Patents
Literature
187 results about "Test setup" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Test setup methods can be time-saving when you need to create reference or prerequisite data for all test methods, or a common set of records that all test methods operate on. Test setup methods can reduce test execution times especially when you’re working with many records.
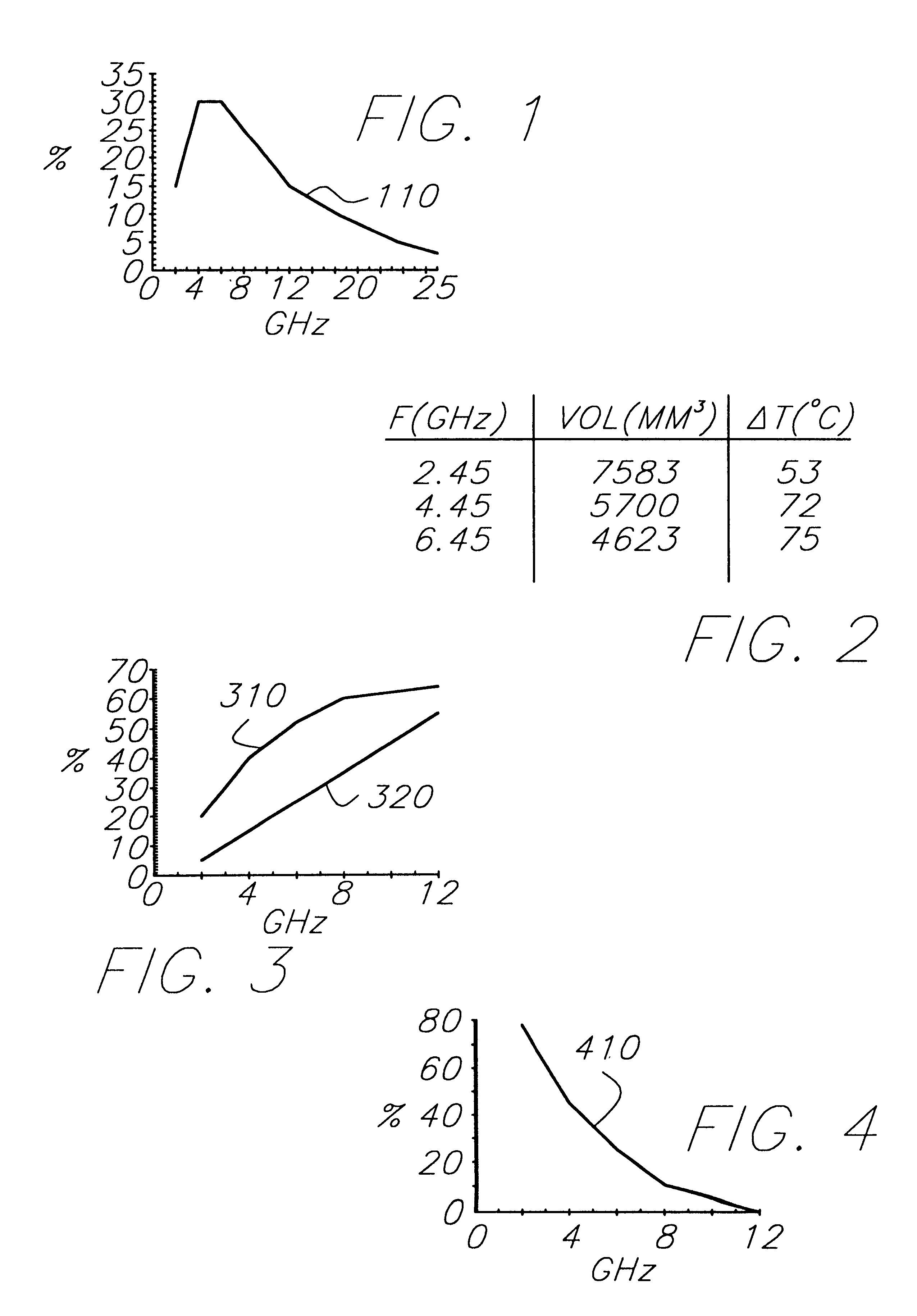
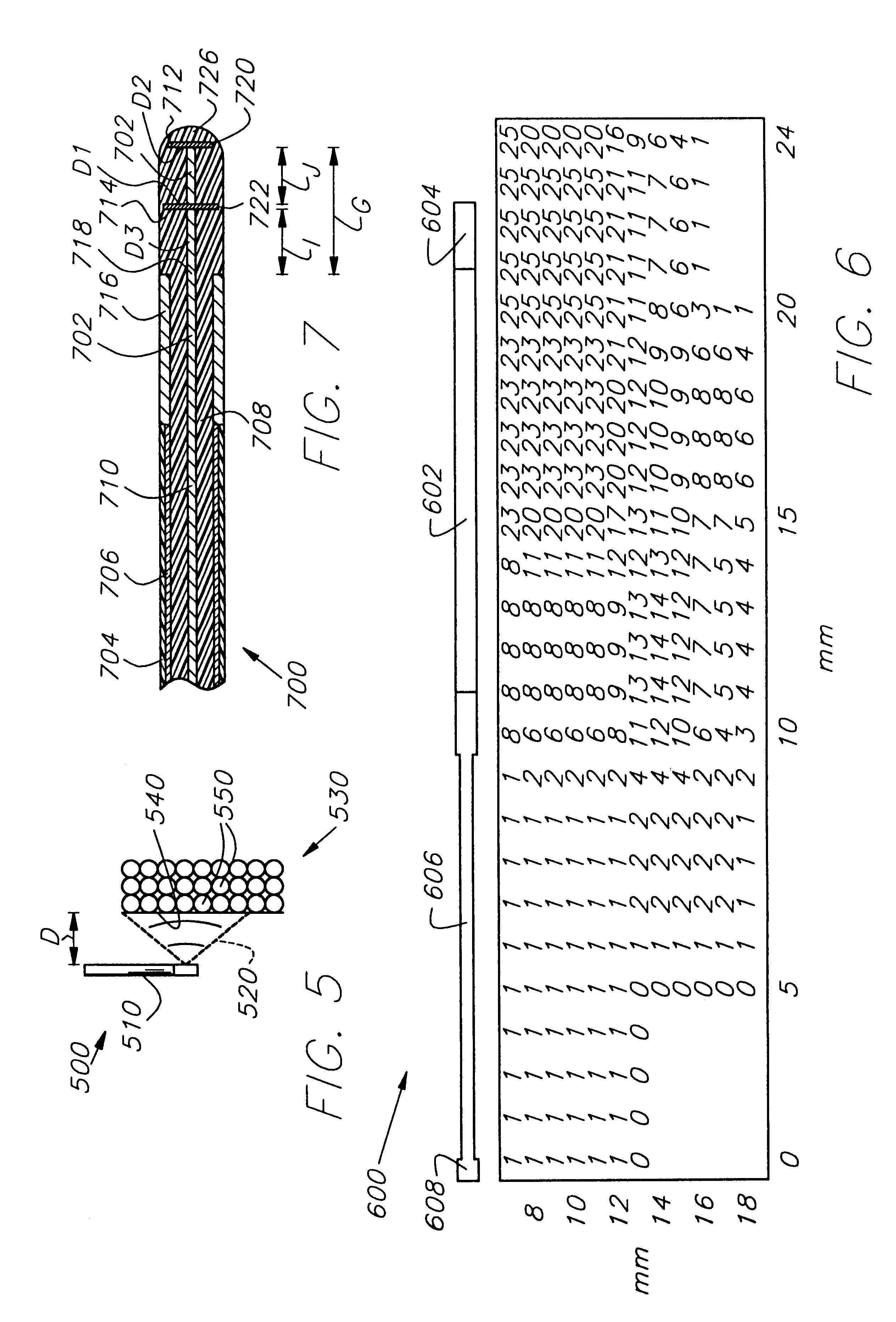
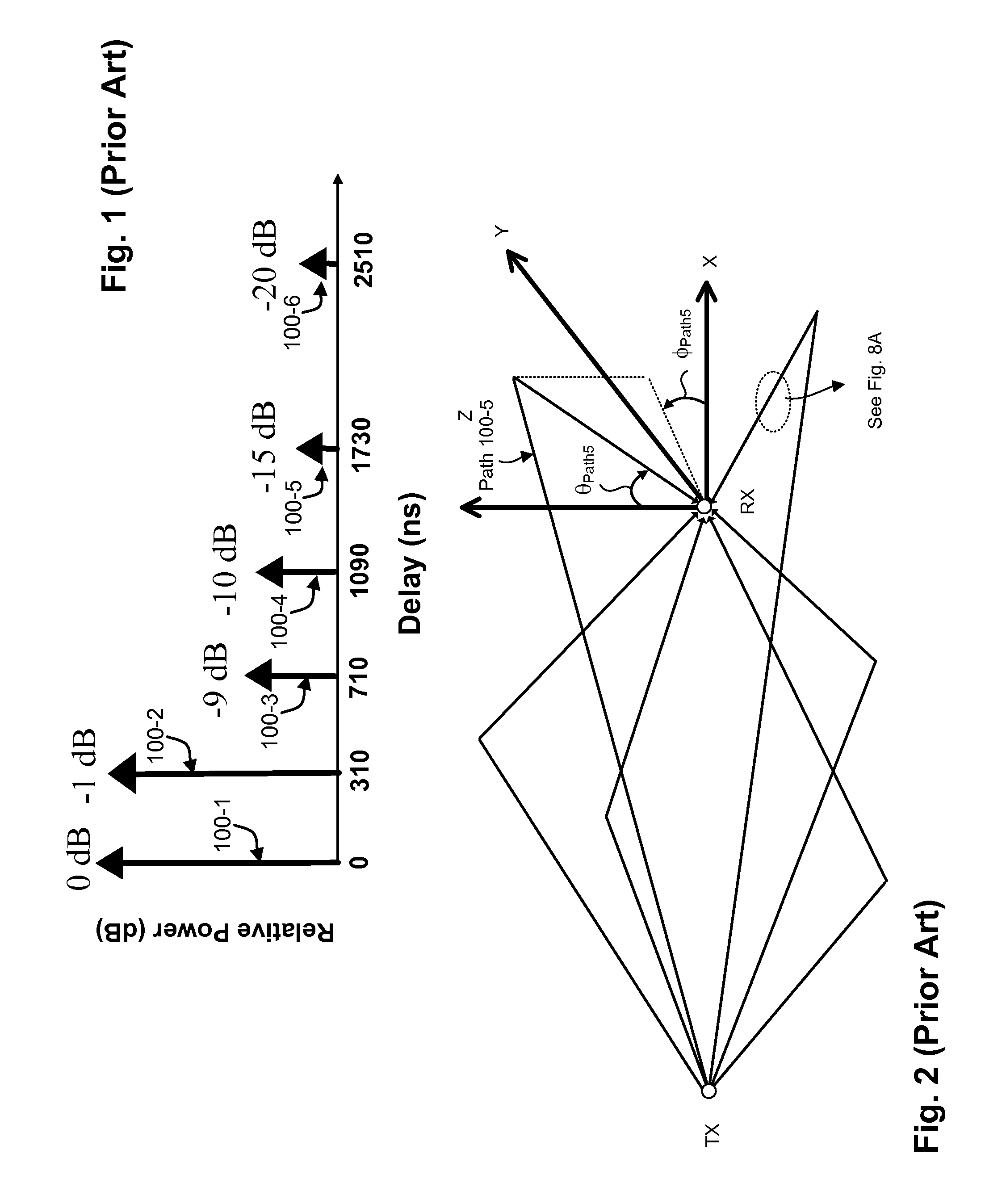
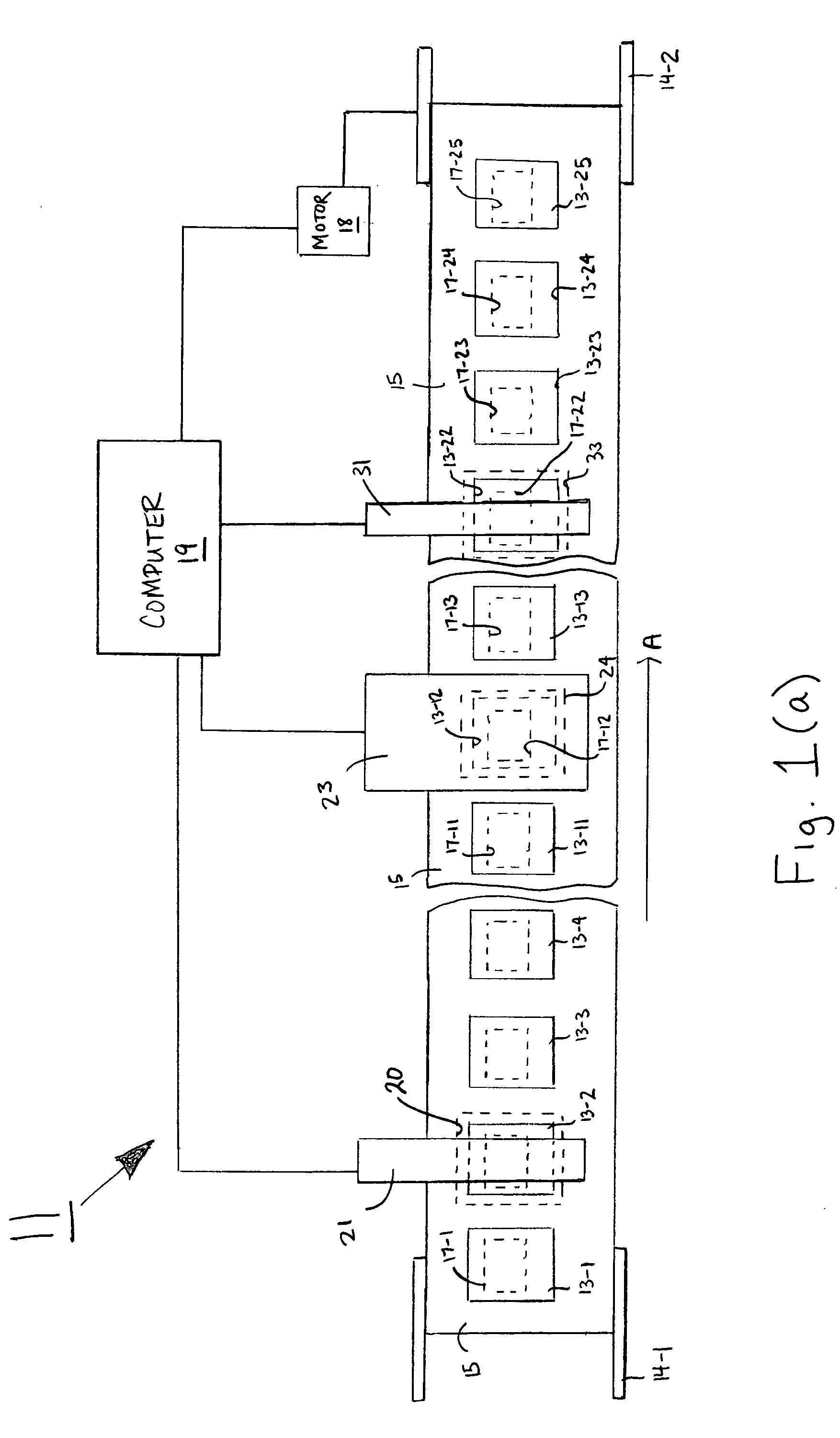
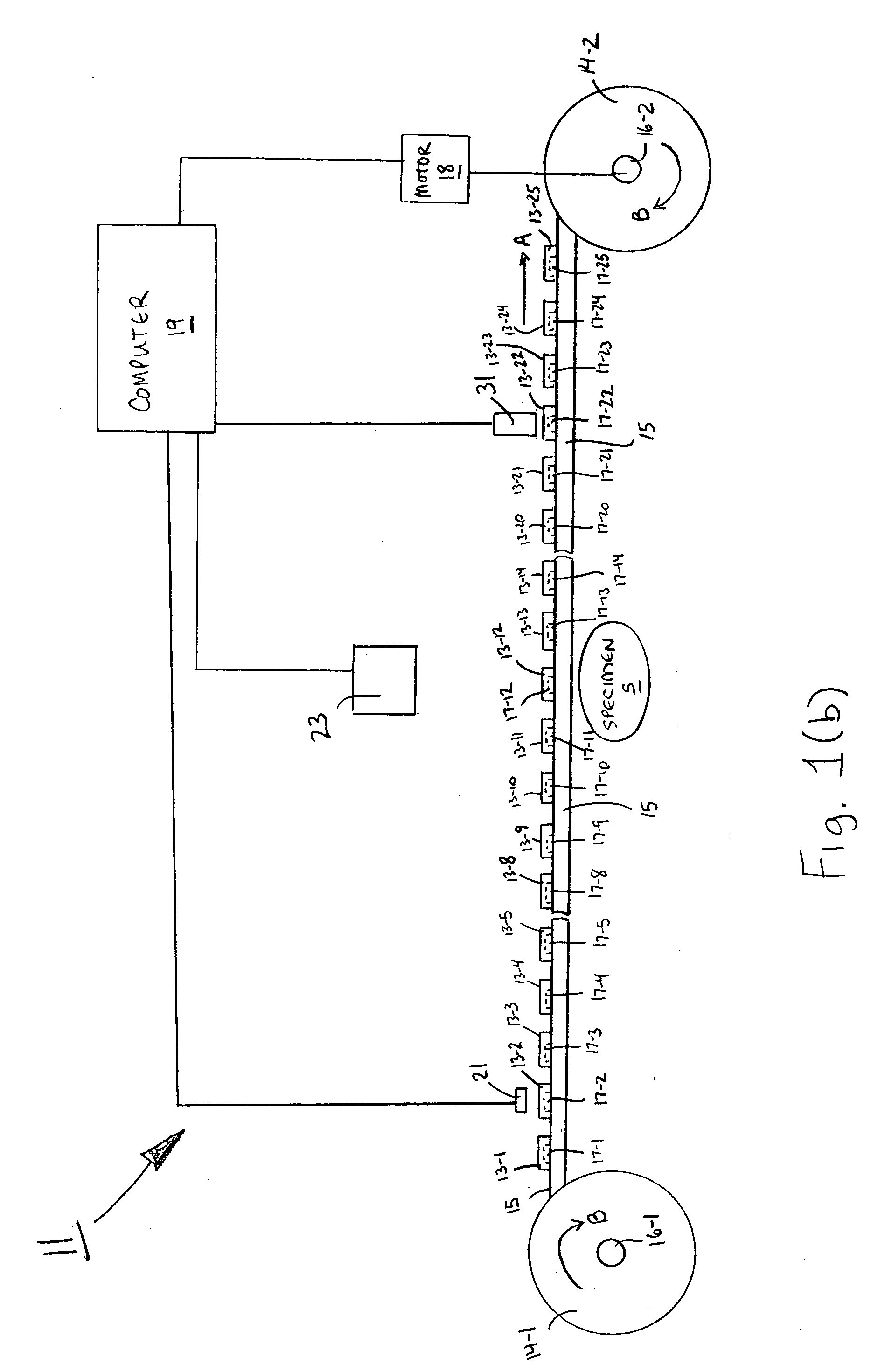
In vivo simulator for microwave treatment
InactiveUS6175768B1Reduce the possibilityWide bandwidthElectrotherapyLavatory sanitoryPeristaltic pumpVentricular tachycardia
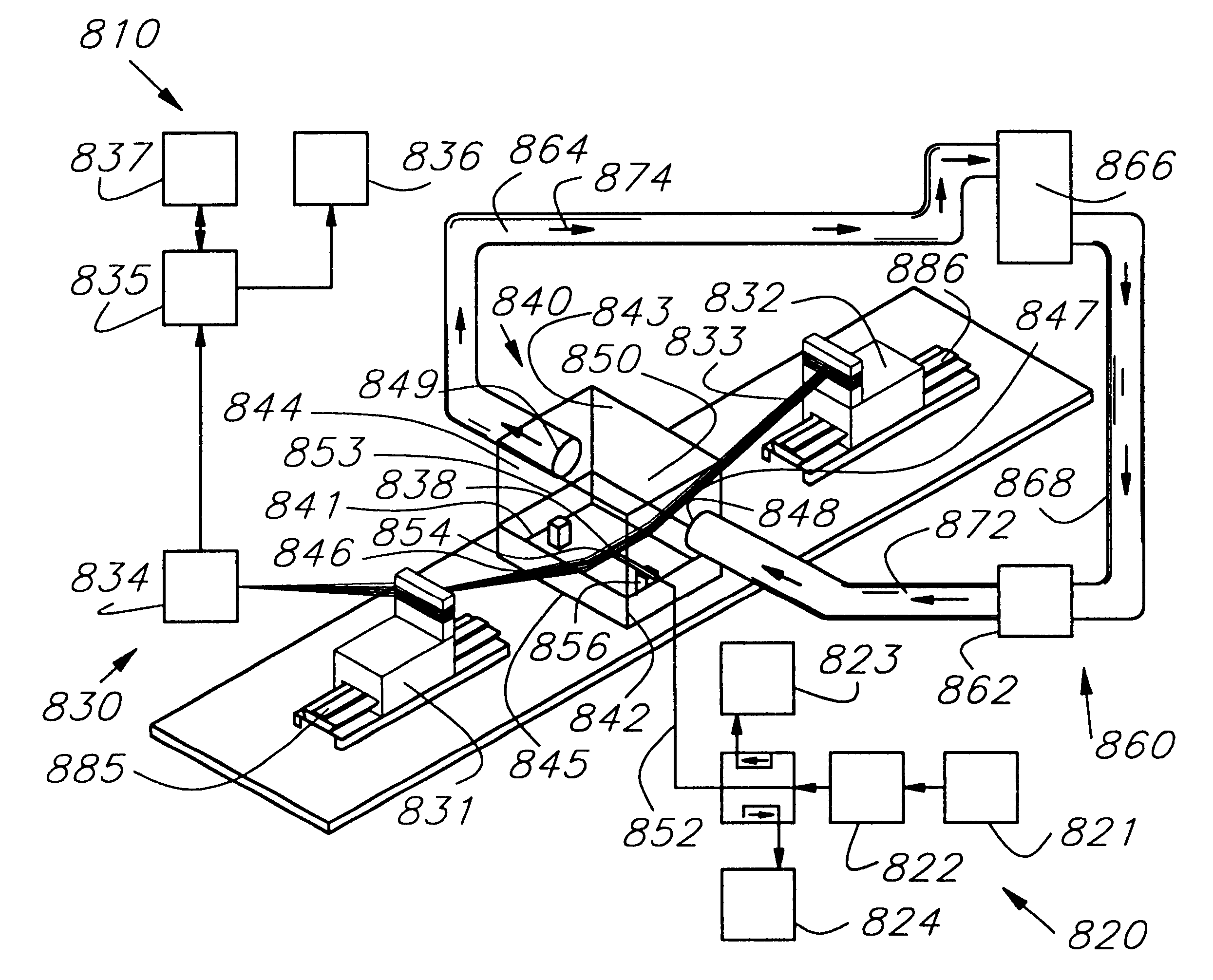
Method and apparatus are provided for propagating microwave energy into heart tissues to produce a desired temperature profile therein at tissue depths sufficient for thermally ablating arrhythmogenic cardiac tissue to treat ventricular tachycardia and other arrhythmias while preventing excessive heating of surrounding tissues, organs, and blood. A wide bandwidth double-disk antenna (700) is effective for this purpose over a bandwidth of about six gigahertz. A computer simulation provides initial screening capabilities for an antenna such as antenna, frequency, power level, and power application duration. The simulation also allows optimization of techniques for specific patients or conditions. In operation, microwave energy between about 1 Gigahertz and 12 Gigahertz is applied to monopole microwave radiator (600) having a surface wave limiter (606). A test setup provides physical testing of microwave radiators (854) to determine the temperature profile created in actual heart tissue or ersatz heart tissue (841). Saline solution (872) pumped over the heart tissue (841) with a peristaltic pump (862) simulates blood flow. Optical temperature sensors (838) disposed at various tissue depths within the heart tissue (841) detect the temperature profile without creating any electromagnetic interference. The method may be used to produce a desired temperature profile in other body tissues reachable by catheter (510) such as tumors and the like.
Owner:NASA
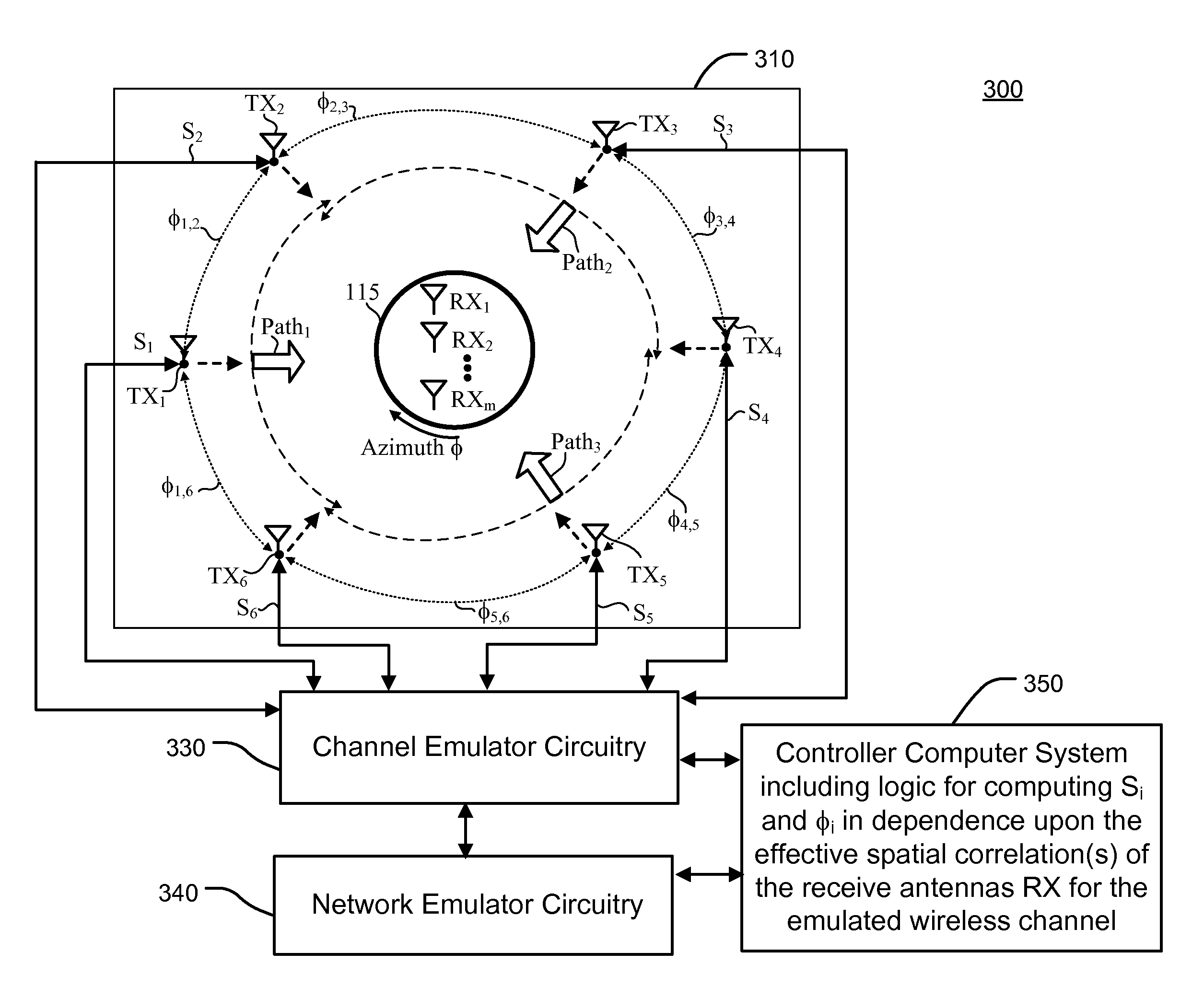
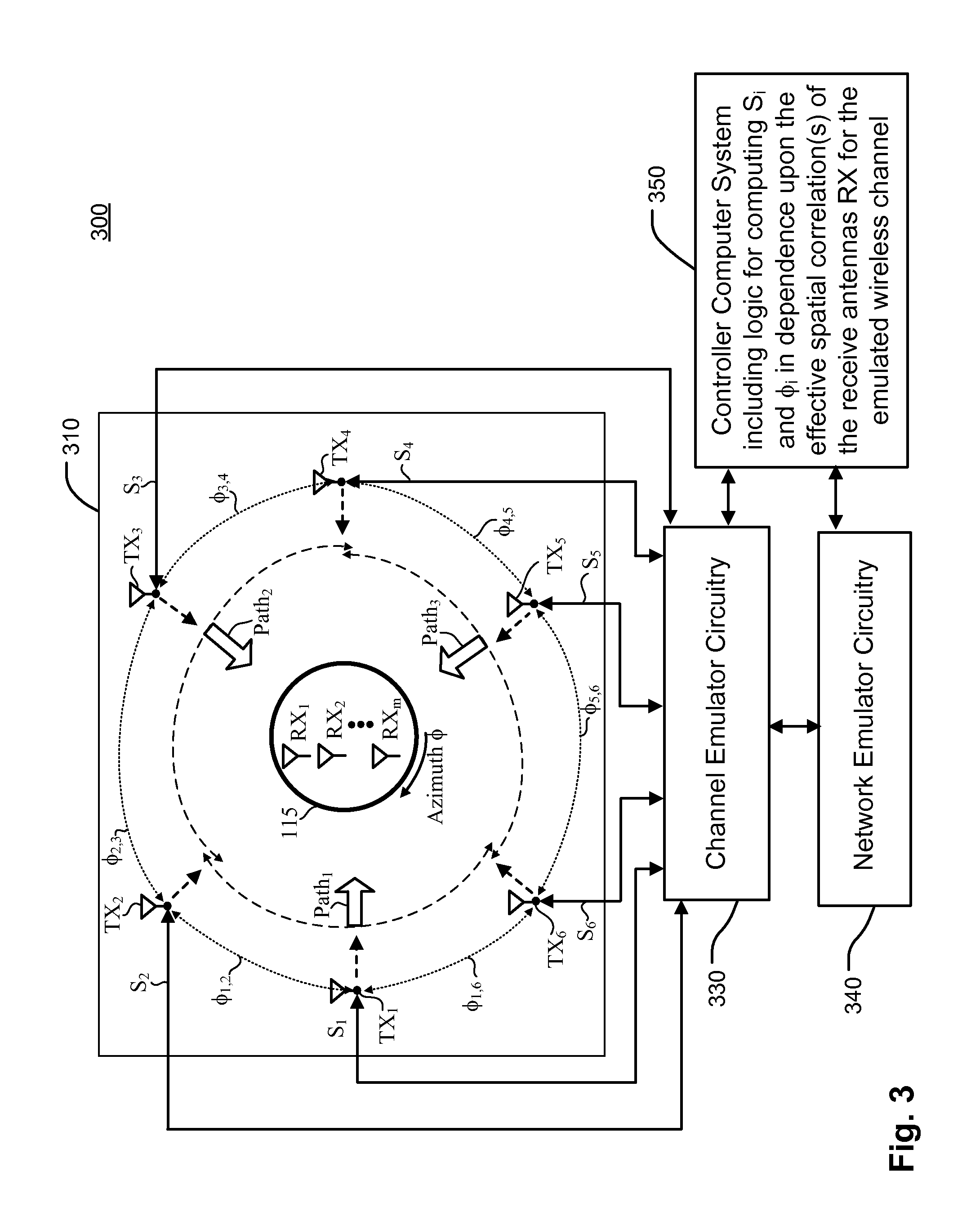
Emulation and controlled testing of MIMO OTA channels
ActiveUS20110299570A1Accurately maintaining desirable characteristic of emulated wireless channelPolarisation/directional diversityTransmission monitoringEngineeringVIT signals
The present invention relates to techniques for OTA testing suitable for producing a test signal to emulate a wireless channel while using a limited number of transmit elements. The techniques described herein enable the number of transmit antennas used to emulate a given signal path in an emulated wireless channel to be less than the number of sub-paths used to characterize the angle spread of the given signal path. As a result, a test setup is provided having a relatively small number of transmit antennas which also accurately maintaining the desirable characteristics of the emulated wireless channel.
Owner:SPIRENT COMM
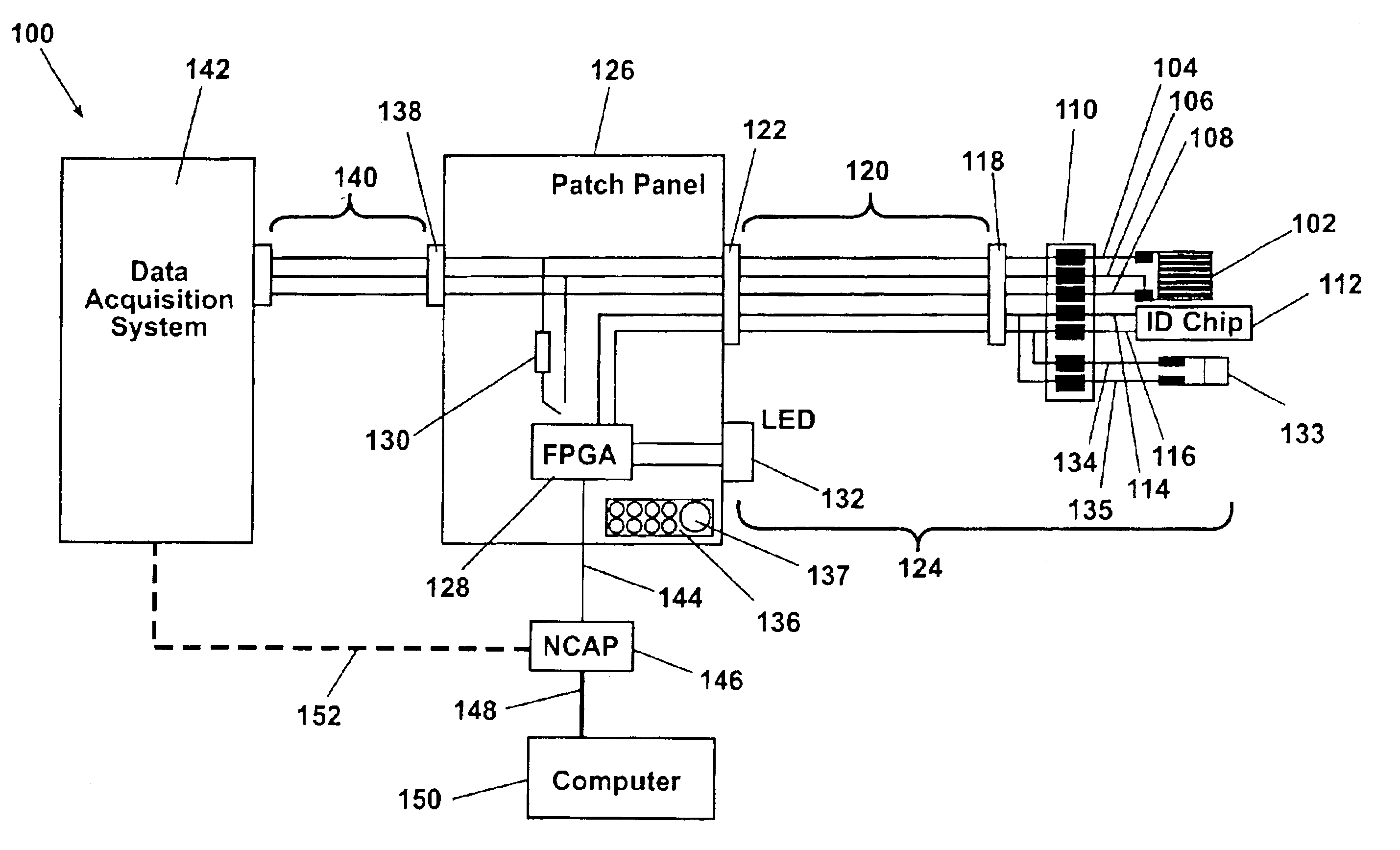
Smart connector patch panel
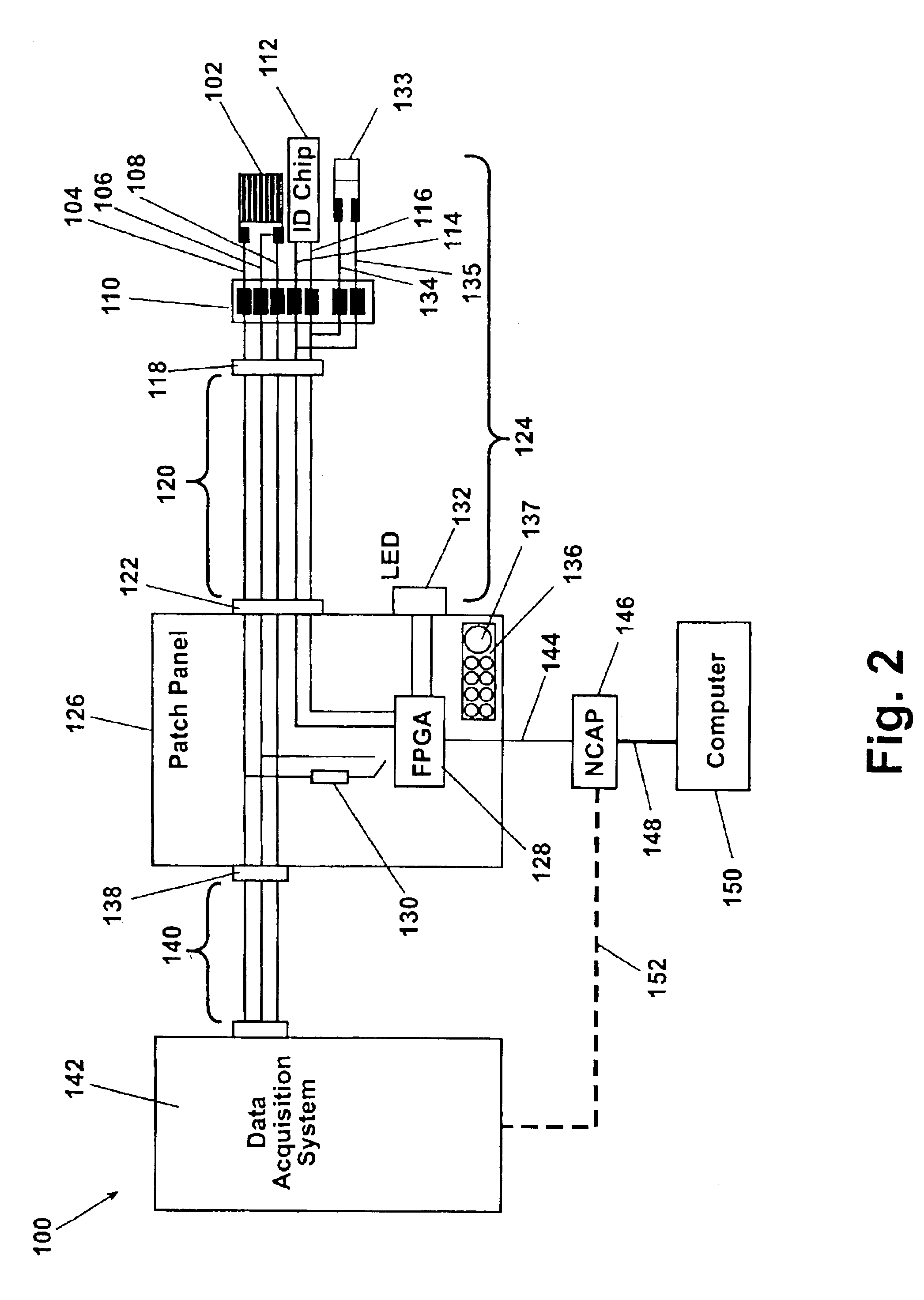
InactiveUS6871156B2Error detection/correctionMeasurement arrangements for variablePatch panelData acquisition
A system remotely collects test data from a test platform using platform attached sensors. Identification chips, each having a unique identification code, are each paired with an associated sensor to form sensor / chip pairs. At least one patch panel having a plurality of connections is positioned approximate to the platform. Connections are communicatively linked to each of the sensor / chip pairs. A computer system is communicatively linked to additional patch panel connections. The identification of selected sensors is queried by a computer command to the patch panels, and a group of sensors for a given test is identified and selected. Test data from each of the selected sensors is transferred through the patch panels to the computer system for collation and generation of a test setup compatible with a data acquisition system. Test setup information is downloaded to the data acquisition system in preparation for the next test.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
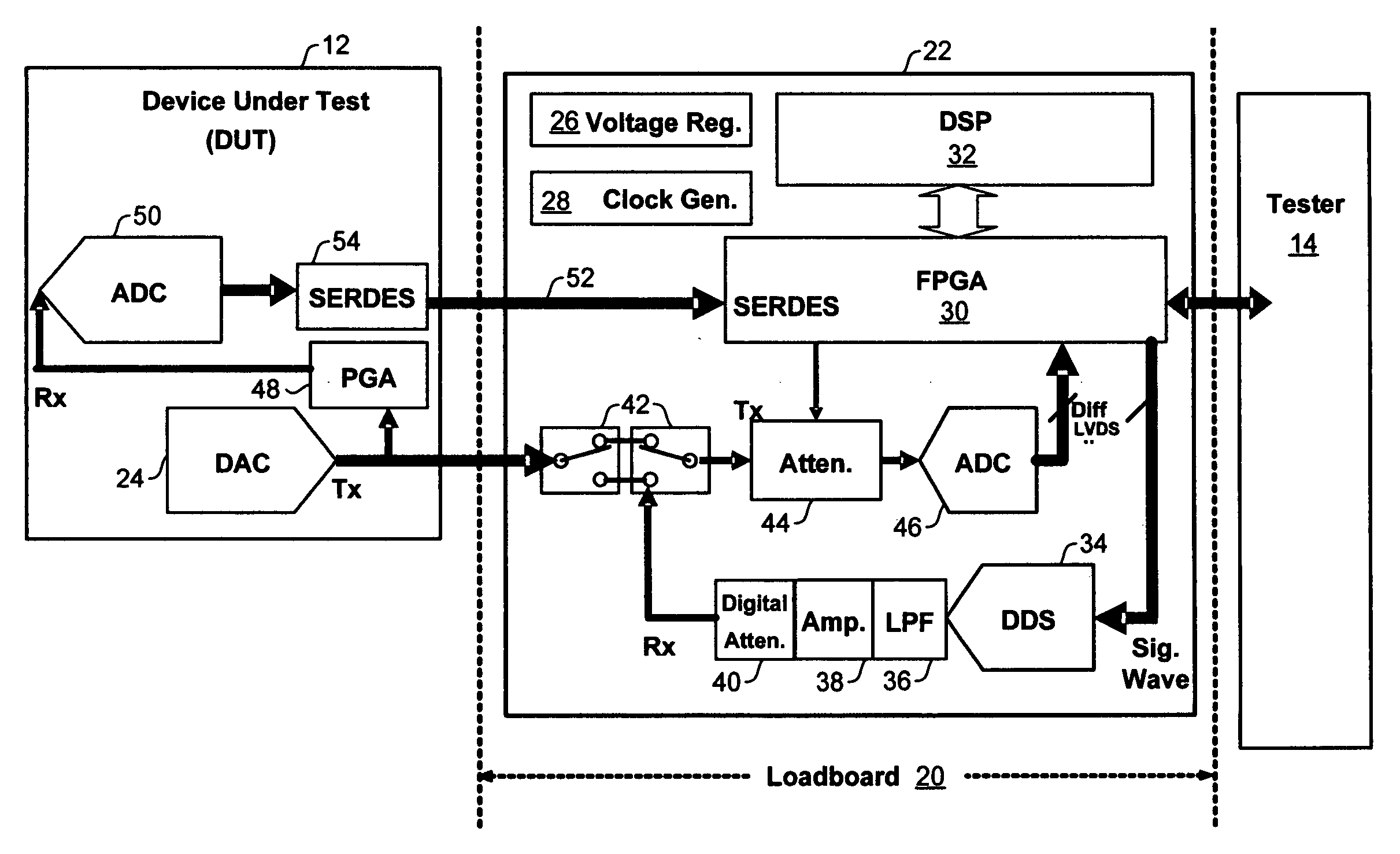
Analog built-in self-test module
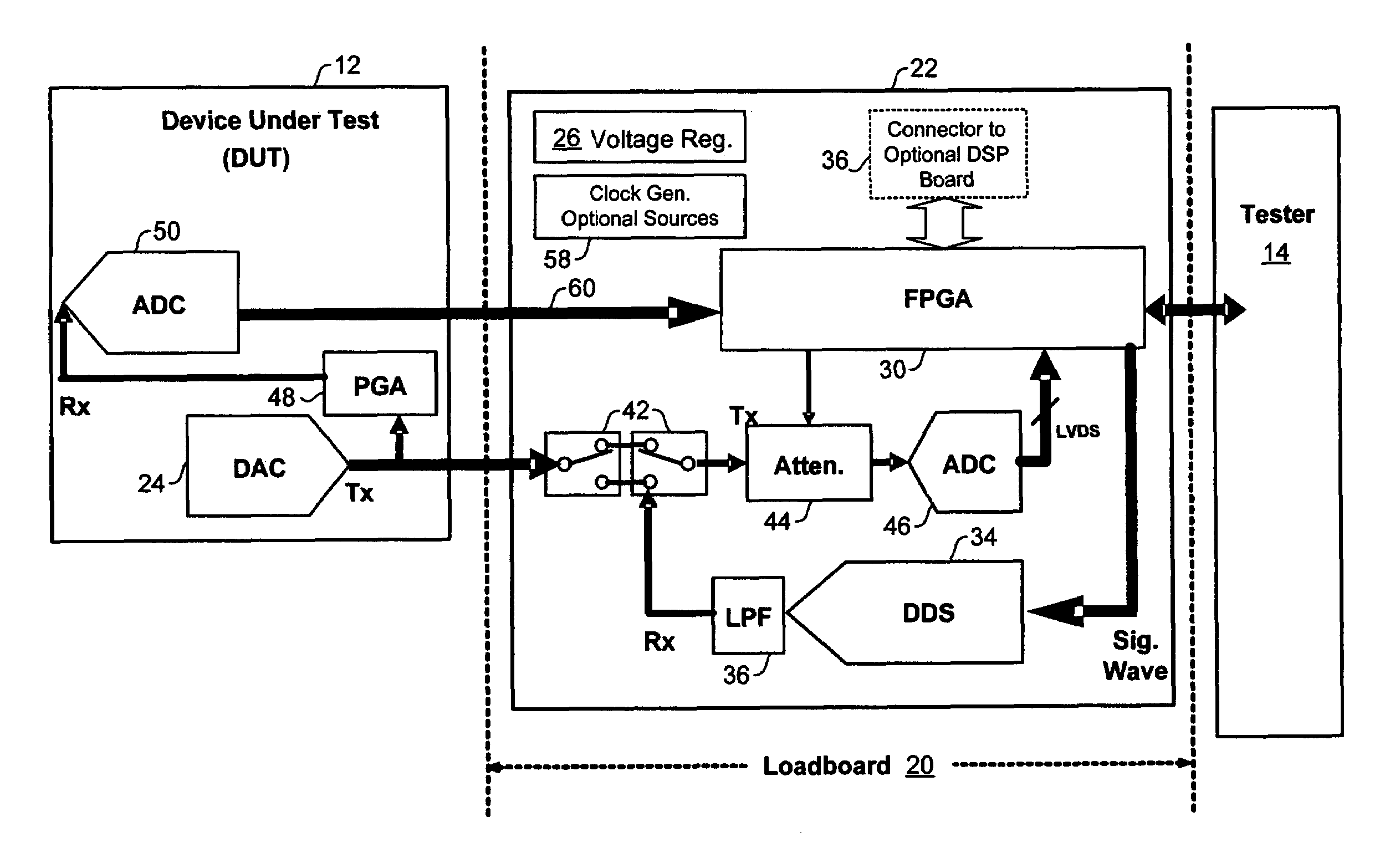
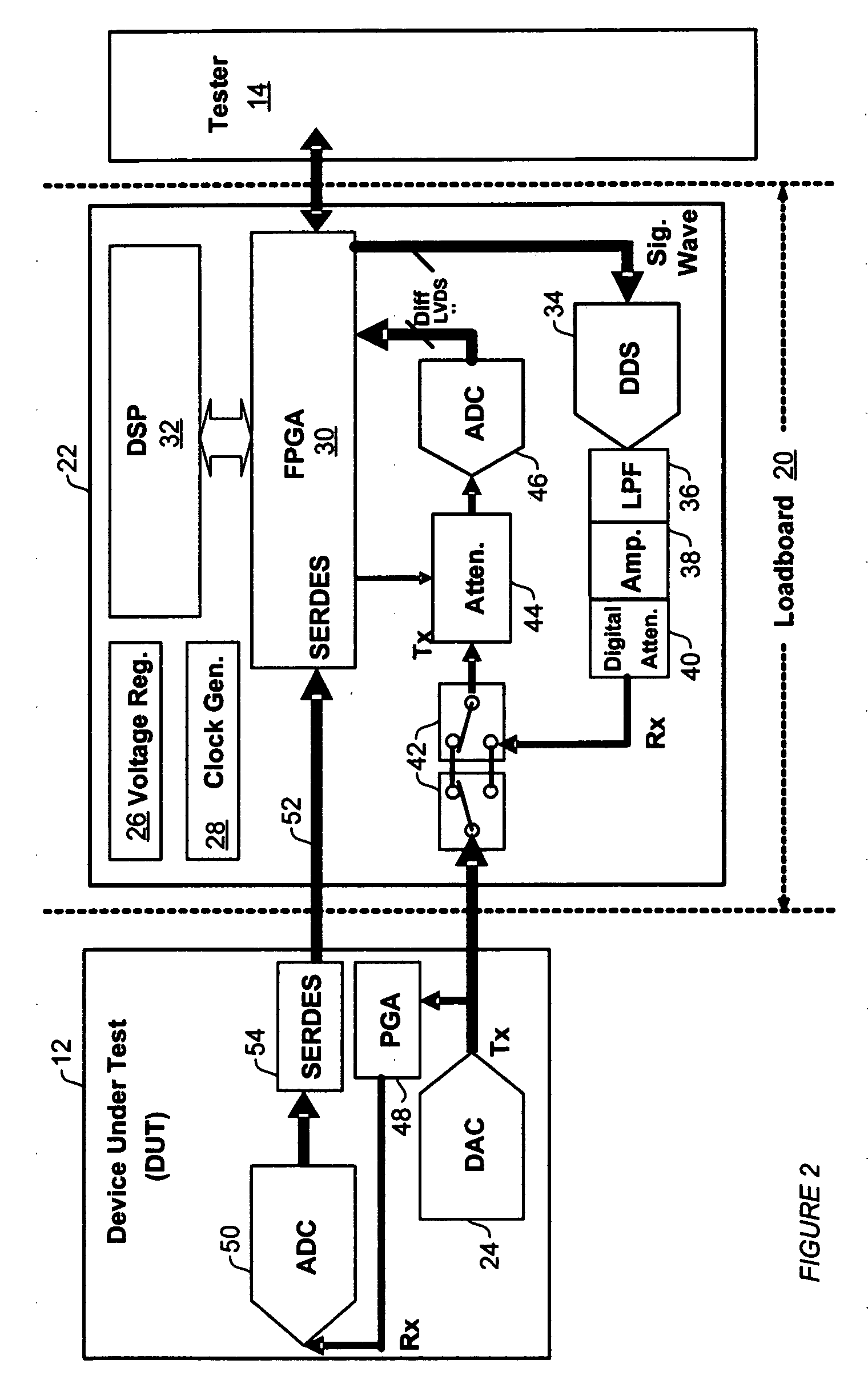
ActiveUS7327153B2Quick testImprove efficiencyElectronic circuit testingError detection/correctionOn boardTester device
An analog BIST (Built-in Self-Test) module for a load board in a test system for testing Integrated Chips (IC) and other devices-under-test (DUTs). Components of the test module perform test setup, transmission of analog test signals to a DUT, capture of analog and digital test data from the DUT, and on-board analysis of the test data using DSPs without sending the test data to a tester. Modules may be add-on boards to load boards an contain one or more processors and multiple components to test DUTs in parallel, significantly decreasing test and analysis times of a test system such as a Very Low Cost Tester (VLCT).
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Architecture, system and method for testing resistive type memory
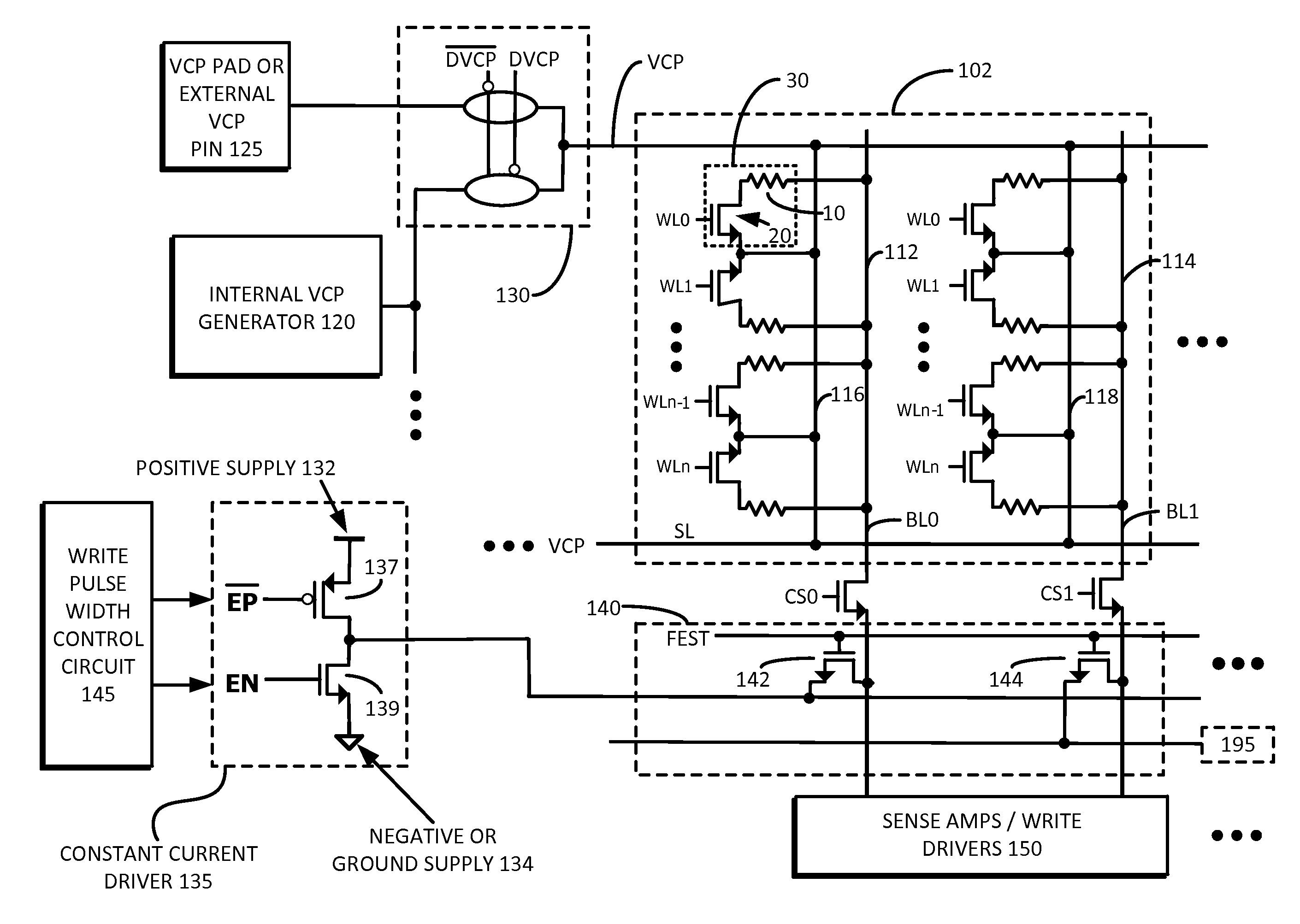
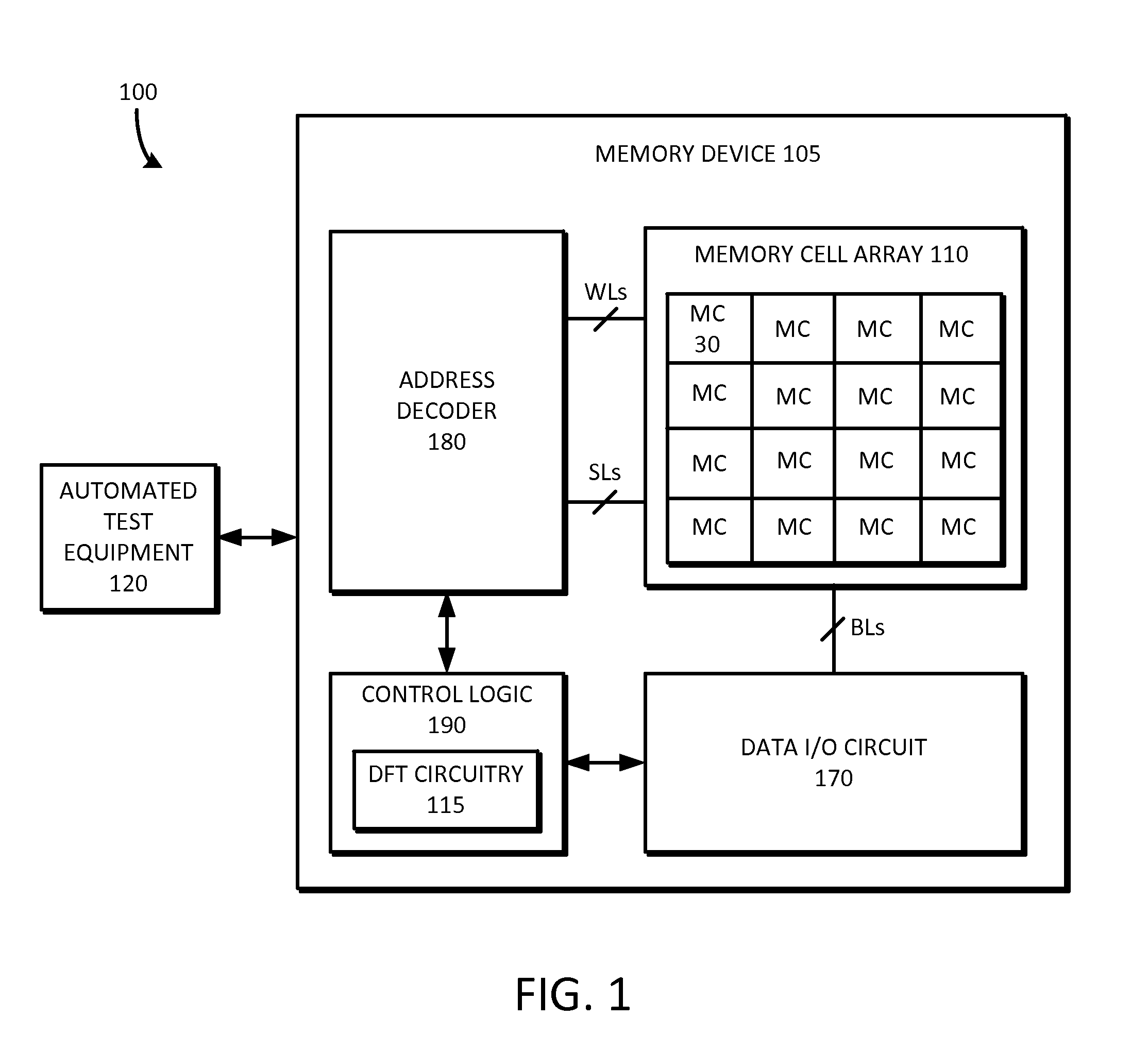
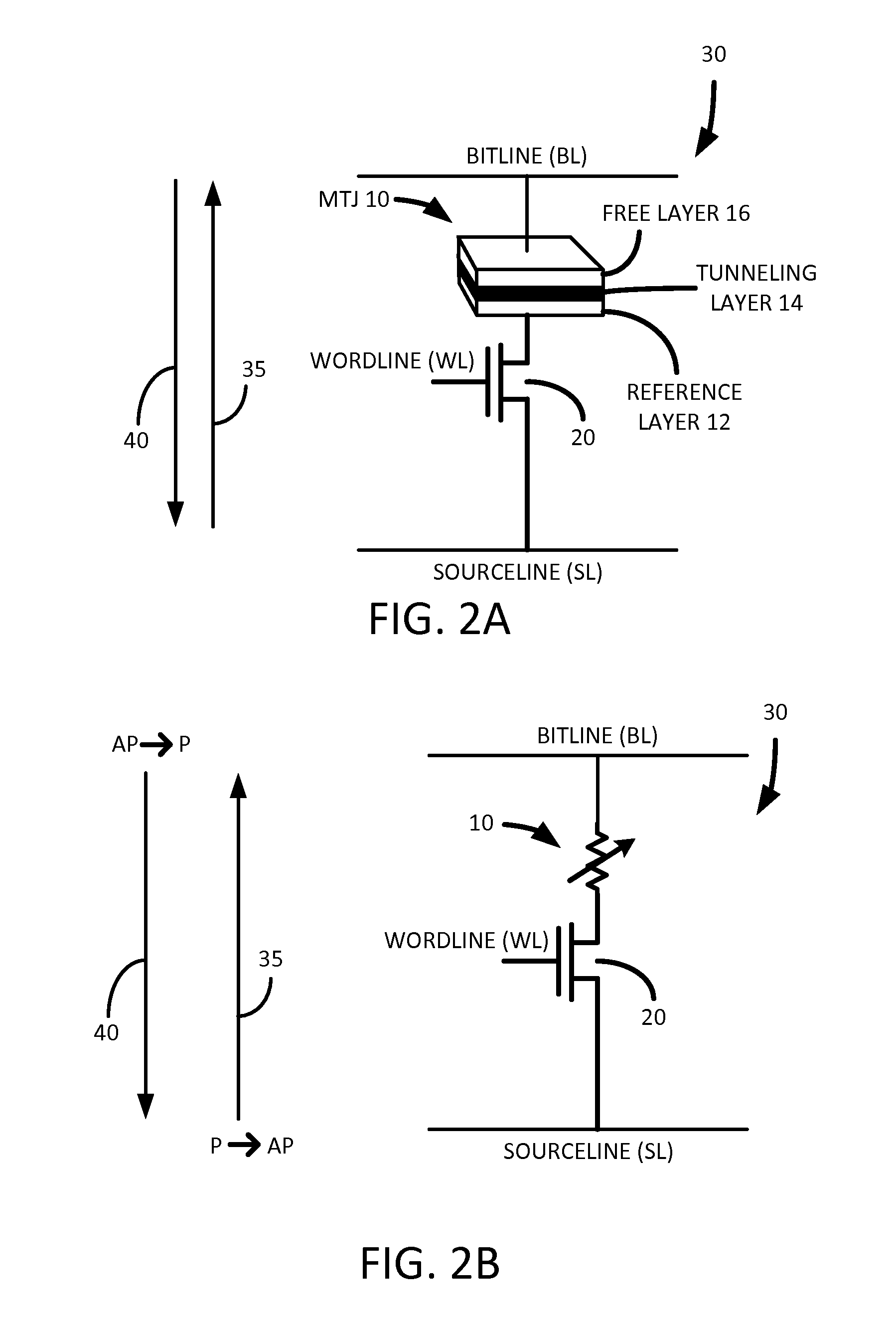
Example embodiments include a method for massive parallel stress testing of resistive type memories. The method can include, for example, disabling one or more internal analog voltage generators, configuring memory circuitry to use a common plane voltage (VCP) pad or external pin, connecting bit lines of the memory device to a constant current driver, which works in tandem with the VCP pad or external pin to perform massive parallel read or write operations. The inventive concepts include fast test setup and initialization of the memory array. The data can be retention tested or otherwise verified using similar massive parallel testing techniques. Embodiments also include a memory test system including a memory device having DFT circuitry configured to perform massive parallel stress testing, retention testing, functional testing, and test setup and initialization.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method and system for testing RFID devices
ActiveUS20060145710A1Precise positioningTesting sensing arrangementsMemory record carrier reading problemsUnique identifierCommon carrier
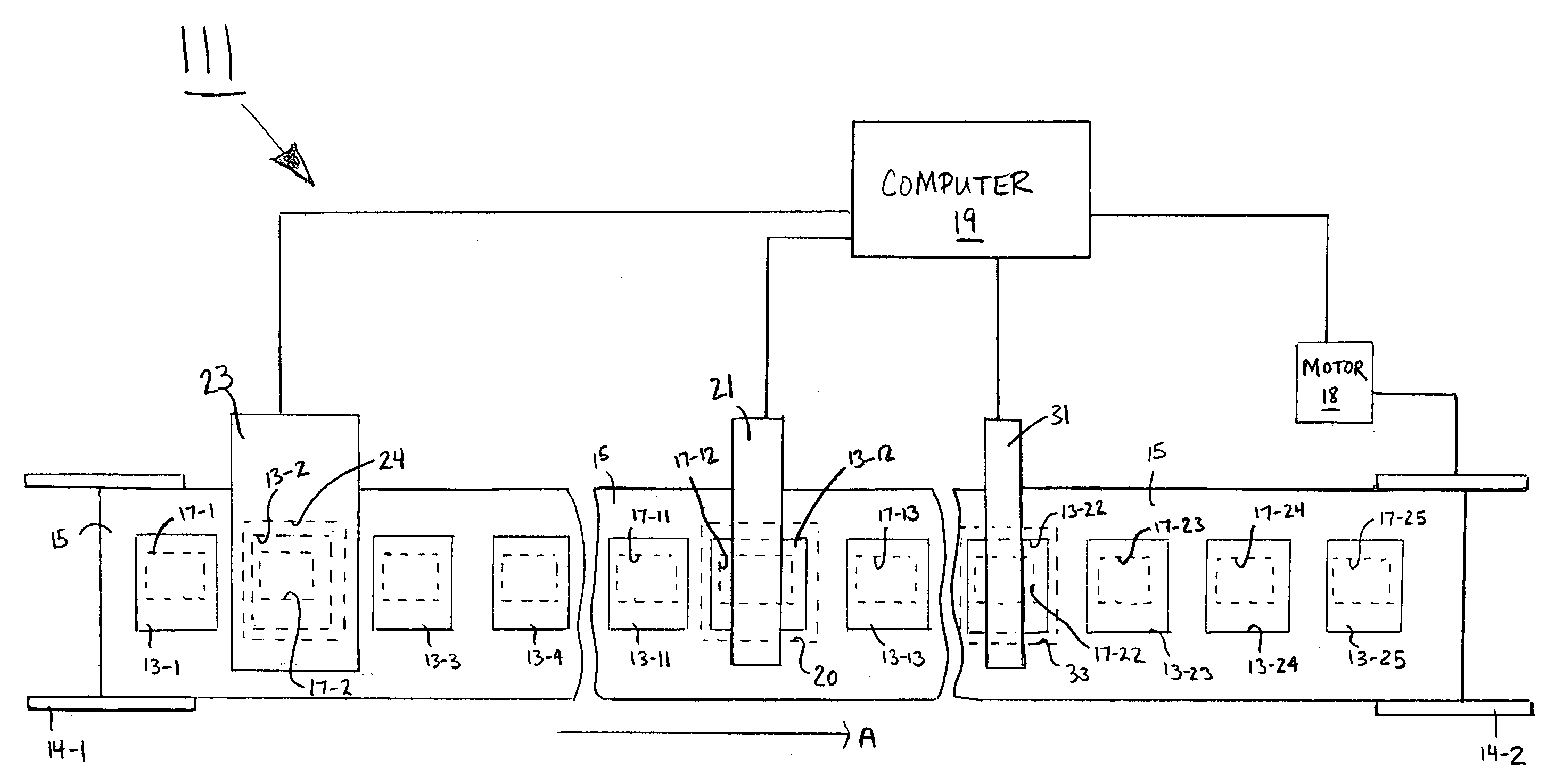
A method and system for testing a plurality of RFID devices disposed on a common carrier. In one embodiment, the RFID devices are evenly spaced along the length of the carrier, and the system comprises a short-range tester, a long-range tester and a computer, the short-range tester being coupled to the computer and having a short-range testing position, the long-range tester being coupled to the computer and having a long-range testing position, the long-range testing position being spaced downstream from the short-range testing position by a known number of device positions. In use, an RFID device of interest is first positioned at the short-range testing position, and the short-range tester reads a unique identifier for that RFID device and communicates the identifier to the computer. The carrier is then advanced so that subsequent RFID devices are read by the short-range tester. When the RFID device of interest has advanced to the long-range testing position, the long-range tester conducts a performance test and communicates any detected results to the computer. Because the distance between the two testing positions is known, the computer knows when the RFID device of interest is at the long-range testing position and uses the identifier to distinguish the results for that device from the results of any other devices.
Owner:AVERY DENNISON CORP
Dynamic changing tier service on test device
ActiveUS20120076015A1Operation efficiency can be improvedImprove technical effectError preventionTransmission systemsComputer hardwareBroadband communication
A test device is located within a broadband communications network. The test device is interconnected with a policy enforcement point of the broadband communications network. Responsive to commencement of a test to be conducted with the test device, the policy enforcement point is signaled, from a policy server of the broadband communications network, so as to set a bandwidth tier for the test to be conducted with the test device. The test is conducted with the test device in accordance with the bandwidth tier. One or more additional tests can be conducted for additional, different, bandwidth tier(s). Related methods, systems, apparatuses, and computer program products are also disclosed.
Owner:TIME WARNER CABLE ENTERPRISES LLC
Method and system for testing RFID devices
ActiveUS7164353B2Testing sensing arrangementsMemory record carrier reading problemsTester deviceCommon carrier
A method and system for testing a plurality of RFID devices disposed on a common carrier. In one embodiment, the RFID devices are evenly spaced along the length of the carrier, and the system comprises a short-range tester, a long-range tester and a computer, the short-range tester being coupled to the computer and having a short-range testing position, the long-range tester being coupled to the computer and having a long-range testing position, the long-range testing position being spaced downstream from the short-range testing position by a known number of device positions. In use, an RFID device of interest is first positioned at the short-range testing position, and the short-range tester reads a unique identifier for that RFID device and communicates the identifier to the computer. The carrier is then advanced so that subsequent RFID devices are read by the short-range tester. When the RFID device of interest has advanced to the long-range testing position, the long-range tester conducts a performance test and communicates any detected results to the computer. Because the distance between the two testing positions is known, the computer knows when the RFID device of interest is at the long-range testing position and uses the identifier to distinguish the results for that device from the results of any other devices.
Owner:AVERY DENNISON CORP
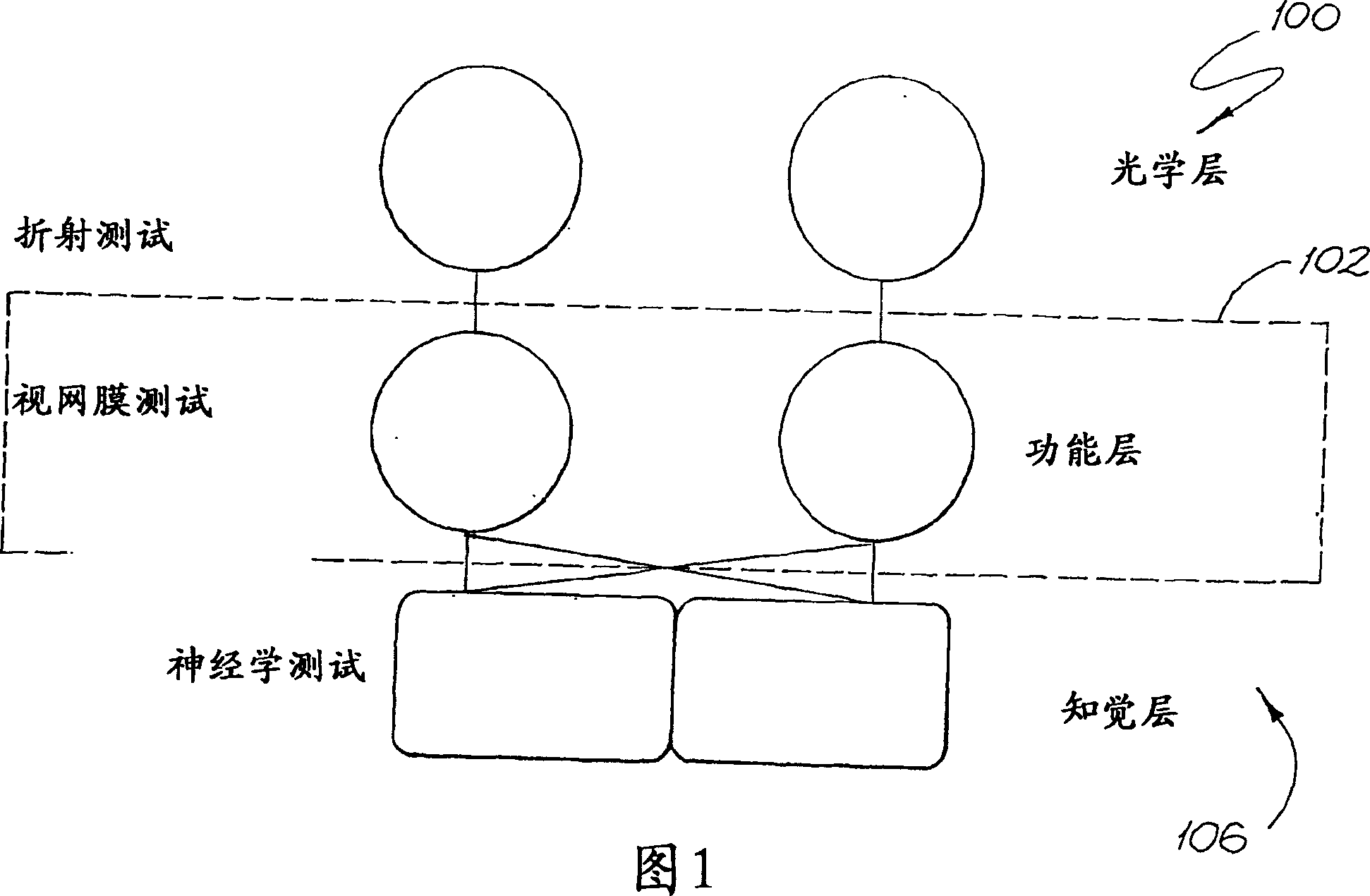
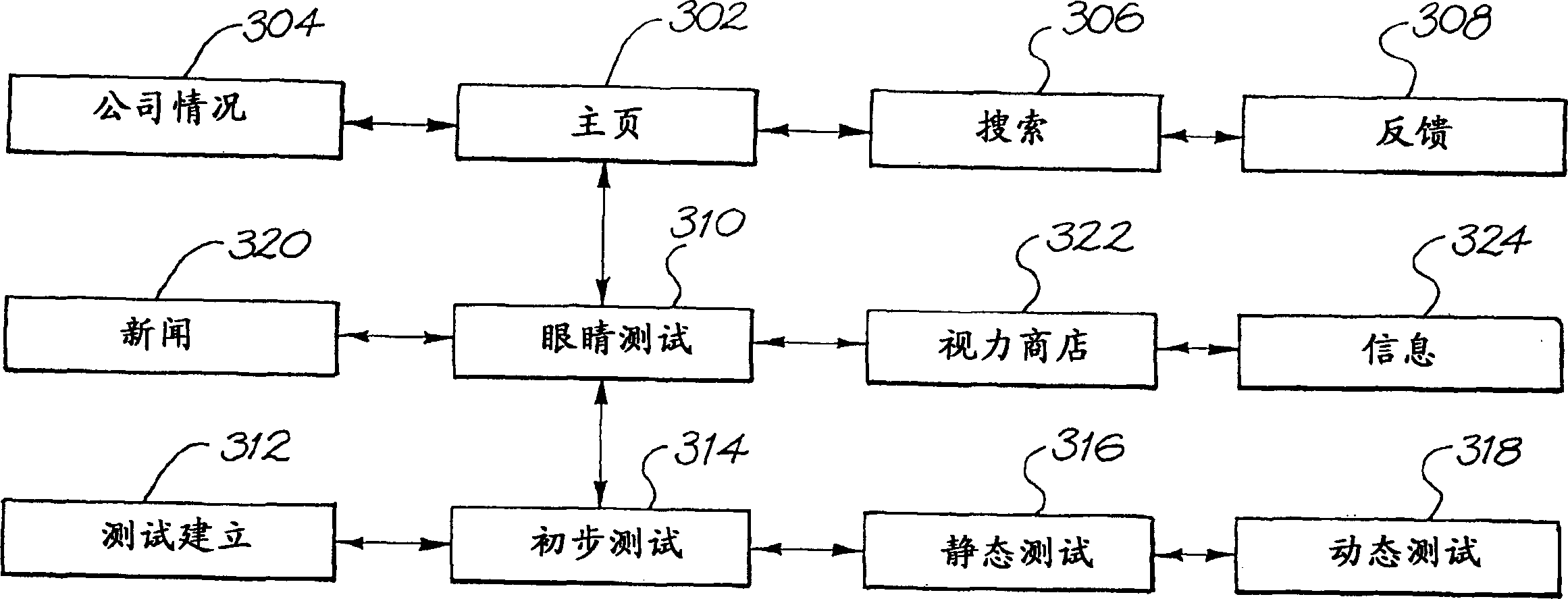
Vision testing system
A method and apparatus are provided for testing the vision of a human subject using a series of eye tests (310). A test setup procedure (312) is run to adjust the settings of a display device (1914) such that graphic objects displayed on the device (1914) conform to a pre-defined appearance. A series of preliminary tests (314), static tests (316) and dynamic tests (318) are displayed on the device (1914), and the responses of the subject are recorded. The tests (310) may be run remotely, for example over the Internet. No lenses are required to run the tests (310).
Owner:AIVISION PTY LTD
Analog built-in self-test module
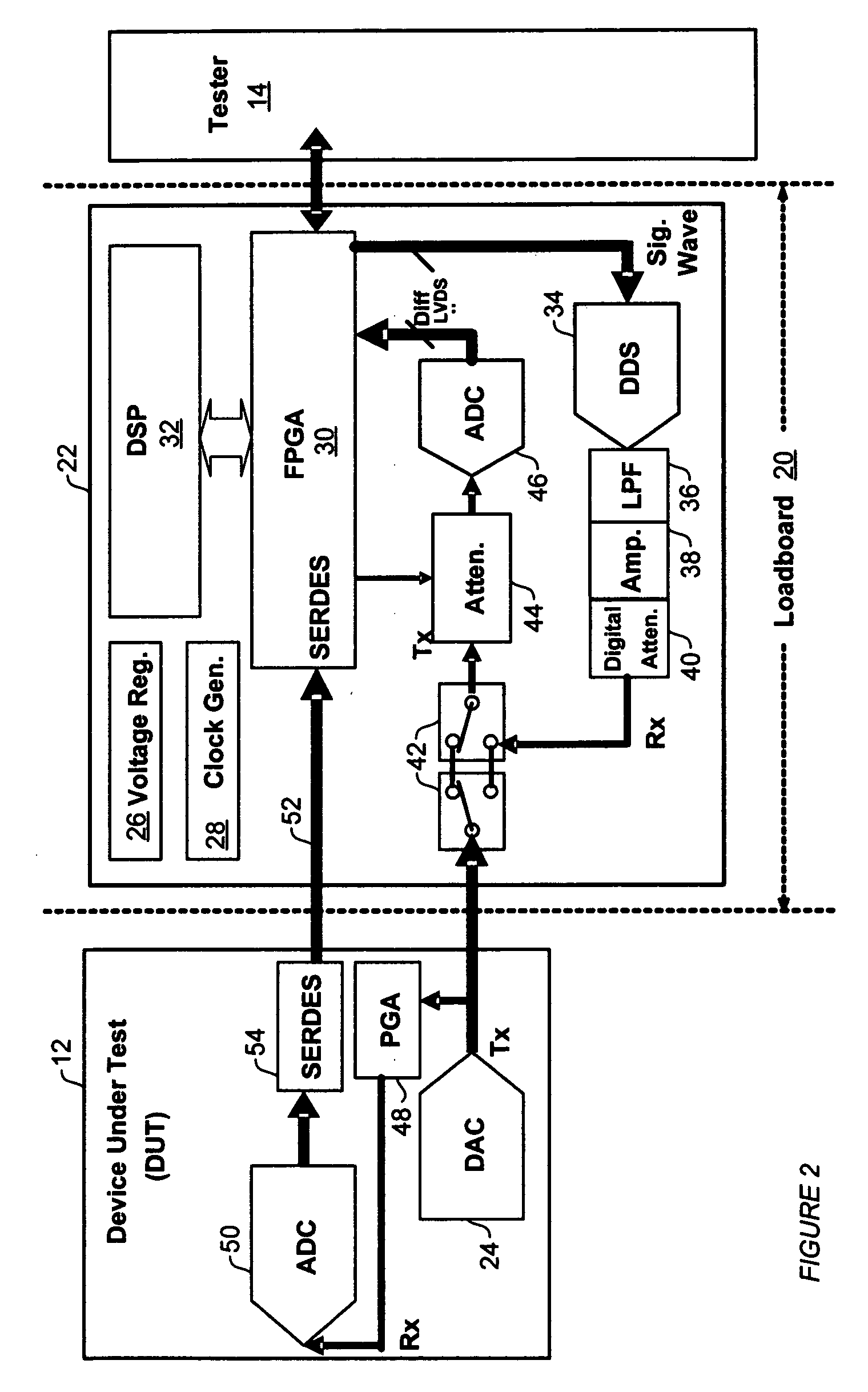
ActiveUS20070096759A1Increase flexibilityFast analog final test analogElectronic circuit testingOn boardTester device
An analog BIST (Built-in Self-Test) module for a load board in a test system for testing Integrated Chips (IC) and other devices-under-test (DUTs). Components of the test module perform test setup, transmission of analog test signals to a DUT, capture of analog and digital test data from the DUT, and on-board analysis of the test data using DSPs without sending the test data to a tester. Modules may be add-on boards to load boards an contain one or more processors and multiple components to test DUTs in parallel, significantly decreasing test and analysis times of a test system such as a Very Low Cost Tester (VLCT).
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Systems and methods for configuring a test setup
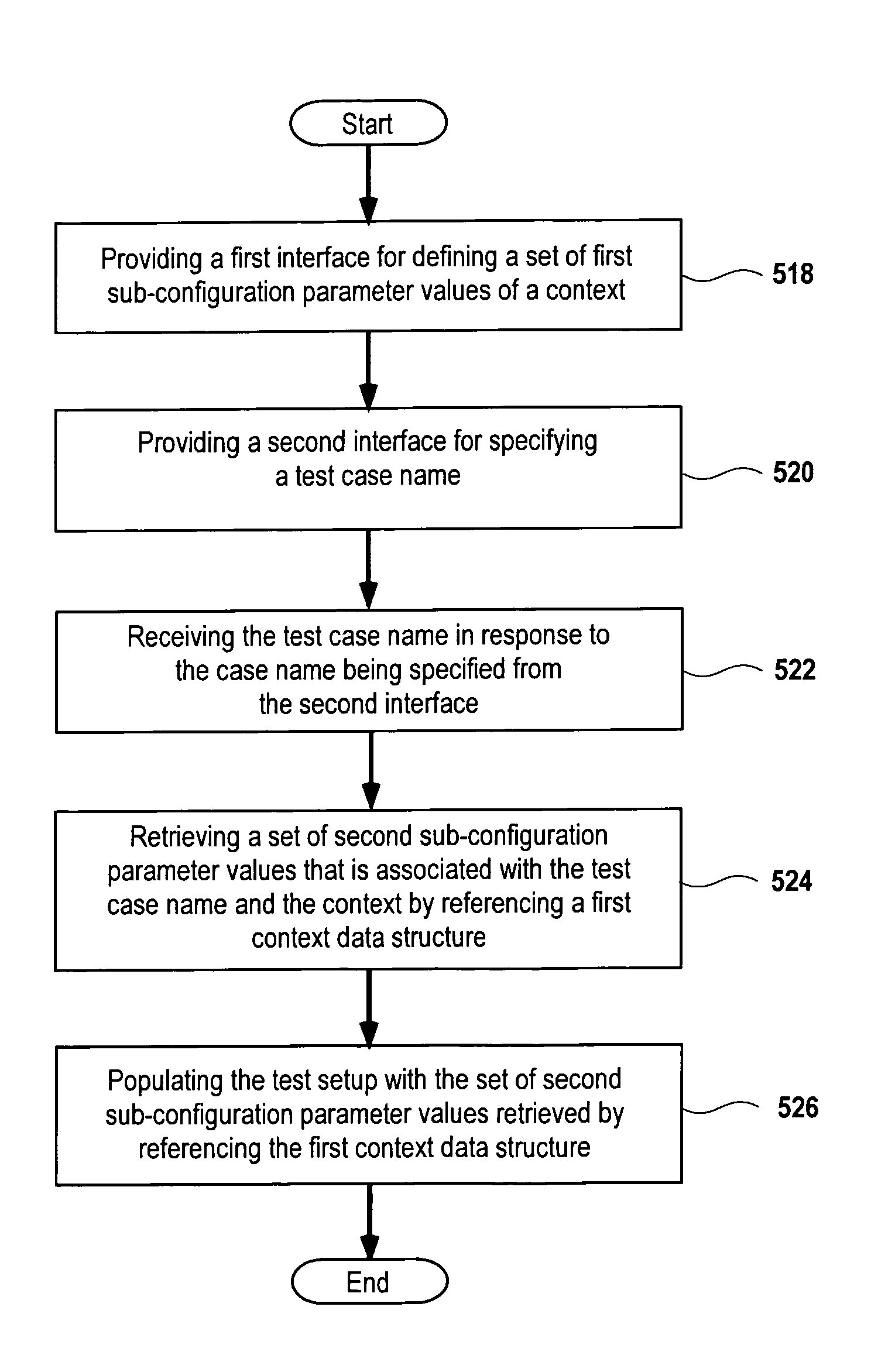
InactiveUS7158907B1Error detection/correctionGeneral purpose stored program computerComputer hardwareContext data
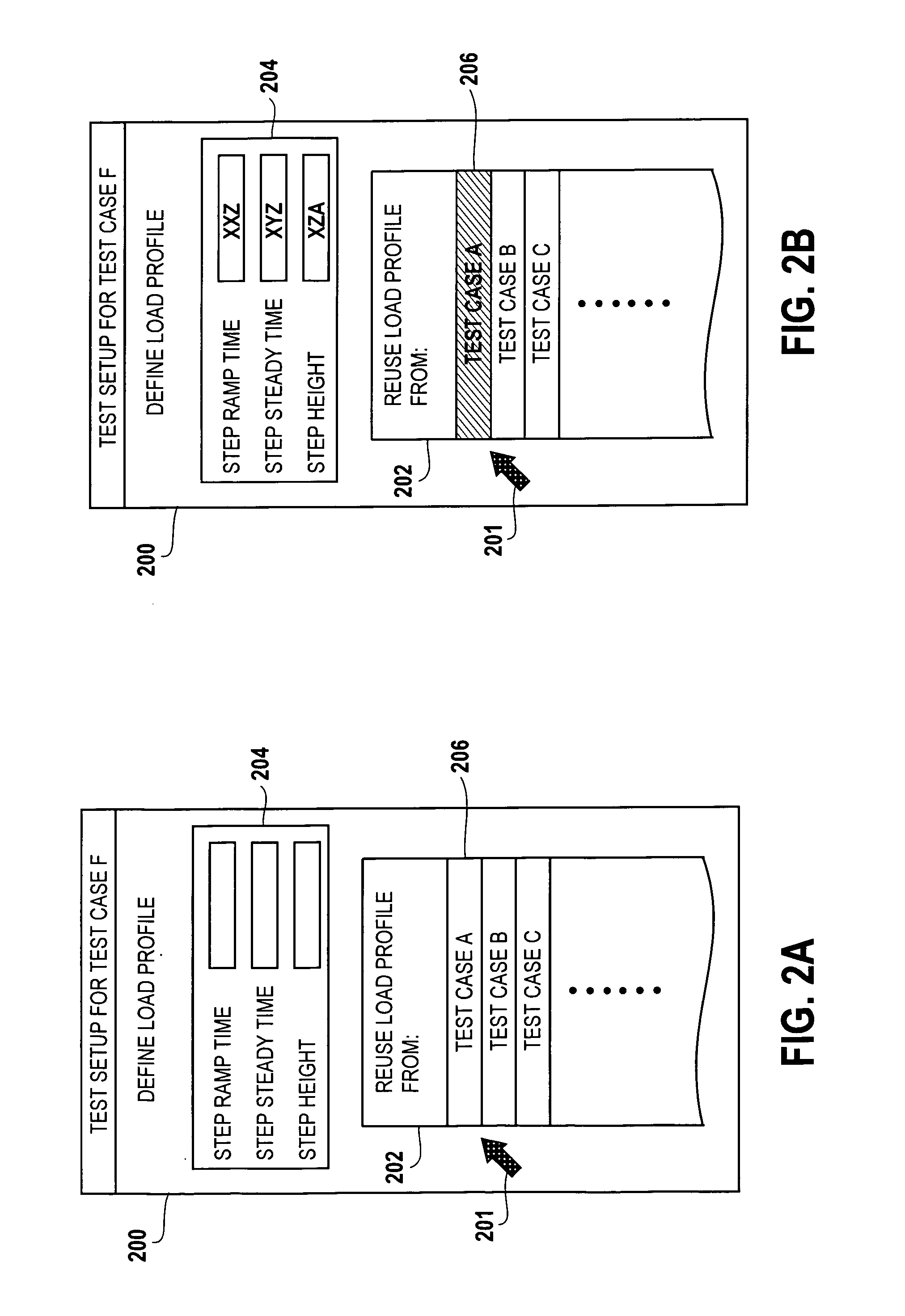
Methods for configuring a test setup that support reuse of previously defined sub-configuration parameter values without reference to individually-named sub-configuration files are provided. In these methods, each sub-configuration parameter value is automatically associated with a test case name within the test, and this association is represented in context data structures. During test configuration, for each set of sub-configuration parameter values, the user may reuse previously-defined values simply by specifying the name of the test associated with the previously-defined values. A system and a user interface for configuring a test setup are also described.
Owner:SPIRENT COMM
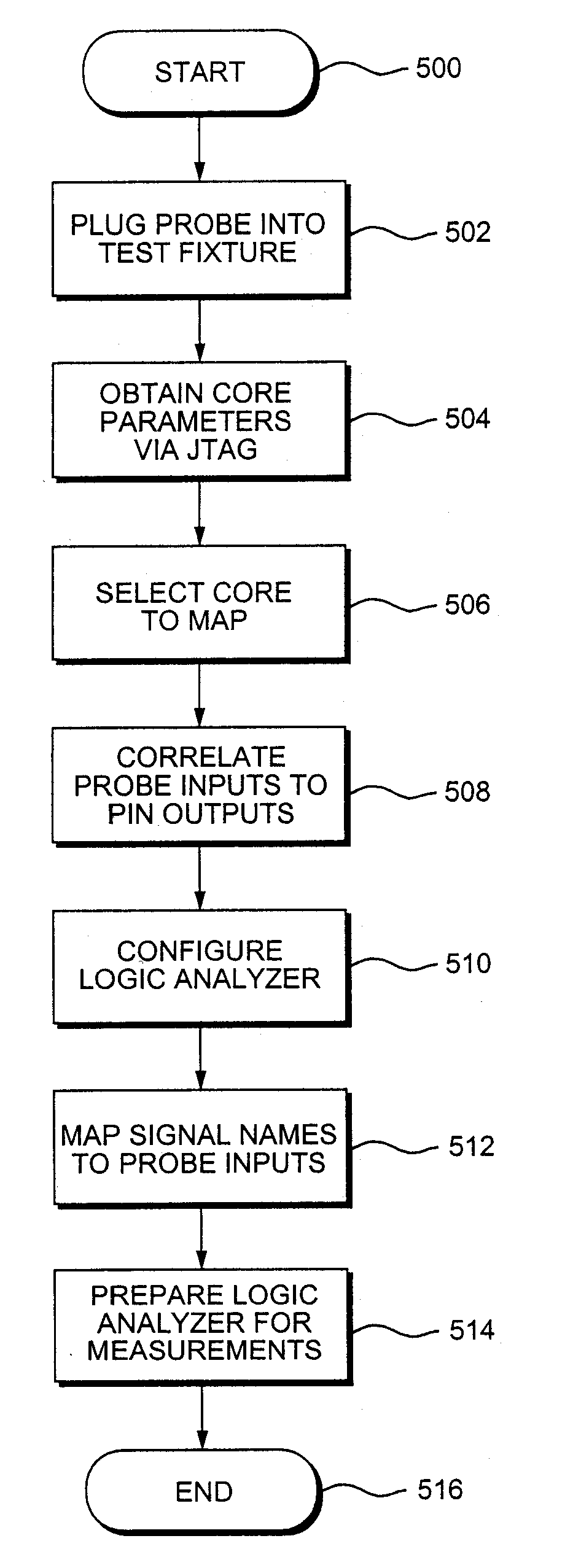
Apparatus and method for automated test setup
Apparatus and methods for setting up a test instrument to perform measurements on a circuit having a plurality of signal applied to a plurality of output pins. Configuration parameters including an identification of the output pins are retrieved and the test instrument is configured to interface with the output pins based on the configuration parameters. A list of output pins and a list of input lines associated with the test instrument are graphically displaying on a screen associated with the test instrument. Interacting with the graphical display, the user then associates each output pin with an input line to which each output pin is connected.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Method and algorithm for functional critical paths selection and critical path sensors and controller insertion
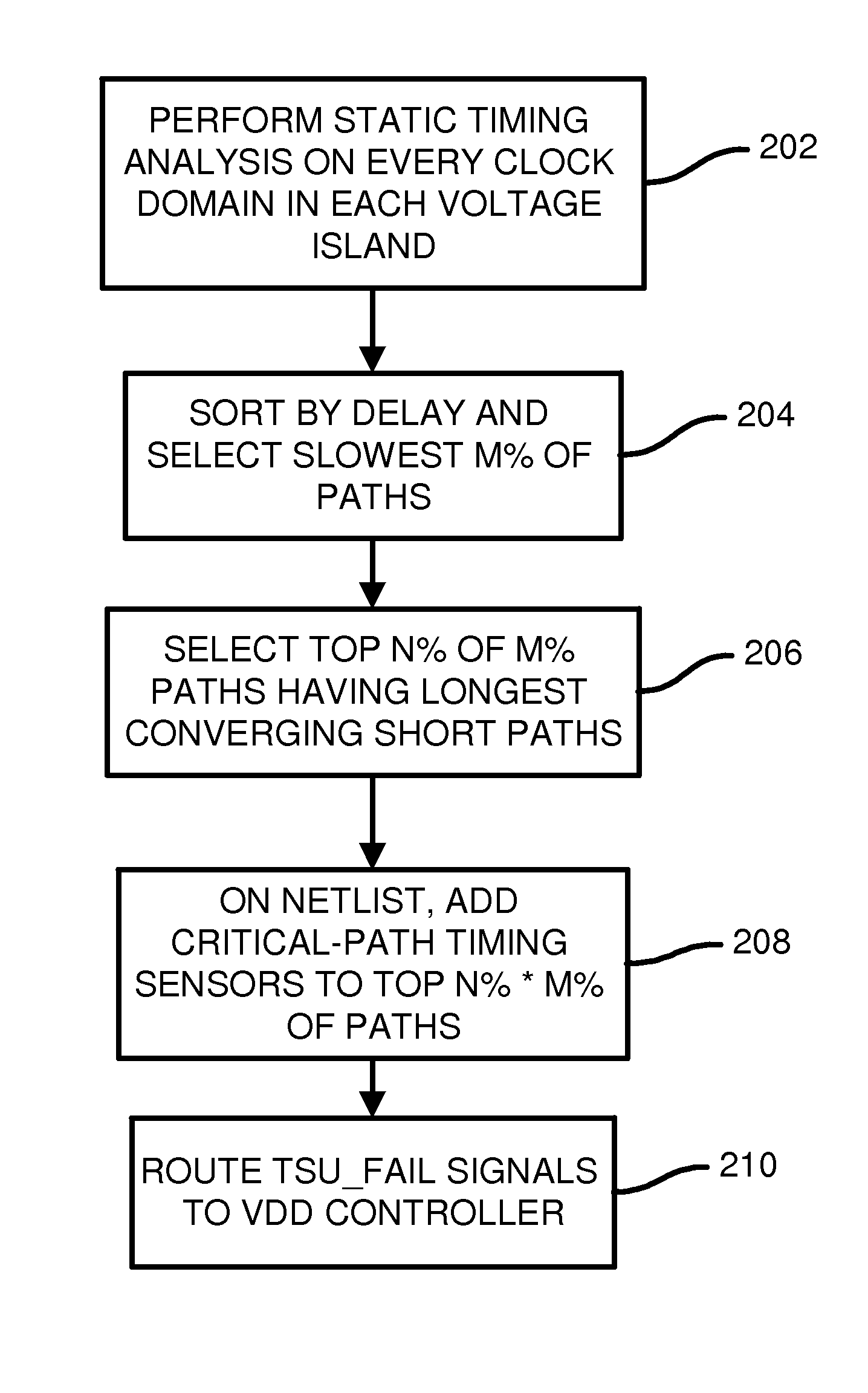
InactiveUS9536038B1CAD circuit designSpecial data processing applicationsDesign engineerCritical path method
CAD software examines delays of paths in a design from design engineers and first selects the longest paths. Then all paths that converge with these longest paths are examined for delays, and a fastest converging path is selected for each of the longest paths. The longest paths are again sorted by the fastest converging delay, and paths with slower converging paths are selected to be Functional Critical Paths (FCP's). Functional critical path timing sensors are added to each FCP to test setup time with an added margin delay. When the margined path delays fail to meet setup requirements, the functional critical path timing sensors signal a controller to increase VDD. When no failures occur over a period of time, the controller decreases VDD. The CAD software can replicate some of the FCP's and add toggle pattern generators and timing sensors and a margin controller to adjust the margin delay.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
System and method for calibrating signal paths connecting a device under test to a test system
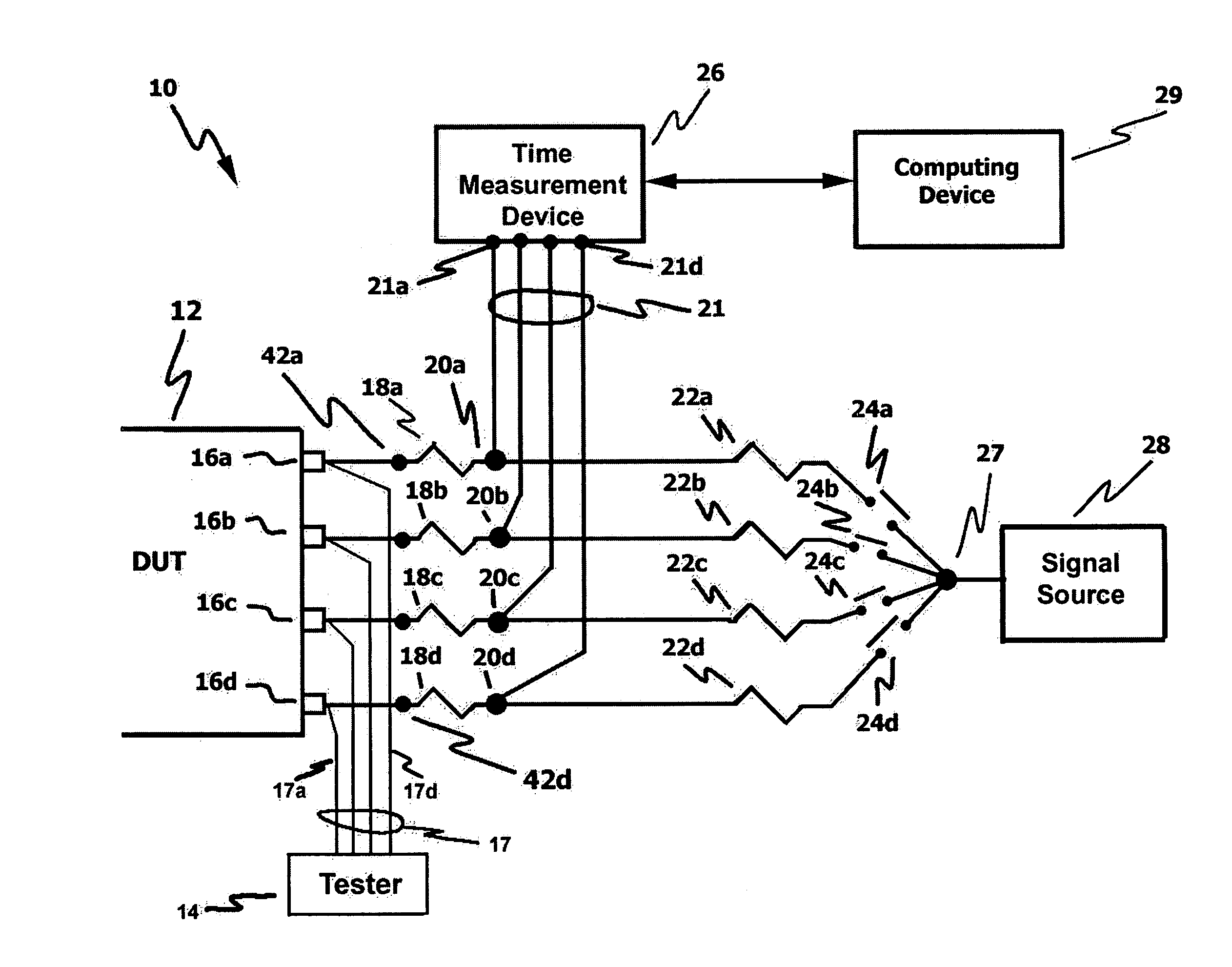
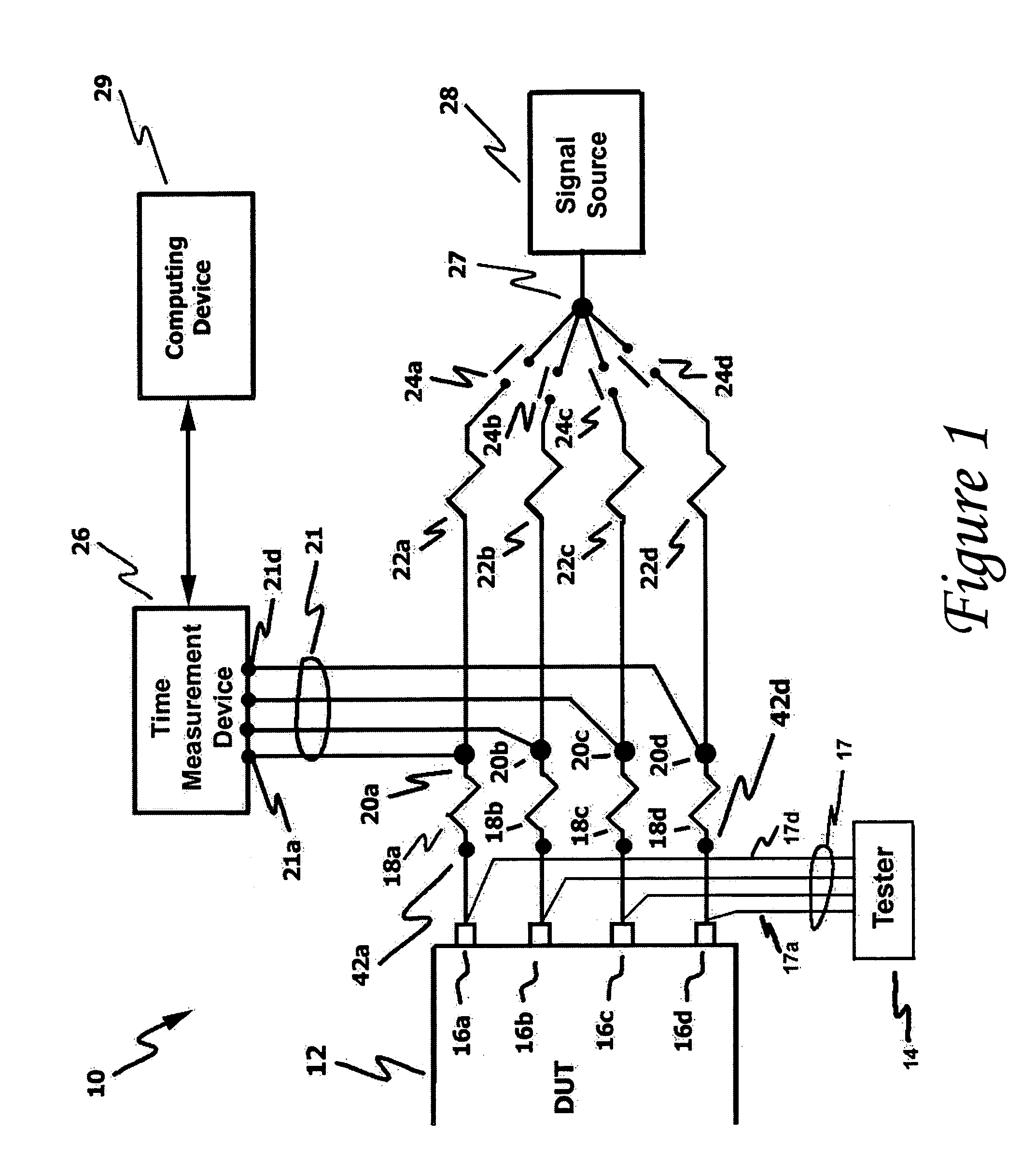
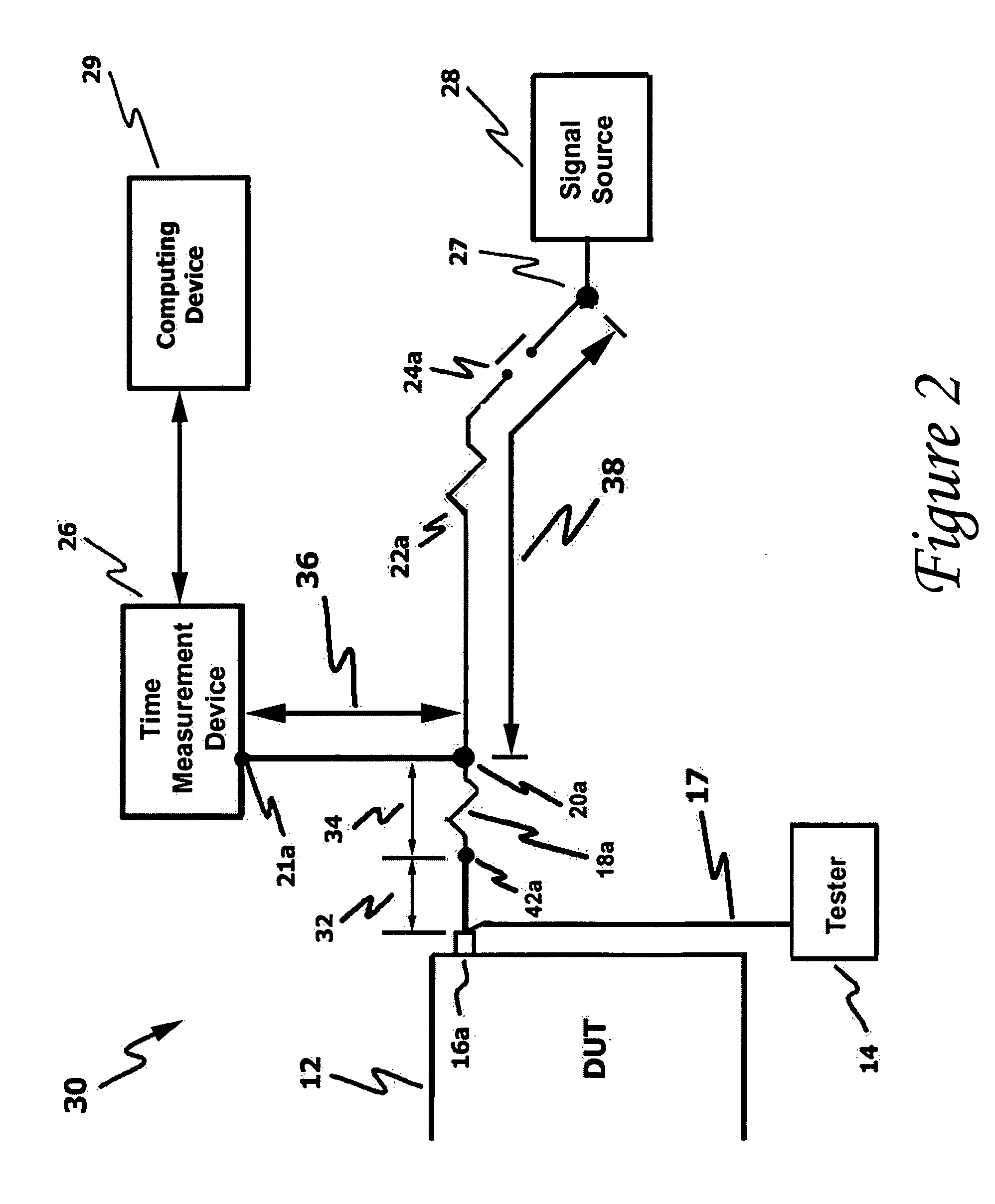
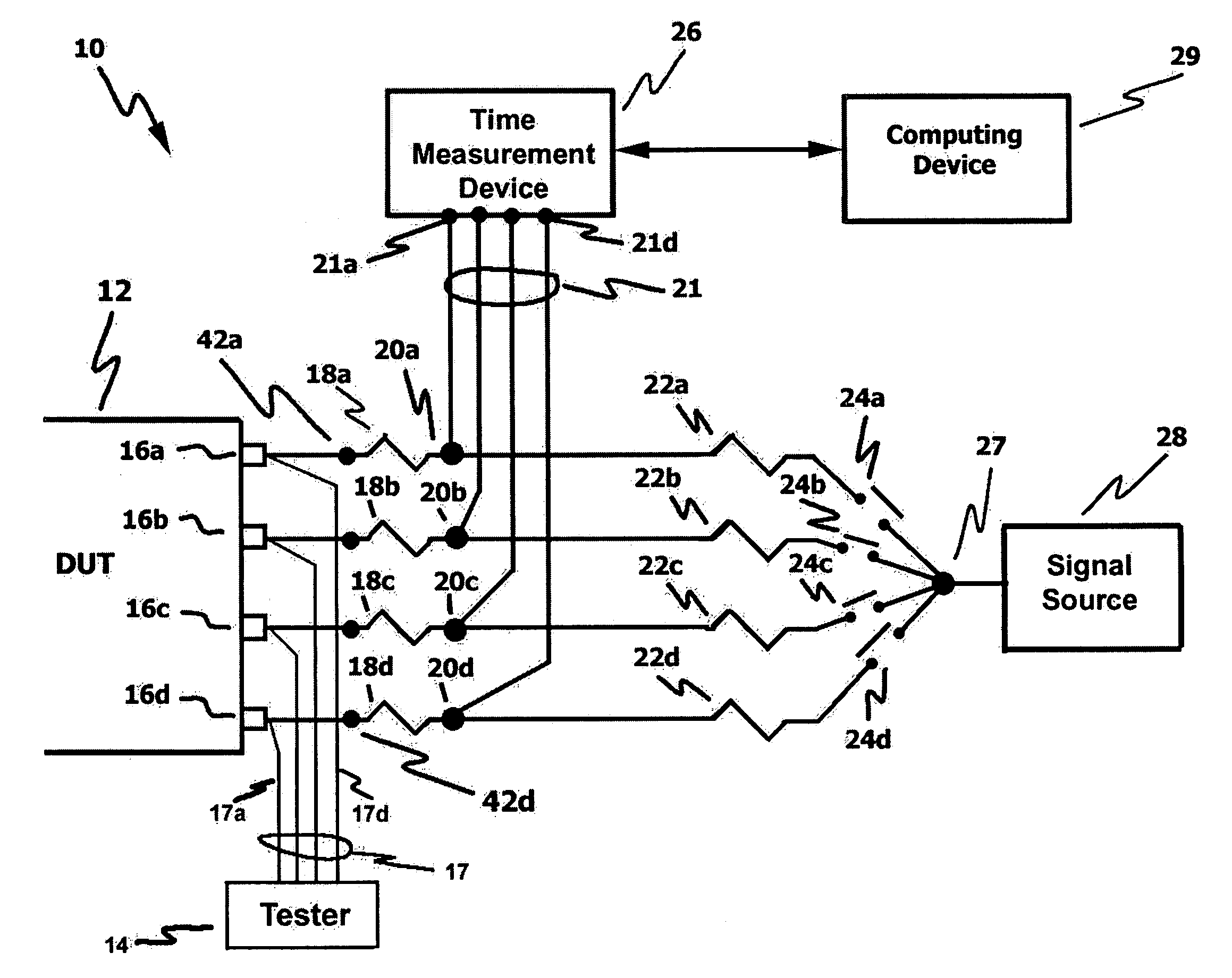
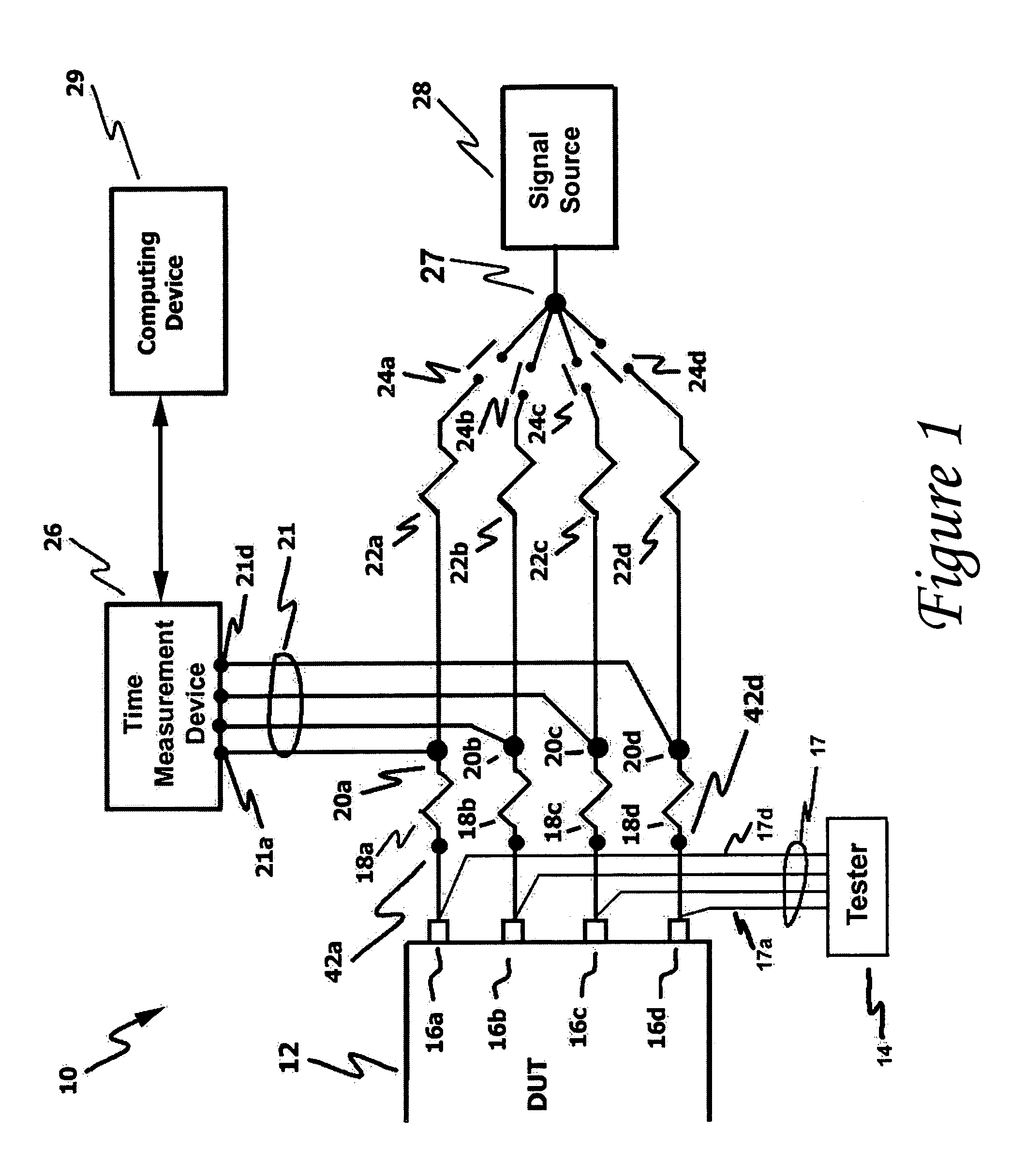
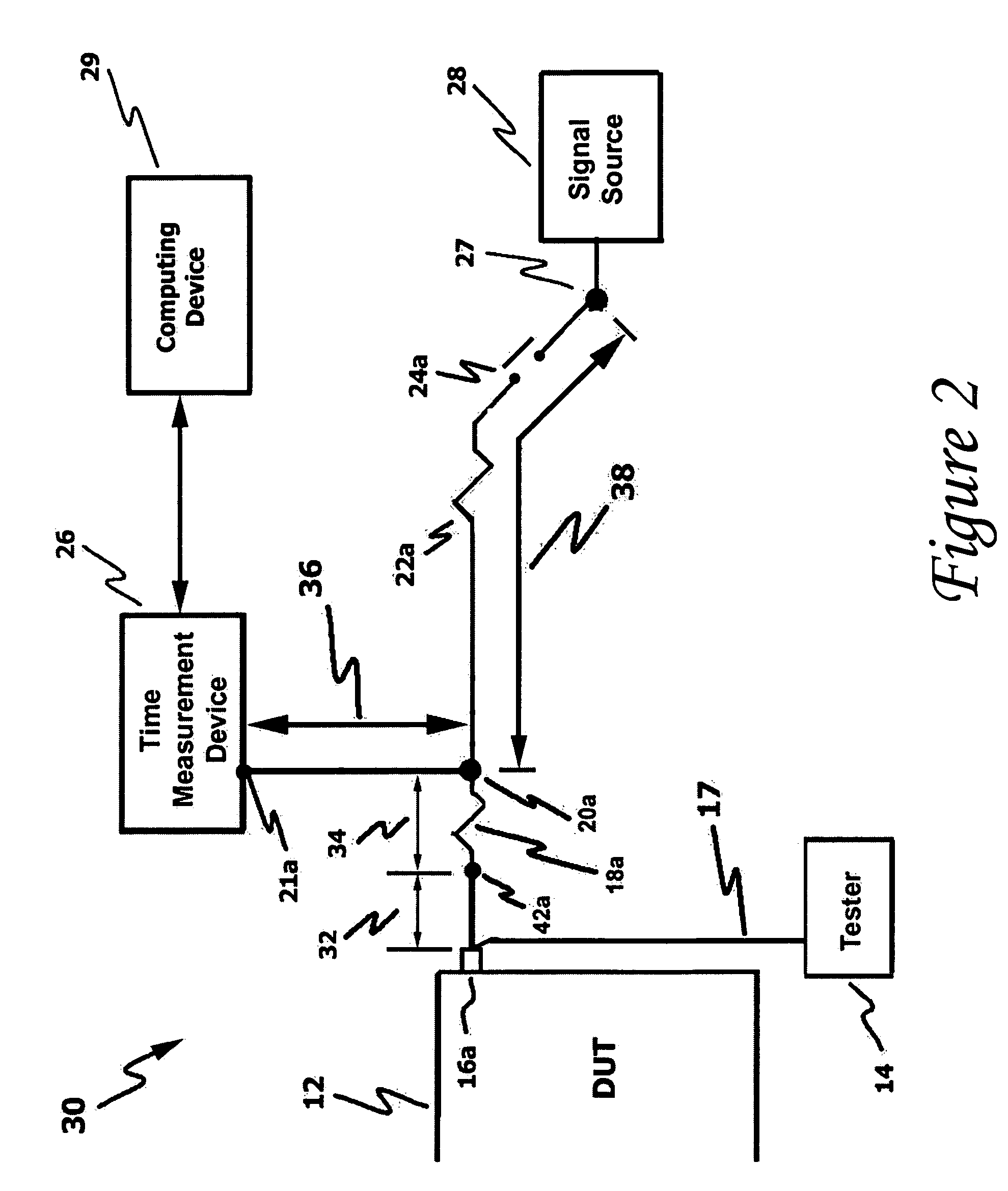
InactiveUS20060111861A1Improve developmentHigh precisionTime indicationSynchronous motors for clocksExternal storageMeasurement device
The present technology involves an apparatus and method for calibrating a plurality of distinct signal paths connecting a device under test (DUT) to a time measurement device. The disclosed calibration circuit, which may be connected to the test setup throughout the testing process, measures the signal skew associated with each distinct signal path connecting a DUT, such as an integrated circuit, to a time measurement device, such as a time interval analyzer. The measured skew values, which may be collected throughout the testing process, are stored in memory. Such memory may be within the time measure device, an external storage device or a computing device that may be in communication with the time measurement device. The time measurement device uses the stored skew values to adjust the test signals to compensate for signal path related signal skew. In addition, the stored skew values are used to perform signal path diagnostics. This is accomplished by comparing newly measured skew values to stored skew values and generating a signal path failure signal when the newly measured skew values fall outside a user programmable range of acceptable skew values.
Owner:GUIDE TECH
Integrated menu-driven manufacturing method and system
ActiveUS20110178627A1Easy to processProgramme controlTotal factory controlManufacturing technologyQuality control
A menu-driven manufacturing technique includes determining a product and product configuration, along with process steps to be carried out in manufacturing workstations. Display screens corresponding to the particular manufacturing process steps are accessed and displayed on monitors at the workstations to lead operators through the processes. Control circuitry may verify that the correct components and tools are utilized as called for by the various process steps. Powered tools and test setups may be integrated with the system to enable improved quality control.
Owner:ROCKWELL AUTOMATION TECH
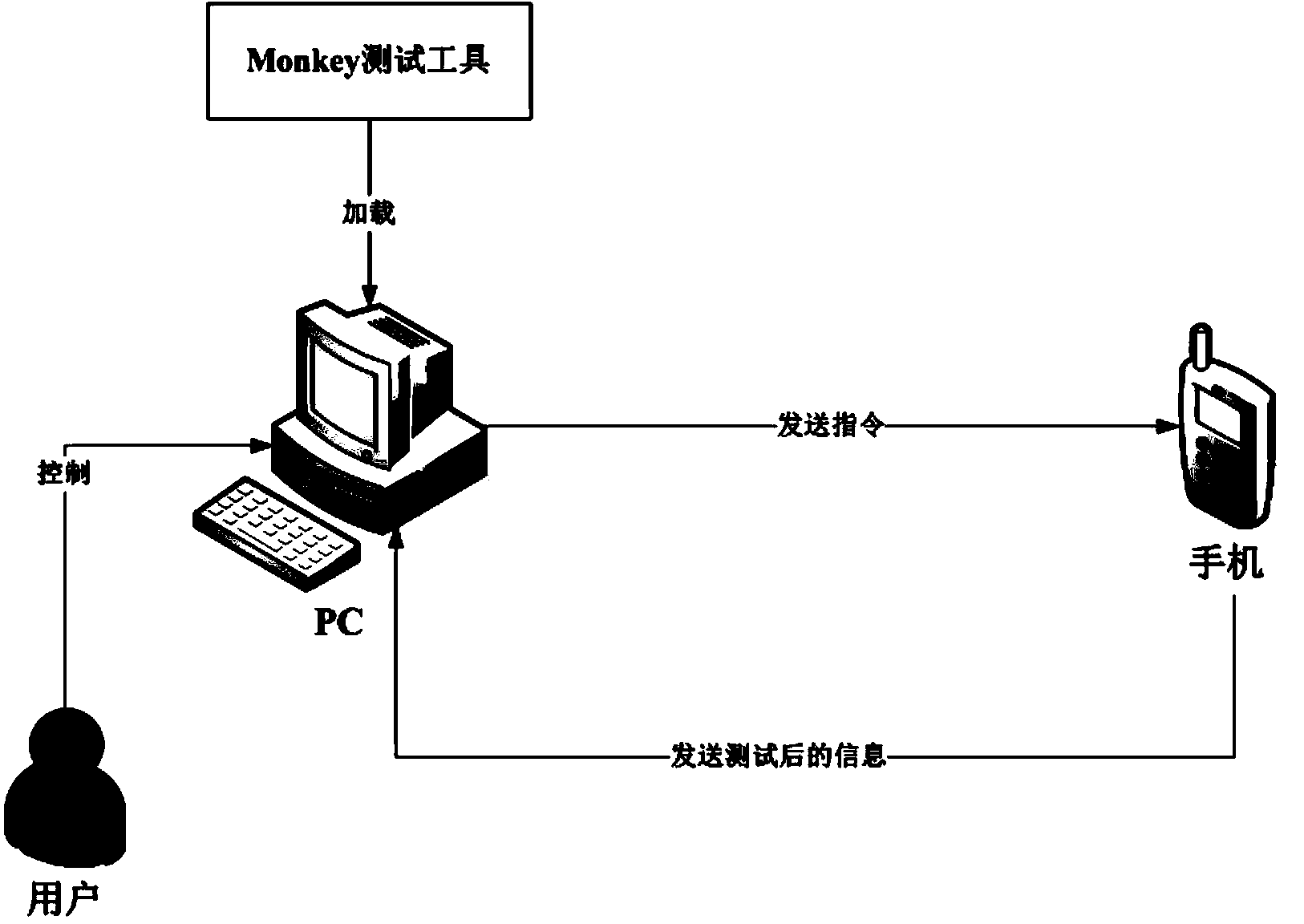
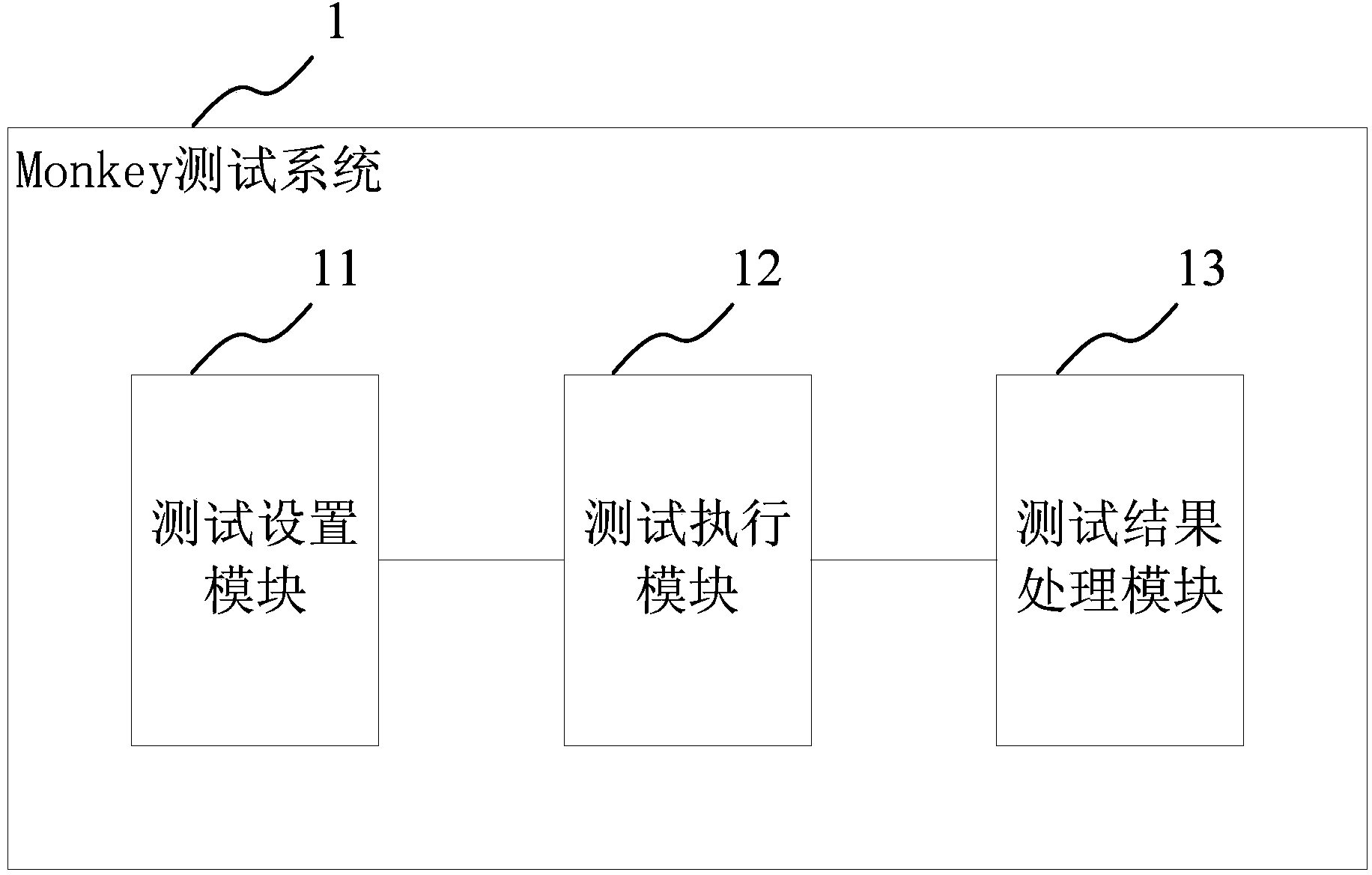
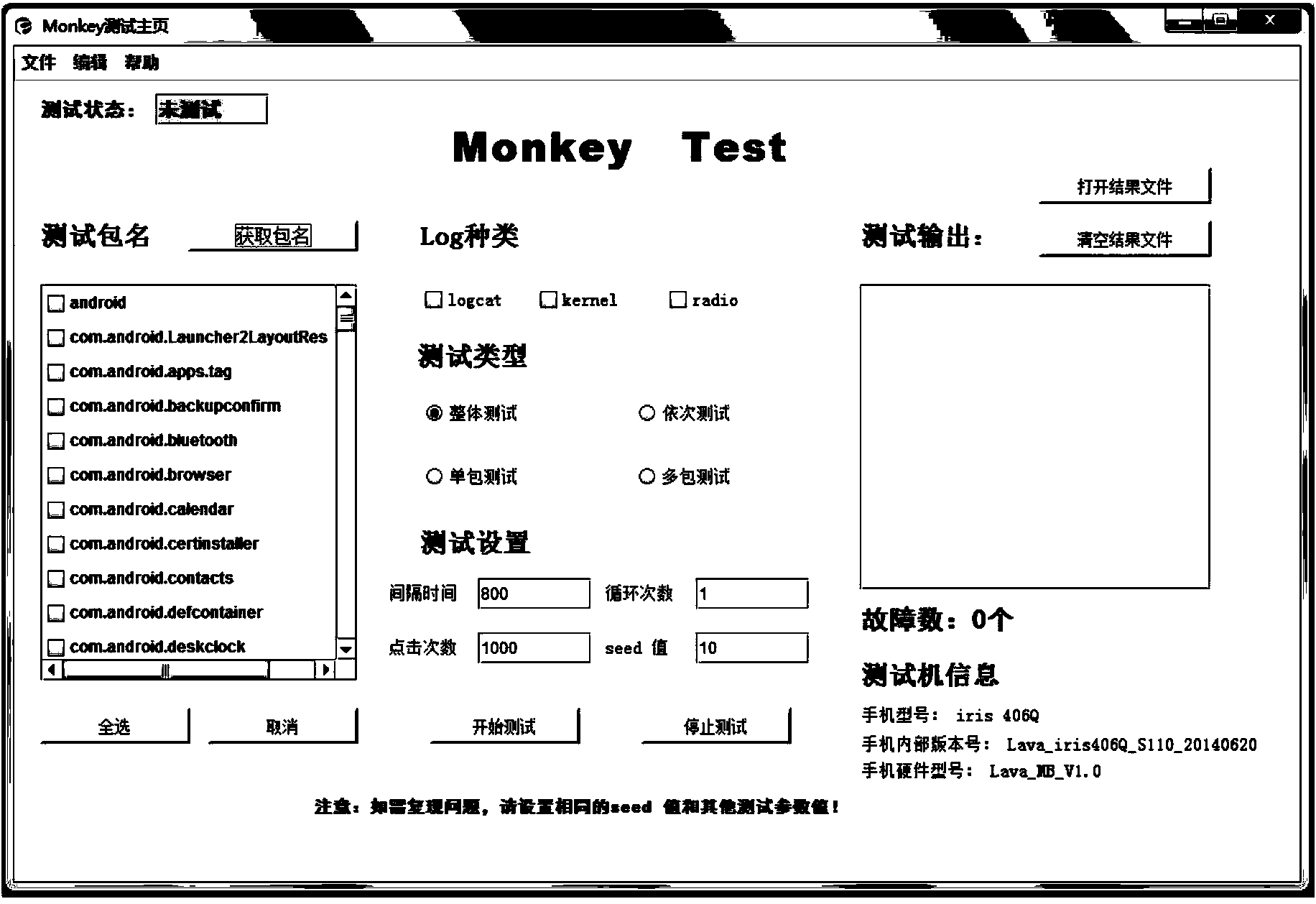
Monkey test system and method
InactiveCN104331373AMeet generationMeet sendSoftware testing/debuggingProcess moduleTest requirements
The invention discloses a Monkey test system and a Monkey test method. The Monkey test system comprises a test setting module for acquiring a test pack mounted on a mobile terminal, setting related test information and generating a corresponding test command; a test execution module which is connected to the test setting module and for testing depending on the test command, and acquiring screenshot information under an abnormal test state when any abnormity is tested; and a test result processing module which is connected to the test execution module and is used for processing a result obtained from test and generating a corresponding test result. The technical scheme of the invention can obtain a final test result through different setting before test and different tests, and can acquire log information of a whole test process and a mobile terminal screenshot in case of abnormity, so as to meet different test requirements and better relieve working strength of a tester.
Owner:PHICOMM (SHANGHAI) CO LTD
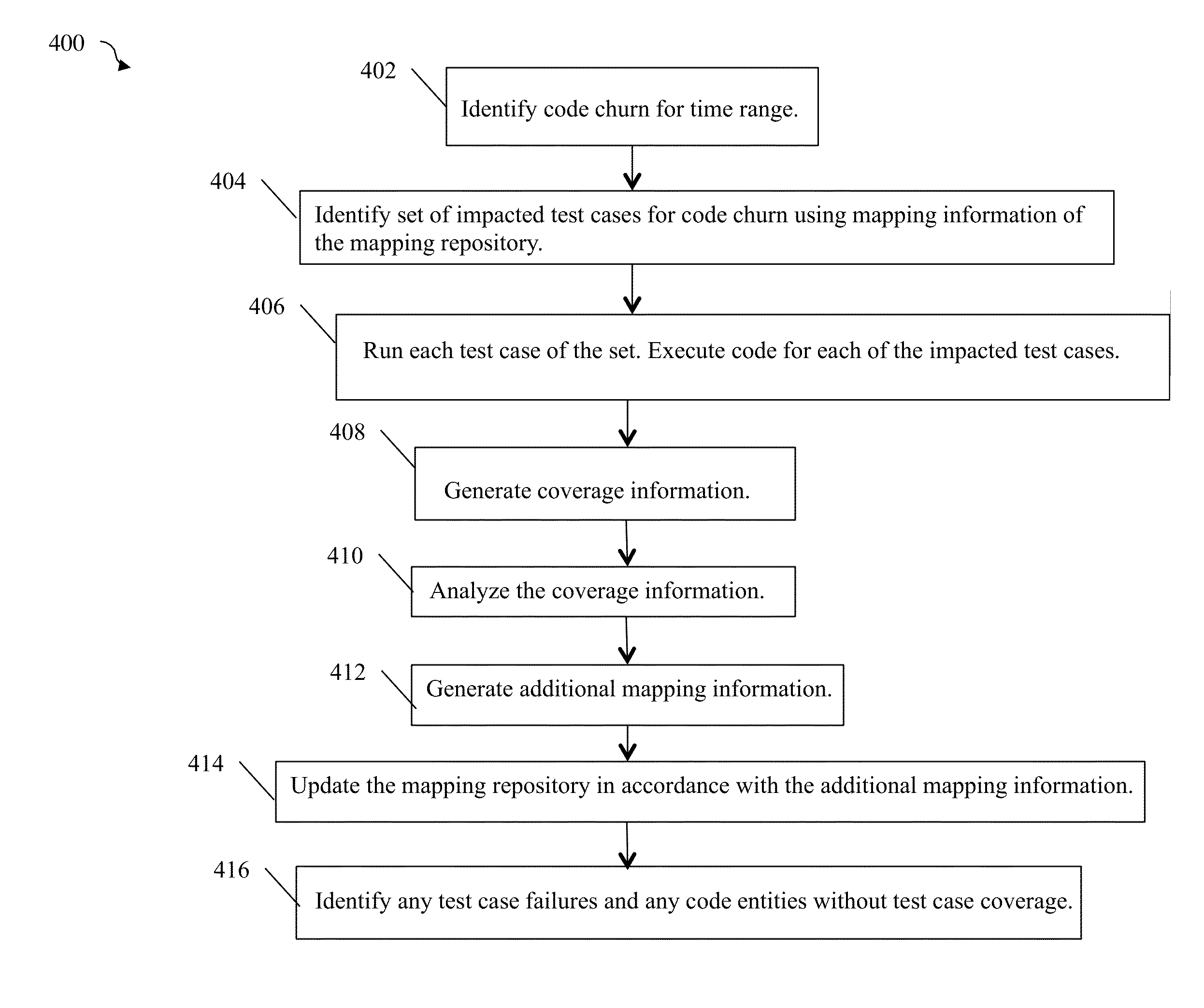
Automated test coverage analysis, execution and reporting
Described are techniques for testing software. The techniques may include identifying, at a first point in time, first code that has been modified, identifying, using first mapping information, a testing set of one or more test cases wherein the first mapping information identifies each test case of the testing set as a test case used to test the first code, running the testing set, generating coverage information in accordance with executing; analyzing the coverage information, generating second mapping information in accordance with said analyzing, and updating the first mapping information in accordance with the second mapping information.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
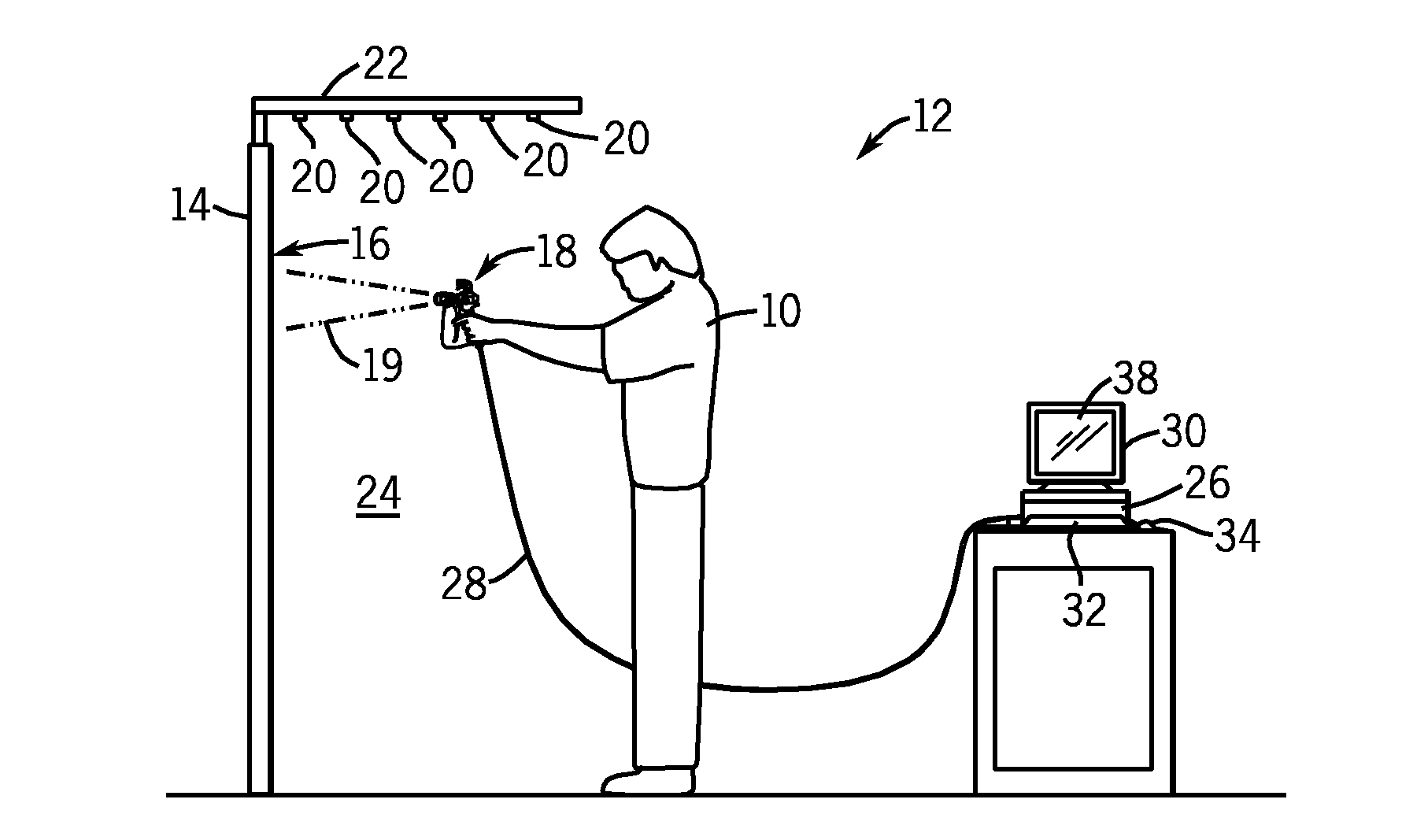
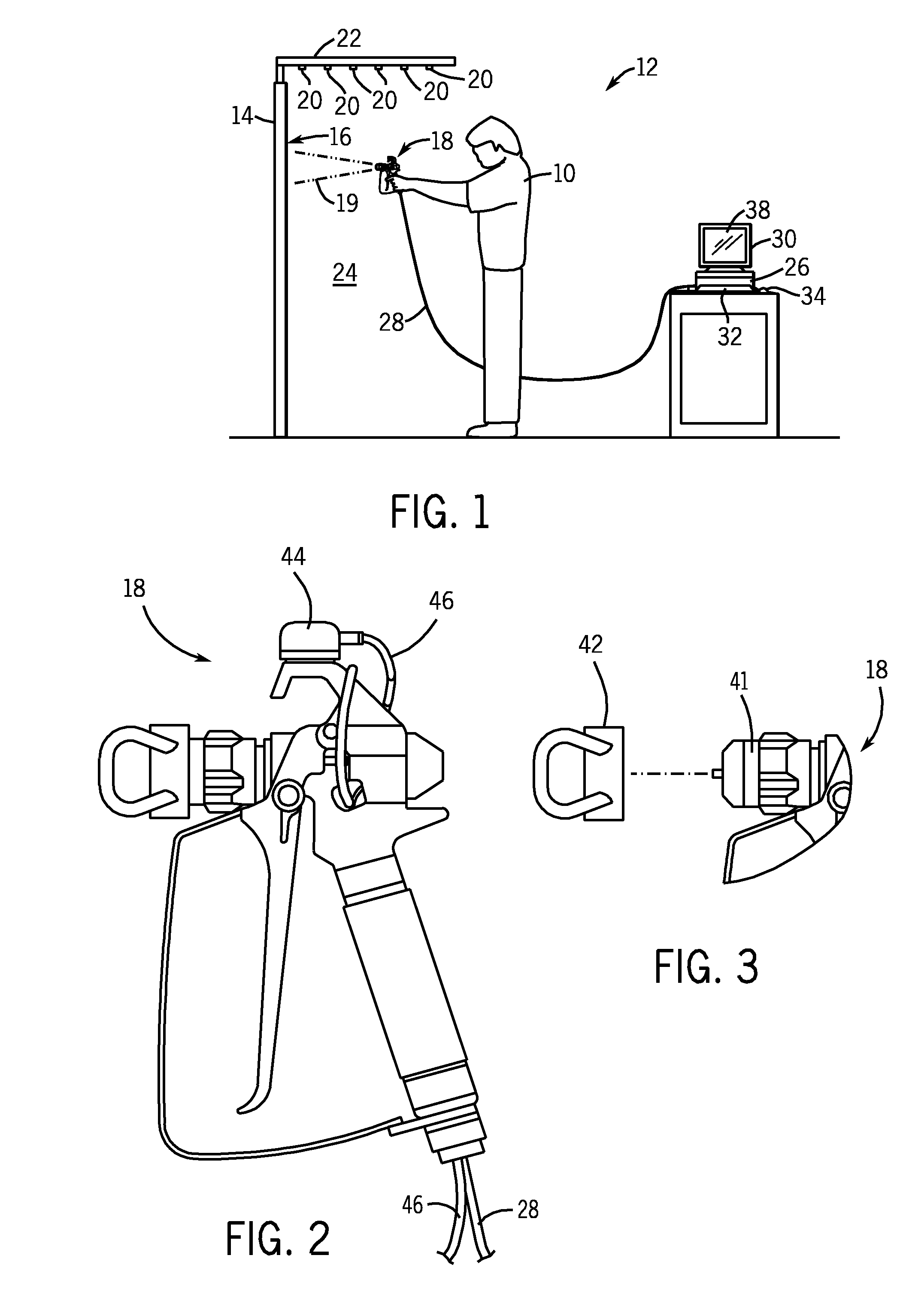
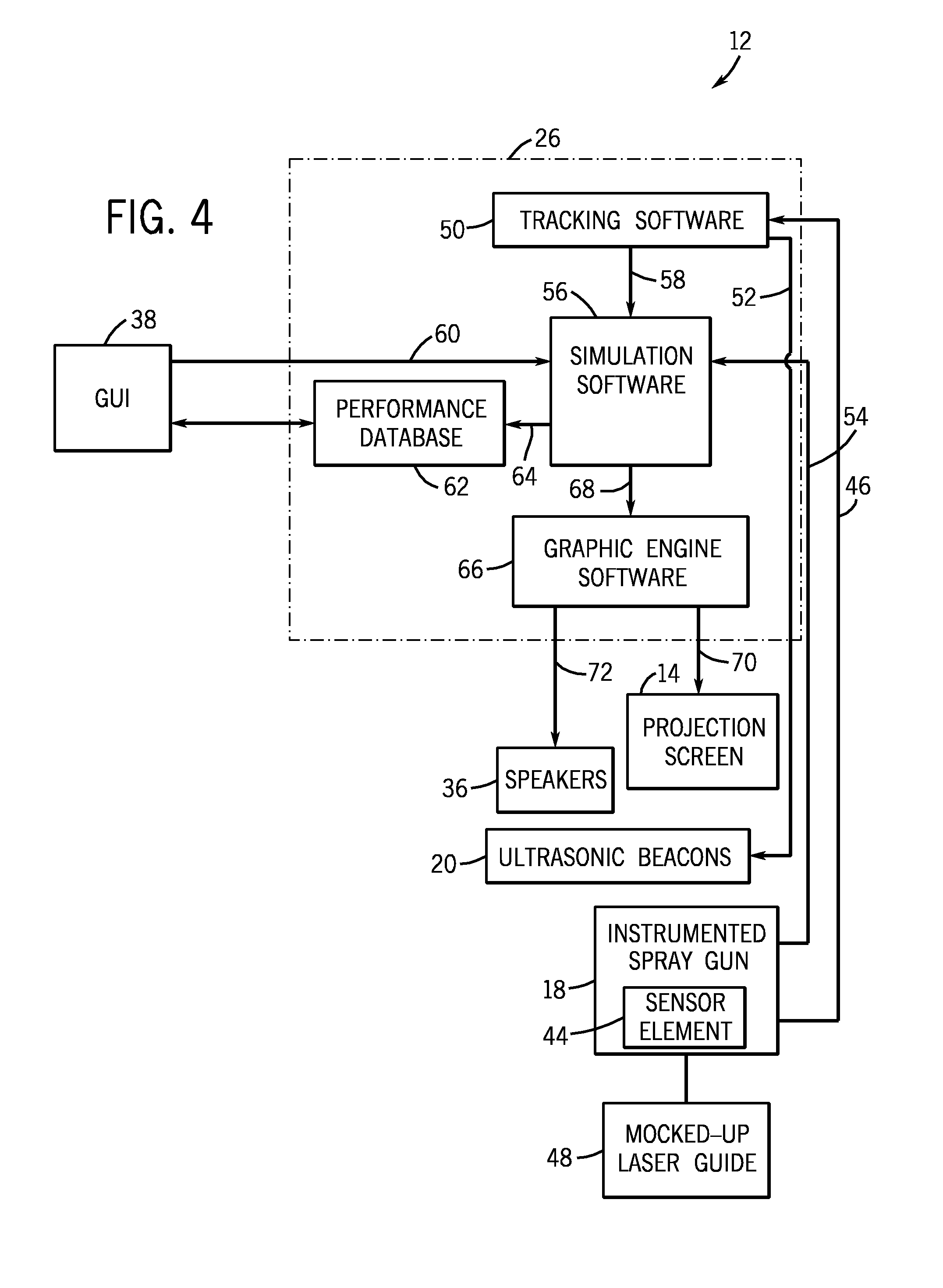
Airless spray gun virtual coatings application system
InactiveUS20100077959A1Reduce calculationFacilitating system responsivenessLiquid surface applicatorsLiquid spraying apparatusEngineeringMotion tracking system
A virtual coatings application system realistically simulates airless spray painting. The system generally includes a display screen on which is defined a virtual surface that is intended to be virtually painted or coated by the user. The user operates the instrumented airless spray gun controller which is instrumented with a tracking device and an electronic on / off switch for the trigger. The system also has a motion tracking system that tracks the position and orientation of the airless spray gun controller with respect to the virtual surface defined on the display screen. Simulation software generates virtual spray pattern data in response to the setup parameters and the position and orientation of the airless spray gun controller with respect to the virtual surface. Virtual spray pattern images are displayed in real time on the display screen in accordance with the accumulation of virtual spray pattern data at each location on the virtual surface. The primary purpose of the system is to enhance training. In addition to providing virtual painting of a part, the system also provides for virtual practice sessions in which the user can test setup parameters by painting virtual practice paper.
Owner:UNIV OF NORTHERN IOWA RES FOUND
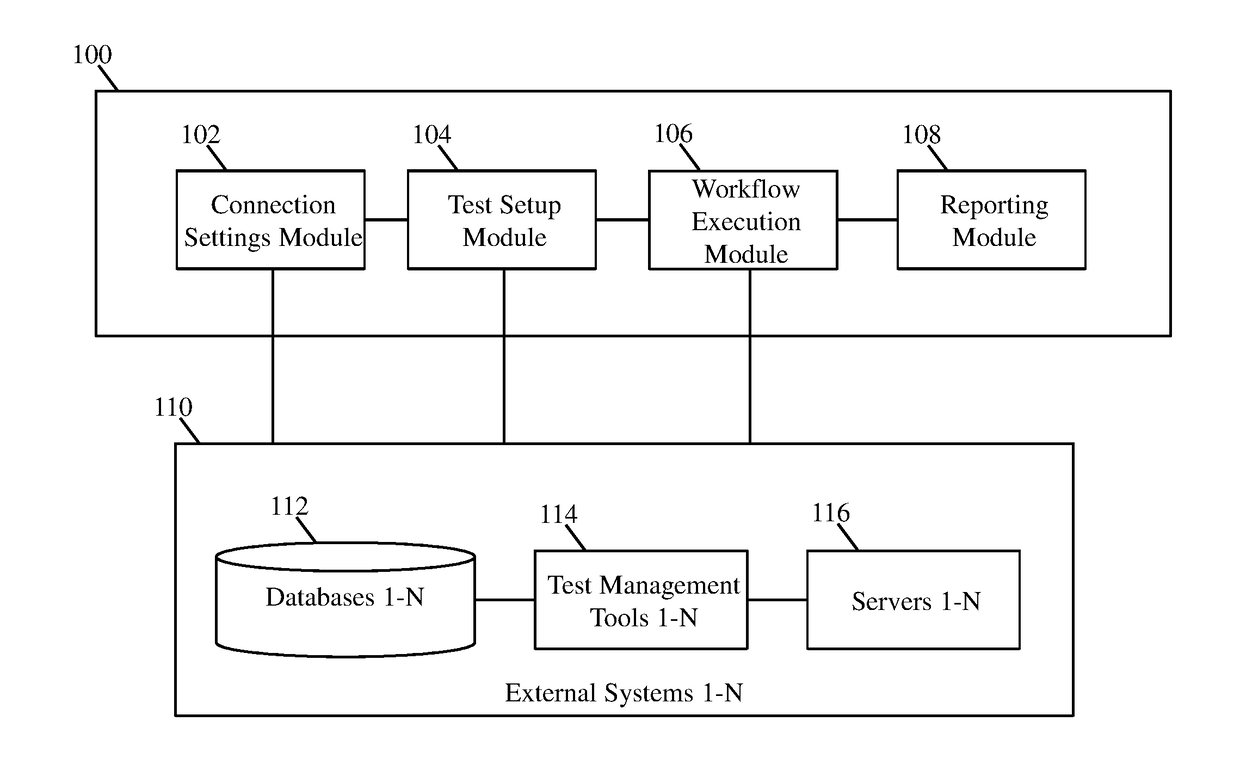
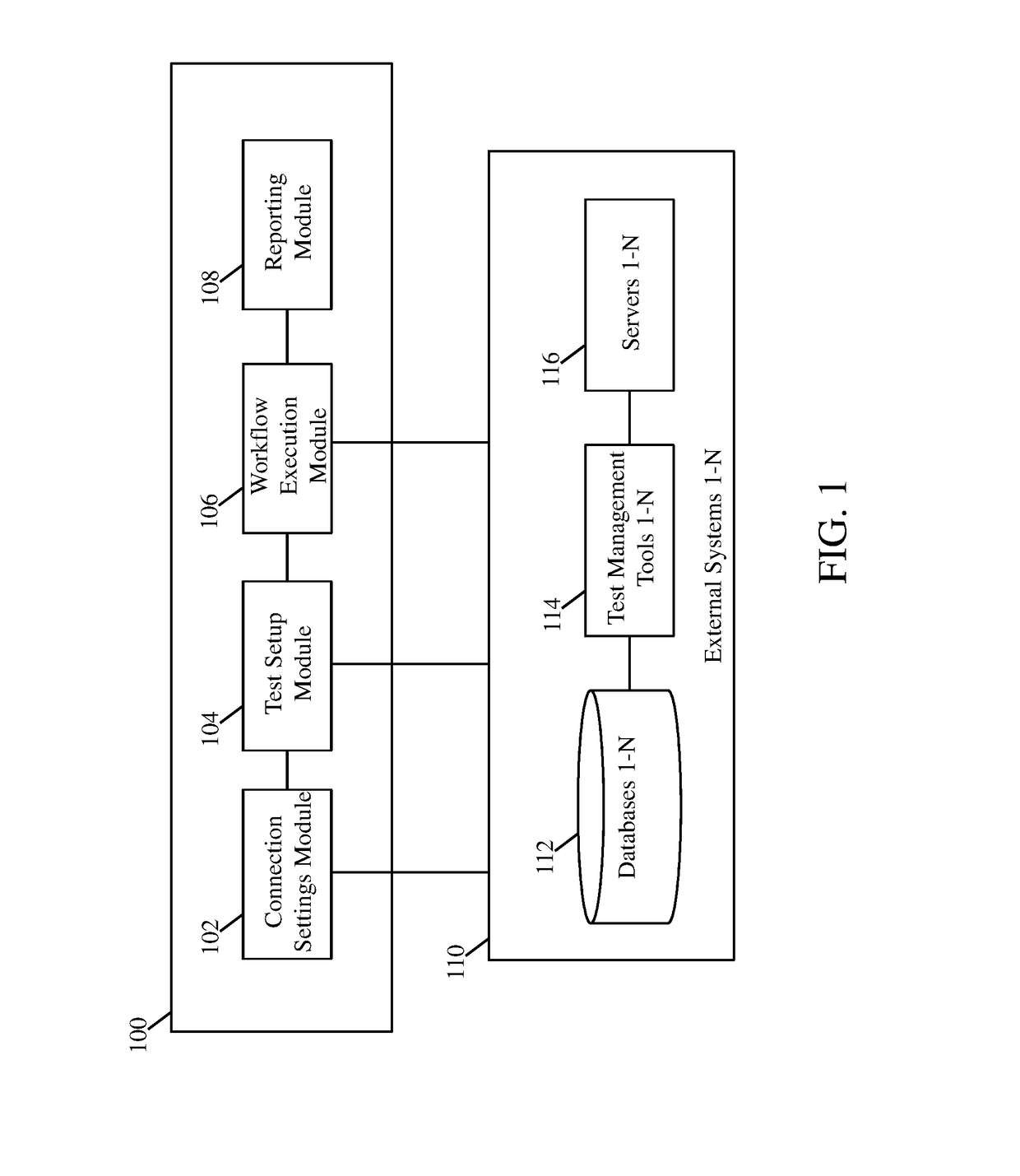
System and method for automating testing without scripting
A system and computer-implemented method for automating end-to end testing is provided. The system comprises a connection settings module to receive information for connecting with one or more external systems. The system further comprises a test setup module to create test workflows, wherein creating the test workflows comprise selecting one or more pre-stored source files and corresponding one or more pre-stored target files and mapping input and output of each of the one or more selected pre-stored source files with the corresponding one or more selected pre-stored target files for testing additional source files associated with the one or more external systems. Furthermore, the system comprises a workflow execution module to connect with the one or more external systems using the received information to retrieve the additional source files and execute the created test workflows corresponding to the retrieved one or more additional source files.
Owner:COGNIZANT TECH SOLUTIONS INDIA PVT
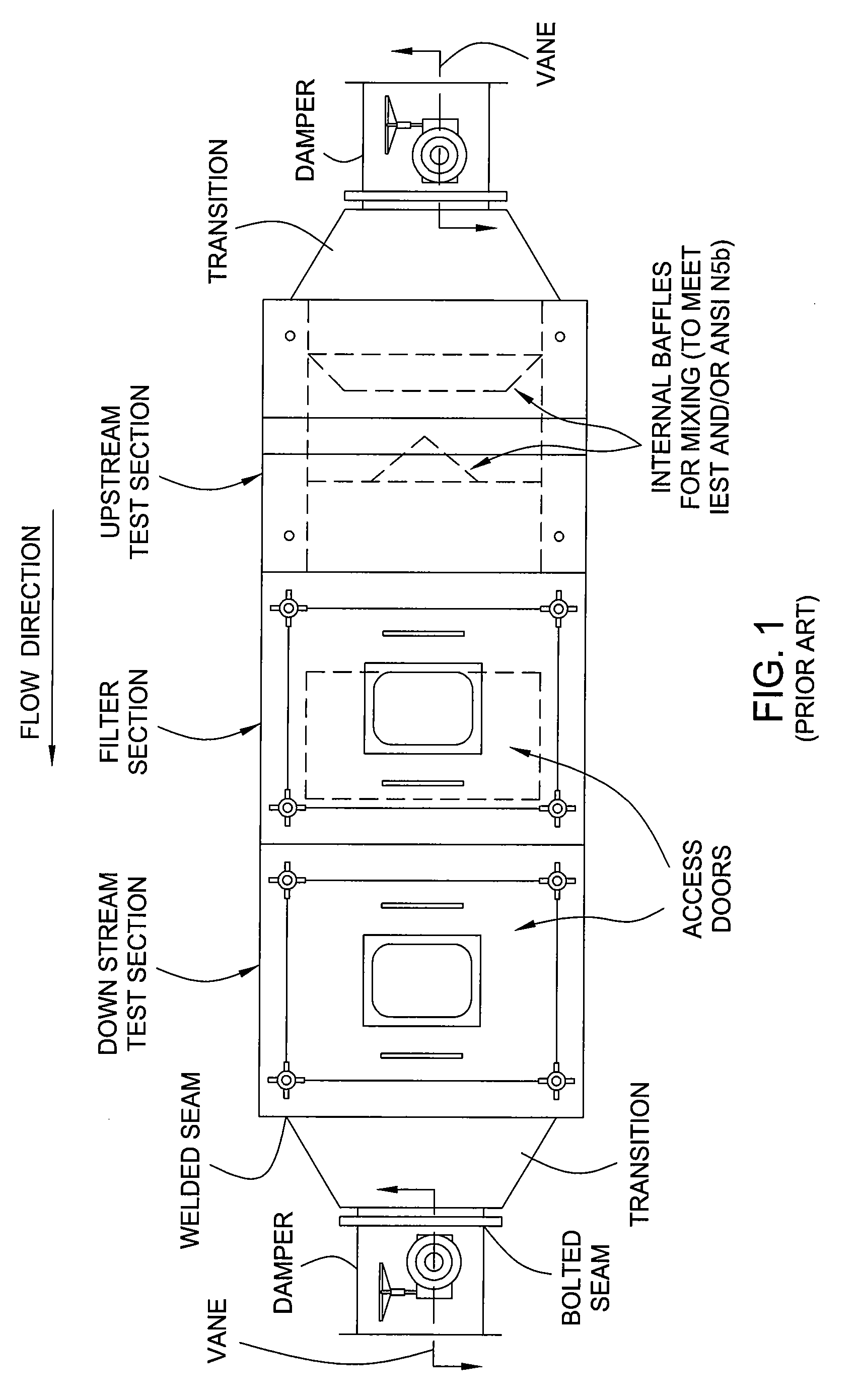
Method and apparatus for in-situ testing of filtration systems
Embodiments of the invention generally provide an apparatus and method for certifying a filter in a containment system without decontaminating the containment system prior to certification. The apparatus generally comprises a valve assembly selectable between at least three operational states. A first state prevents flow from prevents flow through a port of a housing. A second state fluidly couples the port to test equipment necessary to test a filter disposed within the housing. A third state seals the port but fluidly couples the test equipment to a decontamination system.
Owner:CAMFIL USA
System and method for calibrating signal paths connecting a device under test to a test system
InactiveUS7076385B2High precisionDesired calibration measurementsTime indicationSynchronous motors for clocksMeasurement deviceExternal storage
The present technology involves an apparatus and method for calibrating a plurality of distinct signal paths connecting a device under test (DUT) to a time measurement device. The disclosed calibration circuit, which may be connected to the test setup throughout the testing process, measures the signal skew associated with each distinct signal path connecting a DUT, such as an integrated circuit, to a time measurement device, such as a time interval analyzer. The measured skew values, which may be collected throughout the testing process, are stored in memory. Such memory may be within the time measure device, an external storage device or a computing device that may be in communication with the time measurement device. The time measurement device uses the stored skew values to adjust the test signals to compensate for signal path related signal skew. In addition, the stored skew values are used to perform signal path diagnostics. This is accomplished by comparing newly measured skew values to stored skew values and generating a signal path failure signal when the newly measured skew values fall outside a user programmable range of acceptable skew values.
Owner:GUIDE TECH
Wideband I-V probe and method
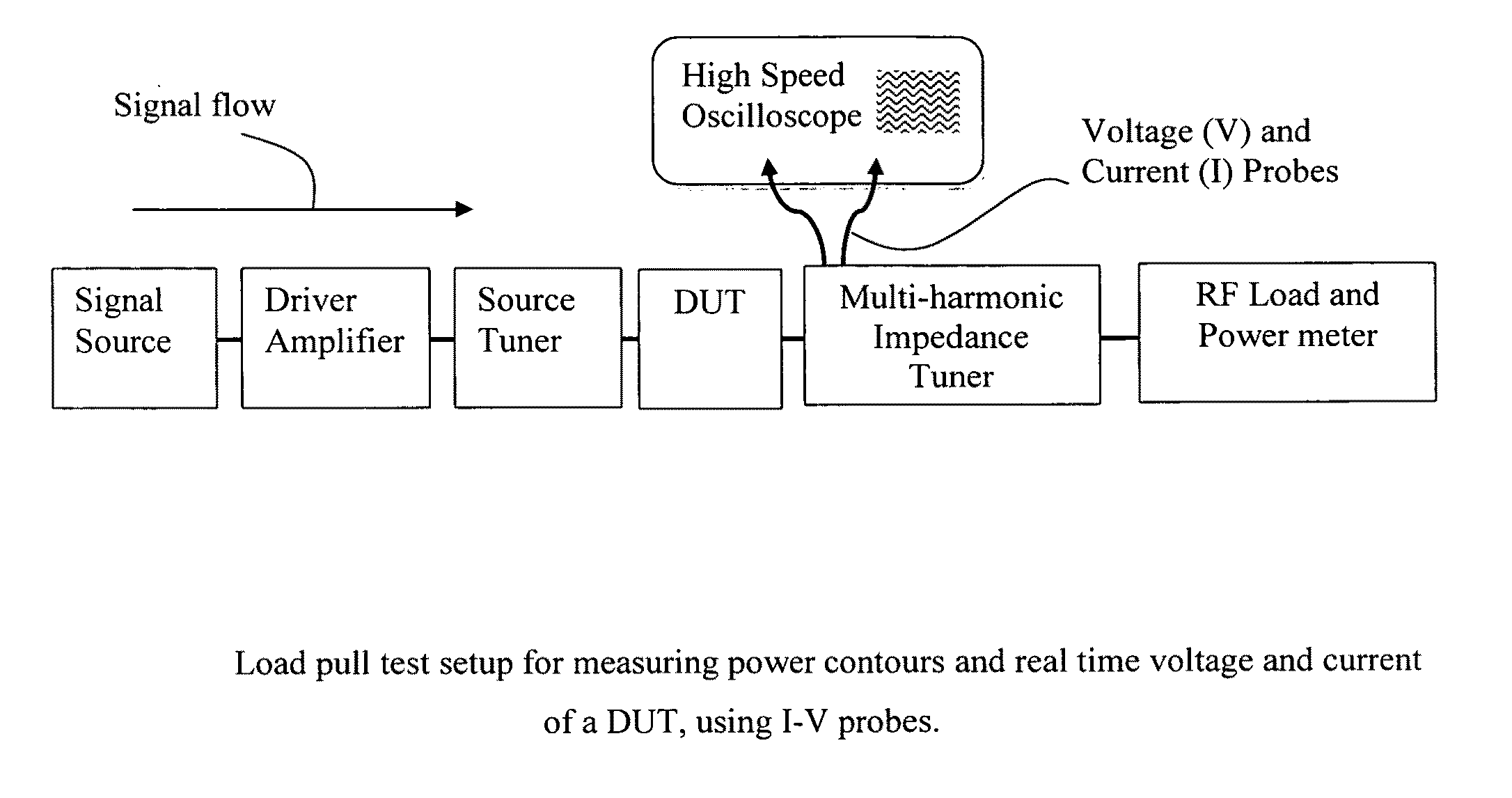
InactiveUS20110204906A1Resistance/reactance/impedenceFault location by increasing destruction at faultParallel plateFourier transform on finite groups
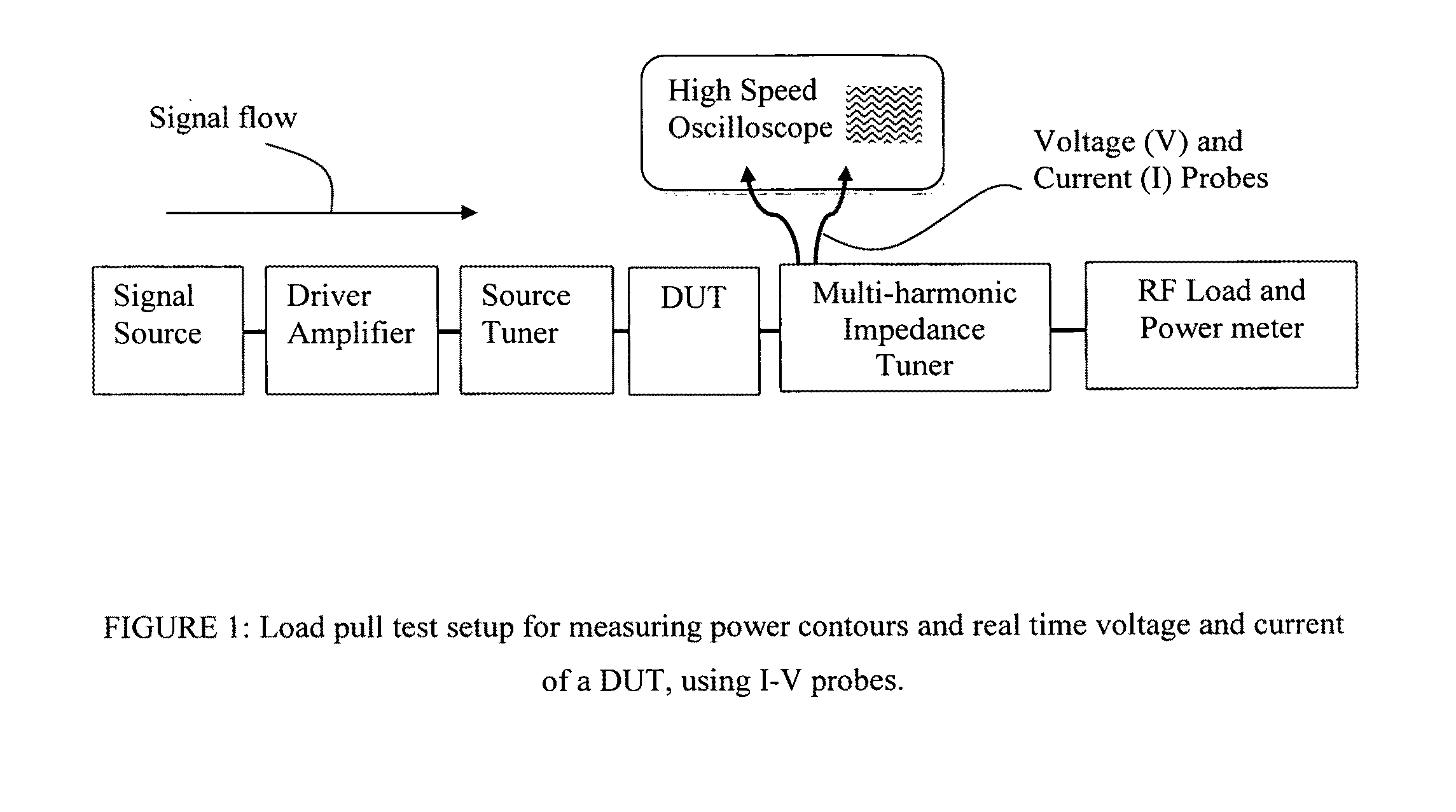
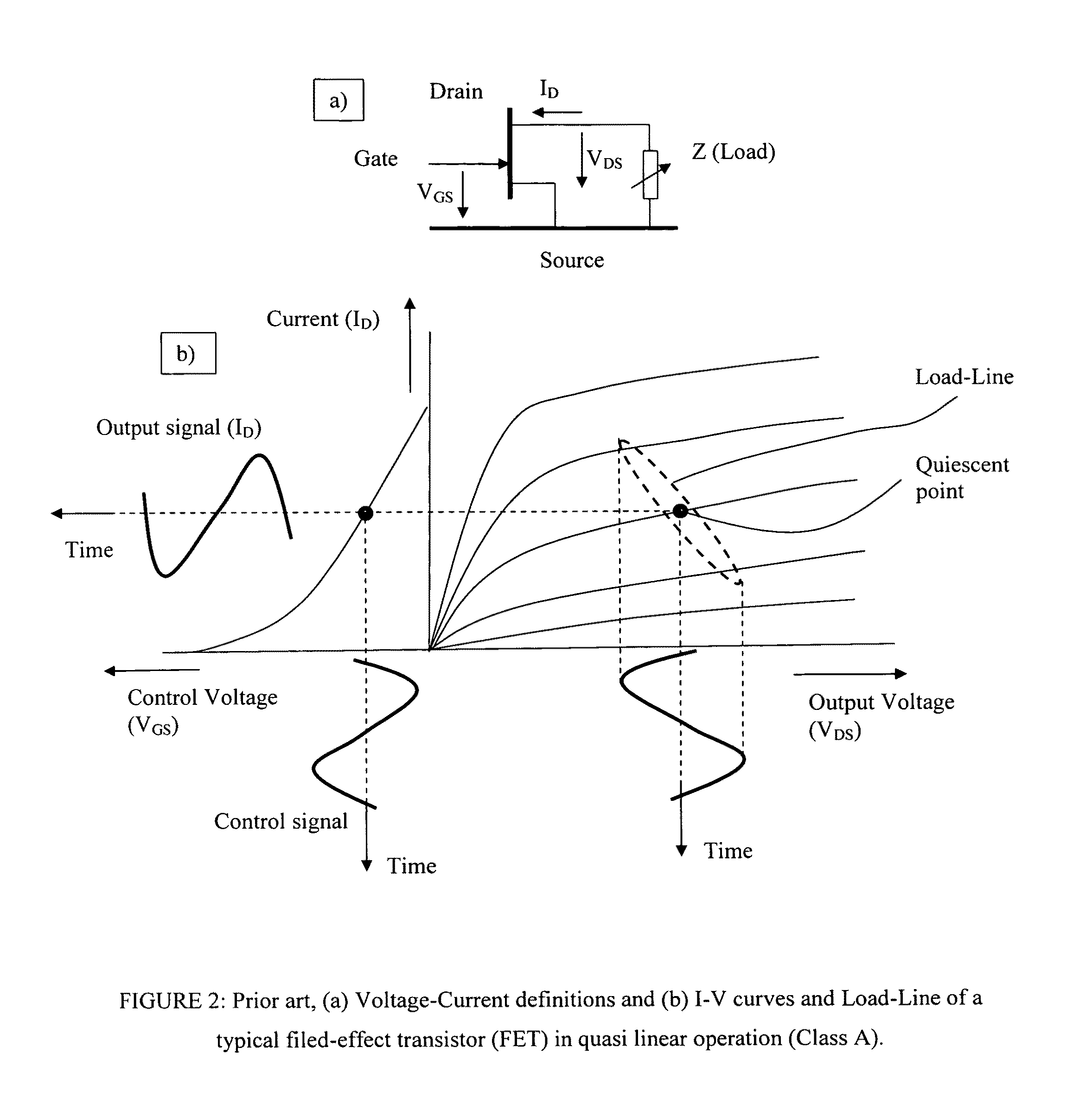
Low loss current and voltage probes are integrated in parallel plate airlines (slablines) to be used either as separate modules inserted between tuner and DUT in load pull test setups, or integrated in the impedance tuners themselves. The probes are inserted orthogonally at exactly the same reference plane relative to the DUT, maximizing bandwidth and the minimizing deformation of the detected electric and magnetic fields. The probes are used to detect the actual voltage and current waveforms and feed into an amplitude-and-phase calibrated high speed oscilloscope, including several harmonic frequencies. The actual real time voltage and current time domain waves are transformed into the frequency domain using fast Fourier transformation (FFT), de-embedded to the DUT reference plane and inverse transformed into the time domain using inverse Fourier transformation (FFT−1). The result of this real-time operation is the actual dynamic load line of the DUT at its terminals.
Owner:TSIRONIS CHRISTOS
Calibration method for audio MACSYM
InactiveCN101437191AEasy to understandGuaranteed accuracyElectrical apparatusArtificial mouthControl system
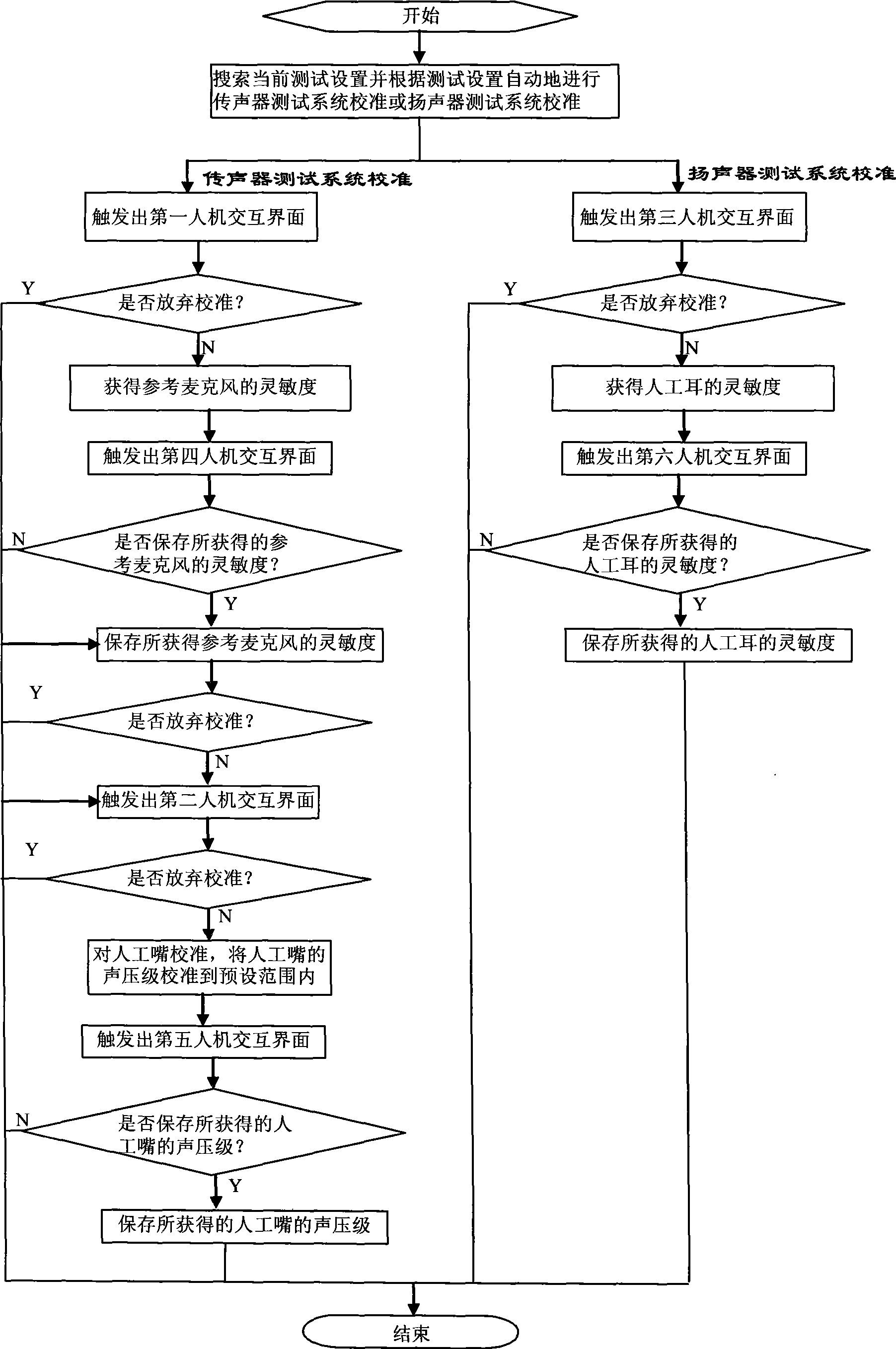
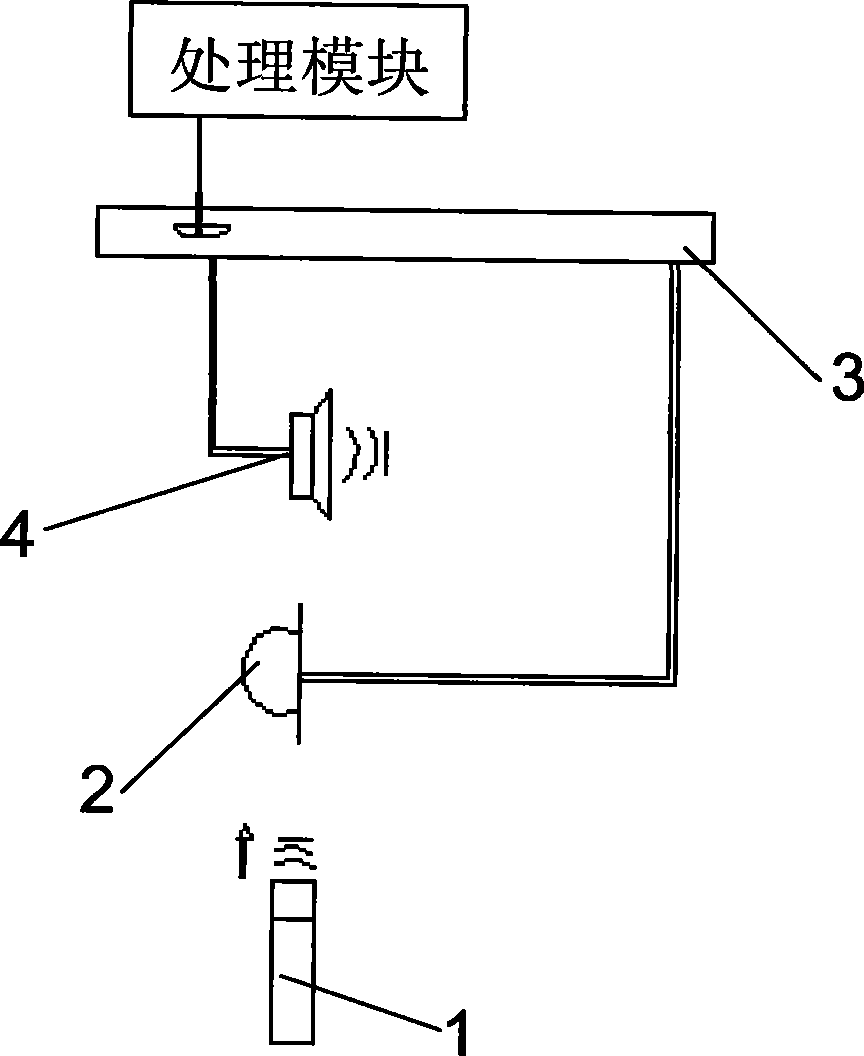
The invention discloses a method for calibrating an audio measurement and control system, which comprises the following steps: searching the current test configuration and automatically performing calibration on a microphone test system or a loudspeaker test system. The calibration on the microphone test system comprises the following steps sequentially: calibrating a reference microphone to obtain the sensitivity of the reference microphone; and calibrating an artificial mouth to calibrating the sound pressure level of the artificial mouth to a preset range. The method does not need an operator to judge calibration items to be carried out currently or know well about an acoustic product or an acoustic instrument. The method is simple and convenient to use. The calibration on the microphone test system comprises performing the calibration on the reference microphone at first automatically and then performing the calibration on the artificial mouth, and does not need the operator to perform the selection between the calibration on the reference microphone and the calibration on the artificial mouth, thus the accuracy of the calibration result is ensured and the quality management and control quality of a factory product is provided.
Owner:海宁市盐官工业投资有限公司
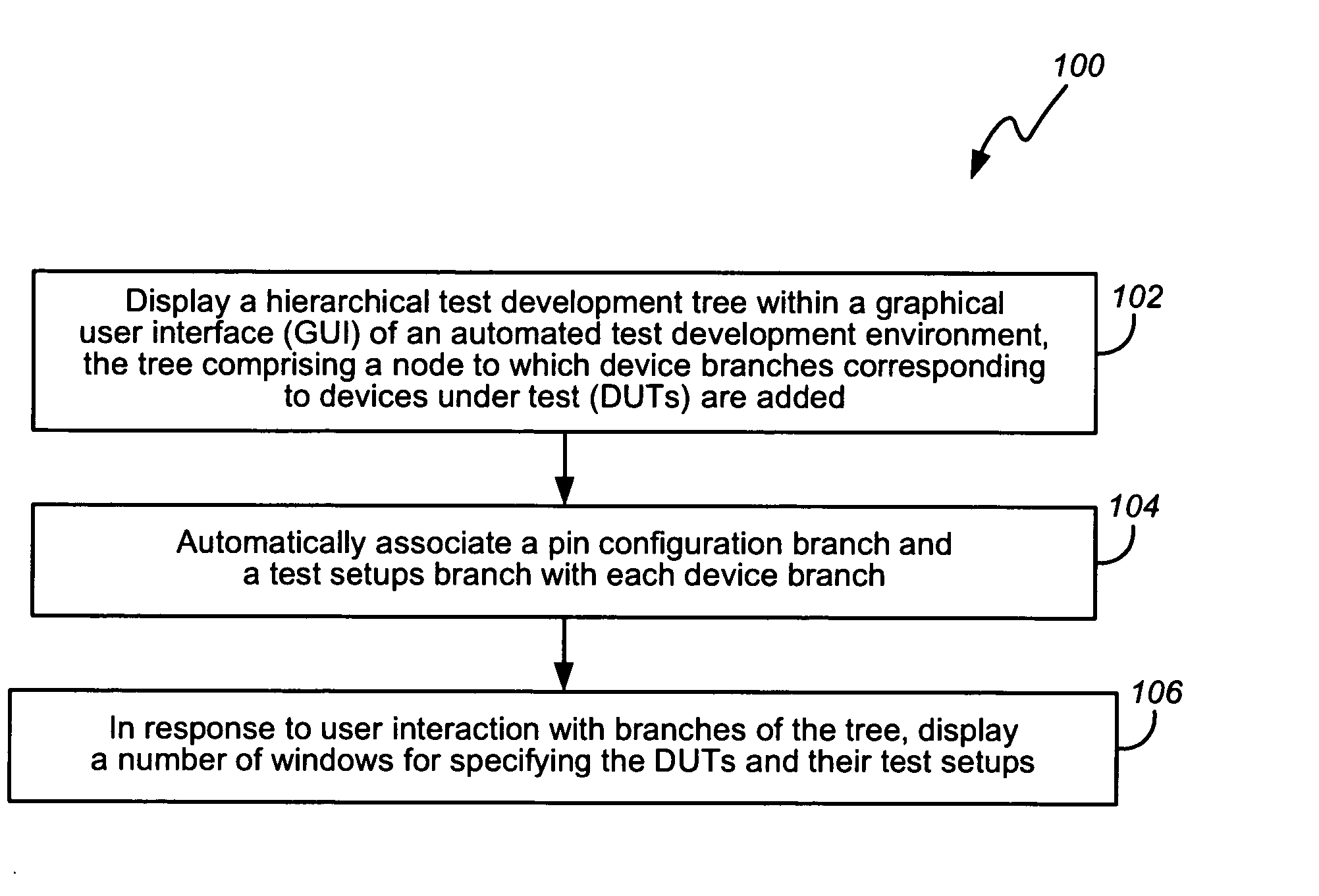
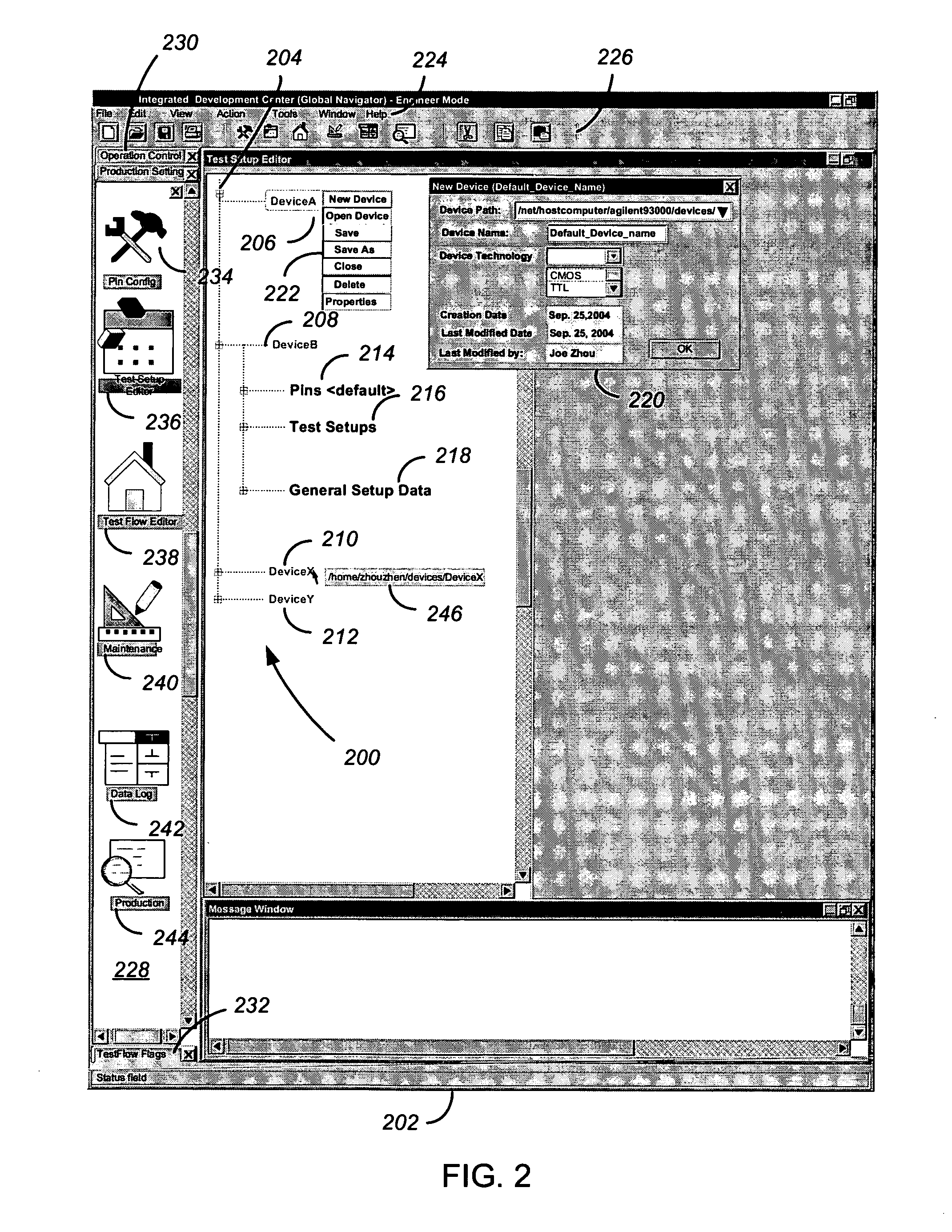
Methods and apparatus using a hierarchical test development tree to specify devices and their test setups
In one embodiment, a computer program is provided with code to display a hierarchical test development tree within a GUI of an automated test development environment. The tree has a node to which device branches corresponding to DUTs are added. The computer program is also provided with code to automatically associate a pin configuration branch and a test setups branch with each device branch; and code to, in response to user interaction with branches of the tree, display a number of windows for specifying the DUTs and their test setups. Other embodiments are also disclosed.
Owner:VERIGY PTE
Storage test circuit
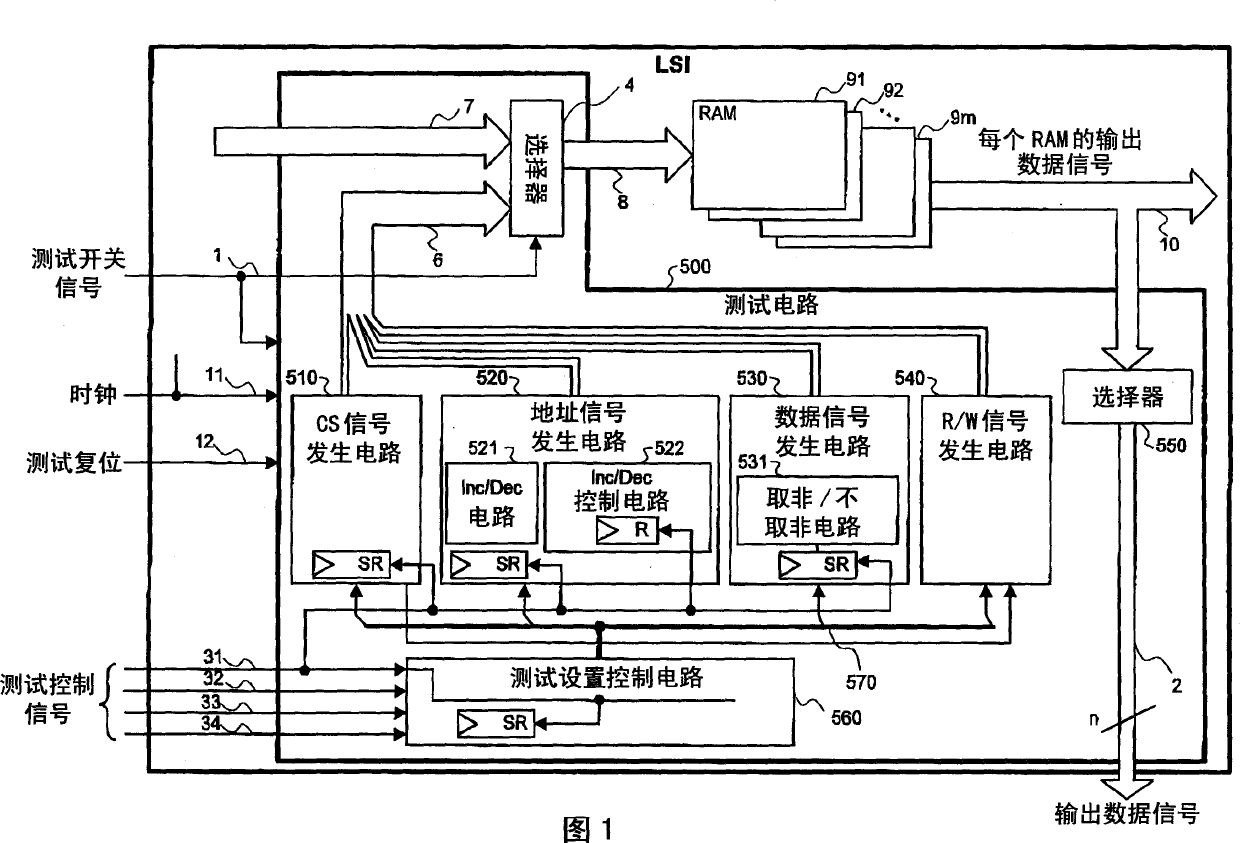
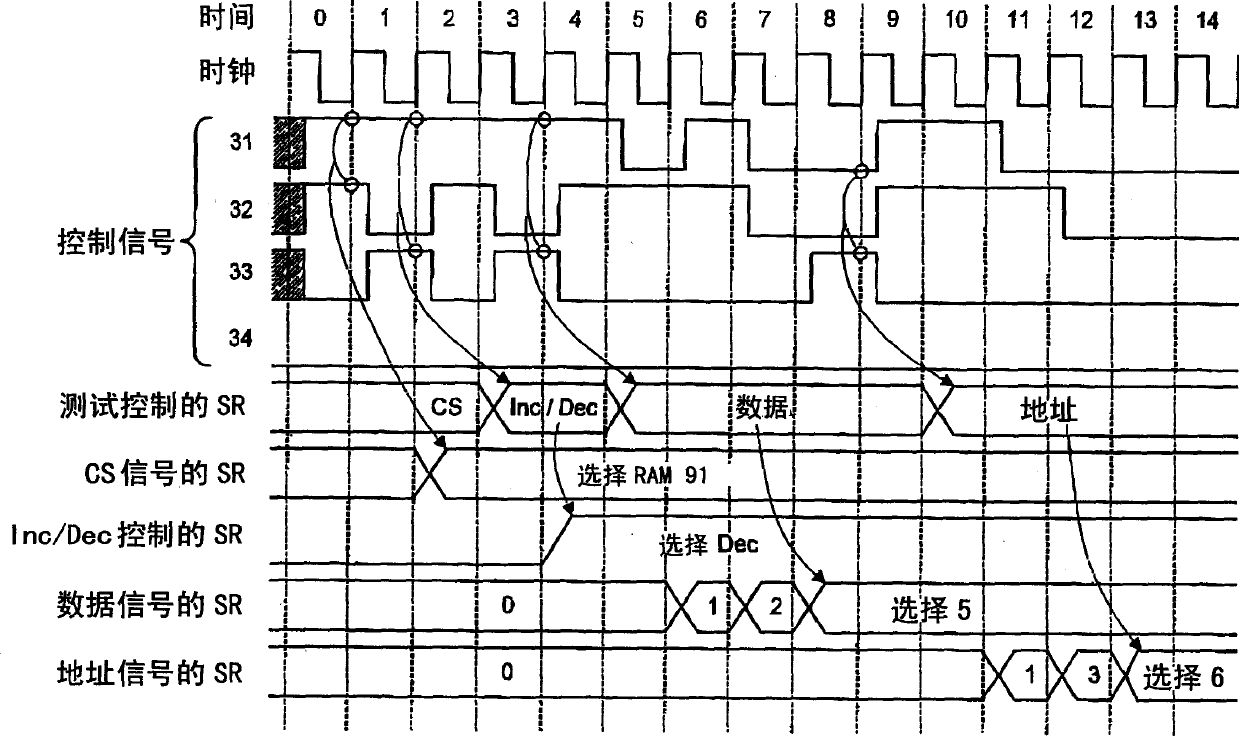
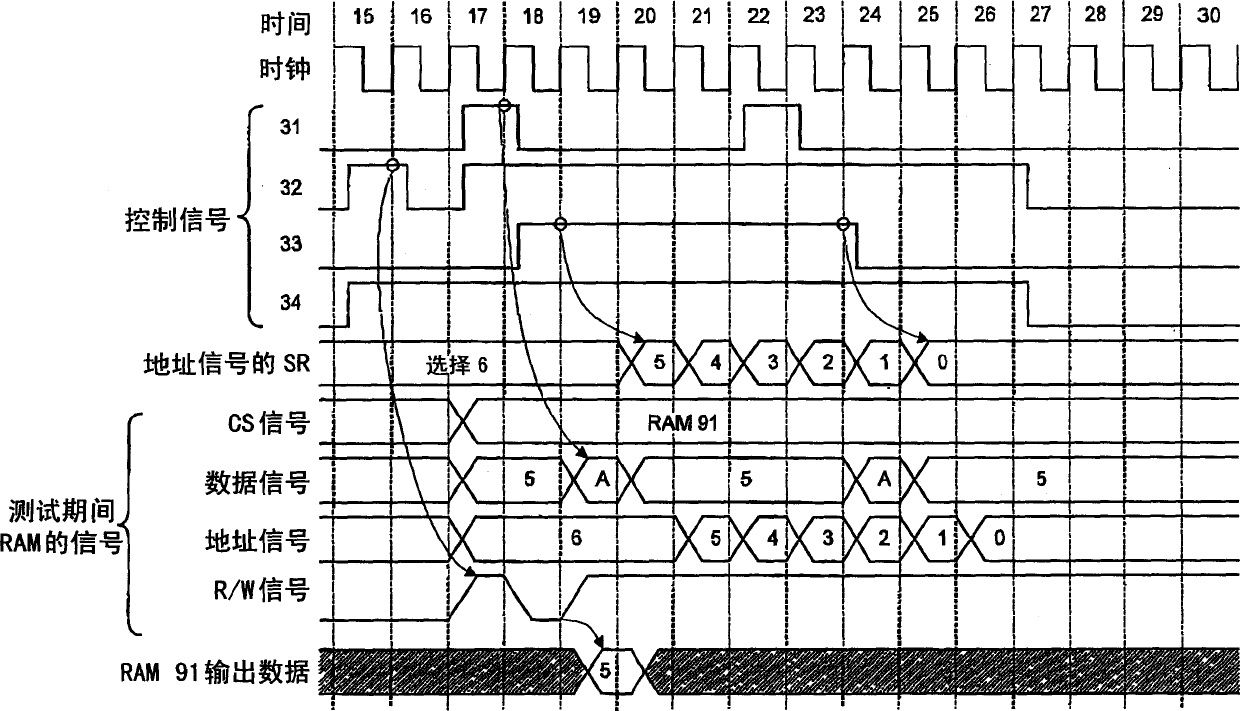
InactiveCN1489156AChange test contentElectronic circuit testingSolid-state devicesShift registerData signal
Each signal generating circuit for generating a CS signal, an address signal, a data signal or an R / W signal of a memory to be tested, and a test setting control circuit for generating a control data of these signal generating circuits are provided. The signal generating circuits and the test setting control circuit have shift registers, and a control data and a test data are serially input to these shift registers from external terminals.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Integrated containment system
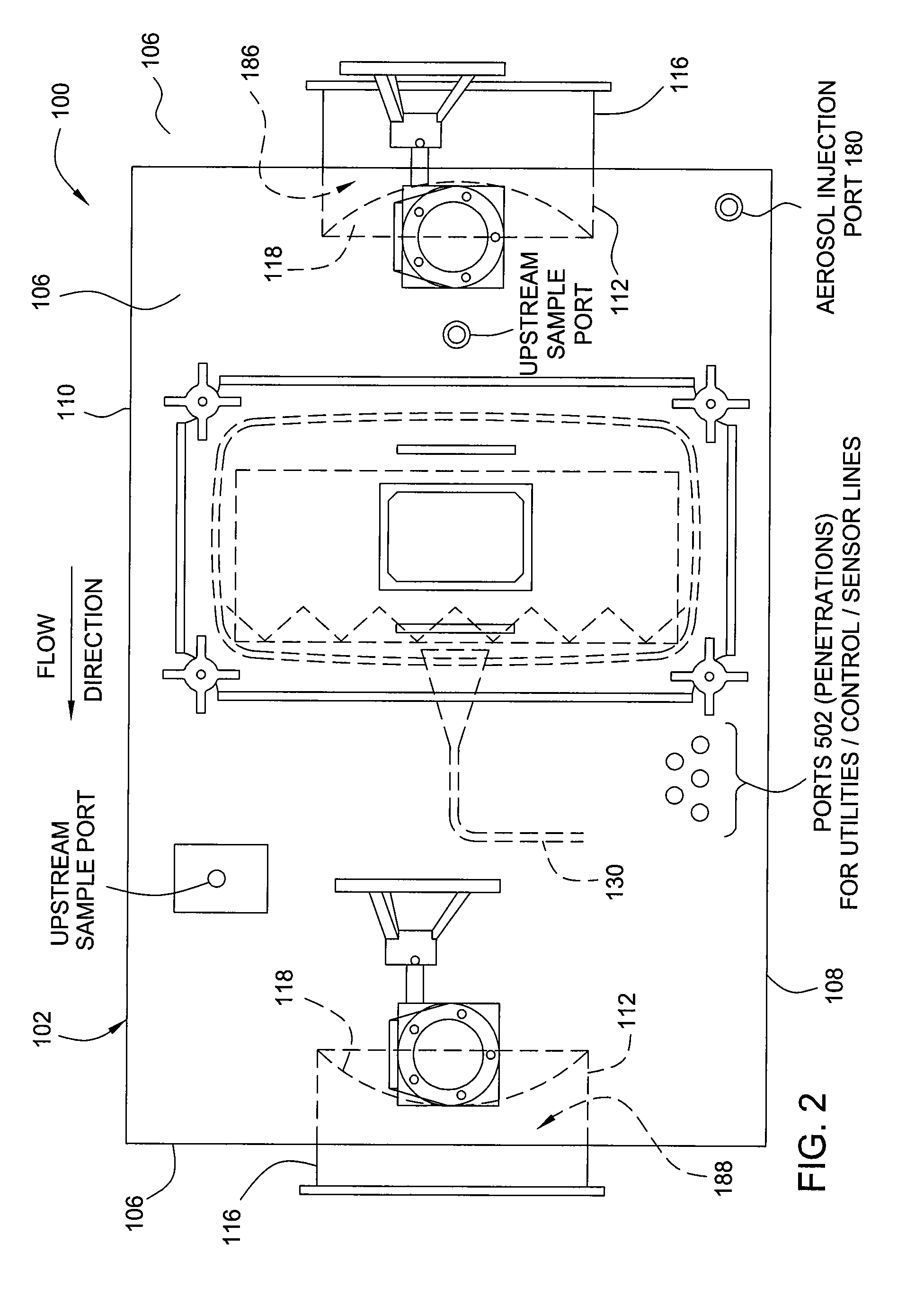
Embodiments of the invention generally provide a containment system having integrated bubble tight-dampers. In another embodiment, the containment system includes an integral auto-scan mechanism disposed in the housing of the containment system so that a filter element, disposed in the housing, may be leak tested without accessing the interior of the housing. In yet another embodiment, a method for testing a filter disposed in a containment system includes challenging an upstream side of a filter element disposed in a housing of the containment system with a test aerosol, and automatically moving a probe disposed within the housing to obtain samples for leak testing.
Owner:CAMFIL USA
Acoustic signal transfer device
InactiveUS6968053B1Supervisory/monitoring/testing arrangementsSubstation equipmentEngineeringRadio frequency
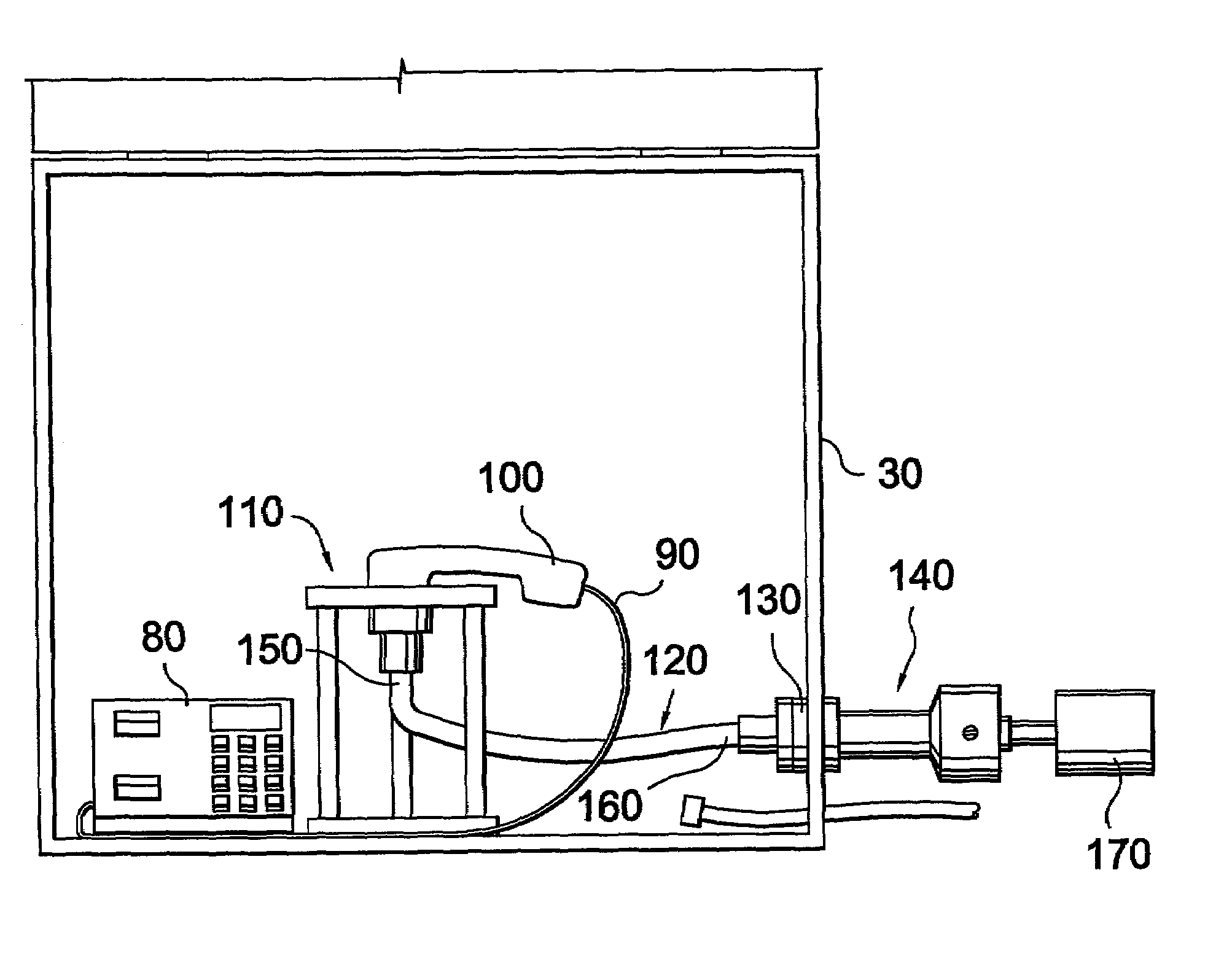
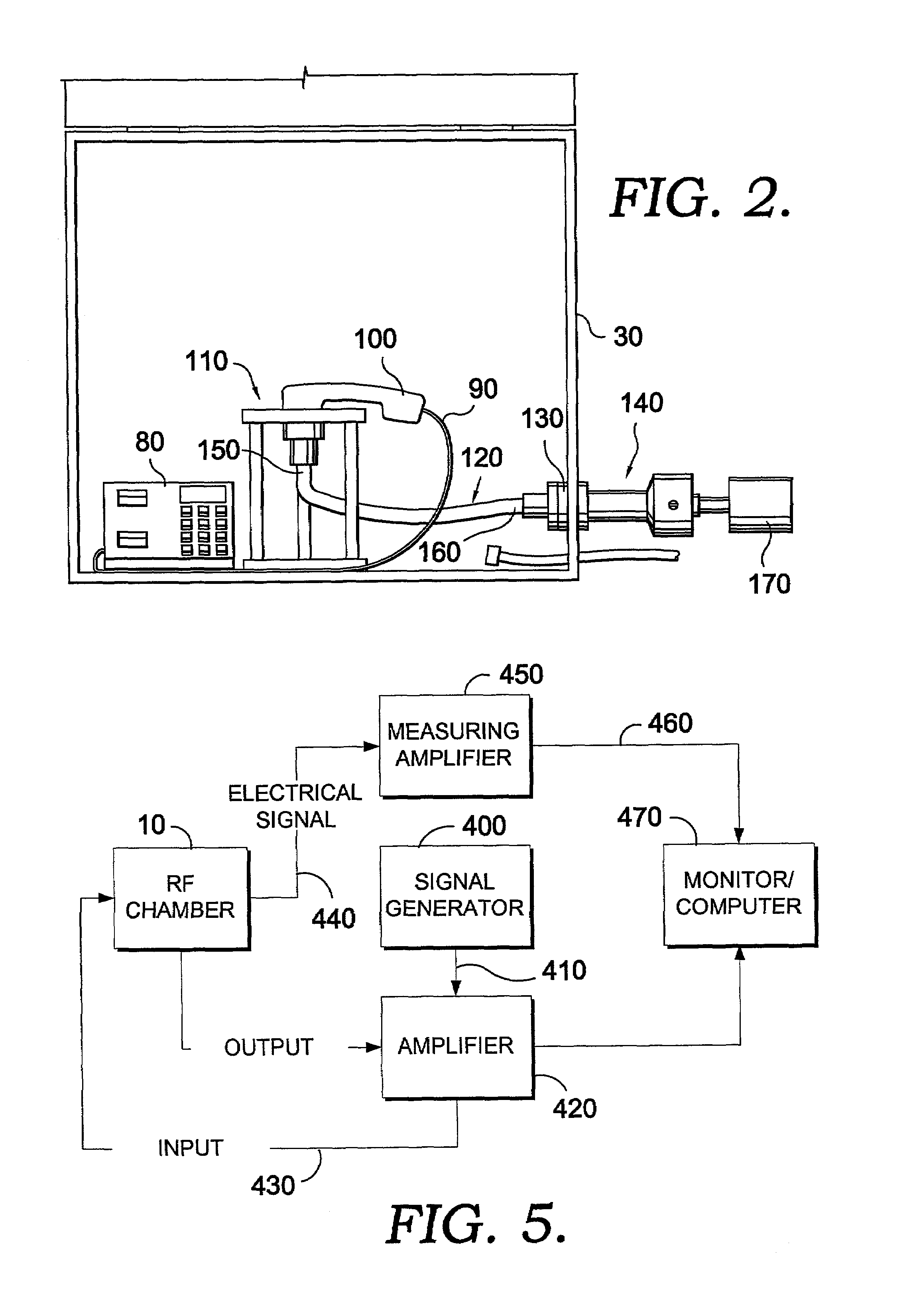
The present invention is directed to an acoustic signal transfer device for transferring an acoustic signal produced by a telephone handset in a test setup. The device comprises a handset holder, a microphone holder and an acoustic pathway that extends from the handset holder to the microphone holder. The handset holder supports a telephone handset and allows an acoustic signal to travel from the telephone handset to one end of the acoustic pathway. The microphone holder supports a microphone and allows an acoustic signal to travel from a second end of the acoustic pathway to the microphone. A system and method for utilizing the acoustic signal transfer device in a radio frequency immunity test for a telephone are also disclosed.
Owner:EMBARQ HLDG
Sensor alignment method for 3D measurment systems
InactiveUS20030210406A1Improve the test environmentImage analysisDigital computer detailsPolarizerPhysics
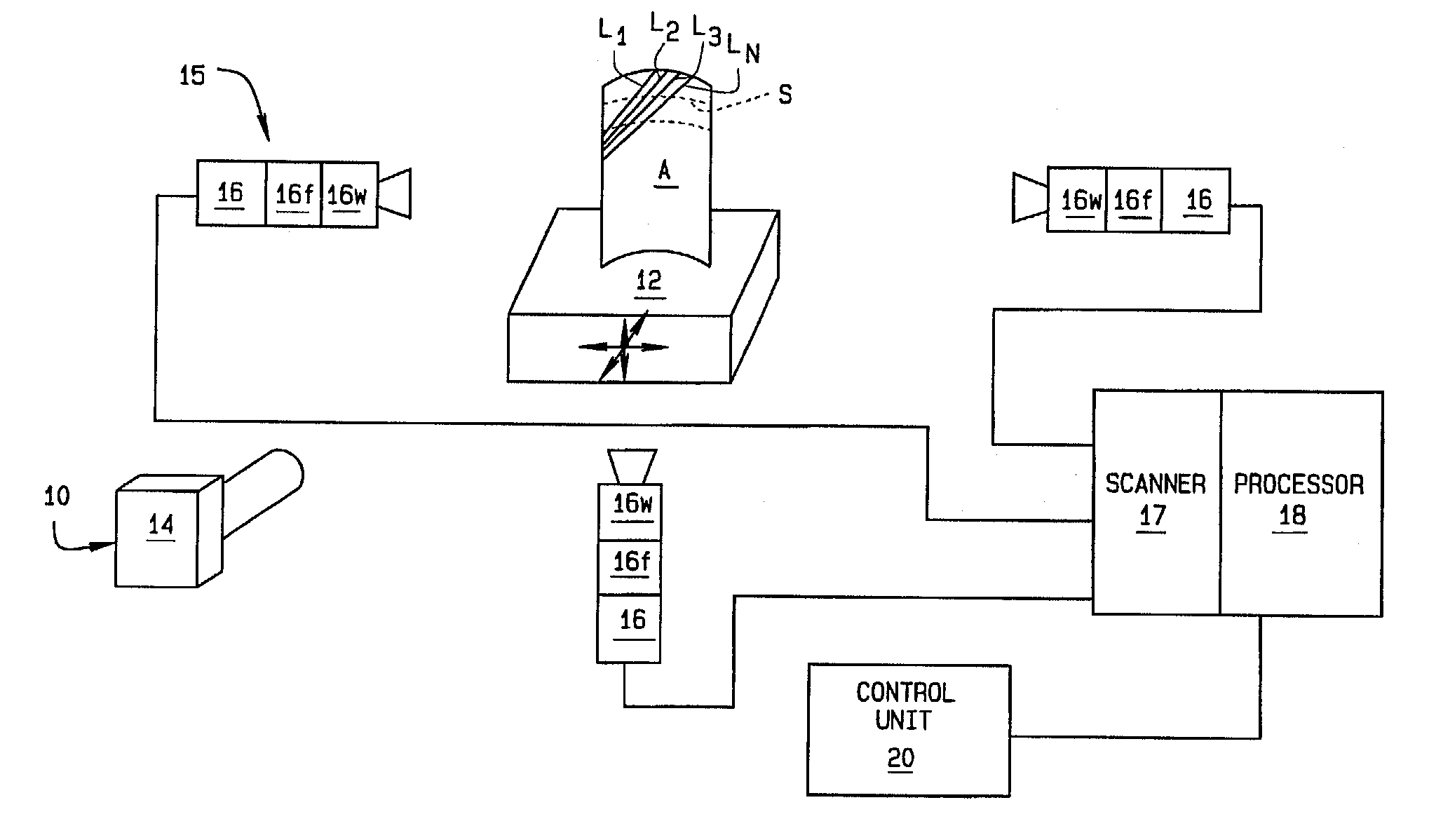
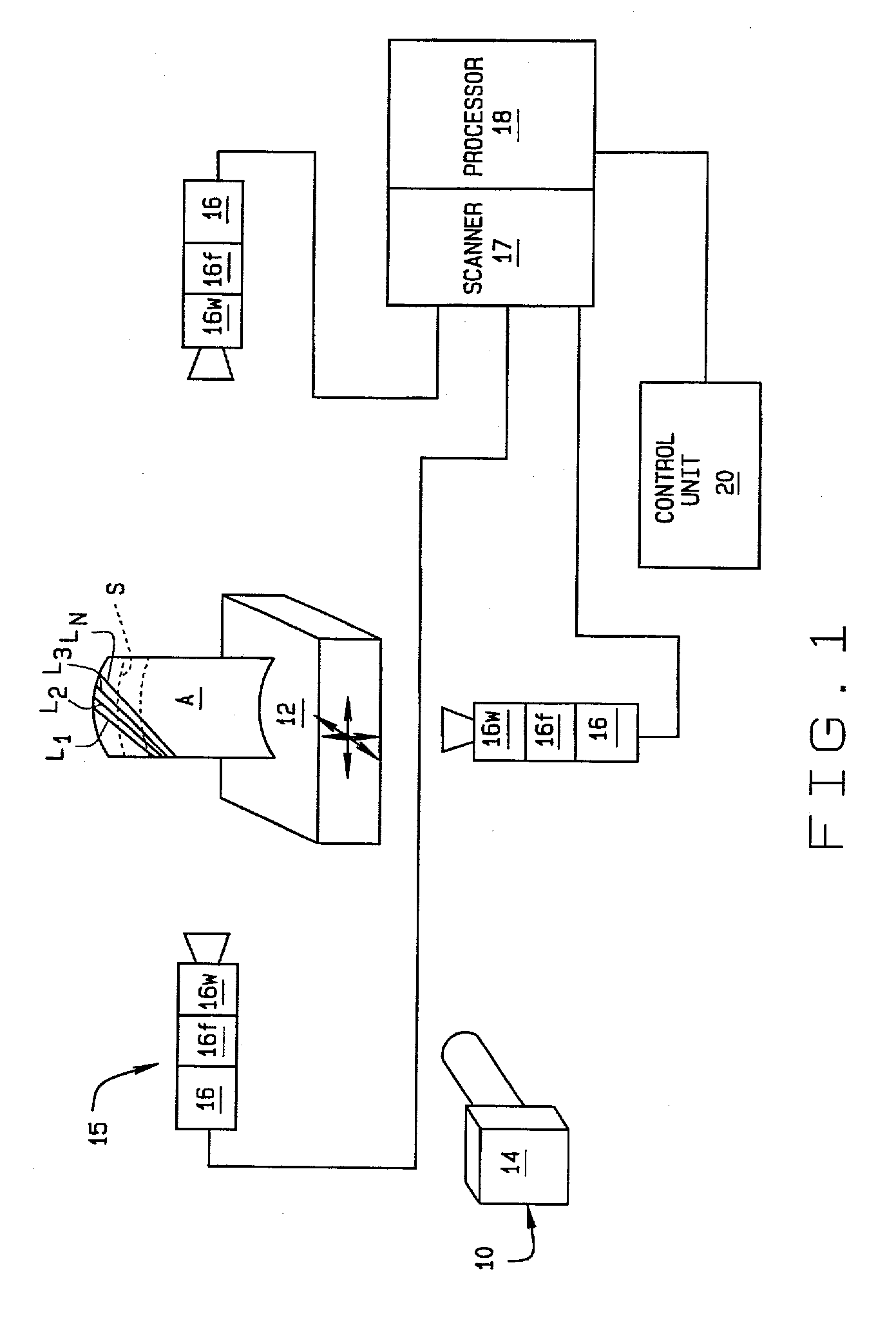
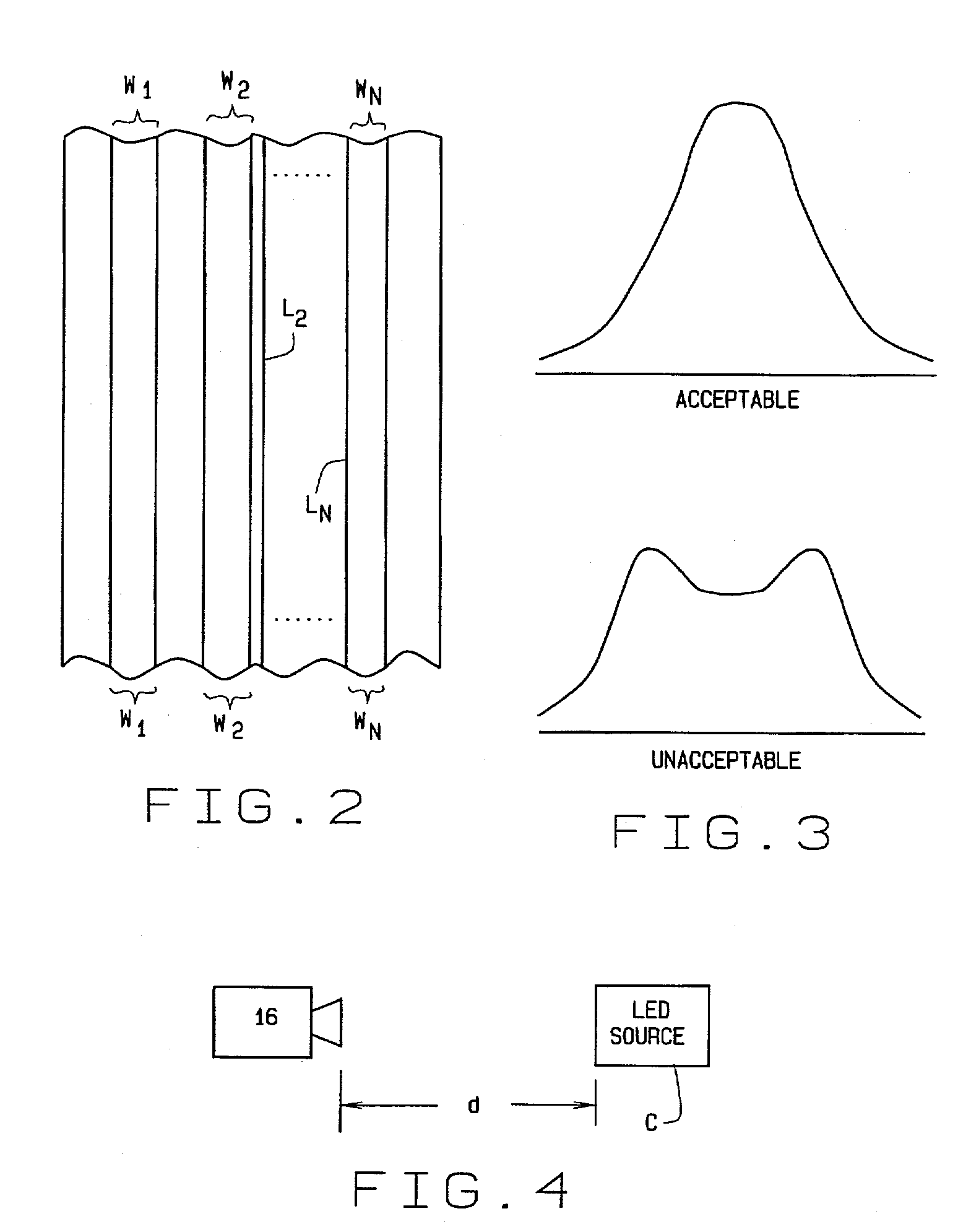
A method of set up and alignment of a structured light system for light gauge testing of an object (A). An initial alignment is made of the system with a test specimen mounted in a fixture. Light stripes (L1-Ln) generated by the structured light system are projected onto the part and images of the reflections are captured by cameras and evaluated to determine the characteristics of each stripe over a section of the specimen. The characteristics checked include the number of pixels extending across the width of a line, centeredness of the line, and the distribution of light intensity. If the former two features are not within predetermined limits, or if intensity distribution is not Gaussian, the test setup is adjusted and the process repeated. An imaging system used in the test is also checked to verify the quality of the images captured and processed. If necessary, viewing windows, polarizers, and other electrical components are evaluated to insure the imaging system is properly focused. The temperature and humidity of the test facility are also controlled to provide an optimal testing environment in which performance of the components is not effected by extremes of either.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method for the development and quality control of flow-optimized shaped charges
ActiveUS20090217739A1Rapid turnaround testingQuick and efficient progressExplosive chargesAmmunition testingShaped chargeDesign engineer
An improved test setup facility, referred to as a “Quick Development Cell” (QDC), which allows for rapid turnaround testing with valuable feedback to a design engineer. Because the QDC allows for quick and efficient testing at a sufficient frequency, QDC tests are compatible with production quality control. In addition to fostering improvement of the API's Section 2 type tests using stressed natural rock for benchmark experiments, the QDC tests allow for progress to be made towards the development of a flow-optimized shape charge and superior well performance.
Owner:WELLS FARGO BANK NAT ASSOC +1
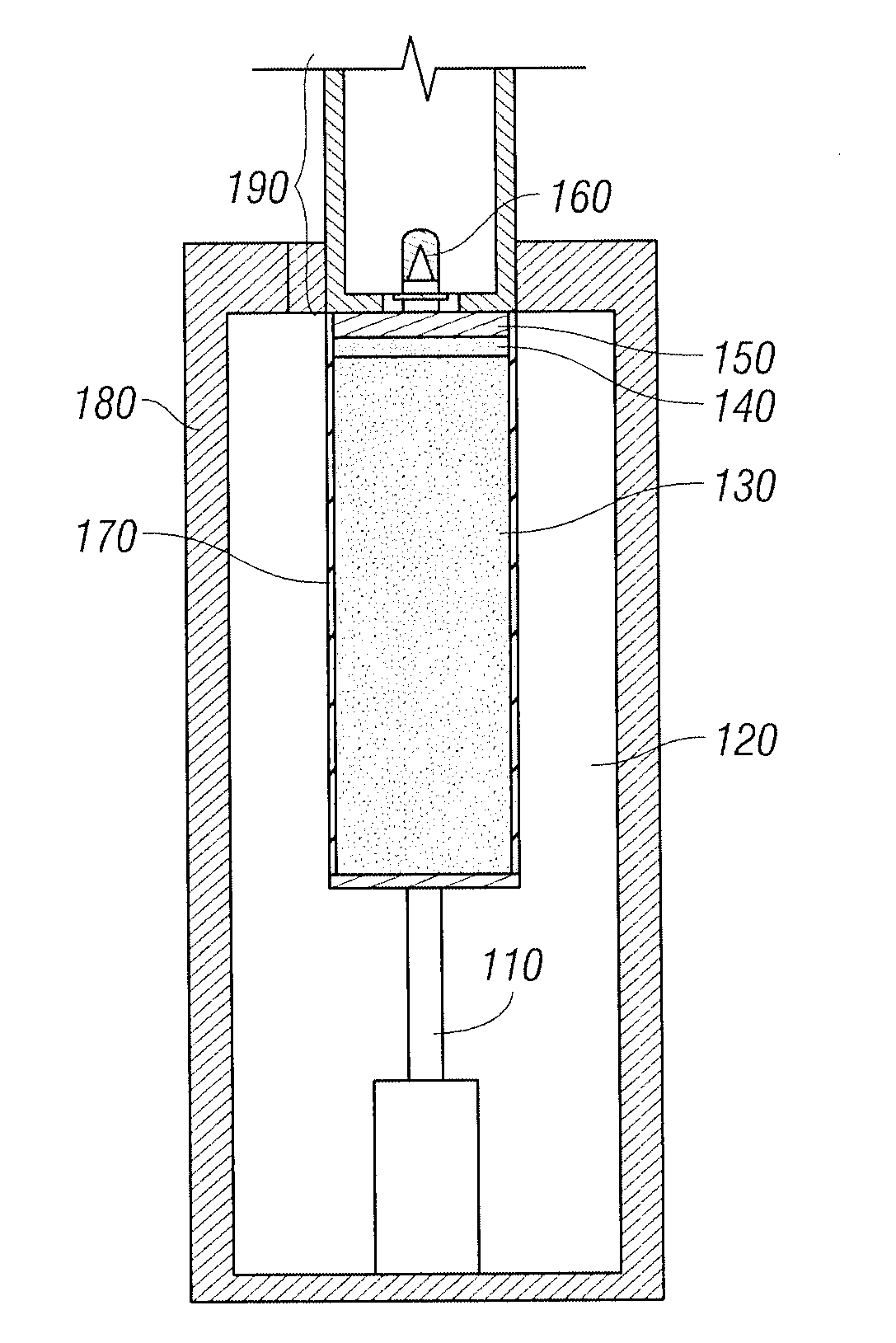
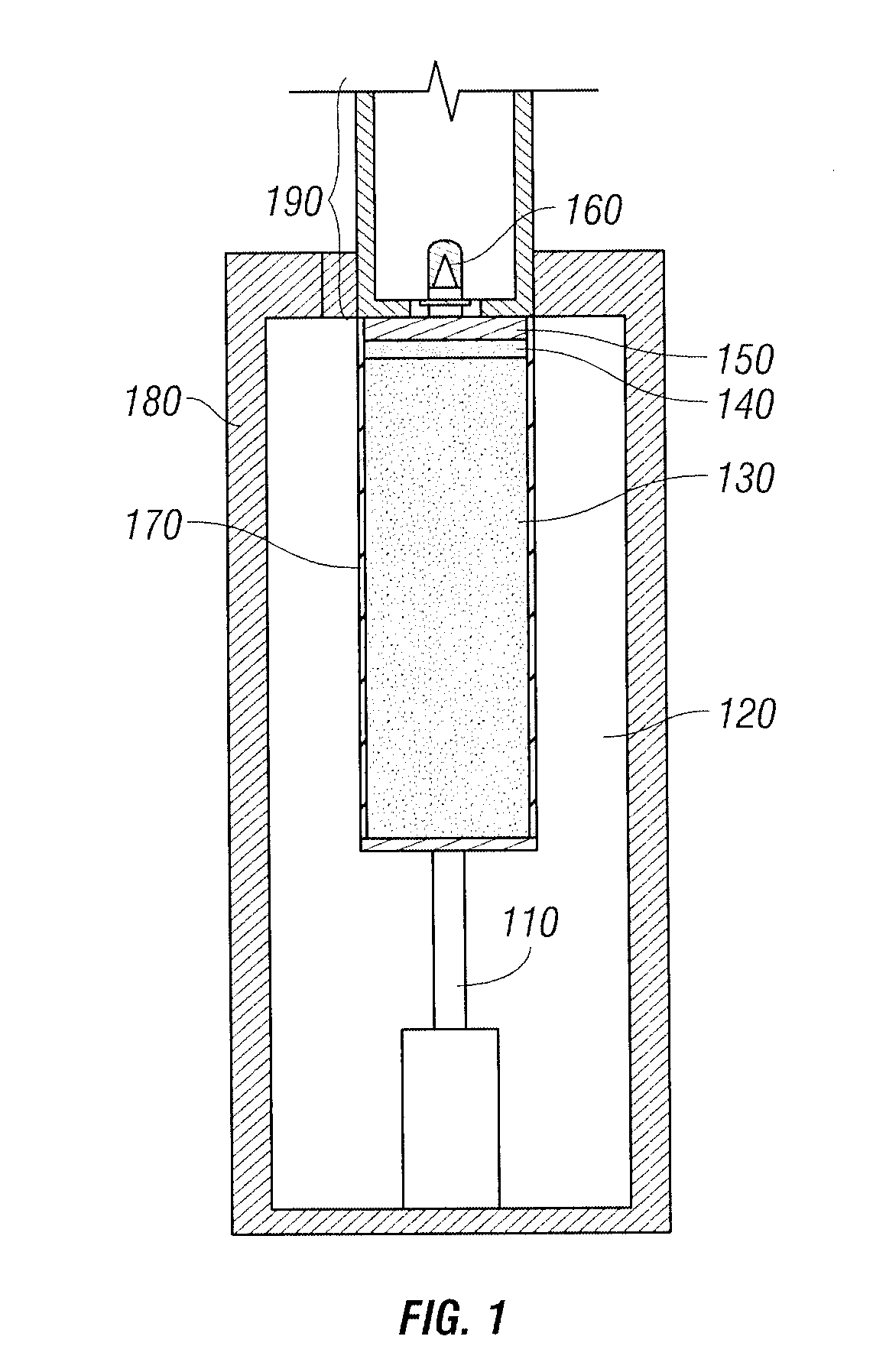
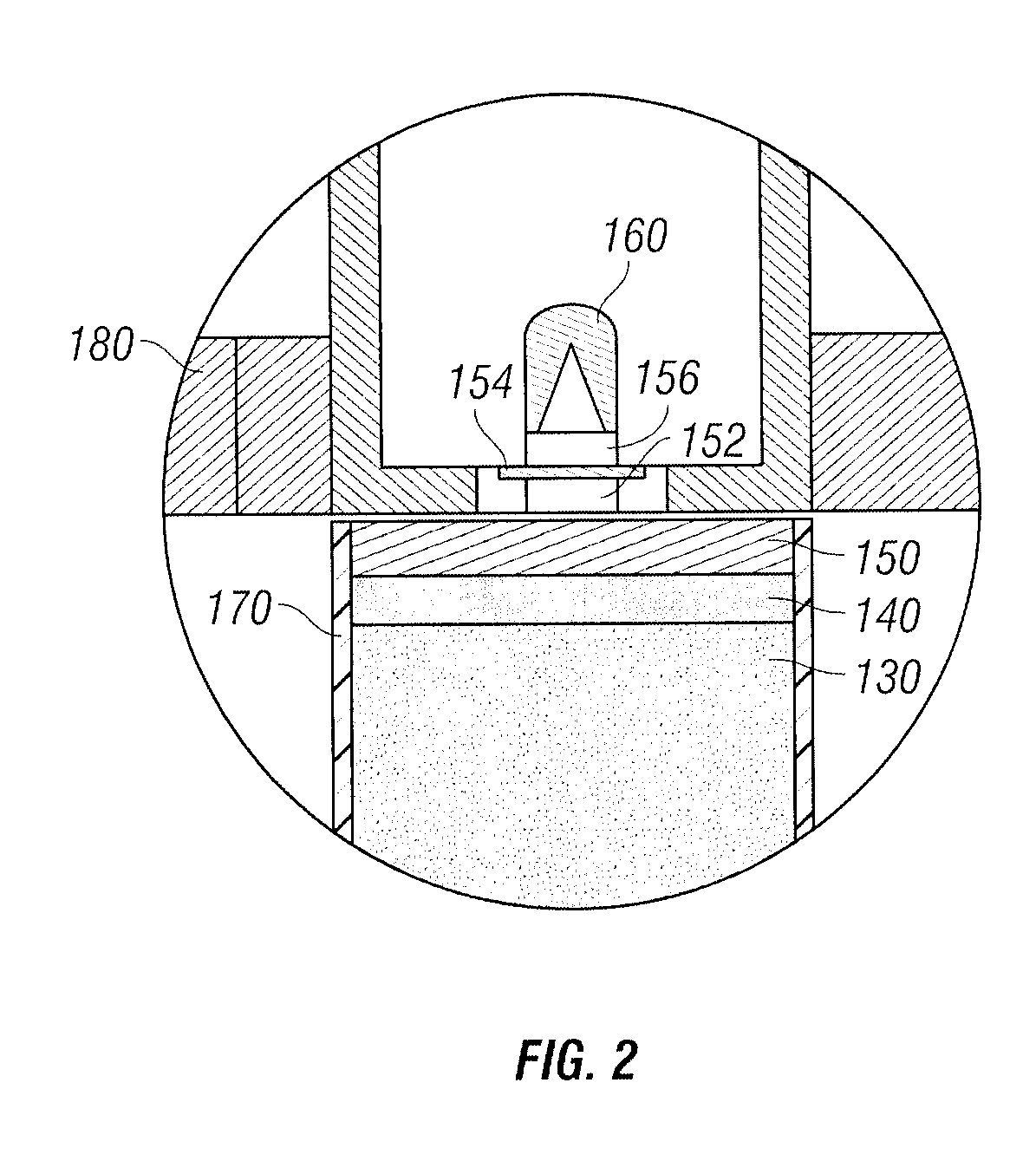
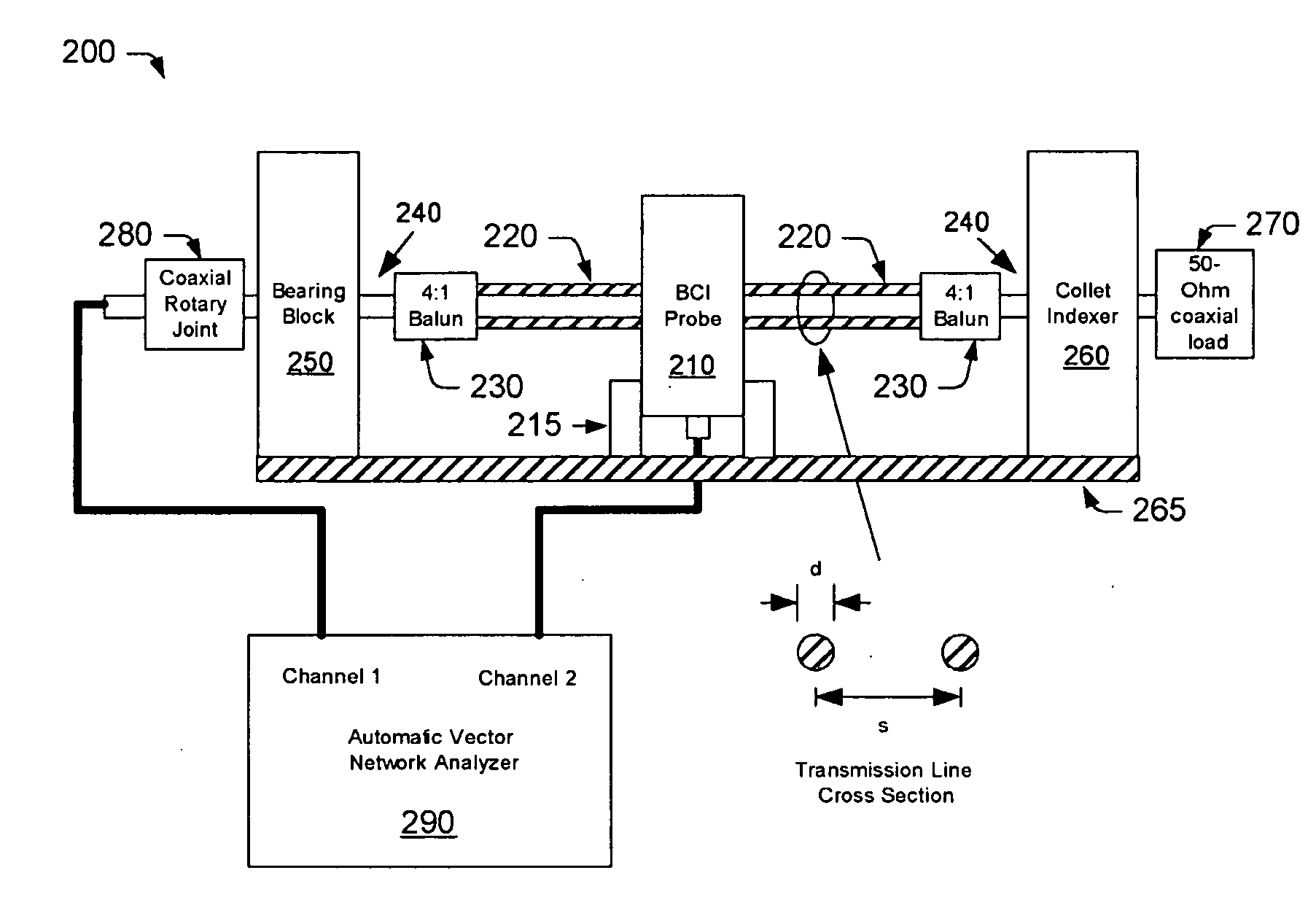
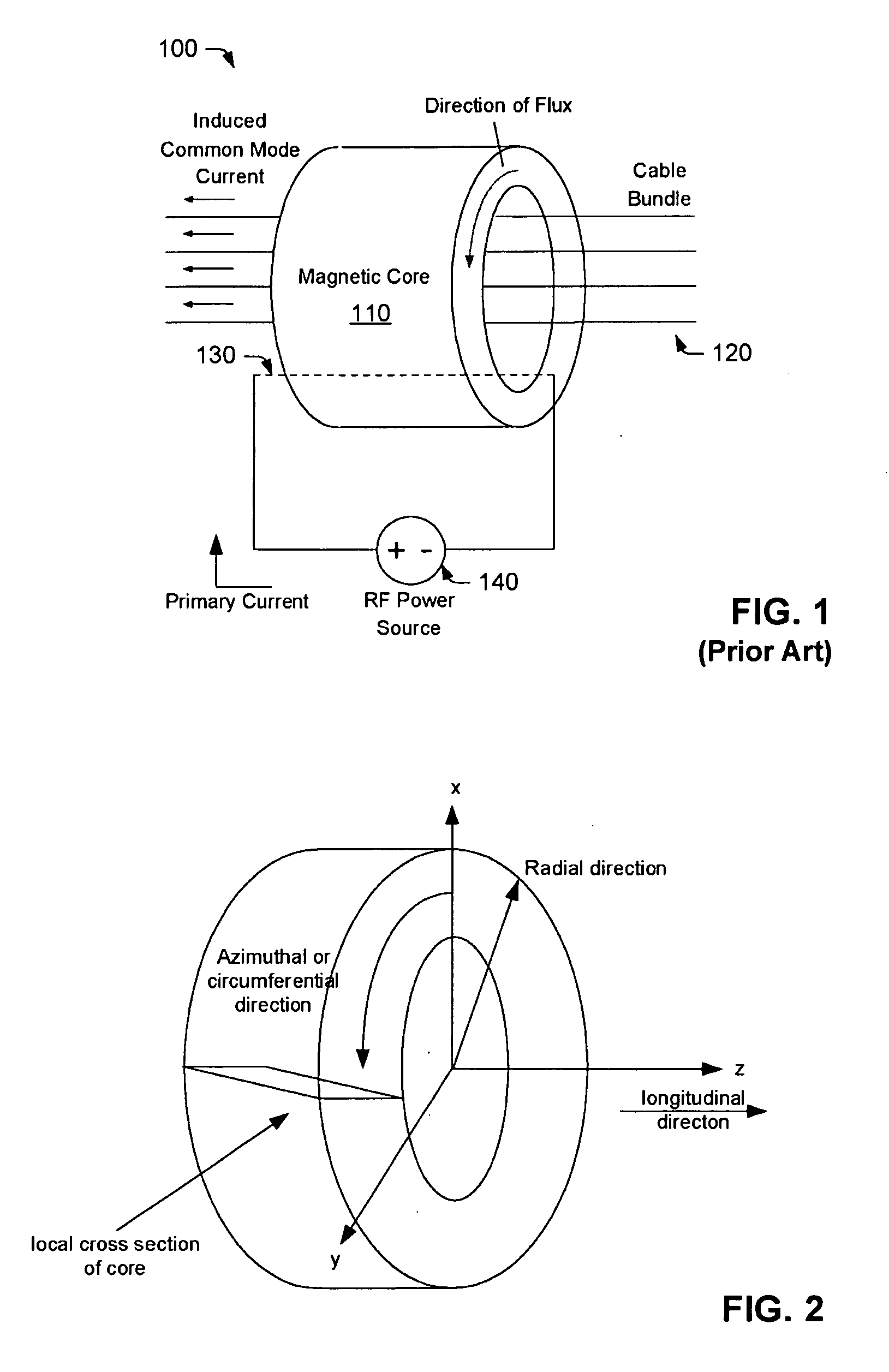
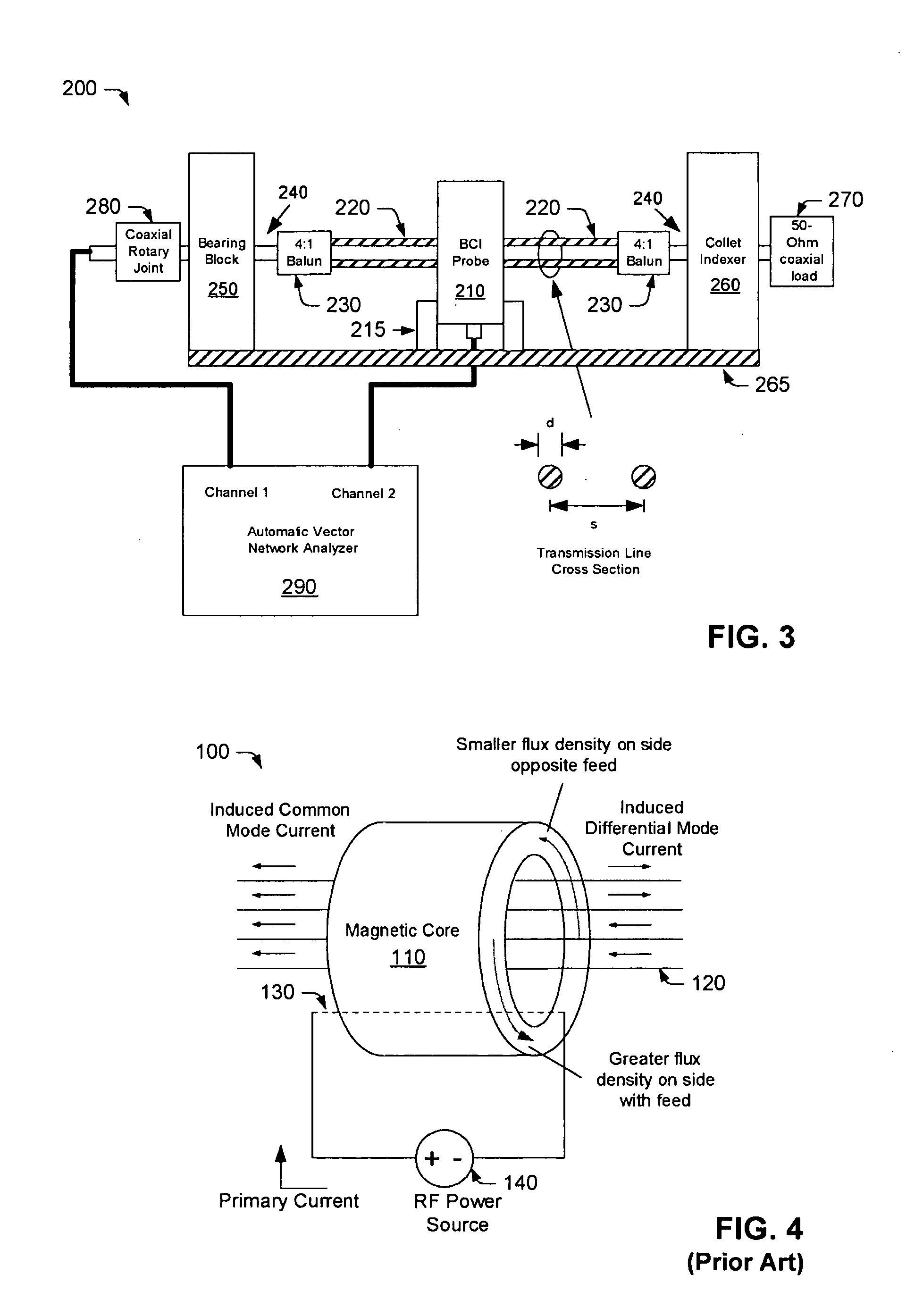
Bulk Current Injection (BCI) Probe with Multiple, Symmetrically Spaced Feeds
ActiveUS20100176817A1Uniform flux densityTransformersResistance/reactance/impedenceElectricityElectrical conductor
A Bulk Current Injection (BCI) transformer is provided herein with a magnetic core and a plurality of windings. The magnetic core is configured for encircling one or more electrical conductors under test. Each of the plurality of windings are wrapped, at least in part, around a longitudinal dimension of the magnetic core and spaced apart around an azimuthal dimension of the magnetic core. During injection tests, a power source may be coupled for supplying current to each of the windings at a respective “feed point.” Arranging multiple feed points around the magnetic core enables current flow through the windings to generate an azimuthally-uniform magnetic flux density in the magnetic core. The uniform magnetic flux density enables the BCI transformer to excite only common mode currents in the electrical conductors under test. BCI test methods, including injection tests and current sensing tests are also provided herein, along with a test setup for characterizing BCI transformers.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com