Patents
Literature
329 results about "Basic mode" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Basic Mode is the name of the mode without Aero enabled. So, basically if you disable Aero you enable the basic mode, but there’s a special theme exactly for that purpose. Tip: There are also various High Contrast themes with inverted colors.
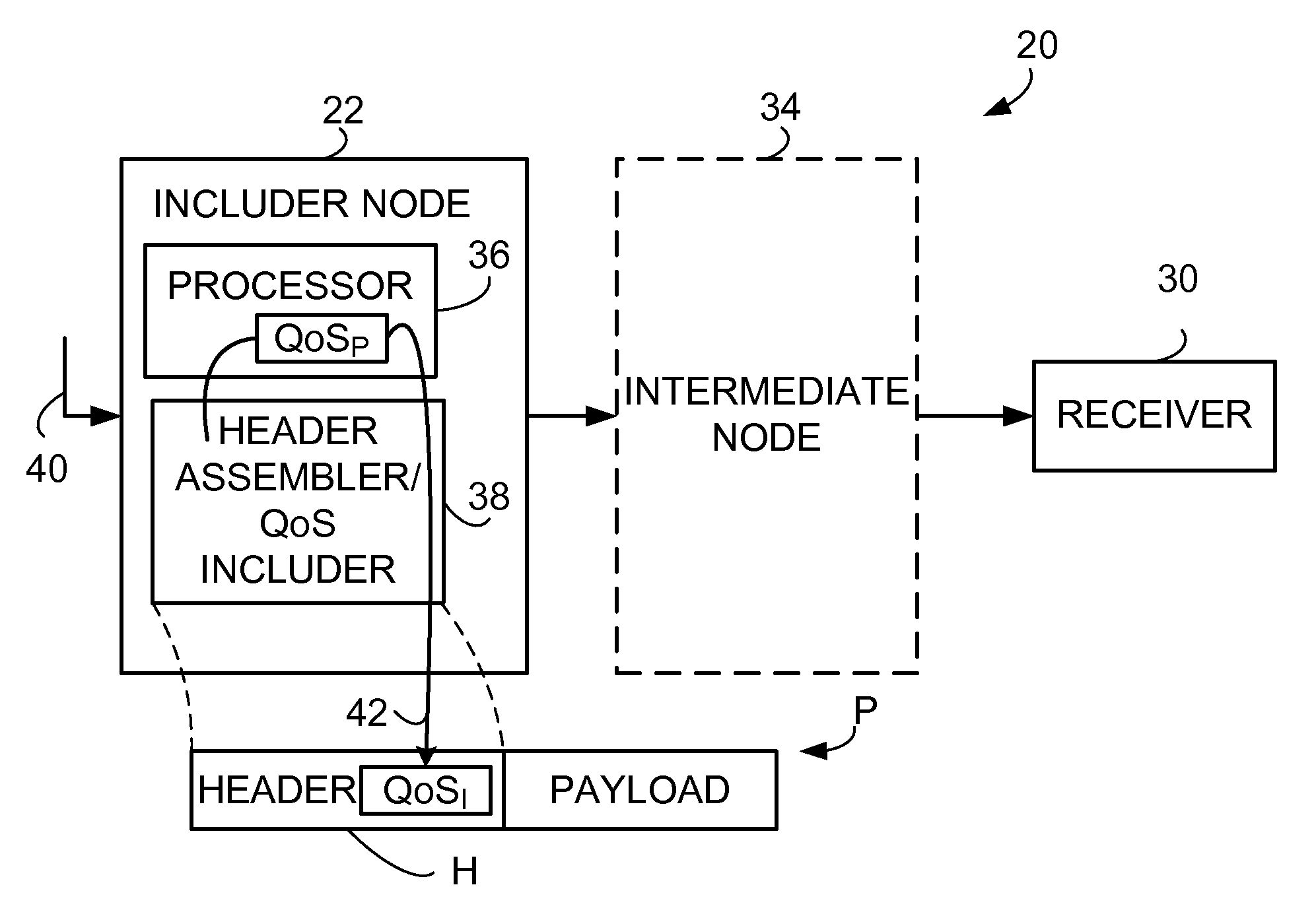
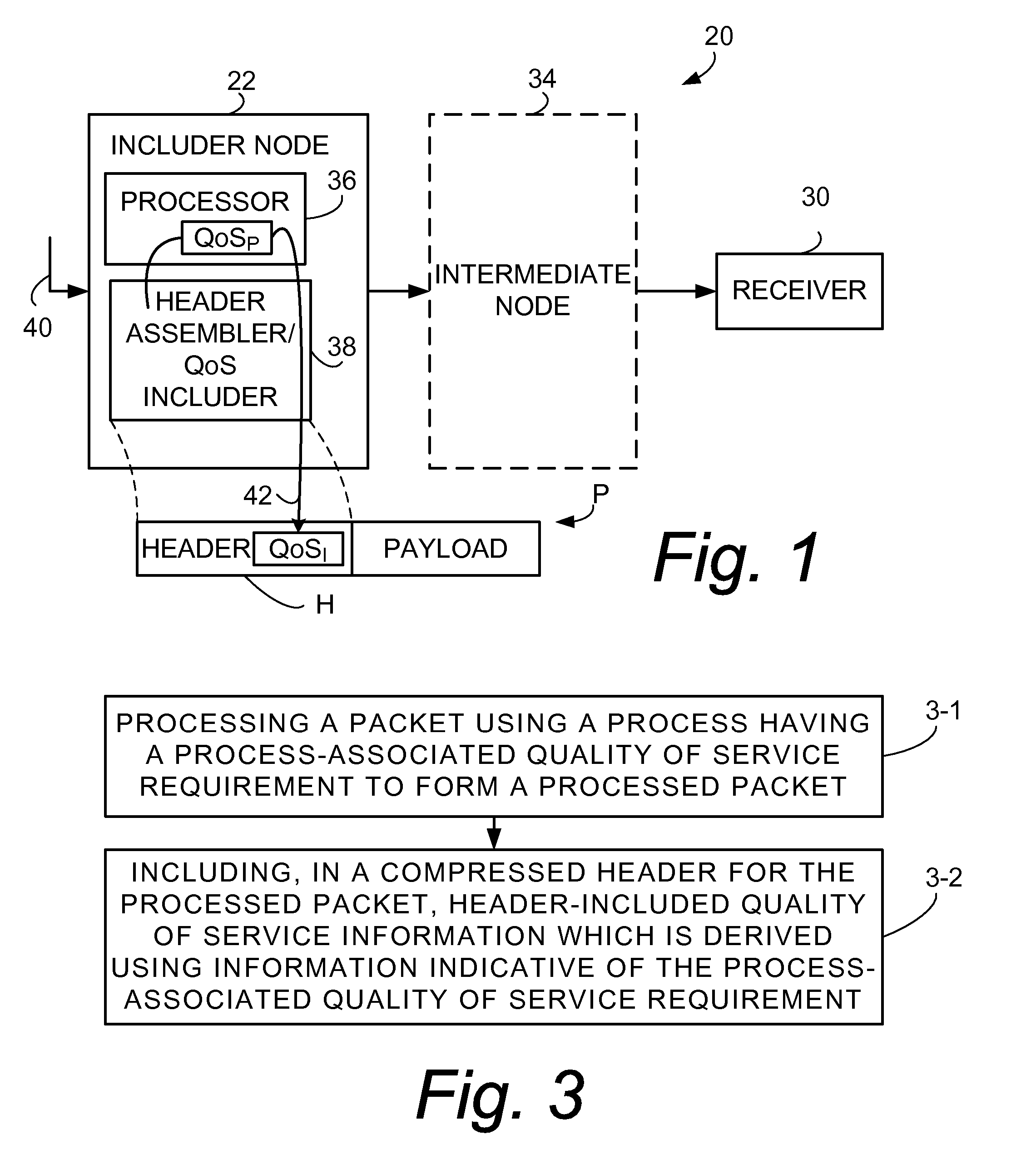
Inclusion of Quality of Service Indication in Header Compression Channel
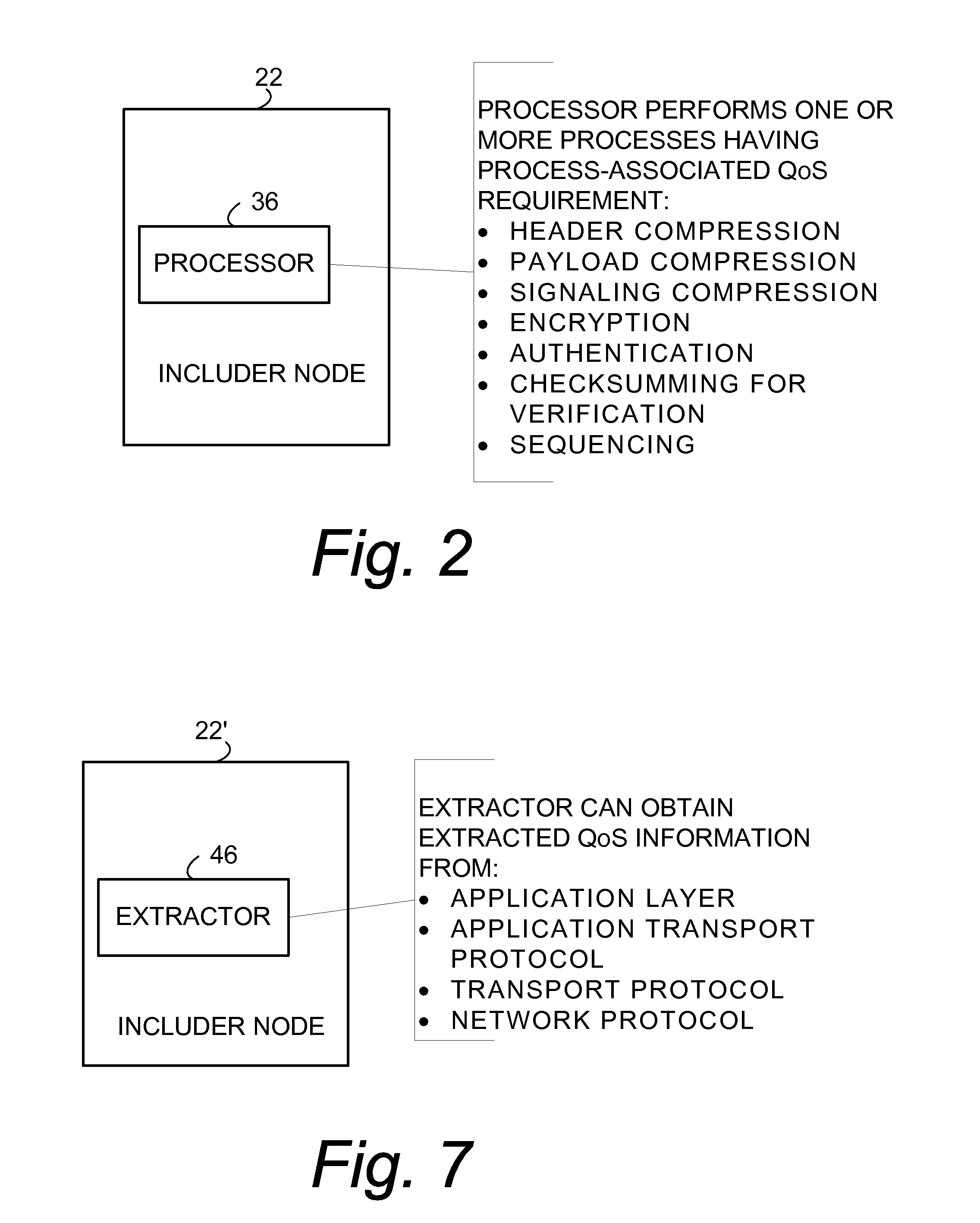
Quality of service information (QoSI) is included with a compressed header of a data packet and can be utilized by nodes supporting the header compression channel to perform QoS enforcements at a sub-flow granularity level. A basic mode of a method comprises (1) processing a packet using a process having a process-associated quality of service requirement to form a processed packet, and (2) including, with a compressed header for the processed packet, the header-included quality of service information which is derived using information indicative of the process-associated quality of service requirement. In another mode the header-included quality of service information is derived both from the process-associated quality of service requirement and quality of service information extracted from the received packet.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Hexagonal array structure of dielectric rod to shape flat-topped element pattern
InactiveUS7167139B2Wide beam scanning rangeConstant electric performanceIndividually energised antenna arraysLeaky-waveguide antennasCouplingEngineering
A hexagonal array structure of a dielectric rod for shaping a flat-topped element pattern (FTEP) is provided. The hexagonal structure of dielectric rods forming a flat-topped element pattern (FTEP) includes: a center element for forming a unit radiation pattern of the FTEP through an electromagnetic wave mutual coupling by receiving a polarization signal of a basic mode; a plurality of first ring elements arranged at vertexes of a regular hexagon based on the center element for forming the unit radiation pattern by electromagnetic wave mutual coupling with the center element and an electromagnetic wave; and a circular waveguide array supporting unit for supporting the center element and the plurality of first ring elements.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
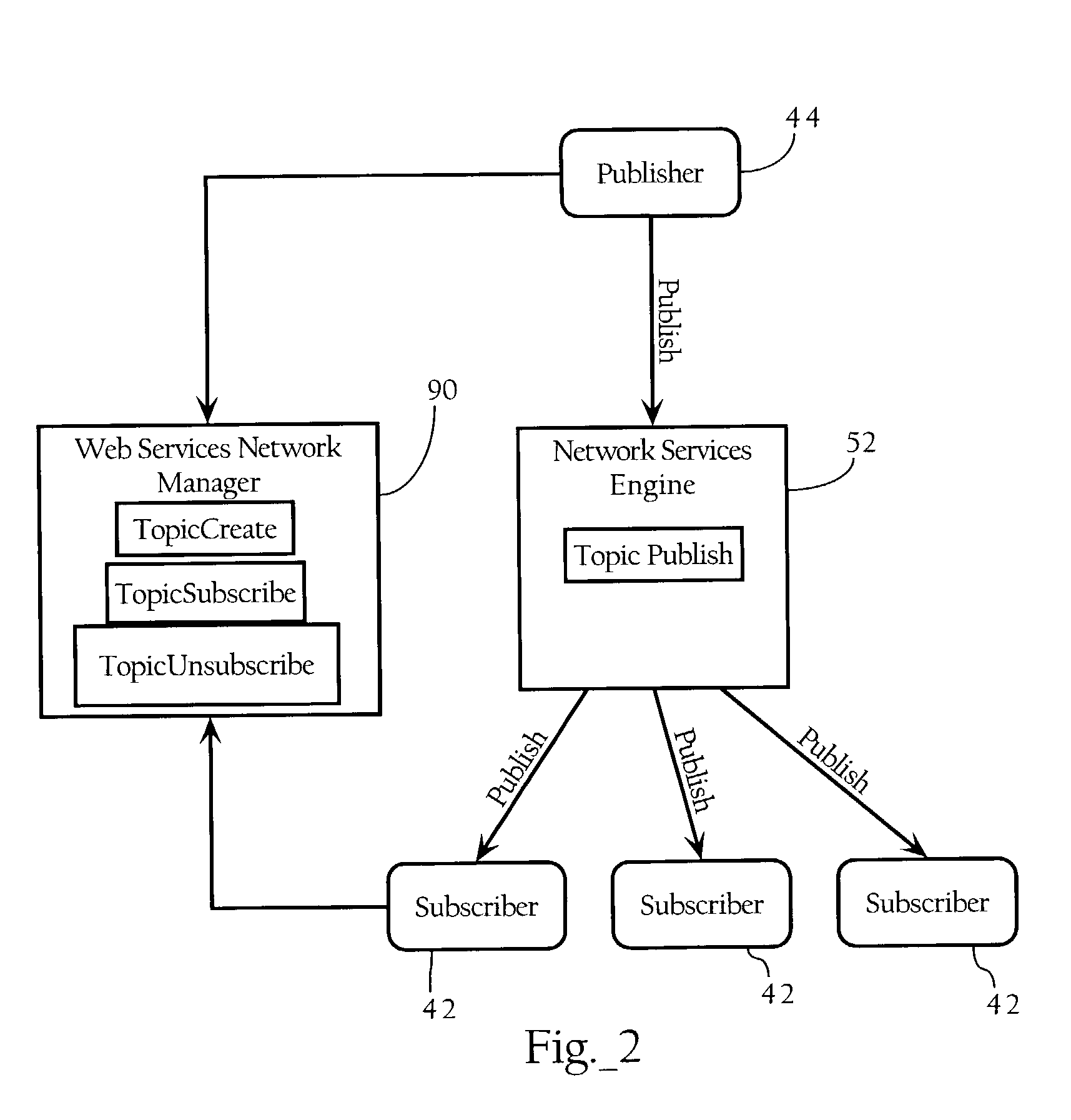
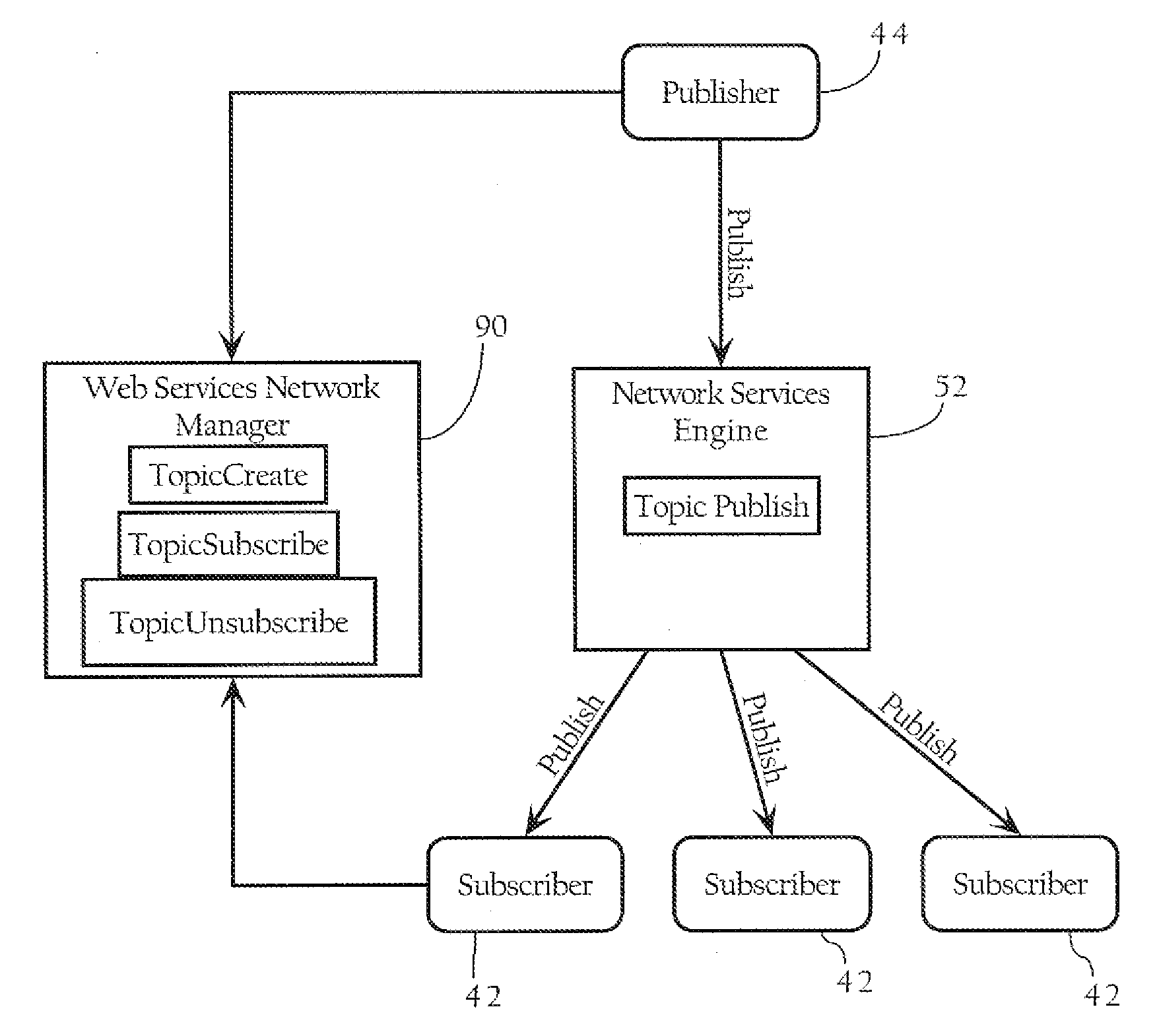
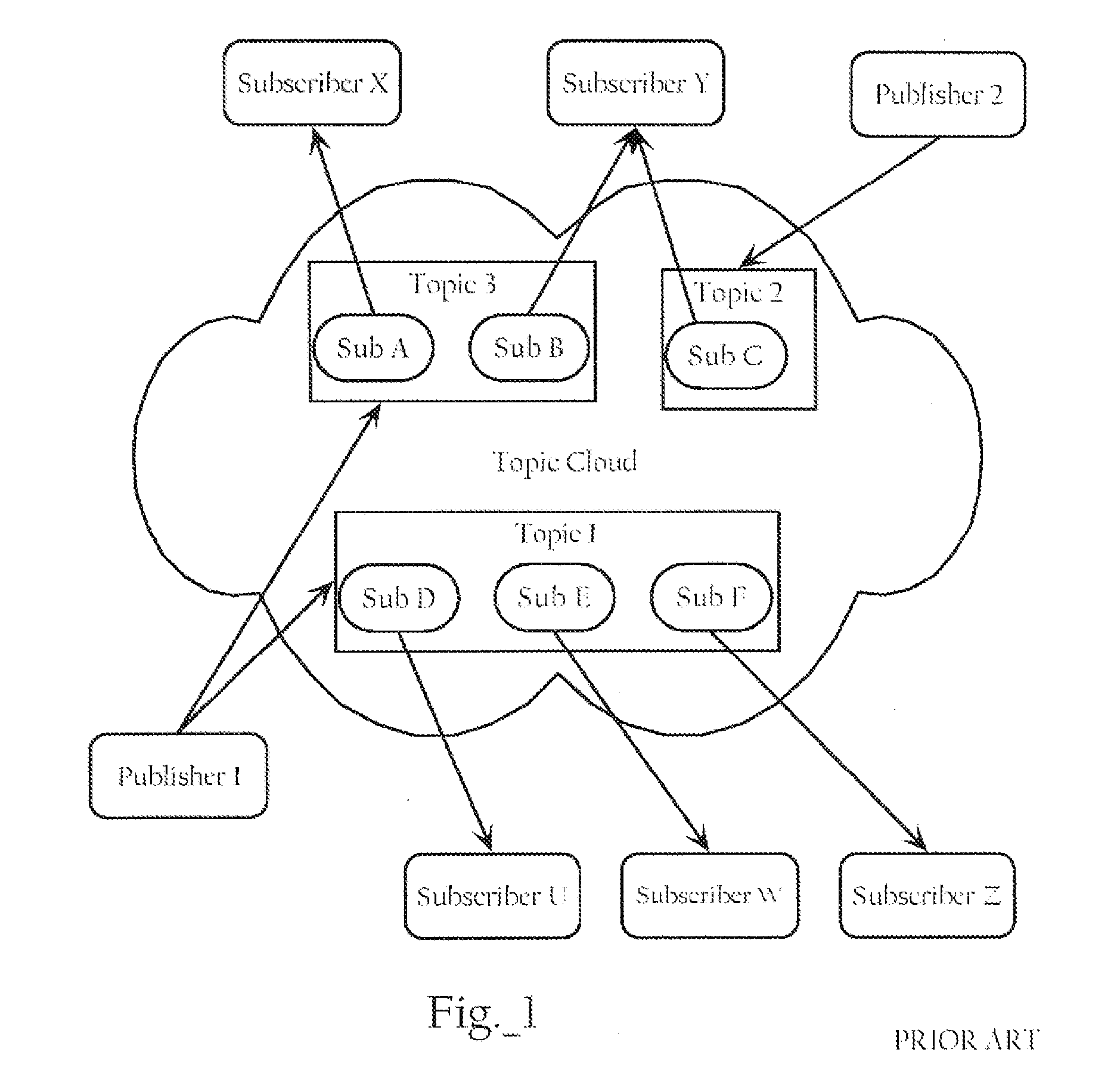
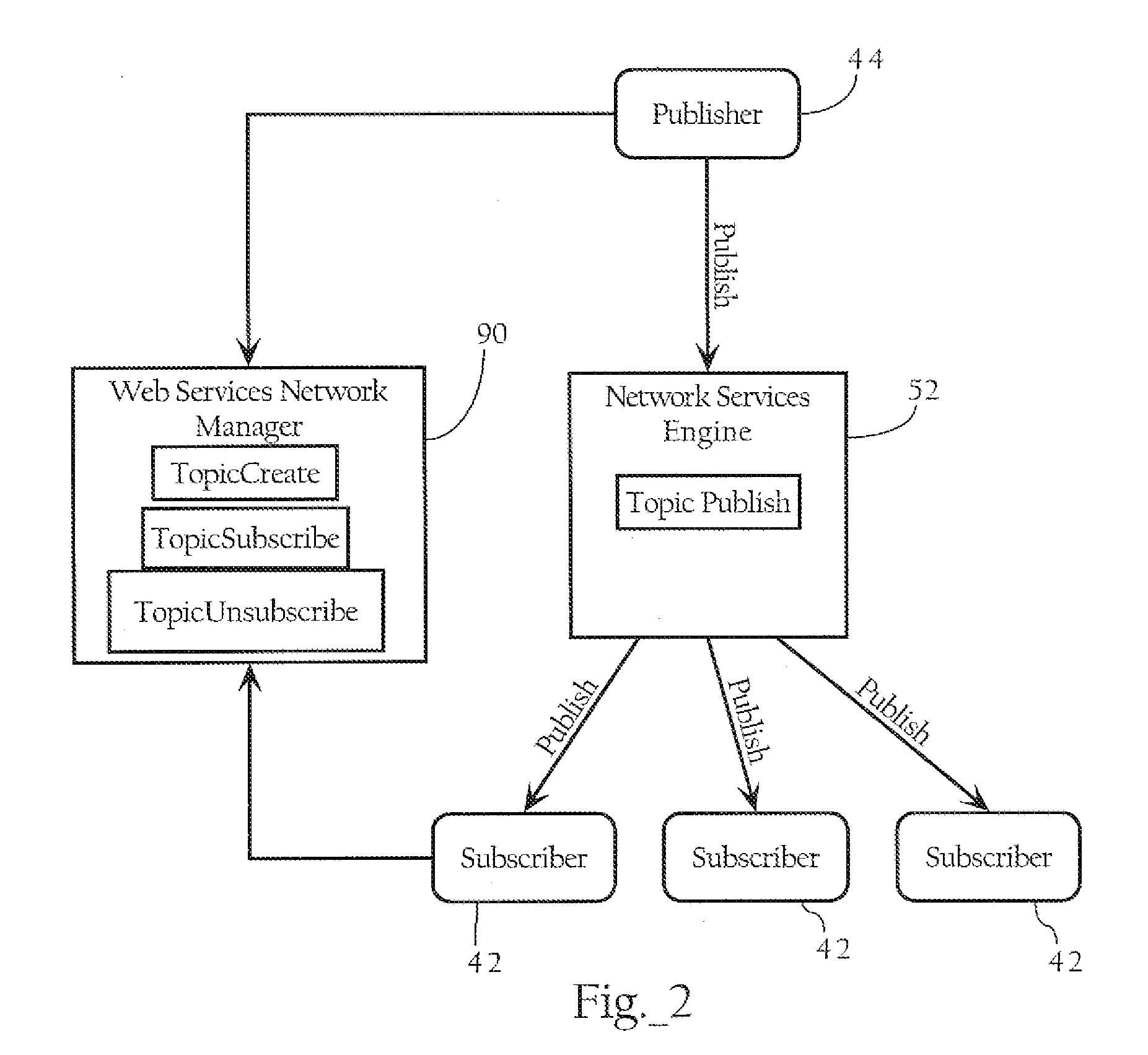
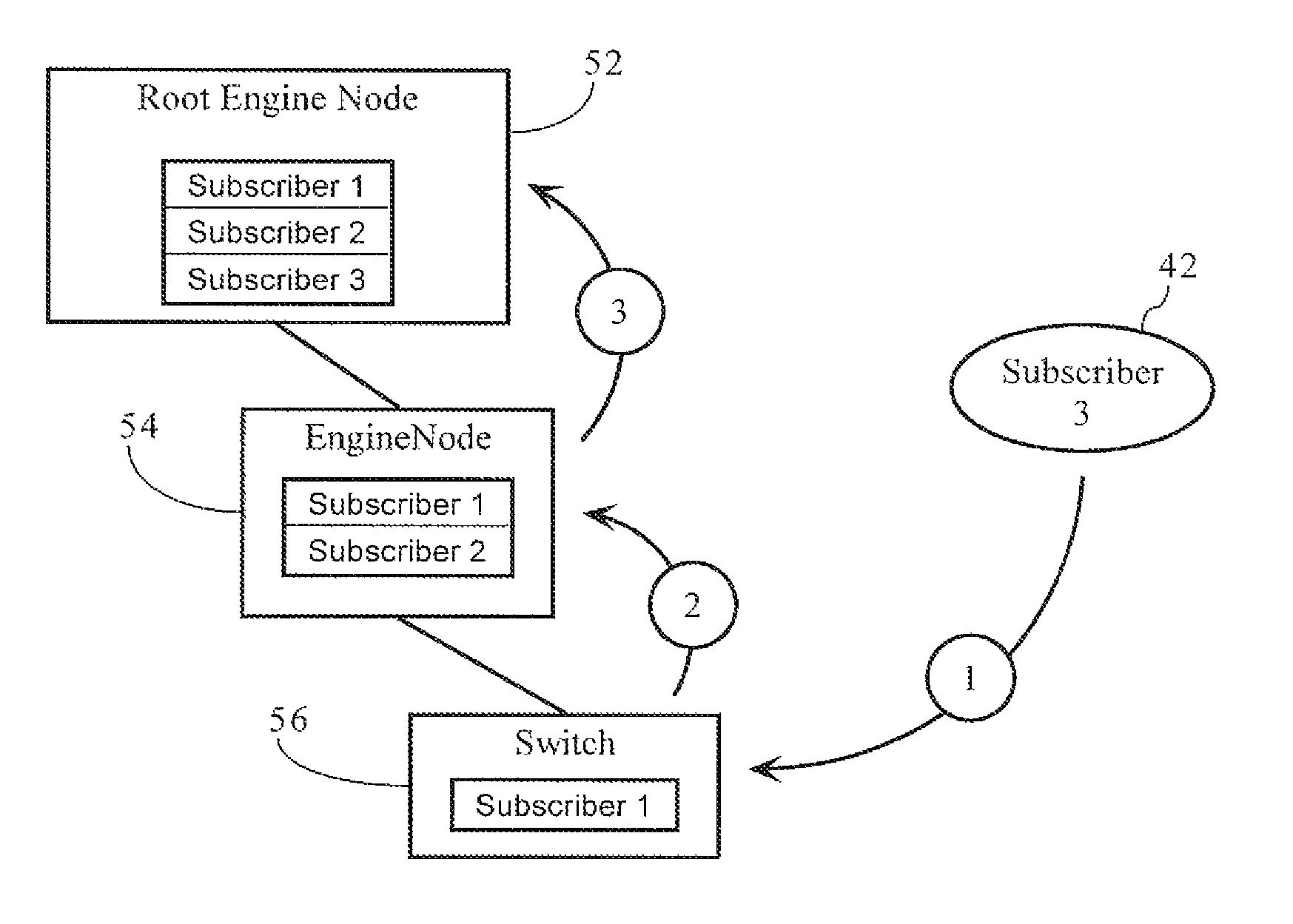
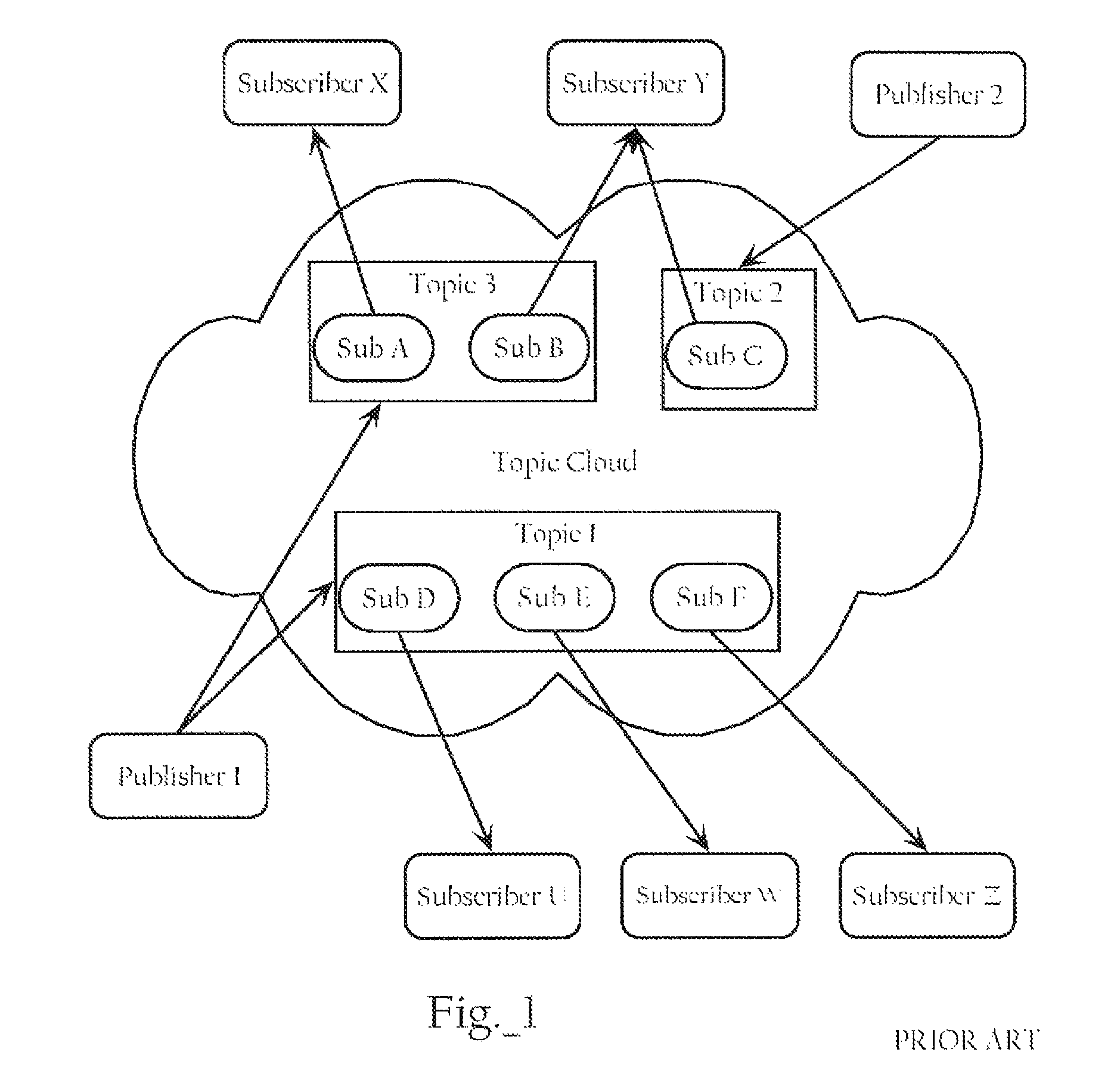
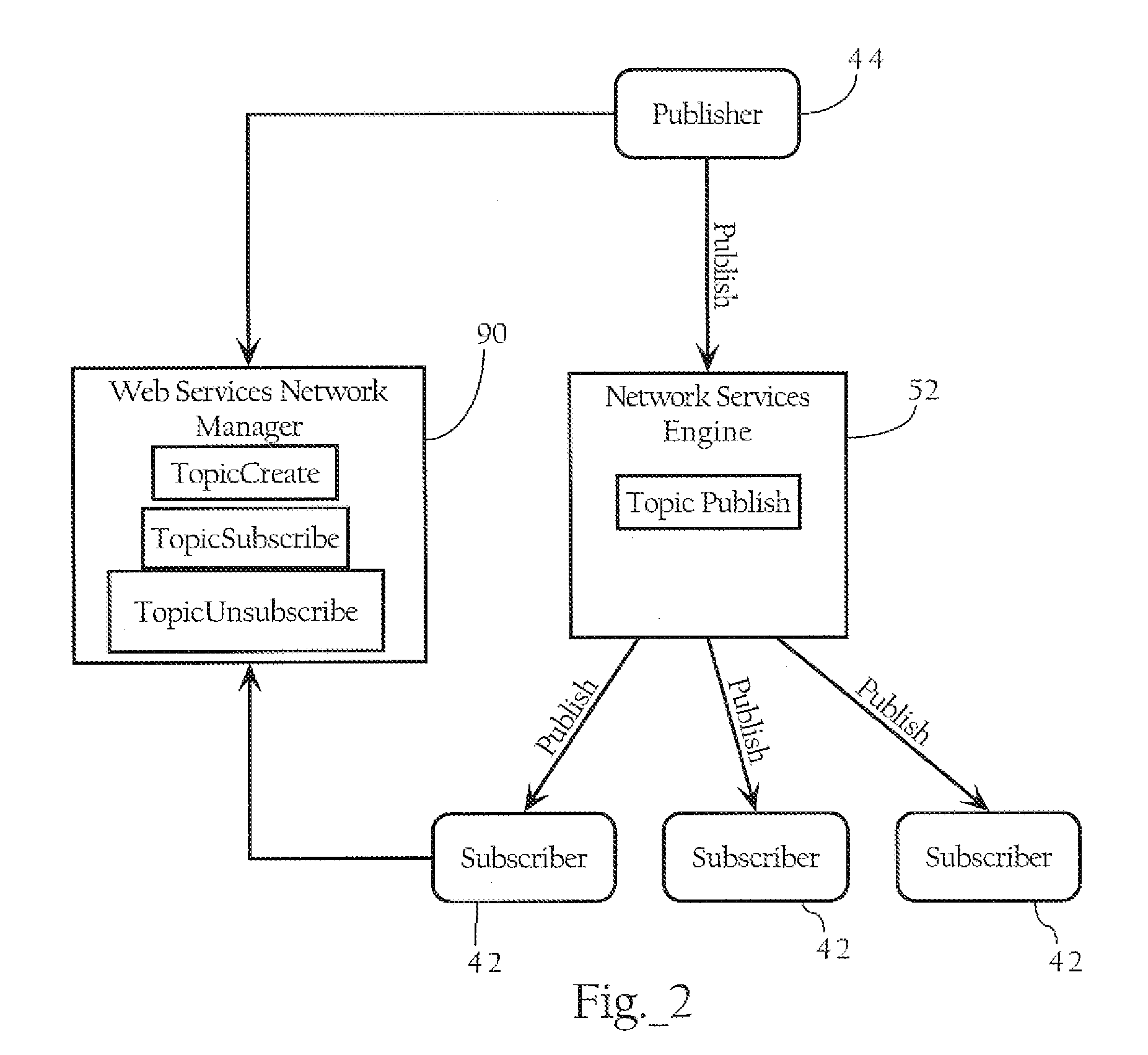
Network publish/subscribe system incorporating Web services network routing architecture
ActiveUS7349980B1Facilitating deployment and configuration and maintenanceMultiple digital computer combinationsWebsite content managementWeb serviceNetwork architecture
Methods, apparatuses, and systems facilitating the deployment, configuration and maintenance of publication / subscription systems within the context of Web service networks. In one embodiment, the present invention provides Web services network system that presents a topic as a routing entity and includes functionality facilitating topic creation, subscription and publication in a manner consistent with the basic modes of Web services development and deployment, allowing such tasks to be approached in an intuitive, cost-effective and manageable manner. In a preferred embodiment, the publication / subscription system functionality according to the present invention is integrated into a distributed Web services network architecture as more fully described below. The Web services network architecture and integrated publication / subscription system according to the present invention can be implemented across any suitable computer network, including a local area network, an intranet or the Internet.
Owner:AKANA
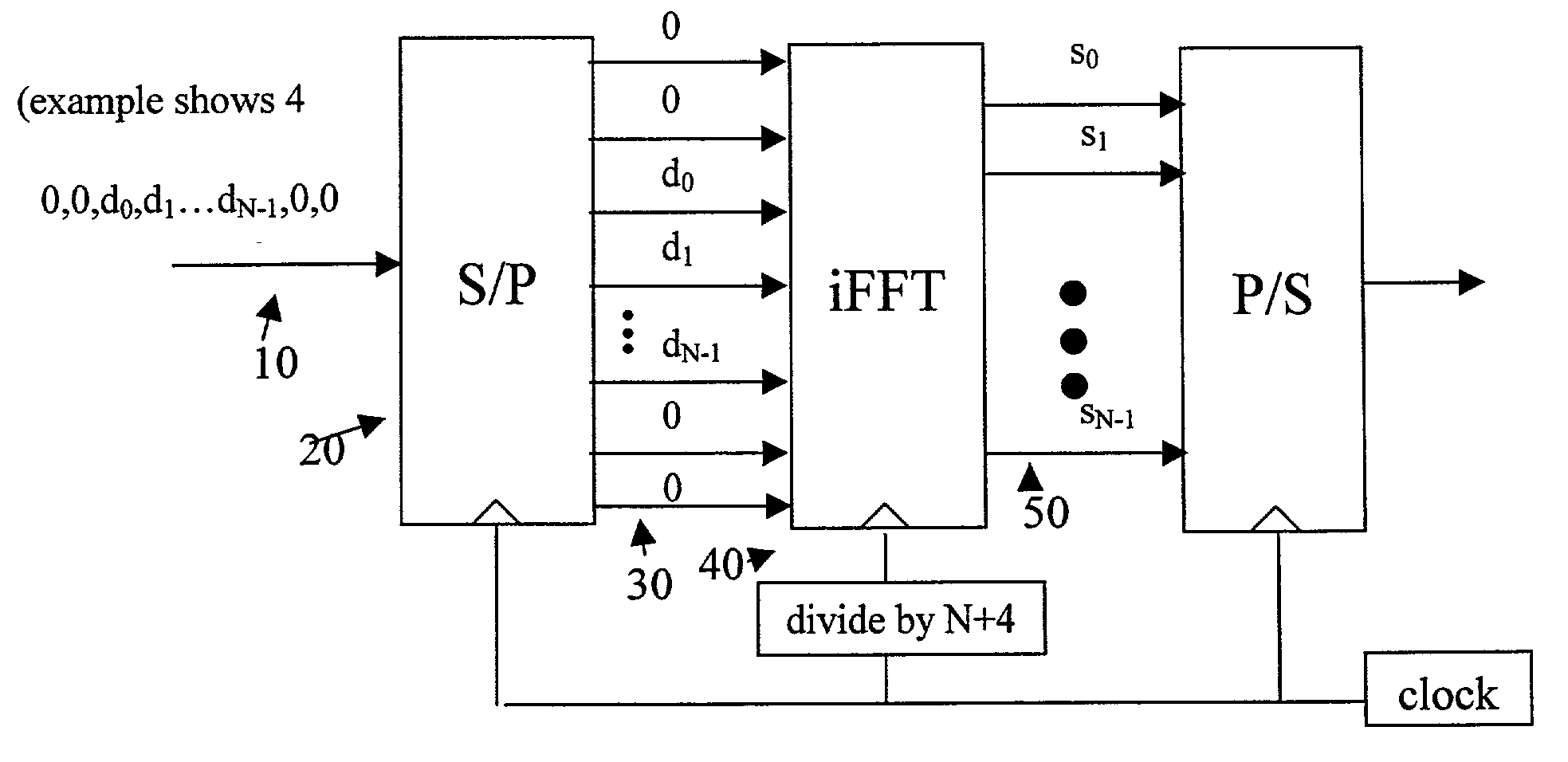
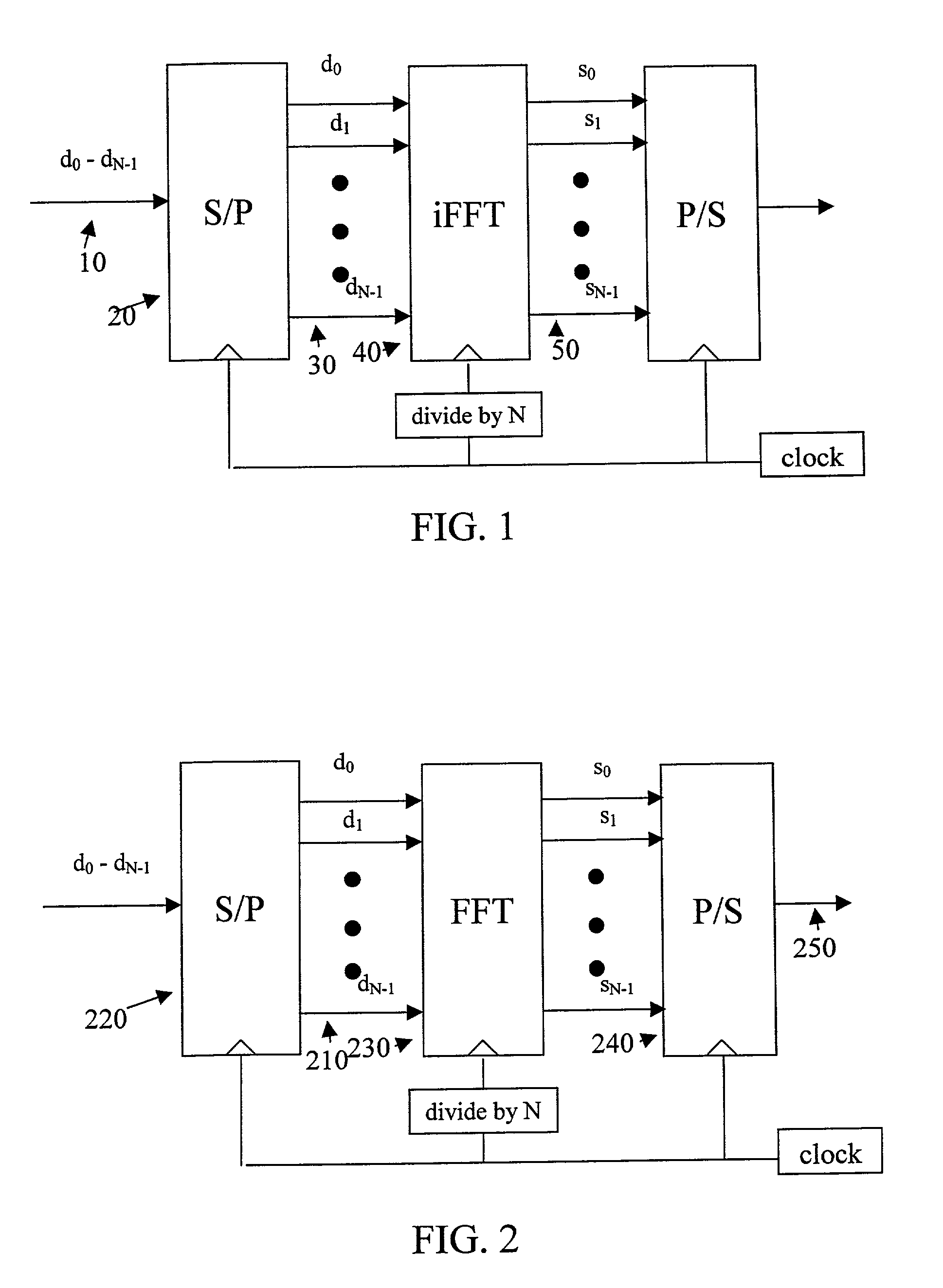
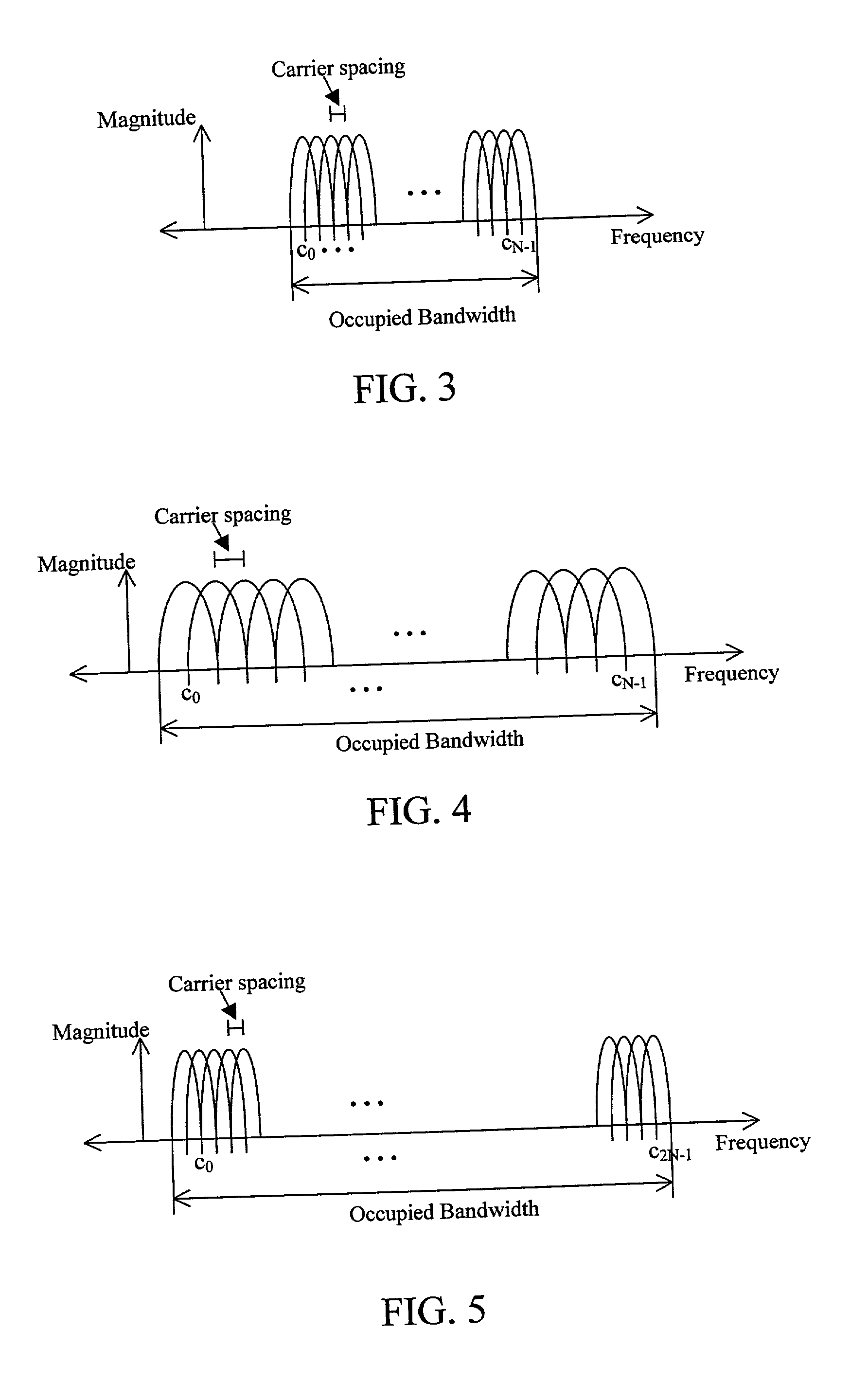
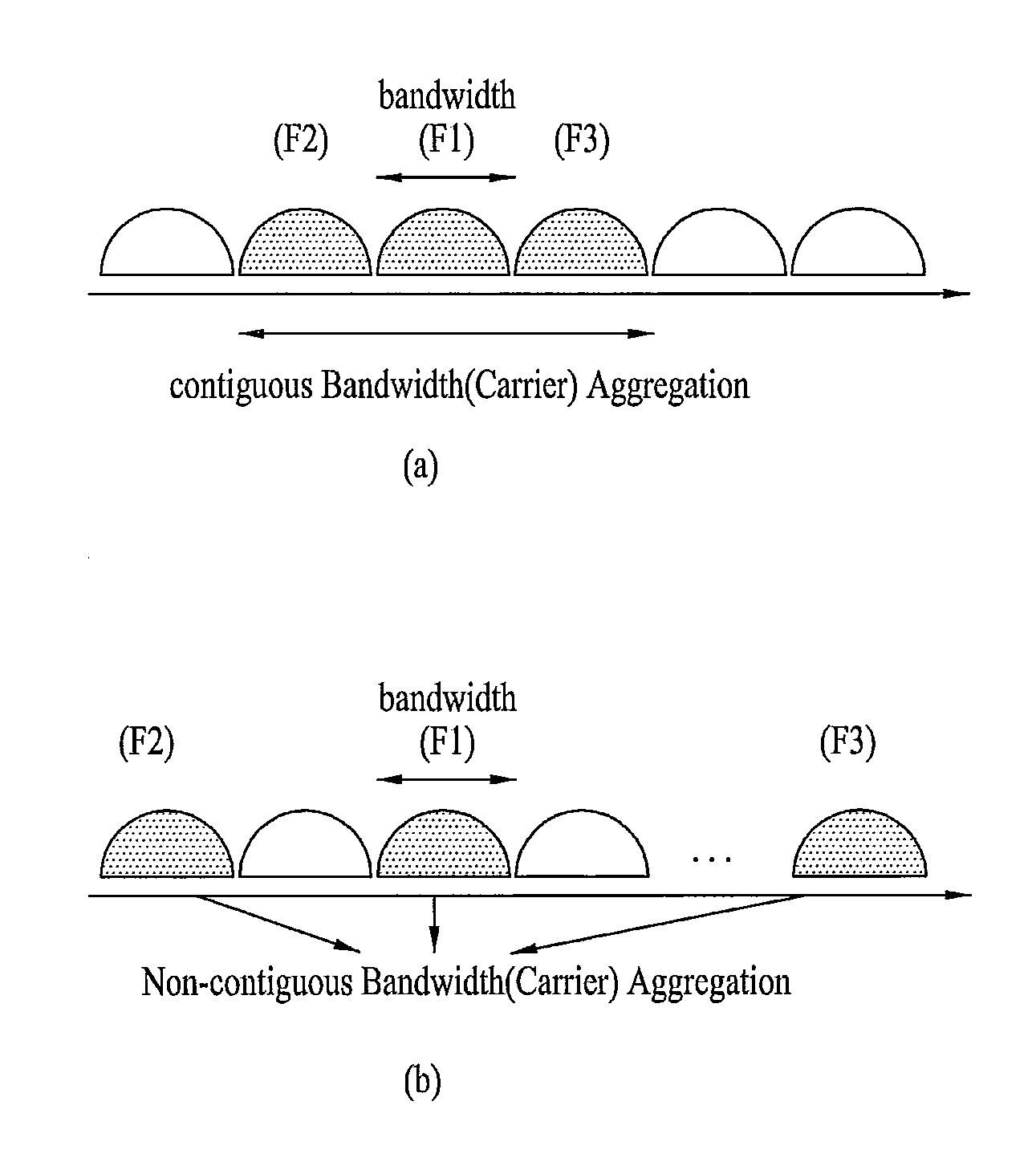
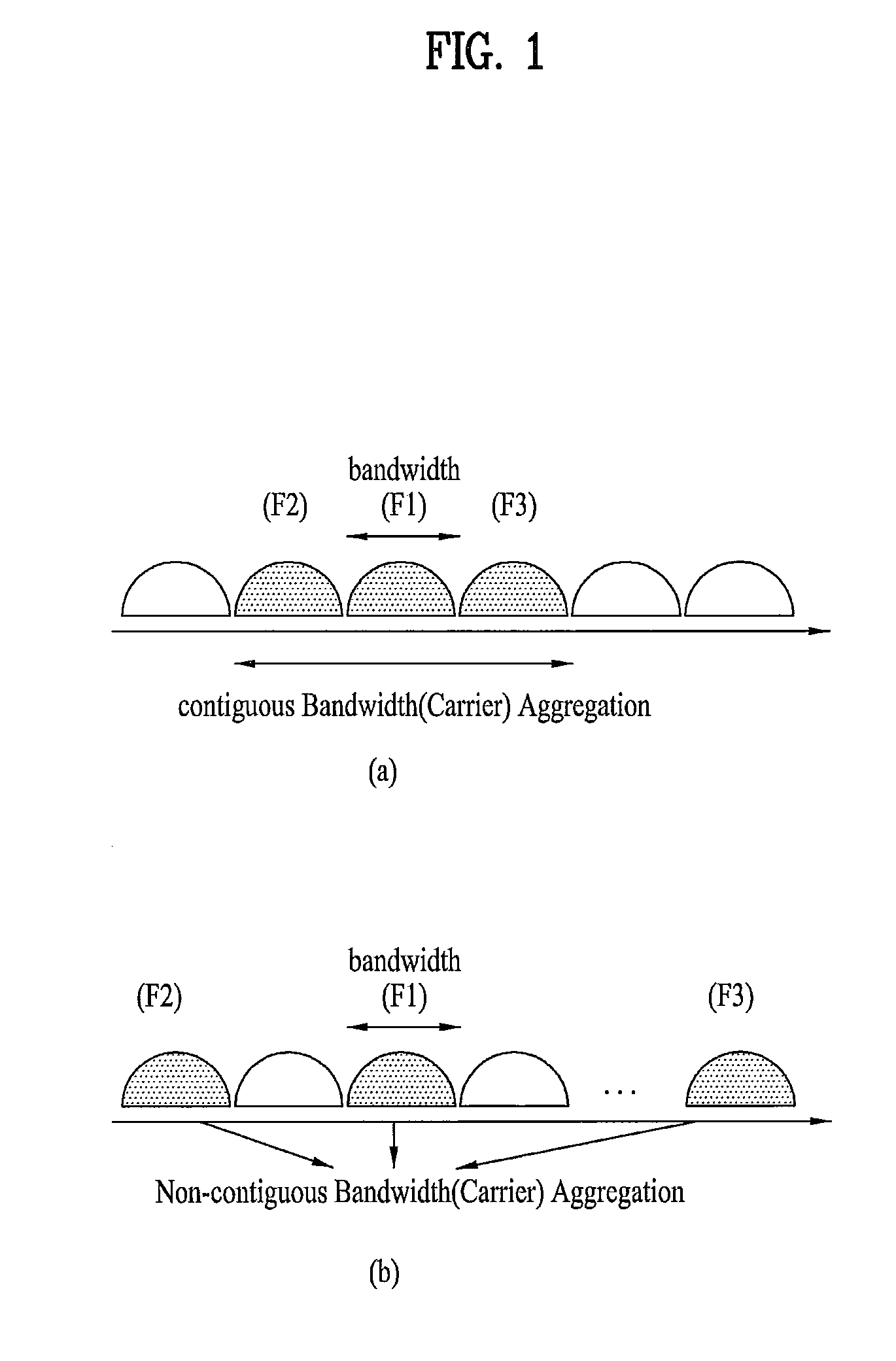
Multi-carrier communication systems employing variable symbol rates and number of carriers
ActiveUS20020006167A1Error detection/prevention using signal quality detectorTransmission path divisionCommunications systemClock rate
A multi-carrier communication system such as an OFDM or DMT system has nodes which are allowed to dynamically change their receive and transmit symbol rates, and the number of carriers within their signals. Changing of the symbol rate is done by changing the clocking frequency of the nodes' iFFT and FFT processors, as well as their serializers and deserializers. The nodes have several ways of dynamically changing the number of carriers used. The selection of symbol rate and number of carriers can be optimized for a given channel based on explicit channel measurements, a priori knowledge of the channel, or past experience. Provision is made for accommodating legacy nodes that may have constraints in symbol rate or the number of carriers they can support. The receiver can determine the correct symbol rate and number of carriers through a priori knowledge, a first exchange of packets in a base mode that all nodes can understand, or an indication in the header of the data packet which is transmitted in a base mode of operation that all nodes can understand.
Owner:THE CONNECTIVITY PATENT TRUST
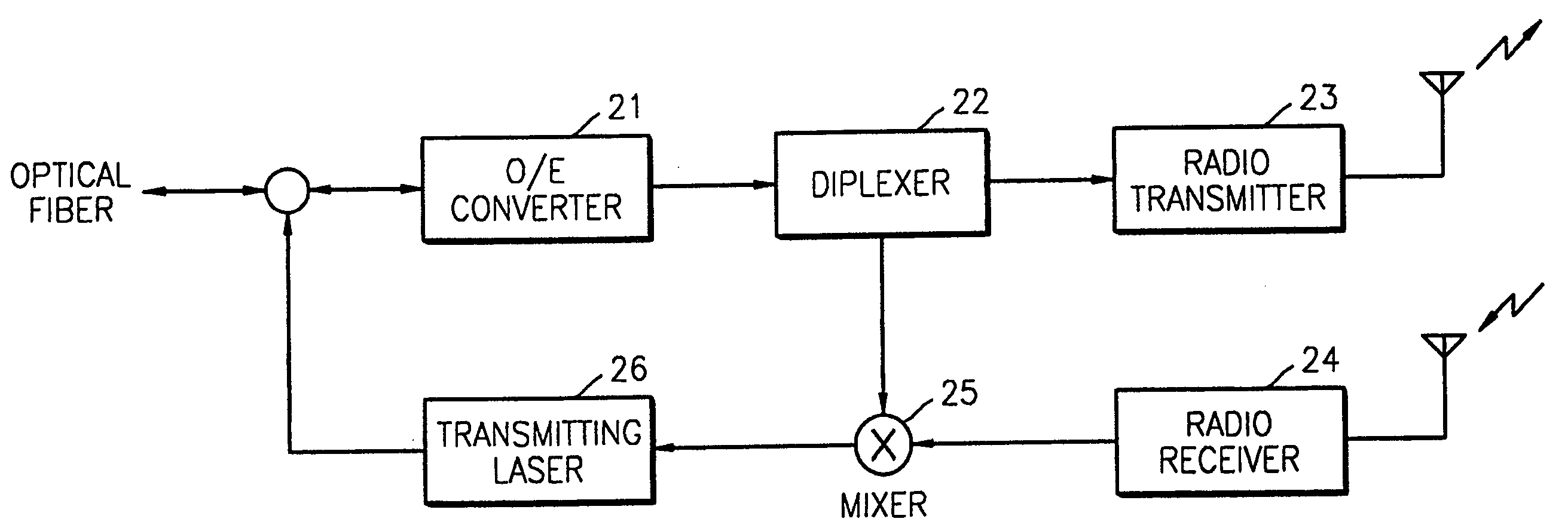
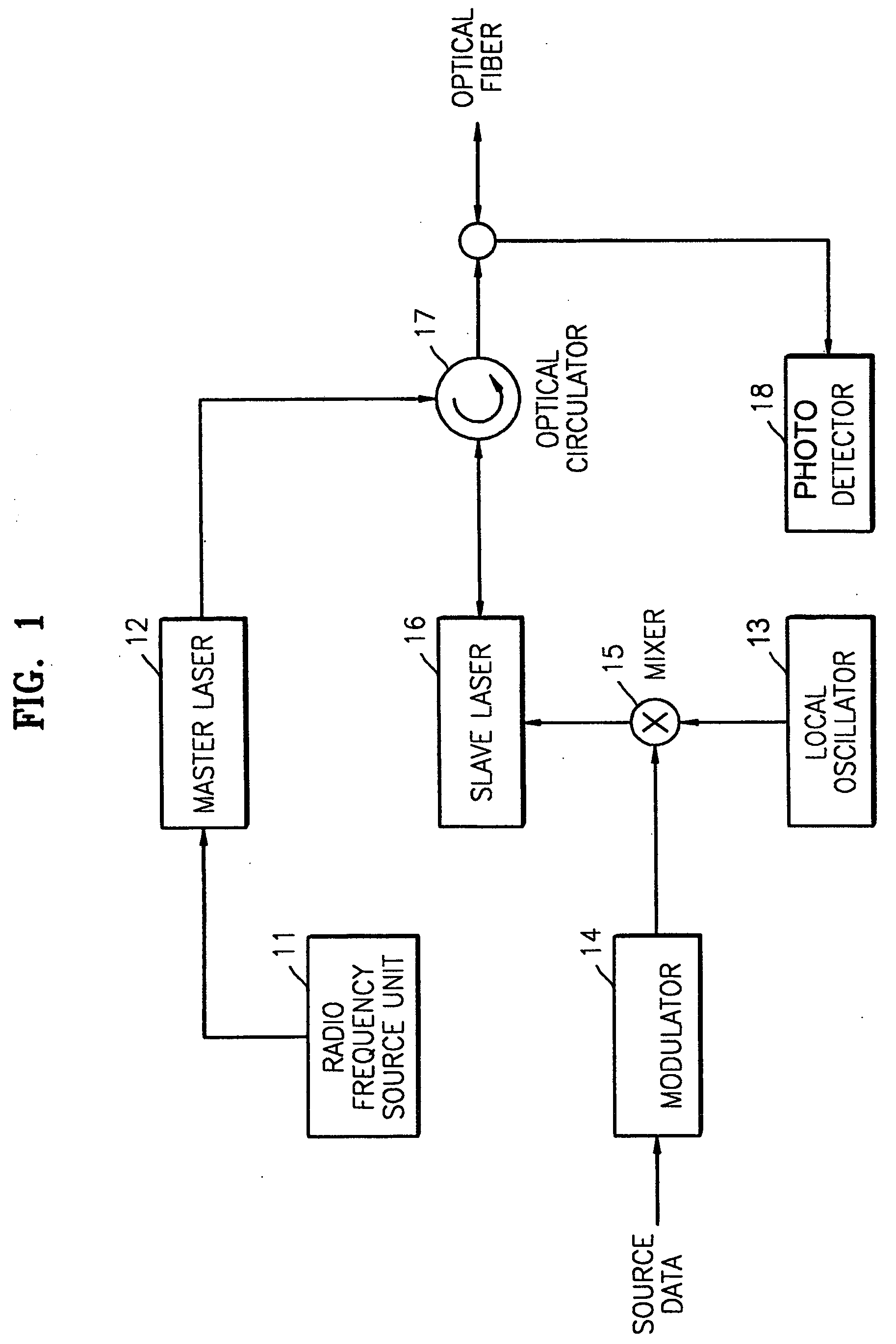
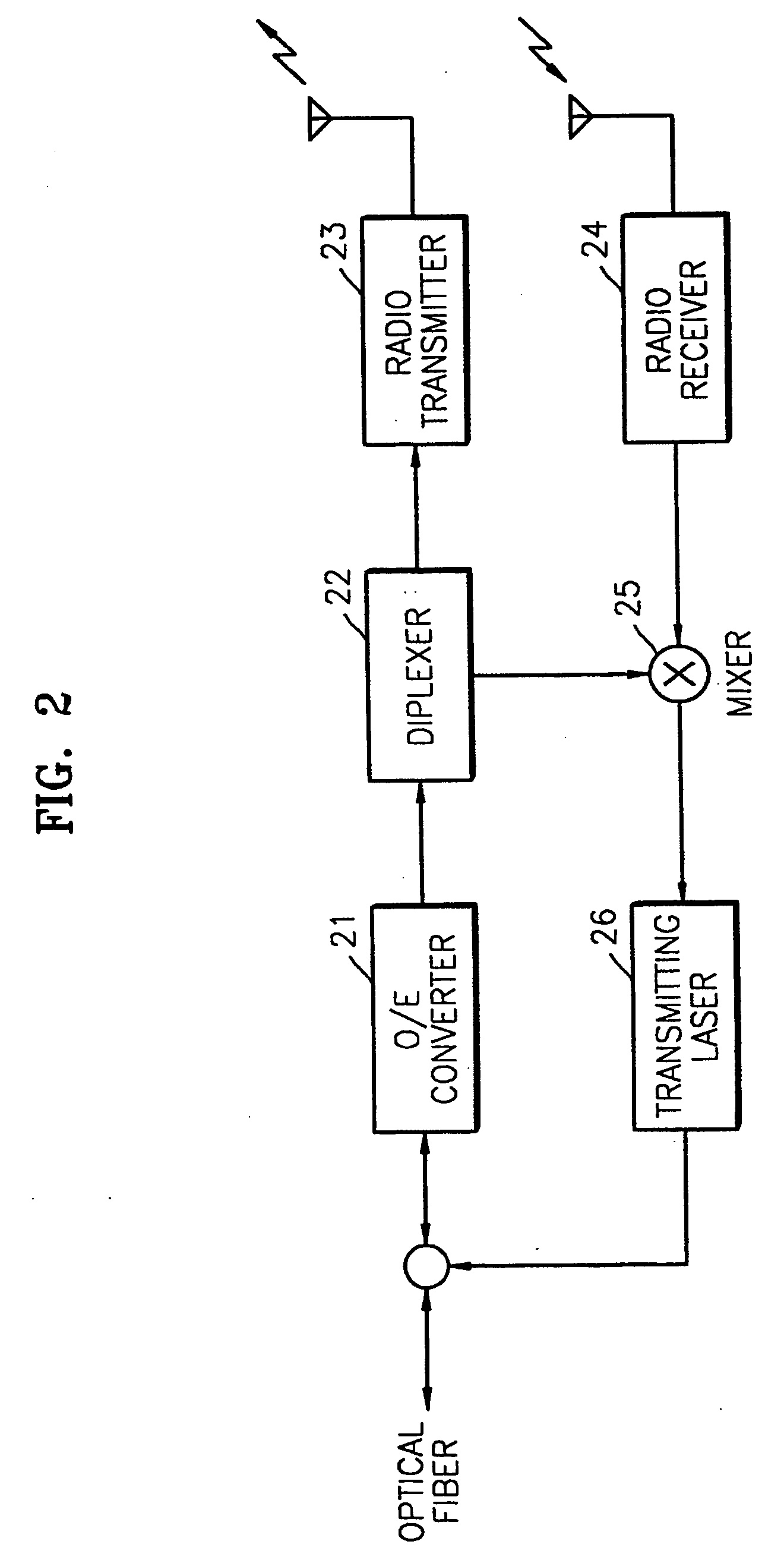
Method and apparatus for duplex communication in hybrid fiber-radio systems
InactiveUS20080232799A1Enabling duplex communicationEfficient methodWavelength-division multiplex systemsRadio-over-fibreFiberInjection locked
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
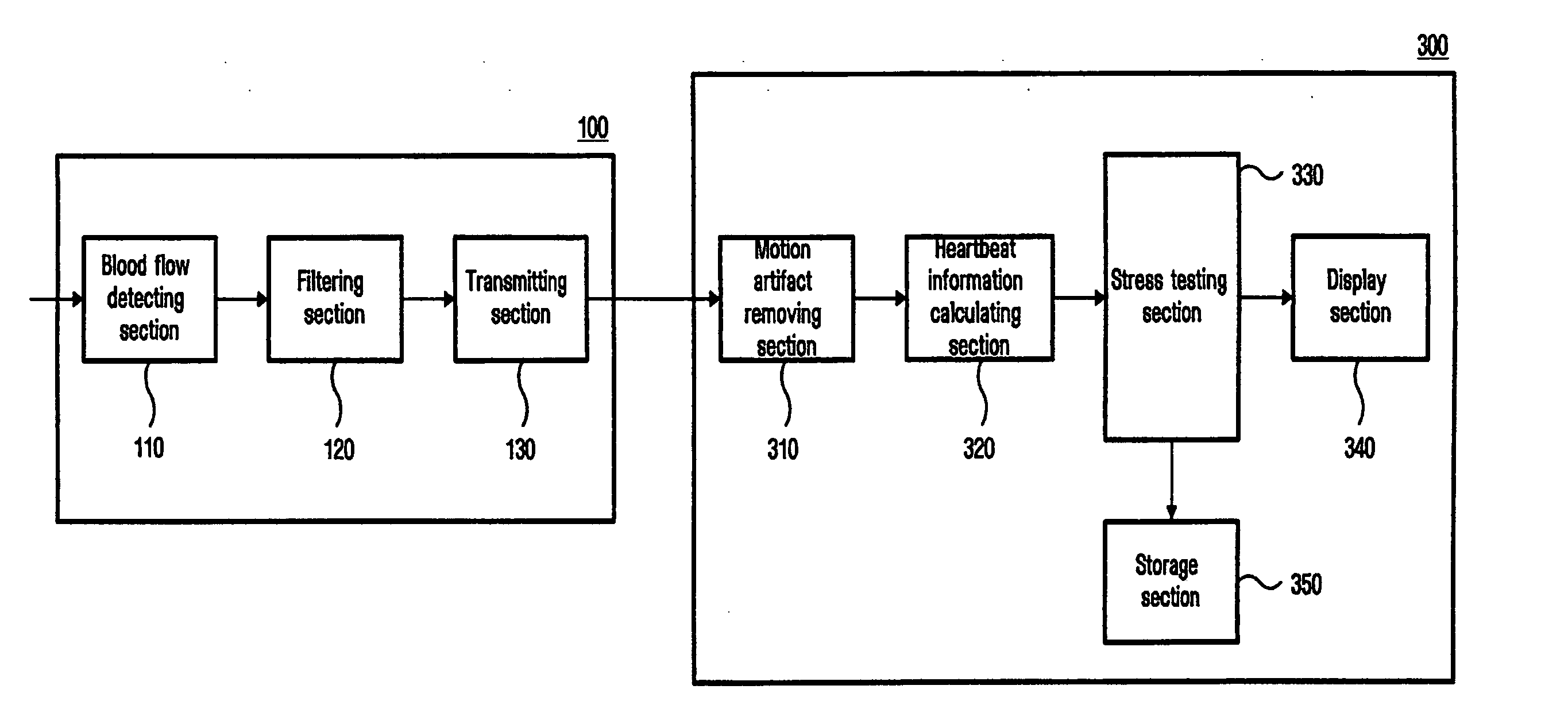
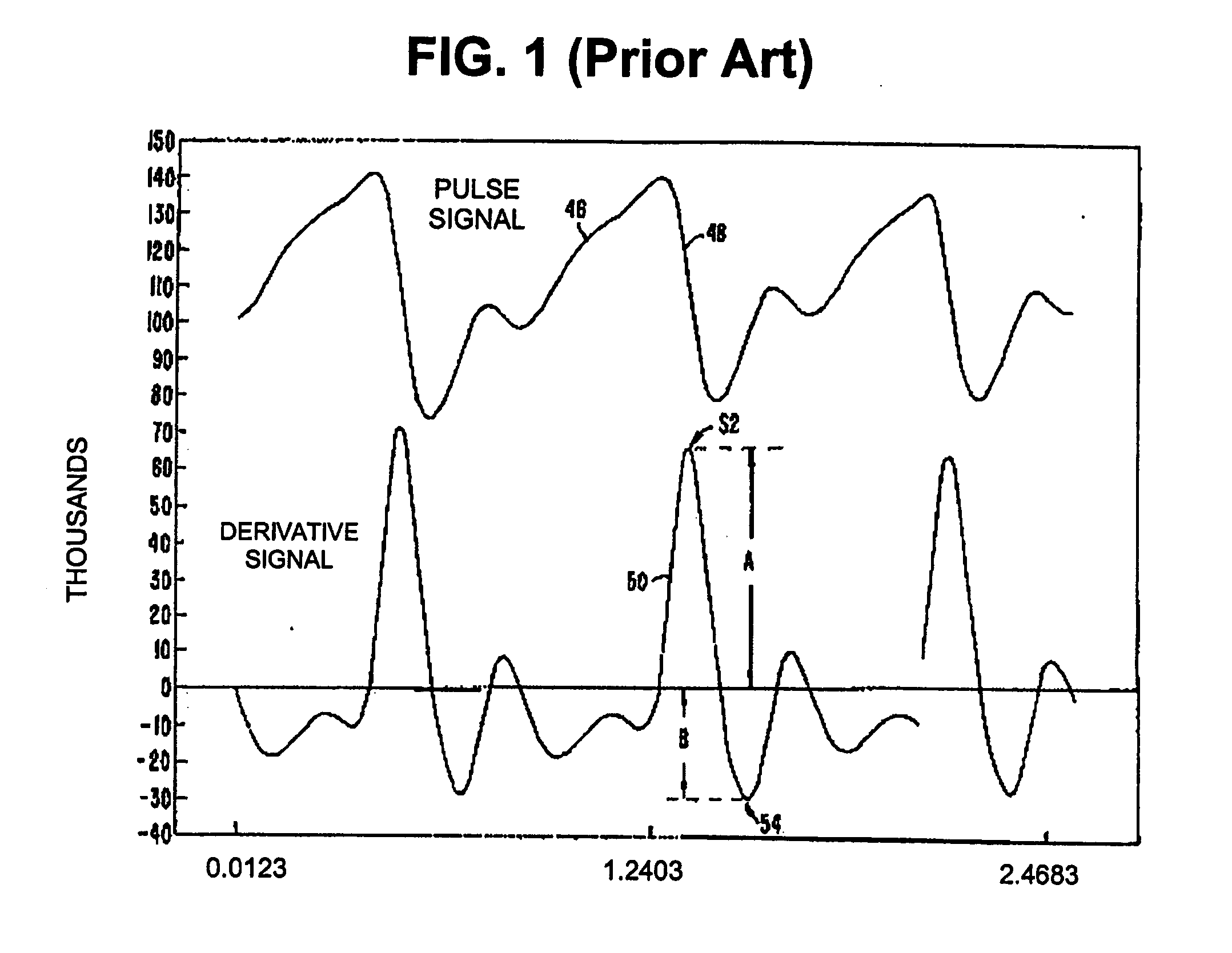
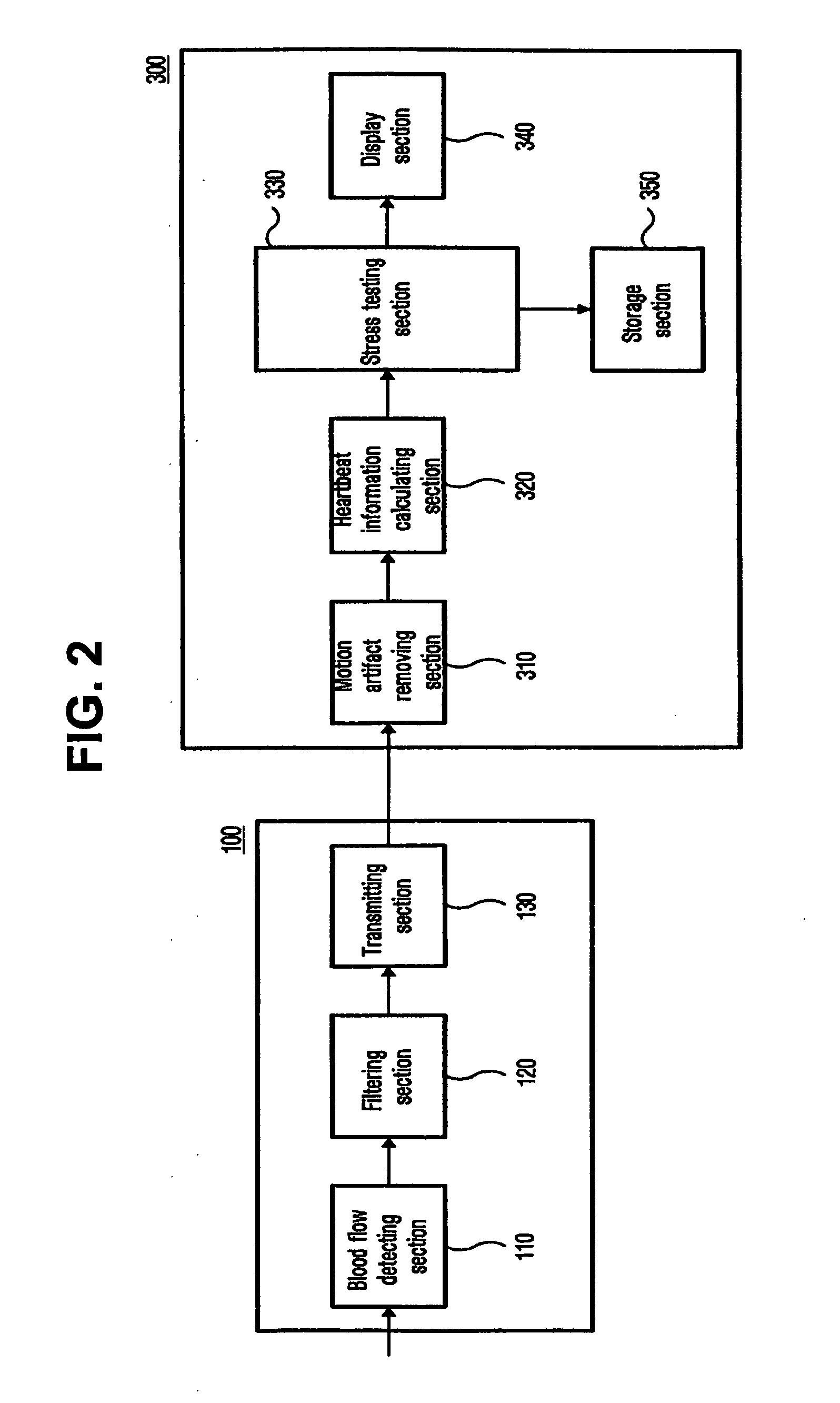
Apparatus and method for detecting blood flow signal free from motion artifact and stress test apparatus using the same
An apparatus and method to detect a blood flow signal free from a motion artifact, and a stress test apparatus using the same, enhance data reliability of the blood flow signal by removing the motion artifact from the blood flow signal detected by photo-plethysmography. The apparatus to detect the blood flow signal includes a base pattern correlation coefficient calculating unit to determine peak points in the blood flow signal sensed from a body of an examinee using a blood flow sensing unit, and to calculate correlation coefficients of each peak point using a predetermined base pattern, and a motion artifact processing unit to determine the motion artifact using the calculated correlation coefficients and to remove the motion artifact from the blood flow signal. Thus, reliability of the blood flow signal is enhanced by effectively removing the motion artifact from the blood flow signal detected by the photo-plethysmography.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
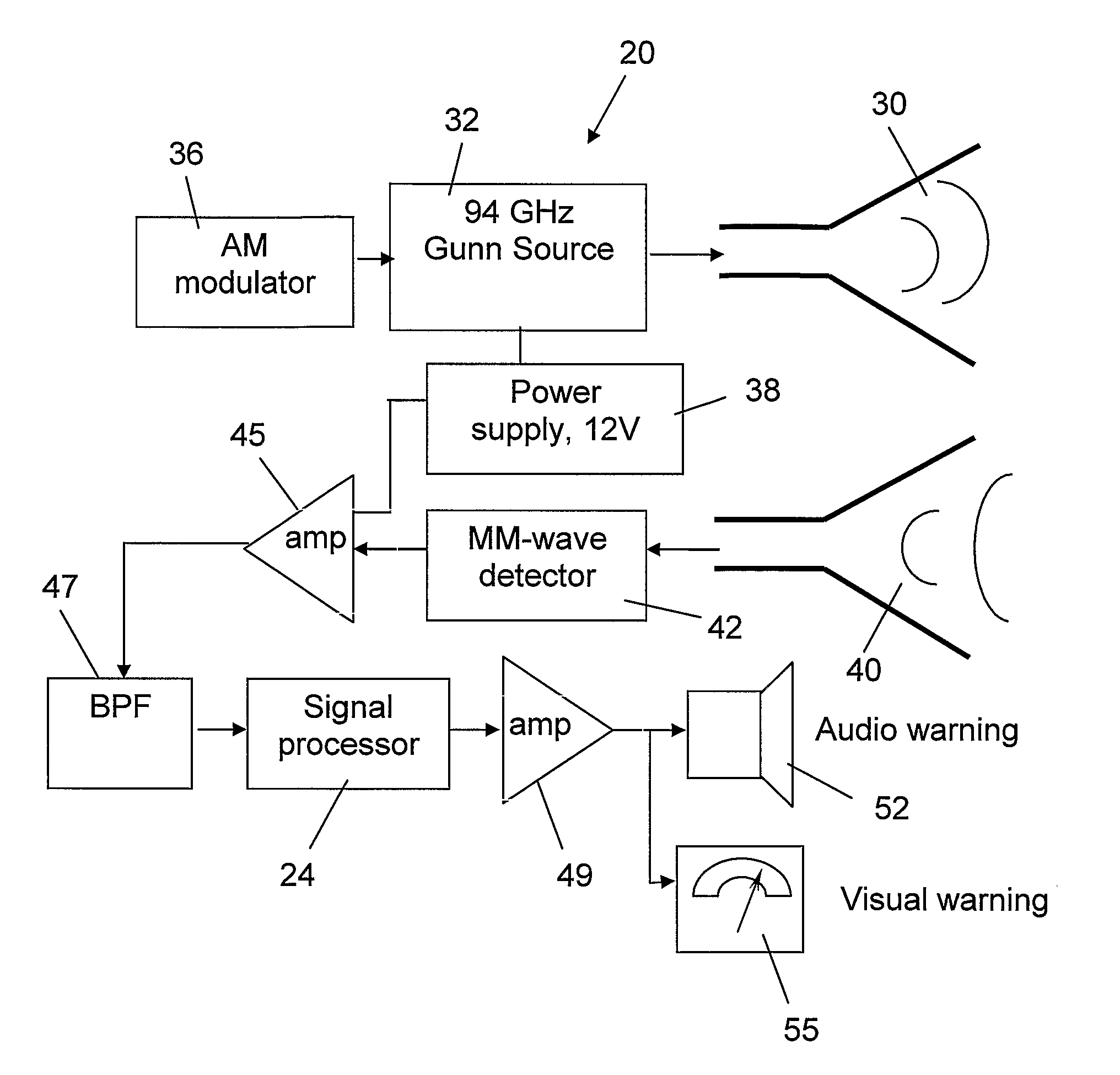
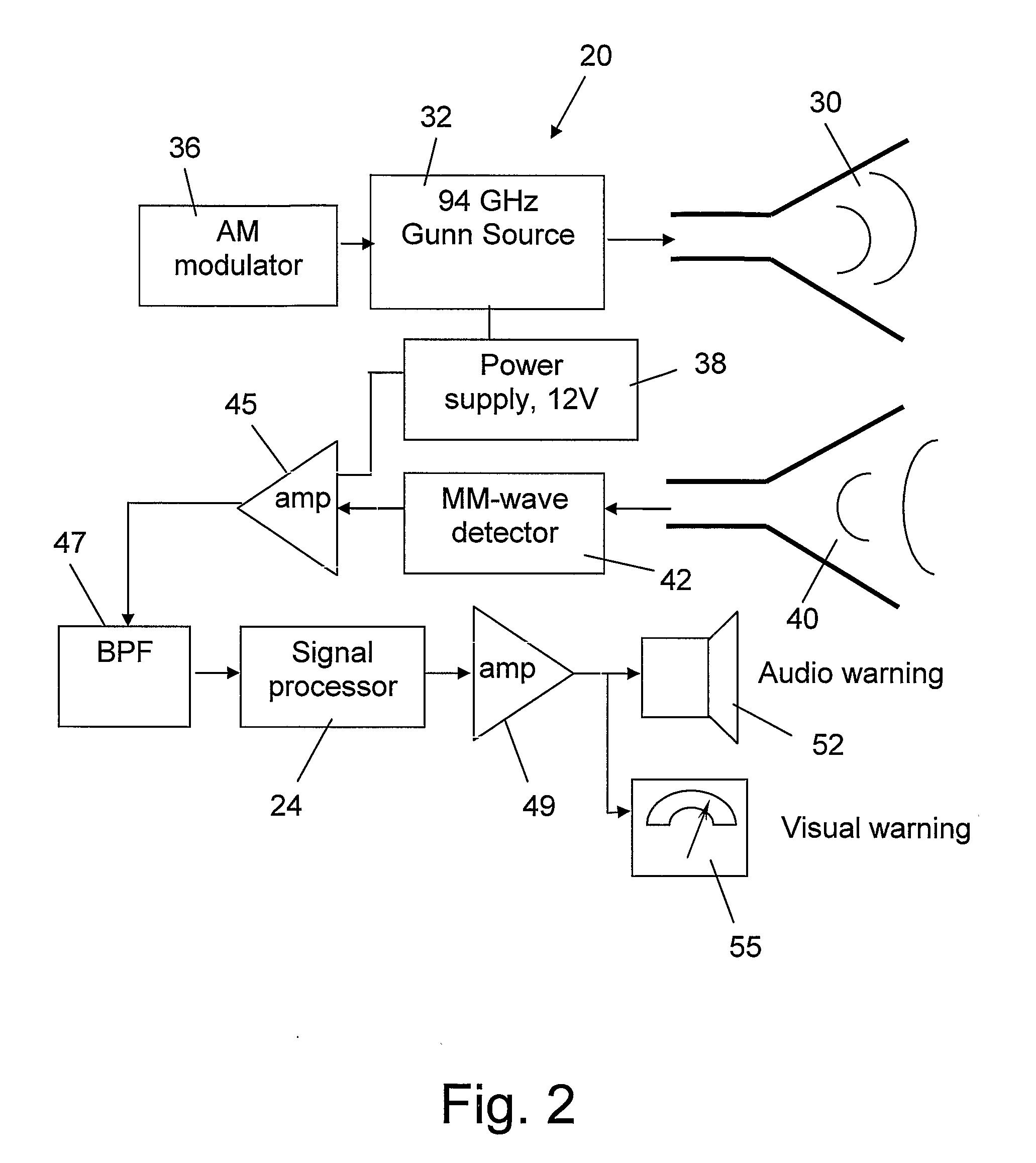
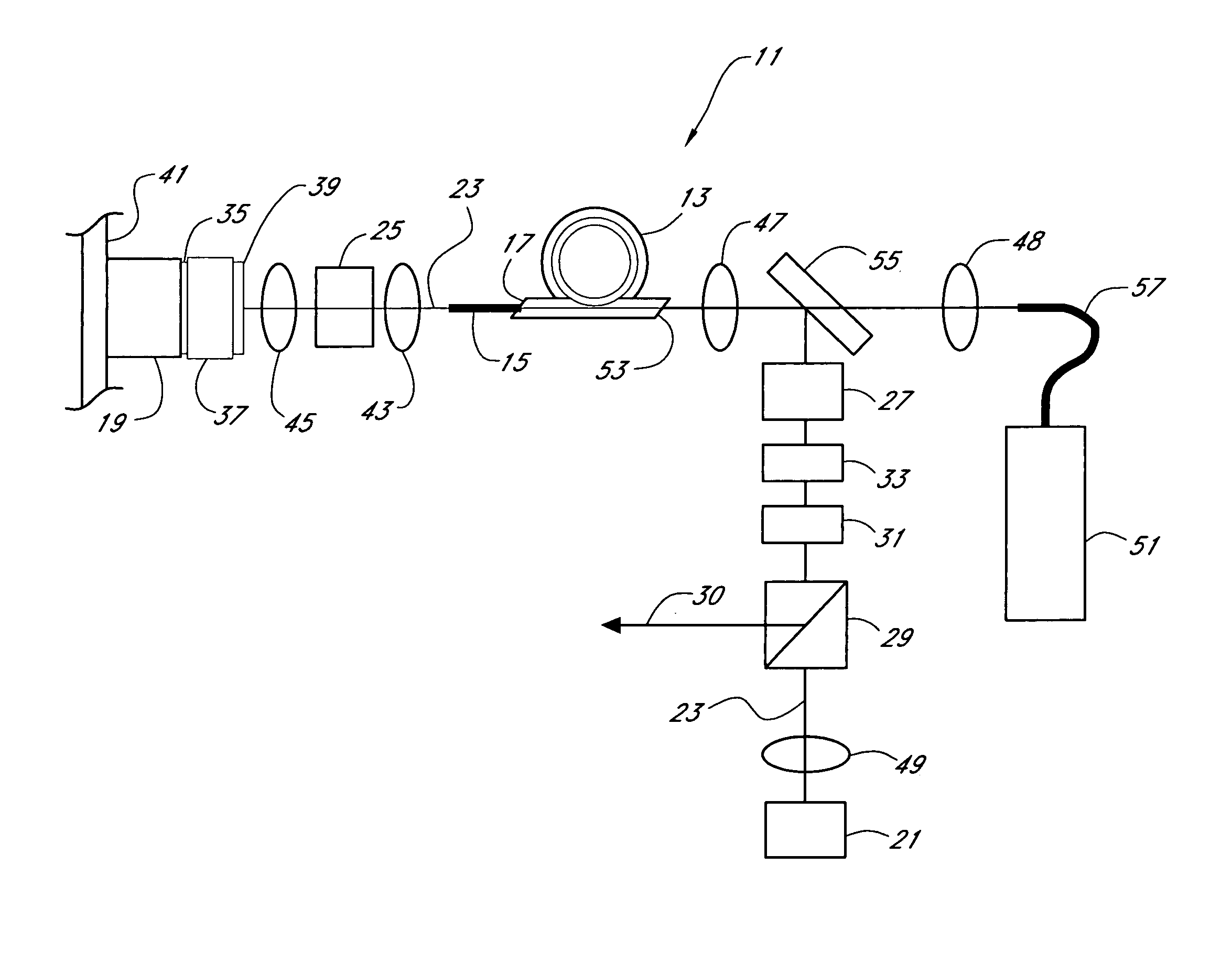
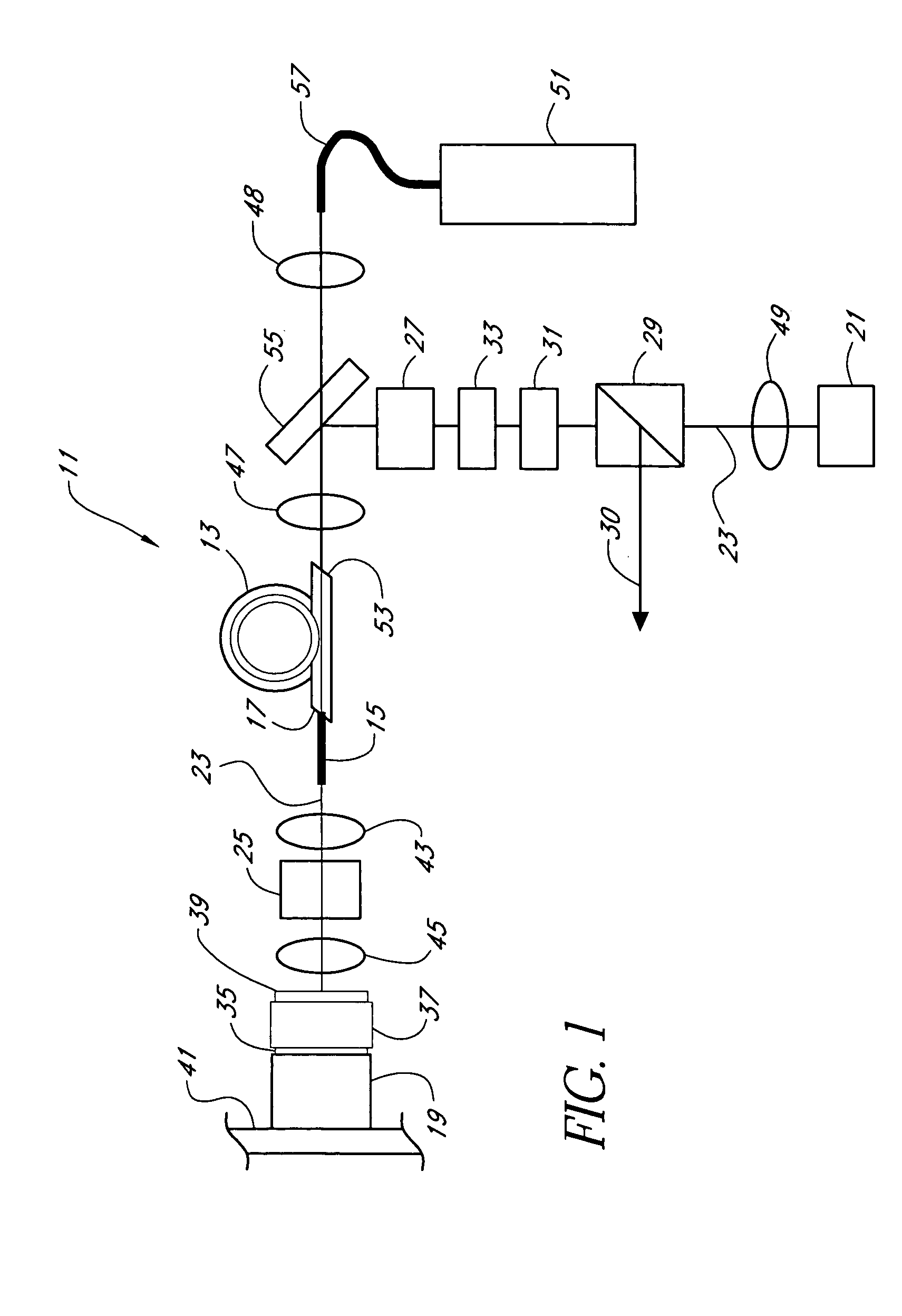
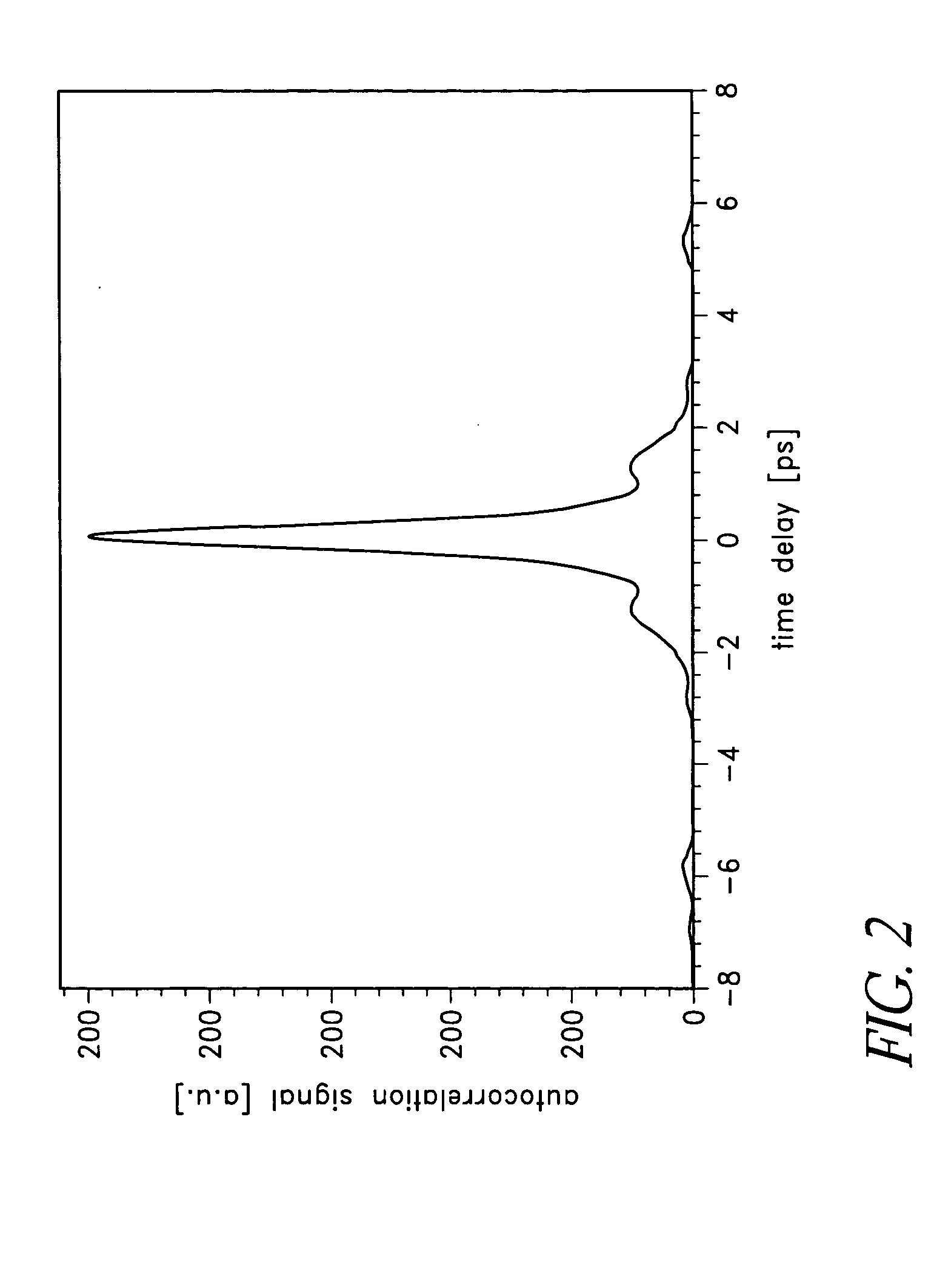
Hand-held device and method for detecting concealed weapons and hidden objects
InactiveUS20090195435A1Improve uniformityGeological detection using milimetre wavesRadio wave reradiation/reflectionWave detectionDisplay device
The present invention is an inexpensive, hand-held, and easy to operate millimeter-wave detection device that employs a non-imaging sensor which radiates a pulse of millimeter waves of a certain amplitude and frequency towards a target located at a distance from the detection device. The sensor receives pulses of millimeter waves that are reflected from the target and generates a voltage waveform that is characteristic mainly of the target material, while other parameters such as distance to the target are known. The processor of the detection device measures both the peak voltage and the rate of increase of the voltage until it reaches the maximum. Using an algorithm stored in a software module, the deviation between the rate of the voltage rise and the peak voltage is compared with values of similar parameters for a number of test targets made of different materials that were previously collected and stored in a calibration table in the memory of the device. A concealed object, e.g. a weapon, is positively identified when the measured voltage rise is found to be similar to one of the stored voltage rises. The circuitry of the detection device generates a visual and / or audio output to a display device which is indicative to the operator as to whether a concealed object is present and, if a match is found with the data in the calibration table, the nature of the concealed object is also displayed. In addition to the basic mode of operation described, various other operation modes can be employed with the detection device of the invention.
Owner:ARIEL UNIV RES & DEV
Mode-locked multi-mode fiber laser pulse source
InactiveUS20050008044A1High energy storageIncrease the sectionCoupling light guidesActive medium shape and constructionHigh power lasersPeak value
A laser utilizes a cavity design which allows the stable generation of high peak power pulses from mode-locked multi-mode fiber lasers, greatly extending the peak power limits of conventional mode-locked single-mode fiber lasers. Mode-locking may be induced by insertion of a saturable absorber into the cavity and by inserting one or more mode-filters to ensure the oscillation of the fundamental mode in the multi-mode fiber. The probability of damage of the absorber may be minimized by the insertion of an additional semiconductor optical power limiter into the cavity. To amplify and compress optical pulses in a multi-mode (MM) optical fiber, a single-mode is launched into the MM fiber by matching the modal profile of the fundamental mode of the MM fiber with a diffraction-limited optical mode at the launch end, The fundamental mode is preserved in the MM fiber by minimizing mode-coupling by using relatively short lengths of step-index MM fibers with a few hundred modes and by minimizing fiber perturbations. Doping is confined to the center of the fiber core to preferentially amplify the fundamental mode, to reduce amplified spontaneous emission and to allow gain-guiding of the fundamental mode. Gain-guiding allows for the design of systems with length-dependent and power-dependent diameters of the fundamental mode. To allow pumping with high-power laser diodes, a double-clad amplifier structure is employed. For applications in nonlinear pulse-compression, self phase modulation and dispersion in the optical fibers can be exploited. High-power optical pulses may be linearly compressed using bulk optics dispersive delay lines or by chirped fiber Bragg gratings written directly into the SM or MM optical fiber. High-power cw lasers operating in a single near-diffraction-limited mode may be constructed from MM fibers by incorporating effective mode-filters into the laser cavity. Regenerative fiber amplifiers may be constructed from MM fibers by careful control of the recirculating mode. Higher-power Q-switched fiber lasers may be constructed by exploiting the large energy stored in MM fiber amplifiers.
Owner:FERMANN MARTIN E +1
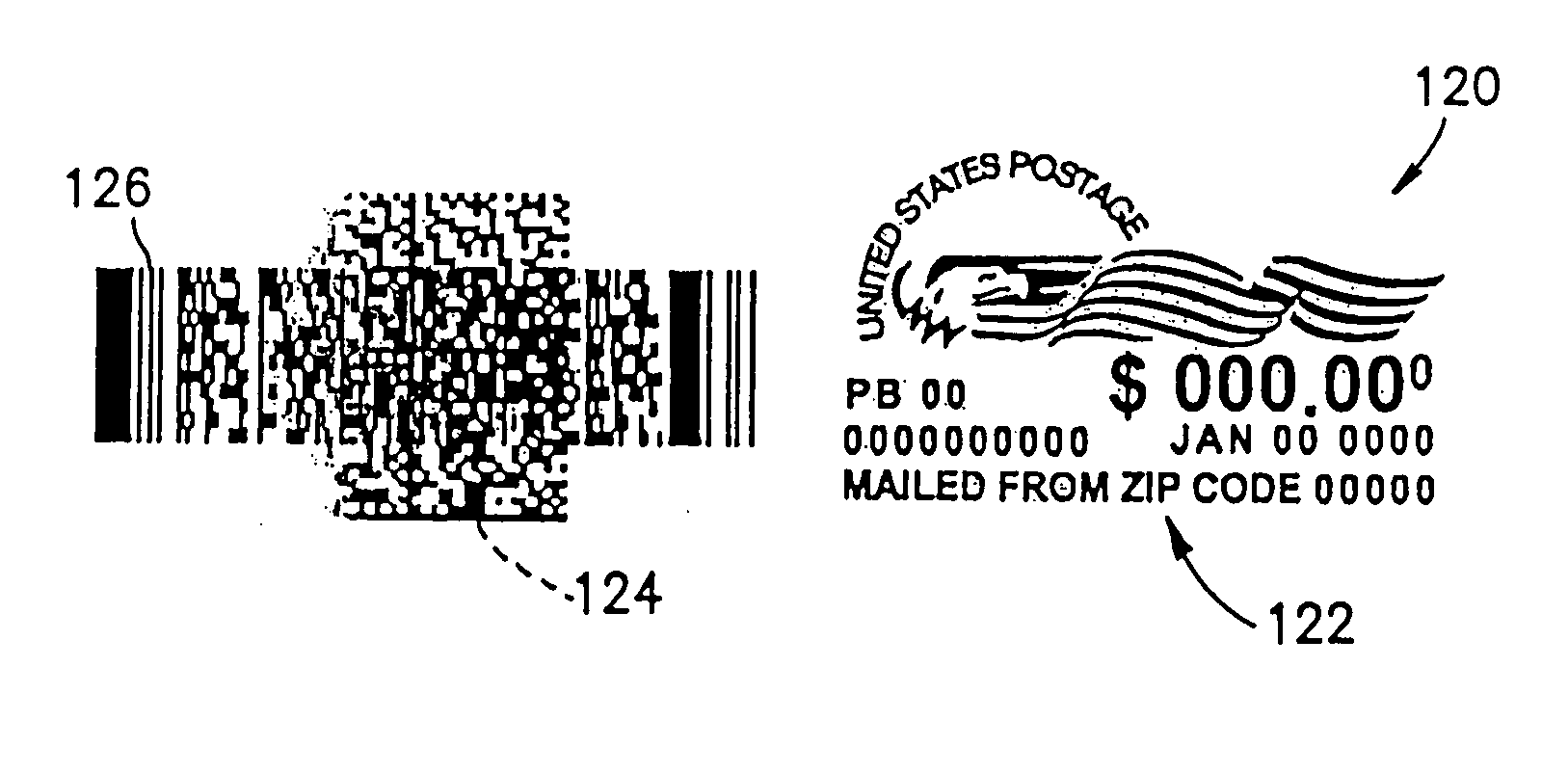
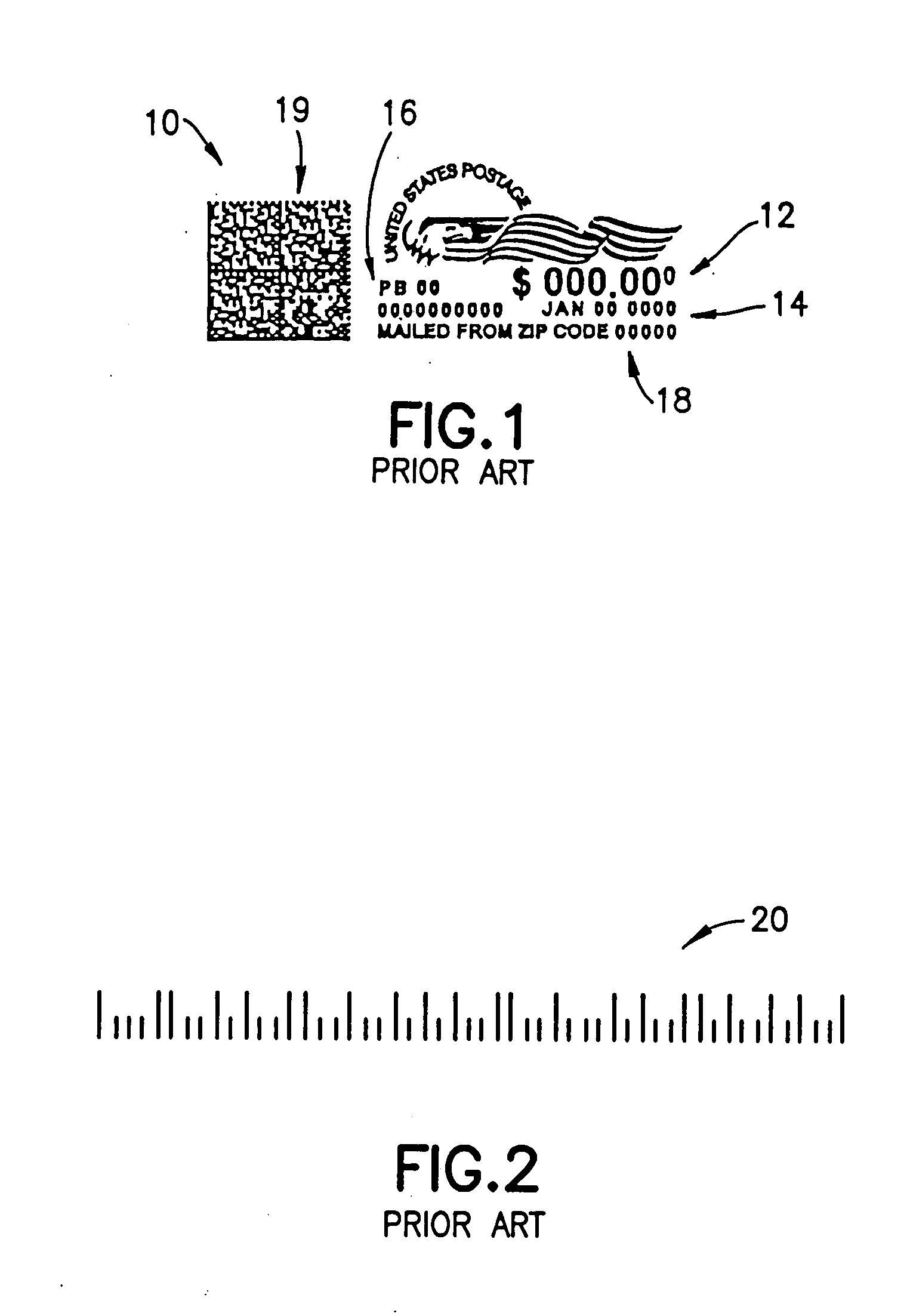
Barcode with enhanced additional stored data
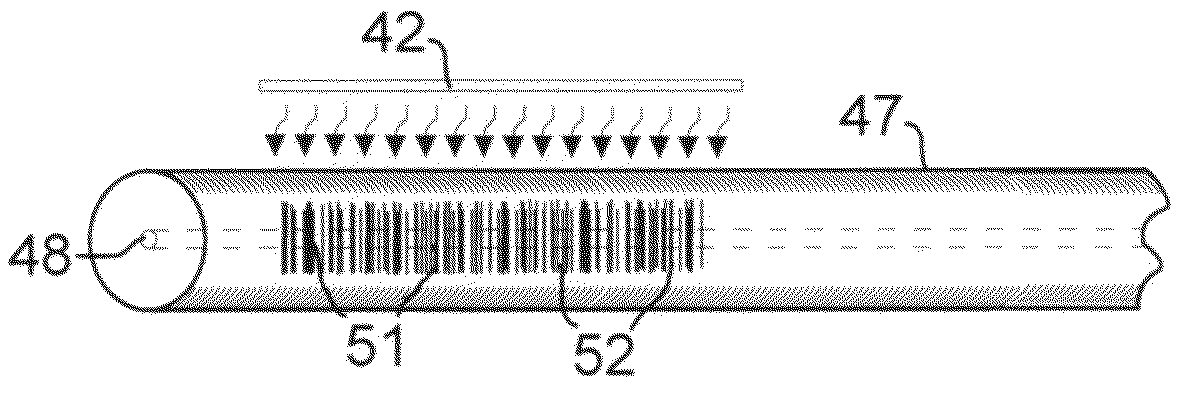
InactiveUS20050269416A1Eliminate needCharacter and pattern recognitionRecord carriers used with machinesBarcode readerBasic mode
A printed barcode including first basic barcode information stored in a first basic mode of printed data storage, and second additional enhanced barcode information stored in a second enhanced mode of printed data storage. The second information is printed, at least partially, as a component of the first information. The first information is adapted to be read by a basic barcode reader. The second information is adapted to be read by an enhanced barcode reader and cannot be read by the basic barcode reader.
Owner:PITNEY BOWES INC
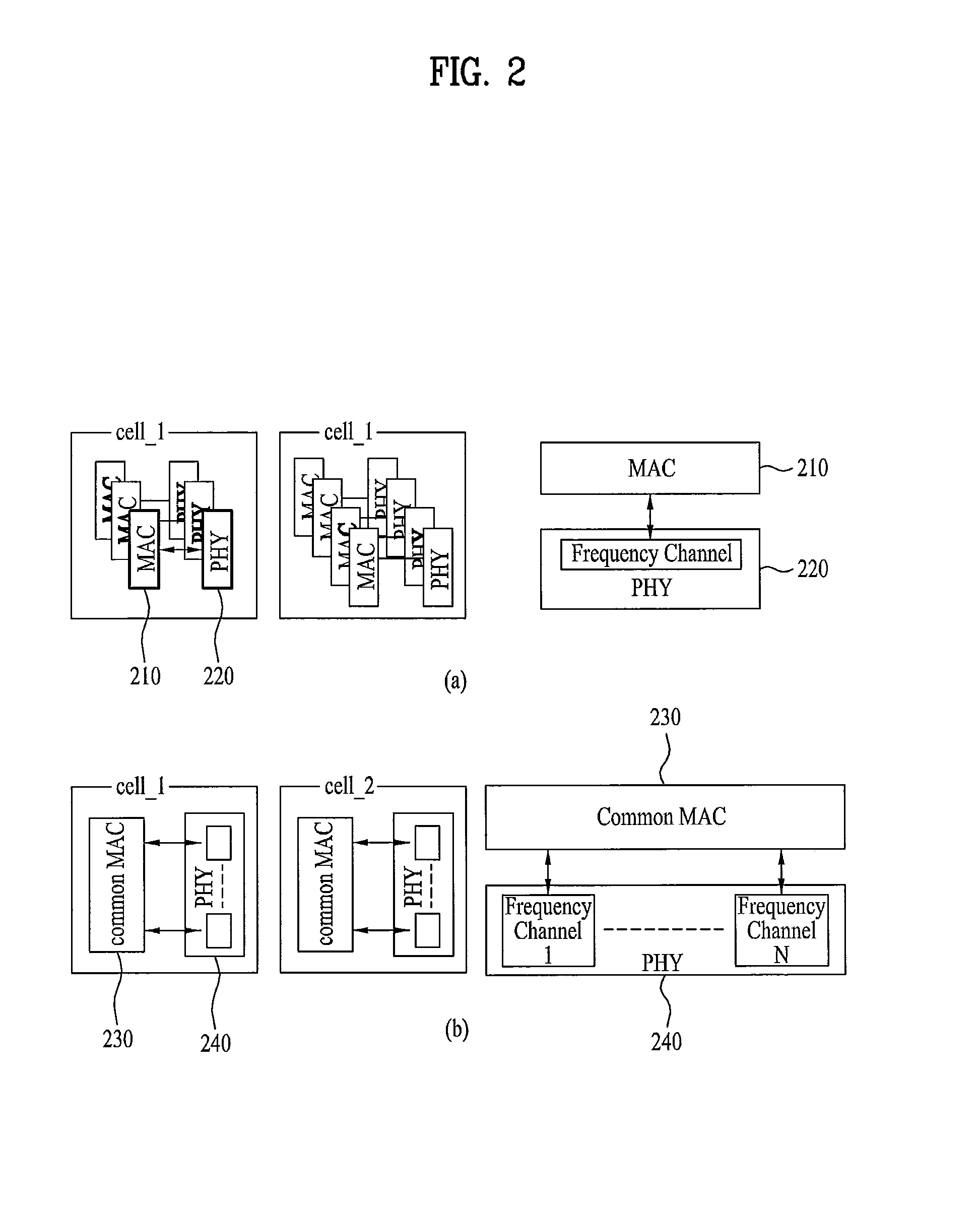
Method for performing carrier management procedure in a multi-carrier supported wideband wireless communication system and apparatus for the same
ActiveUS20110026495A1Efficient managementEffectively performing carrier managementError preventionTransmission path divisionAction CodeCommunications system
A method and apparatus performing carrier management in a broadband wireless communication system supporting multi-carrier (MC) are disclosed. A method for a single-carrier supported mobile station (MS) to perform a carrier change with a MC supported base station (BS) includes transmitting a message indicating a support of a basic MC mode in which the MS is aware of a MC operation of the BS, receiving a carrier management command message including an action code and an action time on a serving carrier, transmitting, in response to the carrier management command message, a confirmation message indicating readiness of signal transmission / reception through a target carrier on a target carrier, and receiving a control signal and data from the BS on the target carrier, wherein the serving carrier and the target carrier are controlled by a common Medium Access Control (MAC) of the BS.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Network Publish/Subscribe System Incorporating Web Services Network Routing Architecture
InactiveUS20080294794A1Facilitating deployment and configuration and maintenanceDigital computer detailsWebsite content managementWeb serviceNetwork architecture
Methods, apparatuses, and systems facilitating the deployment, configuration and maintenance of publication / subscription systems within the context of Web service networks. In one embodiment, the present invention provides Web services network system that presents a topic as a routing entity and includes functionality facilitating topic creation, subscription and publication in a manner consistent with the basic modes of Web services development and deployment, allowing such tasks to be approached in an intuitive, cost-effective and manageable manner. In a preferred embodiment, the publication / subscription system functionality according to the present invention is integrated into a distributed Web services network architecture as more fully described below. The Web services network architecture and integrated publication / subscription system according to the present invention can be implemented across any suitable computer network, including a local area network, an intranet or the Internet.
Owner:AKANA
Barcode with enhanced additional stored data
InactiveUS7229025B2Eliminate needRecord carriers used with machinesSensing by electromagnetic radiationBarcode readerBasic mode
Owner:PITNEY BOWES INC
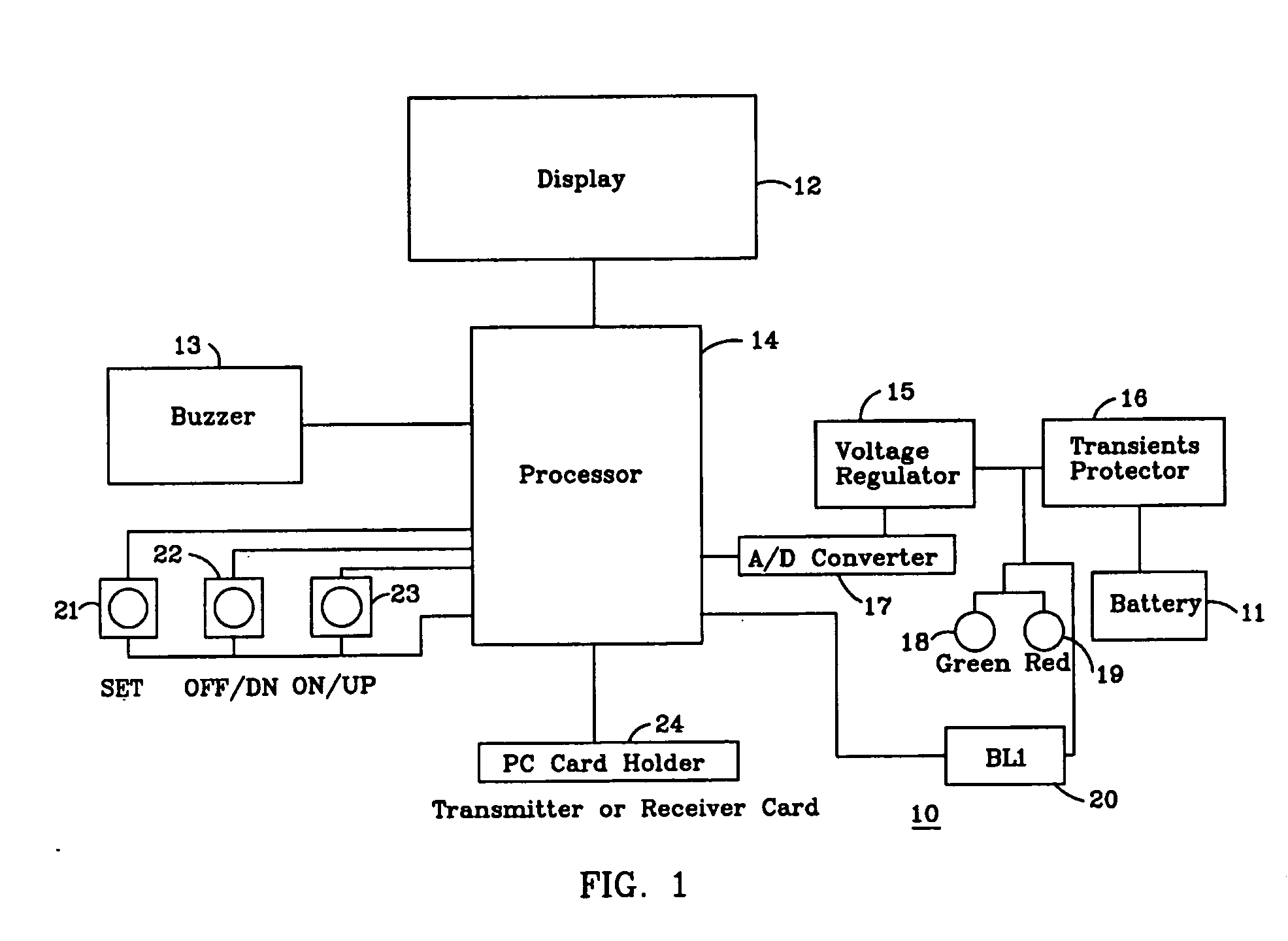
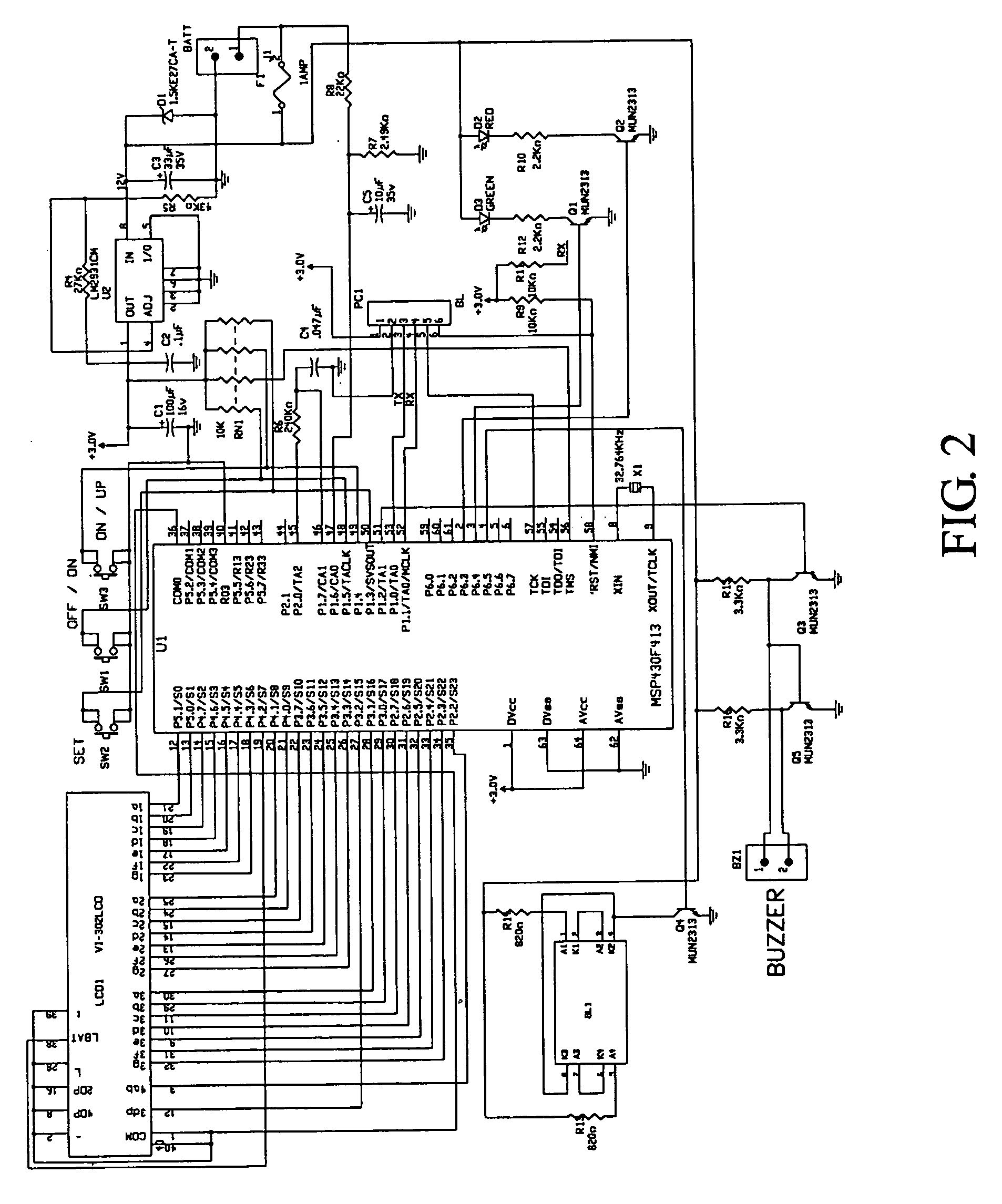
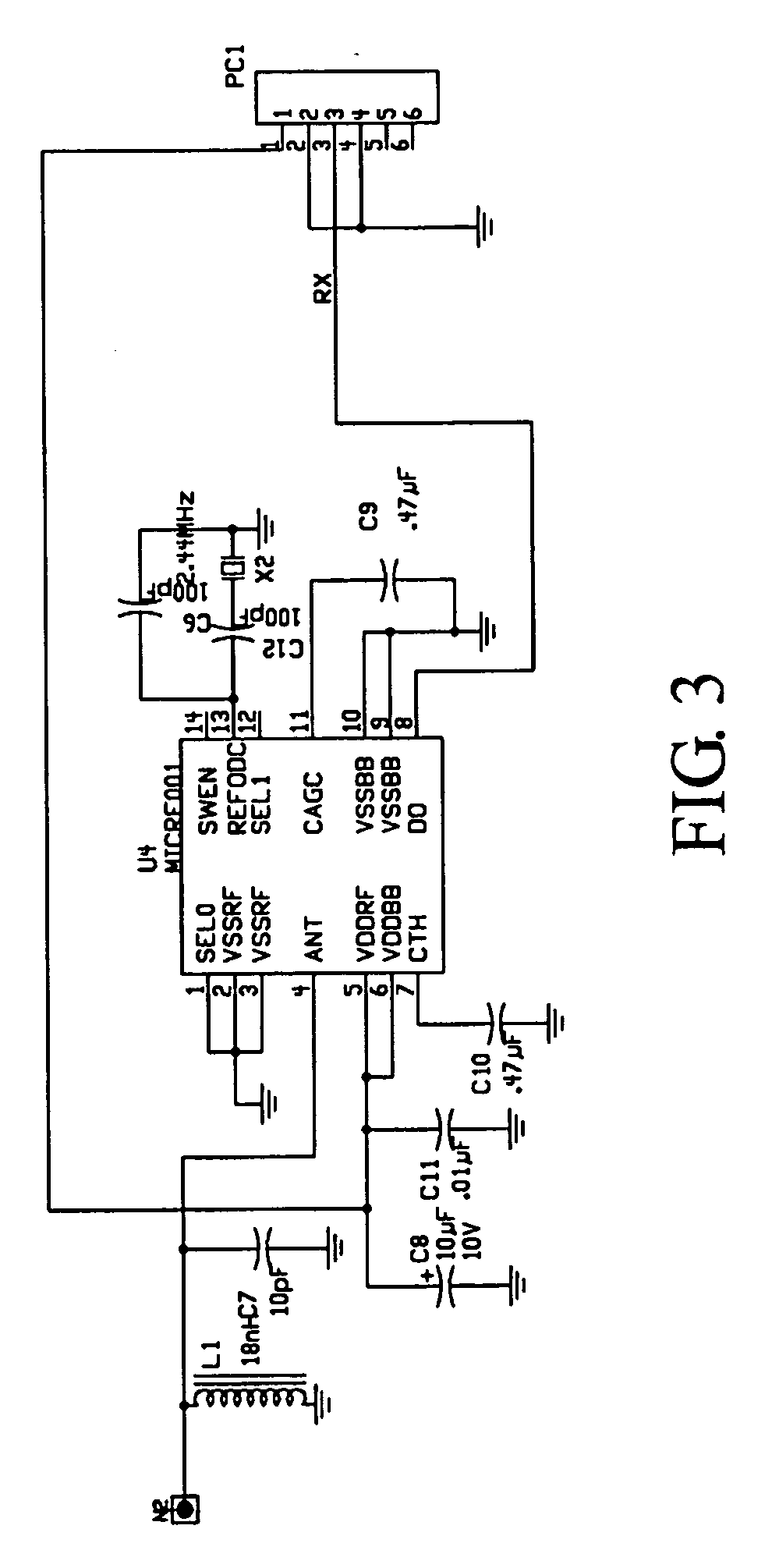
Battery voltage monitor
InactiveUS20060043933A1Batteries circuit arrangementsCurrent/voltage measurementData transmissionBasic mode
A voltage monitor that is operable in two distinct modes. The first mode is the basic model without a transmitter or receiver. The only functions are battery voltage and audible alarm. The second mode is the Voltminder with a alarm and data transmission capability. The standard Voltminder placed in the second mode by adding a transmitter board to the vehicle located Voltminder and a receiver to the home located Voltminder. A programmable monitor reads and tracks a battery voltage, and indicates when a battery voltage drops below a predetermined value. A display shows battery status, and an audible signal is produced when the battery falls below a predetermined voltage.
Owner:VOLTMINDER
Network publish/subscribe system incorporating web services network routing architecture
InactiveUS7788403B2Facilitating deployment and configuration and maintenanceMultiple digital computer combinationsWebsite content managementWeb serviceNetwork architecture
Methods, apparatuses, and systems facilitating the deployment, configuration and maintenance of publication / subscription systems within the context of Web service networks. In one embodiment, the present invention provides Web services network system that presents a topic as a routing entity and includes functionality facilitating topic creation, subscription and publication in a manner consistent with the basic modes of Web services development and deployment, allowing such tasks to be approached in an intuitive, cost-effective and manageable manner. In a preferred embodiment, the publication / subscription system functionality according to the present invention is integrated into a distributed Web services network architecture as more fully described below. The Web services network architecture and integrated publication / subscription system according to the present invention can be implemented across any suitable computer network, including a local area network, an intranet or the Internet.
Owner:AKANA
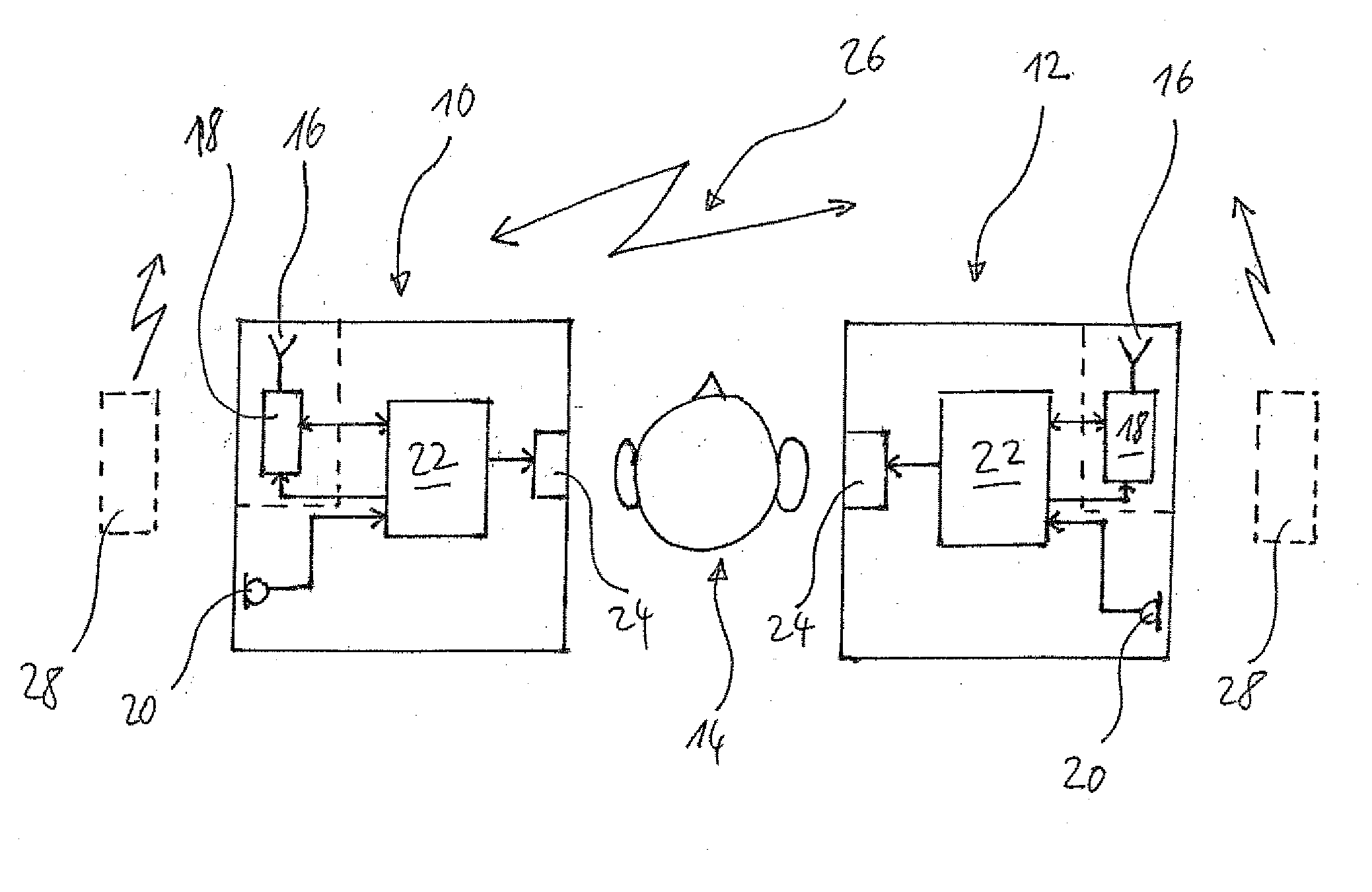
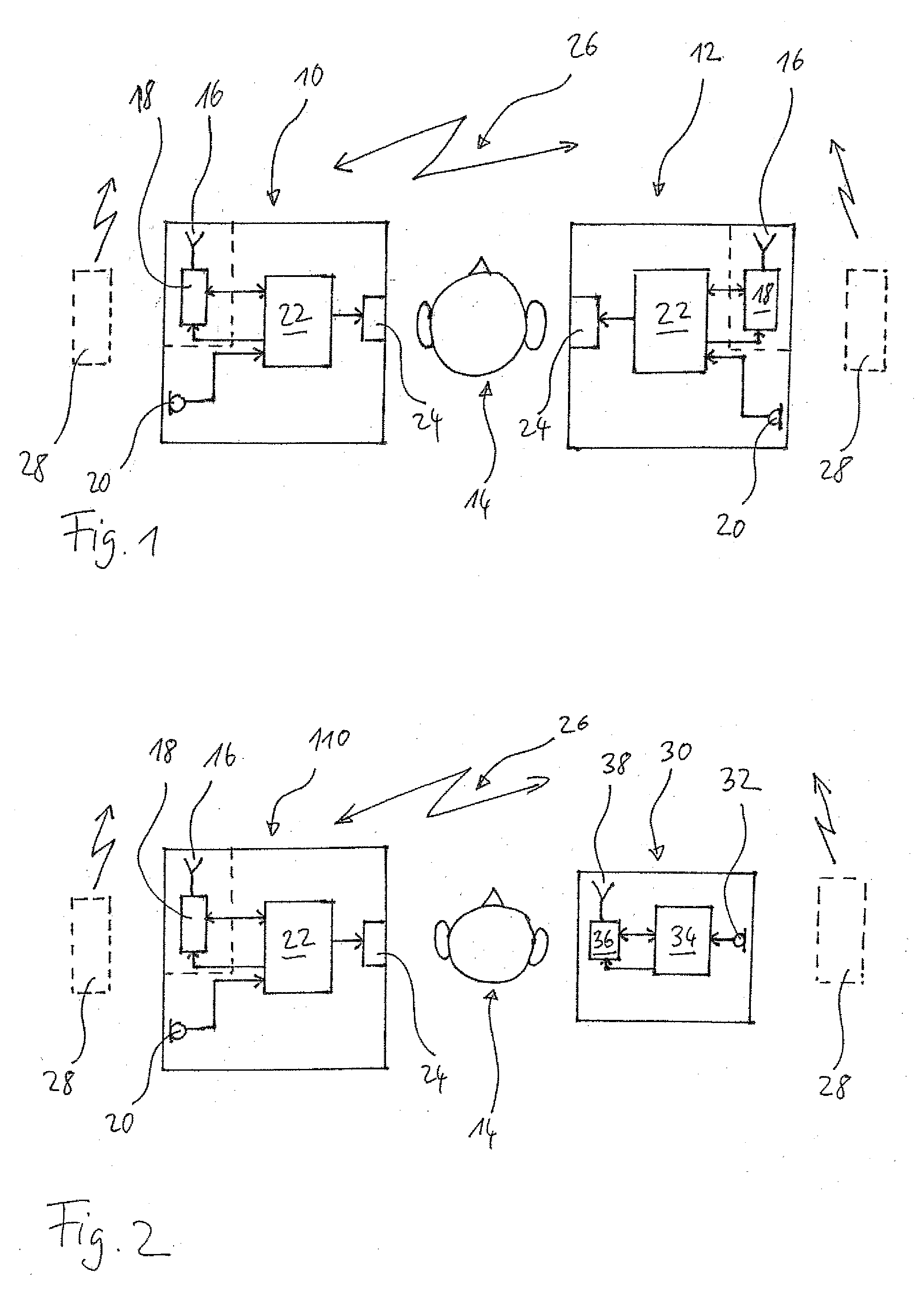
Hearing assistance system and method of operating the same
ActiveUS20070274550A1Avoid failureBreakdown of the link can be avoidedDeaf-aid setsOperational systemRadio frequency signal
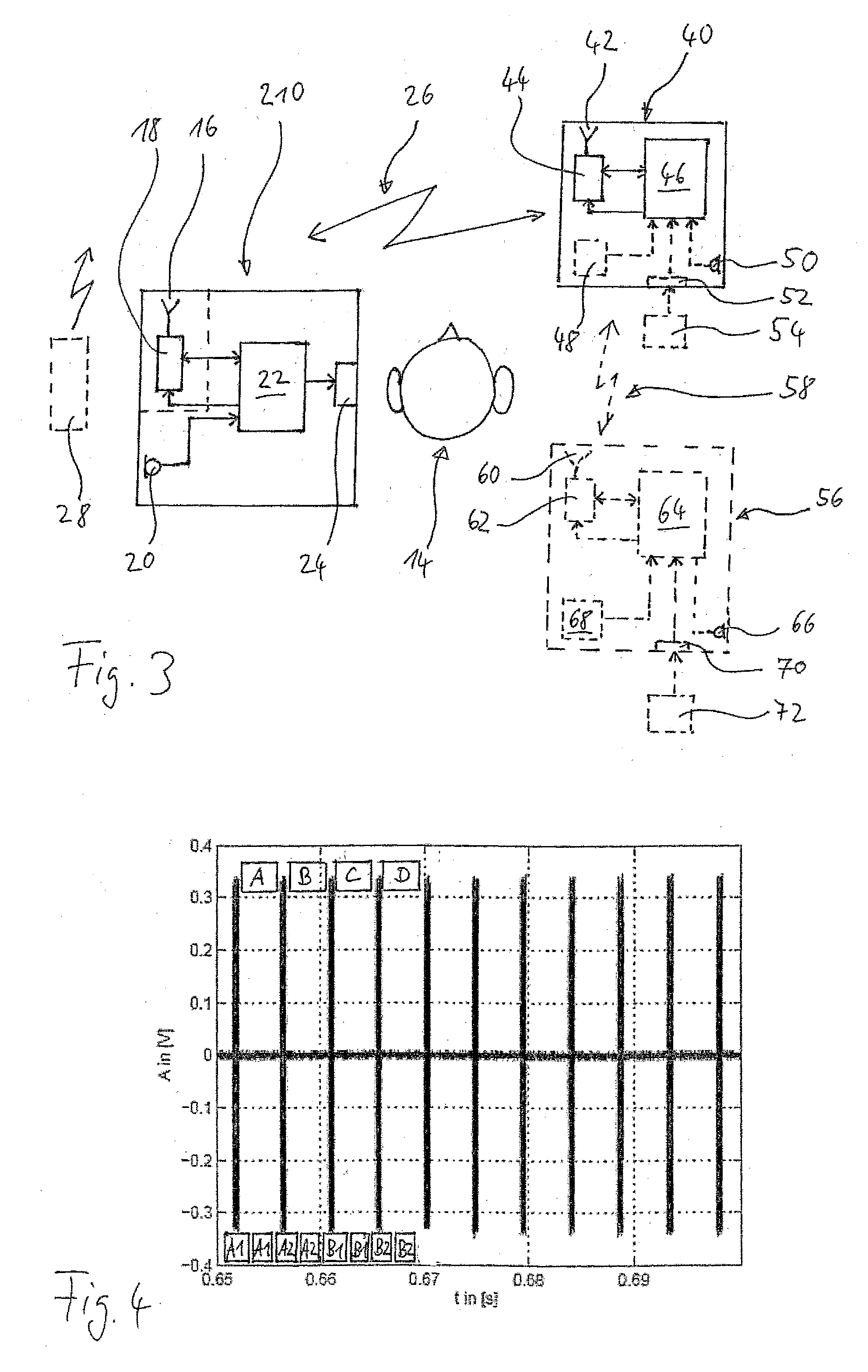
There is provided a method of operating a hearing assistance system comprising a hearing device (10, 110, 210), which comprises means (24) for stimulating a user's hearing and which is worn at one of the user's ears, and a remote device (12, 30, 40) spaced apart from the hearing device. The method comprises: establishing a wireless link (26) between the hearing device and the remote device for transmitting signals from the remote device to the hearing device, and operating the system in a base mode; detecting whether a source (28) of radio frequency signals interfering with the wireless link and having a transmission power changing according to a predictable scheme between low power regimes and high power regimes is present in the vicinity of the hearing device; and operating the system in an interference mode as long as the presence of such source of periodic signals interfering with the wireless link is detected, in which interference mode the transmission of the signals from the remote device to the hearing device is synchronized to the detected power scheme of the interfering signals in such a manner that the signals are transmitted only during the low power regimes.
Owner:SONOVA AG
Optical fiber and integrated optic lasers with enhanced output power
InactiveUS6018533AEfficient pumpingIncrease powerCladded optical fibreLaser using scattering effectsBasic modeLaser source
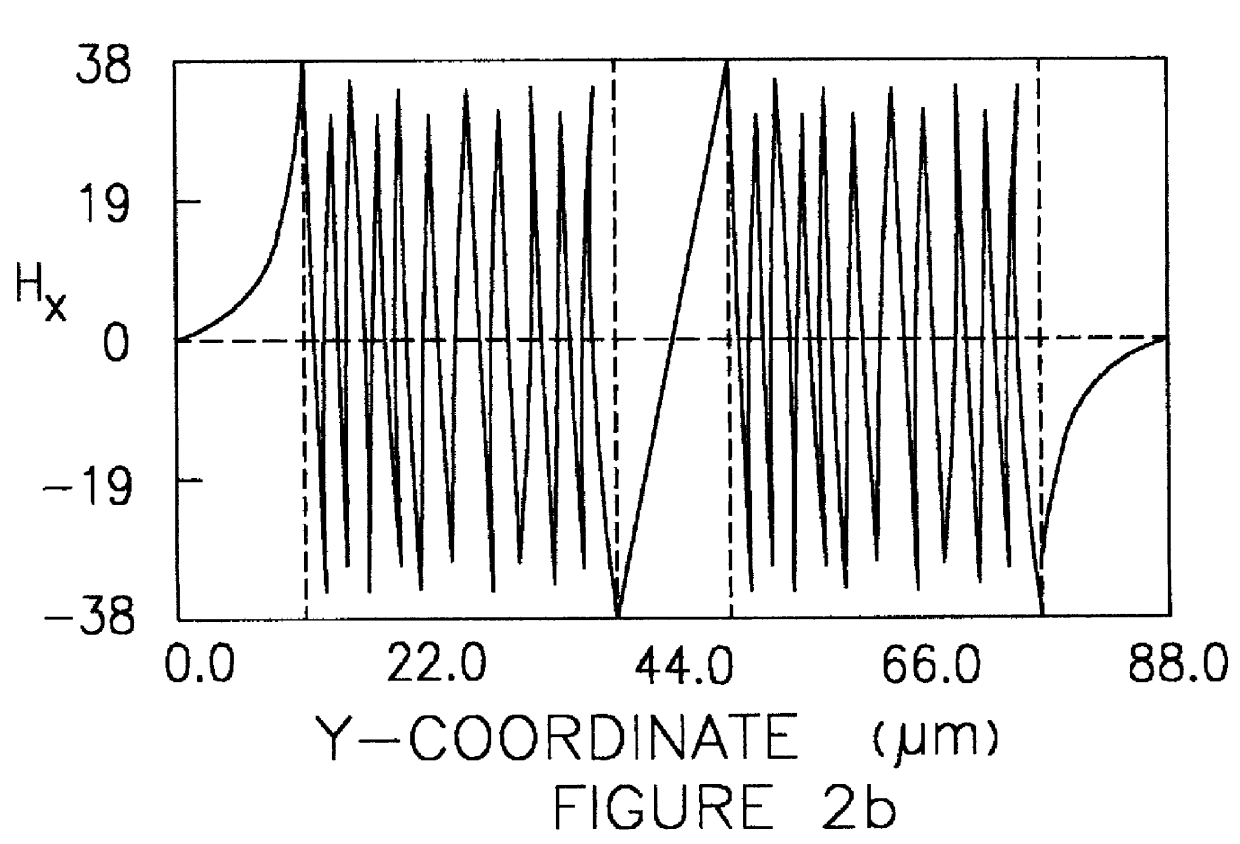
The invention describes a method of single-transverse-mode generation for waveguide lasers of various kinds having a large cross section of their active core and thus providing a possibility of efficient pump of the active core region. This results in a laser beam with enhanced power and high spatial quality for high efficiency coupling to standard single-mode optical fiber networks. It is found that a multimode waveguide having a central dip of special shape in the refractive index profile of its core is able to guide a higher order mode with sharp central peak of its field carrying the considerable part on the mode energy and whose width is well compatible with the width of the fundamental mode of standard single-mode fibers. The useful properties of this higher order mode can be employed to provide the single-transverse-mode regime of generation in optical fiber lasers, integrated optical micro-lasers and various semiconductor laser sources.
Owner:CERAMOPTEC IND INC
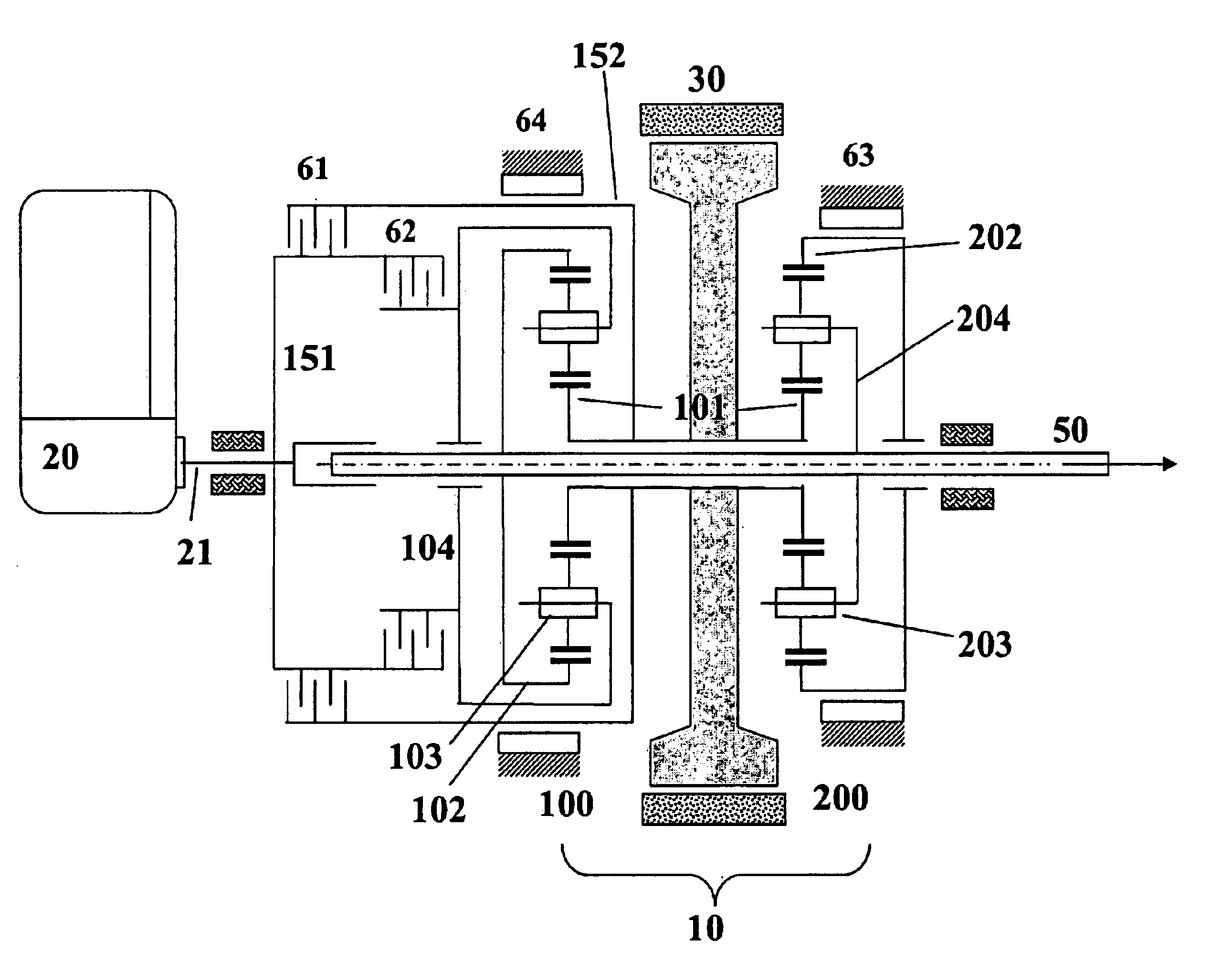
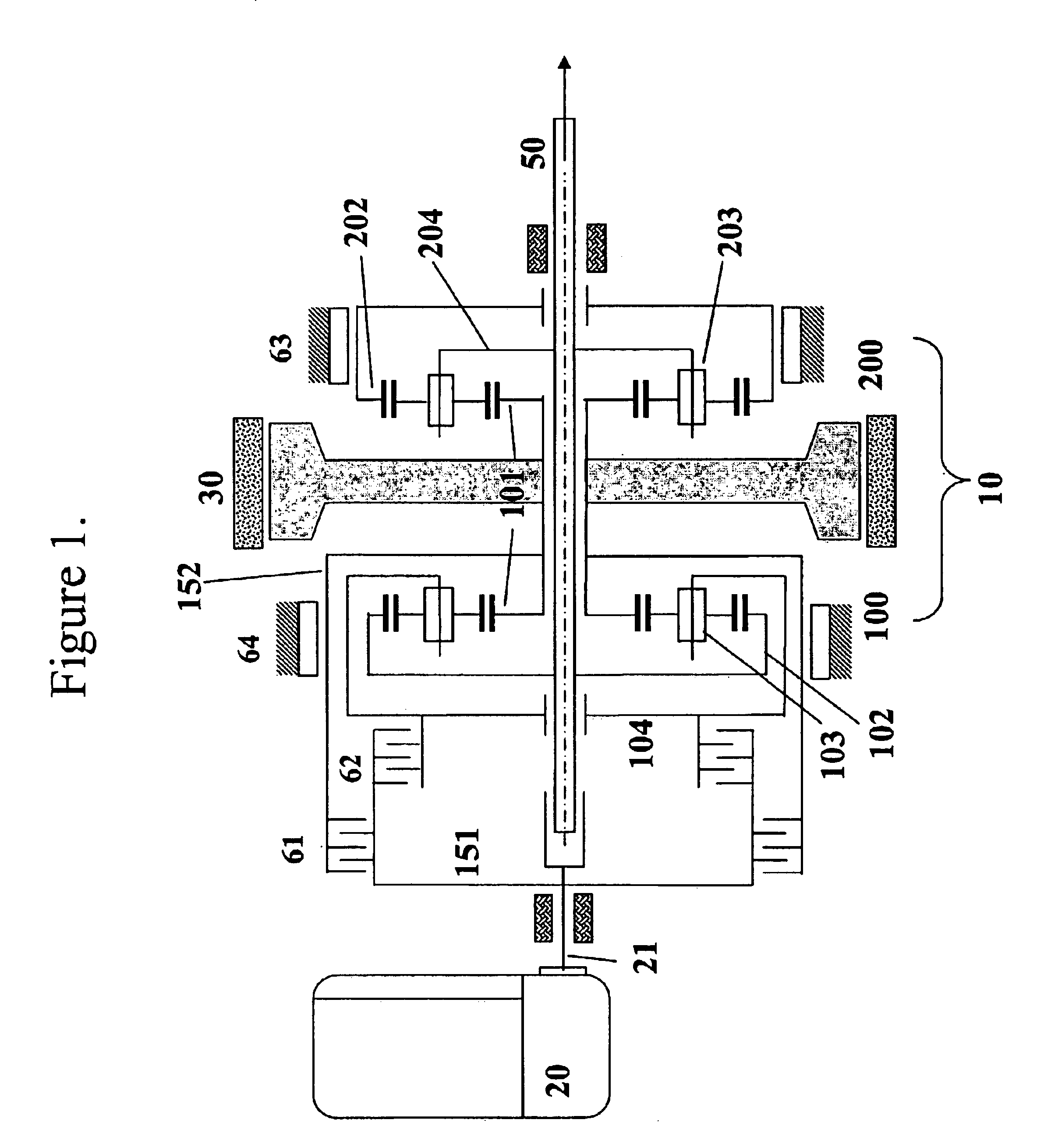
Motor integrated parallel hybrid transmission
InactiveUS6837816B2Improve versatilitySimplified and reliable transmission constructionToothed gearingsGas pressure propulsion mountingVariatorBasic mode
A motor-integrated transmission mechanism for use in parallel hybrid electric vehicles. The transmission can provide five basic modes of operation that can be further classified into sixteen sub-modes: one electric motor mode, four engine modes, four engine / charge modes, three power modes and four regenerative braking modes. Each of these sub-modes can be grouped into like clutching conditions, providing the functional appearance of a conventional 4-speed automatic transmission, with electric launch, engine-only, engine / charge, power-assist, and regeneration capability. CVT capability is provided with one of the engine / charge modes. The transmission can be incorporated in front-wheel drive and in rear-wheel drive vehicles.
Owner:TSAI LUNG WEN +1
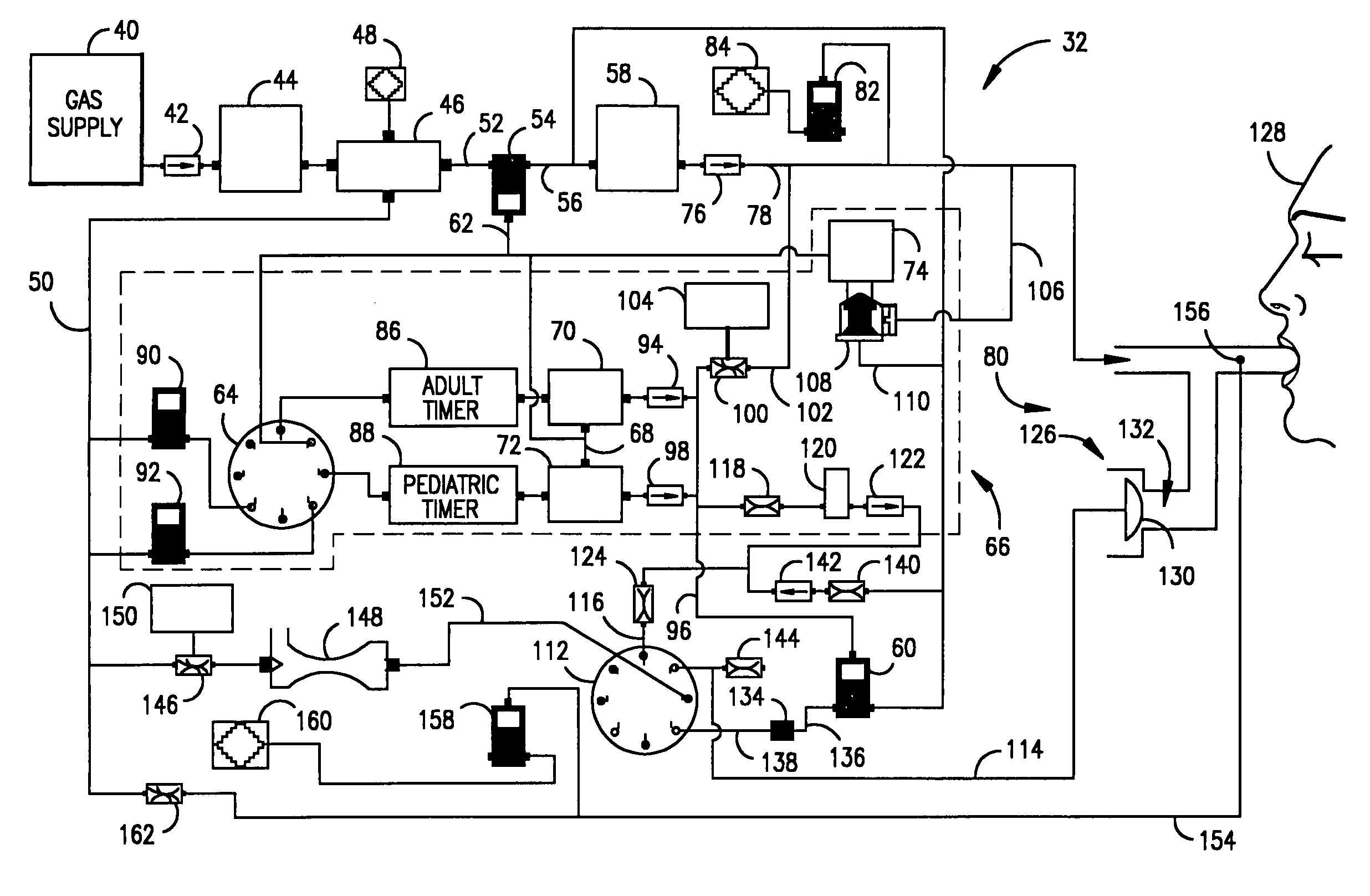
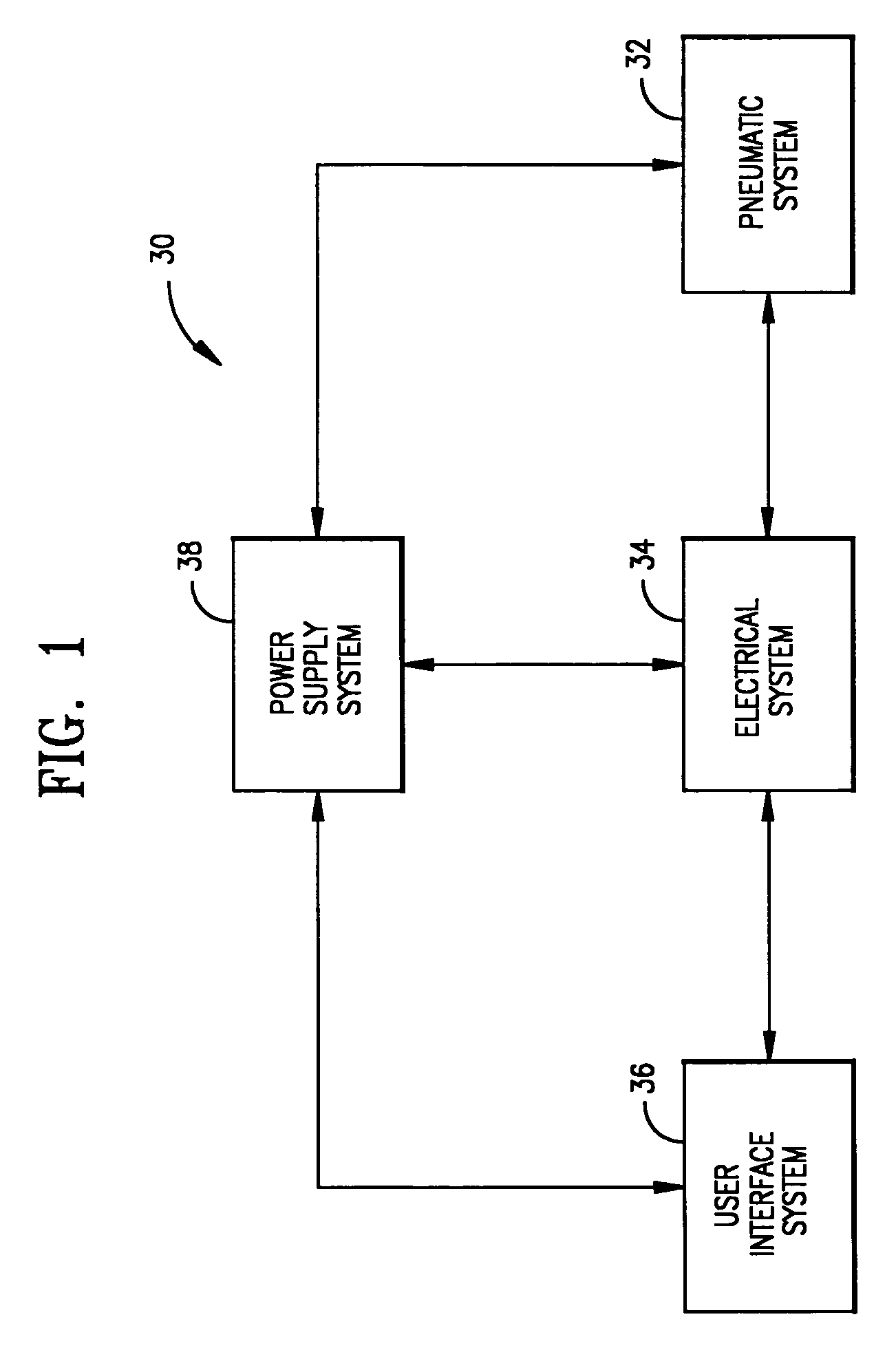
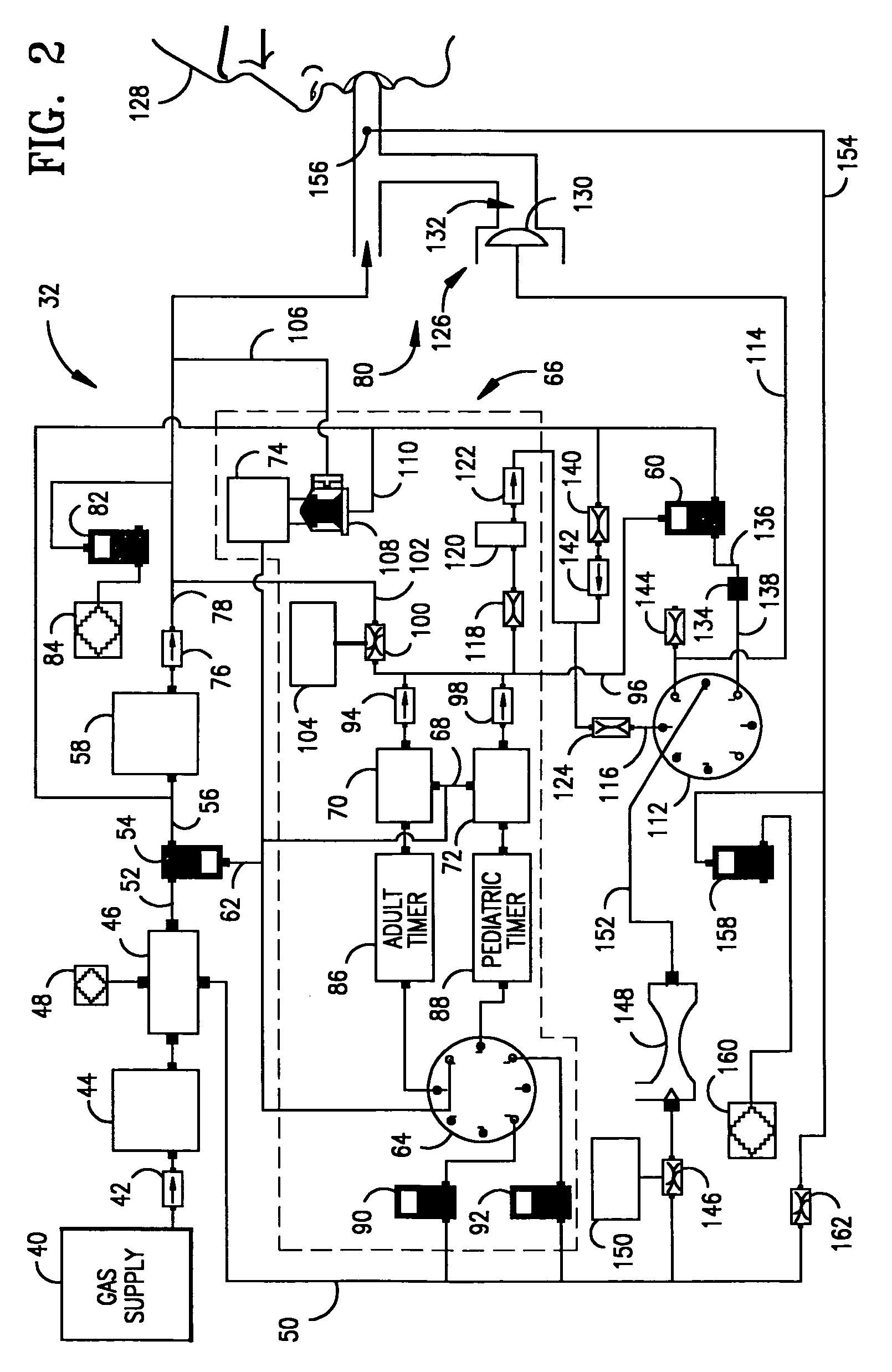
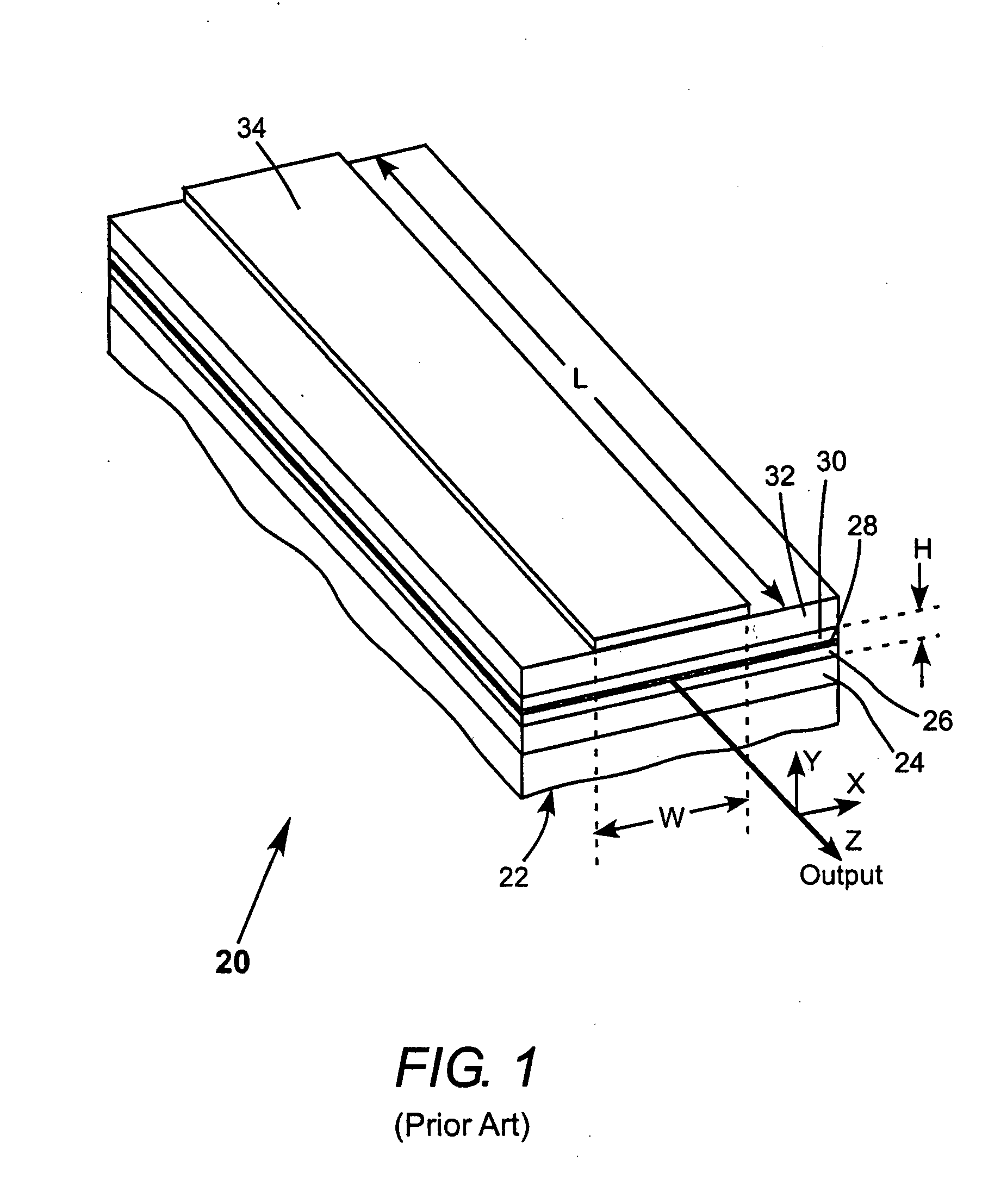
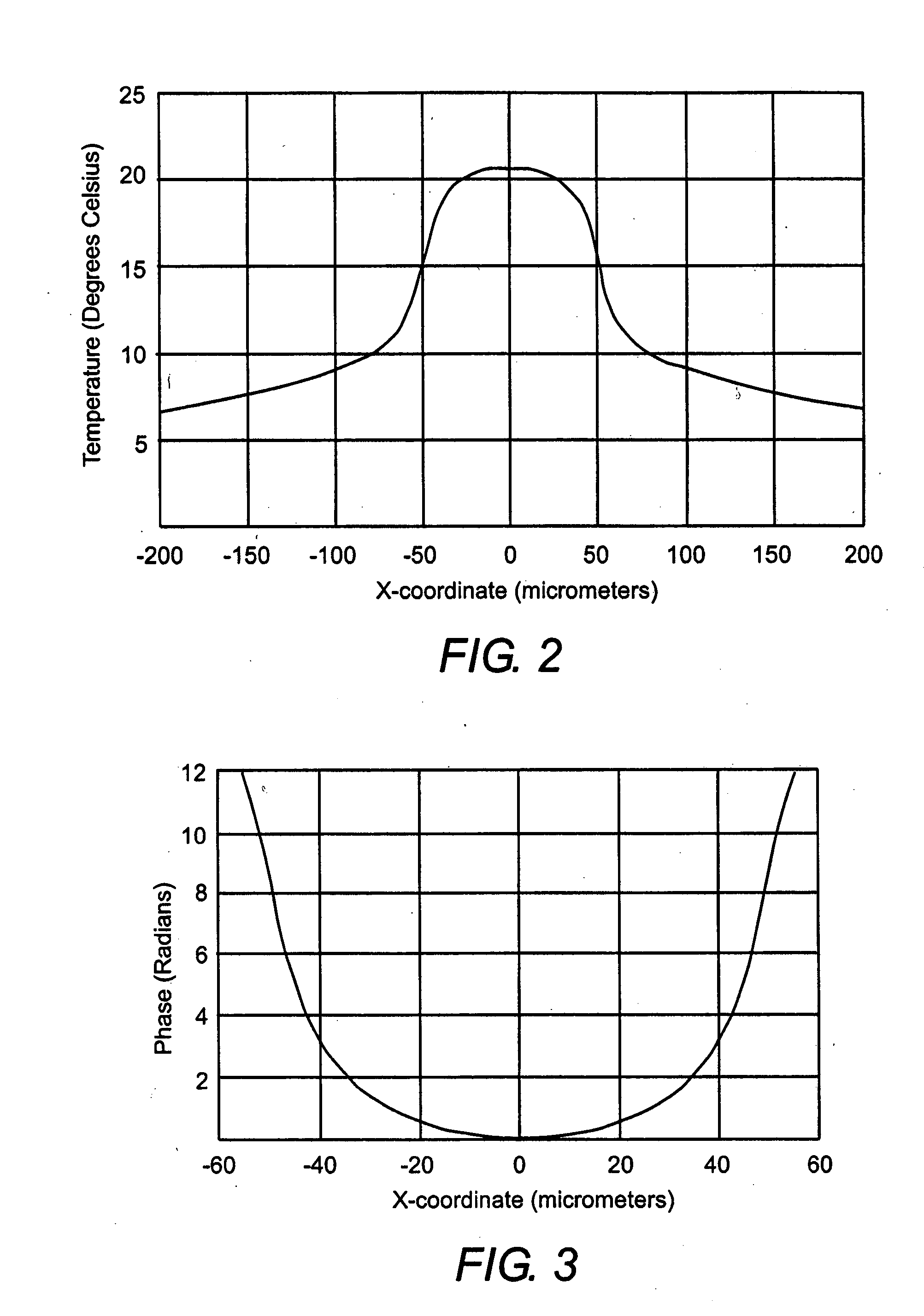
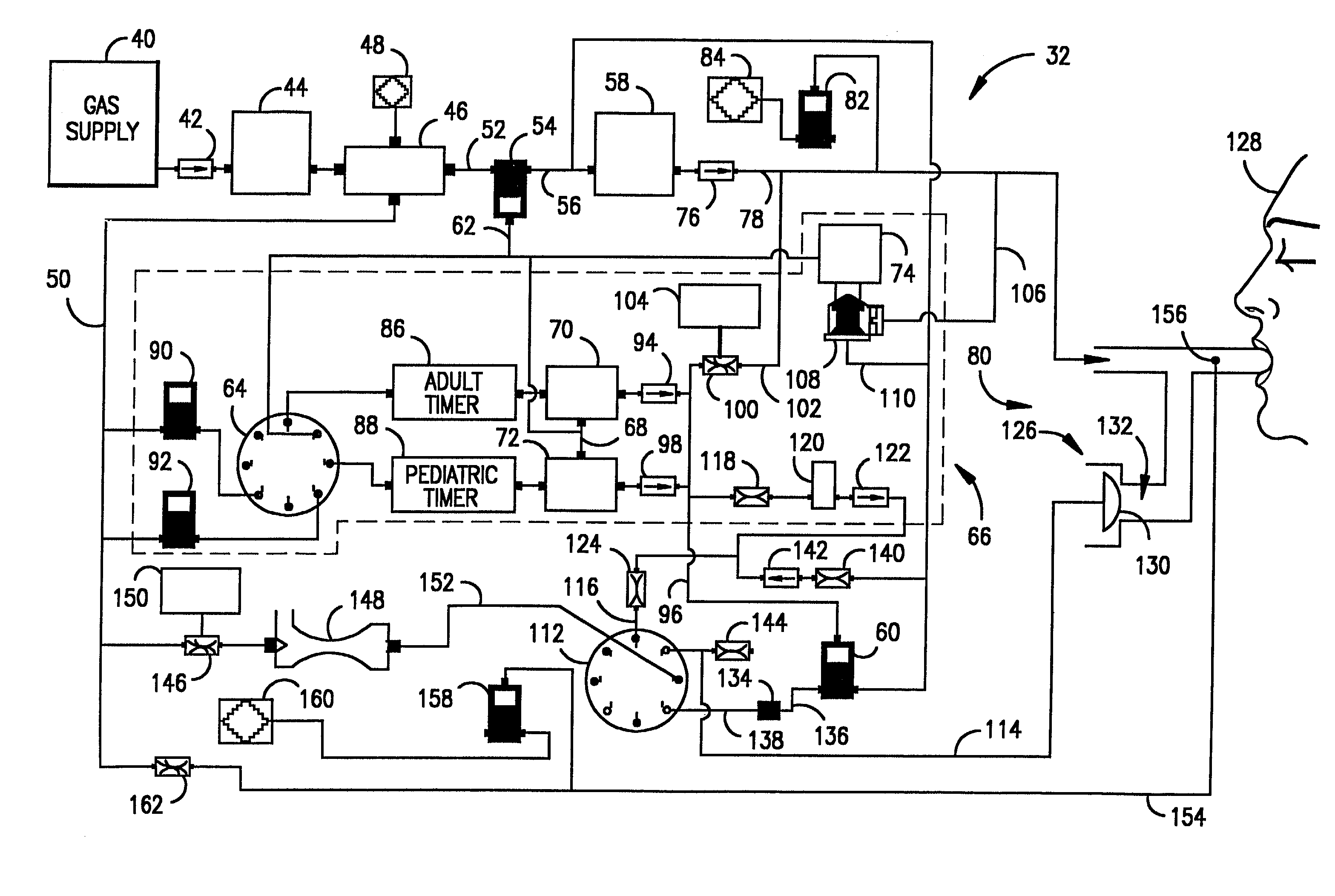
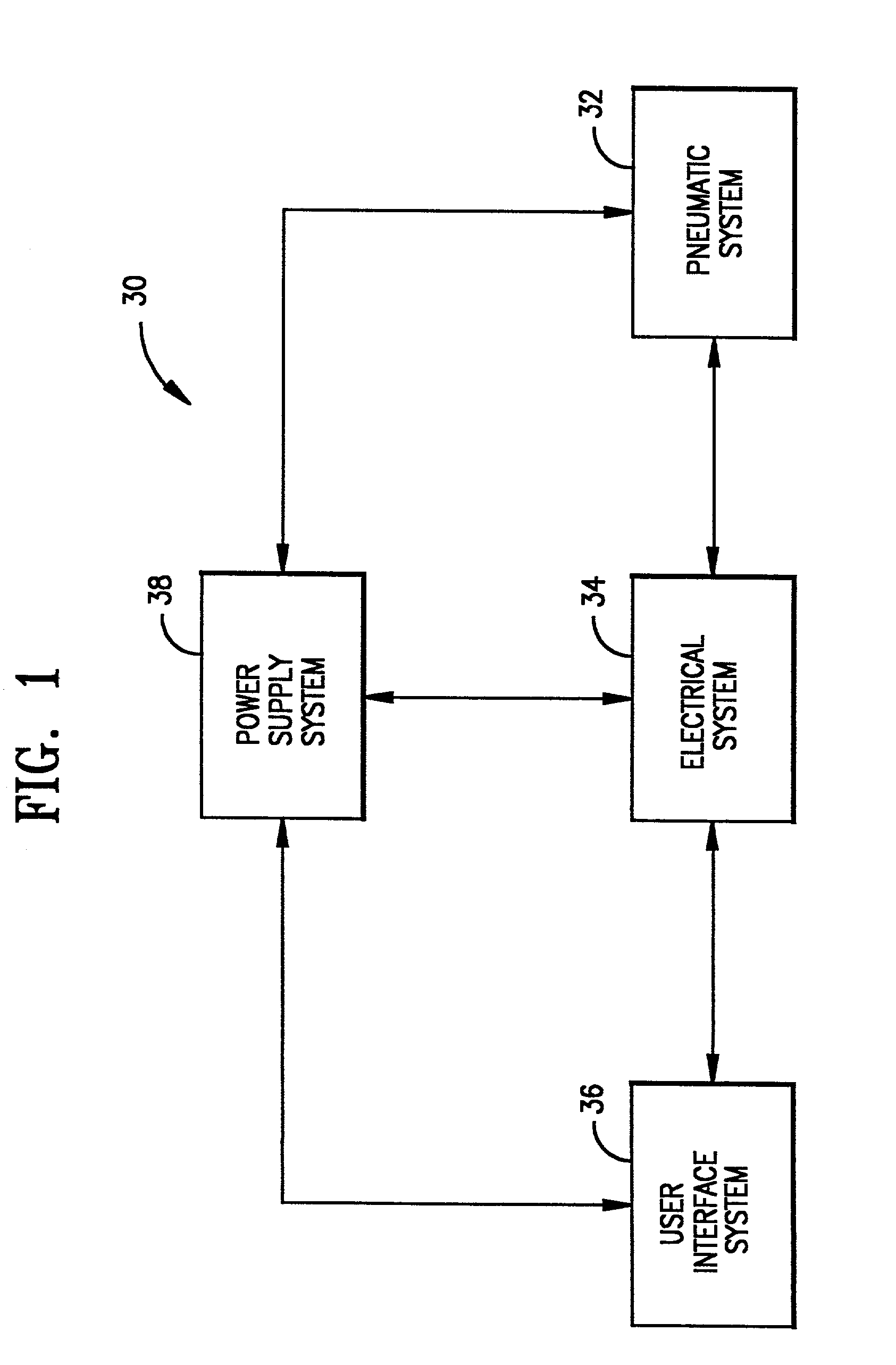
Ventilatory method utilizing body length-based parameter calculations
InactiveUS6976487B1Work lessAvoid dangerRespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesEngineeringBasic mode
A method and apparatus for operating a ventilator in a primary electronic mode or in a back-up pneumatic mode during primary electronic mode failure. A method and apparatus for operating a ventilator in an advanced mode, having a number of ventilatory modes, or in a basic mode, having a limited number of ventilatory modes is also disclosed.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
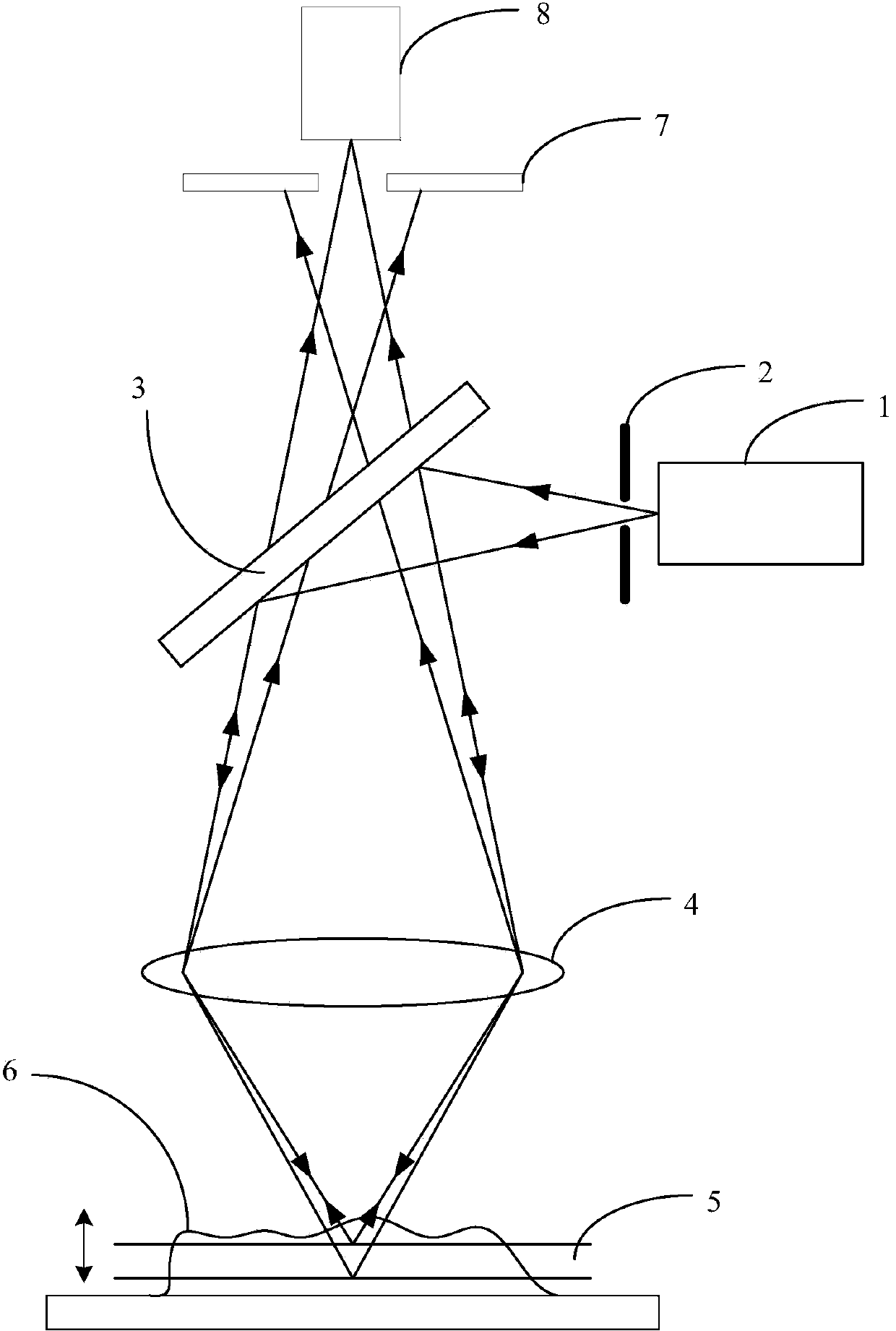
Super-resolution confocal microimaging method and device based on column polarization vortex beam
The invention provides a super-resolution confocal microimaging device based on a column polarization vortex beam. The super-resolution confocal microimaging device comprises a pinhole filter, a collimating lens, a polarization and phase transformation system, a pupil filter, an optical filter, a detector and a three-dimensional translational platform, wherein a beam emitted from a laser passes the pinhole filter to obtain a Gauss basic mode beam, the collimating lens collimates the Gauss basic mode beam into the parallel beam, the polarization and phase transformation system allows the parallel beam to pass and obtain the column polarization vortex beam with preset polarization and phase distribution, the pupil filter allows the column polarization vortex beam to pass and to be reflected through a beam splitter and focused on a to-be-detected sample through a collecting lens, light signals reflected from the sample pass the collecting lens and the beam splitter to be incident on the optical filter, and the optical filter only allows a fluorescence signal of the light signals to be transmitted, the fluorescence signal is focused on a detecting pinhole through the collecting lens and is detected and converted, through the detector, into an electrical signal to be output, the sample is placed on the three-dimensional translational platform, detection of the sample at different positions can be realized by moving the three-dimensional translational platform, and accordingly three-dimensional scanning imaging of the sample can be realized.
Owner:BEIJING INFORMATION SCI & TECH UNIV
Wide-stripe single-mode diode-laser
InactiveUS20050041709A1Laser optical resonator constructionSemiconductor laser arrangementsQuantum wellBroadband
A wide-stripe diode-laser includes a lower cladding region, a lower waveguide region, an active region, an upper waveguide region, and an upper cladding region all comprising semiconductor layers epitaxially grown on a semiconductor substrate. An elongated rectangular electrode on the upper cladding layer defines a stripe or pumped section. Adjacent the electrode is an unpumped section in which at least the quantum-well layer has been treated to cause the active region to be disordered. In this unpumped section, at least one area of the area is etched to a depth equal to or less than the thickness of the cladding region. The etched area provides a diverging lens effect in the waveguide region. The diverging lens effect expands the fundamental mode of the laser in the stripe to a width sufficient to improve single mode performance.
Owner:COHERENT INC
Hybrid microprocessor controlled ventilator unit
InactiveUS7156095B2Restricting trainingReduce stepsRespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesEngineeringBasic mode
A method and apparatus for operating a ventilator in a primary electronic mode or in a back-up pneumatic mode during primary electronic mode failure. A method and apparatus for operating a ventilator in an advanced mode, having a number of ventilatory modes, or in a basic mode, having a limited number of ventilatory modes is also disclosed.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
Efficient nonlinear optical waveguide using single-mode, high v-number structure
InactiveUS20070297732A1Increase the number ofIntuitive presentationOptical light guidesNon-linear opticsBasic modeWaveguide
Owner:CARR & FERRELL
Systems and methods that schematize audio/video data
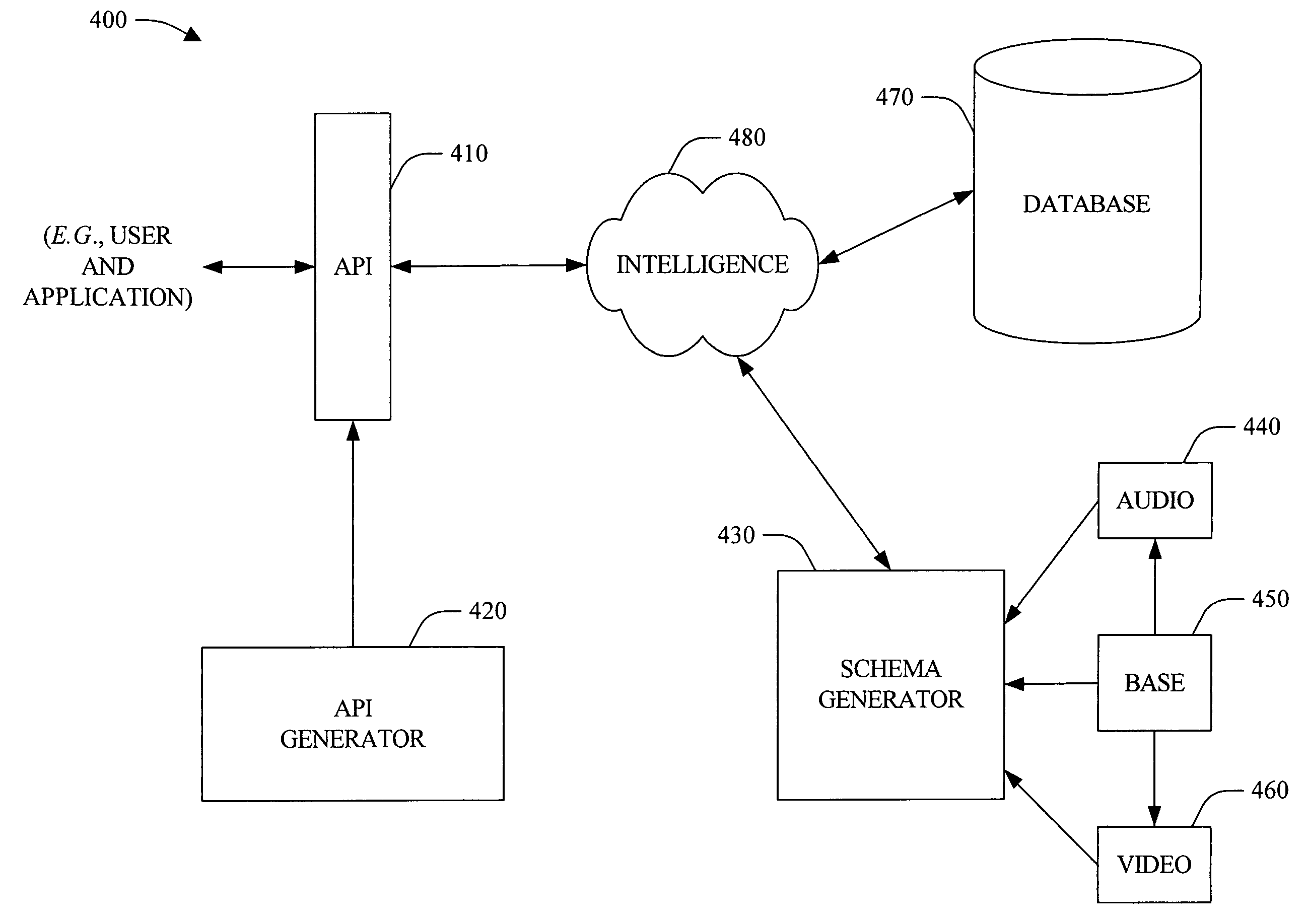
InactiveUS20050091271A1Efficient developmentConsume resourcesData processing applicationsMetadata multimedia retrievalModelicaOperational system
The present invention provides a novel file management approach. The systems and methods comprise a schema-based file management technique that can be integrated within an operating system to provide application developers an efficient and powerful develop utility to build applications. In addition, the system and methods provide for applications that can be employed uniformly across disparate data (e.g., audio and video data) within the operating environment. The schema can include a base schema that is related to known types of data and derived schema that extend the base schema with respect to one or more characteristics of the data. The schema can be employed to generate APIs that can be employed by users and / or applications to exchange information with a file system. In addition, the systems and methods can include configurable intelligence that can be utilized perform actions and / or make decisions, which can automate processes and / or facilitate data storage and / or management.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Bragg refractive waveguide edge transmitting semiconductor laser with low horizontal divergence angle
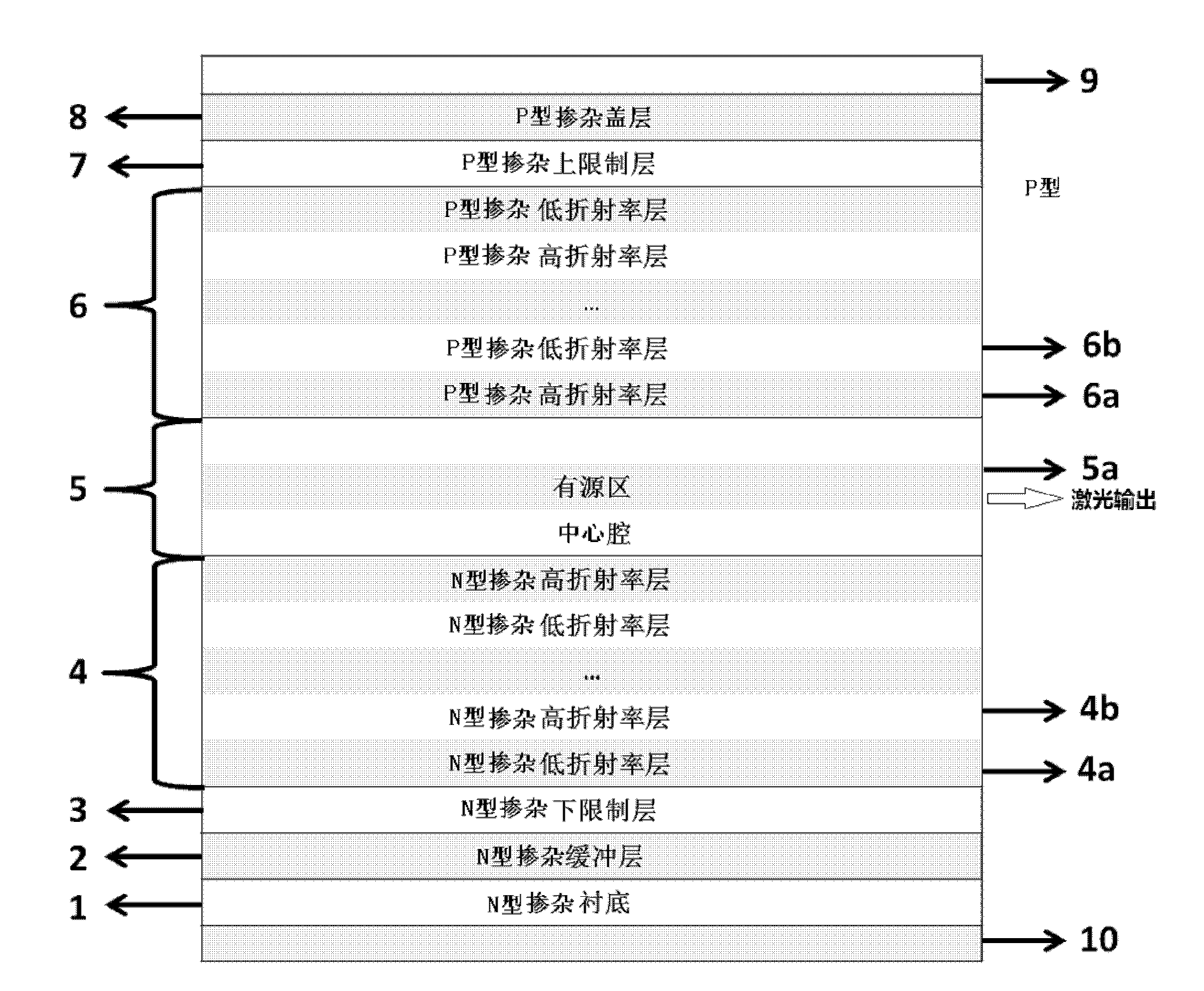
ActiveCN102324696AReduce complexityImprove coupling efficiencyOptical wave guidanceFull waveRefractive index
The invention relates to a Bragg refractive waveguide edge transmitting semiconductor laser with a low horizontal divergence angle, wherein the P electrode of the laser is placed on the top face of a cover layer and is electrically connected onto the cover layer; the N electrode is positioned on the back face of a substrate and is electrically connected to the substrate; a center cavity is positioned between an upper waveguide layer and a lower waveguide layer; an active area is inserted in the center cavity; a Bragg refractive waveguide formed by periodically distributing a plurality of layers of N-doped materials with a high refractive index and a low refractive index is adopted in the lower waveguide layer on; and a Bragg refractive waveguide formed by periodically distributing a plurality of layers of P-doped materials with a high refractive index and a low refractive index is adopted in the upper waveguide layer. The Bragg refractive waveguide edge transmitting semiconductor laser with the low horizontal divergence angle has the advantages that: effects such as catastrophic damage, hole burning, electric heat overburning, beam filamentization and the like on the end face of the traditional edge transmitting semiconductor laser can be effectively improved, and the laser can realize the large mode-volume and stable single-transverse-mode work because of the great gain loss difference between a basic mode and a high-order mode, the full wave at half maximum (FWHM) of the transverse far-field divergence angle of the laser can reach below 10 DEG.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
High non-linear single polarization single-mould photonic crystal fiber
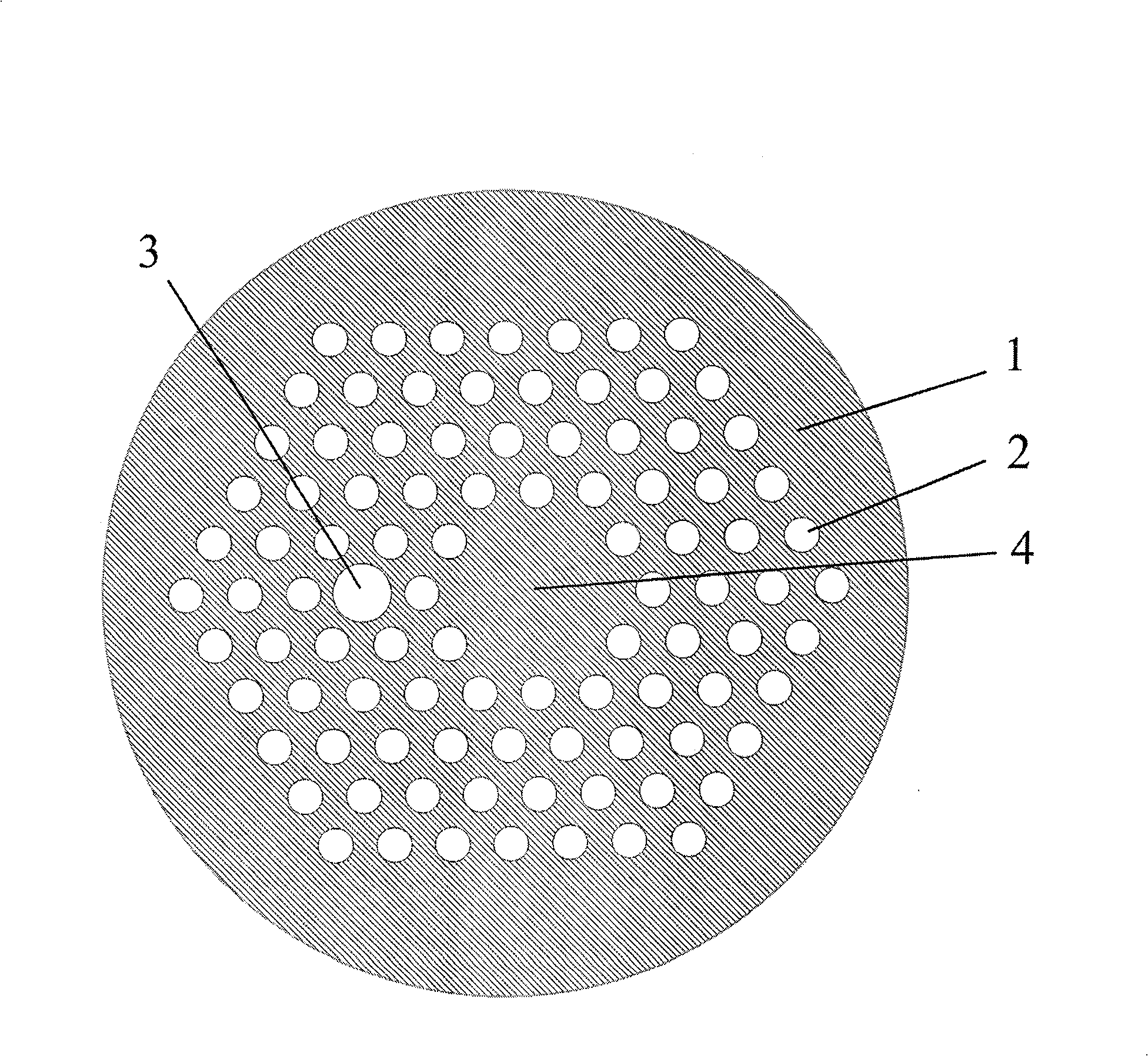
InactiveCN101414026AAdd nonlinearitySmall mode areaCladded optical fibreOptical waveguide light guideFilling rateBasic mode
The invention discloses a single-polarization single-mode photonic crystal fiber with high nonlinearity. The cross section of the photonic crystal fiber comprises a fiber core and a cladding. The-cladding is a peripheral region which is the same as the normal photonic crystal fiber and is formed by evenly distributed air holes (2) with the same structure. The fiber core is composed of a substrate material (1) which is arranged on the center of the optical fiber end face as well as four high-ellipticity air holes (3) which are closely arranged, not mutually overlapped and in rectangular distribution. In the photonic crystal fiber, a cut off characteristic of two polarization modes of a basic mode can be adjusted by finely adjusting distance between centers of air holes, which causes one of the polarization modes to be cut off in the applied waveband, thus realizing the wide-bandwidth single polarization transmission. Meanwhile, the air holes (3) suppress the generation of high order mode, which allows the cladding to use a higher air filling rate on the premise of not changing the single-mode transmission characteristic of the optical fiber, therefore the mode area and the confinement loss are reduced. The single-polarization single-mode photonic crystal fiber with the high nonlinearity solves the problem that the high nonlinearity, low confinement loss and wide band single-polarization single-mode characteristic can not be realized at the same time in the existing photonic crystal fiber technology.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
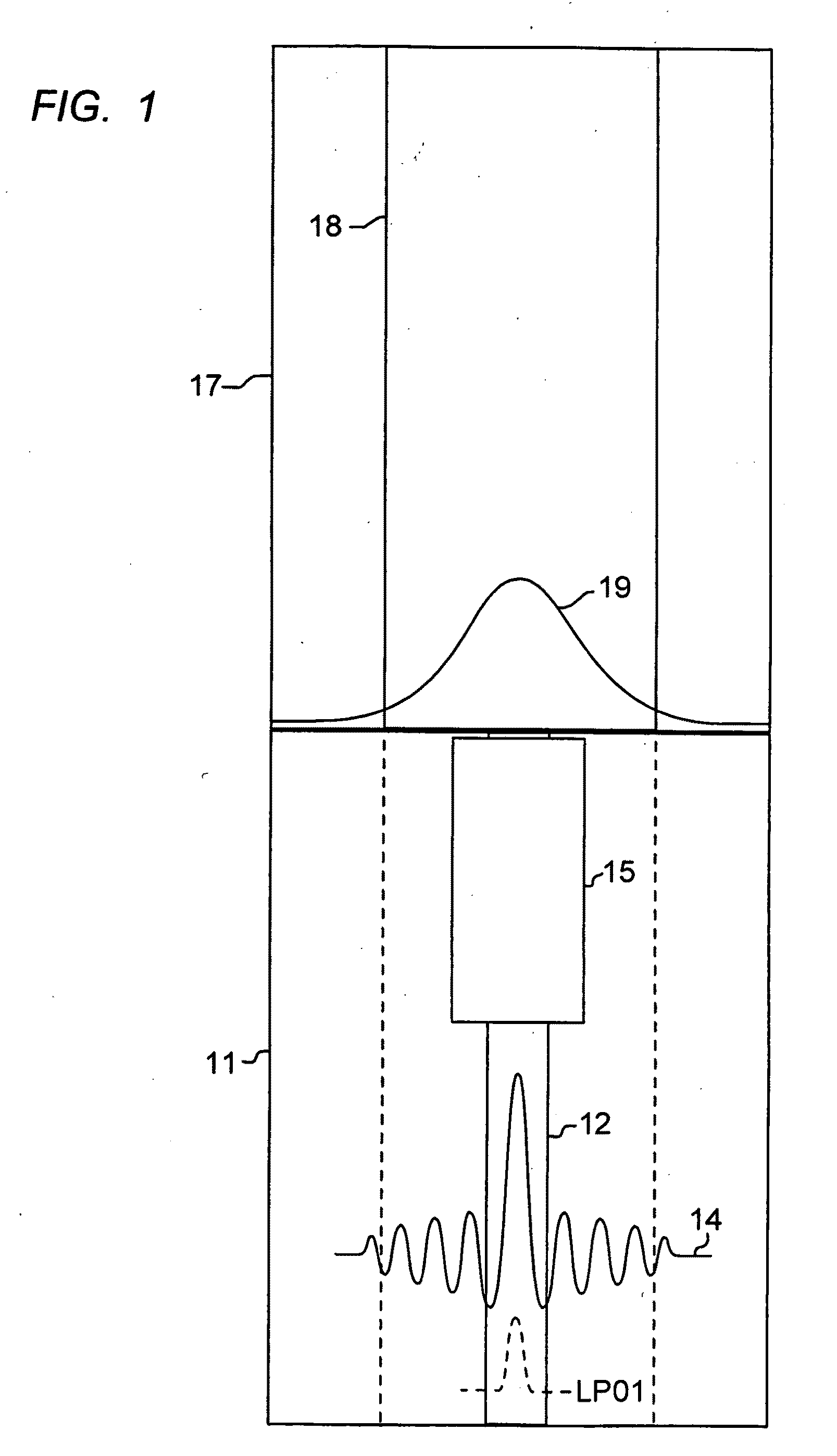
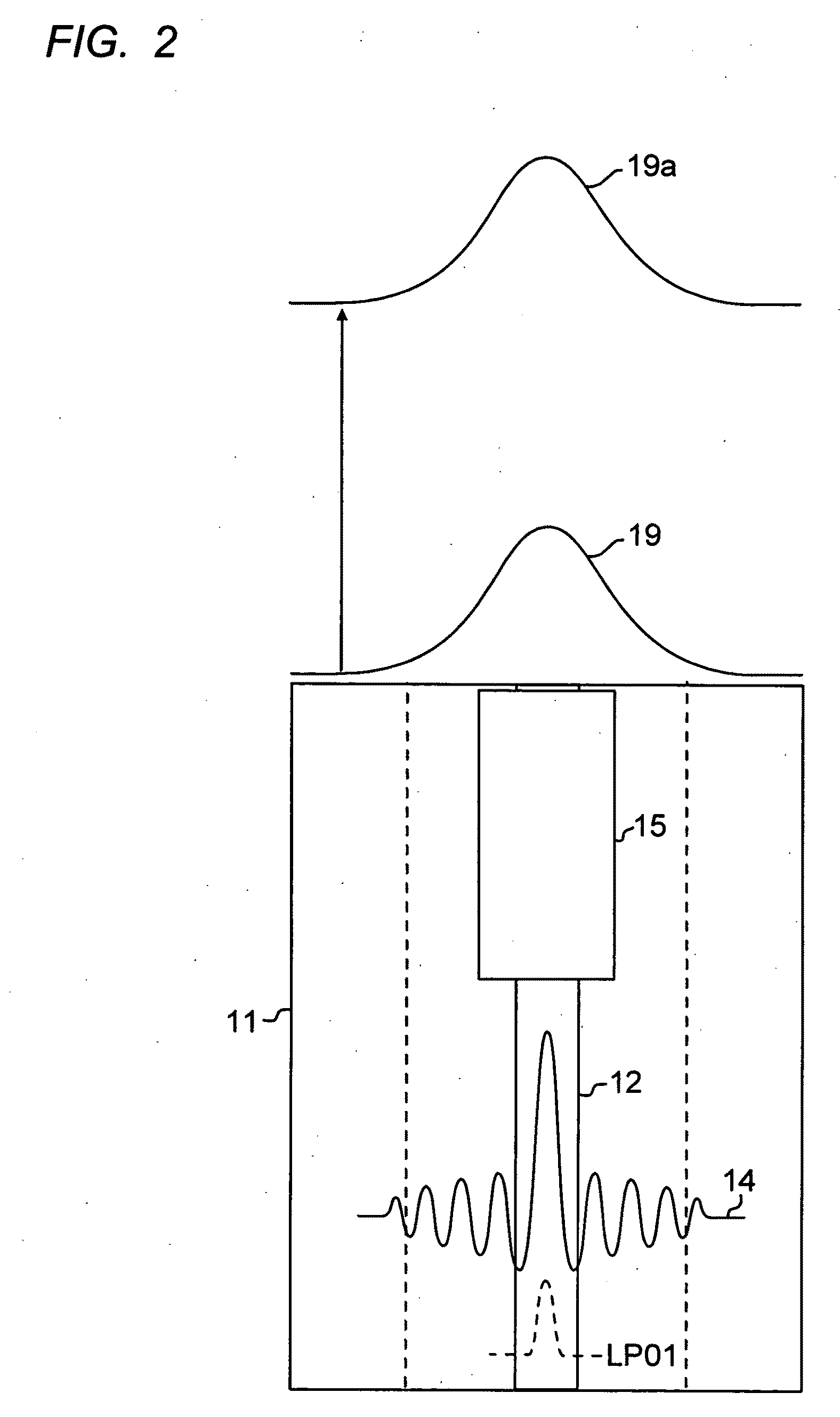
Optical fiber mode couplers
Described are optical devices and related methods wherein a multiple mode input in a Higher Order Mode (an HOM) optical fiber is converted by a complex mode transformer to produce a fundamental mode output in an optical medium with an E-field that is substantially different than that exiting the HOM optical fiber. The medium is preferably a Large Mode Area (LMA) optical fiber, or free space. The mode transformer may be a series of refractive index perturbations created either by photo-induced gratings or by gratings formed by physical deformations of the optical fiber.
Owner:OFS FITEL LLC
Face-shaped element configuring method in computer graphics
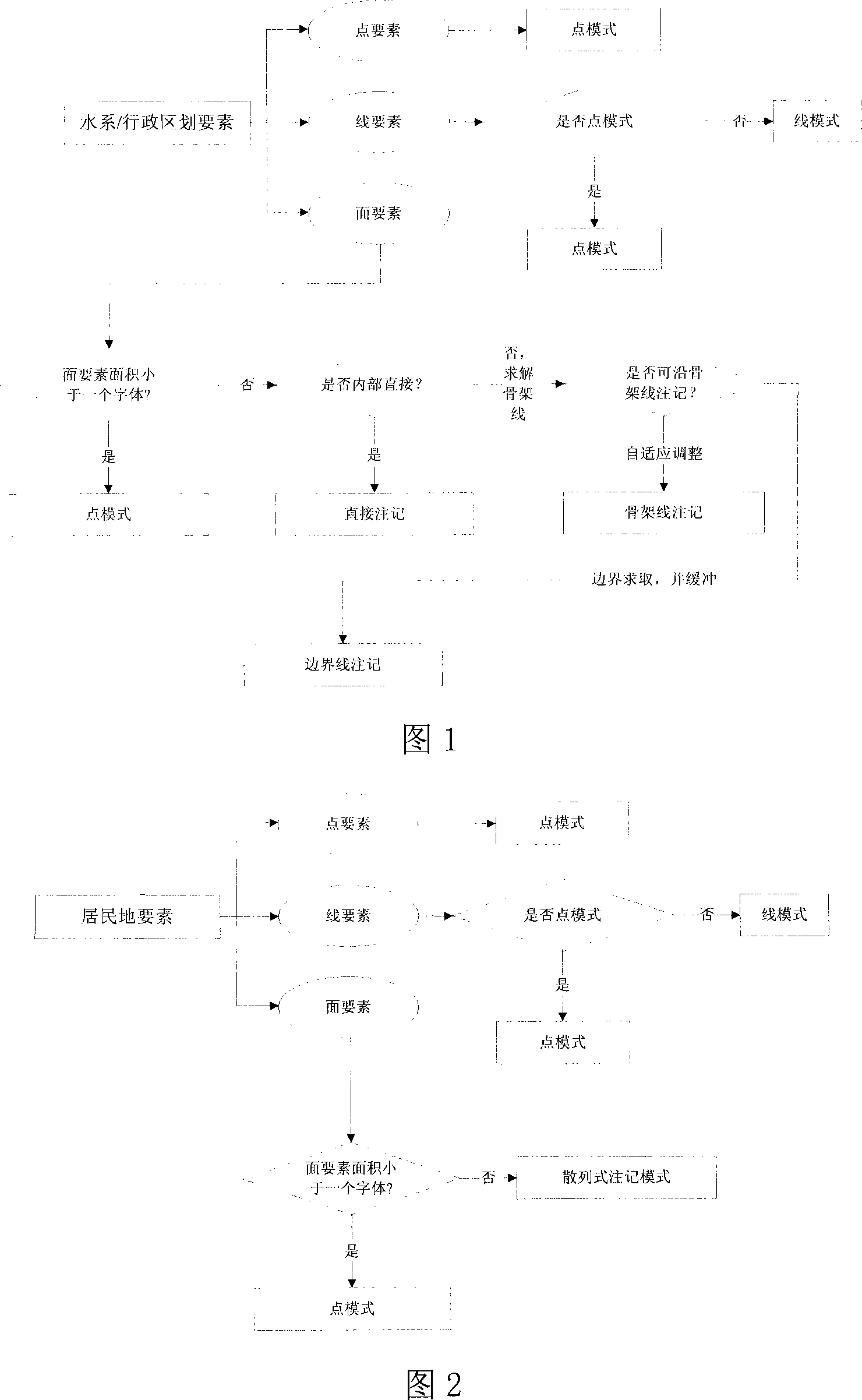
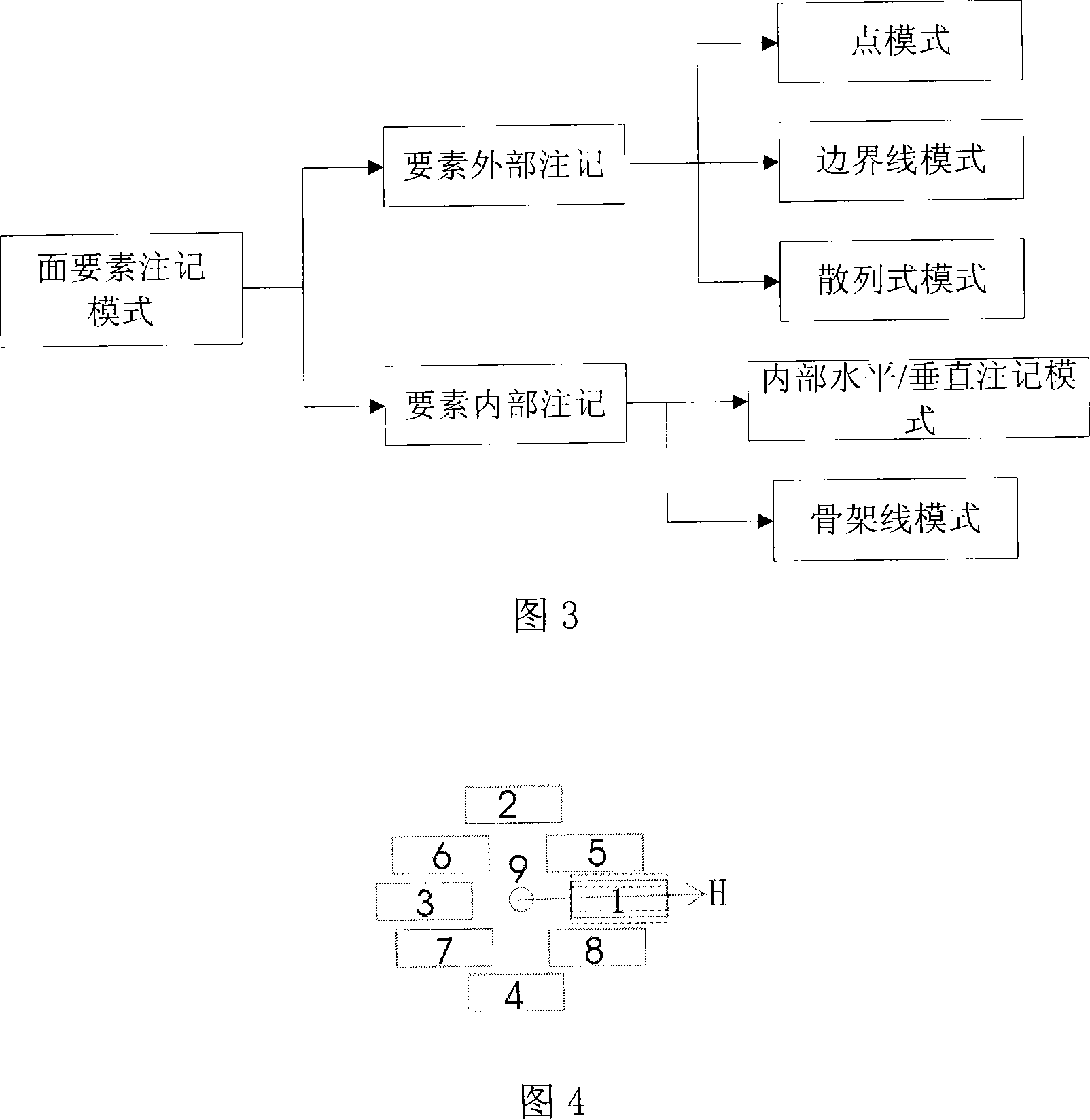
InactiveCN101183461AImprove the efficiency of automatic annotationSolve the problem of intelligent configurationMaps/plans/chartsSpecial data processing applicationsComputerized systemTopographic map
The invention relates to a configuration method for area pattern in computer drawing, belonging to the technical field of computer drawing, which comprises the following steps: step one, importing the geography data into the computer and then judging the pattern type waiting for noting in the geography data; step two, deciding the noting mode type of the noting pattern according to the pattern type; step three, configuring the pattern waiting for noting according to the configuration rule of the noting mode type. The invention divides the noting configuration of the area pattern into five basic modes according to the substantive characteristics and the configuration rules of the patterns of the water system and settlement place, provides the automatic configuration arithmetic of noting of different modes according to the geometrical characteristics of the modes, and resolves the problems of collision or shelter of the different noting modes in topographic maps with full elements. The invention has the advantages of improved efficiency of automatically noting the area pattern and enhanced noting quality of the map.
Owner:常熟紫金知识产权服务有限公司
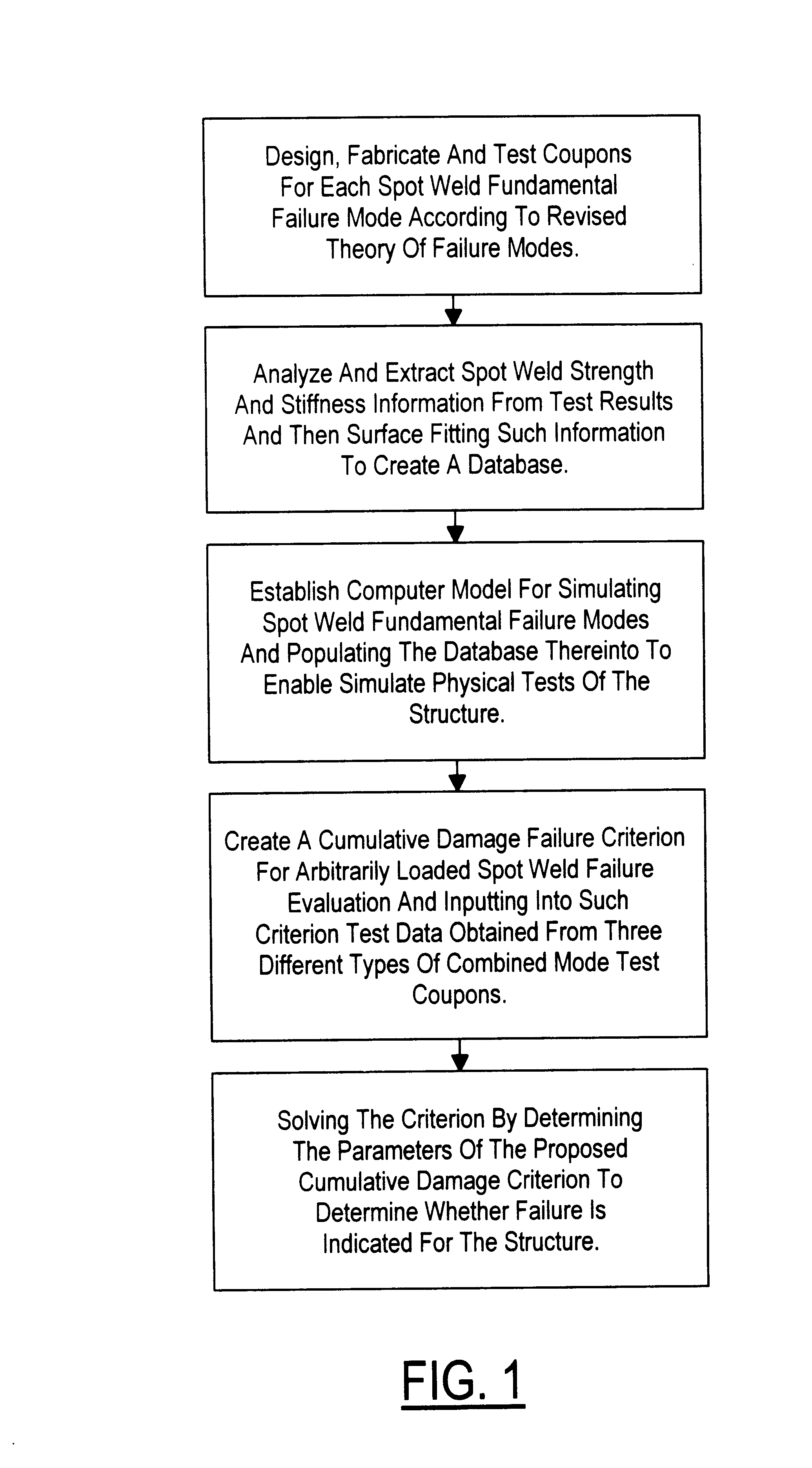
Method of analyzing spot welded structures
InactiveUS6186011B1Improve accuracyMaterial strength using steady bending forcesResistance welding apparatusIn planeMathematical model
Method of analyzing spot welded sheet metal structures subjected to forces that promote one or more basic failure modes of either shear tension, in-plane rotation, coach peel, normal tension, or any combination of such basic modes, the method comprising: (i) providing spot welded sheet metal test coupons for analysis of the selected failure mode for the structure to be analyzed and subjecting such test coupons to progressively increasing forces that eventually achieve failure in the selected failure mode to thereby generate measured load and displacement test data; (ii) analyzing the data from the basic modes to derive and extract spot weld strength and stiffness information and then surface fitting such extracted data to create a database; (iii) establishing a computer math model for simulating the spot weld failure modes of the structure and populating the database thereinto to enable simulated physical tests of the structure; (iv) creating a cumulative-damage failure criterion for the spot welded structure that ratios (a) the resultant strength information from the populated math model for selected combinations of load and selected combinations of time and structure thickness, and (b) the measured strength information derived for such combinations of load derived from the test data; and (v) solving the criterion to determine whether it indicates failure for the combination of resultant strength and other values selected.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Method and Apparatus for Providing Light Having a Selected Polarization With an Optical Fiber
ActiveUS20080095199A1Increases bend lossIncreased bend lossLaser using scattering effectsOptical fibre with polarisationRare earthLength wave
Optical apparatus (110, 500, 600, 800, 1000) for providing light having a selected linear polarization having a polarization ratio, the apparatus (110, 500, 600, 800, 1000) comprising a length of optical fiber (120, 504, 604, 804, 1001) comprising a rare earth for providing light having a first wavelength responsive to receiving pump light having a second wavelength that is different than said first wavelength, wherein if the length of optical fiber (120, 504, 604, 804, 1004) were placed in a first position between the length of fiber (120, 504, 604, 804, 1004) is substantially linearly oriented (20) the fiber (120, 504, 604, 804, 1004) could propagate at the first wavelength a fundamental mode and a plurality of higher order modes and the apparatus (110, 500, 600, 800, 1000) could provide light having a first polarization ratio for the selected linear polarization and an M2 parameter, and wherein the length of fiber (120, 504, 604, 804, 1004) is positioned in a second position that increases the bend loss of the fiber relative to the first position such that, responsive to the increased bend loss, the apparatus (110,500, 600, 800, 1000) can provide light having a reduced M2parameter as well as a second polarization ratio for the selected polarization that is increased relative to the first polarization ratio, the increase being at least 6 dB greater than the first polarization ratio, and wherein when the length of fiber (120, 504, 604, 804, 1004) is in the second position the apparatus (110, 500, 600, 800, 1000) can provide a slope efficiency that is at least 50% of the ratio of the second wavelength to the first wavelength.
Owner:NUFERN
Optical fibre mode converter
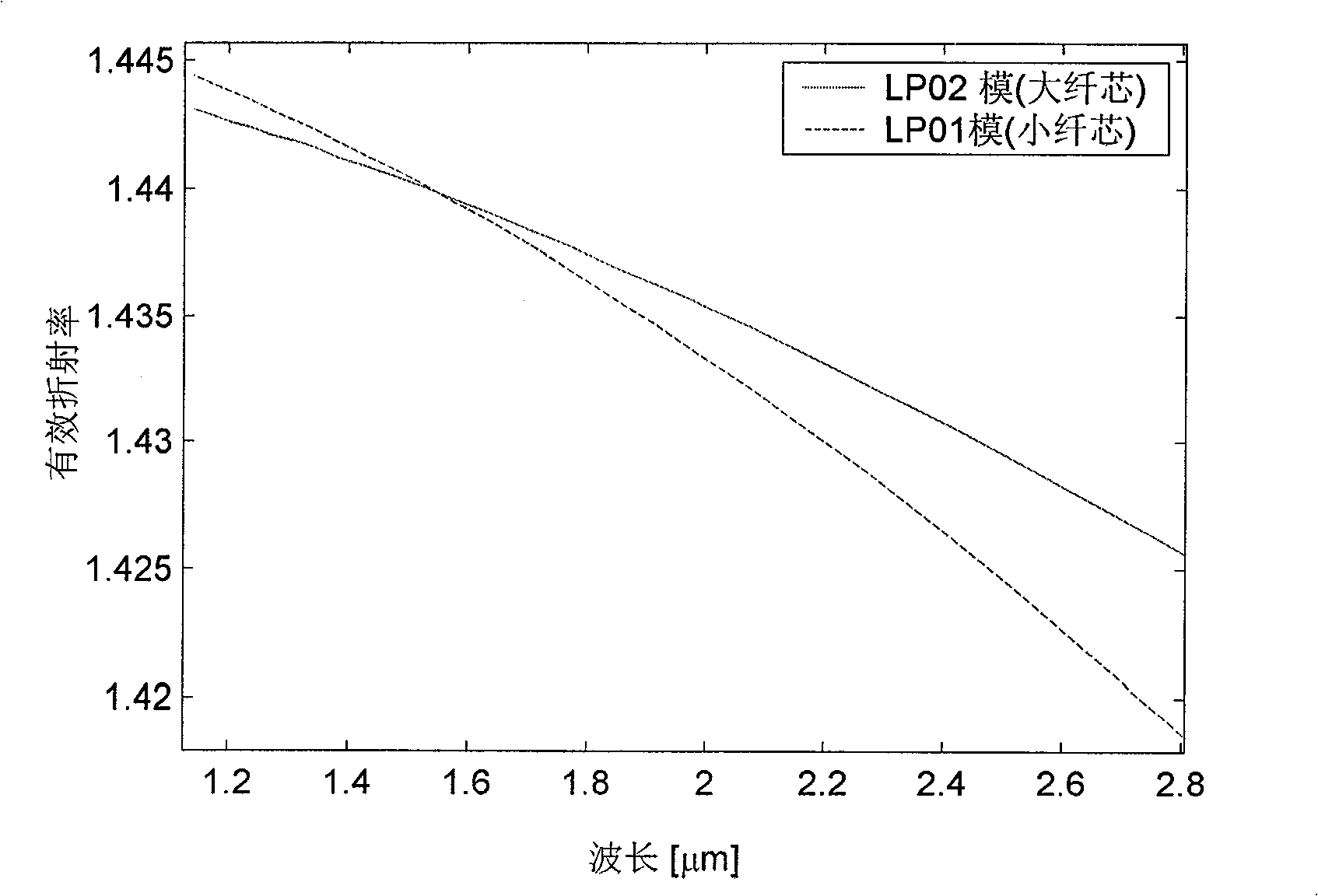
InactiveCN101339273AMode pureEase of mass productionCladded optical fibreOptical waveguide light guideManufacturing technologyGrating
The invention provides an optical fiber mode converter for realizing the conversion between modes, and the optical fiber mode converter is a twin-core photonic crystal fiber, comprising a matrix material and a cladding and fiber cores formed by air vents. The converter is characterized in that two fiber cores are of different sizes, wherein, the smaller fiber core is used for transmitting a basic mode, whereas the larger fiber core is used for transmitting a high-order mode; the effective refractive index of the basic mode of the smaller fiber core is equal to that of the corresponding high-order mode of the larger fiber core at an operating wavelength position. The optical fiber mode converter of the invention uses the energy coupling between the basic mode and the high-order mode of the two fiber cores to realize the conversion between the basic mode and the high-order mode, which ensures a purer conversion mode. Meanwhile, as a twin-core photonic crystal fiber structure is adopted, the converter has no particular requirements in manufacturing technology, and can be put into mass production easily, thus possessing better competitive strength when compared with a converter that adopts a fiber grating.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com