Patents
Literature
298 results about "Catheter sheath" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
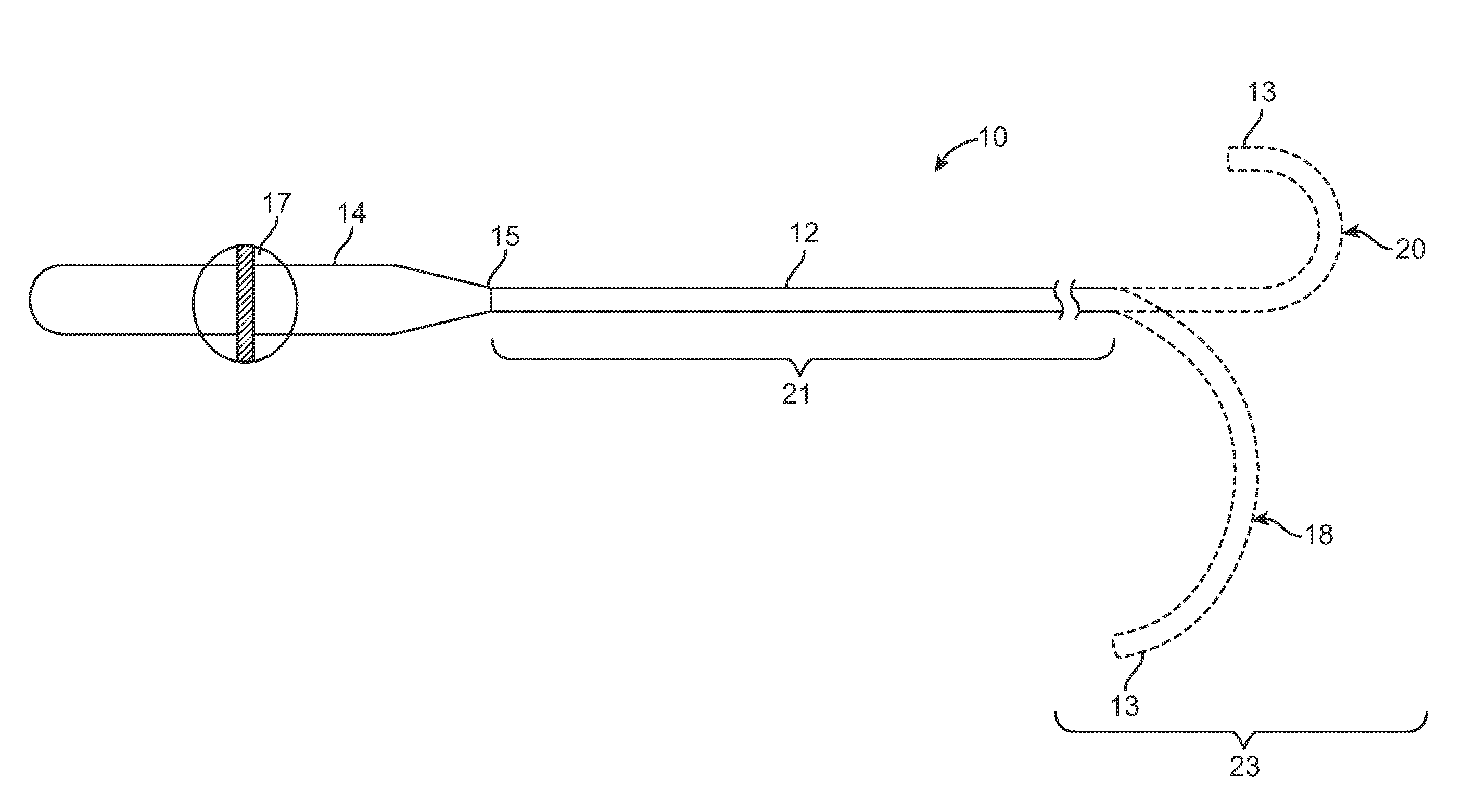
A catheter sheath is a plastic tube of larger diameter than an intravenous catheter, used in the process of introducing the catheter to limit pain and increase accuracy. Companies may package sheaths with catheters, and it is also possible to purchase them as standalone items.
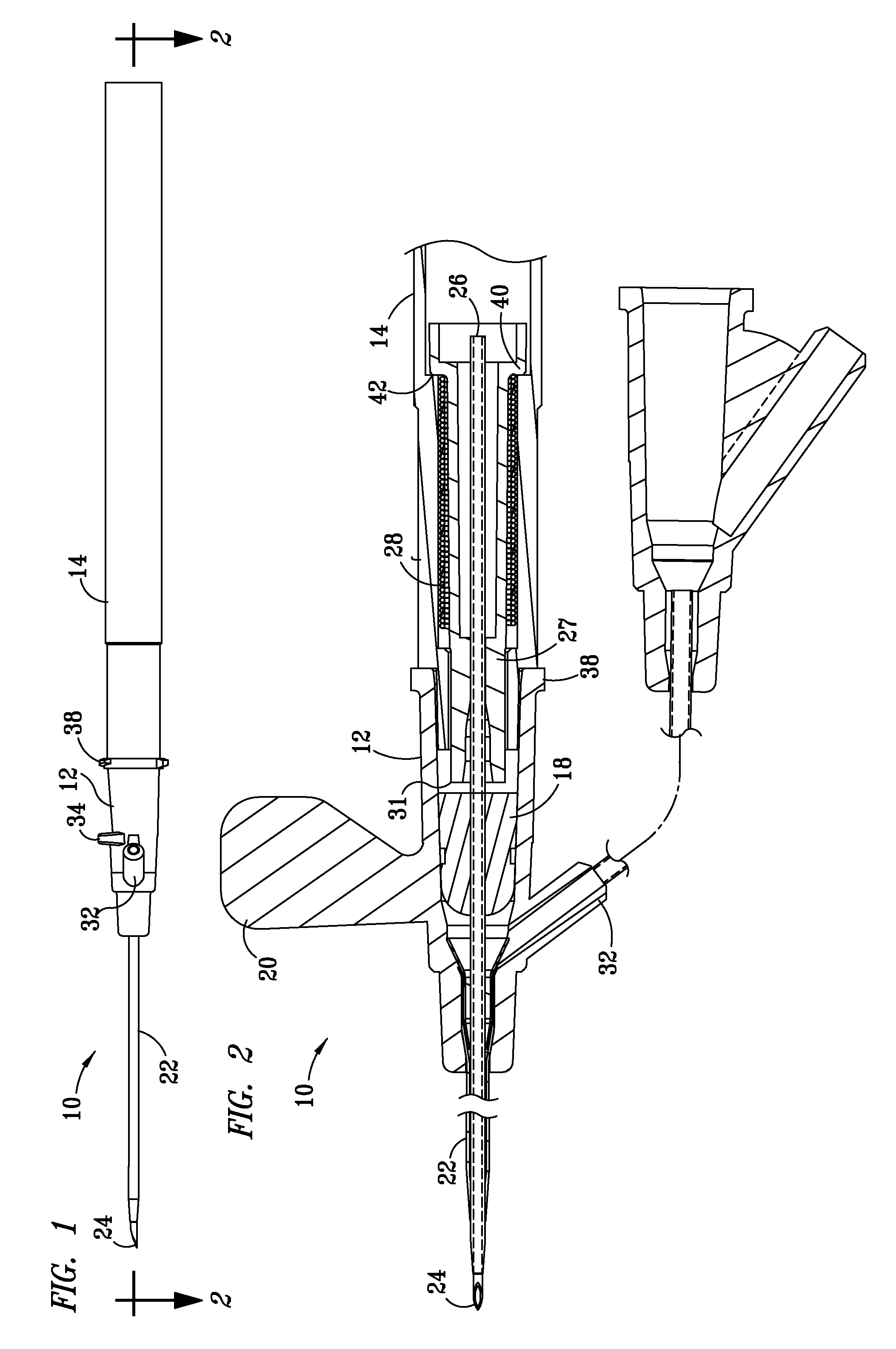
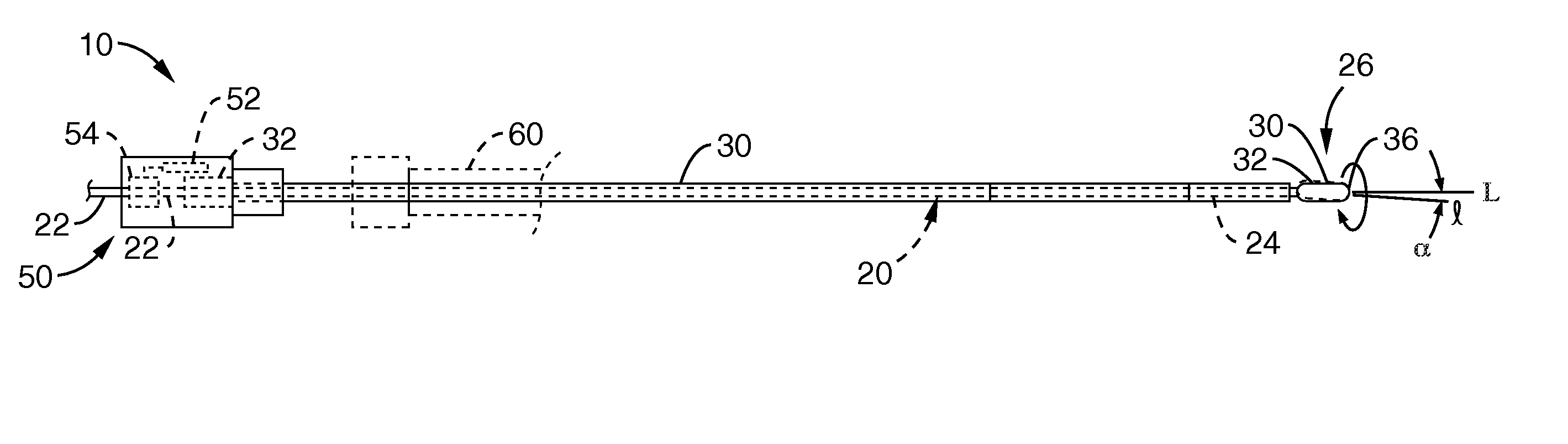
Catheter sheath for implant delivery
ActiveUS9060894B2Increase deflectionLarge radiusStentsBlood vesselsBiomedical engineeringCatheter sheath
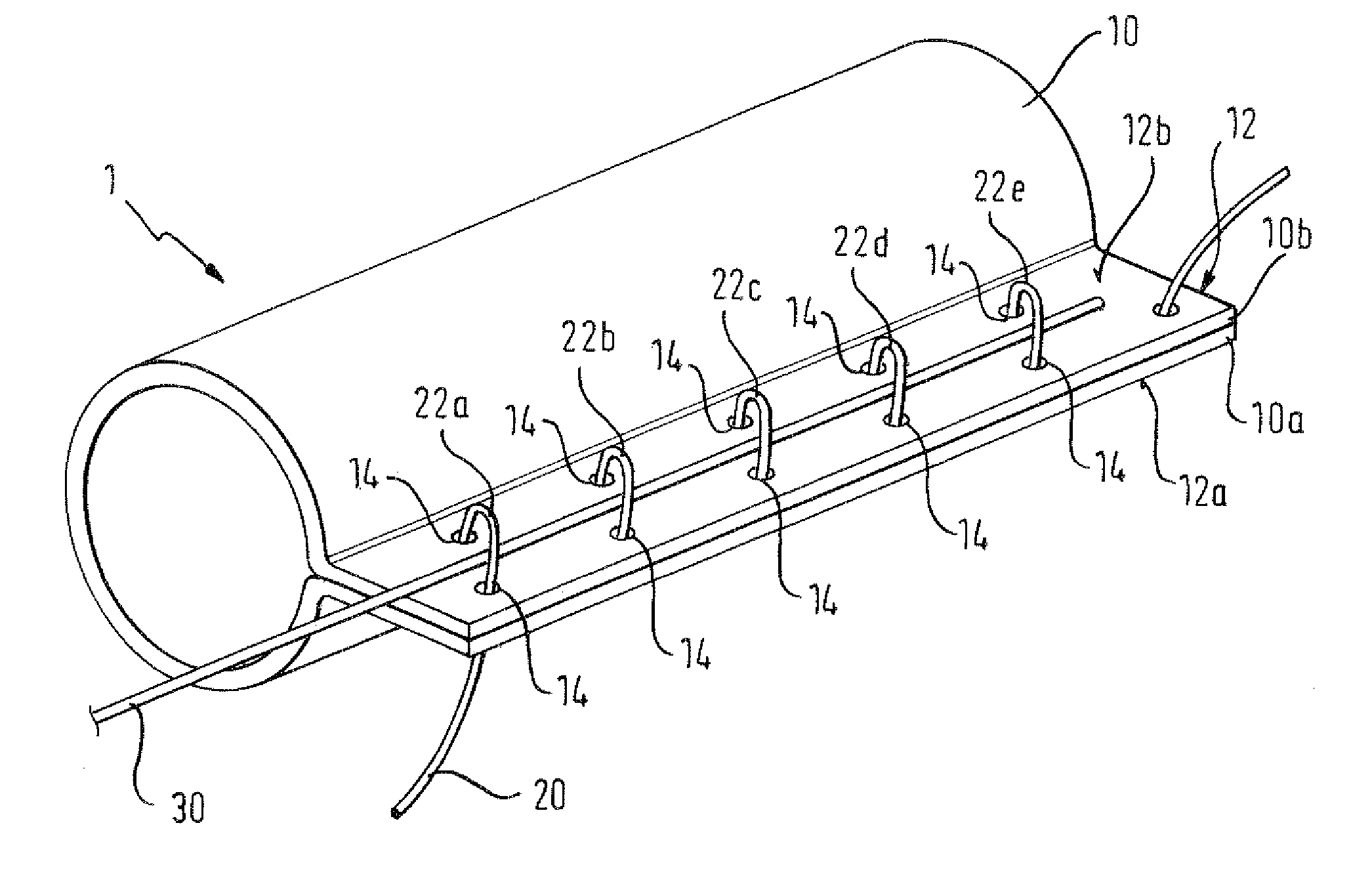
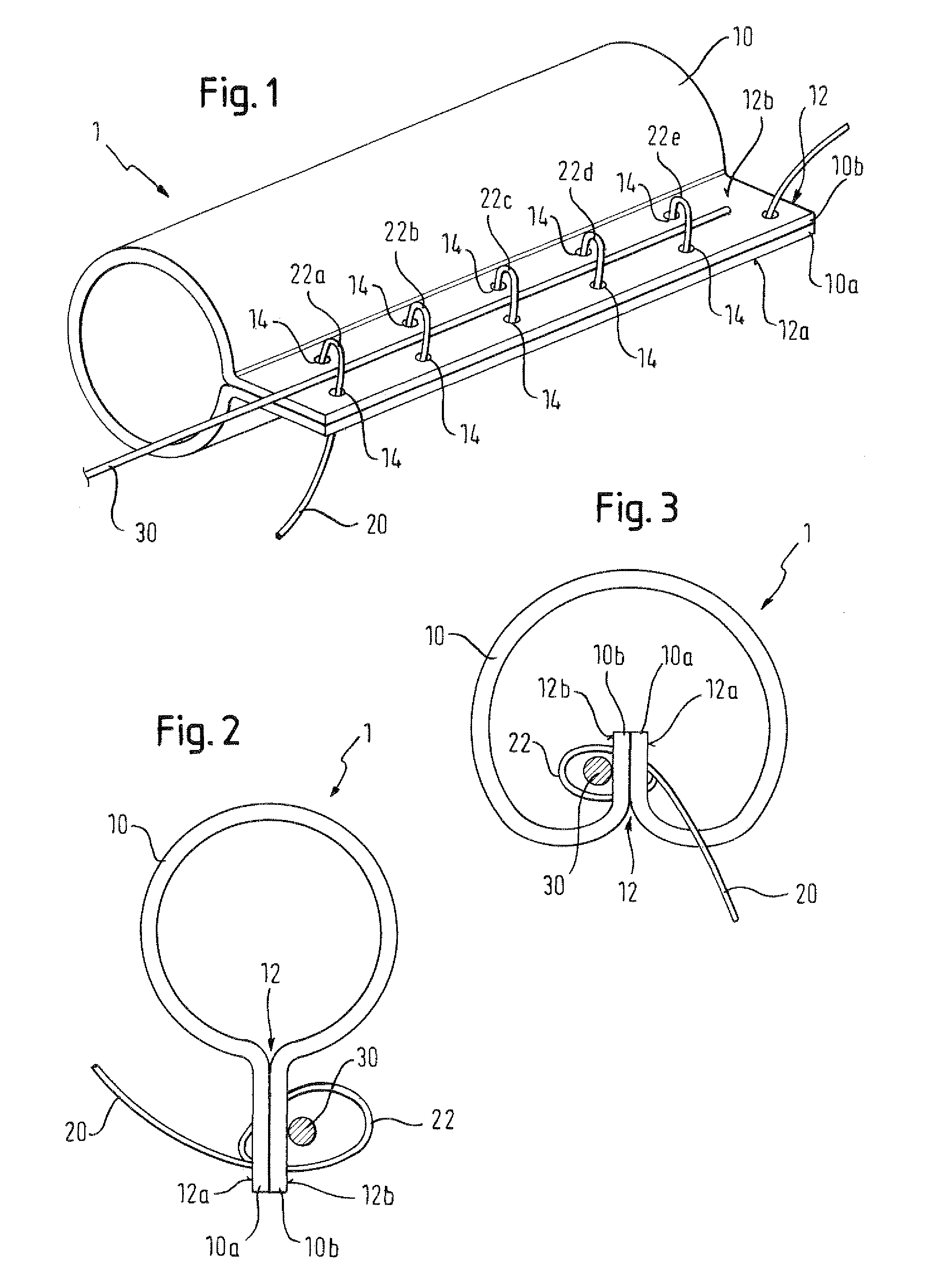
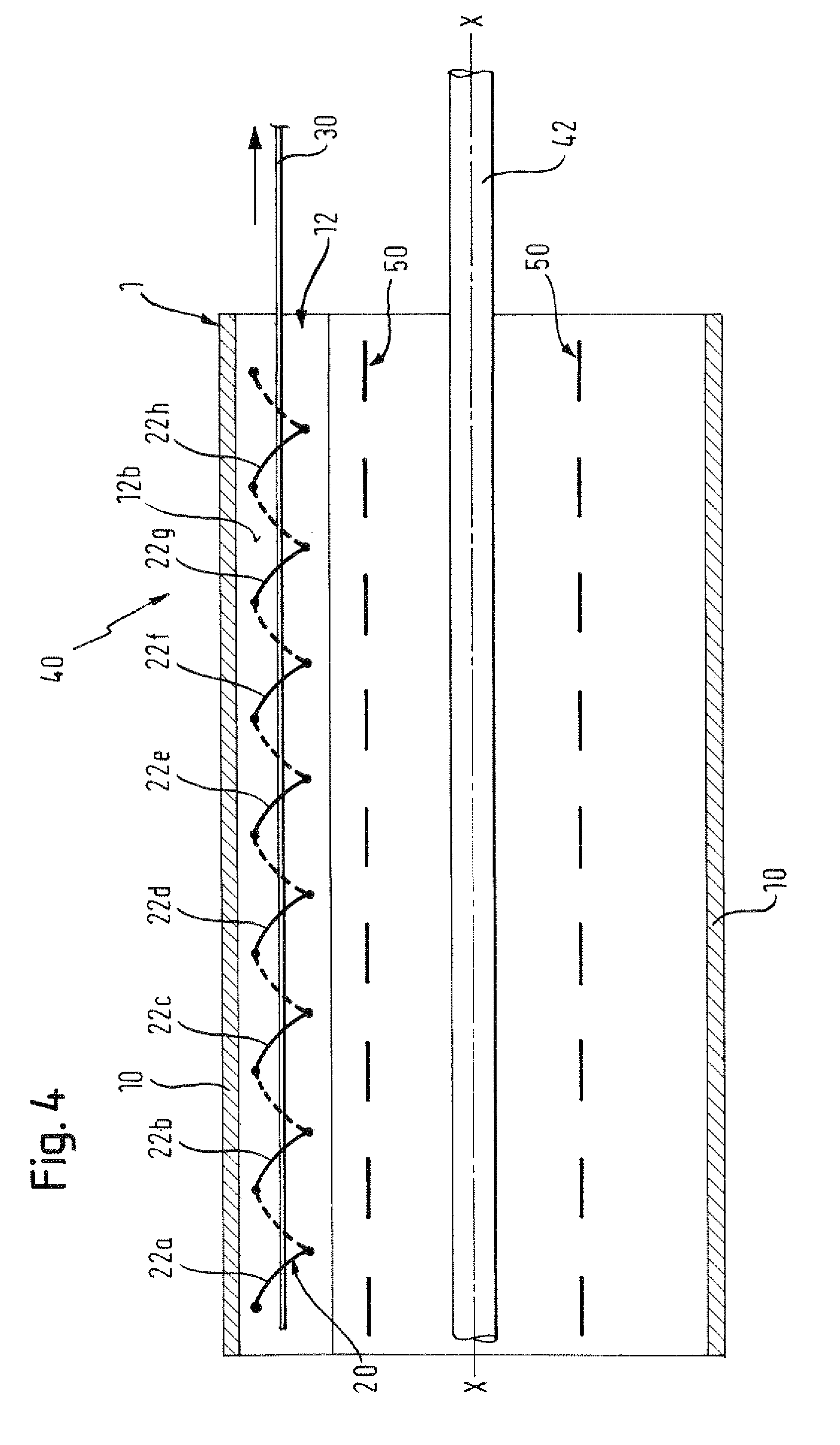
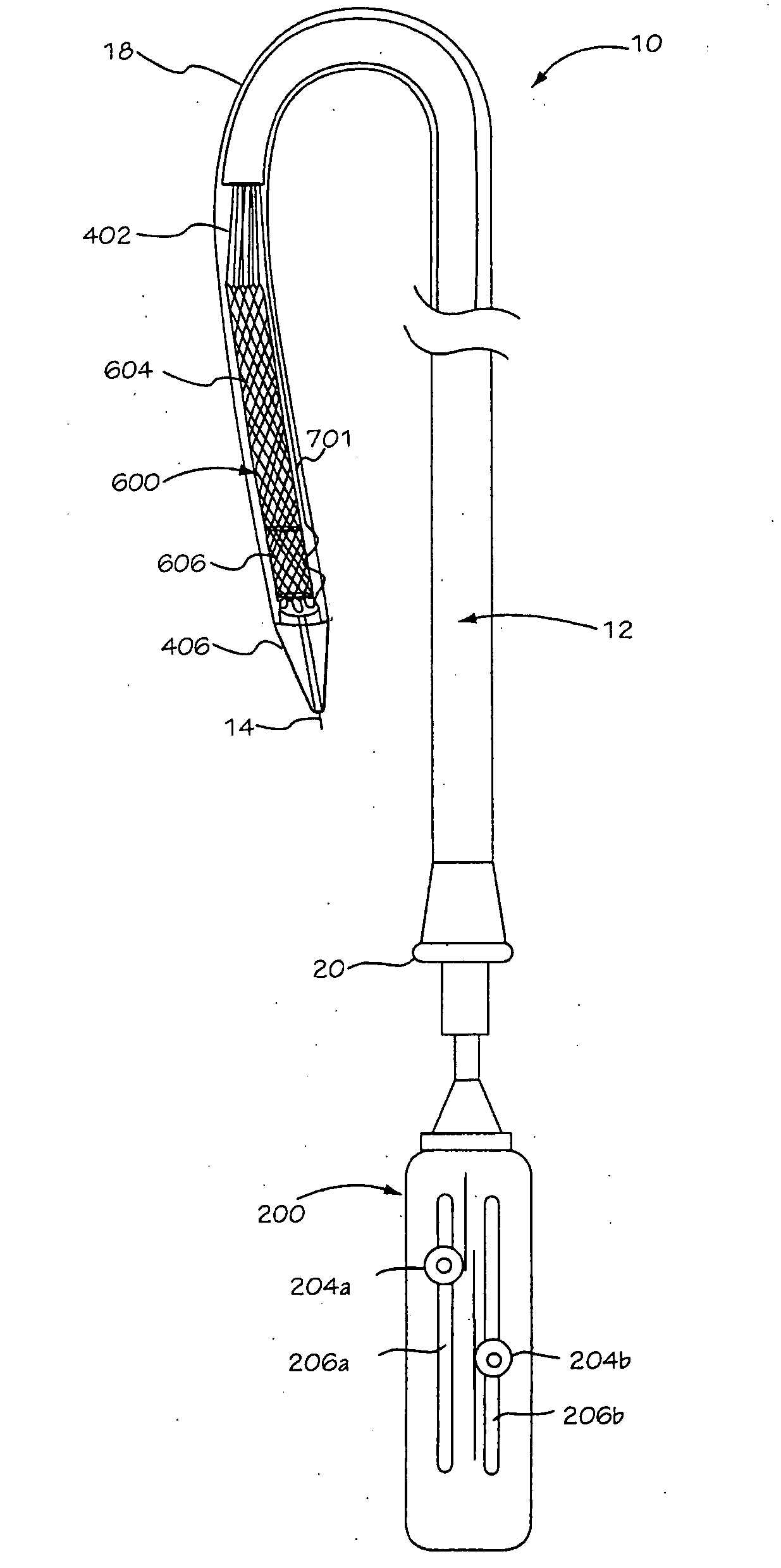
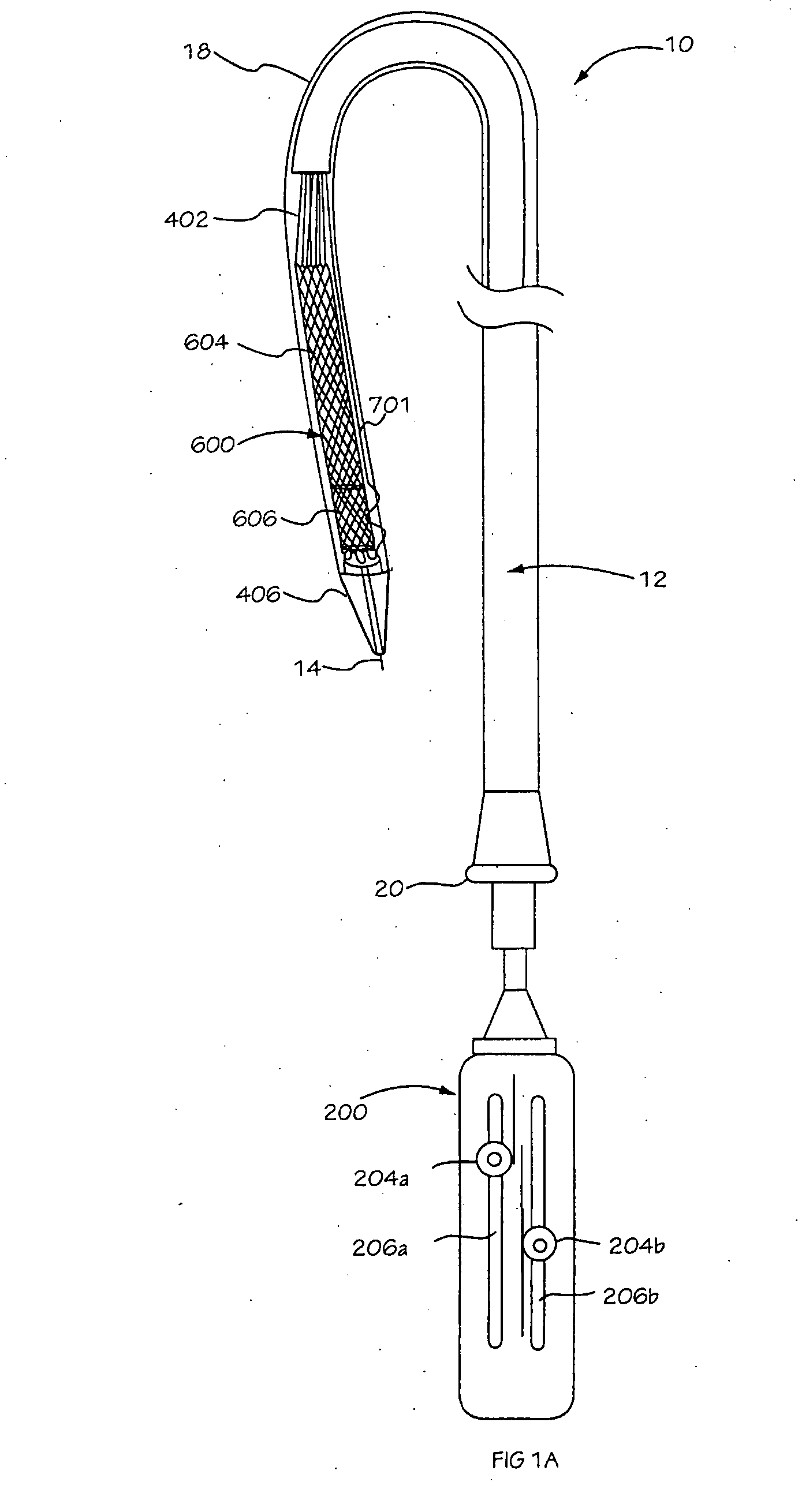
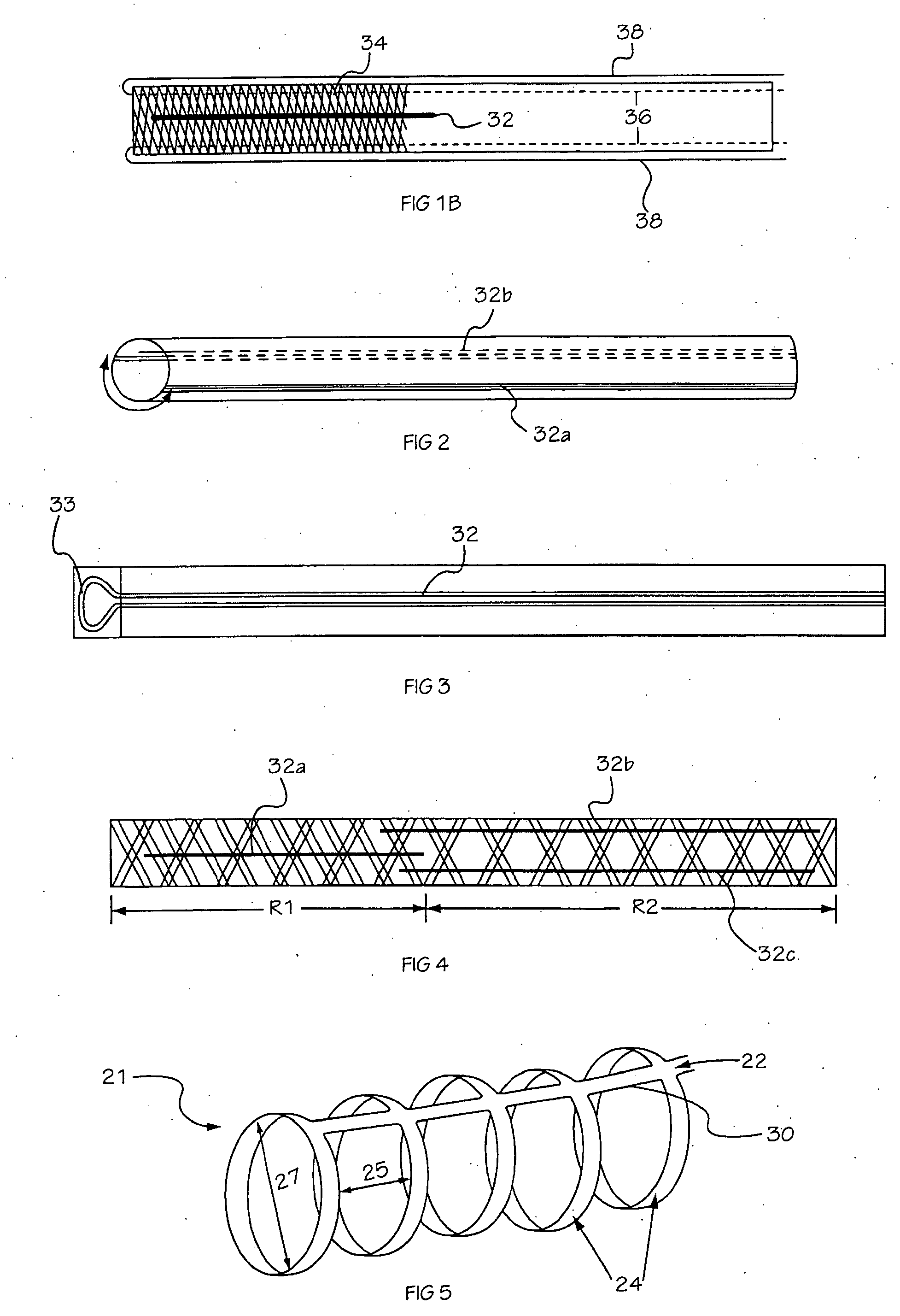
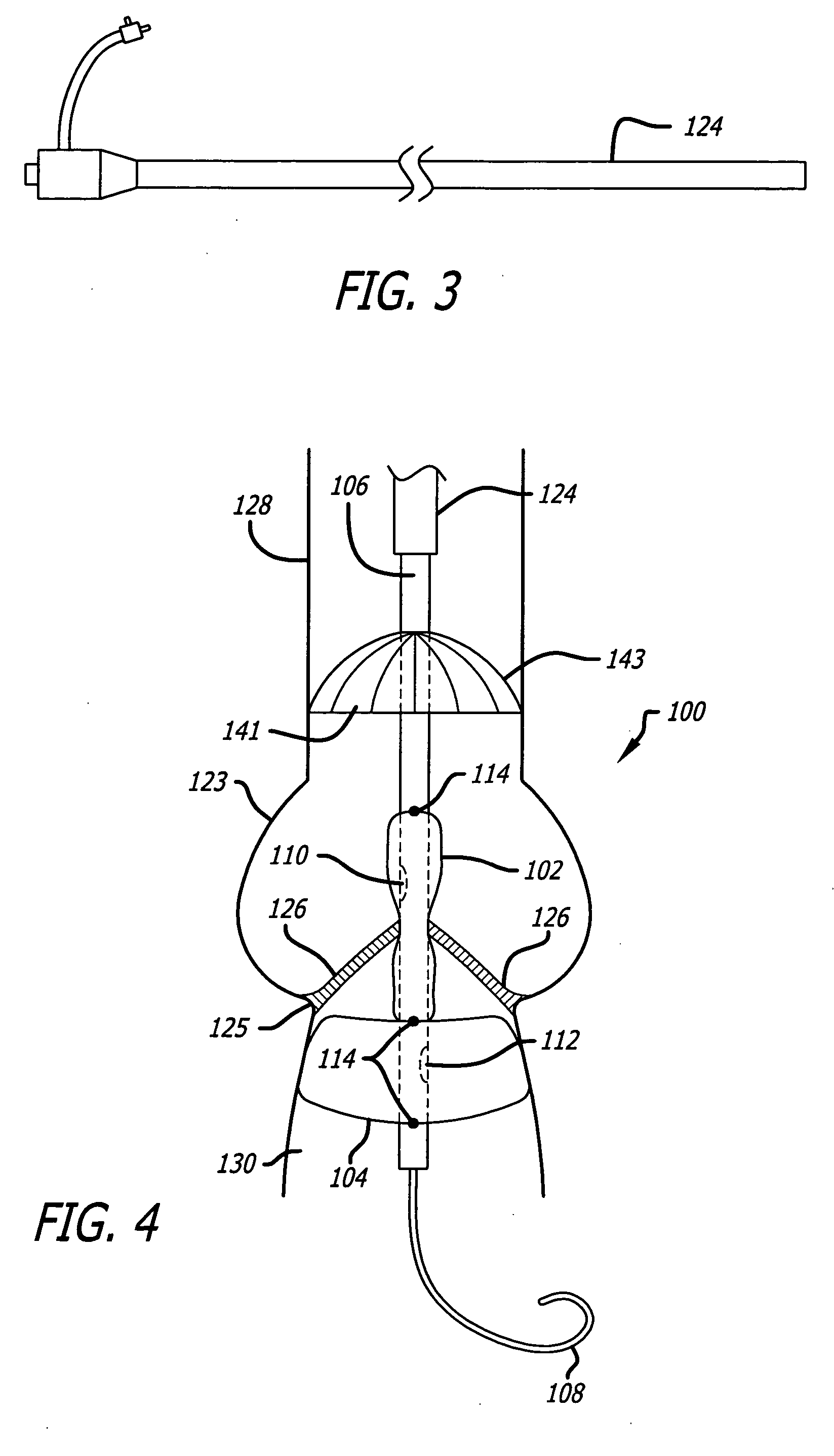
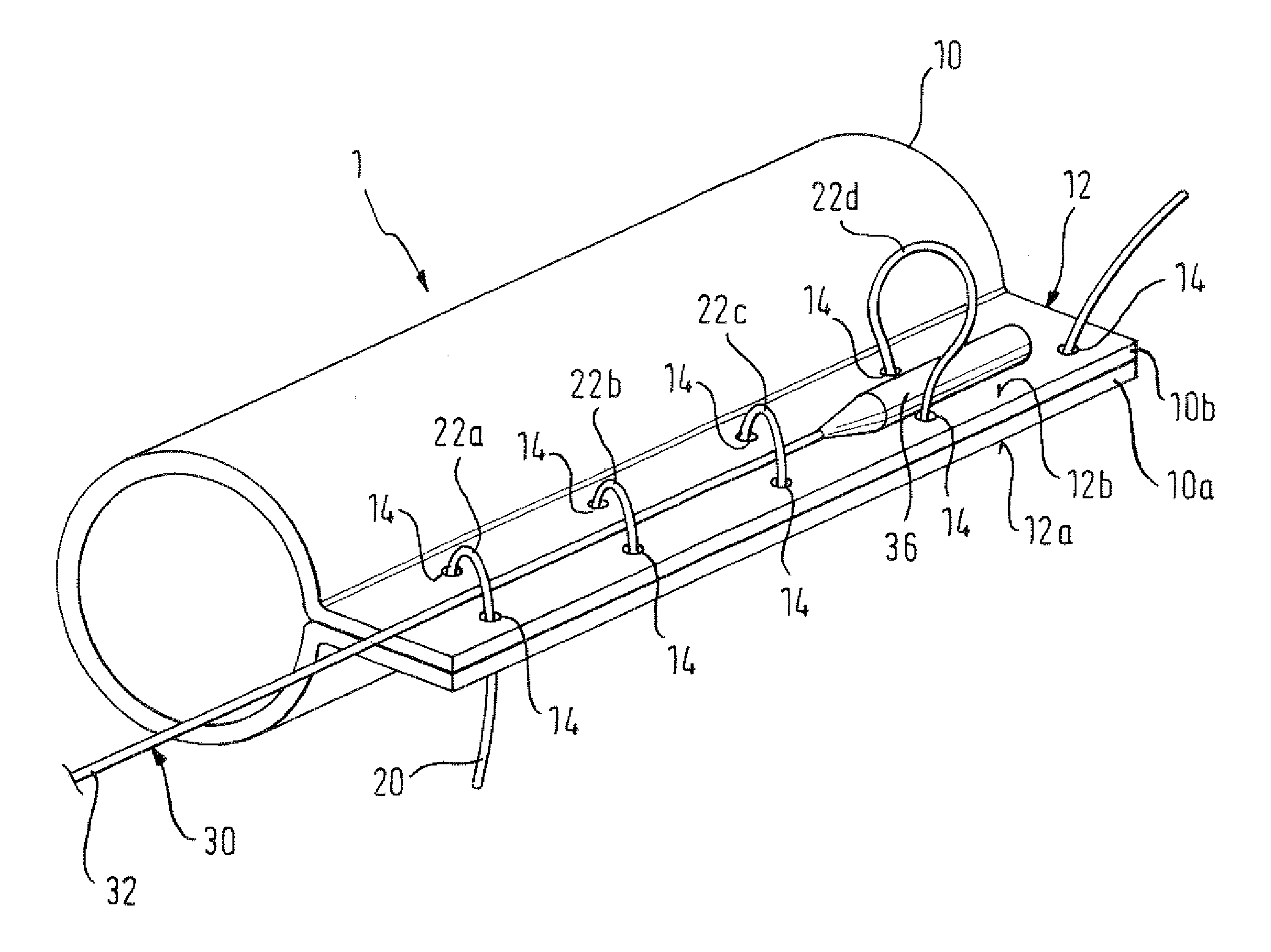
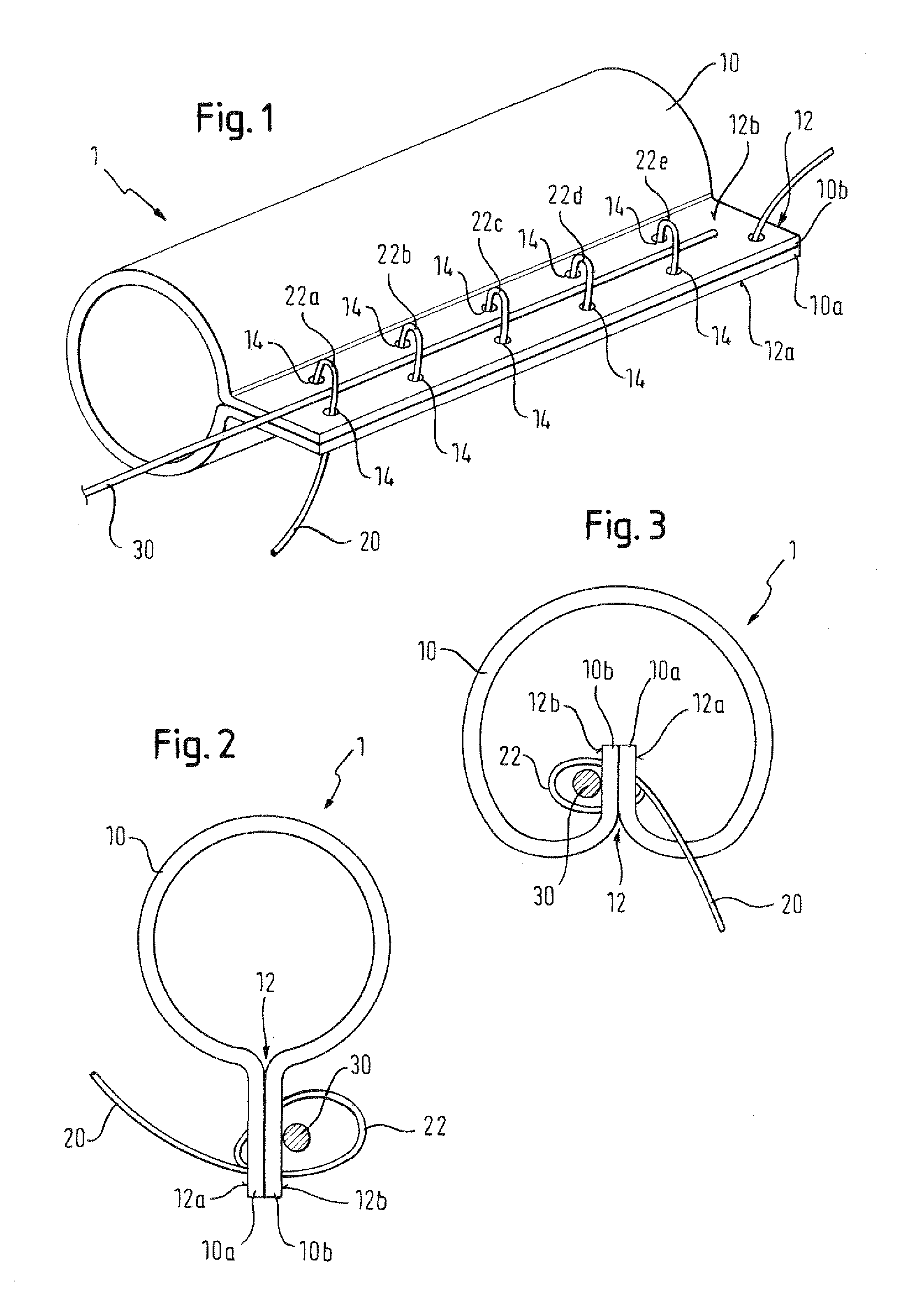
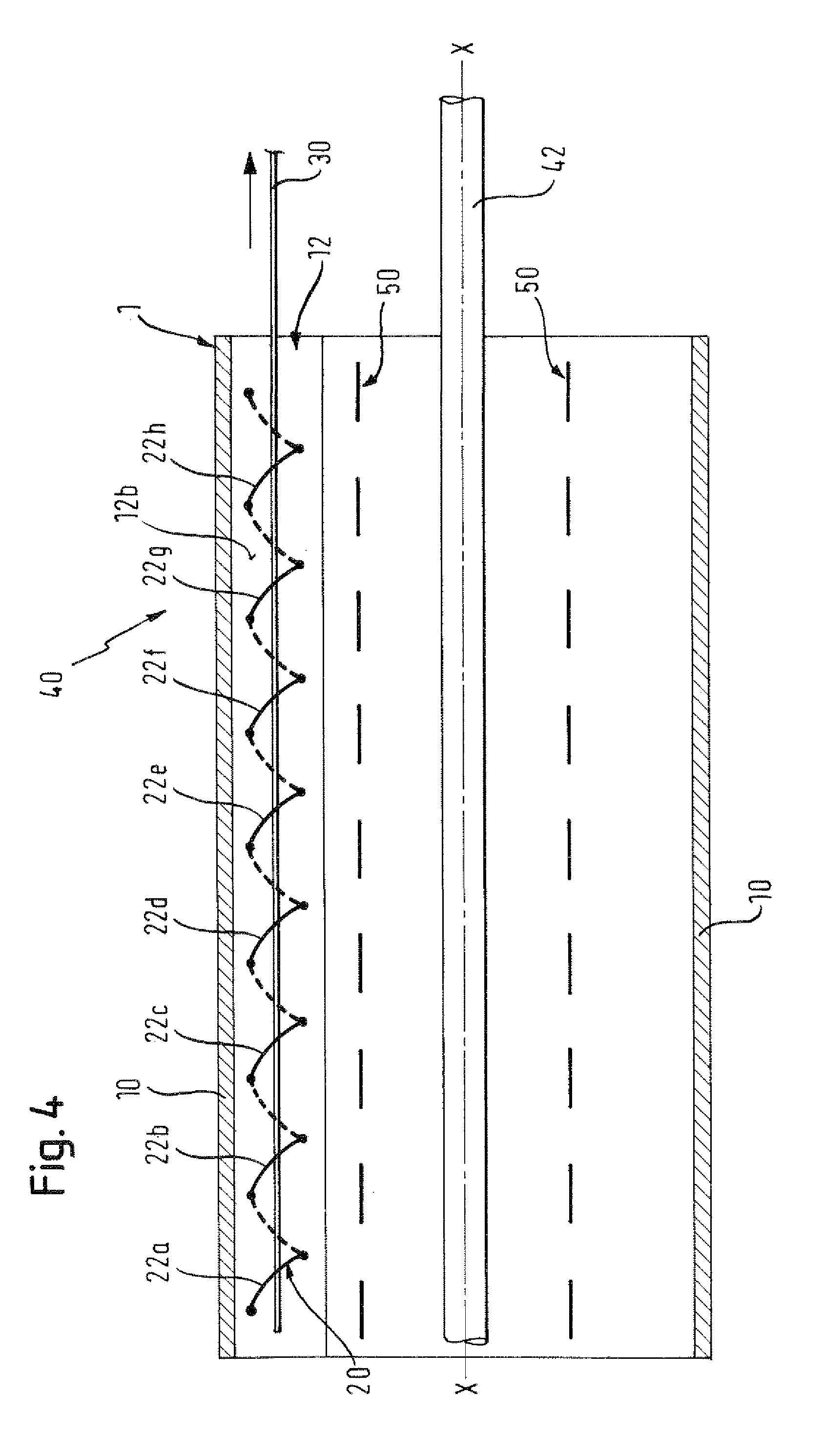
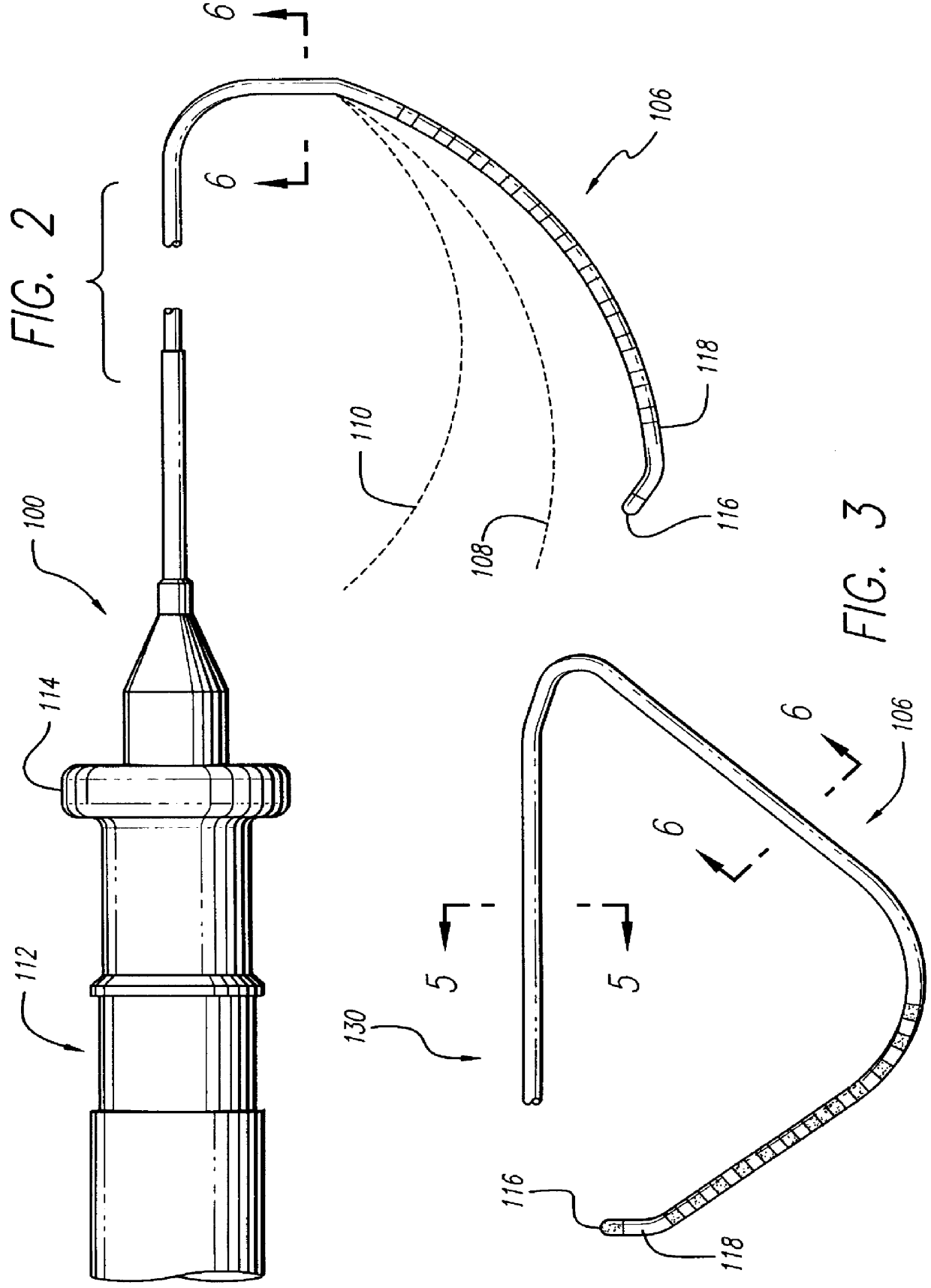
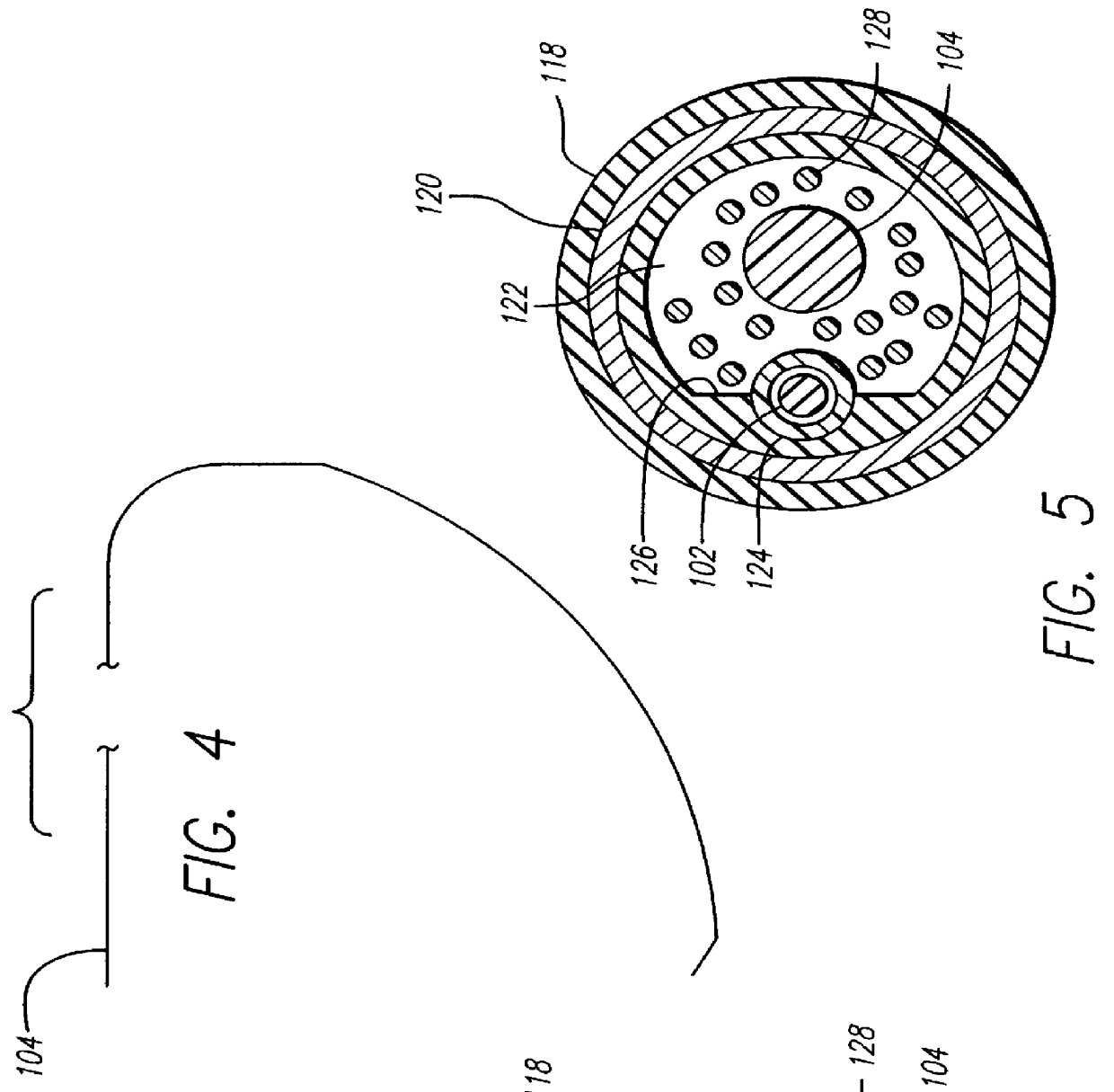
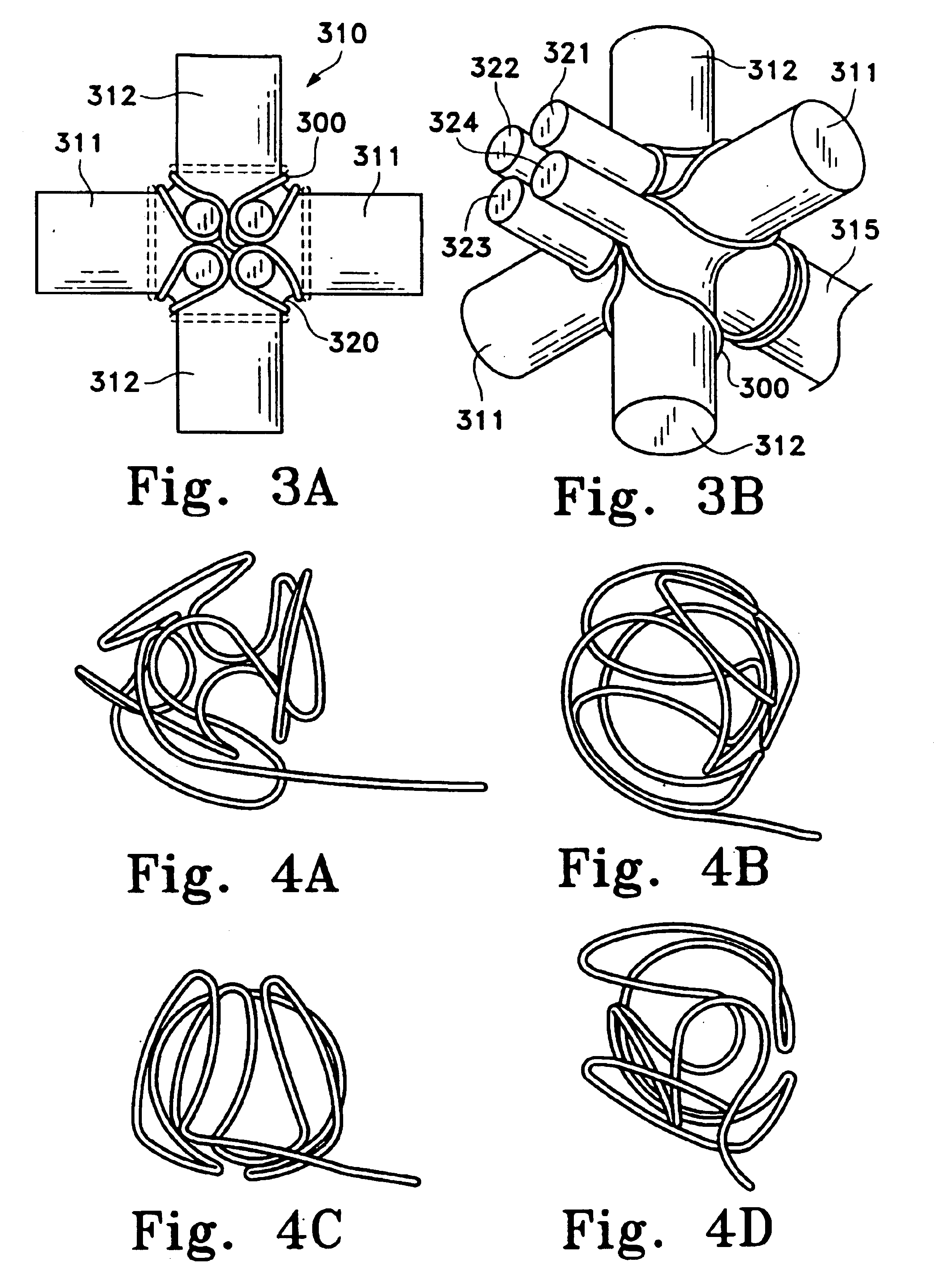
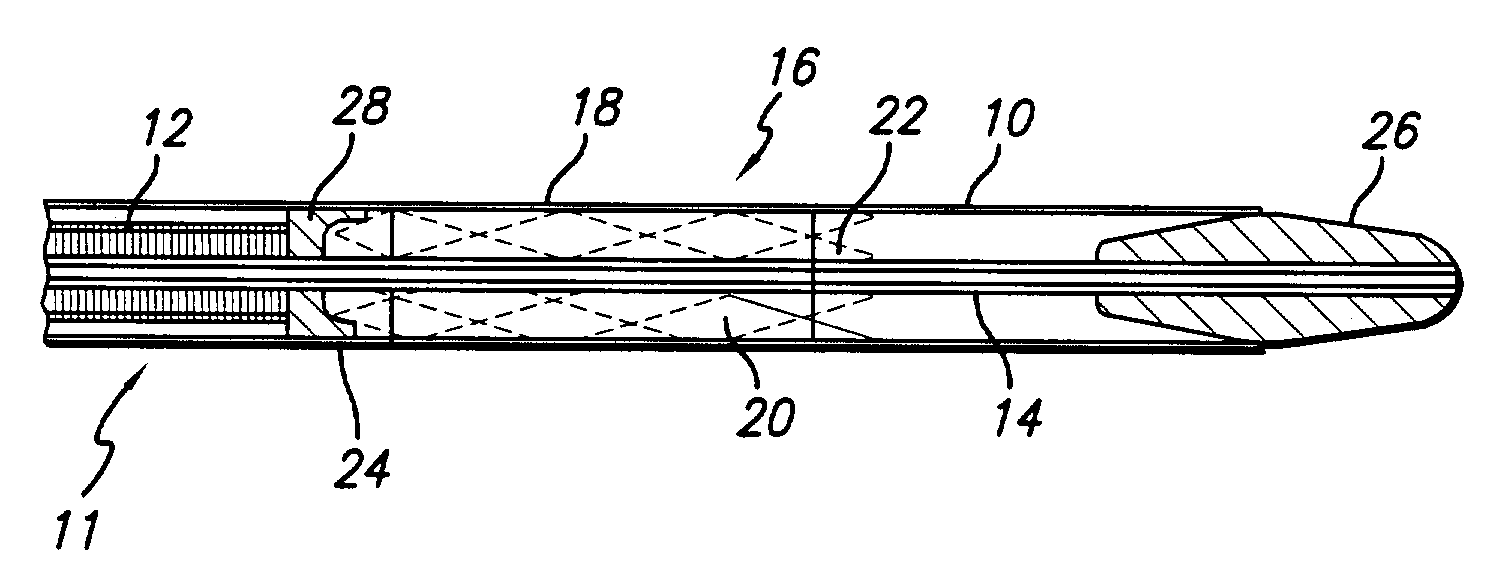
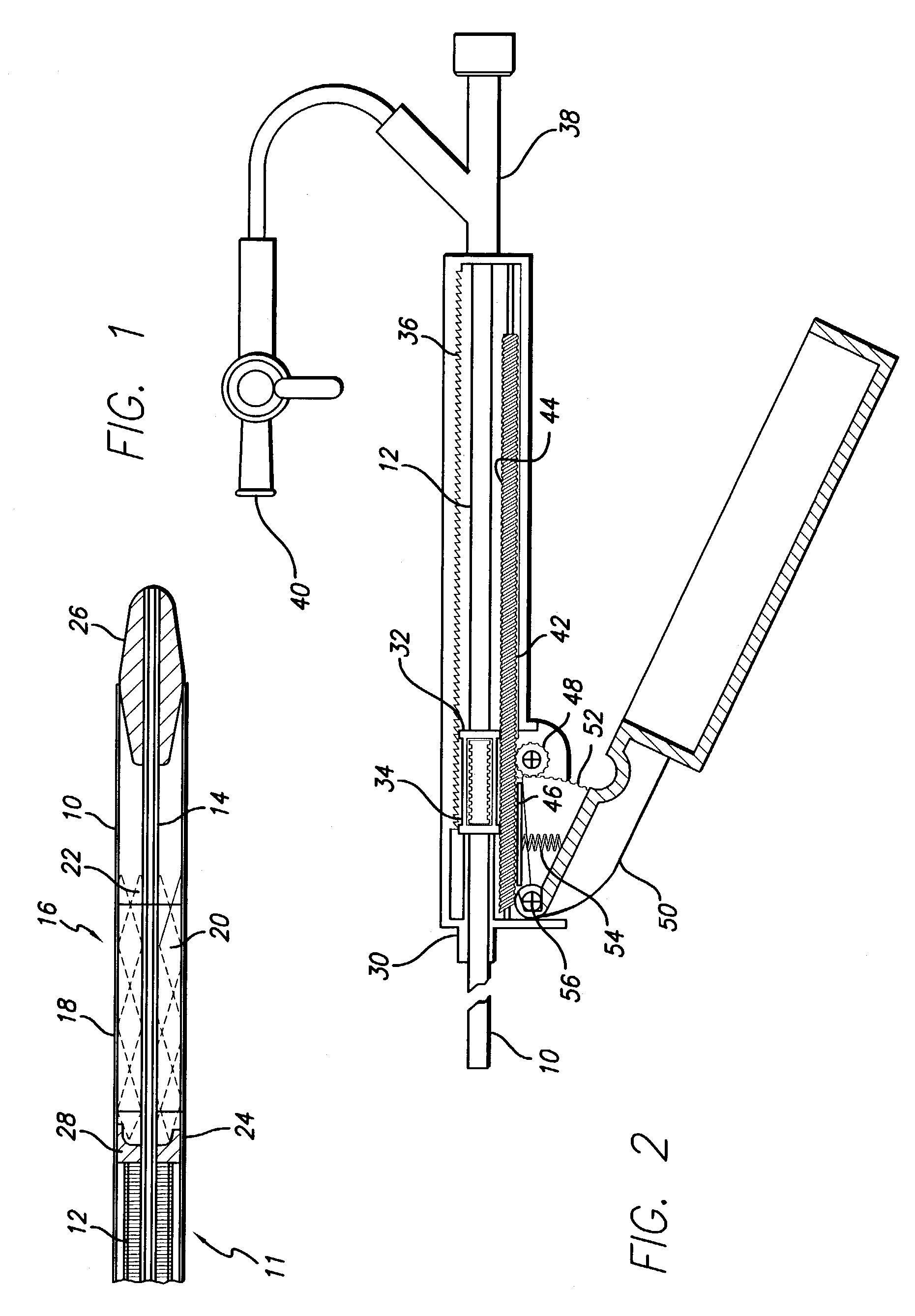
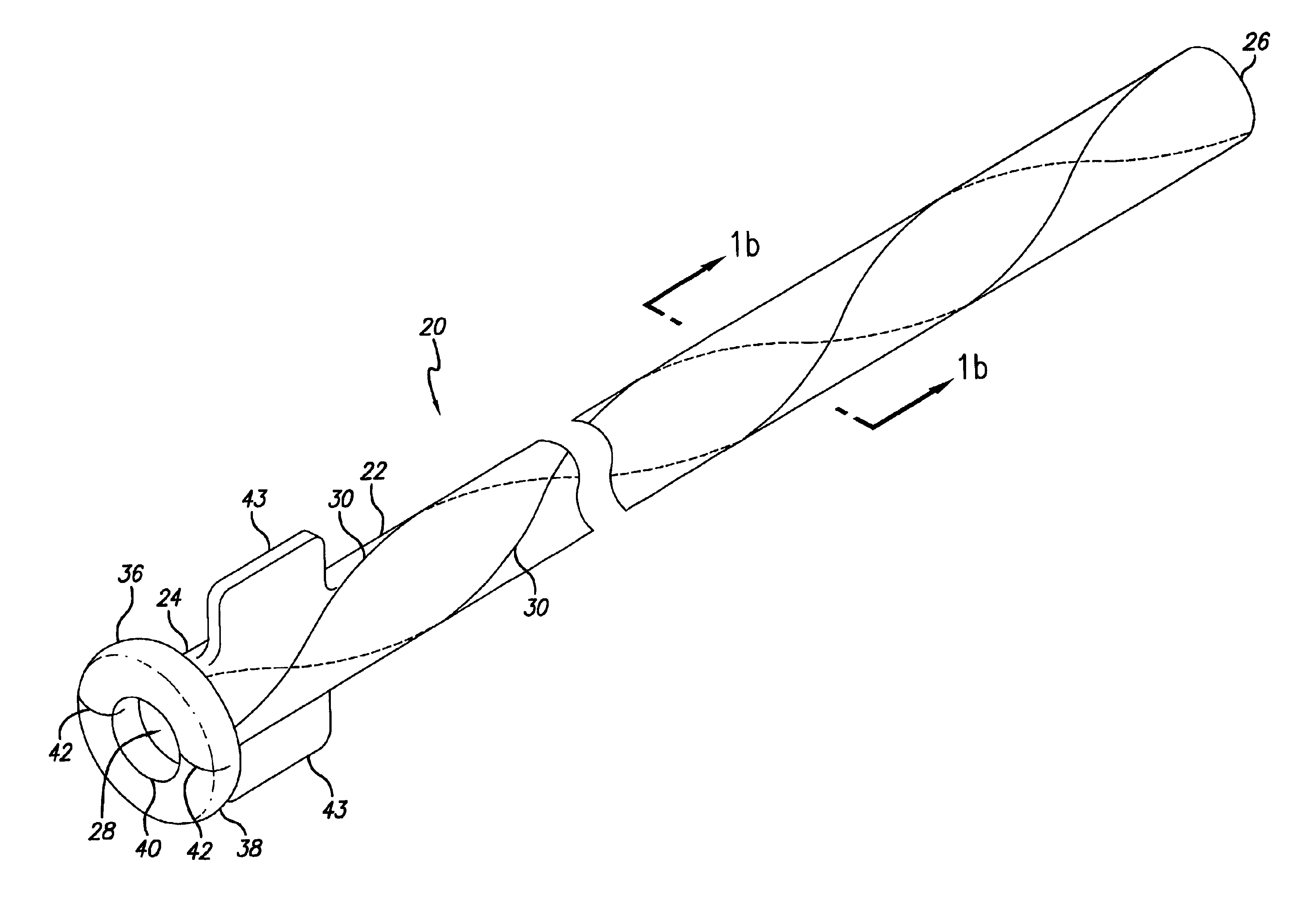
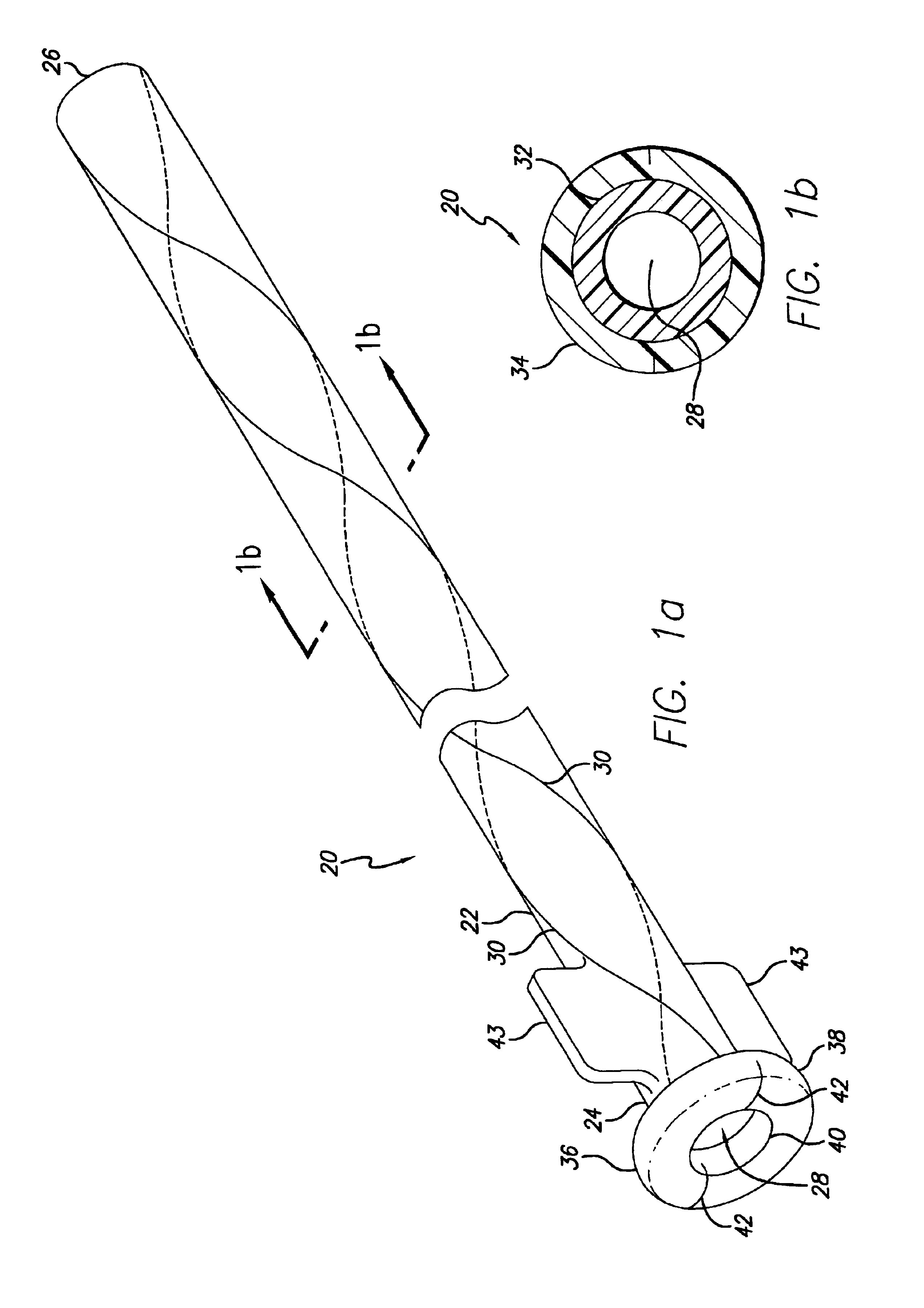
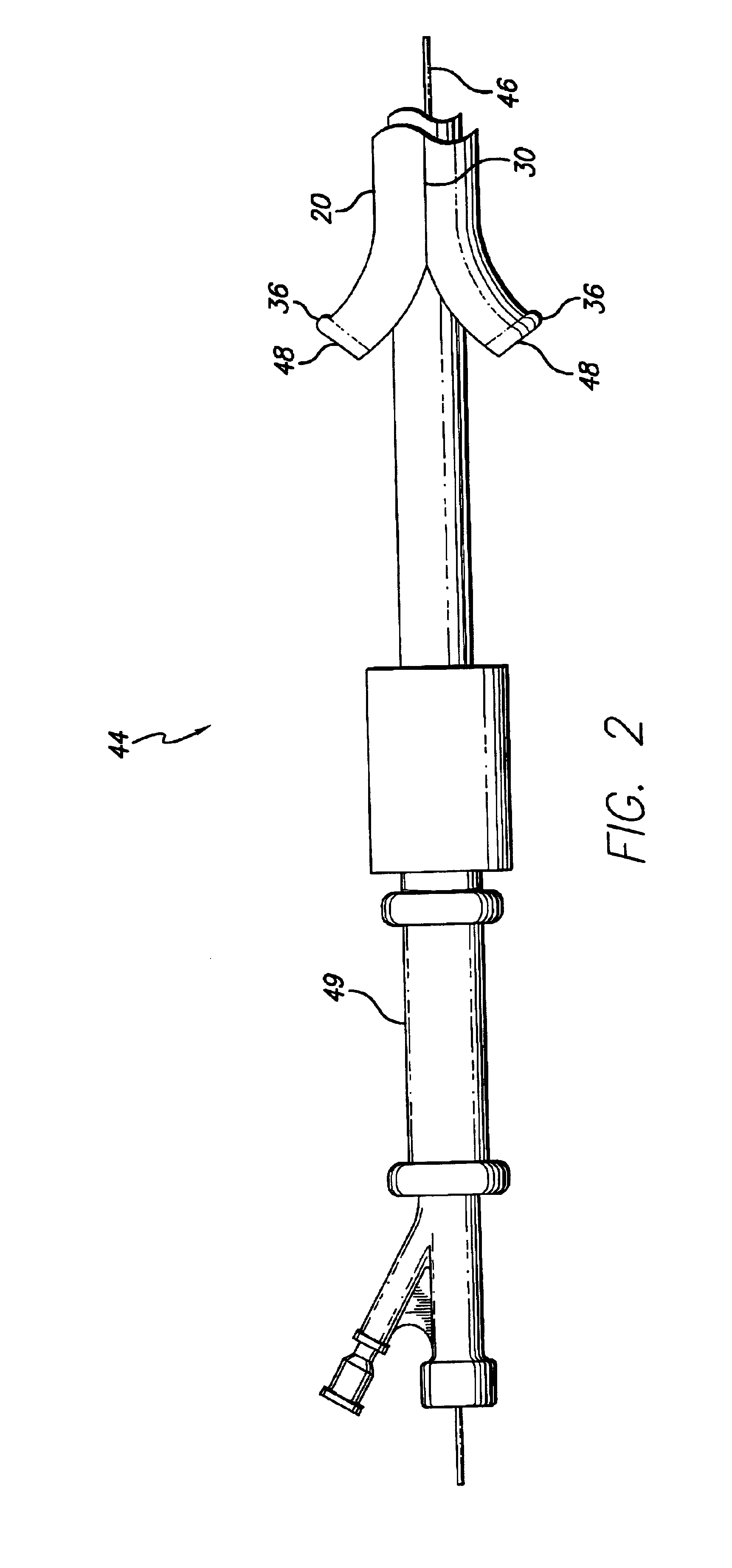
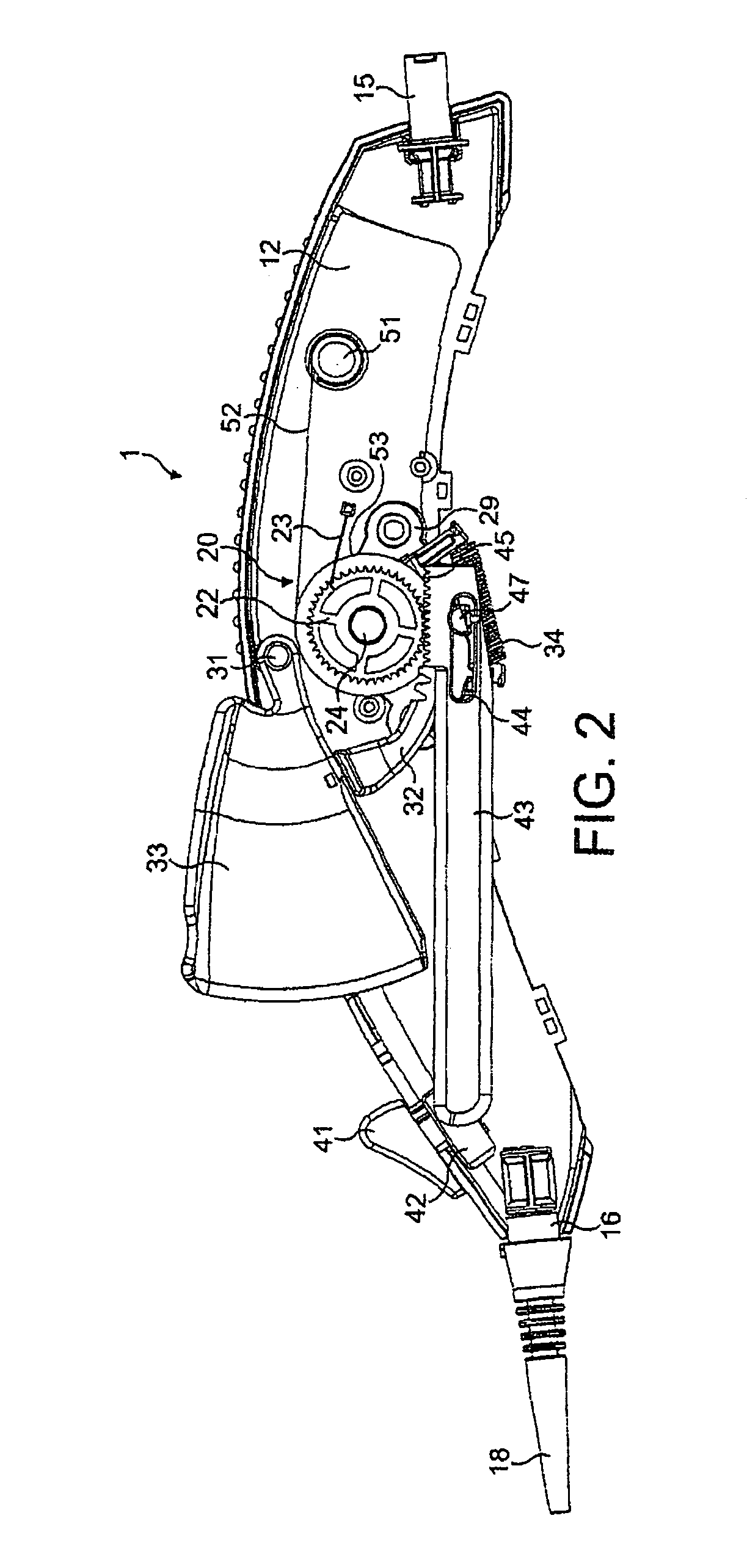
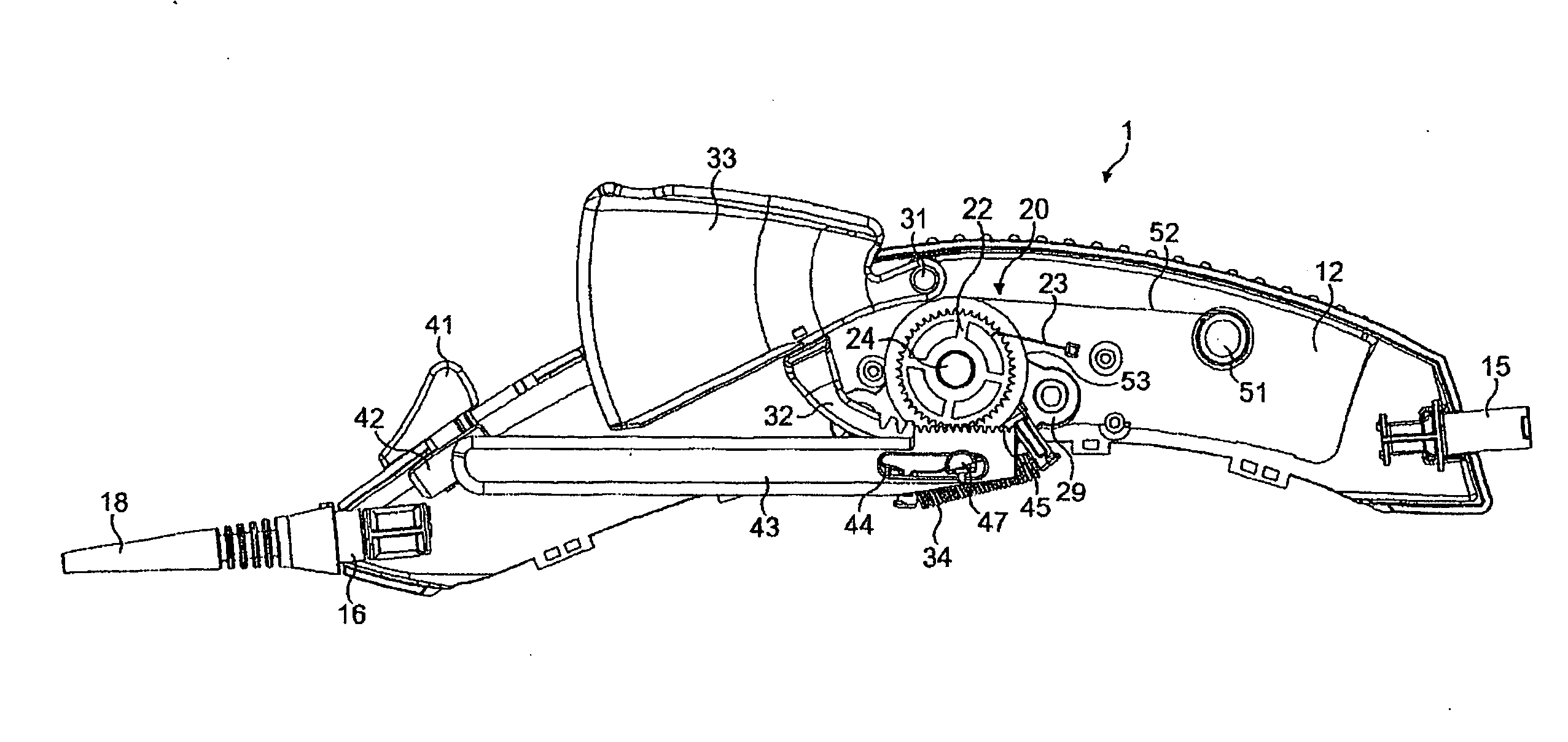
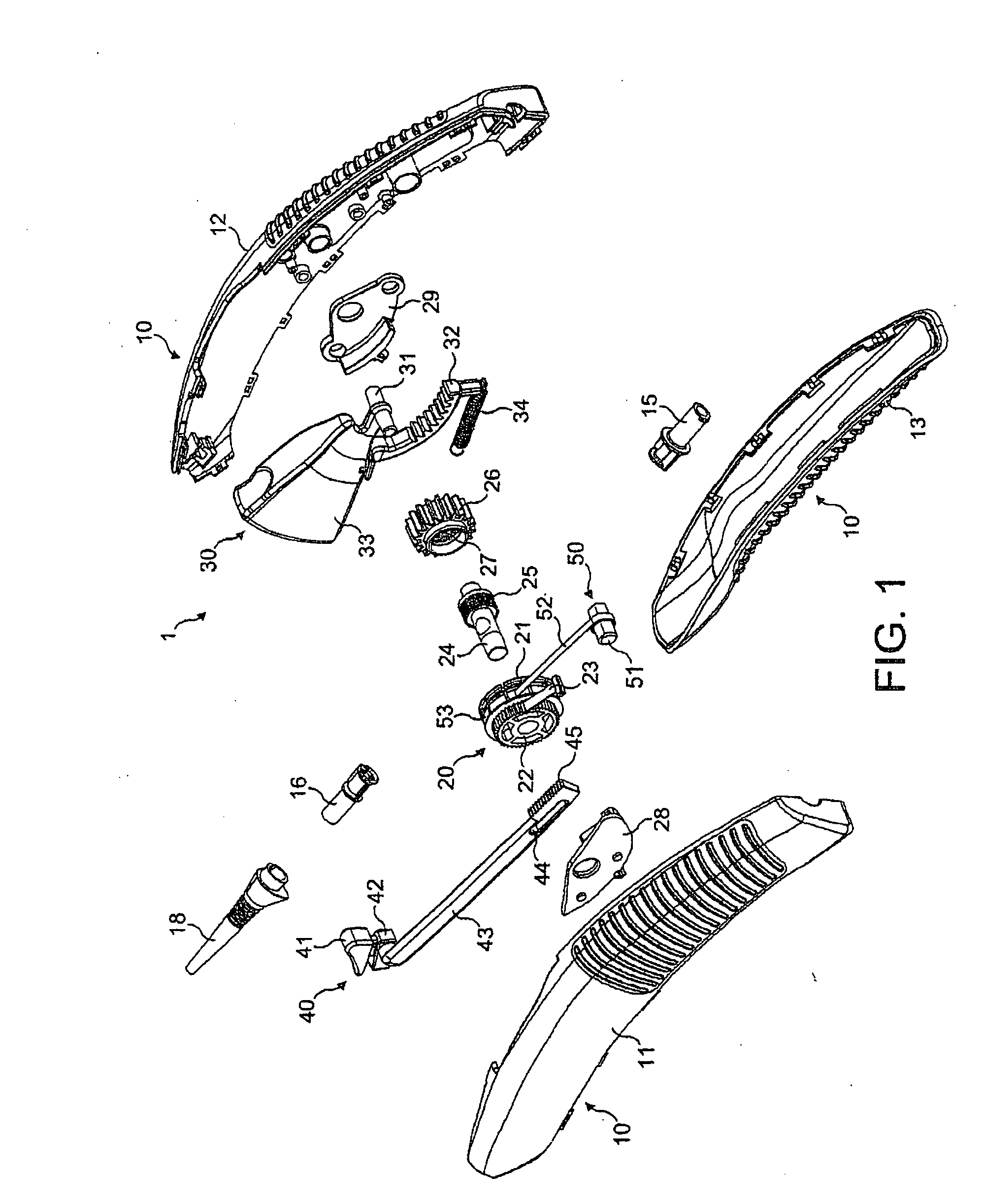
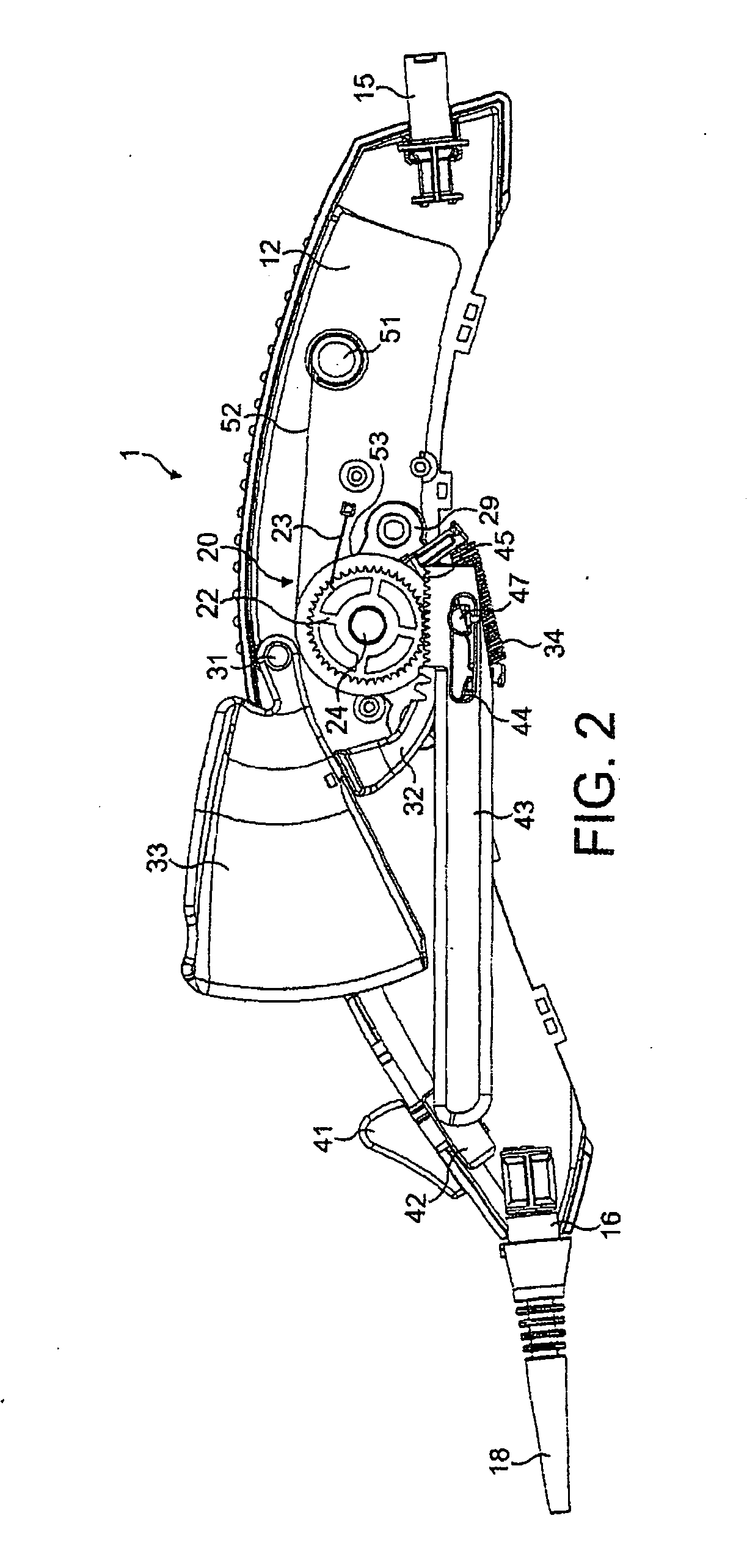
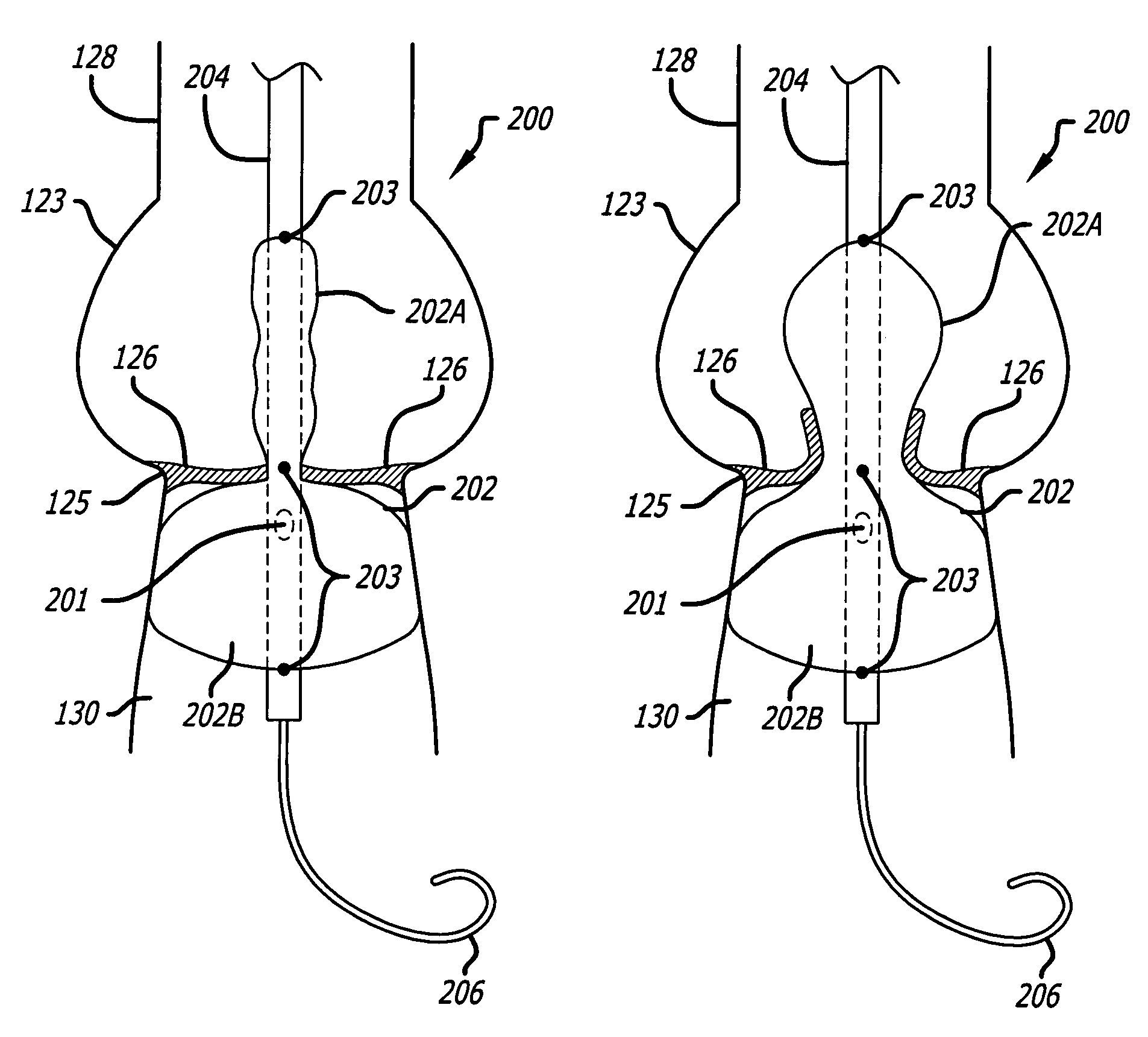
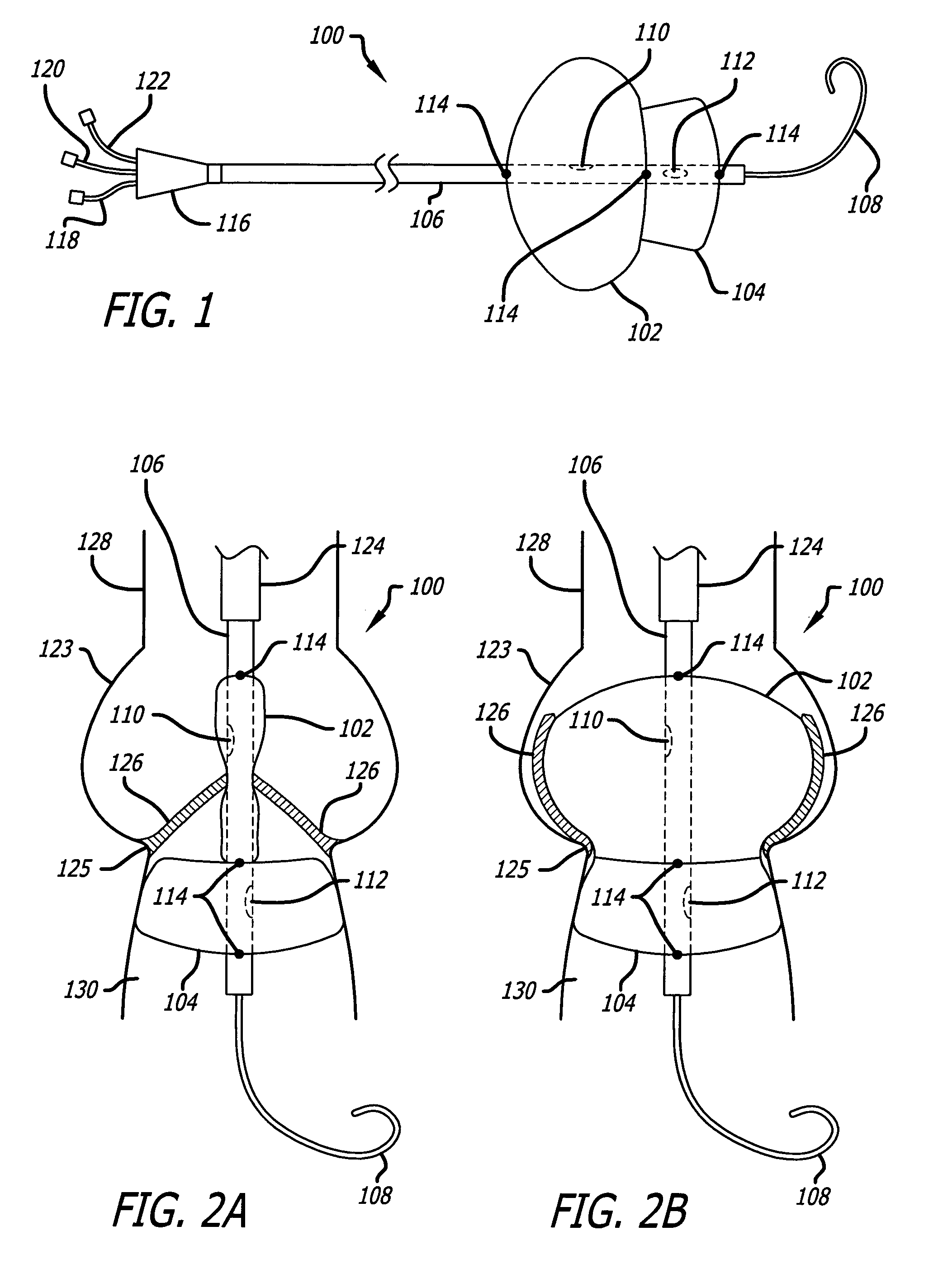
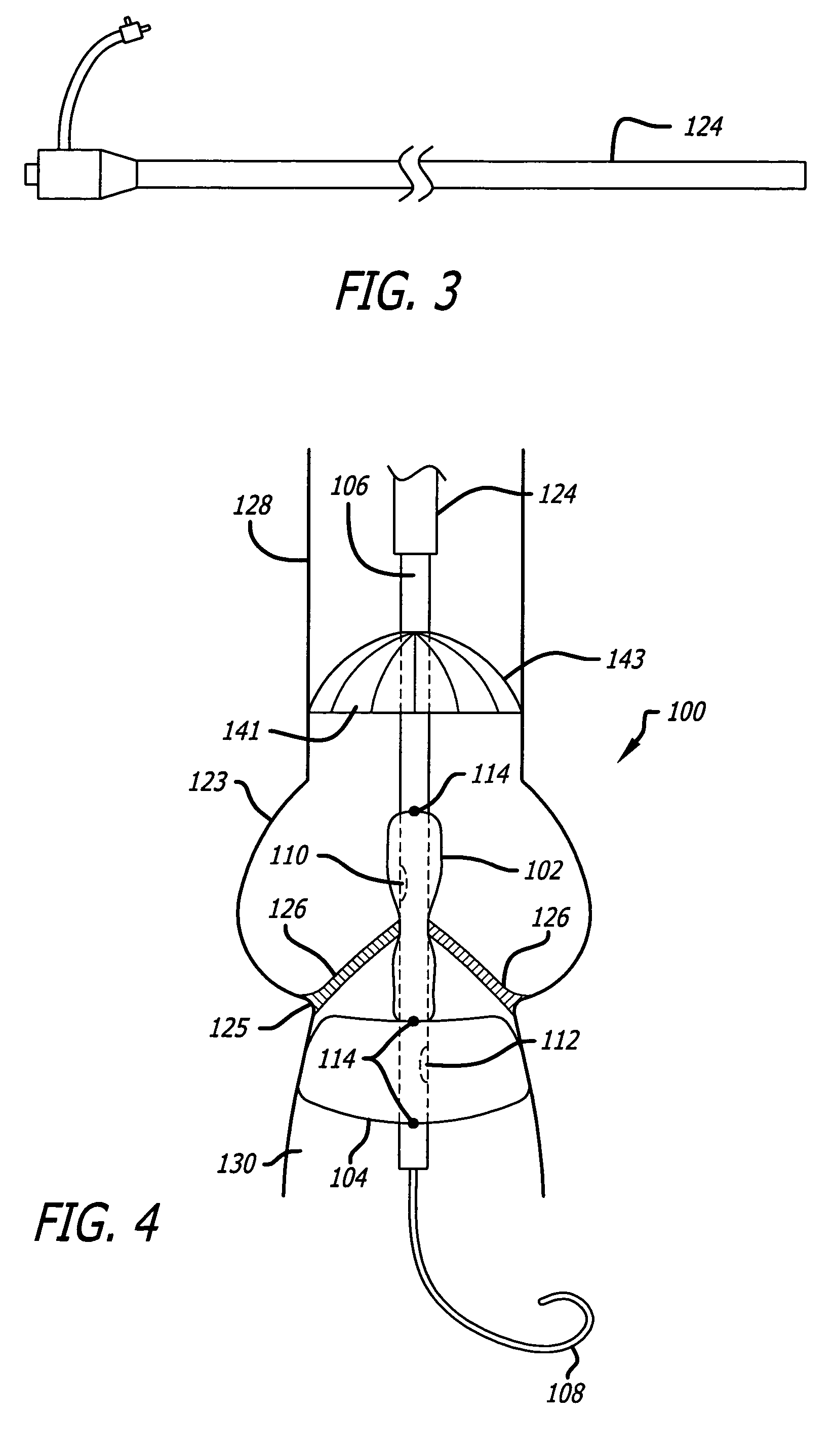
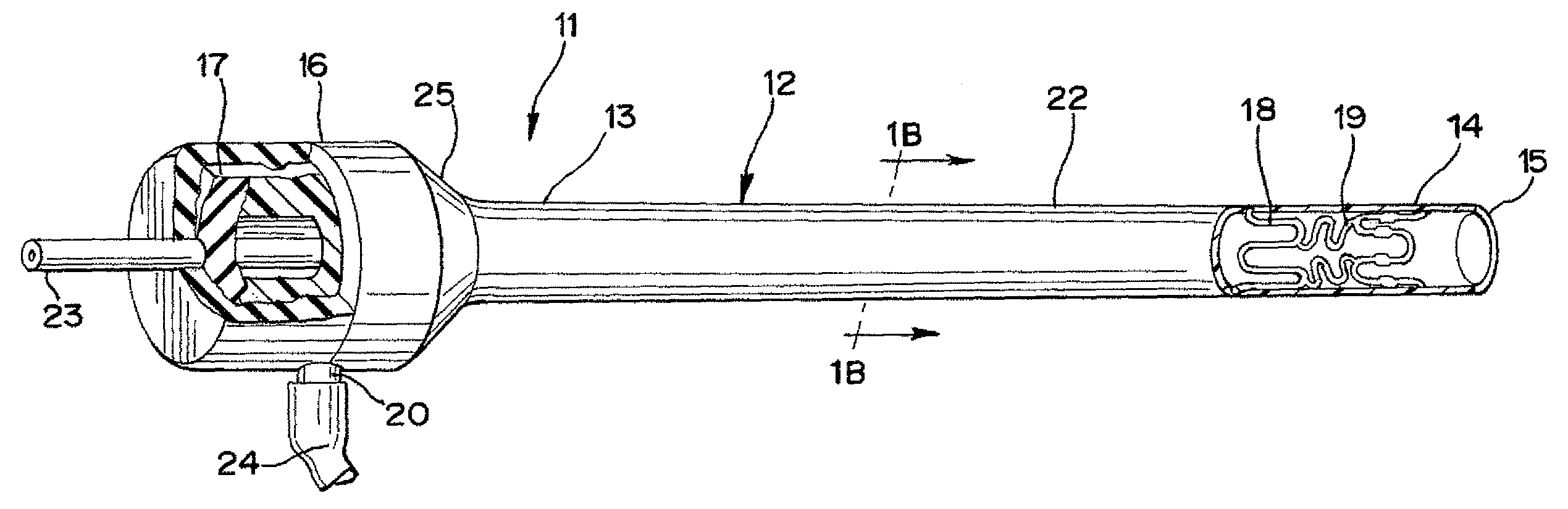
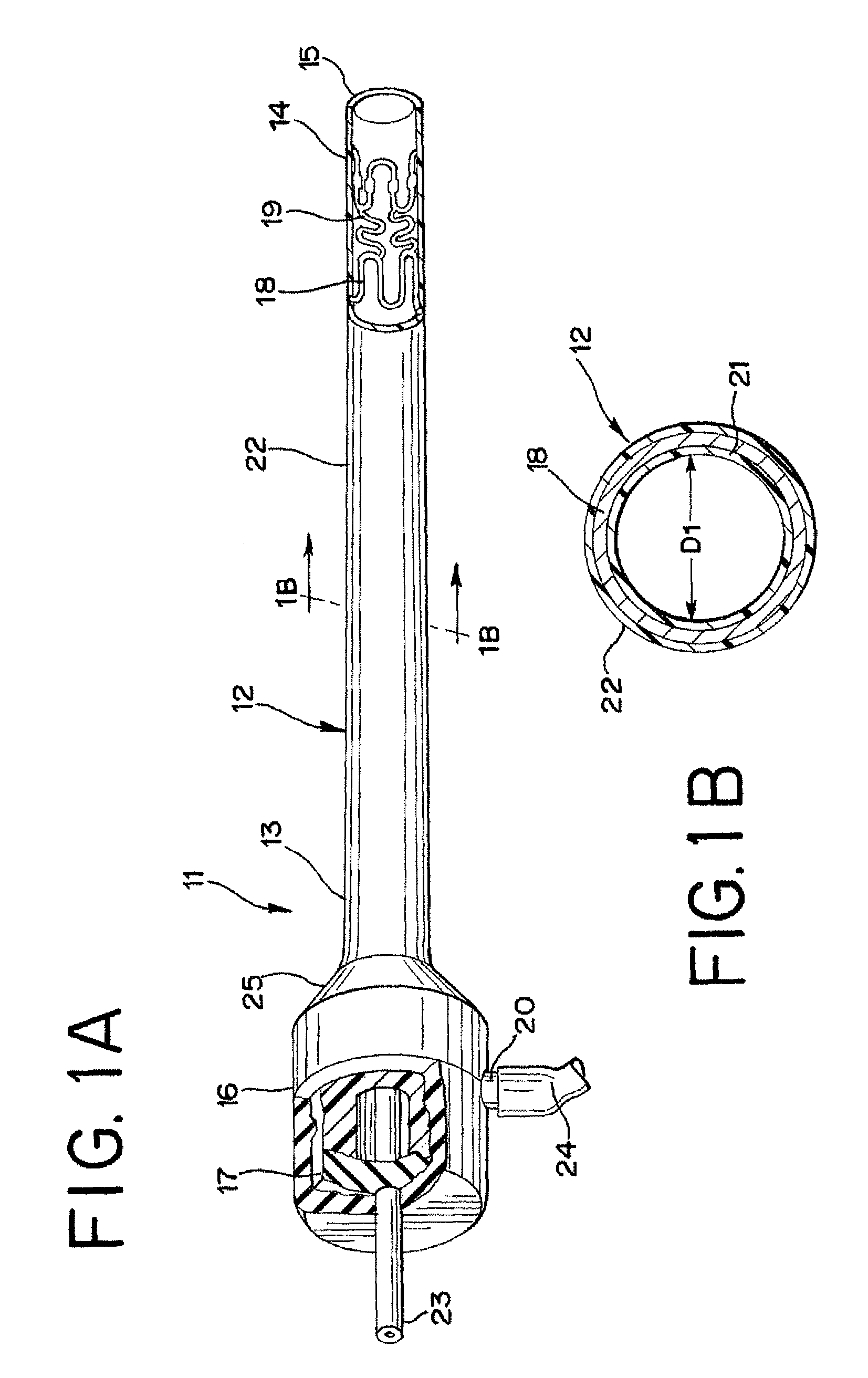
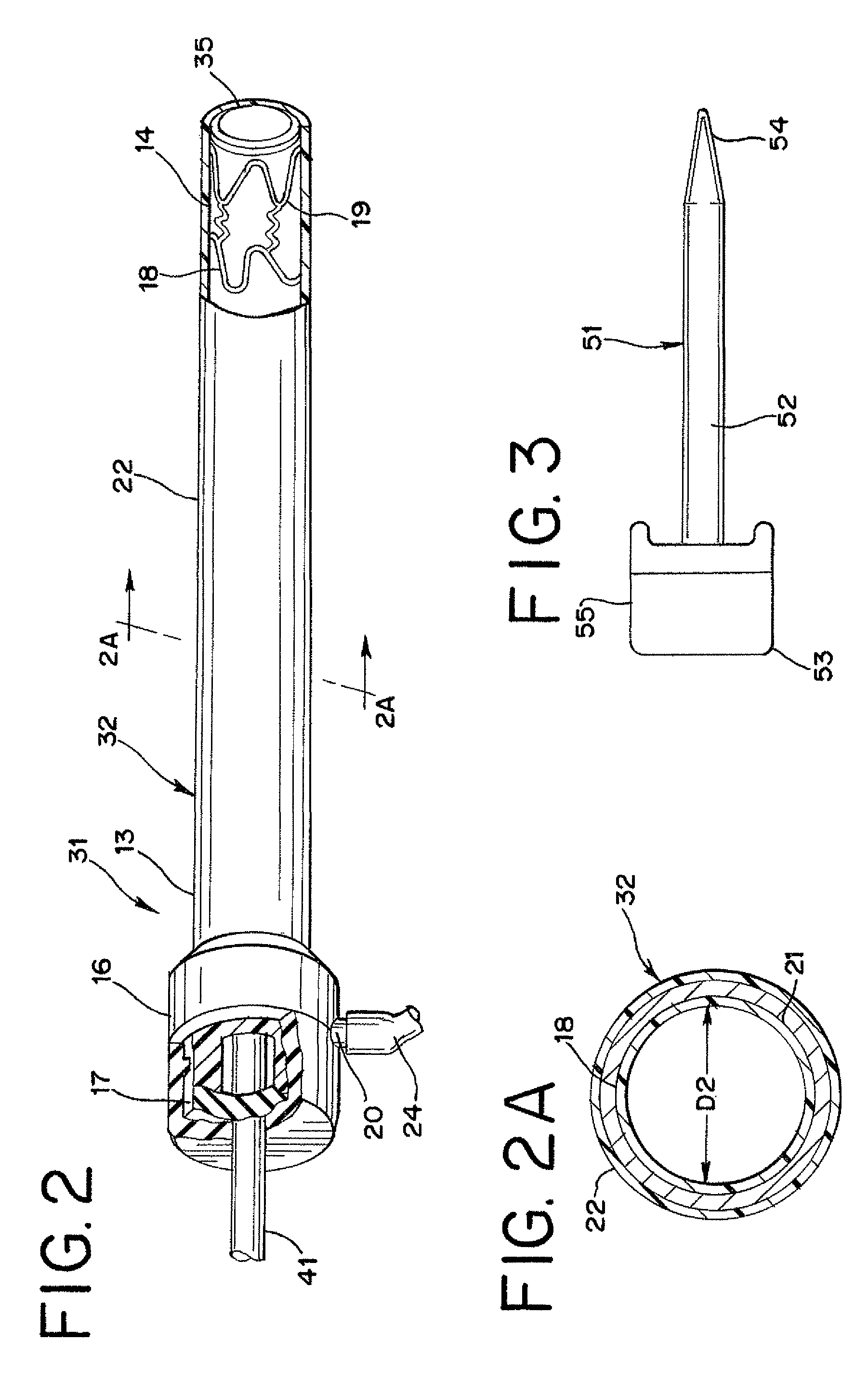
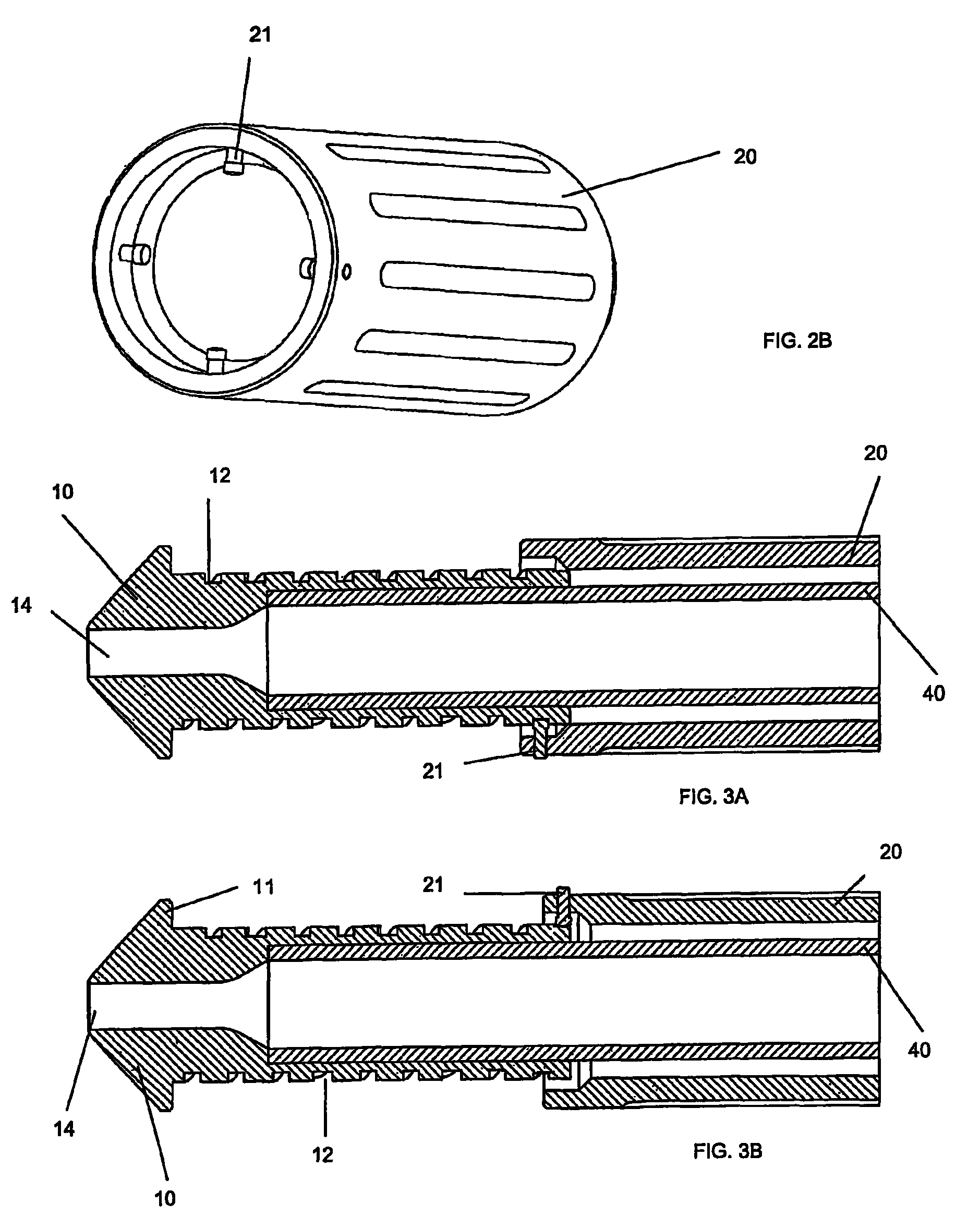
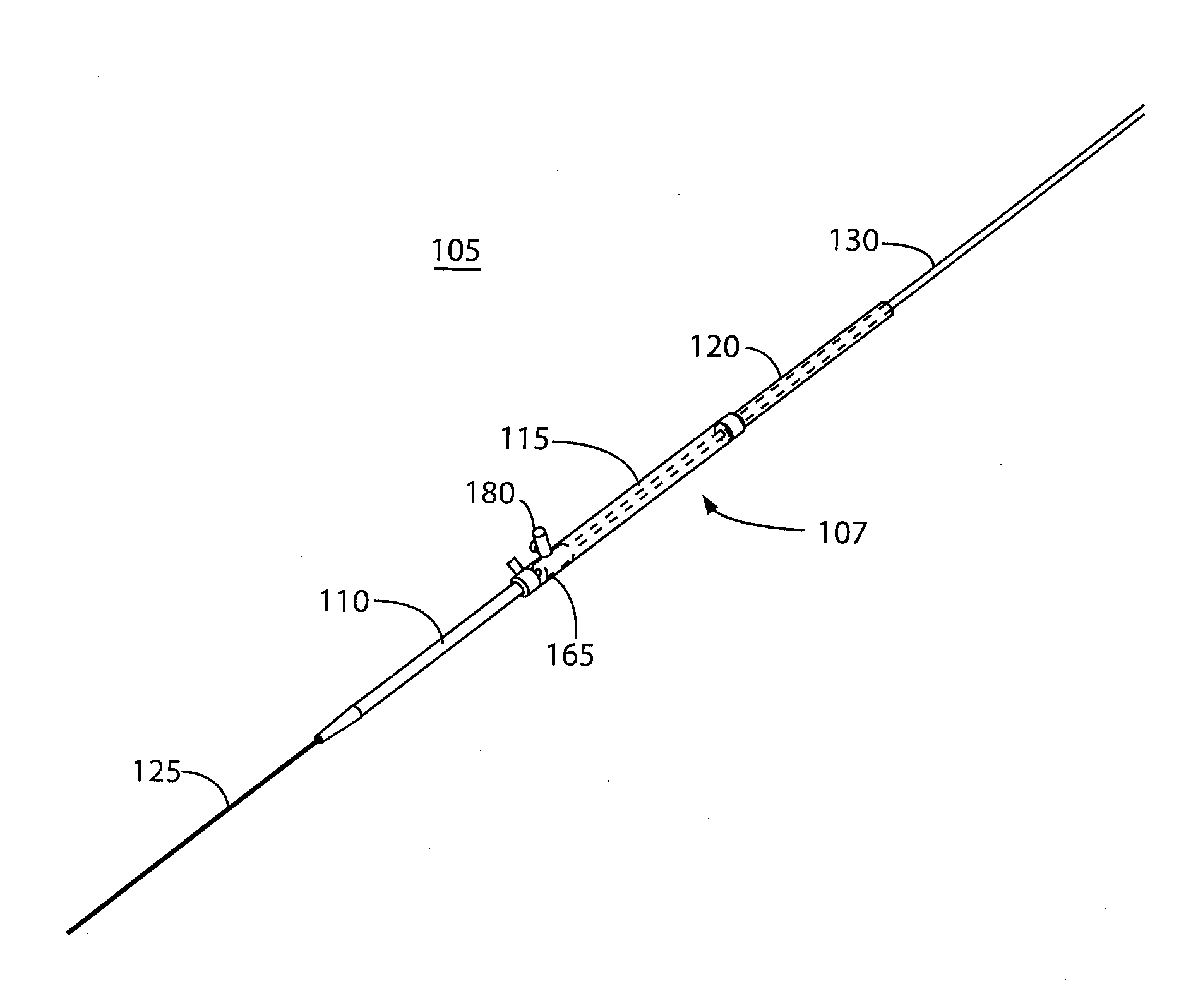
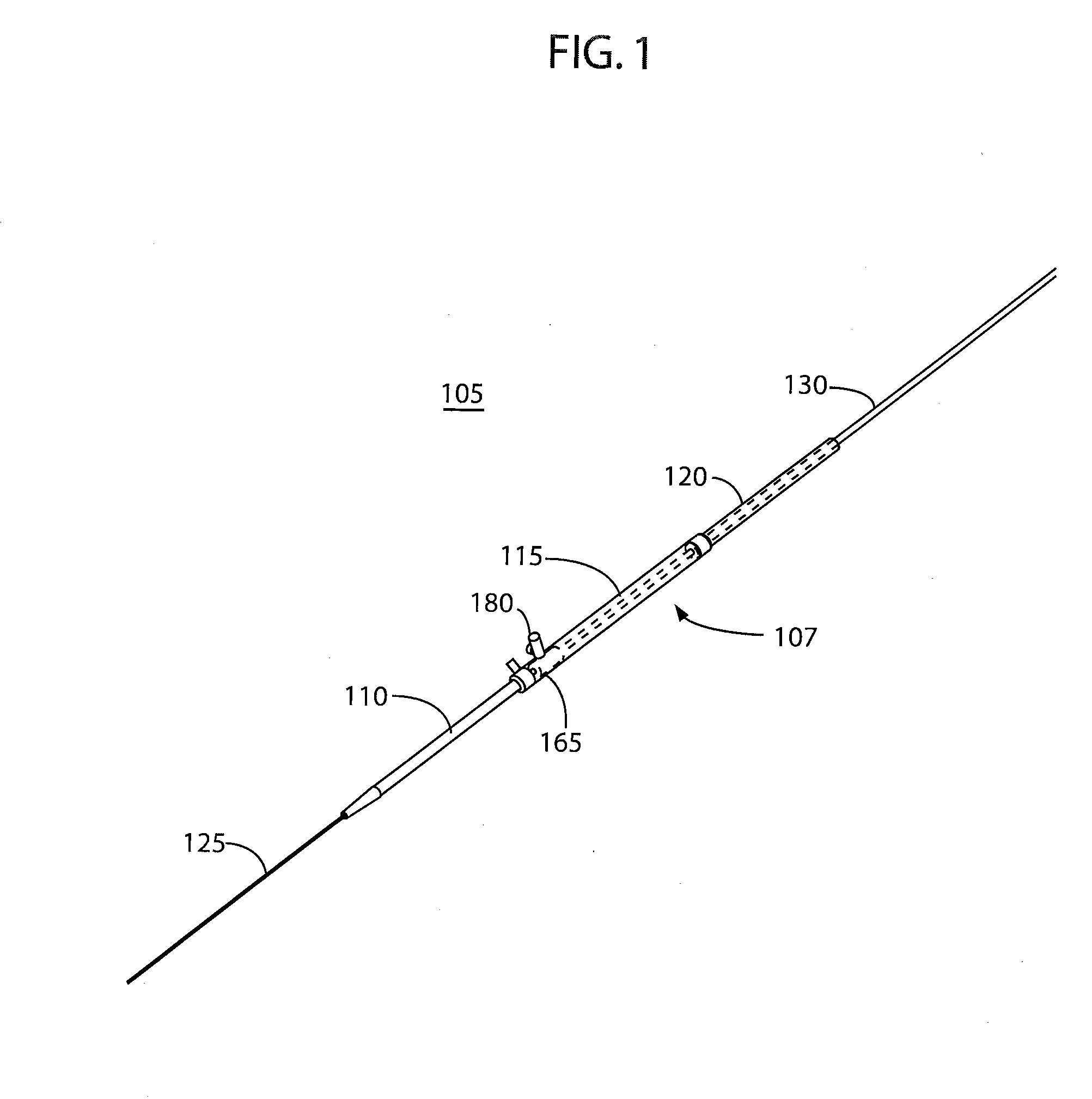
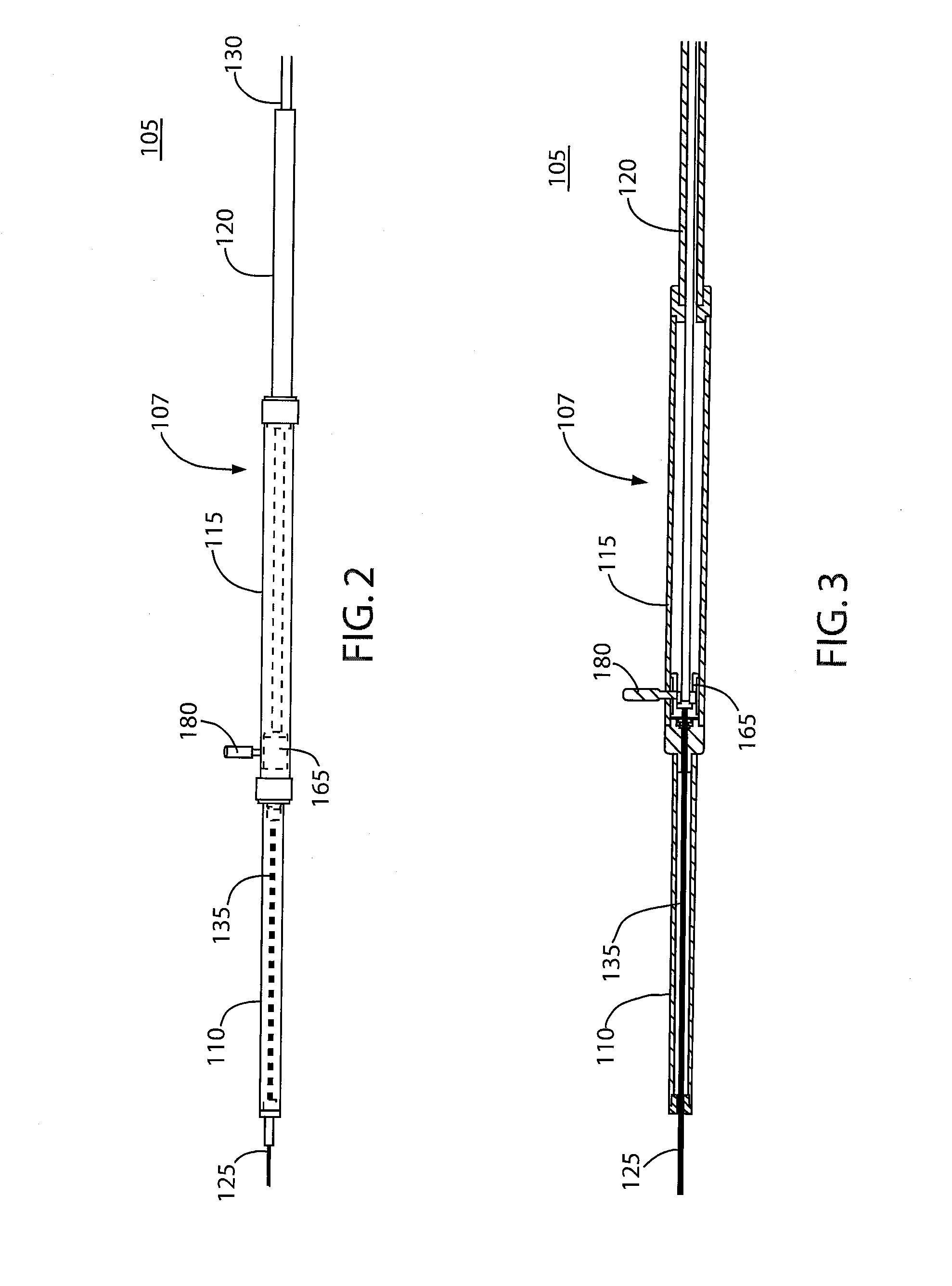
There is disclosed herein a tube of material (1) having a seam (12) extending between a proximal end and a distal end, two edges (10a, 10b) of the material meeting and at least partially overlapping along the seam (12) and being sewn together at the seam by stitches (21, 22, 24) of relatively flexible thread (20), the thread of one or more of the stitches (22, 24) passing from a first side (12a) of the overlapped edges (10a, 10b) of material, through both layers of overlapped material, crossing a relatively rigid member (30) which is disposed on a second, opposite side (12b) of the overlapped edges of material, and passing back to the first side (12a). There is further disclosed an implant delivery catheter (40) incorporating the tube of material (1), and associated methods for its manufacture.
Owner:CR BARD INC
Medical device delivery sheath
InactiveUS20080188928A1Easy to collapseFacilitate resheathingStentsHeart valvesMedical deviceGuide tube
A support member for a catheter sheath is disclosed. The support member has a series of ribs with a distal member having integrated fingers for providing radial compliance. The support member provides sufficient axial stiffness to provide a desired pushability of a minimally invasive device for replacing a heart valve. Various alternative embodiments are also described.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Valvuloplasty devices and methods
ActiveUS20050090846A1Stable positionAvoid structureBalloon catheterCannulasAortic valvuloplastyAortic sinus
The present invention provides an aortic valvuloplasty catheter which, in one preferred embodiment, has a tapered distal balloon segment that anchors within the left ventricle outflow track of the patient's heart and a rounded proximal segment which conforms to the aortic sinuses forcing the valve leaflets open. In addition, this embodiment of the valvuloplasty catheter includes a fiber-based balloon membrane, a distal pigtail end hole catheter tip, and a catheter sheath.
Owner:INTERVALVE MEDICAL INC
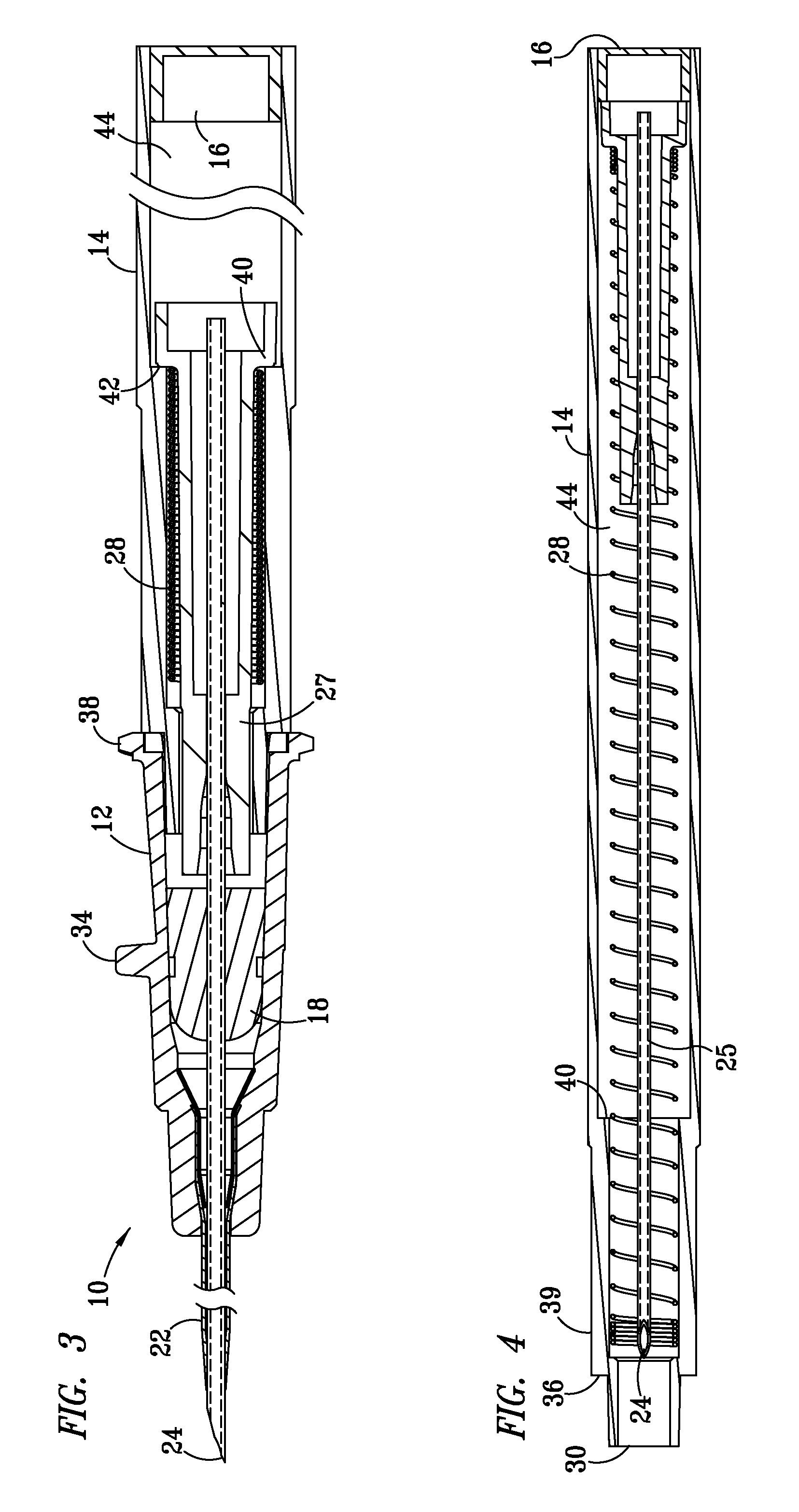
Catheter sheath for implant delivery
ActiveUS20120022630A1Increase deflectionLarge radiusStentsLeather sewingBiomedical engineeringCatheter sheath
There is disclosed herein a tube of material (1) having a seam (12) extending between a proximal end and a distal end, two edges (10a, 10b) of the material meeting and at least partially overlapping along the seam (12) and being sewn together at the seam by stitches (21, 22, 24) of relatively flexible thread (20), the thread of one or more of the stitches (22, 24) passing from a first side (12a) of the overlapped edges (10a, 10b) of material, through both layers of overlapped material, crossing a relatively rigid member (30) which is disposed on a second, opposite side (12b) of the overlapped edges of material, and passing back to the first side (12a). There is further disclosed an implant delivery catheter (40) incorporating the tube of material (1), and associated methods for its manufacture.
Owner:CR BARD INC
Cryocatheter for introduction into a body vessel together with medical investigation and treatment equipment
ActiveUS20070093710A1Load minimizationUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsGuide needlesTherapeutic DevicesBlood vessel
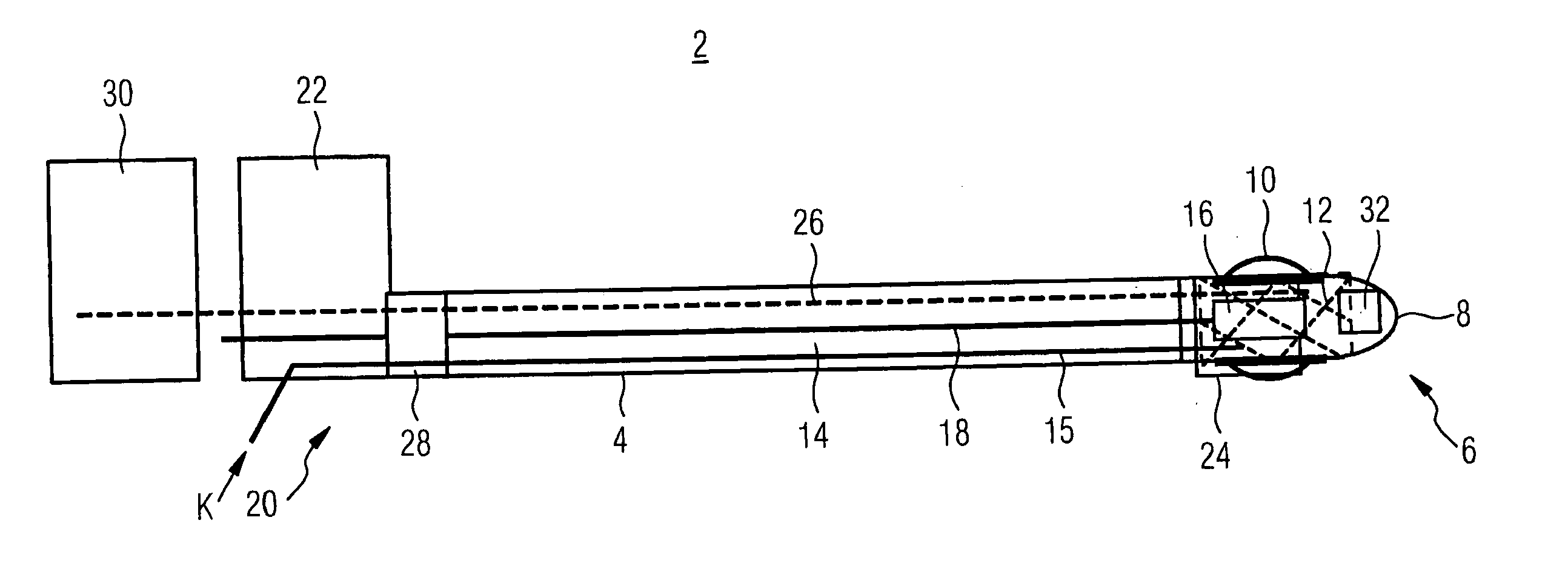
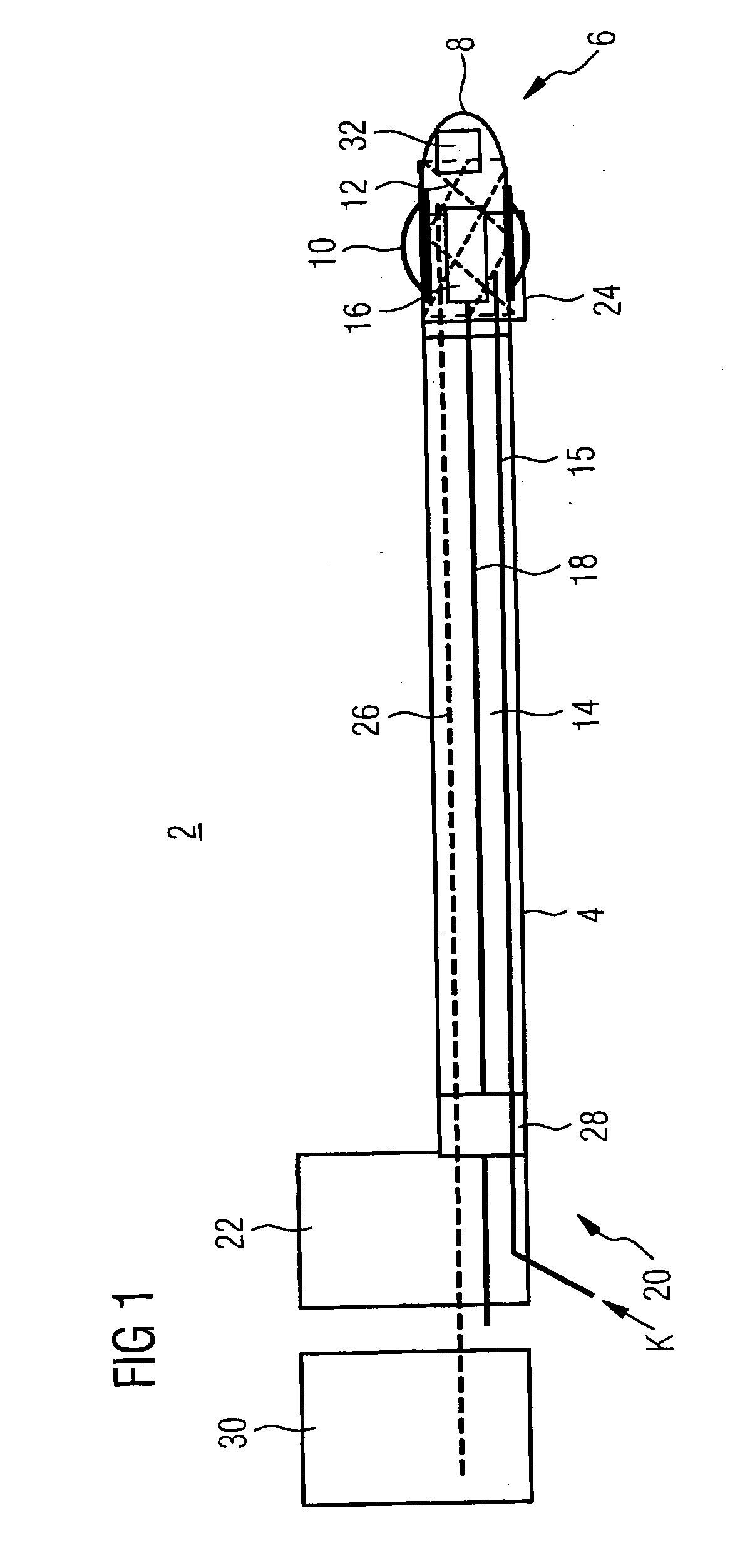
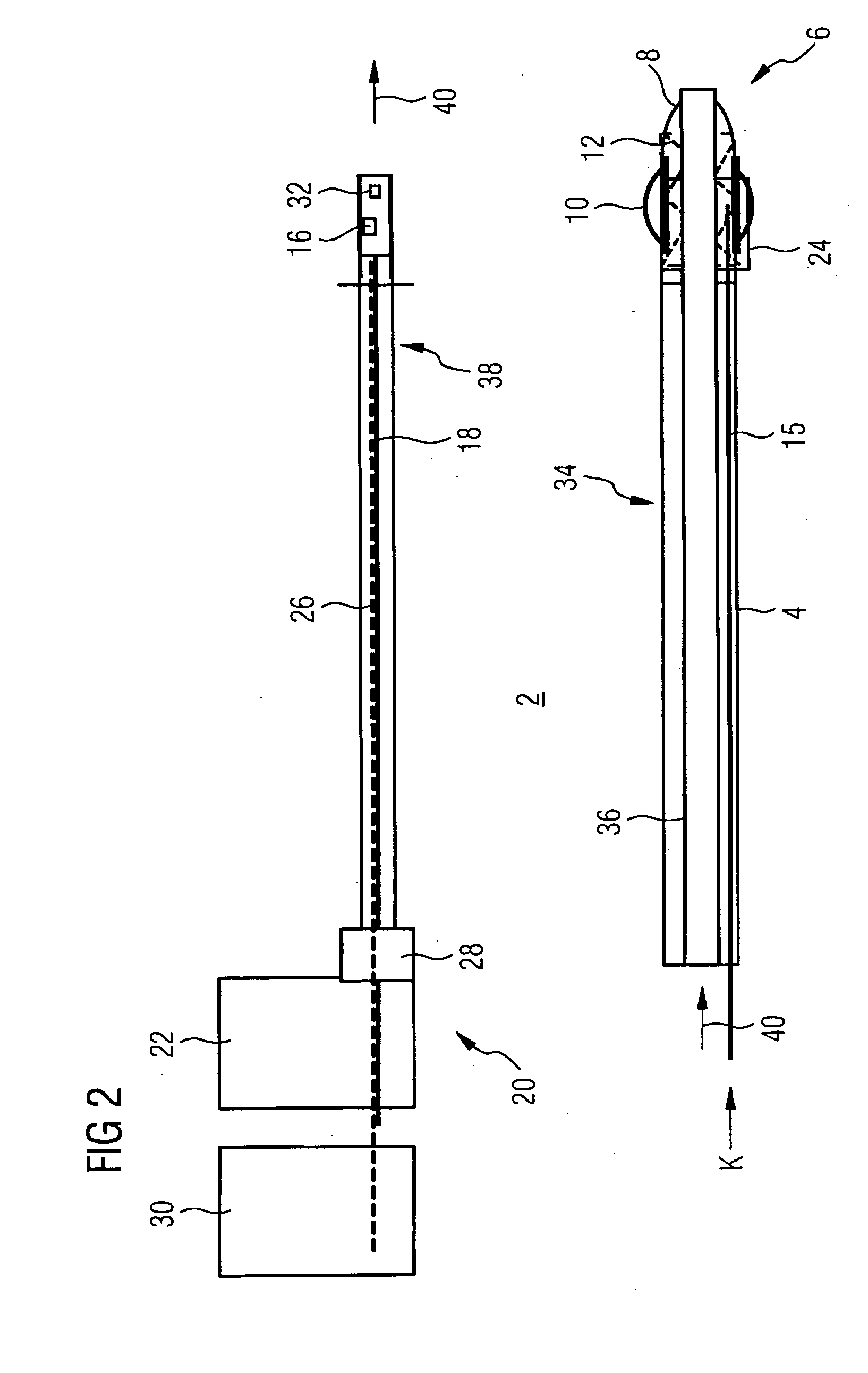
A cryocatheter for introduction into a body vessel or into an organ, with a catheter inner surrounded by a catheter sheath, and with a catheter tip arranged at its distal end, with a feed line for an expansion or cooling agent arranged in the catheter sheath or the catheter inner, and with a balloon, arranged close to the catheter tip, which can be expanded and contracted again by means of the expansion and cooling agent, is to be constructed in such a way that by simple manipulation it can be positioned at a precise target position in the body vessel and, in addition, it minimizes the burden on the patient from invasive interventions. For this purpose, in accordance with the invention an image capture device, with at least one imaging sensor for mapping the region of the vessel around the balloon, is positioned in the region of the catheter tip.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Steerable catheter with preformed distal shape and method for use
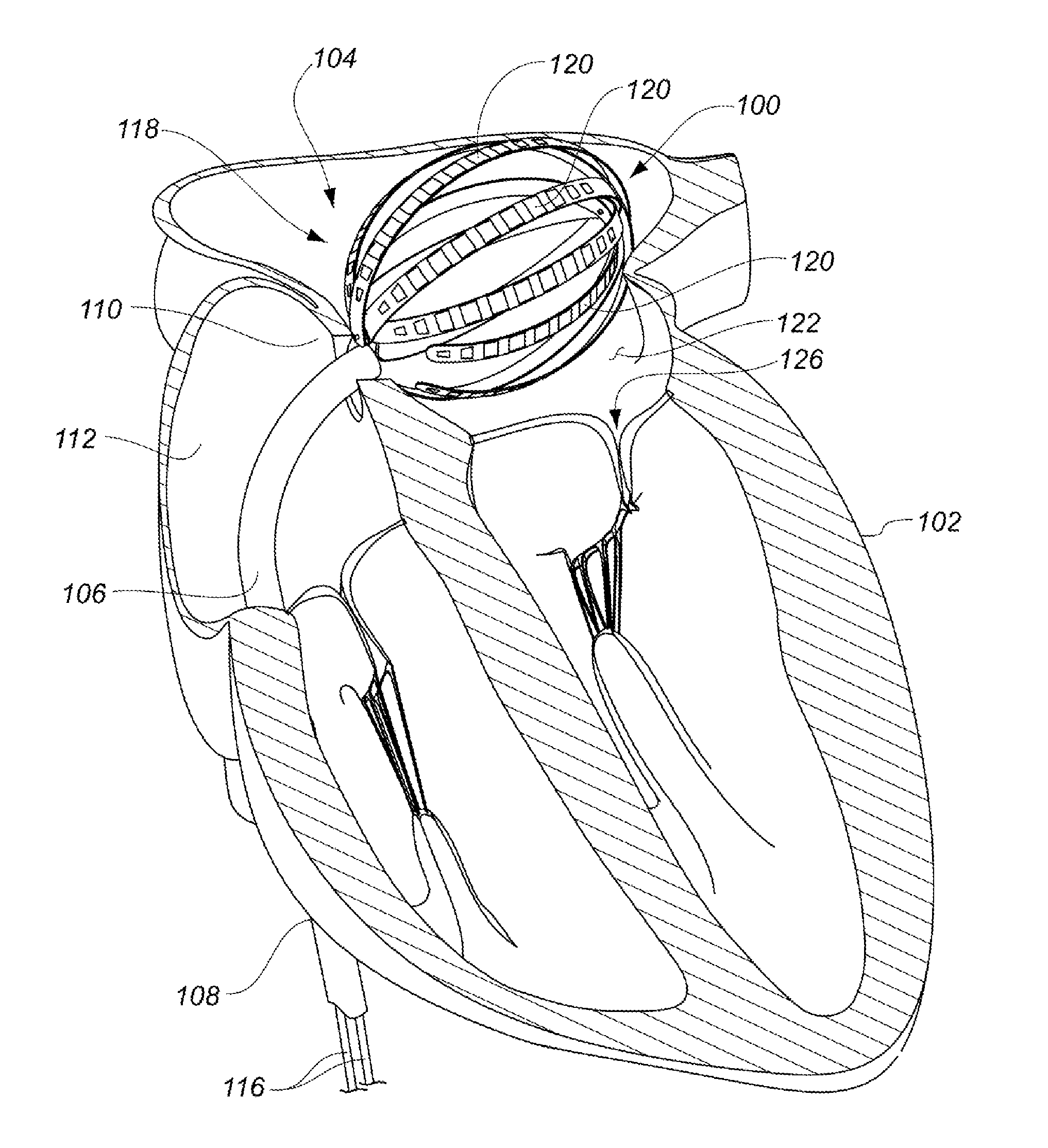
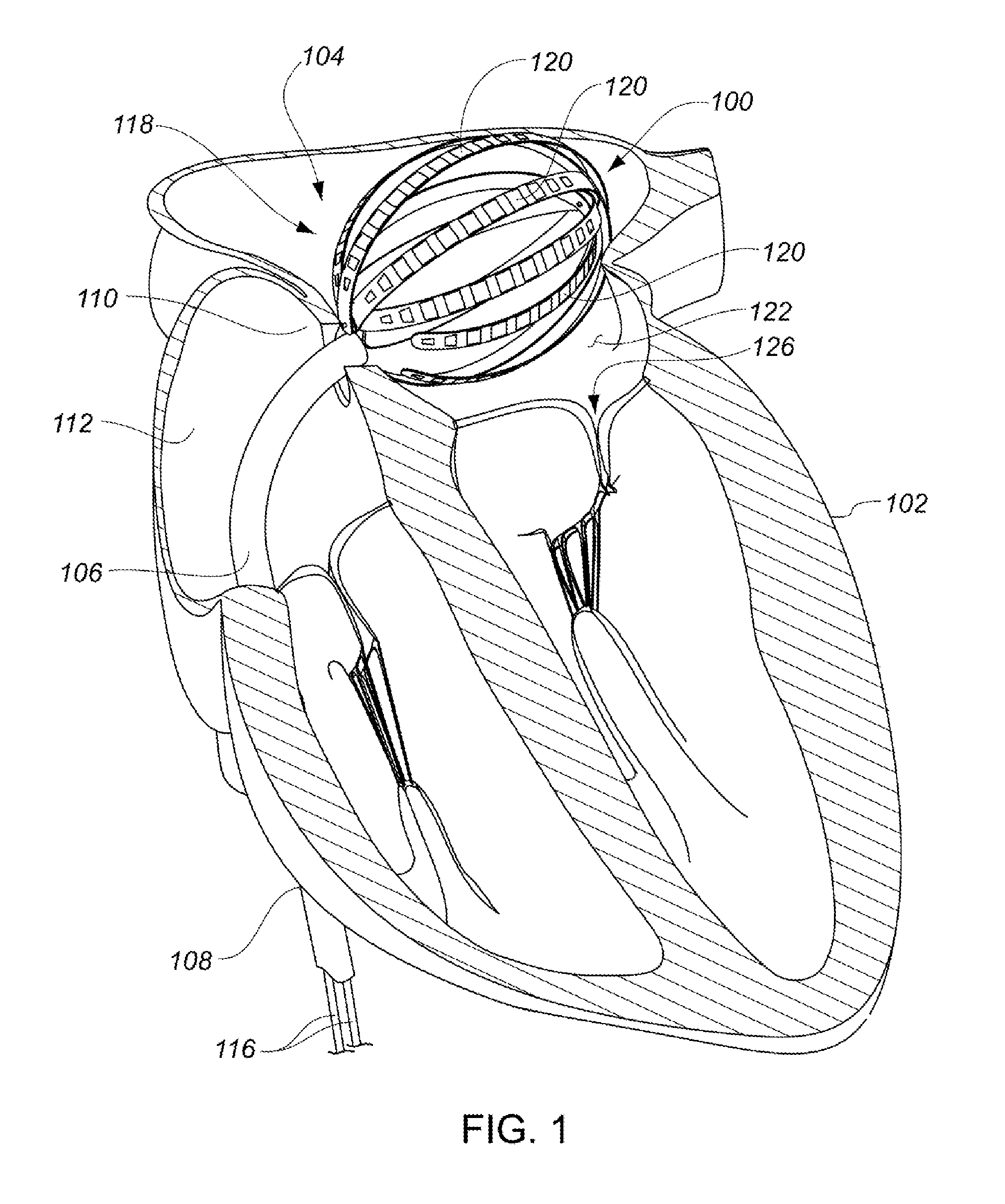
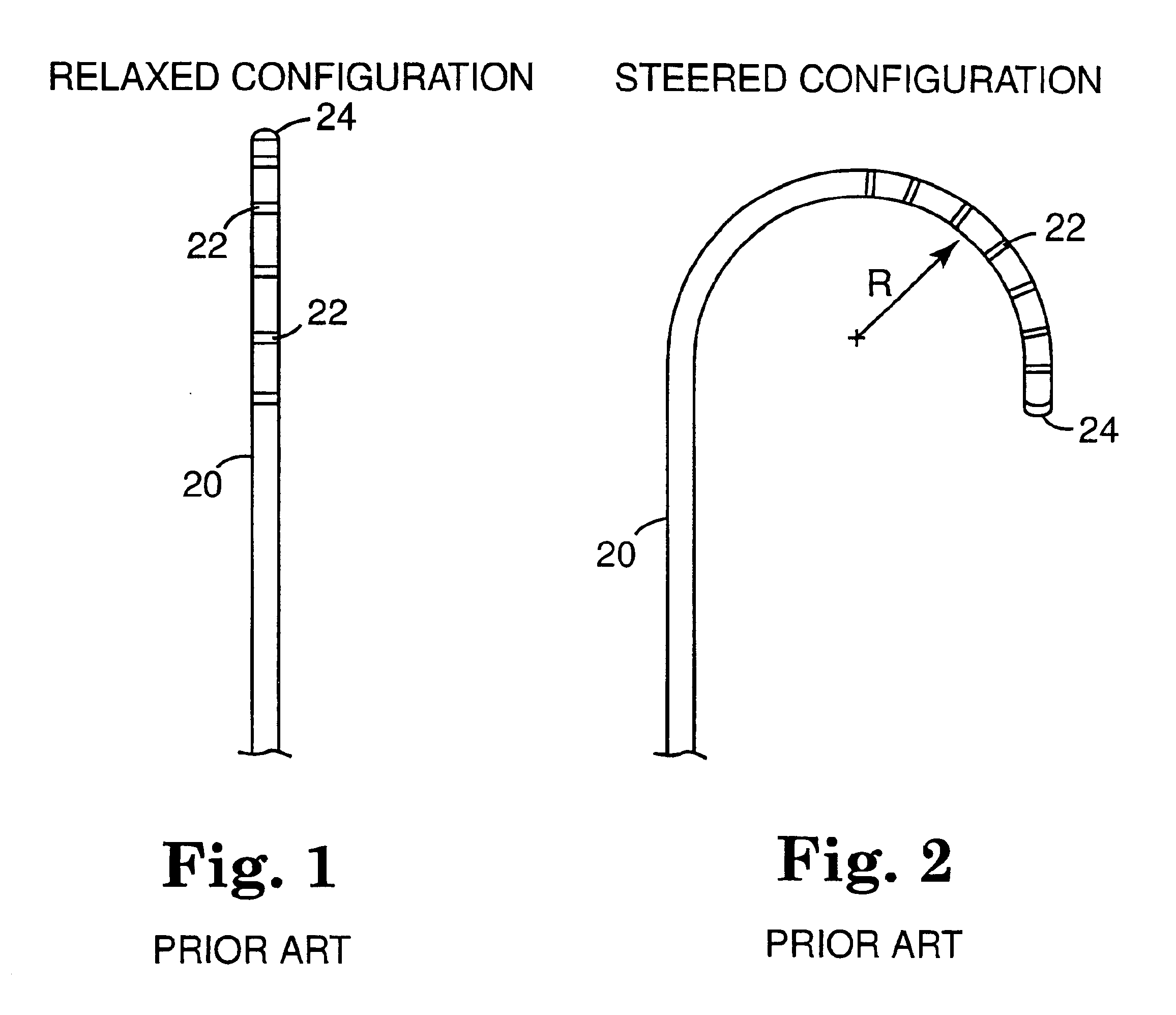
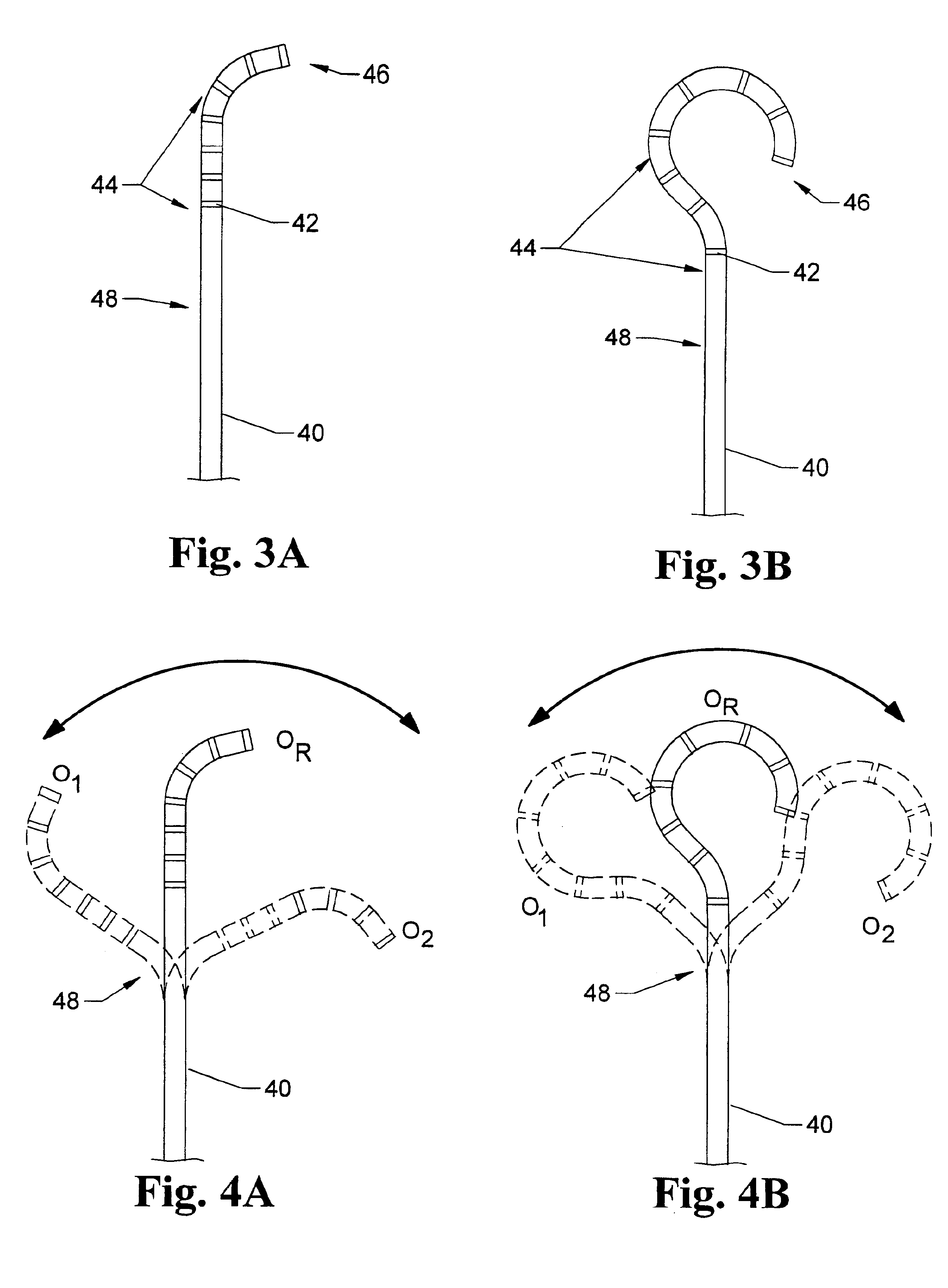
InactiveUS6096036AReduce curvatureTransvascular endocardial electrodesSurgical instrument detailsHeart chamberCurve shape
A catheter has a stylet formed of a shape-retentive and resilient material having a preformed curved shape at its distal end resulting in the catheter sheath having the preformed curved shape. The catheter sheath has a plurality of electrodes at its distal end for contacting selected biological tissue for imparting ablation energy thereto. The catheter sheath also has an axially mounted tendon for causing deflection of the distal end. The stylet material permits straightening the catheter sheath during insertion into the patient and advancing the electrodes to the target tissue. Upon removal of the straightening forces, such as by entry into a chamber of the heart, the stylet material resumes its preformed curved distal shape thereby forcing the catheter distal end with the electrodes into the same preformed curved shape. The operator may place the curved distal end into contact with the target tissue and axially move the tendon as desired to gain greater control over the bend in the distal end of the catheter sheath to adjust the radius of curvature of the distal end to obtain greater contact of the electrodes with the heart tissue. Preferably, the stylet is formed of nitinol.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Stable coil designs
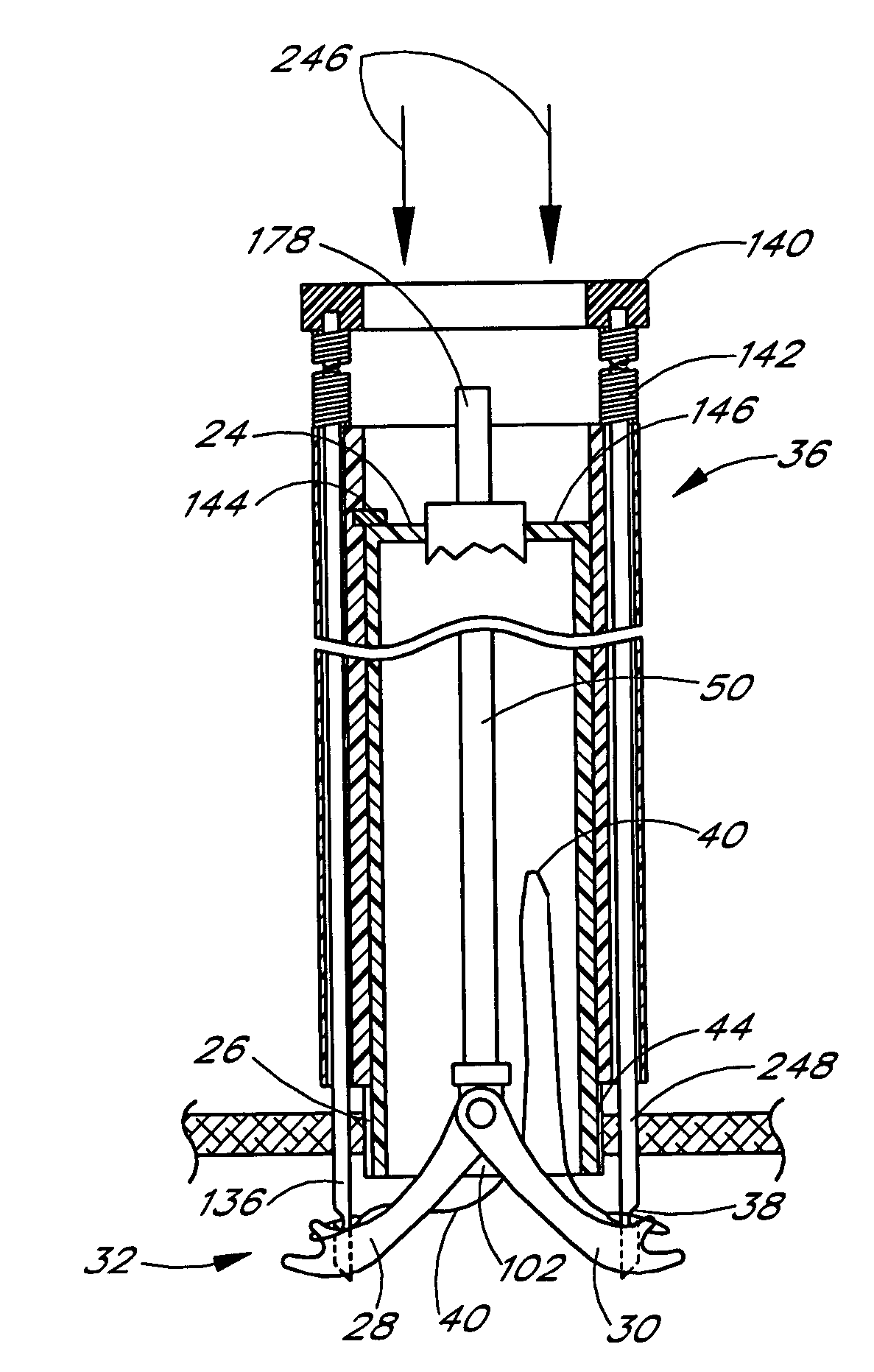
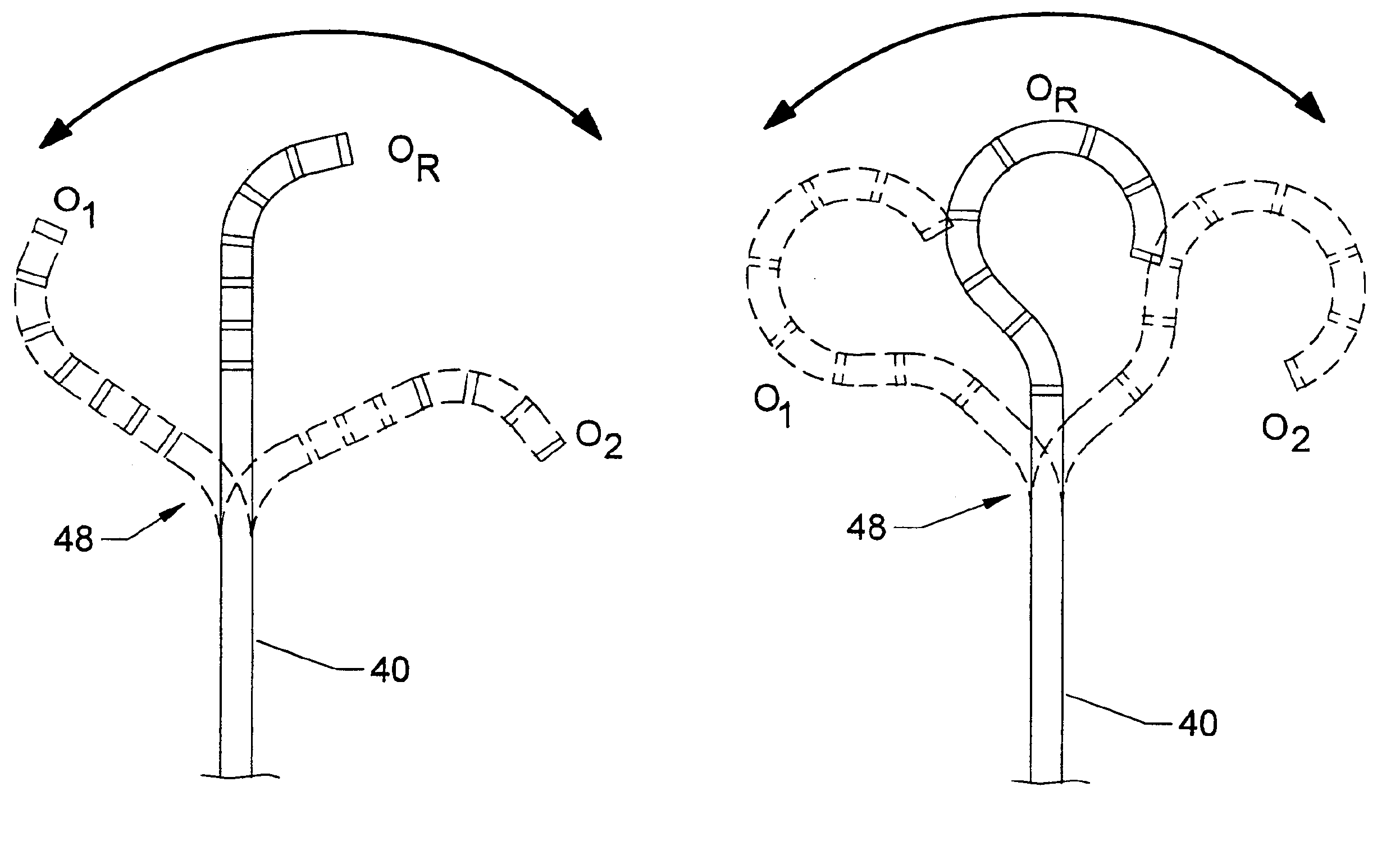
This is an implantable vaso-occlusive device. The device has a complex, three-dimensional structure in a relaxed configuration that may be used in the approximate shape of an anatomical cavity. It may be deployed in the approximate shape of a sphere, an ovoid, a clover, a box-like structure or other distorted spherical shape. The loops forming the relaxed configuration may pass through the interior of the structure. The device is a self-forming shape made from a pre-formed linear vaso-occlusion member. Fibers may be introduced onto the device and affixed to the pre-formed linear member. The constituent member may be also be covered with a fibrous braid. The device is typically introduced through a catheter. The device is passed axially through the catheter sheath and assumes its form upon exiting the catheter without further action. The invention also includes methods of winding the anatomically shaped vaso-occlusive device into appropriately shaped forms and annealing them to form various devices.
Owner:STRYKER CORP +1
Suturing device and method for sealing an opening in a blood vessel for other biological structure
InactiveUS7004952B2Many of complicationMany of costSuture equipmentsSurgical needlesDistal portionVia incision
A suturing device allows a physician to remotely seal an incision in a blood vessel or other biological tissue. The device comprises an elongated tubular body having a distal portion which is adapted to be inserted percutaneously through the incision and into the blood vessel. The distal portion has first and second retractable arms which extend from the distal portion of the body and releasably hold a suture within the blood vessel. First and second retractable needles, each of which is configured to catch the suture from a respective arm, are provided along the body proximal to the retractable arms. The arms and the needles are remotely movable by the physician using a handle or other control mechanism provided at a distal portion of the device. In operation, the arms are initially deployed within the blood vessel to hold the ends of the suture beyond the circumference of the tubular body. The needles are then deployed from and then retracted into the body, during which time the needles pierce the vessel wall on opposite sides of the incision, release the suture ends from the retractable arms, and pull the suture through the vessel wall. The device is particularly useful for closing an incision in an artery following a catheterization procedure. In one embodiment, the catheter sheath introducer (CSI) used to perform the catheterization procedure is left in place during the suturing procedure.
Owner:WHITEBOX CAPITAL ARBITRAGE PARTNERS +1
Delivery mechanism for implantable stent
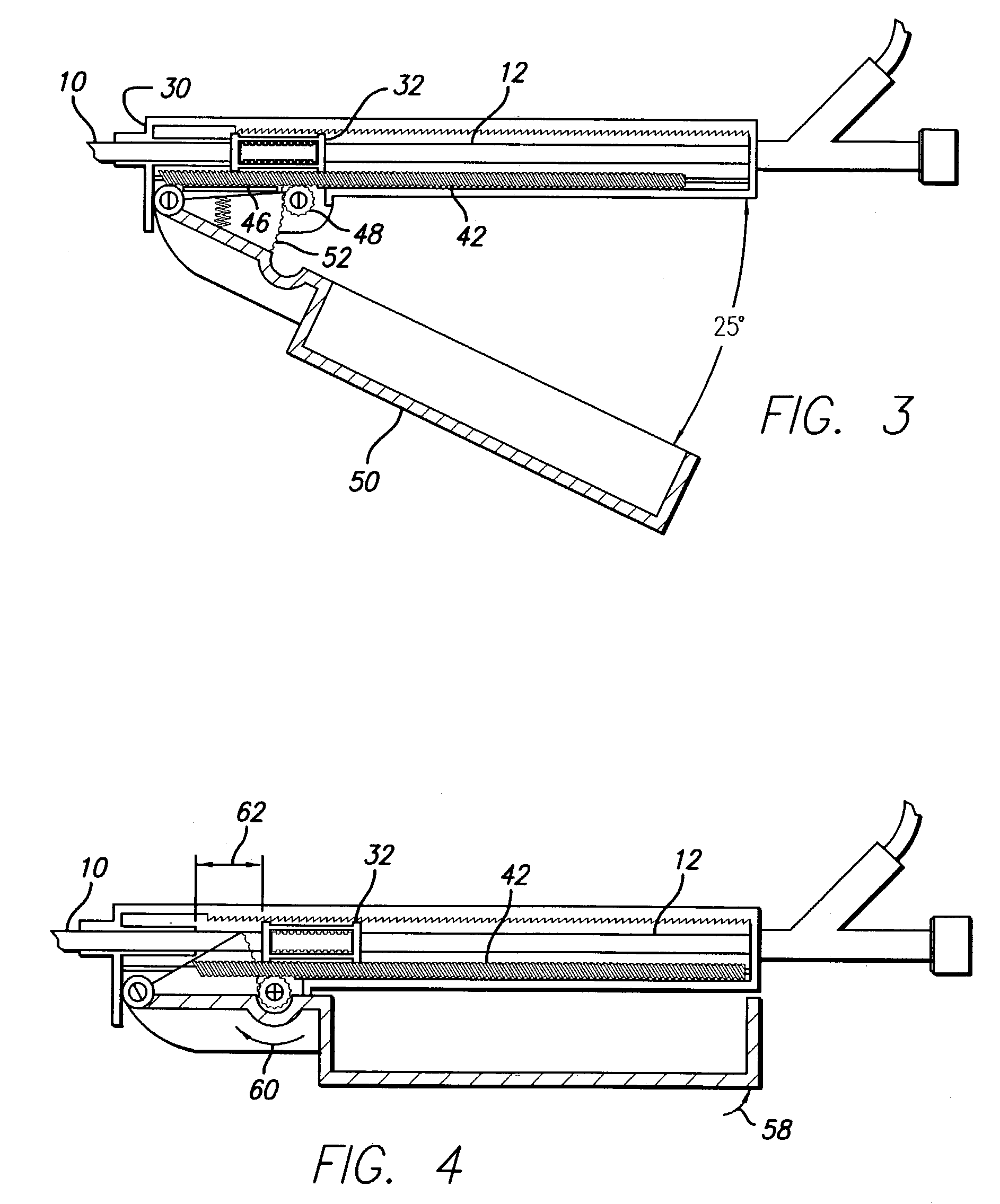
A delivery mechanism for an implantable stent which provides a high mechanical advantage to the surgeon and convenient operation so as to facilitate smooth withdrawal of an outer catheter sheath following placement of the stent in the desired location within the patient's vessel. Preferred embodiments include a moving rail actuated by a V-shaped lever, a hydraulic actuator, a rack and pinion drive, and a power screw system. The delivery mechanism has a movable member that is attached to the outer catheter sheath so that actuating the mechanism results in an incremental movement of the moveable member, which in turn results in an incremental movement of the outer catheter sheath. Once the outer catheter sheath is retracted from the stent, the stent is deployed into the patient's vessel and the remaining parts of the mechanism, including an inner tube, an atraumatic tip, and a stabilizing element, are easily removed.
Owner:BARD PERIPHERAL VASCULAR
Peel-away sheath
A peel-away sheath for a catheter includes at least one weakened area in a non-longitudinal pattern, such as a helical pattern, along the length of the sheath. One embodiment of a catheter sheath includes a tube having at least one pull wire integrally located within its wall. Another embodiment of a catheter sheath includes a tube having at least one integral lumen within its wall. The integral lumen may house a filling material. One embodiment of a catheter may include a first sheath which is positioned within a second sheath, with each of the first and second sheaths having at least one weakened area along its length. A reinforcing guide for a guide catheter includes a tube having a lumen with a diameter at least as large as the guide catheter diameter. The reinforcing guide includes a gap with a width which is less than the guide catheter diameter.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Device for catheter sheath retraction
Owner:CR BARD INC
Instrument and method for implanting an interbody fusion device
A holder is provided which couples to the spine. In an embodiment, the holder has two conduits into which sleeves may be inserted during a spinal fusion procedure. The holder may have a distractor extending from the bottom of the holder. The distractor secures the holder to the spine and maintains a proper separation distance between adjacent vertebrae. The sides of the distractor may be serrated to better secure the holder to the spine. The sleeves and conduits serve as alignment guides for instruments and implants used during the procedure. In an embodiment, the holder may include holes for fasteners that fixably secure the holder to vertebrae adjacent to a disc space. A flange may be placed around the holder to shield surrounding tissue and to provide a placement location for adjacent blood vessels during the spinal fusion procedure.
Owner:ZIMMER SPINE INC
Device for catheter sheath retraction
Owner:CR BARD INC
Driveable catheter systems and methods
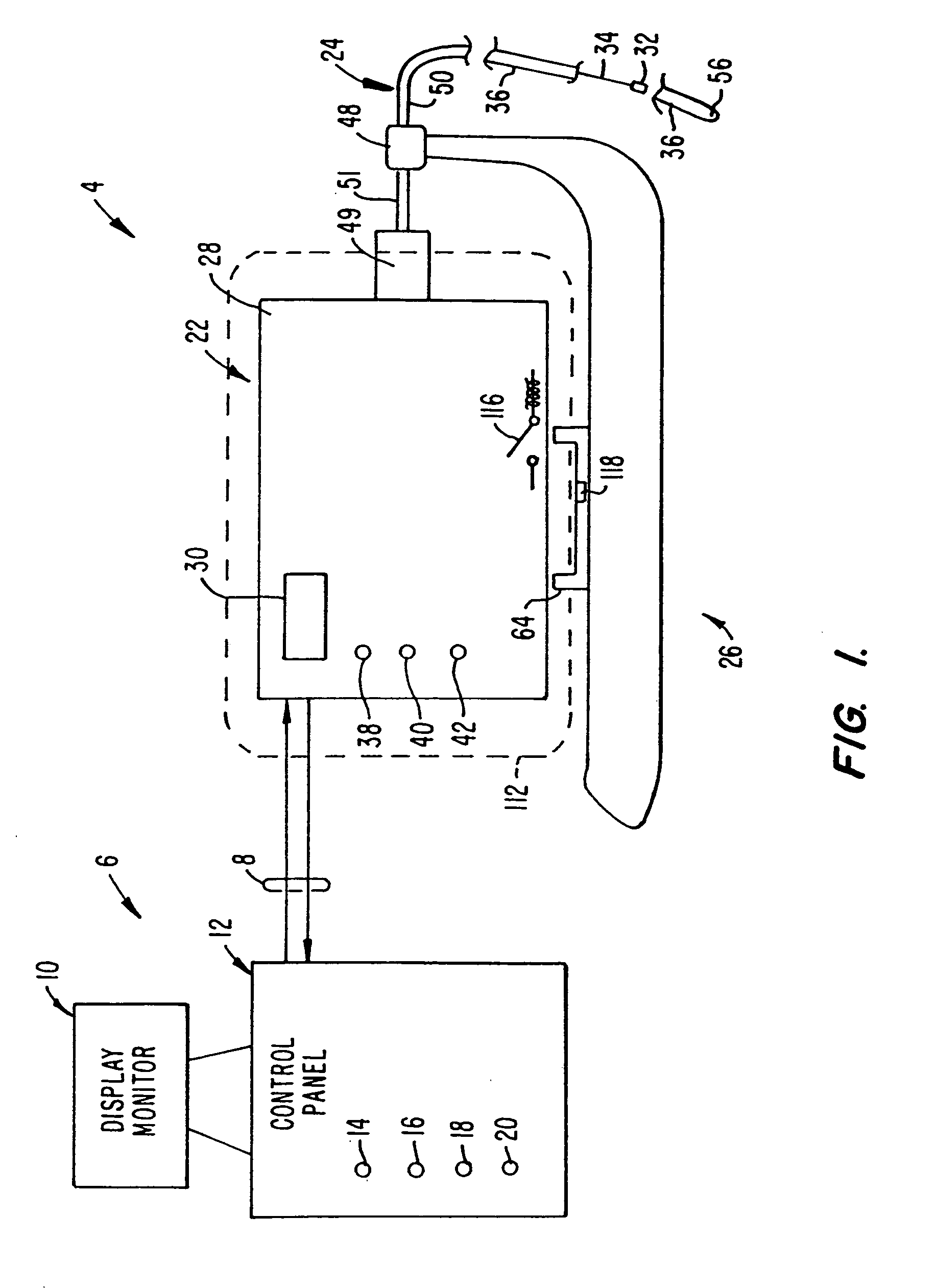
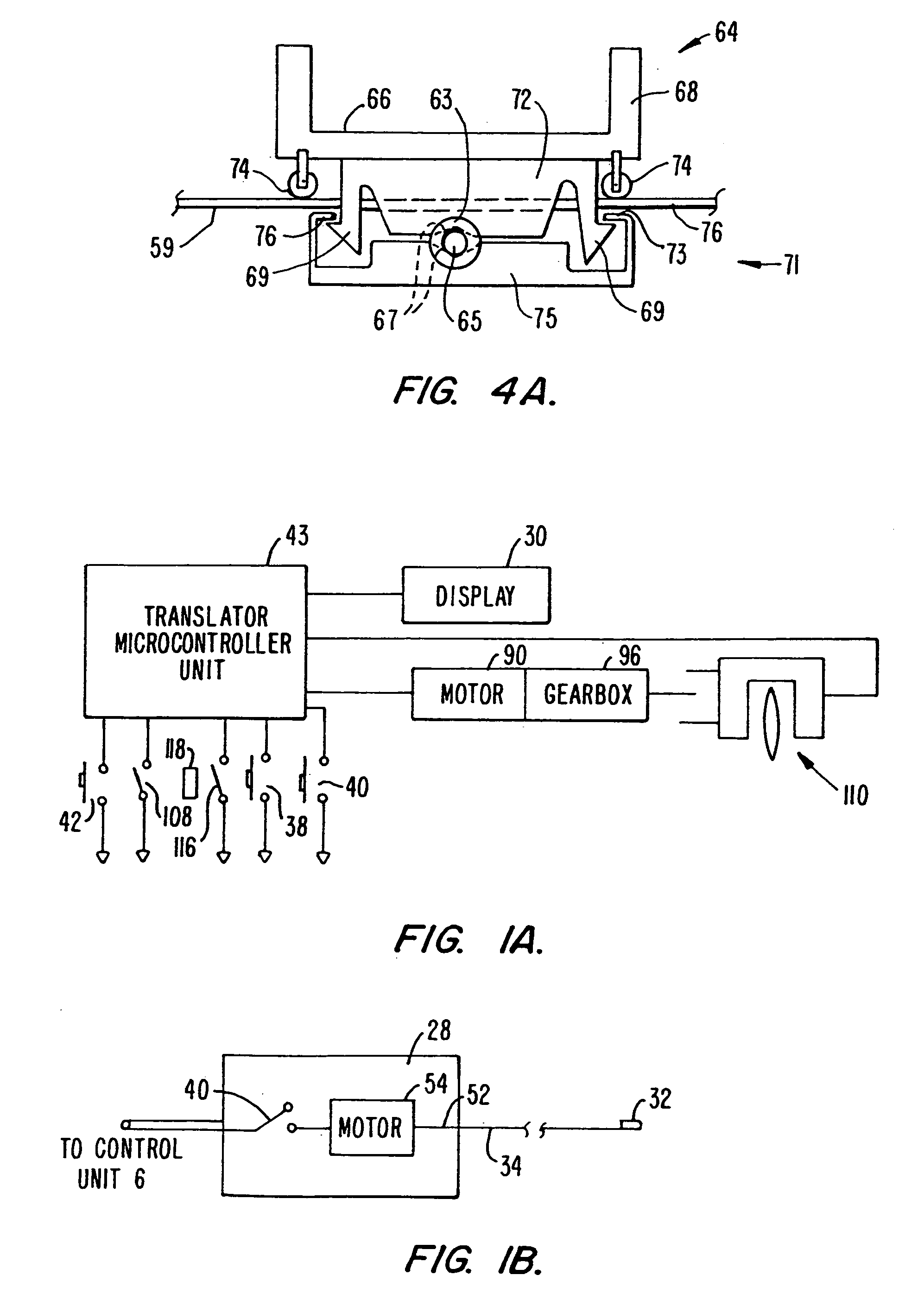
InactiveUS20060084911A1Easy to set upTranslational movement is simplifiedUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsEar treatmentDisplay deviceDrive motor
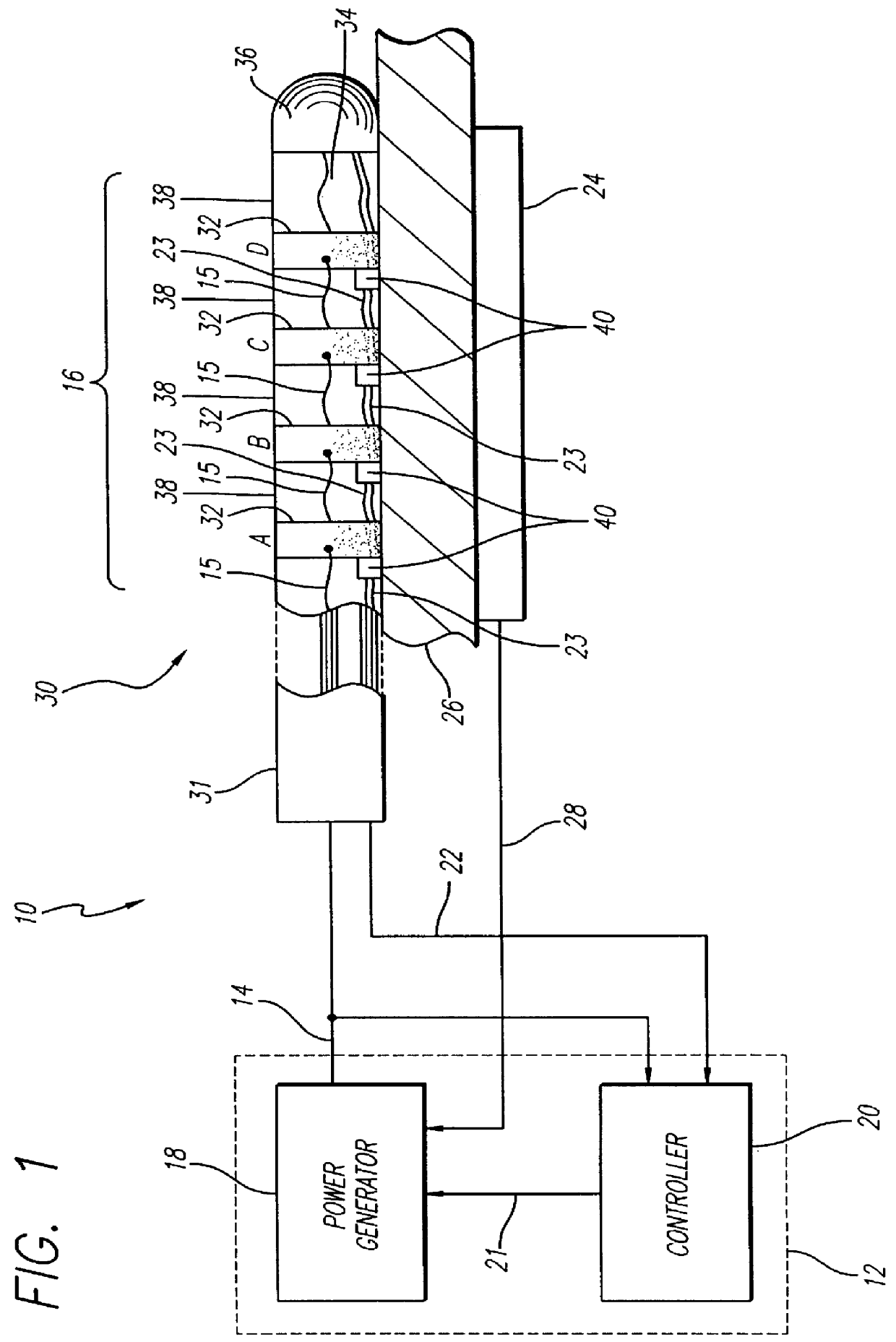
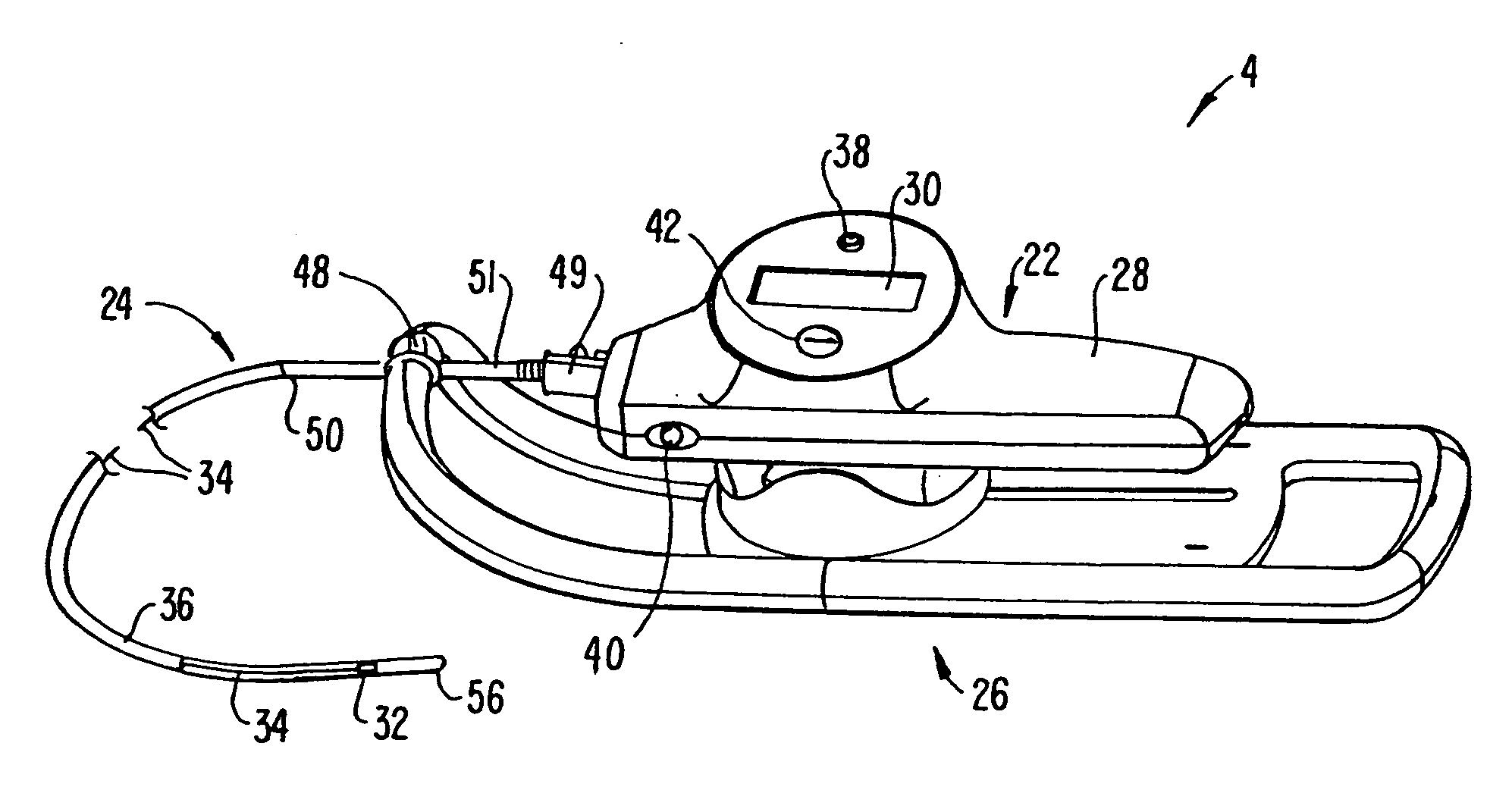
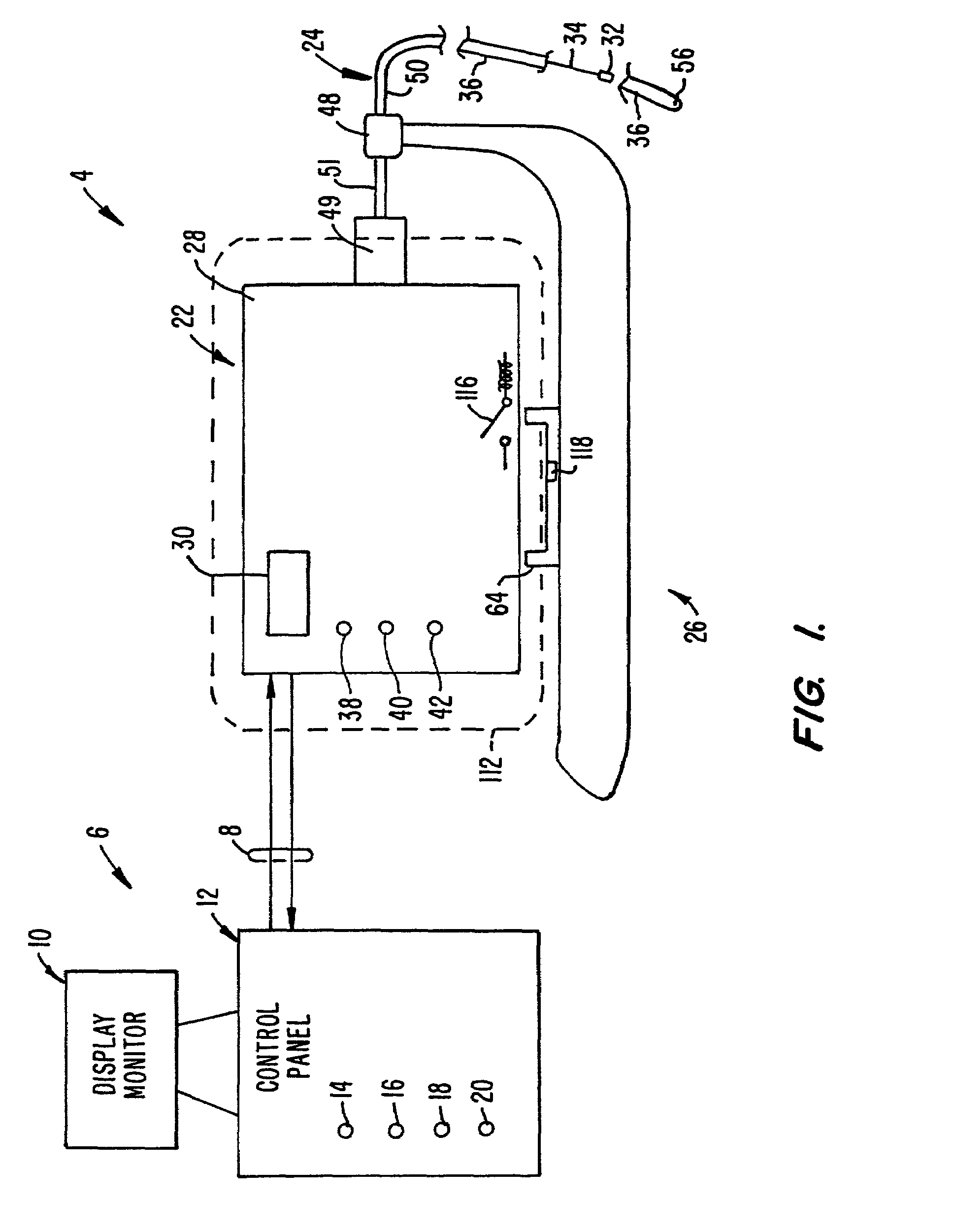
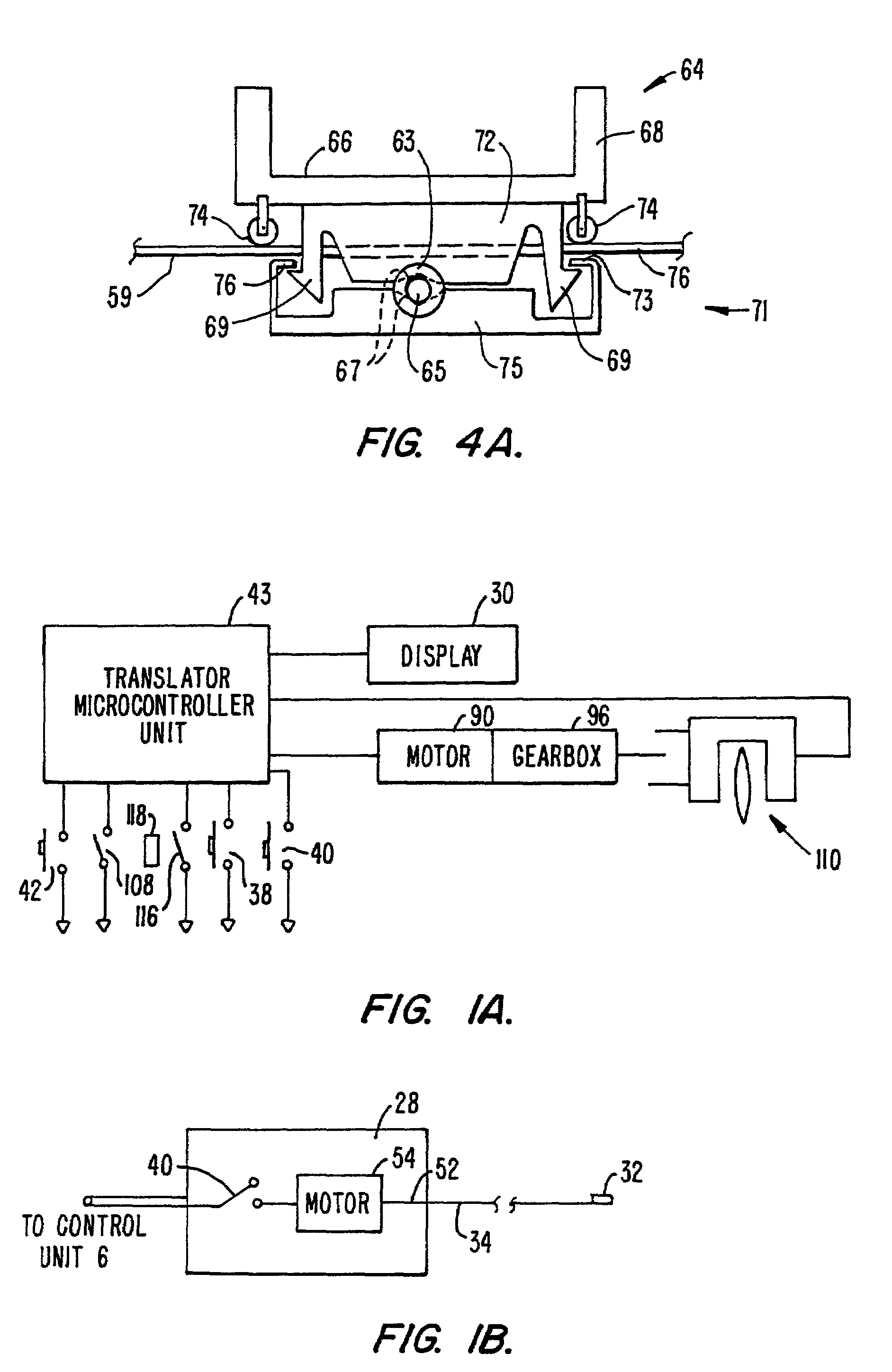
The system (2) includes a catheter drive unit (22) and a catheter (24) extending therefrom movably mounted to a catheter drive sled (26). The catheter drive unit rotates and translates the catheter core (34) within the catheter sheath (36). The sled has a serrated, conical drive unit interface (82), with a bag-piercing tip (86) mateable with a translator drive output (92) so that a sterile drape (112) enclosing the catheter drive unit is automatically pierced when the catheter drive unit is mounted to the sled. A control unit (6) is spaced apart from the catheter drive unit and provides power and commands to the catheter drive unit and receives information and data from the catheter drive unit. The rotator and translator drive motors (54, 90) are operated from both the control unit and the catheter drive unit. Both the control unit and catheter drive unit have translation displacement displays (10, 30).
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
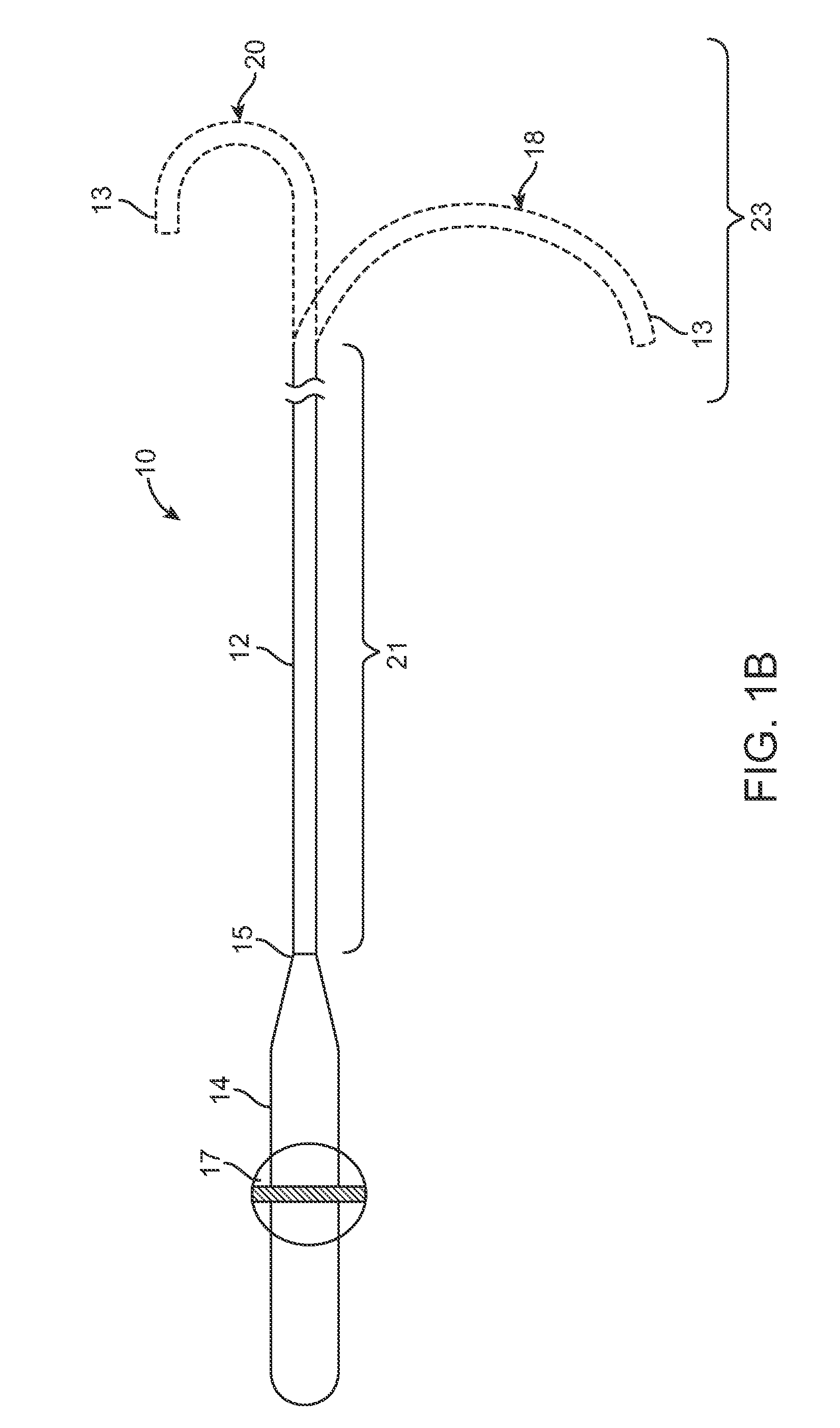
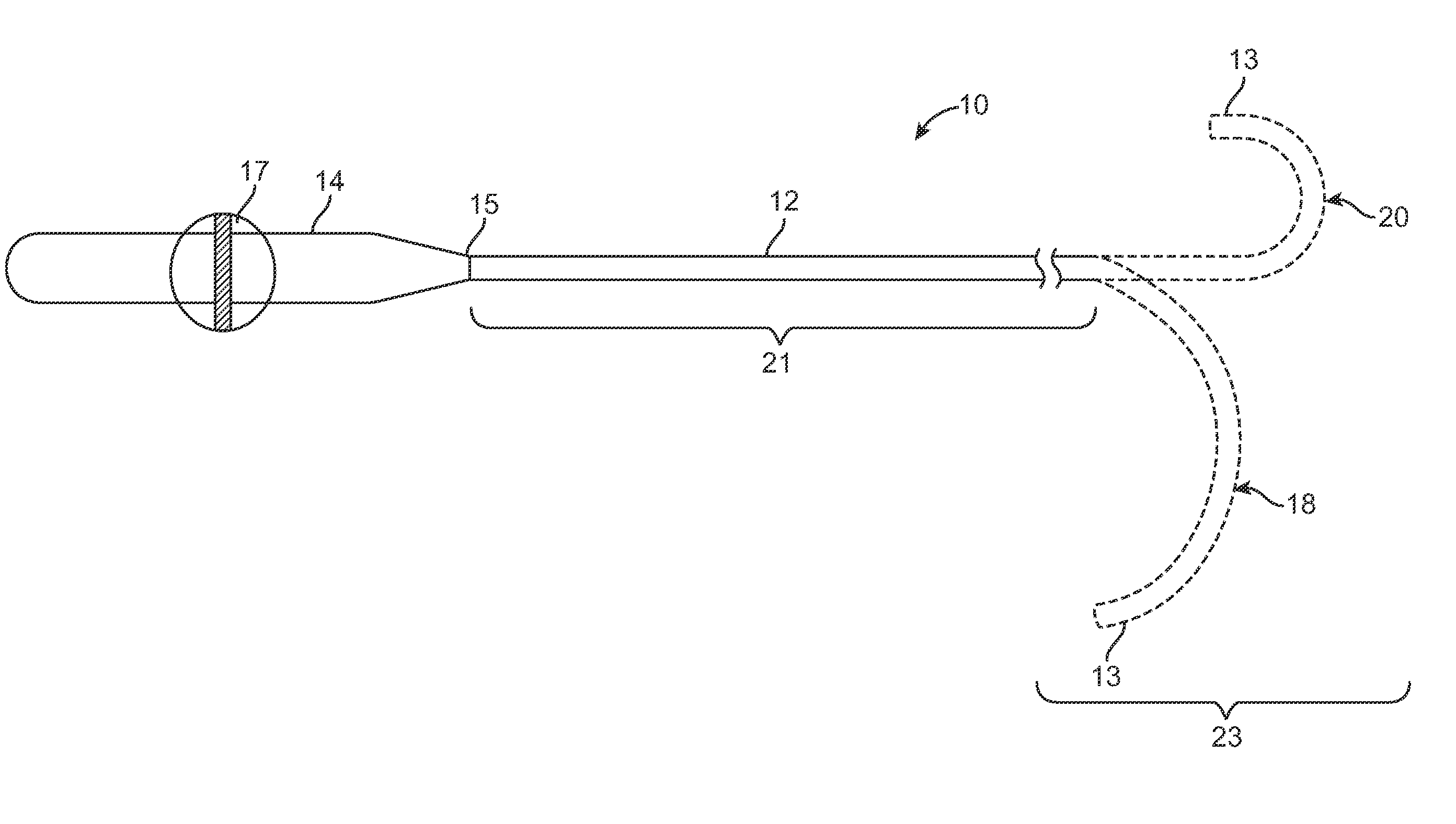
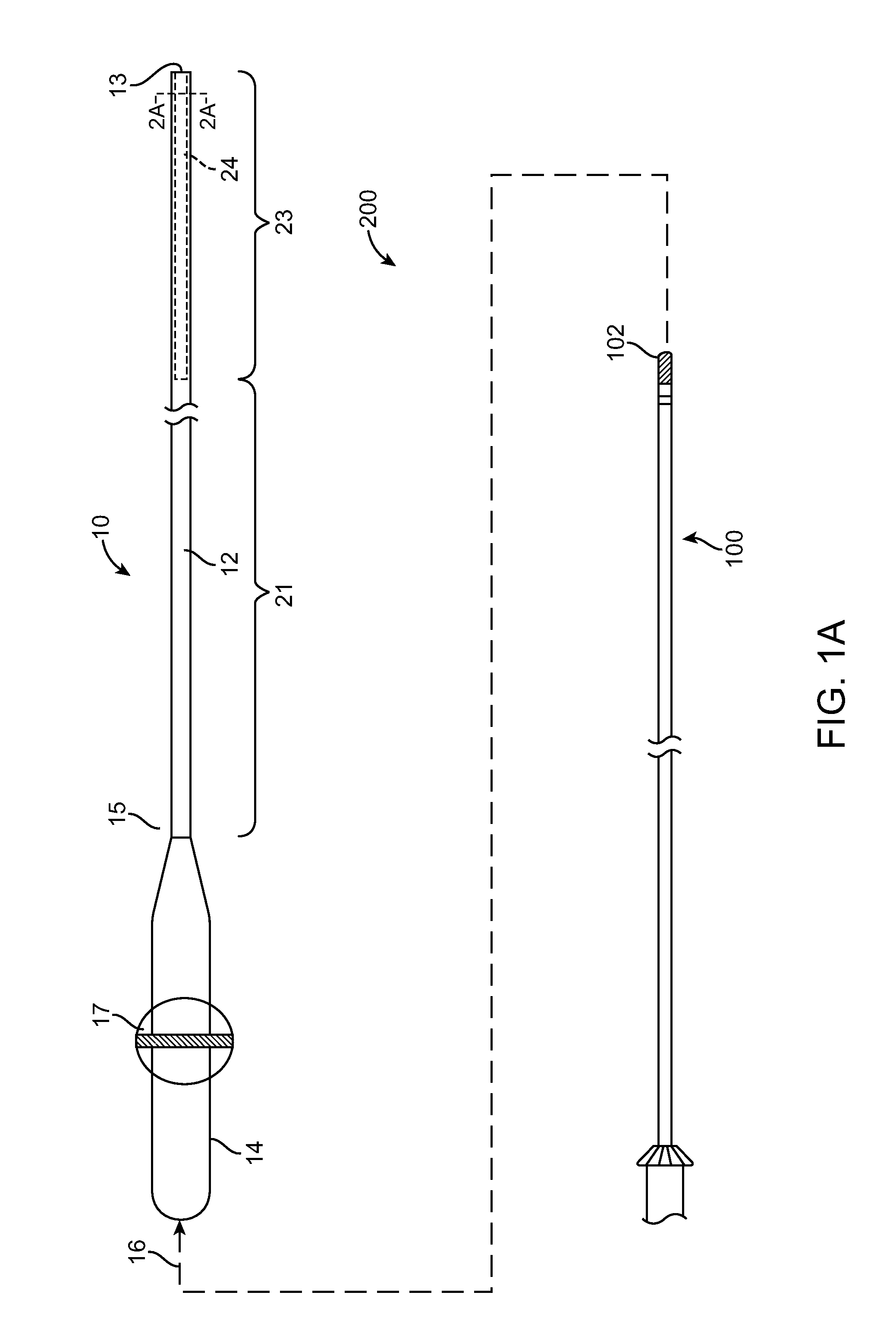
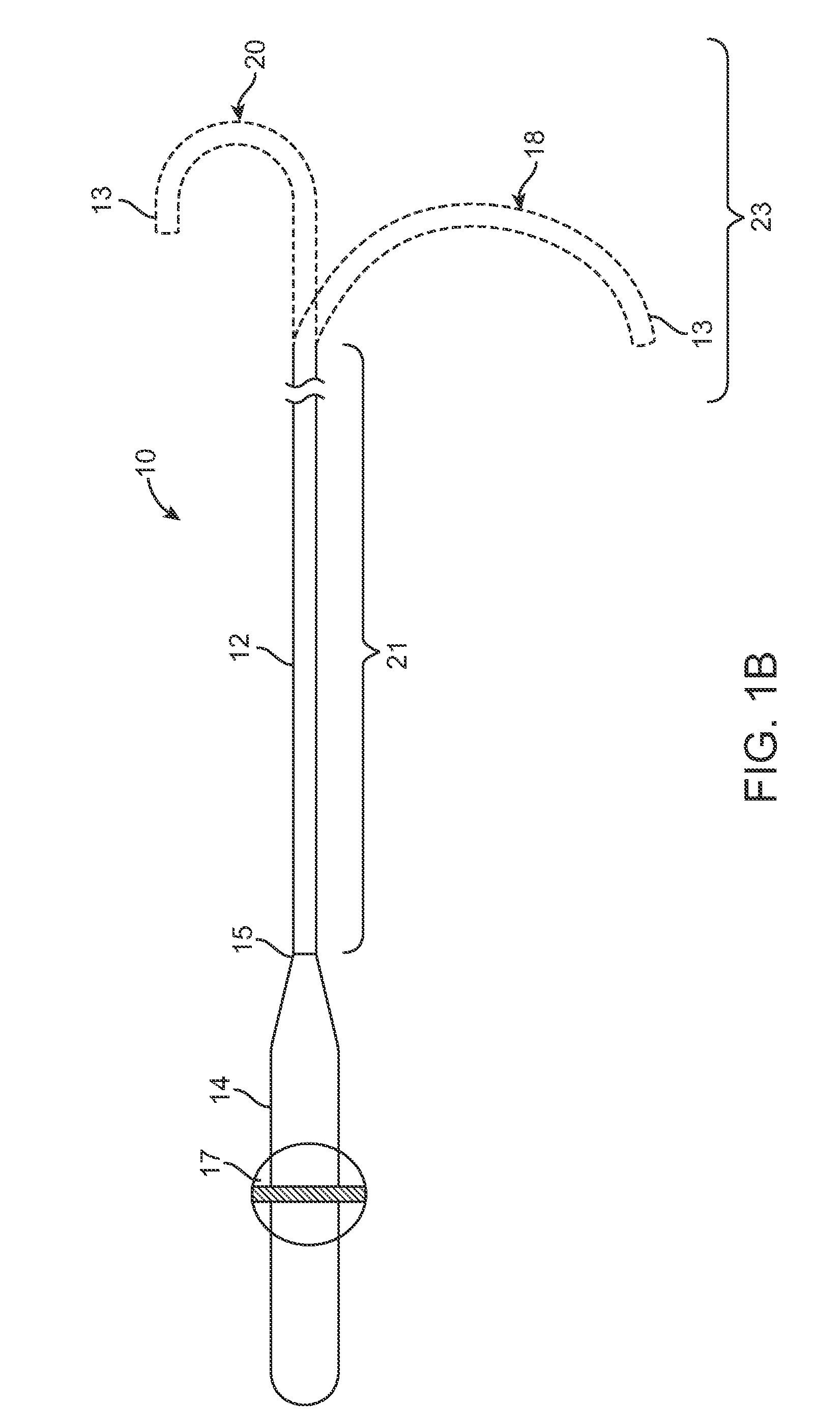
Asymmetric dual directional steerable catheter sheath
ActiveUS8500733B2Shorten travel distanceImprove usabilityMedical devicesCatheterMedicineDistal portion
A steerable catheter sheath for use in directing a catheter into a desired position is provided. The sheath includes an elongated member configured to receive the catheter therein. The distal end of the elongated member is steerable in two directions, each direction having a different bent configuration, e.g., a sharp curve in one direction and an open arching curve in the other direction. A resilient structure having different bending properties in each of its lateral sides is carried in the distal portion of the elongated member and causes the asymmetric bending. In one embodiment, the resilient structure includes a hypotube with a plurality of notches and slits in the sides. In another embodiment, the resilient structure is covered in an outer coating having different durometer portions. The sheath is particularly useful for accessing left and right pulmonary veins when a transeptal entry approach is used into the left atrium.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Asymmetric dual directional steerable catheter sheath
ActiveUS20100217261A1Shorten travel distanceImprove usabilityMedical devicesCatheterDistal portionBiomedical engineering
A steerable catheter sheath for use in directing a catheter into a desired position is provided. The sheath includes an elongated member configured to receive the catheter therein. The distal end of the elongated member is steerable in two directions, each direction having a different bent configuration, e.g., a sharp curve in one direction and an open arching curve in the other direction. A resilient structure having different bending properties in each of its lateral sides is carried in the distal portion of the elongated member and causes the asymmetric bending. In one embodiment, the resilient structure includes a hypotube with a plurality of notches and slits in the sides. In another embodiment, the resilient structure is covered in an outer coating having different durometer portions. The sheath is particularly useful for accessing left and right pulmonary veins when a transeptal entry approach is used into the left atrium.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Valvuloplasty devices and methods
ActiveUS7618432B2Stable positionAvoid structureBalloon catheterCannulasAortic valvuloplastyAortic sinus
Owner:INTERVALVE MEDICAL INC
Expandable sheath introducer
The disclosure relates to an a catheter sheath introducer that is capable of being expanded from first diameter to second diameter in order to accommodate differently sized medical devices to be introduced by the sheath introducer. The device is structured such that it does not foreshorten when expanded.
Owner:CARDINAL HEALTH SWITZERLAND 515 GMBH
Enhanced medical device for use in bodily cavities, for example an atrium
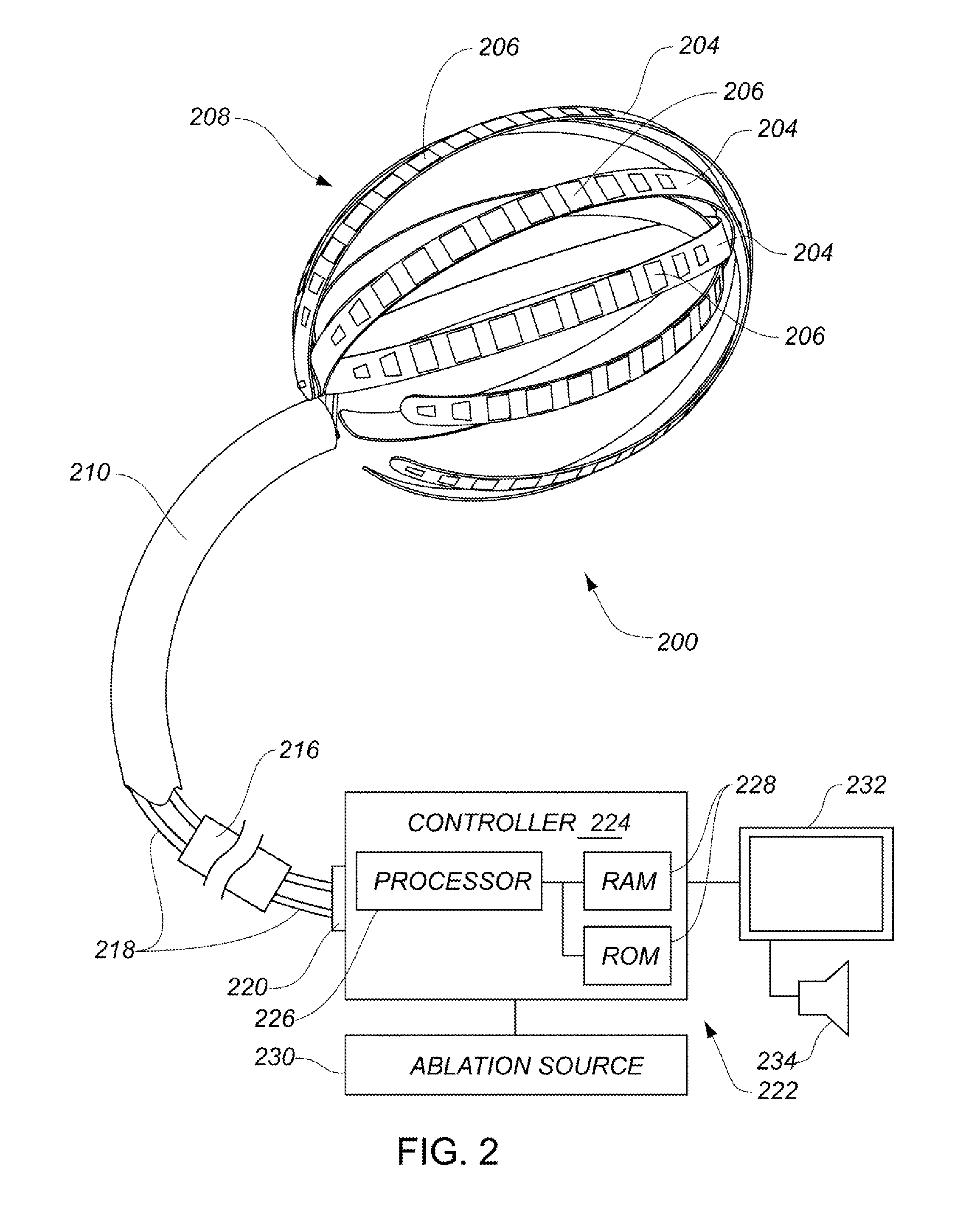
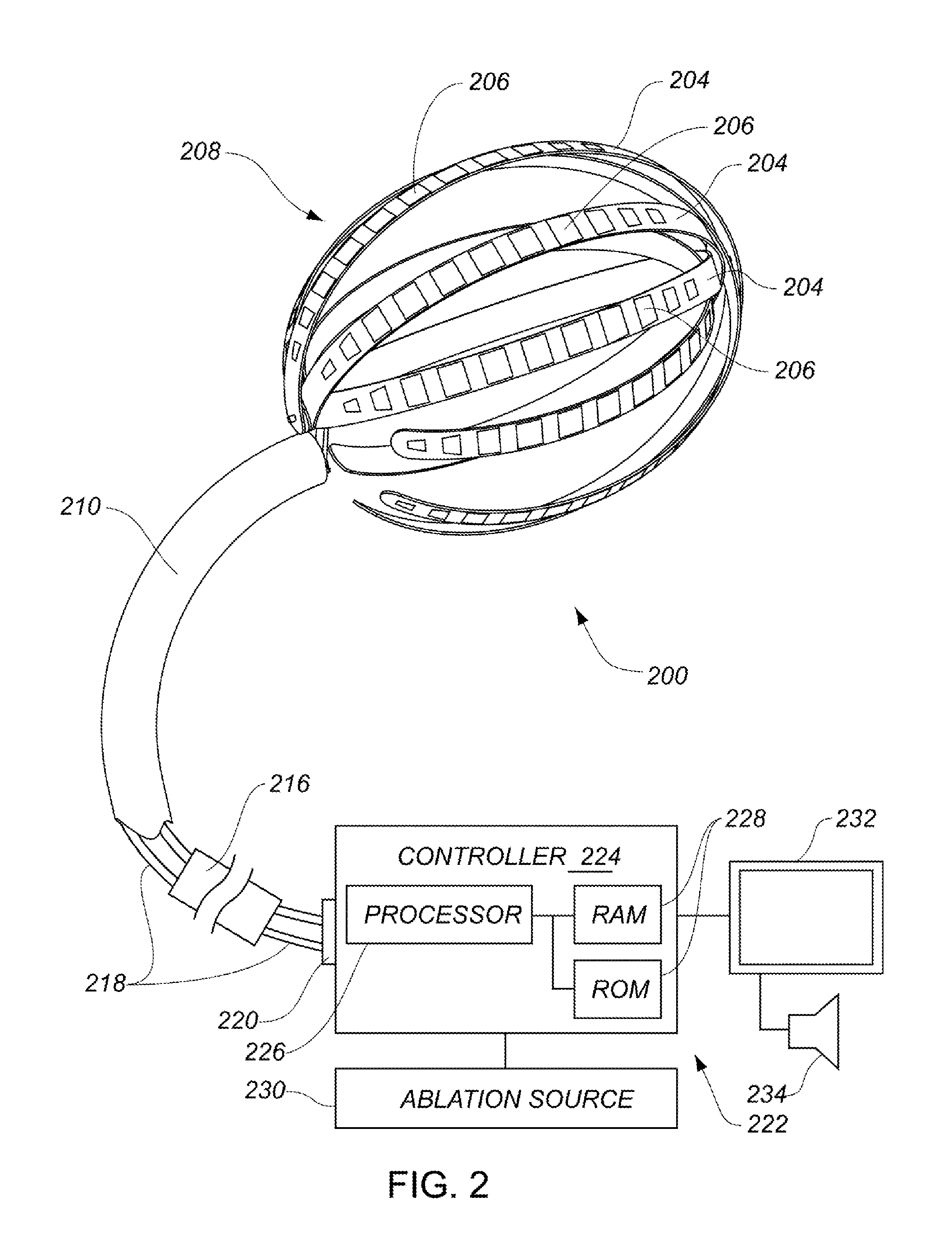
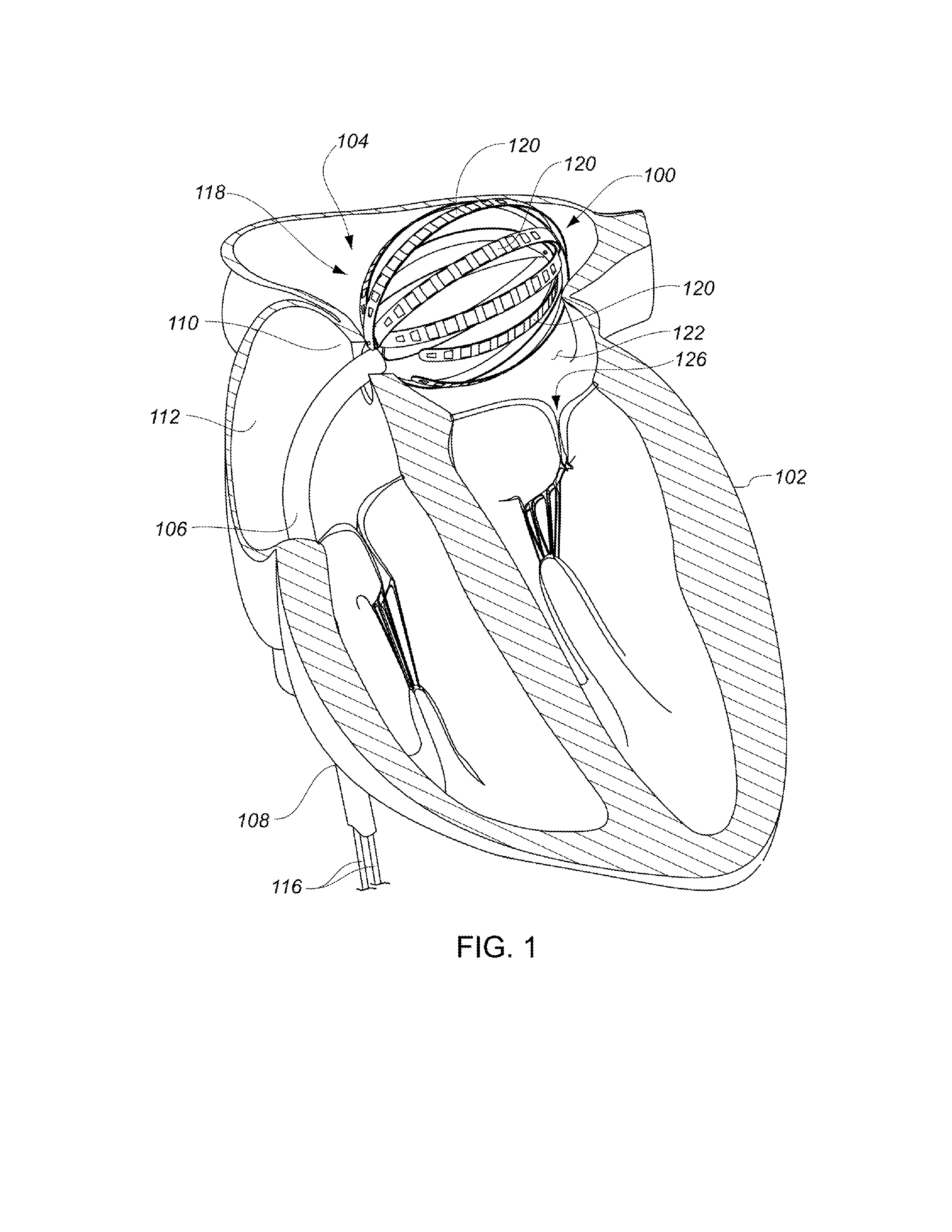
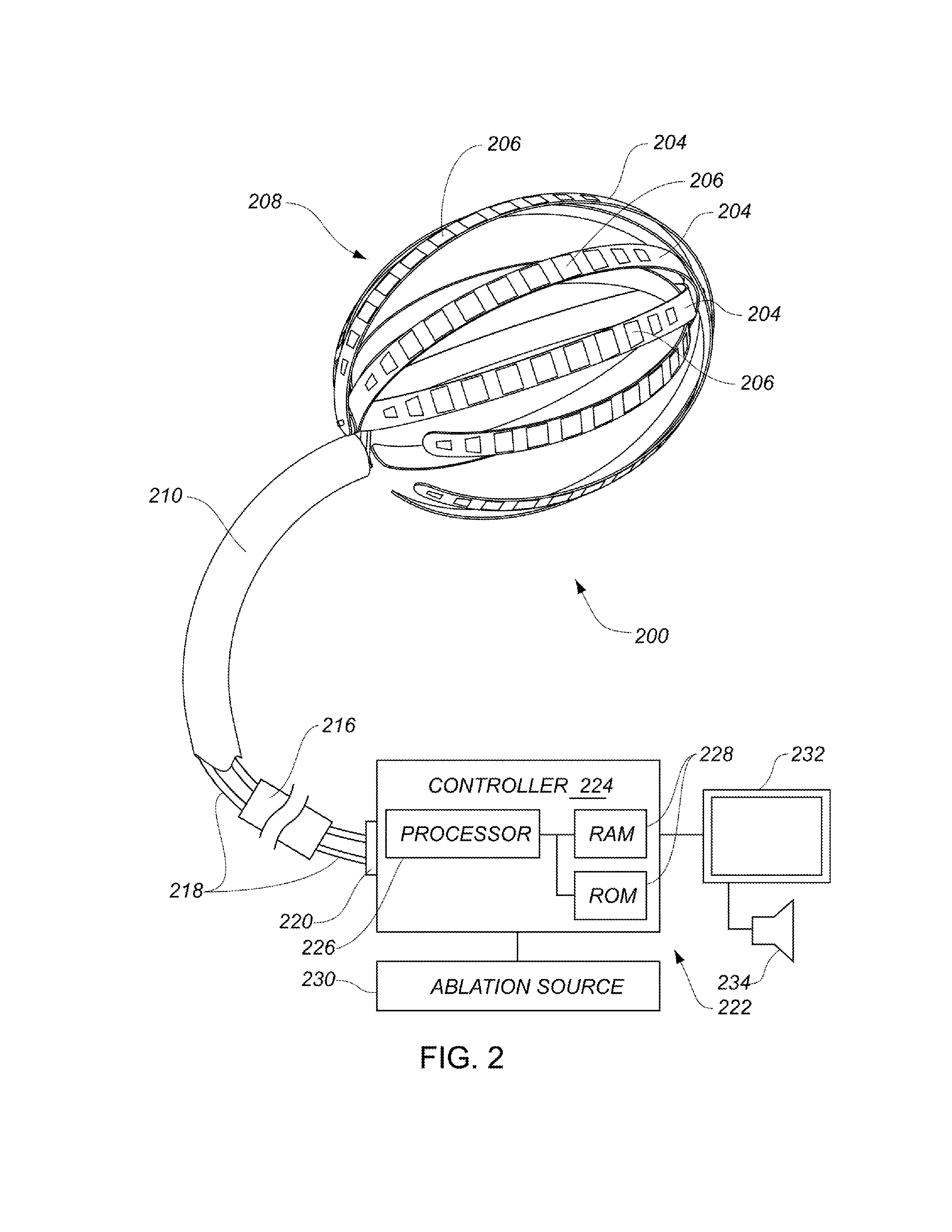
ActiveUS20130304065A1Enhanced for deployment and positioningImprove ablationCatheterSensorsTransducerMedical device
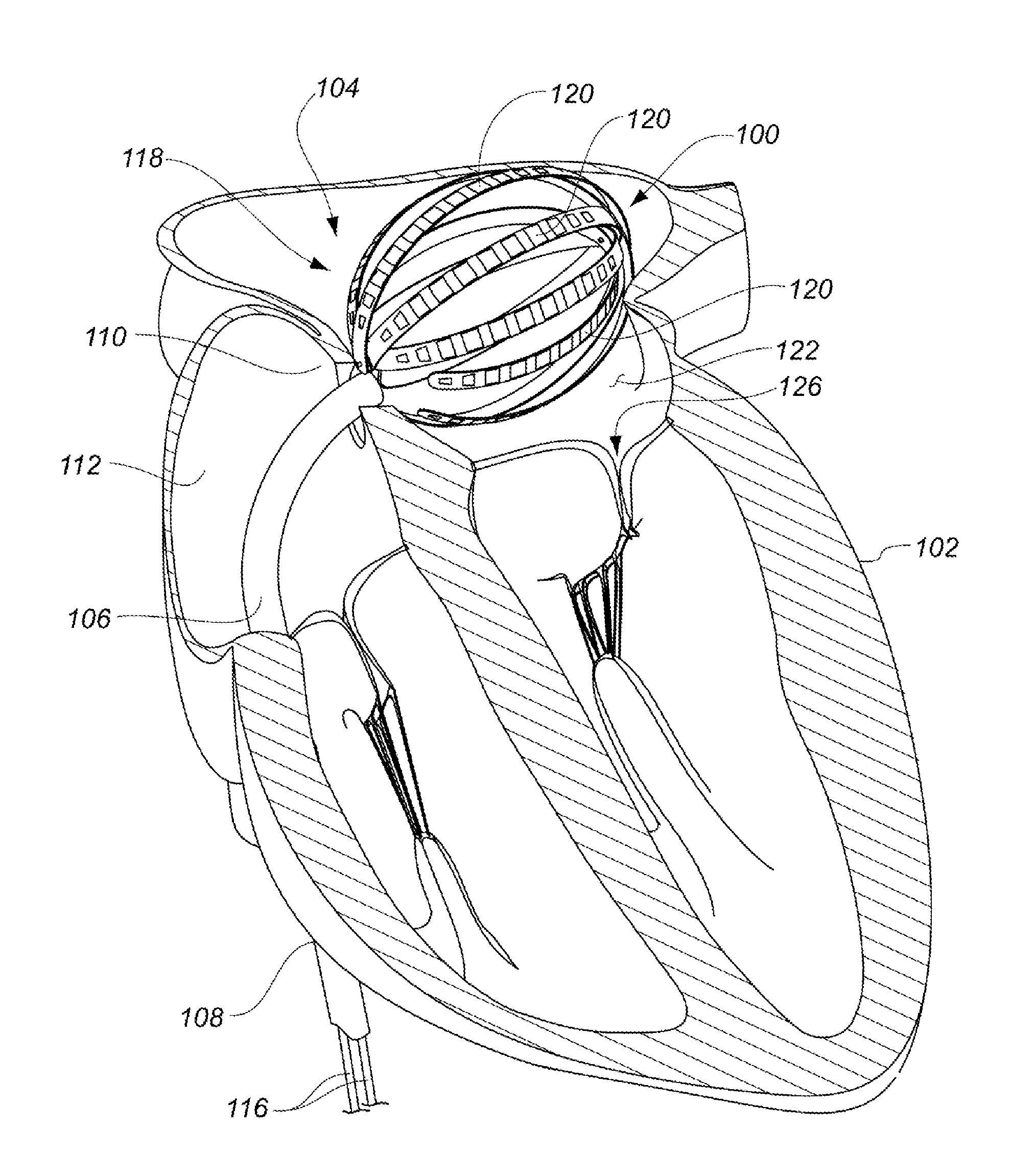
Systems, methods, and devices allow intravascular or percutaneous mapping, orientation or ablation, or combinations thereof in bodily cavities or lumens. A device includes a plurality of elongate members which are moveable between an unexpanded configuration, a bent or coiled stack configuration and an expanded or fanned configuration. The elongate members form a stack arrangement in the unexpanded configuration to fit through a catheter sheath. The elongate members follow respective arcuate or curvilinear paths as advanced from the sheath into the bent or coiled stack configuration, adopting volute, scroll or rho shapes, and may be nested. The elongated members are fanned or radially spaced circumferentially with respect to one another into the expanded or fanned configuration. Transducers carried by elongate members may sense various physiological characteristics of or proximate tissue, for instance temperature, and / or may apply energy to or proximate tissue, for example to perform ablation. The device is retractable.
Owner:KARDIUM
Endovenous ablation mechanism with feedback control
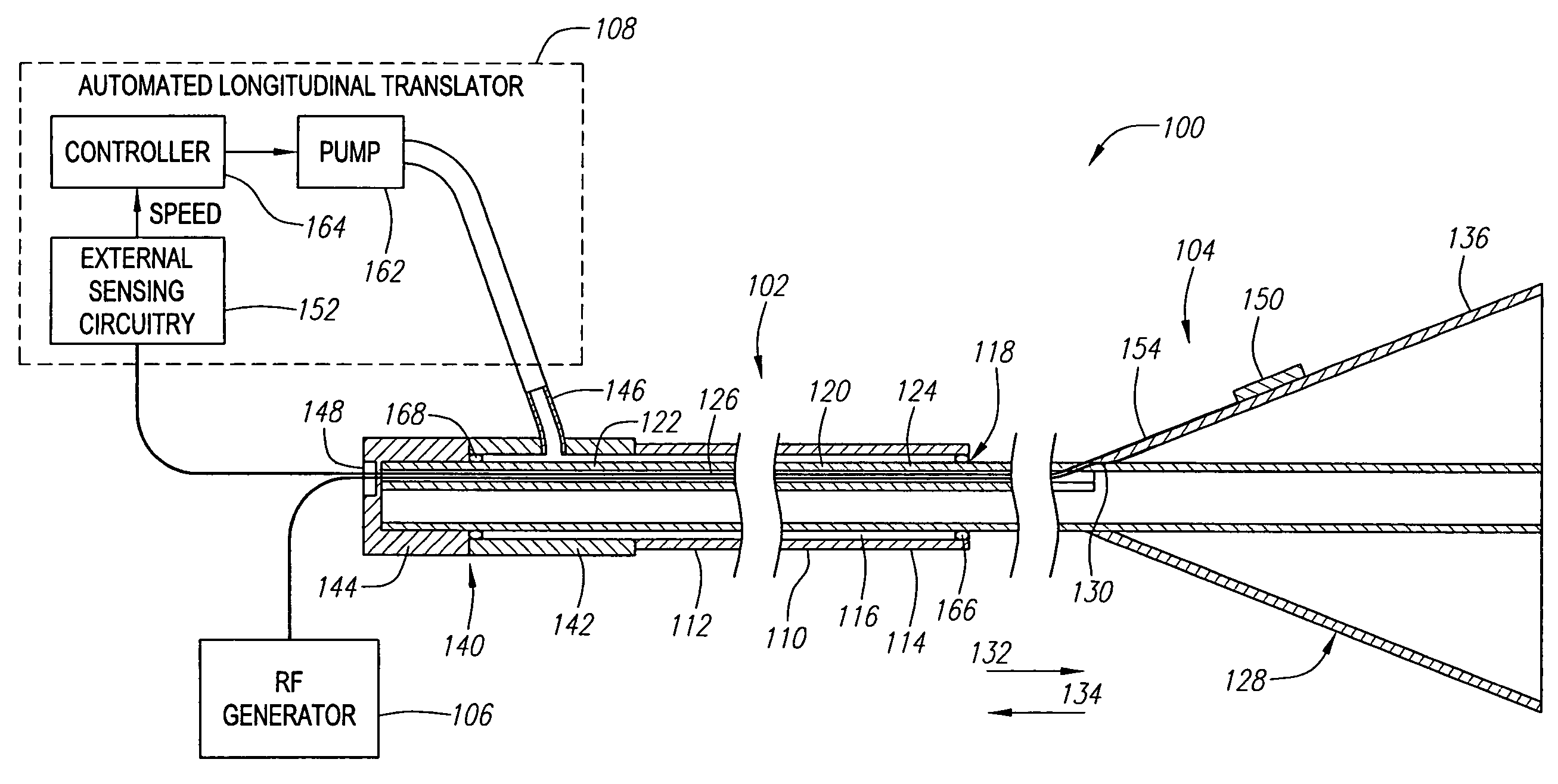
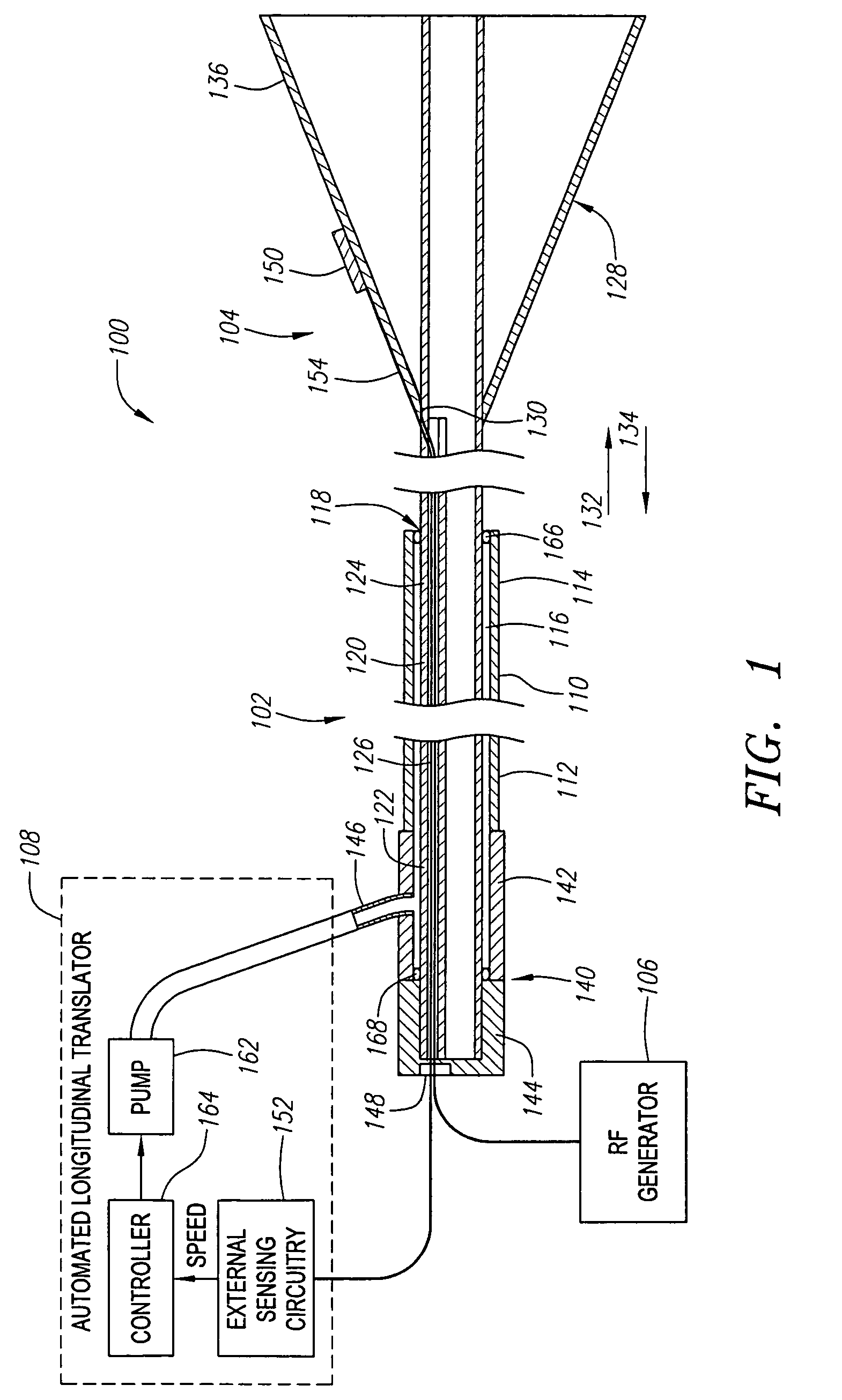
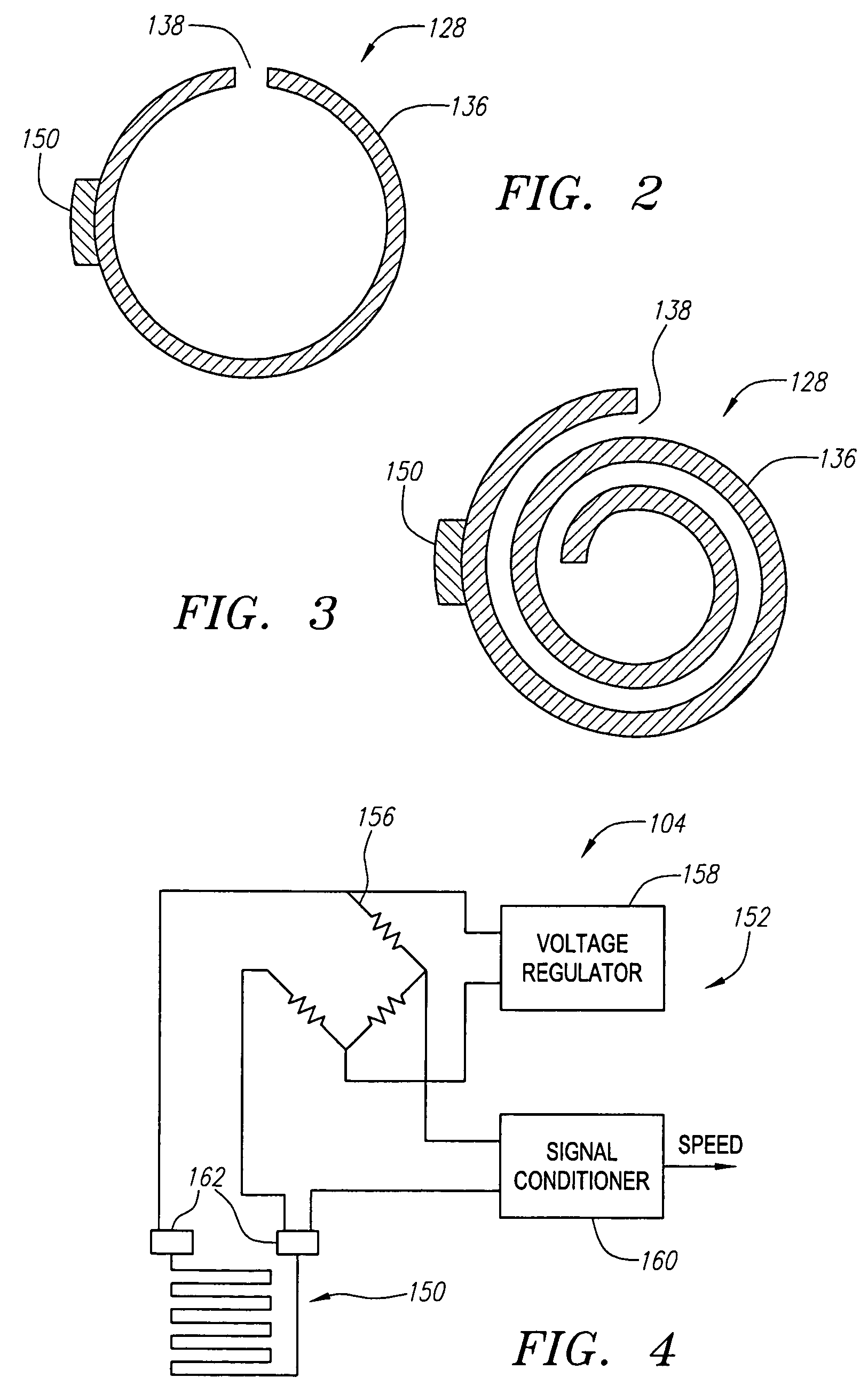
InactiveUS6964661B2Automate the moveCatheterDiagnostic recording/measuringEndovenous ablationFeedback control
A vessel occlusion system includes one or more ablation elements that, when activated, is configured for at least partially closing a vessel segment of a patient. The vessel occlusion system further includes a sensor assembly that is configured for generating feedback indicative of a state of closure of the vessel segment, and an automated longitudinal translator configured for longitudinally translating the one or more ablation elements based on the feedback from the sensor assembly. The one or more ablation elements may be associated with a catheter member that slides within the catheter sheath.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Enhanced medical device for use in bodily cavities, for example an atrium
ActiveUS20130172883A1Enhanced for deployment and positioningImprove ablationElectrocardiographyCatheterProximateTransducer
Systems, methods, and devices allow intravascular or percutaneous mapping, orientation or ablation, or combinations thereof in bodily cavities or lumens. A device includes a plurality of elongate members which are moveable between an unexpanded configuration, a bent or coiled stack configuration and an expanded or fanned configuration. The elongate members form a stack arrangement in the unexpanded configuration to fit through a catheter sheath, The elongate members follow respective arcuate or curvilinear paths as advanced from the sheath into the bent or coiled stack configuration, adopting volute, scroll or rho shapes, and may be nested. The elongated members are fanned or radially spaced circumferentially with respect to one another into the expanded or fanned configuration. Transducers carried by elongate members may sense various physiological characteristics of or proximate tissue, for instance temperature, and / or may apply energy to or proximate tissue, for example to perform ablation. The device is retractable.
Owner:KARDIUM
Intravenous Catheter Introducer with Needle Retraction Controlled by Catheter Hub Seal
A passive intravenous (“IV”) catheter introducer having a spring-biased needle retraction system that is triggered when the needle is manually withdrawn through a catheter hub seal. The catheter hub seal constricts to block the rearward flow of bodily fluid and wipe potentially infectious fluids off the outer surface of the needle as the needle is manually withdrawn through the catheter sheath and seal following insertion of the catheter into a patient's vein. No additional steps are needed to activate the needle retraction mechanism beyond manual removal of the needle from the catheter hub seal.
Owner:RETRACTABLE TECH INC
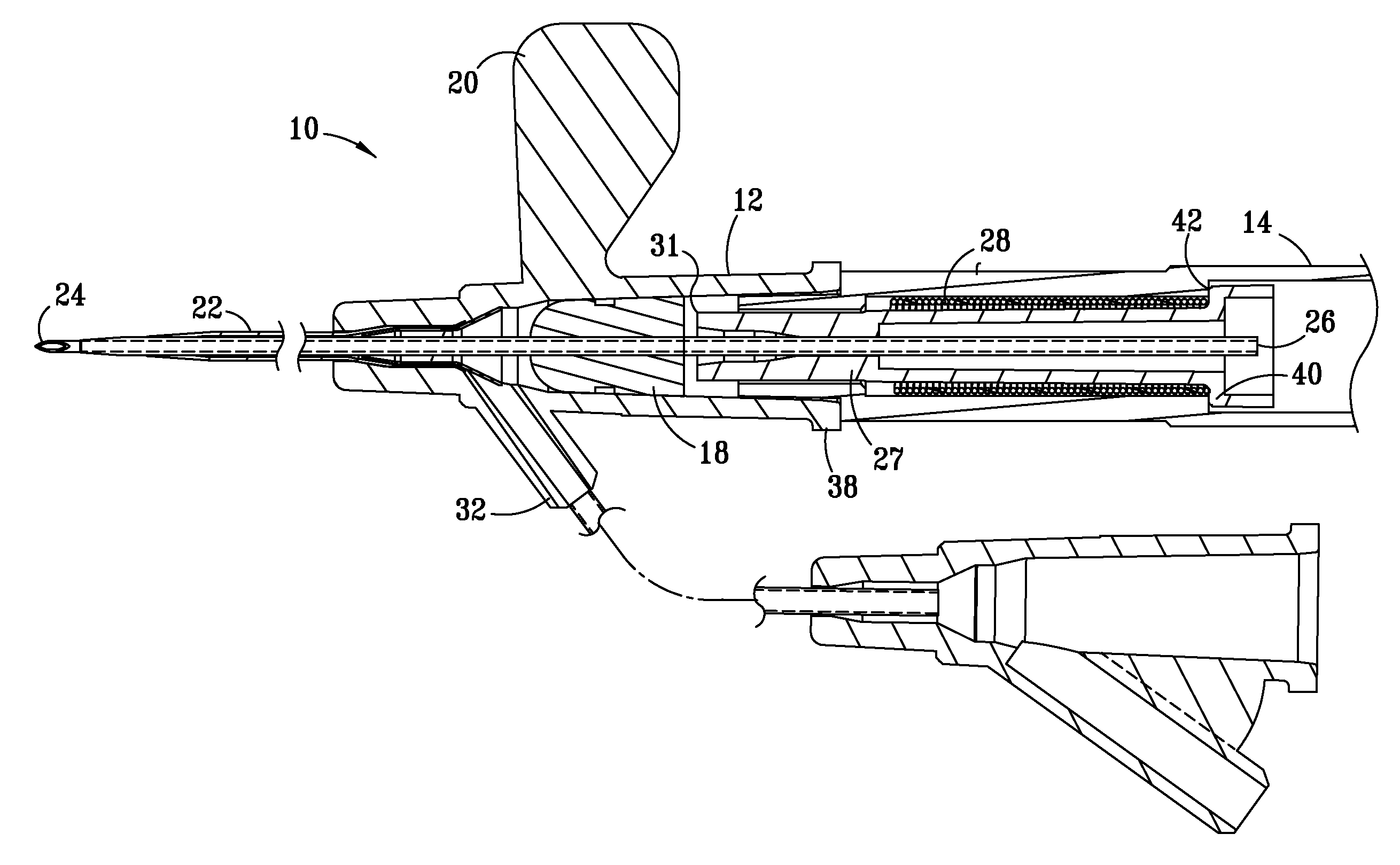
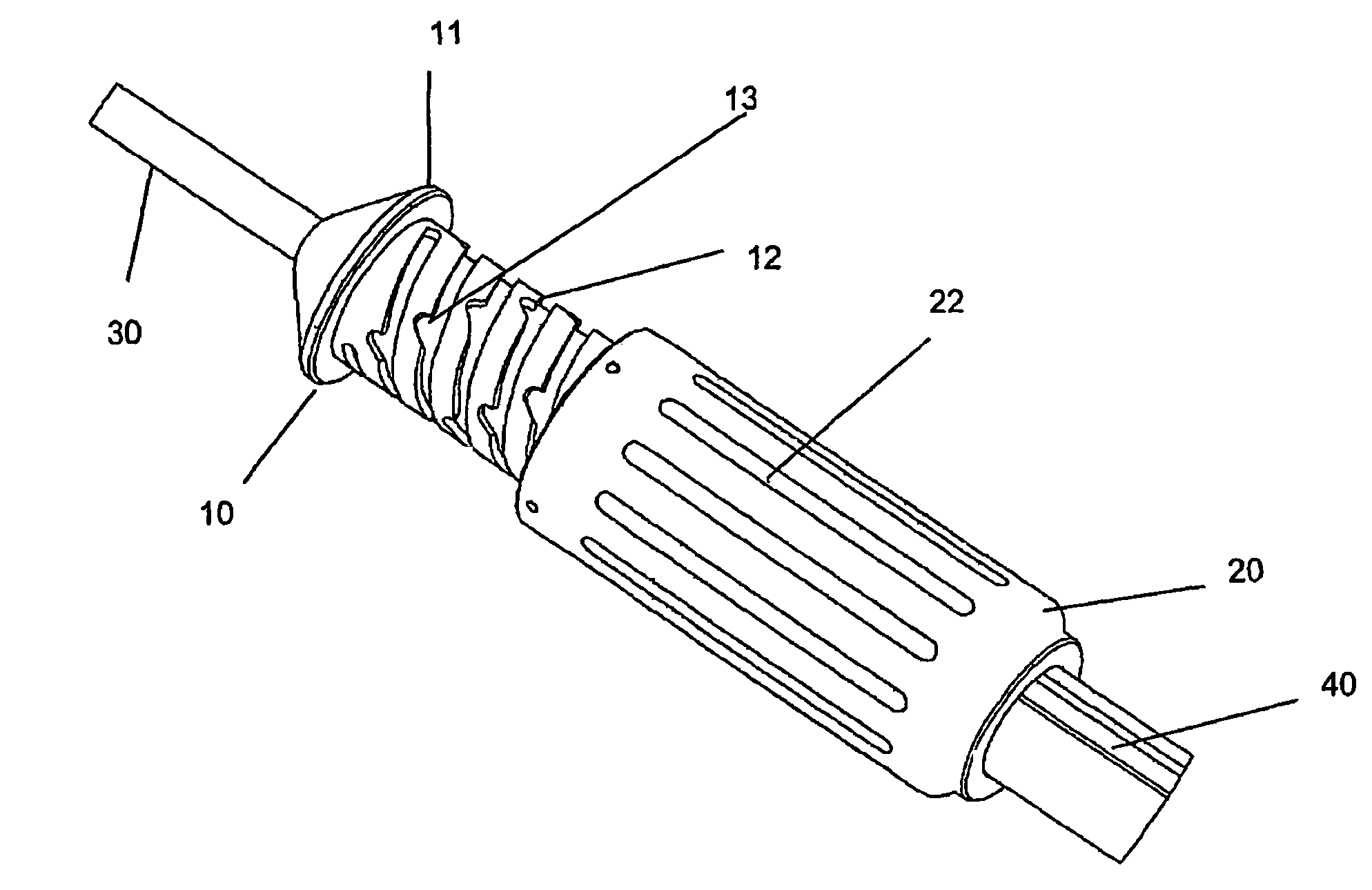
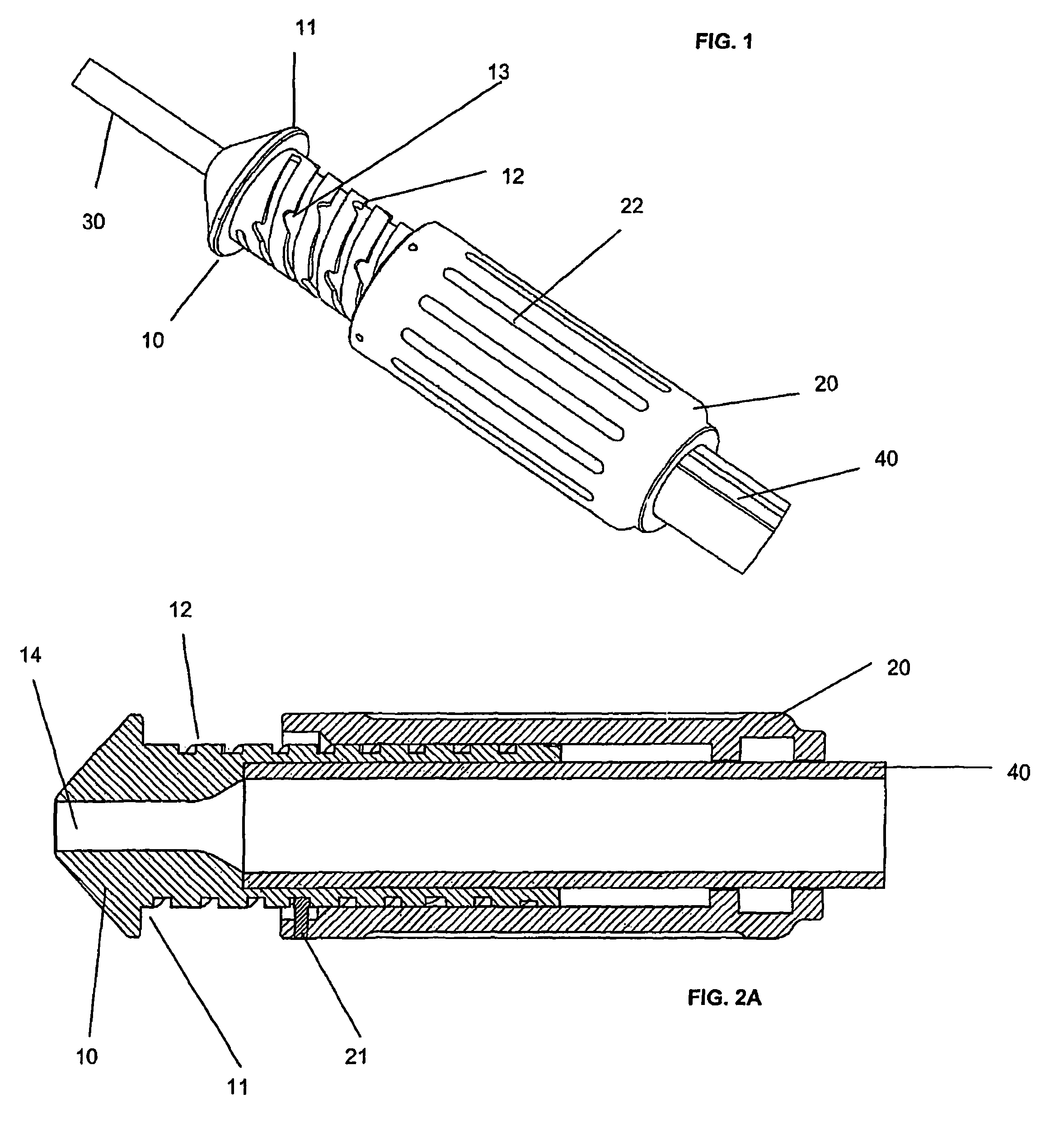
Control device for medical catheters
InactiveUS7837724B2Improve reliabilityInexpensive to fabricateStentsSurgeryEngineeringCatheter sheath
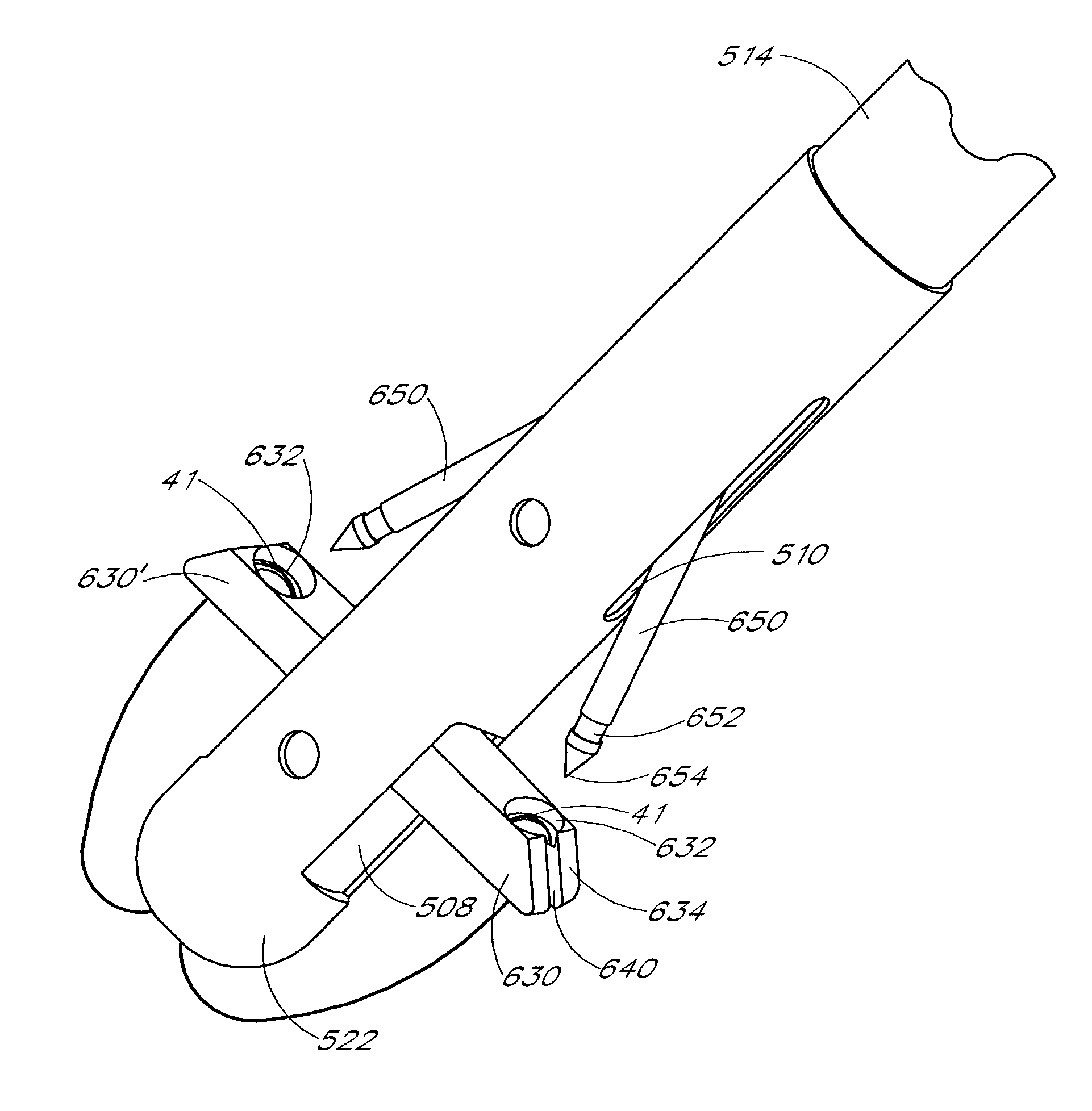
A control mechanism comprises an elongate handle 10 having an external thread 12 and a barrel 20 with internally projecting pins 21 threaded over handle 10. Rotation of barrel 20 causes handle 10 to move back and forth along its longitudinal axis to retract and advance a catheter sheath to which handle 10 is coupled, thereby enabling an implant to be deployed by the catheter. Rotation movement of barrel 20 and longitudinal movement of handle 10 can be disassociated to enable speedy retraction or advancement of the catheter sheath.
Owner:ANSON MEDICAL LTD
Suturing device and method for sealing an opening in a blood vessel or other biological structure
InactiveUS20060195120A1Many of complicationMany of costSuture equipmentsSurgical needlesDistal portionVia incision
Owner:NOBLES ANTHONY A +2
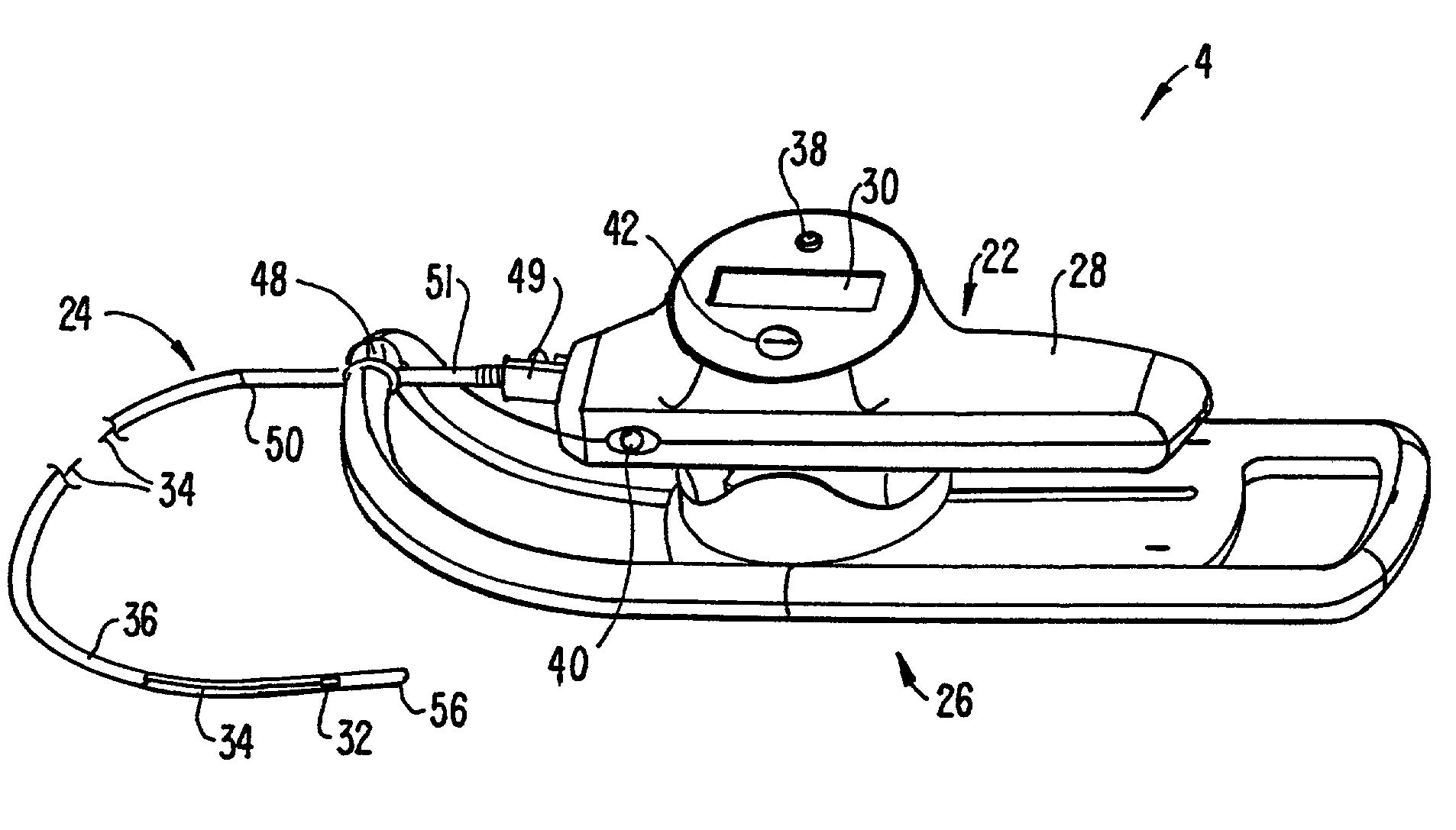
Imaging catheter
ActiveUS20090270737A1Easy to handleEasy to maneuverUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsCatheterMotor driveSTERILE FIELD
Described herein are imaging catheter system. In an exemplary embodiment, a catheter comprises a handle assembly having distal and proximal ends, a catheter sheath connected to the distal end of the handle assembly, and an elongated flexible tube connected to the proximal end of the handle assembly. The catheter further comprises an imaging core slidably received within the catheter sheath, the handle assembly and the elongated tube. The imaging core also includes a slide member, e.g., knob, extending from the imaging core and passing through an elongated slot in the handle assembly, allowing a physician to manually pullback and advance the imaging core within the catheter by sliding the slide member back and forth. Preferably, the elongated tube is long enough so that the motor drive coupled to the proximal end of the catheter is kept outside the sterile field during the imaging procedure.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Enhanced medical device for use in bodily cavities, for example an atrium
ActiveUS20130178851A1Enhanced for deployment and positioningImprove ablationElectrocardiographyCatheterAtrial cavityProximate
Systems, methods, and devices allow intravascular or percutaneous mapping, orientation and / or ablation, in bodily cavities or lumens. A device includes elongate members, moveable between an unexpanded configuration and an expanded or fanned configuration. The elongate members form a stack in the unexpanded configuration to fit through a catheter sheath. The elongate members follow respective arcuate or curvilinear paths as advanced from the sheath into the bent or coiled stack configuration, adopting volute, scroll or rho shapes, and may be nested. The elongated members are fanned or radially spaced circumferentially with respect to one another into the expanded or fanned configuration. Transducer elements carried by elongate members sense various physiological characteristics of or proximate tissue, and / or may apply energy to or proximate tissue. The elongate members are rotatable in groups or as a group in the expanded configuration. The device is retractable.
Owner:KARDIUM
Pre-shaped catheter with proximal articulation and pre-formed distal end
A catheter employs a pre-formed distal end and a proximal deflection mechanism for steering the catheter. A shaped member extends from a shaped region of the catheter sheath to at least a portion of an anchor region. A steering ribbon extends from a proximal region of the sheath and passes within at least a portion of the anchor region. A distal end of the steering ribbon is joined with a proximal portion of the shaped member. At least one steering tendon is disposed within the sheath and has a first end attached at the anchor region and a second end located at the proximal region of the sheath. Movement of the steering tendon in a proximal direction causes the deflection region to deflect relative to the longitudinal axis of the catheter while the shape of shaped region of the sheath is substantially maintained.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Enhanced medical device for use in bodily cavities, for example an atrium
ActiveUS20130178850A1Enhanced for deployment and positioningImprove ablationElectrocardiographySurgical instrument detailsTransducerMedical device
Systems, methods, and devices allow intravascular or percutaneous mapping, orientation or ablation, or combinations thereof in bodily cavities or lumens. A device includes a plurality of elongate members which are moveable between an unexpanded configuration, a bent or coiled stack configuration and an expanded or fanned configuration. The elongate members form a stack arrangement in the unexpanded configuration to fit through a catheter sheath, The elongate members follow respective arcuate or curvilinear paths as advanced from the sheath into the bent or coiled stack configuration, adopting volute, scroll or rho shapes, and may be nested. The elongated members are fanned or radially spaced circumferentially with respect to one another into the expanded or fanned configuration. Transducers carried by elongate members may sense various physiological characteristics of or proximate tissue, for instance temperature, and / or may apply energy to or proximate tissue, for example to perform ablation. The device is retractable.
Owner:KARDIUM
Total vascular occlusion treatment system and method
InactiveUS20080033423A1Avoid resistanceSufficient torqueElectrotherapySurgical instruments for heatingActuatorConductor Coil
Owner:EMERGE MEDSYST
Driveable catheter system
InactiveUS6974465B2User setTranslational movement is simplifiedUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsEar treatmentCatheter sheathControl unit
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com