Patents
Literature
795 results about "Built-in self-test" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
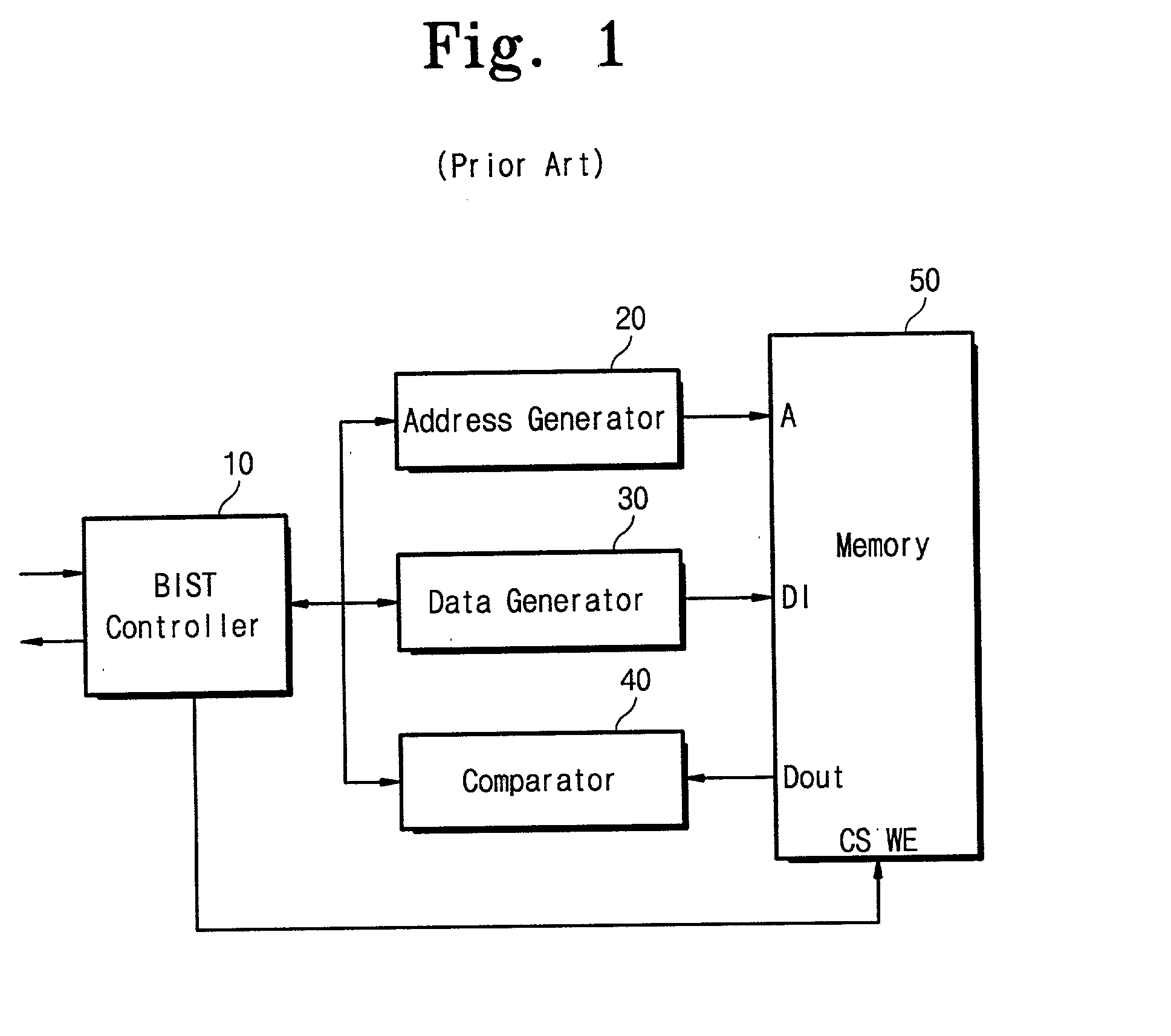
A built-in self-test (BIST) or built-in test (BIT) is a mechanism that permits a machine to test itself.
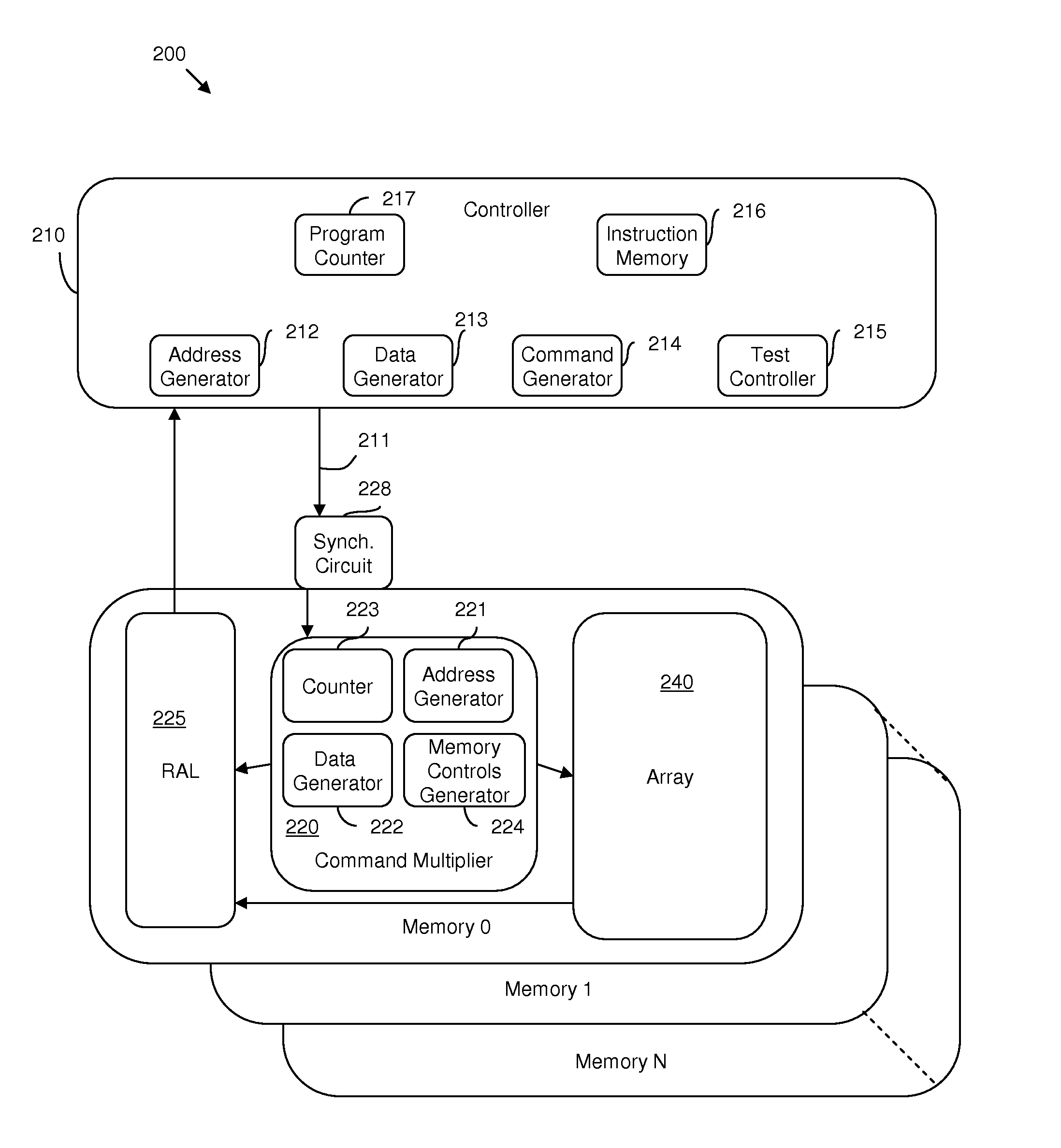
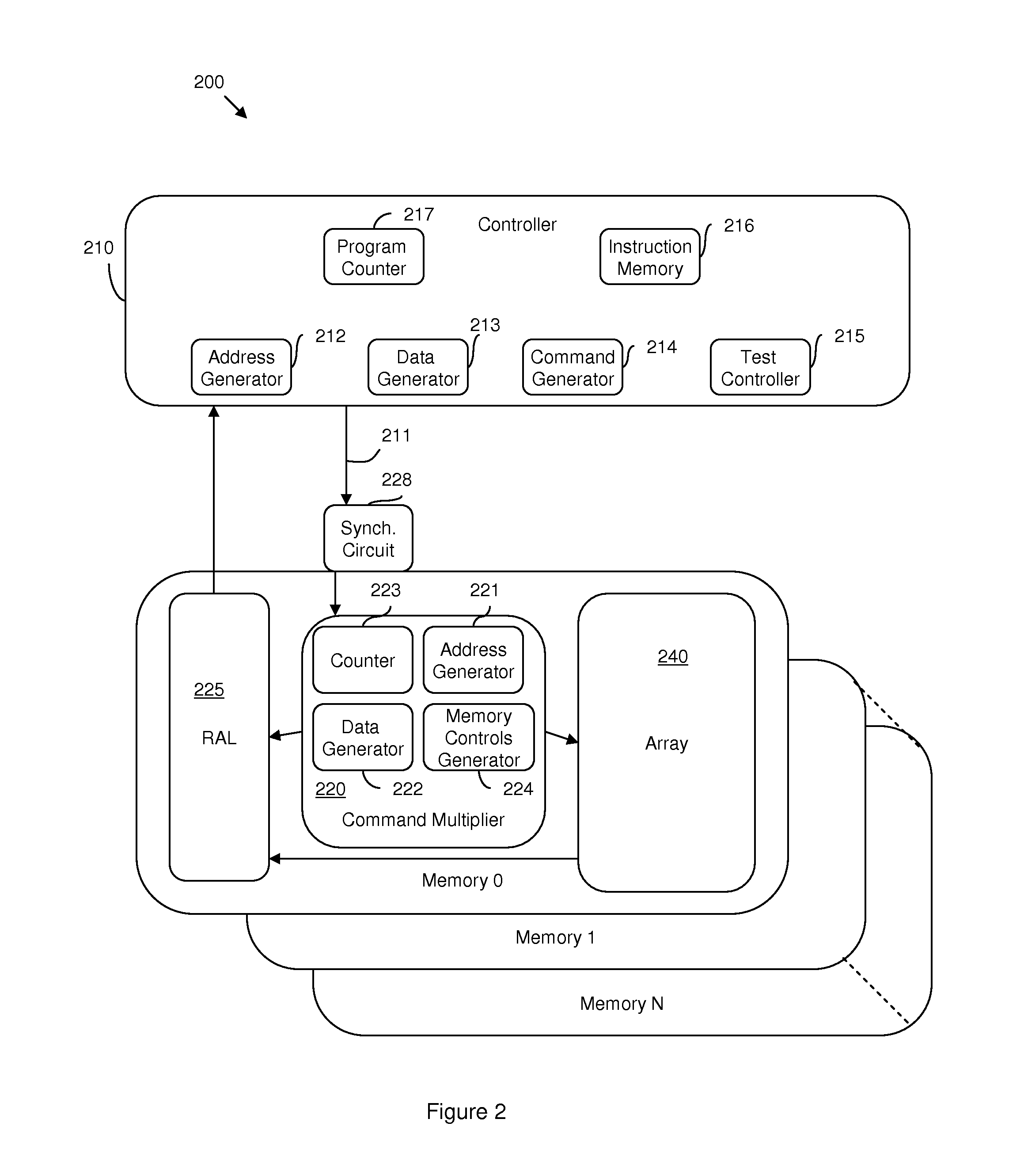
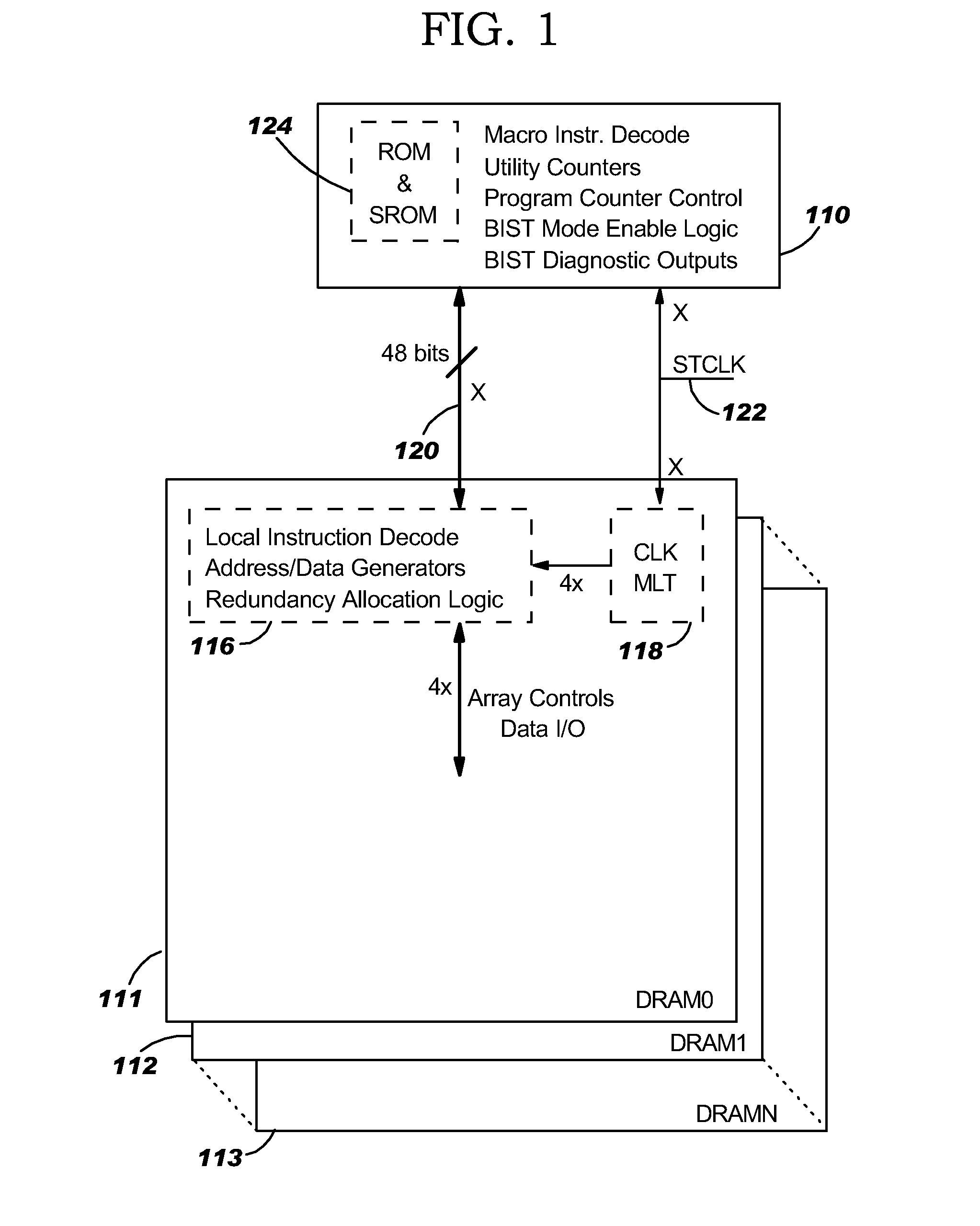
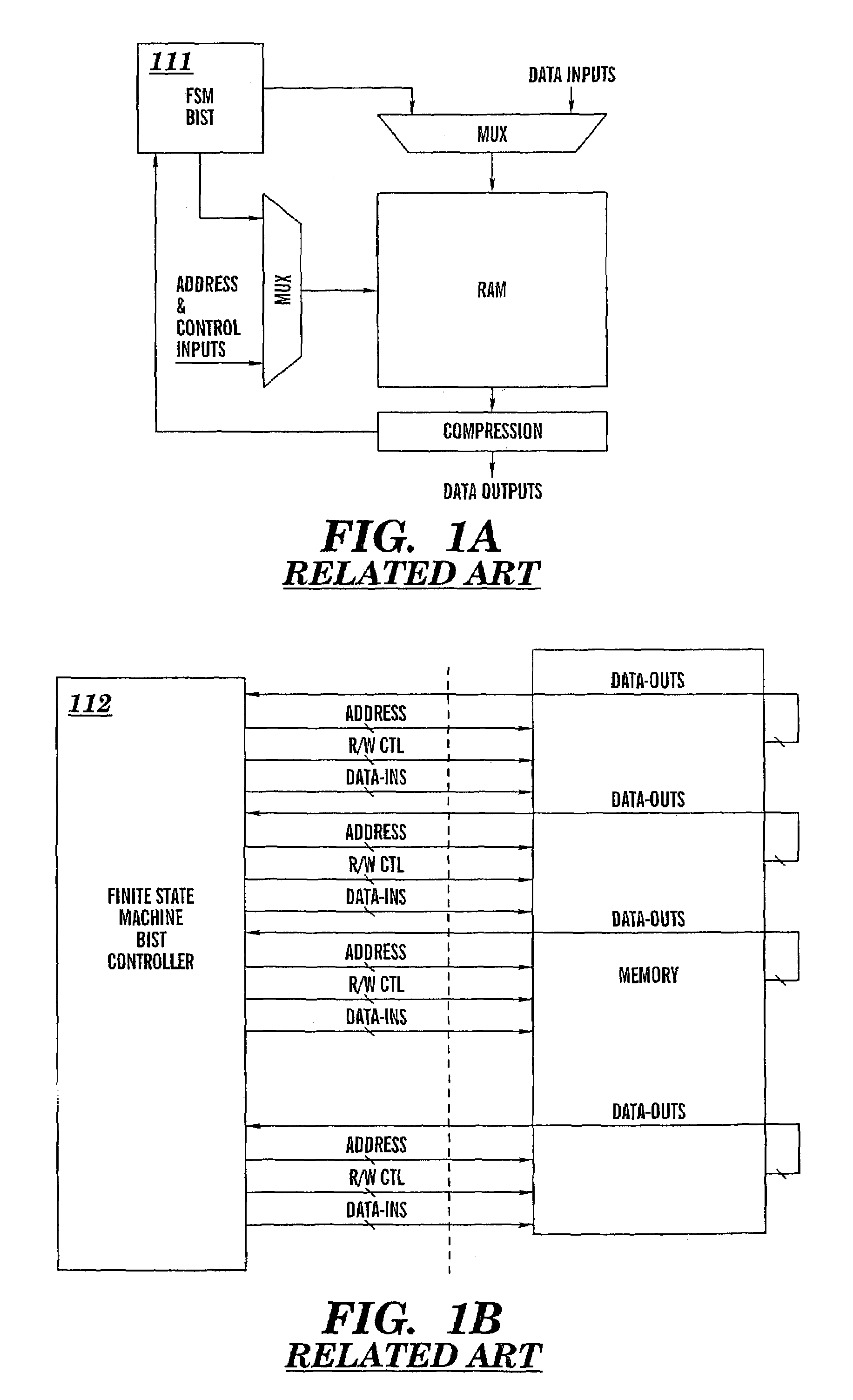
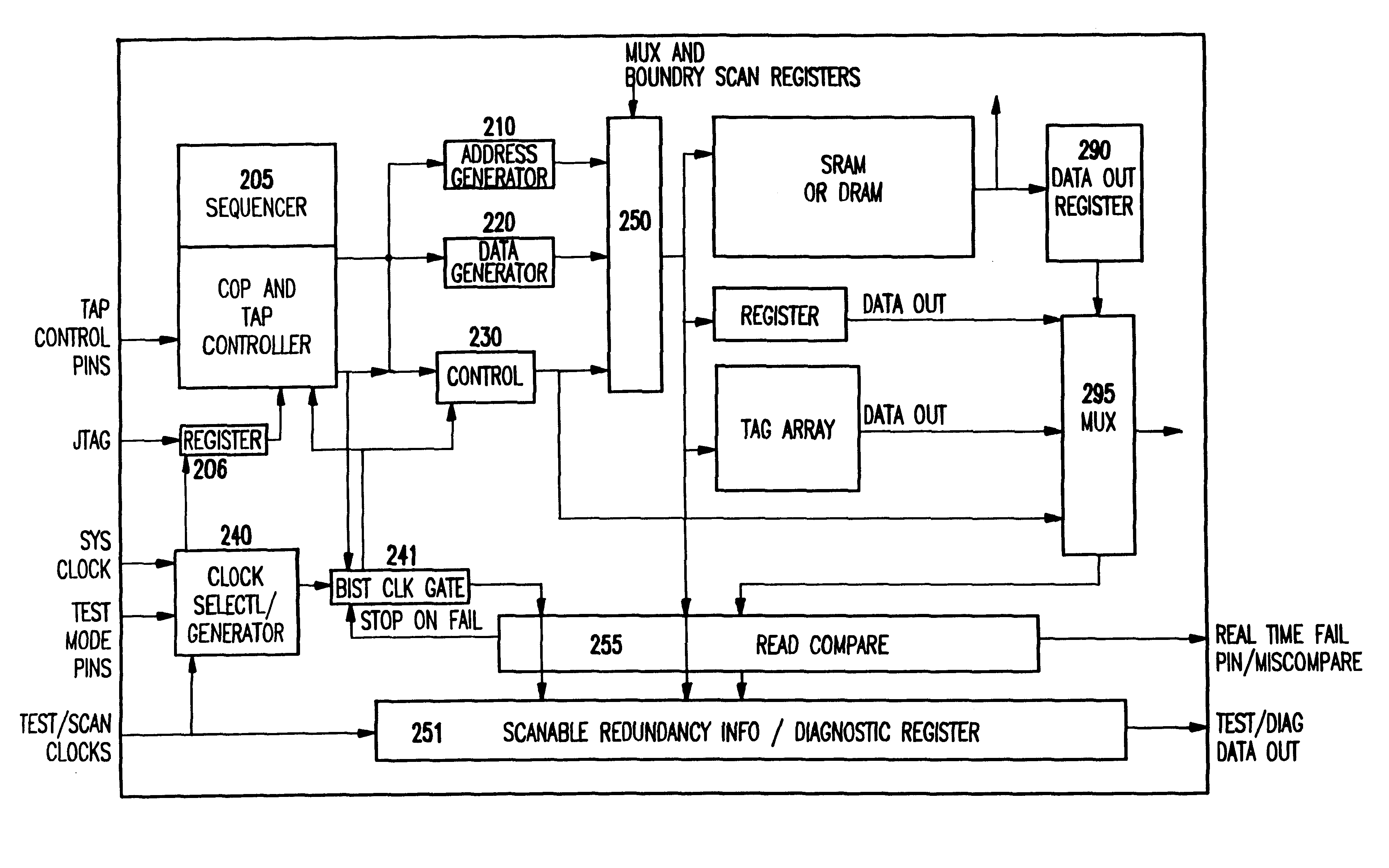
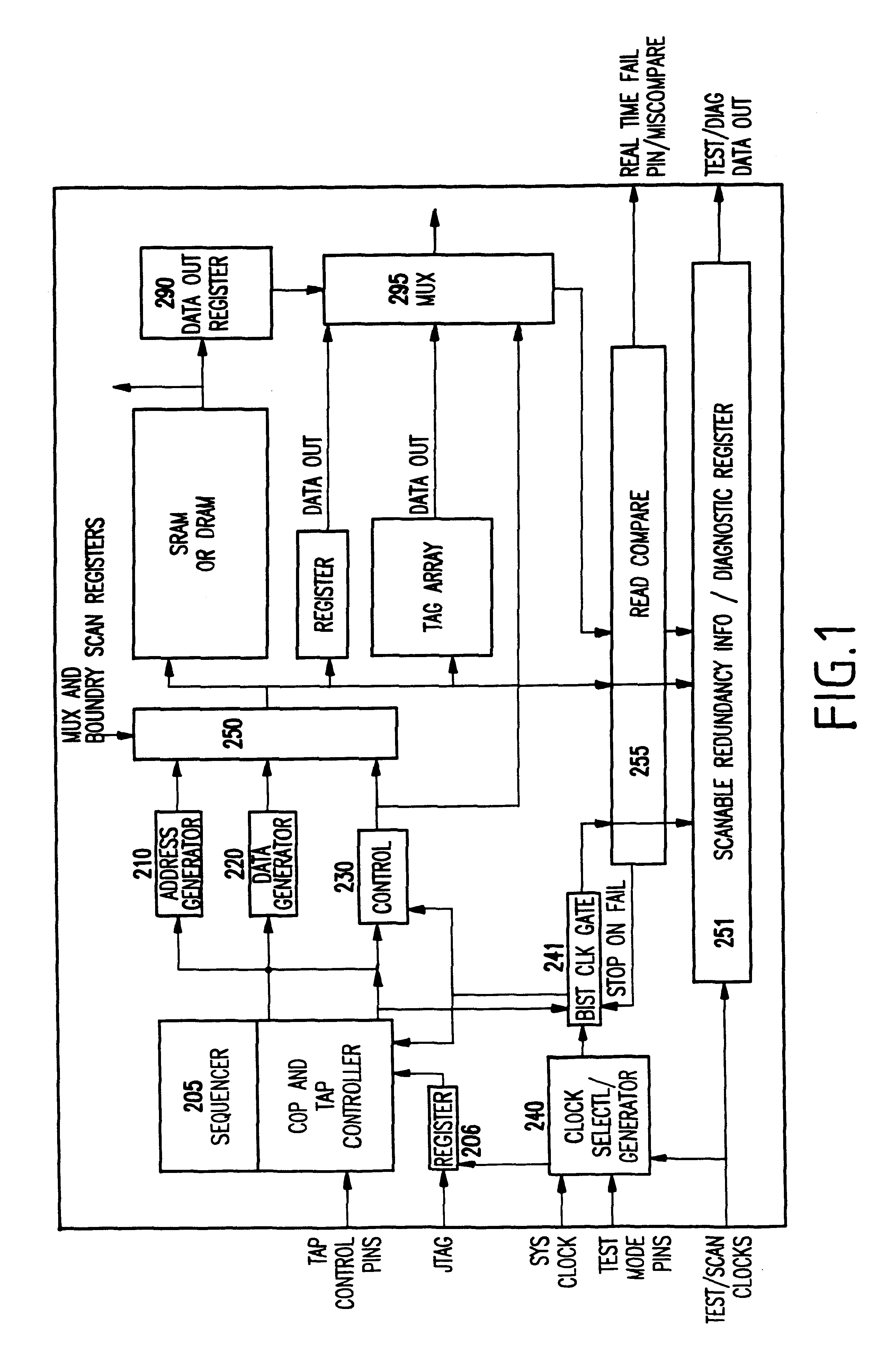
Hybrid built-in self test (BIST) architecture for embedded memory arrays and an associated method
ActiveUS20080178053A1Reduce frequencyMore test pattern flexibilityElectronic circuit testingFunctional testingSpecific testNormal mode
Disclosed are embodiments of a built-in self-test (BIST) architecture that incorporates a standalone controller that operates at a lower frequency to remotely perform test functions common to a plurality of embedded memory arrays. The architecture also incorporates command multipliers that are associated with the embedded memory arrays and that selectively operate in one of two different modes: a normal mode or a bypass mode. In the normal mode, instructions from the controller are multiplied so that memory array-specific test functions can be performed locally at the higher operating frequency of each specific memory array. Whereas, in the bypass mode, multiplication of the instructions is suspended so that memory array-specific test functions can be performed locally at the lower operating frequency of the controller. The ability to vary the frequency at which test functions are performed locally, allows for more test pattern flexibility.
Owner:META PLATFORMS INC
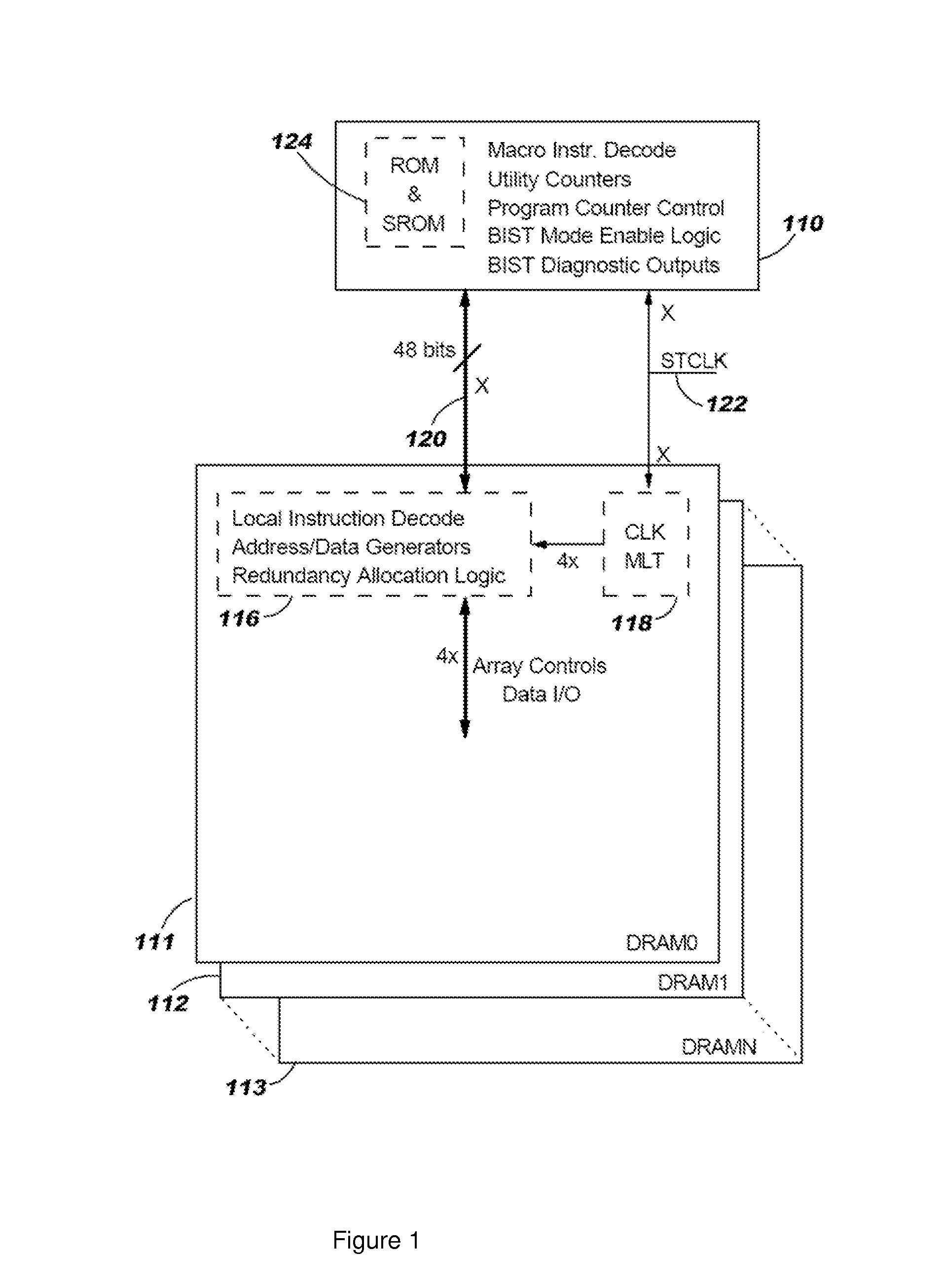
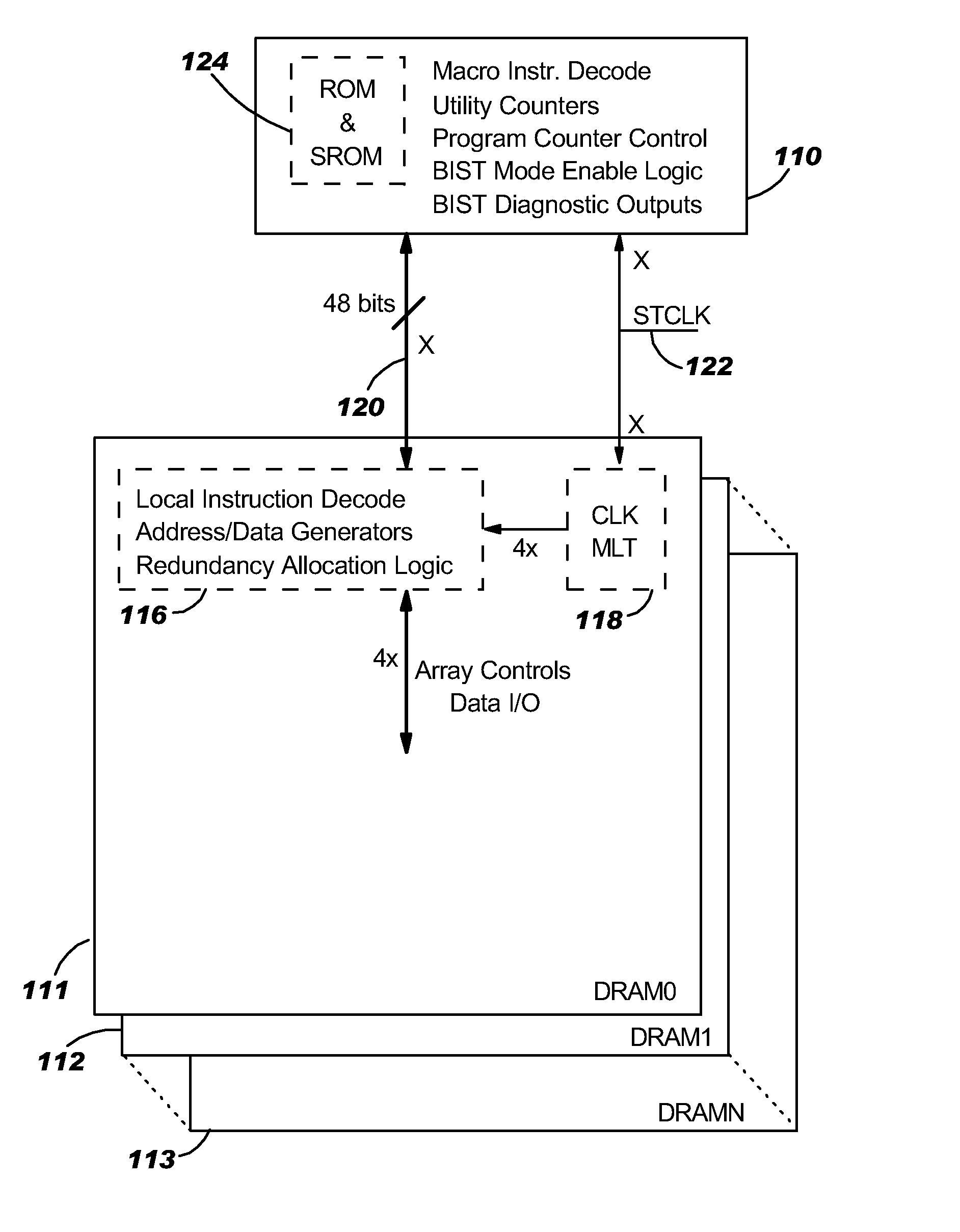
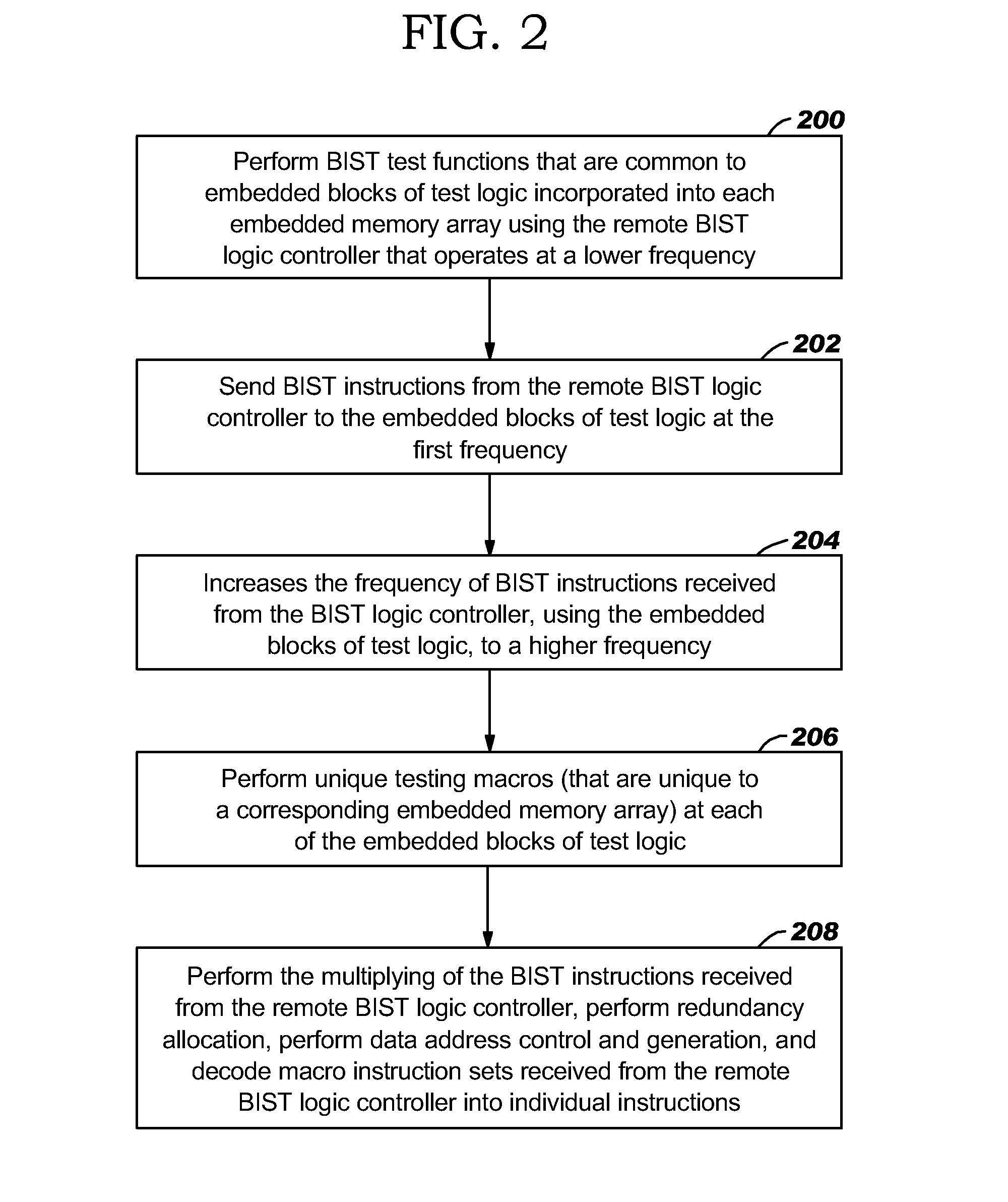
Remote bist for high speed test and redundancy calculation
InactiveUS20080215937A1Reduce frequencyIncrease processing frequencyDigital circuit testingFunctional testingLow speedSpeed test
Disclosed in a hybrid built-in self test (BIST) architecture for embedded memory arrays that segments BIST functionality into remote lower-speed executable instructions and local higher-speed executable instructions. A standalone BIST logic controller operates at a lower frequency and communicates with a plurality of embedded memory arrays using a BIST instruction set. A block of higher-speed test logic is incorporated into each embedded memory array under test and locally processes BIST instructions received from the standalone BIST logic controller at a higher frequency. The higher-speed test logic includes a multiplier for increasing the frequency of the BIST instructions from the lower frequency to the higher frequency. The standalone BIST logic controller enables a plurality of higher-speed test logic structures in a plurality of embedded memory arrays.
Owner:META PLATFORMS INC
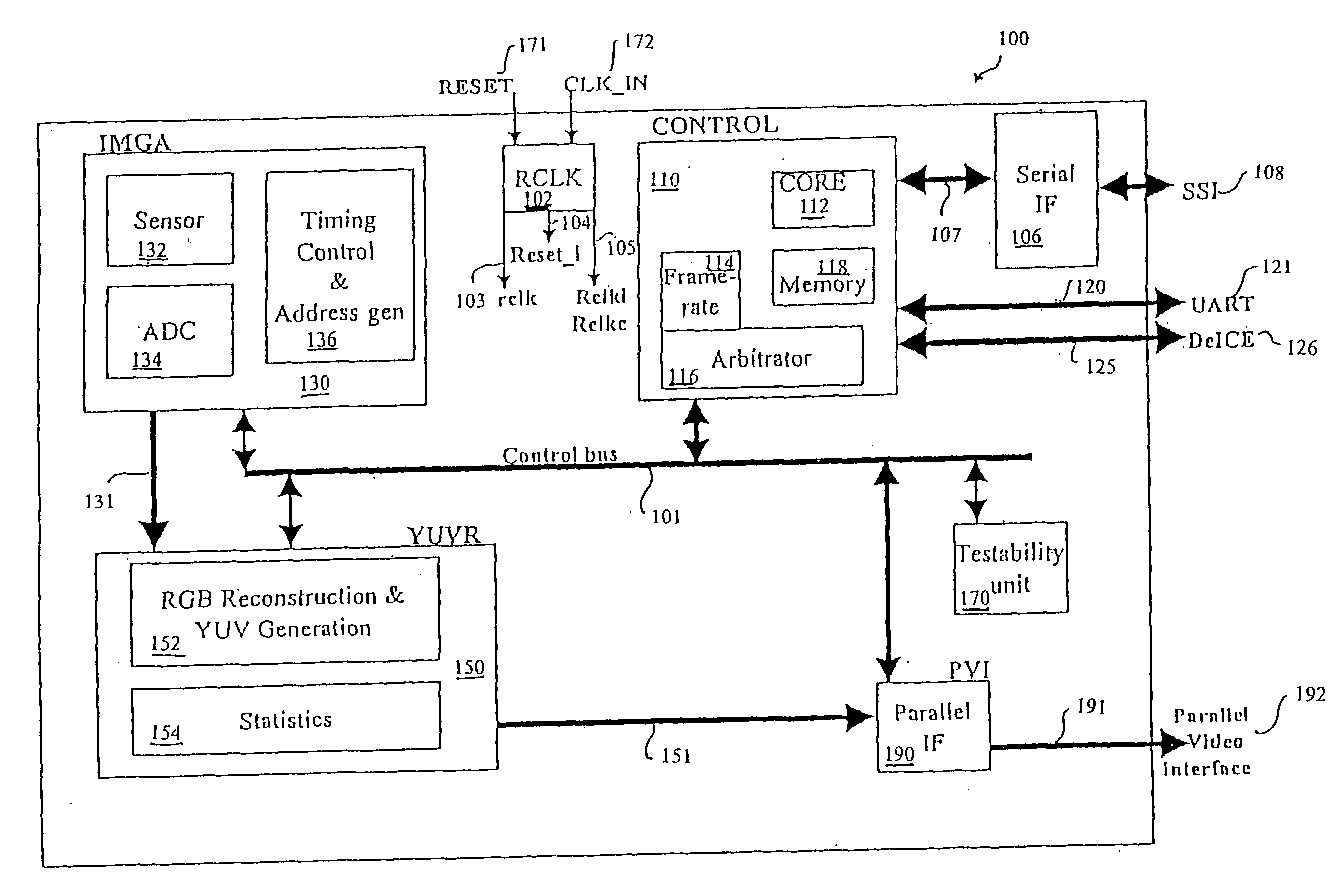
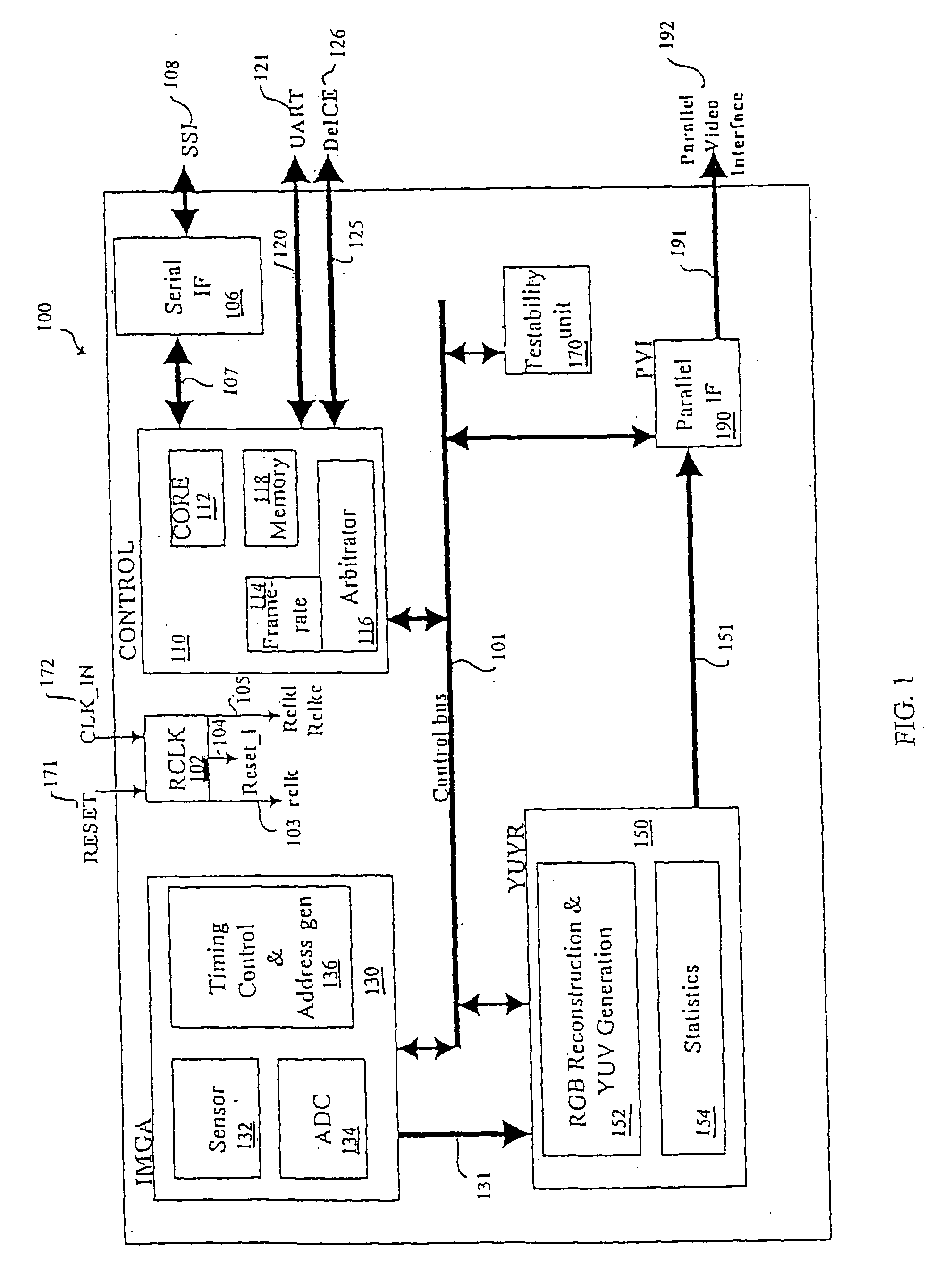
CMOS imager for cellular applications and methods of using such
ActiveUS20050068436A1Reduce power consumptionMeet the noiseTelevision system detailsColor signal processing circuitsCMOSTransformation unit
Systems, methods and devices related to detecting and transmitting images. Imaging system and devices, as well as methods of using such that are provided herein include flicker detection and / or correction; and / or built-in self test (170) associated with various analog circuitry in the imaging devices; and / or power reduction ability; and / or pixels with charge evacuation functionality; and / or parallel to serial conversion (190) unit and associated serial output interface (106); and / or other advanced functionality.
Owner:TRANSCHIP ISRAEL
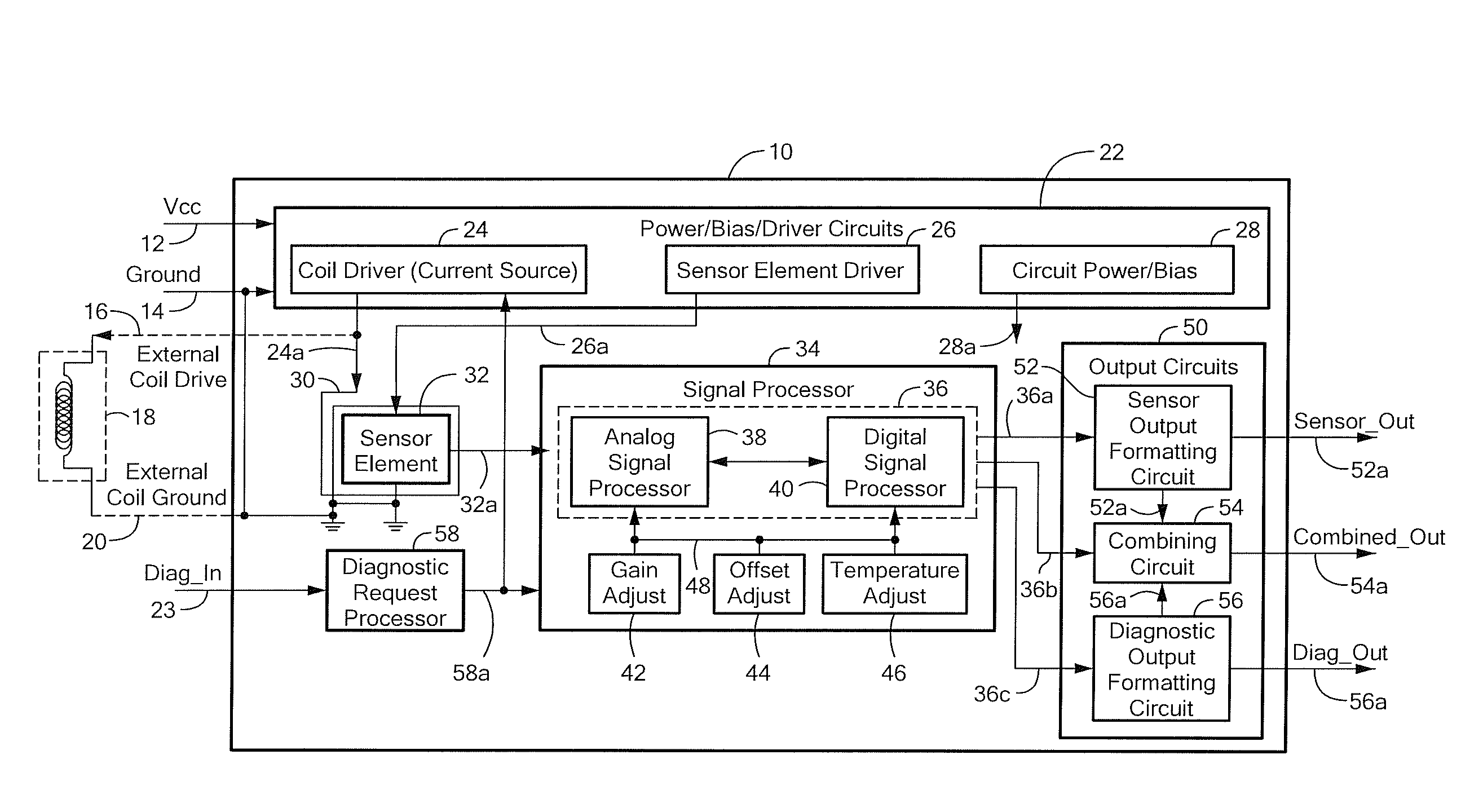
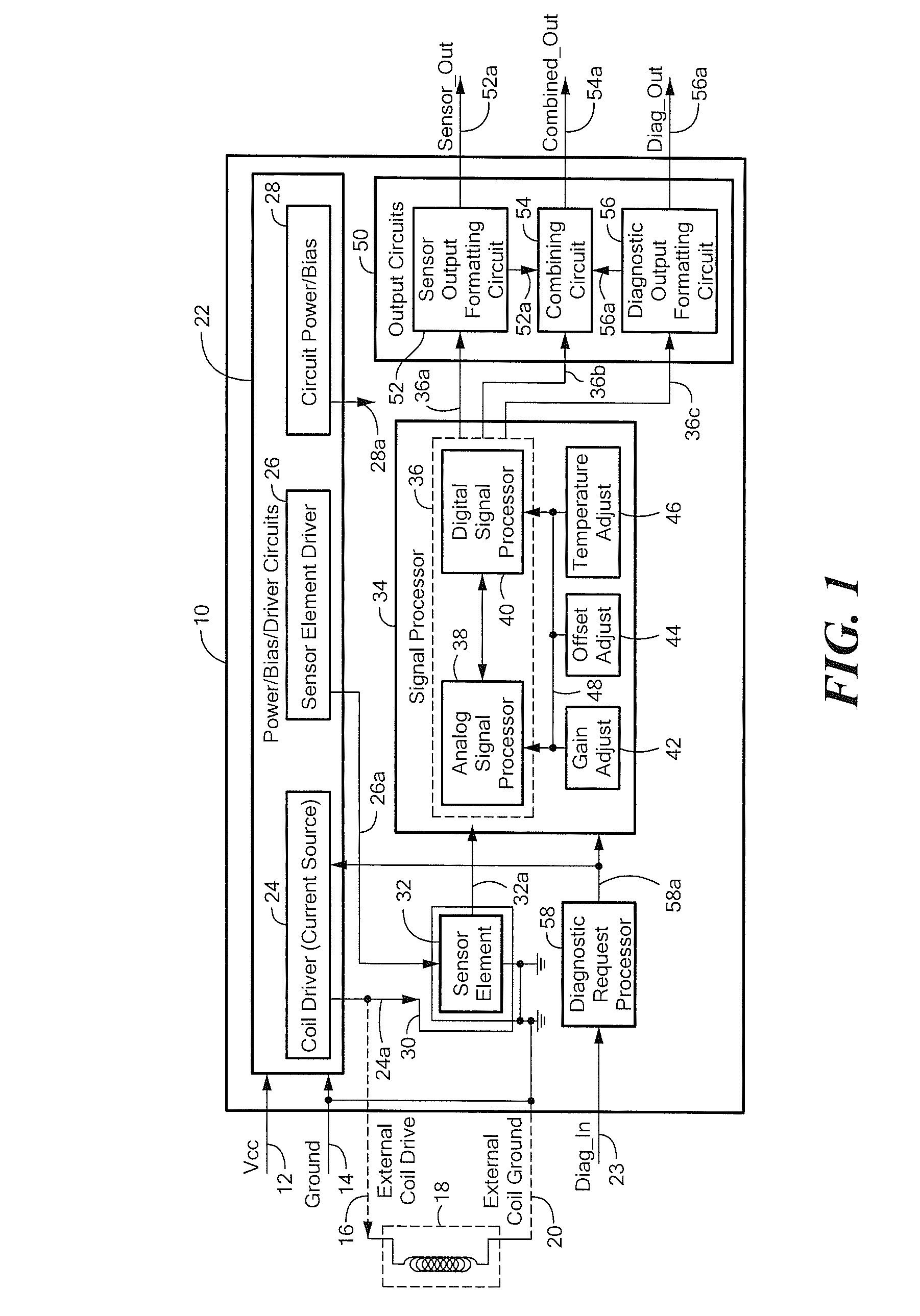
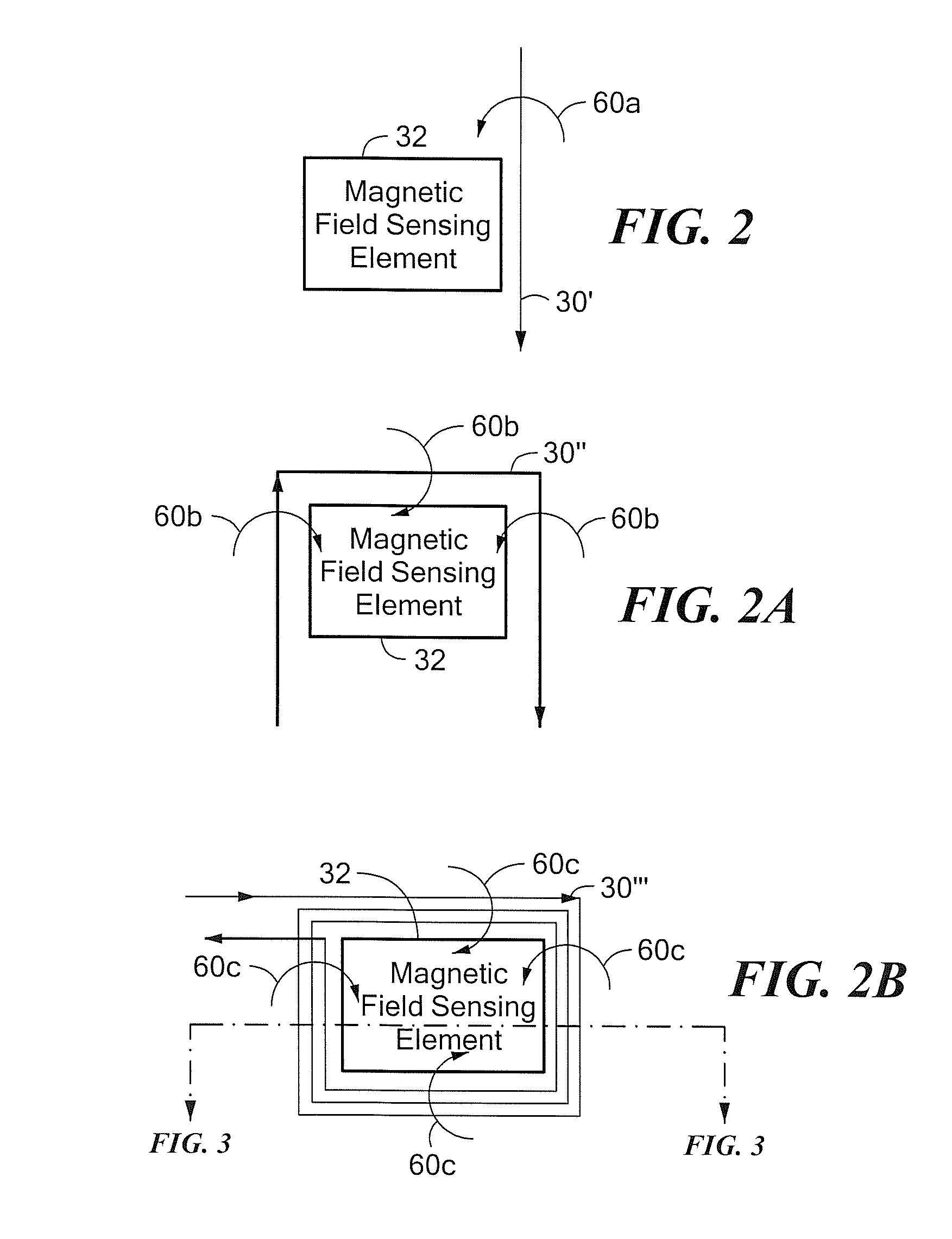
Circuits and Methods for Generating a Self-Test of a Magnetic Field Sensor
ActiveUS20100211347A1Magnetic measurementsAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceBuilt-in self-testCondensed matter physics
A magnetic field sensor includes built in self-test circuits that allow a self-test of most of, or all of, the circuitry of the magnetic field sensor, including self-test of a magnetic field sensing element used within the magnetic field sensor, while the magnetic field sensor is functioning in normal operation.
Owner:ALLEGRO MICROSYSTEMS INC
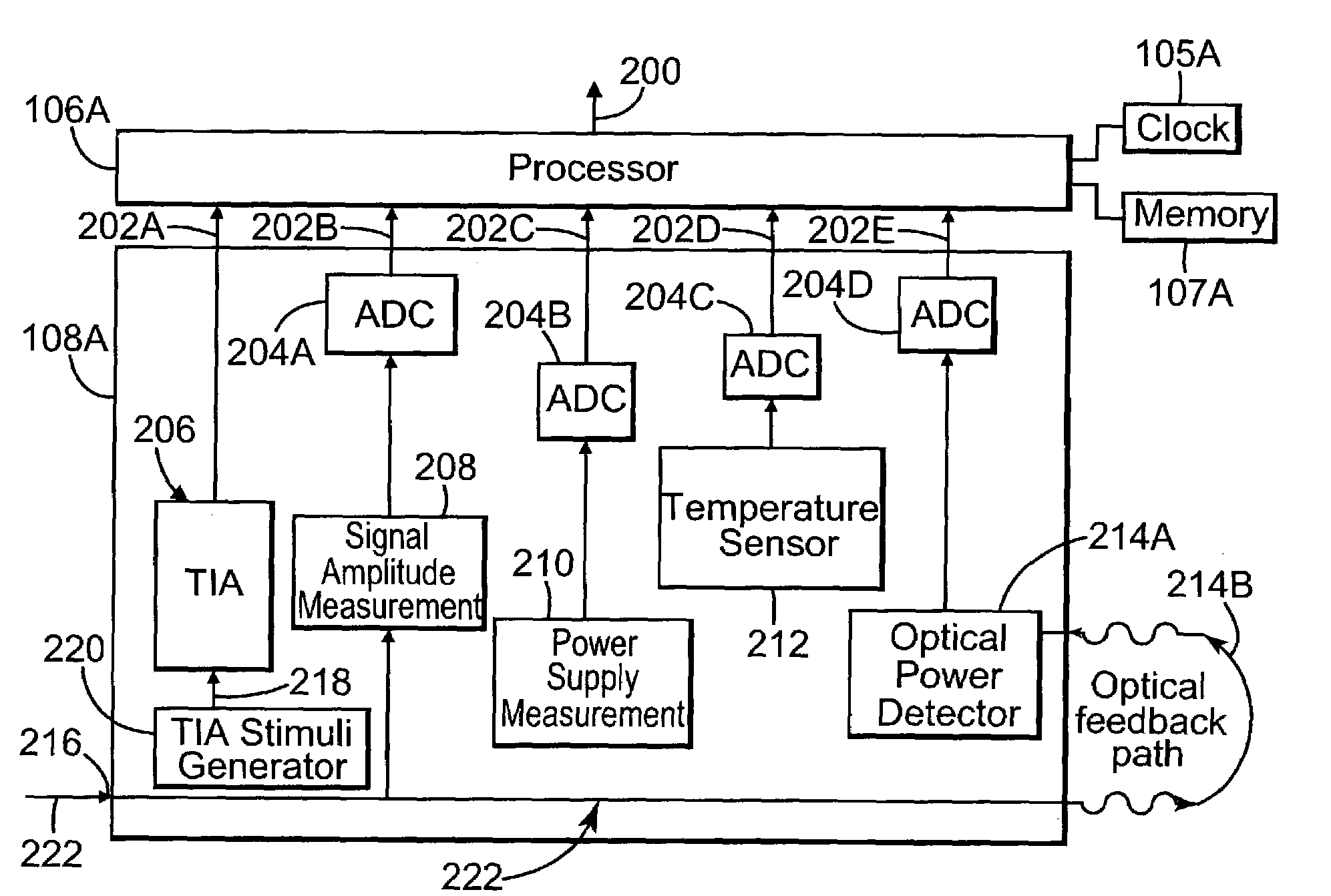
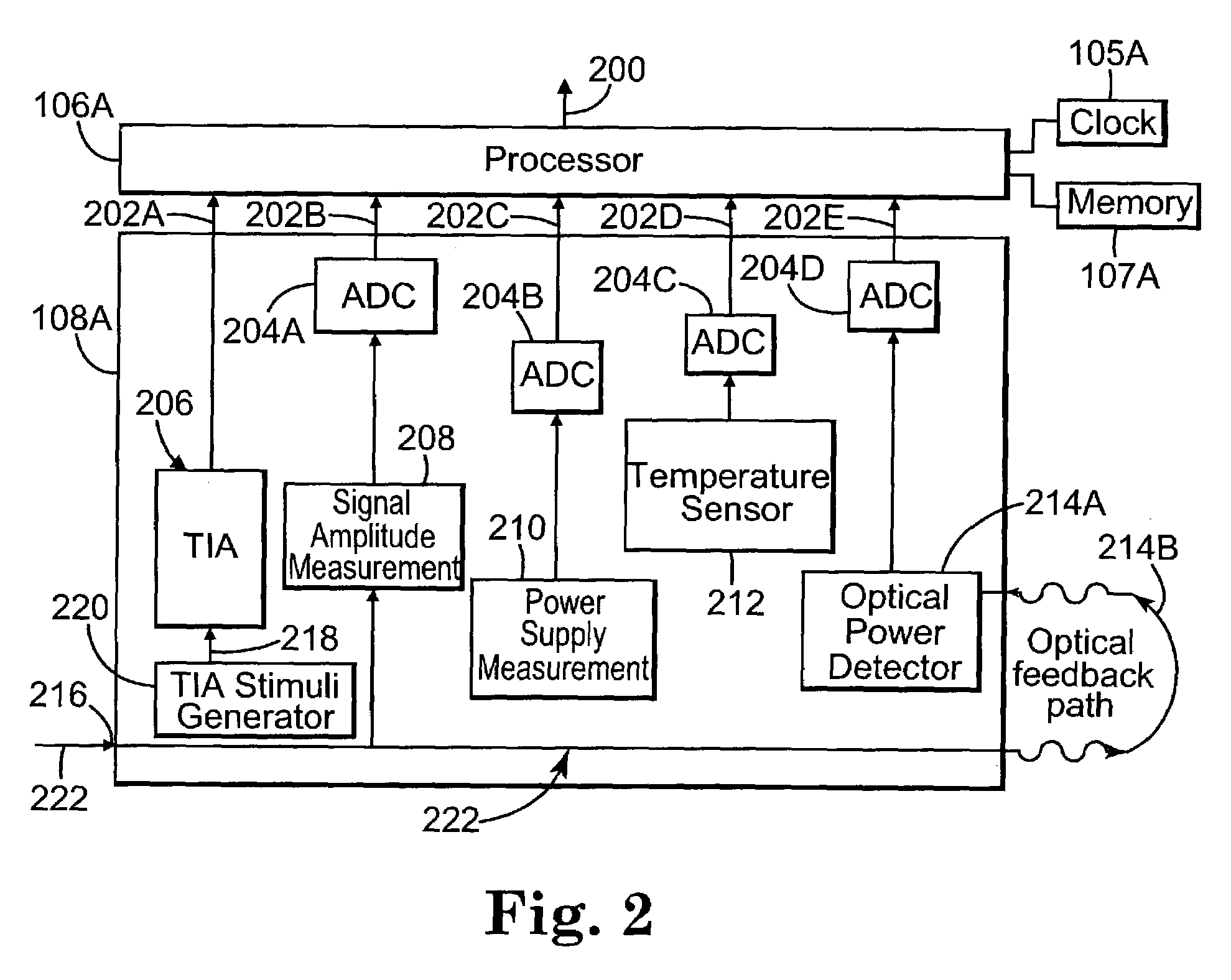
Monitoring system for a communications network
ActiveUS7136772B2Resistance/reactance/impedenceTransmission monitoringMonitoring systemComputer science
A monitoring system for a communications network includes a set of components for transmitting and receiving data signals over the communications network. Each component includes a built-in self-test system for performing tests within the component and outputting corresponding test results. Each self-test system is configured to non-invasively determine waveform characteristics of the data signals. The system includes a set of processors. Each processor is coupled to a subset of the set of components, and is configured to evaluate the test results output by the components coupled to the processor. Each processor is configured to detect and predict faults in the communications network based on the evaluation of the test results.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Method and system for providing a smart memory architecture
ActiveUS20140157065A1High rateHigh error rateError detection/correctionDigital computer detailsMemory chipSmart memory
A smart memory system preferably includes a memory including one or more memory chips, and a processor including one or more memory processor chips. The system may include a smart memory controller capable of performing a bit error rate built-in self test. The smart memory control may include bit error rate controller logic configured to control the bit error rate built-in self test. A write error rate test pattern generator may generate a write error test pattern for the bit error rate built-in self test. A read error rate test pattern generator may generate a read error test pattern for the built-in self test. The smart memory controller may internally generate an error rate timing pattern, perform built-in self test, measure the resulting error rate, automatically adjust one or more test parameters based on the measured error rate, and repeat the built-in self test using the adjusted parameters.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
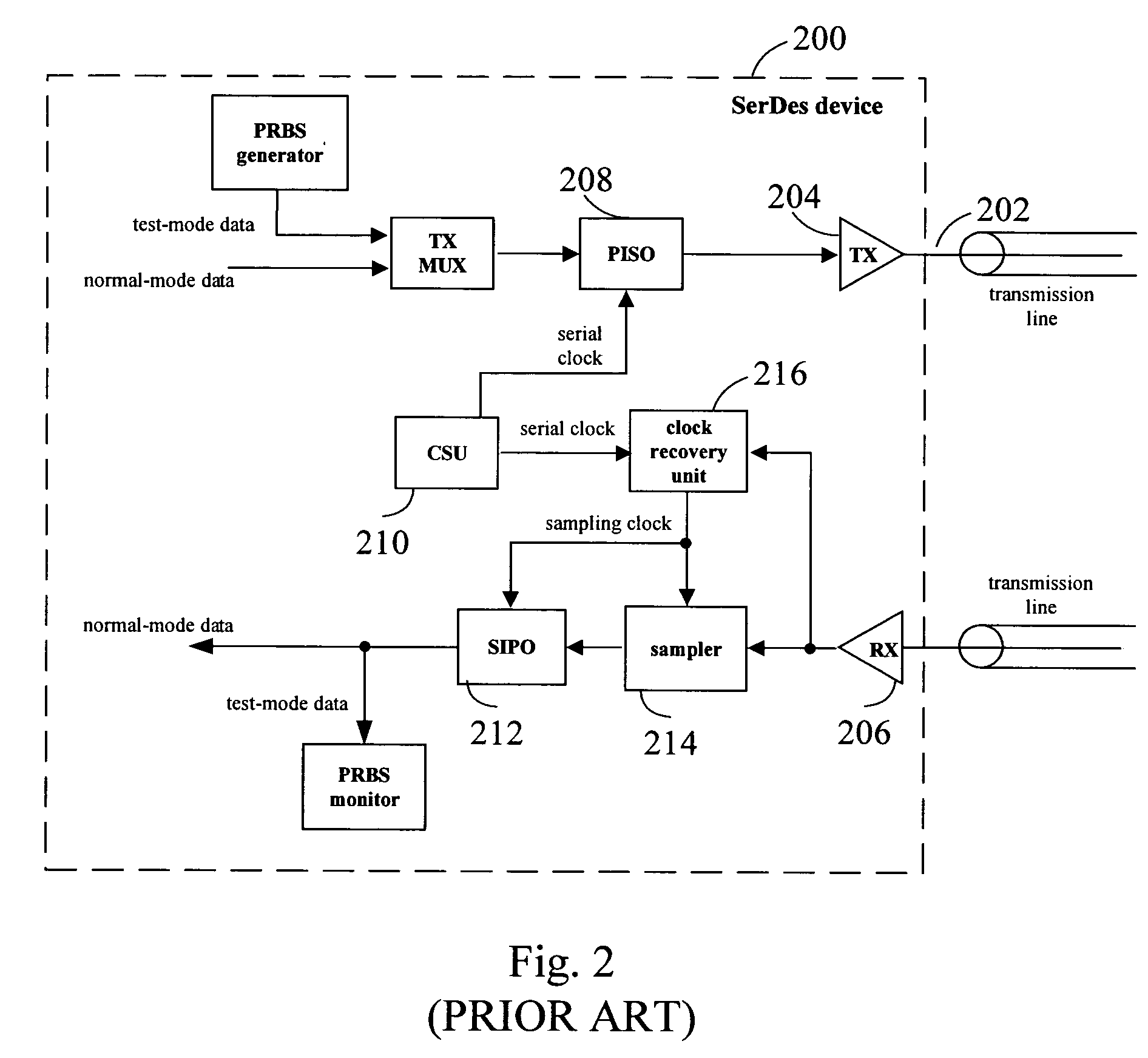
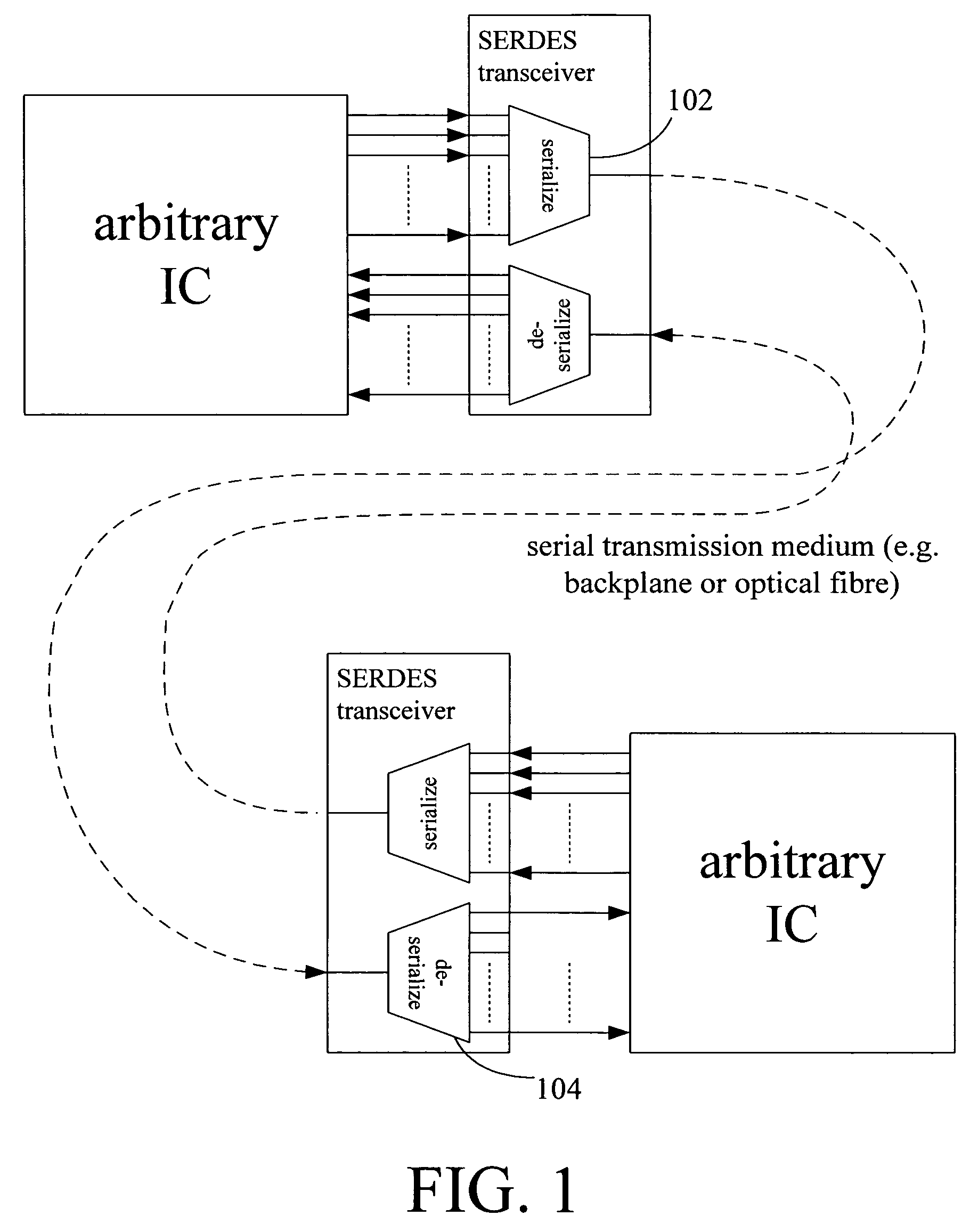
Systems and methods for a built in test circuit for asynchronous testing of high-speed transceivers
ActiveUS7363563B1Maintain performanceCost prohibitiveError preventionPulse automatic controlBuilt-in self-testSerializer
Methods and apparatus provide a transceiver, such as a serializer / deserializer device (SerDes), with enhanced built-in self test (BIST). A built-in self test circuit is provided that decouples a clock signal used for receiving data from a clock signal used in transmitting data. This permits data tracking circuitry of a receiver to be efficiently tested with a relatively simple loop back test.
Owner:MICROSEMI STORAGE SOLUTIONS
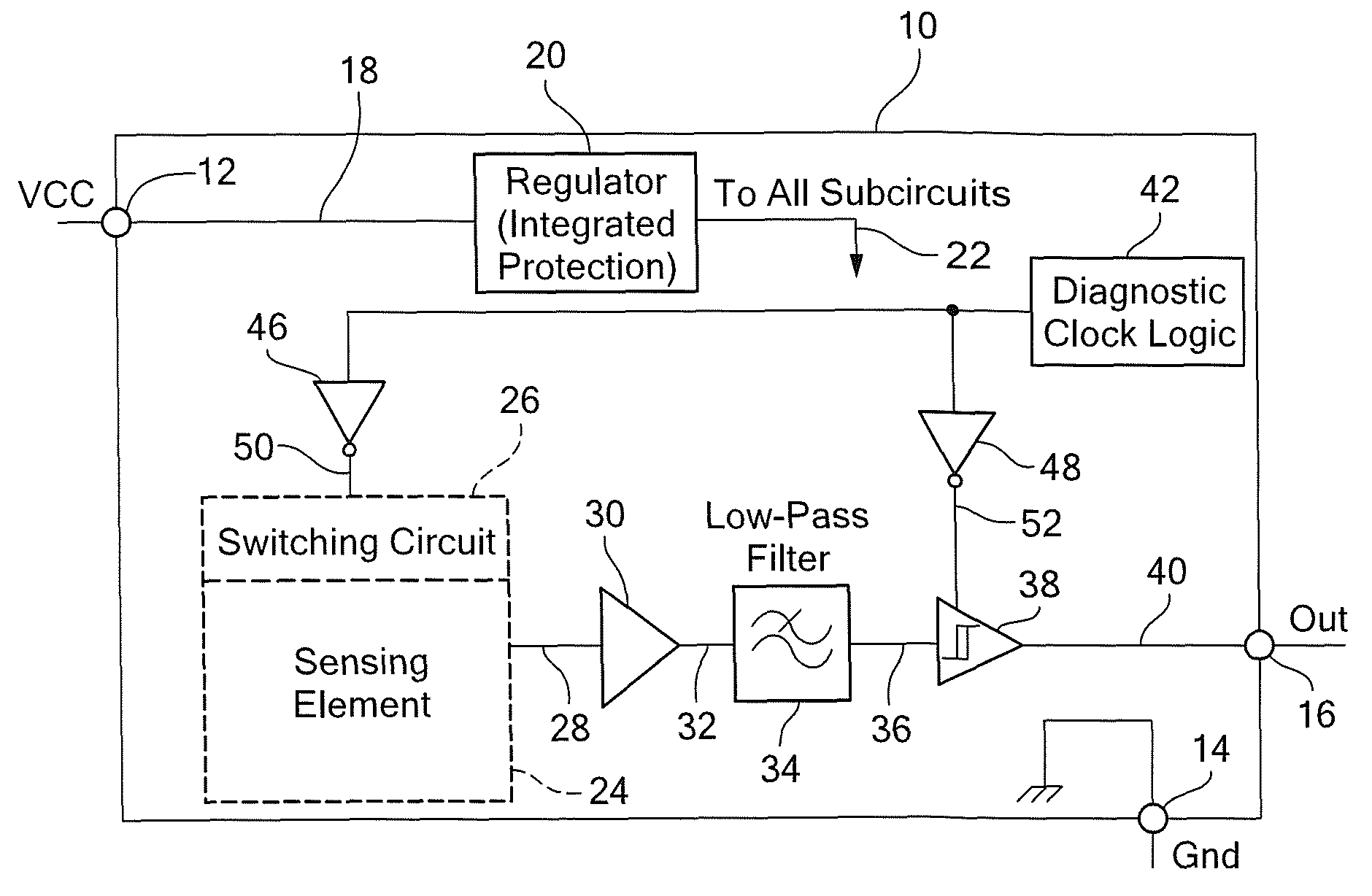
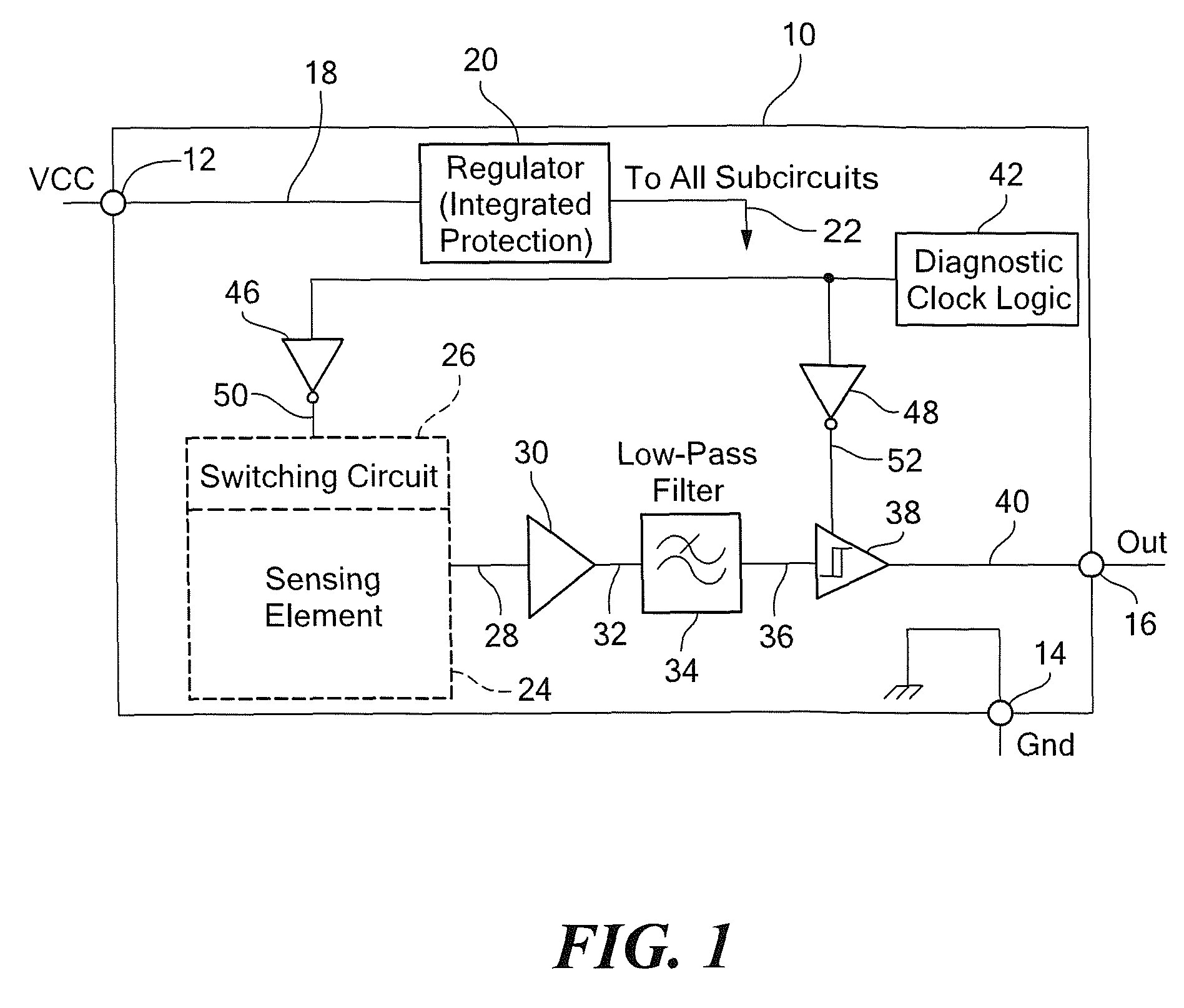
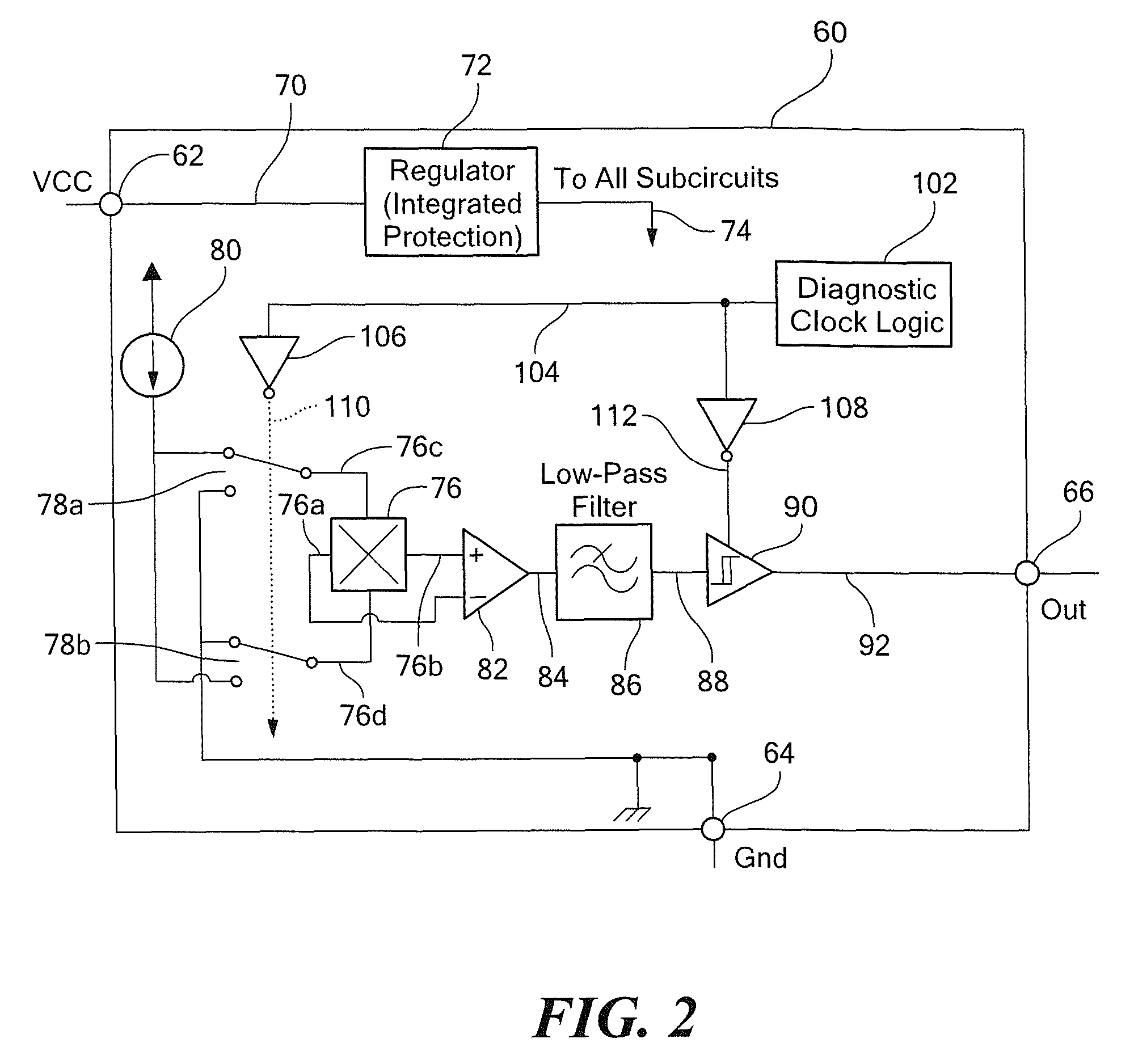
Integrated circuit having built-in self-test features
ActiveUS7800389B2Electronic circuit testingIndividual semiconductor device testingEngineeringBuilt-in self-test
An integrated circuit includes a sensor for providing a sensor output signal and a diagnostic circuit coupled to the sensor for providing a self-diagnostic signal. The self-diagnostic signal comprises the sensor output signal during a first time duration and an inverted sensor output signal during a second different time duration.
Owner:ALLEGRO MICROSYSTEMS INC
Resizable Cache Memory
InactiveUS20100131812A1Reduce power consumptionElectronic circuit testingError detection/correctionMemory addressParallel computing
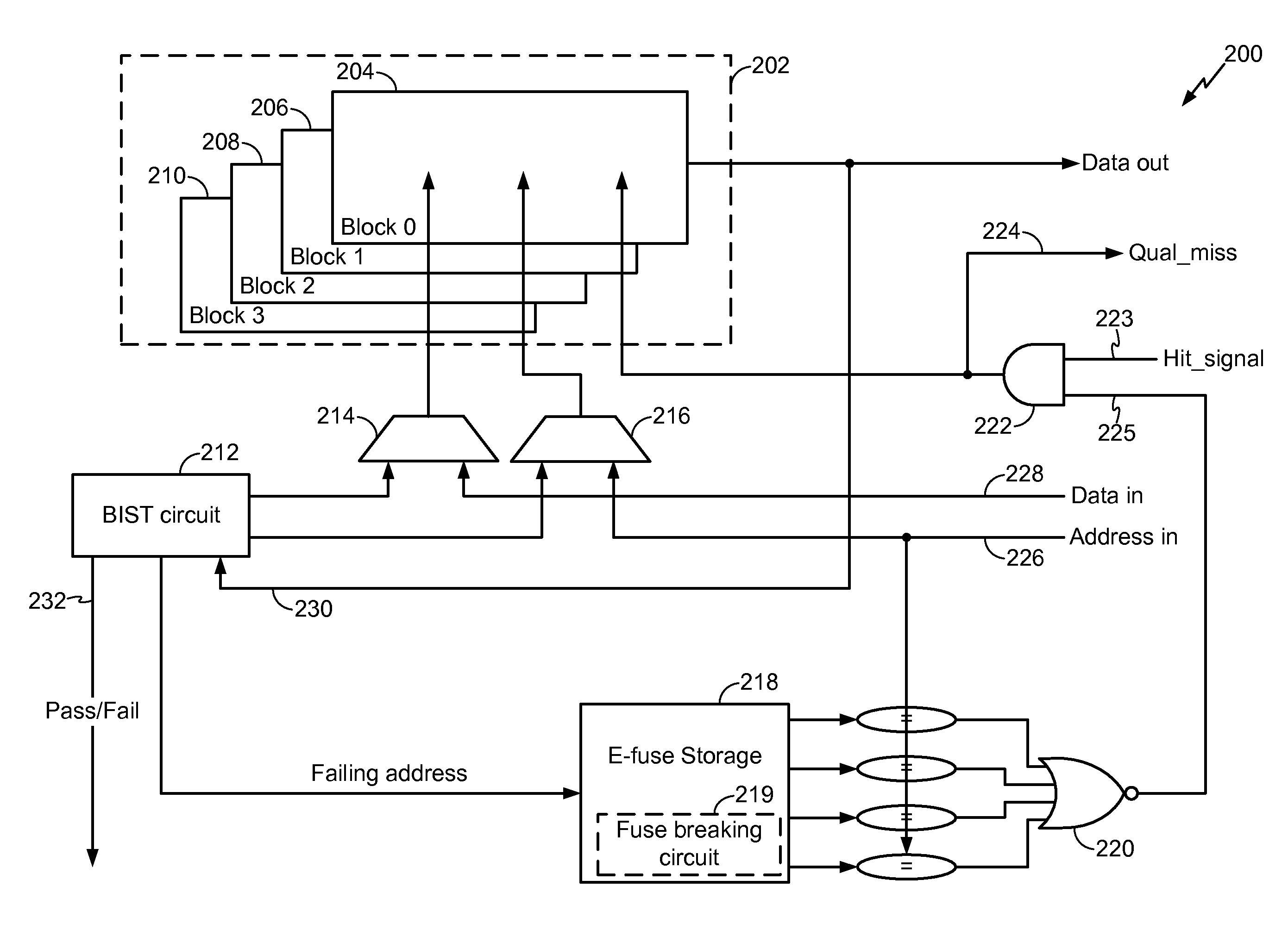
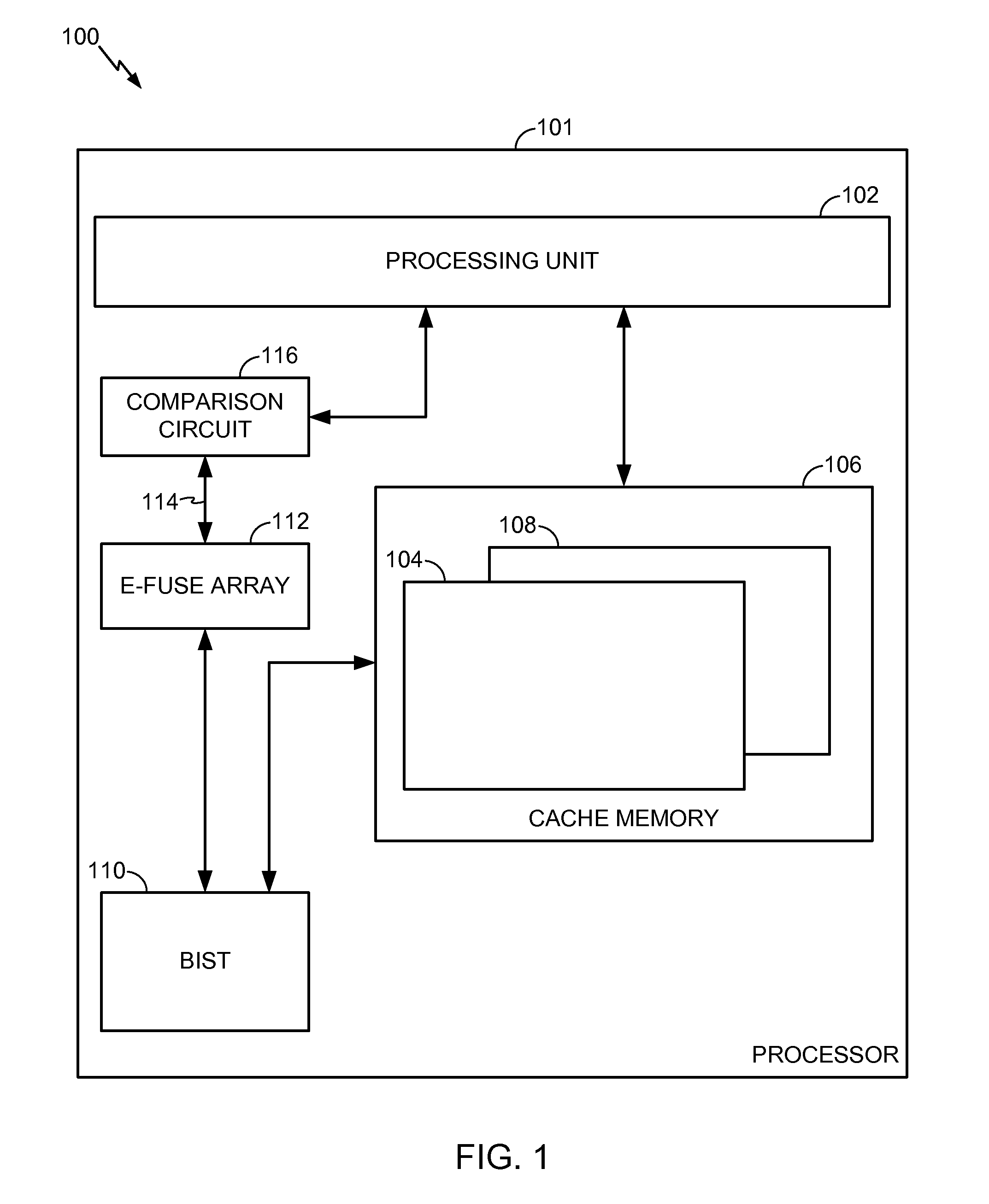
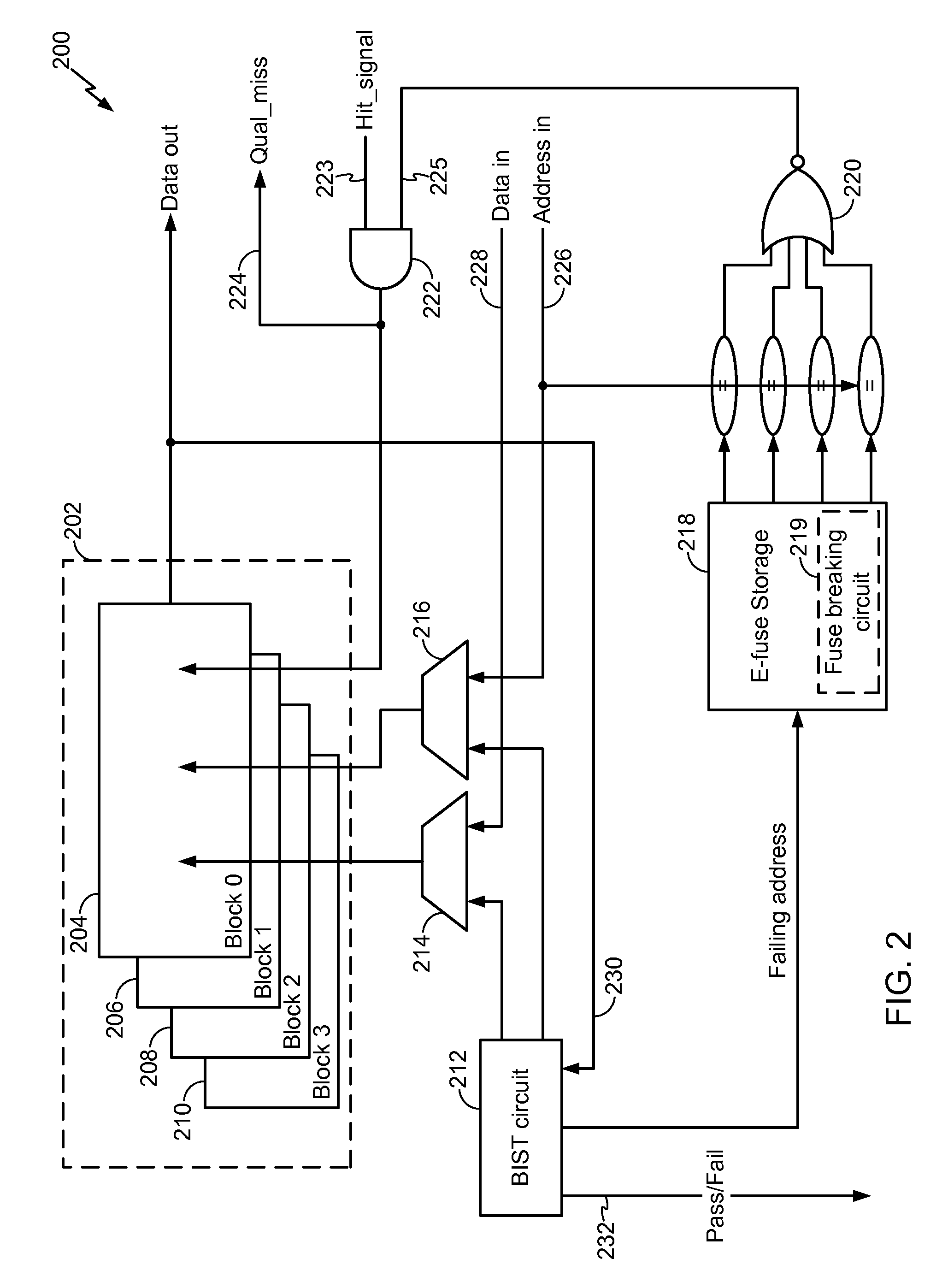
A resizable cache memory is disclosed. In a particular embodiment, a system is disclosed and includes a Built-In Self Test (BIST) circuit configured to test a cache memory. The system further includes a non-volatile storage device including an E-fuse array to store one or more indicators. Each indicator identifies a corresponding memory address of a failed location of the cache memory that has been detected by the BIST circuit.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
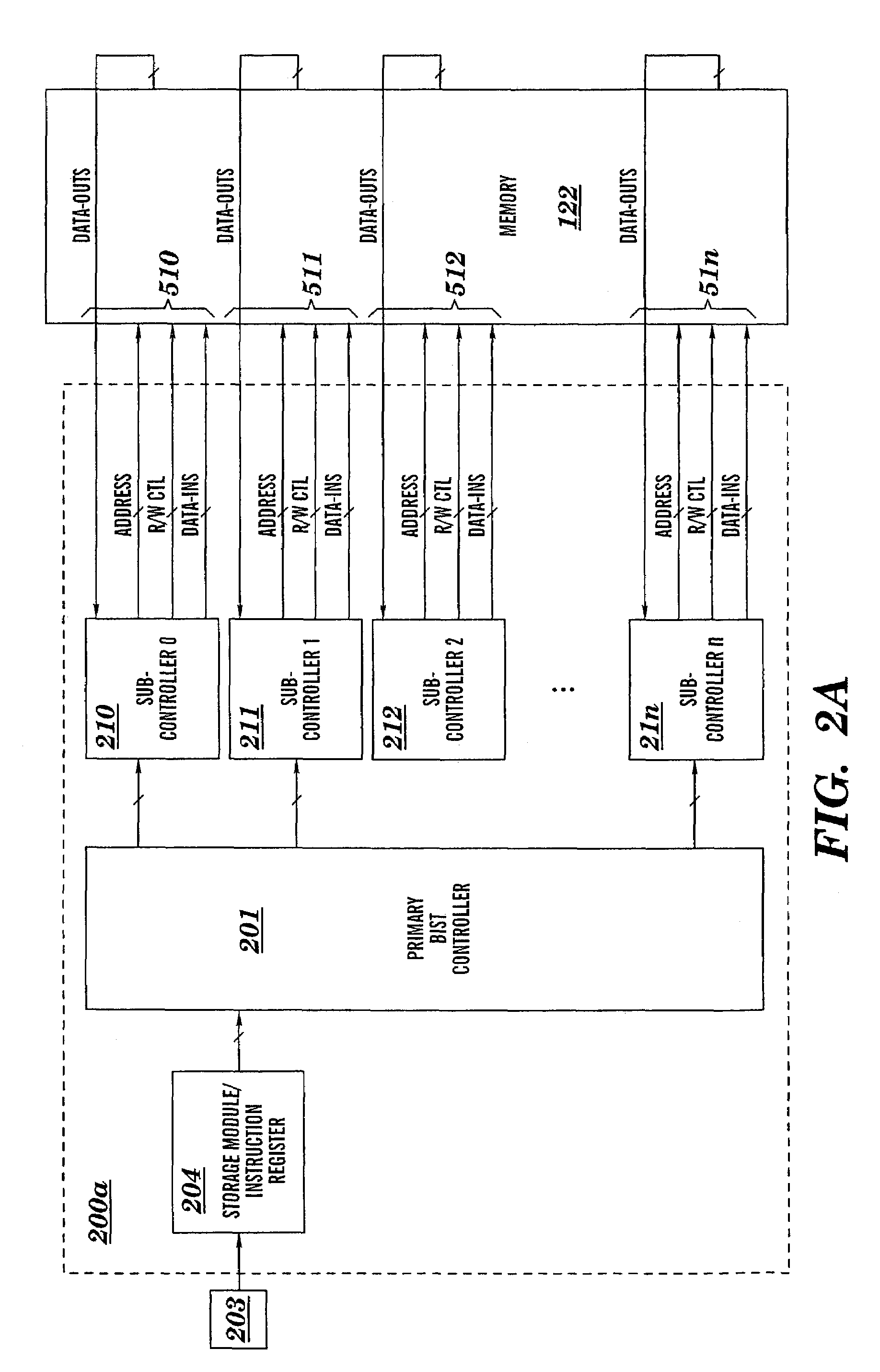
Programable multi-port memory BIST with compact microcode
InactiveUS7168005B2Easy to testIncrease flexibilityElectronic circuit testingFunctional testingAs DirectedMaster controller
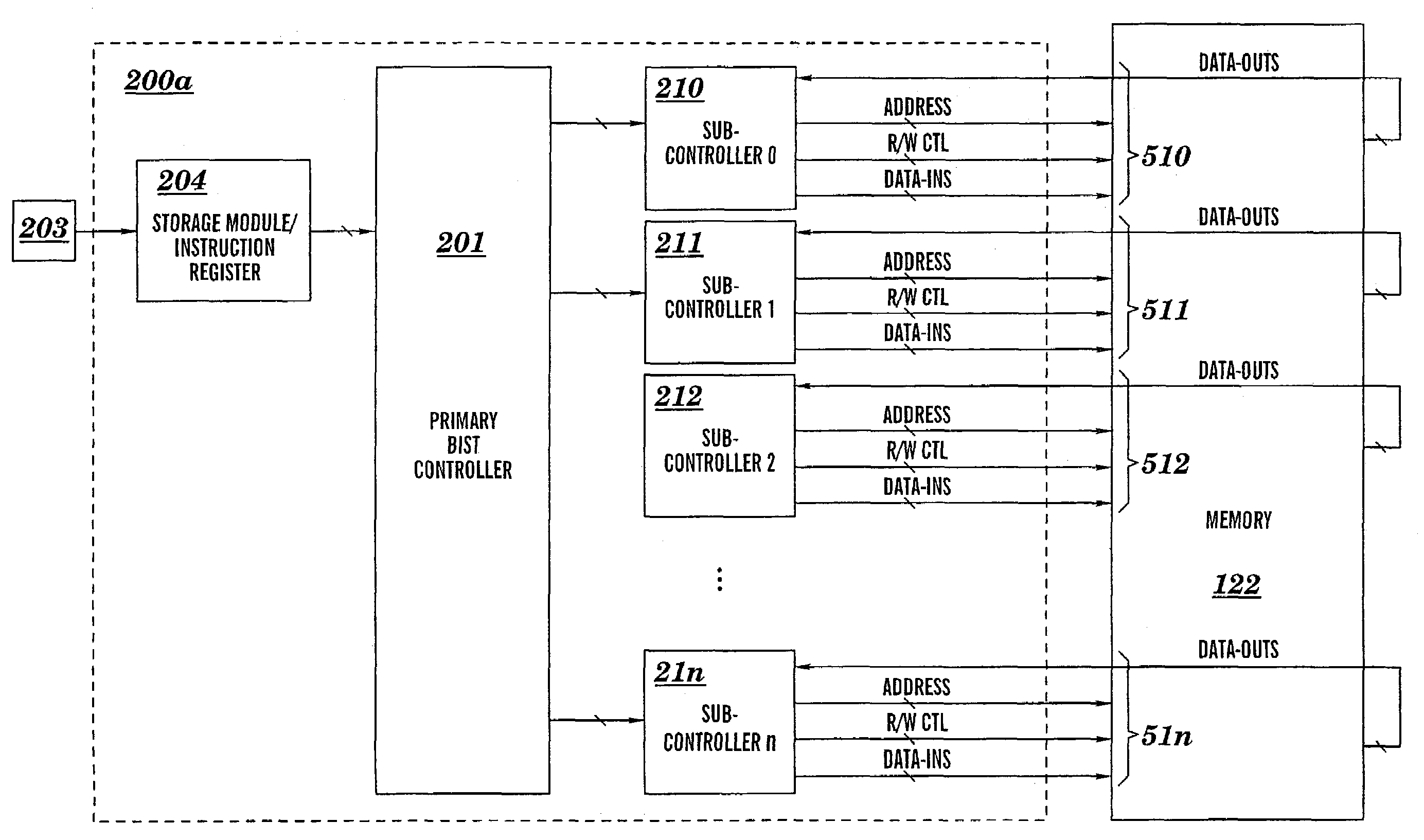
A microcode programmable built-in-self-test (BIST) circuit and method for testing a multiported memory via multiple ports, either simultaneously or sequentially, as directed by a microcode instruction word. The microcode instruction word contains a plurality of executable subinstructions and one bit of information that controls whether the test operations prescribed in the plurality of subinstructions shall be executed in parallel or in series. The executable subinstructions are dispatched by a primary controller to subcontrollers which perform test operations at each port according to the subinstructions. The microcode programable BIST architecture flexibly facilitates the testing of multiple devices, multiported devices, including multiported memory structures and complex dependent multiported memory structures. The BIST supports in-situ testing of the functionality of the memory at wafer, module, and burn-in, as well as system-level testing.
Owner:CADENCE DESIGN SYST INC
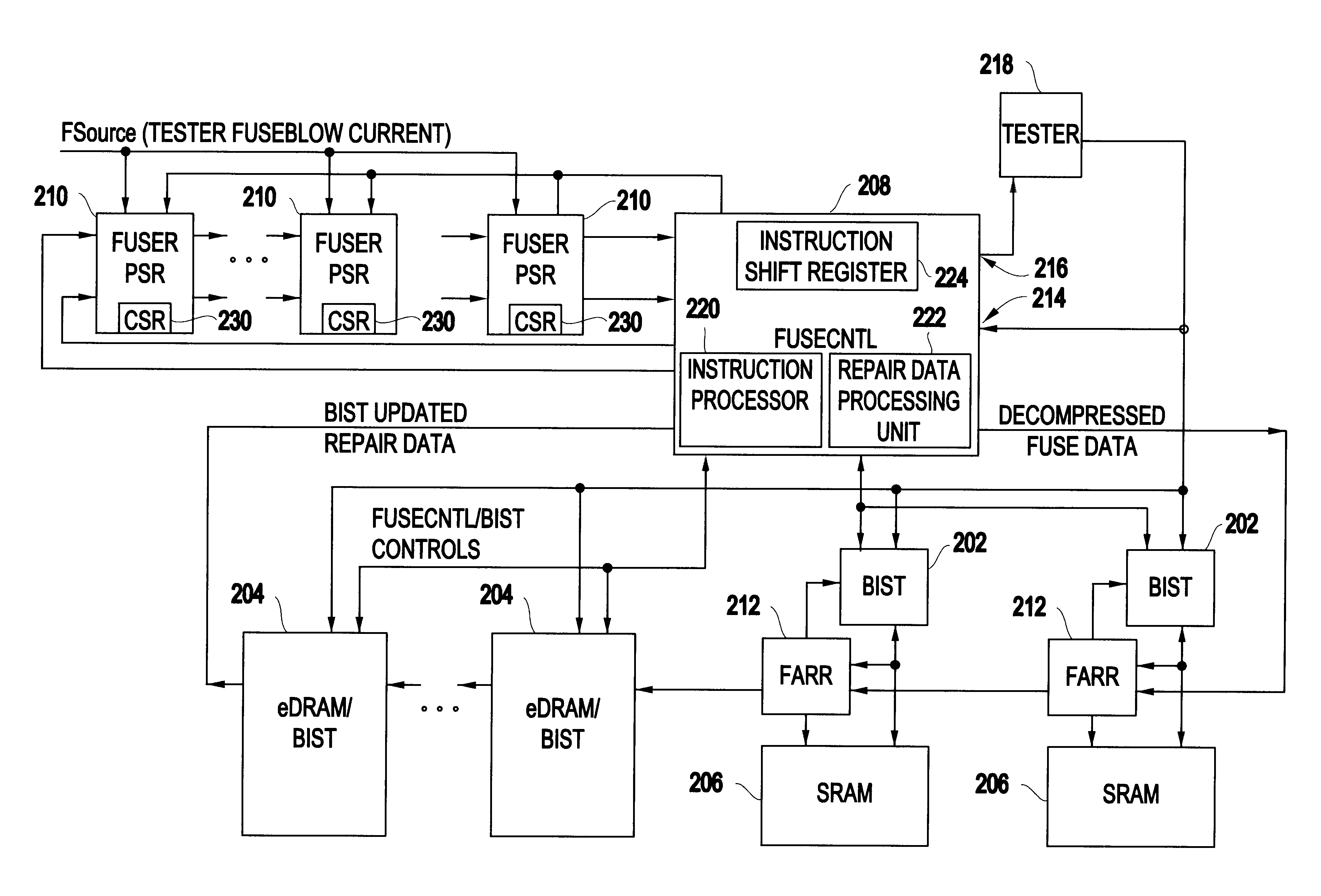
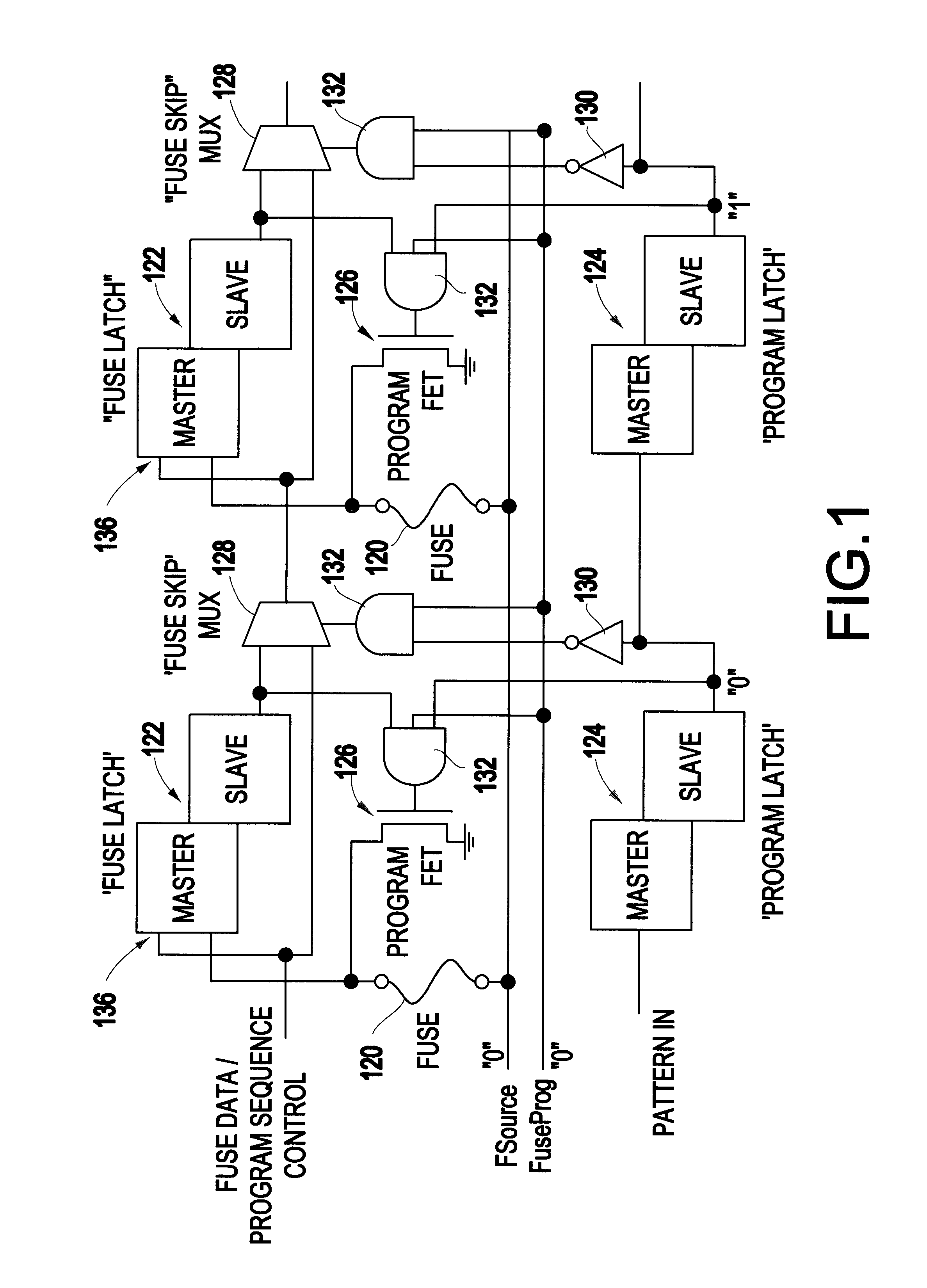
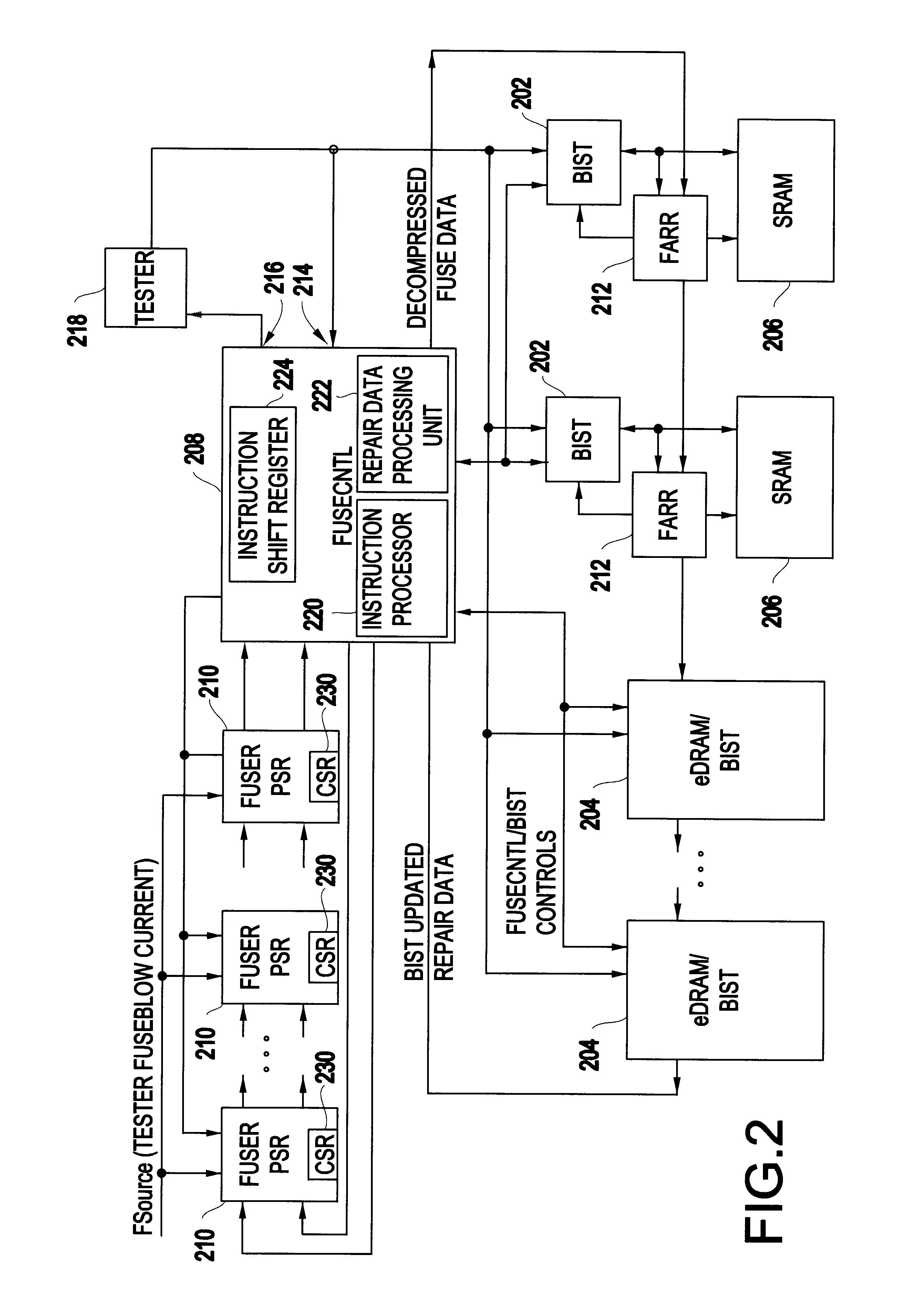
Method of electrically blowing fuses under control of an on-chip tester interface apparatus
A chip repair system designed for automated test equipment independent application on many unique very dense ASIC devices in a high turnover environment is disclosed. During test, the system will control on chip built-in self-test (BIST) engines collect and compress repair data, program fuses and finally decompress and reload the repair data for post fuse testing. In end use application this system decompresses and loads the repair data at power-up or at the request of the system.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
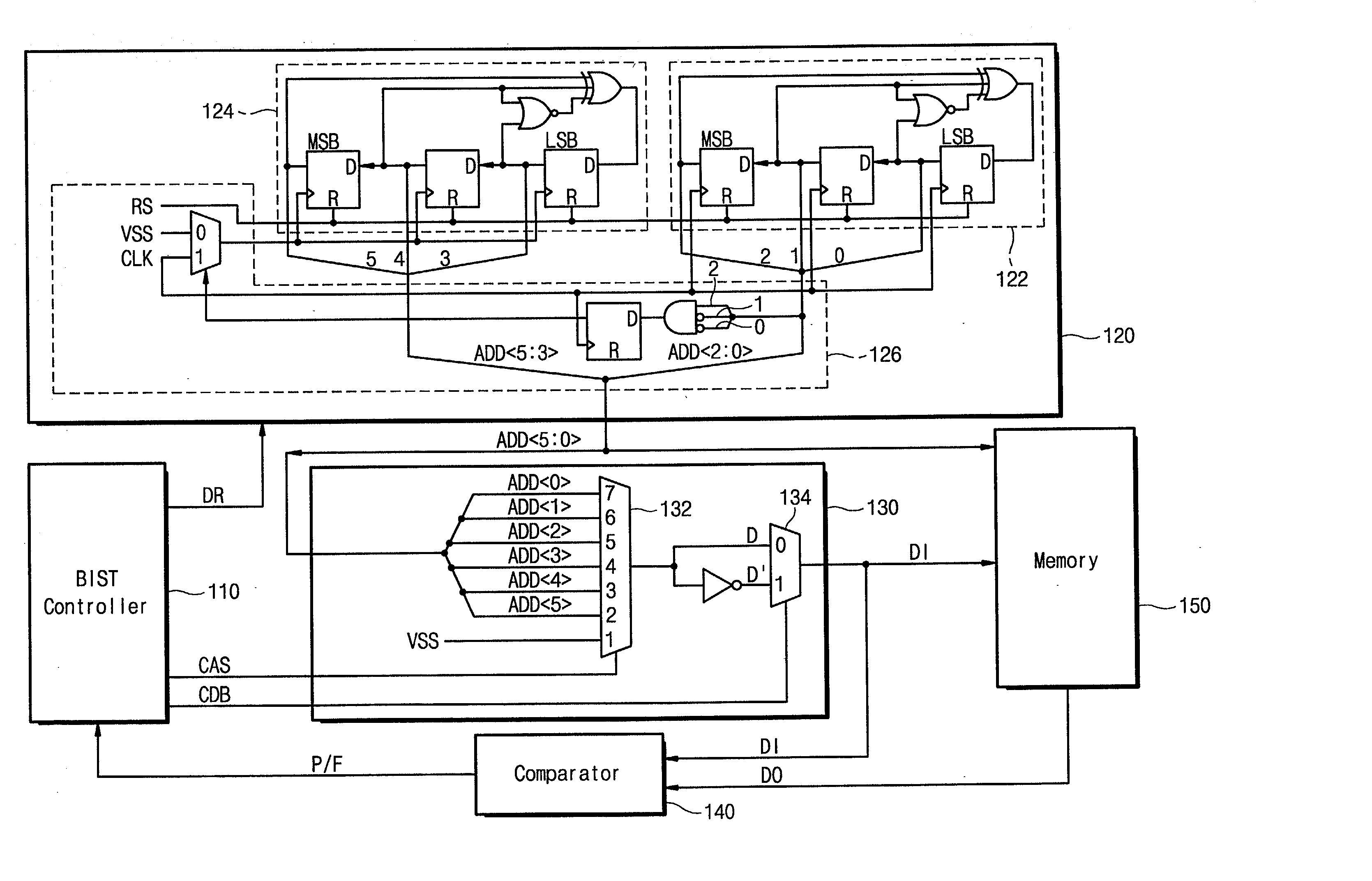
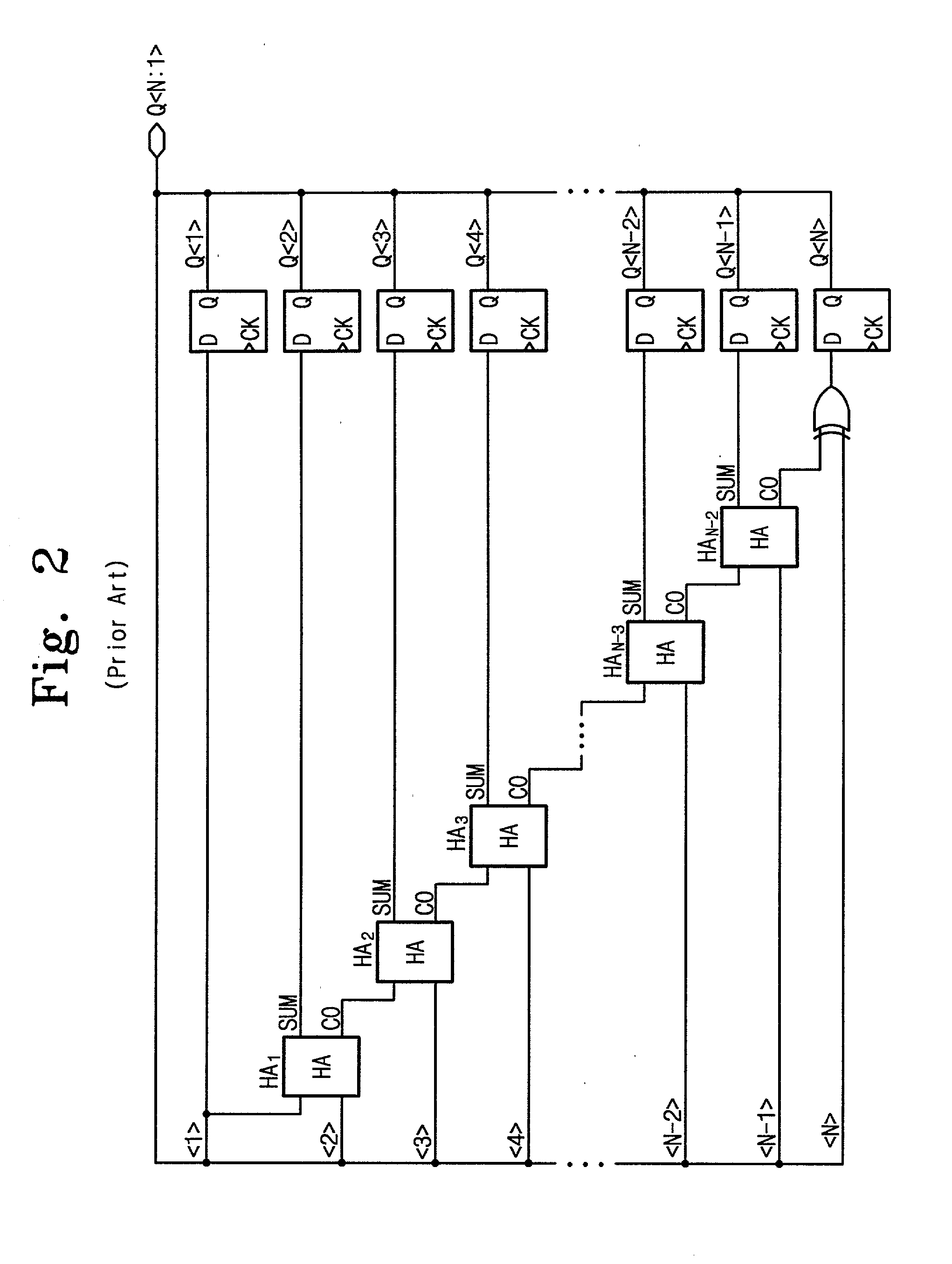
Built-in self test circuit using linear feedback shift register
A built-in self test (BIST) circuit comprising a linear feedback shift register is disclosed. The BIST circuit comprises a controller for controlling a self-testing operation of a memory chip embedded in an integrated circuit, an address generator for generating pseudo-random address patterns under control of the controller, a data generator for producing test data associated with data backgrounds of the address bits under the control of the controller, and a comparator for comparing the test data with memory data output from the memory chip to detect a defect, if any, of the memory chip. The pseudo-random random pattern comprises a single-random pseudo-random address pattern.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
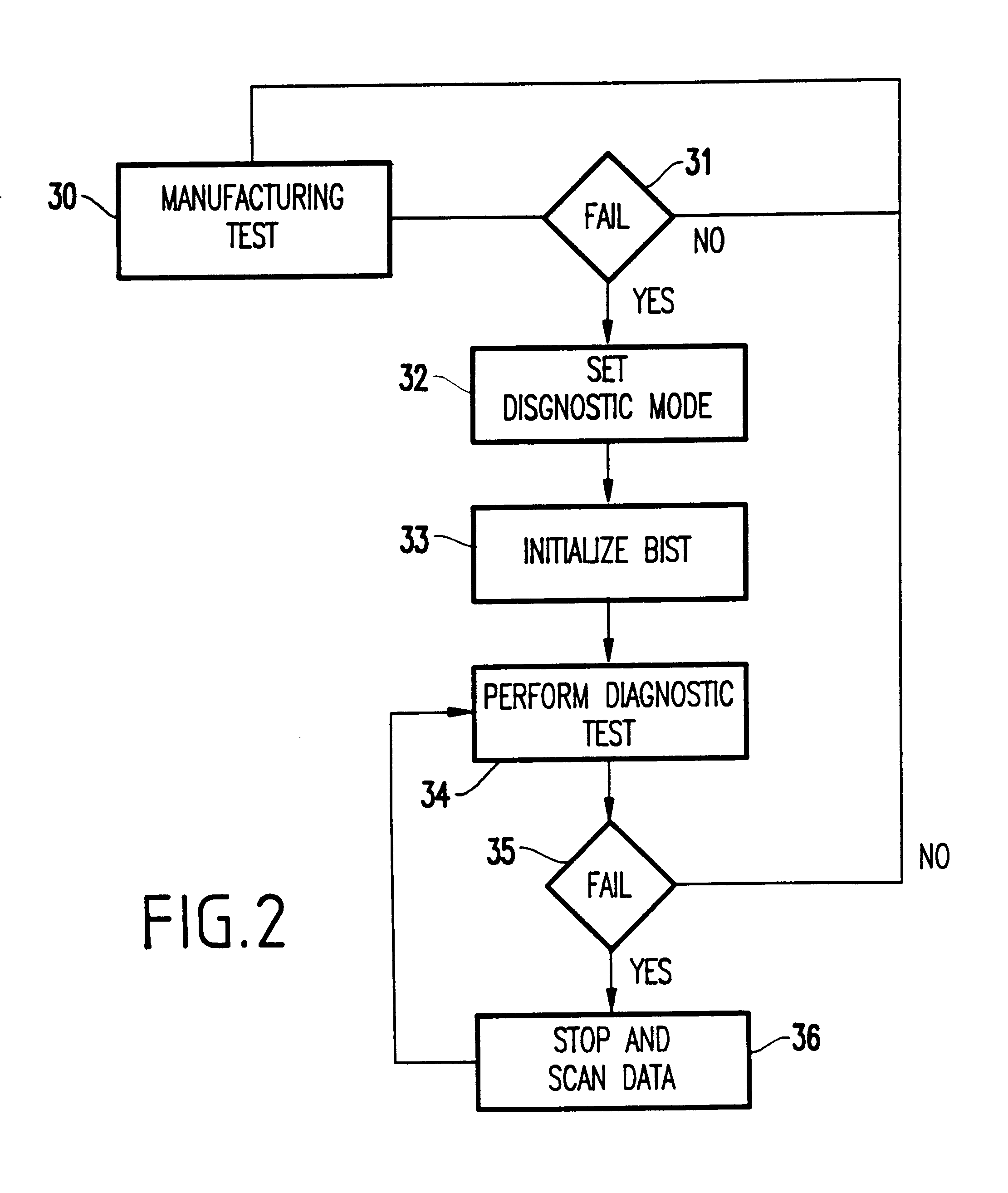
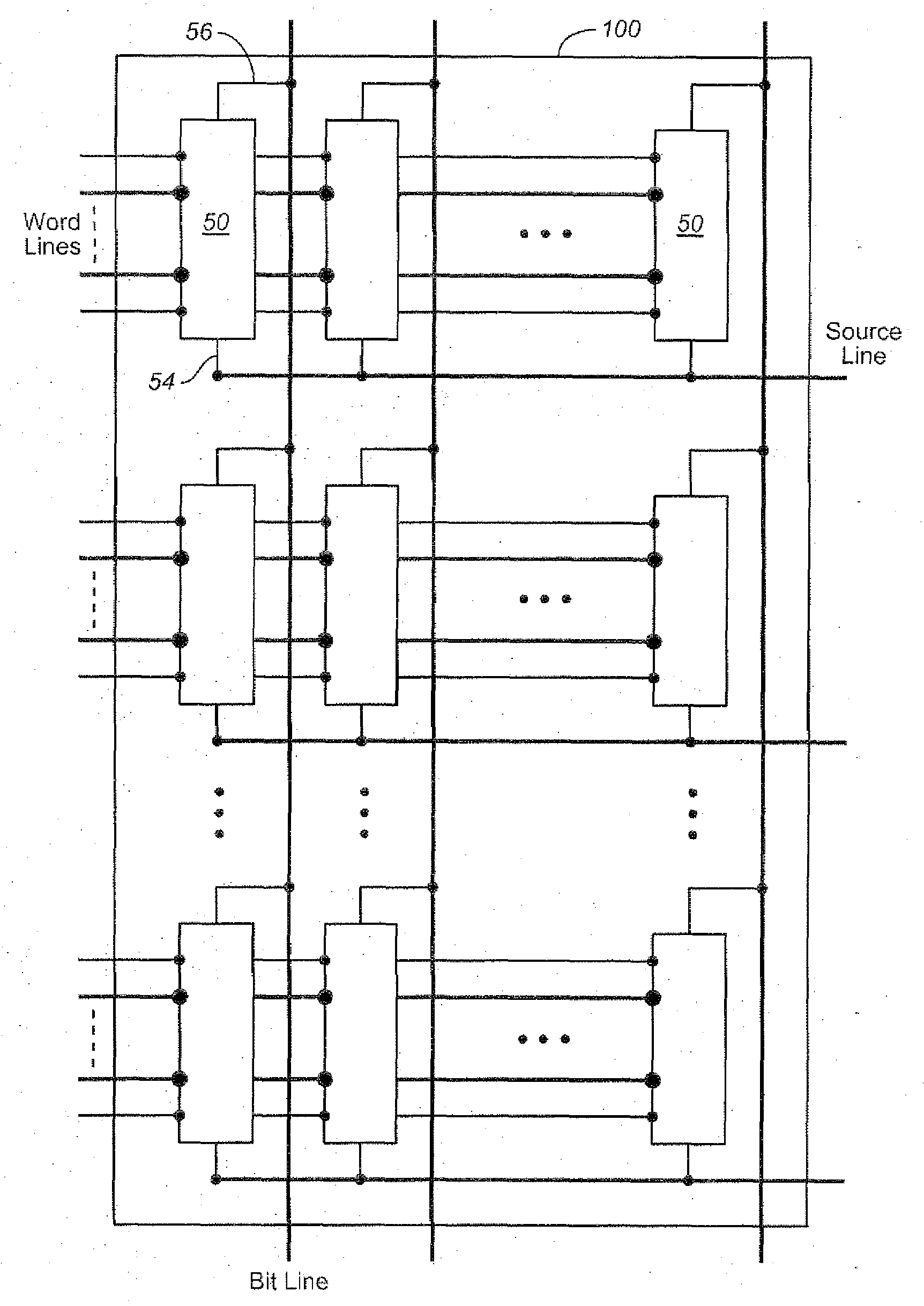
Array-built-in-self-test (ABIST) for efficient, fast, bitmapping of large embedded arrays in manufacturing test
A structure and method for an integrated circuit which includes read / write memory having a plurality of memory devices, each of the memory devices having a unique address; a built-in self-test (BIST) engine, the BIST engine having a controller responsive to a test enable signal and operative to generate and store test data in the read / write memory; a comparator operative to compare retrieved data read from the read / write memory and the test data during a first pass test, the comparator identifying failed cycles where the retrieved data does not correspond correctly to the test data; and a diagnostic unit operative to store the failed cycles and being responsive to the controller generating and storing the test data in the read / write memory and operative to store failed data and failing addresses during a first pass test, wherein the BIST engine stops only at each of the failed cycles during the first pass test.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
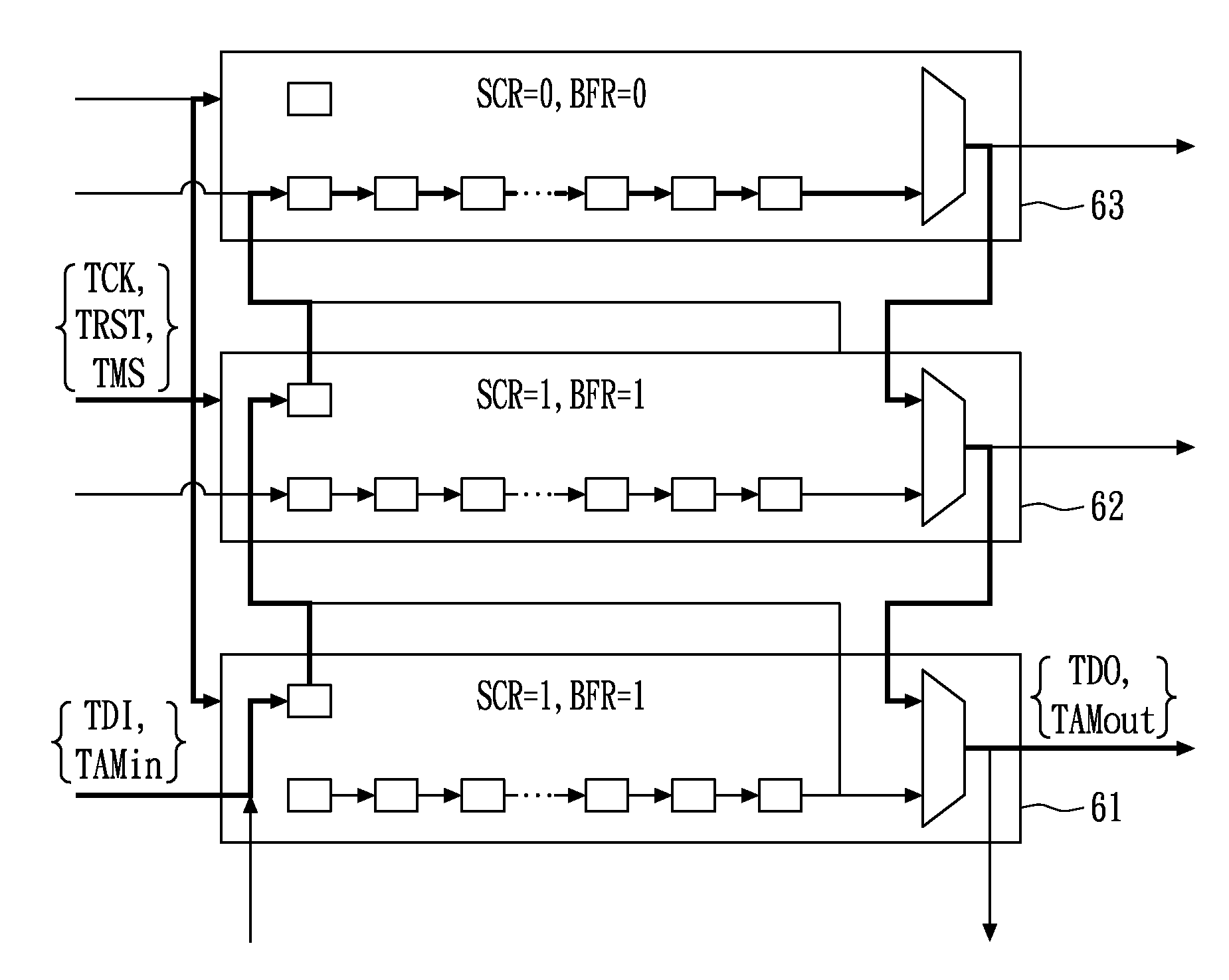
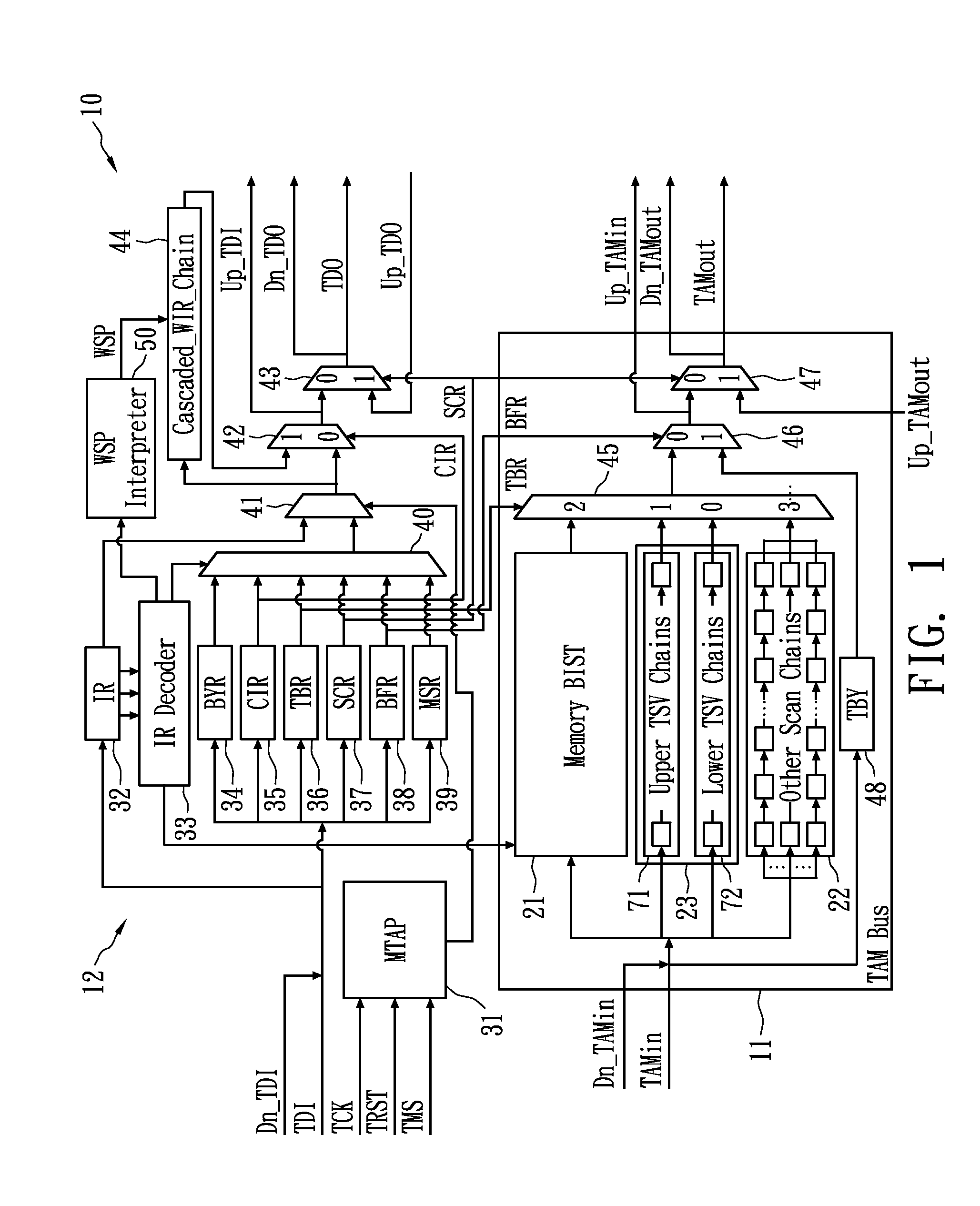
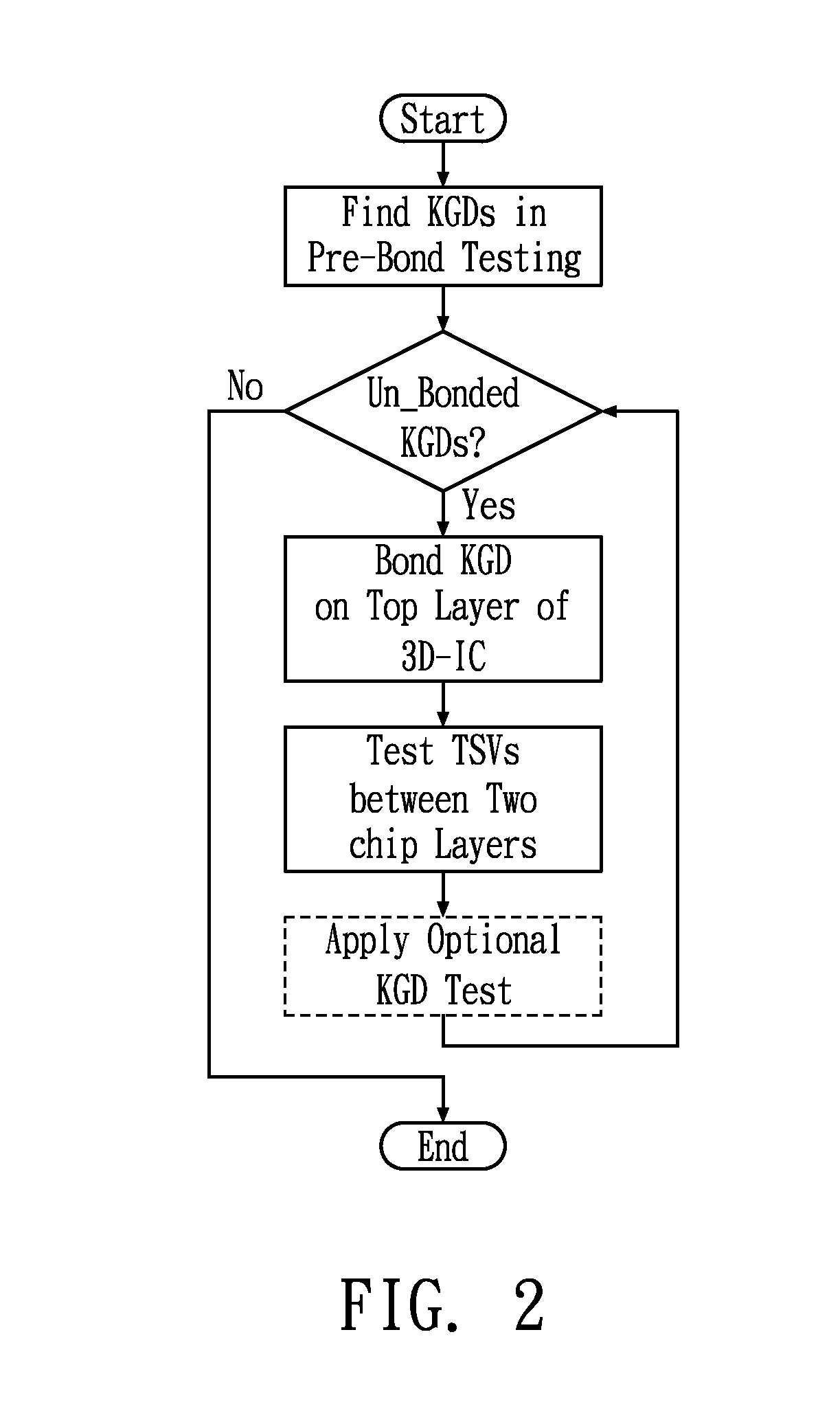
Test access control apparatus and method thereof
InactiveUS20100332177A1High yieldResistance/reactance/impedenceStatic storageEngineeringBuilt-in self-test
A test access control apparatus includes test access mechanism (TAM) buses and an extended IEEE 1149.1 Test Access Port (TAP) Controller. The TAM buses support memory built-in-self-test (BIST) circuit for the memory known-good-die (KGD) test, scan chains for the logic KGD test; and through-silicon-via (TSV) chains that are configured to conduct the TSV test that verifies any defect in vertical interconnects between any two chip layers of the stacked chip device. The TAP Controller is coupled to the TAM buses and is configured to control the memory KGD test, the logic KGD test and the TSV test between two chip layers. A cost-effective connection or configuration of test access control apparatus in 3D-IC is also present. In accordance with an embodiment of the present invention, a test access control method includes a yield-concerned test methodology for 3D-IC, and an integrated flow of test access control apparatus supporting heterogeneous test protocols of SOC
Owner:NATIONAL TSING HUA UNIVERSITY
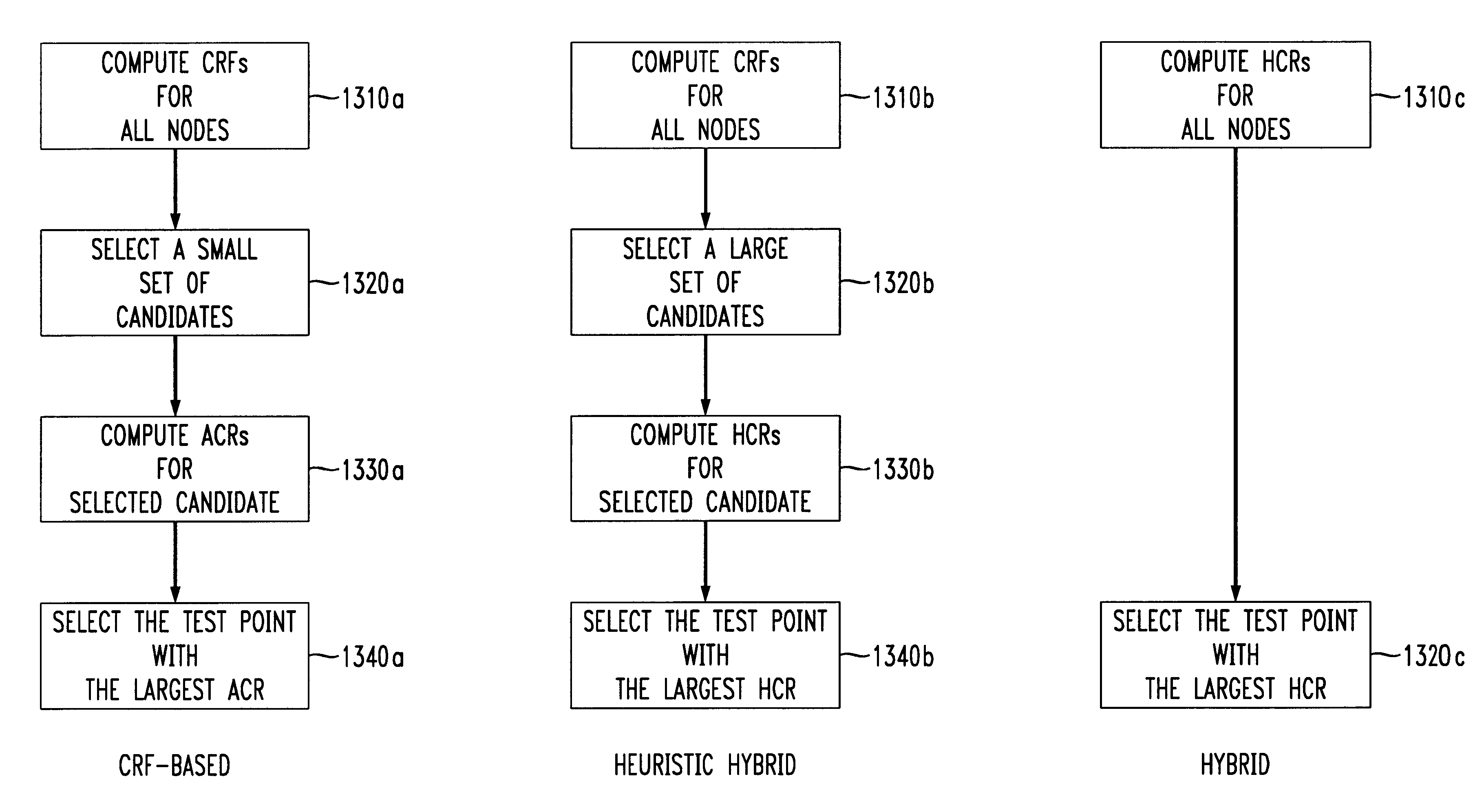
Hybrid algorithm for test point selection for scan-based BIST
A test point selection method for scan-based built-in self-test (BIST). The method calculates a hybrid cost reduction (HCR) value as an estimated value of the corresponding actual cost reduction for all nodes in a circuit under test. A test point is then selected having a largest HCR. This iterative process continues until the fault coverage of the circuit under test reaches a desired value or the number of test points selected is equal to a maximum number of test points. In an alternative embodiment, the cost reduction factor is calculated for all nodes in the circuit under test, the HCR is calculated for only a selected set of candidates, and the candidate having the largest HCR is selected as the test point. The test point selection method achieves higher fault coverage results and reduces computational processing relative to conventional selection methods.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC +1
Runtime programmable BIST for testing a multi-port memory device
One embodiment provides a runtime programmable system which comprises methods and apparatuses for testing a multi-port memory device to detect a multi-port memory fault, in addition to typical single-port memory faults that can be activated when accessing a single port of a memory device. More specifically, the system comprises a number of mechanisms which can be configured to activate and detect any realistic fault which affects the memory device when two simultaneous memory access operations are performed. During operation, the system can receive an instruction sequence, which implements a new test procedure for testing the memory device, while the memory device is being tested. Furthermore, the system can implement a built-in self-test (BIST) solution for testing any multi-port memory device, and can generate tests targeted to a specific memory design based in part on information from the instruction sequence.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
Method and apparatus for testing a serial transmitter circuit
InactiveUS6865222B1Easy to testNeed can be addressedCorrect operation testingAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsComputer scienceBuilt-in self-test
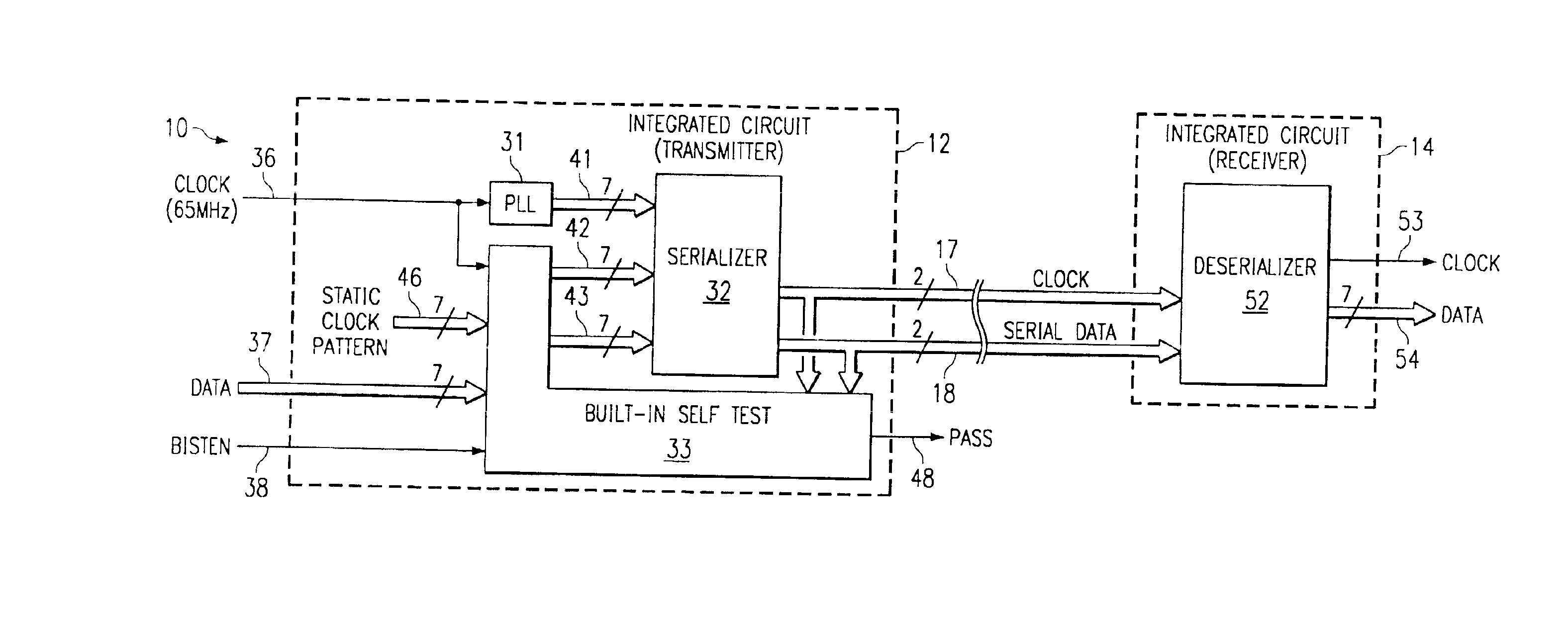
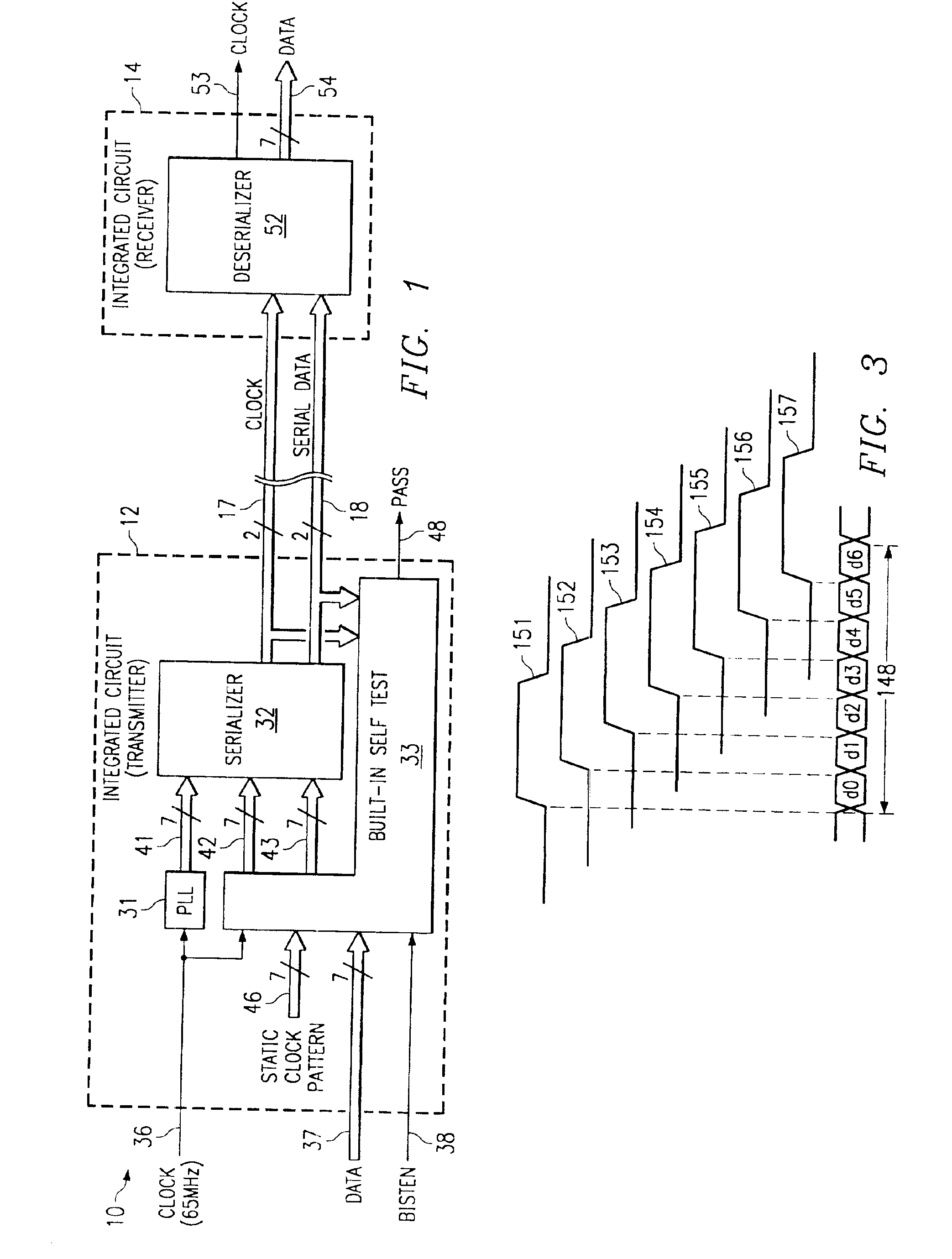
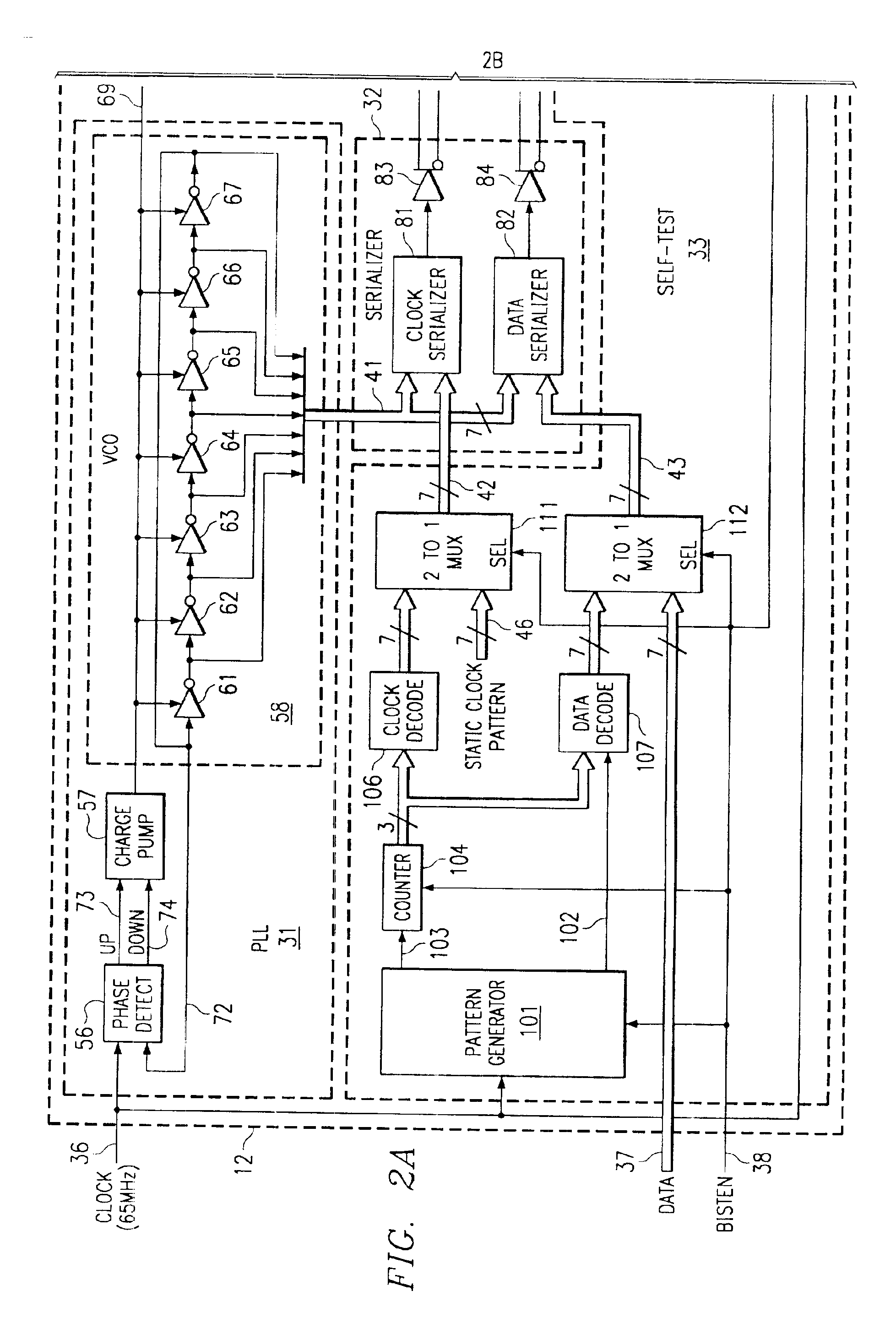
An integrated circuit (12) contains a serializing transmitter, including a phase locked loop (31) that supplies seven clocks (41) with different phases to a serializer circuit (32). The serializer circuit accepts 7-bit words at a parallel input (42), and outputs these words serially in an end-to-end manner on a twisted pair (17), as a clock signal. The serializer circuit also accepts 7-bit words on a further parallel input (43), and transmits them serially in an end-to-end manner on a twisted pair (18), as serialized data. The integrated circuit also includes a built-in self-test circuit (33), which can supply test information to the two parallel inputs of the serializer circuit, and which can monitor the two twisted pairs while the serializer circuit operates at high data rates typical of normal operation, in order to detect any errors introduced by the serializer circuit. The self-test circuit produces a single digital output (48) to indicate whether an error has been detected.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
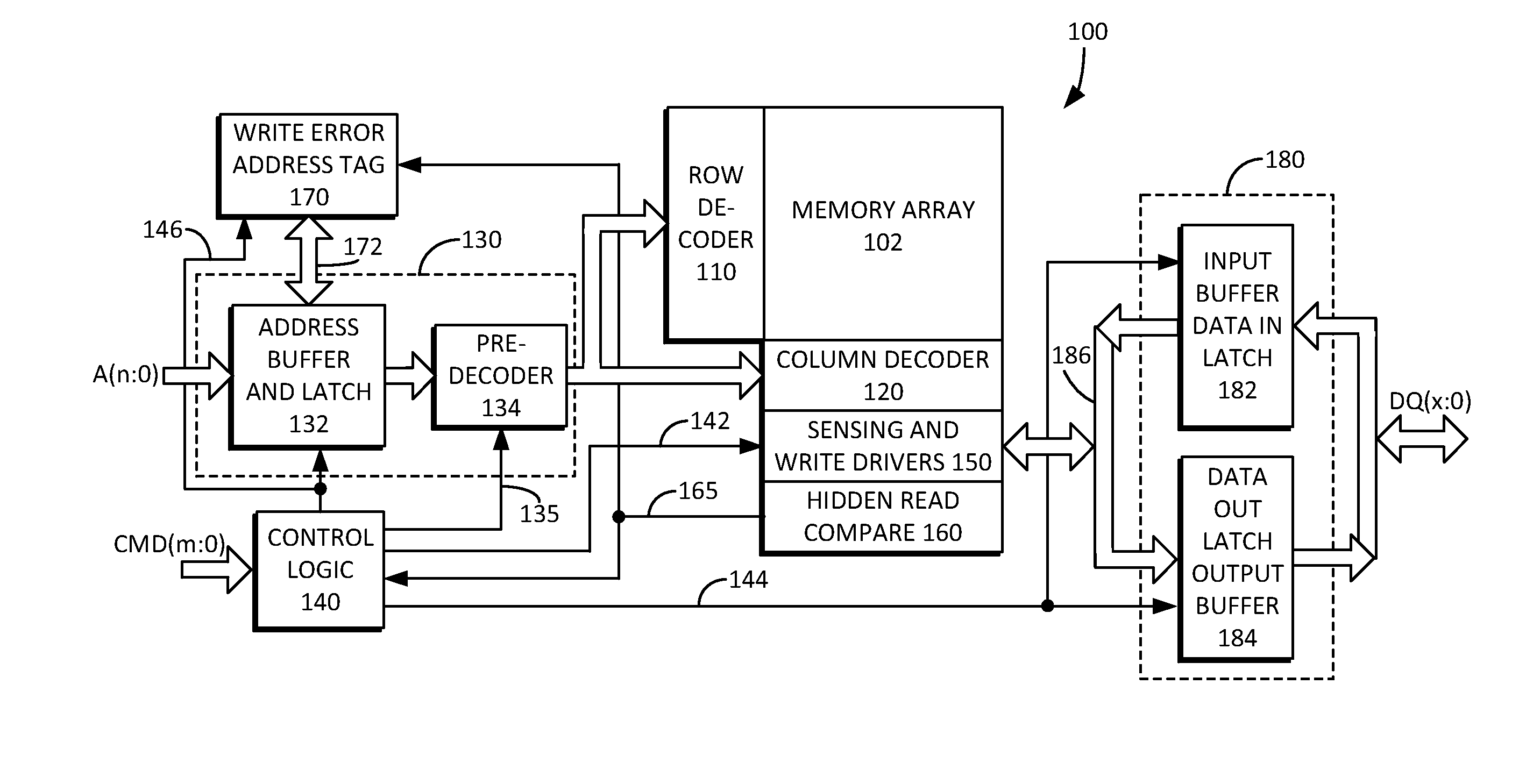
Bad Column Management with Bit Information in Non-Volatile Memory Systems
Column based defect management techniques are presented. Each column of the memory has an associated isolation latch or register whose value indicates whether the column is defective, but in addition to this information, for columns marked as defective, additional information is used to indicate whether the column as a whole is to be treated as defective, or whether just individual bits of the column are defective. The defective elements can then be re-mapped to a redundant element at either the appropriate bit or column level based on the data. When a column is bad, but only on the bit level, the good bits can still be used for data, although this may be done at a penalty of under programming for some bits, as is described further below. A self contained Built In Self Test (BIST) flow constructed to collect the bit information through a set of column tests is also described. Based on this information, the bad bits can be extracted and re-grouped into bytes by the controller or on the memory to more efficiently use the column redundancy area.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
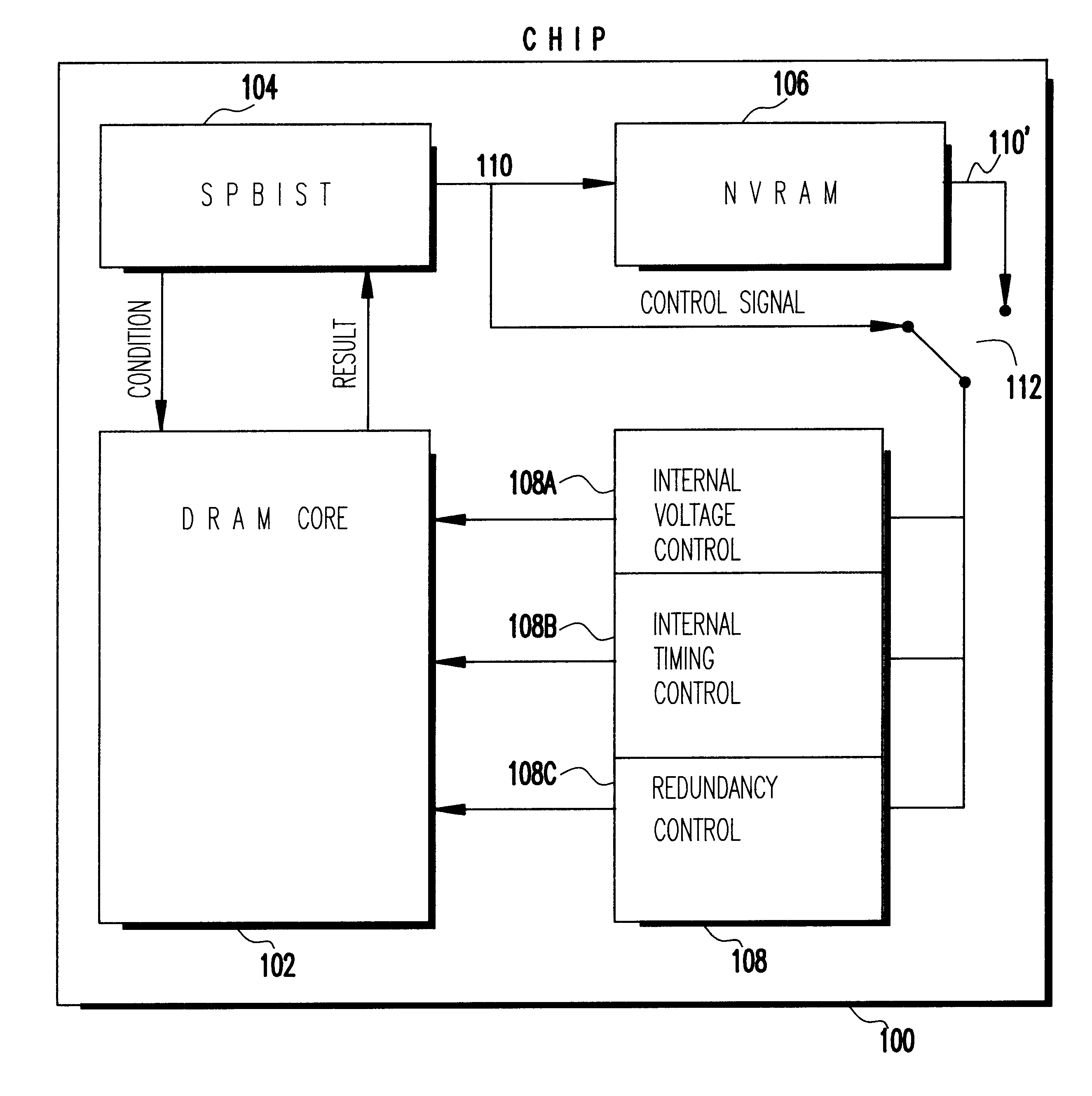
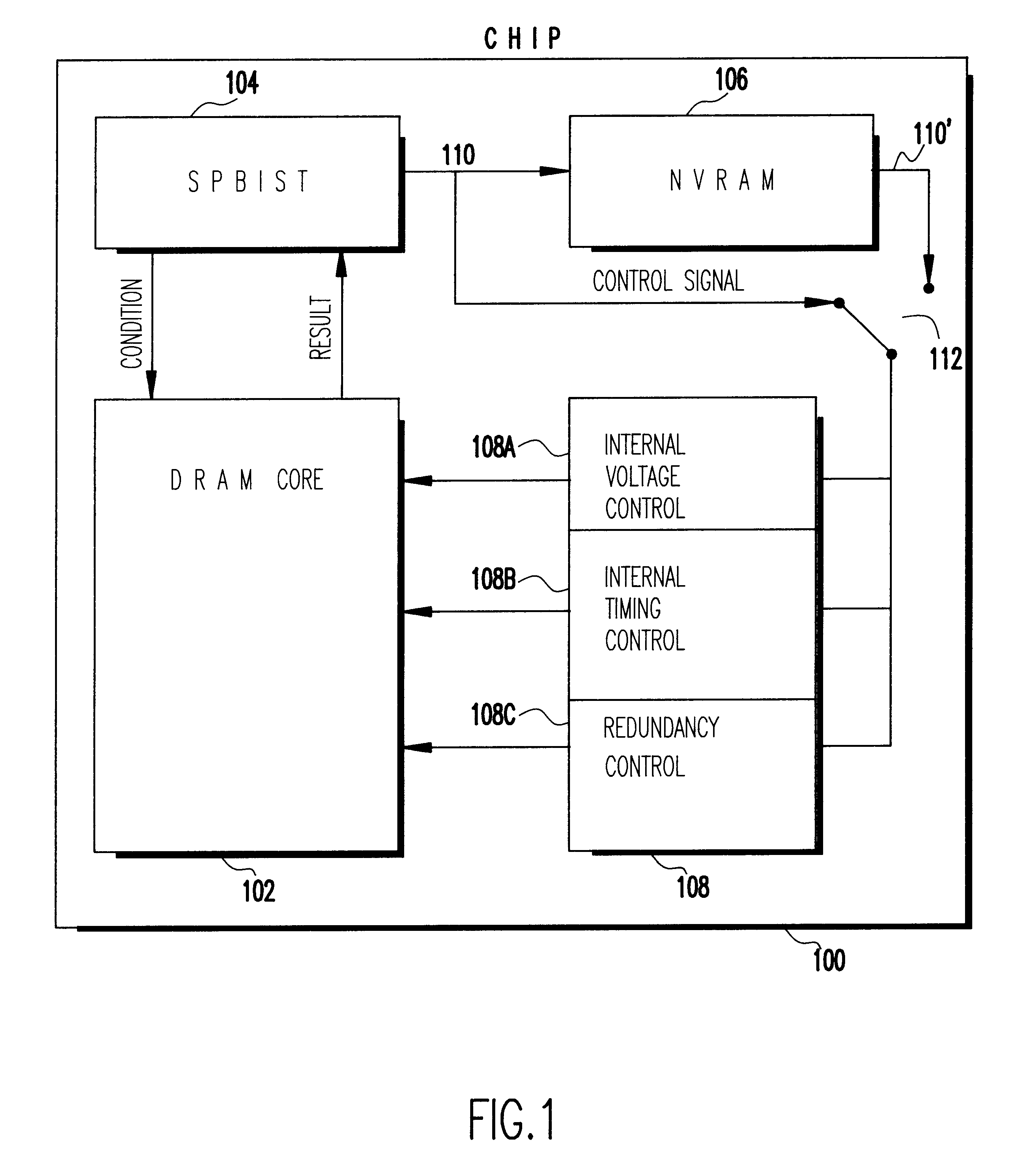
Chip performance optimization with self programmed built in self test
An integrated circuit (IC) chip wherein a built-in self test determines the IC's optimum electrical performance. A corresponding optimum performance setting is stored in NVRAM on the chip. Upon each chip power-up, the optimum performance setting is retrieved and provided to chip control which sets the chip for its best performance.
Owner:IBM CORP
Built-in self test for memory arrays using error correction coding
InactiveUS7254763B2Increased and improved IC manufacturing yieldShorten test timeElectronic circuit testingError detection/correctionIntegratorControl circuit
A memory self-testing system, apparatus, and method are provided which allow for testing for a plurality of bit errors and passing memory arrays having an error level which is correctable using selected error correction coding. An exemplary system embodiment includes a memory array, a comparator, an integrator, and a test control circuit. The memory array is adapted to store input test data and output stored test data during a plurality of memory read and write test operations. The comparator compares the input test data and the stored test data for a plurality of bit positions, and provides a corresponding error signal when the stored test data is not identical to the input test data for each bit position of the plurality of bit positions. The integrator receives the corresponding error signal and maintains the corresponding error signal for each bit position during the plurality of test operations. The test control circuit provides a fail signal when a predetermined level of corresponding error signals have been provided for the plurality of bit positions.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
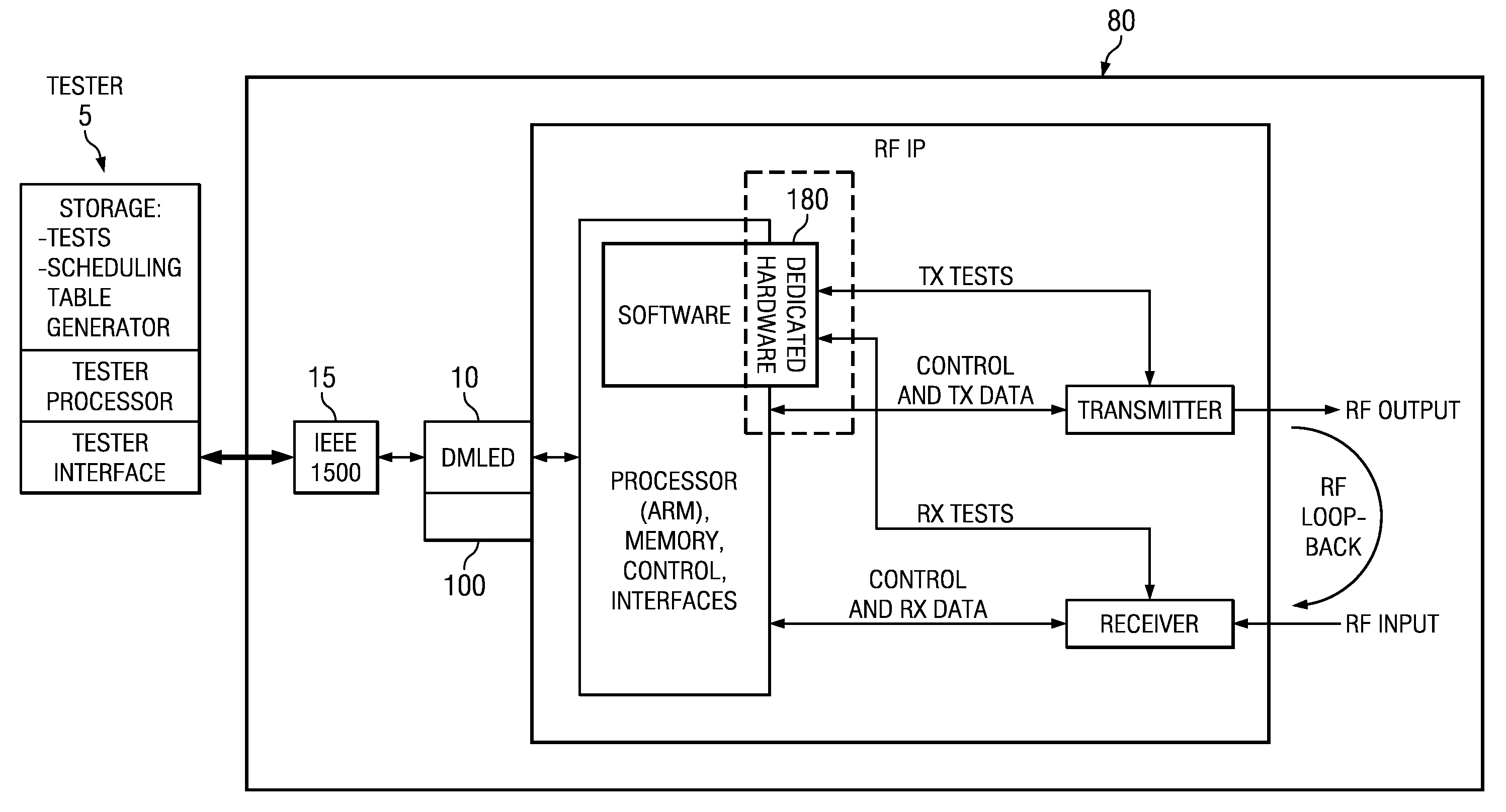
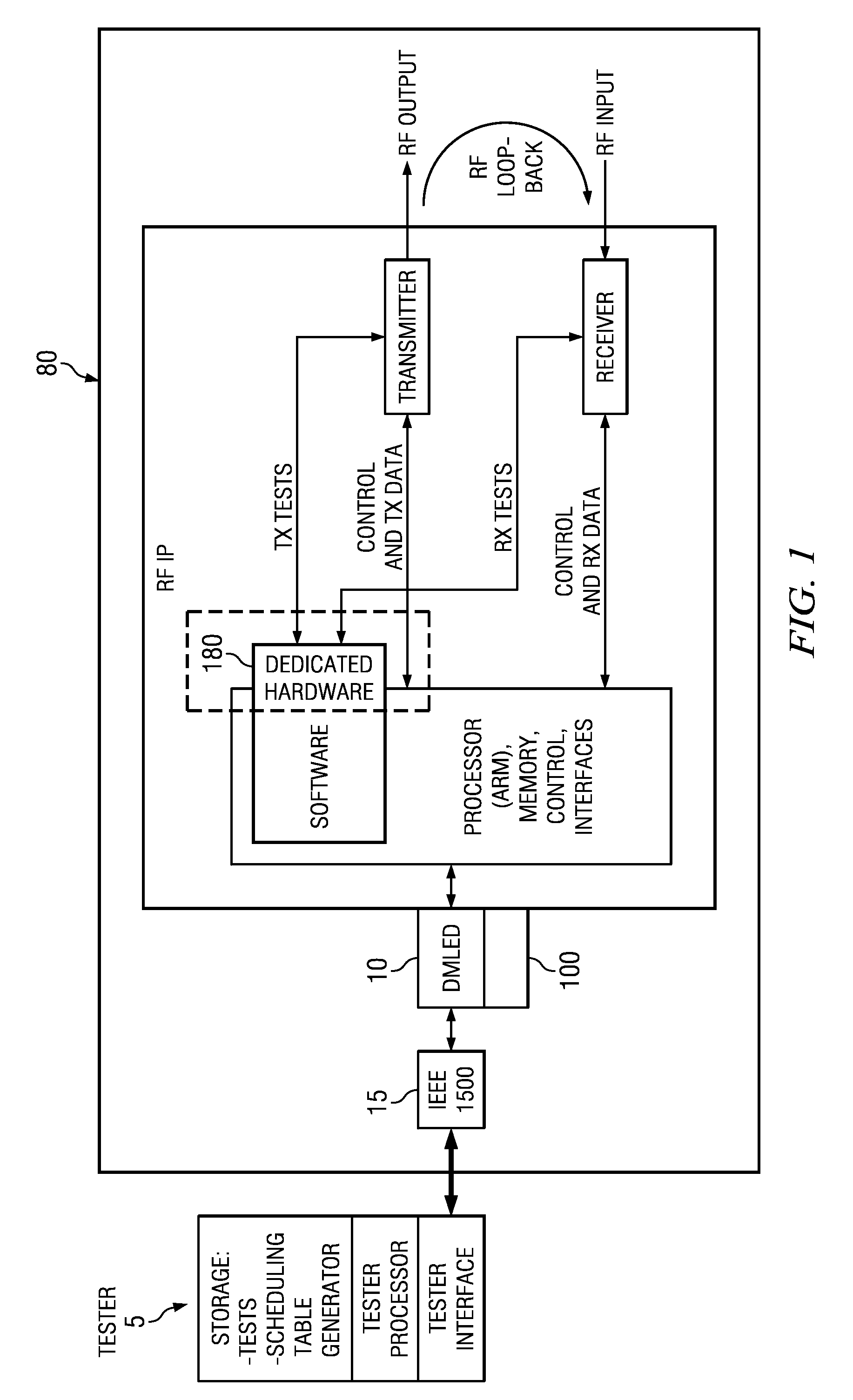
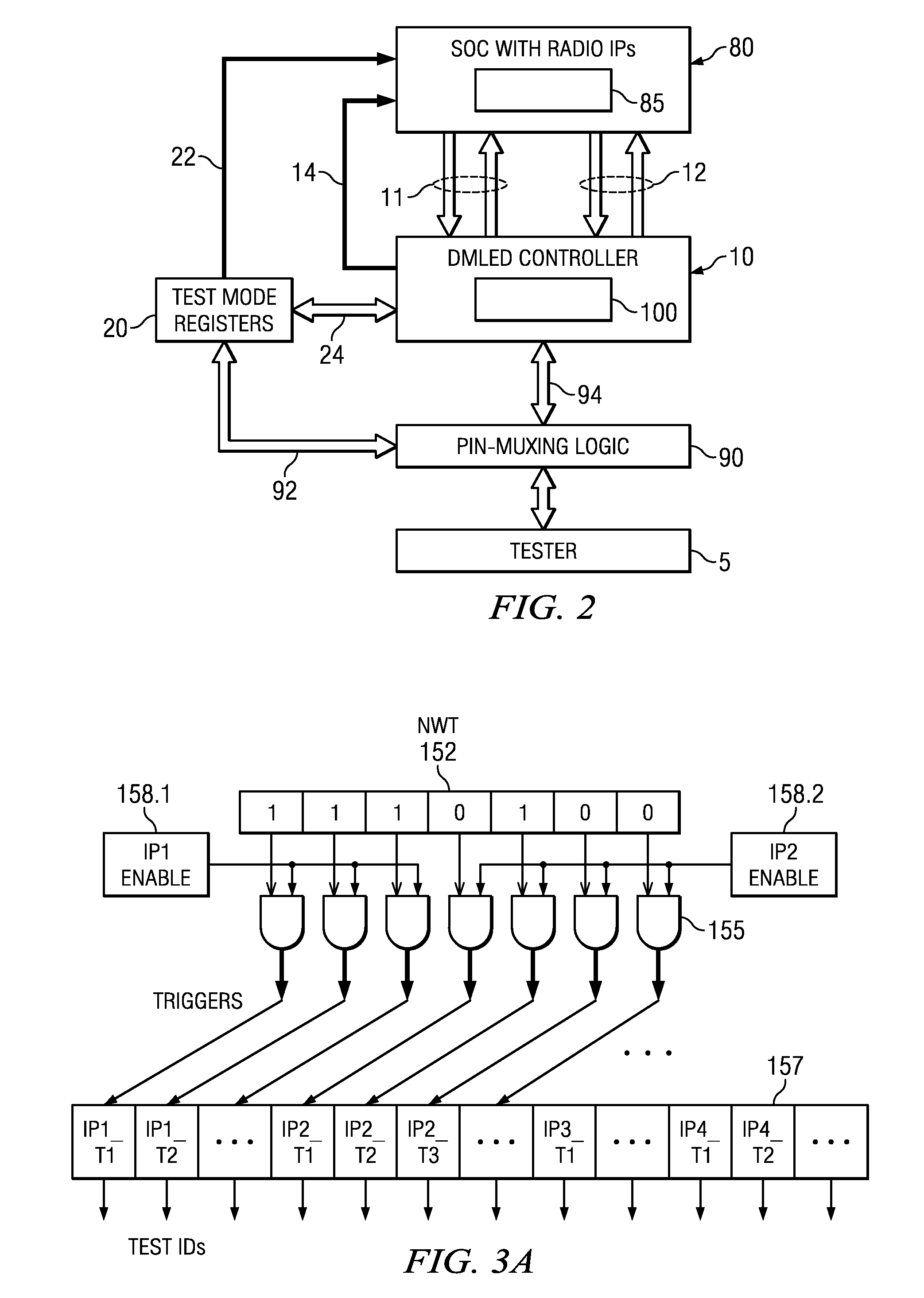
Built-in self-test methods, circuits and apparatus for concurrent test of RF modules with a dynamically configurable test structure
ActiveUS20120191400A1Resistance/reactance/impedenceSpecial data processing applicationsEngineeringBuilt-in self-test
A testable integrated circuit chip (80, 100) includes a functional circuit (80) having modules (IP.i), a storage circuit (110) operable to hold a table representing sets of compatible tests that are compatible for concurrence, and an on-chip test controller (140, 150) coupled with said storage circuit (110) and with said functional circuit modules (IP.i), said test controller (140, 150) operable to dynamically schedule and trigger the tests in those sets, whereby promoting concurrent execution of tests in said functional circuit modules (IP.i). Other circuits, wireless chips, systems, and processes of operation and processes of manufacture are disclosed.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
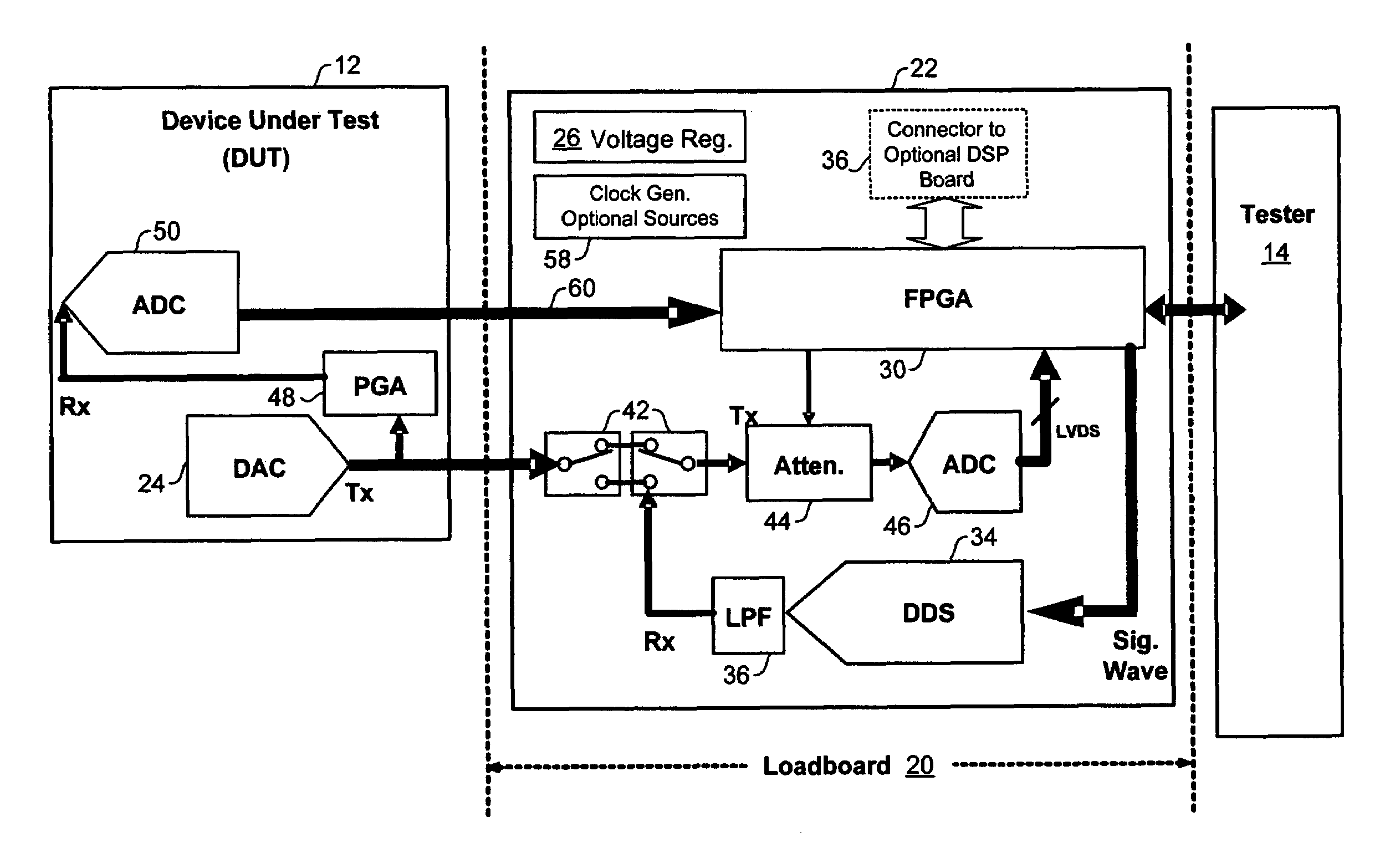
Analog built-in self-test module
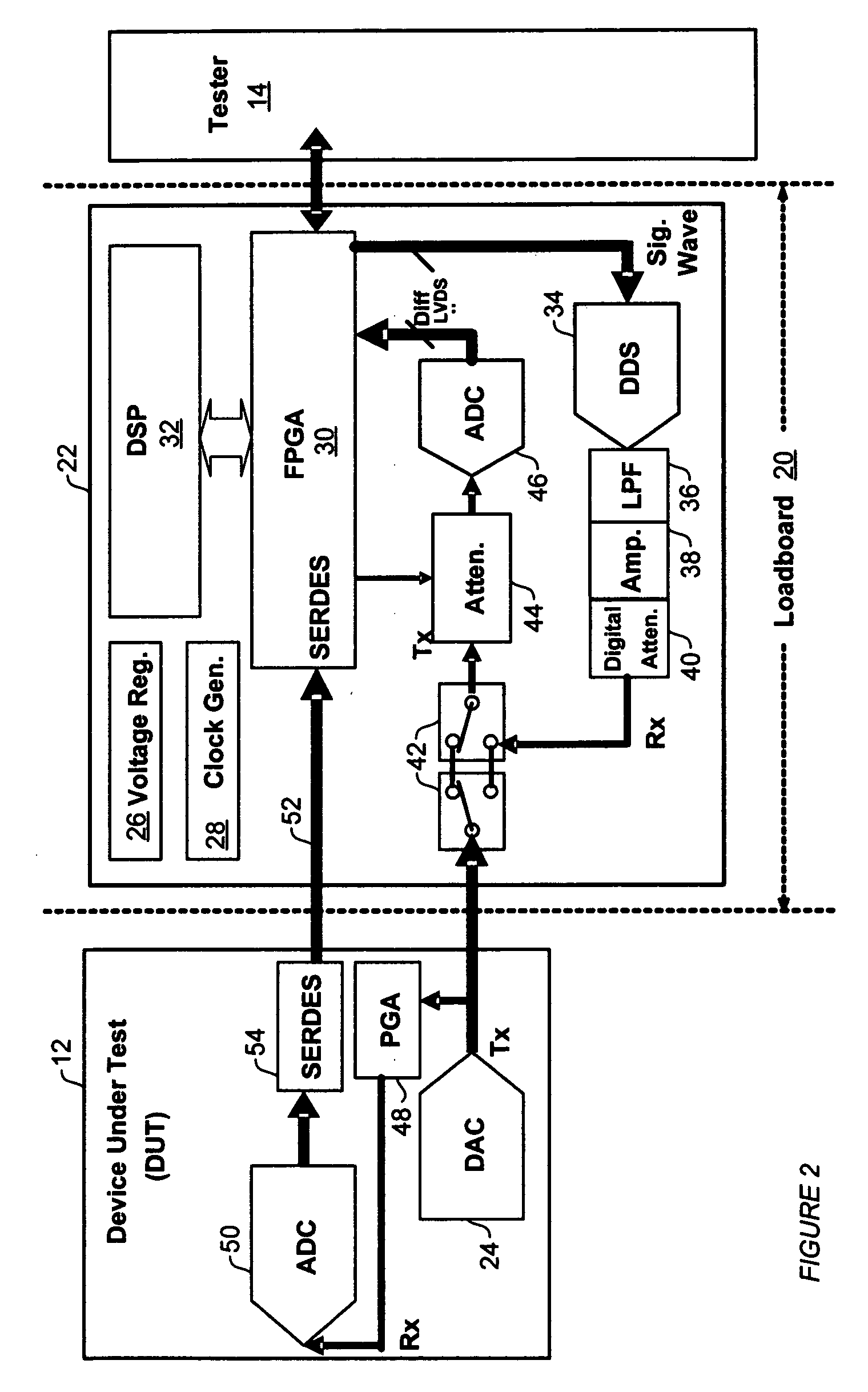
ActiveUS7327153B2Quick testImprove efficiencyElectronic circuit testingError detection/correctionOn boardTester device
An analog BIST (Built-in Self-Test) module for a load board in a test system for testing Integrated Chips (IC) and other devices-under-test (DUTs). Components of the test module perform test setup, transmission of analog test signals to a DUT, capture of analog and digital test data from the DUT, and on-board analysis of the test data using DSPs without sending the test data to a tester. Modules may be add-on boards to load boards an contain one or more processors and multiple components to test DUTs in parallel, significantly decreasing test and analysis times of a test system such as a Very Low Cost Tester (VLCT).
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
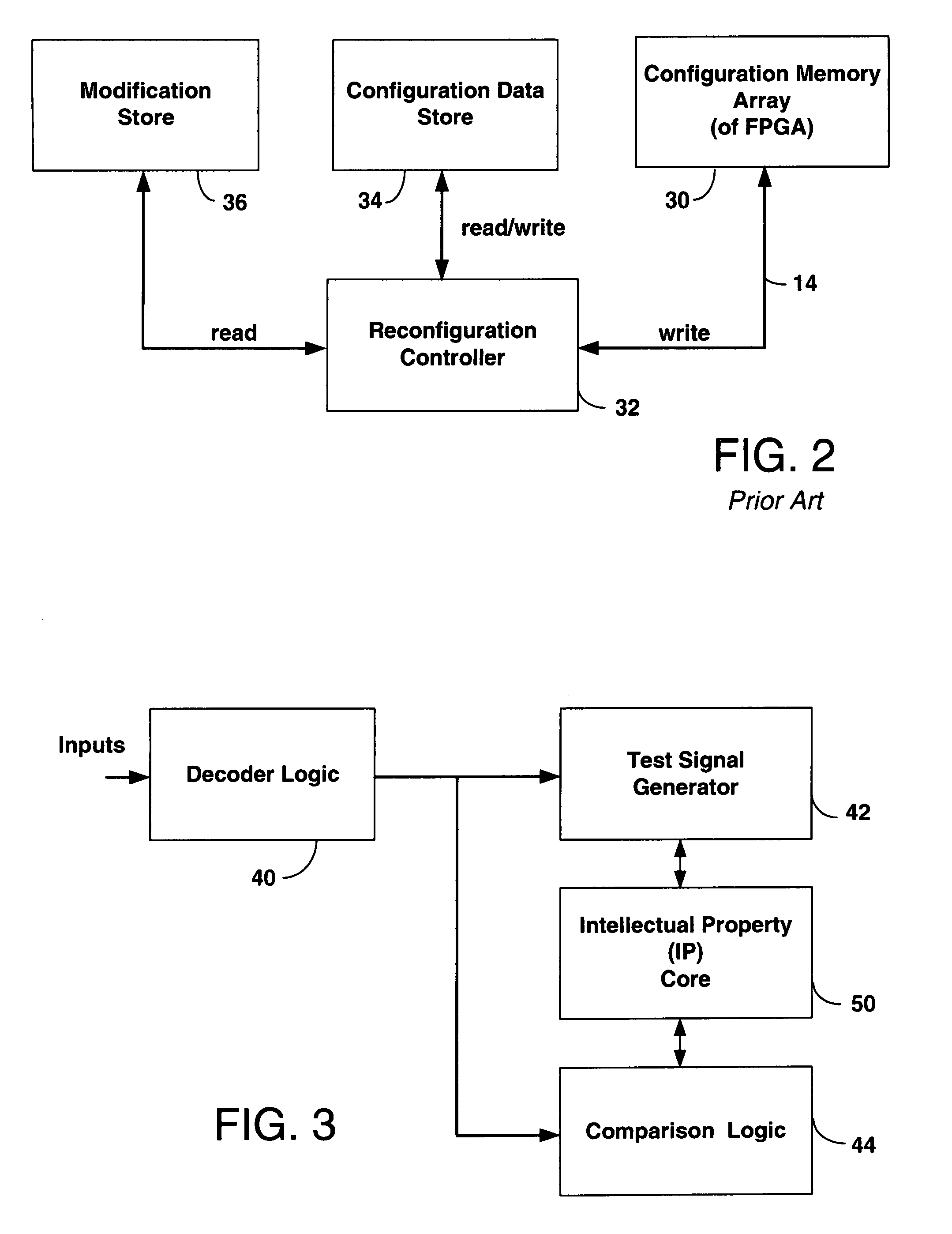
Built-in self test (BIST) technology for testing field programmable gate arrays (FPGAs) using partial reconfiguration
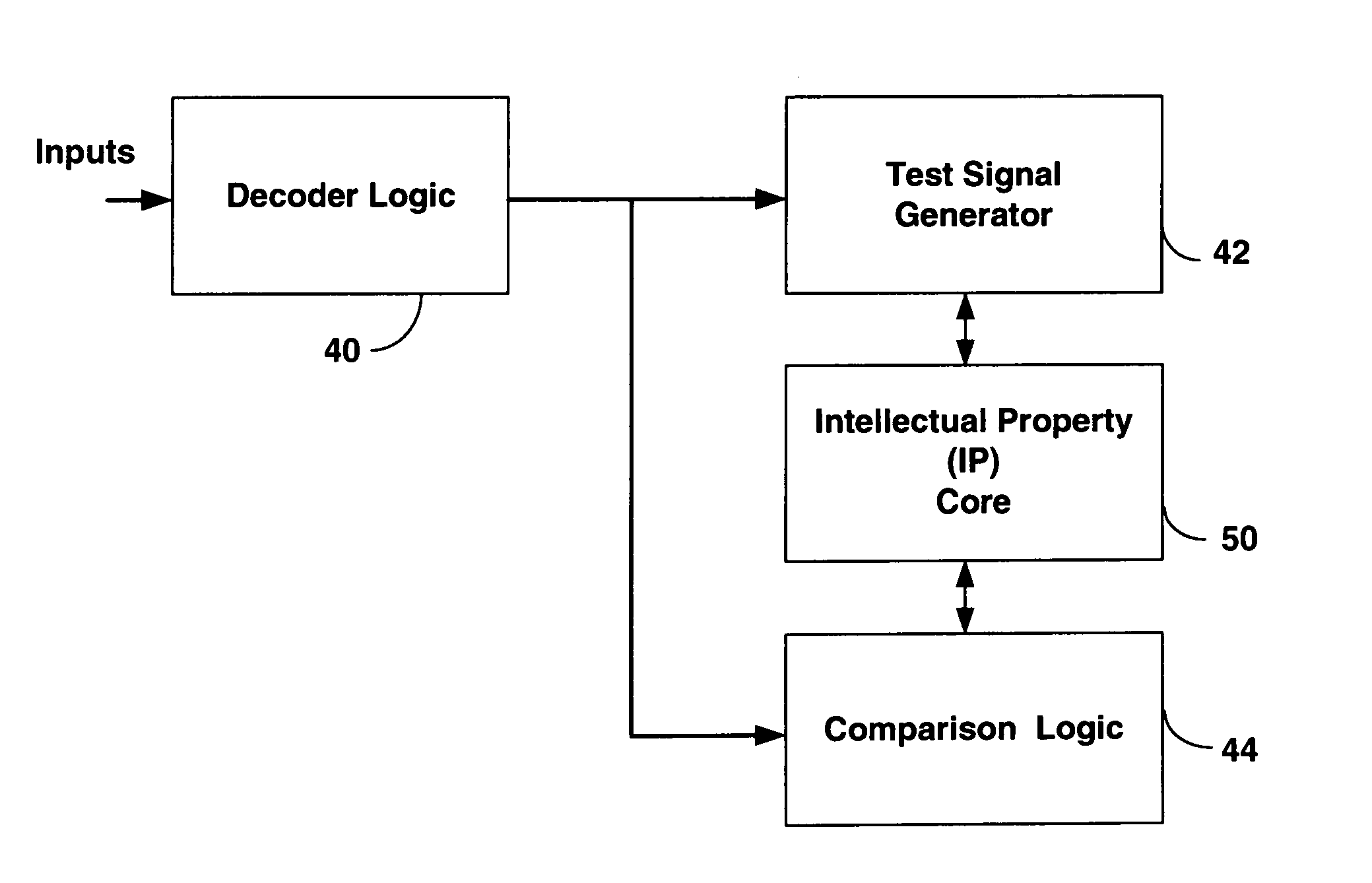
ActiveUS7302625B1Shorten test timeElectronic circuit testingCAD circuit designSignal generatorComputer science
A Built-in Self Test (BIST) system is provided in a Field Programmable Gate Array (FPGA) that can adjust test signal patterns provided for testing after partial reconfiguration of the FPGA. The BIST system includes a decoder that monitors I / O signals and provides an output indicating when I / O signals change indicating partial reconfiguration has occurred. The decoder output is provided to a BIST test signal generator providing signals to an IP core of the FPGA as well as a BIST comparator for monitoring test results to change test signals depending on the partial configuration mode.
Owner:XILINX INC
Built-in self test method and apparatus for jitter transfer, jitter tolerance, and FIFO data buffer
InactiveUS20050193290A1Easy to testTransmitters monitoringReceivers monitoringTransceiverControl manner
Testing a transceiver includes providing a sequence of test signals. A serialization clock is generated and jitter is added to the clock in a known and controlled manner. The test signals can then be transmitted using the serialization clock. After the test signals are recovered by the clock and data recovery mechanism, the recovered sequence is compared to the original sequence, to test for jitter tolerance. Preferably, each of these steps is performed on chip. In other aspects, a jitter transfer test and / or a FIFO test can be performed.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Method and apparatus for programmable logic device (PLD) built-in-self-test (BIST)
InactiveUS6839873B1Digital circuit testingSpecial data processing applicationsProgrammable logic deviceBuilt-in self-test
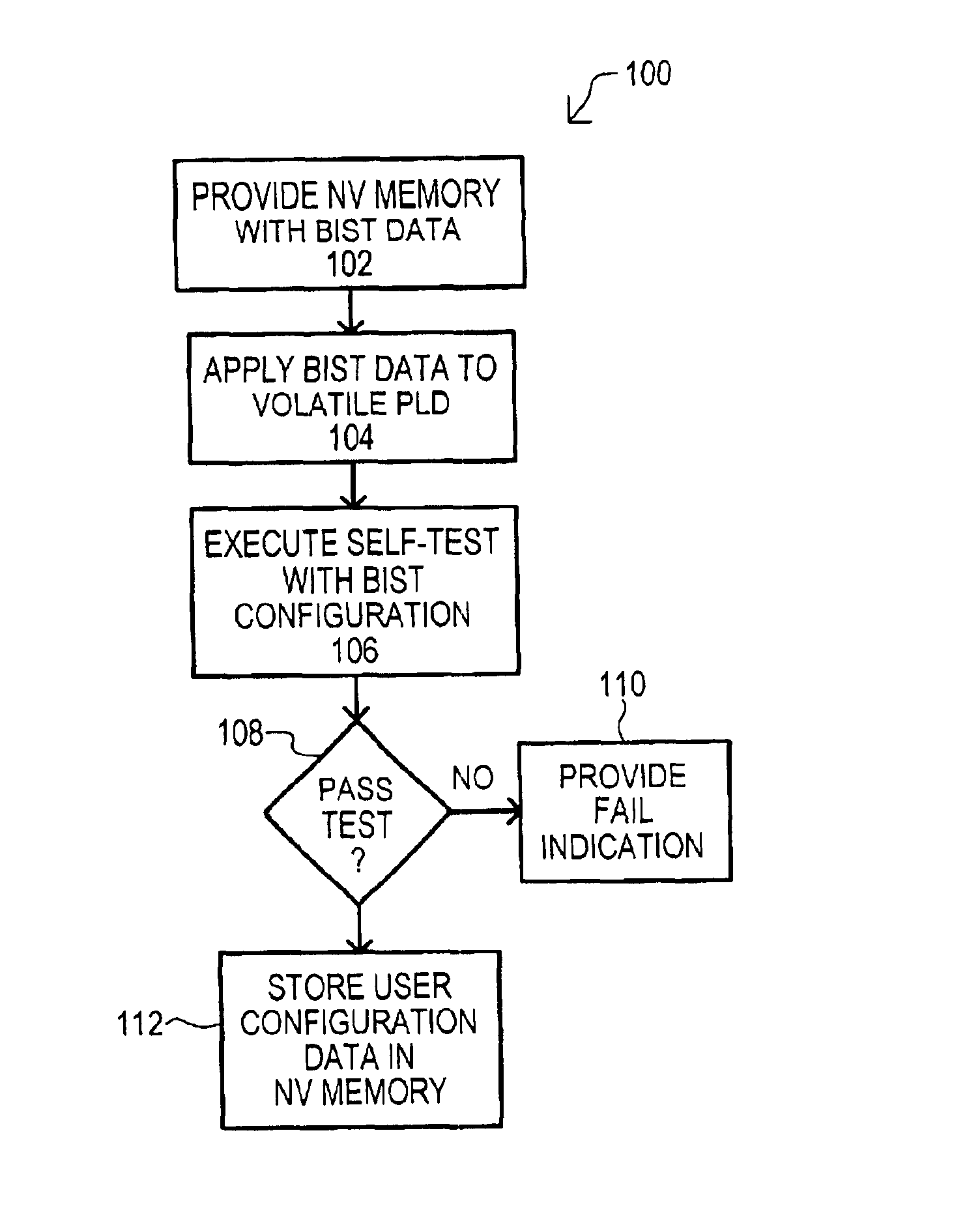
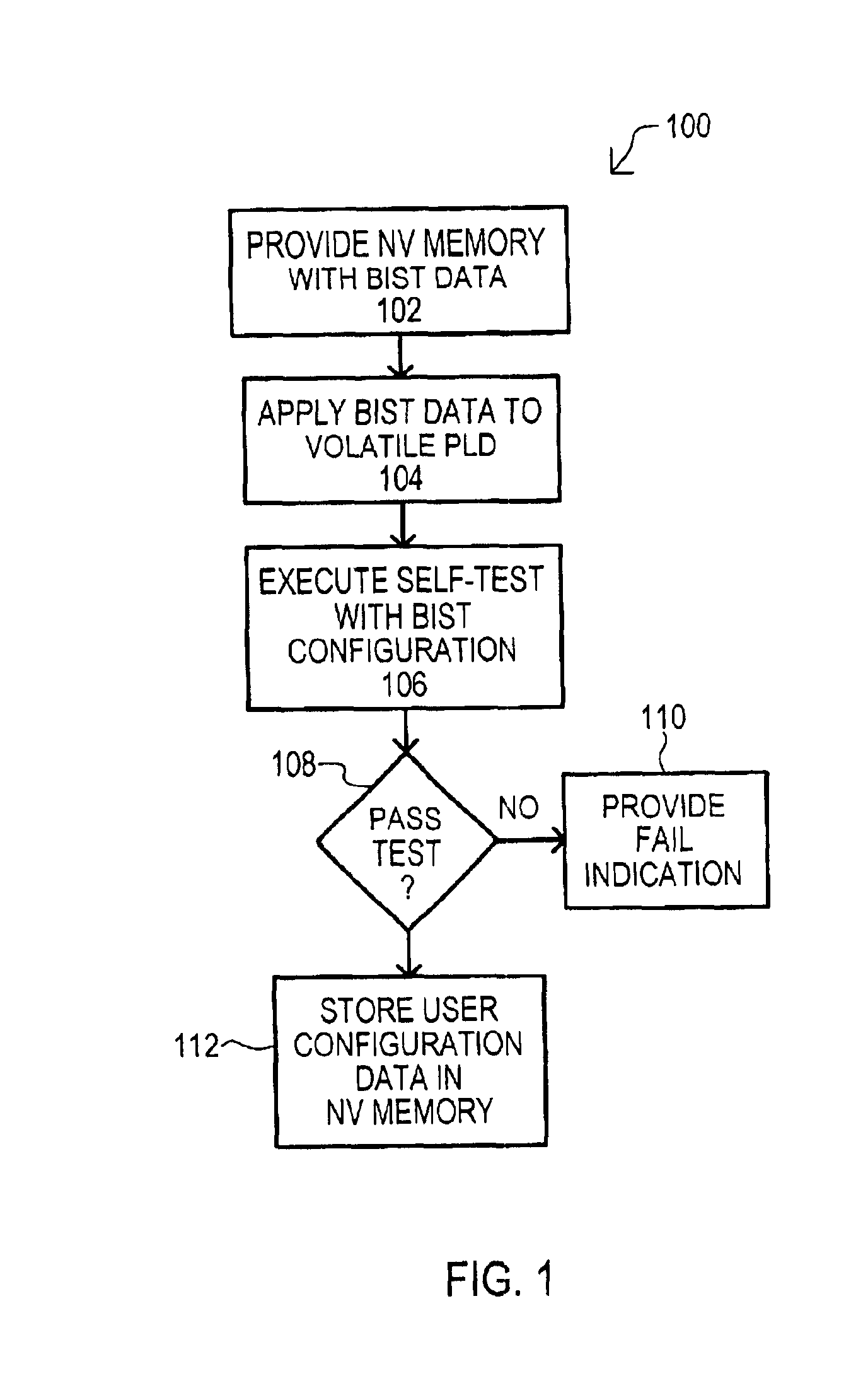
According to one embodiment, a programmable logic assembly (200) may include a nonvolatile memory (202) may be coupled to an associated volatile programmable logic device (PLD) (204). Built-in-self-test (BIST) data (208) may be stored in a nonvolatile memory (202) that places the volatile PLD (204) in a self-test configuration. If a volatile PLD (204) passes a self-test, user data (210) may be stored in a nonvolatile memory (202) that places a volatile PLD (204) into a user determined configuration.
Owner:CYPRESS SEMICON CORP
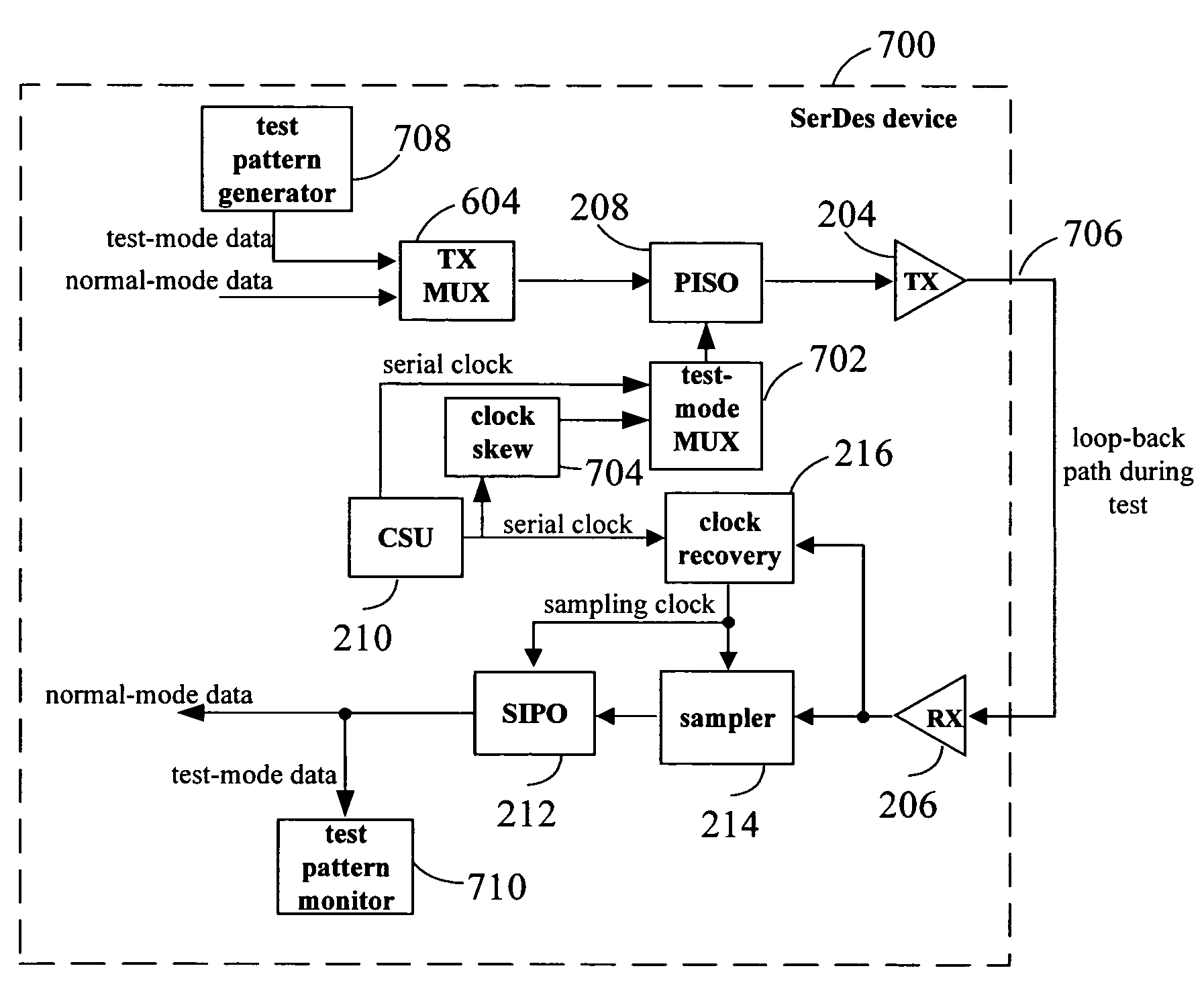
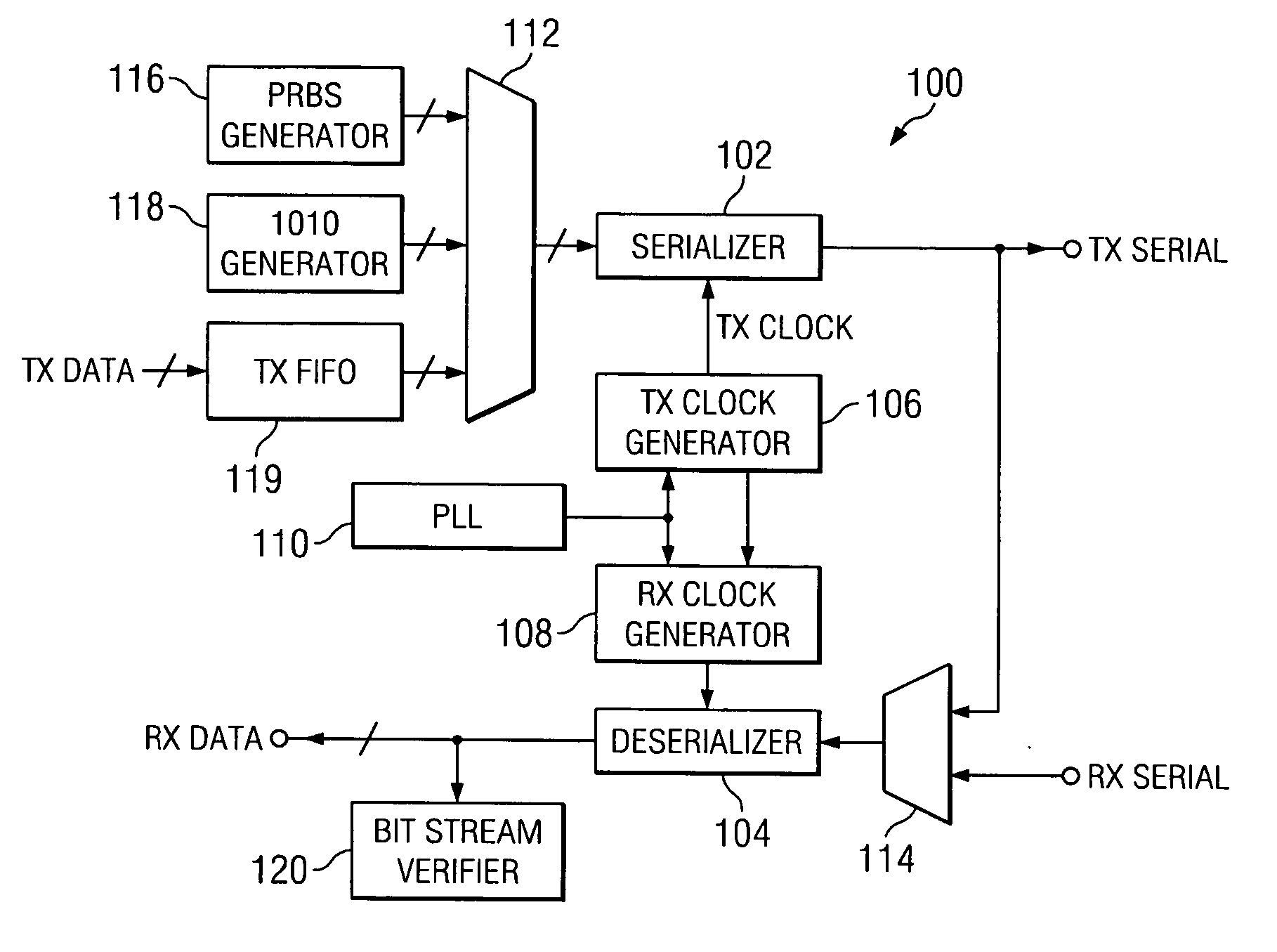
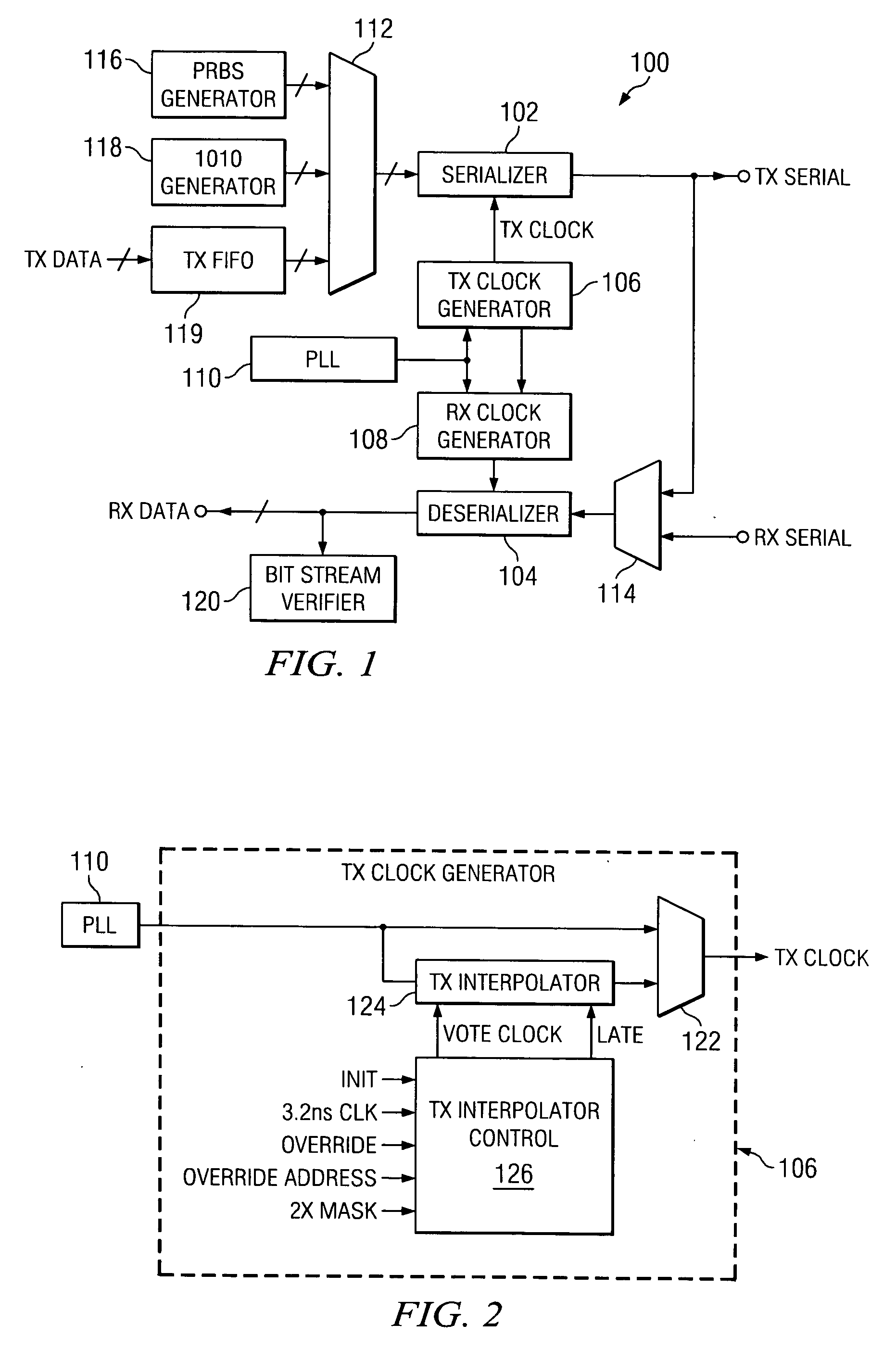
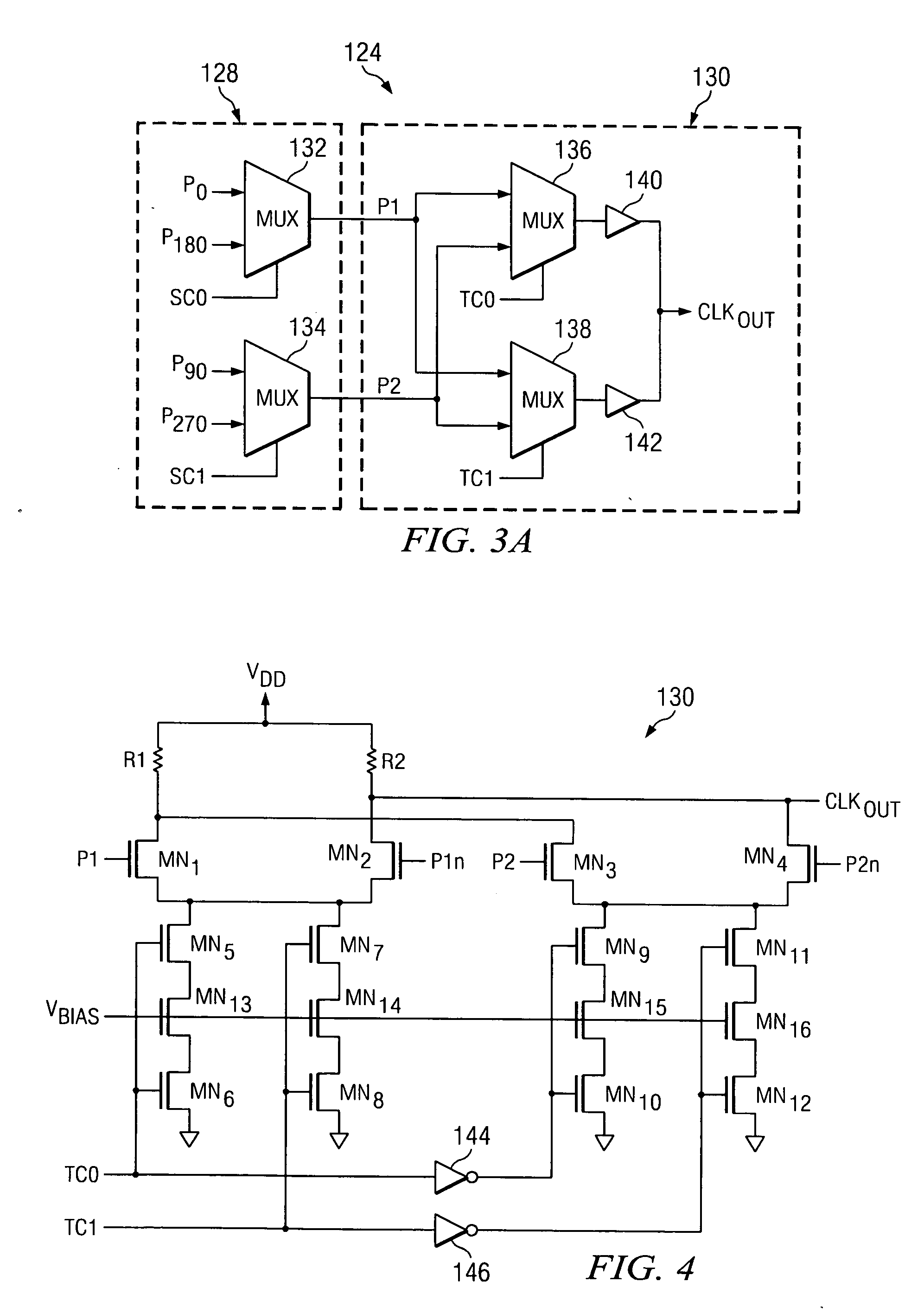
Built in self test (BIST) for high-speed serial transceivers
InactiveUS7756197B1Advantageously highly scaleableIncrease data rateCorrect operation testingTransmission monitoringFinite impulse responseTransceiver
A relatively high-speed serial data transmitter incorporates built in self test (BIST). The BIST circuit advantageously provides tests modes to obviate the need to build expensive test equipment for high-speed serial data devices, such as a serializer / deserializer (SerDes) or other transceivers. Multiple data paths in a finite impulse response (FIR) filter of transmitter of the SerDes or a transceiver can be independently tested. The transmitter output can also be selectively degraded to test a receiver of a transceiver. An attenuated output signal can be provided to test receiver sensitivity. A low-pass filter can be invoked to emulate a backplane, while a loopback circuit can provide the emulated backplane attenuation to the receiver to permit testing of the equalization circuitry of a receiver without requiring the presence of an actual backplane for testing.
Owner:MICROSEMI STORAGE SOLUTIONS
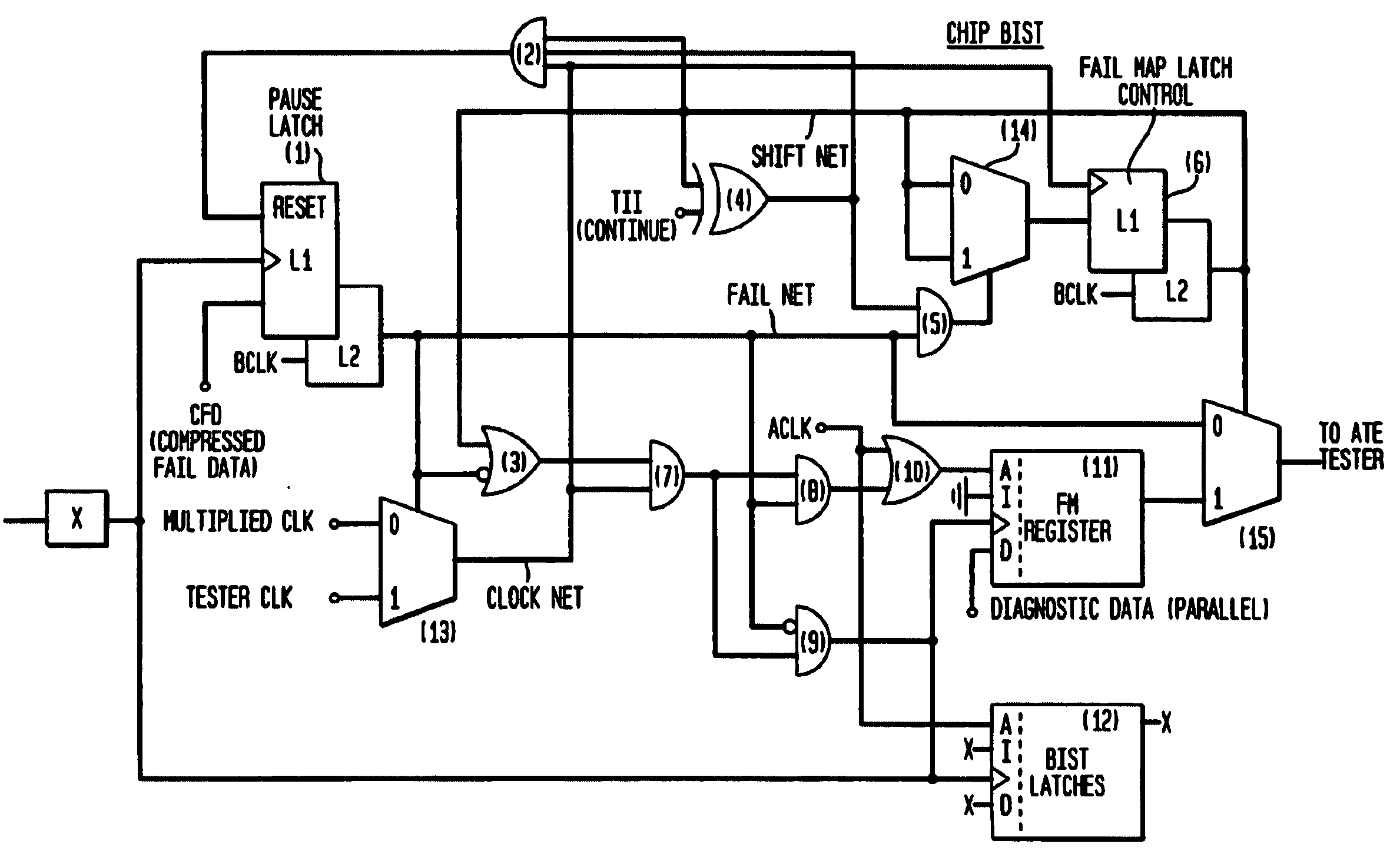
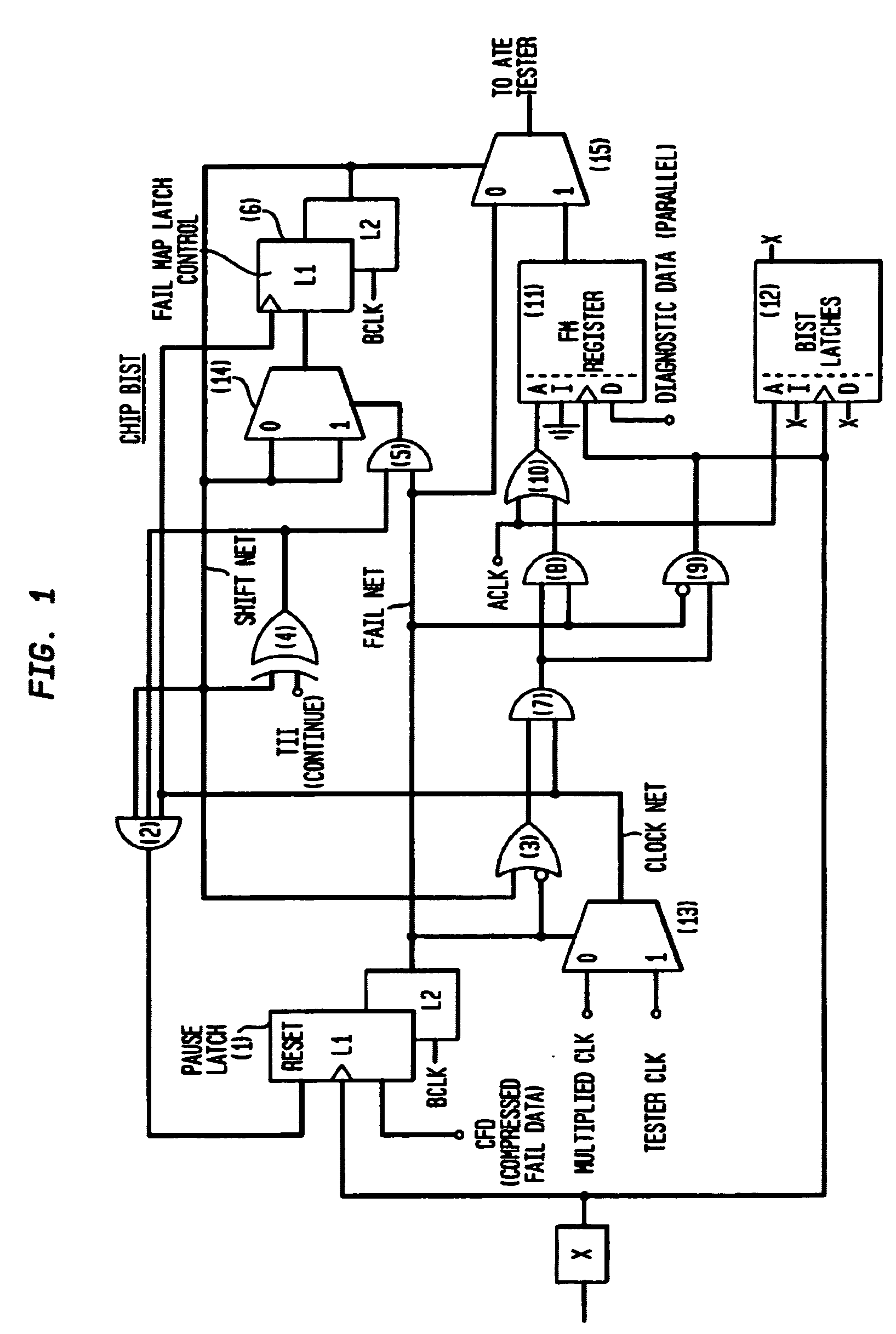
Automatic bit fail mapping for embedded memories with clock multipliers
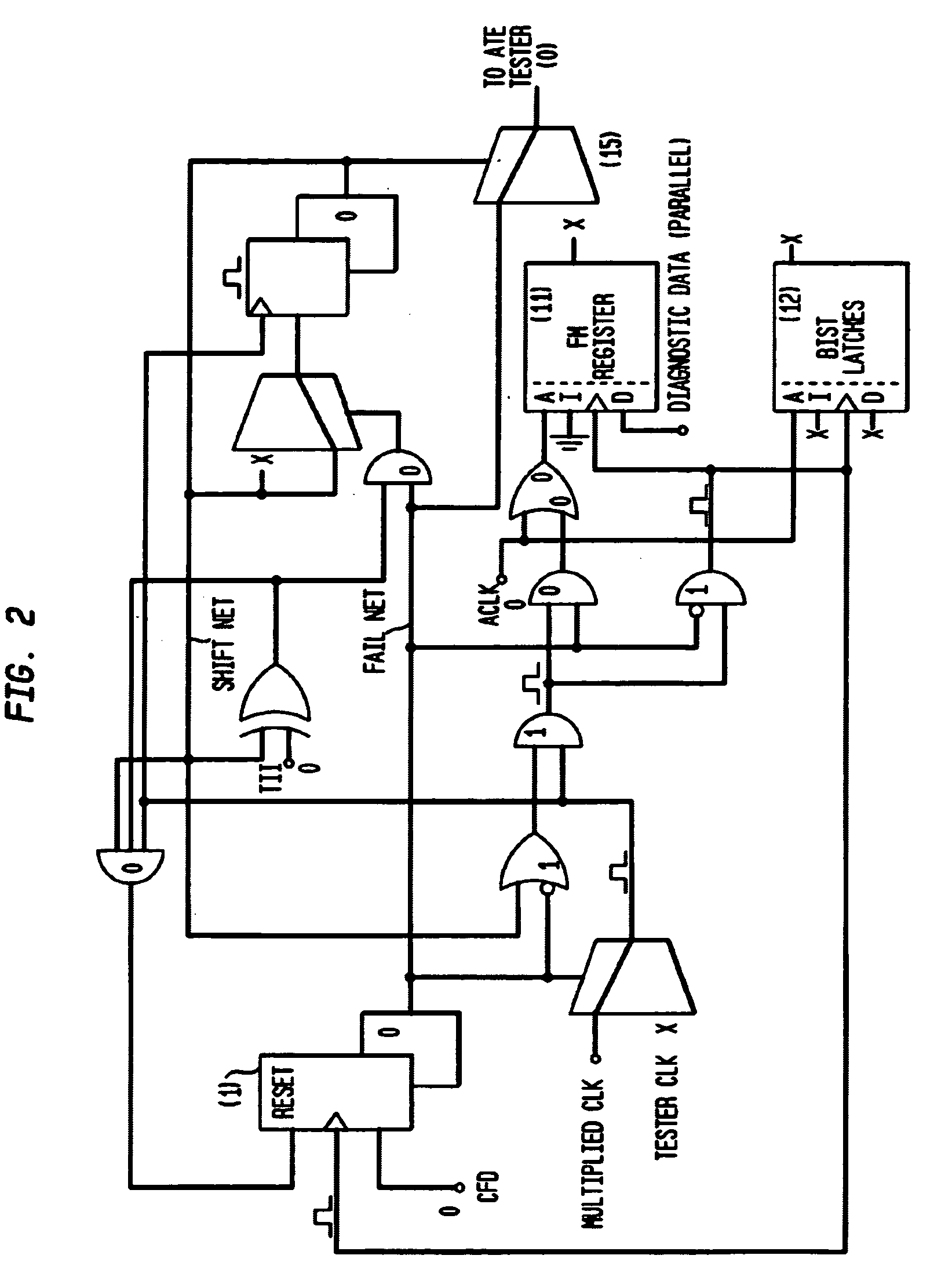
A bit fail map circuit accurately generates a bit fail map of an embedded memory such as a DRAM by utilizing a high speed multiplied clock generated from a low-speed Automated Test Equipment (ATE) tester. The circuit communicates between the ATE tester, the embedded memory under test, Built-In Self-Test (BIST) and Built-In Redundancy Analysis (BIRA). An accurate bit fail map of an embedded DRAM memory is provided by pausing the BIST test circuitry at a point when a fail is encountered, namely a mismatch between BIST expected data and the actual data read from the array, and then shifting the bit fail data off the chip using the low-speed ATE tester clock. Thereafter, the high-speed test is resumed from point of fail by again running the BIST using the high-speed internal clock, to provide at-speed bit Fail Maps.
Owner:IBM CORP
Built-in at-speed bit error ratio tester
InactiveUS7743288B1Low-cost solutionEfficient testingError preventionTransmission systemsEqualizationBuilt-in self-test
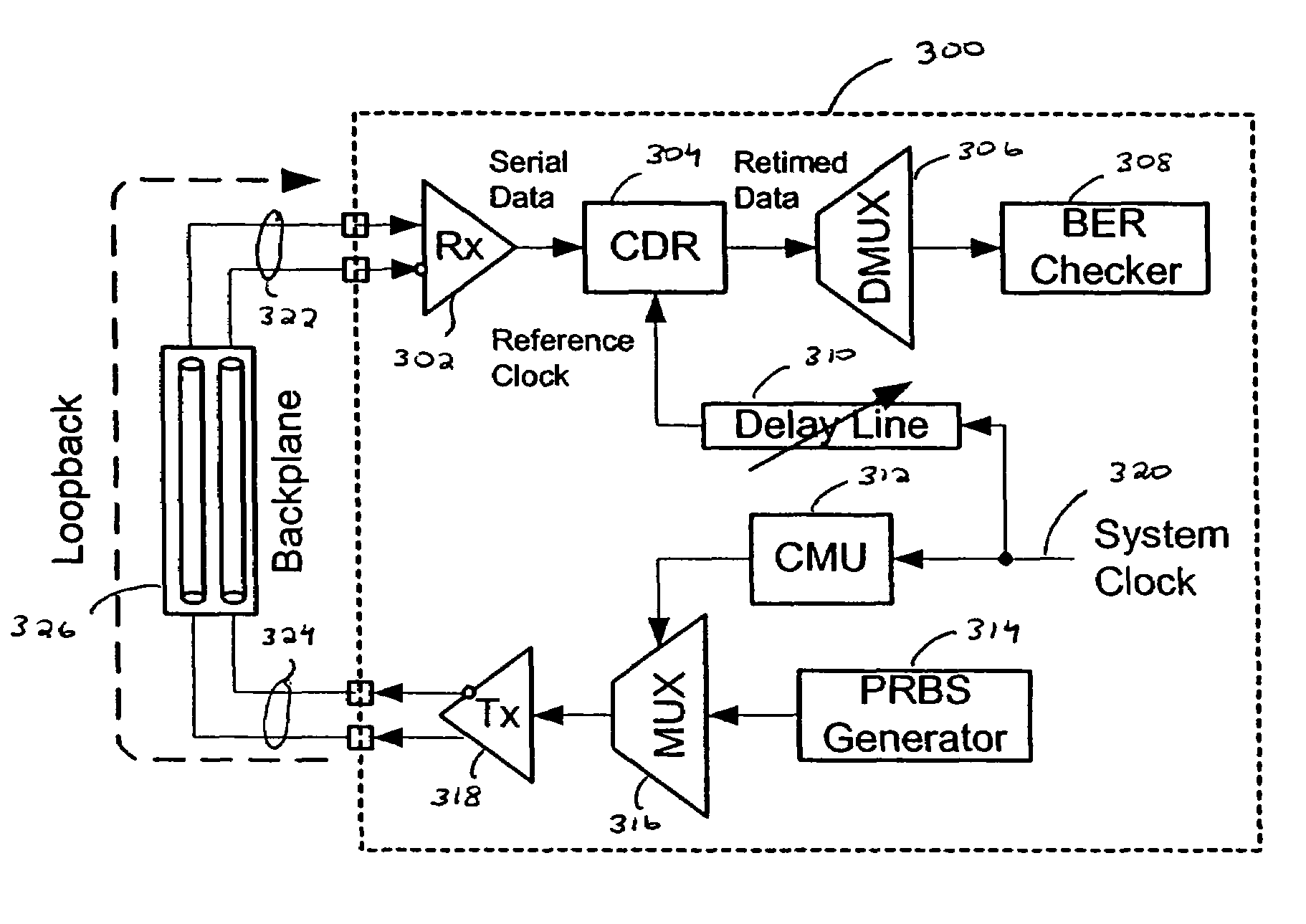
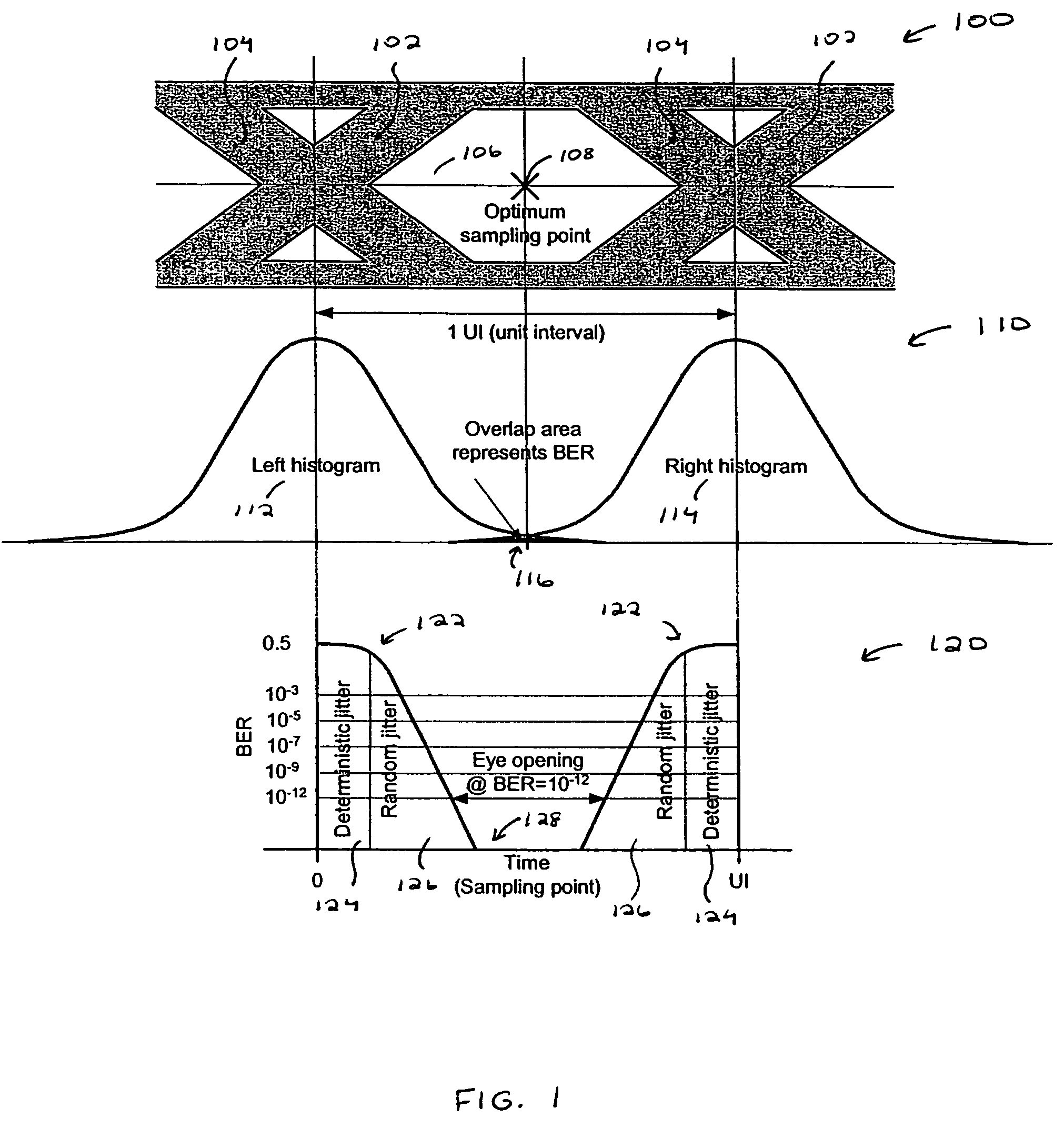
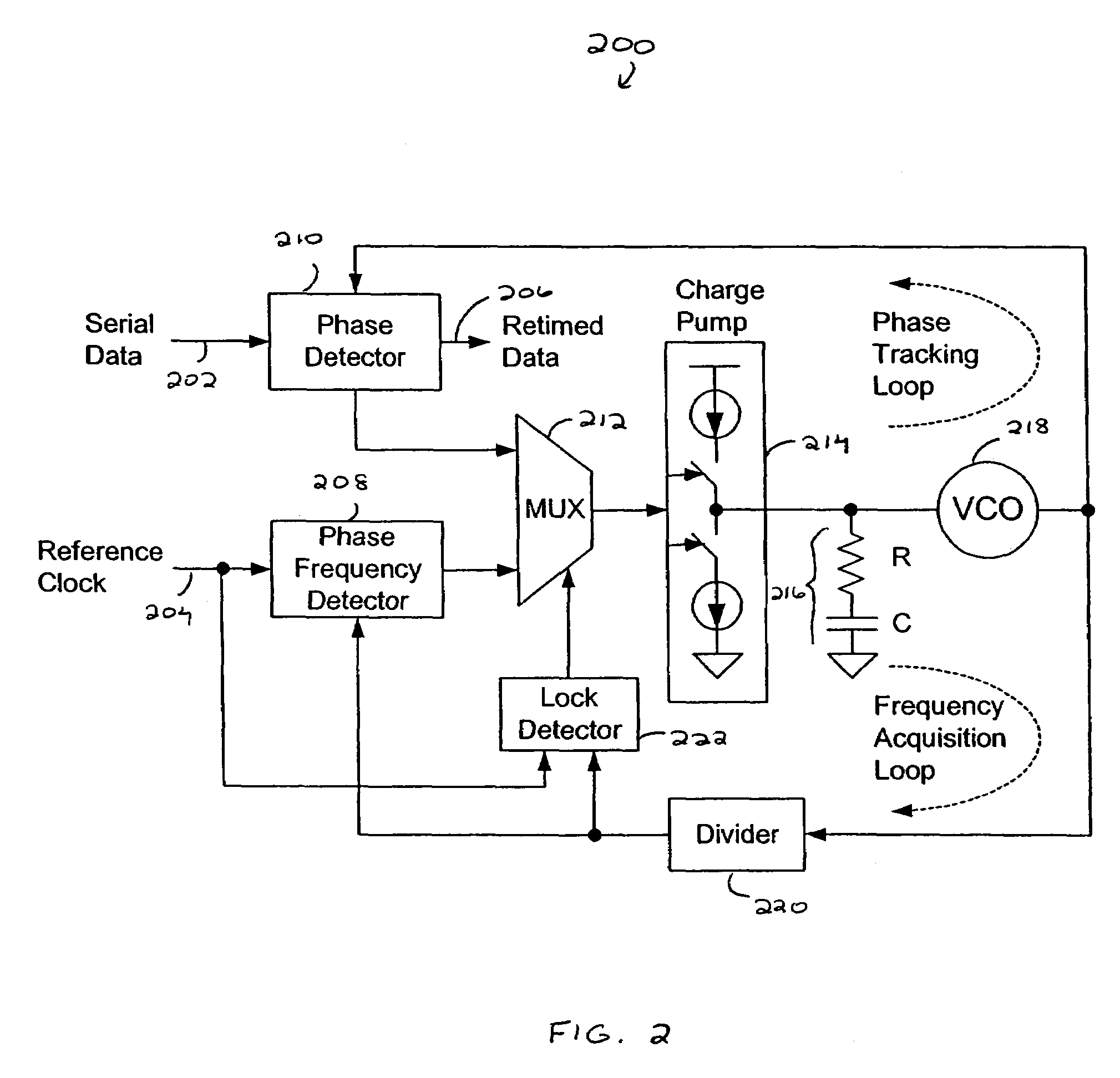
A built-in, at-speed BERT is provided that may be part of high-speed serial interface circuitry implemented on an integrated circuit. The built-in, at-speed BERT takes advantage of an existing clock data recovery (CDR) dual-loop architecture and built-in self test (BIST) circuitry. The built-in, at-speed BERT provides a low-cost solution for production testing of high-speed serial links, facilitating jitter analysis and evaluation of pre-emphasis and equalization performance. This further allows adaptation of pre-emphasis and equalization.
Owner:ALTERA CORP
Method and apparatus for embedded built-in self-test (BIST) of electronic circuits and systems
InactiveUS6957371B2Facilitates testing and debuggingLow costElectronic circuit testingError detection/correctionController architectureElectronic systems
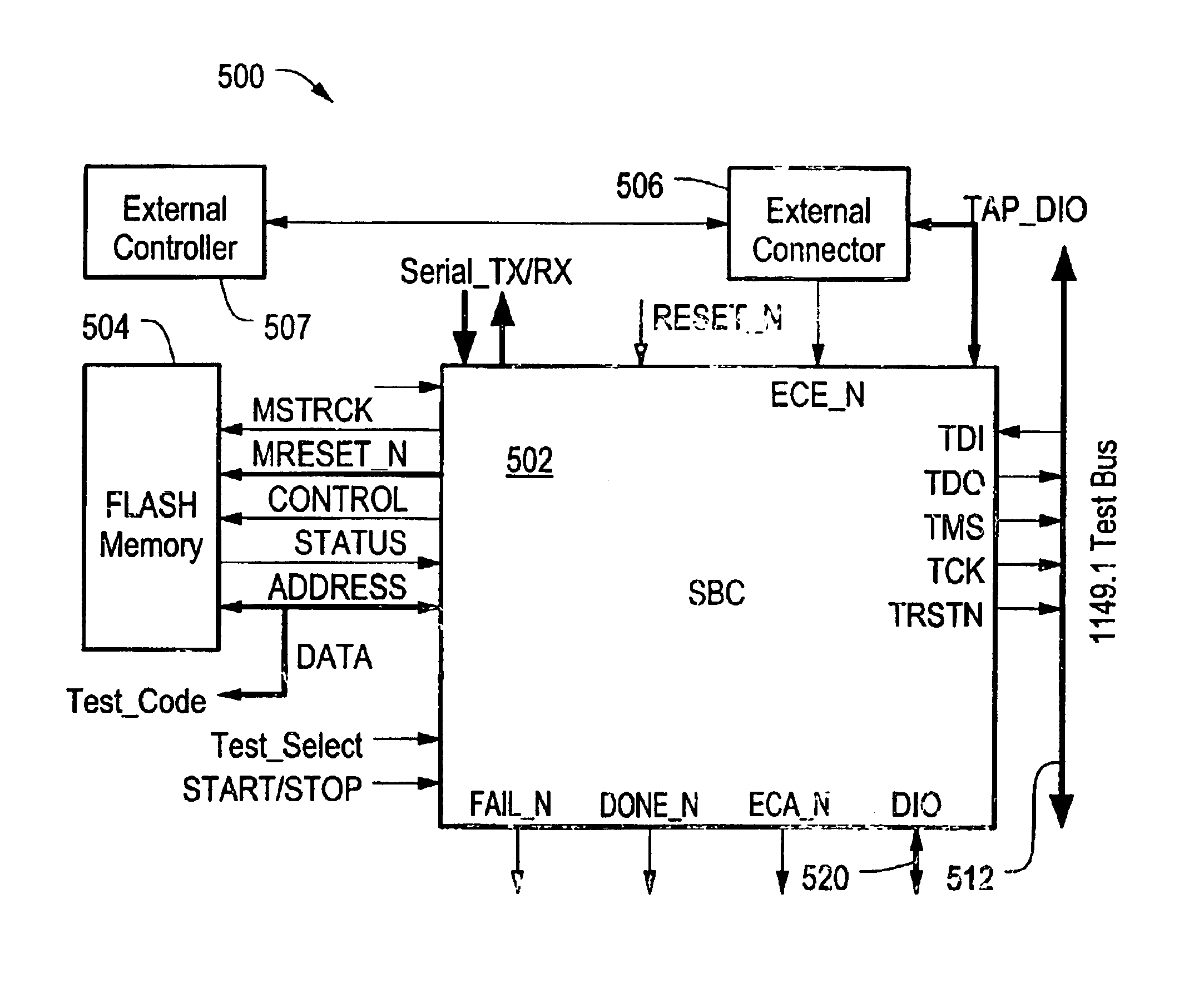
An embedded electronic system built-in self-test controller architecture that facilitates testing and debugging of electronic circuits and in-system configuration of programmable devices. The system BIST controller architecture includes an embedded system BIST controller, an embedded memory circuit, an embedded IEEE 1149.1 bus, and an external controller connector. The system BIST controller is coupled to the memory circuit and the IEEE 1149.1 bus, and coupleable to an external test controller via the external controller connector. The external test controller can communicate over the IEEE 1149.1 bus to program the memory and / or the system BIST controller circuitry, thereby enabling scan vectors to be debugged by the external test controller and then downloaded into the memory for subsequent application to a unit under test by the system BIST controller.
Owner:INTELLITECH INC
Semiconductor integrated circuit, design support apparatus, and test method
InactiveUS20030229886A1Electronic circuit testingSolid-state devicesBuilt-in self-testLogic circuitry
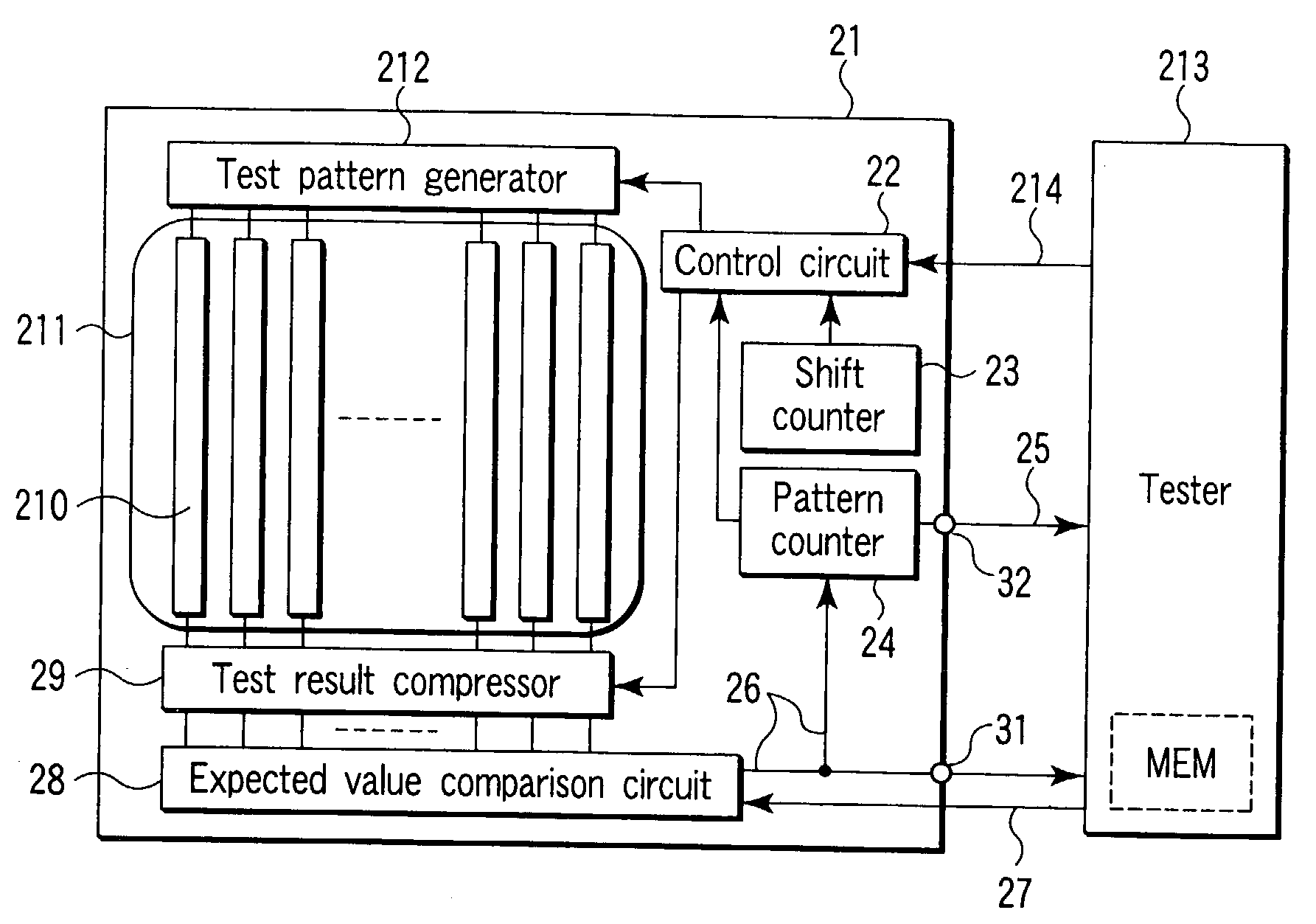
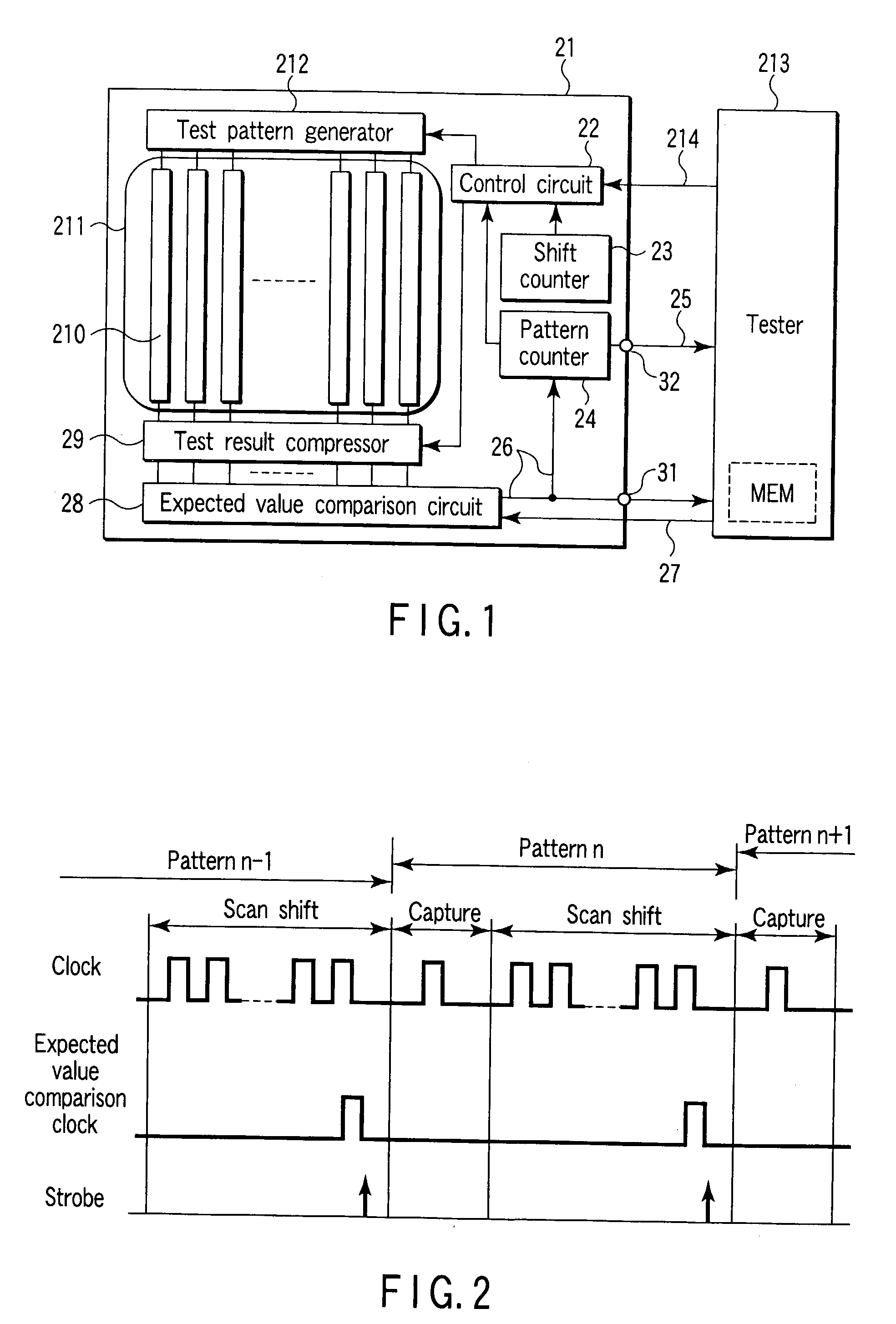
There is disclosed a semiconductor integrated circuit comprising a logic BIST circuit which includes a test pattern generator and test result compressor and which performs a built-in self test (logic BIST) of a logic circuit, a pattern counter which counts test patterns during the logic BIST, an expected value comparison circuit which compares a compressed value output of the test result compressor with an expected value input from an external tester for each test pattern and which outputs a failure flag at a mismatch detection time, an external terminal which outputs the failure flag from the LSI, and an external terminal which outputs from the LSI a pattern count signal at a time when the pattern counter receives the failure flag.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com