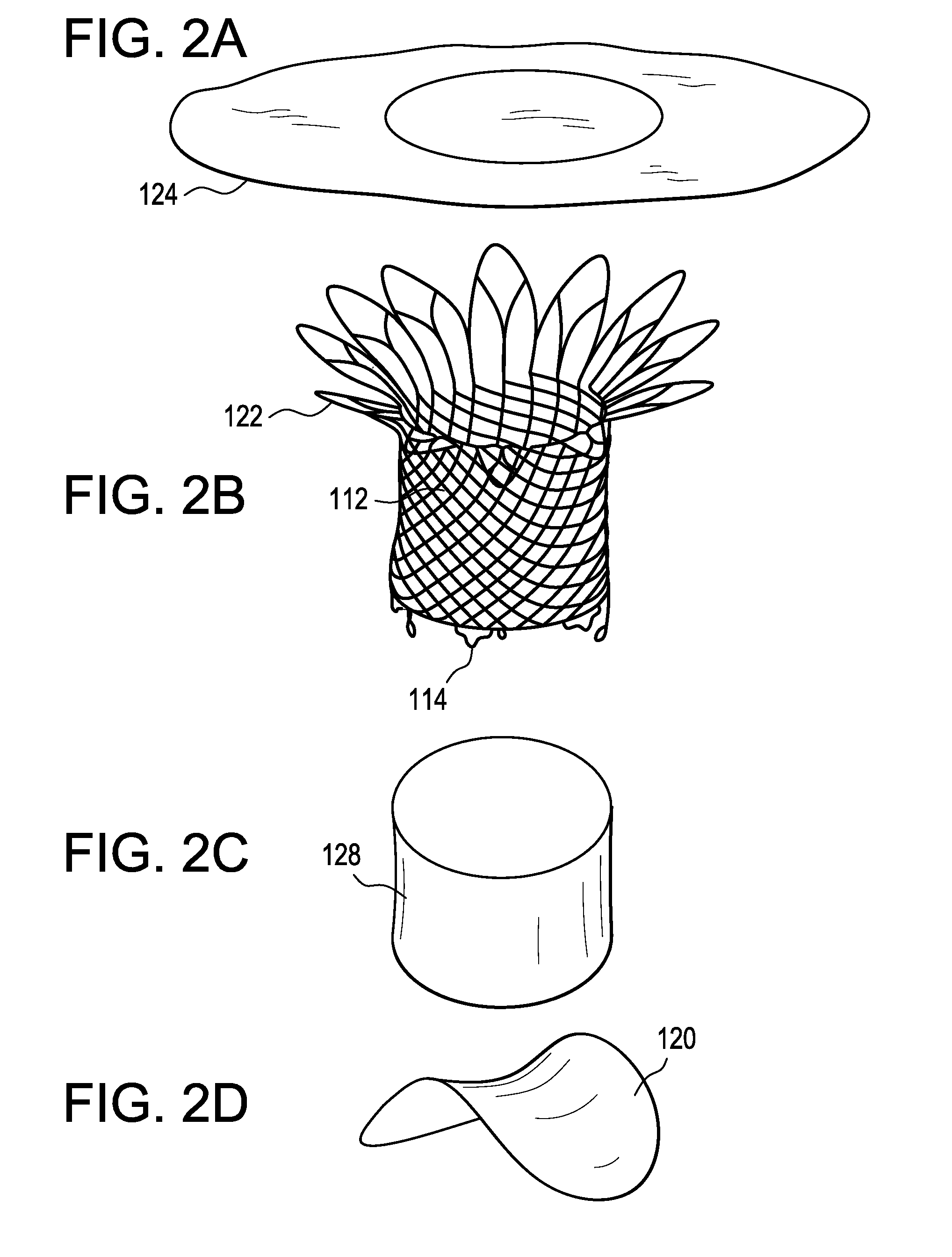
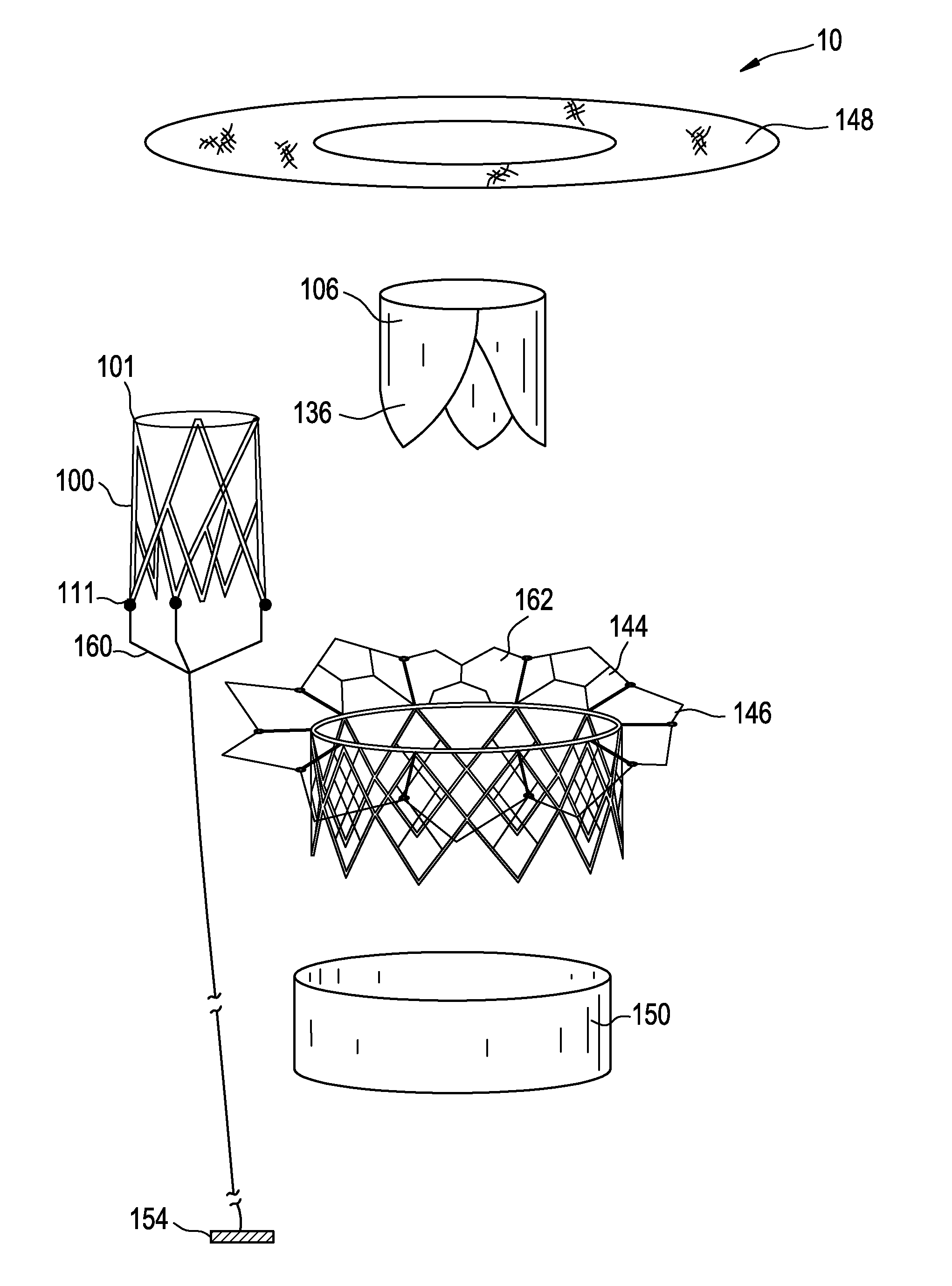
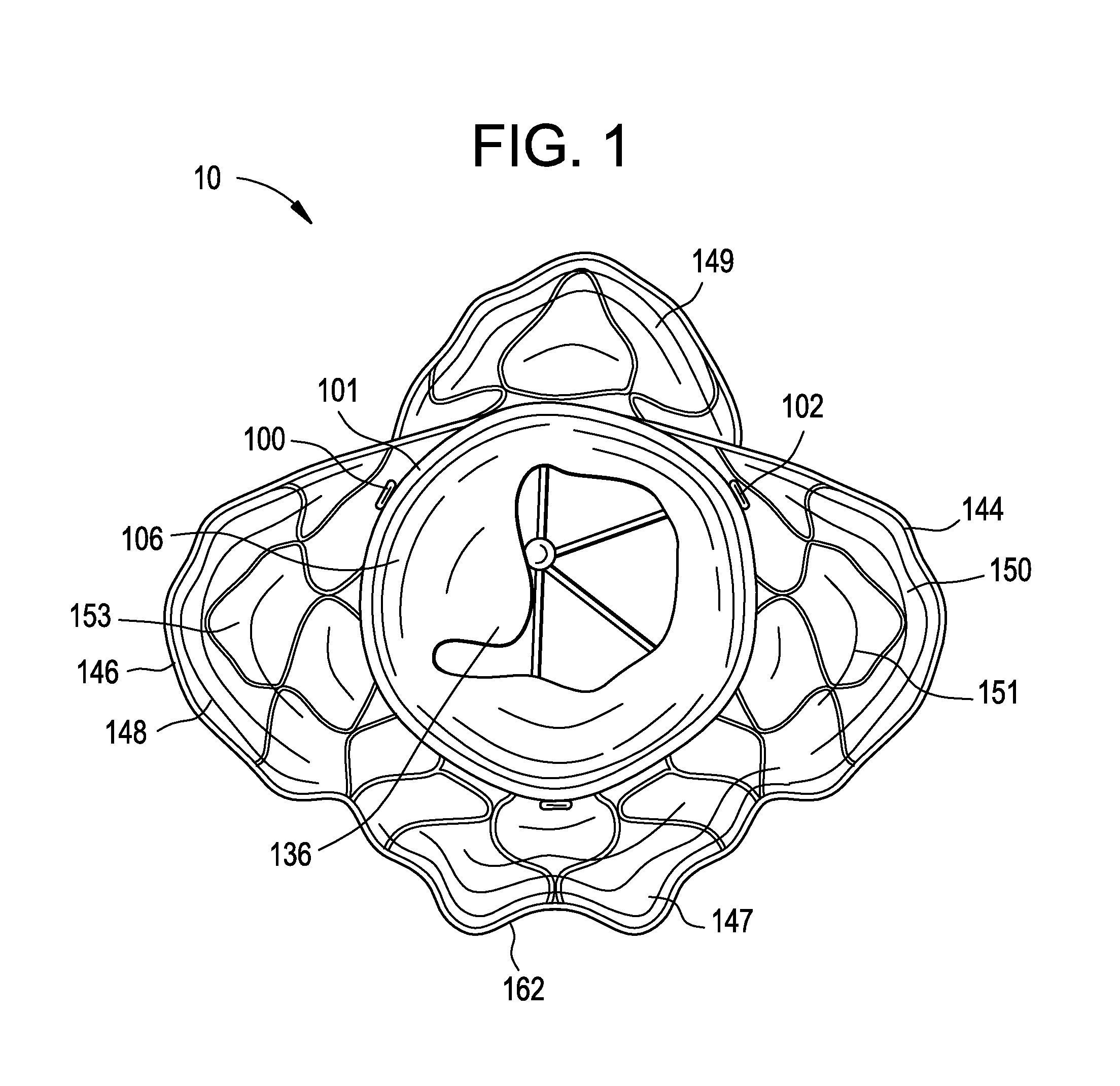
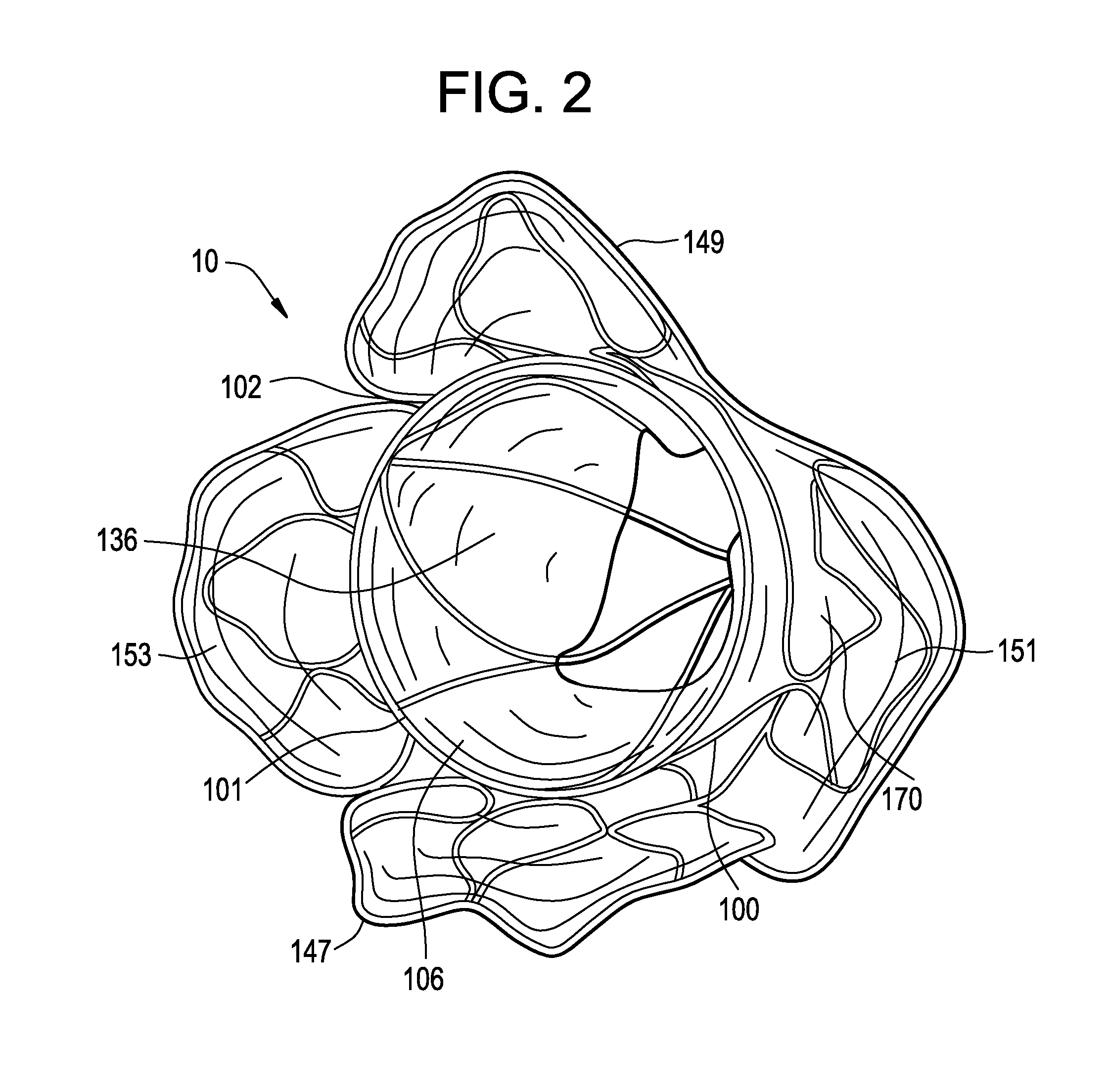
Patents
Literature
138 results about "Tricuspid valve" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
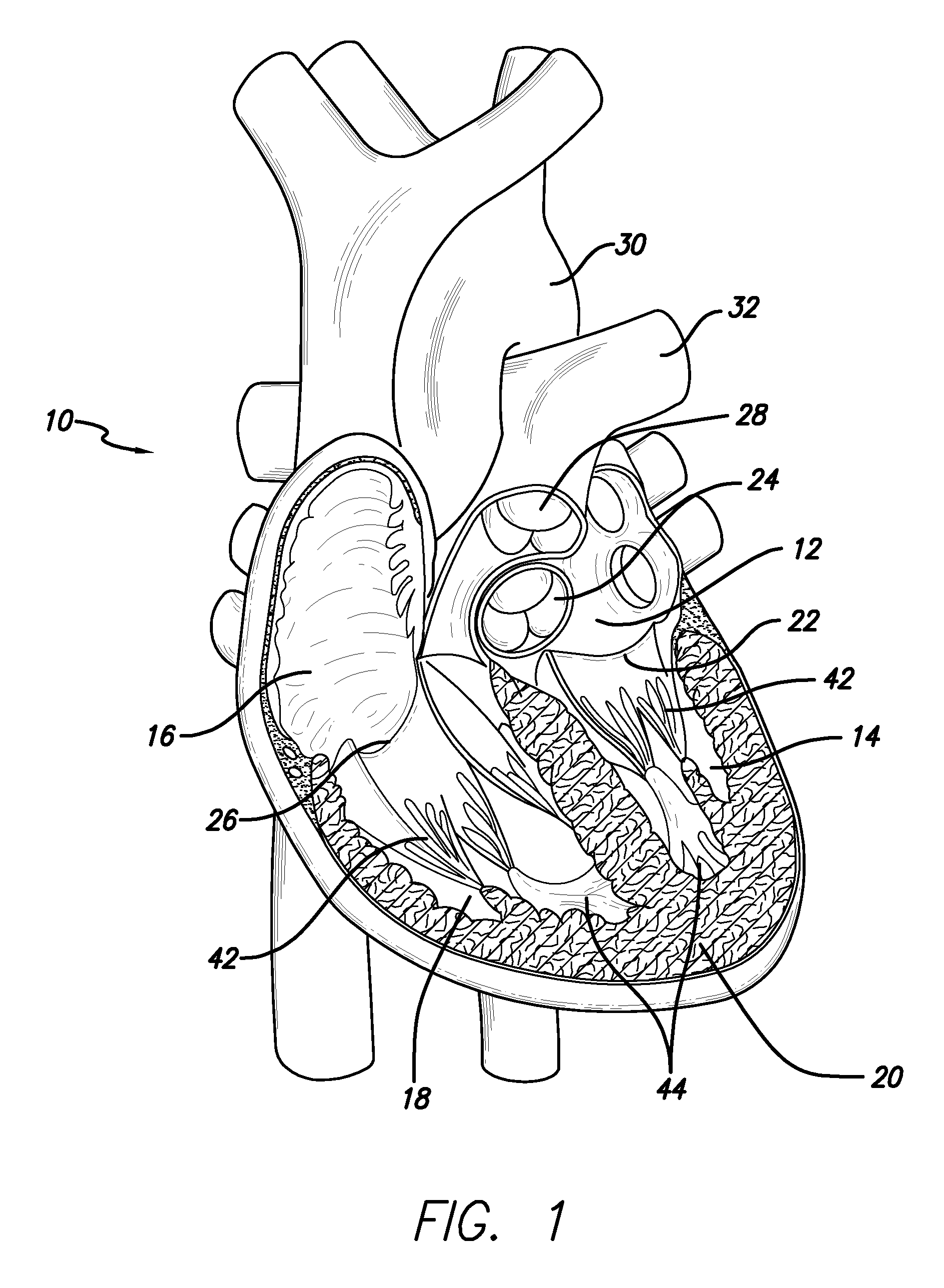
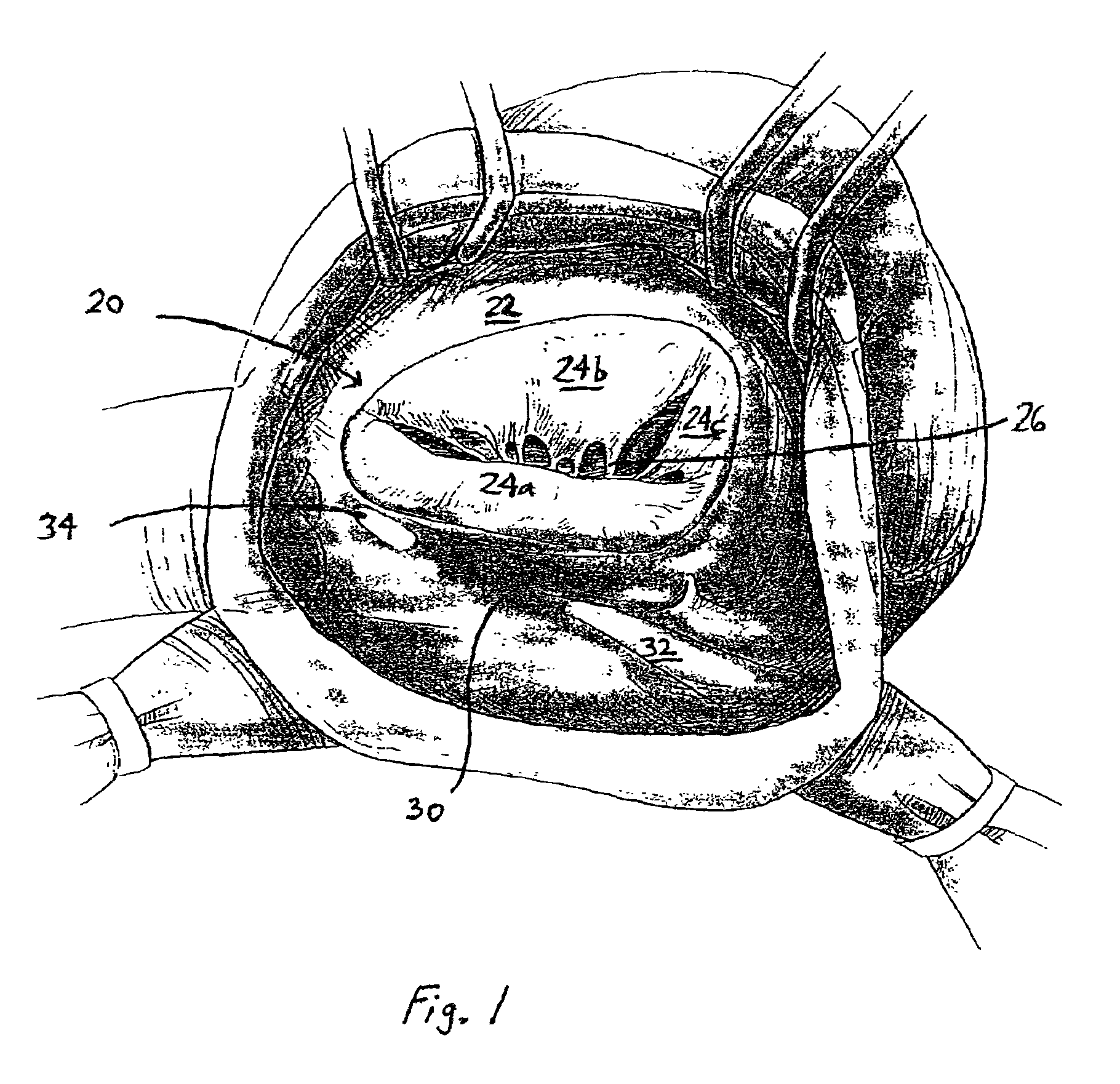
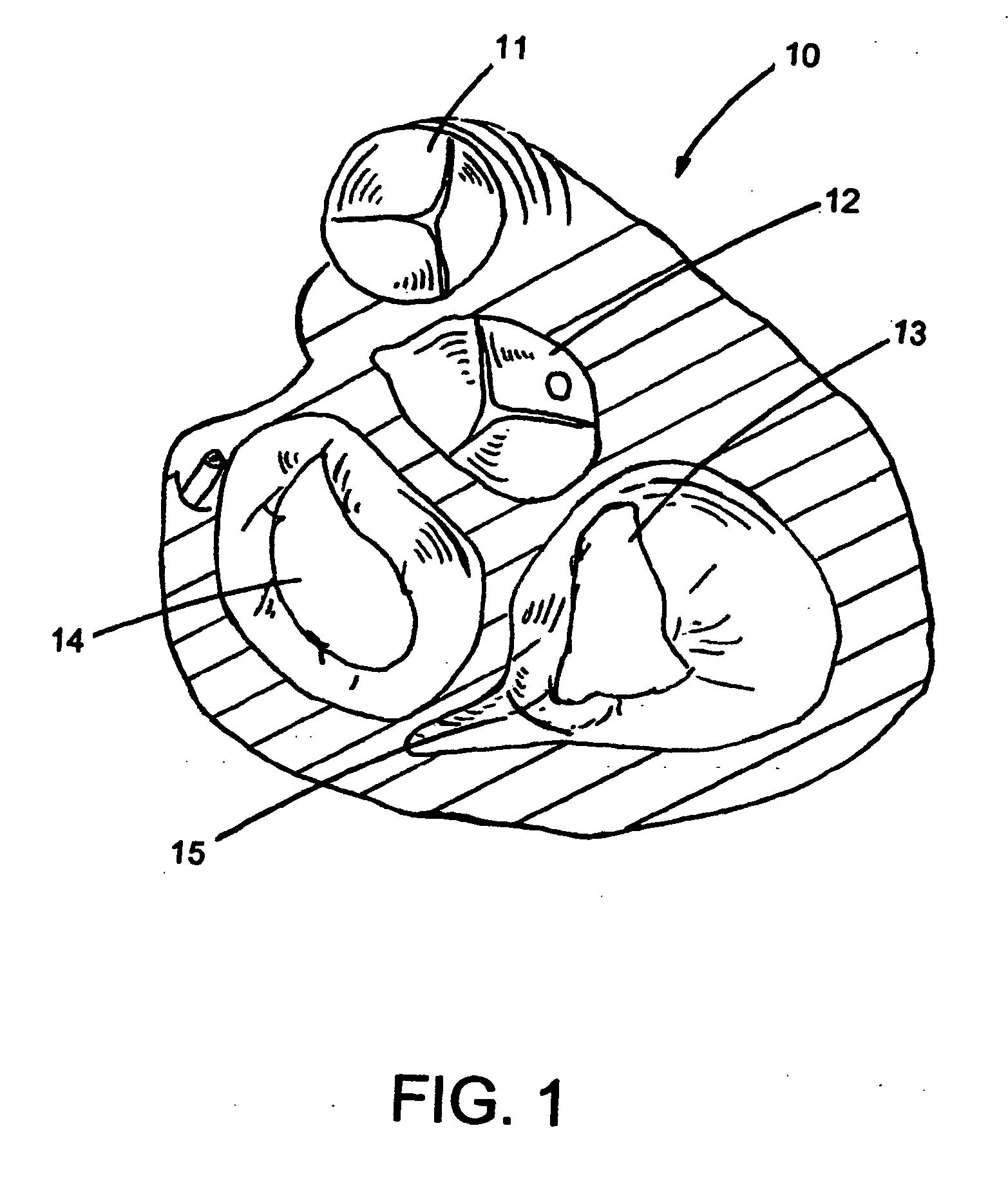
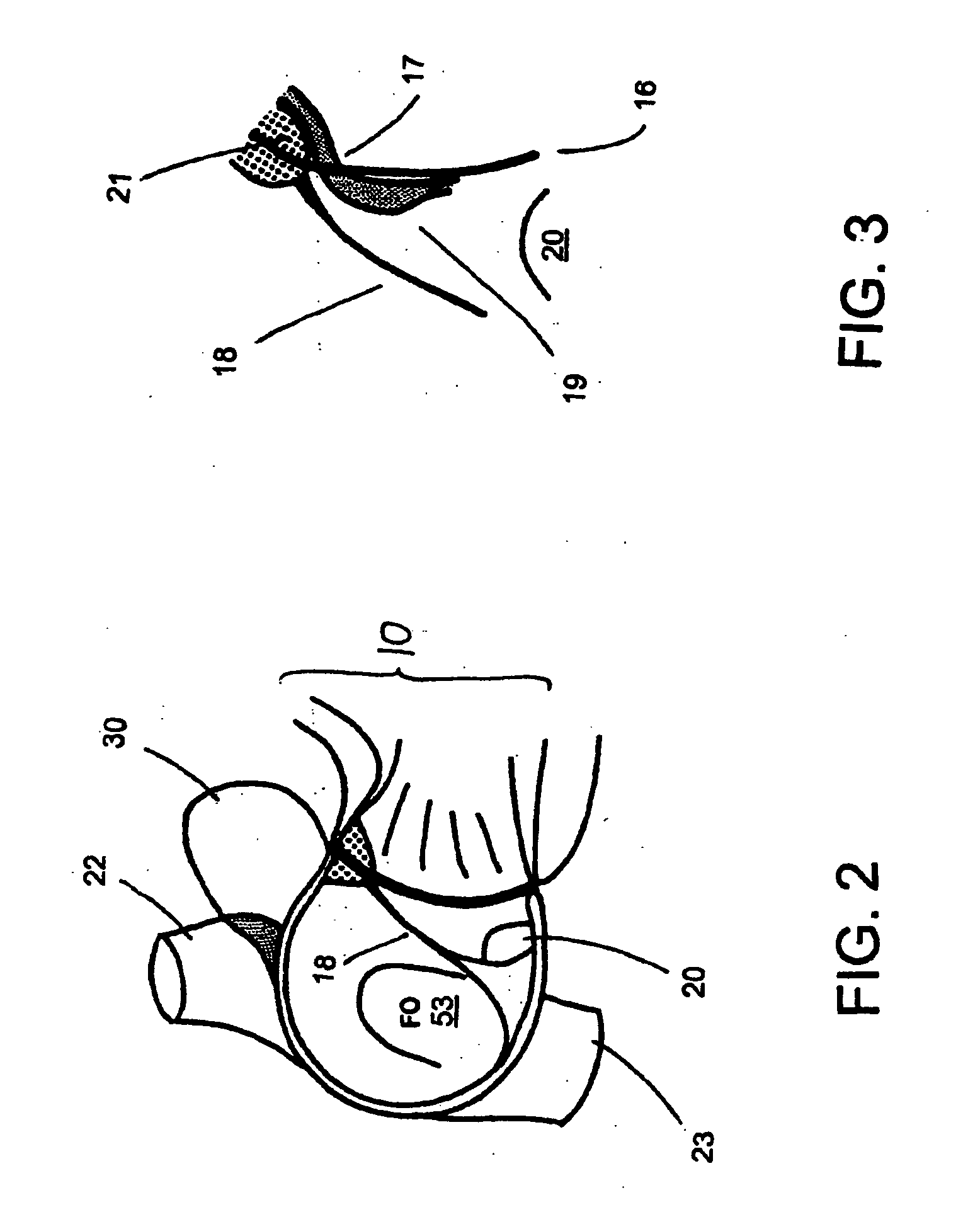
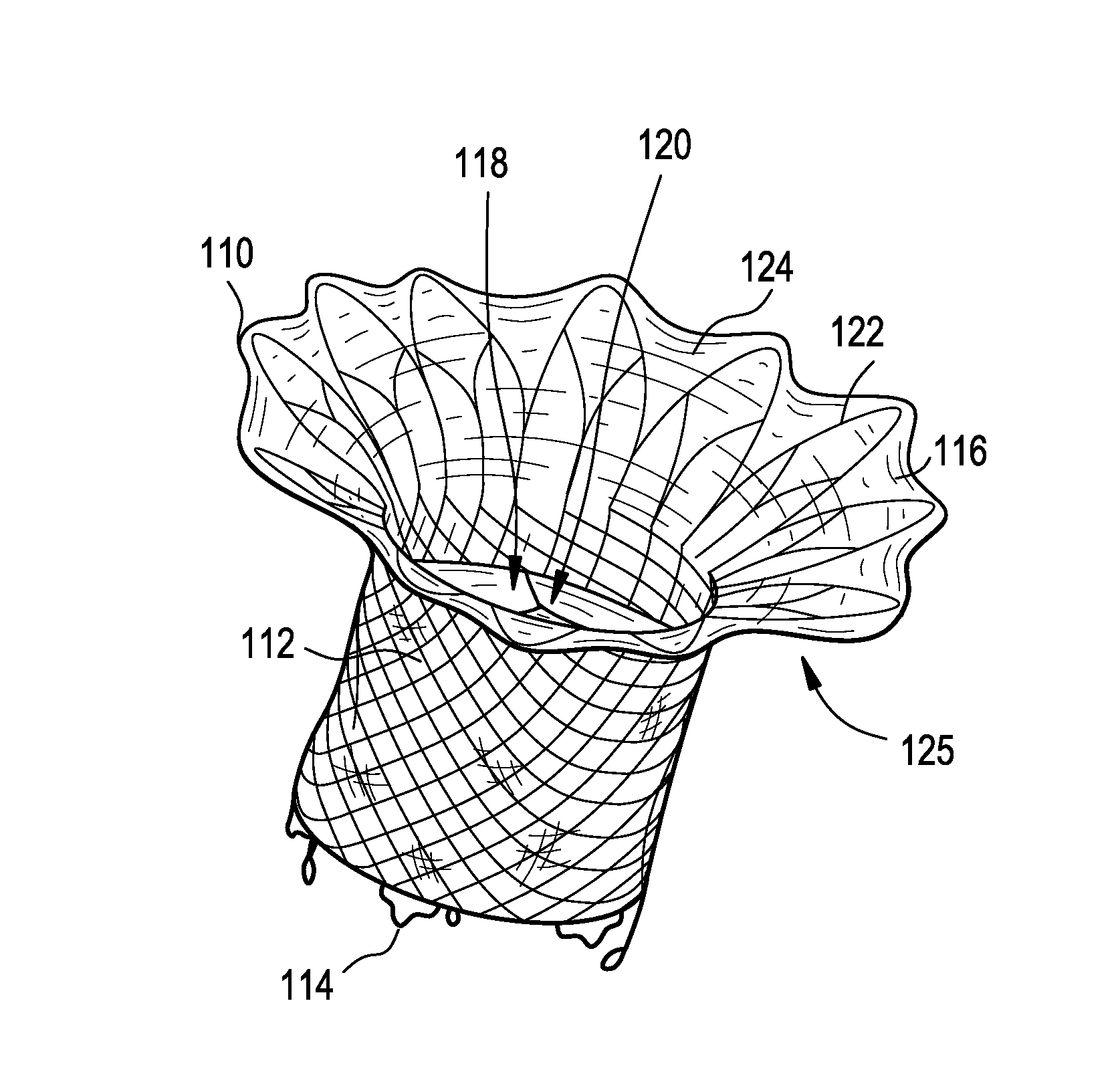
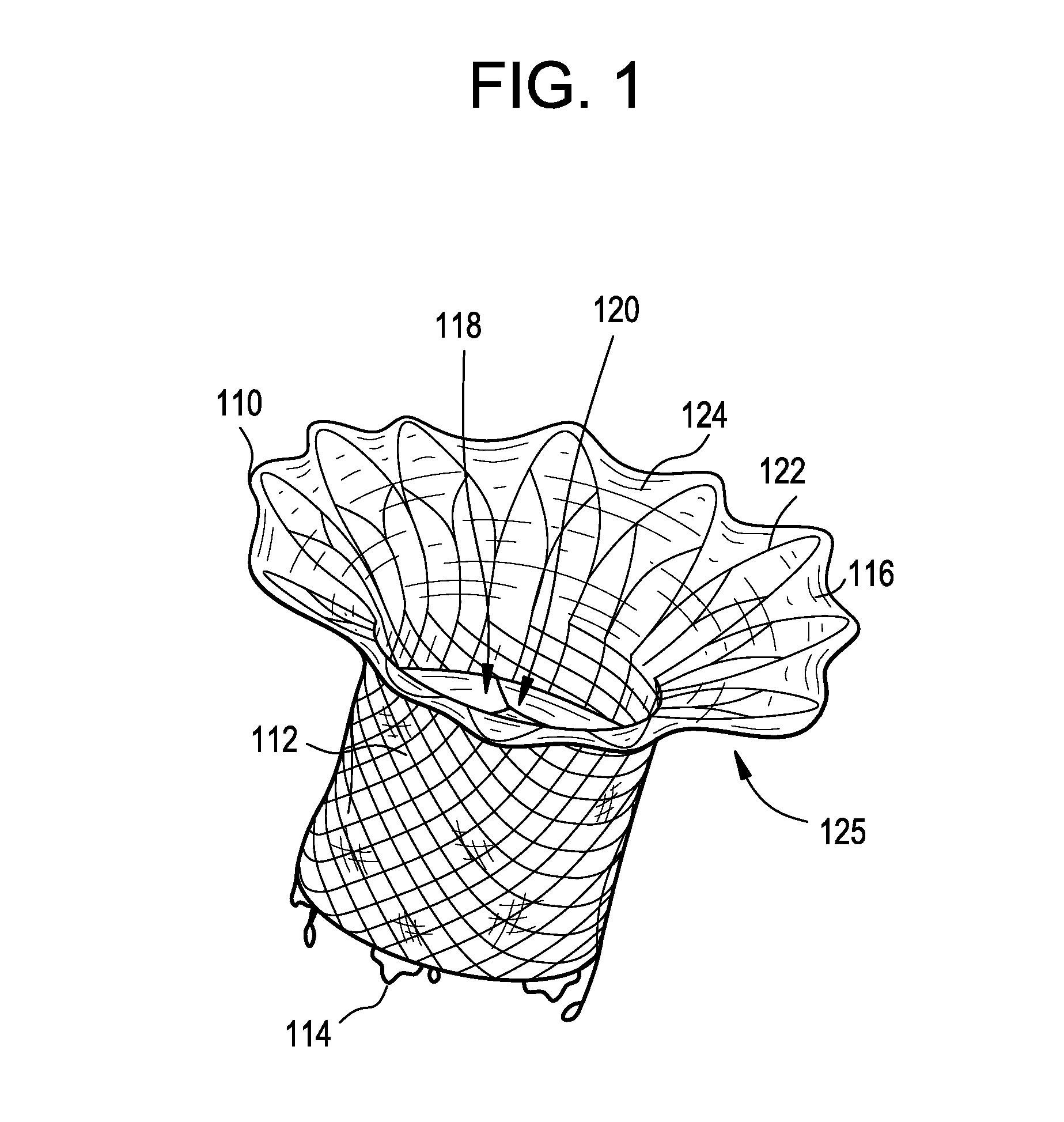
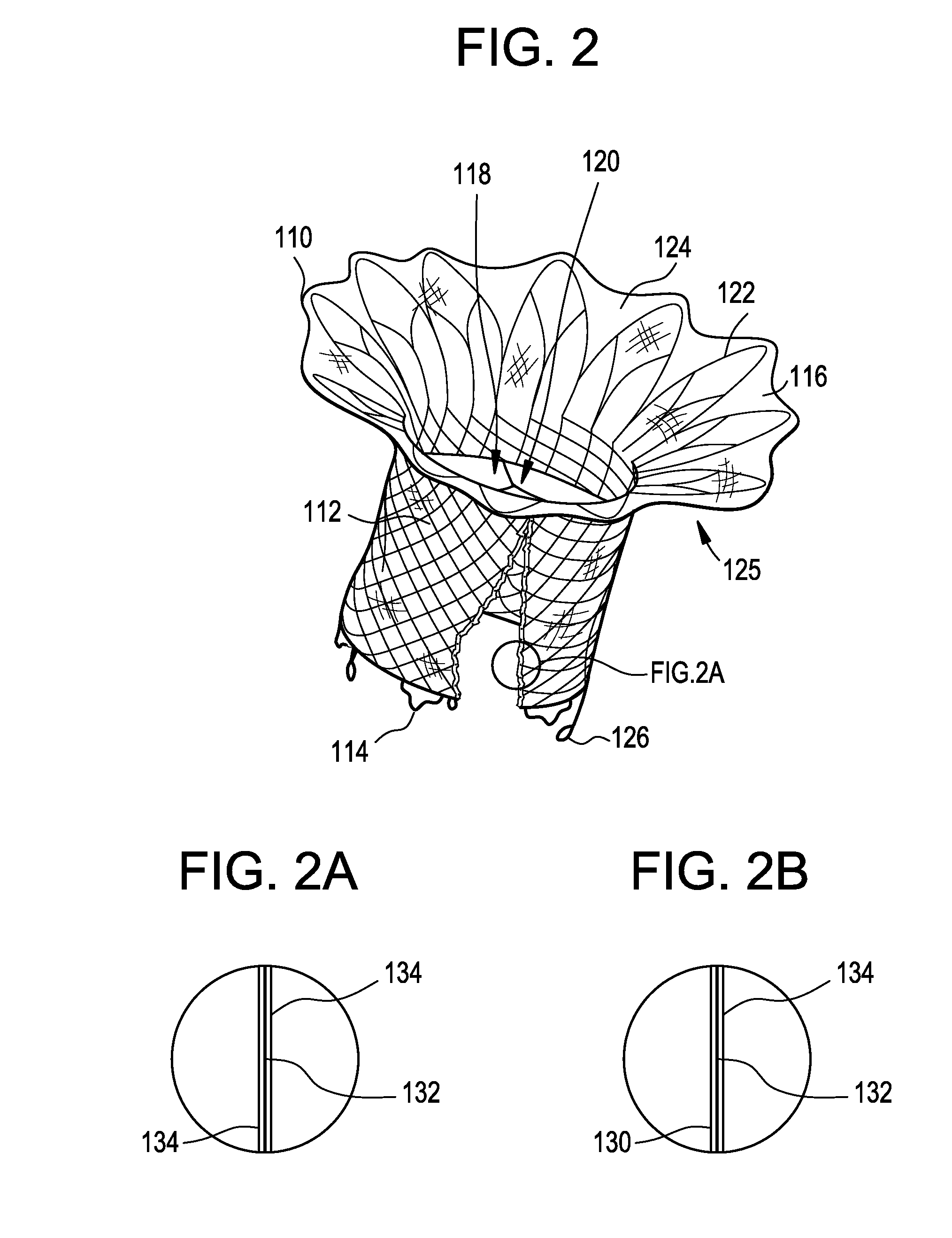
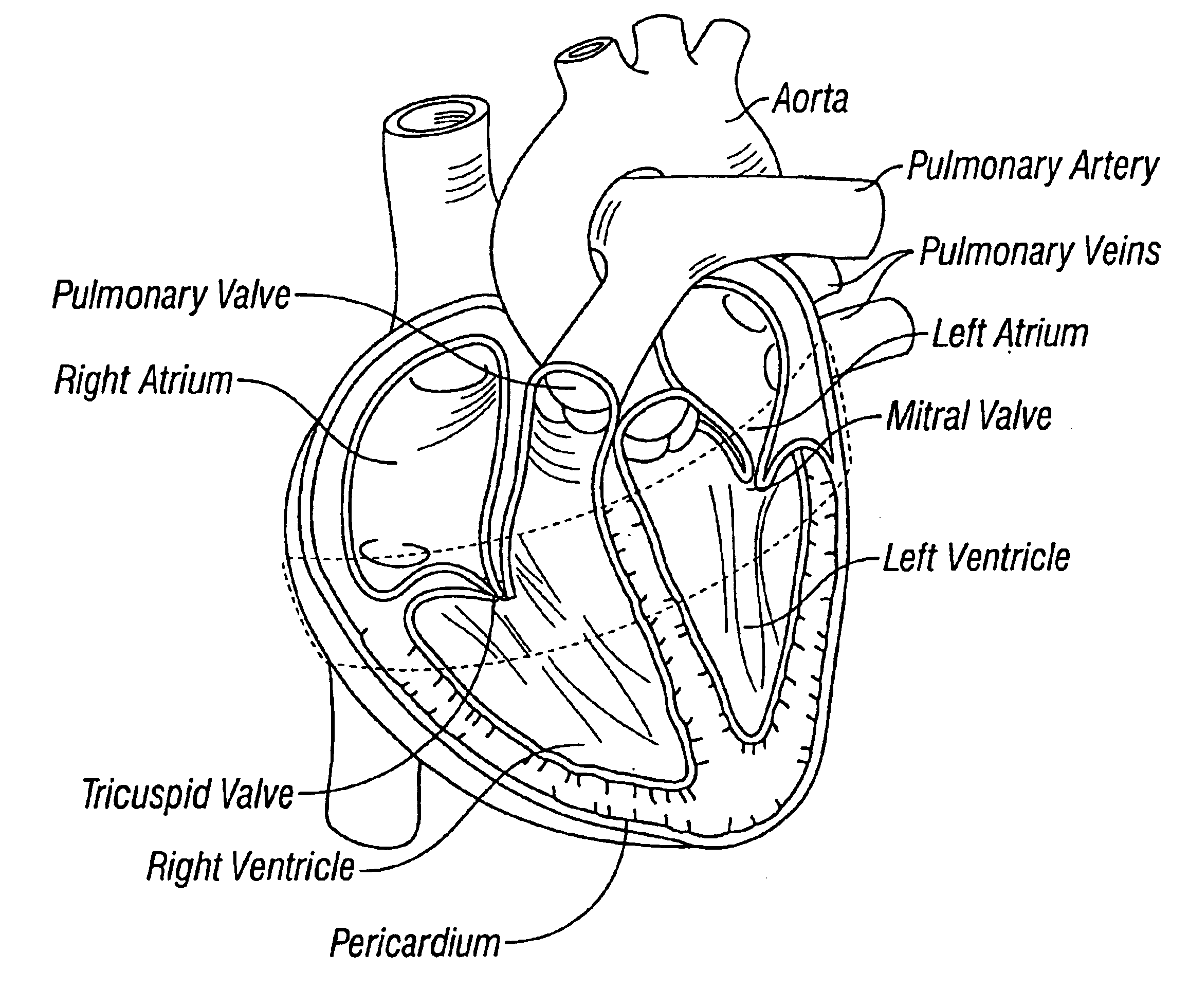
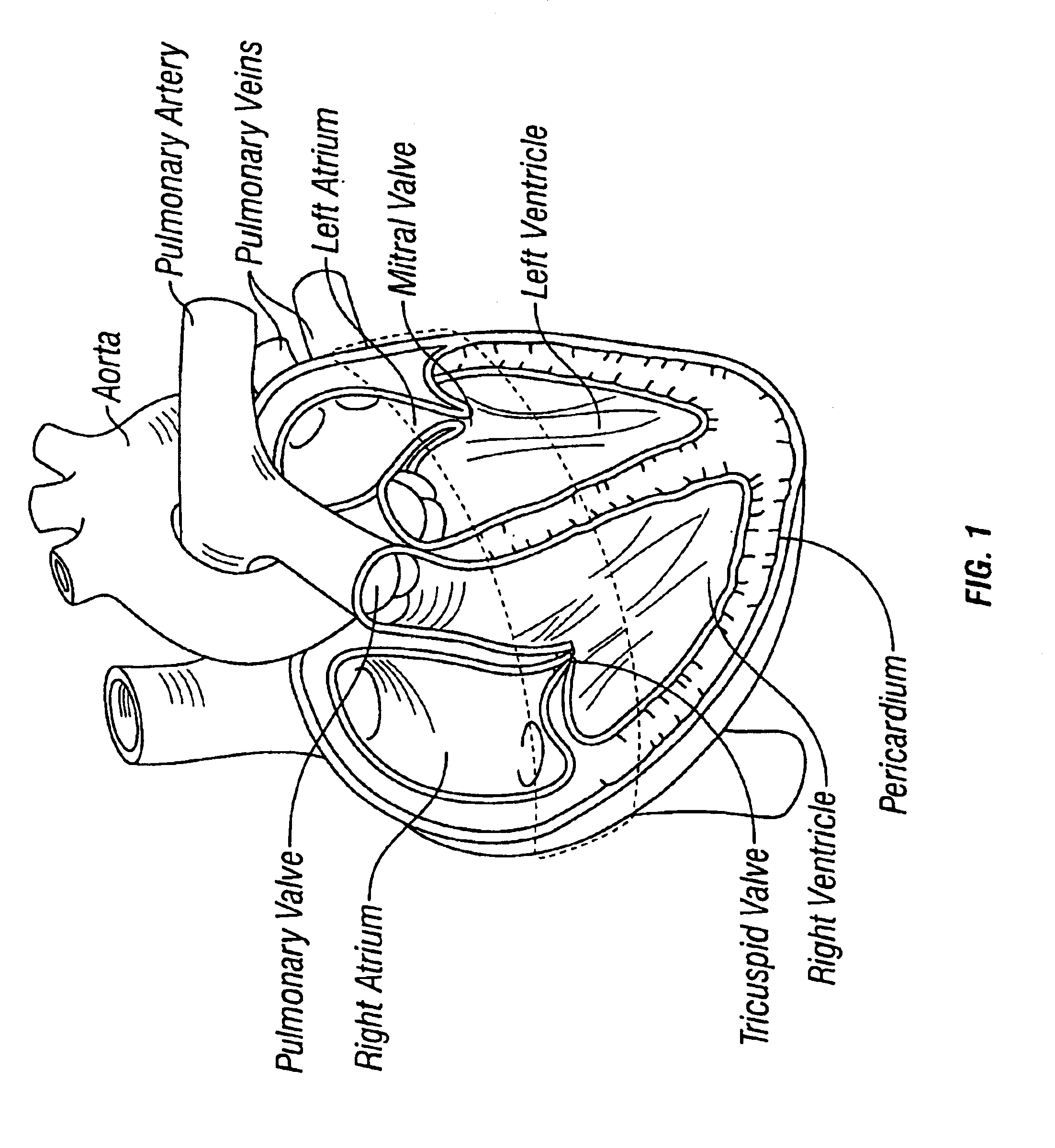
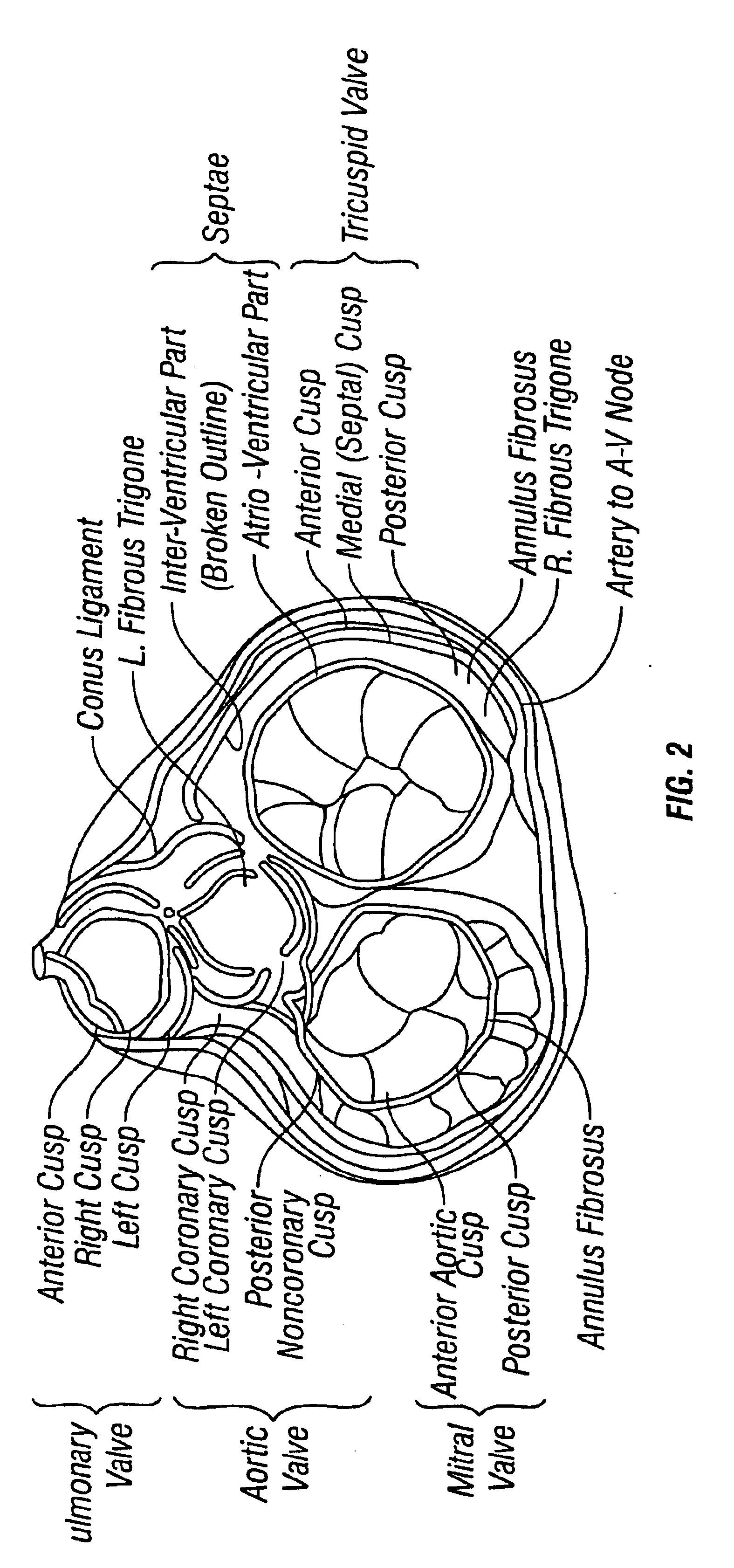
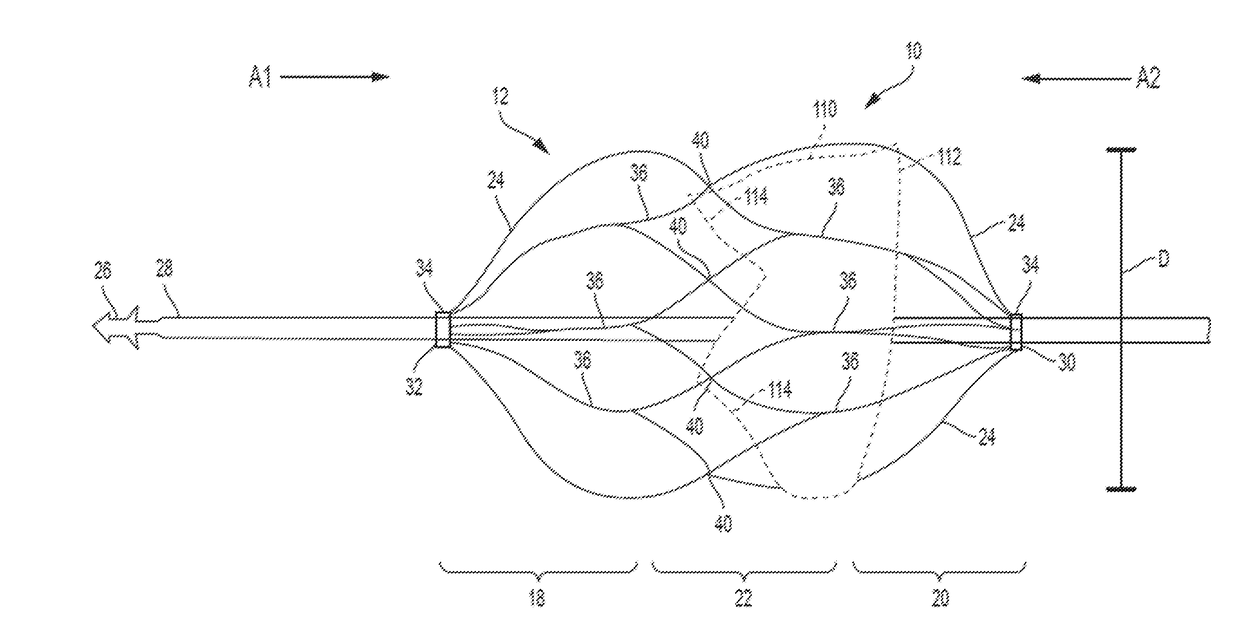
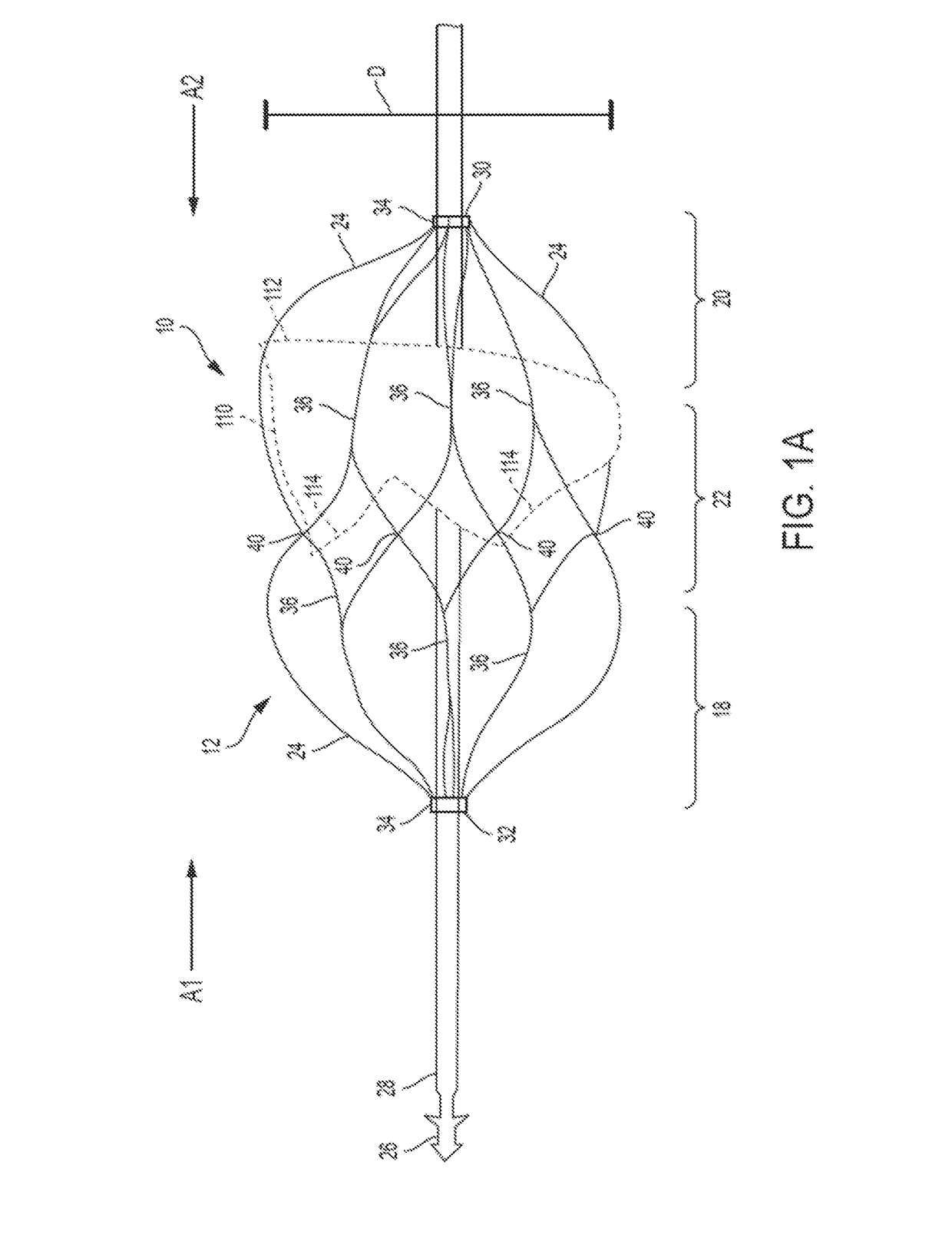
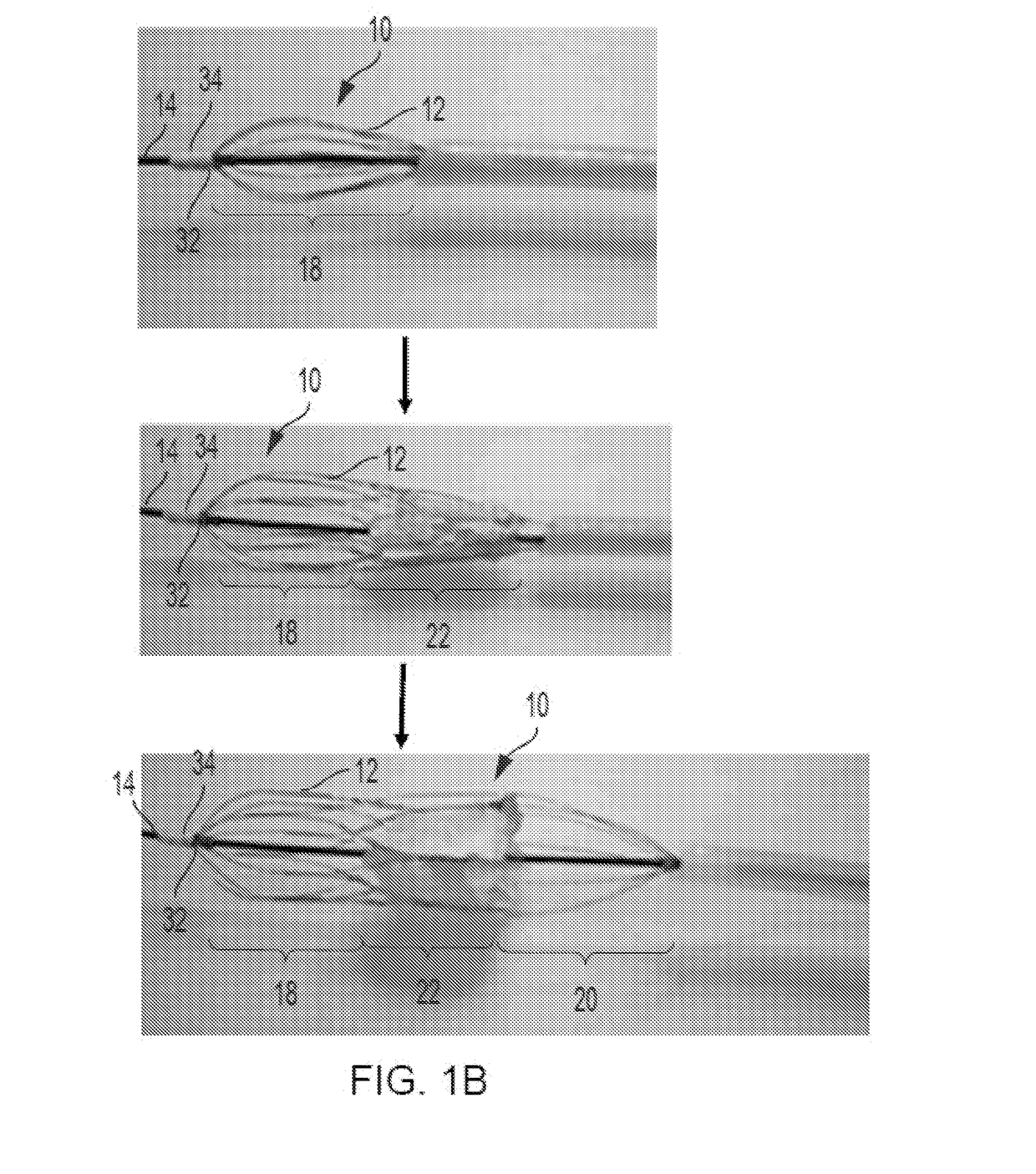
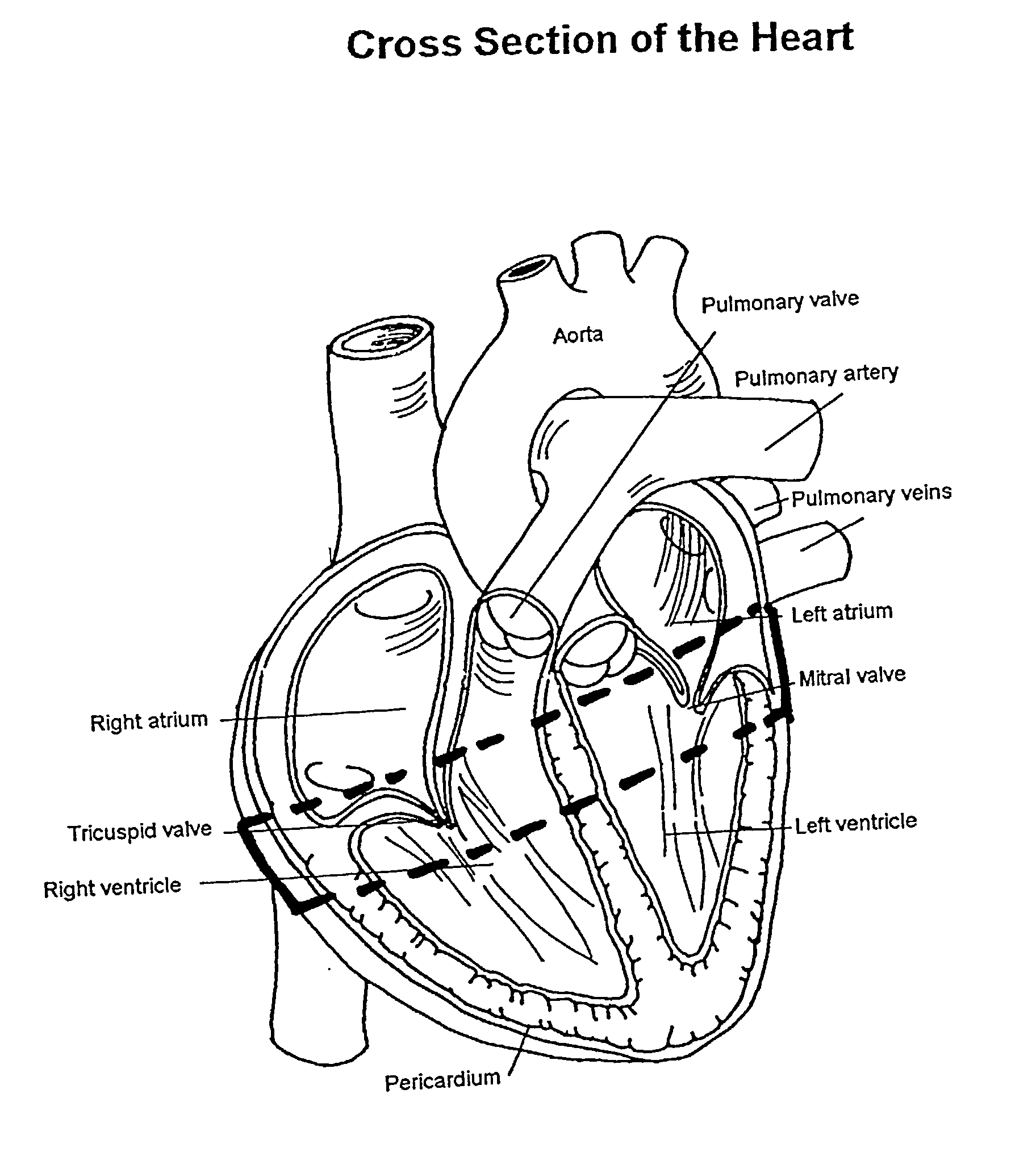
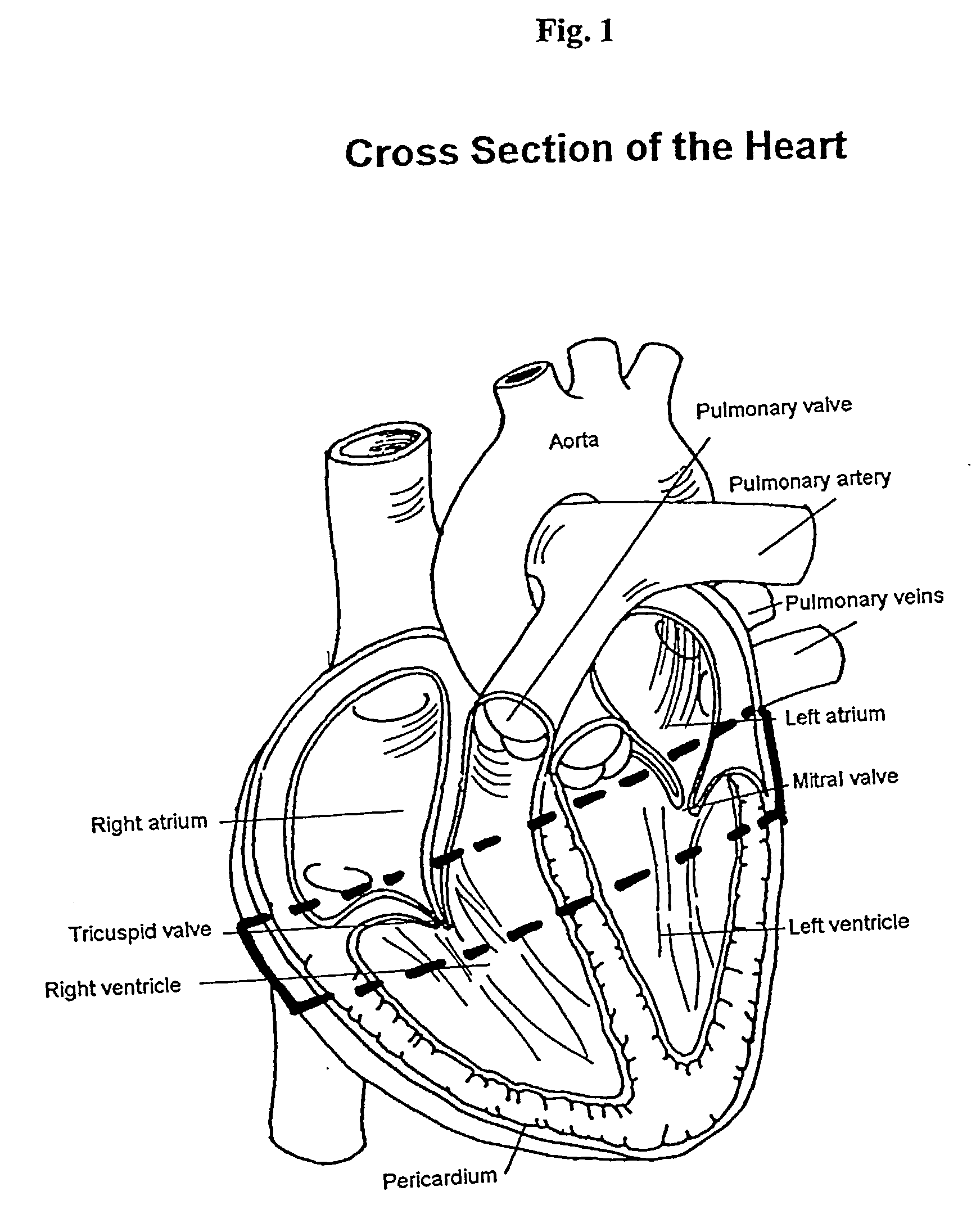
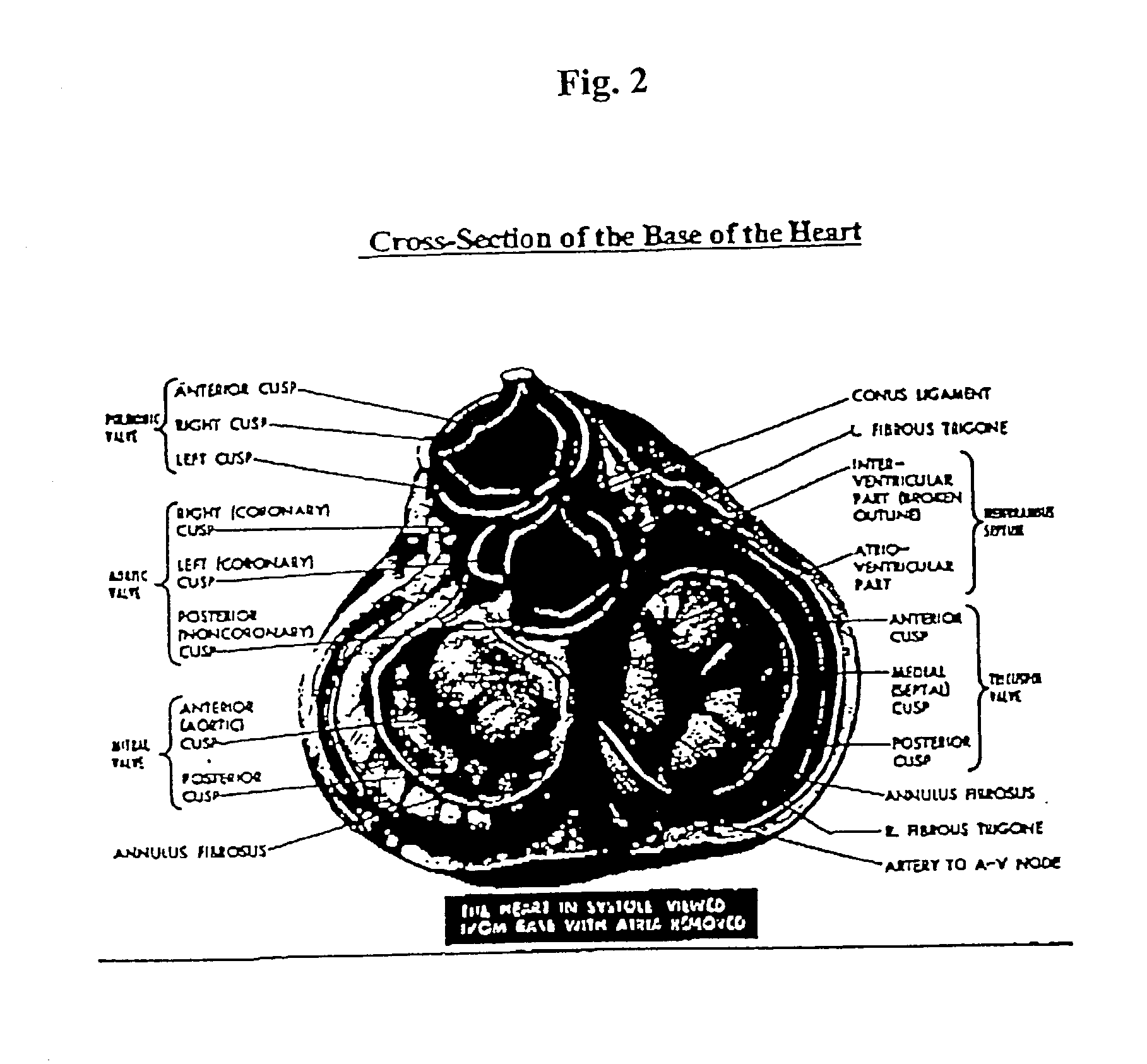
The tricuspid valve, or right atrioventricular valve, is on the right dorsal side of the mammalian heart, at the superior portion of the right ventricle. The function of the valve is to prevent back flow (regurgitation) of blood from the right ventricle into the right atrium during right ventricular contraction: systole.
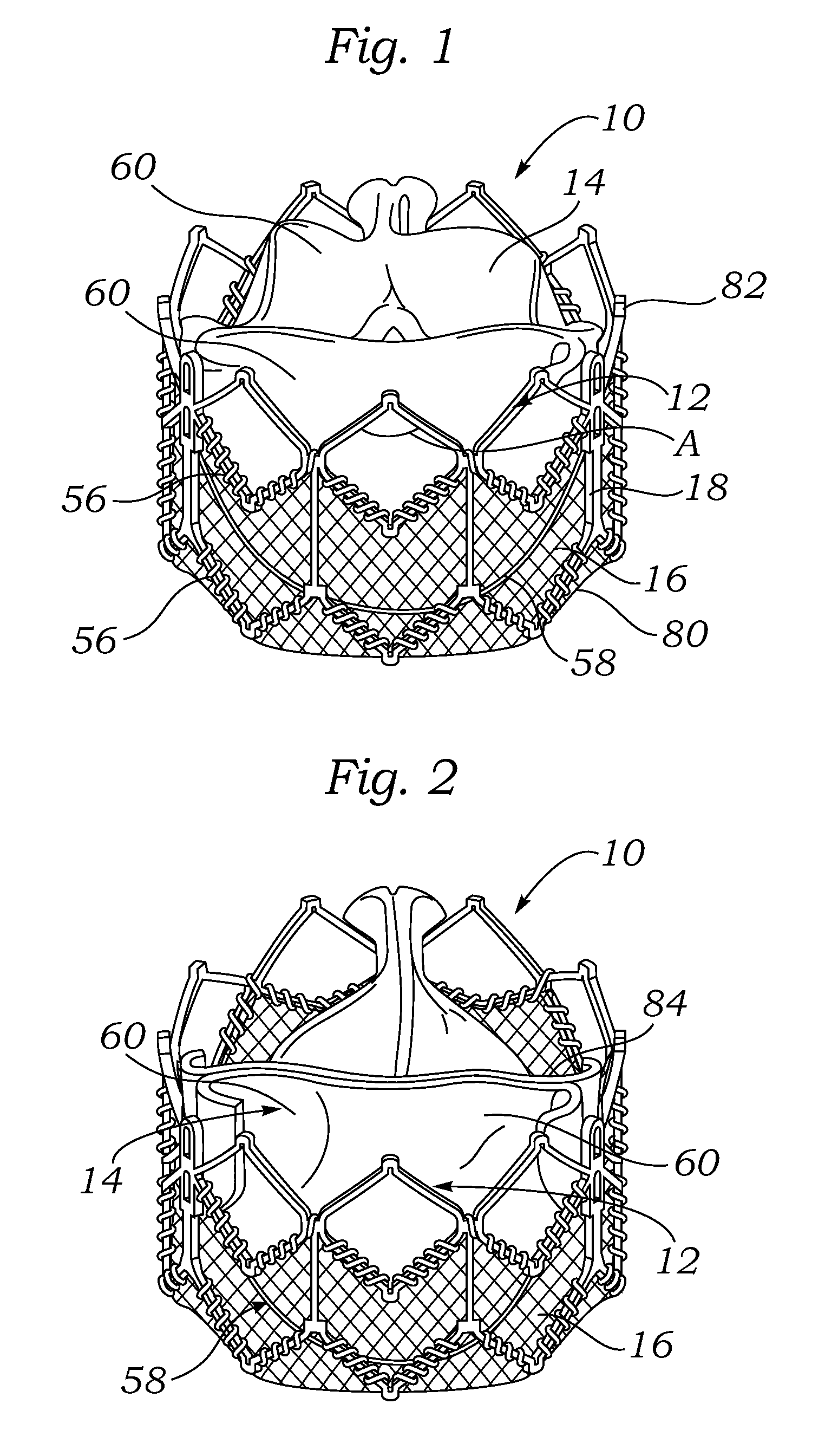
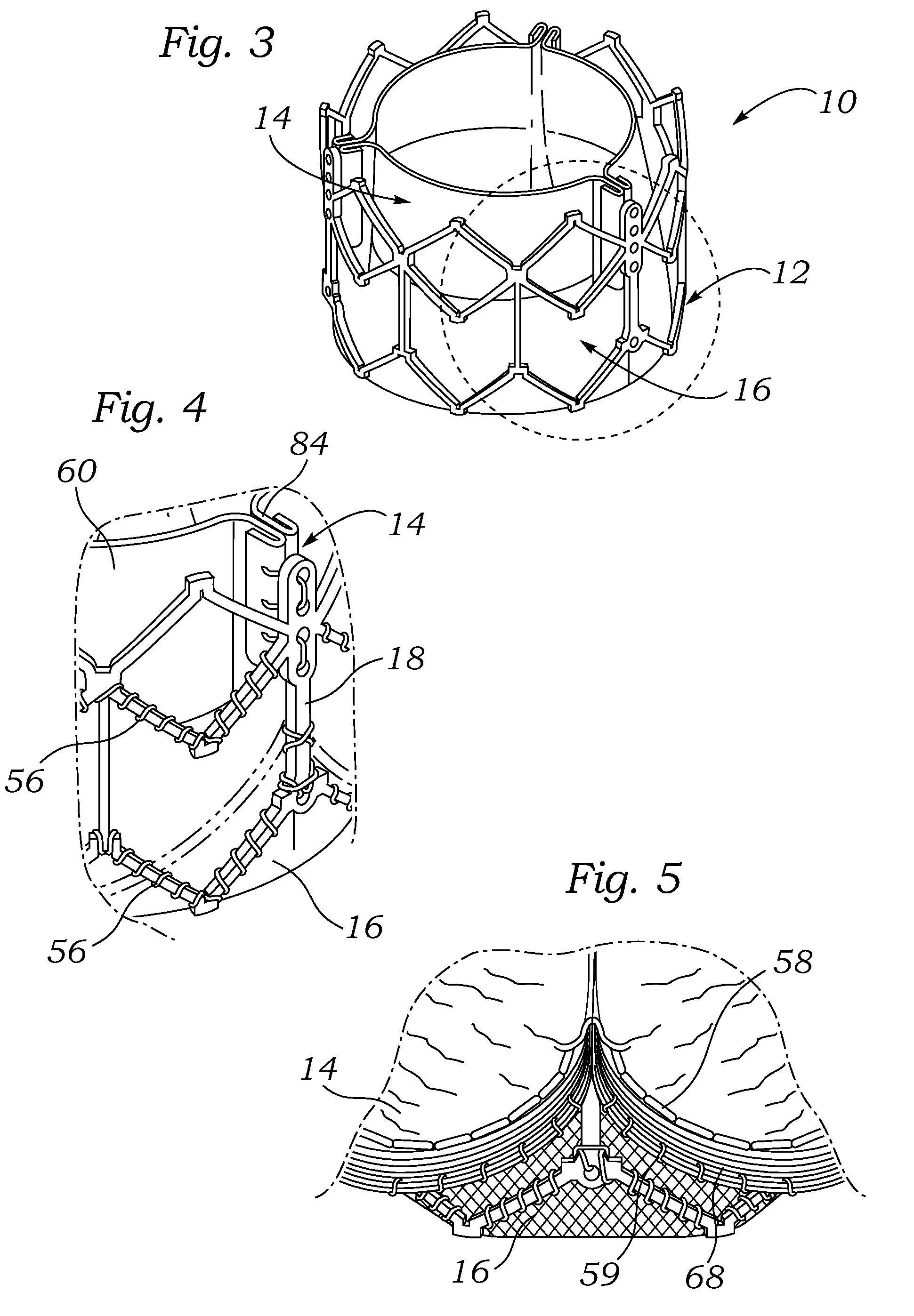
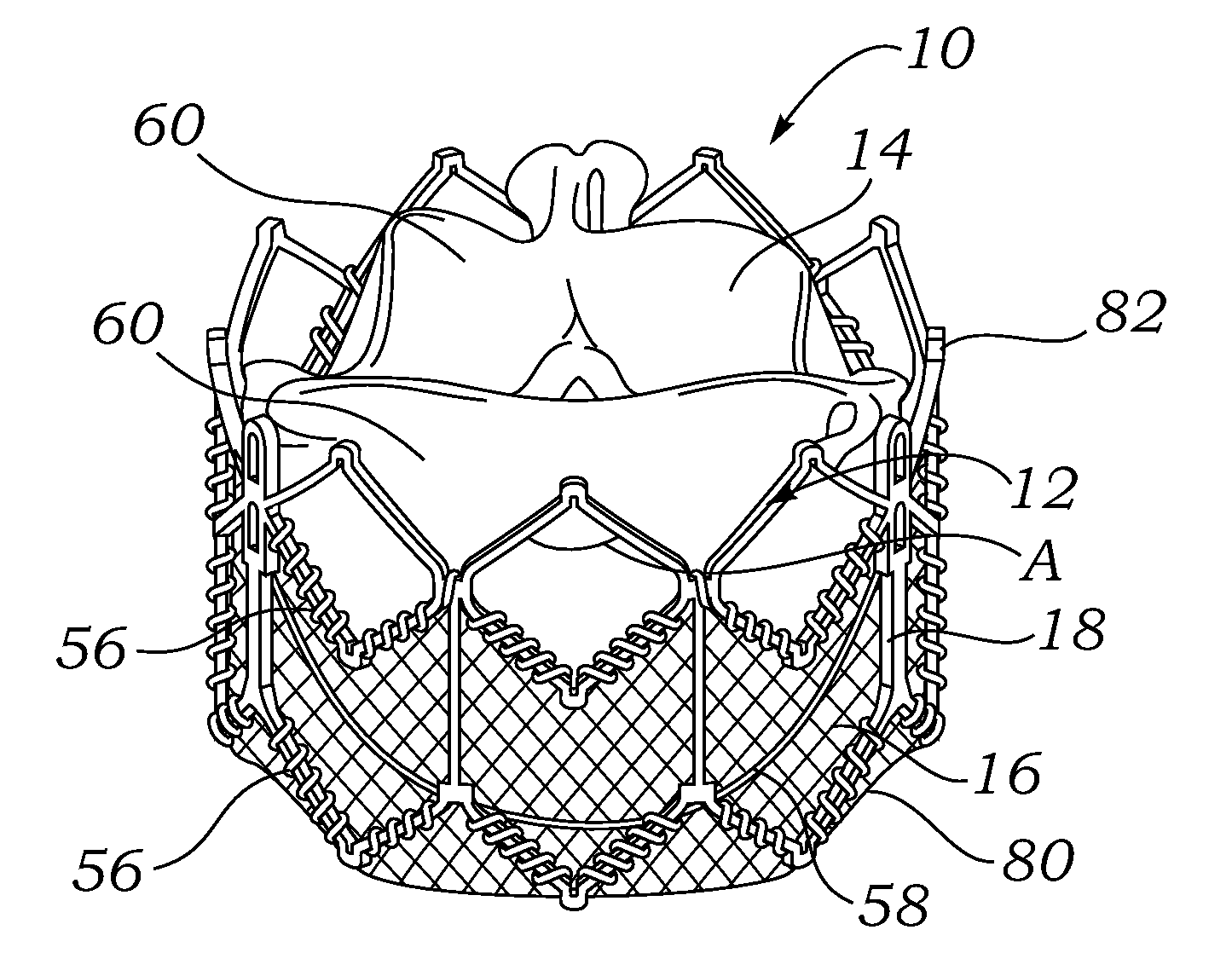
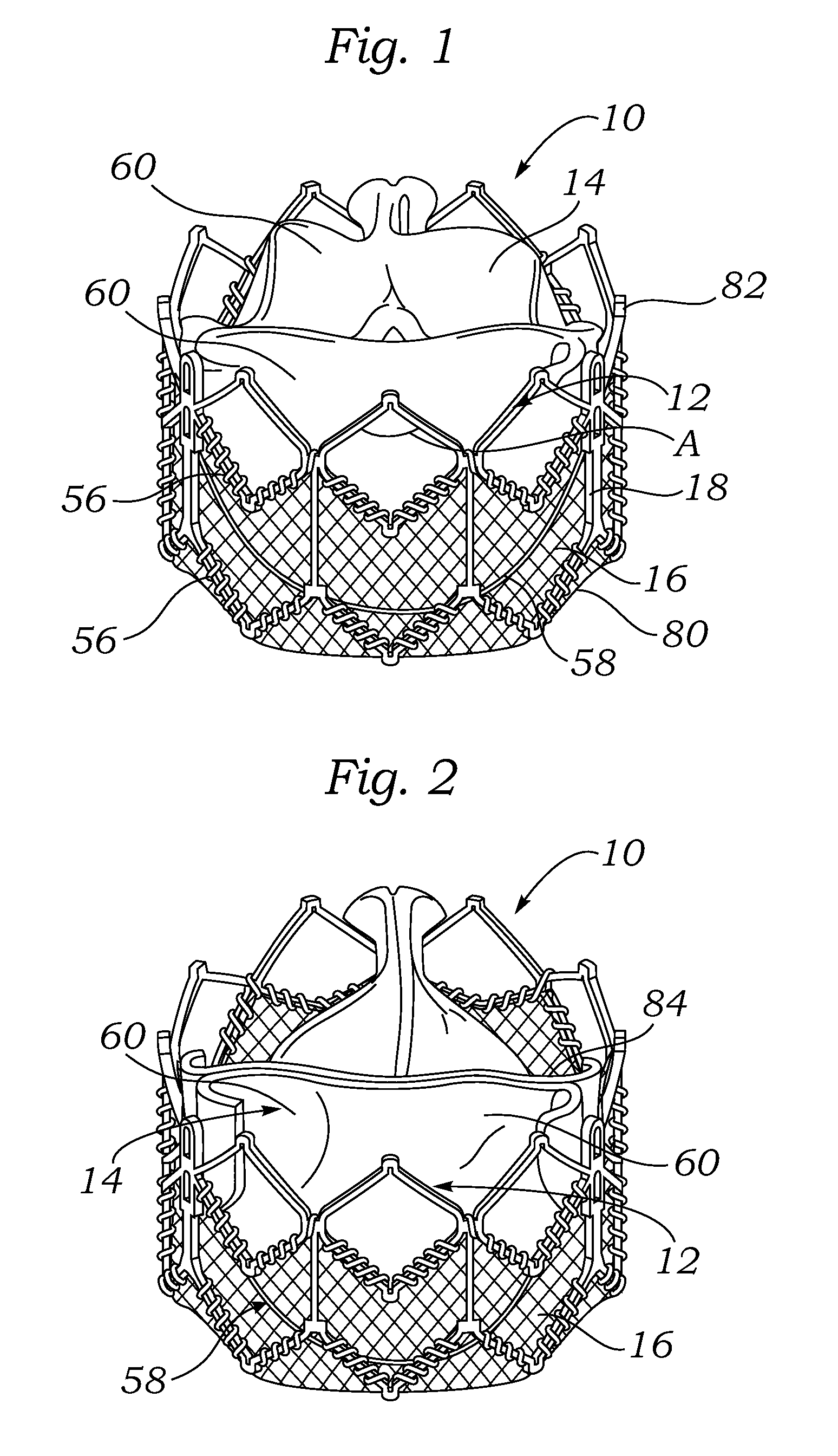
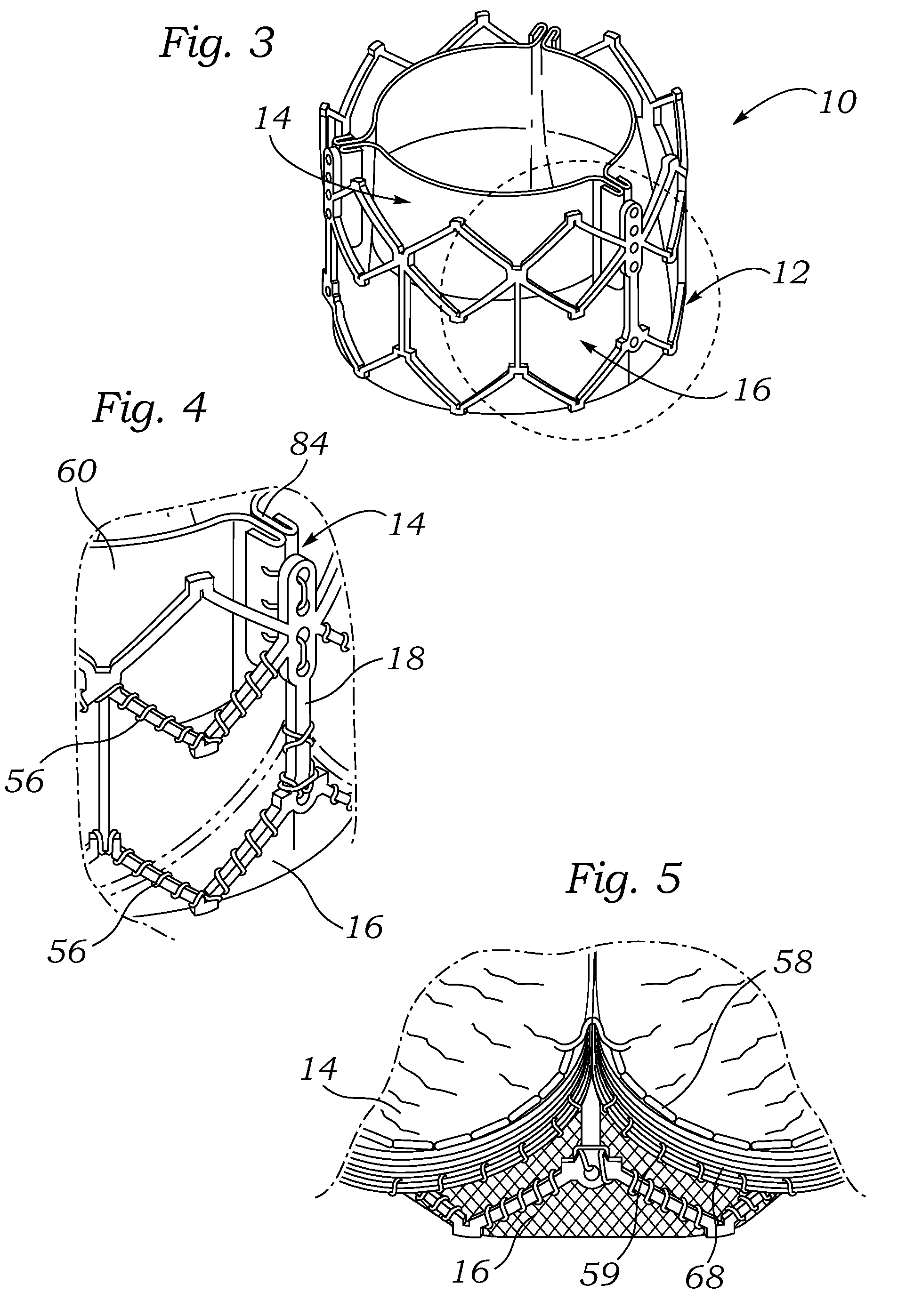
Percutaneous heart valve
ActiveUS20070016286A1Avoid flowStability and functioning of the heart valve are satisfactoryHeart valvesBlood flowValvular prosthesis
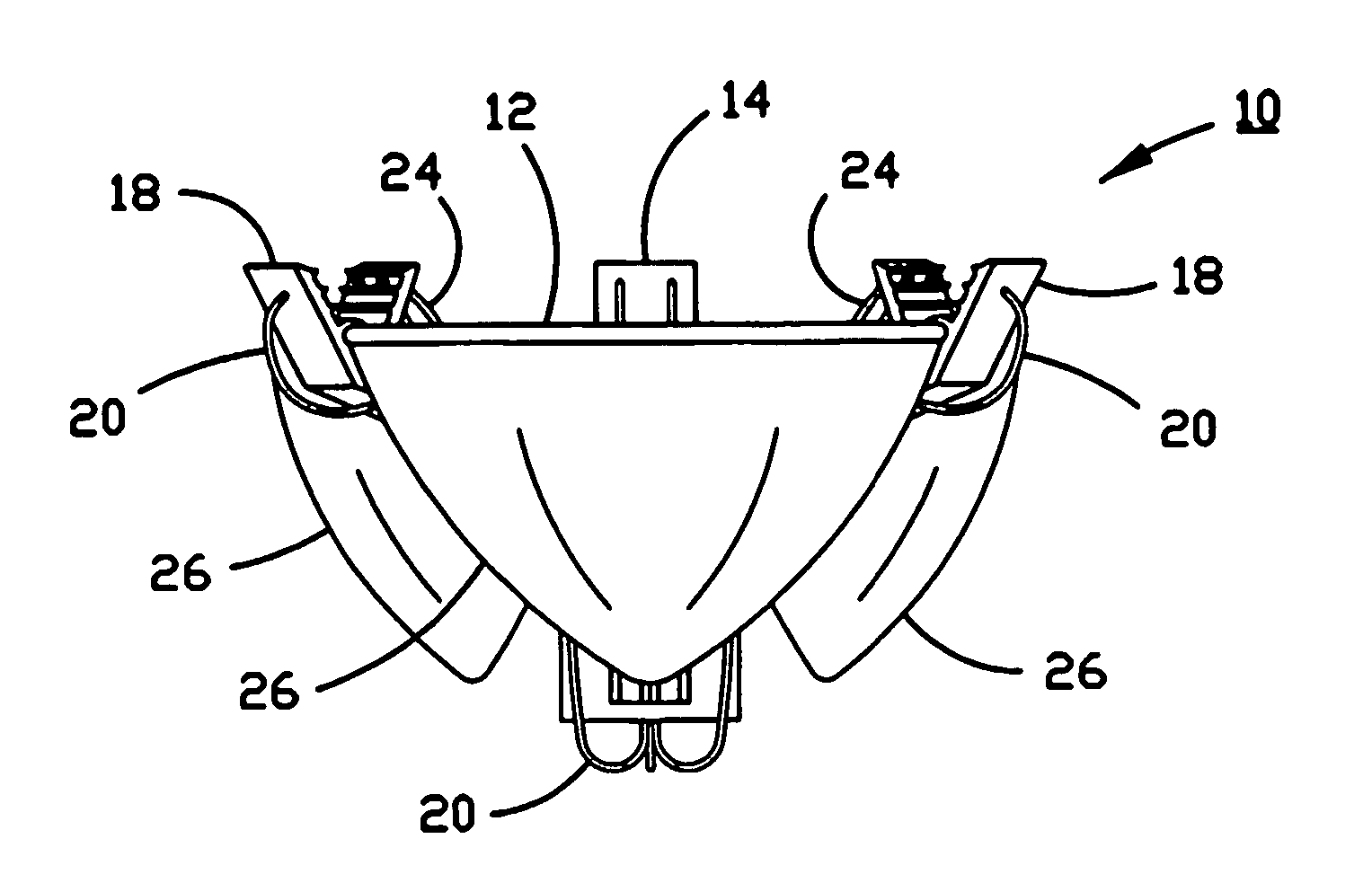
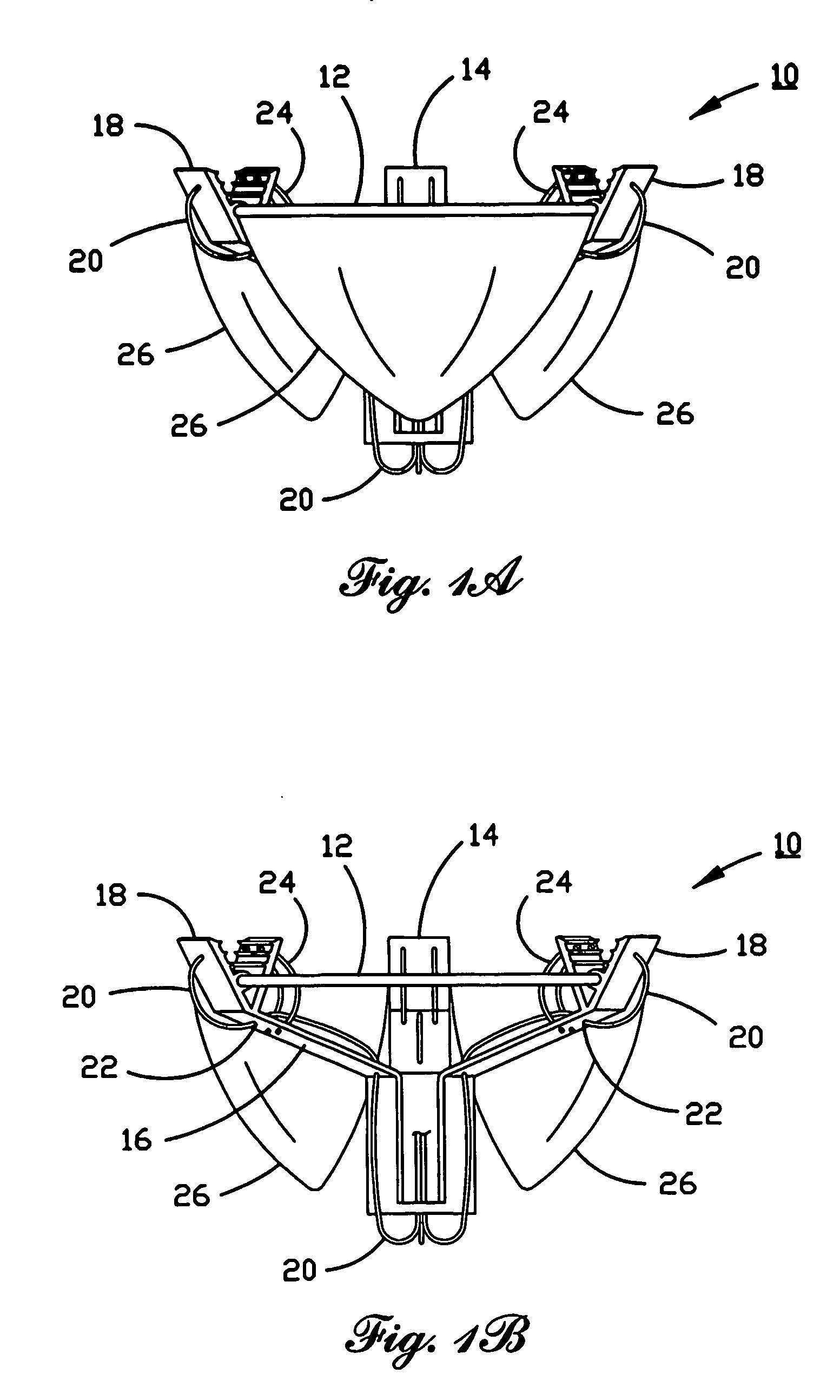
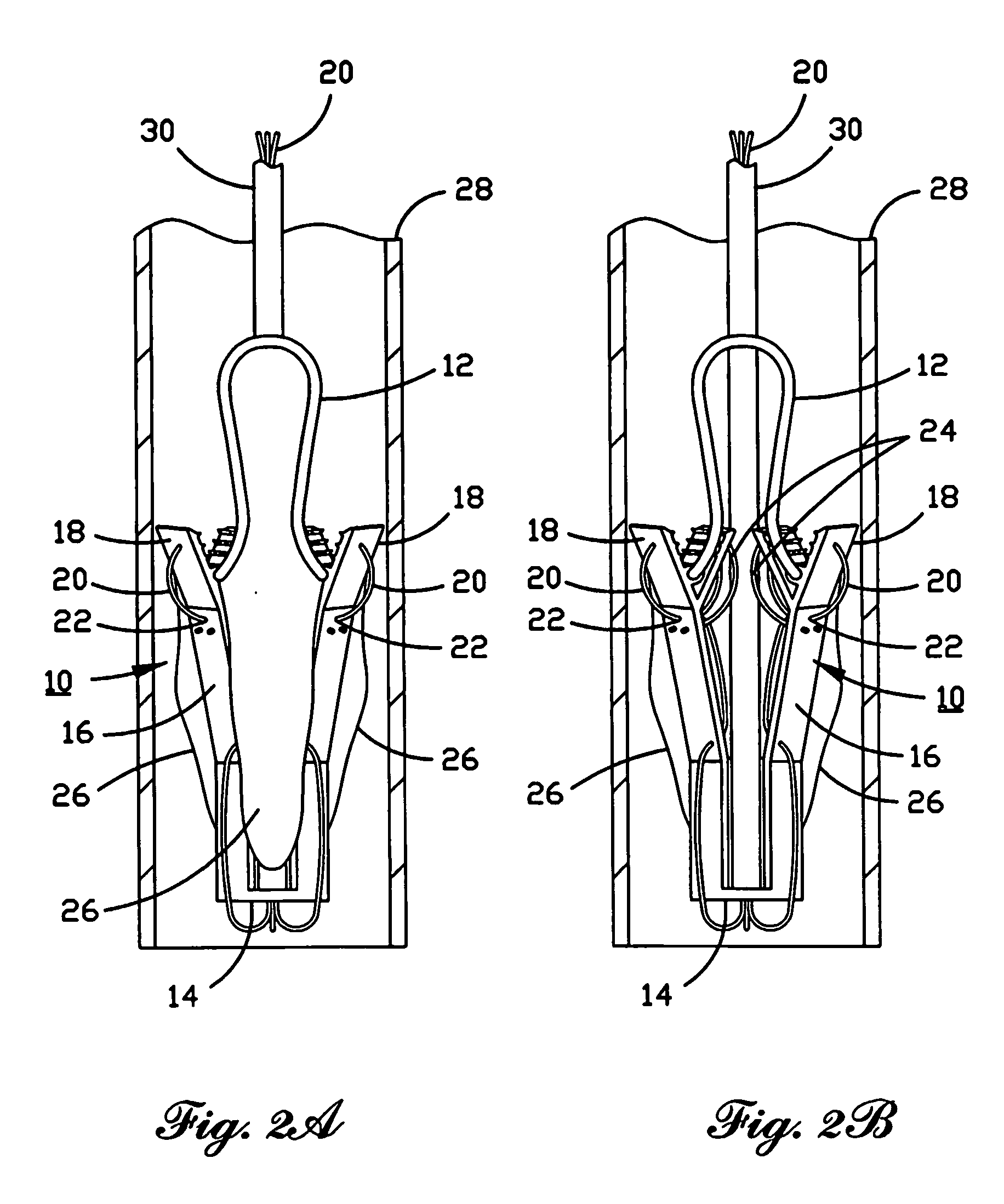
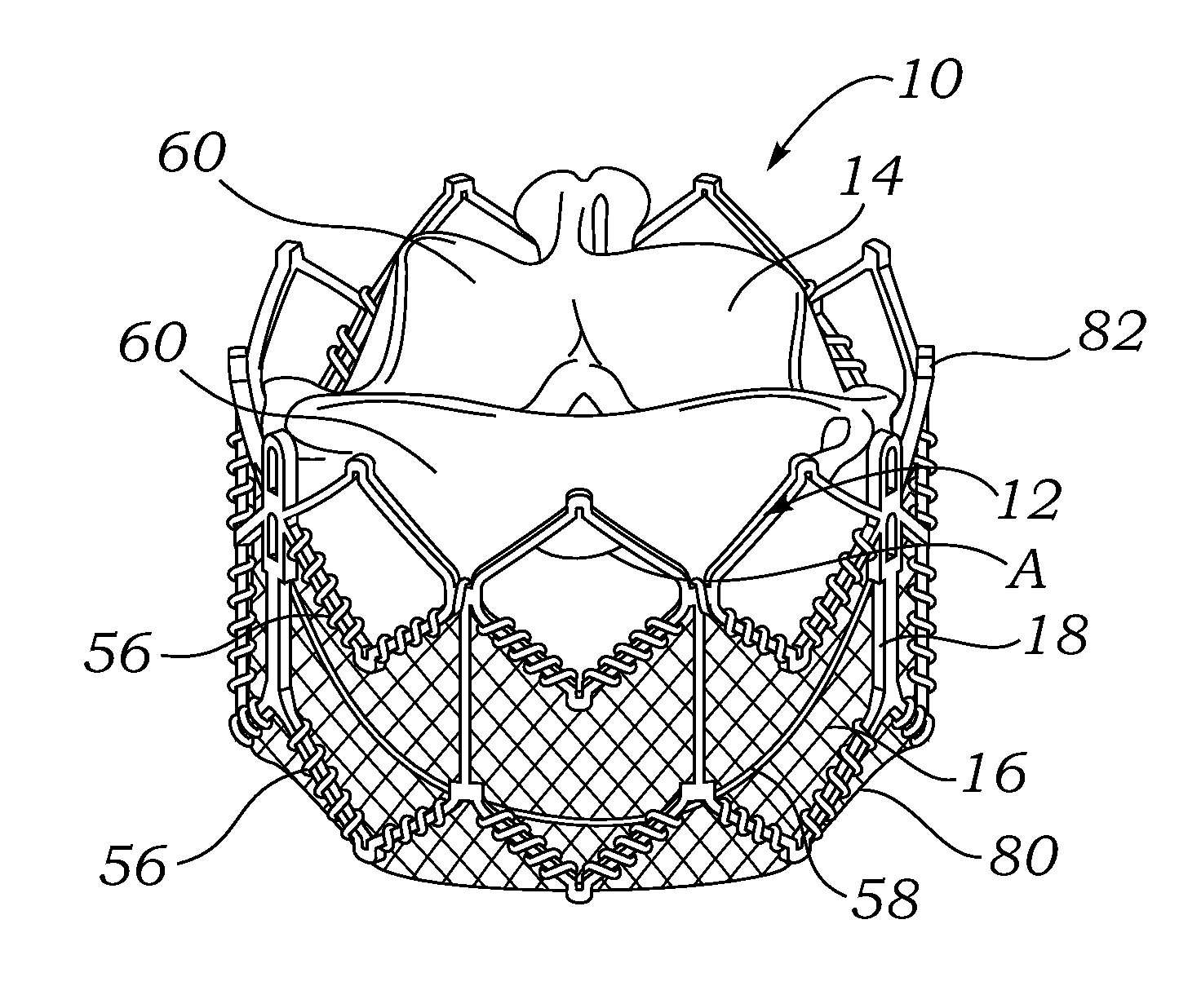
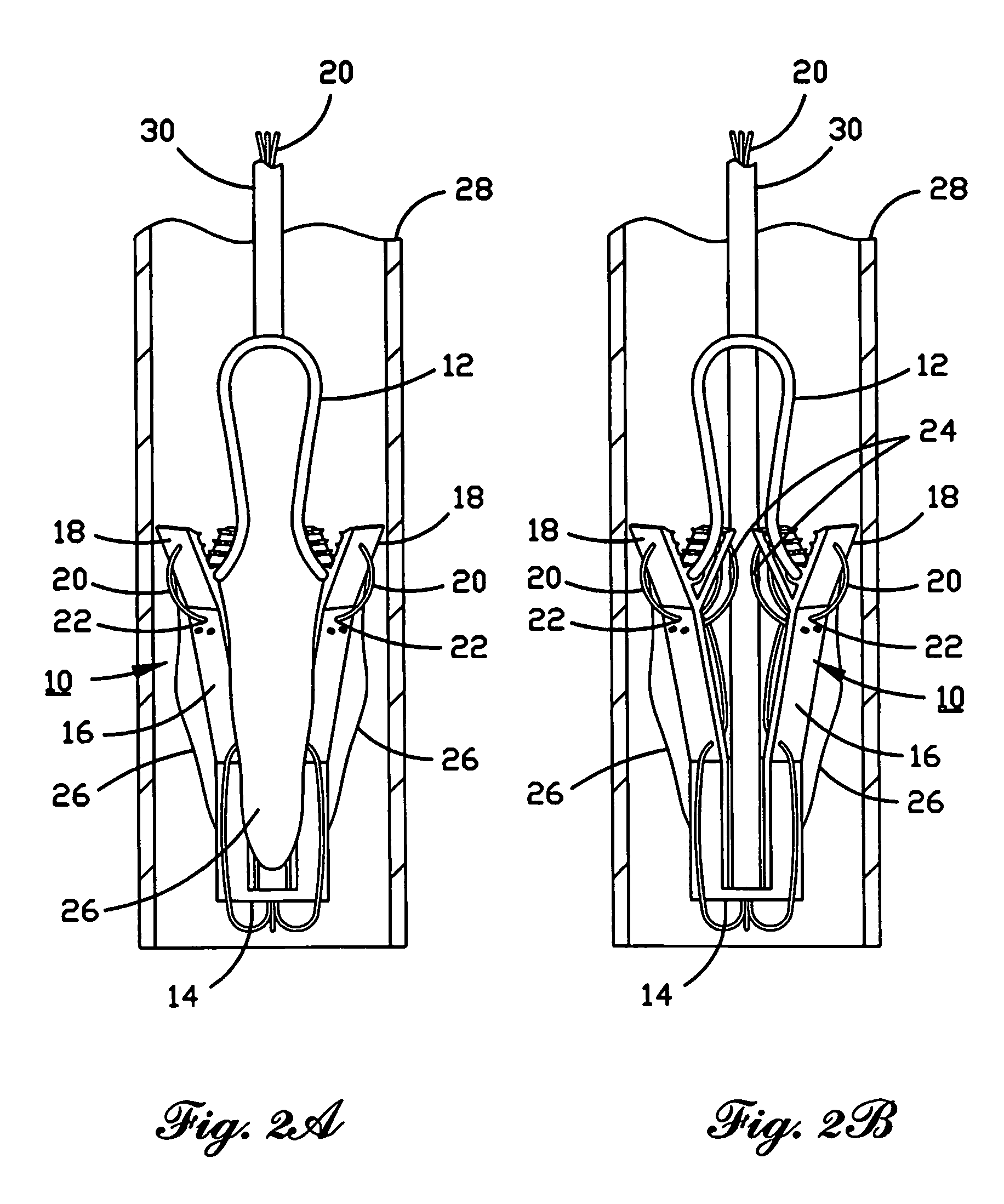
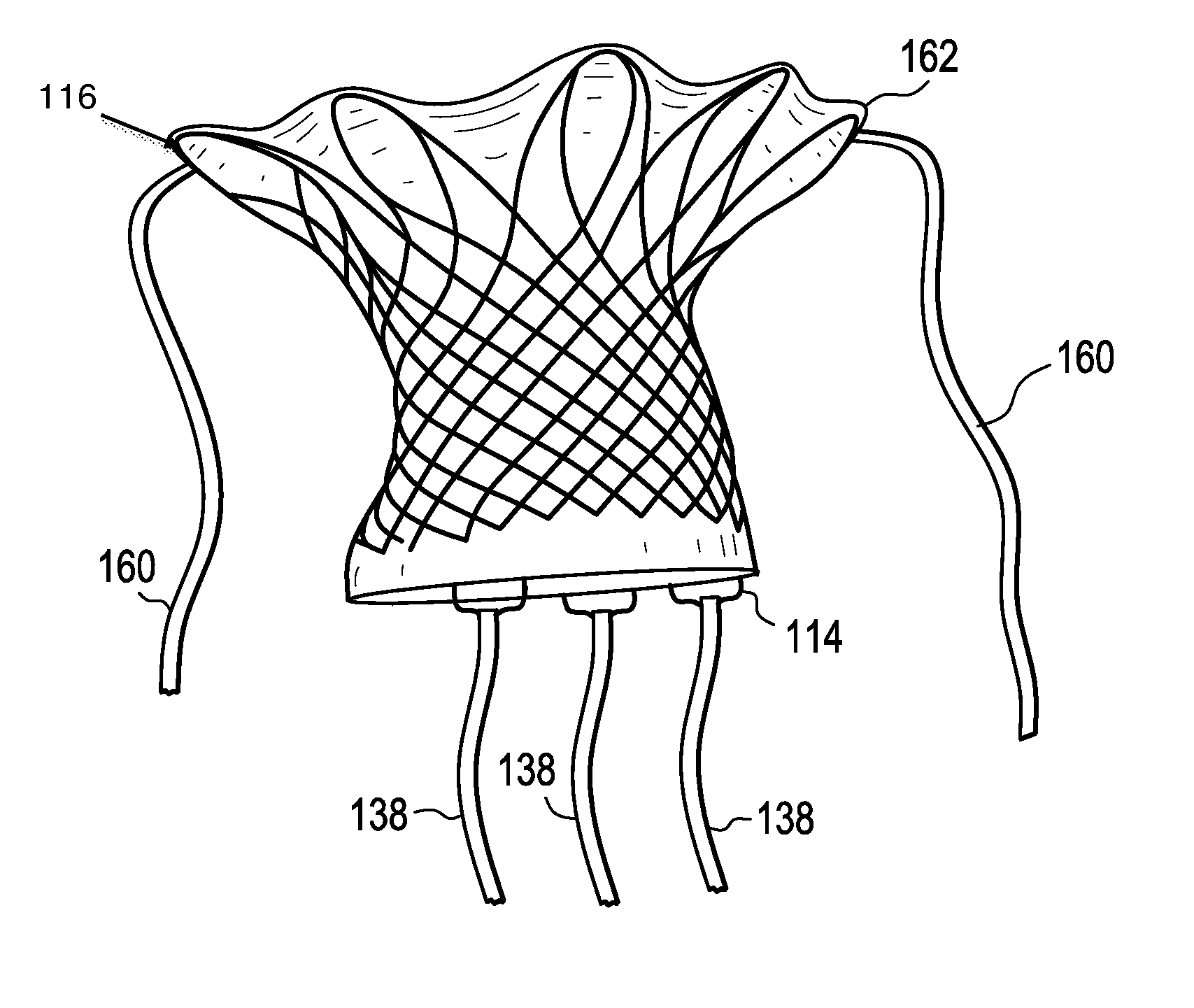
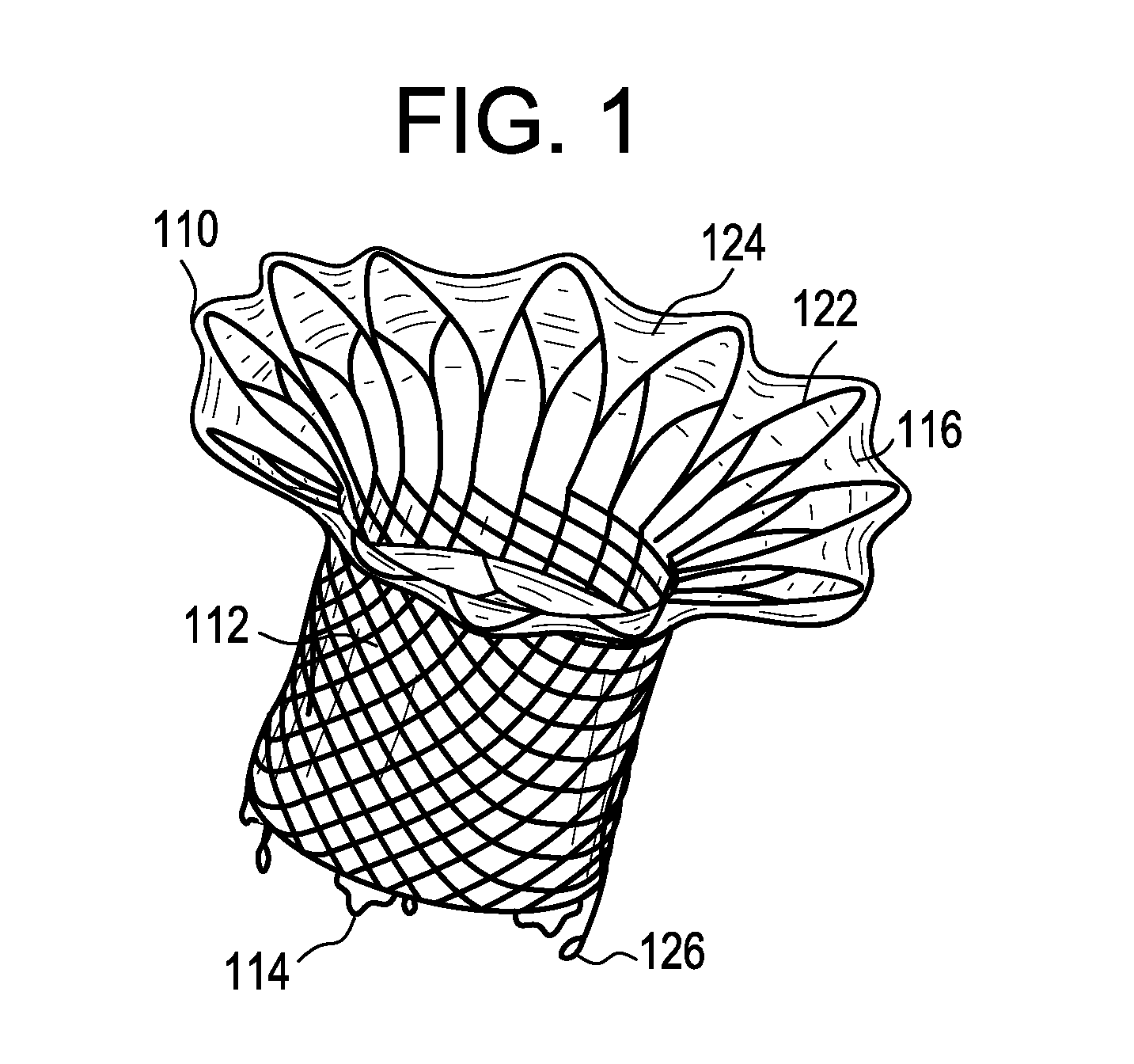
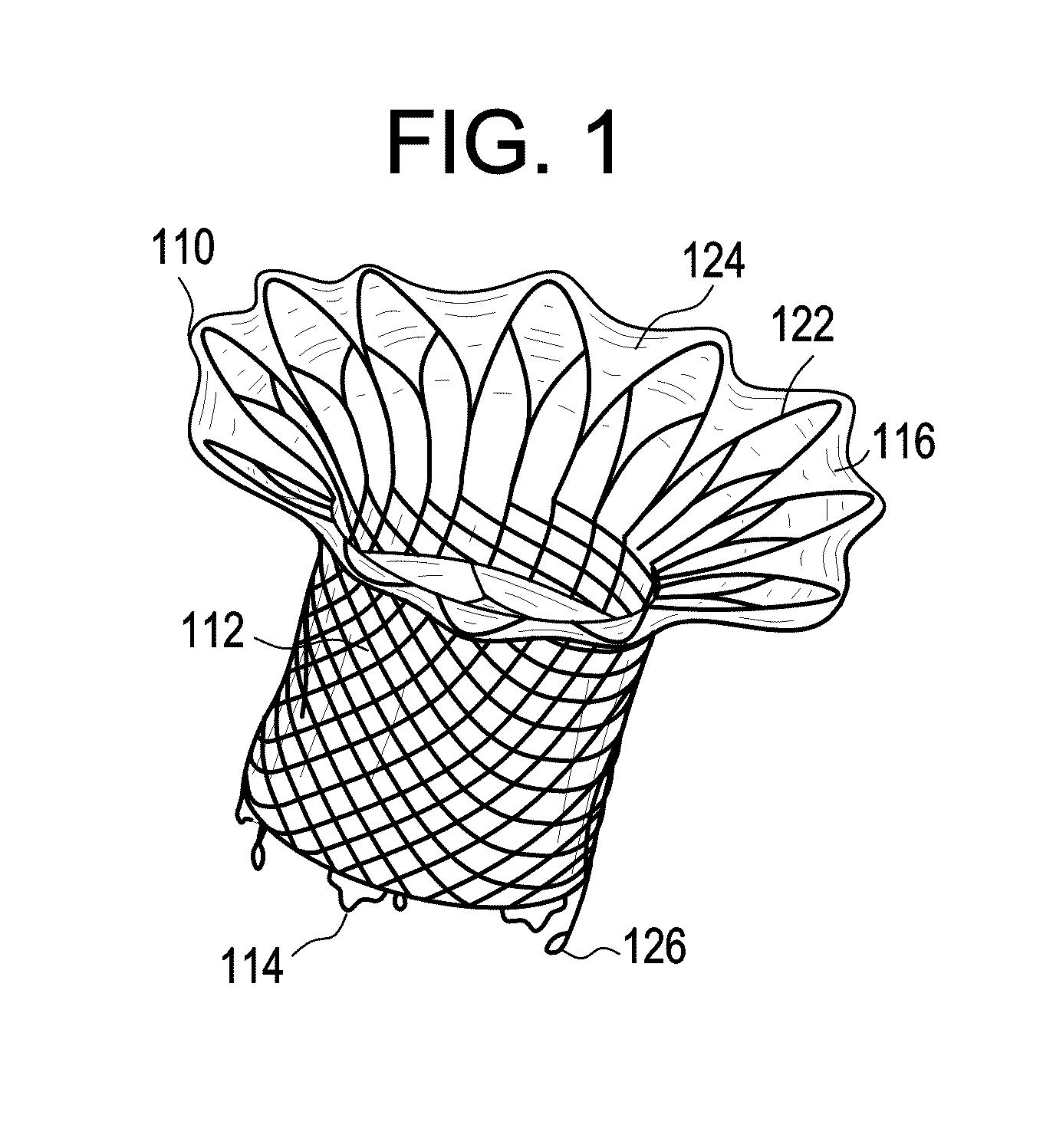
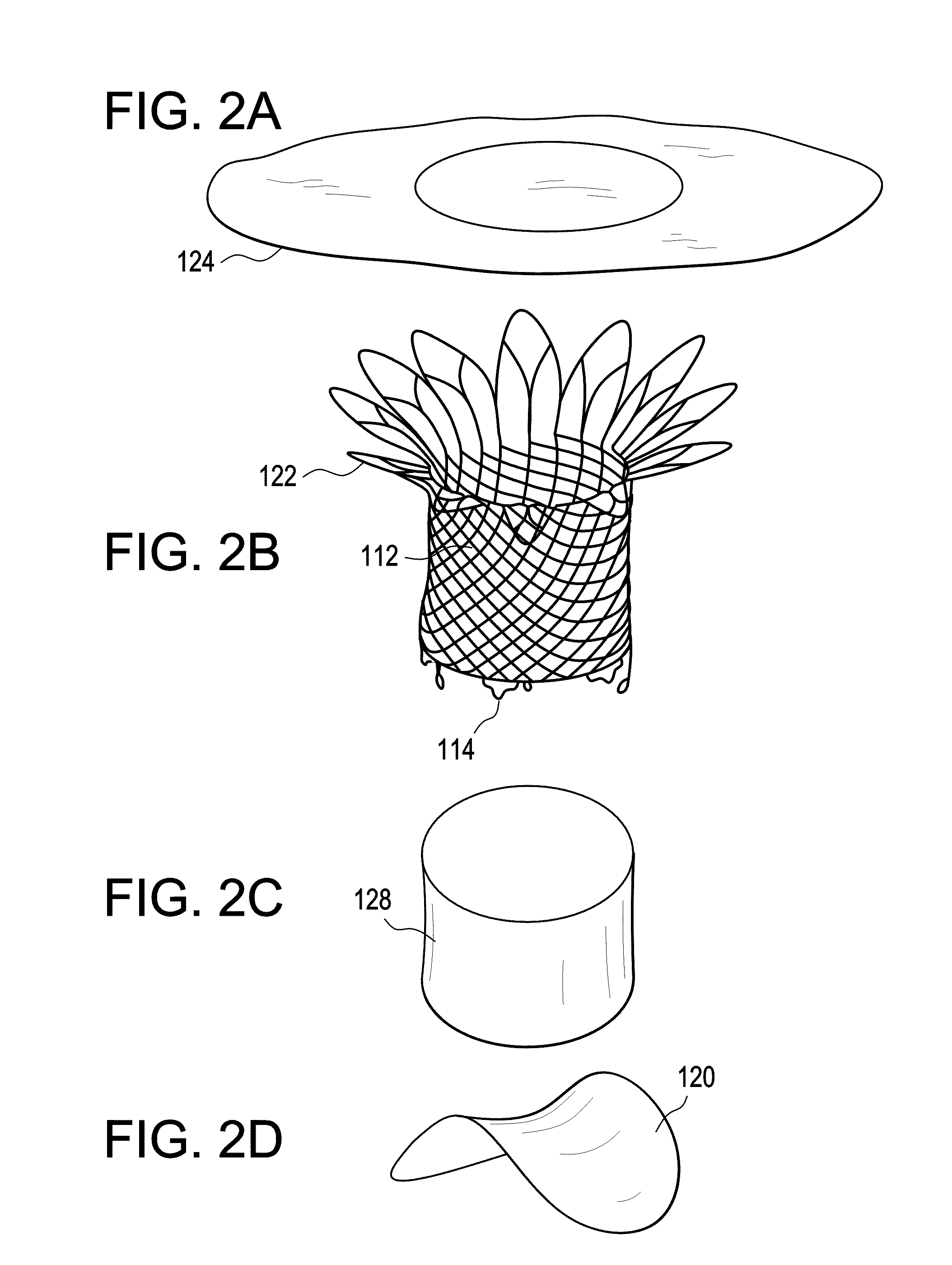
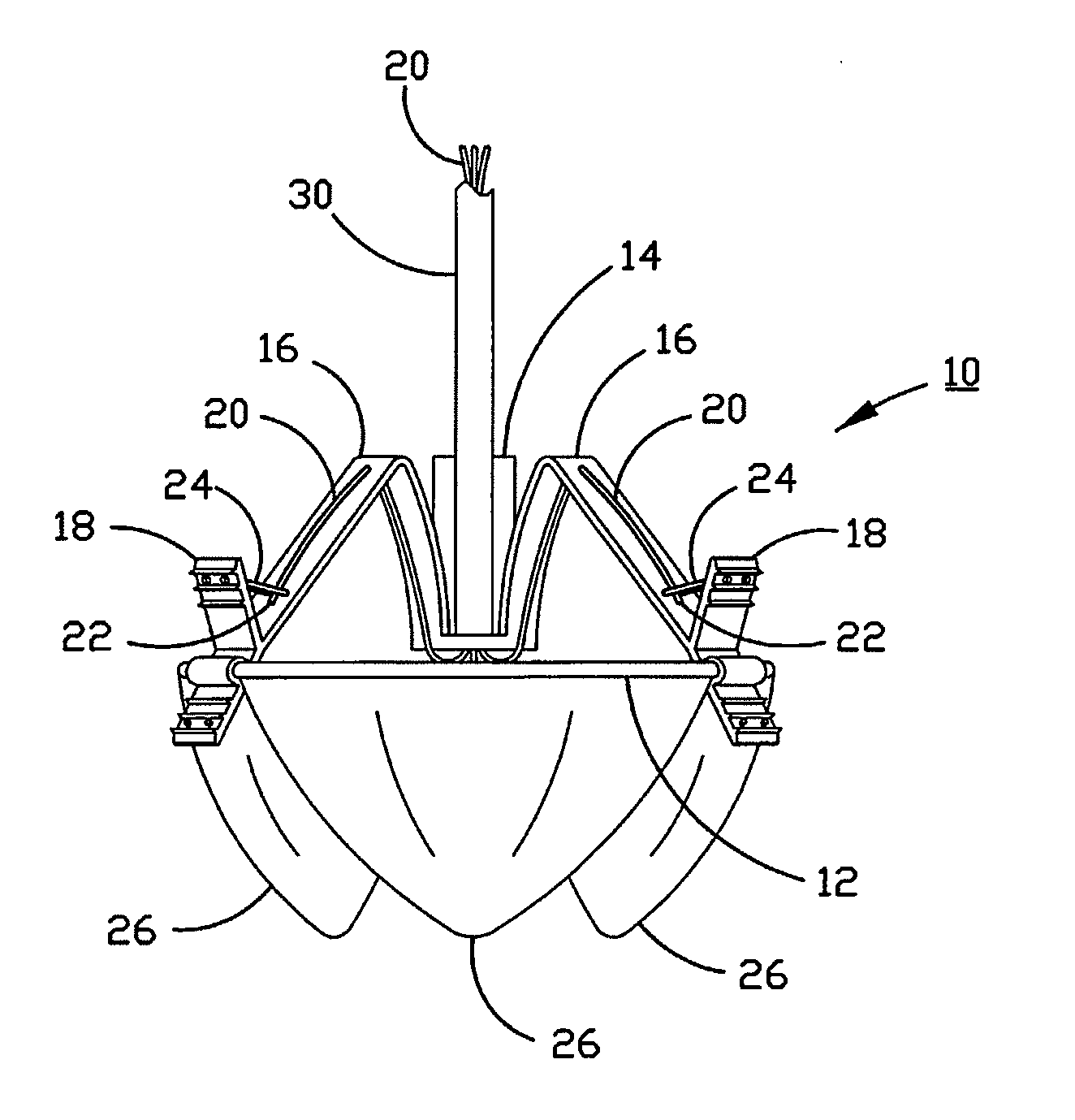
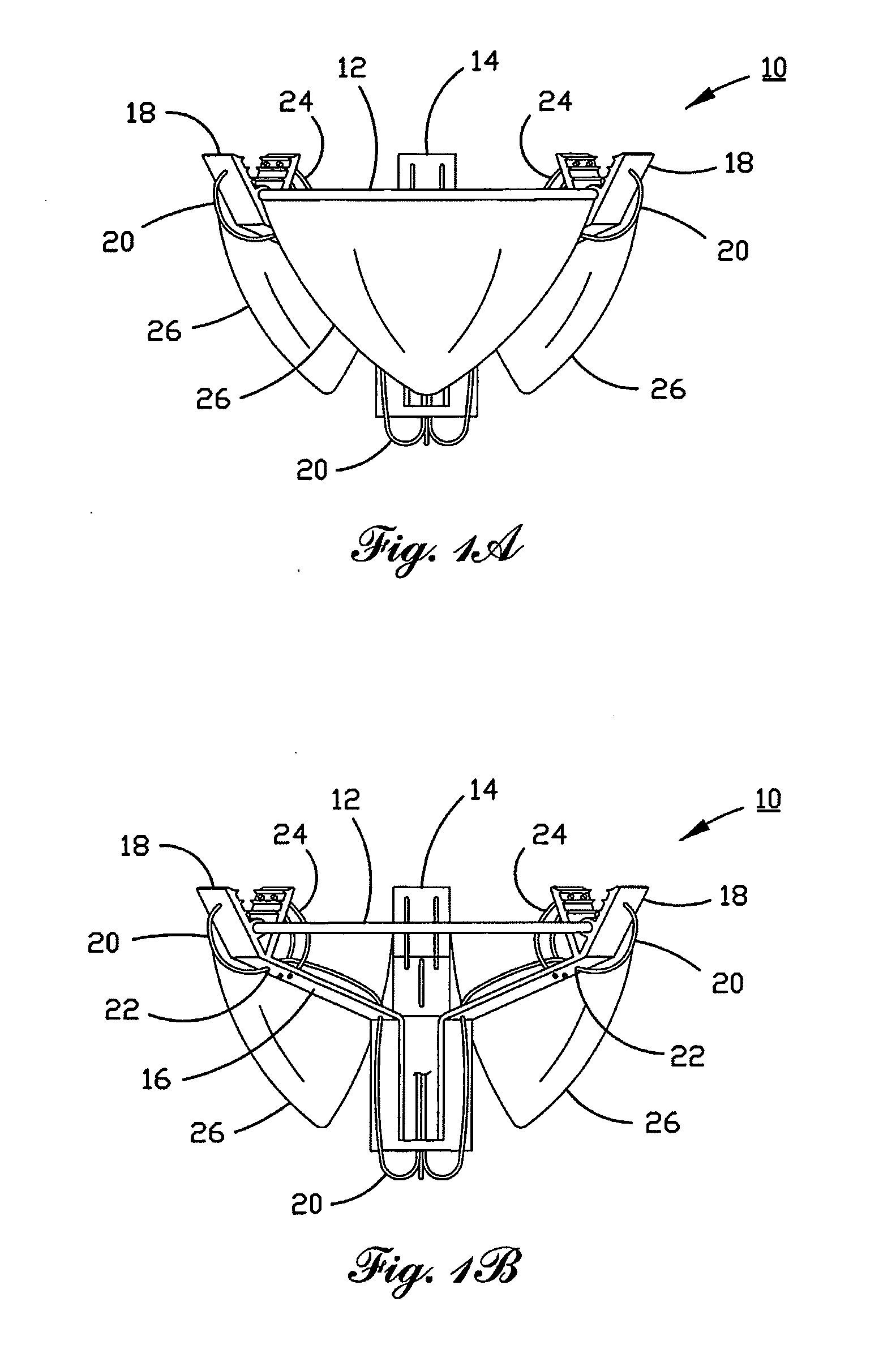
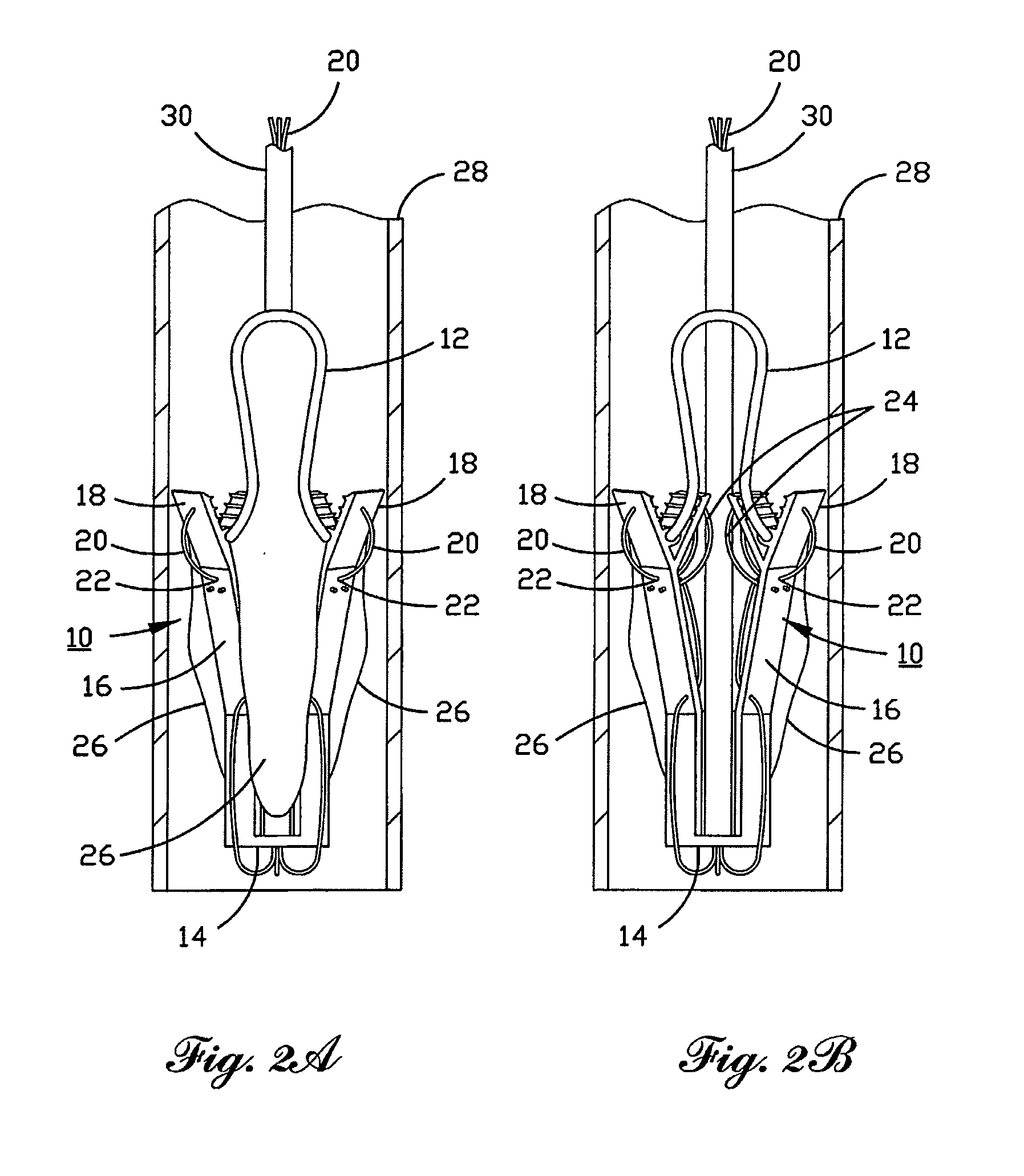
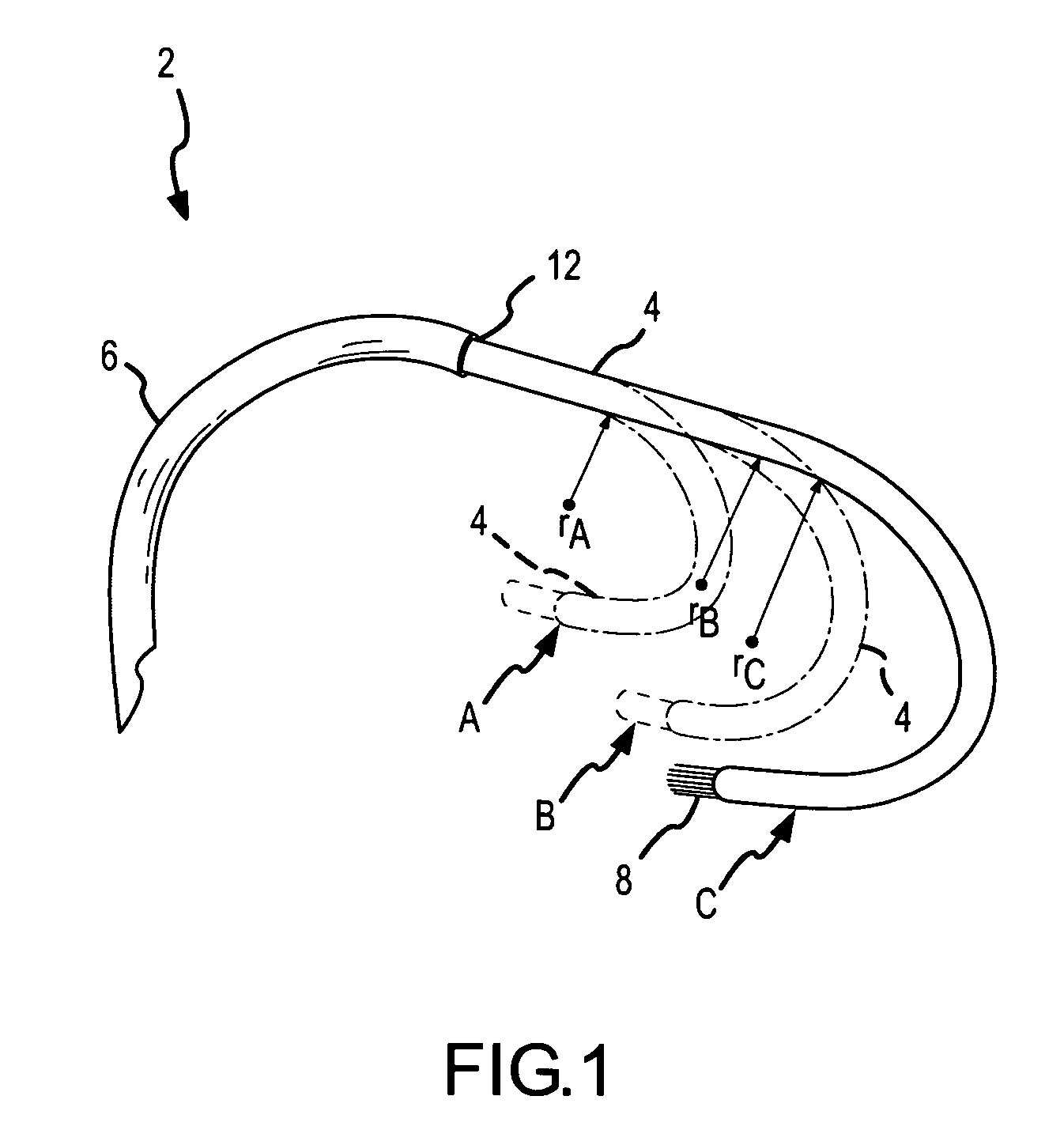
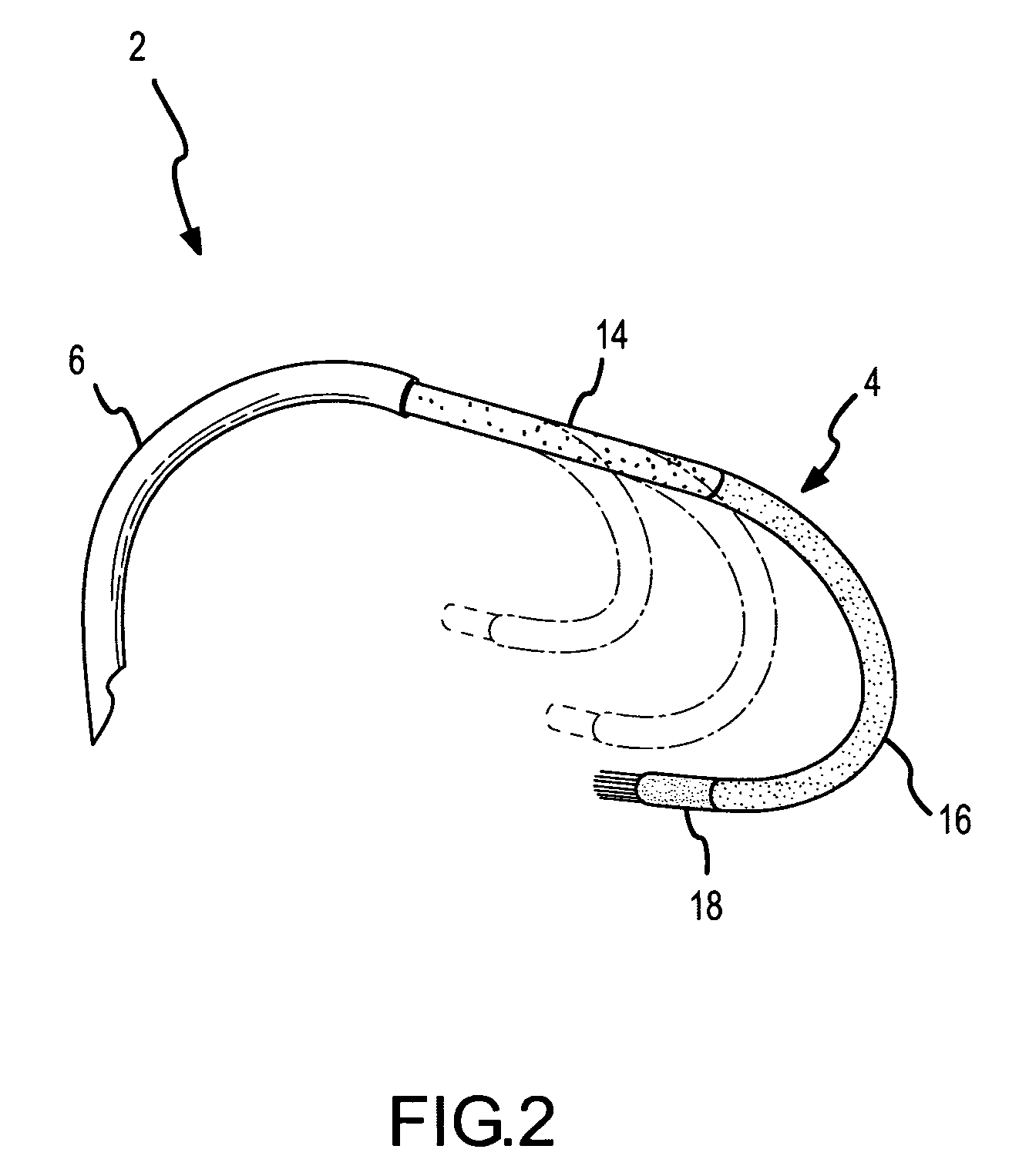
A percutaneously inserted bistable heart valve prosthesis is folded inside a catheter for transseptal delivery to the patient's heart for implantation. The heart valve has an annular ring, a body member having a plurality of legs, each leg connecting at one end to the annular ring, claws that are adjustable from a first position to a second position by application of external force so as to allow ingress of surrounding heart tissue into the claws in the second position, and leaflet membranes connected to the annular ring, the body member and / or the legs, the leaflet membranes having a first position for blocking blood flow therethrough and a second position for allowing blood flow therethrough. The heart valve is designed such that upon removal of the external force the claws elastically revert to the first position so as to grip the heart tissue positioned within the claws, thereby holding the heart valve in place. The body member and claws may be integrated into a one-piece design. The heart valve may be used as a prosthesis for the mitral valve, aortic valve, pulmonary valve, or tricuspid valve by adapting the annular ring to fit in a respective mitral, aortic, pulmonary, or tricuspid valve opening of the heart.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Low profile transcatheter heart valve
An implantable prosthetic valve, according to one embodiment, comprises a frame, a leaflet structure, and a skirt member. The frame can have a plurality of axial struts interconnected by a plurality of circumferential struts. The leaflet structure comprises a plurality of leaflets (e.g., three leaflets arrange to form a tricuspid valve). The leaflet structure has a scalloped lower edge portion secured to the frame. The skirt member can be disposed between the leaflet structure and the frame.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
Percutaneous heart valve
ActiveUS7621948B2Avoid flowStability and functioning of the heart valve are satisfactoryHeart valvesJoint implantsGuide tubeElastance
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Prosthetic valves and related inventions
ActiveUS20140214159A1Low height to width profilePrevent perivalvular leakSuture equipmentsHeart valvesExtracorporeal circulationProsthetic valve
This invention relates to the design and function of a compressible valve replacement prosthesis, collared or uncollared, which can be deployed into a beating heart without extracorporeal circulation using a transcatheter delivery system. The design as discussed focuses on the deployment of a device via a minimally invasive fashion and by way of example considers a minimally invasive surgical procedure preferably utilizing the intercostal or subxyphoid space for valve introduction. In order to accomplish this, the valve is formed in such a manner that it can be compressed to fit within a delivery system and secondarily ejected from the delivery system into the annulus of a target valve such as a mitral valve or tricuspid valve.
Owner:TENDYNE HLDG
Low profile transcatheter heart valve
An implantable prosthetic valve, according to one embodiment, comprises a frame, a leaflet structure, and a skirt member. The frame can have a plurality of axial struts interconnected by a plurality of circumferential struts. The leaflet structure comprises a plurality of leaflets (e.g., three leaflets arrange to form a tricuspid valve). The leaflet structure has a scalloped lower edge portion secured to the frame. The skirt member can be disposed between the leaflet structure and the frame.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
Methods and devices for performing cardiac valve repair
The present invention is directed to methods and devices for repairing a cardiac valve. Generally, the methods involve a minimally invasive procedure that includes creating an access in the apex region of the heart through which one or more instruments may be inserted so as to repair a cardiac valve, for instance, a mitral or tricuspid valve. Accordingly, the methods are useful for performing a variety of procedures to effectuate a repair. For instance, in one embodiment, the methods are useful for repairing a cardiac valve by implanting one or more artificial heart valve chordae tendinae into one or more cardiac valve leaflet tissues so as to restore the proper leaflet function and thereby prevent reperfusion. In another embodiment, the methods are useful for repairing a cardiac valve by resecting a portion of one or more cardiac valve leaflets and implanting one or more sutures into the resected valve tissues, which may also include the implantation of an annuloplasty ring. In an additional embodiment, the methods are useful for performing an edge to edge bow-tie repair (e.g., an Alfieri repair) on cardiac valve tissues. Devices for performing the methods of the invention are also provided.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND BALTIMORE
Device and System for Transcatheter Mitral Valve Replacement
InactiveUS20120179244A1Prevent perivalvular leakStentsHeart valvesExtracorporeal circulationBioprosthetic mitral valve replacement
This invention relates to the design and function of a compressible valve replacement prosthesis which can be deployed into a beating heart without extracorporeal circulation using a transcatheter delivery system. The design as discussed focuses on the deployment of a device via a minimally invasive fashion and by way of example considers a minimally invasive surgical procedure preferably utilizing the intercostal or subxyphoid space for valve introduction. In order to accomplish this, the valve is formed in such a manner that it can be compressed to fit within a delivery system and secondarily ejected from the delivery system into the annulus of a target valve such as a mitral valve or tricuspid valve.
Owner:COLORADO STATE UNIVERSITY +1
Halo Wire Fluid Seal Device for Prosthetic Mitral Valves
This invention relates to a self-expanding pre-configured compressible transcatheter prosthetic cardiovascular valve that comprises an atrial halo fluid sealing device mounted on a self-expanding inner wire frame having a leaflet structure comprised of articulating leaflets that define a valve function, said inner wire frame is disposed within a self-expanding annular tissue-covered outer wire frame, said outer wire frame having an articulating collar, forming a multi-component prosthetic valve assembly for anchoring within the mitral valve or triscuspid valve of the heart, and methods for deploying such a valve for treatment of a patient in need thereof
Owner:TENDYNE HLDG
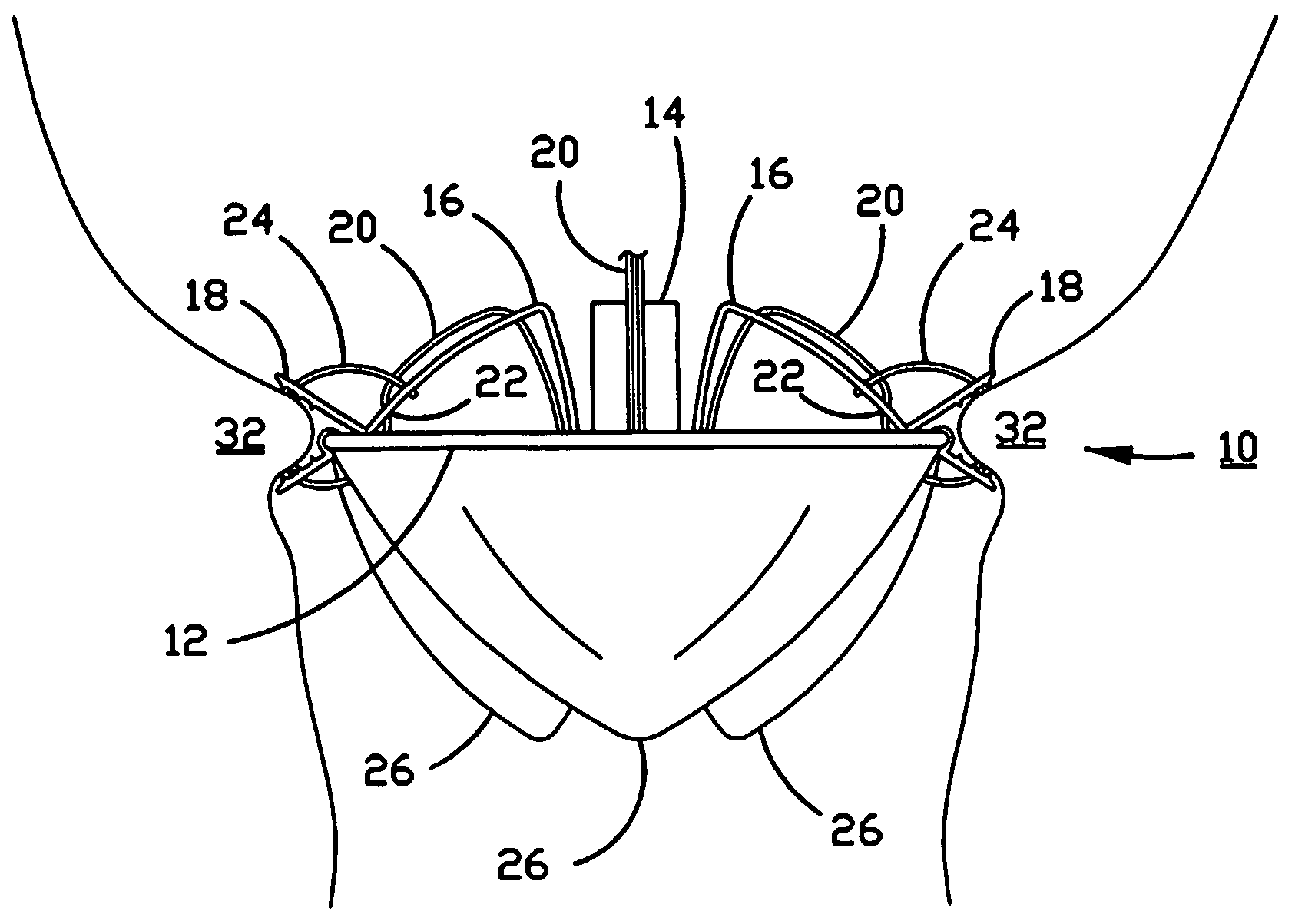
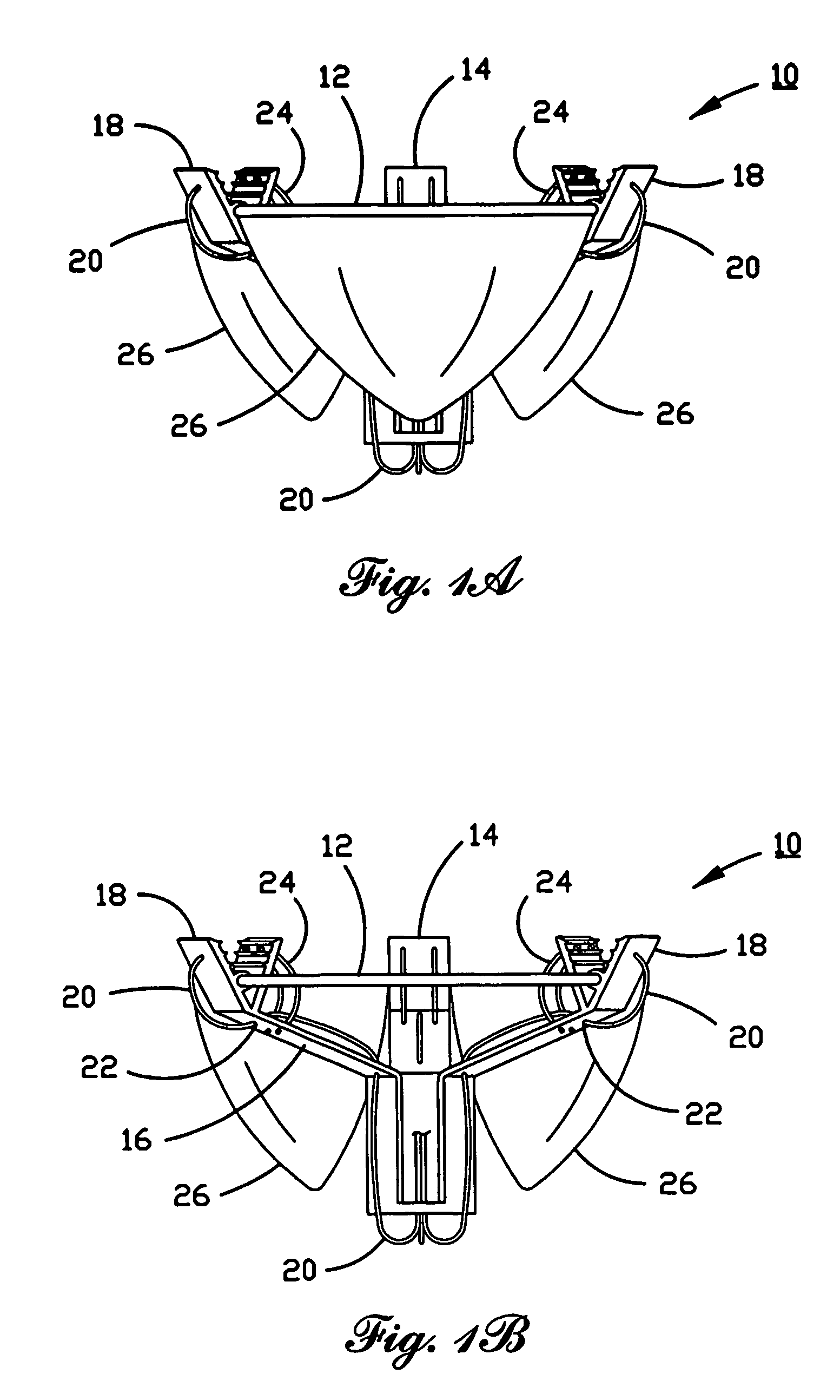
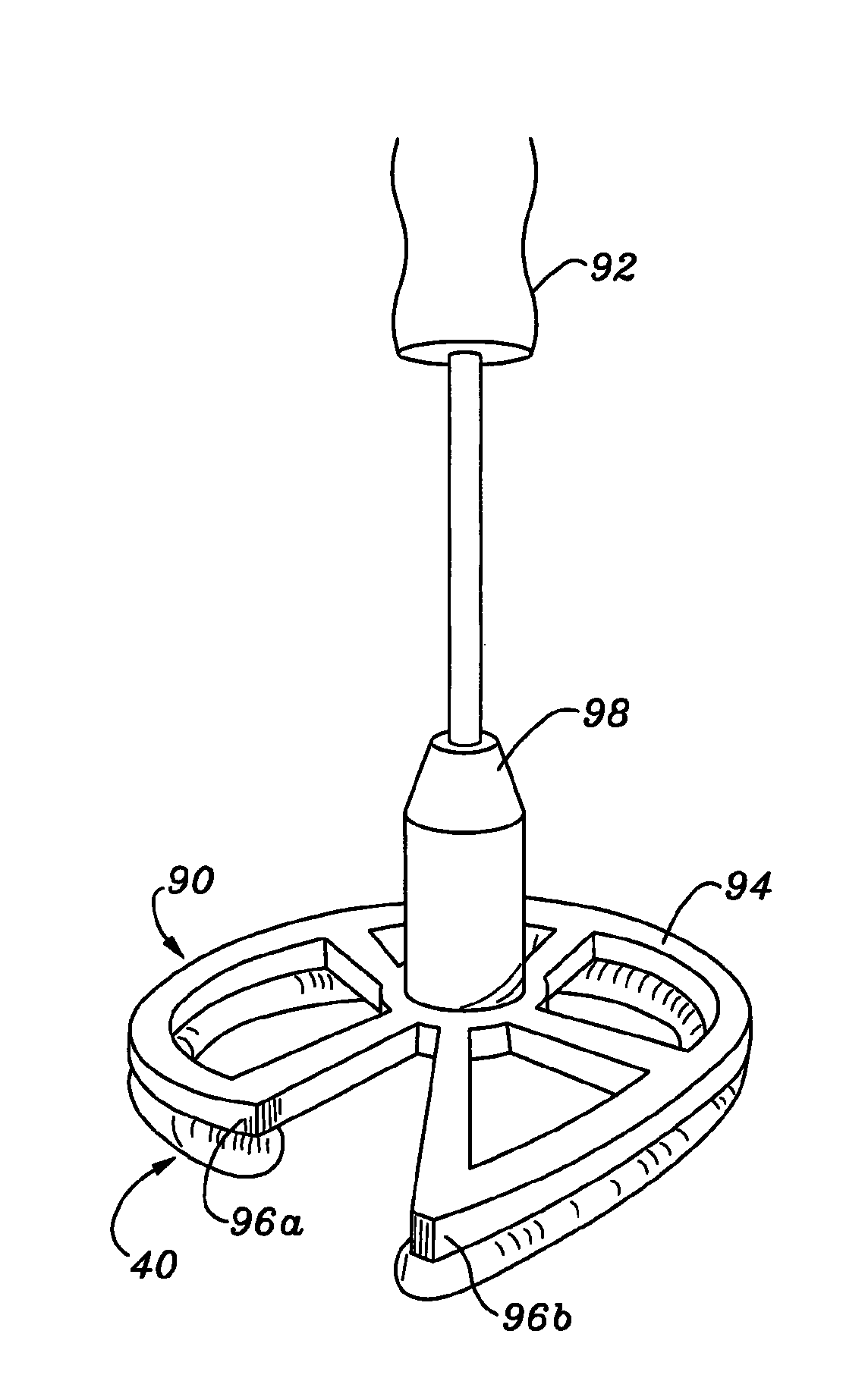
Three-dimensional annuloplasty ring and template
InactiveUS6908482B2Reduce frictionPromote sportsBone implantAnnuloplasty ringsEngineeringAnnuloplasty rings
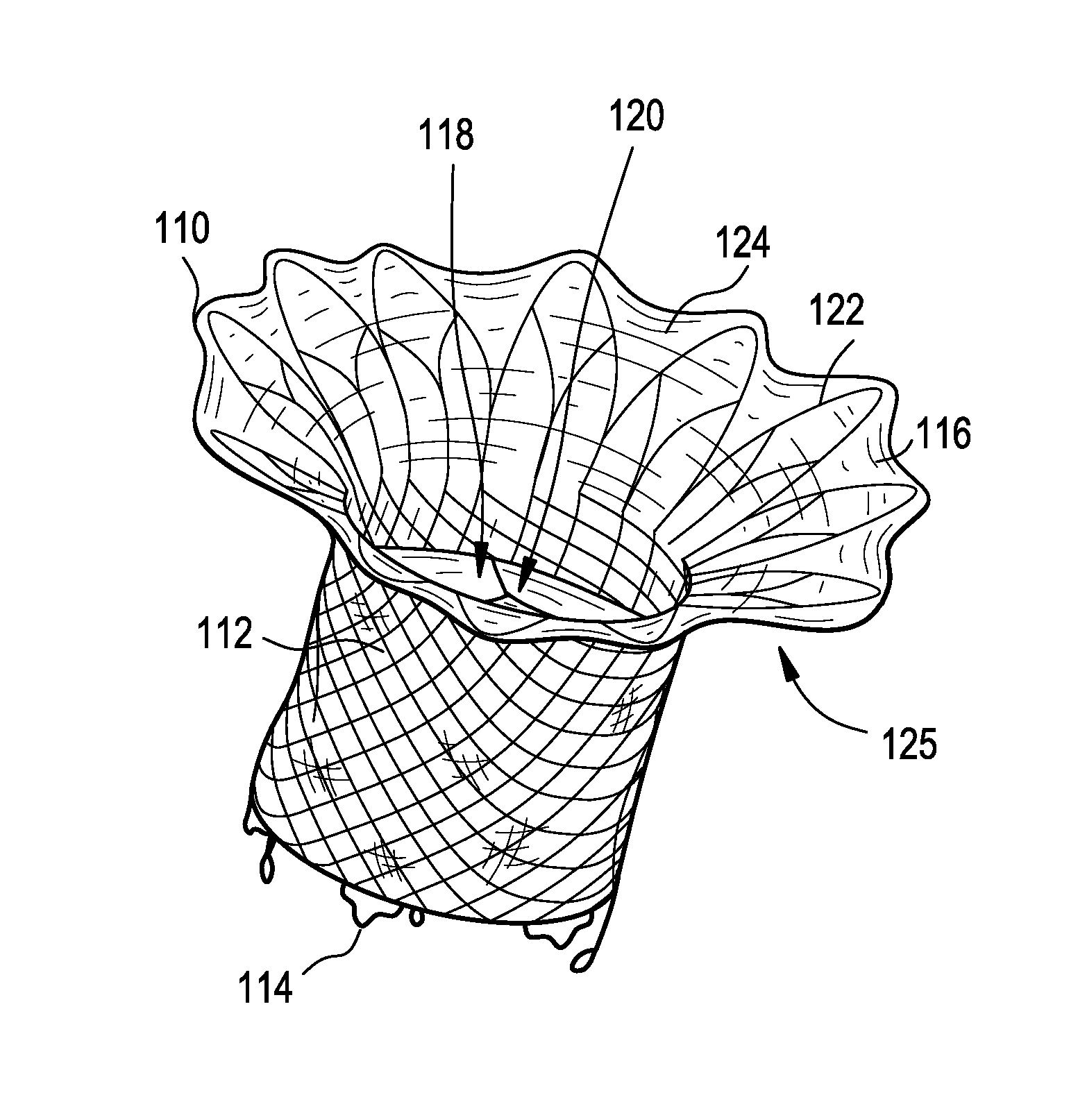
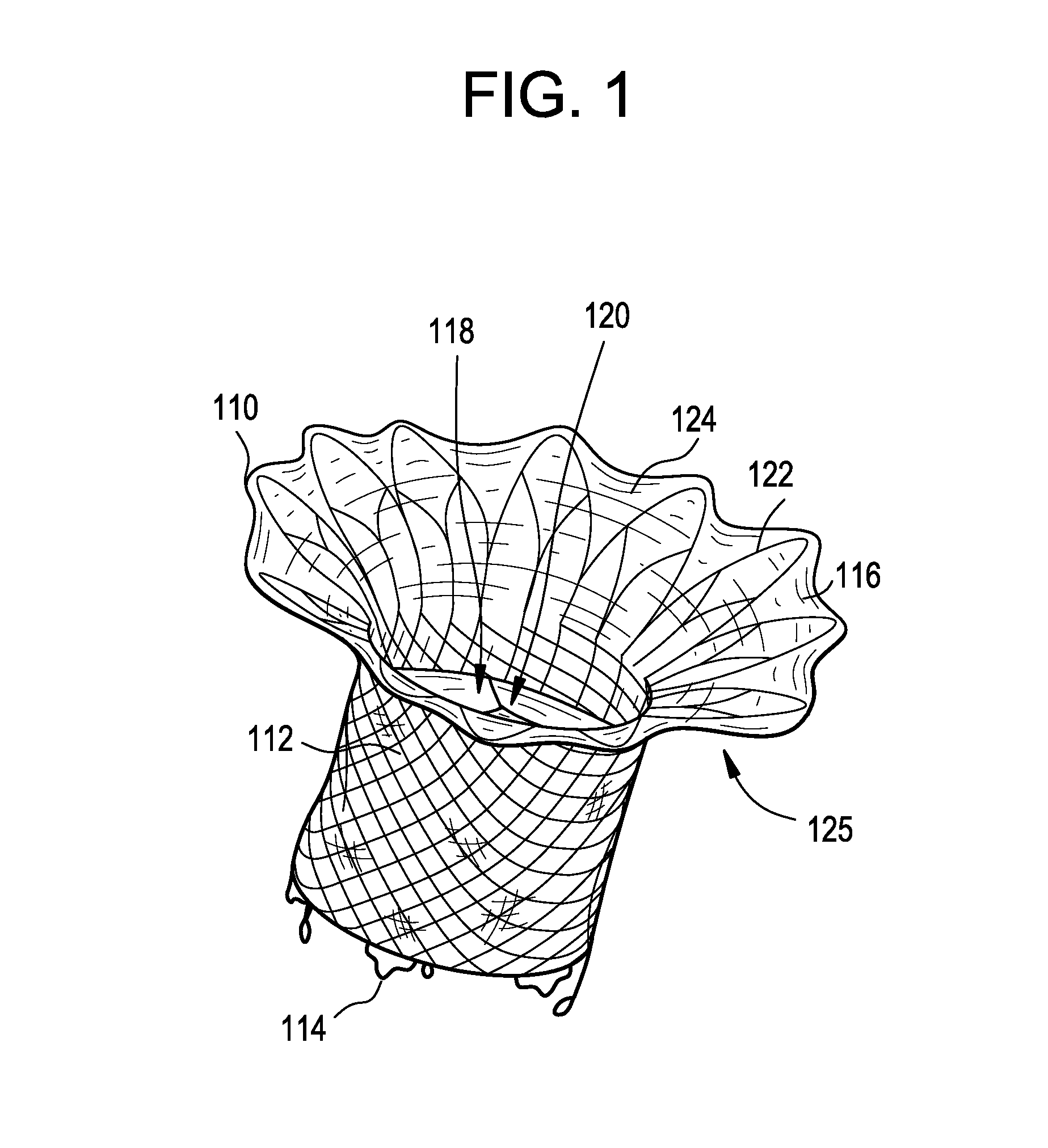
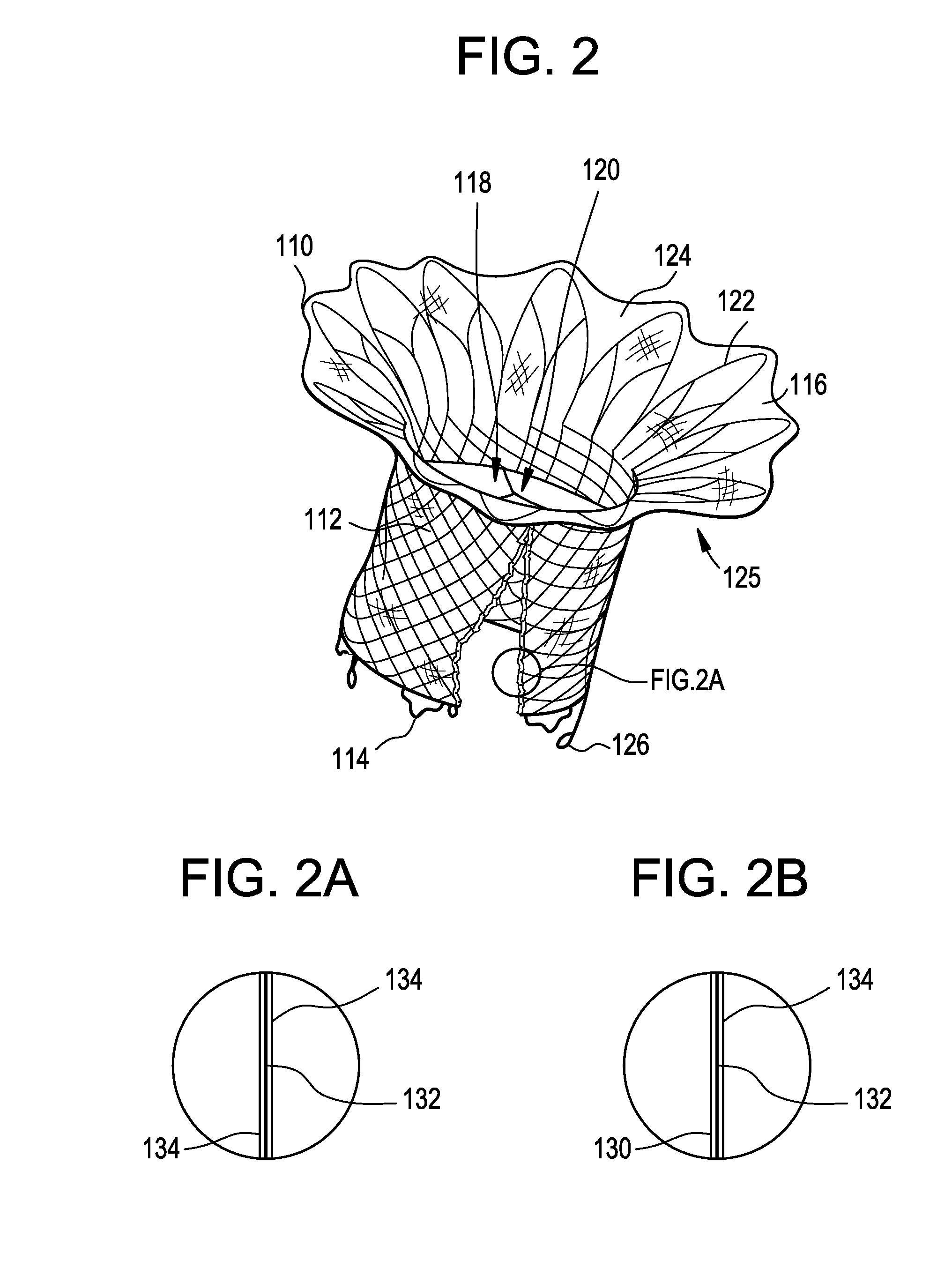
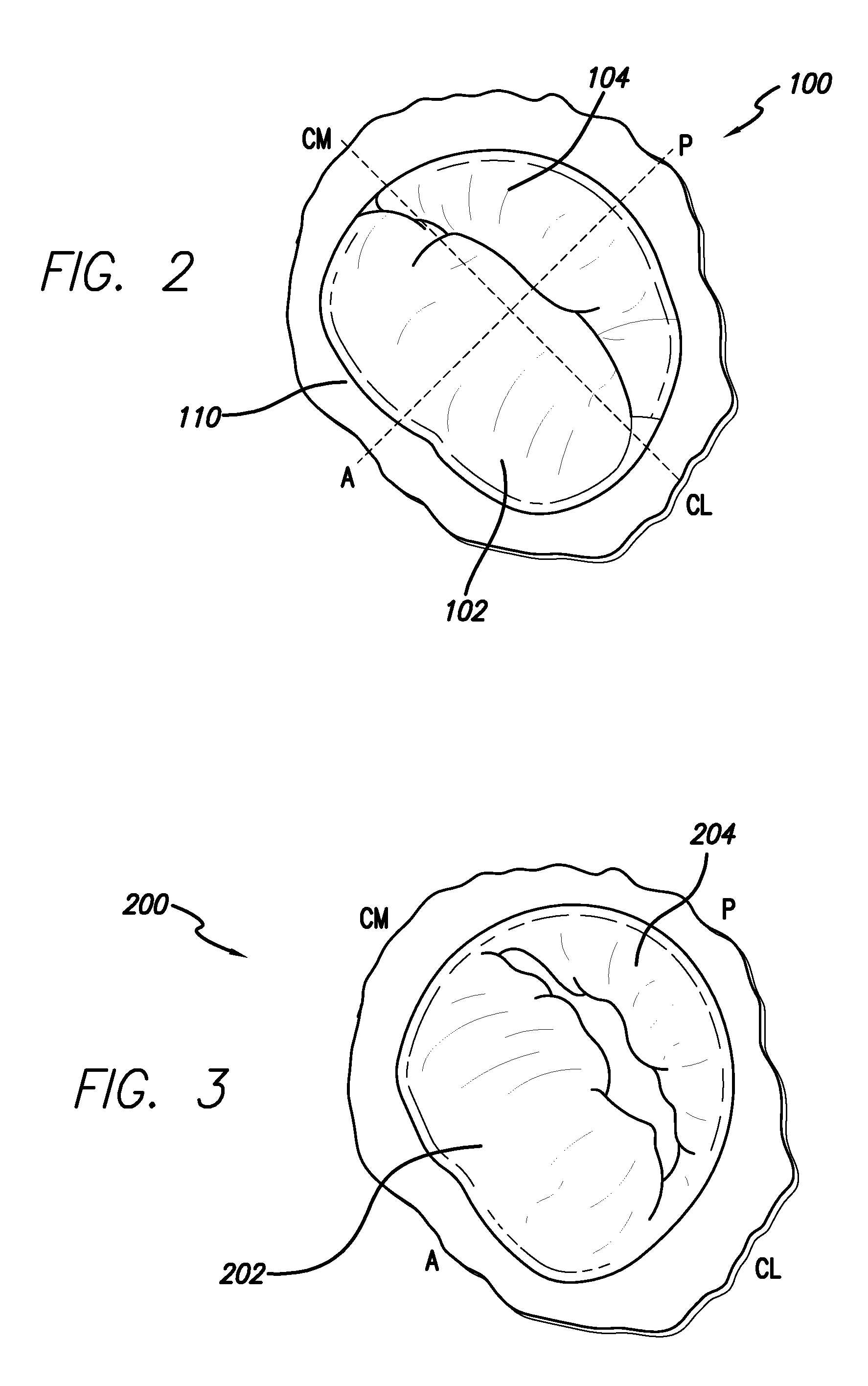
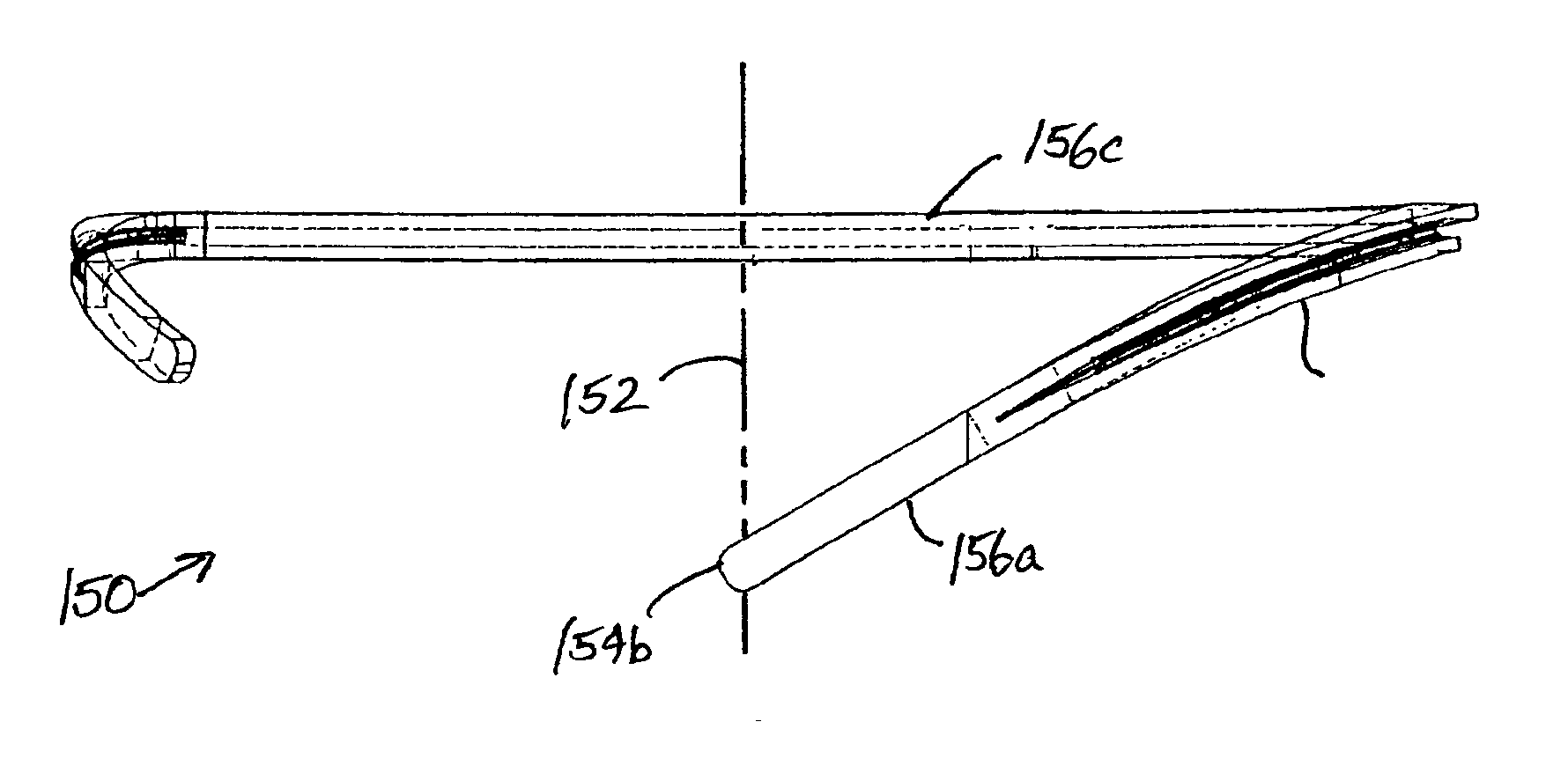
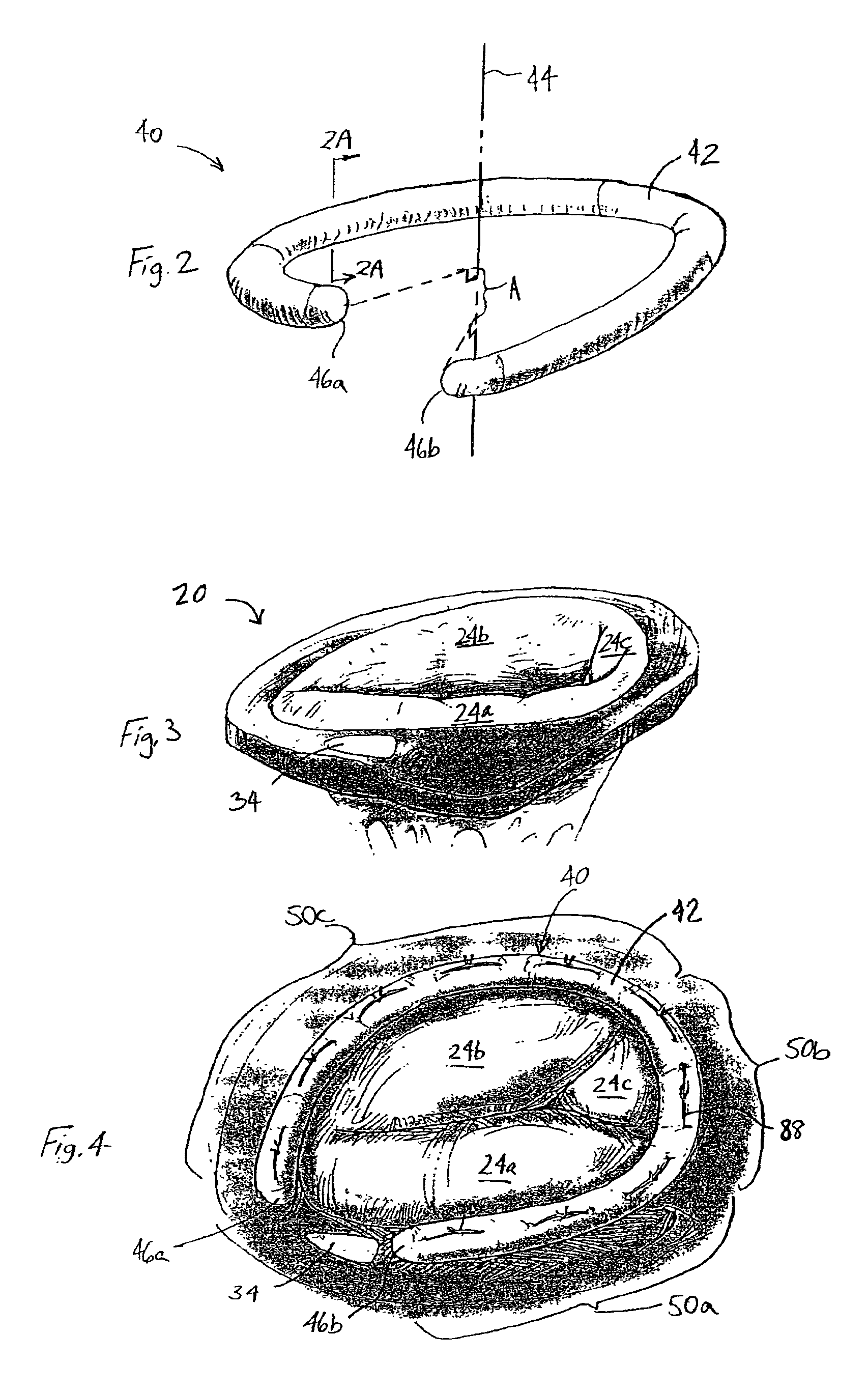
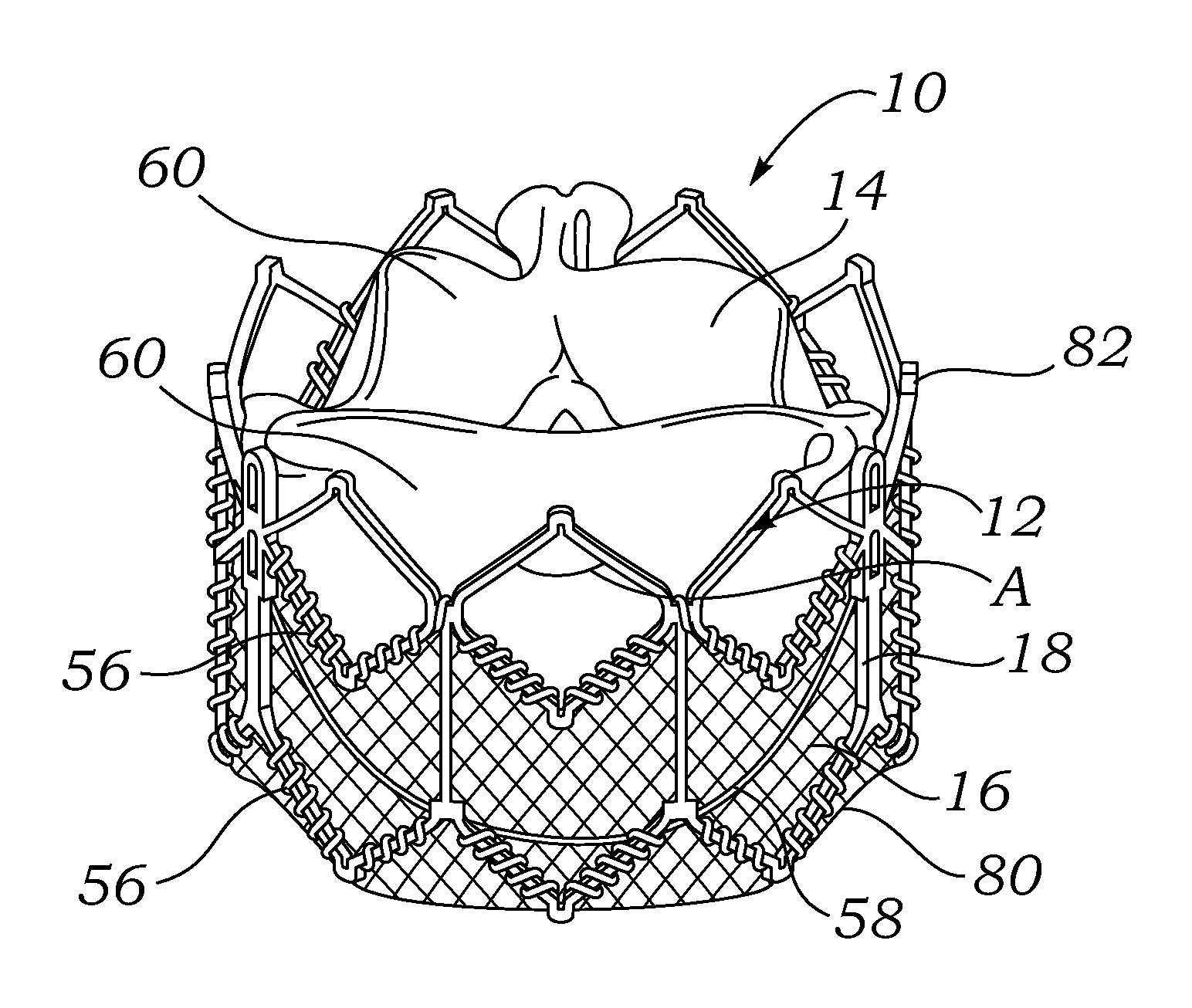
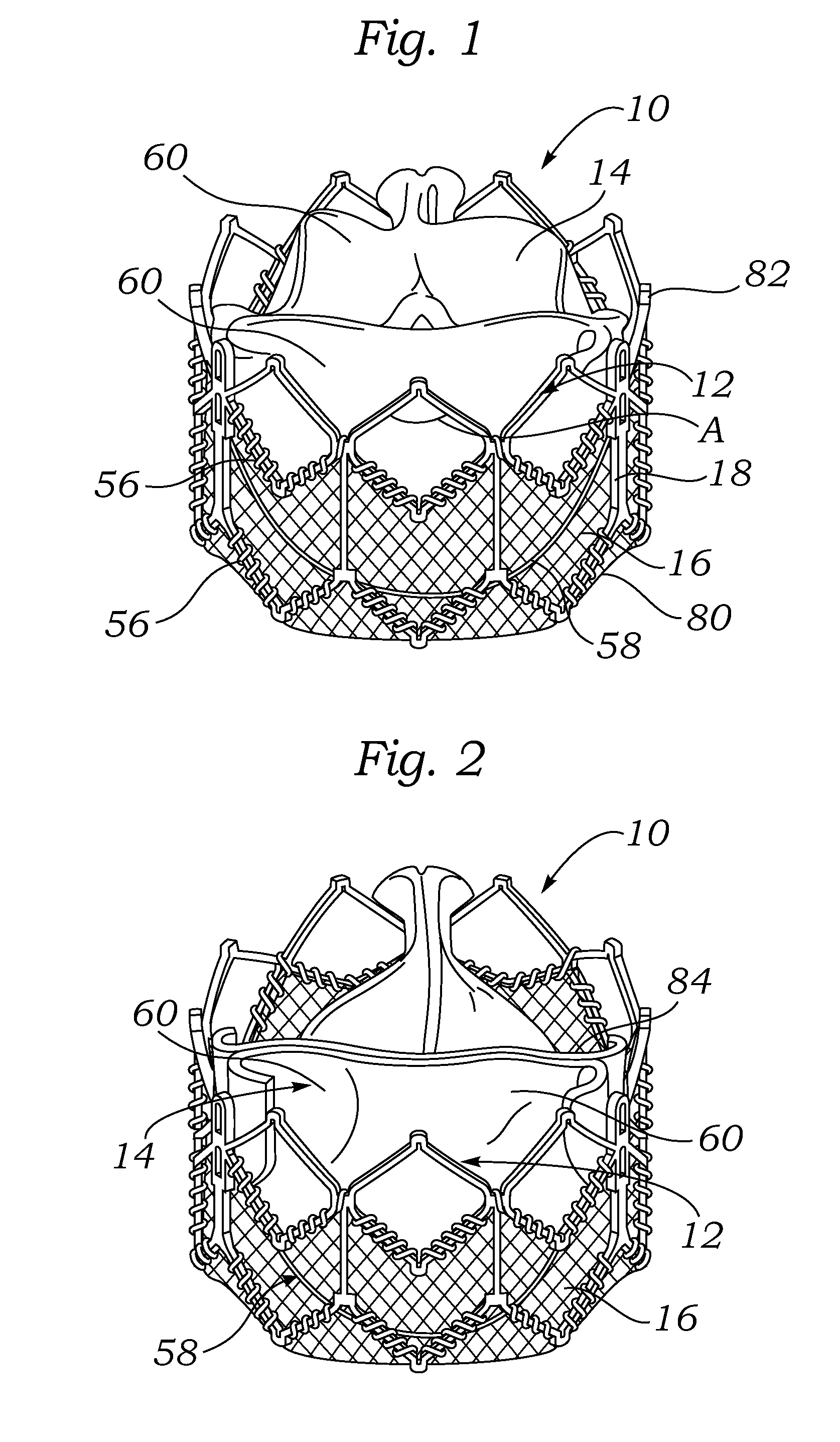
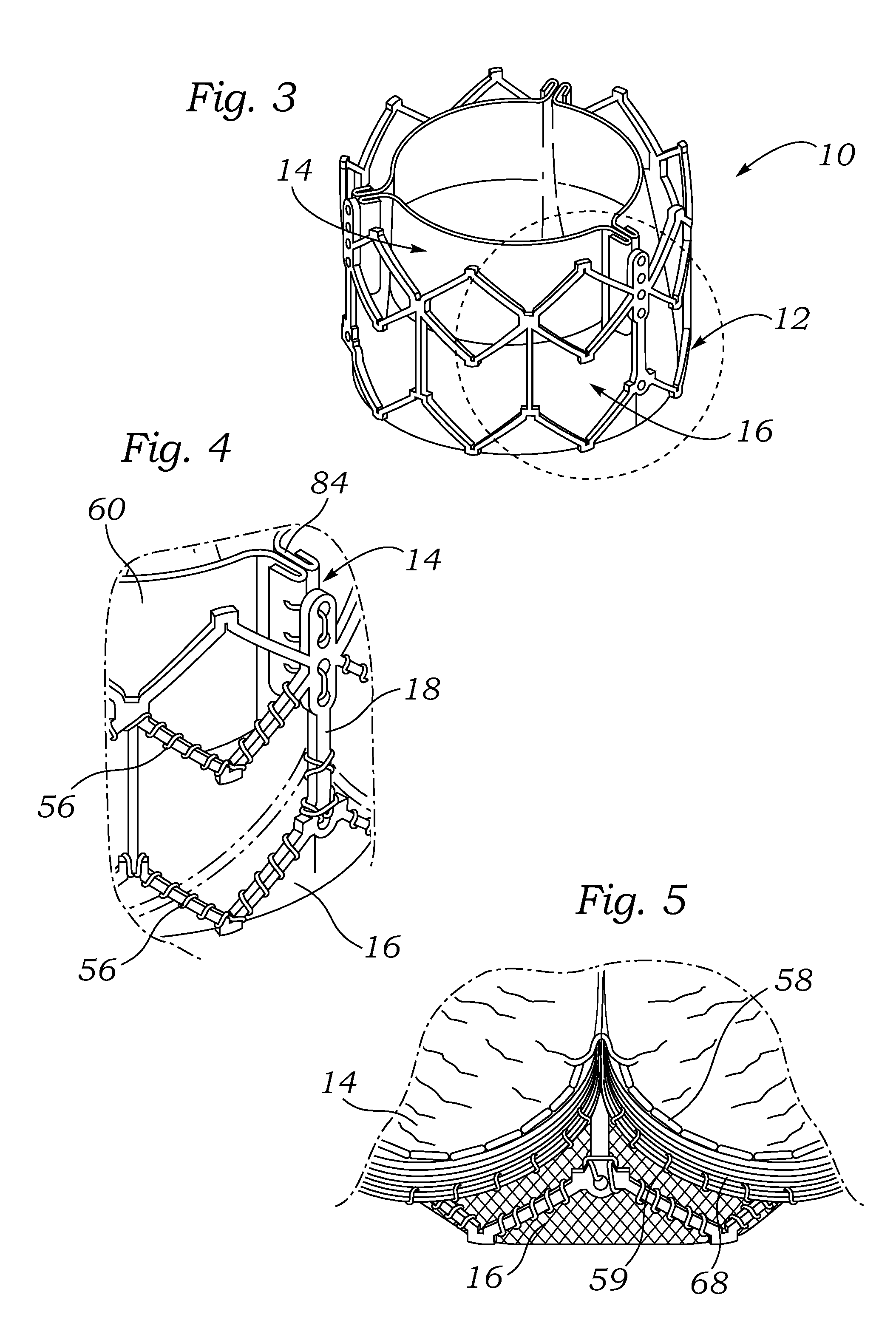
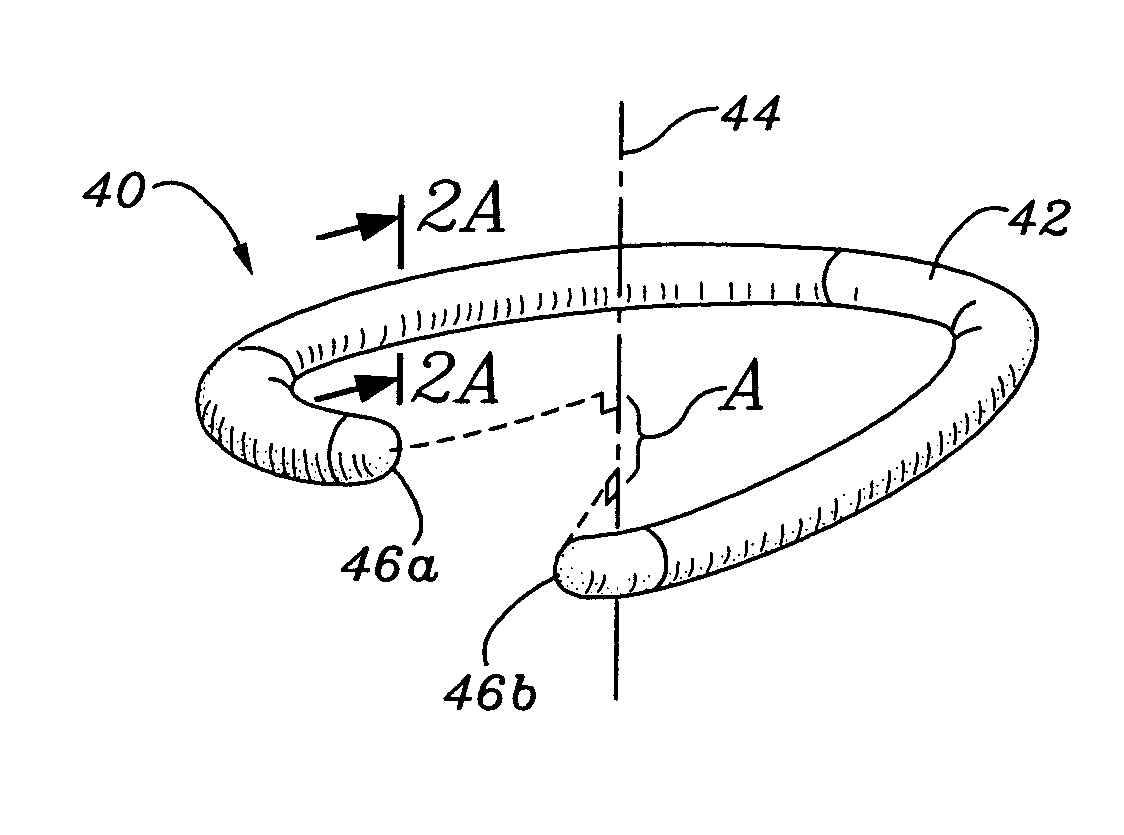
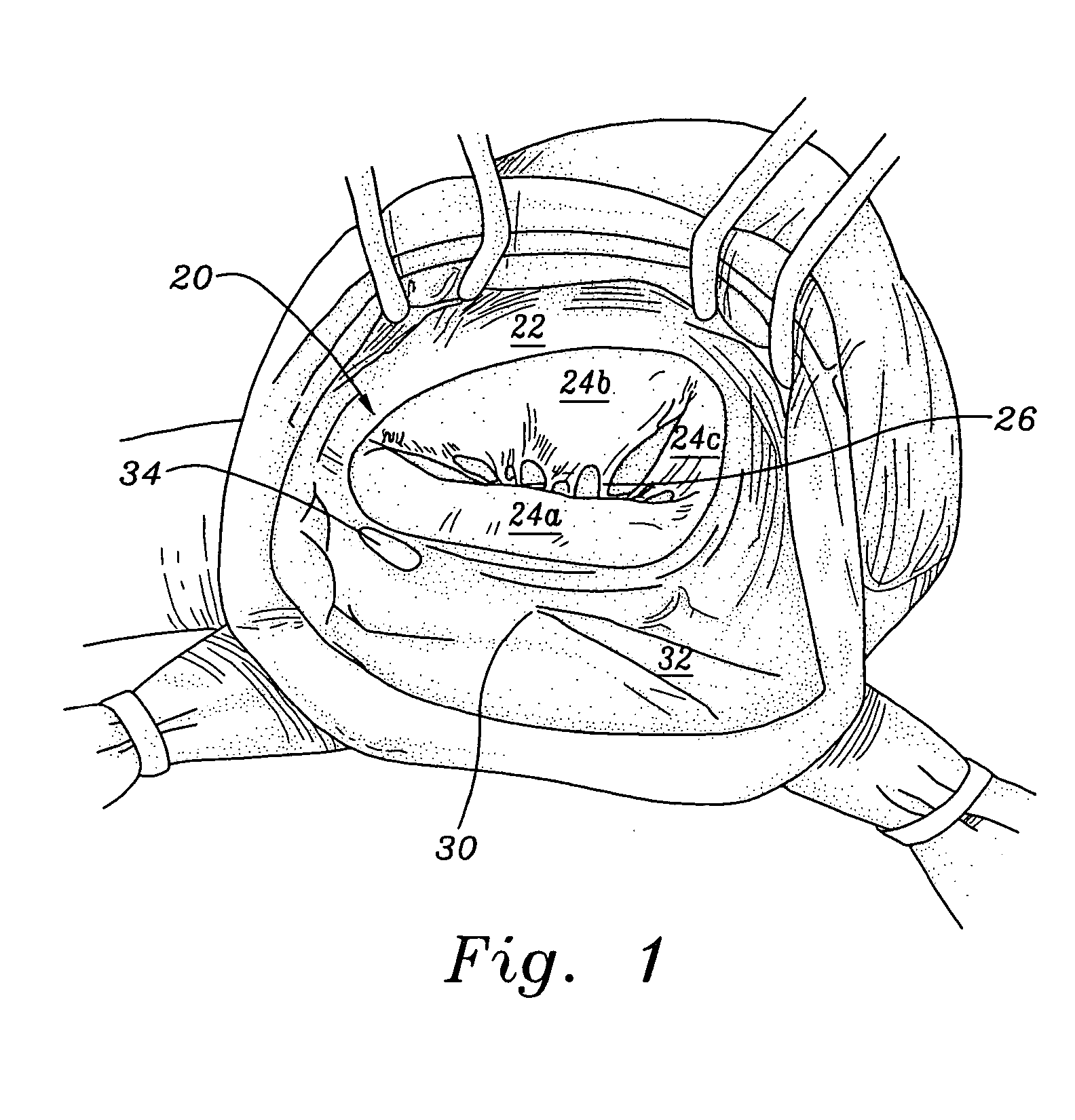
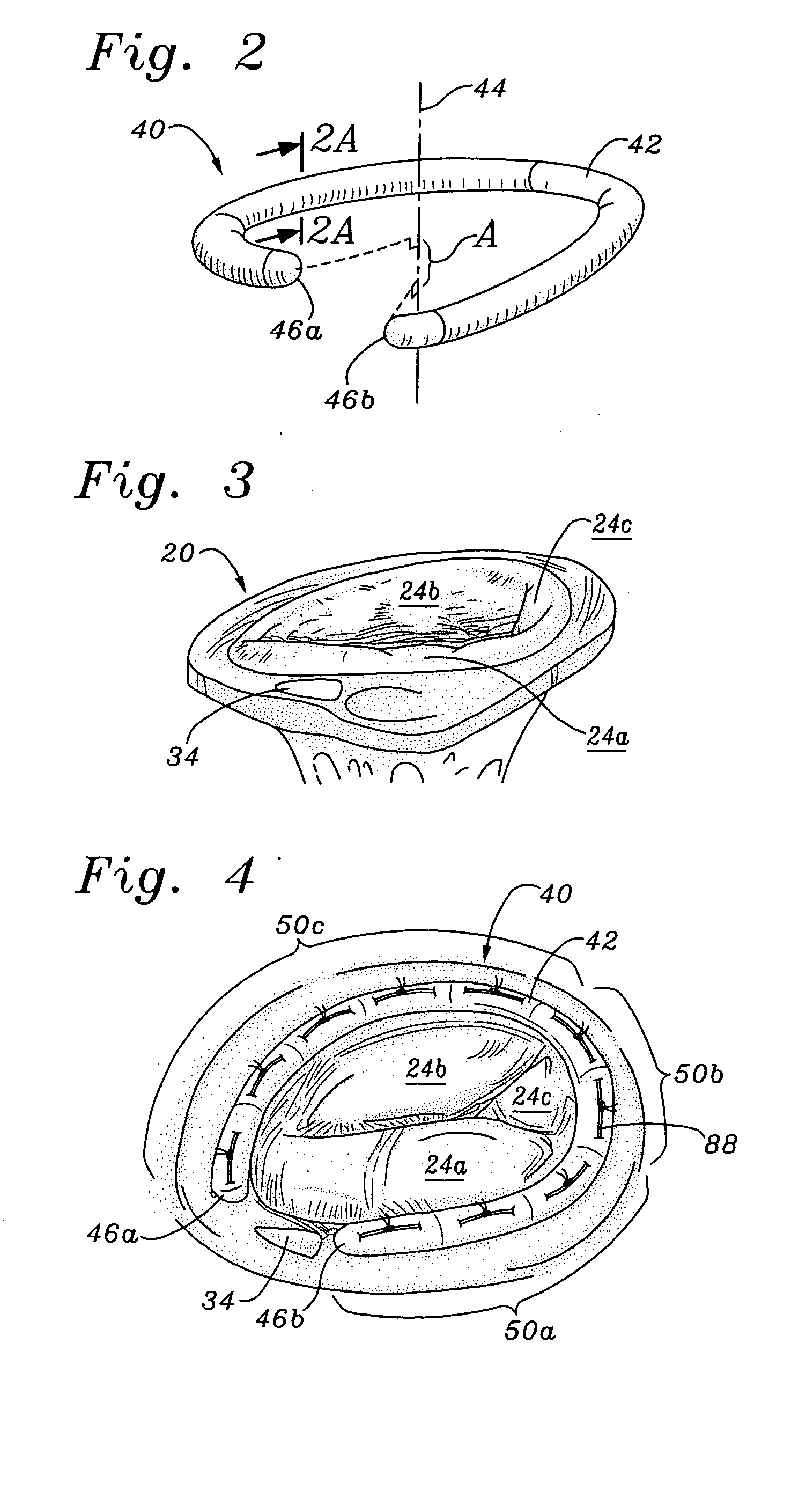
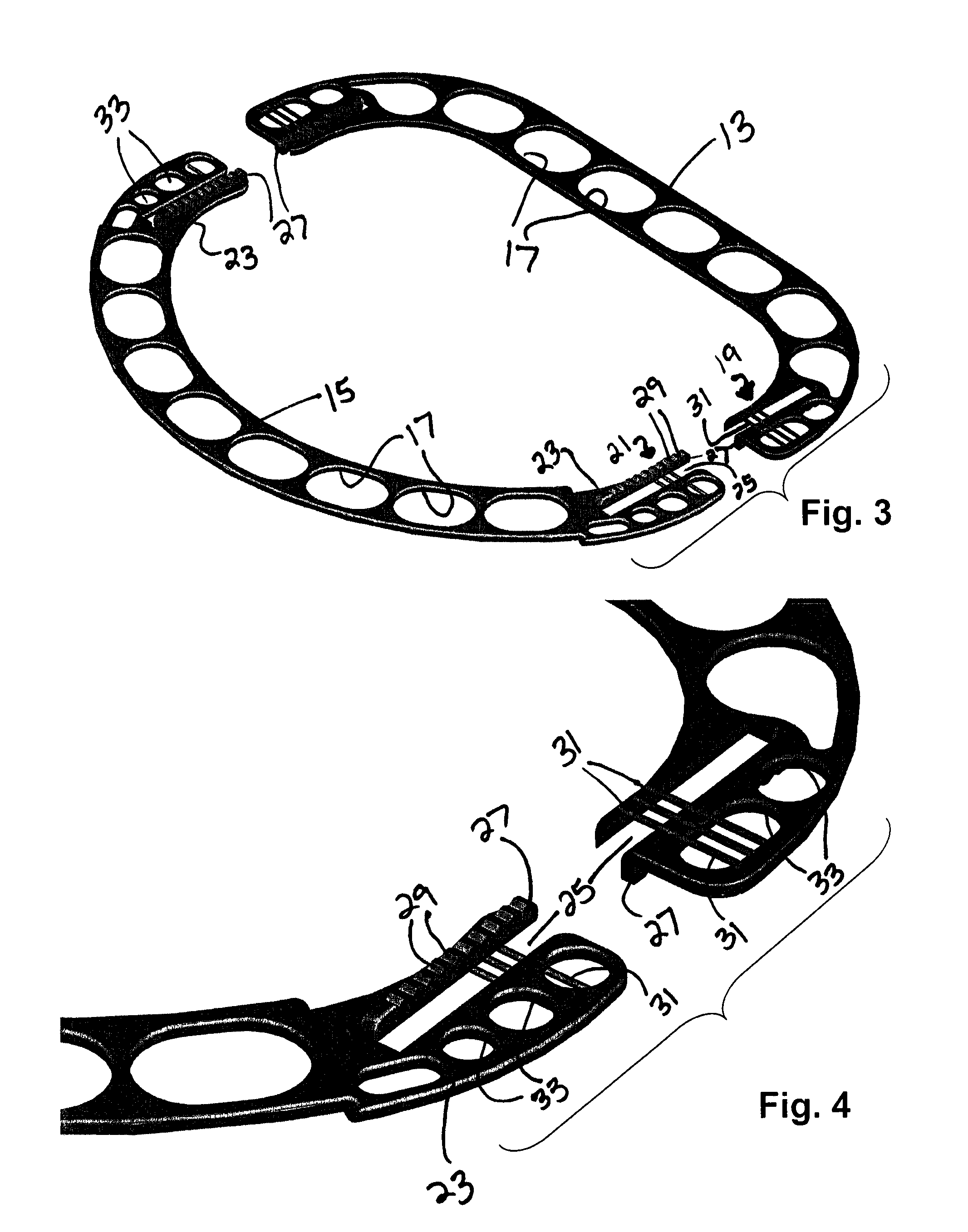
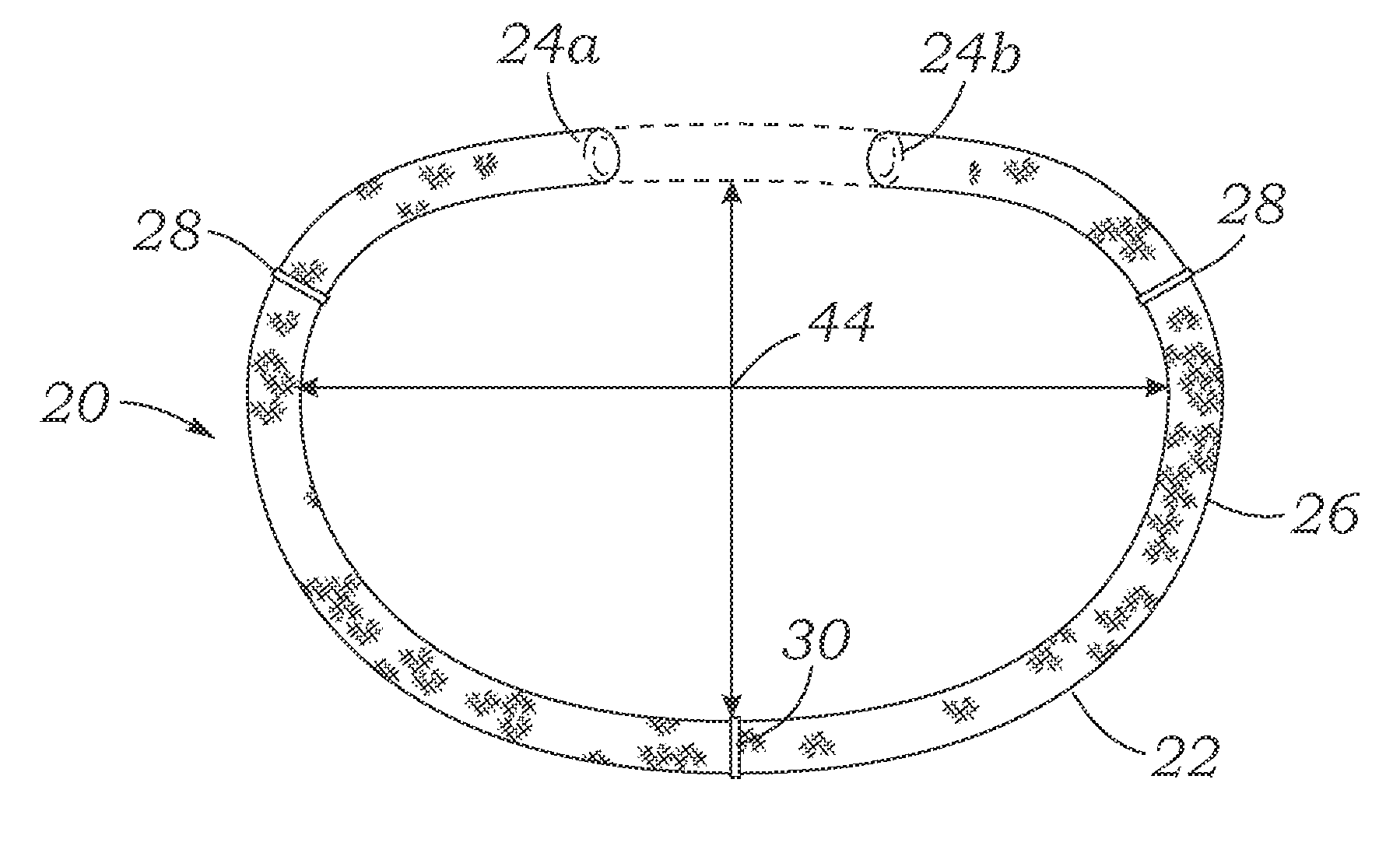
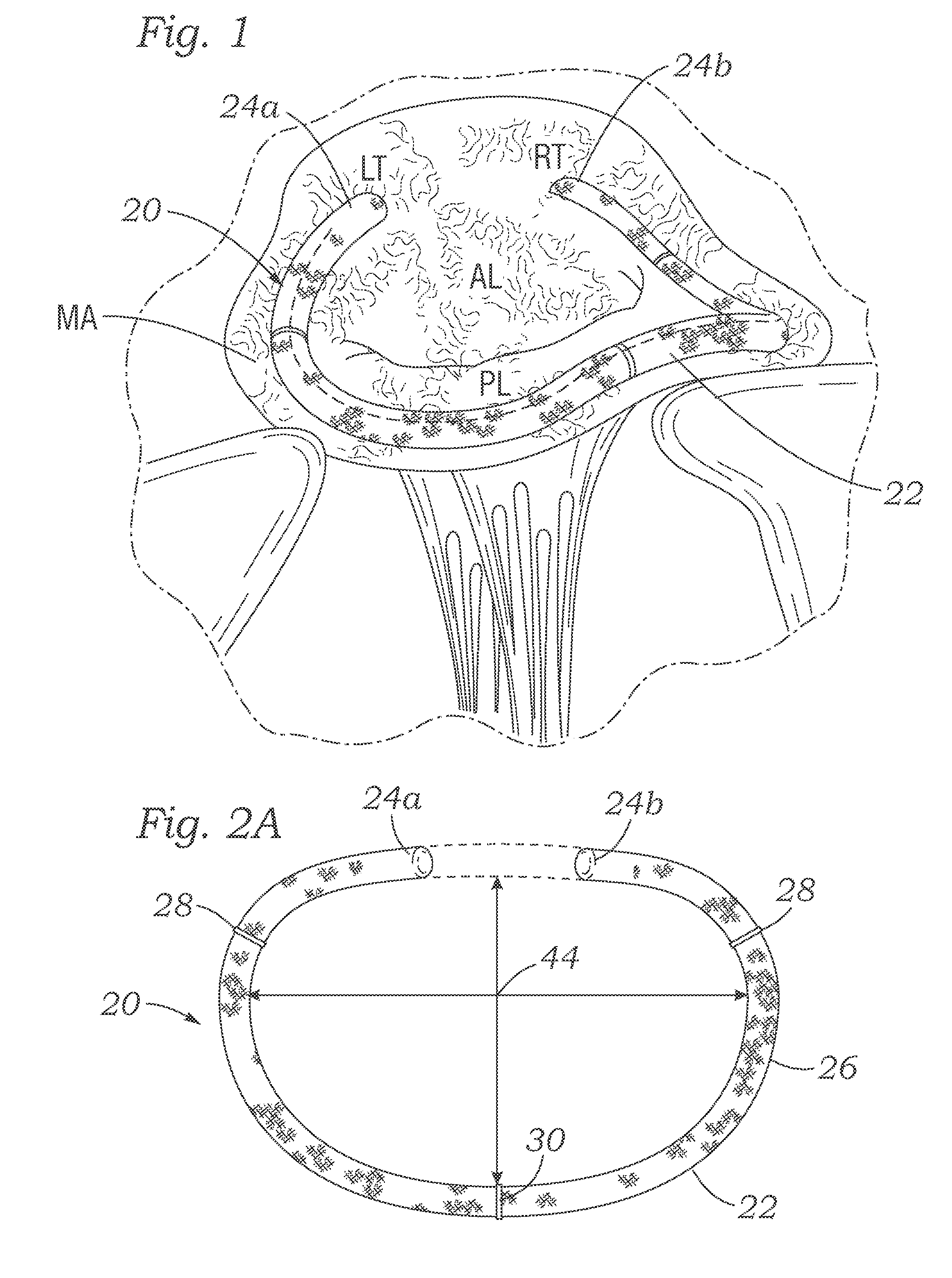
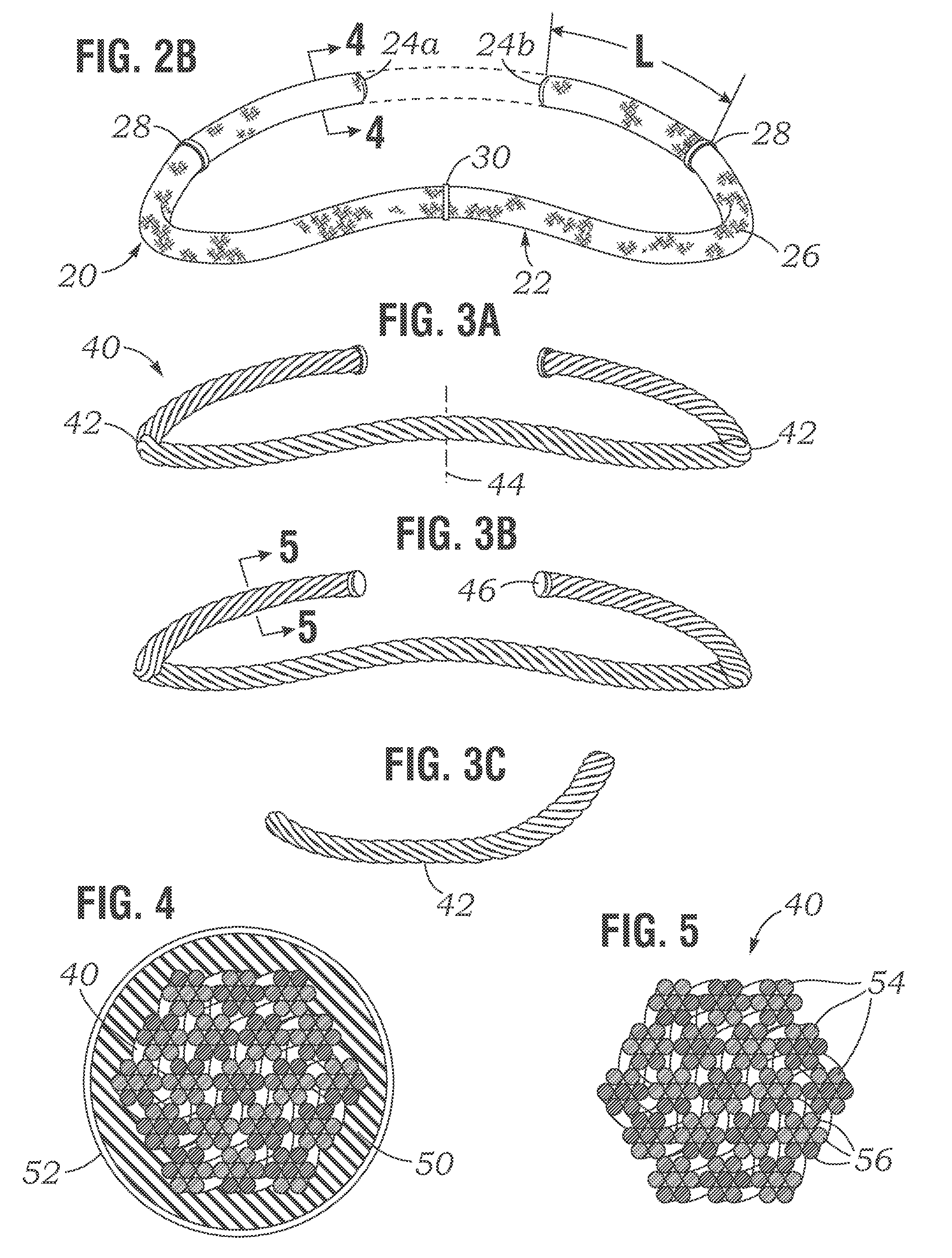
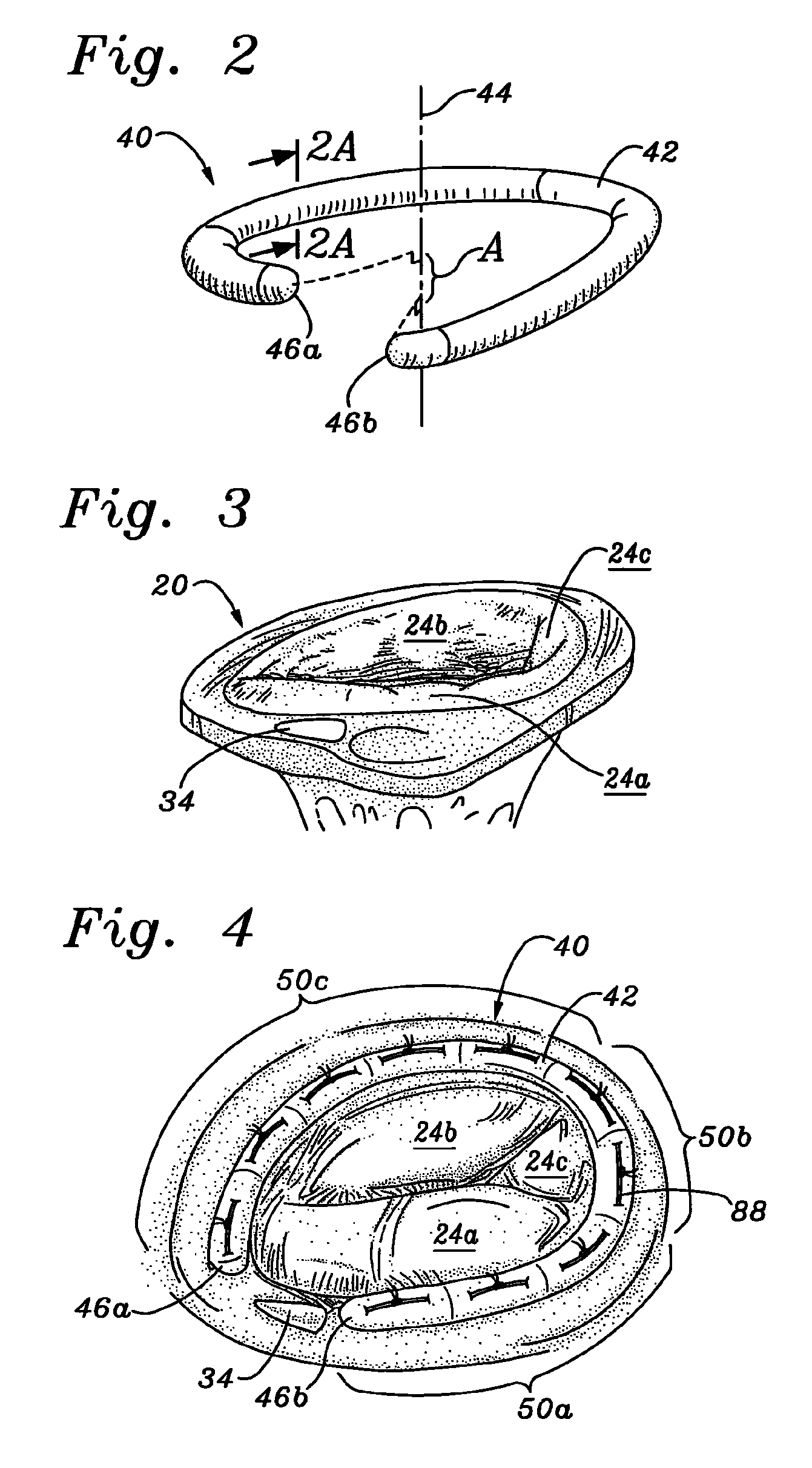
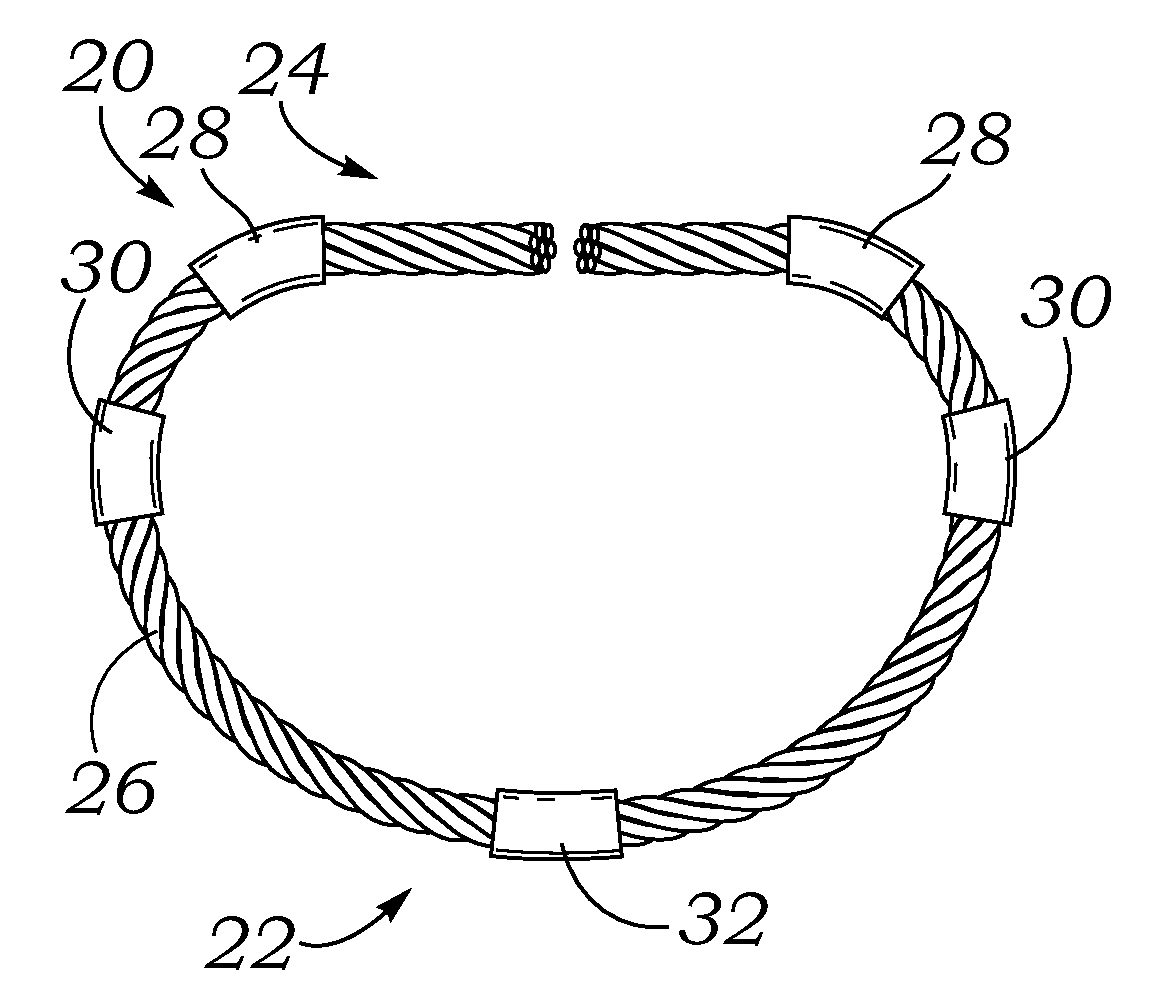
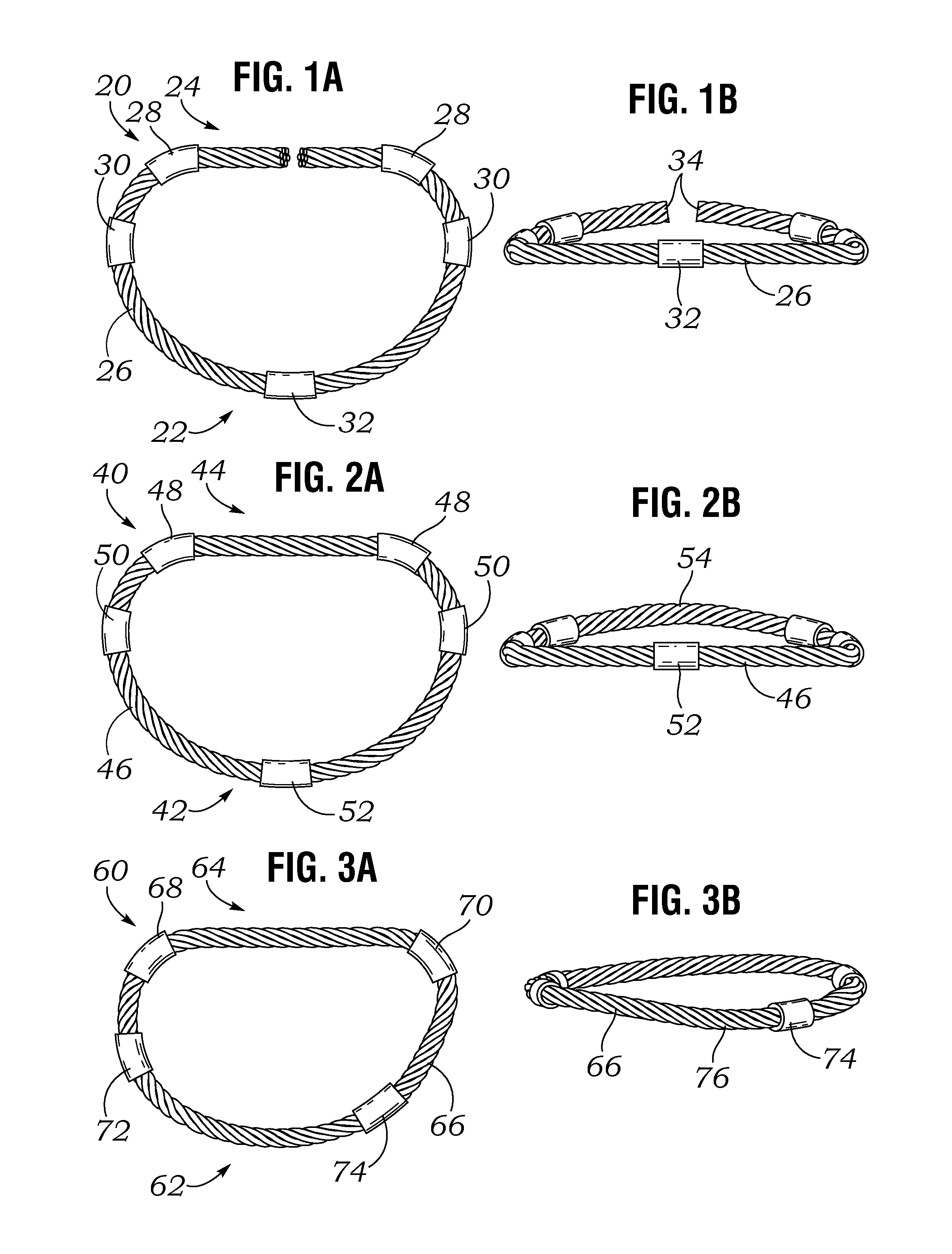
An annuloplasty ring having a three-dimensional discontinuous form generally arranged about an axis with two free ends that are axially offset. The ring is particularly suited for repair of the tricuspid valve, and more closely conforms to the annulus shape. The ring is more flexible in bending about radially extending axes than about the central axis. The ring may have an inner structural support covered by a pliable sleeve and / or a fabric tube. The structural support may have a varying cross-section, such as a C-shaped cross-section in a mid-section between two free ends and a rectangular cross-section at the free ends. A deliver template having a mounting ring with about the same shape as the ring facilitates implant, and may be releasably attached to a delivery handle. The deliver template may include a plurality of cutting guides for releasably attaching the annuloplasty ring thereto while presenting maximum outer surface area of the ring. The template may have an outwardly-facing groove to receive and retain the ring.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
Method and apparatus for percutaneous reduction of anterior-posterior diameter of mitral valve
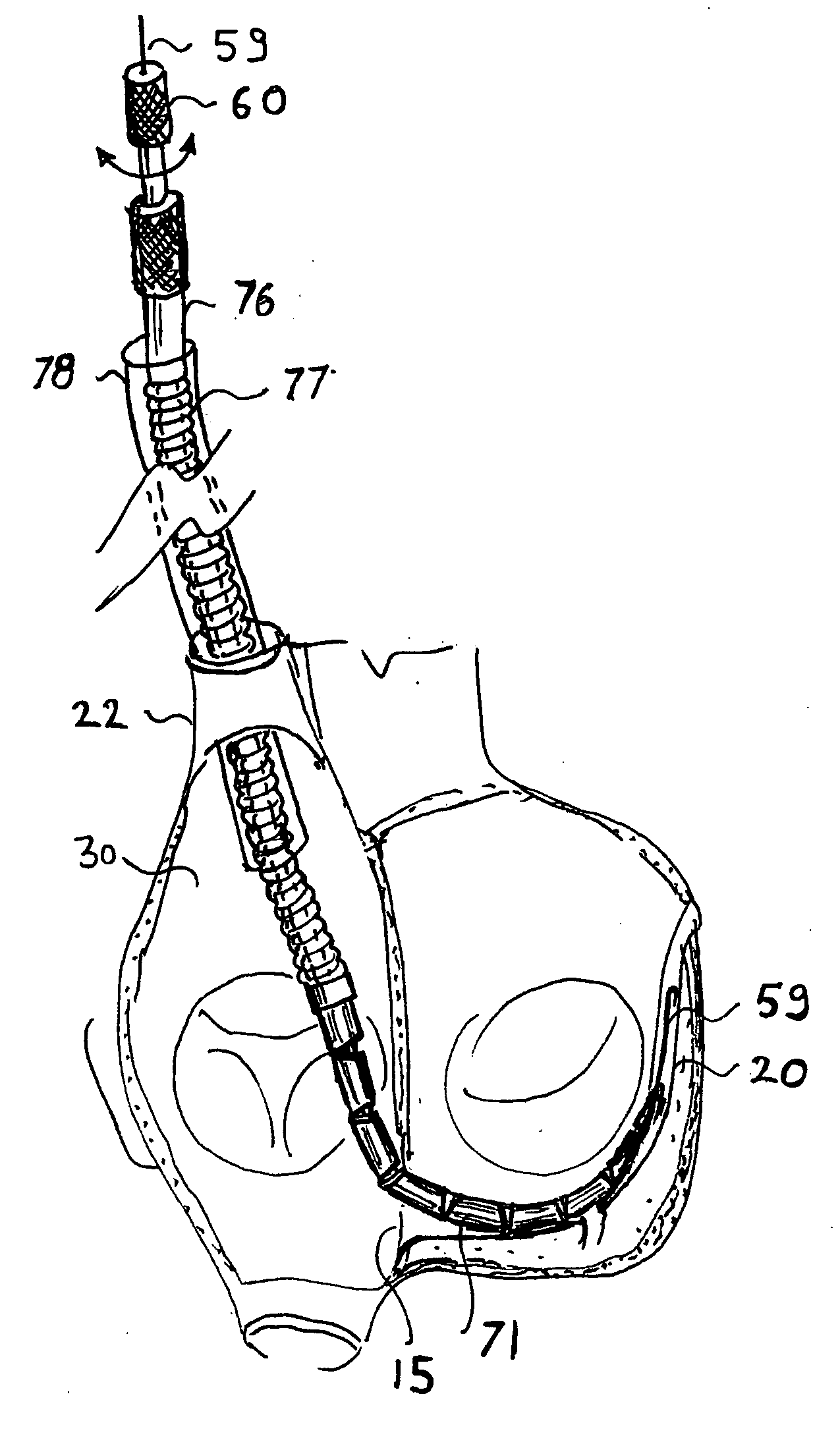
A method and apparatus for treating mitral regurgitation by approximating the septal and lateral (clinically referred to as anterior and posterior) annulus of the mitral valve. The distal end of the device is inserted into the coronary sinus of the heart and the proximal end of the device rests within the right atrium along the tendon of Todaro and extends to at least the membranous septum of the tricuspid valve. Because the coronary sinus approximates the lateral (posterior) annulus of the mitral valve and the tendon of Todaro approximates the septal (anterior) annulus of the mitral valve, the device encircles approximately one half of the mitral valve annulus. The apparatus is then adapted to deform the underlying structures i.e. the septal annulus and lateral annulus of the mitral valve in order to move the posterior leaflet anteriorly and the anterior leaflet posteriorly and thereby improve leaflet coaptation and eliminate mitral regurgitation.
Owner:KARDIUM
Low Profile Transcatheter Heart Valve
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
Device and System for Transcatheter Mitral Valve Replacement
InactiveUS20110319988A1Prevent perivalvular leakStentsHeart valvesExtracorporeal circulationBioprosthetic mitral valve replacement
This invention relates to the design and function of a compressible valve replacement prosthesis which can be deployed into a beating heart without extracorporeal circulation using a transcatheter delivery system. The design as discussed focuses on the deployment of a device via a minimally invasive fashion and by way of example considers a minimally invasive surgical procedure preferably utilizing the intercostal or subxyphoid space for valve introduction. In order to accomplish this, the valve is formed in such a manner that it can be compressed to fit within a delivery system and secondarily ejected from the delivery system into the annulus of a target valve such as a mitral valve or tricuspid valve.
Owner:AVALON MEDICAL +1
Prosthetic valves and related inventions
ActiveUS9480559B2Low height to width profilePrevent perivalvular leakSuture equipmentsHeart valvesExtracorporeal circulationProsthetic valve
This invention relates to the design and function of a compressible valve replacement prosthesis, collared or uncollared, which can be deployed into a beating heart without extracorporeal circulation using a transcatheter delivery system. The design as discussed focuses on the deployment of a device via a minimally invasive fashion and by way of example considers a minimally invasive surgical procedure preferably utilizing the intercostal or subxyphoid space for valve introduction. In order to accomplish this, the valve is formed in such a manner that it can be compressed to fit within a delivery system and secondarily ejected from the delivery system into the annulus of a target valve such as a mitral valve or tricuspid valve.
Owner:TENDYNE HLDG
Atrial Thrombogenic Sealing Pockets for Prosthetic Mitral Valves
This invention relates to a self-expanding pre-configured compressible transcatheter prosthetic cardiovascular valve that comprises atrial thrombogenic sealing pocket cover mounted on a self-expanding inner wire frame having a leaflet structure comprised of articulating leaflets that define a valve function, said inner wire frame is disposed within a self-expanding annular tissue-covered outer wire frame, said outer wire frame having an articulating collar, forming a multi-component prosthetic valve assembly for anchoring within the mitral valve or triscuspid valve of the heart, and methods for deploying such a valve for treatment of a patient in need thereof.
Owner:TENDYNE HLDG
Method and apparatus for external stabilization of the heart
The present disclosure is directed to an external cardiac basal annuloplasty system (ECBAS or BACE-System: basal annuloplasty of the cardia externally) and methods for treatment of regurgitation of mitral and tricuspid valves. The BACE-System provides the ability to correct leakage of regurgitation of the valves with or without the use of cardiopulmonary bypass, particularly when the condition is related to dilation of the base of the heart. This ECBAS invention can be applied to the base of the heart epicardially, either to prevent further dilation or to actively reduce the size of the base of the heart.
Owner:COMPASS CONSULTING INT CORP
Three-dimensional annuloplasty ring and template
InactiveUS20050043791A1Reduce frictionPromote sportsMulti-lumen catheterBone implantEngineeringAnnuloplasty rings
An annuloplasty ring having a three-dimensional discontinuous form generally arranged about an axis with two free ends that are axially offset. The ring is particularly suited for repair of the tricuspid valve, and more closely conforms to the annulus shape. The ring is more flexible in bending about radially extending axes than about the central axis. The ring may have an inner structural support covered by a pliable sleeve and / or a fabric tube. The structural support may have a varying cross-section, such as a C-shaped cross-section in a mid-section between two free ends and a rectangular cross-section at the free ends. A deliver template having a mounting ring with about the same shape as the ring facilitates implant, and may be releasably attached to a delivery handle. The deliver template may include a plurality of cutting guides for releasably attaching the annuloplasty ring thereto while presenting maximum outer surface area of the ring. The template may have an outwardly-facing groove to receive and retain the ring.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
Adjustable annuloplasty rings
Adjustable annuloplasty rings for repair of a mitral or tricuspid valve which incorporate at least two separate parts that are adjustably interconnectable to create a ring the circumference of which can be changed in dimension. Rings having interconnections at spaced-apart lateral locations, which interconnections allow bidirectional movement to either shorten or lengthen the ring at either such location, afford a surgeon opportunity to make further adjustments to the dimensions of the annuloplasty ring after its initial partial securing to the heart valve tissue and thereby adjust the AP diameter of the valve being repaired. The mating interconnections at two lateral locations on the ring can be constructed so as to allow hinged movement about an axis defined by the interconnections to permit hinged movement between the two separate parts.
Owner:QUICKRING MEDICAL TECH LTD
Three-dimensional annuloplasty ring and template
An annuloplasty ring having a three-dimensional discontinuous form generally arranged about an axis with two free ends that are axially offset. The ring is particularly suited for repair of the tricuspid valve, and more closely conforms to the annulus shape. The ring is more flexible in bending about radially extending axes than about the central axis. The ring may have an inner structural support covered by a pliable sleeve and / or a fabric tube. The structural support may have a varying cross-section, such as a C-shaped cross-section in a mid-section between two free ends and a rectangular cross-section at the free ends. A deliver template having a mounting ring with about the same shape as the ring facilitates implant, and may be releasably attached to a delivery handle. The deliver template may include a plurality of cutting guides for releasably attaching the annuloplasty ring thereto while presenting maximum outer surface area of the ring. The template may have an outwardly-facing groove to receive and retain the ring.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
Multi-stranded heat set annuloplasty rings
ActiveUS20140277420A1Improve deployment flexibilitySufficient flexibilityBone implantAnnuloplasty ringsCardiac cycleEngineering
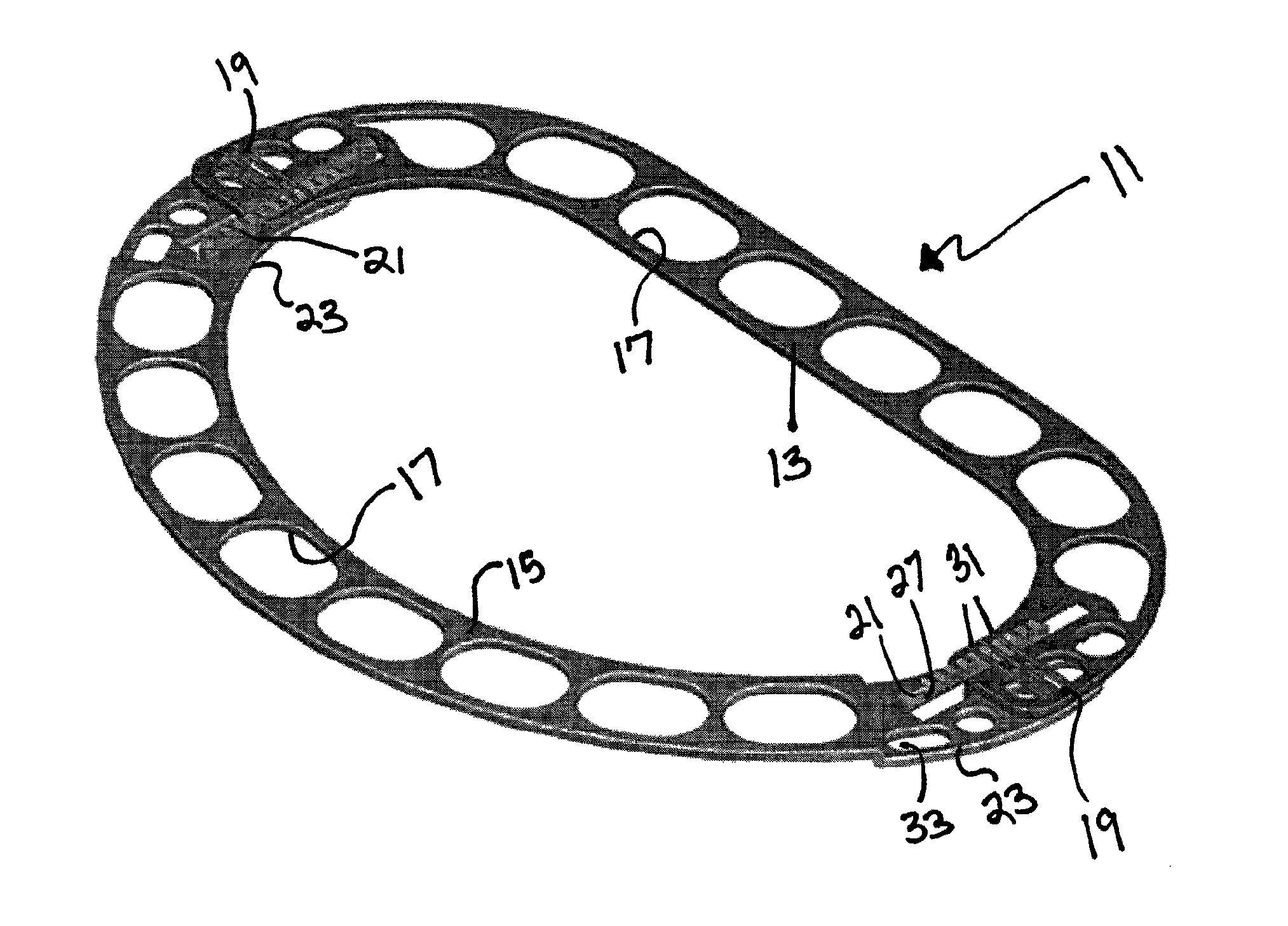
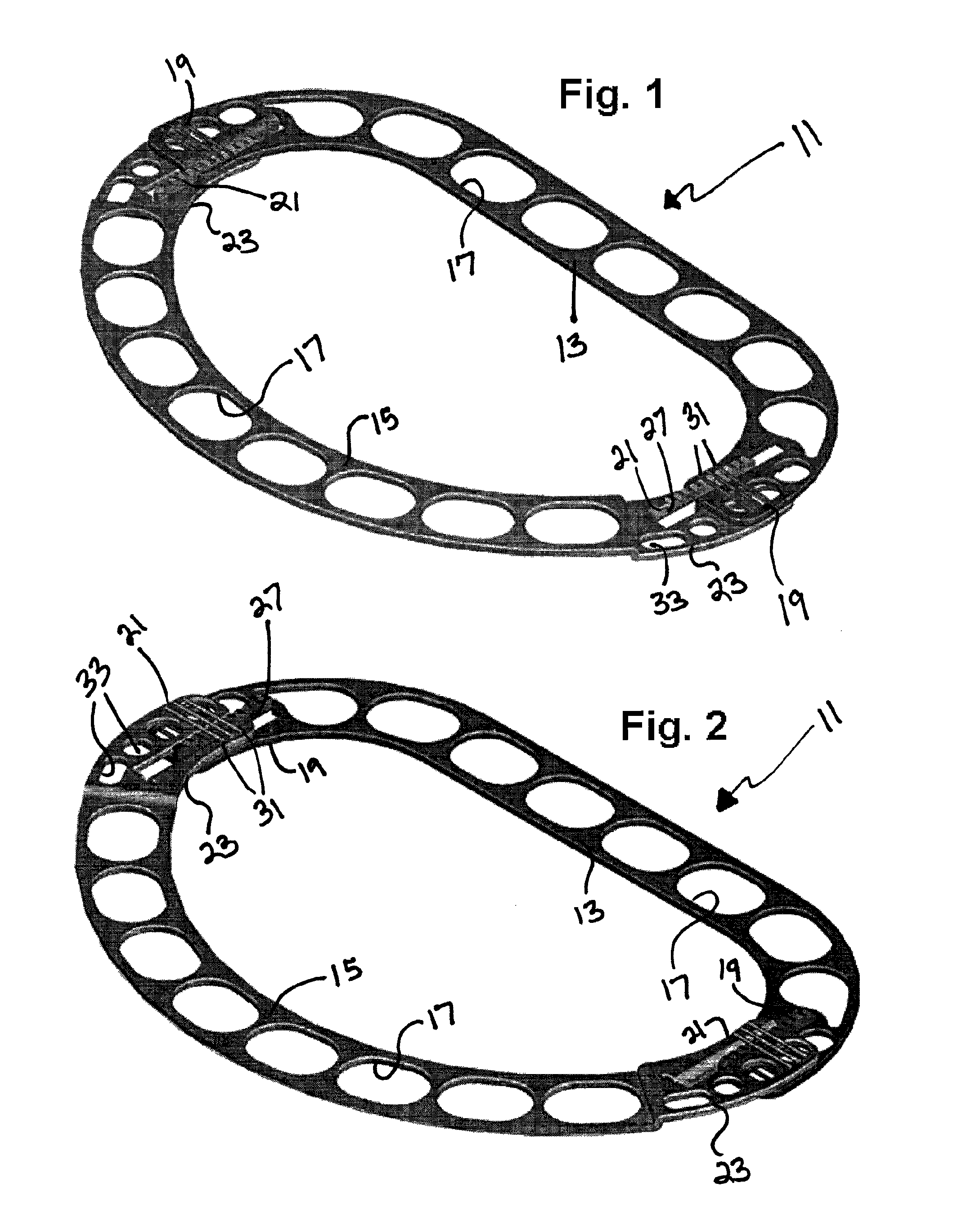
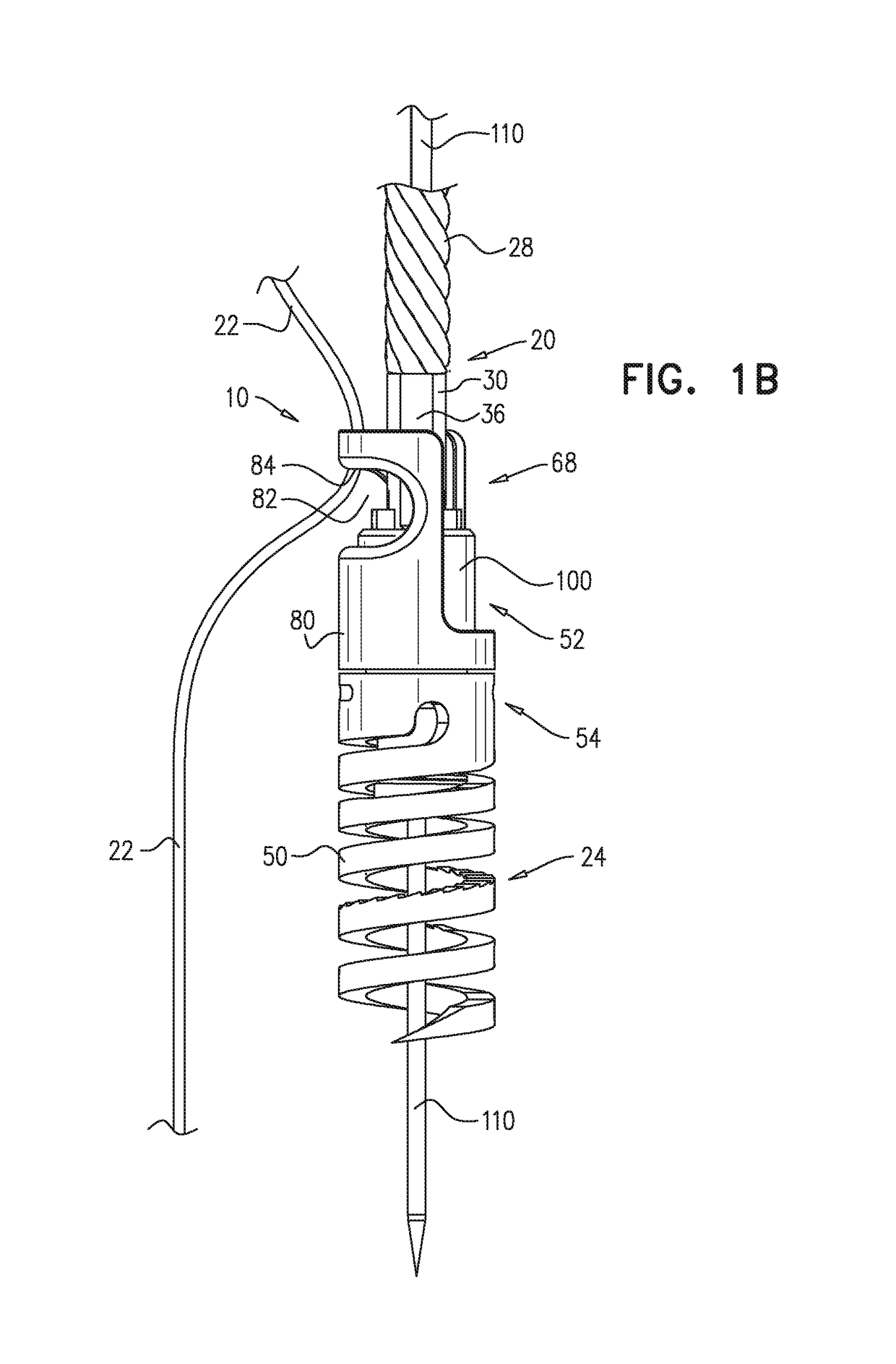
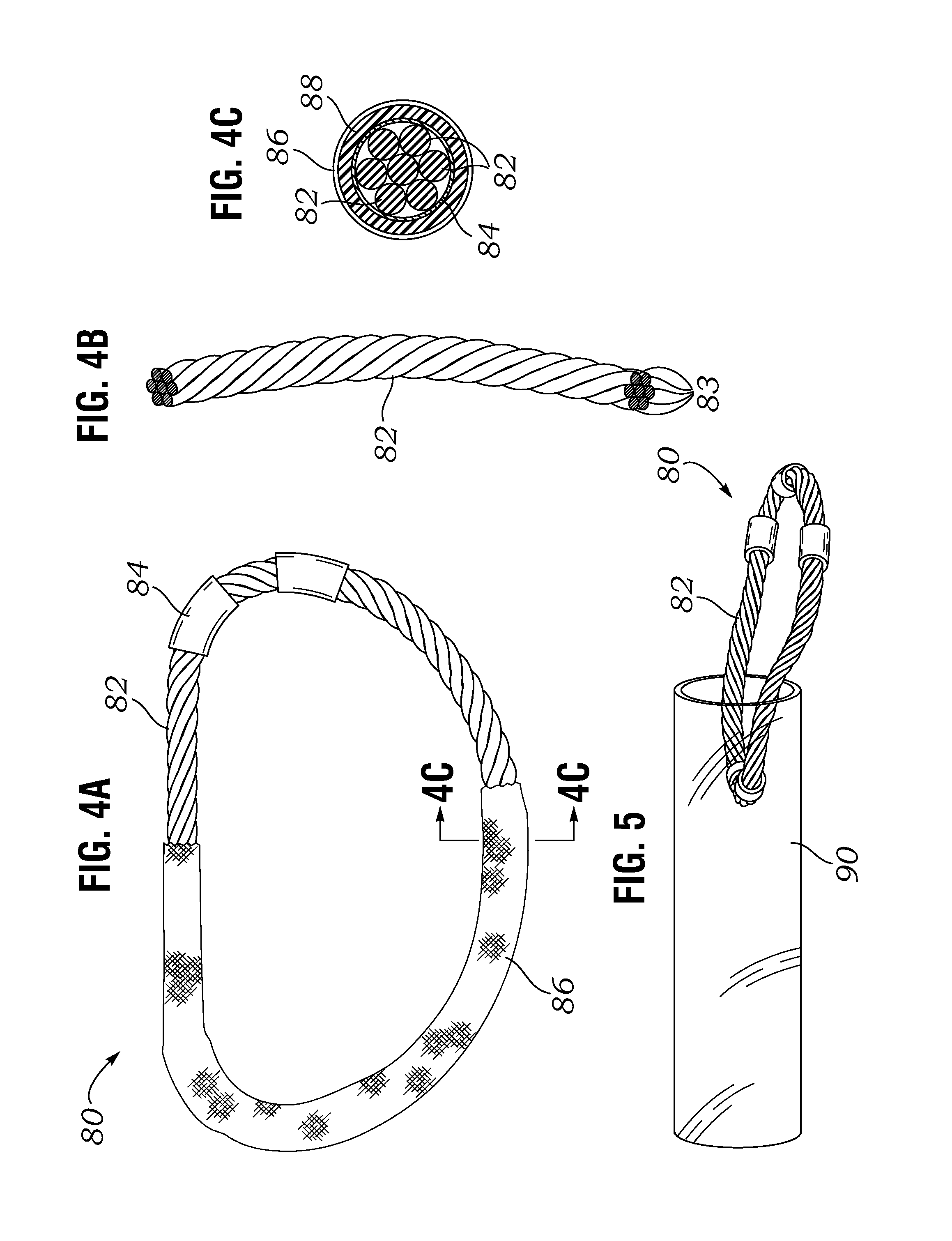
An annuloplasty repair segment for heart valve annulus repair. In one embodiment a multi-stranded cable replaces solid core wire for both the tricuspid and mitral valves. Cable allows for greater deployment flexibility for minimally-invasive surgical (MIS) implant, while still maintaining the required strength and similar tensile properties of solid-core wire. Stranded cable provides a MIS annuloplasty ring with sufficient flexibility in the x-y plane to allow a surgeon to squeeze the ring into a small incision, such as being able to pass through an 18Fr or smaller catheter, while maintaining structural rigidity under forces exerted on the implanted ring by the cardiac cycle. The particular shape of the annuloplasty ring is fixed using a heat setting process.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
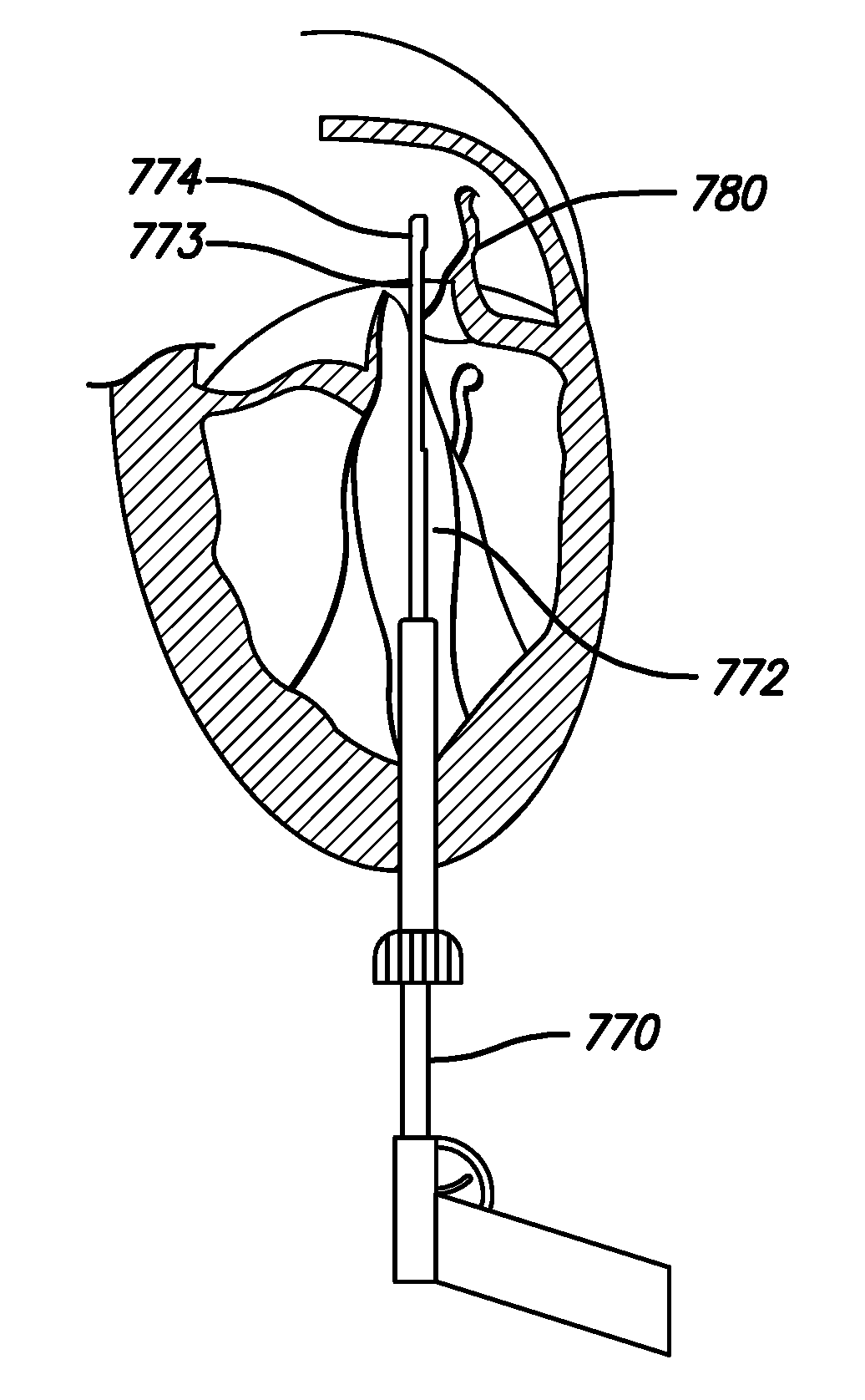
Ablation catheter with suspension system incorporating rigid and flexible components
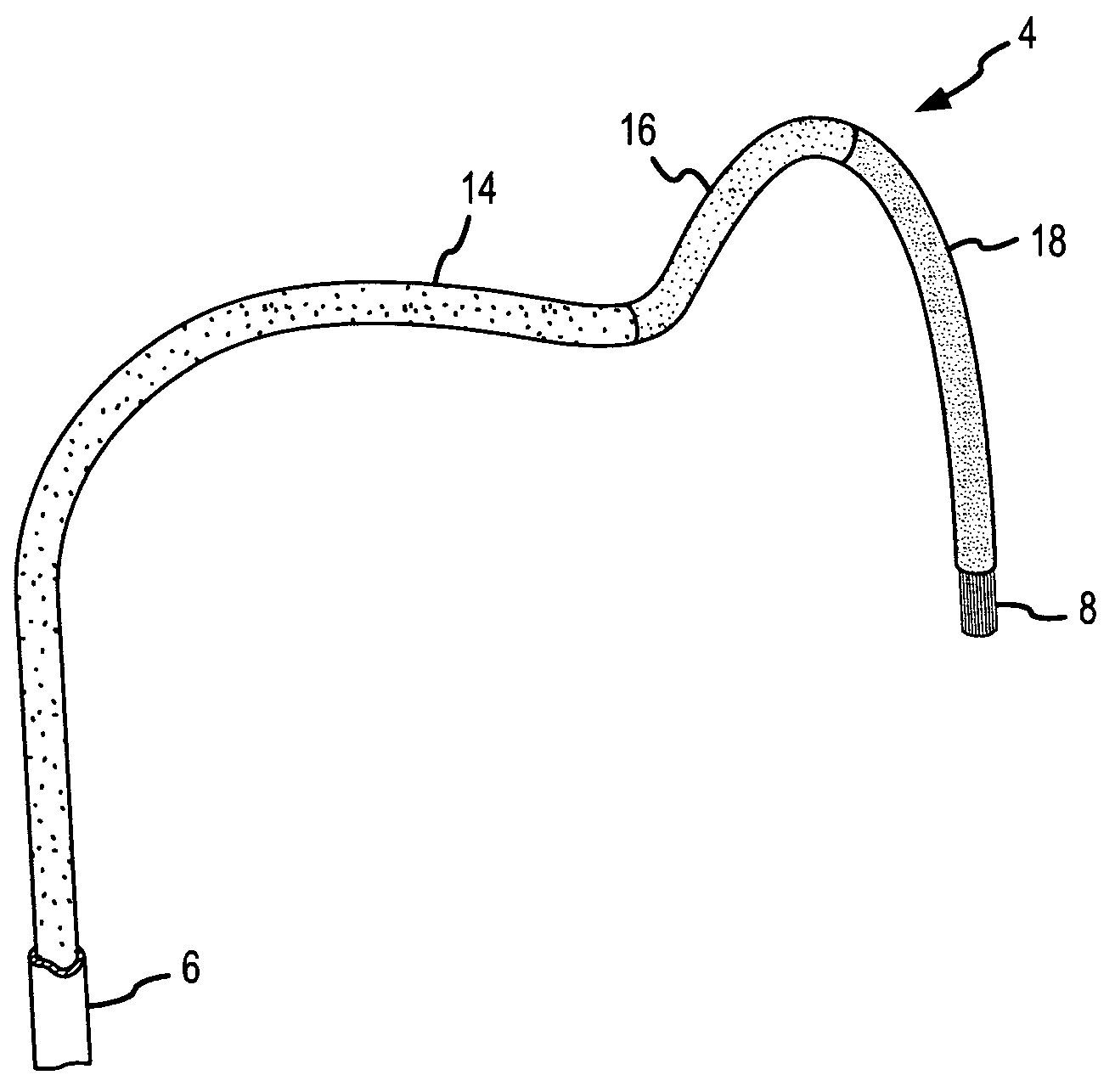
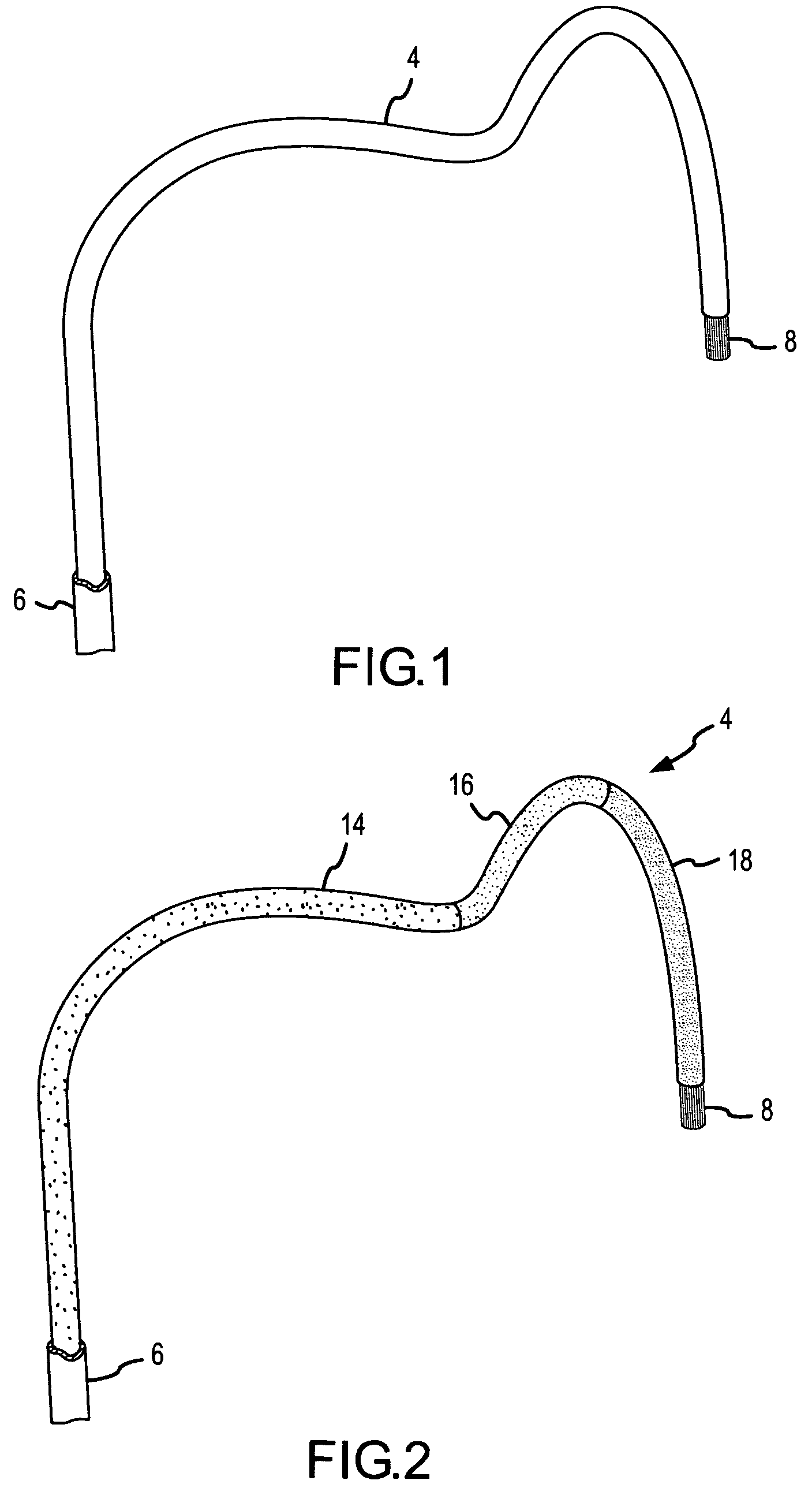
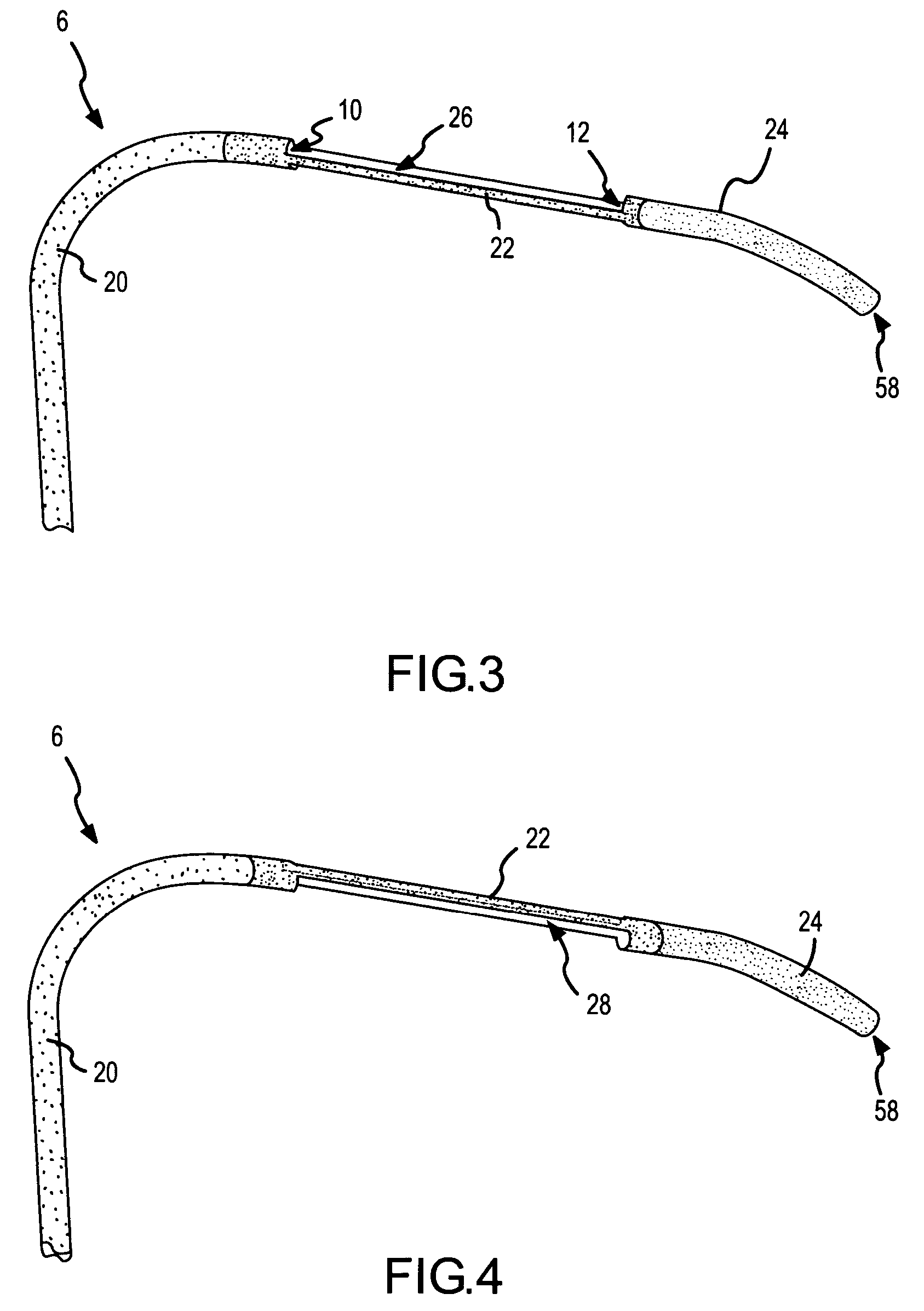
A curved ablation catheter imparts ablative energy to target tissue, for example, along a trabecular slope, e.g., in the right atrium along the isthmus between the ostium of the inferior vena cava and the tricuspid valve. The catheter is formed with a preset curvature that, when deployed, both translates linearly and increases in radius to aid in the formation of spot or continuous linear lesions. A method of treating atrial flutter employs the curved ablation catheter.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
Three-dimensional annuloplasty ring and template
ActiveUS8123800B2Reduce frictionPromote sportsBone implantAnnuloplasty ringsAnnuloplasty ringsCutting guide
An annuloplasty ring having a three-dimensional discontinuous form generally arranged about an axis with two free ends that are axially offset. The ring is particularly suited for repair of the tricuspid valve, and more closely conforms to the annulus shape. The ring is more flexible in bending about radially extending axes than about the central axis. The ring may have an inner structural support covered by a pliable sleeve and / or a fabric tube. The structural support may have a varying cross-section, such as a C-shaped cross-section in a mid-section between two free ends and a rectangular cross-section at the free ends. A deliver template having a mounting ring with about the same shape as the ring facilitates implant, and may be releasably attached to a delivery handle. The deliver template may include a plurality of cutting guides for releasably attaching the annuloplasty ring thereto while presenting maximum outer surface area of the ring. The template may have an outwardly-facing groove to receive and retain the ring.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
Catheter electrode and rail system for cardiac ablation
The instant invention is directed toward an ablation catheter and sheath incorporating wire rail system. The catheter may have a combination of rigid and flexible components to orient an ablation electrode at the distal tip toward the target tissue. The wire rail acts to guide an ablation tip along the tissue to aid in the formation of spot or continuous linear lesions on a trabecular surface, e.g., in the right atrium along the isthmus between the ostium of the inferior vena cava and the tricuspid valve.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
Percutaneous Heart Valve
A percutaneously inserted bistable heart valve prosthesis is folded inside a catheter for transseptal delivery to the patient's heart for implantation. The heart valve has an annular ring, a body member having a plurality of legs, each leg connecting at one end to the annular ring, claws that are adjustable from a first position to a second position by application of external force so as to allow ingress of surrounding heart tissue into the claws in the second position, and leaflet membranes connected to the annular ring, the body member and / or the legs, the leaflet membranes having a first position for blocking blood flow therethrough and a second position for allowing blood flow therethrough. The heart valve is designed such that upon removal of the external force the claws elastically revert to the first position so as to grip the heart tissue positioned within the claws, thereby holding the heart valve in place. The body member and claws may be integrated into a one-piece design. The heart valve may be used as a prosthesis for the mitral valve, aortic valve, pulmonary valve, or tricuspid valve by adapting the annular ring to fit in a respective mitral, aortic, pulmonary, or tricuspid valve opening of the heart.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Curved ablation catheter
A curved ablation catheter imparts ablative energy to target tissue, for example, along a trabecular slope, e.g., in the right atrium along the isthmus between the ostium of the inferior vena cava and the tricuspid valve. The catheter is formed with a preset curvature that, when deployed, both translates linearly and increases in radius to aid in the formation of spot or continuous linear lesions. A method of treating atrial flutter employs the curved ablation catheter.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
Transcatheter atrial anchors and methods of implantation
Anchor assemblies for endovascular introduction and implantation for tethering a replacement heart valve to a cardiac wall. An anchor delivery system introduces the assembly. The anchor may be either implanted with a tether connected thereto or implanted and then connected to a tether. If the latter, a tether assembly is mounted to the implanted anchor to connect the anchor to the valve. The anchors may be implanted into any cardiac wall including the interventricular septum or the epicardial space and the valve may replace the mitral or tricuspid valve.
Owner:OPUS MEDICAL THERAPIES LLC
Curved ablation catheter
ActiveUS20050267459A1Easy to operateImproved linear lesionCatheterDiagnostic recording/measuringVeinRight atrium
A curved ablation catheter imparts ablative energy to target tissue, for example, along a trabecular slope, e.g., in the right atrium along the isthmus between the ostium of the inferior vena cava and the tricuspid valve. The catheter is formed with a preset curvature that, when deployed, both translates linearly and increases in radius to aid in the formation of spot or continuous linear lesions. A method of treating atrial flutter employs the curved ablation catheter.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
Retrievable Self-expanding Non-thrombogenic Low-profile Percutaneous Atrioventricular Valve Prosthesis
ActiveUS20180071088A1Reduce deliveryMitigates concerns regarding heart blockStentsHeart valvesDistal portionProsthesis
An atrioventricular prosthesis device is provided. The device includes a frame at least partially defining and enclosing a central cavity, the frame having a distal portion, a proximal portion, and a middle portion connected therebetween. The device further includes a valve construct formed, at least in part, from a cell growth scaffold, at least partially disposed within the central cavity defined by the frame. The valve construct includes: an annular portion defining an aperture and being connected to the frame for positioning the valve construct within the central cavity of the frame, and a plurality of leaflets extending longitudinally and radially inward from the annular portion. The frame and valve construct are transitionable to a deployed state, in which a diameter of at least a portion of the frame and the valve construct substantially conform to a diameter of a tricuspid and / or mitral valve opening.
Owner:RI MED FOUND
Method and apparatus for external stabilization of the heart
The present disclosure is directed to an external cardiac basal annuloplasty system (ECBAS or BACE-System: basal annuloplasty of the cardia externally) and methods for treatment of regurgitation of mitral and tricuspid valves. The BACE-System provides the ability to correct leakage of regurgitation of the valves with or without the use of cardiopulmonary bypass, particularly when the condition is related to dilation of the base of the heart. This ECBAS invention can be applied to the base of the heart epicardially, either to prevent further dilation or to actively reduce the size of the base of the heart.
Owner:MUPPIRALA GOPAL
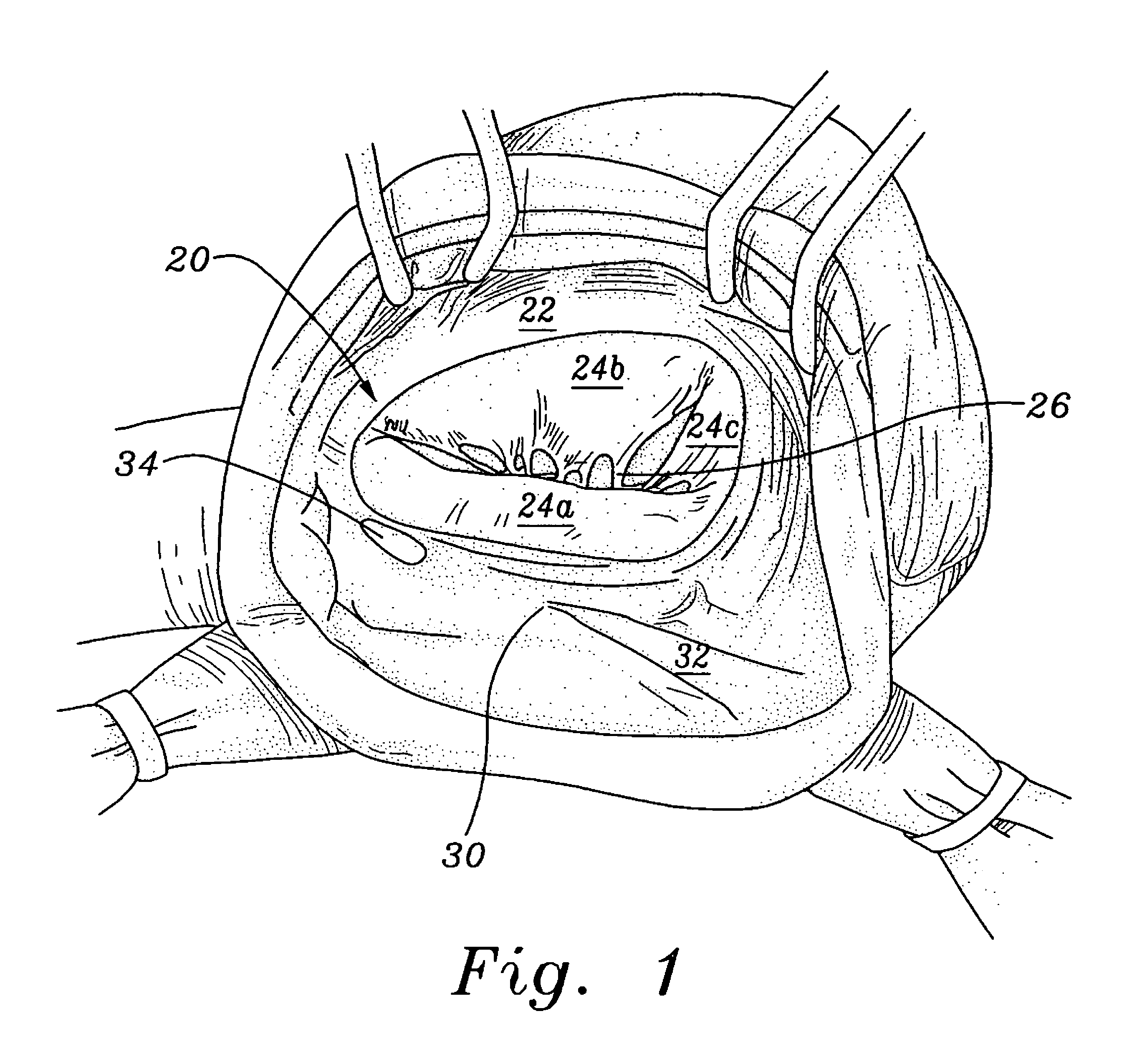
Cardiac tissue cinching
ActiveUS20170086975A1Reduce refluxMaintains distanceSuture equipmentsHeart valvesMitral valve leafletRight atrium
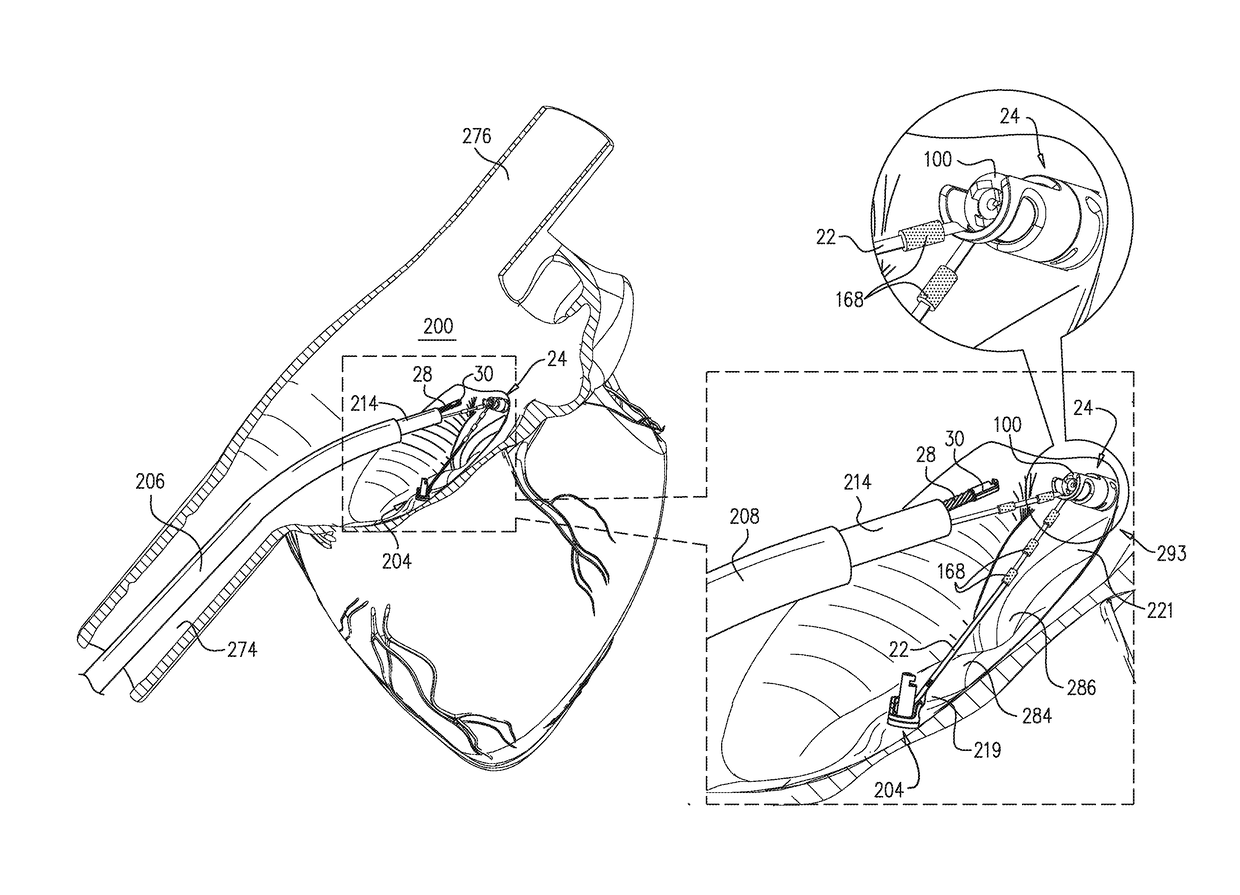
A method is provided including making an opening (300) through an atrial septum (302) at a septal site (304) at least 5 mm from a fossa ovalis (330). A first tissue anchor (204) is endovascularly advanced to a left-atrial site (306) on an annulus of a mitral valve (310) or a wall of a left atrium (308) above the annulus. The first tissue anchor (204) is implanted at the left-atrial site (306). A second tissue anchor (24) is endovascularly advanced to a right-atrial site (320) on an annulus of a tricuspid valve (207) or a wall of a right atrium (200) above the annulus. The second tissue (24) anchor is implanted at the right-atrial site (320). The left-atrial site (306) and the right-atrial site (320) are approximated by tensioning a tether (22) that passes through the opening (300) of the atrial septum (302) and connects the first and the second tissue anchors (204, 24). Other embodiments are also described.
Owner:4TECH INC OXO CAPITAL
Flexible Annuloplasty Ring With Select Control Points
ActiveUS20120053687A1Improve deployment flexibilitySufficient flexibilityAnnuloplasty ringsTubular organ implantsCardiac cycleMitral valve leaflet
An annuloplasty repair segment for heart valve annulus repair. In one embodiment a multi-stranded cable replaces solid core wire for both the tricuspid and mitral valves. Cable allows for greater deployment flexibility for minimally-invasive surgical (MIS) implant, while still maintaining the required strength and similar tensile properties of solid-core wire. In addition, selective placement of point-welds or other such control points locally control other parameters such as the amount and direction of displacement as the ring undergoes external loading. Cable with well-placed control points result in a MIS annuloplasty ring with sufficient flexibility in the x-y plane to allow a surgeon to squeeze the ring into a small incision, such as for example 1 cm×1 cm, while maintaining structural rigidity under forces exerted on the implanted ring by the cardiac cycle and allowing for asymmetrical deflection to be designed into the product.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com