Patents
Literature
466results about "Testing sensing arrangements" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Testing automatic data collection devices, such as barcode, RFID and/or magnetic stripe readers
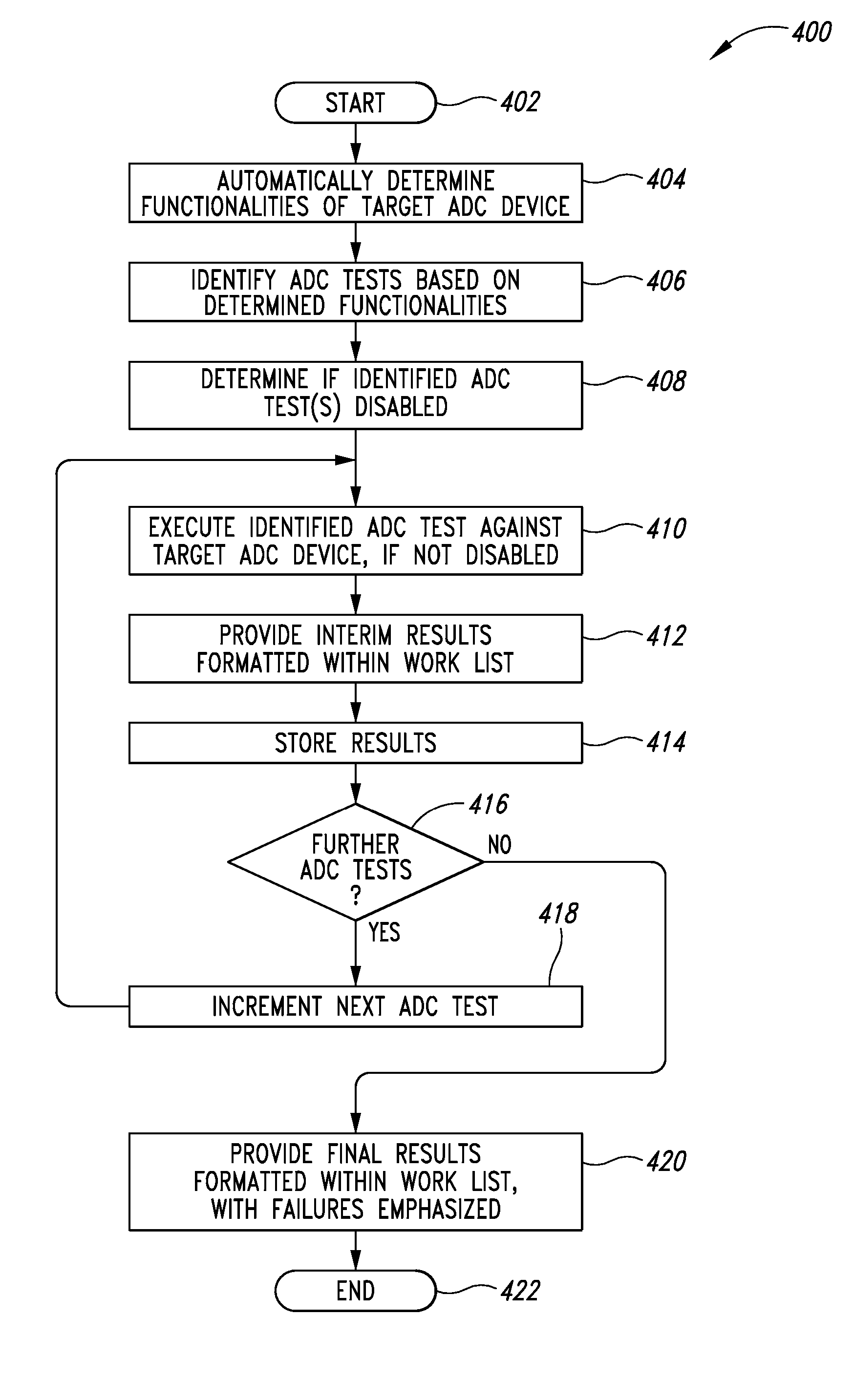
ActiveUS8944332B2Conveying record carriersTesting sensing arrangementsData acquisitionBarcode reader
Automatic data collection devices such as barcode readers, RFID readers, magnetic stripe readers and the like may be tested using ADC device test executables, modules or processes stored at a variety of network locations. One or more sets of tests or work lists may be defined to facilitate testing. Tests may be identified by name and / or keyword. Keywords may be indicative one or more functionalities tested by the respective ADC device test module.
Owner:INTERMEC IP CORP
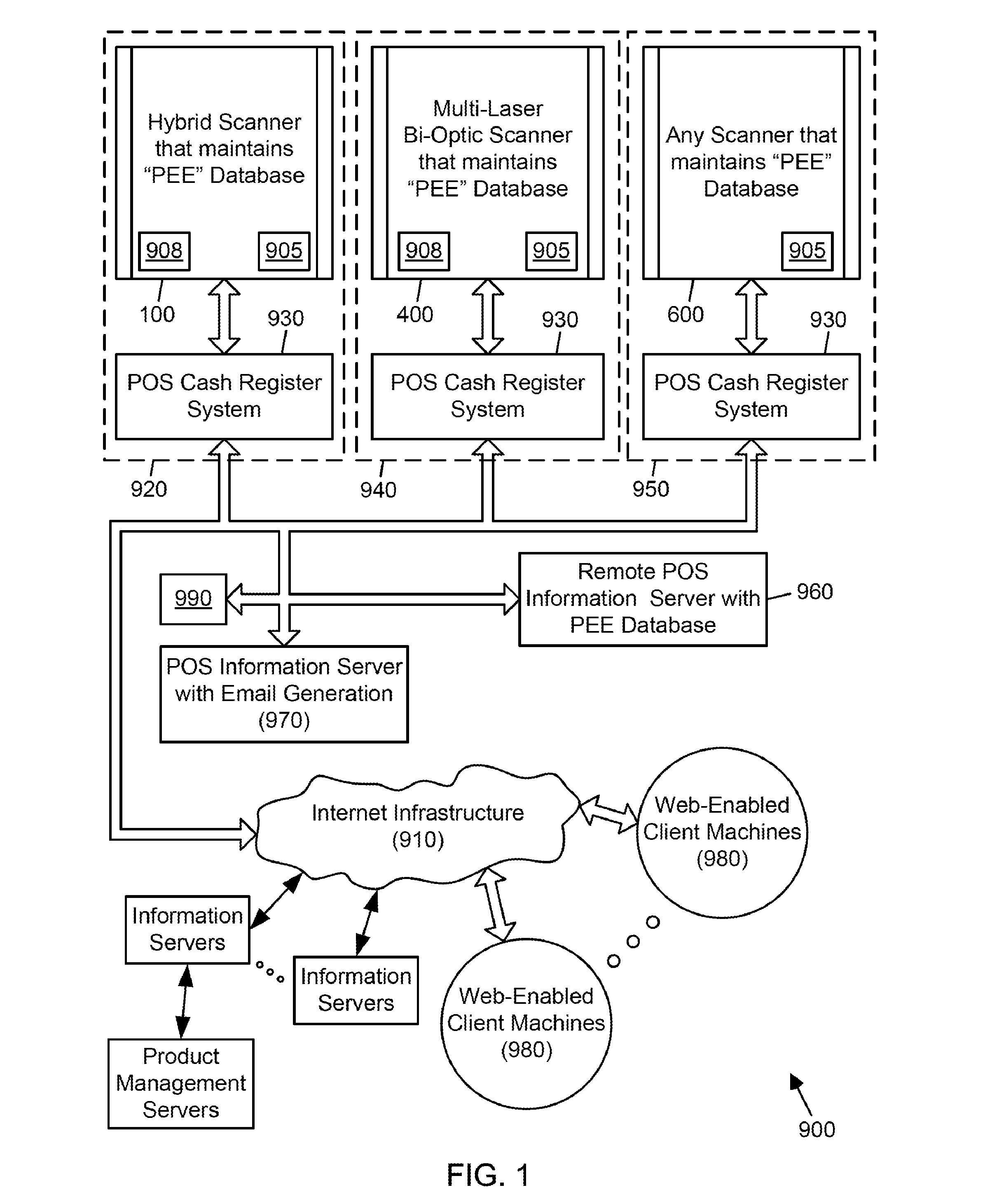
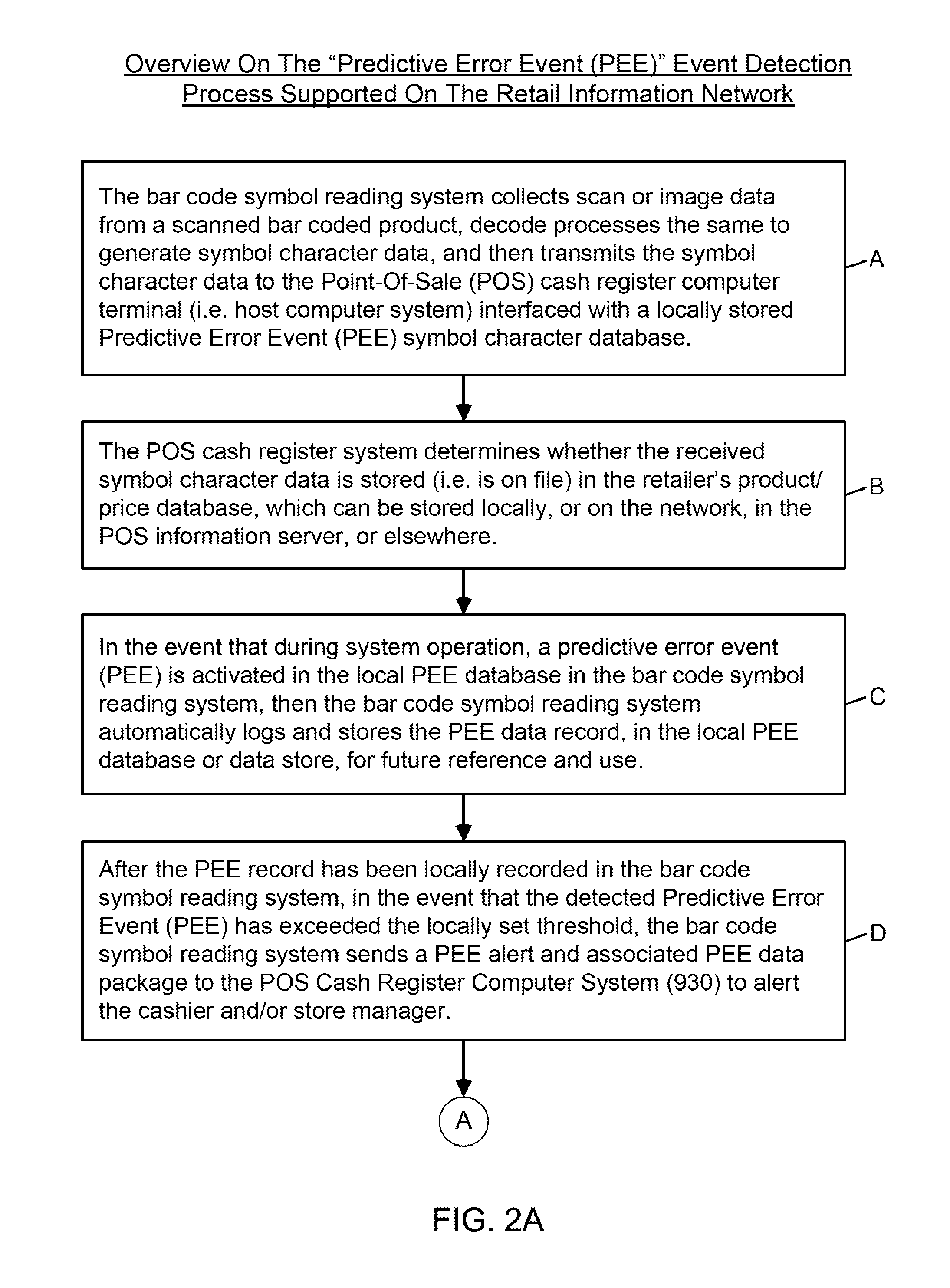
Symbol reading system having predictive diagnostics
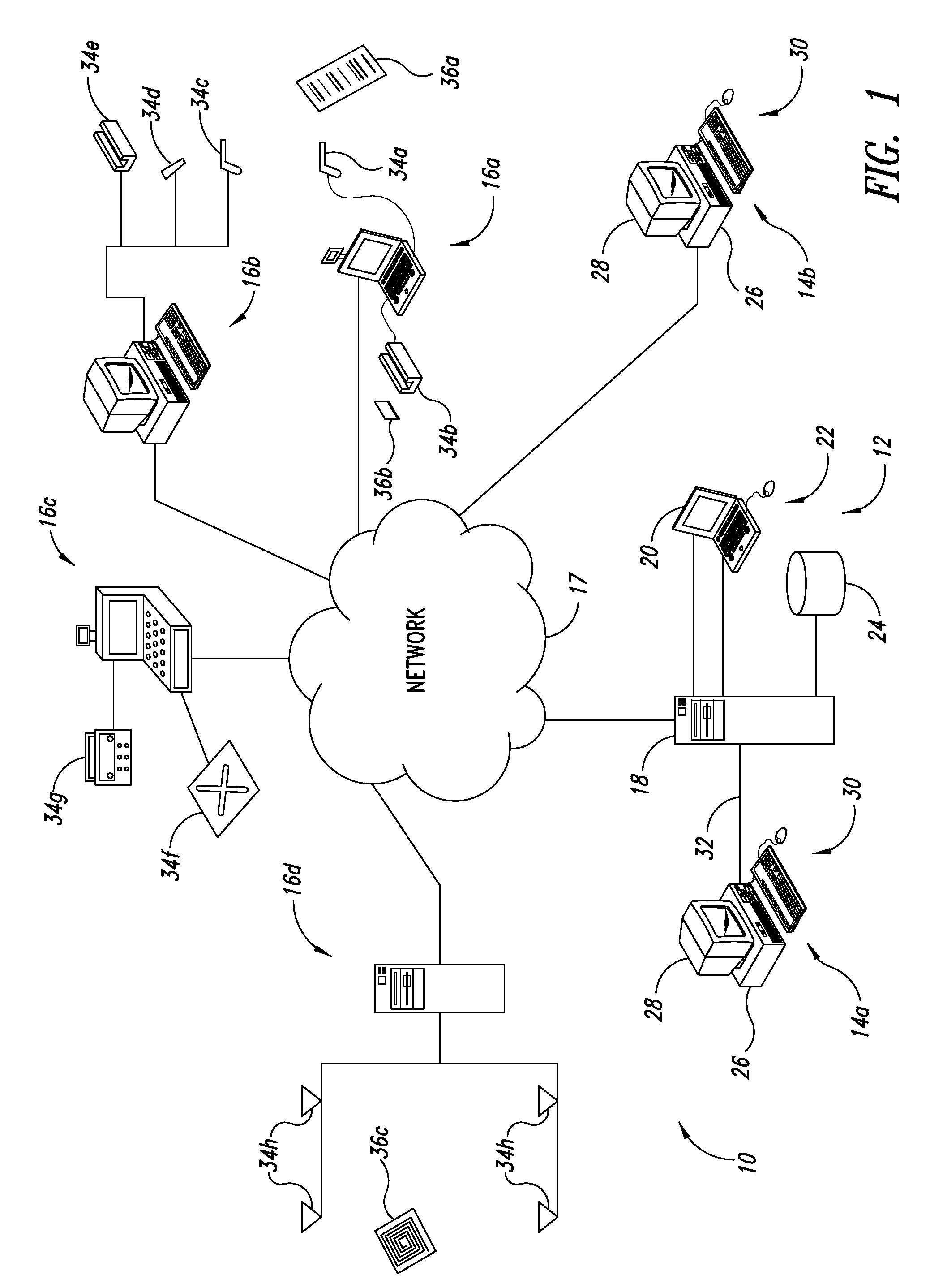
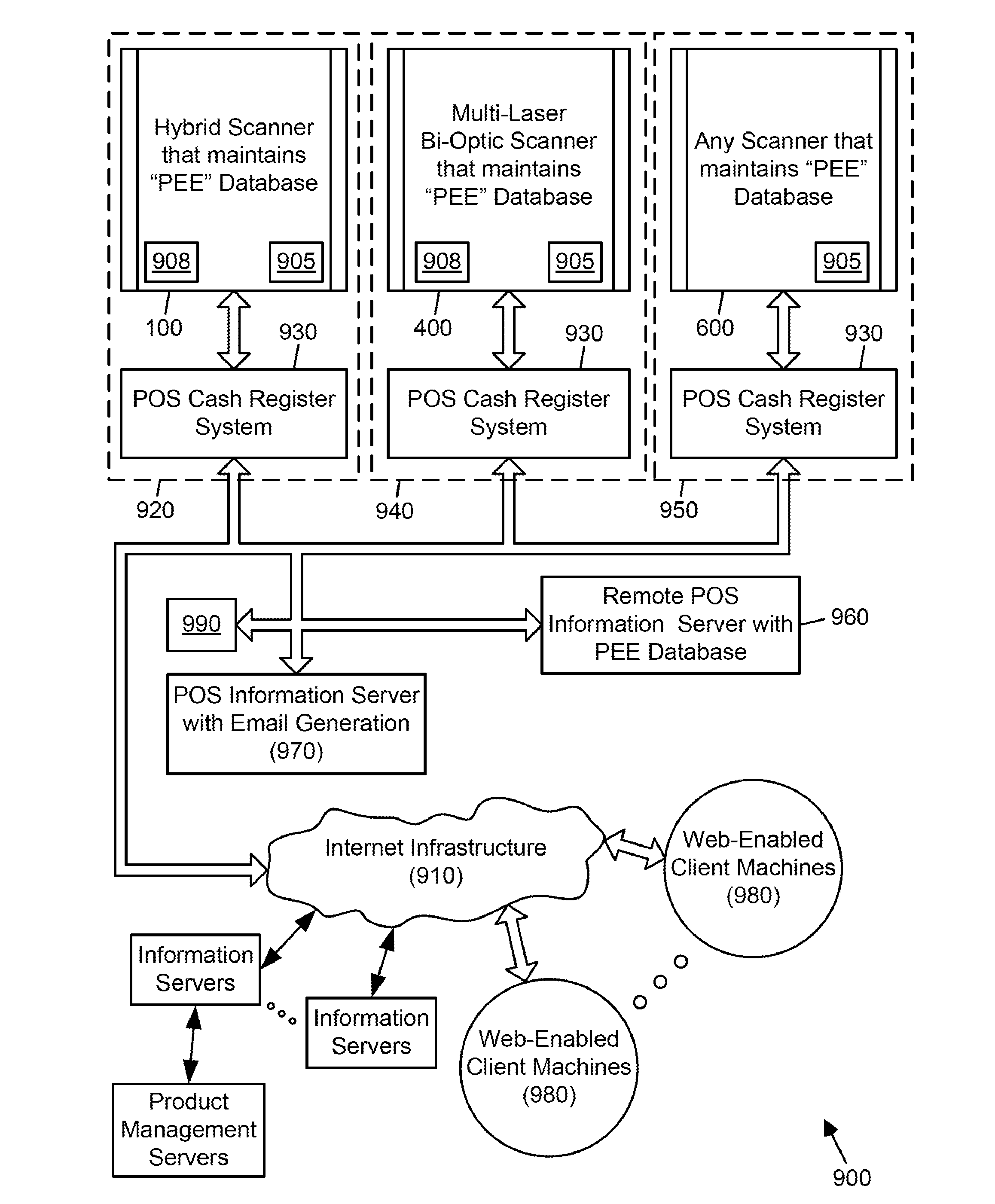
ActiveUS9022288B2Improve the level ofEasy maintenanceTesting sensing arrangementsSensing by electromagnetic radiationInformation networksBarcode
A retail information network includes one or more POS scanning and checkout systems, each including (i) a bar code symbol reading subsystem, and (ii) a cash register computer subsystem interfaced with the bar code symbol reading subsystem and a network infrastructure, and each having access to product and price data maintained in a product / price database. The bar code symbol reading subsystem includes a local predictive error event (PEE) data store for logging and storing predictive error events (PEEs) detected within the bar code symbol reading system, wherein said PEEs are subsequently sent to POS information servers used to create predictive error alerts (PEAs) and corresponding instructions to maintain and / or repair certain aspects of the bar code symbol reading system.
Owner:METROLOGIC INSTR
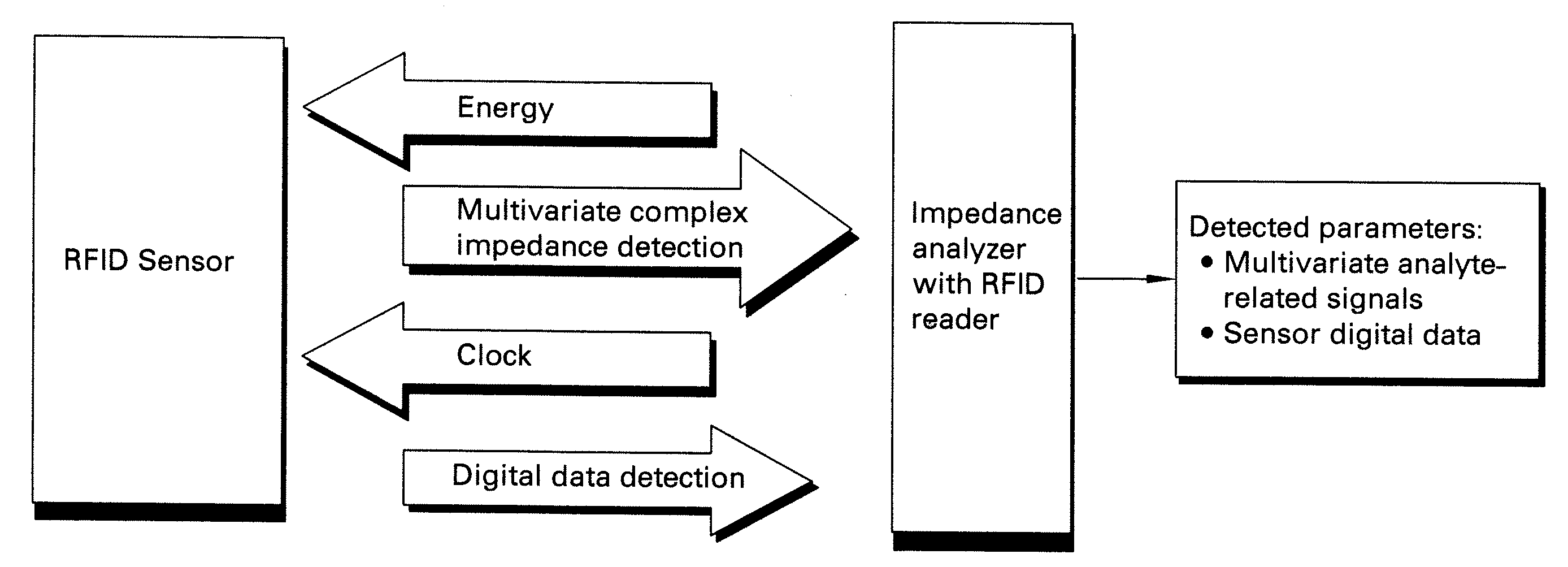
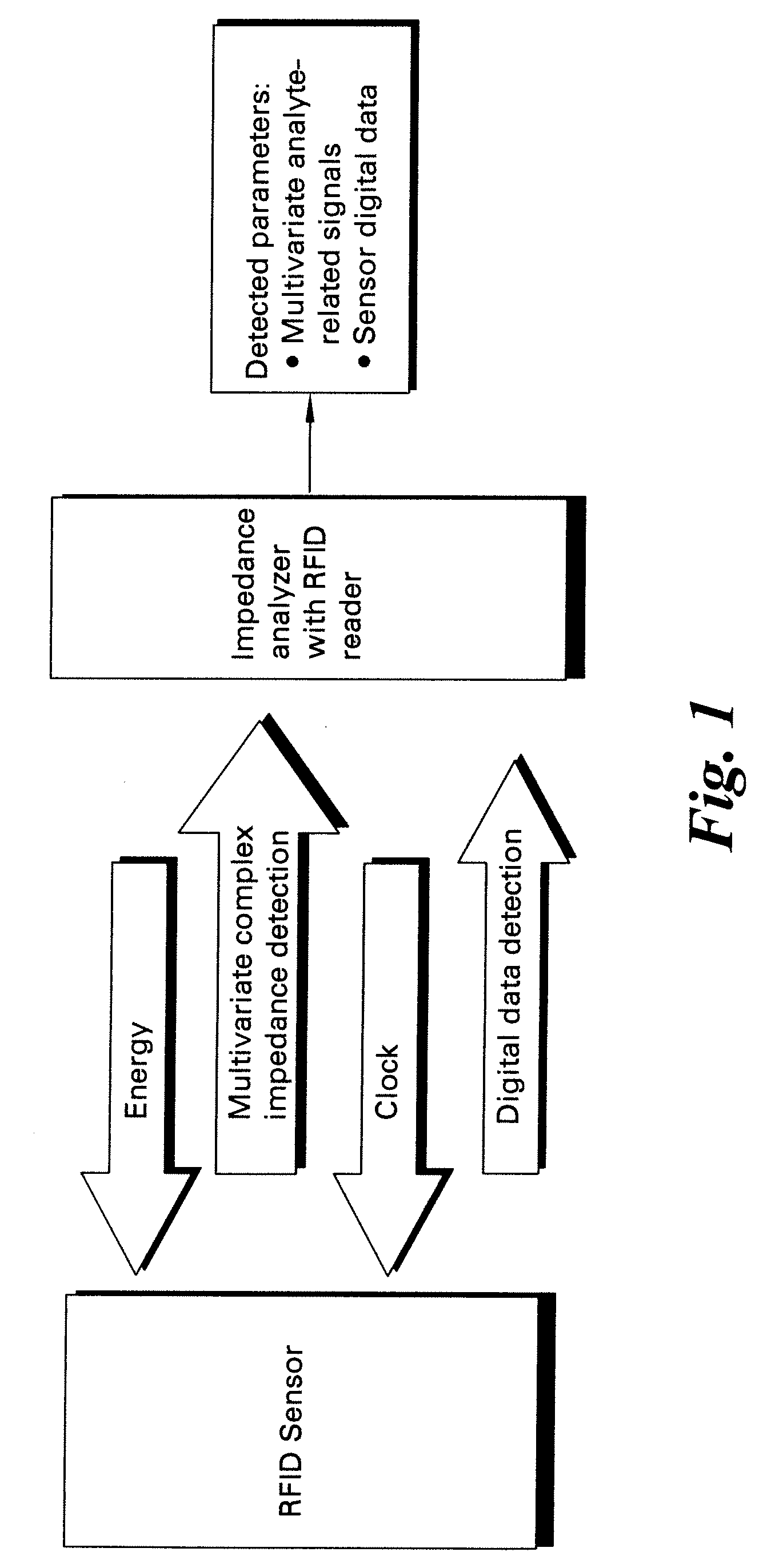
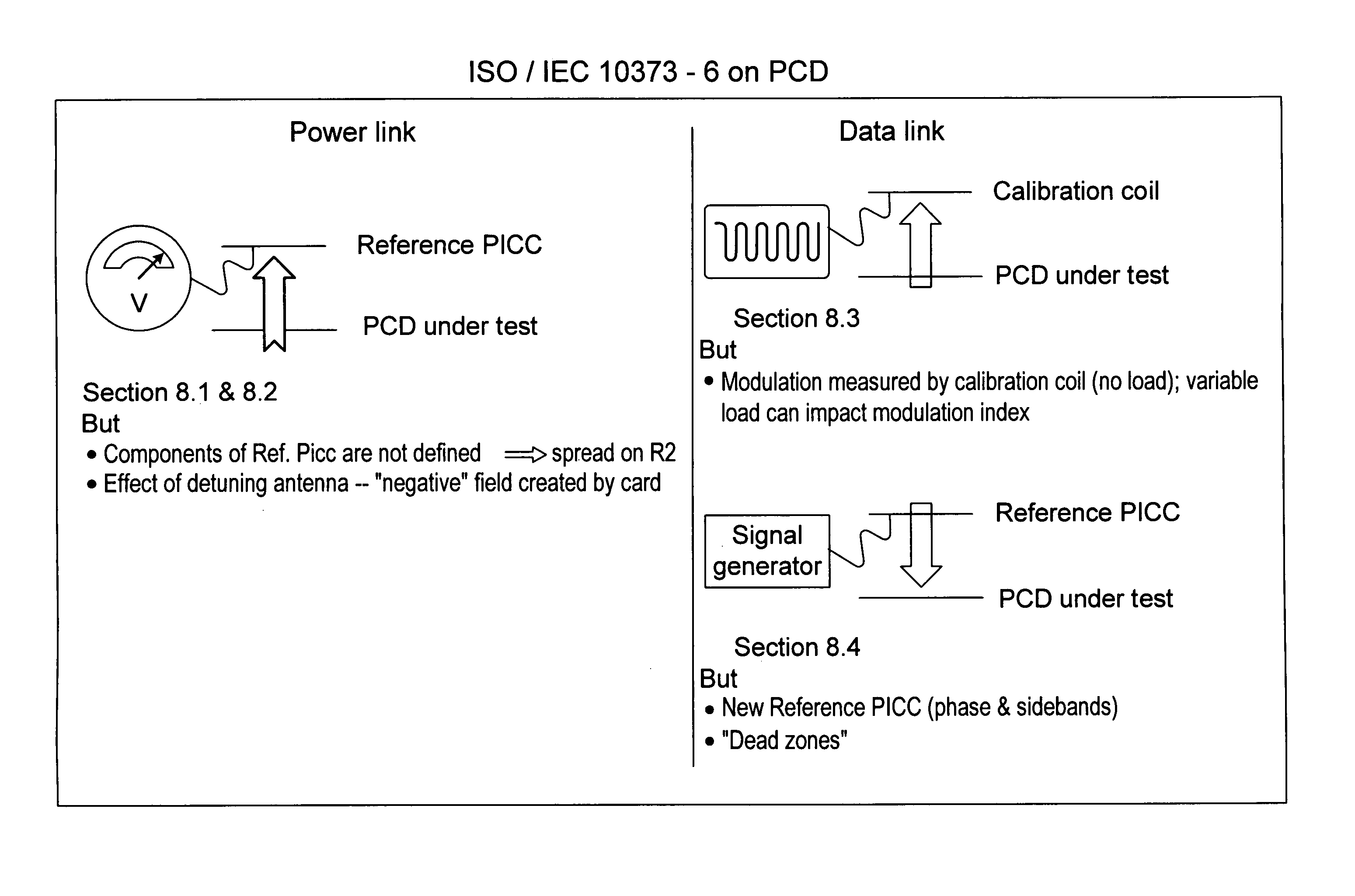
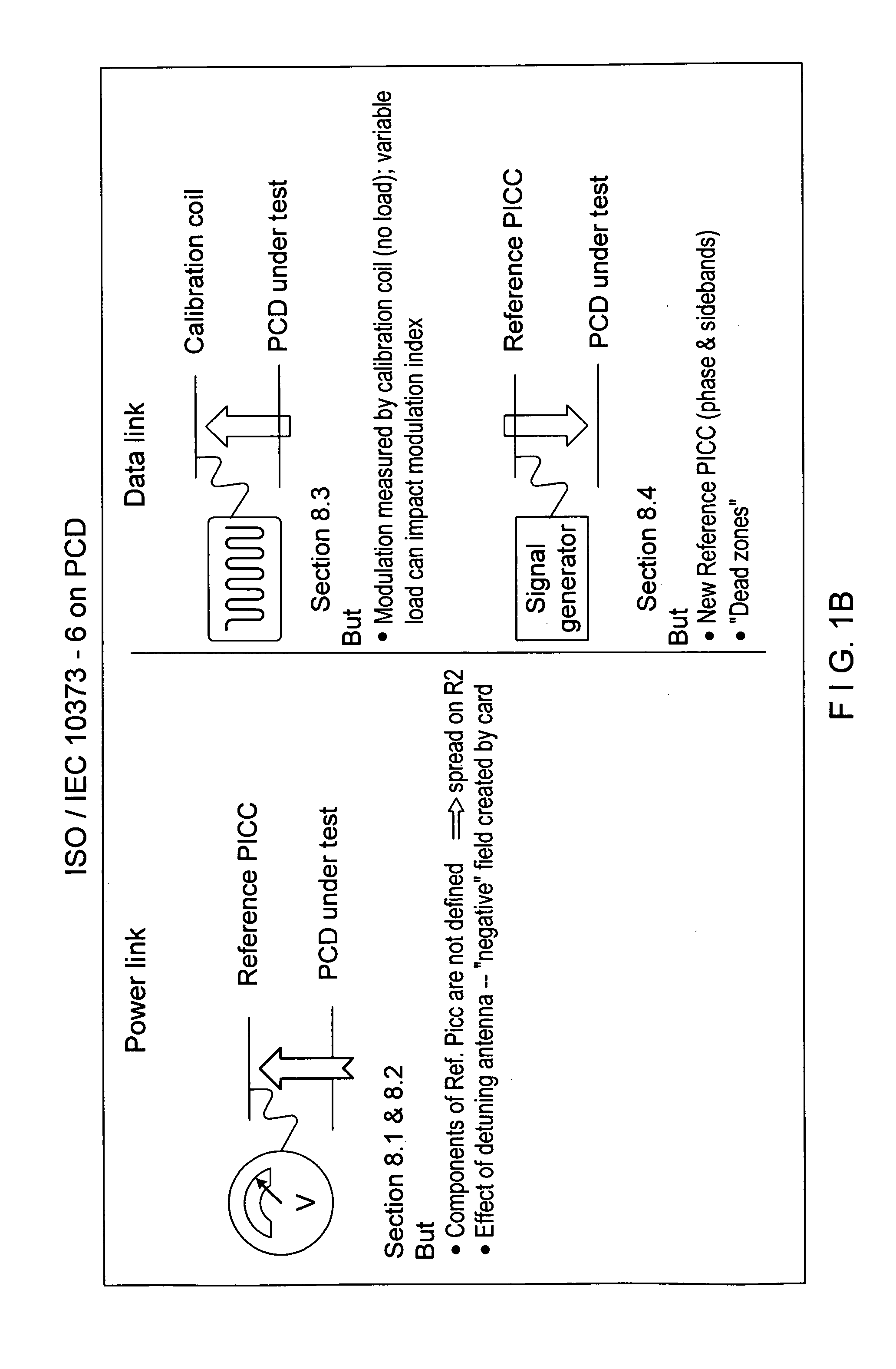
Methods and systems for calibration of RFID sensors
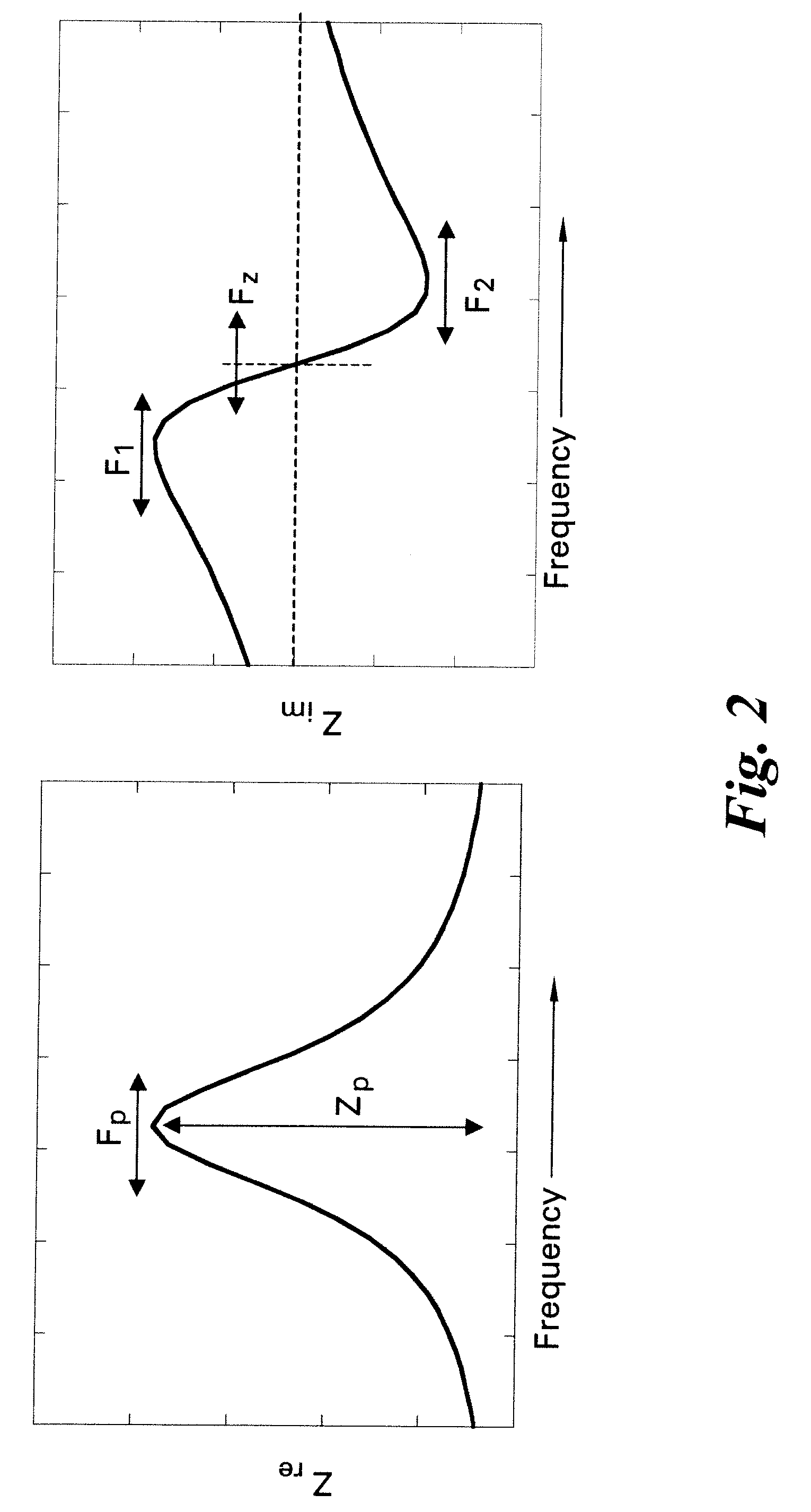
ActiveUS20090278685A1Testing sensing arrangementsGas analyser calibrationMemory chipComplex impedance spectra
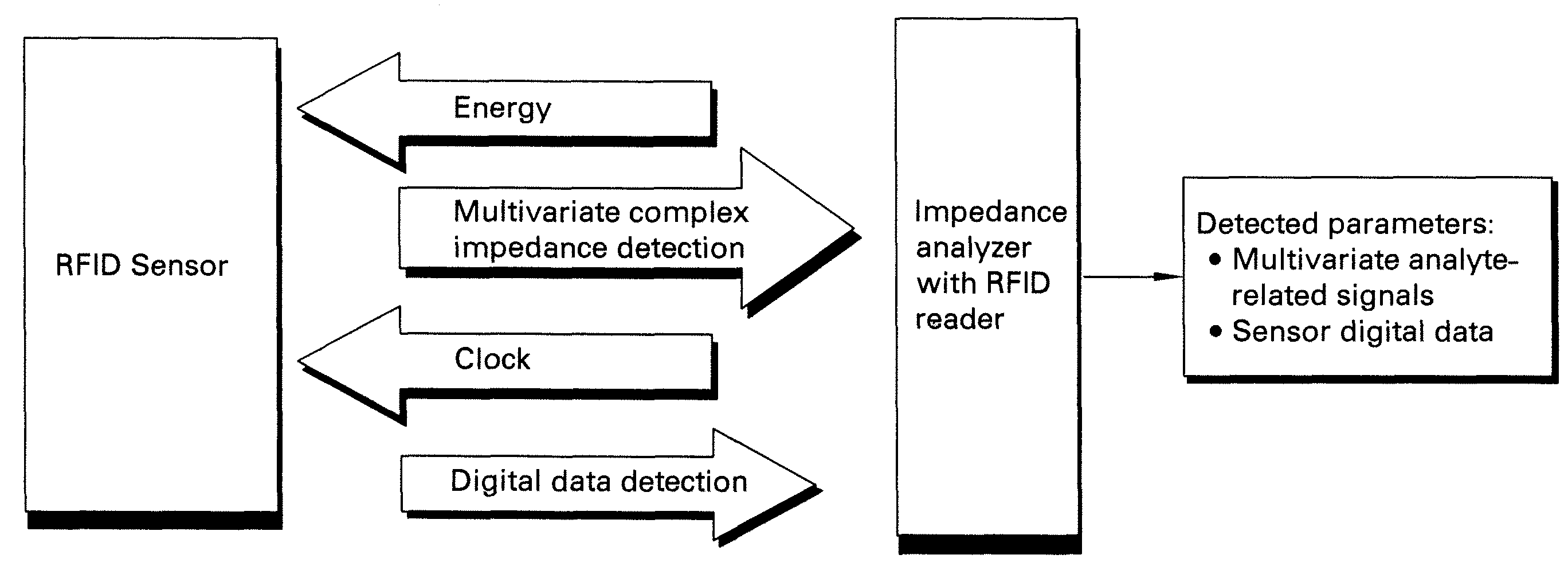
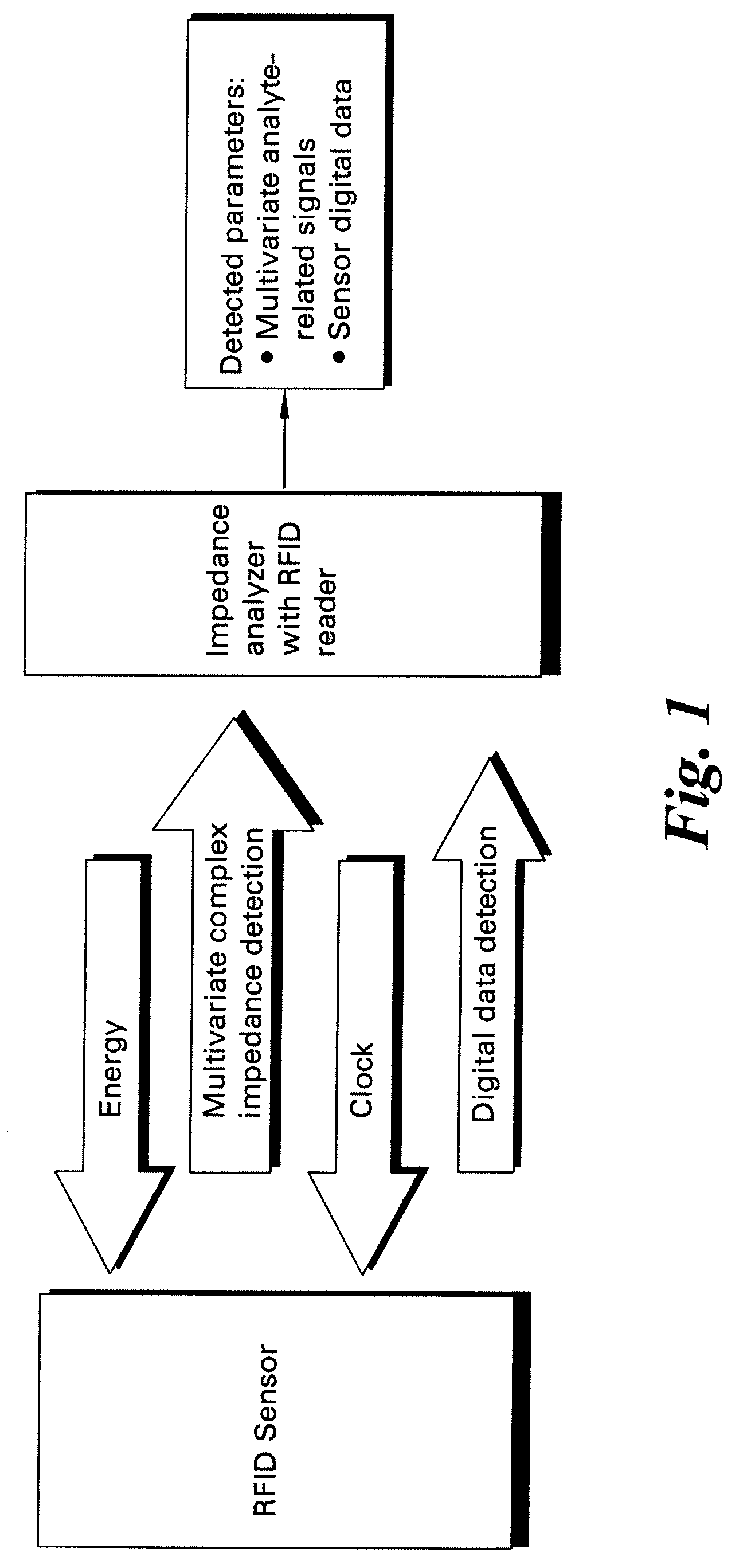
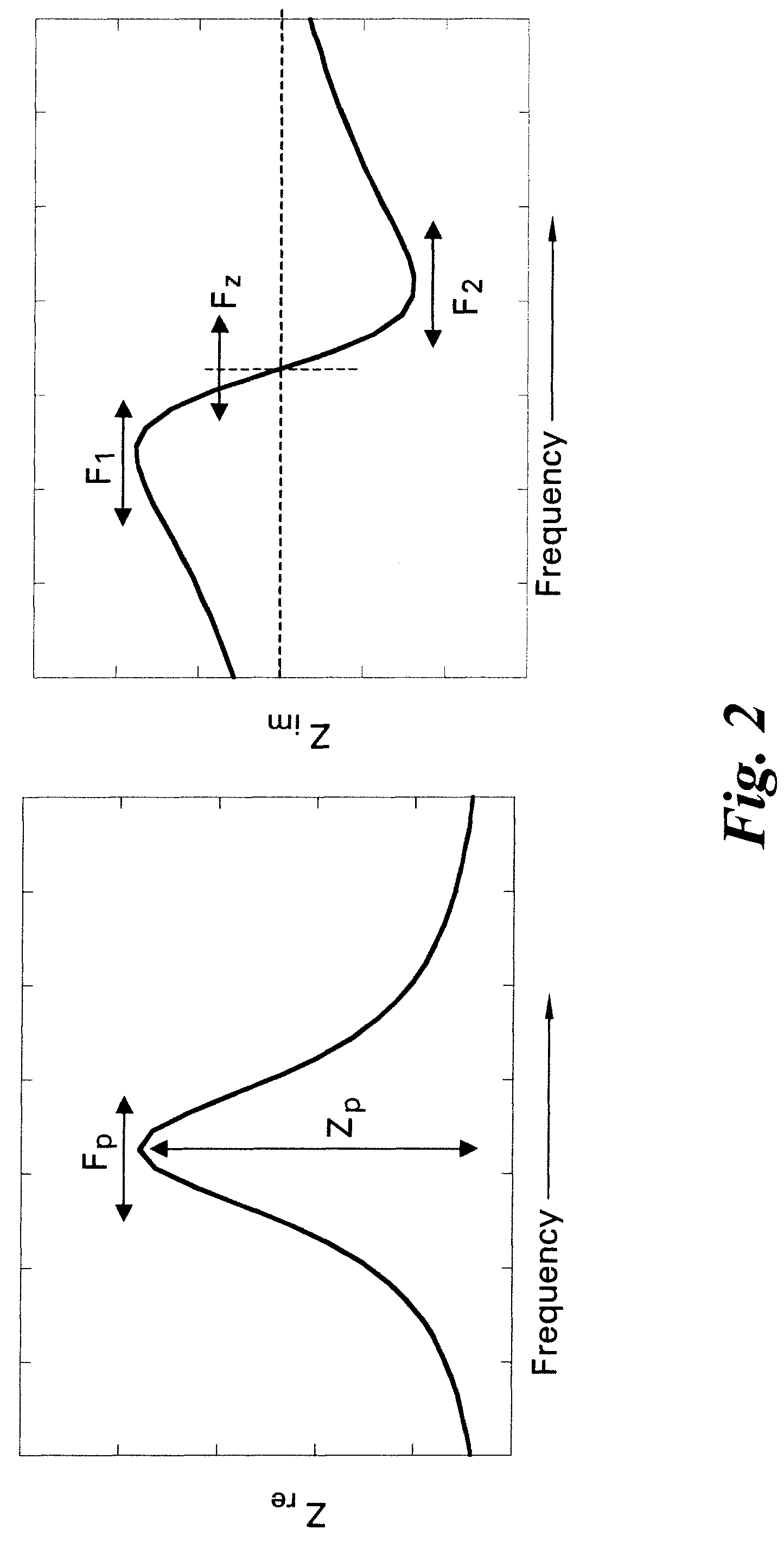
Methods and systems for calibration of RFID sensors used in manufacturing and monitoring systems are provided. The methods include measuring impedance of an RFID sensor antenna, relating the measurement of impedance to one or more parameters (such as physical, chemical and biological properties), computing one or more analytical fit coefficients, and storing the one or more analytical fit coefficients on a memory chip of the RFID sensor. Measuring impedance of the RFID sensor may comprise measuring complex impedance which involves measuring complex impedance spectrum, phase angle and magnitude of the impedance, at least one of frequency of the maximum of the real part of the complex impedance, magnitude of the real part of the complex impedance, zero-reactance frequency, resonant frequency of the imaginary part of the complex impedance, and antiresonant frequency of the imaginary part of the complex impedance. Also provided are manufacturing or monitoring systems comprised of an RFID sensor wherein the RFID sensor comprises, a memory chip, an antenna, and a sensing film wherein analytical fit coefficients are stored on the memory chip to allow calibration of the RFID sensor. Also provided are manufacturing or monitoring systems comprised of an RFID sensor wherein the RFID sensor comprises, a memory chip, an antenna, and a complementary sensor attached to the antenna where the complementary sensor in a pre-calibrated fashion predictably affects the impedance of the antenna.
Owner:WESTINGHOUSE AIR BRAKE TECH CORP
Calibration of Beamforming Nodes in a Configurable Monitoring Device System
InactiveUS20110080267A1Function increaseMultiplex system selection arrangementsTesting sensing arrangementsMonitoring systemEngineering
A system for radio frequency identification of a tag in an interrogation zone, includes a calibration node disposed in the interrogation zone to measure a signal strength of radio frequency identification signals from a beamforming system and provide signal data in accordance with the signal strength. A reader node is configured to receive the signal data and adjust the radio frequency identification signals generated by the beamforming system based upon the signal data. At least one of the calibration node, the reader node and the beamforming system is a configurable monitoring system. The calibration node, the reader node, and the beamforming system are coupled in a feedback control loop. The beamforming system includes a plurality of beamforming nodes. A signal of at least one beamforming node is optimized in accordance with the feedback control loop.
Owner:CHECKPOINT SYST INC
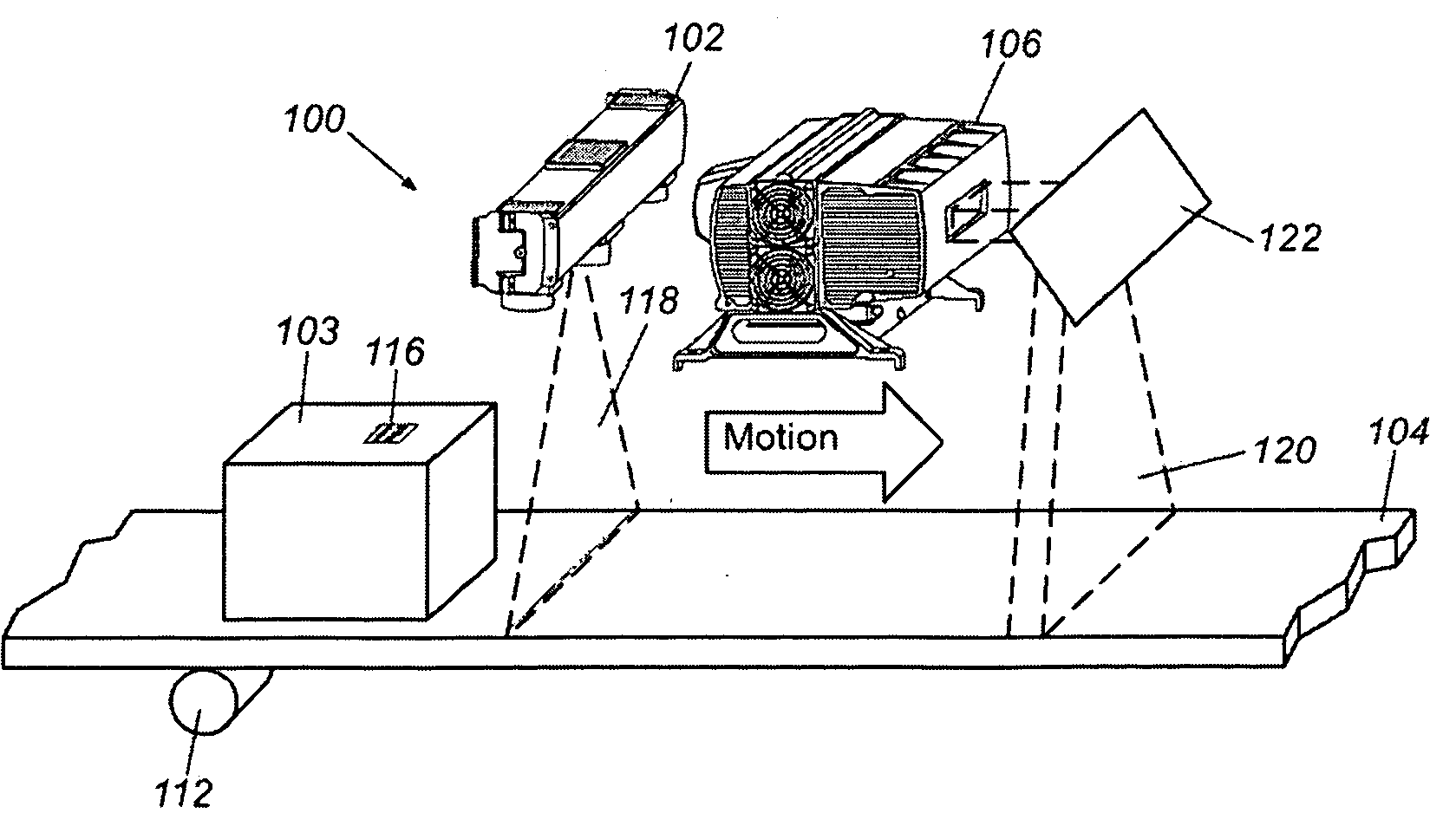
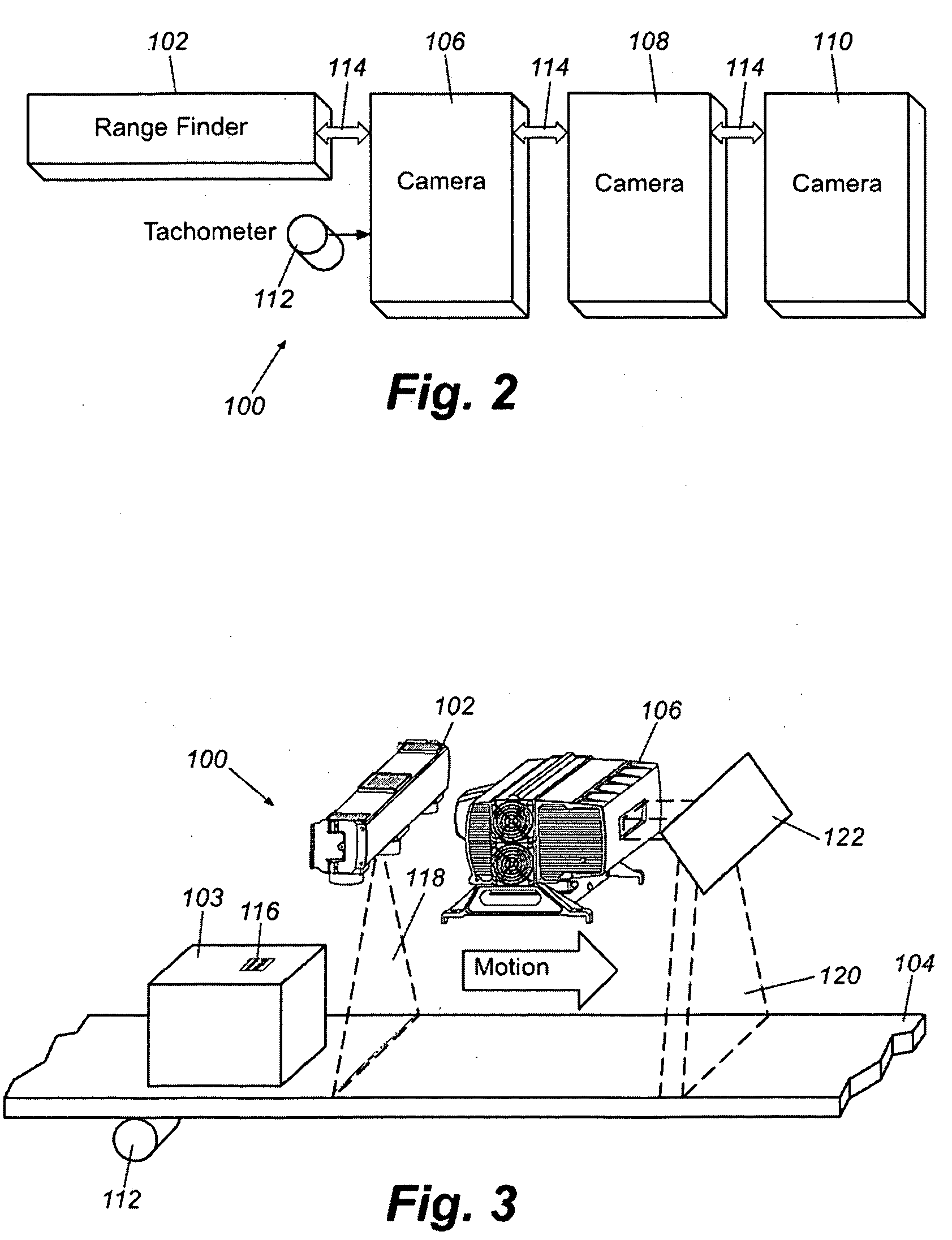
Dimensioning and barcode reading system
InactiveUS20090095047A1Wave based measurement systemsTesting sensing arrangementsBarcodeCamera orientation
A system and method for auto-calibrating a barcode scanning tunnel to determine the orientation of one or more cameras with respect to a range finder and a conveyor belt comprises providing a scanning tunnel having a moveable surface, at least one range finder having an orientation, at least one camera having an orientation and at least one calibration object having at least one indicia disposed in a predetermined relationship to one or more features of the at least one calibration object, capturing at least one image of the at least one calibration object by the at least one camera, electronically detecting the at least one calibration object at least one indicia and the one or more object features and electronically calculating at least one component of the at least one camera orientation with respect to the moveable surface in response to information obtained from the image and the at least one calibration object at least one indicia.
Owner:ACCU SORT SYST
Inspection system, inspection method, and method for manufacturing semiconductor device
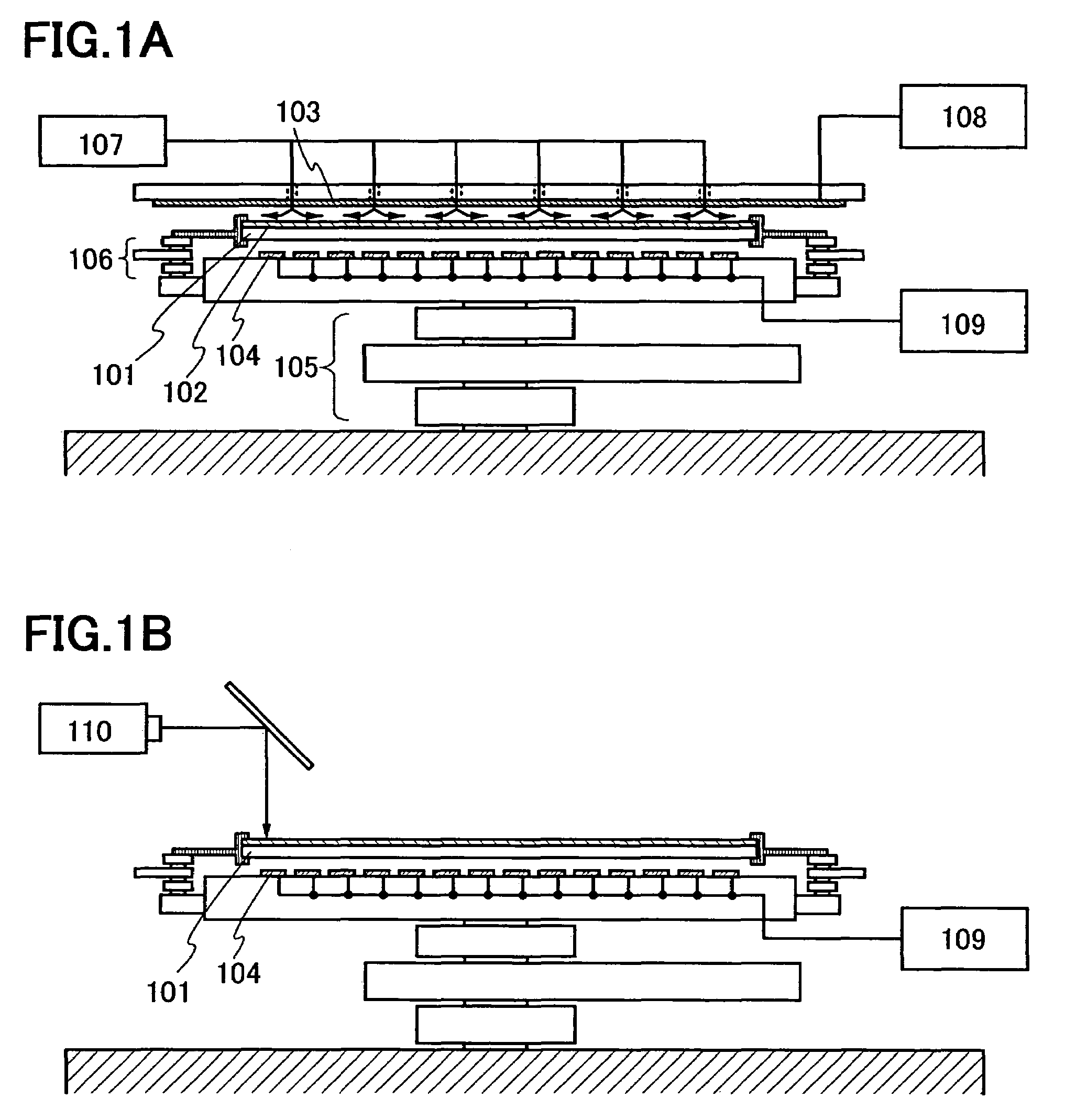
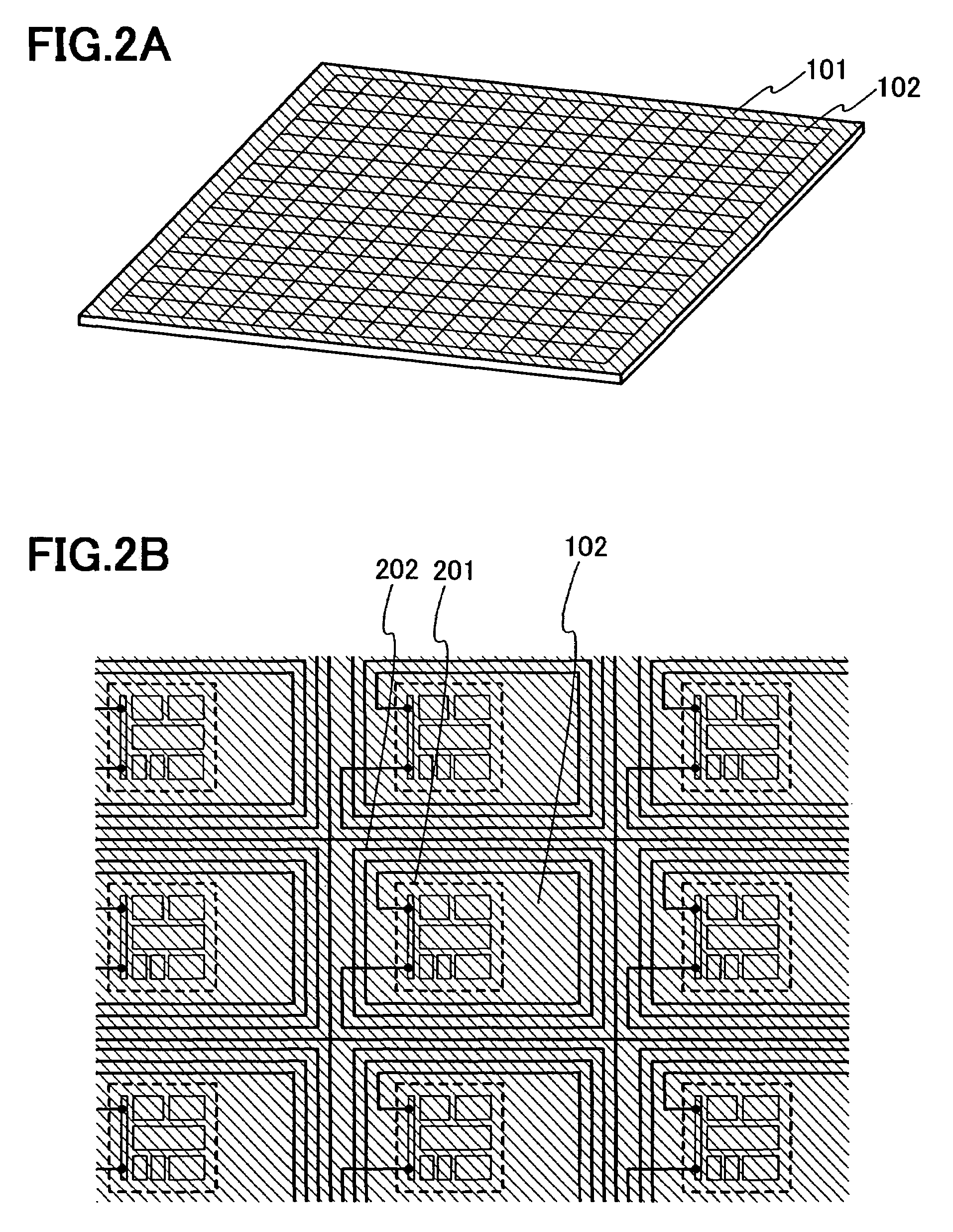
InactiveUS7112952B2Reduce in quantityImprove throughputTesting sensing arrangementsSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementPosition controlSemiconductor
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
RFID device tester and method
InactiveUS7225992B2Ticket-issuing apparatusTesting sensing arrangementsCapacitanceCapacitive coupling
Owner:AVERY DENNISON CORP
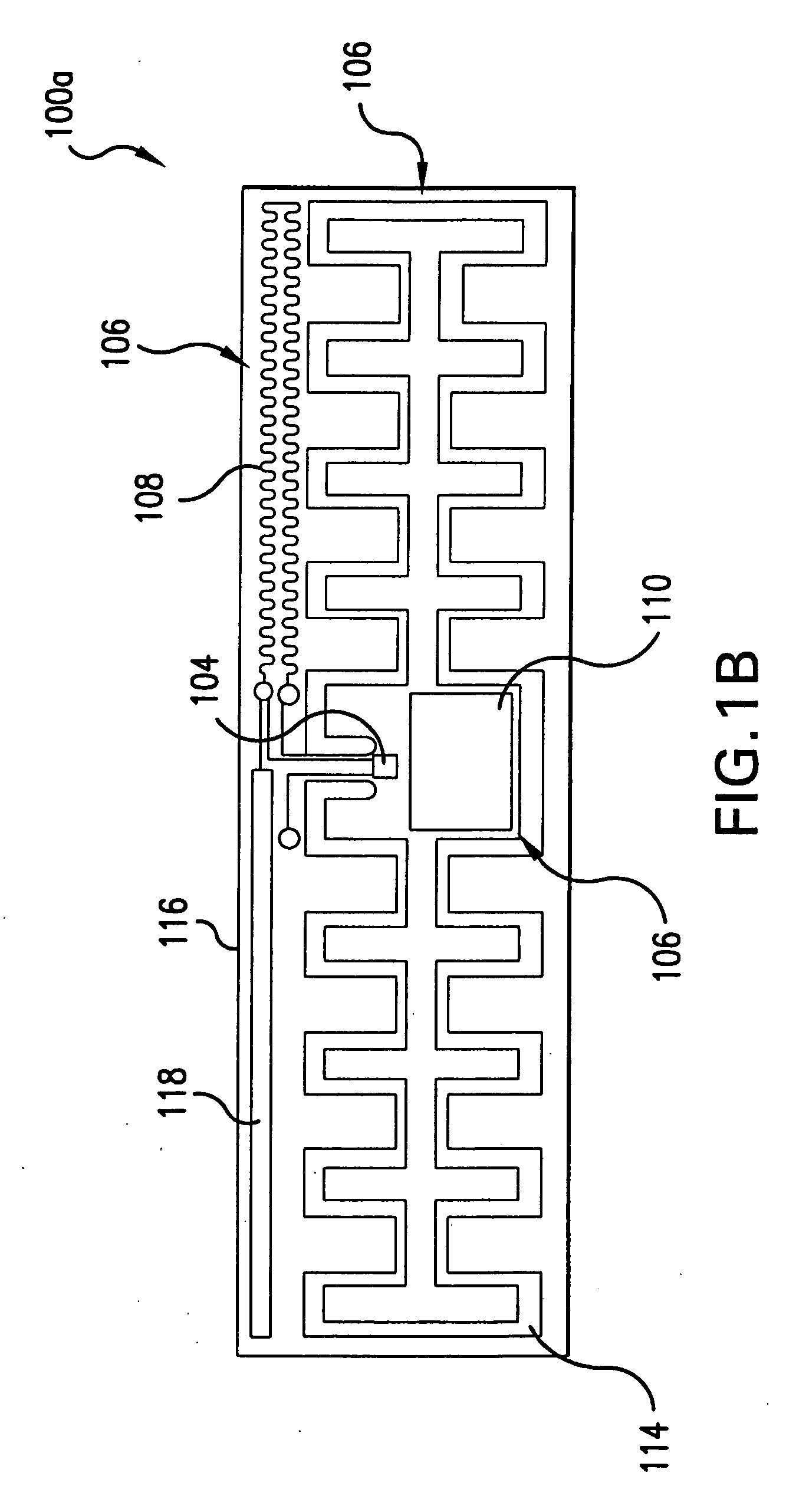
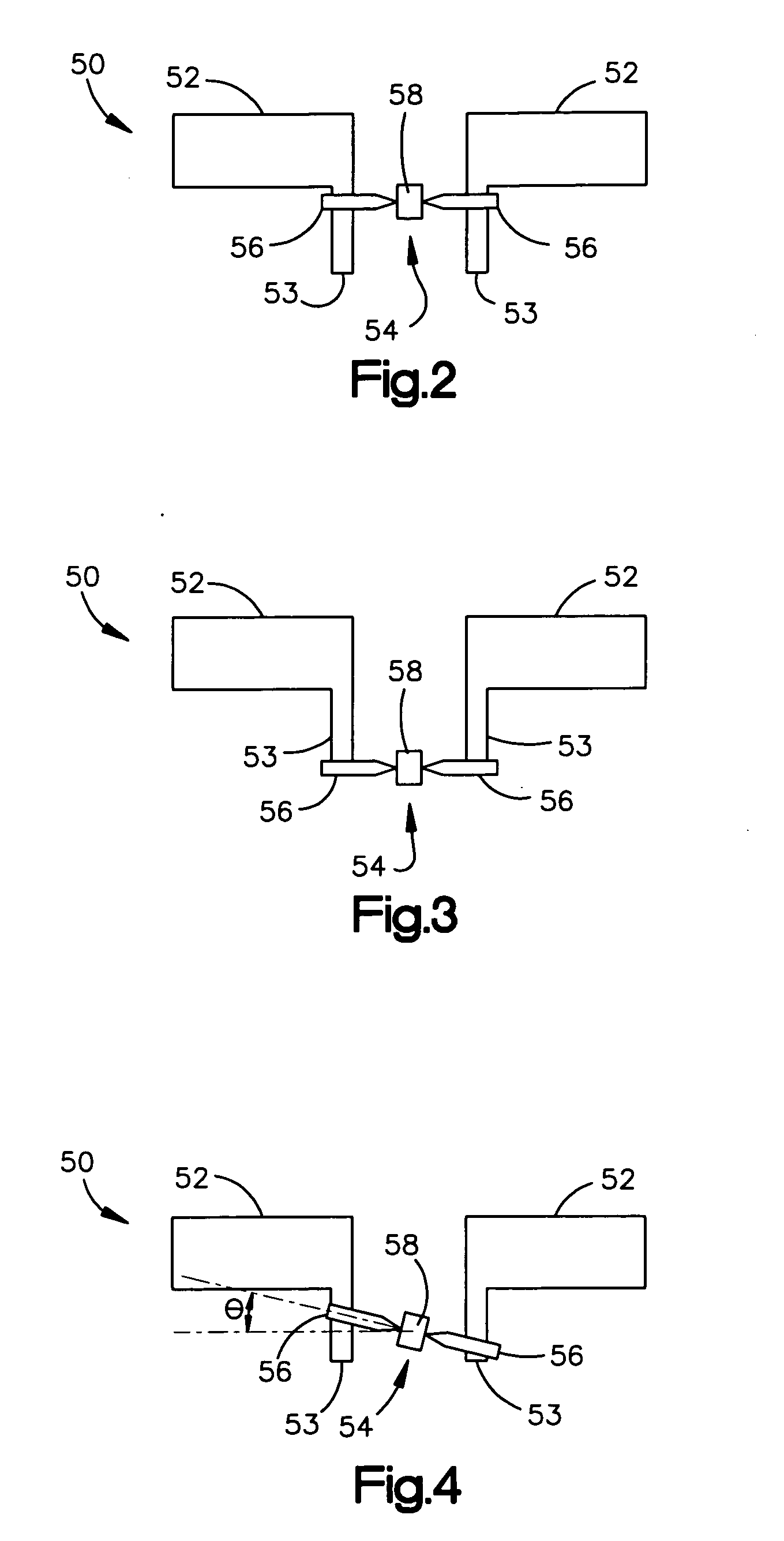
Low cost method of producing radio frequency identification tags with straps without antenna patterning
ActiveUS20050206524A1Low costTesting sensing arrangementsPrinted circuit manufactureEngineeringConductive materials
A web of radio frequency identification (RFID) devices includes a conductive layer atop an insulating layer, the conductive layer having one or more apertures therein. Alternatively, the web may not include an insulating layer. RFID chips or straps are electrically coupled to portions of the conductive layer on either side of an aperture, for use as antennas when the RFID devices are separated from one another, as by cutting. The apertures may be formed by creasing portions of the web, and removing parts of the creased portion. There may be one or more apertures in a longitudinal or transverse direction of the web. The antenna shapes of various of the RFID devices may be tessellated, nesting within one another or having the same boundary, thereby improving efficiency by using substantially all of the conductive material. The RFID devices may be tested and / or programmed while remaining in the web format.
Owner:AVERY DENNISON CORP
Methods and systems for calibration of RFID sensors
ActiveUS7911345B2Testing sensing arrangementsMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansMemory chipComplex impedance spectra
Methods and systems for calibration of RFID sensors used in manufacturing and monitoring systems are provided. The methods include measuring impedance of an RFID sensor antenna, relating the measurement of impedance to one or more parameters (such as physical, chemical and biological properties), computing one or more analytical fit coefficients, and storing the one or more analytical fit coefficients on a memory chip of the RFID sensor. Measuring impedance of the RFID sensor may comprise measuring complex impedance which involves measuring complex impedance spectrum, phase angle and magnitude of the impedance, at least one of frequency of the maximum of the real part of the complex impedance, magnitude of the real part of the complex impedance, zero-reactance frequency, resonant frequency of the imaginary part of the complex impedance, and antiresonant frequency of the imaginary part of the complex impedance. Also provided are manufacturing or monitoring systems comprised of an RFID sensor wherein the RFID sensor comprises, a memory chip, an antenna, and a sensing film wherein analytical fit coefficients are stored on the memory chip to allow calibration of the RFID sensor. Also provided are manufacturing or monitoring systems comprised of an RFID sensor wherein the RFID sensor comprises, a memory chip, an antenna, and a complementary sensor attached to the antenna where the complementary sensor in a pre-calibrated fashion predictably affects the impedance of the antenna.
Owner:WESTINGHOUSE AIR BRAKE TECH CORP
Low cost method of producing radio frequency identification tags with straps without antenna patterning
ActiveUS7158037B2Low costTesting sensing arrangementsPrinted circuit manufactureConductive materialsEngineering
Owner:AVERY DENNISON CORP
Read-write processing device for RFID tag
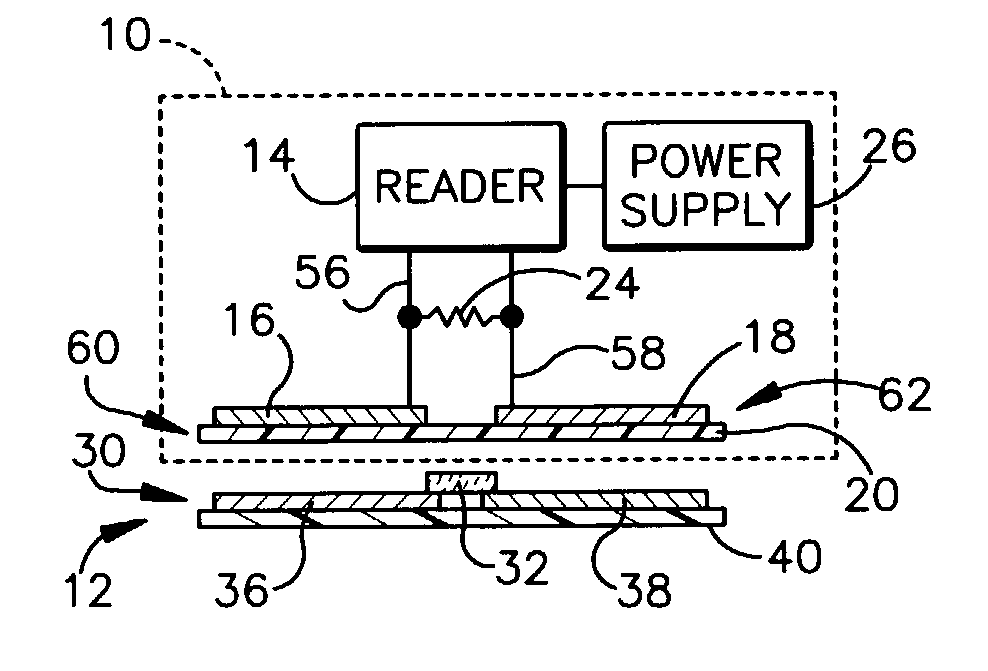
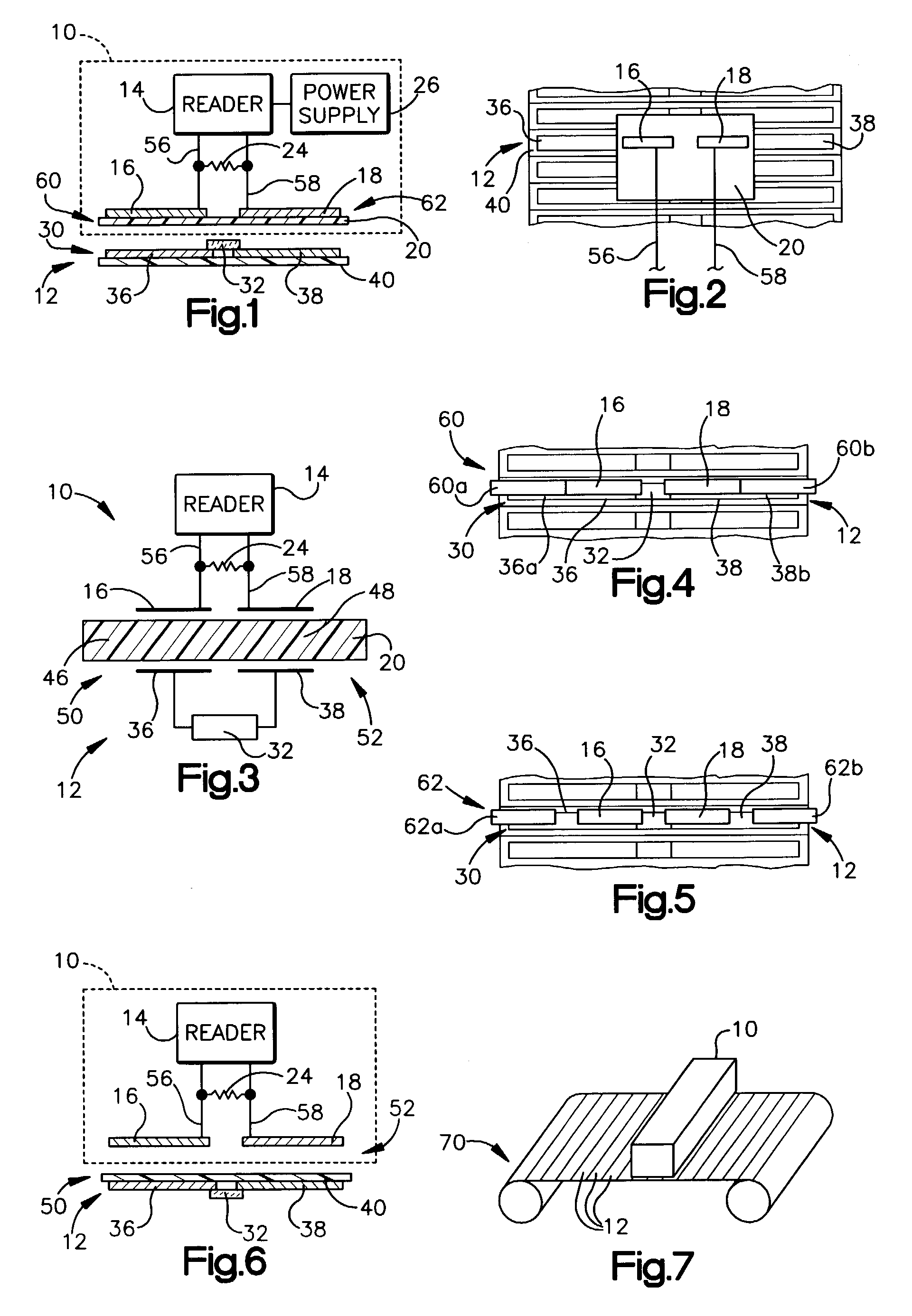
InactiveUS20050159913A1Large marginEasy to understandTesting sensing arrangementsMemory record carrier reading problemsOutput deviceMargin of safety
A read-write processing device communicates with an RFID tag provided with a semiconductor memory to carry out read and write processes. A communication processing device executes communication processes with the RFID tag, exchanging commands and responses, and a data creating device creates safety data indicative of a margin of safety of communication based on communication results by the communication processing device. The created safety data are displayed or outputted to the outside by an output device.
Owner:ORMON CORP
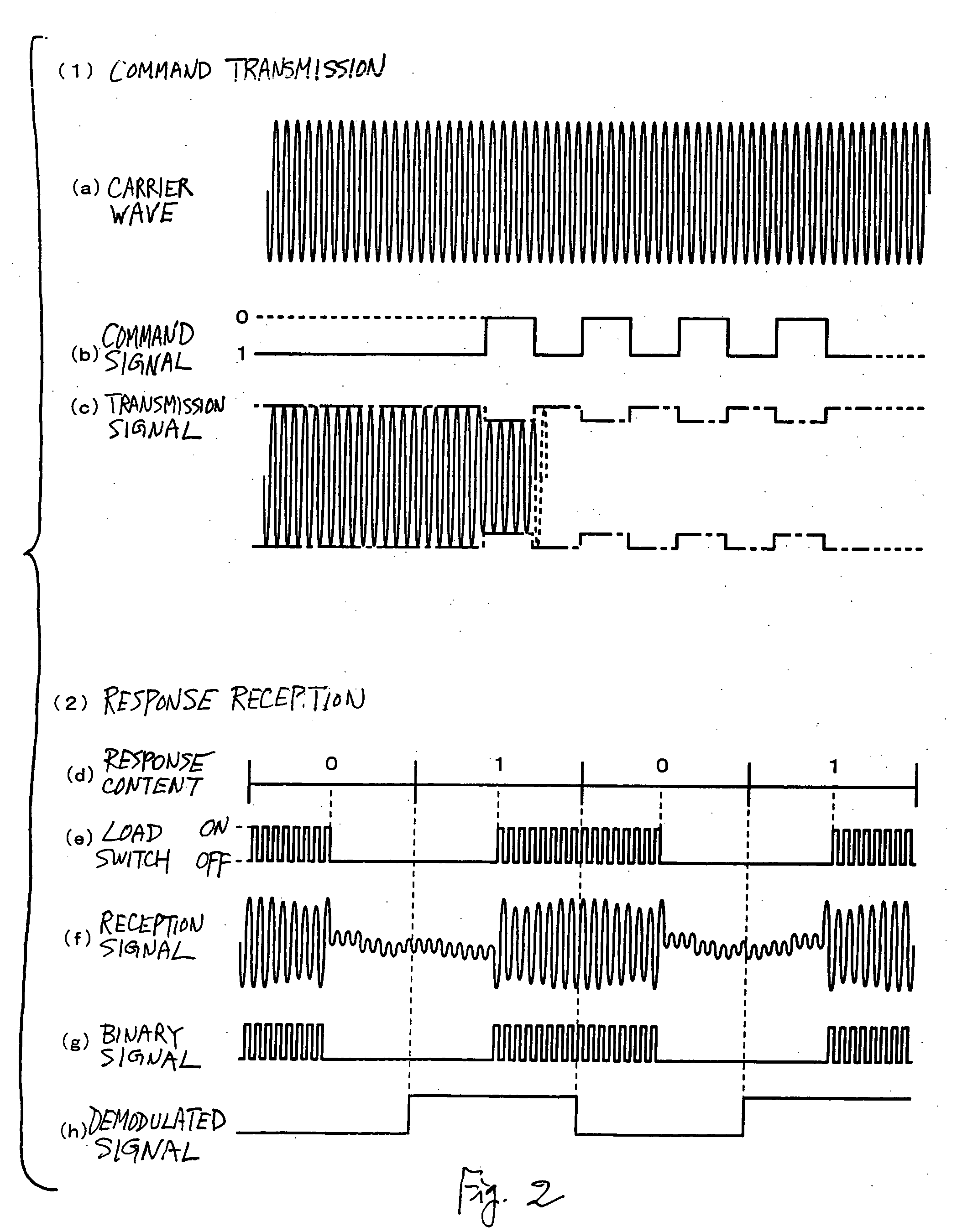
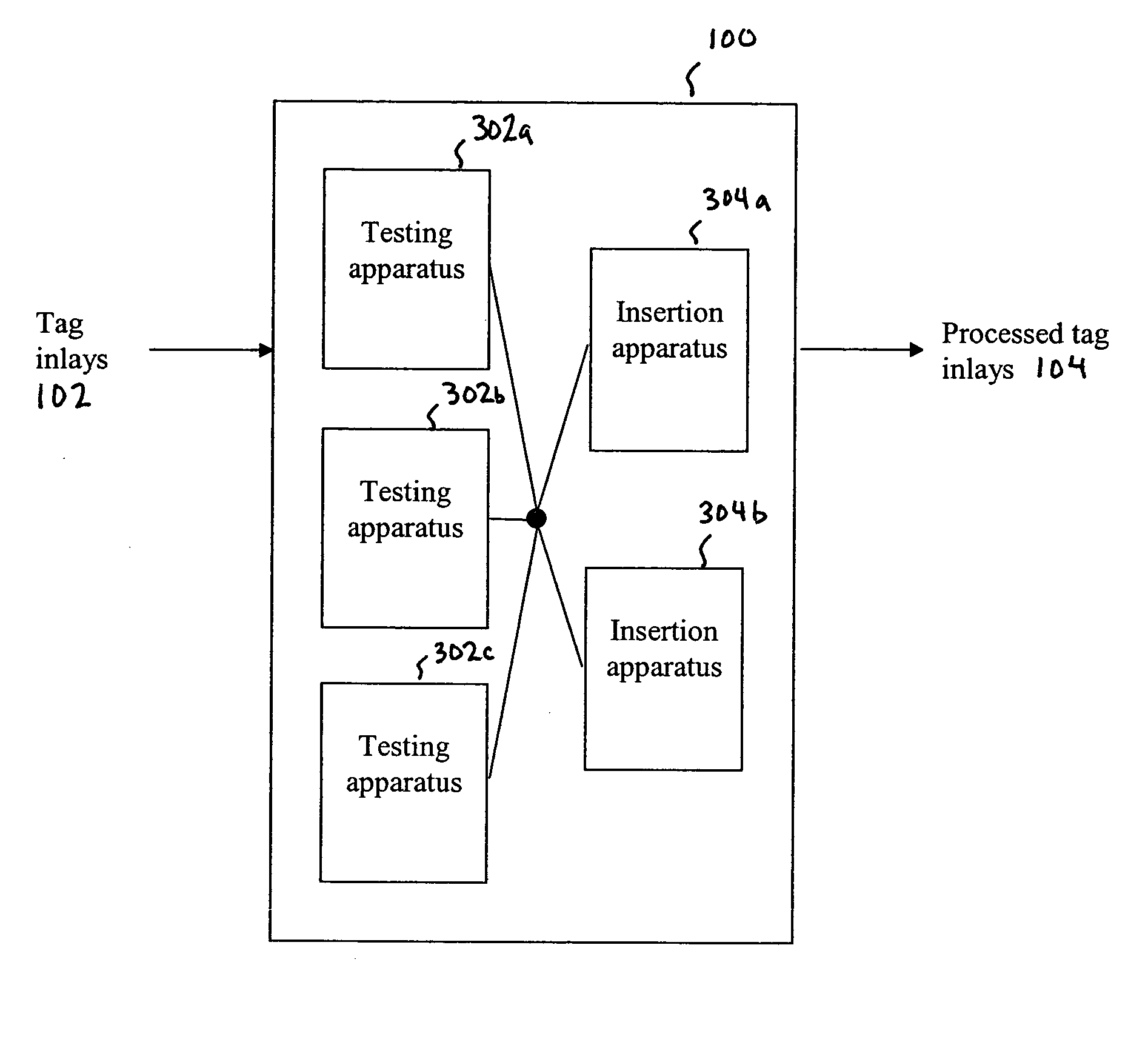
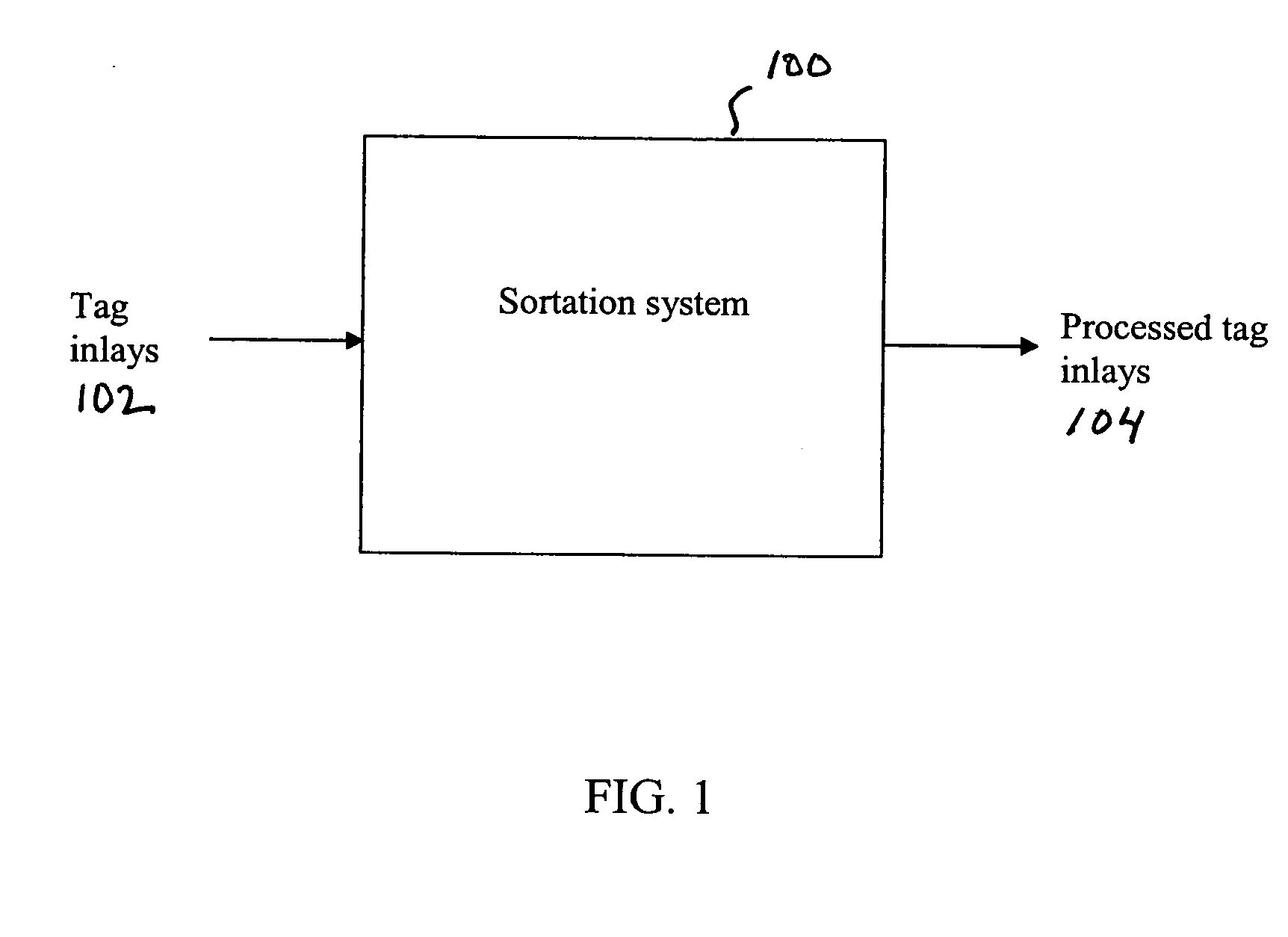
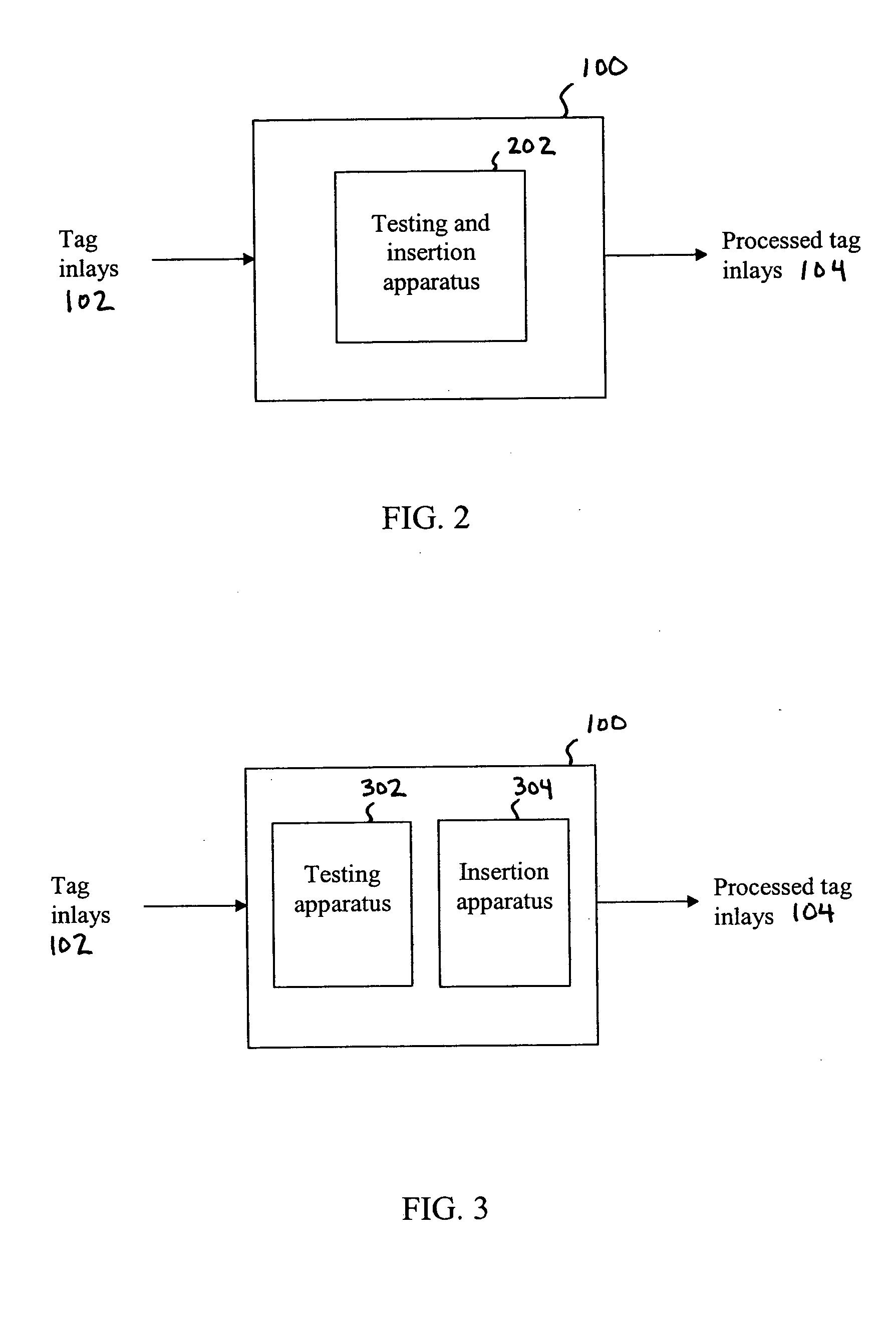
Radio frequency identification tag inlay sortation and assembly
ActiveUS20050155213A1Testing sensing arrangementsElectrical measurement instrument detailsComputer hardwareRadio frequency
A method, system, and apparatus for a radio frequency identification (RFID) tag inlay tester and sorter system are described. A tag inlay is received. A characteristic of the tag inlay is tested. The tag inlay is disposed if the tag inlay is determined to fail the test of characteristic. The tag inlay is transported to a processing station if the tag inlay is determined to have passed the test of characteristic. The tag inlay is processed at the processing station. In an aspect, the tag inlay testing and tag inlay processing is performed in a single apparatus. In an alternative aspect, the tag inlay testing is performed by a first apparatus, and the tag inlay processing is performed by a second apparatus.
Owner:SYMBOL TECH LLC
Method of determining performance of RFID devices
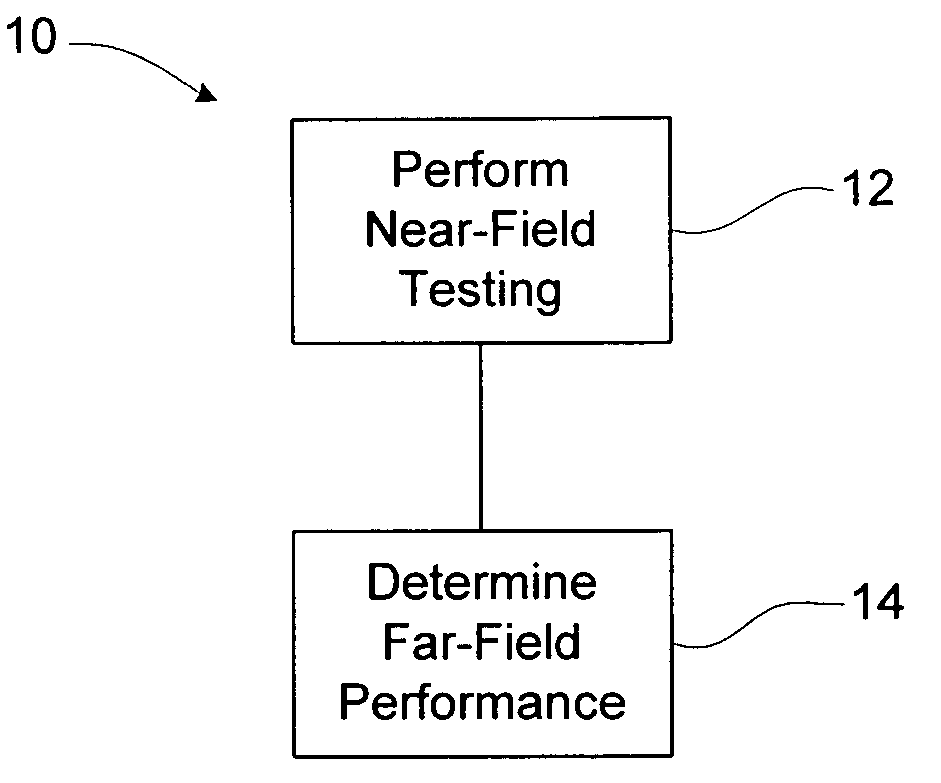
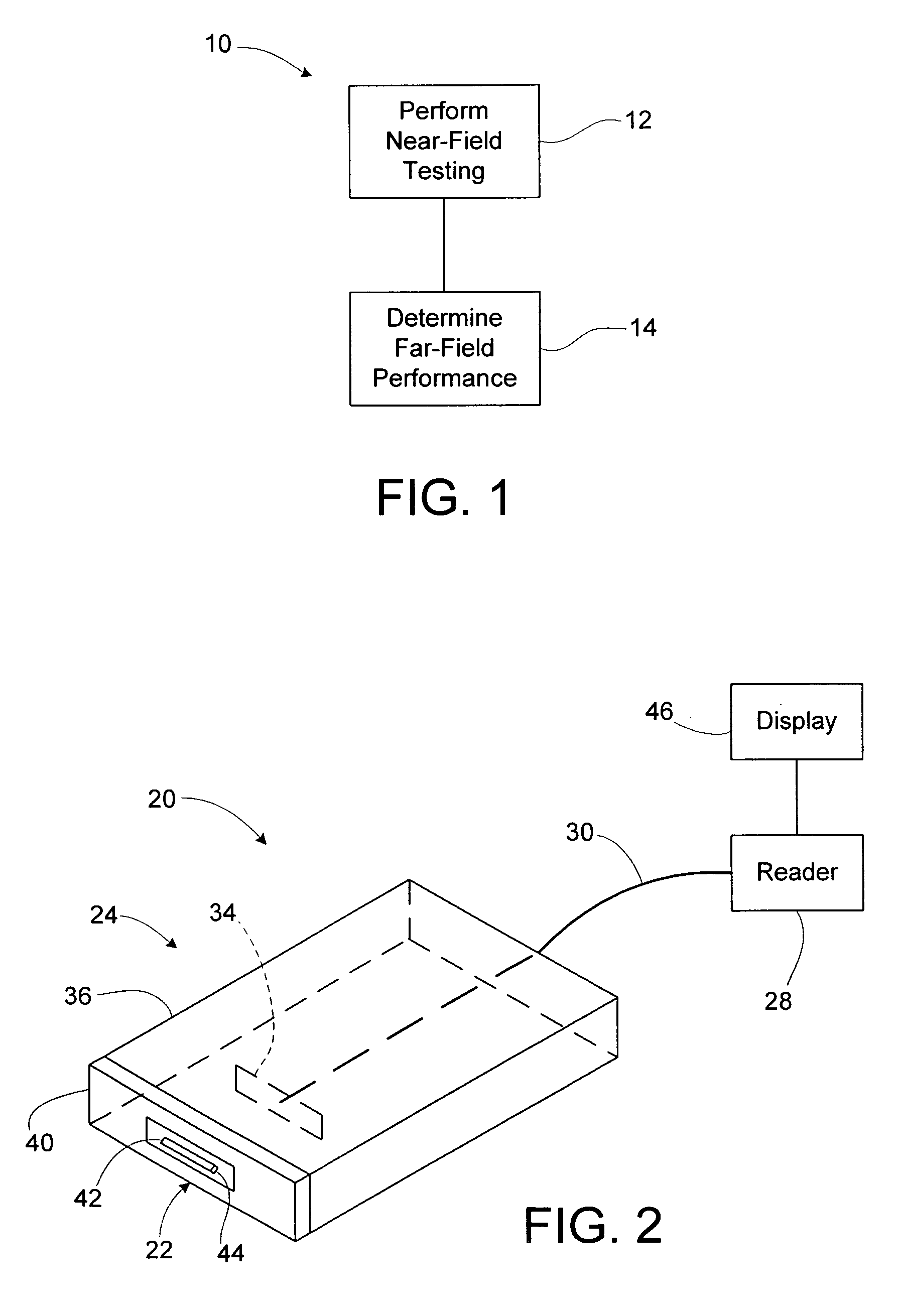
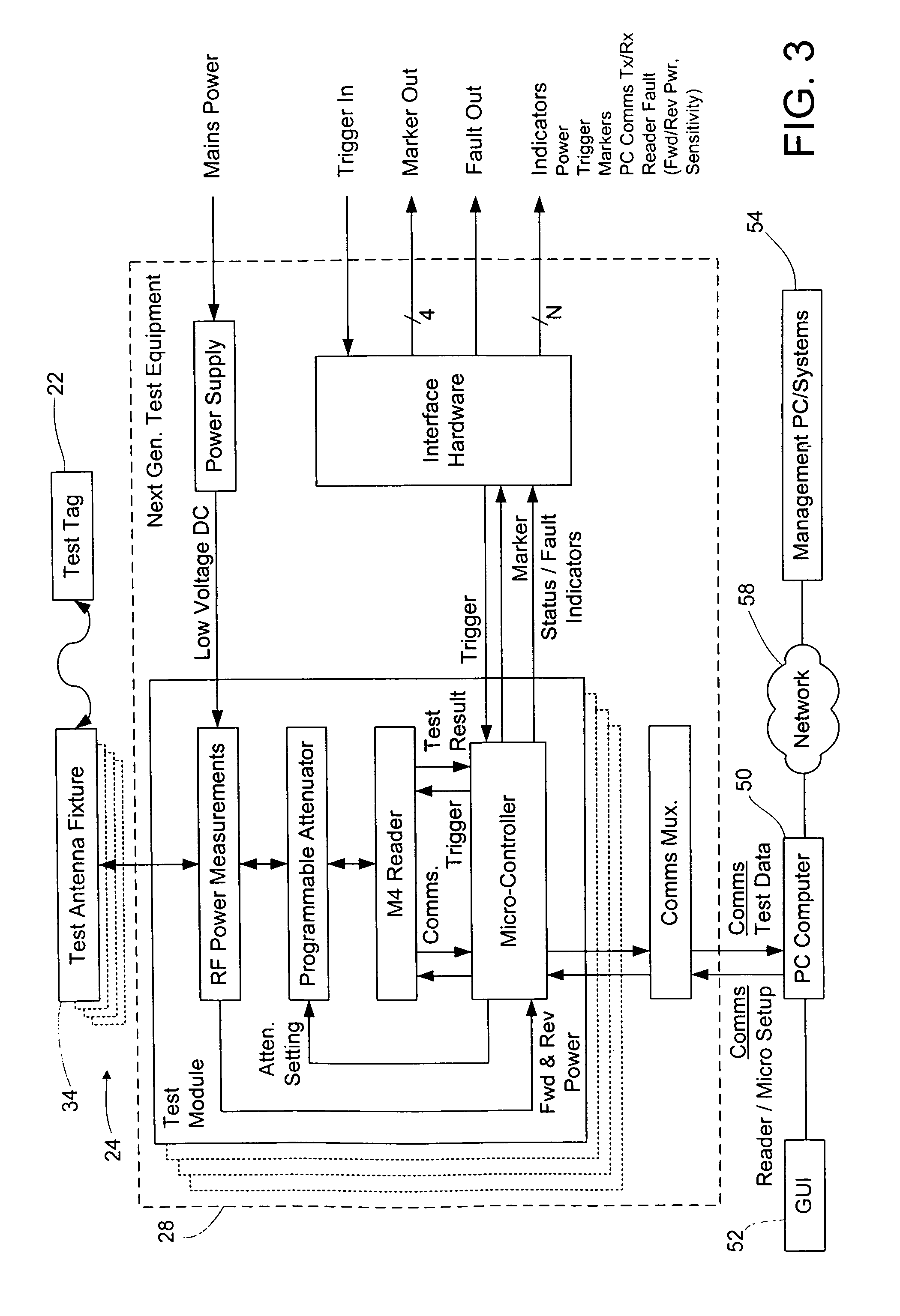
A method of determining far-field performance of an RFID device, such as in or on a tag, label, package, film, carton, wrap, or a portion of any of these, includes performing near-field testing or measurement of the RFID device, and determining or predicting far-field performance based on the results of the near-field testing or measurement. The determining or predicting of far-field performance may involve calculating a measure of far-field performance based on near-field results or measurements. The predicted far-field performance may include any of a variety of performance factors, including range, sensitivity, frequency performance, read sensitivity, write sensitivity, peak operating frequency, and / or average sensitivity over a given frequency band. Using near-field testing results to predict far-field performance may allow use of compact testing facilities, in situ testing of RFID devices, and / or faster and / or less costly testing of RFID devices.
Owner:AVERY DENNISON CORP
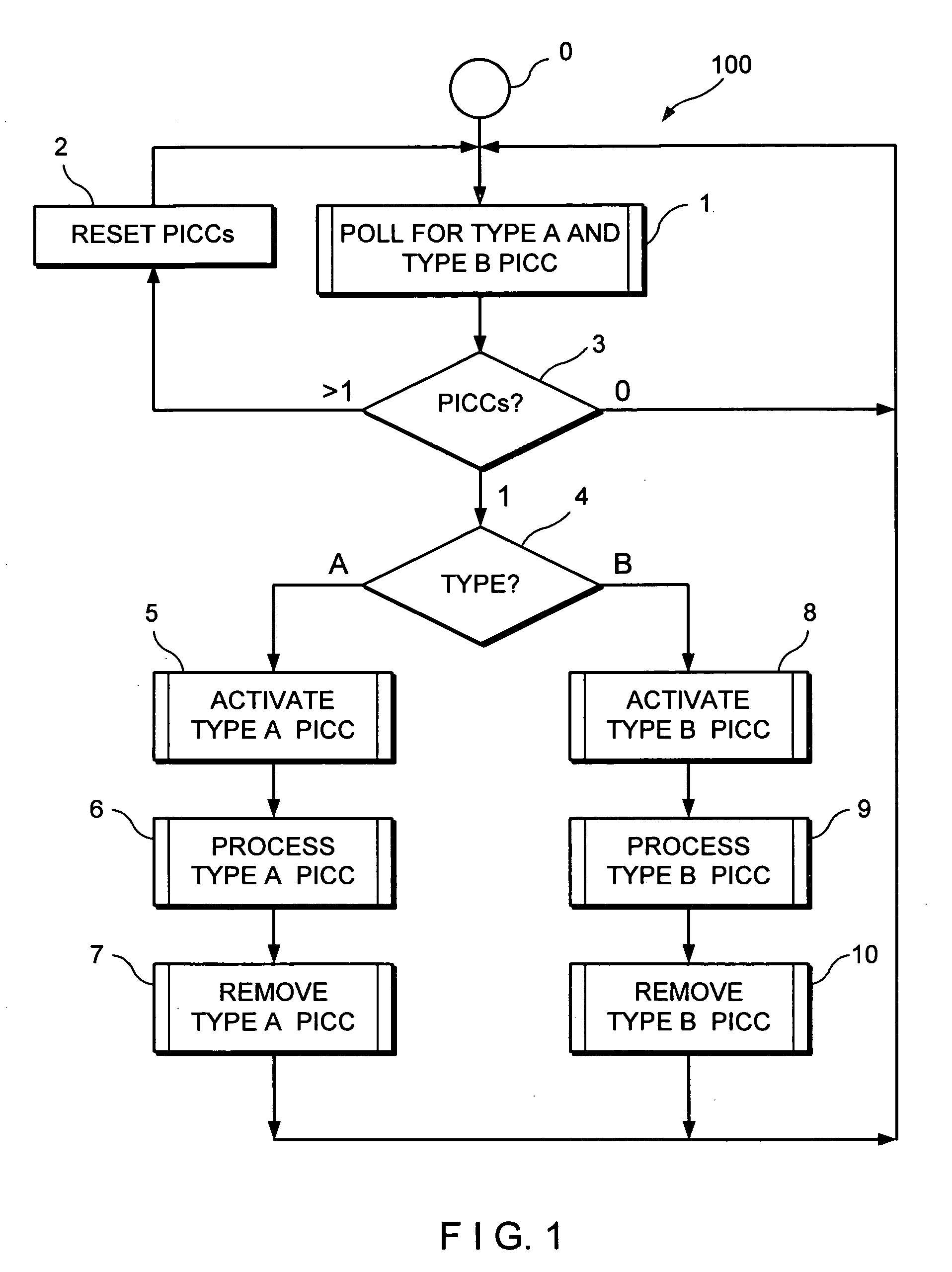
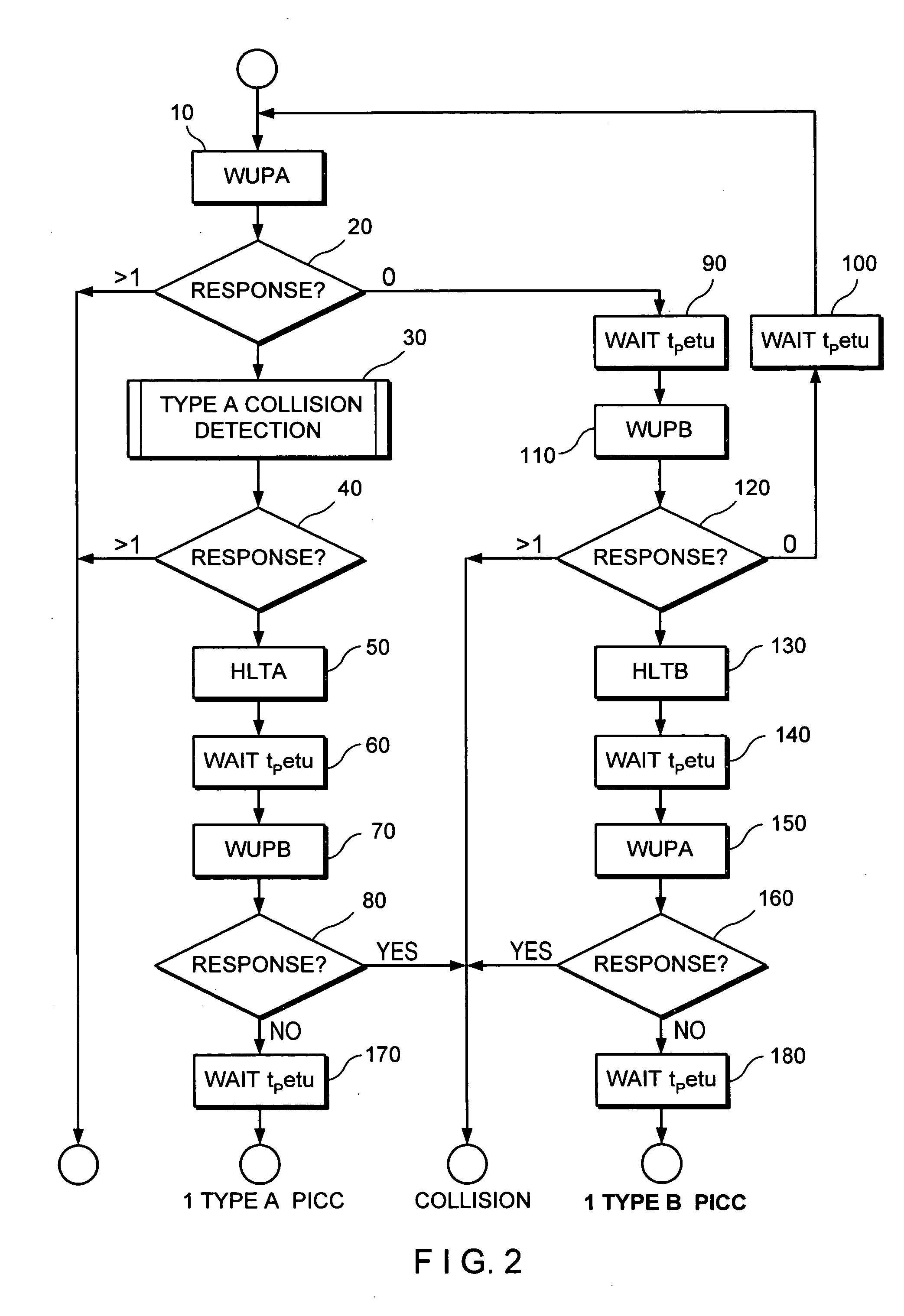
Collision detection and avoidance scheme for contactless card payment systems
ActiveUS20060022042A1Transaction processing is haltedAcutation objectsTicket-issuing apparatusCollision detectionCard reader
An electronic payment system for conducting transactions by presenting a contactless payment card to a card reader. The card reader is configured to process transactions when only one card is present in its operating field. The card reader uses collision detection and avoidance algorithms to detect and report instances where multiple cards are present in the operating field. In response to a reported collision, the collision may be cleared by manual intervention, i.e., by physically removing excess cards from the reader's operating field.
Owner:MASTERCARD INT INC
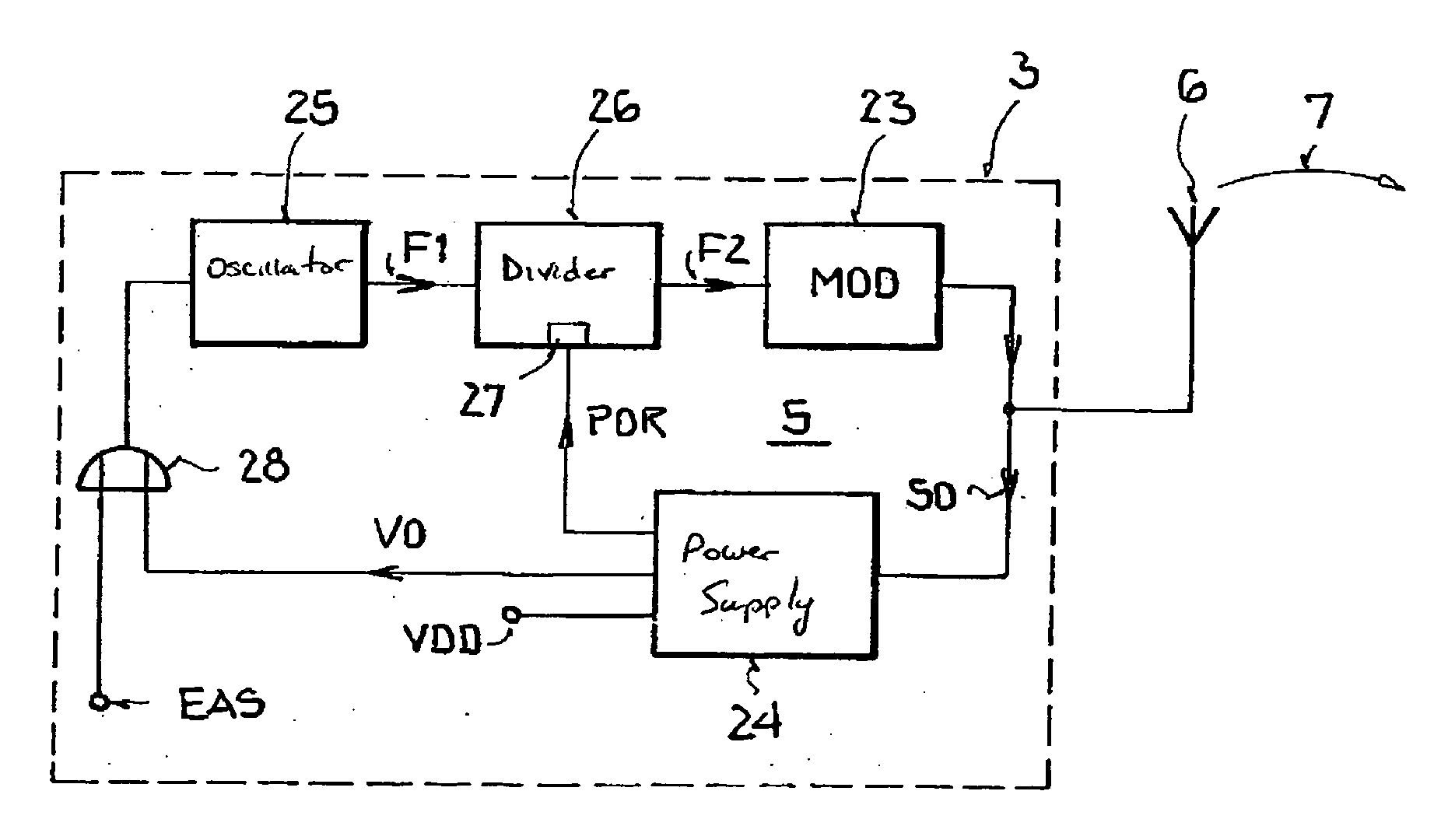
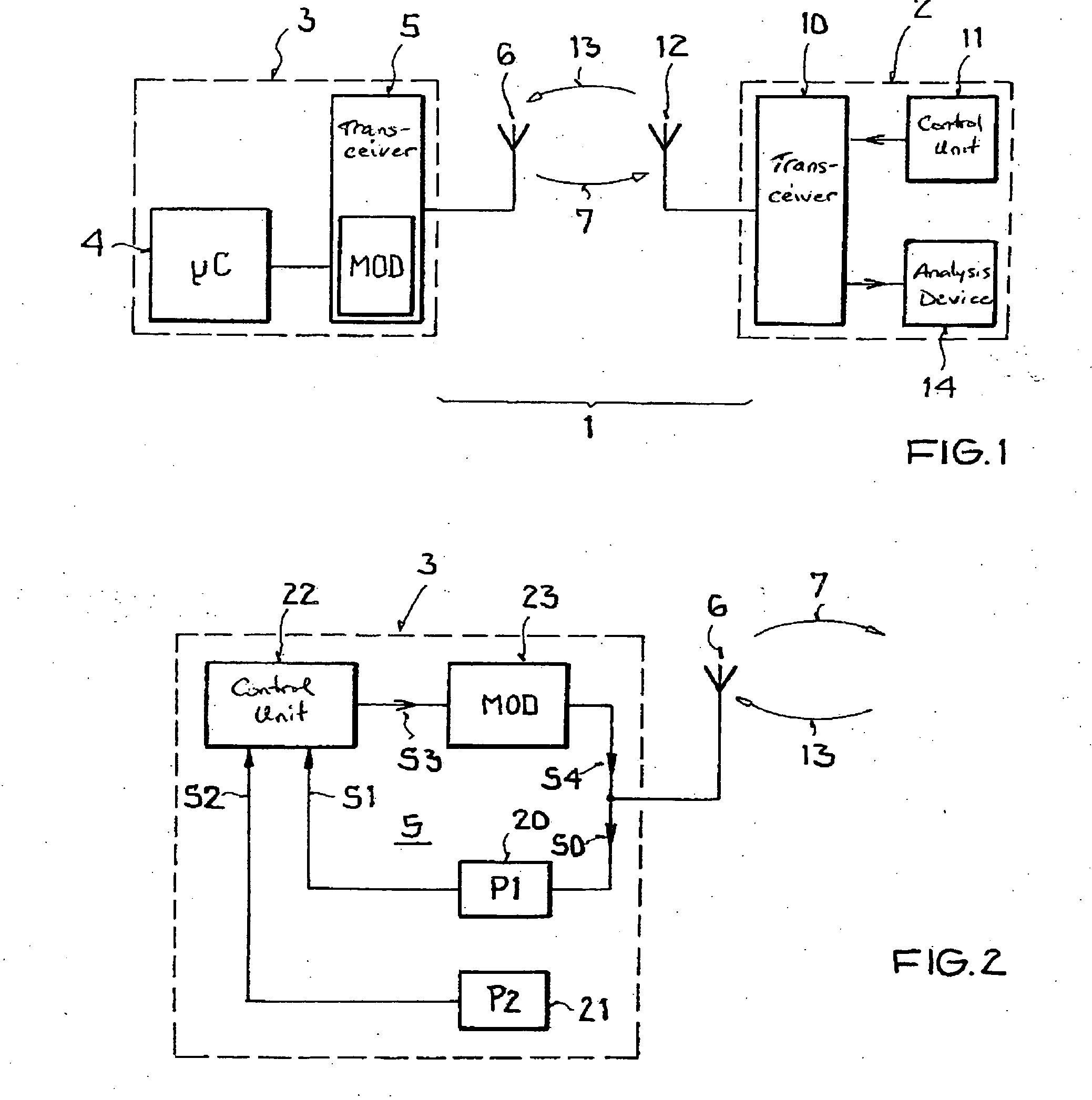
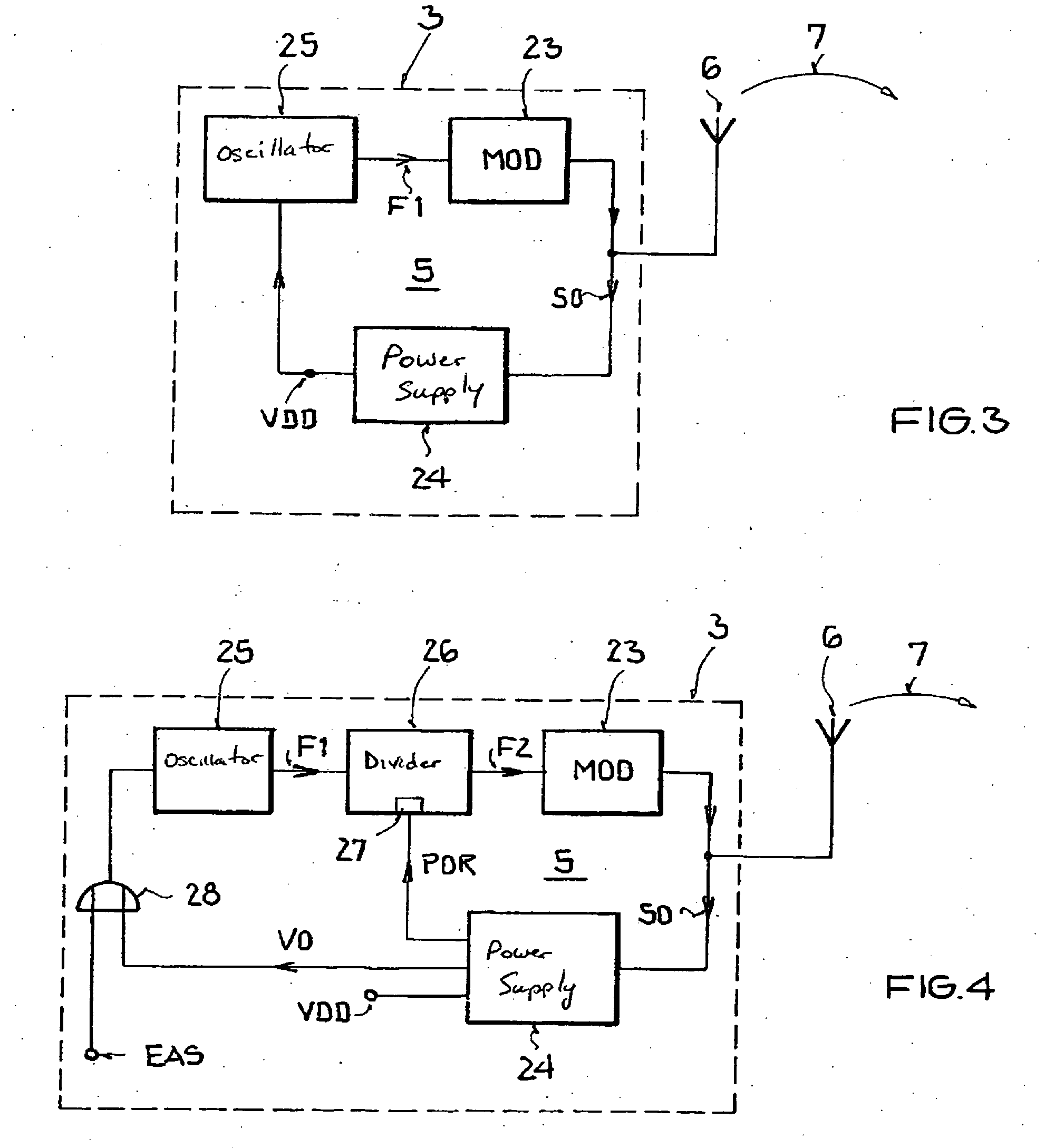
Backscatter transponder
InactiveUS20080136646A1Testing sensing arrangementsSubscribers indirect connectionCommunications systemCarrier signal
A backscatter transponder for an HF communication system with modulated reradiation, is provided that includes an antenna for receiving high-frequency carrier signals, wherein the antenna has reflective characteristics, a control unit for providing transponder-specific parameters, and a modulator that can be driven by the control unit. The modulator altering the reflective characteristics of the antenna in accordance with at least one transponder-specific parameter.
Owner:ATMEL CORP
High-speed RFID circuit placement method and device
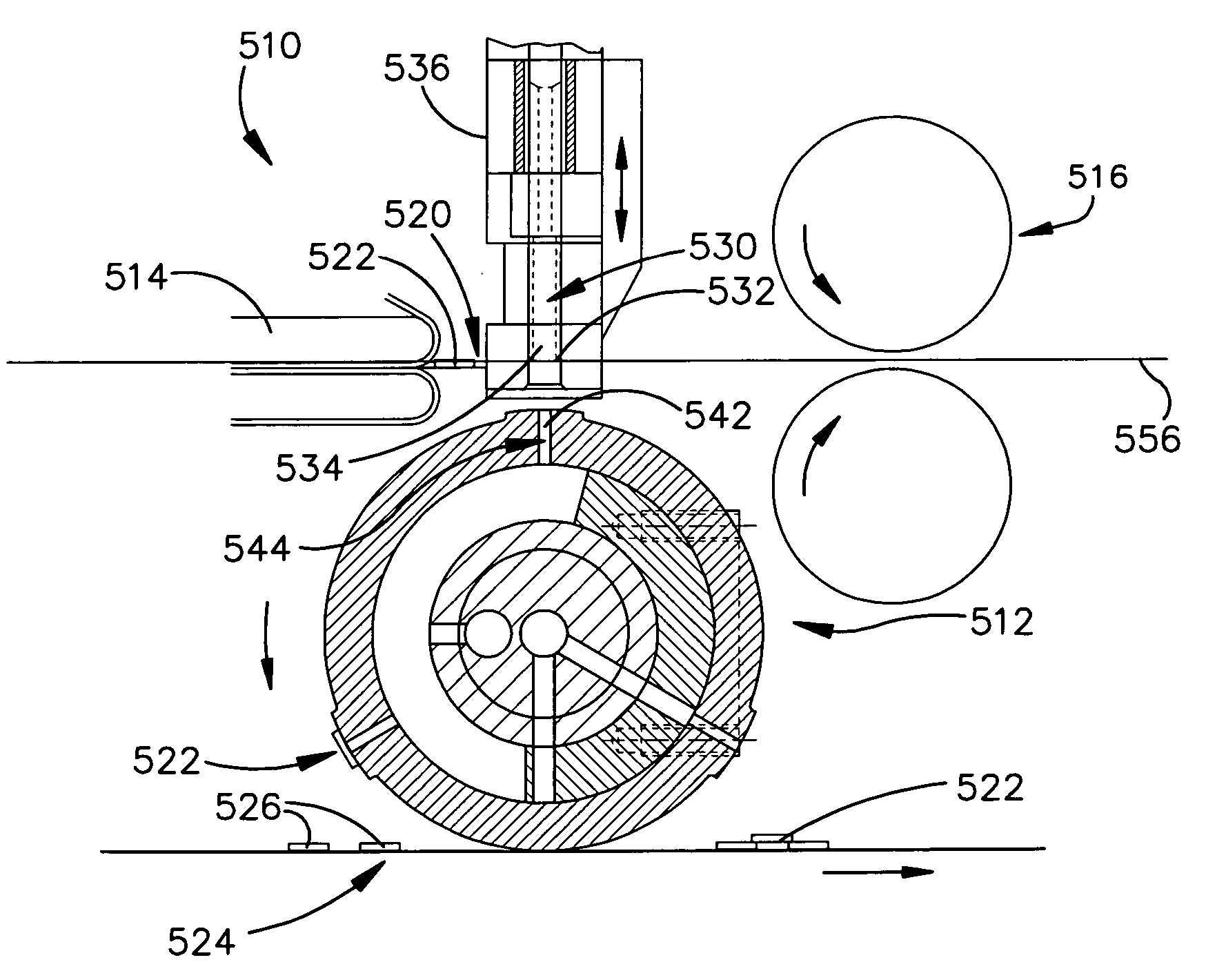
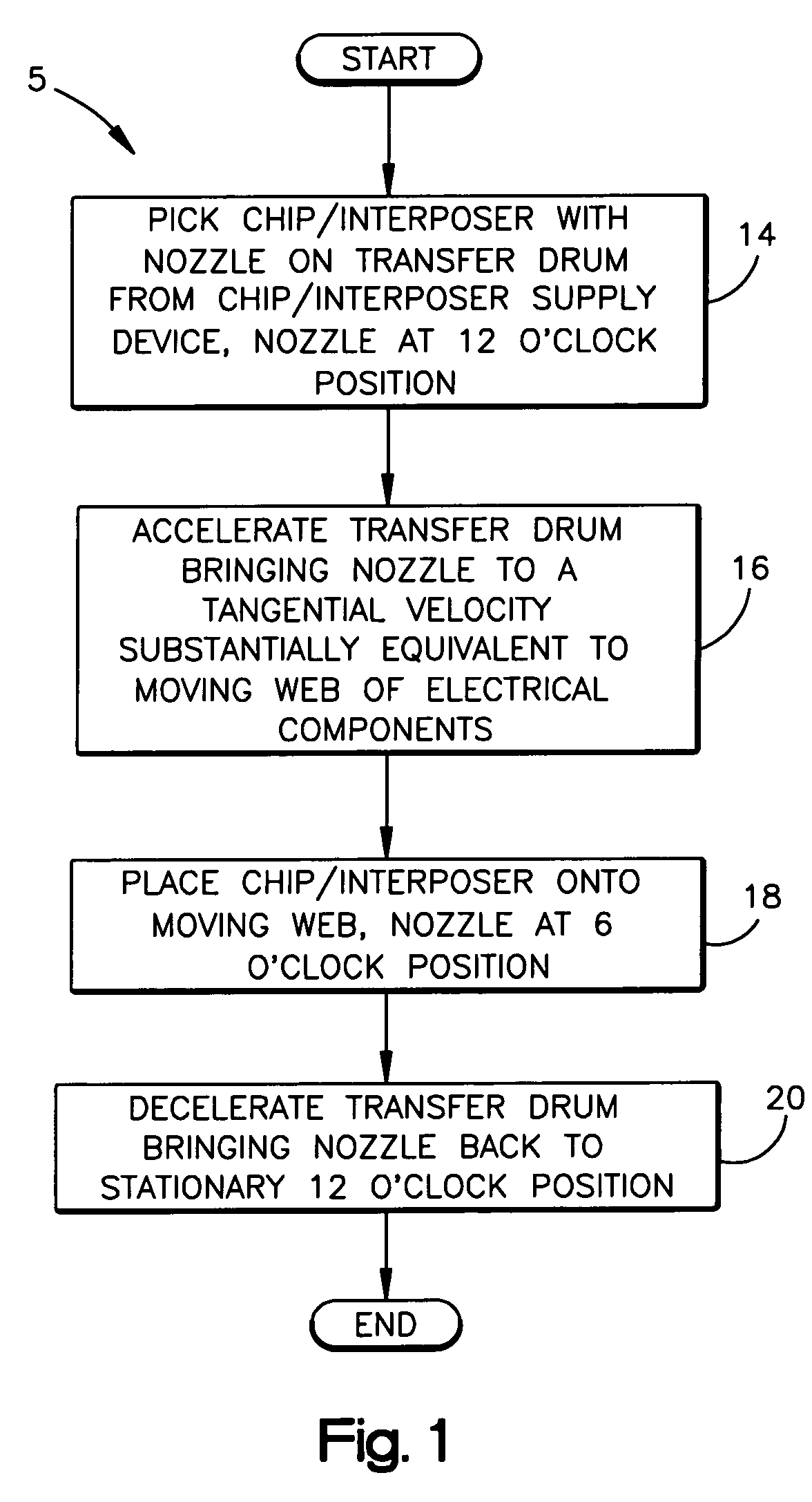
ActiveUS7623034B2Prevent bucklingPrinted circuit assemblingTesting sensing arrangementsInterposerEngineering
A high-speed machine and method for placing an RFID circuit onto an electrical component includes separating an RFID circuit from a web of RFID circuits, and placing the RFID circuit onto an electrical component with a placing device. The separating includes directing the RFID circuit onto a transfer drum of the placement device and separably coupling the RFID circuit to the transfer drum. According to one method, a separator device separates and directs chips or interposers onto a placement device. According to another method, chips or interposers are tested before being separated from a web, and if good, are separated from the web, directed onto a placement device, and placed on an electrical component. If defective, the chips or interposers are not directed onto a placement device and are removed by a scrap web removal device.
Owner:AVERY DENNISON CORP
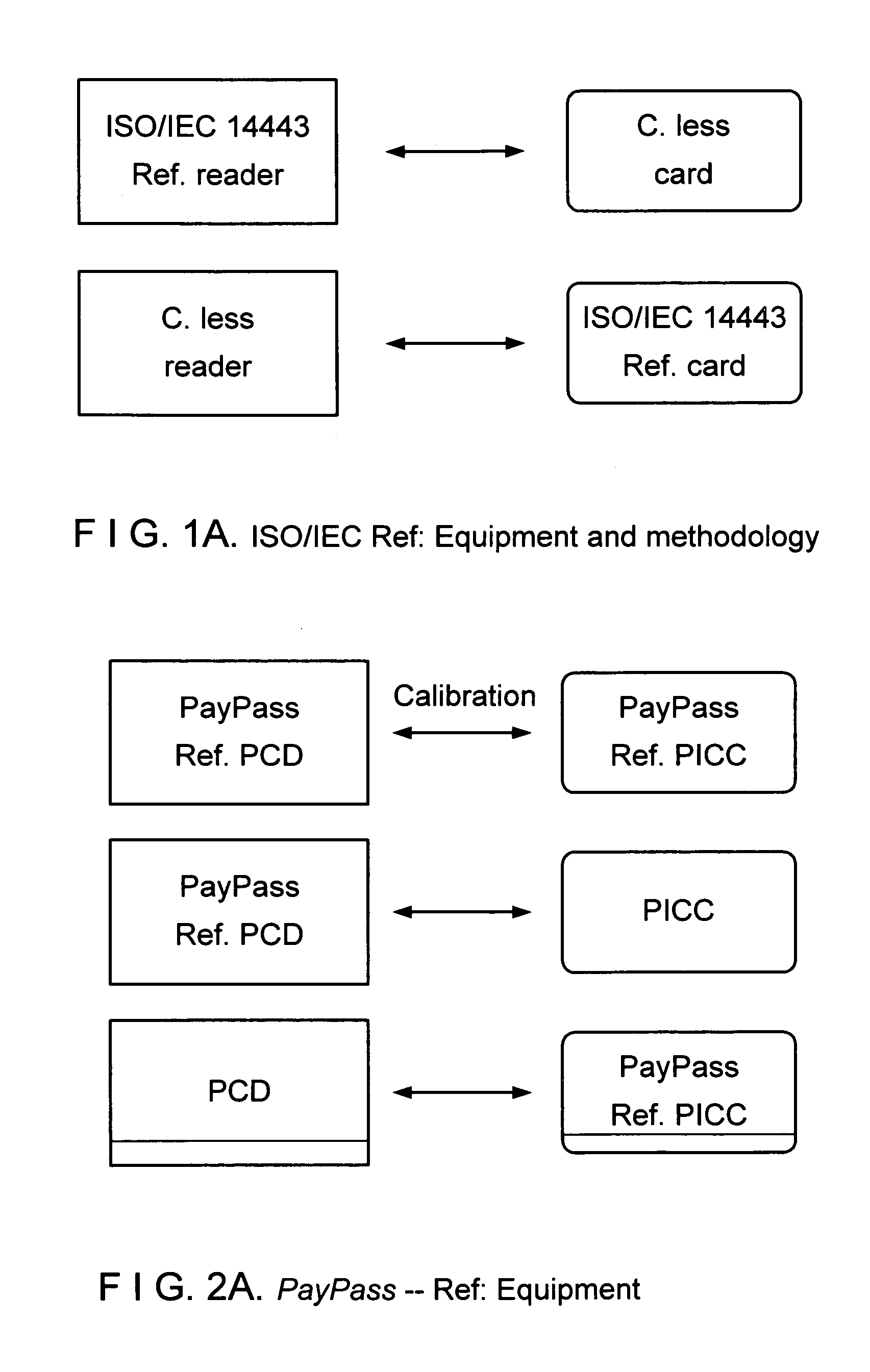
Method and system for conducting contactless payment card transactions
InactiveUS20060027655A1Improve interoperabilityAcutation objectsTesting sensing arrangementsCouplingPayment transaction
A system and method for enhancing functional interoperability of contactless payment devices that are used for conducting electronic payment transactions between consumers and merchants. The contactless payment devices include RFID-embedded cards issued to consumers and proximity coupling devices such as RFID-enabled readers deployed by merchants. The system and method involve use of a reference card and a reference reader to establish acceptable specifications for issued cards and deployed readers, respectively. The reference card and reference reader are cross-calibrated to link the operational specifications for the cards and the readers. A suitable selection of overlapping specification ranges or tolerances for proper card and reader functions, the enhances the interoperability of the issued cards with a deployed reader, and also the interoperability of deployed readers with an issued card.
Owner:MASTERCARD INT INC
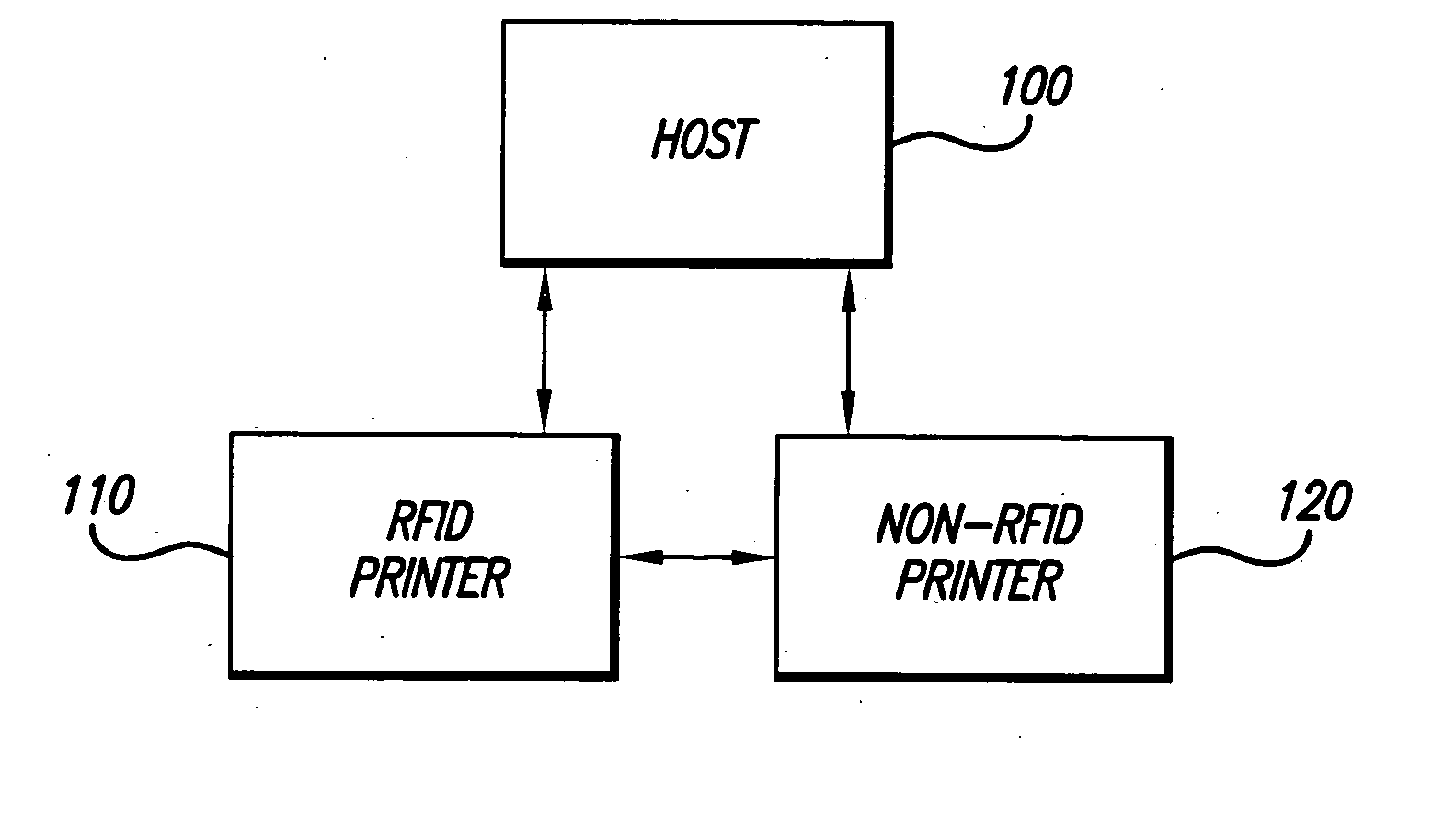
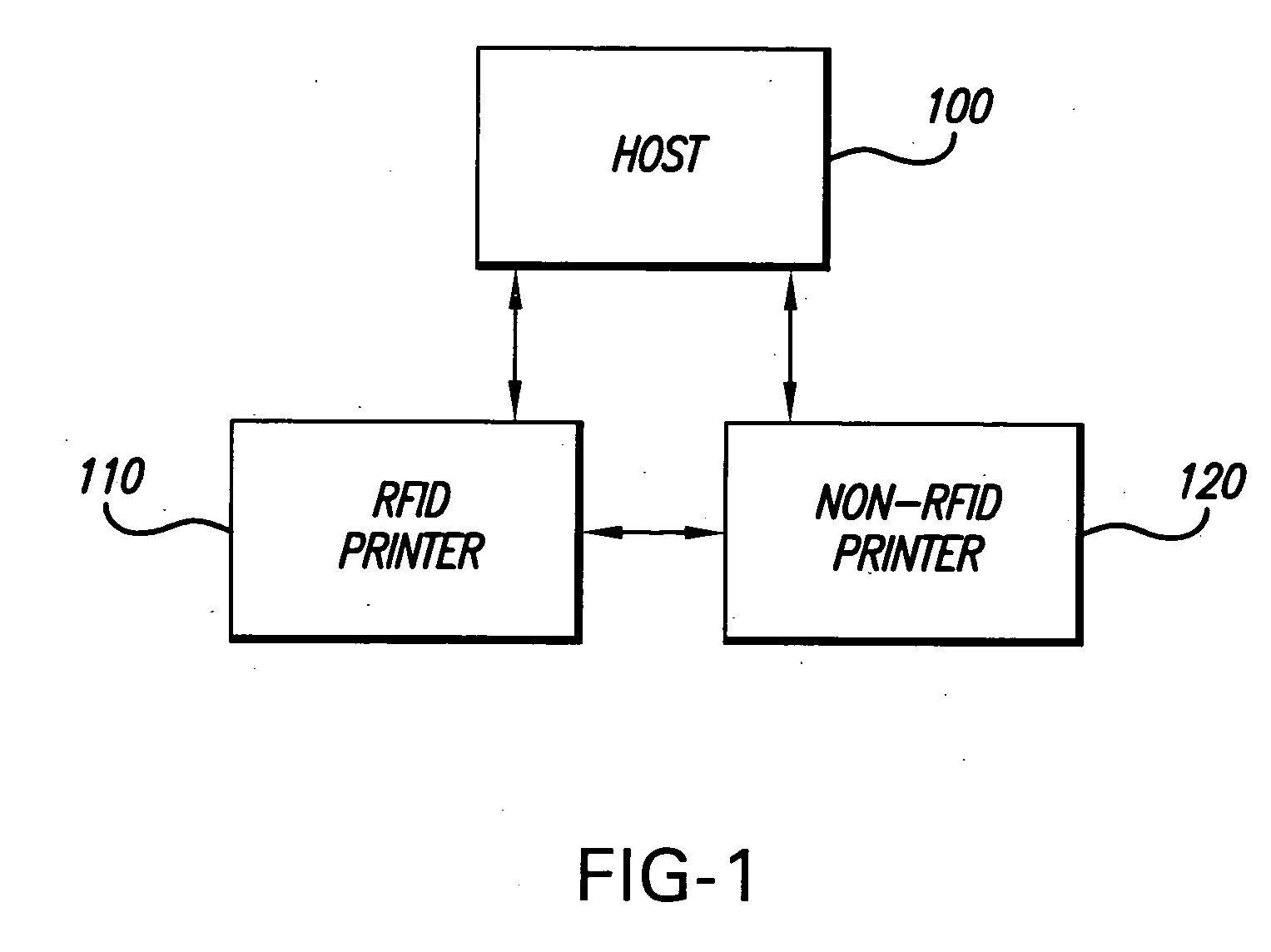
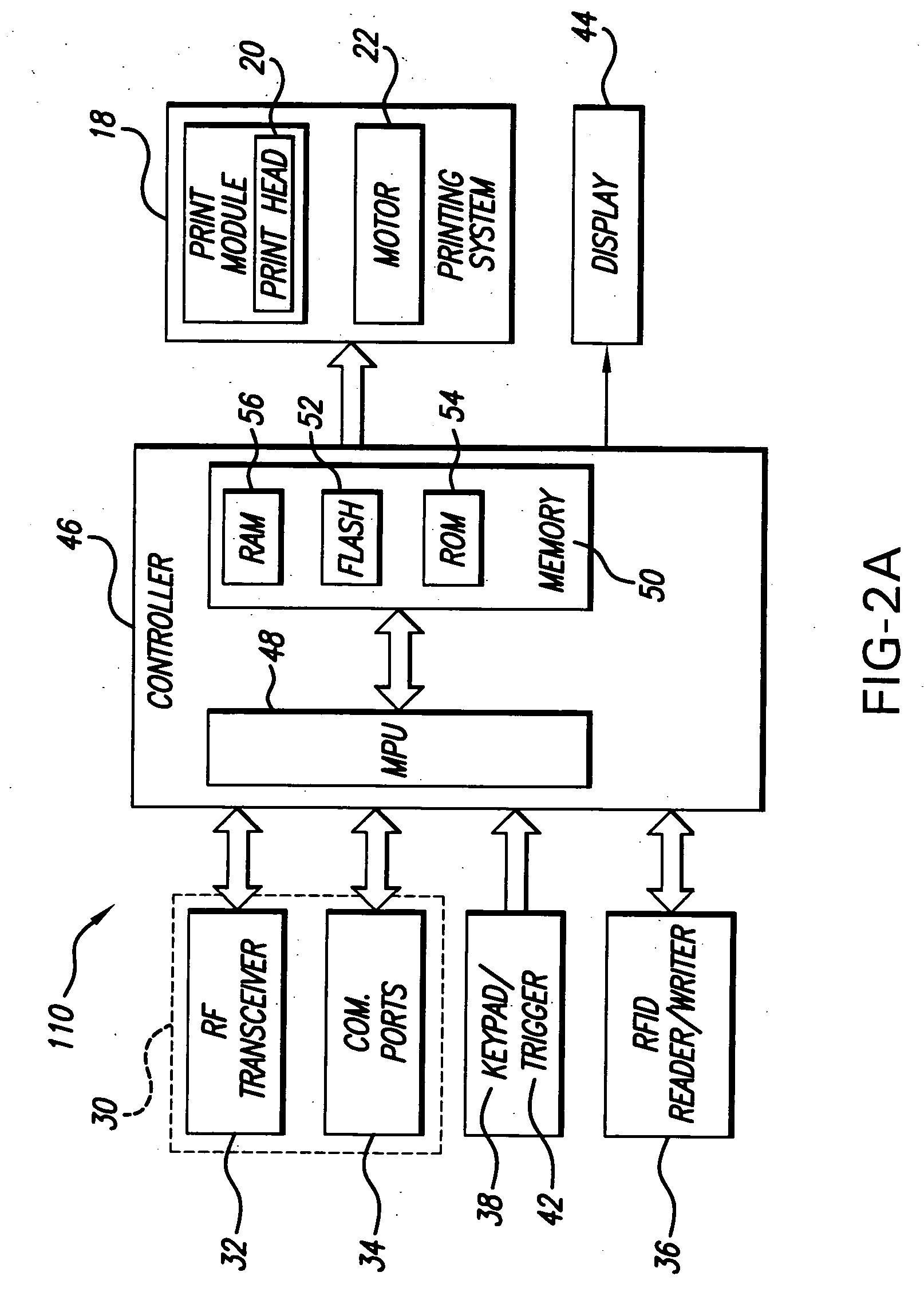
RFID printer system, method of printing and sets of record members
InactiveUS20060071063A1Not possibleInking apparatusTesting sensing arrangementsEngineeringTransponder
A system and method for printing both record members having RFID transponders disposed thereon and record members not having RFID transponders disposed thereon. In one embodiment, a RFID printer receives data to be printed on a record member and determines if the data includes RFID data to be written to a RFID transponder embedded on a record member. If the received data includes RFID data, the RFID printer prints a RFID record member according to the received data. If the received data does not include RFID data, the RFID printer transmits the data to a non-RFID printer for printing. In another embodiment, a non-RFID printer receives data to be printed on a record member and determines if the data includes RFID data to be written to a RFID transponder embedded on a record member. If the received data does not include RFID data, the non-RFID printer prints a record member according to the received data. If the received data does include RFID data, the non-RFID printer transmits the data to a RFID printer for printing. At least one set of RFID record members in a RFID web is written to and printed with data. At least one set of non-RFID record members in a non-RFID web is printed with the same data. The set(s) of RFID record members are associated with the set(s) of non-RFID members by the same indicium which is printed on at least one RFID record member and in at least one non-RFID record member having related data. When there are plural sets of RFID record members, wherein the sets of RFID record members have different data, and there are plural sets of non-RFID record members, wherein the sets of non-RFID record members have different data, and the data of the sets of RFID record members and the sets of non-RFID record members have related data, differing indicia are printed on at least one record member of each set to associate the sets of RFID and non-RFID record members.
Owner:AVERY DENNISON CORP
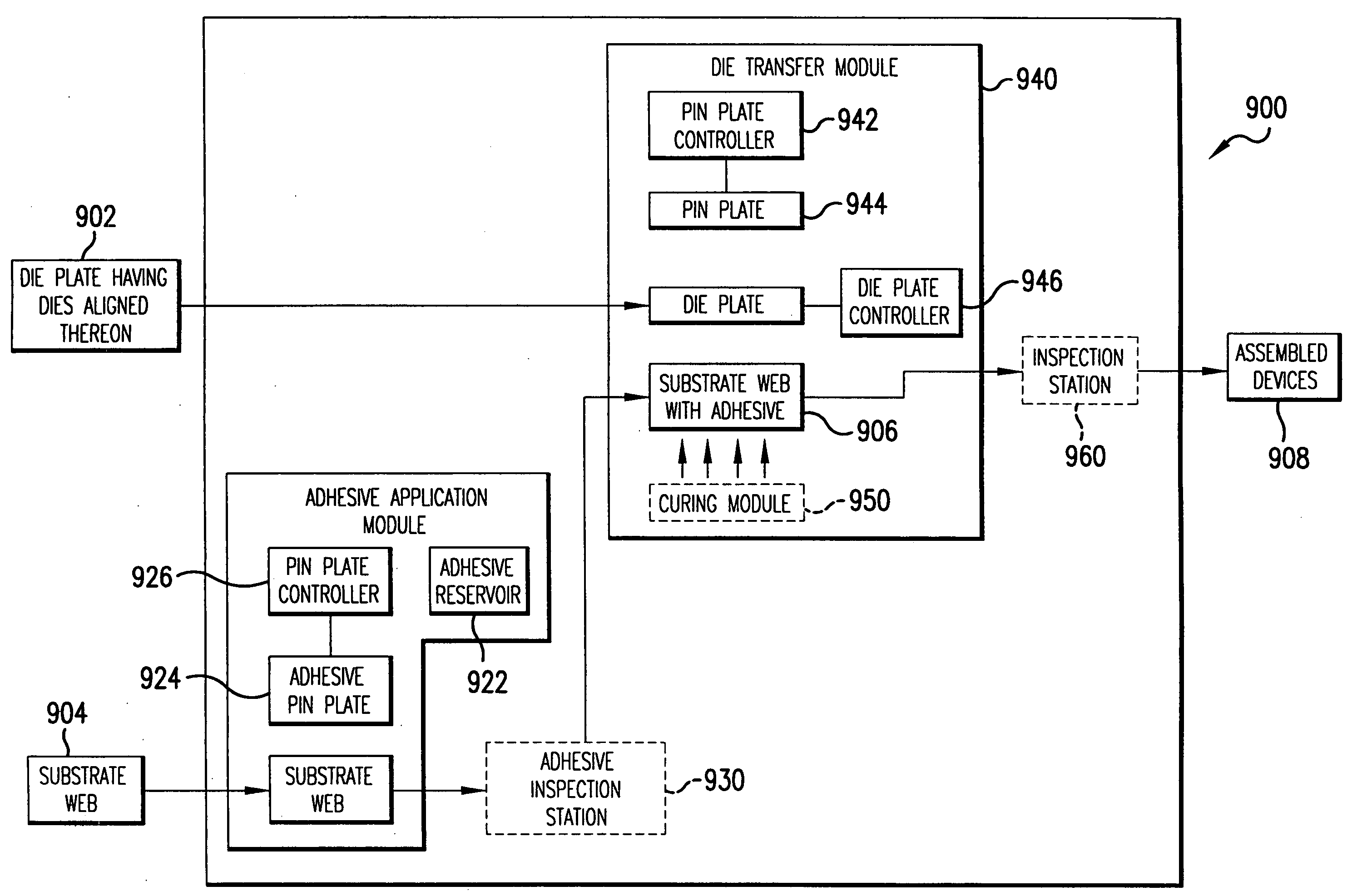
Method, system, and apparatus for transfer of dies using a pin plate
InactiveUS20050015970A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPunchingEngineering
A method and system for device assembly and a method, system, and apparatus for transfer of dies using a pin plate are described herein. A die plate is received having dies. The body of the die plate has a plurality of holes extending therethrough. Each die covers a corresponding hole on a first surface of the die plate. The die plate is positioned to be closely adjacent to the web of substrates. The punching device has a plurality of punching members extending from an outer surface. The punching device is planar or alternatively cylindrical. The punching device is applied to a second surface of the die plate to cause a set of the punching members to extend through a set of holes in the die plate, causing dies to be transferred from the die plate to one or more destination substrates or other surfaces.
Owner:SYMBOL TECH INC
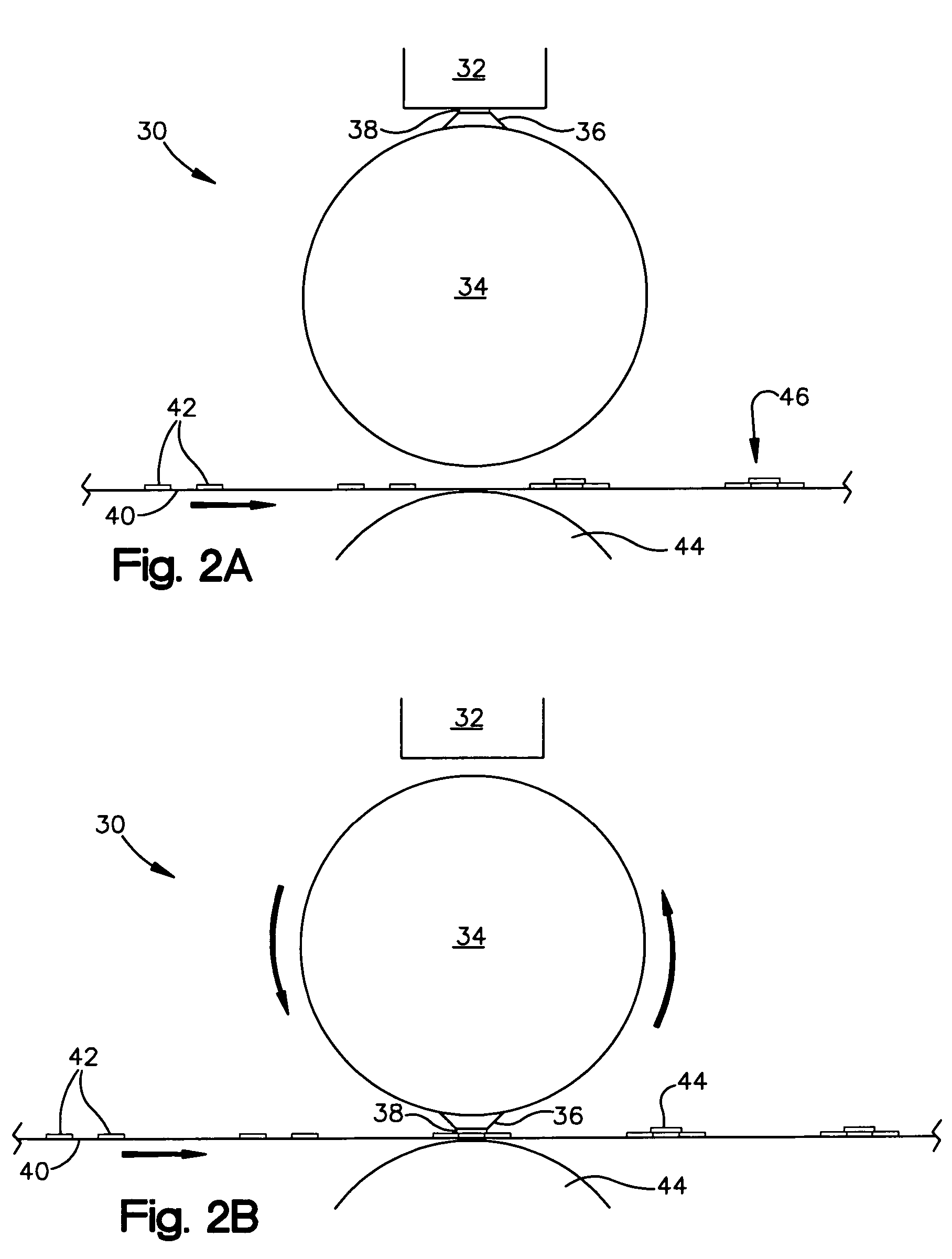
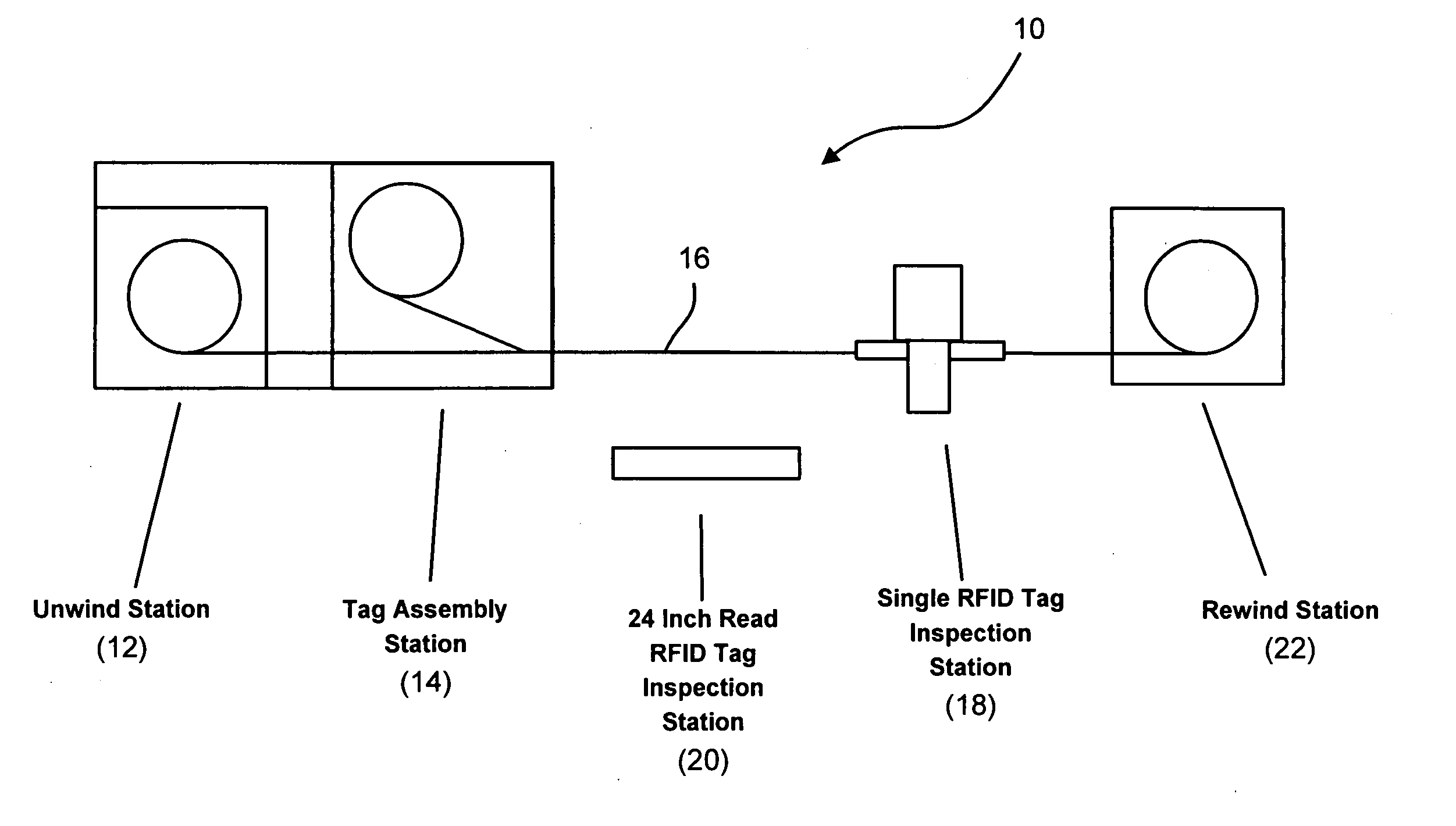
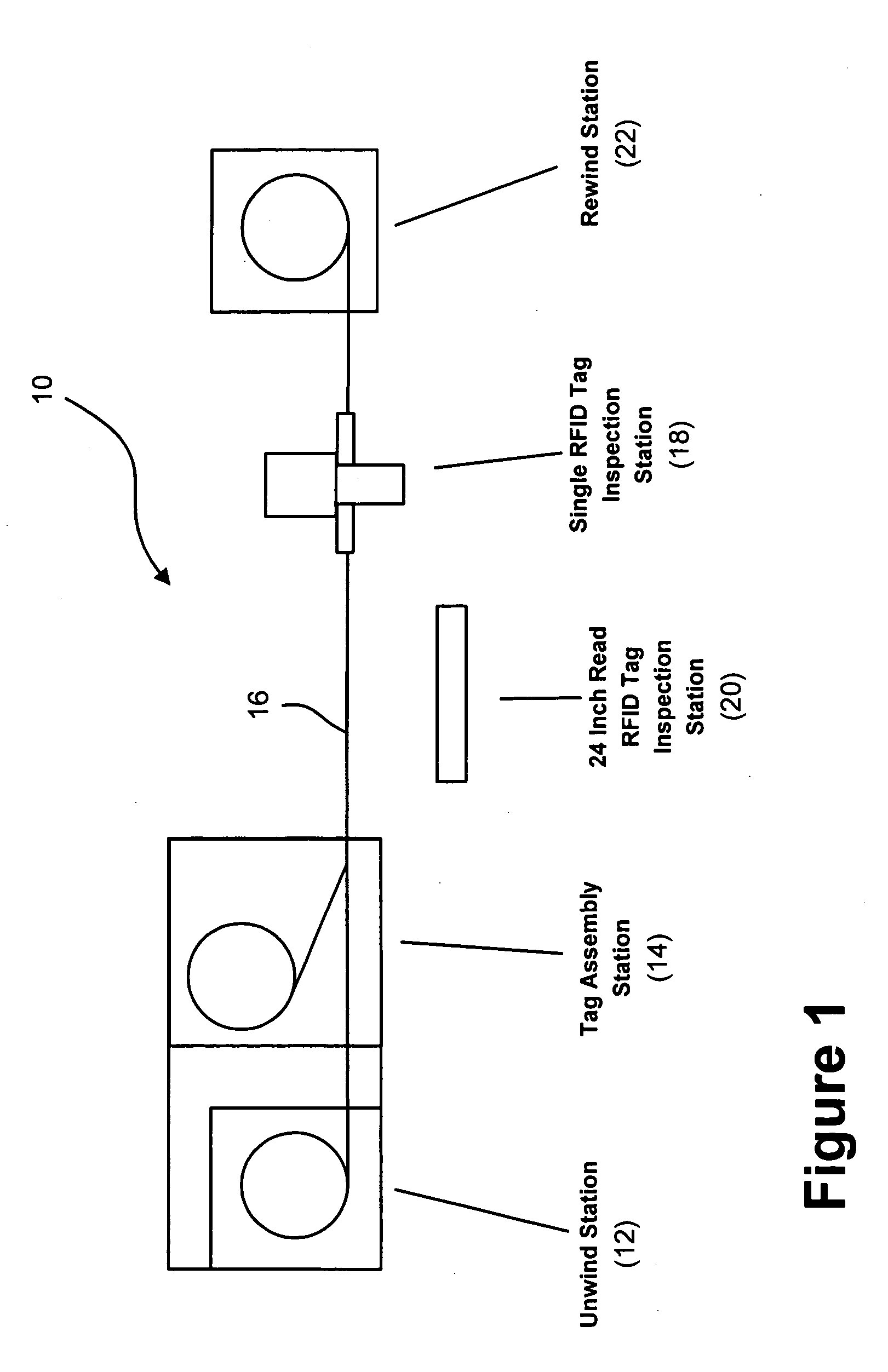
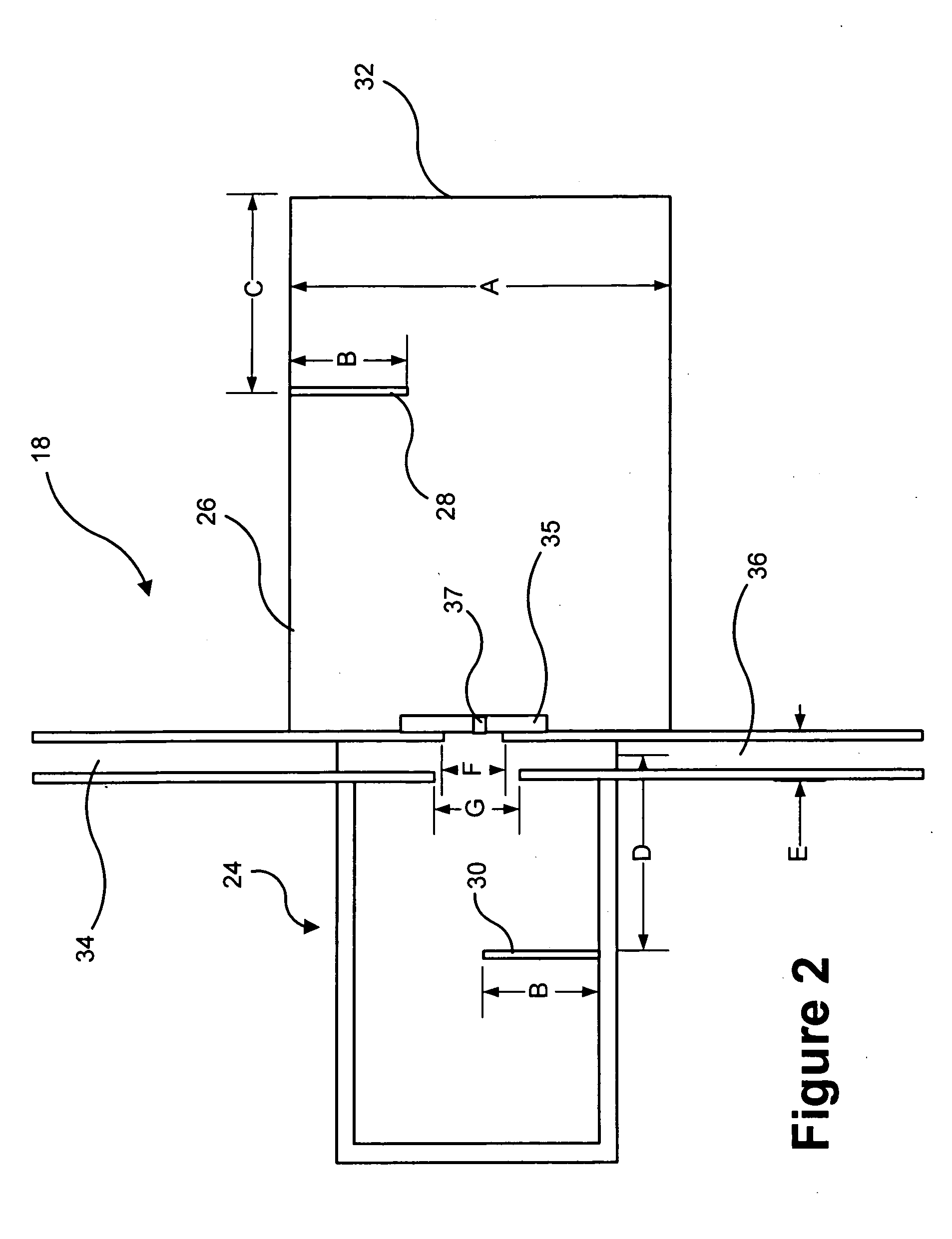
System and method for validating radio frequency identification tags
InactiveUS20050150102A1High speedPrecise functionTesting sensing arrangementsElectrical measurement instrument detailsNarrow angleRadio frequency
A system for validating each of a plurality of radio frequency identification tags disposed on a web in close proximity to one another to ensure proper functioning thereof includes a narrow angle radio frequency identification tag reading station which reads a designation of each radio frequency identification tag individually in order to generate a first list of tag designations read thereby and a wide angle radio frequency identification tag reading station which reads designations of a plurality of radio frequency identification tags simultaneously from a long range in order to generate a second list of tag designations read thereby. The system also includes a processor which compares the first list of tag designations with the second list of tag designations and evaluates the functionality of the plurality of radio frequency identification tags based at least in part upon the comparison.
Owner:GEORGE SCHMITT & CO
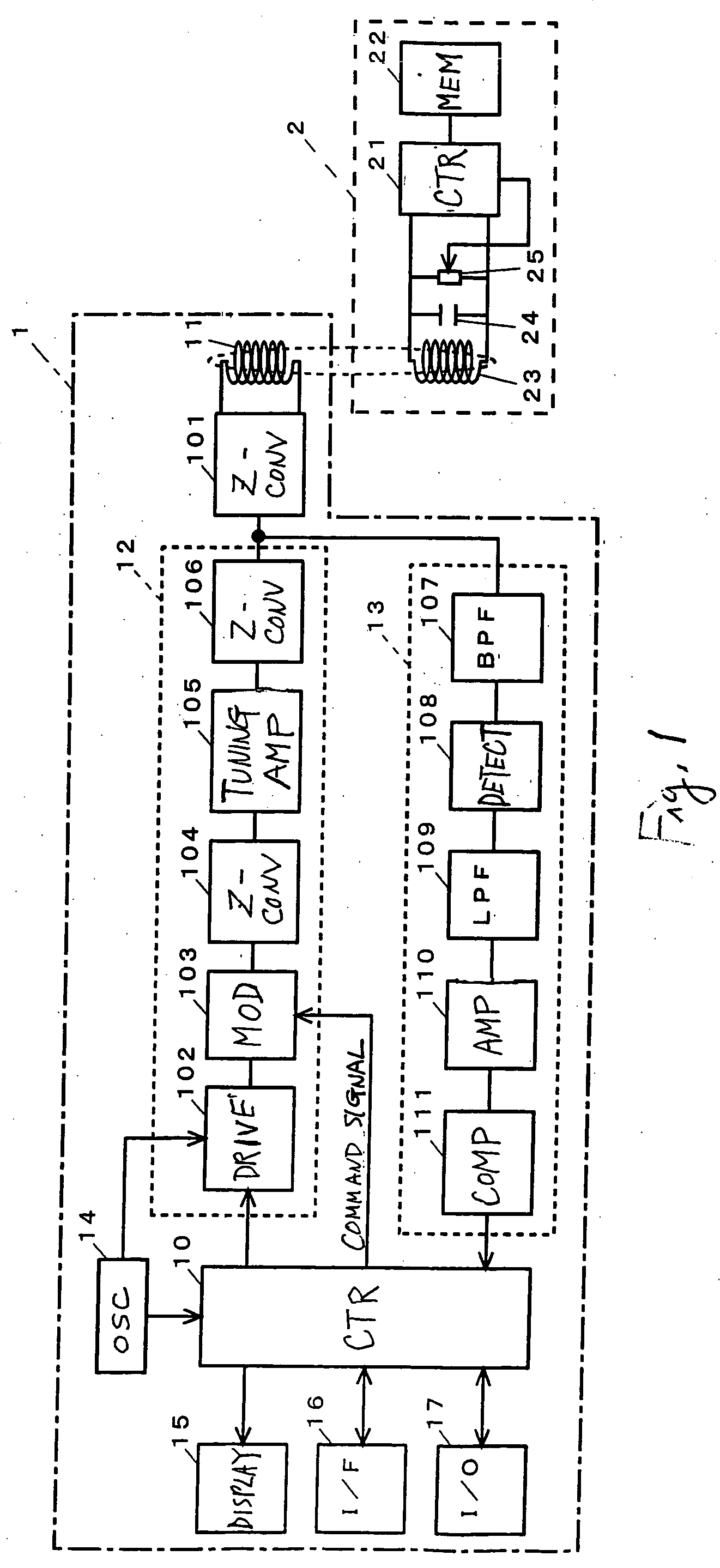
Method and system for testing RFID devices
ActiveUS20060145710A1Precise positioningTesting sensing arrangementsMemory record carrier reading problemsUnique identifierCommon carrier
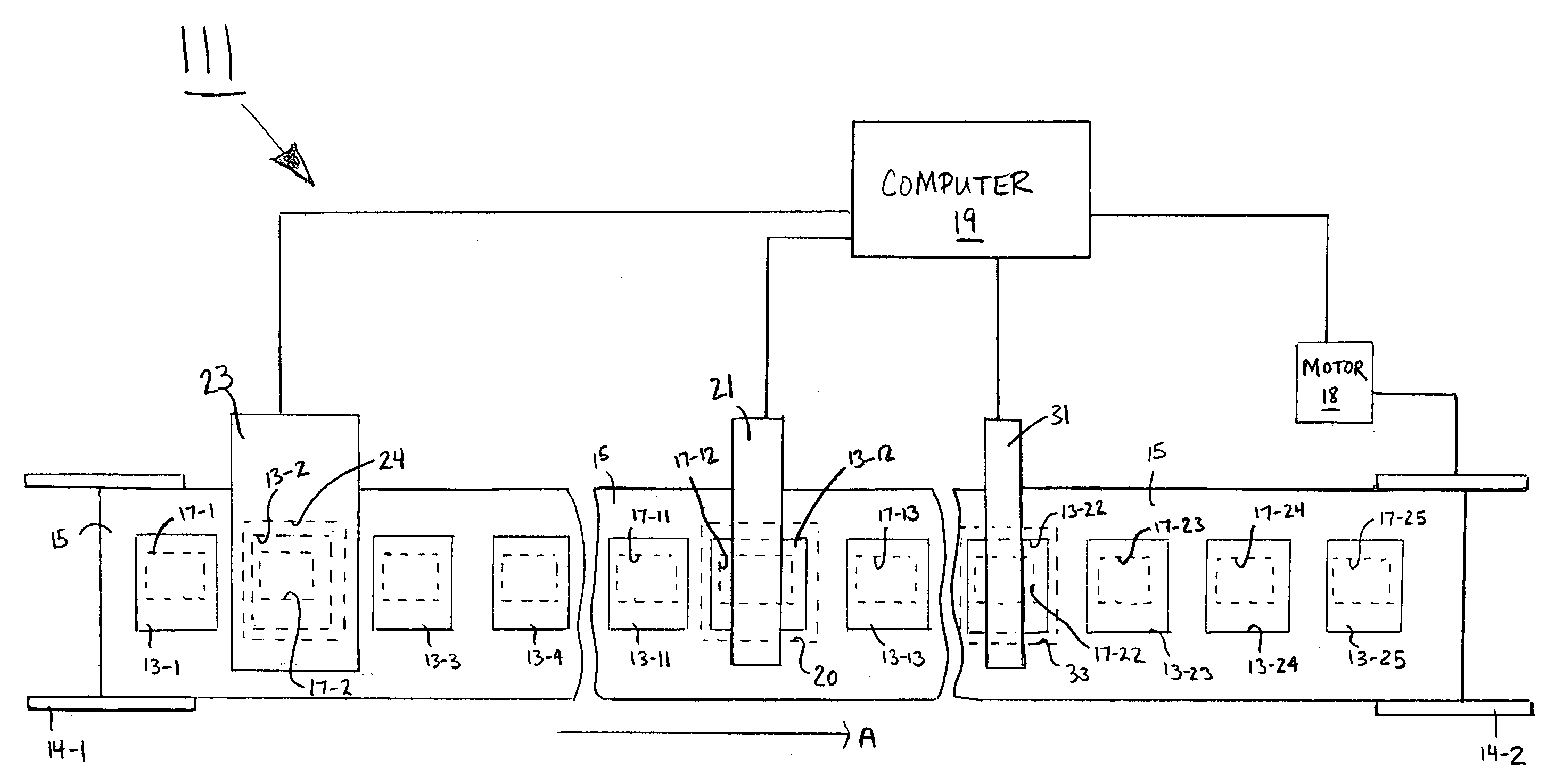
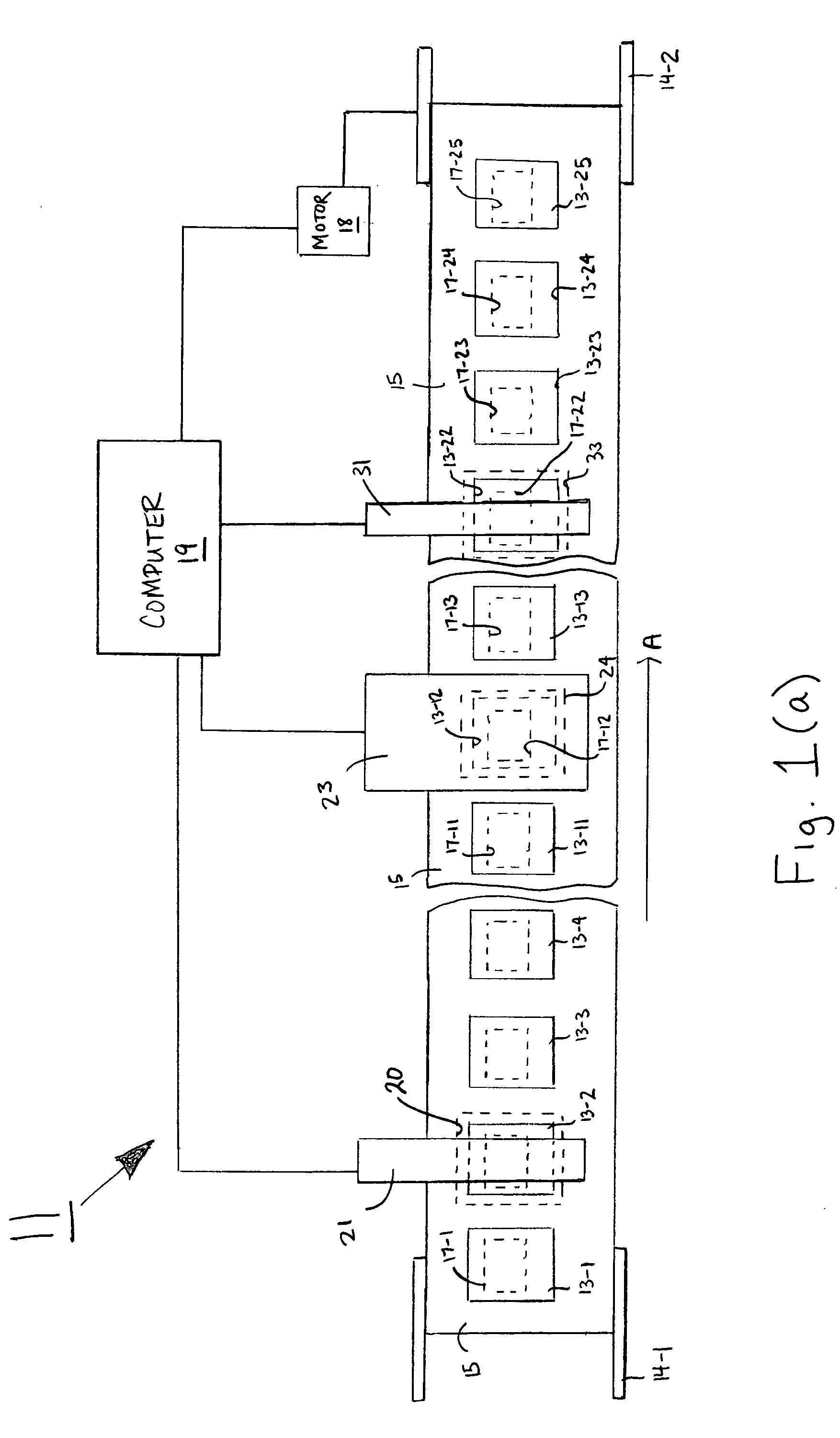
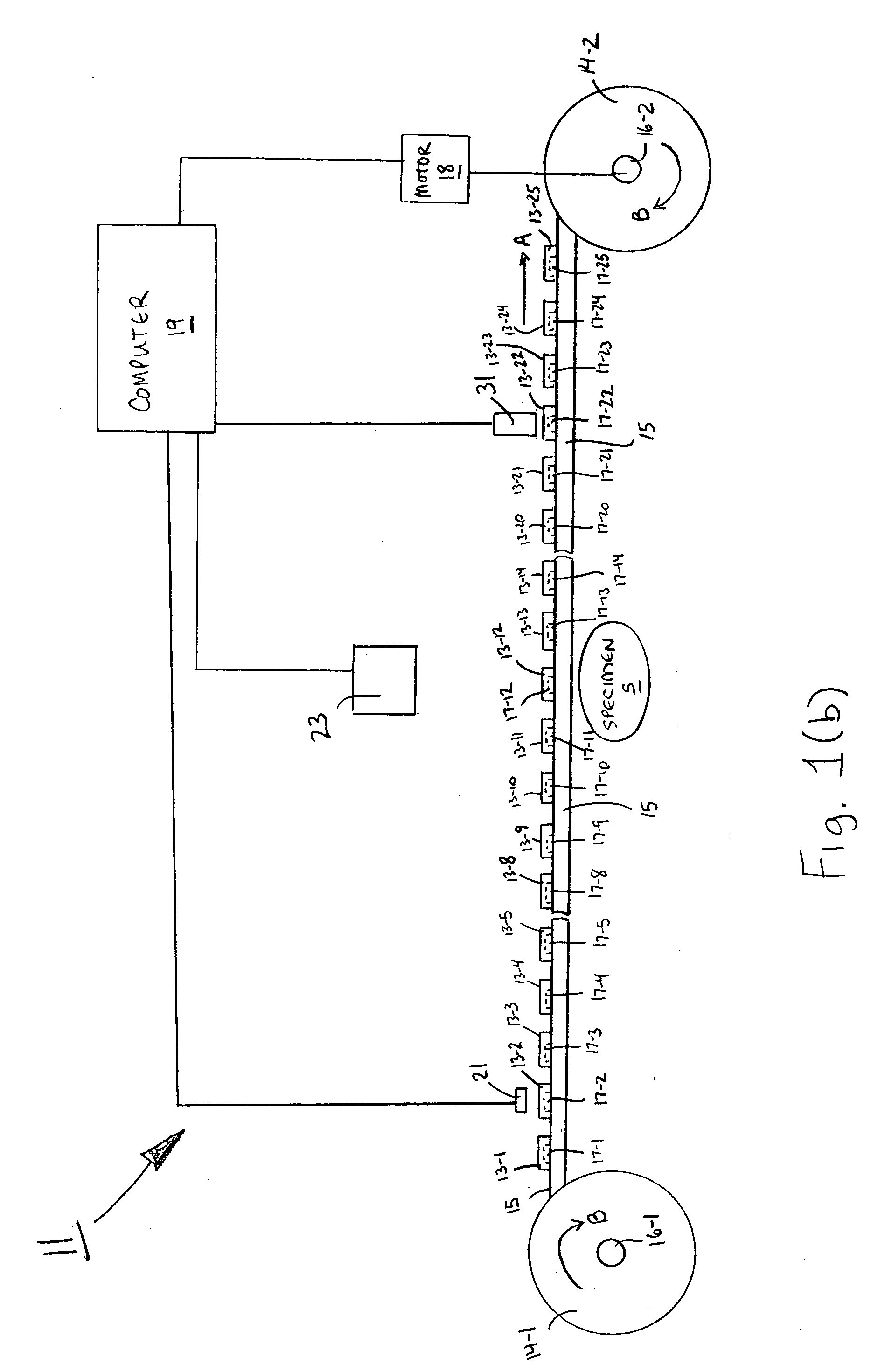
A method and system for testing a plurality of RFID devices disposed on a common carrier. In one embodiment, the RFID devices are evenly spaced along the length of the carrier, and the system comprises a short-range tester, a long-range tester and a computer, the short-range tester being coupled to the computer and having a short-range testing position, the long-range tester being coupled to the computer and having a long-range testing position, the long-range testing position being spaced downstream from the short-range testing position by a known number of device positions. In use, an RFID device of interest is first positioned at the short-range testing position, and the short-range tester reads a unique identifier for that RFID device and communicates the identifier to the computer. The carrier is then advanced so that subsequent RFID devices are read by the short-range tester. When the RFID device of interest has advanced to the long-range testing position, the long-range tester conducts a performance test and communicates any detected results to the computer. Because the distance between the two testing positions is known, the computer knows when the RFID device of interest is at the long-range testing position and uses the identifier to distinguish the results for that device from the results of any other devices.
Owner:AVERY DENNISON CORP
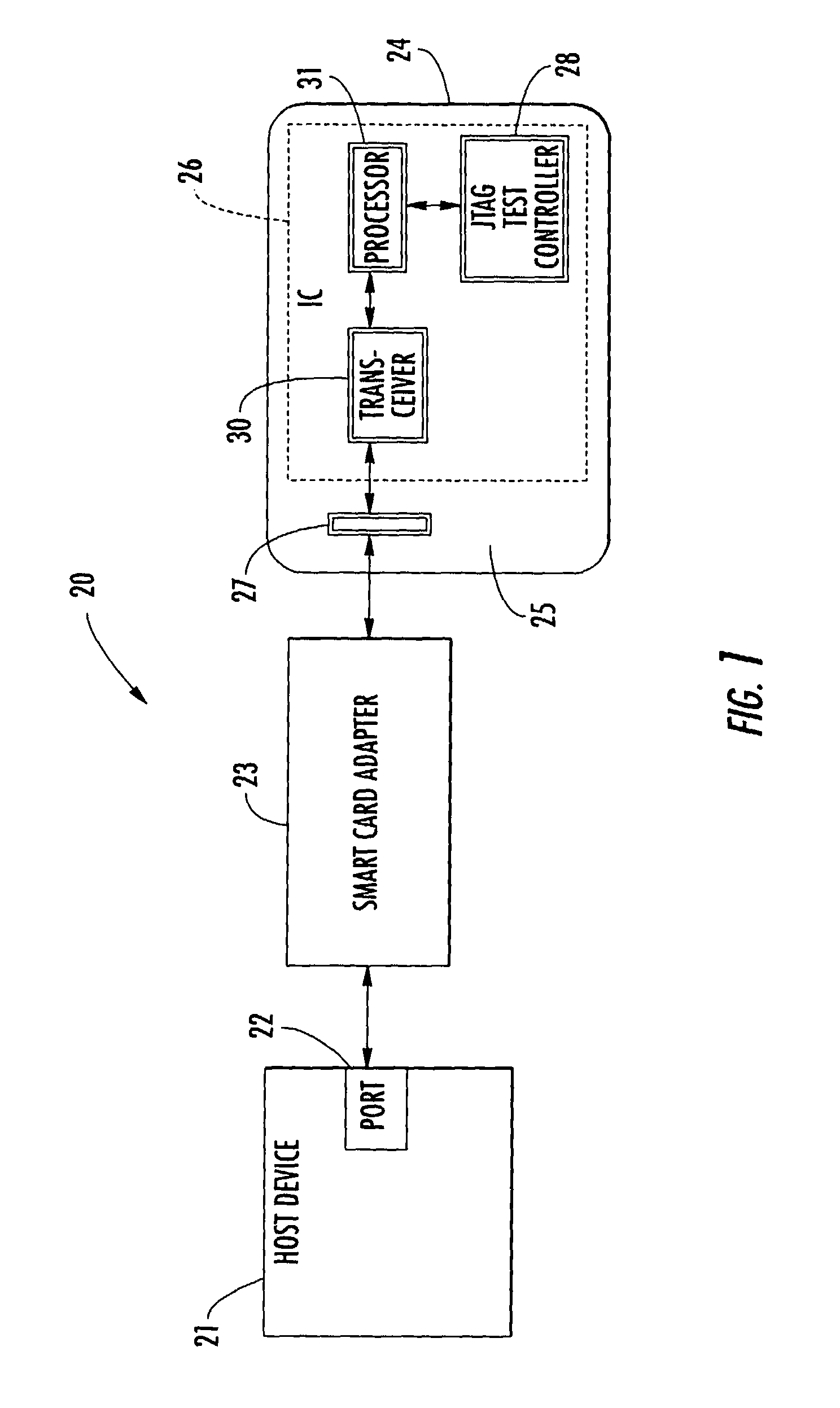
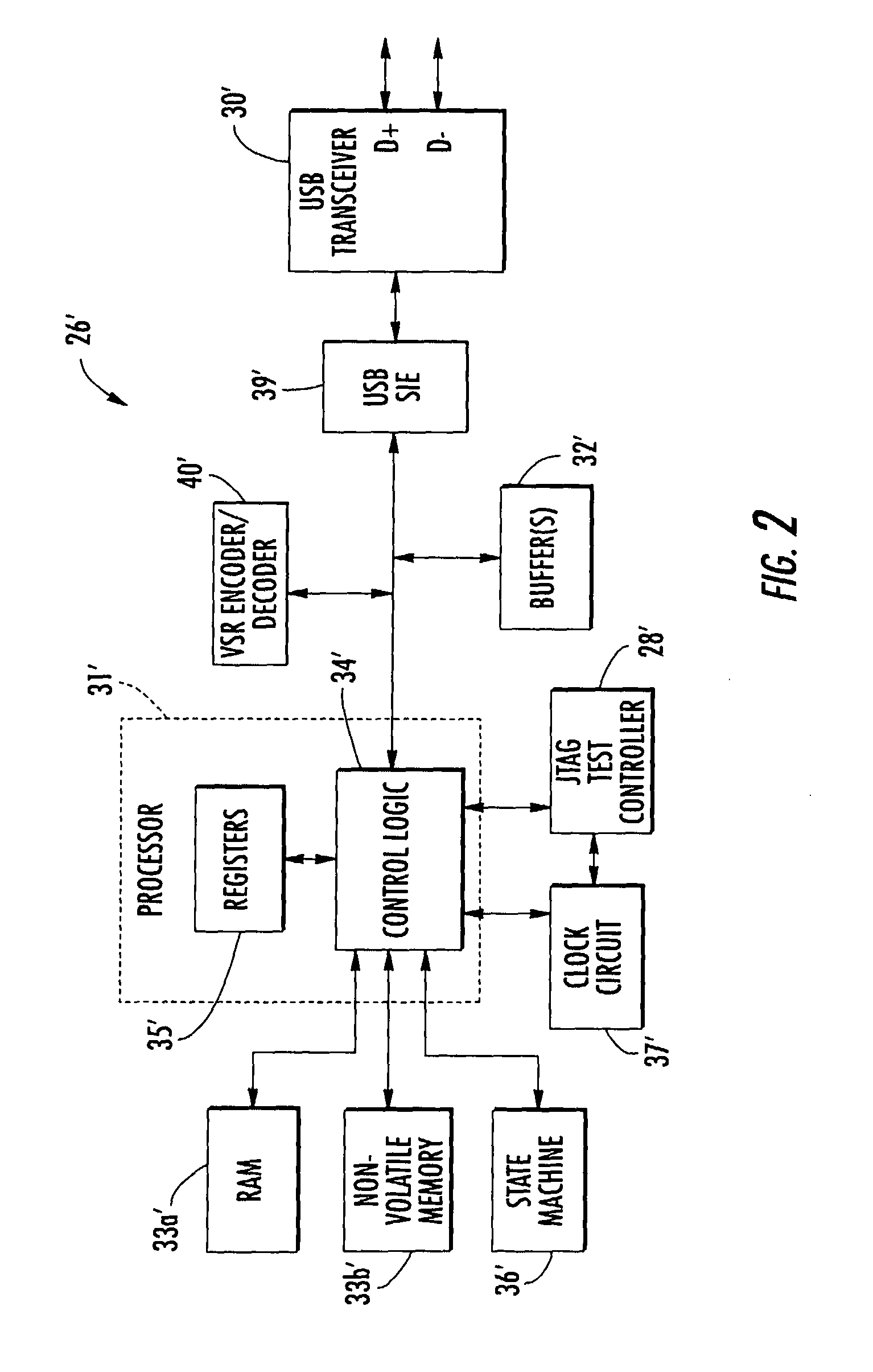
Smart card including a JTAG test controller and related methods
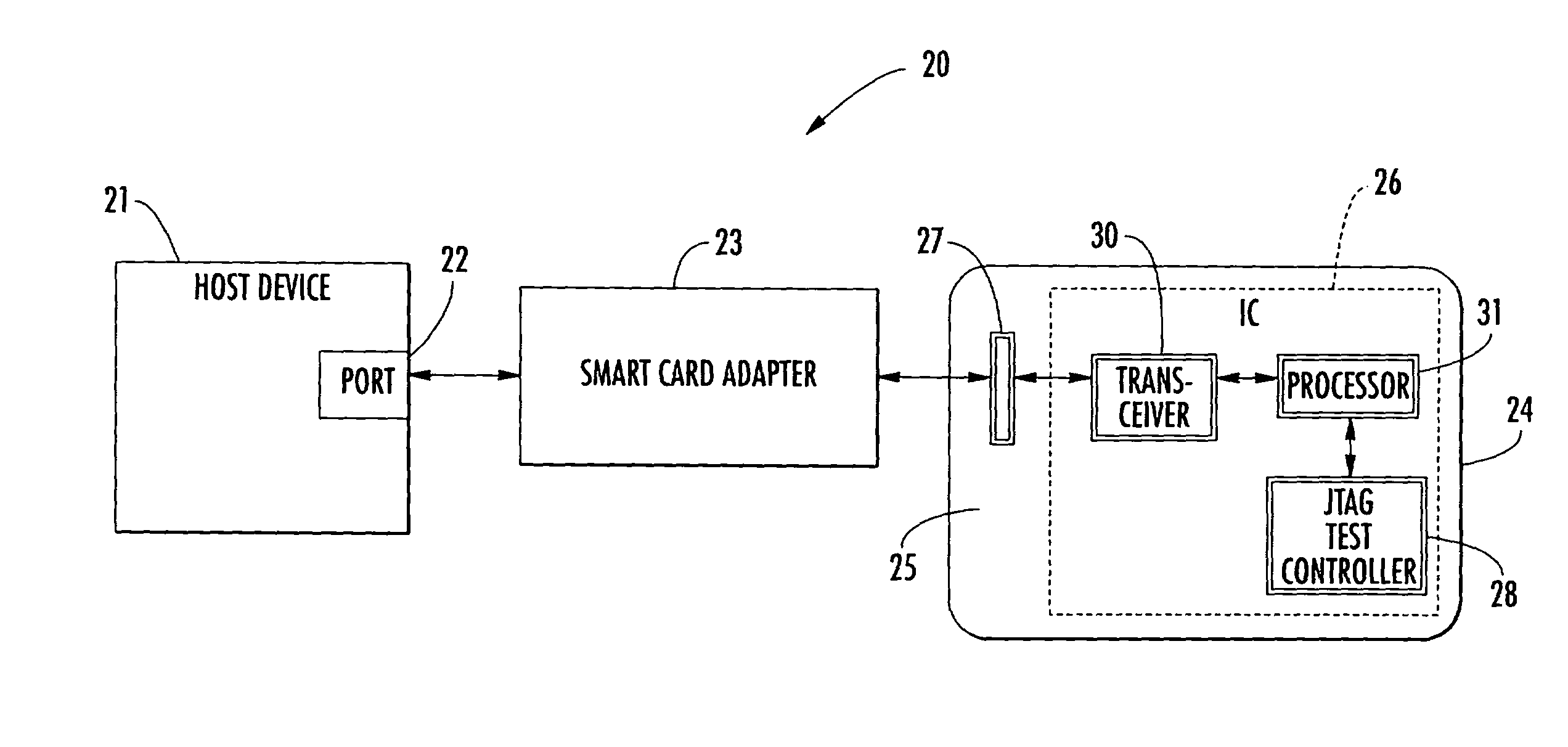
ActiveUS7080789B2Meet growth requirementsTesting sensing arrangementsError preventionTransceiverTest requirements
An integrated circuit for a smart card may include a transceiver for communicating with a host device and a Joint Test Action Group (JTAG) test controller for performing at least one test operation. Further, the integrated circuit may also include a processor for causing the JTAG test controller to initiate the at least one test operation based upon receiving at least one test request from the host device via the transceiver. More particularly, the processor may convert the at least one test request to JTAG data for the JTAG test controller. That is, the integrated circuit advantageously allows communications between the host device and the JTAG controller via a system bus, for example, without the need for a dedicated JTAG test access port (TAP) which is typically required for accessing JTAG controllers.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
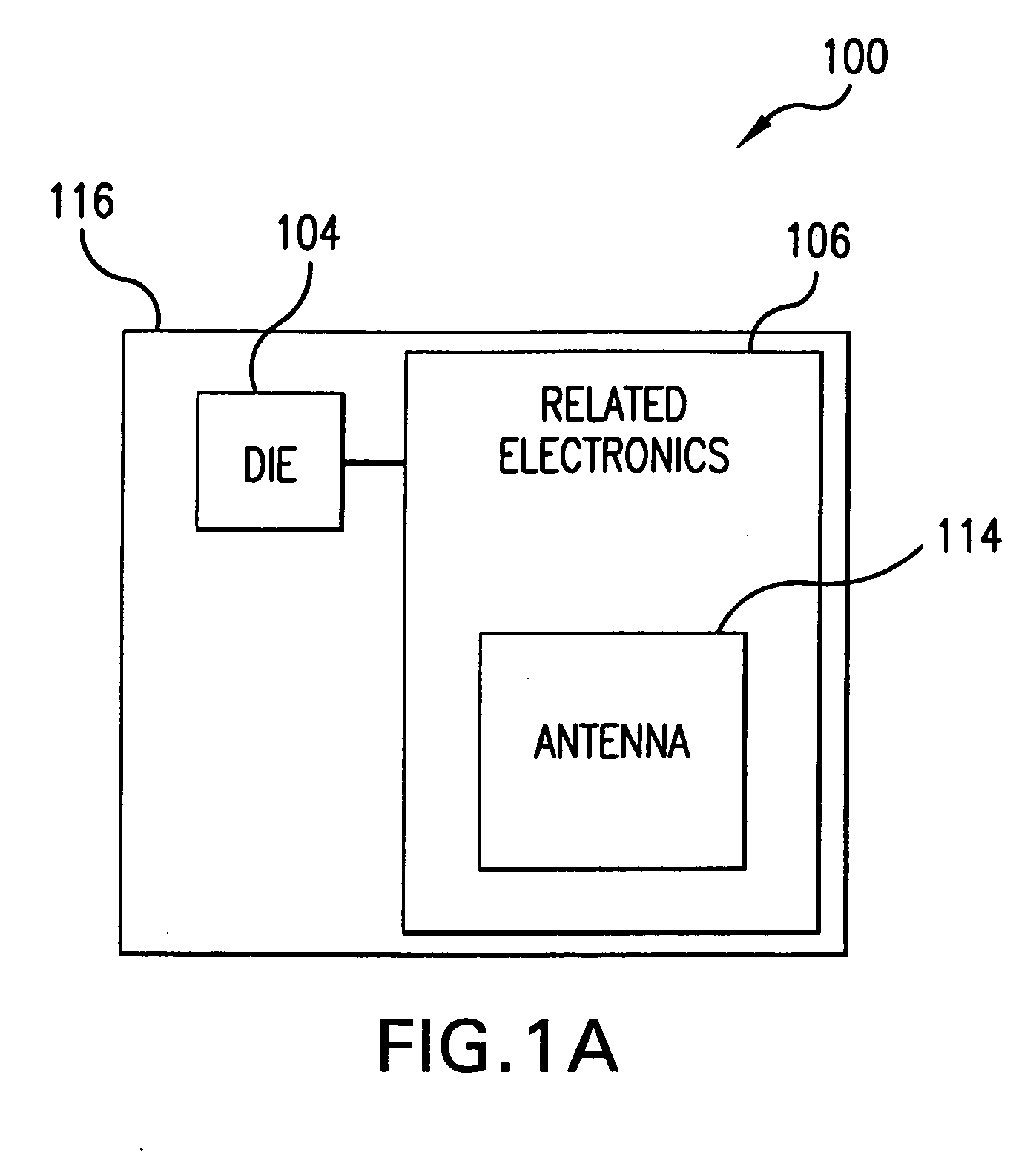
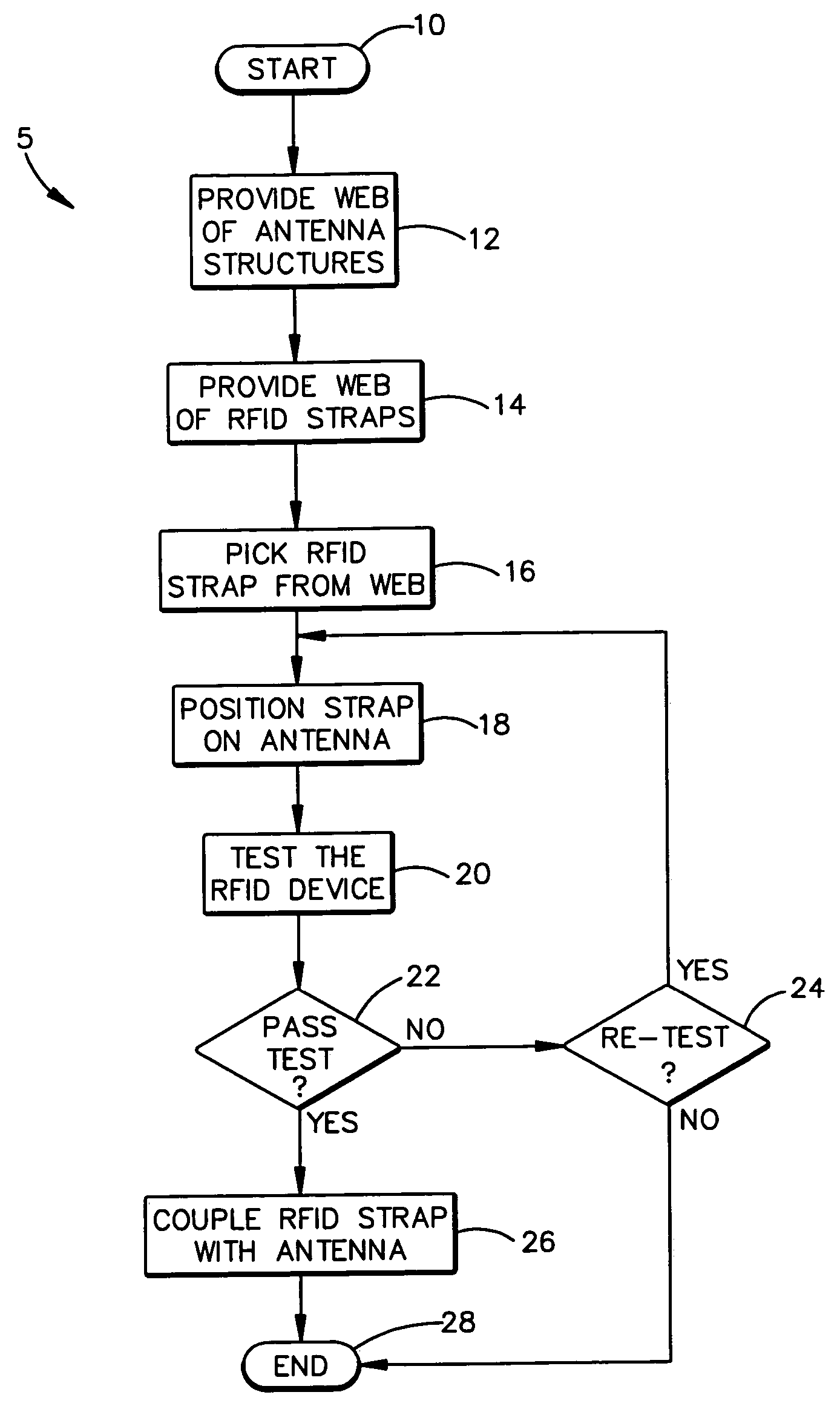
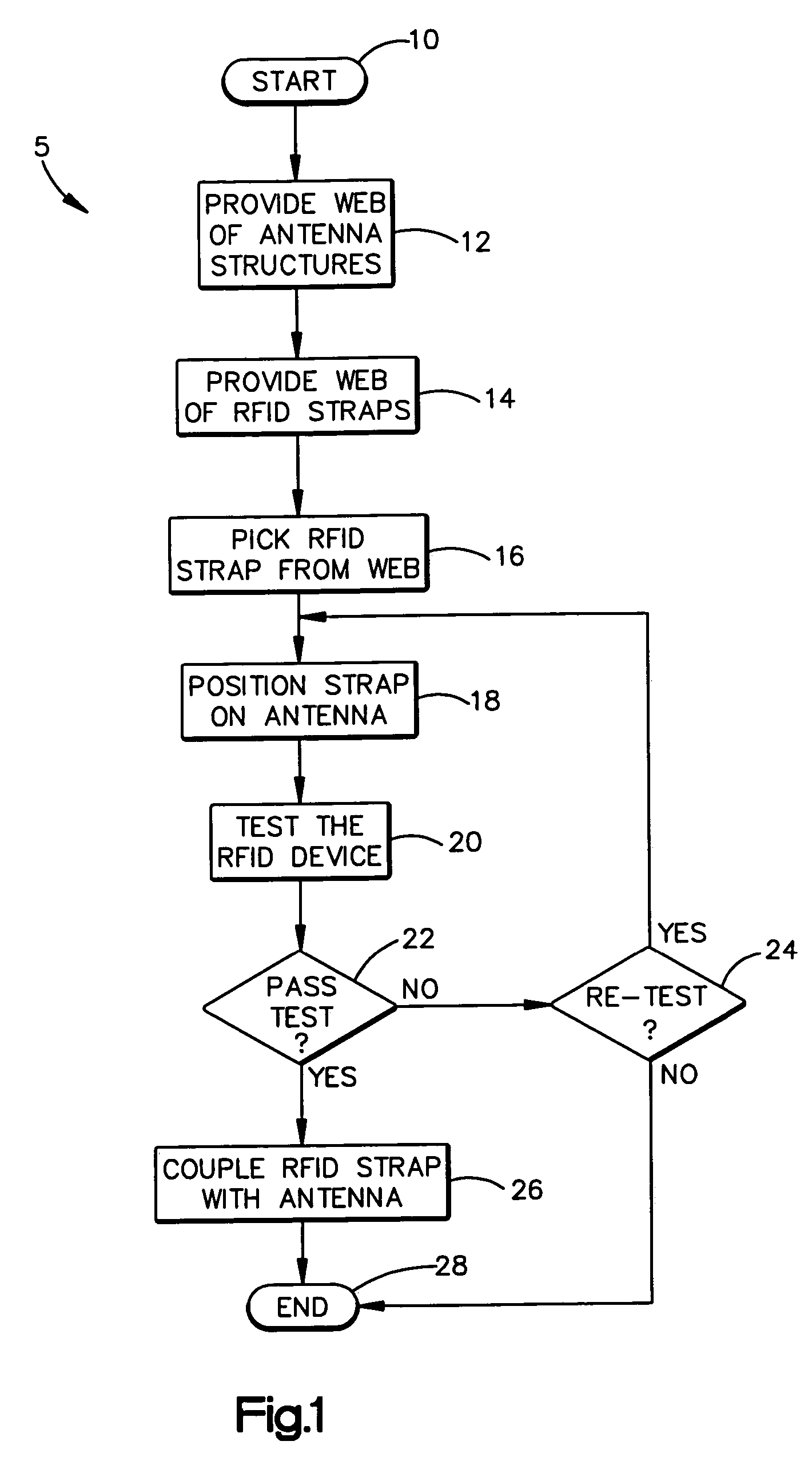
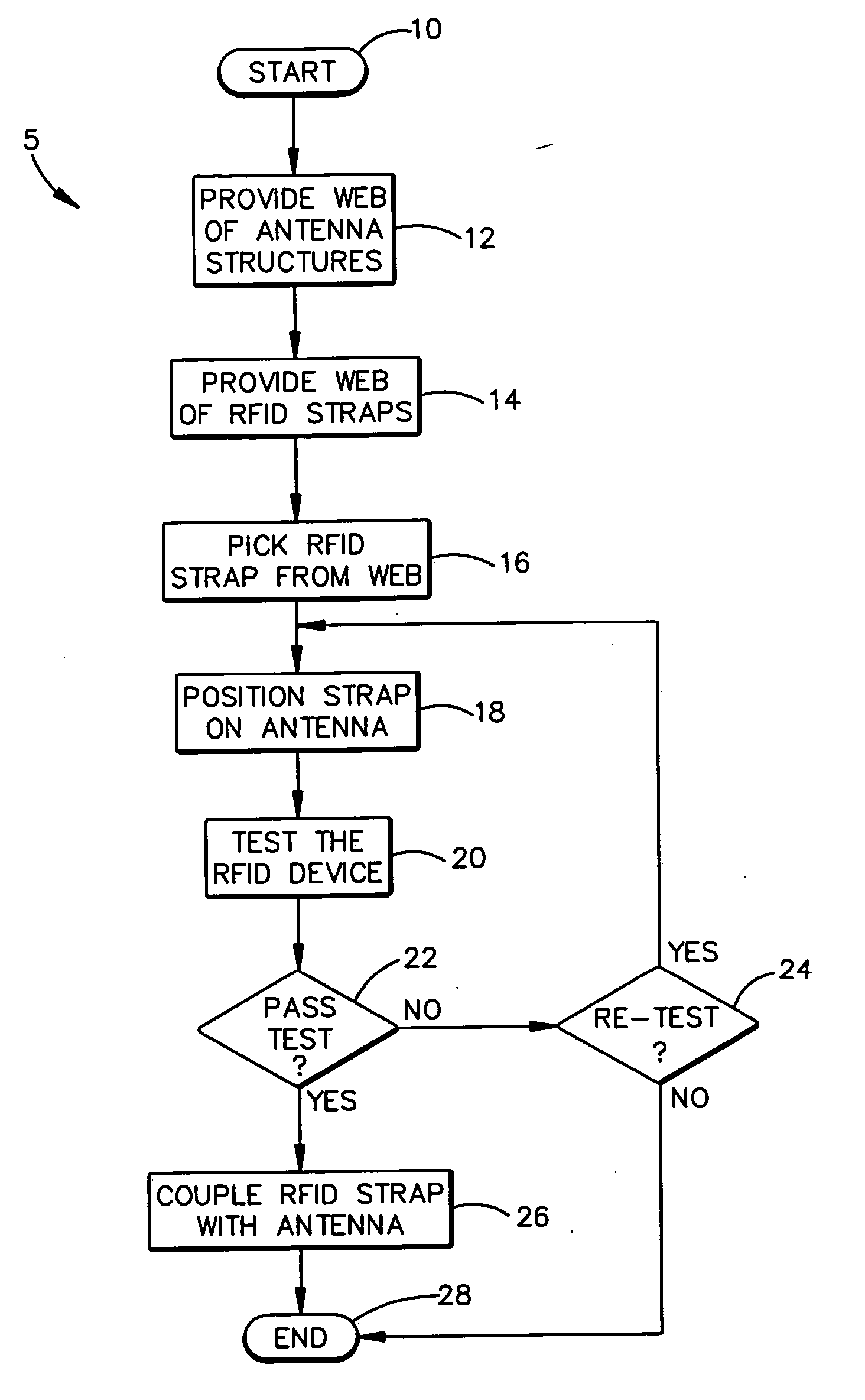
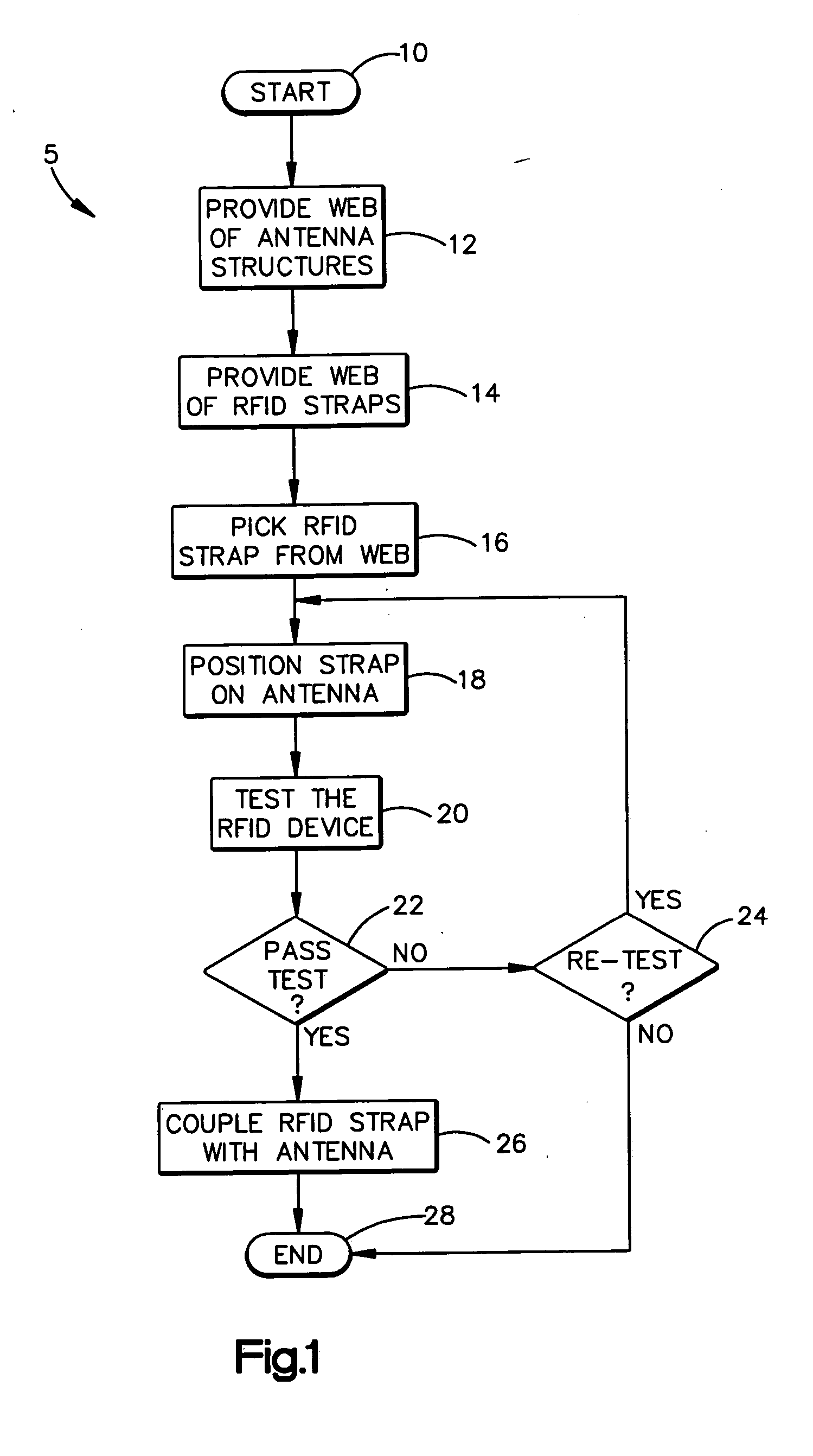
Method of variable position strap mounting for RFID transponder
ActiveUS7292148B2Simultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsEngineeringElectrical and Electronics engineering
A method of coupling an RFID chip to an antenna includes the steps of, iteratively until a test criterion is met, positioning an RFID chip relative to an antenna and testing the RFID chip and antenna. Once the test criterion is met, the RFID chip is coupled with the antenna. A method of coupling an RFID chip to one of a plurality of various antennas is also provided. A method of coupling an RFID chip to an antenna on an object is also provided.
Owner:AVERY DENNISON CORP
Method and system for testing RFID devices
ActiveUS7164353B2Testing sensing arrangementsMemory record carrier reading problemsTester deviceCommon carrier
A method and system for testing a plurality of RFID devices disposed on a common carrier. In one embodiment, the RFID devices are evenly spaced along the length of the carrier, and the system comprises a short-range tester, a long-range tester and a computer, the short-range tester being coupled to the computer and having a short-range testing position, the long-range tester being coupled to the computer and having a long-range testing position, the long-range testing position being spaced downstream from the short-range testing position by a known number of device positions. In use, an RFID device of interest is first positioned at the short-range testing position, and the short-range tester reads a unique identifier for that RFID device and communicates the identifier to the computer. The carrier is then advanced so that subsequent RFID devices are read by the short-range tester. When the RFID device of interest has advanced to the long-range testing position, the long-range tester conducts a performance test and communicates any detected results to the computer. Because the distance between the two testing positions is known, the computer knows when the RFID device of interest is at the long-range testing position and uses the identifier to distinguish the results for that device from the results of any other devices.
Owner:AVERY DENNISON CORP
Method of variable position strap mounting for RFID transponder
ActiveUS20050282495A1Near-field transmissionRadiating elements structural formsEngineeringElectrical and Electronics engineering
A method of coupling an RFID chip to an antenna includes the steps of, iteratively until a test criterion is met, positioning an RFID chip relative to an antenna and testing the RFID chip and antenna. Once the test criterion is met, the RFID chip is coupled with the antenna. A method of coupling an RFID chip to one of a plurality of various antennas is also provided. A method of coupling an RFID chip to an antenna on an object is also provided.
Owner:AVERY DENNISON CORP
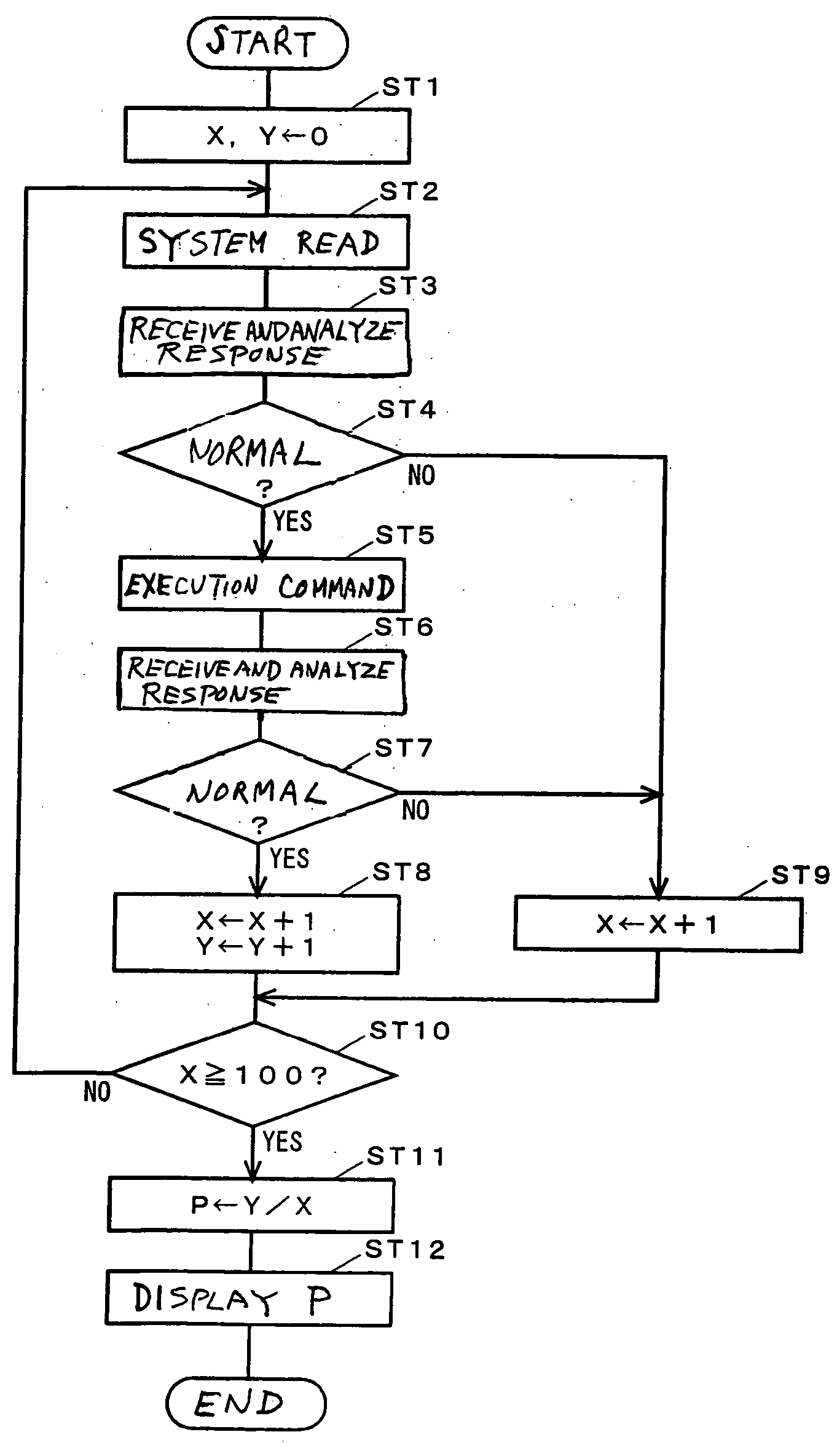
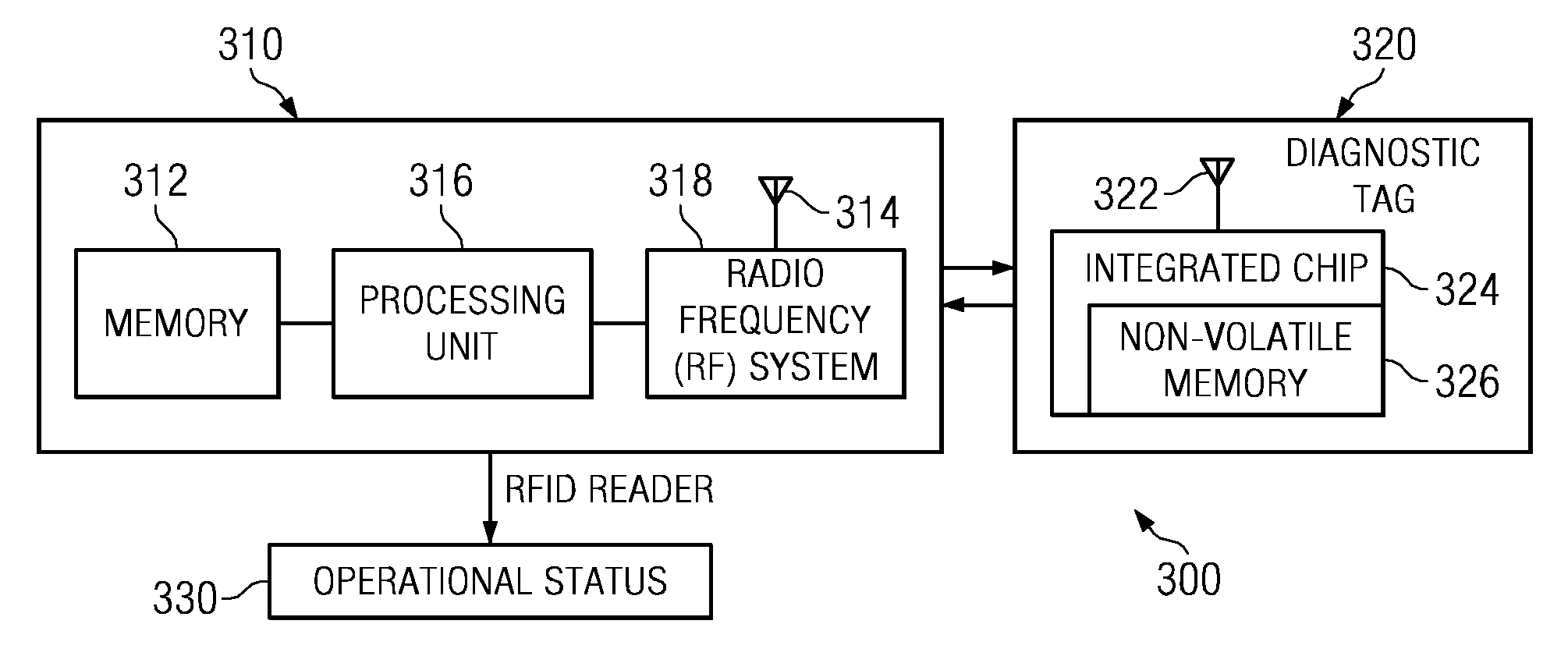
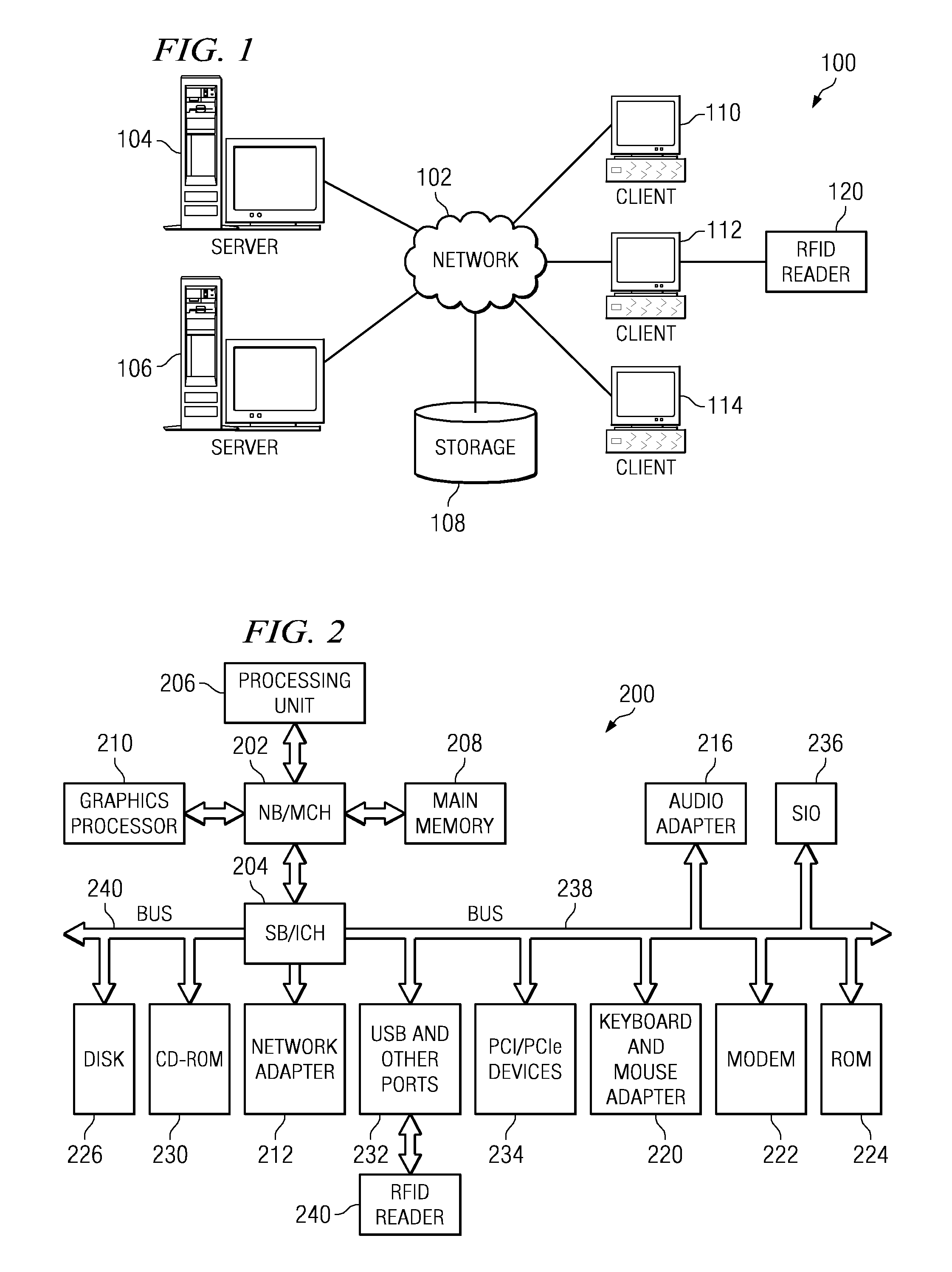
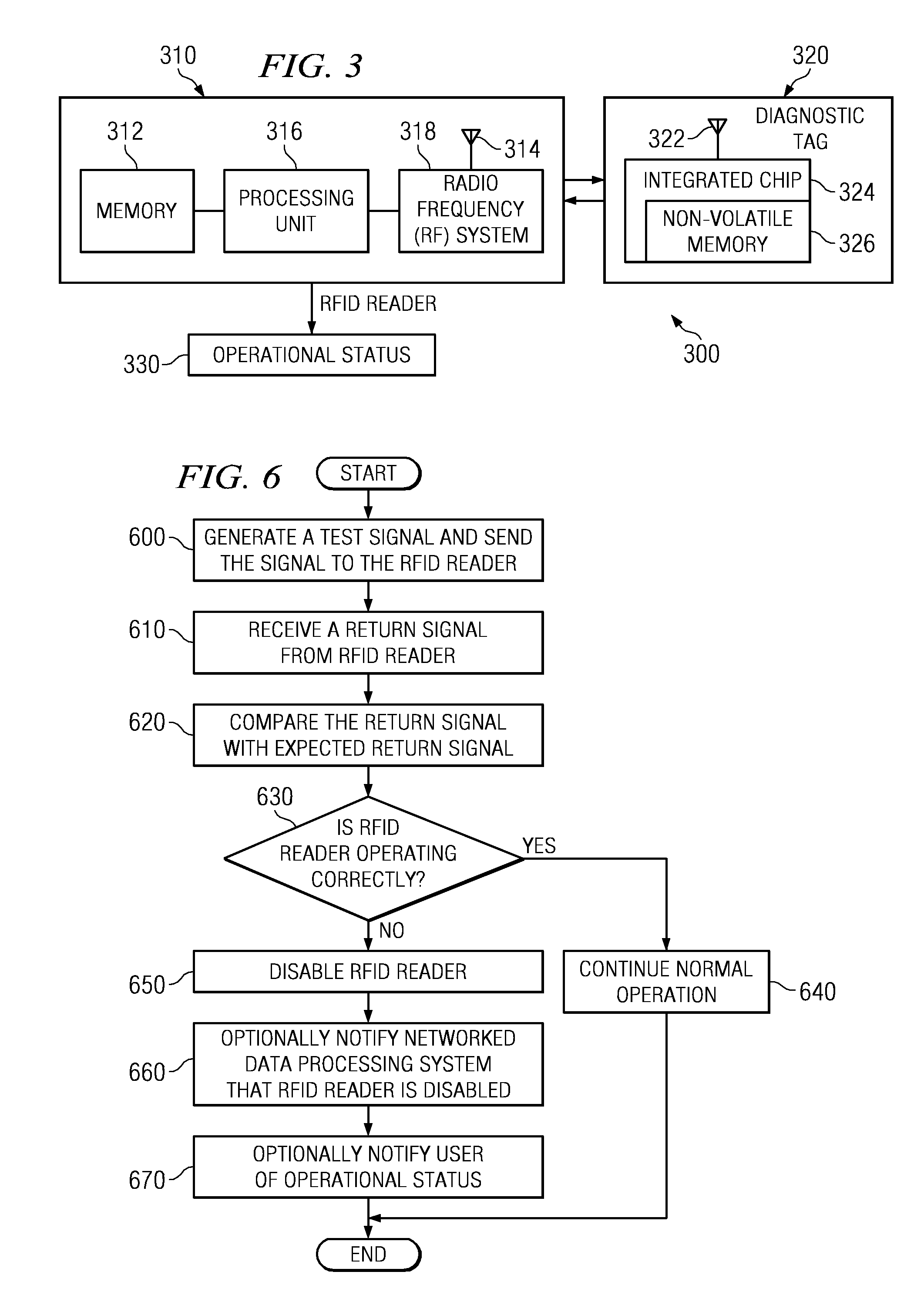
Diagnosing a radio frequency identification reader
The illustrative embodiments provide a computer implemented method, an apparatus, and a computer program product for testing a radio frequency identification reader. The radio frequency identification reader transmits a test signal to a diagnostic tag during a diagnostic period. Responsive to receiving a return signal from the diagnostic tag, the radio frequency identification reader compares the return signal with an expected return signal to form a comparison. The radio frequency identification reader identifies an operational status for the radio frequency identification reader using the comparison.
Owner:TOSHIBA GLOBAL COMMERCE SOLUTIONS HLDG
RFID device tester and method
InactiveUS7306162B2Ticket-issuing apparatusTesting sensing arrangementsCapacitanceCapacitive coupling
Owner:AVERY DENNISON CORP
System for testing, verifying legitimacy of smart card in-situ and for storing data therein
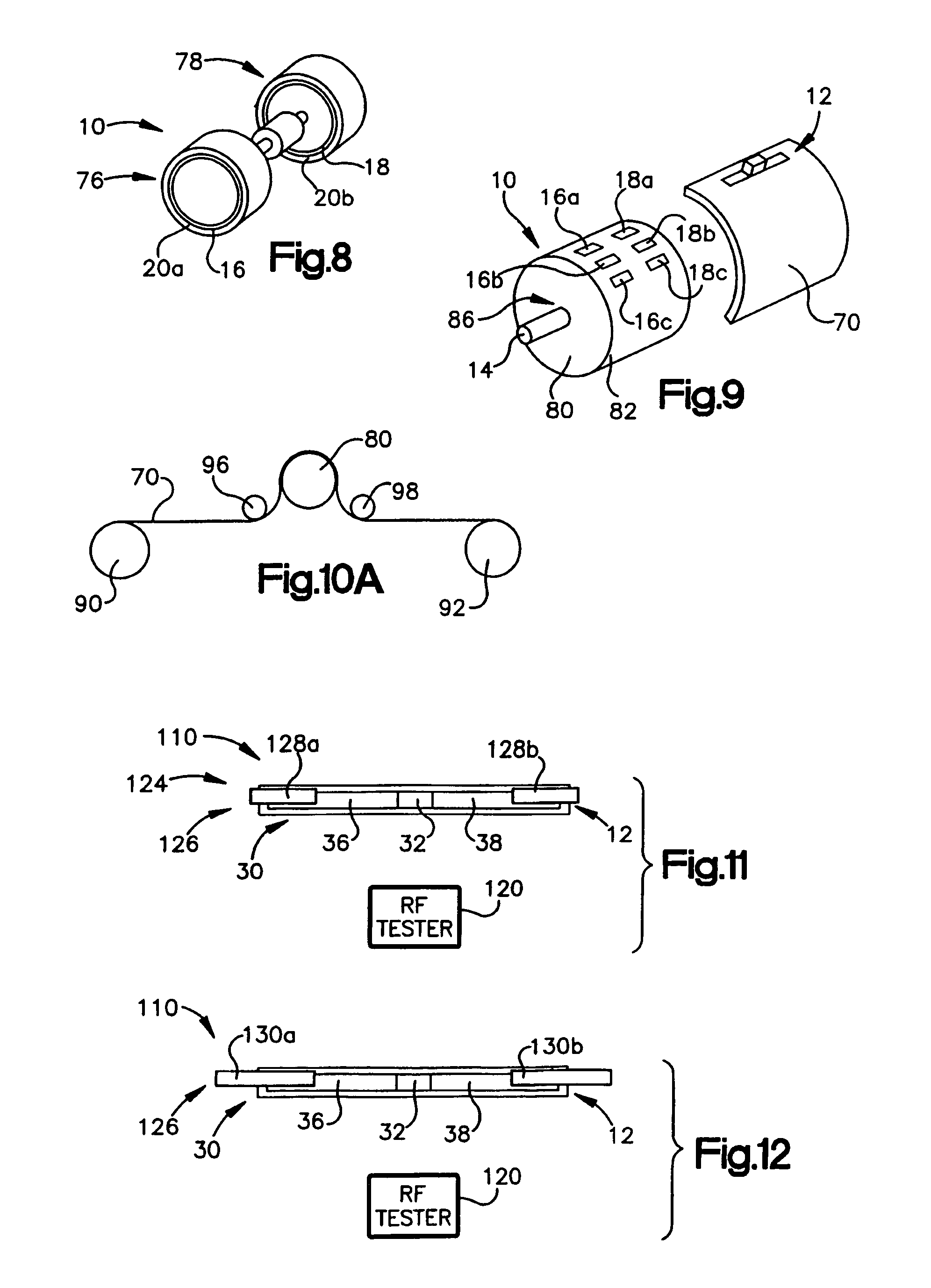
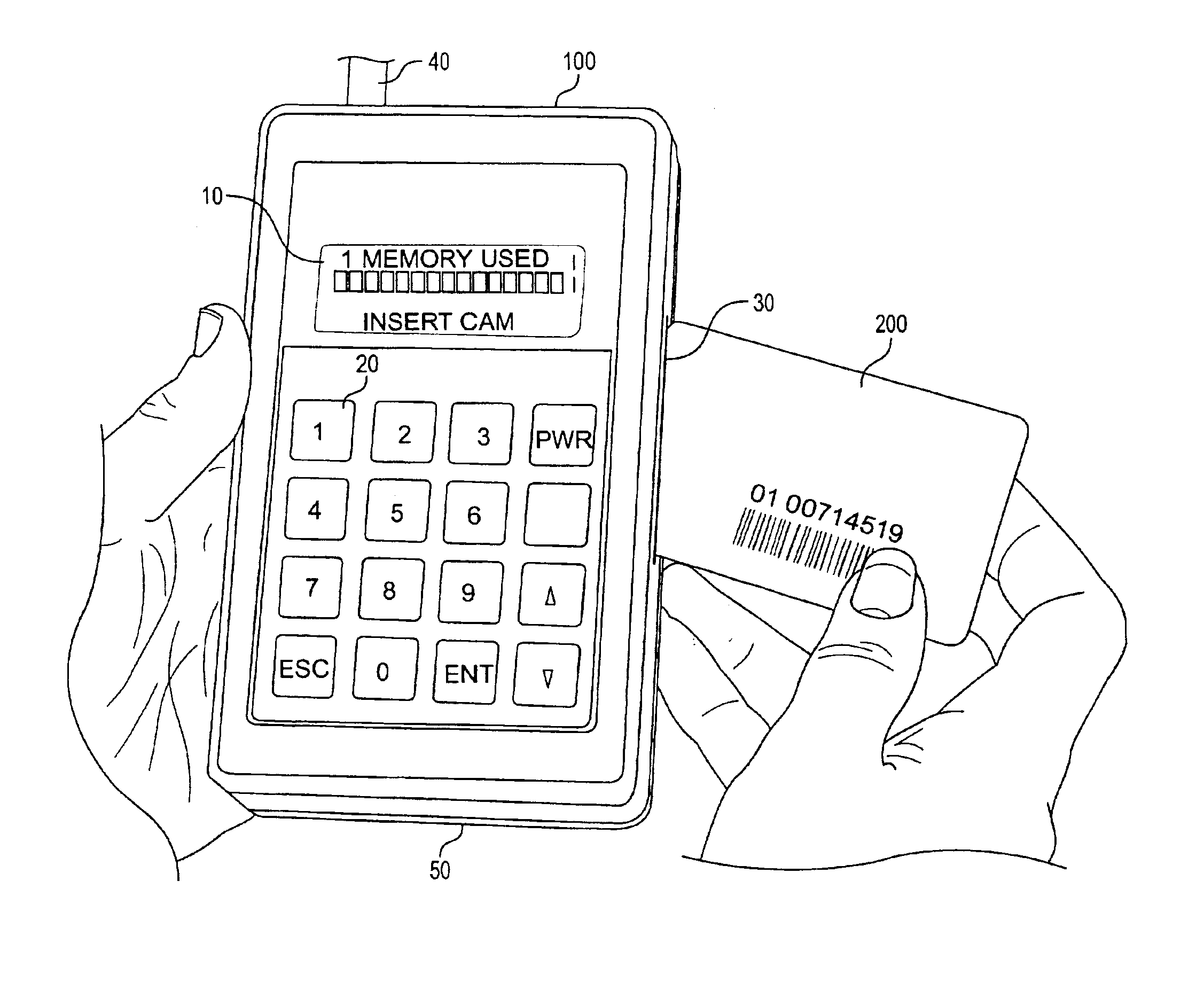
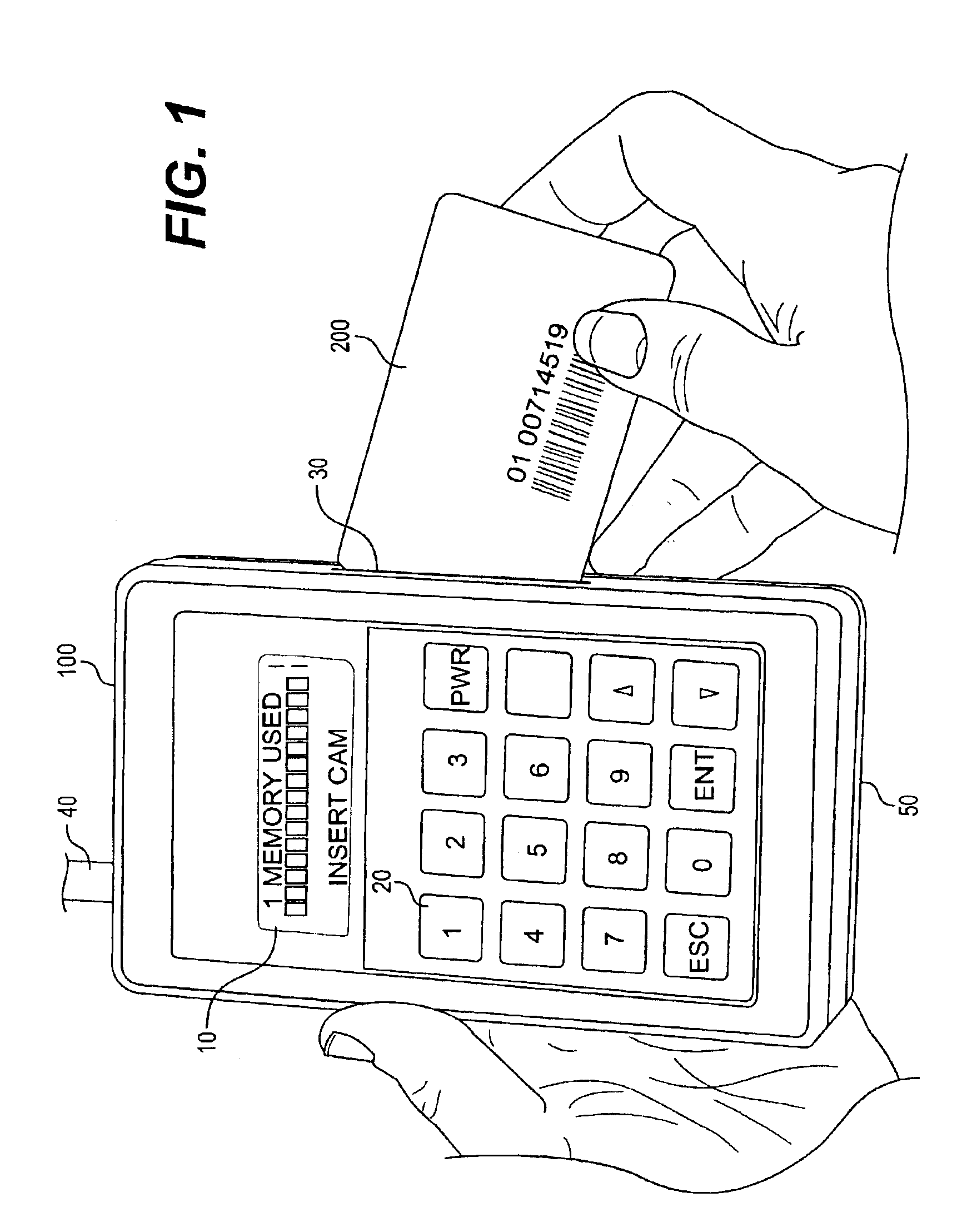
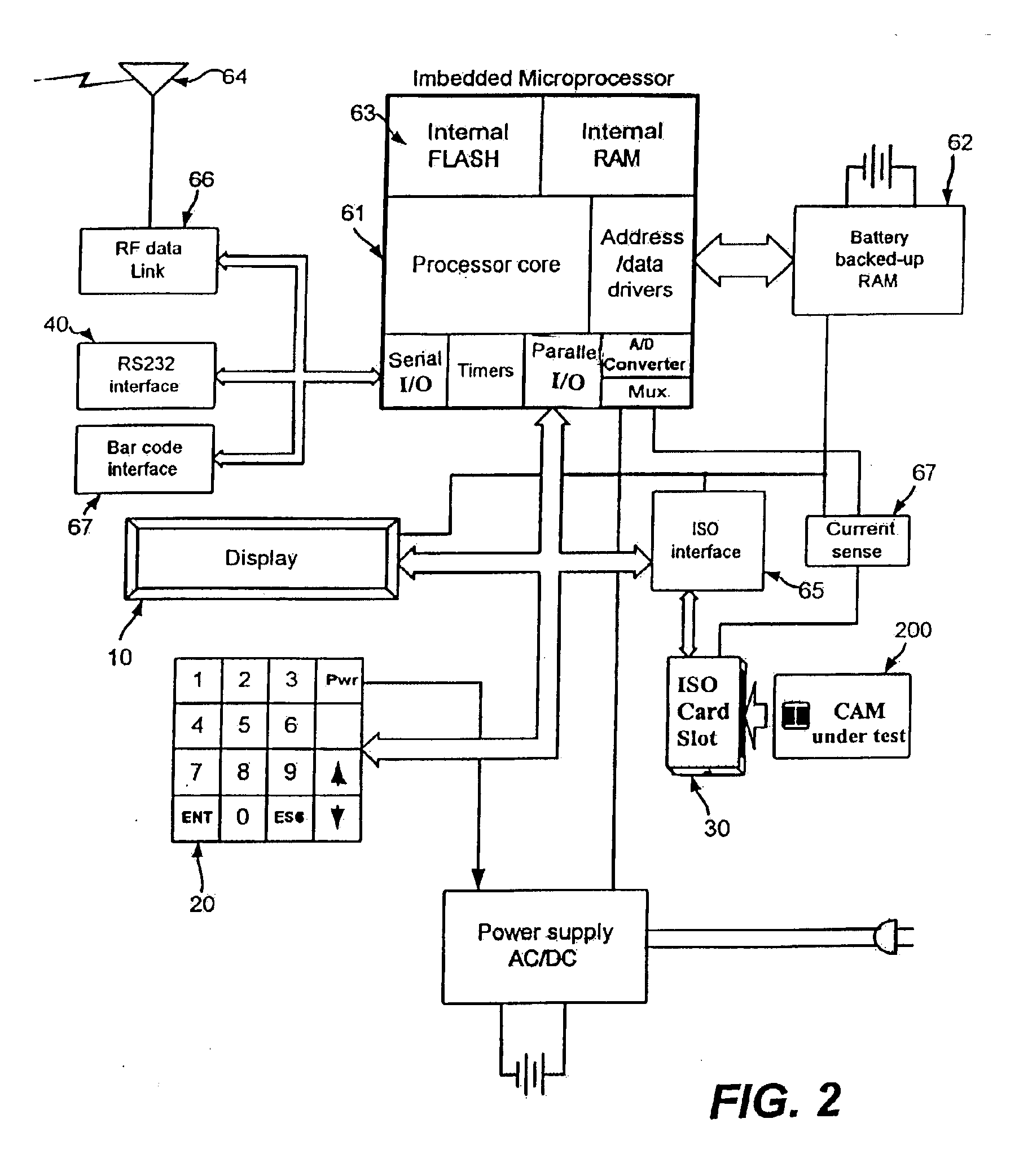
A hand-held battery-operated device for interrogating and / or programming ISO7816 smart cards by means of an ISO7816 compliant card slot, in conjunction with a display, a keypad and barcode reader for data entry, a battery backup RAM for temporary storage of collected data, flash memory for storage of proprietary information provided by a smart card issuer, a RS232 port and RF link for communication with a host computer, in-system programming port for updating the flash program, all connected operatively to an internal microprocessor which perform clock or power glitching to access internal information of a smart card to determine whether the card has been tampered, compromised, and functionality.
Owner:NDS
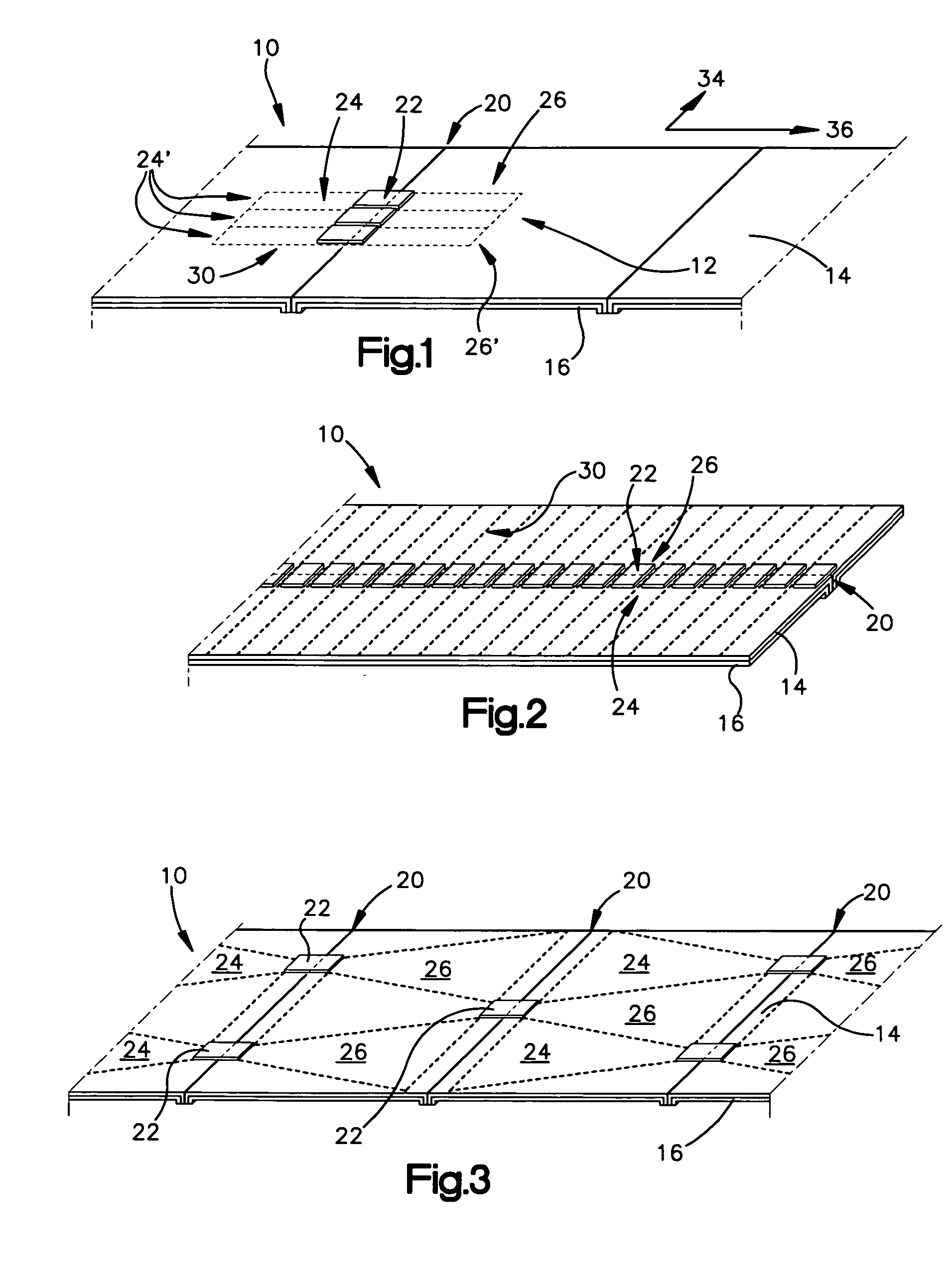
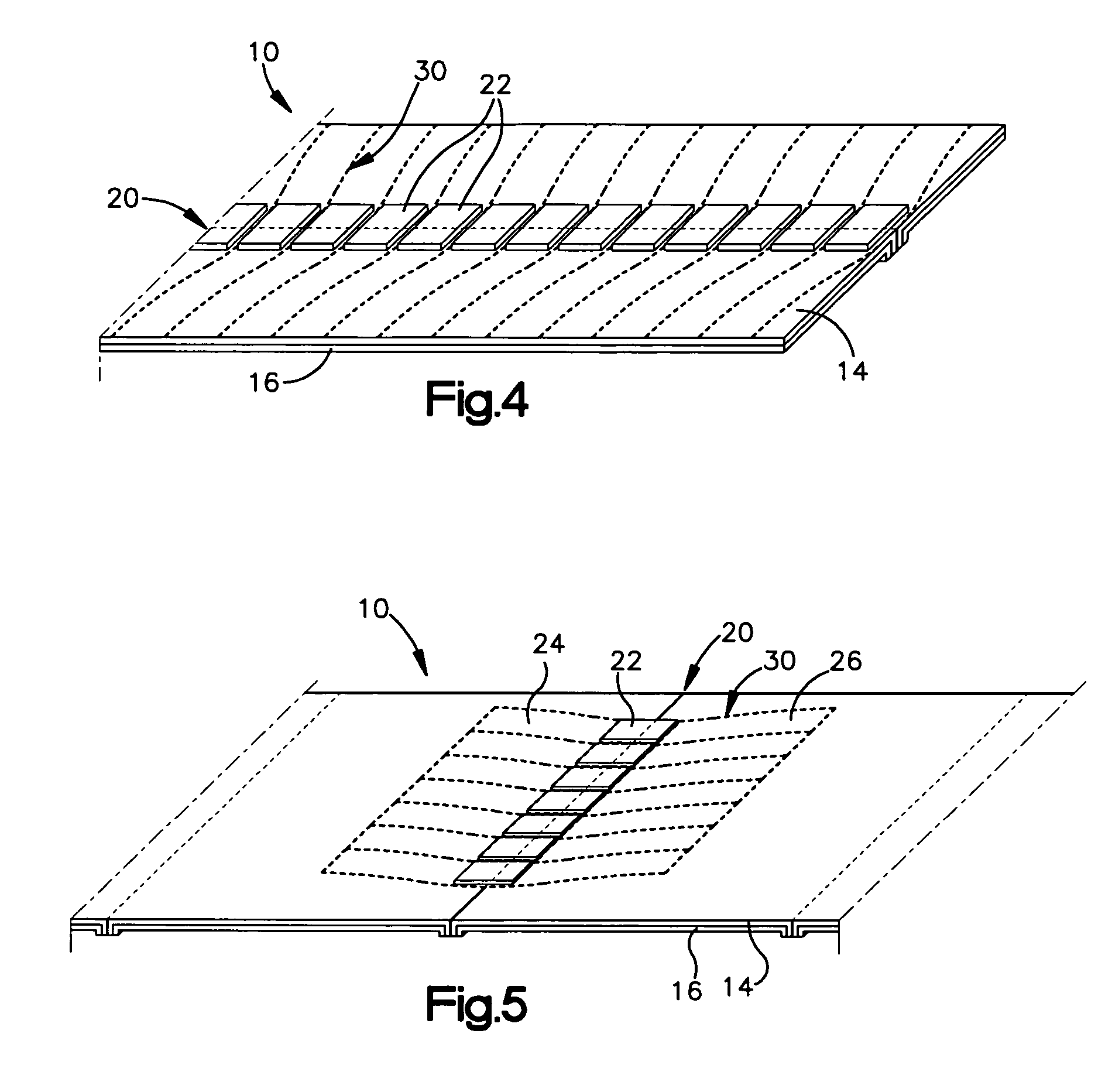
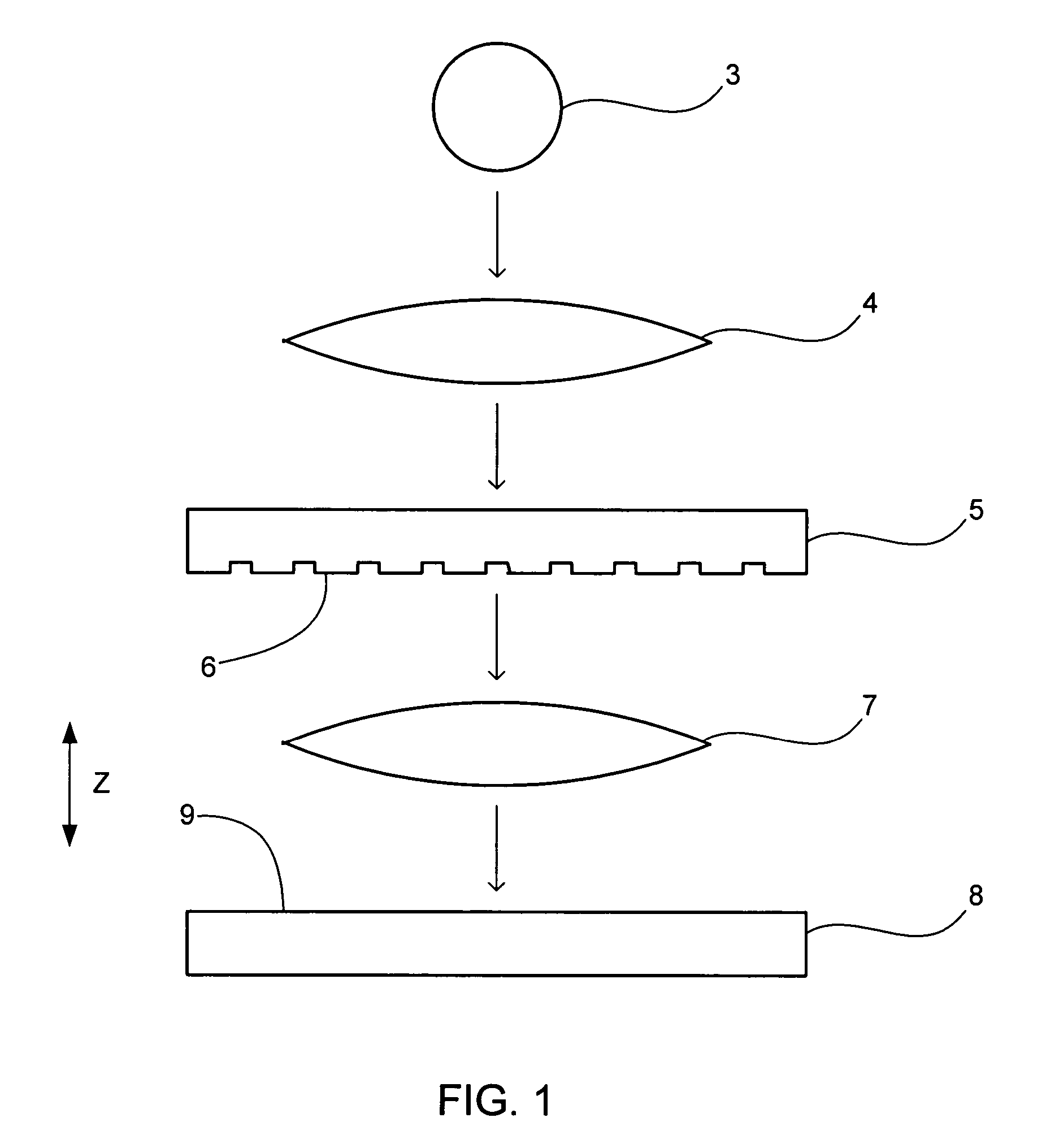
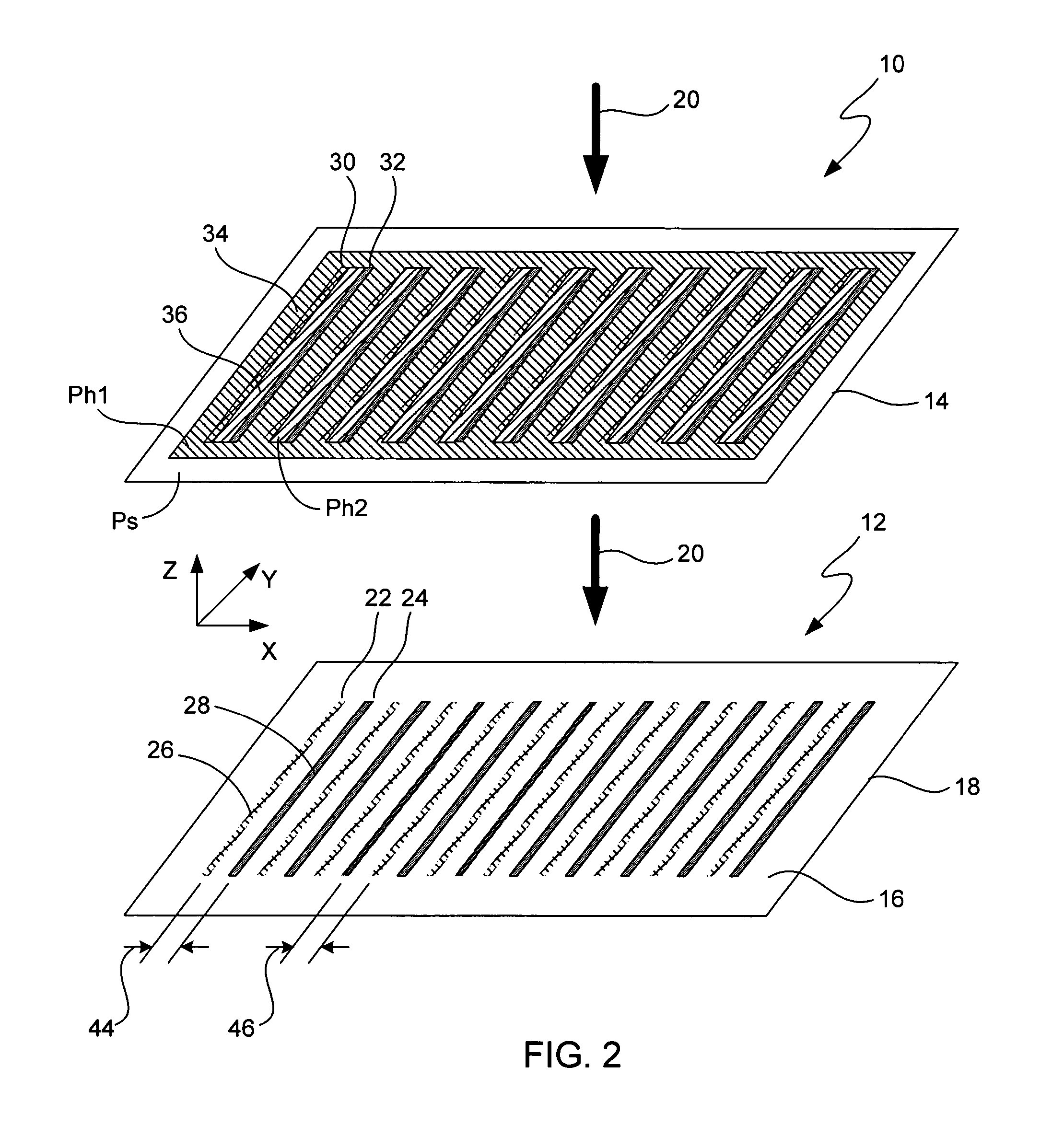
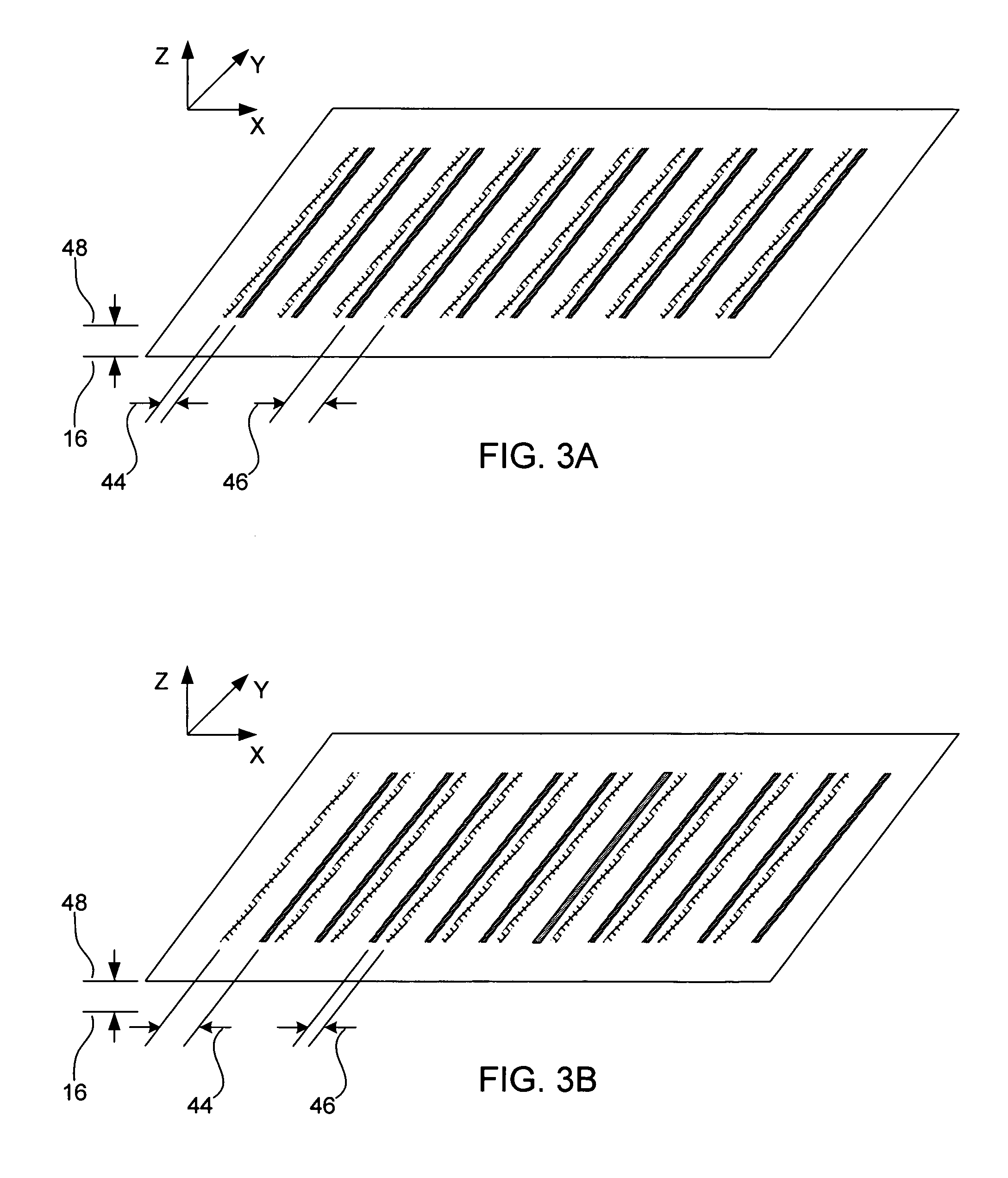
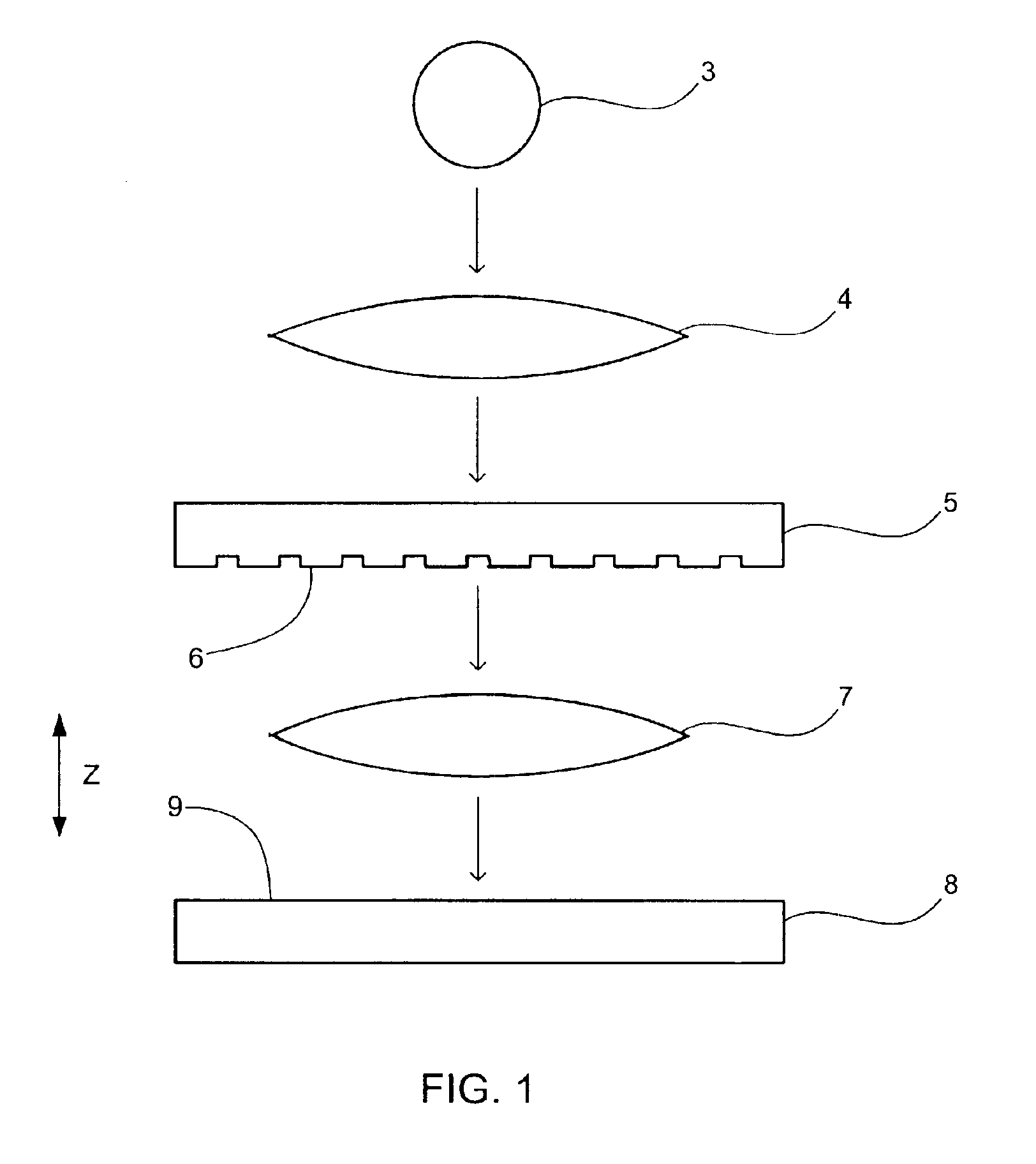
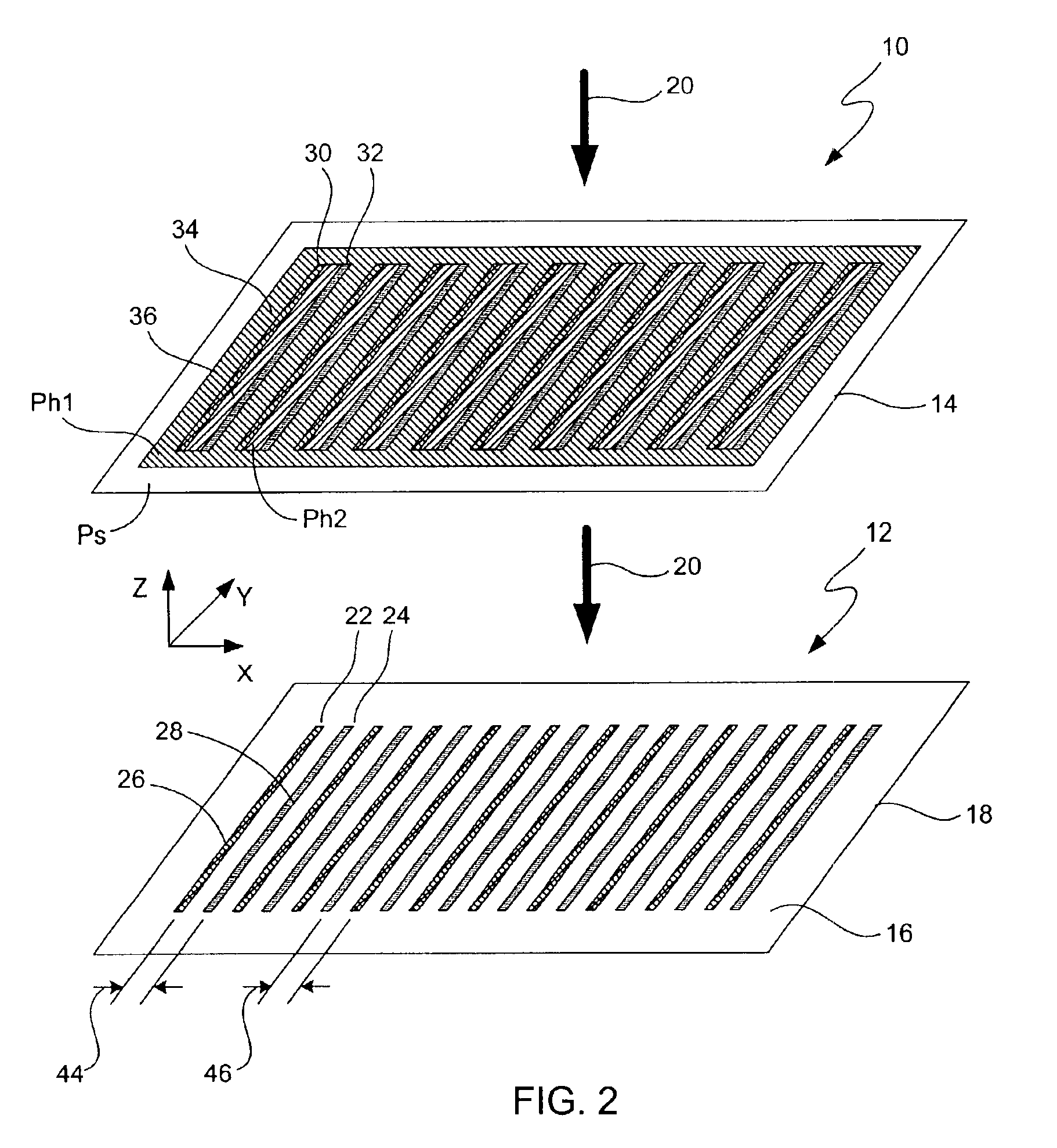
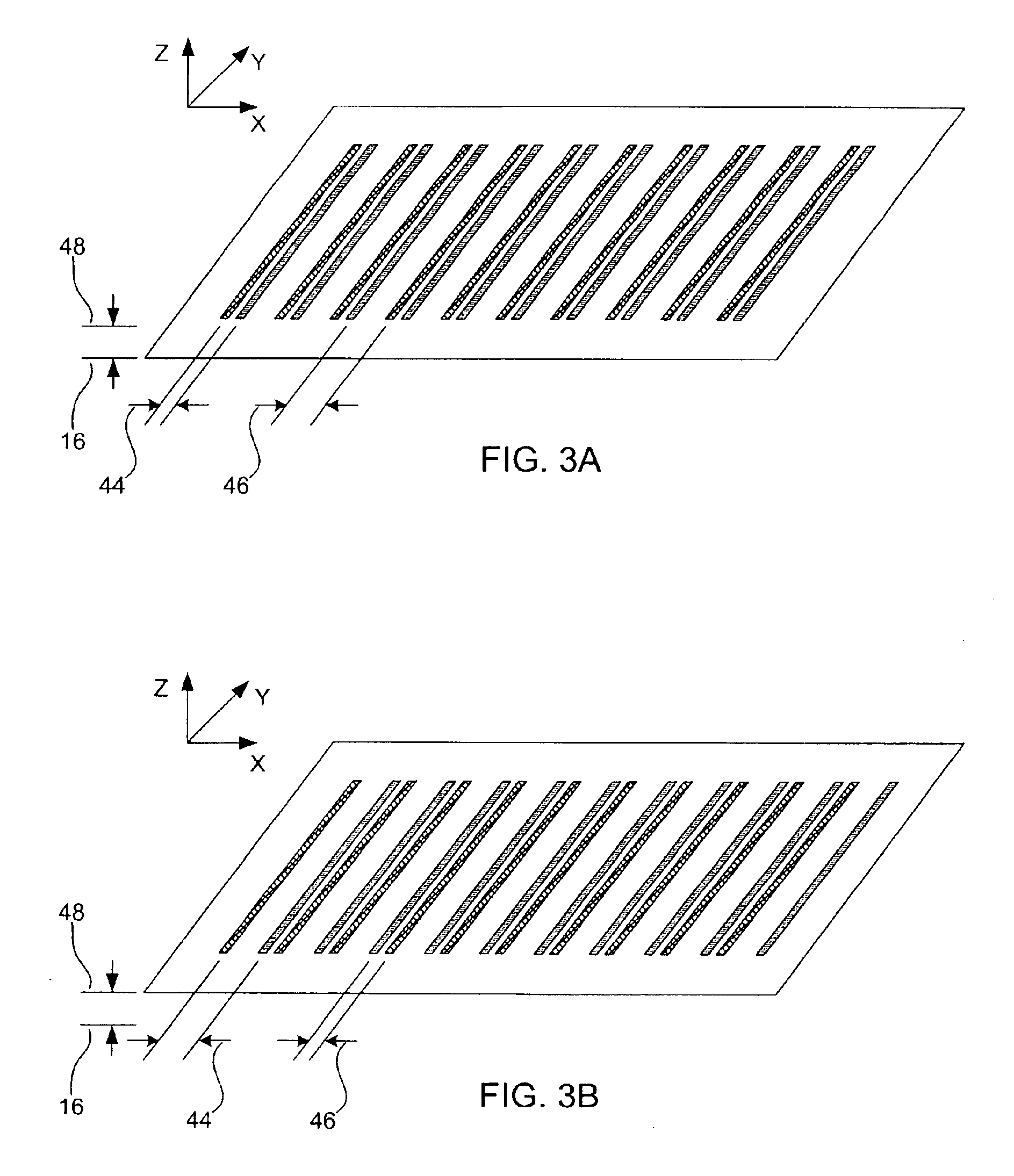
Focus masking structures, focus patterns and measurements thereof
InactiveUS7175945B2Testing sensing arrangementsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhase shiftedEngineering
Methods and device structures used to determine the focus quality of a photolithographic pattern or a photolithographic system are disclosed. One aspect of the invention relates to focus masking structures configured to form focus patterns that contain focus information relating to the focus quality. The focus masking structures generally include a plurality of parallel source lines that are separated by alternating phase shift zones. Another aspect of the invention relates to focus patterns that change with changes in focus. The focus patterns generally include a plurality of periodic structures that form measurable shifts therebetween corresponding to the sign and magnitude of defocus. Another aspect of the invention relates to a method of determining the focus quality of a photolithographic pattern or a photolithographic system. The method generally includes: providing a focus masking structure, forming a focus pattern on a work piece with the focus masking structure, and obtaining focus information from the focus pattern. The focus information may be obtained using a variety of techniques, as for example, scatterometry techniques, scanning techniques, imaging techniques, phase based techniques, and the like.
Owner:KLA CORP
Focus masking structures, focus patterns and measurements thereof
InactiveUS6884552B2Testing sensing arrangementsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhase shiftedEngineering
Methods and device structures used to determine the focus quality of a photolithographic pattern or a photolithographic system are disclosed. One aspect of the invention relates to focus masking structures configured to form focus patterns that contain focus information relating to the focus quality. The focus masking structures generally include a plurality of parallel source lines that are separated by alternating phase shift zones. Another aspect of the invention relates to focus patterns that change with changes in focus. The focus patterns generally include a plurality of periodic structures that form measurable shifts therebetween corresponding to the sign and magnitude of defocus. Another aspect of the invention relates to a method of determining the focus quality of a photolithographic pattern or a photolithographic system. The method generally includes: providing a focus masking structure, forming a focus pattern on a work piece with the focus masking structure, and obtaining focus information from the focus pattern. The focus information may be obtained using a variety of techniques, as for example, scatterometry techniques, scanning techniques, imaging techniques, phase based techniques, and the like.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
Popular searches
Detecting faulty hardware by remote test Multiple digital computer combinations Non-redundant fault processing Verifying markings correctness Record carriers used with machines Burglar alarm by hand-portable articles removal Burglar alarm electric actuation Radio transmission Burglar alarm High level techniques
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com