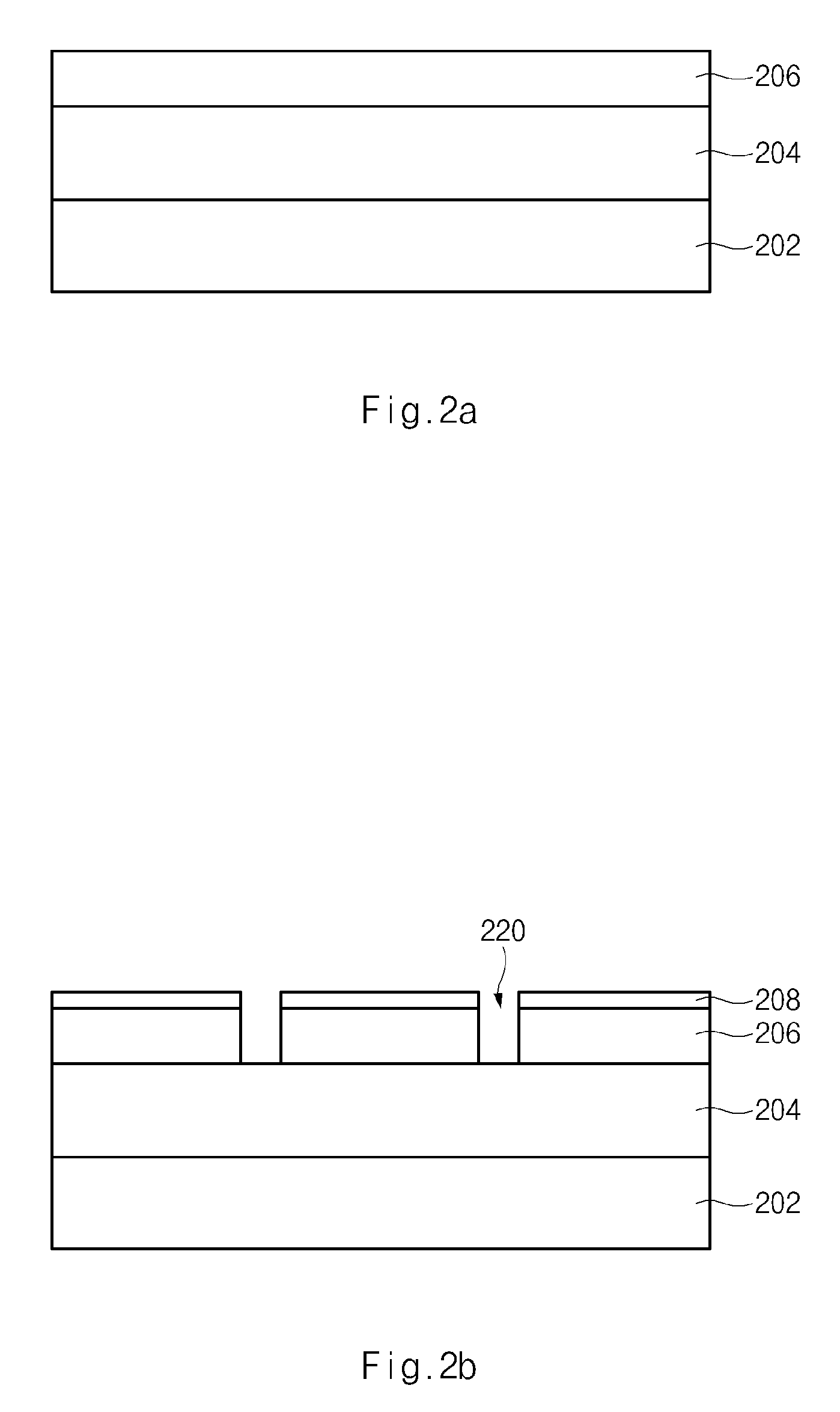
Method For Manufacturing Semiconductor Device Having Bulb-Type Recessed Channel
ActiveUS20080160700A1Increase the effective channel lengthExcellent characteristicsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesIsolation layerGate stack
A method for manufacturing a semiconductor device having a bulb-type recessed channel including: forming a trench that defines an active region including a channel region having a sidewall and a junction region in a semiconductor substrate; forming a device isolation layer that buries the trench, and forming a sidewall pattern that covers the sidewall of the channel region; forming a bulb-type trench by overlapping with the channel region in the semiconductor substrate, and forming a bottom protrusion having a predetermined space parted from the device isolation layer by removing the sidewall pattern; and forming a gate stack that overlaps with the bulb-type trench and the bottom protrusion.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
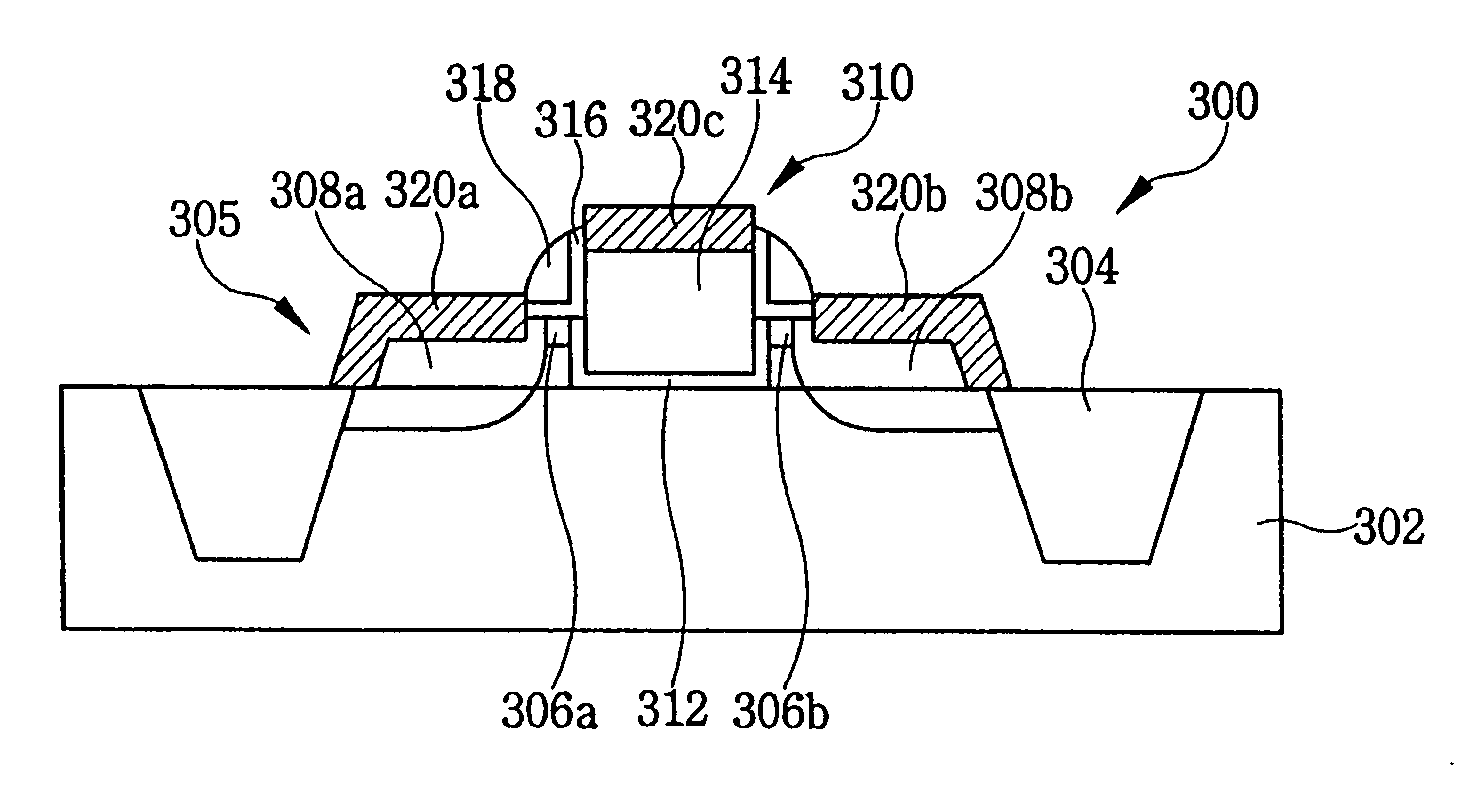
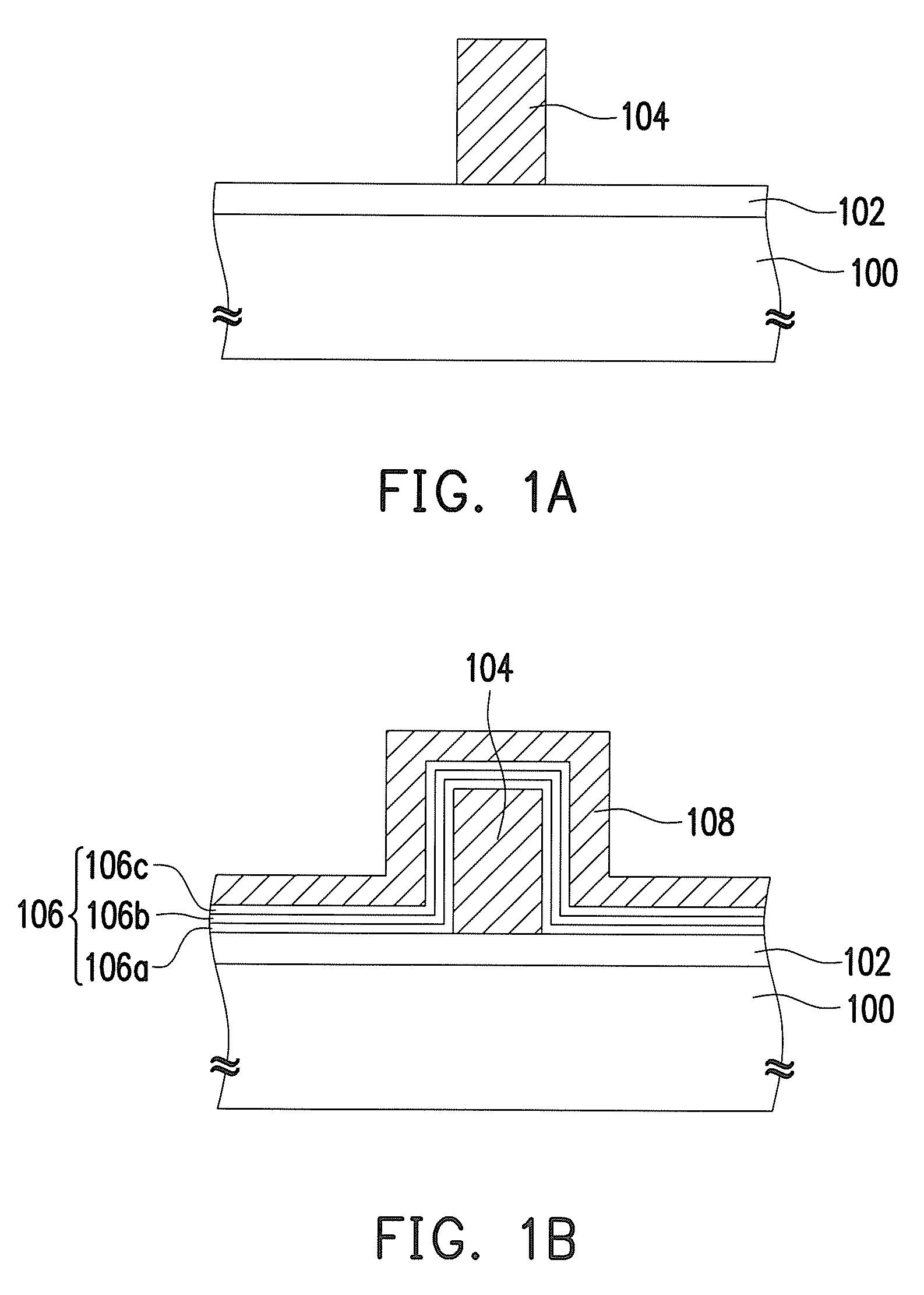
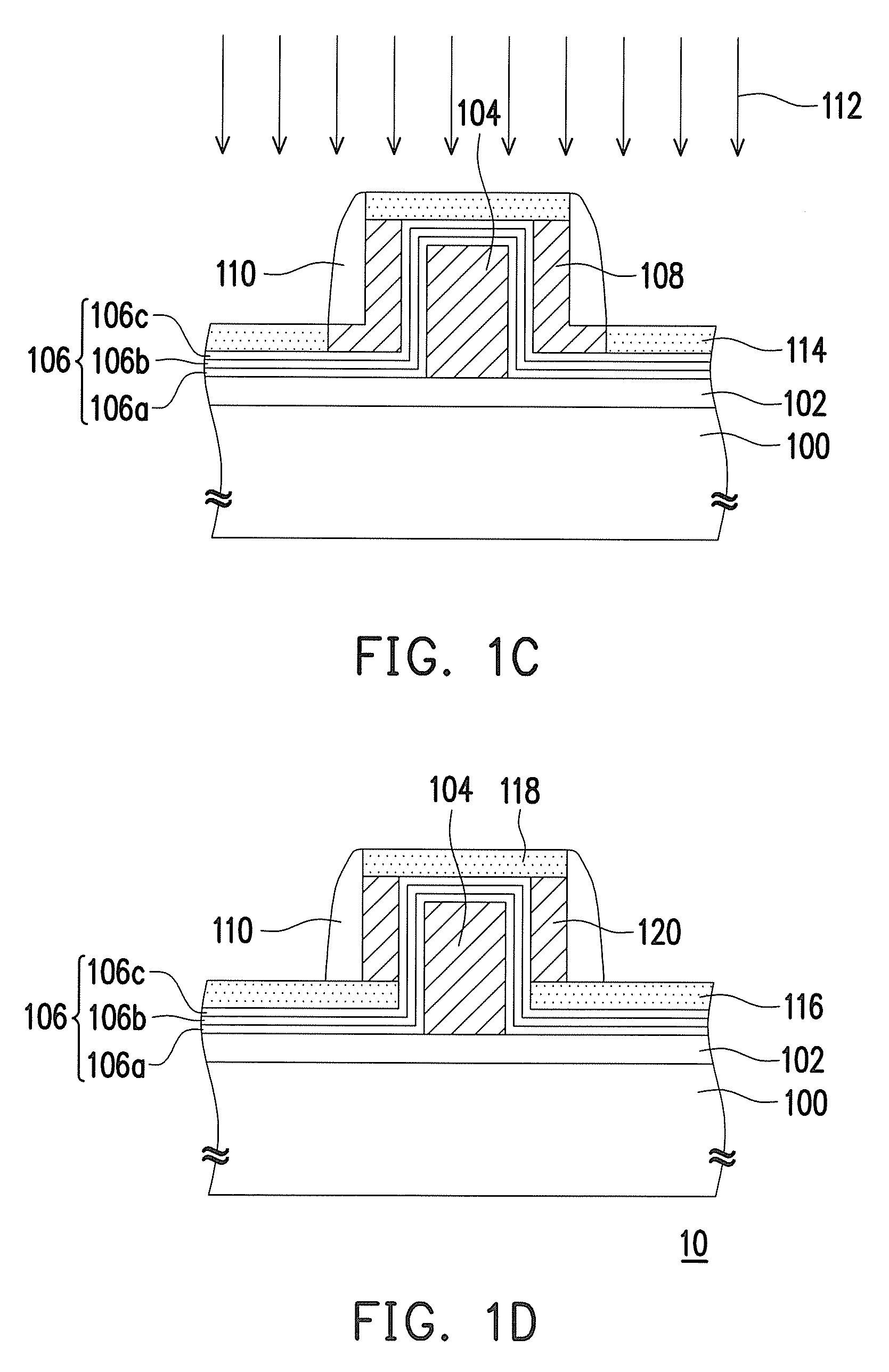
MOS transistor with elevated source and drain structures and method of fabrication thereof
InactiveUS20070164354A1Controlled diffusionIncrease the effective channel lengthTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDopantEngineering
A transistor and method of formation thereof includes source and drain extension regions in which the diffusion of dopants into the channel region is mitigated or eliminated. This is accomplished, in part, by elevating the source and drain extension regions into the epitaxial layer formed on the underlying substrate. In doing so, the effective channel length is increased, while limiting dopant diffusion into the channel region. In this manner, performance characteristics of the transistor can be accurately determined by controlling the respective geometries (i.e. depths and widths) of the source / drain extension regions, the source / drain regions, the channel width and an optional trench formed in the underlying substrate. In the various embodiments, the source / drain regions and the source / drain extension regions may extend partially, or fully, through the epitaxial layer, or even into the underlying semiconductor substrate.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
EEPROM device and method of fabricating the same
InactiveUS20060199334A1Increase the effective channel lengthLower threshold voltageTransistorSolid-state devicesBit lineSemiconductor
A memory device comprises a semiconductor substrate of a first conductive type, a memory transistor, a select transistor, a floating junction region, a common source region, and a bit line junction region. The memory transistor positions on the semiconductor substrate and comprises a gate insulating film formed on the semiconductor substrate and a memory transistor gate formed on the gate insulating film. The gate insulating film includes a tunnel insulating film. The select transistor positions on the semiconductor substrate and is separated from the memory transistor gate. The select transistor comprises a gate insulating film formed on the semiconductor substrate and a select transistor gate formed on the gate insulating film. A floating junction region is formed of a second conductive type on the semiconductor substrate below the tunnel insulating film. The common source region of a second conductive type is formed on the semiconductor substrate adjacent to the memory transistor gate and separated from the floating junction region. A bit line junction region of a second conductive type is formed on the semiconductor substrate adjacent to the select transistor gate and is separated from the floating junction region, wherein the common source region includes a single junction region with a first doping concentration, and a depth of the common source region is shallower than a depth of the floating junction region and the bit line junction region.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
SONOS flash memory unit and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN101740576AImplementing Substrate BiasingOvercoming the disadvantages of programming difficultiesSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingComputational physicsIon implantation
The invention discloses an SONOS flash memory unit and a manufacturing method thereof, wherein an SONOS component and a selected transistor both adopt enhanced PMOS components, therefore, the substrate bias of the components can be realized without a deep N-well process. A P-type buried channel on the surface of an N-well can provide a great deal of cavities for the programming of the SONOS component, thereby greatly improving the programming efficiency and overcoming the defects of large effective quality and difficult programming of the cavities. The P-type SONOS component can obtain a programming and erasing threshold voltage which is more symmetrical than that of an N-type SONOS component; furthermore, the invention ensures that the drain electrode implantation volume is larger than that of a source electrode, increases the effective channel length and creates conditions for shortening the size of the components by fully utilizing the characteristic of small grid spacing between the two components of the flash memory unit and adopting source-drain ion implantation with large angle and light dope; and finally, the invention further reduces the short channel effect by carrying out bag-shaped ion implantation on the two components of the flash memory unit.
Owner:SHANGHAI HUAHONG GRACE SEMICON MFG CORP
MOS transistor with elevated source and drain structures and method of fabrication thereof
ActiveUS20070166926A1Controlled diffusionIncrease the effective channel lengthTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDopantChannel width
A transistor and method of formation thereof includes source and drain extension regions in which the diffusion of dopants into the channel region is mitigated or eliminated. This is accomplished, in part, by elevating the source and drain extension regions into the epitaxial layer formed on the underlying substrate. In doing so, the effective channel length is increased, while limiting dopant diffusion into the channel region. In this manner, performance characteristics of the transistor can be accurately determined by controlling the respective geometries (i.e. depths and widths) of the source / drain extension regions, the source / drain regions, the channel width and an optional trench formed in the underlying substrate. In the various embodiments, the source / drain regions and the source / drain extension regions may extend partially, or fully, through the epitaxial layer, or even into the underlying semiconductor substrate.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Semiconductor device
InactiveUS8106444B2Potential barrier is preventedTotal current dropTransistorSolid-state devicesSemiconductorSilicon
Owner:NEC CORP
Pixel structure
ActiveCN109003579AIncrease the effective channel lengthStatic indicating devicesActive layerTransistor
The invention provides a pixel structure comprising a thin film transistor having a first gate electrode and a second gate electrode and an active layer having a first strip part and a second strip part. The first gate electrode is inclined in the extending direction of the orthogonal projection on the plane of the active layer and the extending direction of the first strip part. The second gate electrode is inclined in the extending direction of the orthogonal projection on the plane of the active layer and the extending direction of the second strip part. The first gate electrode and the first strip part of the active layer are obliquely overlapped and the second gate electrode and the second strip part of the active layer are obliquely overlapped so that the effective channel length ofthe channel region of the thin film transistor can be enhanced.
Owner:WUHAN CHINA STAR OPTOELECTRONICS SEMICON DISPLAY TECH CO LTD
MOS transistor with elevated source and drain structures and method of fabrication thereof
InactiveUS20070164373A1Controlled diffusionIncrease the effective channel lengthTransistorSolid-state devicesDopantChannel width
A transistor and method of formation thereof includes source and drain extension regions in which the diffusion of dopants into the channel region is mitigated or eliminated. This is accomplished, in part, by elevating the source and drain extension regions into the epitaxial layer formed on the underlying substrate. In doing so, the effective channel length is increased, while limiting dopant diffusion into the channel region. In this manner, performance characteristics of the transistor can be accurately determined by controlling the respective geometries (i.e. depths and widths) of the source / drain extension regions, the source / drain regions, the channel width and an optional trench formed in the underlying substrate. In the various embodiments, the source / drain regions and the source / drain extension regions may extend partially, or fully, through the epitaxial layer, or even into the underlying semiconductor substrate.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
High-integration-level and high-mobility-ratio source, drain and gate auxiliary control type junction-free transistor
InactiveCN104282751ALow source-drain resistanceIncrease the effective channel lengthSemiconductor devicesShort-channel effectDrain resistance
The invention relates to a high-integration-level and high-mobility-ratio source, drain and gate auxiliary control type junction-free transistor. Two independently-controlled gate electrodes including the source and drain control gate electrode and the gate electrode are adopted, so that the high mobility ratio of the device in a channel with the low doping concentration can be guaranteed, and the device mobility ratio reduction and the device stability reduction caused by strengthening of the random scattering effect under the high doping concentration are avoided; meanwhile, the low source and drain resistance can be obtained through the independent control effect of the source and drain control gate electrode and the gate electrode, and therefore the contradictions that the source and drain resistance will be increased if the doping concentration of a channel of a common junction-free transistor is excessively low, and the device mobility ratio reduction and the device stability reduction will be caused if the doping concentration is excessively high are overcome; in addition, the groove-shaped channel design is adopted; compared with a common plane structure, on the premise that a chip area is not additionally increased, the effective channel length is obviously increased to reduce the short channel effect of the device under the deep nanoscale, and therefore the high-integration-level and high-mobility-ratio source, drain and gate auxiliary control type junction-free transistor is suitable for application and popularization.
Owner:SHENYANG POLYTECHNIC UNIV
Double-vertical-channel transistor, integrated circuit memory and preparation method thereof
PendingCN110931558AHighly integratedIncrease the effective channel lengthTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectrical connectionStructural engineering
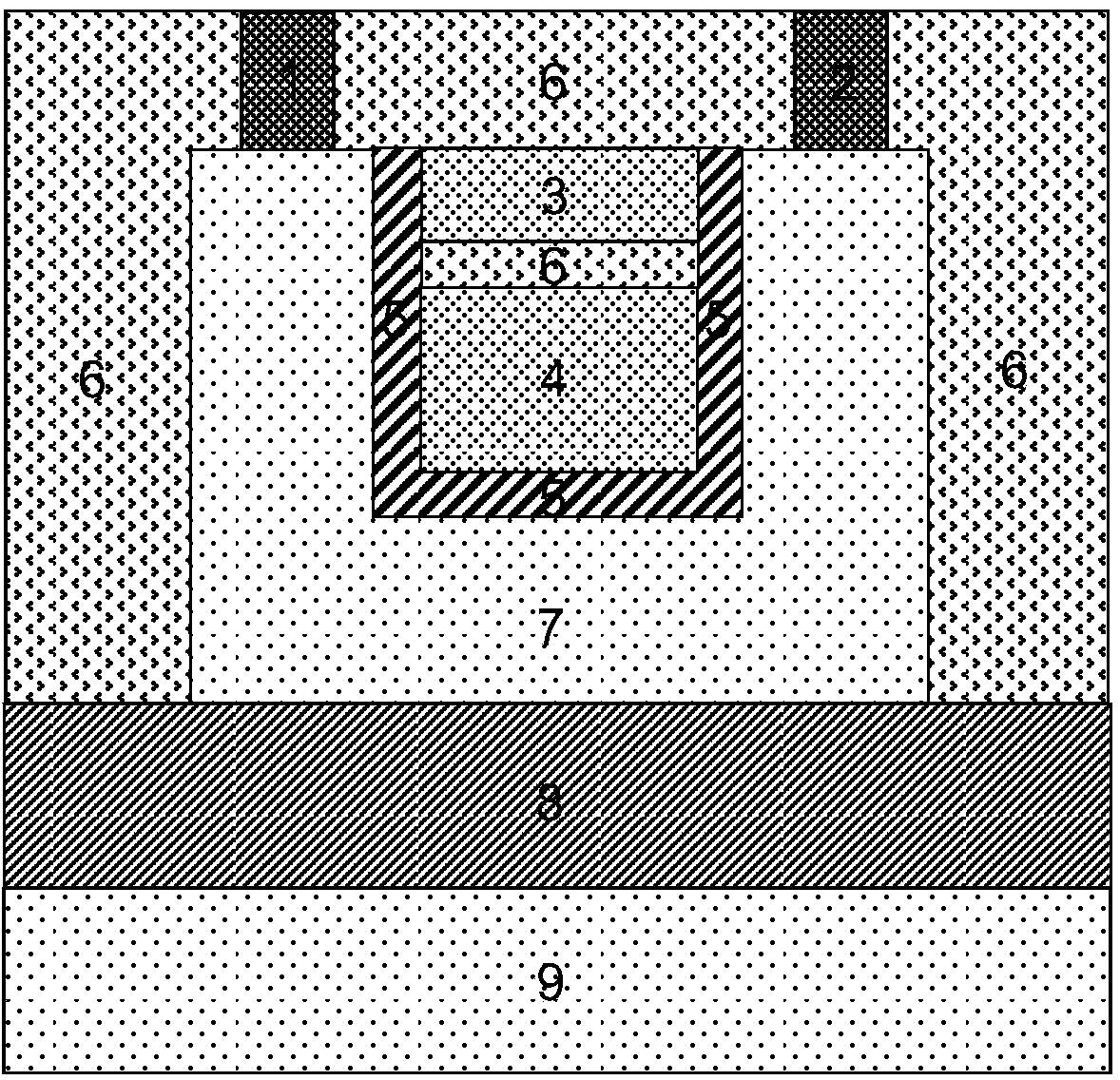
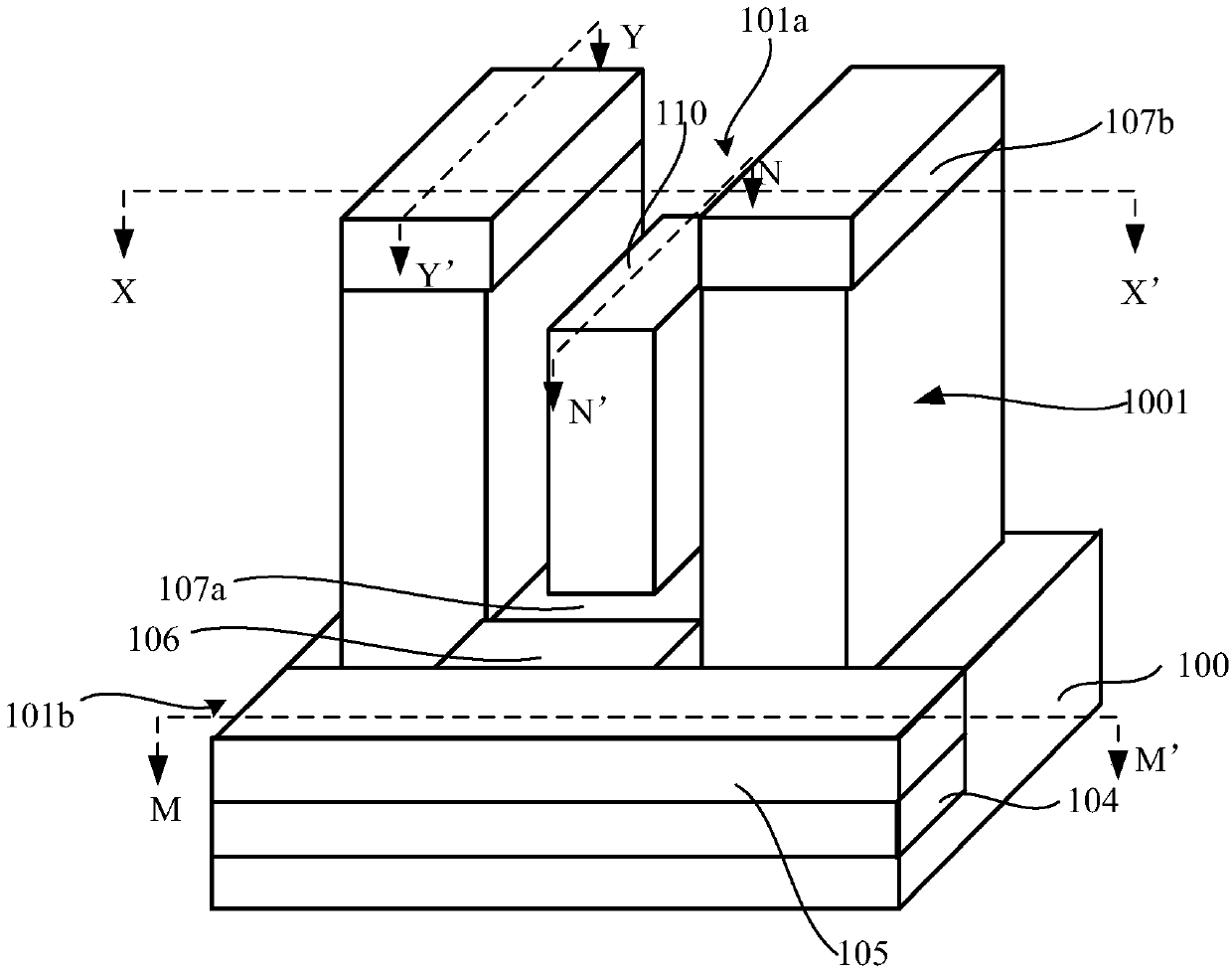
The invention provides a double-vertical-channel transistor, an integrated circuit memory and a preparation method thereof. A first trench extending along a first direction is formed in the vertical fin; first source / drain regions are formed in the fins at the tops of the two sides of the first trench; a second source / drain region is formed in the fin at the bottom of the first trench; a first gate structure is filled in the first trench and extends along the first direction; the embedded wires are filled in the second trench in the side wall, extending along the second direction, of the vertical fins, so that the first source / drain regions on the two sides of the first trench and the second source / drain region at the bottoms of the first trench respectively form double vertical L-shaped channels, the effective channel length is increased, and the short channel effect is overcome; and the second source / drain region and the electric connection embedded wire thereof are positioned at thebottom of the transistor and do not need to be directly led out from the upper surface, so that isolation at the periphery of the transistor is easier to form, the device area is reduced, the processis simplified and the performance is improved.
Owner:CHANGXIN MEMORY TECH INC
Method for manufacturing semiconductor device having bulb-type recessed channel
ActiveUS7838405B2Increase the effective channel lengthExcellent characteristicsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesIsolation layerGate stack
A method for manufacturing a semiconductor device having a bulb-type recessed channel including: forming a trench that defines an active region including a channel region having a sidewall and a junction region in a semiconductor substrate; forming a device isolation layer that buries the trench, and forming a sidewall pattern that covers the sidewall of the channel region; forming a bulb-type trench by overlapping with the channel region in the semiconductor substrate, and forming a bottom protrusion having a predetermined space parted from the device isolation layer by removing the sidewall pattern; and forming a gate stack that overlaps with the bulb-type trench and the bottom protrusion.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
Non-volatile memory location and producing method thereof
InactiveCN1674292AImprove component integrationIncrease the effective channel lengthSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingStorage cellNon-volatile memory
A non- volatile storage cell is composed of substrate, grid, the first source electrode / drain electrode area, composite dielectric layer and the second source electrode / drain electrode area. It is featured as setting a slot on substrate; placing grid in slot, the first source electrode / drain electrode area at slot bottom; setting composite dielectric layer between grid and slot surface and placing the second source electrode / drain electrode area in substrate at two side of grid.
Owner:POWERCHIP SEMICON CORP
Semiconductor device with a metal insulator semiconductor transistor
InactiveUS20050169050A1Increase the effective channel lengthTransistorSolid-state devicesDevice materialTrapping
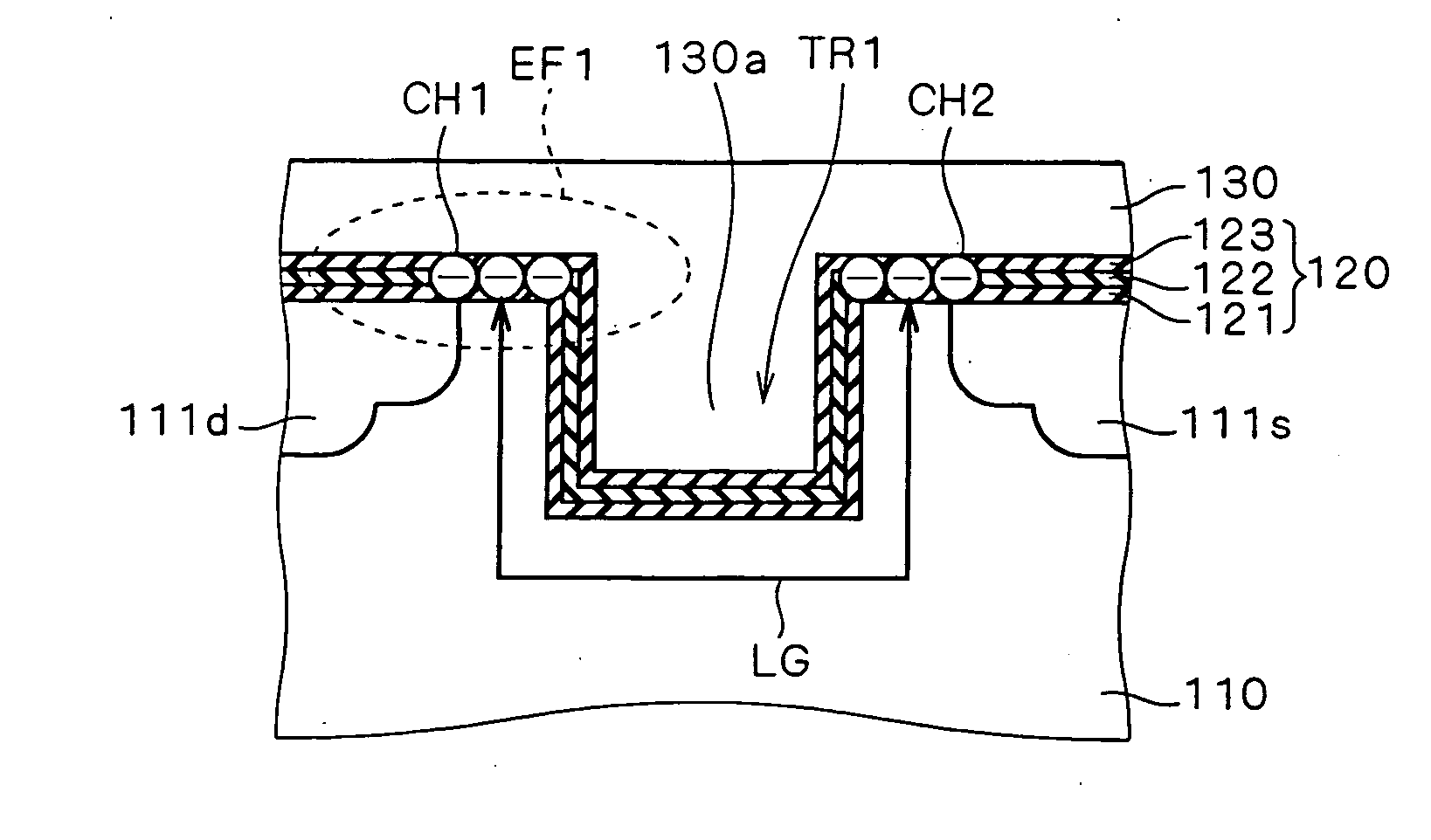
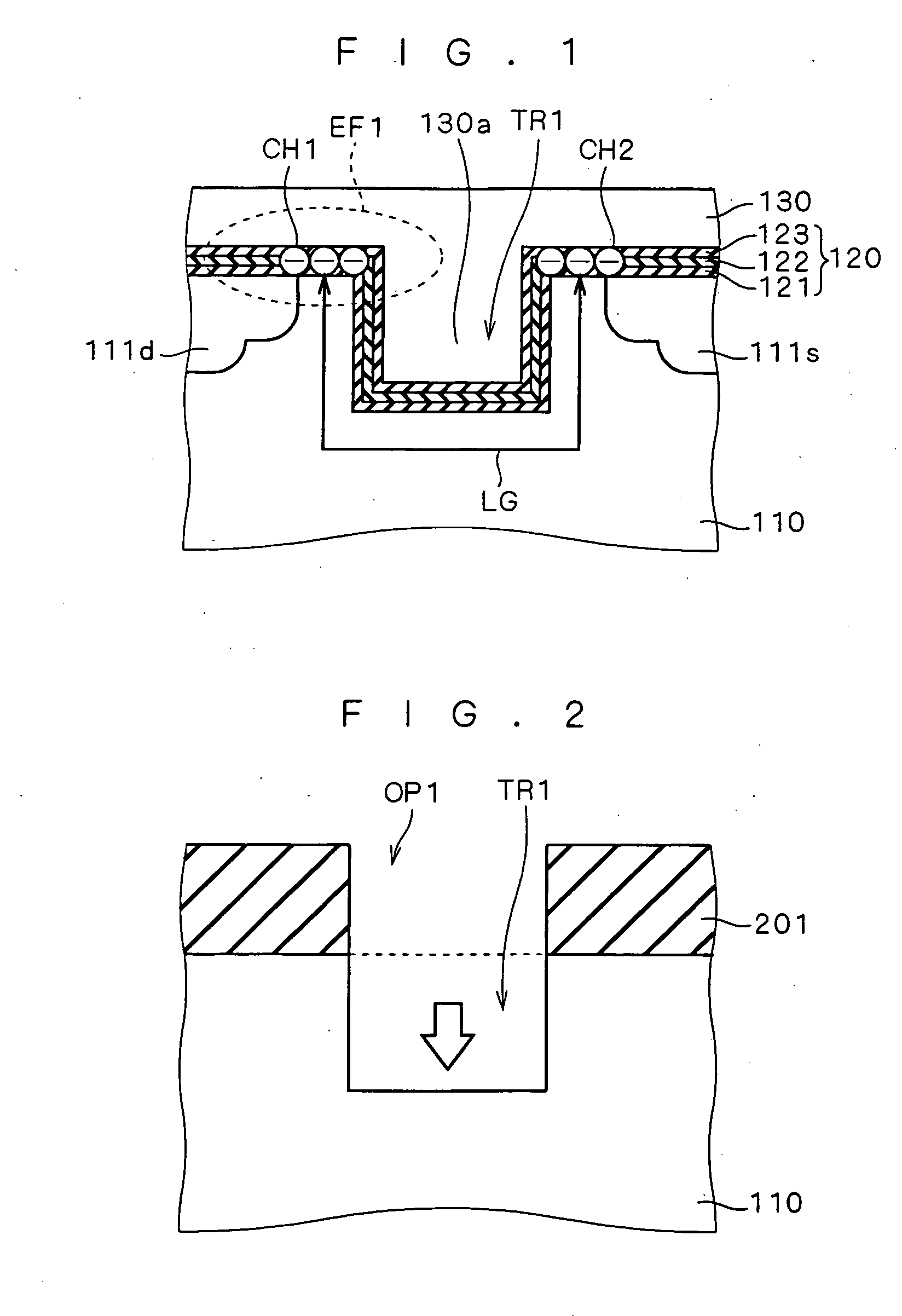
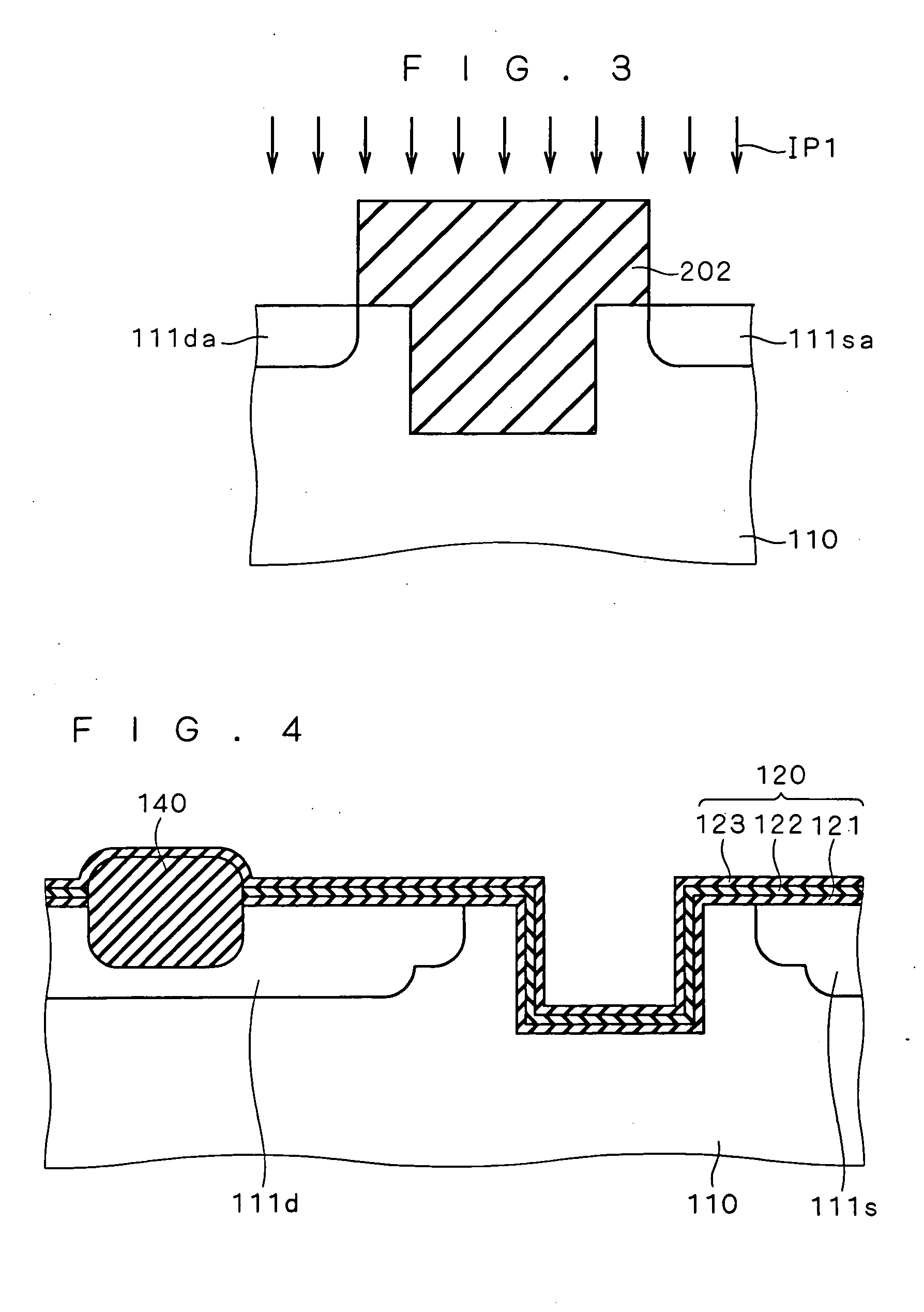
It is an object to provide a semiconductor device capable of holding multibit information in one memory cell also when scaling for a nonvolatile memory progresses, and a method of manufacturing the semiconductor device. A trench (TR1) is formed in a channel portion of an MONOS transistor. Then, a source side portion and a drain side portion in a silicon nitride film (122) of a gate insulating film (120) which interpose the trench (TR1) are caused to function as first and second electric charge holding portions capable of holding electric charges (CH1) and (CH2). In the case in which the electric charges (CH1) are trapped and the electric charges (CH2) are then trapped, thus, a portion (130a) of a gate electrode (130) in the trench (TR1) functions as a shield. If a fixed potential is given to the gate electrode (130), the second electric charge holding portion is not influenced by an electric field (EF1) induced by the electric charges (CH1) so that the trapping of the electric charges (CH2) is not inhibited.
Owner:RENESAS TECH CORP
CMOS inverter layout for increasing effective channel length
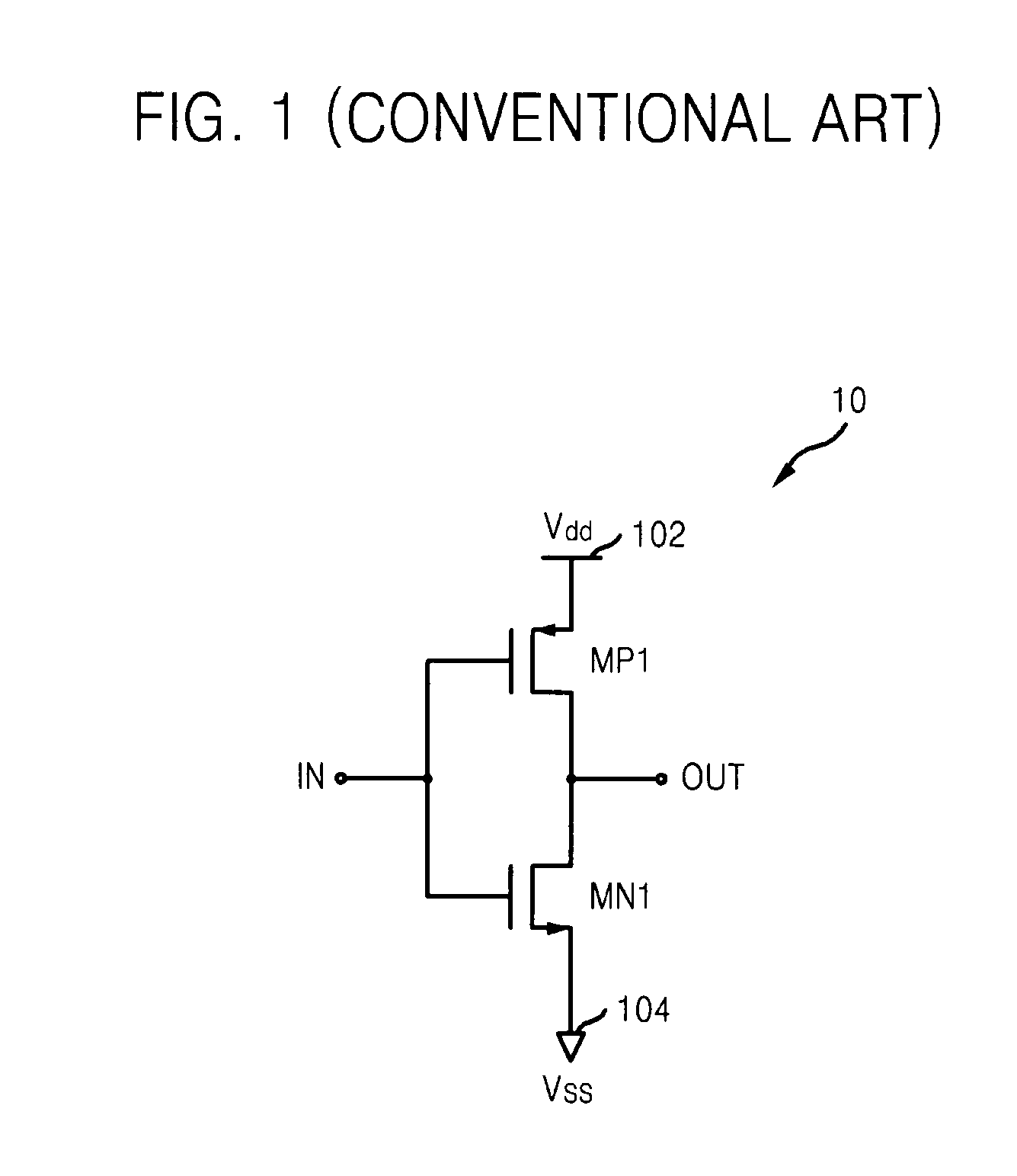
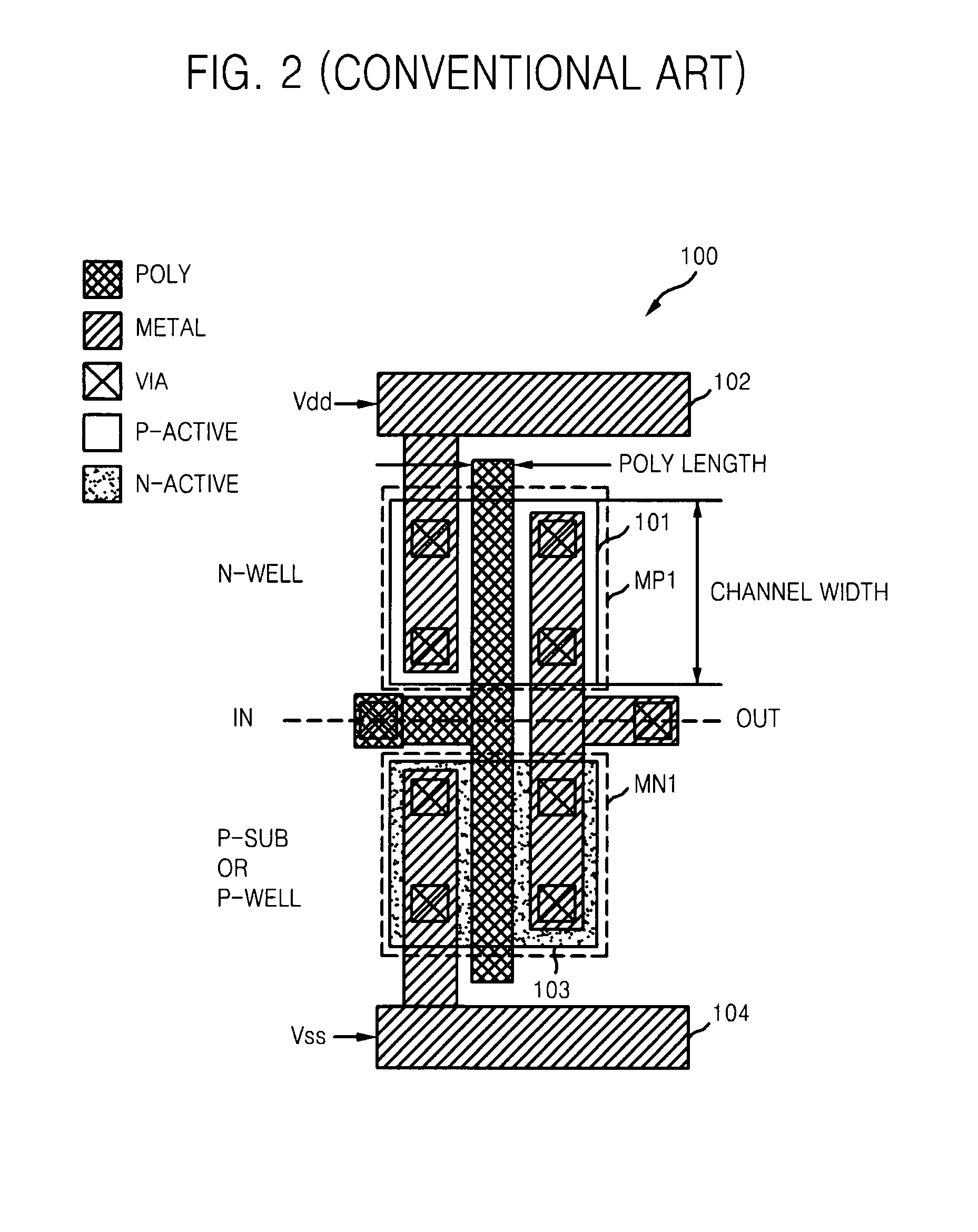
ActiveUS7849431B2Long delayIncrease effective channel lengthTransistorSolid-state devicesOxide semiconductorCMOS
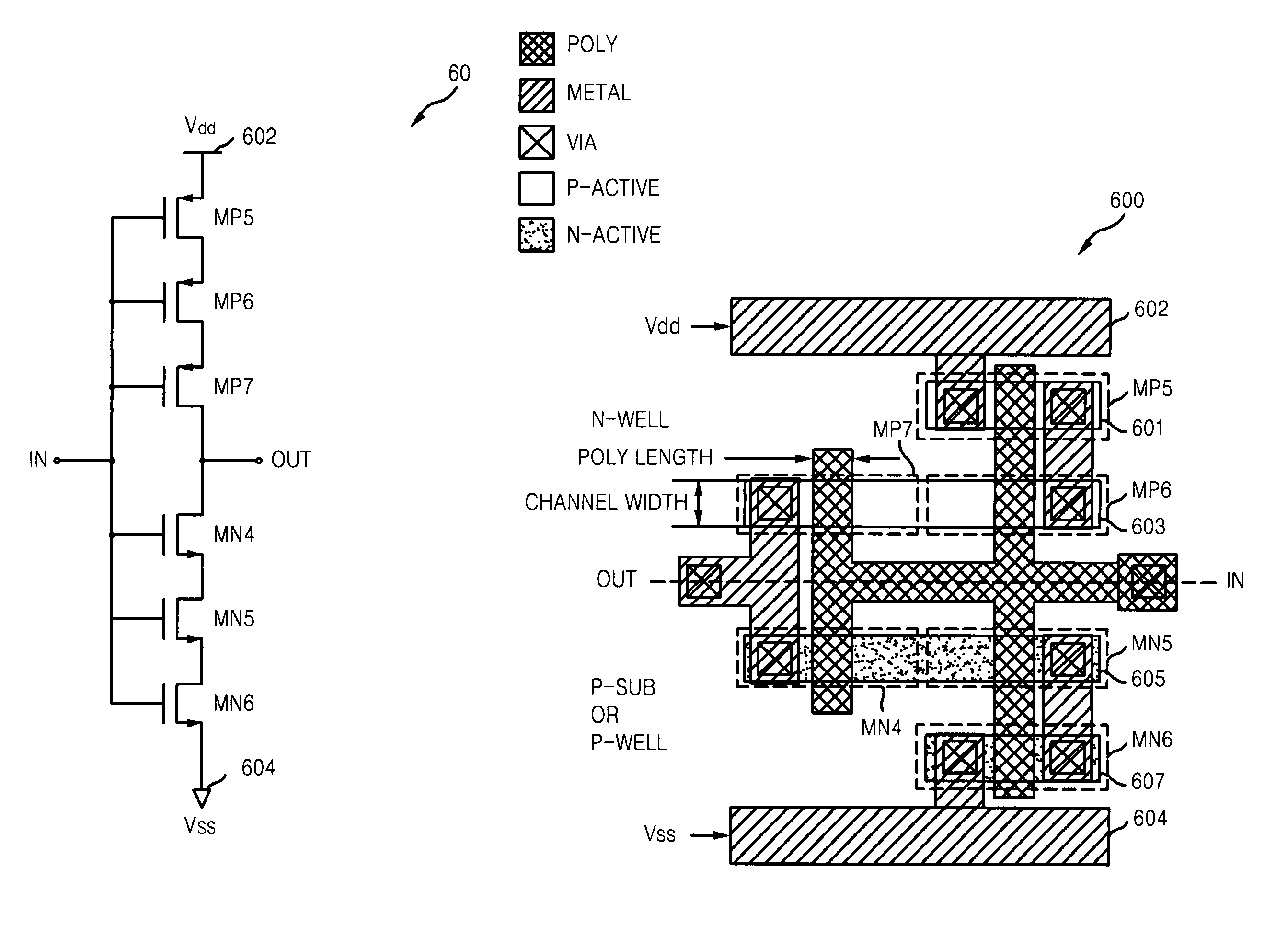
Provided is a complementary metal oxide semiconductor (CMOS) inverter layout for increasing an effective channel length. The CMOS inverter layout may include first and second conductive MOS transistors respectively formed in first and second active regions, metal lines electrically connecting the first and second conductive MOS transistors, and one or more gate electrodes electrically connecting the gates of the first and second conductive MOS transistors. The widths of one or more gate electrodes may be set to a reduced and / or minimum feature size to reduce and / or minimize a process variation and a layout area of the CMOS inverter. Also, the first and second conductive MOS transistors may be connected in series via the metal lines to increase an effective channel length, thereby realizing a layout of the CMOS inverter having a longer delay than a conventional CMOS inverter.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Trench construction in MOS transistor
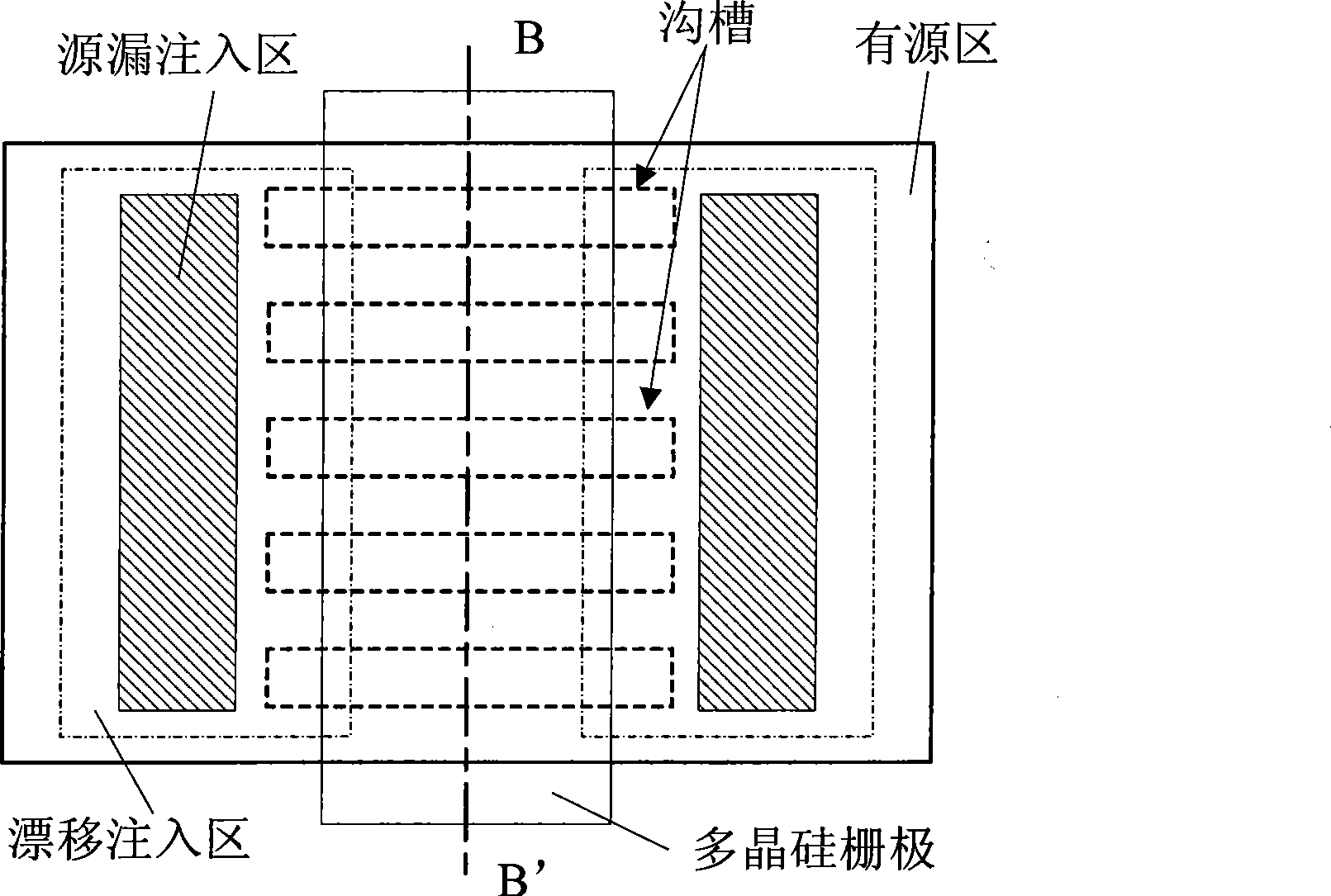
InactiveCN101452954AIncrease the effective channel lengthImprove driving abilitySemiconductor devicesEffective lengthEngineering
The invention discloses a channel structure of an MOS transistor, which is used in the power MOS transistor. The surface of a silicon substrate in a channel zone is provided with a plurality of slots of which the lengthwise direction is the same as the moving direction of the current in the channel zone when the MOS transistor works. Because the channel zone is additionally provided with the slots, the channel is changed from a single plane to multi-planes, so that under conditions of not changing the size of the device, the effective length of the channel of the device is increased, and the driving capacity of the device is also enhanced.
Owner:SHANGHAI HUA HONG NEC ELECTRONICS
High-integration-level source, drain and gate auxiliary control U-shaped channel high-mobility-ratio junction-free transistor shaped like Chinese character 'ri'
InactiveCN104282753ALow source-drain resistanceImprove mobilitySemiconductor devicesElectrical resistance and conductanceChinese characters
The invention relates to a high-integration-level source, drain and gate auxiliary control U-shaped channel high-mobility-ratio junction-free transistor shaped like the Chinese character 'ri'. Two independently-controlled gate electrodes including the auxiliary control gate electrode shaped like the Chinese character 'ri' and the gate electrode are adopted, it is guaranteed that the dosing concentration of the device is reduced to improve the mobility ratio, and the device mobility ratio reduction and the device stability reduction caused by strengthening of the random scattering effect under the high doping concentration are avoided; meanwhile, the resistance of source and drain areas is effectively reduced through the auxiliary control gate electrode shaped like the Chinese character 'ri', so that the contradictions that the source and drain resistance will be increased if the doping concentration of a channel of a common junction-free transistor is excessively low, and the device mobility ratio reduction and the device stability reduction will be caused if the doping concentration is excessively high are overcome; meanwhile, U-shaped monocrystalline silicon serves a channel part of the device; compared with a common plane structure, on the premise that the chip area is not additionally increased, the effective channel length is obviously increased to reduce the short channel effect of the device under the deep nanoscale, and therefore the high-integration-level source, drain and gate auxiliary control U-shaped channel high-mobility-ratio junction-free transistor shaped like the Chinese character 'ri' is suitable for application and popularization.
Owner:SHENYANG POLYTECHNIC UNIV
Method of manufacturing semiconductor device
ActiveUS20100052054A1Increase the effective channel lengthIncrease the lengthTransistorSolid-state devicesDevice materialEngineering
The present invention relates to a method of manufacturing a semiconductor memory device and a semiconductor memory device manufactured using the same. A method of manufacturing a semiconductor device comprises defining source / drain regions in semiconductor substrate through an etch process using a mask, and forming a gate and source / drain by depositing a conductive material over the defined regions and the semiconductor substrate and patterning the conductive material.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
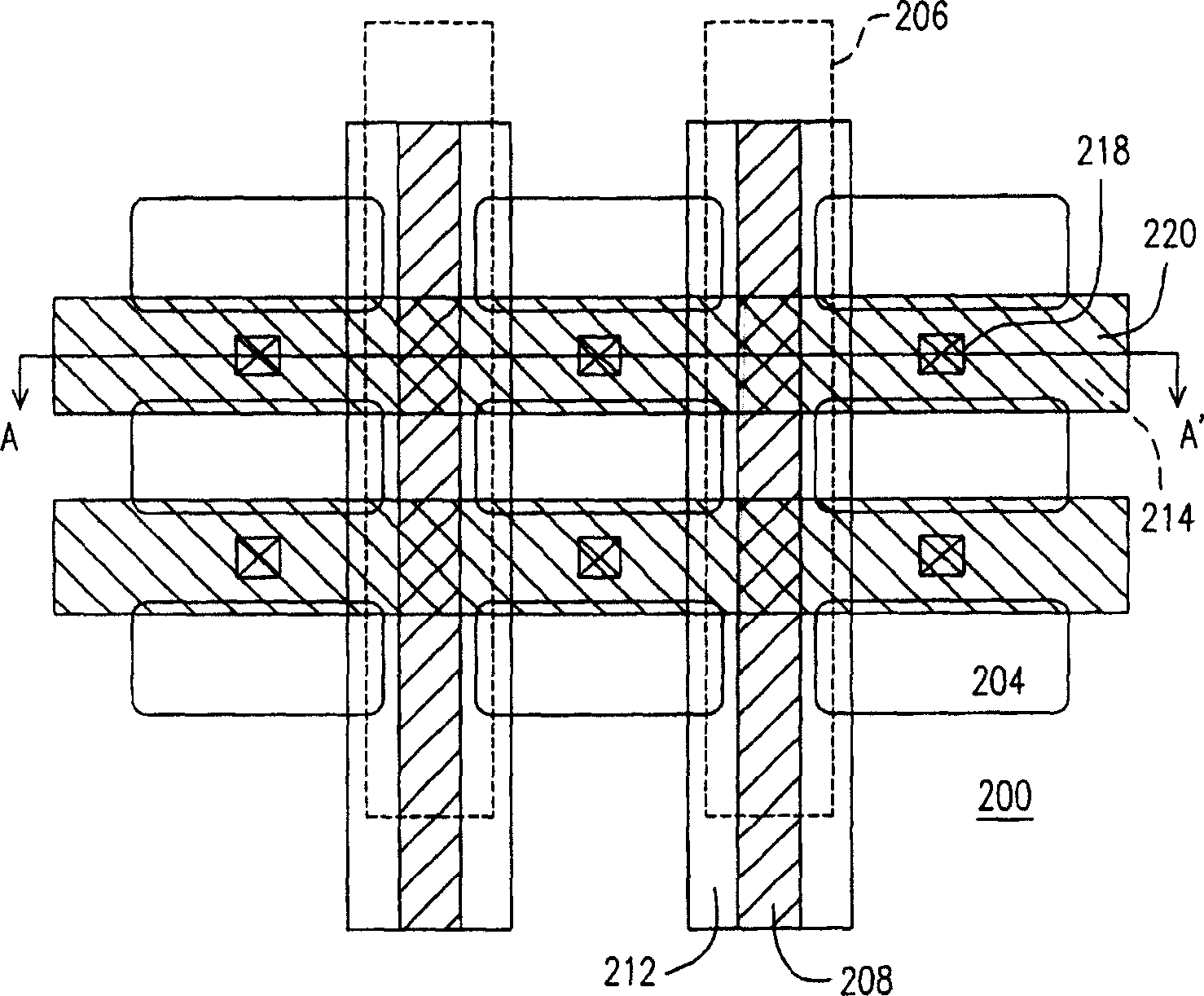
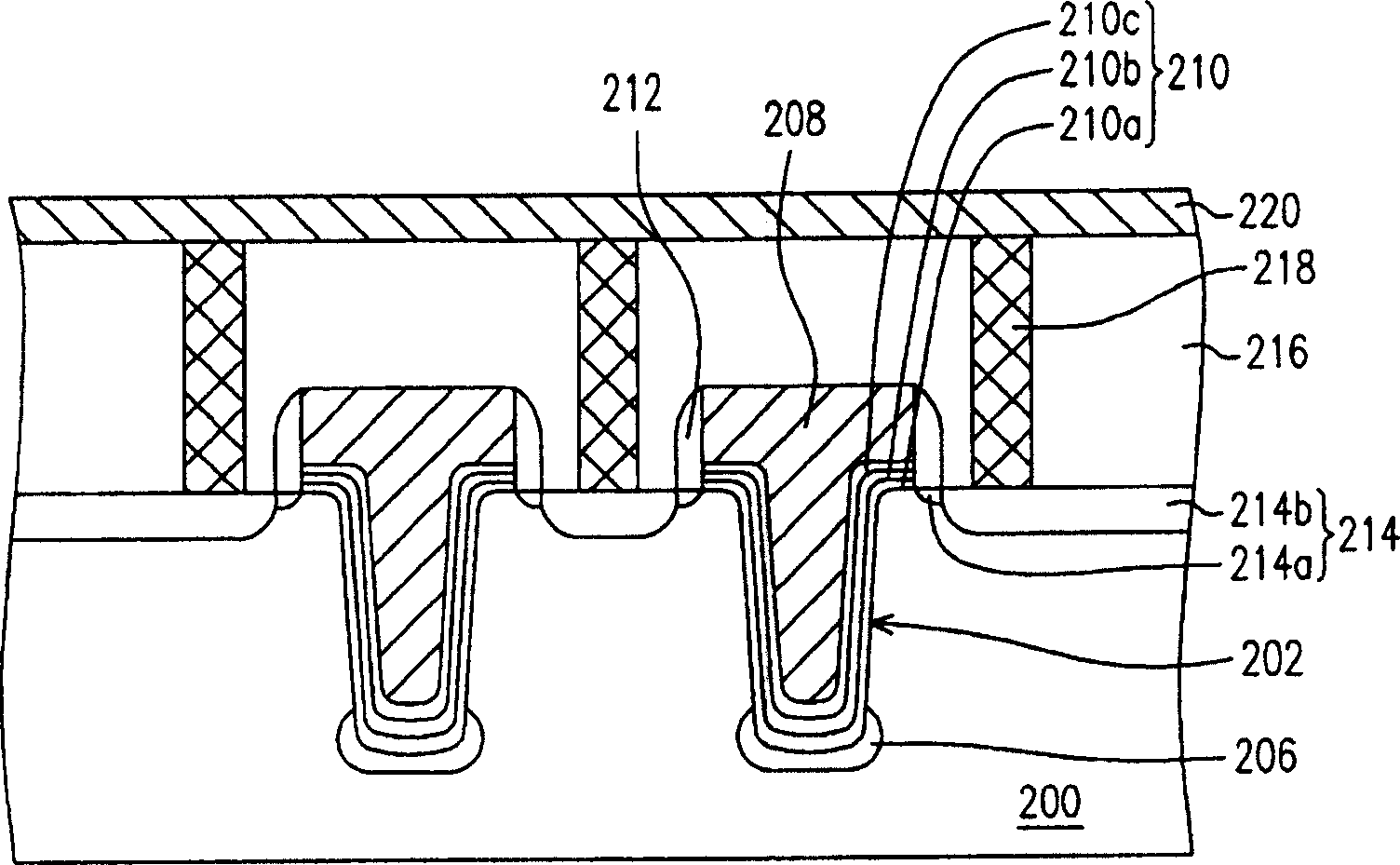
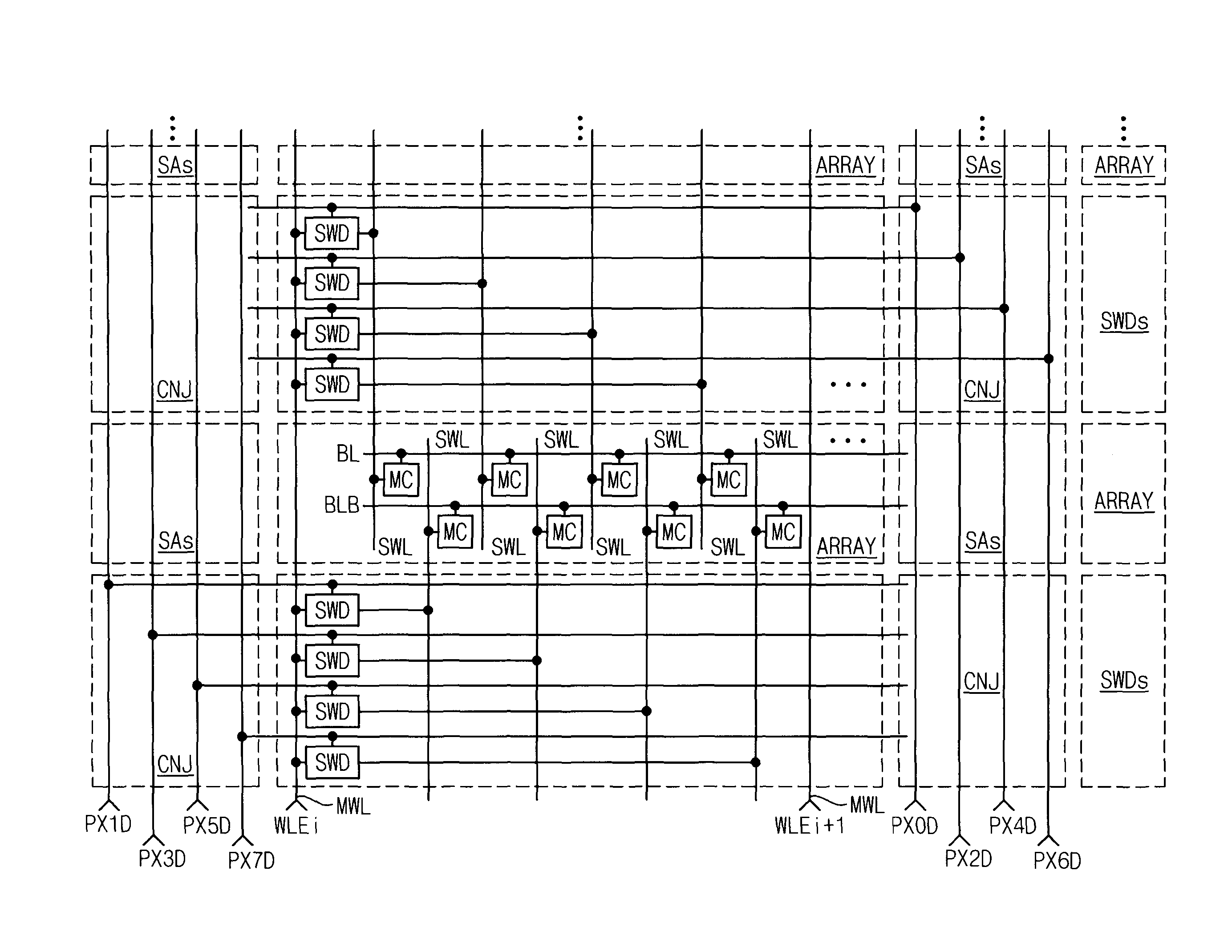
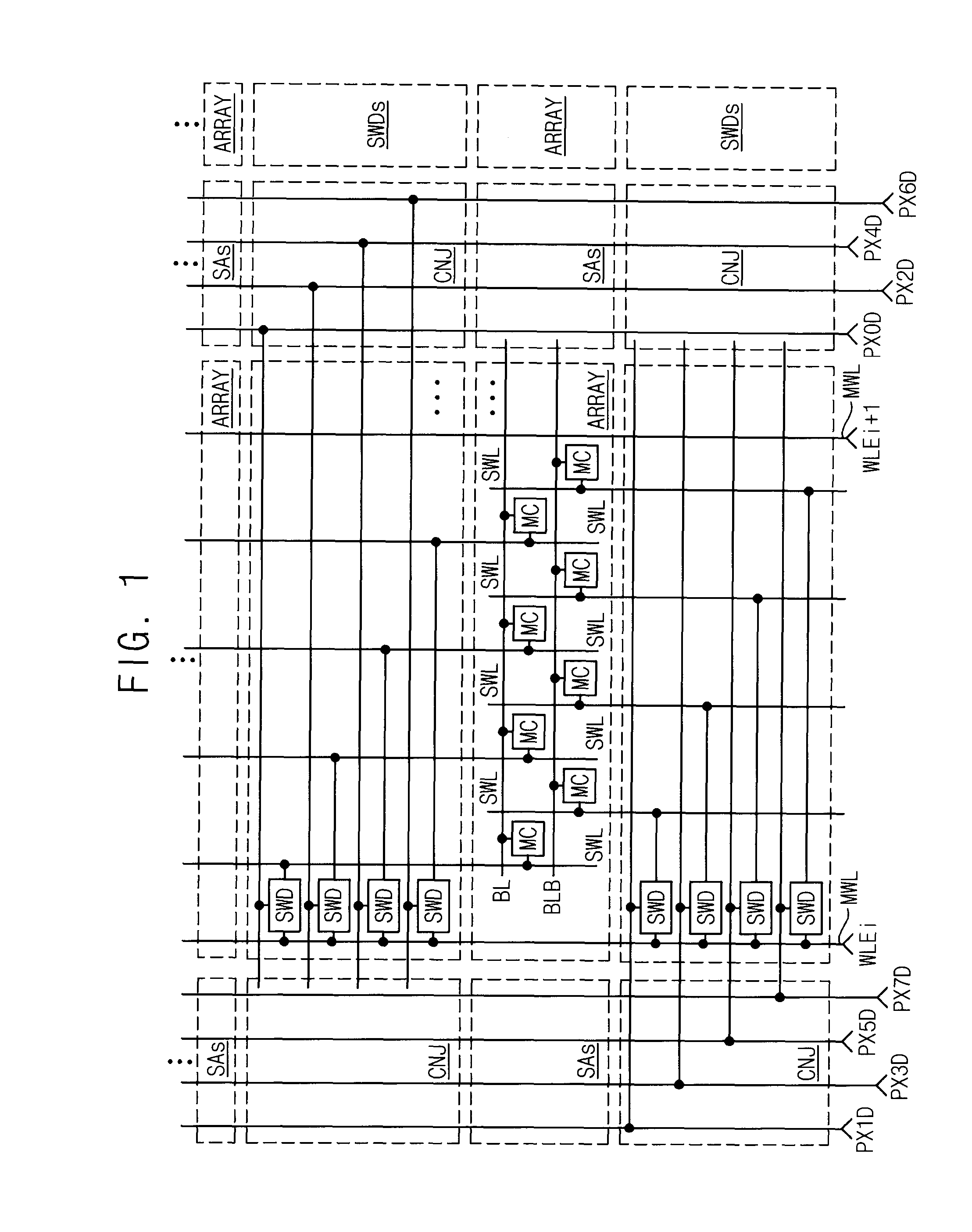
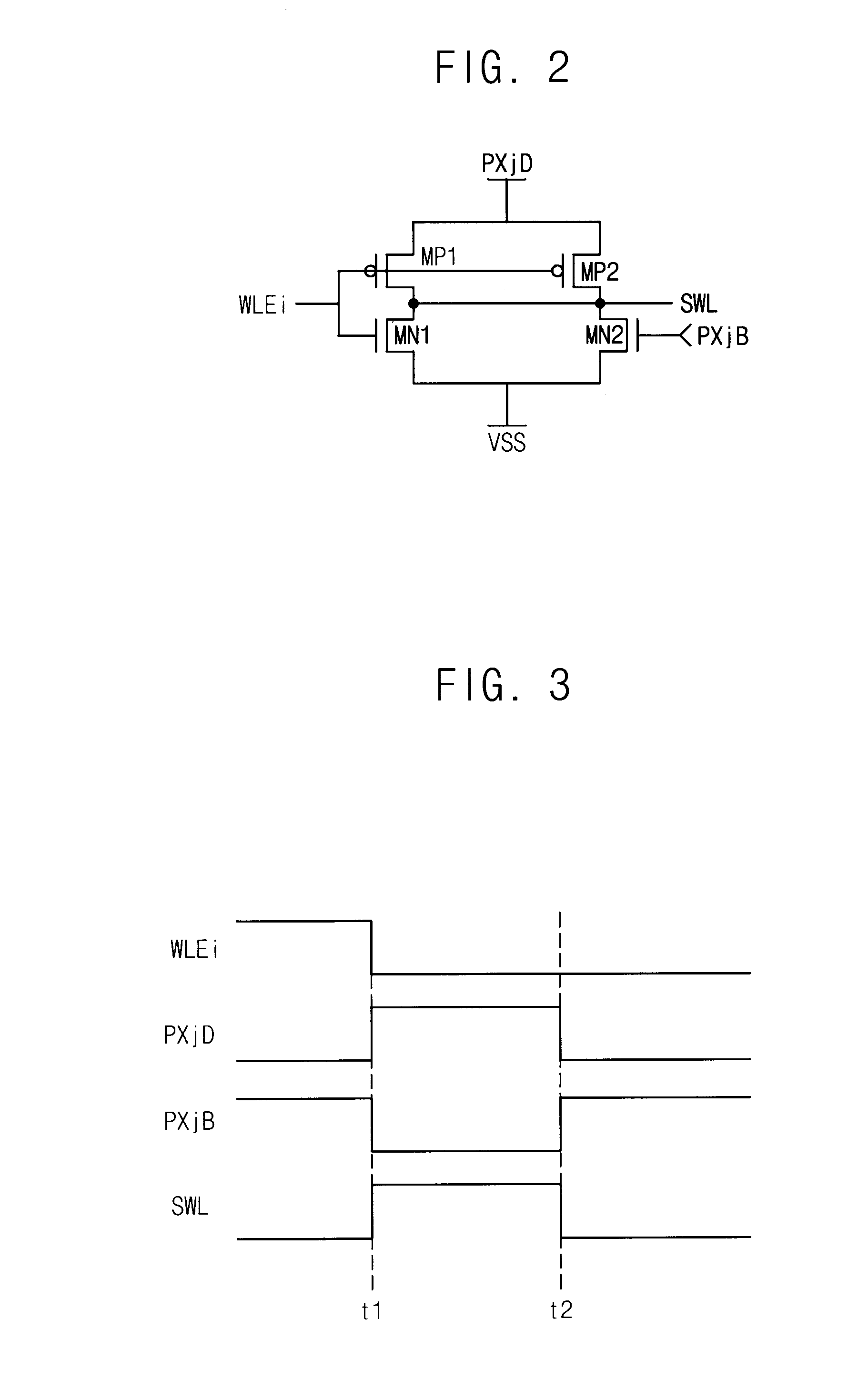
Sub-word line driver circuit and semiconductor memory device having the same
ActiveUS8279703B2Increase the effective channel lengthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDigital storageDriver circuitEngineering
A sub-word line driver includes a substrate, a plurality of gate lines and at least one gate tab. The substrate includes a plurality of isolation areas and a plurality of active areas, where the two active areas are separated by each isolation area, and the isolation areas and the active areas are extended in a first direction and are arranged in a second direction perpendicular to the first direction. The plurality of gate lines are formed on the substrate, where the gate lines are extended in a second direction and are arranged in the first direction. The at least one gate tab is formed on the substrate, where the at least one gate tab is extended in the first direction to cover the isolation area. Incorrect operation of the sub-word line driver may be prevented, and a power consumption of the sub-word line driver may be reduced.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Nonvolatile memory device and method for fabricating the same
InactiveUS7803691B2Increase the effective channel lengthSecure characteristicTransistorSolid-state devicesInsulation layerDielectric layer
A nonvolatile memory device includes a control gate formed along a first direction over a substrate, an active region formed over the substrate, the active region being defined along a second direction crossing the control gate and including a fin type protruding portion having rounded top corners at a region where the control gate and the active region overlap, a floating gate formed over a surface of the protruding portion of the active region below the control gate and formed to a substantially uniform thickness along the surface profile of the protruding portion of the active region, a tunneling insulation layer formed between the floating gate and the active region, and a dielectric layer formed between the floating gate and the control gate.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
Method for reducing dark current of image sensor
ActiveCN104992954AReduce dark currentIncrease the effective channel lengthRadiation controlled devicesThermal electronEngineering
The invention provides a method for reducing dark current of an image sensor. The method comprises preparation of a photodiode and a transistor. The preparation of the transistor comprises following steps of firstly forming grid electrodes of four transistors; forming light dope drain regions of a reset pipe, an amplifying pipe and a selecting pipe; then, forming corresponding side walls on grid electrode side walls of the rest pipe, the amplifying pipe, the selection pipe and a transferring pipe; and at last, forming a light dope drain region of the transferring pipe on the substrate of a semiconductor at the bottom of the outer side of the side wall of the transferring pipe. Thus, effective channel length of the transferring pipe is increased, electric field in the channel direction is reduced and probability of generation of thermal electrons is reduced, thereby reducing dark current of the image sensor.
Owner:SHANGHAI HUALI MICROELECTRONICS CORP
Field effect transistor
InactiveUS7511344B2Transistor size to be scaledIncrease the effective channel lengthSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsNanoinformaticsField-effect transistorSemiconductor
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Semiconductor device and method for fabricating the same
ActiveUS11227926B2Suppression of short channel effectsIncrease the effective channel lengthTransistorSolid-state devicesDevice materialConductive materials
The present disclosure provides a semiconductor device. The semiconductor device comprises a substrate, a plurality of isolation regions in the substrate and an active region surrounded by the isolation regions. A p-type doped region is interposed between two n-type doped regions in the substrate. A buried gate structure is formed in the substrate and disposed between the p-type doped region and the n-type doped region. The buried gate structure comprises a gate conductive material, a gate insulating layer disposed over the gate conductive material and a gate liner surrounding the gate conductive material and the gate insulating layer. A plurality of contact plugs are formed on the p-type doped region and the plurality of n-type doped regions.
Owner:NAN YA TECH
Method for increasing length of effective channel of PMOS
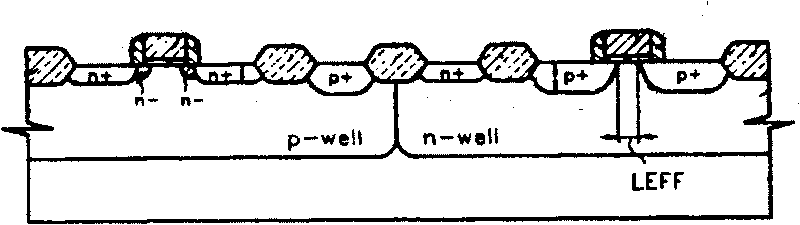
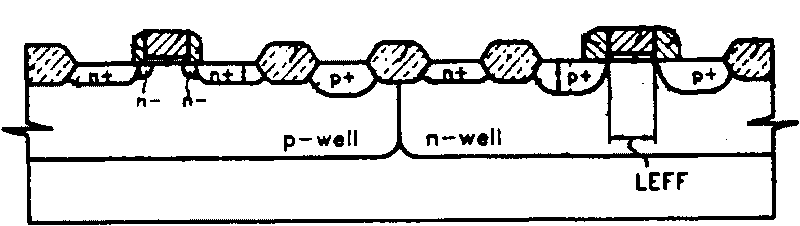
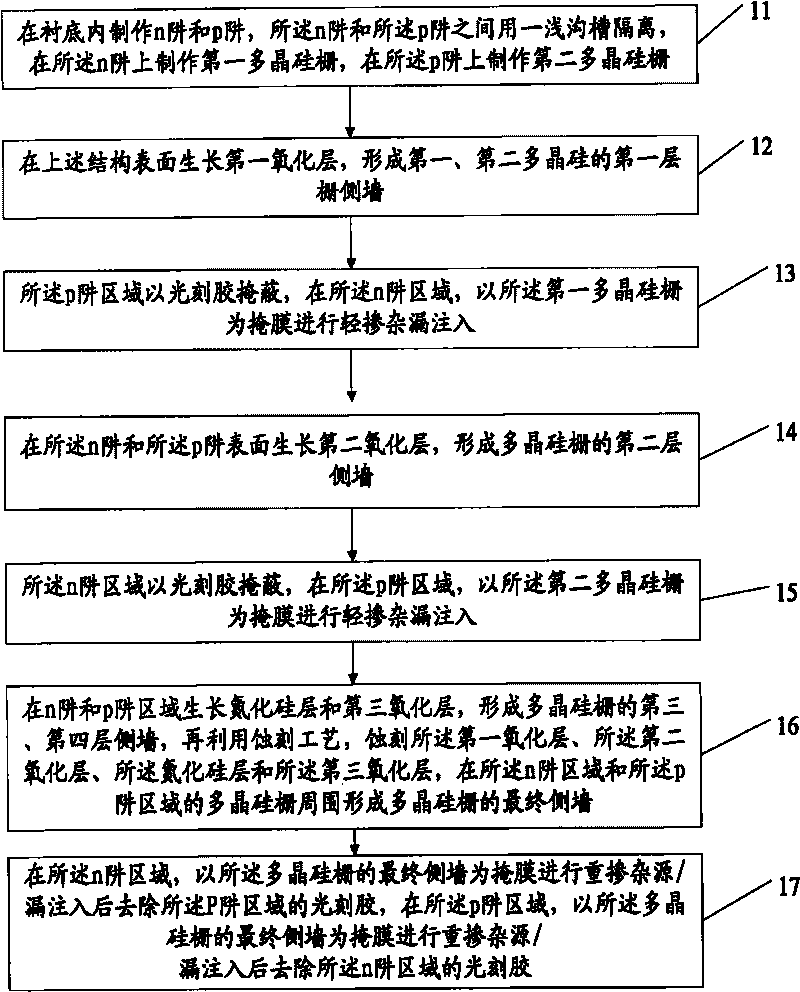
ActiveCN101697346AIncrease the effective channel lengthCost controlSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringPolysilicon gate
The invention provides a method for increasing the length of an effective channel of a PMOS, which comprises the following steps of: making an n-well and a p-well in a substrate; making a first polysilicon gate on the n-well and making a second polysilicon gate on the p-well; growing a first oxidation layer; injecting lightly doped source / drain in an n-well area; respectively growing a second oxidation layer on the surface of the n-well and the p-well; injecting lightly doped source / drain in a p-well area; respectively growing a silicon nitride layer and a third oxidation layer in the n-well and the p-well areas; etching the first oxidation layer, the second oxidation layer, the silicon nitride layer and the third oxidation layer; respectively forming a side wall around the polysilicon gates of the n-well and the p-well; injecting heavily doped source / drain in the n-well area; and injecting heavily doped source / drain in the p-well area. The method moves the step of injecting the lightly doped source / drain in the p-well area between the step of growing the second oxidation layer and the step of growing the silicon nitride layer and increases the length of the effective channel of the PMOS by using the second oxidation layer.
Owner:SHANGHAI HUAHONG GRACE SEMICON MFG CORP
Memory cell and manufacturing method thereof and memory structure
InactiveUS20110079840A1Superior channel boosting capabilityAvoid leakage currentSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingIsolation layerEngineering
A memory cell is provided. The memory cell includes a substrate, an isolation layer, a gate, a charge storage structure, a first source / drain region, a second source / drain region and a channel layer. The isolation layer is disposed over the substrate. The gate is disposed over the isolation layer. The charge storage structure is disposed over the isolation layer and the gate. The first source / drain region is disposed over the charge storage structure at two sides of the gate. The second source / drain region is disposed over the charge storage structure at top of the gate. The channel layer is disposed over the charge storage structure at sidewall of the gate and is electrically connected with the first source / drain region and the second source / drain region.
Owner:MACRONIX INT CO LTD
MOSFET structure
InactiveCN107195680AReduce electric field peaksImprove performanceSemiconductor devicesDevice materialPlanar channel
The invention discloses a MOSFET structure which belongs to the technical field of semiconductor devices and comprises a substrate electrode, a substrate, a channel region, a source region, a drain region, a source electrode, a drain electrode, a gate oxide layer and a gate electrode. The channel region with a non-planar surface is formed in a substrate region built in the substrate, and the source region and the drain region are arranged on both sides of the channel region respectively. The source electrode and the drain electrode are correspondingly arranged in the source region and the drain region respectively. The gate oxide layer covers the surface of the non-planar channel region. The gate electrode is arranged on the surface of the gate oxide layer, and both ends of the gate electrode are spaced from the source electrode and the drain electrode. Both ends of the gate electrode respectively extend to the source region and the drain region to form overlap. According to the invention, the non-planar channel MOSFET structure is used to reduce the electric field peak of the drain region and increase the effective channel length of a device; a leakage-induced barrier reducing effect is improve and suppressed; a short channel effect is suppressed; the high electric field of the drain region is reduced; the generation of hot carriers is suppressed; and the stability of the device is improved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Semiconductor device and preparation method thereof
PendingCN110931557AReduce areaHighly integratedSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesDevice materialEngineering
The invention provides a semiconductor device and a preparation method thereof. A second trench extending along a second direction is formed in a semiconductor substrate. U-shaped fins are arranged onthe two sides of the second trench in a staggered mode. The U-shaped fin is provided with a first trench extending along a first direction. The first source / drain regions are formed in the fins at the tops of the two sides of the first trench; a second source / drain region is formed in the fin at the bottom of the first trench; a gate line is filled in the first trench and extends along the firstdirection; the embedded wire is filled in the second trench extending along the second direction, so that the two first source / drain regions in the U-shaped fin respectively form double vertical L-shaped channels with the second source / drain region, the effective channel length is favorably increased, the short channel effect is overcome, and the smaller feature size and the higher integration degree are further favorably realized; and the U-shaped fins on the two sides of the second trench are arranged in a staggered manner, so that the coupling effect between adjacent active regions can be improved, and the device performance can be improved.
Owner:CHANGXIN MEMORY TECH INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com