Patents
Literature
399 results about "Small incision" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
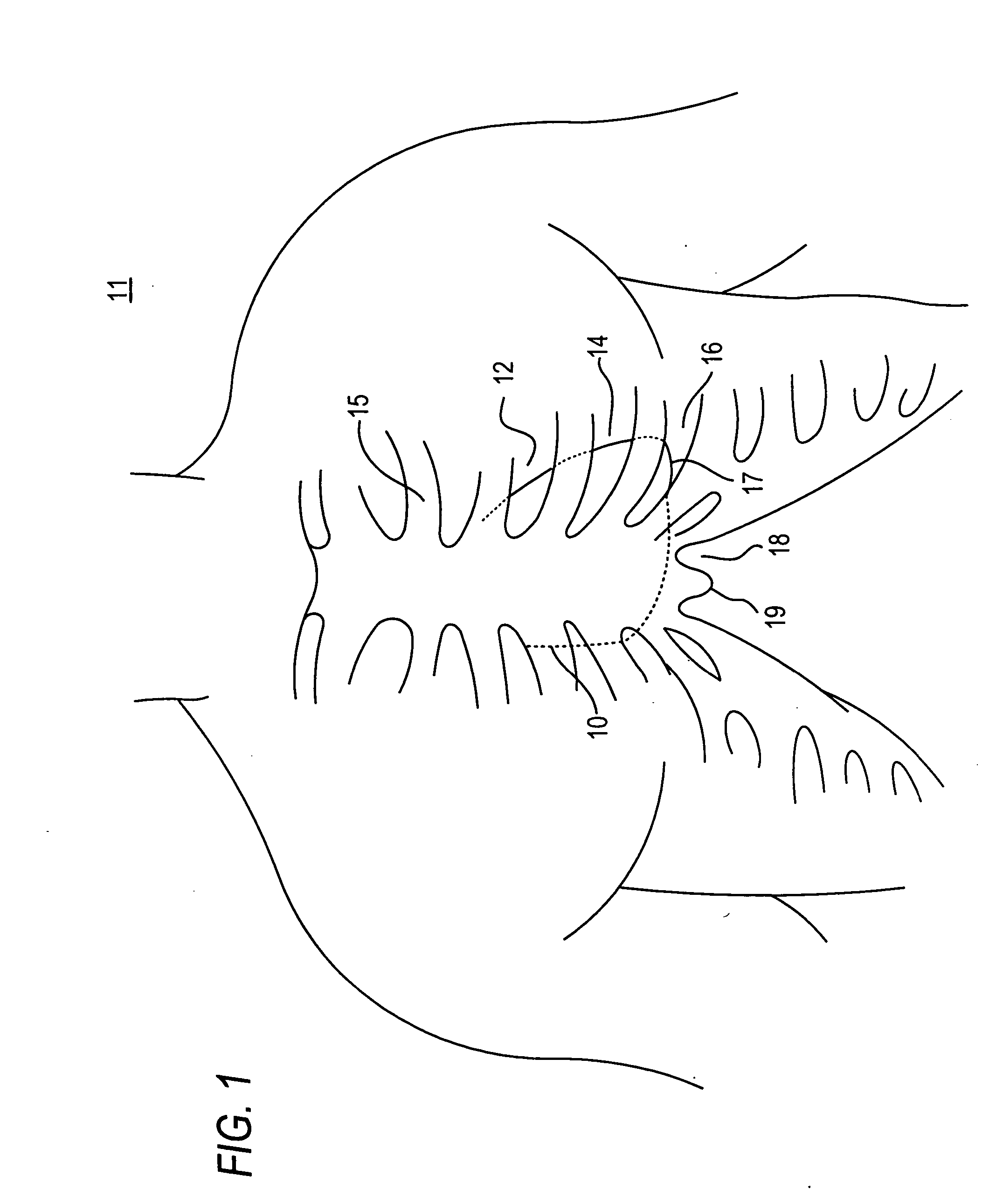
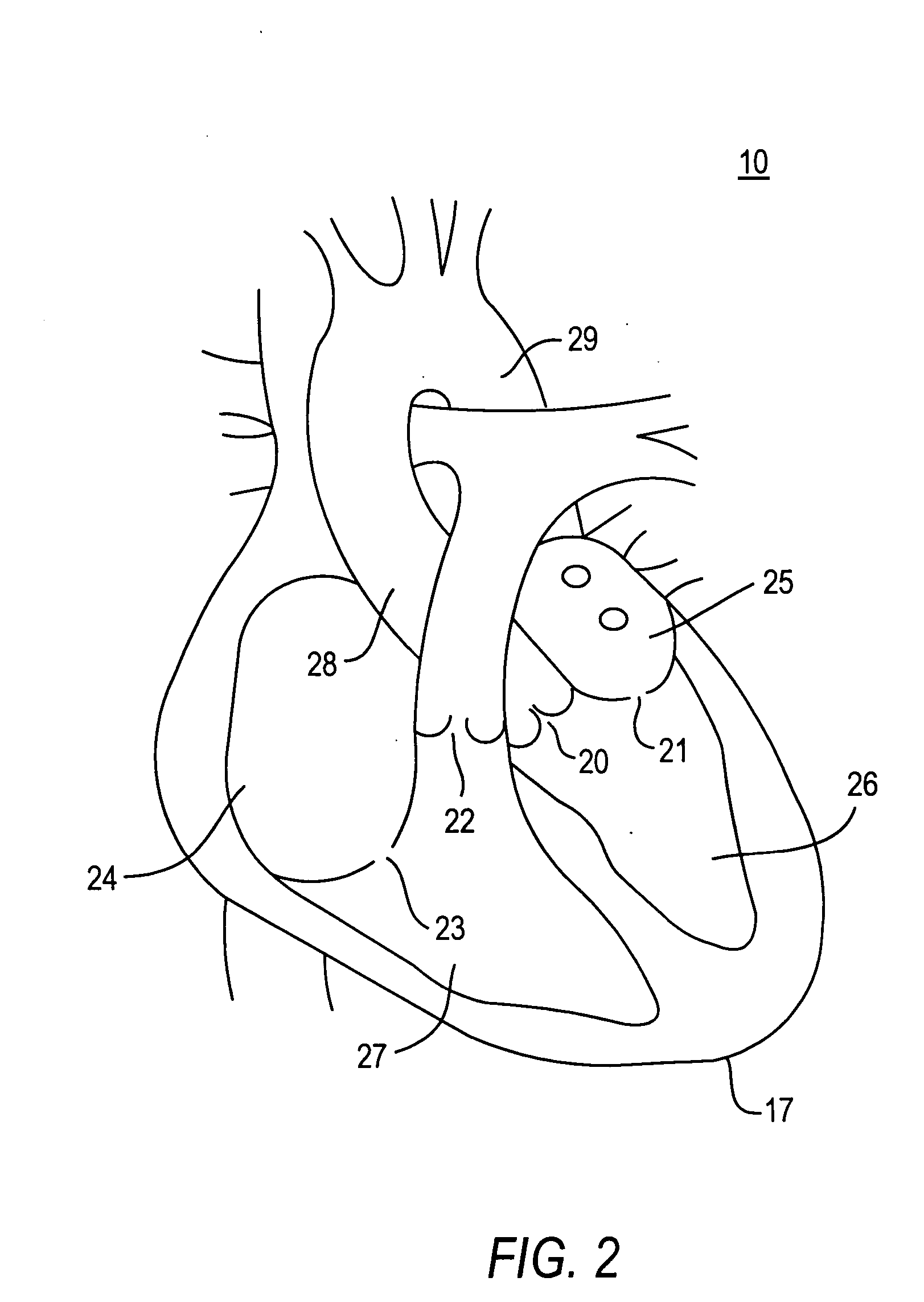
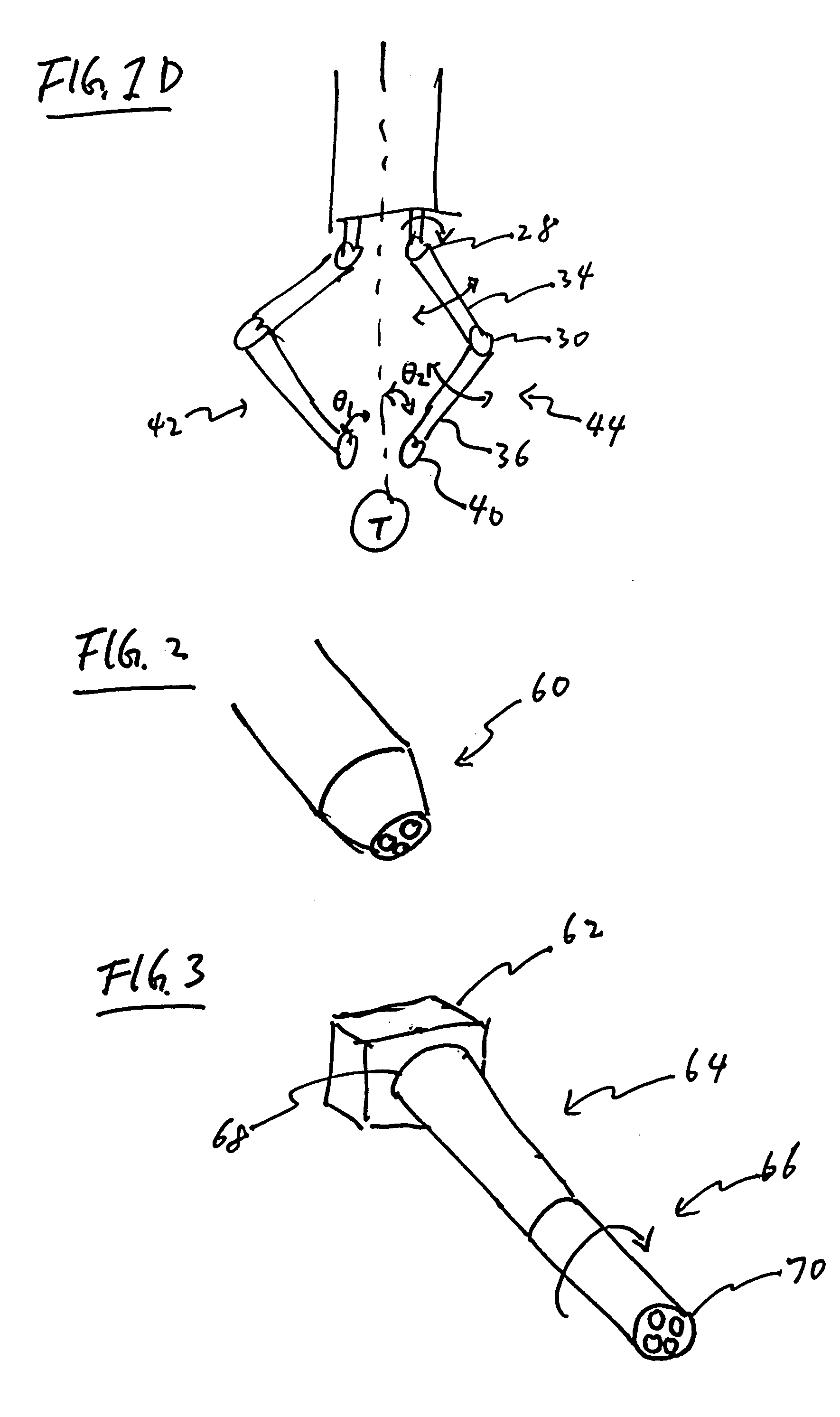
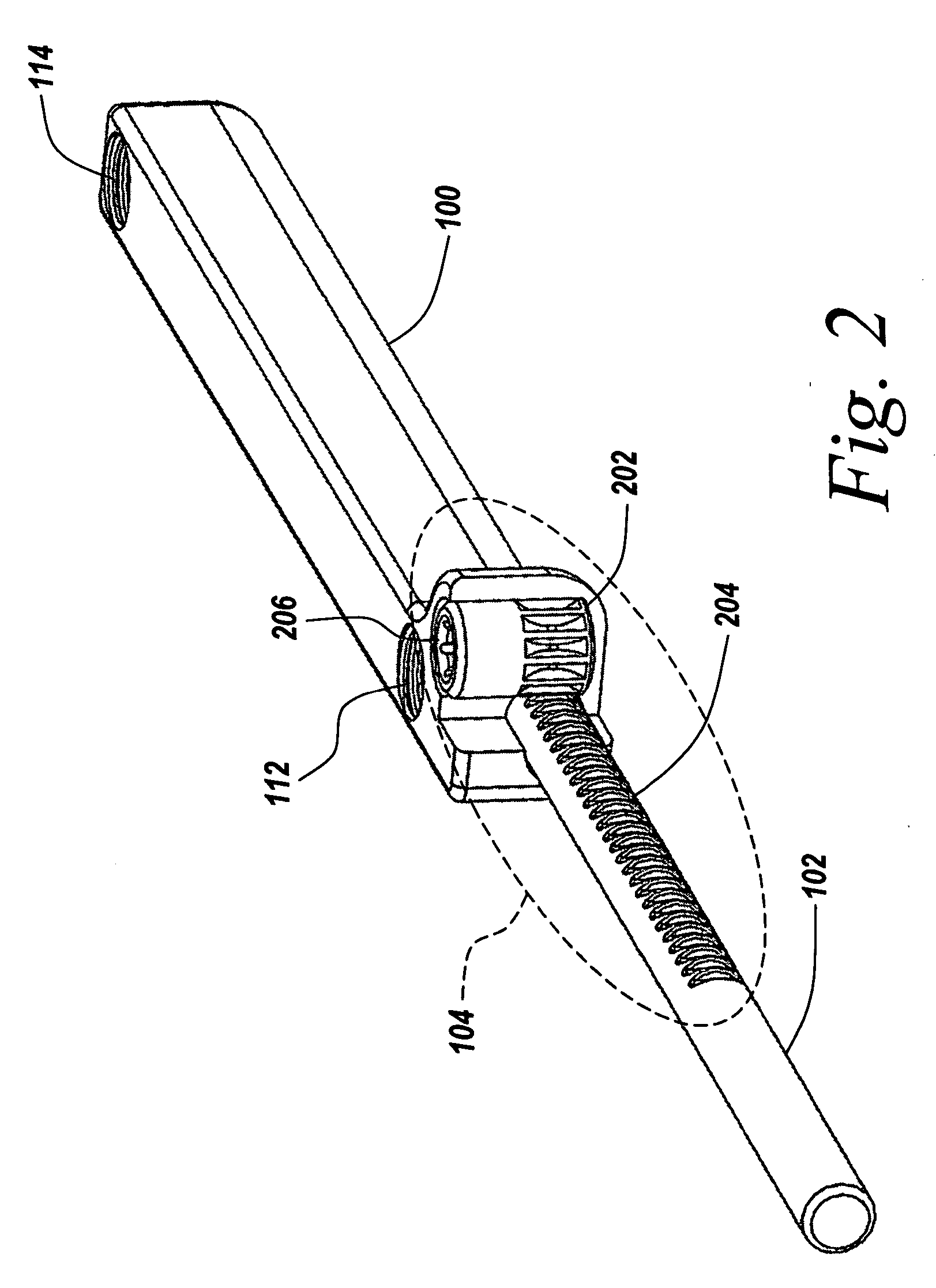
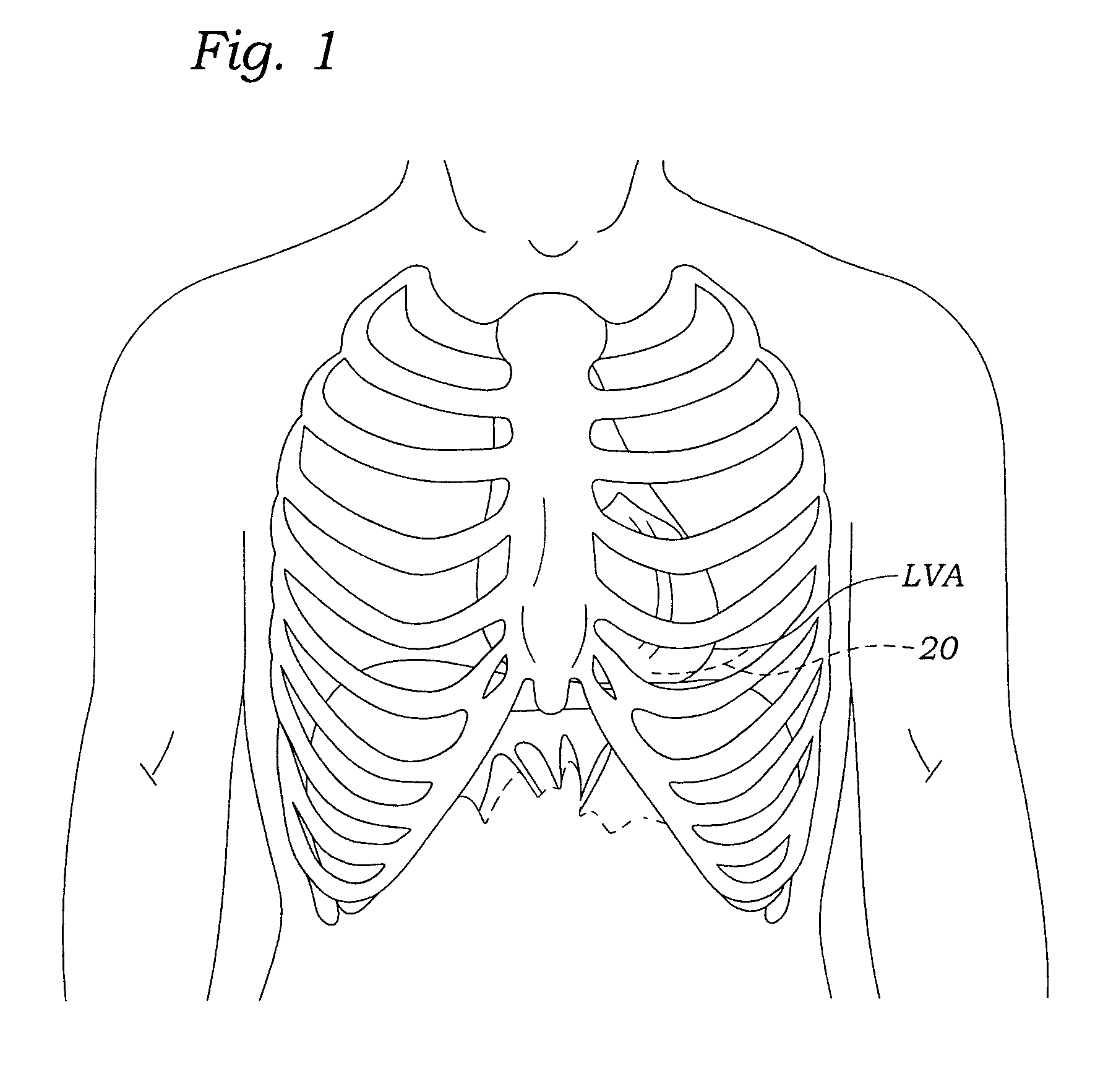
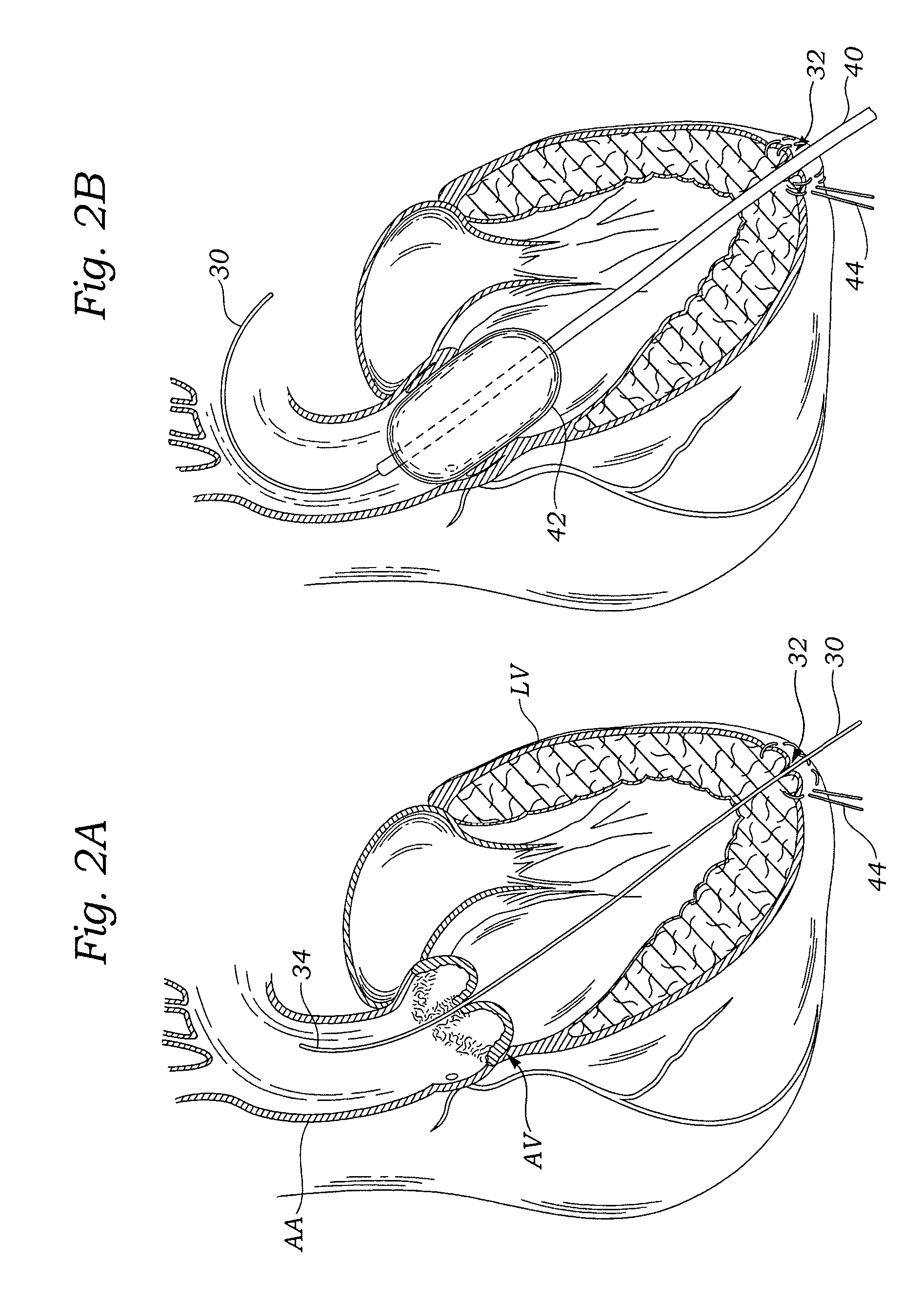
Transapical heart valve delivery system and method
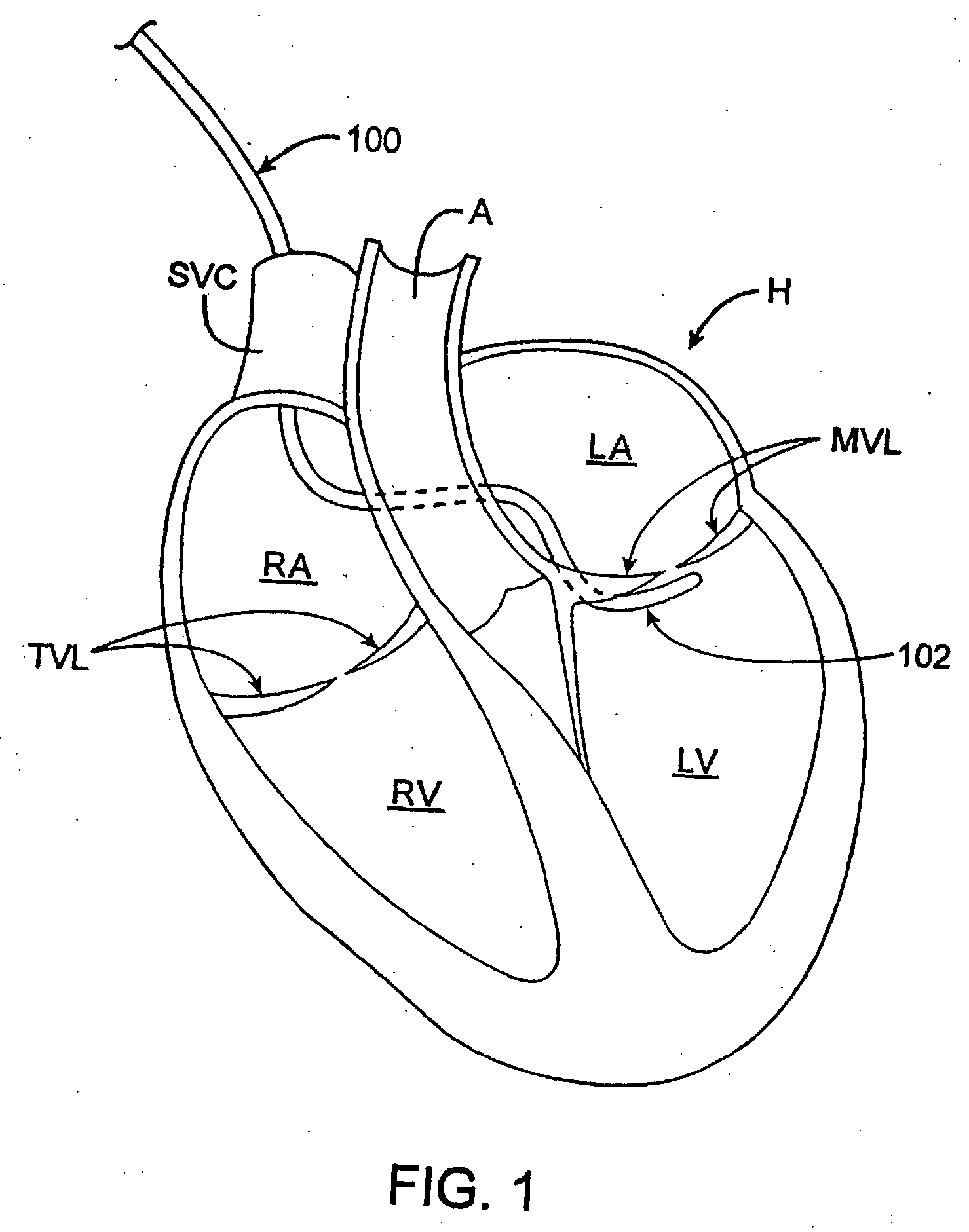
ActiveUS20070112422A1Facilitate positioning of valveHelp positioningStentsBalloon catheterProsthetic heartLeft ventricular apex
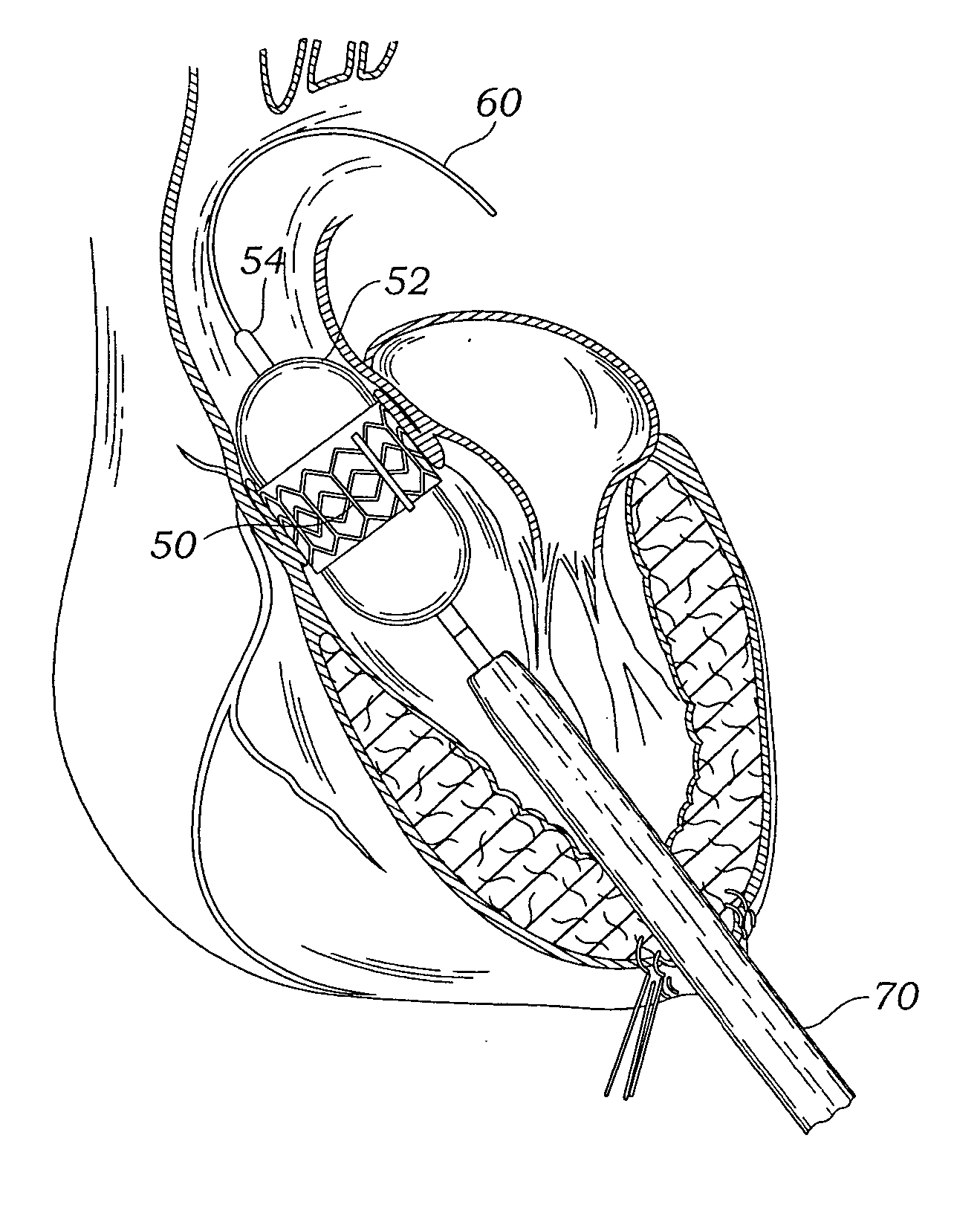
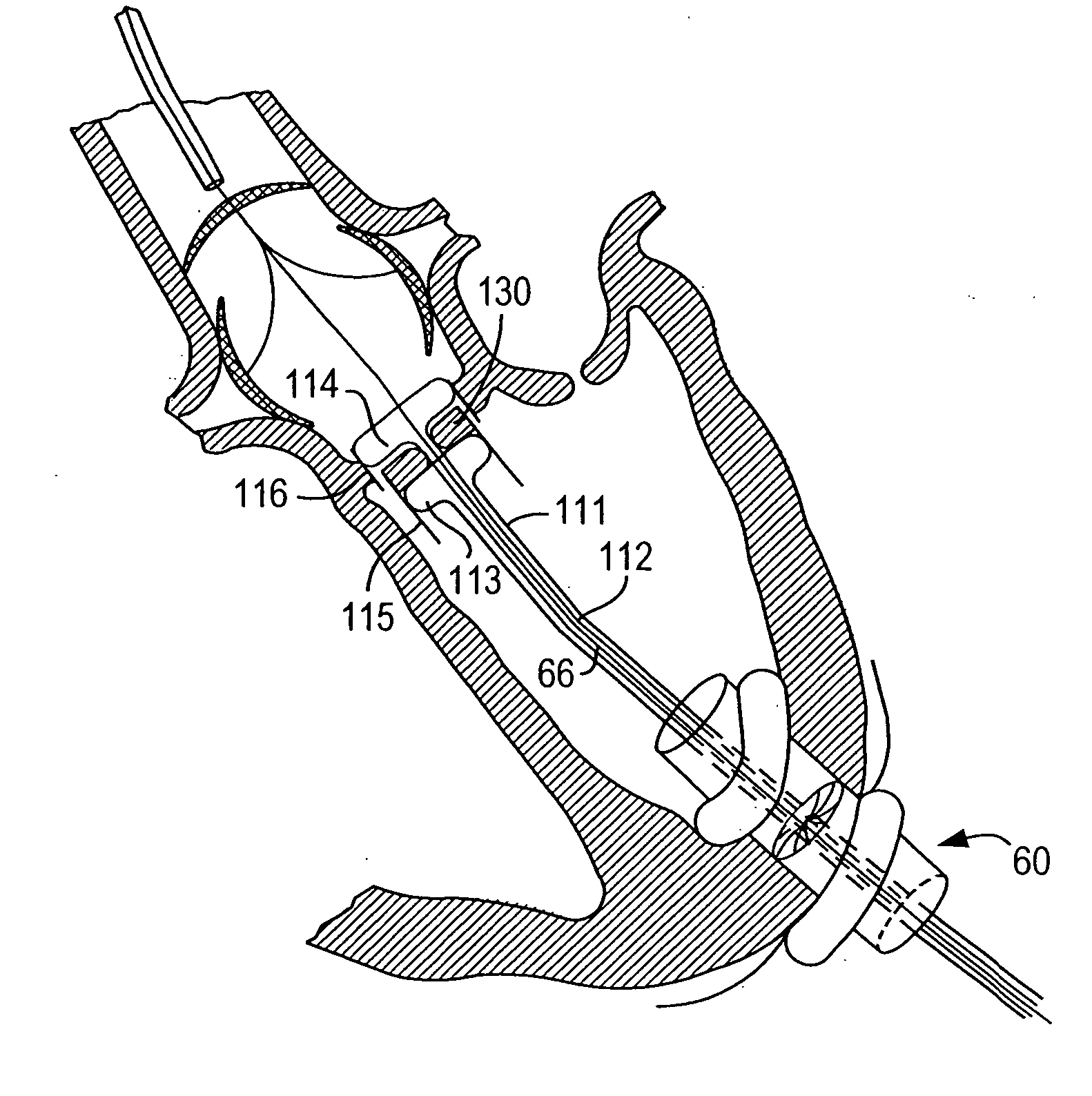
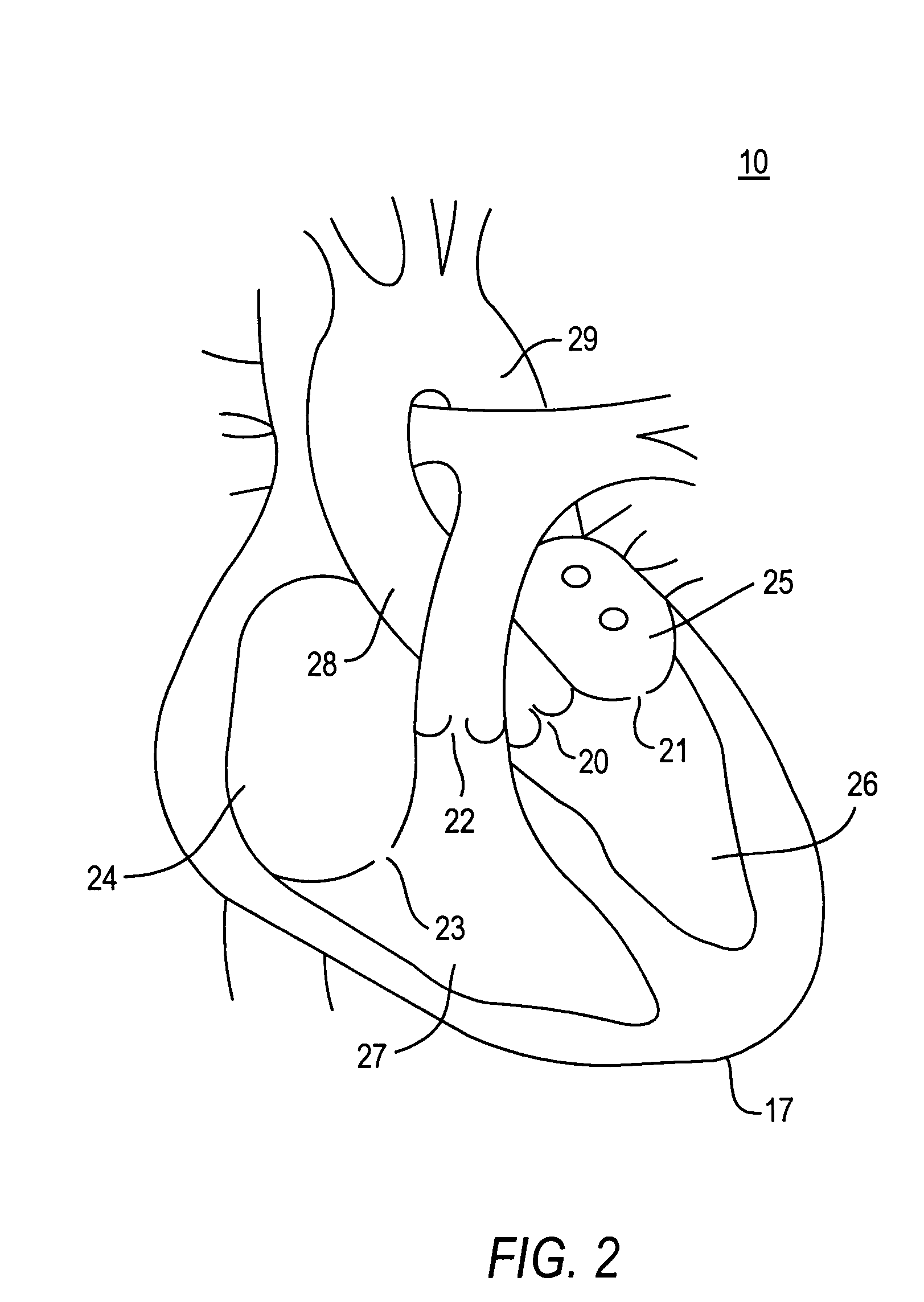
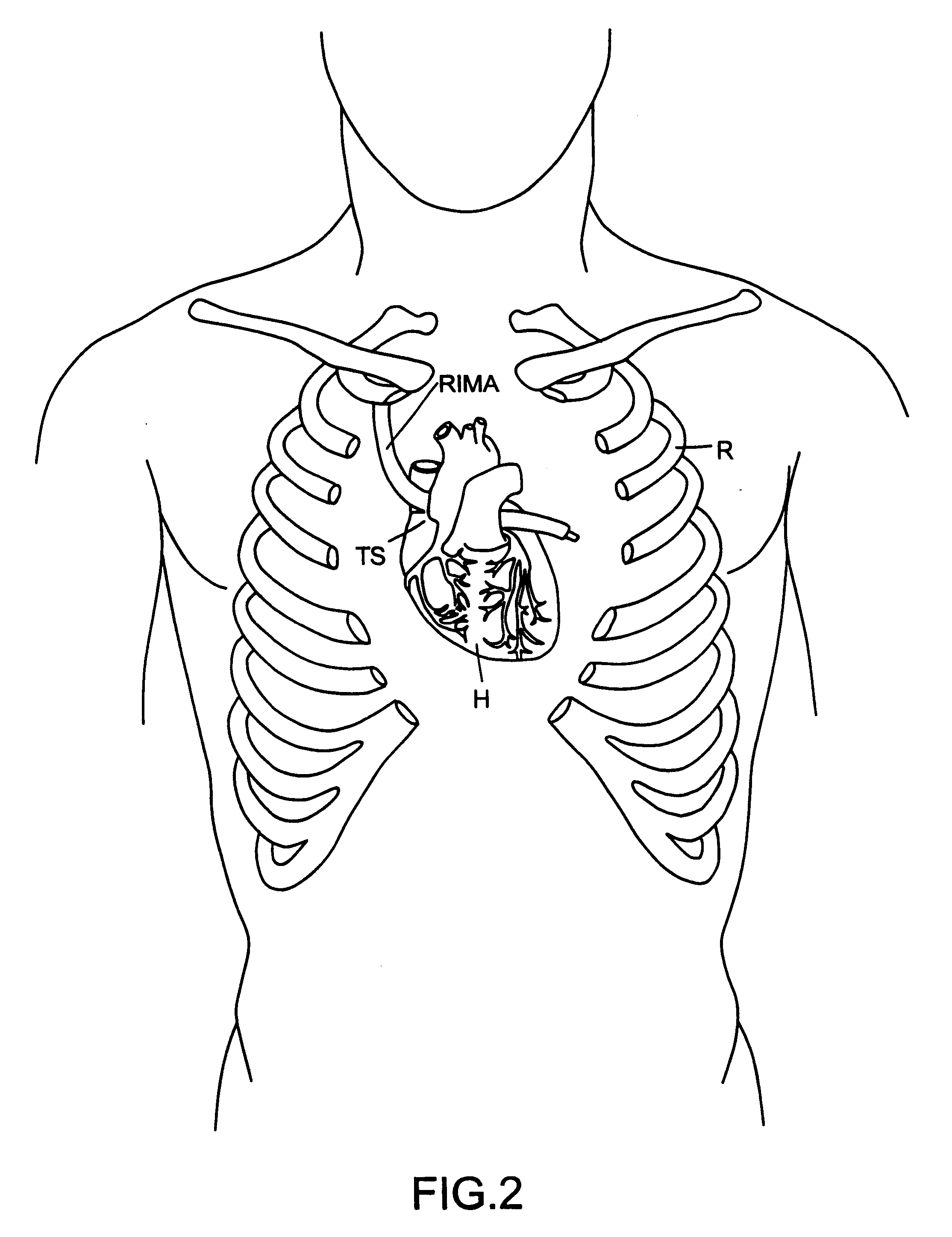
A delivery system and method for delivering a prosthetic heart valve to the aortic valve annulus. The system includes a balloon catheter having a steering mechanism thereon for delivering a balloon-expandable prosthetic heart valve through an introducer in an antegrade fashion to the aortic annulus. The balloon catheter passes through an introducer that accesses the left ventricle through its apex and a small incision in the chest wall. The balloon catheter includes a deflecting segment just proximal to the distal balloon to facilitate positioning of the prosthetic heart valve in the proper orientation within the aortic annulus. A slider in a deflection handle may be coupled to a deflection wire that actuates the deflecting segment. The method includes using two concentric rings of purse-string sutures around the puncture in the left ventricular apex to maintain a good seal around instruments passed therethrough. The prosthetic heart valve may be installed over the existing calcified leaflets, and a pre-dilation valvuloplasty procedure may also be utilized.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
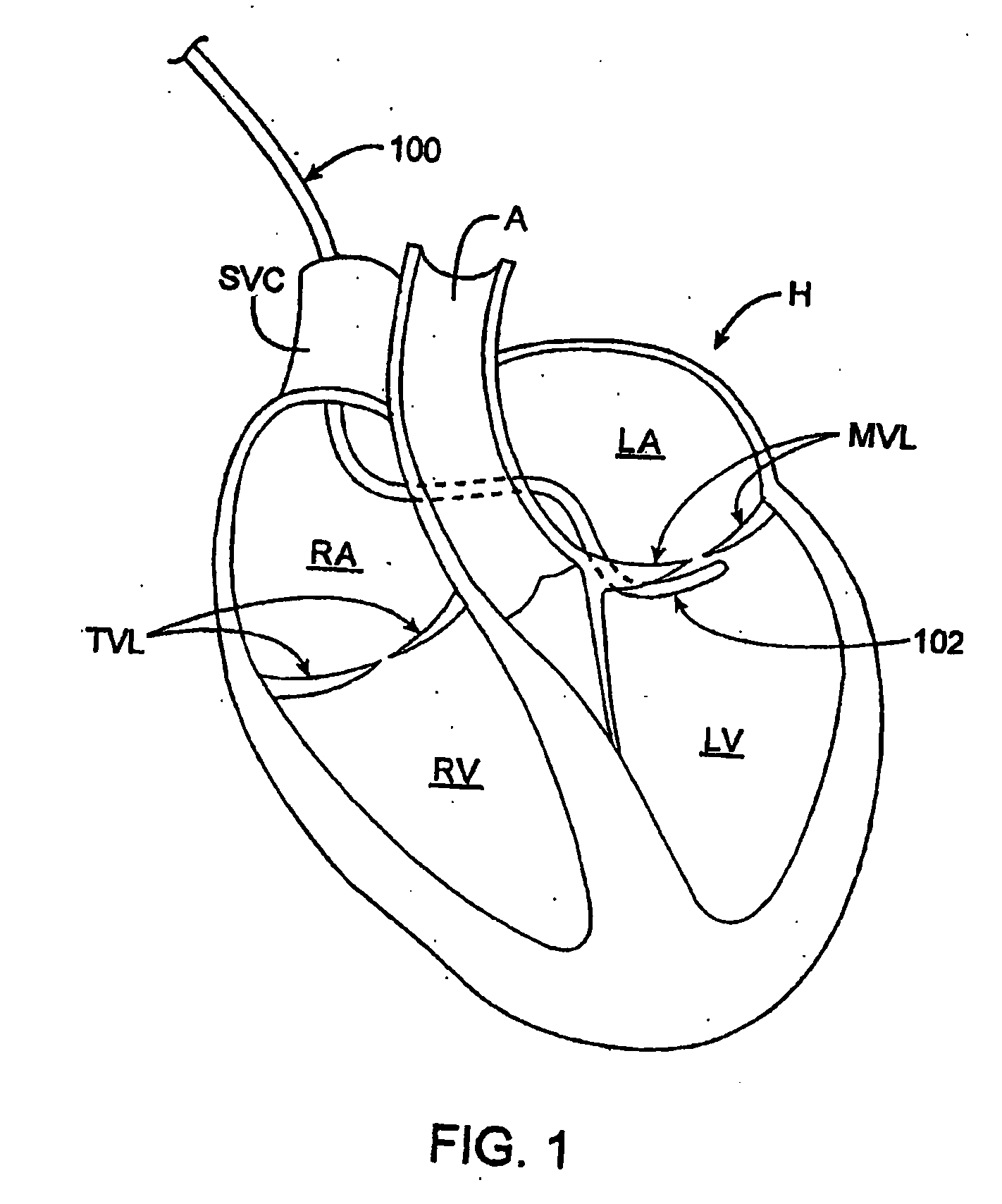
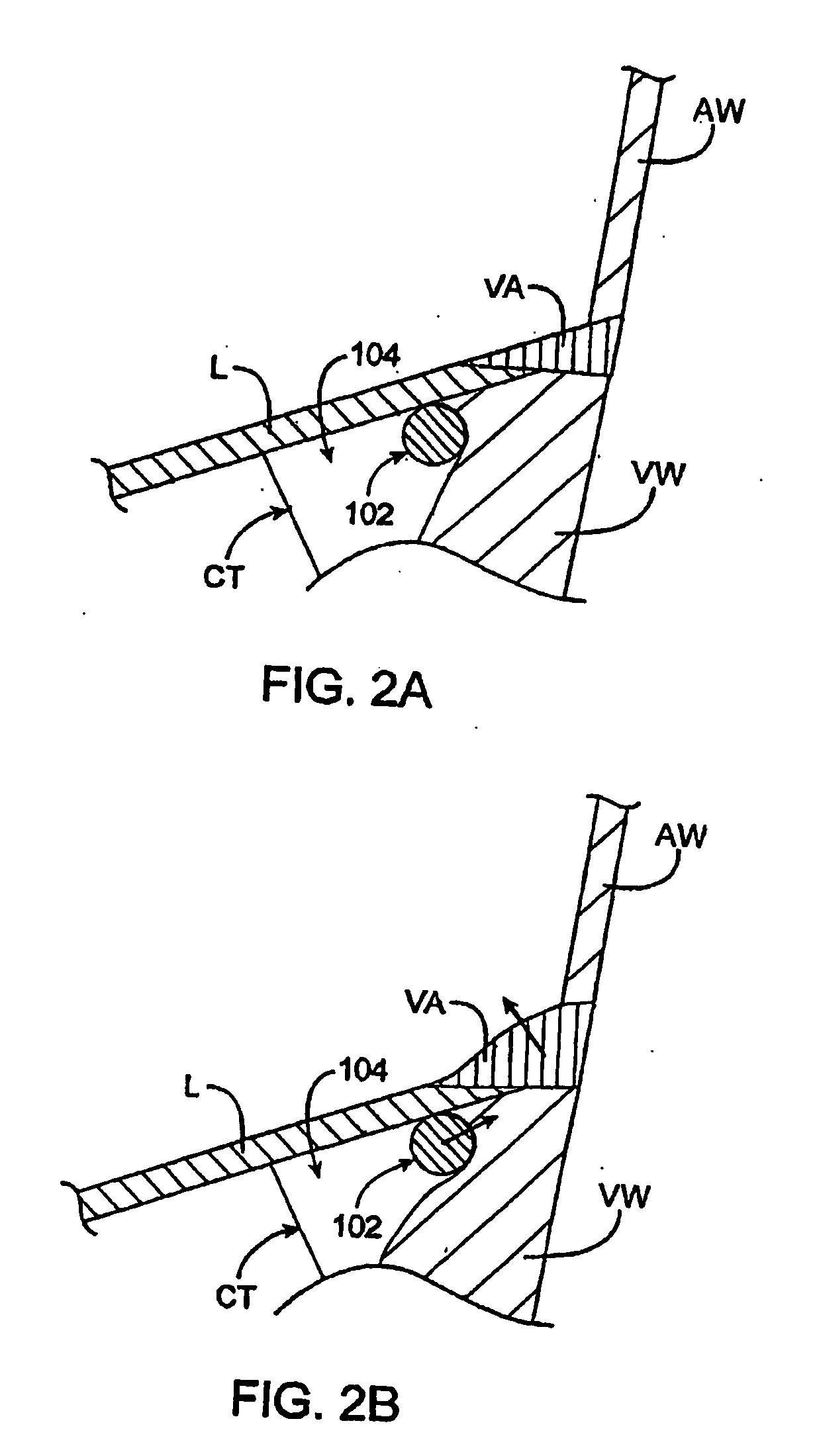
Methods and devices for repair or replacement of heart valves or adjacent tissue without the need for full cardiopulmonary support
ActiveUS20060074484A1Reduce in quantityEliminate needEar treatmentCannulasAortic dissectionVentricular aneurysm
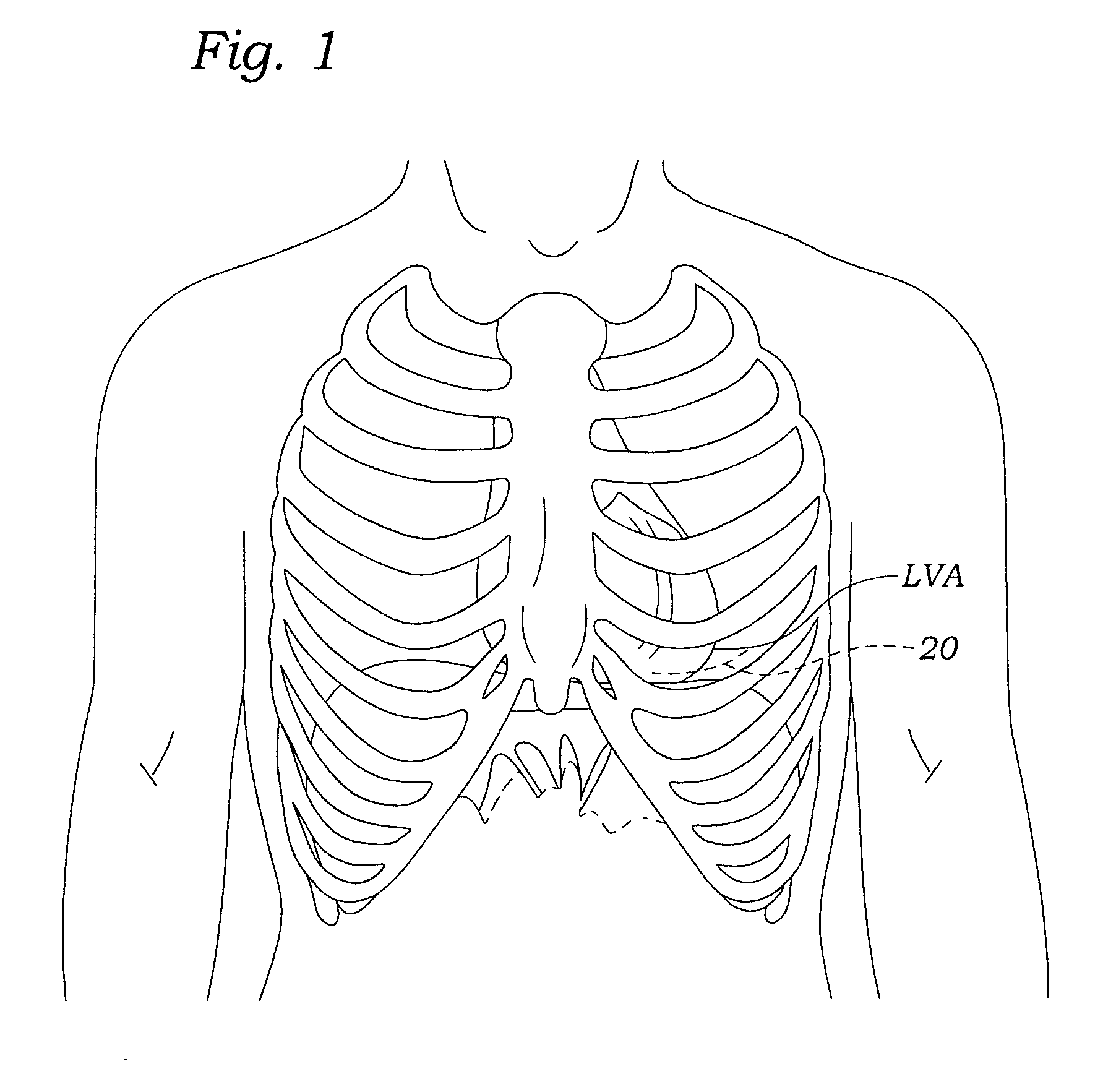
Methods and systems for endovascular, endocardiac, or endoluminal approaches to a patient's heart to perform surgical procedures that may be performed or used without requiring extracorporeal cardiopulmonary bypass. Furthermore, these procedures can be performed through a relatively small number of small incisions. These procedures may illustratively include heart valve implantation, heart valve repair, resection of a diseased heart valve, replacement of a heart valve, repair of a ventricular aneurysm, repair of an arrhythmia, repair of an aortic dissection, etc. Such minimally invasive procedures are preferably performed transapically (i.e., through the heart muscle at its left or right ventricular apex).
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCI CARDIAQ
Robotic surgical device
InactiveUS20050096502A1Minimize traumaShorten preoperative preparation timeEndoscopesLaproscopesRobotic armDistal portion
Described herein is a robotic surgical device configured for performing minimally invasive surgical procedures. The robotic surgical device comprises an elongated body for insertion into a patient's body through a small incision. In one variation, the elongated body houses a plurality of robotic arms. Once the distal portion of the elongated body is inserted into the patient body, the operator may then deploy the plurality of robotic arms to perform surgical procedures within the patient's body. An image detector may be positioned at the distal portion of the elongated body or on one of the robotic arms to provide visual feedback to the operator of the device. In another variation, each of the robotic arms comprises two or more joints, allowing the operator to maneuver the robotic arms in a coordinated manner within a region around the distal end of the device.
Owner:CEDARS SINAI MEDICAL CENT
Rotatable lead introducer
Minimally invasive introducers and methods that can be used for rotationally securing devices within the human body. Introducers can include a distal element for releasably engaging a lead head controllable from a proximal control located outside of the body. An inner stem can extend between a proximal portion and a distal portion, and be pivotally and rotatably coupled to the distal lead engagement mechanism. An outer tube can be rotatably disposed over the inner stem and be flexibly coupled over the pivot to rotationally drive the distal element. A helical epicardial-myocardial lead electrode can be secured and oriented straight ahead and introduced through a port or small incision with the introducer in a straight configuration. The introducer can then be bent and rotated to screw the helical electrode into the heart.
Owner:WILSON GREATBATCH LTD
Easily placeable and removable wound retractor
InactiveUS20060149137A1Easy to placeGood for scrollingCannulasSurgical needlesSurgical departmentBody tissue
The invention is directed to a surgical wound retractor for retracting and sealing an incision and forming a functional opening or channel through which a surgical procedure may be executed. The wound retractor provides a path for a surgeon to insert his hand and / or instruments through the opening formed by the wound retractor. The wound retractor is sized and configured to be easily placed through a small incision and removed without further insult to the body tissue adjacent to the incision. The wound retractor is adapted to dilate a surgical wound incision to a desired diameter, and comprises a first ring having a diameter greater than the desired diameter of the wound incision and being adapted for disposition interiorly of the wound incision; a second ring having an annular axis and a diameter greater than the desired diameter of the wound incision and being adapted for disposition exteriorly of the wound incision; and a flexible sleeve disposed in a generally cylindrical form between the first ring and the second ring, the first ring having at least one notch to facilitate folding or collapsing of the first ring during insertion and removal of the first ring through the wound incision. The first ring may further comprise a second notch disposed on an opposing end of the first notch to further facilitate folding or collapsing of the first ring. With this aspect, the first ring is folded by squeezing between the first and second notches during insertion and removal of the retractor from the incision. In another aspect, the wound retractor may further comprise a tether having a length, a first end attached to the first ring interiorly of the sheath, and a second end disposed outside of the wound incision, wherein the tether facilitates removal of the first ring by pulling on the second end to retrieve the first ring through the wound incision.
Owner:APPL MEDICAL RESOURCES CORP
Systems and methods for stabilization of bone structures
Owner:EXACTECH INC
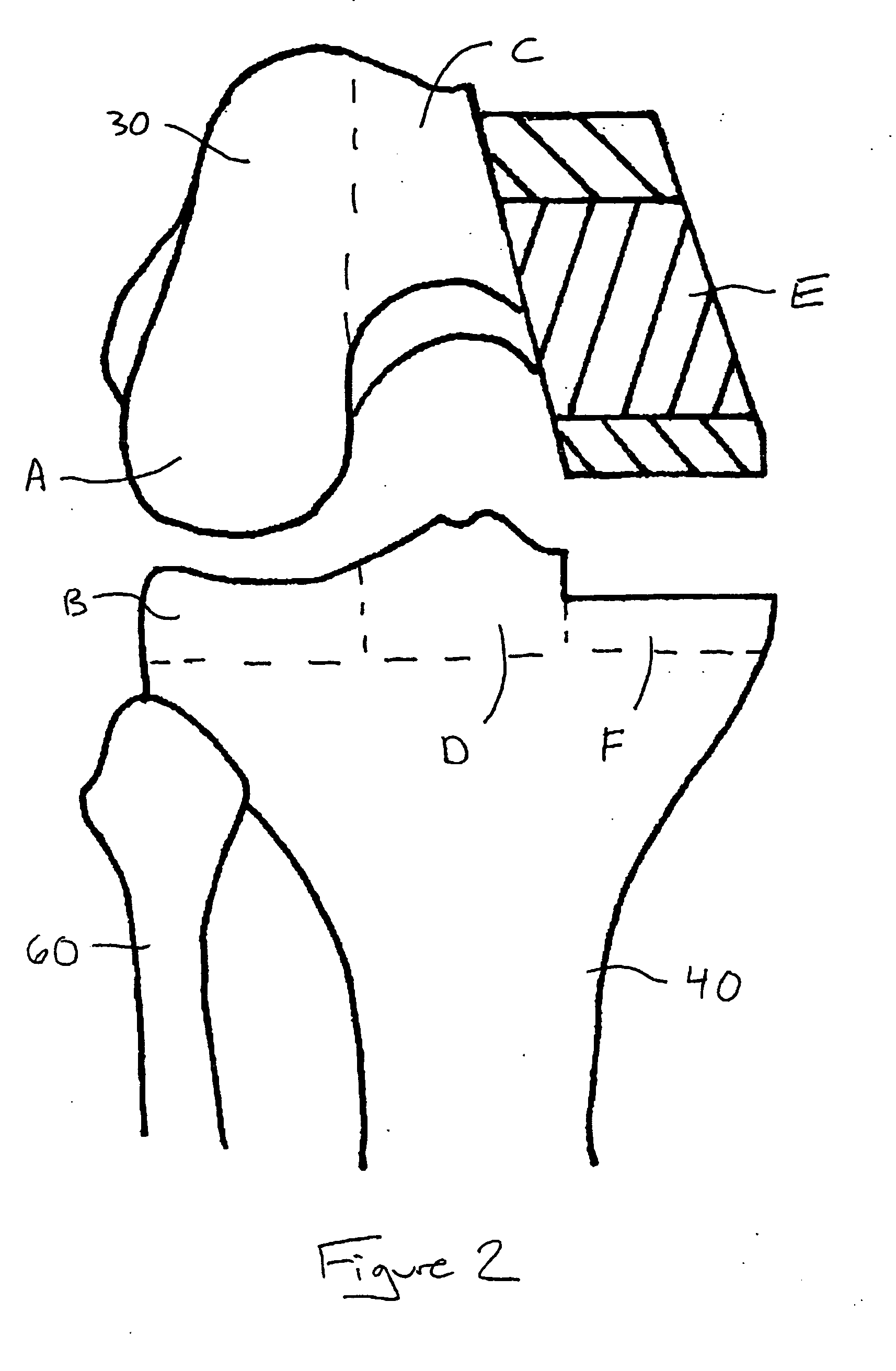
Knee implant
A modular prosthetic device is provided for replacement of the knee. The device is assembled from a plurality of components, each of which can be inserted through a small incision. After inserting the components through the incision, the device can be assembled within the knee cavity. The modularity of the device enables a surgeon to replace only those regions of the knee that are diseased or damaged, thereby avoiding a complete knee replacement. If, at a later time, additional regions of the knee become diseased or damaged, those additional regions of the knee can be replaced by additional device components and those additional components can be connected to the previously implanted components. By replacing only those regions of the knee that are diseased or damaged and by implanting each of the components through the small incision, the surgery is minimally invasive and, therefore, requires reduced time for healing and rehabilitation.
Owner:MAKO SURGICAL CORP
Methods and devices for termination
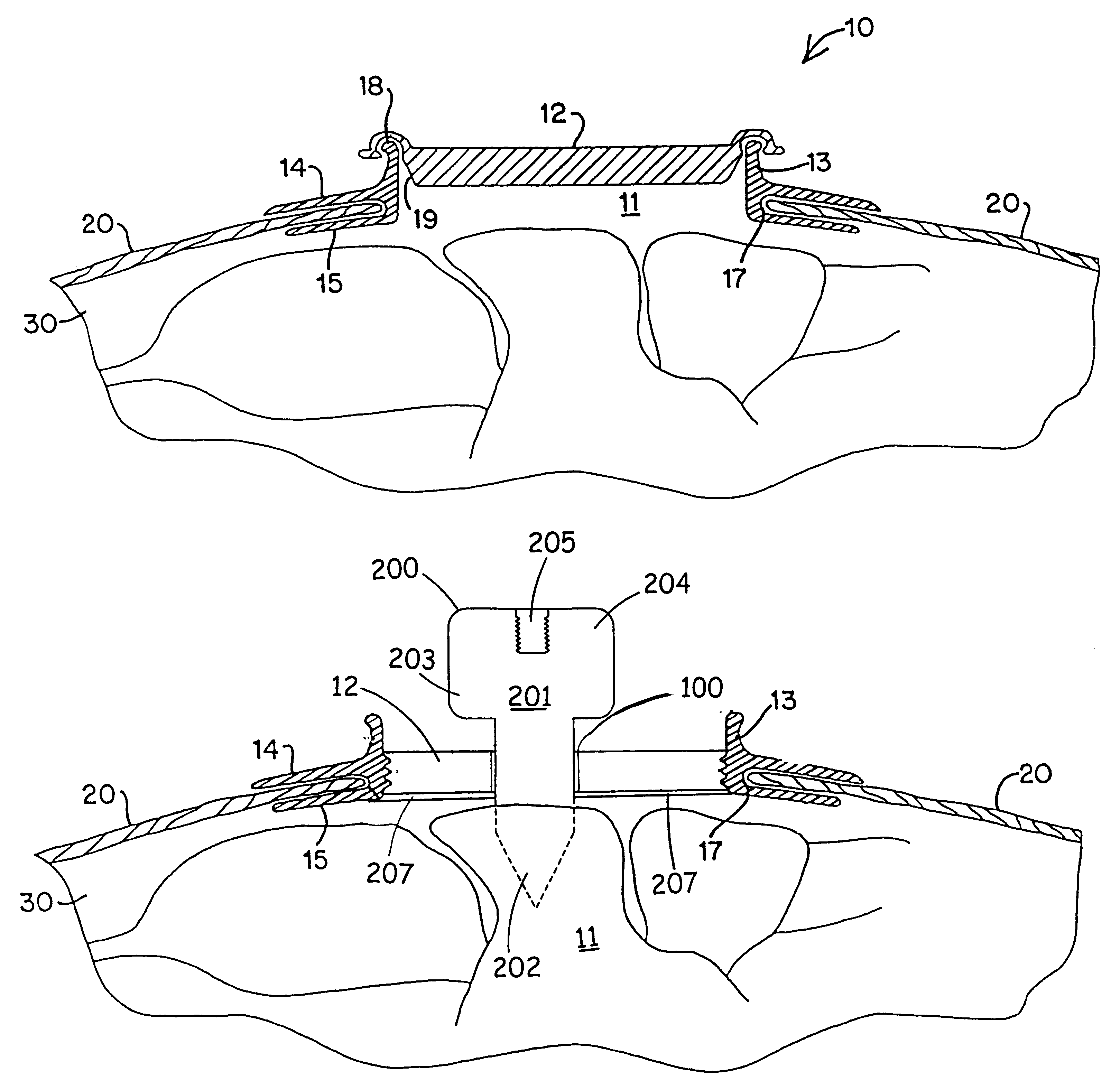
Devices and methods used in termination of a tissue tightening procedure are described. Termination includes the cinching of a tether to tighten the tissue, locking the tether to maintain tension, and cutting excess tether. In procedures involving anchors secured to the tissue, the tether is coupled to the anchors and the tissue is tightened via tension applied to the anchors by cinching the tether. In general, the devices and methods can be used in minimally invasive surgical procedures, and can be applied through small incisions or intravascularly. A method for tightening tissue by fixedly coupling a first anchor to a tether and slidably coupling a second anchor to the tether, securing both anchors to the tissue, applying tension to the tether intravascularly, fixedly coupling the tether to the second anchor, and cutting the tether is described. The tissue to be tightened can comprise heart tissue, in particular heart valve annulus tissue. Various devices and methods for locking the tether in place and cutting excess tether are described.
Owner:GUIDED DELIVERY SYST INC
Apparatus and Method for Ocular Treatment
InactiveUS20080058704A1Reduce releaseFacilitate tissue targetingUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsLaser surgeryLess invasive surgerySuprachoroidal space
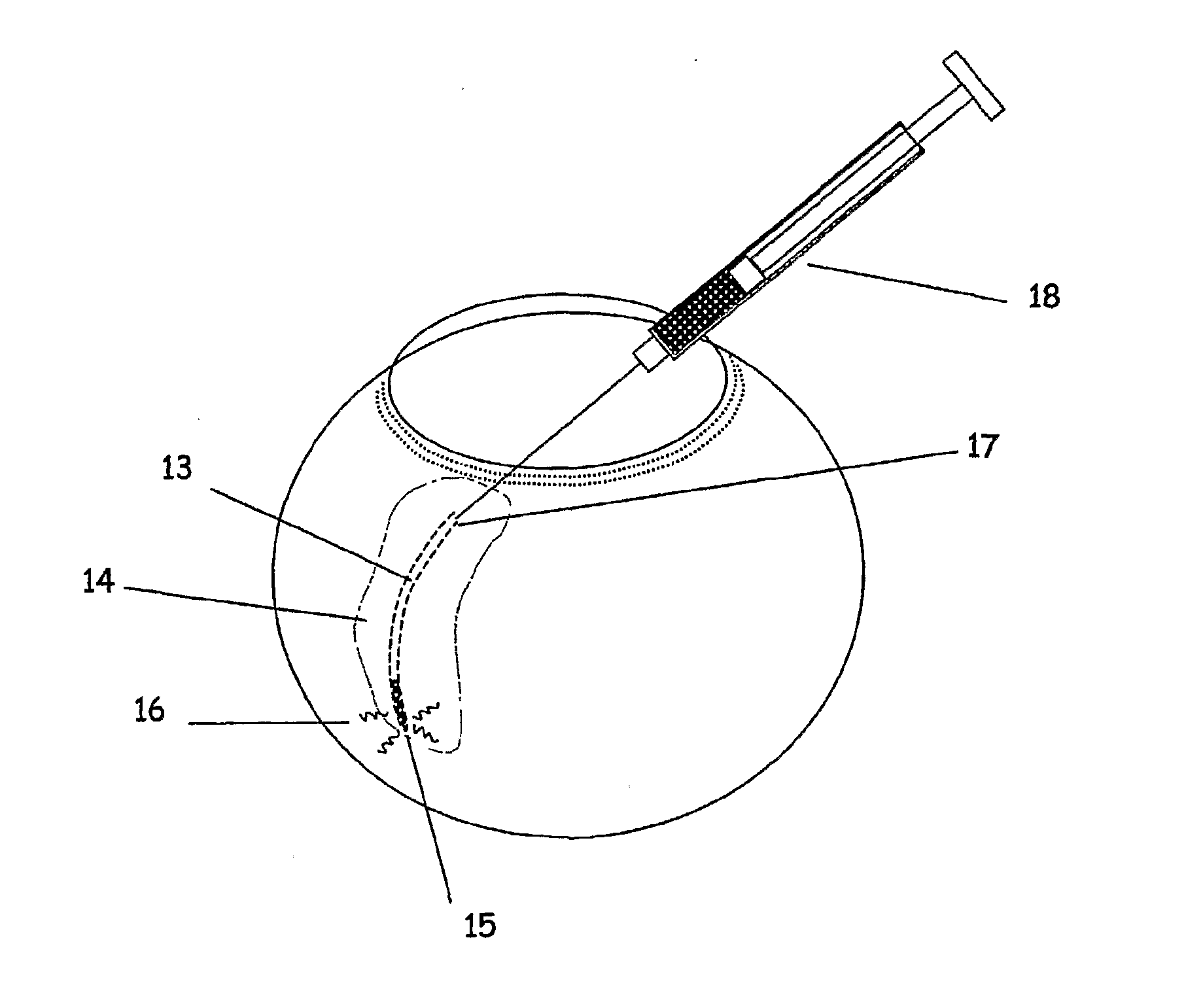
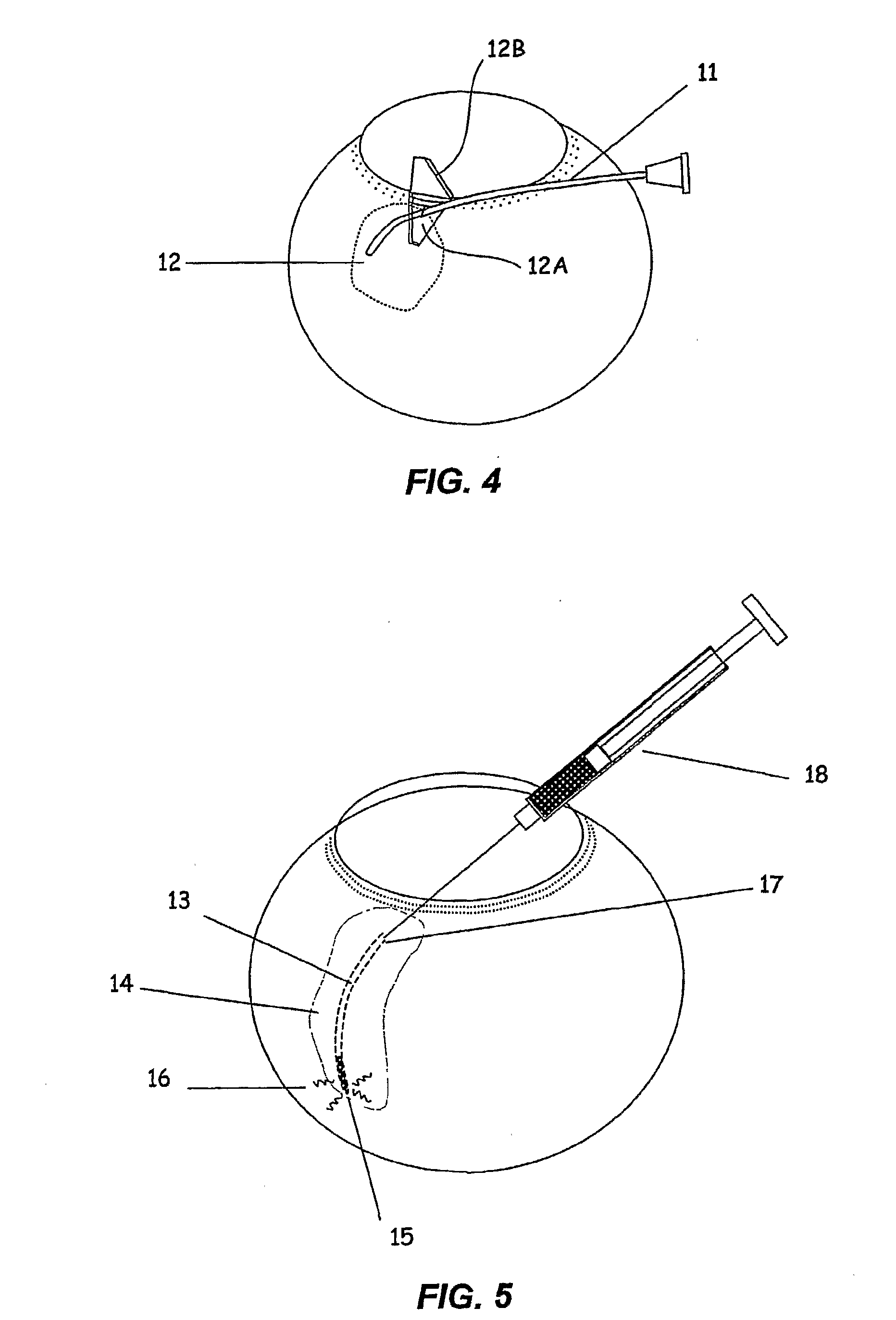
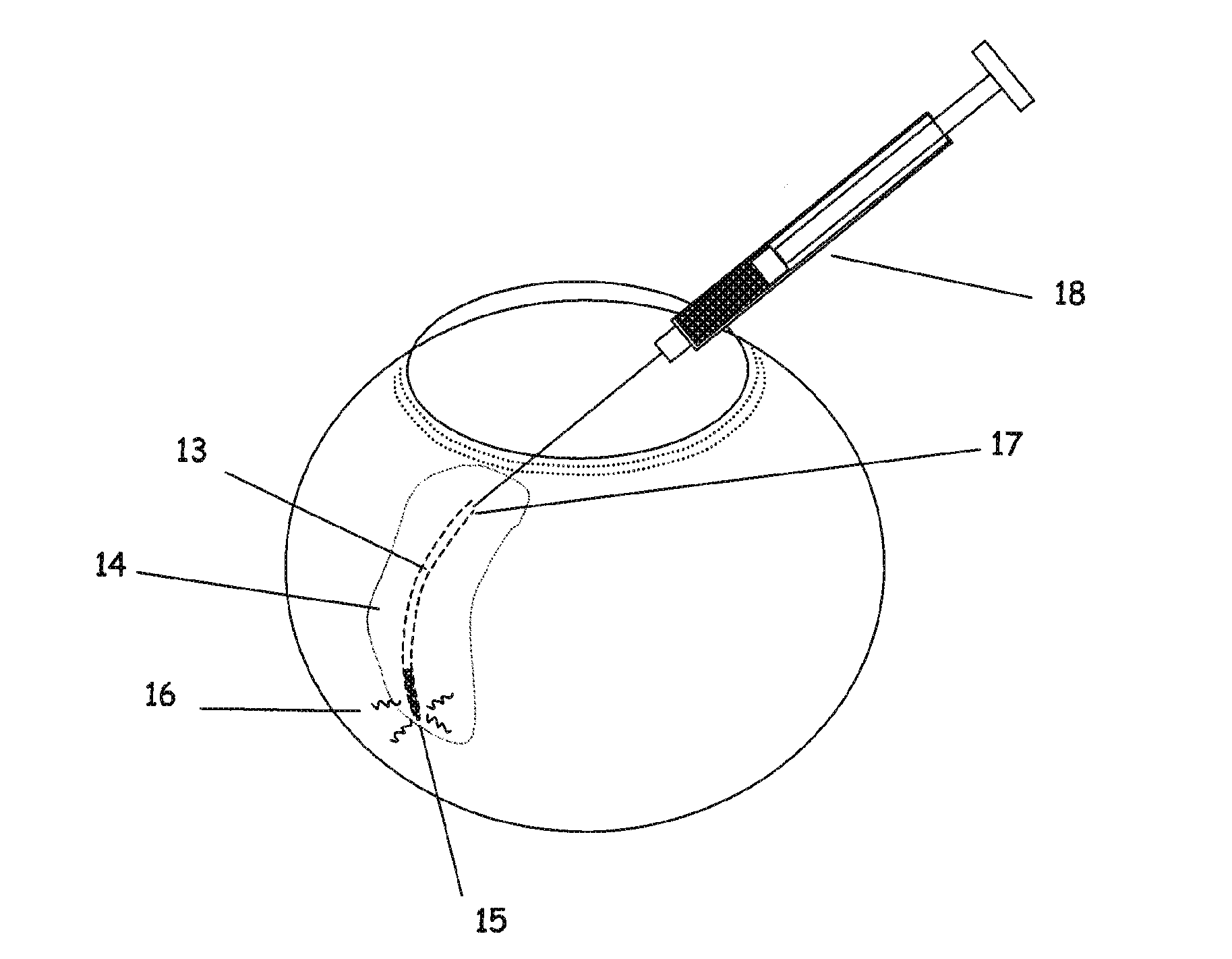
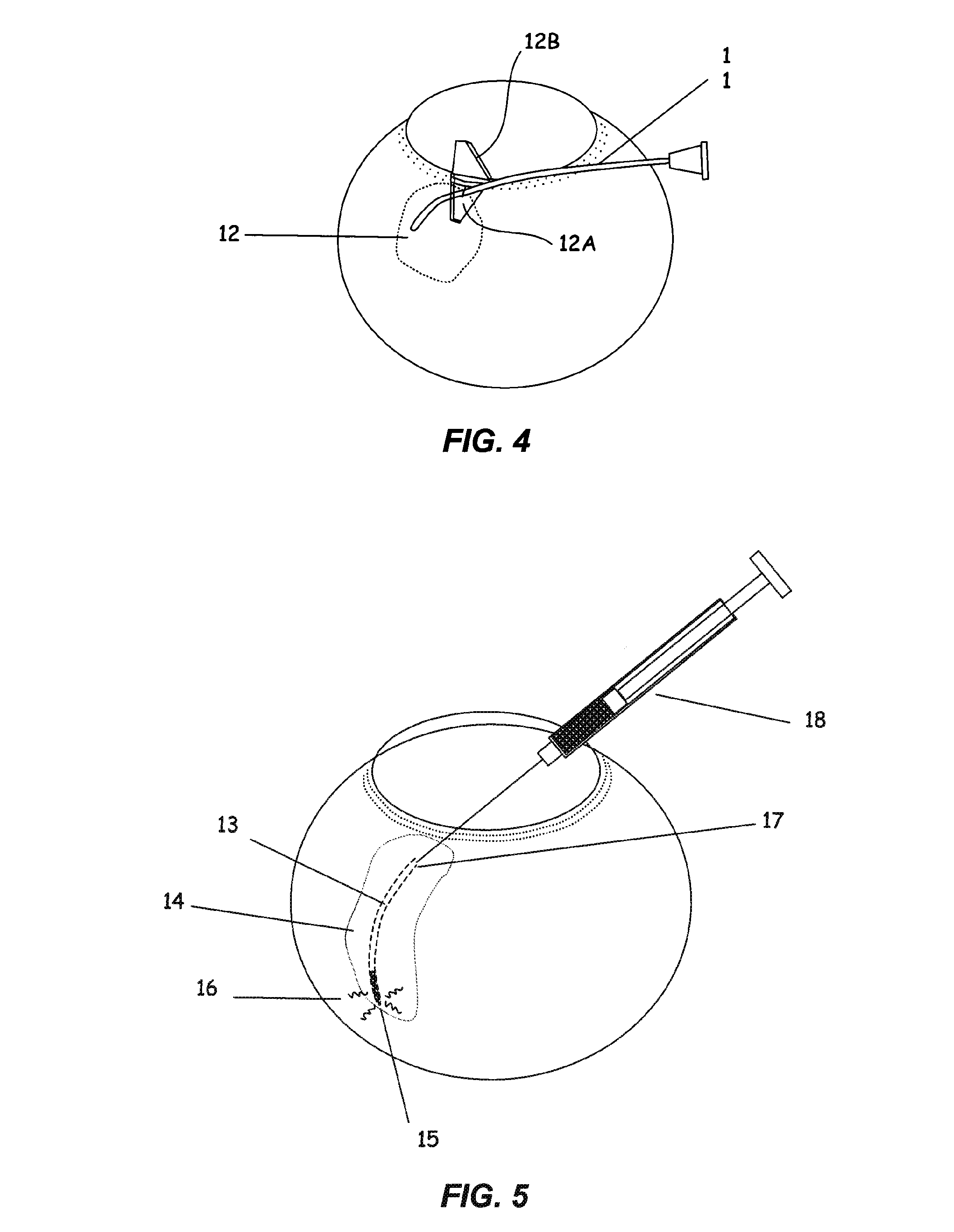
The invention provides tools, materials and related methods to surgically access the suprachoroidal space of an eye for the purpose of performing minimally invasive surgery or to deliver drugs to the eye. The invention provides a flexible microcannula device (11, 13) that may be placed into the suprachoroidal space (12, 14) through a small incision (12A) of the overlying tissues, maneuvered into the appropriate region of the space, and then activated to treat tissues adjacent to the distal tip of the device.
Owner:ISCI INTERVENTIONAL CORP
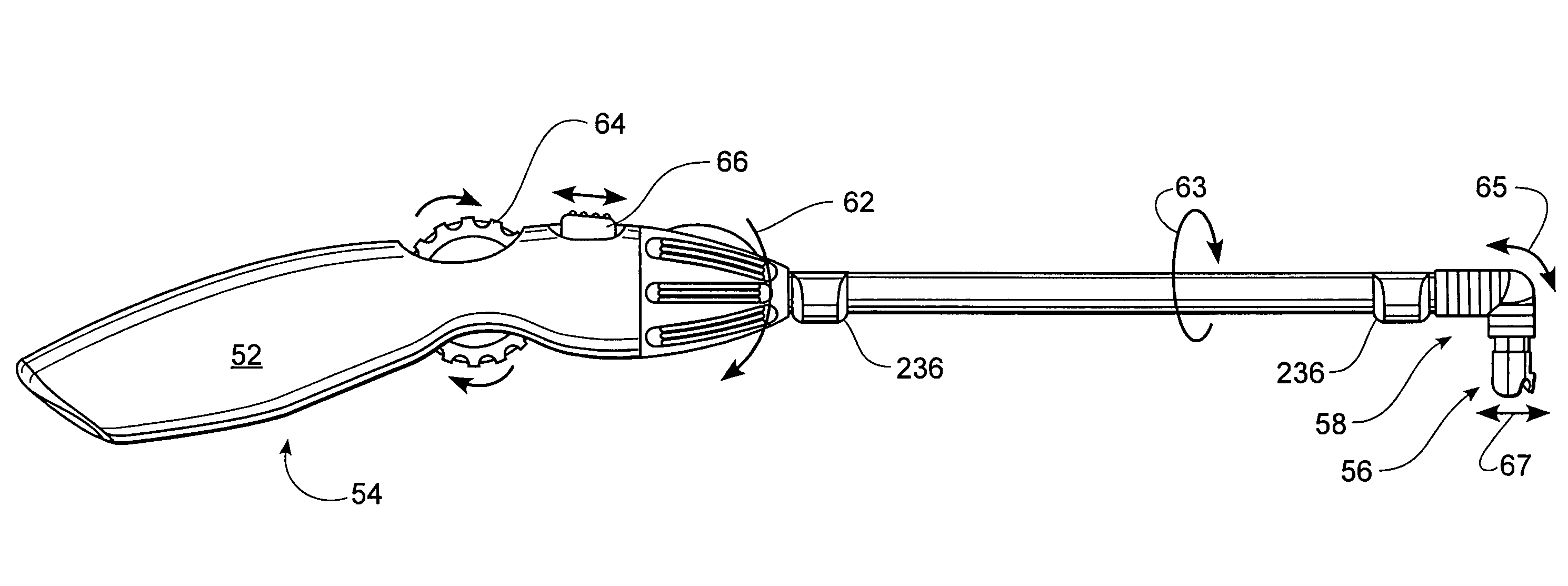
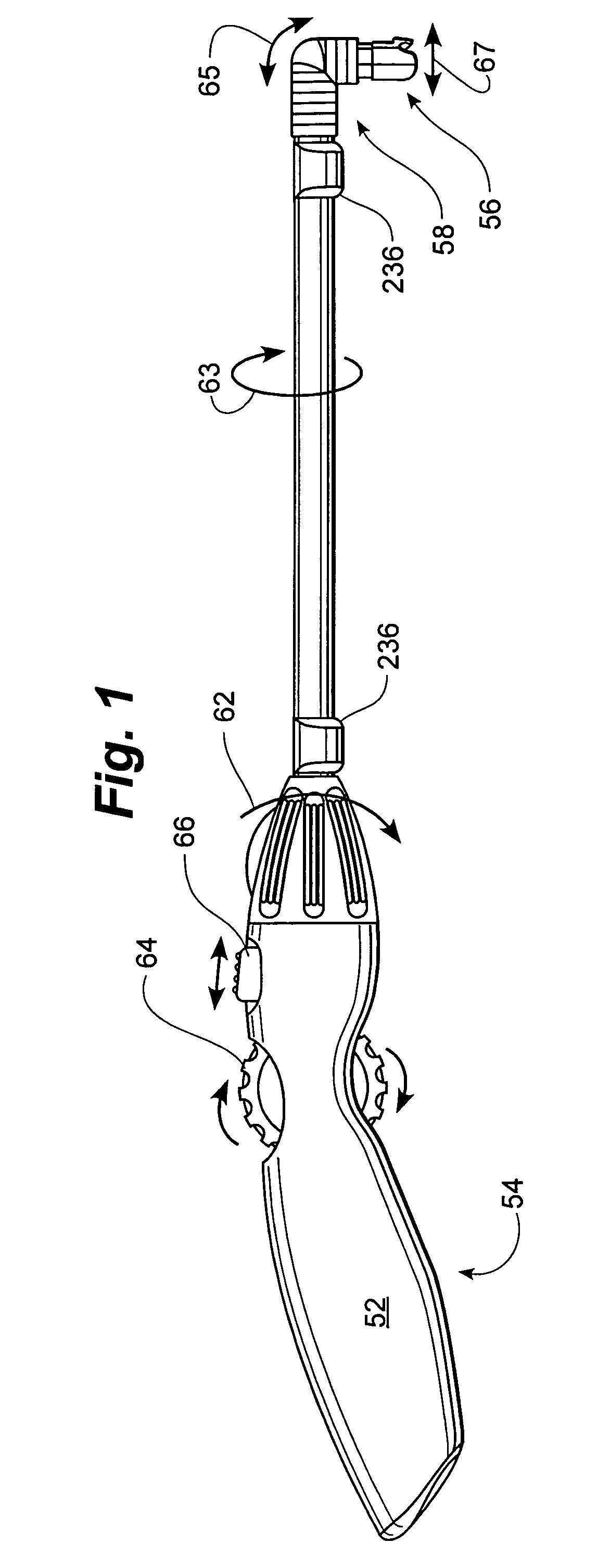
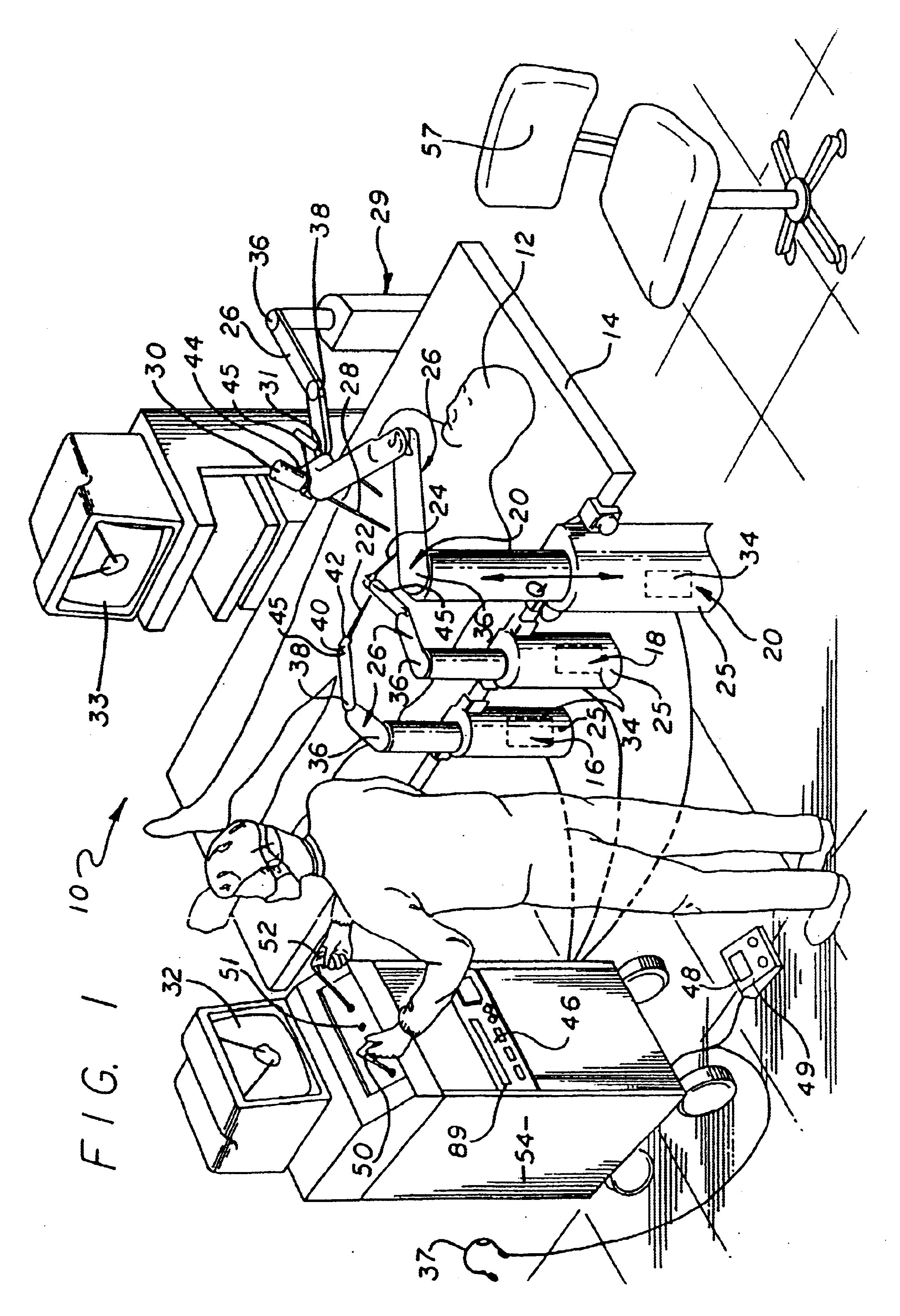
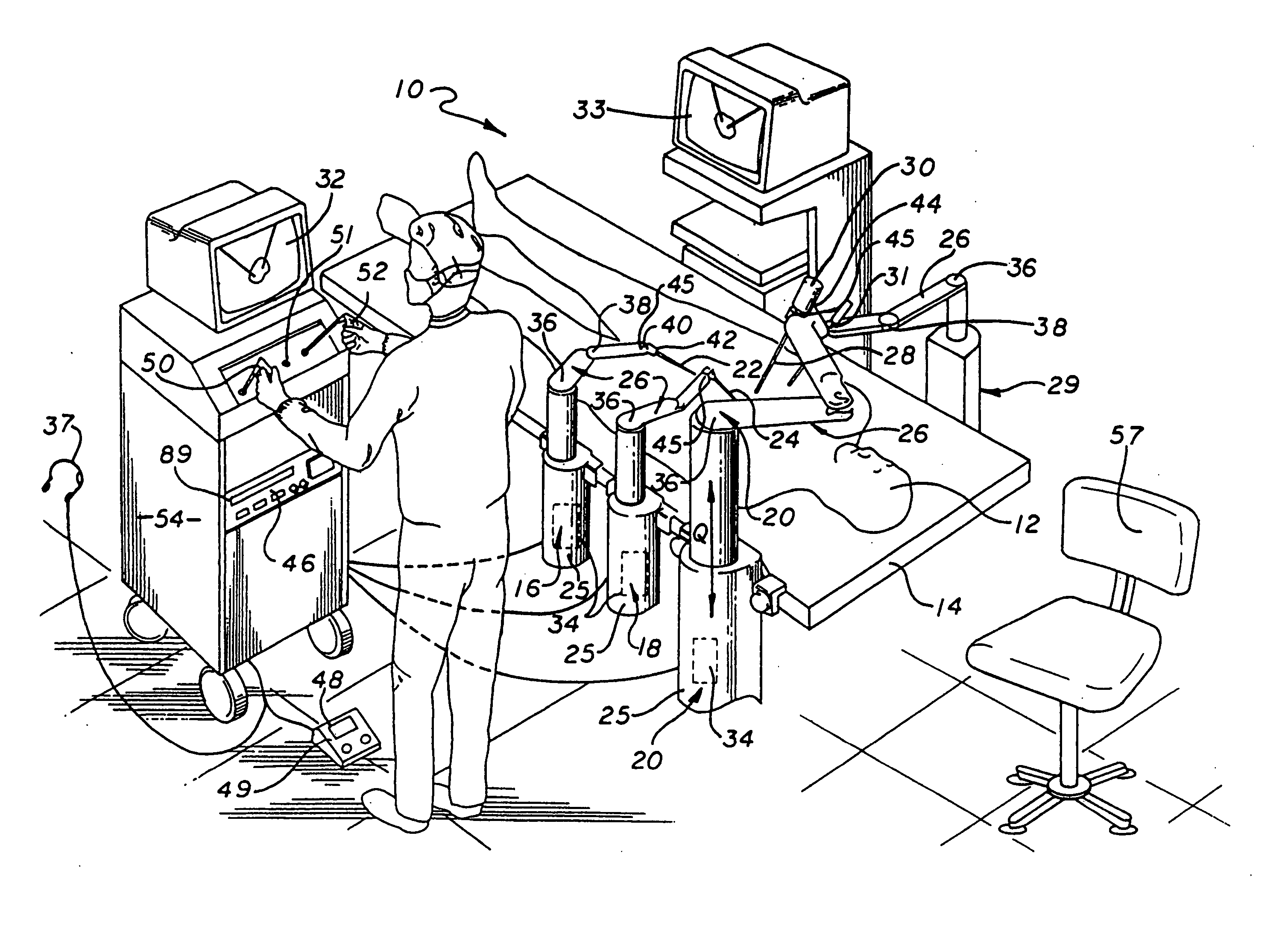
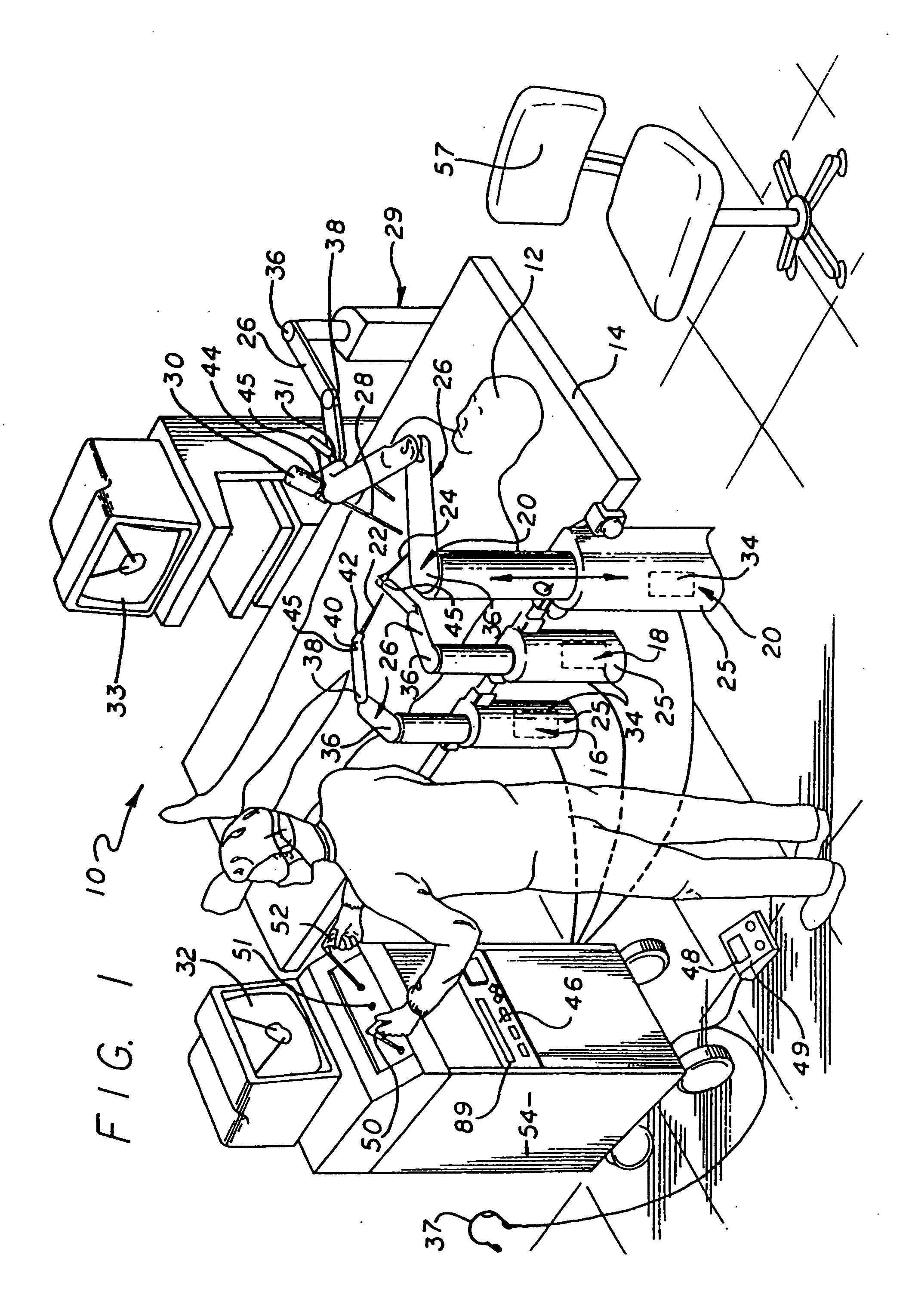
Method and apparatus for performing minimally invasive surgical procedures
InactiveUS6905460B2Reserved functionHigh precisionProgramme controlSuture equipmentsRobotic armSurgical site
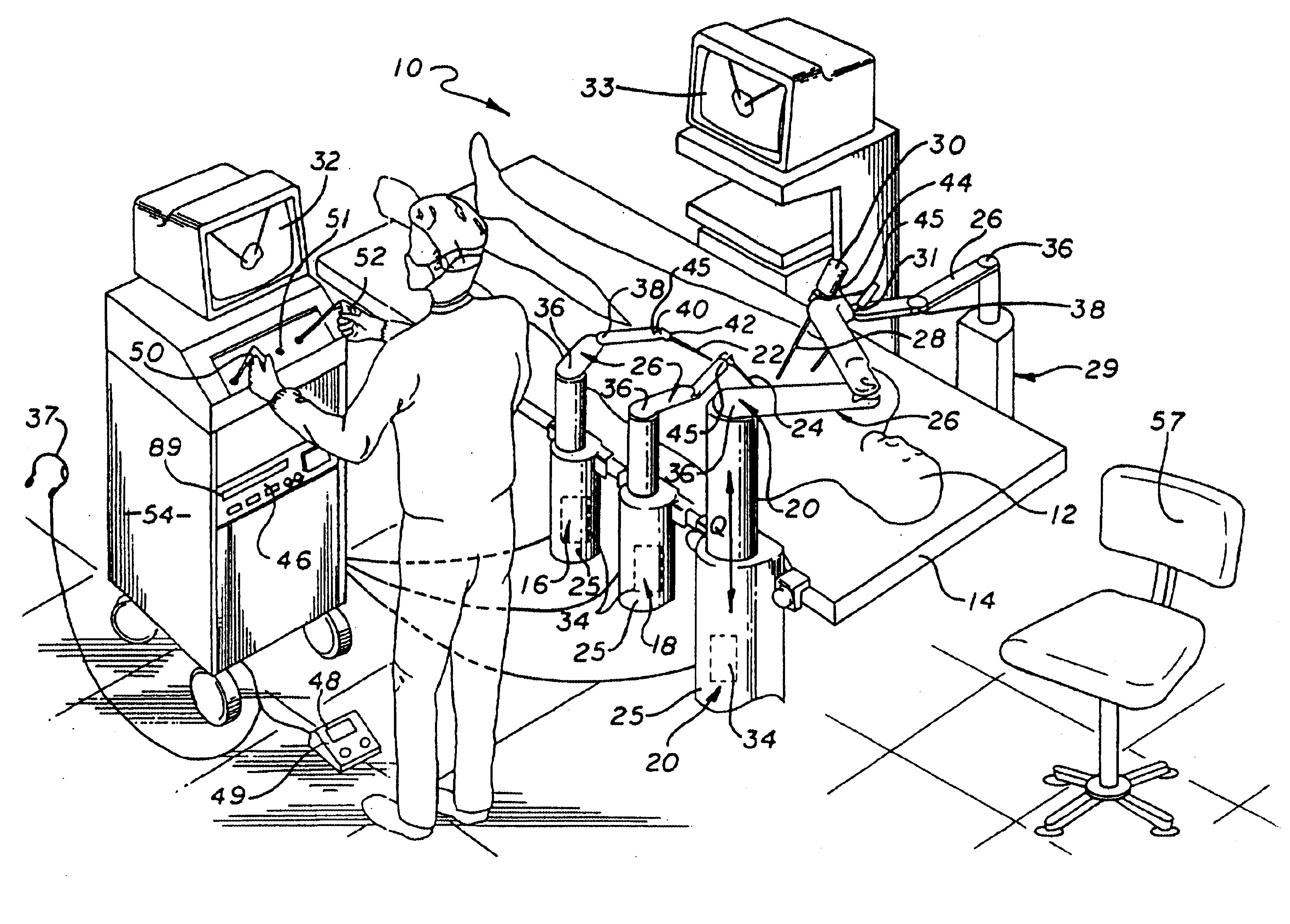
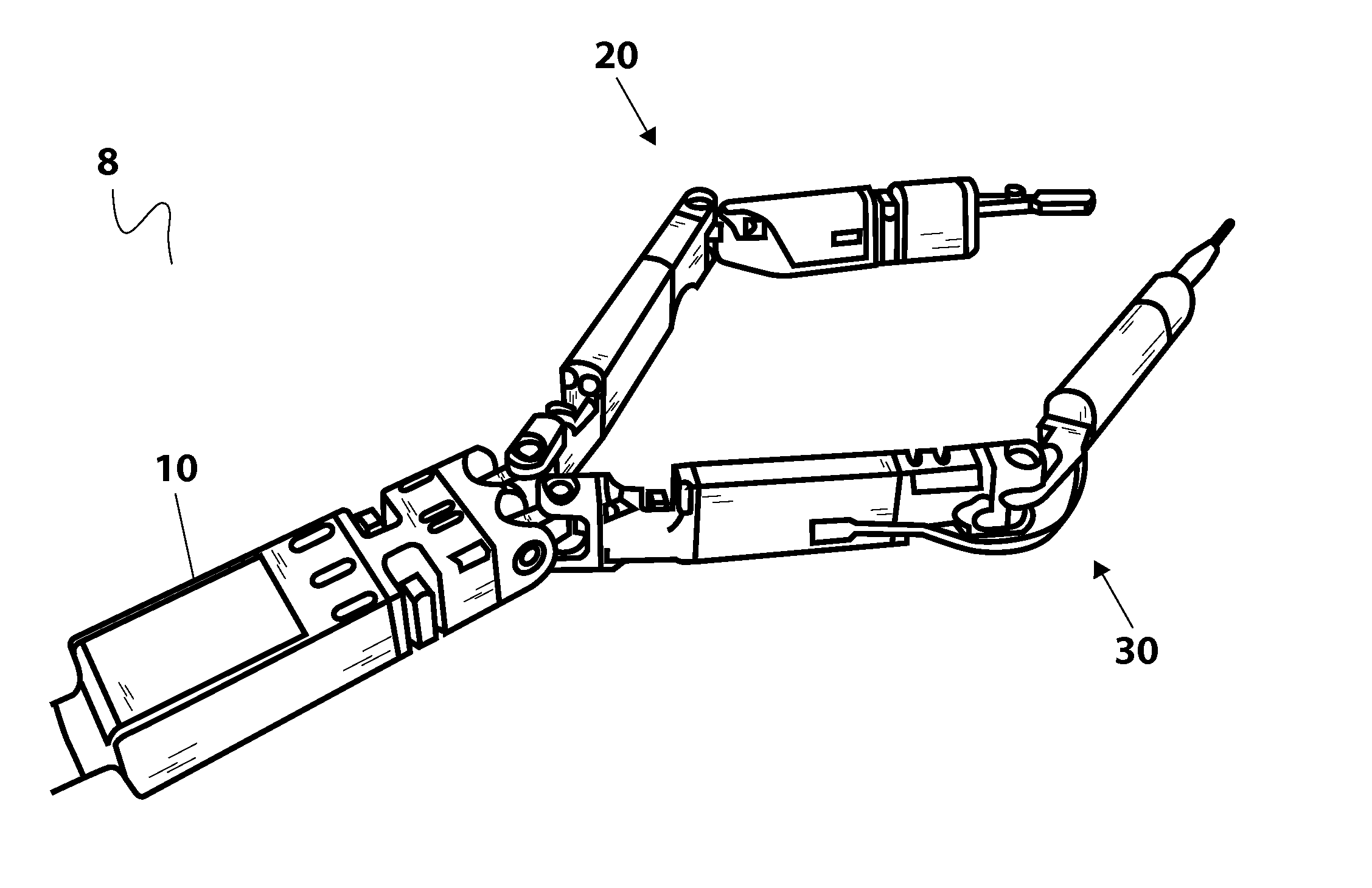
A system for performing minimally invasive cardiac procedures. The system includes a pair of surgical instruments that are coupled to a pair of robotic arms. The instruments have end effectors that can be manipulated to hold and suture tissue. The robotic arms are coupled to a pair of master handles by a controller. The handles can be moved by the surgeon to produce a corresponding movement of the end effectors. The movement of the handles is scaled so that the end effectors have a corresponding movement that is different, typically smaller, than the movement performed by the hands of the surgeon. The scale factor is adjustable so that the surgeon can control the resolution of the end effector movement. The movement of the end effector can be controlled by an input button, so that the end effector only moves when the button is depressed by the surgeon. The input button allows the surgeon to adjust the position of the handles without moving the end effector, so that the handles can be moved to a more comfortable position. The system may also have a robotically controlled endoscope which allows the surgeon to remotely view the surgical site. A cardiac procedure can be performed by making small incisions in the patient's skin and inserting the instruments and endoscope into the patient. The surgeon manipulates the handles and moves the end effectors to perform a cardiac procedure such as a coronary artery bypass graft.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
Systems and methods for stabilization of bone structures
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Apparatus and method for ocular treatment
InactiveUS20100173866A1Facilitate tissue targetingSafely reachedLaser surgeryOrganic active ingredientsLess invasive surgerySuprachoroidal space
The invention provides tools, materials and related methods to surgically access the suprachoroidal space of an eye for the purpose of performing minimally invasive surgery or to deliver drugs to the eye. The invention provides a flexible microcannula or microcatheter device (11, 13) that may be placed into the suprachoroidal space (12, 14) through a small incision (12A) of the overlying tissues, maneuvered into the appropriate region of the space, and then activated to treat tissues adjacent to the distal tip of the device.
Owner:ISCI INTERVENTIONAL CORP
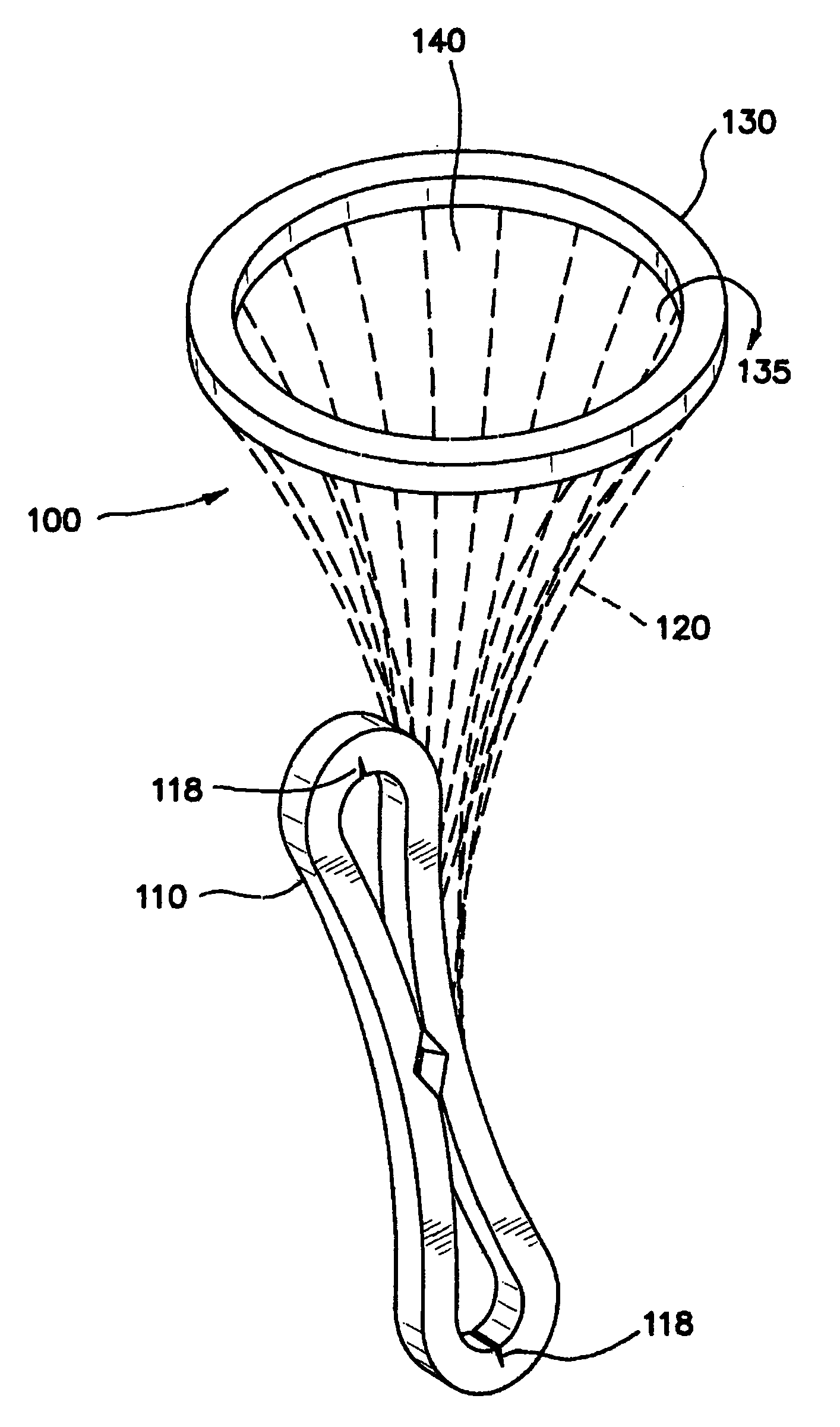
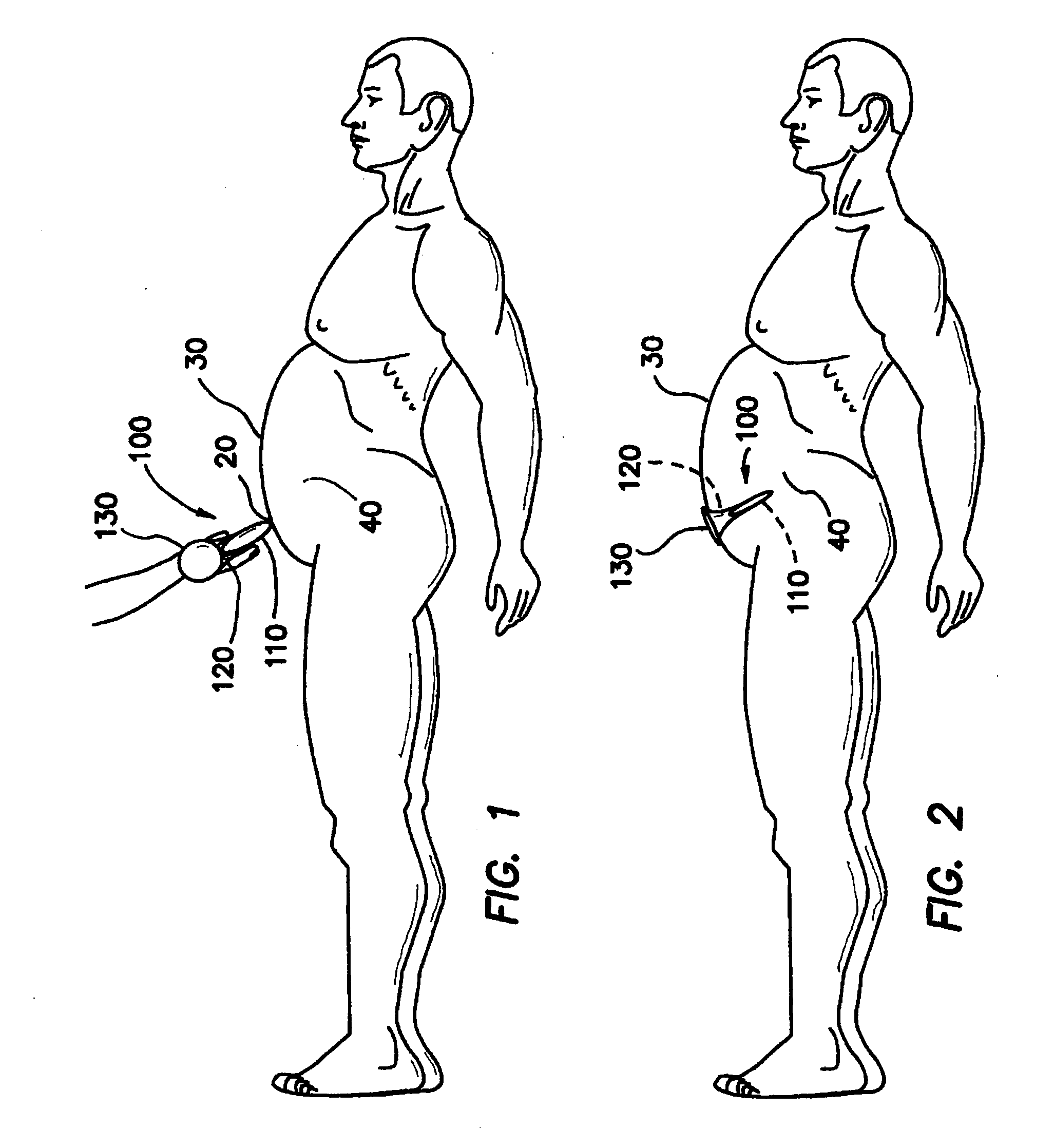
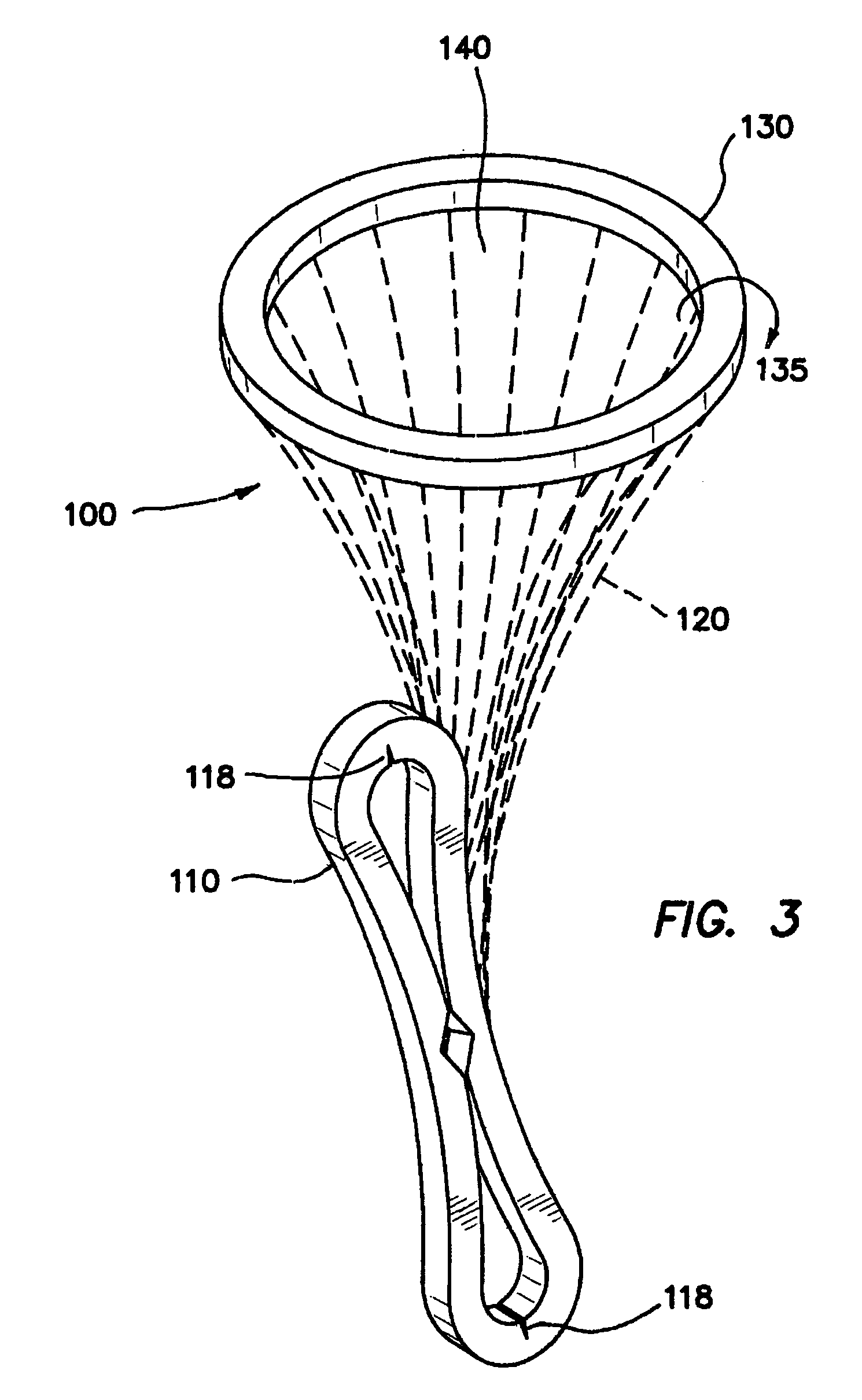
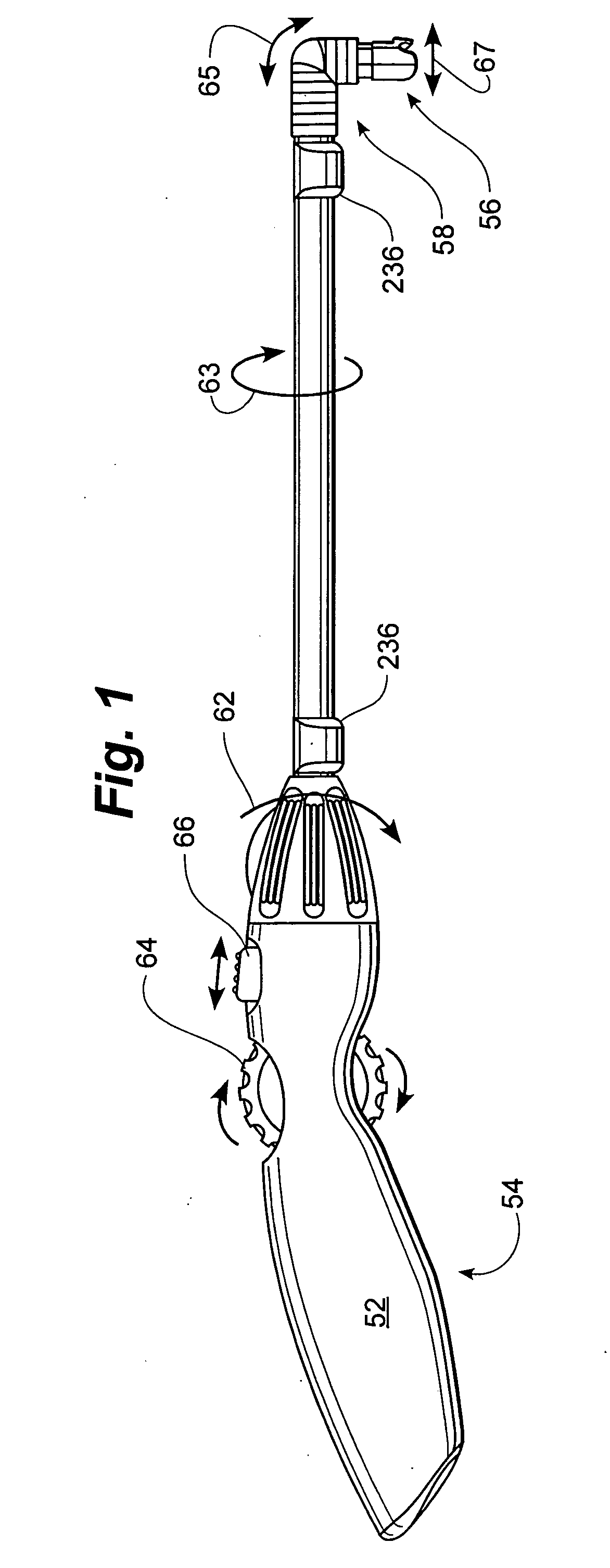
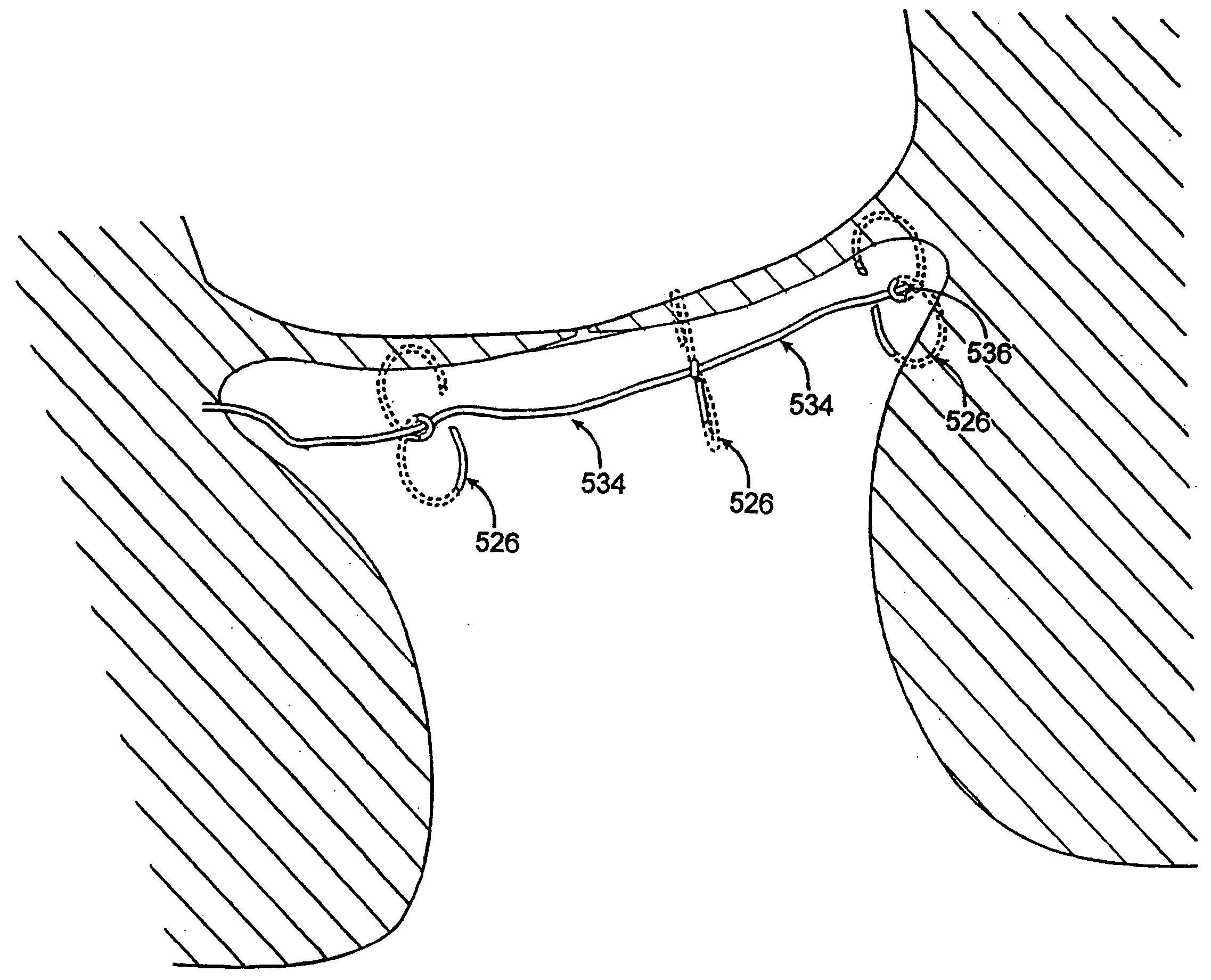
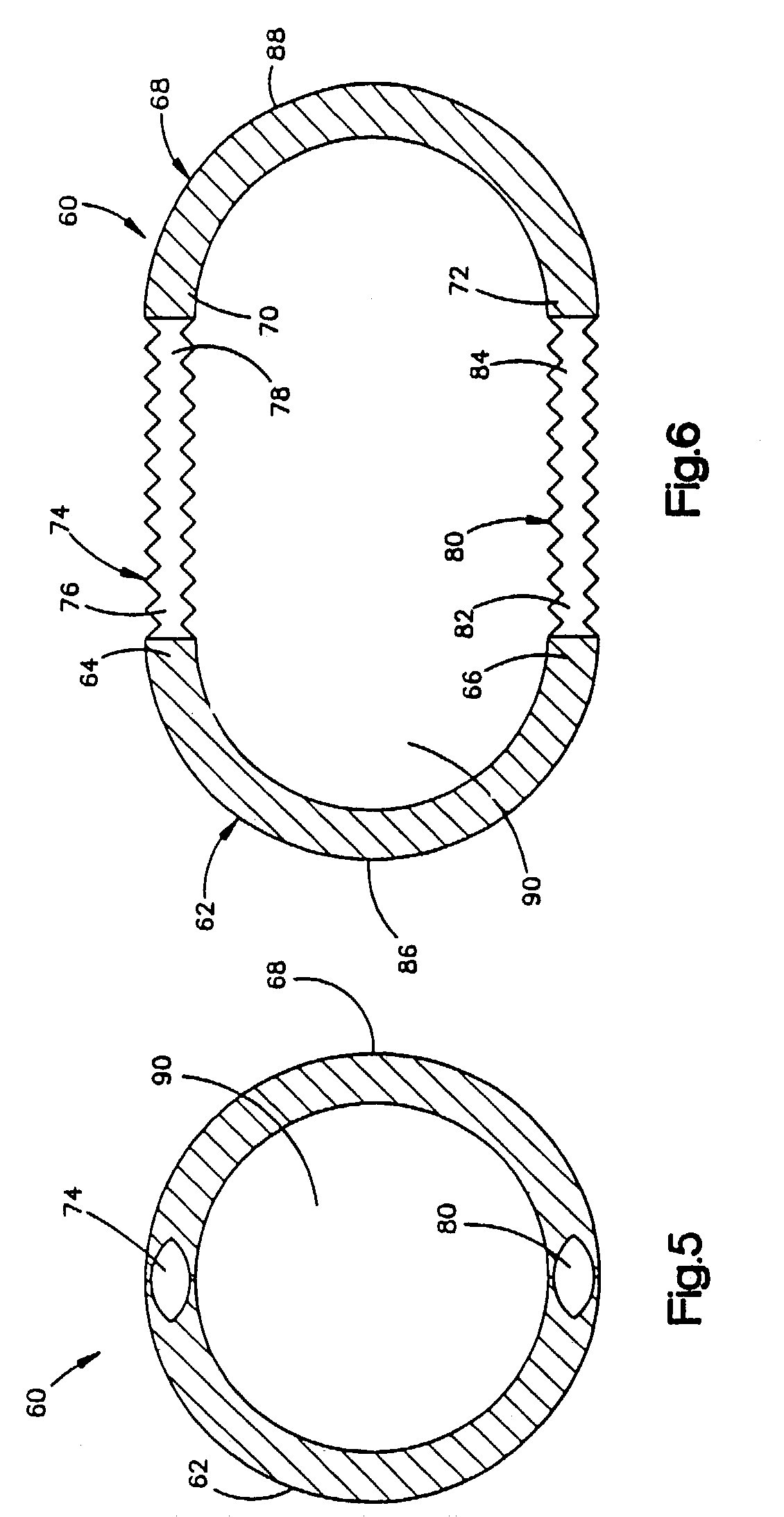
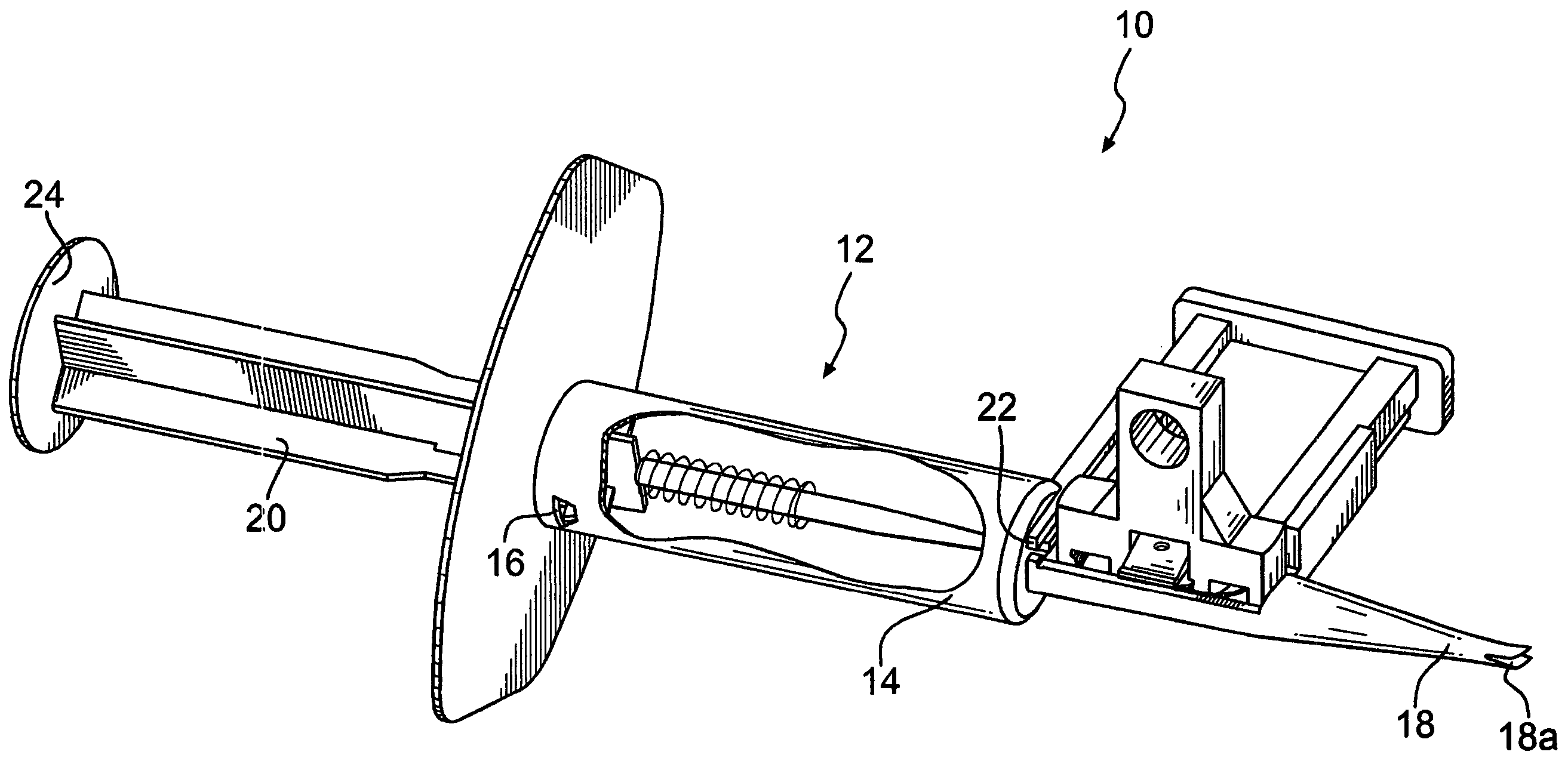
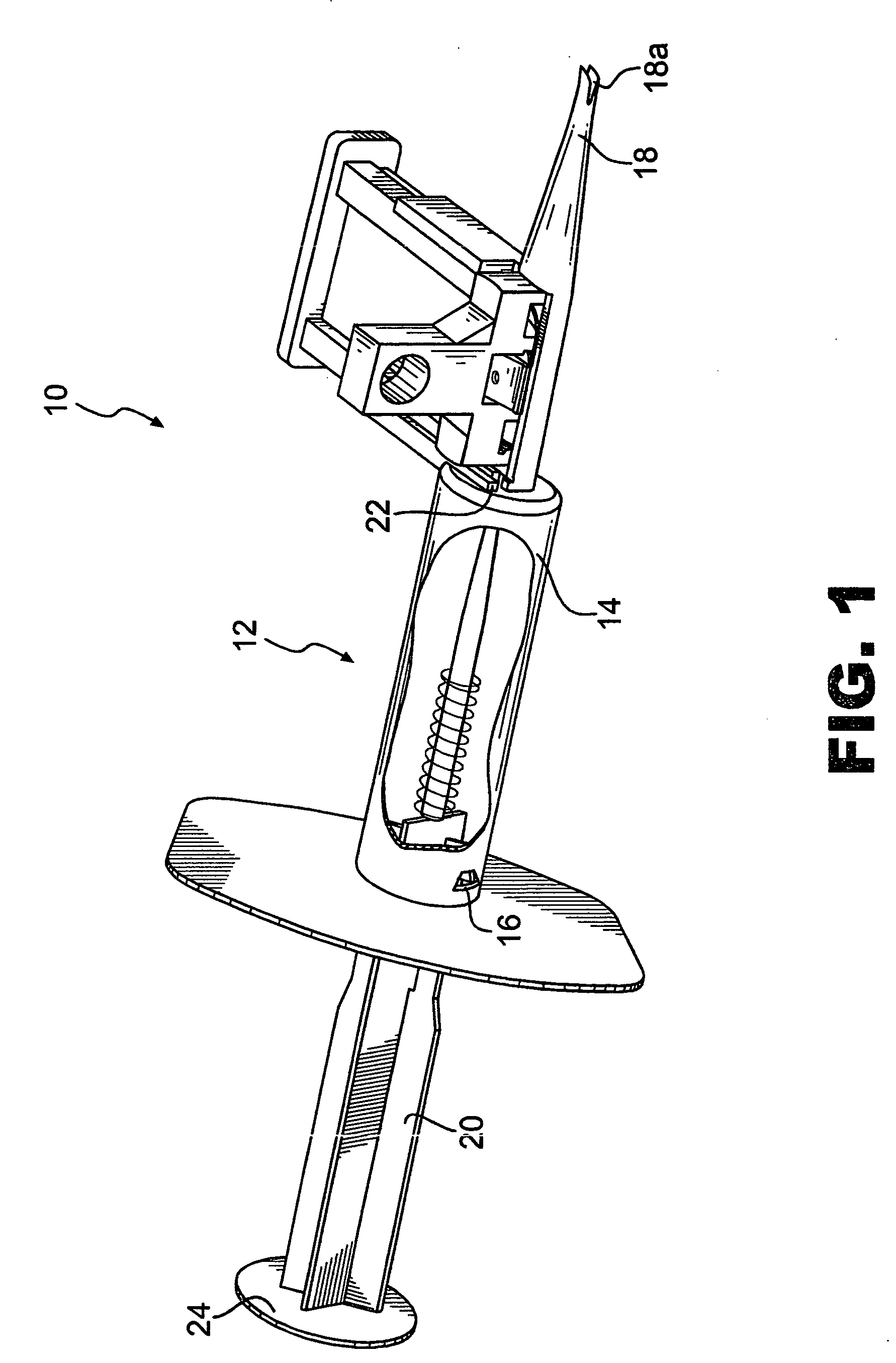
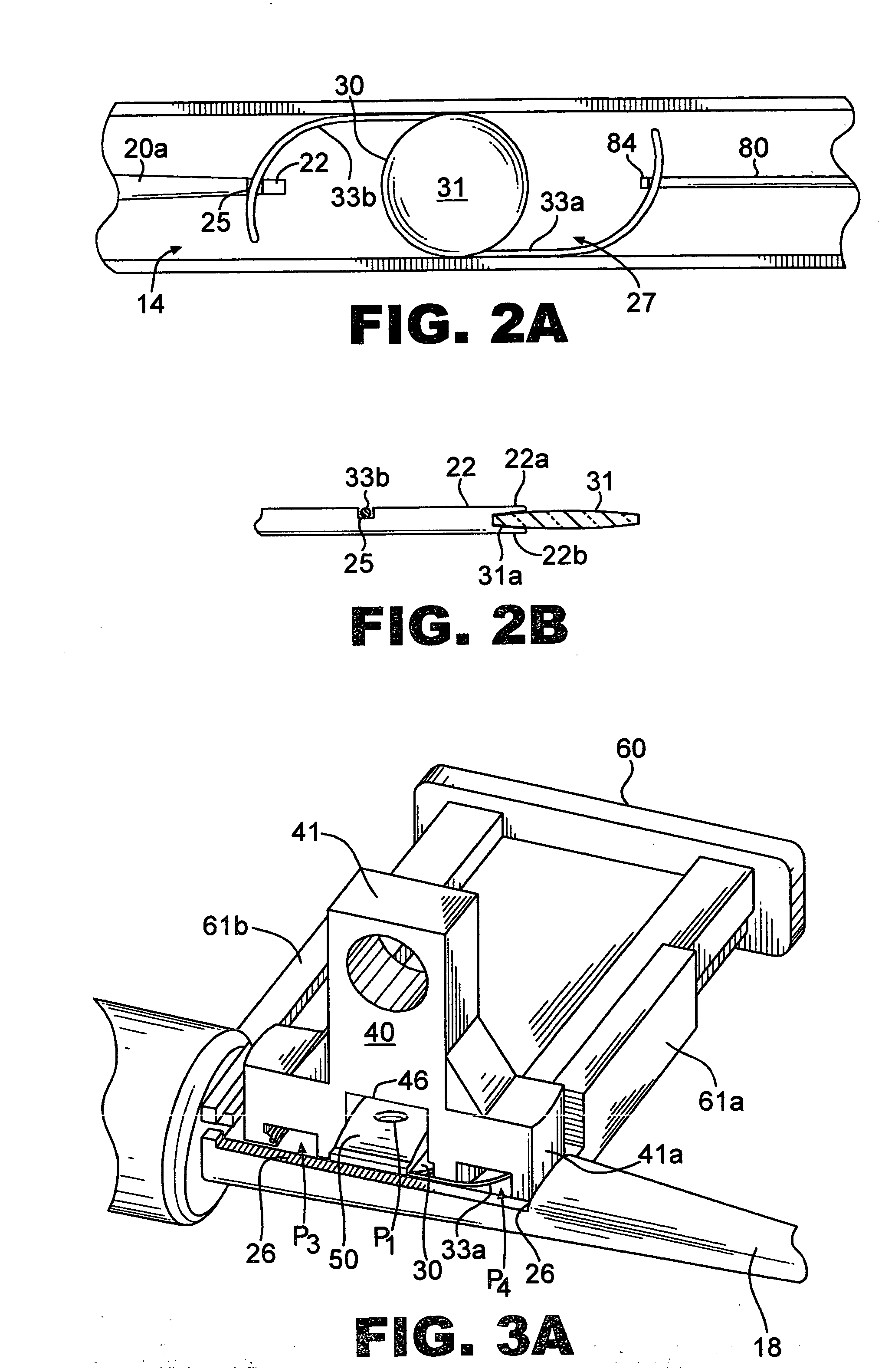
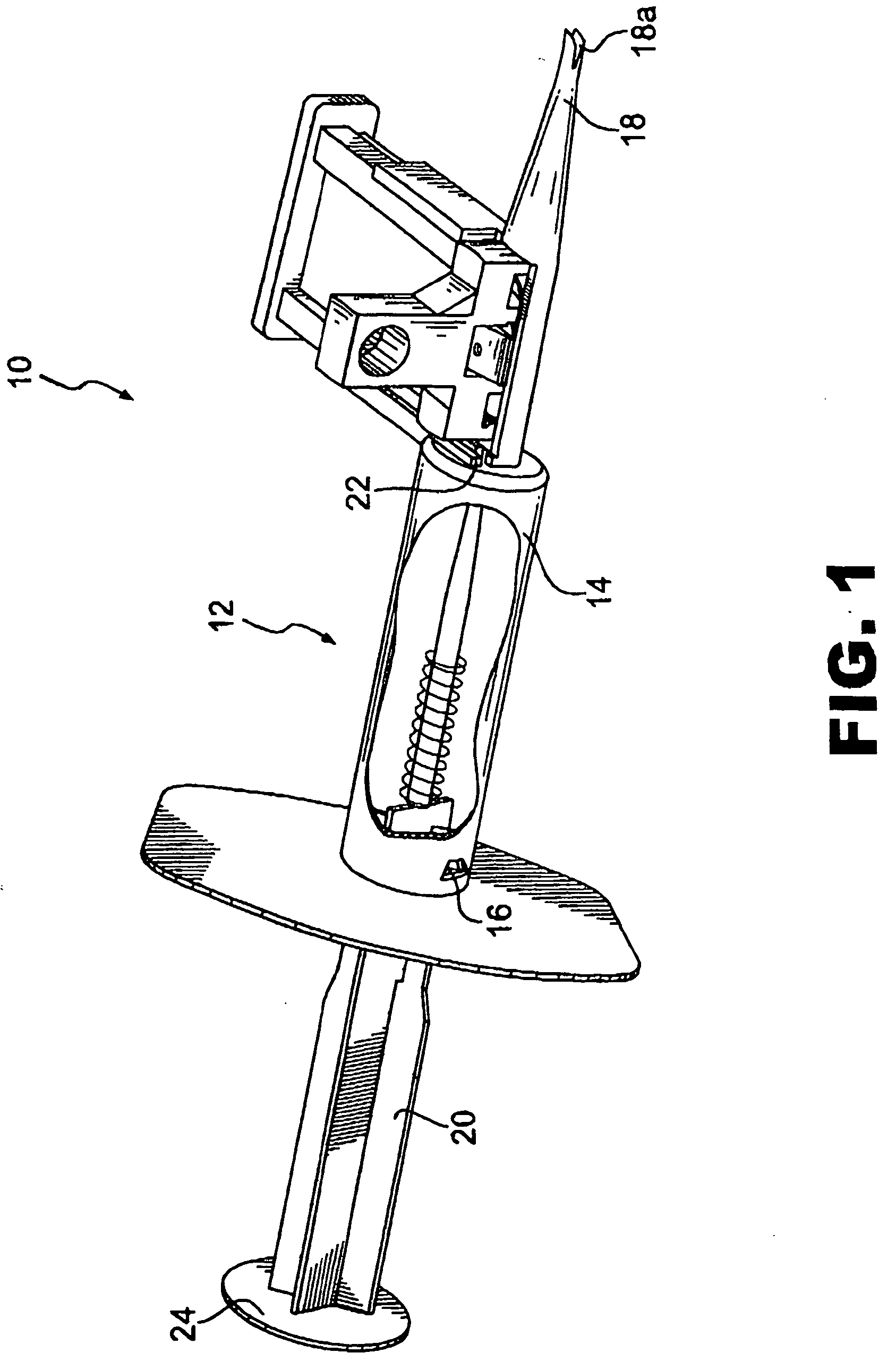
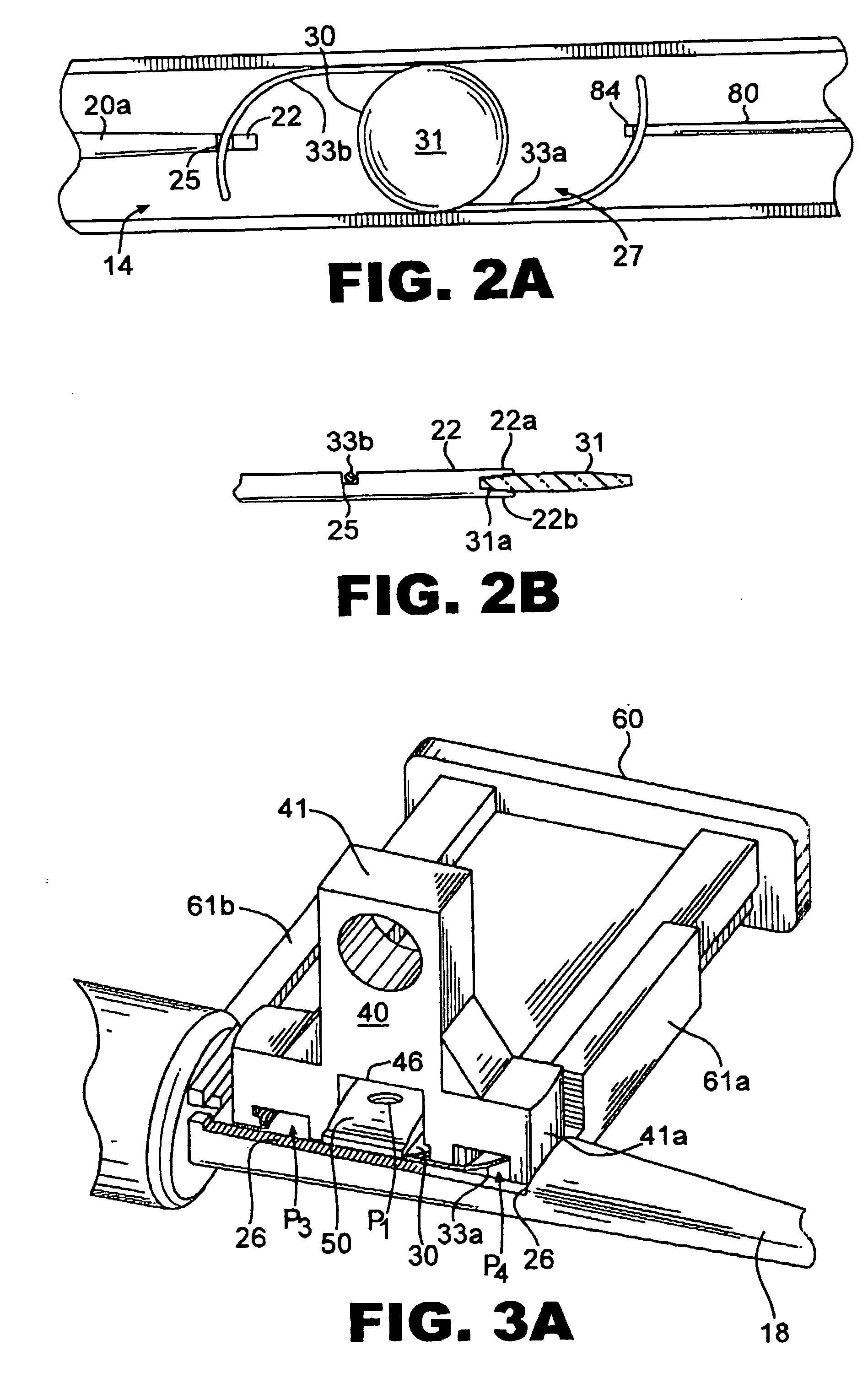
Active holder for annuloplasty ring delivery
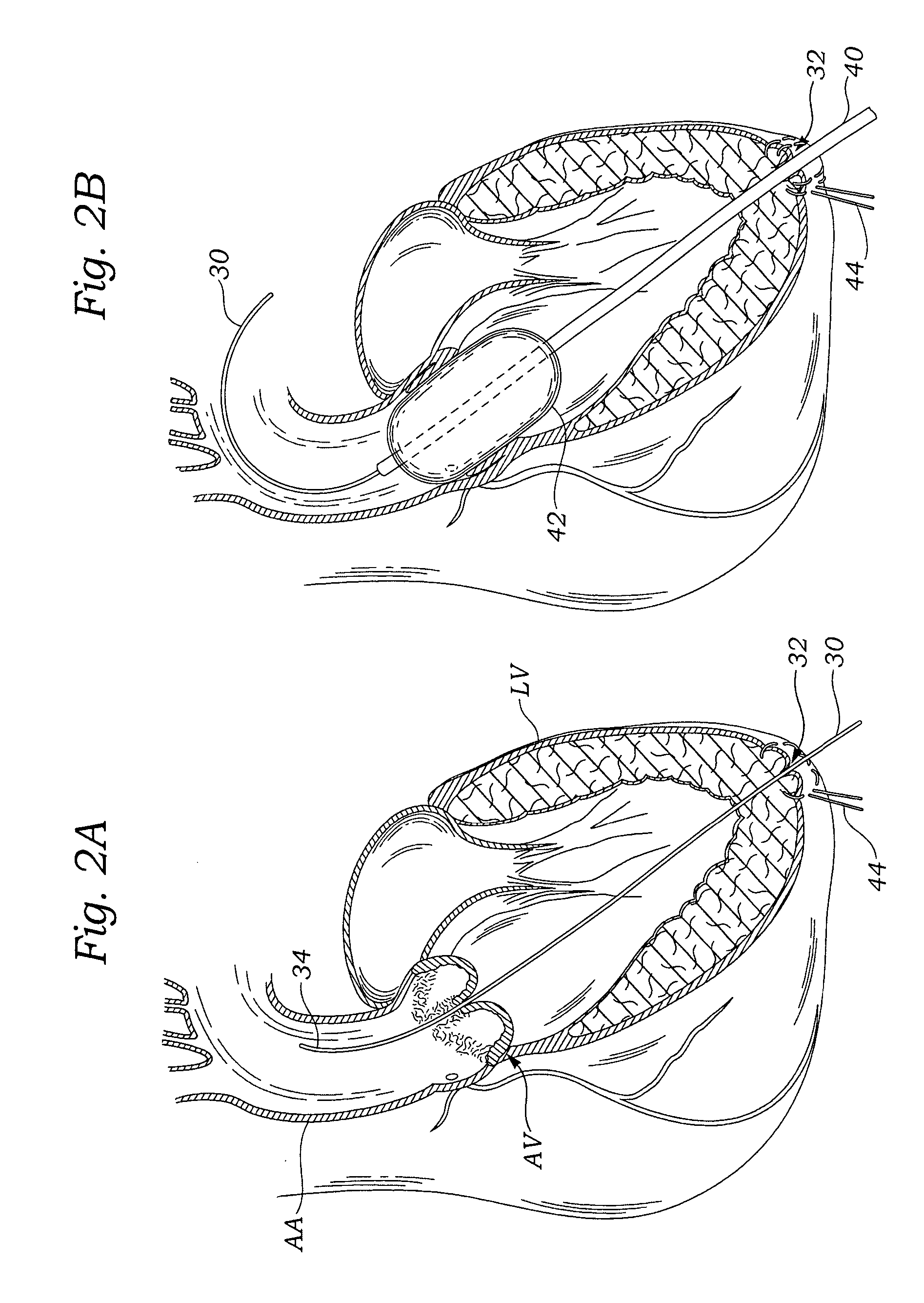
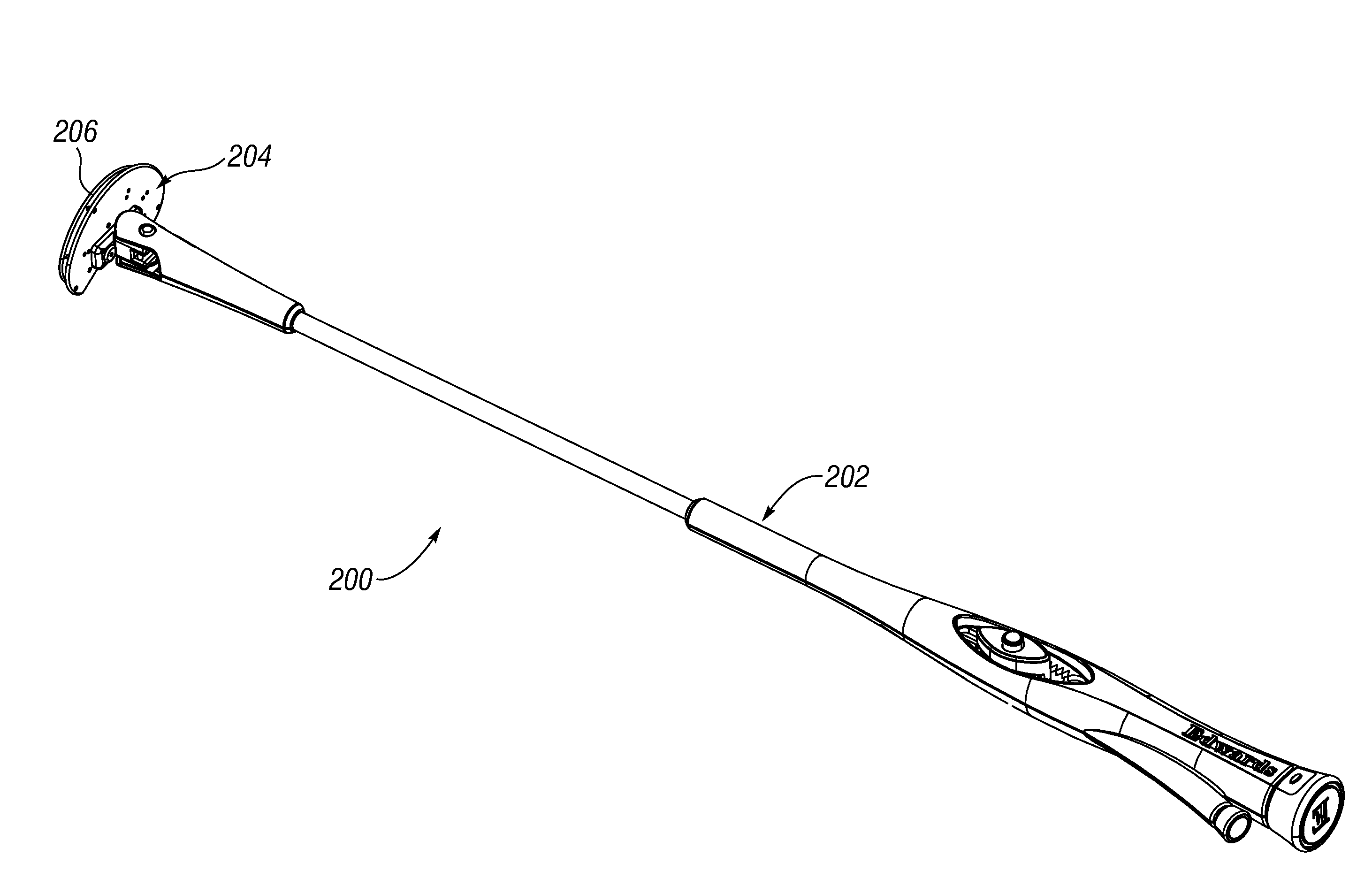
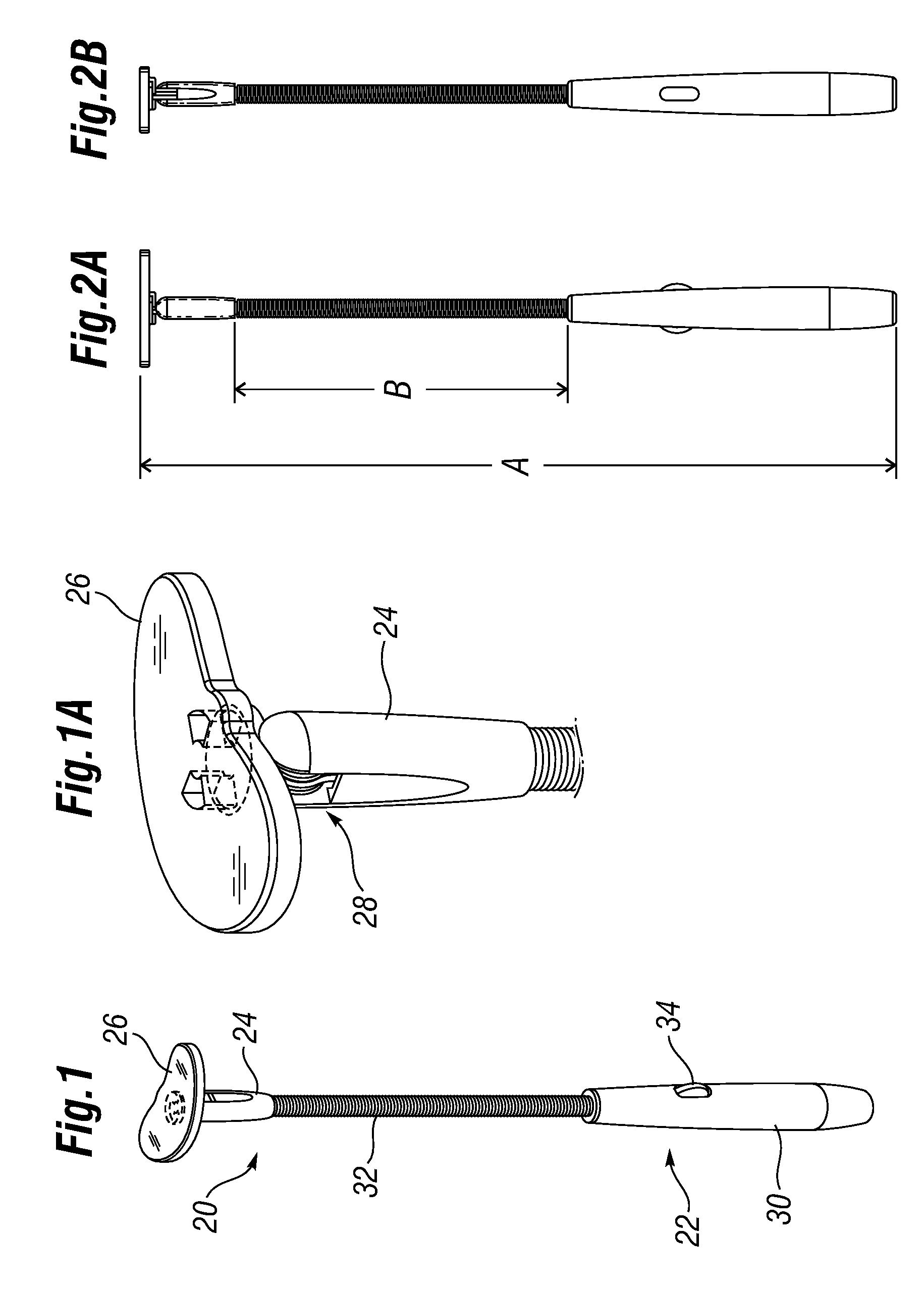
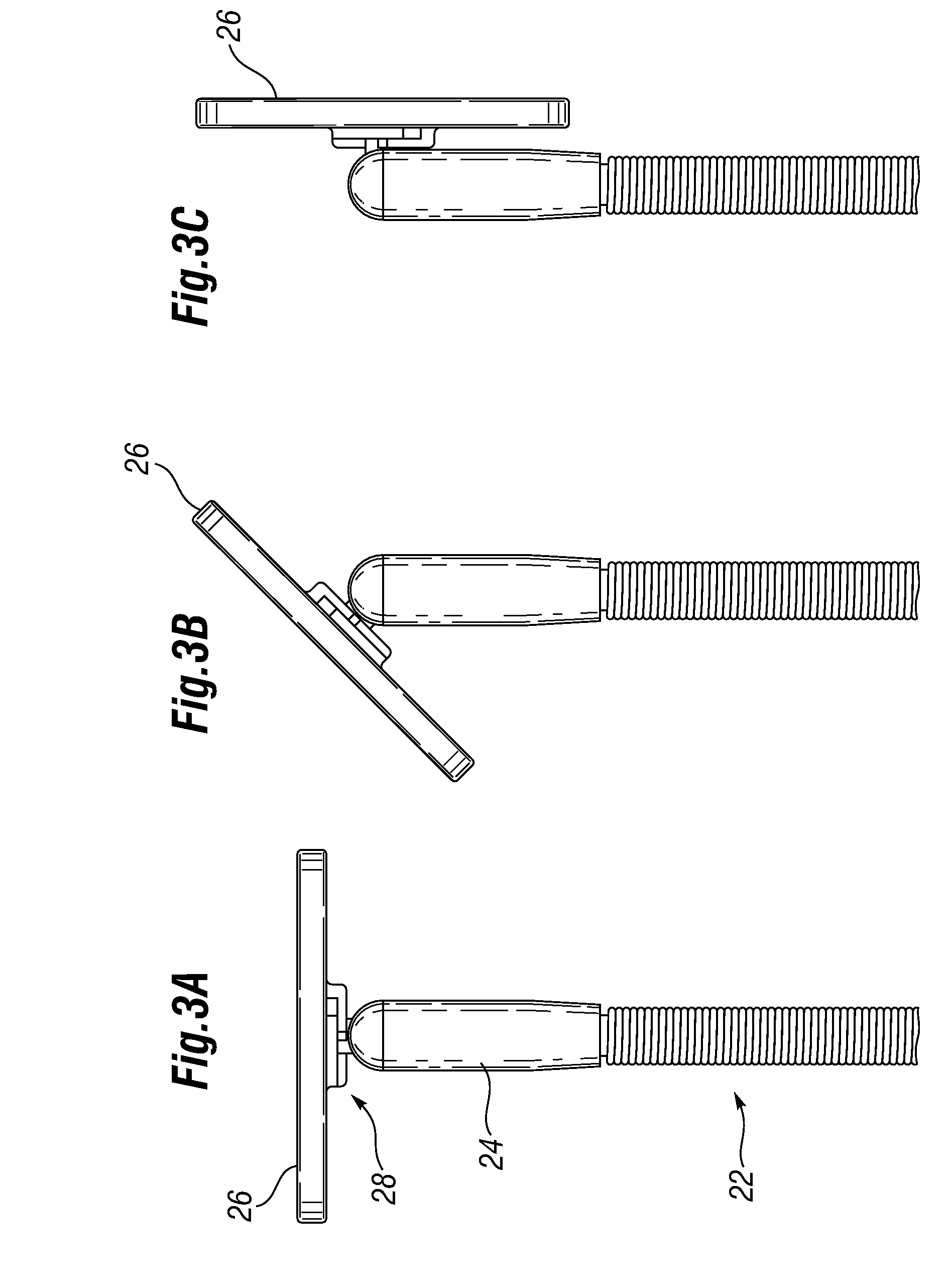
An active annuloplasty ring holder having a template that can be folded or pivoted to the side allowing the template to align longitudinally with the handle and enter the patient's chest through a small incision. The holder may include a mechanism to remotely detach sutures fastening the ring to the holder, thereby detaching the ring while avoiding the risk associated with introducing a scalpel into the operating field. A detachment mechanism may include a movable pin actuated by a pull wire that releases a plurality of holding sutures, or a hot wire, knives, or pull wire that severs the sutures. The holder may have a built-in light source for better visualization of the ring inside the heart. The holder may also have an optical means of visualizing the inside of the heart from the proximal end of the handle.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
Local Control Robotic Surgical Devices and Related Methods
The various embodiments disclosed herein relate to various robotic medical devices, including robotic devices that are disposed within a body cavity and positioned using a support component disposed through an orifice or opening in the body cavity. Additional embodiments relate to devices having arms coupled to a device body wherein the device has a minimal profile such that the device can be easily inserted through smaller incisions in comparison to other devices without such a small profile. Further embodiments relate to methods of operating the above devices.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT UNIV OF NEBRASKA
Methods and devices for repair or replacement of heart valves or adjacent tissue without the need for full cardiopulmonary support
ActiveUS8182530B2Reduce in quantityEliminate needEar treatmentCannulasAortic dissectionVentricular aneurysm
Methods and systems for endovascular, endocardiac, or endoluminal approaches to a patient's heart to perform surgical procedures that may be performed or used without requiring extracorporeal cardiopulmonary bypass. Furthermore, these procedures can be performed through a relatively small number of small incisions. These procedures may illustratively include heart valve implantation, heart valve repair, resection of a diseased heart valve, replacement of a heart valve, repair of a ventricular aneurysm, repair of an arrhythmia, repair of an aortic dissection, etc. Such minimally invasive procedures are preferably performed transapically (i.e., through the heart muscle at its left or right ventricular apex).
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCI CARDIAQ
Rotatable lead introducer
Minimally invasive introducers and methods that can be used for rotationally securing devices within the human body. Introducers can include a distal element for releasably engaging a lead head controllable from a proximal control located outside of the body. An inner stem can extend between a proximal portion and a distal portion, and be pivotally and rotatably coupled to the distal lead engagement mechanism. An outer tube can be rotatably disposed over the inner stem and be flexibly coupled over the pivot to rotationally drive the distal element. A helical epicardial-myocardial lead electrode can be secured and oriented straight ahead and introduced through a port or small incision with the introducer in a straight configuration. The introducer can then be bent and rotated to screw the helical electrode into the heart.
Owner:WILSON GREATBATCH LTD
Methods and devices for termination
Devices and methods used in termination of a tissue tightening procedure are described. Termination includes the cinching of a tether to tighten the tissue, locking the tether to maintain tension, and cutting excess tether. In procedures involving anchors secured to the tissue, the tether is coupled to the anchors and the tissue is tightened via tension applied to the anchors by cinching the tether. In general, the devices and methods can be used in minimally invasive surgical procedures, and can be applied through small incisions or intravascularly. A method for tightening tissue by fixedly coupling a first anchor to a tether and slidably coupling a second anchor to the tether, securing both anchors to the tissue, applying tension to the tether intravascularly, fixedly coupling the tether to the second anchor, and cutting the tether is described. The tissue to be tightened can comprise heart tissue, in particular heart valve annulus tissue. Various devices and methods for locking the tether in place and cutting excess tether are described.
Owner:ANCORA HEART INC
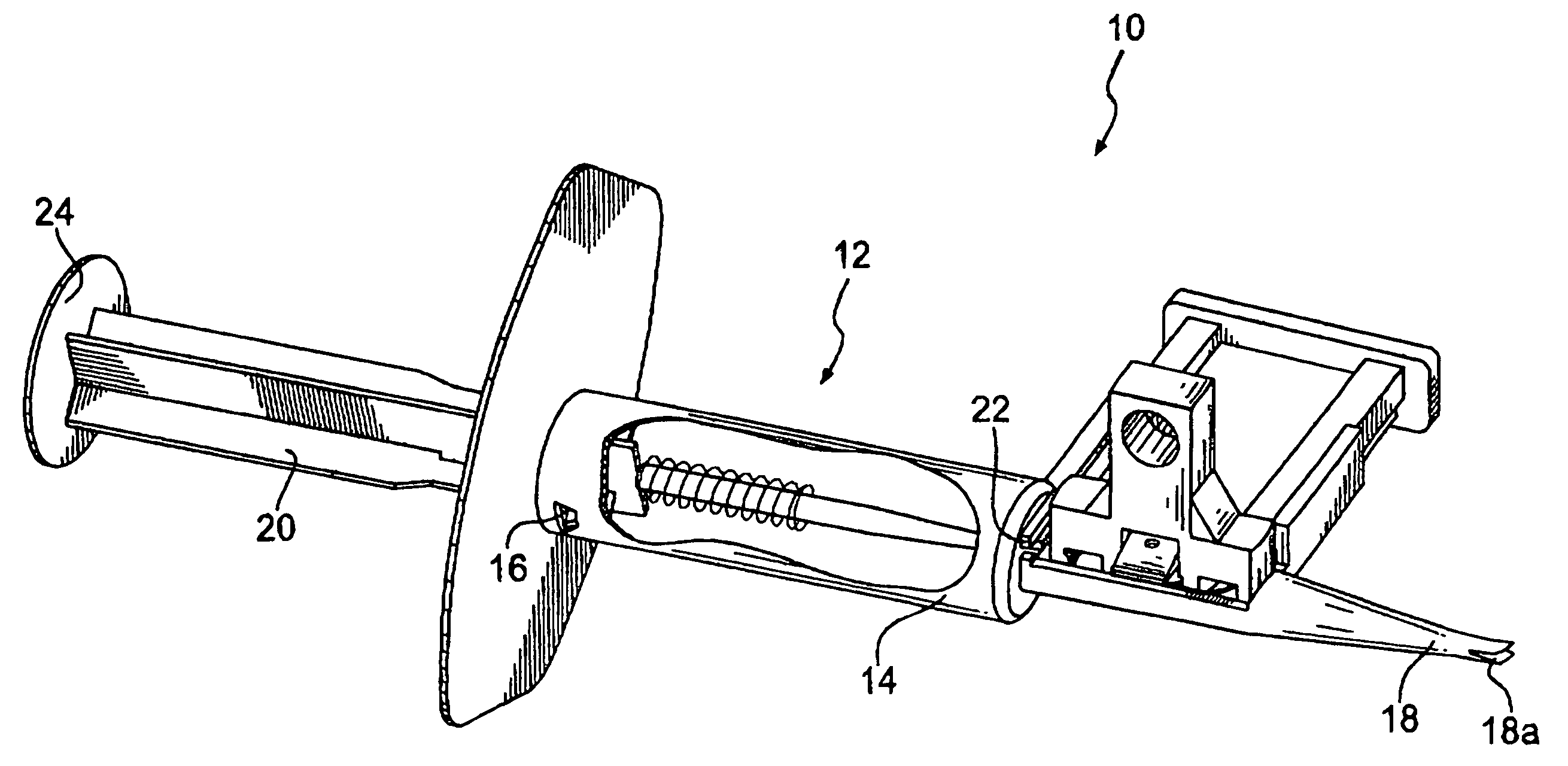
Modified trocar and methods of use
A modified trocar system to assist in surgical procedures. In one embodiment, the system is designed to assist in lifting lift a body wall in order to perform surgical procedures within the body cavity without establishing insufflation. The flanged trocar embodiment includes an extended flange forming a portion of the trocar body wall that may be inserted through the incision and deployed against either the interior surface of the body wall, or the interior surface of a protective sealing ring. A lifting mechanism forming a portion of the upper part of the flanged trocar is used in conjunction with the extended flange to enable the surgeon to draw the retained trocar upward in order to provide additional access to the body cavity under the tented body wall. In a more general embodiment of the invention, the modified trocar is directed through an existing incision and is used in an inward-to-outward manner to create a second smaller incision. The second smaller incision is designed to enable the deployment of some operating equipment or attachment device. Larger equipment may then be deployed through the larger first incision and coupled to the unit inserted into the smaller incision. In this way, a variety of manipulations may take place within the body cavity with minimal incision sizes and reduced traffic into and out of the incisions.
Owner:MACLEOD CATHEL
Adjustable length implant
ActiveUS20060195088A1Reducing patient discomfortGreat medical benefitInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsSurgical implantSurgery procedure
A method and apparatus for providing an adjustable length surgical implant is provided, wherein the surgical implant is readily adjustable by a surgeon using a surgical tool sized for use with the surgical implant. Adjustment of the surgical implant further requires a small incision through the skin prior to the adjustment of the length of the implant, such that the potential for infection is greatly reduces and the associated trauma of surgery is lessened for the patient.
Owner:DEPUY SPINE INC (US)
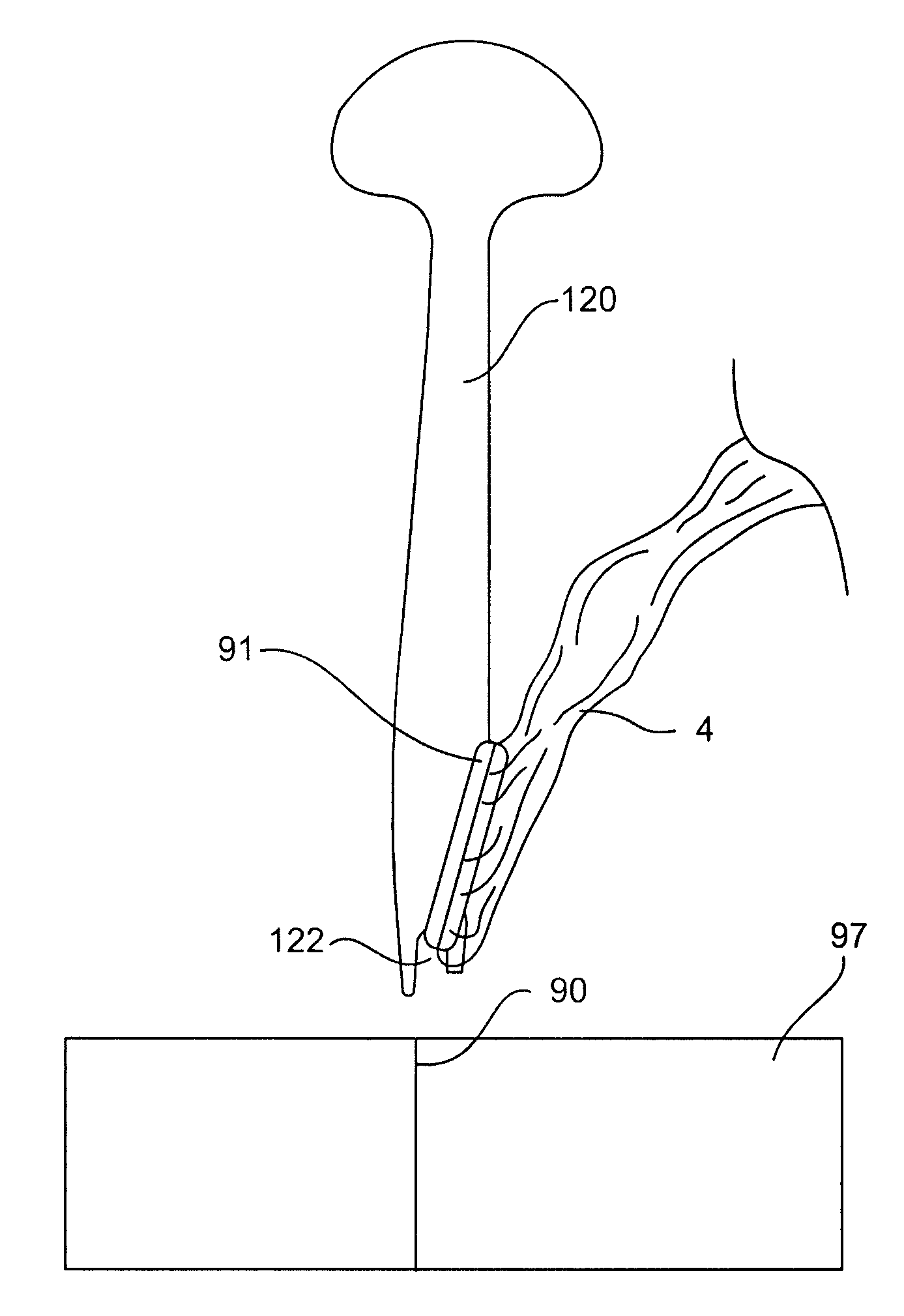
Wound retractor system
A wound retractor system comprises a retractor having a distal ring 91 and a retracting sleeve 4 extending from the ring. An insertion tool 120 has a distal groove 122 to hold the ring for insertion of the ring through a small incision 90 in the abdominal wall 97. The retractor may be used for retracting an incision to receive an instrument therethrough. A seal or valve may be mounted to the retractor through which an instrument can pass.
Owner:ATROPOS LTD
Methods and devices for termination
Devices and methods used in termination of a tissue tightening procedure are described. Termination includes the cinching of a tether to tighten the tissue, locking the tether to maintain tension, and cutting excess tether. In procedures involving anchors secured to the tissue, the tether is coupled to the anchors and the tissue is tightened via tension applied to the anchors by cinching the tether. In general, the devices and methods can be used in minimally invasive surgical procedures, and can be applied through small incisions or intravascularly. A method for tightening tissue by fixedly coupling a first anchor to a tether and slidably coupling a second anchor to the tether, securing both anchors to the tissue, applying tension to the tether intravascularly, fixedly coupling the tether to the second anchor, and cutting the tether is described. The tissue to be tightened can comprise heart tissue, in particular heart valve annulus tissue. Various devices and methods for locking the tether in place and cutting excess tether are described.
Owner:ANCORA HEART INC
Systems and methods for stabilization of bone structures
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Devices and methods for port-access multivessel coronary artery bypass surgery
InactiveUS6478029B1Reduce oxygen demandReduce the temperatureSuture equipmentsDiagnosticsDiseaseSurgical approach
Surgical methods and instruments are disclosed for performing port-access or closed-chest coronary artery bypass (CABG) surgery in multivessel coronary artery disease. In contrast to standard open-chest CABG surgery, which requires a median sternotomy or other gross thoracotomy to expose the patient's heart, post-access CABG surgery is performed through small incisions or access ports made through the intercostal spaces between the patient's ribs, resulting in greatly reduced pain and morbidity to the patient. In situ arterial bypass grafts, such as the internal mammary arteries and / or the right gastroepiploic artery, are prepared for grafting by thoracoscopic or laparoscopic takedown techniques. Free grafts, such as a saphenous vein graft or a free arterial graft, can be used to augment the in situ arterial grafts. The graft vessels are anastomosed to the coronary arteries under direct visualization through a cardioscopic microscope inserted through an intercostal access port. Retraction instruments are provided to manipulate the heart within the closed chest of the patient to expose each of the coronary arteries for visualization and anastomosis. Disclosed are a tunneler and an articulated tunneling grasper for rerouting the graft vessels, and a finger-like retractor, a suction cup retractor, a snare retractor and a loop retractor for manipulating the heart. Also disclosed is a port-access topical cooling device for improving myocardial protection during the port-access CABG procedure. An alternate surgical approach using an anterior mediastinotomy is also described.
Owner:HEARTPORT
Anthro-centric multisensory interface for sensory augmentation of telesurgery
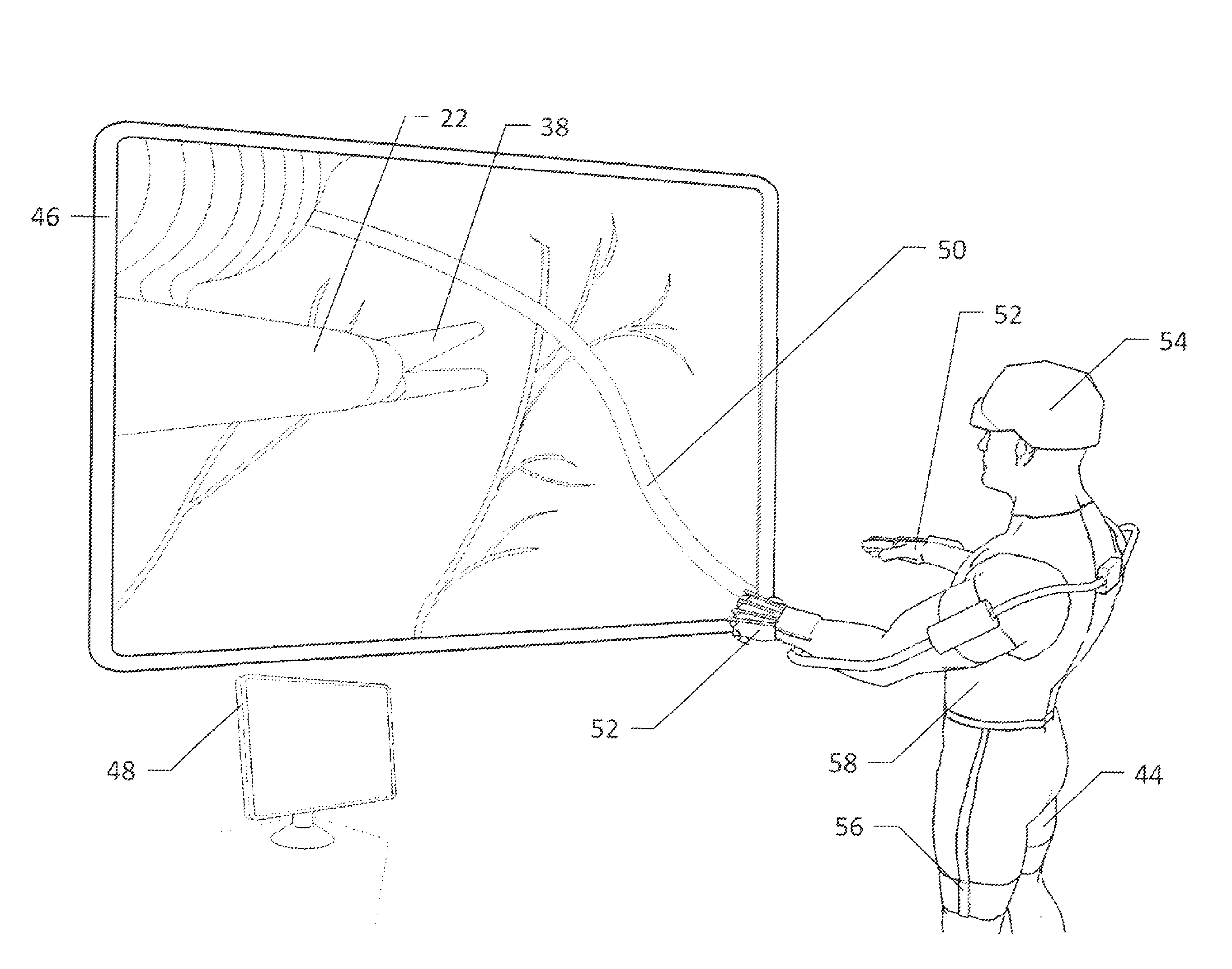
InactiveUS8880223B2Good awareness of situationThe process is simple and easy to understandComputer controlSimulator controlRemote surgeryControl system
A multisensory interface for a tele-robotic surgical control system. The invention allows the surgeon to use natural gestures and motions to control the actions of end effectors in the robotic surgical apparatus. Multiple feedback mechanisms are provided to allow the physician a more intuitive understanding of what is being controlled, along with a greater situational awareness. Prior art robotic end effectors are inserted into the patient through a small incision—as is already known in the art. The invention presents an improved method of controlling these effectors.
Owner:FLORIDA INST FOR HUMAN & MACHINE COGNITION
Adjustable length implant
ActiveUS20060195087A1Reducing patient discomfortGreat medical benefitInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsSurgical operationSurgical implant
A method and apparatus for providing an adjustable length surgical implant is provided, wherein the surgical implant is readily adjustable by a surgeon using a surgical tool sized for use with the surgical implant. Adjustment of the surgical implant further requires a small incision through the skin prior to the adjustment of the length of the implant, such that the potential for infection is greatly reduces and the associated trauma of surgery is lessened for the patient.
Owner:HYLIGHTER +1
Transapical heart valve delivery system and method
ActiveUS8764820B2Help positioningShorten balloonStentsBalloon catheterProsthetic heartLeft ventricular apex
A delivery system and method for delivering a prosthetic heart valve to the aortic valve annulus. The system includes a balloon catheter having a steering mechanism thereon for delivering a balloon-expandable prosthetic heart valve through an introducer in an antegrade fashion to the aortic annulus. The balloon catheter passes through an introducer that accesses the left ventricle through its apex and a small incision in the chest wall. The balloon catheter includes a deflecting segment just proximal to the distal balloon to facilitate positioning of the prosthetic heart valve in the proper orientation within the aortic annulus. A slider in a deflection handle may be coupled to a deflection wire that actuates the deflecting segment. The method includes using two concentric rings of purse-string sutures around the puncture in the left ventricular apex to maintain a good seal around instruments passed therethrough. The prosthetic heart valve may be installed over the existing calcified leaflets, and a pre-dilation valvuloplasty procedure may also be utilized.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
Active cannulas
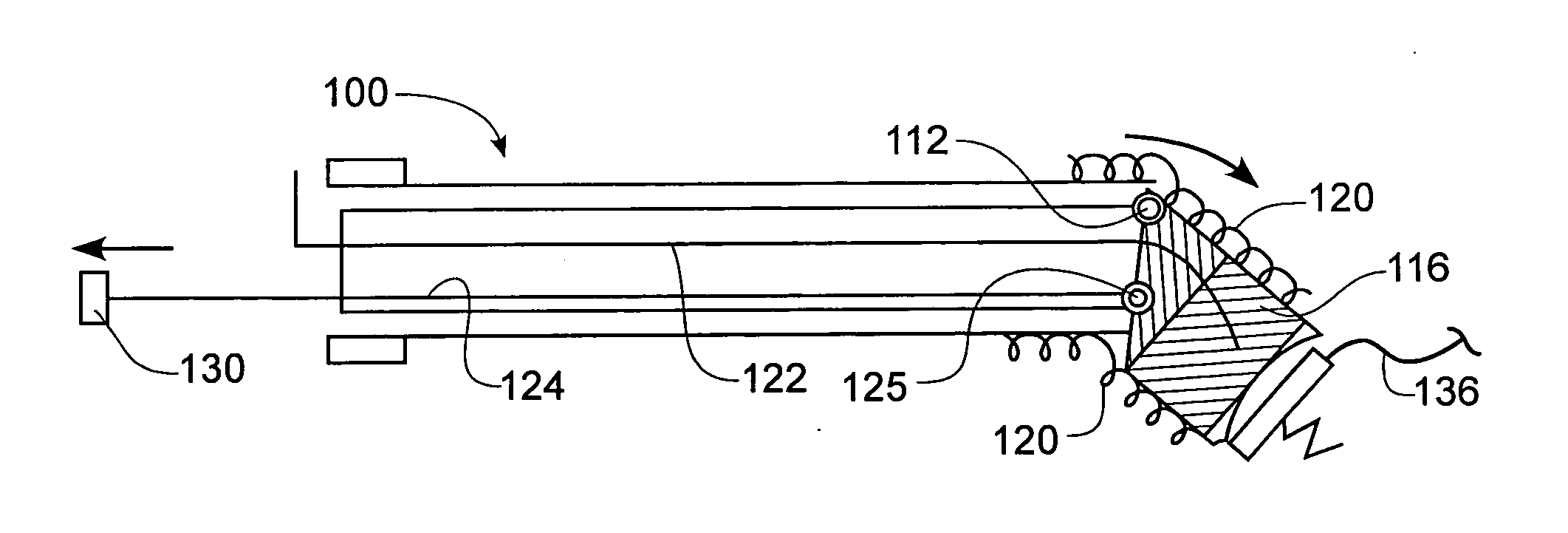
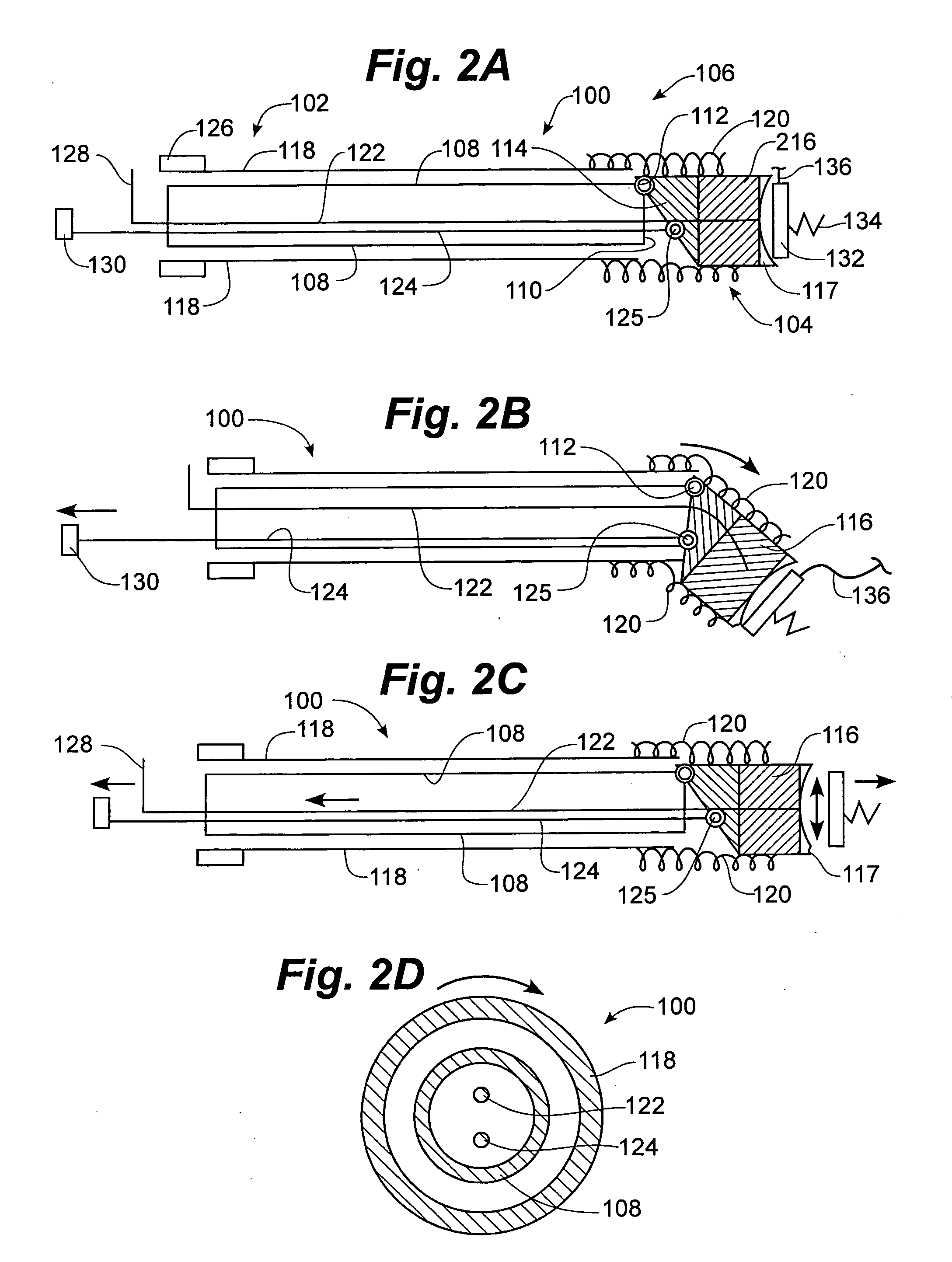
InactiveUS7311719B2Simple and safe processSafely visualize appropriate tissue and operateStentsGuide needlesMedicineSkin opening
An active cannula which does more than merely maintain a passage is usable to create and / or enlarge a passage, to position a scope or instrument, to move or locate tissue, etc. The cannula can vary in size or shape as needed, intraoperatively. Because a cannula of the present invention is expandable, the surgeon can make a relatively small incision, stretch the tissue with the expandable cannula, contract the cannula and remove it, allowing the skin to come back to its unstretched condition. Thus, a smaller incision can be made to fit the same size instrument. The cannulas can assume such a non-circular shape, to fit into a natural skin opening and cause less trauma. The devices can be used to seal off a space, expand an existing space or a potential space for working or visualization, move tissue (for example, to stretch an incision), or protect tissue.
Owner:GEN SURGICAL INNOVATIONS
Preloaded IOL injector
ActiveUS20050049606A1Facilitate manual decouplingEye treatmentIntraocular lensIntraocular lensEngineering
A preloaded intraocular lens injection device includes a retainer for releasably holding an IOL in an unstressed state. The retainer and IOL are removably attached to an injector body and are sealed in the same package for delivery to a surgeon. In an alternate embodiment, the retainer and IOL are coupled together and sealed in one package and the injector body is sealed in a separate package with the surgeon attaching the retainer to the injector body at the time of surgery. To deliver the IOL through the injector body, the retainer is removed from the injector body causing the IOL to release from the retainer and become located in an unstressed state in the injector body. A compressor is moved to the closed position to compress the IOL, the injector tip is inserted through a small incision in an eye and a plunger is advanced to push the IOL through and out the injector body tip and into an eye.
Owner:BAUSCH & LOMB INC
Method and apparatus for performing minimally invasive surgical procedures
InactiveUS20050228365A1Reserved functionHigh precisionProgramme controlSuture equipmentsRobotic armSurgical site
The system includes a pair of surgical instruments that are coupled to a pair of robotic arms. The instruments have end effectors that can be manipulated to hold and suture tissue. The robotic arms are coupled to a pair of master handles by a controller. The handles can be moved by the surgeon to produce a corresponding movement of the end effectors. The movement of the handles is scaled so that the end effectors have a corresponding movement that is different, typically smaller, than the movement performed by the hands of the surgeon. The scale factor is adjustable so that the surgeon can control the resolution of the end effector movement. The movement of the end effector can be controlled by an input button, so that the end effector only moves when the button is depressed by the surgeon. The input button allows the surgeon to adjust the position of the handles without moving the end effector, so that the handles can be moved to a more comfortable position. The system may also have a robotically controlled endoscope which allows the surgeon to remotely view the surgical site. A cardiac procedure can be performed by making small incisions in the patient's skin and inserting the instruments and endoscope into the patient. The surgeon manipulates the handles and moves the end effectors to perform a cardiac procedure such as a coronary artery bypass graft.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
Preloaded IOL injector
InactiveUS20050049605A1Facilitate manual decouplingEye treatmentIntraocular lensIntraocular lensEngineering
A preloaded intraocular lens injection device includes a retainer for releasably holding an IOL in an unstressed state. The retainer and IOL are removably attached to an injector body and are sealed in the same package for delivery to a surgeon. In an alternate embodiment, the retainer and IOL are coupled together and sealed in one package and the injector body is sealed in a separate package with the surgeon attaching the retainer to the injector body at the time of surgery. To deliver the IOL through the injector body, the retainer is removed from the injector body causing the IOL to release from the retainer and become located in an unstressed state in the injector body. A compressor is moved to the closed position to compress the IOL, the injector tip is inserted through a small incision in an eye and a plunger is advanced to push the IOL through and out the injector body tip and into an eye.
Owner:BAUSCH & LOMB INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com