Patents
Literature
64 results about "Chordae tendinae" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
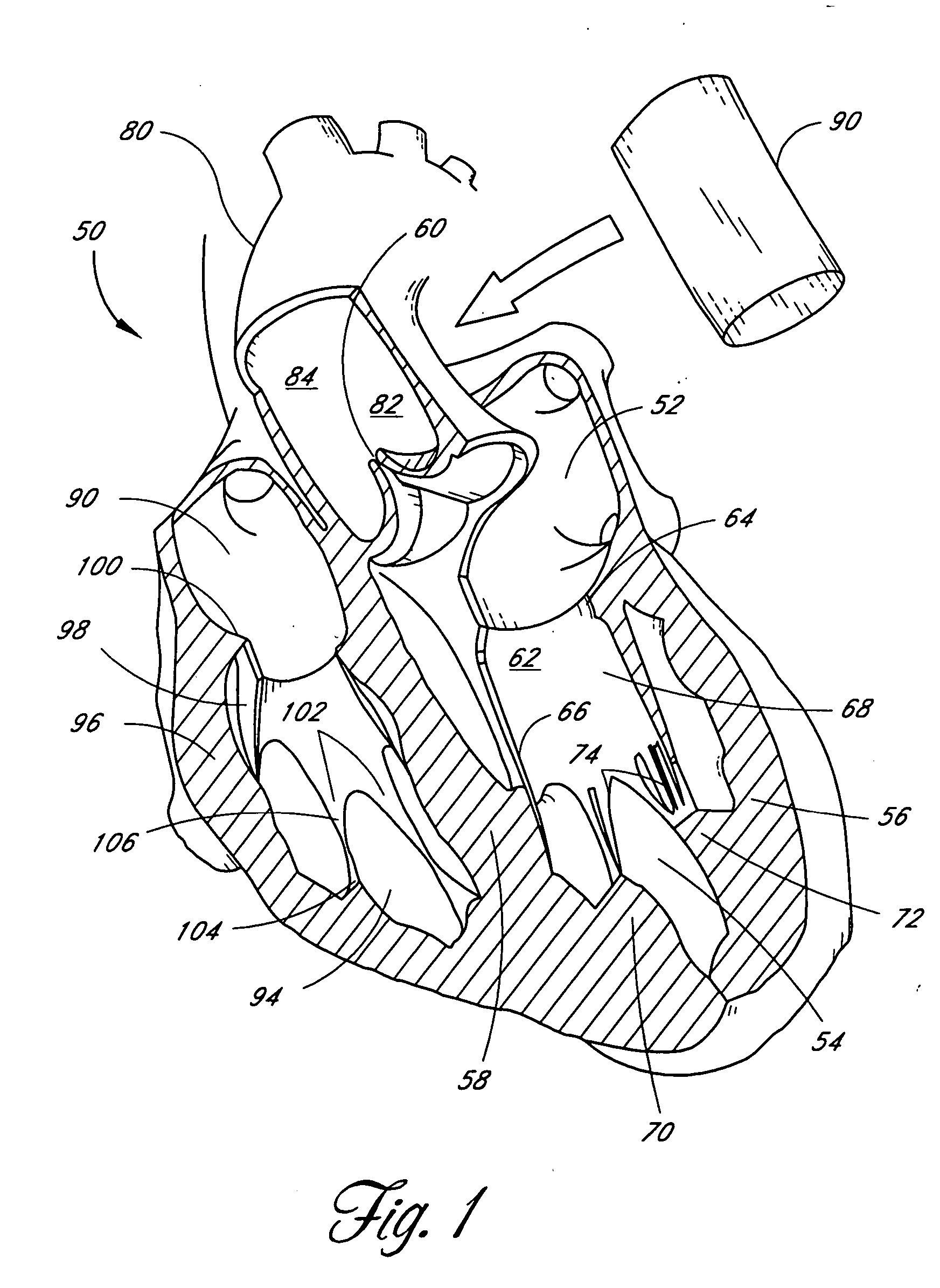
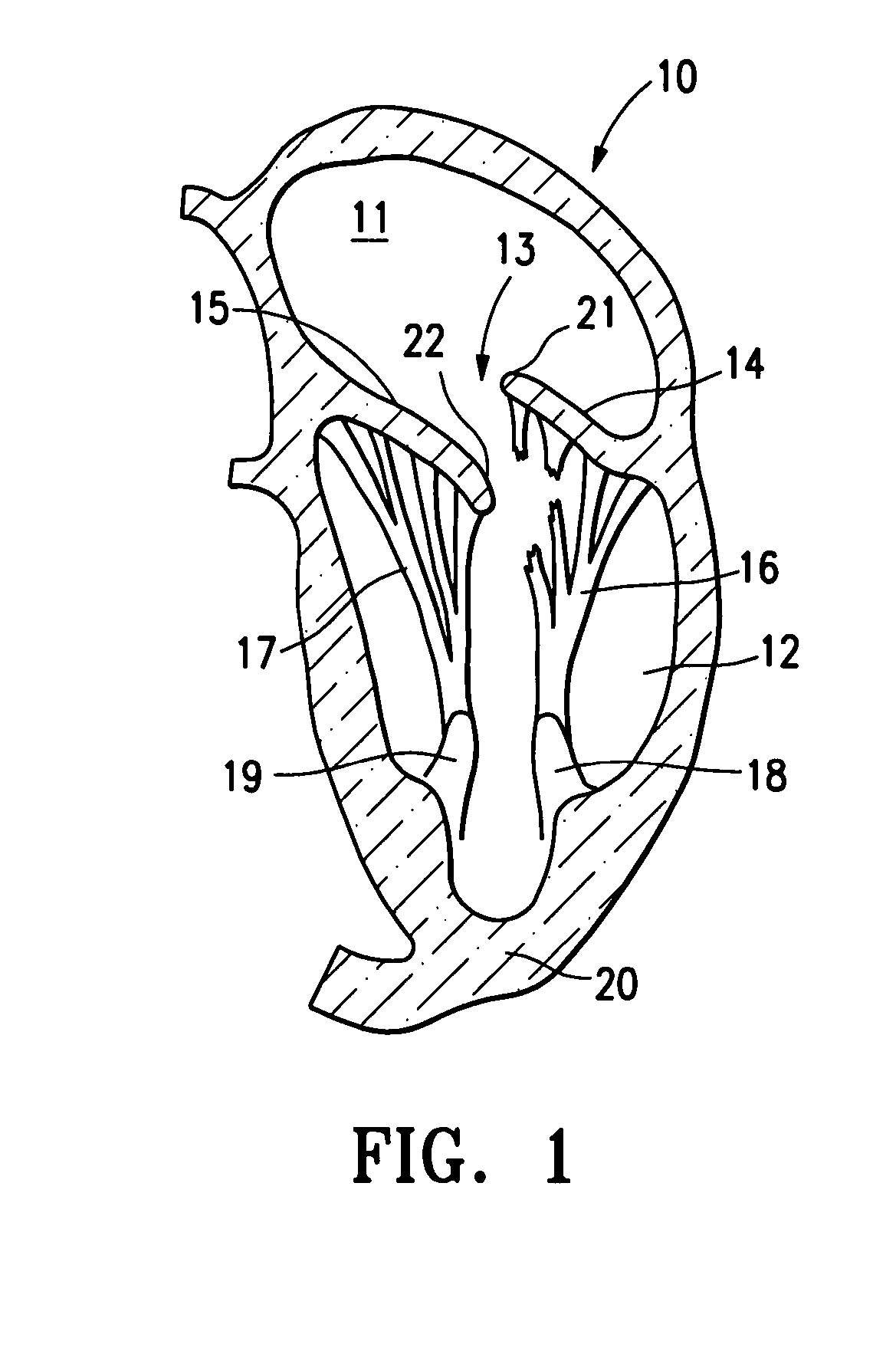
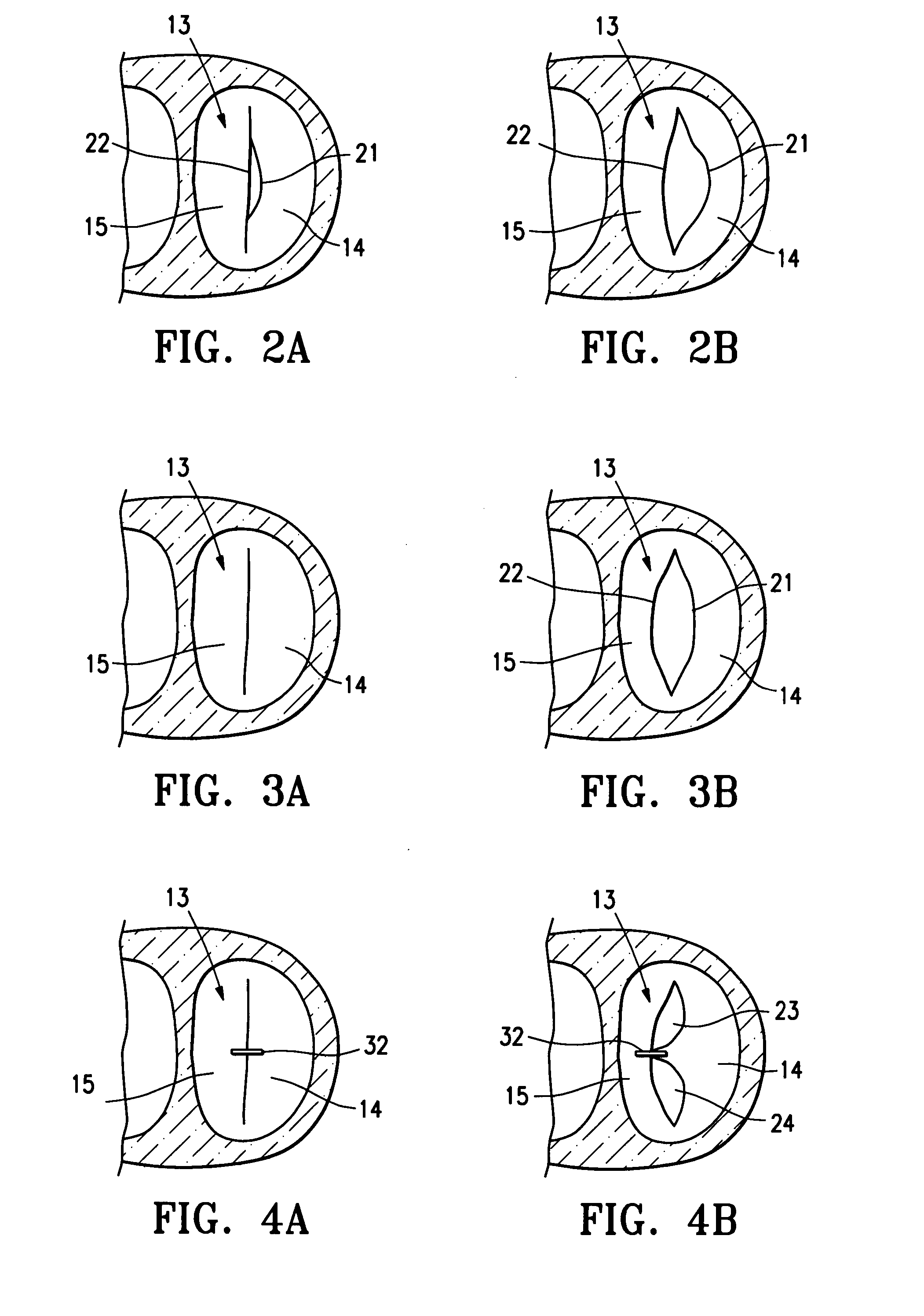
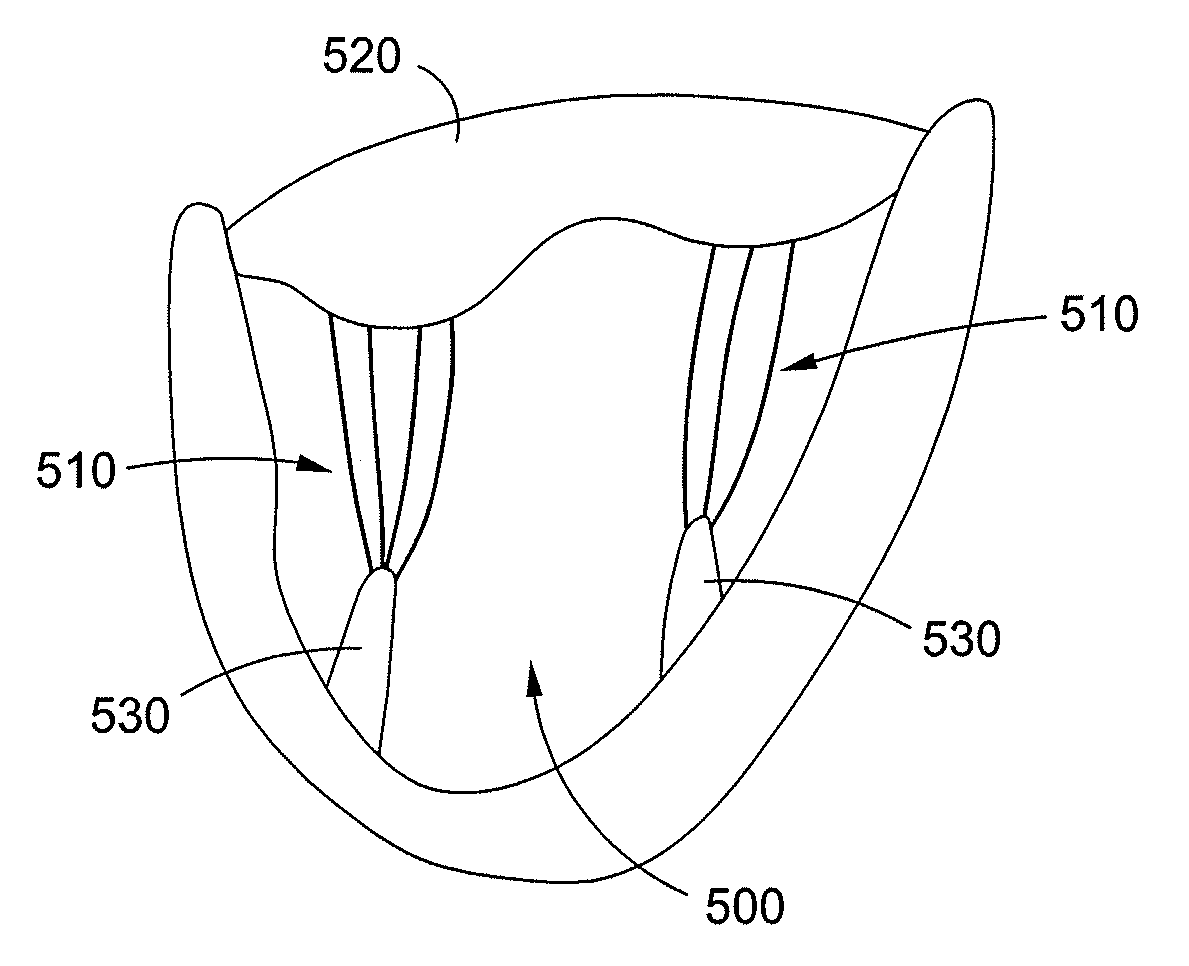
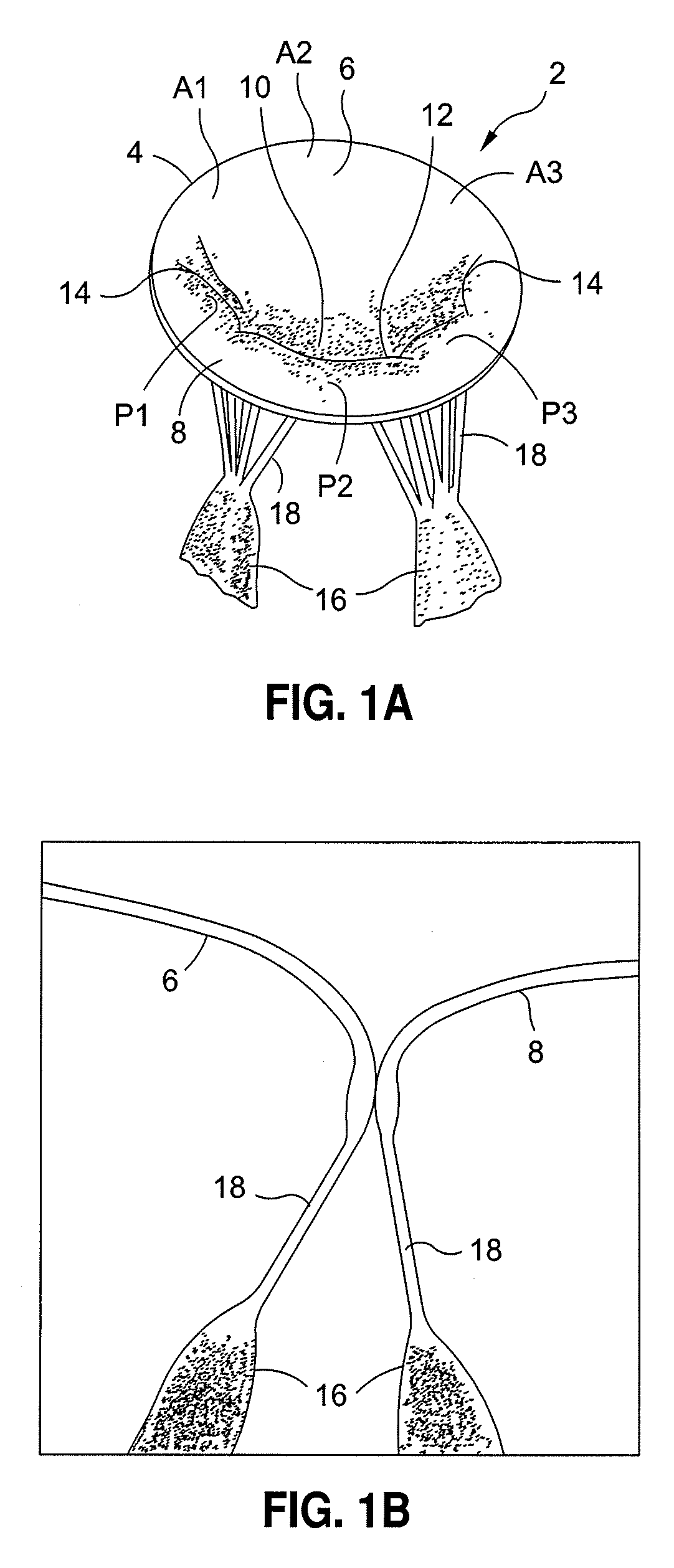
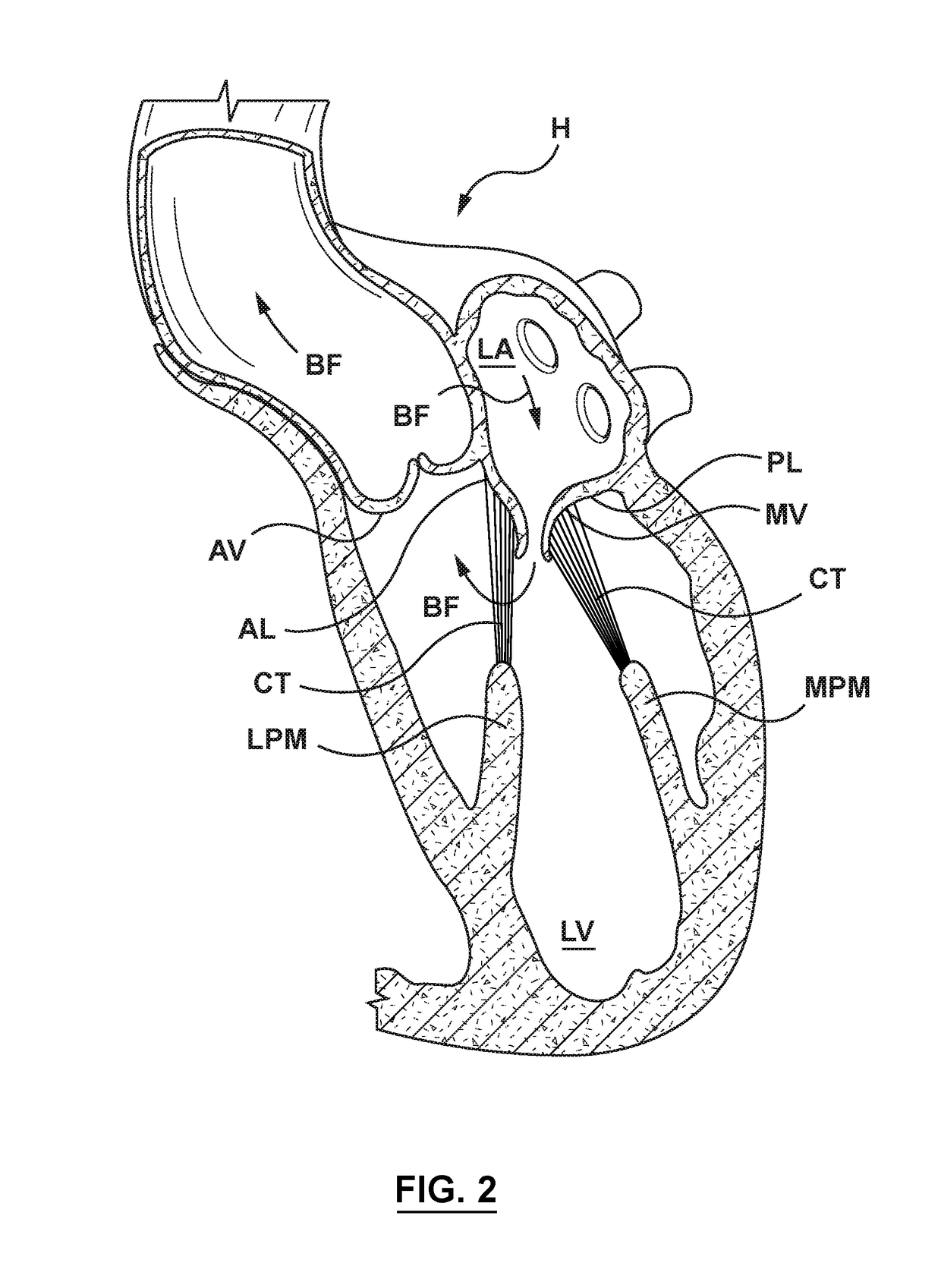
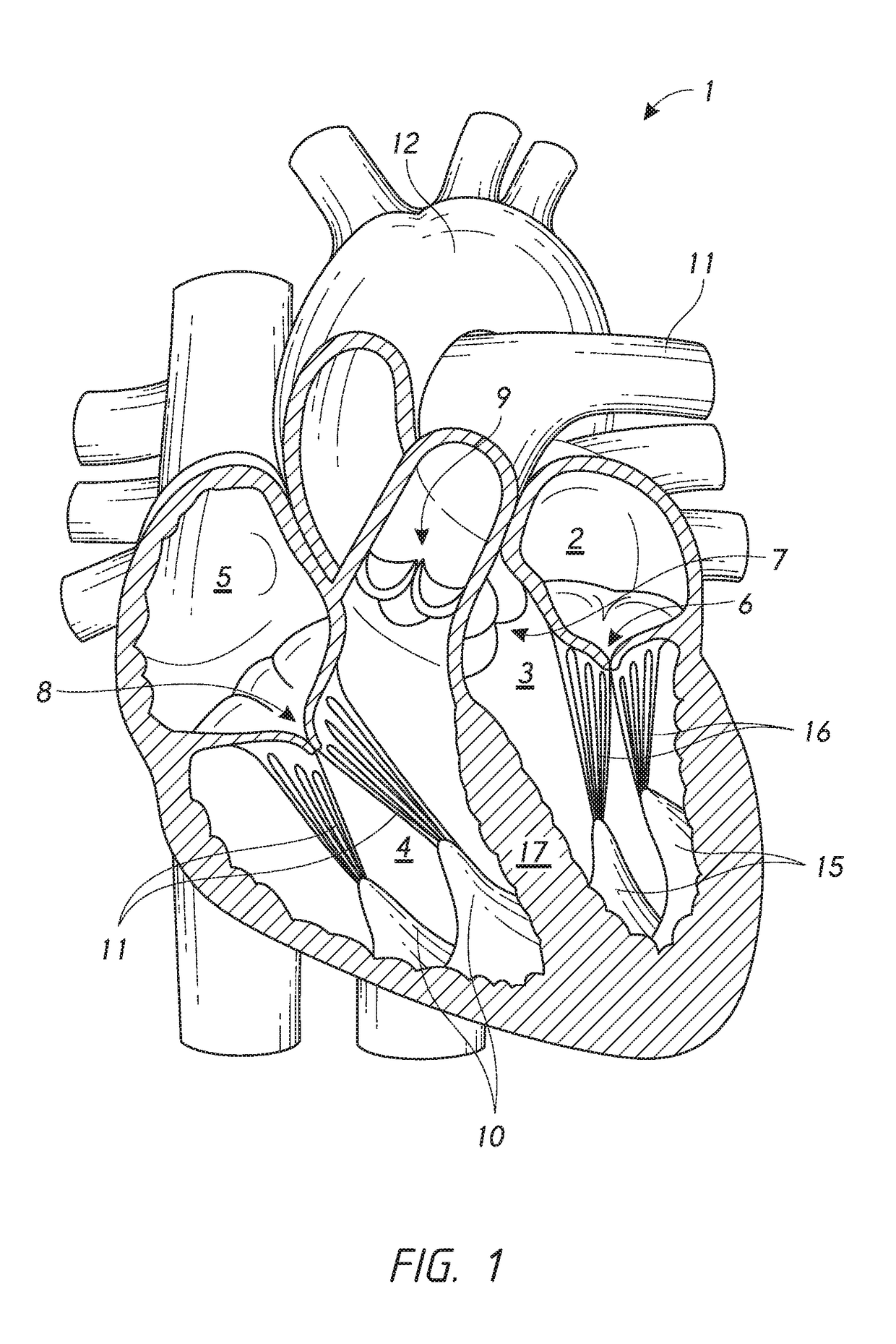
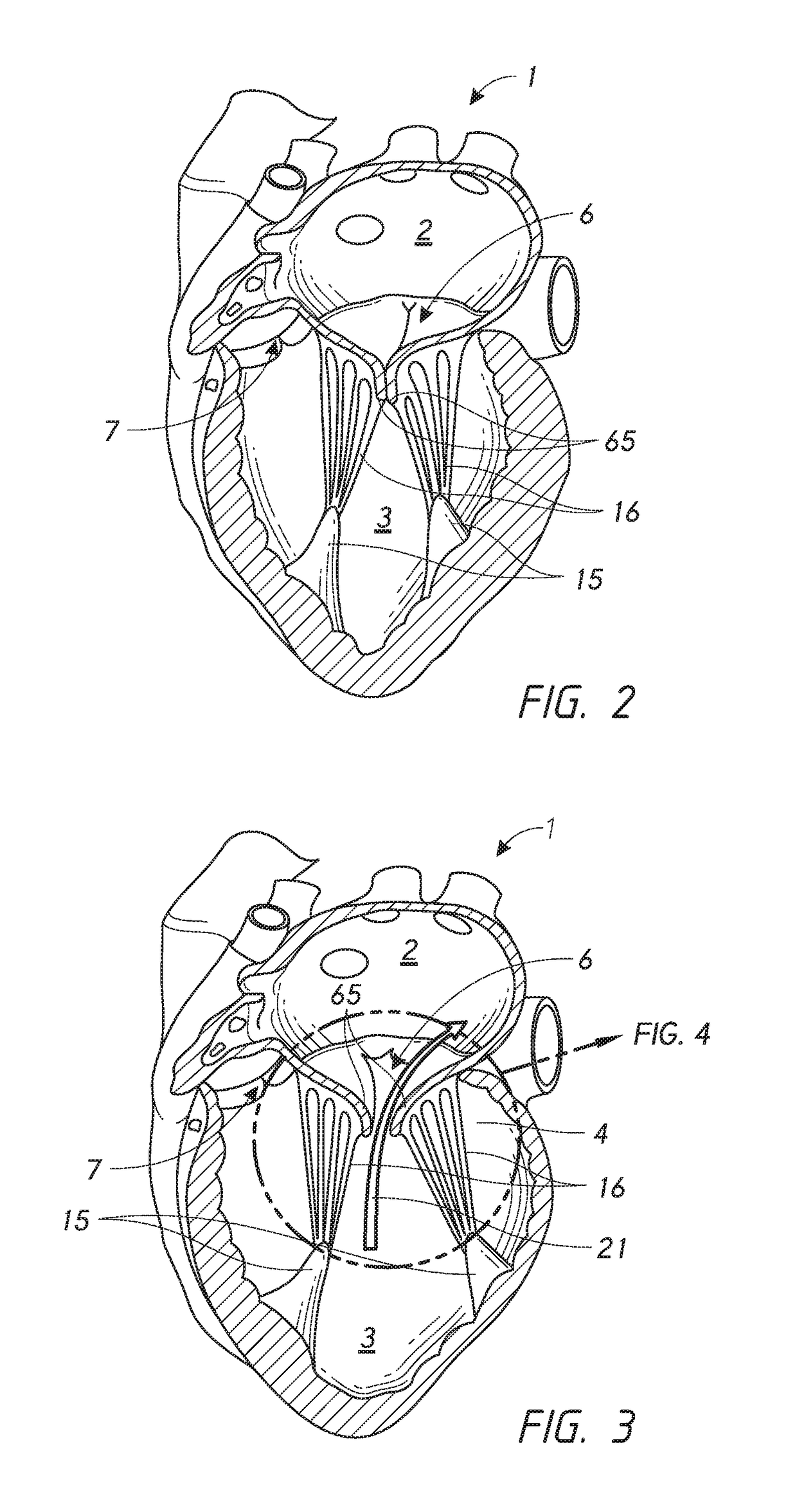
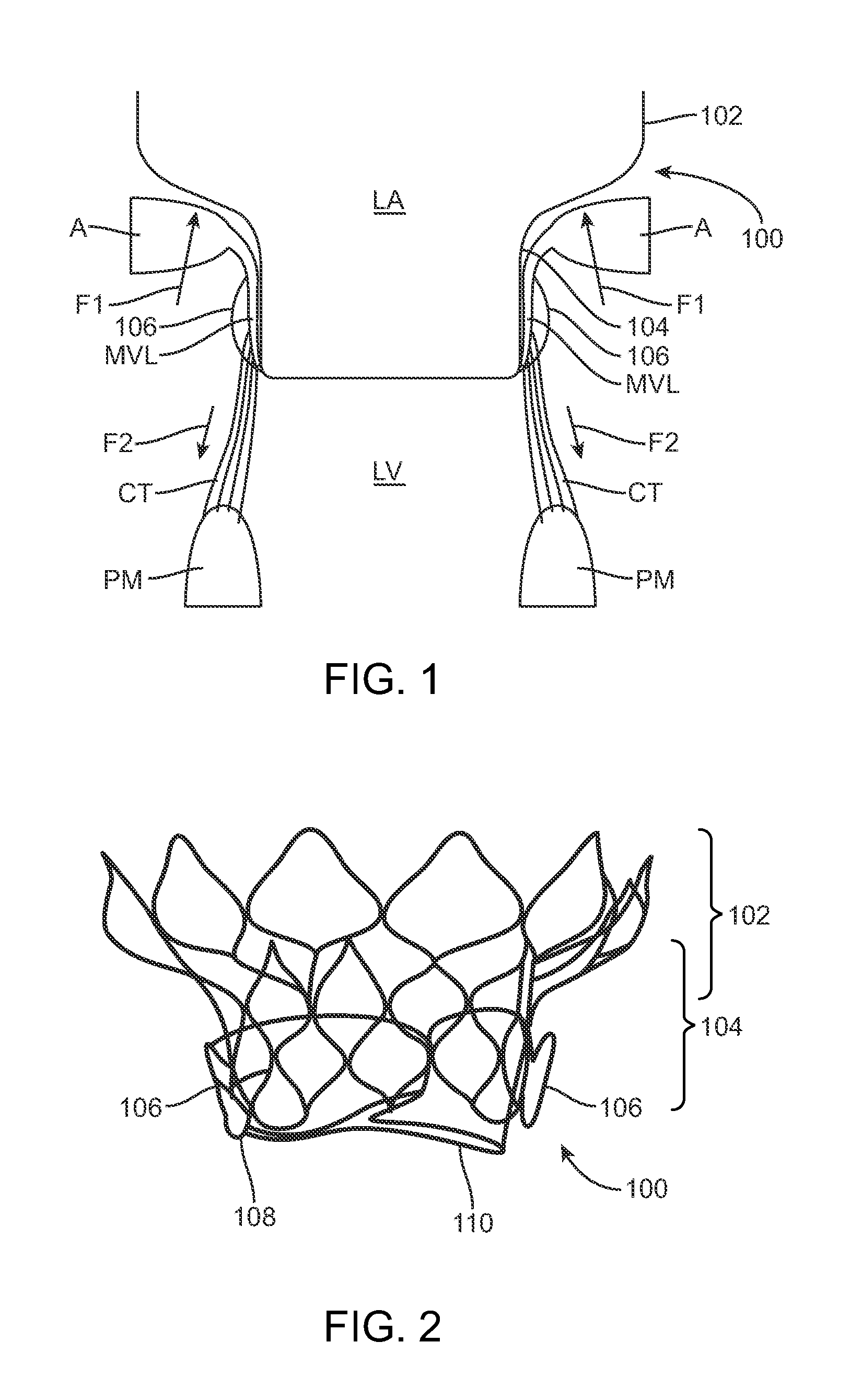
The chordae tendineae (tendinous chords), colloquially known as the heart strings, are tendon-resembling fibrous cord connective tissue that connect the papillary muscles to the tricuspid valve and the bicuspid valve in the heart.
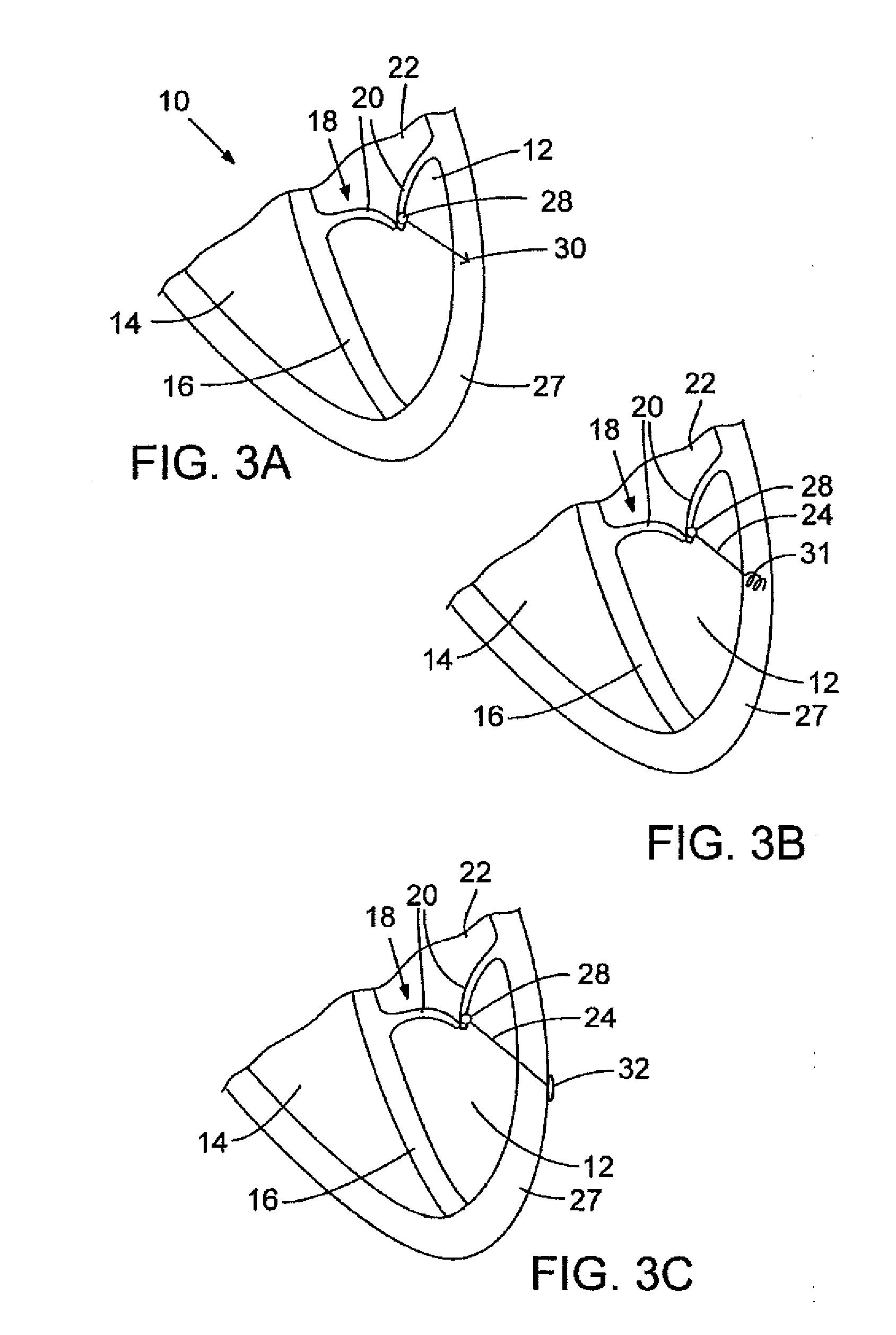
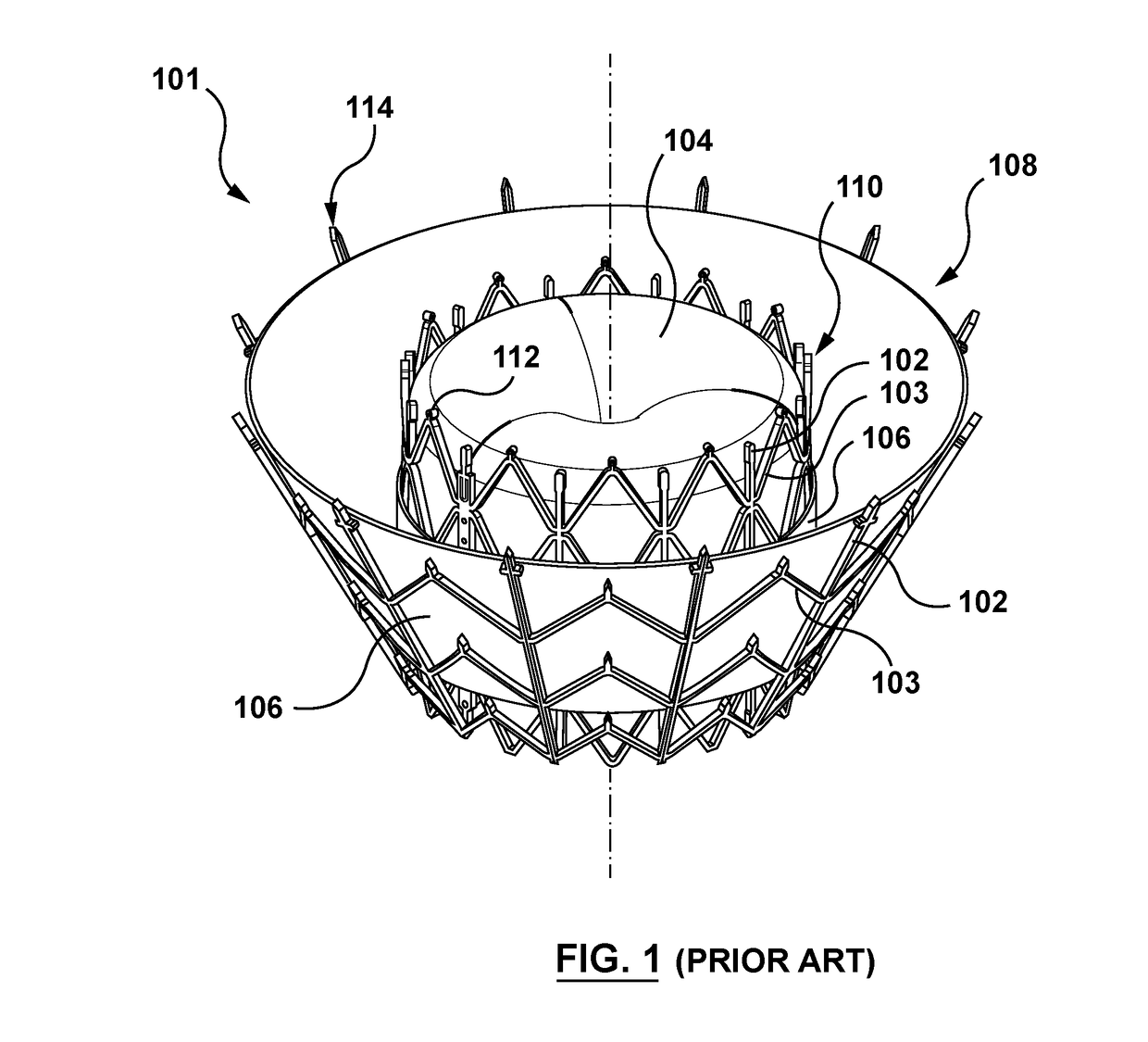
Mitral valve prosthesis
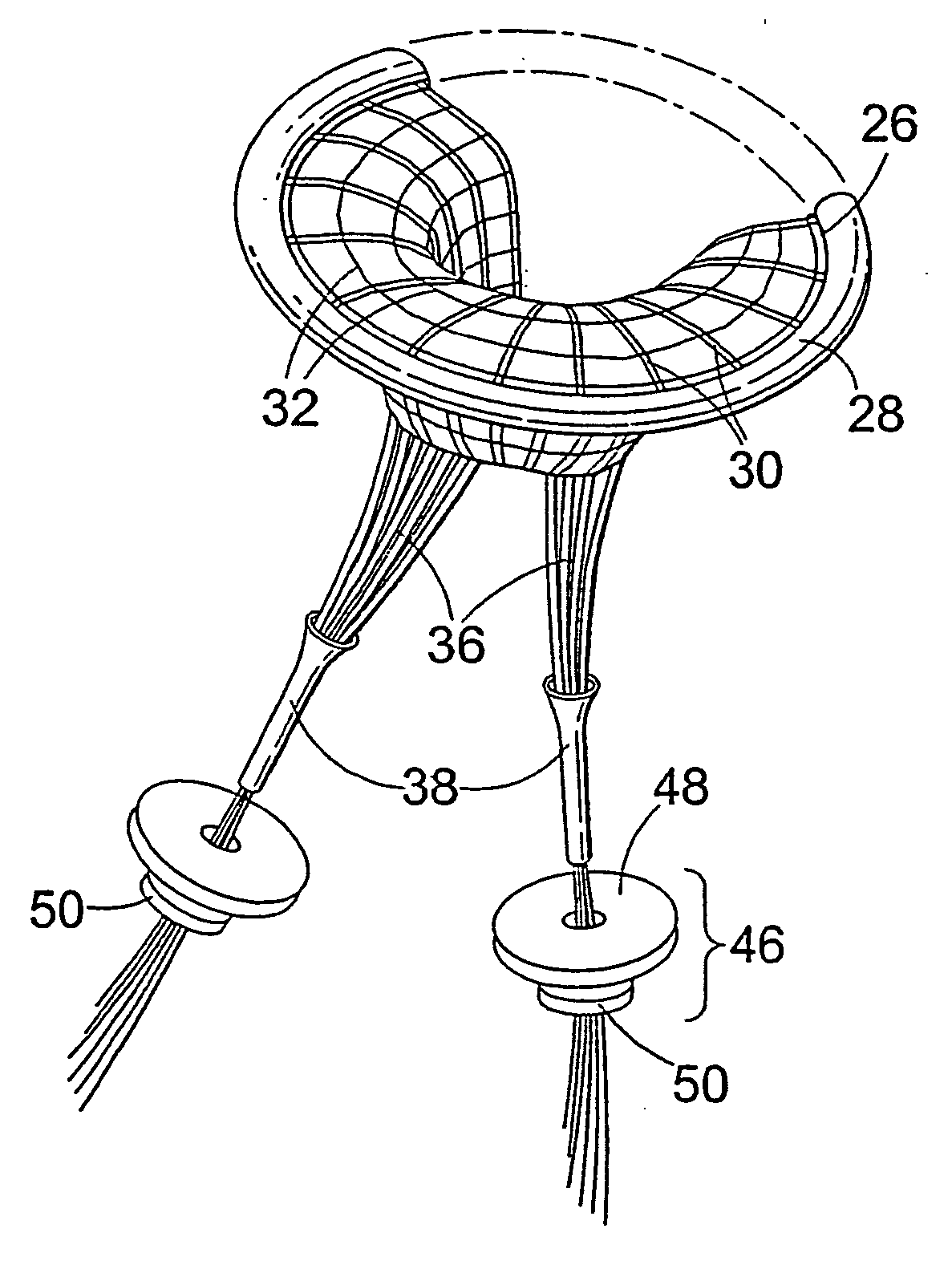
The present invention relates to a mitral valve prosthesis comprising flexible leaflet-like elements with curved coapting surfaces and means for maintaining continuity of the valve when inserted into the mitral annulus, which mimics the continuity between the papillary muscles, the chordae tendineae, the mitral valve leaflets and the mitral annulus of a natural valve. The present invention also relates to a method of fitting such a prosthesis to heart of a patient.
Owner:THE UNIV COURT OF THE UNIV OF GLASGOW
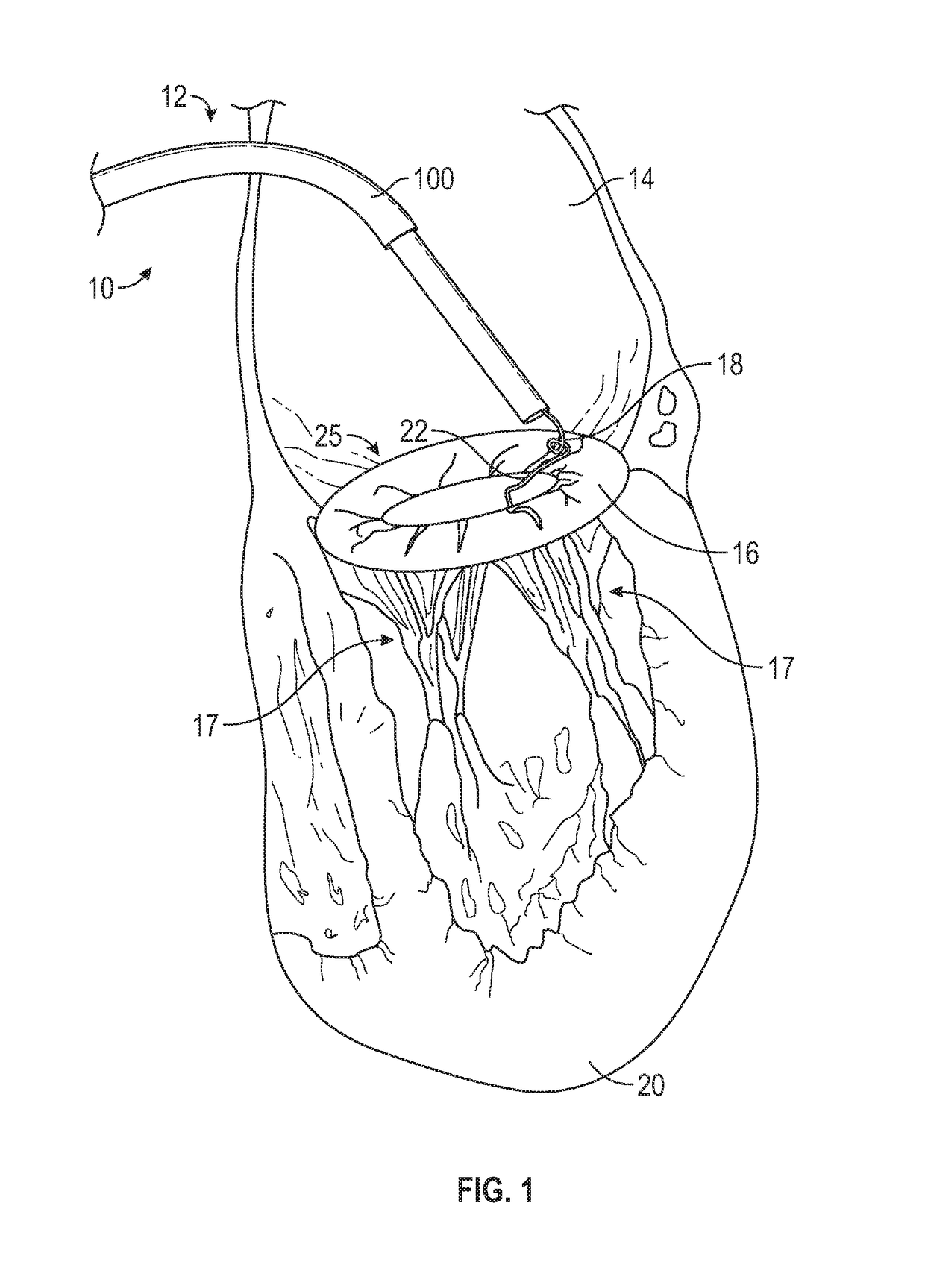
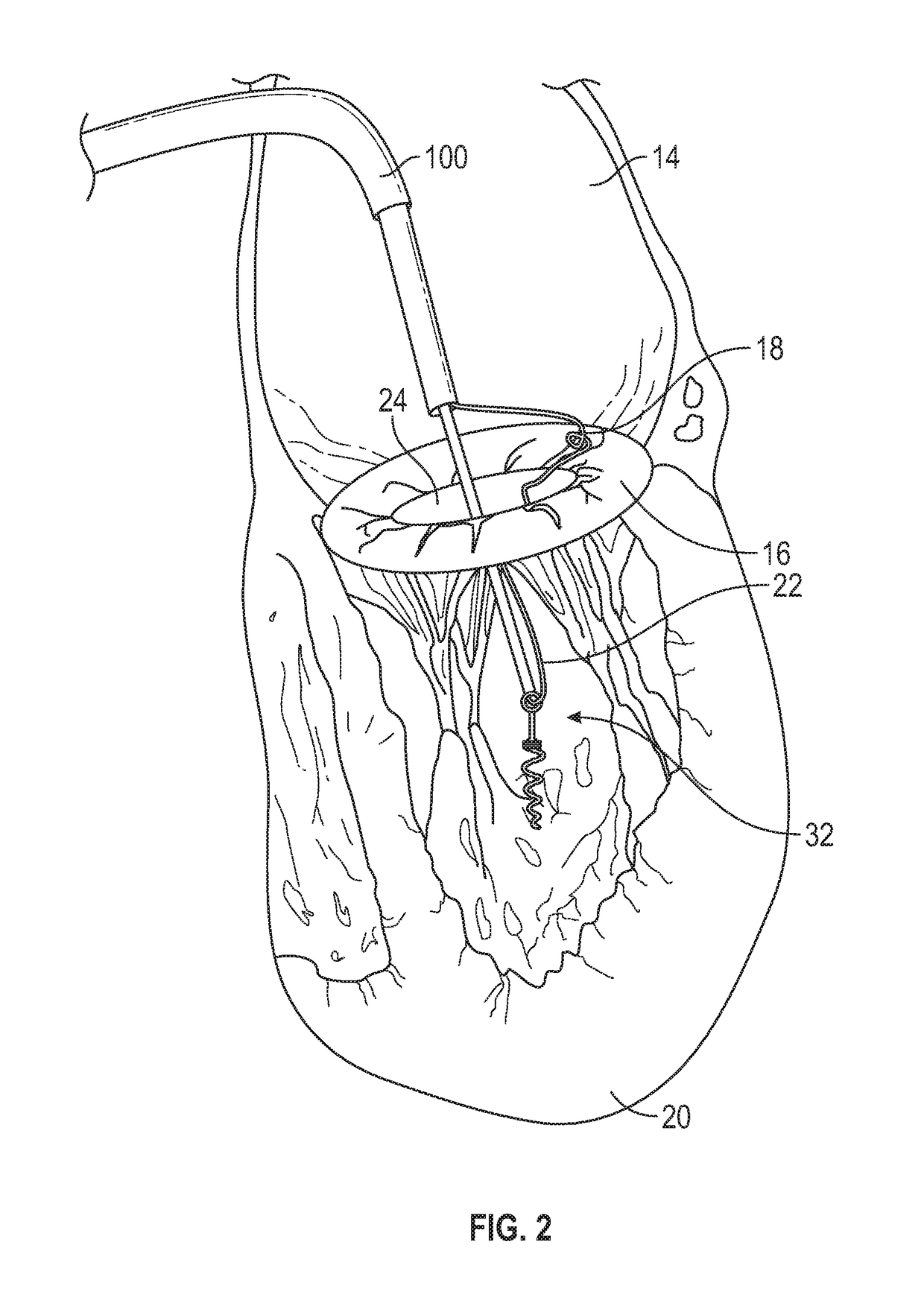
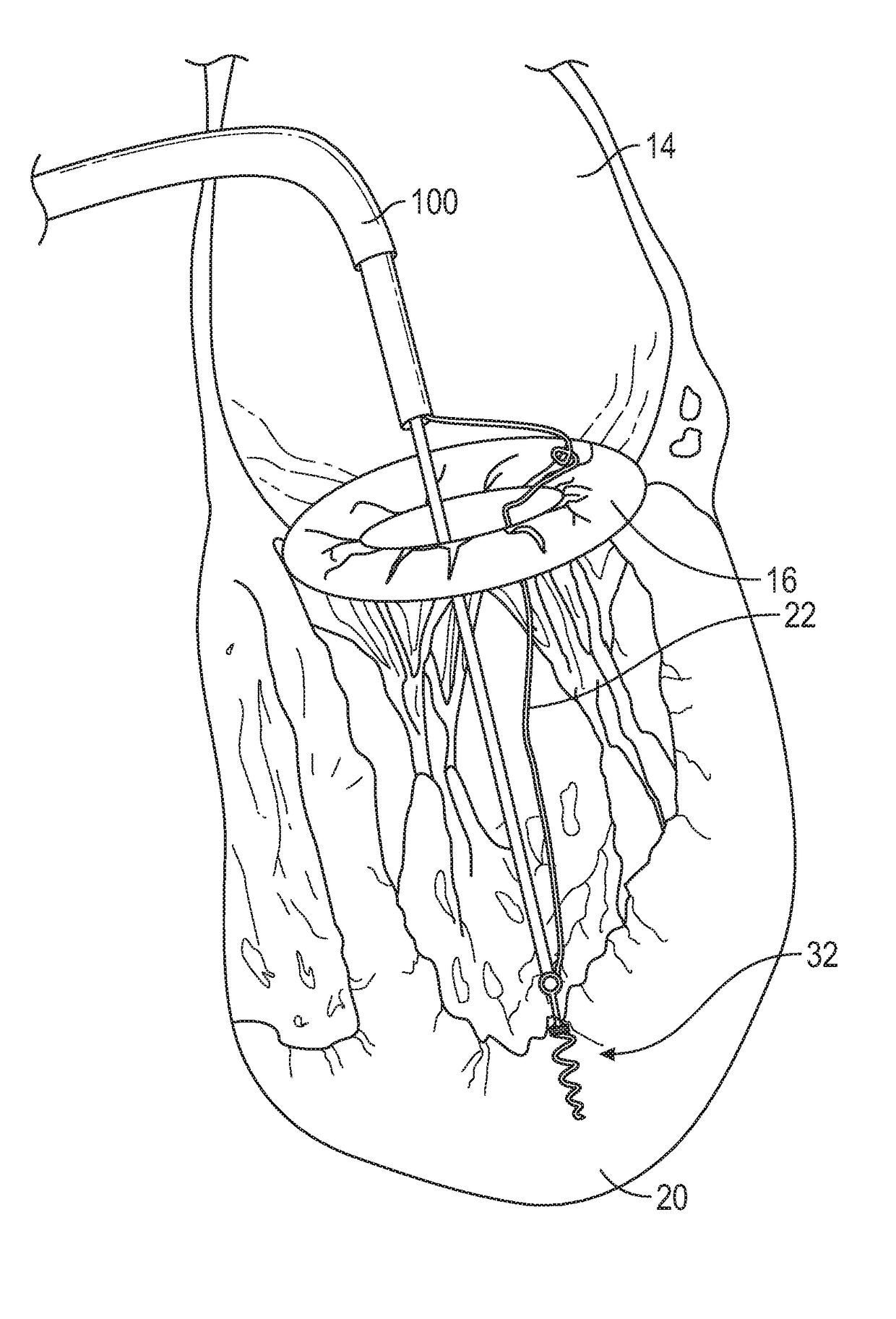
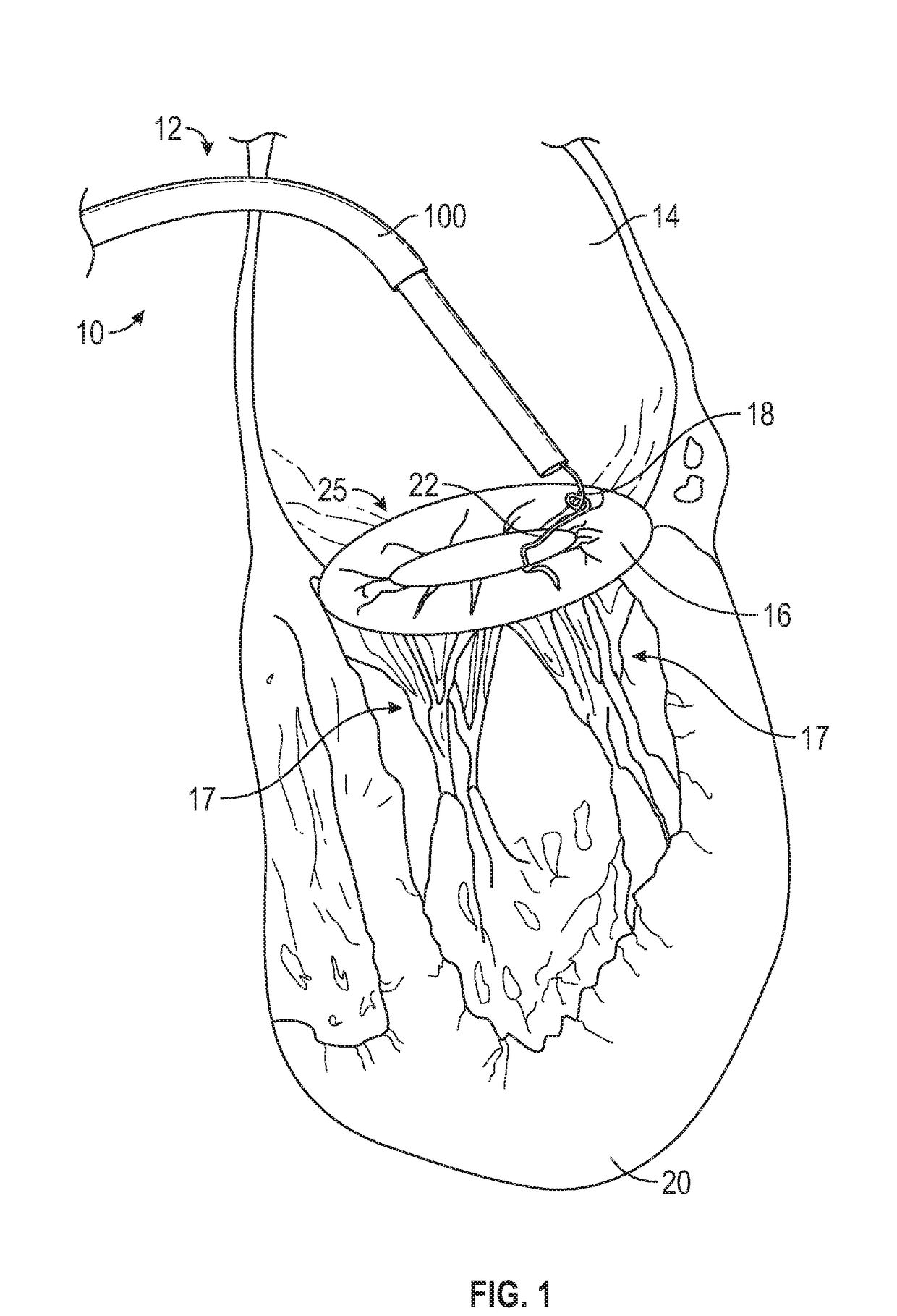
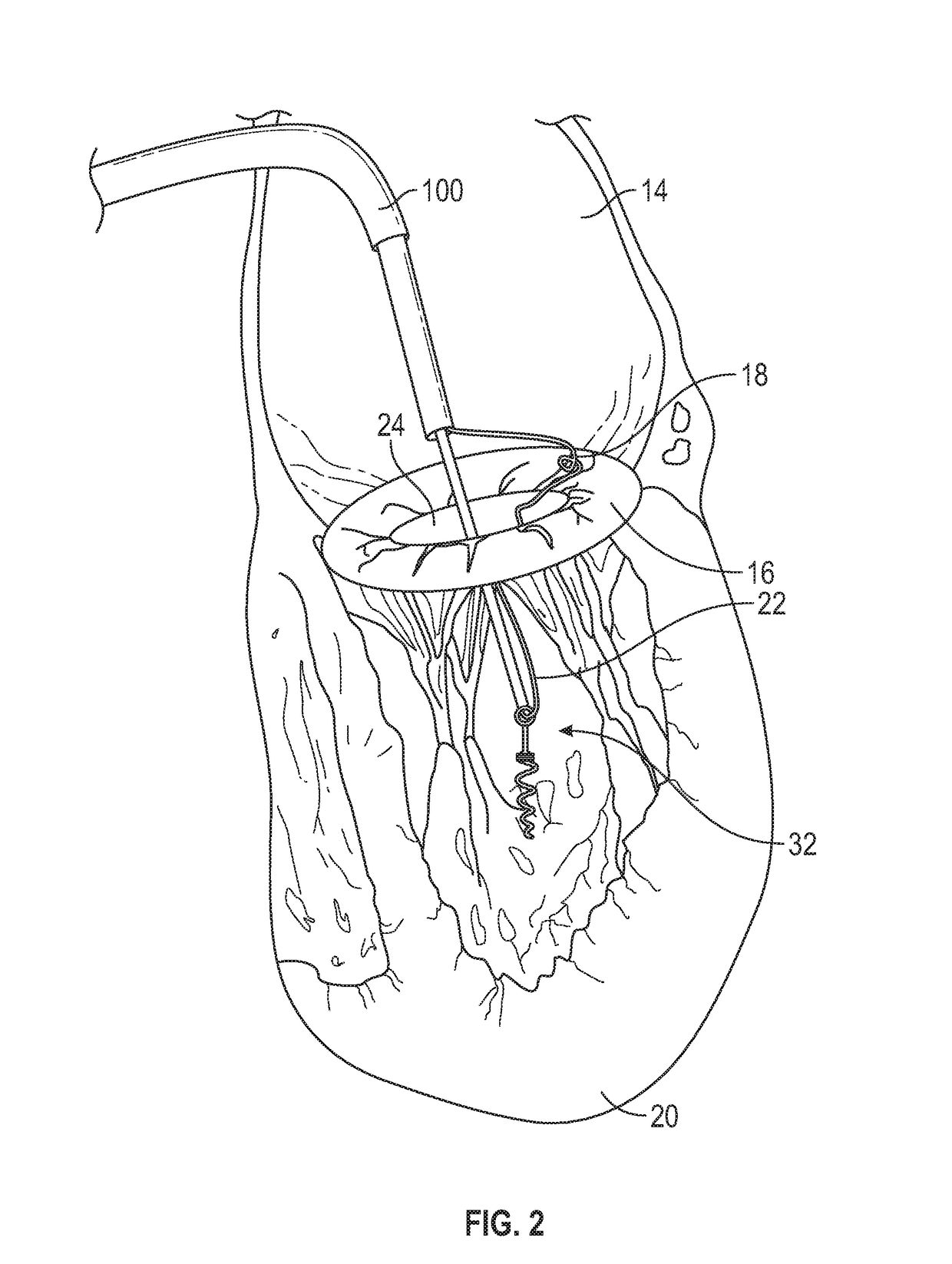
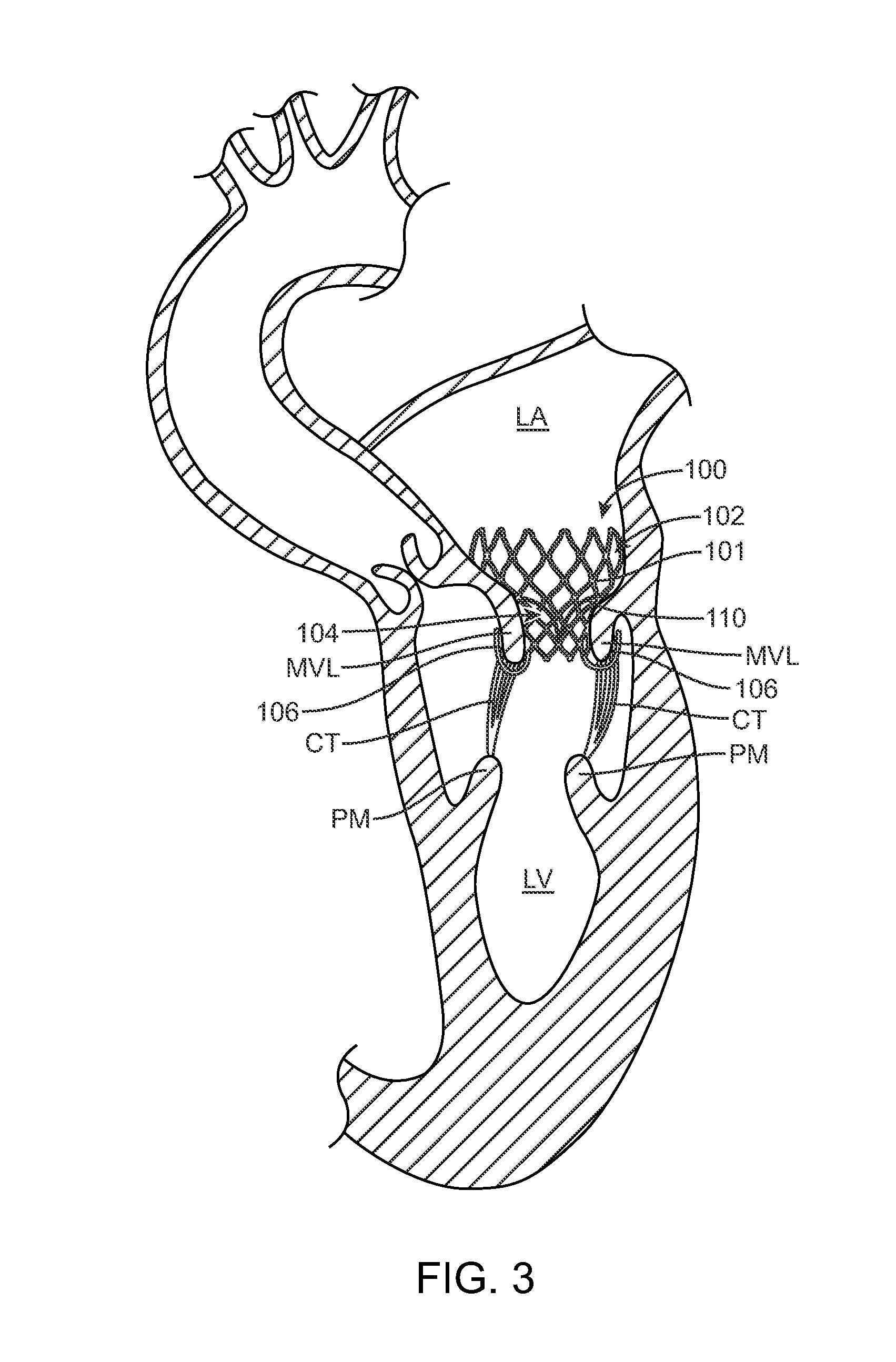
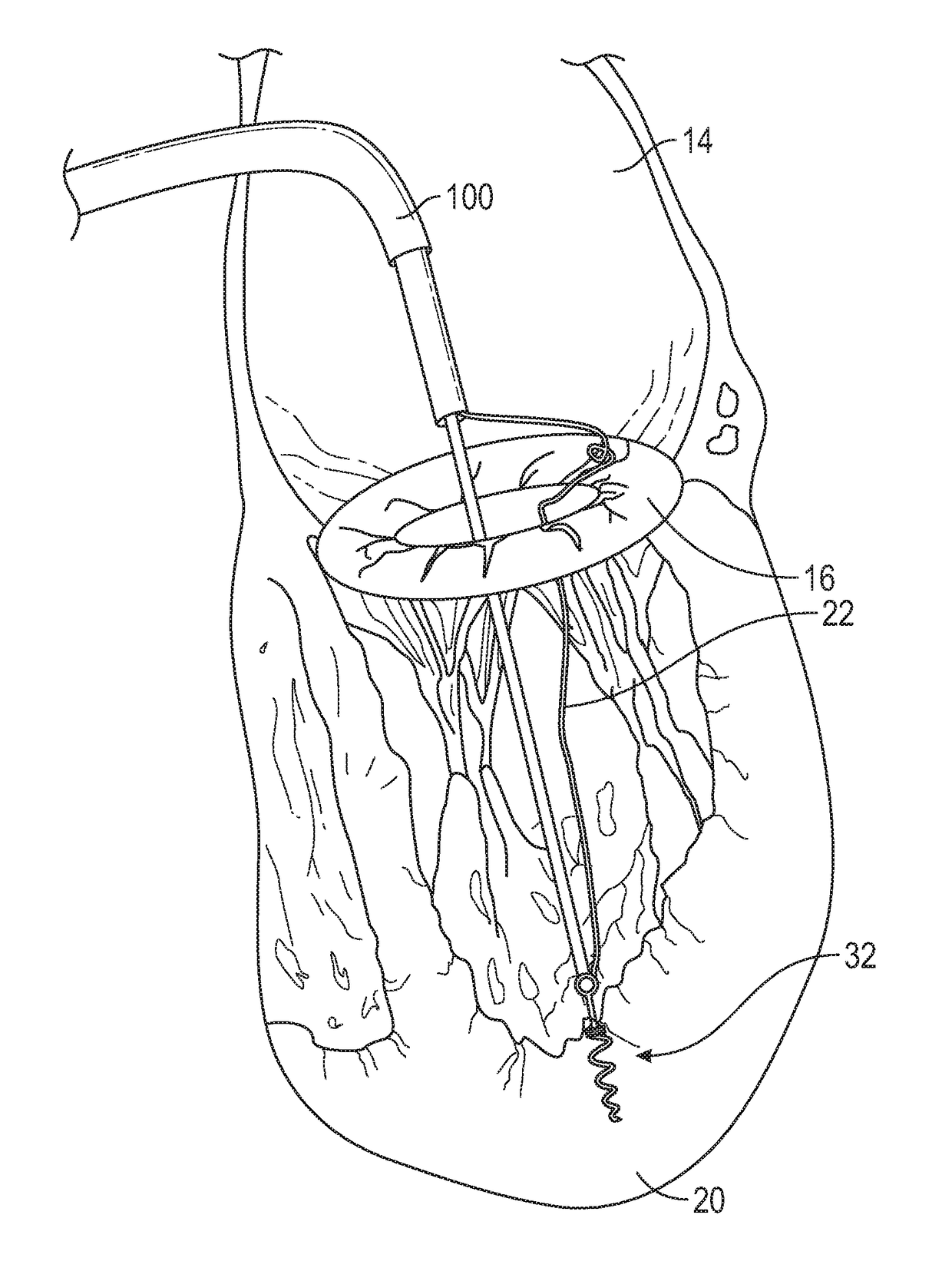
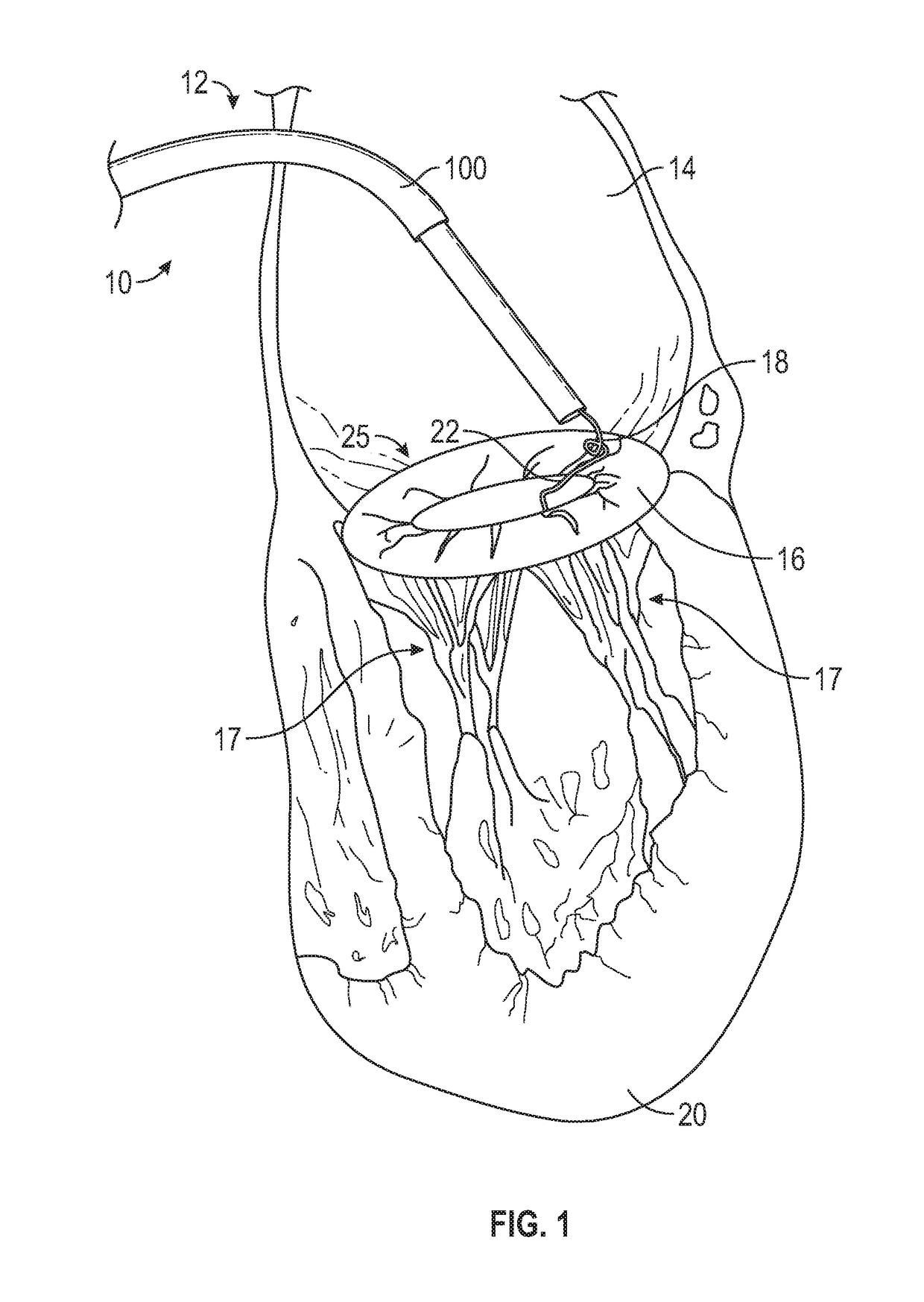
Methods and devices for performing cardiac valve repair
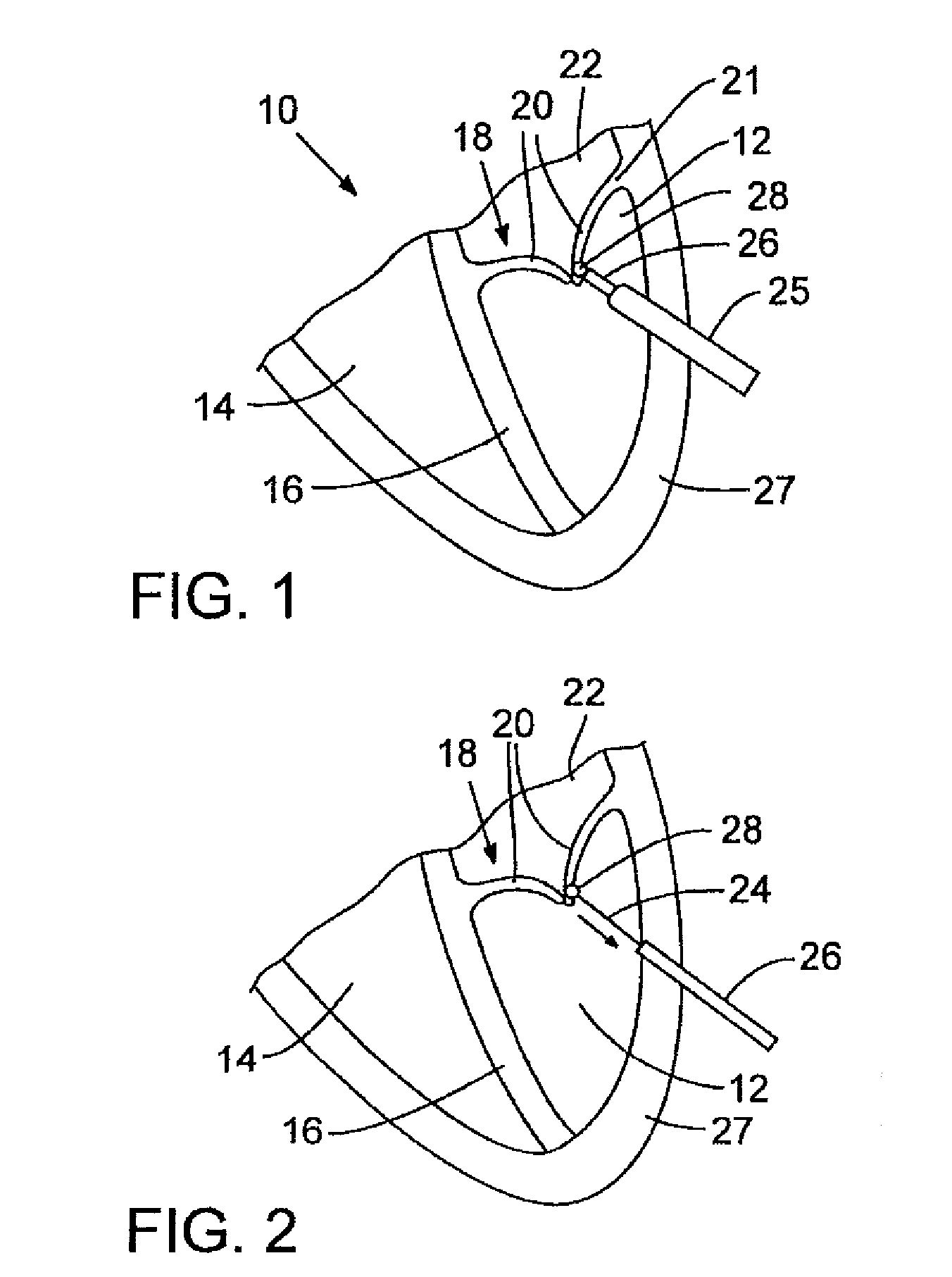
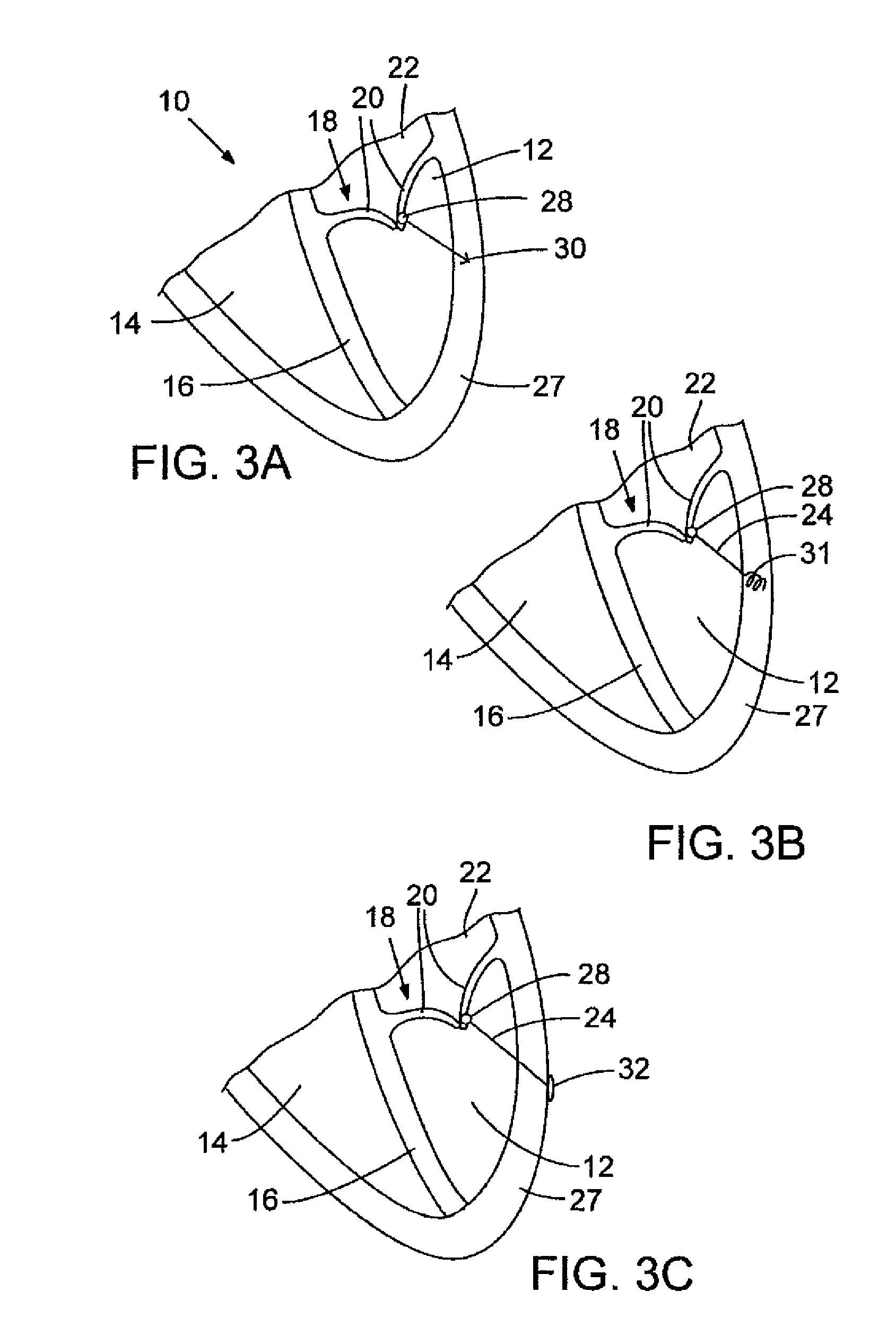
The present invention is directed to methods and devices for repairing a cardiac valve. Generally, the methods involve a minimally invasive procedure that includes creating an access in the apex region of the heart through which one or more instruments may be inserted so as to repair a cardiac valve, for instance, a mitral or tricuspid valve. Accordingly, the methods are useful for performing a variety of procedures to effectuate a repair. For instance, in one embodiment, the methods are useful for repairing a cardiac valve by implanting one or more artificial heart valve chordae tendinae into one or more cardiac valve leaflet tissues so as to restore the proper leaflet function and thereby prevent reperfusion. In another embodiment, the methods are useful for repairing a cardiac valve by resecting a portion of one or more cardiac valve leaflets and implanting one or more sutures into the resected valve tissues, which may also include the implantation of an annuloplasty ring. In an additional embodiment, the methods are useful for performing an edge to edge bow-tie repair (e.g., an Alfieri repair) on cardiac valve tissues. Devices for performing the methods of the invention are also provided.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND BALTIMORE
Prosthetic mitral valve
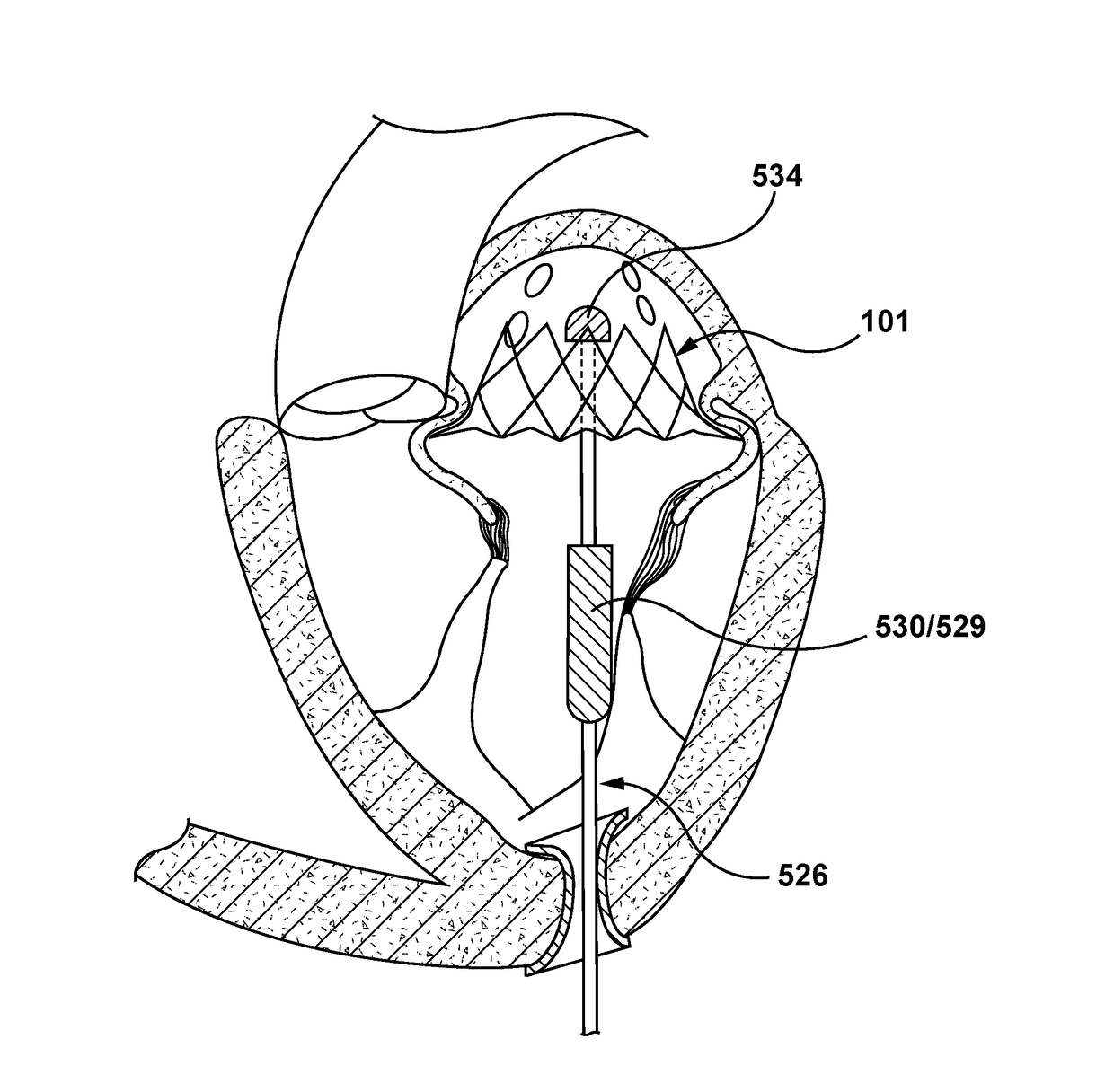
A prosthetic mitral valve with a frame comprises at least one arm shaped to deploy among a region of chordae tendineae of the native mitral valve to deflect these chords in order to pull the native valve leaflets around the frame to avoid paravalvular leaks. The frame may be made from two parts that are connected by sutures. The prosthetic valve may be deployed by a catherer comprising a deployment clamp attached to the valve frame where the deployment clamp is actuable to induce rotation of the frame.
Owner:TEL HASHOMER MEDICAL RES INFRASTRUCTURE & SERVICES
Prosthetic heart value
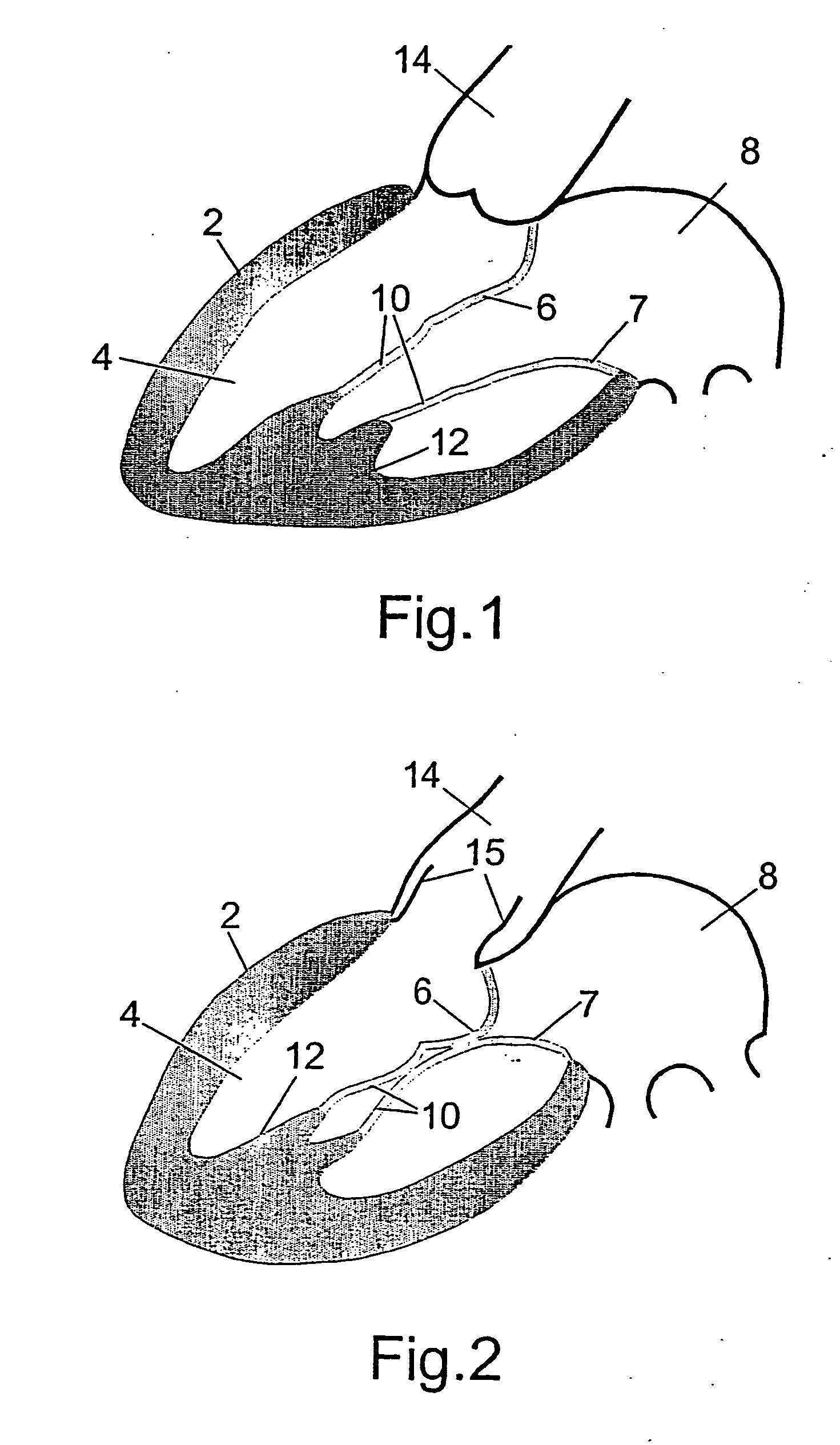
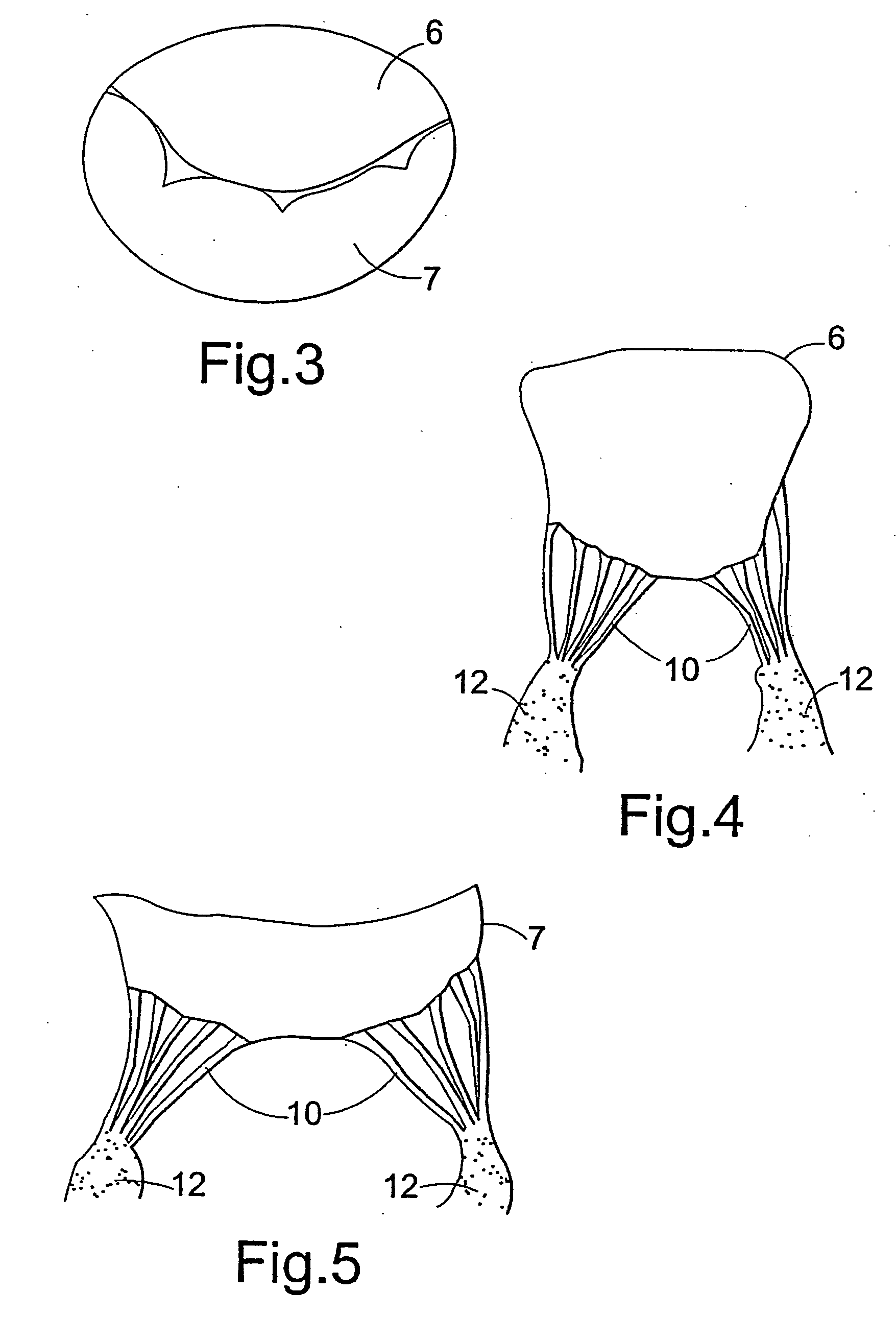
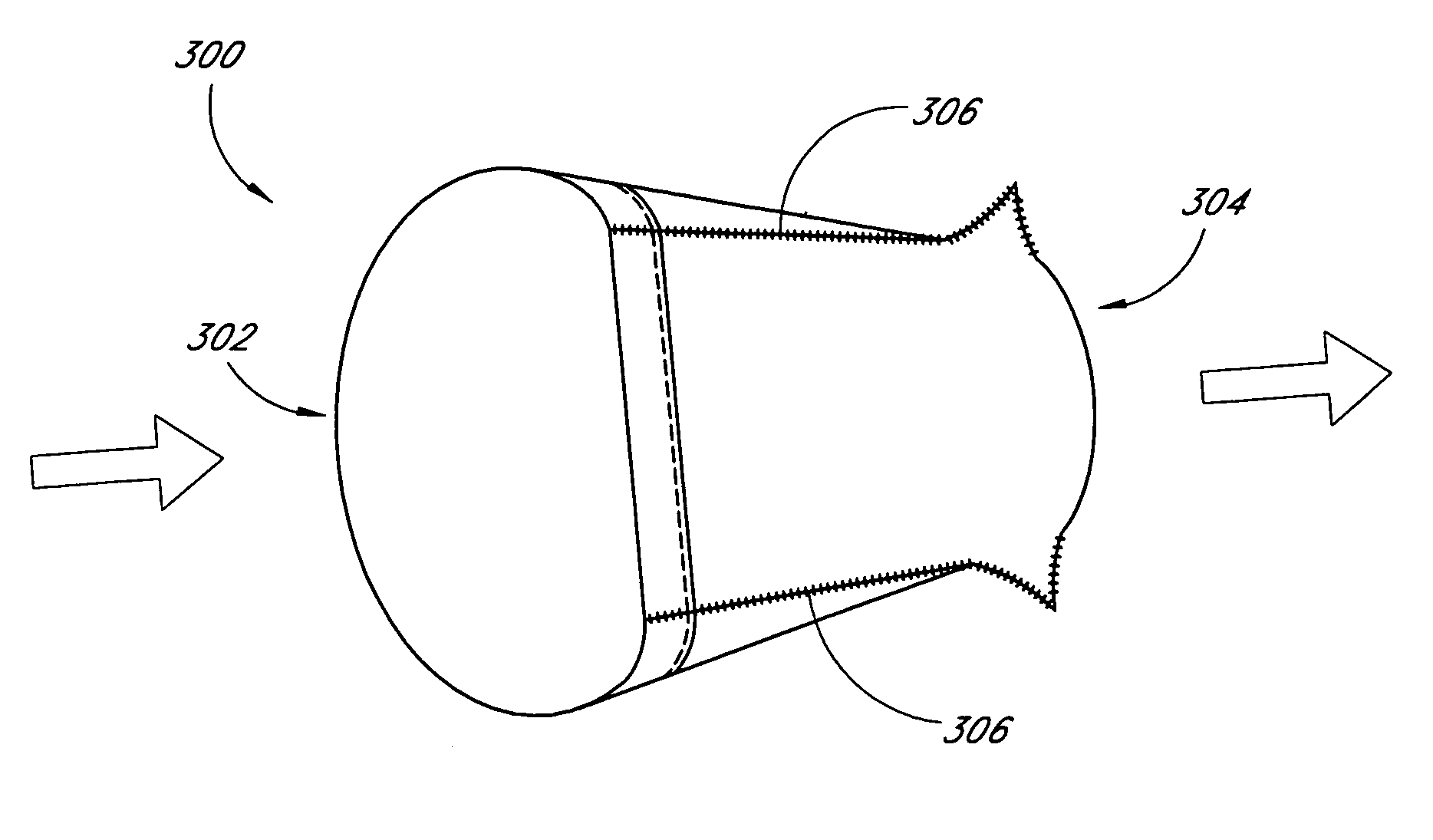
A tubular prosthetic semilunar or atrioventricular heart valve is formed by cutting flat, flexible leaflets according to a pattern. The valve is constructed by aligning the side edges of adjacent leaflets so that the leaflet inner faces engage each other, and then suturing the leaflets together with successive stitches along a fold line adjacent the side edges. The stitches are placed successively from a proximal in-flow end of each leaflet toward a distal out-flow end. During operation, when the leaflets open and close, the leaflets fold along the fold line. Distal tabs extend beyond the distal end of each leaflet. The successive stitches terminate proximal of the distal tab portion so that no locked stitches are placed along the distal portion of the fold line. The tab portions of adjacent leaflets are folded over each other and sewn together to form commissural attachment tabs. The commissural tabs provide commissural attachment points to accommodate sutures and the like in order to secure the tab to a vessel wall, if a semilunar valve, and papillary muscles and / or chordae tendineae if an atrioventricular valve.
Owner:MEDTRONIC 3F THERAPEUTICS
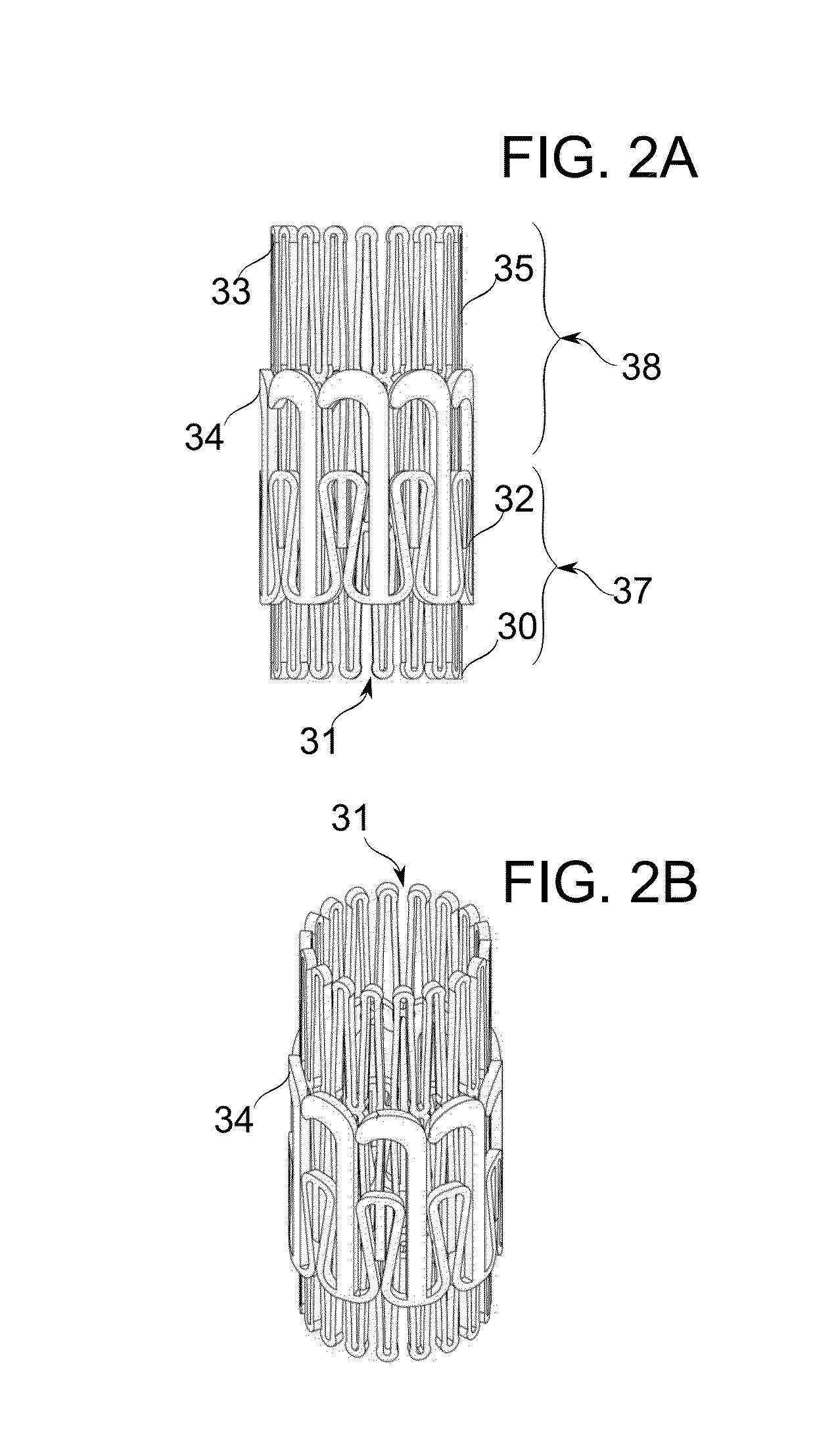
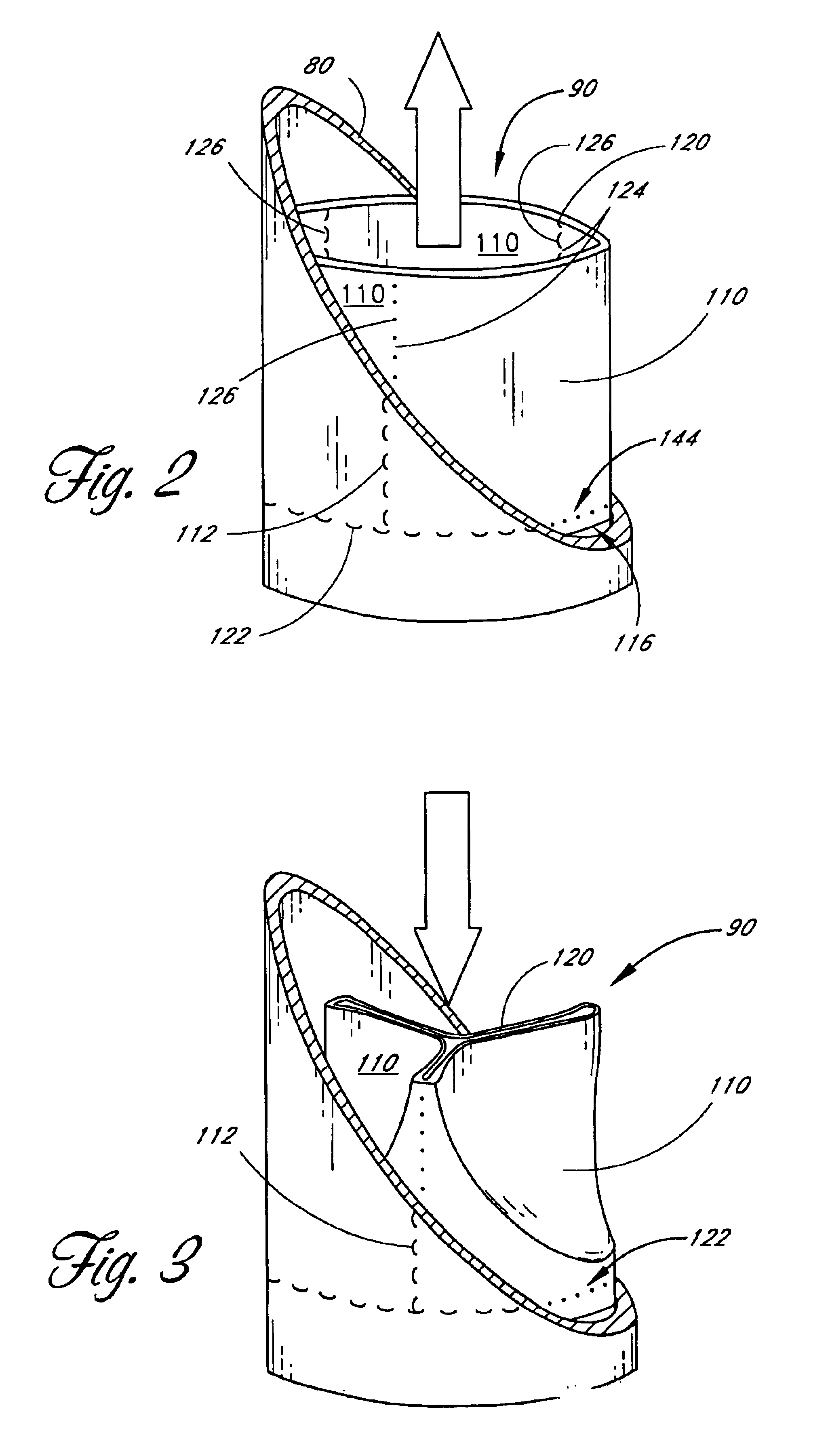
Chordae tendinae restraining ring
InactiveUS20070100439A1Reduce decreaseImprove valve functionAnnuloplasty ringsValve leafletCatheter device
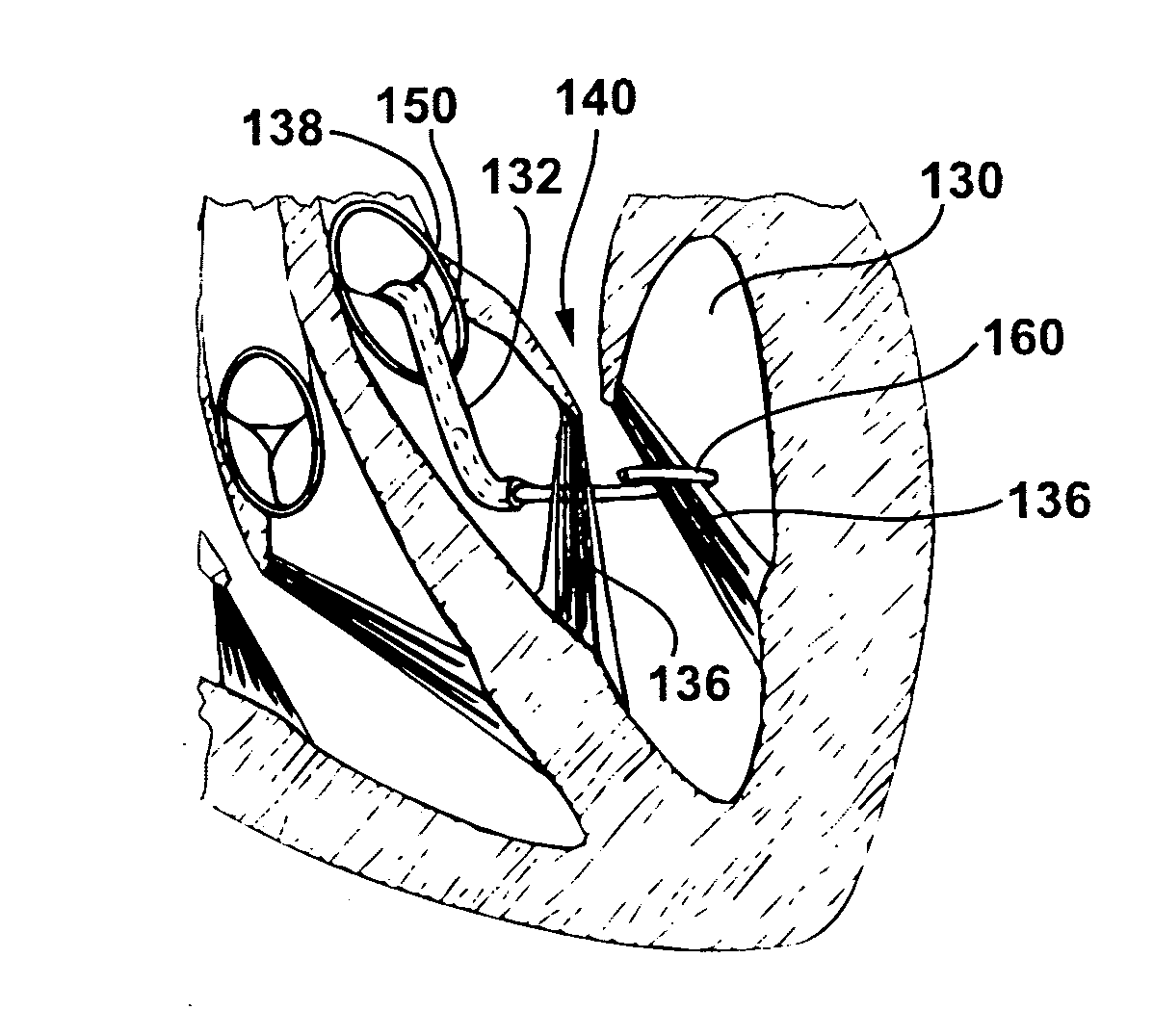
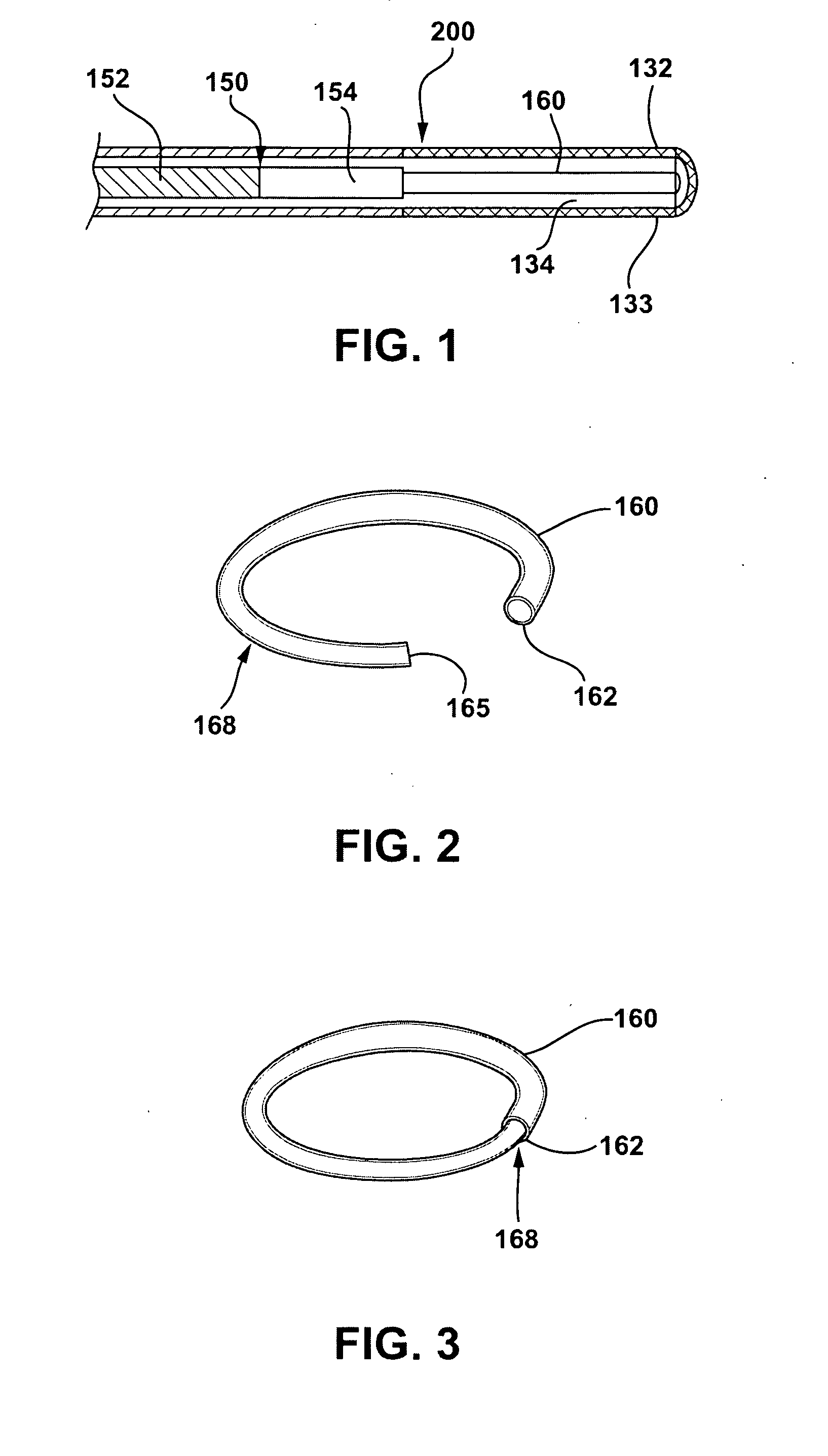
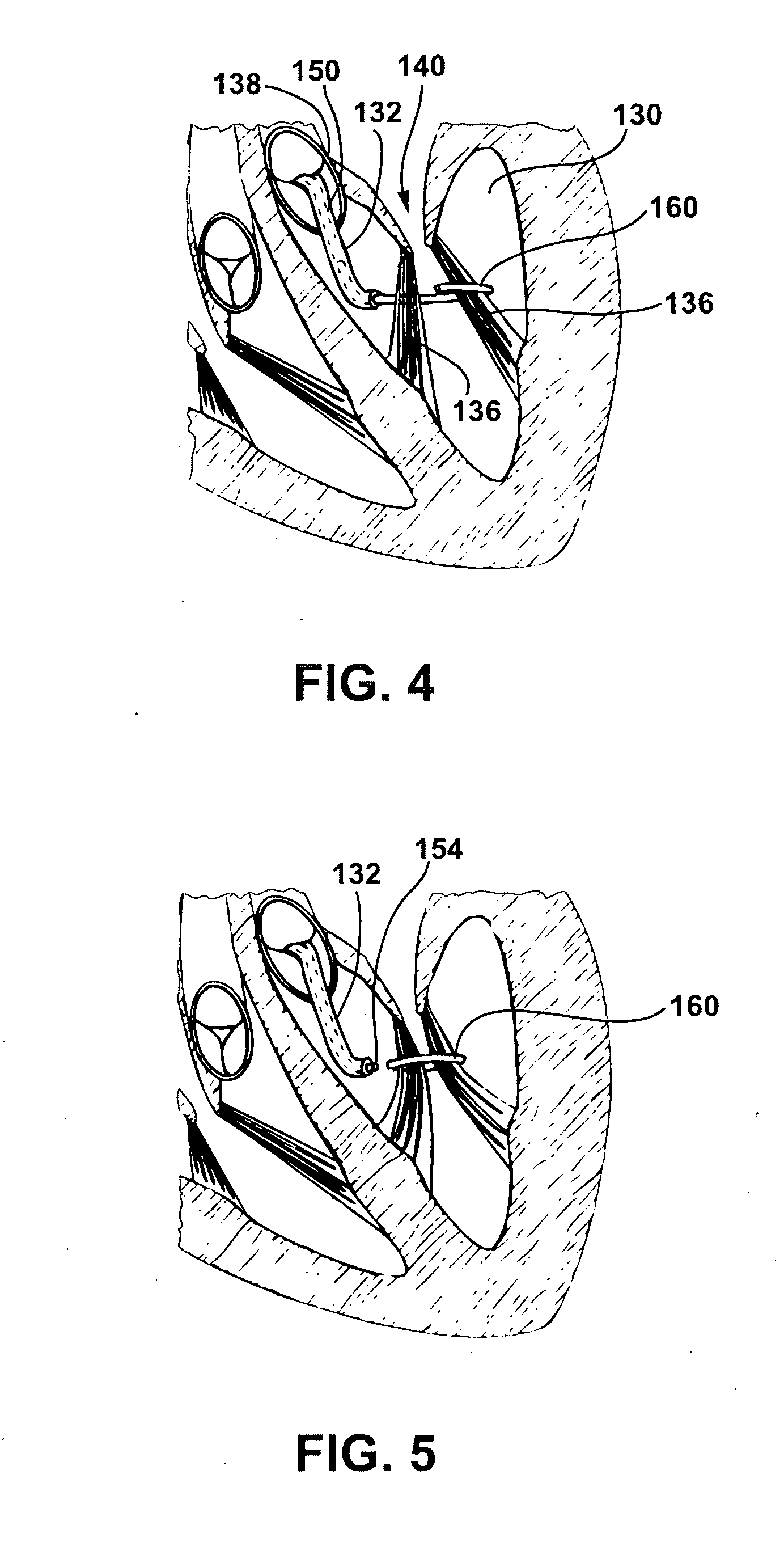
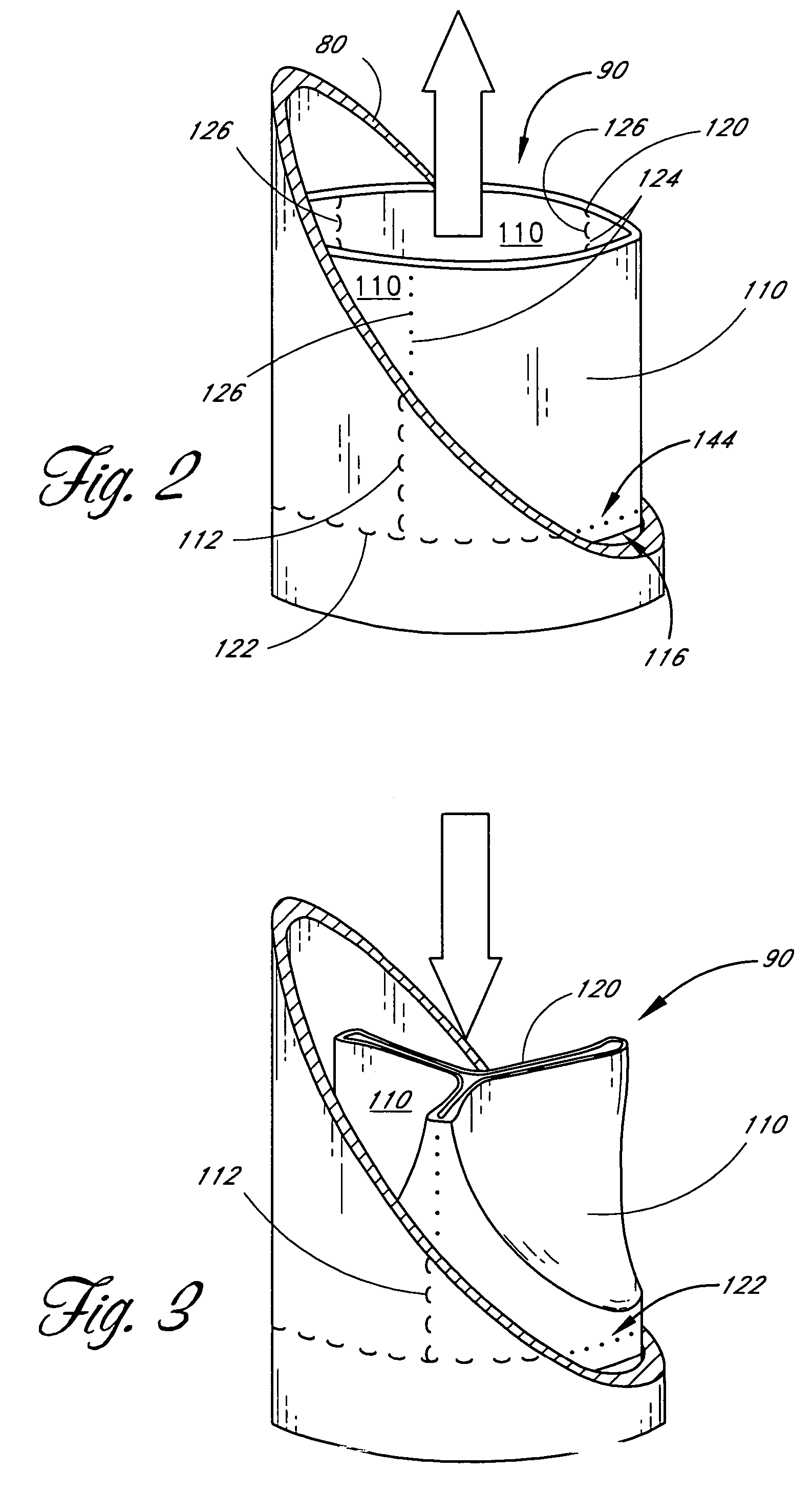
A ring for surrounding the chordae tendinae of a heart valve, and a system for delivering the ring. The ring gathers the chordae tendinae into a bundle to effectively shorten the chordae tendinae to resolve or reduce valve leaflet prolapse. The body of the ring has an elongated generally linear delivery configuration and a plurality of annular treatment configurations. The body of the ring is releasably carried within a delivery catheter to a treatment location, and a push rod expels the ring from the delivery catheter. Upon being expelled from the delivery catheter, a second end of the ring body will co-axially align with and insert into a first end of the body to form the ring.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
Prosthetic heart valve
A tubular prosthetic semilunar or atrioventricular heart valve is formed by cutting flat, flexible leaflets according to a pattern. The valve is constructed by aligning the side edges of adjacent leaflets so that the leaflet inner faces engage each other, and then suturing the leaflets together with successive stitches along a fold line adjacent the side edges. The stitches are placed successively from a proximal in-flow end of each leaflet toward a distal out-flow end. During operation, when the leaflets open and close, the leaflets fold along the fold line. Distal tabs extend beyond the distal end of each leaflet. The successive stitches terminate proximal of the distal tab portion so that no locked stitches are placed along the distal portion of the fold line. The tab portions of adjacent leaflets are folded over each other and sewn together to form commissural attachment tabs. The commissural tabs provide commissural attachment points to accommodate sutures and the like in order to secure the tab to a vessel wall, if a semilunar valve, and papillary muscles and / or chordae tendineae if an atrioventricular valve.
Owner:MEDTRONIC 3F THERAPEUTICS
Prosthetic heart value
InactiveUS6911043B2Increased durabilityImprove performanceHeart valvesBlood vesselsDistal portionProsthesis
A tubular prosthetic semilunar or atrioventricular heart valve is formed by cutting flat, flexible leaflets according to a pattern. The valve is constructed by aligning the side edges of adjacent leaflets so that the leaflet inner faces engage each other, and then suturing the leaflets together with successive stitches along a fold line adjacent the side edges. The stitches are placed successively from a proximal in-flow end of each leaflet toward a distal out-flow end. During operation, when the leaflets open and close, the leaflets fold along the fold line. Distal tabs extend beyond the distal end of each leaflet. The successive stitches terminate proximal of the distal tab portion so that no locked stitches are placed along the distal portion of the fold line. The tab portions of adjacent leaflets are folded over each other and sewn together to form commissural attachment tabs. The commissural tabs provide commissural attachment points to accommodate sutures and the like in order to secure the tab to a vessel wall, if a semilunar valve, and papillary muscles and / or chordae tendineae if an atrioventricular valve.
Owner:MEDTRONIC 3F THERAPEUTICS
Chrodae Tendinae Girdle
InactiveUS20070255396A1Shortens the chordae tendinae to resolve or reduce valve leaflet prolapseAnnuloplasty ringsBlood vesselsLocking mechanismValve leaflet
A girdle for surrounding the chordae tendinae of a heart valve, and a system and method for delivering the girdle. The girdle gathers the chordae tendinae into a bundle to effectively shorten the chordae tendinae to resolve or reduce valve leaflet prolapse. The system includes a girdle releaseably carried within a delivery catheter, and a push rod to release the girdle from the delivery catheter. The girdle has a filamentous linear delivery configuration and one of several annular treatment configurations. The girdle may have a locking mechanism for locking the girdle in an annular treatment configuration.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
Prosthetic heart valve
InactiveUS7037333B2Increased durabilityImprove performanceHeart valvesBlood vesselsProsthetic valvePapillary muscle
A tubular prosthetic semilunar or atrioventricular heart valve is formed by cutting flat, flexible leaflets according to a pattern. The valve is constructed by aligning the side edges of adjacent leaflets so that the leaflet inner faces engage each other, and then suturing the leaflets together with successive stitches along a fold line adjacent the side edges. The stitches are placed successively from a proximal in-flow end of each leaflet toward a distal out-flow end. During operation, when the leaflets open and close, the leaflets fold along the fold line. Distal tabs extend beyond the distal end of each leaflet. The successive stitches terminate proximal of the distal tab portion so that no locked stitches are placed along the distal portion of the fold line. The tab portions of adjacent leaflets are folded over each other and sewn together to form commissural attachment tabs. The commissural tabs provide commissural attachment points to accommodate sutures and the like in order to secure the tab to a vessel wall, if a semilunar valve, and papillary muscles and / or chordae tendineae if an atrioventricular valve.
Owner:MEDTRONIC 3F THERAPEUTICS
Suture and method for repairing a heart
InactiveUS20080195126A1Eliminate needSmall sizeSuture equipmentsHeart valvesLocking mechanismPapillary muscle
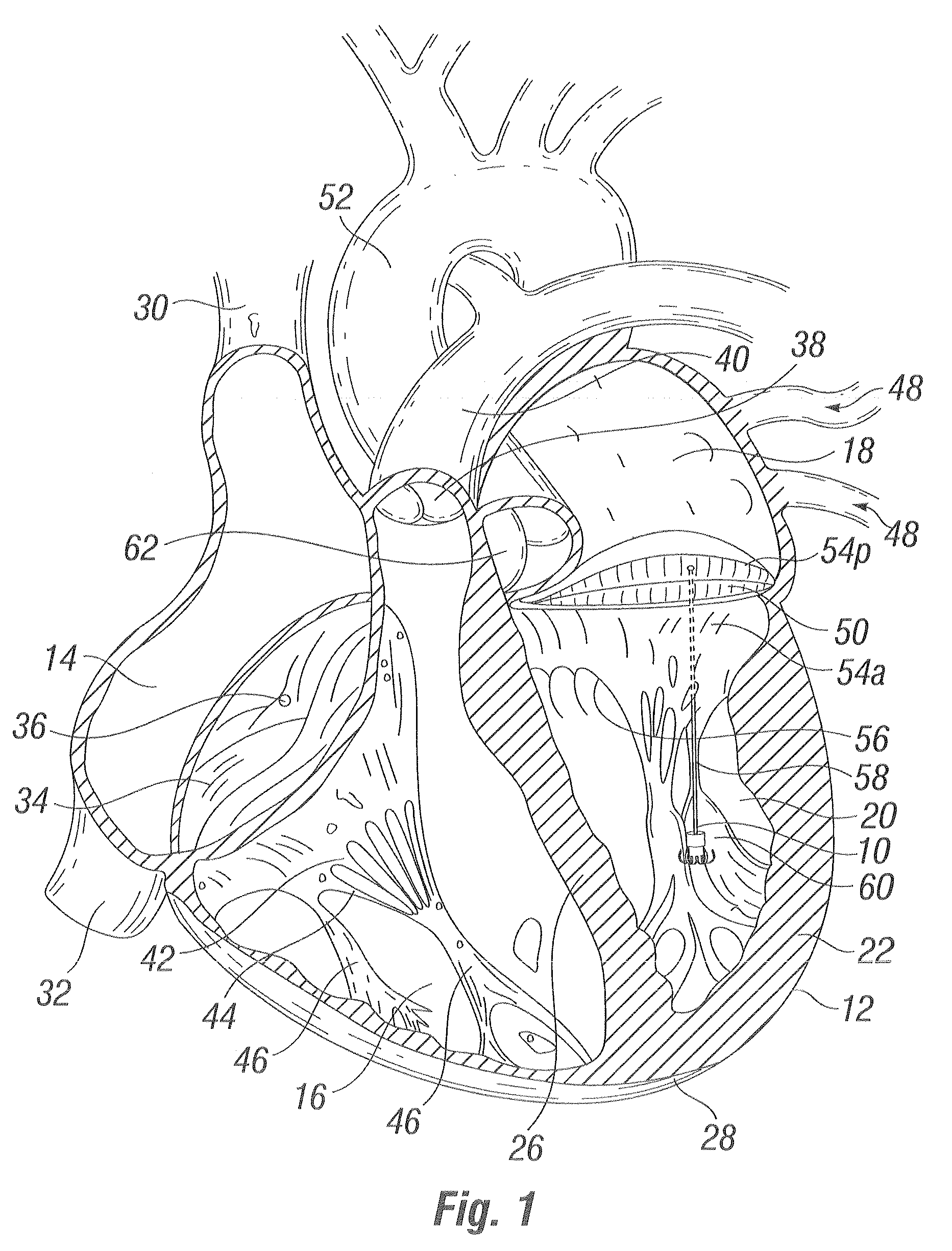
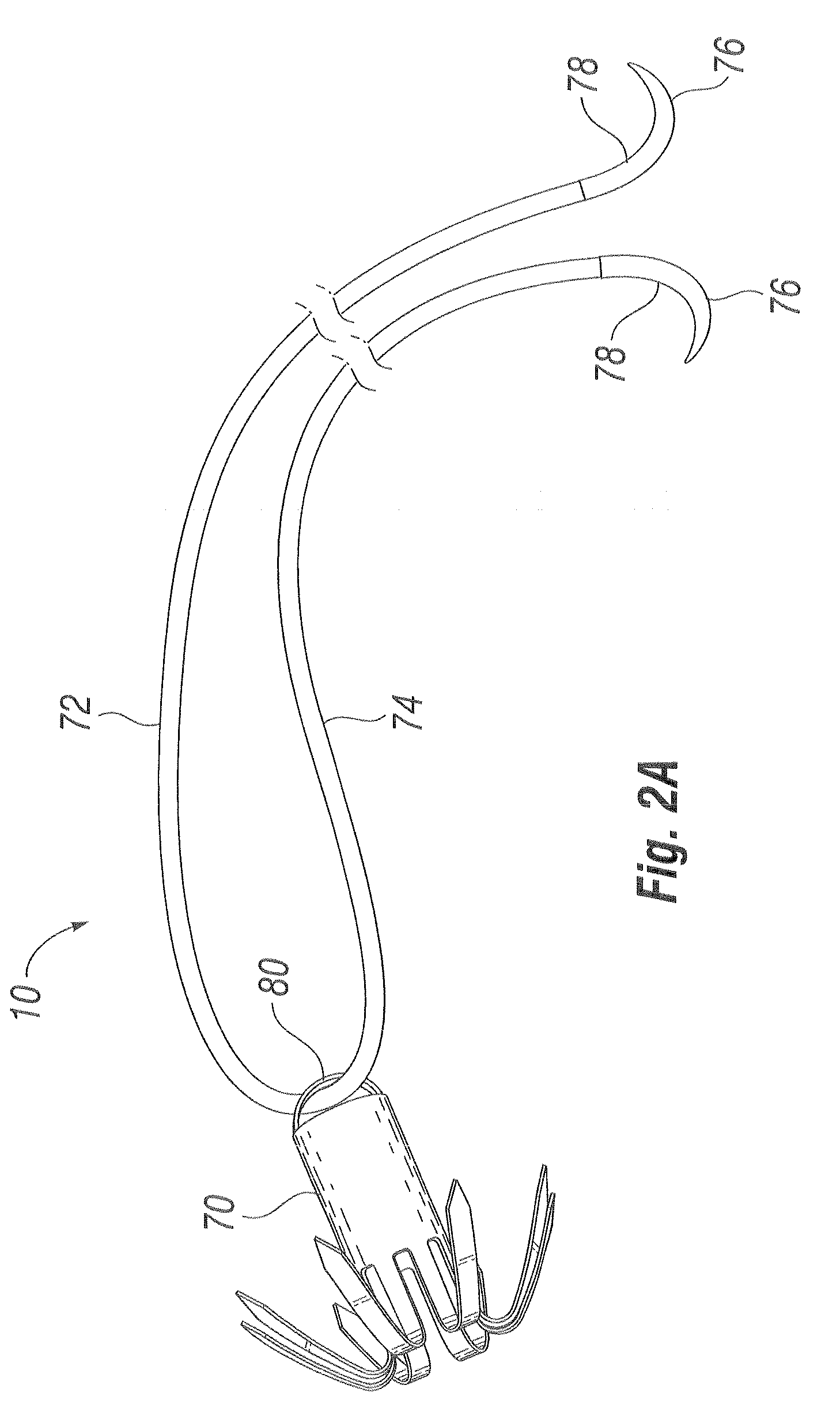
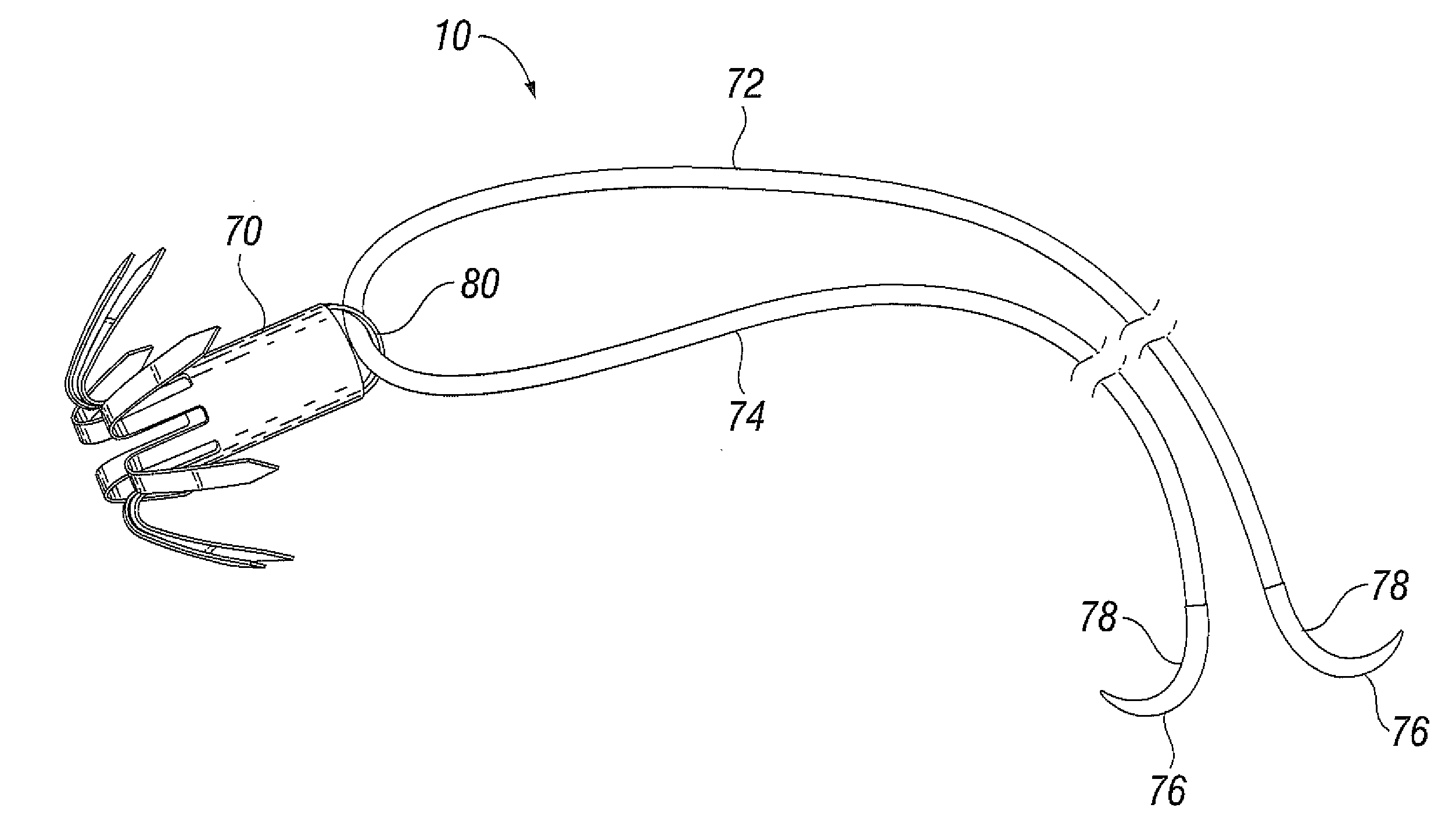
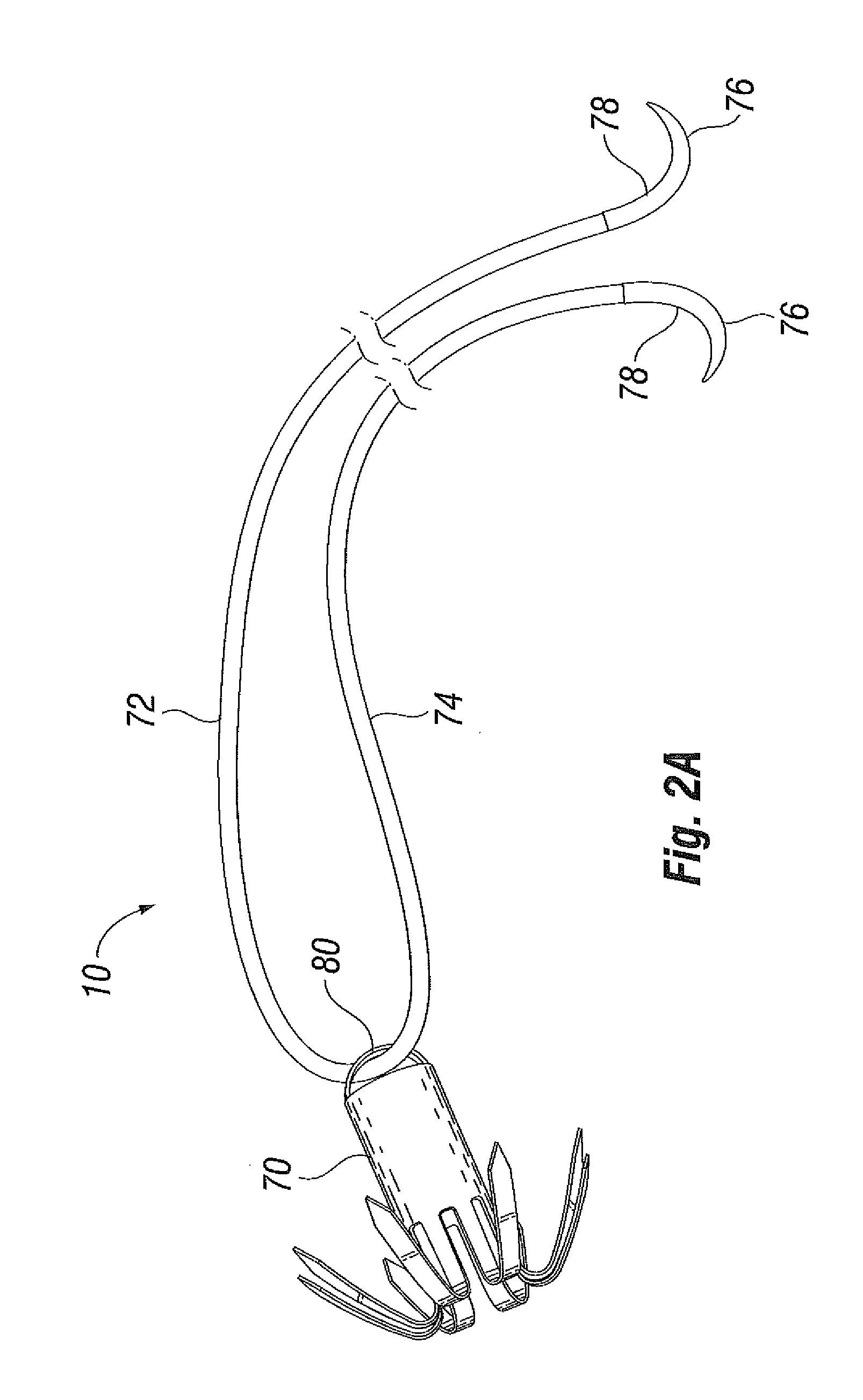
Devices and methods for treating or repairing a heart are disclosed. The device includes at least one anchor configured to engage tissue of a heart and a thread or other elongate member adapted to be coupled to the anchor and secured to heart tissue. The anchor may be attached to papillary muscle tissue and an elongate member may be attached to a valve leaflet for creating artificial chordae tendinae, thereby treating mitral valve prolapse. In another application, multiple anchors may be deployed within a ventricle and the threads pulled together for reducing dilation of a ventricle. A locking mechanism is provided for capturing and locking the threads together, thereby maintaining the ventricle in the reshaped condition.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
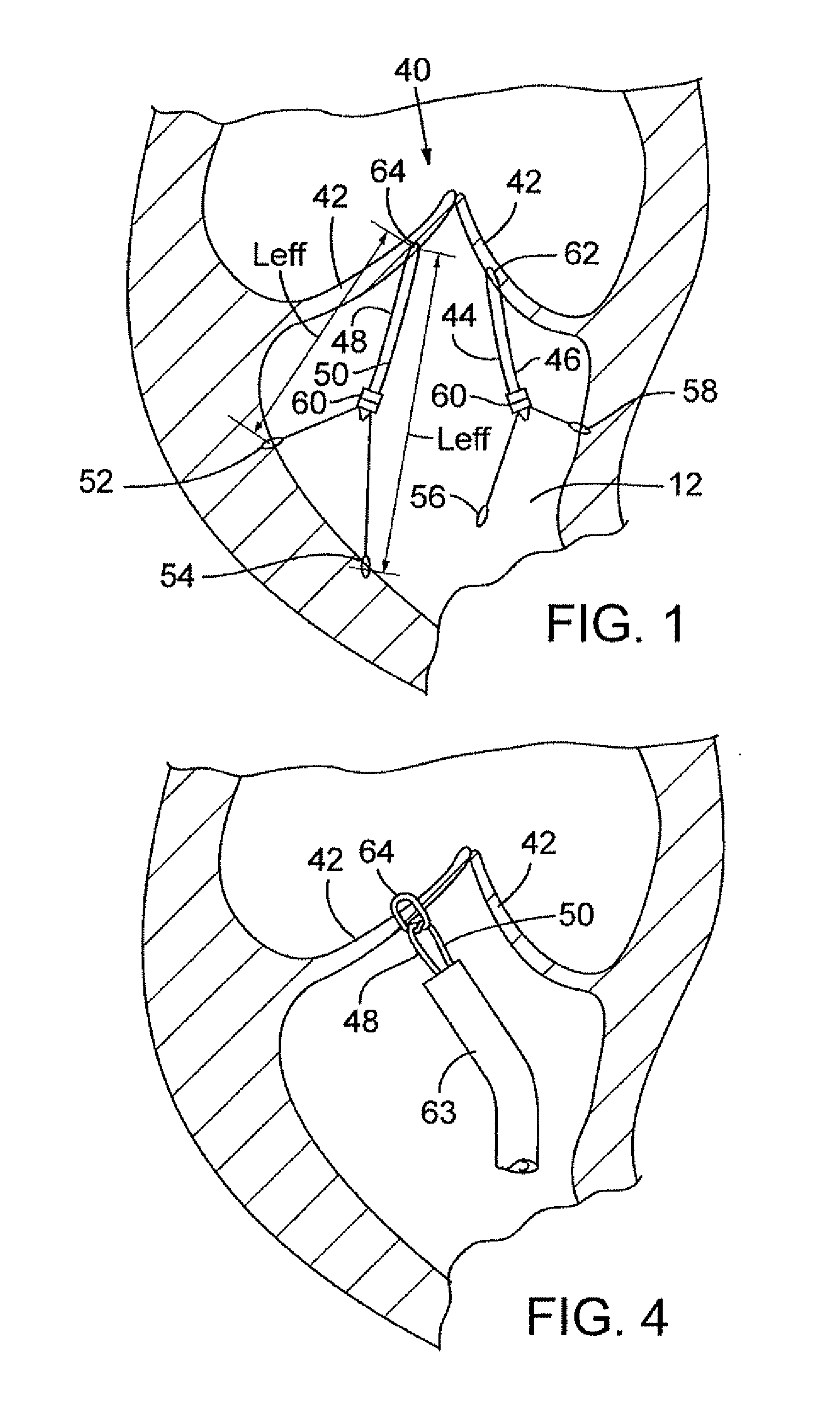
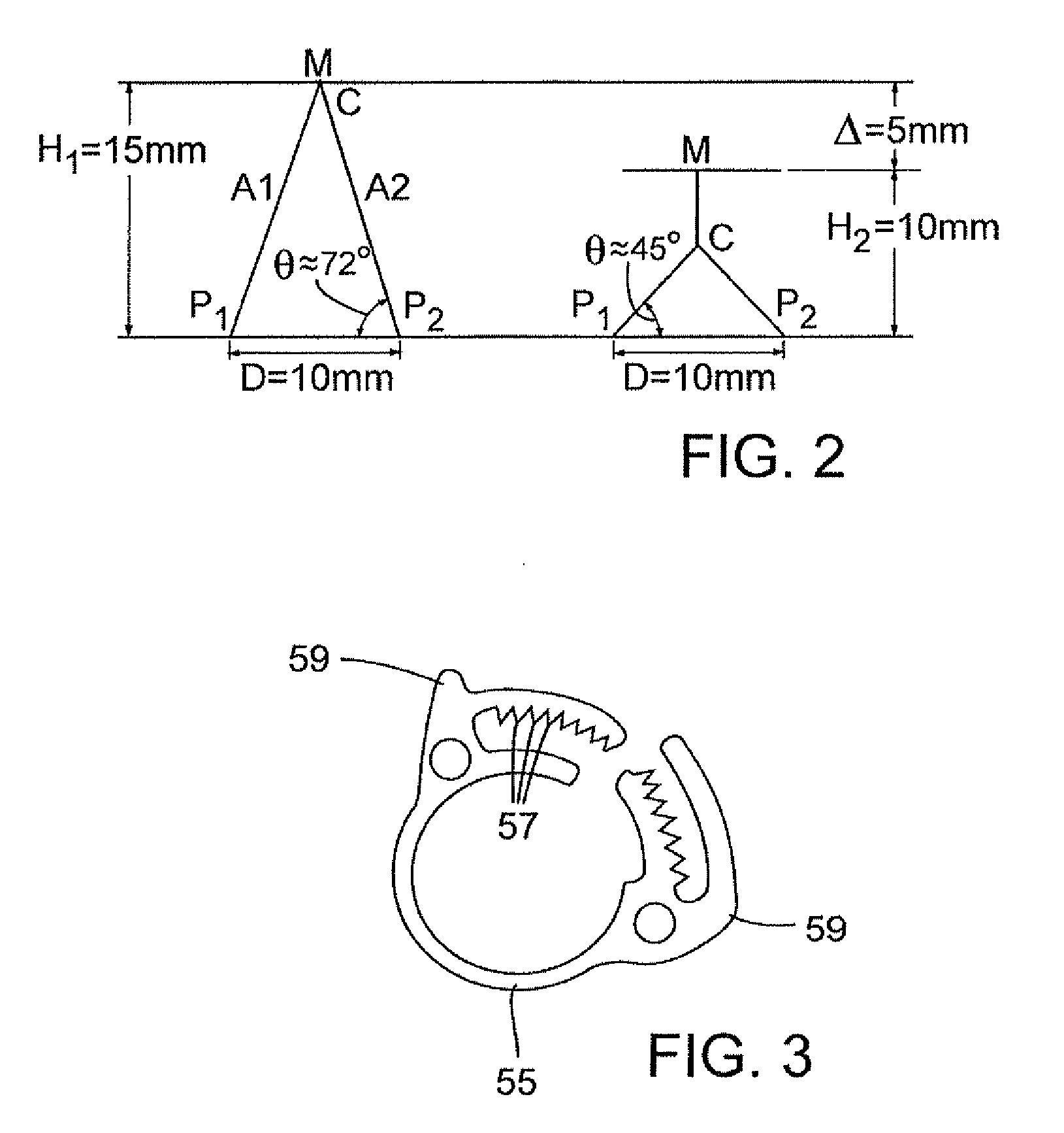
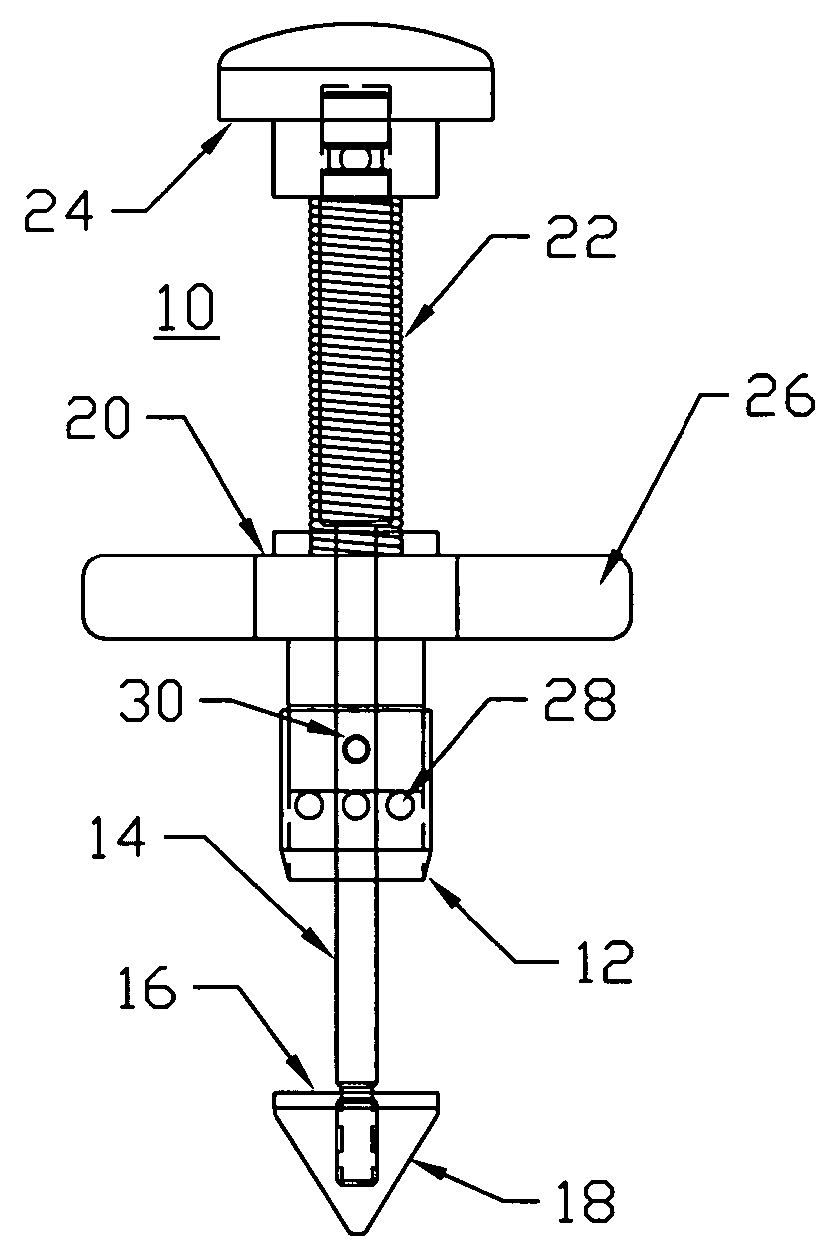
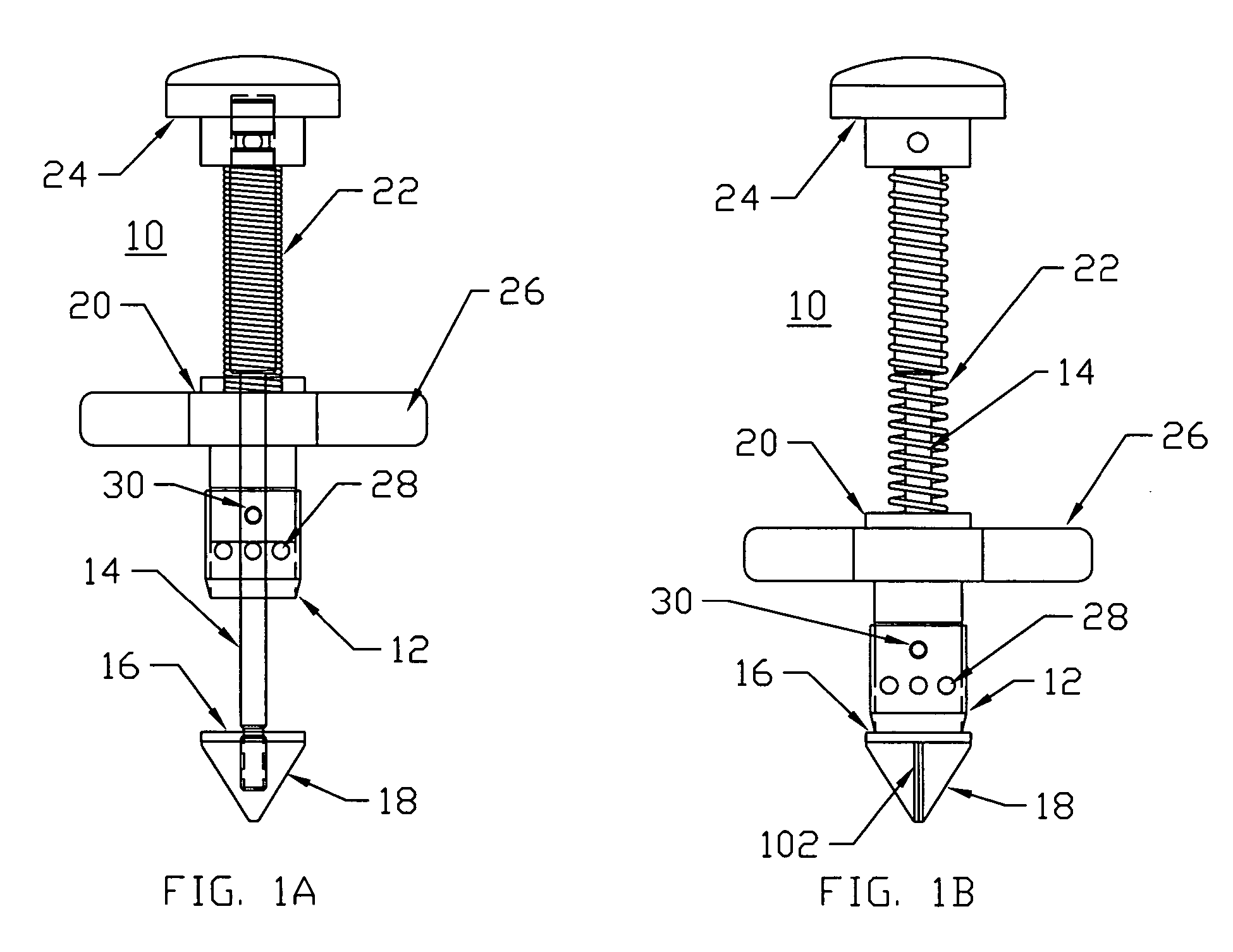
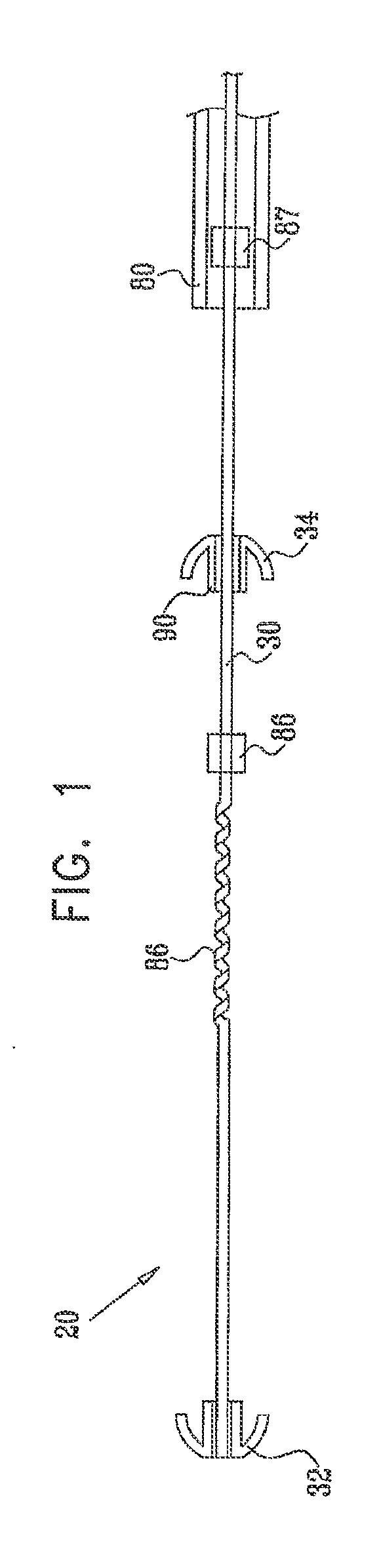
Method and apparatus for repairing or replacing chordae tendinae
ActiveUS20100042147A1Adjustable lengthFunction increaseSuture equipmentsHeart valvesPapillary muscleMitral valve leaflet
A method and apparatus for performing mitral valve chordal repair on a patient include attaching at least one filament to a mitral valve leaflet and to a papillary muscle. A first end of a filament can be attached to the mitral valve leaflet and the length of the filament can be adjusted by adjusting the tension of the filament in a catheter. The second end of the filament can be attached to an attachment site.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
Method and apparatus for repairing or replacing chordae tendinae
A method and apparatus for performing mitral valve chordal repair on a patient include attaching at least one filament to a mitral valve leaflet and to a papillary muscle. The length of filaments can be adjusted by adjusting tension in a filament or by altering the effective length of a filament by cutting filament strands or by moving an adjustment member along the length of the filaments.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
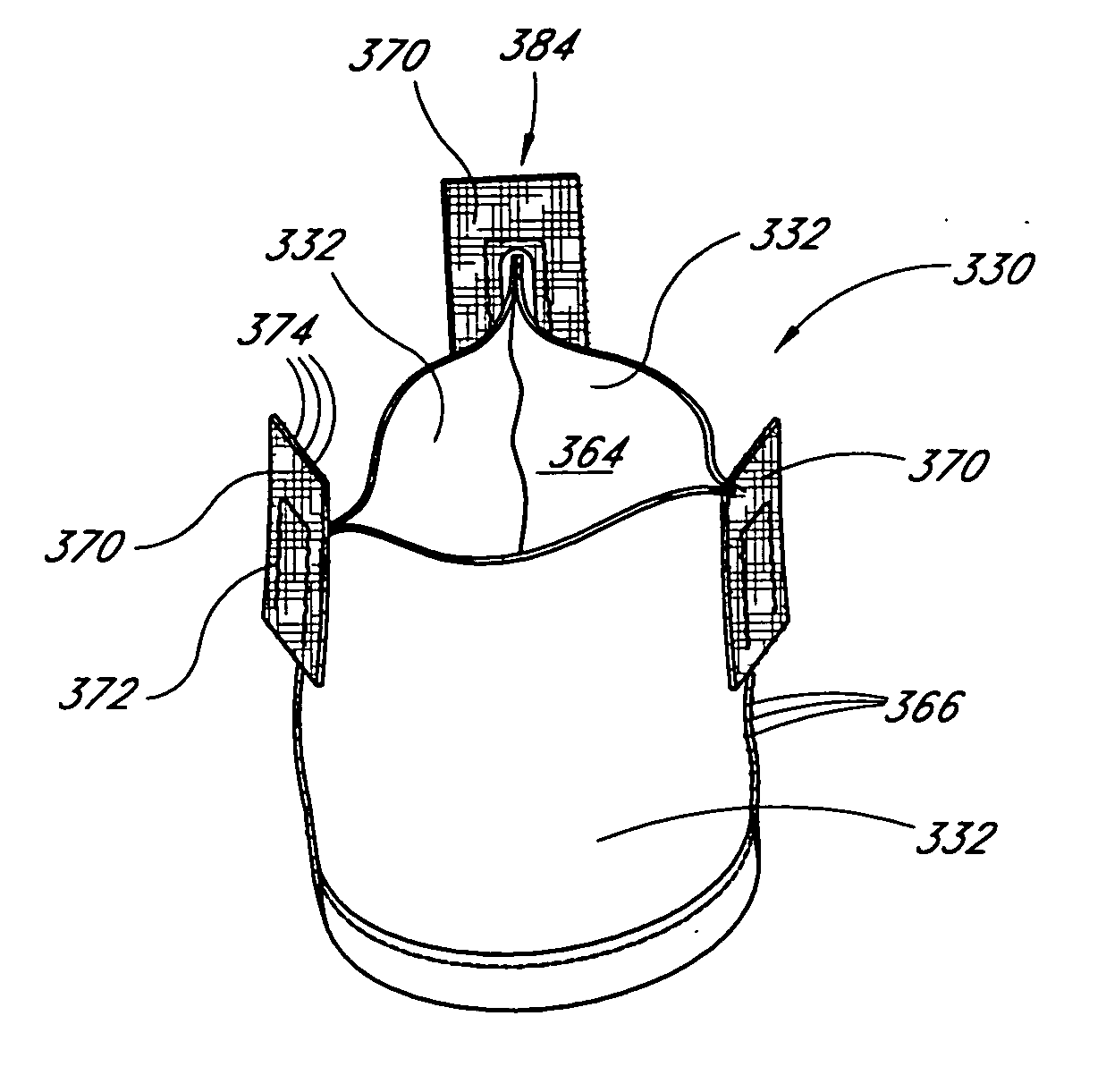
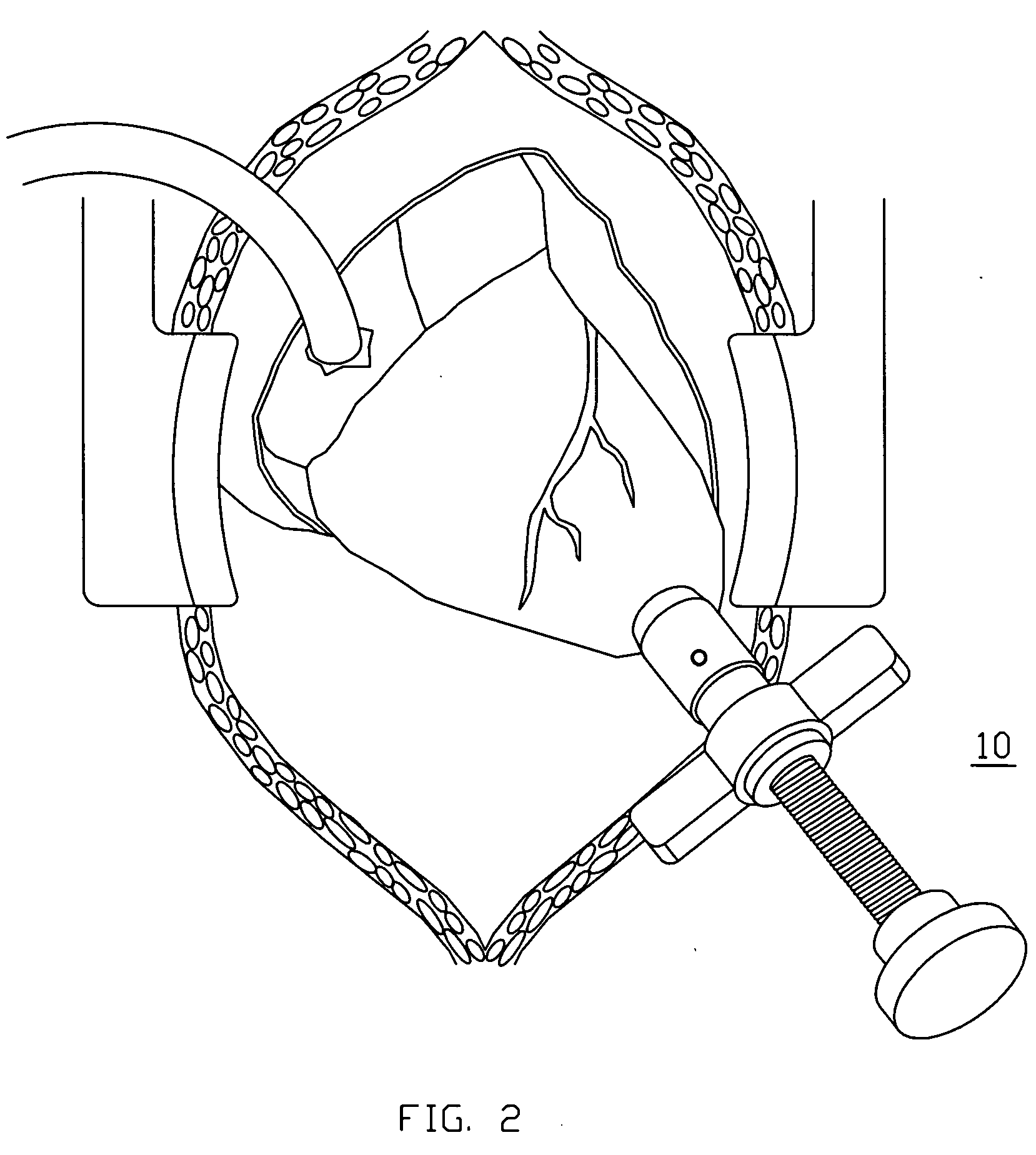
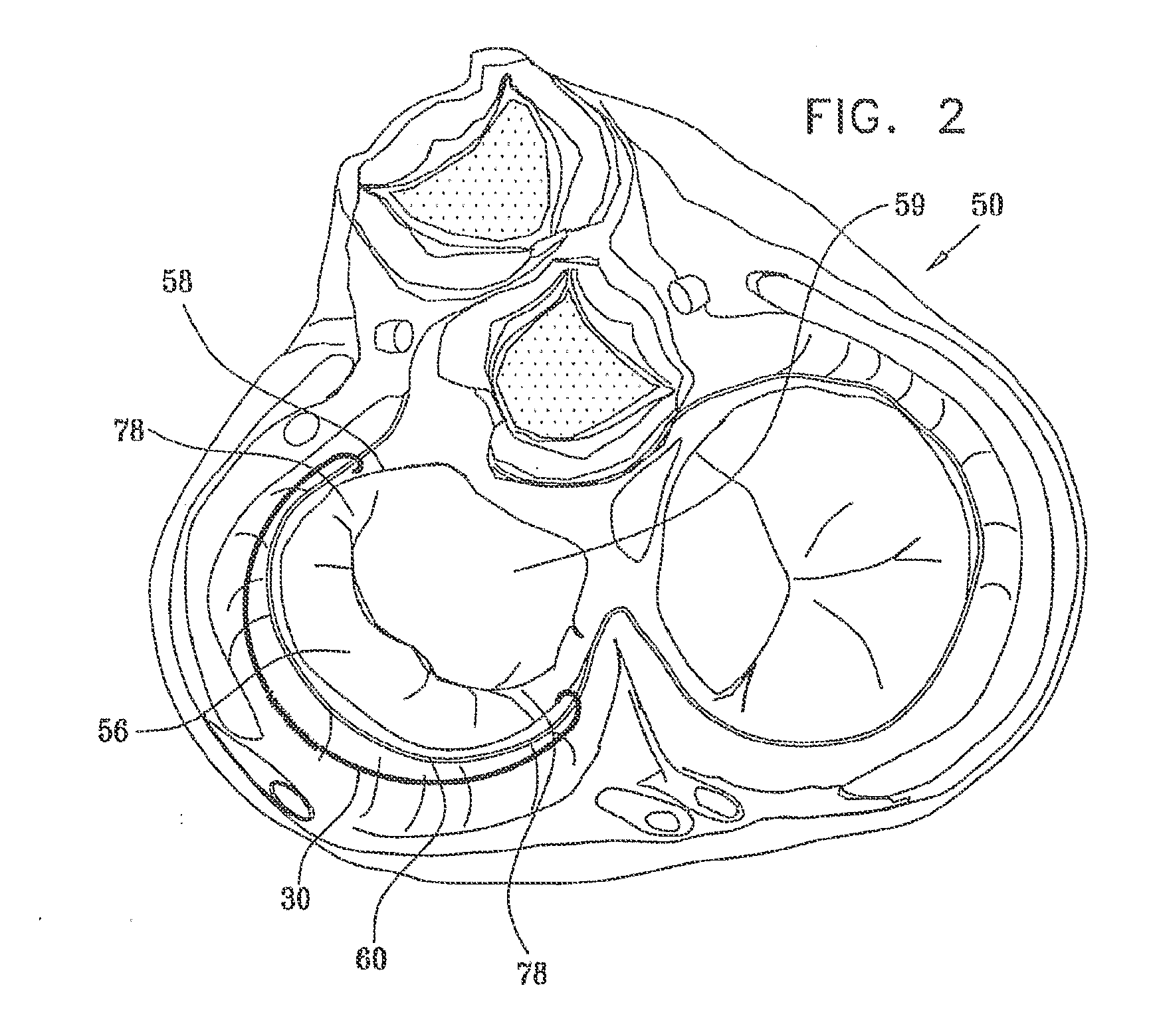
Mitral valve treatment techniques
ActiveUS8608797B2Enhance fibrosisReduce distanceBone implantAnnuloplasty ringsCouplingMitral valve leaflet
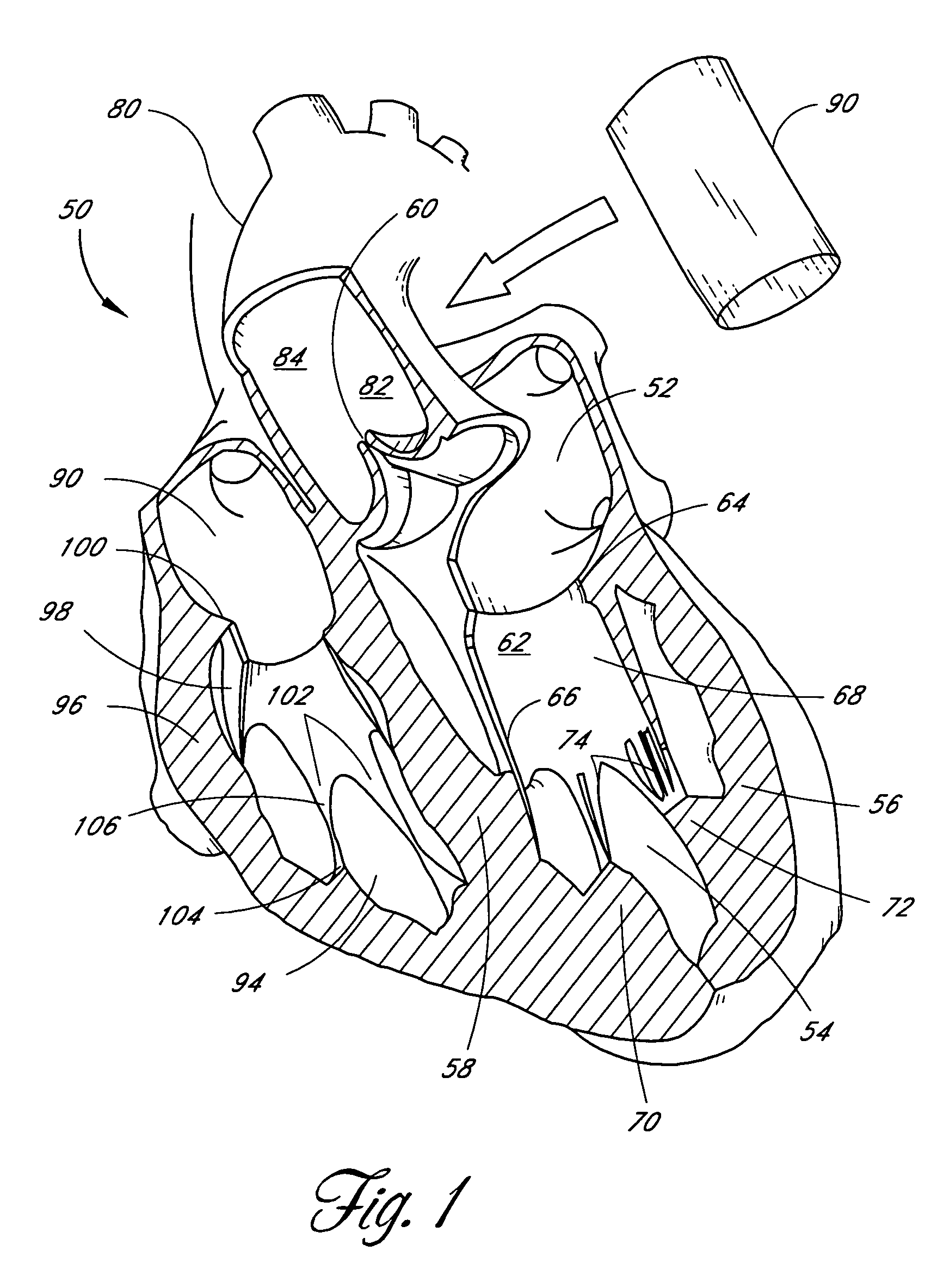
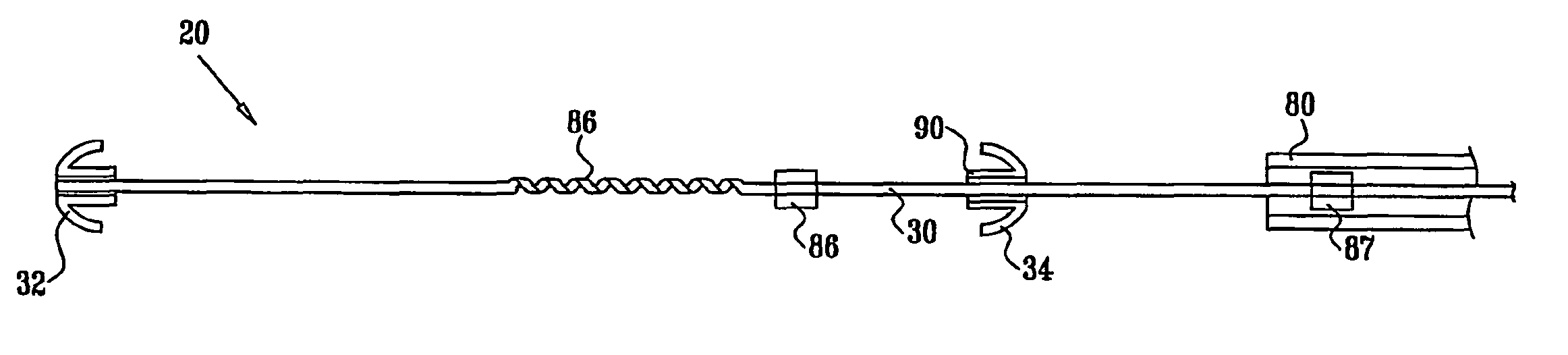
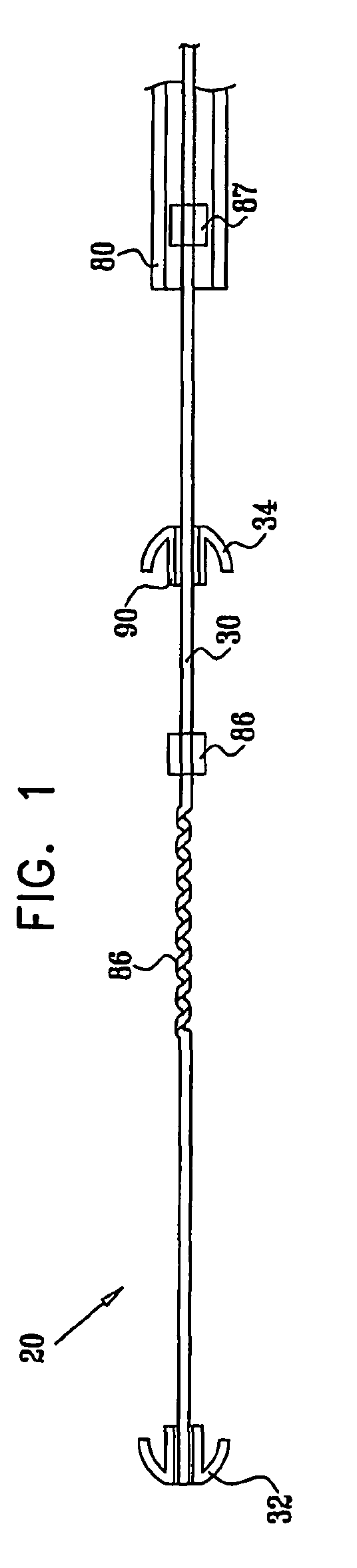
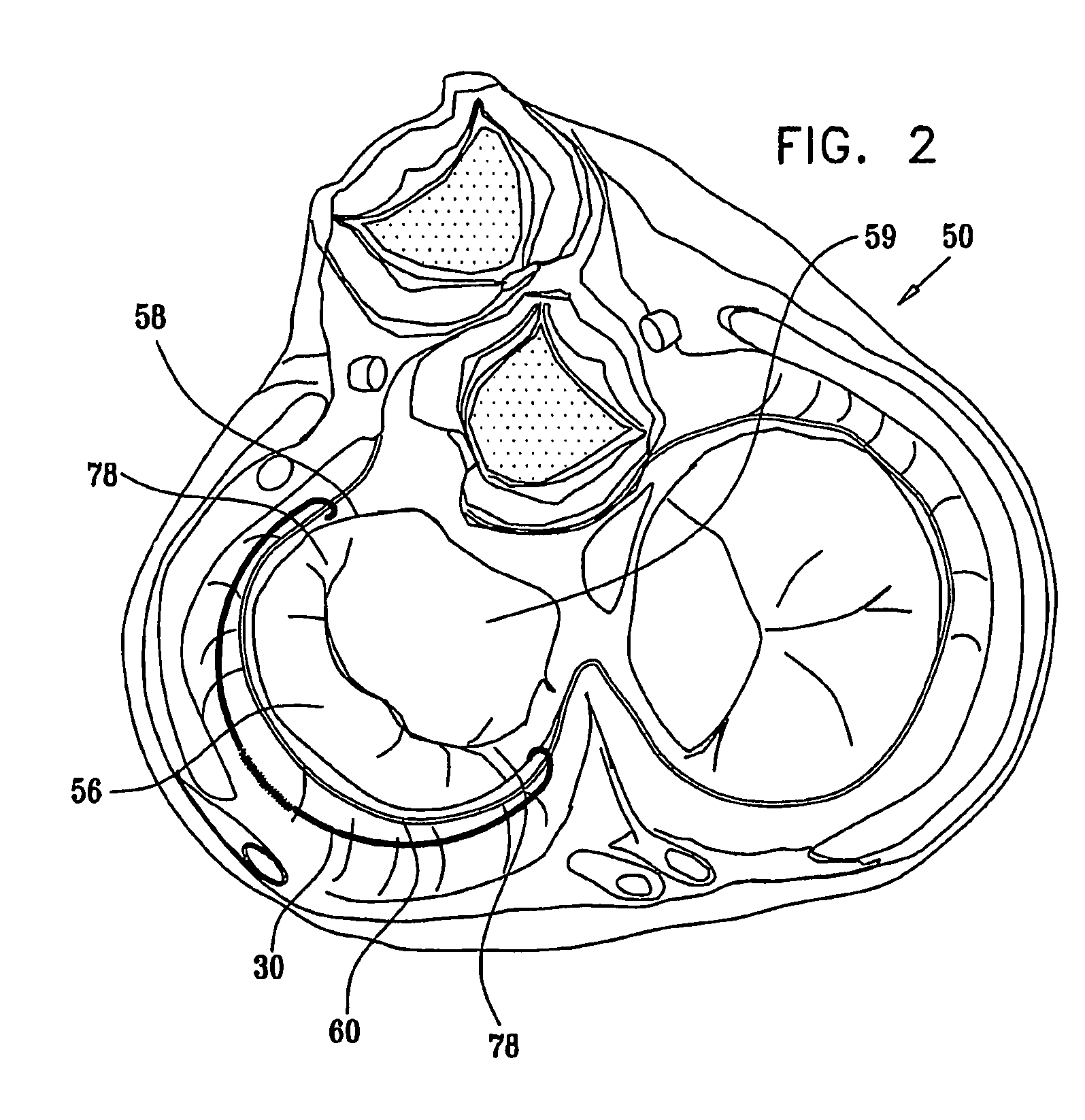
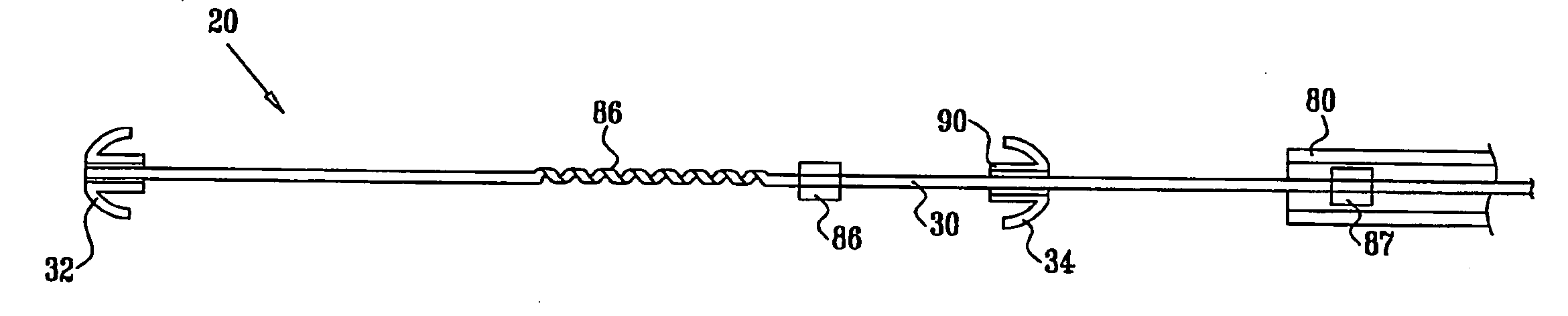
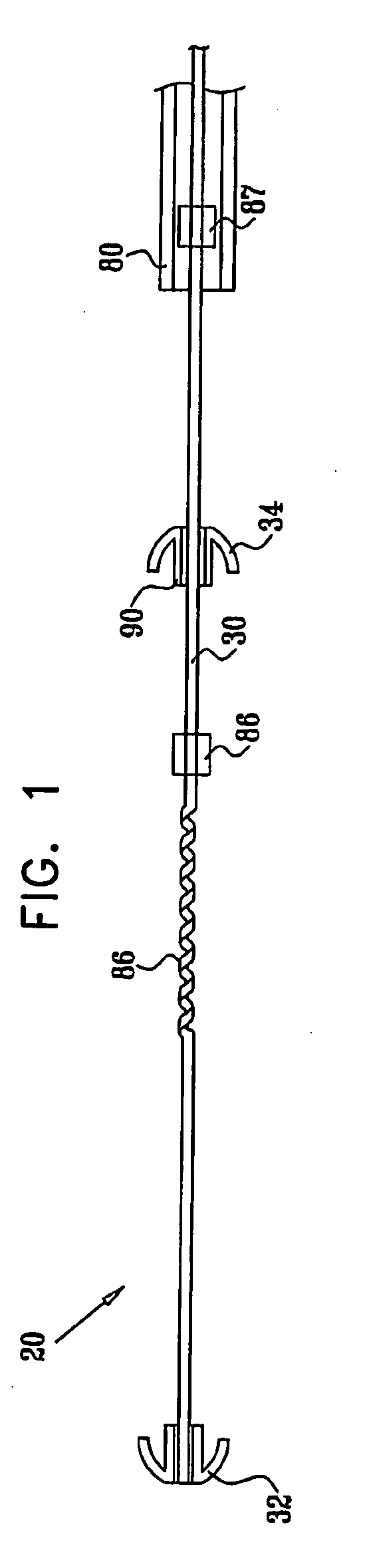
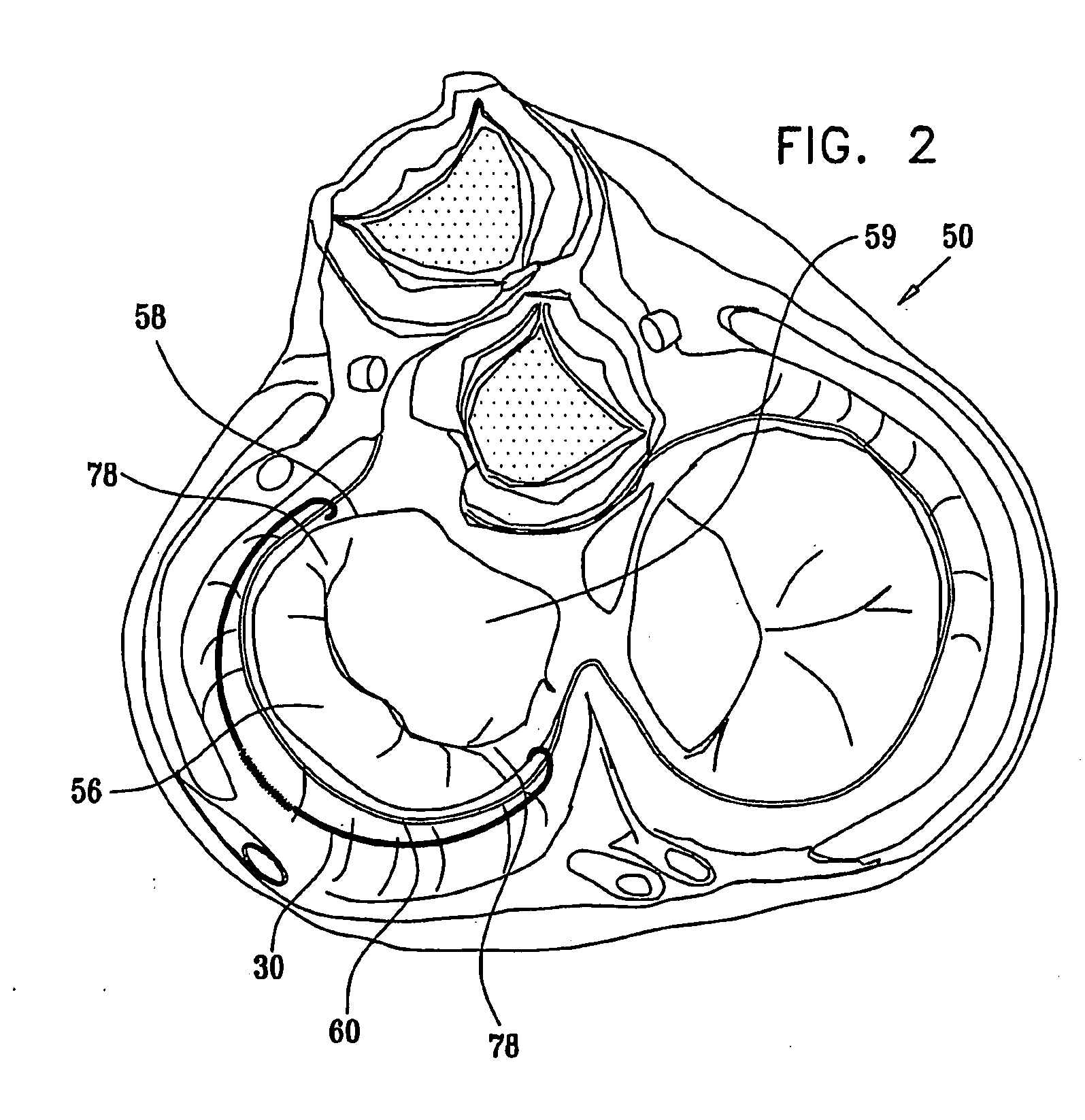
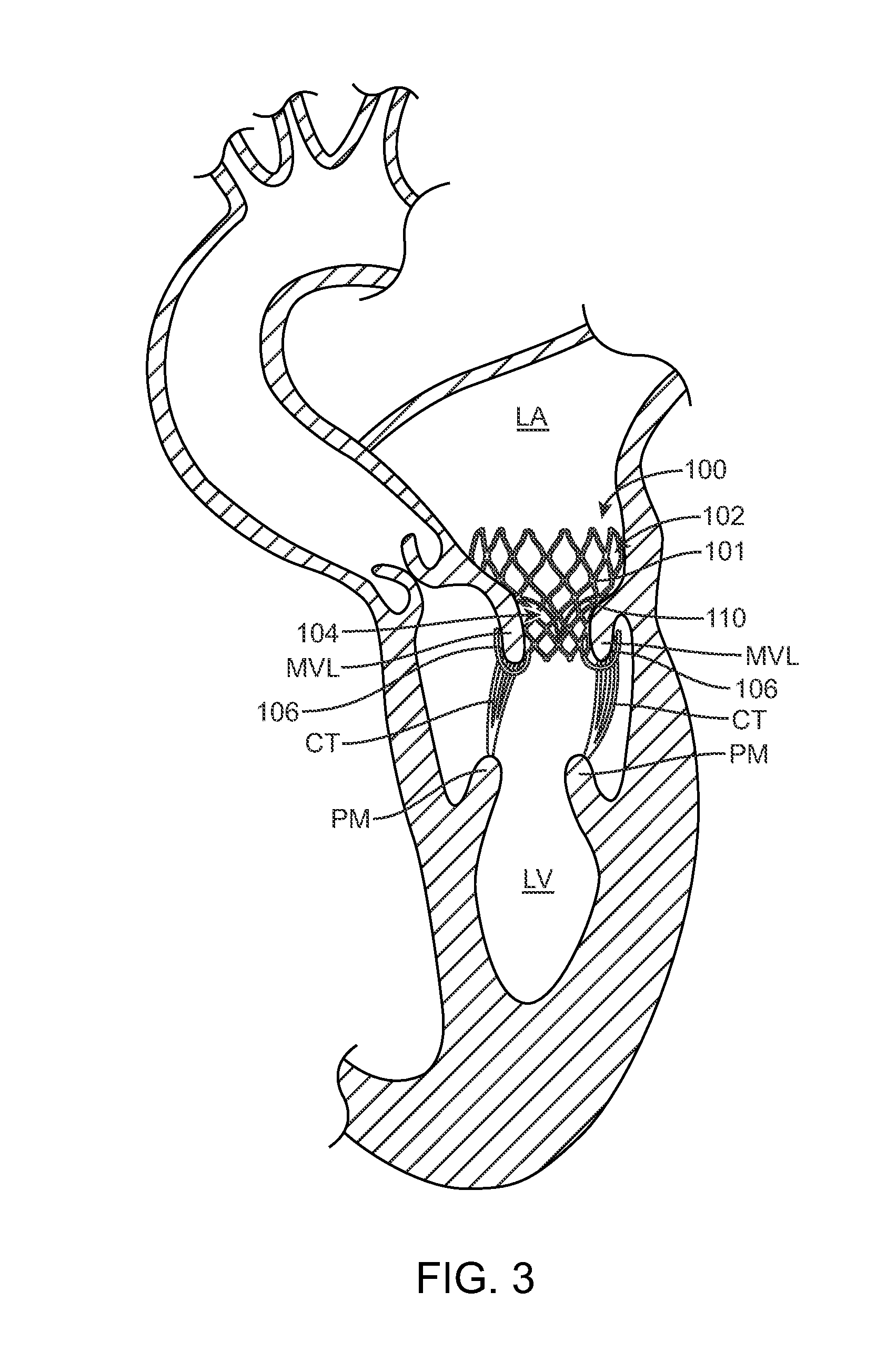
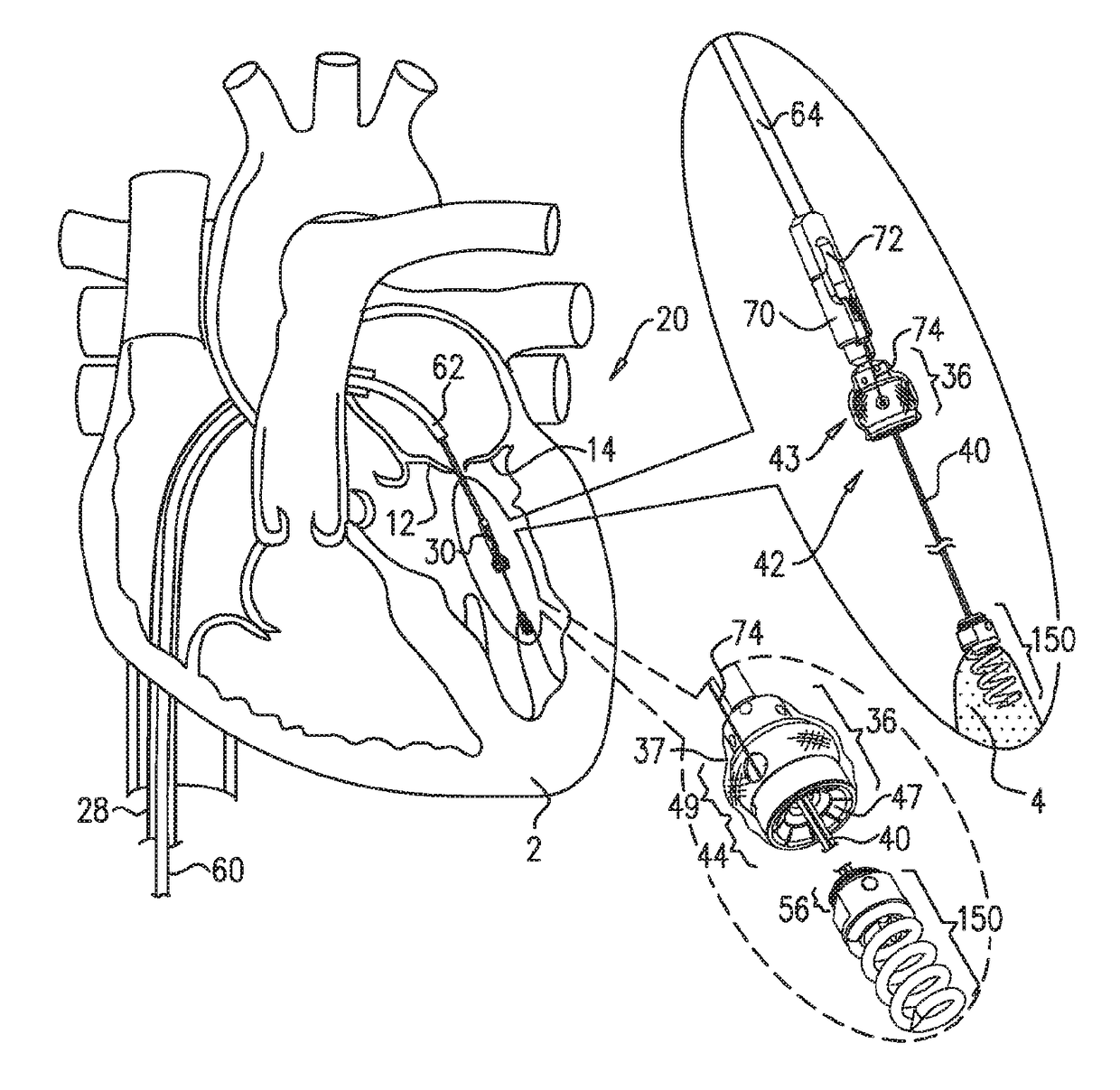
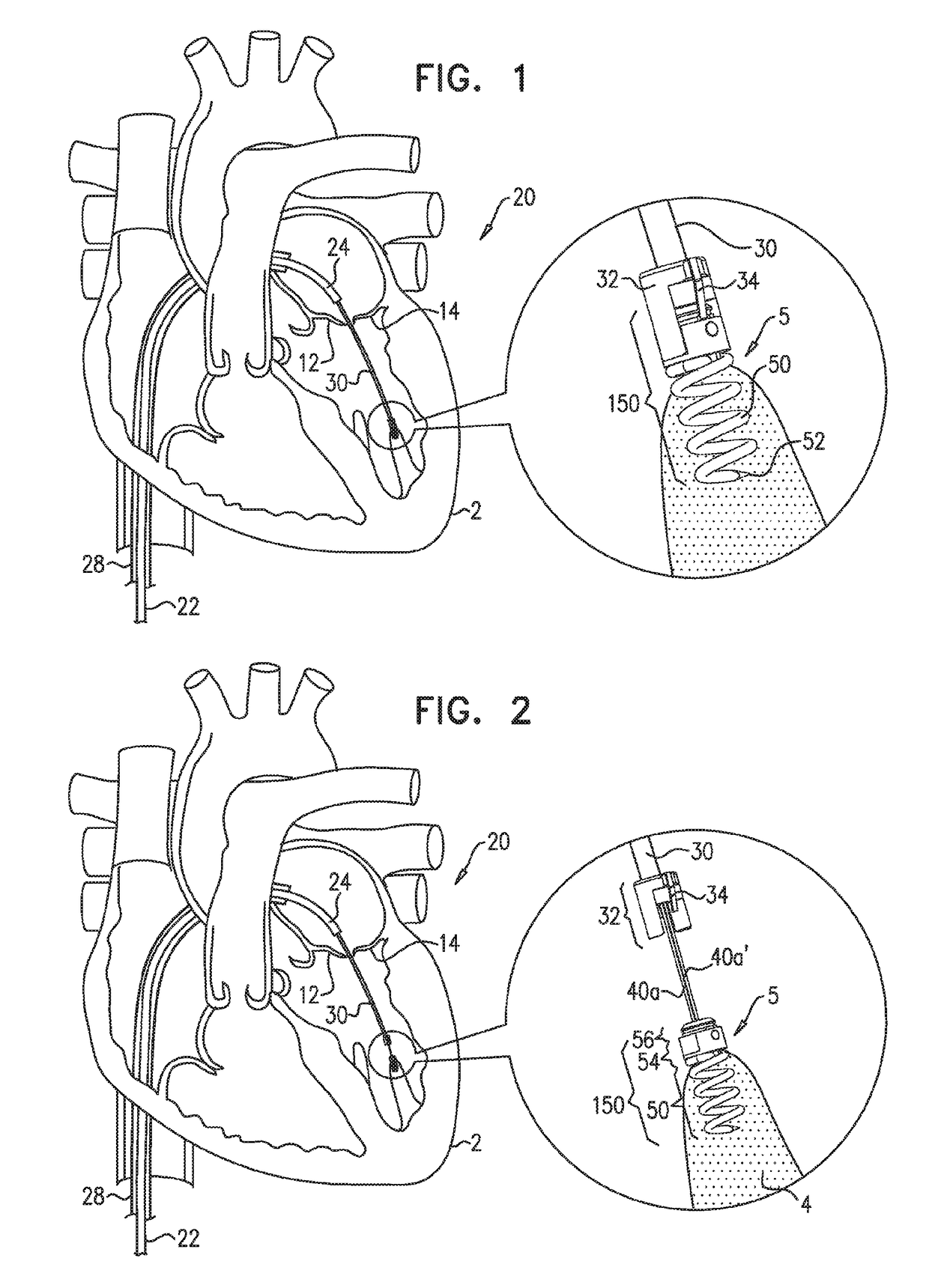
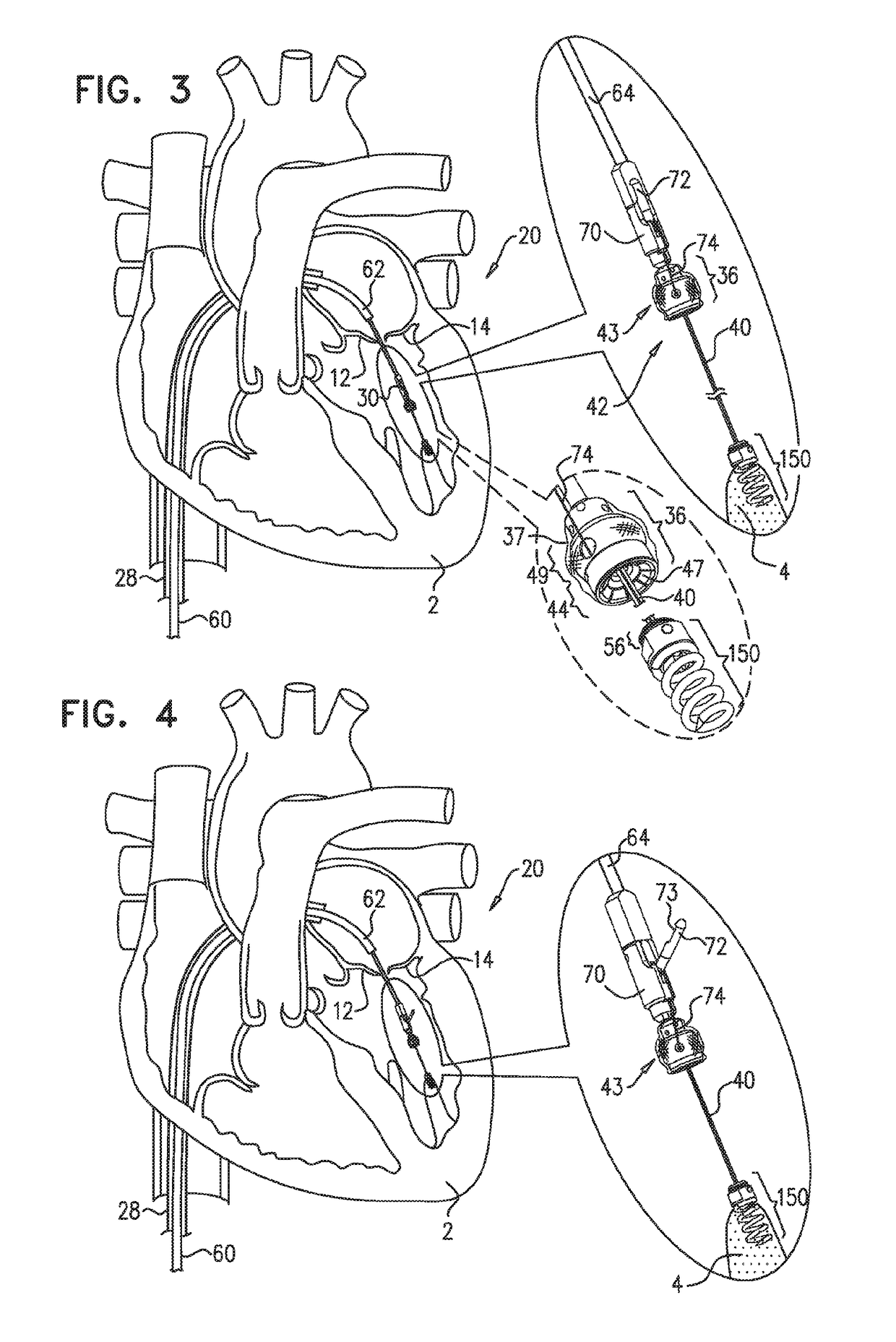
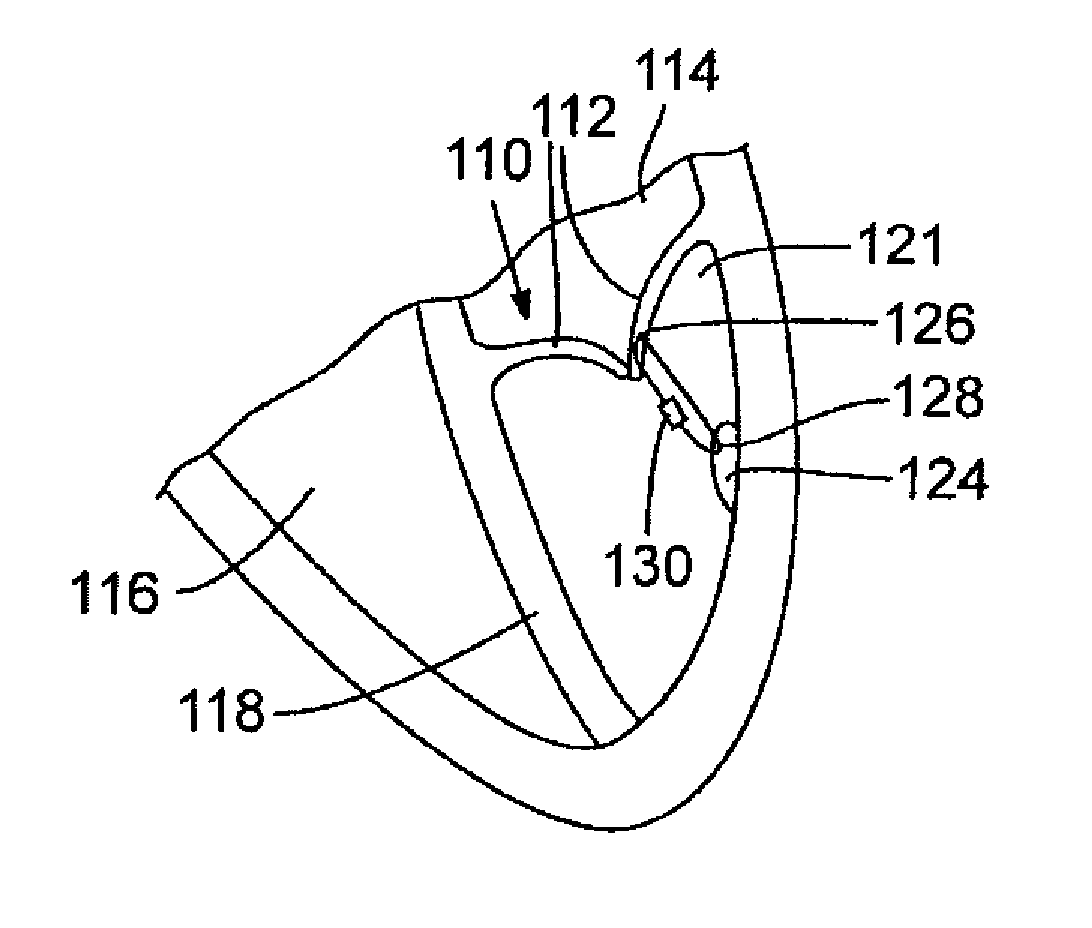
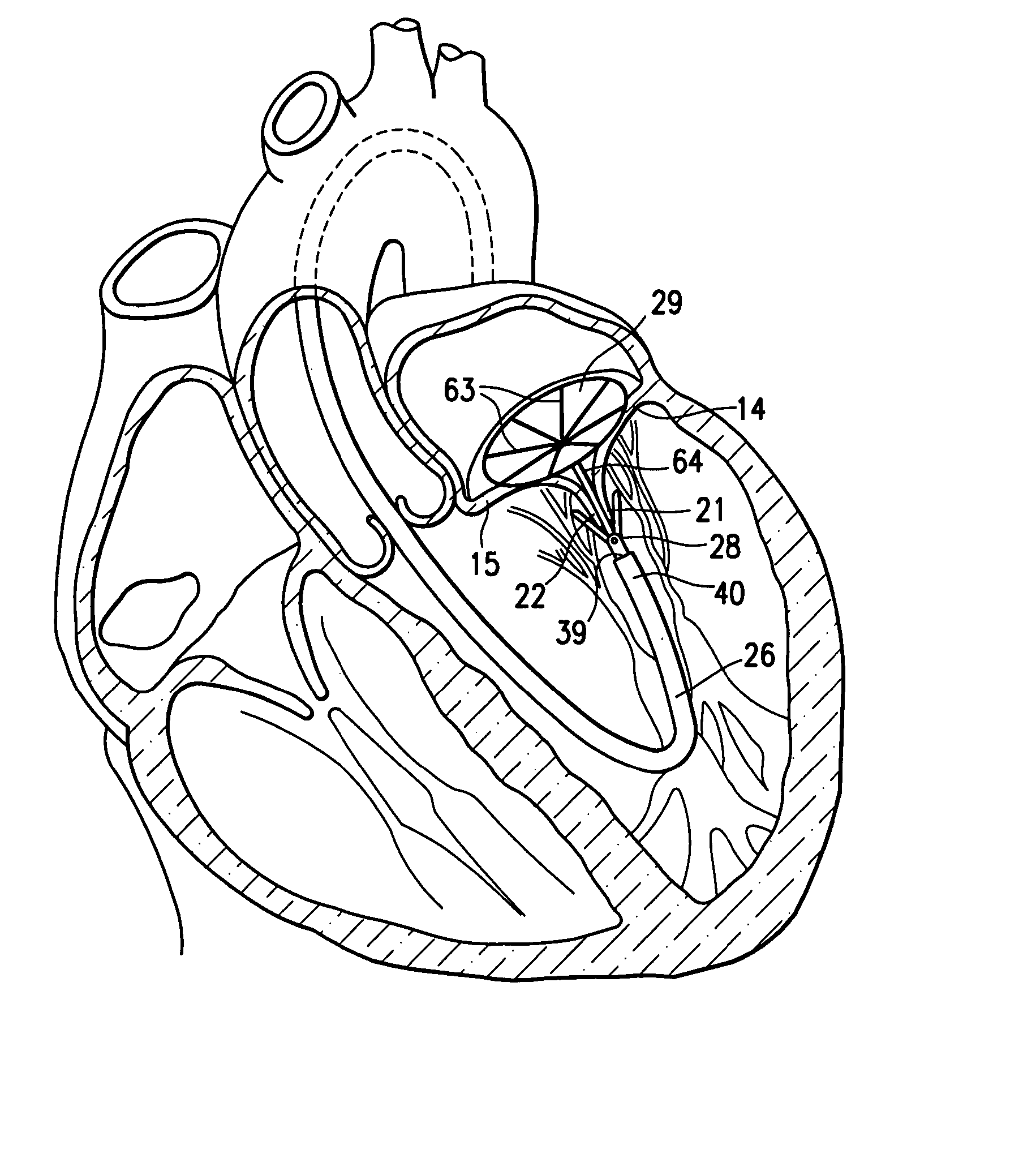
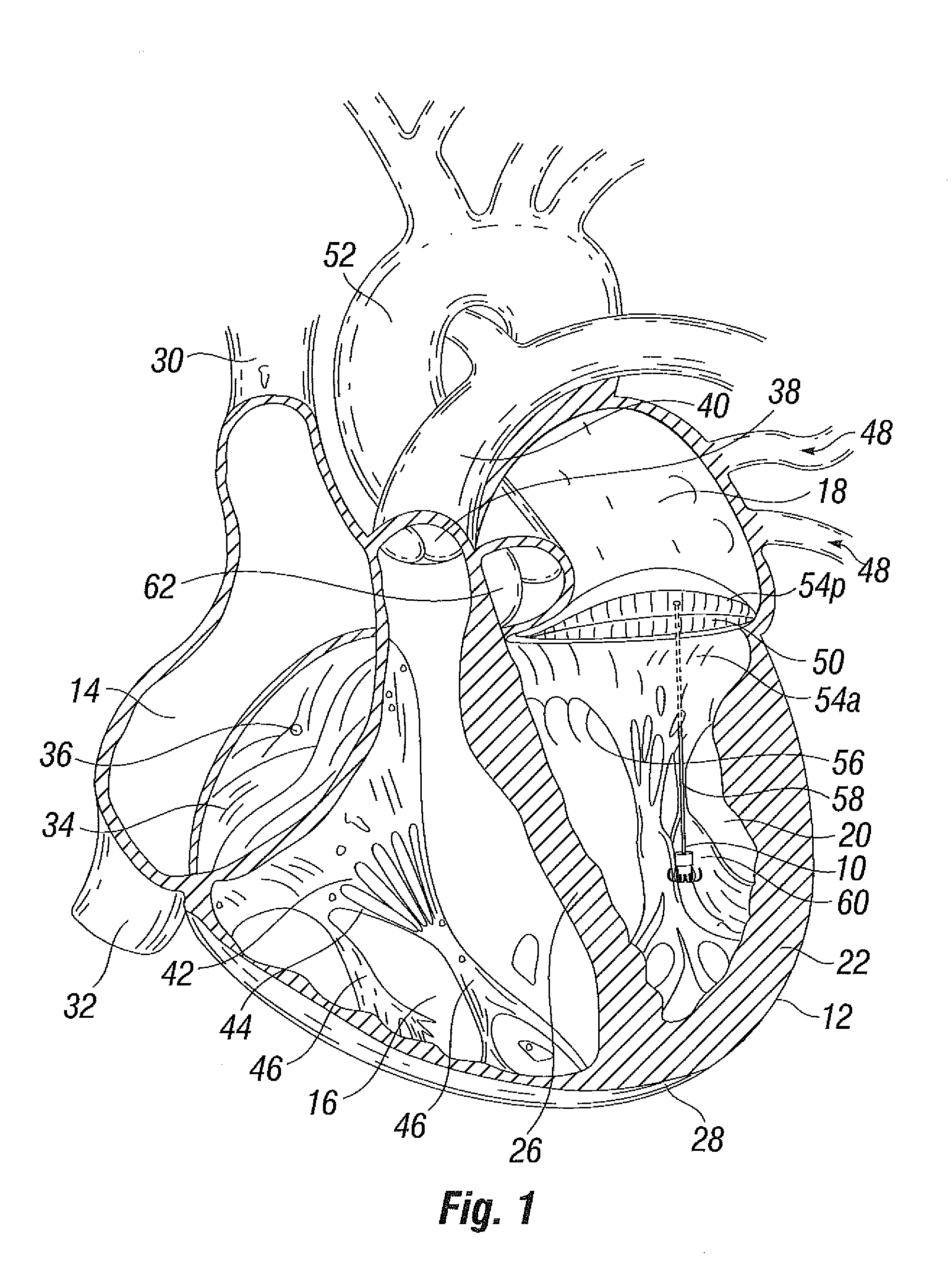
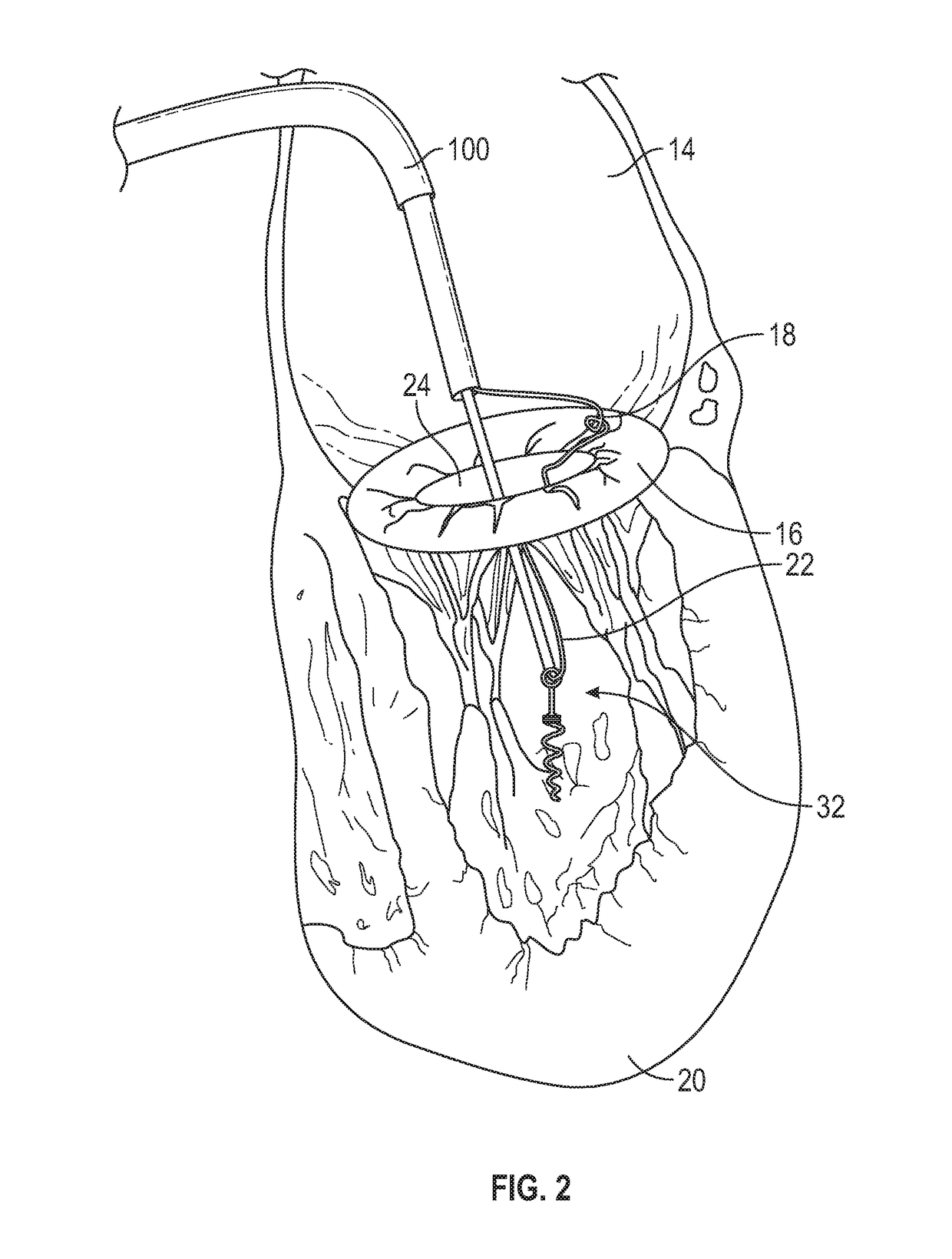
Apparatus (20) is provided for treating mitral valve regurgitation, including a band (30) having distal and proximal ends, the band (30) adapted to be placed: around between 90 and 270 degrees of a mitral valve (58), including around at least a portion of a posterior cusp (56) of the valve (58), in a space defined by (a) a ventricular wall (70), (b) a ventricular surface of the posterior cusp (56) in a vicinity of an annulus (60) of the mitral valve (58), and (c) a plurality of third-order chordae tendineae (74). The apparatus (20) further includes distal and proximal coupling elements (32, 34), coupled to the band (30) at the distal and proximal ends thereof, respectively, and adapted to be coupled to a first chorda tendinea and a second chorda tendinea, respectively, each of the first and second chordae tendineae selected from the group consisting of: one of the plurality of third-order chordae tendineae (74), and a first-order chorda tendinea that inserts on a commissural cusp (78) of the mitral valve (58). Additional embodiments are also described.
Owner:VALTECH CARDIO LTD
Mitral valve treatment techniques
ActiveUS20090149872A1Enhance fibrosisReduce distanceAnnuloplasty ringsNon-surgical orthopedic devicesCouplingMitral valve leaflet
Apparatus (20) is provided for treating mitral valve regurgitation, including a band (30) having distal and proximal ends, the band (30) adapted to be placed: around between 90 and 270 degrees of a mitral valve (58), including around at least a portion of a posterior cusp (56) of the valve (58), in a space defined by (a) a ventricular wall (70), (b) a ventricular surface of the posterior cusp (56) in a vicinity of an annulus (60) of the mitral valve (58), and (c) a plurality of third-order chordae tendineae (74). The apparatus (20) further includes distal and proximal coupling elements (32, 34), coupled to the band (30) at the distal and proximal ends thereof, respectively, and adapted to be coupled to a first chorda tendinea and a second chorda tendinea, respectively, each of the first and second chordae tendineae selected from the group consisting of: one of the plurality of third-order chordae tendineae (74), and a first-order chorda tendinea that inserts on a commissural cusp (78) of the mitral valve (58). Additional embodiments are also described.
Owner:VALTECH CARDIO LTD
Method of Treating Paravalvular Leakage After Prosthetic Valve Implantation
A method for treating paravalvular leakage at a location of a stented prosthetic valve includes the steps of delivering a clip to a location adjacent chordae tendinae of a native valve, and deploying the clip such that the clip captures at least some of the chordae tendinae of the native valve, thereby increasing tension in the captured chordae tendinae. The clip is delivered to the location in a collapsed stated and is released from a sheath convert to an undeflected or relaxed state. After the clip is released from the sheath, the clip is rotated to capture the chordae tendinae. The clip is then released from the delivery system and the delivery system is retracted.
Owner:MEDTRONIC ARDIAN LUXEMBOURG SARL
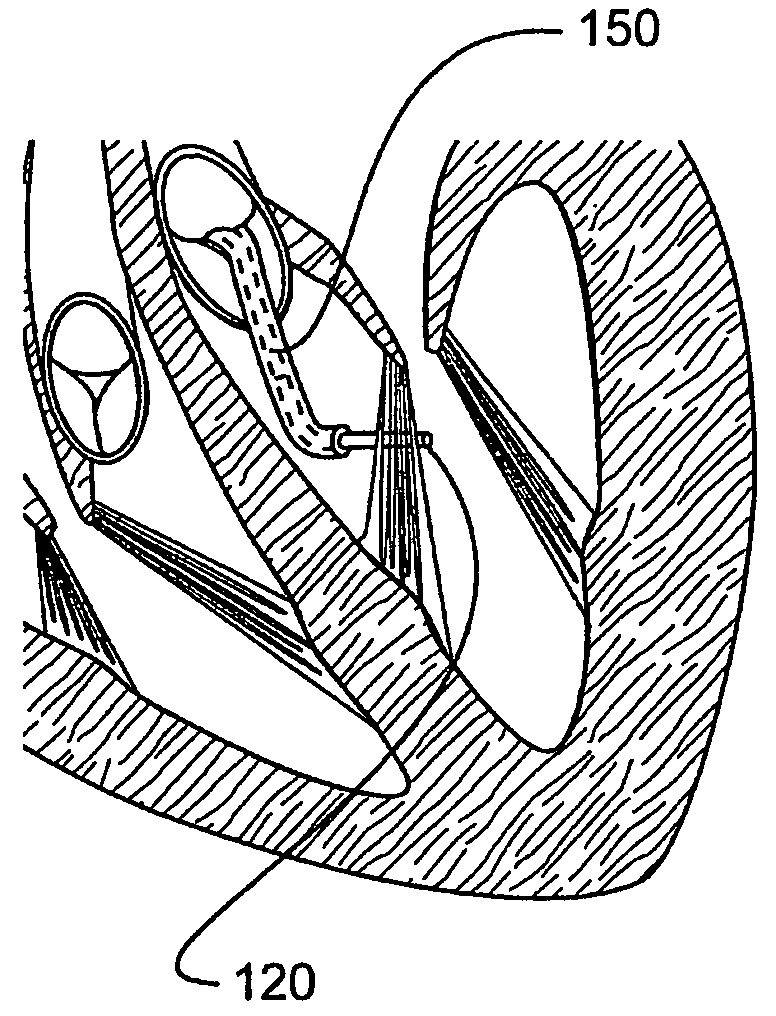
Techniques for guide-wire based advancement of a tool
ActiveUS9730793B2Facilitates bidirectional rotationEffect tensioningSuture equipmentsIncision instrumentsDistal portionPapillary muscle
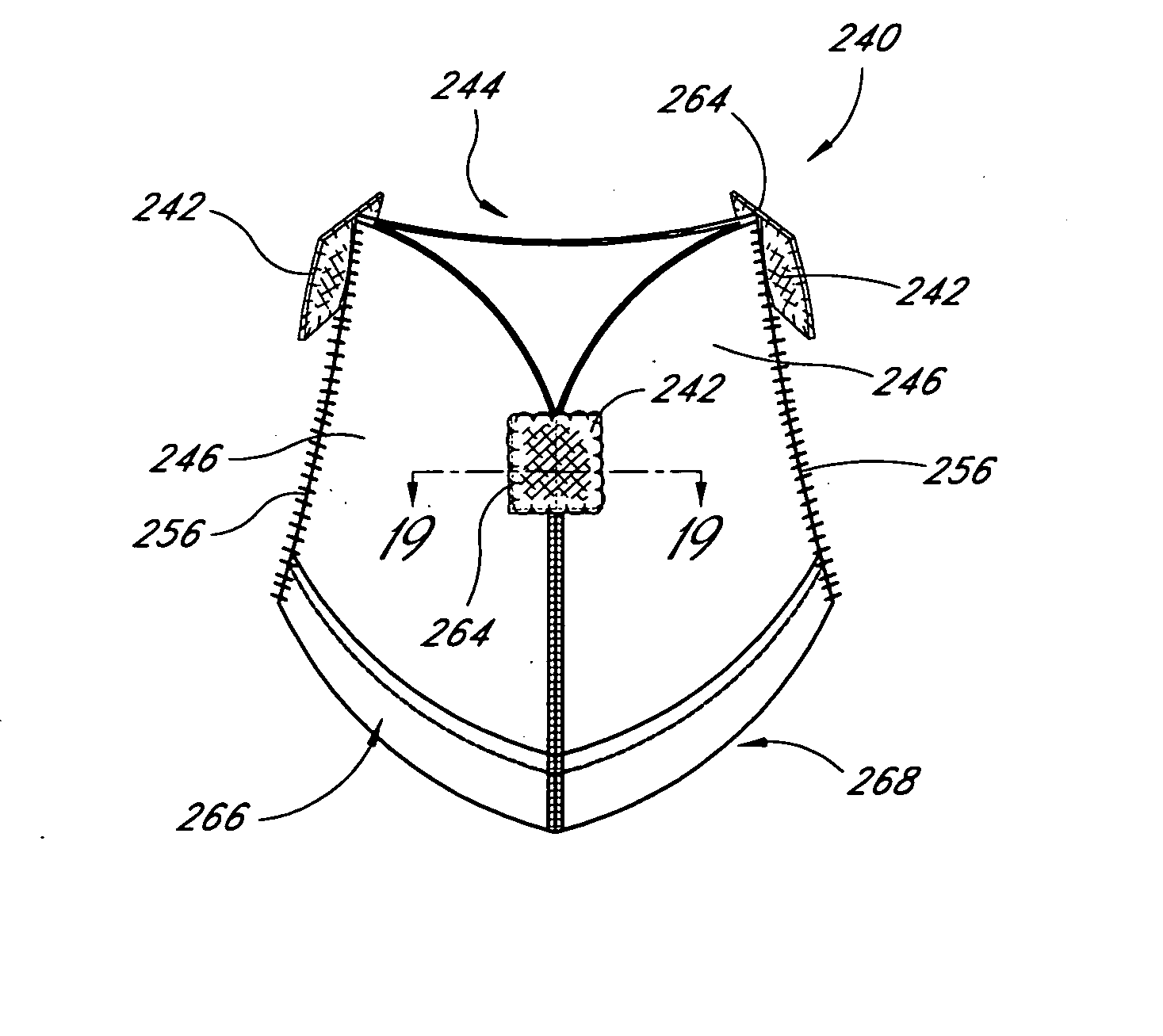
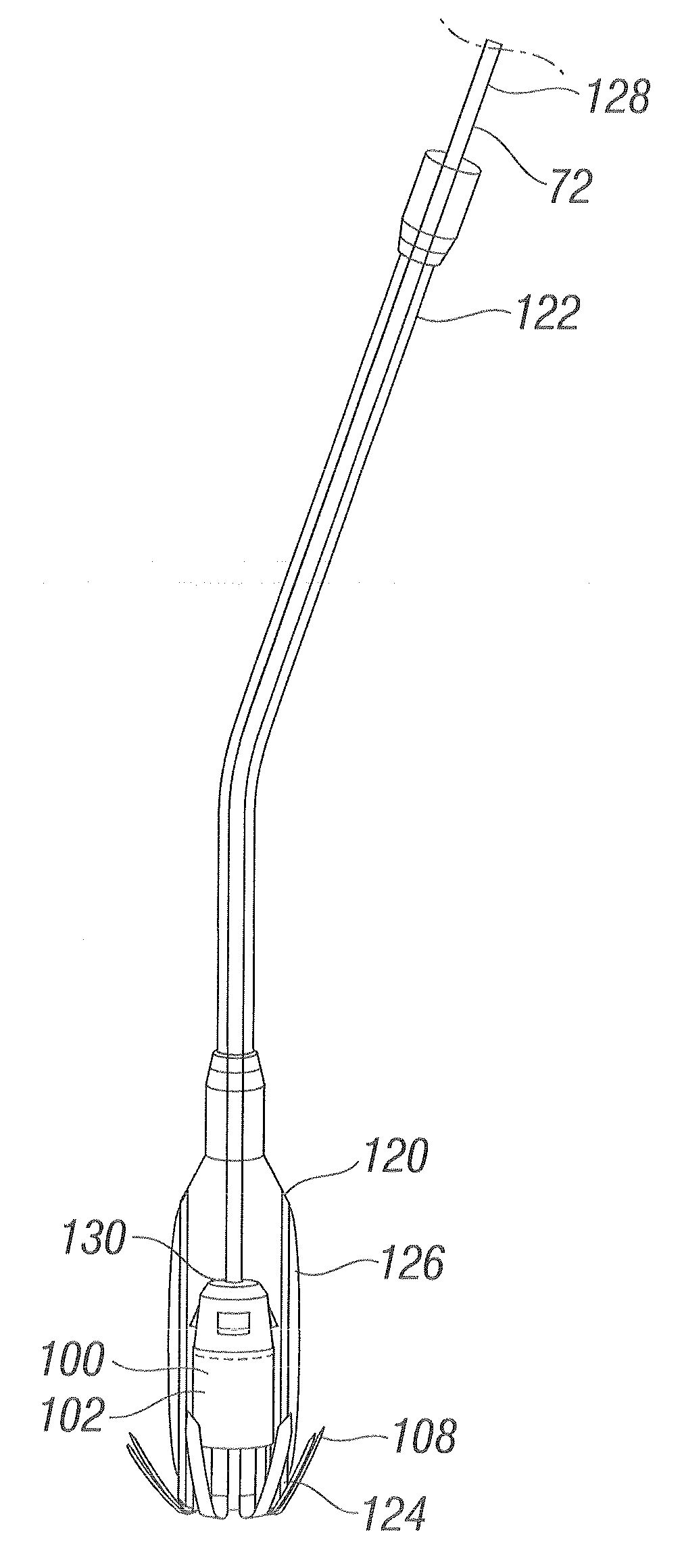
Apparatus comprises: (A) a housing (248), percutaneously deliverable to a heart of a subject, slidable along a guidewire (242), and shaped to define at least one opening (249); (B) a guide member (250), percutaneously deliverable to the heart, percutaneously removable from the subject, couplable to the housing, and having: (i) a distal portion, comprising a chord-engaging element (252), configured to be percutaneously slidably coupled to and decouplable from at least one chordae tendineae (244), and (ii) a proximal portion, comprising a longitudinal element (251); and (C) a deployment tool, configured (i) to be reversibly coupled to a tissue anchor (50,280), (ii) to be slidably coupled to the longitudinal element of the guide member, and (iii) to anchor the tissue anchor to a papillary muscle (254) of the subject. Other embodiments are also described.
Owner:VALTECH CARDIO LTD
Method and apparatus for trephinating body vessels and hollow organ walls
InactiveUS6863677B2Improve permeabilityReduce cleaningSurgical needlesSurgical instrument detailsPapillary muscleBone trephine
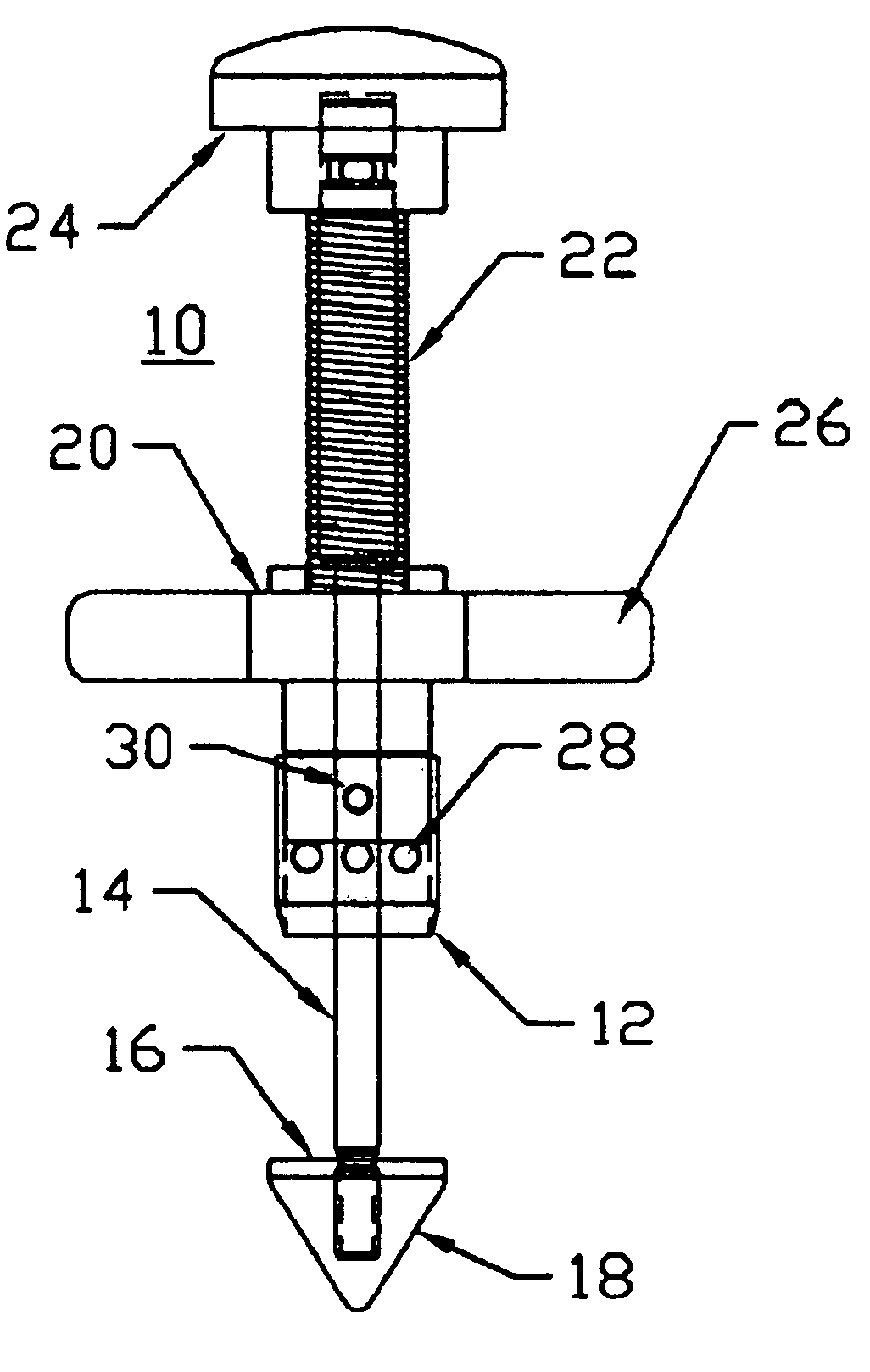
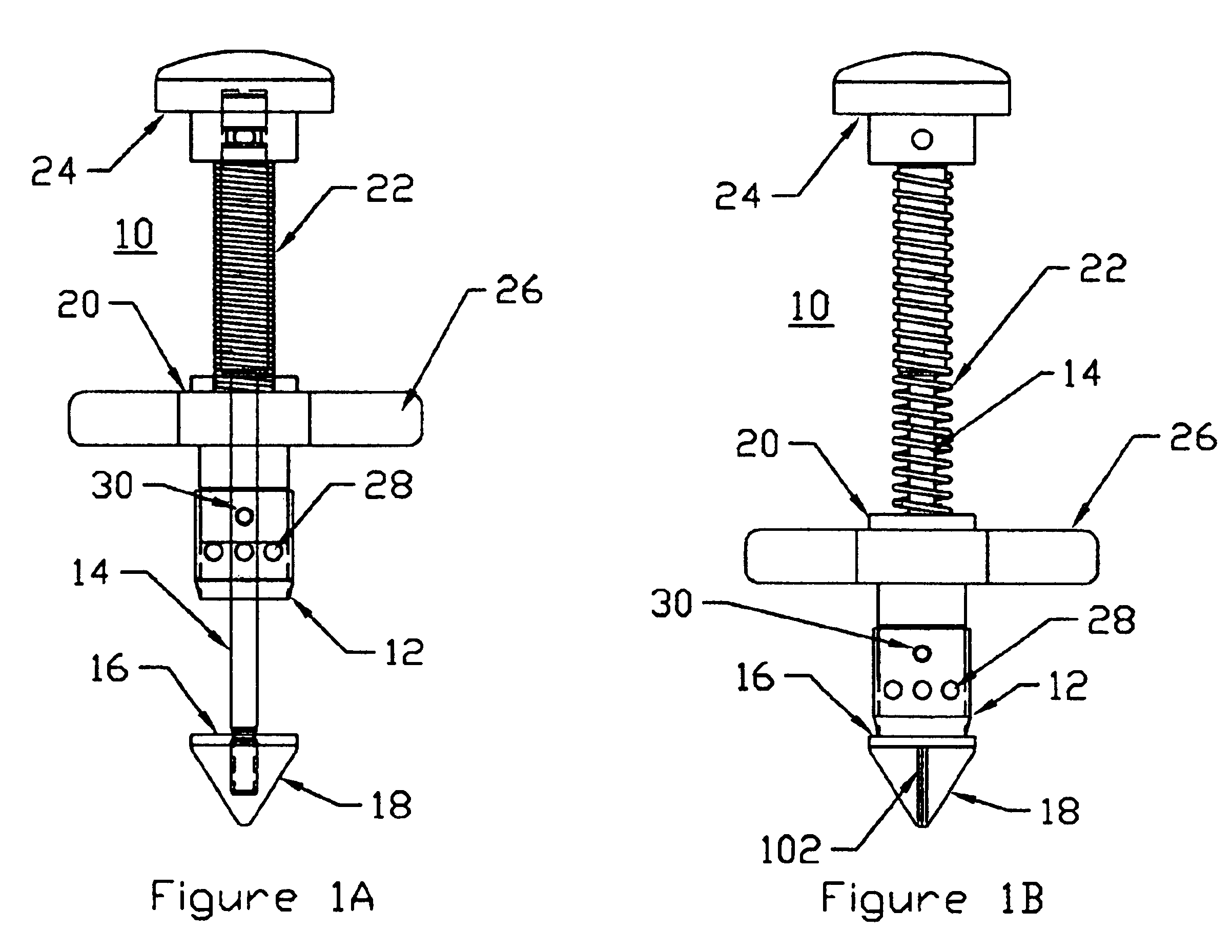
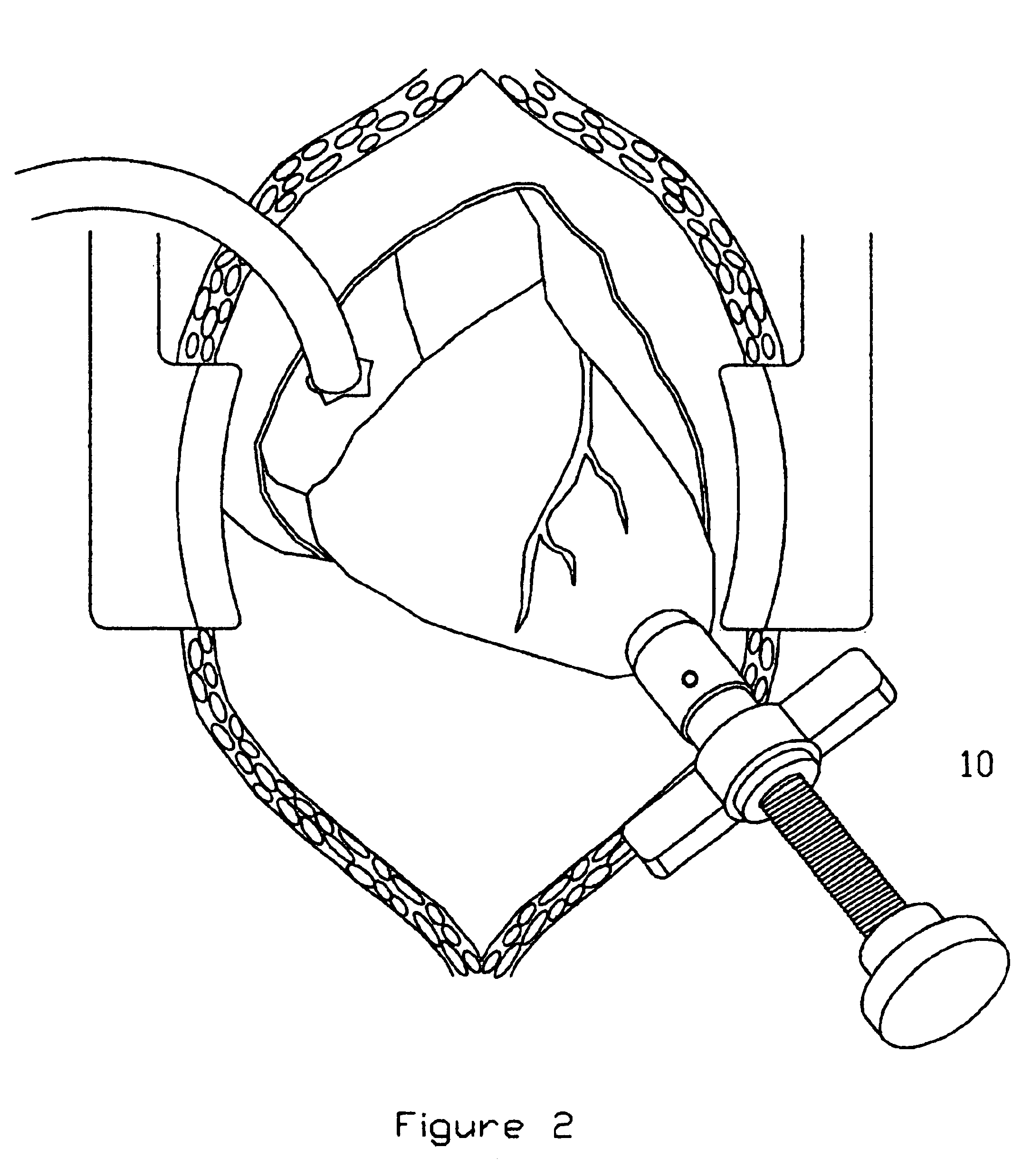
A system is disclosed for creating a hole in a body vessel or hollow organ. Such holes are useful in surgically preparing the hollow organ or body vessel for connection with another hollow organ, body vessel or prosthetic conduit. For example, an assist device is generally connected to the left ventricle through a ventriculotomy created at the apex of the left ventricle. This ventriculotomy is most easily created with a punch or trephine. Control over such a procedure must be precise so as not to damage the ventricular wall or intracardiac structures such as papillary muscles, chordae tendinae, etc. The punch of the current invention allows for precise location and alignment of the cutting segment. The punch of the current invention also allows for precise advance of the cutting blade and a very clean cut of the tissue. Such clean cuts improve the healing when the hole in the body vessel or hollow organ is closed or attached to a connection, either prosthetic or natural.
Owner:INDIAN WELLS MEDICAL
Method and apparatus for repairing or replacing chordae tendinae
ActiveUS8778016B2Adjustable lengthFunction increaseSuture equipmentsDiagnosticsPapillary muscleMitral valve leaflet
A method and apparatus for performing mitral valve chordal repair on a patient include attaching at least one filament to a mitral valve leaflet and to a papillary muscle. A first end of a filament can be attached to the mitral valve leaflet and the length of the filament can be adjusted by adjusting the tension of the filament in a catheter. The second end of the filament can be attached to an attachment site.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
Percutaneous treatment for heart valves
InactiveUS20070265702A1Avoid problemsReduce ventricular outputSuture equipmentsHeart valvesCongestive heart failure chfBlood vessel
The invention is directed to percutaneous transvascular therapeutic procedures, particularly for patients with congestive heart failure, and systems for such procedures. A system of the invention for a “Bow-tie” procedure has an elongated guide catheter, a leaf stabilizing device and a tissue grasping device for grasping the free edges of the patient's heart valve slidably disposed within the guide catheter. Preferably, an artificial cordae tendenae is provided if a natural cordae tendenae of the patient has been torn.
Owner:TRANSCARDIAC THERAPEUTICS
Method and apparatus for trephinating body vessels and hollow organ walls
InactiveUS20050154411A1Improve permeabilityReduce cleaningSurgical needlesSurgical instrument detailsPapillary muscleBone trephine
A system is disclosed for creating a hole in a body vessel or hollow organ. Such holes are useful in surgically preparing the hollow organ or body vessel for connection with another hollow organ, body vessel or prosthetic conduit. For example, an assist device is generally connected to the left ventricle through a ventriculotomy created at the apex of the left ventricle. This ventriculotomy is most easily created with a punch or trephine. Control over such a procedure must be precise so as not to damage the ventricular wall or intracardiac structures such as papillary muscles, chordae tendinae, etc. The punch of the current invention allows for precise location and alignment of the cutting segment. The punch of the current invention also allows for precise advance of the cutting blade and a very clean cut of the tissue. Such clean cuts improve the healing when the hole in the body vessel or hollow organ is closed or attached to a connection, either prosthetic or natural.
Owner:BREZNOCK EUGENE M +1
Suture and method for repairing a heart
InactiveUS20130110230A1Eliminate needSmall sizeSuture equipmentsHeart valvesLocking mechanismPapillary muscle
Devices and methods for treating or repairing a heart are disclosed. The device includes at least one anchor configured to engage tissue of a heart and a thread or other elongate member adapted to be coupled to the anchor and secured to heart tissue. The anchor may be attached to papillary muscle tissue and an elongate member may be attached to a valve leaflet for creating artificial chordae tendinae, thereby treating mitral valve prolapse. In another application, multiple anchors may be deployed within a ventricle and the threads pulled together for reducing dilation of a ventricle. A locking mechanism is provided for capturing and locking the threads together, thereby maintaining the ventricle in the reshaped condition.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
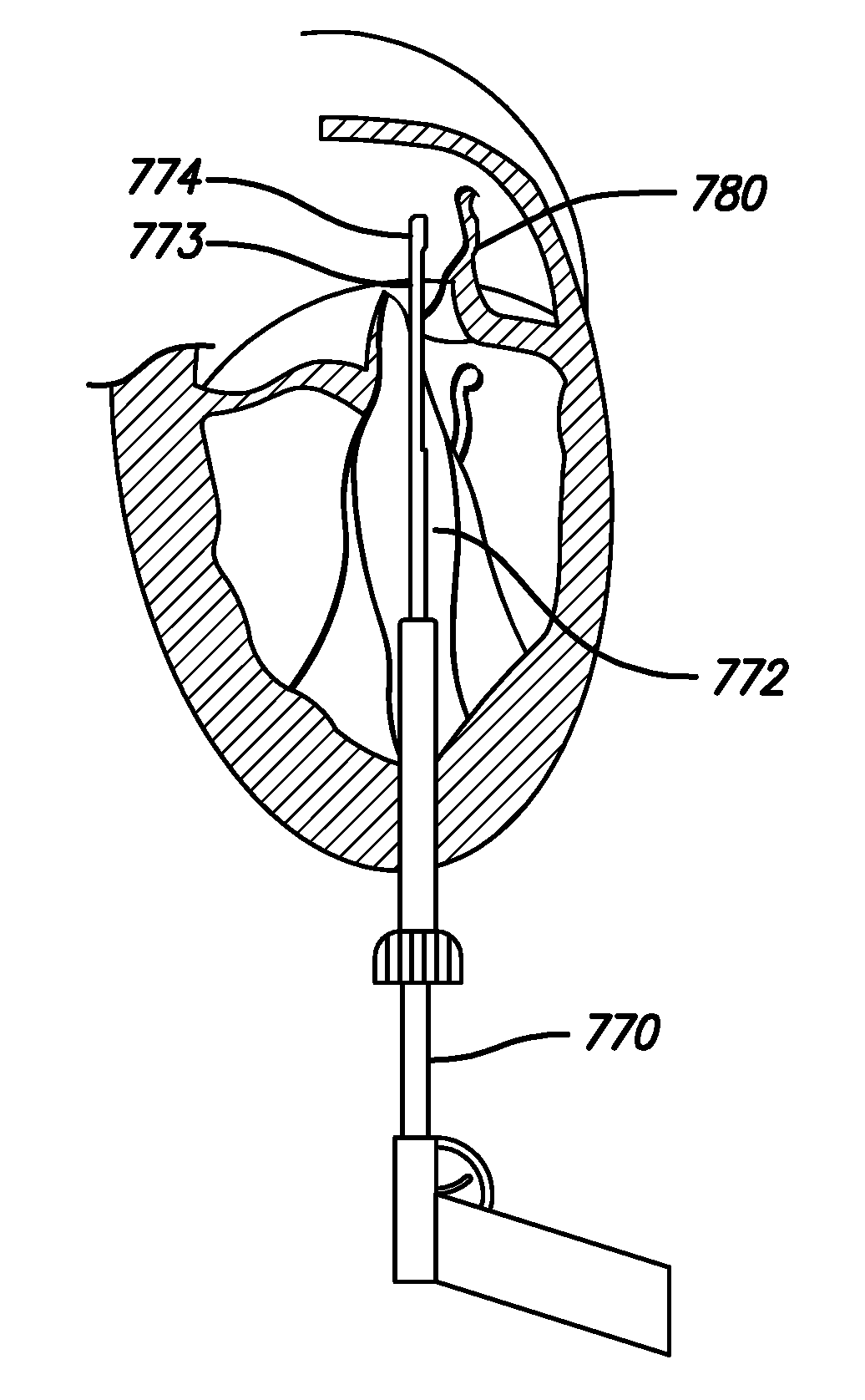
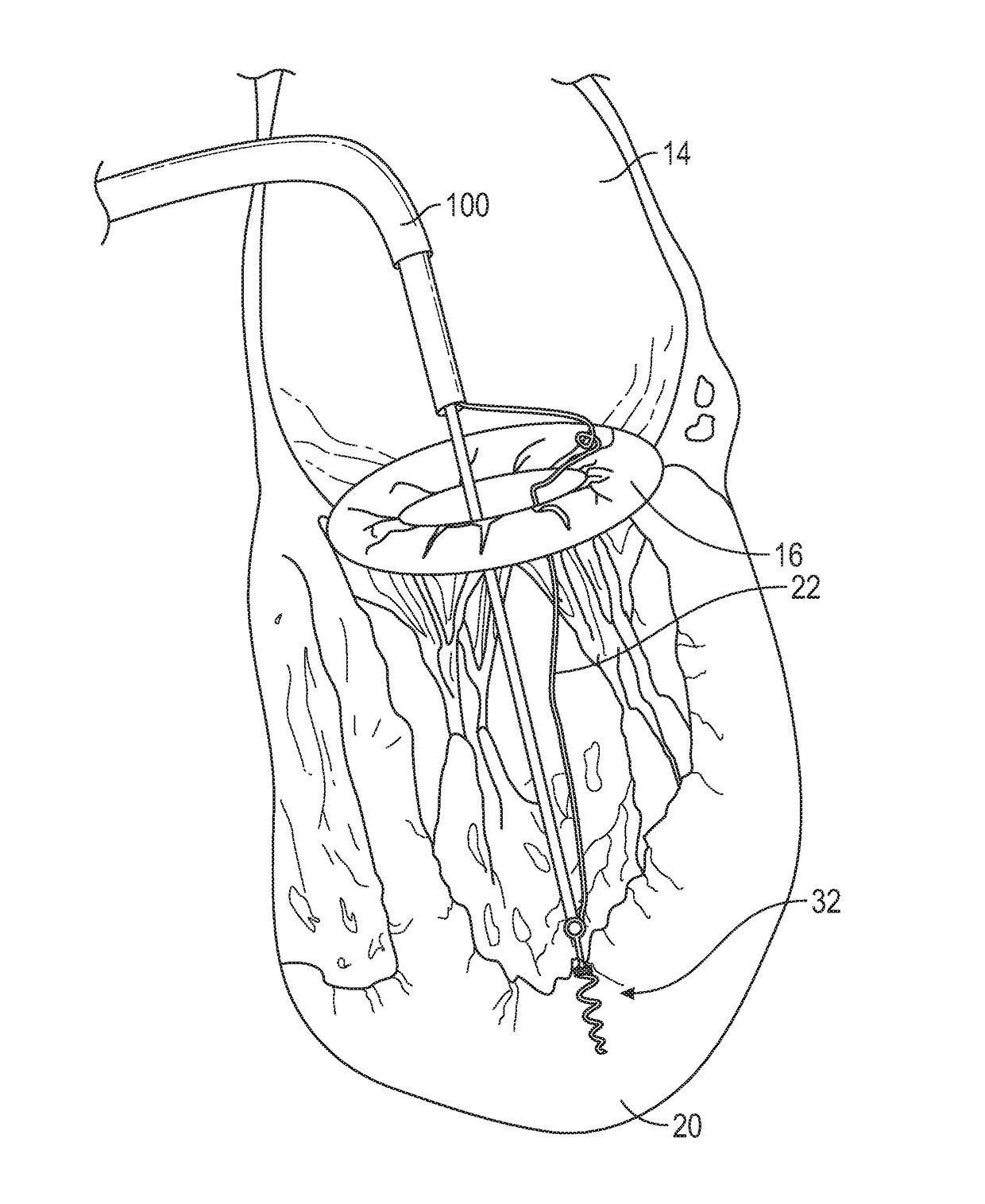
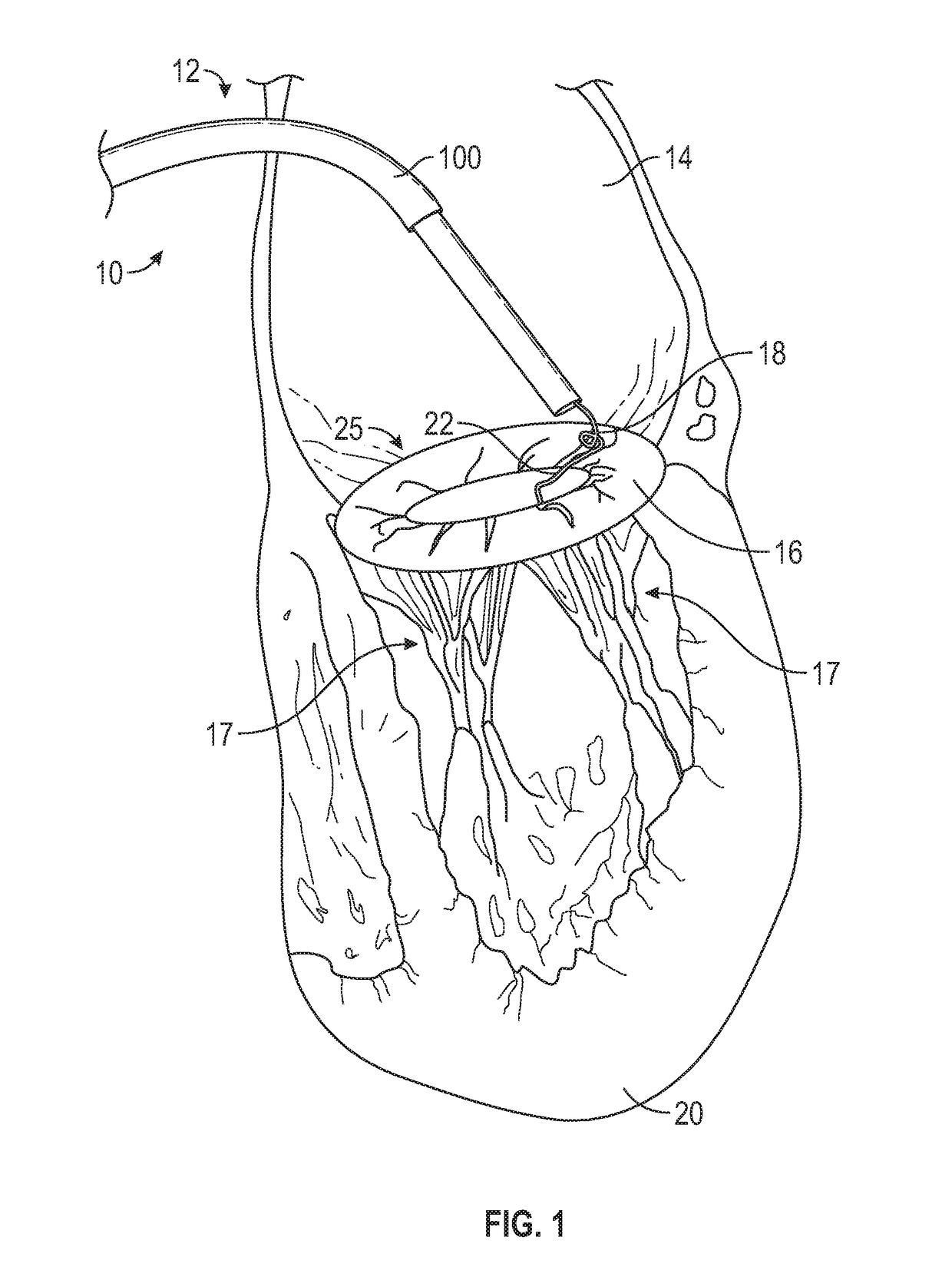
Method and apparatus for transvascular implantation of neo chordae tendinae
ActiveUS9877833B1Limiting range of travelFunction increaseSuture equipmentsHeart valvesPapillary muscleMitral valve leaflet
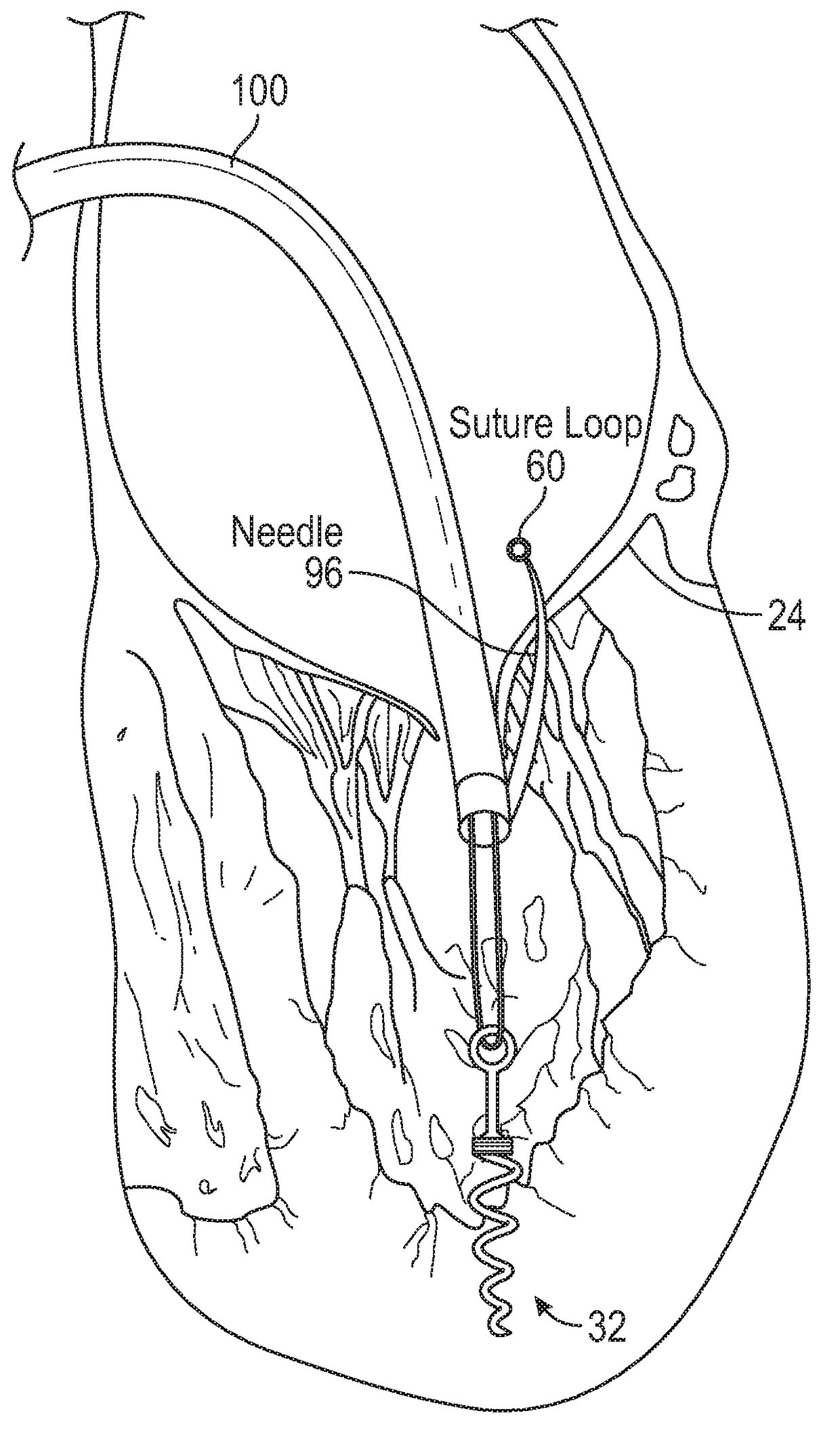
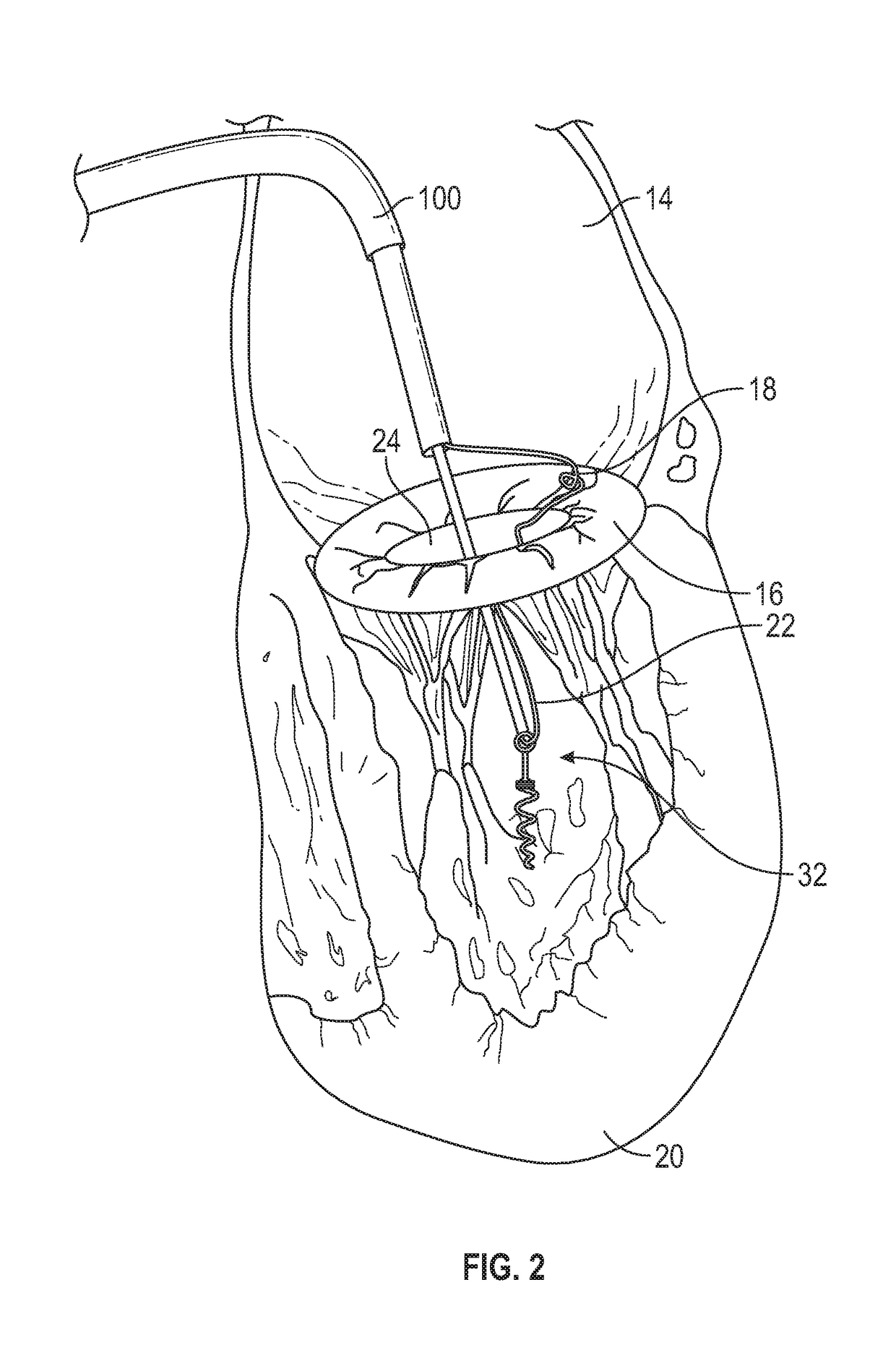
Methods and devices for transvascular prosthetic chordae tendinea implantation are disclosed. A catheter is advanced into the left atrium, through the mitral valve, and into the left ventricle. A ventricular anchor is deployed from the catheter and into a wall of the left ventricle, leaving a ventricular suture attached to the ventricular anchor and extending proximally through the catheter. A leaflet anchor is deployed to secure a mitral valve leaflet to a leaflet suture, with the leaflet suture extending proximally through the catheter. The leaflet suture is secured to the ventricular suture to limit a range of travel of the leaflet in the direction of the left atrium. Also disclosed is an assembled in situ mitral valve leaflet restraint, having a neo papillary muscle and a neo chordae tendinea.
Owner:PIPELINE MEDICAL TECH INC
Mitral valve treatment techniques
ActiveUS20140148898A1Enhance fibrosisReduce distanceAnnuloplasty ringsSurgeryMitral valve leafletVALVE PORT
A method is provided for treating mitral valve regurgitation, including inserting a band around between 90 and 270 degrees of a mitral valve of a heart, including around at least a portion of a posterior cusp of the valve, in a space defined by (a) a ventricular wall, (b) a ventricular surface of the posterior cusp in a vicinity of an annulus of the valve, and (c) a plurality of chordae tendineae of one or more types of chordae tendineae selected from the group consisting of: second-order chordae tendineae and third-order chordae tendineae. The method also includes applying pressure to the posterior cusp by inflating the band.
Owner:VALTECH CARDIO LTD
Dynamically adjustable suture and chordae tendinae
InactiveUS20080228272A1Lower activation energyIncreased riskHeart valvesLigamentsThermal energyLight energy
Embodiments of a dynamically adjustable artificial chordae tendinae implant are described. In some embodiments the implant includes a body portion, including an adjustable portion. In some embodiments, the implant includes a plurality of adjustable portions. In some embodiments the adjustable element can include a shape memory material. The adjustable portion can be configured to transform from a first conformation to a second conformation in response to an activation energy. In some embodiments, the activation energy can be one of electromagnetic energy, acoustic energy, light energy, thermal energy, electrical energy, mechanical energy, or a combination of energies. The implant couples a heart valve leaflet to a papillary muscle. Activation of the shape memory material regulates tension between the muscle and valve leaflet improving coaptation of heart valve leaflets, and reducing or eliminating regurgitation.
Owner:MICARDIA CORP
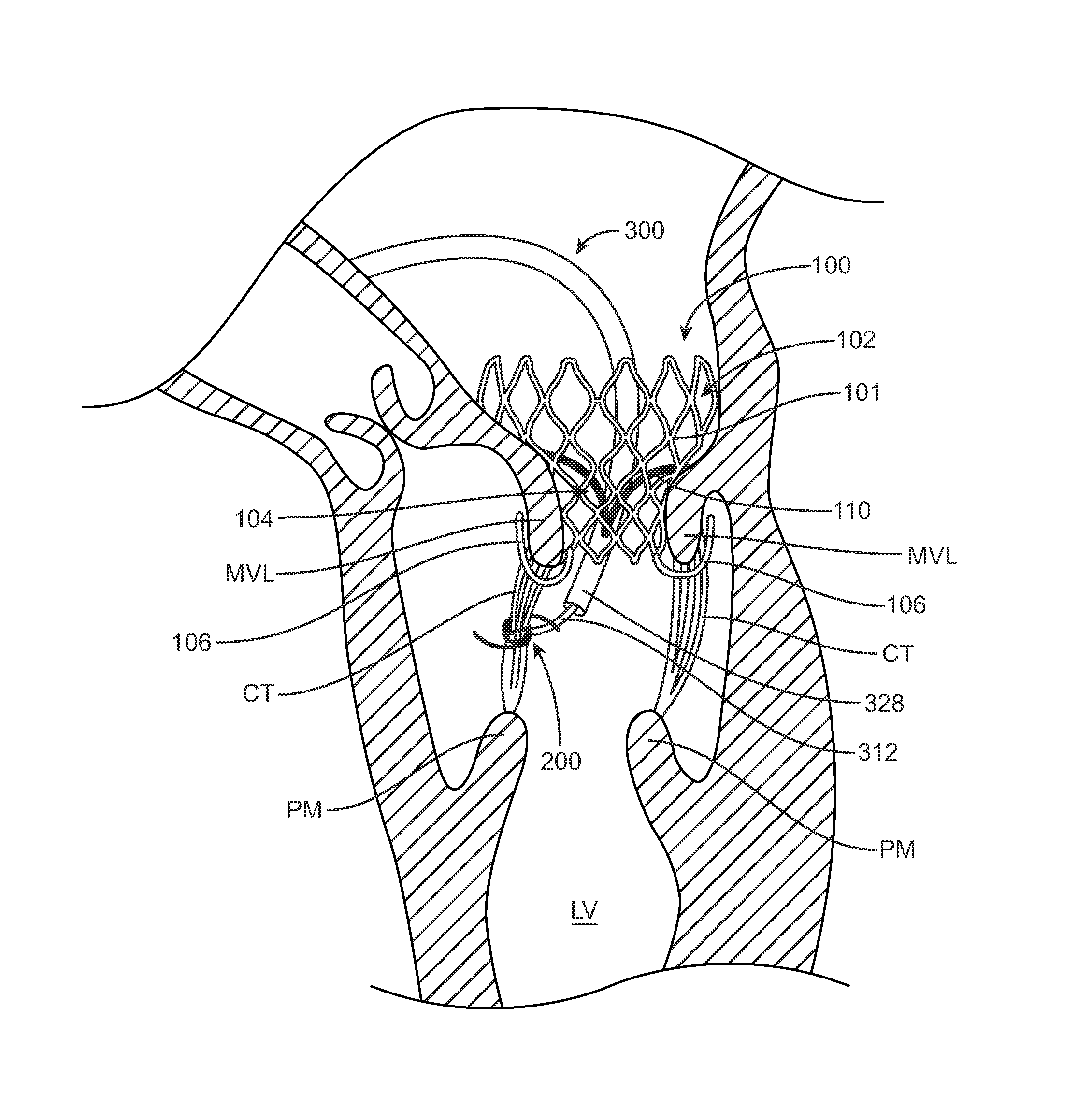
Valve delivery system having an integral displacement component for managing chordae tendineae in situ and methods of use thereof
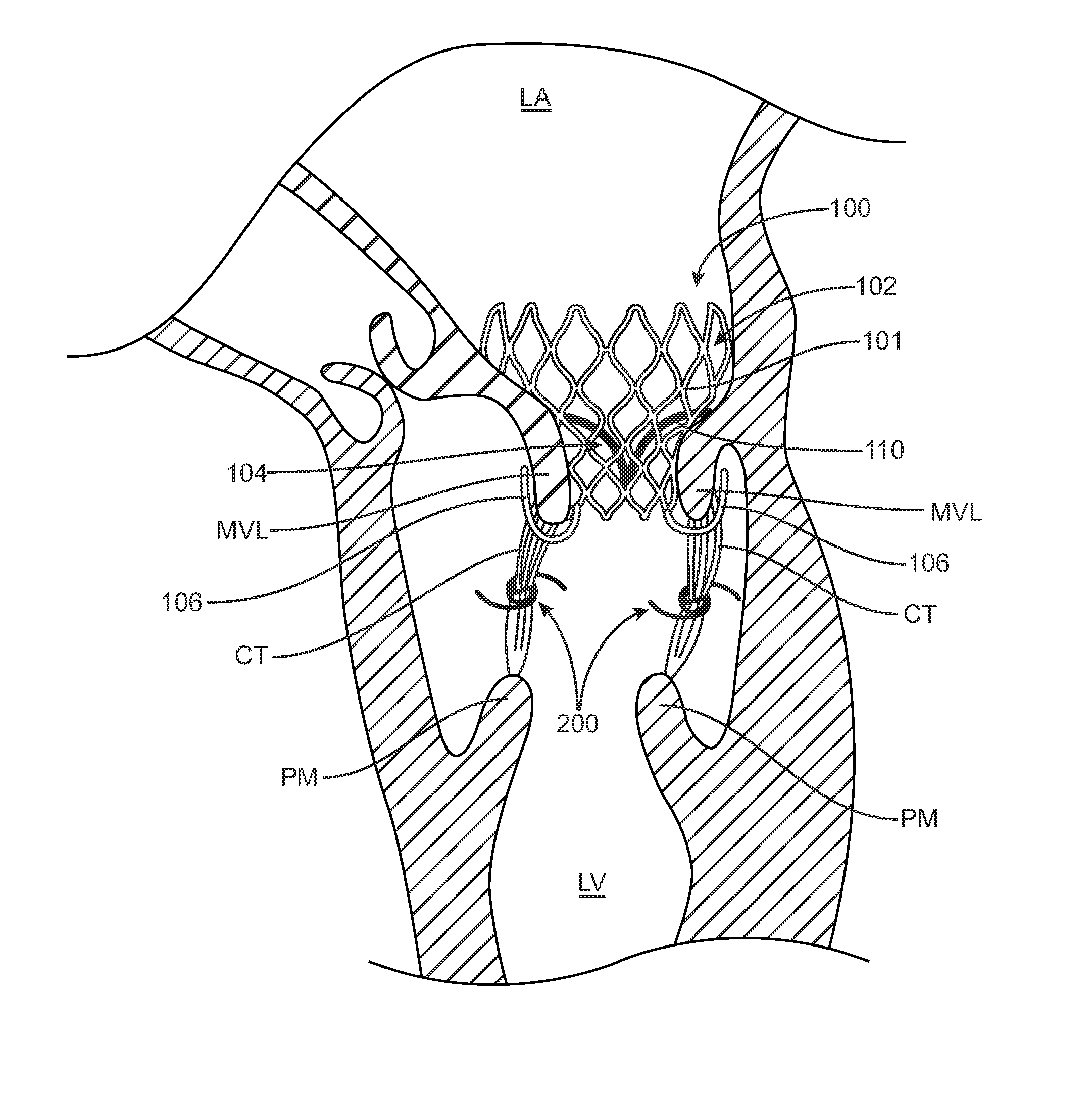
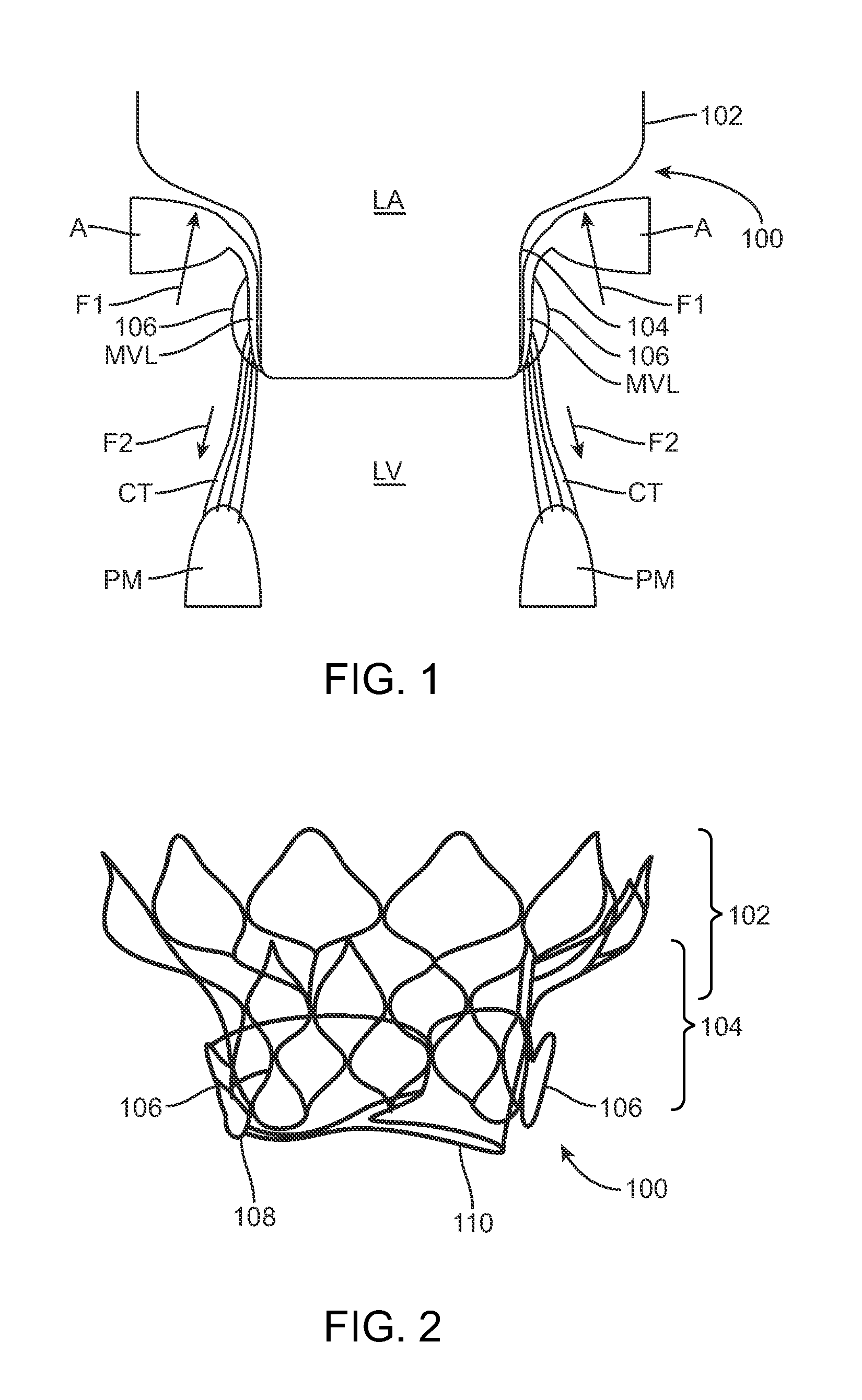
Embodiments hereof relate methods of delivering a valve prosthesis to an annulus of a native valve of a heart. A valve delivery system is introduced into a ventricle of the heart via a ventricular wall of the heart. The valve delivery system has a displacement component at the distal portion thereof. The valve prosthesis is in a delivery configuration and the displacement component is in a delivery state in which the displacement component has a first outer diameter. While the valve prosthesis is in the delivery configuration, the displacement component of the valve delivery system is radially expanded into an expanded state in which the displacement component has a second outer diameter greater than the first outer diameter. The valve delivery system is advanced towards the annulus of the native valve of the heart with the displacement component in the expanded state to displace chordae tendineae.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
Method for transvascular implantation of neo chordae tendinae
ActiveUS20180185151A1Limiting range of travelFunction increaseSuture equipmentsHeart valvesPapillary muscleMitral valve leaflet
Methods and devices for transvascular prosthetic chordae tendinea implantation are disclosed. A catheter is advanced into the left atrium, through the mitral valve, and into the left ventricle. A ventricular anchor is deployed from the catheter and into a wall of the left ventricle, leaving a ventricular suture attached to the ventricular anchor and extending proximally through the catheter. A leaflet anchor is deployed to secure a mitral valve leaflet to a leaflet suture, with the leaflet suture extending proximally through the catheter. The leaflet suture is secured to the ventricular suture to limit a range of travel of the leaflet in the direction of the left atrium. Also disclosed is an assembled in situ mitral valve leaflet restraint, having a neo papillary muscle and a neo chordae tendinea.
Owner:PIPELINE MEDICAL TECH INC
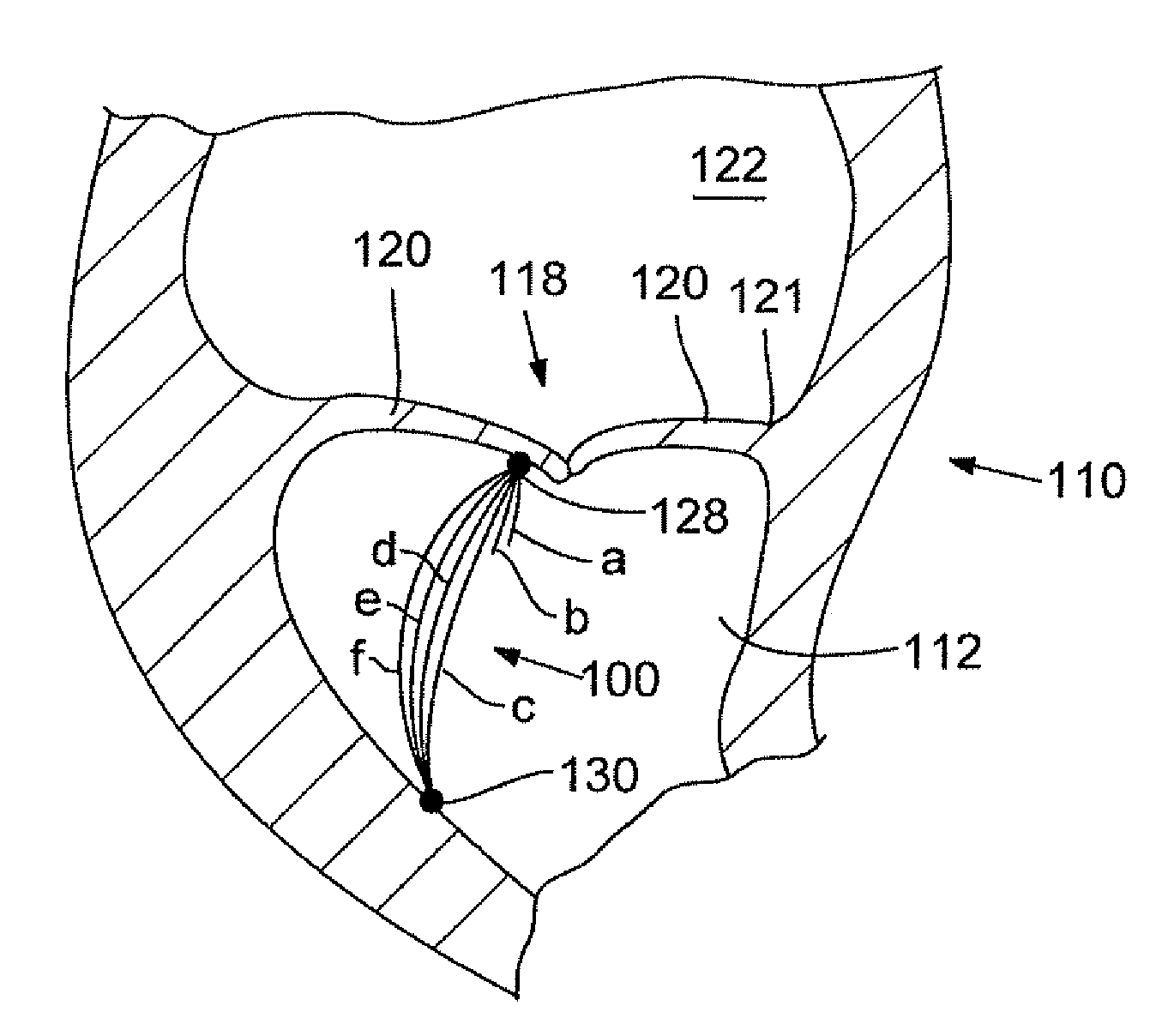
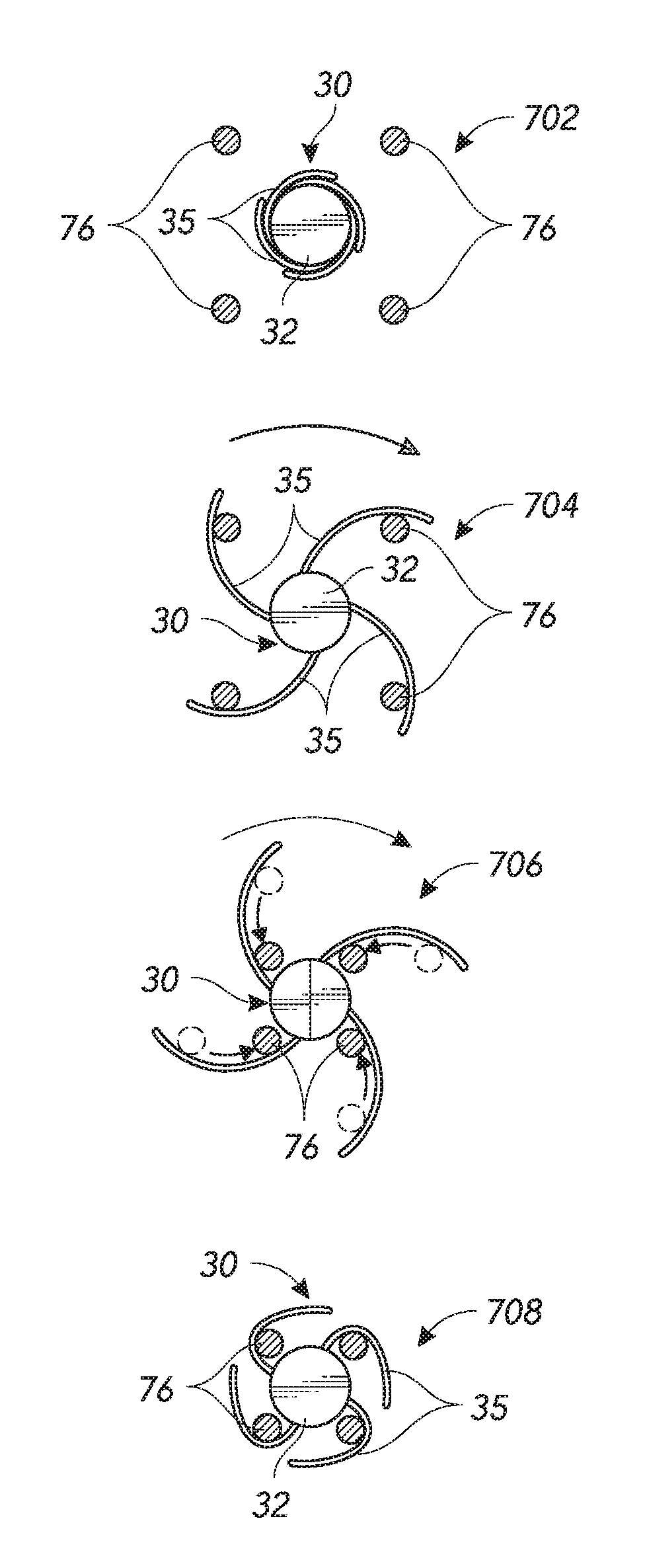
Chordae tendineae adjustment
ActiveUS20180206992A1Accelerating prolapseSuture equipmentsHeart valvesBiomedical engineeringChordae tendinae
A method for improving leaflet prolapse and / or valve regurgitation associated with a heart valve involves introducing a chordae tendineae capturing device into a ventricle of a heart, the chordae tendineae capturing device comprising a central hub component and a plurality of spokes, extending the plurality of spokes outward from the central hub component, rotating the chordae tendineae capturing device in a first direction to bring at least one of the plurality of spokes into physical contact with one or more cords of chordae tendineae disposed in the ventricle, further rotating the chordae tendineae capturing device in the first direction to bring the one or more cords inward towards the central hub component, and closing the plurality of spokes at least partially over the one or more cords to secure the one or more cords.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
Apparatus for transvascular implantation of neo chordae tendinae
ActiveUS20180185150A1Limiting range of travelFunction increaseSuture equipmentsHeart valvesPapillary muscleMitral valve leaflet
Owner:PIPELINE MEDICAL TECH INC
Method of treating paravalvular leakage after prosthetic valve implantation
Owner:MEDTRONIC ARDIAN LUXEMBOURG SARL
Method and apparatus for transvascular implantation of neo chordae tendinae
ActiveUS20180185152A1Limiting range of travelFunction increaseSuture equipmentsHeart valvesPapillary muscleCatheter
Owner:PIPELINE MEDICAL TECH INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com