Methods and devices for termination
a technology of termination and method, applied in the field of medical devices and methods, can solve the problems of difficulty in manipulating the knotting or tying material of the suture, the difficulty of heart valve surgery candidates, and the difficulty of valve repair and replacemen
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
examples
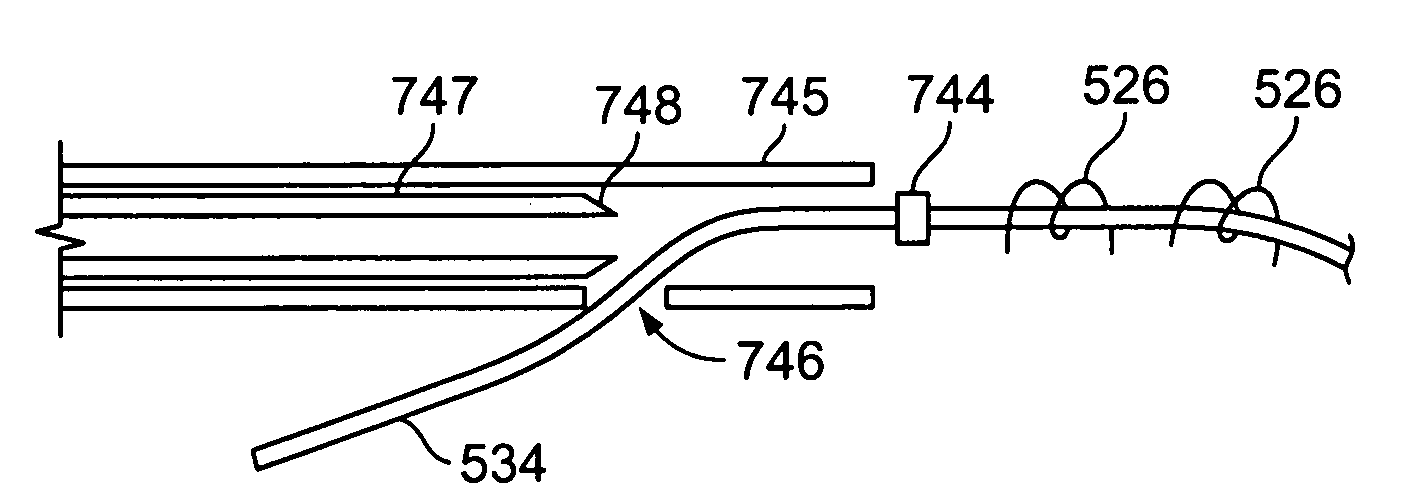
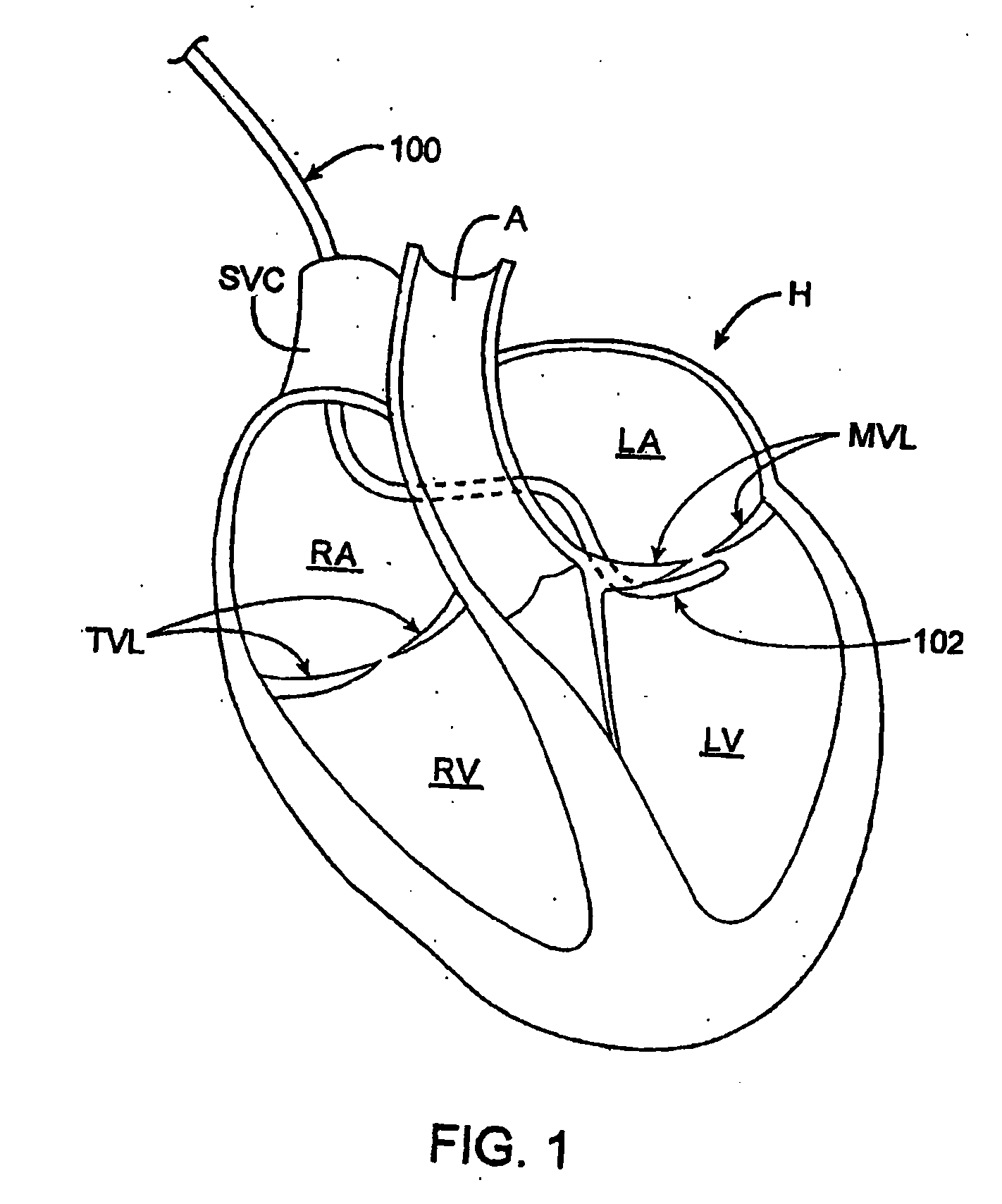
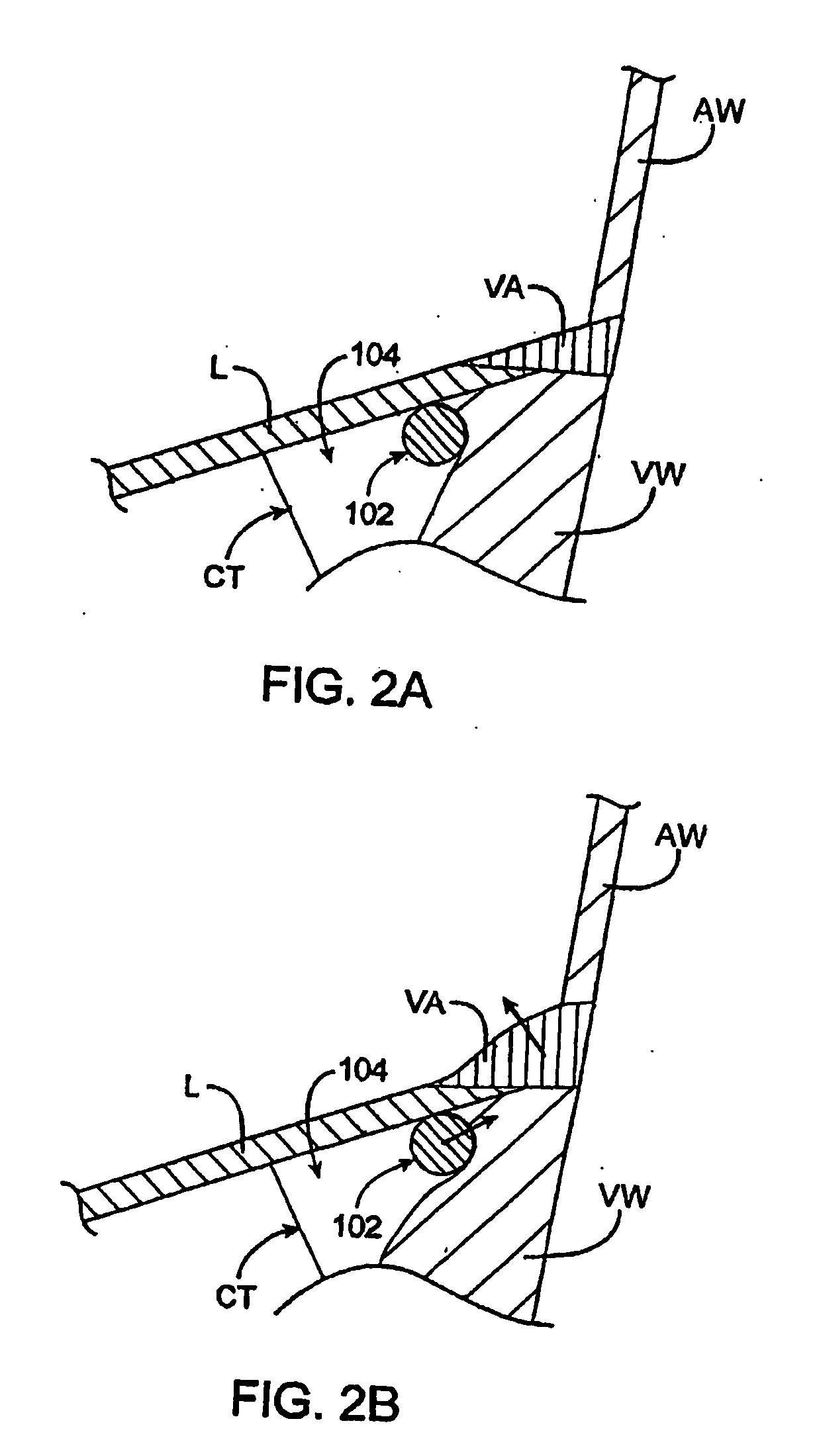
[0169] In general, termination devices are designed to cinch, lock, and / or cut a tether (e.g., a suture or cable) as described herein. These devices can be used for any surgery where these functions (or combinations of them) are desired. FIG. 39 shows a termination device 3901 having a detachable locking feature 3905 that is releasably attached at the distal end of the termination device. This variation of a termination device has an elongated tubular body 3903 which may be flexible over all (or a portion) of its length. Thus, the termination device may be used in non-invasive procedures (e.g., percutaneously) or in invasive (e.g., open-heart) surgeries. The termination device shown in FIG. 39 is configured as a termination device catheter.
[0170] The termination device 3901 shown in cross-section in FIG. 39 is coupled to a tether 3910. The tether is threaded through the distal region of the termination device, particularly through the locking feature 3905 region at the distal end o...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com