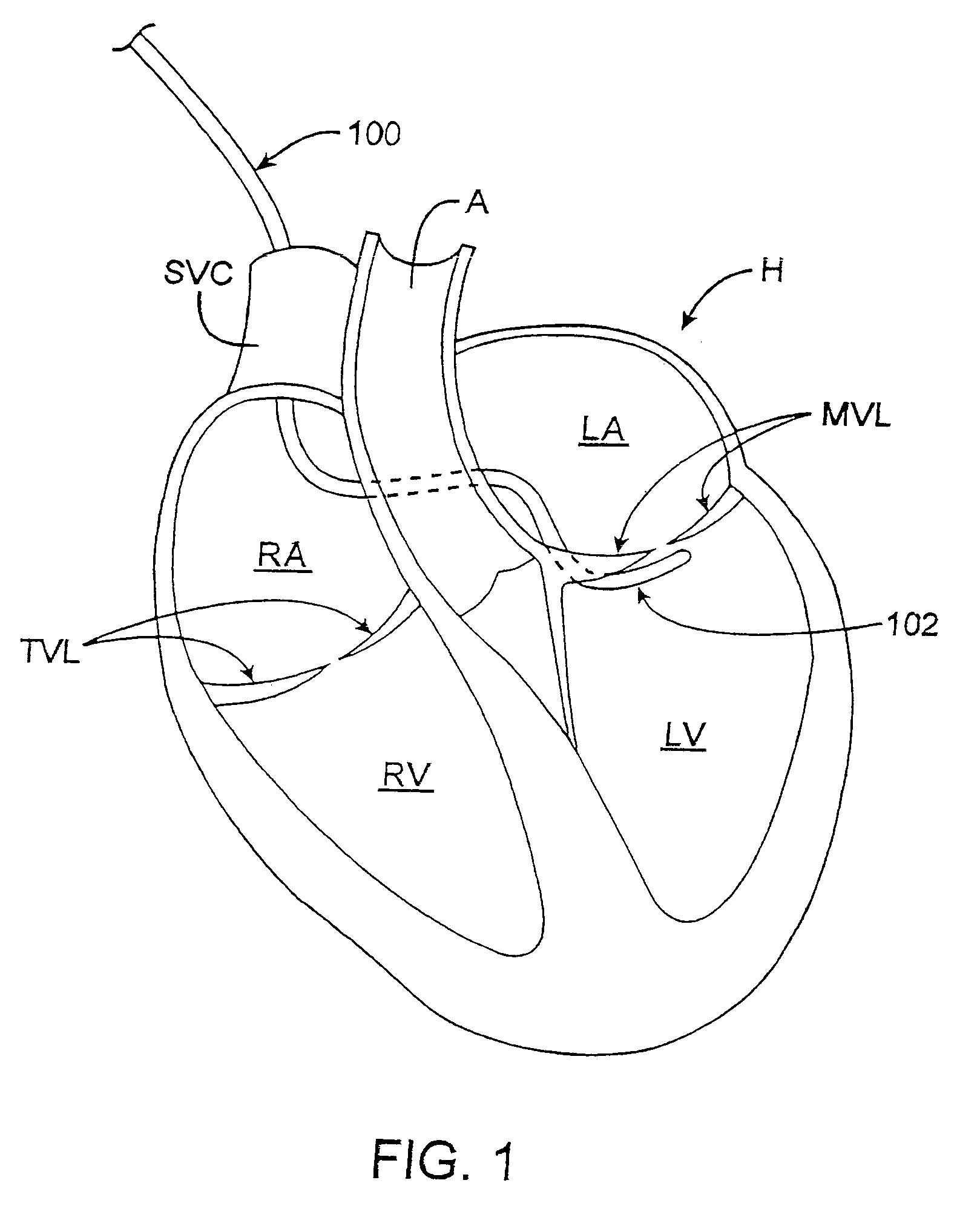
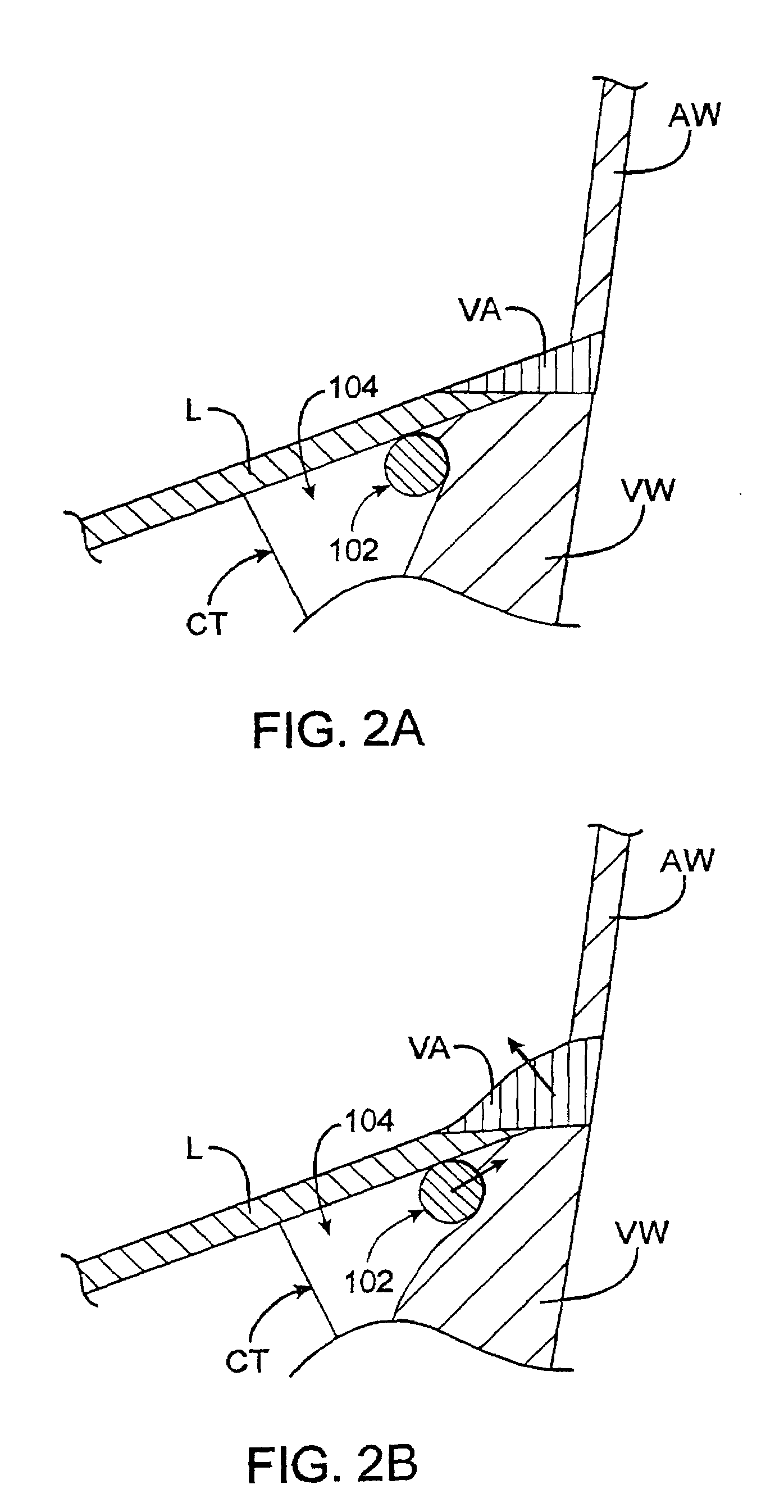
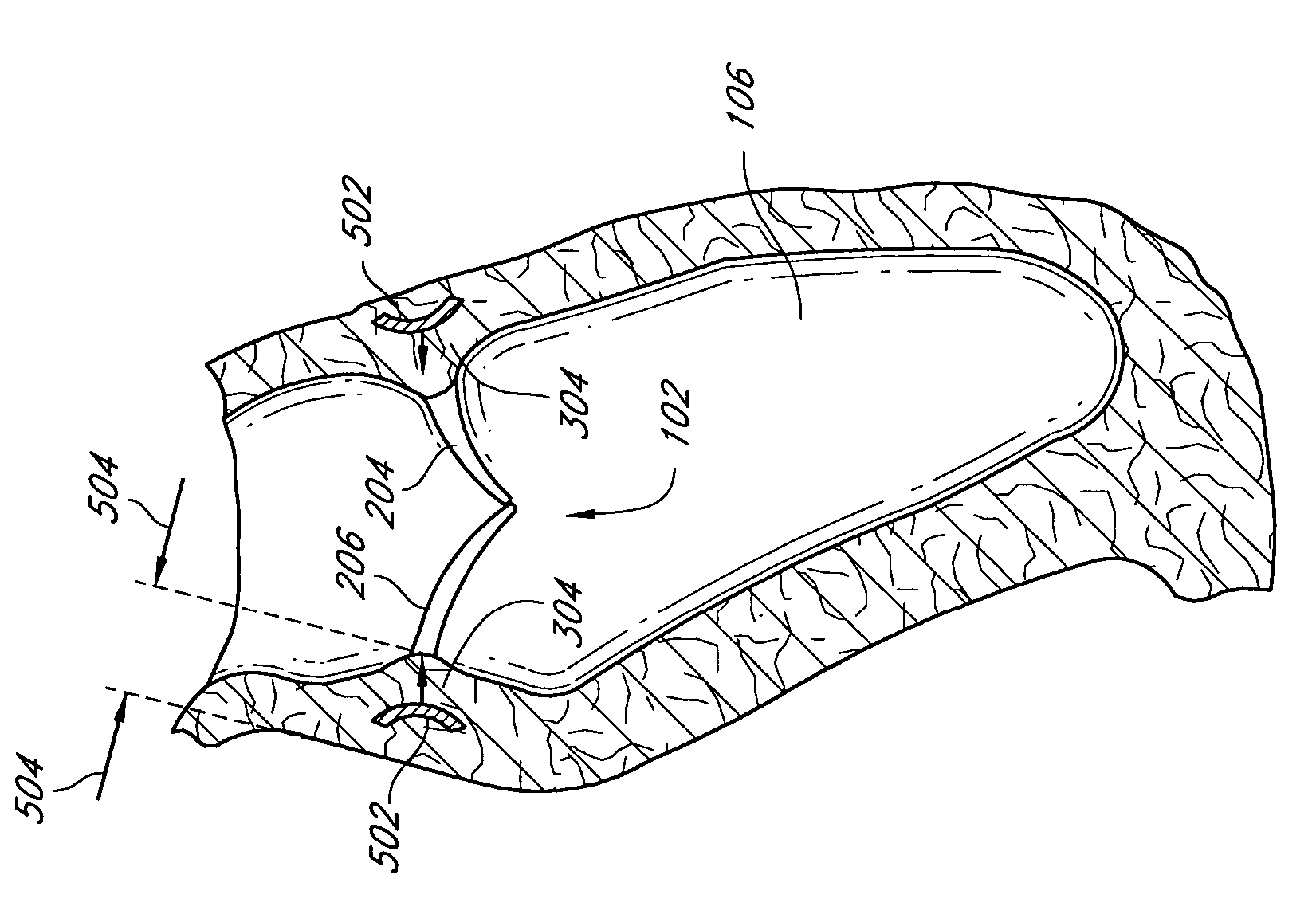
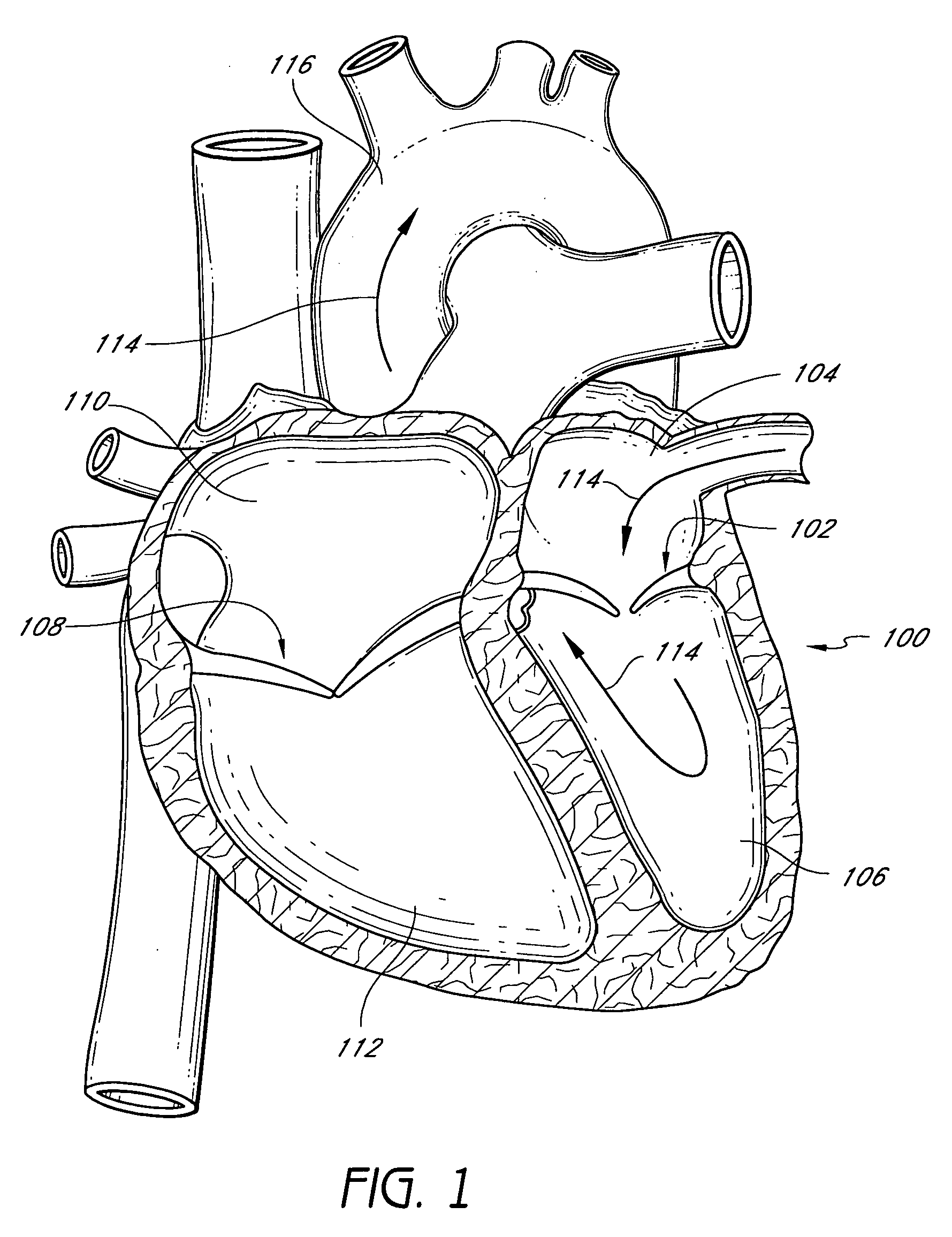
Patents
Literature
736 results about "Heart tissues" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
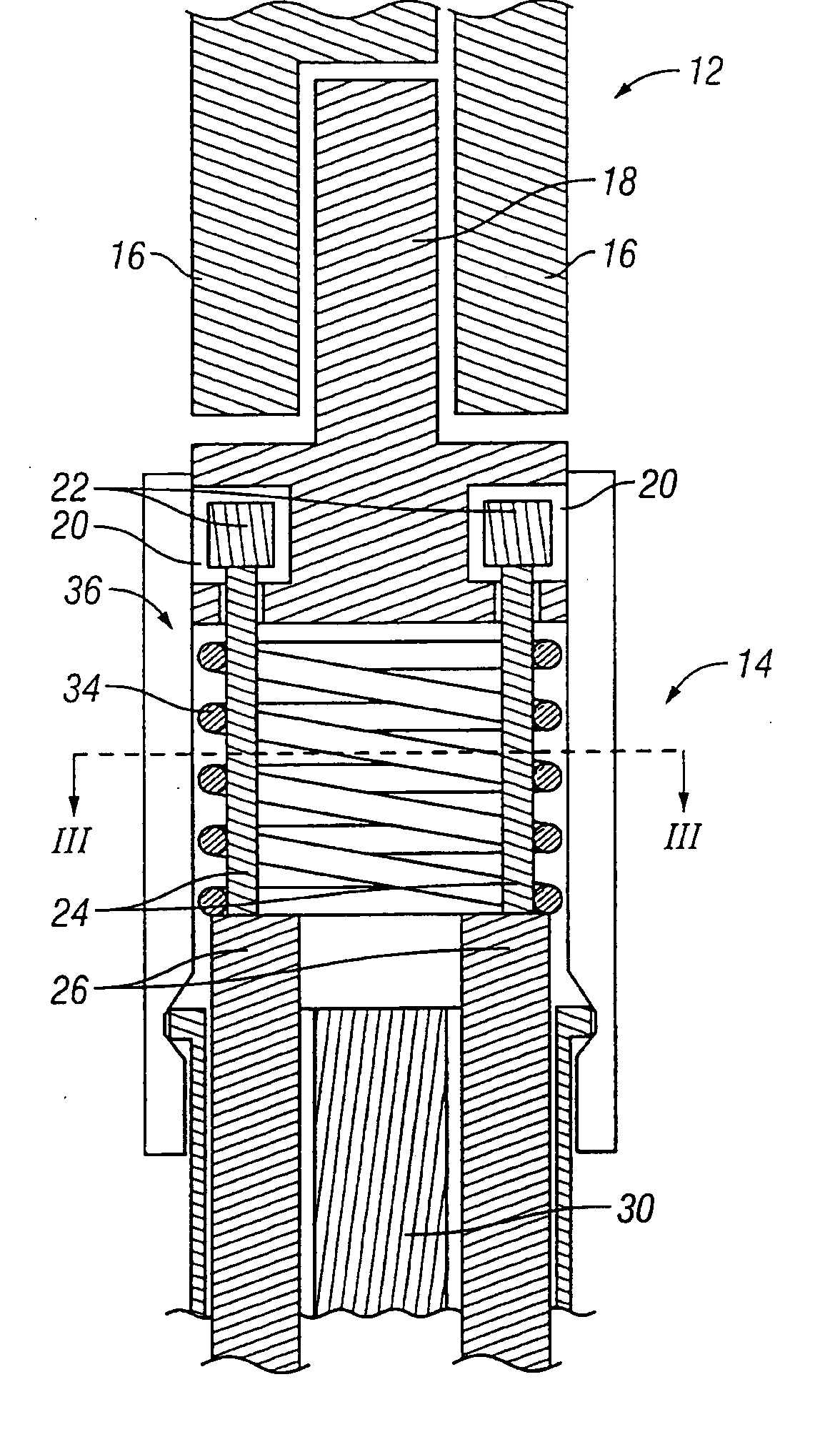
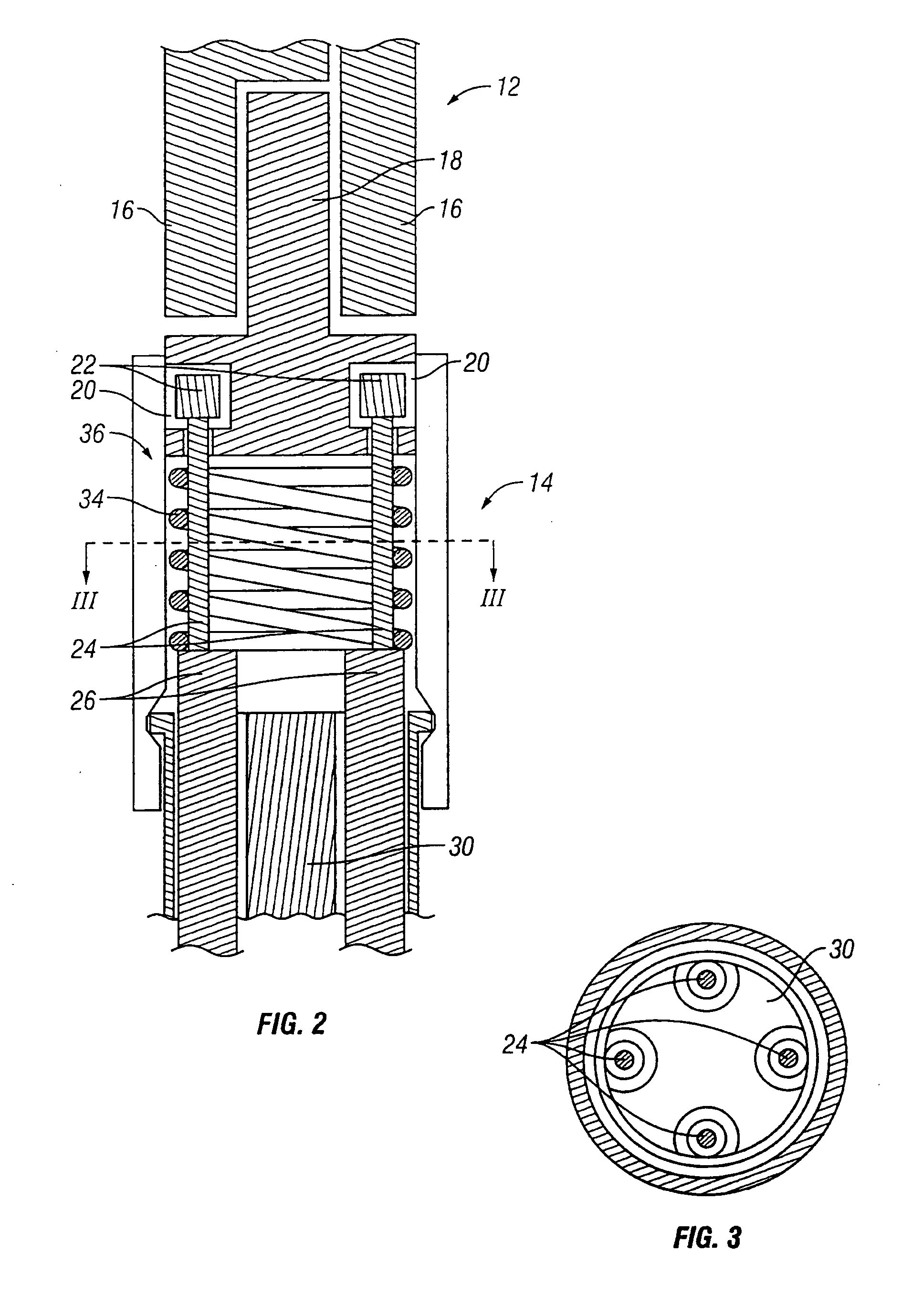
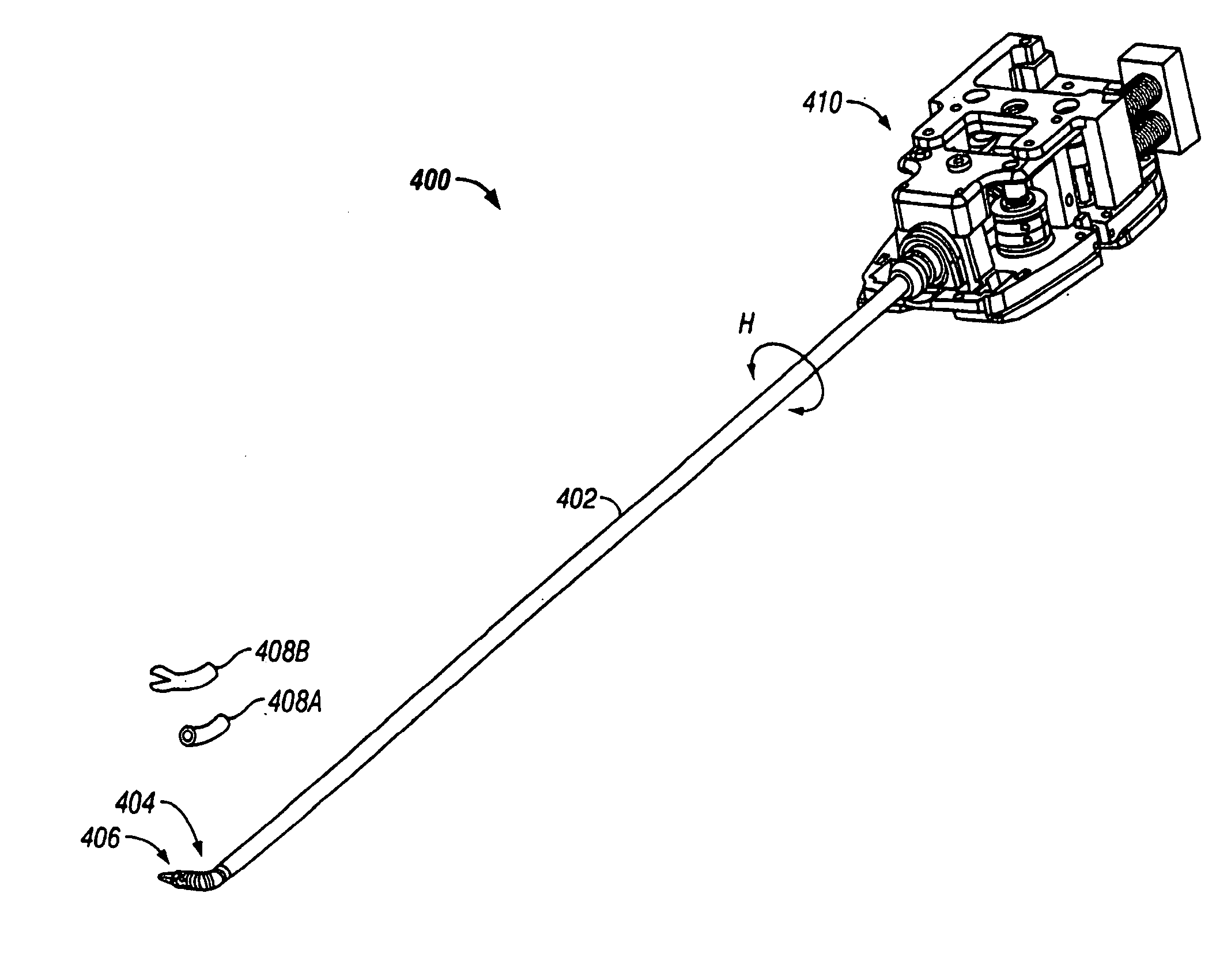
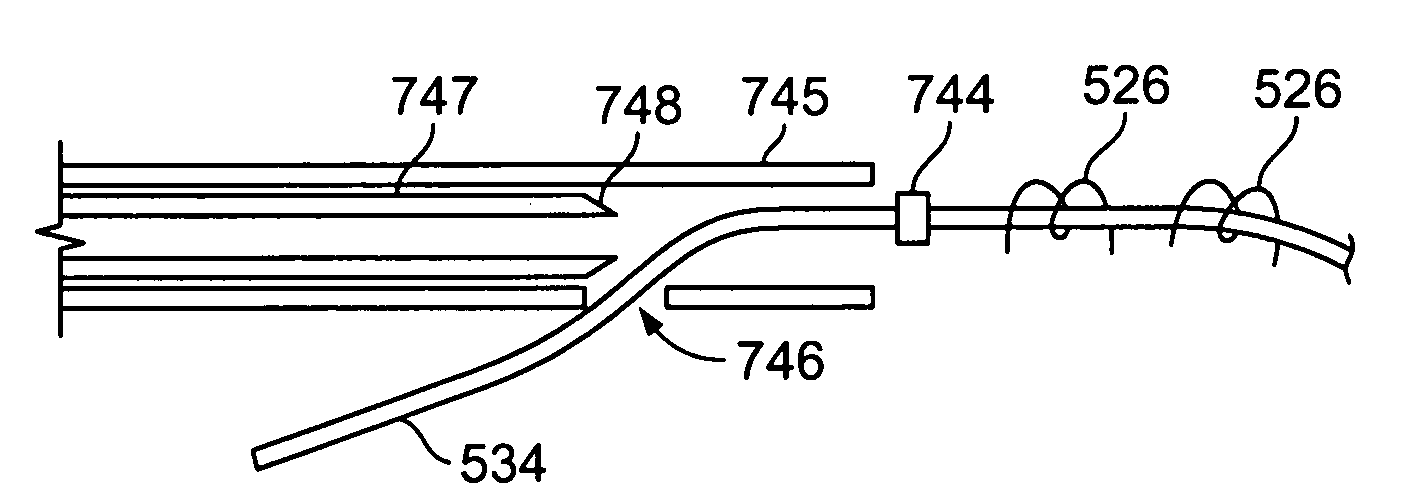
Cardiac tissue ablation instrument with flexible wrist
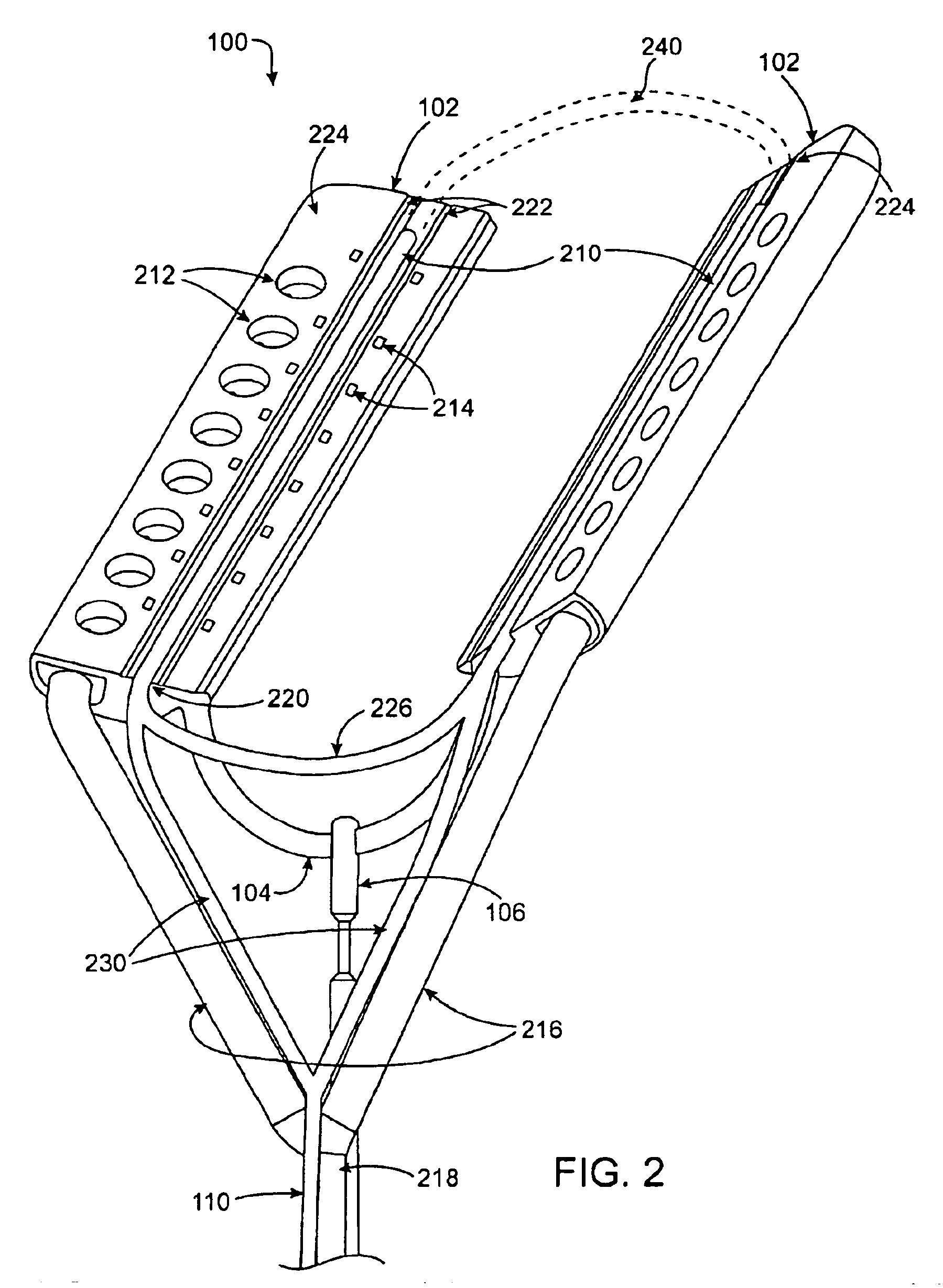
The present invention is directed to an articulate minimally invasive surgical instrument with a flexible wrist to facilitate the safe placement and provide visual verification of the ablation catheter or other devices in Cardiac Tissue Ablation (CTA) treatments. In one embodiment, the instrument is an endoscope which has an elongate shaft, a flexible wrist at the working end of the shaft, and a vision scope lens at the tip of the flexible wrist. The flexible wrist has at least one degree of freedom to provide the desired articulation. It is actuated and controlled by a drive mechanism located in the housing at the distal end of the shaft. The articulation of the endoscope allows images of hard-to-see places to be taken for use in assisting the placement of the ablation catheter on the desired cardiac tissue. The endoscope may further include couplings to releasably attach an ablation device / catheter or a catheter guide to the endoscope thereby further utilizing the endoscope articulation to facilitate placement of the ablation catheter on hard-to-reach cardiac tissues. In another embodiment, the articulate instrument is a grasper or any other instrument with a flexible wrist and a built-in lumen to allow an endoscope to insert and be guided to the distal end of the instrument.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL
Cardiac tissue ablation instrument with flexible wrist
InactiveUS20060199999A1Promotes convenient, simplified manufacturing and assembly processesShorten the counting processEndoscopesSurgical manipulatorsWristInstrumentation
An articulate minimally invasive surgical instrument with a flexible wrist to facilitate the safe placement and provide visual verification of the ablation catheter or other devices in Cardiac Tissue Ablation (CTA) treatments is described. In one embodiment, the instrument is an endoscope which has an elongate shaft, a flexible wrist at the working end of the shaft, and a vision scope lens at the tip of the flexible wrist. The flexible wrist has at least one degree of freedom to provide the desired articulation. It is actuated and controlled by a drive mechanism located in the housing at the distal end of the shaft. The articulation of the endoscope allows images of hard-to-see places to be taken for use in assisting the placement of the ablation catheter on the desired cardiac tissue. The endoscope may further include couplings to releasably attach an ablation device / catheter or a catheter guide to the endoscope thereby further utilizing the endoscope articulation to facilitate placement of the ablation catheter on hard-to-reach cardiac tissues. In another embodiment, the articulate instrument is a grasper or any other instrument with a flexible wrist and a built-in lumen to allow an endoscope to insert and be guided to the distal end of the instrument.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
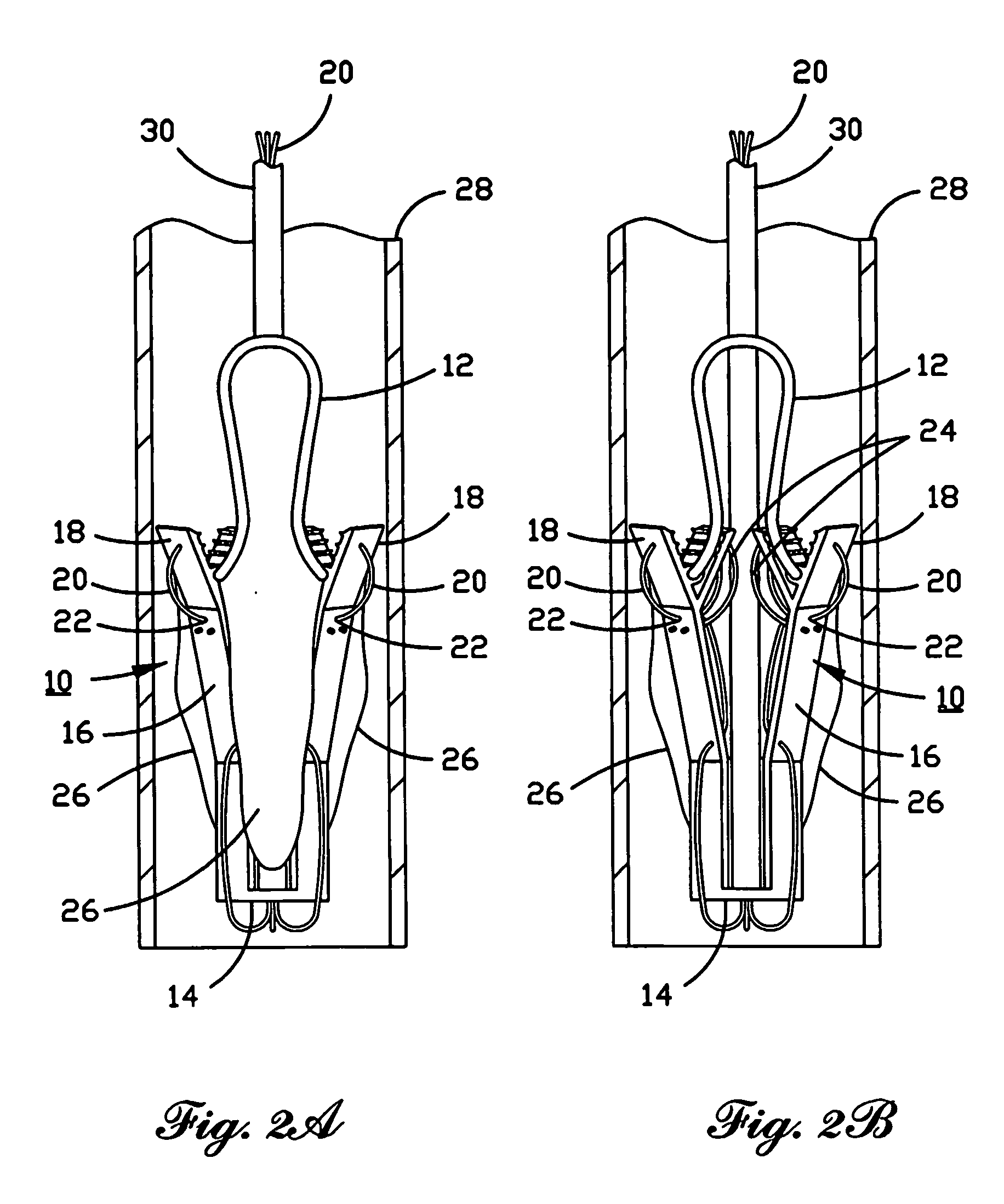
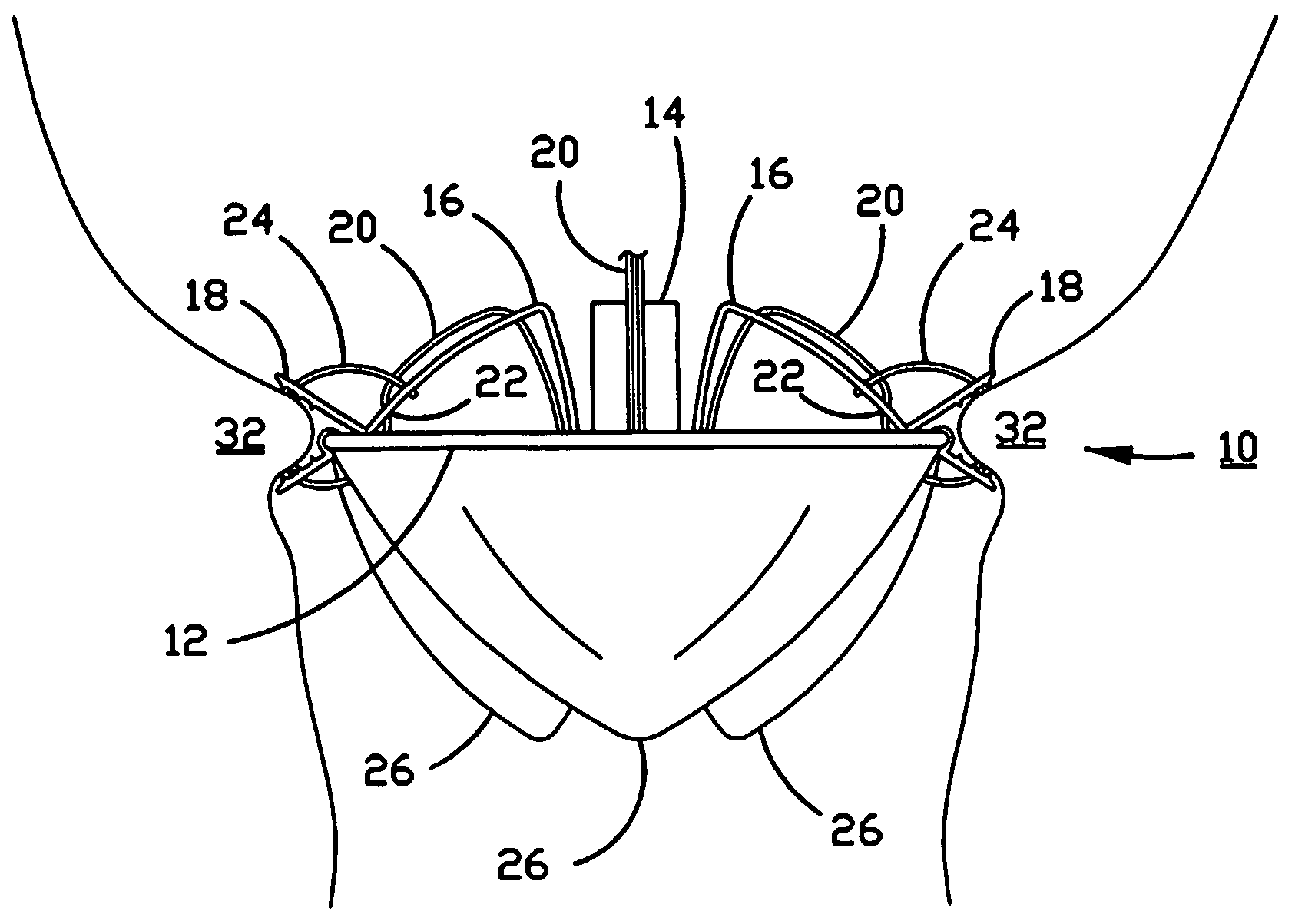
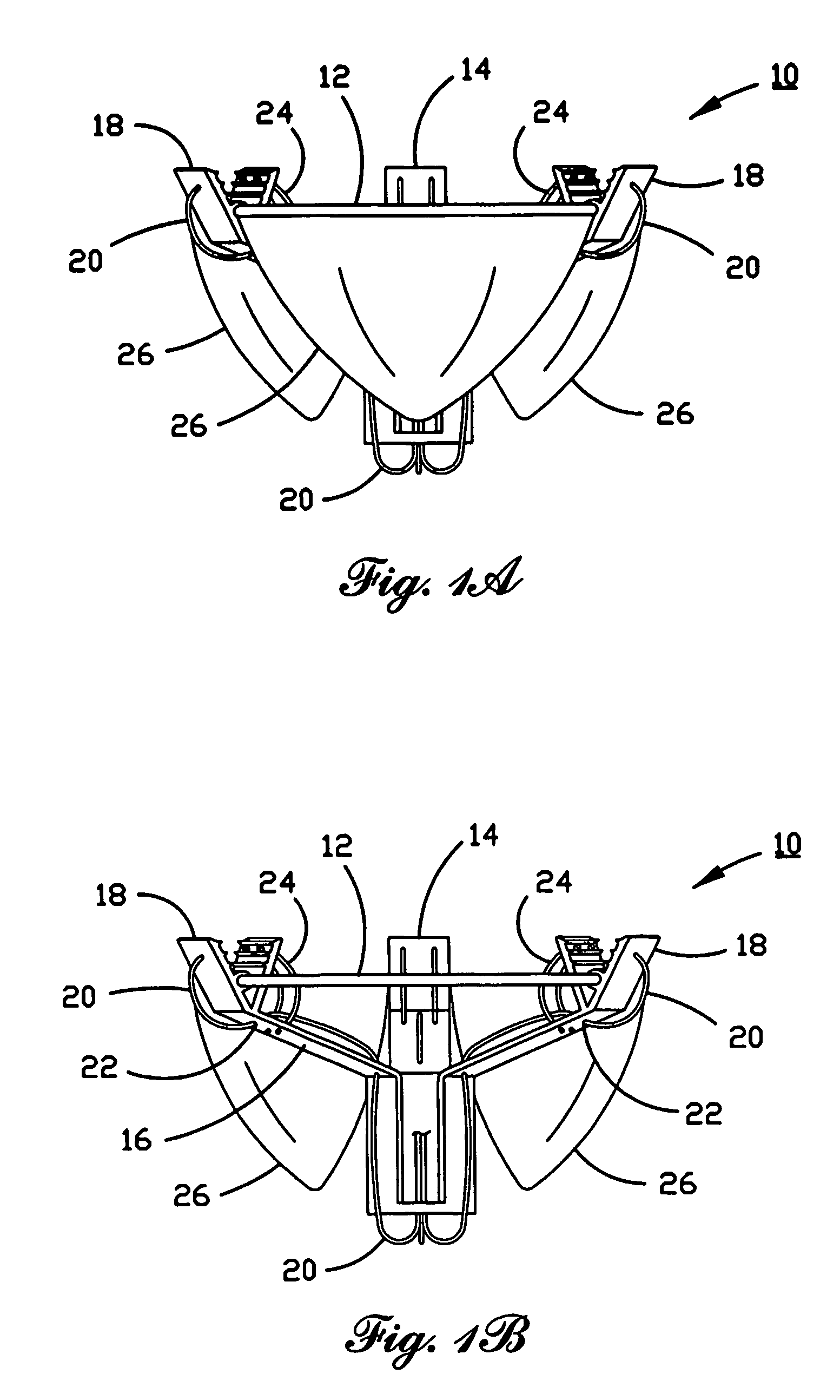
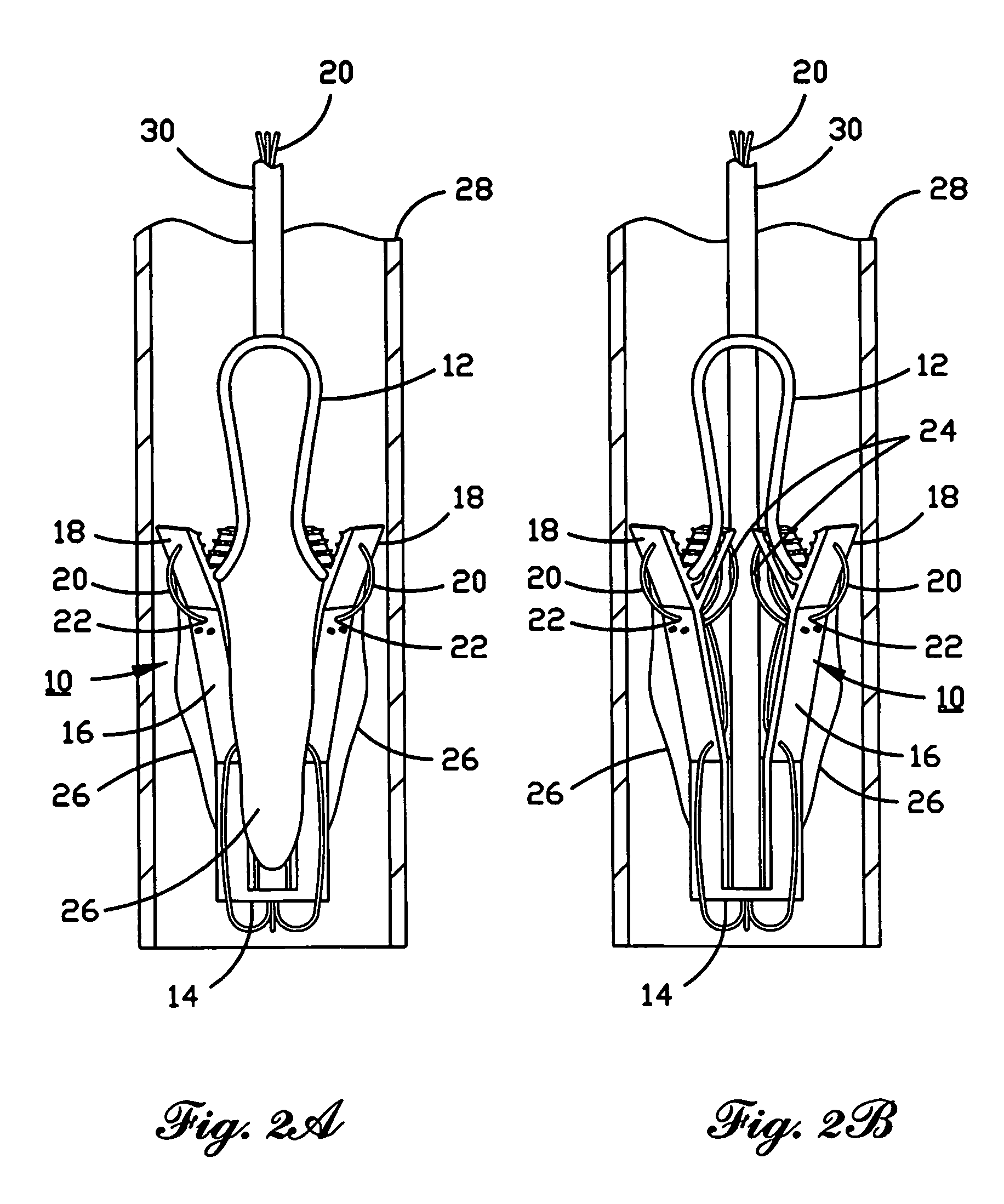
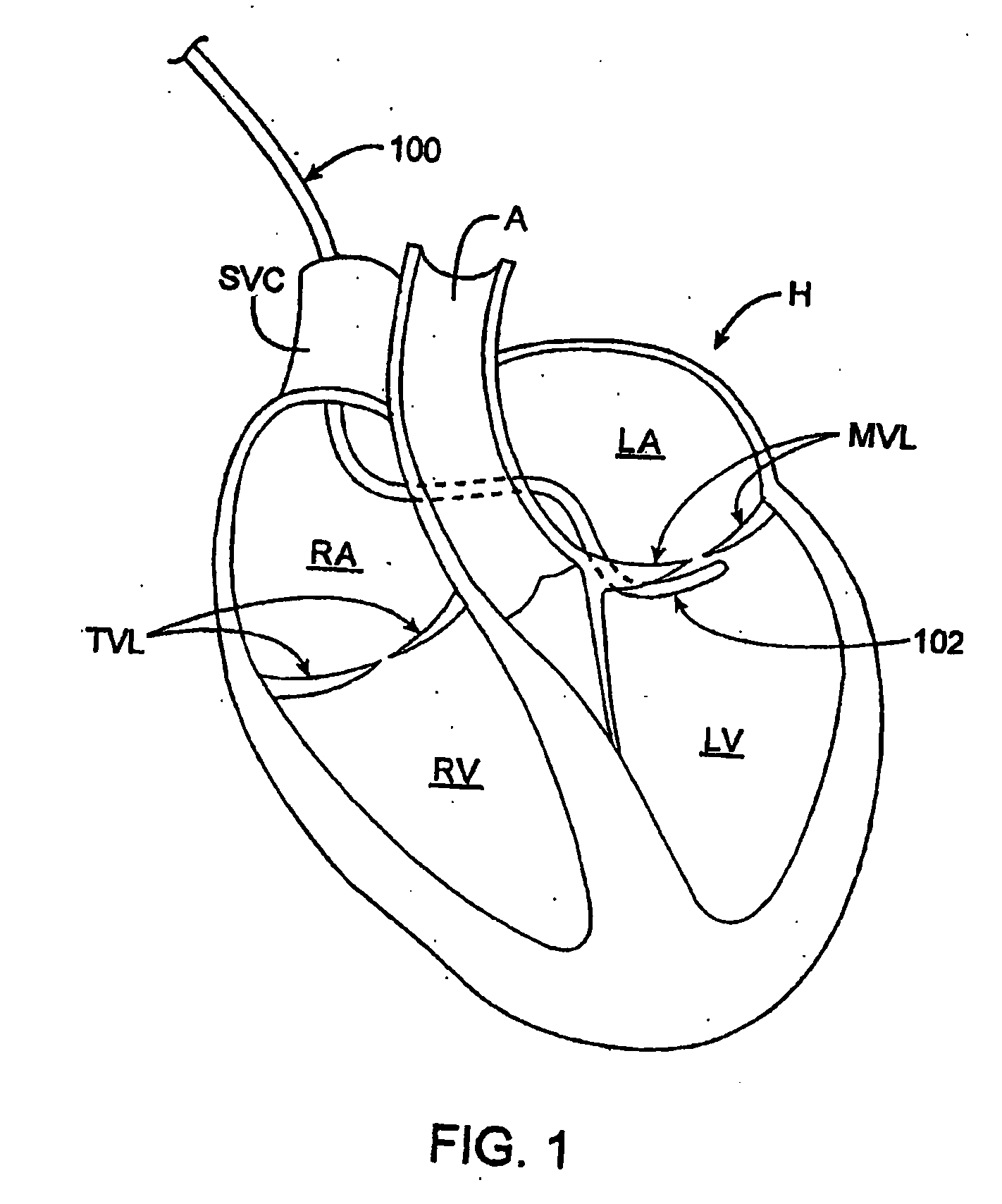
Percutaneous heart valve
ActiveUS20070016286A1Avoid flowStability and functioning of the heart valve are satisfactoryHeart valvesBlood flowValvular prosthesis
A percutaneously inserted bistable heart valve prosthesis is folded inside a catheter for transseptal delivery to the patient's heart for implantation. The heart valve has an annular ring, a body member having a plurality of legs, each leg connecting at one end to the annular ring, claws that are adjustable from a first position to a second position by application of external force so as to allow ingress of surrounding heart tissue into the claws in the second position, and leaflet membranes connected to the annular ring, the body member and / or the legs, the leaflet membranes having a first position for blocking blood flow therethrough and a second position for allowing blood flow therethrough. The heart valve is designed such that upon removal of the external force the claws elastically revert to the first position so as to grip the heart tissue positioned within the claws, thereby holding the heart valve in place. The body member and claws may be integrated into a one-piece design. The heart valve may be used as a prosthesis for the mitral valve, aortic valve, pulmonary valve, or tricuspid valve by adapting the annular ring to fit in a respective mitral, aortic, pulmonary, or tricuspid valve opening of the heart.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Stapling apparatus and method for heart valve replacement
A surgical stapler for securing a prosthetic heart valve within a patient generally includes a first cylindrical portion for carrying at least one staple assembly on a distal end thereof; a second cylindrical portion positioned concentrically about the first cylindrical portion and having a camming arm on a distal end thereof, the camming arm configured to cam the at least one staple assembly radially outward and drive the at least one staple assembly distally such that a first leg of the at least one staple assembly penetrates a cuff of the prosthetic heart valve and a second leg of the at least one staple assembly pierces a portion of heart tissue surrounding the prosthetic heart valve, as the second cylindrical portion is moved distally relative to the first cylindrical portion; and a third cylindrical portion positioned concentrically about the second cylindrical portion and having an anvil flange on a distal end thereof, the anvil flange configured to crimp the second leg of the at least one staple assembly toward the first leg of the at least one staple assembly to secure the prosthetic heart valve to the surrounding heart tissue as the third cylindrical portion is moved relative to the second cylindrical portion. A method of installing a heart valve within a patient which includes the steps of accessing a site within a heart from which a natural heart valve has been removed; lowering a prosthetic heart valve into position within the site in the heart; positioning a surgical stapler having at least one staple assembly removably held on a distal end thereof adjacent the prosthetic heart valve within the site in the heart; driving a first leg of the at least one staple assembly through a peripheral cuff of the prosthetic heart valve; and crimping a second leg of the at least one staple assembly in a direction toward the first leg such that the second leg pierces a portion of heart tissue surrounding the prosthetic heart valve, thereby securing the prosthetic heart valve to the surrounding heart tissue.
Owner:UNITED STATES SURGICAL CORP
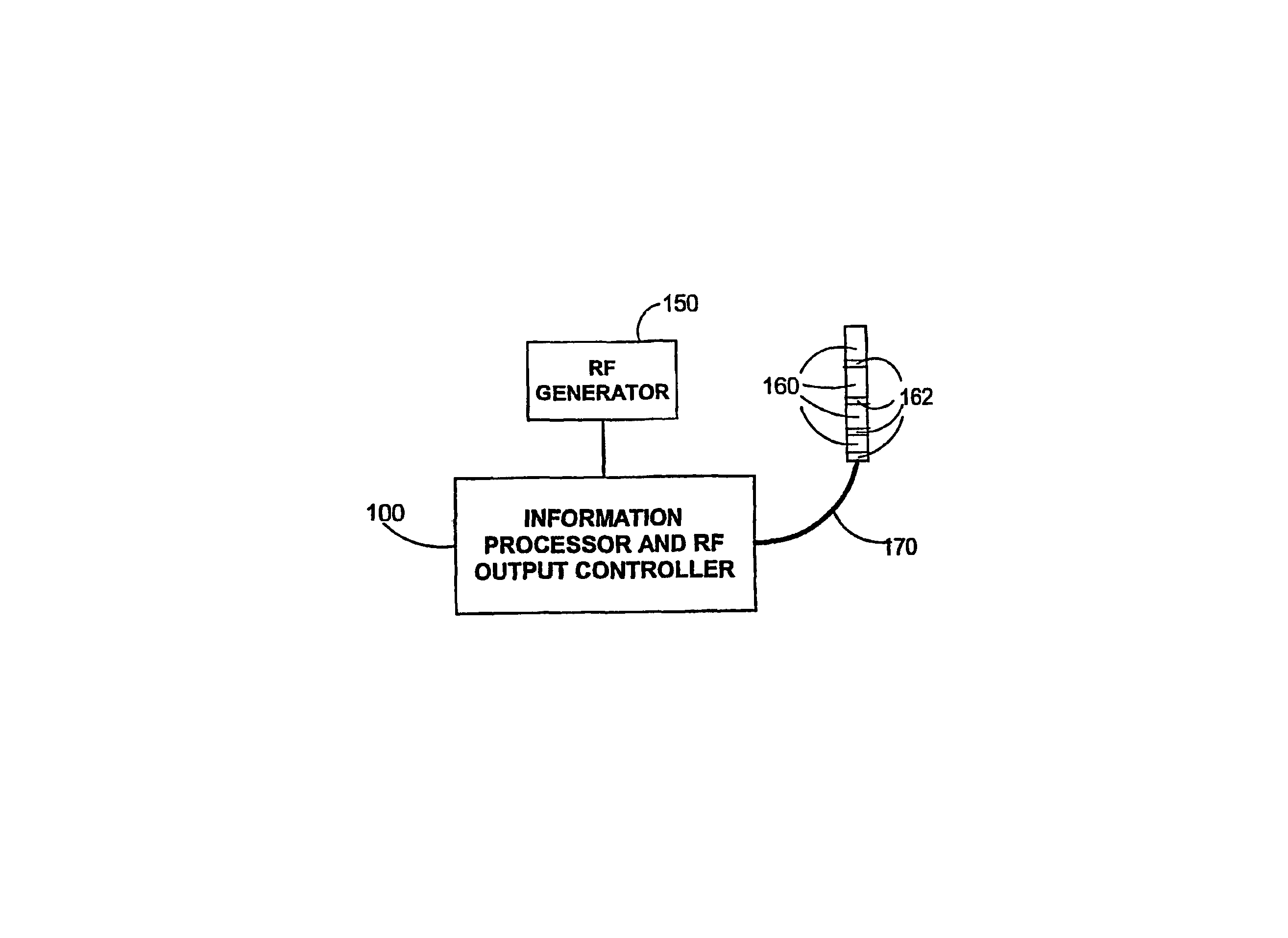
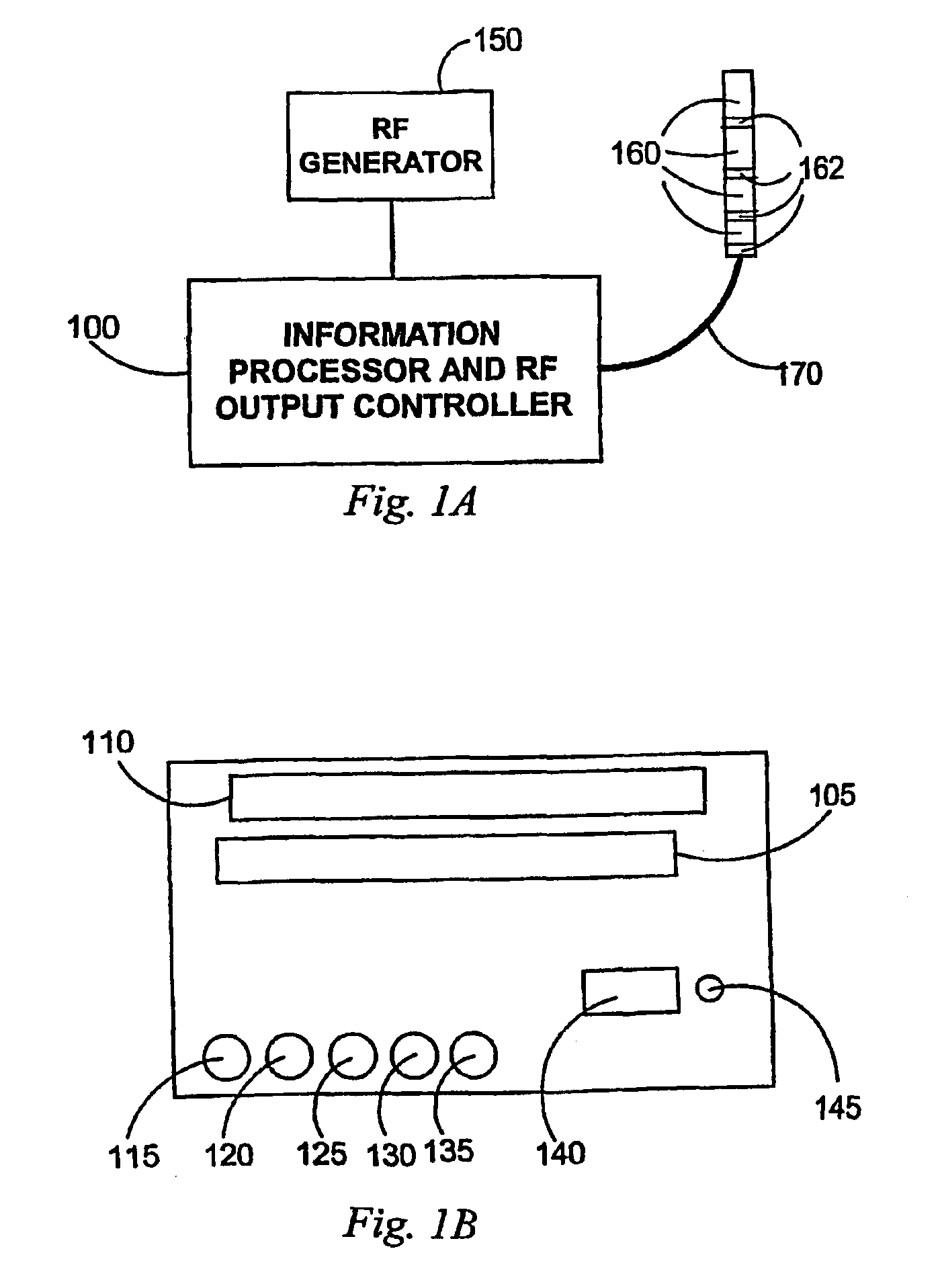
Multi-channel RF energy delivery with coagulum reduction
InactiveUS6936047B2Risk minimizationImprove efficiencySurgical instruments for heatingRf ablationCurrent sensor
A system for efficient delivery of radio frequency (RF) energy to cardiac tissue with an ablation catheter used in catheter ablation, with new concepts regarding the interaction between RF energy and biological tissue. In addition, new insights into methods for coagulum reduction during RF ablation will be presented, and a quantitative model for ascertaining the propensity for coagulum formation during RF ablation will be introduced. Effective practical techniques a represented for multichannel simultaneous RF energy delivery with real-time calculation of the Coagulum Index, which estimates the probability of coagulum formation. This information is used in a feedback and control algorithm which effectively reduces the probability of coagulum formation during ablation. For each ablation channel, electrical coupling delivers an RF electrical current through an ablation electrode of the ablation catheter and a temperature sensor is positioned relative to the ablation electrode for measuring the temperature of cardiac tissue in contact with the ablation electrode. A current sensor is provided within each channel circuitry for measuring the current delivered through said electrical coupling and an information processor and RF output controller coupled to said temperature sensor and said current sensor for estimating the likelihood of coagulum formation. When this functionality is propagated simultaneously through multiple ablation channels, the resulting linear or curvilinear lesion is deeper with less gaps. Hence, the clinical result is improved due to improved lesion integrity.
Owner:SICHUAN JINJIANG ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH CO LTD
Percutaneous heart valve
ActiveUS7621948B2Avoid flowStability and functioning of the heart valve are satisfactoryHeart valvesJoint implantsGuide tubeElastance
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Cardiovascular defect patch device and method
The present invention provides a defect patch device and method that patches a defect in the heart or other cardiovascular tissue. One aspect provides a PFO closure device and method that patches a PFO in the right atrium without the device extending through the PFO into the left atrium. The patch device includes a patch and a heart tissue engaging member for attaching the device over the defect. A deployment device and method includes a device positioner to advance the device out of a catheter and to position the device over the defect to attach the device to the tissue around the defect. The positioner may include a device expander or opener that opens the device for deployment.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
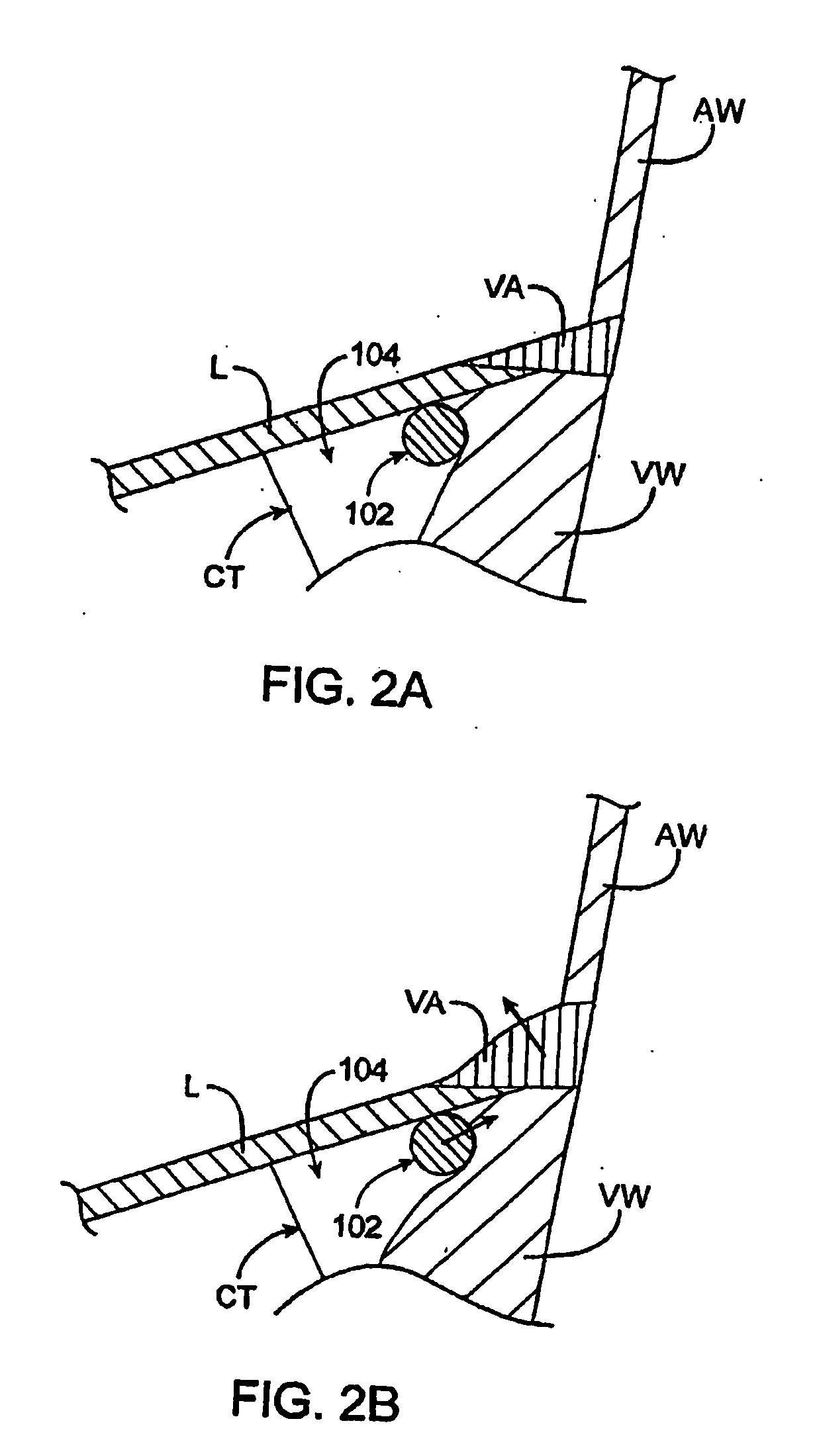
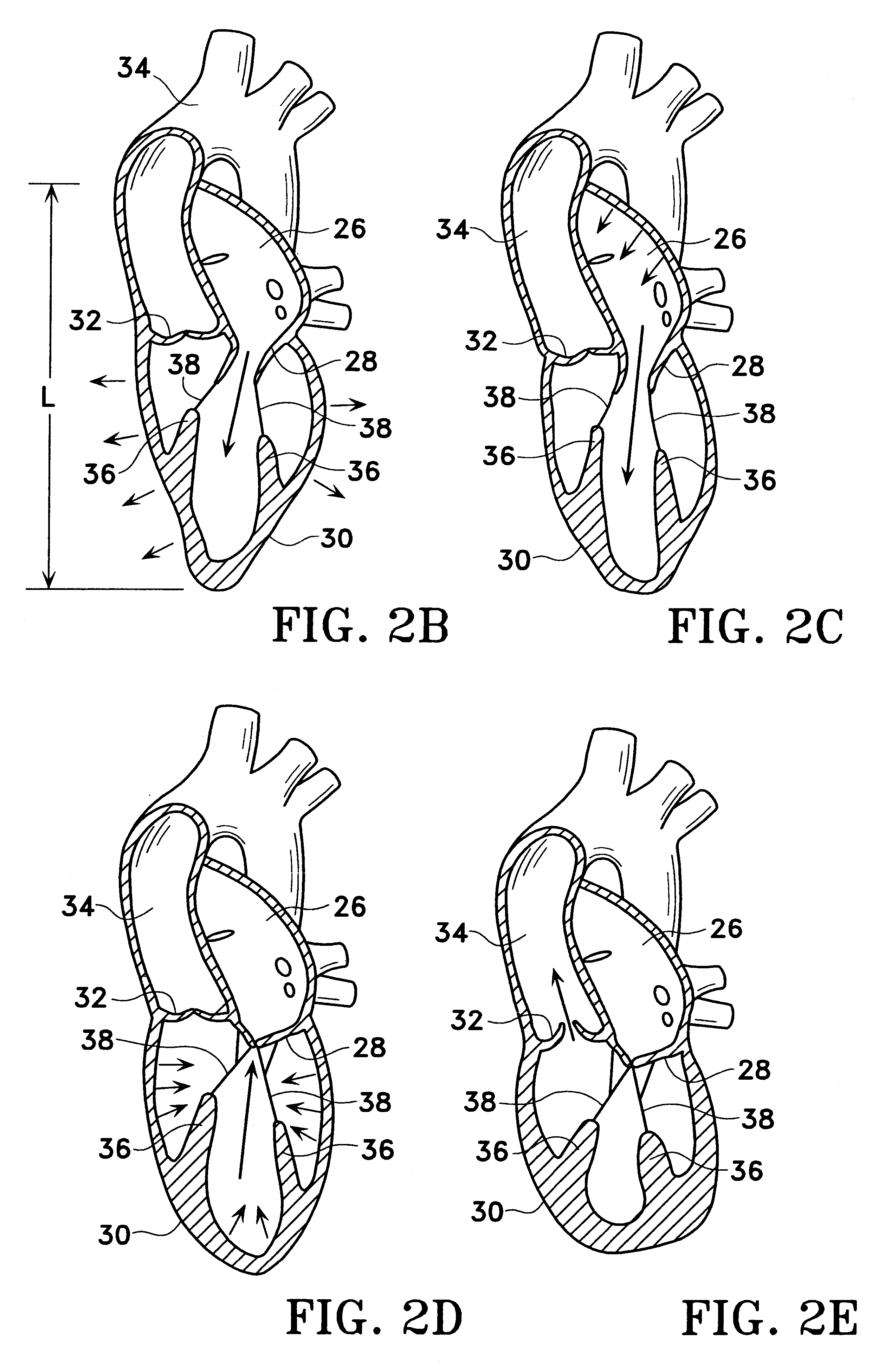
Method of Forming a Lesion in Heart Tissue
InactiveUS7100614B2Facilitate responsive and precise positionabilitySuture equipmentsElectrotherapyDefect repairPatch type
Owner:HEARTPORT
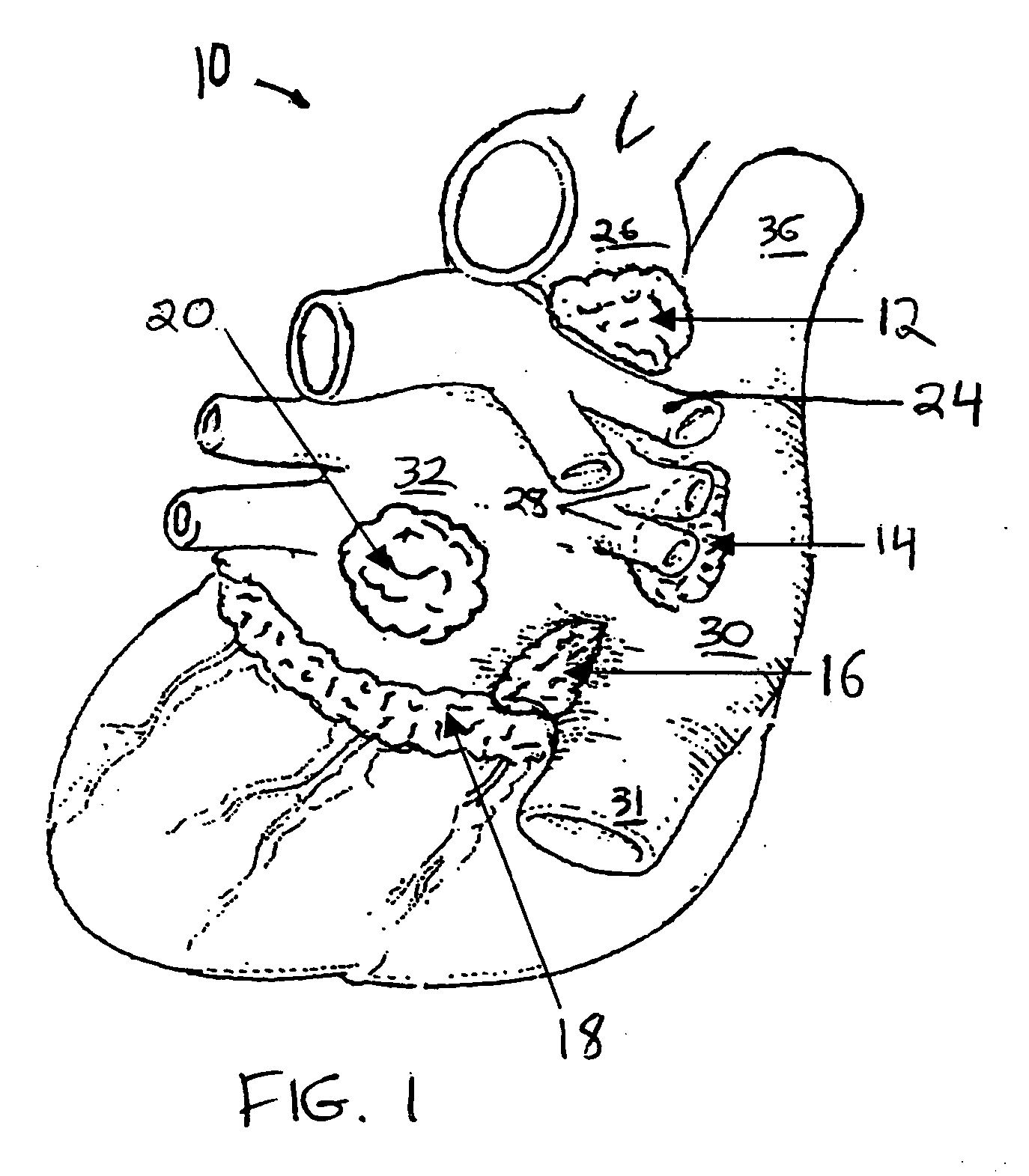
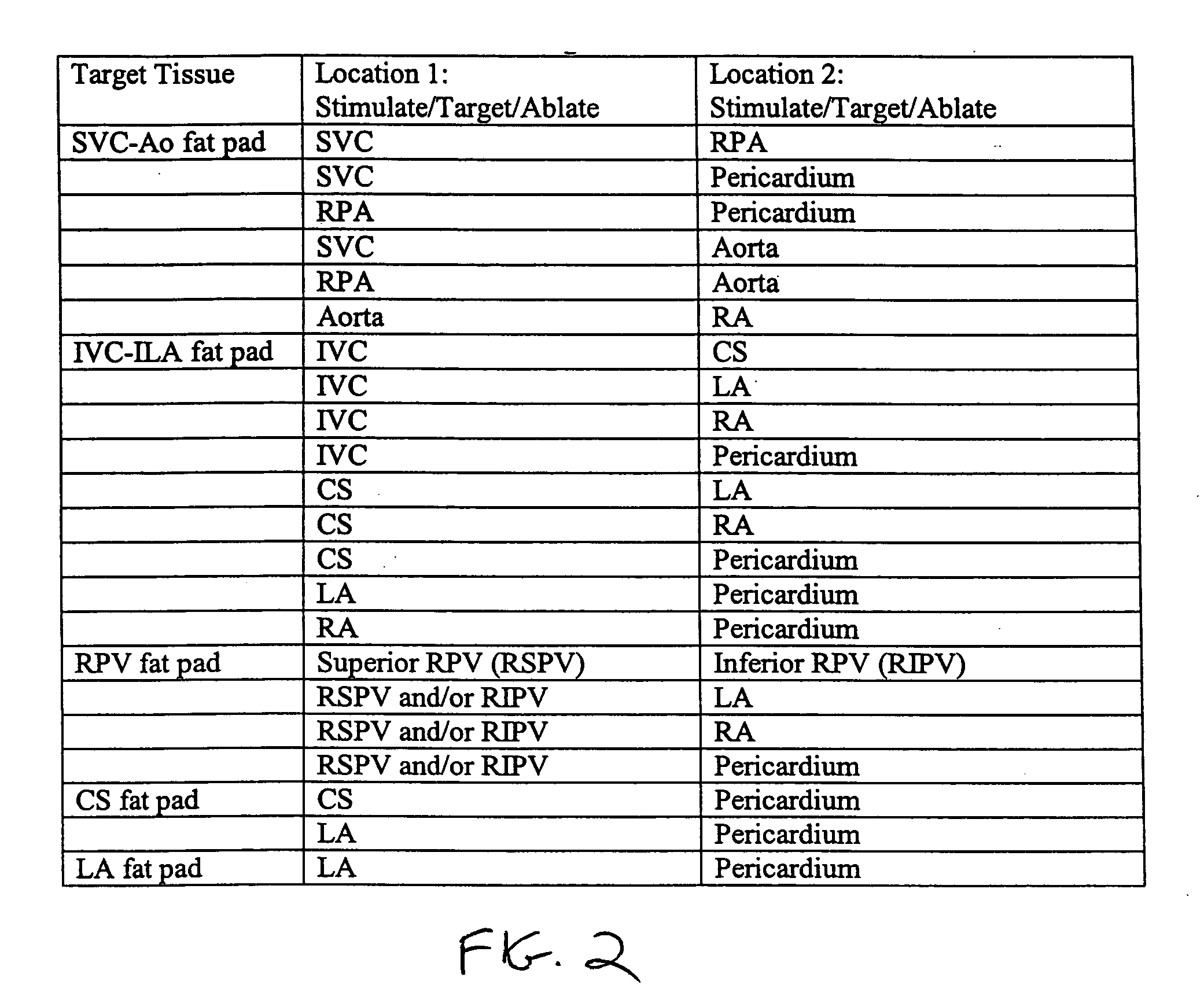
Systems and methods for selective denervation of heart dysrhythmias
InactiveUS20050261672A1Reduce sympathovagal toneAltering autonomic burdenElectrotherapySurgical instruments for heatingConduction pathwayElectroporation
Methods and apparatus are provided for selective denervation of conduction pathways in the heart for the treatment of dysrhythmias, including one or more ablation or electroporation catheters having electrodes for stimulating, targeting, and ablating fat pad tissue and other cardiac tissue to selectively denervate heart tissue.
Owner:ARDIAN
Cardiac Tissue Ablation Instrument with Flexible Wrist
InactiveUS20110028991A1Promotes convenient, simplified manufacturing and assembly processesShorten the counting processEndoscopesSurgical manipulatorsInstrumentationWrist
An articulate minimally invasive surgical instrument with a flexible wrist to facilitate the safe placement and provide visual verification of the ablation catheter or other devices in Cardiac Tissue Ablation (CTA) treatments is described. In one embodiment, the instrument is an endoscope which has an elongate shaft, a flexible wrist at the working end of the shaft, and a vision scope lens at the tip of the flexible wrist. The flexible wrist has at least one degree of freedom to provide the desired articulation. It is actuated and controlled by a drive mechanism located in the housing at the distal end of the shaft. The articulation of the endoscope allows images of hard-to-see places to be taken for use in assisting the placement of the ablation catheter on the desired cardiac tissue. The endoscope may further include couplings to releasably attach an ablation device / catheter or a catheter guide to the endoscope thereby further utilizing the endoscope articulation to facilitate placement of the ablation catheter on hard-to-reach cardiac tissues. In another embodiment, the articulate instrument is a grasper or any other instrument with a flexible wrist and a built-in lumen to allow an endoscope to insert and be guided to the distal end of the instrument.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
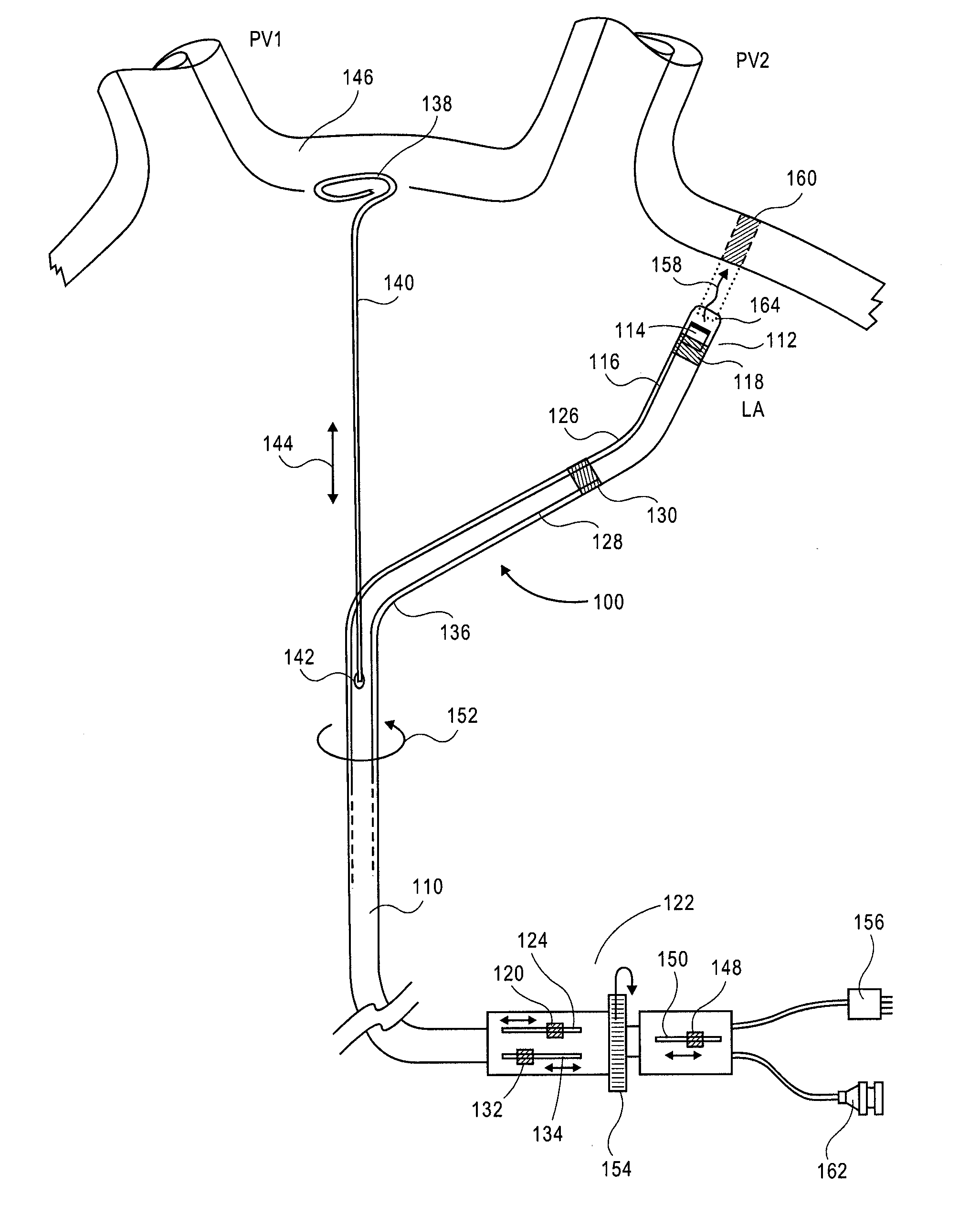
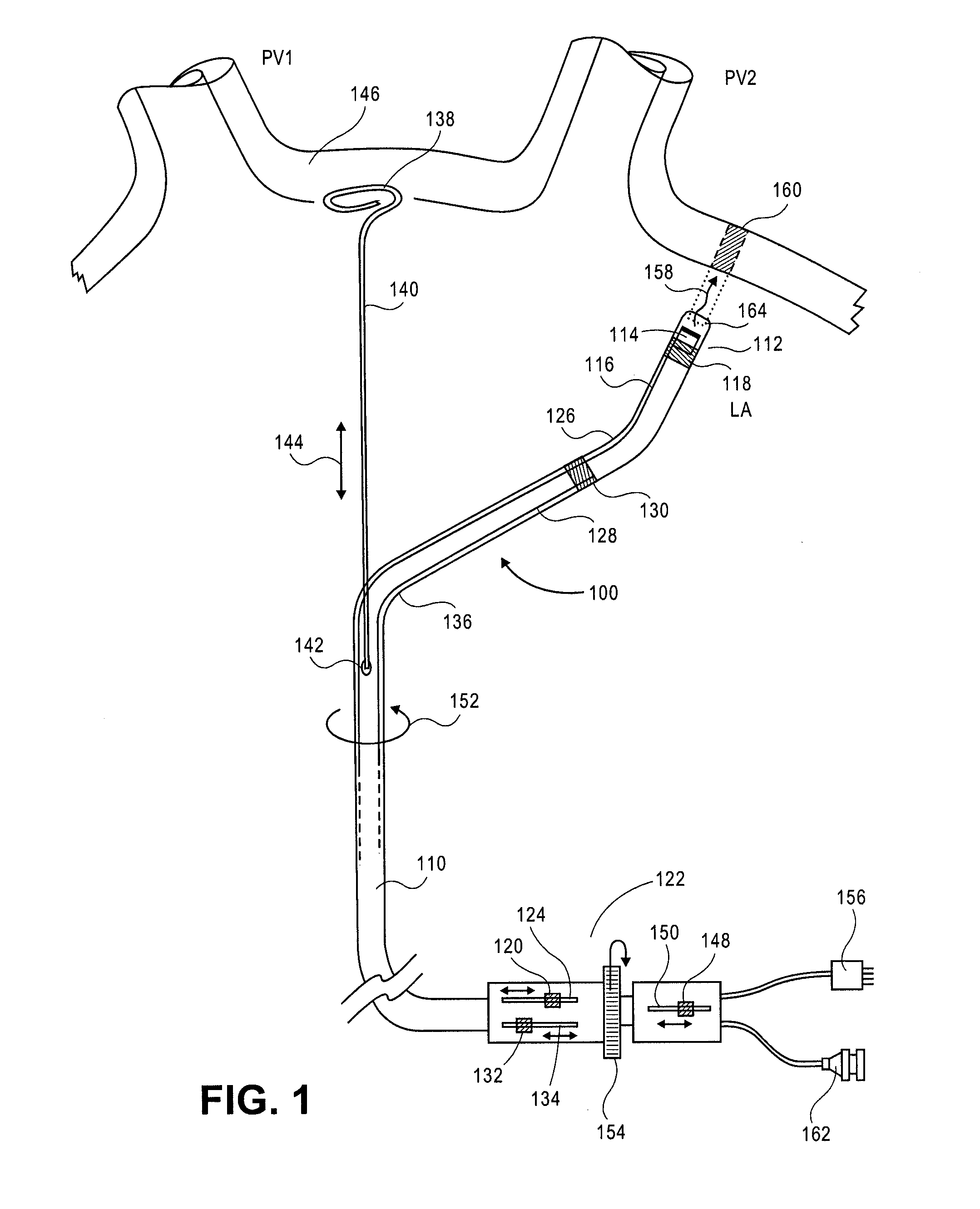
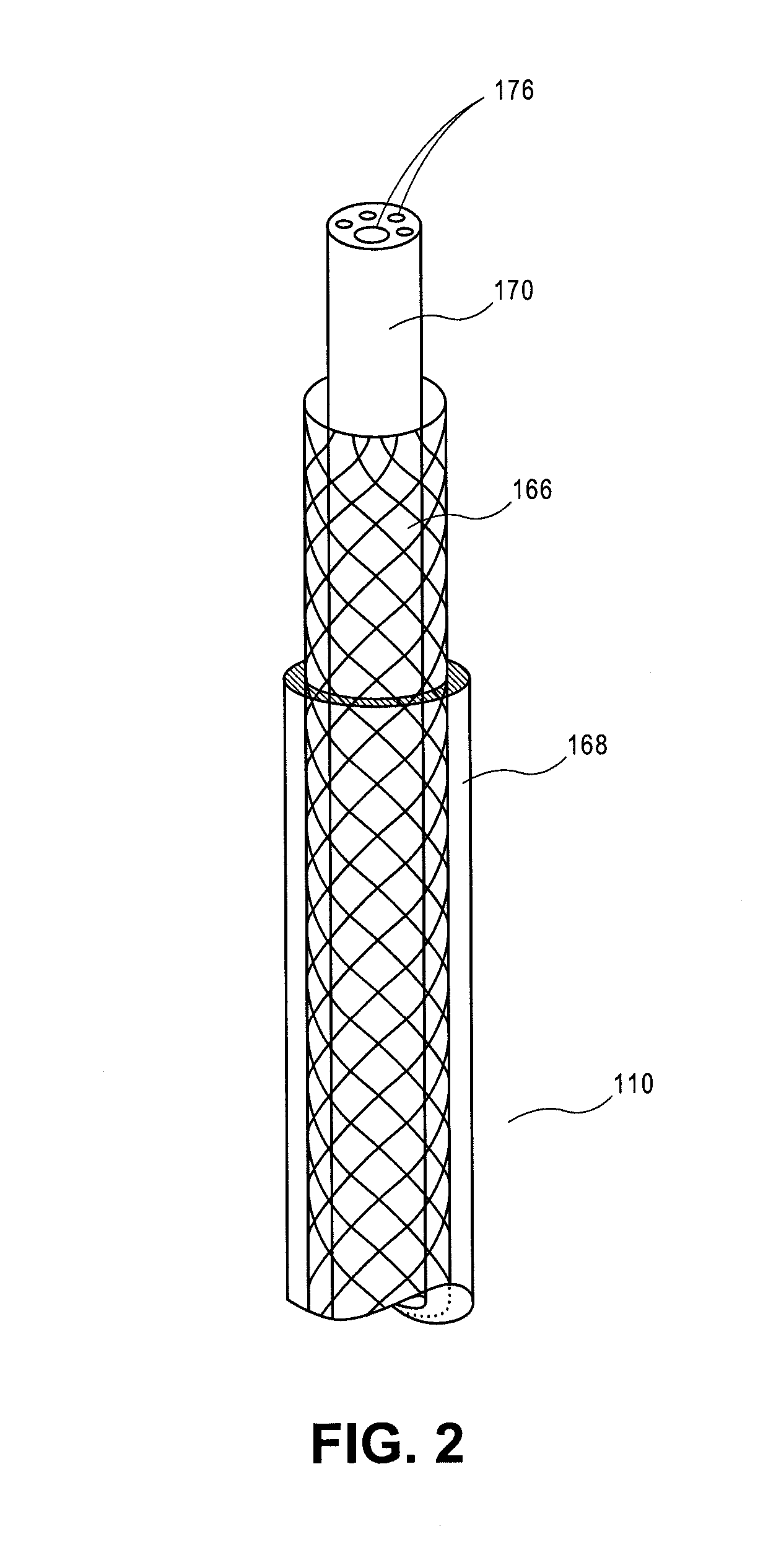
Cardiac treatment devices and methods
Devices and methods provide for ablation of cardiac tissue for treating cardiac arrhythmias such as atrial fibrillation. Although the devices and methods are often be used to ablate epicardial tissue in the vicinity of at least one pulmonary vein, various embodiments may be used to ablate other cardiac tissues in other locations on a heart. Devices generally include at least one tissue contacting member for contacting epicardial tissue and securing the ablation device to the epicardial tissue, and at least one ablation member for ablating the tissue. Various embodiments include features, such as suction apertures, which enable the device to attach to the epicardial surface with sufficient strength to allow the tissue to be stabilized via the device. For example, some embodiments may be used to stabilize a beating heart to enable a beating heart ablation procedure. Many of the devices may be introduced into a patient via minimally invasive introducer devices and the like. Although devices and methods of the invention may be used to ablate epicardial tissue to treat atrial fibrillation, they may also be used in veterinary or research contexts, to treat various heart conditions other than atrial fibrillation and / or to ablate cardiac tissue other than the epicardium.
Owner:ESTECH ENDOSCOPIC TECH +1
Thermal treatment methods and apparatus with focused energy application
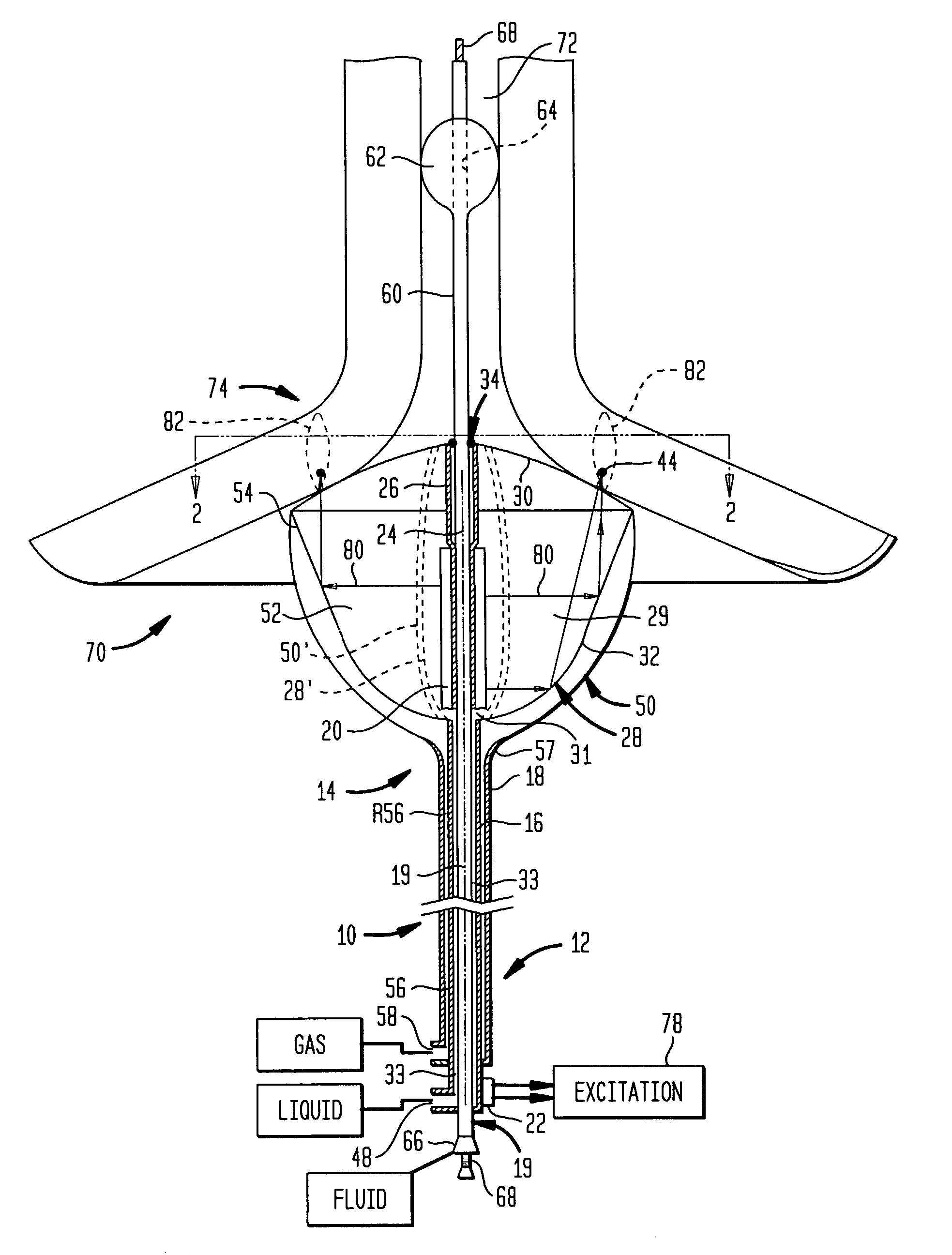
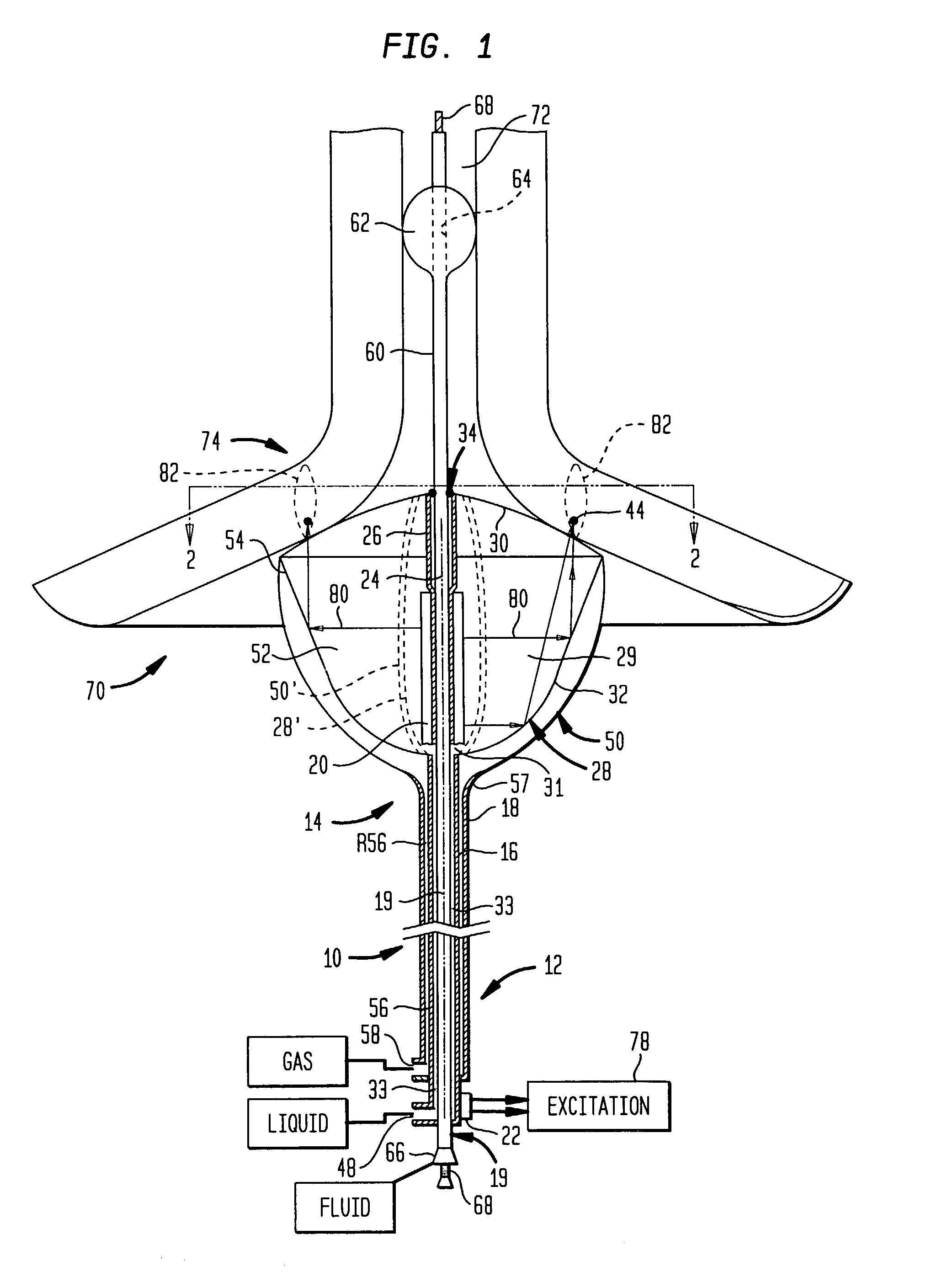
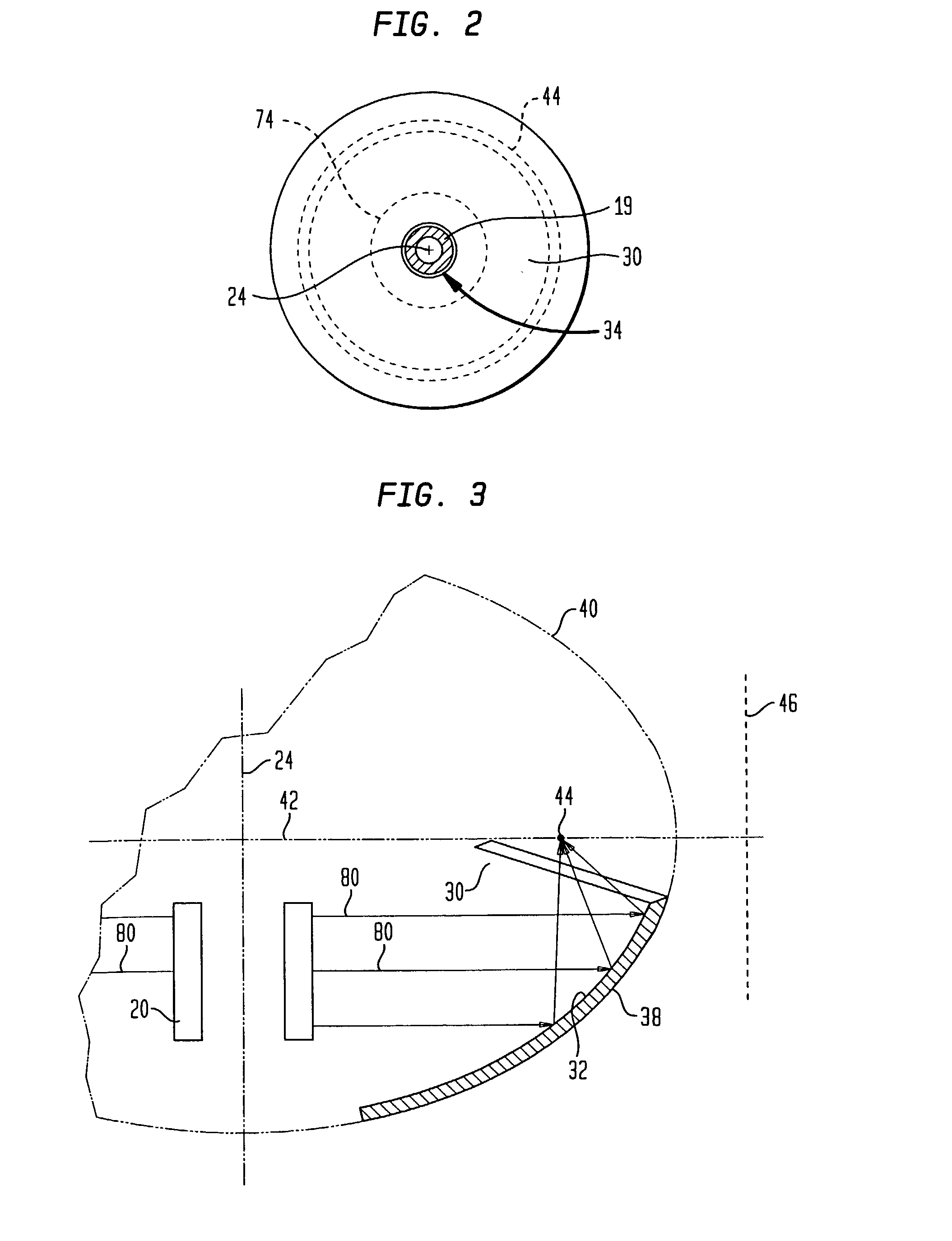
InactiveUS7083614B2Minimize reflectionCollapse of structureUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapyMedicineAcoustic energy
A collapsible ultrasonic reflector incorporates a gas-filled reflector balloon, a liquid-filled structural balloon an ultrasonic transducer disposed within the structural balloon. Acoustic energy emitted by the transducer is reflected by a highly reflective interface between the balloons. In a cardiac ablation procedure, the ultrasonic energy is focused into an annular focal region to ablate cardiac tissue extending in an annular path along the wall. Devices for stabilizing the balloon structure and for facilitating collapse and withdrawal of the balloon structure are also disclosed.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC +1
Magnetic devices and methods for reshaping heart anatomy
InactiveUS20060015003A1Improve shrinkageIncreased total stroke volumeElectrotherapyHeart valvesCardiac surfaceHeart Part
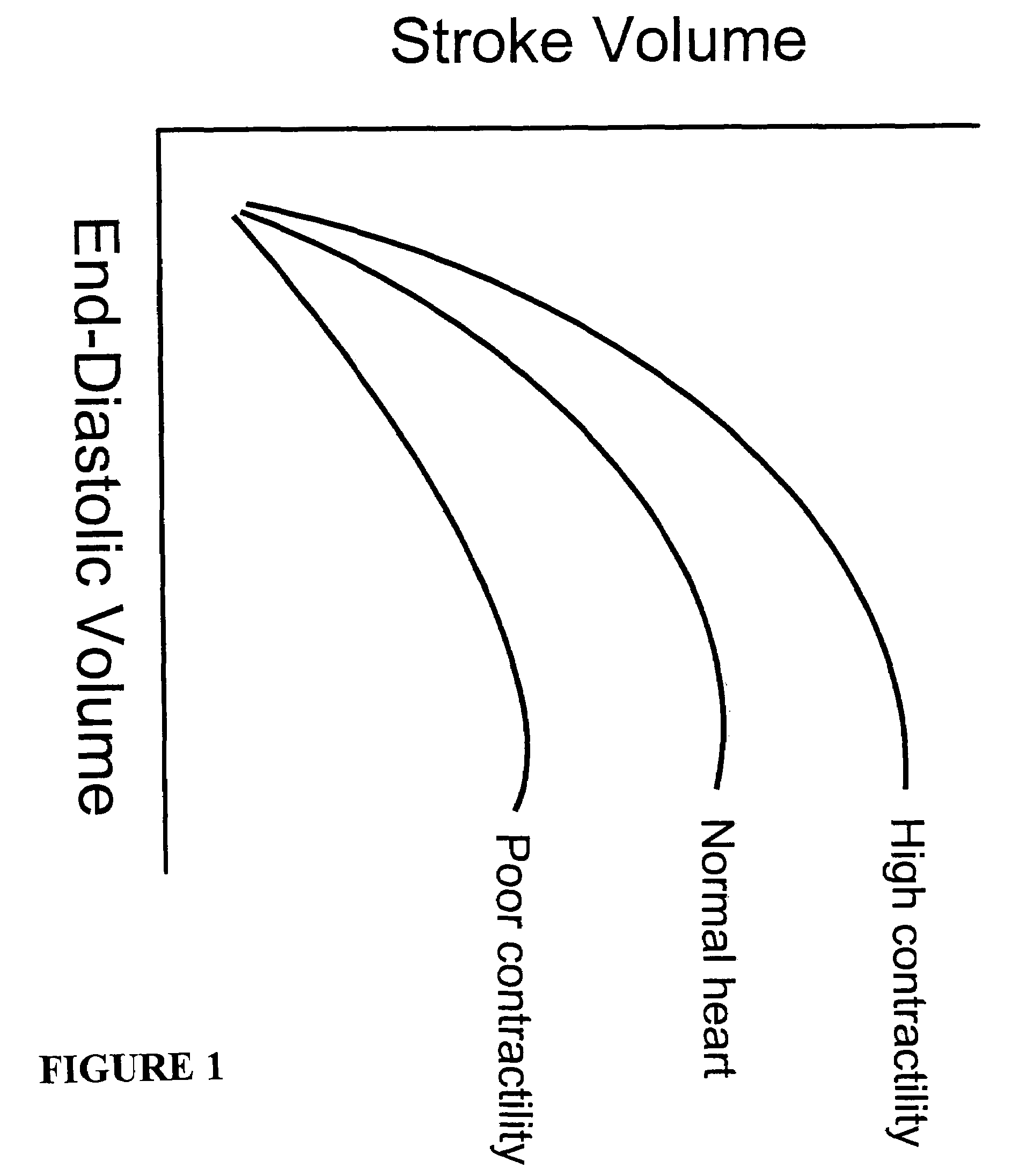
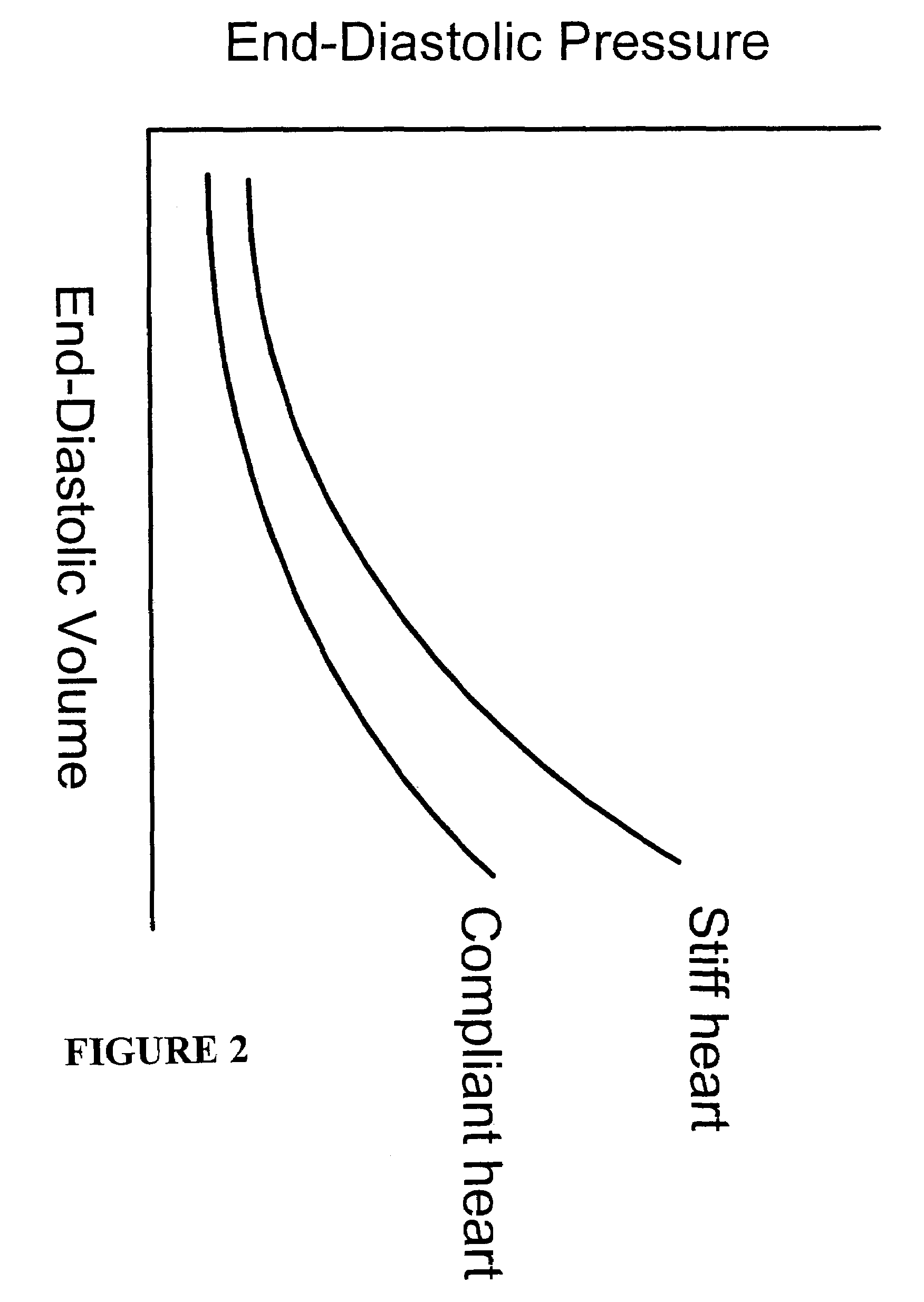
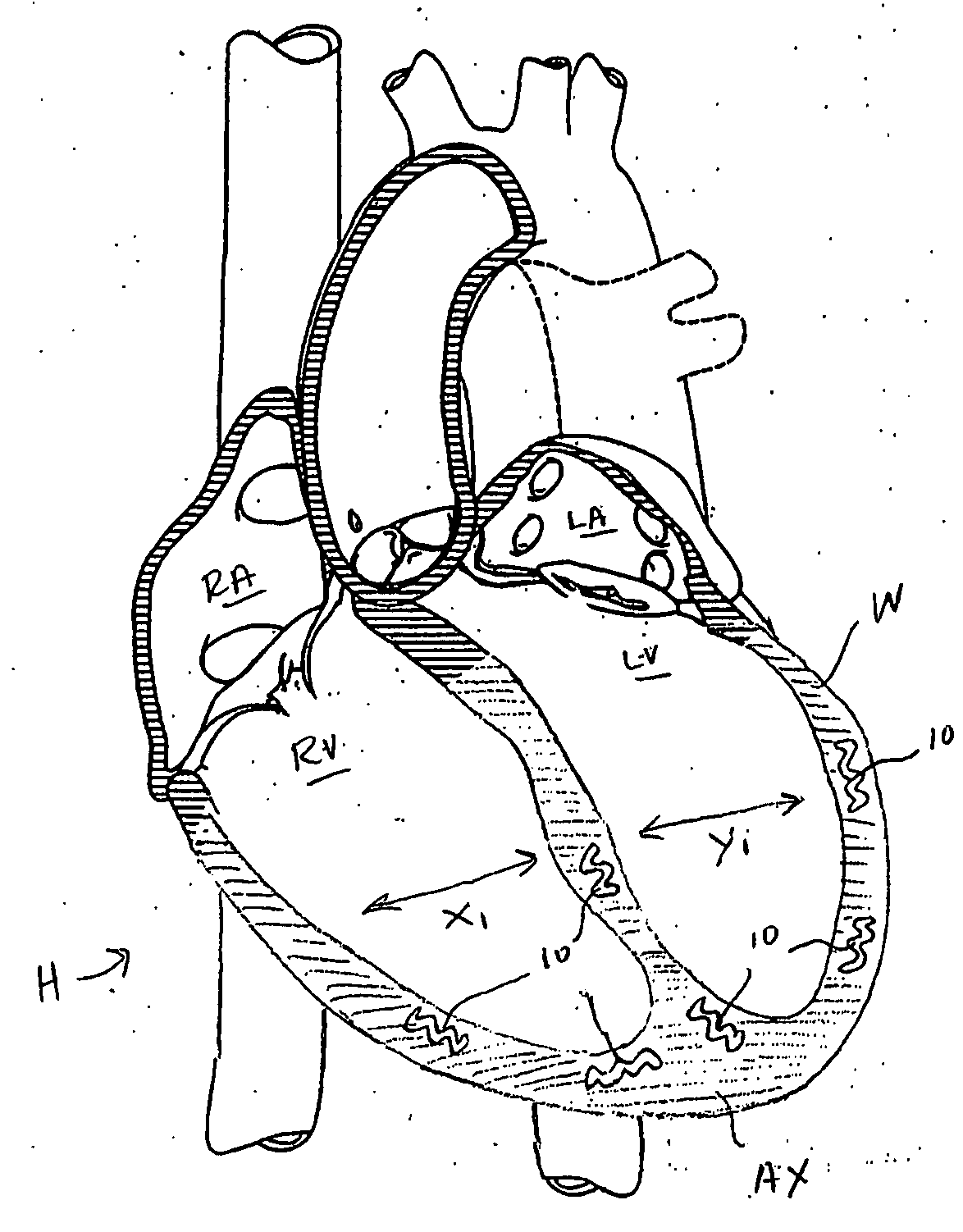
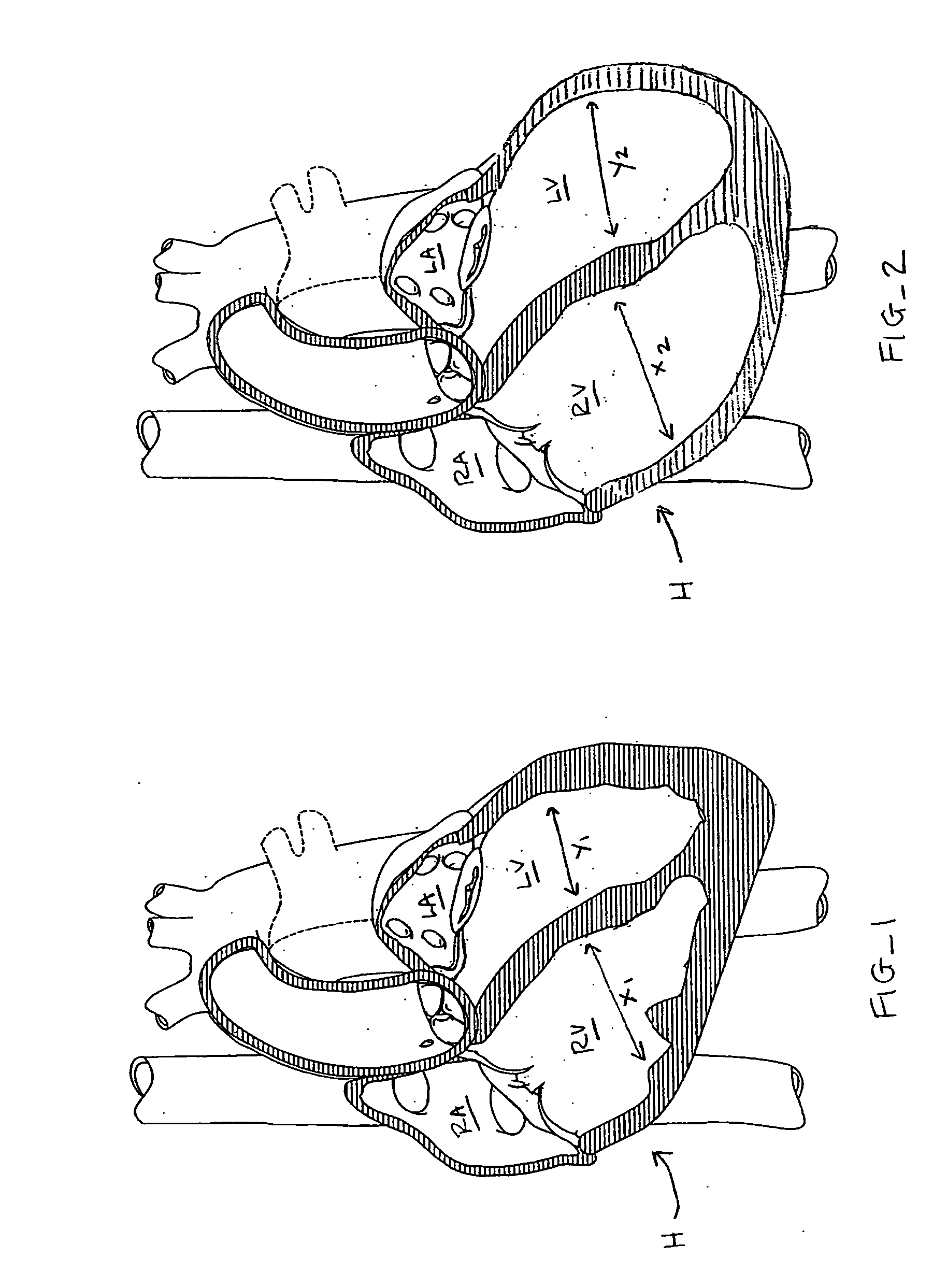
Systems, methods and devices are provided for treating heart failure patients suffering from various levels of heart dilation. Heart dilation treated by reshaping the heart anatomy with the use of magnetic forces. Such reshaping changes the geometry of portions of the heart, particularly the right or left ventricles, to increase contractibility of the ventricles thereby increasing the stroke volume which in turn increases the cardiac output of the heart. The magnetic forces are applied with the use of one or more magnetic elements which are implanted within the heart tissue or attached externally and / or internally to a surface of the heart. The various charges of the magnetic forces interact causing the associated heart tissue areas to readjust position, such as to decrease the width of the ventricles. Such repositioning is maintained over time by the force of the magnetic elements, allowing the damaging effects of heart dilation to slow in progression or reverse.
Owner:MICARDIA CORP
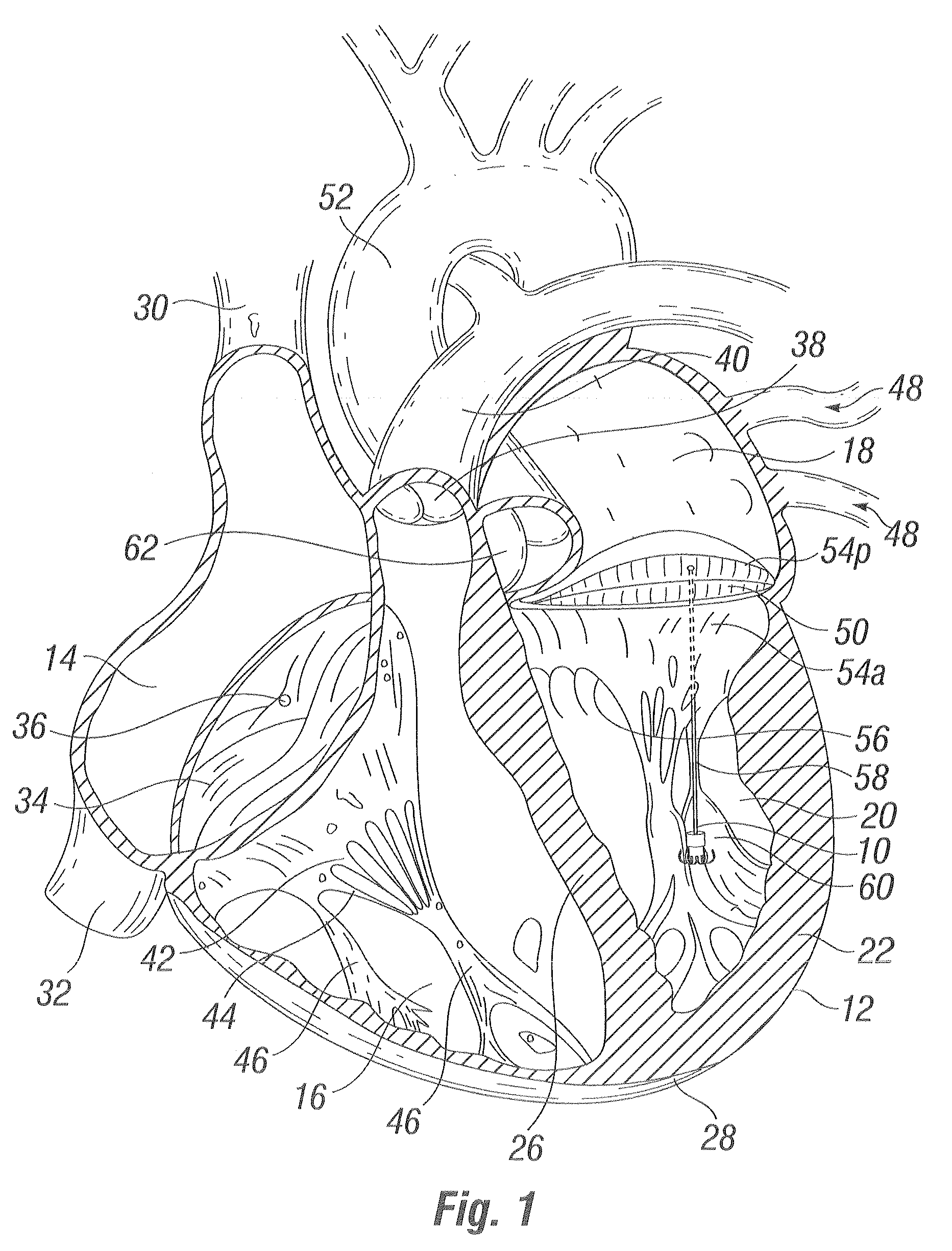
Method and apparatus for thoracoscopic intracardiac procedures
InactiveUS6955175B2Facilitate responsive and precise positionabilitySuture equipmentsElectrotherapyDefect repairThoracic cavity
Devices, systems, and methods are provided for accessing the interior of the heart and performing procedures therein while the heart is beating. In one embodiment, a tubular access device having an inner lumen is provided for positioning through a penetration in a muscular wall of the heart, the access device having a means for sealing within the penetration to inhibit leakage of blood through the penetration. The sealing means may comprise a balloon or flange on the access device, or a suture placed in the heart wall to gather the heart tissue against the access device. An obturator is removably positionable in the inner lumen of the access device, the obturator having a cutting means at its distal end for penetrating the muscular wall of the heart. The access device is preferably positioned through an intercostal space and through the muscular wall of the heart. Elongated instruments may be introduced through the tubular access device into an interior chamber of the heart to perform procedures such as septal defect repair and electrophysiological mapping and ablation. A method of septal defect repair includes positioning a tubular access device percutaneously through an intercostal space and through a penetration in a muscular wall of the heart, passing one or more instruments through an inner lumen of the tubular access device into an interior chamber of the heart, and using the instruments to close the septal defect. Devices and methods for closing the septal defect with either sutures or with patch-type devices are disclosed.
Owner:STEVENS JOHN H +4
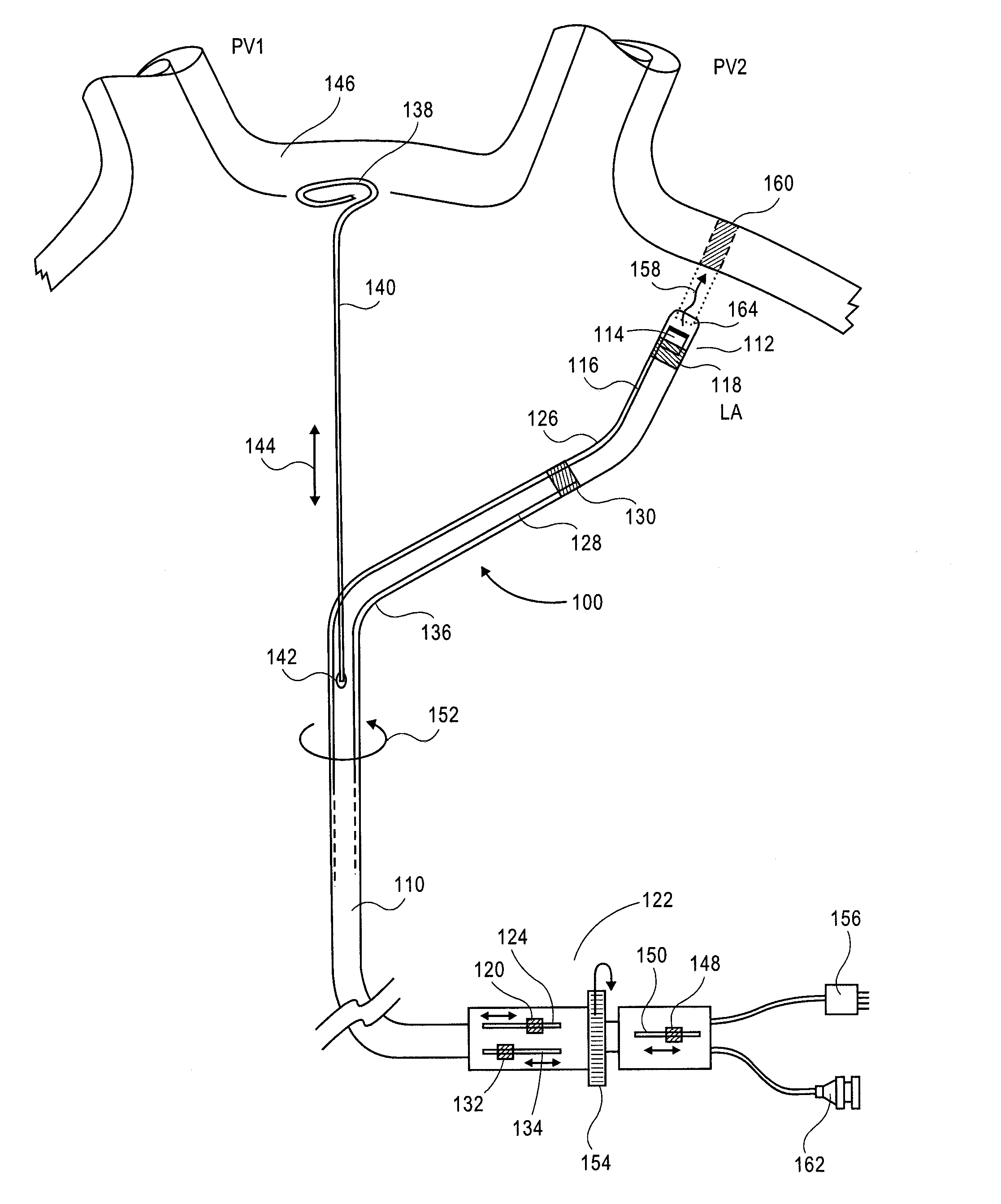
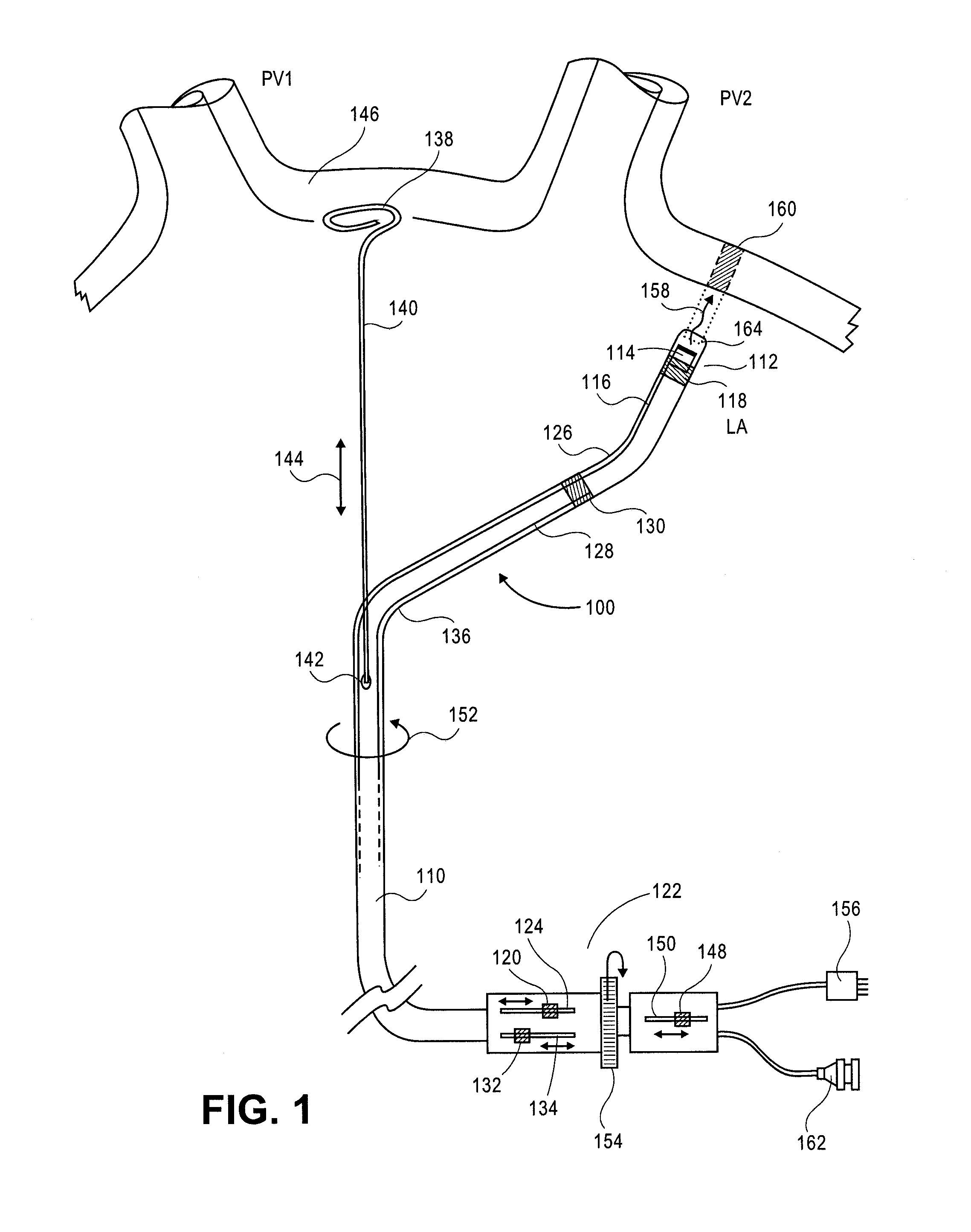
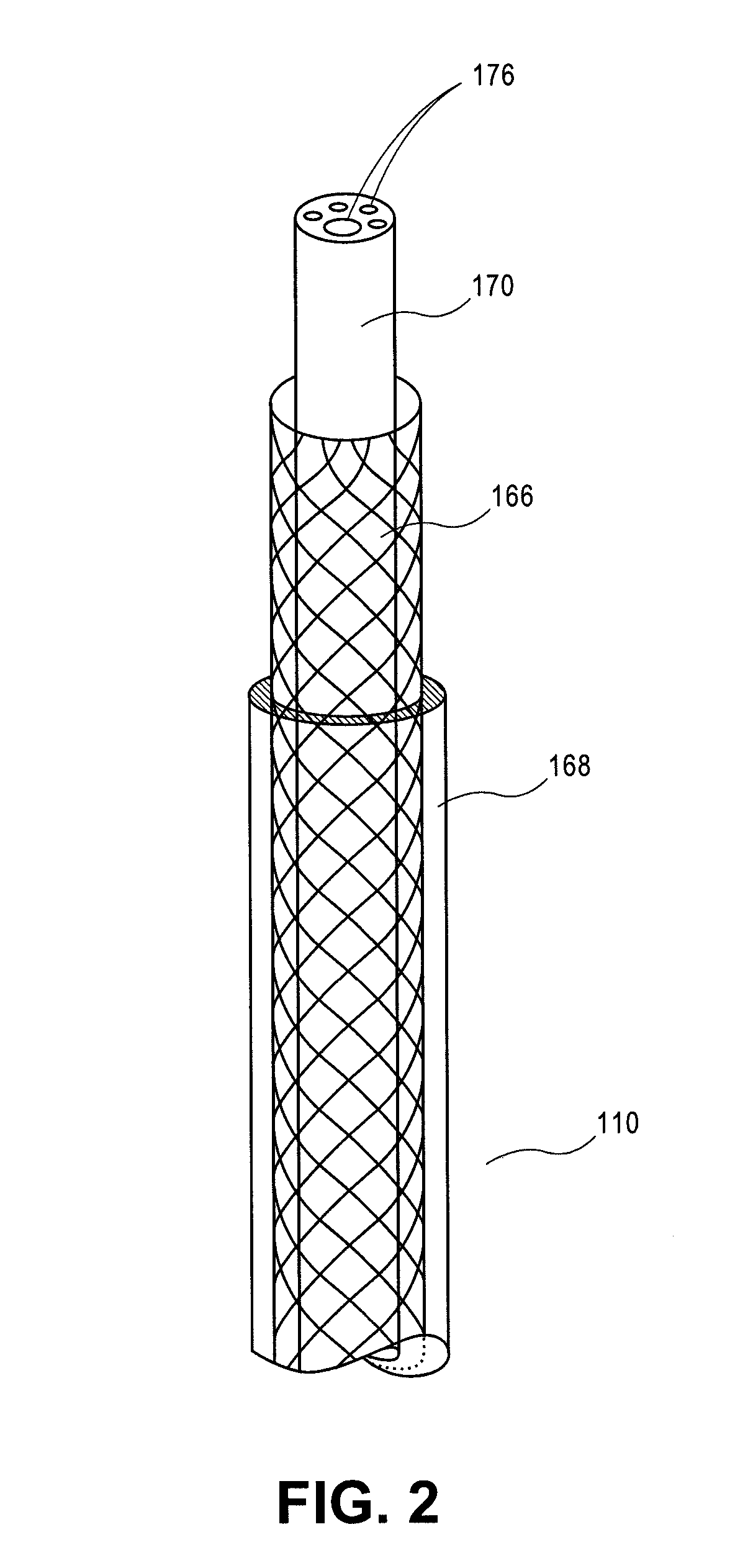
Steerable catheter with preformed distal shape and method for use
InactiveUS6096036AReduce curvatureTransvascular endocardial electrodesSurgical instrument detailsHeart chamberCurve shape
A catheter has a stylet formed of a shape-retentive and resilient material having a preformed curved shape at its distal end resulting in the catheter sheath having the preformed curved shape. The catheter sheath has a plurality of electrodes at its distal end for contacting selected biological tissue for imparting ablation energy thereto. The catheter sheath also has an axially mounted tendon for causing deflection of the distal end. The stylet material permits straightening the catheter sheath during insertion into the patient and advancing the electrodes to the target tissue. Upon removal of the straightening forces, such as by entry into a chamber of the heart, the stylet material resumes its preformed curved distal shape thereby forcing the catheter distal end with the electrodes into the same preformed curved shape. The operator may place the curved distal end into contact with the target tissue and axially move the tendon as desired to gain greater control over the bend in the distal end of the catheter sheath to adjust the radius of curvature of the distal end to obtain greater contact of the electrodes with the heart tissue. Preferably, the stylet is formed of nitinol.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
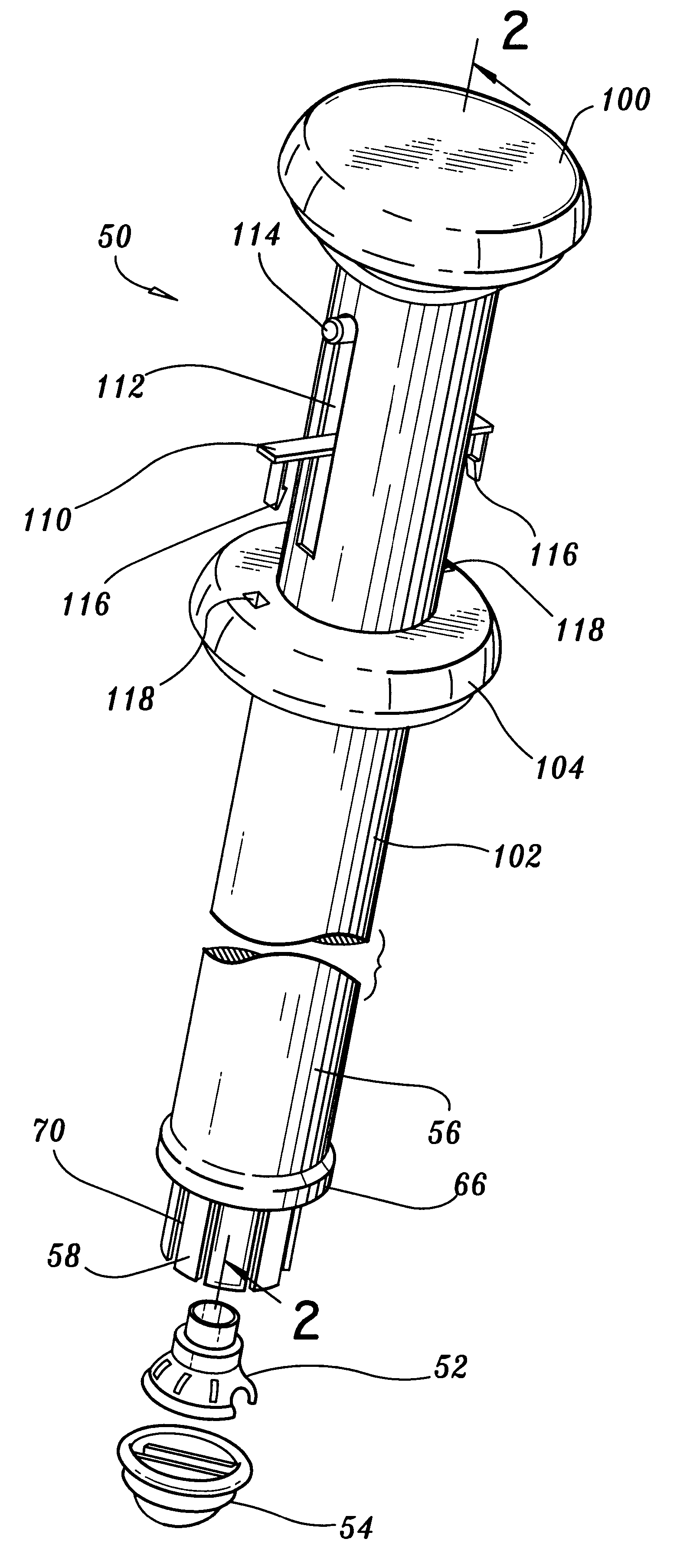
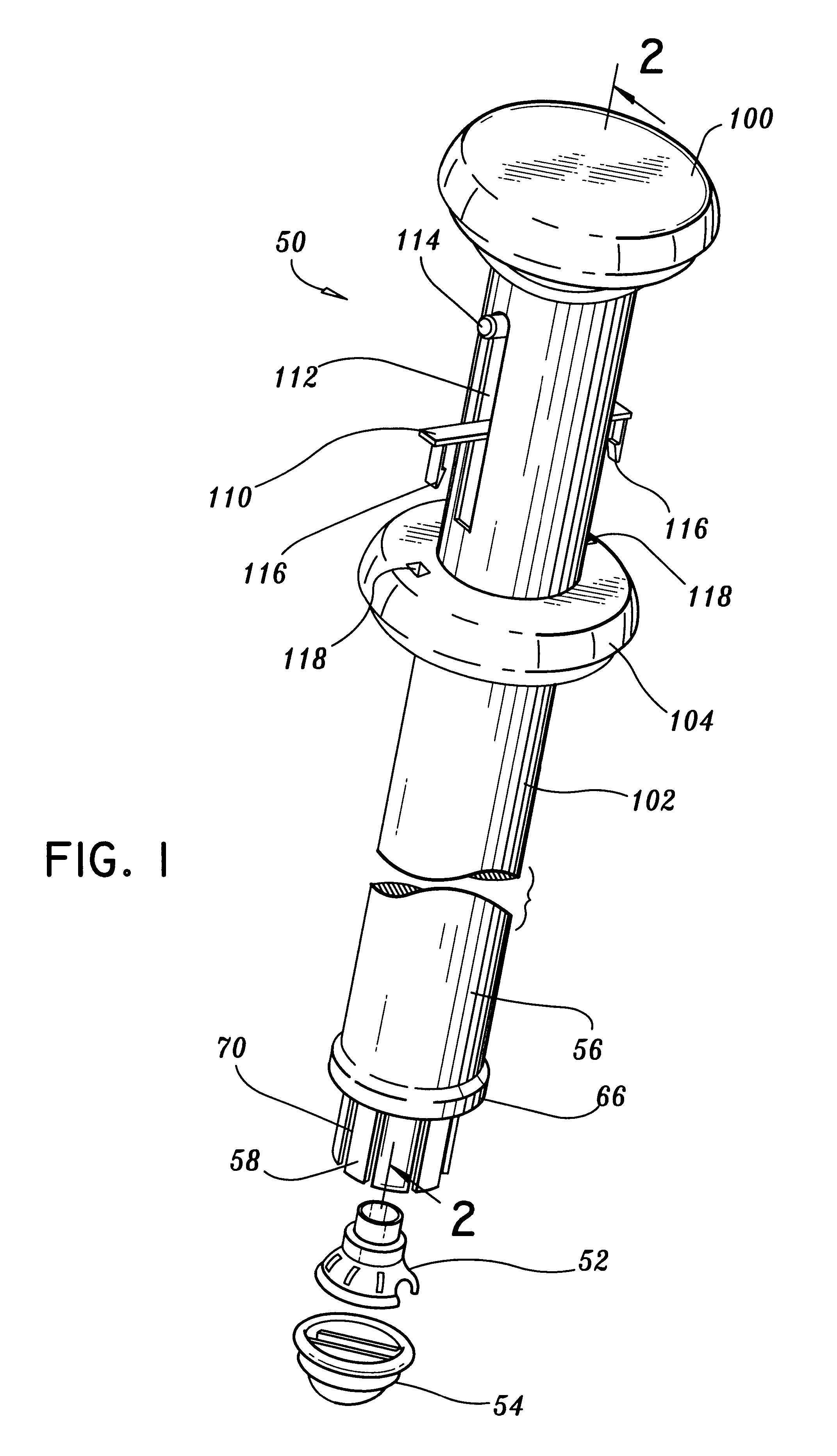
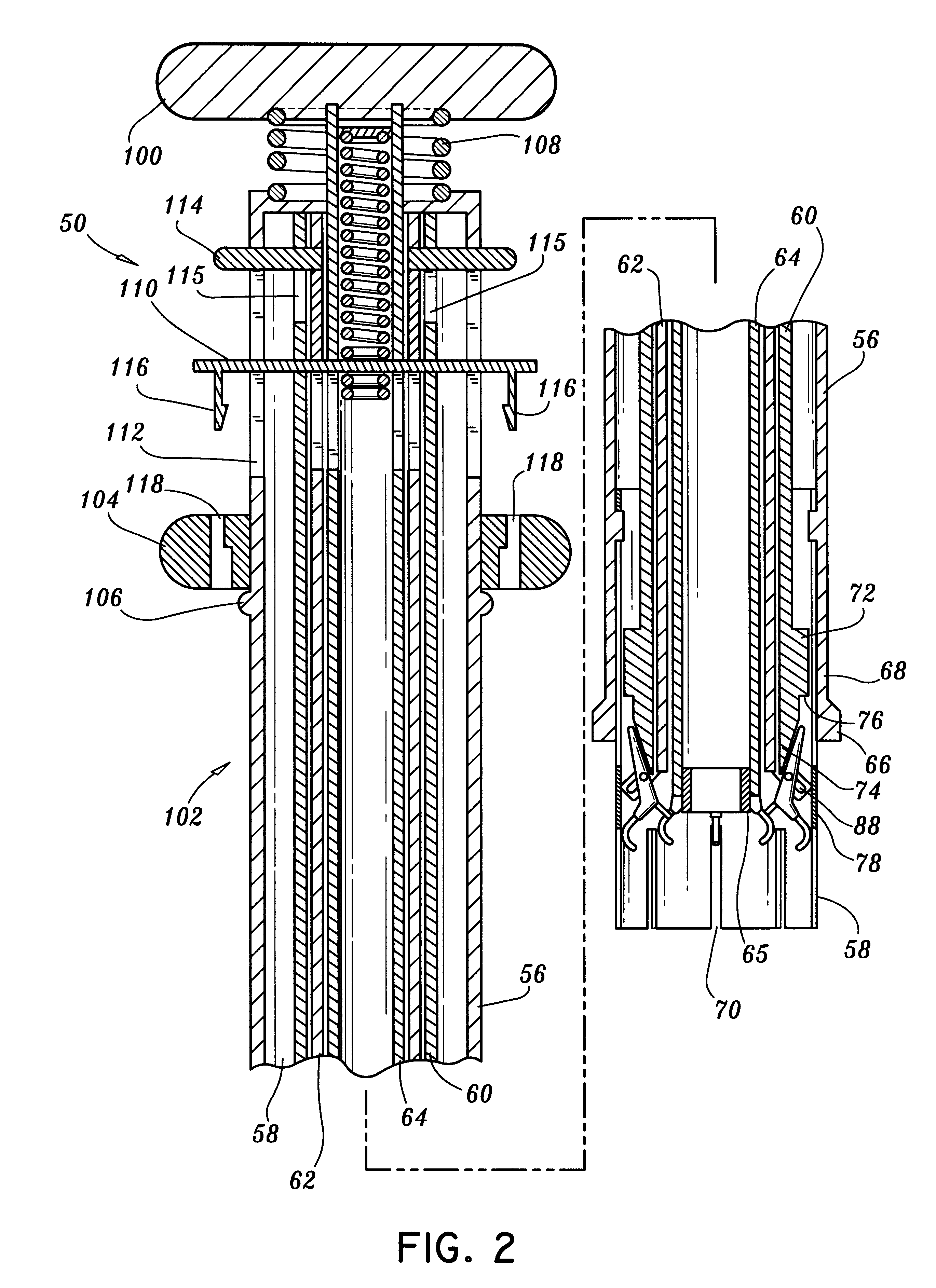
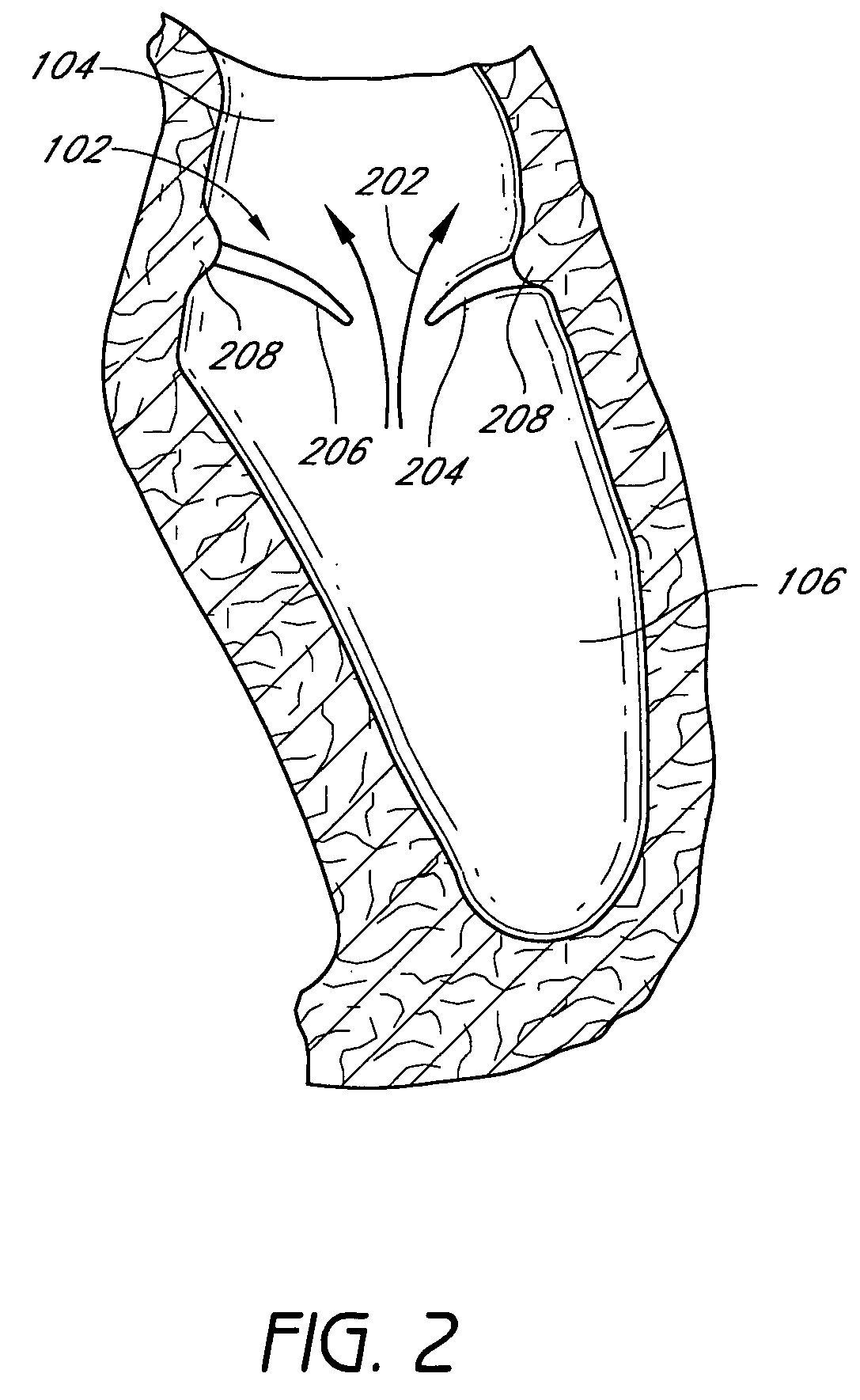
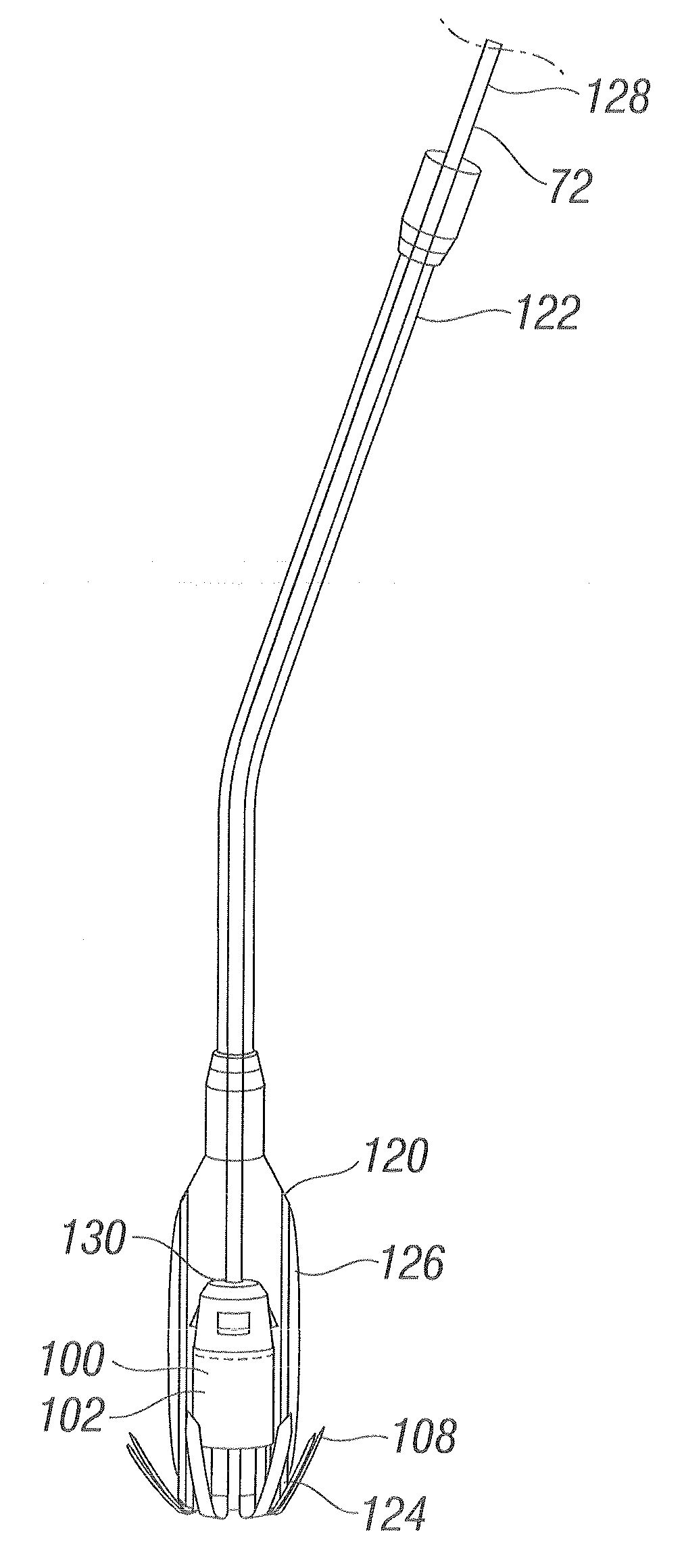
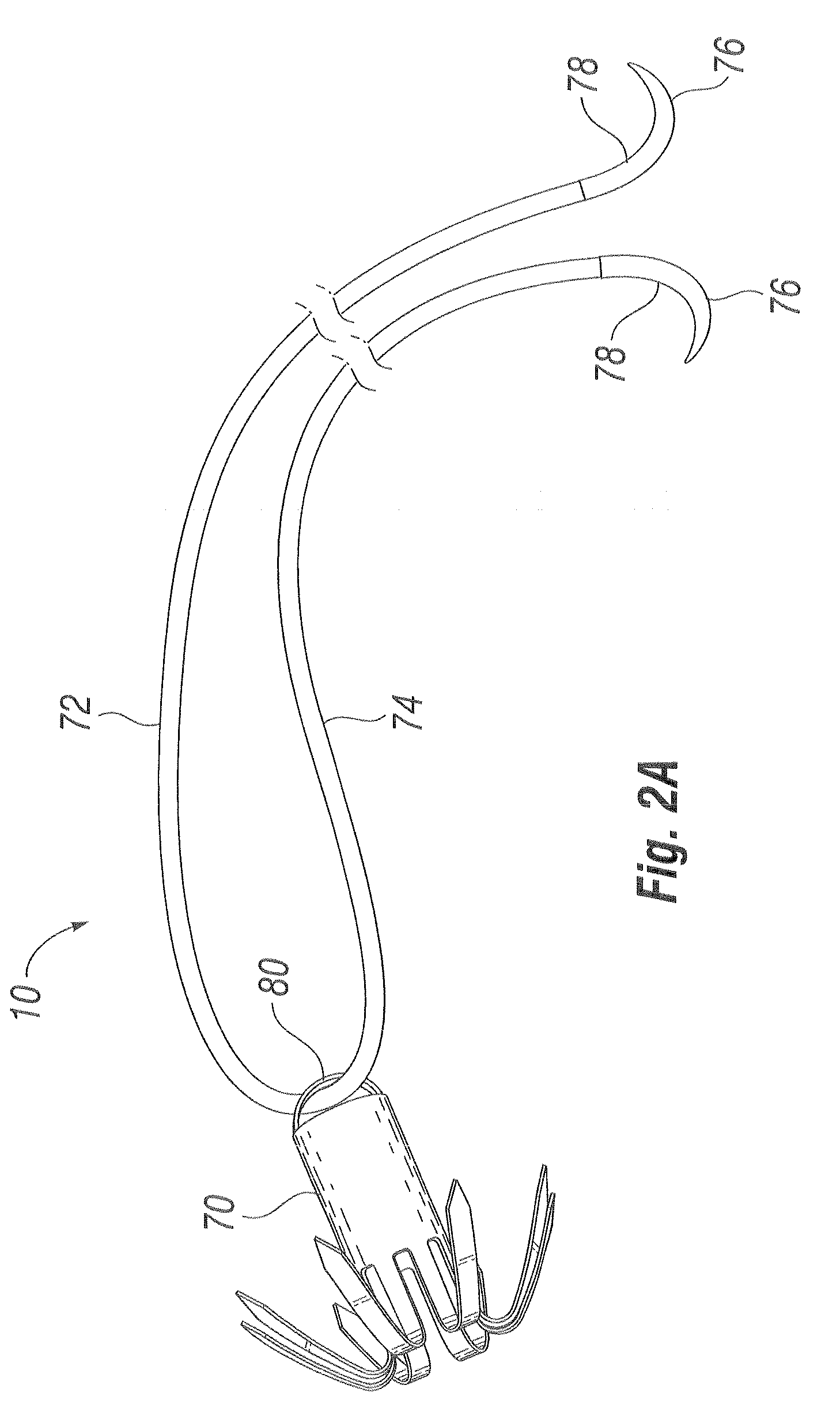
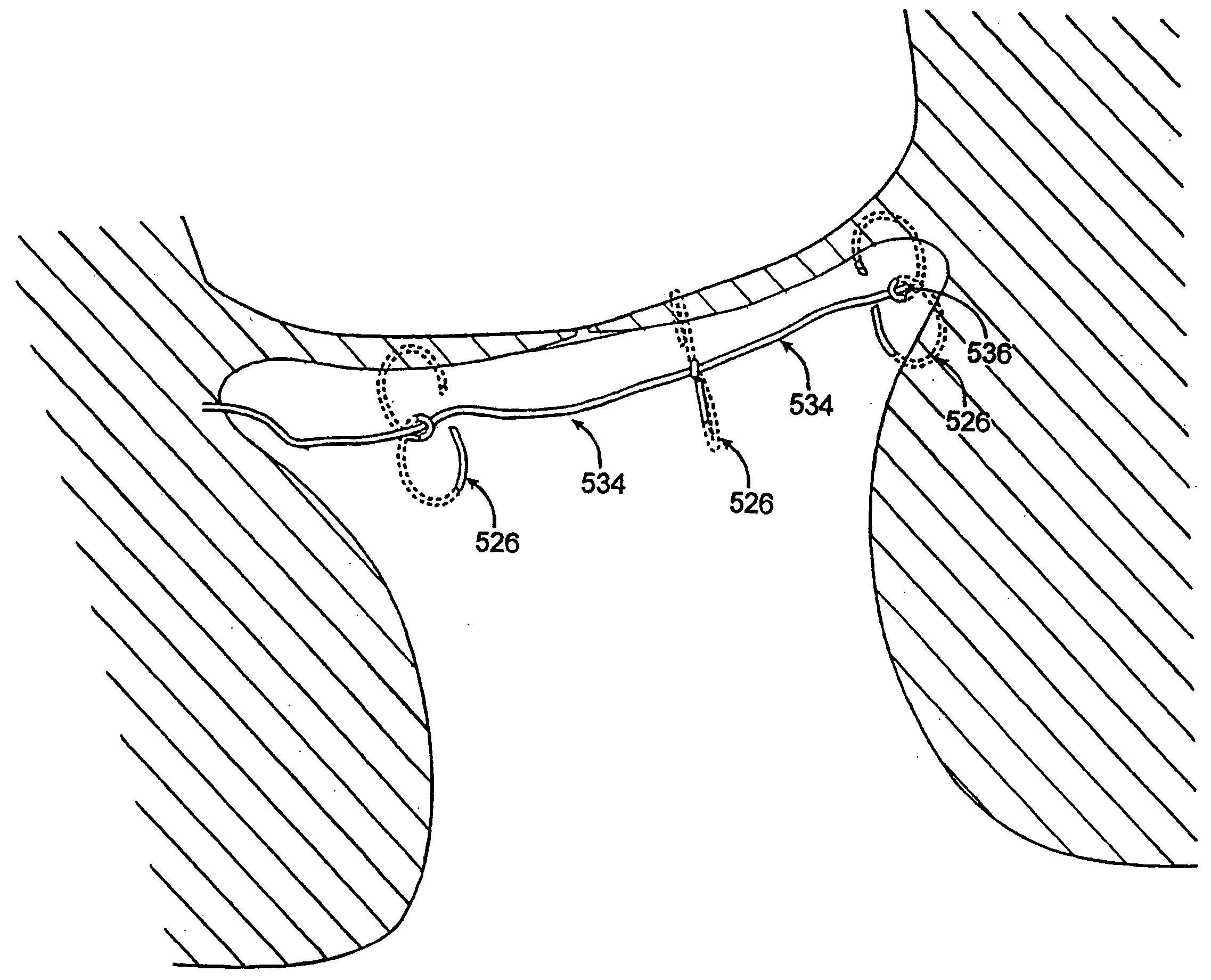
Methods and devices for termination
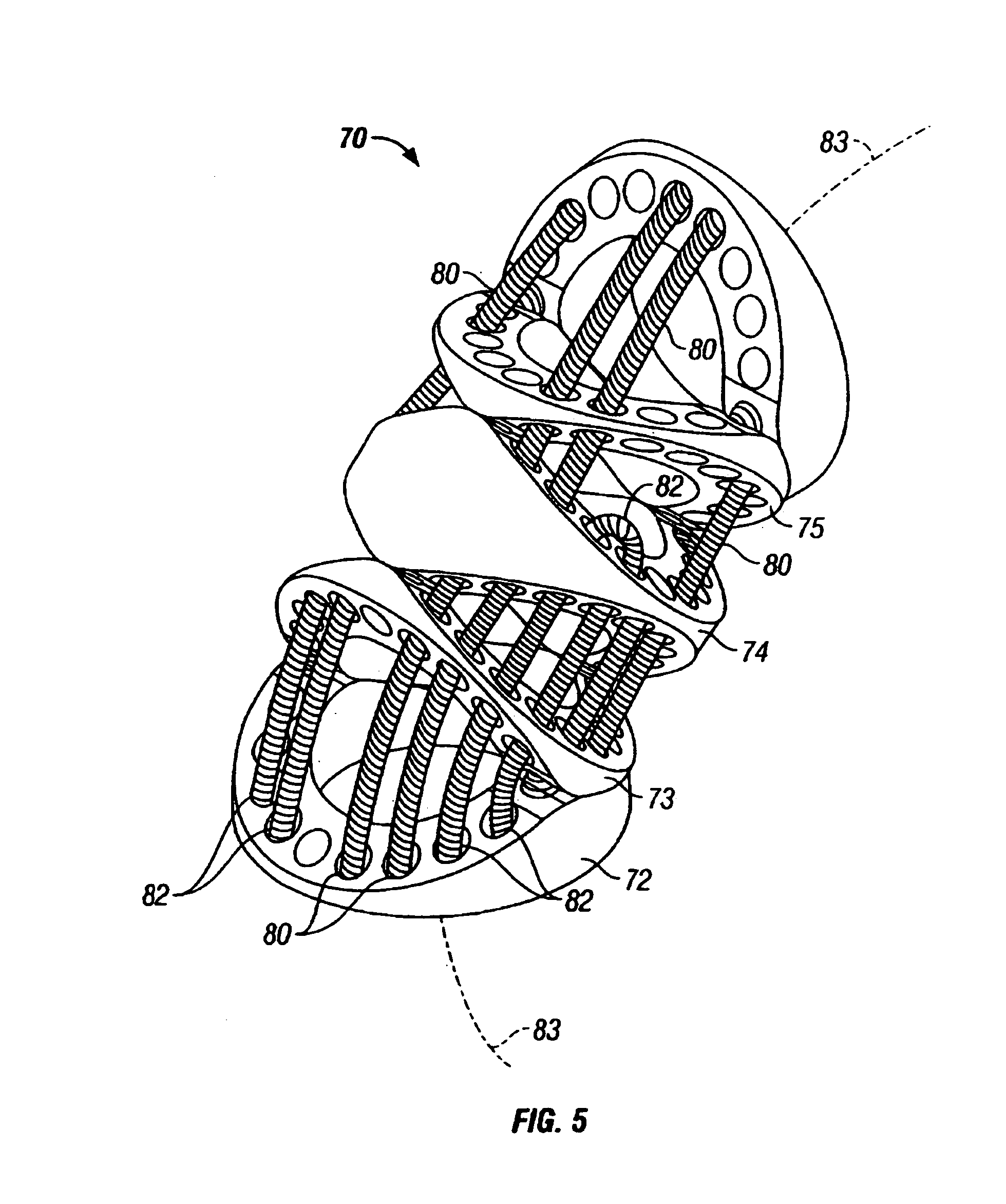
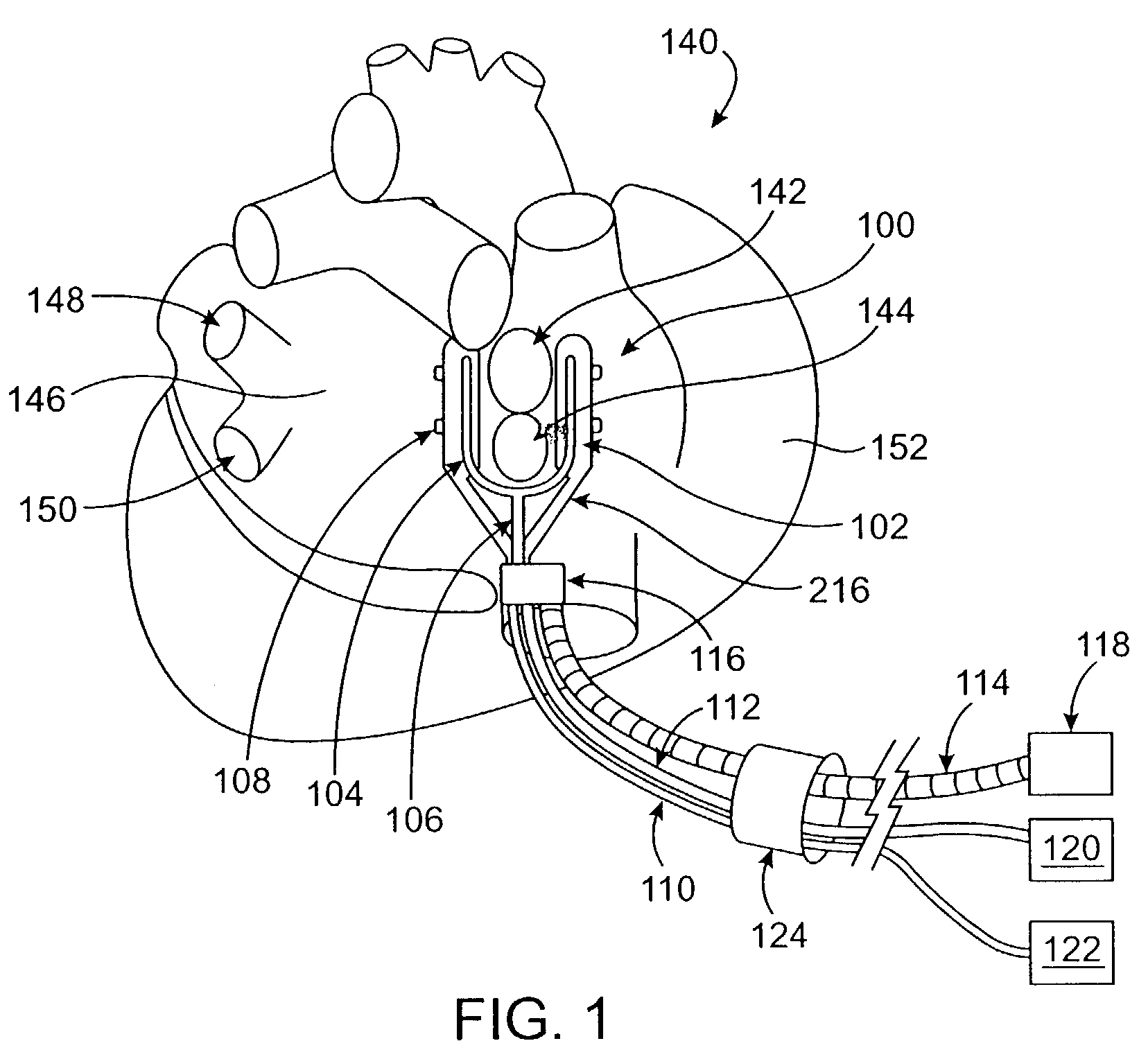
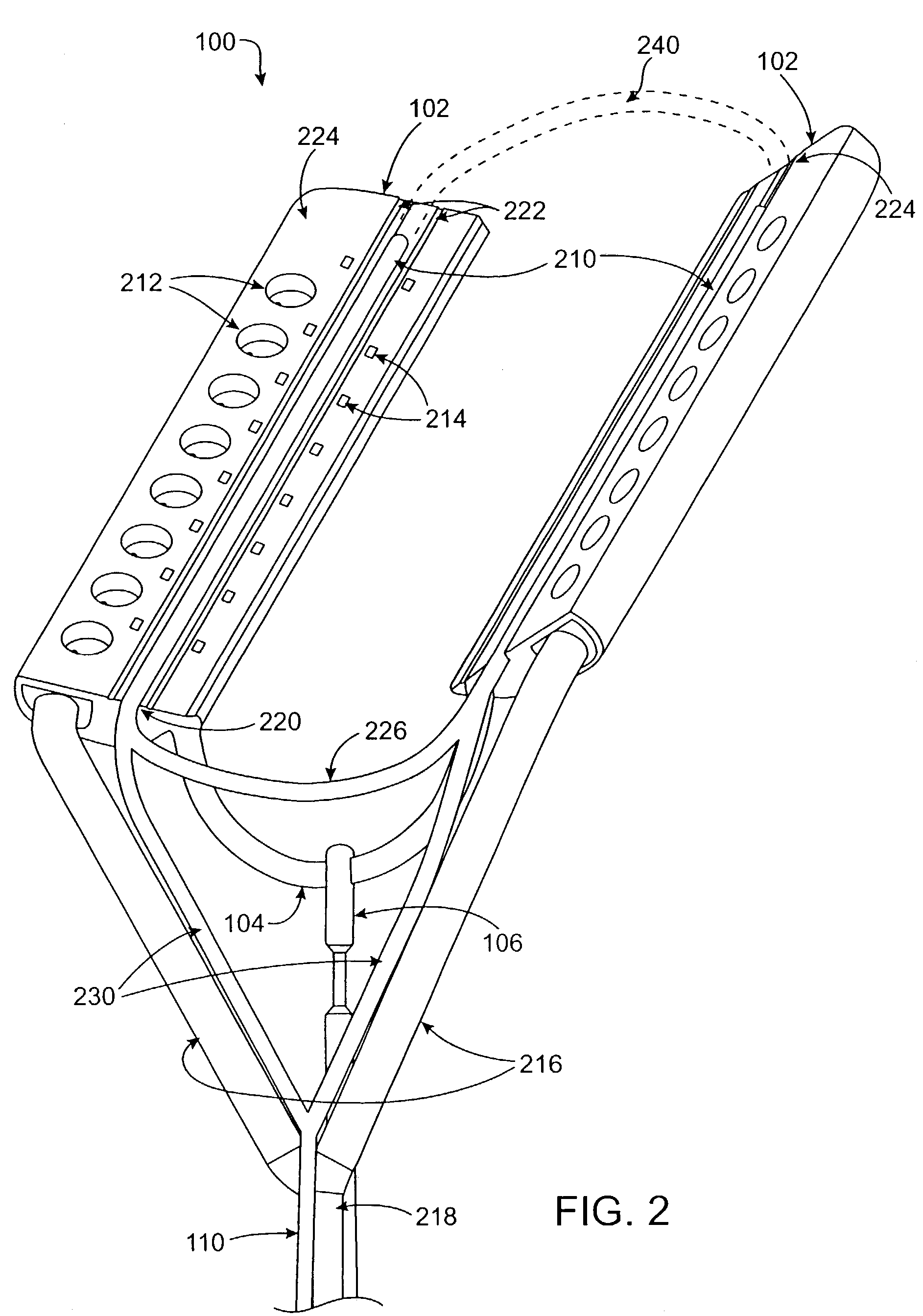
Devices and methods used in termination of a tissue tightening procedure are described. Termination includes the cinching of a tether to tighten the tissue, locking the tether to maintain tension, and cutting excess tether. In procedures involving anchors secured to the tissue, the tether is coupled to the anchors and the tissue is tightened via tension applied to the anchors by cinching the tether. In general, the devices and methods can be used in minimally invasive surgical procedures, and can be applied through small incisions or intravascularly. A method for tightening tissue by fixedly coupling a first anchor to a tether and slidably coupling a second anchor to the tether, securing both anchors to the tissue, applying tension to the tether intravascularly, fixedly coupling the tether to the second anchor, and cutting the tether is described. The tissue to be tightened can comprise heart tissue, in particular heart valve annulus tissue. Various devices and methods for locking the tether in place and cutting excess tether are described.
Owner:GUIDED DELIVERY SYST INC
Methods for remodeling cardiac tissue
InactiveUS7588582B2Convenient treatmentConstricting the valve annulusSuture equipmentsSurgical needlesTethered CordVALVE PORT
Described herein are methods of remodeling the base of a ventricle. In particular, methods of remodeling a valve annulus by forming a new fibrous annulus are described. These methods may result in a remodeled annulus that corrects valve leaflet function without substantially inhibiting the mobility of the leaflet. The methods of remodeling the base of the ventricle include the steps of securing a plurality of anchors to the valve annulus beneath one or more leaflets of the valve, constricting the valve annulus by cinching a tether connecting the anchors, and securing the anchors in the cinched conformation to allow the growth of fibrous tissue. The annulus may be cinched (e.g., while visualizing the annulus) so that the mobility of the valve leaflets is not significantly restricted. The remodeled annulus is typically constricted to shorten the diameter of the annulus to correct for valve dysfunction (e.g., regurgitation).
Owner:ANCORA HEART INC
Implants and methods for reshaping heart valves
Tissue shaping methods and devices are provided for reinforcing and / or remodeling heart valves. In certain embodiments, magnetic tissue shaping devices are implanted in tissue adjacent heart valve leaflets. The devices are mutually attractive or repulsive so as to remodel the heart tissue and improve heart valve function. In certain other embodiments, one or more tissue shaping devices including shape memory material are implanted in a patient's body within or on tissue adjacent a heart valve leaflet. The shape memory material can be activated within the patient in a less invasive or non-invasive manner, such as by applying energy percutaneously or external to the patient's body. The shape memory tissue shaping devices are implanted in a first configuration and then activated to remember a second configuration that displaces tissue so as to remodel the heart valve geometry and improve heart valve function. In certain other embodiments, a brace is crimped to the base of a heart valve leaflet to support the leaflet and improve valve closure.
Owner:MICARDIA CORP
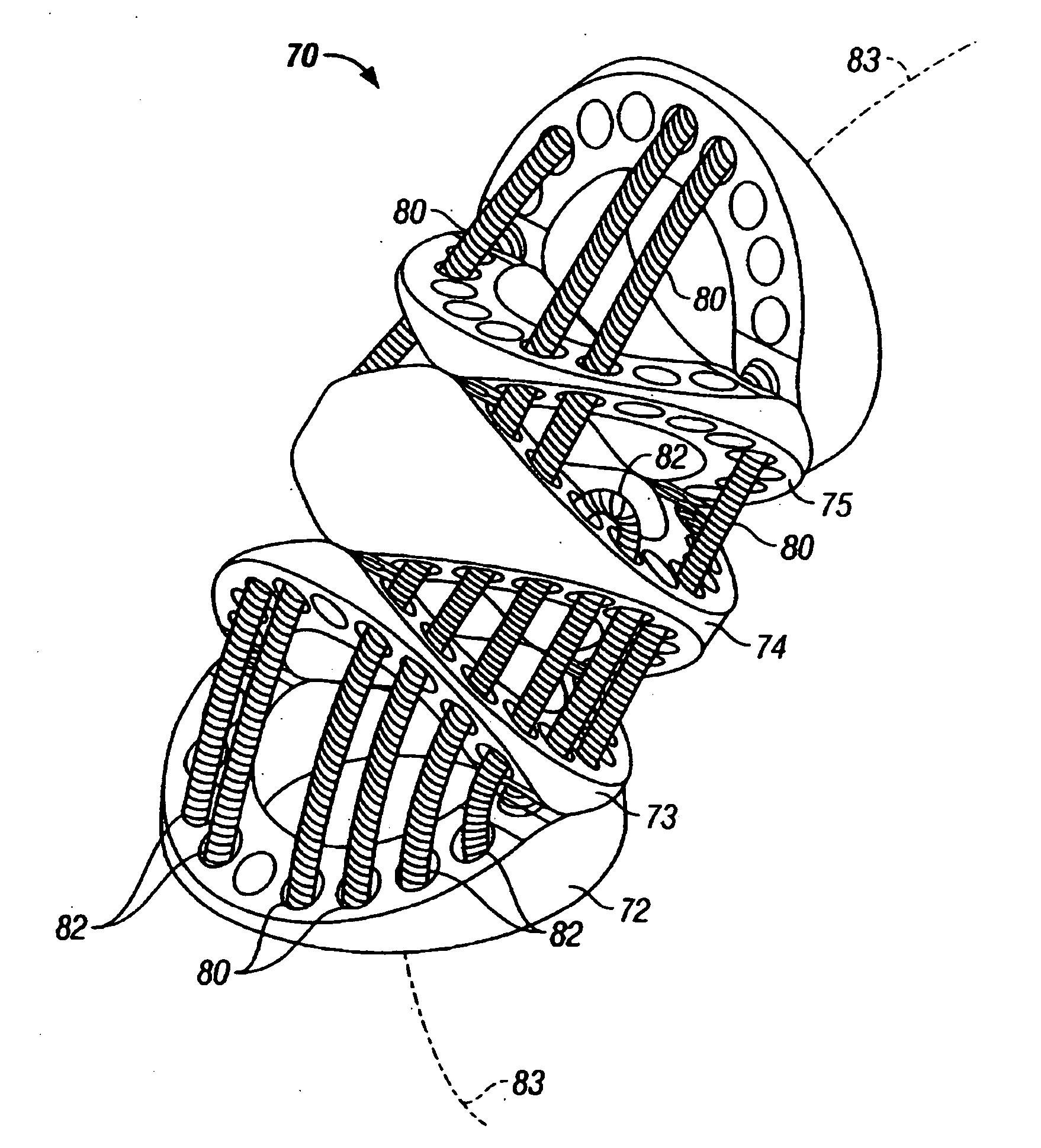
Suture and method for repairing a heart
InactiveUS20080195126A1Eliminate needSmall sizeSuture equipmentsHeart valvesLocking mechanismPapillary muscle
Devices and methods for treating or repairing a heart are disclosed. The device includes at least one anchor configured to engage tissue of a heart and a thread or other elongate member adapted to be coupled to the anchor and secured to heart tissue. The anchor may be attached to papillary muscle tissue and an elongate member may be attached to a valve leaflet for creating artificial chordae tendinae, thereby treating mitral valve prolapse. In another application, multiple anchors may be deployed within a ventricle and the threads pulled together for reducing dilation of a ventricle. A locking mechanism is provided for capturing and locking the threads together, thereby maintaining the ventricle in the reshaped condition.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
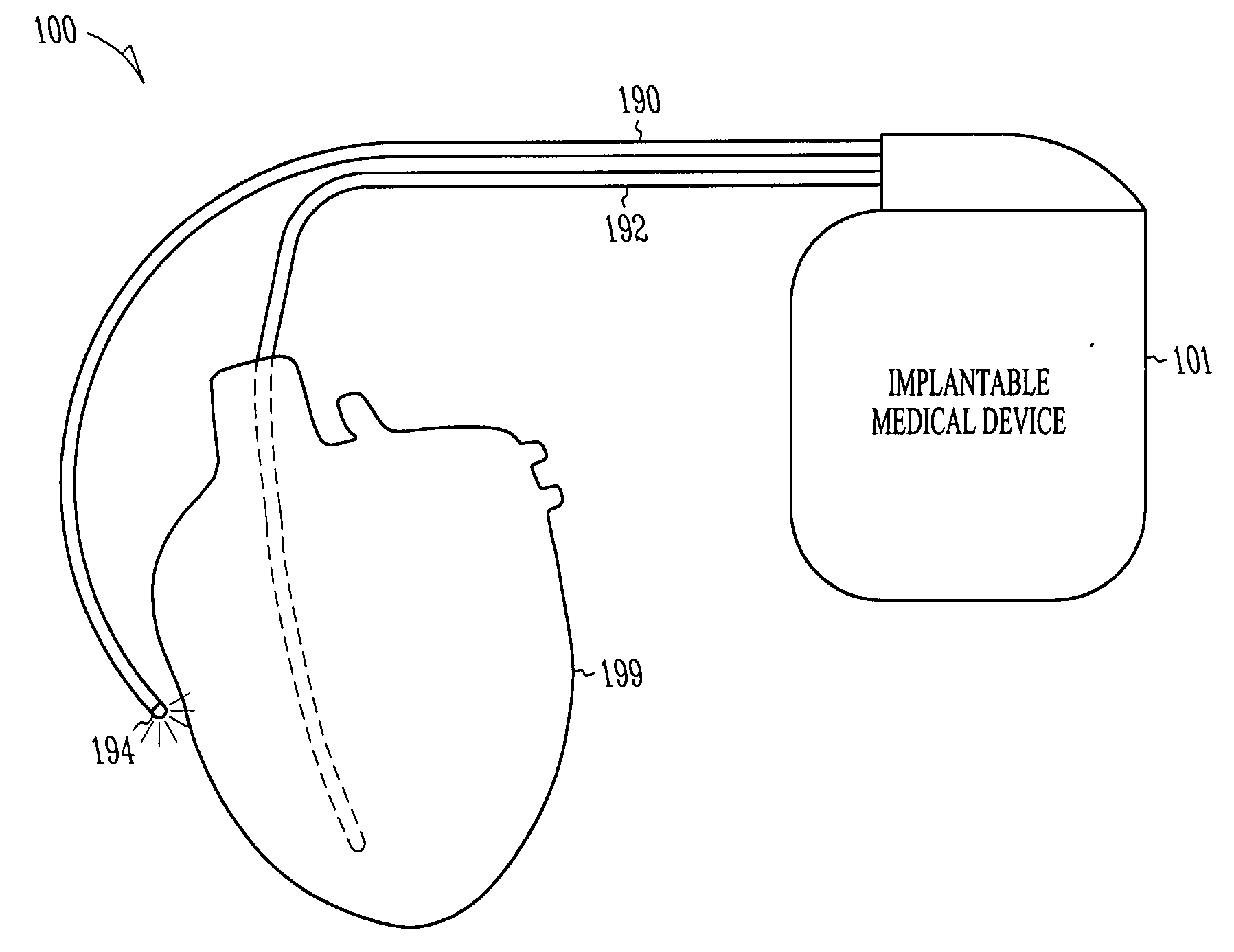
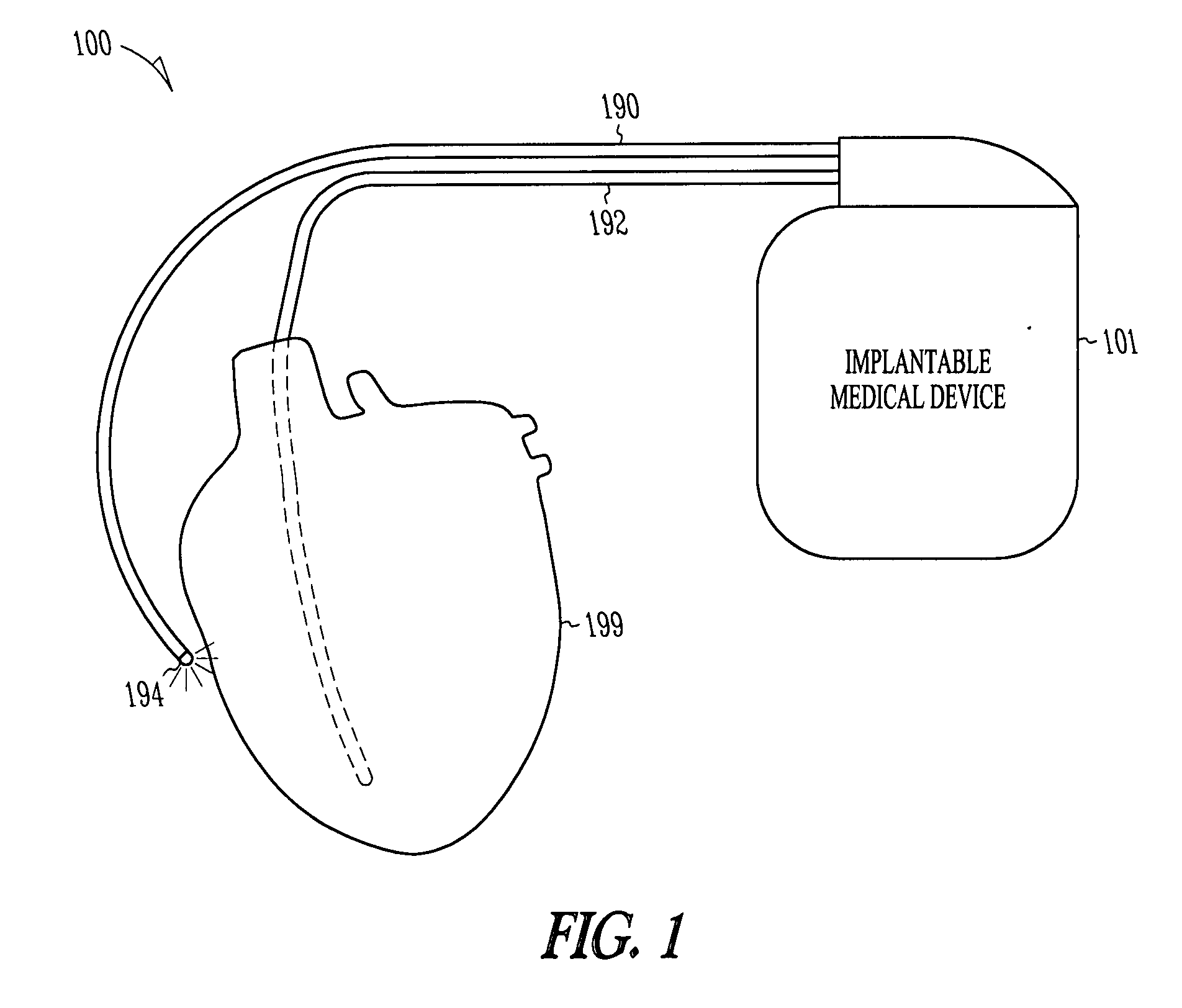
Implantable medical device for monitoring cardiac blood pressure and chamber dimension
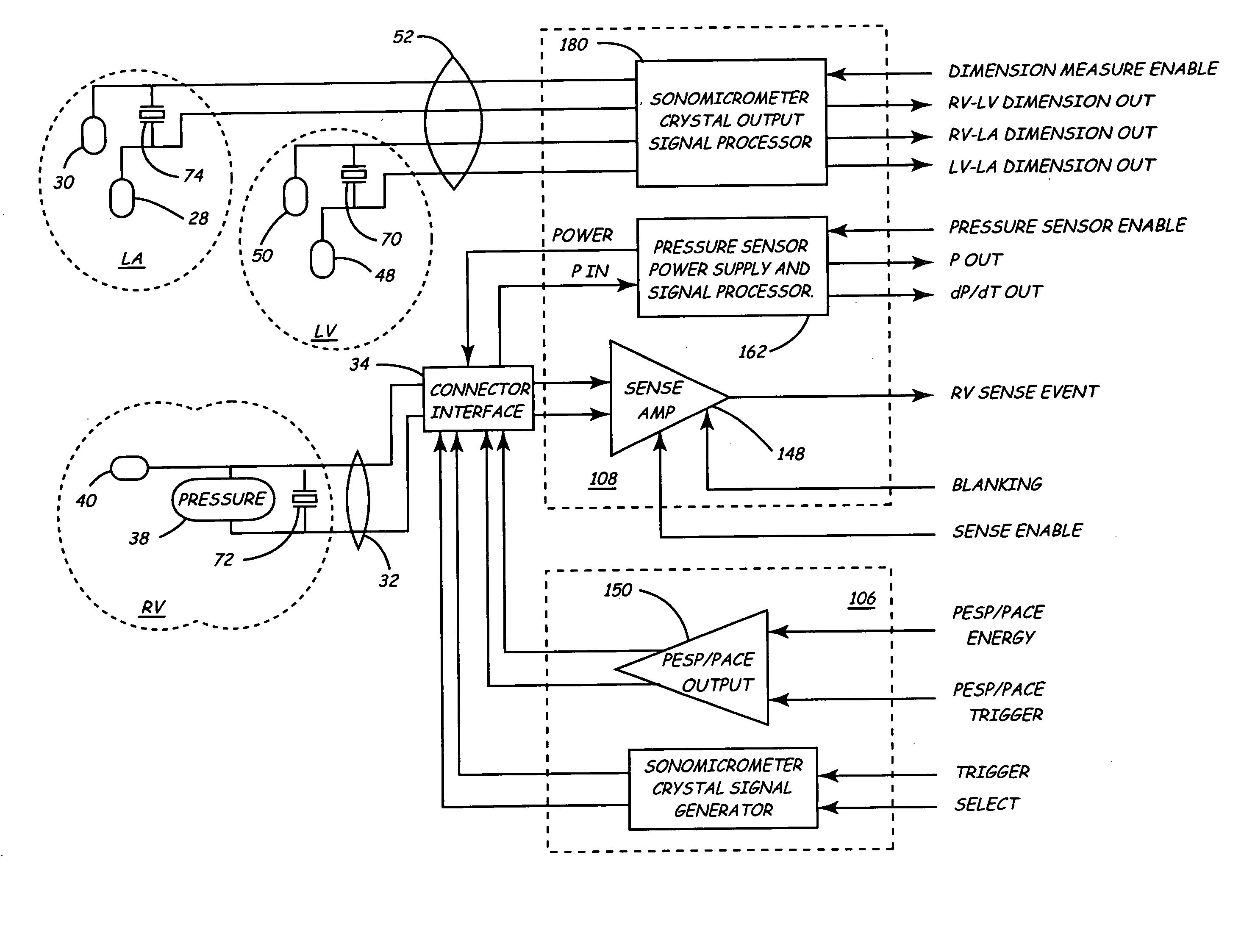
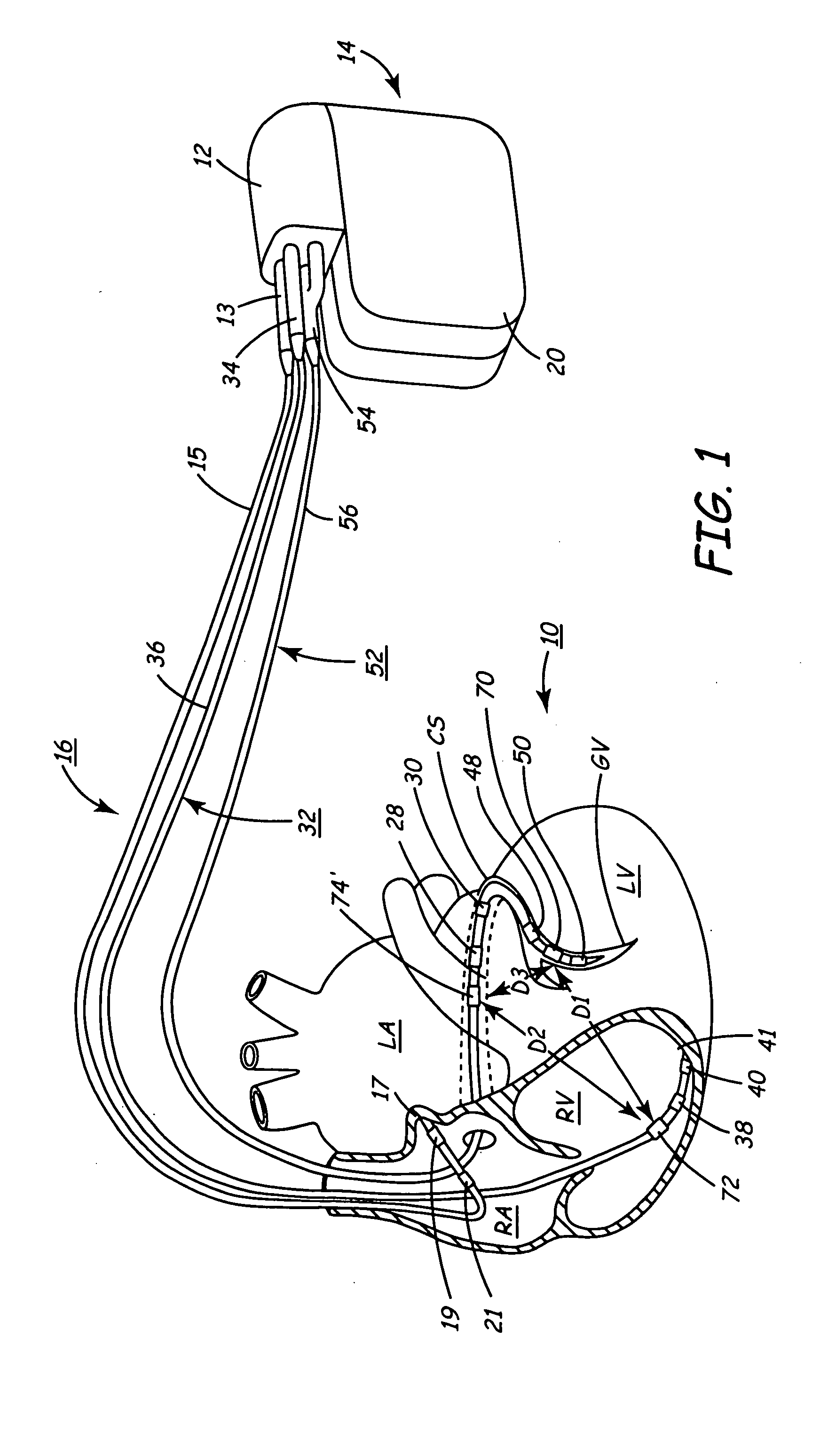
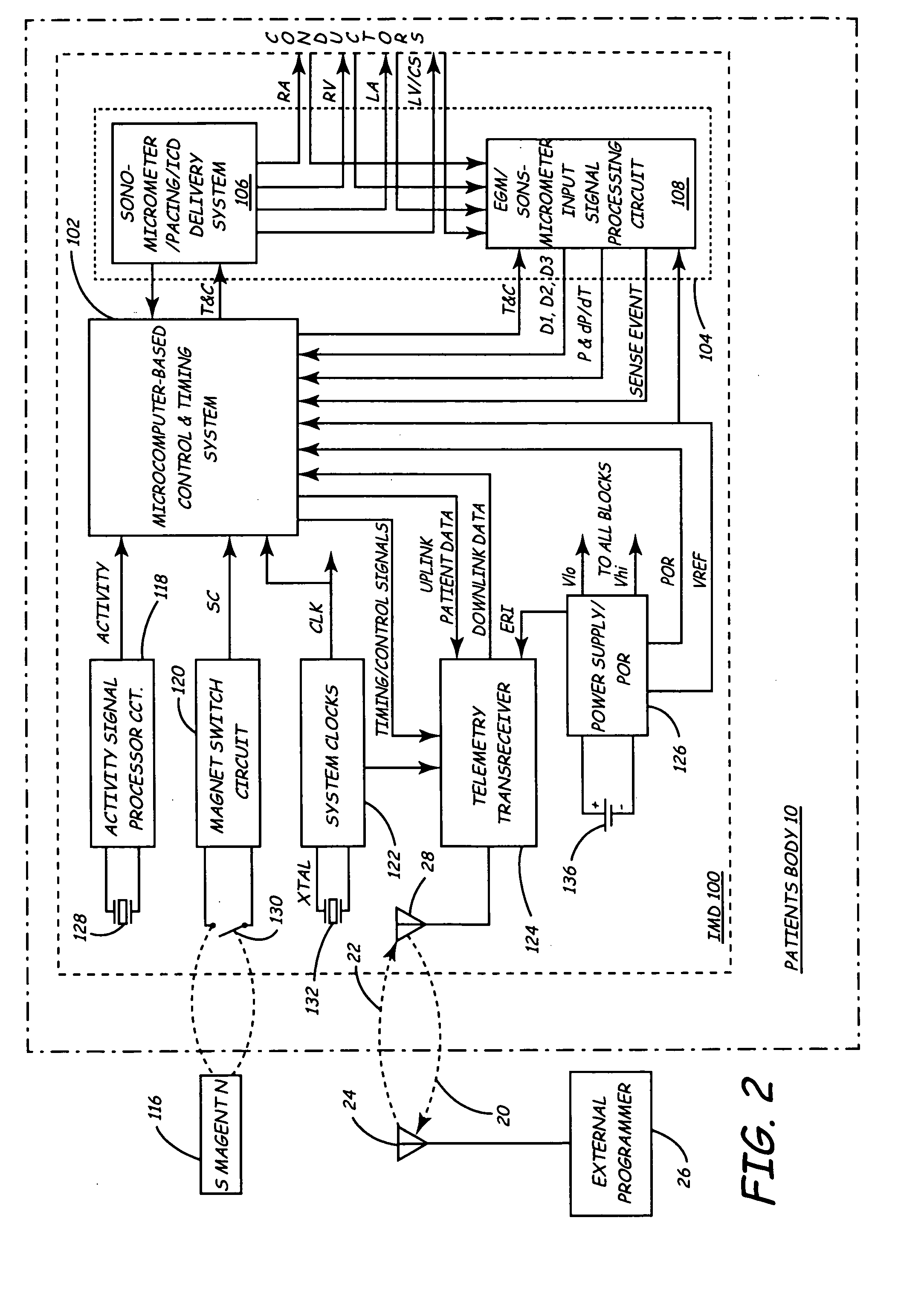
InactiveUS20050027323A1Maximize cardiac outputConvenient timeCatheterHeart stimulatorsSonificationHeart chamber
Implantable medical devices (IMDs) for monitoring signs of acute or chronic cardiac heart failure by measuring cardiac blood pressure and mechanical dimensions of the heart and providing multi-chamber pacing optimized as a function of measured blood pressure and dimensions are disclosed. The dimension sensor or sensors comprise at least a first sonomicrometer piezoelectric crystal mounted to a first lead body implanted into or in relation to one heart chamber that operates as an ultrasound transmitter when a drive signal is applied to it and at least one second sonomicrometer crystal mounted to a second lead body implanted into or in relation to a second heart chamber that operates as an ultrasound receiver. The ultrasound receiver converts impinging ultrasound energy transmitted from the ultrasound transmitter through blood and heart tissue into an electrical signal. The time delay between the generation of the transmitted ultrasound signal and the reception of the ultrasound wave varies as a function of distance between the ultrasound transmitter and receiver which in turn varies with contraction and expansion of a heart chamber between the first and second sonomicrometer crystals. One or more additional sonomicrometer piezoelectric crystal can be mounted to additional lead bodies such that the distances between the three or more sonomicrometer crystals can be determined. In each case, the sonomicrometer crystals are distributed about a heart chamber such that the distance between the separated ultrasound transmitter and receiver crystal pairs changes with contraction and relaxation of the heart chamber walls.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
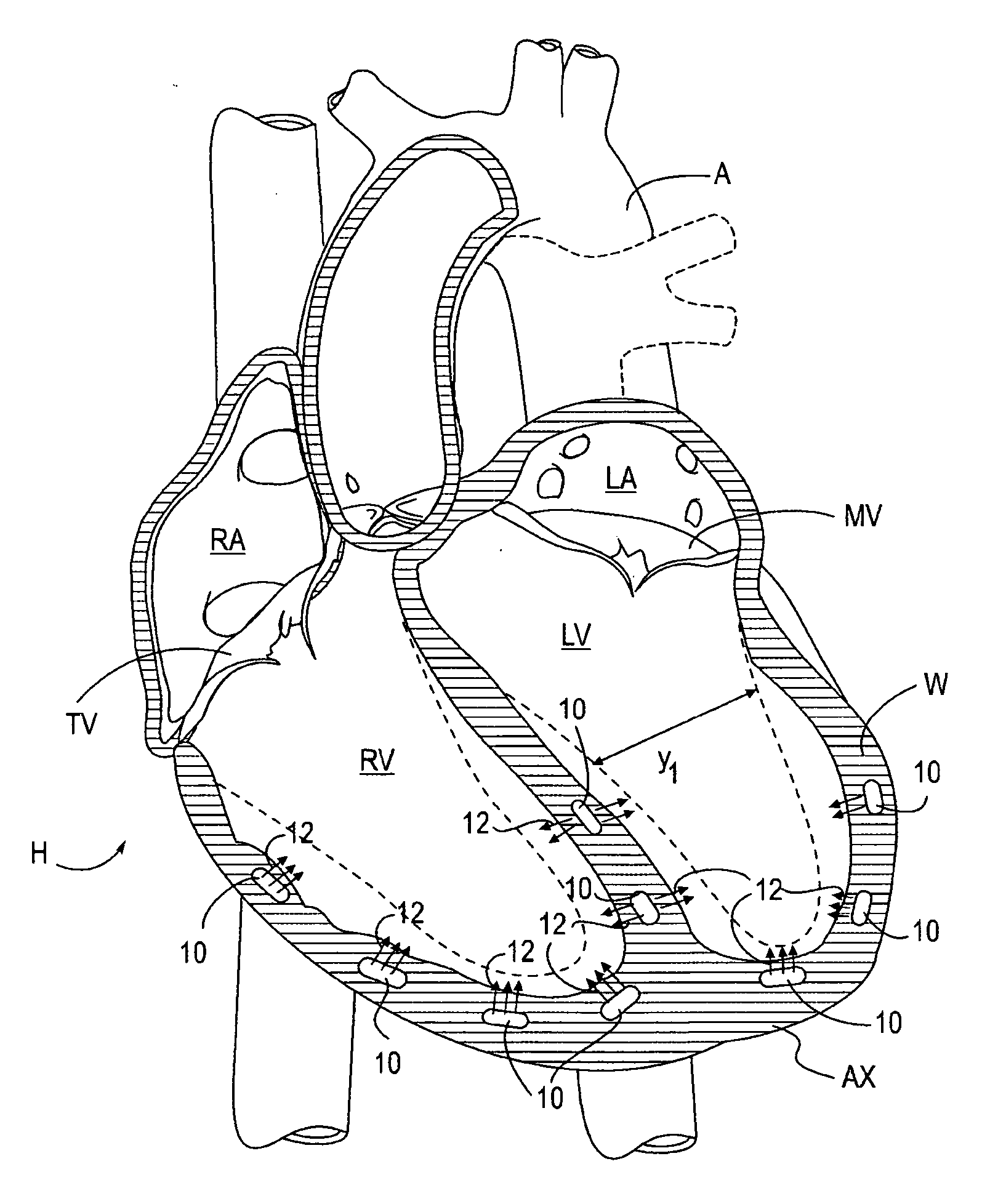
Treating Dysfunctional Cardiac Tissue
ActiveUS20090093670A1Reduce distanceBeneficial heart geometrySuture equipmentsSurgical furnitureCongestive heart failure chfDisease progression
Medical devices, systems, and methods reduce the distance between two points in tissue, often for treatment of congestive heart failure and often in a minimally invasive manner. An anchor is inserted along an insertion path through a first wall of the heart. An arm of the anchor is deployed and rotationally positioned according to a desired alignment. Application of tension to the anchor may draw the first and second walls of the heart into contact along a desired contour so as to effect a desired change in the geometry of the heart. Additional anchors may be inserted and aligned with the first anchor to close off a portion of a ventricle such that the ventricle is geometrically remodeled and disease progression is reversed, halted, and / or slowed.
Owner:BIOVENTRIX A CHF TECH
Device to permit offpump beating heart coronary bypass surgery
Owner:MAQUET CARDIOVASCULAR LLC
Device for Ablating Body Tissue
A cardiac ablation system including an ablation catheter having an anchor adapted to support the ablation catheter within an atrium of a heart and an ultrasound emitter disposed radially outward from a rotation axis and from the anchor, and a control mechanism adapted to rotate the ultrasound emitter about the rotation axis and to provide ablation energy to the ultrasound emitter to ablate heart tissue.
Owner:AURIS HEALTH INC
Method for Ablating Body Tissue
A cardiac ablation method including the following steps: inserting a treatment catheter into an atrium of a heart, the treatment catheter including an ultrasound emitter; positioning the ultrasound emitter to face heart tissue within the left atrium outside of a pulmonary vein; emitting ultrasound energy from the ultrasound emitter while rotating the ultrasound emitter about a rotation axis; and ablating heart tissue with the ultrasound energy to form a lesion outside of a pulmonary vein.
Owner:AURIS HEALTH INC
Systems and methods for making noninvasive assessments of cardiac tissue and parameters
InactiveUS7022077B2Maximize tissue displacementEasy diagnosisBlood flow measurement devicesOrgan movement/changes detectionSonificationUltrasound techniques
Systems and methods for noninvasive assessment of cardiac tissue properties and cardiac parameters using ultrasound techniques are disclosed. Determinations of myocardial tissue stiffness, tension, strain, strain rate, and the like, may be used to assess myocardial contractility, myocardial ischemia and infarction, ventricular filling and atrial pressures, and diastolic functions. Non-invasive systems in which acoustic techniques, such as ultrasound, are employed to acquire data relating to intrinsic tissue displacements are disclosed. Non-invasive systems in which ultrasound techniques are used to acoustically stimulate or palpate target cardiac tissue, or induce a response at a cardiac tissue site that relates to cardiac tissue properties and / or cardiac parameters are also disclosed.
Owner:PHYSIOSONICS +1
Shape memory devices and methods for reshaping heart anatomy
InactiveUS20060015002A1Improve shrinkageReduce widthSuture equipmentsSurgical needlesCardiac surfaceHeart anatomy
Systems, methods and devices are provided for treating heart failure patients suffering from various levels of heart dilation. Such heart dilation is treated by reshaping the heart anatomy with the use of shape memory elements. Such reshaping changes the geometry of portions of the heart, particularly the right or left ventricles, to increase contractibility of the ventricles thereby increasing the stroke volume which in turn increases the cardiac output of the heart. The shape memory elements have an original shape and at least one memory shape. The elements are implanted within the heart tissue or attached externally and / or internally to a surface of the heart when in the original shape. The elements are then activated to transition from the original shape to one of the at least one memory shapes. Transitioning of the elements cause the associated heart tissue areas to readjust position, such as to decrease the width of the ventricles. Such repositioning is maintained over time by the elements, allowing the damaging effects of heart dilation to slow in progression or reverse.
Owner:MICARDIA CORP
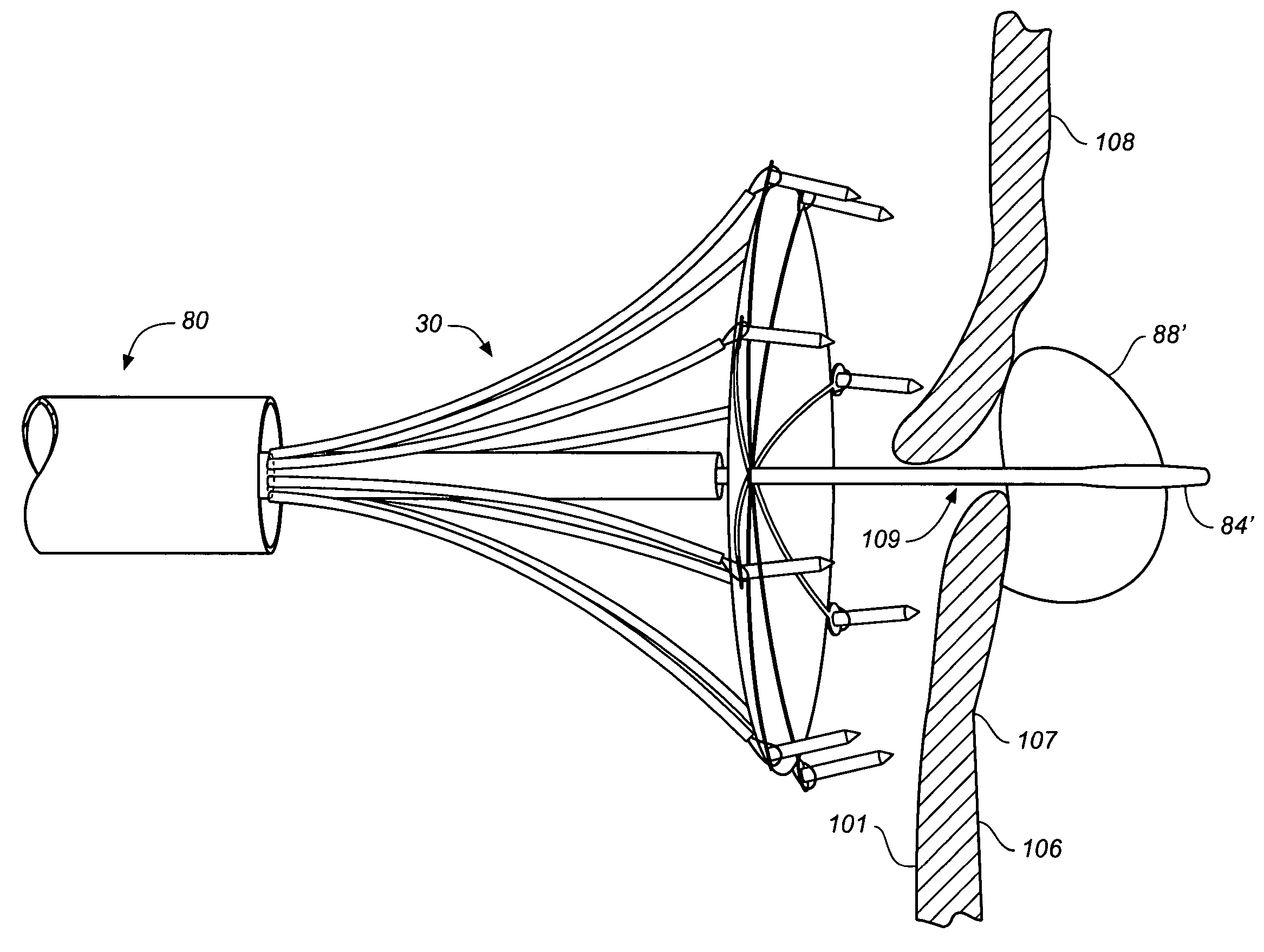
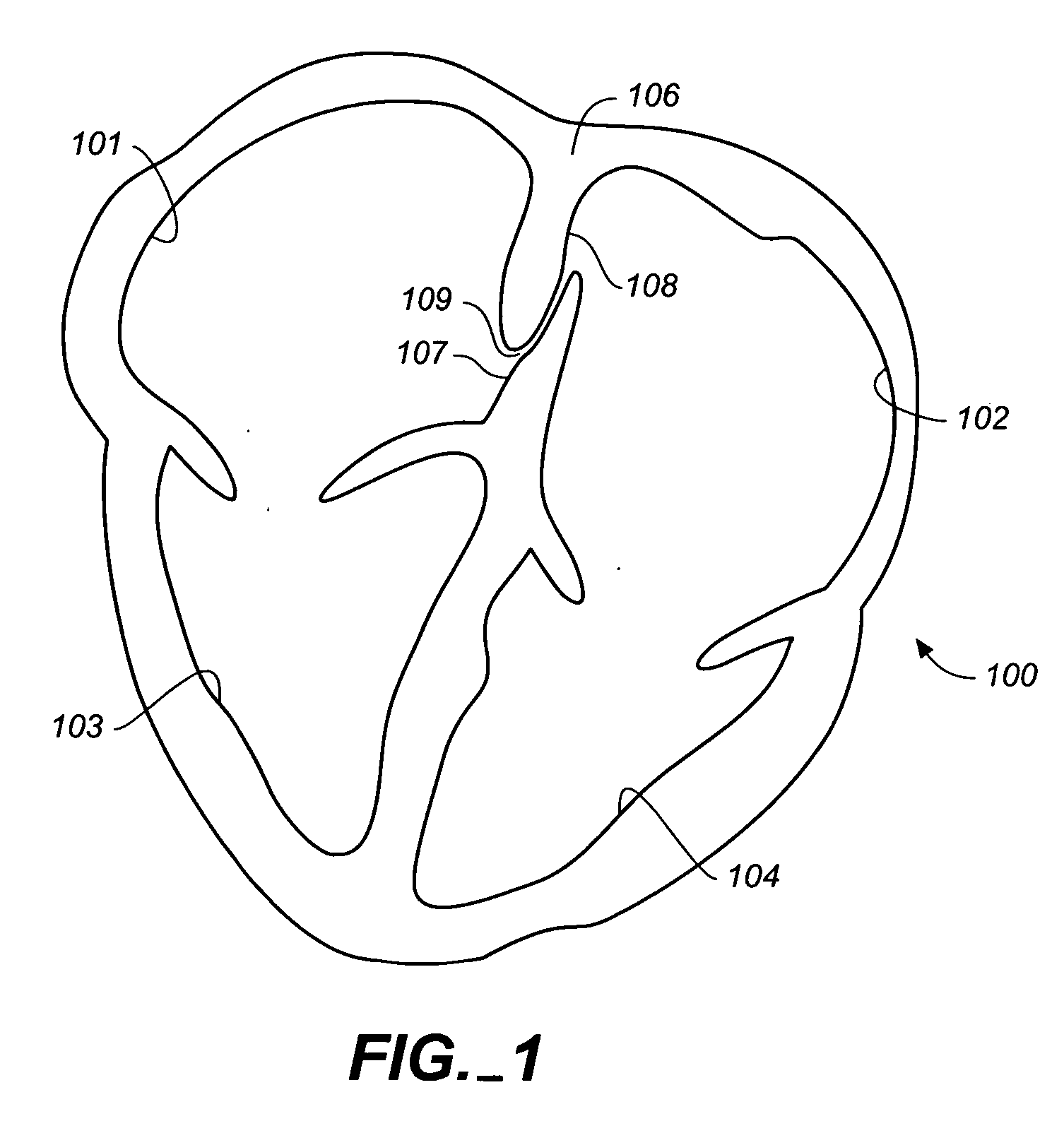
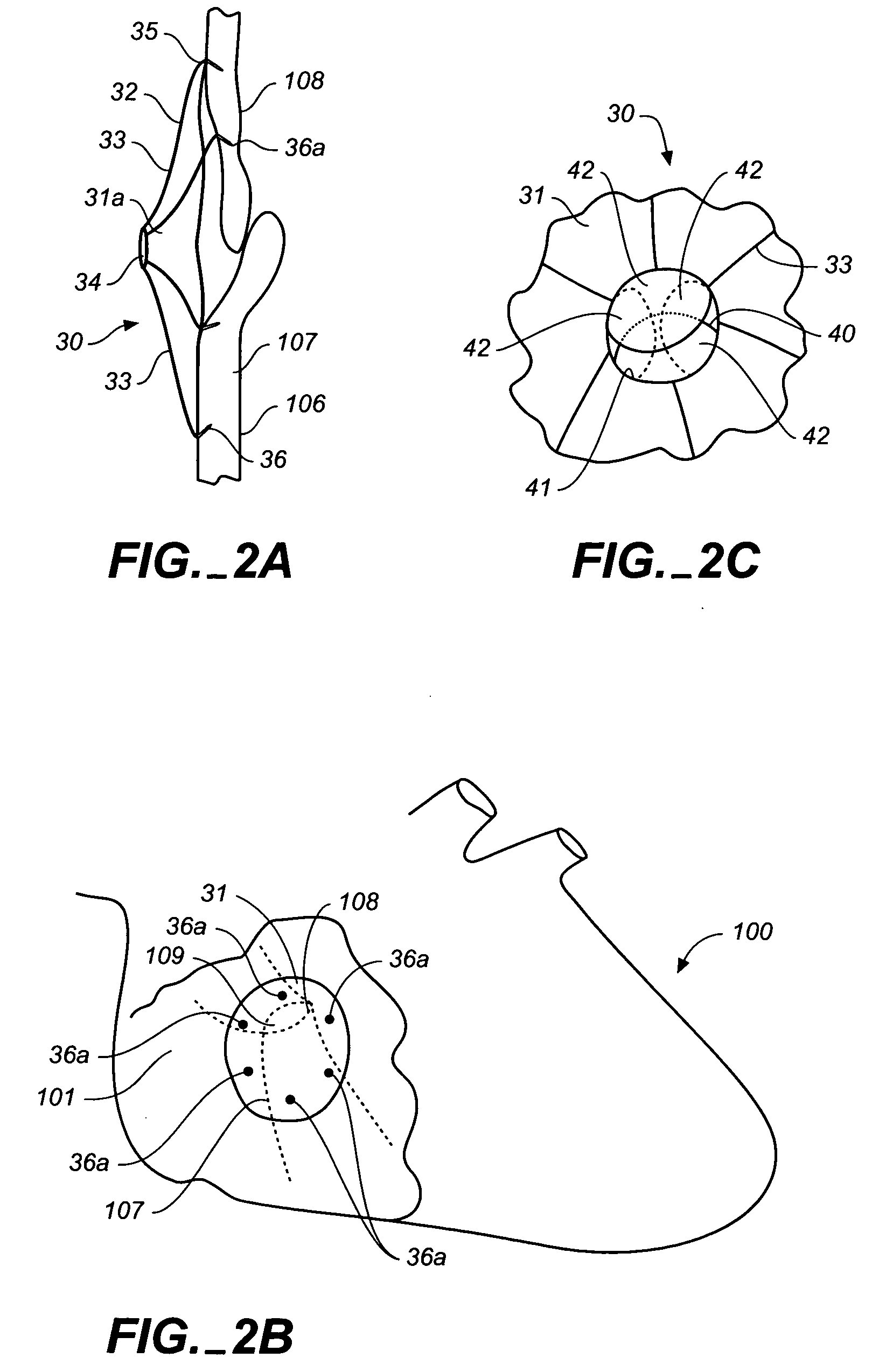
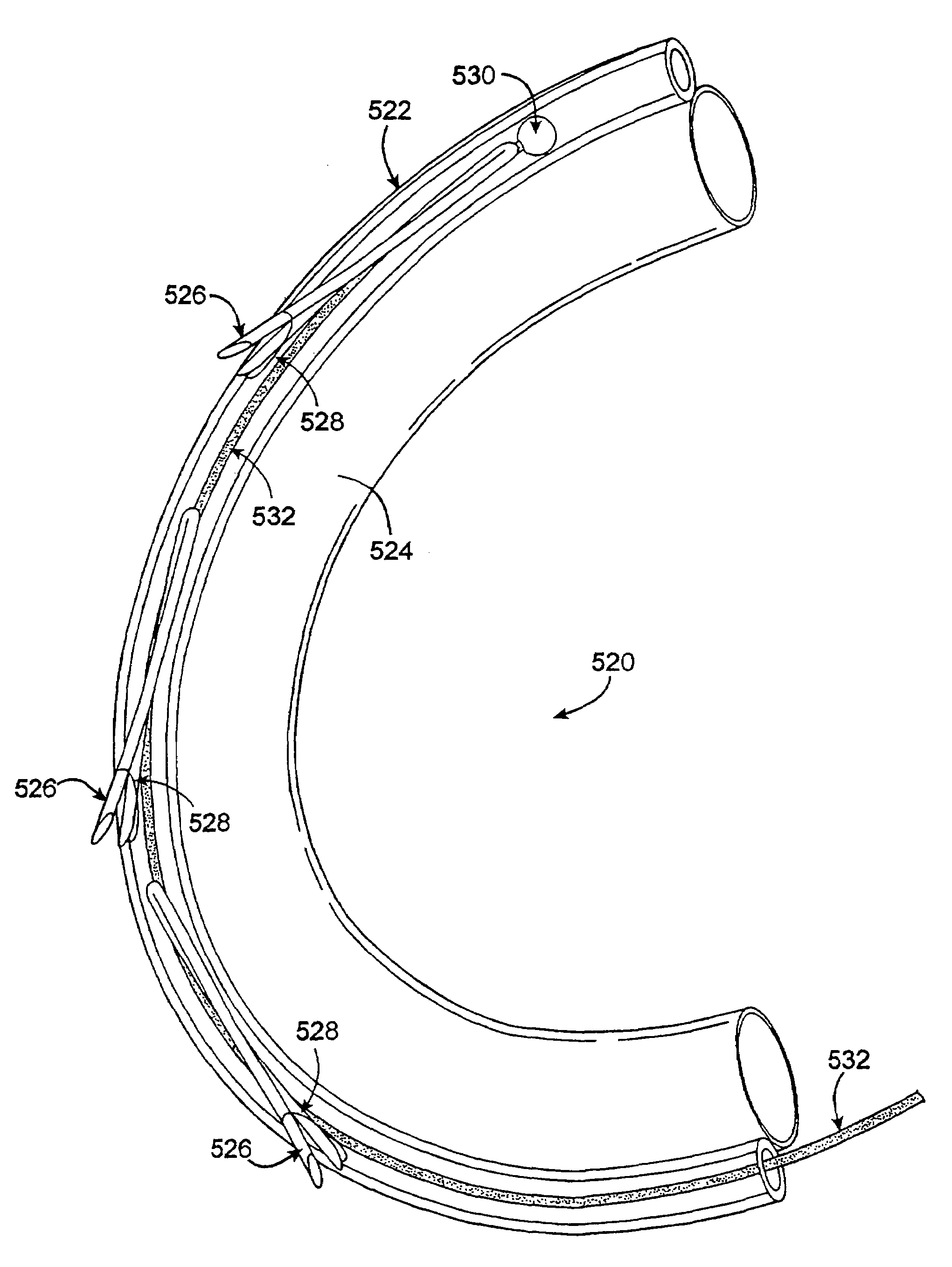
Surgical system and procedure for treatment of medically refractory atrial fibrillation
InactiveUS7387126B2Reduce complicationsShorten the timeSuture equipmentsCannulasMedicineBiomedical engineering
The invention provides surgical systems and methods for ablating heart tissue within the interior and / or exterior of the heart. A plurality of probes is provided with each probe configured for introduction into the chest for engaging the heart. Each probe includes an elongated shaft having an elongated ablating surface of a predetermined shape. The elongated shaft and the elongated ablating surface of each probe are configured to ablate a portion of the heart. A sealing device affixed to the heart tissue forms a hemostatic seal between the probe and the penetration in the heart to inhibit blood loss therethrough.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
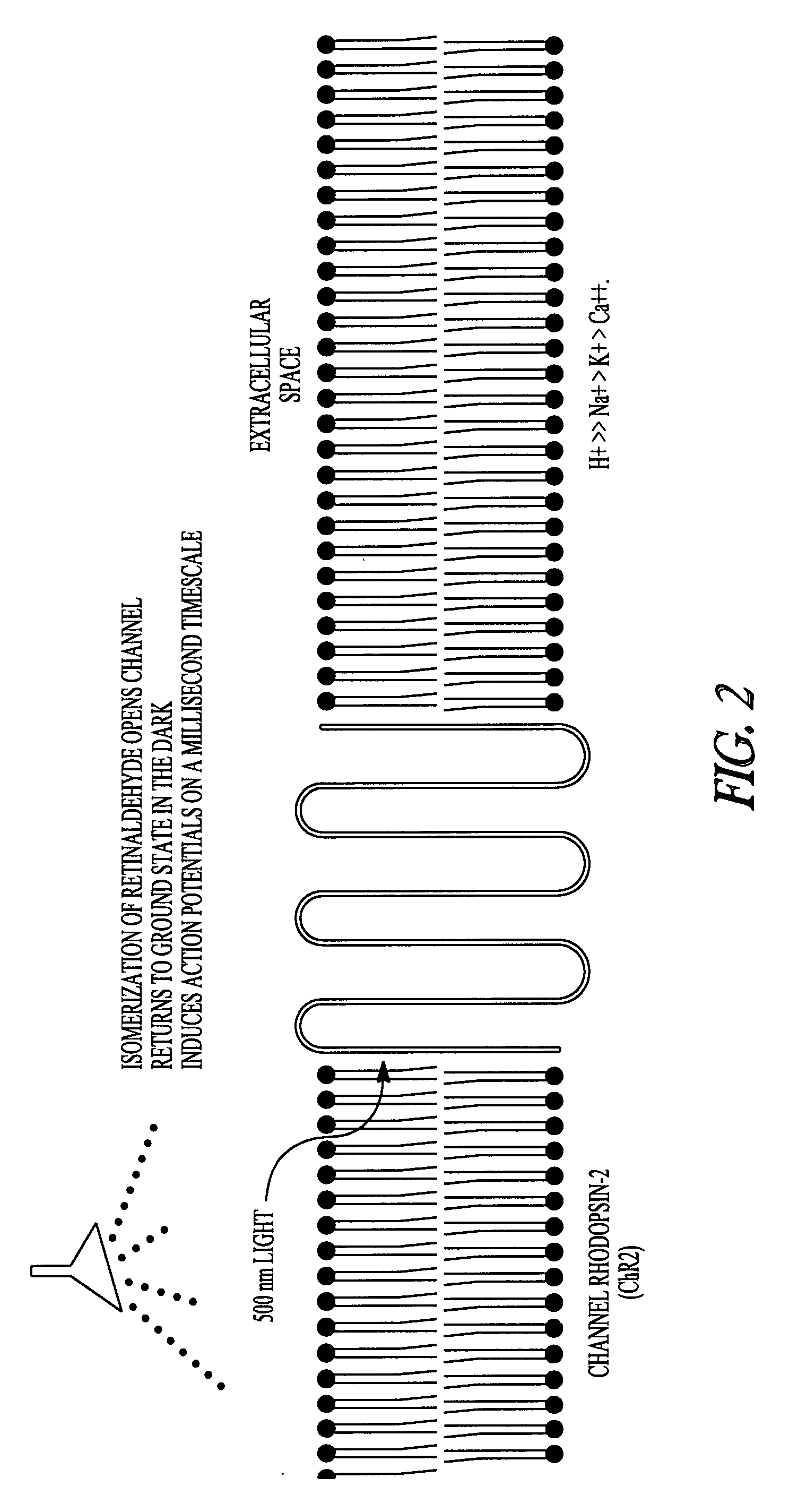
Optical depolarization of cardiac tissue
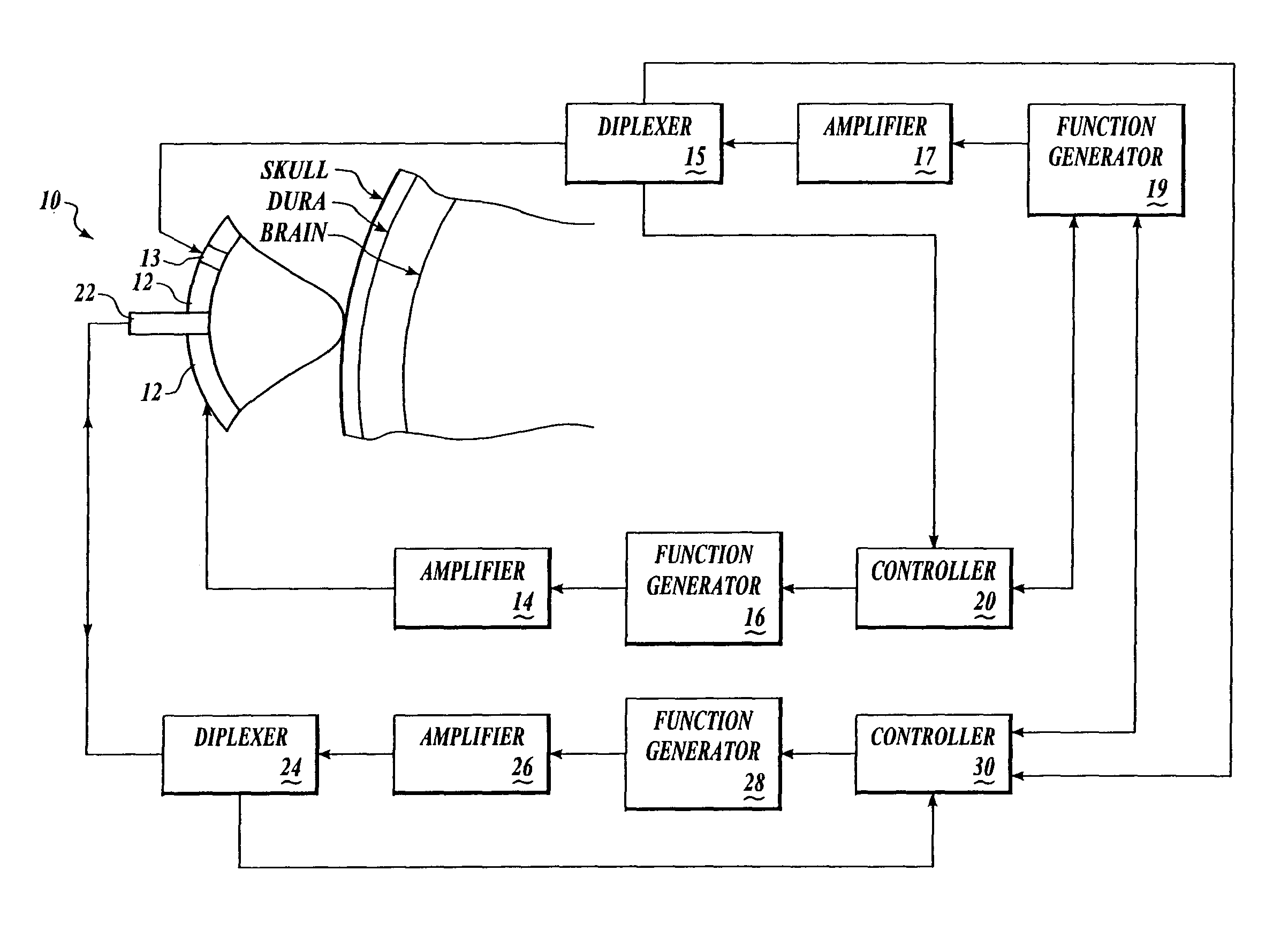
ActiveUS20090054954A1No painIncrease photosensitivitySurgical instrument detailsViruses/bacteriophagesManagement systemDepolarization
The invention provides a cardiac rhythm management system for stimulating a heart having photosensitive tissue, vectors useful to photosensitize cells expressing the vectors, and methods for light induced depolarization of cells.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Methods and devices for termination
Devices and methods used in termination of a tissue tightening procedure are described. Termination includes the cinching of a tether to tighten the tissue, locking the tether to maintain tension, and cutting excess tether. In procedures involving anchors secured to the tissue, the tether is coupled to the anchors and the tissue is tightened via tension applied to the anchors by cinching the tether. In general, the devices and methods can be used in minimally invasive surgical procedures, and can be applied through small incisions or intravascularly. A method for tightening tissue by fixedly coupling a first anchor to a tether and slidably coupling a second anchor to the tether, securing both anchors to the tissue, applying tension to the tether intravascularly, fixedly coupling the tether to the second anchor, and cutting the tether is described. The tissue to be tightened can comprise heart tissue, in particular heart valve annulus tissue. Various devices and methods for locking the tether in place and cutting excess tether are described.
Owner:ANCORA HEART INC
Conduction block verification probe and method of use
ActiveUS20060015165A1Lower impedanceImprove conductivityEpicardial electrodesSurgical needlesVeinCardiac arrhythmia
Devices and methods provide for ablation of cardiac tissue for treating cardiac arrhythmias such as atrial fibrillation. Although the devices and methods are often be used to ablate epicardial tissue in the vicinity of at least one pulmonary vein, various embodiments may be used to ablate other cardiac tissues in other locations on a heart. Devices generally include at least one tissue contacting member for contacting epicardial tissue and securing the ablation device to the epicardial tissue, and at least one ablation member for ablating the tissue. Various embodiments include features, such as suction apertures, which enable the device to attach to the epicardial surface with sufficient strength to allow the tissue to be stabilized via the device. For example, some embodiments may be used to stabilize a beating heart to enable a beating heart ablation procedure. Many of the devices may be introduced into a patient via minimally invasive introducer devices and the like. Although devices and methods of the invention may be used to ablate epicardial tissue to treat atrial fibrillation, they may also be used in veterinary or research contexts, to treat various heart conditions other than atrial fibrillation and / or to ablate cardiac tissue other than the epicardium.
Owner:ATRICURE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com