Patents
Literature
96 results about "Spurious emission" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A spurious emission is any radio frequency not deliberately created or transmitted, especially in a device which normally does create other frequencies. A harmonic or other signal outside a transmitter's assigned channel would be considered a spurious emission.
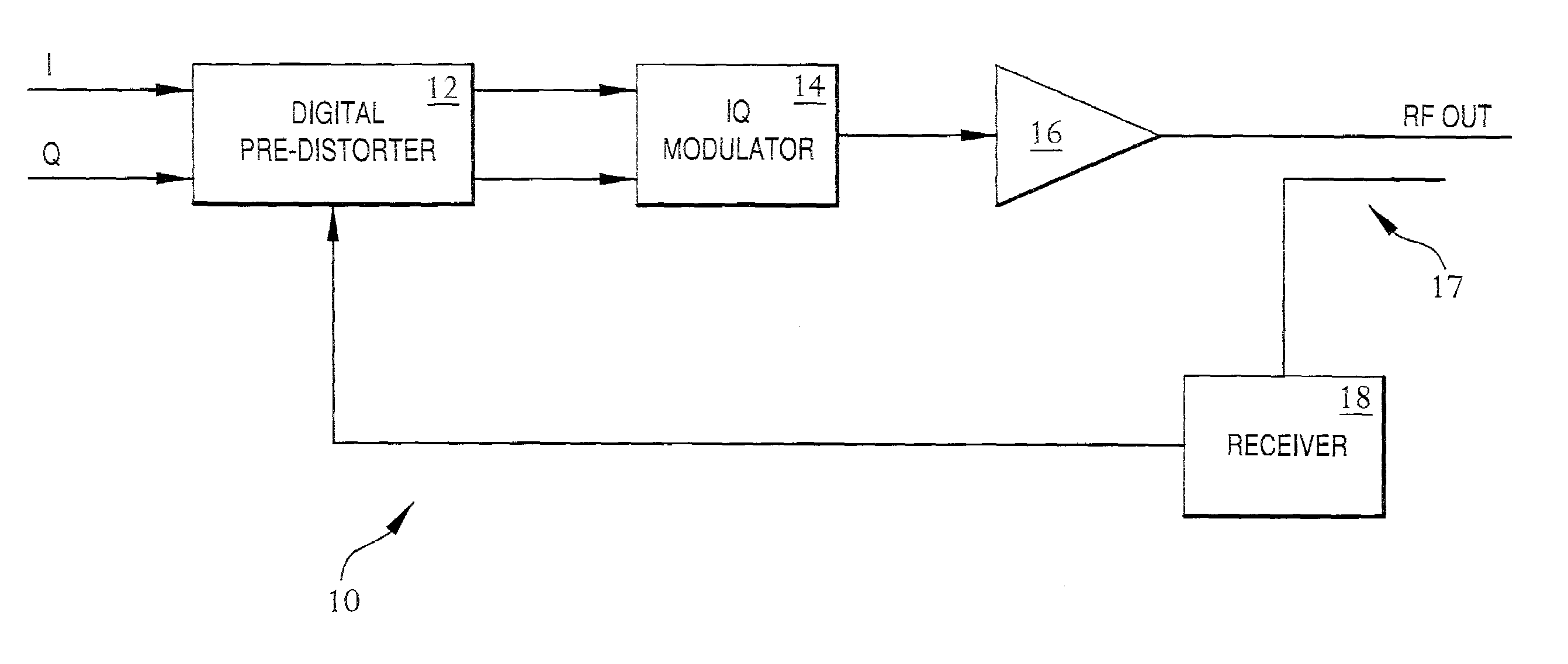
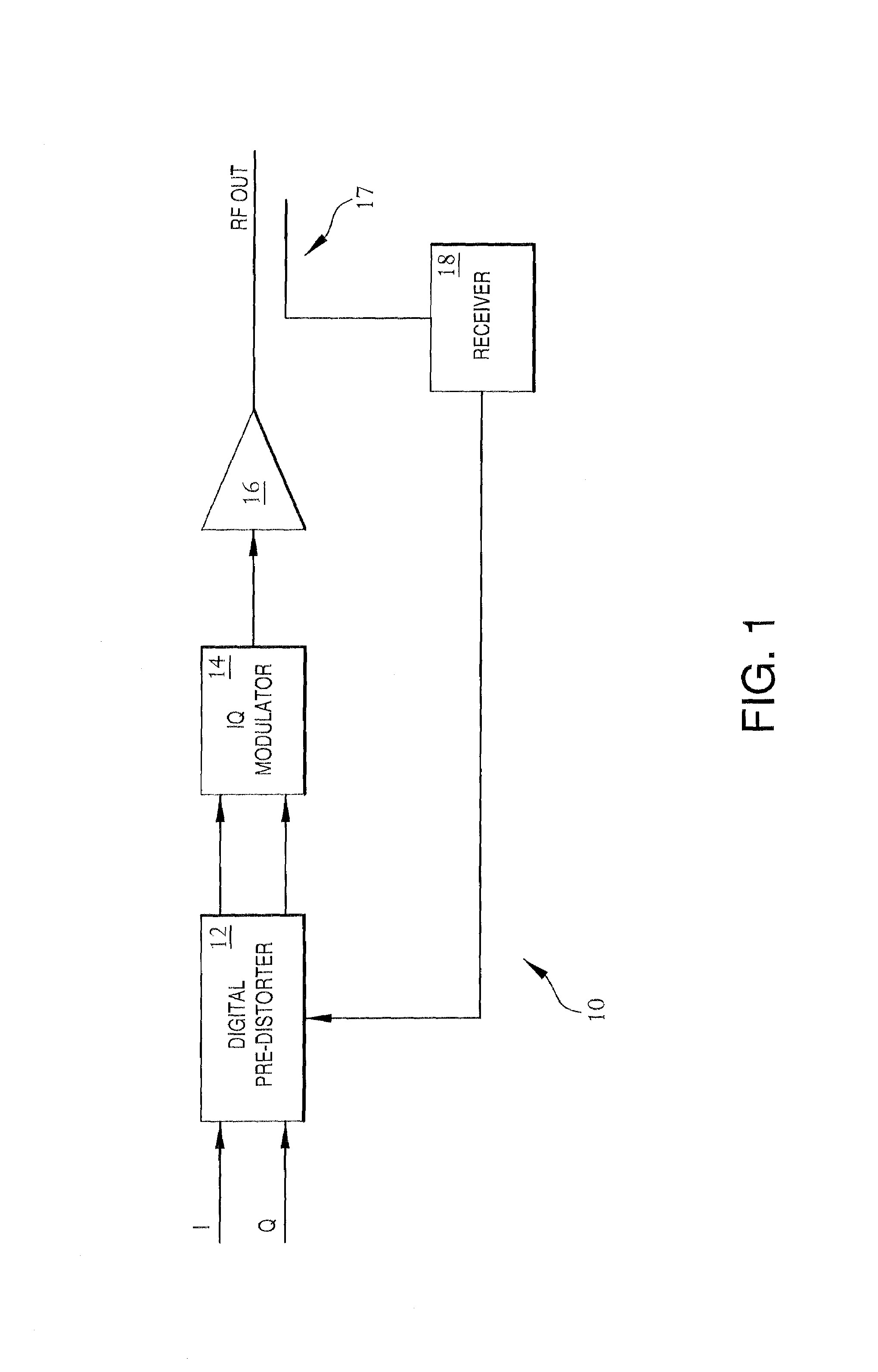
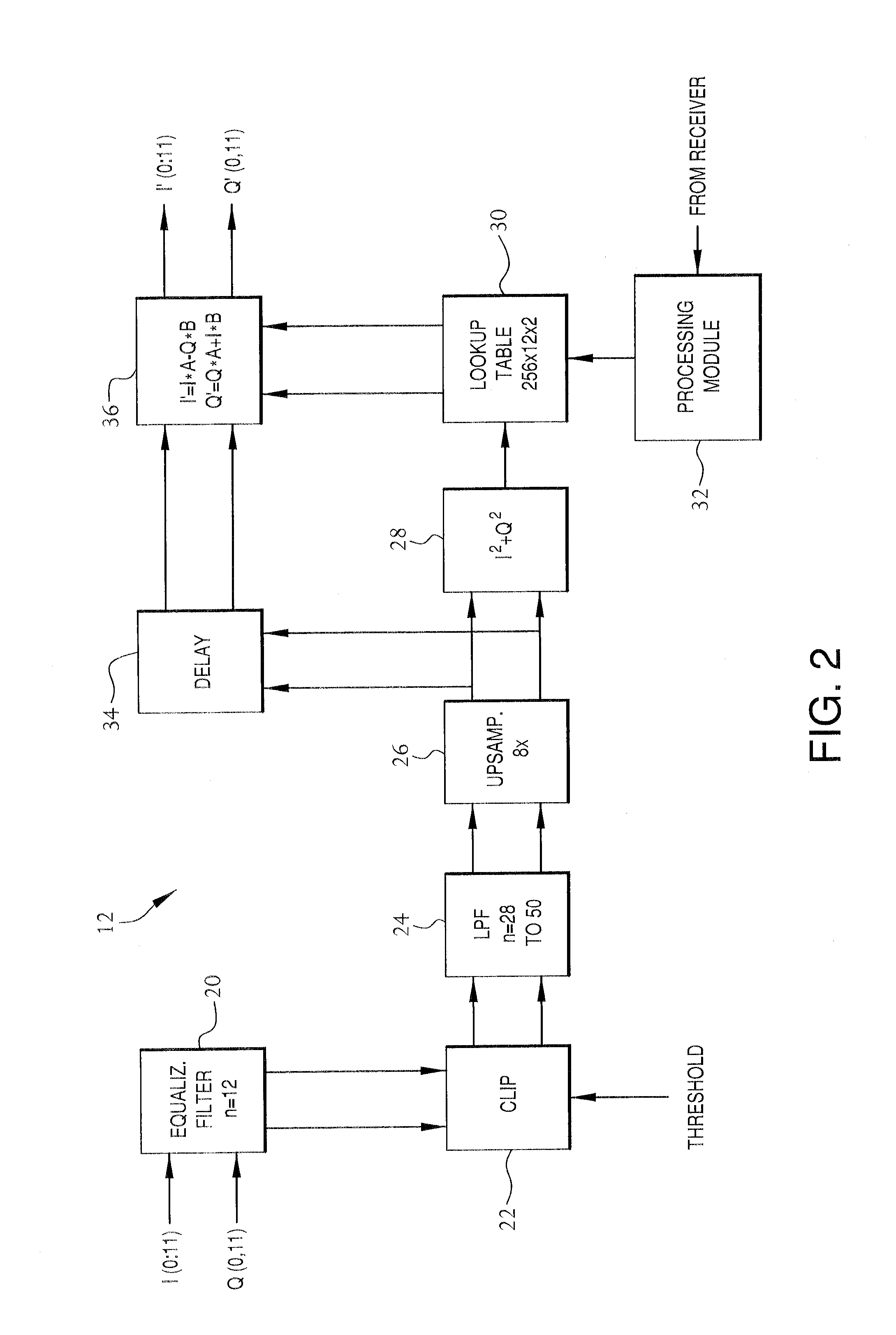
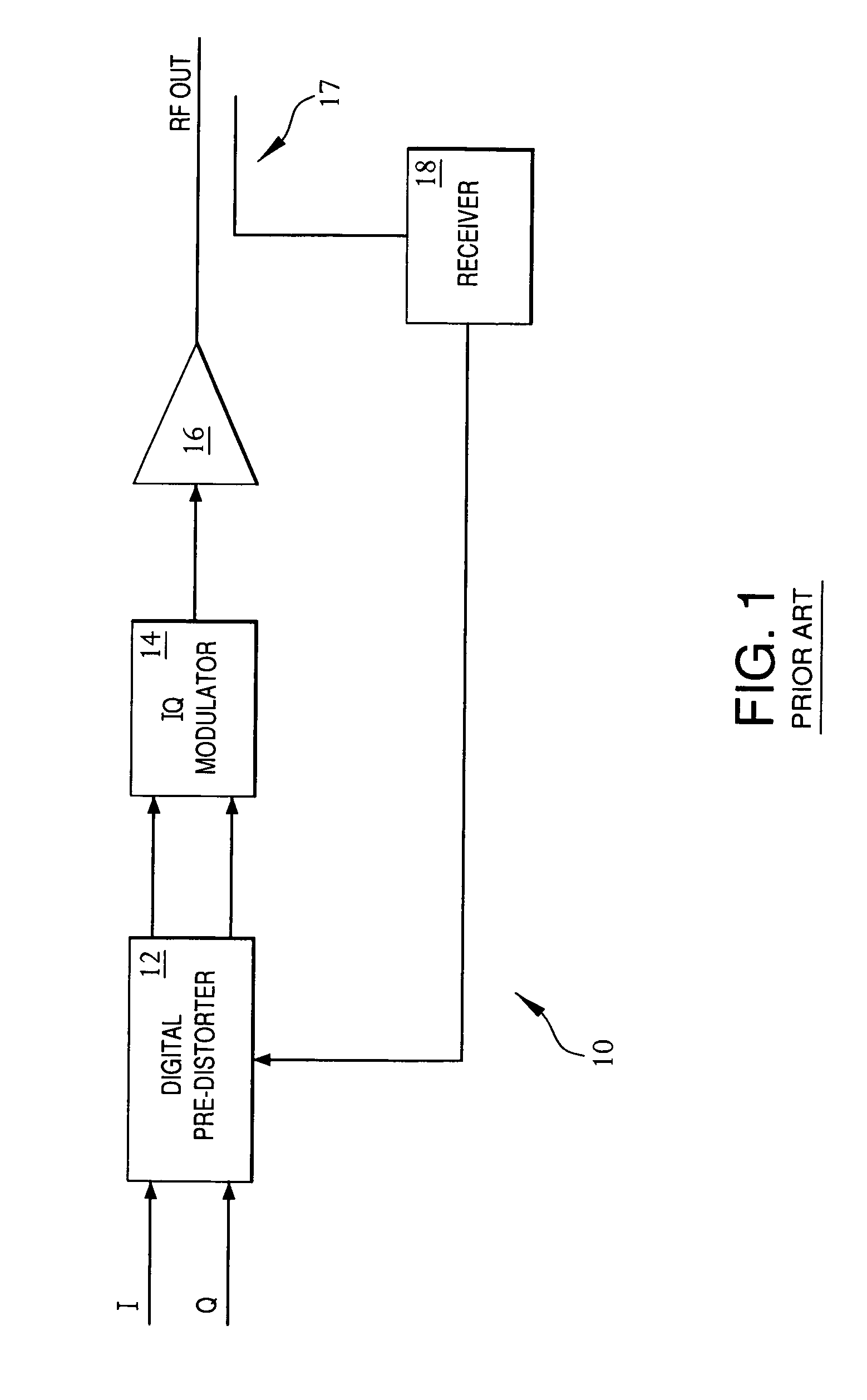
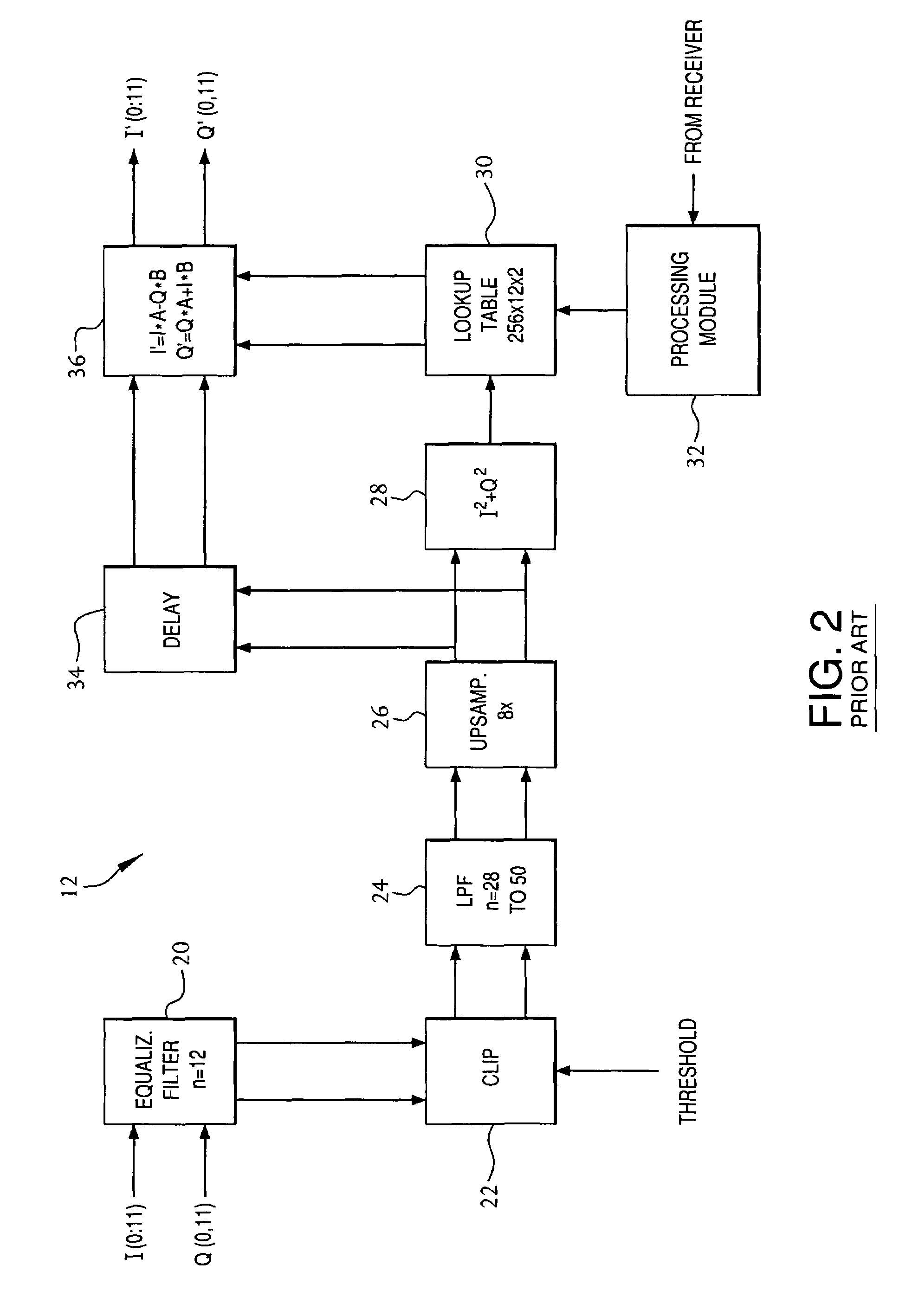
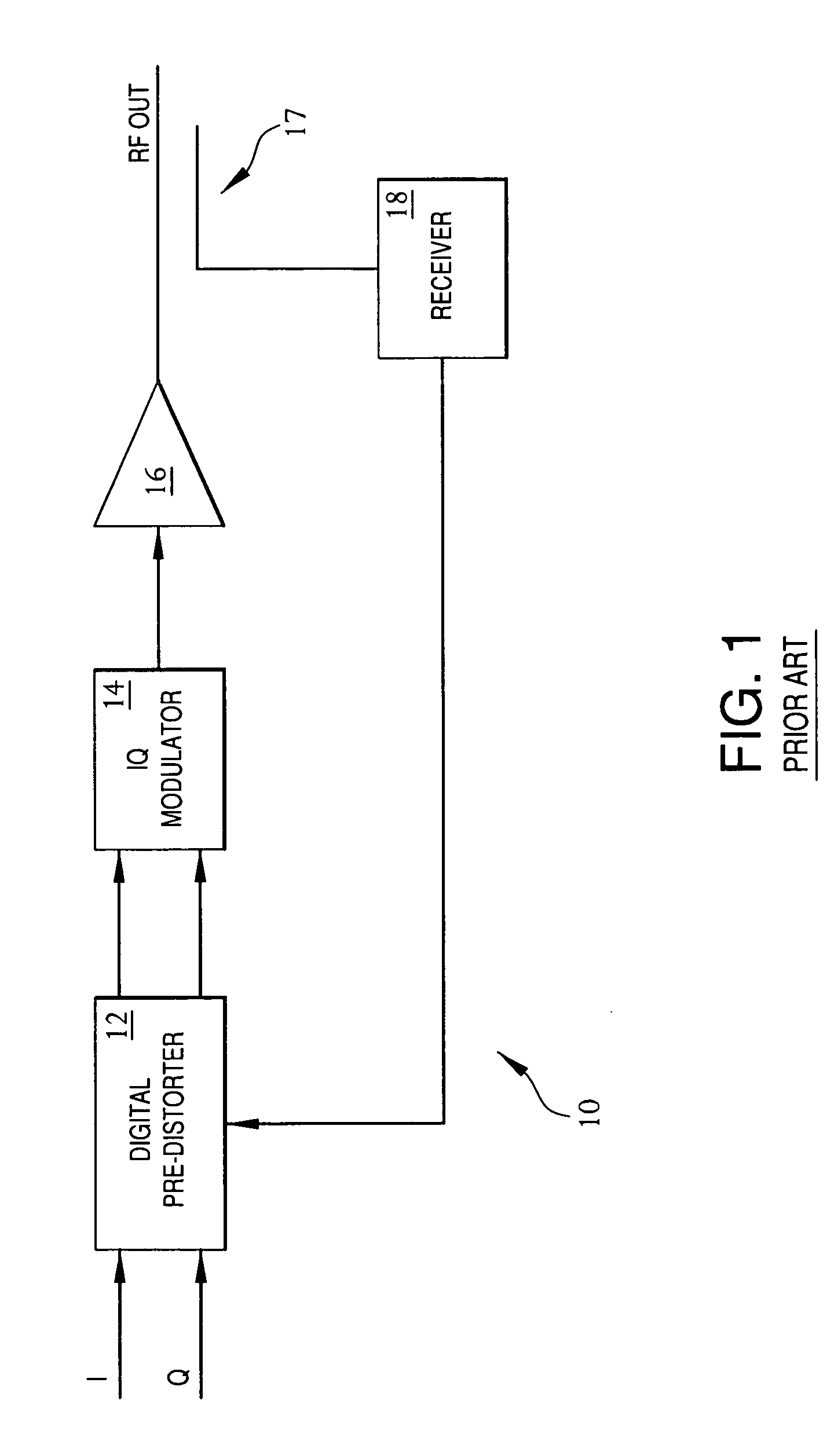
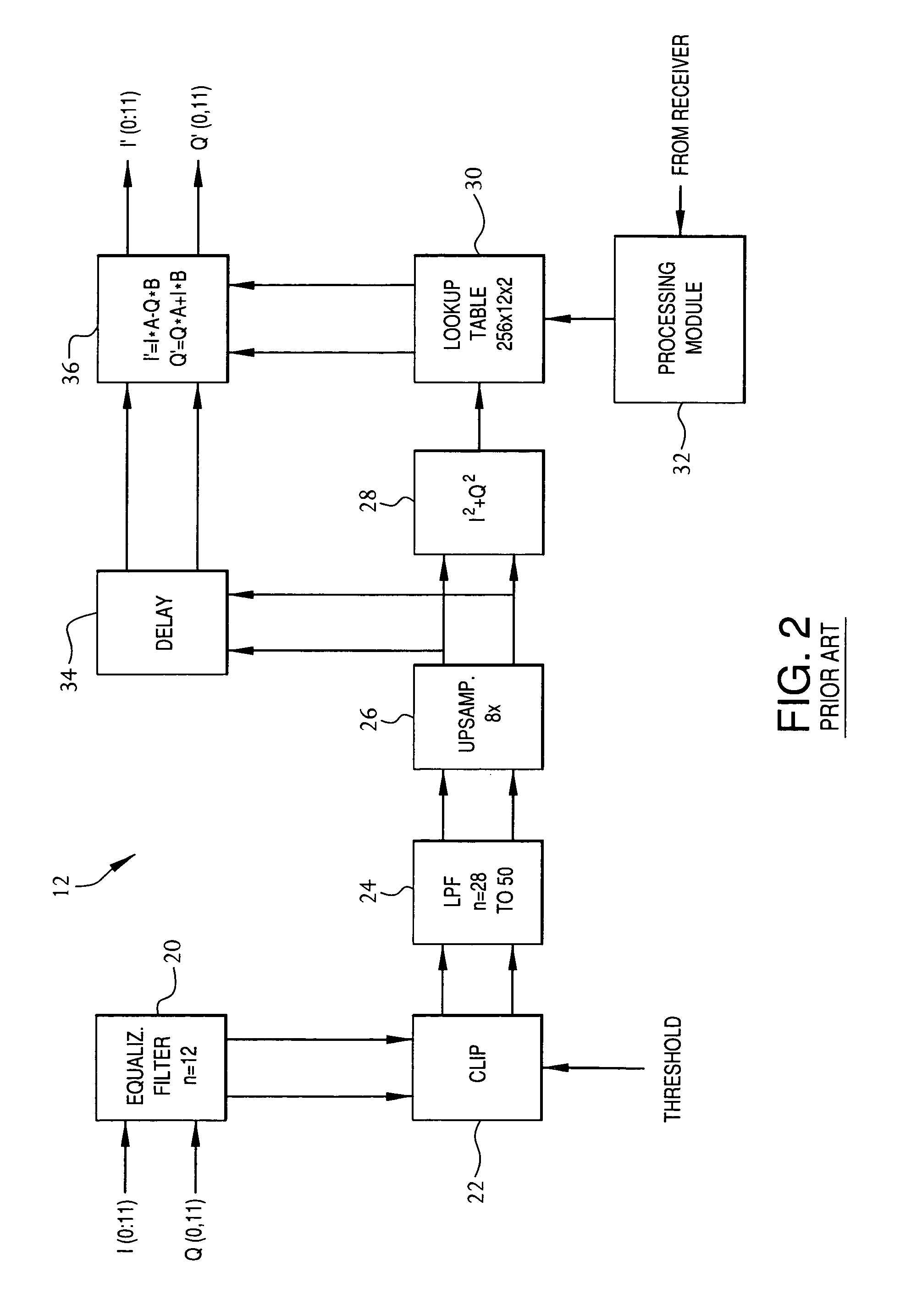
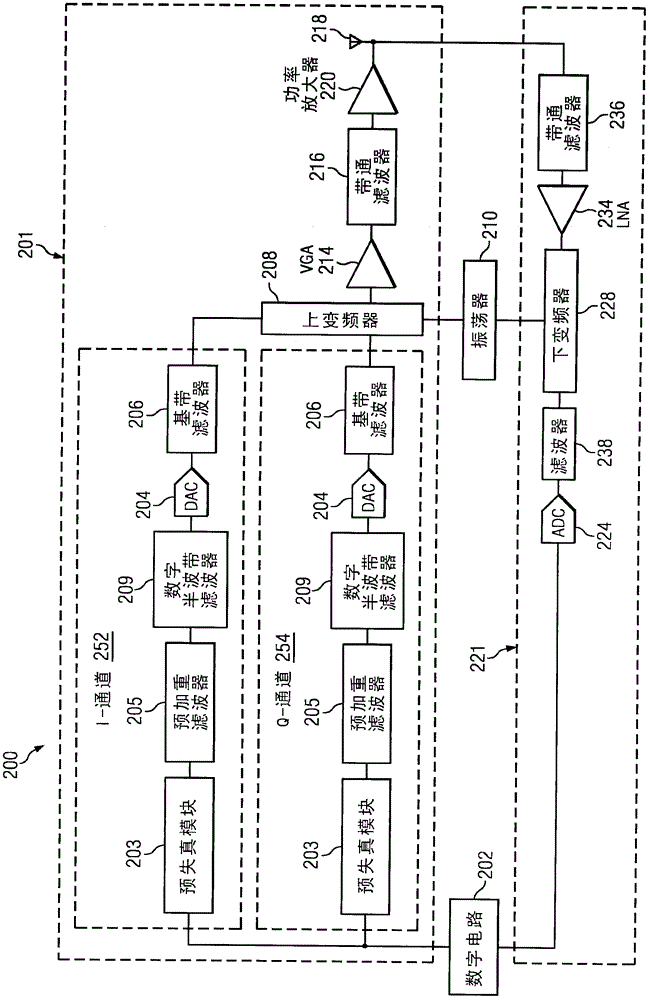
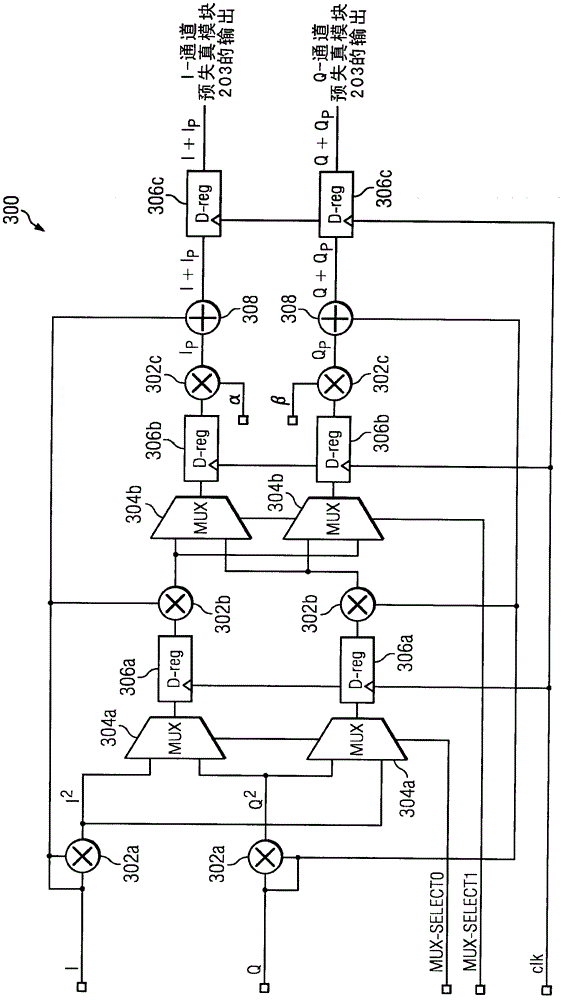
Frequency-dependent phase pre-distortion for reducing spurious emissions in communication networks
InactiveUS7248642B1Spurious emission can be reducedEmission reductionModulated-carrier systemsSecret communicationPhase differenceSpurious emission
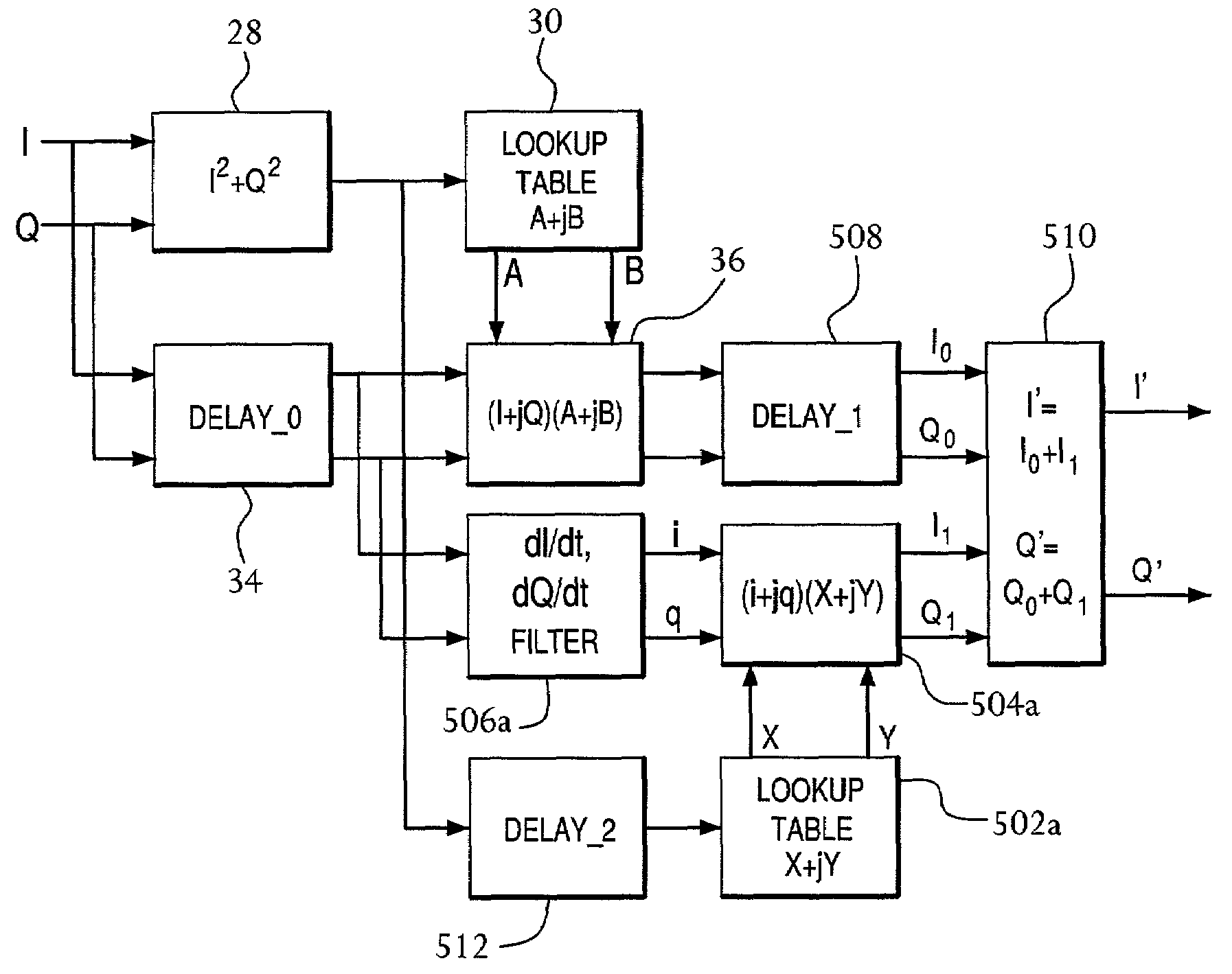
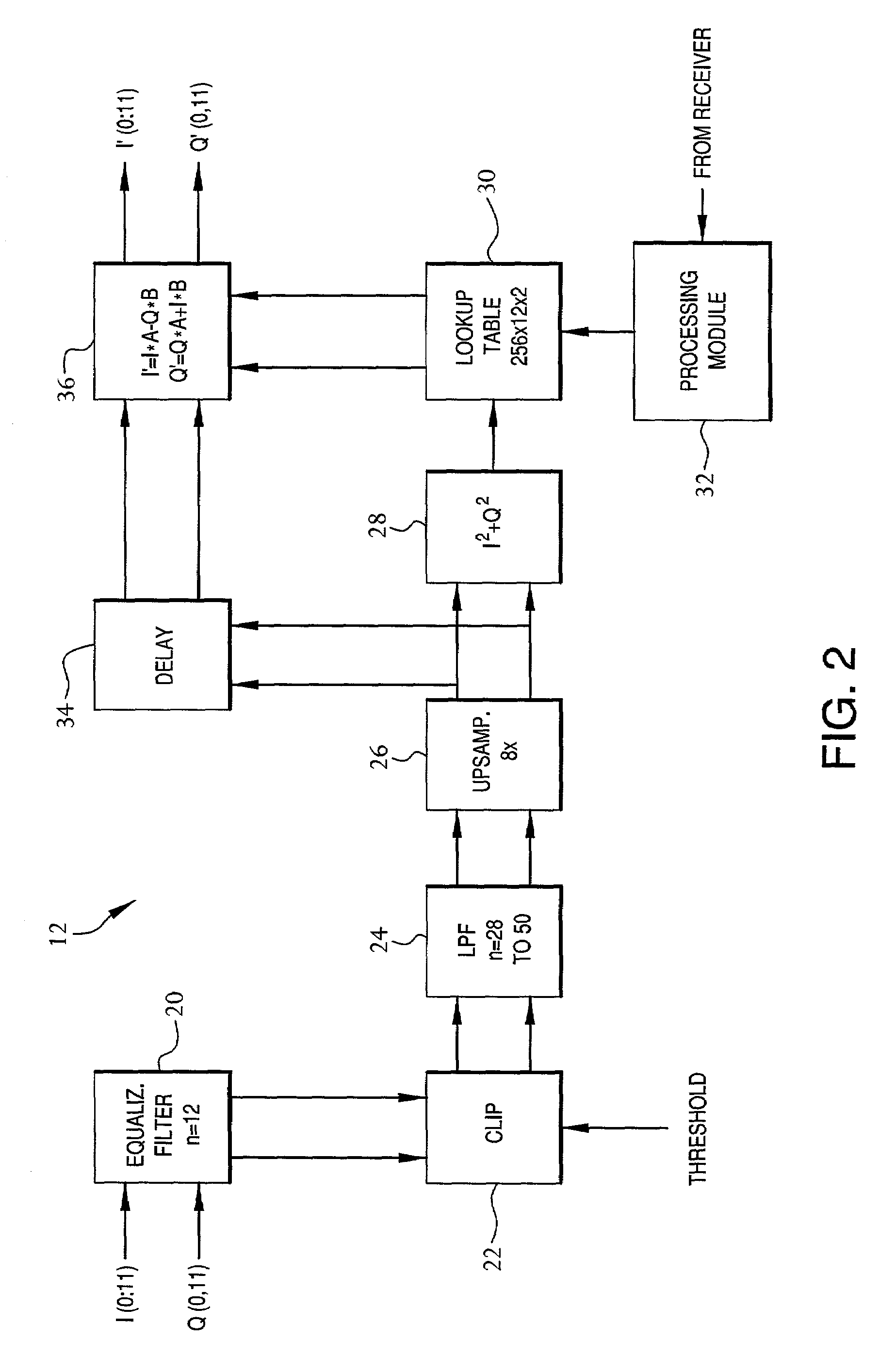
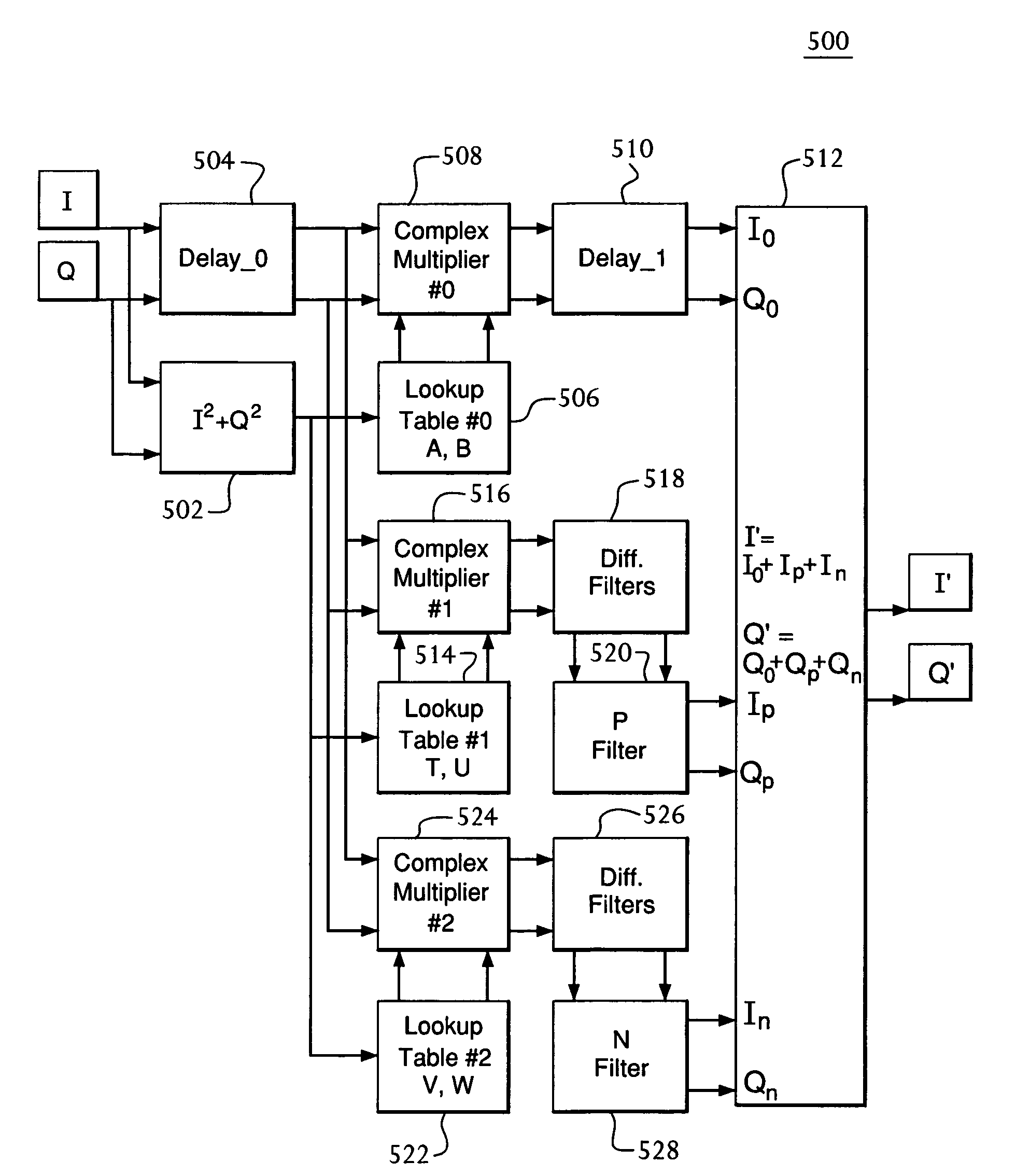
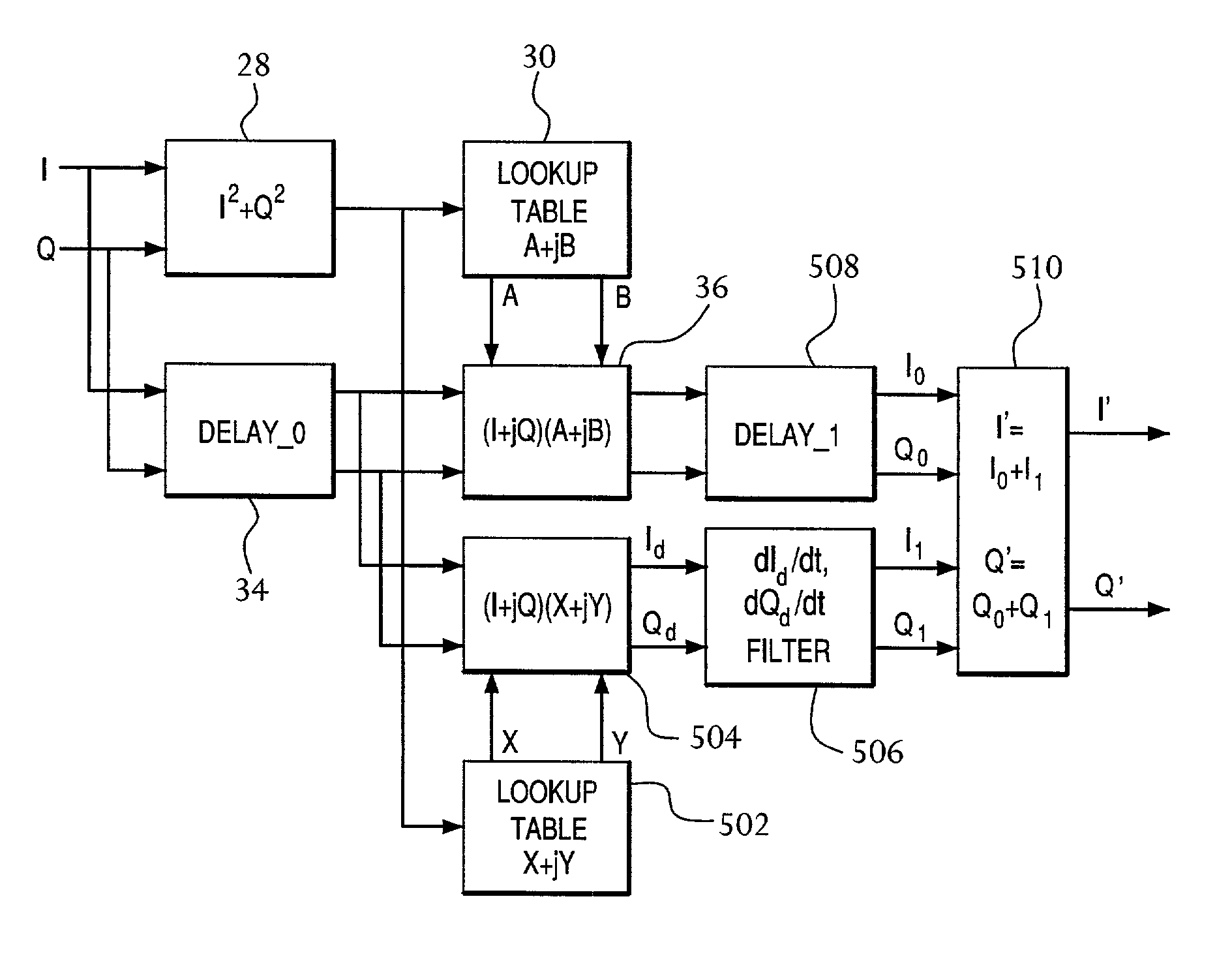
A frequency-dependent phase pre-distortion technique is applied to an input signal in order to reduce spurious emissions resulting from subsequent amplification of the signal. In preferred embodiments, the frequency-dependent phase pre-distortion of the present invention is implemented in combination with the (frequency-independent) magnitude and phase pre-distortion technique described in U.S. patent application Ser. No. 09 / 395,490 (“the '490 application”), where one or more frequency-dependent phase pre-distortion signals are either advanced or delayed relative to the main pre-distorted signal generated in accordance with the '490 application. Each frequency-dependent phase pre-distortion signal is preferably based on a 180° phase difference between a pair of (critical) frequencies located outside (e.g., one on each side) of the signal channel. The magnitude of the frequency difference between the pair of critical frequencies dictates the magnitude of the desired advancement or delay in time of the frequency-dependent pre-distortion signal relative to the main pre-distorted signal. Embodiments of the present invention may be implemented in either the baseband domain or the RF domain. Implementations may also be based on look-up tables that are adaptively updated to ensure optimal performance over time.
Owner:COMMSCOPE TECH LLC
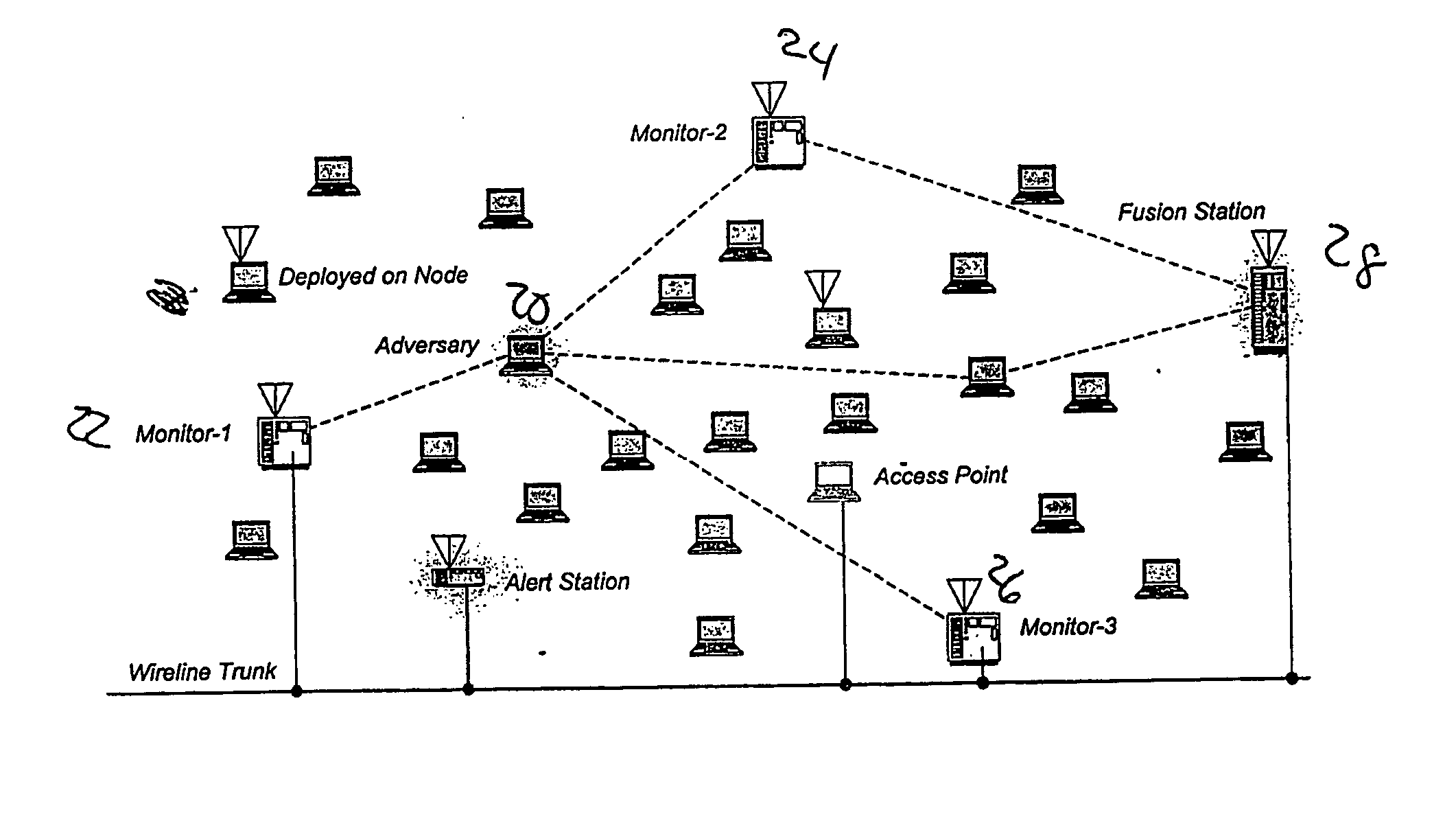
Intrusion detection system for wireless networks
InactiveUS20040162995A1New level of robustness against intrusionReceivers monitoringError preventionSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Physical layer
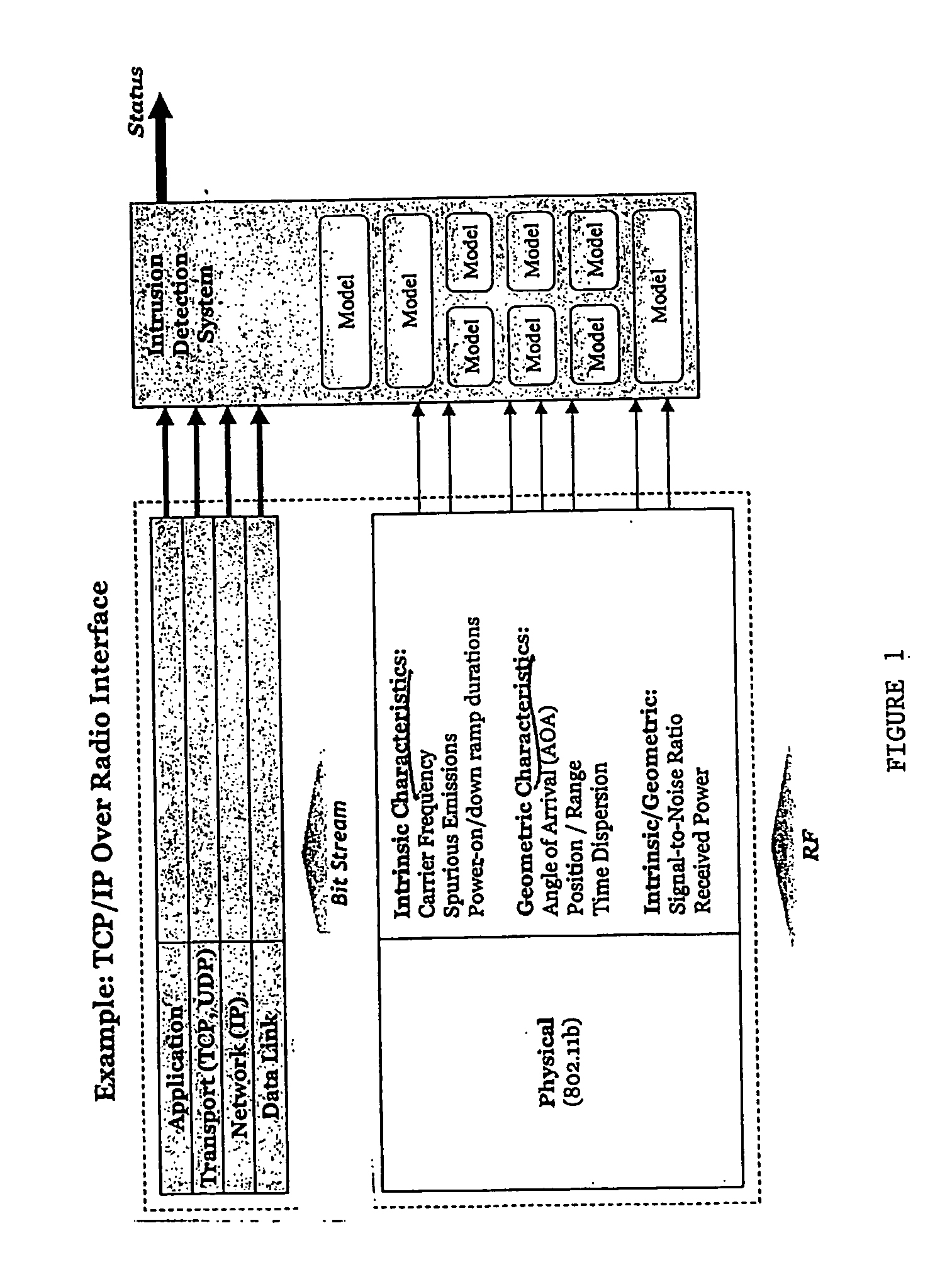
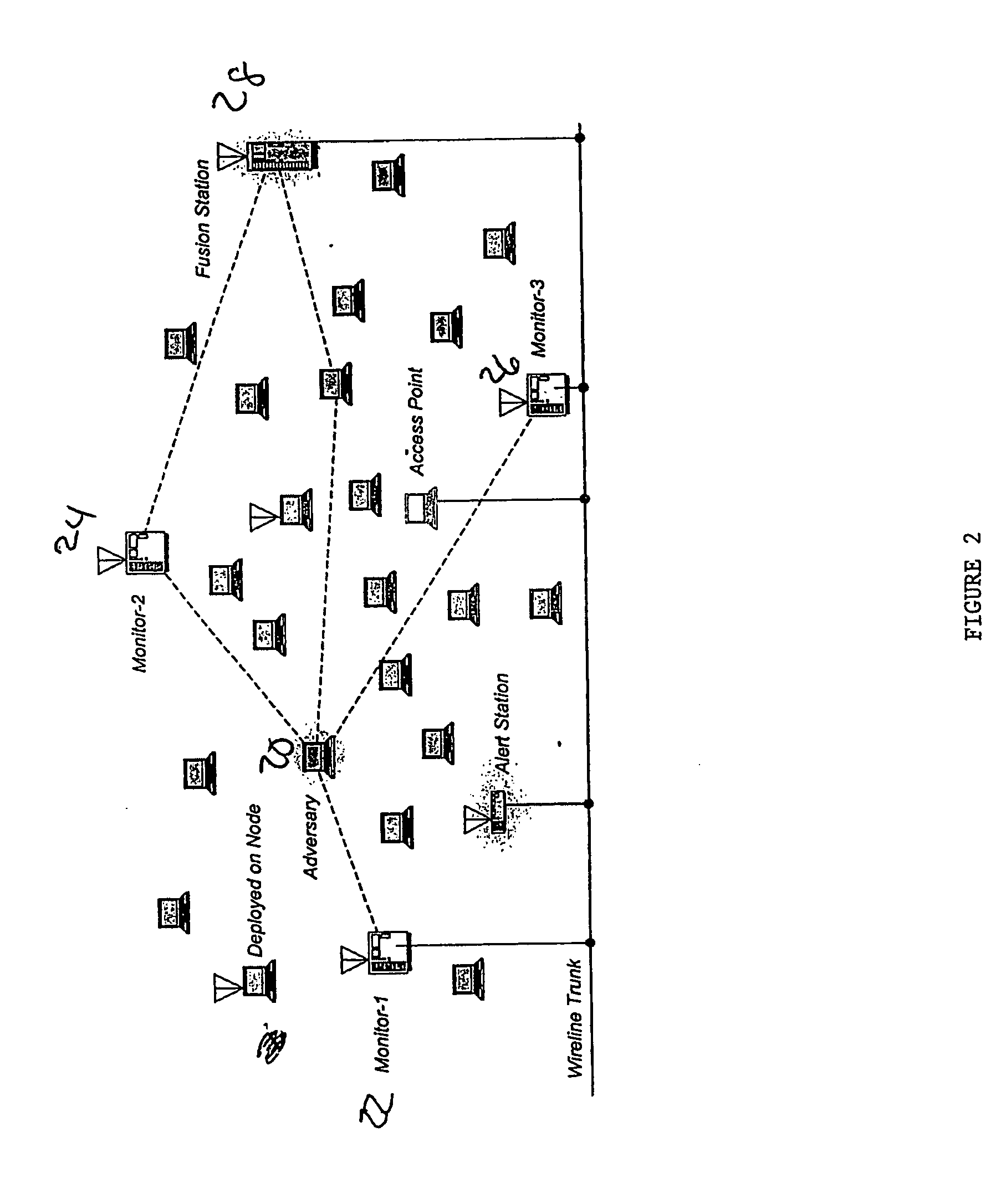
A method and system (FIG. 2) for facilitating detection of intruders into a wireless network, through the use of physical layer anomalies. One or more monitoring stations (22, 24, 26) can be distributed across the potential intruder's sign transmission region. They process these transmissions and extract attributes of the signals, which can then transmit to one or more fusion stations (28), which correlate the calculated attributes with stored attributes of signals of known, authorized users of the network, and transmit alert messages in the case that these signal attributes do not match those of known, authorized users. Signal attributes in accordance with the instant invention include the carrier frequency, spurious emissions, and power-on and power-down transients. Also in accordance with the instant invention are methods and systems using both direct and multipath received signal strength, signal-to-noise ratio, and geometric characteristics such as direction / angle of arrival (AOA), time of arrival, position / range, time dispersion, Doppler shift and polarization.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
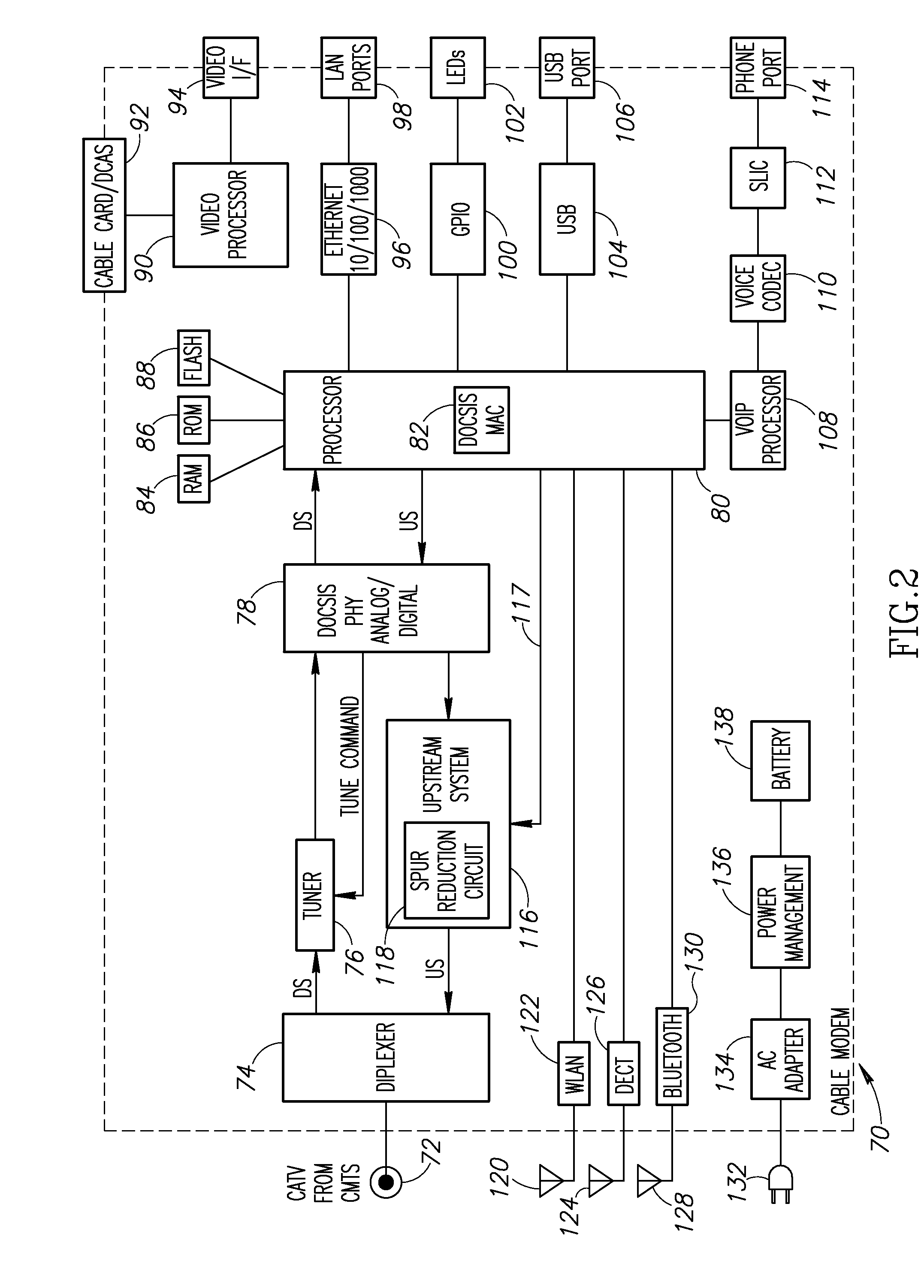
Discrete spurious leakage cancellation for use in a cable modem
InactiveUS20100266000A1Reduced frequency spur energyLow costTwo-way working systemsSelective content distributionPhase shiftedDOCSIS
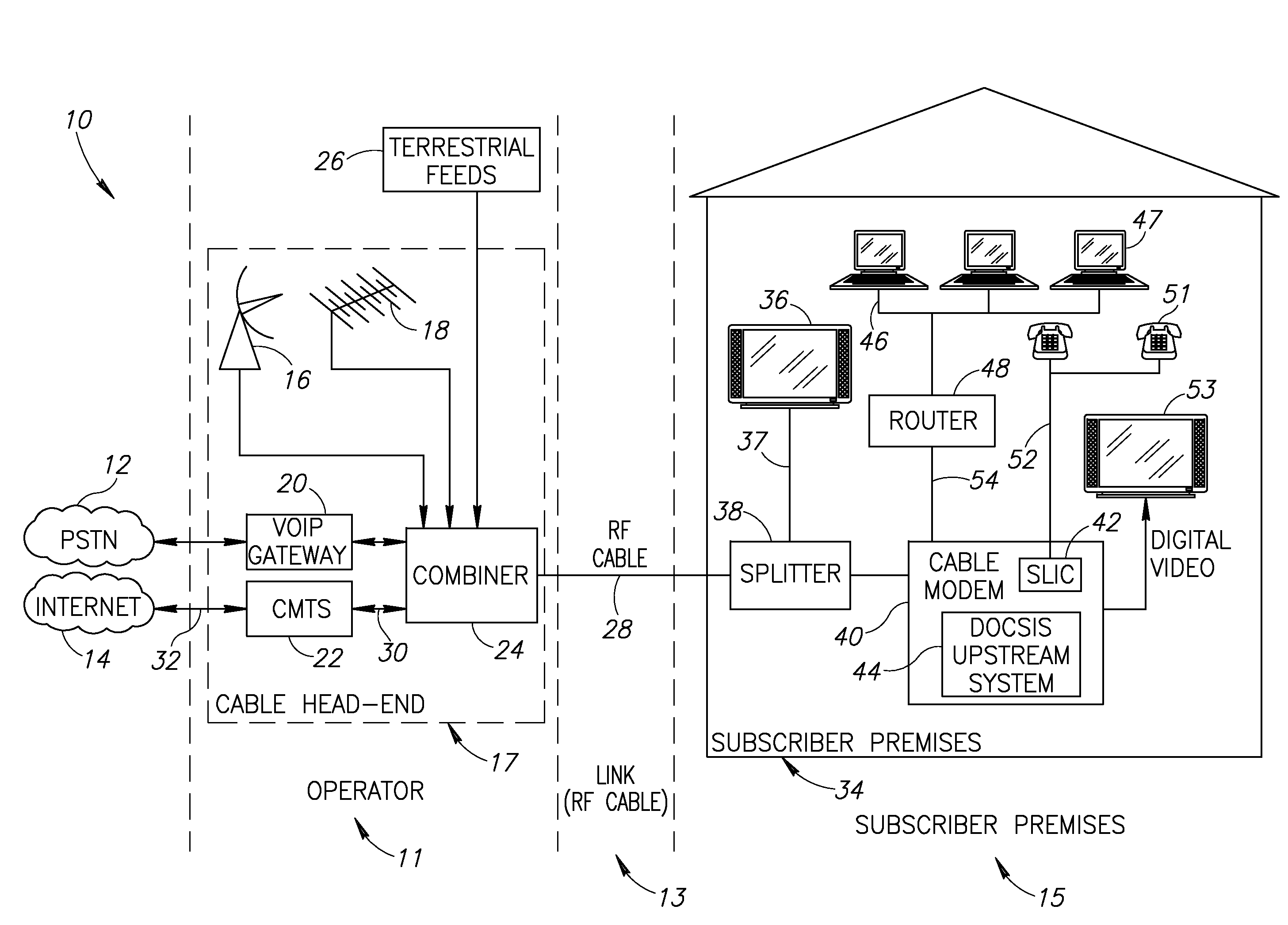
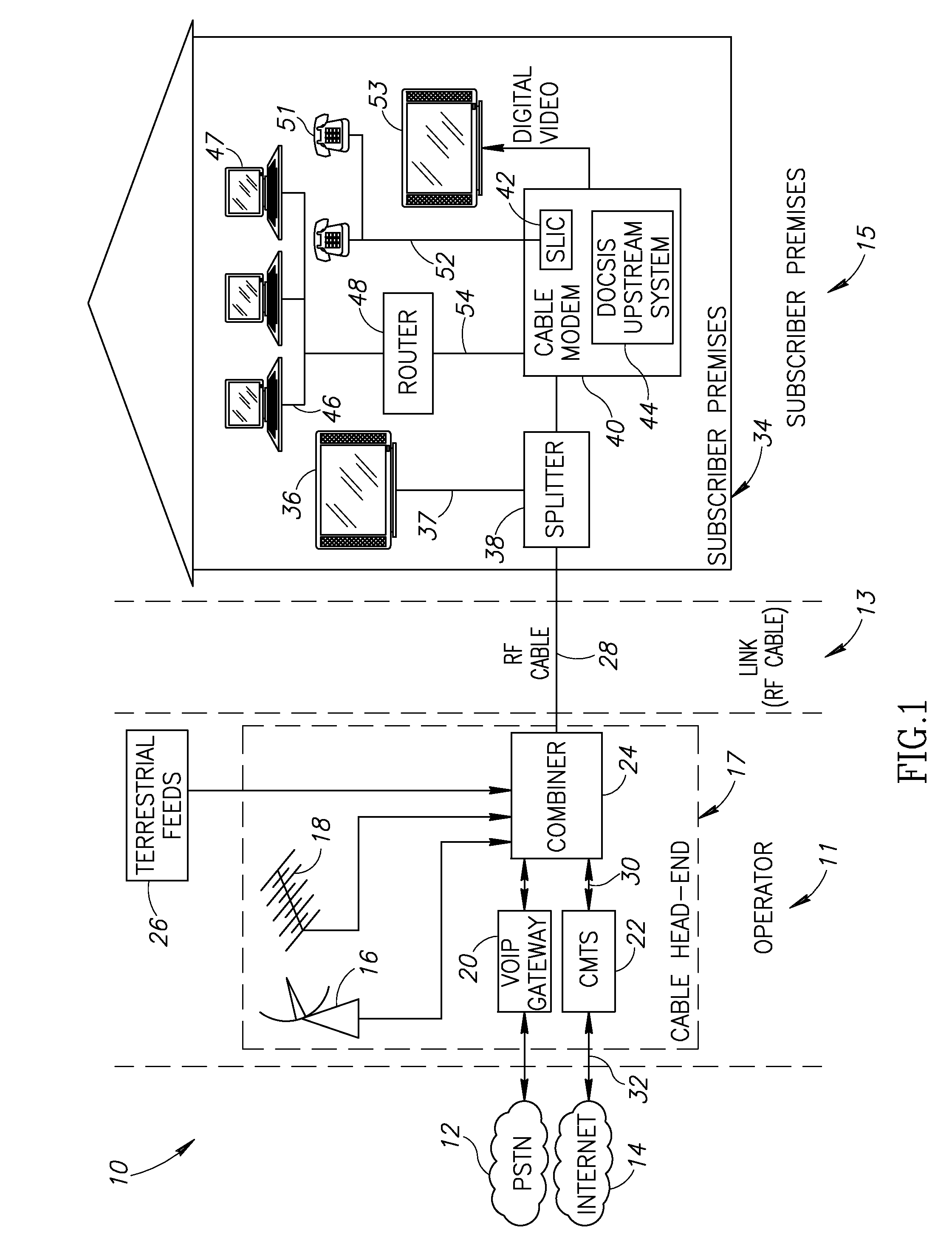
A novel apparatus for and method of discrete spurious frequency leakage cancellation for use in a cable modem. The spurious leakage cancellation mechanism is particularly suitable for use in cable modem systems adapted to implement the DOCSIS 2.0 specification which specifies both downstream and upstream channels. In one embodiment, the spurious emission cancellation mechanism cancels the spurious emissions by first creating a replica of the aggressor clock signal having the same amplitude but 180 degree phase shift as the spurious signal. The phase shifted spurious replica is added to the original spurious signal thus cancelling the spurious signal. In another embodiment, an RF switch is used to couple the upstream path signal to the CATV cable only during transmission bursts. In between transmission bursts, the upstream signal is disconnected from the CATV cable. This embodiment takes advantage of the less stringent spurious requirements in the DOCSIS 2.0 specification for transmission bursts. In between transmission bursts, when stricter spurious requirements apply, the upstream signal is disconnected from the CATV cable.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
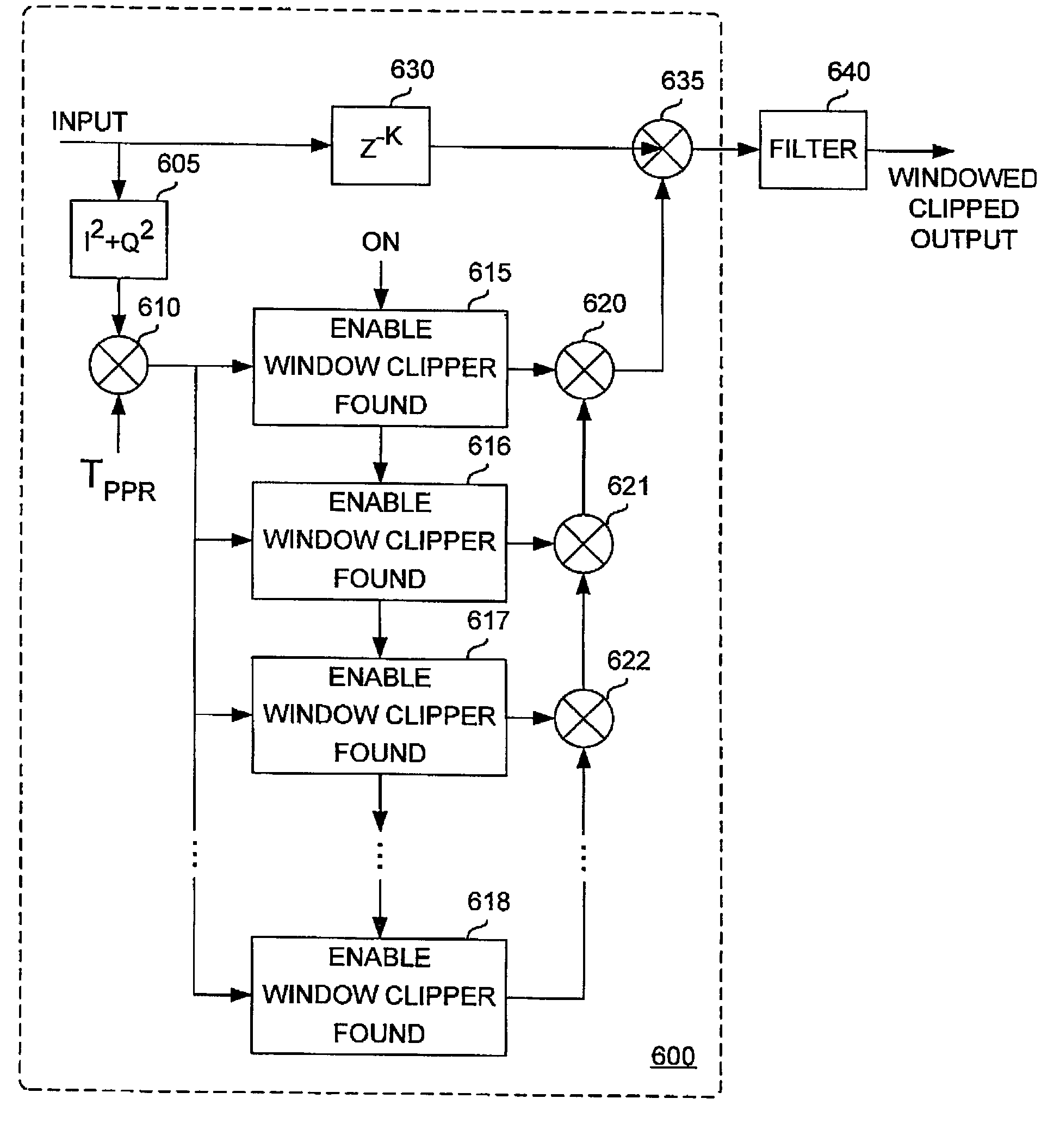
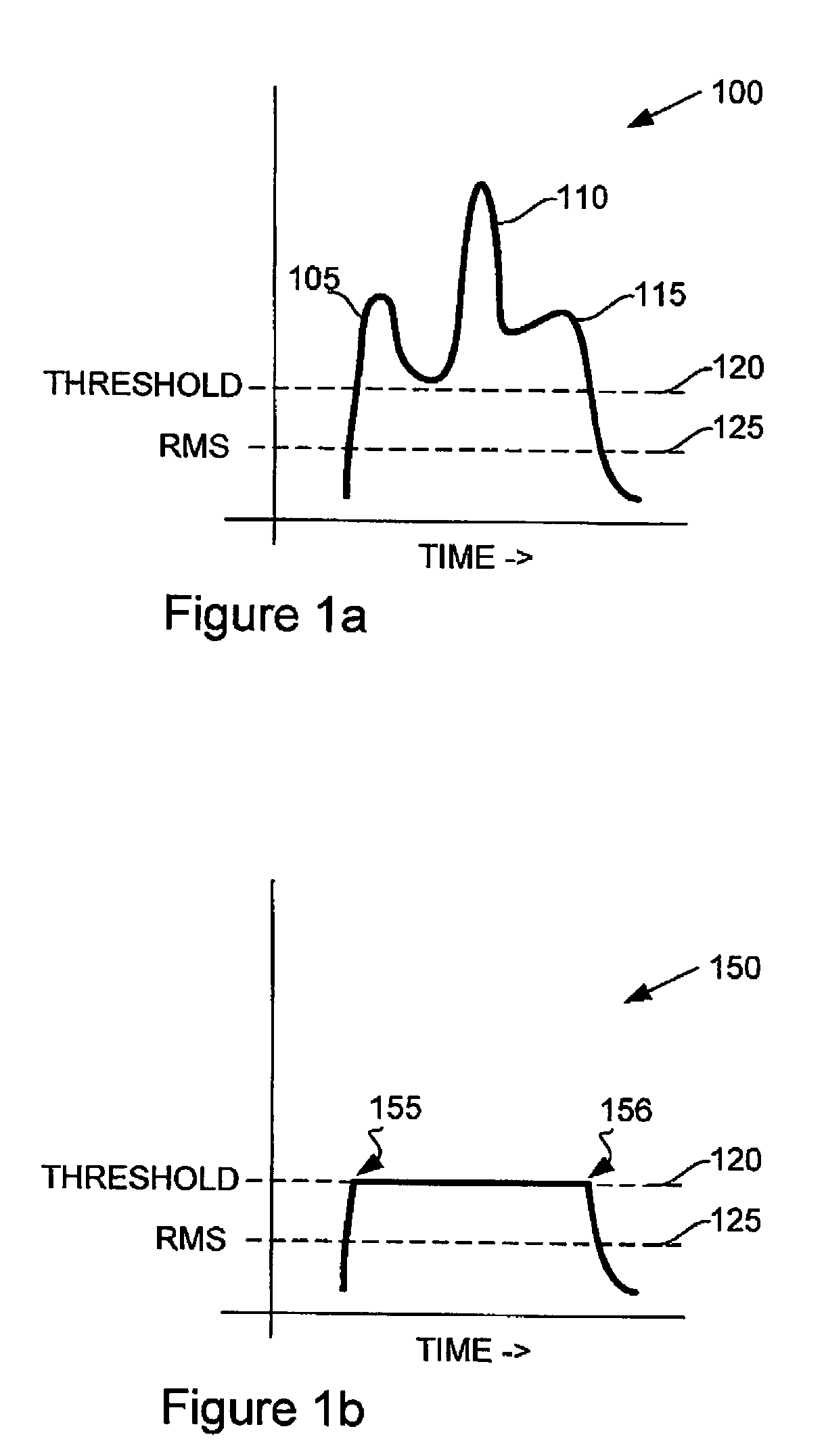
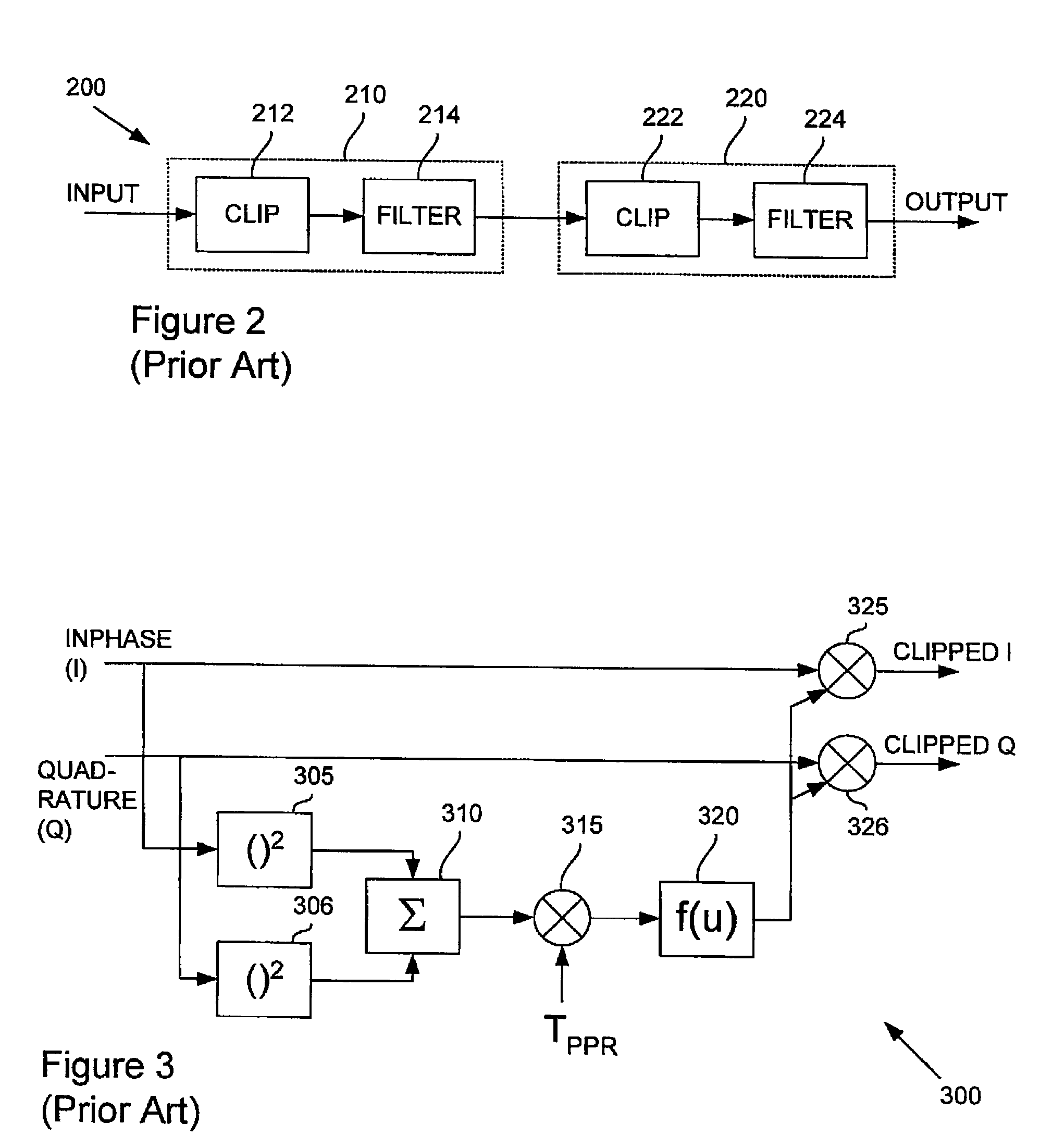
Peak power reduction using windowing and filtering
InactiveUS7013161B2Eliminate emissionsReducing PAPModulation with suppressed carrierVolume compression/expansion in untuned/low-frequency amplifiersAudio power amplifierEngineering
Large signal peaks (for example, peaks 105 and 110) can dramatically increase the cost of a communications device by requiring high grade power amplifiers. Peak reduction can reduce the large peaks at a cost of increasing spurious emissions. A circuit (for example, circuit 500) combining a scaling window peak reducing unit (for example, unit 507) and a filter (for example, filter 509) can effectively reduce the signal peaks without significantly increasing spurious emissions.
Owner:BLACKBERRY LTD
Frequency-dependent magnitude pre-distortion for reducing spurious emissions in communication networks
ActiveUS7197085B1Spurious emission can be reducedEmission reductionAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionSecret communicationDifferentiatorAudio power amplifier
Pre-distortion, whose magnitude—and preferably phase—are frequency-dependent, is applied to an input signal in order to reduce spurious emissions resulting from subsequent amplification of the signal. In preferred embodiments, the pre-distortion technique of the present invention is implemented in combination with the (frequency-independent) magnitude and phase pre-distortion technique described in U.S. patent application Ser. No. 09 / 395,490 (“the '490 application”), where the frequency-dependent pre-distortion corresponds to amplifier distortion that has a magnitude that is proportional to the frequency offset from the carrier frequency and a phase shift of ±90° on either side of the carrier frequency. Since these characteristics match those of a differentiator, a thorough correction of this part of the amplifier's distortion can be achieved using a differentiating filter. Embodiments of the present invention may be implemented in the baseband domain. Implementations may also be based on look-up tables that are adaptively updated to ensure optimal performance over time.
Owner:COMMSCOPE TECH LLC
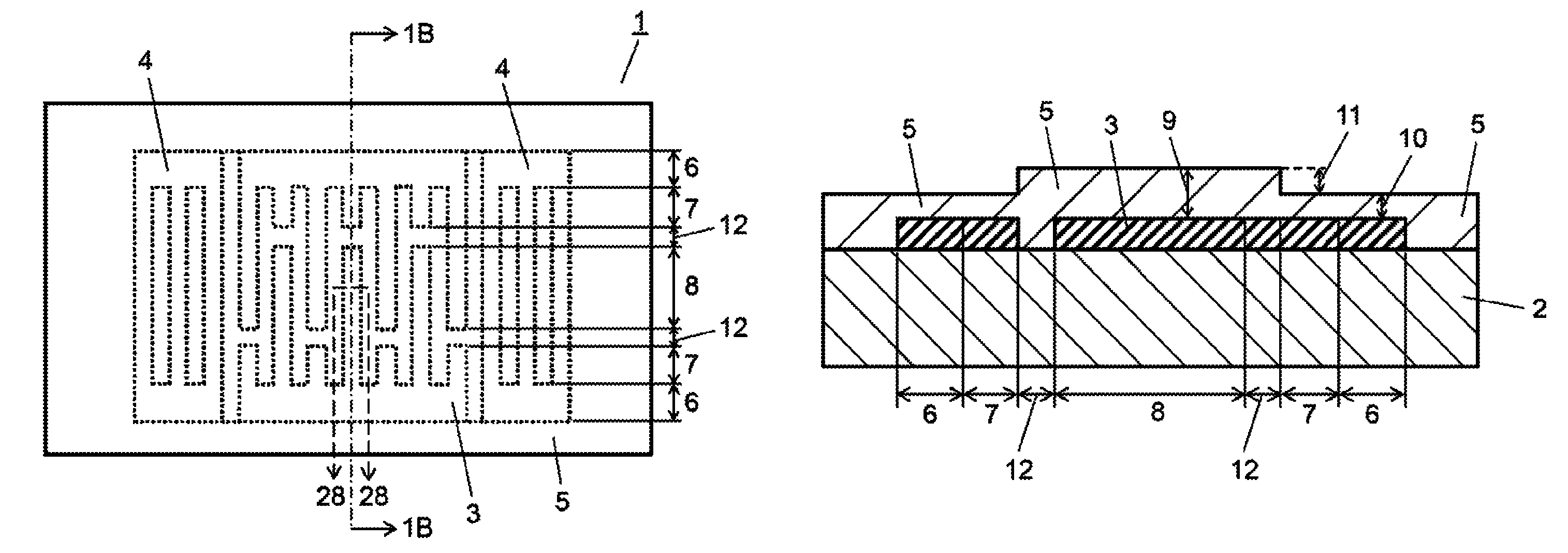
Filter devices having reduced spurious emissions from lamb waves
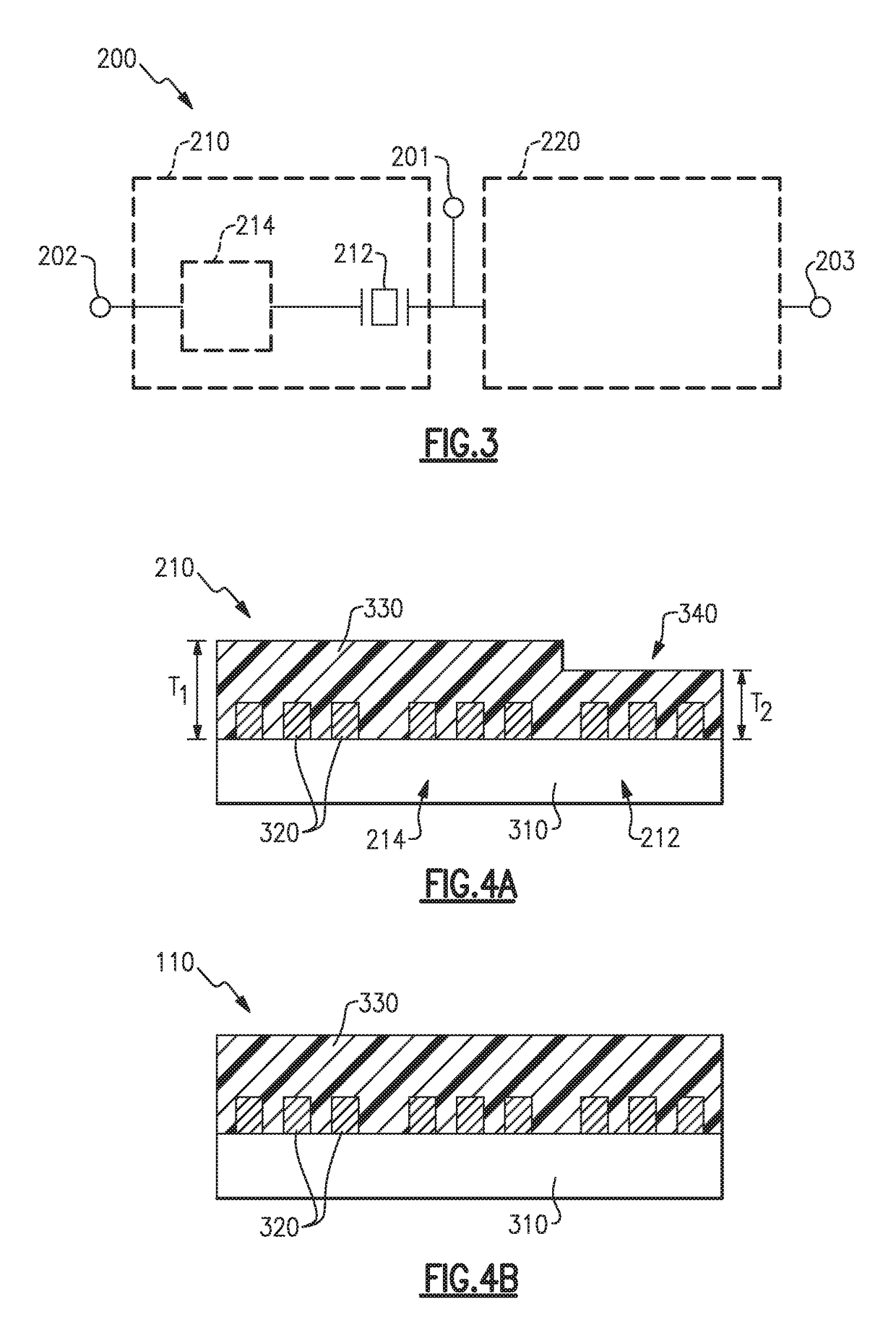
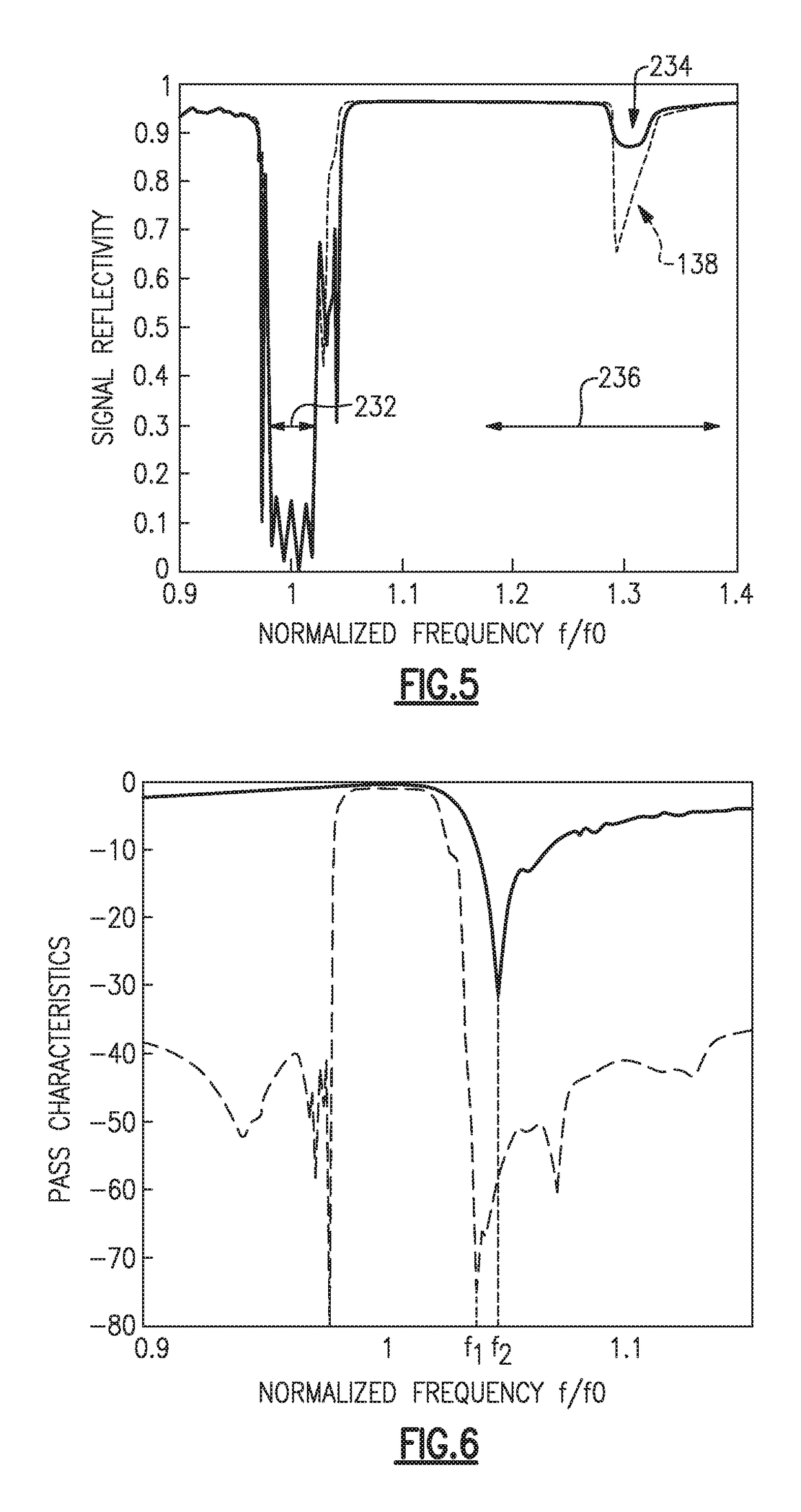
ActiveUS10187039B2Emission reductionImprove communication qualityImpedence networksElectricitySpurious emission
A filter device that reduces spurious emissions generated in a frequency band 1.2 to 1.4 times greater than a center frequency of a passband of a filter. In one example the filter device includes a first filter connected between a common contact and a first signal contact and having a first passband, and a second filter connected between the common contact and a second signal contact and having a second passband with a center frequency in a range of 1.2 to 1.4 times greater than a center frequency of the first passband. The first filter includes a SAW filter formed on a piezoelectric substrate, a SAW resonator formed on the piezoelectric substrate and connected in series between the common contact and the SAW filter, and a dielectric film covering the SAW filter and SAW resonator, the dielectric film having a reduced thickness in a region corresponding to the SAW resonator.
Owner:SKYWORKS PANASONIC FILTER SOLUTIONS JAPAN
Antenna tuning circuit and mobile terminal
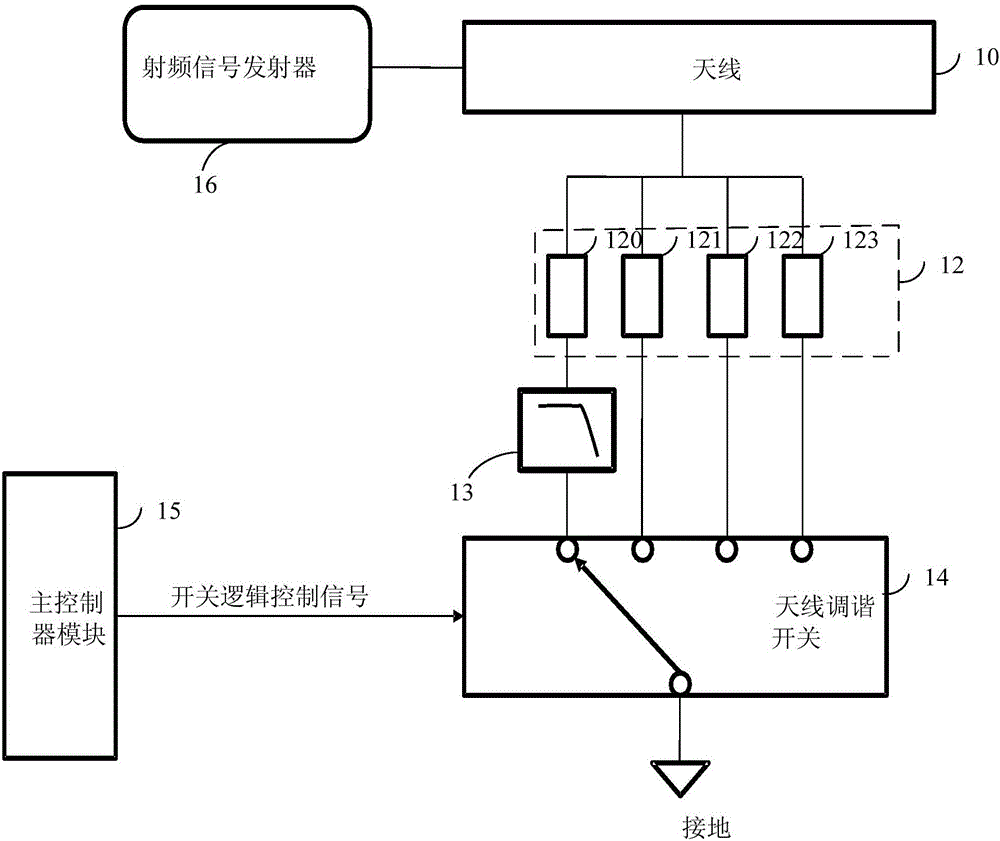
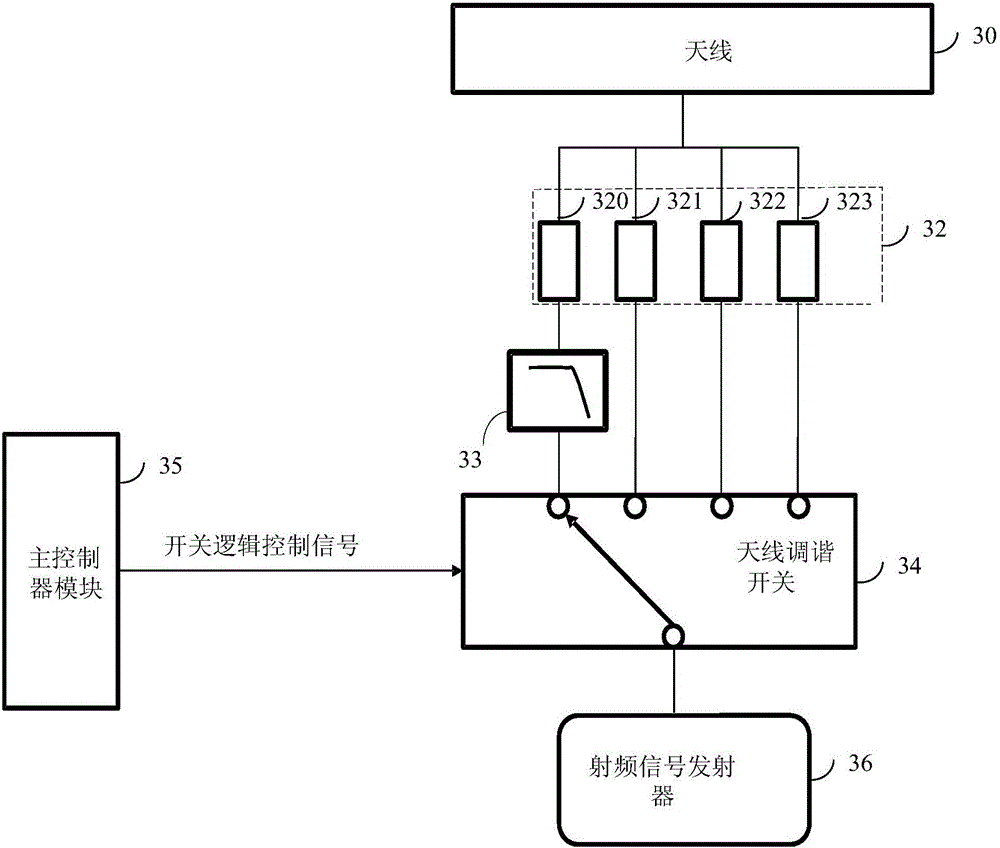
InactiveCN105897280ASolve the problem of radiation spuriousFilter out harmonicsTransmissionLow-pass filterHarmonic
The embodiment of the invention discloses an antenna tuning circuit and a mobile terminal. The antenna tuning circuit comprises an antenna, a frequency band matching circuit and an antenna tuning switch, wherein the frequency band matching circuit is respectively connected with the antenna and the antenna tuning switch; the frequency band matching circuit comprises at least one frequency band matching sub circuit for selecting and matching corresponding frequency band signals from radio frequency signals transmitted by a radio frequency signal transmitter of the mobile terminal, and a low-pass filter serially connected between the frequency band matching sub circuit and the antenna tuning switch for retaining main frequency signals of a corresponding frequency band and filtering harmonics generated by the antenna tuning switch. Thus, the problem of radiated spurious emission brought by switch saturation as the antenna tuning switch generates harmonics can be avoided.
Owner:GUANGDONG OPPO MOBILE TELECOMM CORP LTD
Acoustic wave device
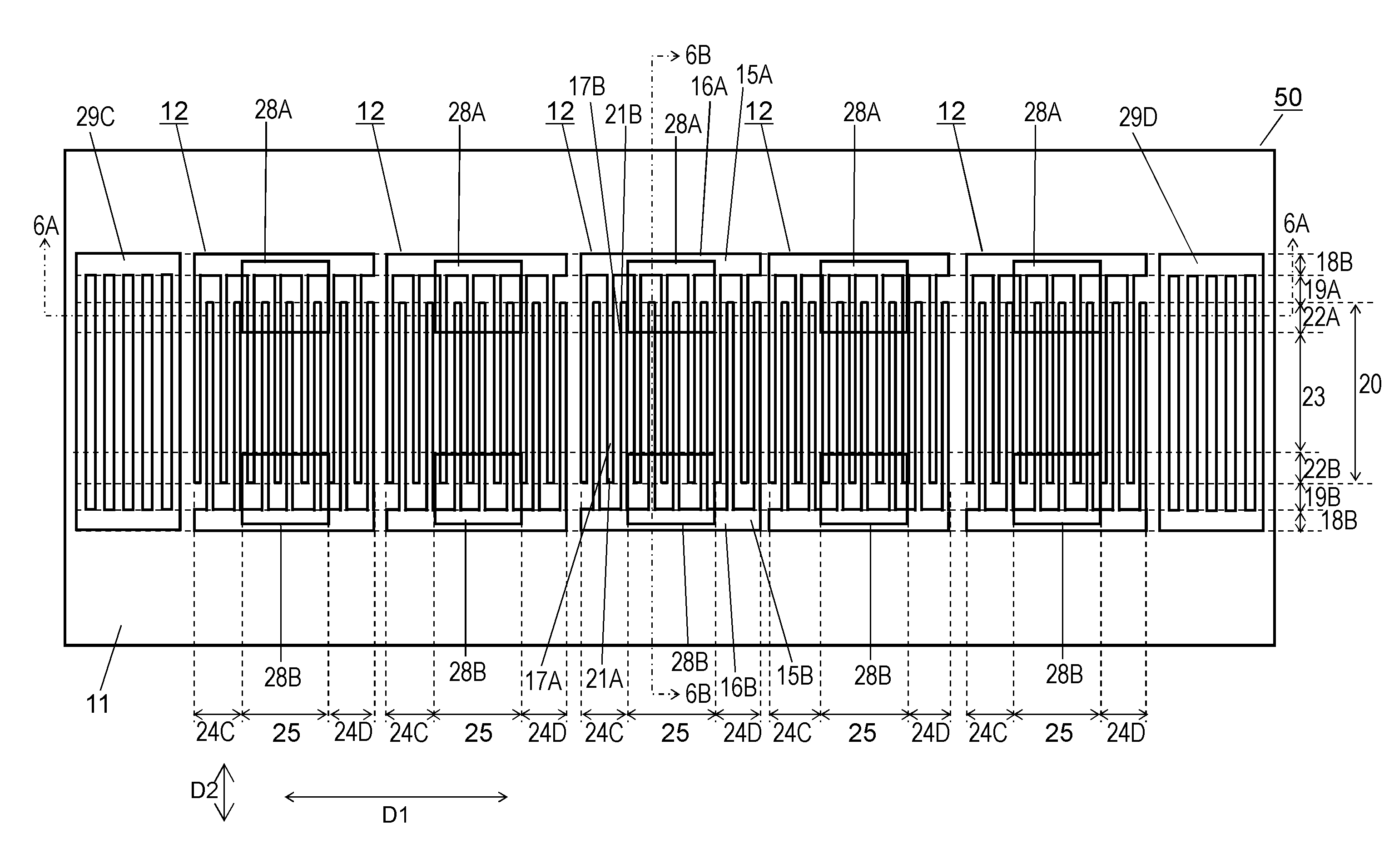
ActiveUS20140285287A1Suppresses spurious emissionSuperior passband characteristicImpedence networksPiezoelectric/electrostrictive devicesDielectricSpurious emission
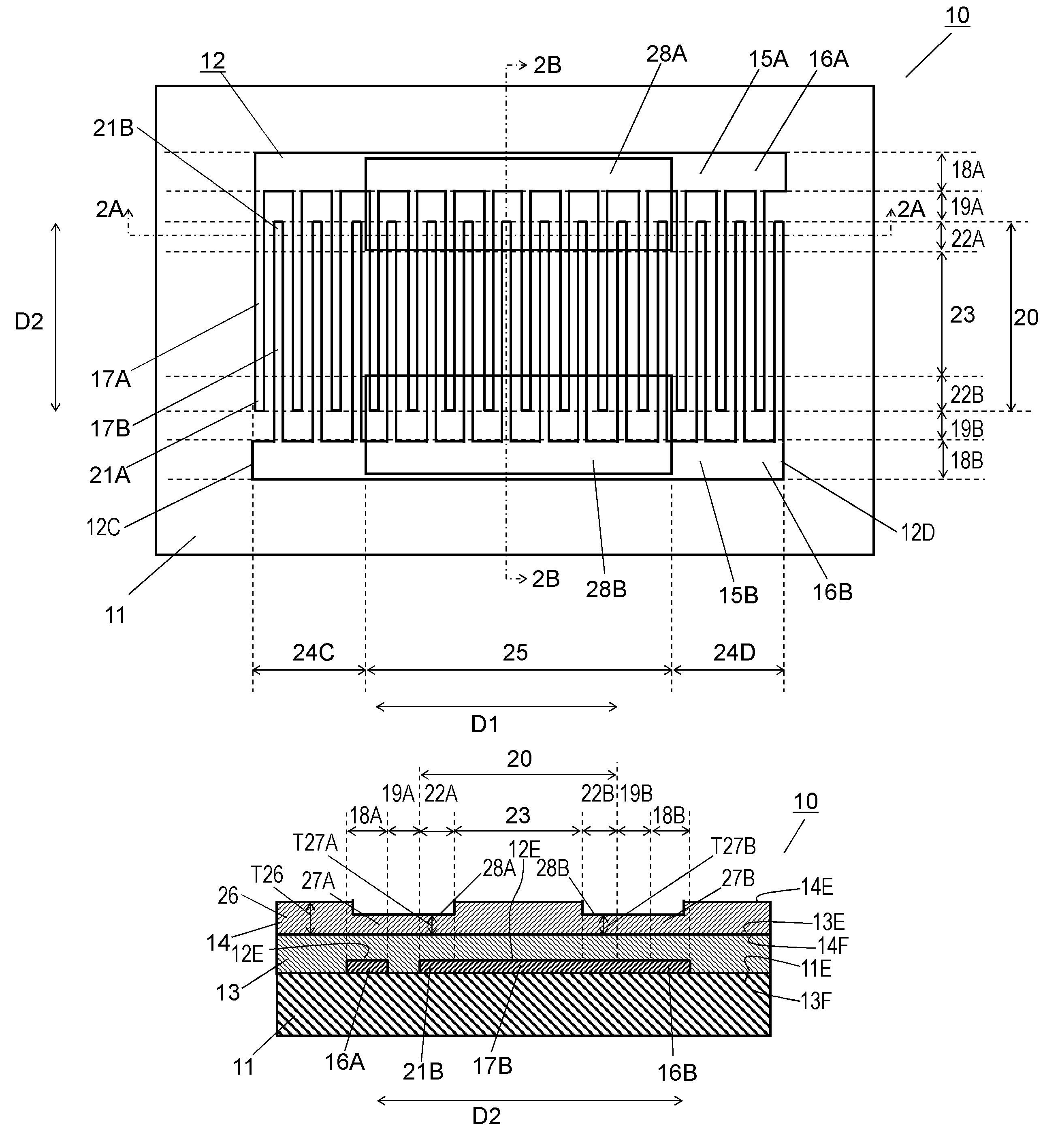
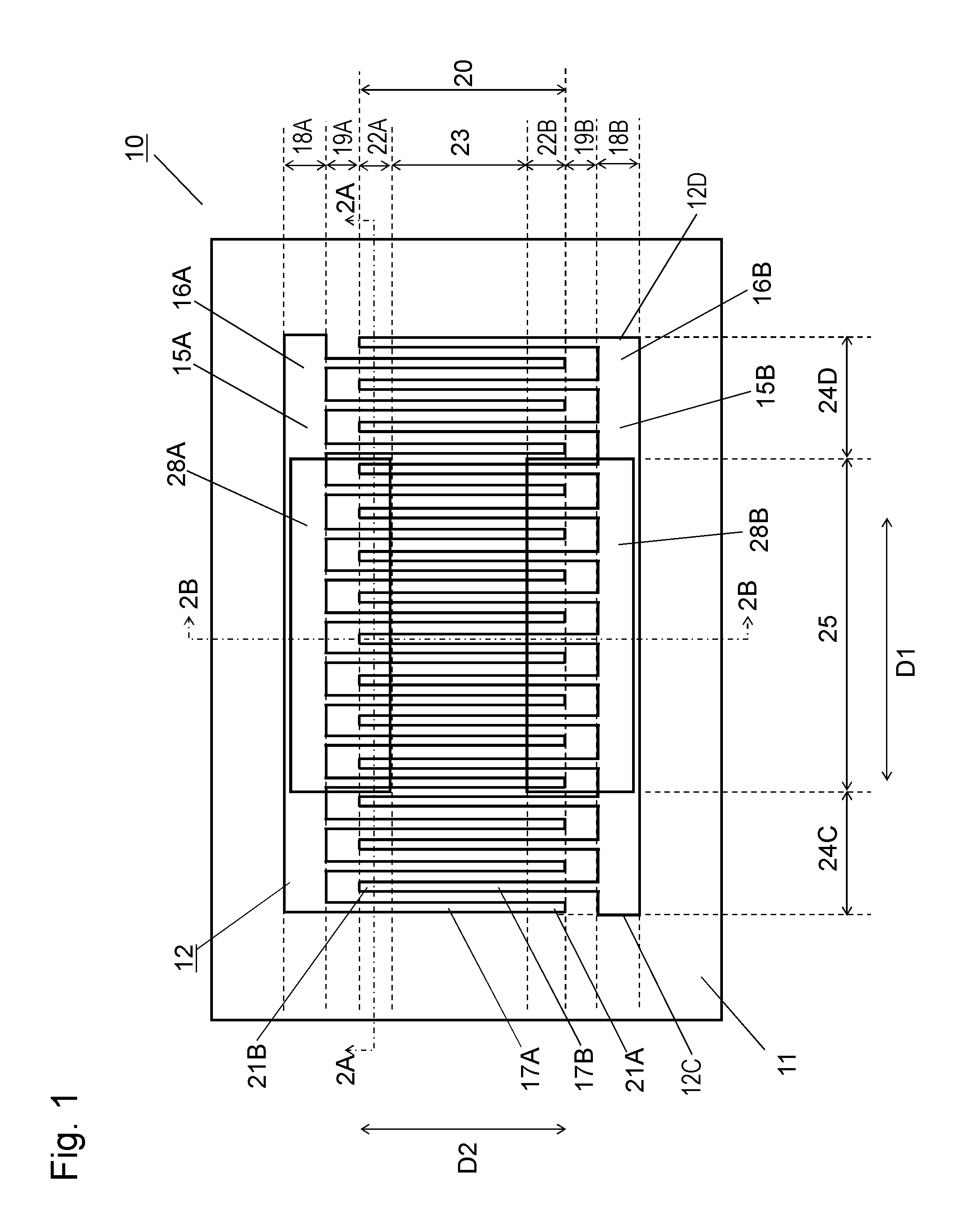
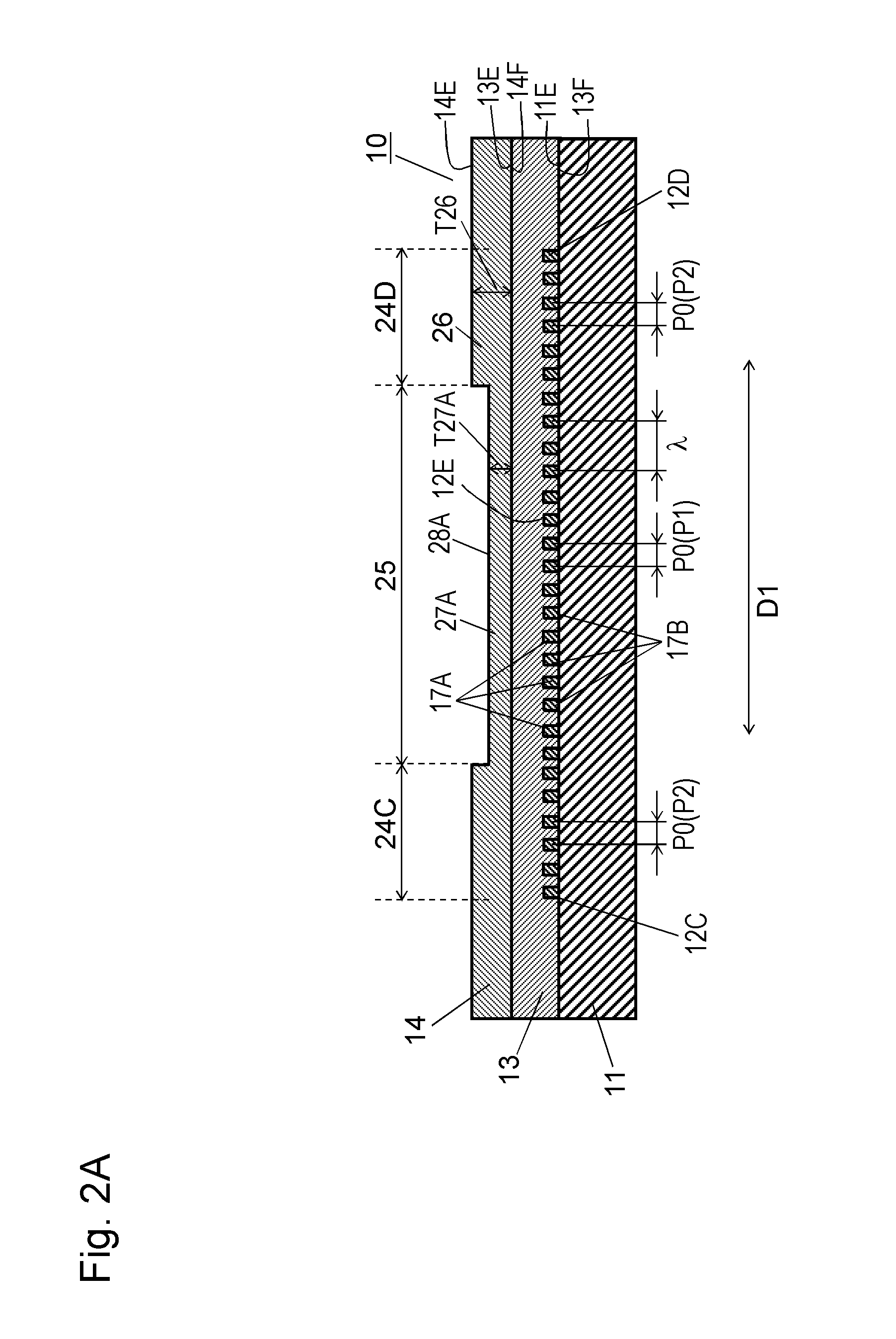
An acoustic wave device includes a piezoelectric substrate, an interdigital transducer (IDT) electrode provided on an upper surface of the piezoelectric substrate, a first dielectric film covering the upper surface of the piezoelectric substrate to cover the IDT electrode, and a second dielectric film covering an upper surface of the first dielectric film. The second dielectric film includes a thin portion positioned in a tip region of electrode fingers of the IDT electrode and a thick portion which is positioned in a middle region of the IDT electrode and is thicker than the thin portion. The acoustic wave device suppresses spurious emission and has superior passband characteristics.
Owner:SKYWORKS PANASONIC FILTER SOLUTIONS JAPAN
Digital pre-distortion for the linearization of power amplifiers with asymmetrical characteristics
InactiveUS7251293B2Amplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influencePower amplifier linearizationEngineering
An input signal is pre-distorted to reduce spurious emissions resulting from subsequent signal amplification. Frequency-dependent pre-distortion is preferably implemented in combination with frequency-independent pre-distortion, where the frequency-dependent pre-distortion corresponds to amplifier distortion that has a magnitude that is proportional to the frequency offset from the carrier frequency and a ±90° phase shift on either side of the carrier frequency. The frequency-dependent pre-distortion is generated by differentiating waveforms corresponding to two different sets of pre-distortion parameters with respect to time. In one embodiment, one of the differentiated waveforms is applied to a positive-frequency filter and the other to a negative-frequency filter to generate positive- and negative-frequency pre-distortion signals, respectively, to account for asymmetries in the amplifier characteristics. In another embodiment, only one of the differentiated waveforms is applied to an asymmetric filter (i.e., either a positive-frequency filter or a negative-frequency filter).
Owner:COMMSCOPE TECH LLC
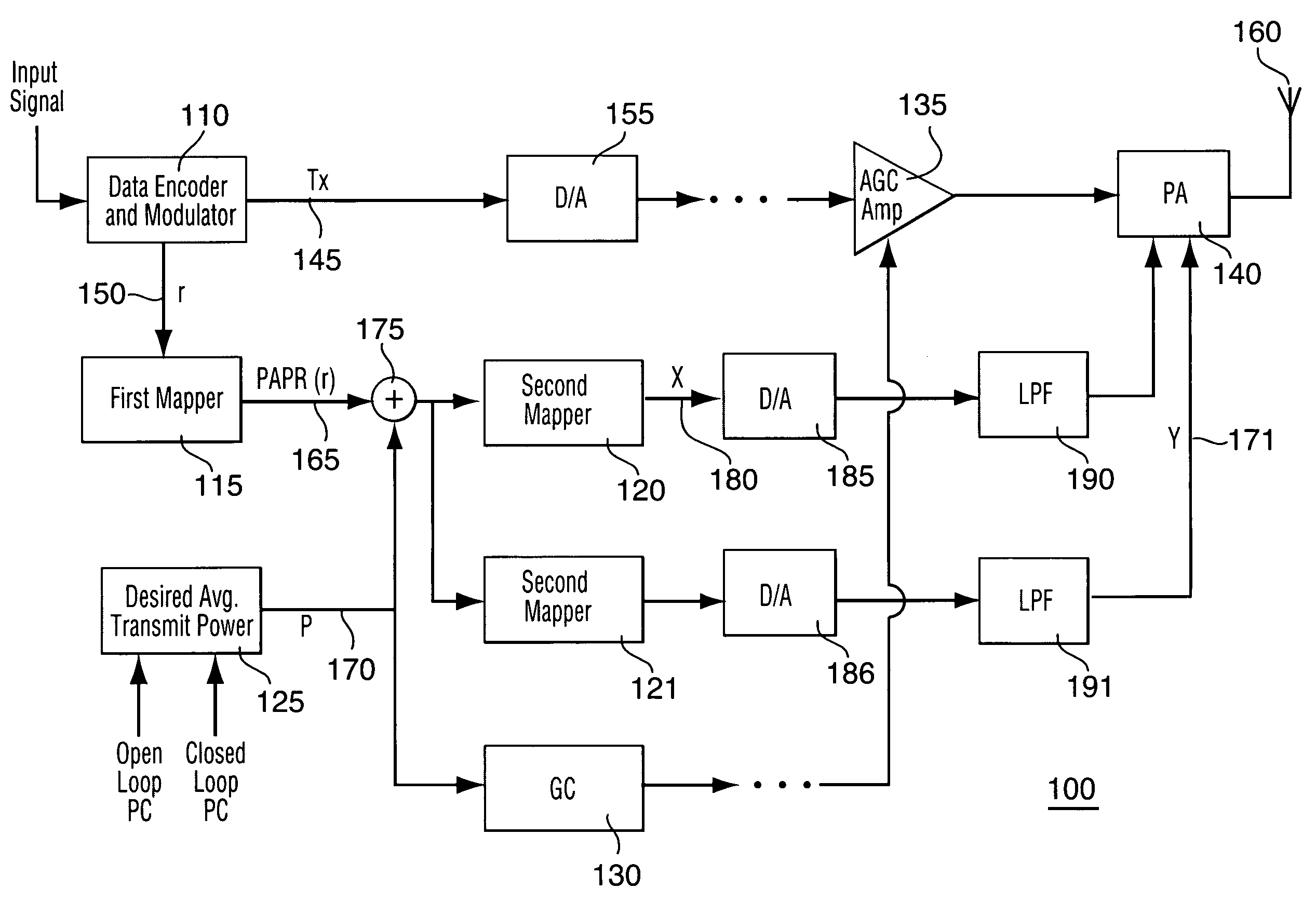
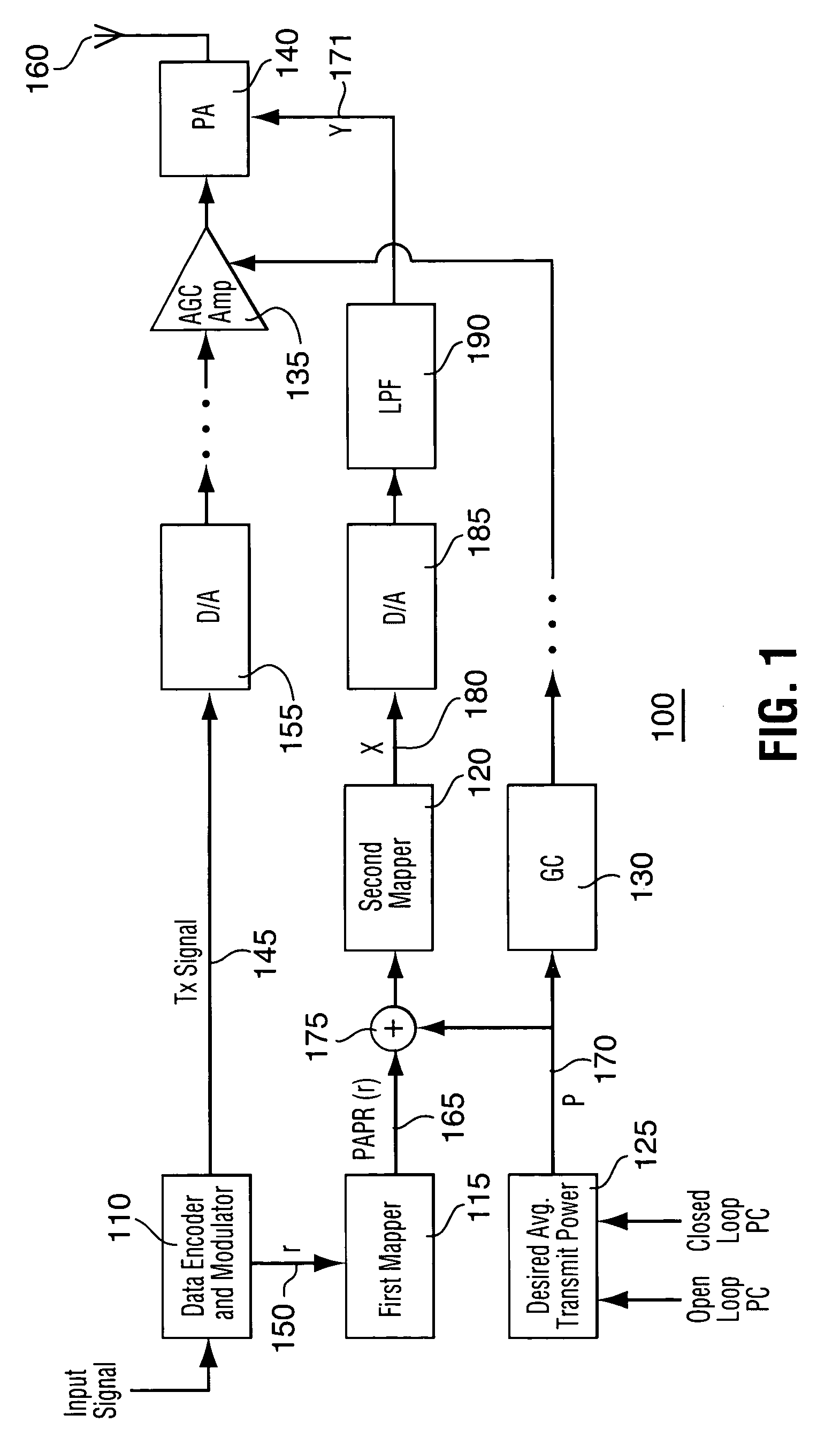
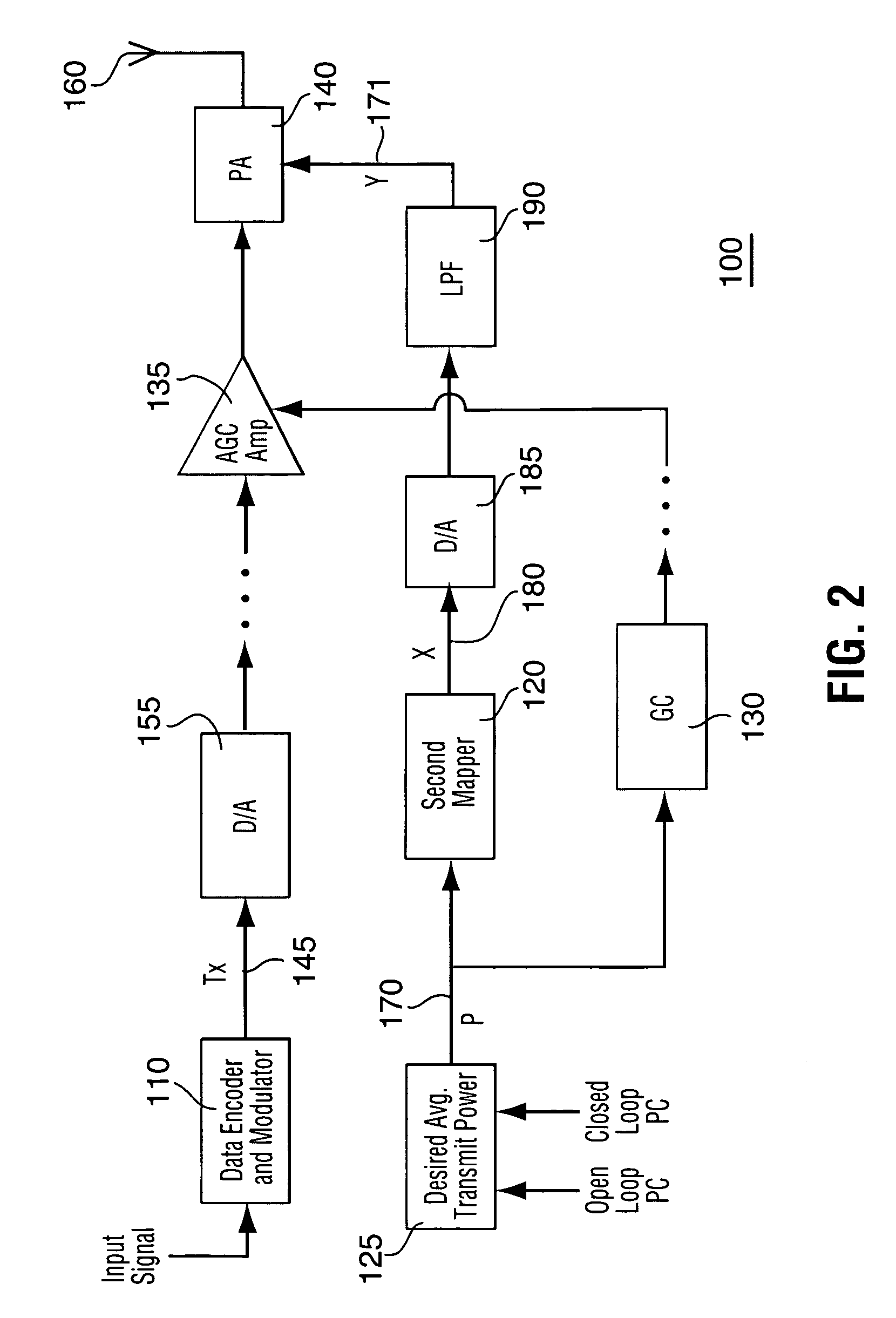
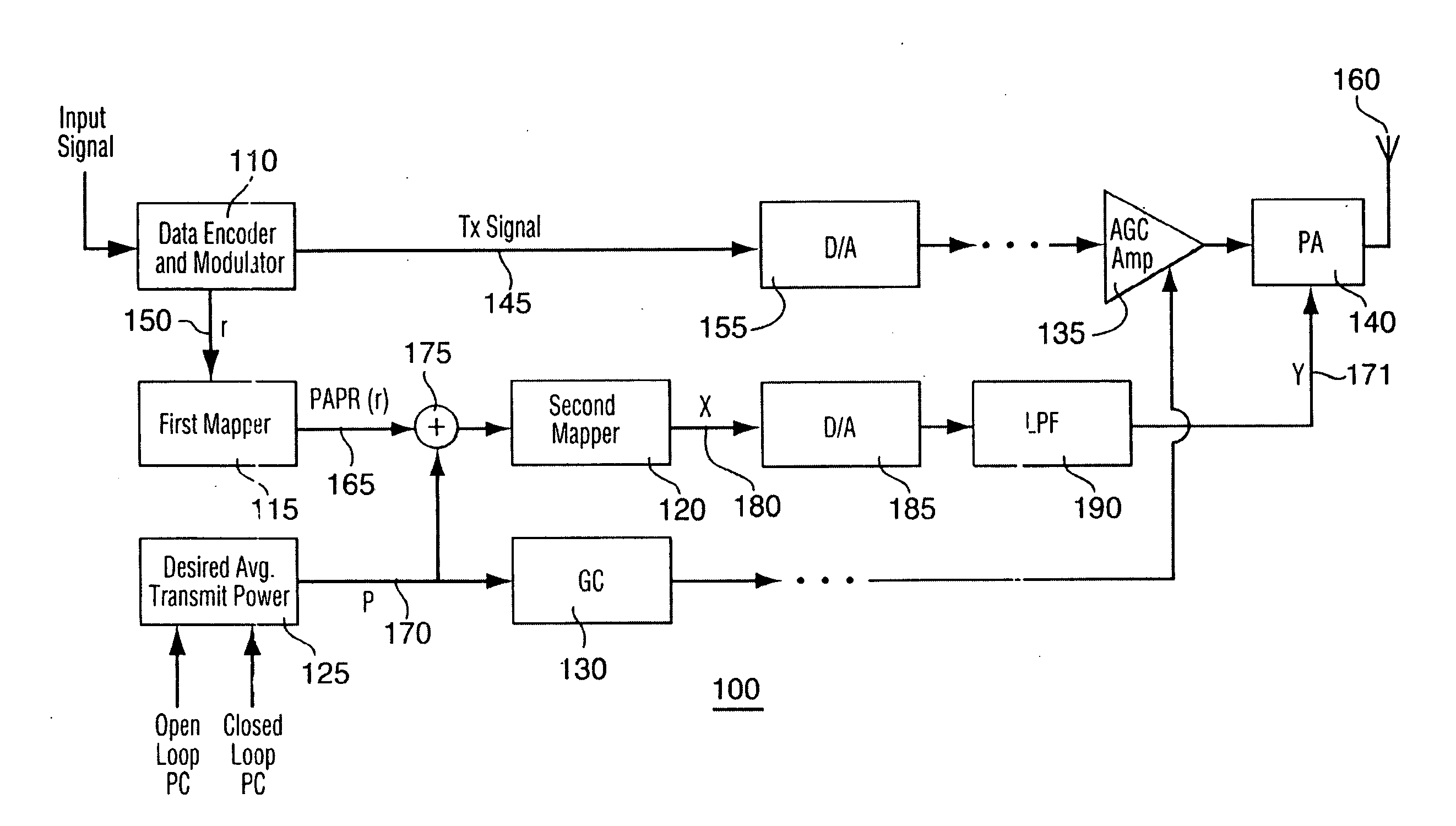
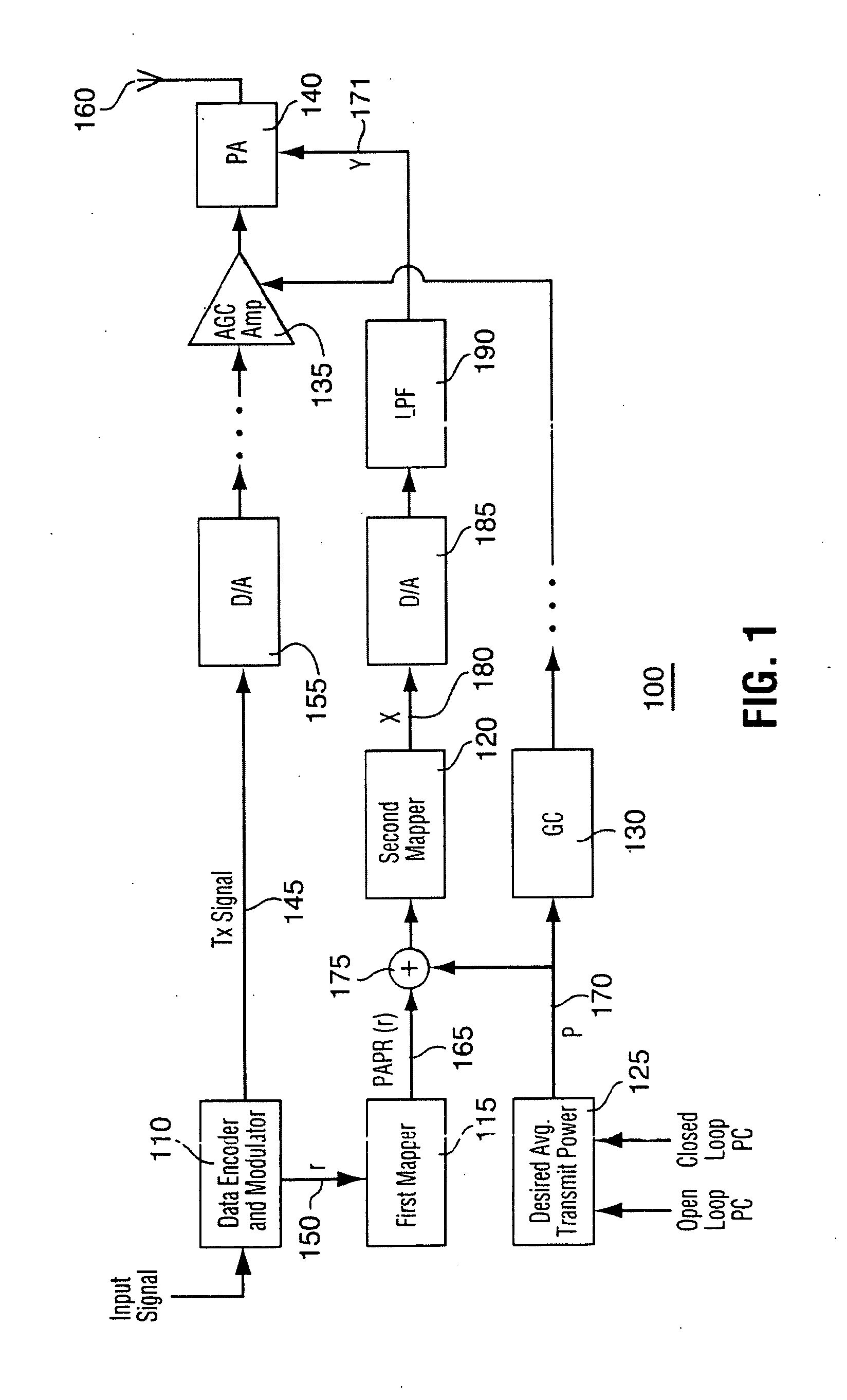
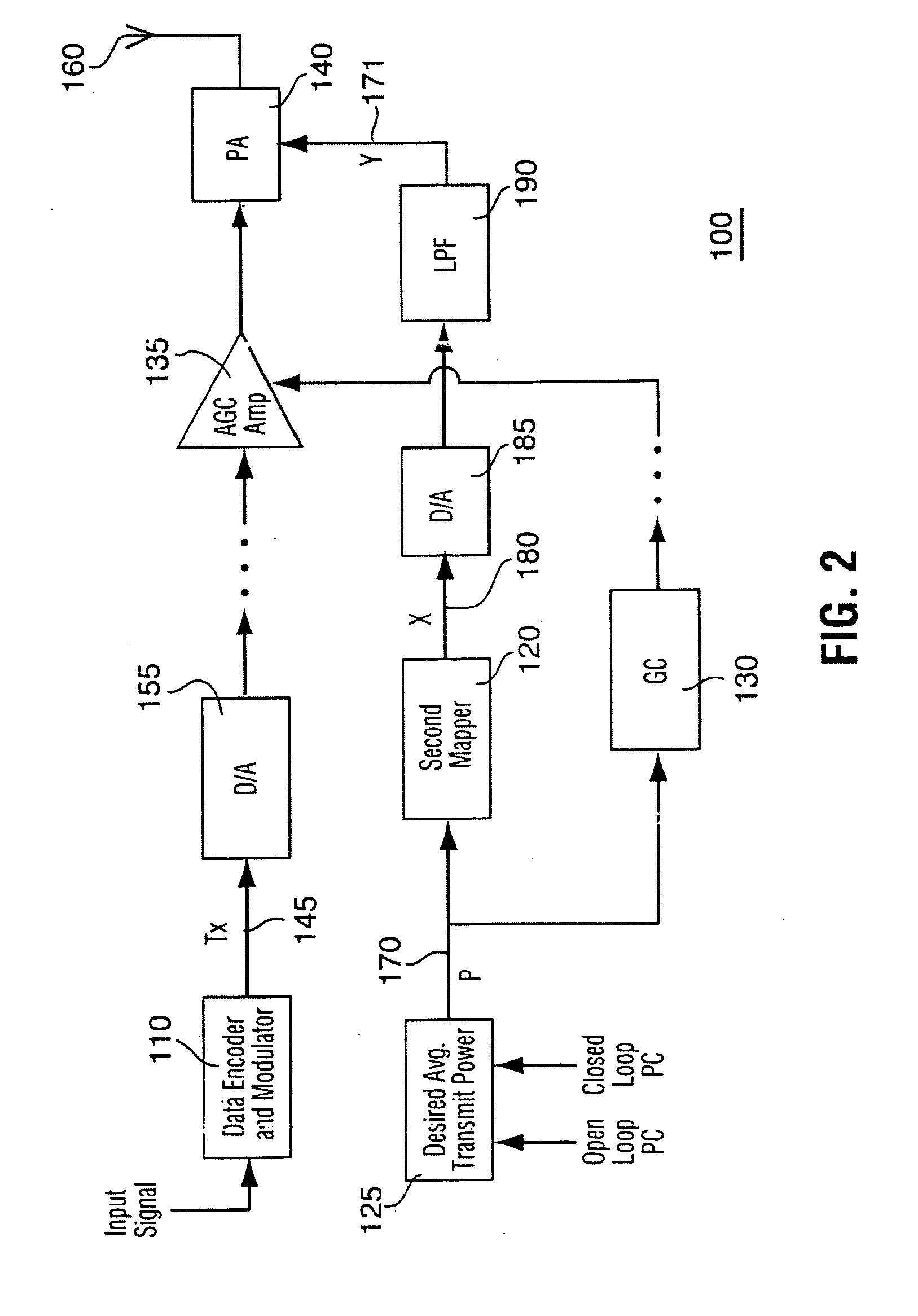
Method and apparatus for optimizing transmitter power efficiency
A peak to average power ratio signal is generated from a first mapping function that selects the peak to average power ratio signal that corresponds to the data rate or data format of the signal to be transmitted. The selected peak to average power ratio signal is summed with a desired average transmit power signal. The resulting summation signal is input to a second effectively continuously valued mapping function comprising a table that has a plurality of power amplifier control signal values each with a corresponding peak transmit power. Each peak transmit power signal value results in a power amplifier control signal value that achieves the best possible transmitter power efficiency while still meeting out of band spurious emissions and waveform quality requirements. The summation signal value maps to one of the power amplifier control signal value that is then used to adjust a parameter such as bias of the power amplifier.
Owner:MALIKIE INNOVATIONS LTD
Method and apparatus for optimizing transmitter power efficiency
Owner:MALIKIE INNOVATIONS LTD
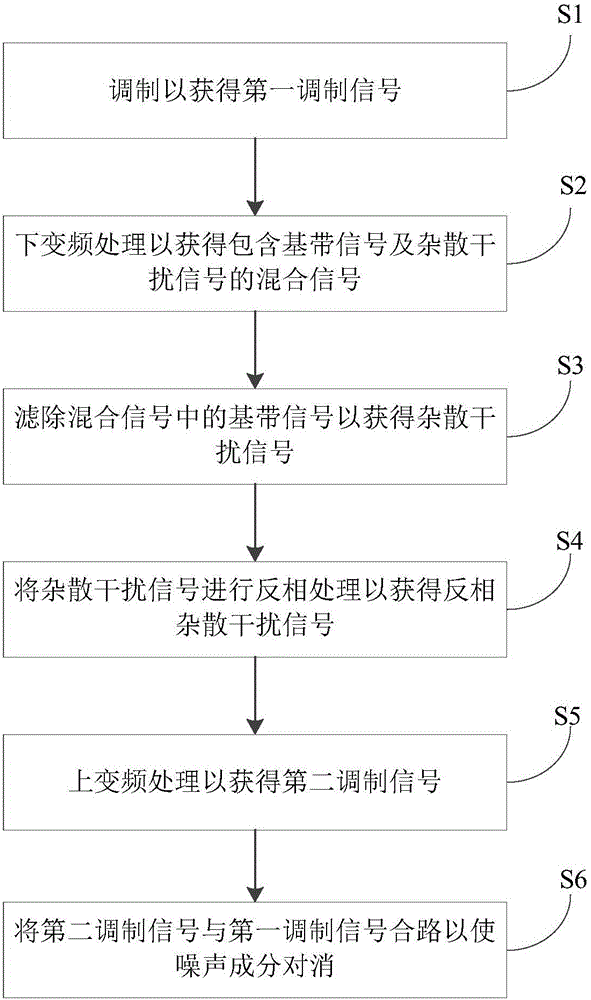
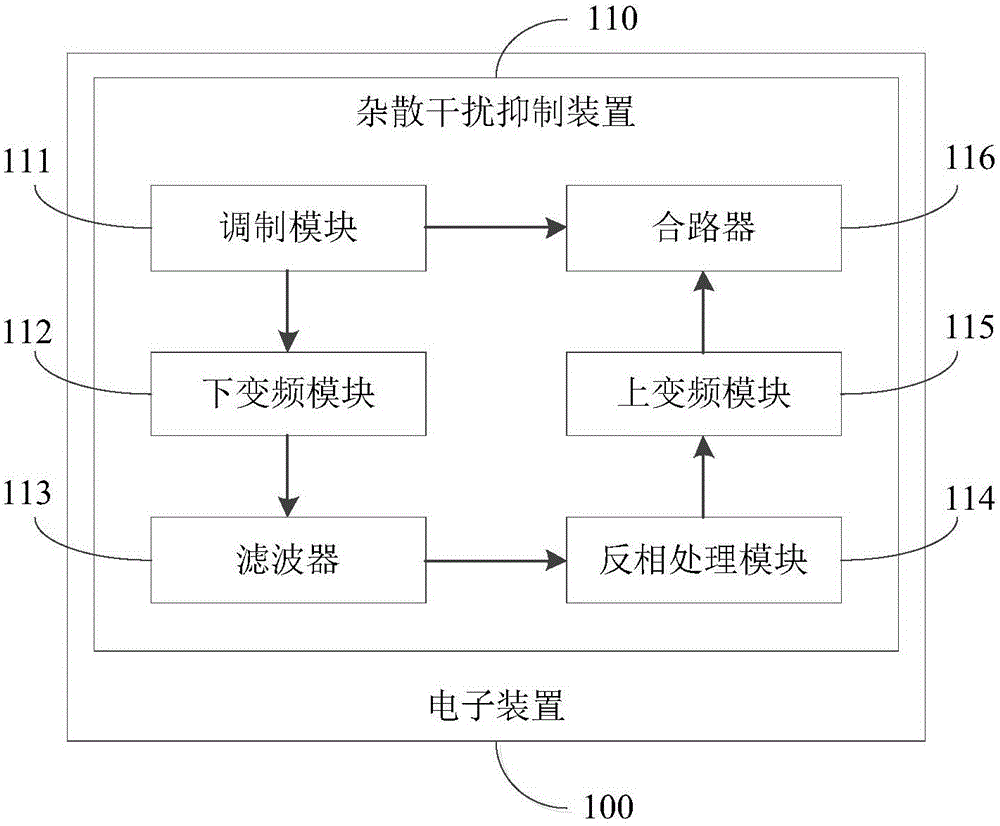
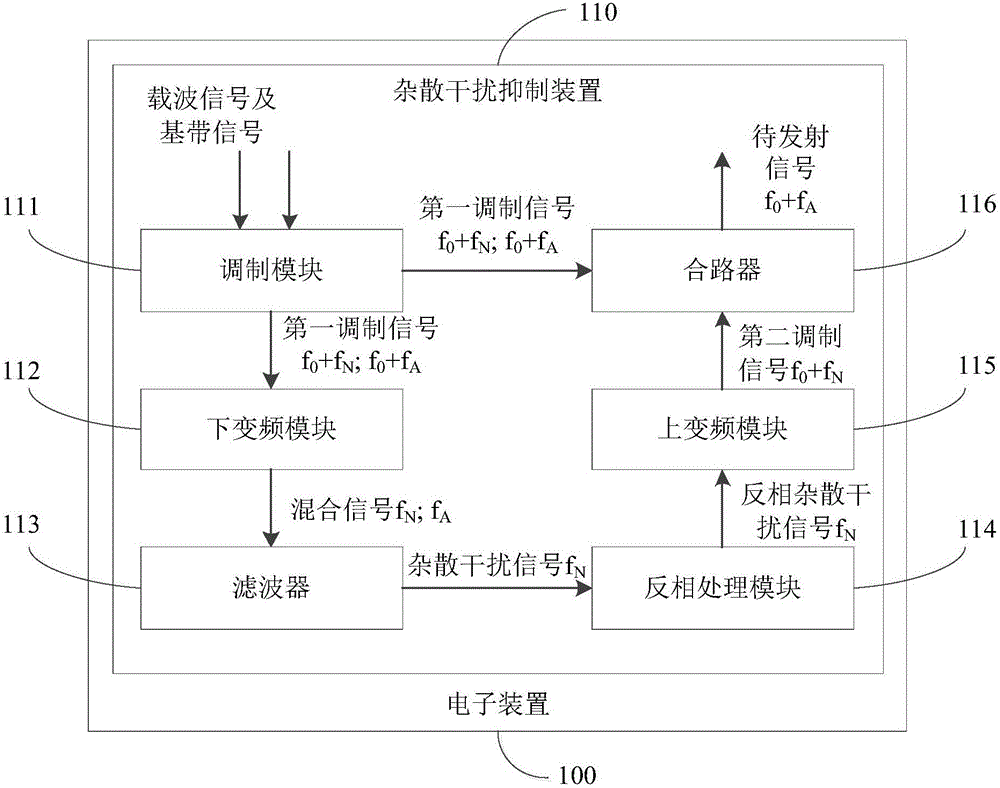
Spurious emission interference suppressing method, spurious emission interference suppressing device and electronic device
The invention discloses a spurious emission interference suppressing method, which can be used for suppressing a spurious emission interference signal of an electronic device. The method comprises the following steps: first of all, modulating an amplitude of a baseband signal to obtain a first modulation signal; then, carrying out down-conversion processing on the first modulation signal to obtain a mixed signal comprising the baseband signal and the spurious emission interference signal; after that, filtering the baseband signal in the mixed signal to obtain the spurious emission interference signal; then, carrying out phase reversal processing on the spurious emission interference signal to obtain a phase reversal spurious emission interference signal; then, carrying out up-conversion processing on the phase reversal spurious emission interference signal to obtain a second modulation signal; and at last, combining the second modulation signal and the first modulation signal to enable the spurious emission interference signal to offset the phase reversal spurious emission interference signal. By adopting the spurious emission interference suppressing method or the spurious emission interference suppressing device disclosed by the embodiment of the invention, spurious emission interference elements in the modulation signals can be effectively suppressed, thereby improving the quality of the modulation signals. And the invention further discloses the spurious emission interference suppressing device and the electronic device.
Owner:GUANGDONG OPPO MOBILE TELECOMM CORP LTD
Intelligent straight placement station and parameter automatic adjustment method
InactiveCN101202573AQuality improvementStable output powerTransmission control/equalisingRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsAutomatic controlTransceiver
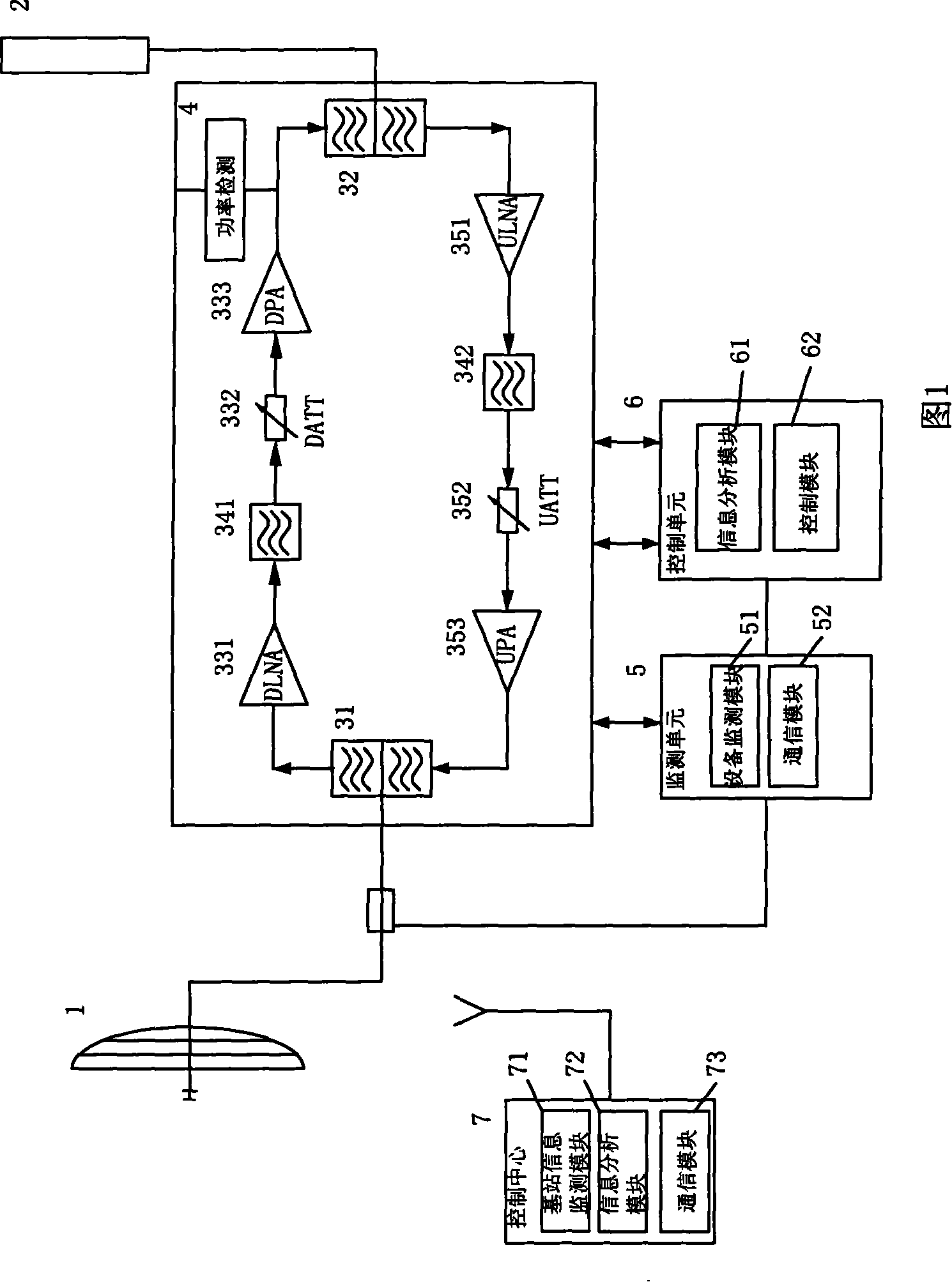
The invention discloses an intelligent repeater and an automatic adjusting method for the parameters thereof. The intelligent repeater station includes a donor antenna, a retransmission antenna, a radio frequency transceiver hardware unit, a power detecting component, a control center and an intelligent control system. The control center includes a base station information monitoring module, an information analyzing module and a communicating module. The intelligent control system includes a monitoring unit and a control unit. The monitoring unit includes a device monitoring module and the communicating module. The control unit includes the information analyzing module and a control module. The invention gathers the information from the base station and the self parameter information of the repeater through the control center and the intelligent control system and carries out analyzing and calculating on the information according to certain arithmetic and automatically adjusts the parameters of the repeater according to the calculating results. Adopting the intelligent station and the automatic adjusting method for the parameters thereof can realize automatic frequency control and adjustment and increases the effectiveness of network coverage as well as realize automatic multi-carrier power control to lead each carrier output power to be stable and improve the quality of network. The invention can automatically control a spurious emission power and prevent the base station from being continuous interrupted.
Owner:厦门特力通信息技术股份有限公司
Apparatuses, systems, and methods for reducing spurious emissions resulting from carrier leakage
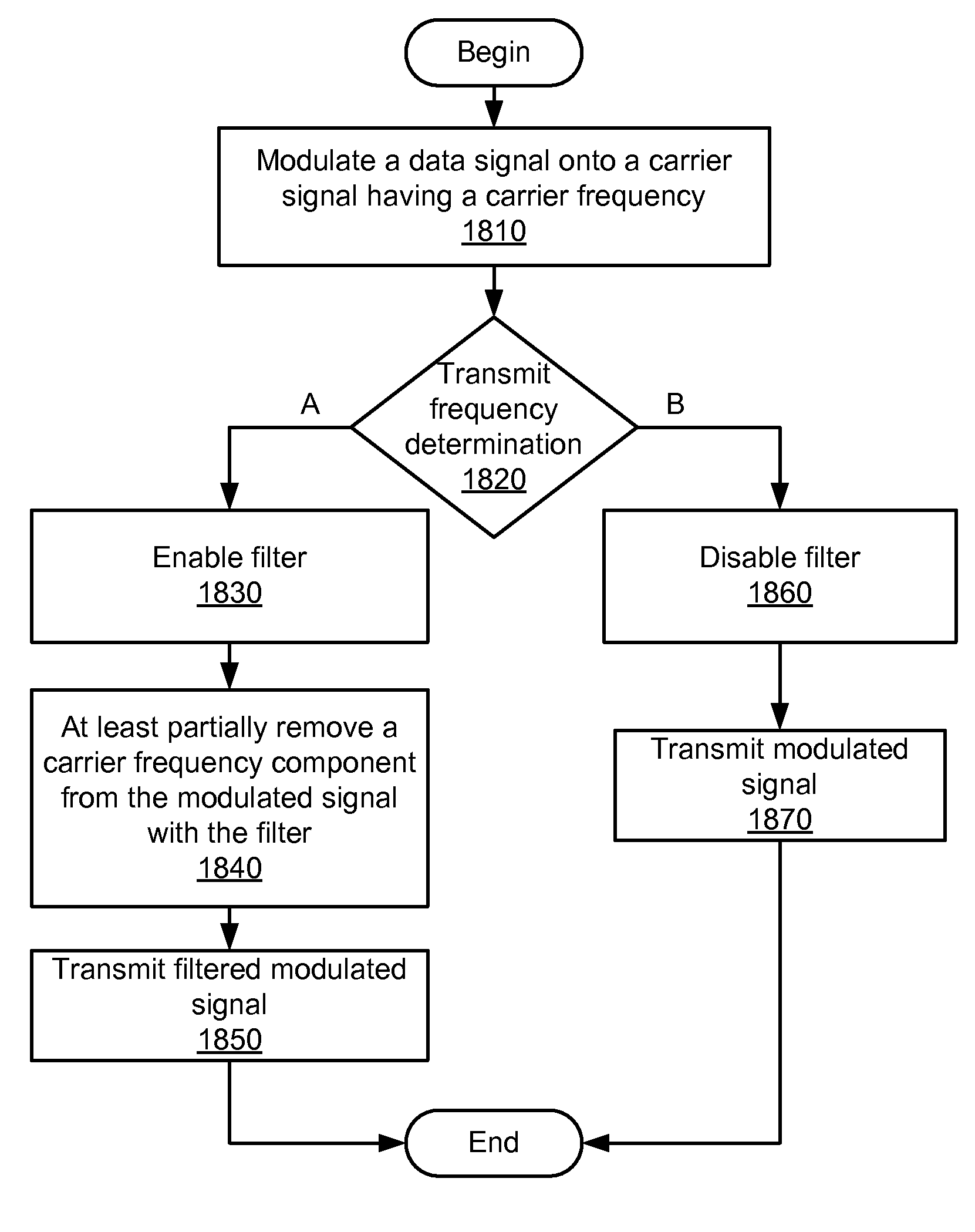
ActiveUS20100189190A1Secret communicationPhase-modulated carrier systemsFrequency filteringCarrier signal
An exemplary apparatus includes a modulator configured to modulate a data signal onto a carrier signal to generate a modulated signal having a transmit frequency within a predefined frequency range adjacent to and within a boundary of an uplink frequency band, a filter configured to at least partially remove a carrier frequency component from the modulated signal to produce a filtered modulated signal, and an antenna configured to transmit the filtered modulated signal.
Owner:VERIZON PATENT & LICENSING INC
High level iboc combining method and apparatus for single input antenna systems
ActiveUS20130287144A1Improve complianceSpatial transmit diversityModulated-carrier systemsHybrid couplerConstant impedance
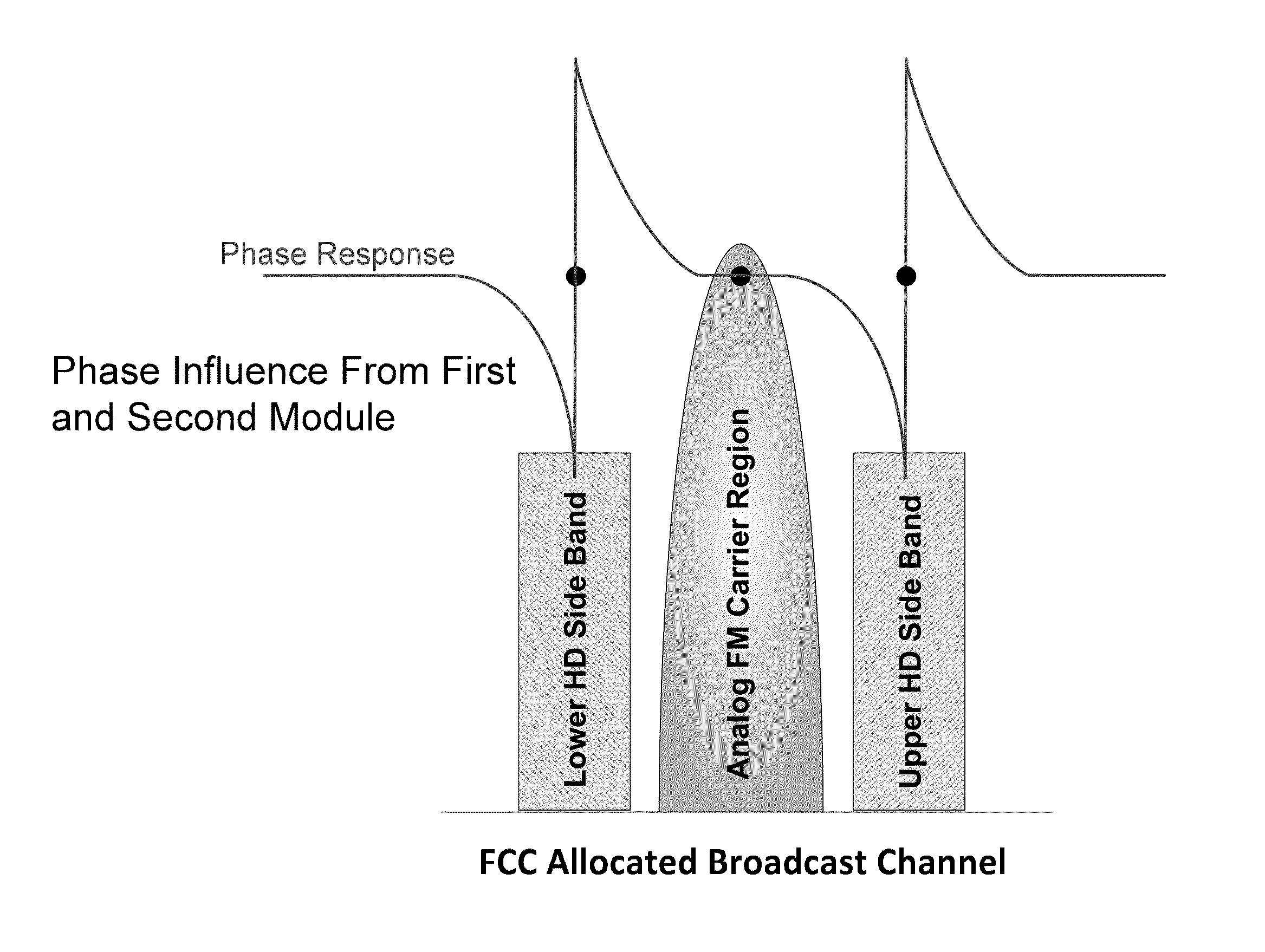
A phase shift is defined as a point in frequency at which the phase is changed from 0 degrees to 180 degrees. A device is provided for combining analog and digital in-band-on-channel (IBOC) signals to feed a common antenna utilizing phase shifting allpass filter modules to provide a 180 degree phase shift to specific IBOC channels within a constant impedance dual-hybrid circuit. The IBOC Allpass combiner includes one input 90 degree 3 dB quadrature hybrid coupler, one output 90 degree 3 dB quadrature hybrid coupler, a load resistor, and two phase shifting allpass filter modules. Each phase shifting allpass filter module is comprised of a two coaxial cavity resonators coupled to a 90 degree 3 dB quadrature hybrid coupler. Components and modules are coupled using mating transmission lines. The four coaxial cavity resonators are used as devices to produce two distinct phase shifts at isolated upper and lower IBOC side band frequencies. The circuit is designed for one center analog frequency and two sideband IBOC OFDM carrier frequencies, such that all frequencies will combine in phase at the common antenna input with minimal loss and minimal group delay. Out of phase and spurious emissions are ported to the load resistor.
Owner:ELECTRONICS RES
Acoustic wave device
ActiveUS9035725B2Suppresses spurious emissionSuperior passband characteristicImpedence networksDielectricSpurious emission
An acoustic wave device includes a piezoelectric substrate, an interdigital transducer (IDT) electrode provided on an upper surface of the piezoelectric substrate, a first dielectric film covering the upper surface of the piezoelectric substrate to cover the IDT electrode, and a second dielectric film covering an upper surface of the first dielectric film. The second dielectric film includes a thin portion positioned in a tip region of electrode fingers of the IDT electrode and a thick portion which is positioned in a middle region of the IDT electrode and is thicker than the thin portion. The acoustic wave device suppresses spurious emission and has superior passband characteristics.
Owner:SKYWORKS PANASONIC FILTER SOLUTIONS JAPAN
Acoustic wave resonator and duplexer using same
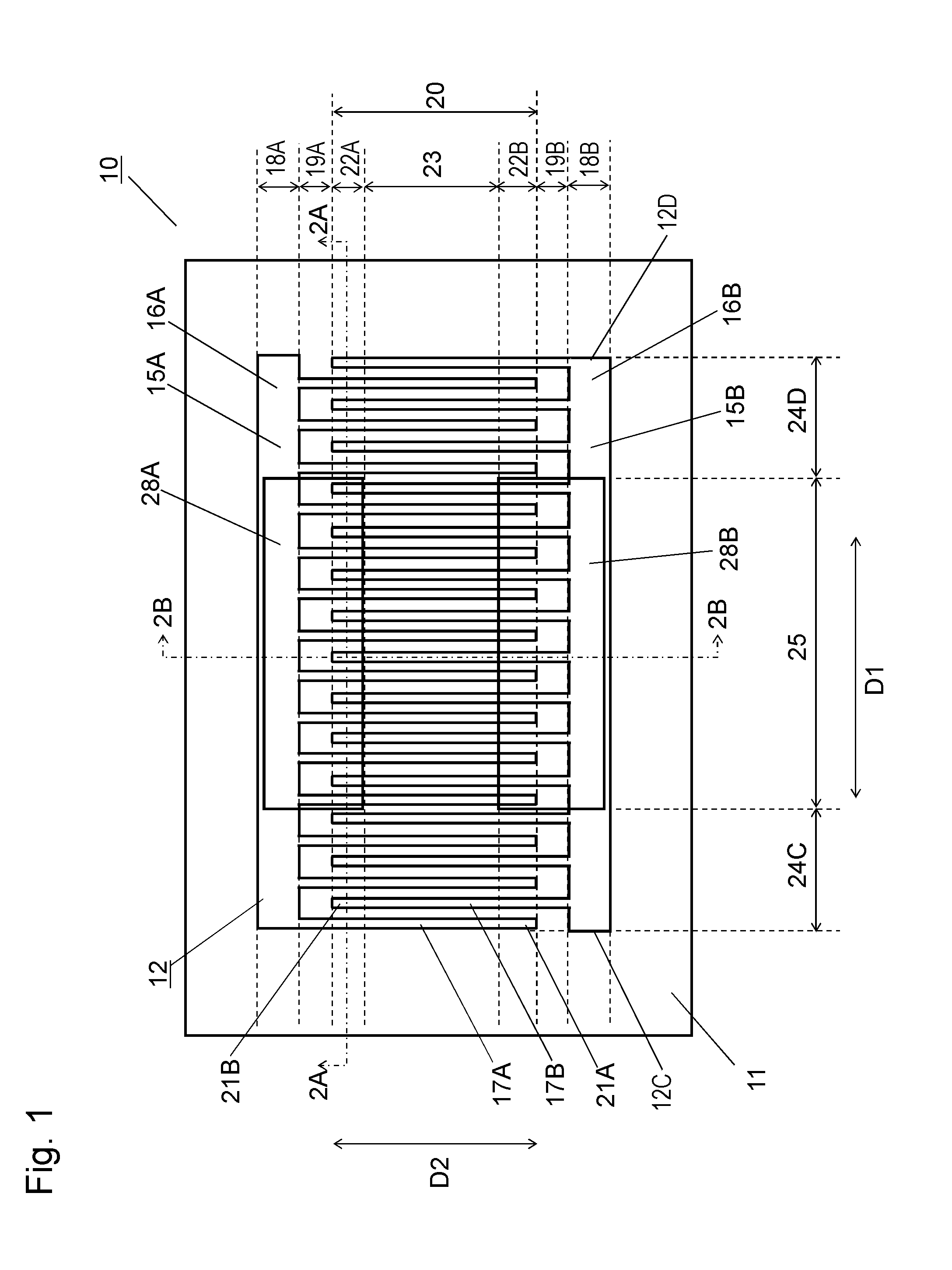
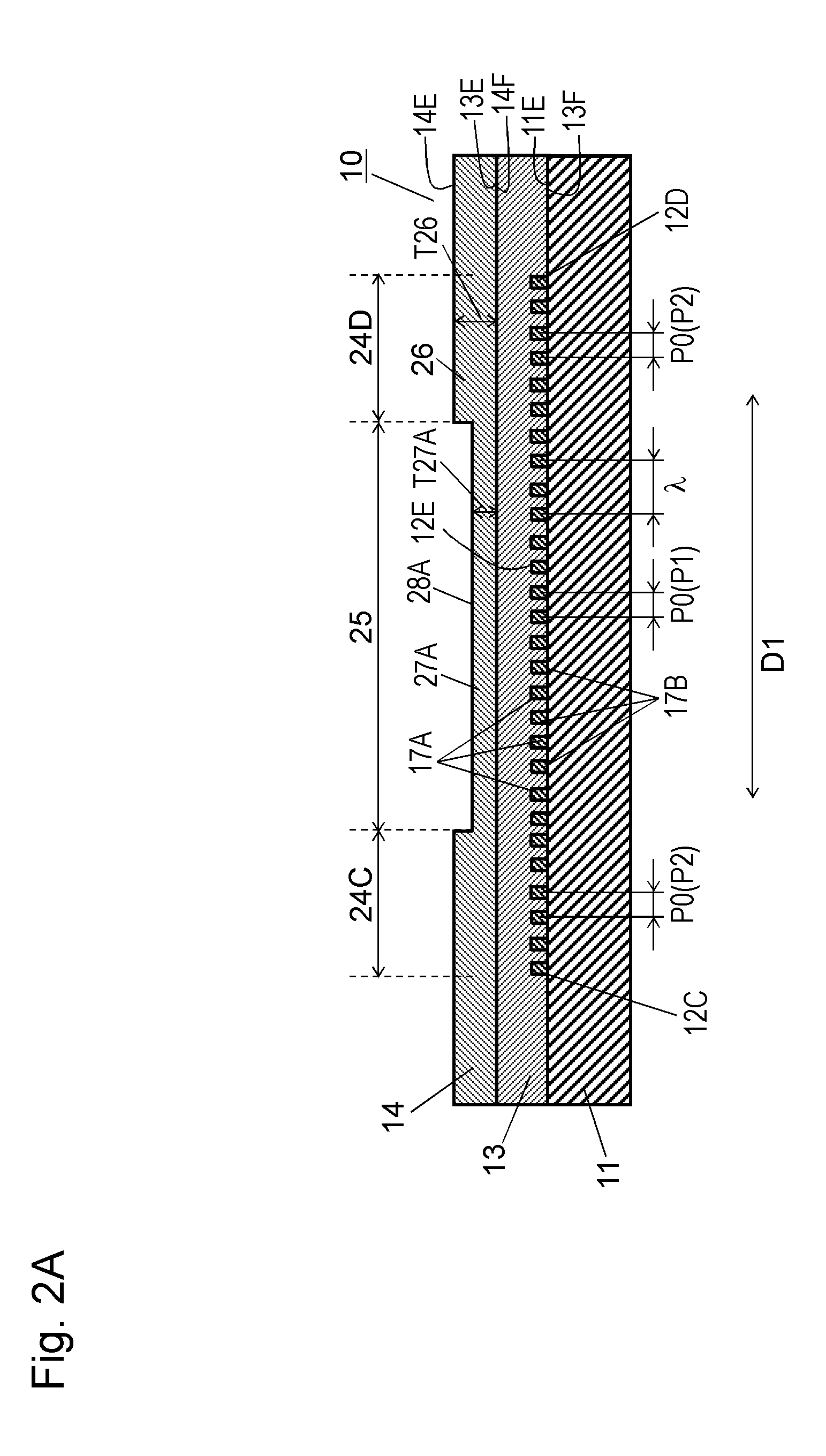
ActiveUS8698578B2Avoid emissionsImpedence networksPiezoelectric/electrostrictive/magnetostrictive devicesTransverse modeAcoustic wave
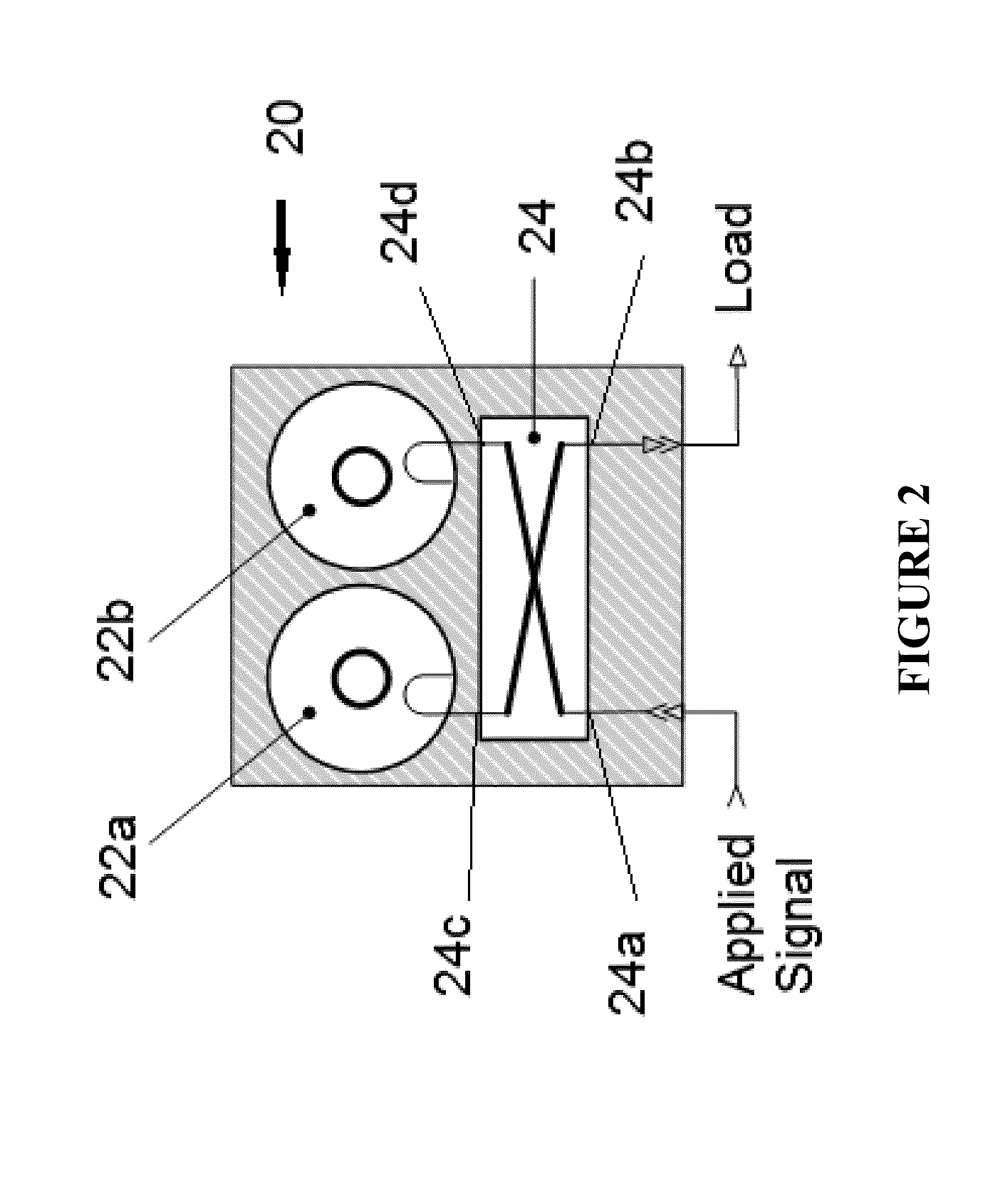
An acoustic wave resonator includes a piezoelectric body, an IDT electrode for exciting an acoustic wave with wavelength λ, and a dielectric thin film provided so as to cover the IDT electrode. The IDT electrode includes a bus bar electrode region, a dummy electrode region, and an IDT cross region in order from outside. The film thickness of the dielectric thin film above at least one of the bus bar electrode region and the dummy electrode region is smaller than that above the IDT cross region by 0.1λ to 0.25λ. This configuration provides an acoustic wave resonator that reduces transverse-mode spurious emission.
Owner:SKYWORKS PANASONIC FILTER SOLUTIONS JAPAN
Frequency-dependent magnitude pre-distortion on non-baseband input signals for reducing spurious emissions in communication networks
InactiveUS7266159B2Spurious emission can be reducedEmission reductionAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceDifferentiatorAudio power amplifier
Pre-distortion, whose magnitude—and preferably phase—are frequency-dependent, is applied to a non-baseband input signal in order to reduce spurious emissions resulting from subsequent amplification of the signal. In preferred embodiments, the pre-distortion technique of the present invention is implemented in combination with the (frequency-independent) magnitude and phase pre-distortion technique described in U.S. patent application Ser. No. 09 / 395,490 (“the '490 application”), where the frequency-dependent pre-distortion corresponds to amplifier distortion that has a magnitude that is proportional to the frequency offset from the carrier frequency and a phase shift of ±90° on either side of the carrier frequency. Since these characteristics match those of a differentiator, a thorough correction of this part of the amplifier's distortion can be achieved using a differentiating circuit. Embodiments of the present invention may be implemented in the RF domain. Implementations may also be based on look-up tables that are adaptively updated to ensure optimal performance over time.
Owner:COMMSCOPE TECH LLC
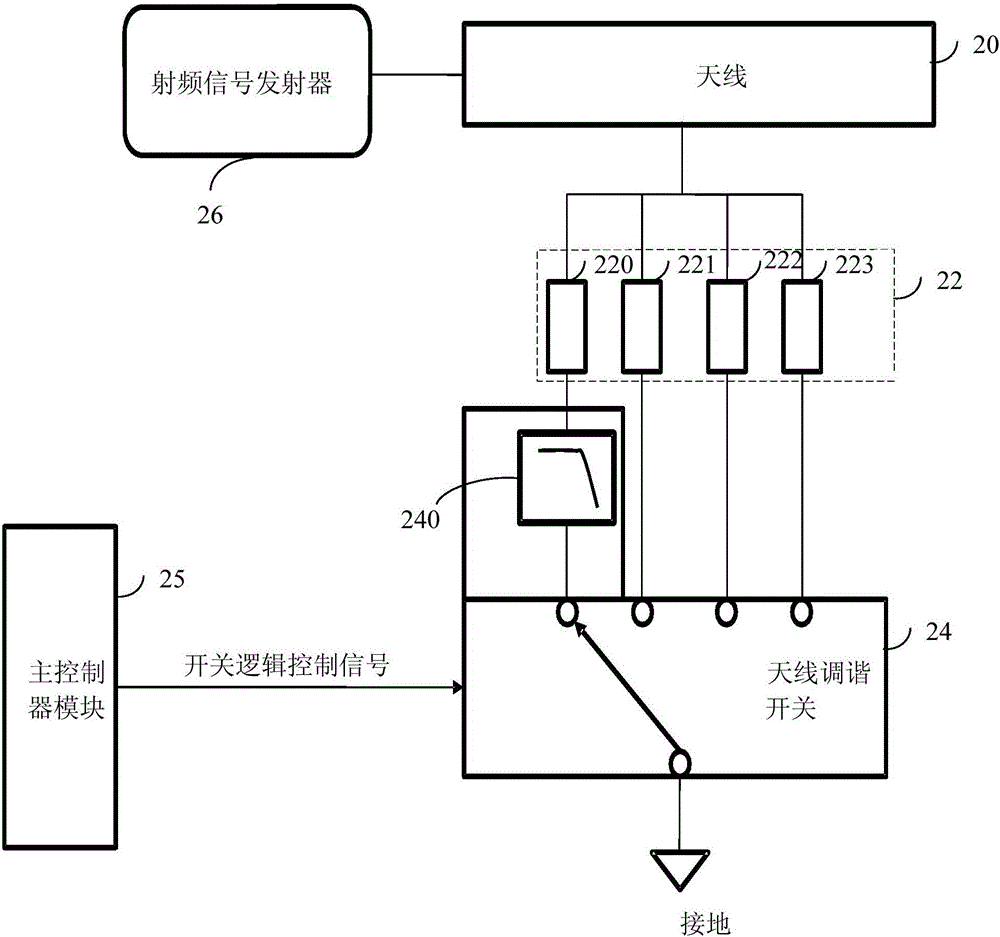
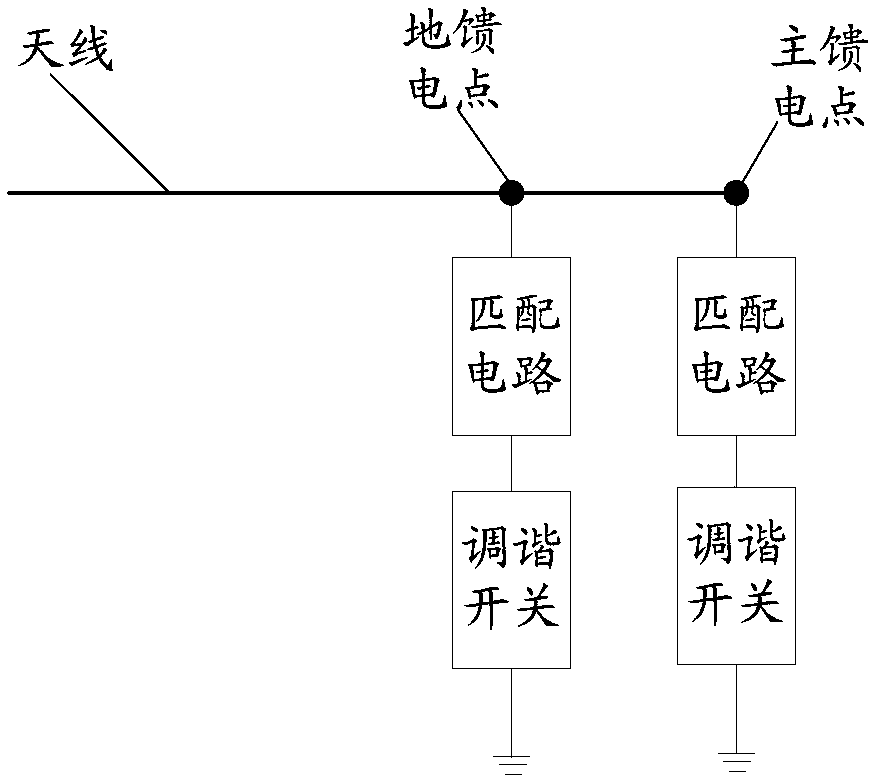
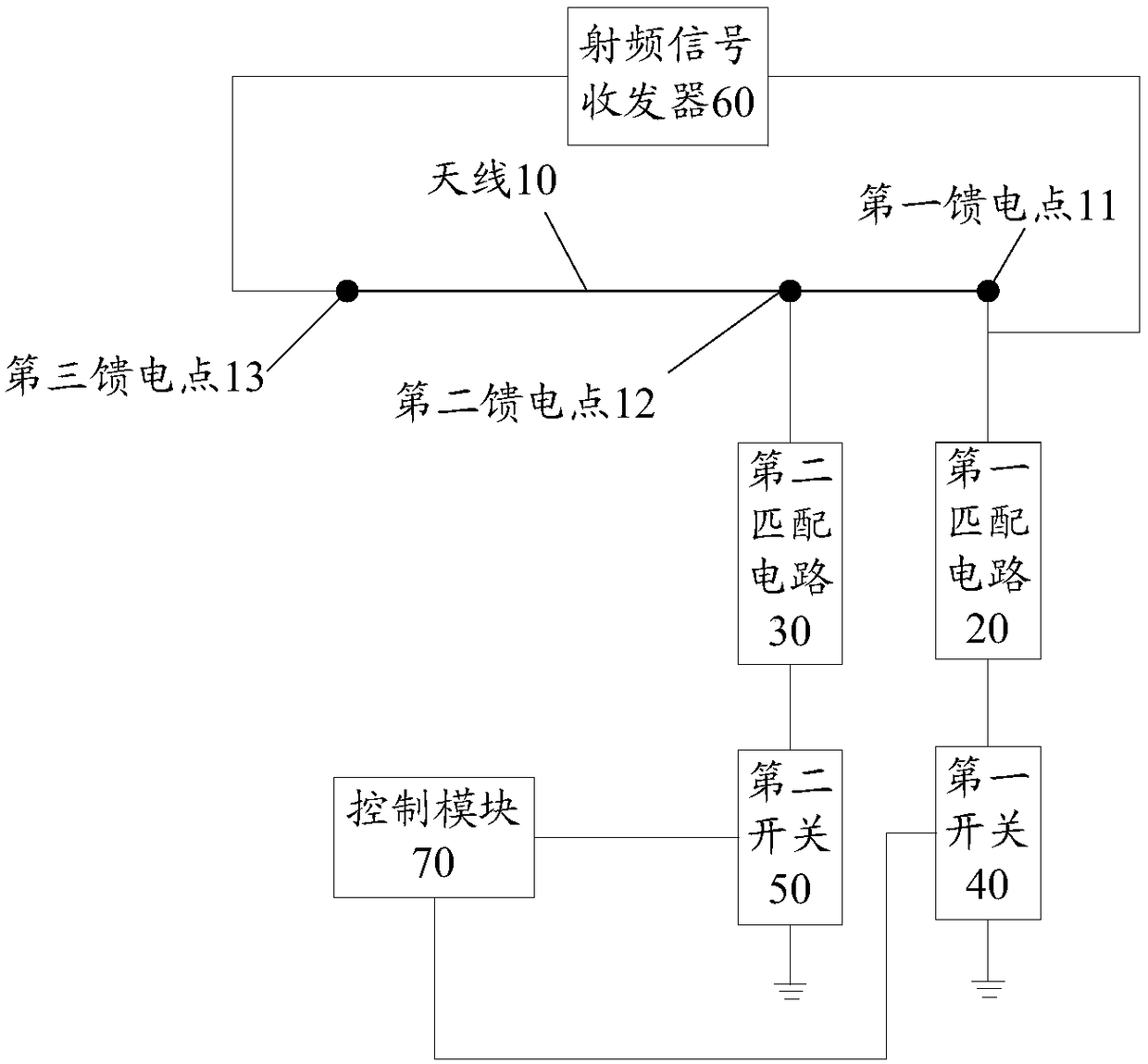
Antenna tuning circuit, antenna device and mobile terminal
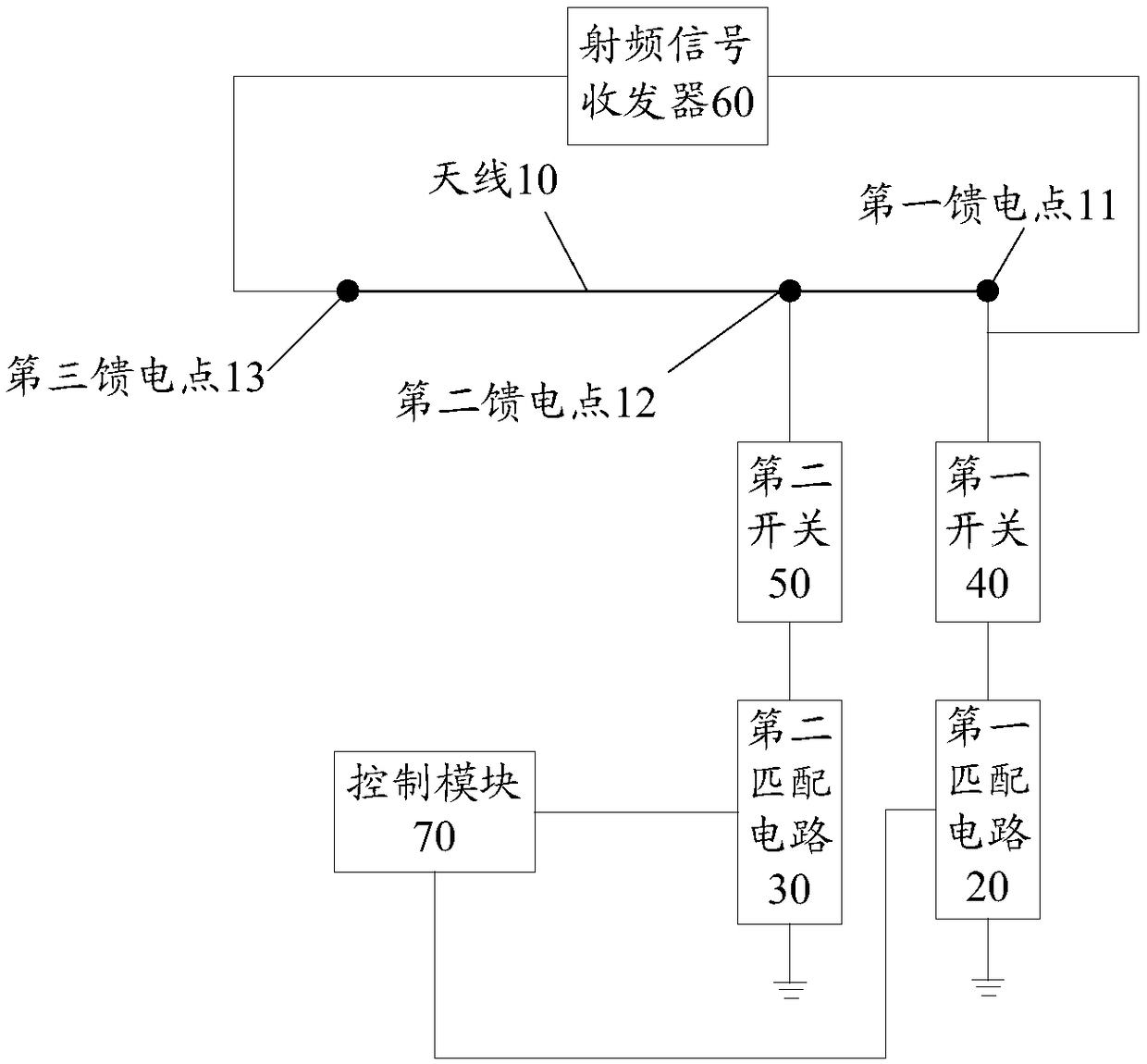
ActiveCN108110423AEliminate saturationSuppression of Radiation StraySimultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsTransceiverRadio frequency signal
The application discloses an antenna tuning circuit and a mobile terminal. The antenna tuning circuit includes an antenna, a first matching circuit, a second matching circuit, a first switch, a secondswitch, and a radio frequency signal transceiver. The antenna includes a first feed point, a second feed point, and a third feed point that are arranged in sequence. The first matching circuit and the first switch are connected in series between the first feed point and the ground. The second matching circuit and the second switch are connected in series between the second feed point and the ground. When the operating frequency band is at a low frequency, a radio frequency signal transmitted by the radio frequency signal transceiver is transmitted to an antenna radiator through the third feedpoint. Both the first switch and the second switch are turned on. The frequency band in the third frequency range is smaller than the frequency band in the second frequency range. With the embodiments of the application, the radiation spurious emission can be suppressed.
Owner:GUANGDONG OPPO MOBILE TELECOMM CORP LTD
Synthesized resonation for an EL driver circuit
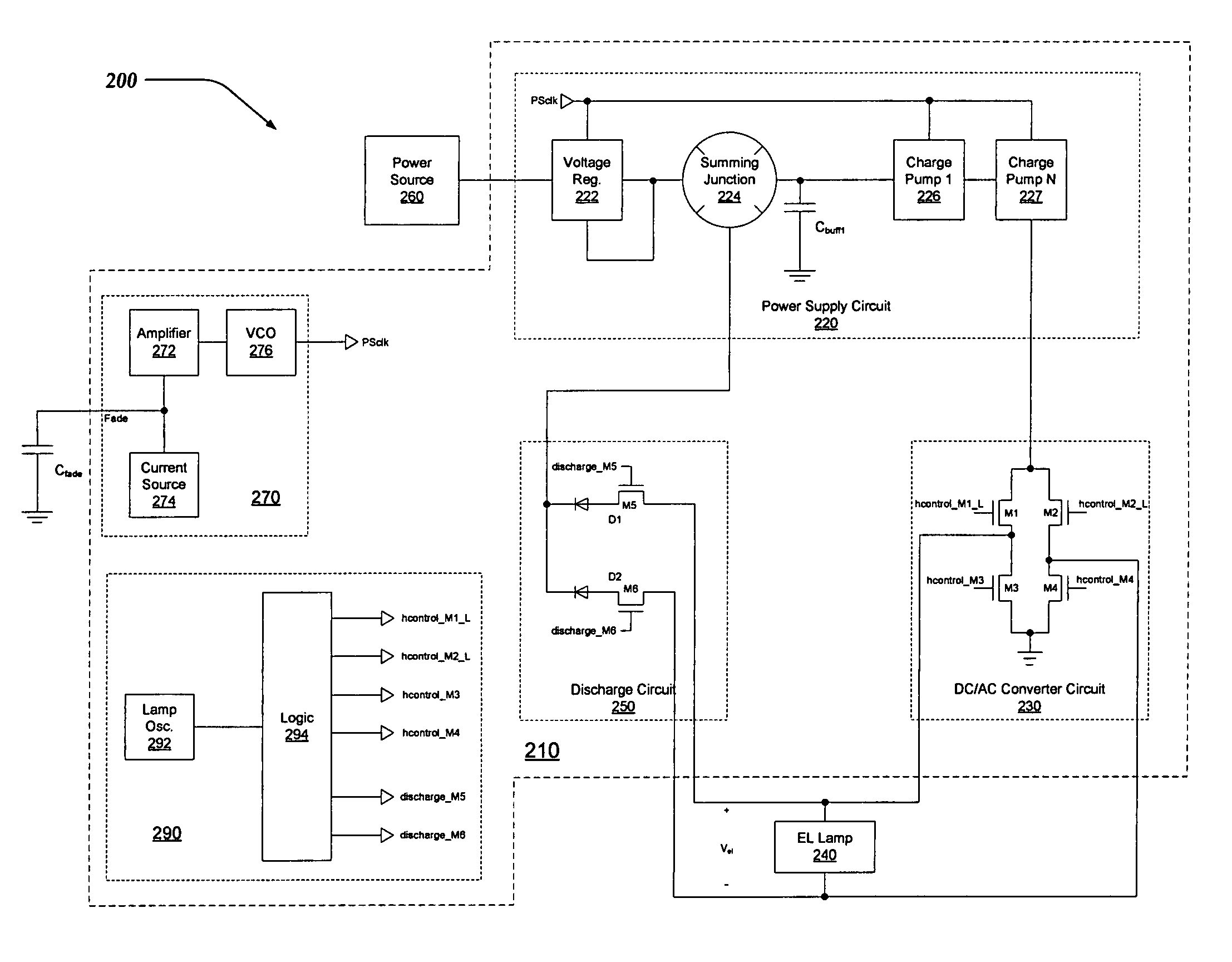
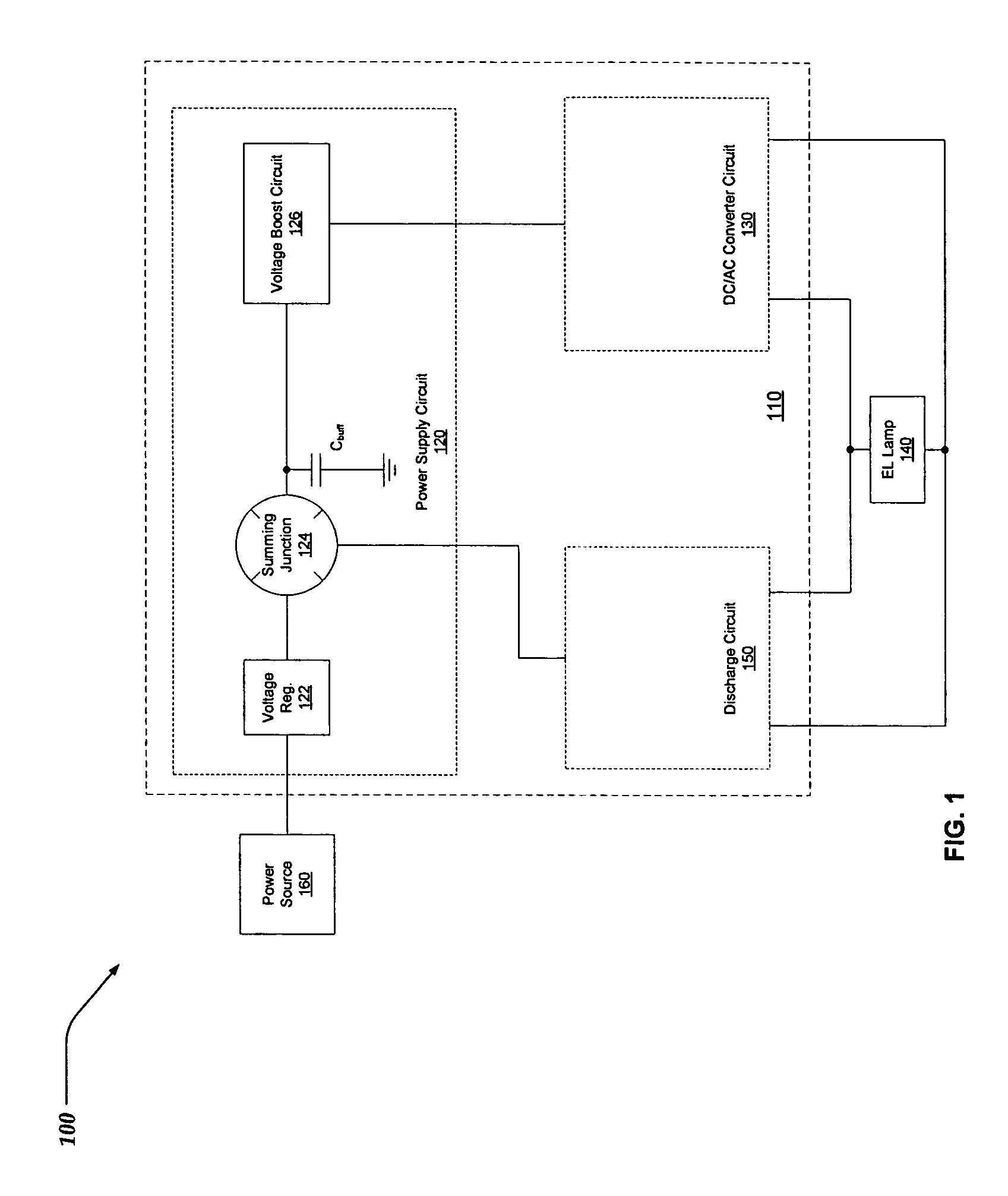
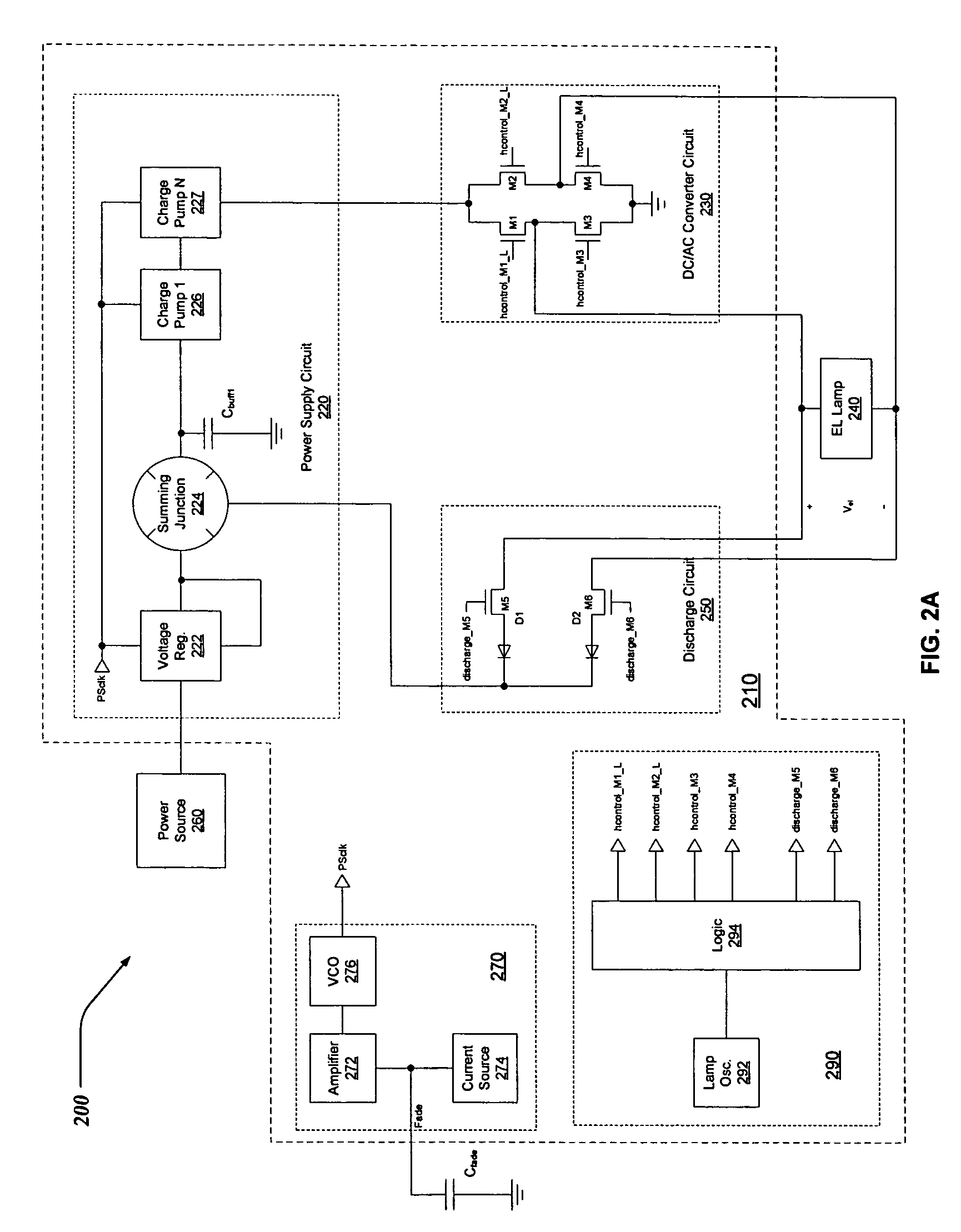
ActiveUS7279958B1Electrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesDriver circuitElectromagnetic interference
A driver circuit for an electroluminescent (EL) lamp that consumes less power and reduces electromagnetic interference (EMI). Electrical charge is stored during a discharge cycle of an AC signal employed to illuminate an EL lamp, and subsequently reused during the AC signal's charging cycle. The reuse of electrical charge enables the driver circuitry to illuminate the EL lamp while drawing the least amount of power from a power supply, such as a battery. Also, multiple charge pumps can be sequentially / serially turned off during the discharge cycles of the AC signal driving the EL Lamp. By sequentially discharging the EL lamp, a waveform for the AC signal can be synthesized that more closely resembles a relatively symmetrical sinusoidal shape. The relatively symmetrical shape of the synthesized AC waveform serves at least in part to reduce spurious emissions of electromagnetic interference (EMI), audio noise, and improve the efficiency of the driver circuitry.
Owner:NAT SEMICON CORP
Method for agile region and band conscious frequency planning for wireless transceivers
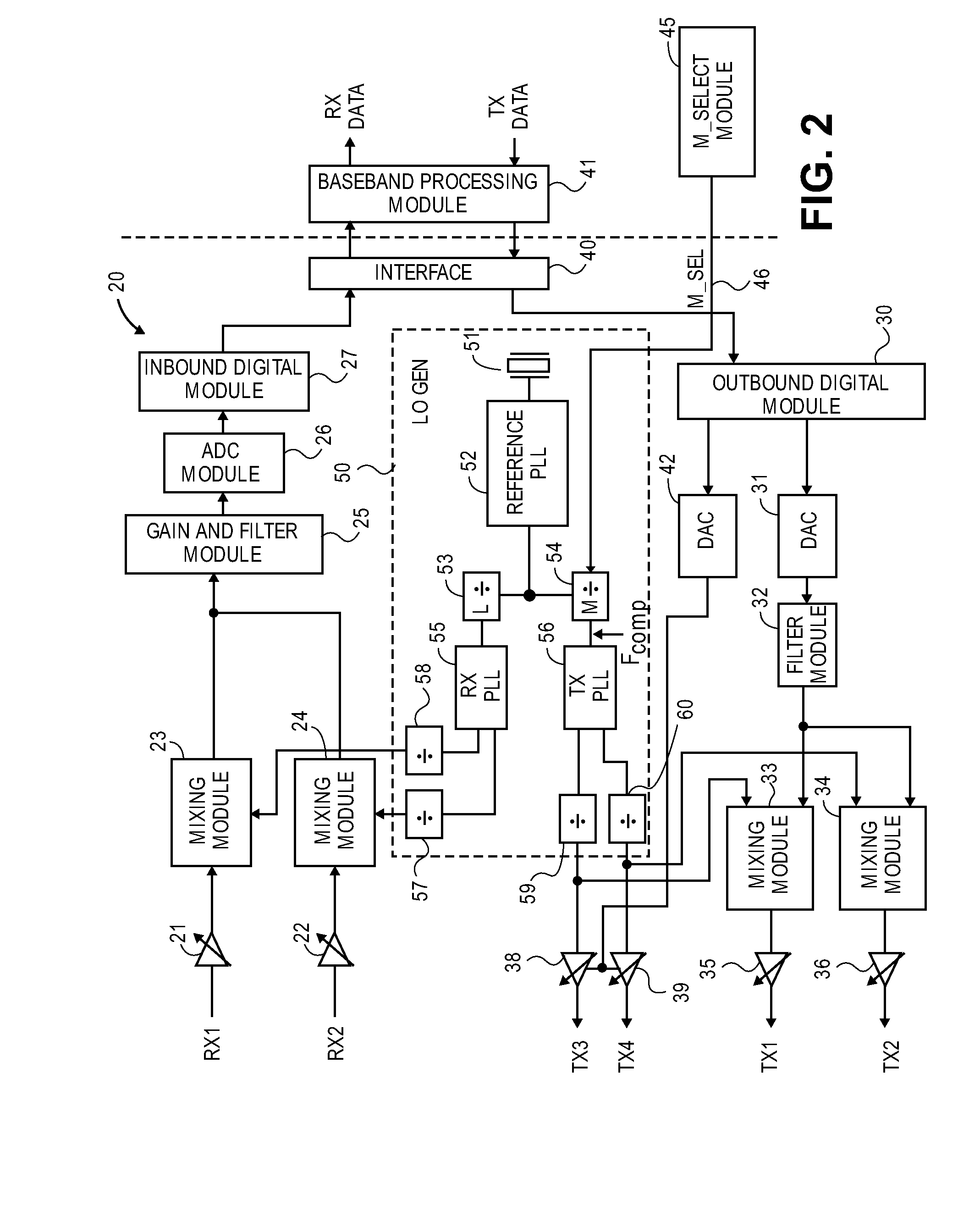
InactiveUS20090213974A1Pulse automatic controlFrequency-modulated carrier systemsWireless transceiverLocal oscillator signal
A technique for agile region and band conscious frequency planning for wireless transceivers in which a comparison frequency is selected for generating a local oscillator signal. The comparison frequency (Fcomp) is selected for a frequency band of a particular communication standard or protocol, in order not to introduce harmonic components of the selected comparison frequency in a transmitted signal from the wireless device that generates spurious emissions restricted by the particular communication protocol or another protocol. The Fcomp selection may also take into consideration restrictive region-specific criteria for out-of band spurious emissions.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Systems and methods for spurious emission cancellation
ActiveCN102751999AEffective Mechanism to Eliminate Spurious EmissionsPower amplifiersAmplifier detailsAmplitude responseSpurious emission
In accordance with some embodiments of the present disclosure, a method may include digitally pre-distorting a digital baseband signal with an opposite phase of a C-IM3 distortion term such that the pre-distortion and C-IM3 distortion cancel each other out in a transmitter. The method may also include digitally conditioning the pre-distorted digital signal in order to provide a flat amplitude response of a composite filter comprising a baseband filter and a digital half-band filter of the transmitter, and to provide a linear phase response for the composite filter.
Owner:APPLE INC
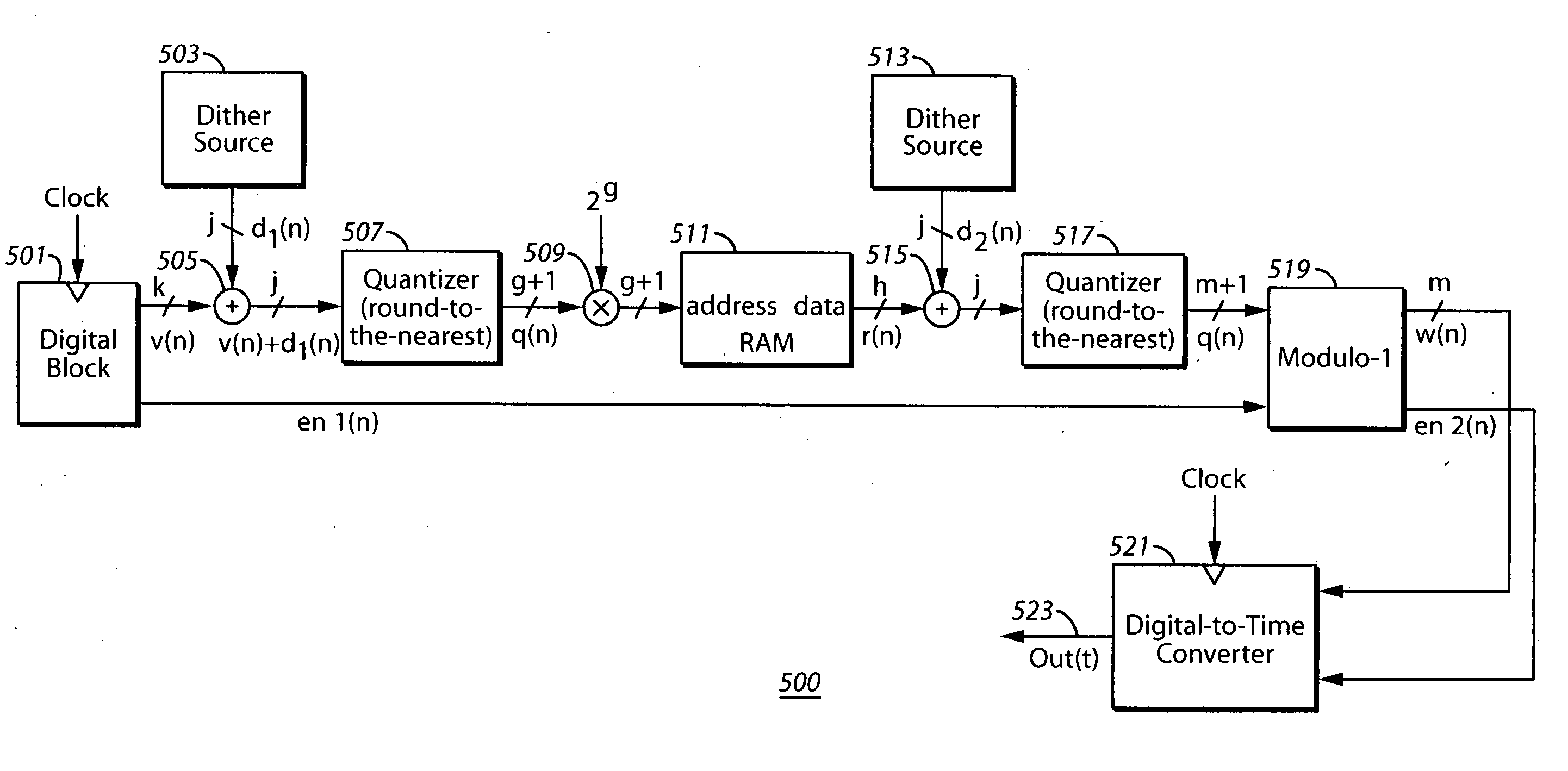
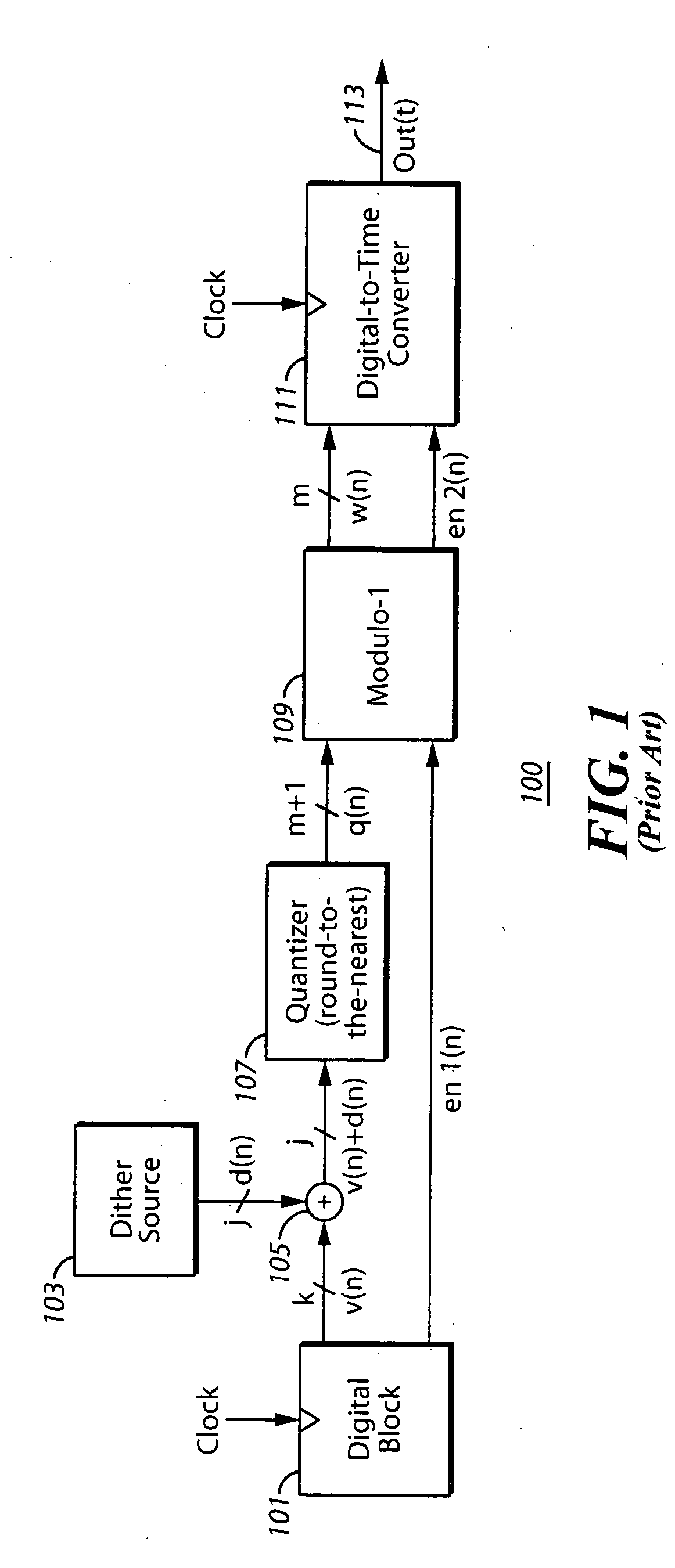
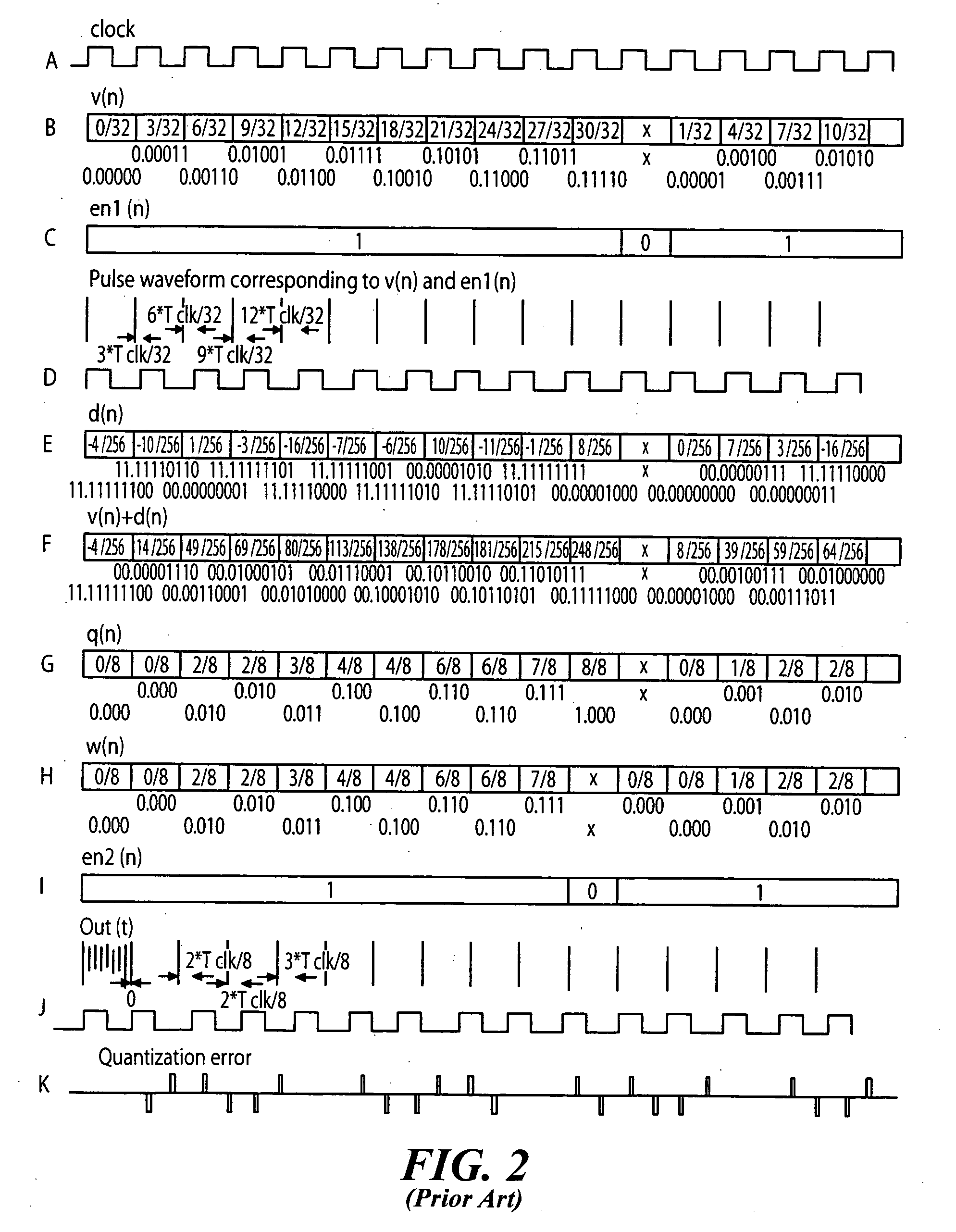
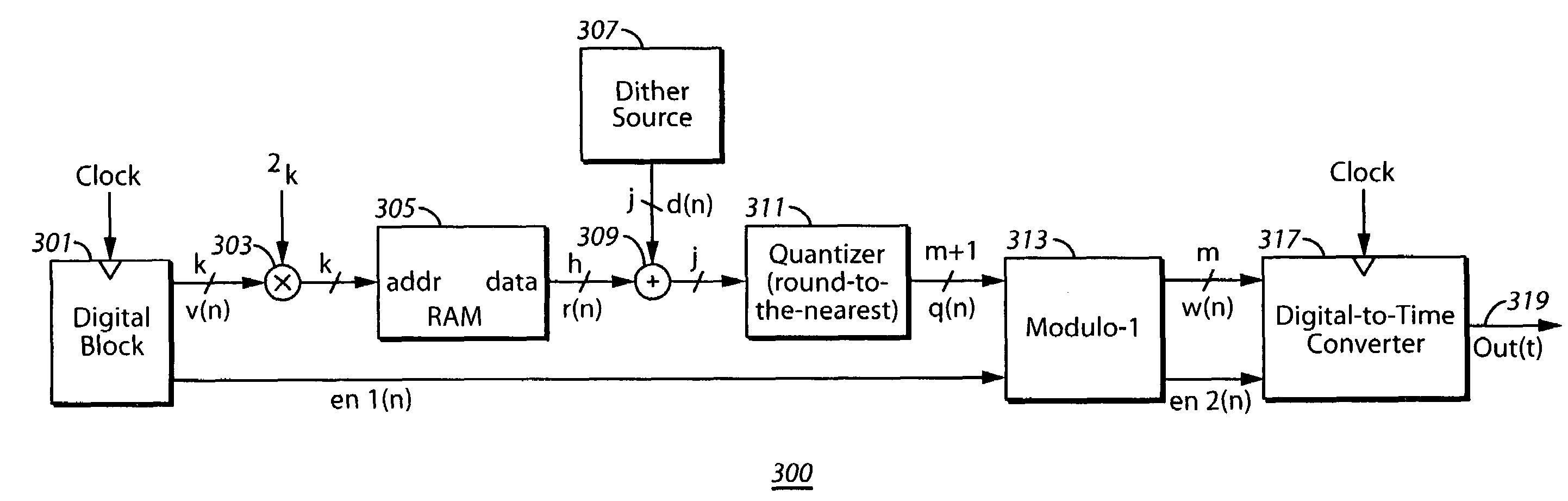
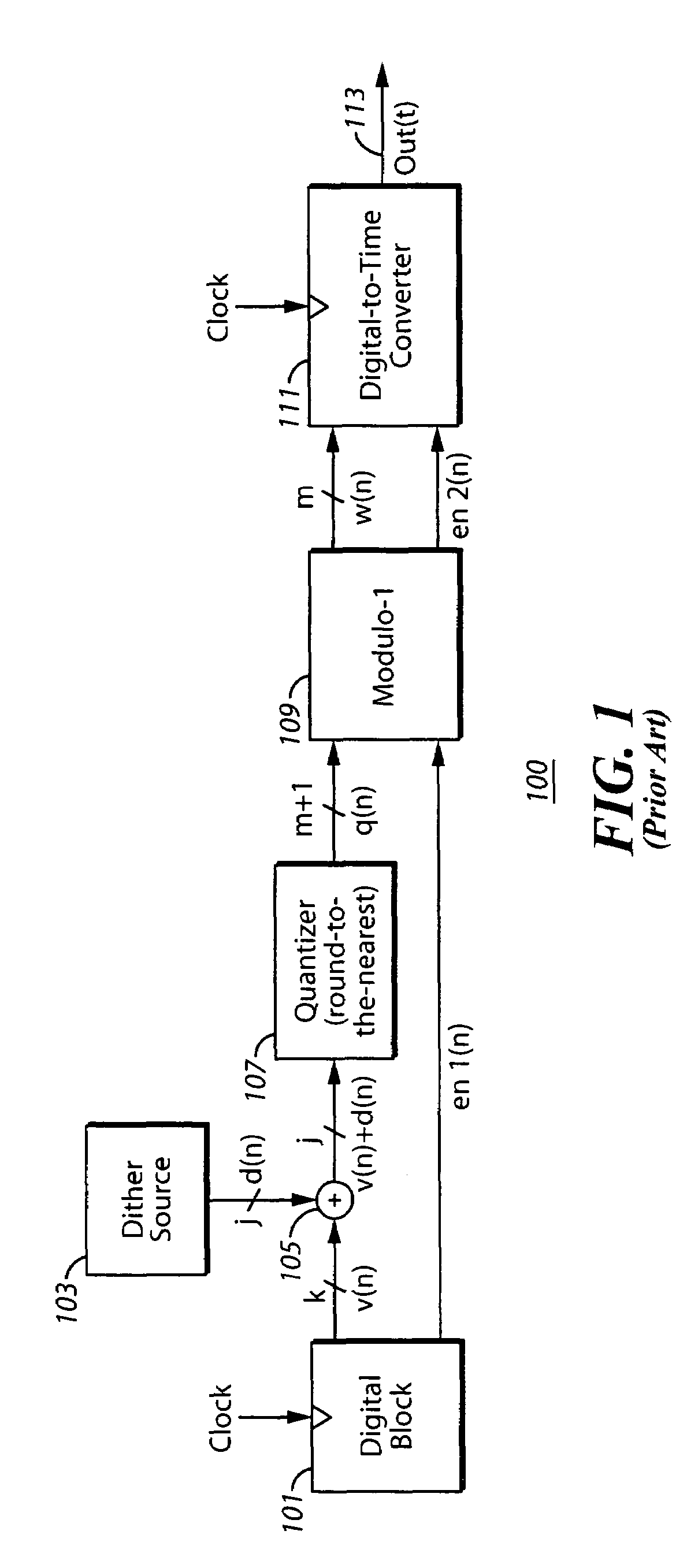
System and method for introducing dither for reducing spurs in digital-to-time converter direct digital synthesis
ActiveUS20060069707A1Eliminate contributionReduce contributionDigital function generatorsRandom access memoryTime transformation
A direct digital synthesizer (DDS) (300) that uses a system for reducing spurious emissions in a digital-to-time converter (DTC) (317). The DDS (300) includes one or more dither sources (307) and a random access memory (RAM) (305). The RAM (305) utilizes a look-up table for storing delay error values by using an output of the look-up table which is combined with the dither source (307) to compensate unequal unit delay values in the DTC (317).
Owner:MOTOROLA SOLUTIONS INC
System and method for introducing dither for reducing spurs in digital-to-time converter direct digital synthesis
ActiveUS7421464B2Reduce contributionEliminate contributionDigital function generatorsTime transformationRandom access memory
A direct digital synthesizer (DDS) (300) that uses a system for reducing spurious emissions in a digital-to-time converter (DTC) (317). The DDS (300) includes one or more dither sources (307) and a random access memory (RAM) (305). The RAM (305) utilizes a look-up table for storing delay error values by using an output of the look-up table which is combined with the dither source (307) to compensate unequal unit delay values in the DTC (317).
Owner:MOTOROLA SOLUTIONS INC
Multiple stream transmission method comprising multicarrier modulation selection according to the associated communication type
ActiveUS20180183641A1Add supportEasily cancels out intercarrier interferenceMulti-frequency code systemsBaseband systemsFrequency filteringCarrier signal
A method for transmitting multiple communications of different types, in particular sporadic (MTC) or cellular (broadband) communication including symbols to be transmitted, corresponding to communication services implementing a modulation having M subcarriers of the FBMC-OQAM or OFDM-OQAM type. The method uses linear frequency filtering of a sequence of length N including symbols having L coefficients that are parametrizable according to the communication, L, N, and M being natural numbers, so as to generate N+L−1 symbols, reducing out-of-band spurious emissions. The method also uses, no matter what the communication is, a single frequency / time transform (IFFT) having a size M, where N<M. For sporadic communications (MTC) in a lower frequency band, the constraints on the out-of-band side-lobes are more stringent on the filter and FBMC modulation is thus better adapted.
Owner:ORANGE SA (FR)
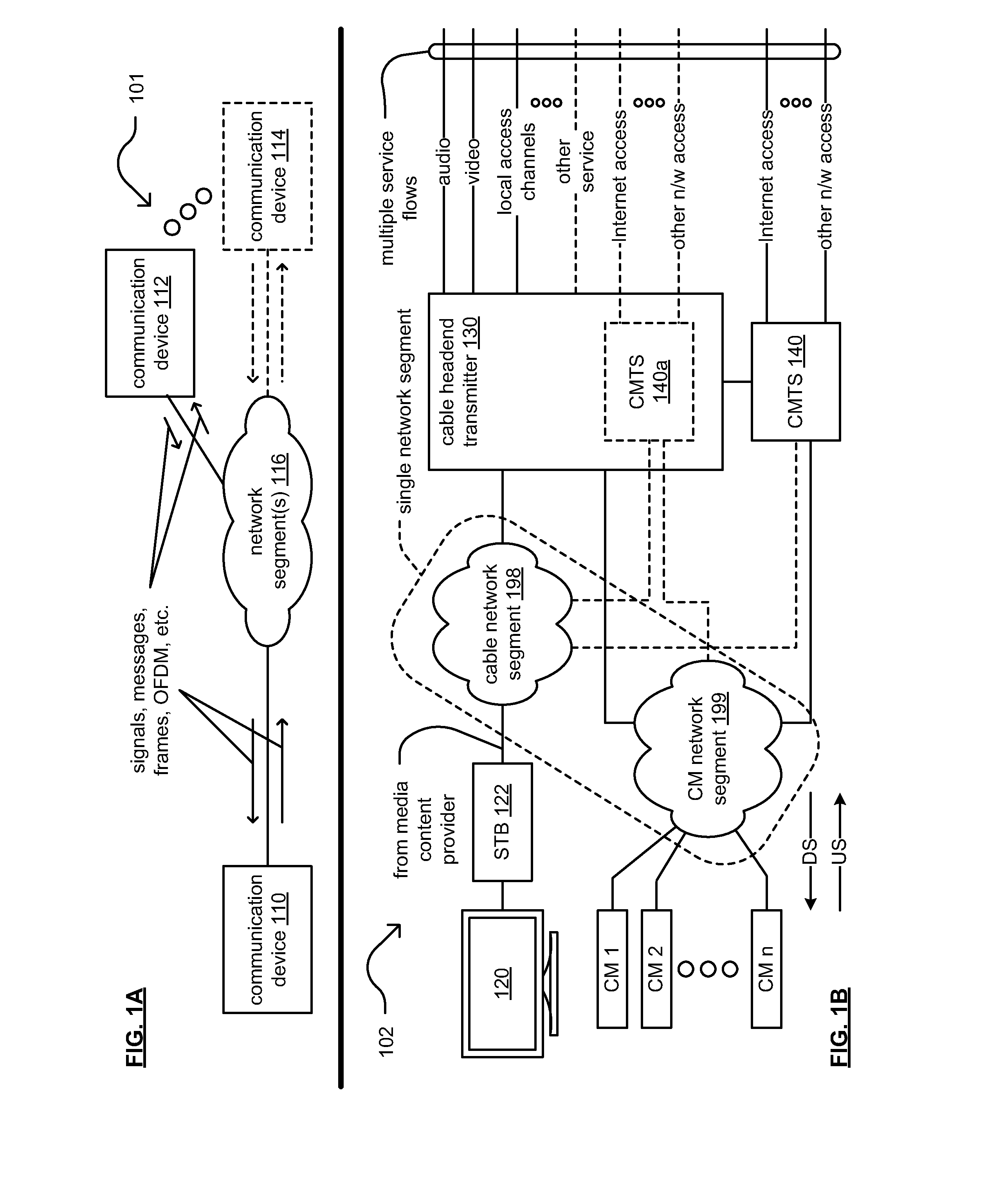
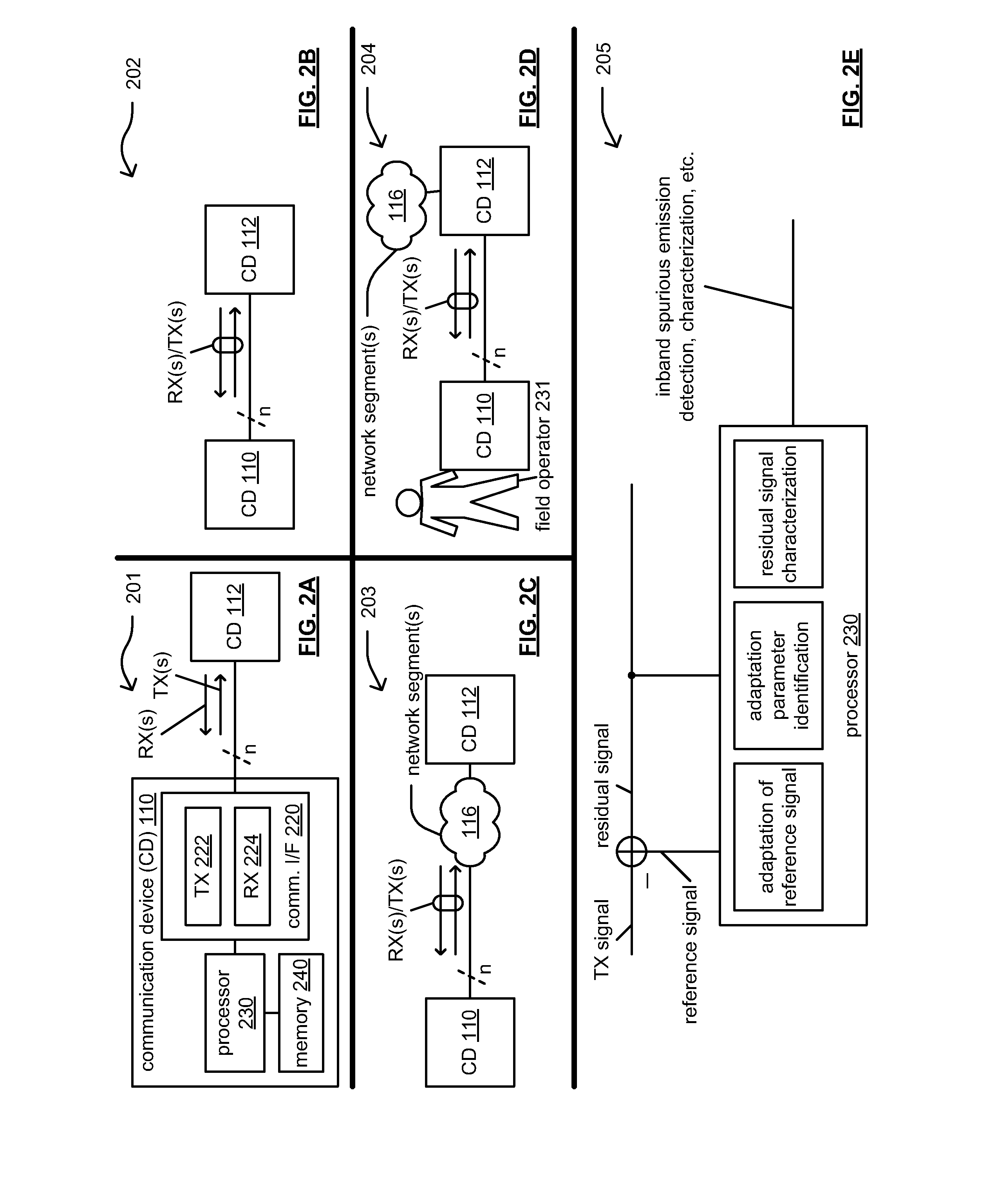
Inband spurious detection and processing within communication systems
ActiveUS20170063489A1Supervisory/monitoring/testing arrangementsTransmission monitoringDigital dataCommunications system
A communication device receives a transmitted signal from another communication device. This transmitted signal is generated within the another communication device based on predetermined digital data. The communication device then generates a first reference signal based on a copy of the predetermined digital data and subtracts the first reference signal from the transmitted signal to generate a first residual signal. The communication device then identifies at least one adaptation parameter based on the first residual signal and adapts the first reference signal using the at least one adaptation parameter to generate a second reference signal so that a first characteristic of the transmitted signal and a second characteristic of the second reference signal are approximately equal. The communication device then subtracts the second reference signal from the transmitted signal to generate a second residual signal processes the second residual signal to characterize inband spurious emission within the transmitted signal.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
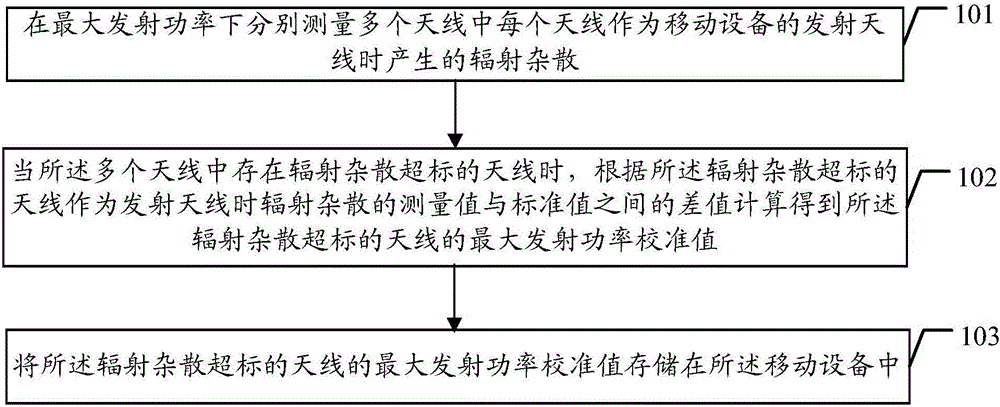
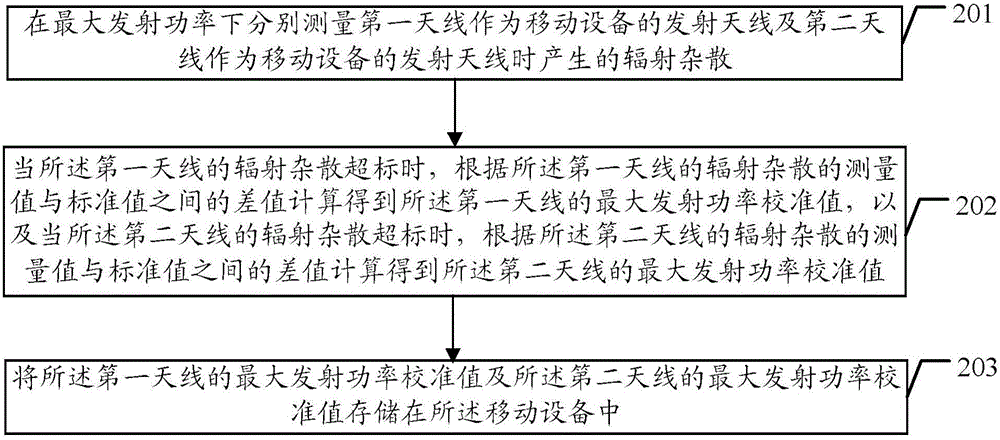
Method for controlling radiated spurious emission standard exceeding, device and mobile device
ActiveCN105827334AReduced maximum transmit powerMeet the standard requirementsPower managementTransmitters monitoringEngineeringSpurious emission
The embodiments of the invention disclose a method for controlling radiated spurious emission standard exceeding, a device for controlling radiated spurious emission standard exceeding and a mobile device. The method includes the following steps that: radiated spurious emissions generated by each antenna in a plurality of antennas is measured respectively under maximum transmitting power when the plurality of antennas are adopted as the transmitting antenna of the mobile device; when an antenna of which the radiated spurious emissions exceed standards exists in the plurality of antennas, the maximum transmitting power calibration value of the antenna of which the radiated spurious emissions exceed standards can be obtained through calculation according to the difference value of the measurement value of the radiated spurious emissions of the antenna adopted as the transmitting antenna and a standard value; and the maximum transmitting power calibration value of the antenna of which the radiated spurious emissions exceed standards is stored in the mobile device. With the method and device provide by the embodiments of the invention adopted, the radiated spurious emissions of the antenna can satisfy the requirements of RSE (radiated spurious emission) standards, and user experience can be enhanced.
Owner:GUANGDONG OPPO MOBILE TELECOMM CORP LTD
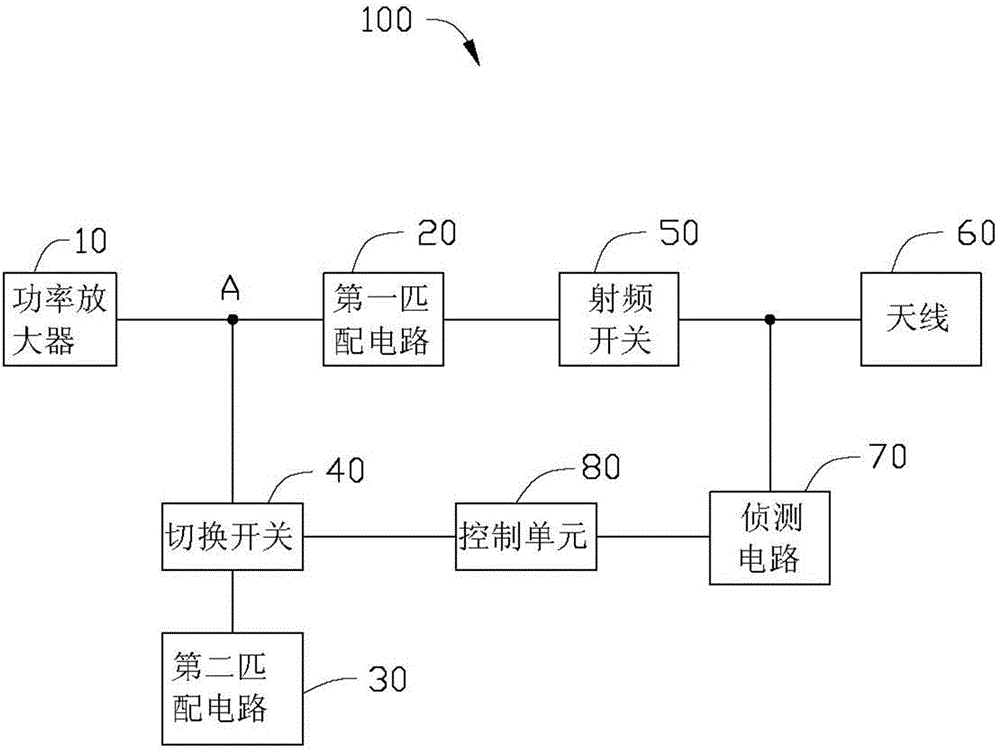
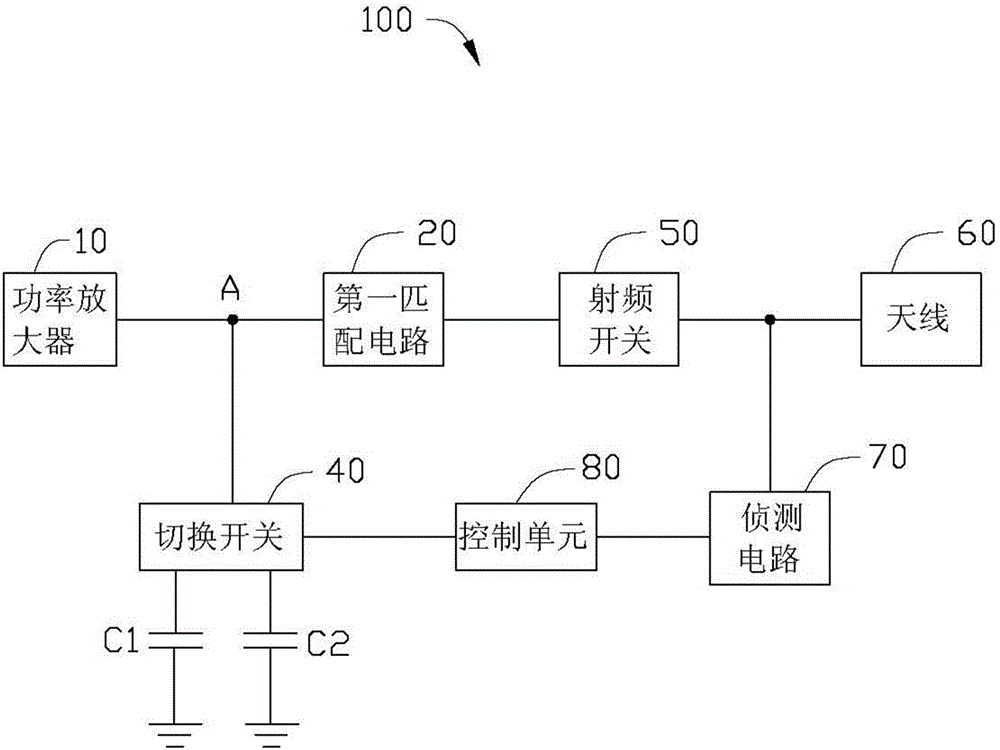
Radiation spurious emission (RSE) auxiliary test circuit
InactiveCN105472082ARSE test improvementElectrical testingSubstation equipmentElectricityAudio power amplifier
The invention provides a radiation spurious emission (RSE) auxiliary test circuit which is applied to an electronic device. The auxiliary test circuit comprises a power amplifier, a first match circuit, a radio frequency switch, an antenna, a second match circuit, a change-over switch, a detecting circuit and a control unit, which are connected electrically in sequence. The second match circuit is electrically connected to the change-over switch; the change-over switch is electrically connected to a node between the power amplifier and the first match circuit; the detecting circuit is electrically connected between the radio frequency switch and the antenna; the control unit is electrically connected between the change-over switch and the detecting circuit; the detecting circuit is used for judging whether the electronic device is subjected to the RSE test and outputting the corresponding detecting result; and the control unit controls the change-over switch to establish or disconnect the electrical connection between the second match circuit and the node according to the detecting result, so that when the electronic device is subjected to the RSE test, the power amplifier and the antenna reach impedance matching therebetween.
Owner:SHENZHEN FUTAIHONG PRECISION IND CO LTD +1
Wireless equipment for transmitting uplink signal through reduced transmission resource block and power, and enodeb
ActiveCN104541459AReduce distractionsSpurious emission reductionTransmission path divisionSignal allocationCommunications systemResource block
According to one embodiment of the present invention, provided is a wireless equipment for transmitting an uplink signal through a reduced transmission resource block (RB) in a wireless communication system. The wireless equipment can comprise: a processor; and a radio frequency (RF) unit for transmitting an uplink signal under control of the processor. When the RF unit is set to a predetermined channel bandwidth and a predetermined frequency range and must satisfy a predetermined maximum allowed value of spurious radiation to protect another frequency range, the uplink signal can be transmitted according to a predetermined maximum number of RBs instead of a total number of RBs for the predetermined channel bandwidth.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Antenna assemblies for use with portable communications devices
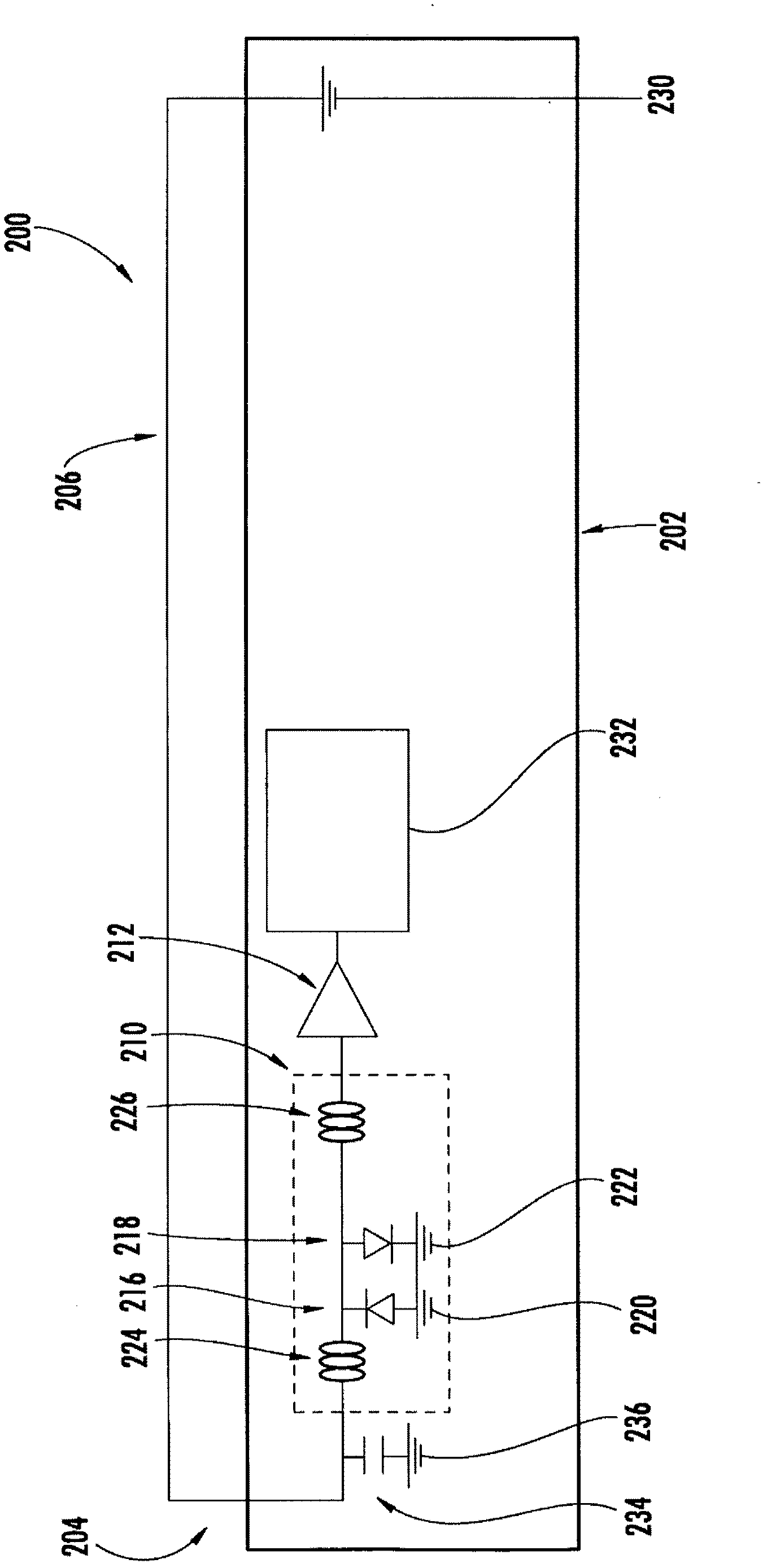
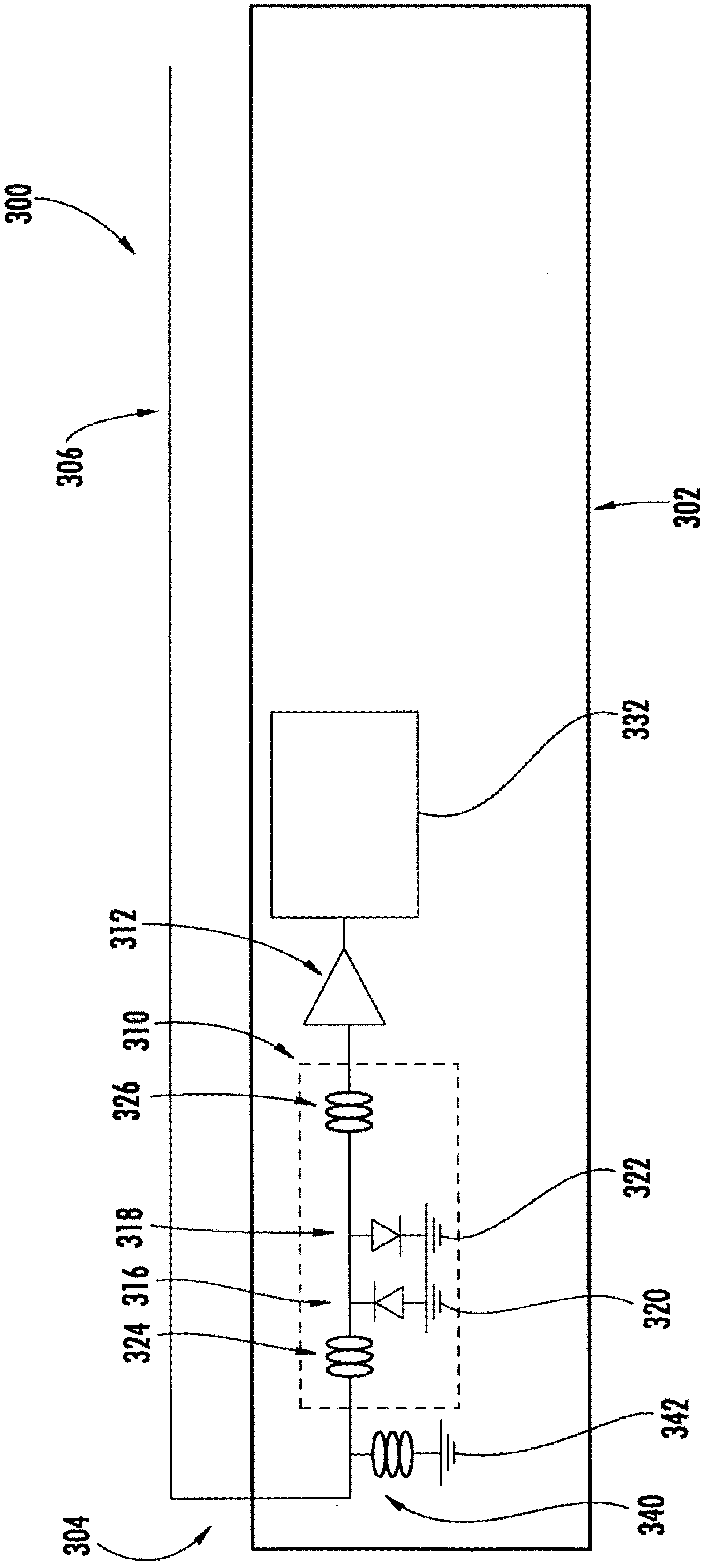
An antenna assembly generally includes an antenna element, an amplifier, and an electronics protection system coupled generally between the antenna element and the amplifier for filtering cross-talk and / or for protecting against electrostatic discharge and / or for suppressing radiated spurious emissions. The electronics protection system generally includes first and second inductors disposed in series generally between the antenna element and the amplifier, and first and second diodes coupled in shunt and disposed generally between the first and second inductors.
Owner:LAIRD TECH INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com