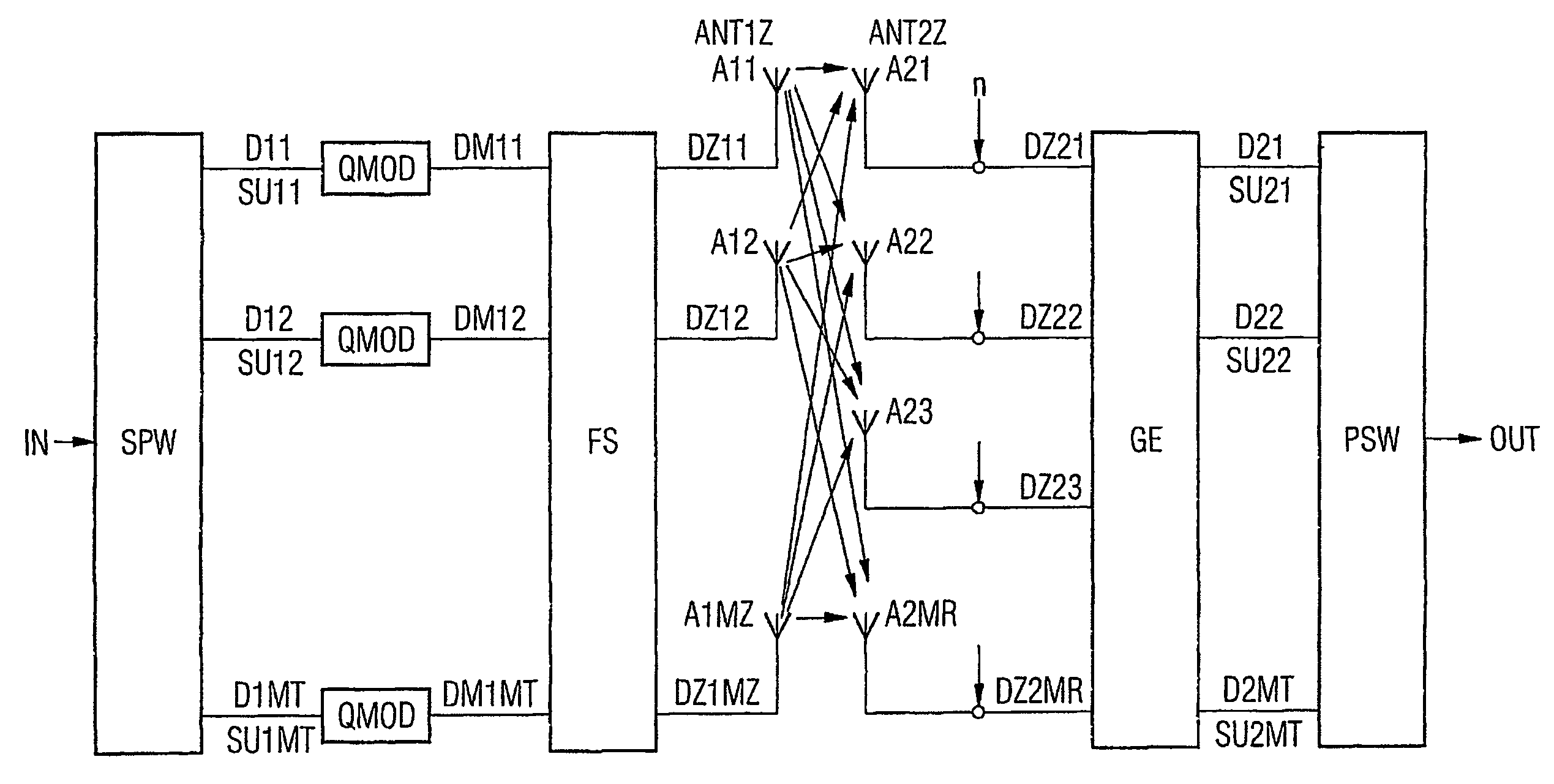
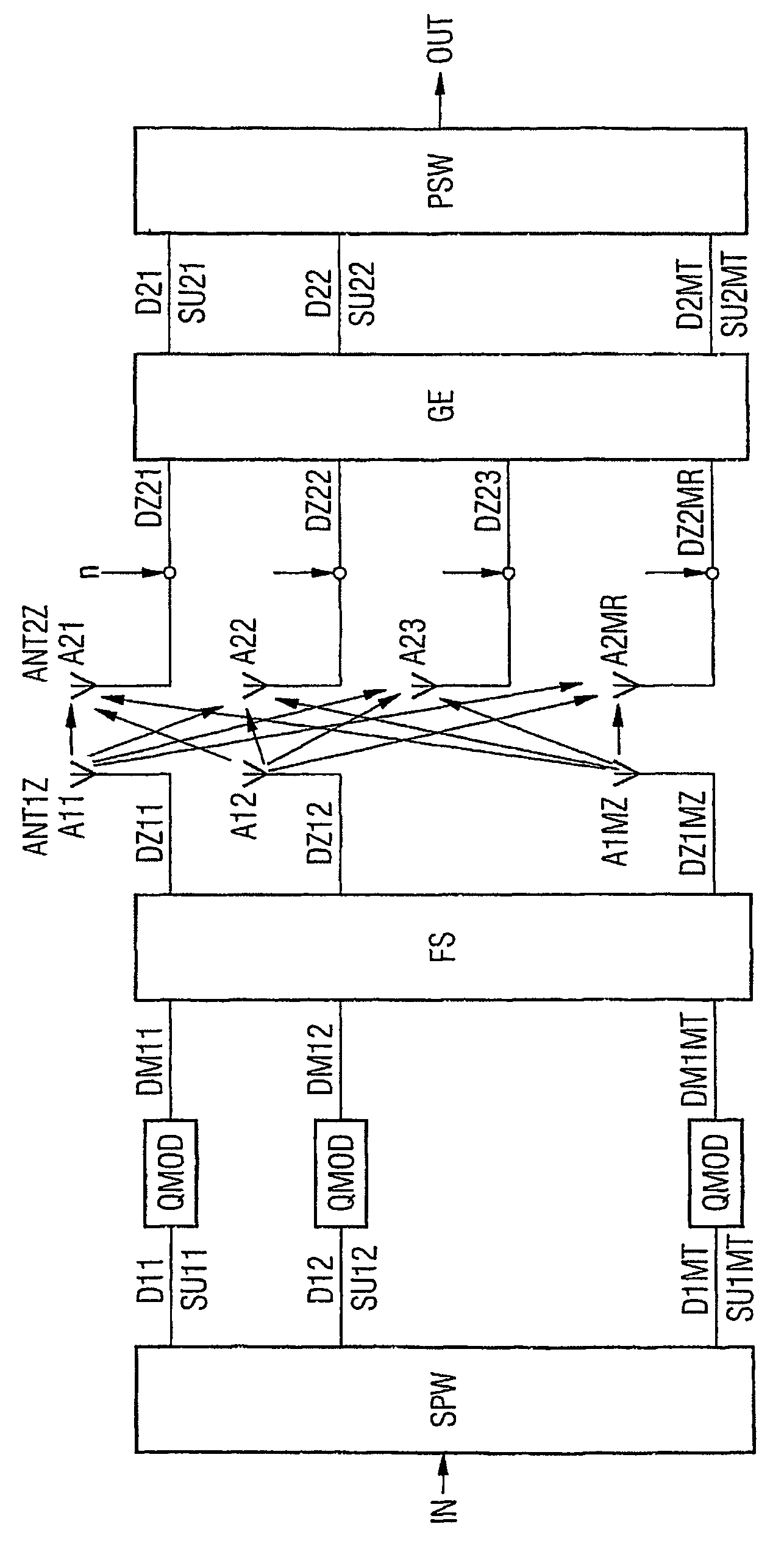
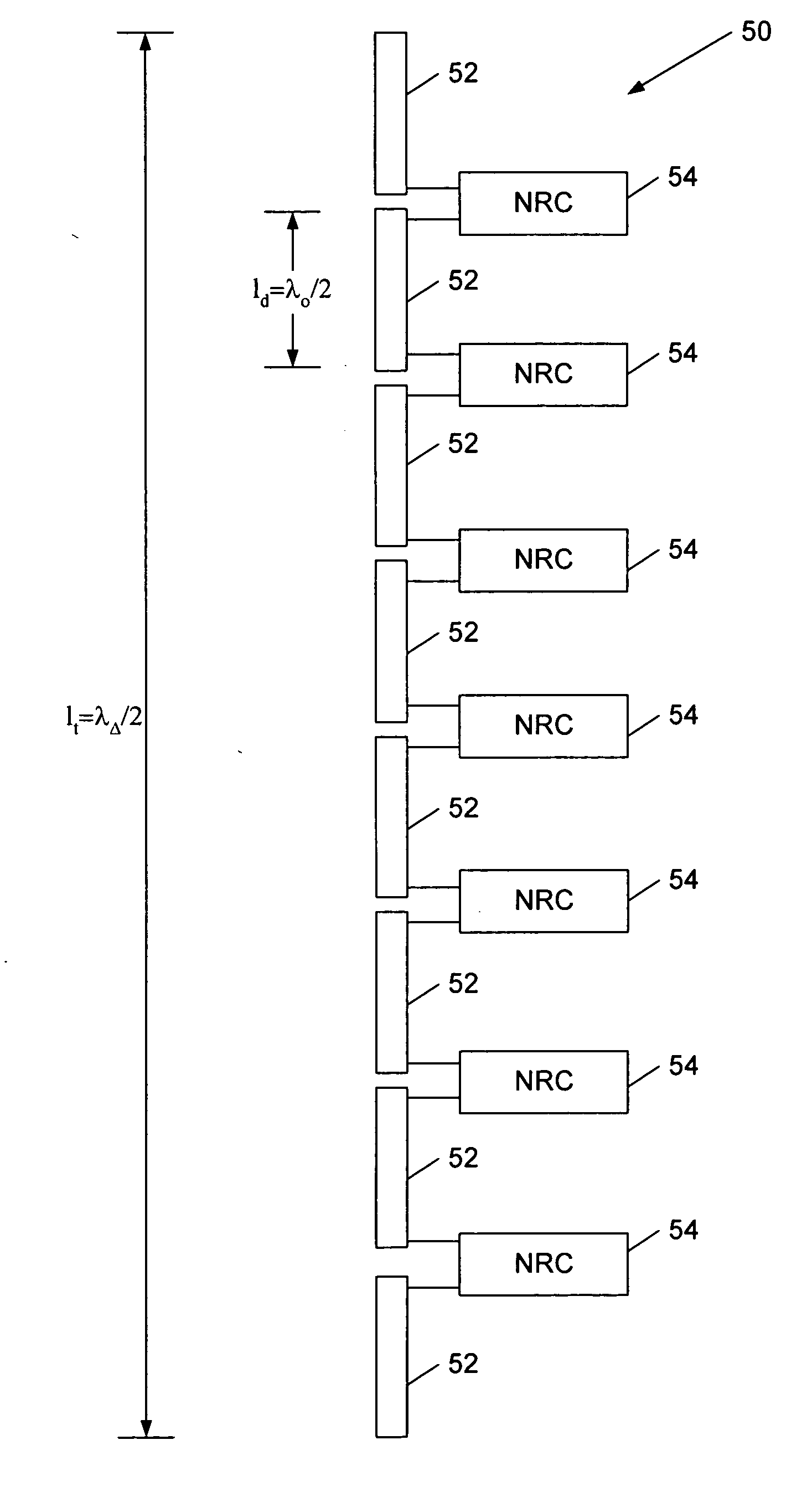
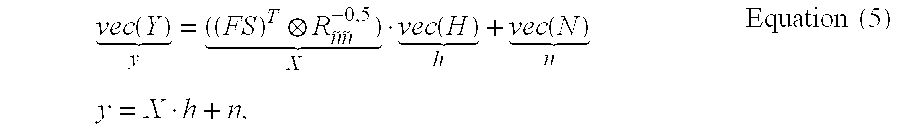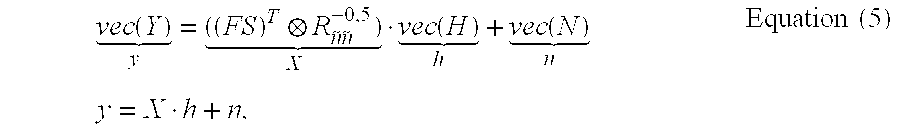Patents
Literature
63 results about "Reradiation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In telecommunication, the term reradiation has the following meanings: Electromagnetic radiation, at the same or different wavelengths, i.e., frequencies, of energy received from an incident wave. Undesirable radiation of signals locally generated in a radio receiver. This type of radiation might cause interference or reveal the location of the device. Near-field effects of an AM antenna may extend out two miles or more. Cellular and microwave towers within this radius can reflect the AM signal out at a different frequency. This process results in interfering frequencies called reradiation. This article incorporates public domain material from the General Services Administration document "Federal Standard 1037C".
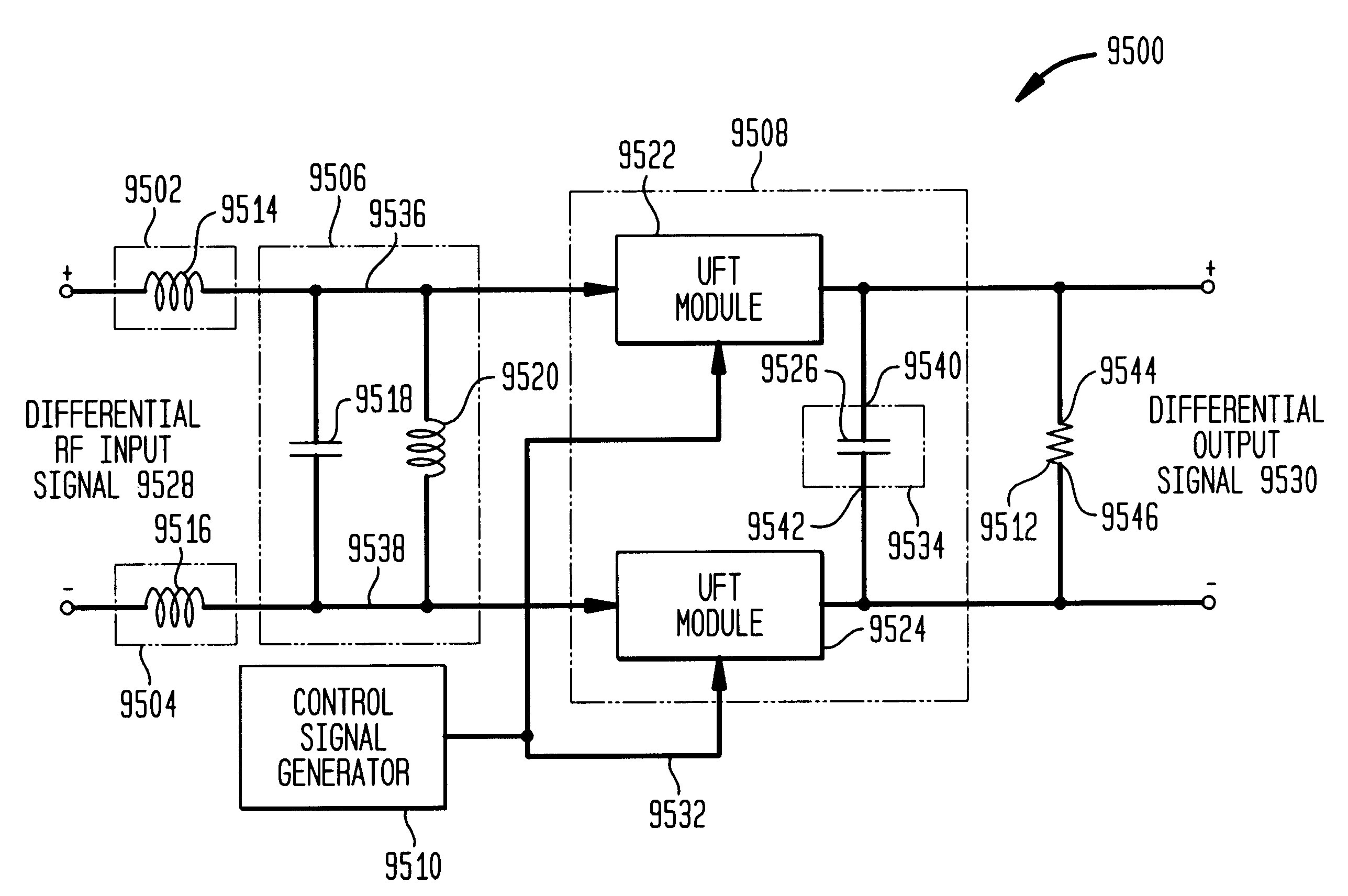
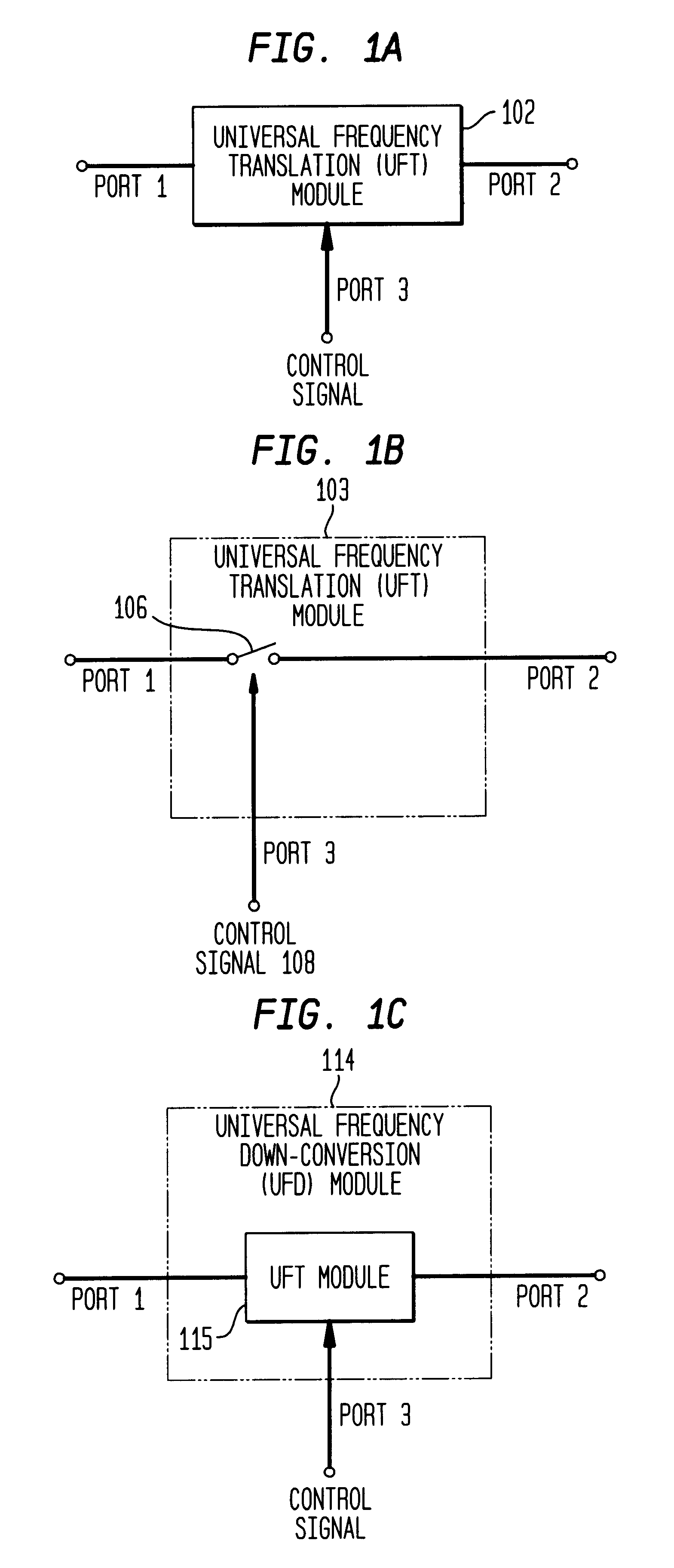
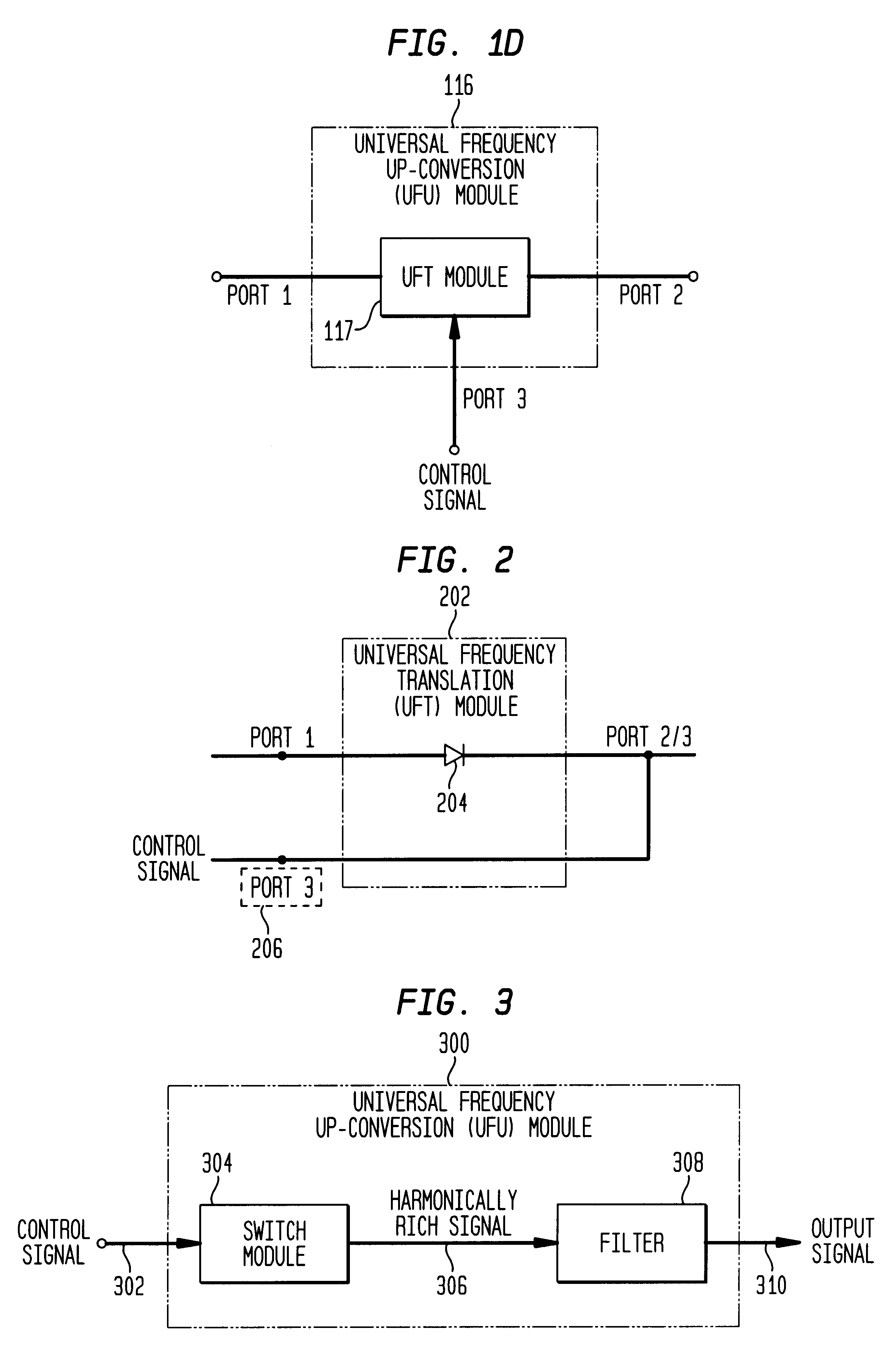
Differential frequency down-conversion using techniques of universal frequency translation technology
InactiveUS6963734B2Reduce voltageImprove dynamic rangeModulation transferenceComputations using contact-making devicesEngineeringDynamic range
Methods, systems, and apparatuses for down-converting an electromagnetic (EM) signal by aliasing the EM signal, and applications thereof are described herein. Reducing or eliminating DC offset voltages and re-radiation generated when down-converting an electromagnetic (EM) signal is also described herein. Down-converting a signal and improving receiver dynamic range is also described herein.
Owner:PARKER VISION INC
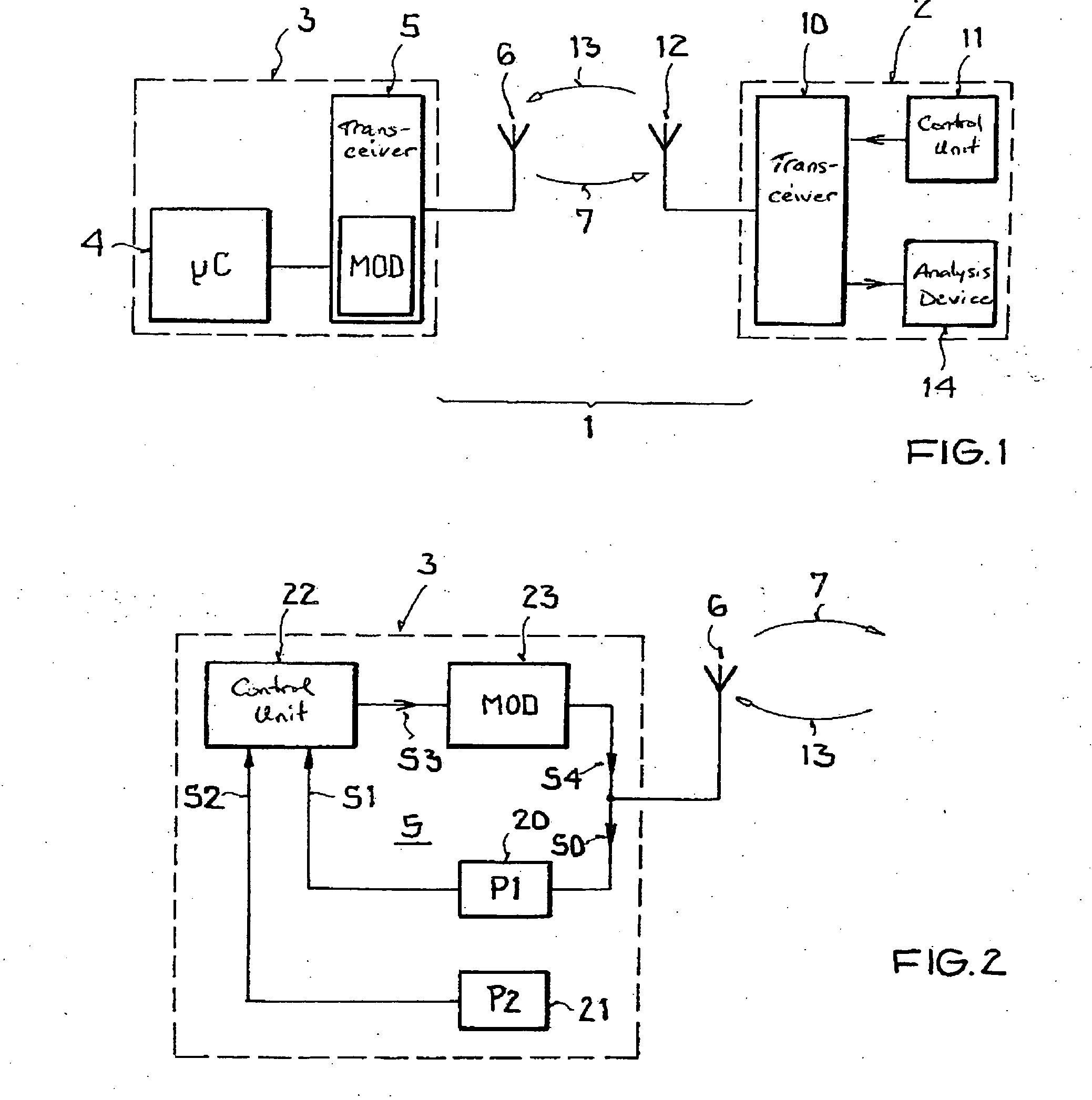
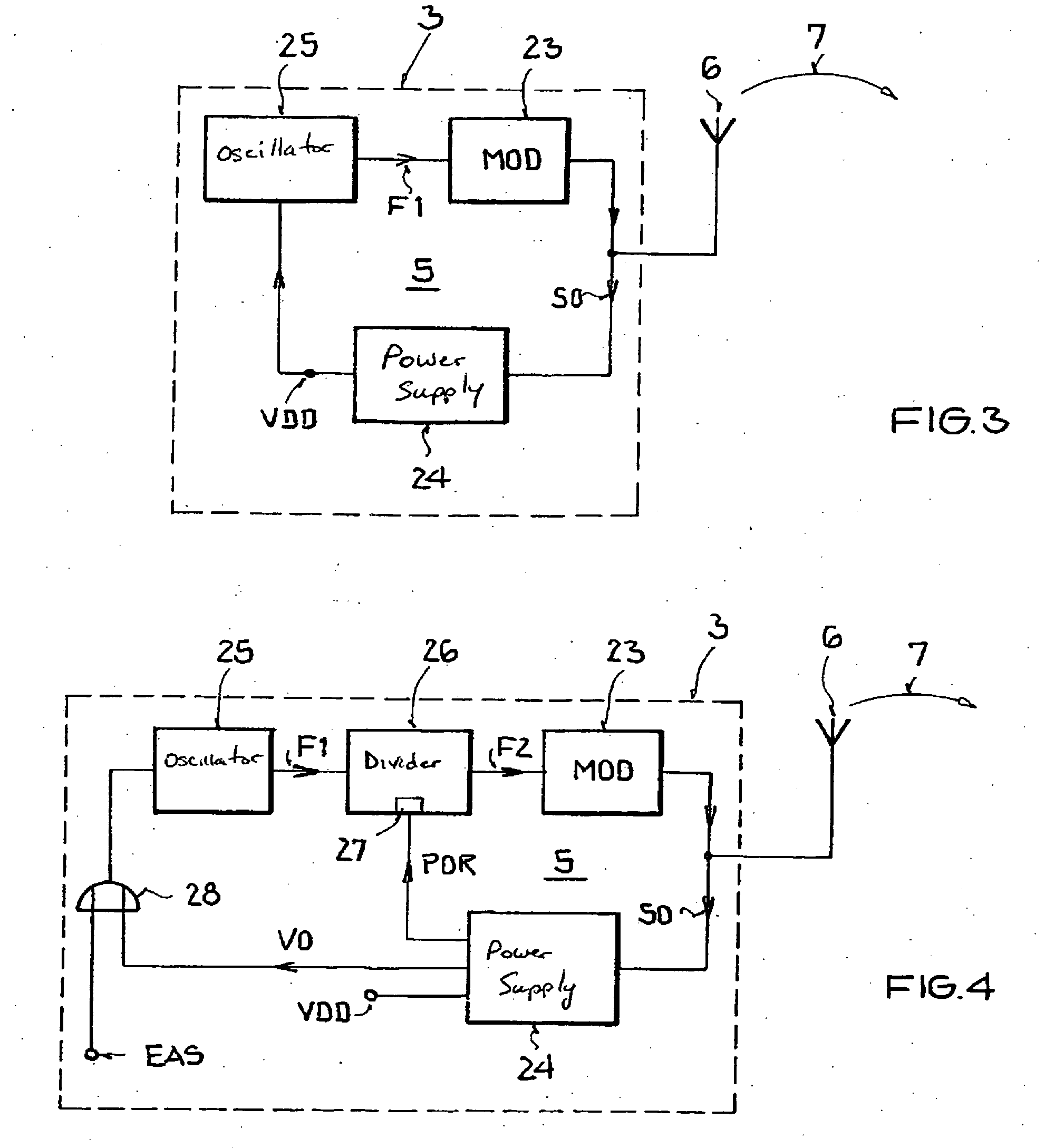
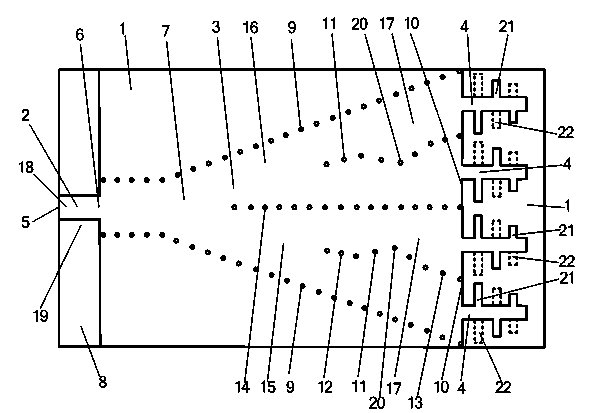
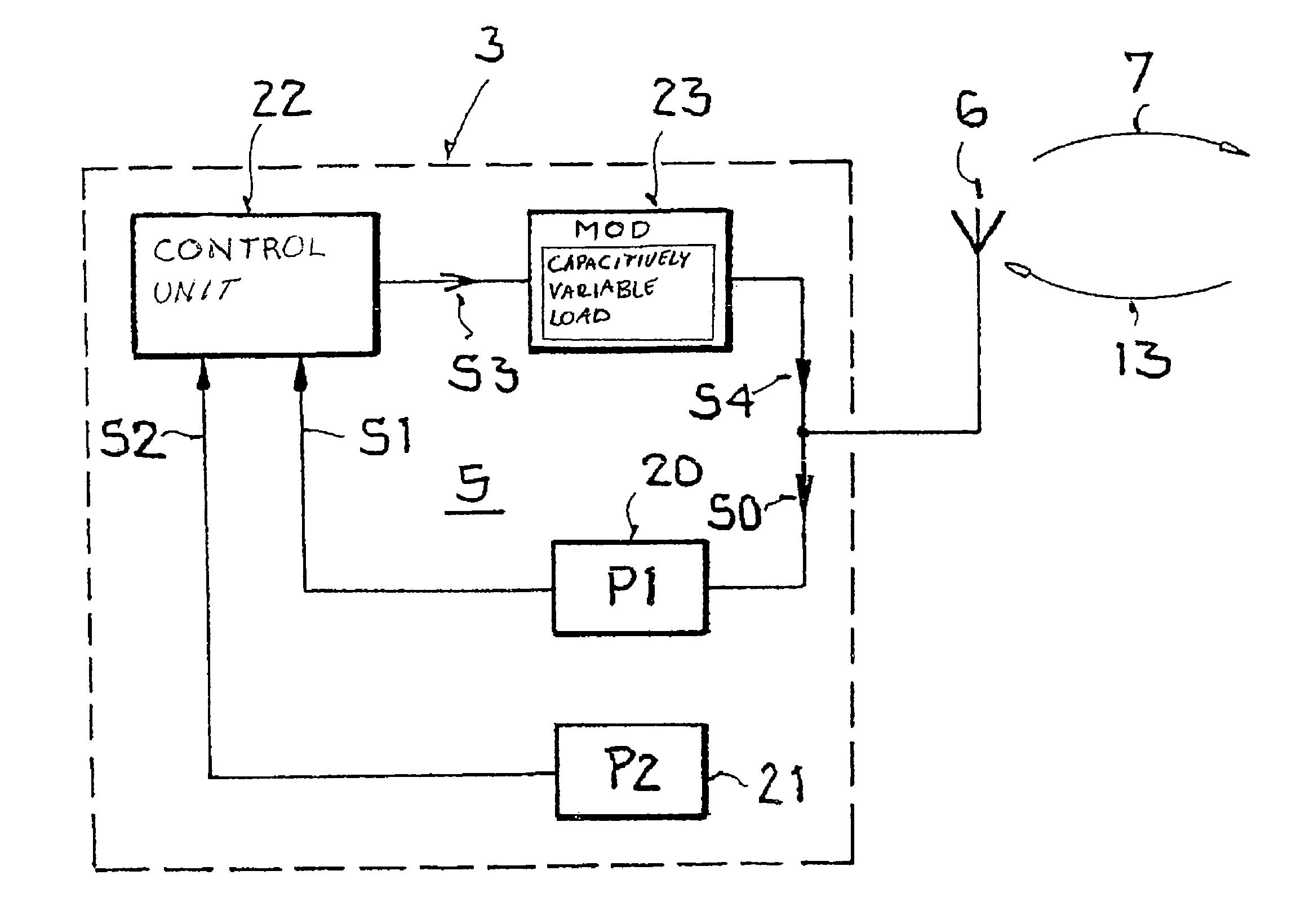
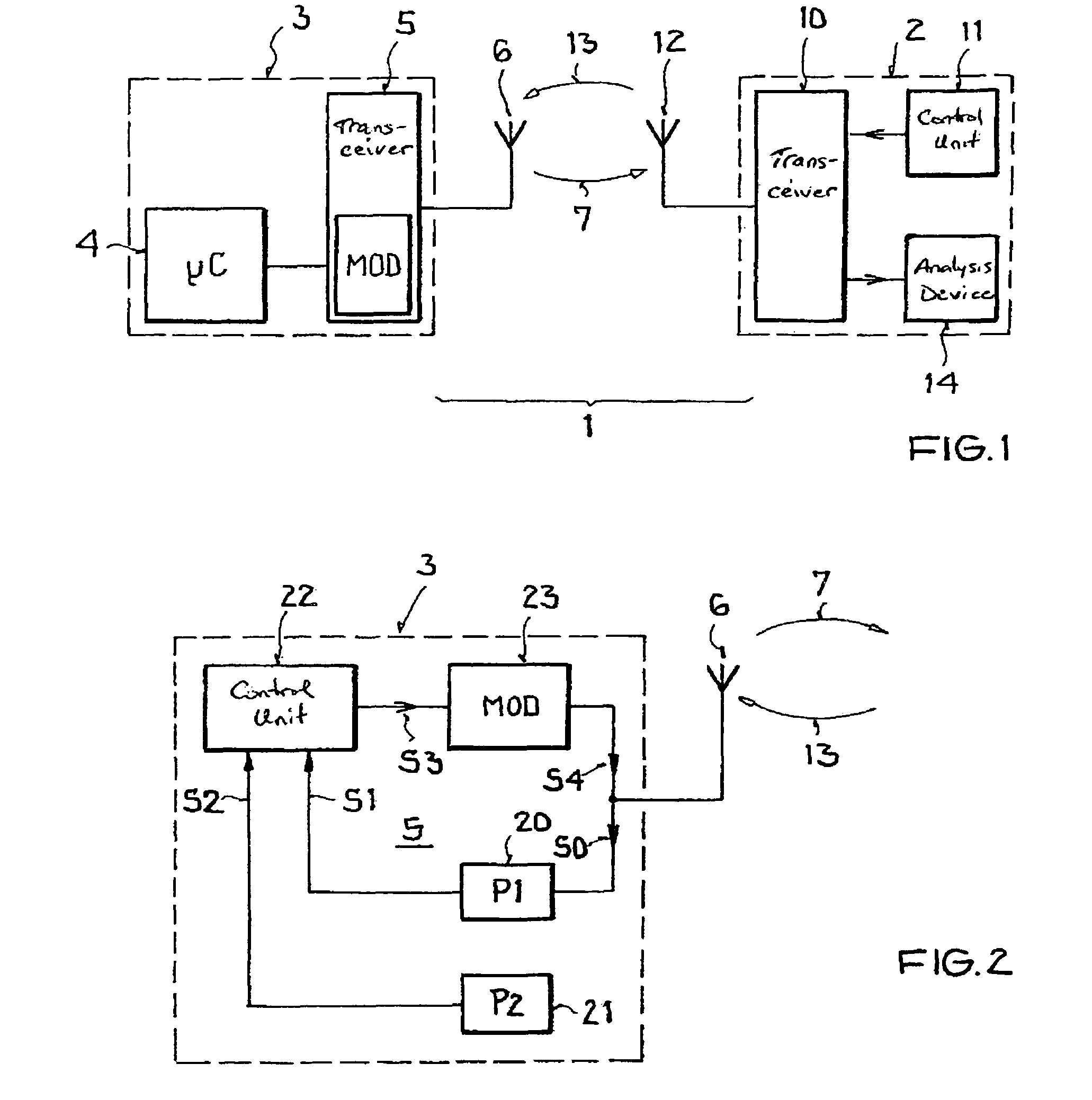
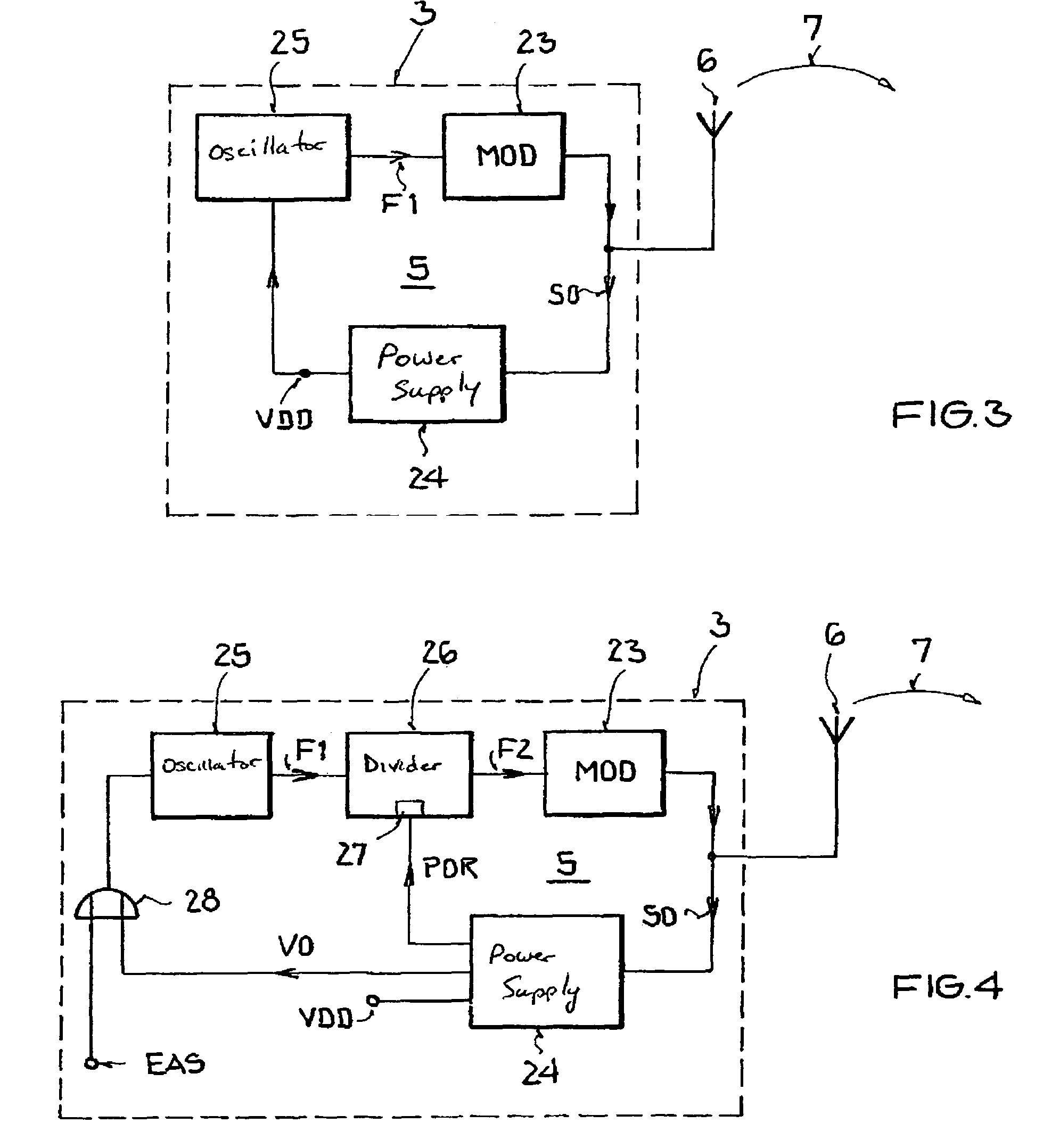
Backscatter transponder
InactiveUS20080136646A1Testing sensing arrangementsSubscribers indirect connectionCommunications systemCarrier signal
A backscatter transponder for an HF communication system with modulated reradiation, is provided that includes an antenna for receiving high-frequency carrier signals, wherein the antenna has reflective characteristics, a control unit for providing transponder-specific parameters, and a modulator that can be driven by the control unit. The modulator altering the reflective characteristics of the antenna in accordance with at least one transponder-specific parameter.
Owner:ATMEL CORP
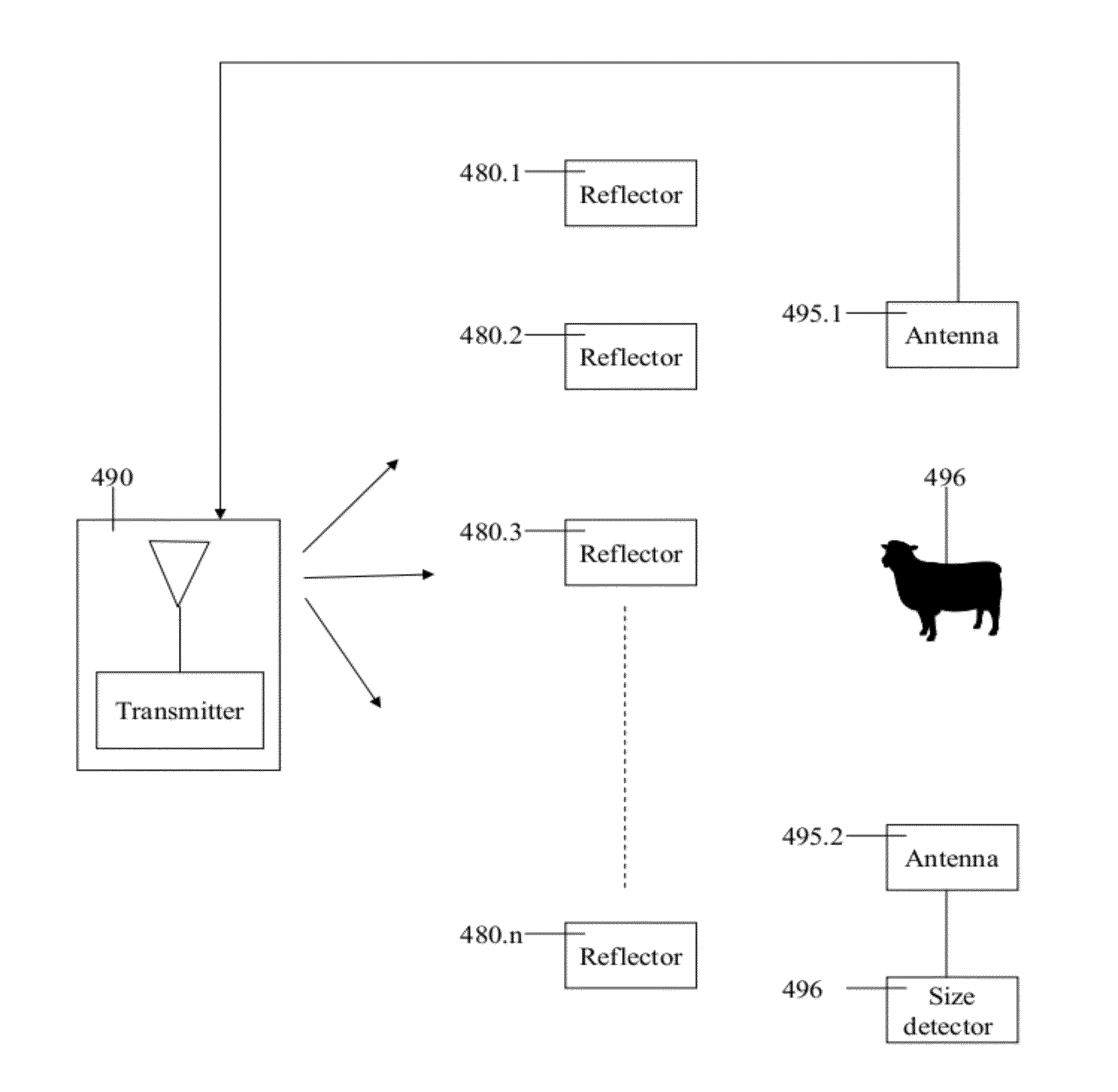
Apparatus and method for concentrating electromagnetic energy on a remotely-located object
InactiveUS7994962B1Reduce undesired reflectionWave based measurement systemsCommunication jammingResonanceElectromagnetic shielding
A method for concentrating radio frequency (RF) radiation on an object located in proximity to a reflector includes the steps of: selecting a target reflector and a level of power for conveying to the target reflector by reradiation from the target reflector, determining a resonance profile of the target reflector, the resonance profile including at least one resonant frequency of the target reflector, selecting a transmission profile matching the resonance profile, the transmission profile comprising the at least one resonant frequency, and transmitting RF radiation in accordance with the transmission profile towards the target reflector.
Owner:DROSERA
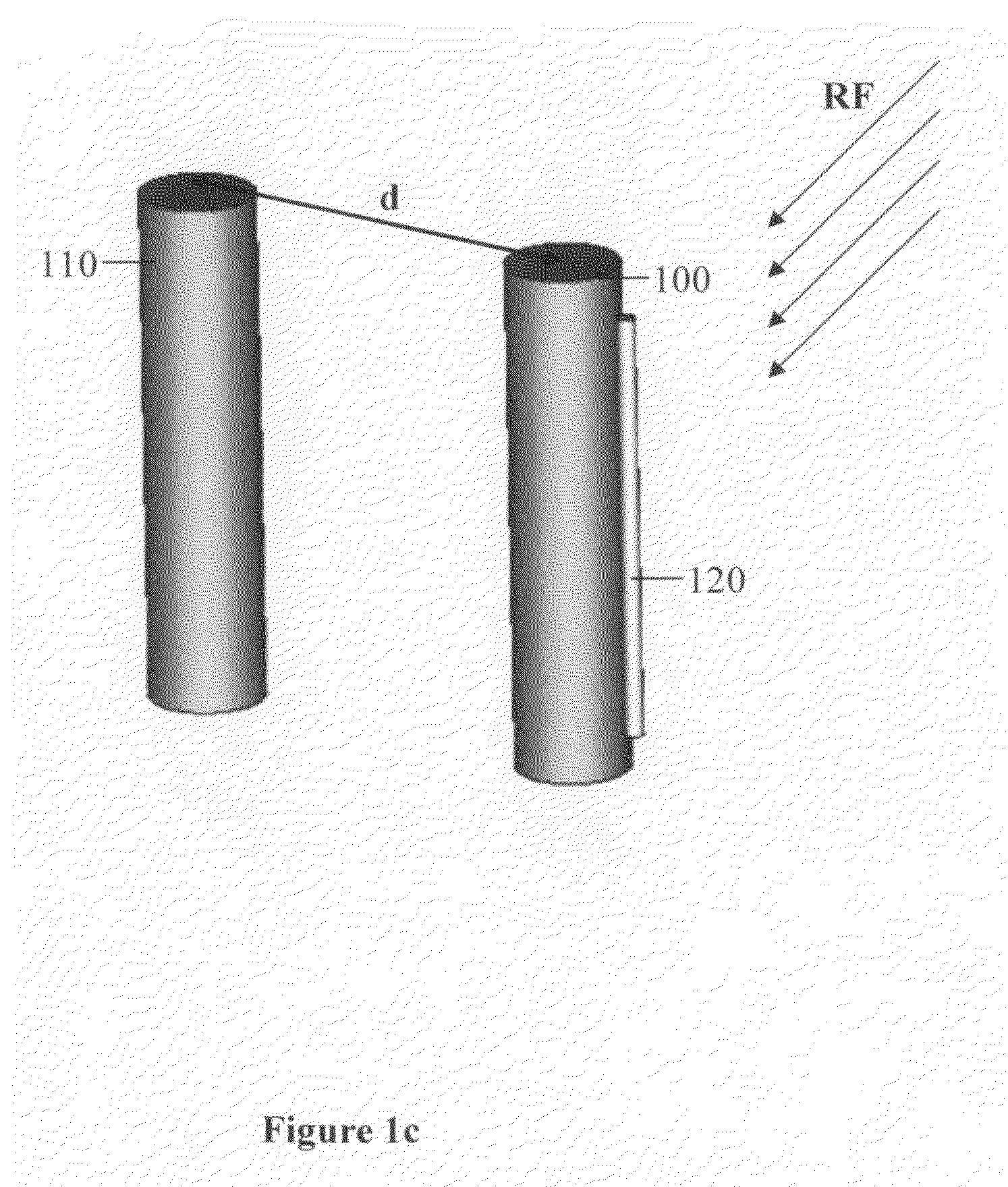
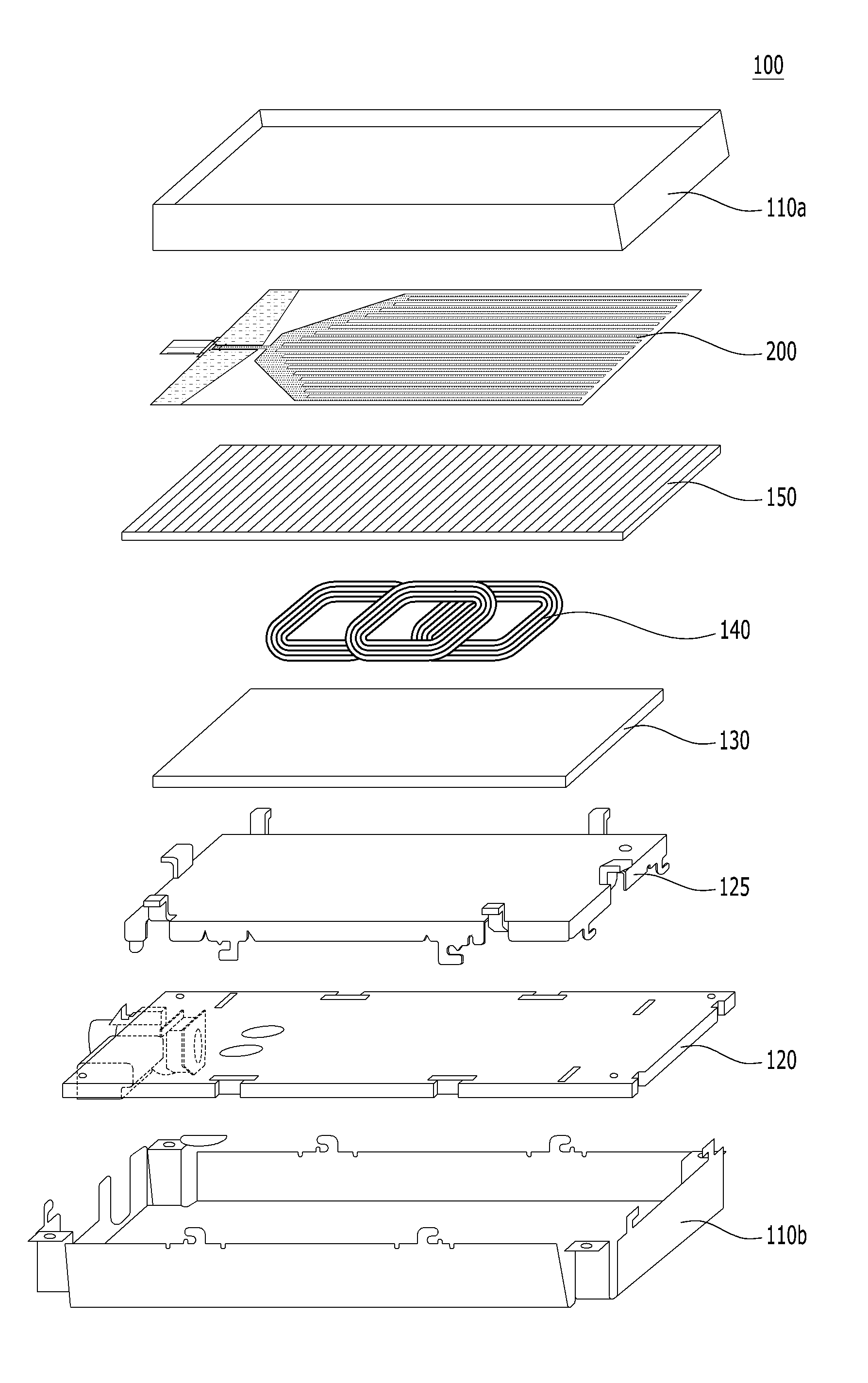
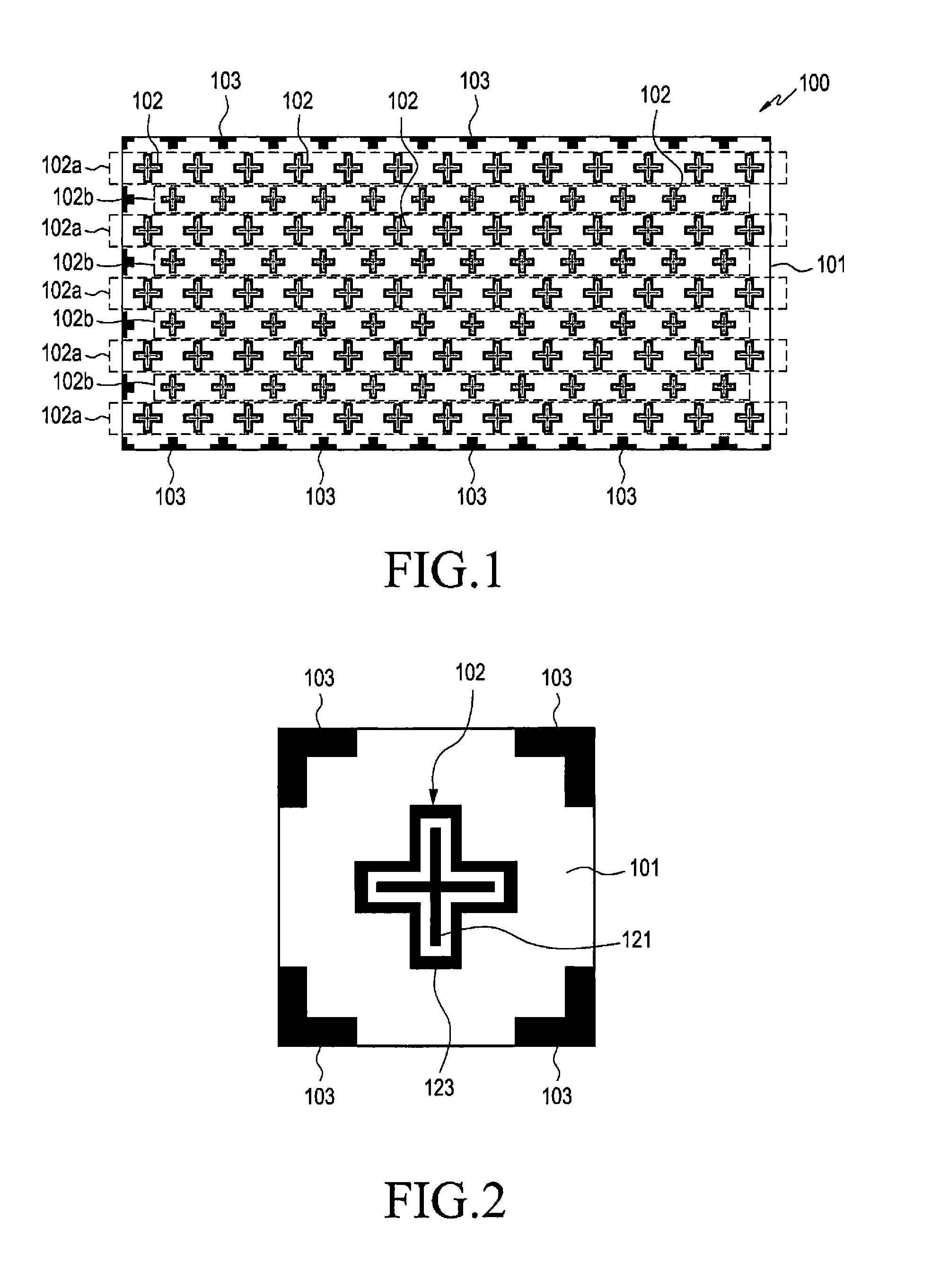
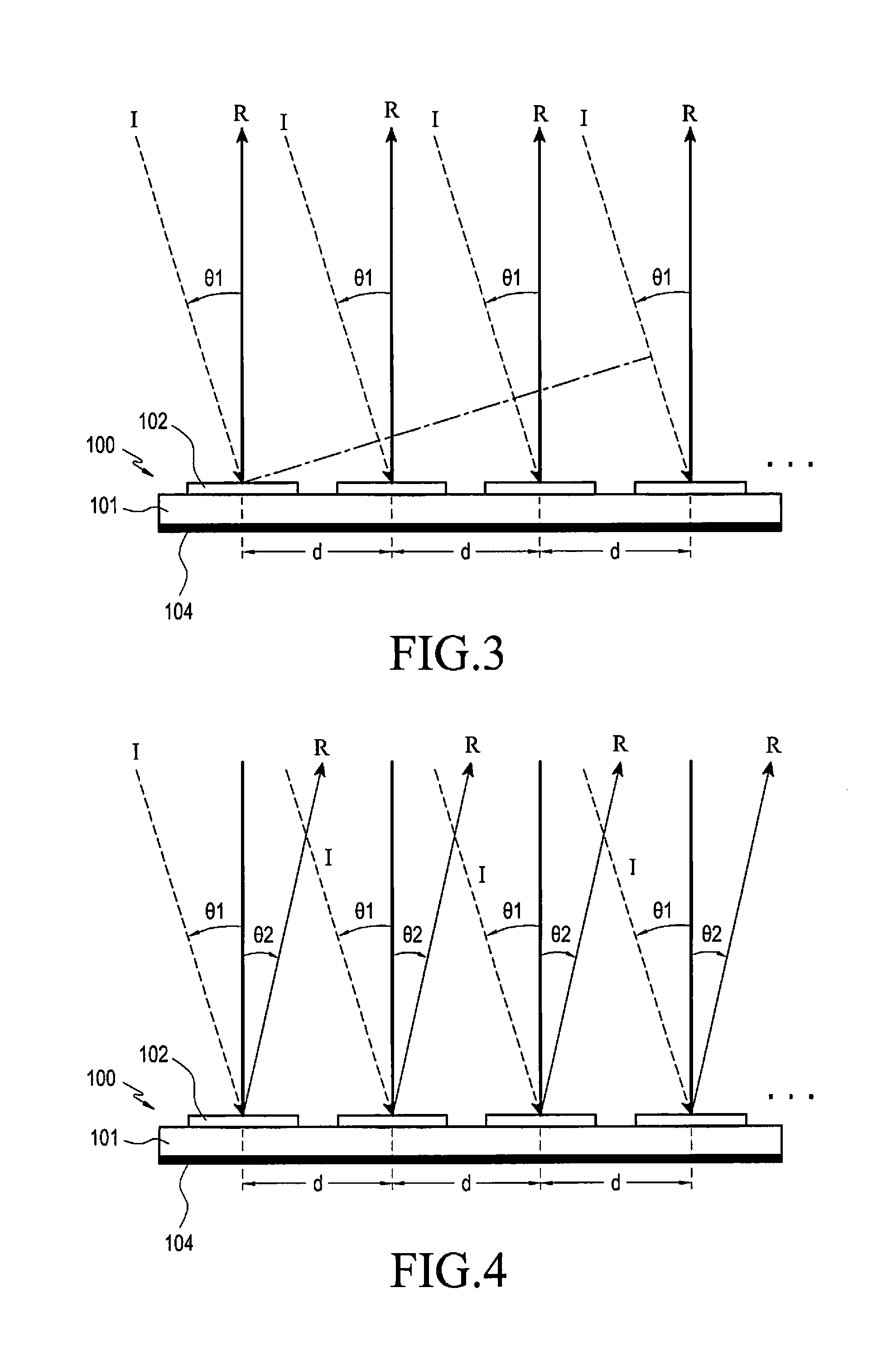
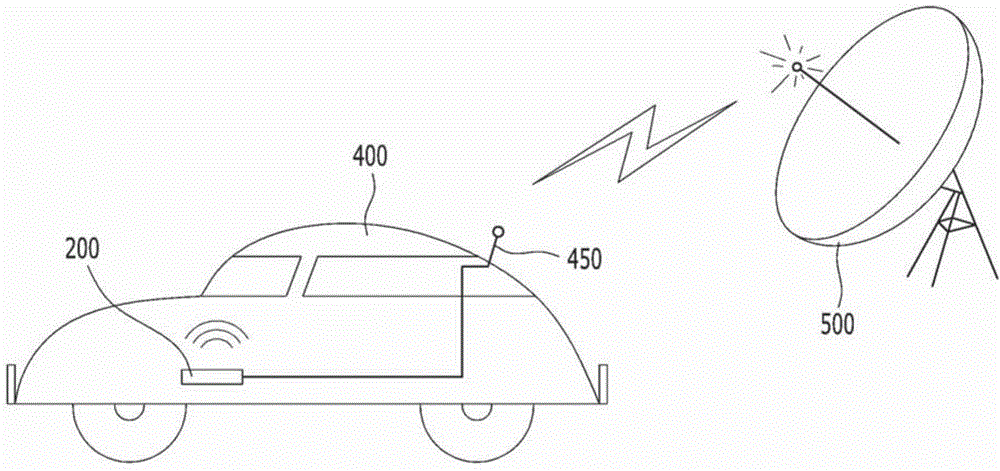
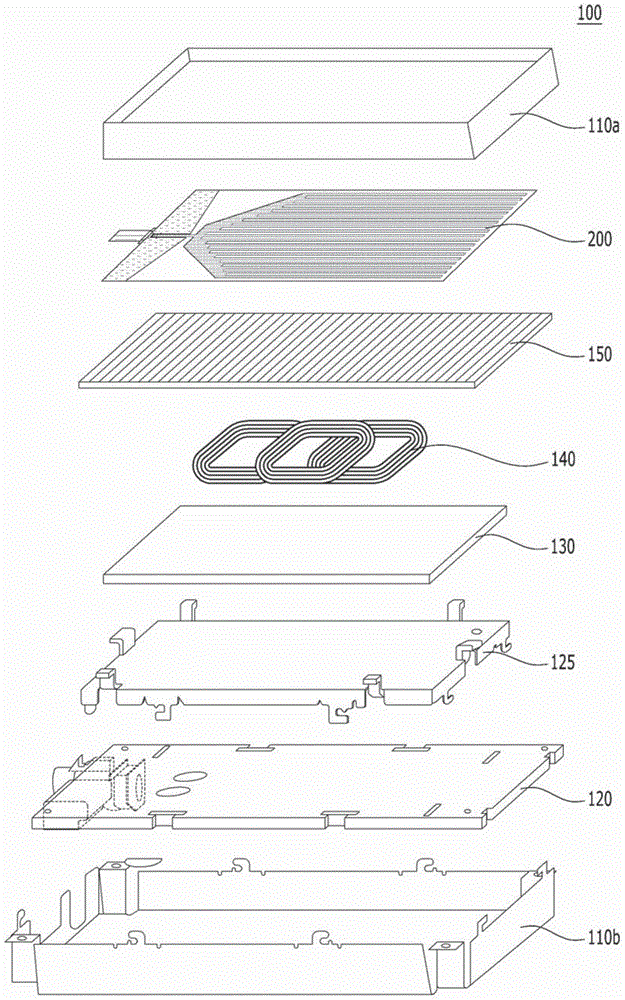
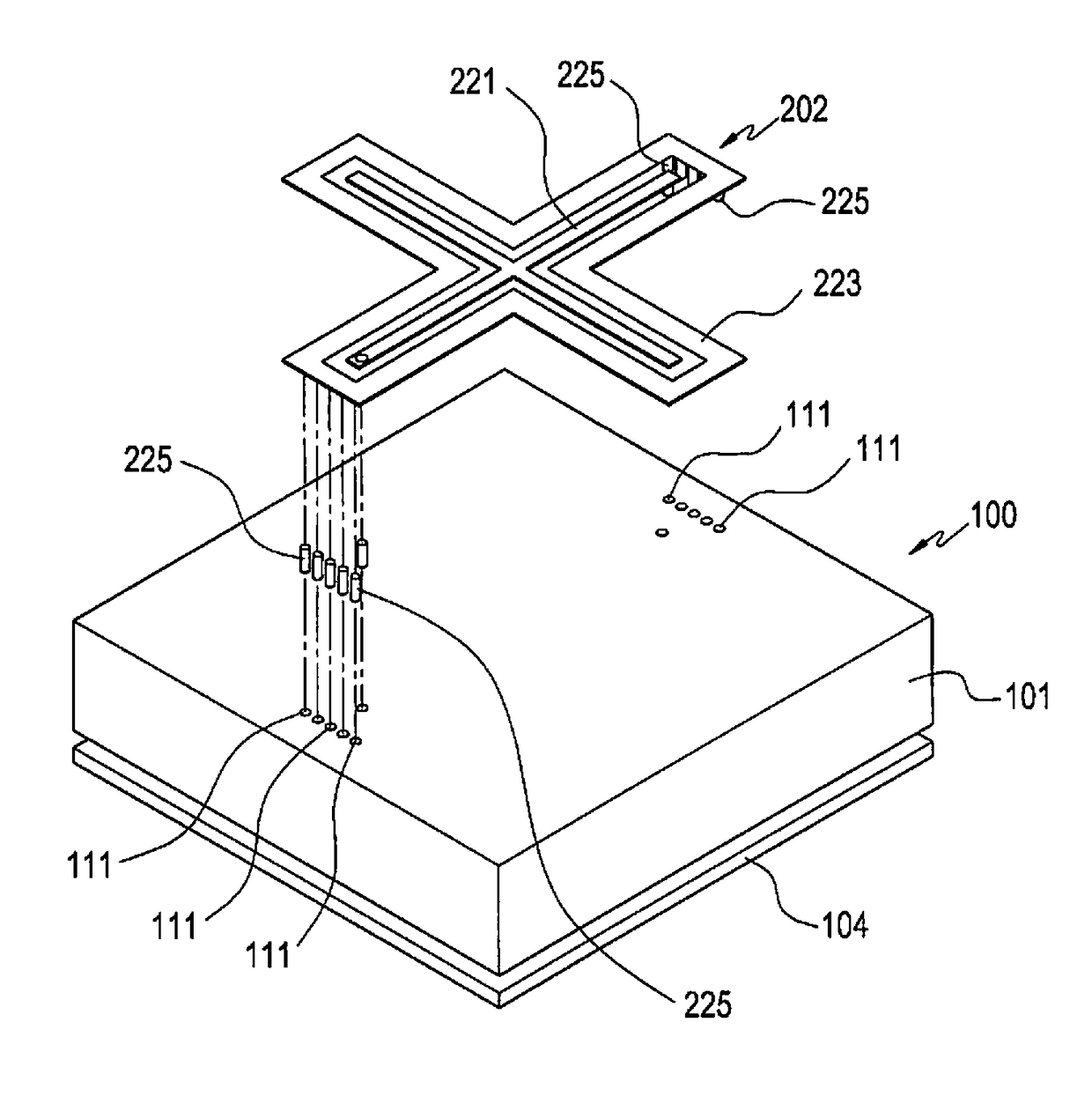
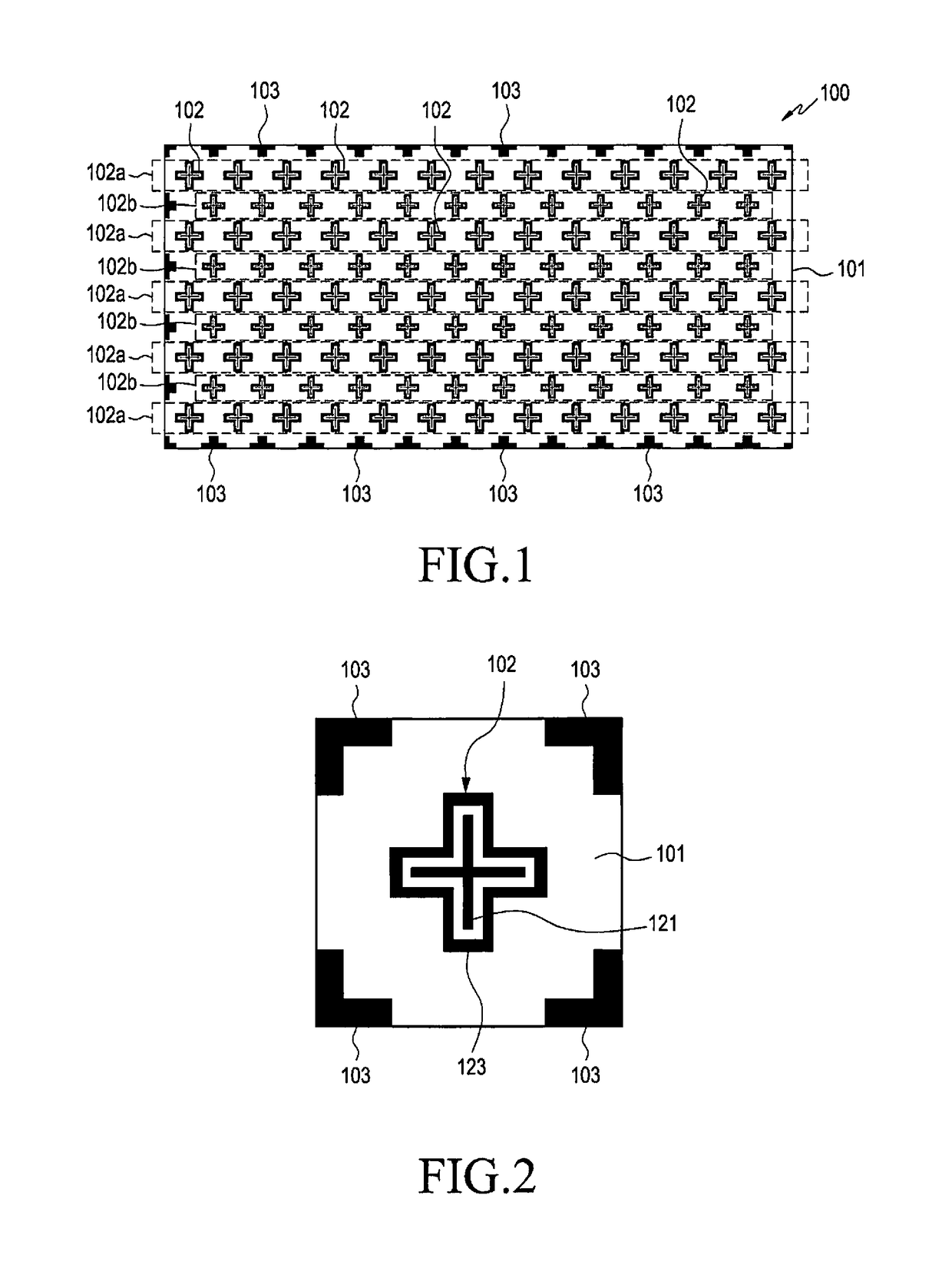
Reradiation antenna and wireless charger
ActiveUS20150288067A1Improve communication environmentNot degrading performanceNear-field transmissionBatteries circuit arrangementsGround contactEngineering
A reradiation antenna including an insulation panel; a ground contact formed on one side of the insulation panel; a slot formed by eliminating a part of the ground contact by exposing the insulation panel; a power feeding unit formed on the insulation panel between the slot and separated from the ground contact and connected with a power source using a first end of the power feeding unit; and a radiation unit formed on one side of the insulation panel, and connected with a second end of the power feeding unit positioned at an opened end of the slot.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Dual frequency antennas and associated down-conversion method
ActiveUS6999041B2Simultaneous aerial operationsIndividually energised antenna arraysDual frequencyResonance
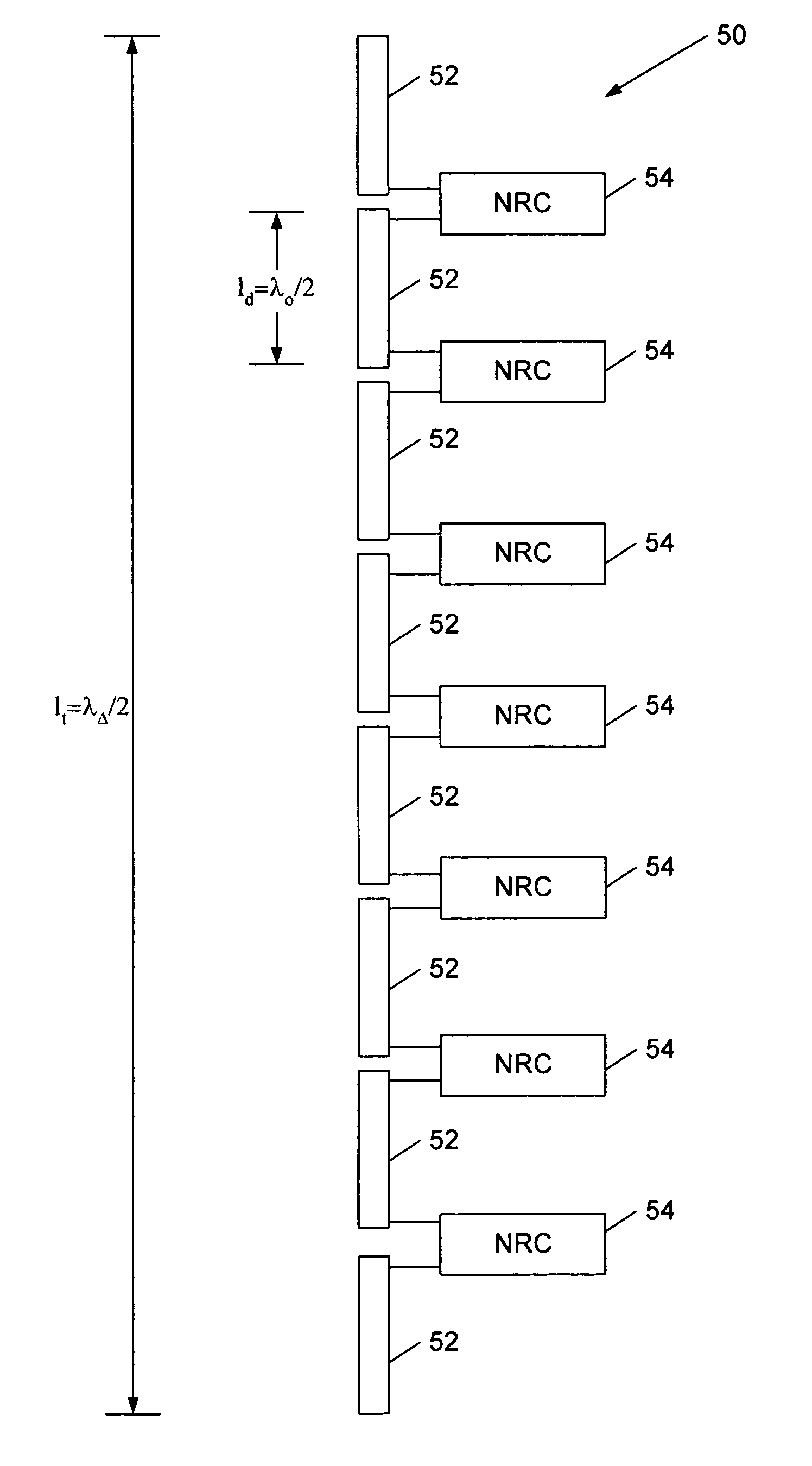
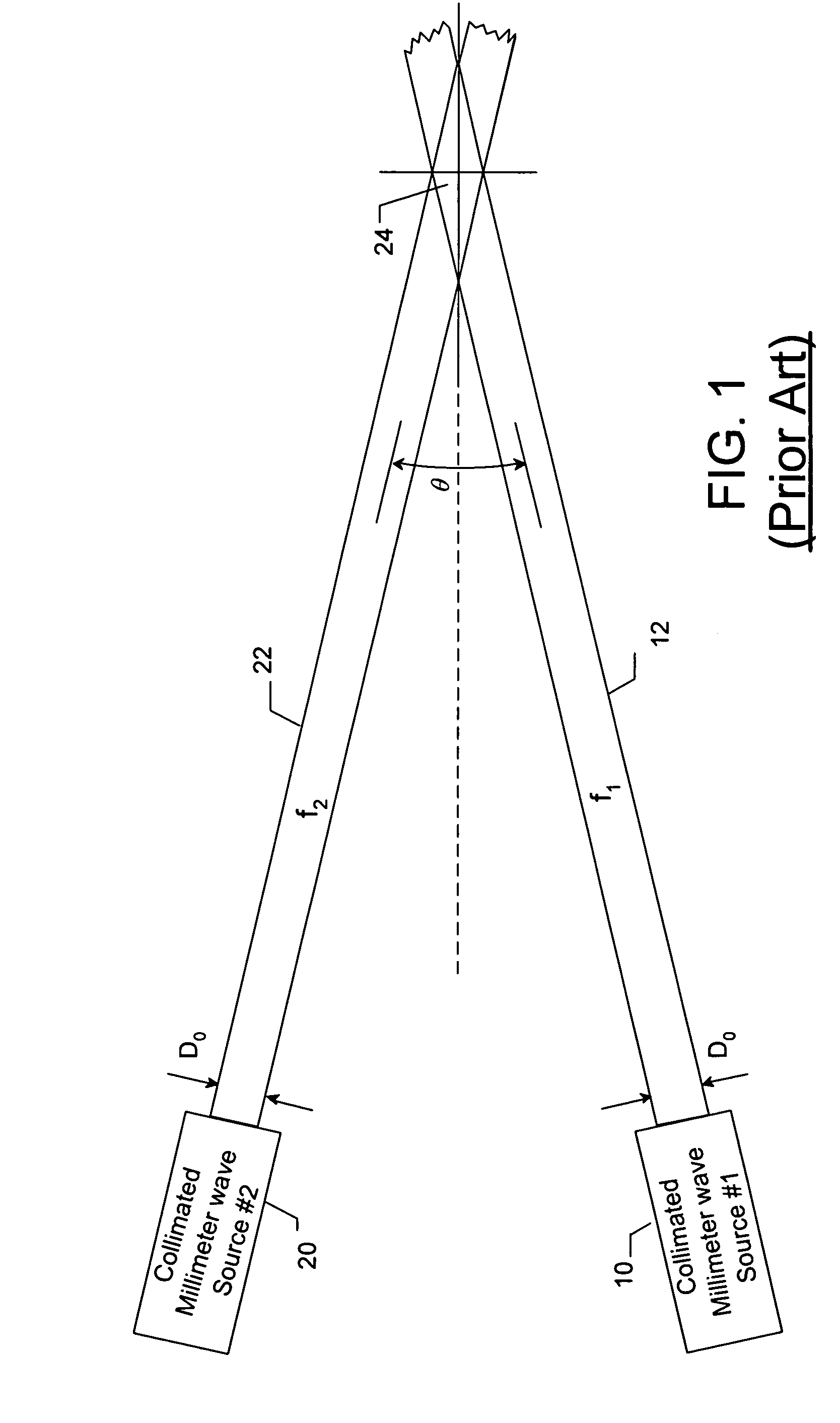
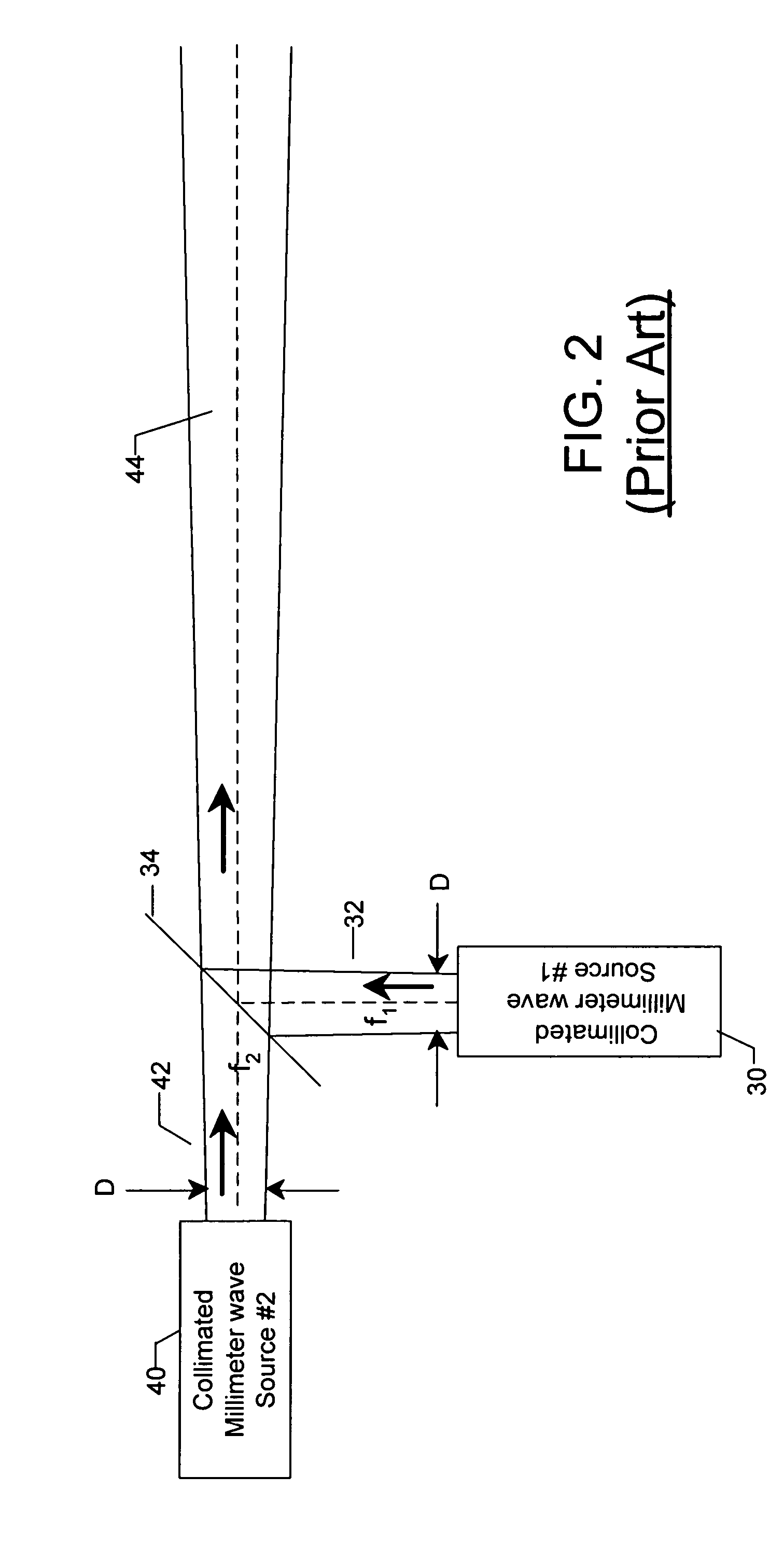
A dual frequency antenna includes a plurality of dipole antennas configured to receive first and second frequencies. The antennas are arrayed to an effective length to reradiate at a third frequency, which is down-converted from the first and second frequencies. A plurality of nonlinear resonant circuits interconnect the plurality of dipole antennas and are configured to permit reradiation of the third frequency over the effective length through its low frequency dipole resonance. A method of down-converting at least first and second electromagnetic radiation frequencies is also provided. The method includes transmitting first and second electromagnetic beams at first and second frequencies, respectively. The first and second frequencies are converted to the difference frequency through a nonlinear resonant circuit coupling the at least two dipole antennas.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
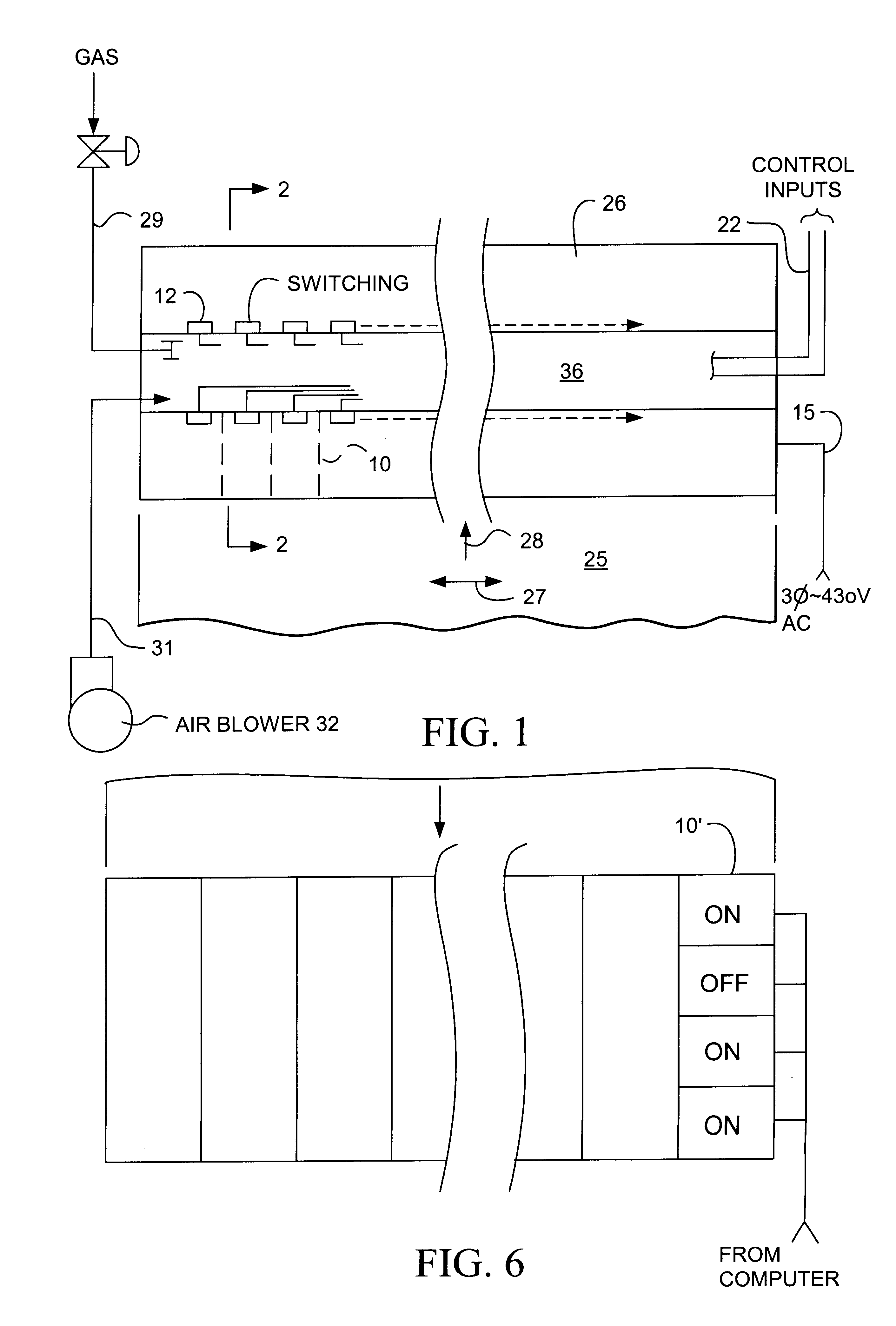
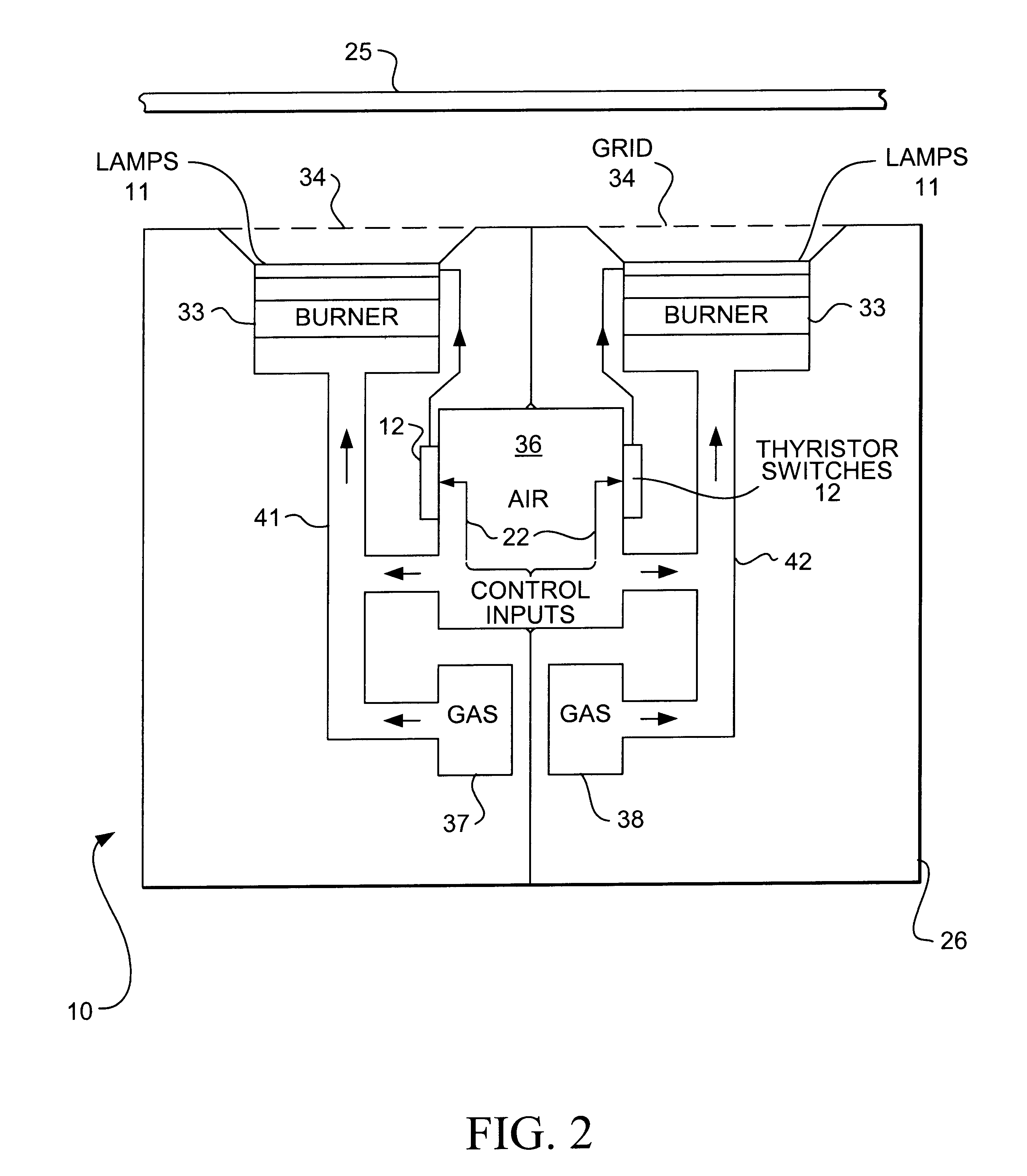
Cross-direction dryer for a machine producing sheet material moving in a machine direction having both gas powered and electric heating portions
A cross-direction dryer for typically drying a continuous web of paper or paper to which coating has just been applied provides both for baseline drying and a linear moisture profile by the use of respectively gas and electric heating portions of the heater units. Profile control is normally provided by control of the voltage to electric heating lamps. Such heating lamps are suspended over a large area gas burner to provide a combined increased infrared heat output. Encapsulation of the heating lamps with quartz provides for reradiation of the medium wavelength radiation produced by the gas burner. Thyristor switching for the quartz halogen heat lamps may be located adjacent to each heater unit and cooled by the combustion air for the gas burners.
Owner:IMPACT SYST
Adaptive antenna for use in wireless communication systems
InactiveUS6989797B2Increase effective transmit powerHigh data rateAntenna arraysAntenna supports/mountingsSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Communications system
An antenna apparatus, which can increase capacity in a cellular communication system or Wireless Local Area Network (WLAN), such as an 802.11 network, operates in conjunction with a mobile subscriber unit or client station. At least one antenna element is active and located within multiple passive antenna elements. The passive antenna elements are coupled to selectable impedance components for phase control of re-radiated RF signals. Various techniques for determining the phase of each antenna element are supported to enable the antenna apparatus to direct an antenna beam pattern toward a base station or access point with maximum gain, and, consequently, maximum signal-to-noise ratio. By directionally receiving and transmitting signals, multipath fading is greatly reduced as well as intercell interference.
Owner:IPR LICENSING INC
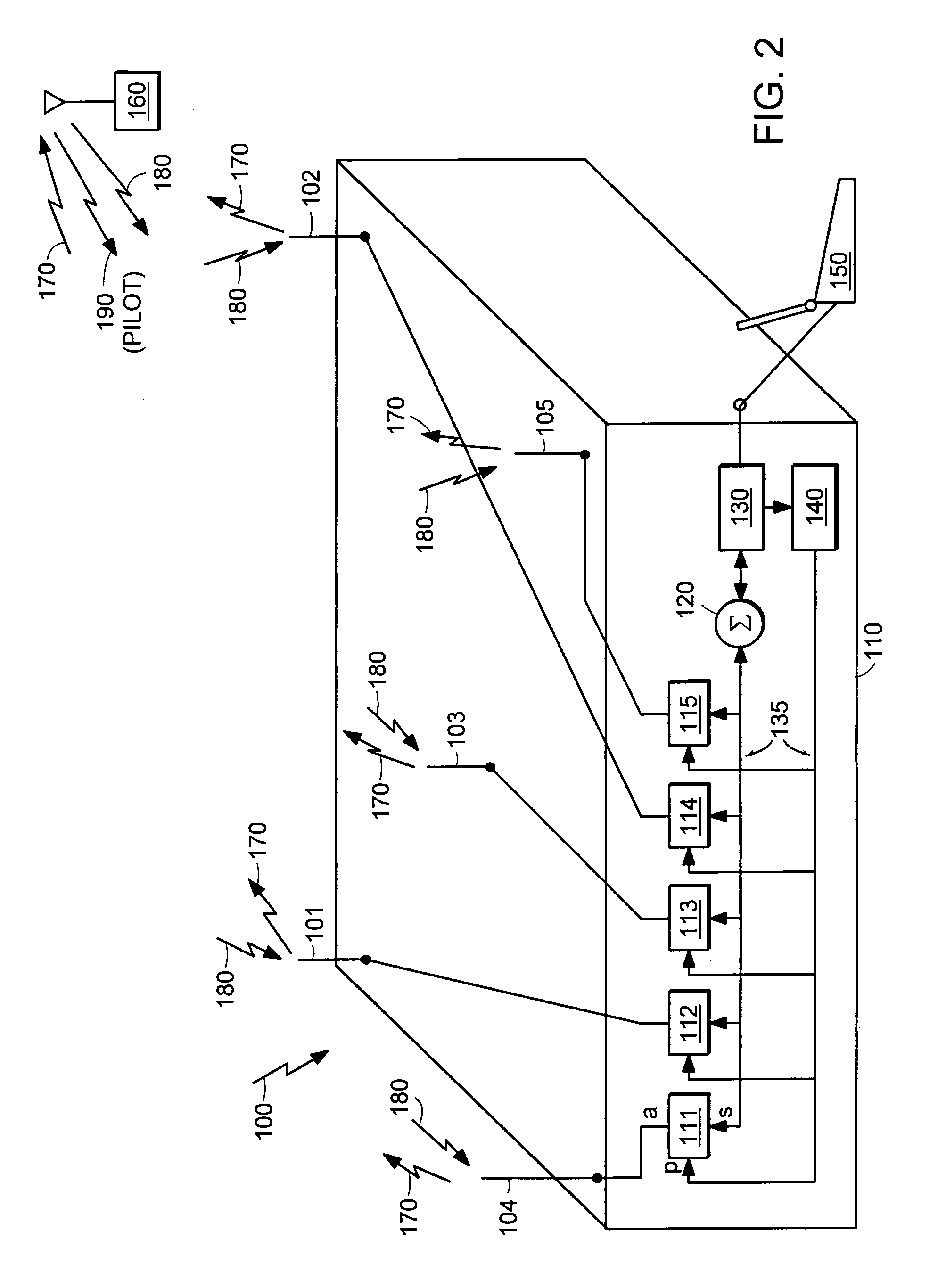
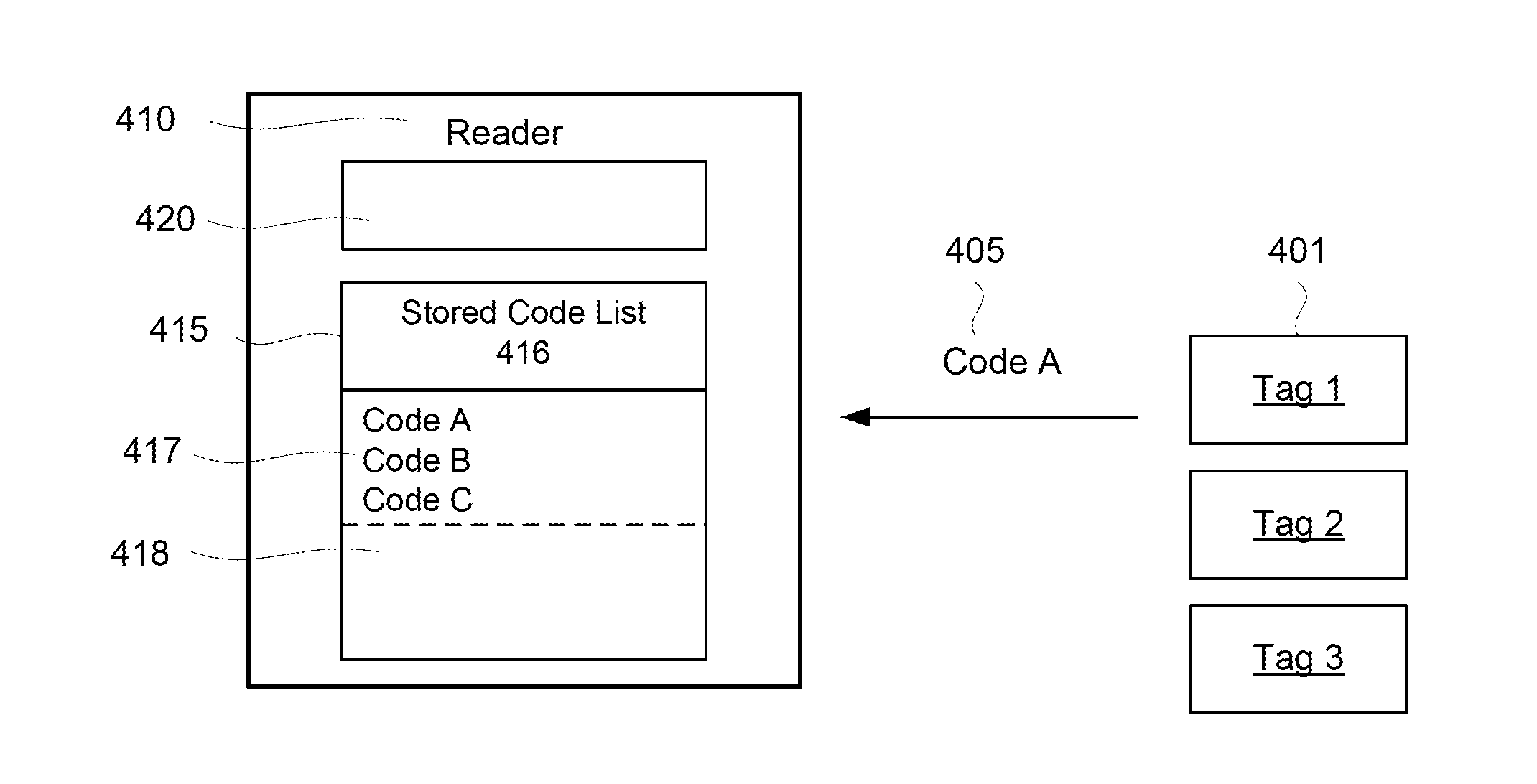
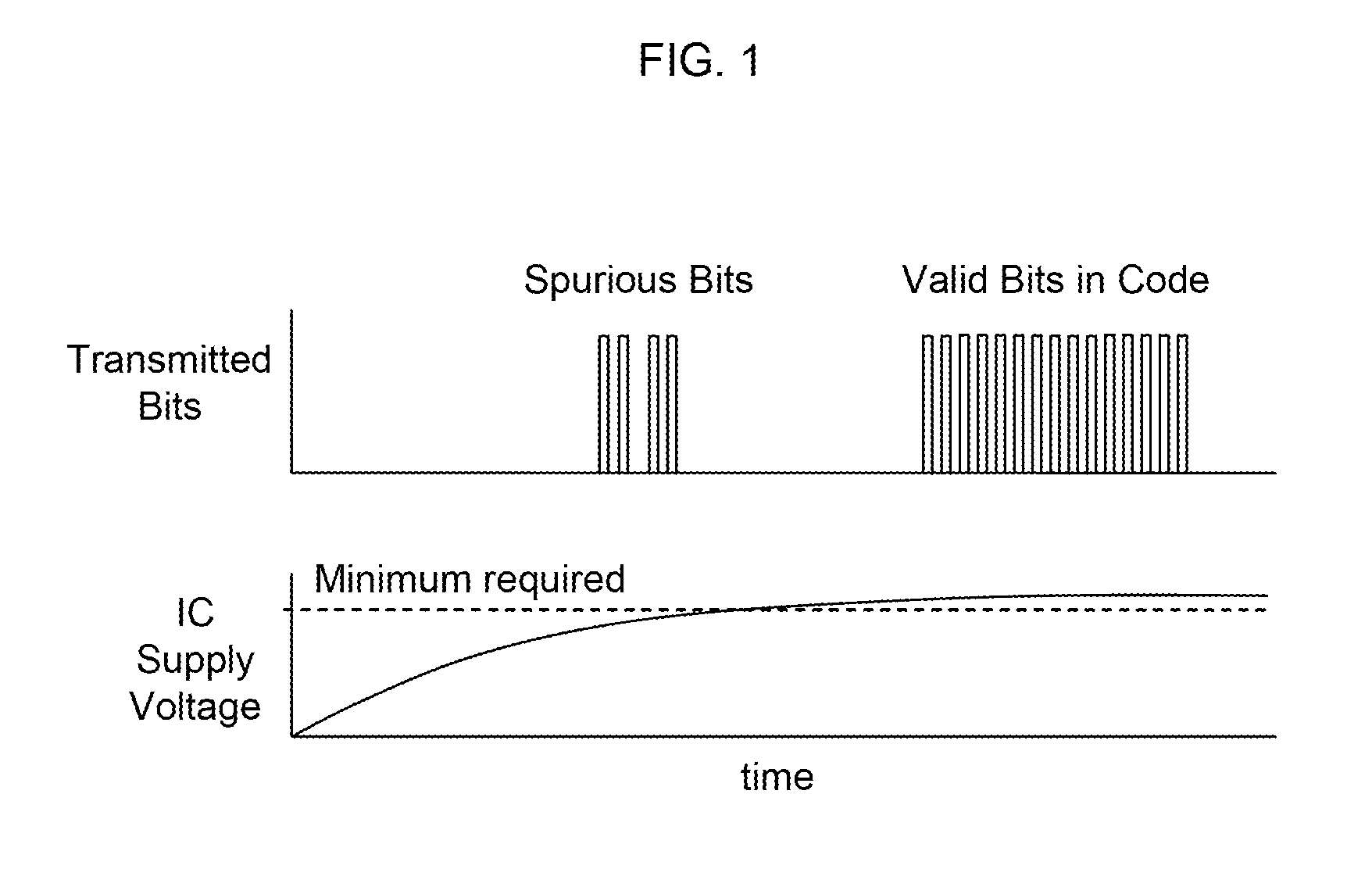
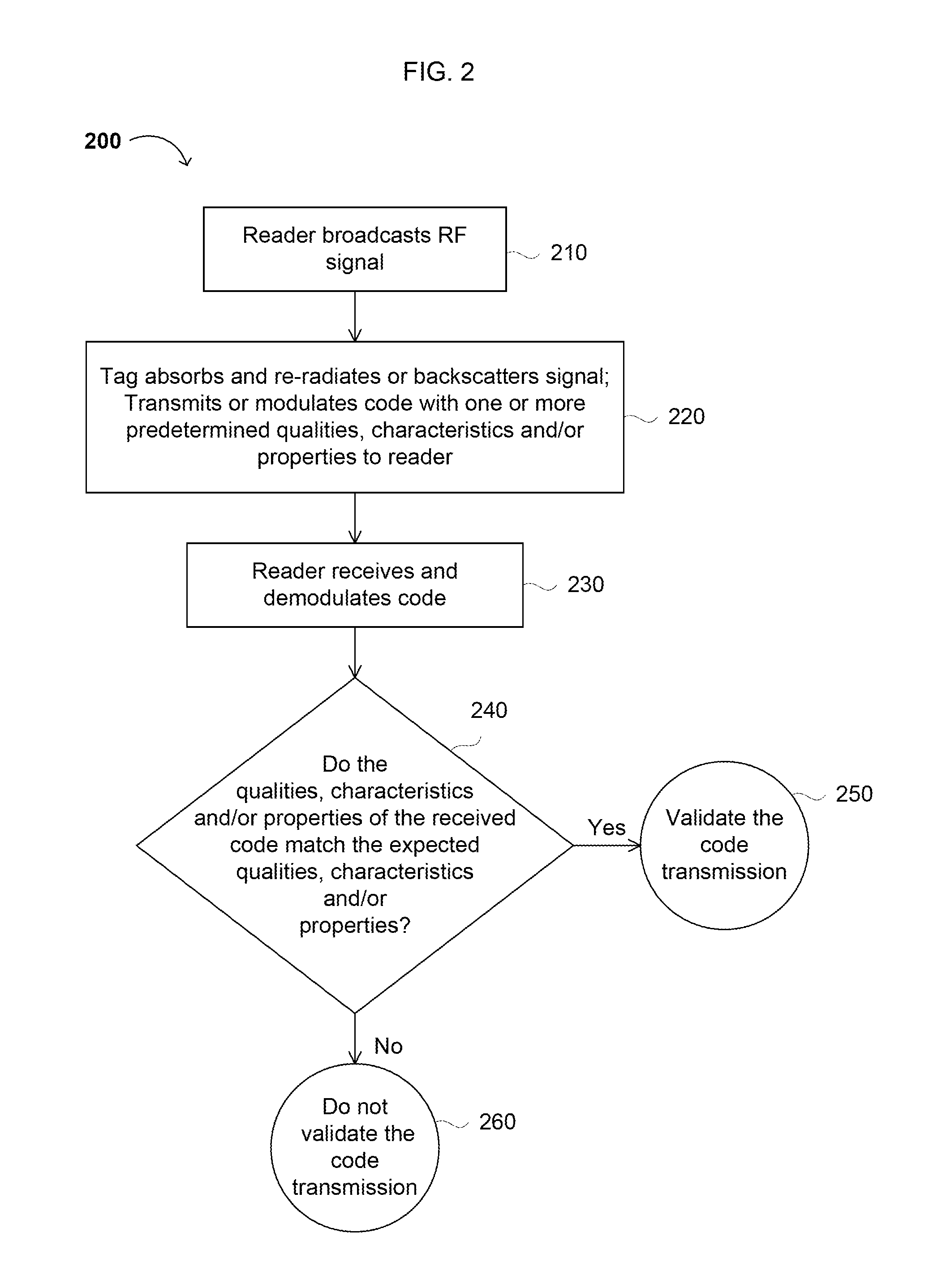
Methods and Systems for Validating Code from a Wireless Device
InactiveUS20110018692A1Reliable methodReadily apparentError preventionSensing detailsIntegrated circuitAloha
Methods, algorithms, architectures, circuits, and / or systems for managing POR-less integrated circuits are disclosed. The method of validating code from a wireless device can include: (i) broadcasting a signal from a reader to the wireless device, (ii) reading a code transmitted, re-radiated, and / or backscattered from the wireless device, the code having a predetermined quality, characteristic, and / or property, (iii) comparing the code to a reference quality, characteristic, and / or property, and (iv) validating the code when the predetermined quality, characteristic, and / or property matches the reference quality, characteristic, and / or property. Embodiments of the present invention can advantageously provide a reliable approach for validating integrated circuits that do not incorporate a POR circuit, and which therefore may transmit spurious bits of data upon being energized. In addition, embodiments of the present invention advantageously allow an Aloha-type anti-collision function to be implemented in a reader based on POR-less integrated circuits.
Owner:ENSURGE MICROPOWER ASA
Method for pre-filtering training sequences in a radiocommunication system
InactiveUS7697602B2Good estimateSave transmission resourcesMultiple-port networksTwo-way loud-speaking telephone systemsSpatial correlationEngineering
A training sequence is pre-filtered in a radiocommunication system having an emitter in the form of an antenna device with several antenna systems, thereby making it possible to transmit the training sequences through a pre-filter to said antenna systems side for reradiation by the emitter. Estimation enabling to form the properties of radio transmission channels described by spatial correlations is formed. The prefilter is dimensioned according to the correlations, thereby minimizing the error value of an algorithm used for estimation the channel on a reception side.
Owner:NOKIA SIEMENS NETWORKS GMBH & CO KG
Dual frequency antennas and associated down-conversion method
ActiveUS20050179609A1Simultaneous aerial operationsIndividually energised antenna arraysDual frequencyResonance
A dual frequency antenna includes a plurality of dipole antennas configured to receive first and second frequencies. The antennas are arrayed to an effective length to reradiate at a third frequency, which is down-converted from the first and second frequencies. A plurality of nonlinear resonant circuits interconnect the plurality of dipole antennas and are configured to permit reradiation of the third frequency over the effective length through its low frequency dipole resonance. A method of down-converting at least first and second electromagnetic radiation frequencies is also provided. The method includes transmitting first and second electromagnetic beams at first and second frequencies, respectively. The first and second frequencies are converted to the difference frequency through a nonlinear resonant circuit coupling the at least two dipole antennas.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Method for pre-filtering training sequences in a radiocommunication system
InactiveUS20070121749A1Good precisionSpend lessTwo-way loud-speaking telephone systemsMultiple-port networksSpatial correlationReradiation
A training sequence is pre-filtered in a radiocommunication system having an emitter in the form of an antenna device with several antenna systems, thereby making it possible to transmit the training sequences through a pre-filter to said antenna systems side for reradiation by the emitter. Estimation enabling to form the properties of radio transmission channels described by spatial correlations is formed. Said prefilter is dimensioned according to said correlations, thereby minimizing the error value of an algorithm used for estimation the channel on a reception side.
Owner:NOKIA SIEMENS NETWORKS GMBH & CO KG
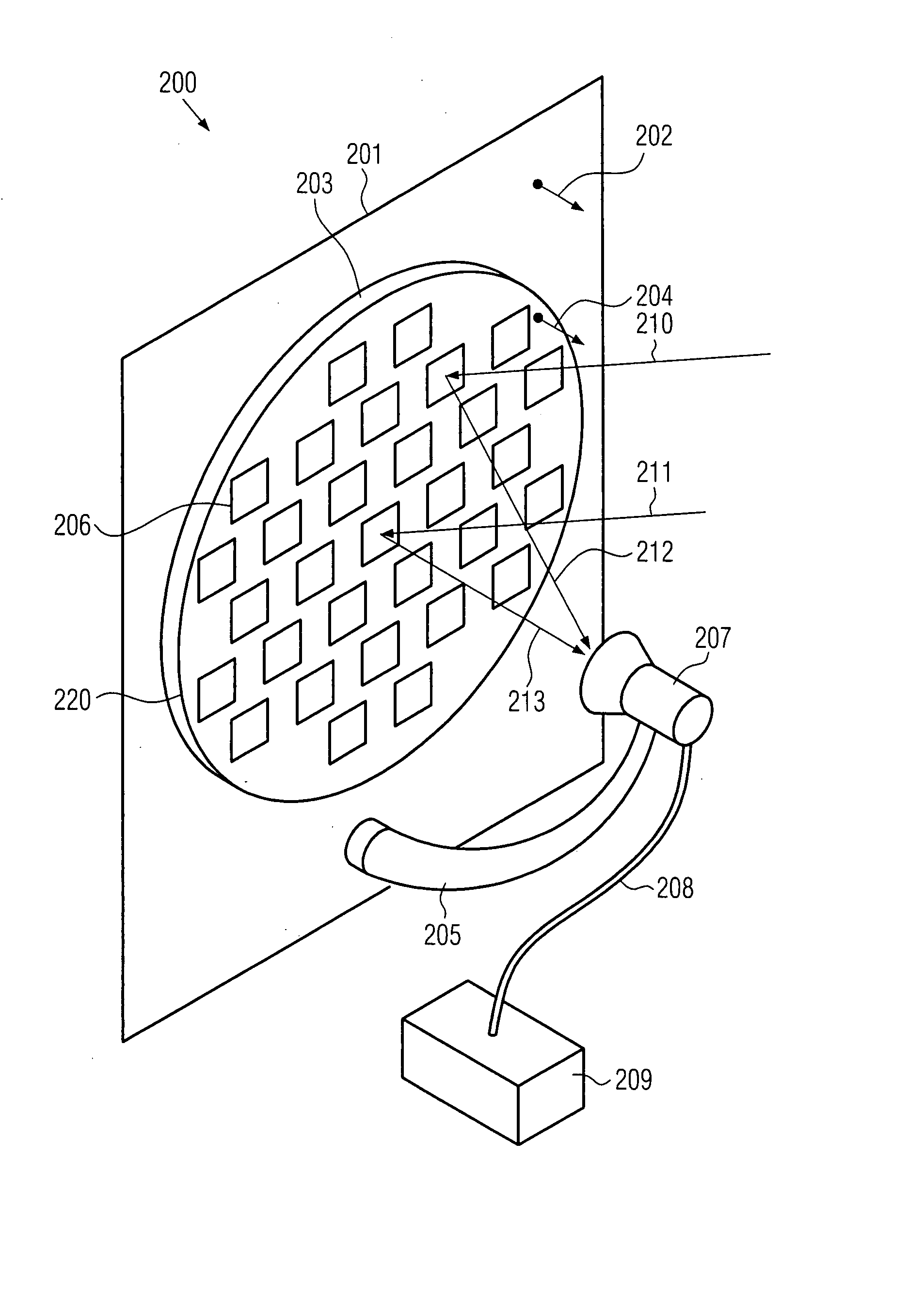
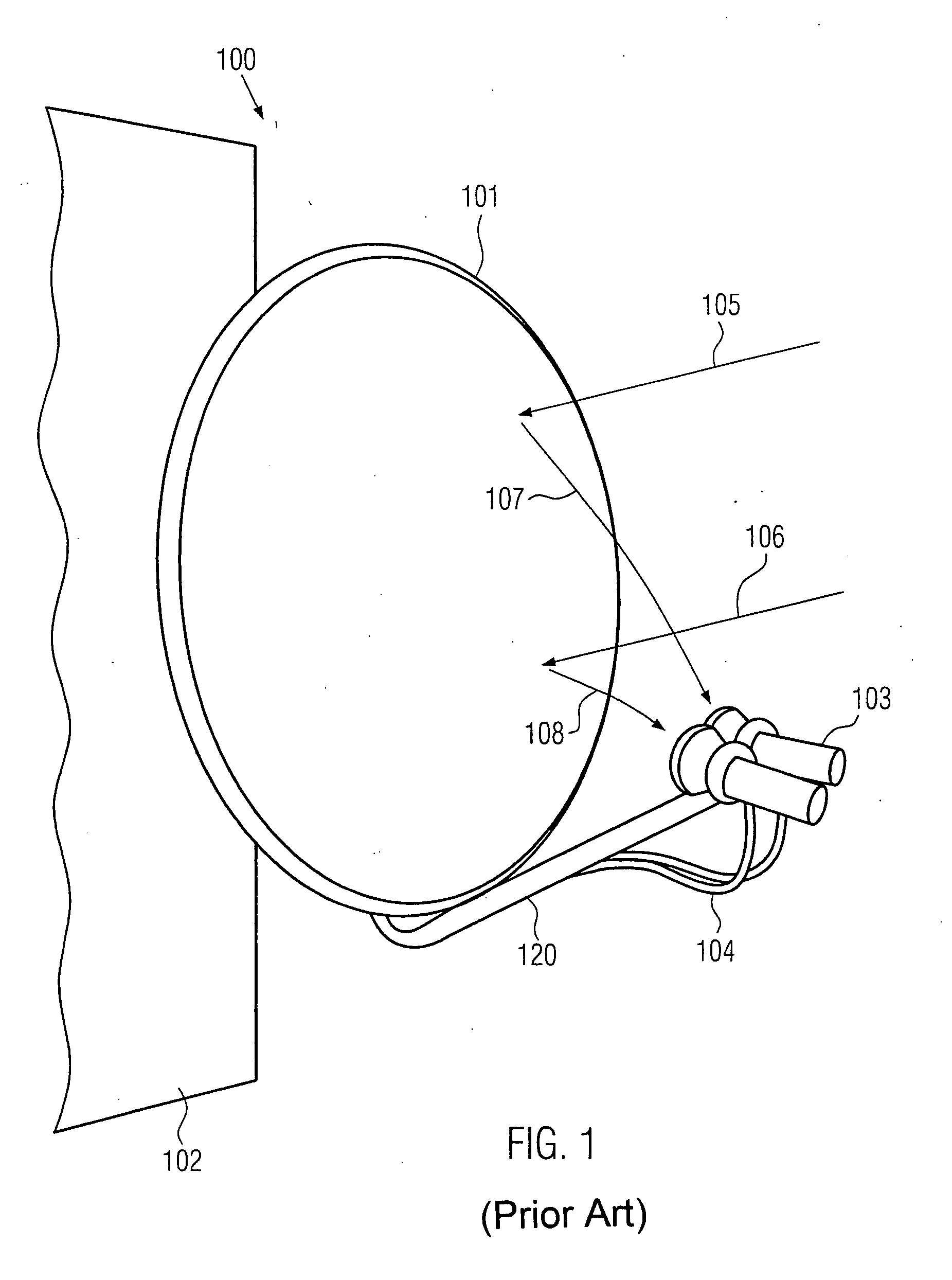
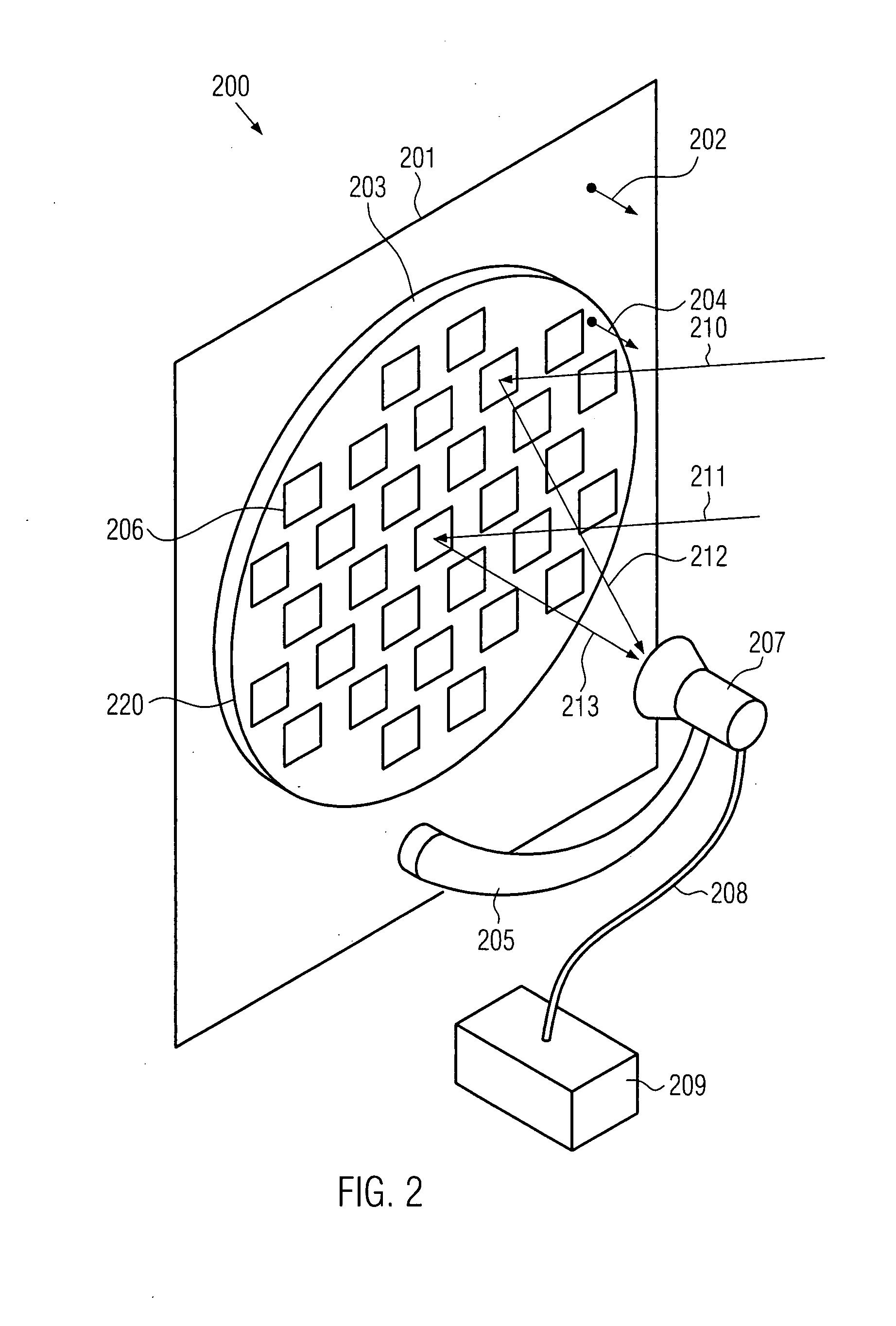
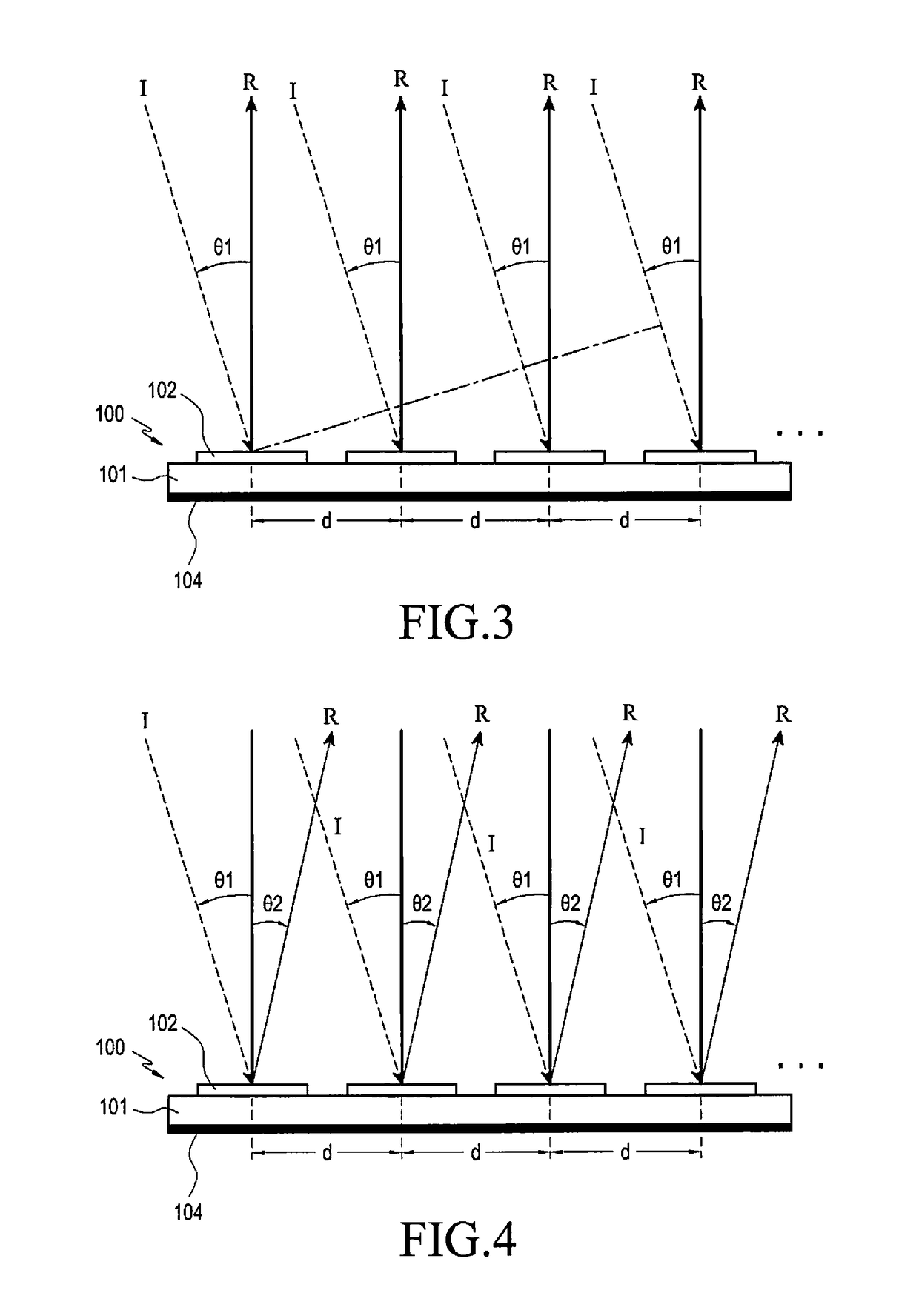
Antenna, method of manufacturing an antenna and apparatus for manufacturing an antenna
InactiveUS20080062059A1Less obtrusive visual appearanceCost-effective manufacturingAntenna supports/mountingsRadiating elements structural formsEngineeringElectromagnetic radiation
An antenna comprising a plurality of re-radiating elements arranged in at least one plane being parallel to a fixed surface. The arrangement is adapted such that electromagnetic radiation emitted from the re-radiating elements in response to electromagnetic radiation arriving from a predetermined direction interferes constructively at a feed location. Additionally, the antenna comprises a feed provided at the feed location. In a method of manufacturing an antenna, the arrangement of the plurality of re-radiating elements may be calculated and the re-radiating elements can be provided in the at least one plane substantially parallel to the substrate. An apparatus for manufacturing an antenna may comprise a data processor adapted to calculate the arrangement of the plurality of re-radiating elements and means for forming the plurality of re-radiating elements.
Owner:FRENI ANGELO +3
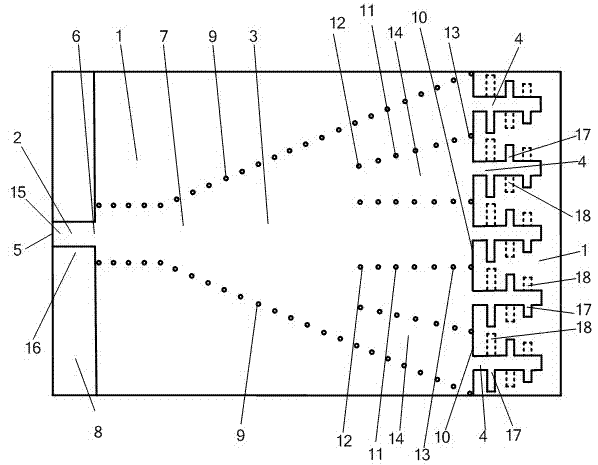
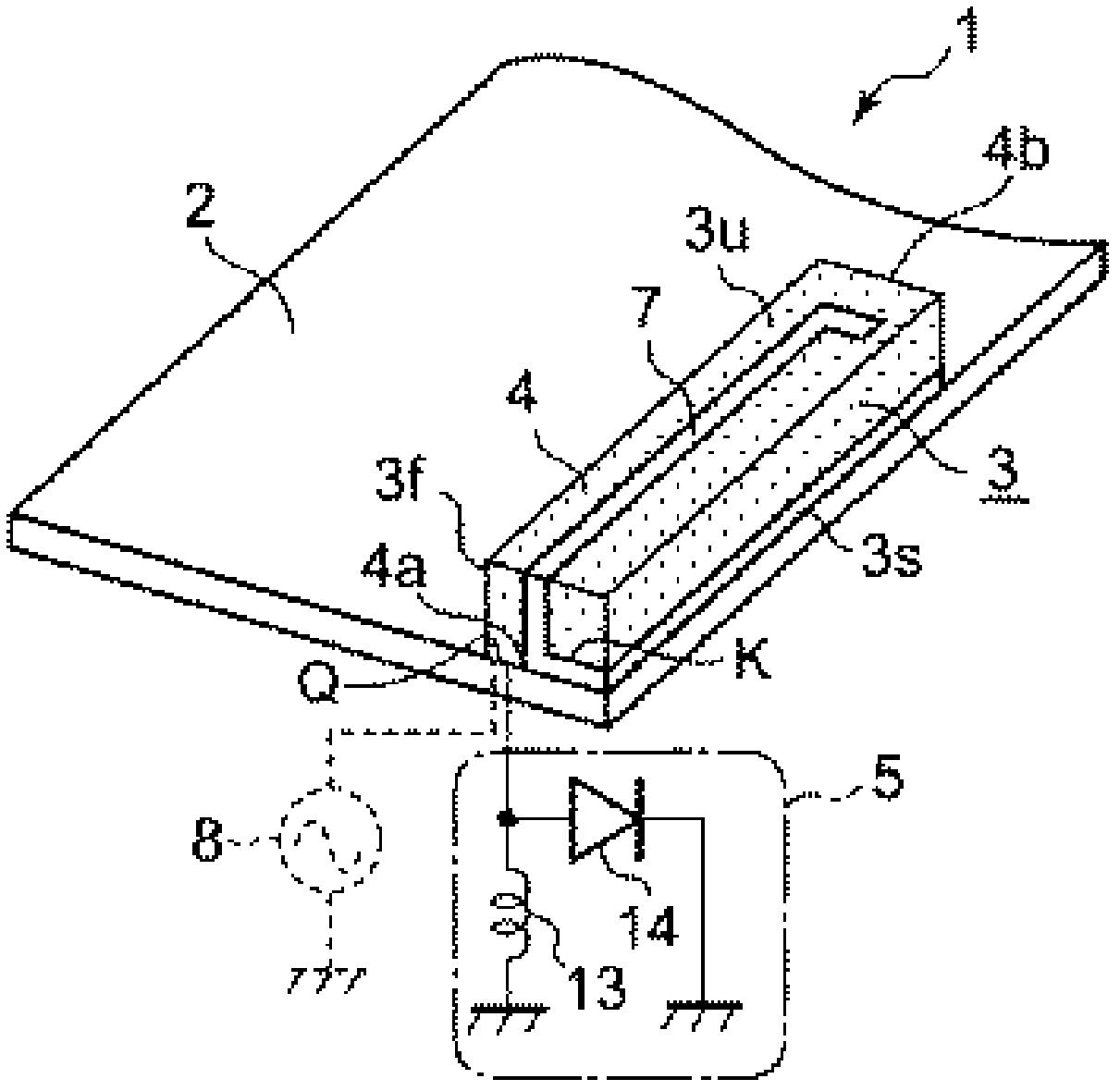
Thin-substrate amplitude correction broadband difference-beam planar horn antenna
InactiveCN103594807ACompact structureFeed loss is smallWaveguide hornsSoftware engineeringDielectric substrate
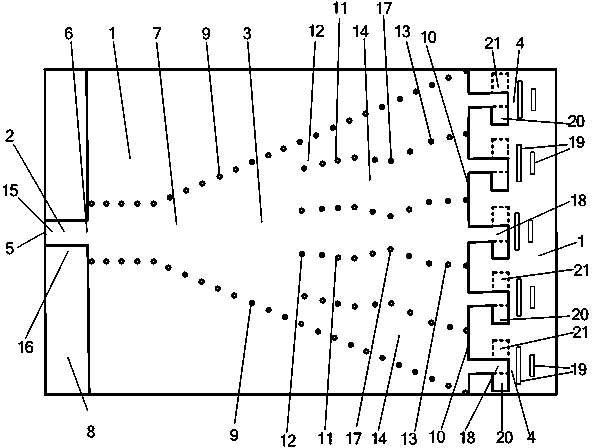
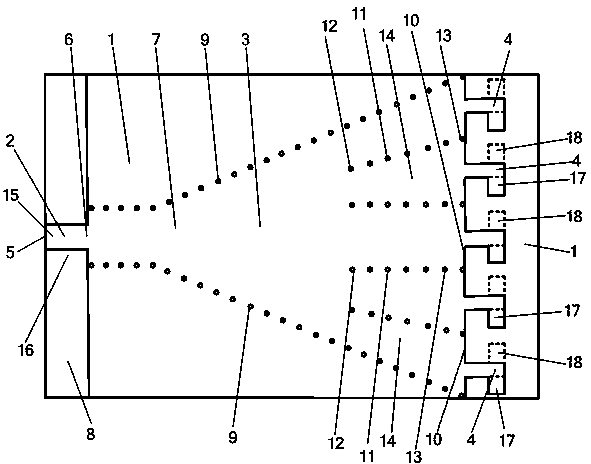
The invention provides a thin-substrate amplitude correction broadband difference-beam planar horn antenna and relates to a horn antenna. The thin-substrate amplitude correction broadband difference-beam planar horn antenna comprises a micro-strip feeder line (2), a horn antenna body (3) and log-periodic oscillators (4) which are located on a dielectric substrate (1), wherein the horn antenna body (3) consists of a first metal plane (7), a second metal plane (8) and two rows of metalized via hole horn side walls (9). The horn antenna body (3) is provided with an odd number of metalized via hole arrays (11) and an even number of dielectric-loaded waveguides (17), the dielectric-loaded waveguides (17) on the caliber face (10) of the horn antenna body (3) are identical in width and respectively connected with one of the log-periodic oscillators (4), and a left-half antenna (15) and the log-periodic oscillators (4) connected with the left-half antenna (15) are symmetric with a right-half antenna (16) and the log-periodic oscillators (4) connected with the right-half antenna (16). Electromagnetic waves can reach to the log-periodic oscillators in a constant-amplitude mode and then are radiated, and the polarization direction of a radiation field is parallel to the substrate. The thin-substrate amplitude correction broadband difference-beam planar horn antenna can be manufactured by using the thin substrate and is wide in frequency band, high in gain, large in null depth, low in cost and compact in structure.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Backscatter transponder
InactiveUS7859387B2Testing sensing arrangementsSubscribers indirect connectionCommunications systemCarrier signal
A backscatter transponder for an HF communication system with modulated reradiation, is provided that includes an antenna for receiving high-frequency carrier signals, wherein the antenna has reflective characteristics, a control unit for providing transponder-specific parameters, and a modulator that can be driven by the control unit. The modulator altering the reflective characteristics of the antenna in accordance with at least one transponder-specific parameter.
Owner:ATMEL CORP
Apparatus and method for concentrating electromagnetic energy on a remotely-located object
A method for transmitting radio frequency (RF) radiation to an object located in proximity to a reflector includes the steps of: selecting a target reflector and a level of power for conveying to the target reflector by reradiation from the target reflector, determining a resonance profile of the target reflector, the resonance profile including at least one resonant frequency of the target reflector, selecting a transmission profile matching the resonance profile, the transmission profile comprising the at least one resonant frequency, and transmitting RF radiation in accordance with the transmission profile towards the target reflector.
Owner:DROSERA
Reradiation repeater
ActiveUS20160352021A1Enhanced radio wave environmentImprove the environmentAntenna supports/mountingsRadiating elements structural formsElectricityElectrical conductor
According to an embodiment of the present invention, a reradiation repeater may comprise a dielectric substrate, a ground conductor provided on a surface of the dielectric substrate, and a plurality of unit cells provided on another surface of the dielectric substrate, wherein the unit cells reradiate radio waves in the same direction by directing the radio waves which are incident onto the unit cells at different angles to a same direction. The reradiation repeater may facilitate to select, e.g., an installation location and secure a good reradiation capability even when the installation environment is changed (e.g., a variation in the installation location of base station facility), contributing to coverage of a shadow zone. The reradiation repeater may be implemented in various manners according to embodiments of the present invention.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
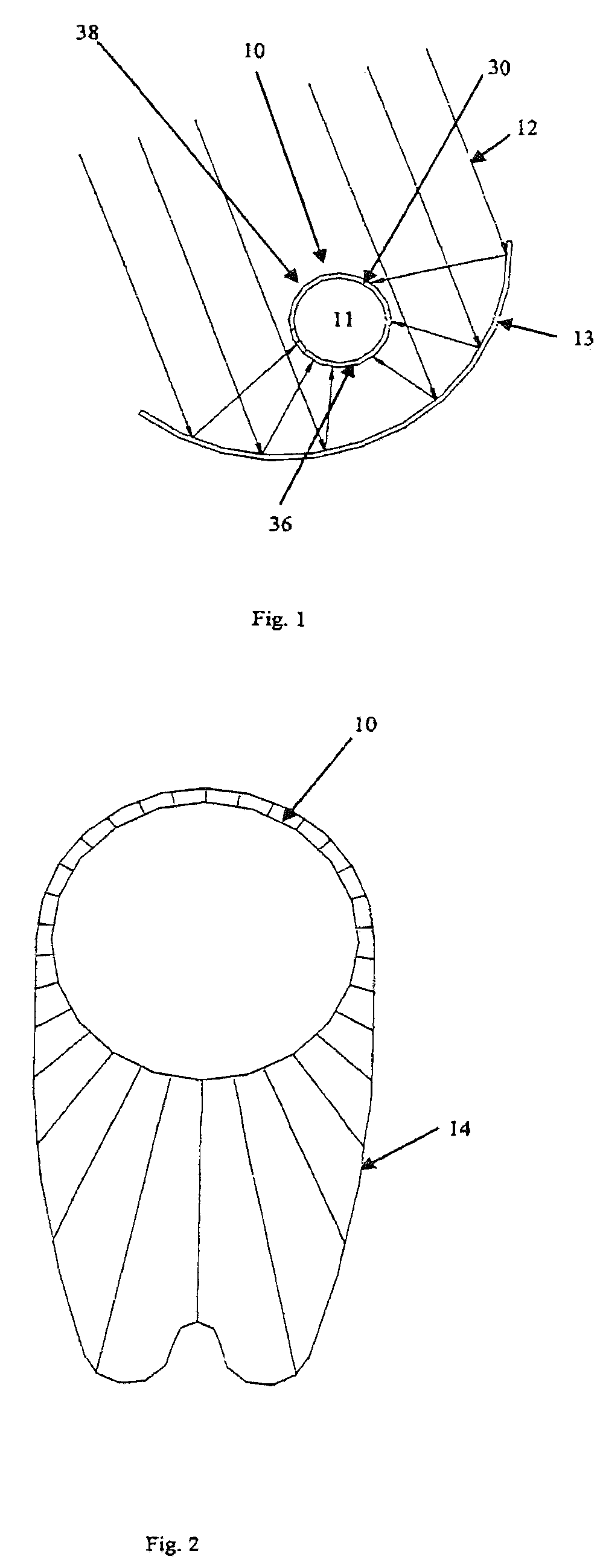
Solar absorber
InactiveUS7607428B2Minimize reradiation lossIncrease productionSolar heating energySolar heat devicesSolar absorberLength wave
The solar absorber is equipped with an absorber body (10) that absorbs incident solar energy (12) and converts it to heat. The absorber body has a selective absorption layer (17) on a side (36) oriented toward the concentrator (13) and another selective absorption layer (18) on an opposite side (38) oriented away from the concentrator (13). The selective absorption layers (17, 18) have threshold wavelengths below which solar radiation is absorbed and above which a reradiation capacity of the absorber body is suppressed. The threshold wavelength of the selective absorption layer (17) on the side (36) of the absorber body that is oriented toward the concentrator is greater than the other threshold wavelength of the other selective absorption layer(18) on the opposite side (38) of the absorber body oriented away from the concentrator.
Owner:SCHOTT AG
Glazing laminates
InactiveUS20060210775A1Minimize transmission of heatReduce heat buildupSynthetic resin layered productsCellulosic plastic layered productsPolyvinyl butyralGram
There is provided a glazing laminate comprising a polyvinyl butyral core layer having polyvinyl butyral / IR dye layers on each side. The dye containing layers are solvent cast from methanol onto the core layer. The dyes in each layer are different comprising BN 18 type PVB containing either 2 mg Epoline III-125 or 2 mg of Epolite III-57 dyes per grams of resin and dissolved in 10 ml of analytical grade of methanol for casting. The polymer is sandwiched between two glass layers under pressure and heat treatment at 135-140° C. An overall concentration of the dyes of ˜0.1 g / m2 results in an energy absorption over 65%. The heating effect of absorption is reduced by conduction through the polymer to the laminate edges, internal reflection, spherical reradiation and the relative insulative effect of the glass layers.
Owner:TROPIGLAS
Thin-substrate phase amplitude correction quari-yagi difference beam planar horn antenna
InactiveCN103606754ACompact structureFeed loss is smallWaveguide hornsRadiating elements structural formsDielectric substrateEngineering
The invention discloses a thin-substrate phase amplitude correction quari-yagi difference beam planar horn antenna, and relates to a horn antenna. The thin-substrate phase amplitude correction quari-yagi difference beam planar horn antenna comprises a micro-strip feeder (2), a horn antenna body (3) and quari-yagi antennas (4), wherein the micro-strip feeder (2), the horn antenna body (3) and the quari-yagi antennas (4) are arranged on a dielectric substrate (1), the horn antenna body (3) comprises a first metal plane (7), a second metal plane (8) and two metallization through hole horn side walls (9), the horn antenna body (3) is provided with metallization through an odd number of hole arrays (11), and an even number of dielectric-loaded waveguides (15), on an aperture surface (10) of the horn antenna body (3), the widths of the dielectric-loaded waveguides (15) are equal, the dielectric-loaded waveguides (15) are connected with the quari-yagi antennas (4) which comprise active oscillators (21) and passive oscillators (22), and a left-half antenna (13) and a right-half antenna (14) are arranged symmetrically. Electromagnetic waves can reach the quari-yagi antennas in an equal-amplitude and in-phase mode and then carry out radiation, and the direction of polarization of a radiation field is parallel to the dielectric substrate; according to the thin-substrate phase amplitude correction quari-yagi difference beam planar horn antenna, the thin substrate can be adopted, and the thin-substrate phase amplitude correction quari-yagi difference beam planar horn antenna is high in gain, large in zero drawdown, low in cost and compact in structure.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Thin substrate phase-position correcting quasi-yagi plane horn antenna
InactiveCN103606750ACompact structureFeed loss is smallWaveguide hornsRadiating elements structural formsDielectric substrateEngineering
The invention relates to a horn antenna, and discloses a thin substrate phase-position correcting quasi-yagi plane horn antenna. The antenna comprises a micro-strip feeder (2), a horn antenna body (3) and a plurality of quasi-yagi antennas (4), wherein the micro-strip feeder (2), the horn antenna body (3) and the quasi-yagi antennas (4) are arranged on a dielectric substrate (1). The horn antenna body (3) is composed of a first metal plane (7), a second metal plane (8) and two rows of metallization through hole horn side walls (9). Metallization through hole arrays (11) and medium filling waveguides (14) are arranged in the horn antenna body (3). Each medium filling waveguide (14) on a caliber plane (10) of the horn antenna body (3) is connected with the corresponding quasi-yagi antenna (4) composed of an active vibrator (17) and a passive vibrator (18). An electromagnetic wave can reach the quasi-yagi antennas in an in-phase mode to be irradiated, and the polarization direction of a radiation field is parallel to the substrate. According to the antenna, a thin substrate can be used for manufacturing the antenna, and the antenna is high in gain, low in cost and compact in structure.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
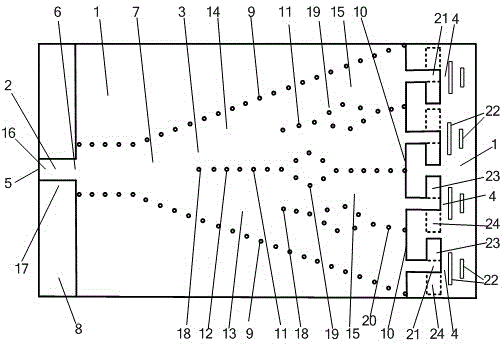
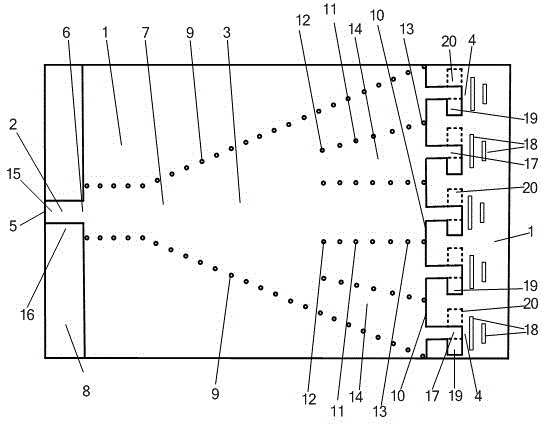
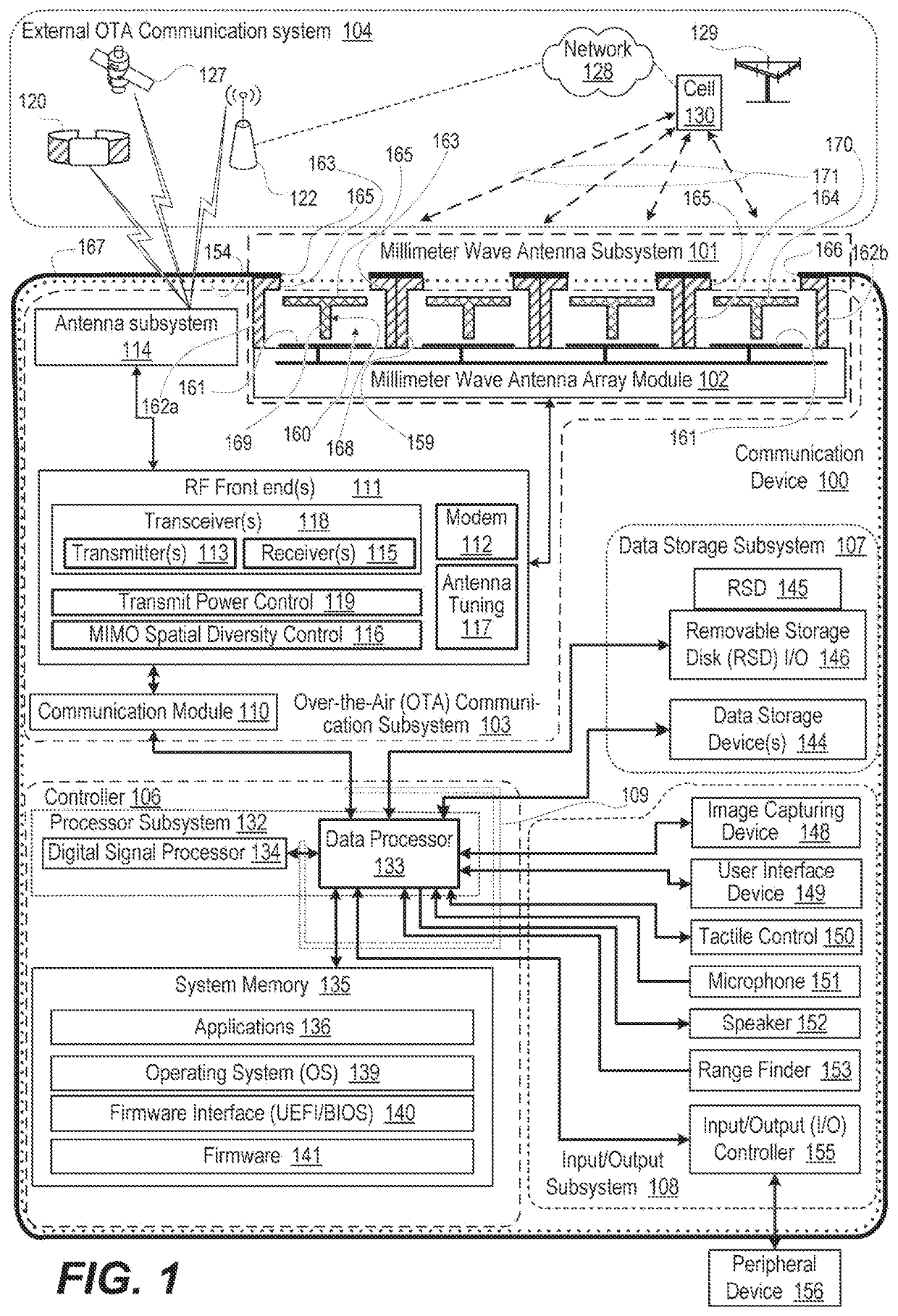
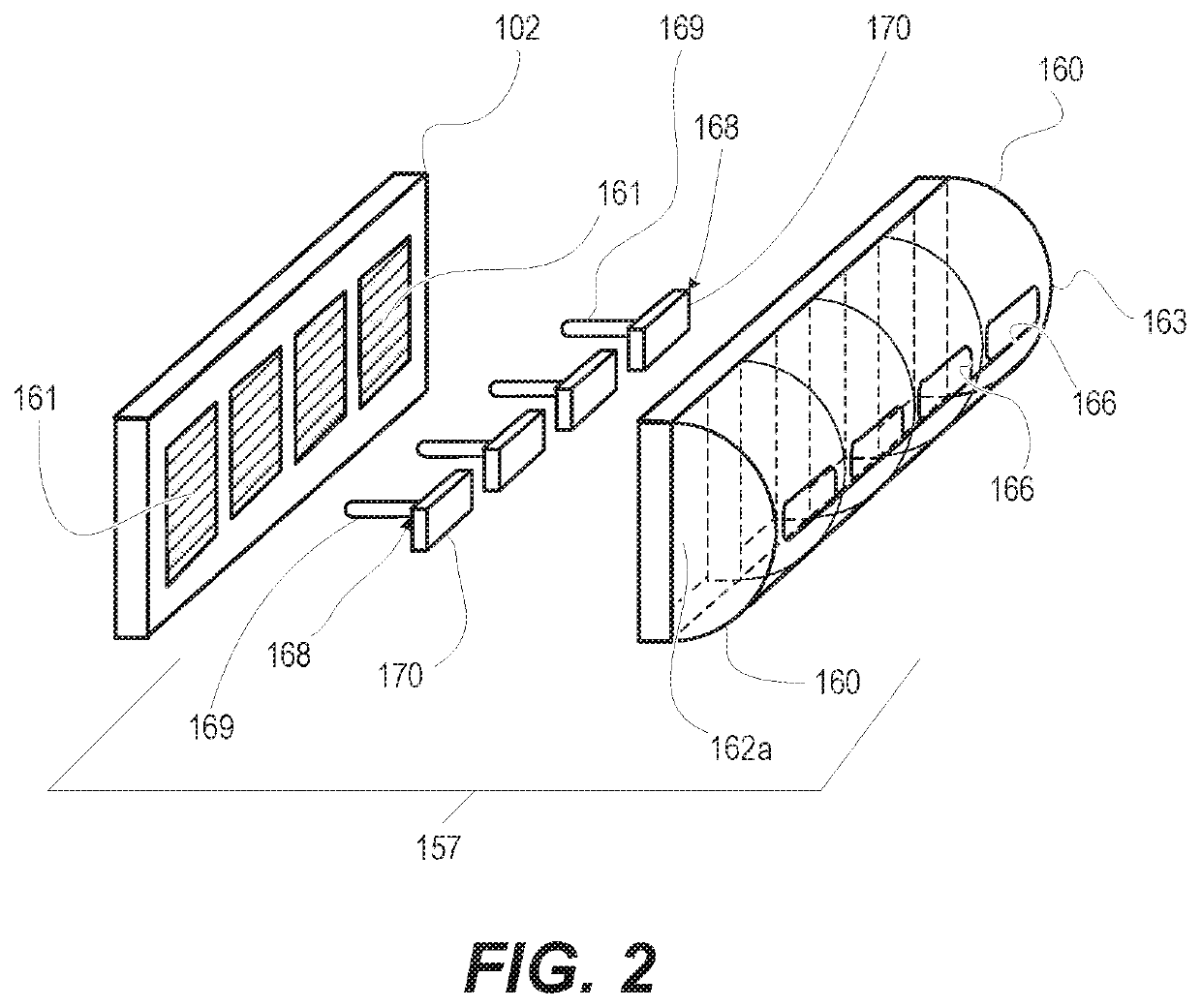
Coupling and re-radiating system for millimeter-wave antenna
ActiveUS10727600B1Easily integrated into metal housing of phoneIncreased beam widthAntenna supports/mountingsAntenna arrays manufactureSoftware engineeringMillimetre wave
An antenna subsystem of a communication device has an open cavity including an inner opening and lateral and outer sides that define a cavity. The cavity is sized less than required for cavity mode resonance at a millimeter-wave operating frequency. A millimeter-wave antenna element placed at the inner opening of the hollowed section cavity excites evanescent electromagnetic fields in the cavity. A slot antenna is formed in a metallic layer of the outer side of the cavity. A metallic sectioned proximity post has a first section positioned adjacent to and spaced apart from the millimeter-wave antenna element to couple to, and conduct, the evanescent electromagnetic field. The metallic proximity post has a second section positioned adjacent to and spaced apart from the slot antenna to couple at the millimeter-wave operating frequency, enabling re-radiation by the slot antenna.
Owner:MOTOROLA MOBILITY LLC
Reradiation apparatus for terrestrial digital broadcasting and method for reradiating terrestrial digital broadcasting
InactiveUS20090122843A1Spatial transmit diversityModulated-carrier systemsDigital broadcastingMobile device
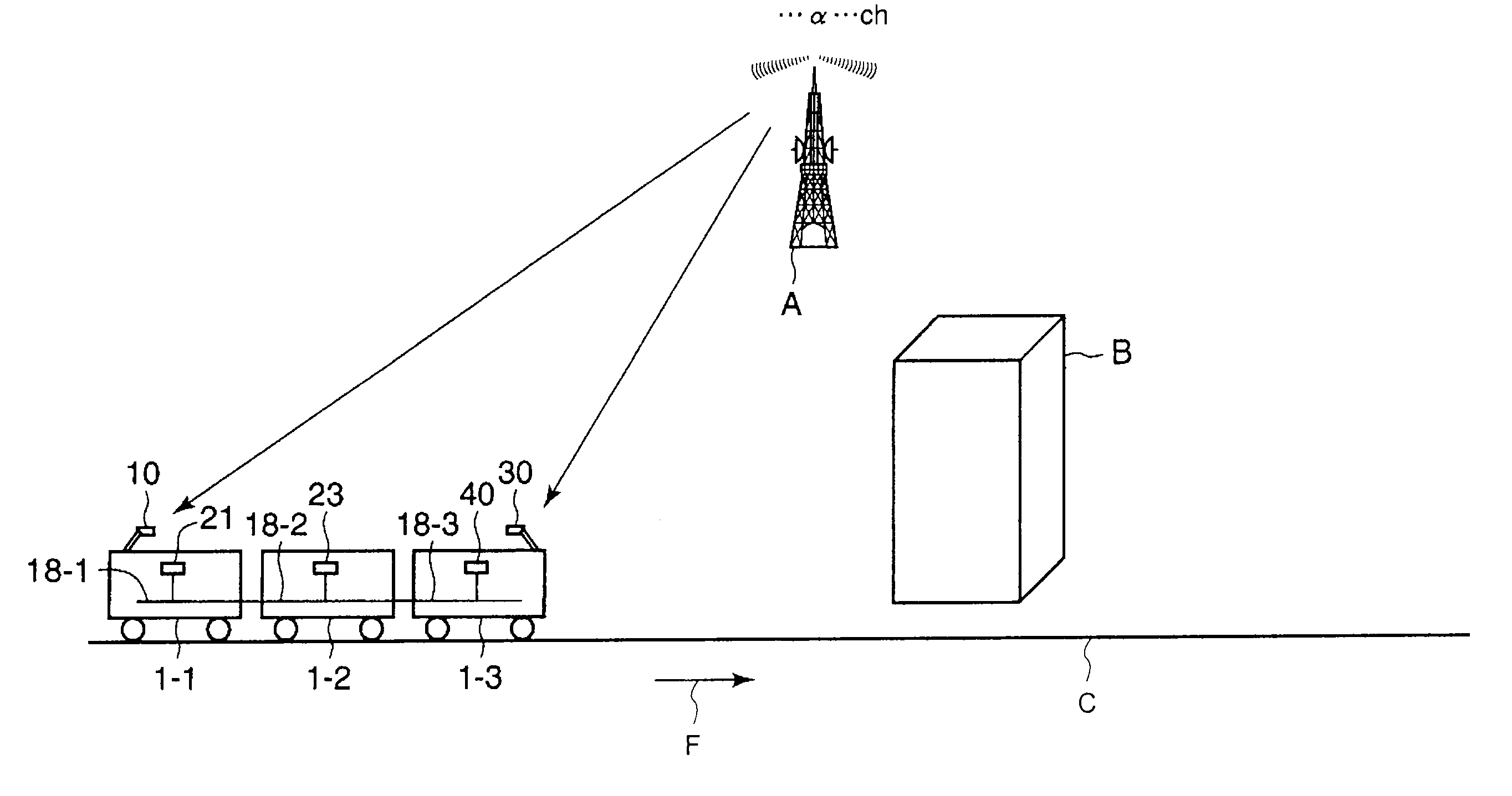
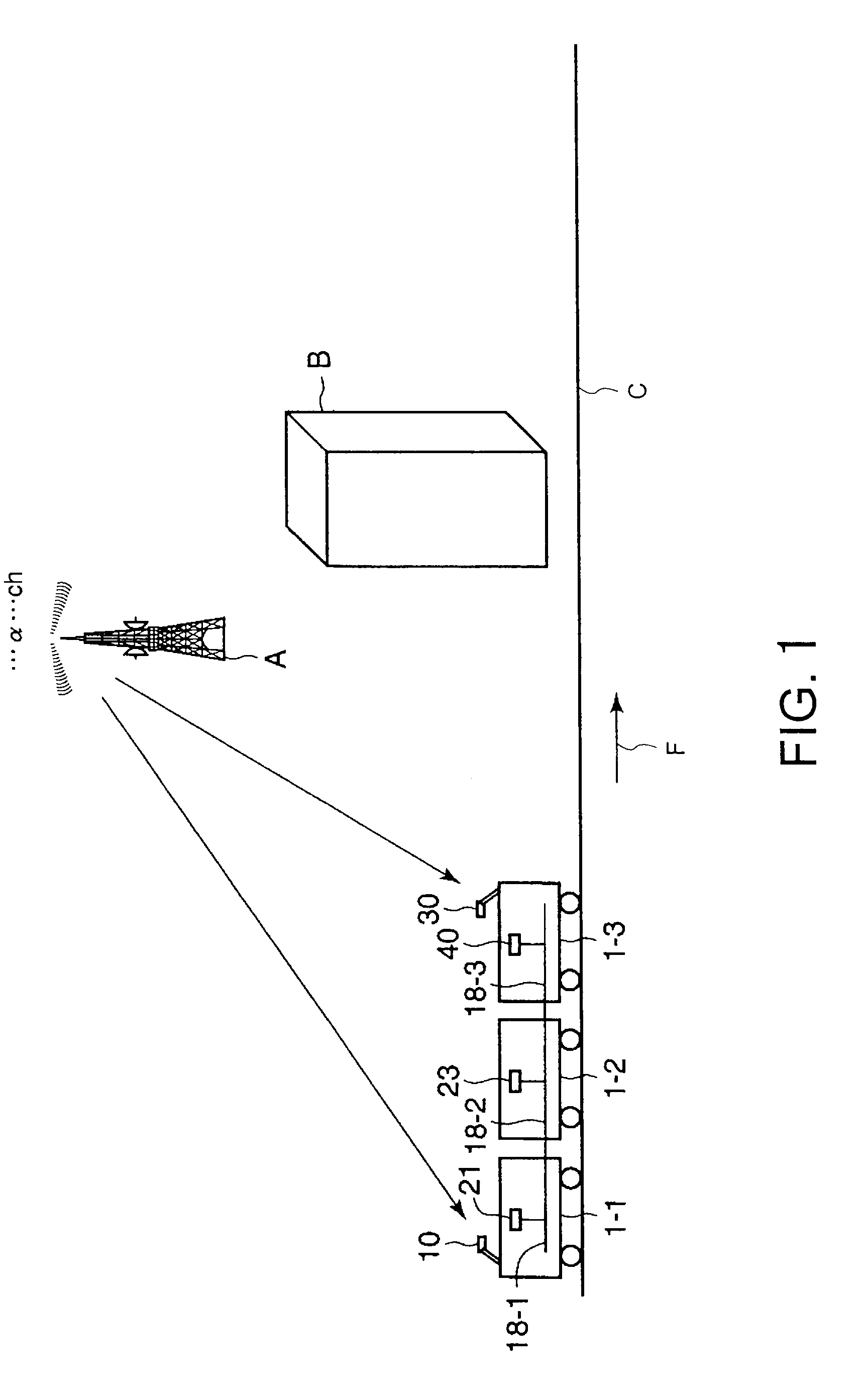
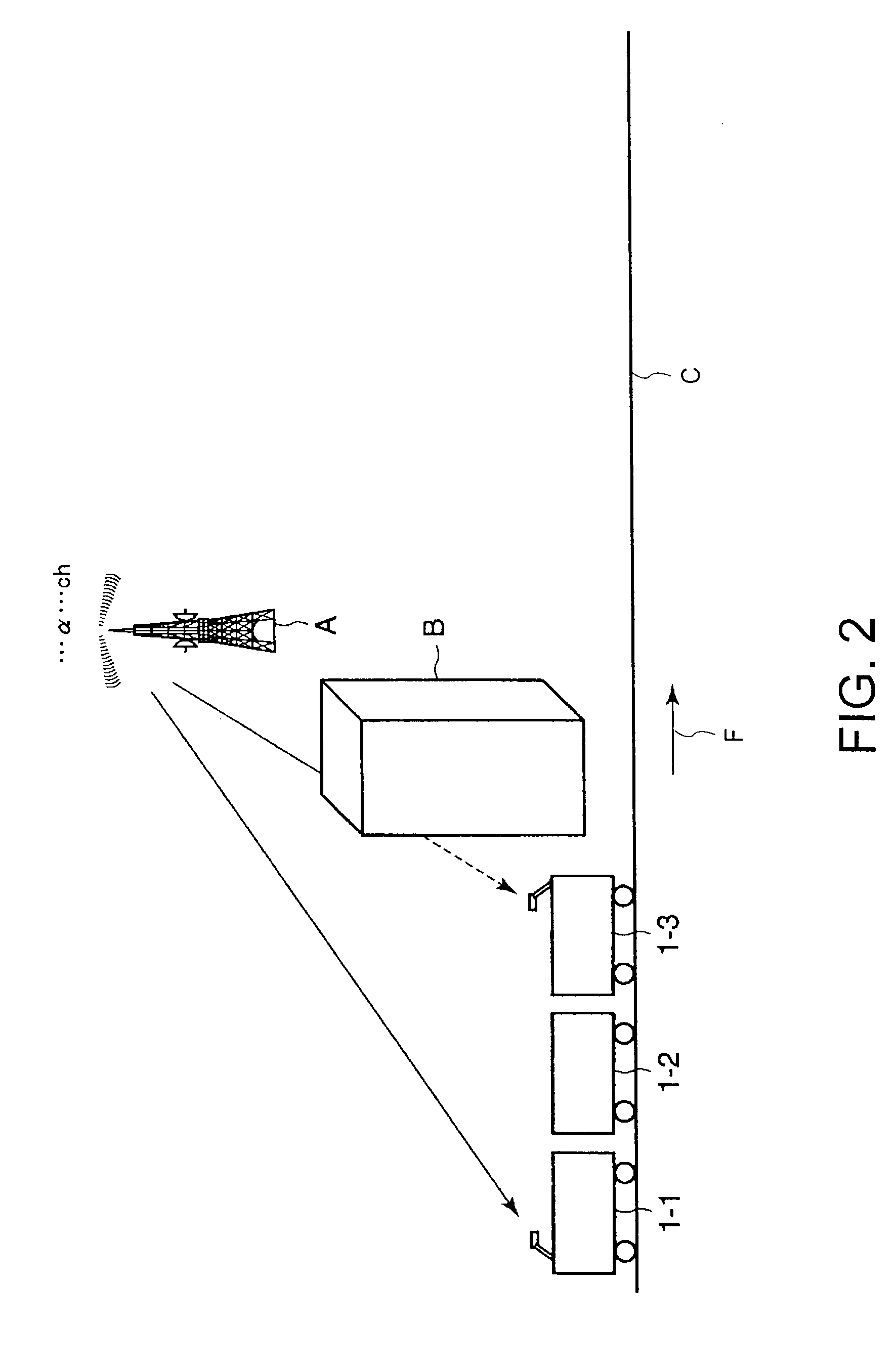
A reradiation apparatus for terrestrial digital broadcasting which can continue to reradiate a broadcasting signal even if the receive state of the broadcasting signal deteriorates intermittently with movement is provided. The reradiation apparatus for the terrestrial digital broadcasting includes plural antennas which are provided in mutually spaced along the running direction of a mobile, plural receiving processing parts provided corresponding to each antenna, a master selecting part which chooses any one of the receiving processing parts as a master, a monitoring part which supervises receive states of the terrestrial digital broadcasting signals of the plural receiving processing parts, a switching part, and a reradiation unit. The switching part chooses the terrestrial digital broadcasting signal received by the receiving processing part selected as a master or the terrestrial digital broadcasting signal received by other receiving processing part based on the receive state of the receiving processing part chosen as the master, and the reradiation unit reradiates the selected terrestrial digital broadcasting signal in the mobile.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Reradiation antenna and wireless charger
ActiveCN104979624AImprove performanceImprove communication environmentNear-field transmissionBatteries circuit arrangementsGround contactElectric power
A reradiation antenna including an insulation panel; a ground contact formed on one side of the insulation panel; a slot formed by eliminating a part of the ground contact by exposing the insulation panel; a power feeding unit formed on the insulation panel between the slot and separated from the ground contact and connected with a power source using a first end of the power feeding unit; and a radiation unit formed on one side of the insulation panel, and connected with a second end of the power feeding unit positioned at an opened end of the slot.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Thin-substrate phase correction broadband plane horn antenna
InactiveCN103618146ACompact structureFeed loss is smallWaveguide hornsSoftware engineeringDielectric substrate
The invention relates to a horn antenna, in particular to a thin-substrate phase correction broadband plane horn antenna which comprises a micro-strip feeder line (2), a horn antenna body (3) and a plurality of log-periodic vibrators (4), and the micro-strip feeder line (2), the horn antenna body (3) and the log-periodic vibrators (4) are arranged on a dielectric substrate (1). The horn antenna body (3) is composed of a first metal plane (7), a second metal plane (8) and two rows of metalized via hole horn side walls (9), metalized via hole arrays (11) and dielectric-loaded waveguides (14) are arranged in the horn antenna body (3), and the dielectric-loaded waveguides (14) are connected with the log-periodic vibrators (4) respectively on the caliber face (10) of the horn antenna body (3). Electromagnetic waves can reach the log-periodic vibrators in an in-phase mode and then are reradiated, and polarization of a radiation field is parallel with the substrate. The antenna can be made through a thin substrate, and is wide in bandwidth, high in gain, low in cost and compact in structure.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Thin-substrate phase amplitude correction oscillator planar horn antenna
InactiveCN103606732ACompact structureFeed loss is smallWaveguide hornsRadiating elements structural formsSoftware engineeringDielectric substrate
The invention discloses a thin-substrate phase amplitude correction oscillator planar horn antenna, and relates to a horn antenna. The thin-substrate phase amplitude correction oscillator planar horn antenna comprises a micro-strip feeder (2), a horn antenna body (3) and a plurality of oscillators (4), wherein the micro-strip feeder (2), the horn antenna body (3) and the oscillators (4) are arranged on a dielectric substrate (1), the horn antenna body (3) comprises a first metal plane (7), a second metal plane (8) and two metallization through hole horn side walls (9), the horn antenna body (3) is provided with metallization through hole arrays (11) and dielectric-loaded waveguides (12), on an aperture surface (10) of the horn antenna body (3), the widths of the dielectric-loaded waveguides (12) are equal, and each dielectric-loaded waveguide (12) is connected with the corresponding oscillator (4). Electromagnetic waves can reach the oscillators (4) in an equal-amplitude and in-phase mode and then carry out radiation, and the direction of polarization of a radiation field is parallel to the dielectric substrate; the thin-substrate phase amplitude correction oscillator planar horn antenna can be manufactured with the thin substrate, and is high in gain, low in cost and compact in structure.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Antenna Radiator with Pre-Configured Cloaking to Enable Dense Placement of Radiators of Multiple Bands
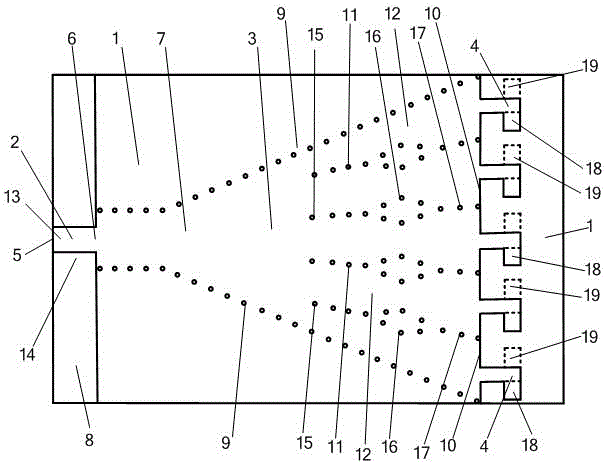
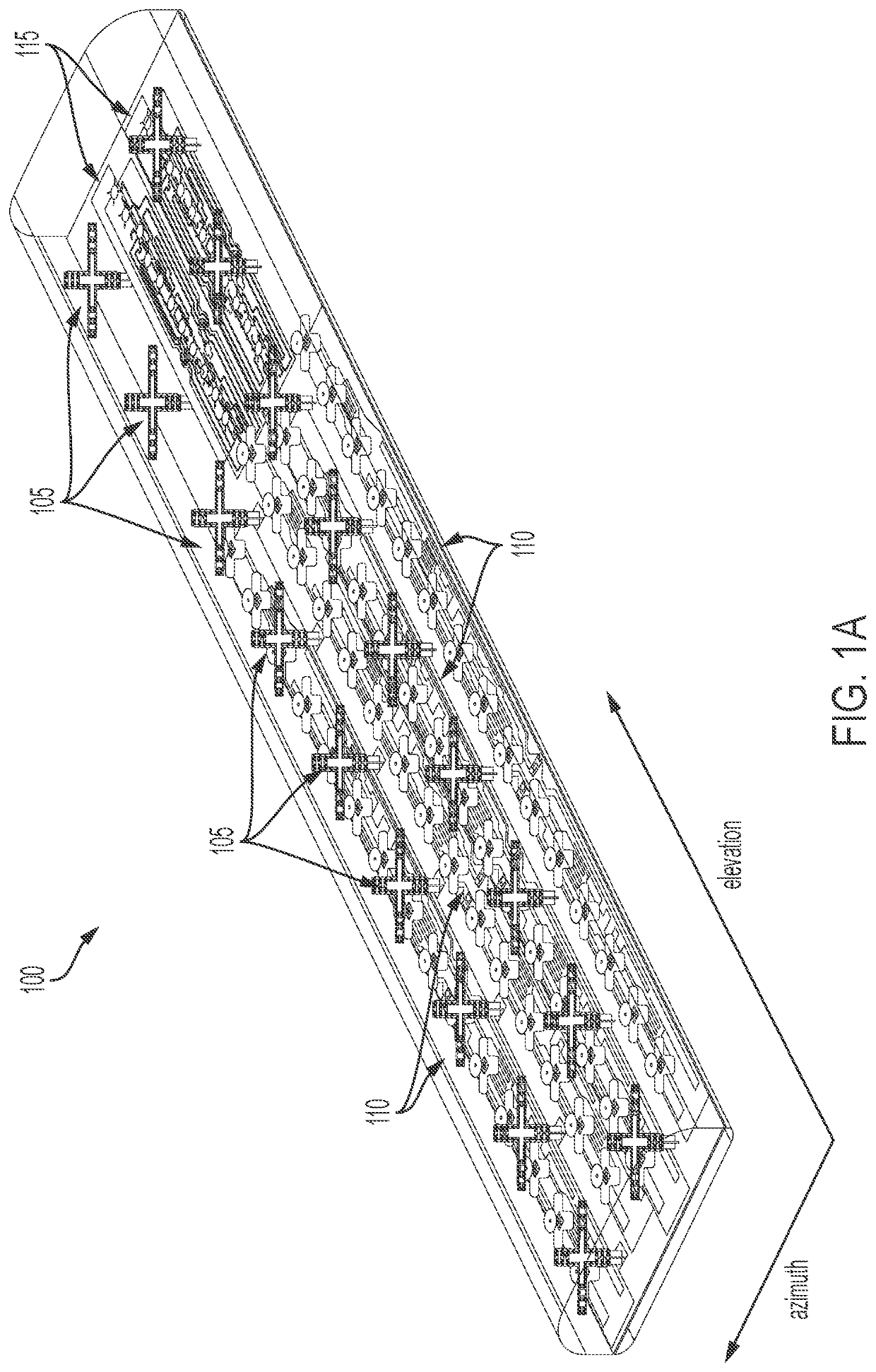
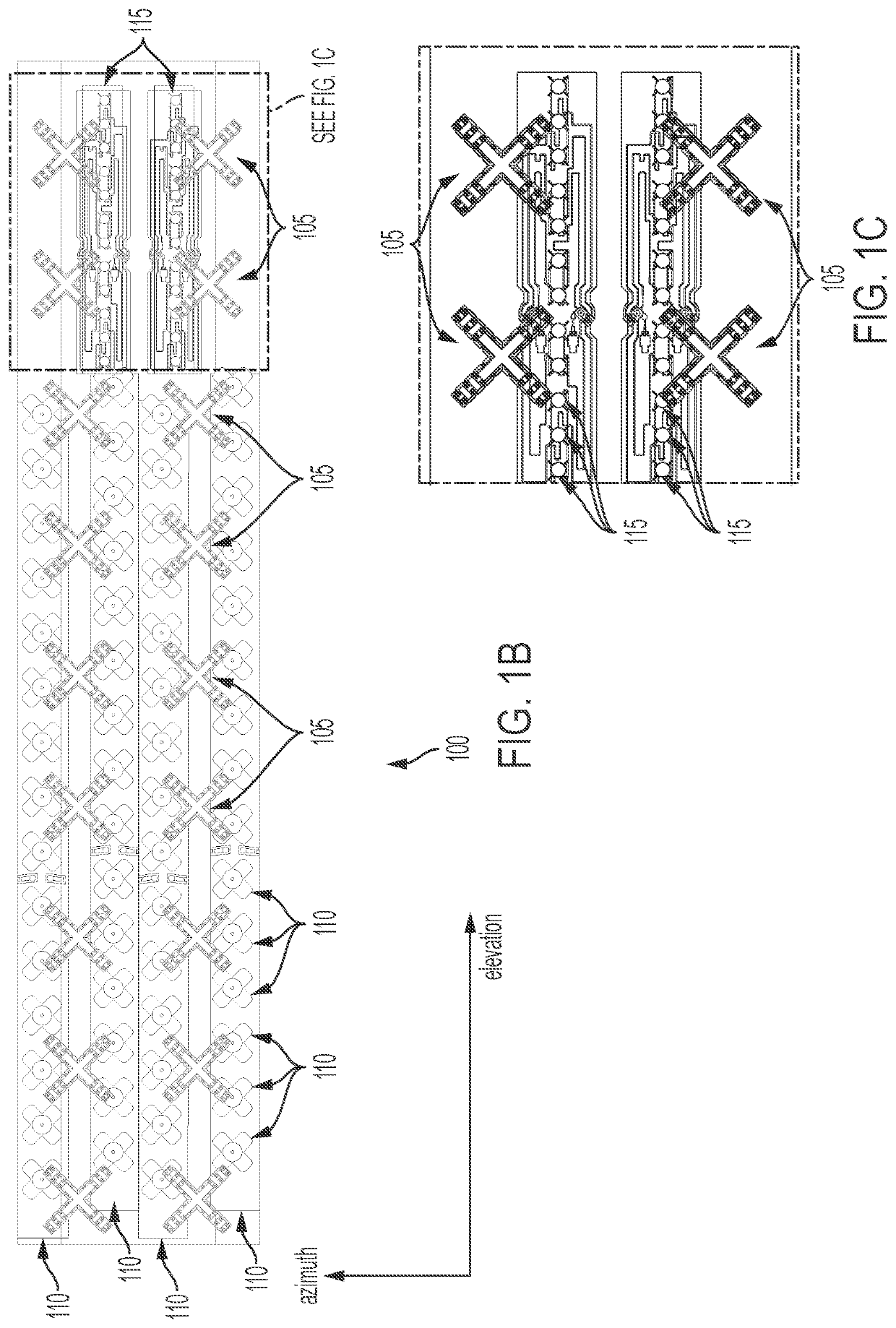
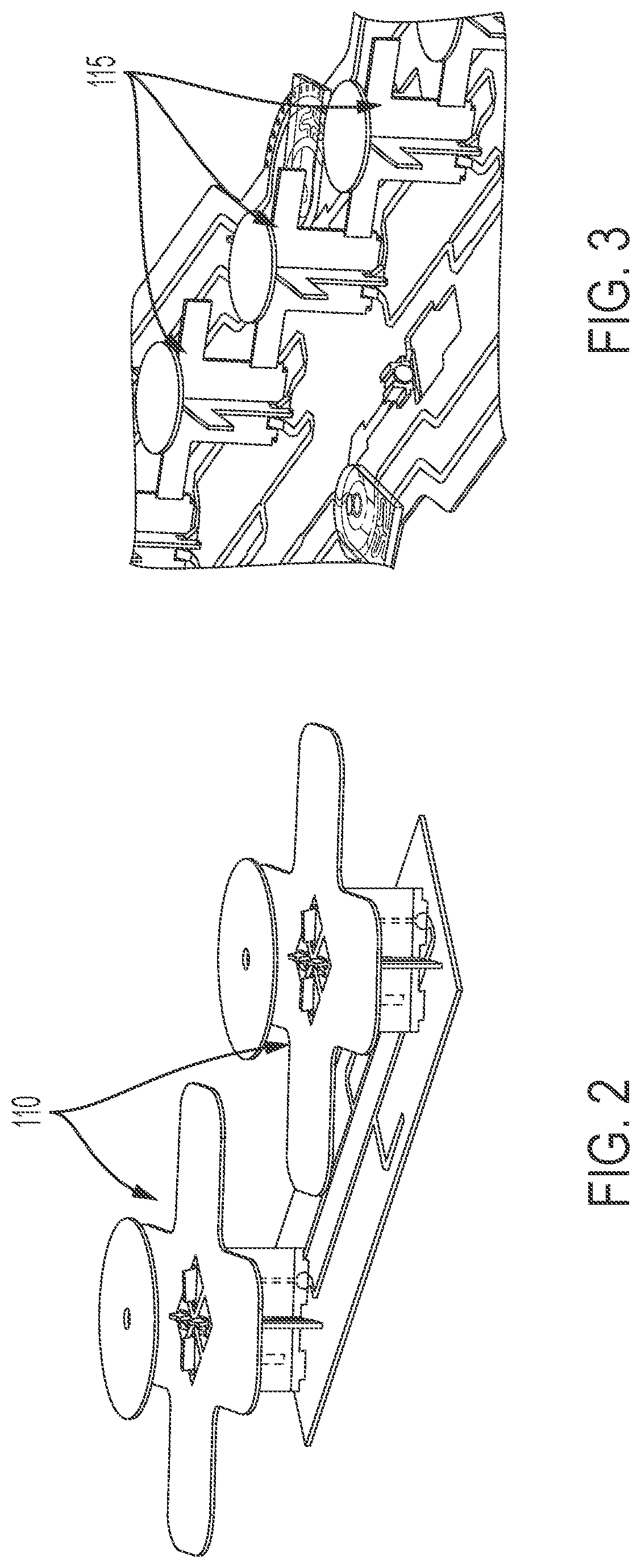
ActiveUS20210359414A1Simultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsEngineeringMechanical engineering
Disclosed is an antenna that enables dense packing of low band, mid band, and C-band radiators. The low band radiators have a plurality of dipole arms that minimize re-radiation of either RF energy emitted by either the mid band or C-Band radiators. In one embodiment, the dipole arms are formed of a two-dimensional structure that has a shape that substantially prevents re-radiation in both the mid band and the C-band. In another embodiment, the dipole arms have two different configurations: a first configuration optimized for preventing re-radiation in the mid band, and a second configuration optimized for preventing re-radiation in the C-Band. In the latter embodiment, the low band radiators in close proximity to the mid band radiators have dipole arms of the first configuration, and the low band radiators in close proximity to the C-Band radiators have dipole arms of the second configuration.
Owner:JOHN MEZZALINGUA ASSOC LLC
Reradiation repeater
ActiveUS10116059B2Improve the environmentImprove abilitiesAntenna supports/mountingsRadiating elements structural formsElectricityDielectric substrate
According to an embodiment of the present invention, a reradiation repeater may comprise a dielectric substrate, a ground conductor provided on a surface of the dielectric substrate, and a plurality of unit cells provided on another surface of the dielectric substrate, wherein the unit cells reradiate radio waves in the same direction by directing the radio waves which are incident onto the unit cells at different angles to a same direction. The reradiation repeater may facilitate to select, e.g., an installation location and secure a good reradiation capability even when the installation environment is changed (e.g., a variation in the installation location of base station facility), contributing to coverage of a shadow zone. The reradiation repeater may be implemented in various manners according to embodiments of the present invention.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Antenna and wireless communication apparatus
InactiveCN102396107AInhibit inputSuppresses higher harmonicsEnergy efficient ICTAntenna supports/mountingsCapacitanceLc resonant circuit
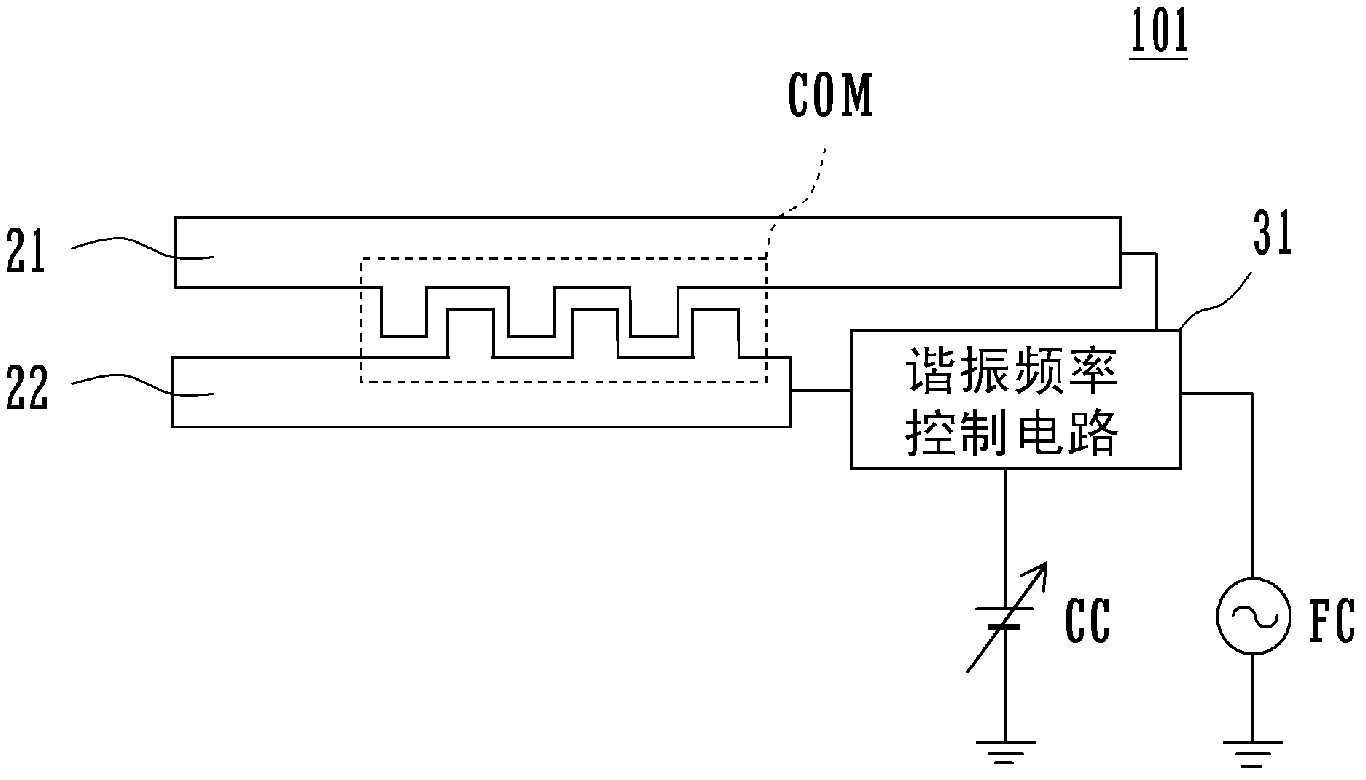
Disclosed are an antenna provided with a resonant frequency control circuit and having a design which suppresses emission (reradiation) of harmonic signals generated when the antenna receives radio waves from the outside, and a wireless communication apparatus provided with the same. A first radiating electrode (21) and a second radiating electrode (22) are provided with comb sections (COM) which generate capacitance by facing each other. If emissions of transmission radio waves from a different antenna near the antenna (101) are received, a portion will be emitted to the antenna (101), and harmonic signals will be generated by a variable capacitance element inside the resonant frequency control circuit (31). However, an LC resonant circuit (tank circuit) is formed by the inductance component of the first radiating electrode (21) and second radiating electrode (22) and the capacitance component generated at the comb sections (COM), so even if emissions from the different antenna are received, the radio waves of the basic mode are confined by the resonant frequency of the LC resonant circuit, and harmonic reradiation (spurious emission) power is reduced.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Thin-substrate amplitude correction regular yagi planar horn antenna
InactiveCN103594813ACompact structureFeed loss is smallWaveguide hornsRadiating elements structural formsDielectric substrateEngineering
The invention provides a thin-substrate amplitude correction regular yagi planar horn antenna and relates to a horn antenna. The thin-substrate amplitude correction regular yagi planar horn antenna comprises a micro-strip feeder line (2), a horn antenna body (3) and multiple regular yagi antennas (4) which are located on a dielectric substrate (1), wherein the horn antenna body (3) consists of a first metal plane (7), a second metal plane (8) and two rows of metalized via hole horn side walls (9). The horn antenna body (3) is provided with metalized via hole arrays (11) and dielectric-loaded waveguides (14), and the dielectric-loaded waveguides (14) on the caliber face (10) of the horn antenna body (3) are identical in width and respectively connected with one of the regular yagi antennas (4) consisting of active oscillators (18) and passive oscillators (19). Electromagnetic waves can reach to the regular yagi antennas in a constant-amplitude mode and then are radiated, and the polarization direction of a radiation field is parallel to the substrate. The thin-substrate amplitude correction regular yagi planar horn antenna can be manufactured by using the thin substrate and is high in gain, low in cost and compact in structure.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Thin-substrate phase correction oscillator planar horn antenna
InactiveCN103594814ACompact structureFeed loss is smallWaveguide hornsPhase correctionSoftware engineering
The invention provides a thin-substrate phase correction oscillator planar horn antenna and relates to a horn antenna. The thin-substrate phase correction oscillator planar horn antenna comprises a micro-strip feeder line (2), a horn antenna body (3) and multiple oscillators (4) which are located on a dielectric substrate (1), wherein the horn antenna body (3) consists of a first metal plane (7), a second metal plane (8) and two rows of metalized via hole horn side walls (9). The horn antenna body (3) is provided with metalized via hole arrays (11) and dielectric-loaded waveguides (14), and the dielectric-loaded waveguides (14) on the caliber face (10) of the horn antenna body (3) are respectively connected with one of the oscillators (4). Electromagnetic waves can reach to the oscillators in an in-phase mode and then are radiated, and the polarization direction of a radiation field is parallel to the substrate. The thin-substrate phase correction oscillator planar horn antenna can be manufactured by using the thin substrate and is high in gain, low in cost and compact in structure.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com