Patents
Literature
1171 results about "Effective length" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
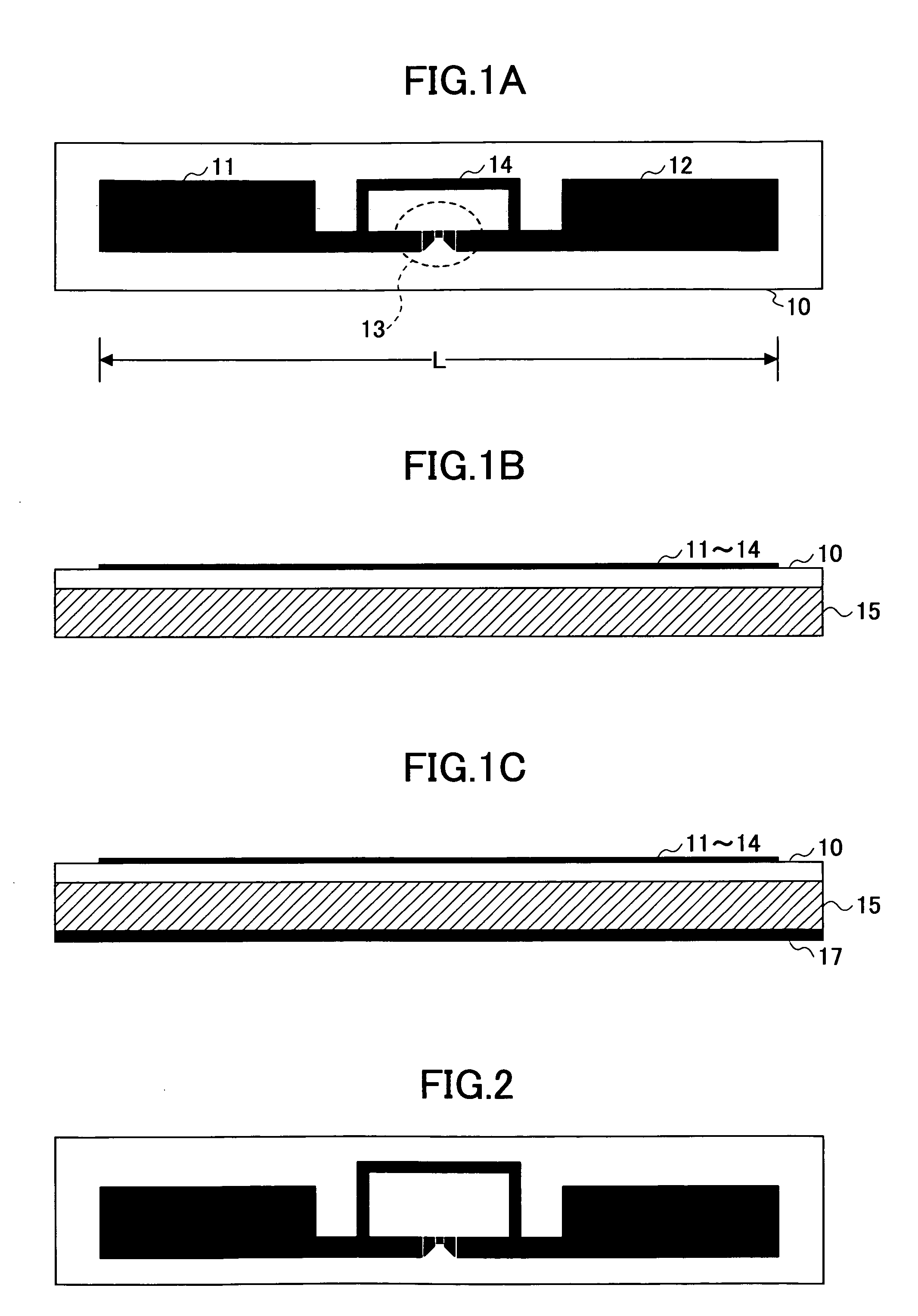
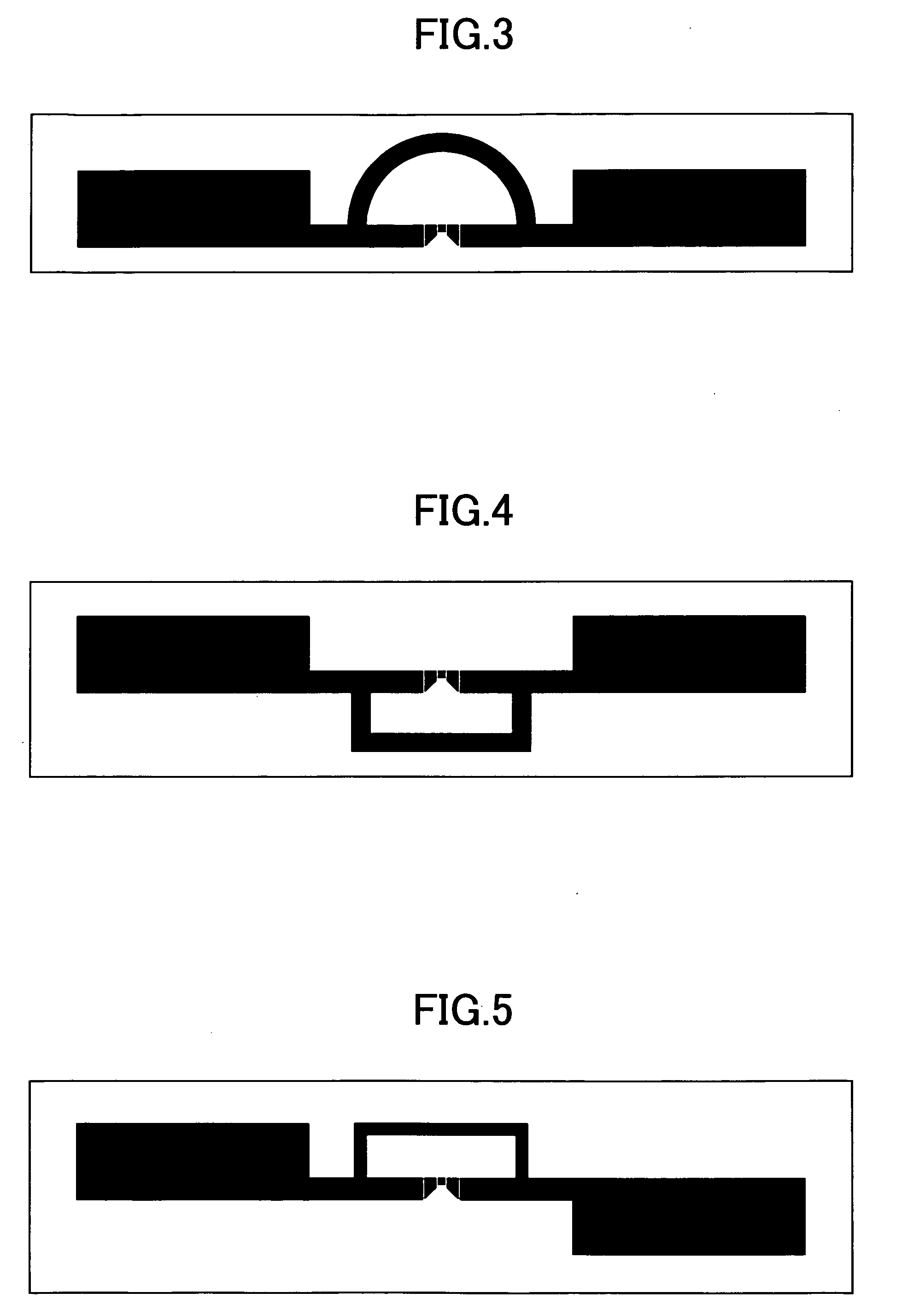
Effective length: The distance between inflection points in a column when it bends. Effective Length. (of an antenna), a parameter of wire antennas that characterizes the antenna’s efficiency in transmitting and receivingelectromagnetic waves.
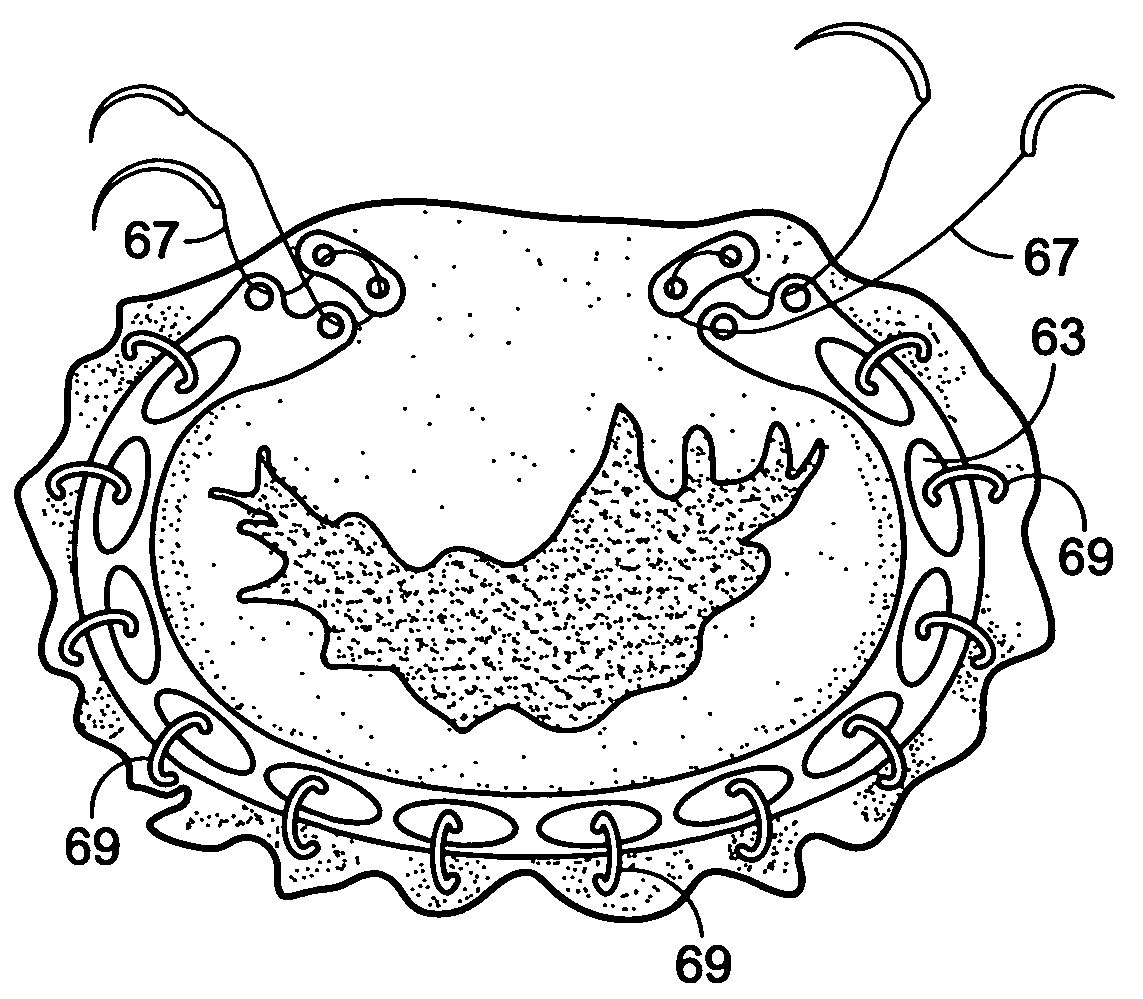
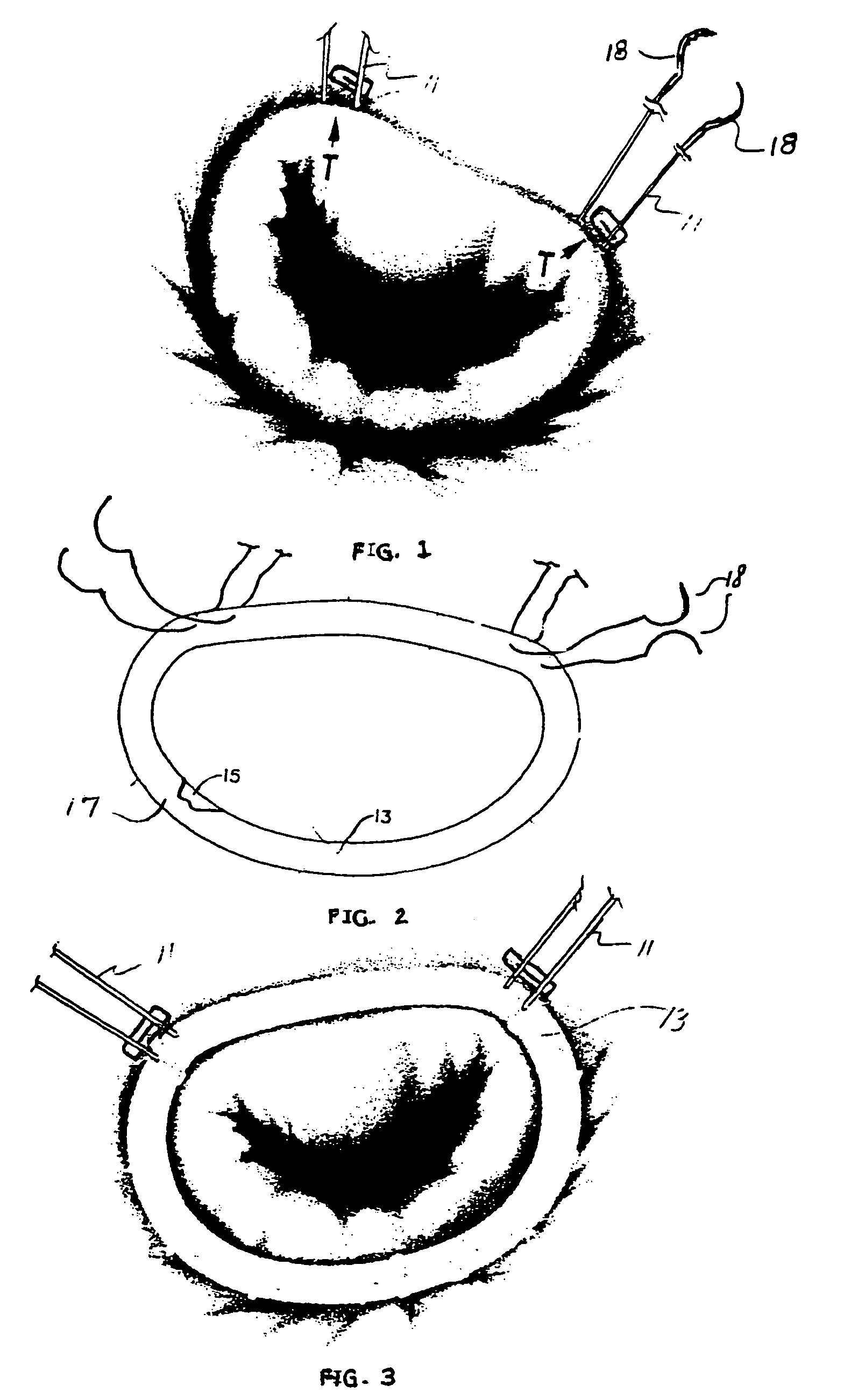
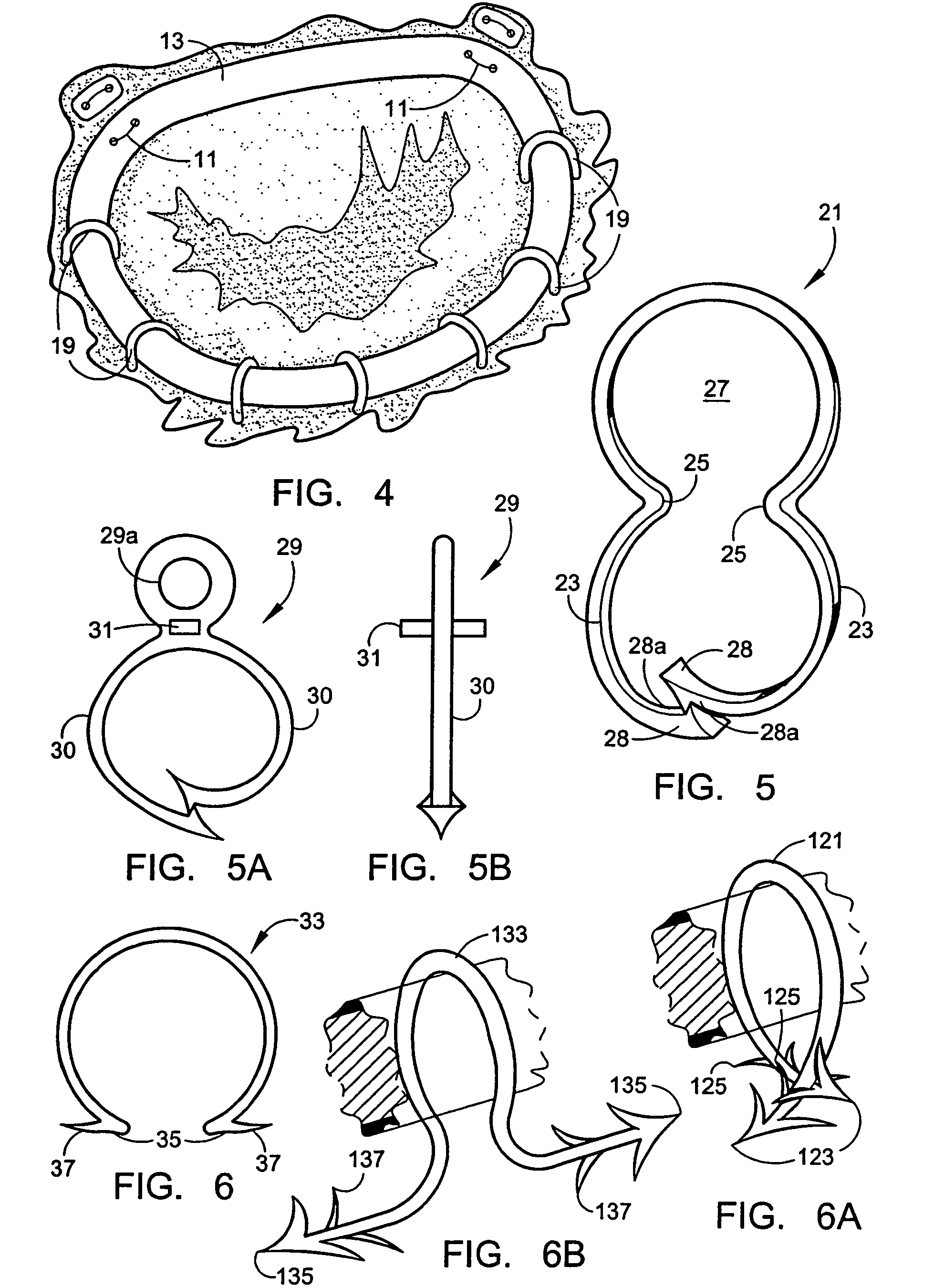
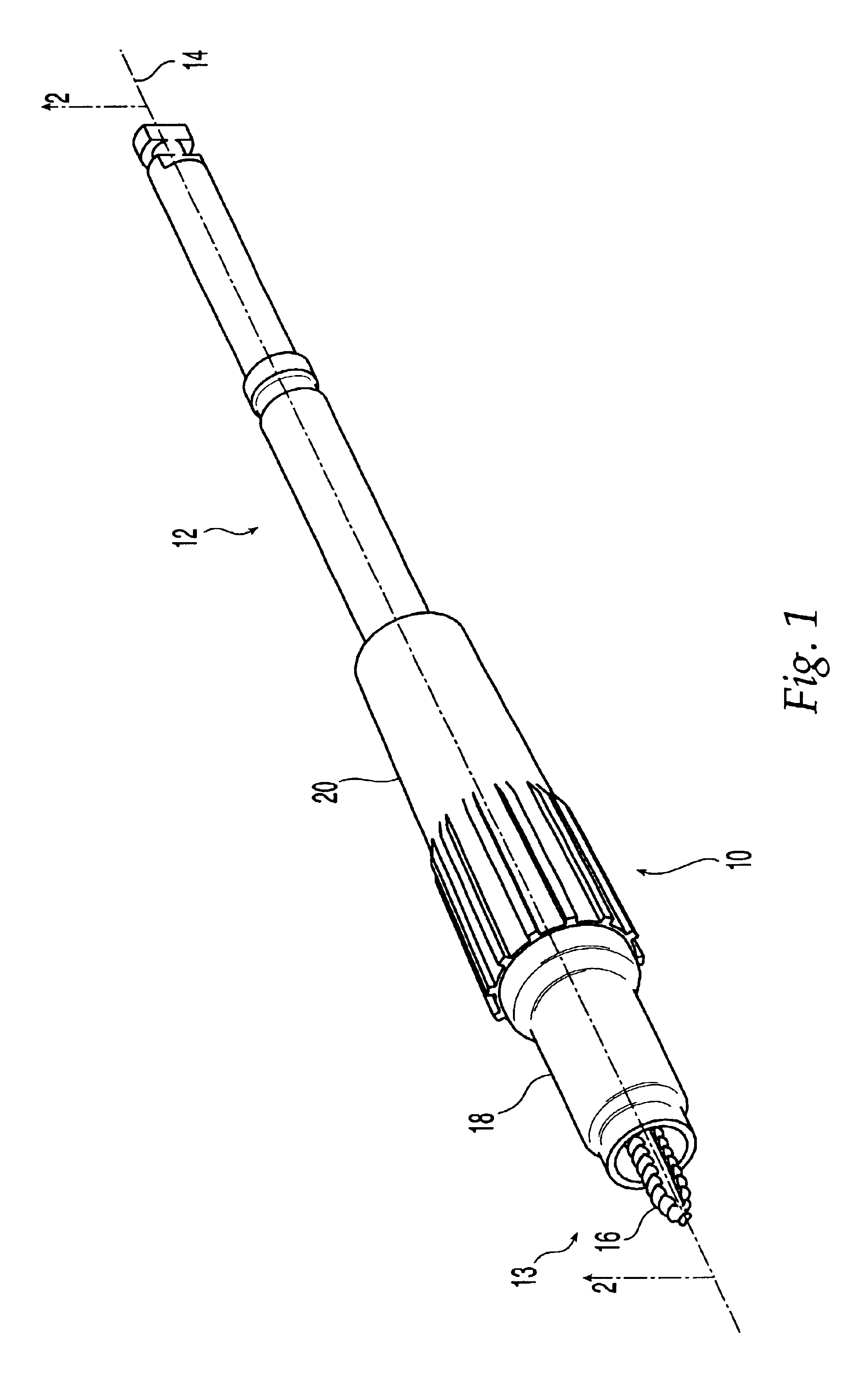
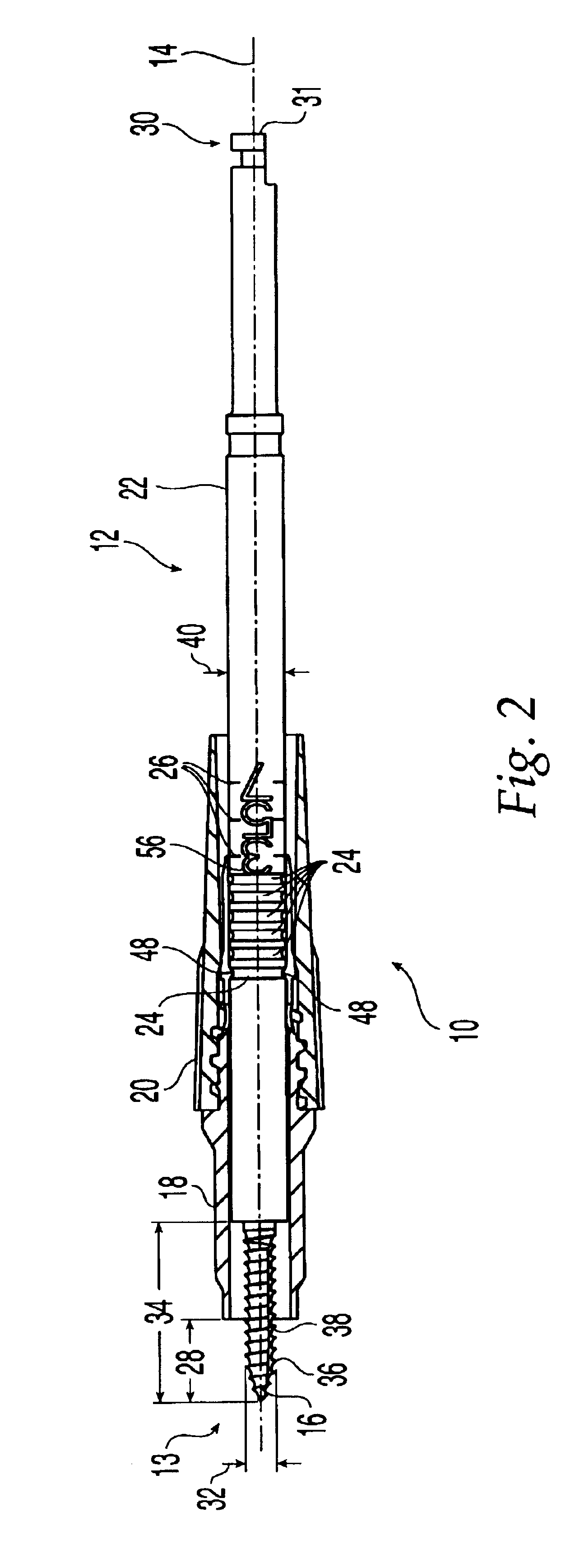
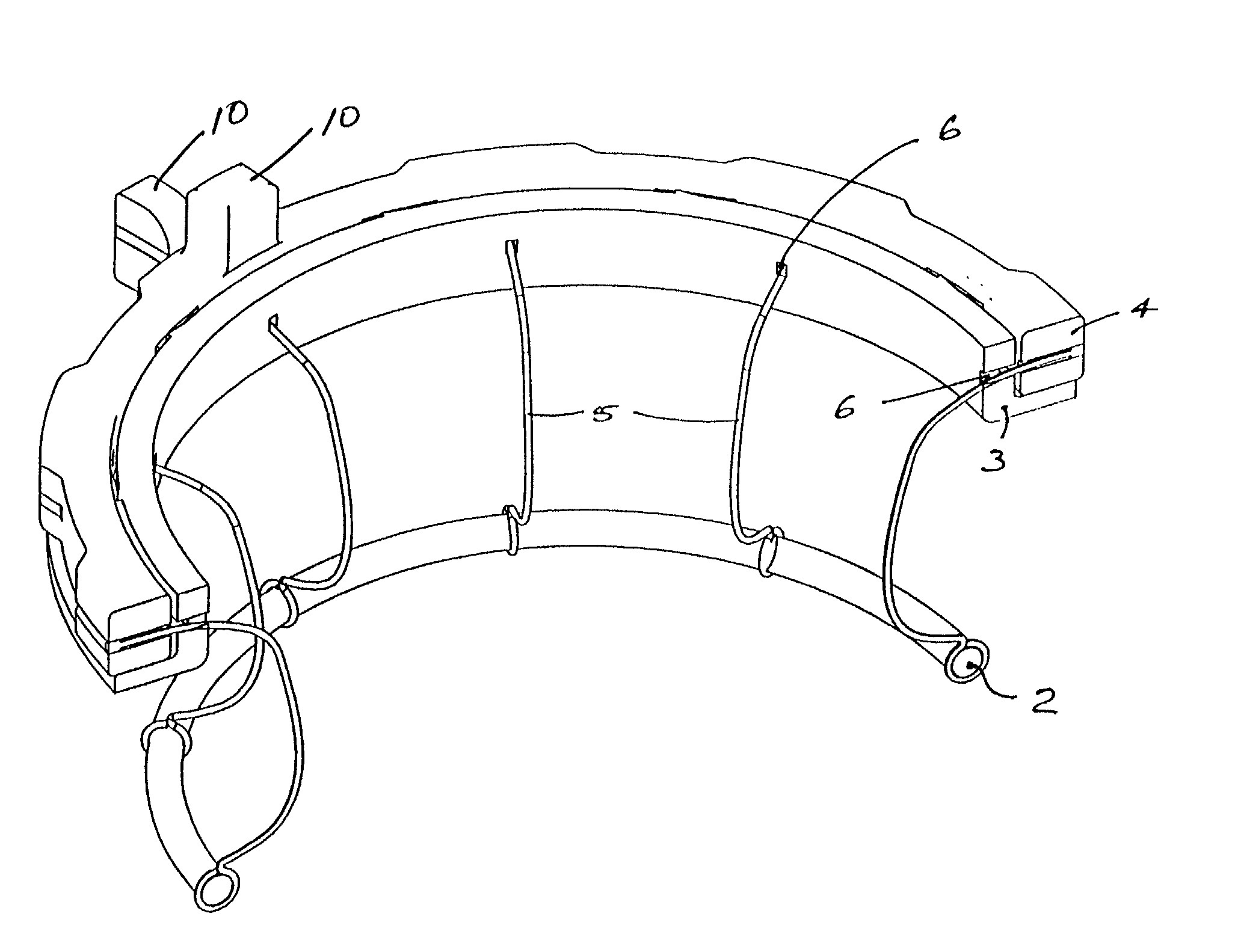
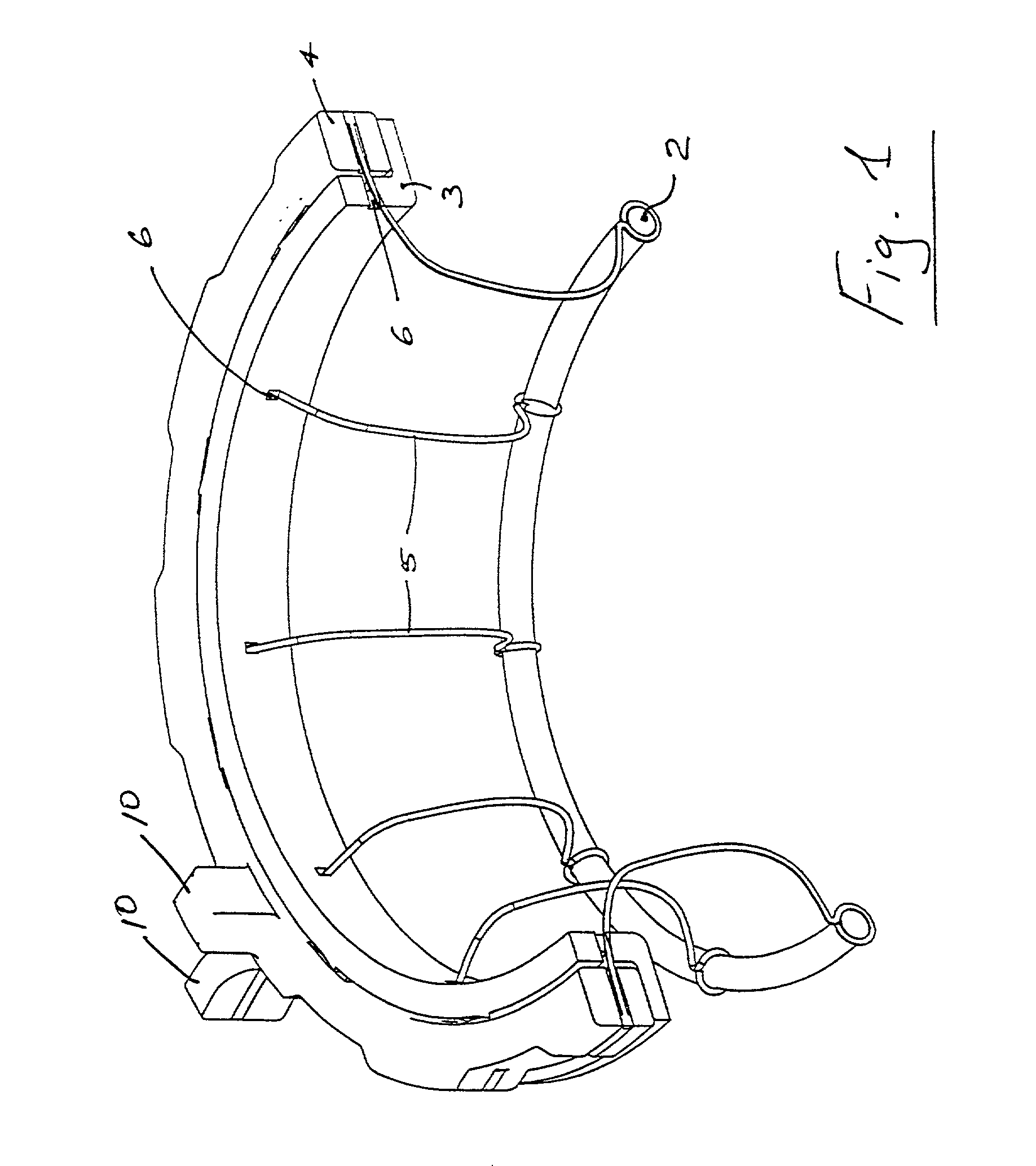
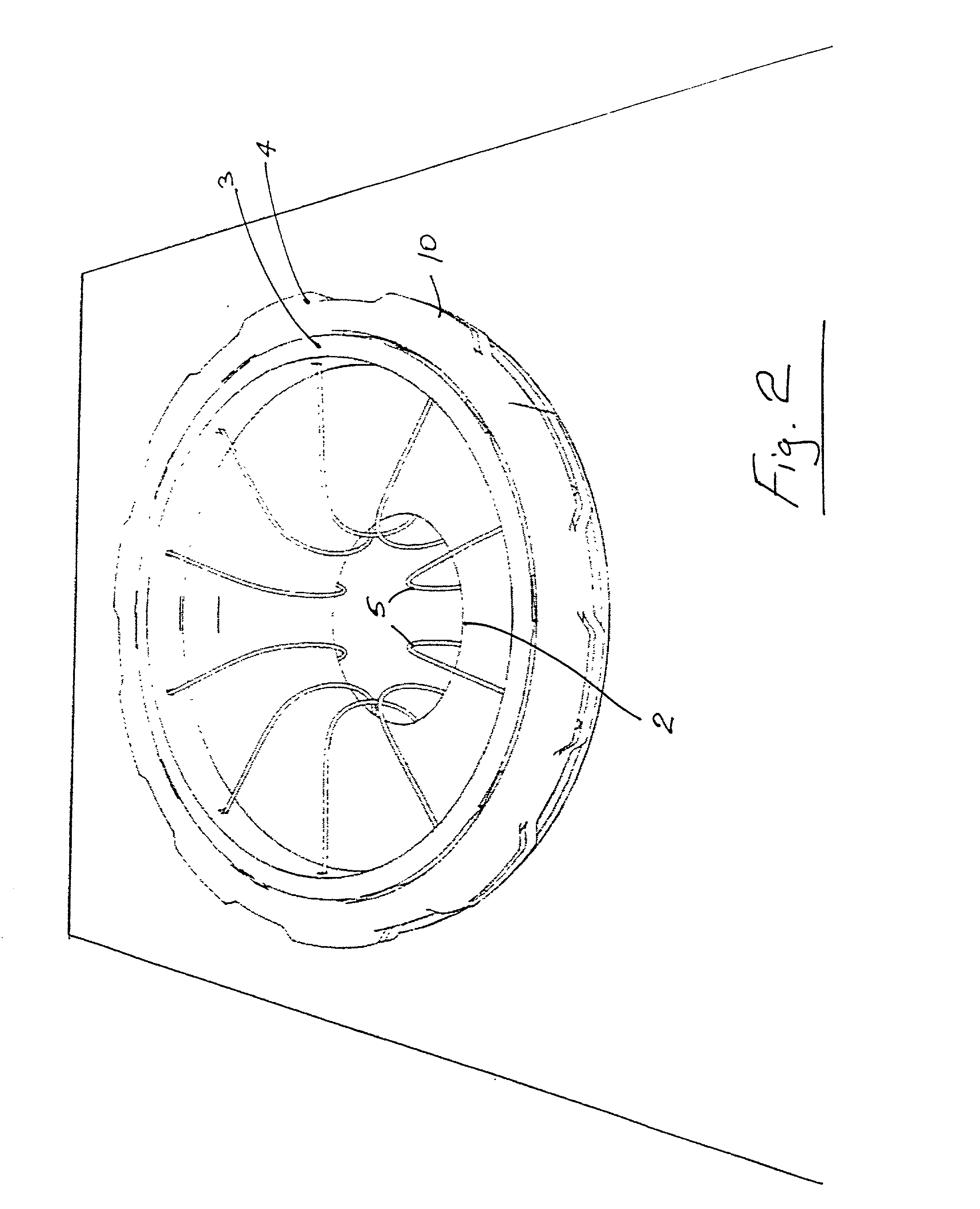
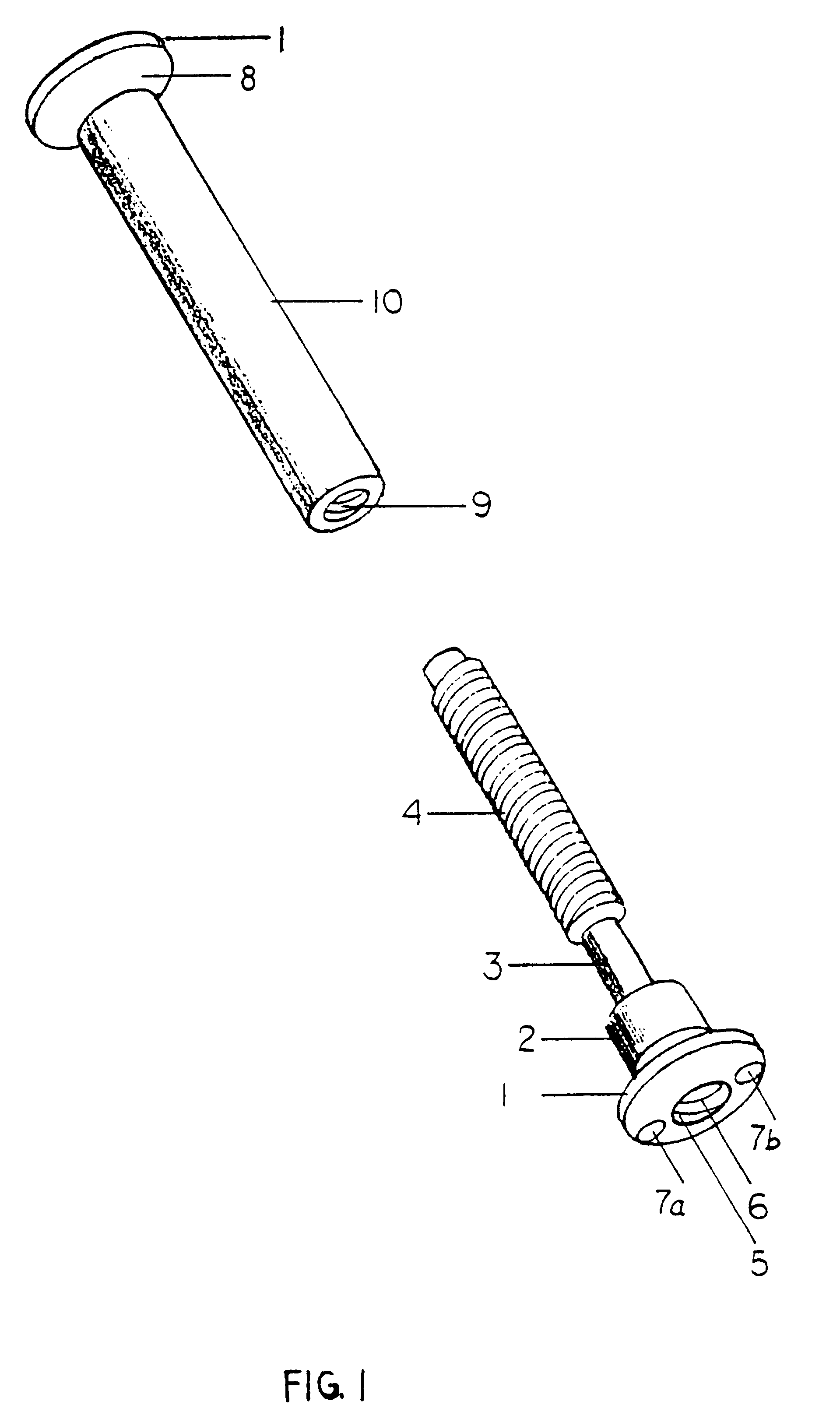
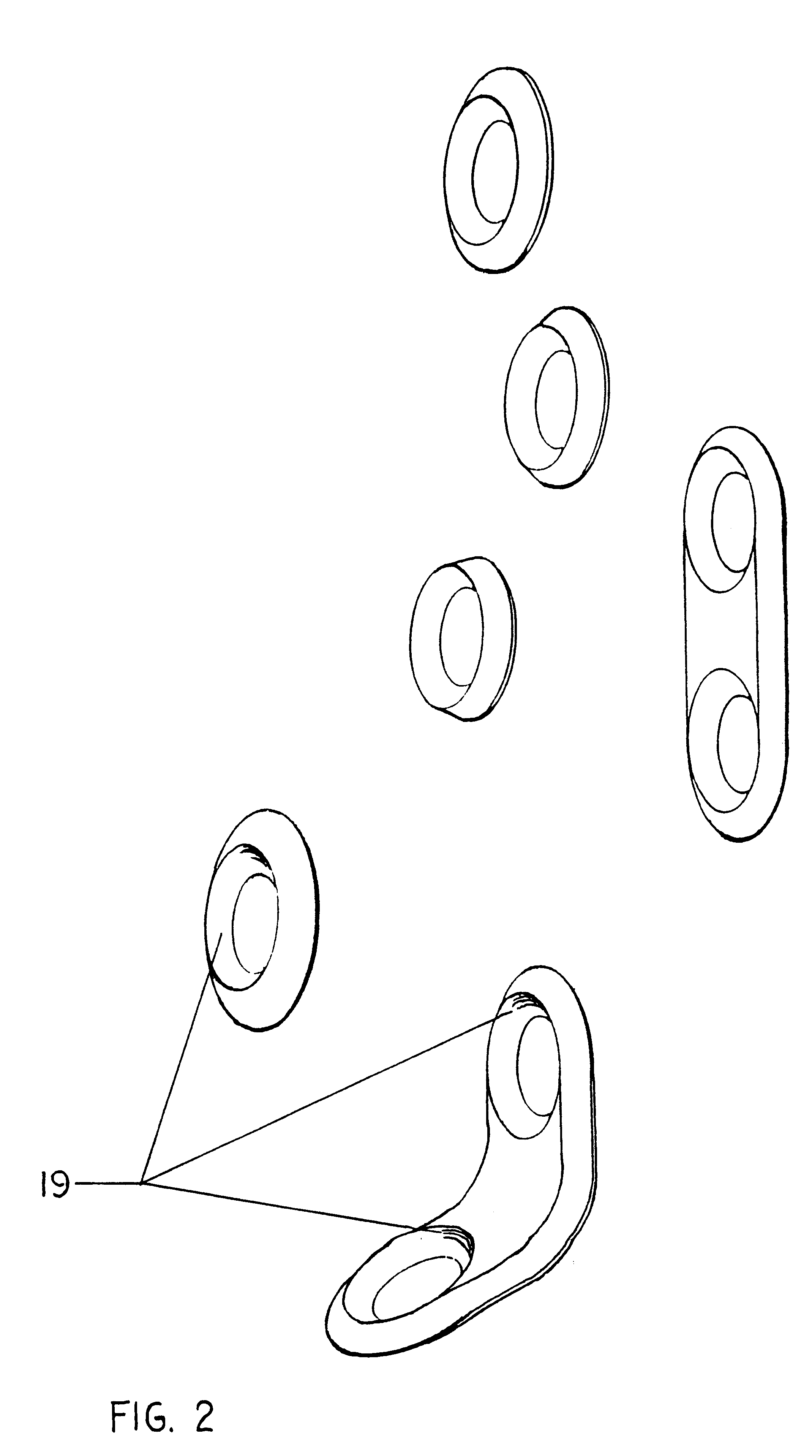
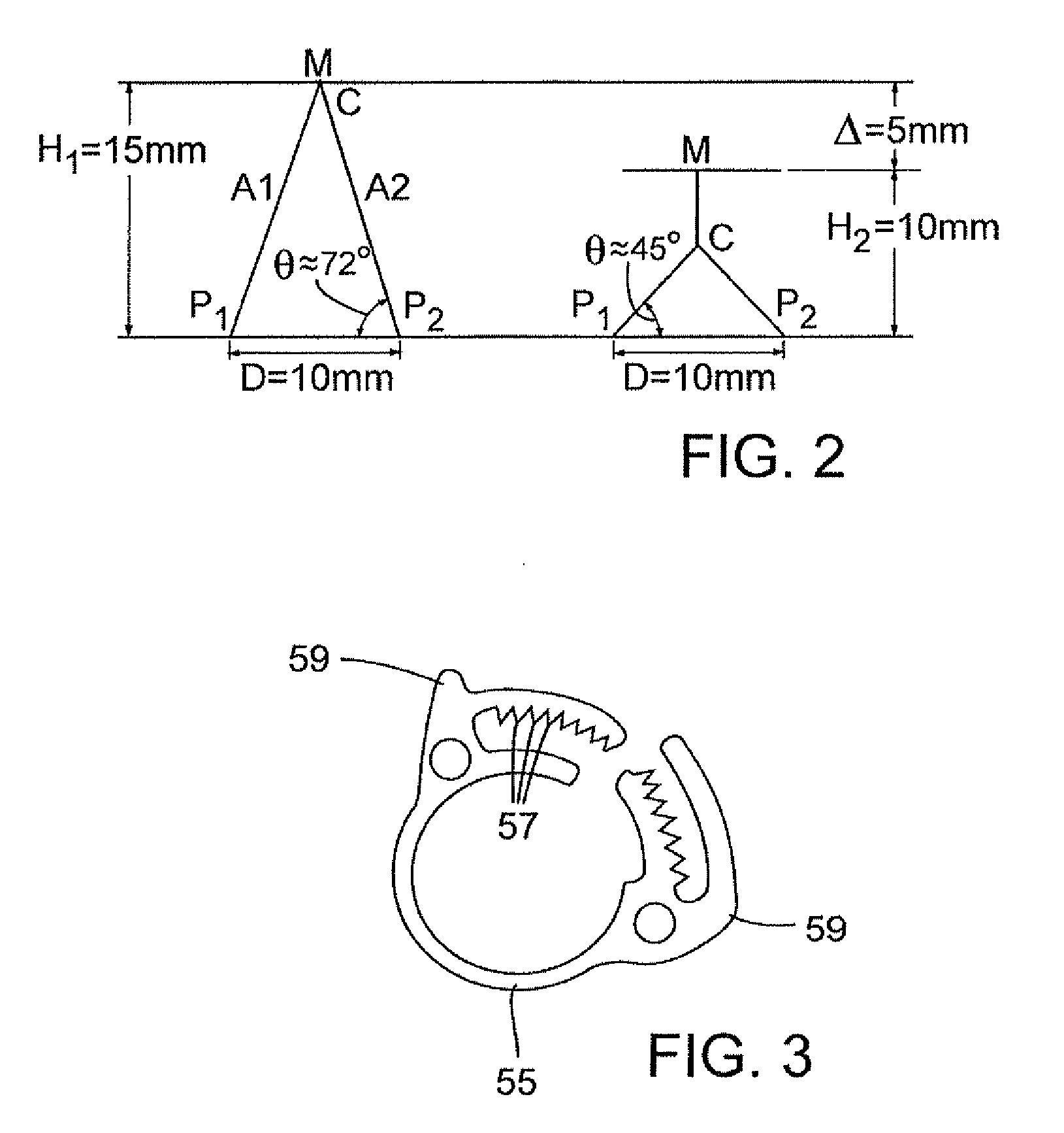
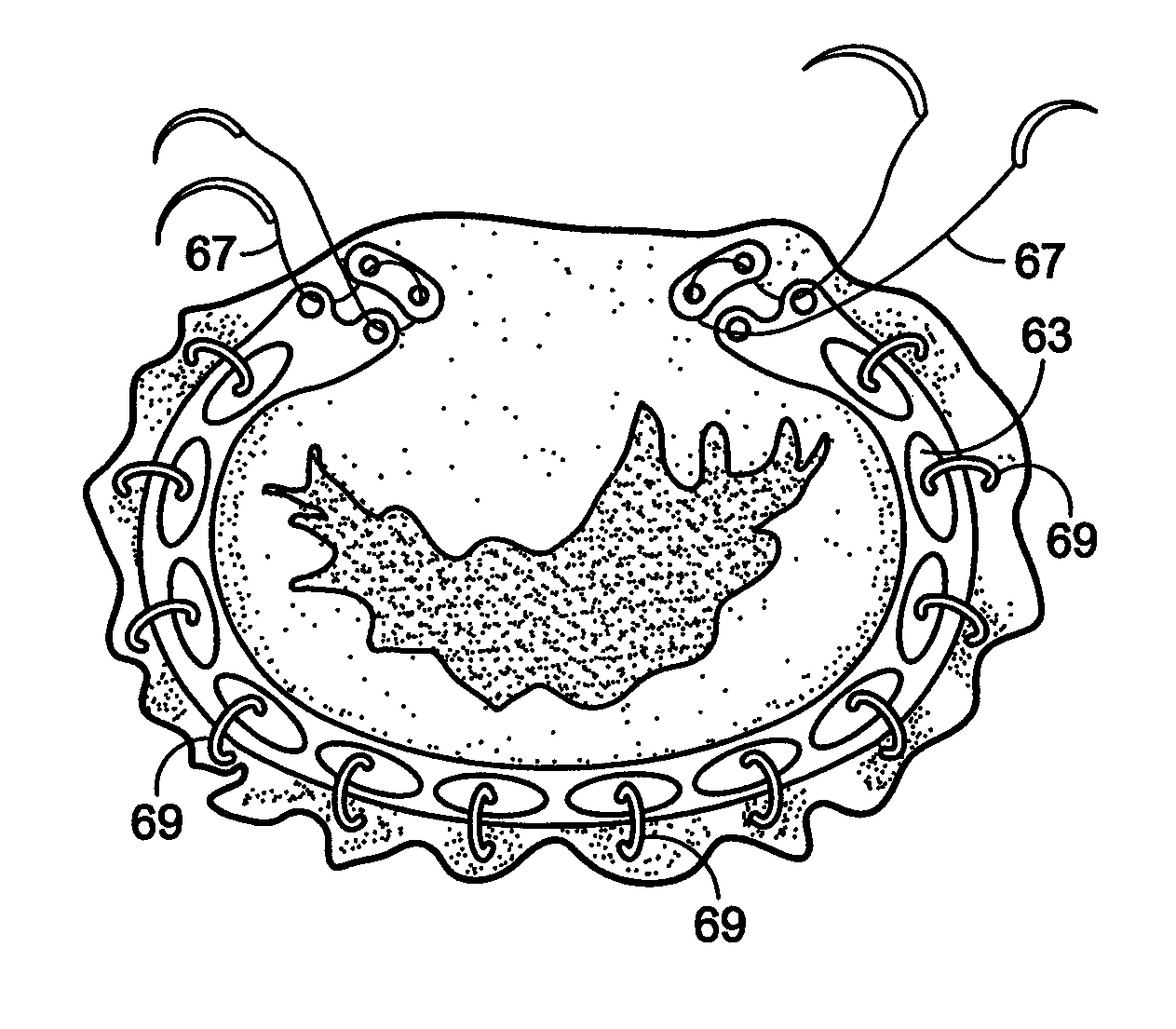
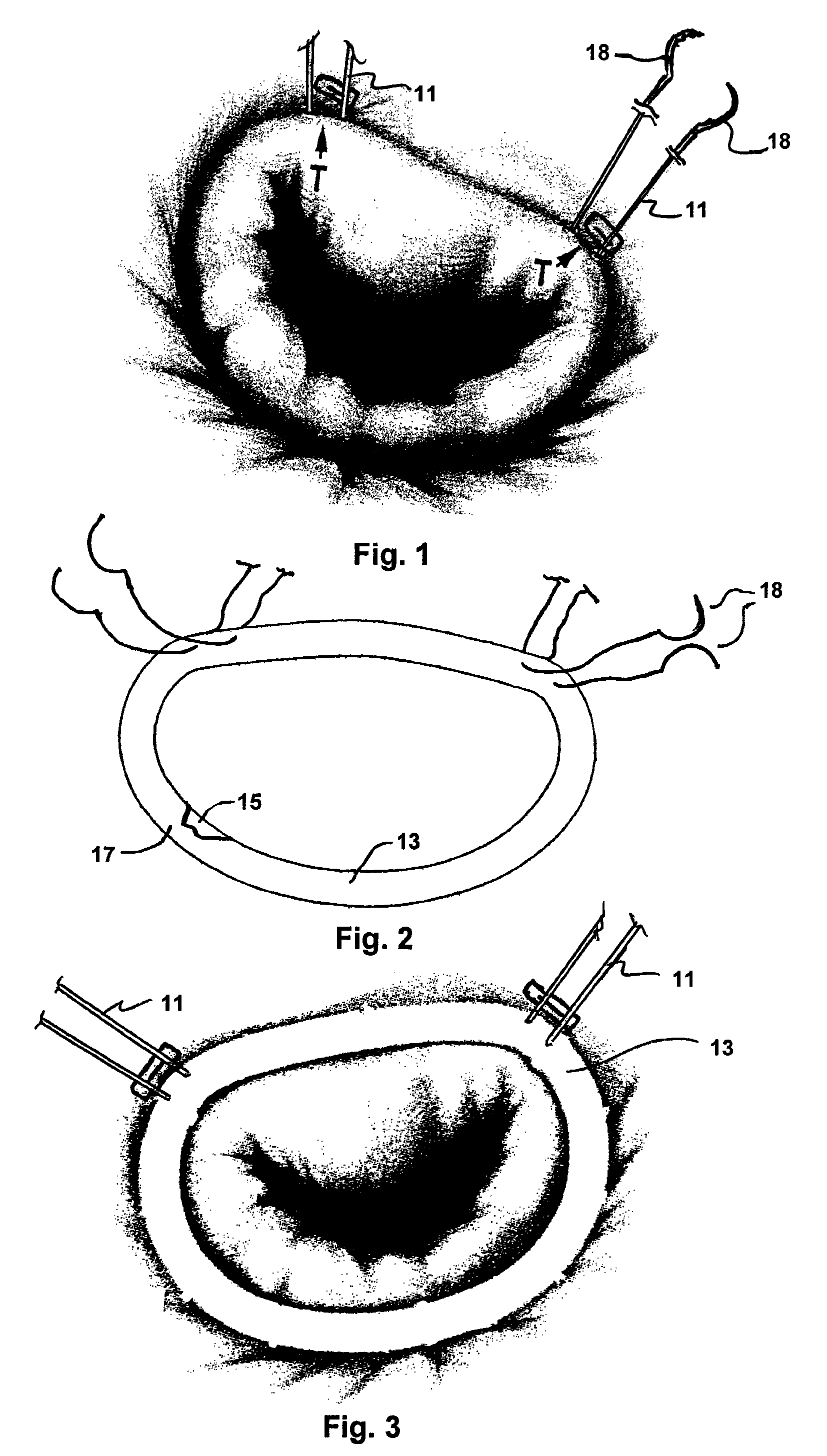
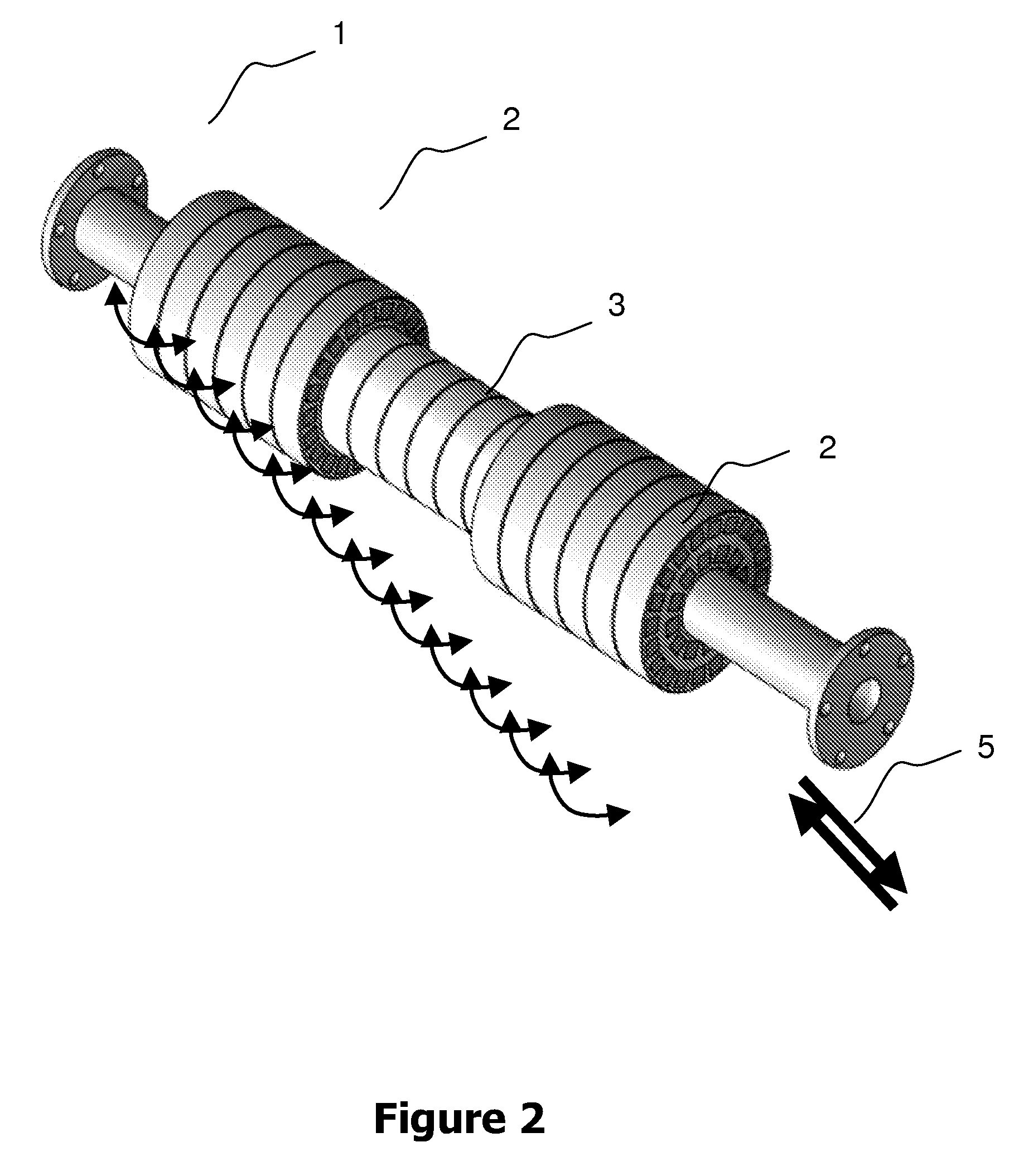
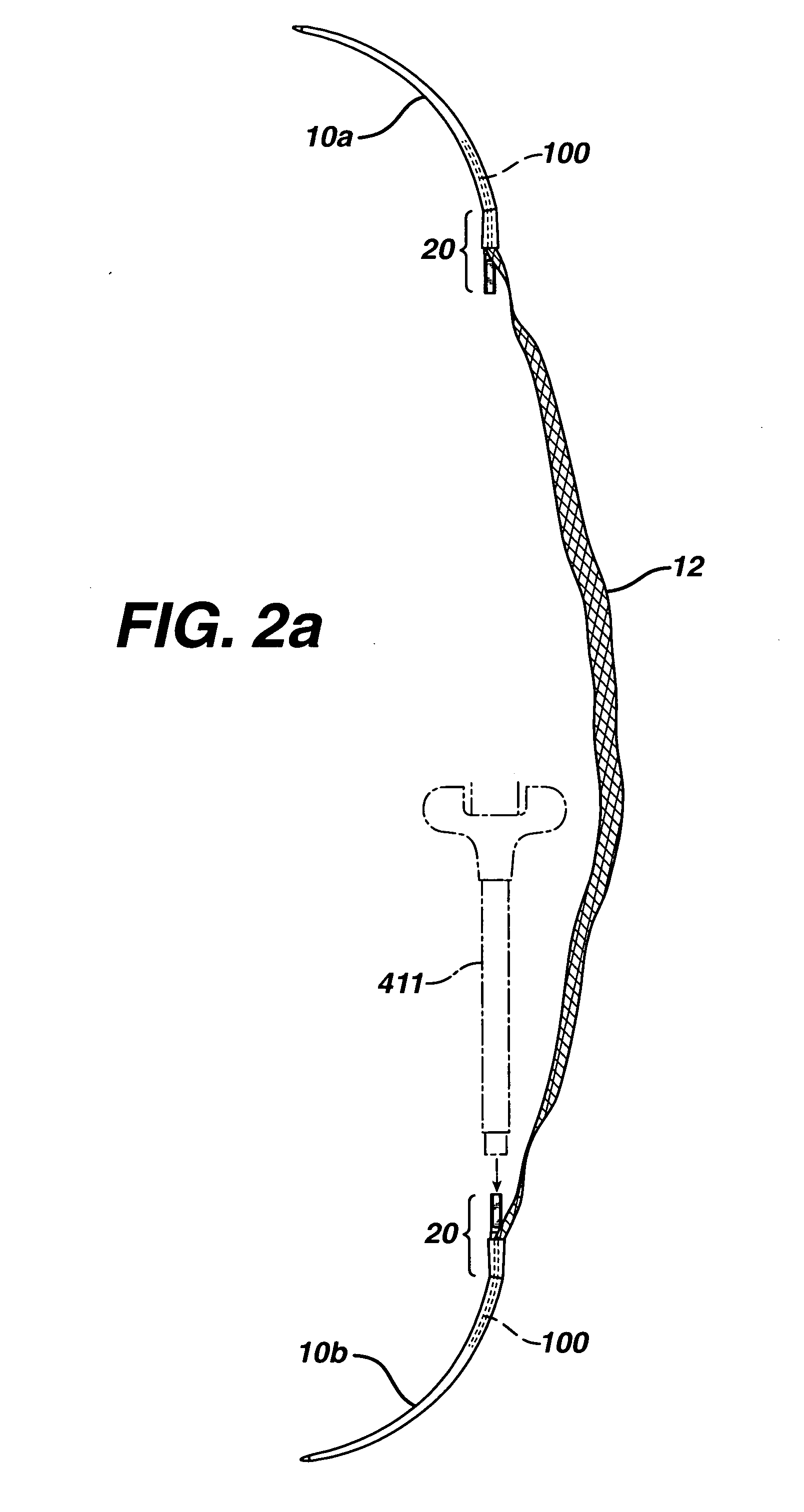
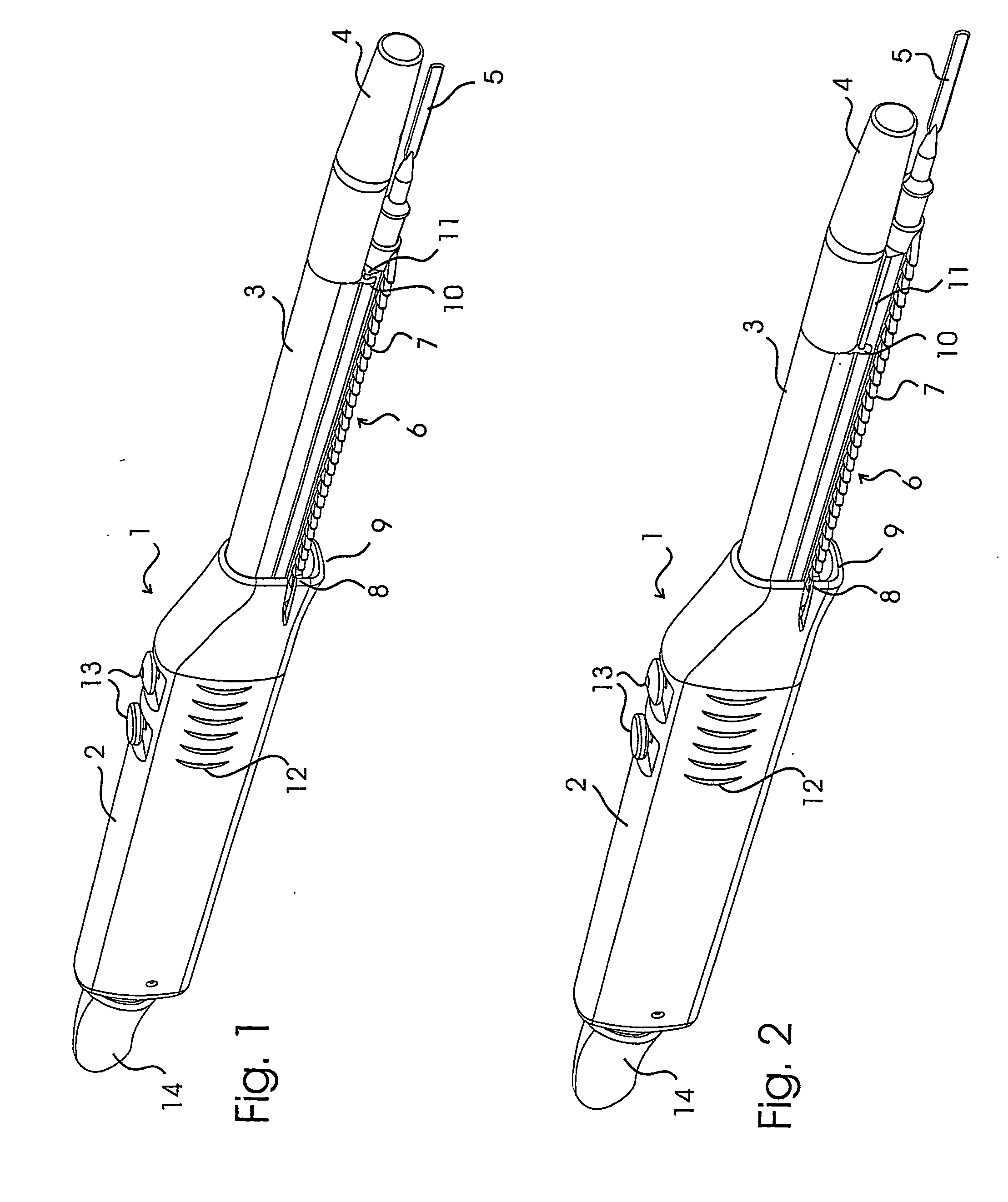
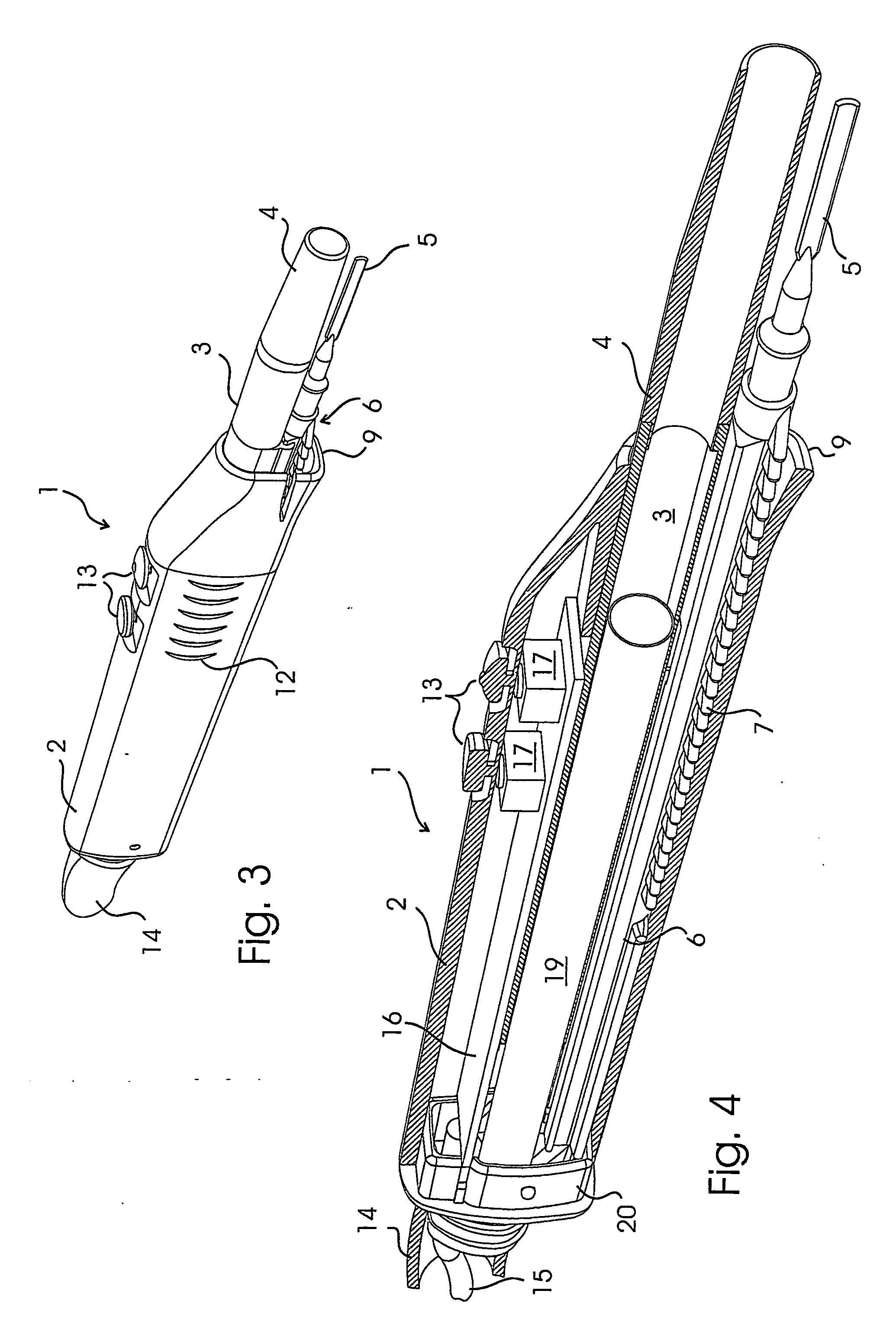
Implantation system for annuloplasty rings
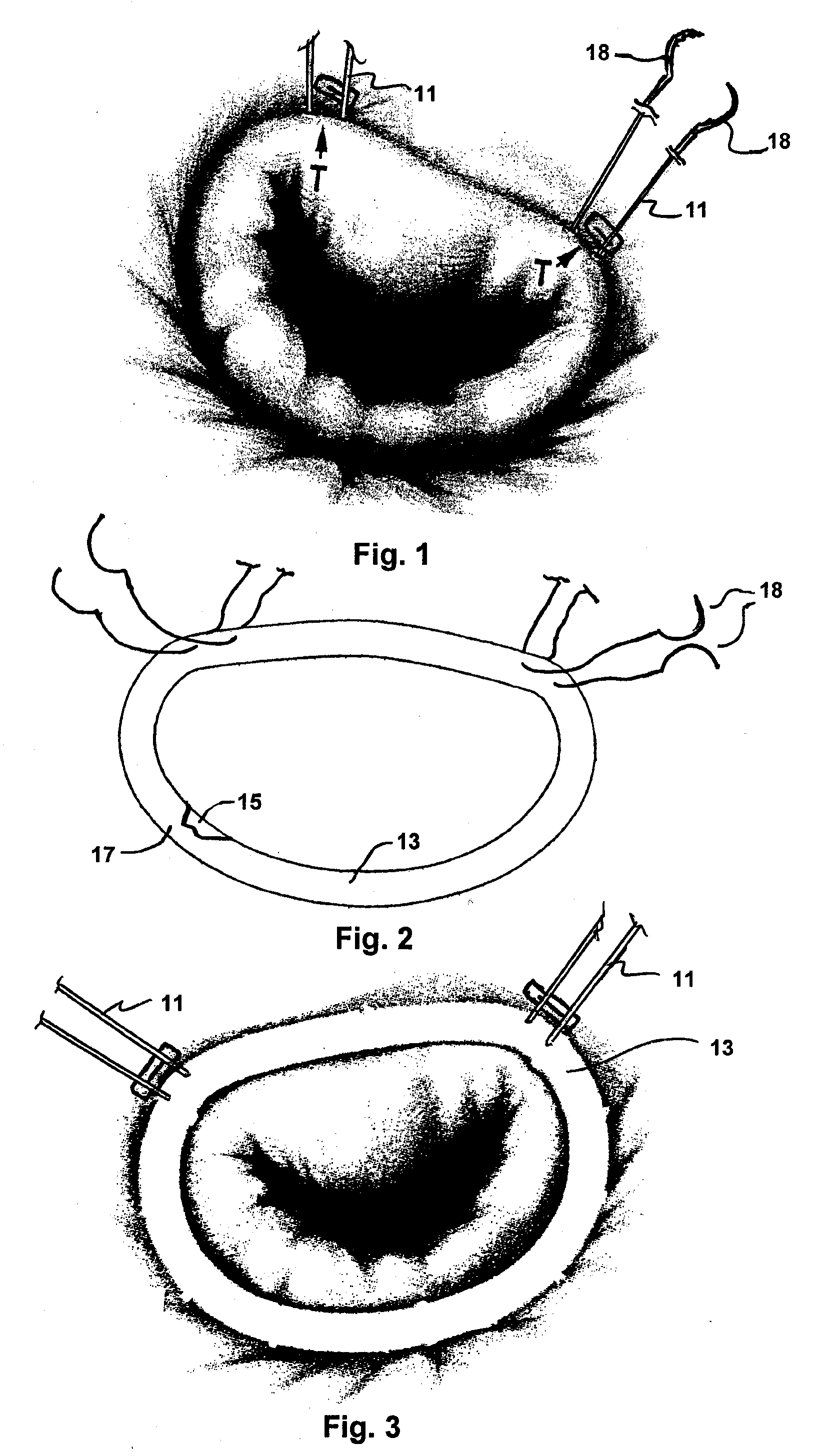
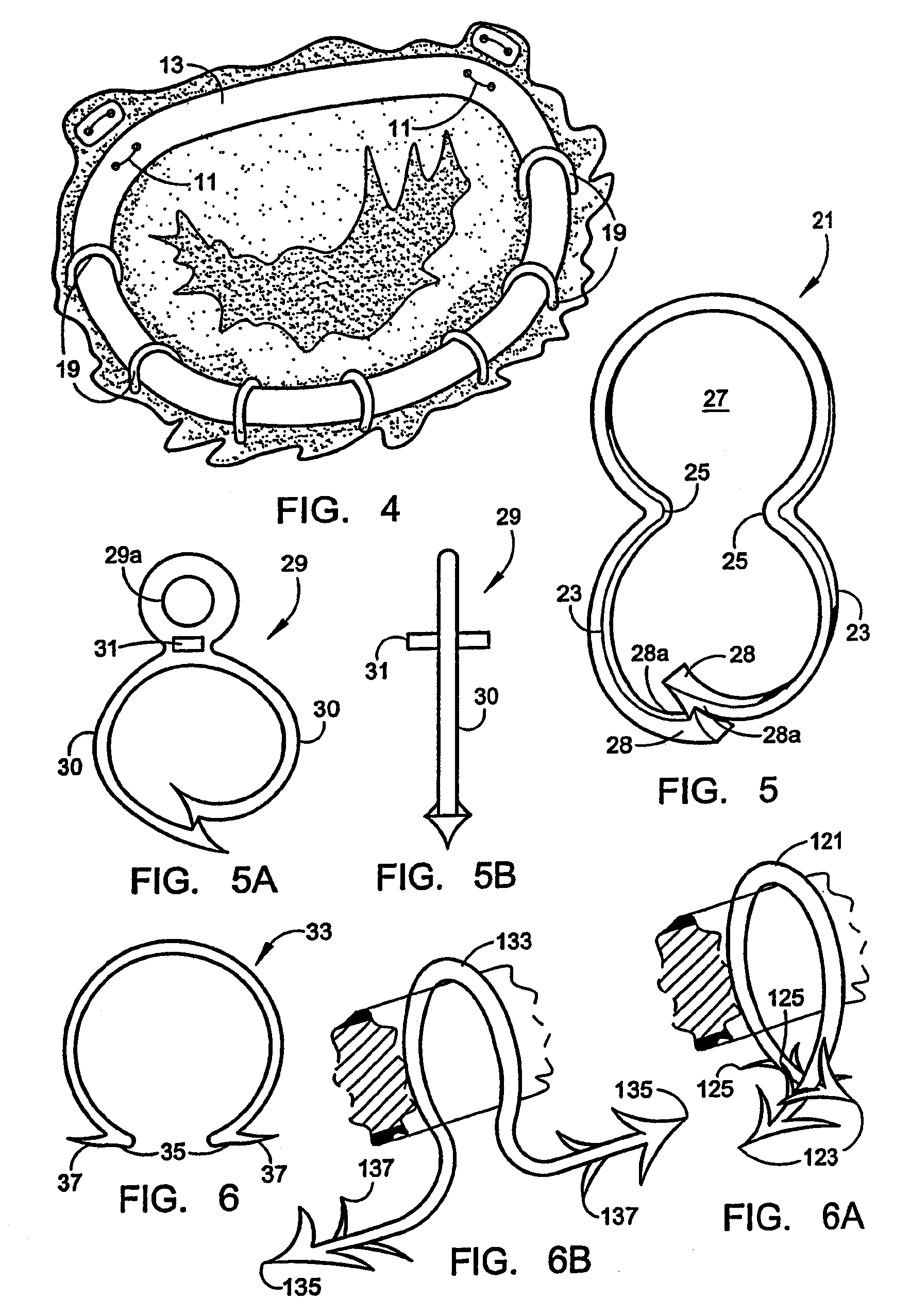
InactiveUS7485142B2Good coaptation of leafletImprove hemodynamic functionSuture equipmentsSurgical needlesEffective lengthShape-memory alloy
Methods for reconfiguring an atrioventricular heart valve that may use systems comprising a partial or complete annuloplasty rings proportioned to reconfigure a heart valve that has become in some way incompetent, a pair of trigonal sutures or implantable anchors, and a plurality of staples which may have pairs of legs that are sized and shaped for association with the ring at spaced locations along its length. These systems permit relative axial movement between the staples and the ring, whereby a patient's heart valve can be reconfigured in a manner that does not deter subtle shifting of the native valve components. Shape-memory alloy material staples may have legs with free ends that interlock following implantation. Annuloplasty rings may be complete or partial and may be fenestrated. One alternative method routes a flexible wire, preferably of shape-memory material, through the bights of pre-implanted staples. Other alternative systems use linkers of shape-memory material having hooked ends to interengage with staples or other implanted supports which, following implantation, decrease in effective length and pull the staples or other supports toward one another so as to create desired curvature of the reconfigured valve. These linkers may be separate from the supports or may be integral with them and may have a variety of shapes and forms. Various of these systems may be implanted non-invasively using a delivery catheter.
Owner:QUICKRING MEDICAL TECH LTD
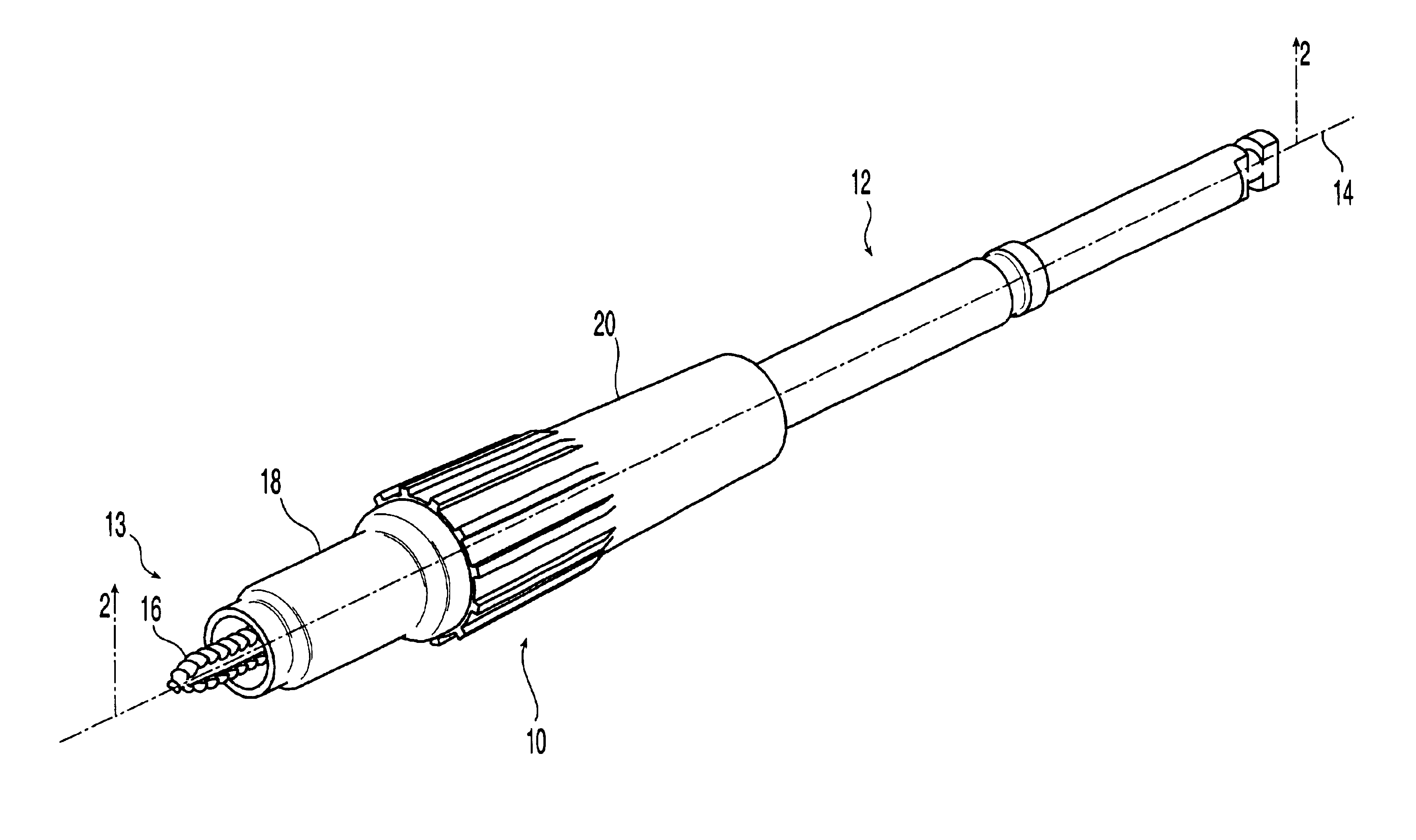
Adjustable length tap and method for drilling and tapping a bore in bone
InactiveUS6951562B2Impeding translational movementDiagnosticsSurgeryEffective lengthOrthopedic Procedures
The present invention is directed to an adjustable self drilling tap assembly and method for drilling and tapping bores in bone for use in orthopedic procedures to treat bone. The adjustable length tap assembly includes a shaft having cutting threads for drilling holes in bone, a stop collar configured and dimensioned to be translatable along the longitudinal axis of the shaft, and a locking collar comprising a member configured and dimensioned to be received over at least a portion of the stop collar. The locking collar preferably is configured and dimensioned to engage with the stop collar to adjustably set the effective length for the cutting threads and to prevent movement of the stop collar along the longitudinal axis of the shaft.
Owner:SYNTHES USA
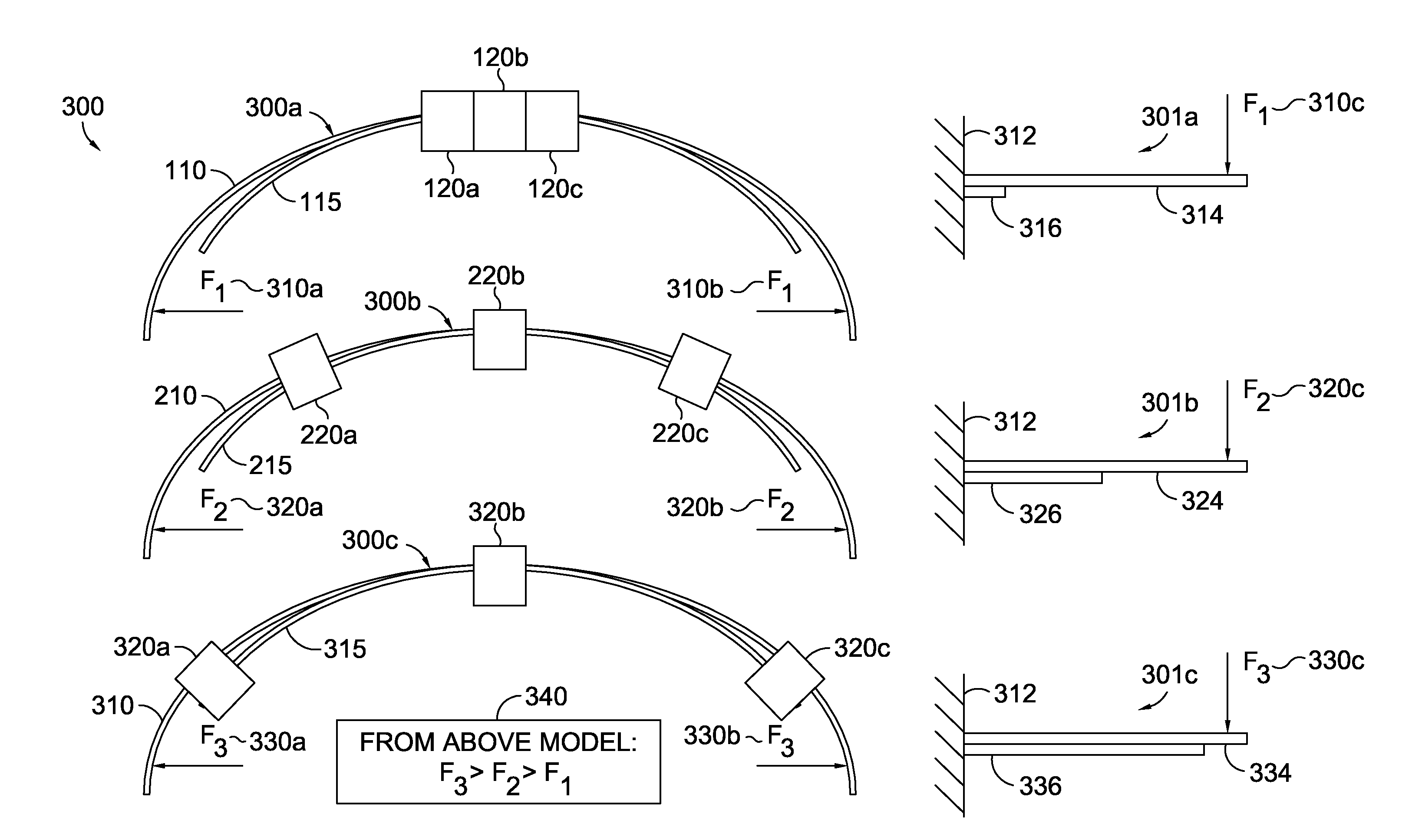
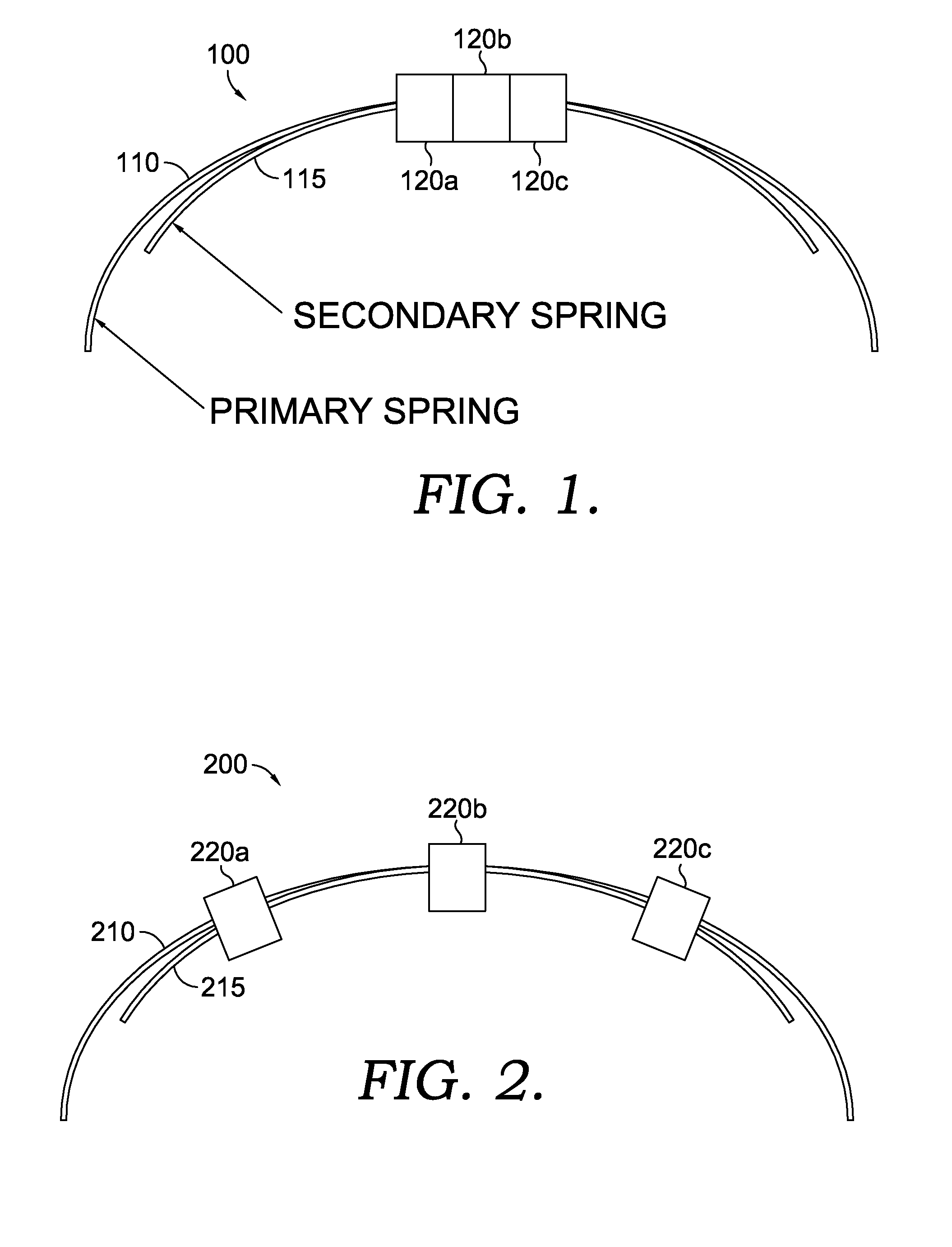
Headband variable stiffness
A method and apparatus are provided for allowing a user to change the stiffness of their headband, thus changing the clamping force of the headset. The section properties of the headband equivalent spring, which is a cantilevered beam, are changed by engaging a secondary spring, which is also a shorter cantilevered beam. The change is achieved by manipulating the effective length of the secondary spring, which can be accomplished with a set of clamps. Thus, the stiffness of the headband can be modified to the desire of the user.
Owner:VOCOLLECT
Microfluidic devices for methods development
InactiveUS6880576B2Material nanotechnologySludge treatmentChromatographic separationFlow resistivity
Microfluidic devices with multiple fluid process regions for subjecting similar samples to different process conditions in parallel are provided. One or more common fluid inputs may be provided to minimize the number of external fluid supply components. Solid materials such as chromatographic separation media or catalyst media is preferably provided in each fluid process region. Solid materials may be supplied to the devices in the form of slurry, with particles retained by porous elements or frits. Different fluid process regions may having different effective lengths, different solid material types or amounts, or may receive different ratios of common fluids supplied to the device. The flow resistances of dissimilar fluid process regions may be balanced passively with the addition of impedance elements in series with each fluid process region.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Device for use in surgery
In one embodiment, a wound retractor includes a plurality of straps connected between an inner ring and an outer ring assembly. The inner ring is positioned internal of the wound so that it rests against the innermost tissue layer, and the outer ring is located outside of the wound adjacent the outermost tissue layer. The outer ring assembly includes an inner ring having guide holes for the passage of the straps and an outer ring to which the straps are affixed. Rotation of the outer ring of the outer ring assembly relative to the inner ring of the outer ring assembly results in a shorting of the effective length of the straps, retraction of the wound edge and exposure of the wound site.
Owner:ATROPOS LTD
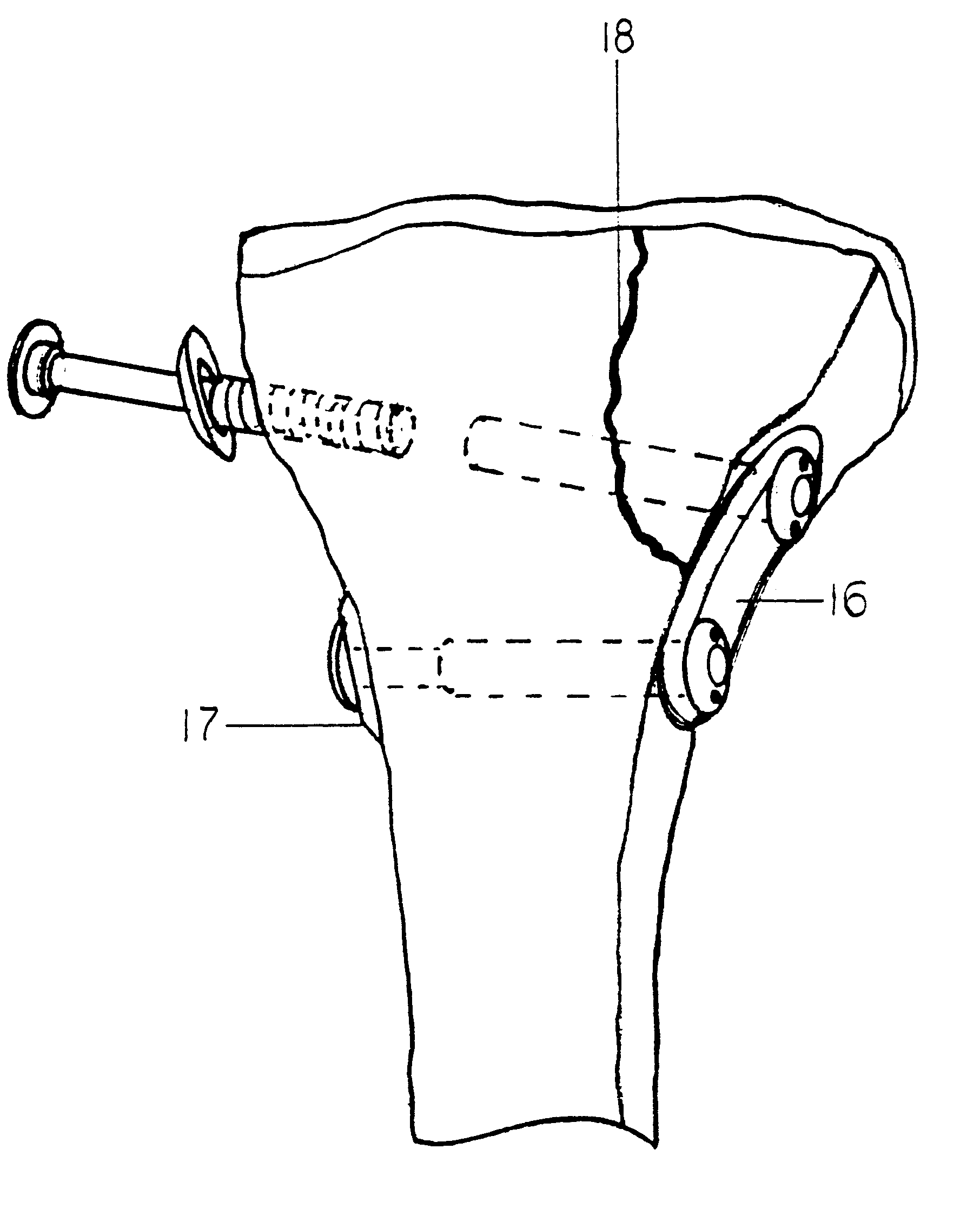
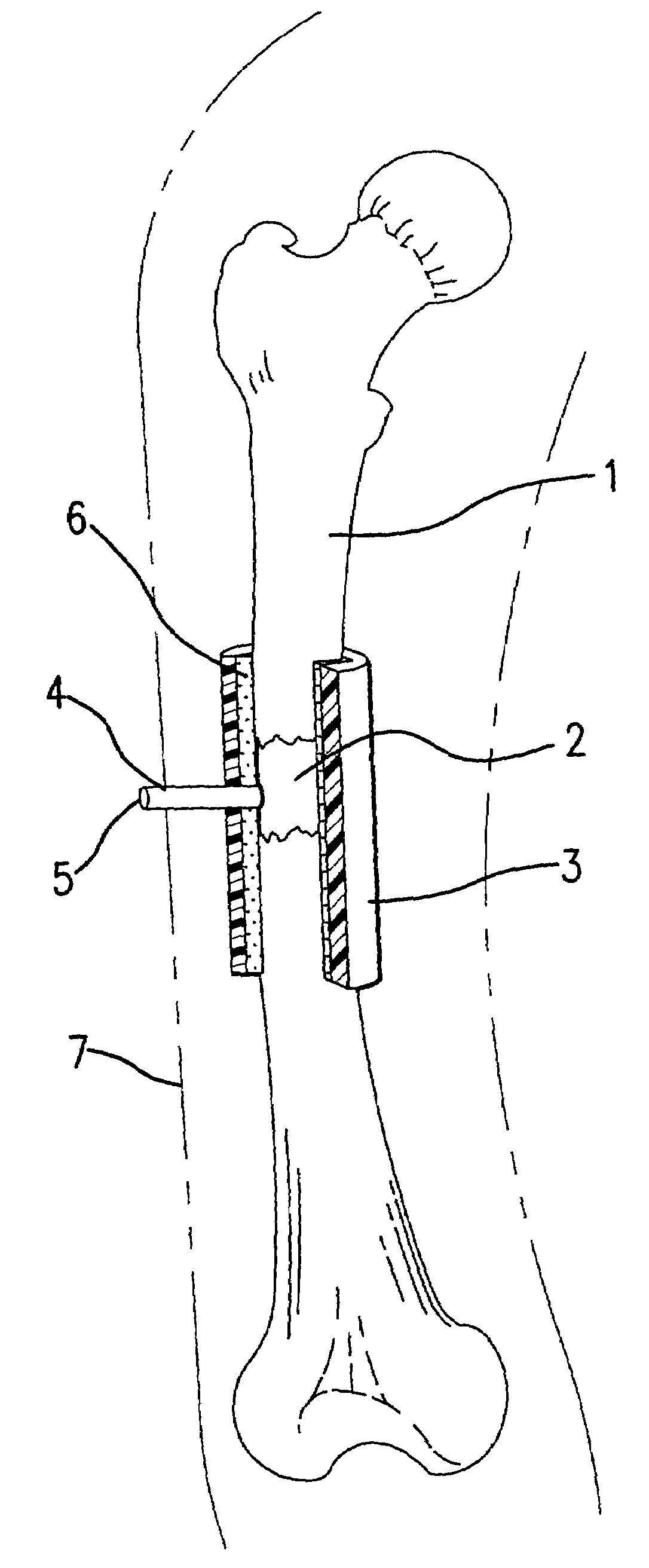
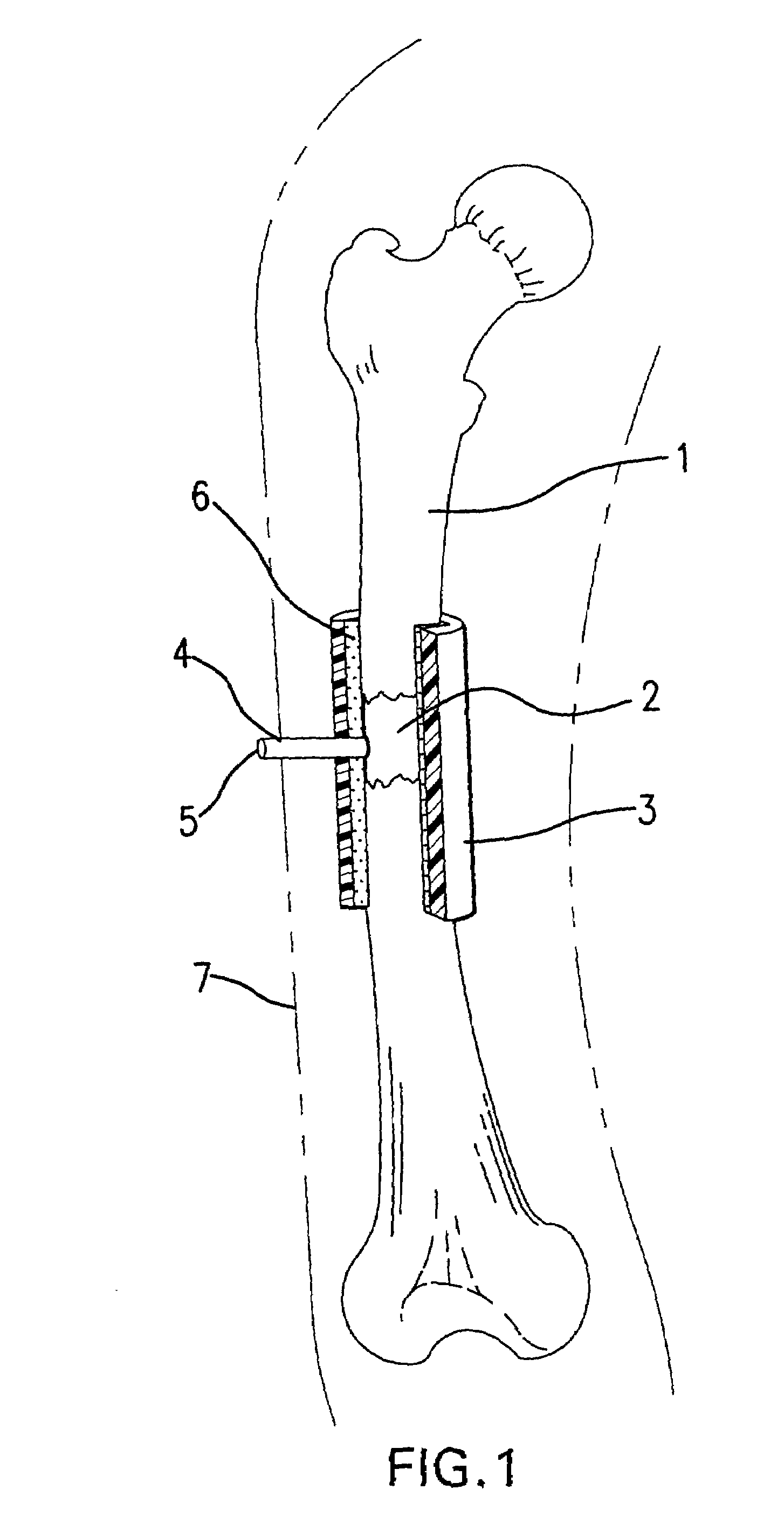
Hardware for high strength fastening of bone
InactiveUS6302887B1High strengthMinimal invasionInternal osteosythesisDiagnosticsShoulder regionEffective length
A high strength fastener for bone fractures. This fastener consists of two members, a male and female. The male member has external machine screw threads that screw into matching internal threads in the female member at a predictable torque so that the force of fixation exerted upon the bone can be approximated by the installer. Because of the effective length of the threads, this fastener is easily adjusted to the proper length without cutting. Both members have a smooth shoulder region proximal to the heads and this shoulder region presents a low-stress bearing surface to each cortical wall. Each member has a head that fits rigidly into an installation tool providing for ease of insertion and fastening in the patient with minimal invasion and little periosteal stripping. Each head has a semi-spherical face that articulates with matching washers and plates, thus allowing the washer to assume the plane of the surrounding bone therefore distributing the load over a greater area.
Owner:ACUMED
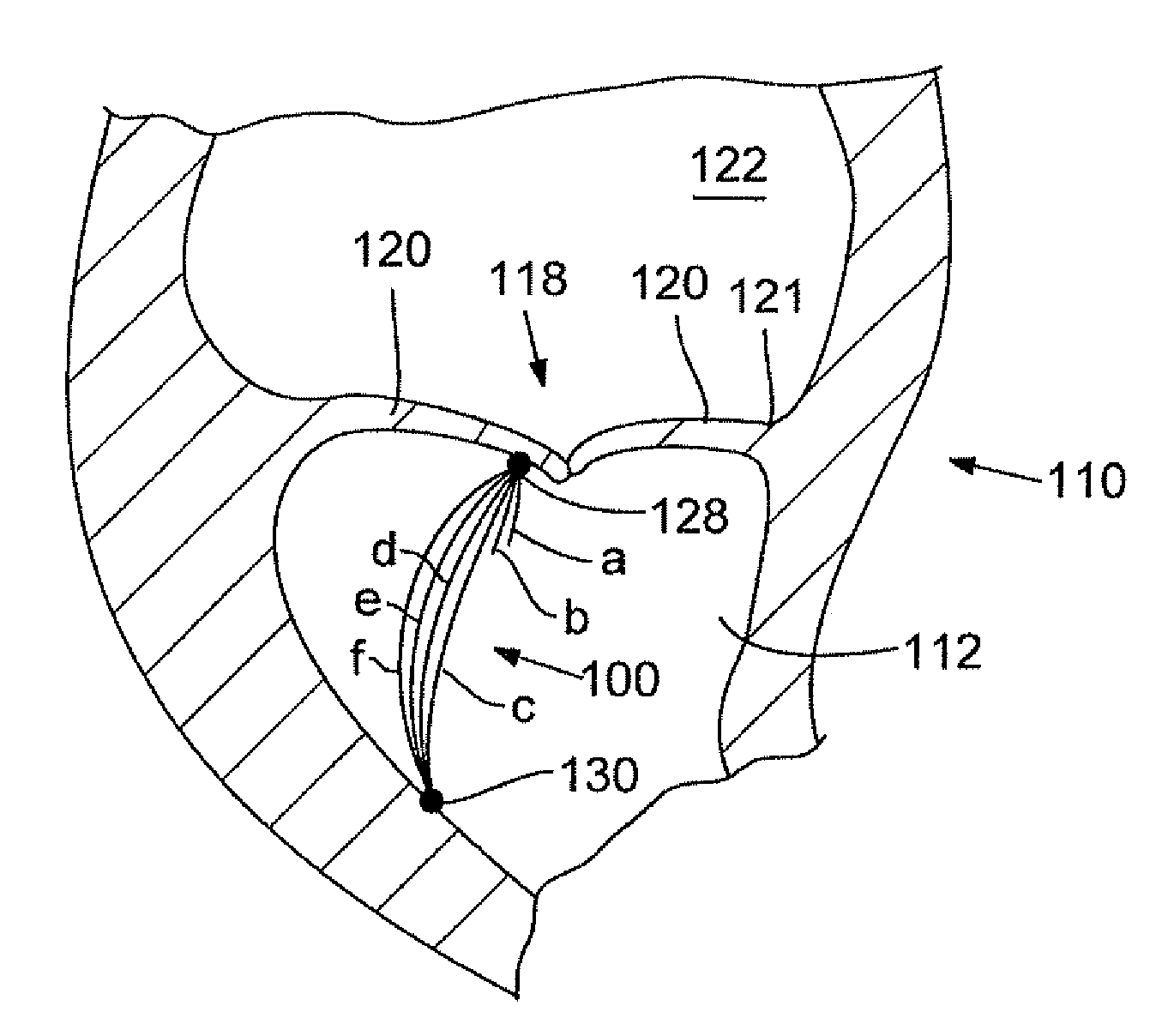
Method and apparatus for repairing or replacing chordae tendinae
A method and apparatus for performing mitral valve chordal repair on a patient include attaching at least one filament to a mitral valve leaflet and to a papillary muscle. The length of filaments can be adjusted by adjusting tension in a filament or by altering the effective length of a filament by cutting filament strands or by moving an adjustment member along the length of the filaments.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
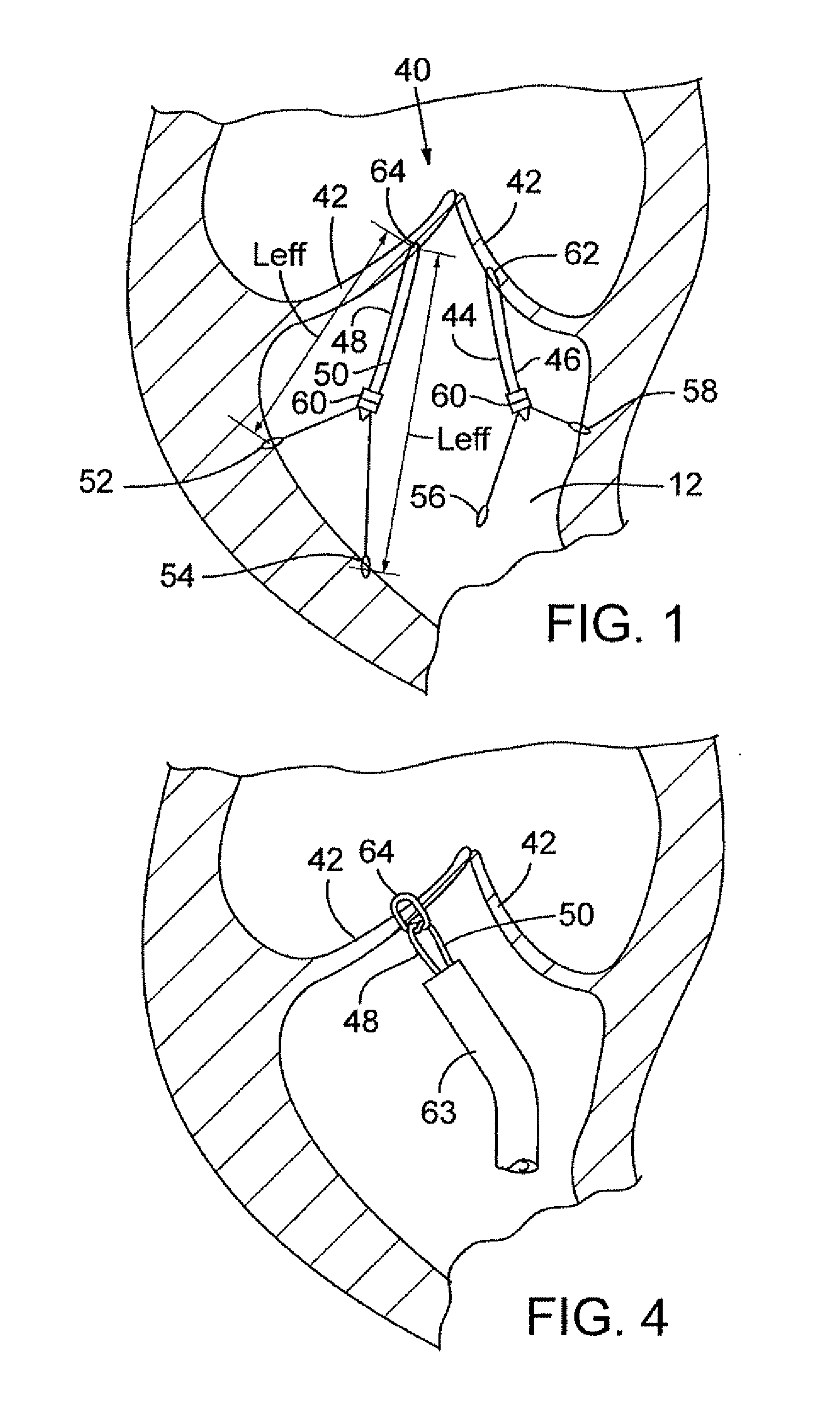
Method and apparatus for adjusting flexible areal polymer implants
A minimally invasive approach to adjusting the amount of support on an anatomical structure. The methods and apparatus described include the use of a tape for supporting an anatomical structure. Adjustment may be achieved by use of bulking agents applied either directly to the site or into a containment device Lo located within proximity of the tape and such that it works in conjunction with the tape to support the anatomic structure. An alternative approach utilizes mechanical means for adjusting the effective length of the supporting arms of the tape used to support the anatomical structure.
Owner:ETHICON GMBH CO KG +1
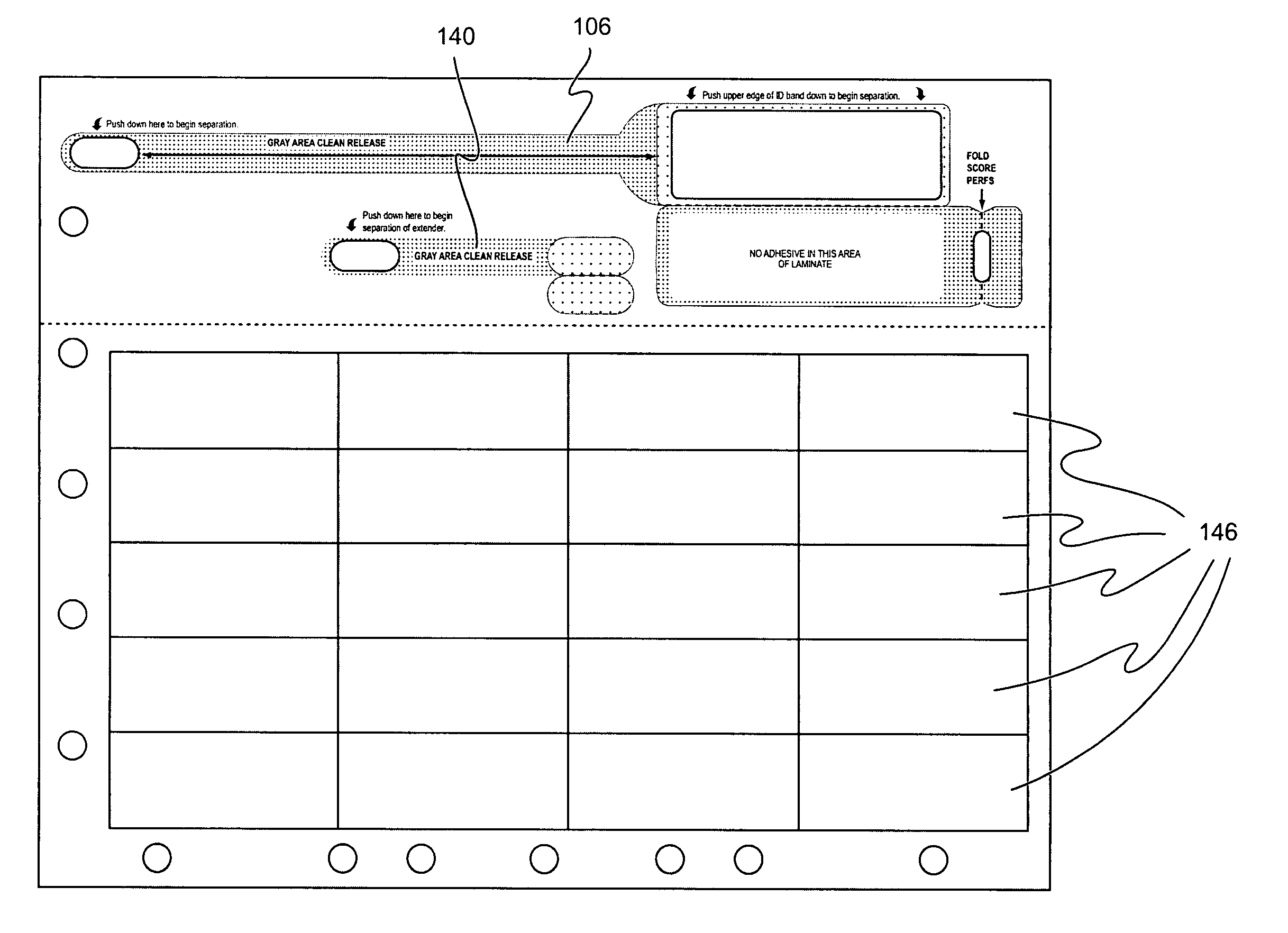
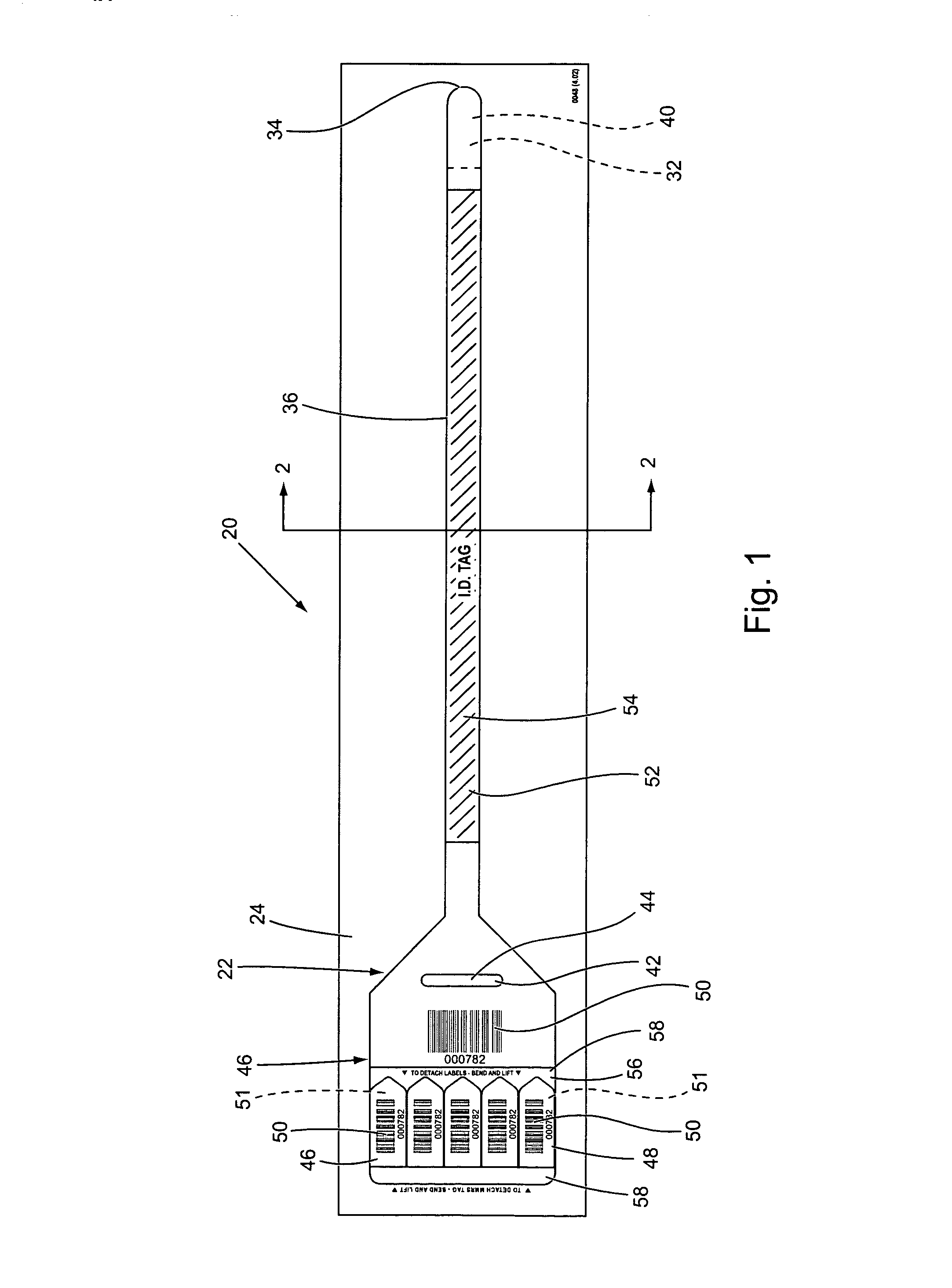
Wristband/cinch with label assembly business form and method
A business form particularly adapted for use in a medical or hospital environment includes in a first embodiment a wristband assembly that is readily separable from a carrier comprised of a layer of face stock and a laminate, with the wristband including a printable face stock region die cut into the face stock and a strap portion, a laminating portion, and a cinch die cut into the laminate layer. The laminating portion includes two halves which fold together about a fold line to enclose the face stock, with the strap portion extending from one of said halves. The cinch may be located in one of two locations, either in an extension from the other side of the face stock or intermediate the face stock and the strap portion. In either case the cinch comprises a slot through which the strap portion is inserted and then adhered to itself after its length has been adjusted by the medical professional. If an extension is provided, it may be folded over to adhere to the strap portion and clamp it in place there as well as being adhered at its end back onto itself, as described. An extender is also described which includes a clamshell joinder and a tail portion. The clamshell portion may be applied to the strap portion anywhere along its length to extend the effective length of the strap portion. Any of the wristband constructions may be provided on a page sized sheet along with a plurality of self adhering labels, in any of a number of configurations, to suit any particular application, as desired by a user.
Owner:ZEBRA TECH CORP
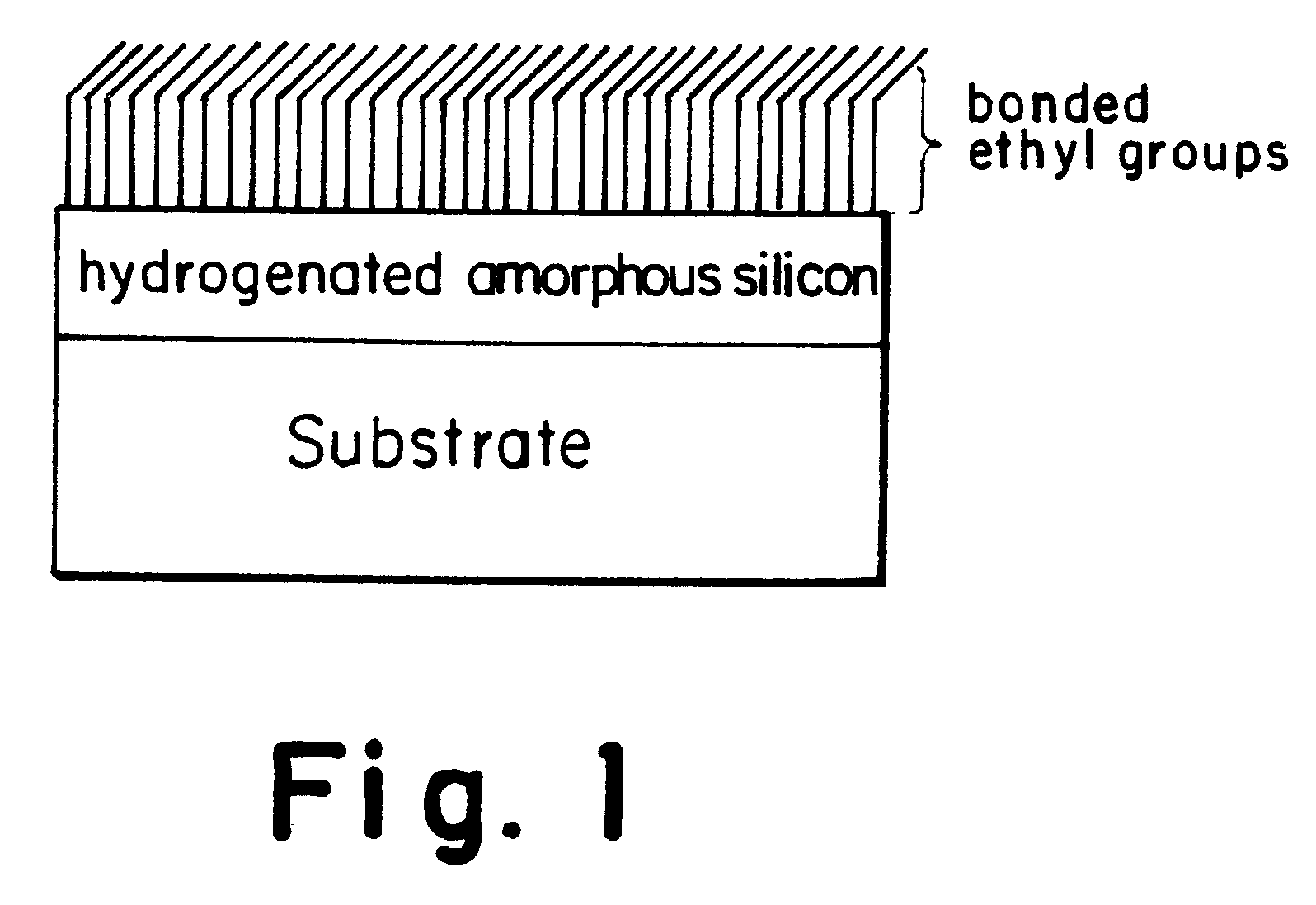
Surface modification of solid supports through the thermal decomposition and functionalization of silanes
InactiveUS6444326B1Inhibition formationGaseous chemical processesOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsUnsaturated hydrocarbonSilanes
Method of modifying the surface properties of a substrate by depositing a coating of hydrogenated amorphous silicon on the surface of the substrate and functionalizing the coated substrate by exposing the substrate to a binding reagent having at least one unsaturated hydrocarbon group under pressure and elevated temperature for an effective length of time. The hydrogenated amorphous silicon coating is deposited by exposing the substrate to silicon hydride gas under pressure and elevated temperature for an effective length of time.
Owner:SILCOTEK CORP
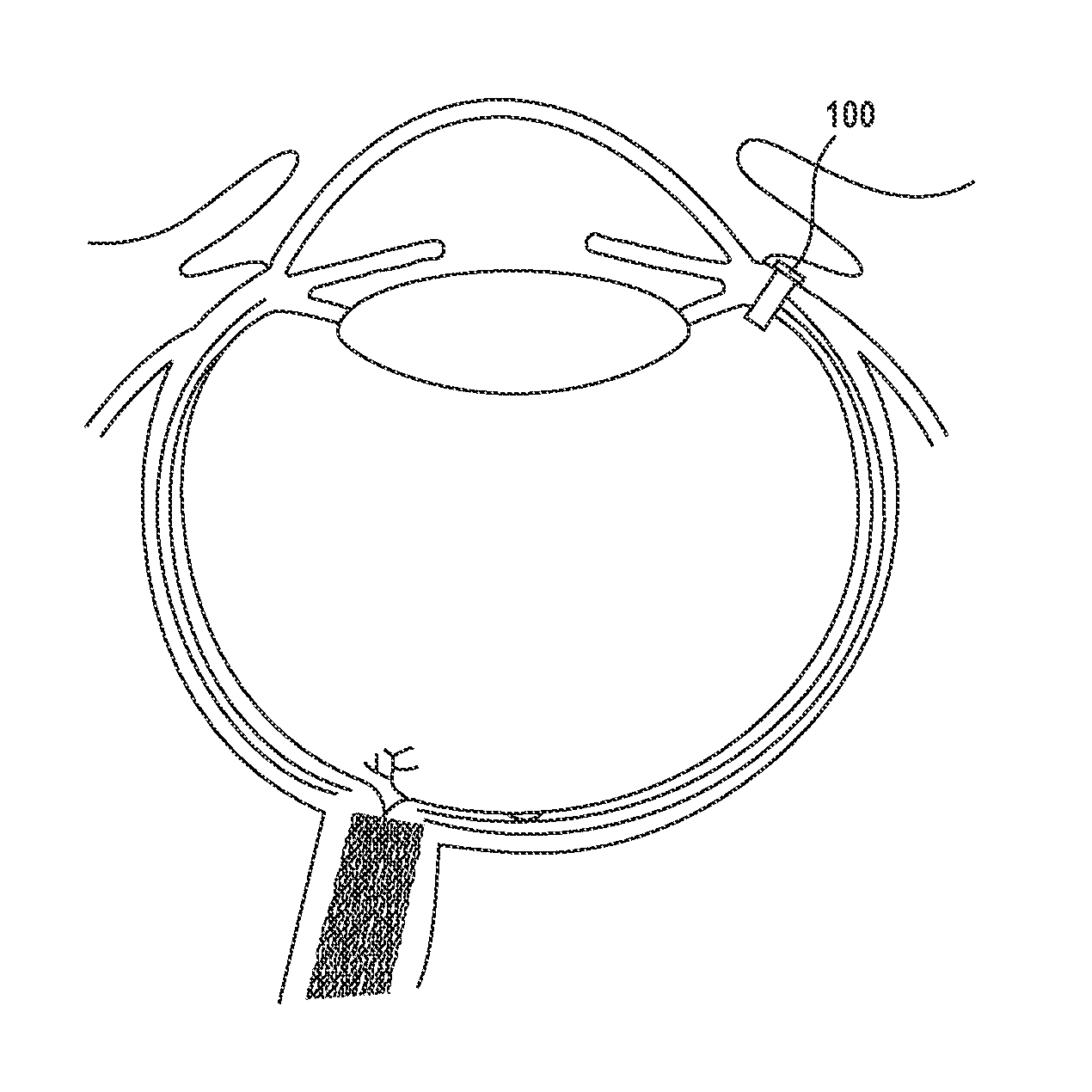
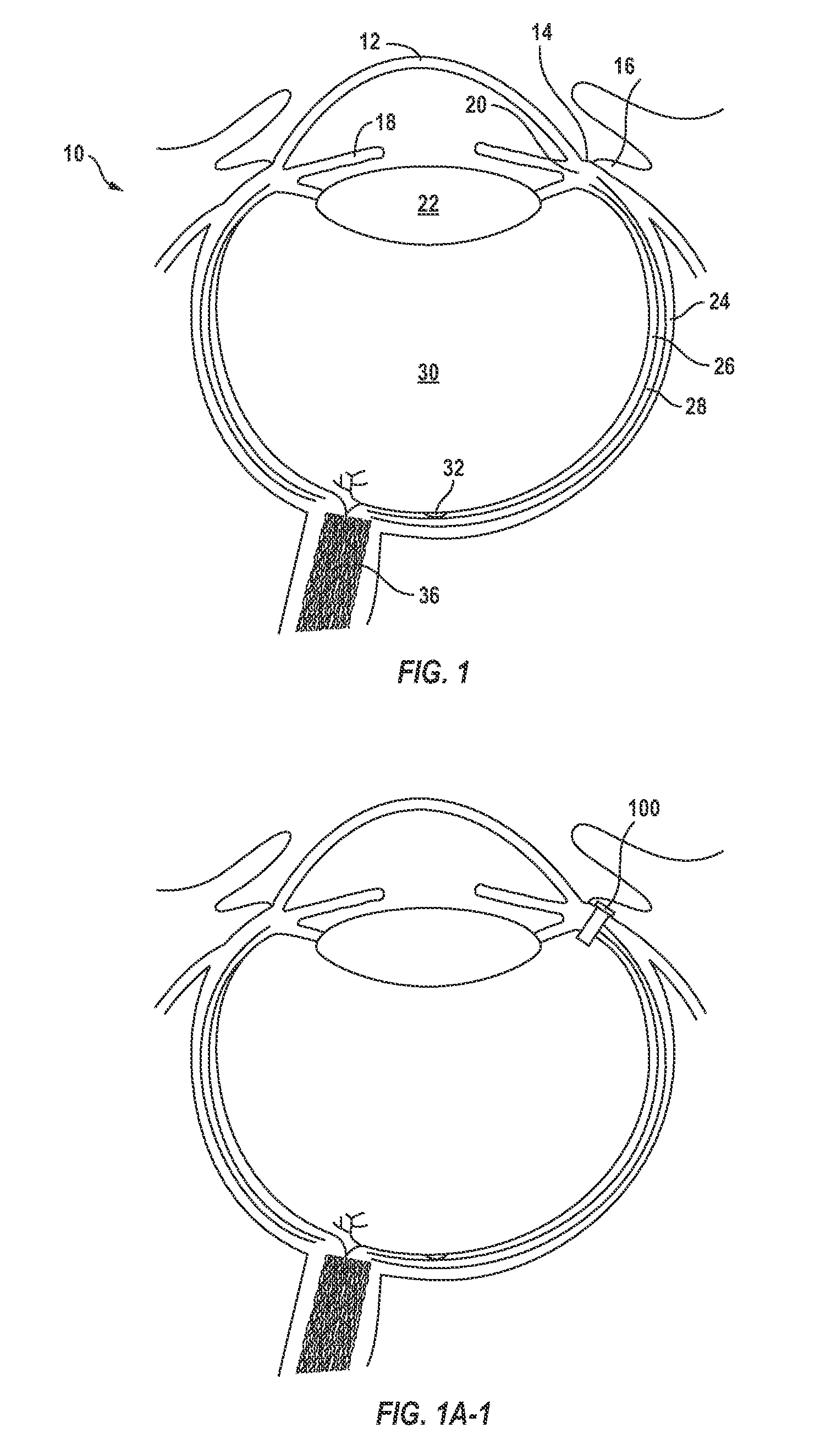
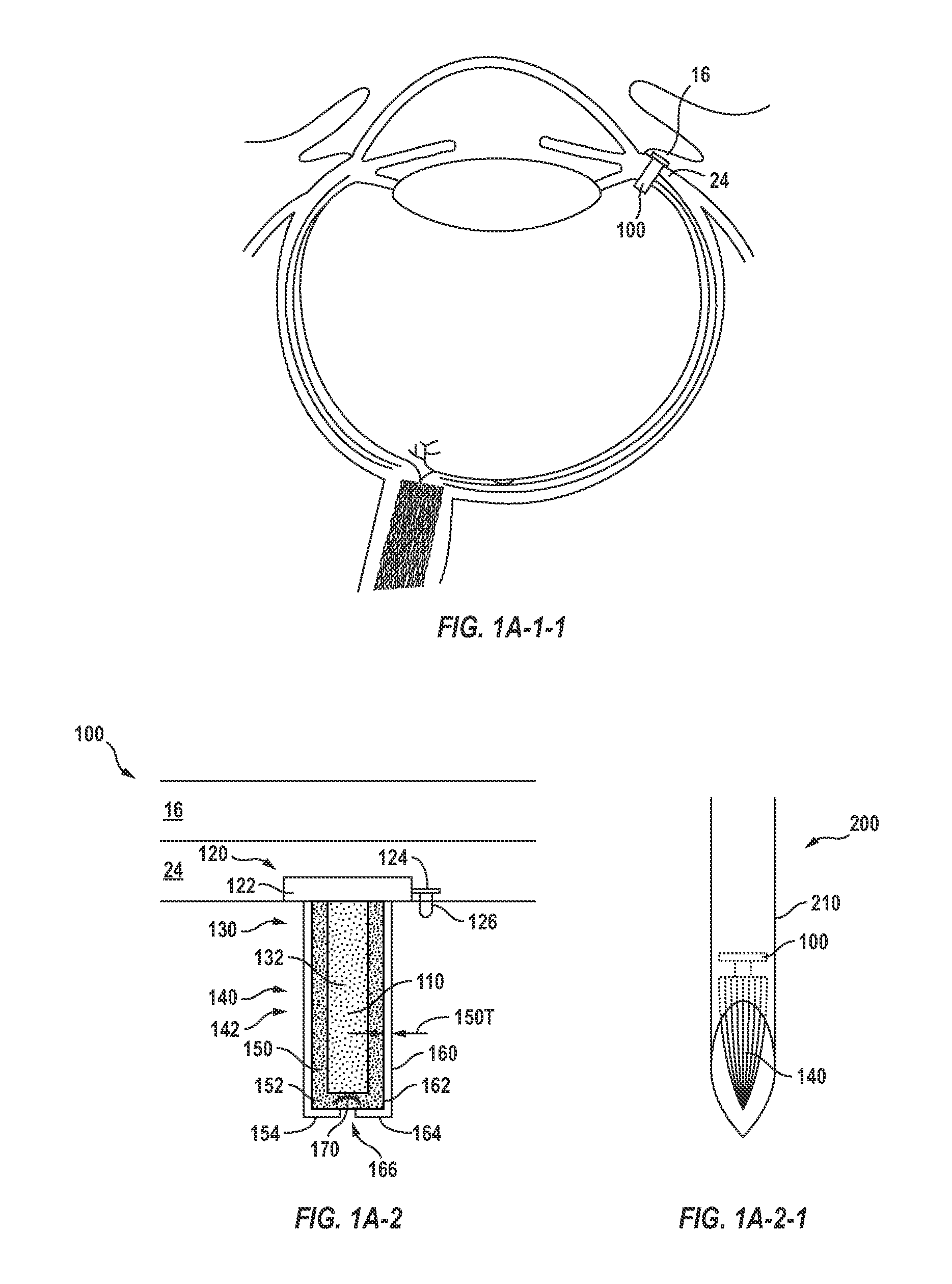
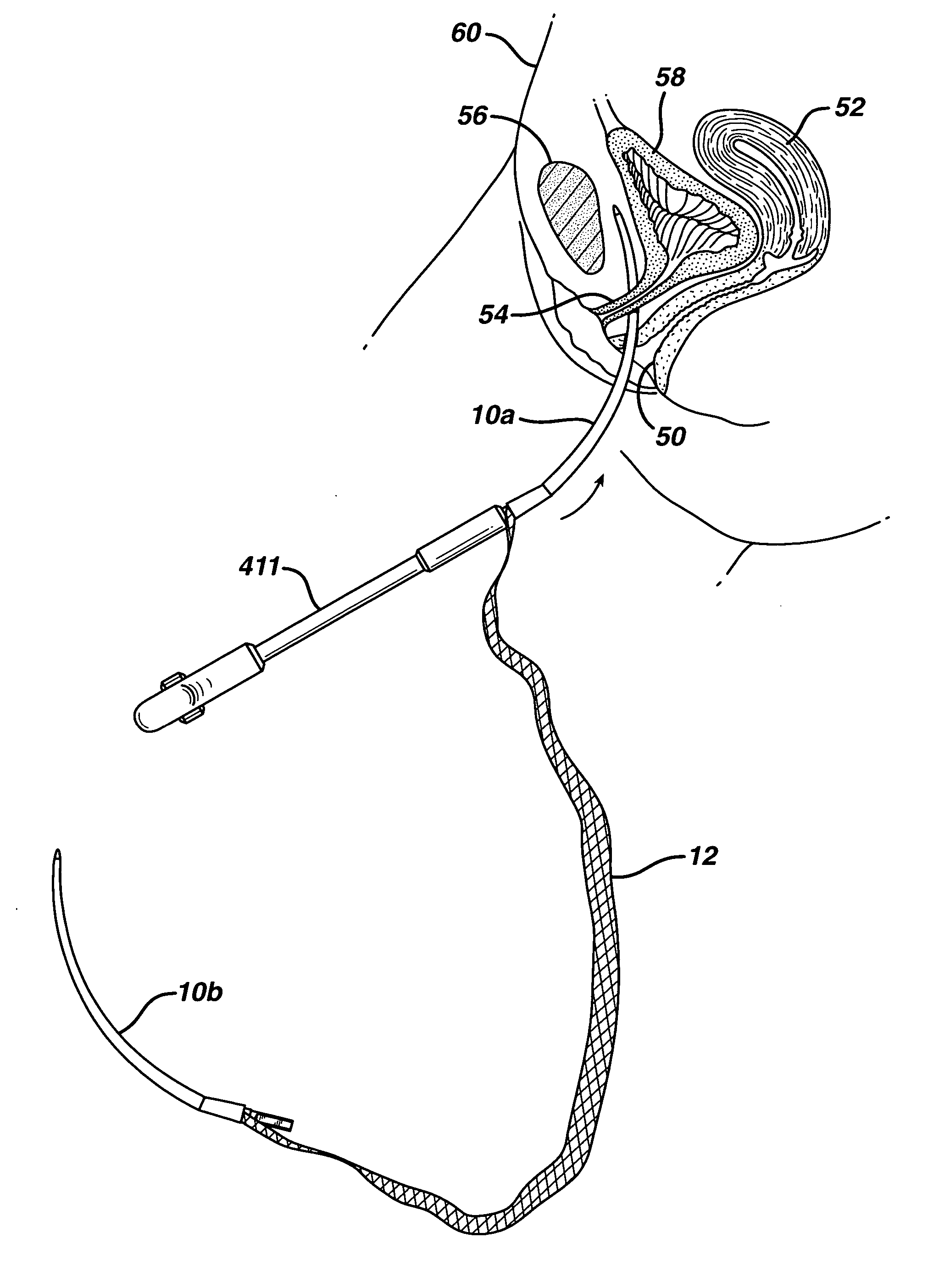
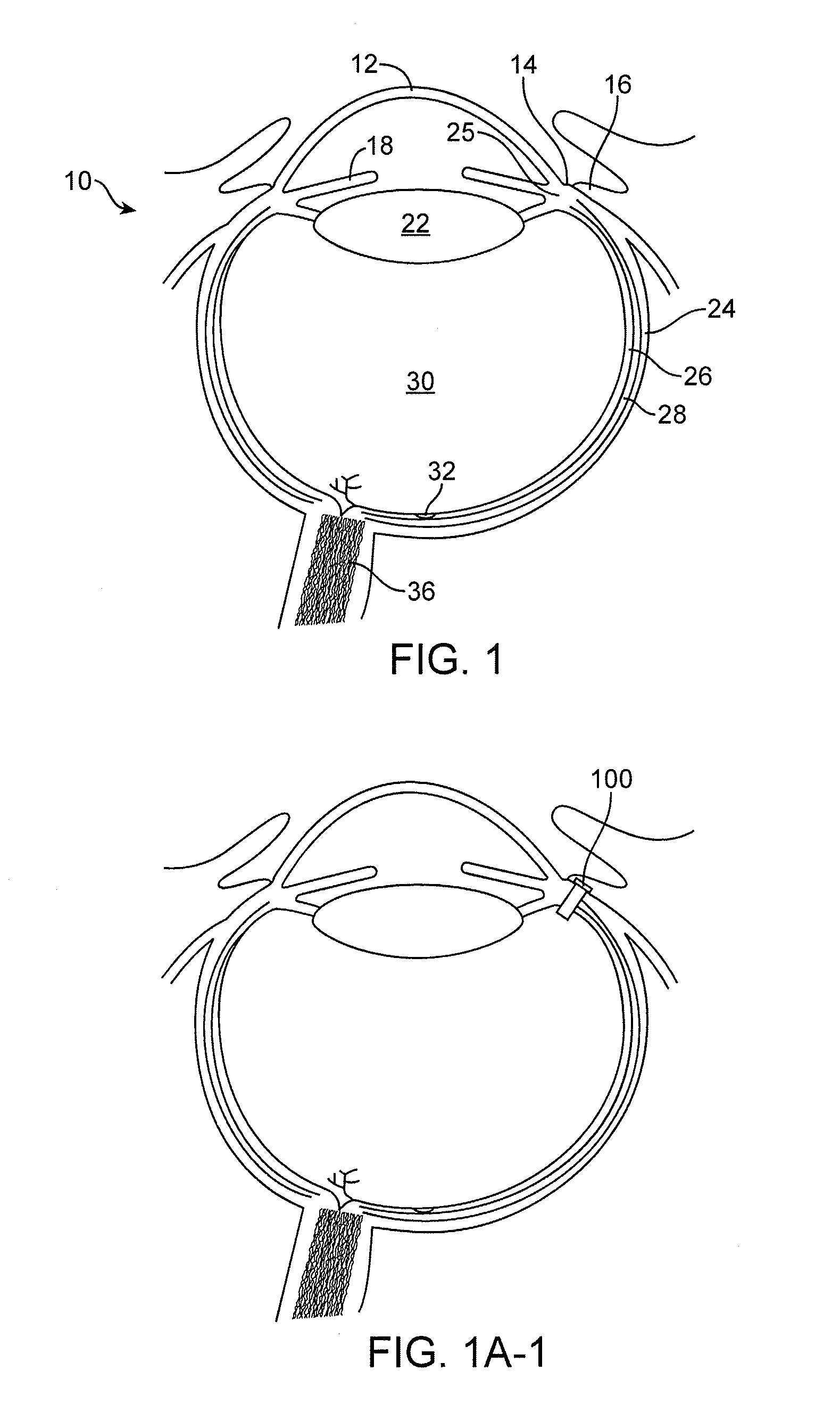
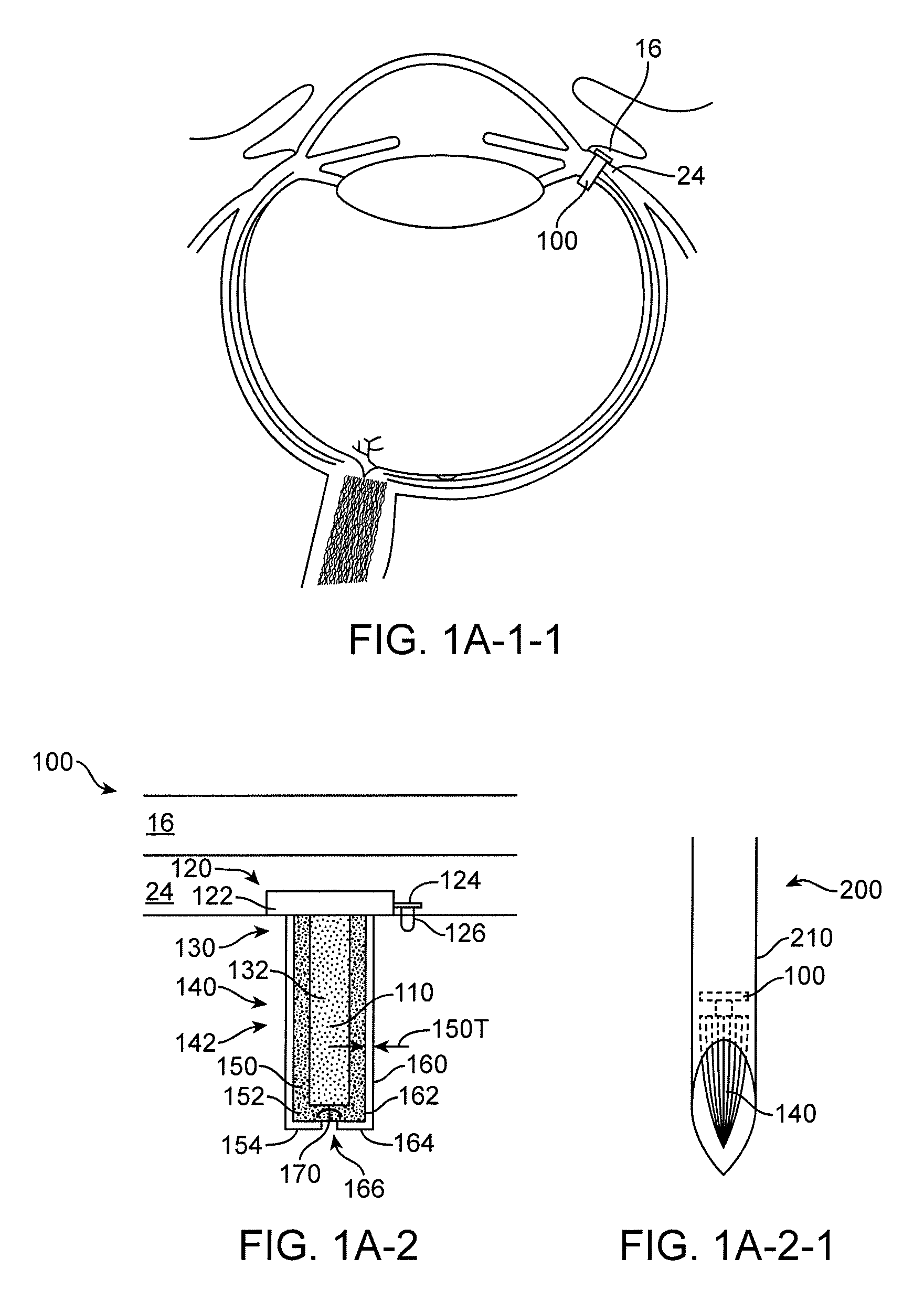
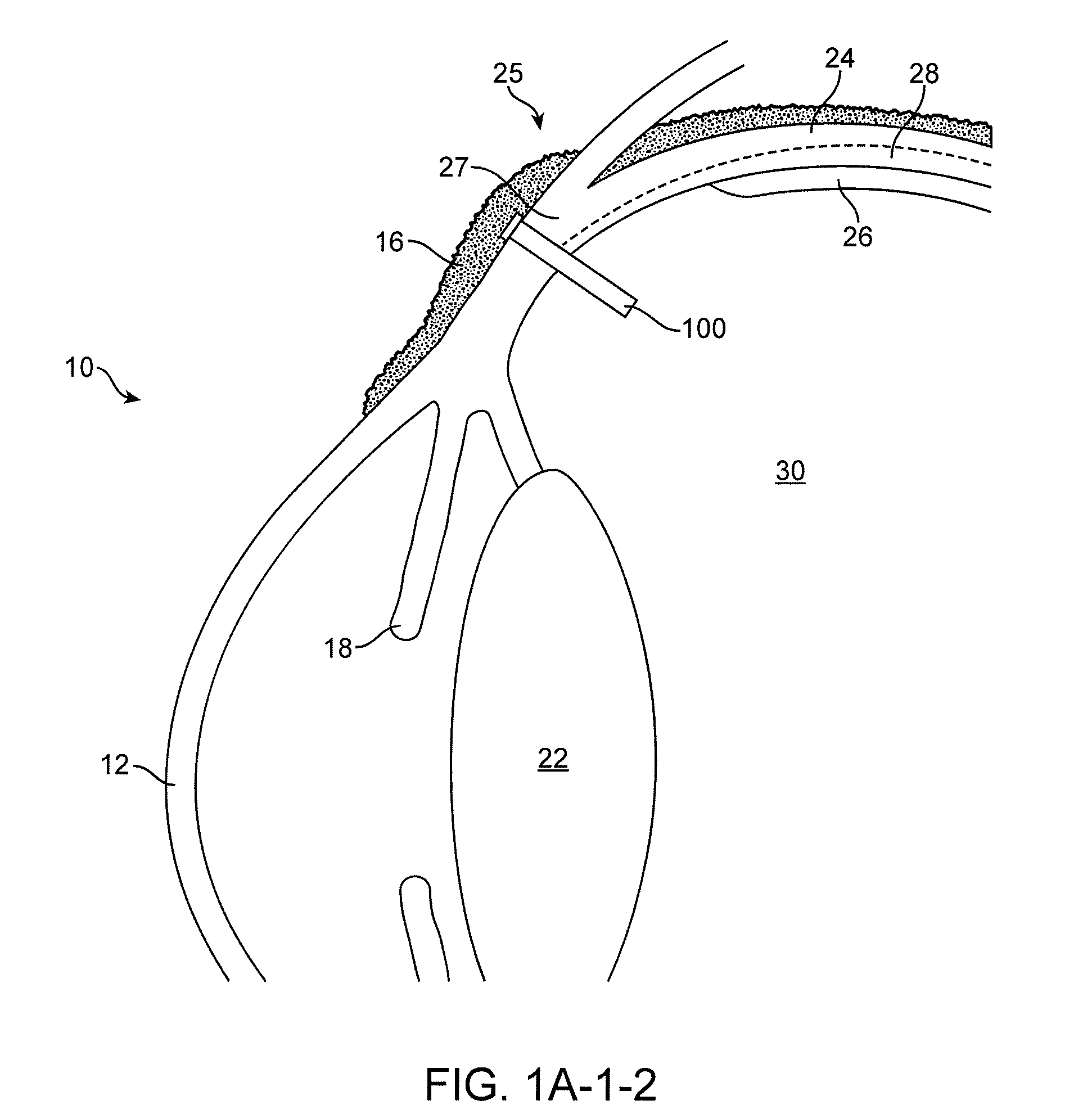
Posterior Segment Drug Delivery
ActiveUS20100255061A1Reduce frequencyReduce riskOrganic active ingredientsSenses disorderTherapeutic DevicesMedicine
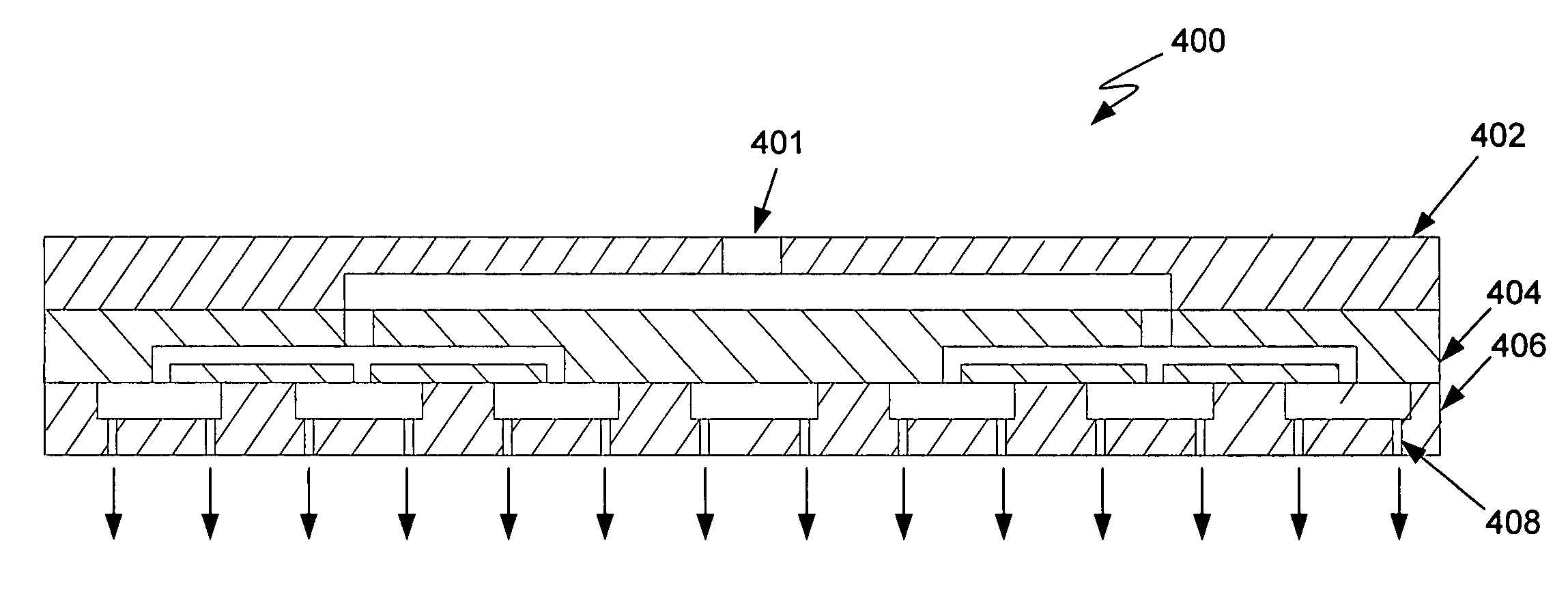
A therapeutic device to release a therapeutic agent comprises a porous structure coupled to a container comprising a reservoir. The reservoir comprises a volume sized to release therapeutic amounts of the therapeutic agent for an extended time when coupled to the porous structure and implanted in the patient. The porous structure may comprise a first side coupled to the reservoir and a second side to couple to the patient to release the therapeutic agent. A plurality of interconnecting channels can extend from the first side to the second side so as to connect a first a plurality of openings on the first side with a second plurality of openings on the second side. Each of the openings on the first side can be connected to each of the openings on the second side with the plurality of interconnecting channels, such that the rate of release of the therapeutic agent can be substantially maintained when one or more of the openings is blocked, for example with particles, cells, bacteria or tissue when the device is implanted for an extended time. The length of the channels extending from the first side to the second side may comprise an effective length greater than a distance across the porous structure from the first side to the second side. The therapeutic device many comprise an expandable retention structure and an expandable reservoir, such that the device can be delivered from a lumen of a delivery device and expand when positioned in the patient. The therapeutic device may comprises a penetrable barrier to inject therapeutic agent into the device when implanted in the patient.
Owner:FORSIGHT VISION5 INC
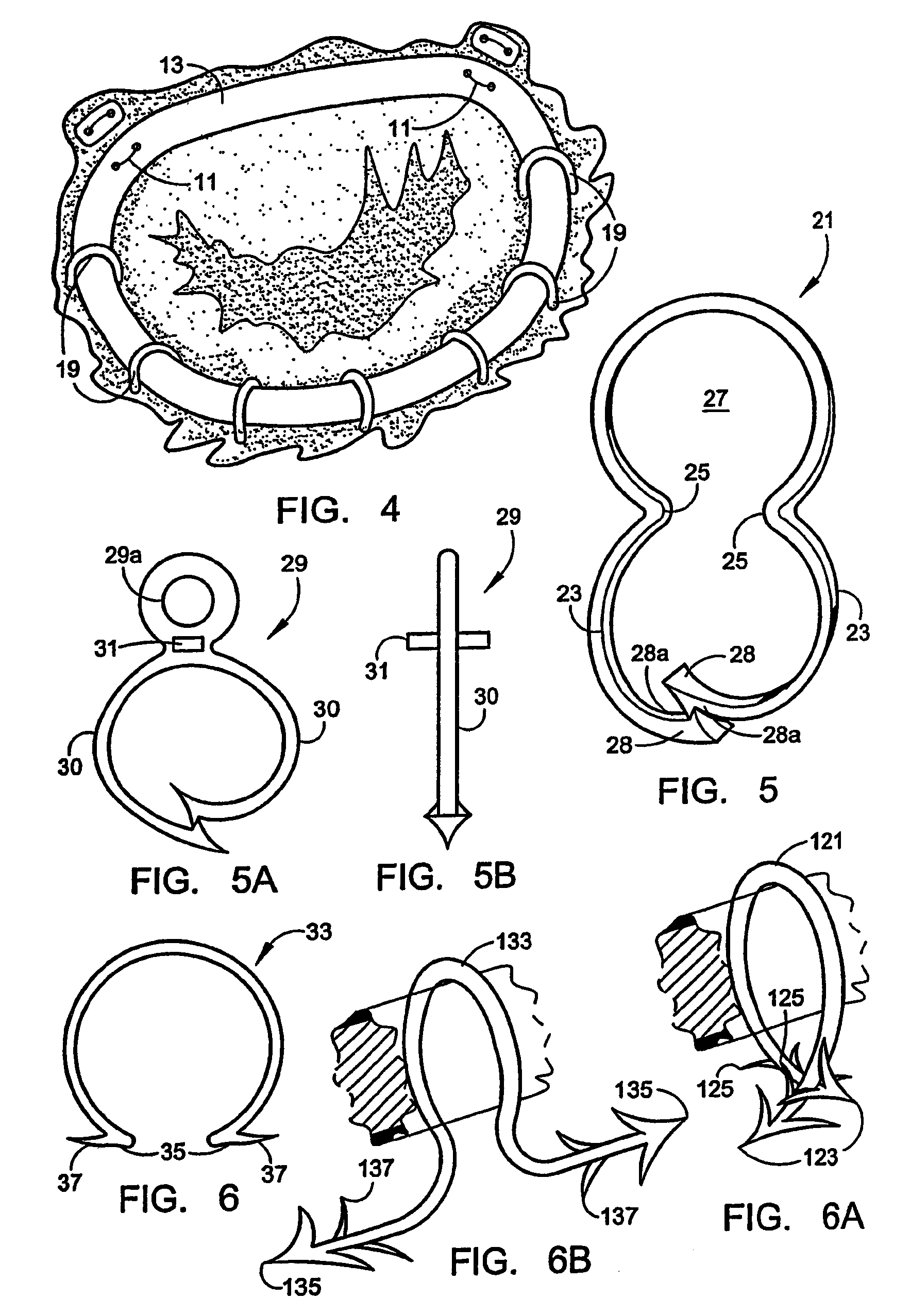
Implantation system for annuloplasty rings
ActiveUS8123801B2Good coaptation of leafletEliminate riskSuture equipmentsSurgical needlesEffective lengthShape-memory alloy
Methods for reconfiguring an atrioventricular heart valve may use systems comprising a partial or complete fenestrated annuloplasty ring proportioned to reconfigure a heart valve that has become in some way incompetent, and a plurality of staples which may have pairs of legs that are sized and shaped for association with the ring at spaced locations along its length. These systems permit relative axial movement between the staples and the ring, whereby a patient's heart valve can be reconfigured in a manner that does not deter subtle shifting of the native valve components. Shape-memory alloy material staples may have legs with free ends that interlock following implantation. One alternative is to use flexible rings that will bend in the plane of the ring as the heart beats. Other alternative systems use linkers of shape-memory material having hooked ends to interengage with staples or other implanted supports which, following implantation, decrease in effective length and pull the staples or other supports toward one another so as to create desired curvature of the reconfigured valve. These linkers may be separate from the supports or may be integral with them and may have a variety of shapes and forms. Various of these systems may be implanted non-invasively using a delivery catheter.
Owner:QUICKRING MEDICAL TECH LTD
Magnetic resonance based apparatus and method to analyze and to measure the bi-directional flow regime in a transport or a production conduit of complex fluids, in real time and real flow-rate
ActiveUS20080174309A1Magnetic property measurementsAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceResonanceData acquisition
An apparatus and a method is provided based on the Magnetic Resonance techniques to analyze and measure a uni- and / or a bi-directional flow regime of multiphase fluids in a transport and production conduct, in real time and flow-rates, based on a magnetic resonance analytical module, two magnetic prepolarization modules of variable effective length and a control computer of data acquisition and transfer, all associated to each other.
Owner:SIEP +1
Bone regeneration device for long bones, and method of use
A method of stimulating bone regeneration in a discontinuous section of a long bone in a subject requiring same, comprising the step of applying to said discontinuous section of the bone an effective vacuum for an effective length of time. A device for carrying out the method consisting of a sealable tubular-shaped sleeve or cuff that fits snugly and sealably around the bone section to be treated and that can be evacuated via a port that is integral to the sleeve or port.
Owner:KCI LICENSING INC
Implantation system for annuloplasty rings
ActiveUS20090177277A1Permit some movementGood coaptation of leafletSuture equipmentsBone implantEffective lengthShape-memory alloy
Methods for reconfiguring an atrioventricular heart valve may use systems comprising a partial or complete fenestrated annuloplasty ring proportioned to reconfigure a heart valve that has become in some way incompetent, and a plurality of staples which may have pairs of legs that are sized and shaped for association with the ring at spaced locations along its length. These systems permit relative axial movement between the staples and the ring, whereby a patient's heart valve can be reconfigured in a manner that does not deter subtle shifting of the native valve components. Shape-memory alloy material staples may have legs with free ends that interlock following implantation. One alternative is to use flexible rings that will bend in the plane of the ring as the heart beats. Other alternative systems use linkers of shape-memory material having hooked ends to interengage with staples or other implanted supports which, following implantation, decrease in effective length and pull the staples or other supports toward one another so as to create desired curvature of the reconfigured valve. These linkers may be separate from the supports or may be integral with them and may have a variety of shapes and forms. Various of these systems may be implanted non-invasively using a delivery catheter.
Owner:QUICKRING MEDICAL TECH LTD
Method and apparatus for adjusting flexible areal polymer implants
InactiveUS20060058574A1Suture equipmentsAnti-incontinence devicesAnatomical structuresEffective length
A minimally invasive approach to adjusting the amount of support on an anatomical structure. The methods and apparatus described include the use of a tape for supporting an anatomical structure. Adjustment may be achieved by use of bulking agents applied either directly to the site or into a containment device located within proximity of the tape and such that it works in conjunction with the tape to support the anatomic structure. An alternative approach utilizes mechanical means for adjusting the effective length of the supporting arms of the tape used to support the anatomical structure.
Owner:ETHICON INC
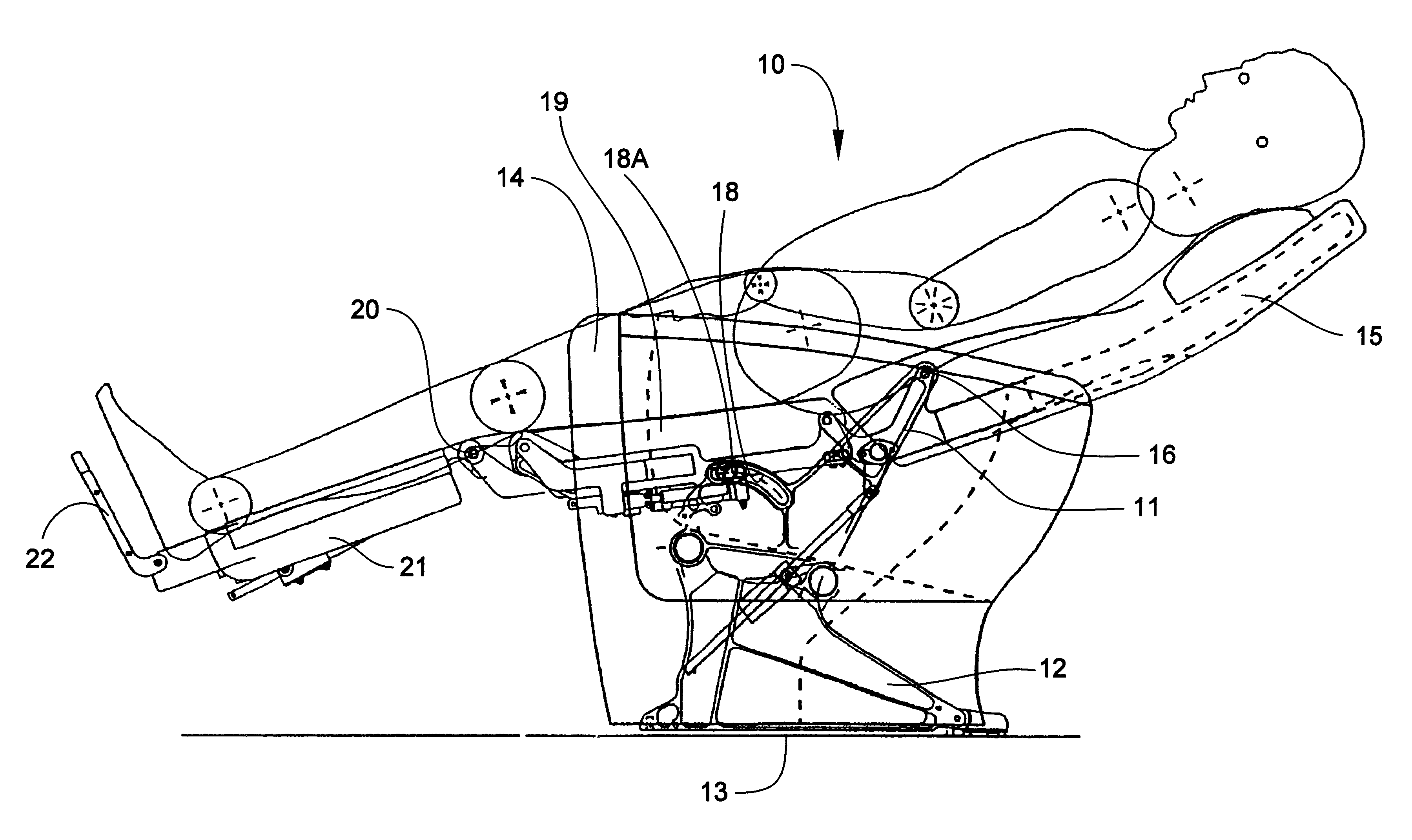
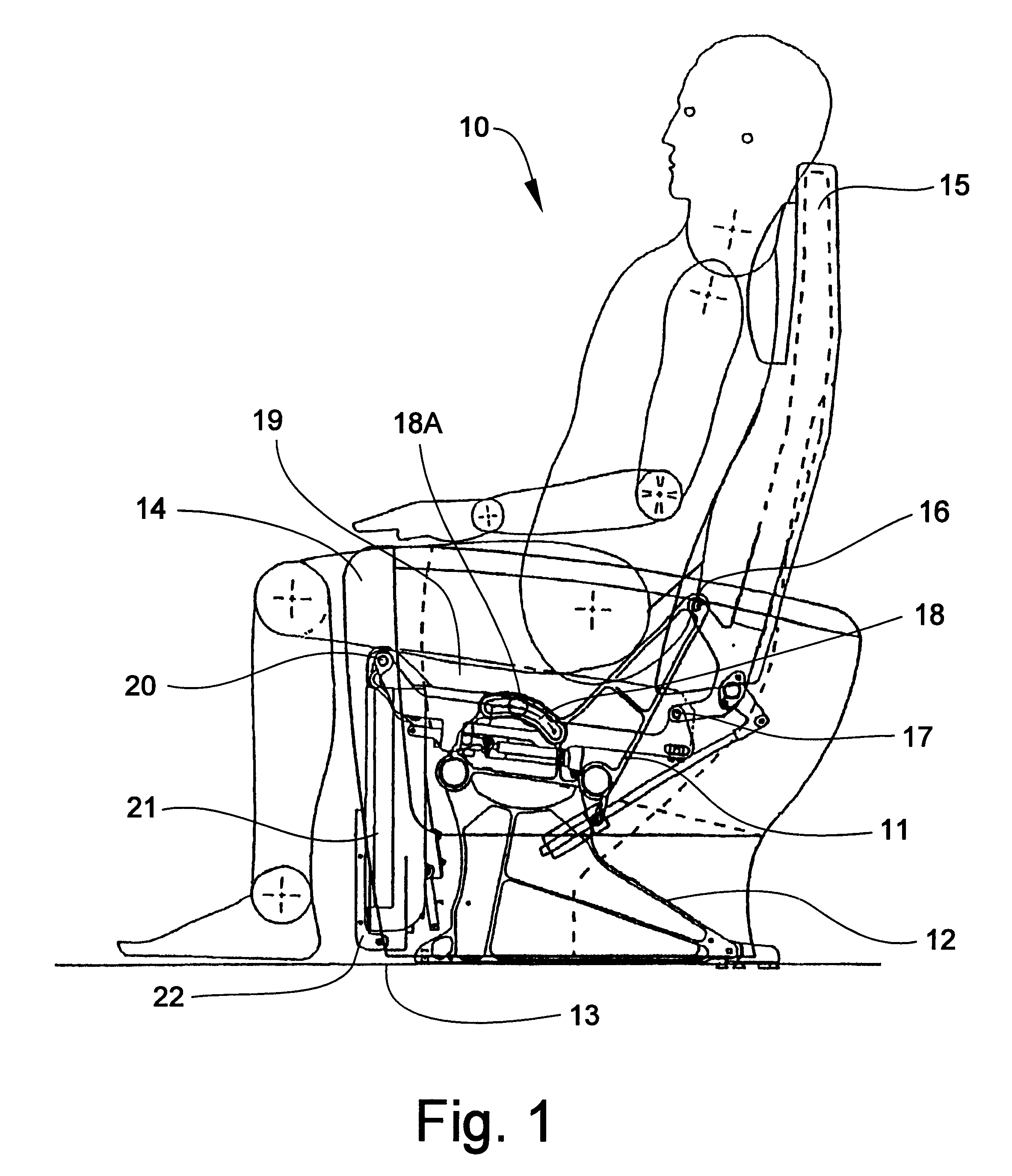
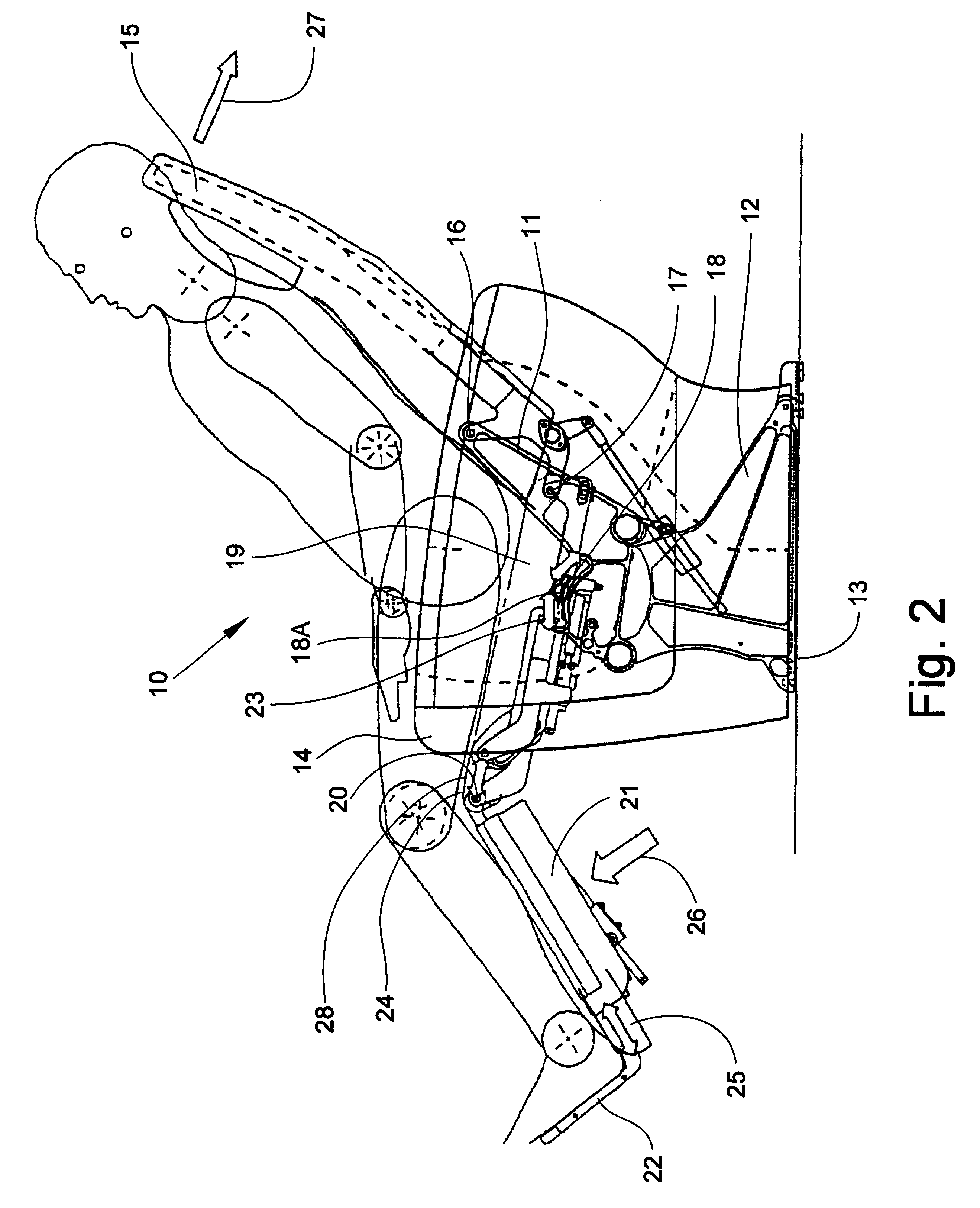
Passenger seat with variable length seat bottom
InactiveUS6494536B2Easy to adjustEconomical to useOperating chairsSeating arrangementsEffective lengthEngineering
A reclinable passenger seat having a seat frame mounting a seat bottom, a seat back extending upwardly from the seat bottom, and a seat bottom / seat back articulation assembly for simultaneously varying the adjustment of the seat bottom and seat back relative to each other. A translation linkage is provided for mounting the seat bottom and seat back for translating movement of the seat bottom relative to the seat back as the seat back is reclined from an upright position and raised to an upright position. The translation linkage extends the effective length of the seat bottom relative to the seat back to provide additional support to the buttocks and legs of the seated passenger.
Owner:BE AEROSPACE INCORPORATED
Implantable therapeutic device
ActiveUS8623395B2Reduce deliveryPrecision injectionSenses disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsTherapeutic DevicesEffective length
A therapeutic device to release a therapeutic agent comprises a porous structure coupled to a container comprising a reservoir. The reservoir comprises a volume sized to release therapeutic amounts of the therapeutic agent for an extended time when coupled to the porous structure and implanted in the patient. The porous structure may comprise a first side coupled to the reservoir and a second side to couple to the patient to release the therapeutic agent. The length of the channels extending from the first side to the second side may comprise an effective length greater than a distance across the porous structure from the first side to the second side. The therapeutic device may comprise a penetrable barrier to inject therapeutic agent into the device when implanted in the patient.
Owner:FORSIGHT VISION5 INC
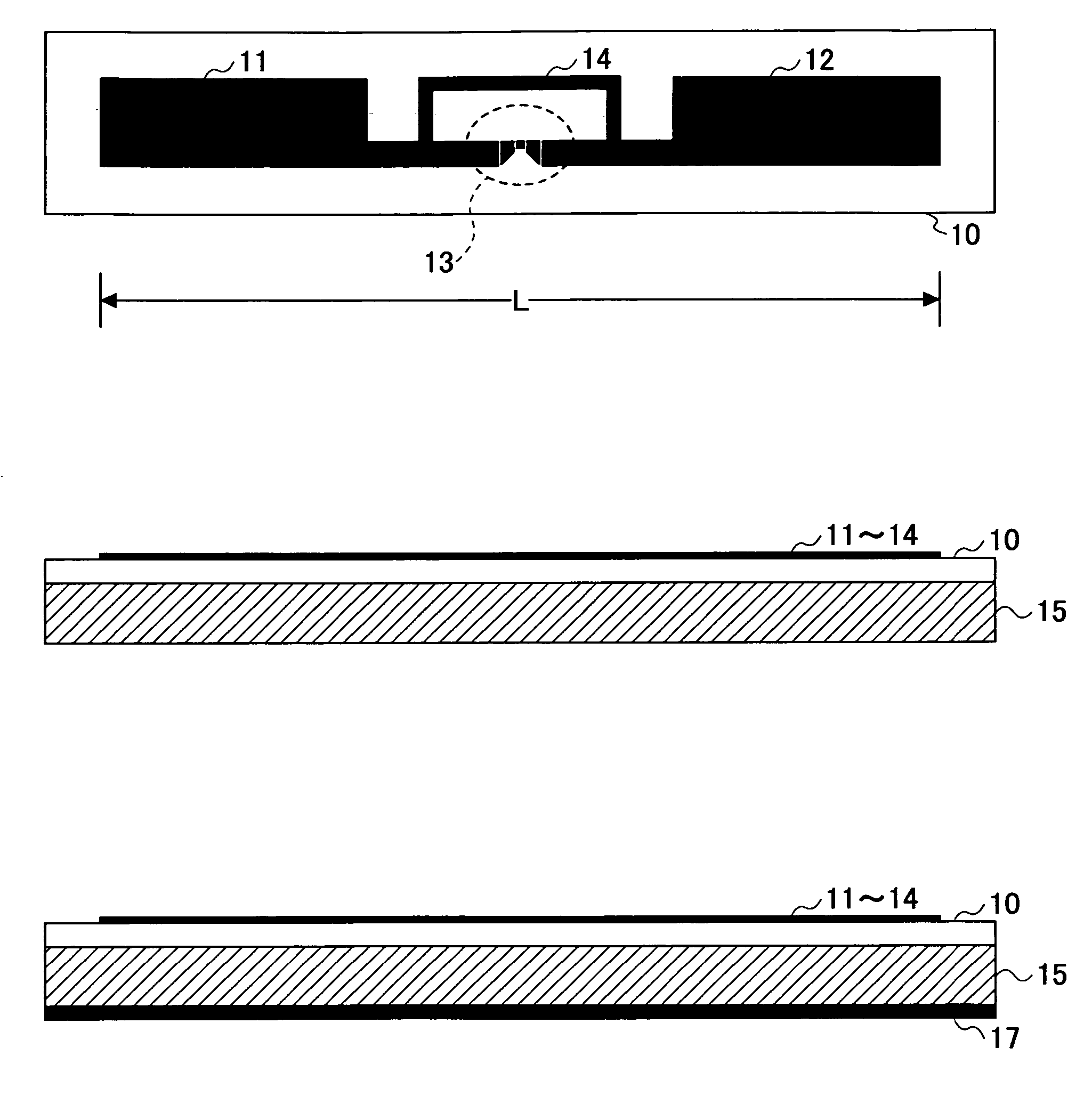
RF tag and method of manufacturing the RF tag
InactiveUS20080111695A1Small sizeRadiating elements structural formsSubscribers indirect connectionEffective lengthLength wave
An RF tag to accompany a conductive object is disclosed that includes an antenna and an integrated circuit connected to the antenna. The antenna includes a first radiating element, a second radiating element, a feeding part connected in series between the first and second radiating elements, and an impedance control part connected parallel to the feeding part. The antenna has an effective length shorter than half of a wavelength used in communication.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Orthopedic fixation device with zero backlash and adjustable compliance, and process for adjusting same
ActiveUS20080269741A1Eliminate backlashAccurately and securely fixedInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsOrthopedic fixation devicesEffective length
An orthopedic fixator for positioning a first element relative to a second element with precision and with controlled compliance which can be adjusted during the healing process. One embodiment comprises a first frame for attachment to the first element, a second frame attached to the first frame through a plurality of adjustable effective length struts, and a third frame for attachment to the second element, wherein the third frame is compliantly attached to the second frame. A preferred embodiment comprises adjustable length preload elements to apply unidirectional forces between the first and second frames so as preload the adjustable effective length struts and substantially reduce the positional tolerance. An alternative embodiment comprises adjustable spring elements allowing the compliance of the attachment of the third frame to the second frame to be adjusted at various points in the healing process.
Owner:KARIDIS SARA LYNN
Ablation catheter with adjustable virtual electrode
An ablation catheter has a virtual electrode tip including a fluid manifold structure for operably varying the active area of the virtual electrode. An array of apertures in the distal end of the catheter form the virtual electrode structure. A movable plug slides within the fluid manifold and seals against the interior walls of the fluid manifold. Conductive fluid cannot flow past the plug to fill the fluid manifold on the side of the plug opposite a fluid inlet channel into the fluid manifold. An electrode is positioned within the fluid manifold between the plug and the end wall of the fluid manifold adjacent the channel. By moving the plug within fluid manifold, only those portholes between the plug and the inlet channel will emit energized fluid. The effective length of an active ablation section of the virtual electrode is changed by repositioning the plug within the fluid manifold.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
Apparatus and method for delivering uniform fluid flow in a chemical deposition system
InactiveUS20080081114A1Spray nozzlesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEffective lengthProduct gas
Uniform fluid delivery to a substrate is provider using a diffuser. The diffuser is designed with a series of fluid (gas and / or liquid) passages of equal effective length / flow resistance, such that as the fluid passes through the diffuser, the gas exits all areas at the same time and with the same mass flux. These passages may not be physically the same, however they have the same effective length and flow resistance. The diffuser can be implemented using single or multiple stacked layers, and from several to many passages. The net effect is a uniform gas curtain to the wafer. Since the passages through the diffuser are effectively the same, the uniform gas curtain to the wafer is not sensitive to the quantity of gas, the gas flow rate or the gas pressure. Additionally, a faceplate can optionally be used to smooth out any jet effects of the diffuser exit holes.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
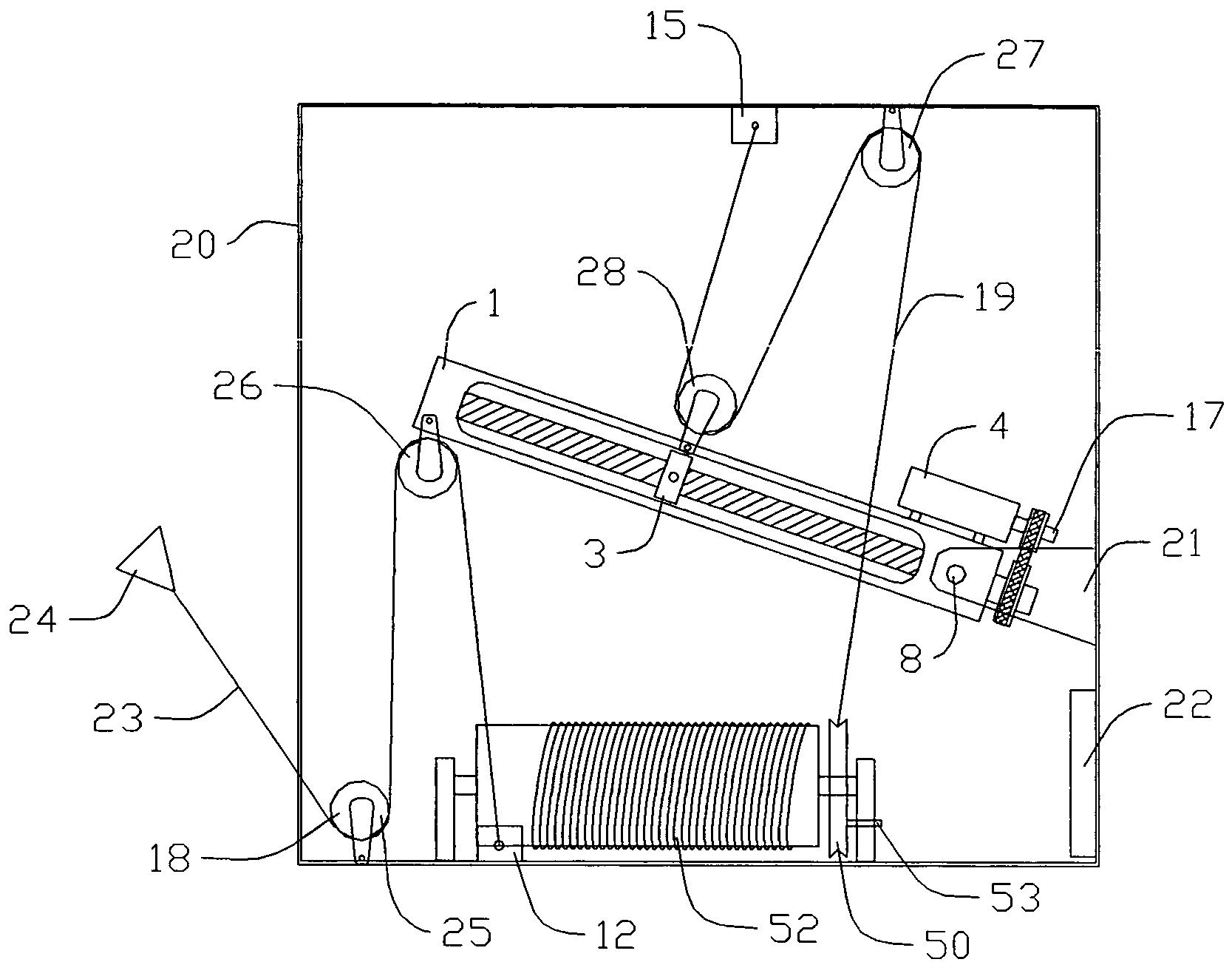
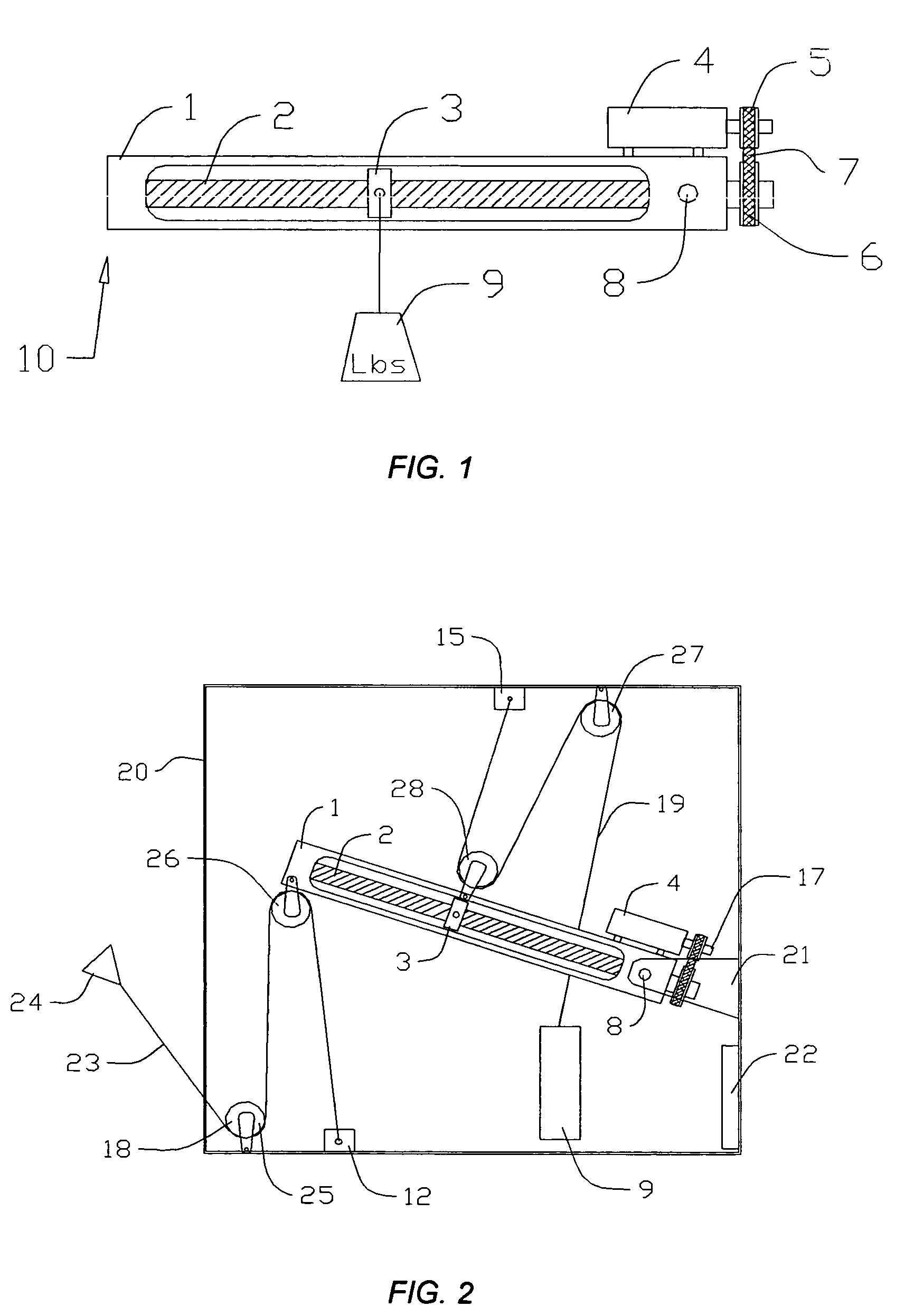
Length adjustable electro-surgical pencil with suction means
InactiveUS20060264928A1Easy to adjustSurgical instruments for heatingSurgical instruments using microwavesEffective lengthEngineering
An electro-surgical (ES) pencil of the kind that includes an elongated housing having a longitudinal axis, a surgical electrode having a tip and a longitudinal axis that is aligned parallel to the longitudinal axis of the housing, the electrode a suction tube having a top and a longitudinal axis that is aligned parallel to the longitudinal axis of the housing and being offset from the longitudinal axis of the electrode, a suction hose connecting the suction tube with a suction unit, an electrical wire for providing electrical power to the pencil and being placed inside the hose. With this arrangement, an ES pencil is provided that is easily adjustable and customizable. In addition, since both the tip of the suction tube and the tip of the electrode are displaceable with respect to the location of the surgeon's hand, the effective length of the ES pencil can be simply and easily changed.
Owner:LINA MEDICAL
Automatic variable resistance exercise system
InactiveUS7278958B2Continuous regulationRealize automatic adjustmentResilient force resistorsWeightsMotor driveEffective length
A variable resistance physical exercise apparatus is provided which provides improved features over prior art devices in that it is more compact, provides a linear resistance profile to the user and provides a variety of modes of operation. The device comprises a motor driven bi-directional linear translation mechanism to vary the effective length of a lever arm and therefore vary the weight of resistance to the user. An alternative embodiment includes a spring winder drum pulley combination.
Owner:MORGAN CURTIS WAYNE
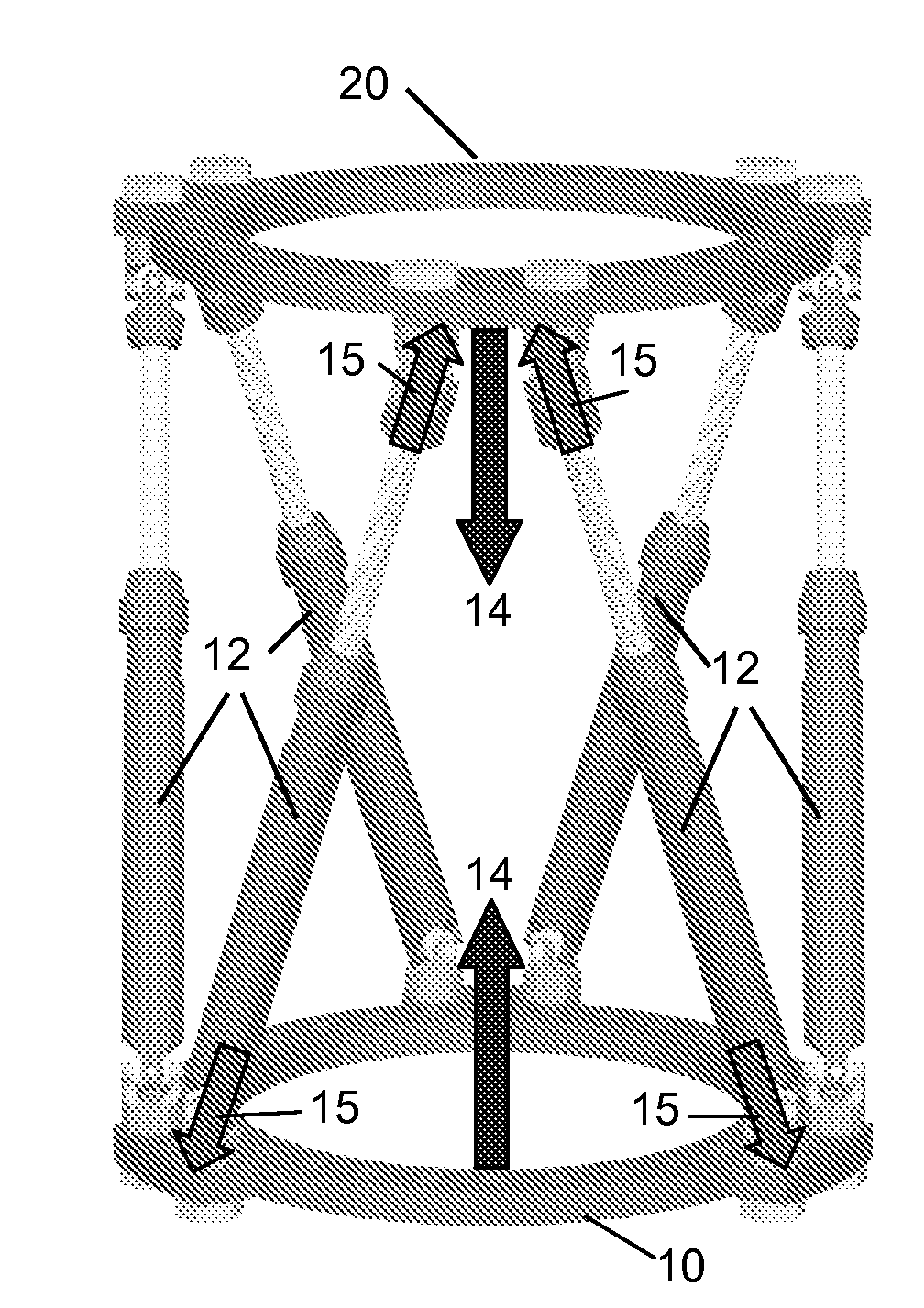
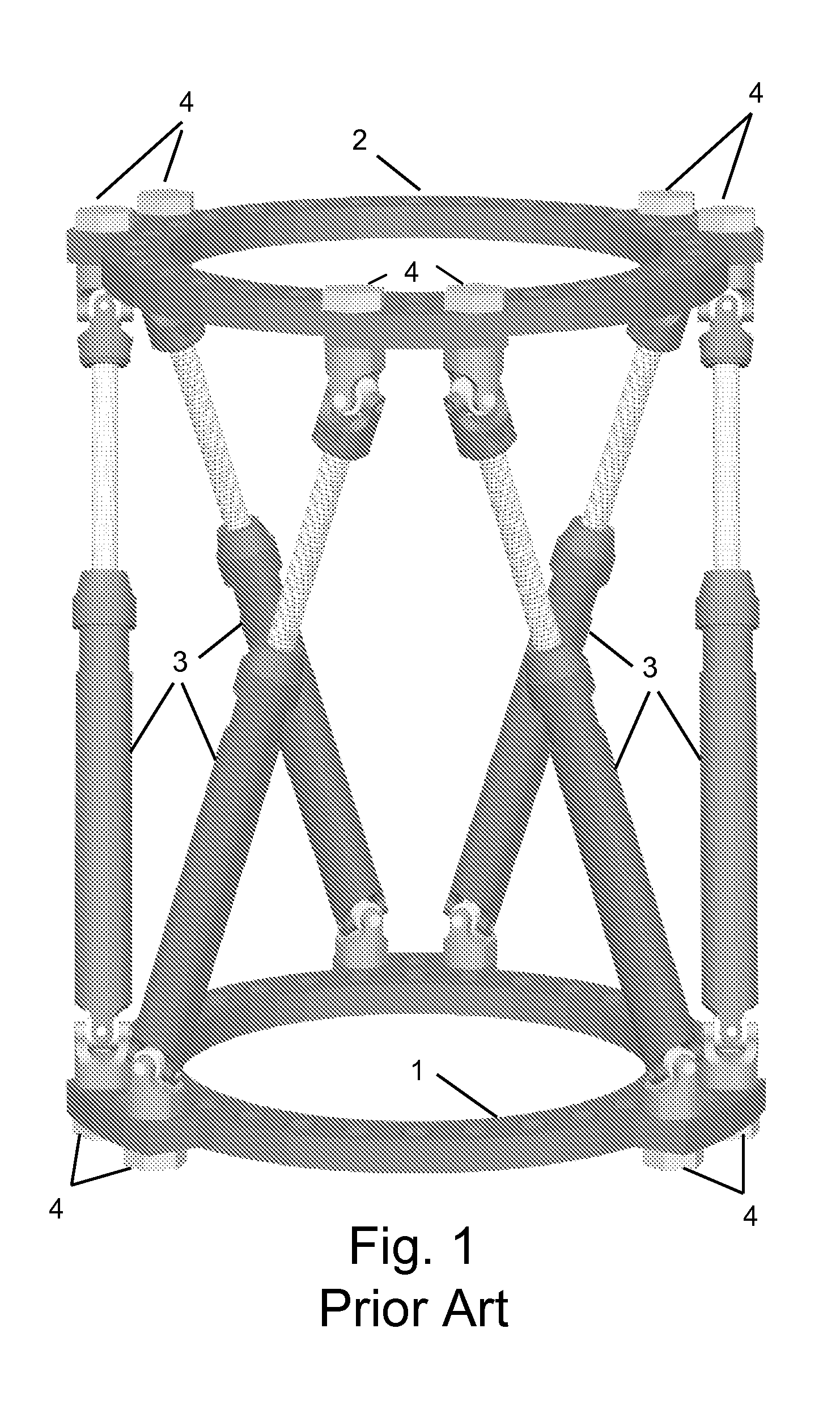
Bearing support
To further isolate imbalances in a rotating structure such as a gas turbine engine, an effective length between two bearings may exceed an actual length. This may be achieved via one or more tapering bearing supports associated with at least one of the bearings.
Owner:RTX CORP
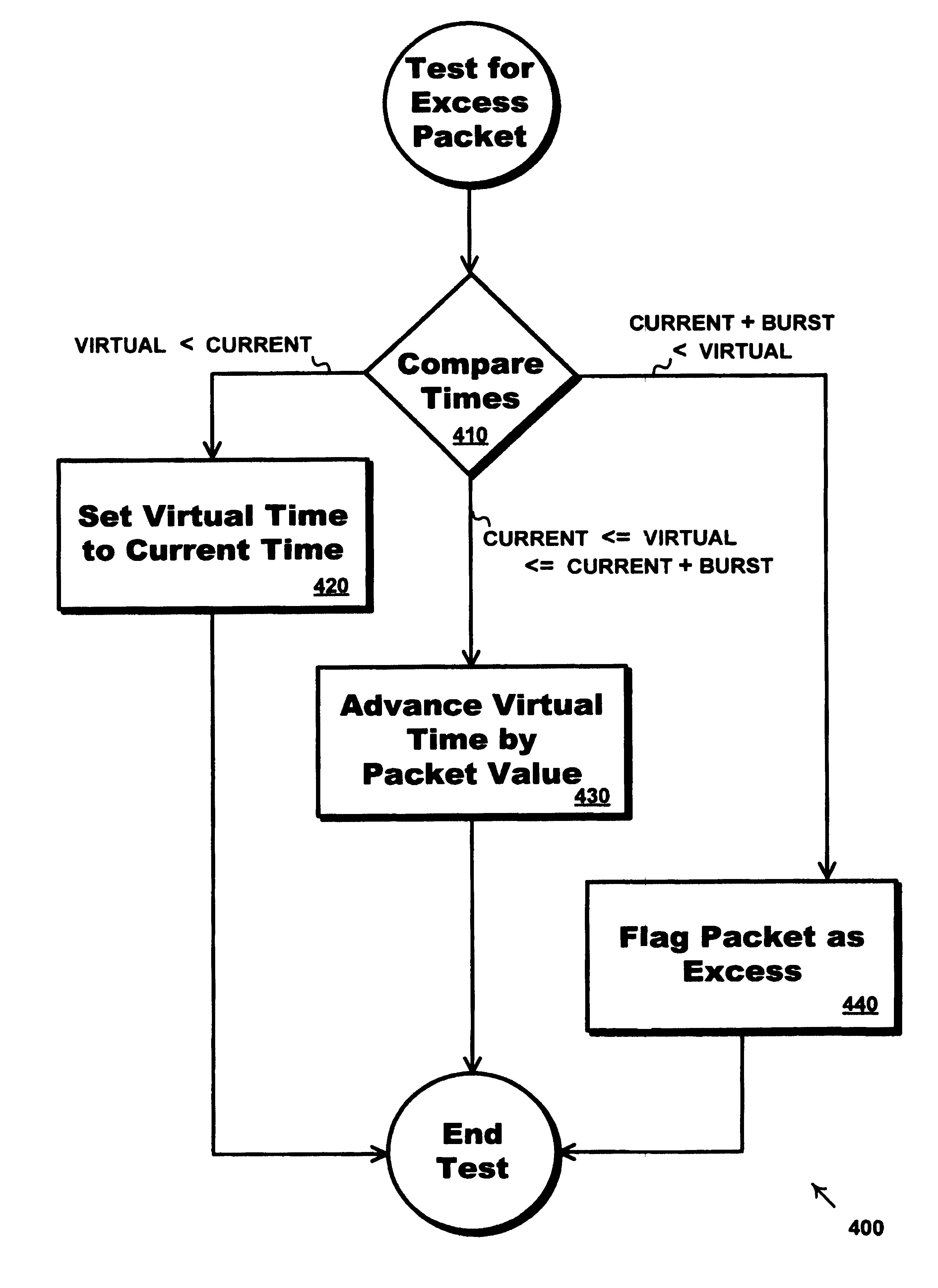
Converting a network device from data rate traffic management to packet rate
A network device that manages the flow rate of a stream of packets traveling within a network is converted from managing based on data rate to managing based on packet rate. In one embodiment, an interface receives from the device an actual length of a packet and provides to the device an effective length for the packet. A multiplexer generates the effective length by selecting the actual length during data rate mode and selecting a virtual length during packet rate mode. Various embodiments work with network devices that use various traffic management techniques. Such techniques include, but are not limited to: virtual time algorithms for determining excess packets; policing techniques that drop excess packets; and shaping techniques that buffer excess packets for possible later transmission.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Adjustable integrated circuit antenna structure
ActiveUS20080158081A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesCouplingEffective length
An adjustable integrated circuit antenna structure includes a plurality of antenna elements, a coupling circuit, a ground plane, and a transmission line circuit. The coupling circuit is operable to couple at least one of the plurality of antenna elements into an antenna based on an antenna structure characteristic signal, wherein the antenna has at least one of an effective length, a bandwidth, an impedance, a quality factor, and a frequency band in accordance with the antenna characteristic signal. The ground plane is proximal to the plurality of antenna elements. The transmission line circuit is coupled to provide an outbound radio frequency (RF) signal to the antenna and receive an inbound RF signal from the antenna.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Trapezoidal shaped magnet flux intensifier motor pole arrangement for improved motor torque density
InactiveUS6879075B2Increase torqueImprove power characteristicsSynchronous generatorsWindingsPermanent magnet synchronous machineElectric machine
A permanent magnet synchronous machine with improved torque and power characteristics. A circumferential-oriented rotor assembly is provided with alternating permanent magnets and magnetic pole pieces. In order to reduce the amount of leakage flux in the rotor and increase the effective length of the permanent magnet, a trapezoidal or otherwise tapered permanent magnet structure is used. By alternating trapezoidal permanent magnet, and magnetic pole pieces, a higher intensity magnetic field is created in the air gap utilizing the same radial space in the motor without altering the weight or volume of the motor compared to conventional machines.
Owner:CURTISS WRIGHT ELECTRO MECHANICAL
Lithographic type microelectronic spring structures with improved contours
InactiveUS7189077B1Reduce processing stepsHigh stiffnessElectrical measurement instrument detailsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsManufacturing cost reductionEffective length
Improved lithographic type microelectronic spring structures and methods are disclosed, for providing improved tip height over a substrate, an improved elastic range, increased strength and reliability, and increased spring rates. The improved structures are suitable for being formed from a single integrated layer (or series of layers) deposited over a molded sacrificial substrate, thus avoiding multiple stepped lithographic layers and reducing manufacturing costs. In particular, lithographic structures that are contoured in the z-direction are disclosed, for achieving the foregoing improvements. For example, structures having a U-shaped cross-section, a V-shaped cross-section, and / or one or more ribs running along a length of the spring are disclosed. The present invention additionally provides a lithographic type spring contact that is corrugated to increase its effective length and elastic range and to reduce its footprint over a substrate, and springs which are contoured in plan view. The present invention further provides combination (both series and parallel) electrical contacts tips for lithographic type microelectronic spring structures. The microelectronic spring structures according to the present invention are particularly useful for making very fine pitch arrays of electrical connectors for use with integrated circuits and other substrate-mounted electronic devices, because their performance characteristics are enhanced, while at the same time, they may be manufactured at greatly reduced costs compared to other lithographic type microelectronic spring structures.
Owner:FORMFACTOR INC
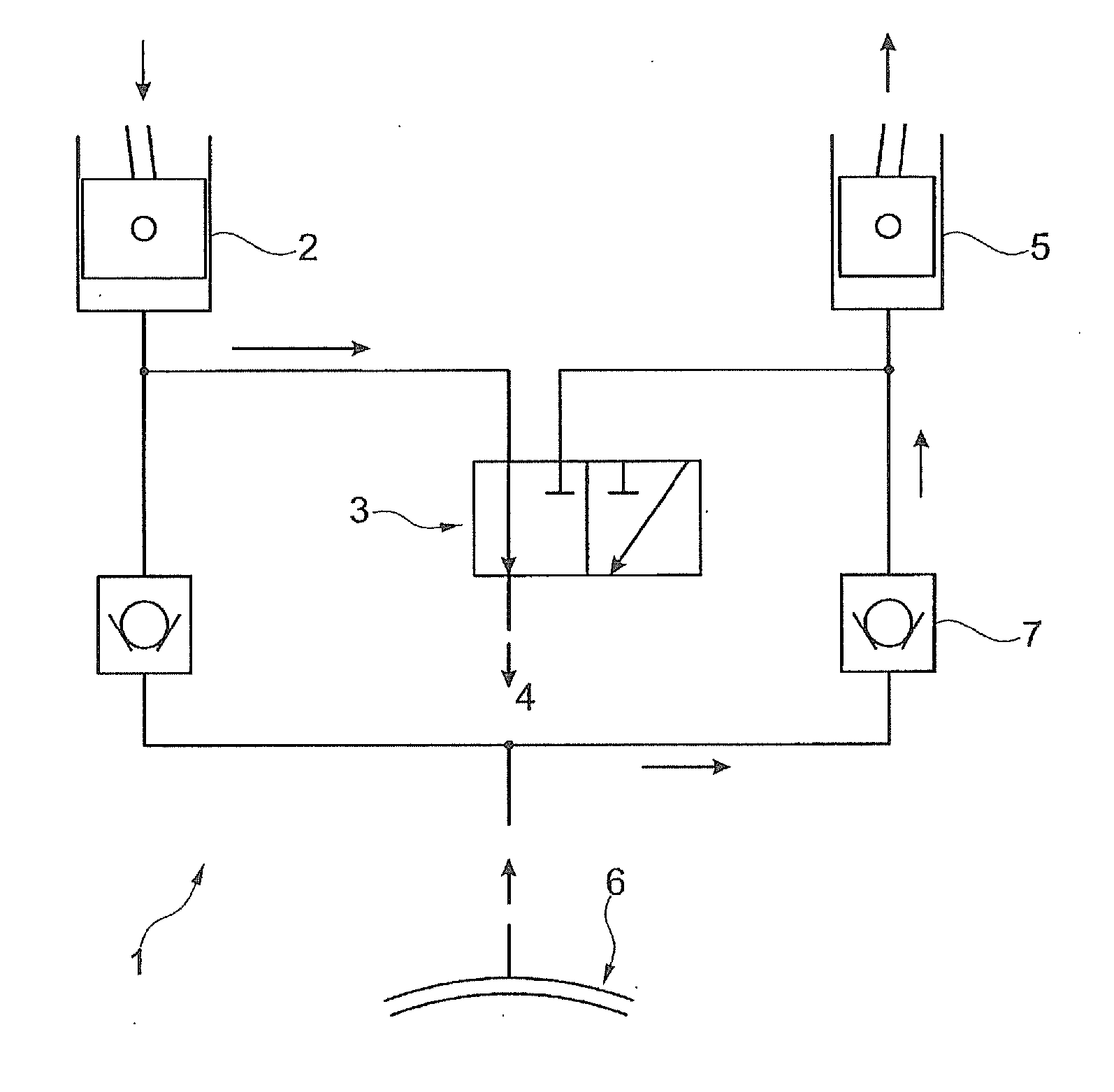
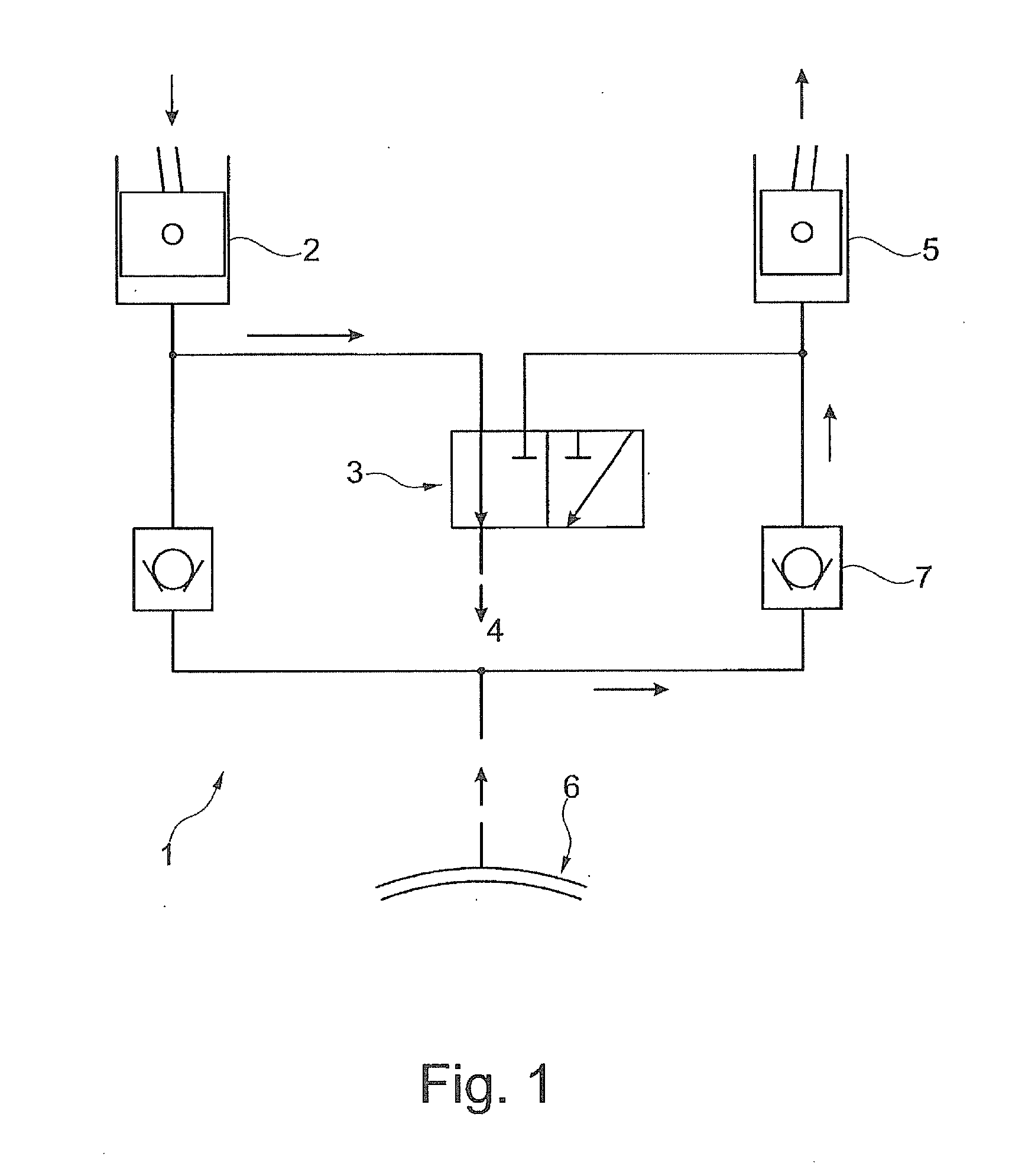
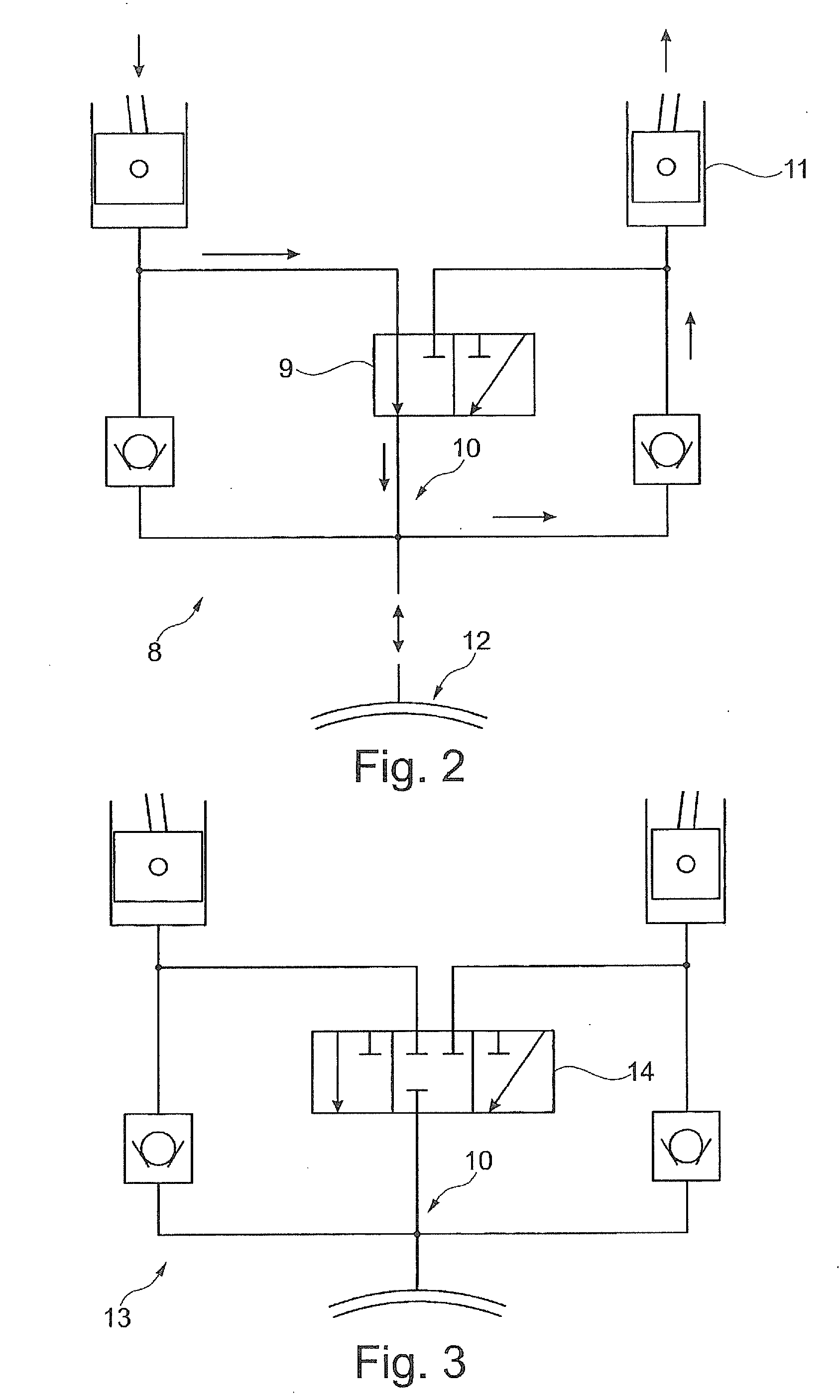
Hydraulic freewheel for an internal combustion engine with variable compression ratio
ActiveUS20150260094A1Little temperature dependenceReduce throttlingRotary bearingsConnecting rodsFlywheelEffective length
A reciprocating-piston internal combustion engine having a hydraulic adjustment mechanism which is assigned to a connecting rod and which comprises at least one eccentric, for adjusting at least one variable compression ratio in at least one cylinder of the reciprocating-piston internal combustion engine by means of a change in an effective length of a connecting rod. Also proposed is a method for changing the effective length of a connecting rod.
Owner:FEV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com