Patents
Literature
68 results about "Random logic" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Random logic is a semiconductor circuit design technique that translates high-level logic descriptions directly into hardware features such as AND and OR gates. The name derives from the fact that few easily discernible patterns are evident in the arrangement of features on the chip and in the interconnects between them. In VLSI chips, random logic is often implemented with standard cells and gate arrays.
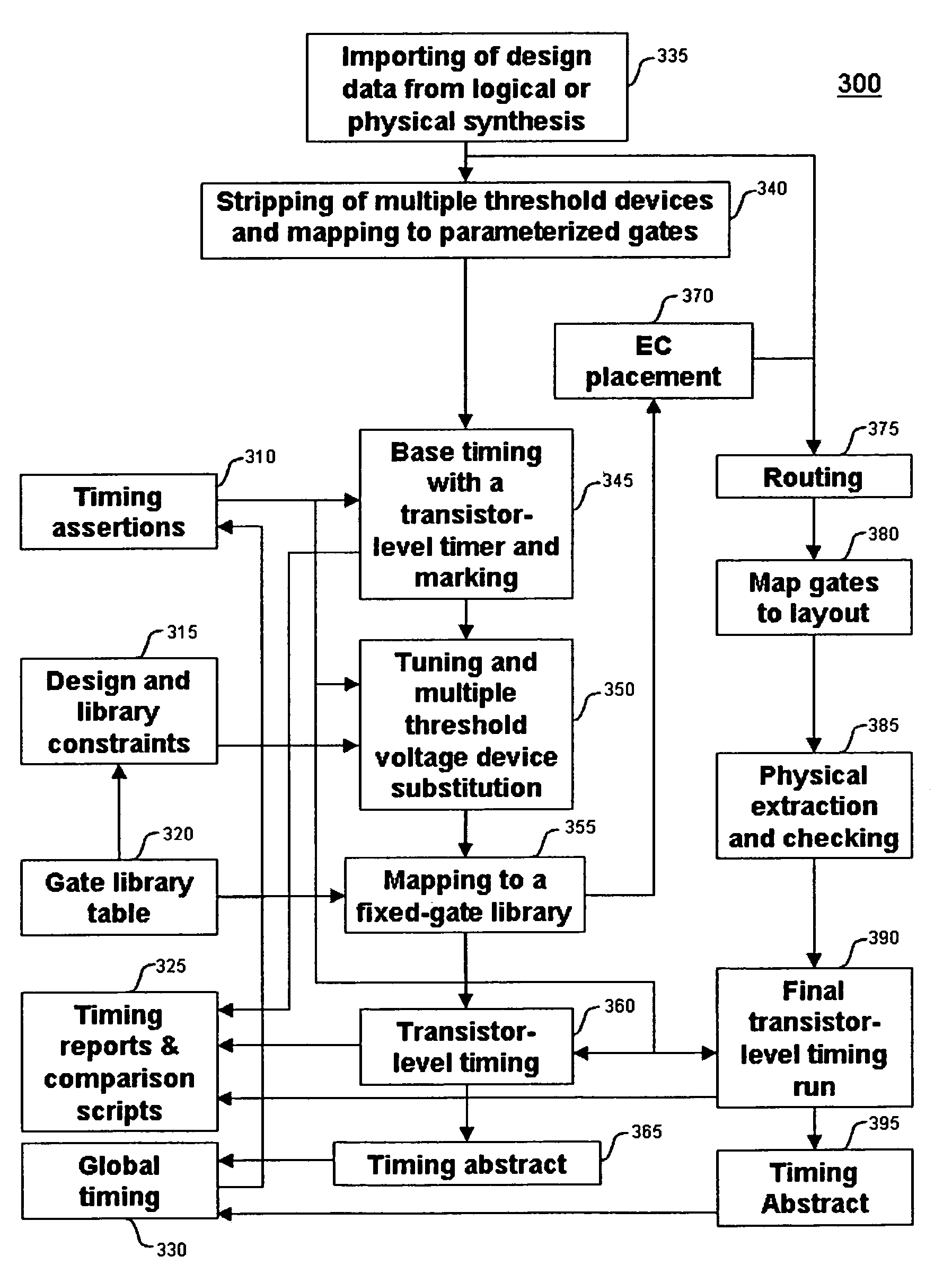
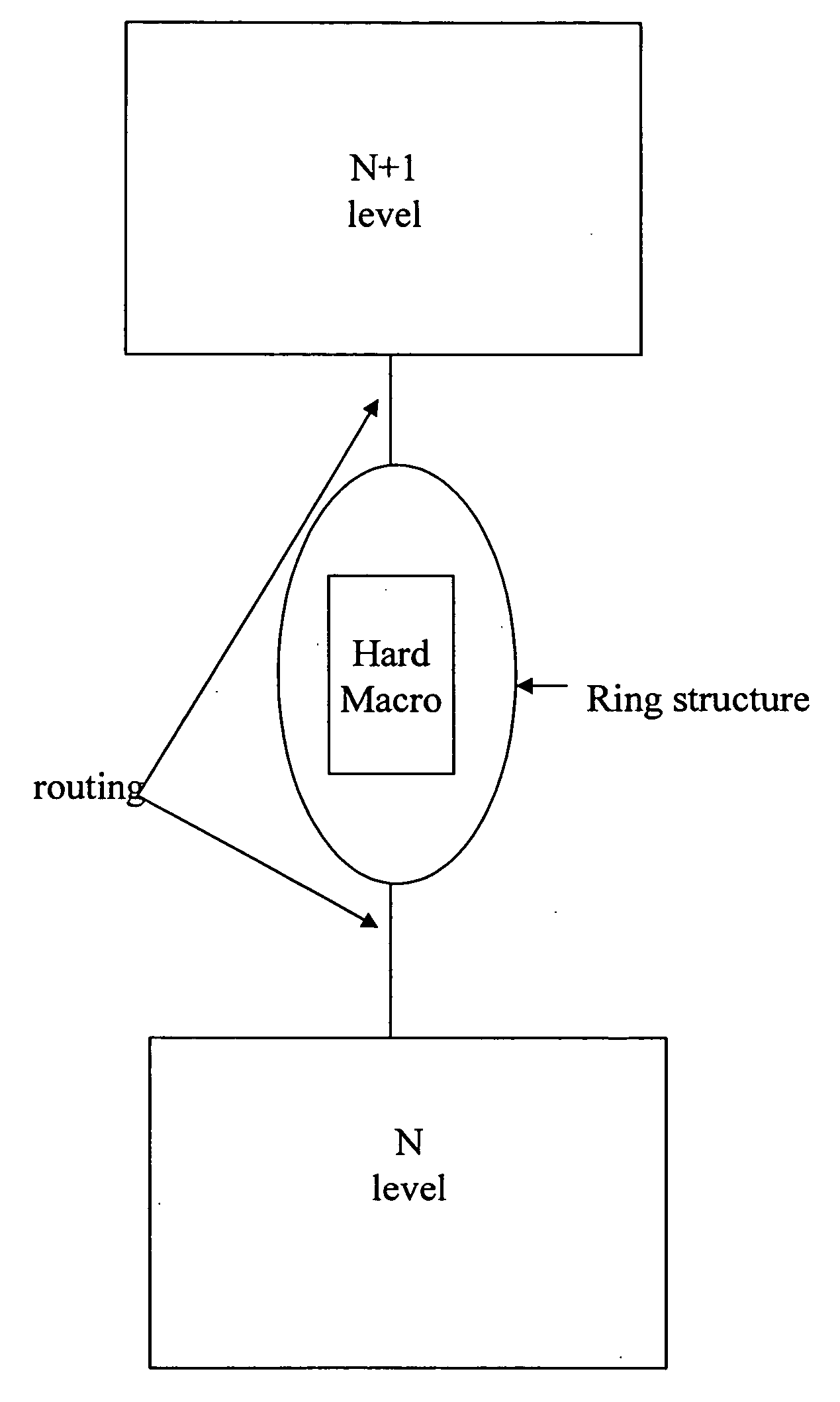
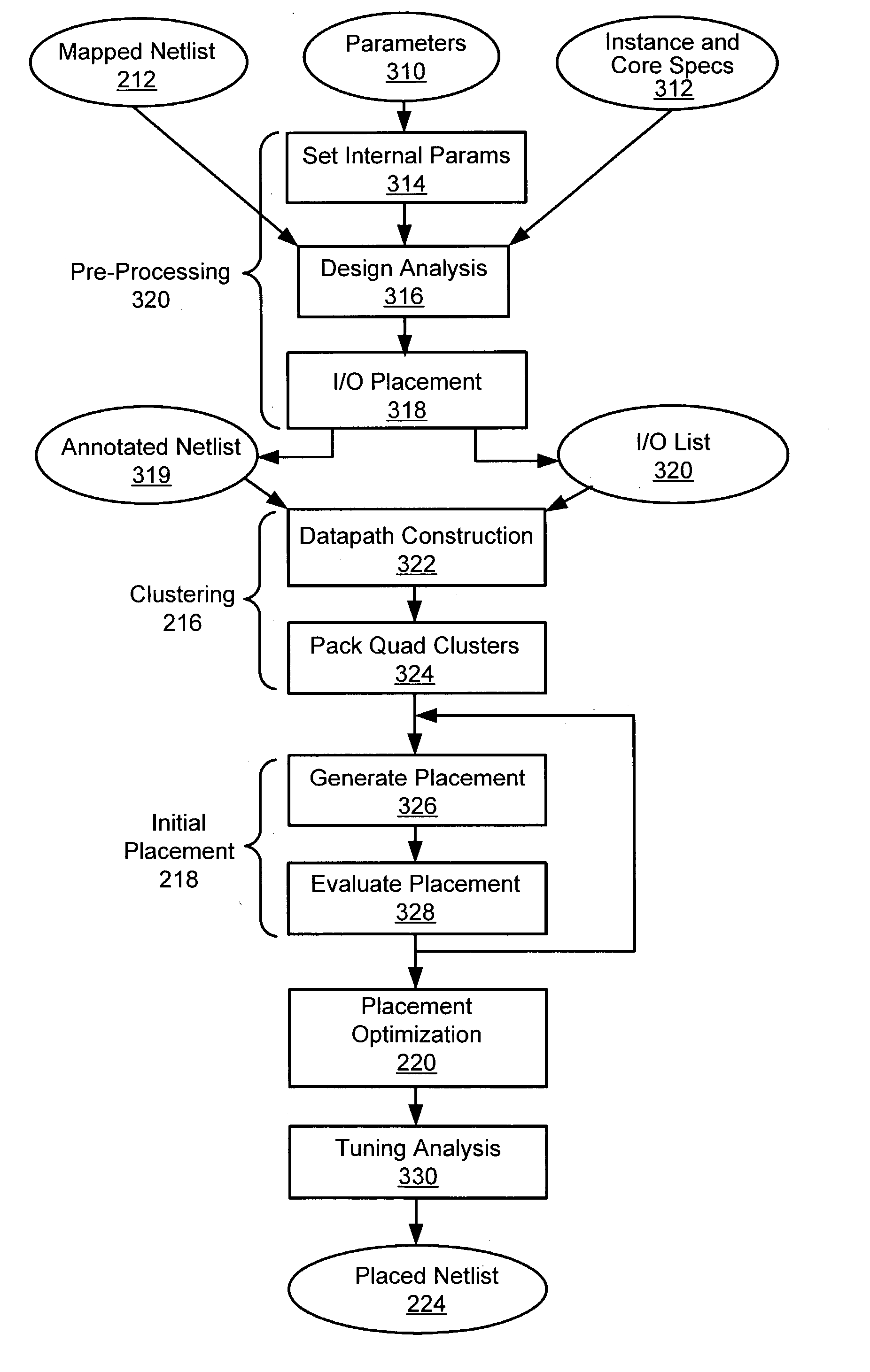
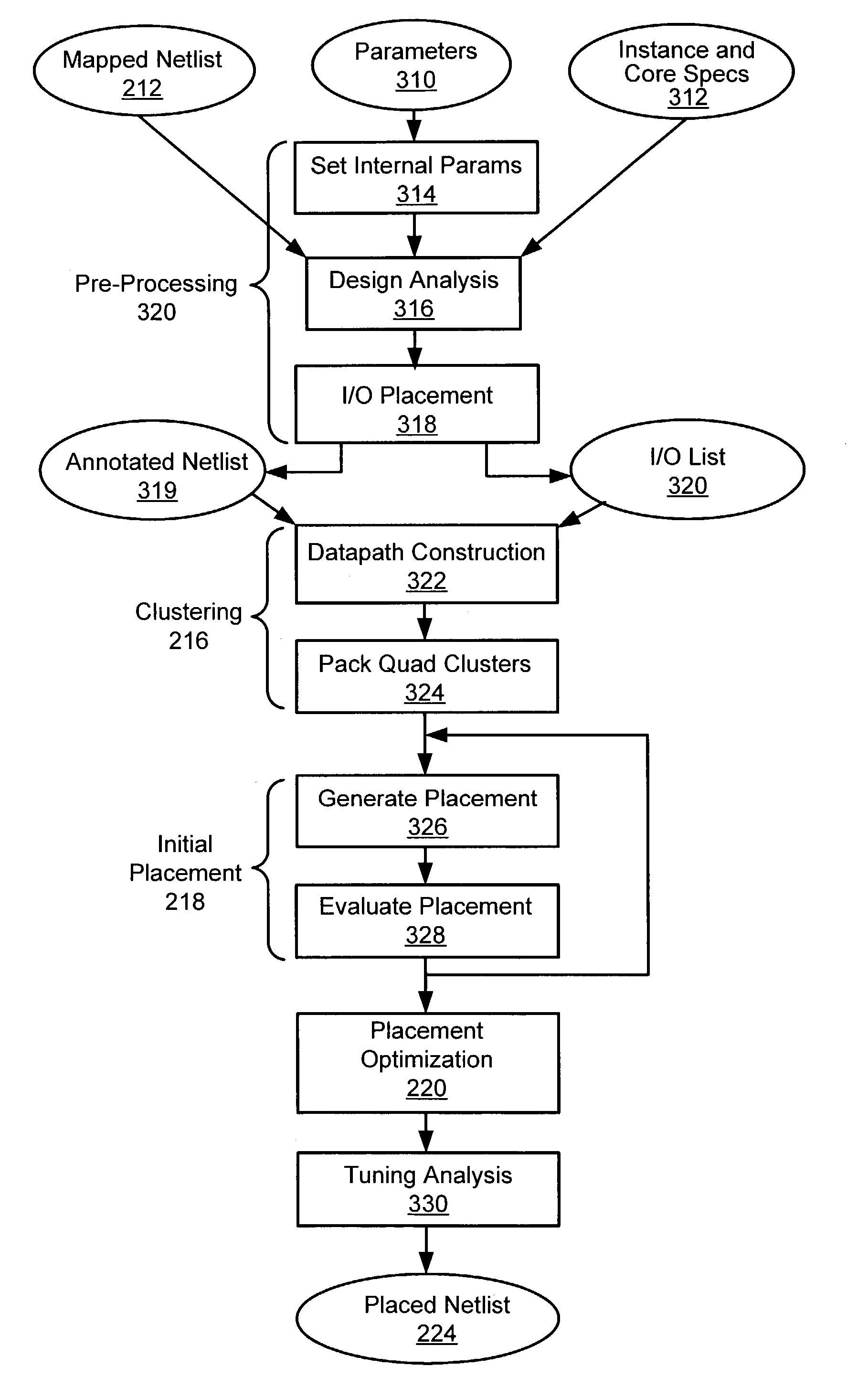
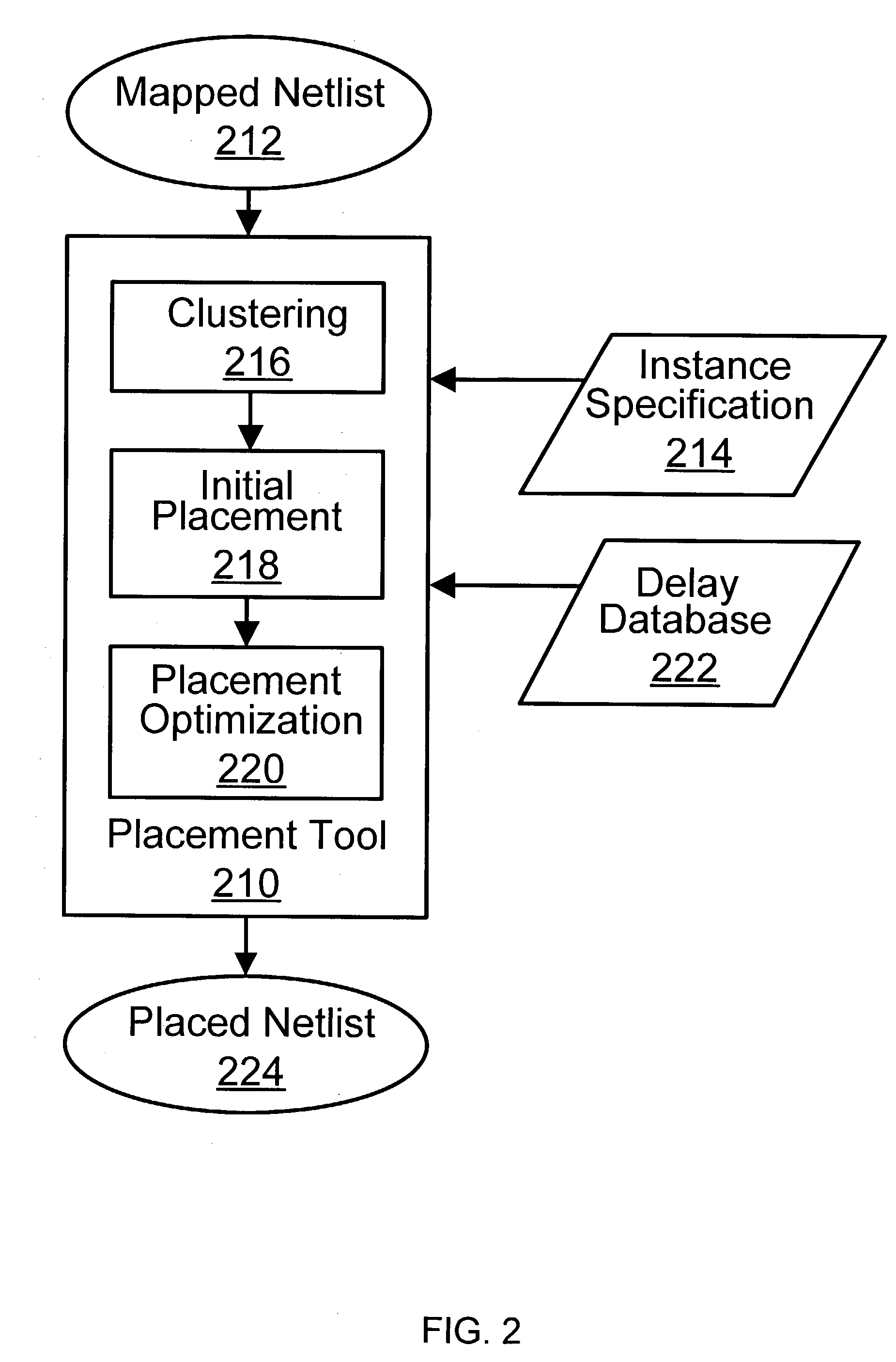
Method for tuning a digital design for synthesized random logic circuit macros in a continuous design space with optional insertion of multiple threshold voltage devices
InactiveUS7093208B2Efficient and effective methodologyError minimizationDigital storageComputer aided designContinuous designCritical section
A Digital Design Method which may be automated is for obtaining timing closure in the design of large, complex, high-performance digital integrated circuits. The methodincludes the use of a tuner on random logic macros that adjusts transistor sizes in a continuous domain. To accommodate this tuning, logic gates are mapped to parameterized cells for the tuning and then back to fixed gates after the tuning. Tuning is constrained in such a way as to minimize “binning errors” when the design is mapped back to fixed cells. Further, the critical sections of the circuit are marked in order to make the optimization more effective and to fit within the problem-size constraints of the tuner. A specially formulated objective function is employed during the tuning to promote faster global timing convergence, despite possibly incorrect initial timing budgets. The specially formulated objective function targets all paths that are failing timing, with appropriate weighting, rather than just targeting the most critical path. Finally, the addition of multiple threshold voltage gates allows for increased performance while limiting leakage power.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
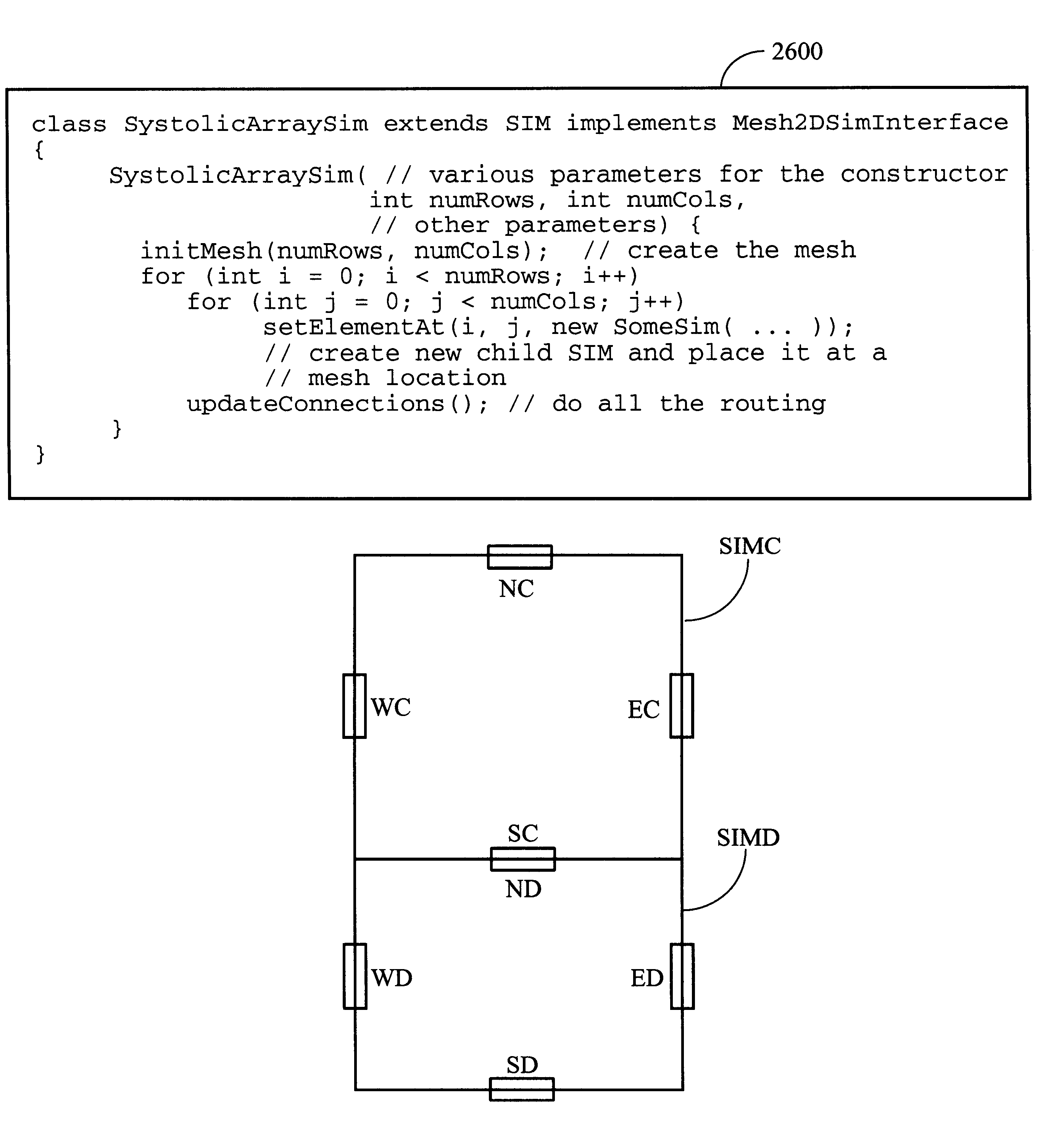
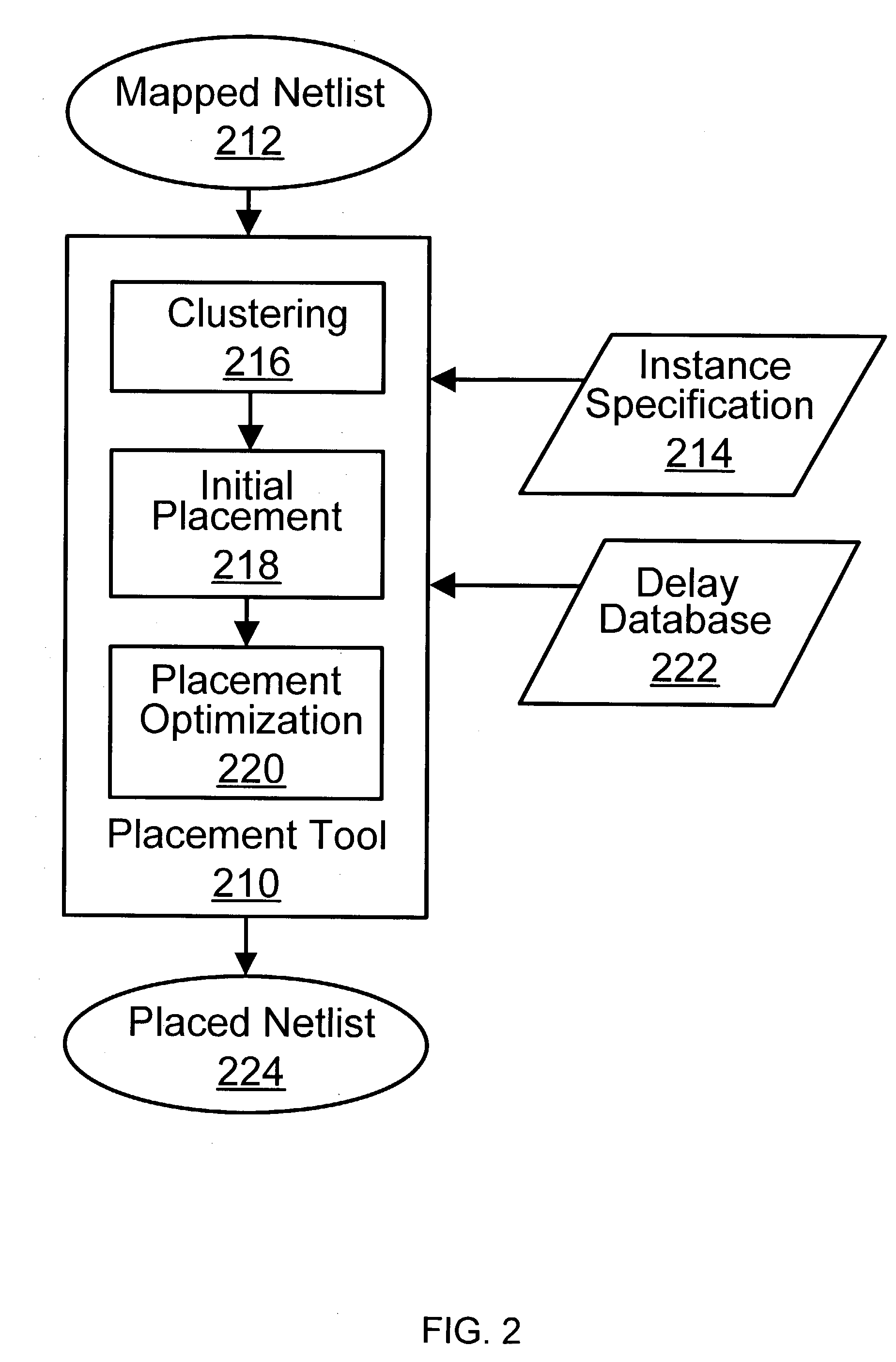
Hetergeneous method for determining module placement in FPGAs
InactiveUS6457164B1Reduce deliverySpeed up the implementation processElectronic switchingComputer programmed simultaneously with data introductionGrid patternSorting algorithm
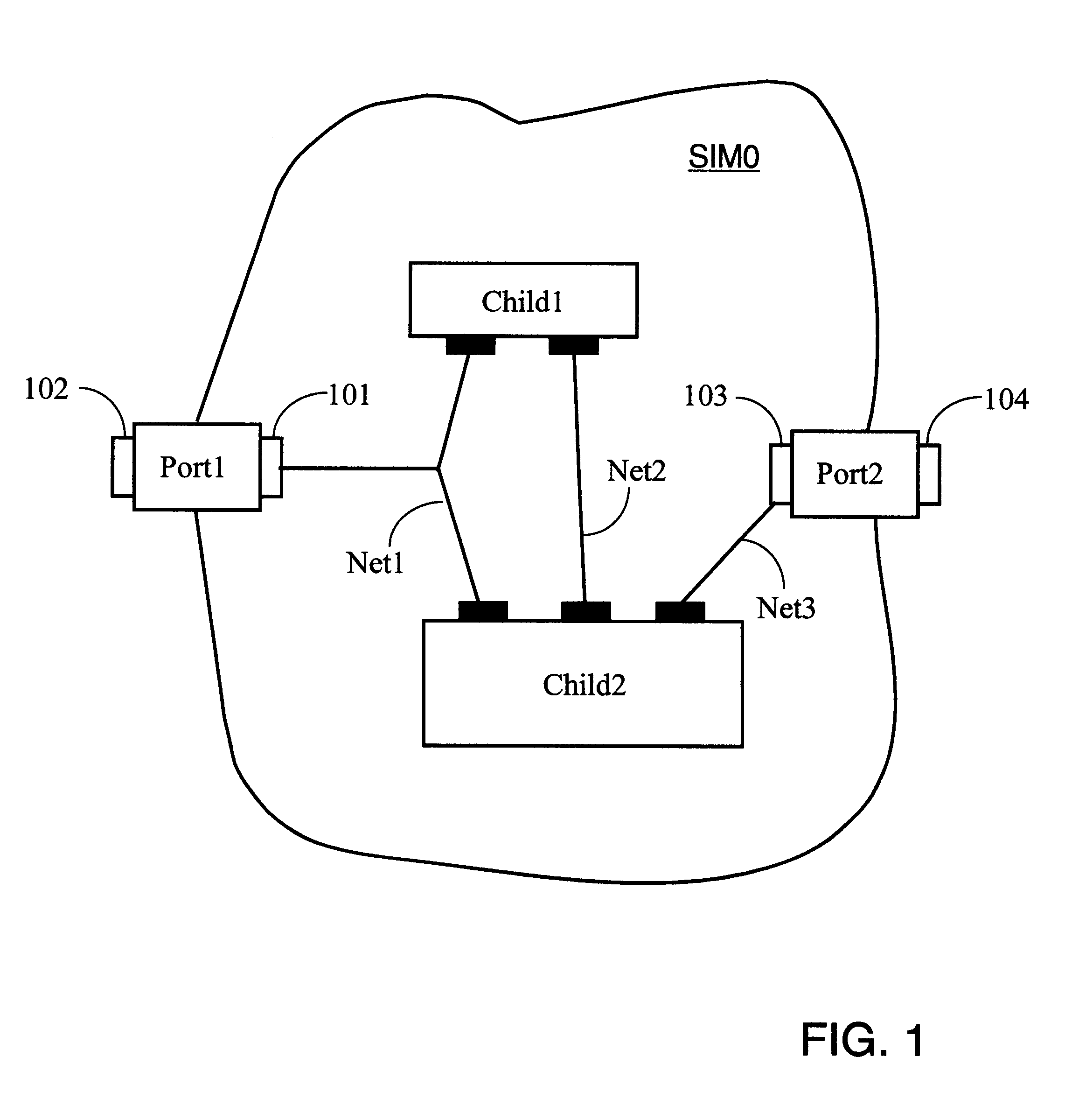
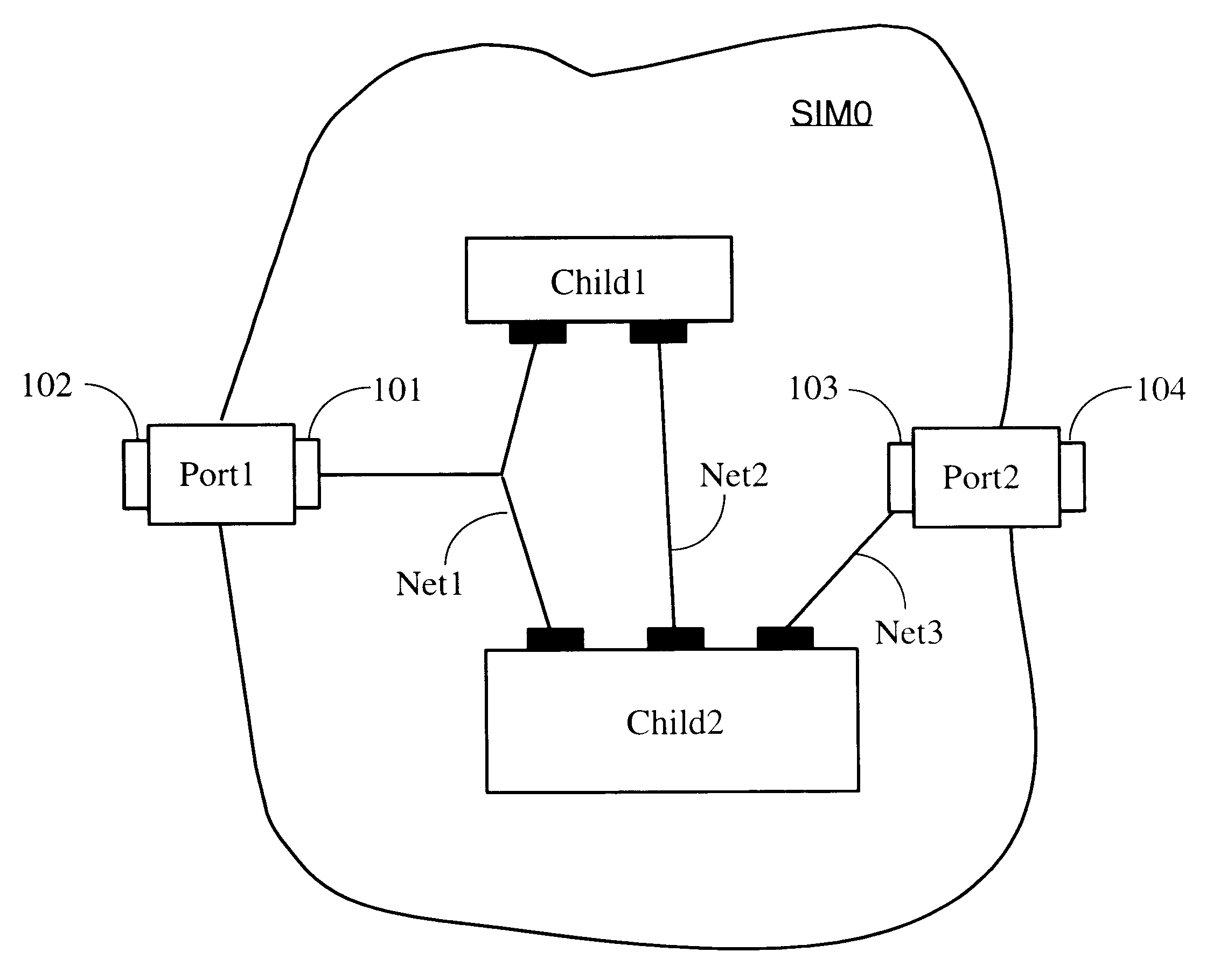
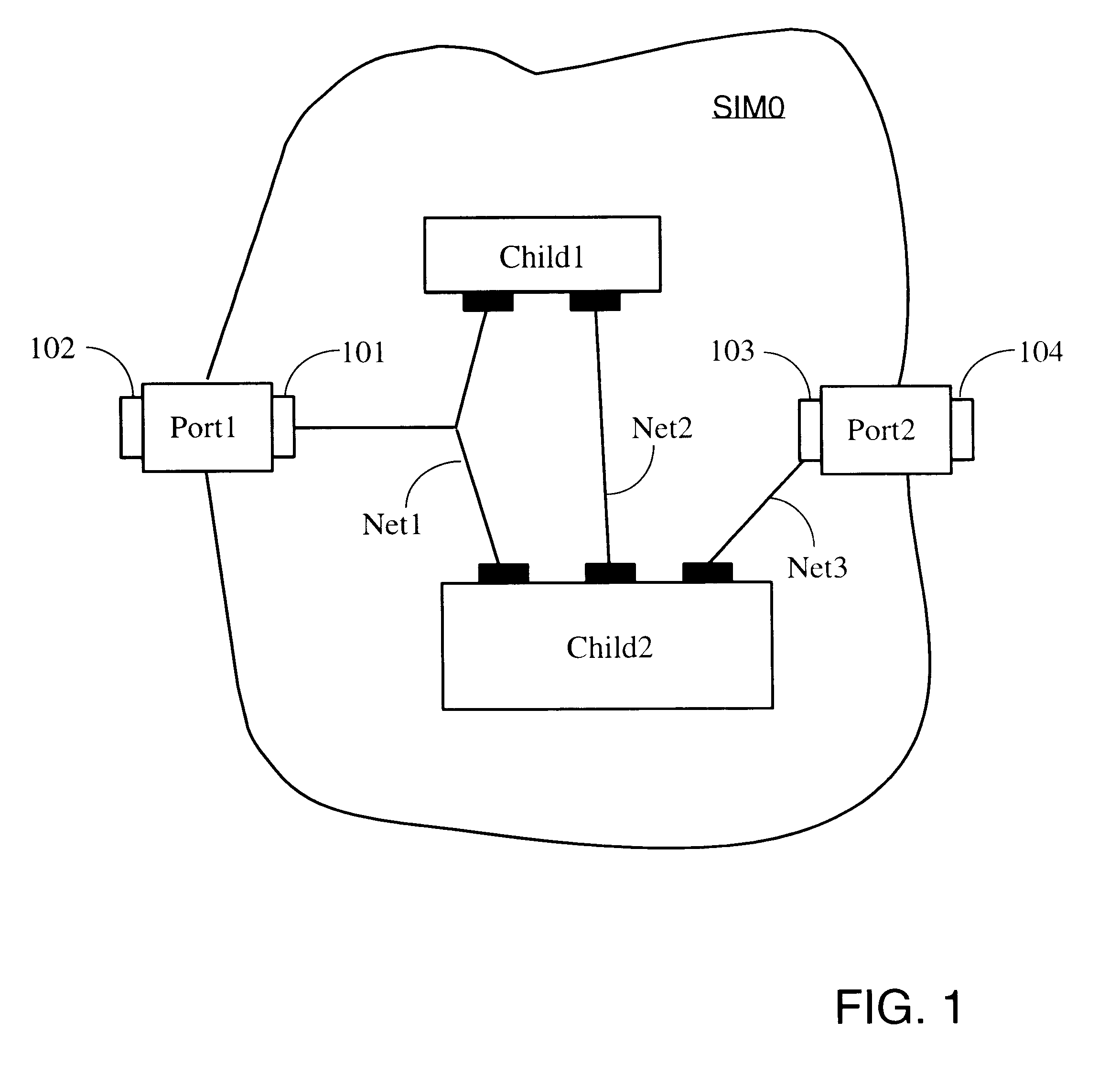
The invention provides parametric modules called Self Implementing Modules (SIMs) for use in programmable logic devices such as FPGAS. The invention further provides tools and methods for generating and using SIMs. SIMs implement themselves at the time the design is elaborated, targeting a specified FPGA according to specified parameters. In one embodiment, a SIM references or includes one or more floorplanners each of which may employ one or more placement algorithms. Such placement algorithms might include, for example: a linear ordering algorithm that places datapath logic bitwise in a regular linear pattern; a rectangular mesh algorithm that implements memory in a grid pattern in distributed RAM; a columnar algorithm for counters and other arithmetic logic; or a simulated annealing algorithm for random logic such as control logic. Therefore, a design including more than one SIM can utilize a plurality of placement algorithms at the same or different levels of hierarchy. The design as a whole can therefore utilize a non-uniform global placement strategy.
Owner:XILINX INC
System and method to power route hierarchical designs that employ macro reuse
InactiveUS20070256044A1Computer aided designSpecial data processing applicationsHierarchical designLinearity
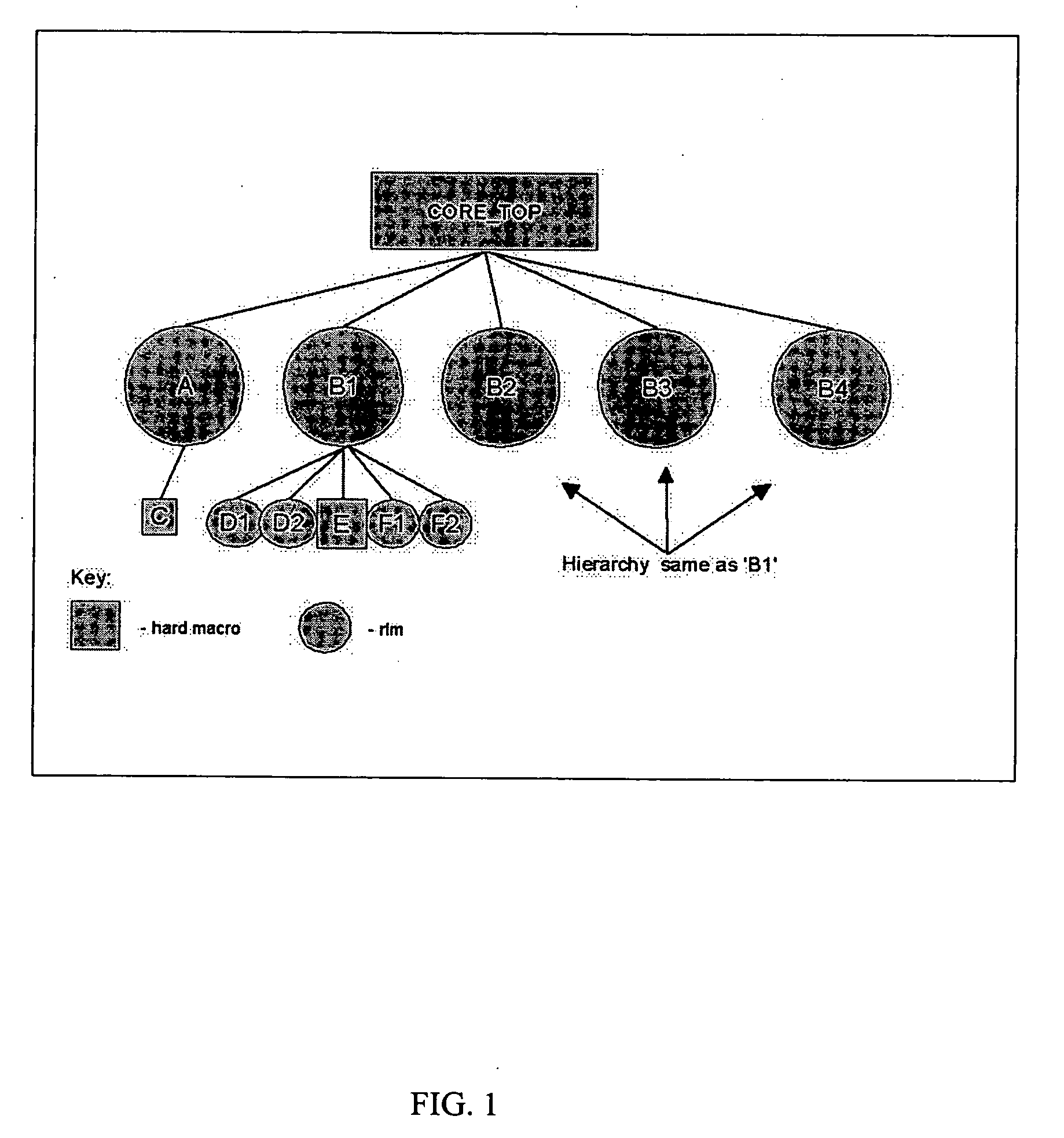
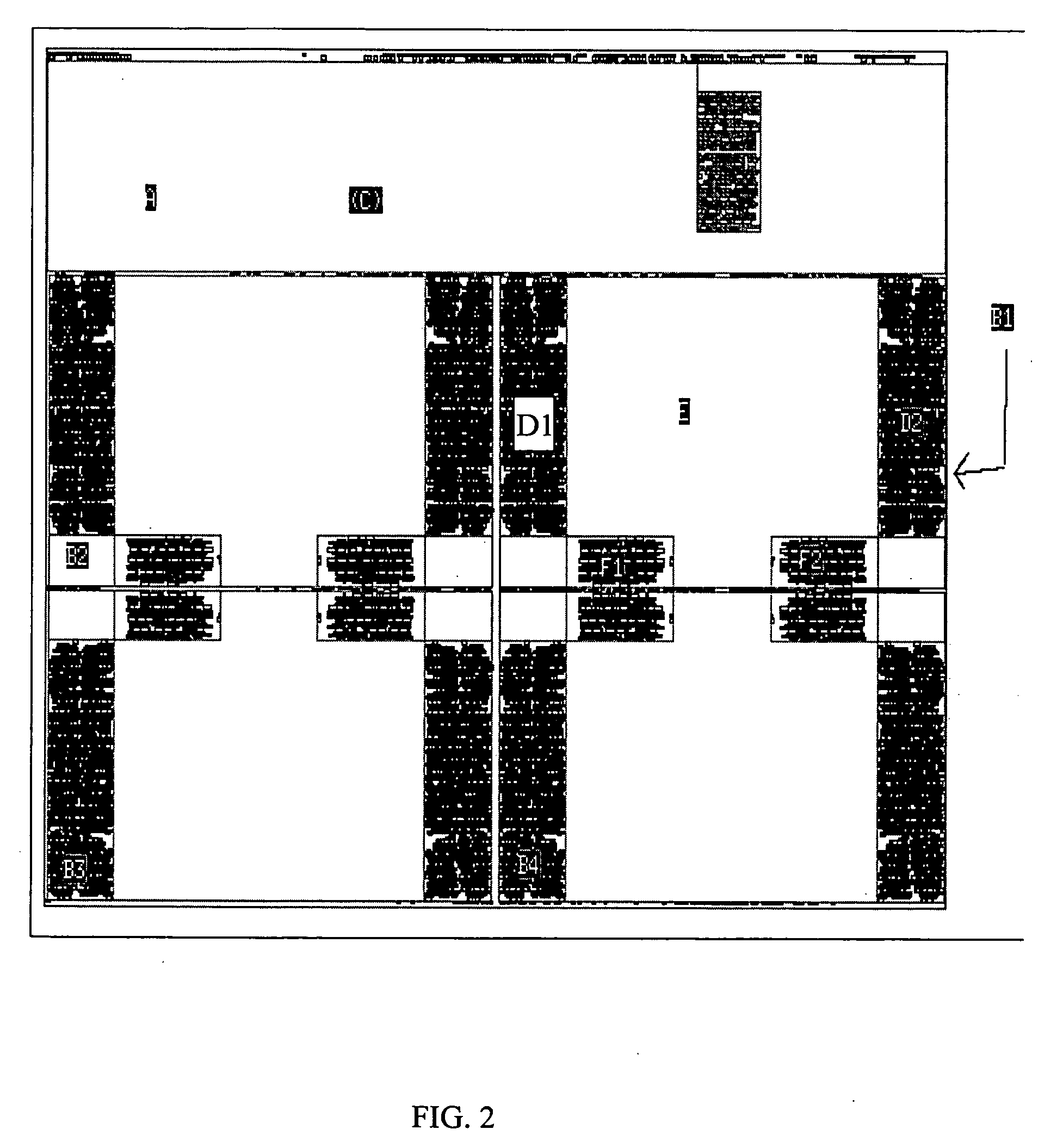
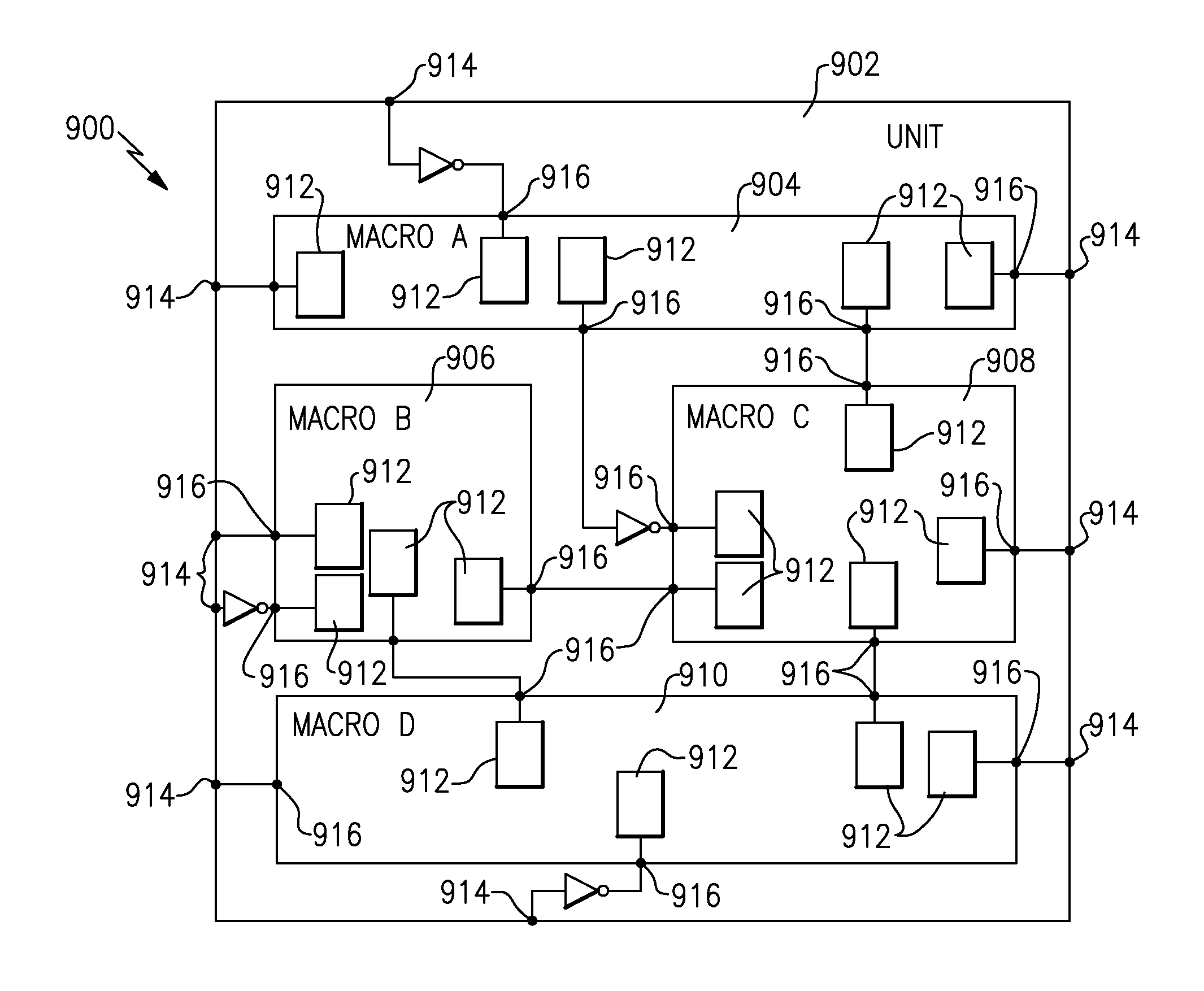
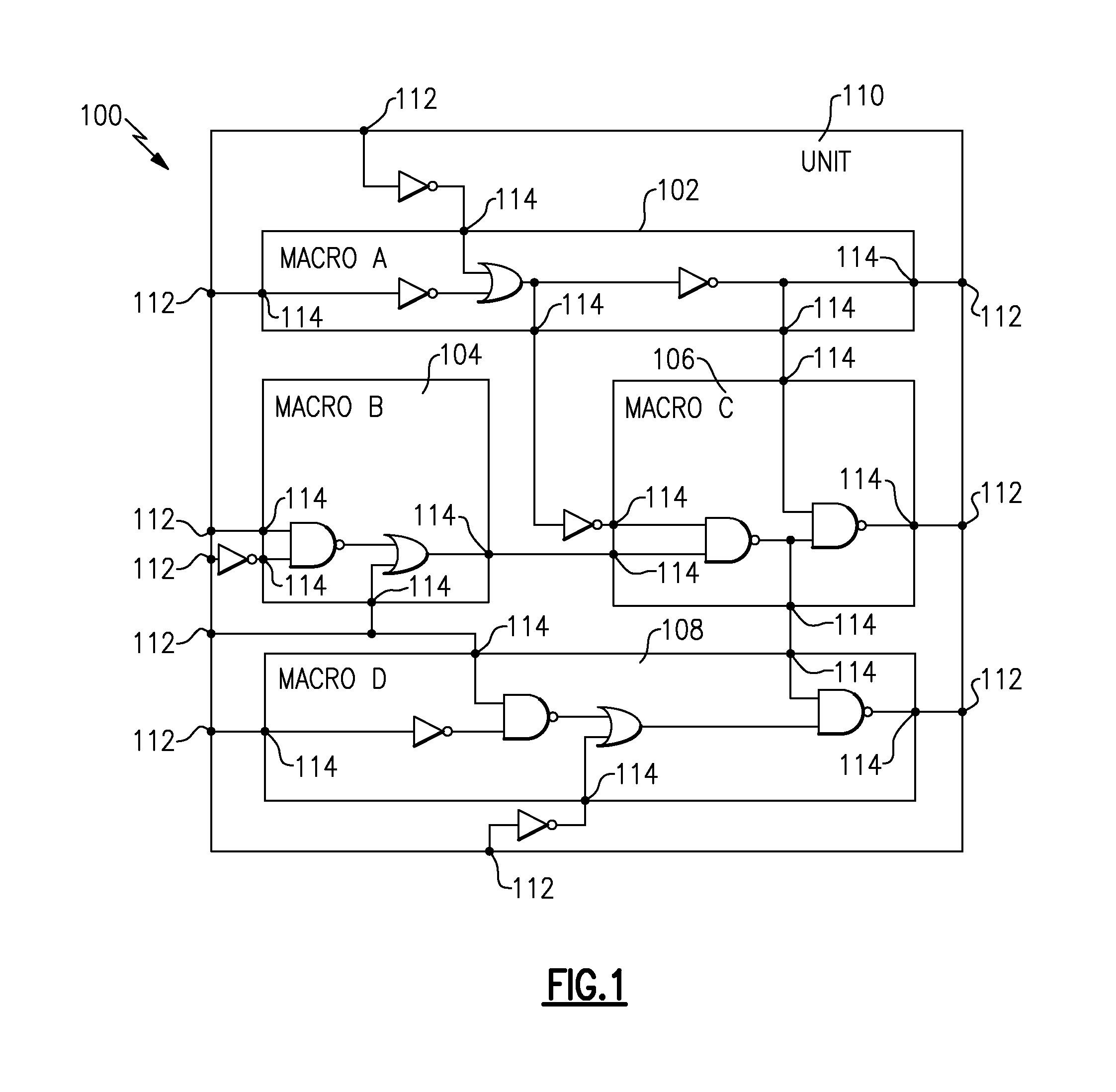
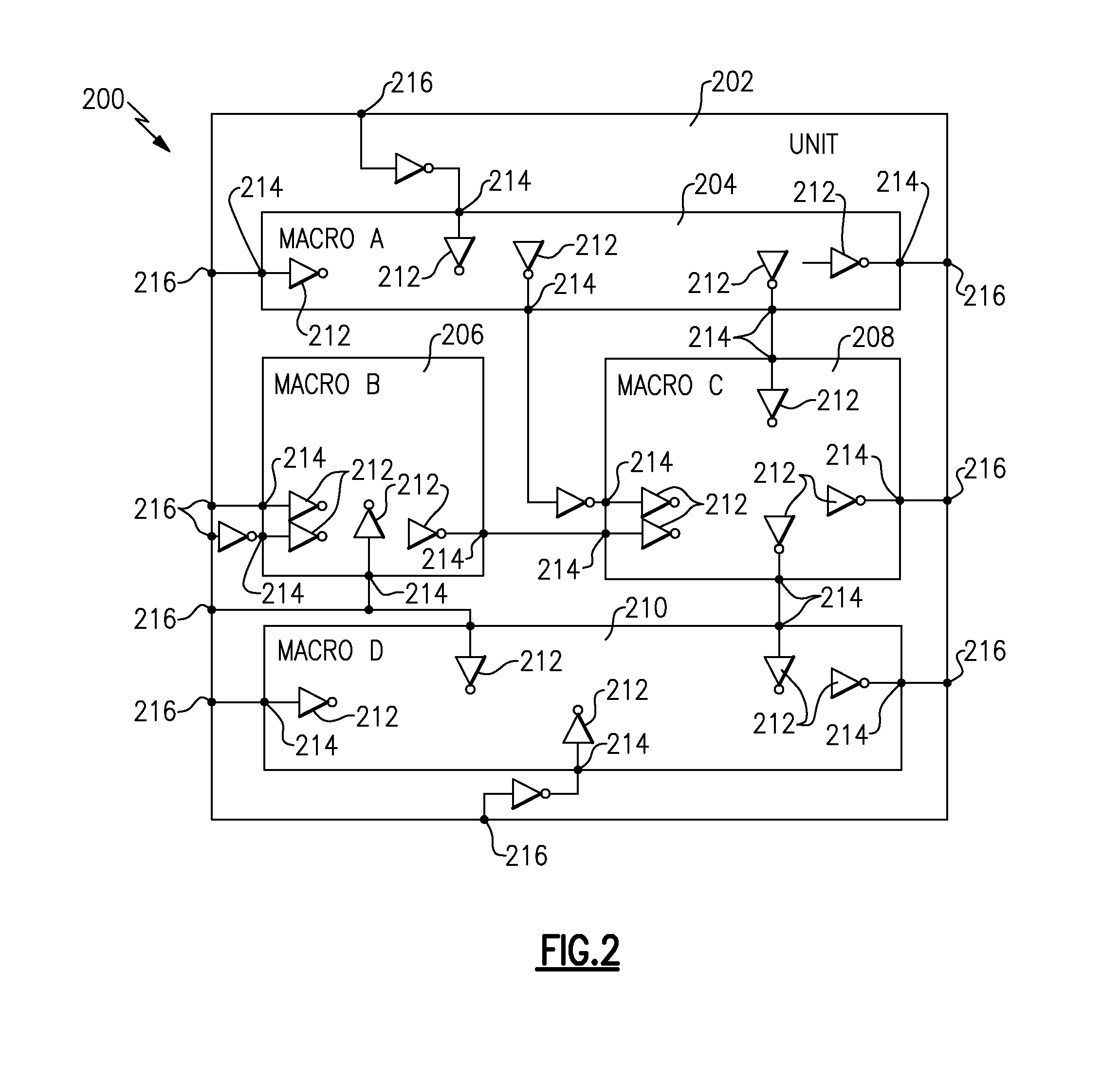
A method of routing a random logic macro (RLM) that is used multiple times in a hierarchical VLSI design without having to route each individual instantiation independently. Once an RLM has been routed and timed it can be copied and reused in a physical design as is, and does not require any wiring changes. This method is an advantage over existing art because it conserves area, improves wireability, and reduces the time required for routing and timing each RLM instance. Furthermore, each RLM possesses the same timing and power characteristics, which improves overall circuit performance.
Owner:IBM CORP
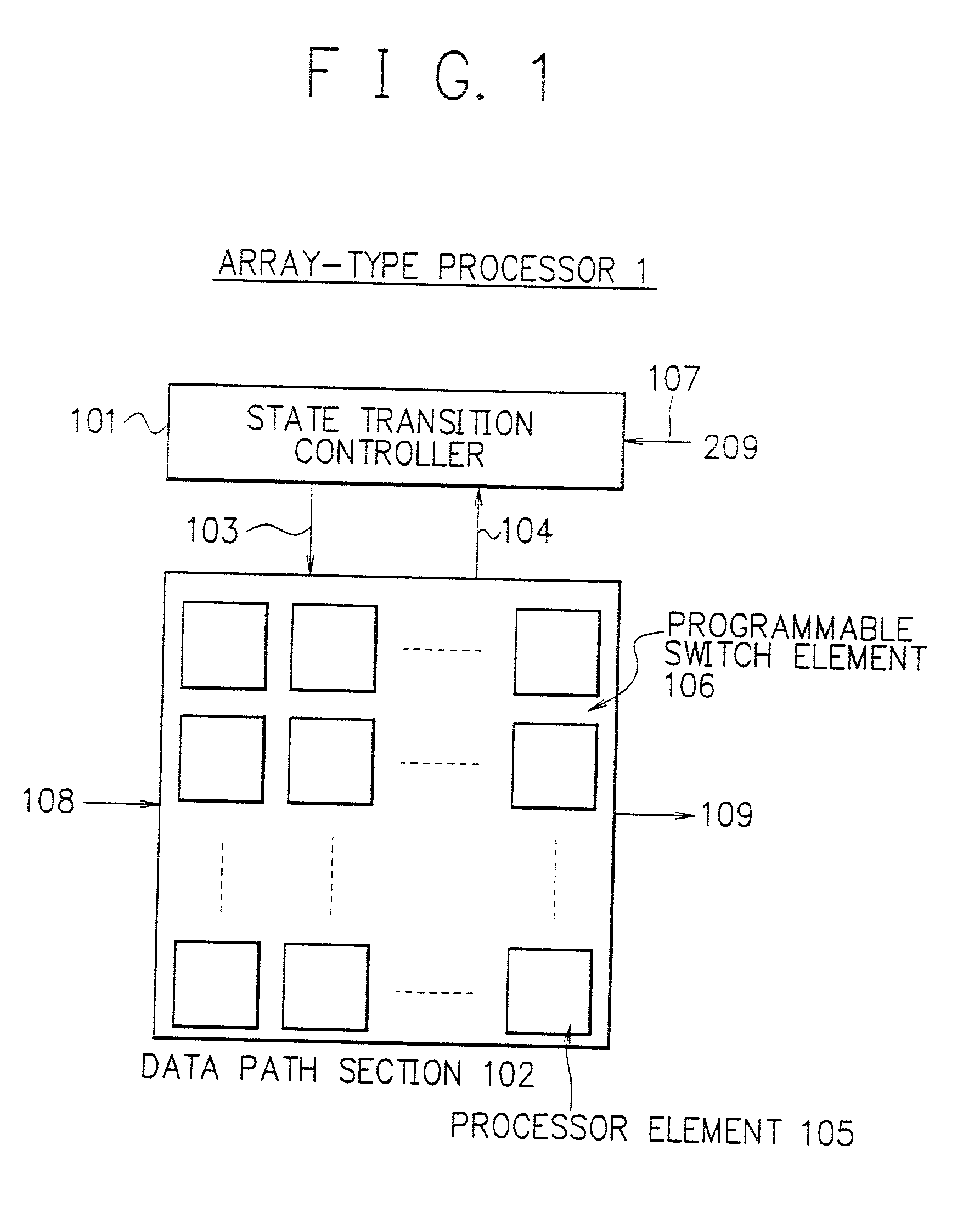
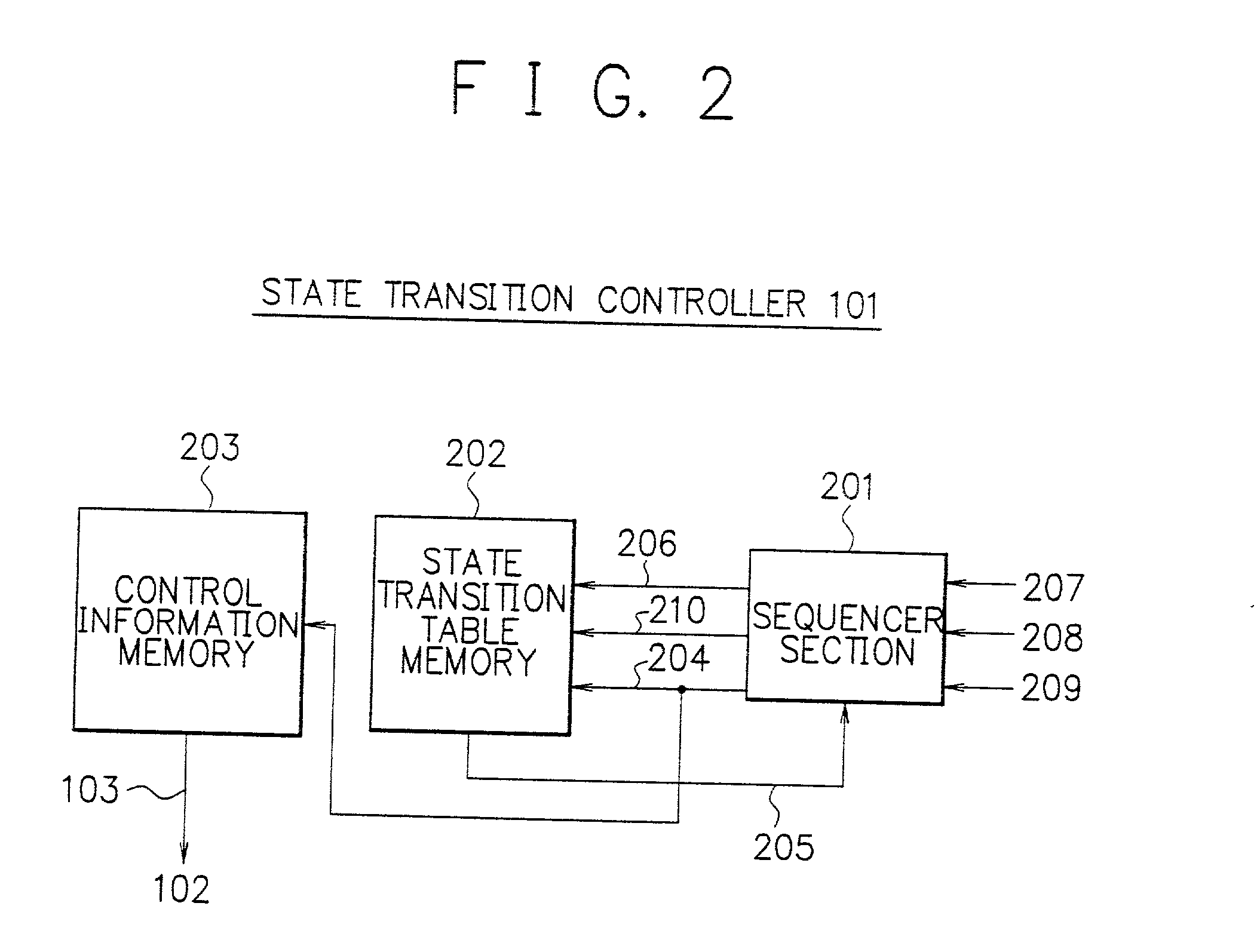
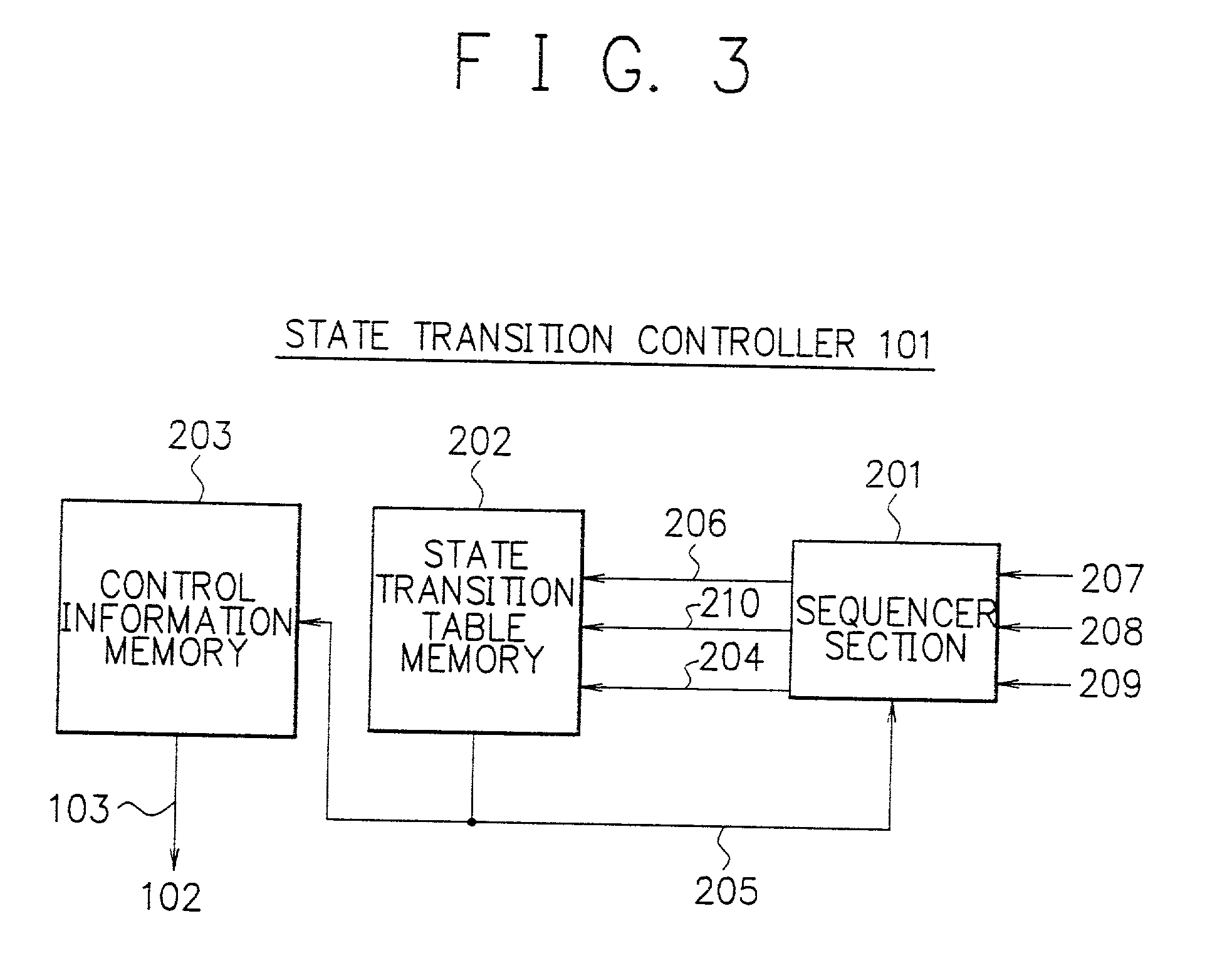
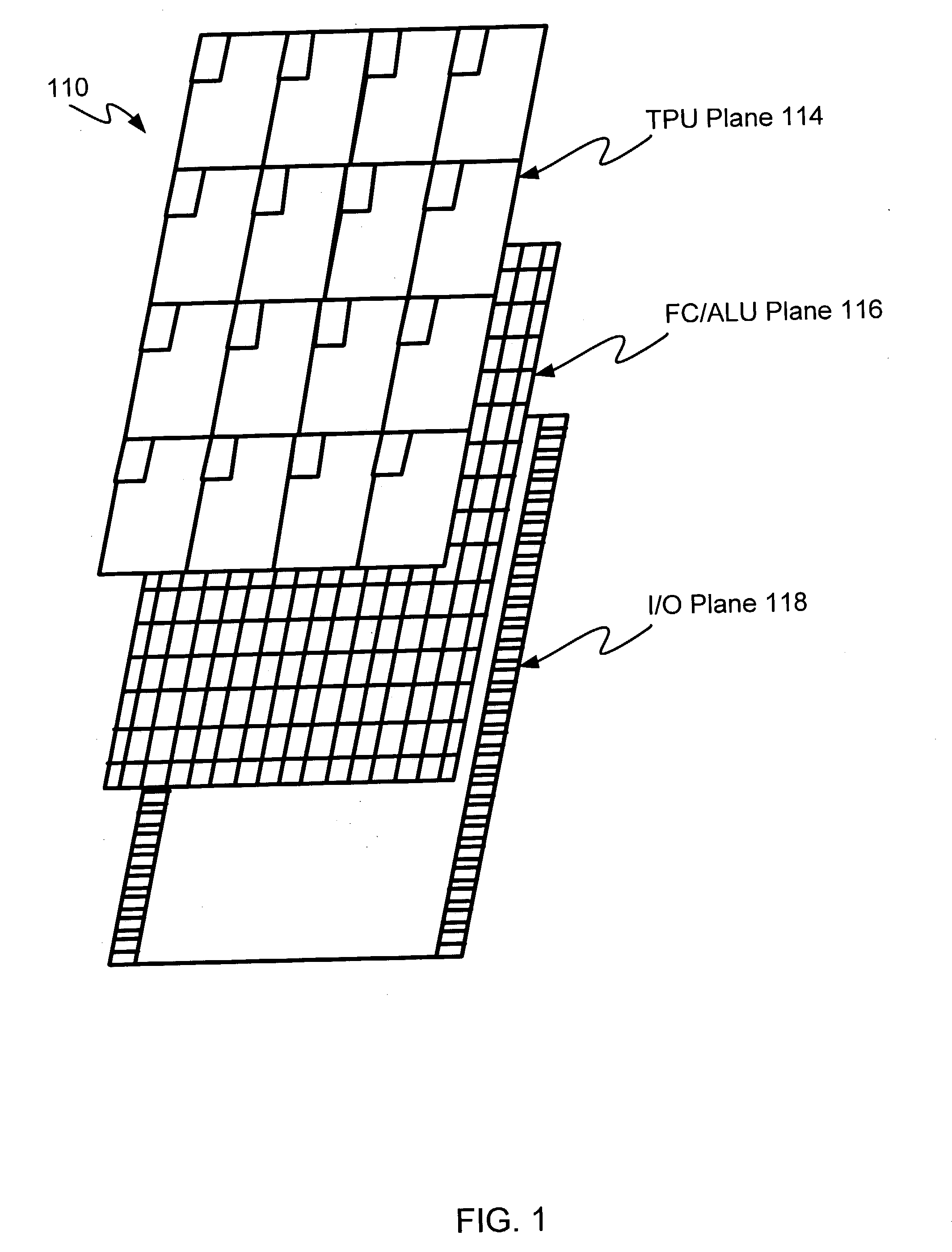
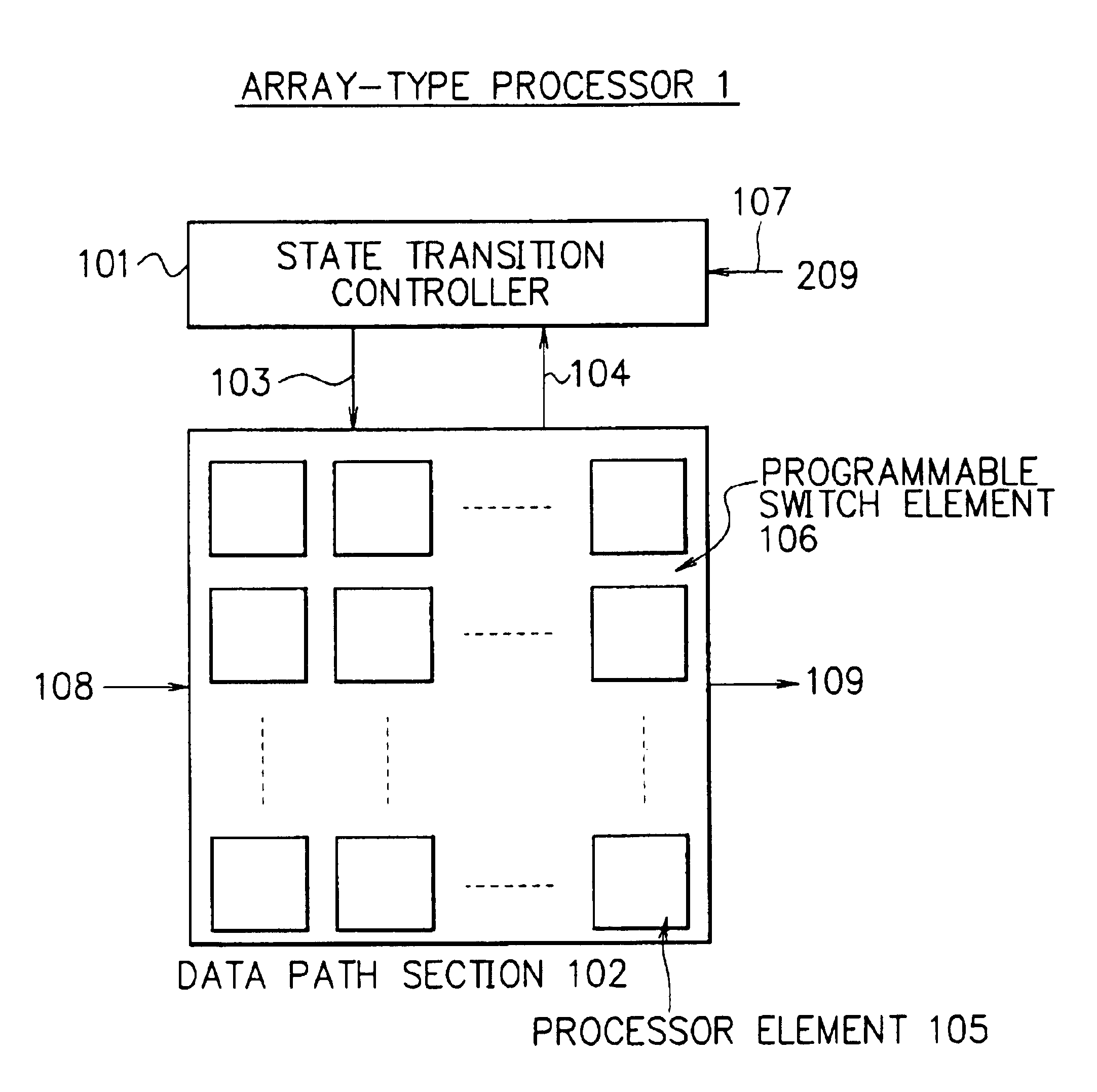
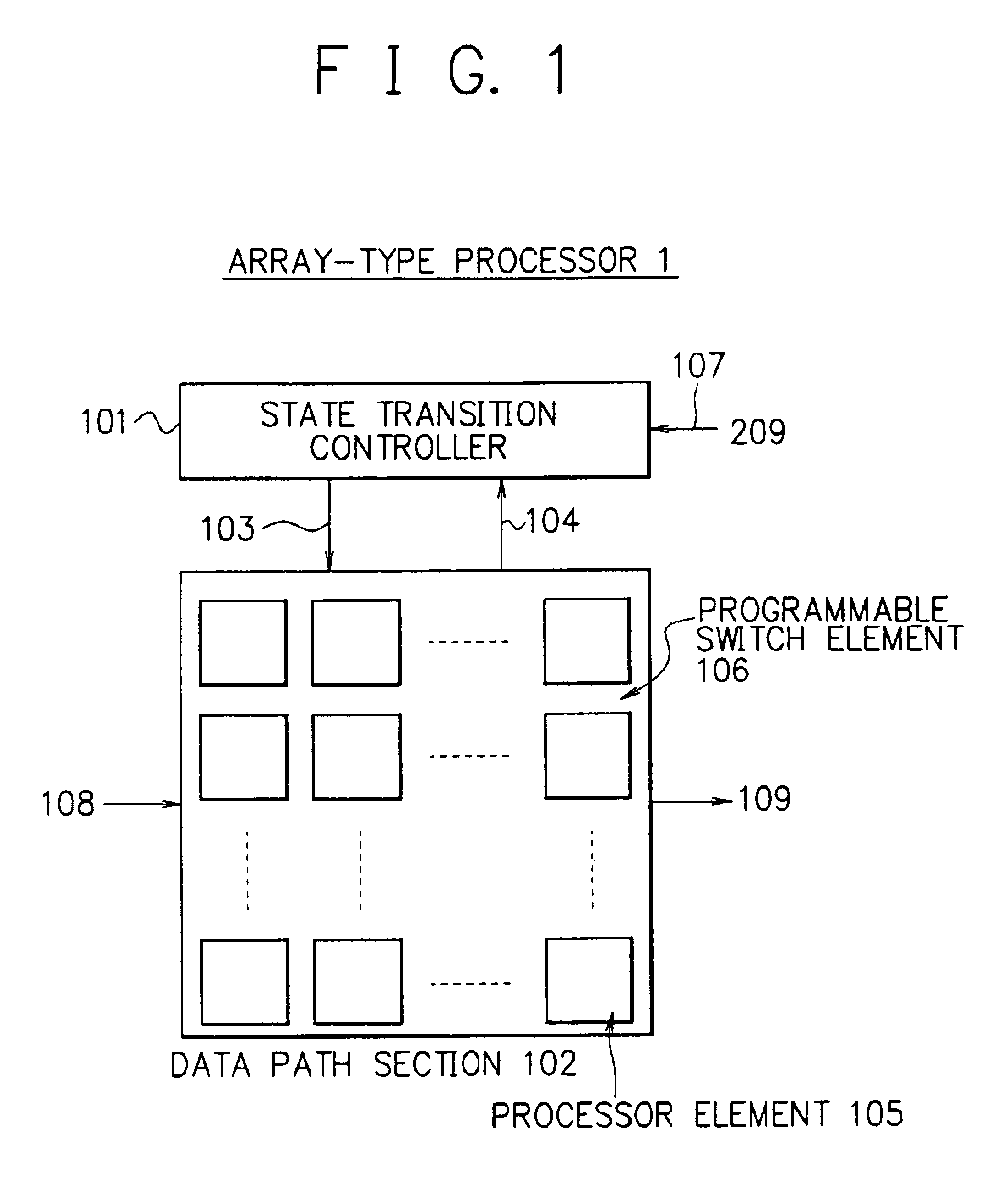
Array-type processor
InactiveUS20010018733A1Efficient implementationEfficient executionSingle instruction multiple data multiprocessorsSpecific program execution arrangementsDatapathState switching
To execute all processing in an array section of an array-type processor, each processor must execute processing of different types, i.e., processing of an operating unit and processing of a random logic circuit, which limits its size and processing performance. A data path section including processors arranged in an array are connected via programmable switches to primarily execute processing of operation and a state transition controller configured to easily implement a state transition function to control state transitions are independently disposed. These sections are configured in customized structure for respective processing purposes to efficiently implement and achieve the processing of operation and the control operation.
Owner:NEC CORP
Data processing system
InactiveUS6859869B1Widely scalable parallelityFlexible and fastGeneral purpose stored program computerSpecial data processing applicationsData processing systemComputer architecture
A data processing system, wherein a data flow processor (DFP) integrated circuit chip is provided which comprises a plurality of orthogonally arranged homogeneously structured cells, each cell having a plurality of logically same and structurally identically arranged modules. The cells are combined and facultatively grouped using lines and columns and connected to the input / output ports of the DFP. A compiler programs and configures the cells, each by itself and facultatively-grouped, such that random logic functions and / or linkages among the cells can be realized. The manipulation of the DFP configuration is performed during DFP operation such that modification of function parts (MACROs) of the DFP can take place without requiring other function parts to be deactivated or being impaired.
Owner:PACT XPP TECH
Heterogeneous method for determining module placement in FPGAs
InactiveUS6243851B1Reduce deliverySpeed up the implementation processElectronic switchingComputer aided designSorting algorithmGrid pattern
The invention provides parametric modules called Self Implementing Modules (SIMs) for use in programmable logic devices such as FPGAs. The invention further provides tools and methods for generating and using SIMs. SIMs implement themselves at the time the design is elaborated, targeting a specified FPGA according to specified parameters. In one embodiment, a SIM references or includes one or more floorplanners each of which may employ one or more placement algorithms. Such placement algorithms might include, for example: a linear ordering algorithm that places datapath logic bitwise in a regular linear pattern; a rectangular mesh algorithm that implements memory in a grid pattern in distributed RAM; a columnar algorithm for counters and other arithmetic logic; or a simulated annealing algorithm for random logic such as control logic. Therefore, a design including more than one SIM can utilize a plurality of placement algorithms at the same or different levels of hierarchy. The design as a whole can therefore utilize a non-uniform global placement strategy.
Owner:XILINX INC
System and method for efficiently mapping heterogeneous objects onto an array of heterogeneous programmable logic resources
ActiveUS20040194048A1Computer aided designSpecial data processing applicationsInto-structureComputer module
A system and method of mapping heterogeneous objects onto an array of heterogeneous programmable logic resources. The method comprises clustering to identify datapath modules from a netlist. The method further comprises aggregating the datapath modules into higher level modules. The method also comprises clustering random logic into structures.
Owner:XILINX INC
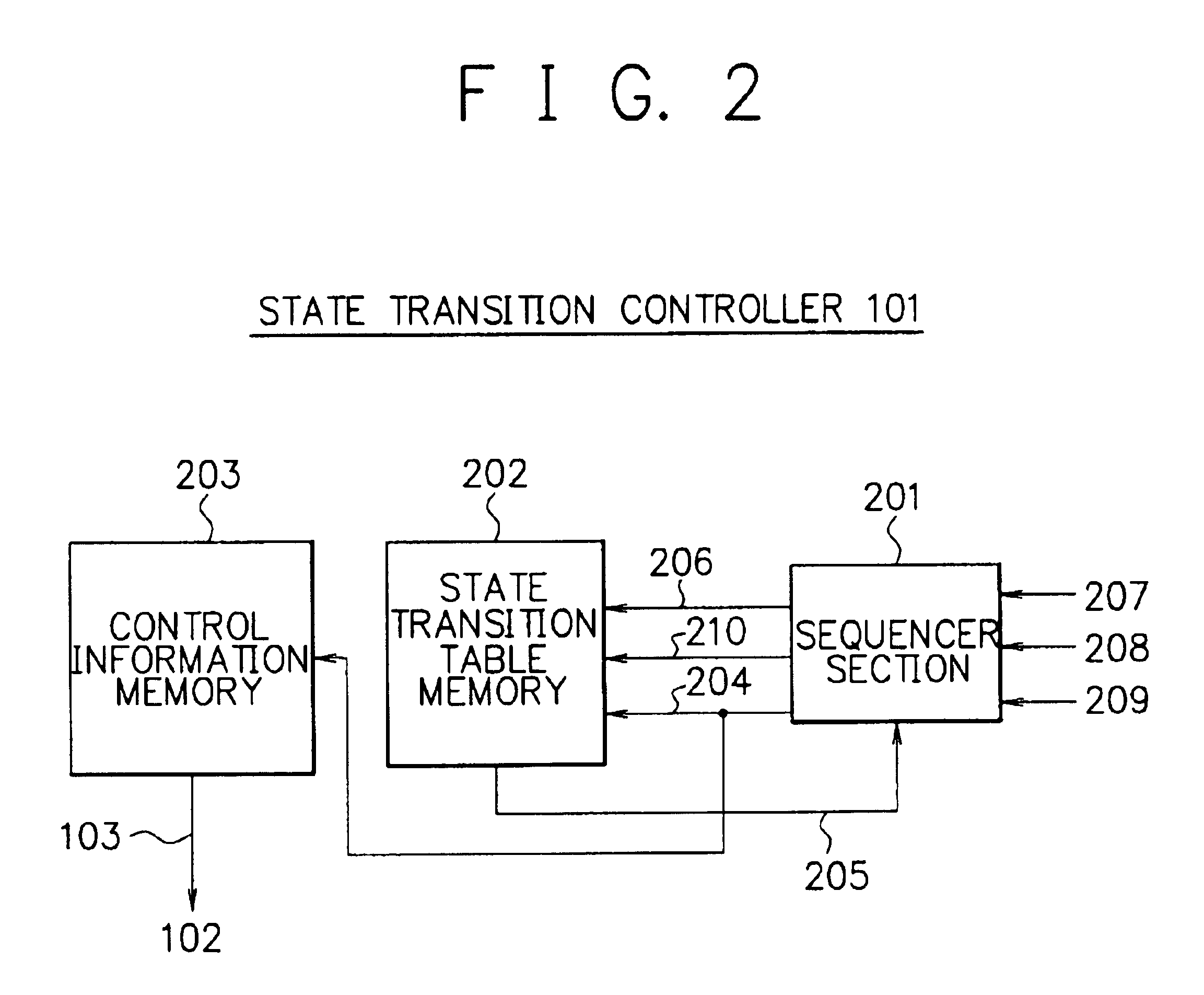
Array type processor with state transition controller identifying switch configuration and processing element instruction address
InactiveUS6738891B2Efficient implementationEfficient executionSingle instruction multiple data multiprocessorsSpecific program execution arrangementsProcessing elementSystem configuration
To execute all processing in an array section of an array-type processor, each processor must execute processing of different types, i.e., processing of an operating unit and processing of a random logic circuit, which limits its size and processing performance. A data path section including processors arranged in an array are connected via programmable switches to primarily execute processing of operation and a state transition controller configured to easily implement a state transition function to control state transitions are independently disposed. These sections are configured in customized structure for respective processing purposes to efficiently implement and achieve the processing of operation and the control operation.
Owner:NEC CORP
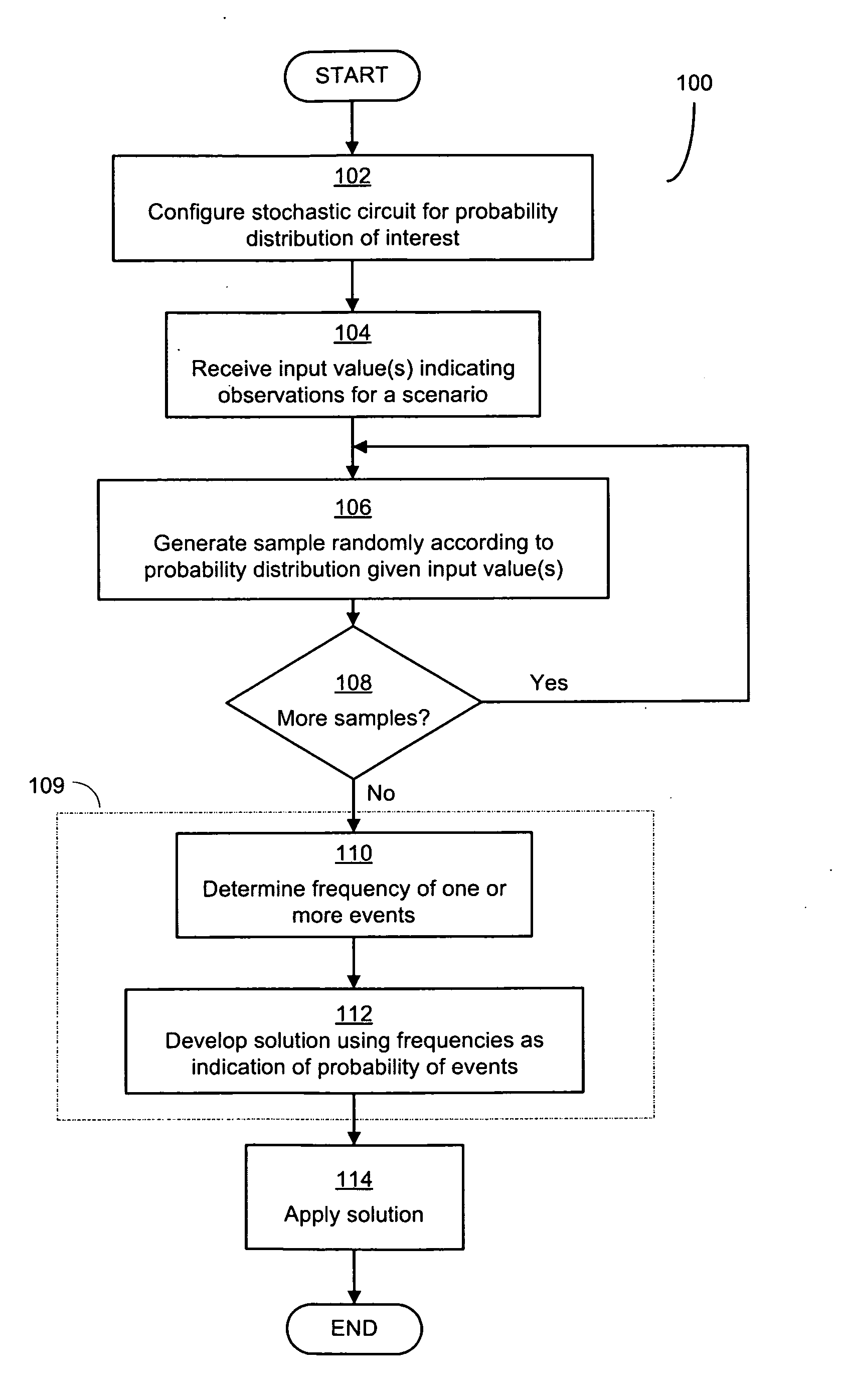
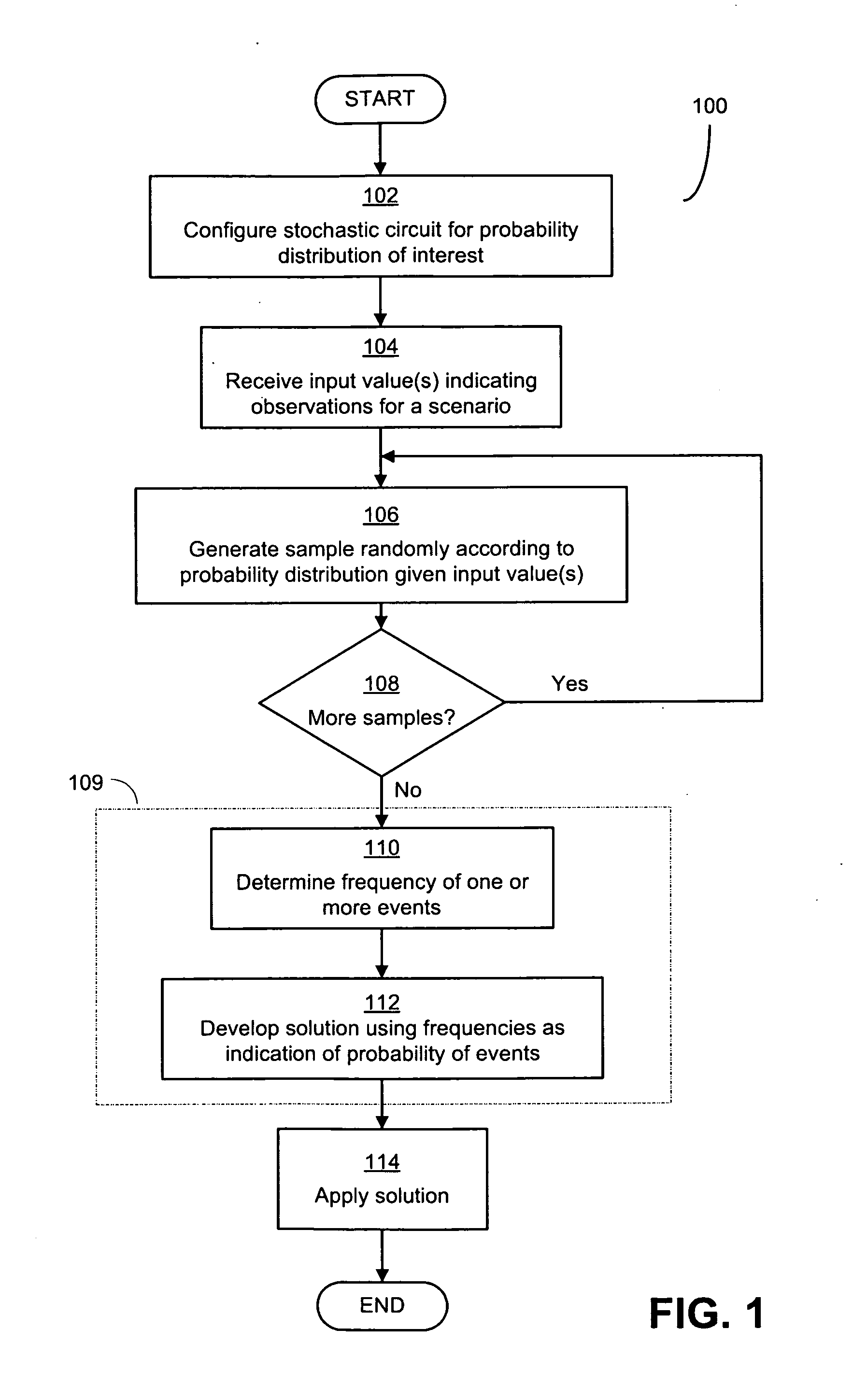
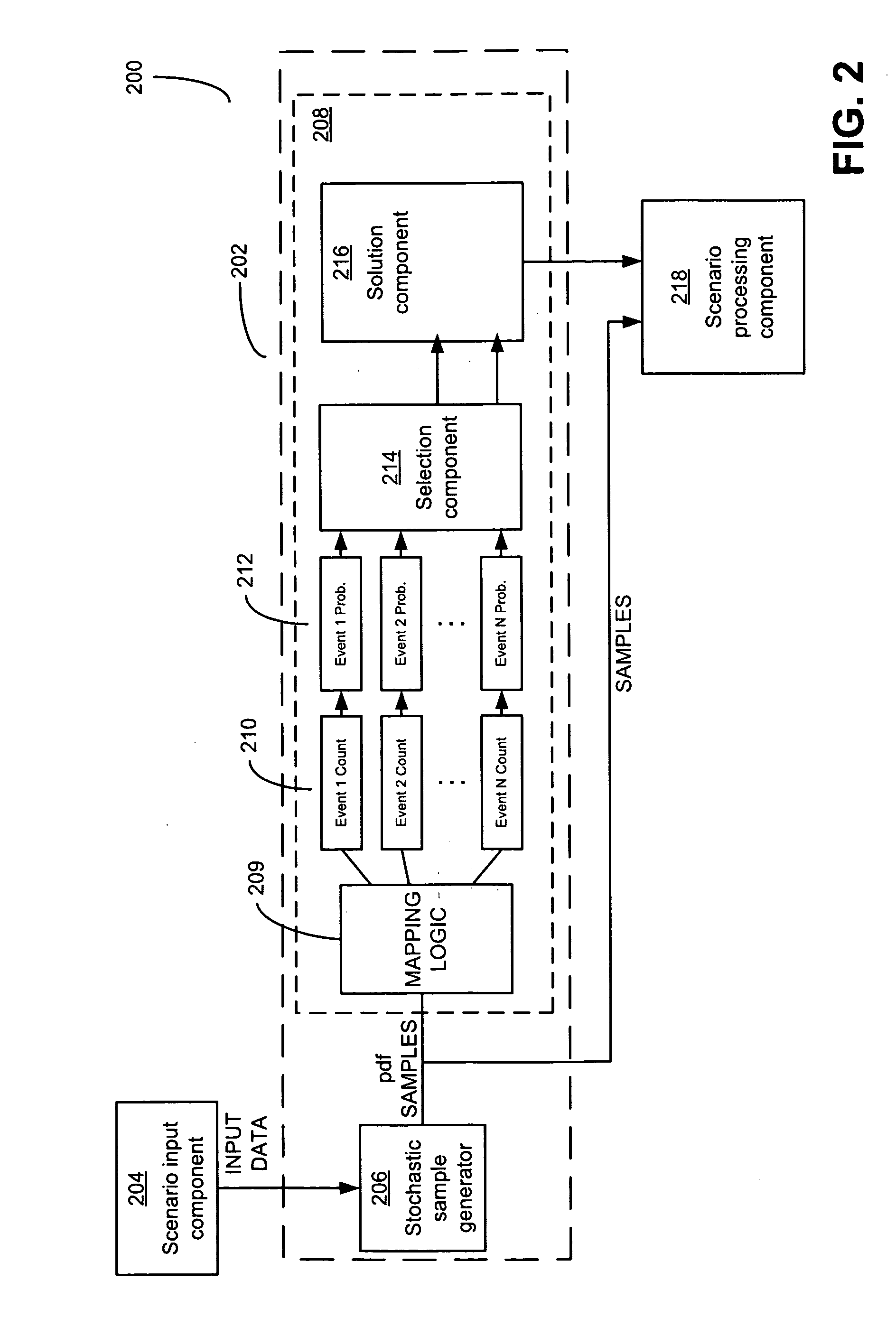
Combinational Stochastic Logic
ActiveUS20090228238A1Analogue computers for electric apparatusDigital computer detailsConditional probabilityComputer science
Circuits that solve stochastic problems and techniques for operating them. These natively stochastic circuits may produce samples from probability distributions of interest for particular stochastic problems, and may be combined together in any suitable way to yield potential solutions to stochastic problems. In some implementations, the stochastic circuits may generate samples from conditional probability distributions conditioned on input data provided to the stochastic circuits. The circuits may be constructed from multiple interconnected stochastic subcircuits such that a circuit may produce a sample from a joint probability distribution, or from a marginal distribution of a joint distribution. These circuits may be used to implement stochastic sampling algorithms to solve stochastic processes, and may include stochastic subcircuits that operate concurrently.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
System and method for efficiently mapping heterogeneous objects onto an array of heterogeneous programmable logic resources
ActiveUS7000211B2Computer aided designSpecial data processing applicationsInto-structureComputer module
A system and method of mapping heterogeneous objects onto an array of heterogeneous programmable logic resources. The method comprises clustering to identify datapath modules from a netlist. The method further comprises aggregating the datapath modules into higher level modules. The method also comprises clustering random logic into structures.
Owner:XILINX INC
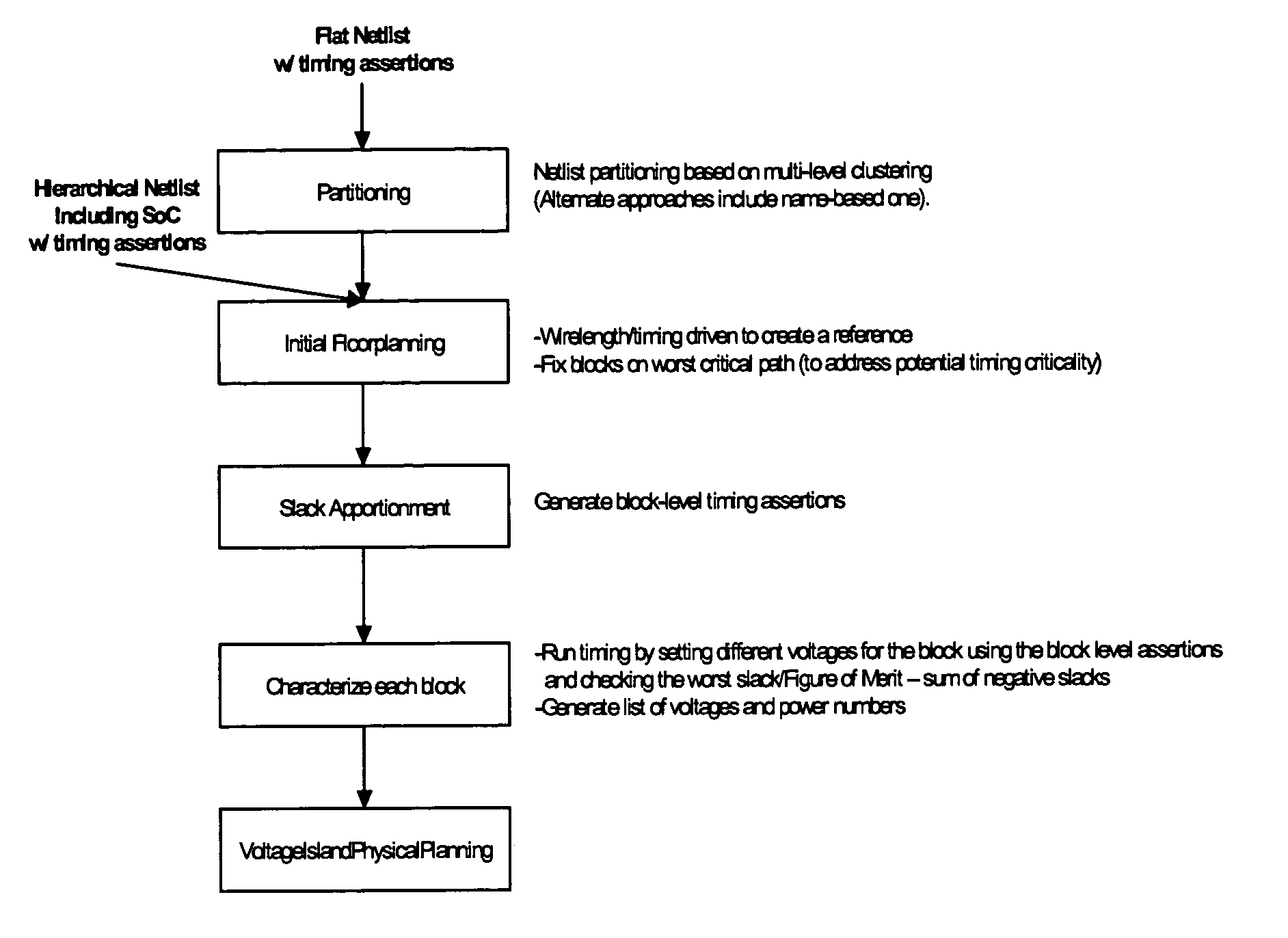
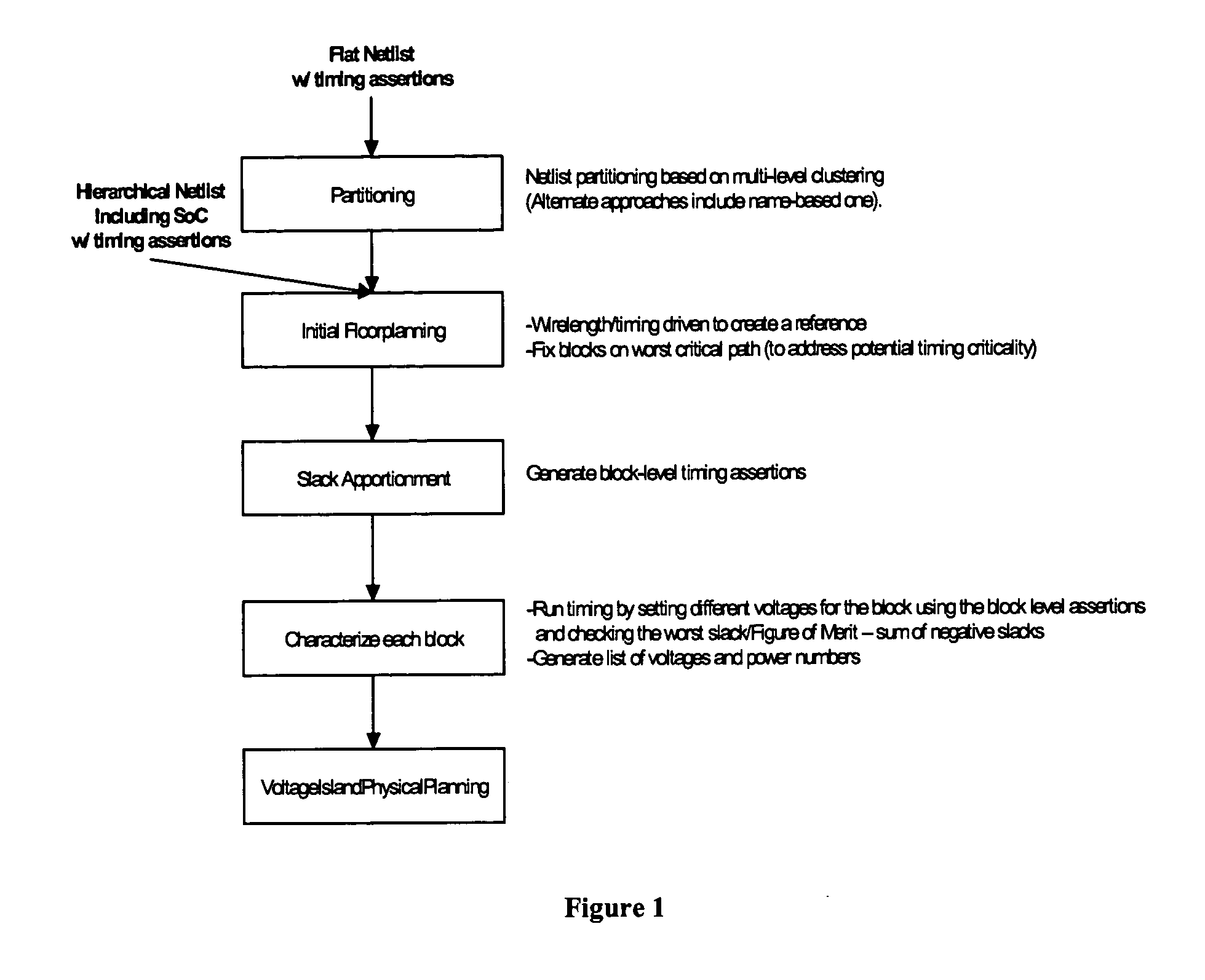
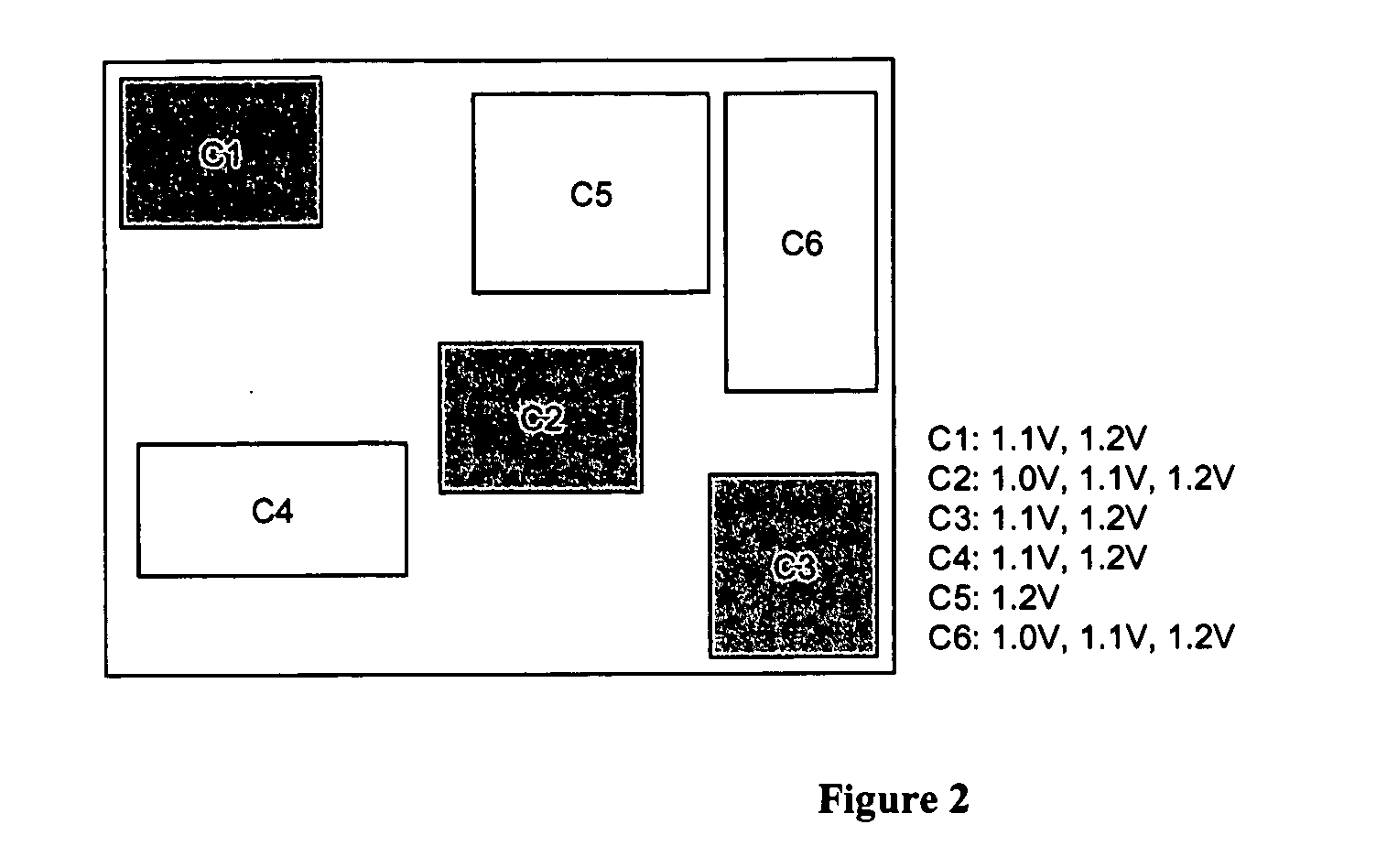
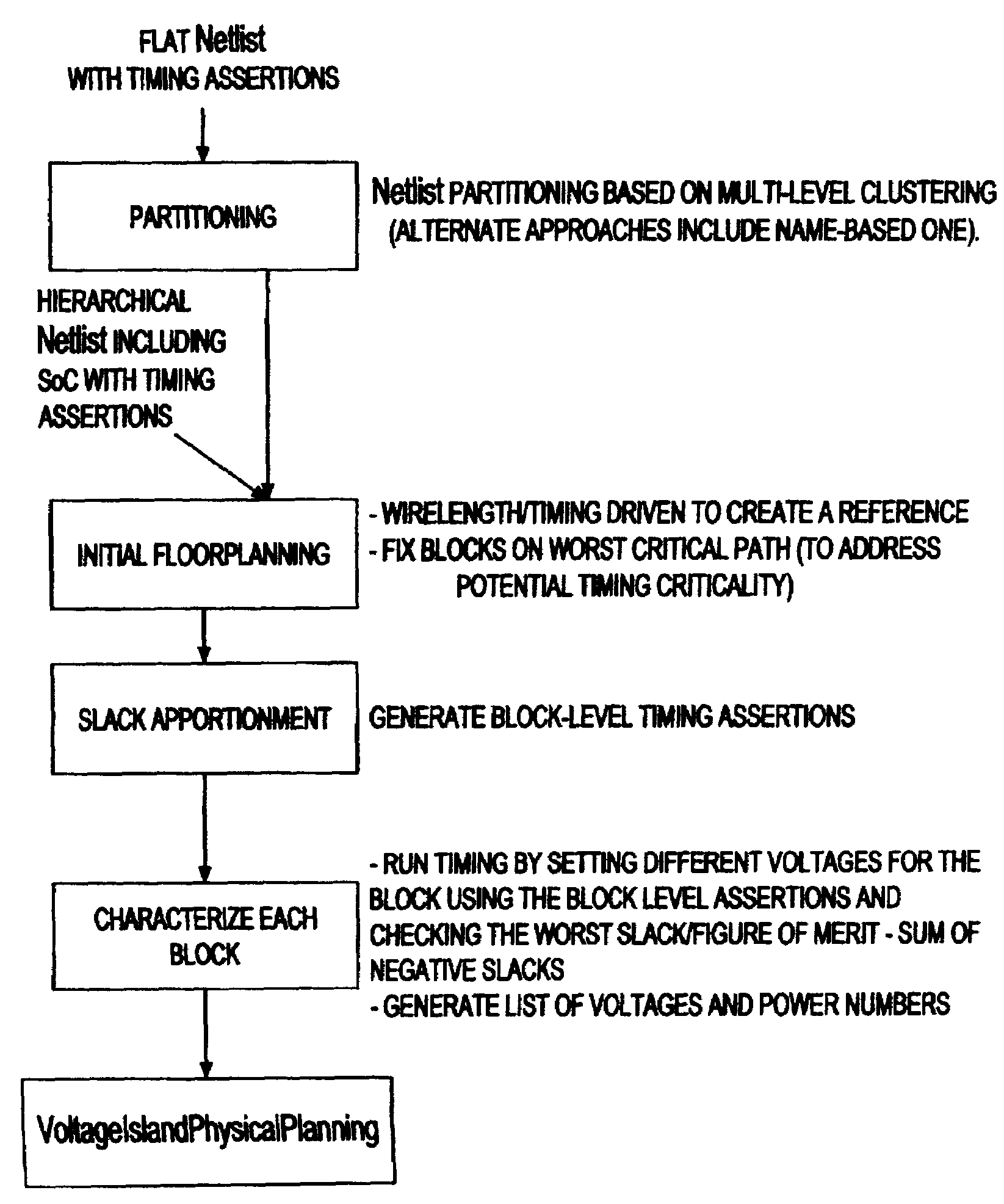
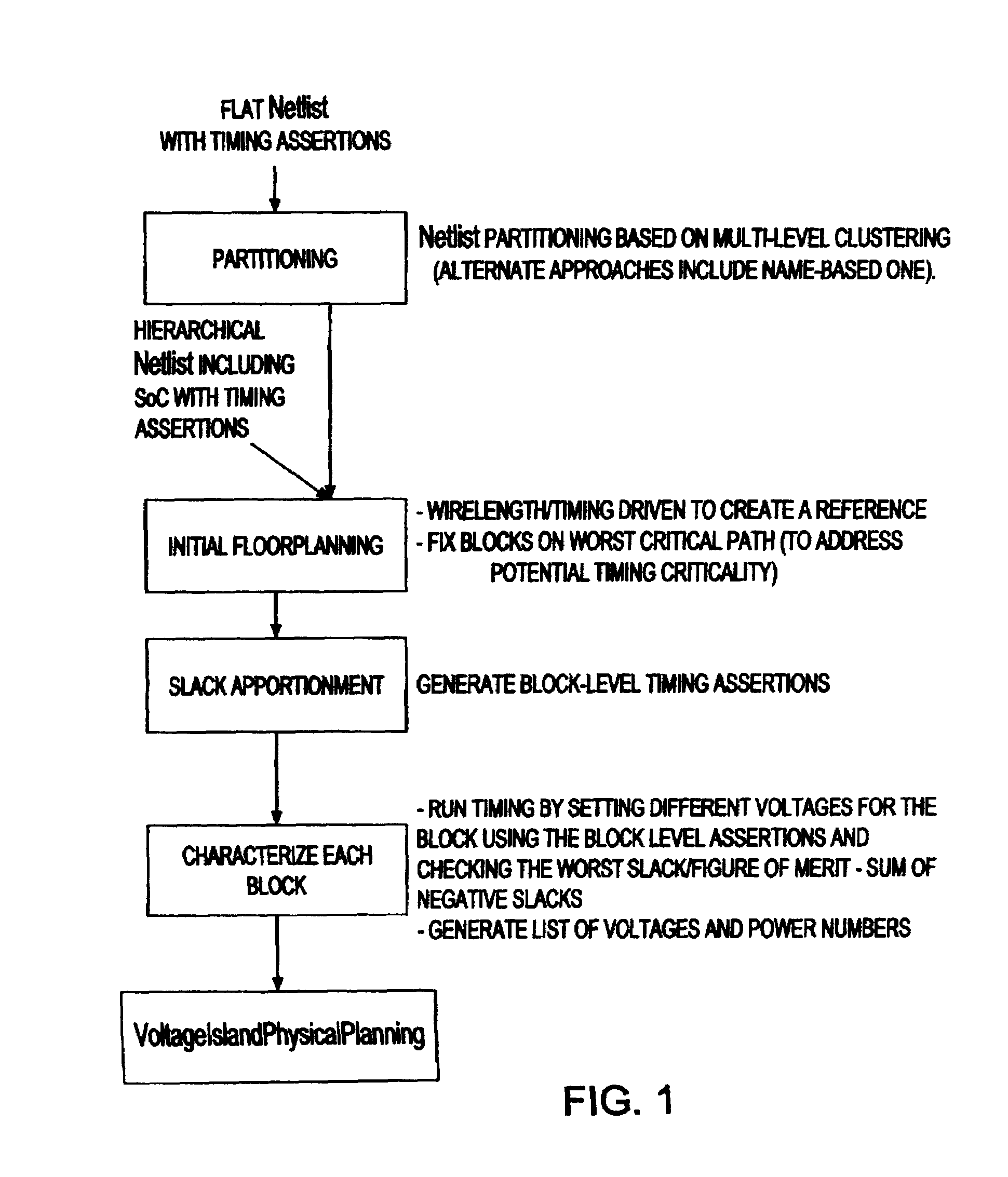
Method of physical planning voltage islands for ASICs and system-on-chip designs
InactiveUS20050278676A1Minimize power consumptionCAD circuit designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationPhysical planningIslanding
Voltage islands enable a core-level power optimization of ASIC / SoC designs by utilizing a unique supply voltage for each cluster of the design. Creating voltage islands in a chip design for optimizing the overall power consumption consists of generating voltage island partitions, assigning voltage levels and floorplanning. The generation of voltage island partitions and the voltage level assignment are performed simultaneously in a floorplanning context due to the physical constraints involved. This leads to a floorplanning formulation that differs from the conventional floorplanning for ASIC designs. Such a formulation of a physically aware voltage island partitioning and method for performing simultaneous voltage island partitioning, level assignment and floorplanning are described, as are the definition and the solution of floorplanning for voltage island based designs executed under area, power, timing and physical constraints. The physical planning of voltage islands includes: a) characterizing cell clusters in terms of voltages and power consumption values; b) providing a set of cell clusters that belong to a single voltage island Random Logic Macro (RLM); and c) assigning voltages for the voltage island RLMs, all within the context of generating a physically realizable floorplan for the design.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
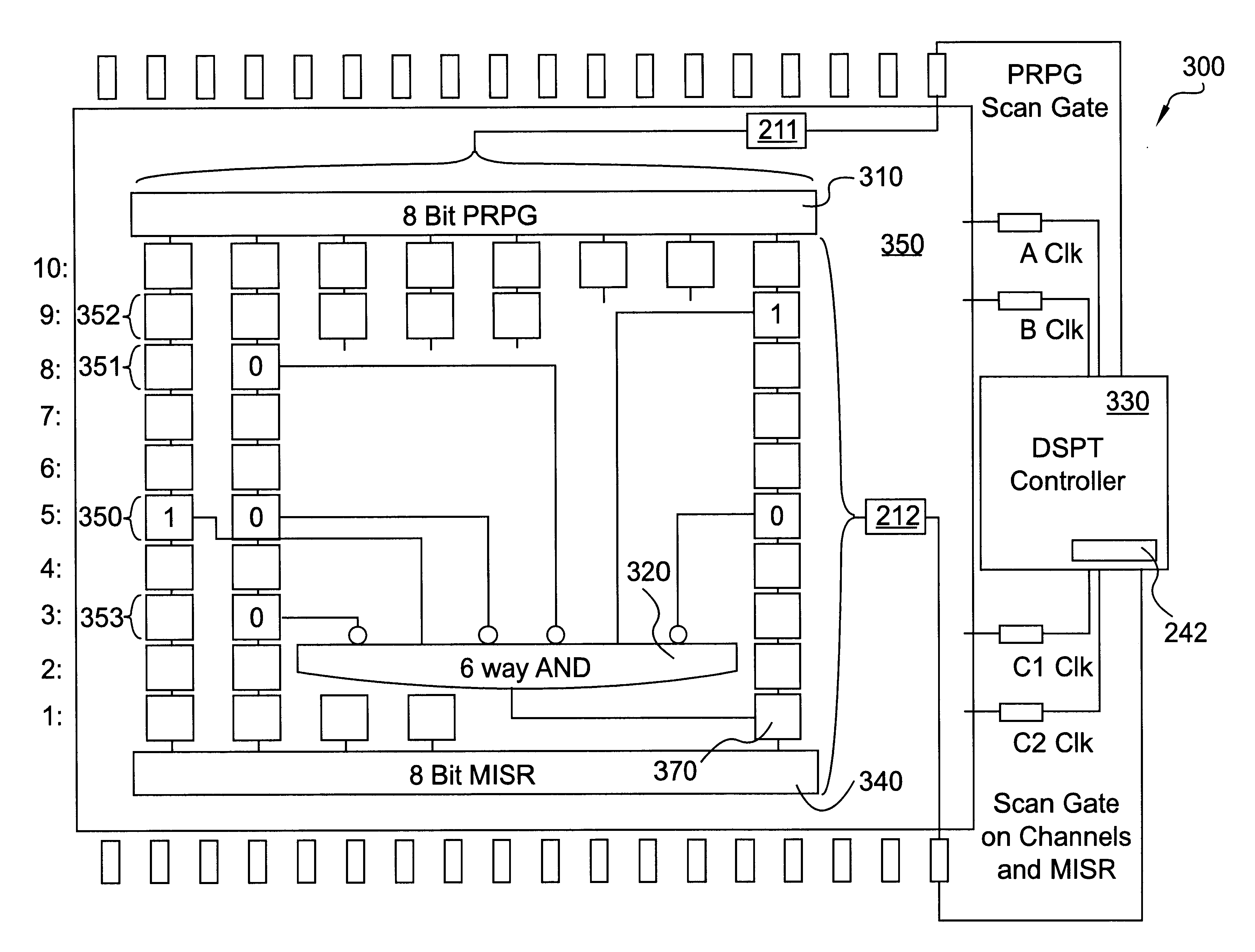
Deterministic random LBIST
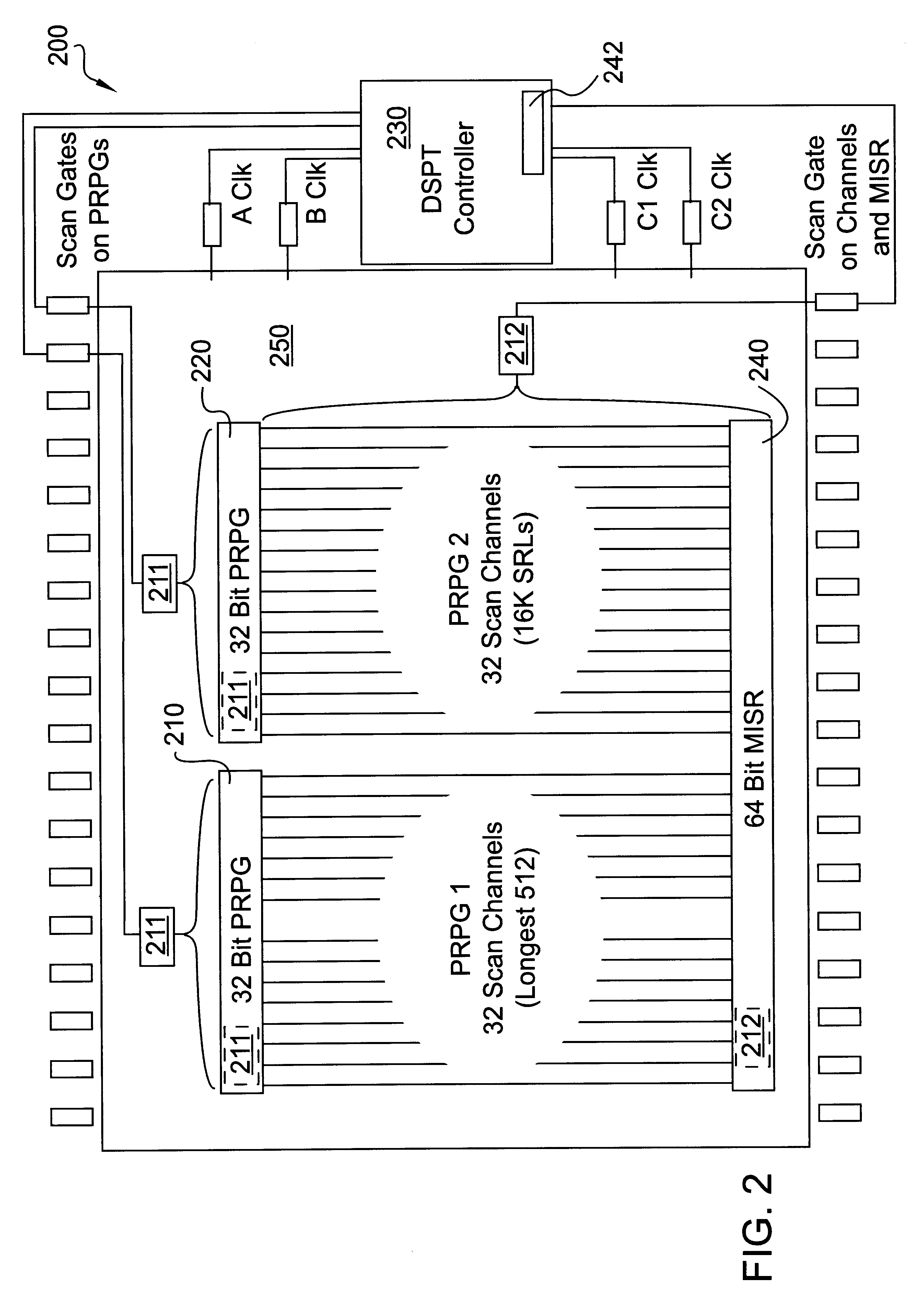
InactiveUS6708305B1Short test timeIncrease costElectronic circuit testingError detection/correctionAlgorithmLogisim
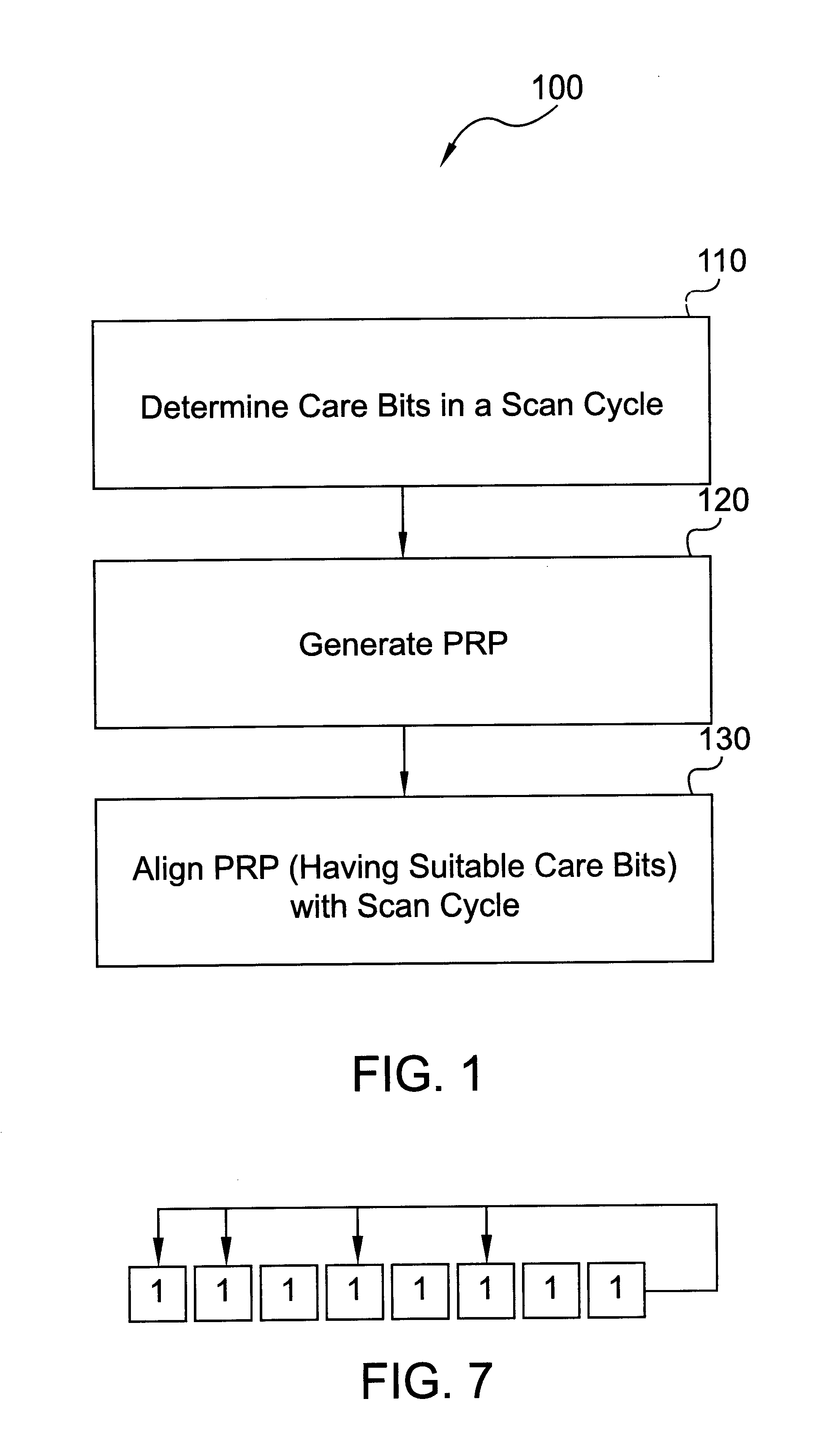
Deterministic random Logic Built In Self Test (LBIST) is disclosed that applies Deterministic Stored Pattern Tests (DSPTs) by using random LBIST. Basically, the present invention selects the appropriate pseudorandom pattern for use with a scan cycle that needs care bits. The scan cycle may be a current or future scan cycle. In particular, the present invention determines care bits for a particular scan cycle. A pseudorandom pattern is generated that is then aligned with the particular scan cycle. If the pseudorandom pattern contains the care bits, with the correct values and in the proper positions within the pattern, this alignment tests one or more logic devices.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
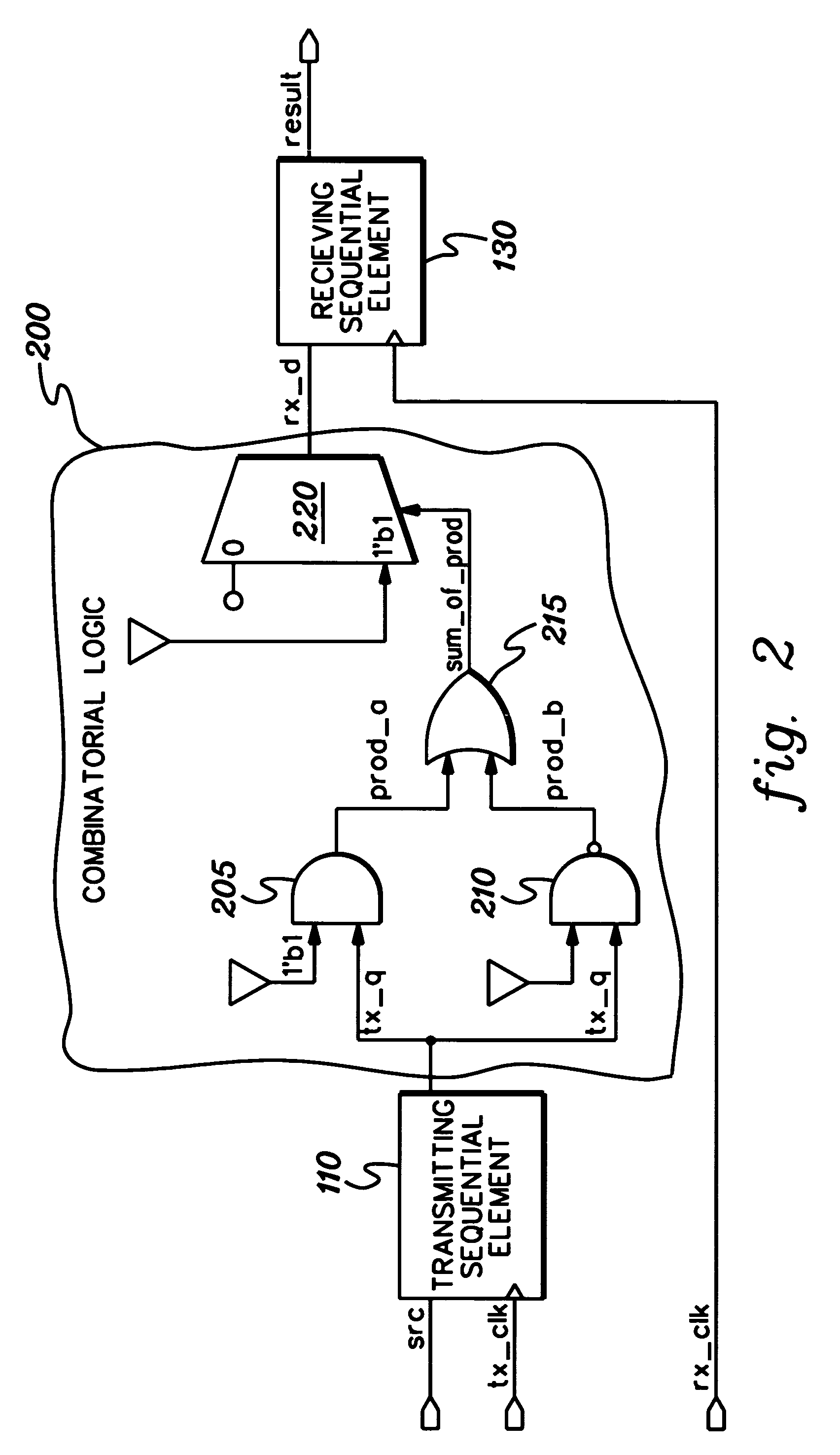
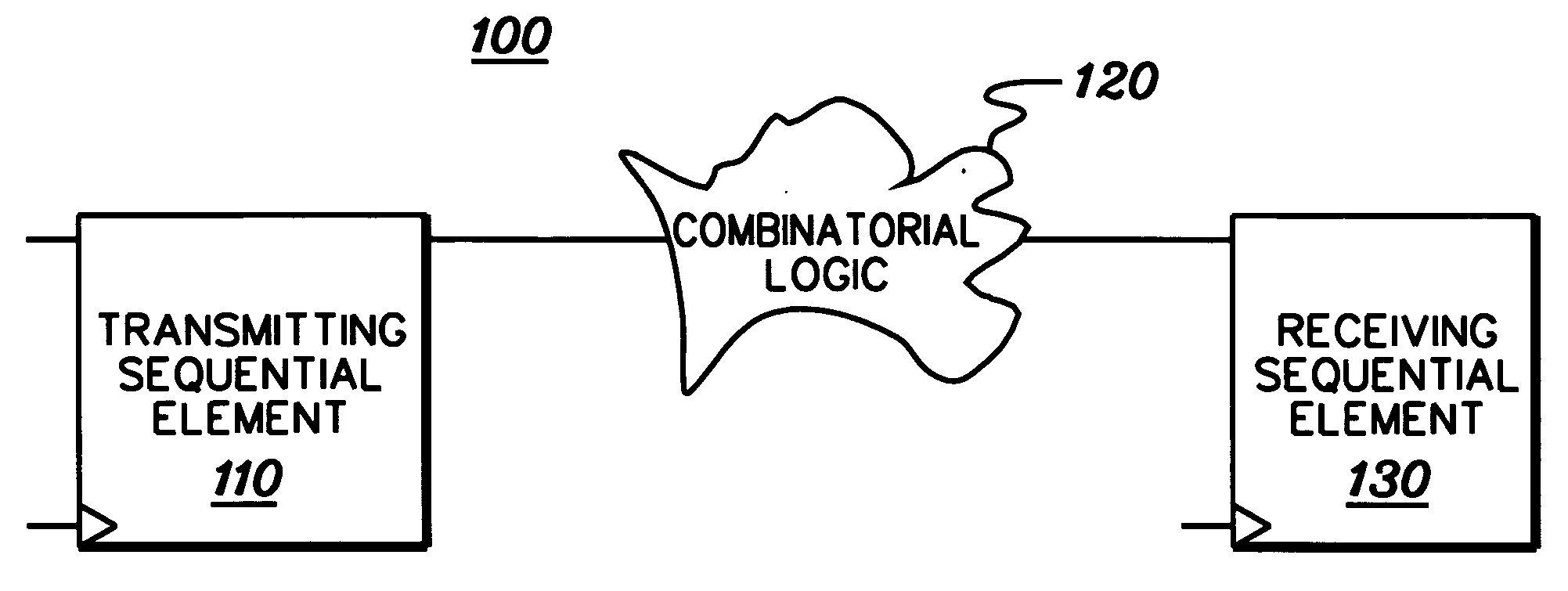
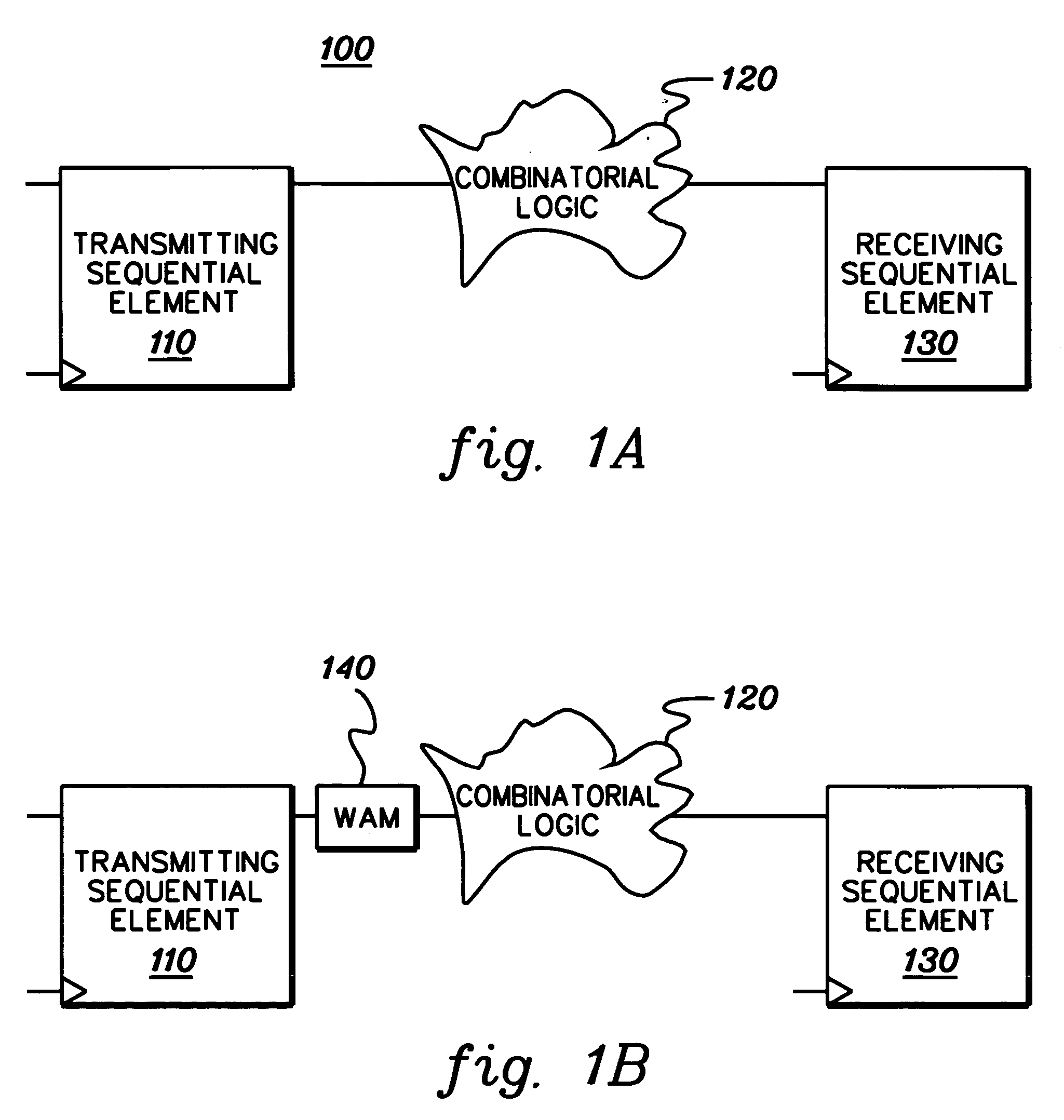
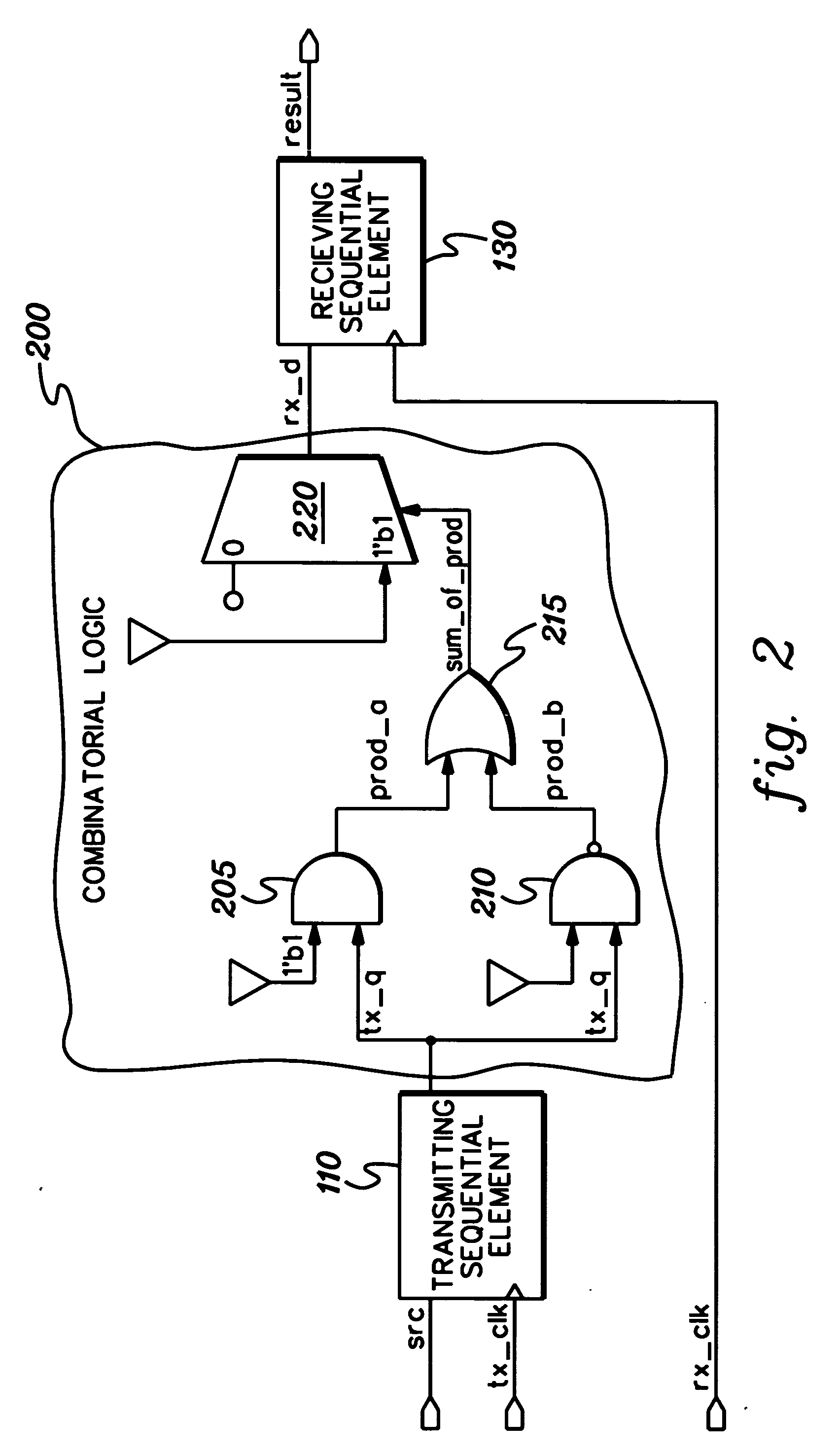
Method, apparatus, and computer program product for facilitating modeling of a combinatorial logic glitch at an asynchronous clock domain crossing
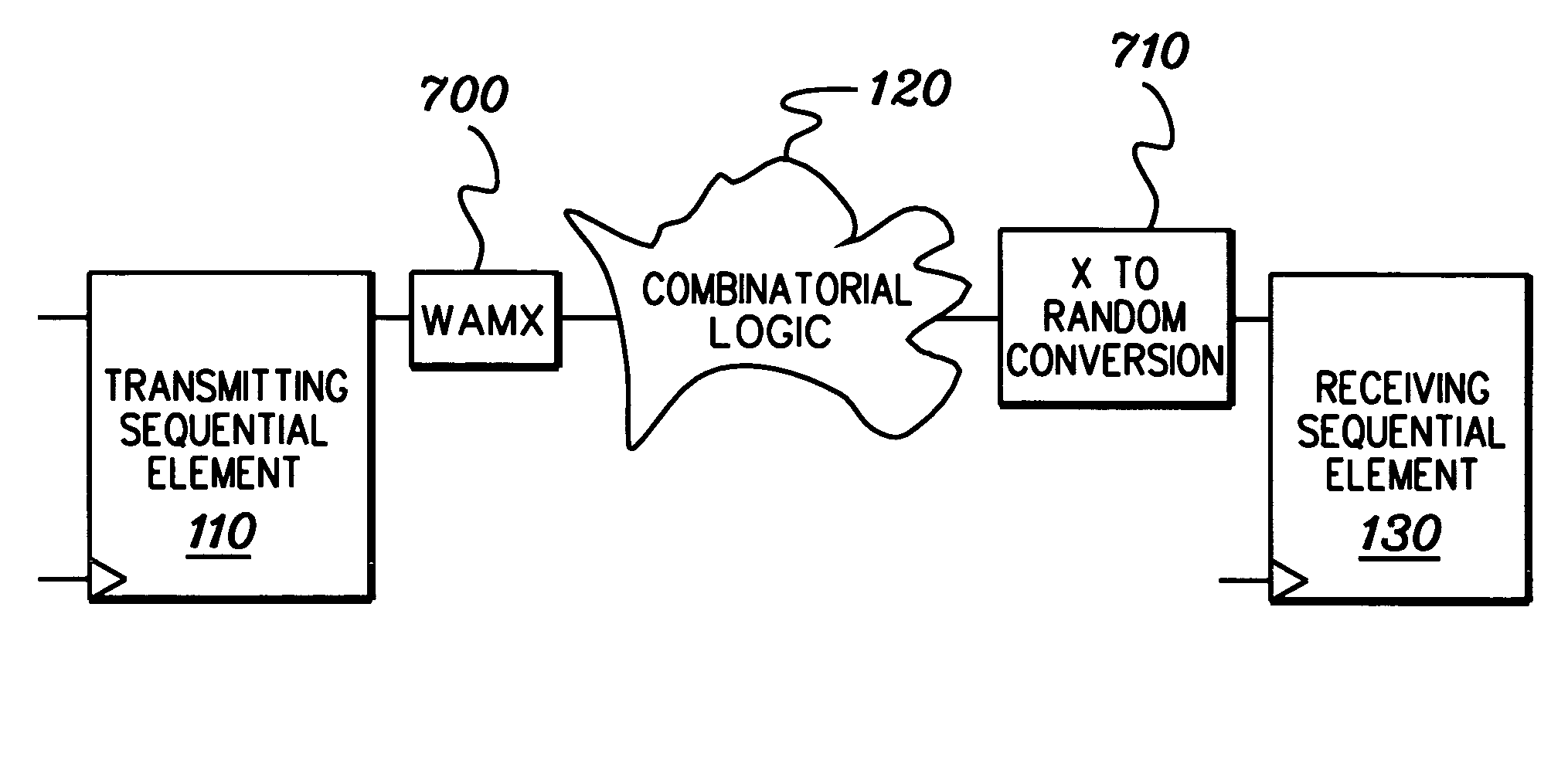
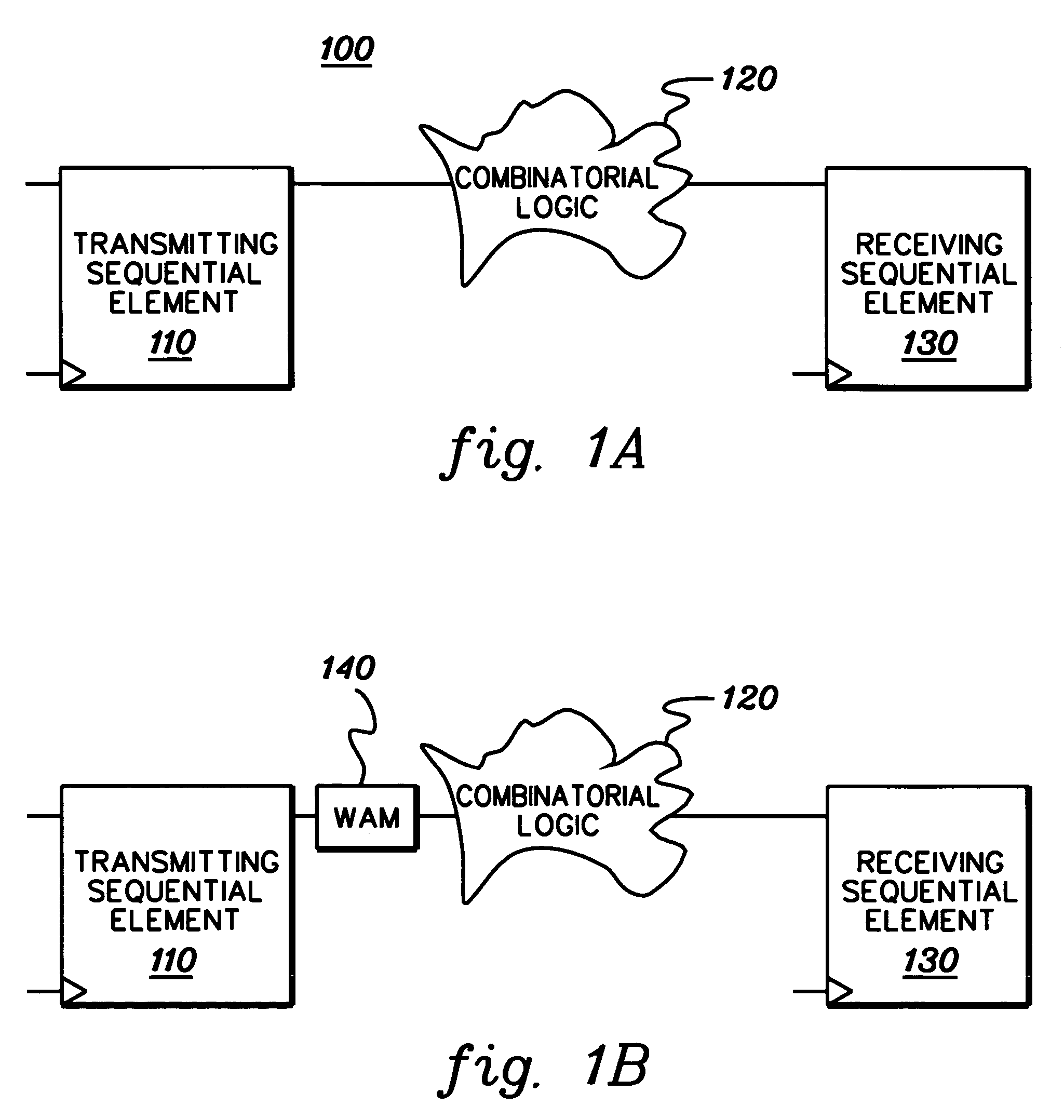
InactiveUS7333926B2Inserting of the simulation value of X into the combinatorial logic can be facilitatedFacilitate automatic propagation of the simulation value XDetecting faulty computer hardwareComputation using non-denominational number representationLogic modelingPath generation
A method, apparatus and computer program product are provided for facilitating combinatorial logic modeling at an asynchronous clock domain crossing. The modeling technique employs a simulation value of X in combinatorial logic at the asynchronous clock domain crossing of a circuit being modeled to facilitate modeling of a potential combinatorial logic glitch at the crossing during metastability periods thereof. Employing the simulation value of X includes: generating one or more equivalent functional equations for one or more combinatorial paths through the combinatorial logic at the crossing; propagating the simulation value of X through the combinatorial logic using the at least one equivalent functional equation; and then converting the simulation value of X at an output of the combinatorial logic of the asynchronous clock domain crossing to a random logic value for further propagation within the circuit being modeled.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
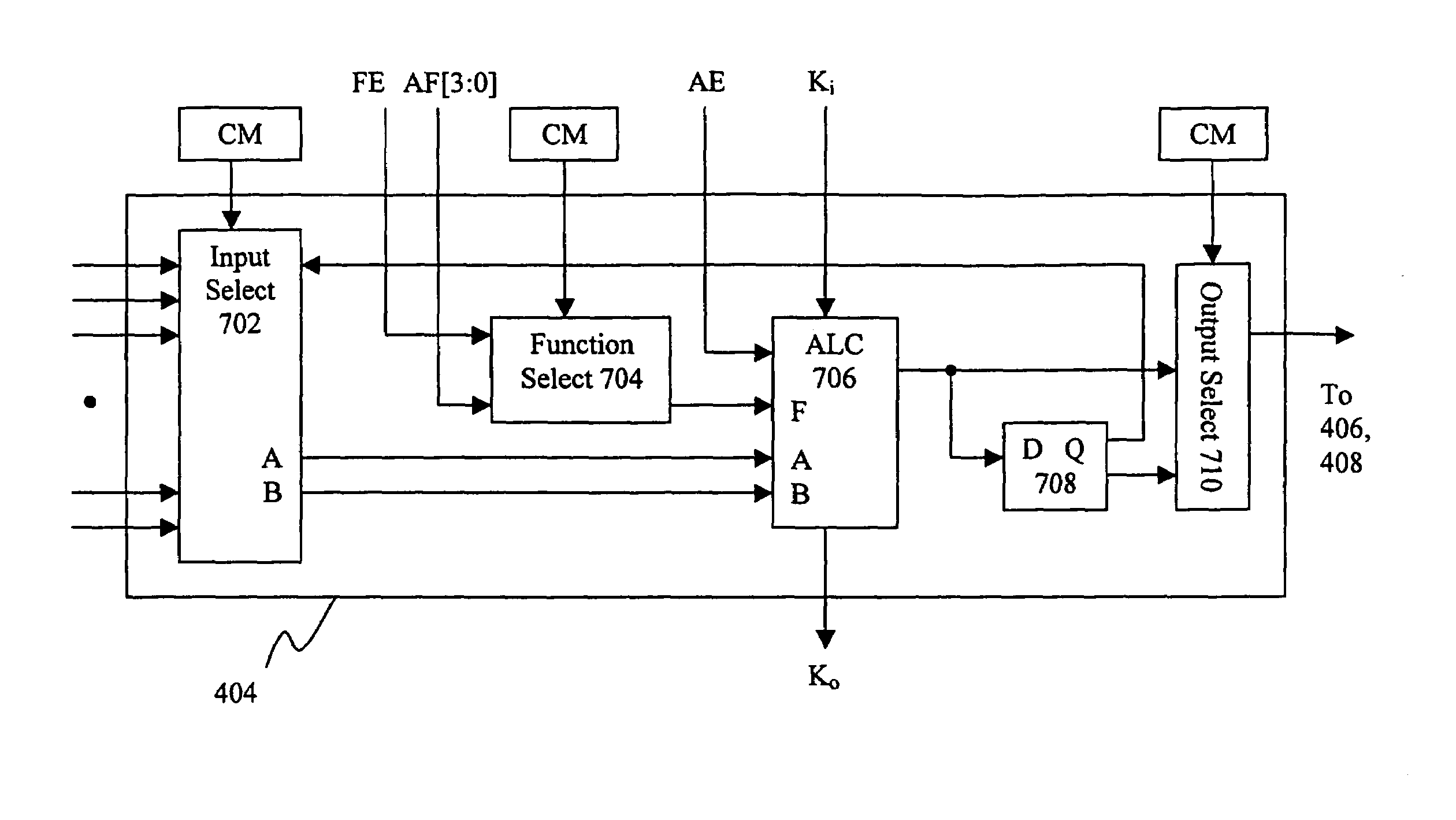
Multi-scale programmable array
InactiveUS7062520B2Lower performance requirementsIncrease costLogic circuits using elementary logic circuit componentsComputation using denominational number representationArithmetic logic unitCall gate
A novel architecture for a multi-scale programmable logic array (MSA) to be used in the design of complex digital systems allows digital logic to be programmed using both small-scale blocks (also called gate level blocks) as well as medium scale blocks (also called Register Transfer Level or RTL blocks). The MSA concept is based on a bit sliceable Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU). Each bit-slice may be programmed to perform a basic Boolean logic operation or may be programmed to contribute to higher-level functions that are further programmed by an ALU controller circuit. The ALU controller level in this new approach also allows the primitive logic operations computed at the bit-slice level to be combined to perform complex random logic operations. The data shifting capability of this new programmable logic architecture reduces the complexity of the programmable routing needed to implement shift operations including multiplier arrays. The new array also allows logic variables under program control to dynamically modify the micro-program of each ALU. This technique is called configuration overlay and simplifies the programming of complex arithmetic and random logic functions.
Owner:XILINX INC
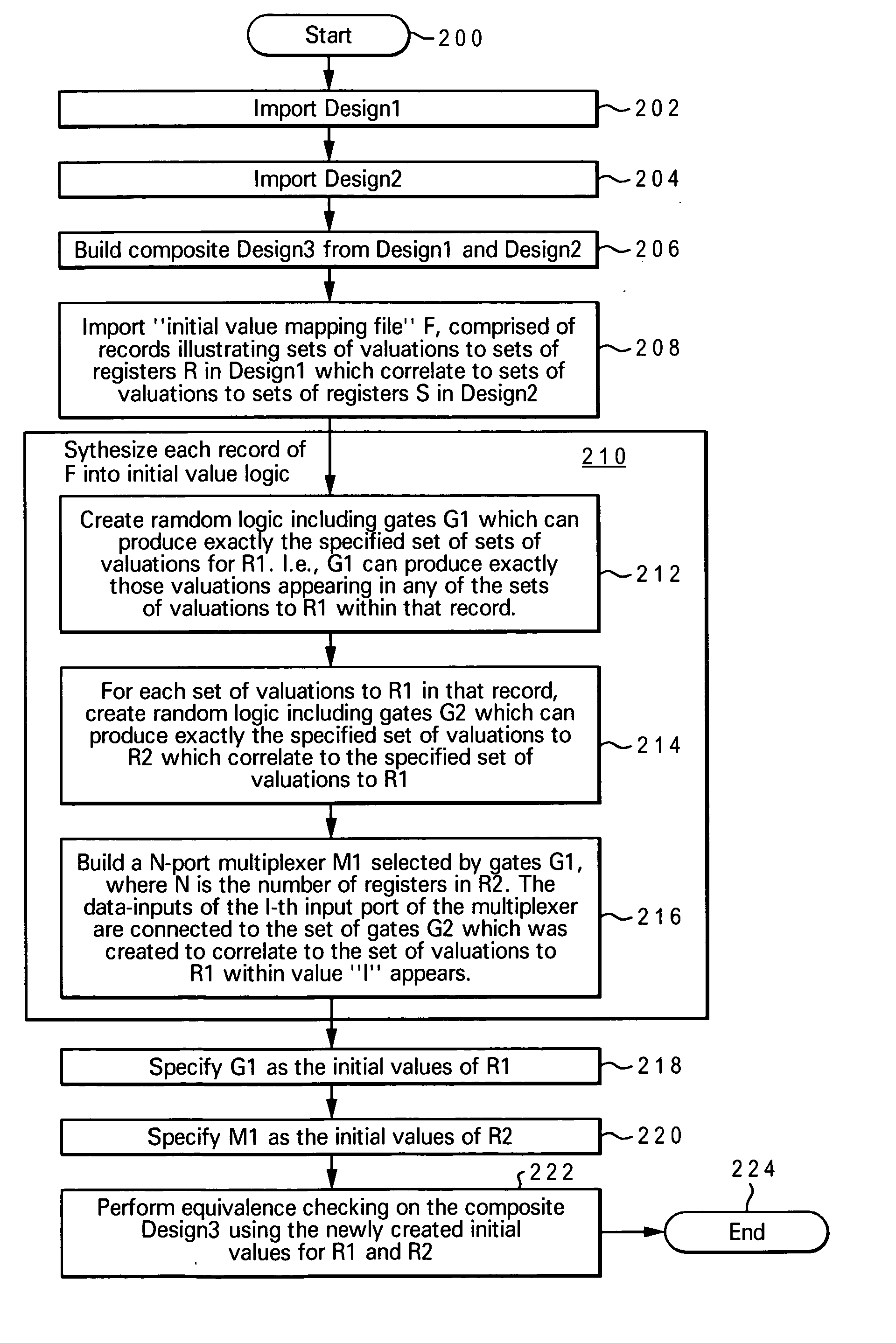
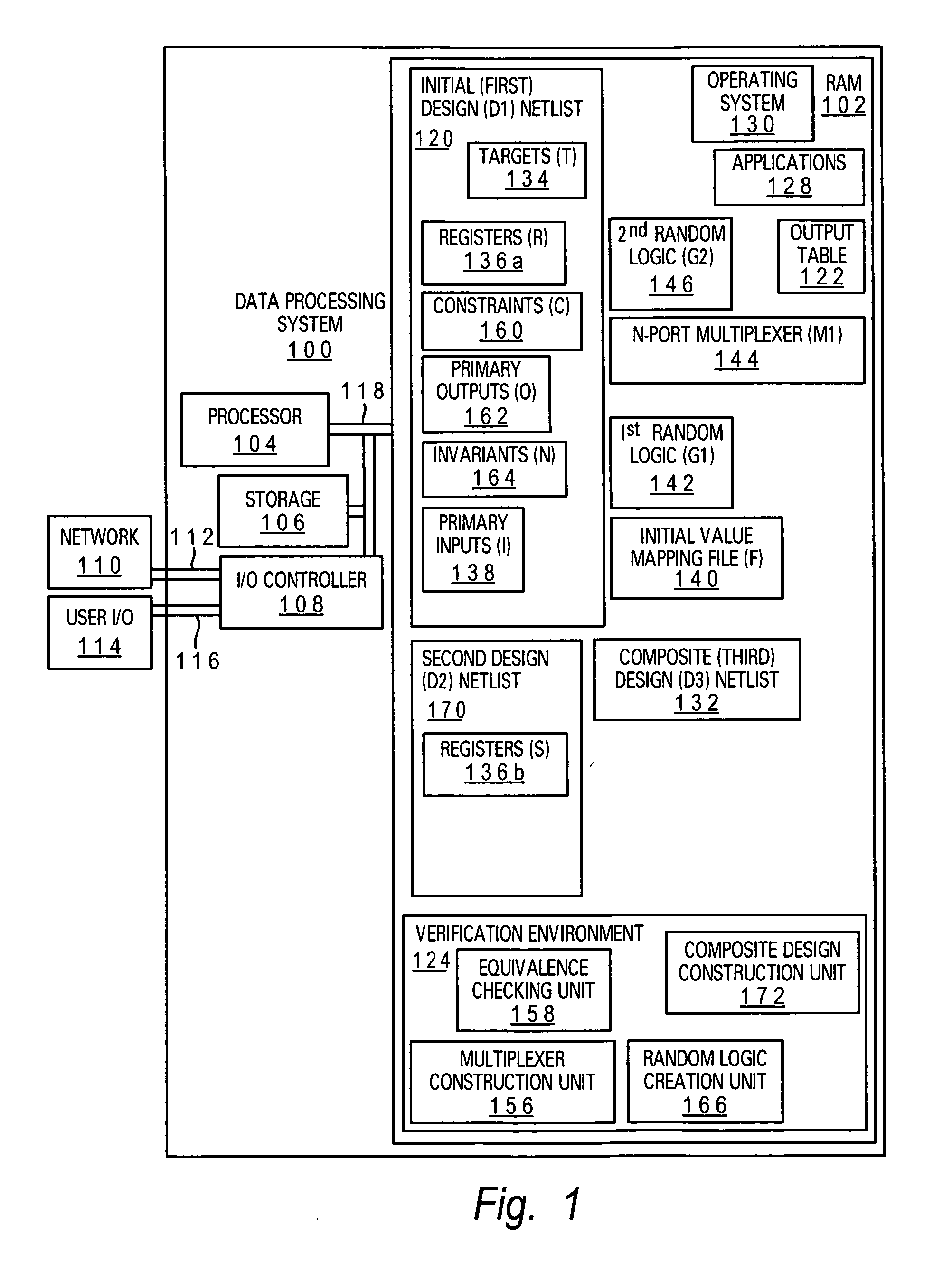
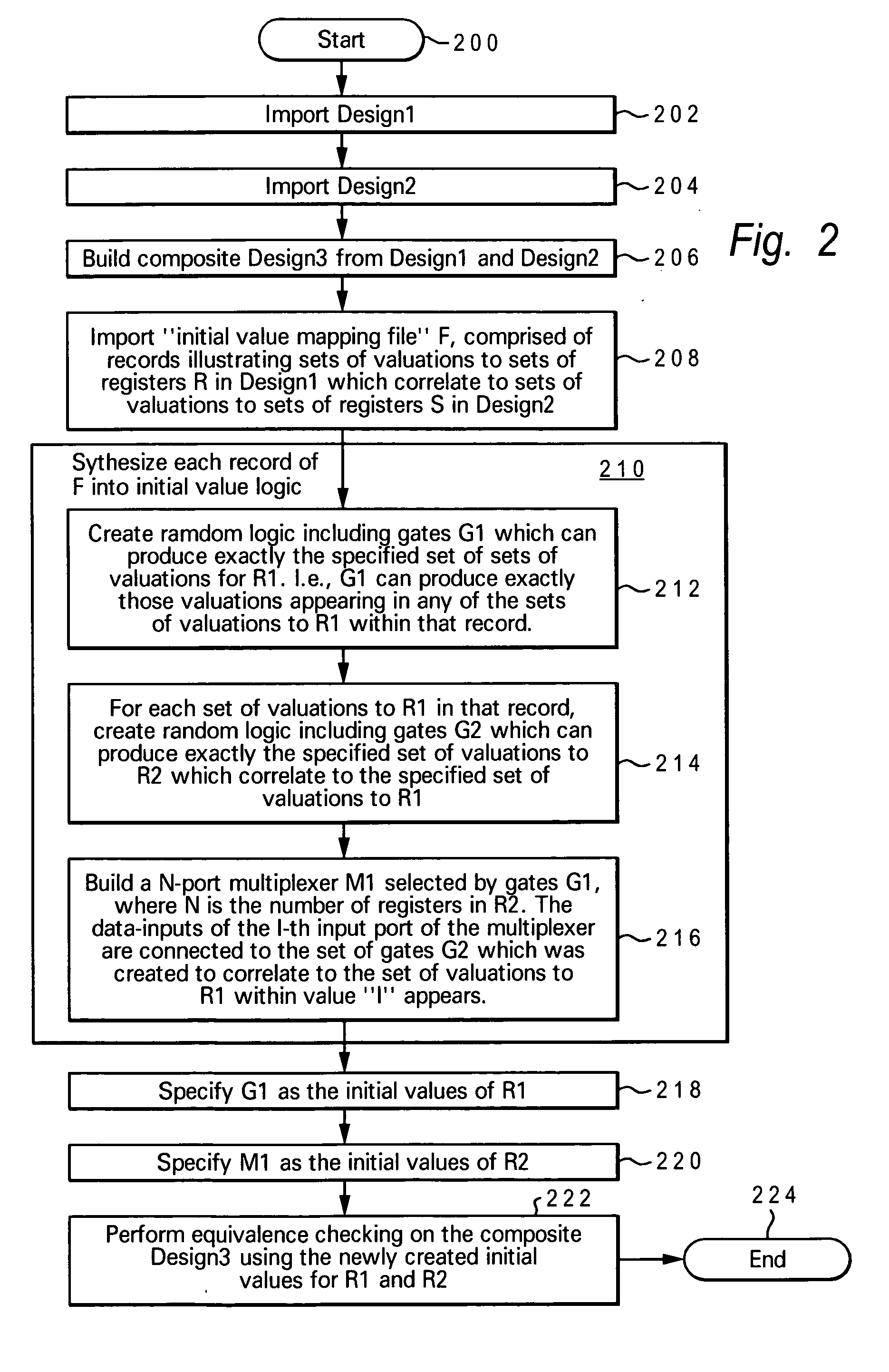
Method and system for sequential equivalence checking with multiple initial states
InactiveUS20070220461A1Computer aided designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationInitTheoretical computer science
A method, system and computer program product for performing equivalence checking of a circuit design are disclosed. The method includes importing a first design comprising a first register set and a different second design comprising a second register set and importing a mapping between corresponding initial states of the first register set and the second register set. A first random logic and a second random logic, respectively representing an application of a set of initial values to the first register set and the second register set are generated and an equivalence check on a third design synthesized from the first design and the second design with an output set from the first random logic as an initialization of the first register set and with an output set of the second random logic as an initialization of the second register set is performed.
Owner:IBM CORP
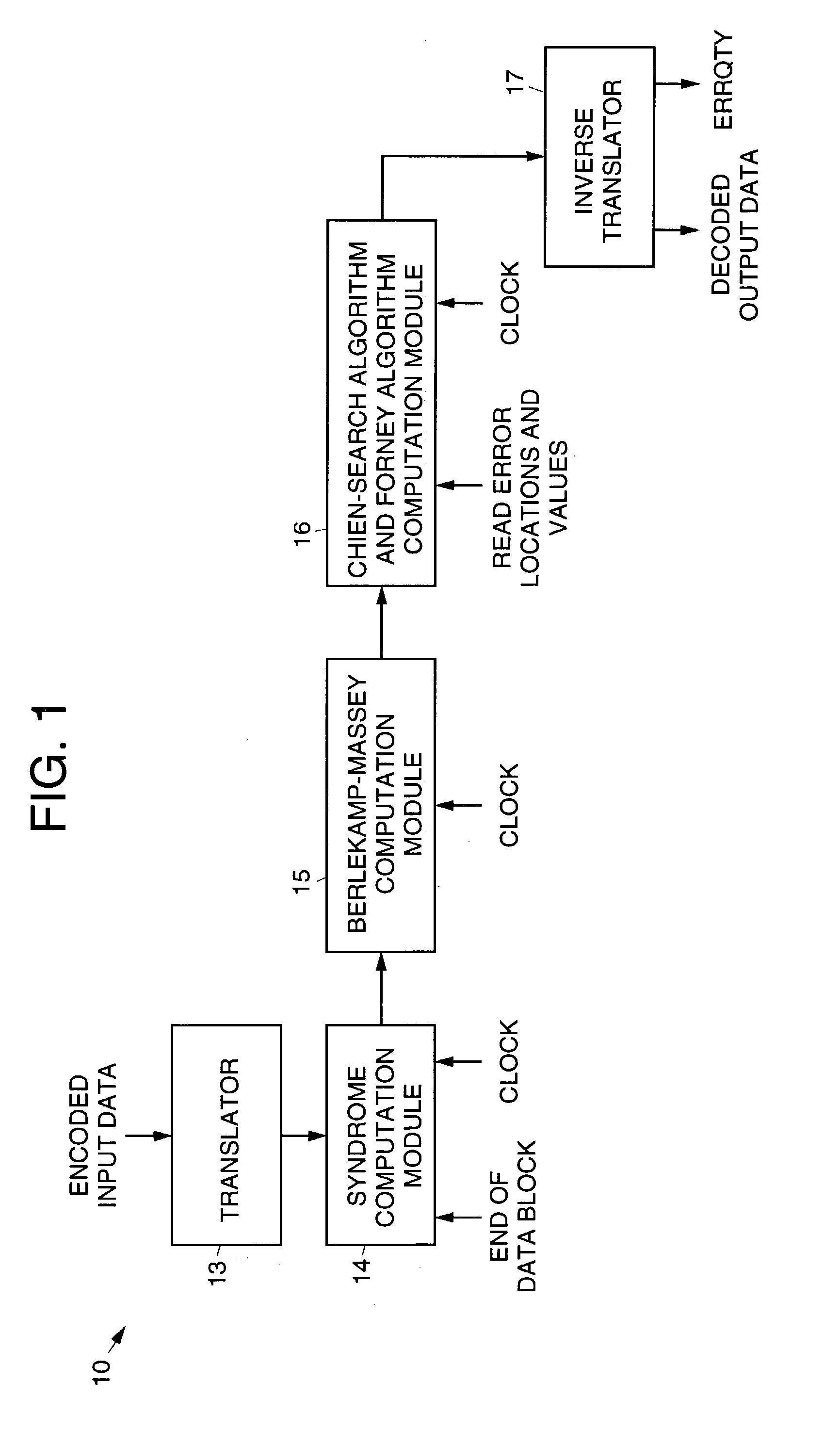
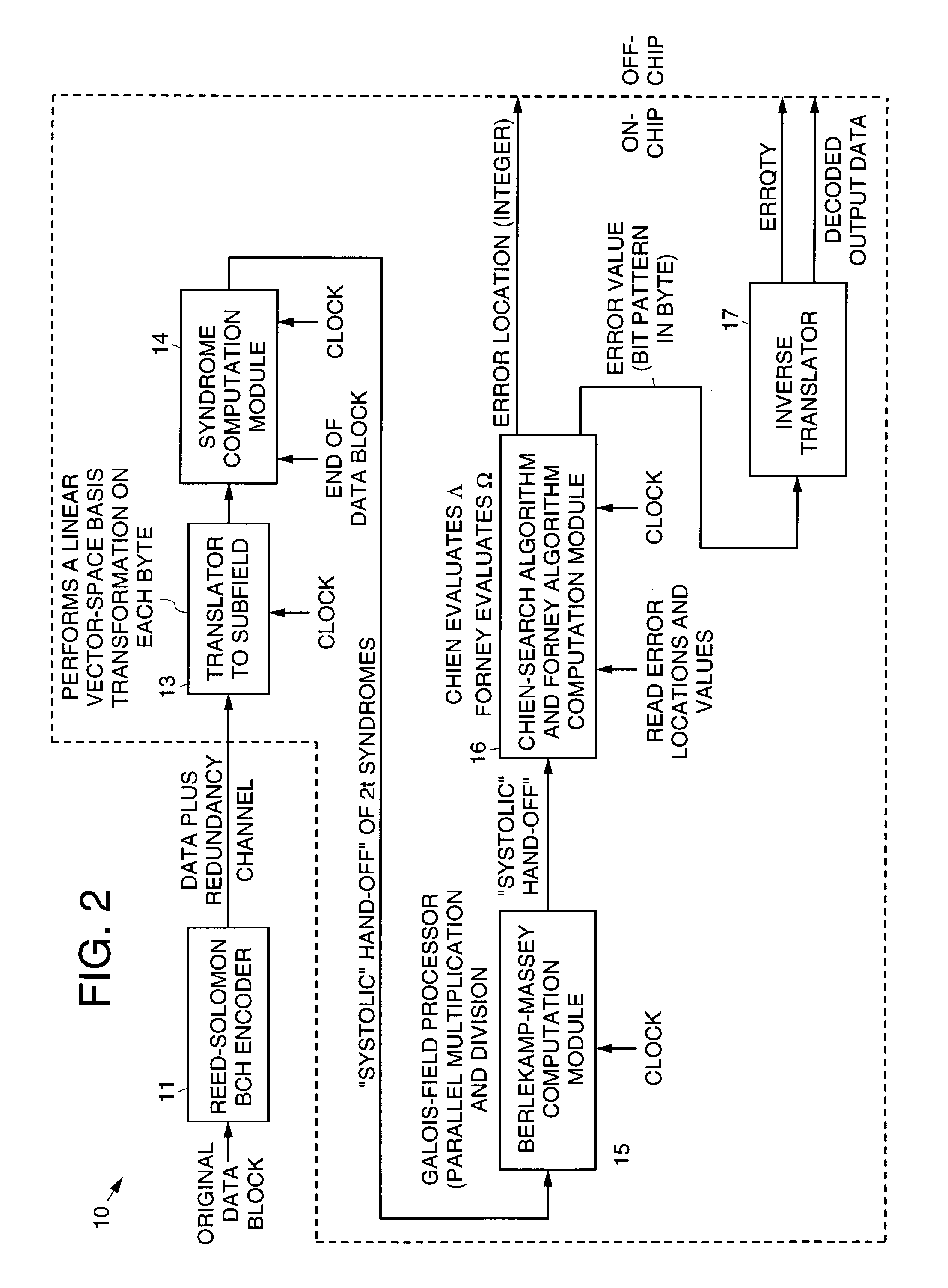
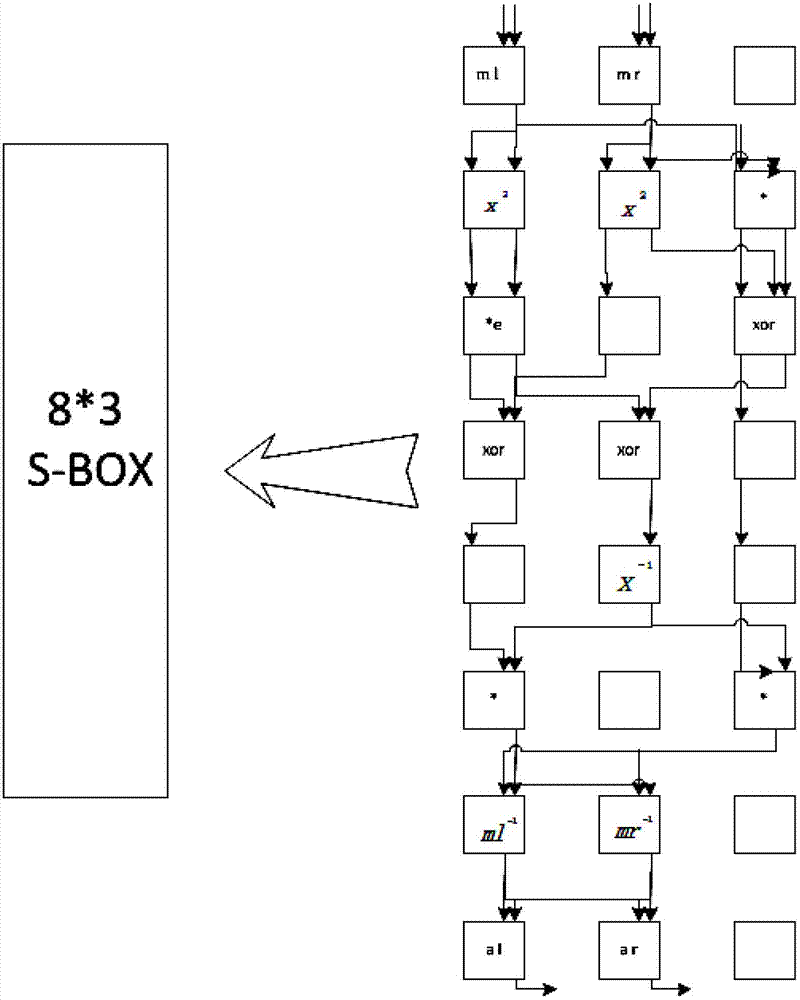
Modular Galois-field subfield-power integrated inverter-multiplier circuit for Galois-field division over GF(256)
ActiveUS7089276B2Lowering gateIncrease computing speedDigital computer detailsComputations using residue arithmeticSystems designModularity
A modular Galois-field subfield-power integrated inverter-multiplier circuit that may be used to perform Galois-field division over GF(245). The integrated inverter-multiplier circuit combines subfield-power and parallel multiplication and inversion operations performed therein. The circuit is modular, has a relatively low gate count, and is easily pipelined because it does not use random logic. The circuit implements mathematical calculations known as “Galois-field arithmetic” that are required for a variety of digital signaling and processing applications such as Reed-Solomon and Bose-Chaudhuri-Hochquenghem (BCH) error-correction coding systems. Galois-field division is particularly difficult, typically requiring either a great deal of time or highly complex circuits, or both. The circuit uses a unique combination of subfield and power inversion techniques to carry out multiplicative inversion. Furthermore, the circuit uniquely implements Galois-field division by carrying out the multiplicative inversion and the multiplication simultaneously and in parallel. This substantially increases computation speed. The modularity and pipelineability of the present invention also make system design easier and increases the speed and reduces the gate count of an integrated circuit embodying the inverter-multiplier circuit.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Method of physical planning voltage islands for ASICs and system-on-chip designs
InactiveUS7296251B2Minimize power consumptionCAD circuit designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationPhysical planningCore level
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Cyclic redundancy check generation via distributed time multiplexed linear feedback shift registers
ActiveUS20140026021A1Less surface areaLess powerCode conversionError detection onlyGeneration rateTheoretical computer science
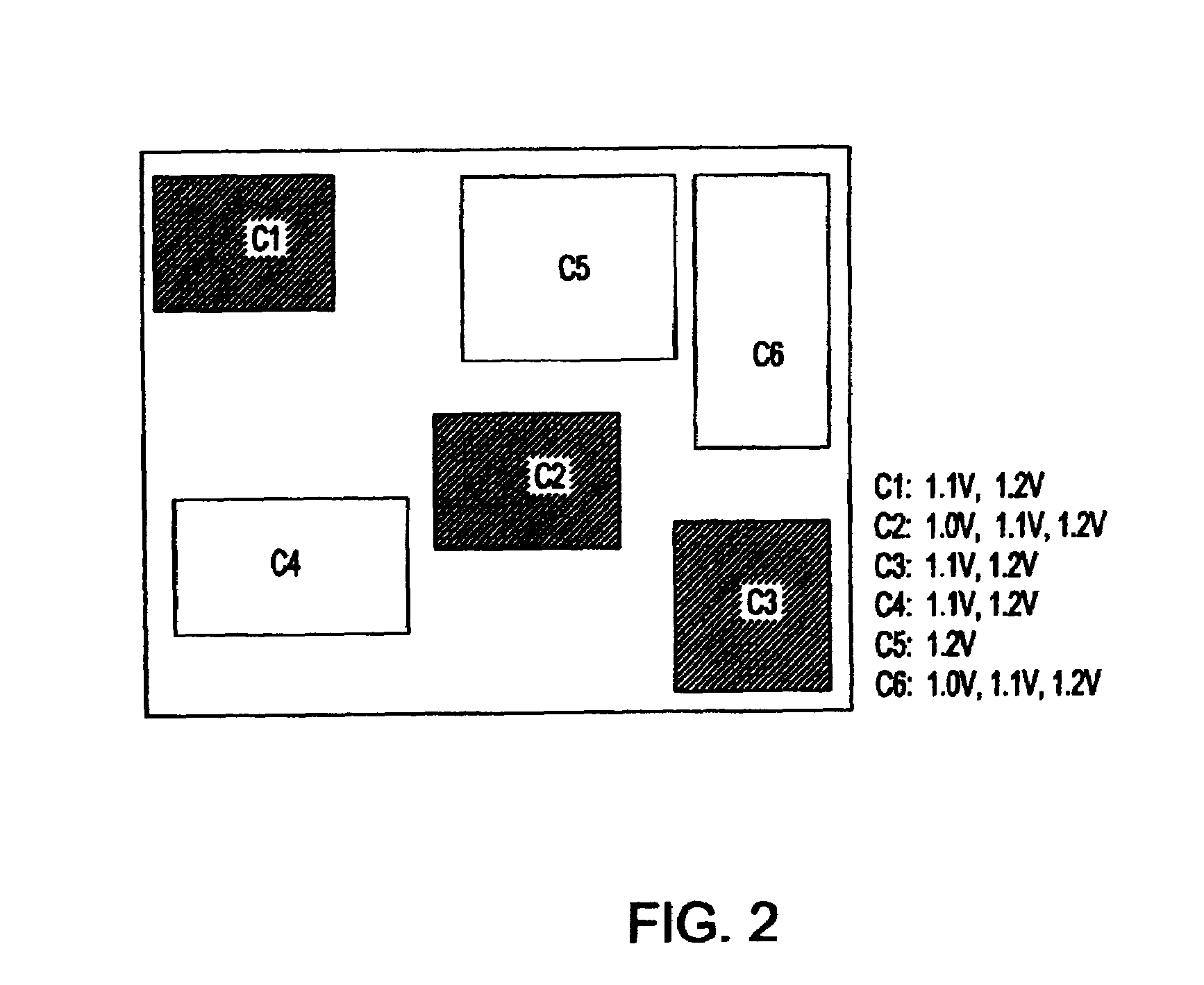
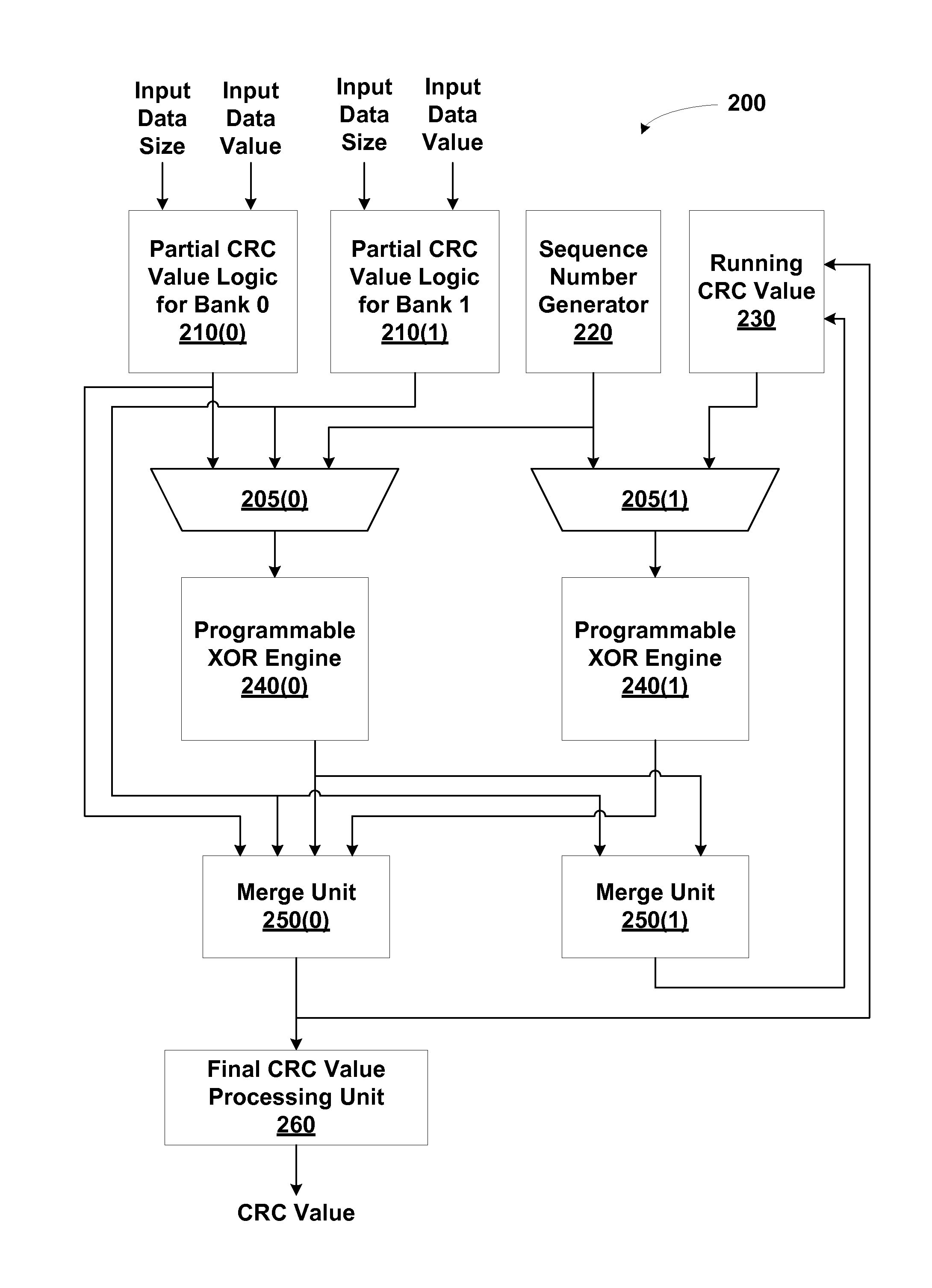
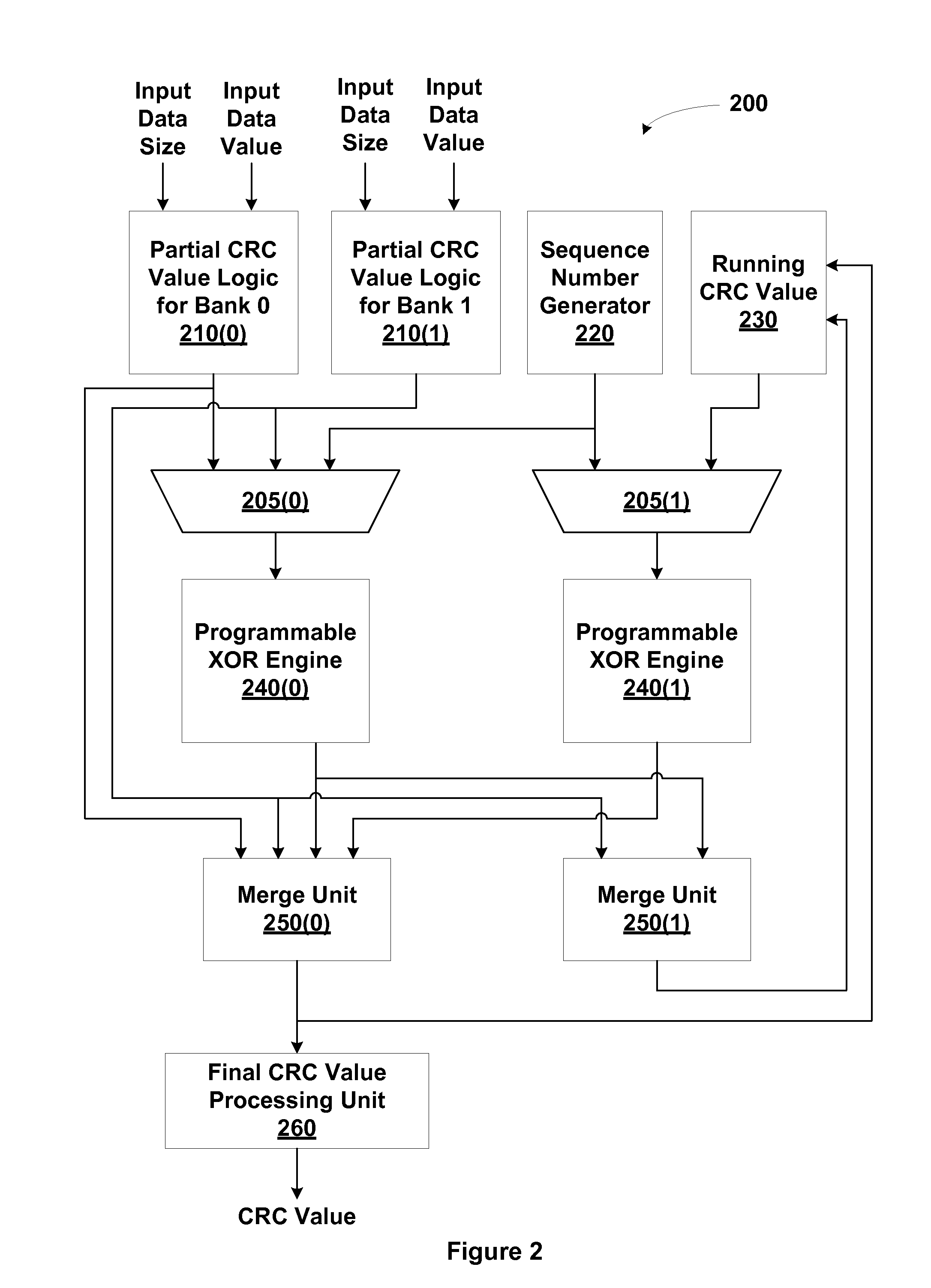
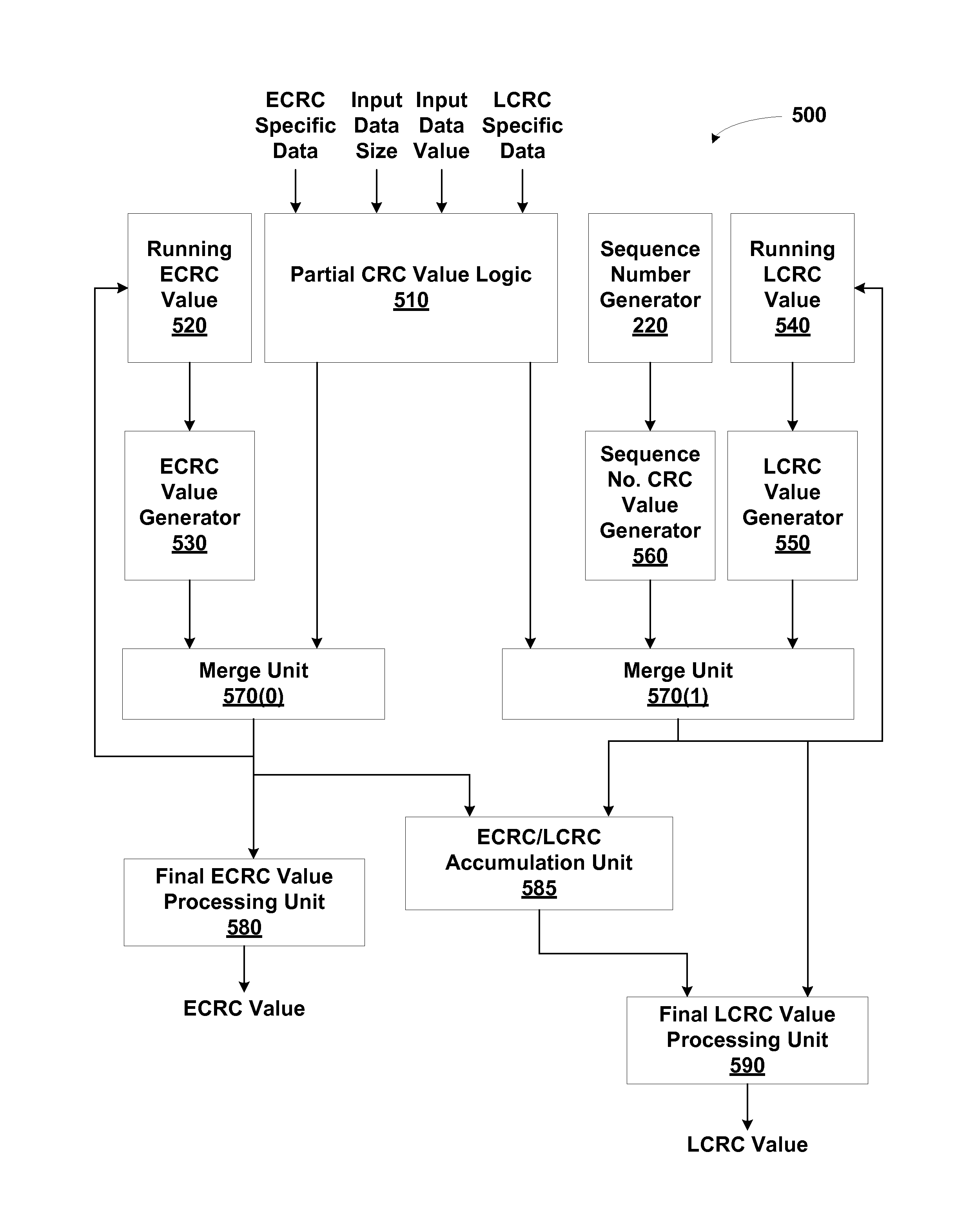
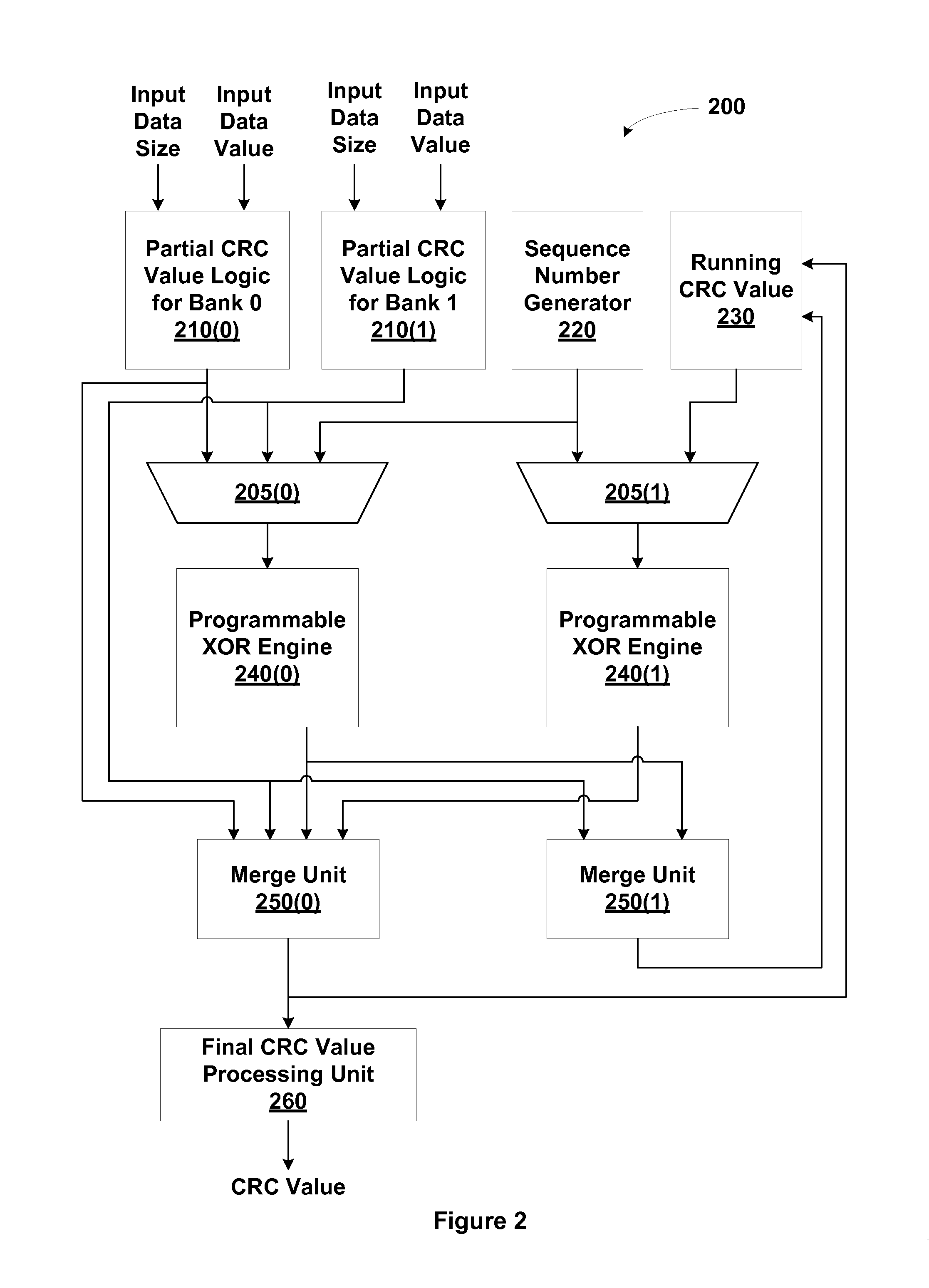
Cyclic redundancy check (CRC) values are efficiently calculated using an improved linear feedback shift register (LFSR) circuit. CRC value generation is separated into two sub-calculations, which are then combined to form a final CRC value. A programmable XOR engine performs logic functions via a table lookup rather than via a random logic circuit. LCRC and ECRC calculations are performed using a single shared LFSR circuit. Multiple links share the same CRC value generator. One advantage of the present invention is that CRC values are generated using smaller and fewer LFSR circuits relative to conventional circuit designs. As a result, a CRC value generator utilizing the disclosed techniques consumes less surface area of an integrated circuit and consumes less power, resulting in cooler operation.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
Reconfigurable technology-based basic operator extraction method in encryption and decryption algorithm
ActiveCN102868532AImprove universalityImprove simplicityPublic key for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationGranularityTheoretical computer science
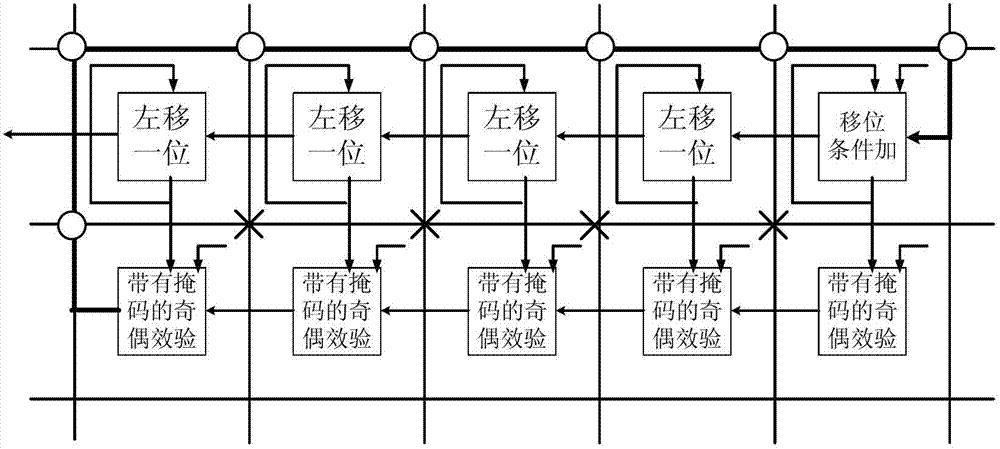
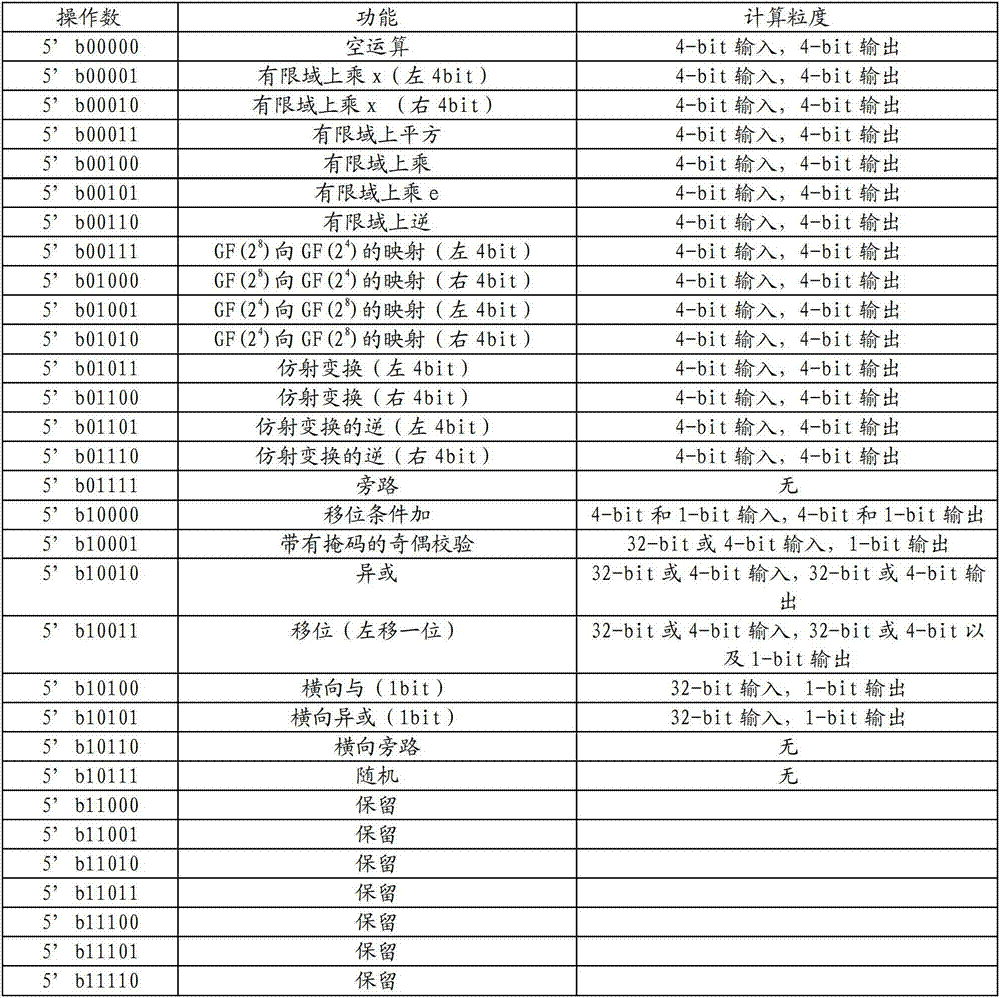
The invention provides a reconfigurable technology-based basic operator extraction method in an encryption and decryption algorithm. The method comprises the following steps of: firstly, analyzing the encryption and decryption algorithm to be realized, drawing data flow graph of each algorithm, dividing submodules, marking the computing granularity of each submodule in the data flow graphs, and computing the length of a critical path in each submodule; secondly, segmenting the submodules in the data flow graphs, thus obtaining a basic operator set; and adding the random logic into the basic operators finally. The basic operator set obtained by the method is very good in universality and simplicity, so that various cryptographic algorithms can be effectively realized by a reconfigurable crypto chip, and the throughput capacity of the crypto chip can be improved. The side channel attack can be disturbed by the basic operators provided by the method, so that the safety of the crypto chip can be improved.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
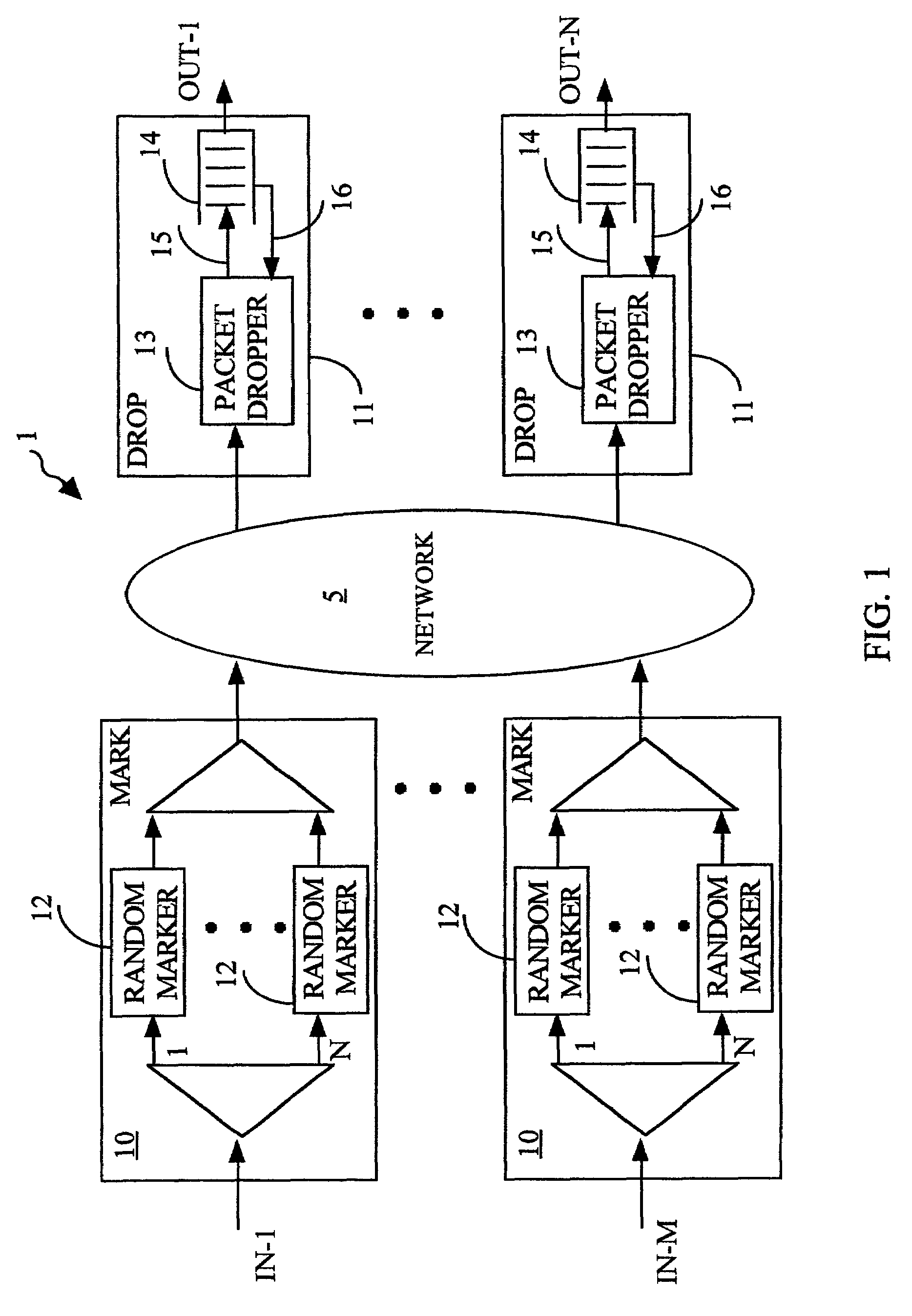
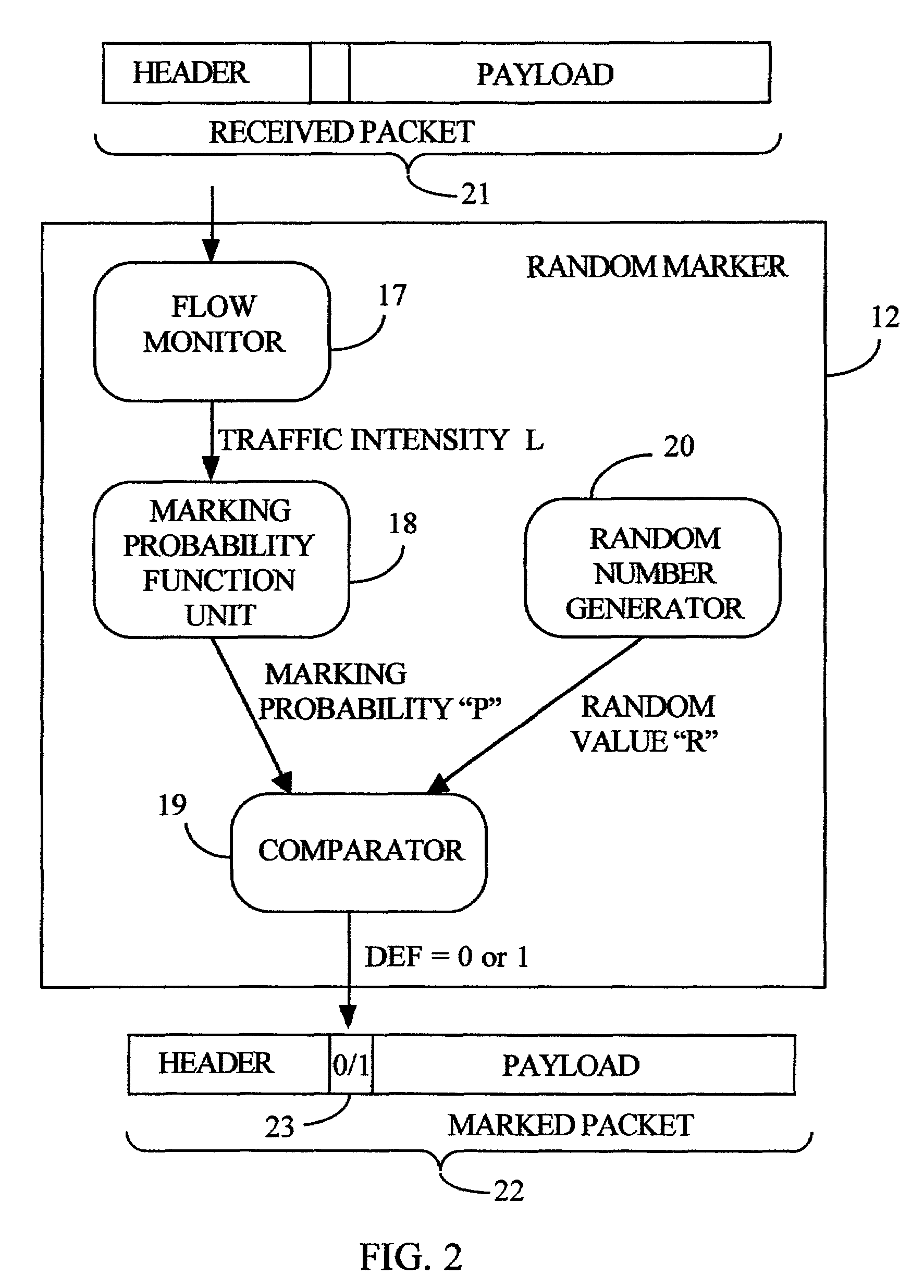
Method and system for traffic management in packet networks using random early marking
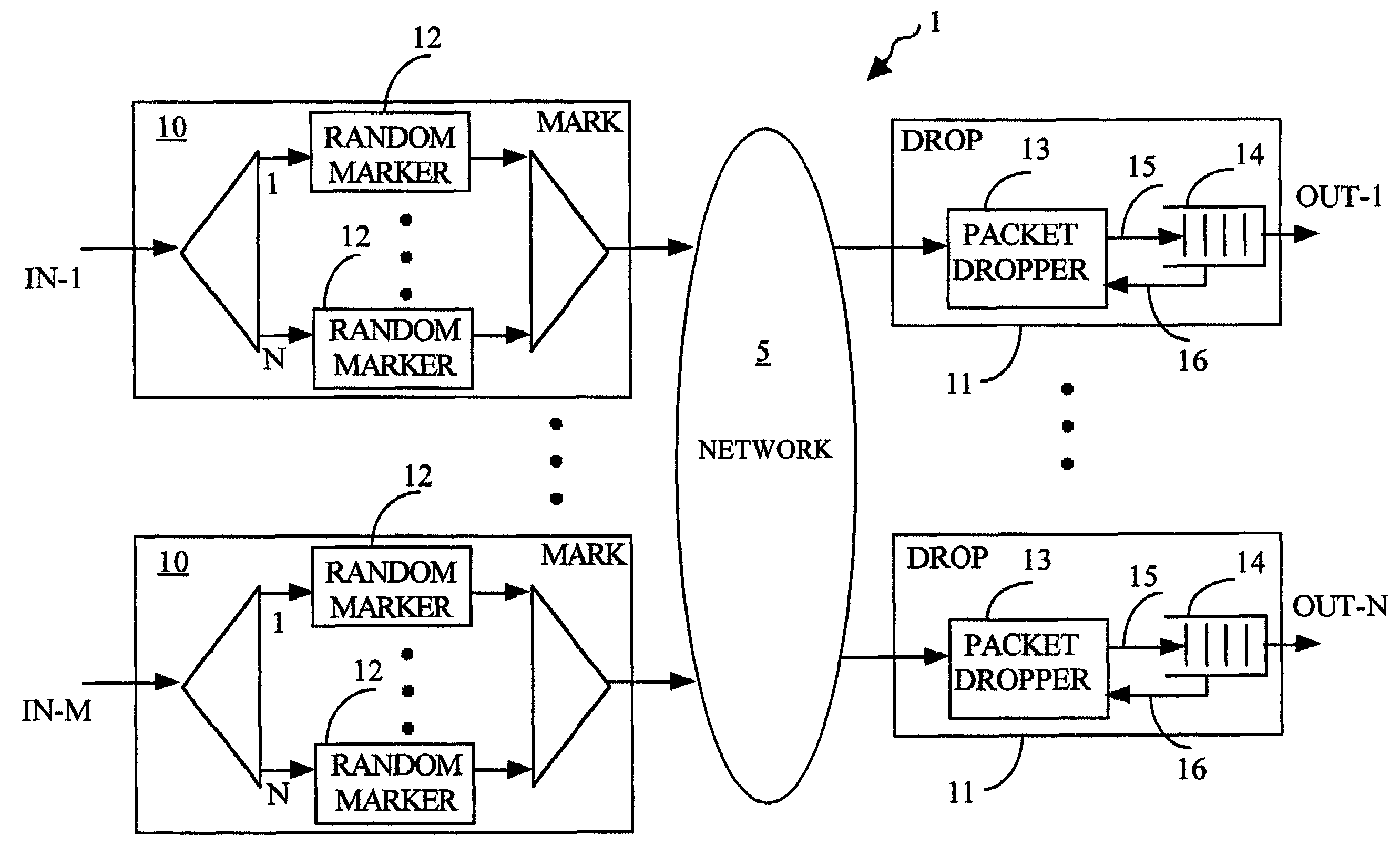
ActiveUS6977943B2Simple processComputational power requiredError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsTraffic capacityData stream
The invention describes a method for traffic management in a packet network using random early marking. For each packet flow, packets are randomly marked at the ingress of the network, while discard of the packets at the egress of the network is performed deterministically, i.e. in accordance with the predetermined rules. The step of random marking includes measuring parameters of the data flow, calculating marking probability by applying a mathematical function to the measured parameters, and generating a mark by applying a random logic function to the calculated marking probability. The packets are dropped at the egress of the network if the corresponding queues where the packets have to be stored are congested or full. A corresponding system for traffic management in packet networks is also provided.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT CANADA +1
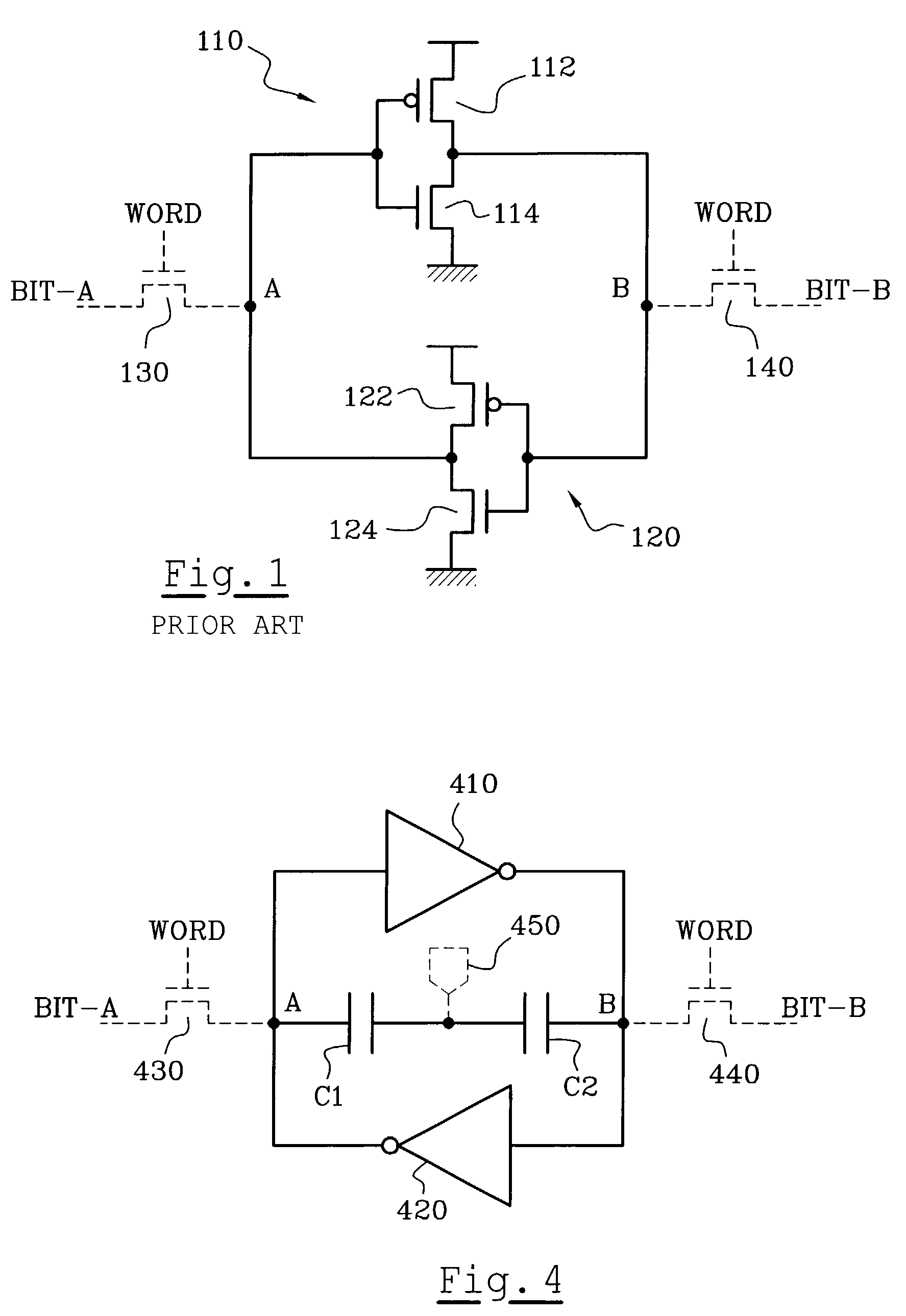
Integrated circuit component, protected against random logic events, and associated method of manufacture
A component of an integrated circuit comprises a first capacitor and a second capacitor series-connected between a first node and a second node of the component. This has application to logic circuits and bistable circuits, for example, SRAM type memories, flip-flop trigger circuits, etc.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
Cyclic redundancy check generation via distributed time multiplexed linear feedback shift registers
ActiveUS20140026022A1Less surface areaLess powerError preventionCode conversionTheoretical computer scienceLinearity
Cyclic redundancy check (CRC) values are efficiently calculated using an improved linear feedback shift register (LFSR) circuit. CRC value generation is separated into two sub-calculations, which are then combined to form a final CRC value. A programmable XOR engine performs logic functions via a table lookup rather than via a random logic circuit. LCRC and ECRC calculations are performed using a single shared LFSR circuit. Multiple links share the same CRC value generator. One advantage of the present invention is that CRC values are generated using smaller and fewer LFSR circuits relative to conventional circuit designs. As a result, a CRC value generator utilizing the disclosed techniques consumes less surface area of an integrated circuit and consumes less power, resulting in cooler operation.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
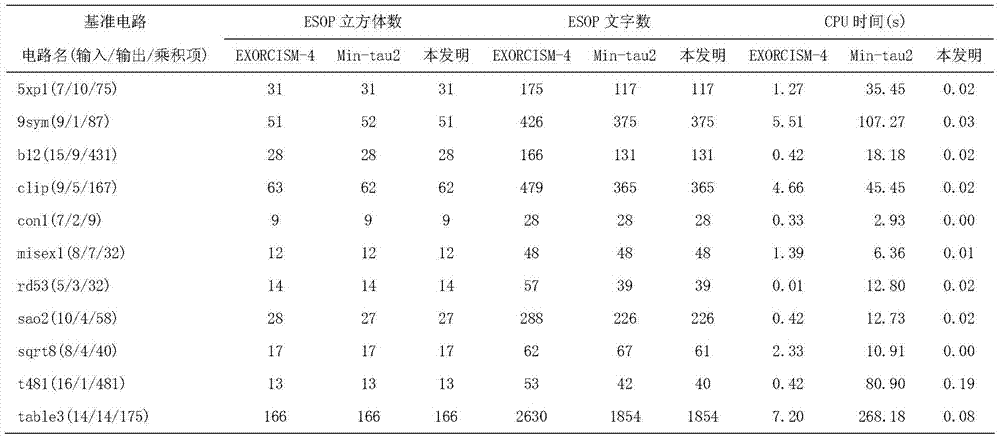
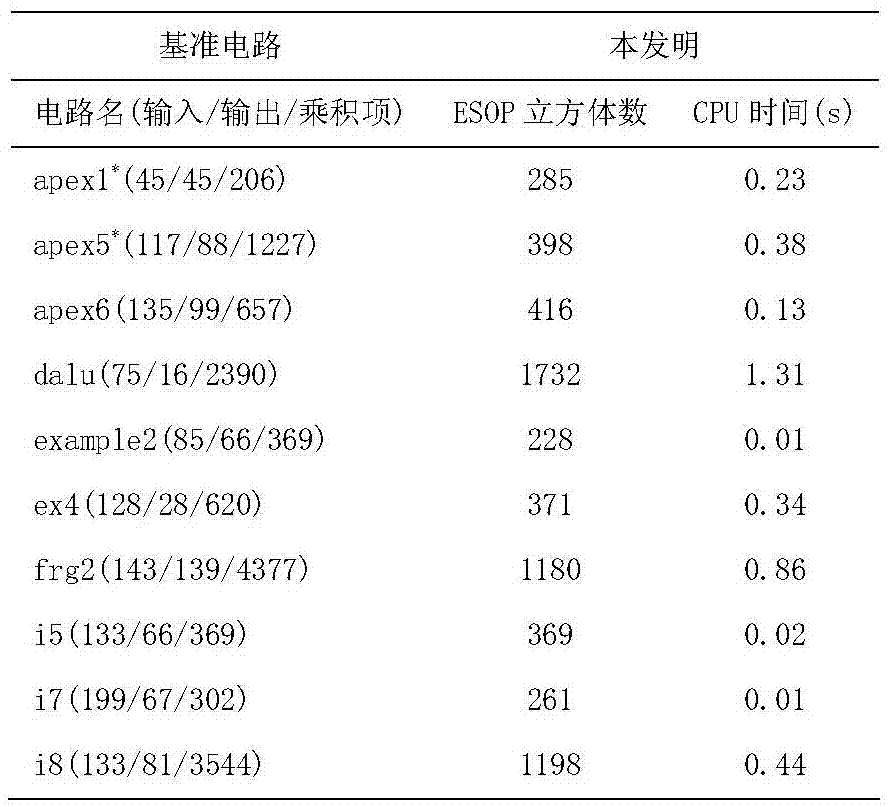
ESOP minimization method for logic function
InactiveCN105447241AMinimizeGet rid of constraintsComputer aided designSpecial data processing applicationsSearch problemRound complexity
The present invention discloses an ESOP minimization method for a logic function. By converting the optimal coverage searching problem of a 3n global space in the ESOP minimization process of an n variable logic function into the simplest connection problem in a plurality of cube blocks, a search space is reduced, thereby breaking away from a constraint of a variable scale; moreover, a cube set is directly operated without being converted into a minterm set, so that limitation to a product term number is avoided; and in order to achieve accurate minimization of rapid ESOP, a minimized conversion algorithm of a cube EXOR conversion diagram is adopted to improve operation efficiency so as to effectively reduce calculation complexity and a memory occupied quantity, and the characteristics that calculation time is insensitive to the number of input variables and is only related to the number of product terms included by the logic function and intersection can effectively achieve an effect that random n variables totally regulate the ESOP minimization of the logic function. The ESOP minimization method has the advantages of no limitation to the number of the product items and the number of the variables in the logic function and capacity of carrying out minimization processing on an ESOP of a random logic function.
Owner:ZHEJIANG WANLI UNIV
Method, apparatus, and computer program product for facilitating modeling of a combinatorial logic glitch at an asynchronous clock domain crossing
InactiveUS20060282251A1Inserting of the simulation value of X into the combinatorial logic can be facilitatedFacilitate automatic propagation of the simulation value XDetecting faulty computer hardwareComputation using non-denominational number representationLogic modelingPath generation
A method, apparatus and computer program product are provided for facilitating combinatorial logic modeling at an asynchronous clock domain crossing. The modeling technique employs a simulation value of X in combinatorial logic at the asynchronous clock domain crossing of a circuit being modeled to facilitate modeling of a potential combinatorial logic glitch at the crossing during metastability periods thereof. Employing the simulation value of X includes: generating one or more equivalent functional equations for one or more combinatorial paths through the combinatorial logic at the crossing; propagating the simulation value of X through the combinatorial logic using the at least one equivalent functional equation; and then converting the simulation value of X at an output of the combinatorial logic of the asynchronous clock domain crossing to a random logic value for further propagation within the circuit being modeled.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
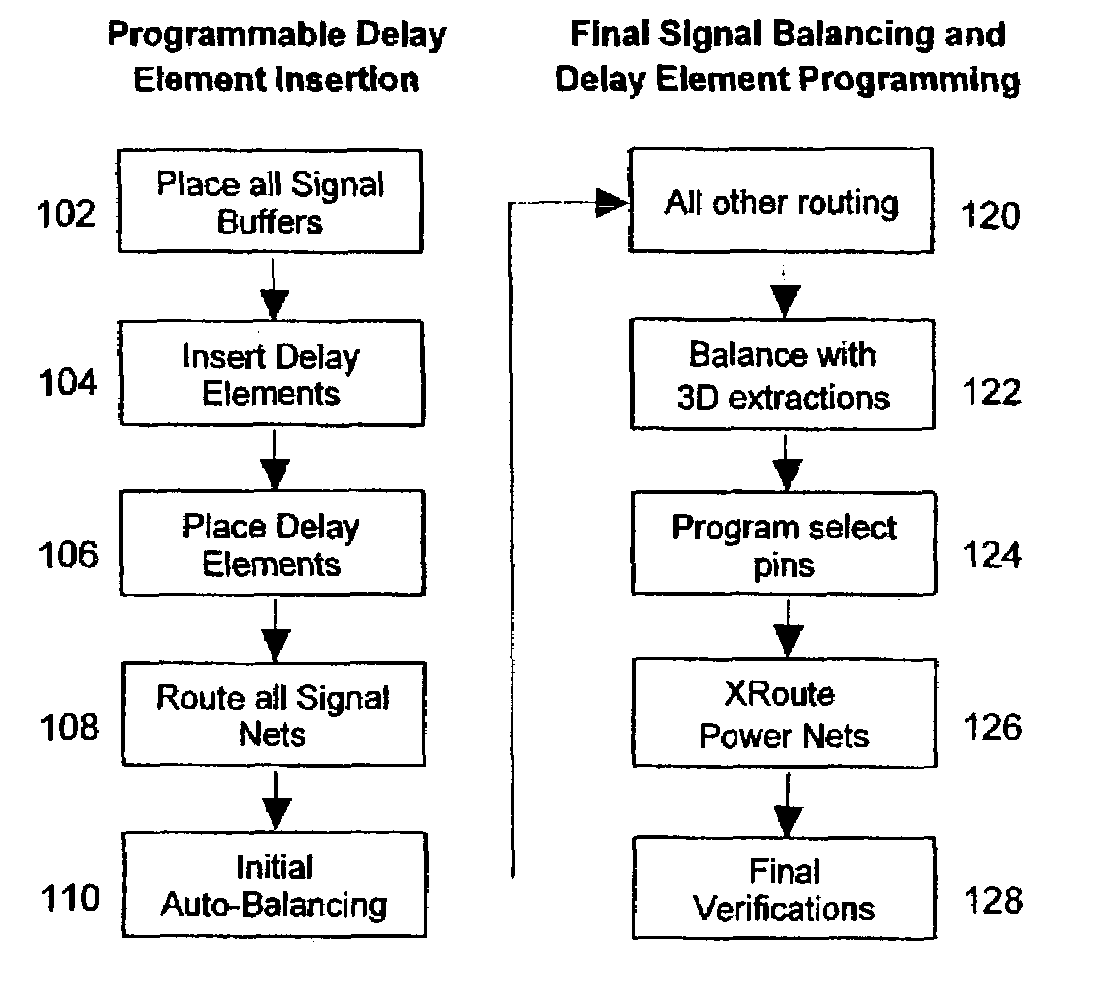
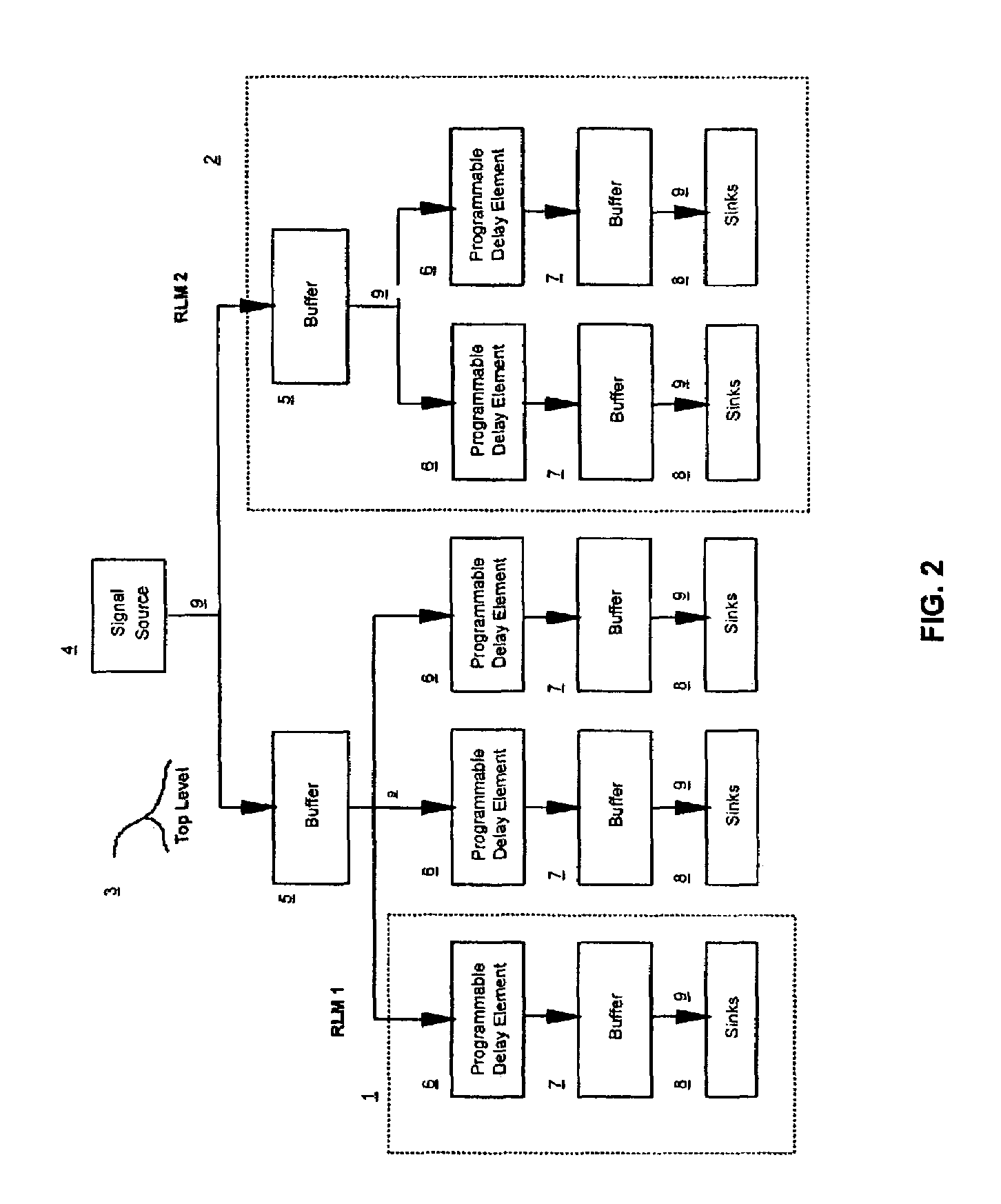
Programmable delay method for hierarchical signal balancing
InactiveUS7073145B2Reduce effortReduce turnaround timeComputer aided designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationComputer scienceSignal delay
A method for signal balancing across multiple random logic macros. The method inserts a programmable delay element into the design before the last buffer level on all signal paths. The random logic macro is then fully designed including cell placement and wiring. With programmable delay buffers in place, the random logic macros may be used within multiple designs, each having varying signal latency requirements.
Owner:TWITTER INC
Circuit Macro Placement Using Macro Aspect Ratio Based on Ports
InactiveUS20110289468A1Improving macro utilization of macroIncrease path lengthComputer aided designSpecial data processing applicationsElectronic circuit designLogic depth
Fixed outline shaped and modifiable outline shaped random logic macros of an electronic circuit design are manipulated by modifying an outline of a modifiable outline shape macro based on criteria consisting of any one of a macro port weight value, a macro port ordering; a macro rapport constraint or a macro logic depth and placing resulting macros at locations on an integrated circuit (chip).
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Logic modules for semiconductor integrated circuits
InactiveCN101258679ASimplify the interconnection networkLogic circuitsTheoretical computer scienceLogic module
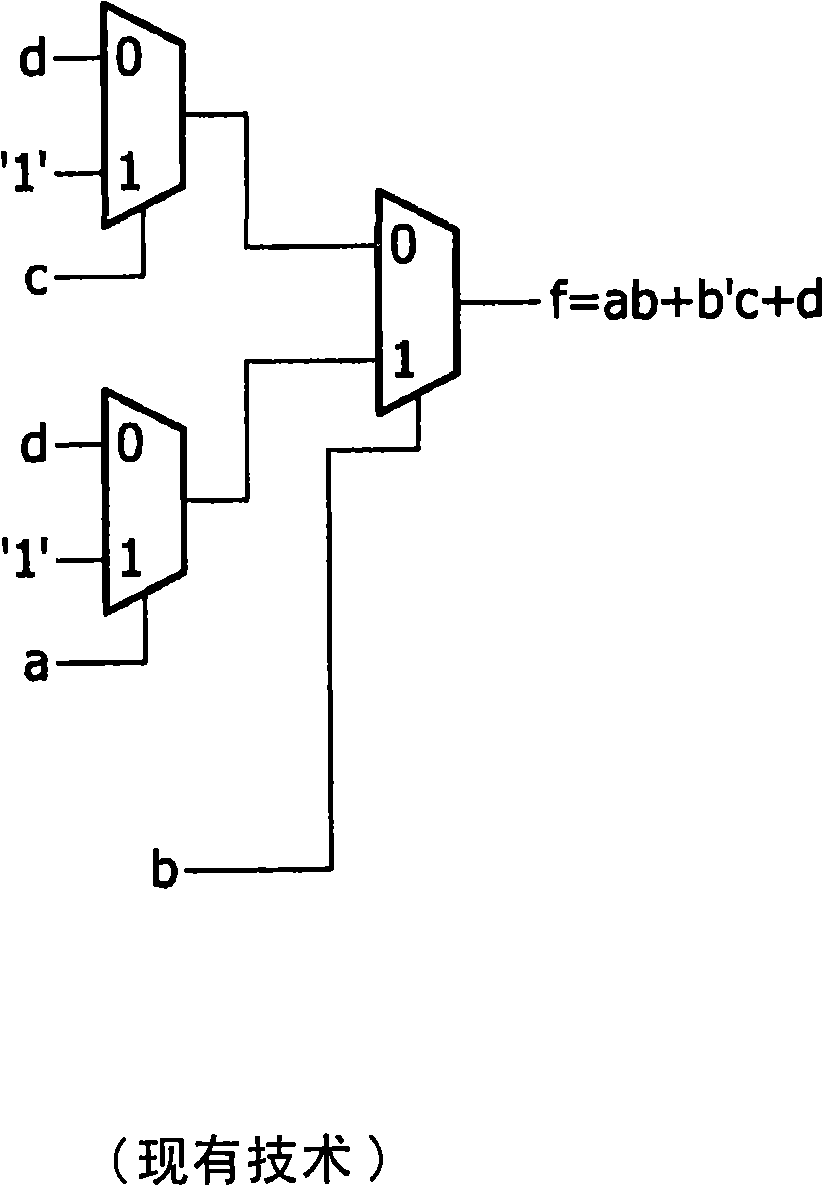
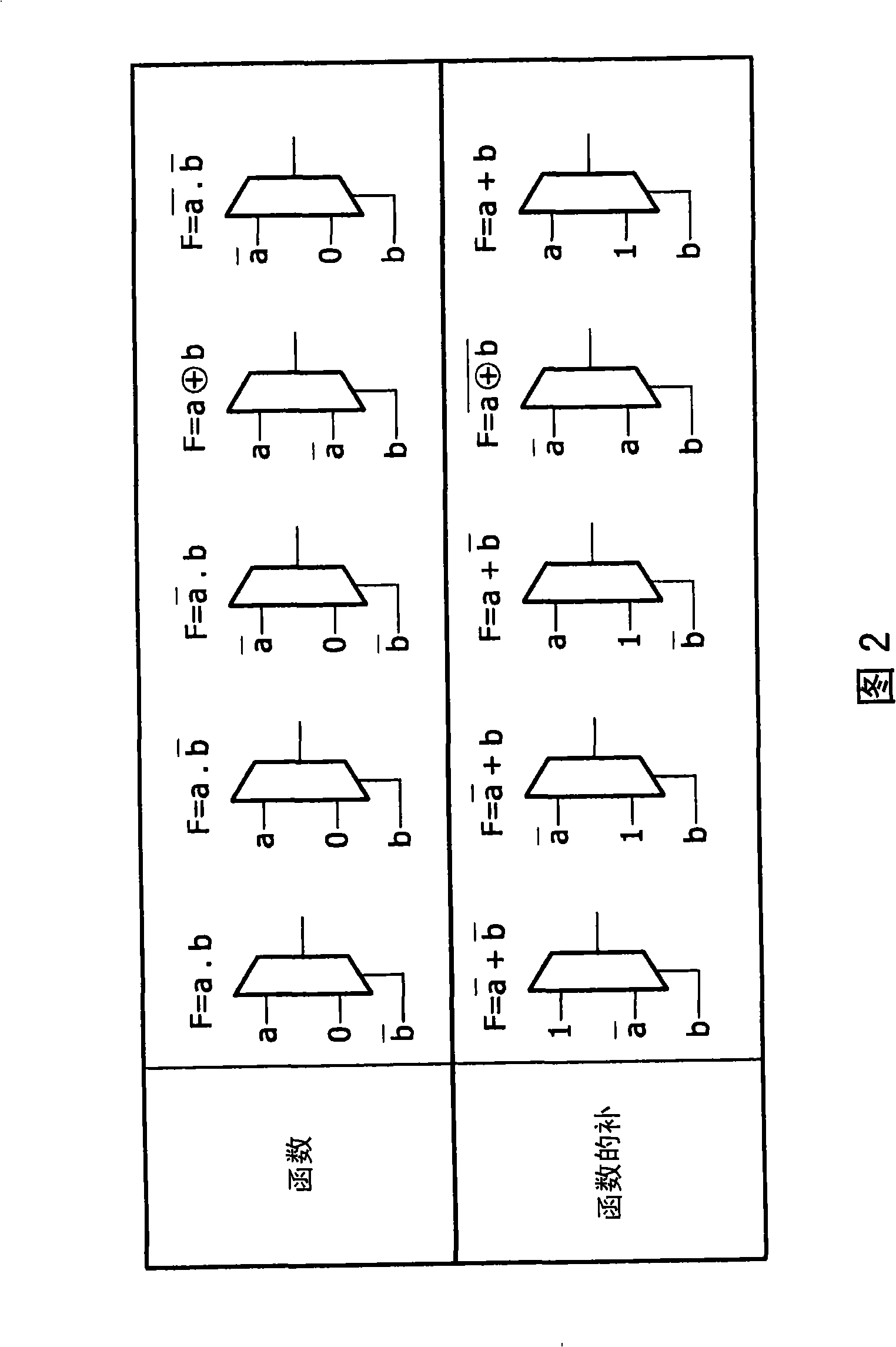
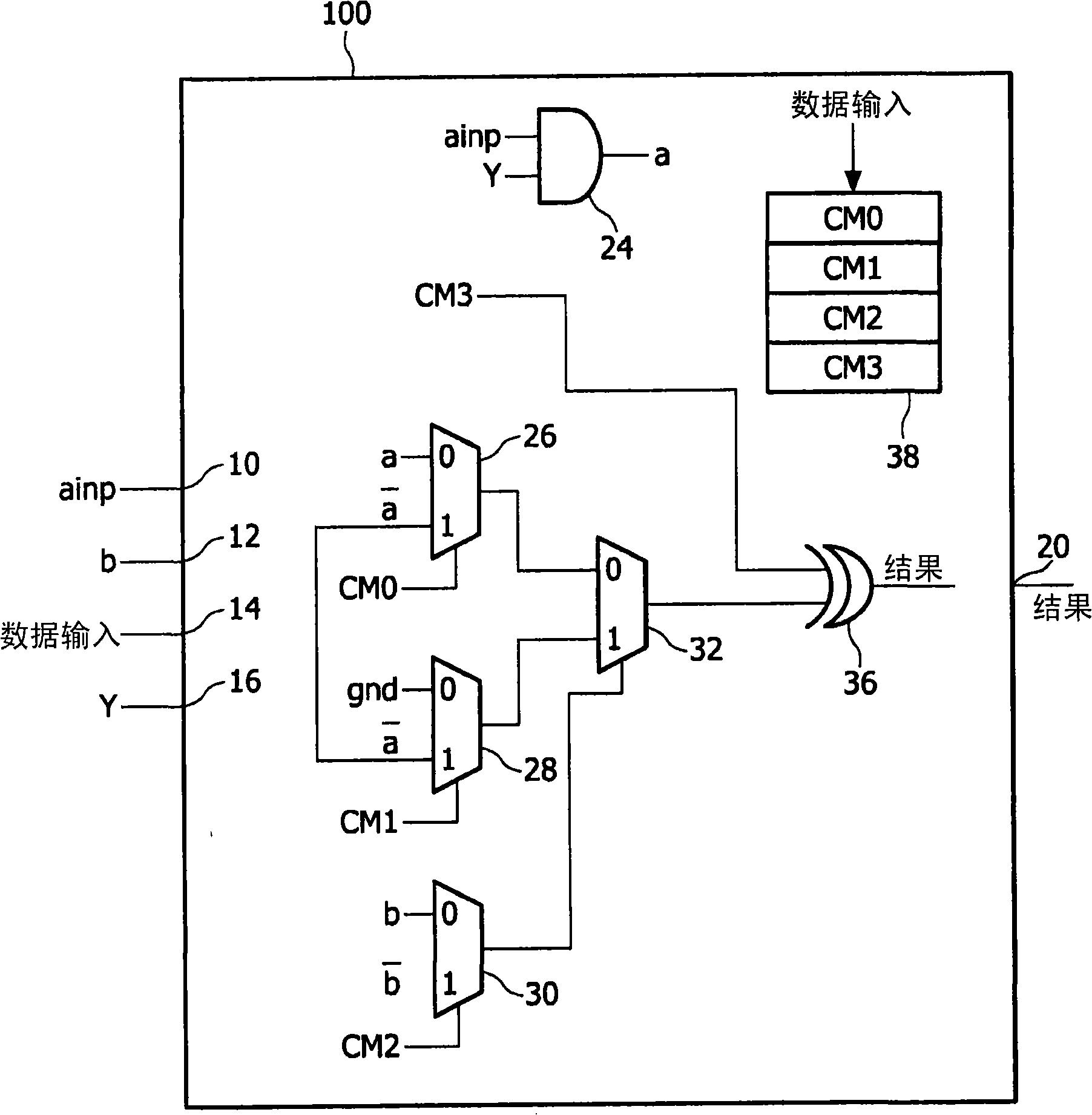
The present invention provides a logic module (400) that is capable of implementing data-path and random logic (command Z in bloc 42) uses control logic for selectively coupling one or more of the input terminals (10, 12, 14, 16, 18, 40) to the at least one output terminal (20) . The control logic comprises a plurality of logic elements (26, 28, 30, 32) arranged to generate a first set of two-input logic functions (f , (a, b)) and a programmable inverter (36) arranged to generate a second set of two-input logic functions, the second set of two-input logic functions being the complement functions of the first set of two-input logic functions. SRAM memory cells (4 bit memory batch (38)) may be used for configuration purposes, realising a compact logic module or block that is also re-programmable .
Owner:NXP BV
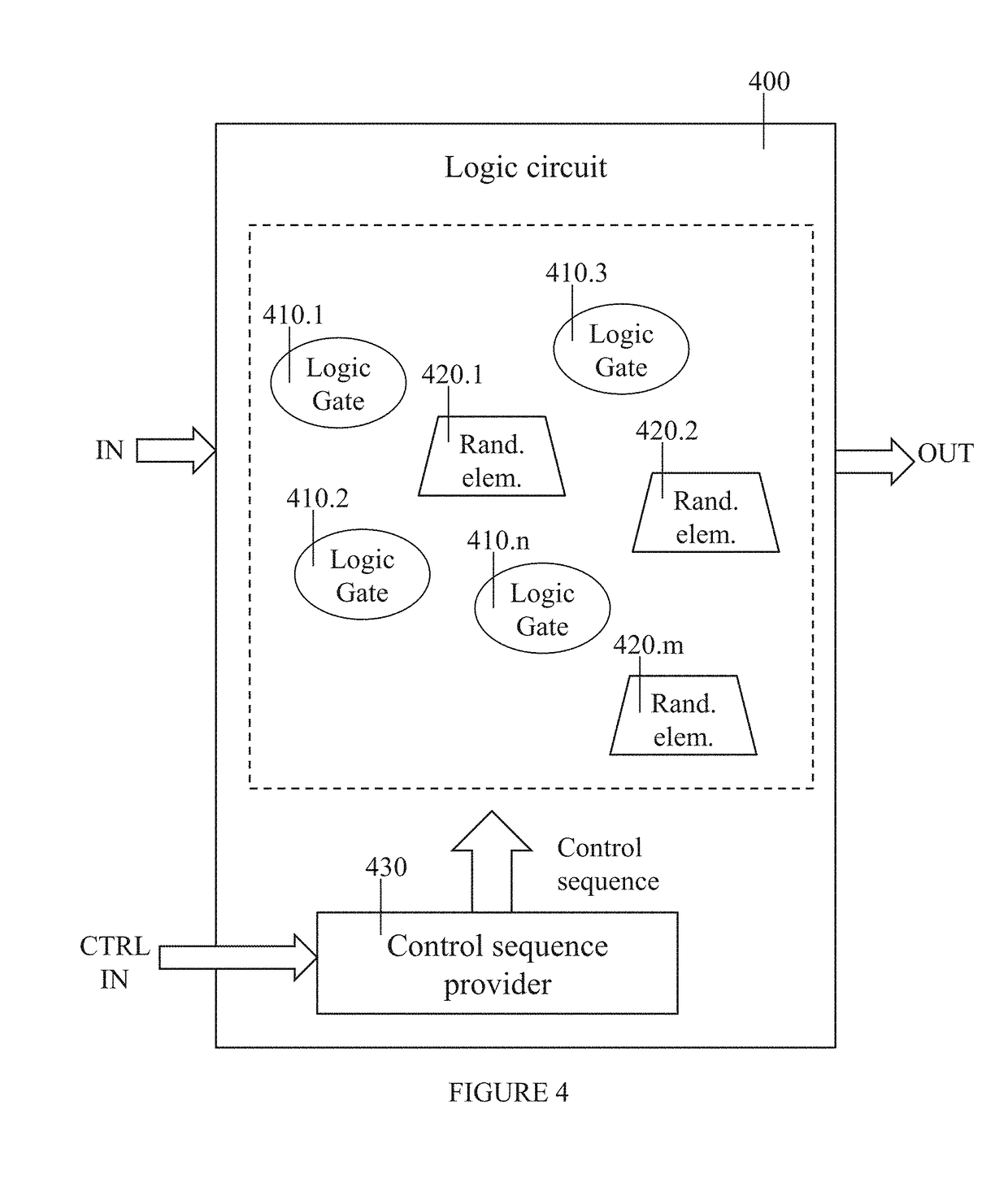
Randomized logic against side channel attacks
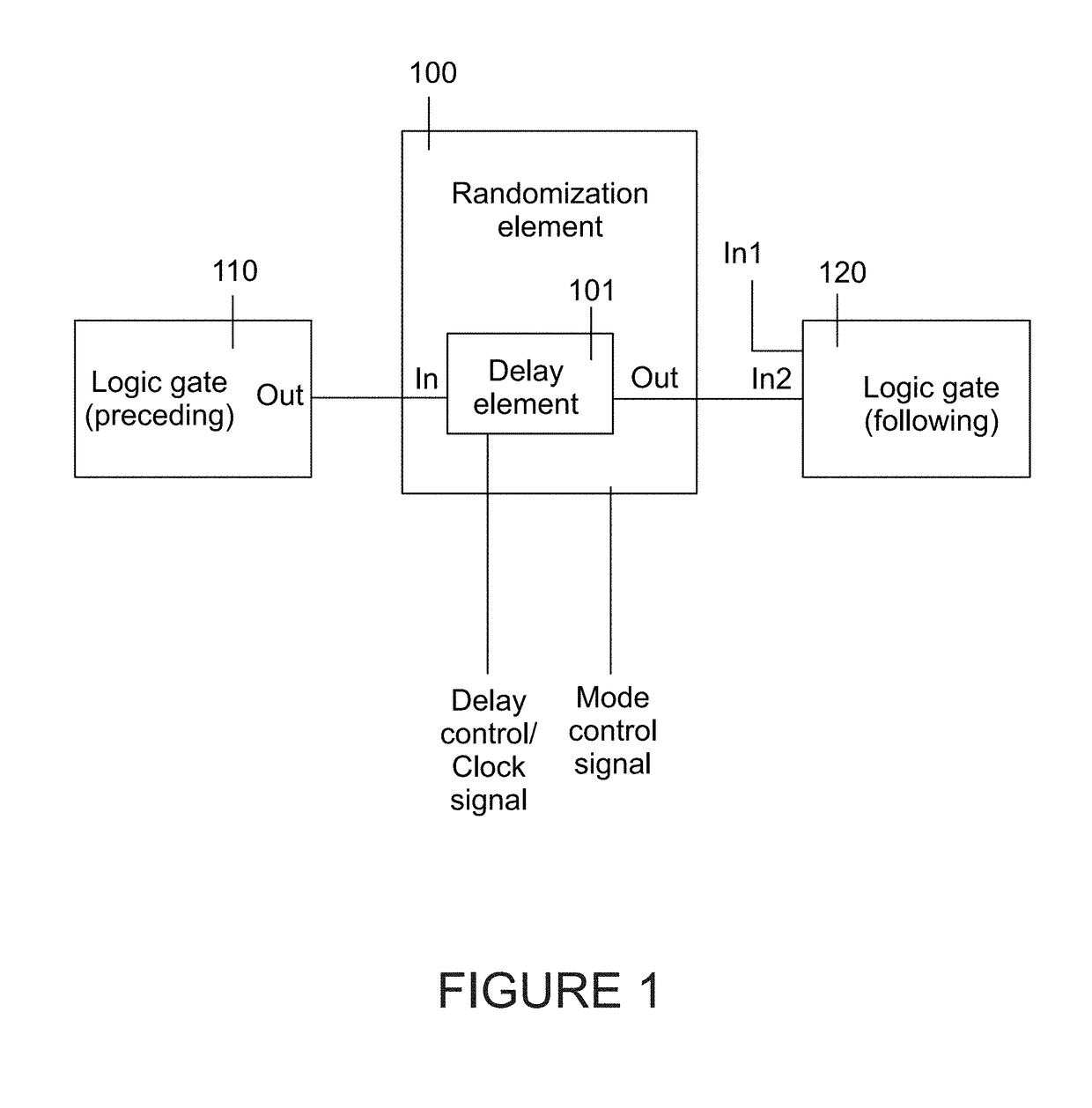
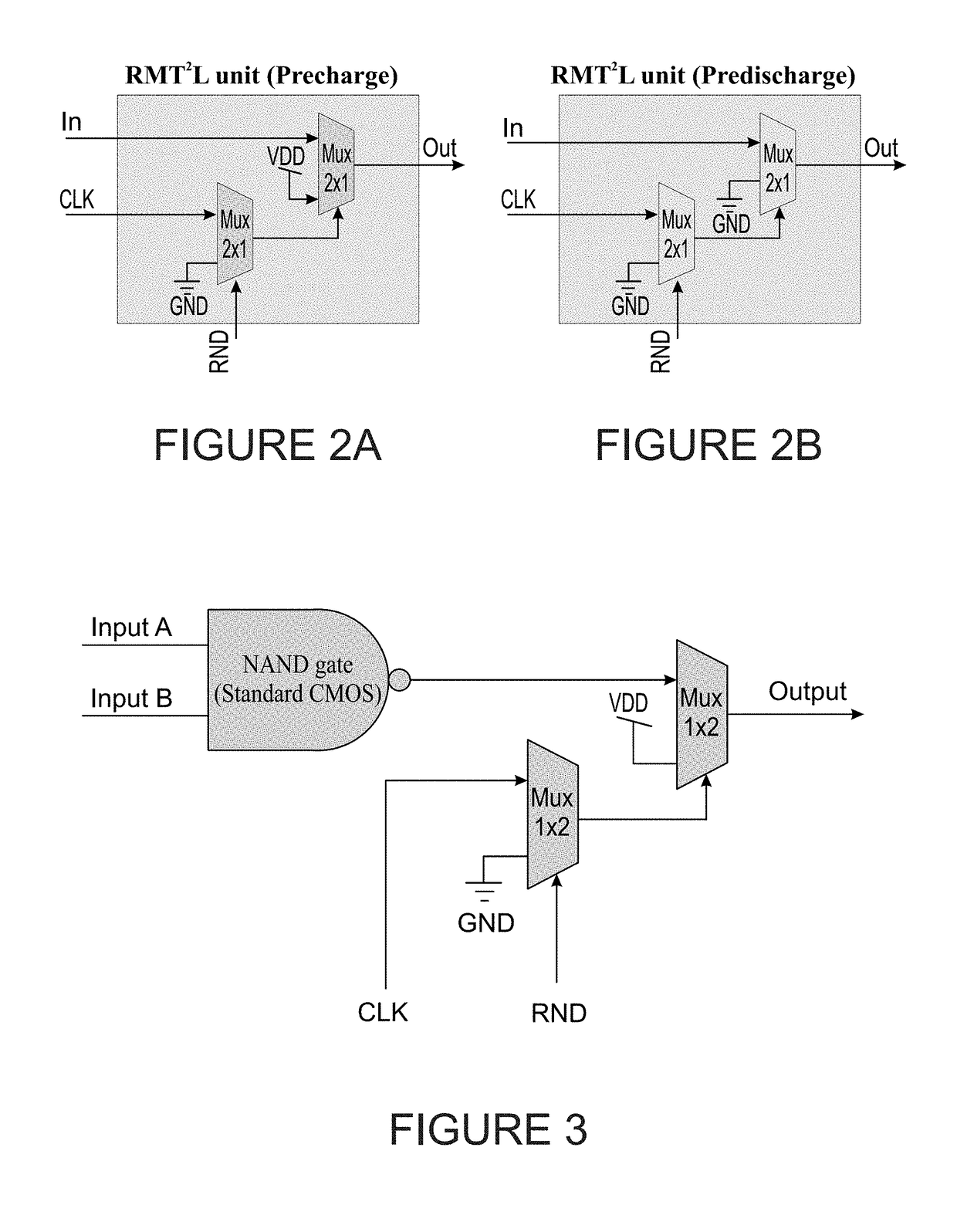
ActiveUS20190028263A1Minimizing propagation delayAddressing slow performanceInternal/peripheral component protectionCryptographic attack countermeasuresControl signalMode control
A randomization element includes a logic input for inputting a logic signal, a logic output for outputting the input logic signal at a delay and a randomization element. The randomization elements introduces the delay between said logic input and said logic output and operates selectably in static mode and in dynamic mode in accordance with a mode control signal. A logic circuit may be formed with randomization elements interspersed amongst the logic gates, to obtain protection against side channel attacks by inputting a selected control sequence into the randomization elements.
Owner:BAR ILAN UNIV
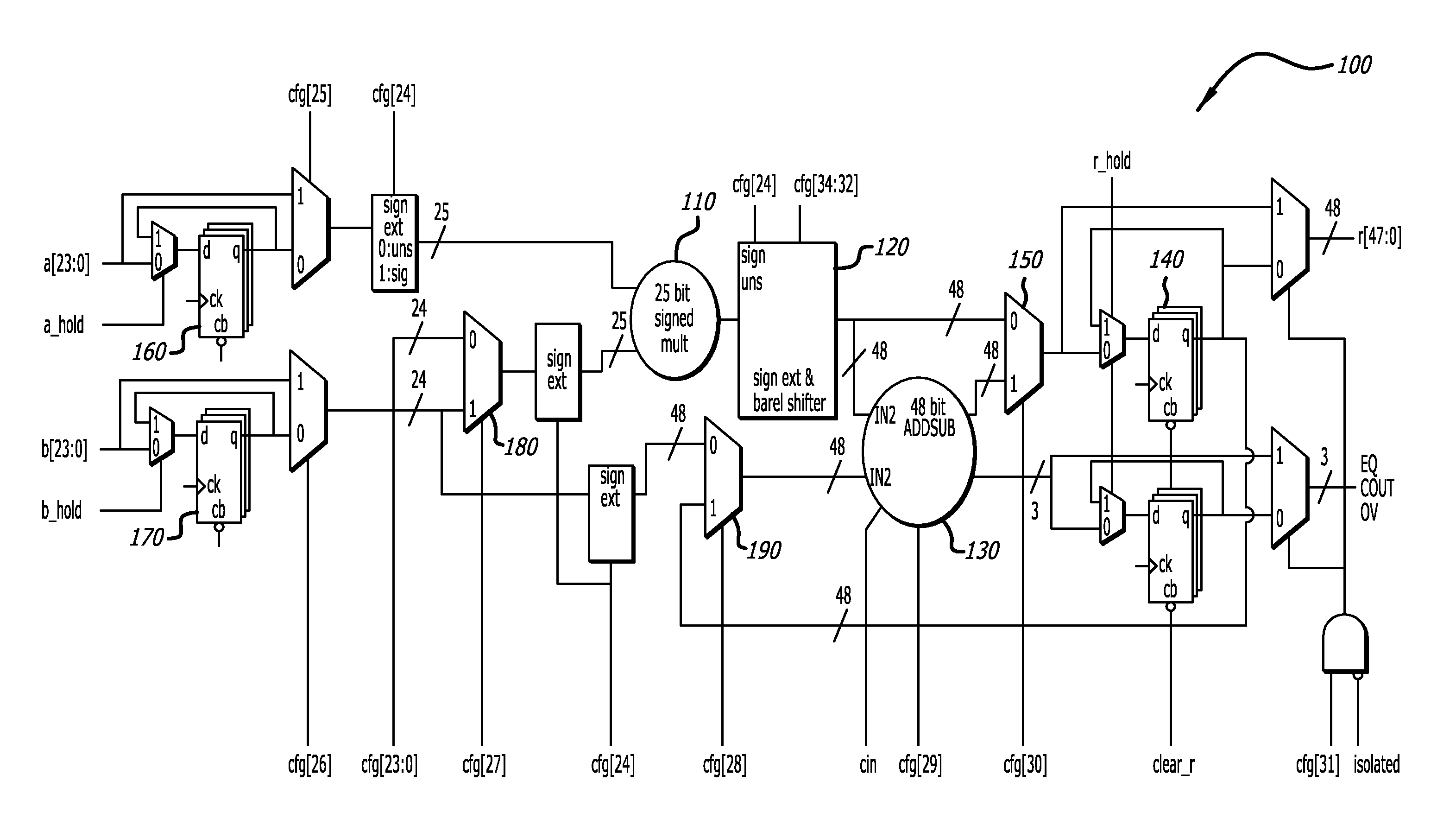
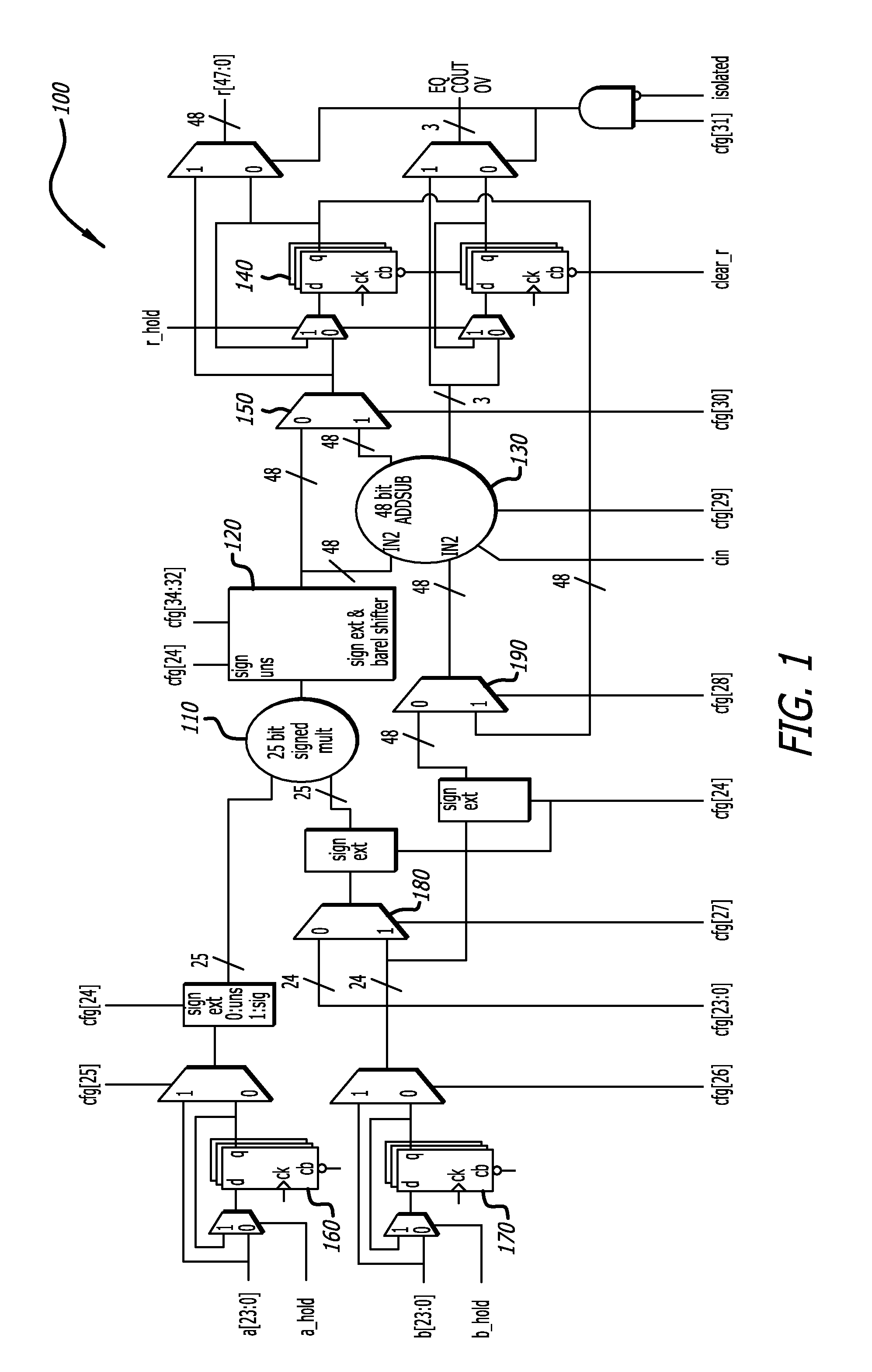
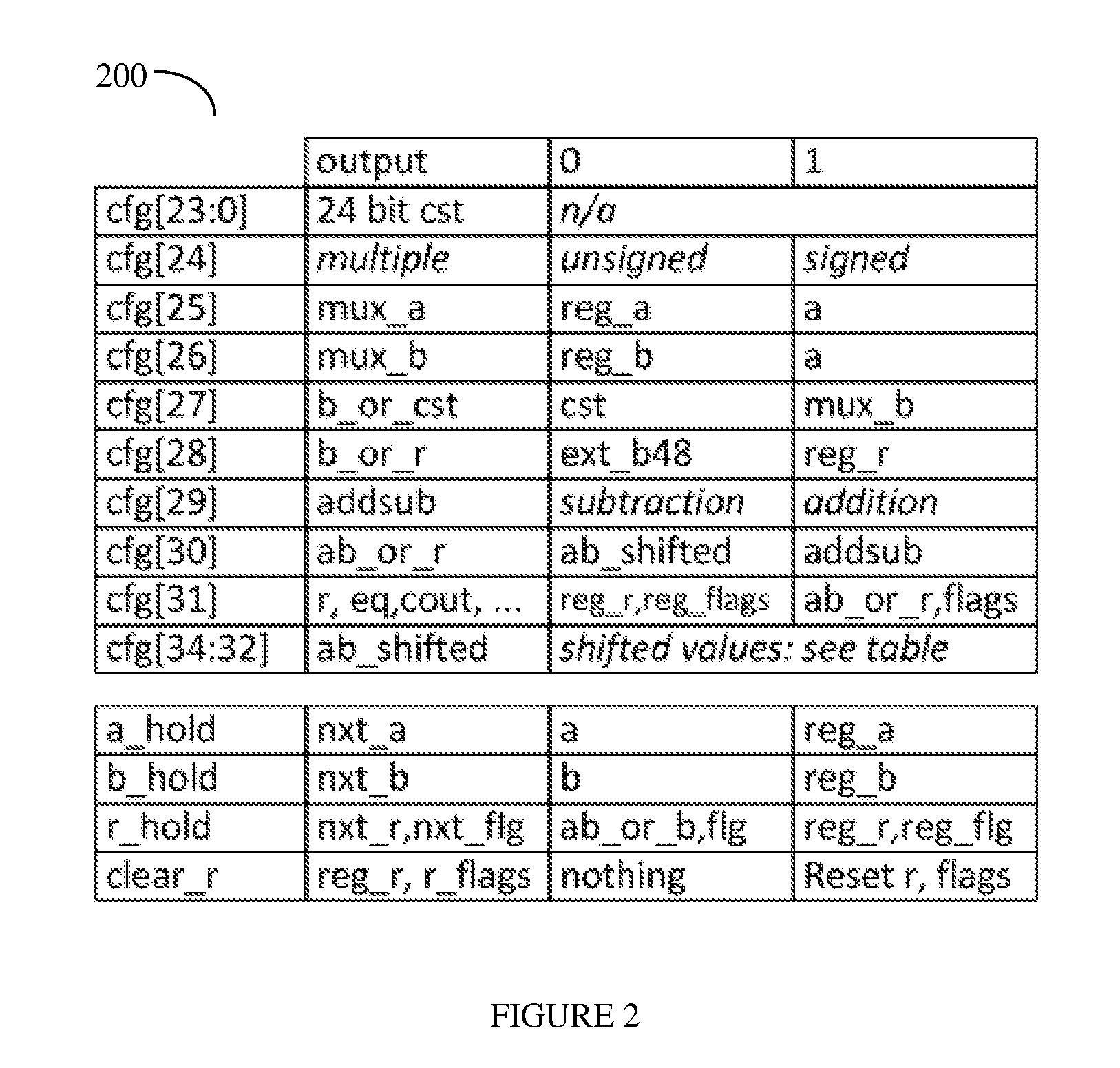
Configurable Multiply-Accumulate
ActiveUS20150095388A1Digital data processing detailsDigital computer detailsComputer hardwareInfinite impulse response
Field programmable gate arrays (FPGA) contain, in addition to random logic, also other components, such as processing units, multiply-accumulate (MAC) units, analog circuits, and other elements, configurable with respect of the random logic, to enhance the capabilities of the FPGA. A circuit for a filed configurable MAC unit is provided to allow various configurations of ADD, SUBTRACT, MULTIPLY and SHIFT functions. Optionally, registered input and registered output support a multi-cycle path. A configuration of a constant facilitates the configuration of the circuit to perform infinite impulse response (IIR) and finite impulse response (FIR) functions in hardware.
Owner:SILICON MOBILITY
Metal wire detection apparatus and chip
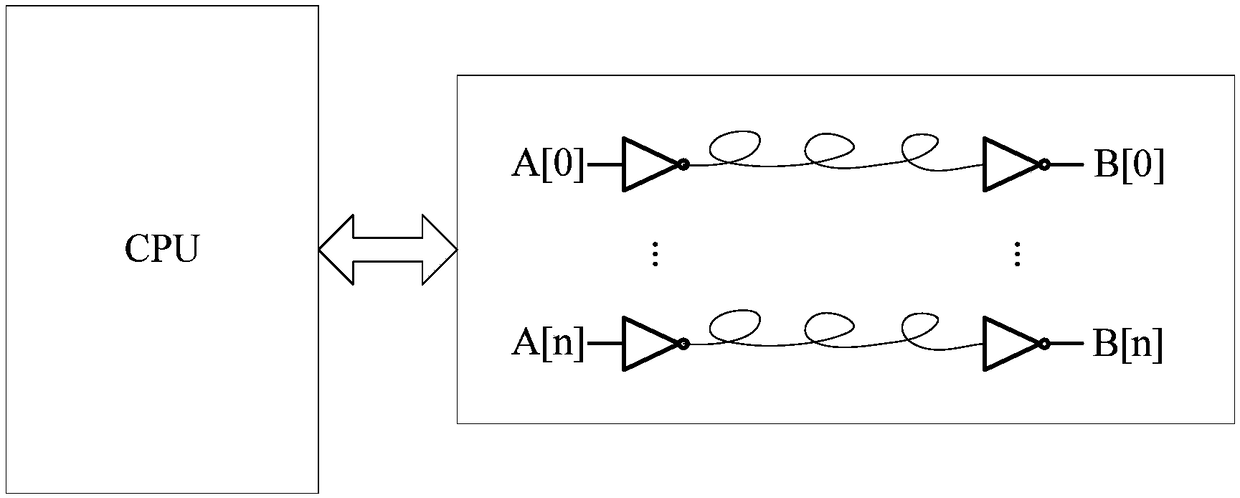
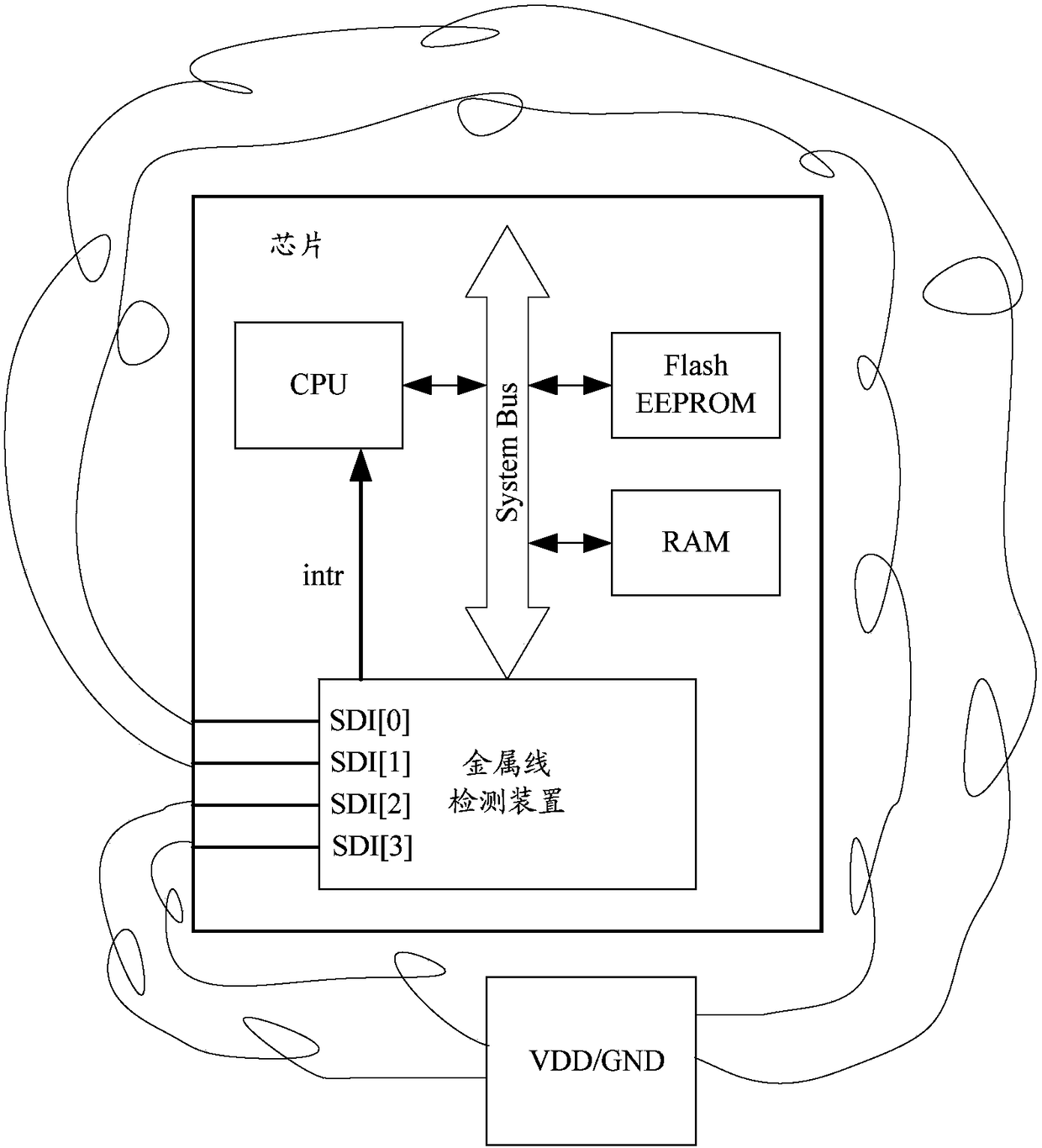
ActiveCN108090384AIncrease the number ofAdd pinInternal/peripheral component protectionOutput compareComputer science
The invention discloses a metal wire detection apparatus and a chip. The apparatus comprises a random number generation module used for generating a random logic value and outputting the random logicvalue to one end of a metal wire, a sampling module used for collecting a logic value output by the other end of the metal wire, and a metal wire detection module used for comparing the logic value collected by the sampling module with the logic value generated by the random number generation module and outputting a comparison result. Through the apparatus, the random number generation module generates the random logic value, so that an illegal user cannot foreknow the logic value transmitted by the metal wire, the illegal user cannot control the logic values at two ends of the metal wire to be kept consistent when the metal wire is broken, and whether the metal wire is broken or not can be accurately detected out; and key data is erased when the metal wire is broken, so that the securityprotection of the key data is improved.
Owner:DATANG MICROELECTRONICS TECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com