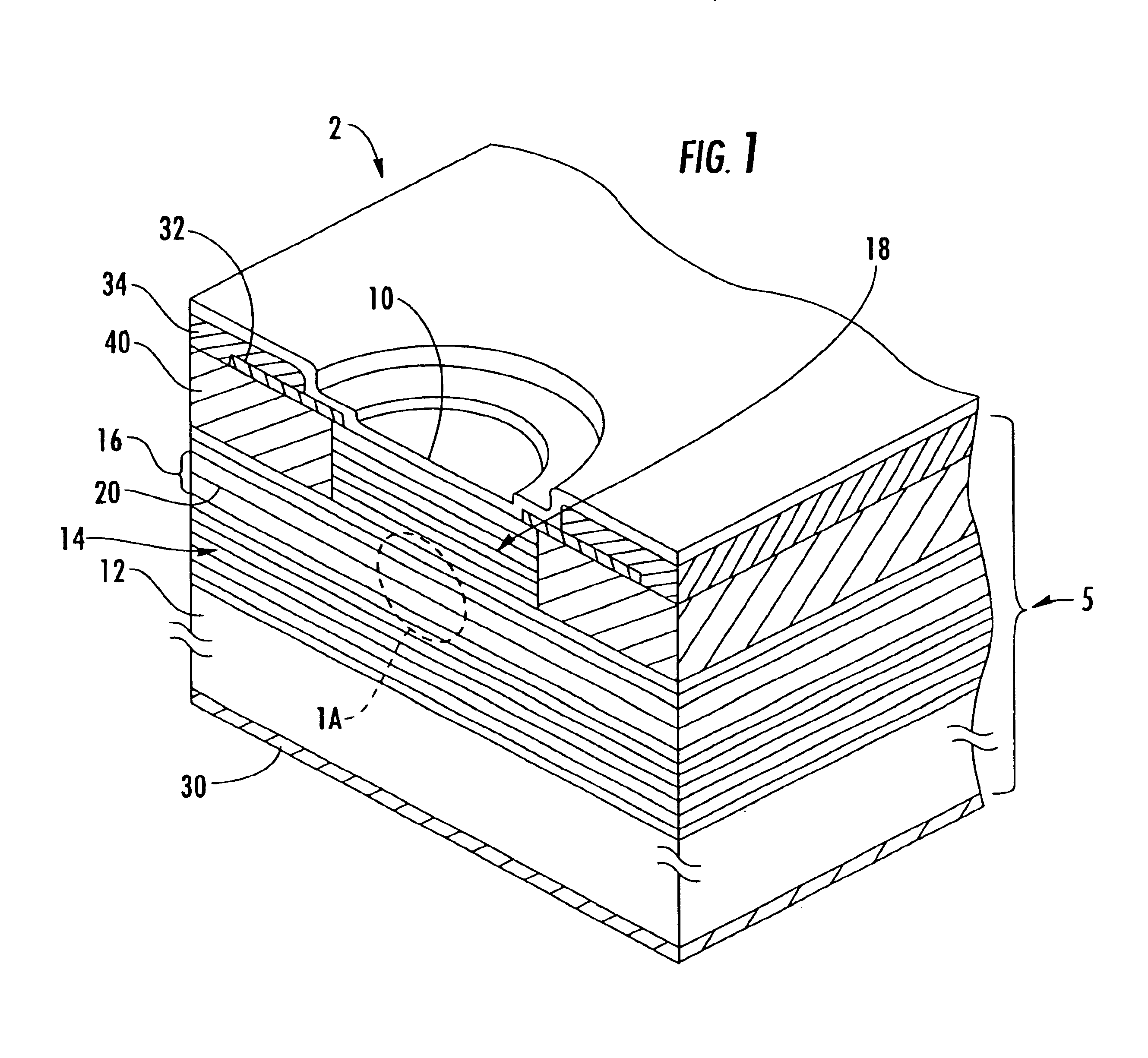
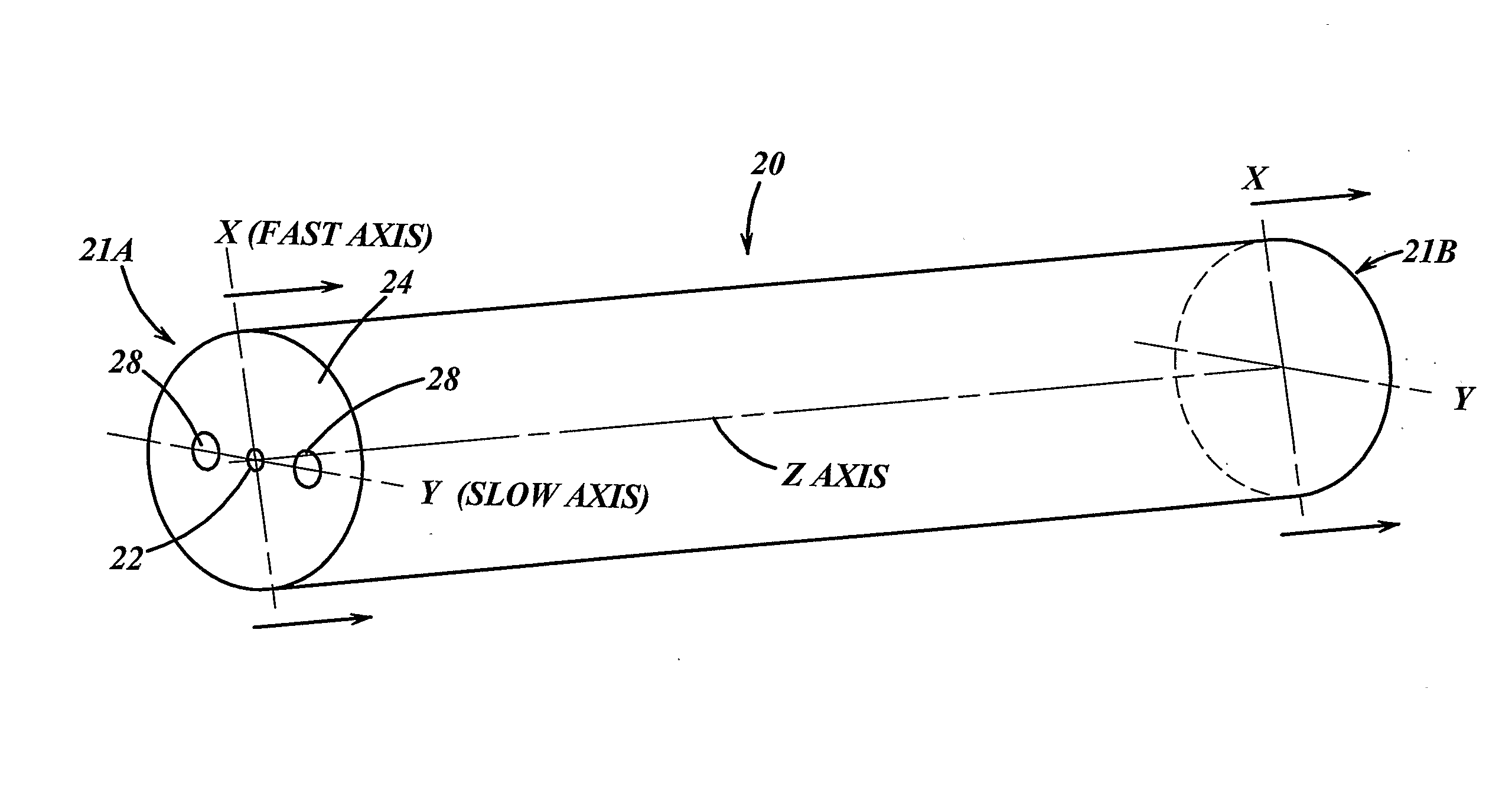
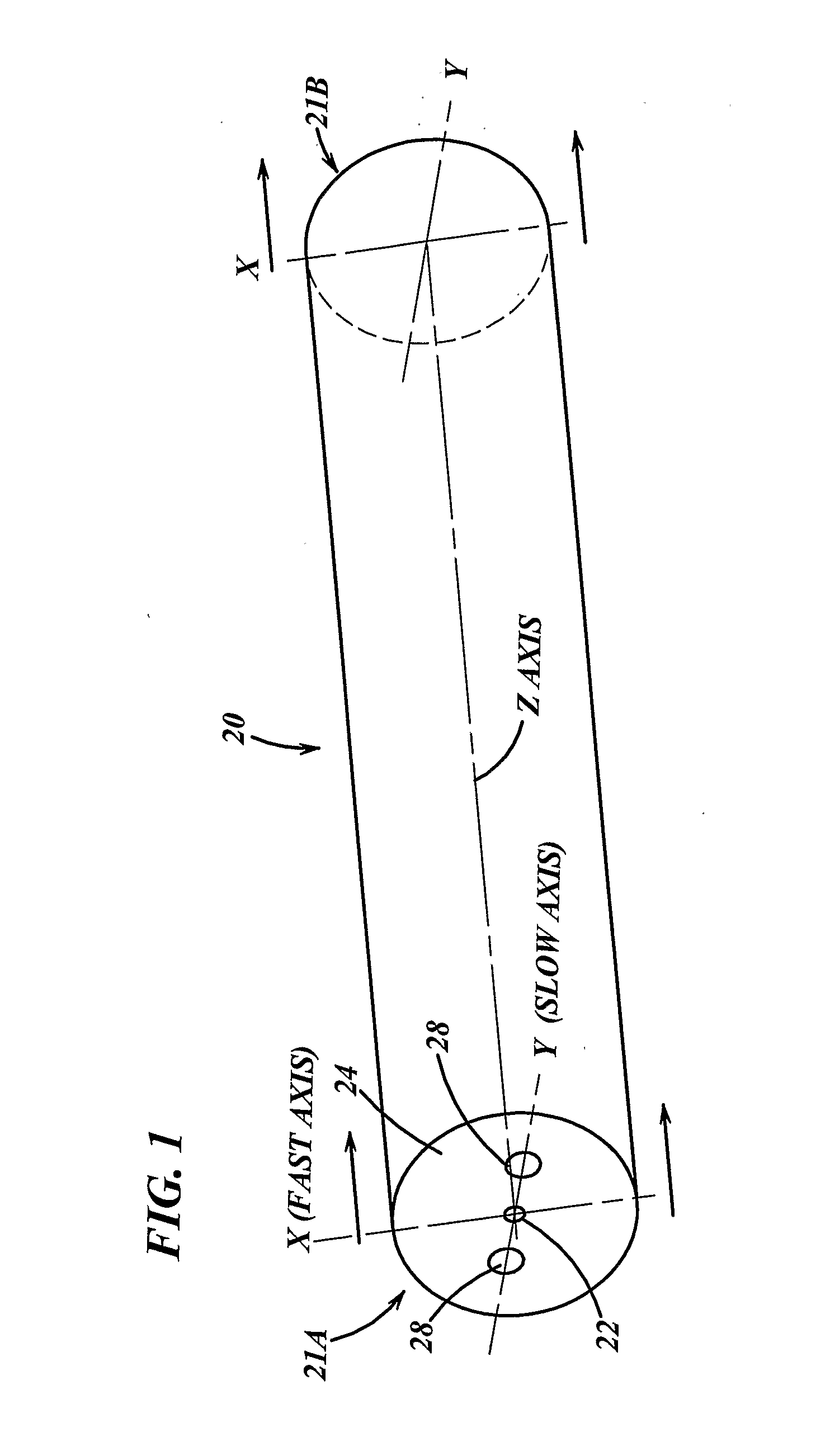
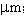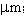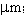Patents
Literature
113 results about "Slope efficiency" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
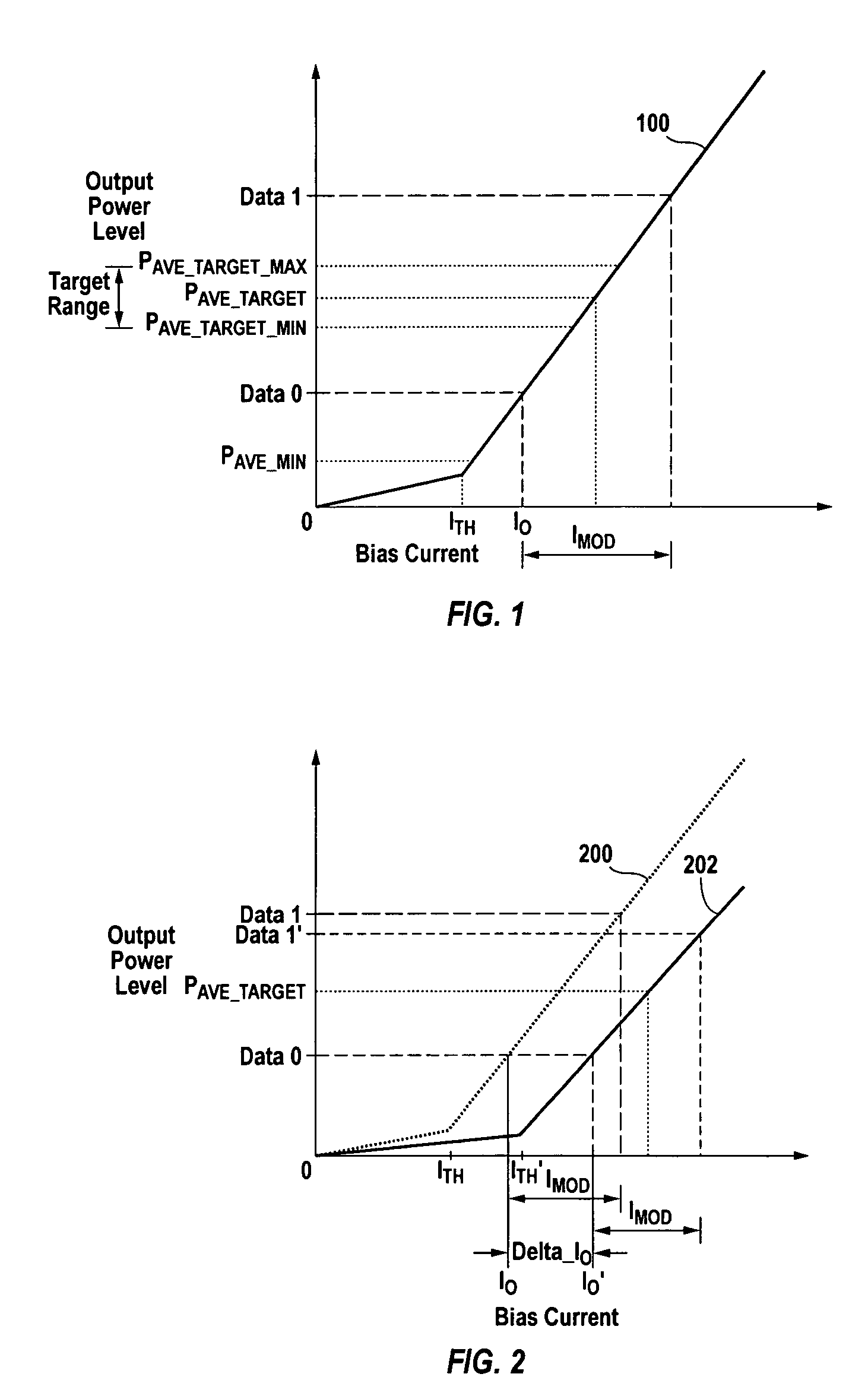
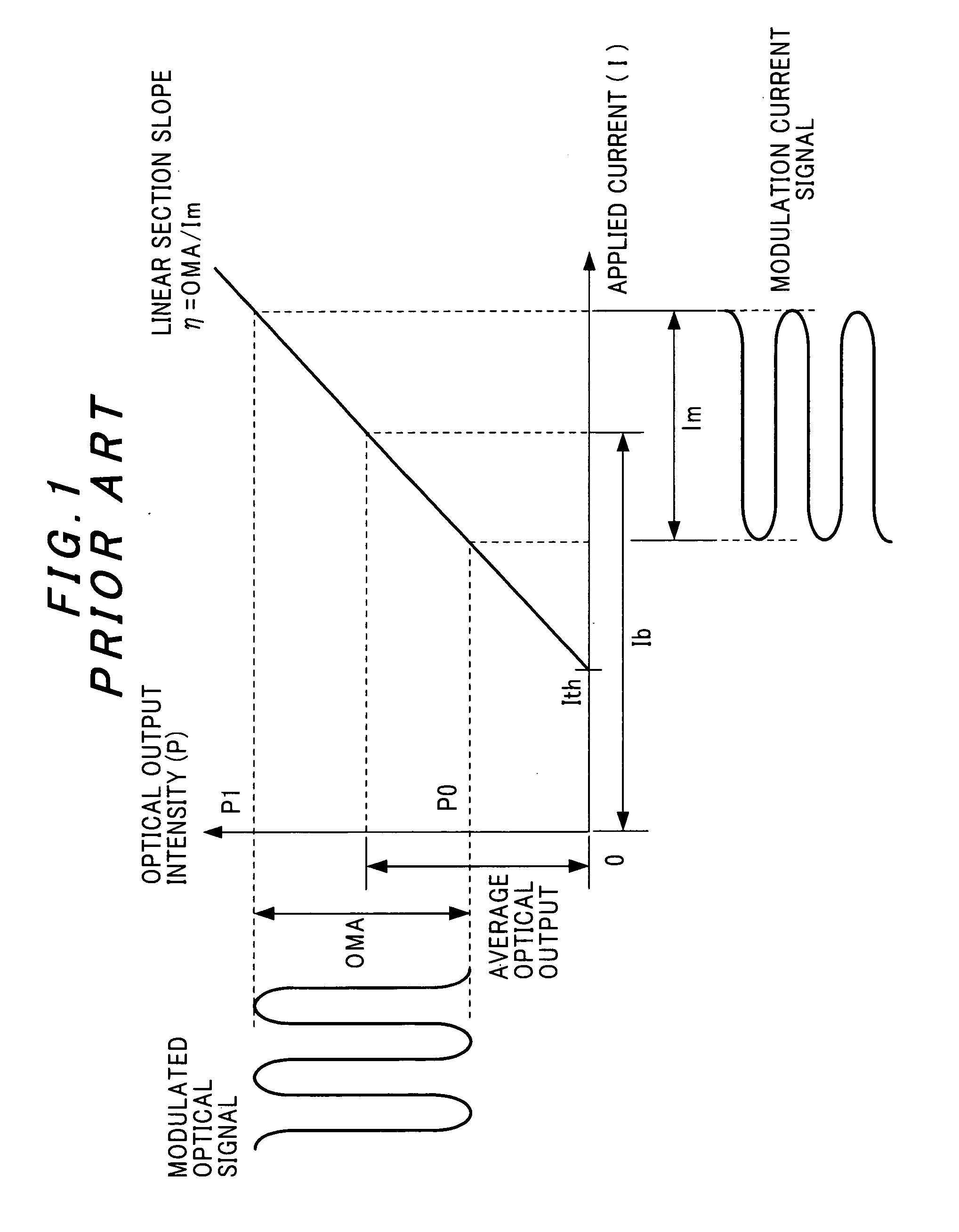
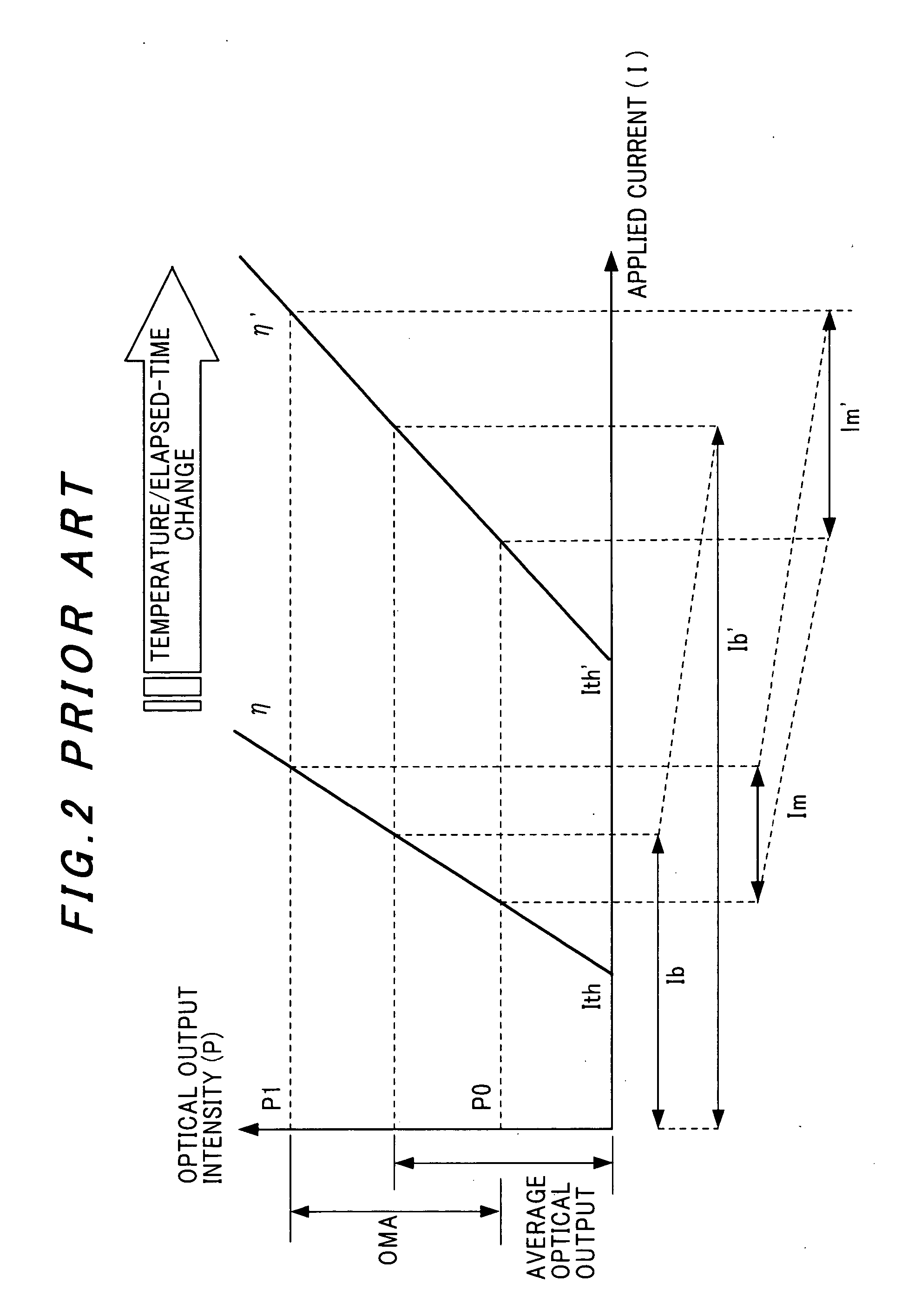
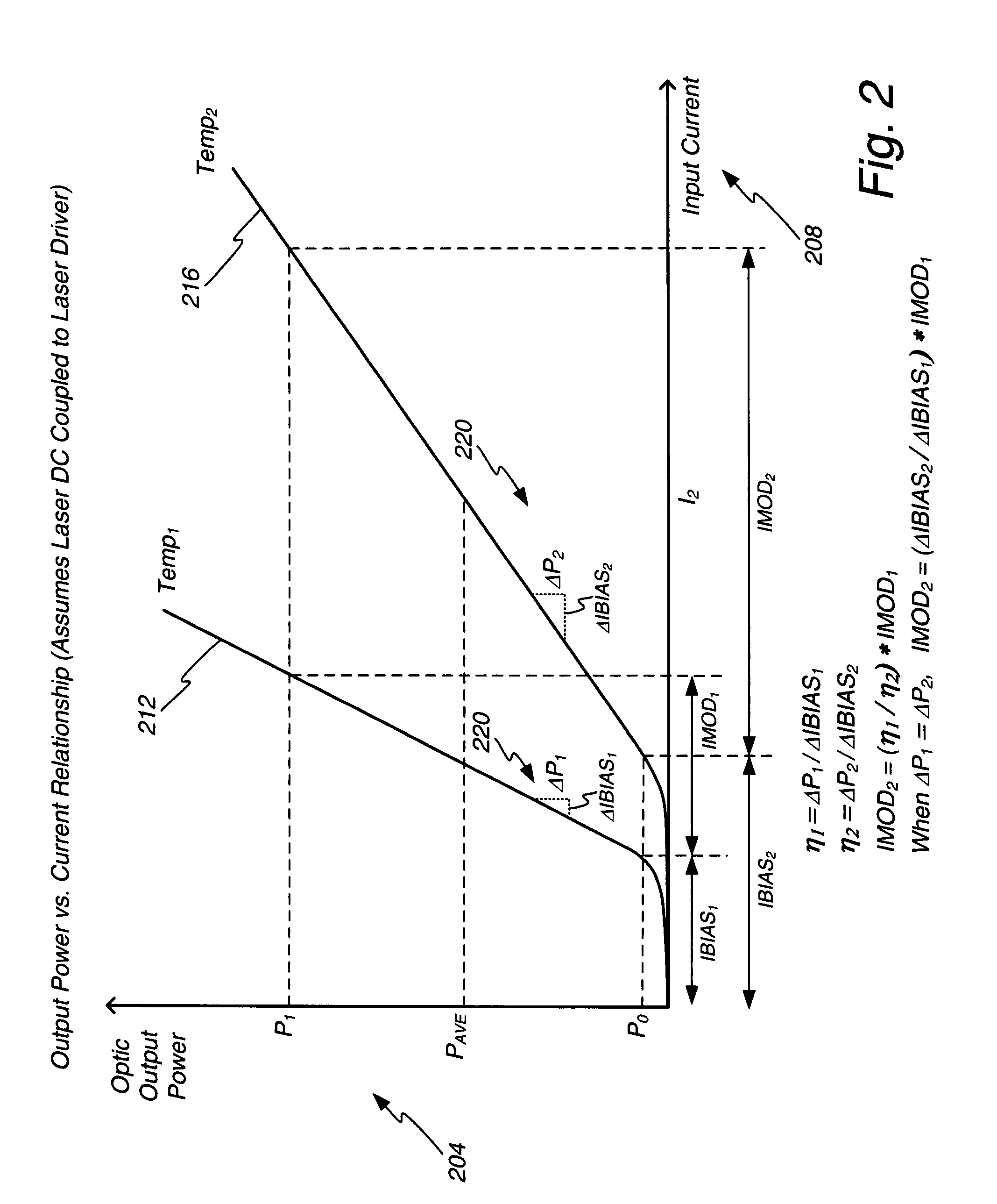
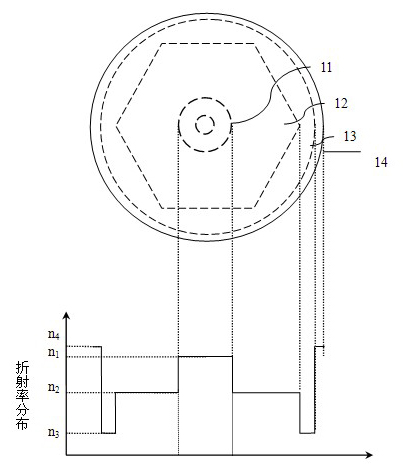
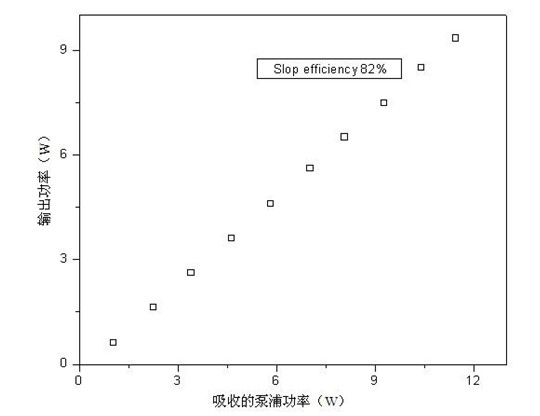
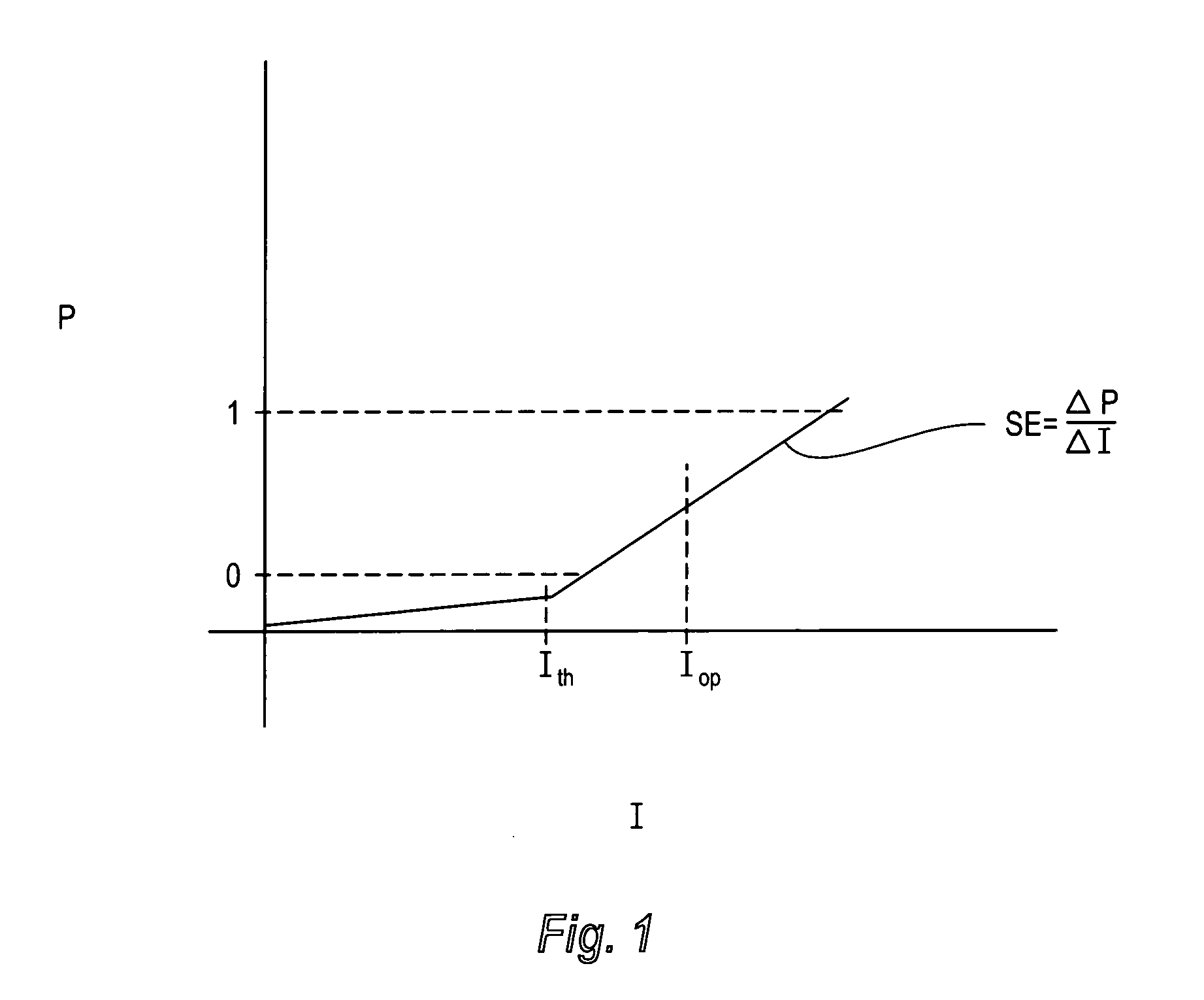
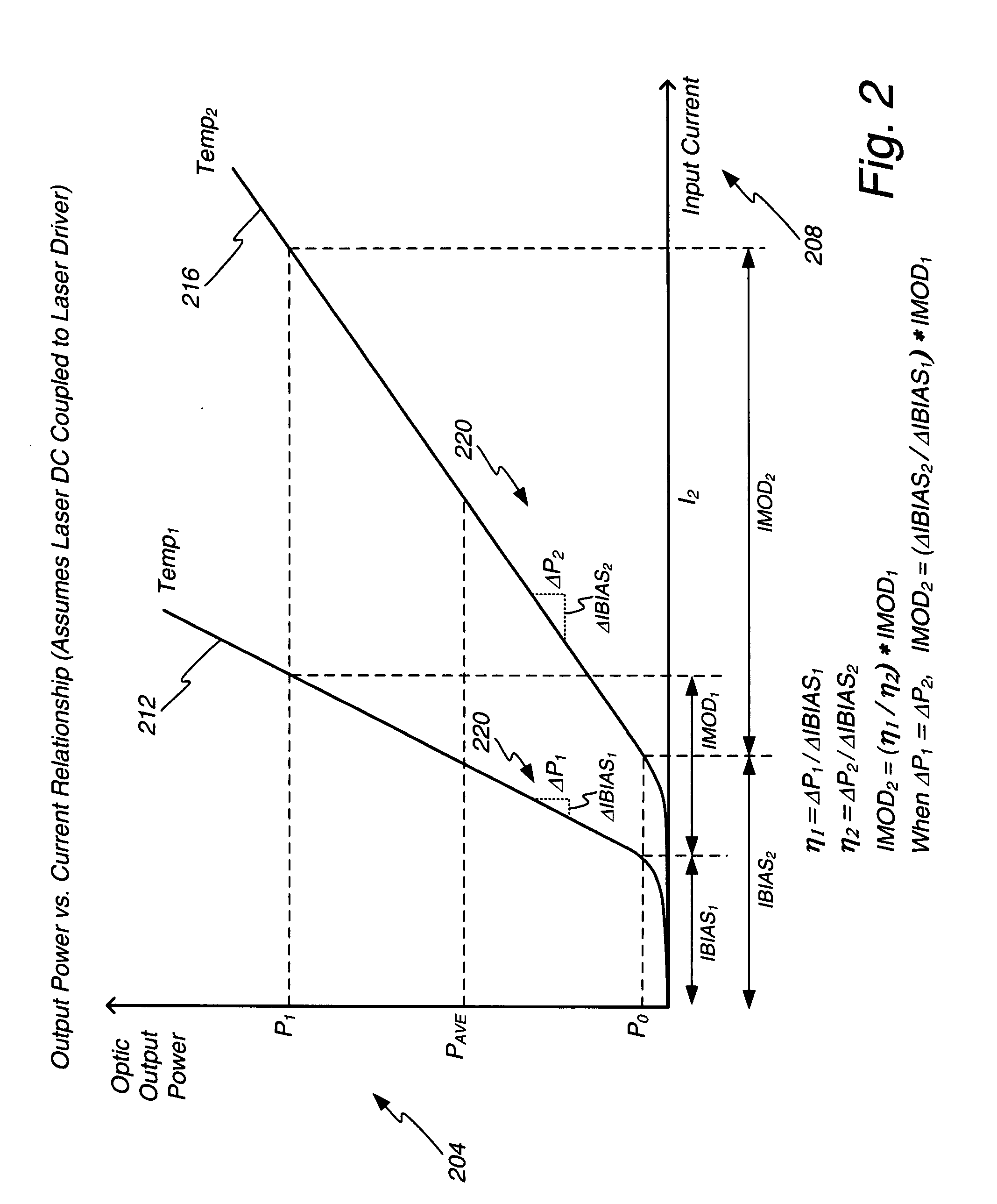
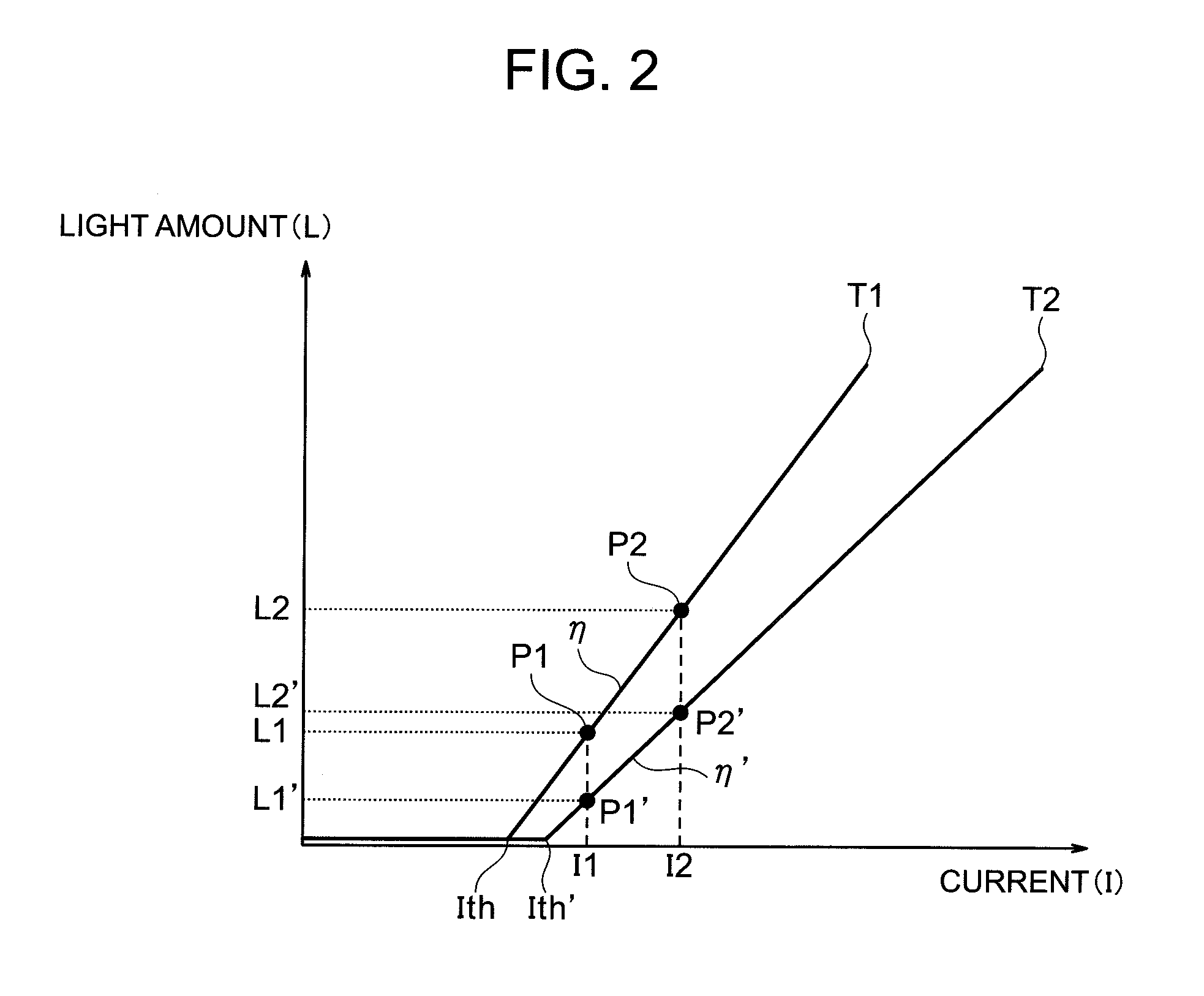
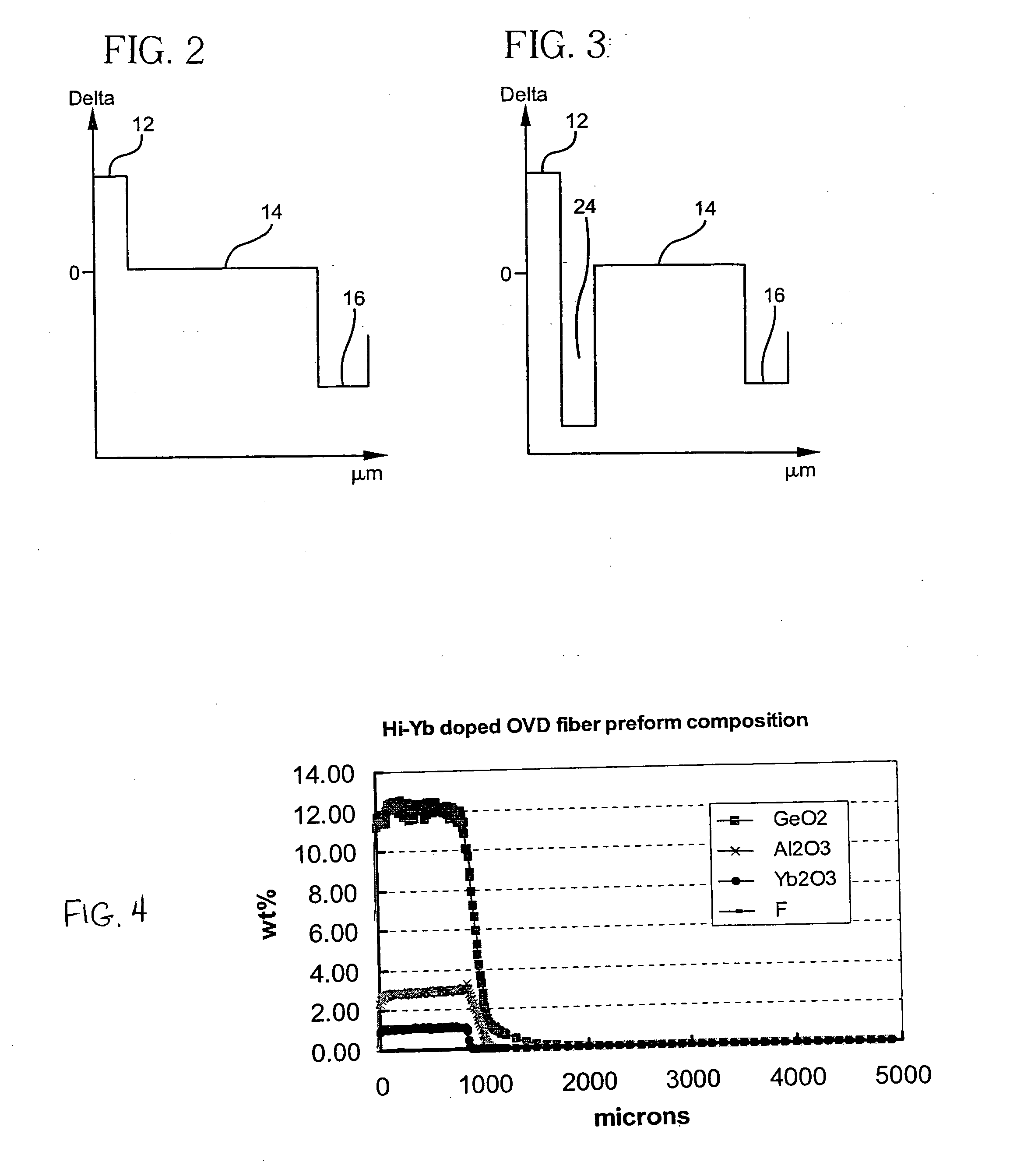
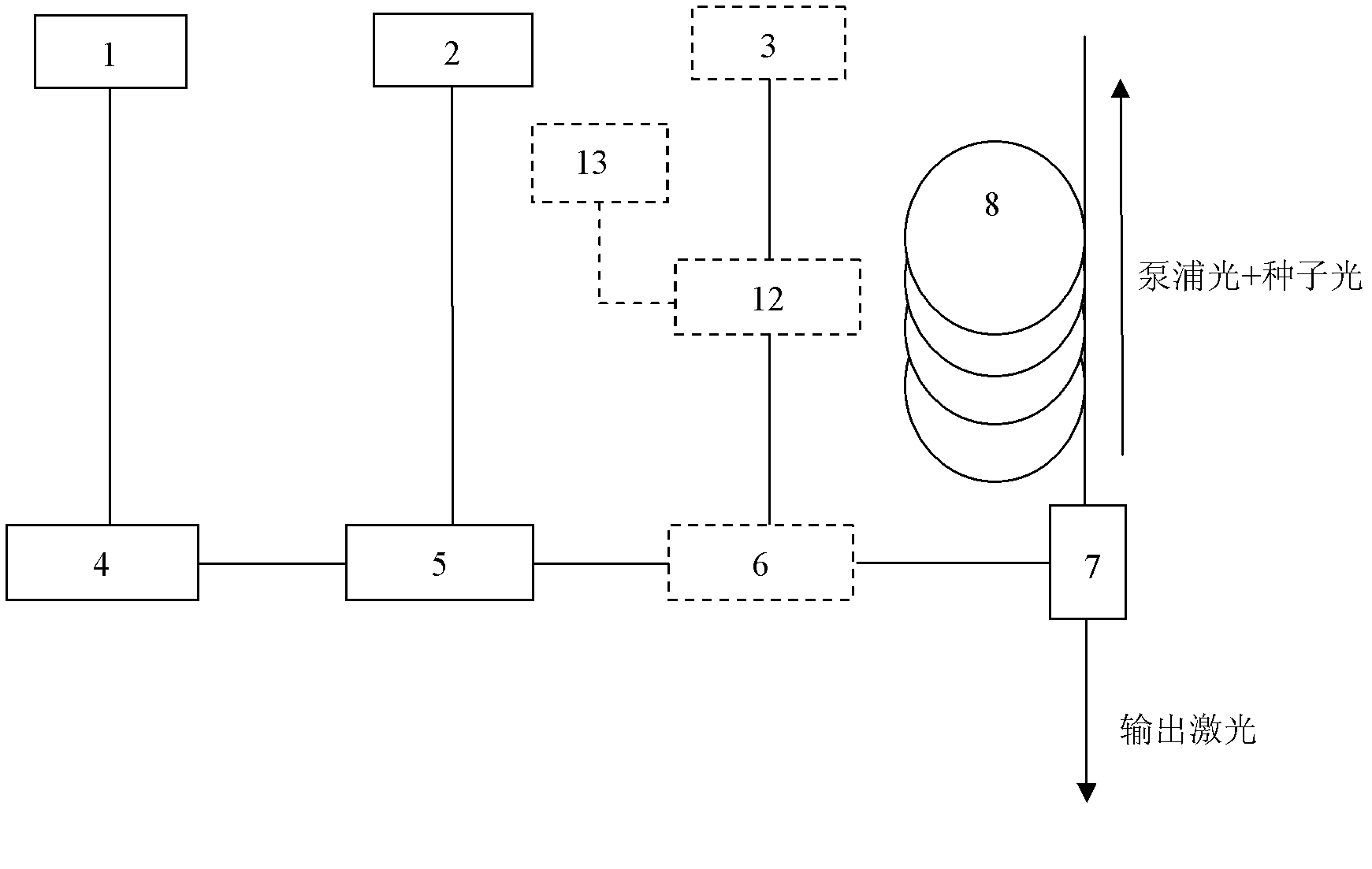
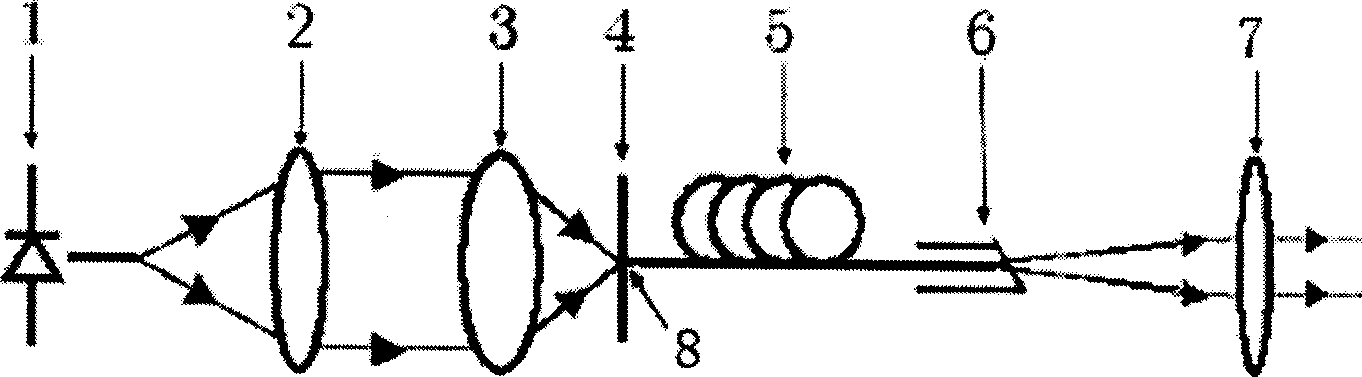
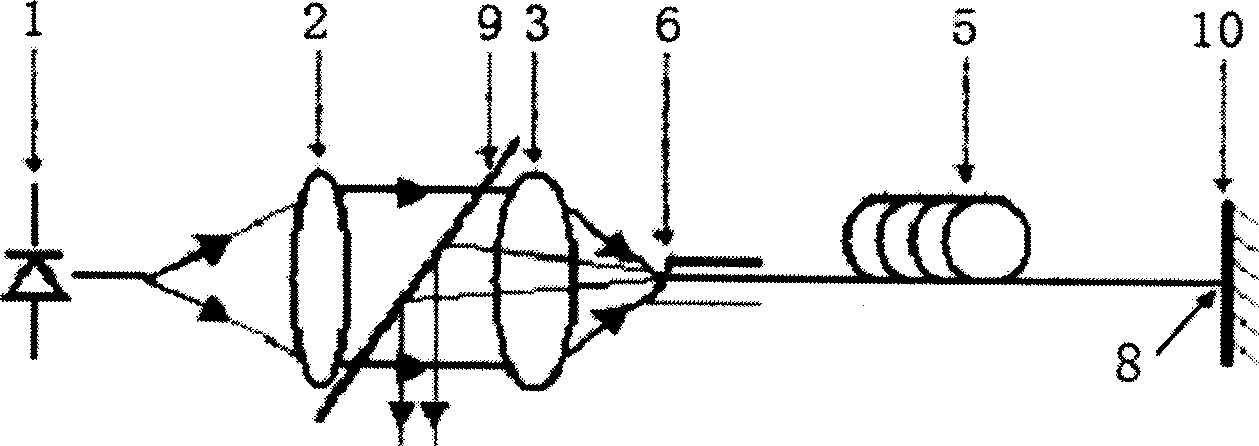
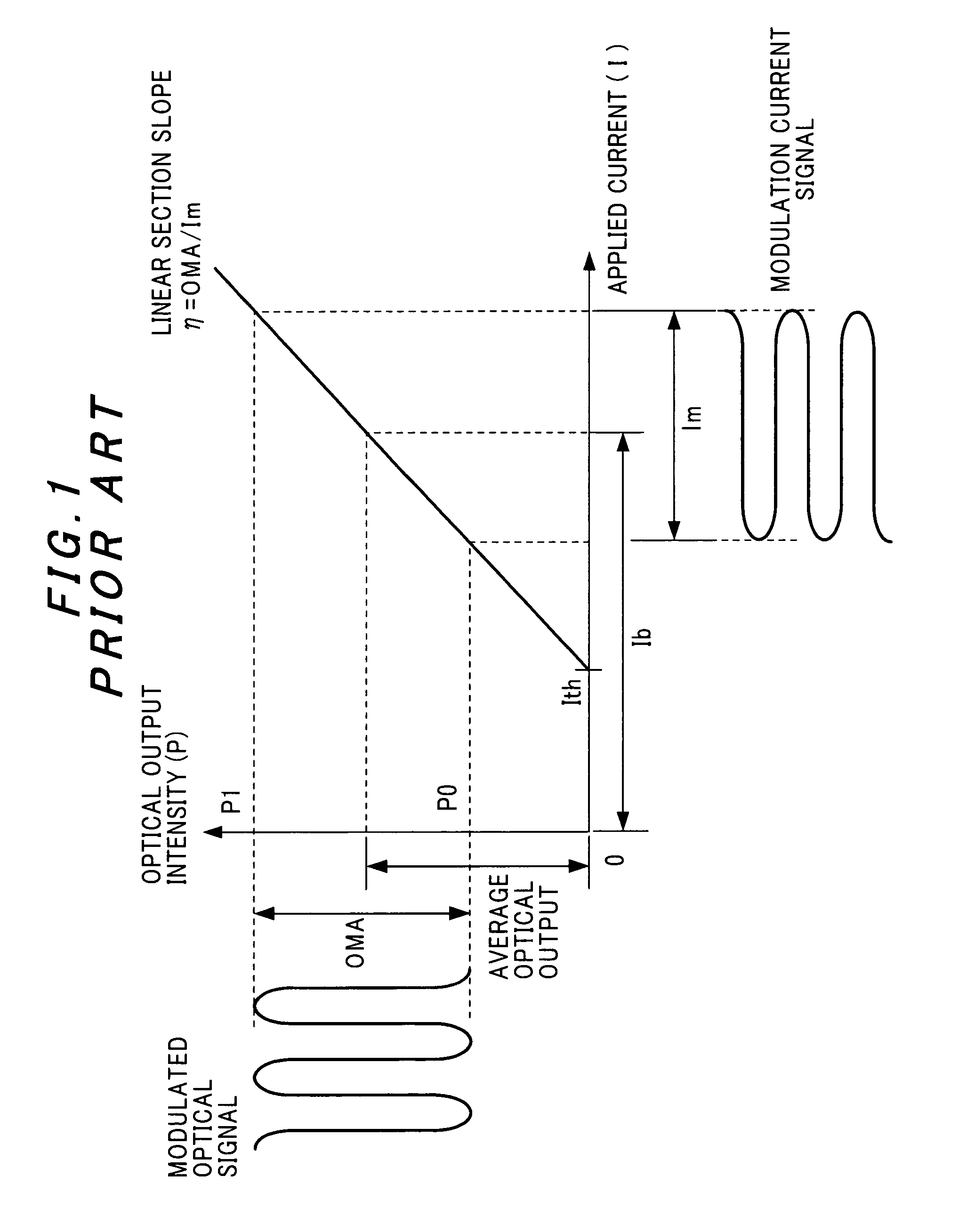
The slope efficiency is an important property of a laser. It is obtained by plotting the laser output power against the input pump power. Above the lasing threshold, the resulting curve is usually close to a straight line. The slope efficiency is the slope of this line. Slope efficiency can similarly be defined in terms of output and input energies instead of powers. This makes it applicable to pulsed lasers.
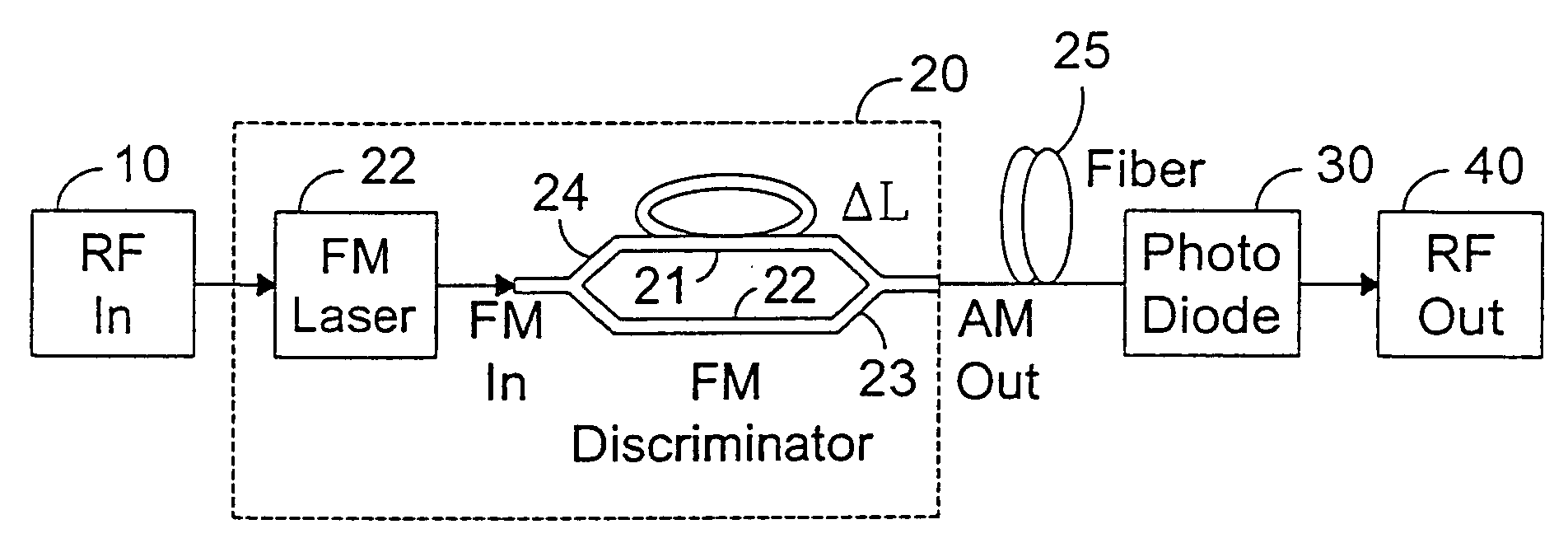
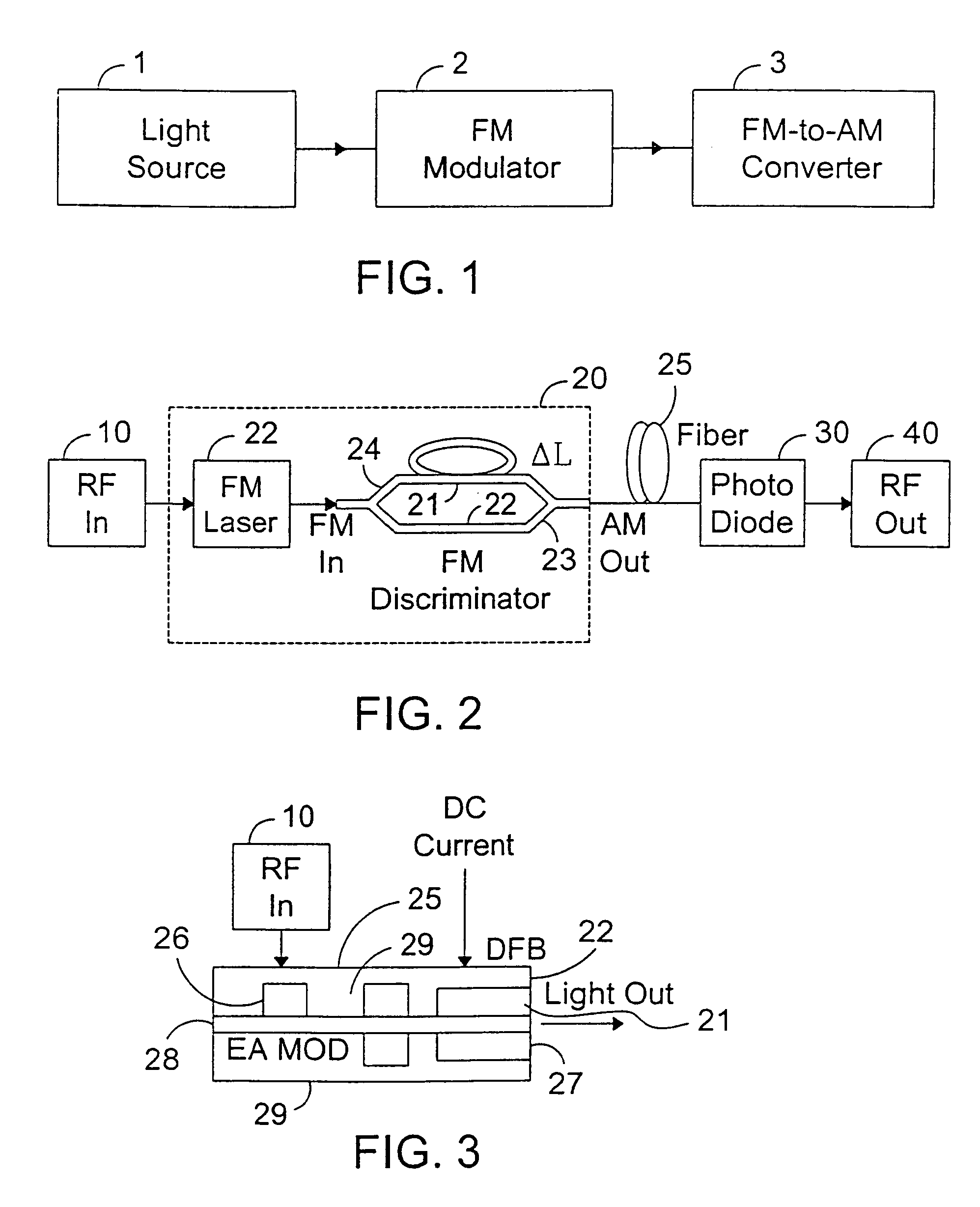
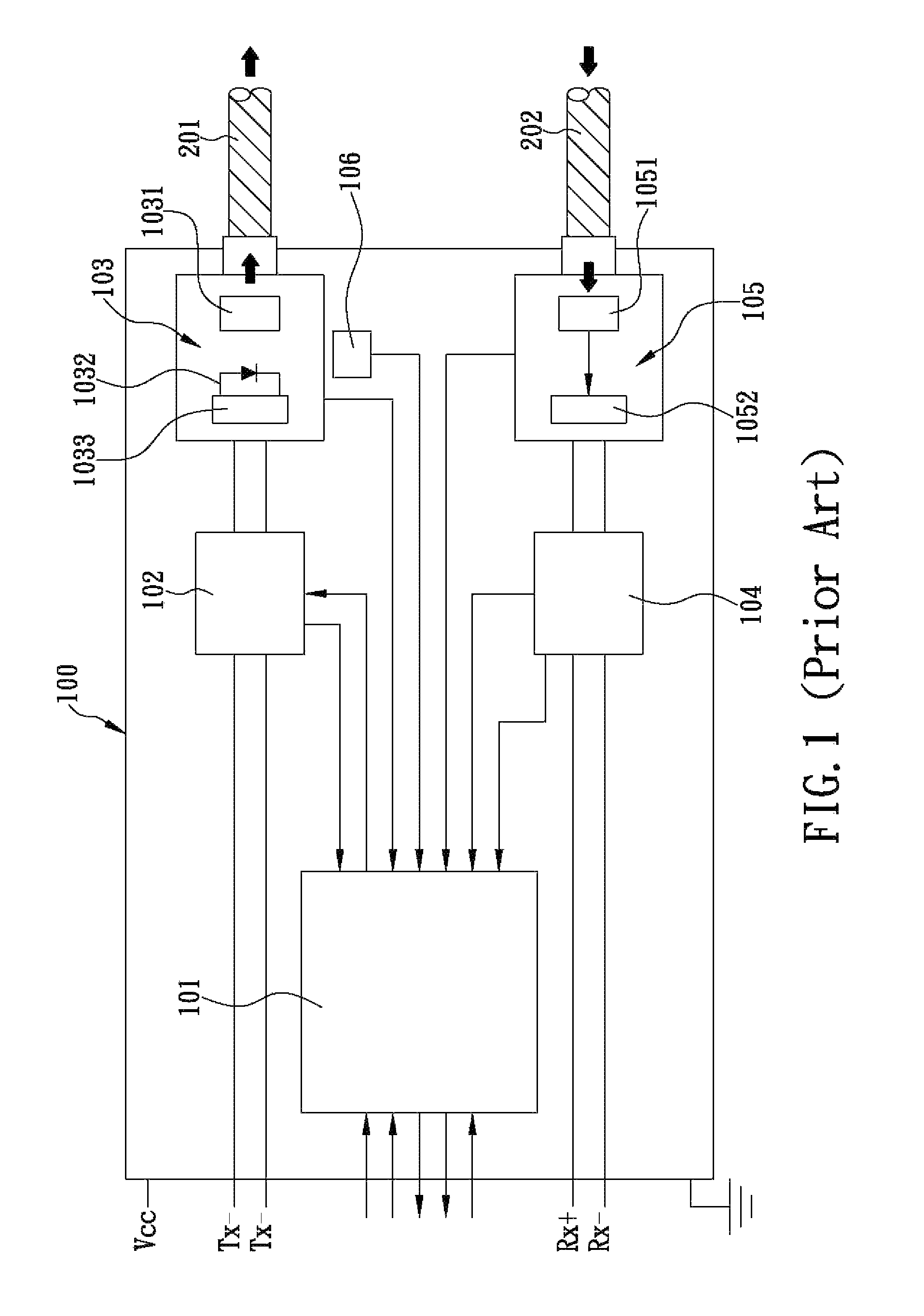
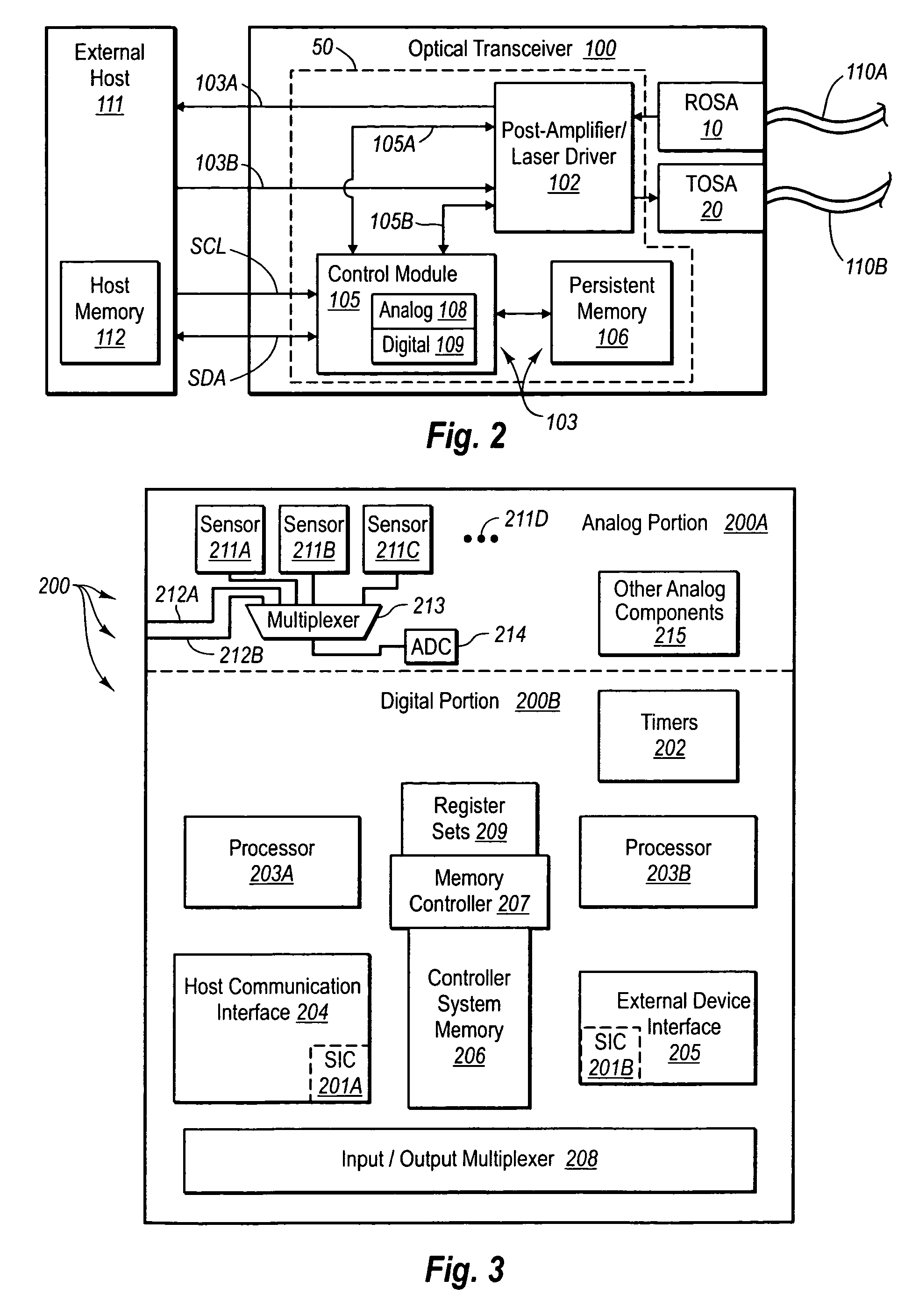
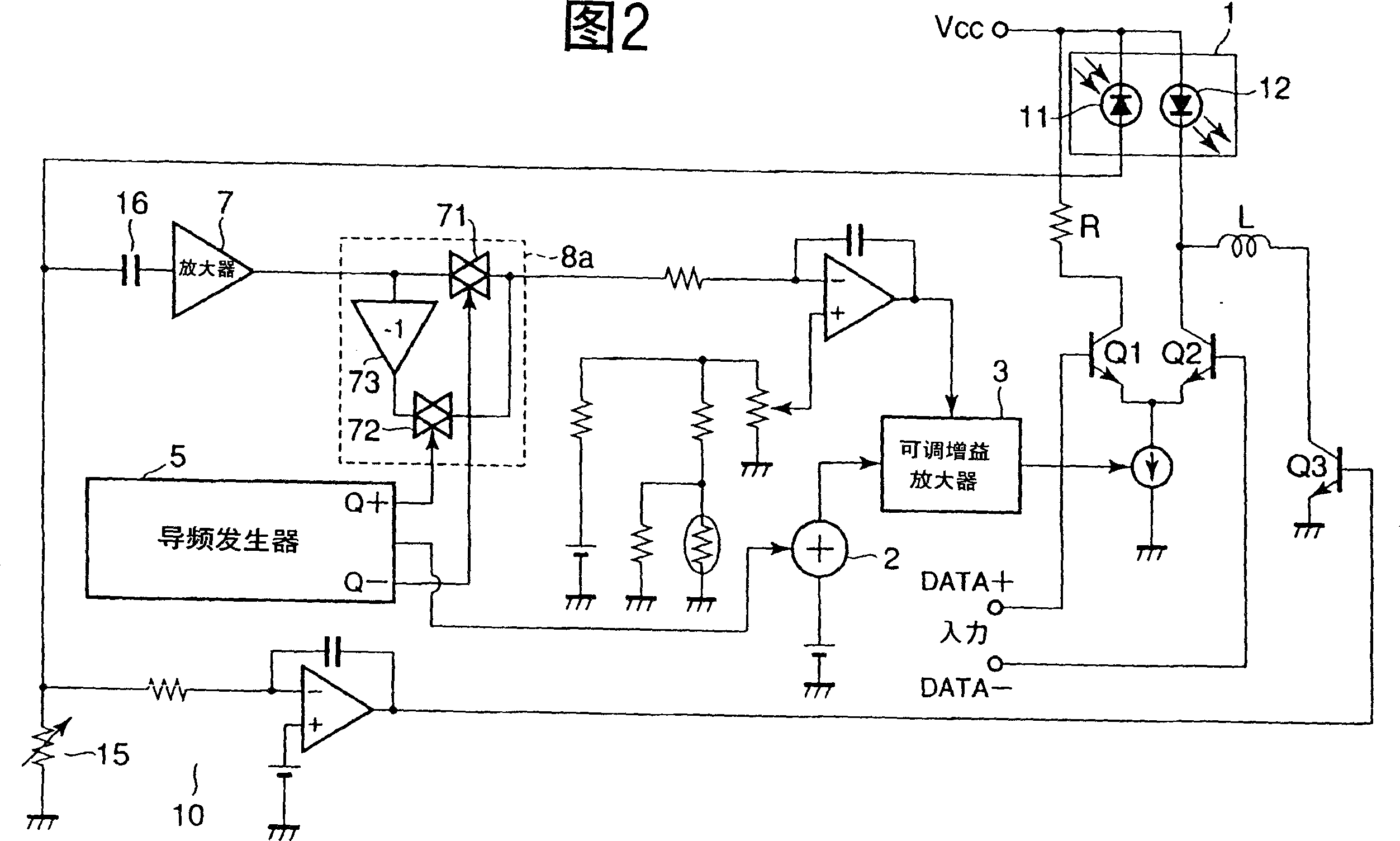
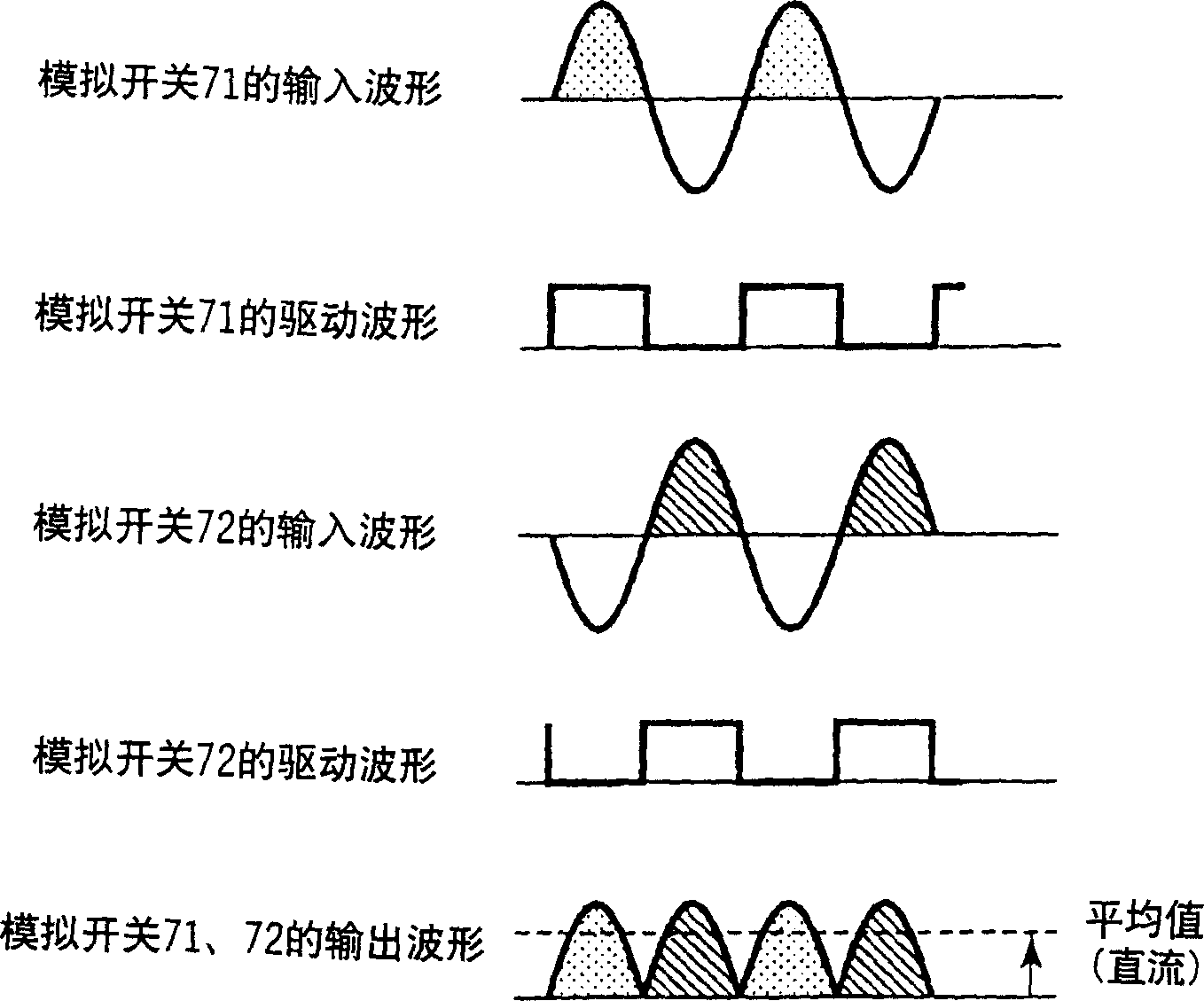
System and method for generating analog transmission signals
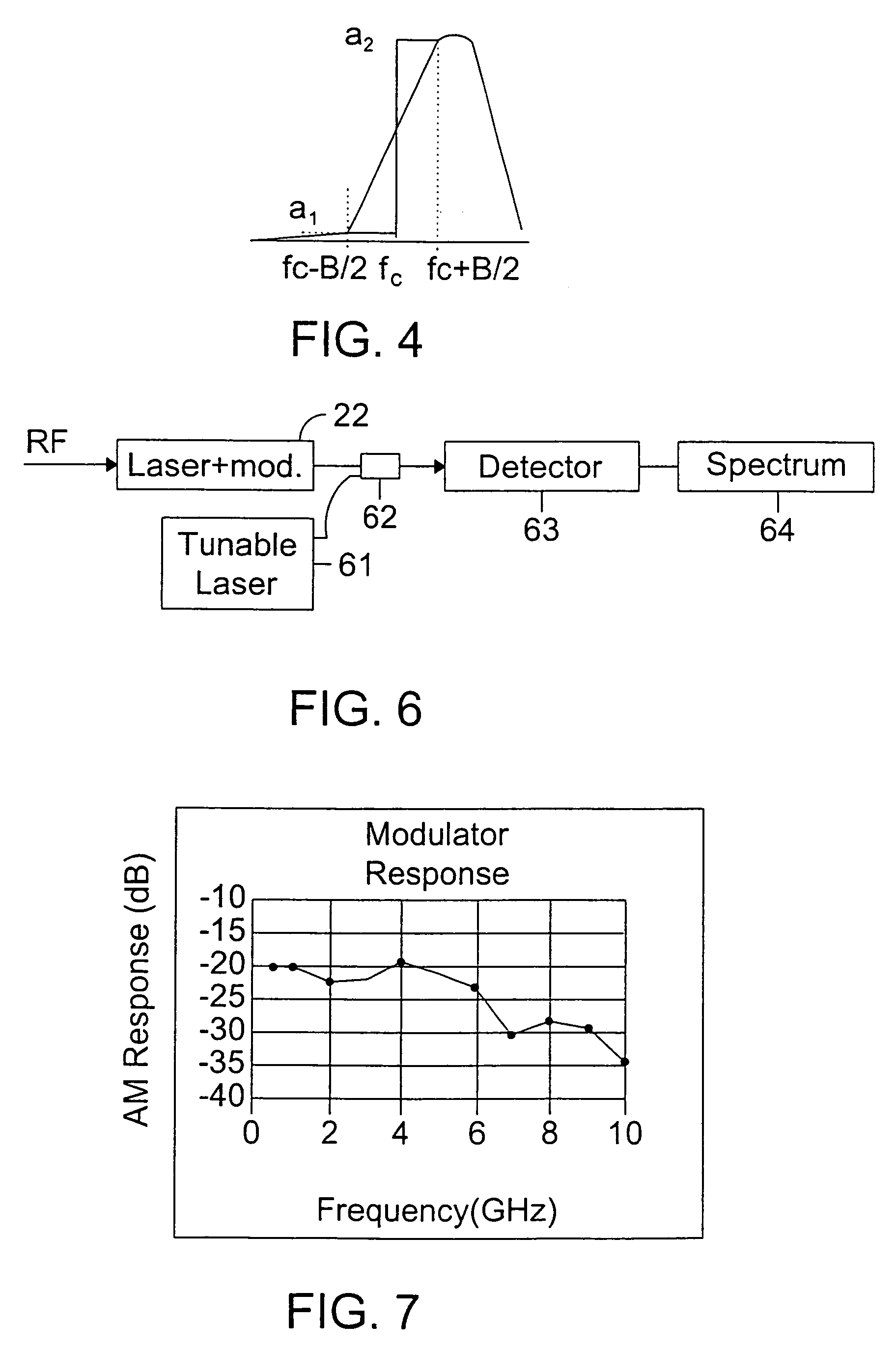
InactiveUS7076170B2Overcomes drawbackImprove dynamic rangeLaser detailsCoupling light guidesLow noiseDiscriminator
An RF-lightwave transmitter performs successive conversions of an information-bearing input signal in order to generate an output signal suitable for transmission in a wireless communications system. The transmitter includes a high-efficiency FM laser connected to a FM discriminator. In operation, the laser converts an RF signal into a frequency-modulated optical signal, and the discriminator converts this signal into an amplitude-modulated optical signal. The discriminator performs its conversion using a high slope-efficiency linear transfer function which ensures that the AM optical signal varies in accordance with a desired operational performance. The transmitter also includes a photodiode which converts the AM signal output from the optical discriminator back into an RF signal for transmission. Experimental results demonstrated that a transmitter of this type is able to realize greater than 10 dB RF insertion gain at less than 0 dBm optical power, with a high spurious-free dynamic range and low noise. A signal processor embodied within the transmitter may be used in a purely optical communication systems or may be used for other types of RF-photonics applications such as those expected for use in next-generation systems.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND BALTIMORE COUNTY
Encapsulated optoelectronic devices with controlled properties
An optoelectronic device, such as a VCSEL, is disclosed whose transmission does not change upon encapsulation by a material such as plastic, epoxy or other suitable encapsulant with a known index of refraction. The surface reflection of the VCSEL surface is very different depending on whether it is terminated in air or the encapsulant, with a much larger reflection in the case of air. It is known that the surface reflection can be made out of phase with the rest of the mirror, effectively increasing the transmission. The amount of the transmission increase can be adjusted by controlling the thickness of the surface layer. Once the VCSEL is encapsulated, the surface reflection is reduced, and the transmission at the facet is increased but the dephased reflection is also reduced. Depositing a surface layer whose index of refraction is similar to the encapsulant, and adjusting the surface layer thickness correctly, the overall transmission from the laser into the terminating material is unchanged, be it air or encapsulation. As a result, the laser properties such as slope efficiency and threshold current are unchanged upon encapsulation. The same procedure may be applied to devices other than VCSELs such as other types of lasers, LEDs, and resonant cavity photodetectors to achieve encapsulated optoelectronic components with controlled properties that remain unchanged upon encapsulation.
Owner:OPTICAL COMM PRODS
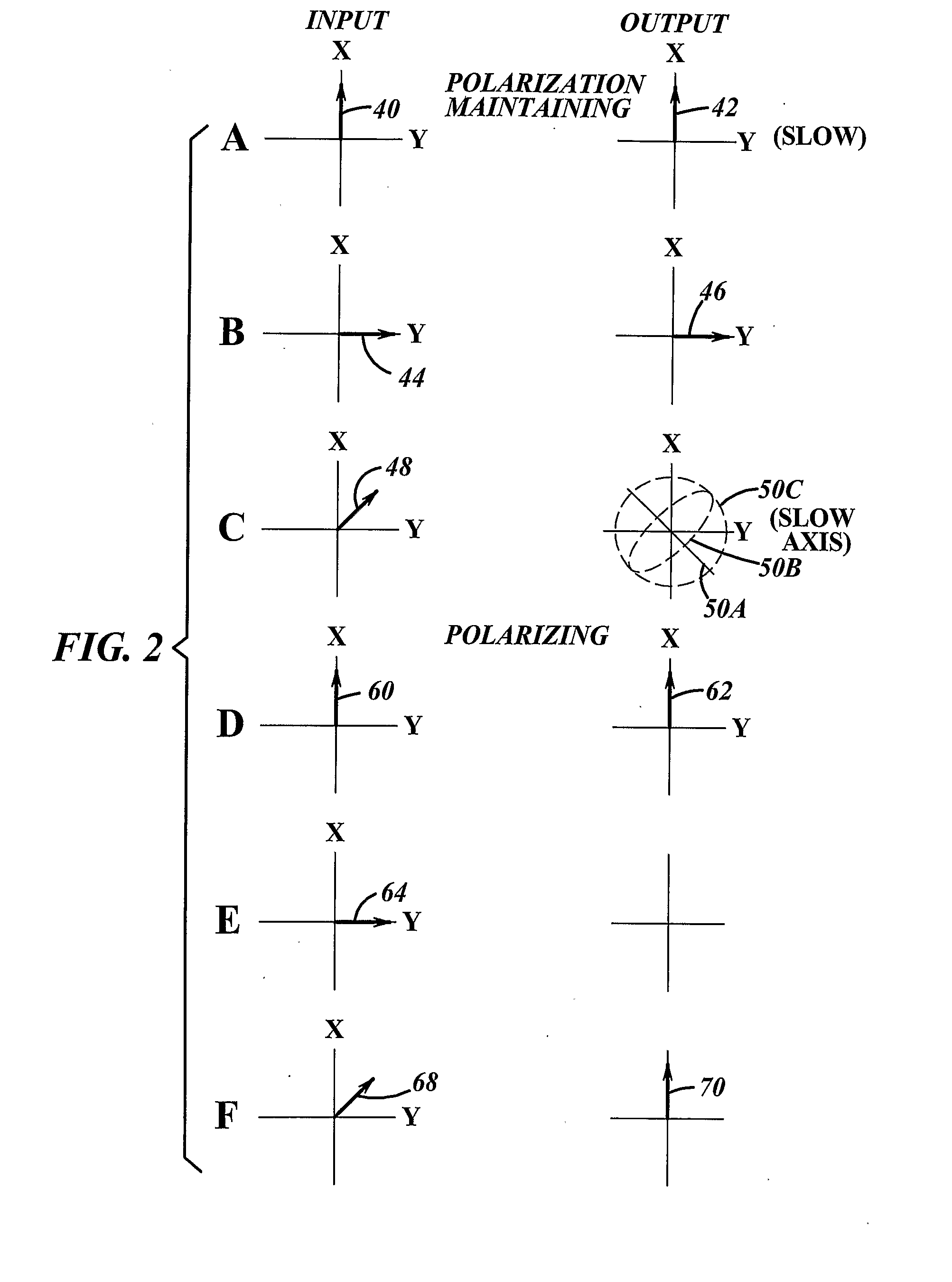
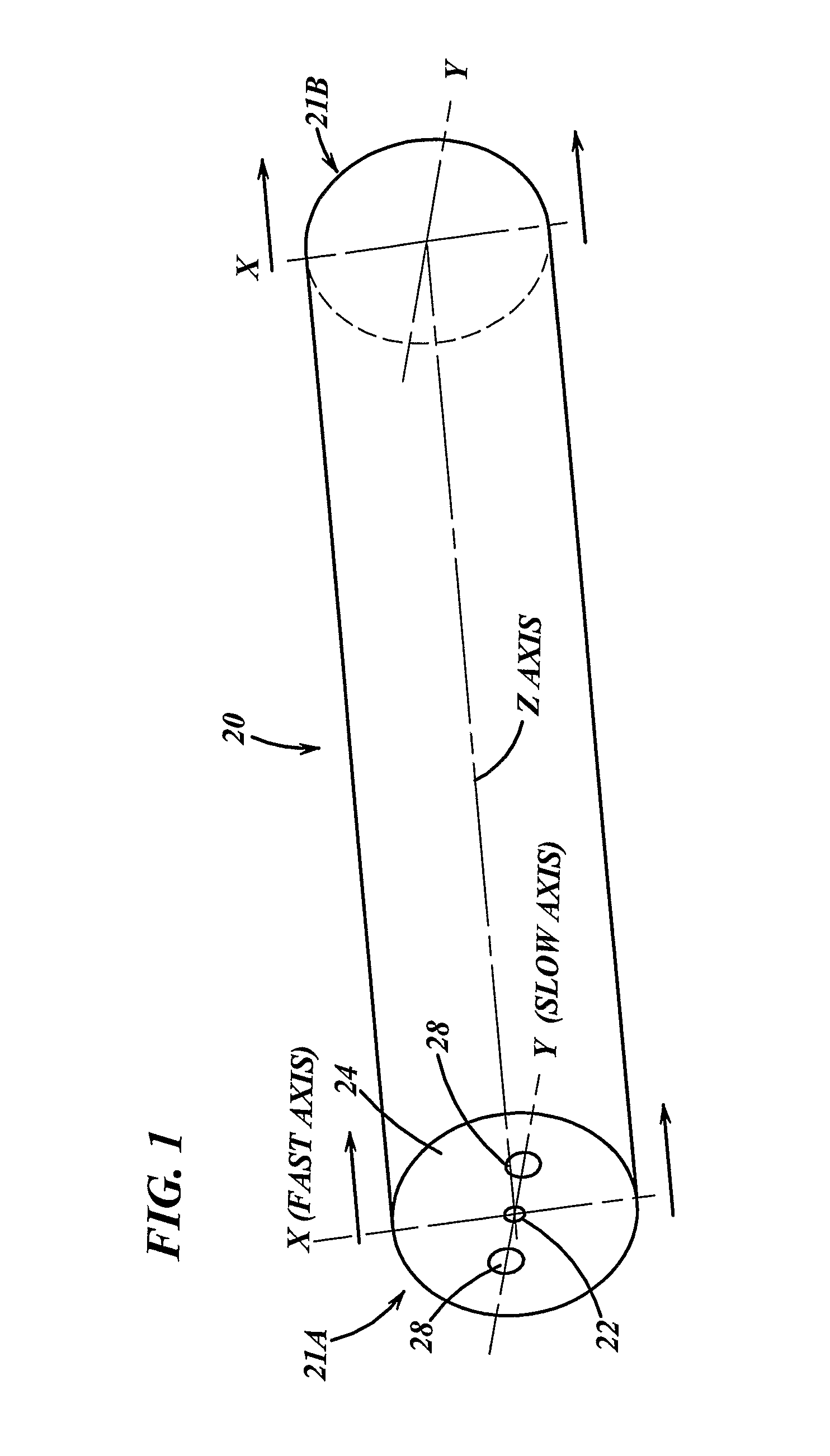
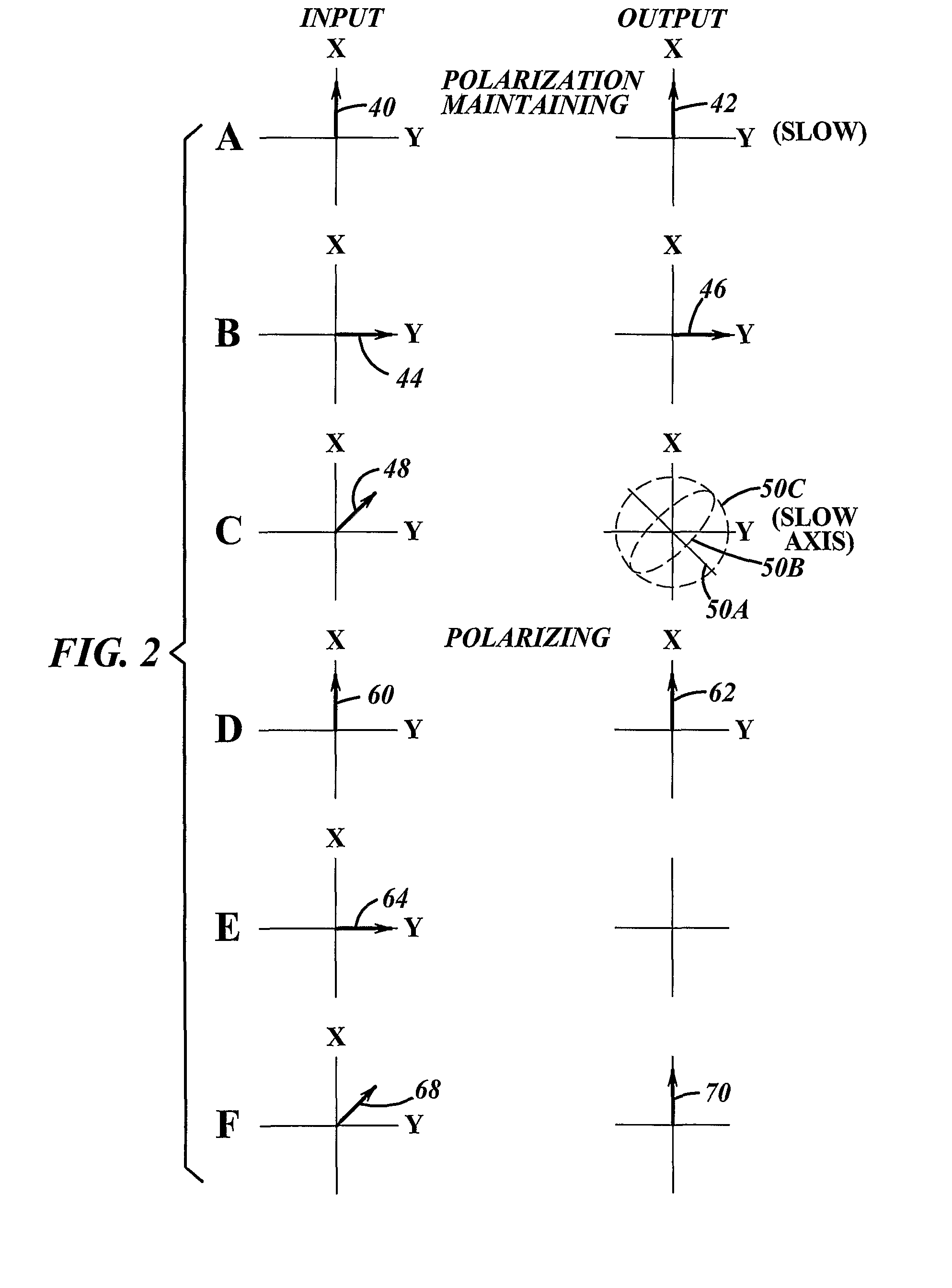
Method and Apparatus for Providing Light Having a Selected Polarization With an Optical Fiber
ActiveUS20080095199A1Increases bend lossIncreased bend lossLaser using scattering effectsOptical fibre with polarisationRare earthLength wave
Optical apparatus (110, 500, 600, 800, 1000) for providing light having a selected linear polarization having a polarization ratio, the apparatus (110, 500, 600, 800, 1000) comprising a length of optical fiber (120, 504, 604, 804, 1001) comprising a rare earth for providing light having a first wavelength responsive to receiving pump light having a second wavelength that is different than said first wavelength, wherein if the length of optical fiber (120, 504, 604, 804, 1004) were placed in a first position between the length of fiber (120, 504, 604, 804, 1004) is substantially linearly oriented (20) the fiber (120, 504, 604, 804, 1004) could propagate at the first wavelength a fundamental mode and a plurality of higher order modes and the apparatus (110, 500, 600, 800, 1000) could provide light having a first polarization ratio for the selected linear polarization and an M2 parameter, and wherein the length of fiber (120, 504, 604, 804, 1004) is positioned in a second position that increases the bend loss of the fiber relative to the first position such that, responsive to the increased bend loss, the apparatus (110,500, 600, 800, 1000) can provide light having a reduced M2parameter as well as a second polarization ratio for the selected polarization that is increased relative to the first polarization ratio, the increase being at least 6 dB greater than the first polarization ratio, and wherein when the length of fiber (120, 504, 604, 804, 1004) is in the second position the apparatus (110, 500, 600, 800, 1000) can provide a slope efficiency that is at least 50% of the ratio of the second wavelength to the first wavelength.
Owner:NUFERN
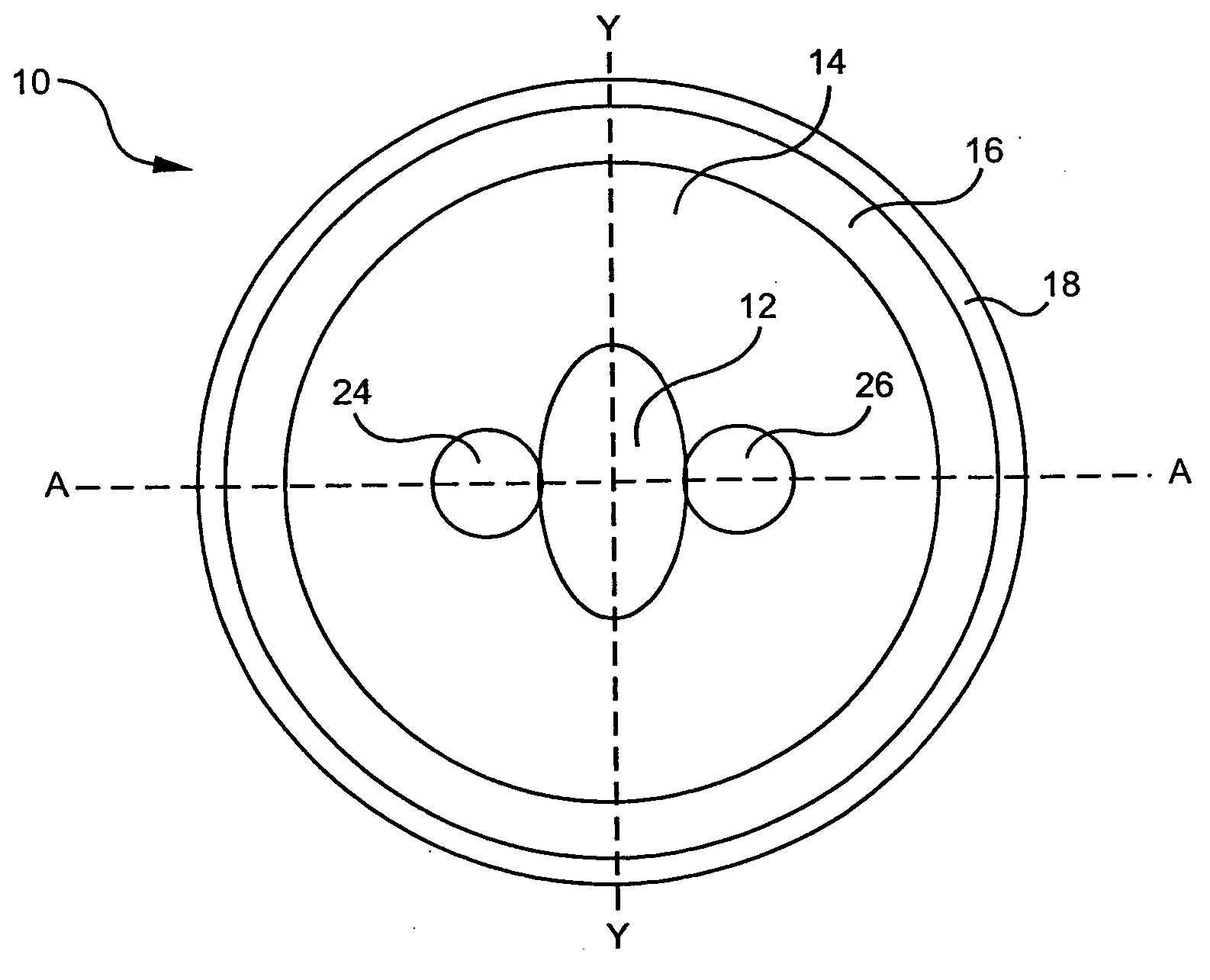
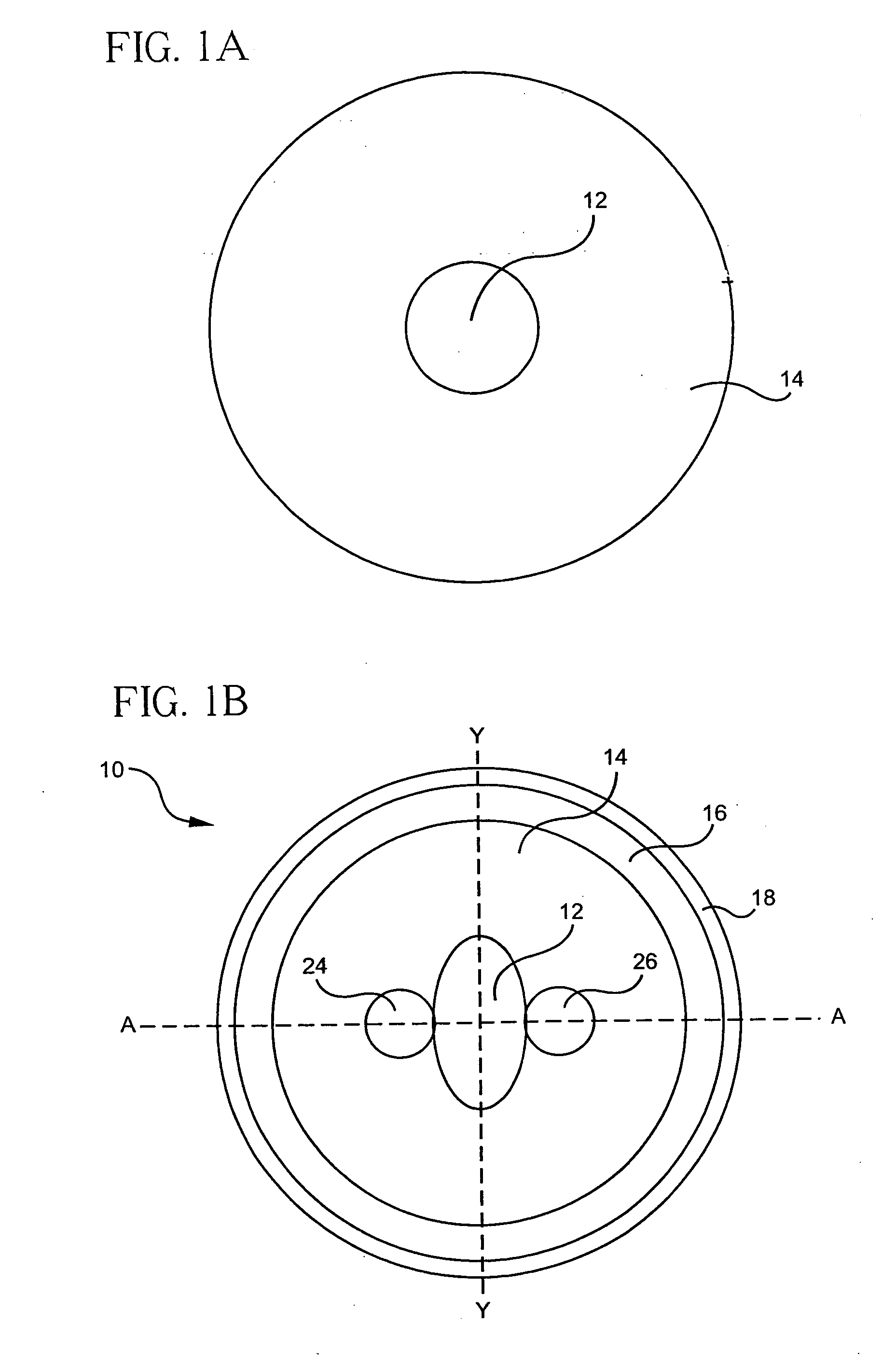
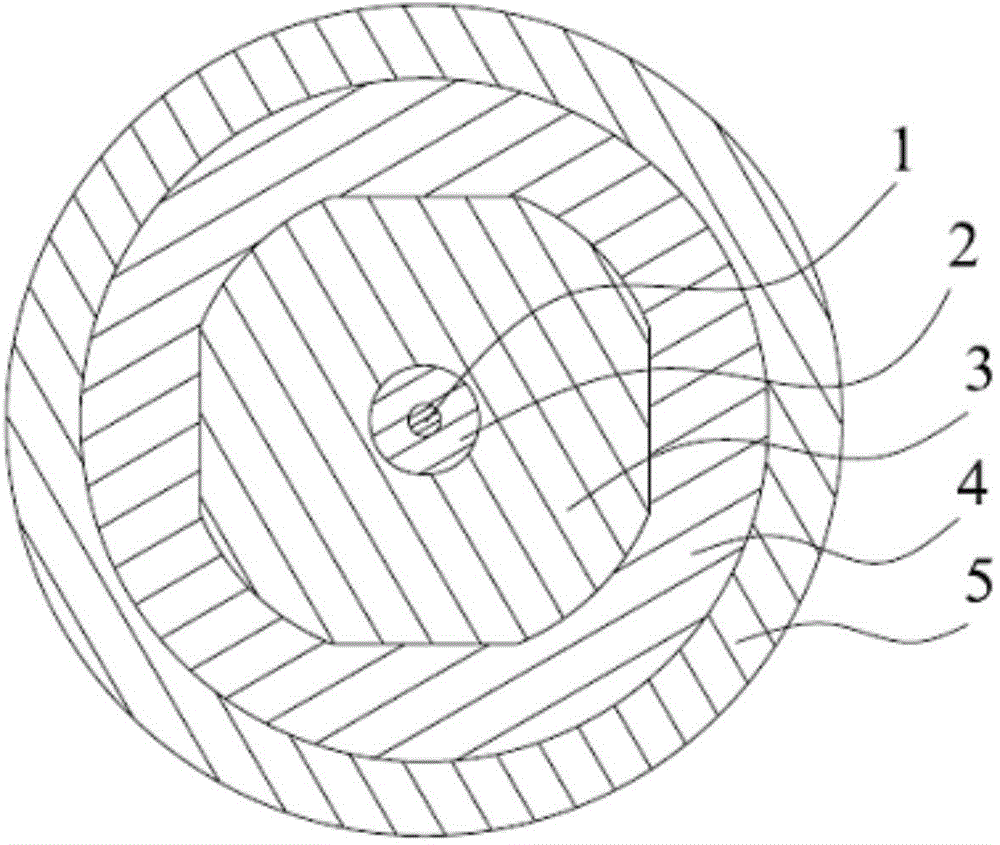
Rare-earth uniformly-doped fiber perform core rod and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102992613AImprove homogeneityHigh Refractive Profile FlatnessGlass shaping apparatusGlass fibre productsFiberRare earth ions
The invention relates to a rare-earth uniformly-doped fiber perform core rod and a preparation method thereof. The core rod adopts silicon dioxide used as a matrix and is at least doped with a rare earth ion and a co-doping ion, wherein the doping concentration of the rare earth element is calculated in the oxide form; the concentration of the doped rare earth oxide is 0.05-0.5mol%; the co-doping ion is at least one of Al and P elements; the co-doping agent concentration is calculated in the oxide form; and the concentration of the co-doping agent oxide is 0.4-10mol%. The core rod is prepared by adopting a powder forming-sintering method. The core rod disclosed by the invention has the advantages that the fiber core has high doping uniformity in the axial direction and the radial direction; the refractive index profile of the fiber core has high flatness; the numerical aperture (NA) of the fiber core is accurate and adjustable; and the optical fiber has high slope efficiency. Based on the rare earth doped core rod, various rare-earth doped optical fibers with different structures can be manufactured by using a core rod through the external cladding technology, i.e., the manufacturing requirements of rare earth doped optical fibers with different structures such as single cladding single mode, double cladding single mode, polarization-maintaining double cladding, large-mode field area air hole double cladding and the like are satisfied.
Owner:YANGTZE OPTICAL FIBRE & CABLE CO LTD
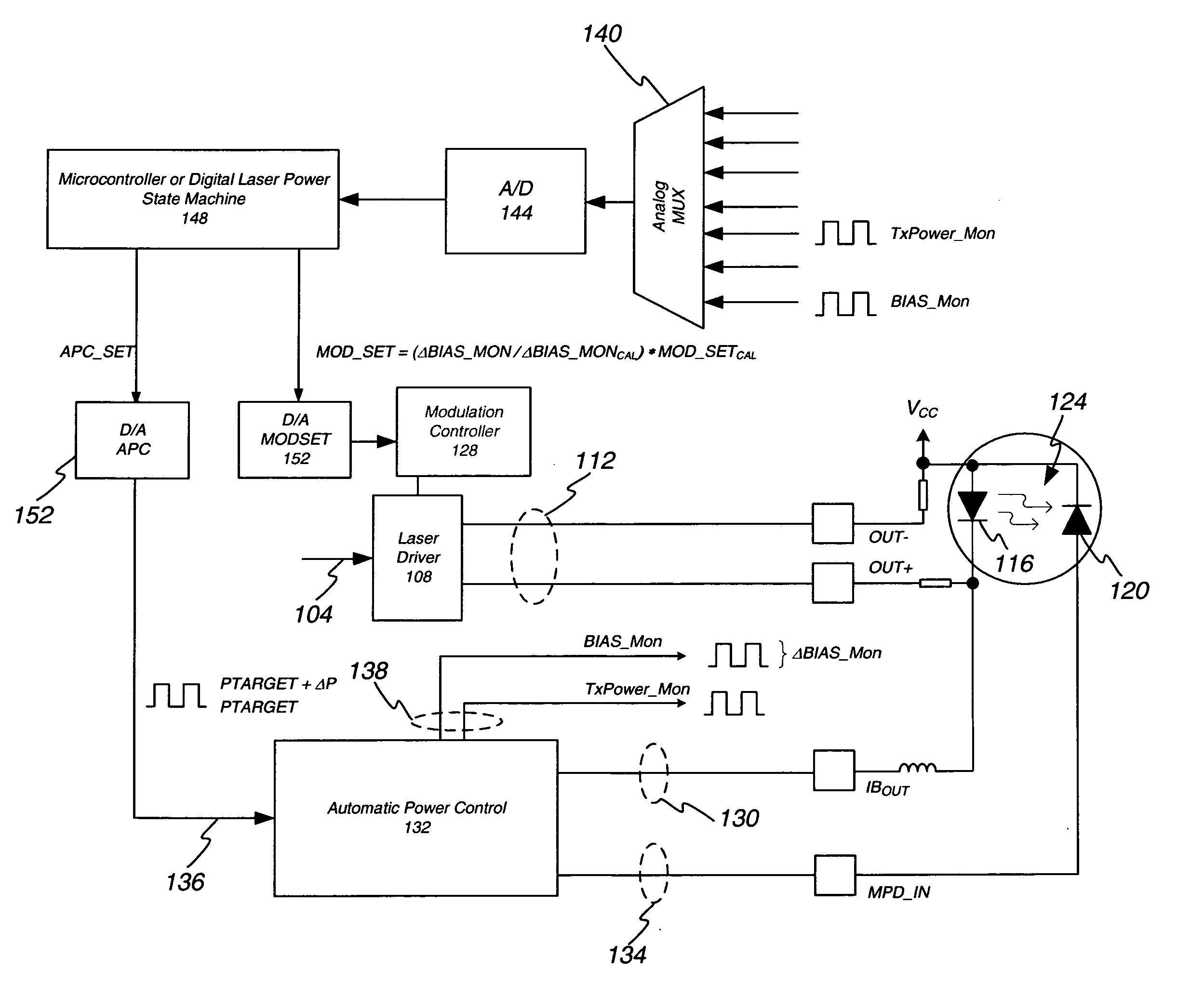
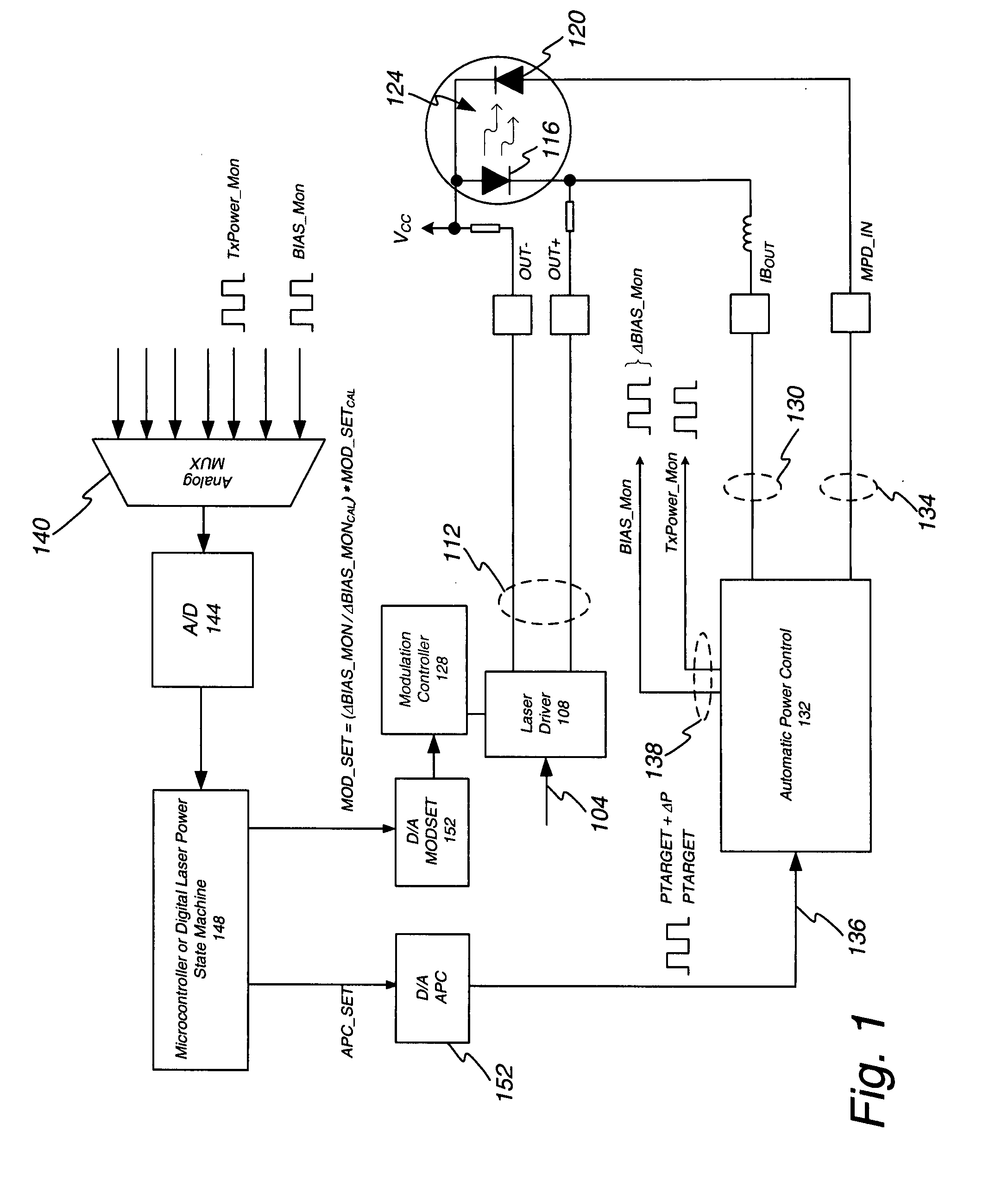
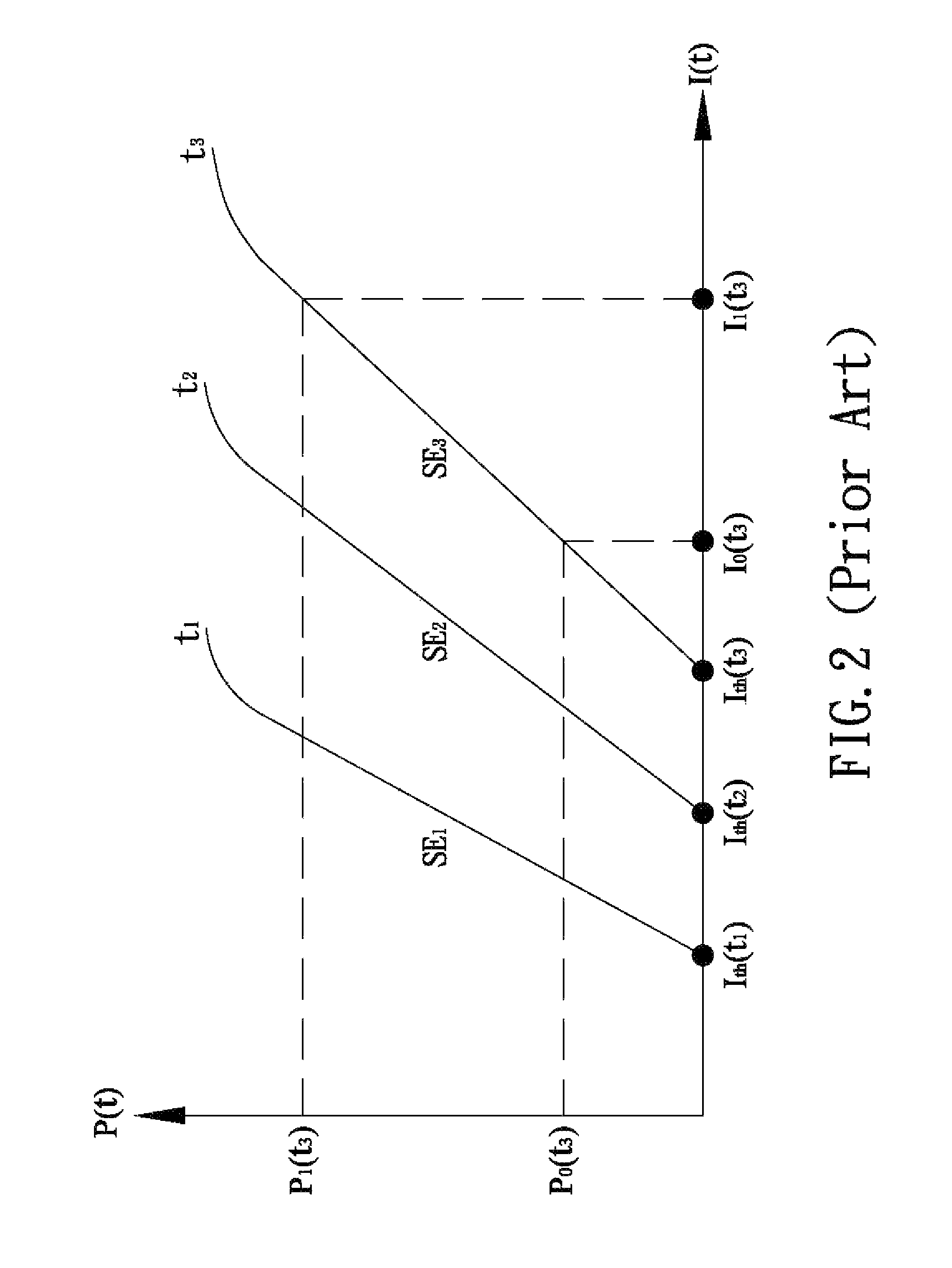
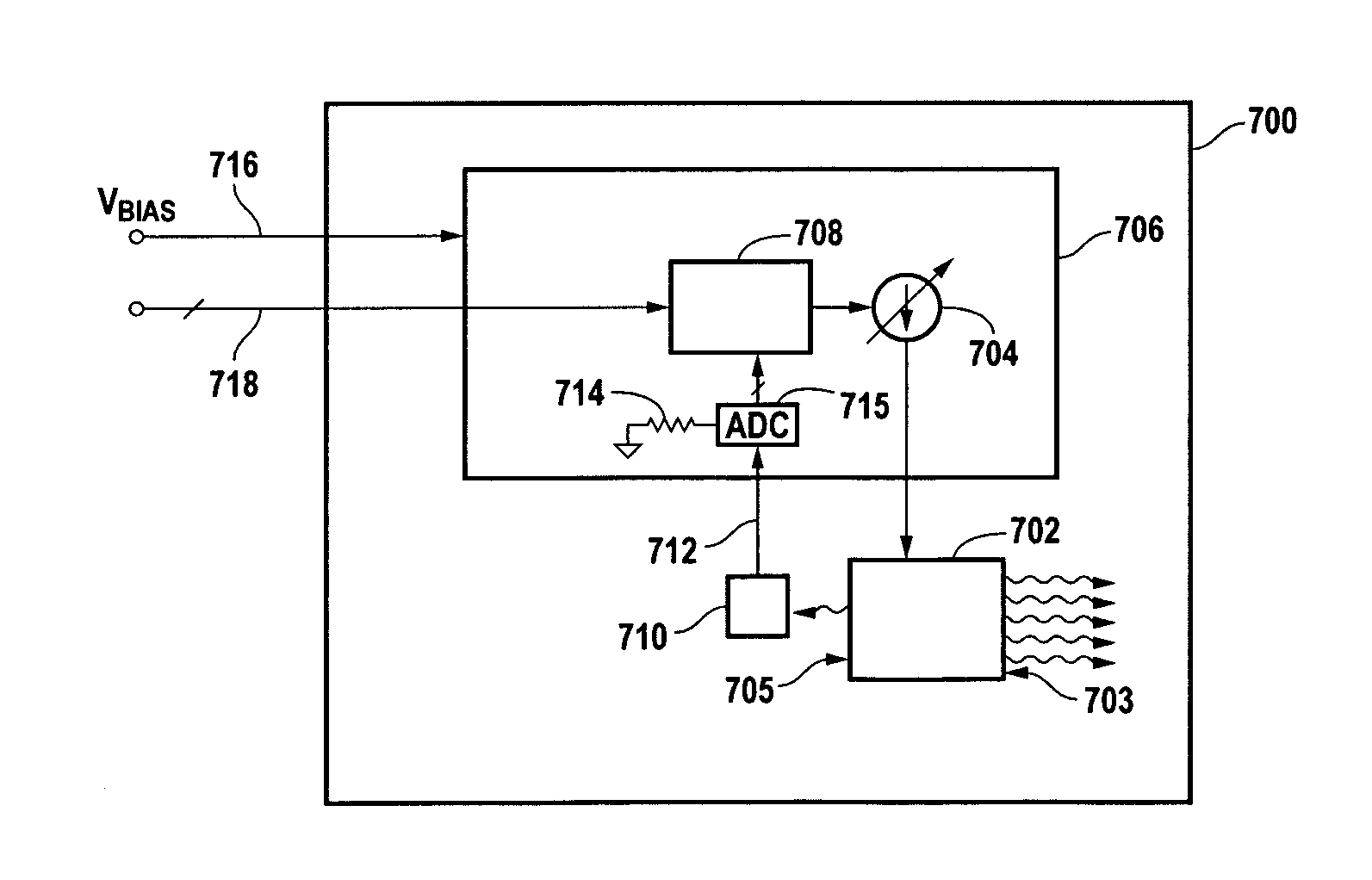
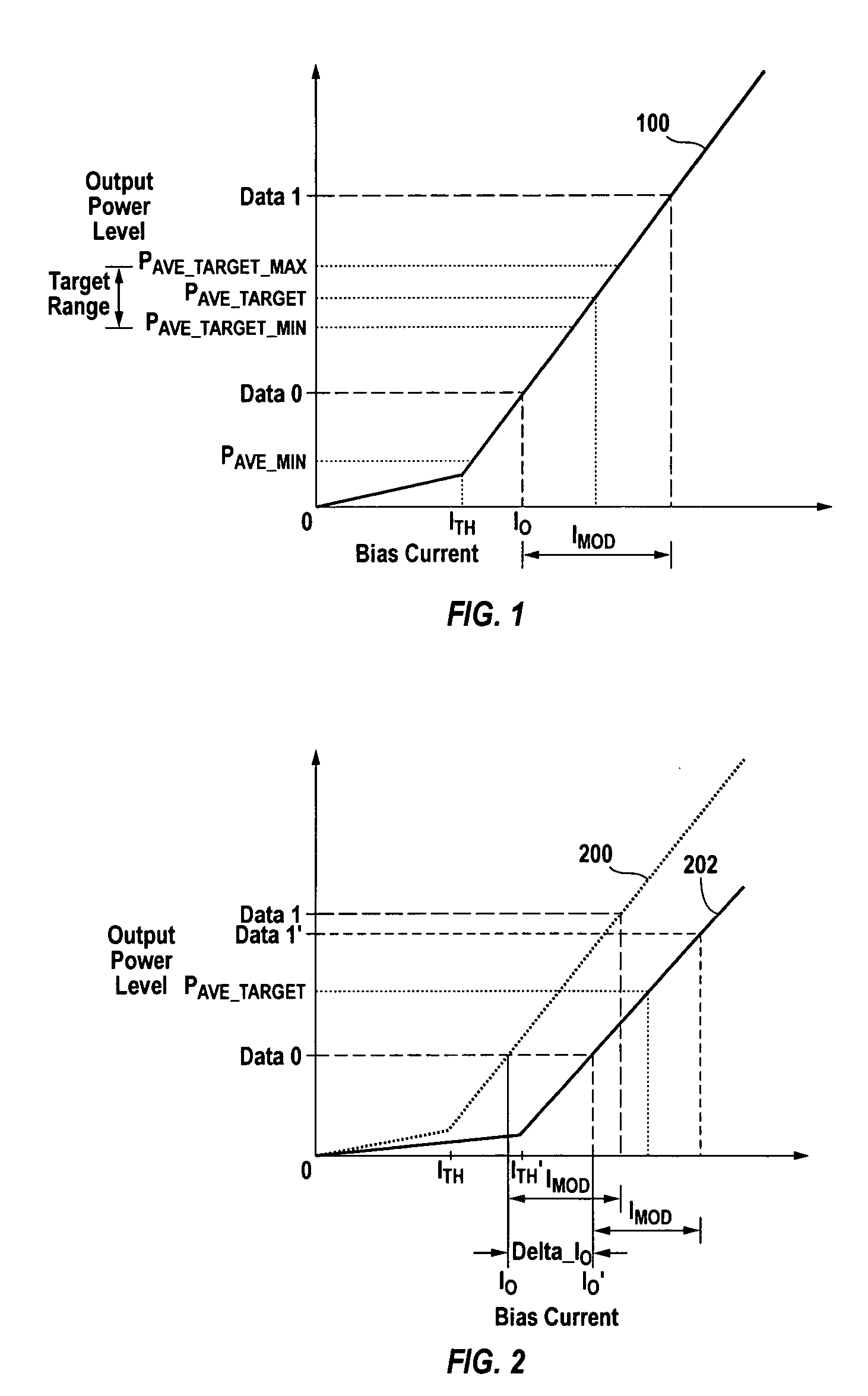
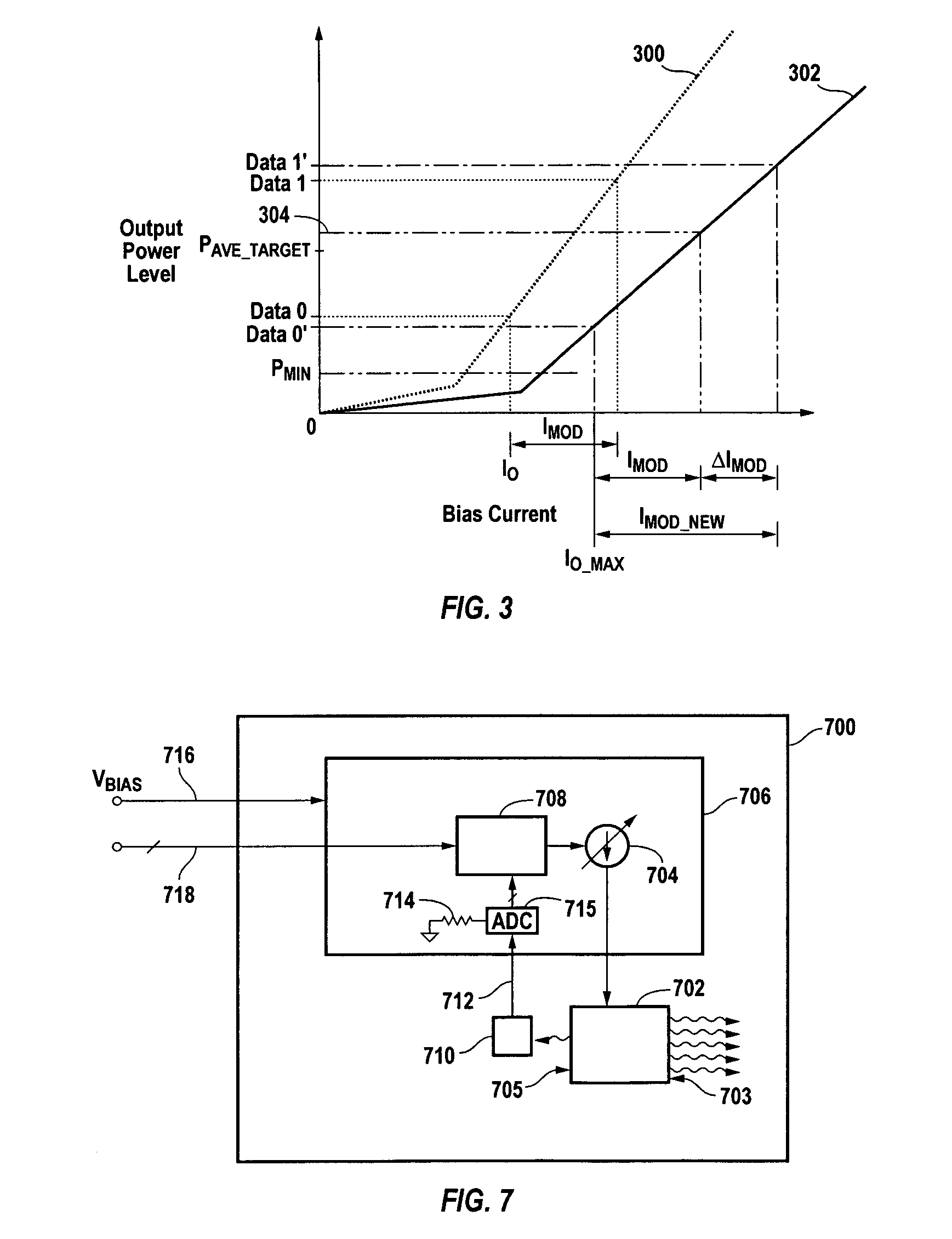
Method of monitoring and controlling a laser diode
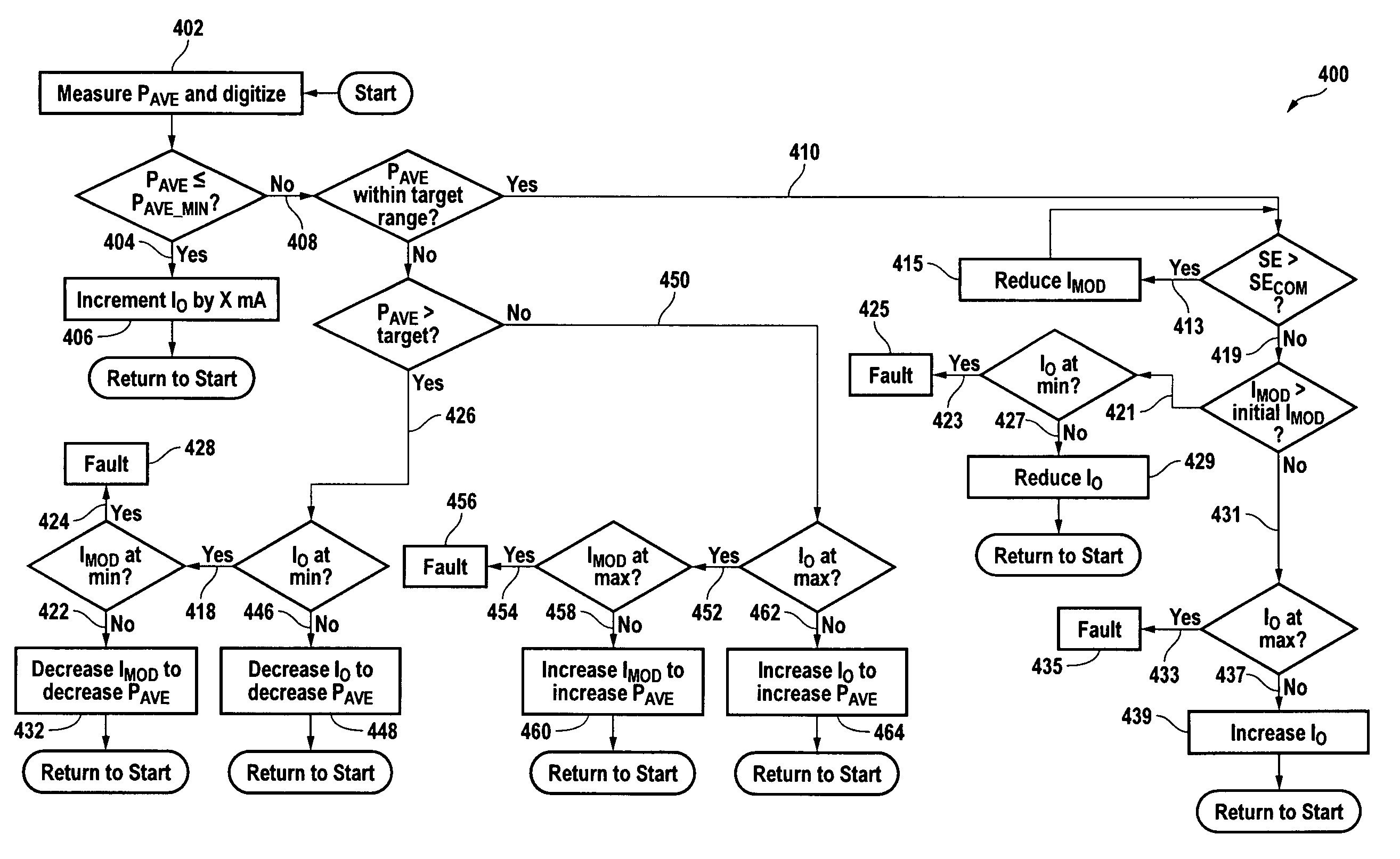
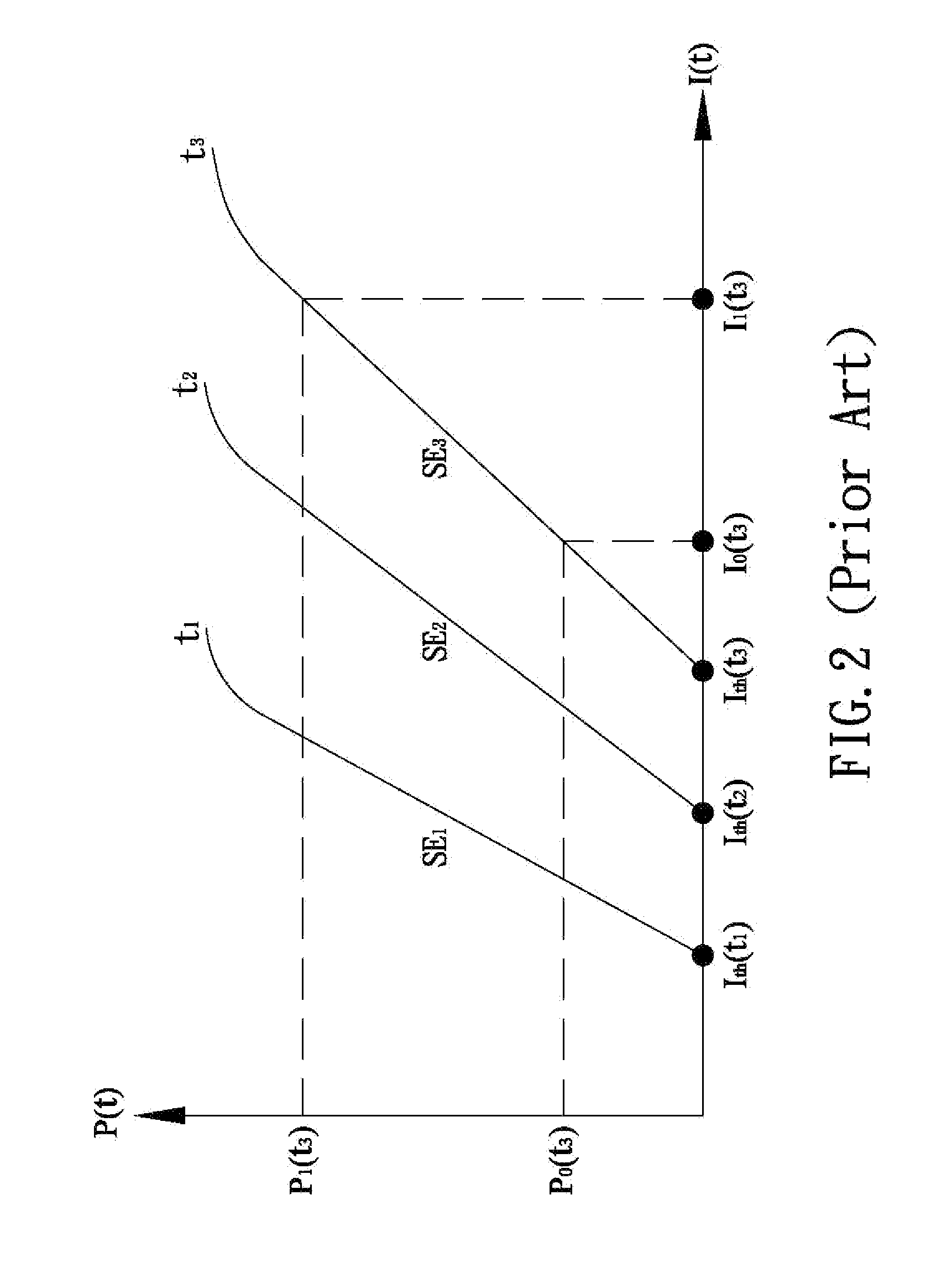
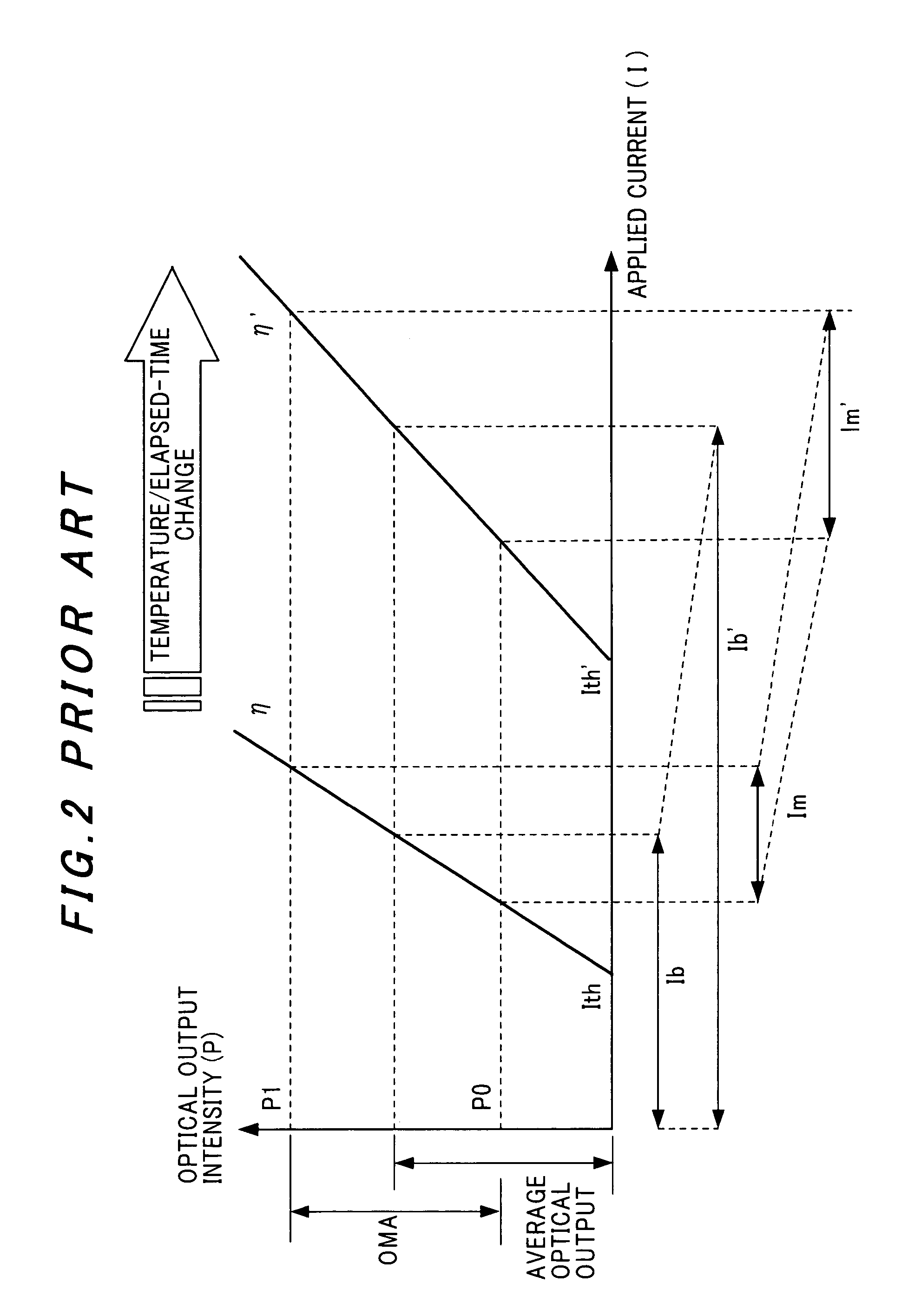
A method of controlling a laser diode measures an average light output power of the laser diode and compares the average light output power to a desired average light output power within a target range. If the average light output power is not within the target range, the slope efficiency is determined by measuring two light output powers at two different bias conditions. Each of the two light output powers is greater than a selected minimum light output power, which insures that each measurement occurs within the slope efficiency portion of the laser diode curve. A new bias current for the laser diode is calculated based on the measured slope efficiency so as to produce a new average light output power within the target range.
Owner:AVAGO TECHNOLOGIED FIBER IP SINGAPORE PTE LTD
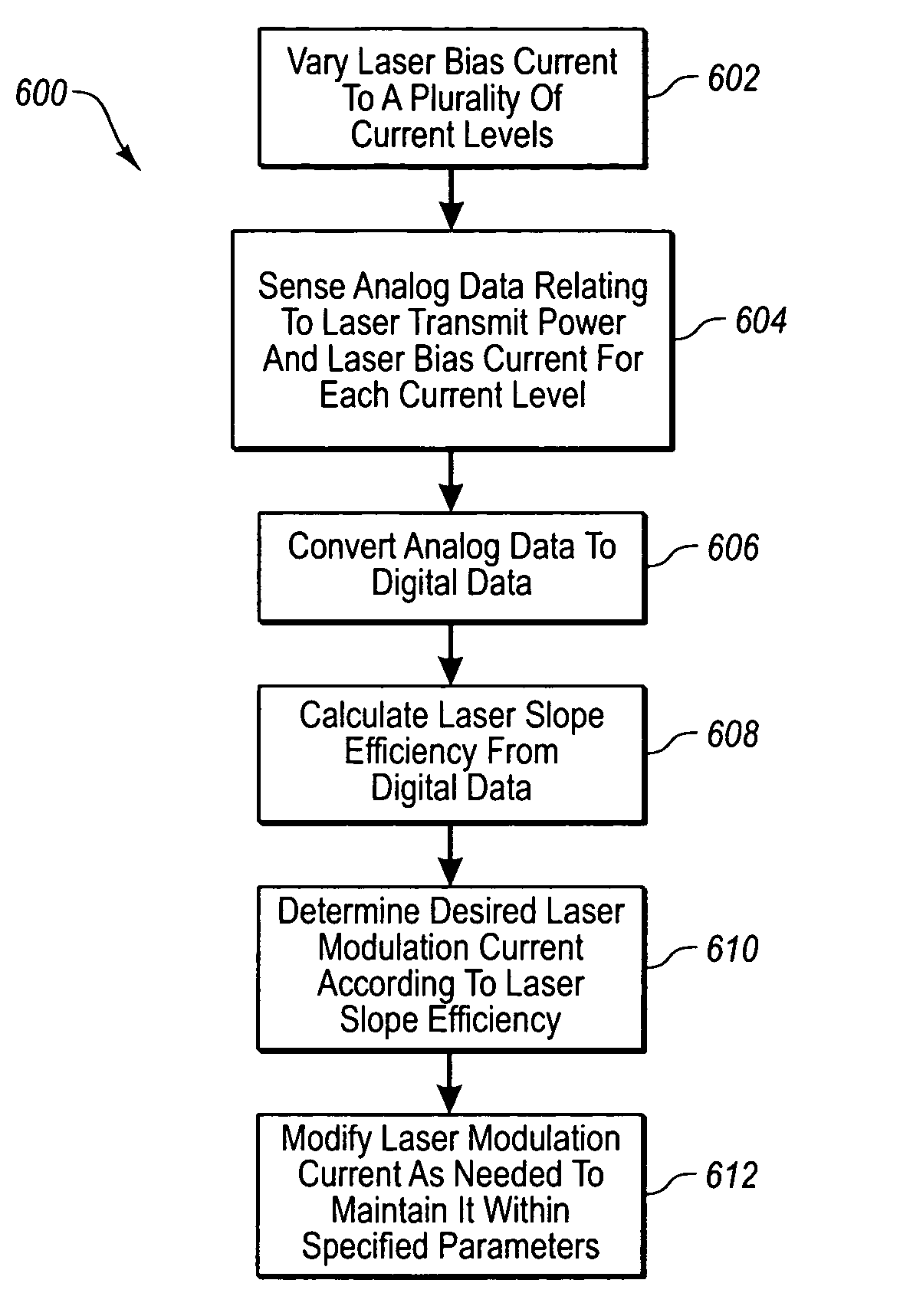
Calculation of laser slope efficiency in an optical transceiver module
ActiveUS20060216040A1Effective calculationAccurate currentTransmission monitoringElectromagnetic transmittersTransceiverOptical transmitter
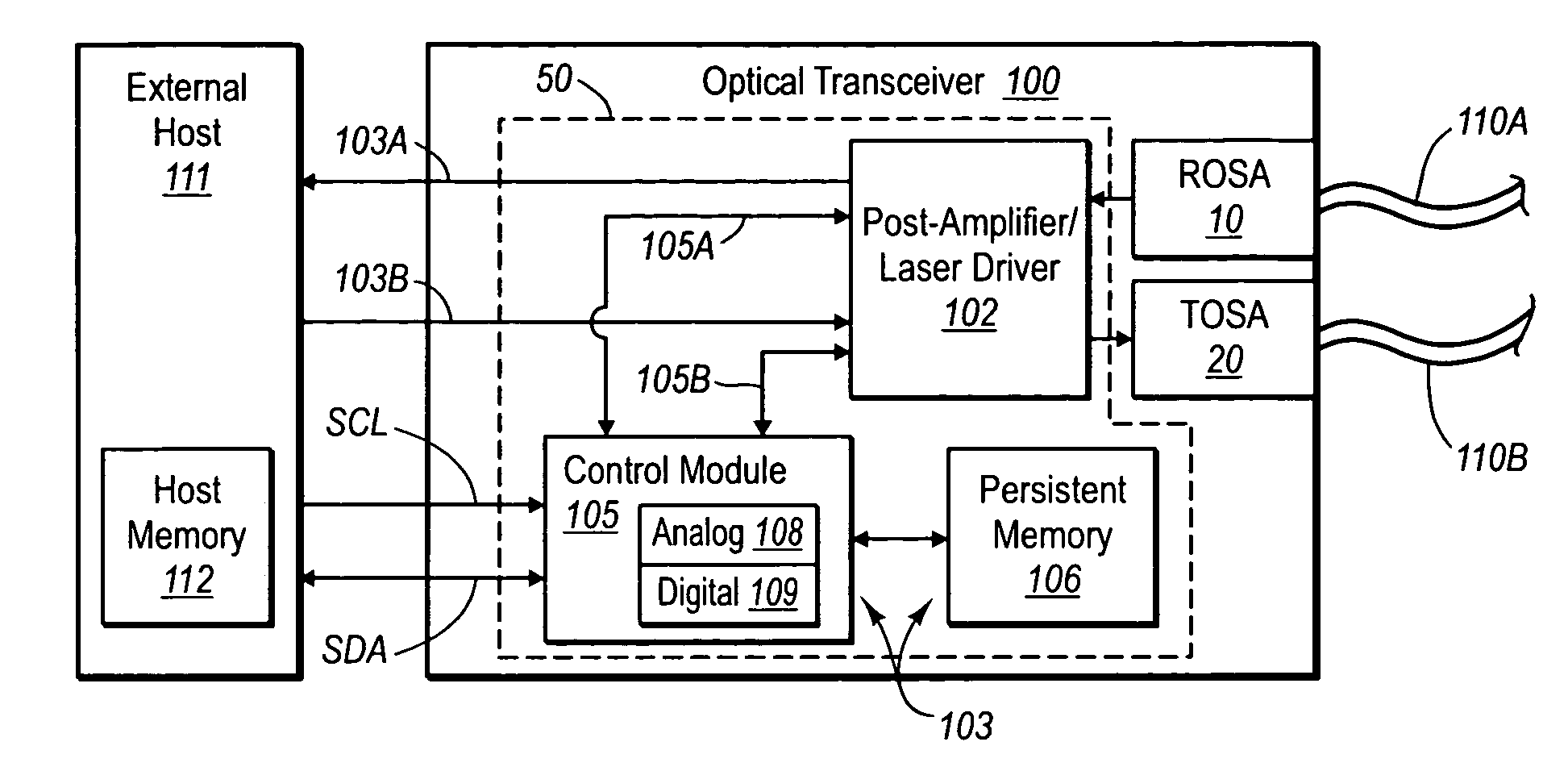
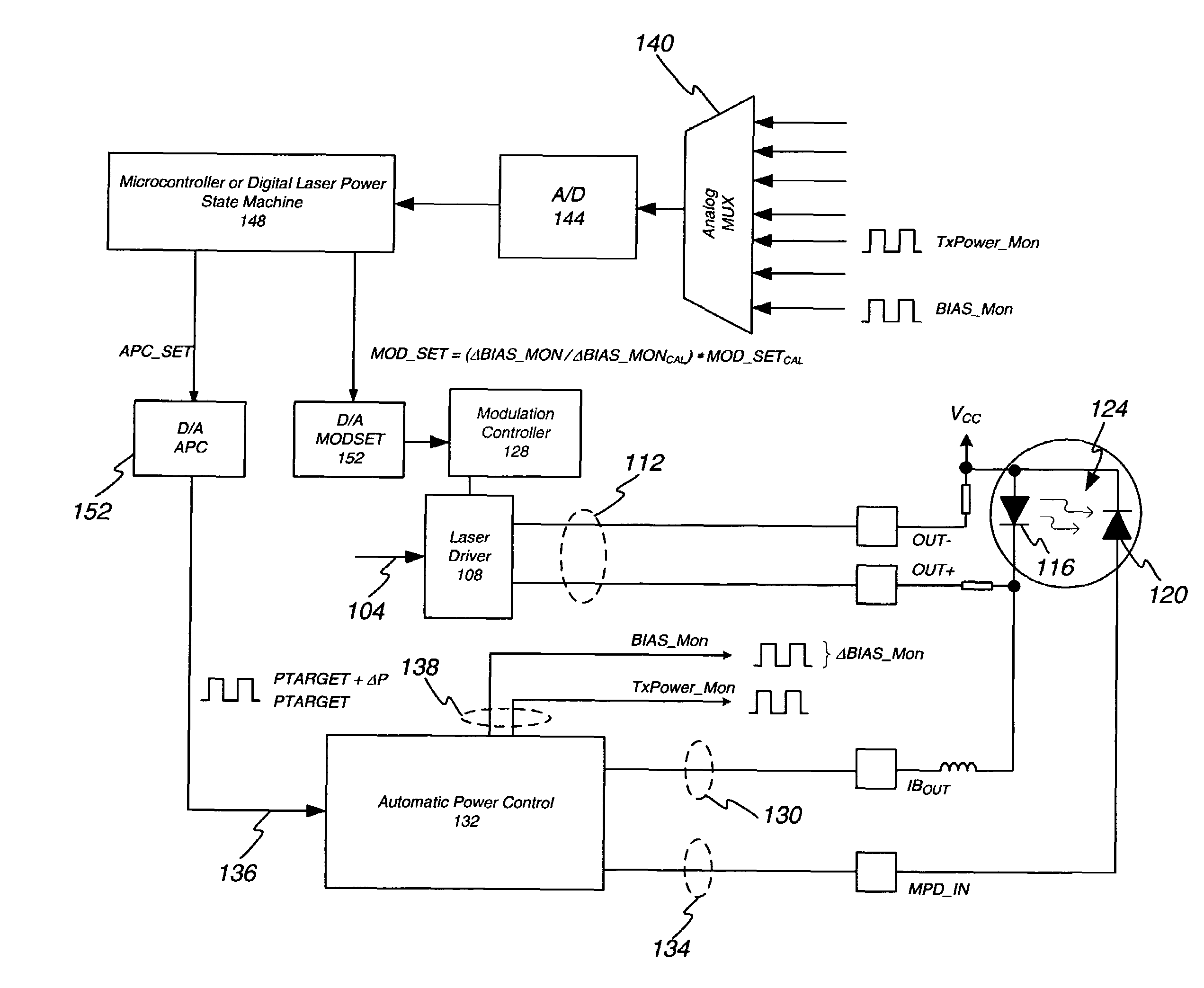
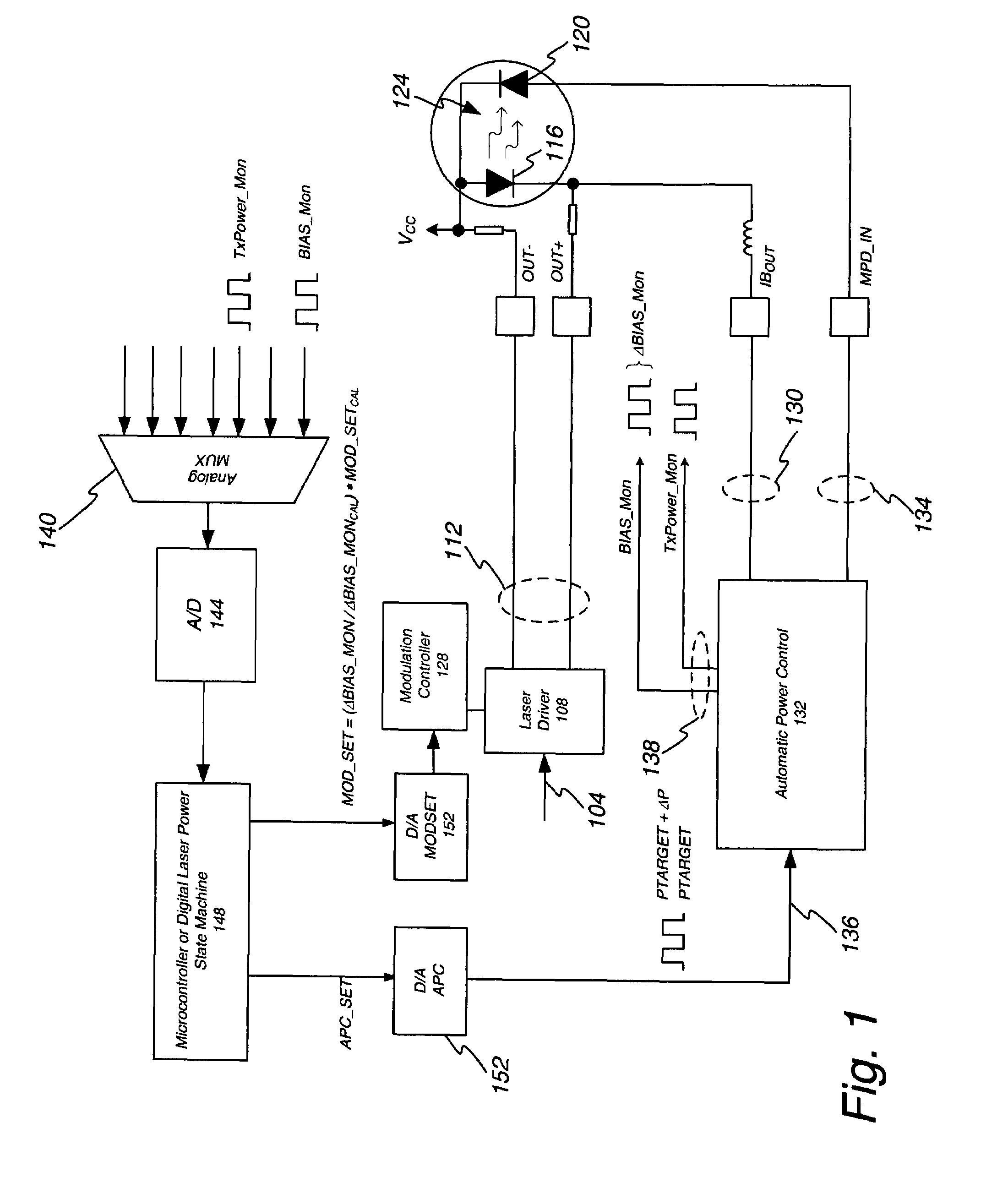
Systems and methods are provided for determining and compensating for the laser slope efficiency of a light source positioned in an optical transmitter in order to properly set a modulation current for the light source. In one embodiment, a method for setting a modulation current for the laser of an optical transmitter is disclosed, wherein data relating to the laser transmit power and laser bias current at a plurality of laser bias current levels are sensed. A processor is then employed to calculate a slope efficiency of the laser using the data. The processor then determines a desired modulation current for the laser using the slope efficiency. Then if needed, the modulation current of the laser is modified to match the desired modulation current.
Owner:II VI DELAWARE INC
Control method and control circuit for laser diode, and optical transmitter using the same
InactiveUS20050286575A1Easy to adjustInhibit deteriorationLaser detailsSemiconductor lasersAutomatic controlAmplitude control
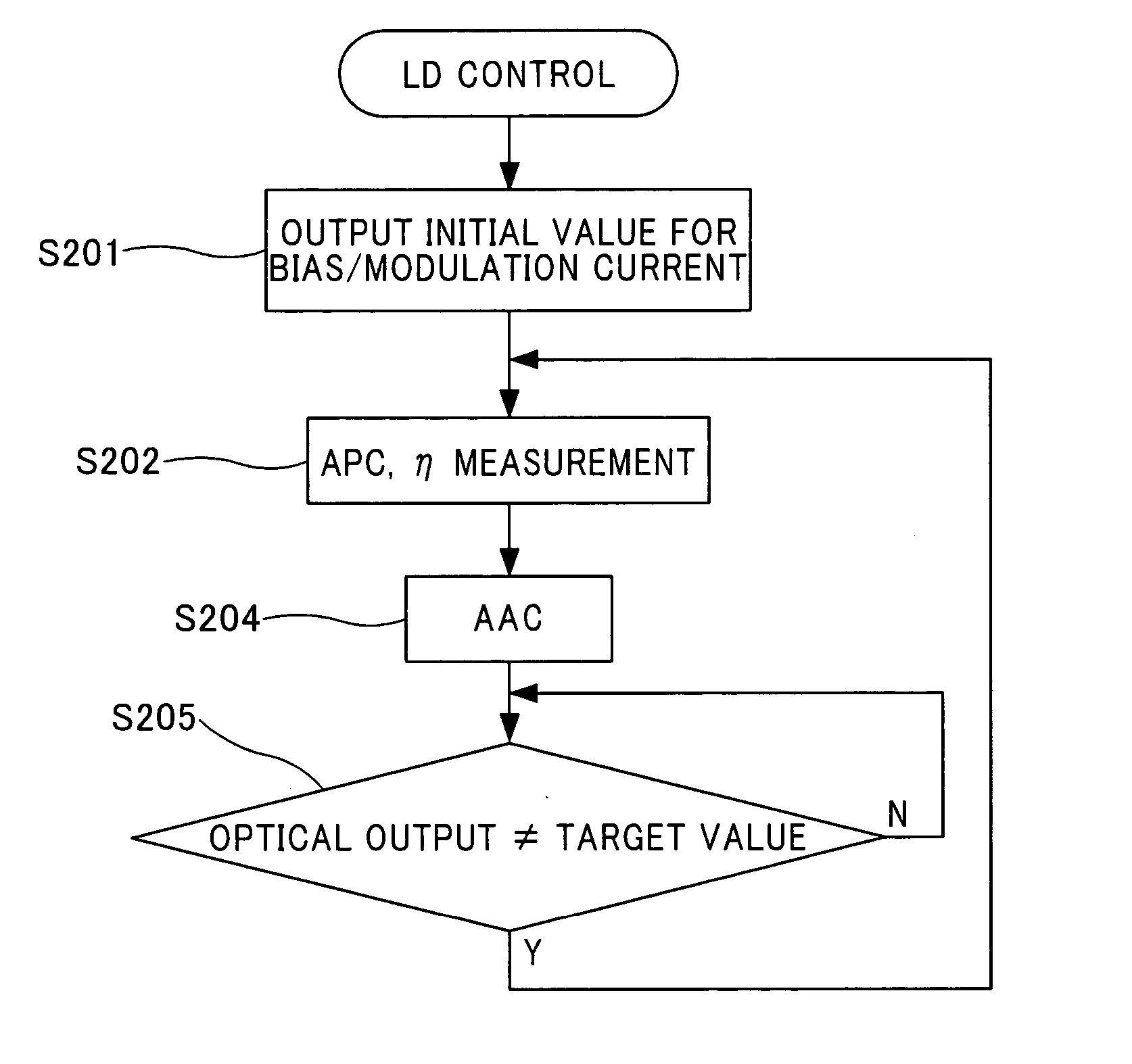
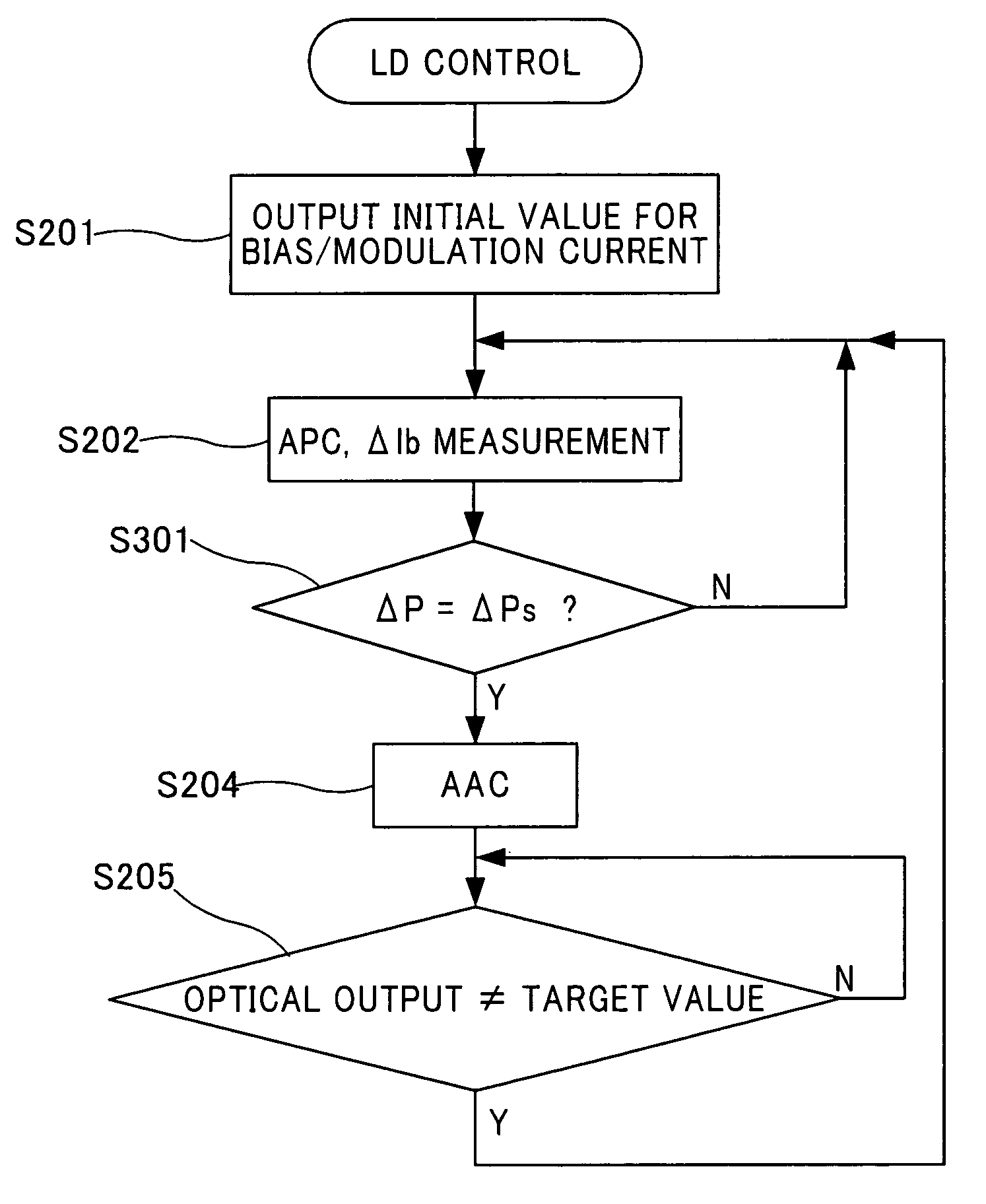
A control method for a laser diode is conducted such that optical output and OMA (optical modulation amplitude) or extinction ratio of the laser diode are controlled while modulating the optical output of the laser diode by applying a bias current and a modulation current to the laser diode. The method has: a first step of measuring the optical output of the laser diode; a second step of measuring a slope efficiency or a corresponding value of the slope efficiency while conducting APC (automatic power control) to adjust the bias current such that the optical output coincides with a predetermined value; and a third step of adjusting the modulation current by AAC (automatic amplitude control) according to the slope efficiency or the corresponding value of the slope efficiency such that the OMA or extinction ratio coincides with a predetermined value.
Owner:APRESIA SYST LTD
Optical modulation amplitude compensation system having a laser driver with modulation control signals
ActiveUS7504610B2Photometry using reference valueMaterial analysis by optical meansPower control systemControl signal
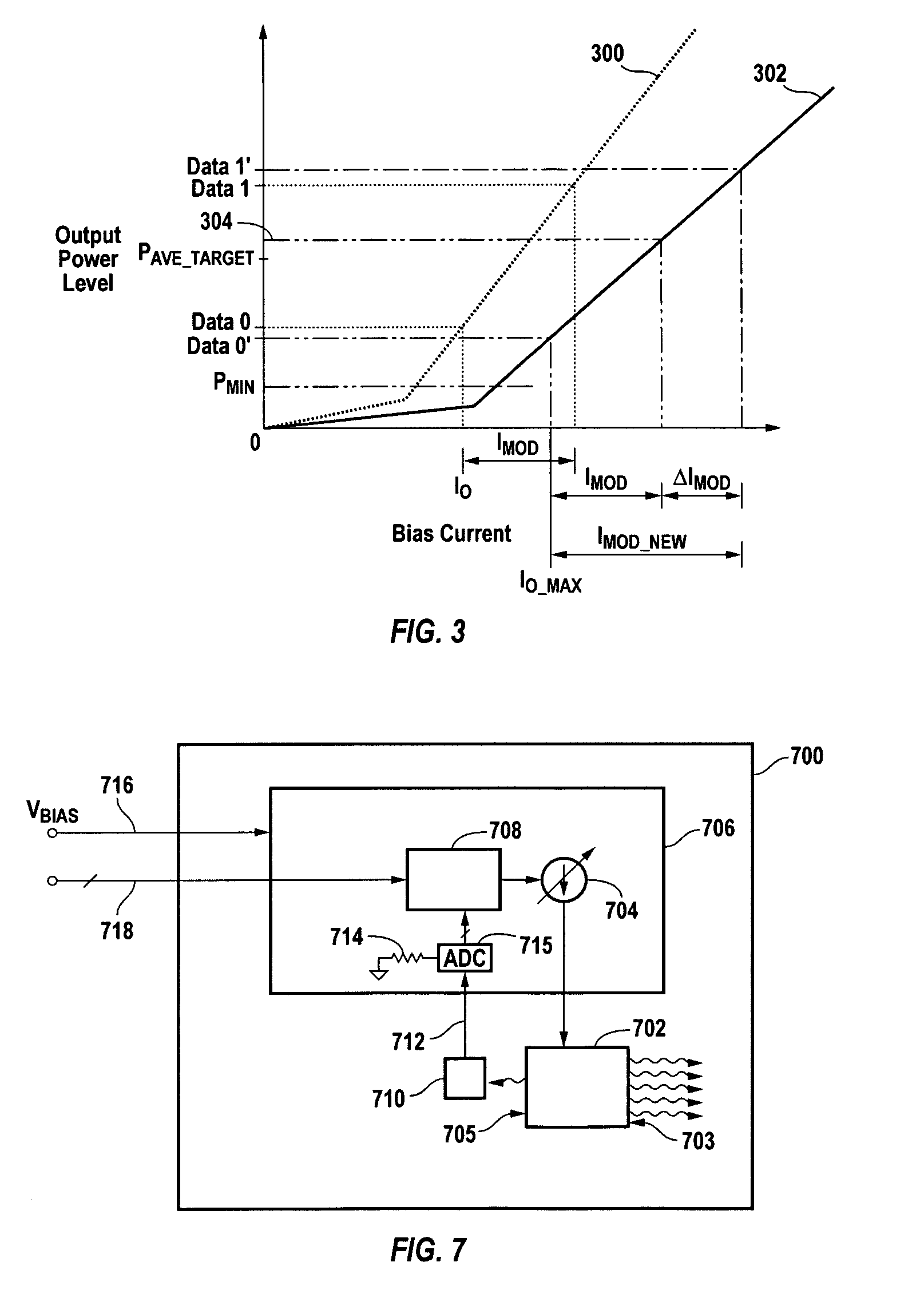
The power control system utilizing a normal average power control loop to control average power and modulation level of an optic signal generated by an optic signal generator. The target average power is adjusted by a small percentage, and the corresponding change in bias current needed to adjust the average power level is monitored. The change in average power divided by the change in bias current is a measure of the optic signal generator's slope efficiency. Modulation current is adjusted up or down based on the change in slope efficiency compared to the slope efficiency stored at the time of module calibration. By adjusting the modulation current, the desired optic signal output from the transmitter may be maintained.
Owner:MACOM TECH SOLUTIONS HLDG INC
Active optical fiber with photon darkening resistance and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102135641ALittle effect on damage thresholdHigh Damage Threshold FeaturesGlass making apparatusOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingCeriumSilicon dioxide
The invention provides an active optical fiber with photon darkening resistance. Silicon dioxide is used as matrix for a fiber core of the active optical fiber which comprises at least one type of active ions and a codoping agent, wherein the active ions are rare earth ions with the atomic number of 57-71; and the codoping agent contains aluminum, yttrium and cerium ions. The invention also provides a preparation method of the active optical fiber with the photon darkening resistance, comprising the following steps of: firstly carrying out polishing treatment on a pure quartz reaction tube; depositing an envelope layer and a core layer, and then soaking in a hydrochloric acid-alcohol mixed solution of the active ions and the cerium and yttrium ions; drying after soaking; vitrifying the pure quartz reaction tube to prepare an optical fiber preformed rod; and finally drawing the prepared optical fiber preformed rod to prepare the active optical fiber. The active optical fiber is greatly enhanced in photon darkening resistant property; and in addition, an optical fiber laser prepared by using the active optical fiber has the slope efficiency kept more than 80 percent and has higher stability and longer service life.
Owner:武汉长进光子技术股份有限公司
Method for optimizing laser diode operating current
ActiveUS20070253454A1Sufficient speed of operationMinimum currentLaser detailsSemiconductor lasersMinimum biasDriving current
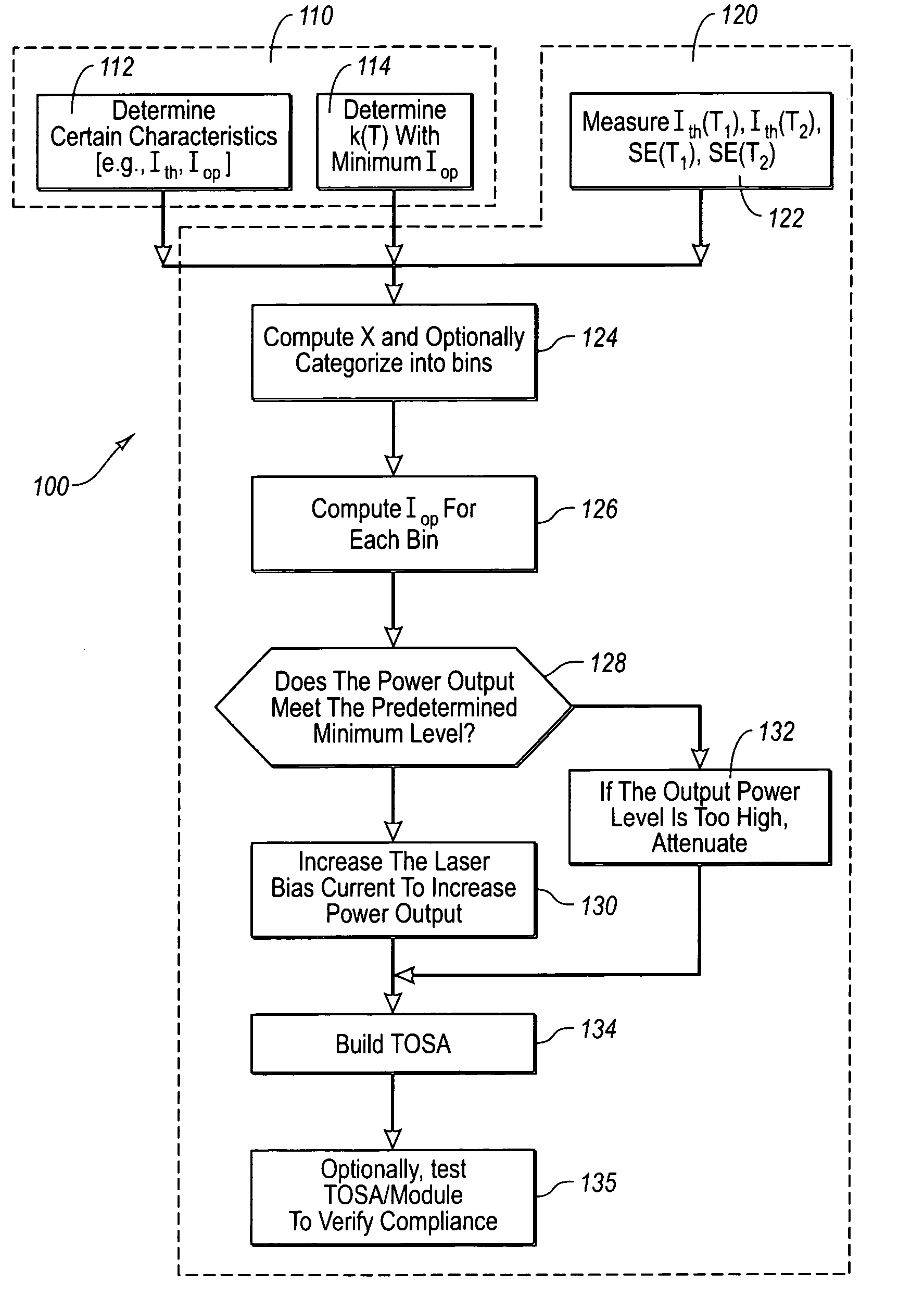
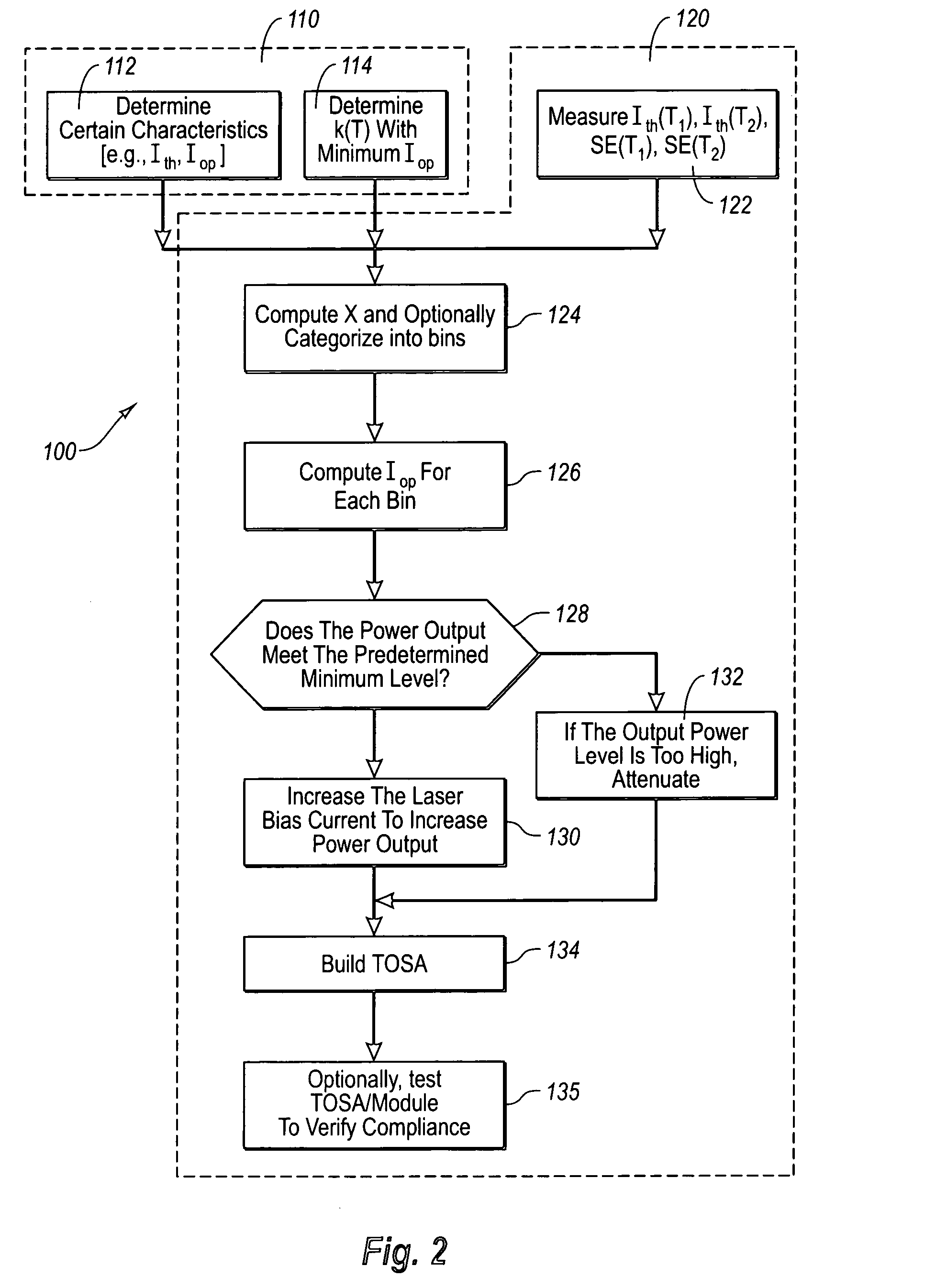
A method for optimizing a dc operating drive current of a laser diode is presented. Lasers of a particular type are characterized in terms of the dependency of certain parameters on temperature and of the minimum bias current required for adequate laser speed. The minimum bias current is determined using the operating bias current minus the threshold current all normalized by the threshold current. For individual laser diodes, the threshold current and slope efficiency are obtained at various temperatures to allow calculation at operating temperatures of interest. The minimum laser bias current for speed can then be determined over the operating temperature range. This may be done by setting the optical power to the highest value calculated using this minimum acceptable bias criterion over the operating temperature range. The ac and dc laser driver current sourcing requirements may be computed to ensure laser and module compatibility.
Owner:II VI DELAWARE INC
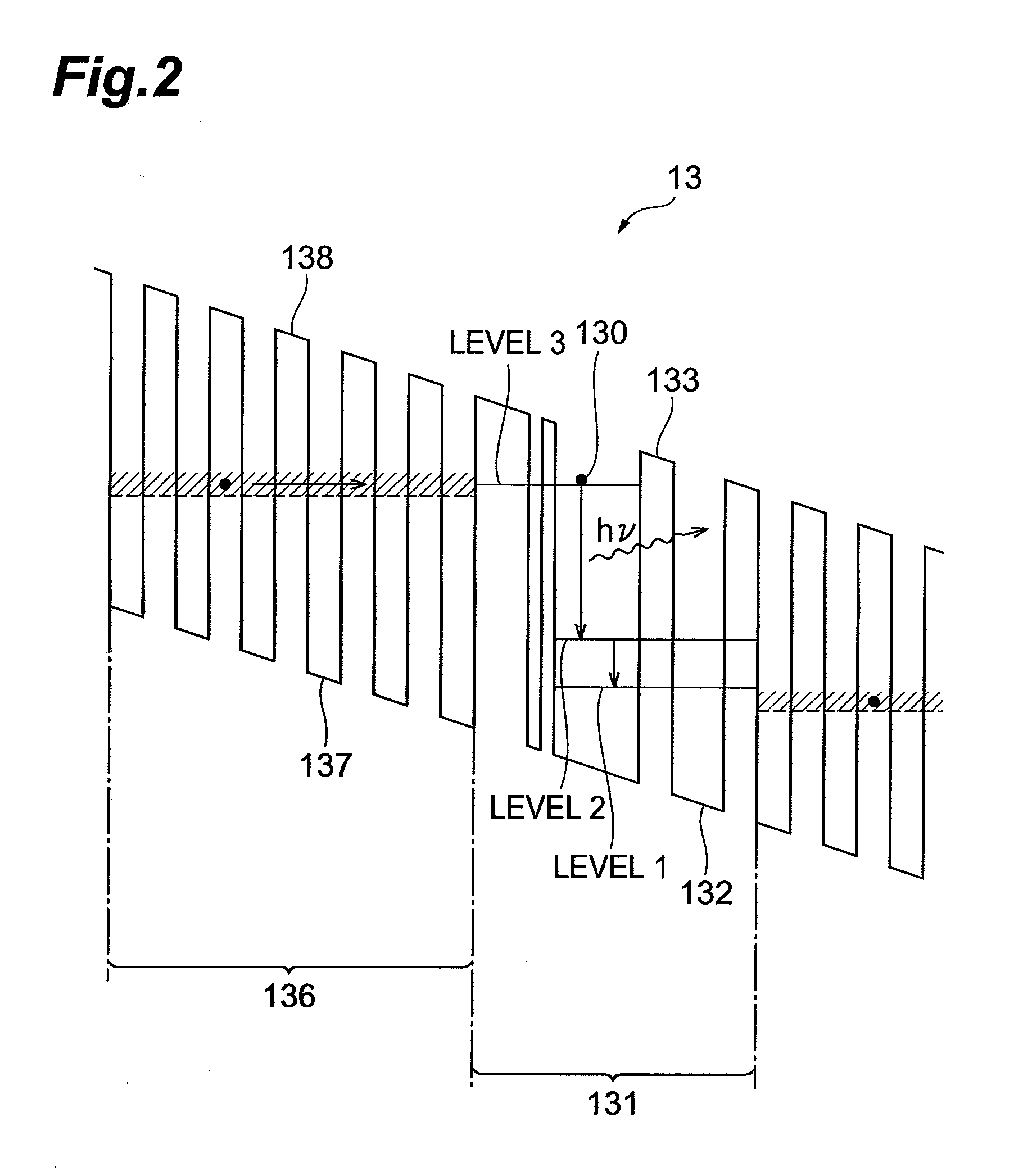
Quantum cascade laser device
InactiveUS20080219312A1Improve slope efficiencyStably realizing single transverse mode operationLaser detailsLaser active region structureQuantum wellOptoelectronics
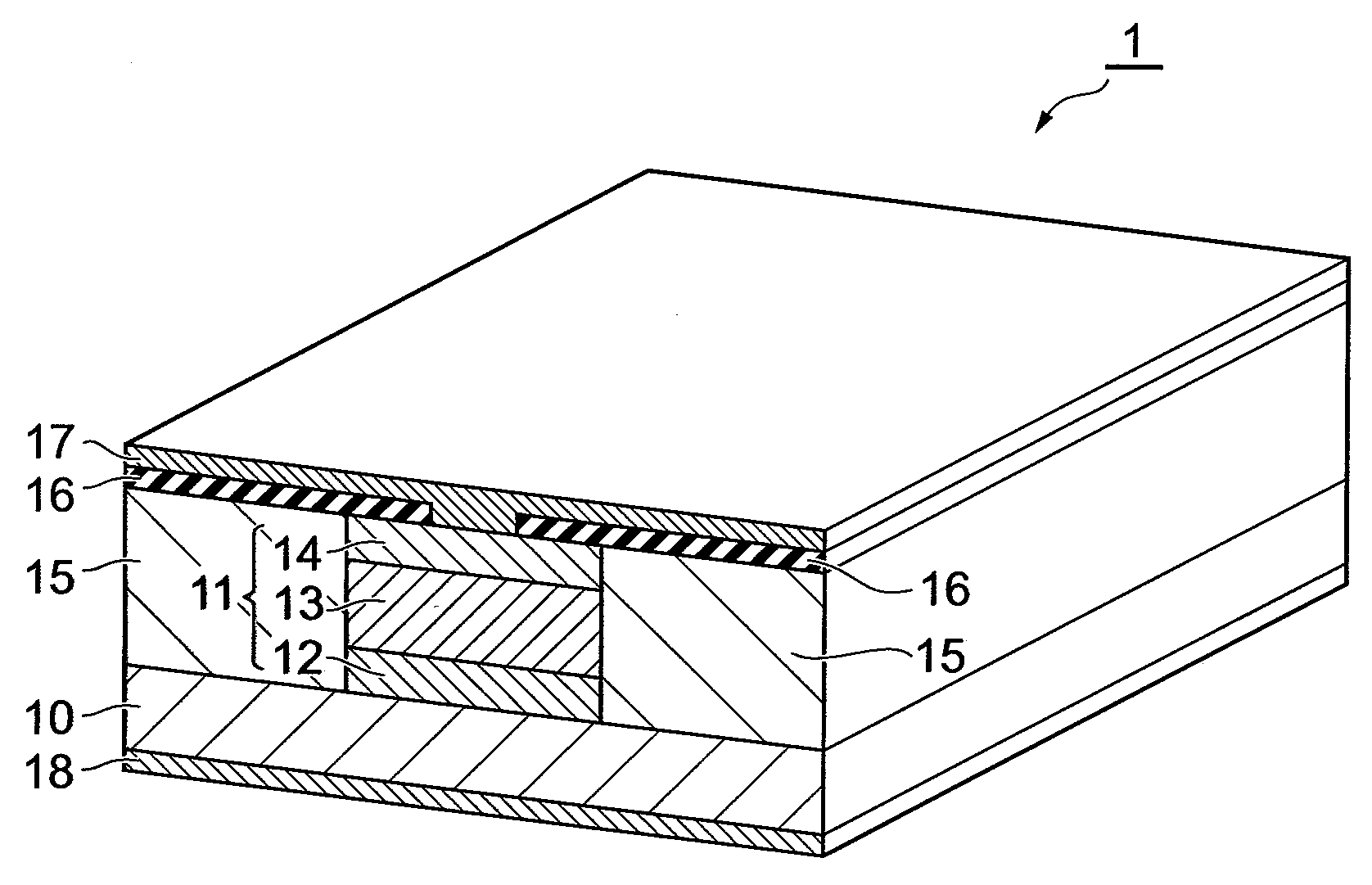
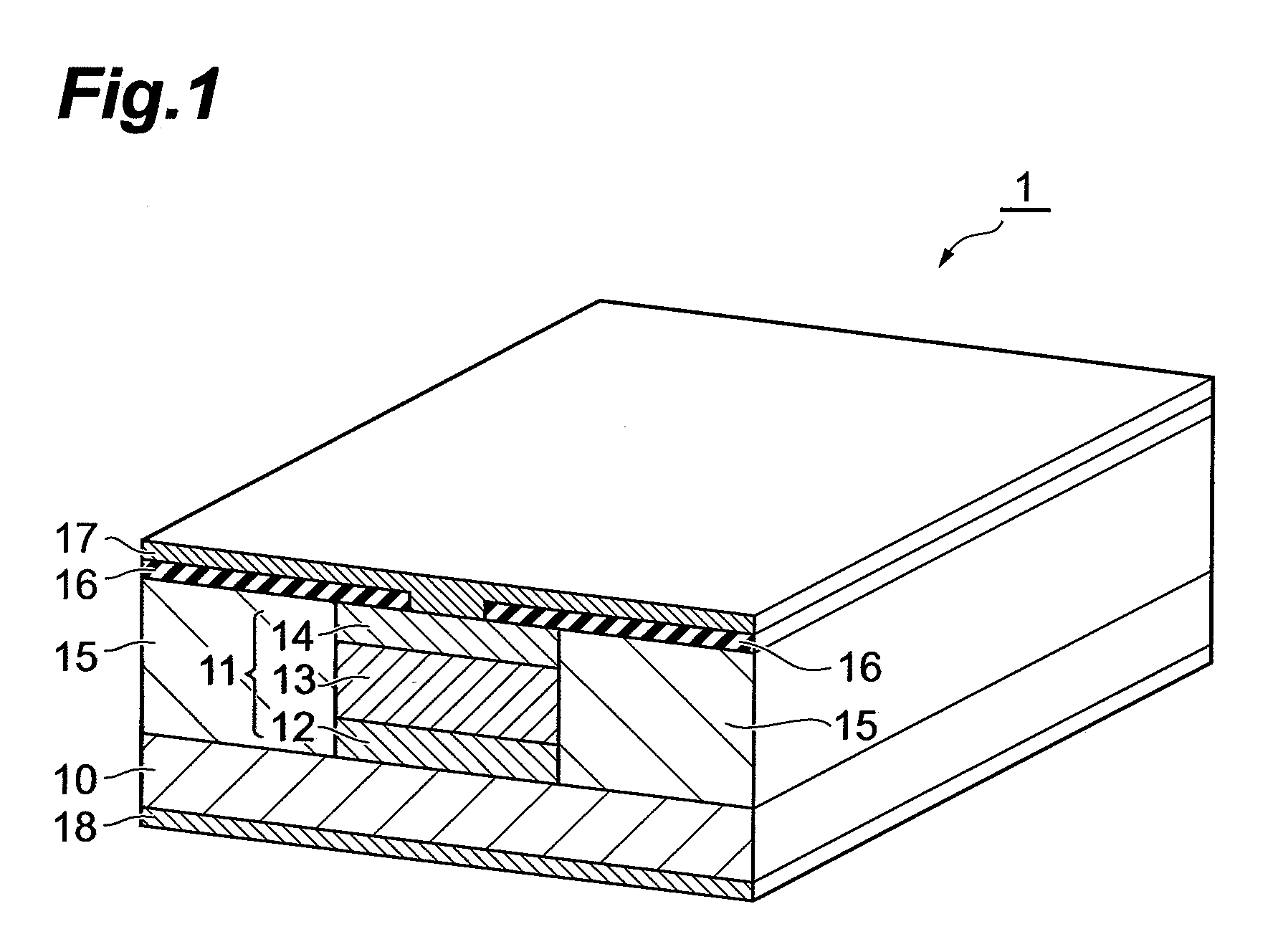
In a quantum cascade laser device 1, a laminate structure 11 is formed into a stripe shape along a predetermined direction on a principal surface at one side of a substrate 10, and insulating layers 15 are formed on bilateral sides of the laminate structure 11, and an insulating layer 16 and a metal layer 17 are formed in sequence on the laminate structure 11 and the insulating layers 15. The laminate structure 11 is formed such that a cladding layer 12, an active layer 13, and a cladding layer 14 are formed in sequence from the side of the substrate 10. In the active layer 13, light emitting layers and injection layers are alternately laminated, and the active layer 13 generates light due to intersubband electron transition in a quantum well structure. A shape in a cross section of the laminate structure 11 perpendicular to the direction in which the laminate structure 11 is provided to extend is formed into a rectangle or an inverted mesa shape. In accordance therewith, it is possible to realize a quantum cascade laser device having high slope efficiency, and being capable of stably realizing a single transverse mode operation.
Owner:HAMAMATSU PHOTONICS KK
Optical modulation amplitude compensation
ActiveUS20080013151A1Overcomes drawbackEnhanced advantagePhotometry using reference valueMaterial analysis by optical meansControl systemPower control system
The power control system utilizing a normal average power control loop to control average power and modulation level of an optic signal generated by an optic signal generator. The target average power is adjusted by a small percentage, and the corresponding change in bias current needed to adjust the average power level is monitored. The change in average power divided by the change in bias current is a measure of the optic signal generator's slope efficiency. Modulation current is adjusted up or down based on the change in slope efficiency compared to the slope efficiency stored at the time of module calibration. By adjusting the modulation current, the desired optic signal output from the transmitter may be maintained.
Owner:MACOM TECH SOLUTIONS HLDG INC
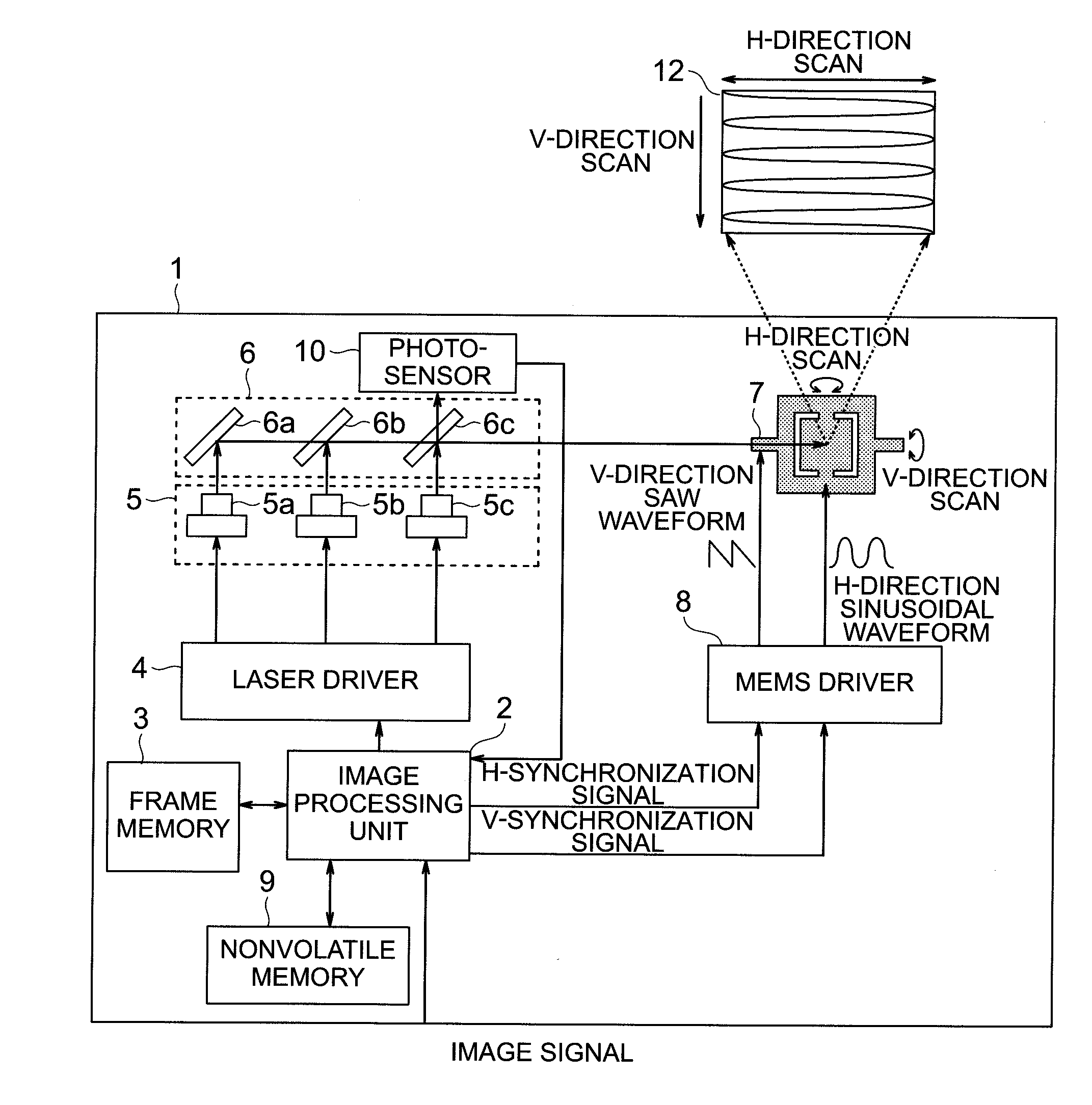
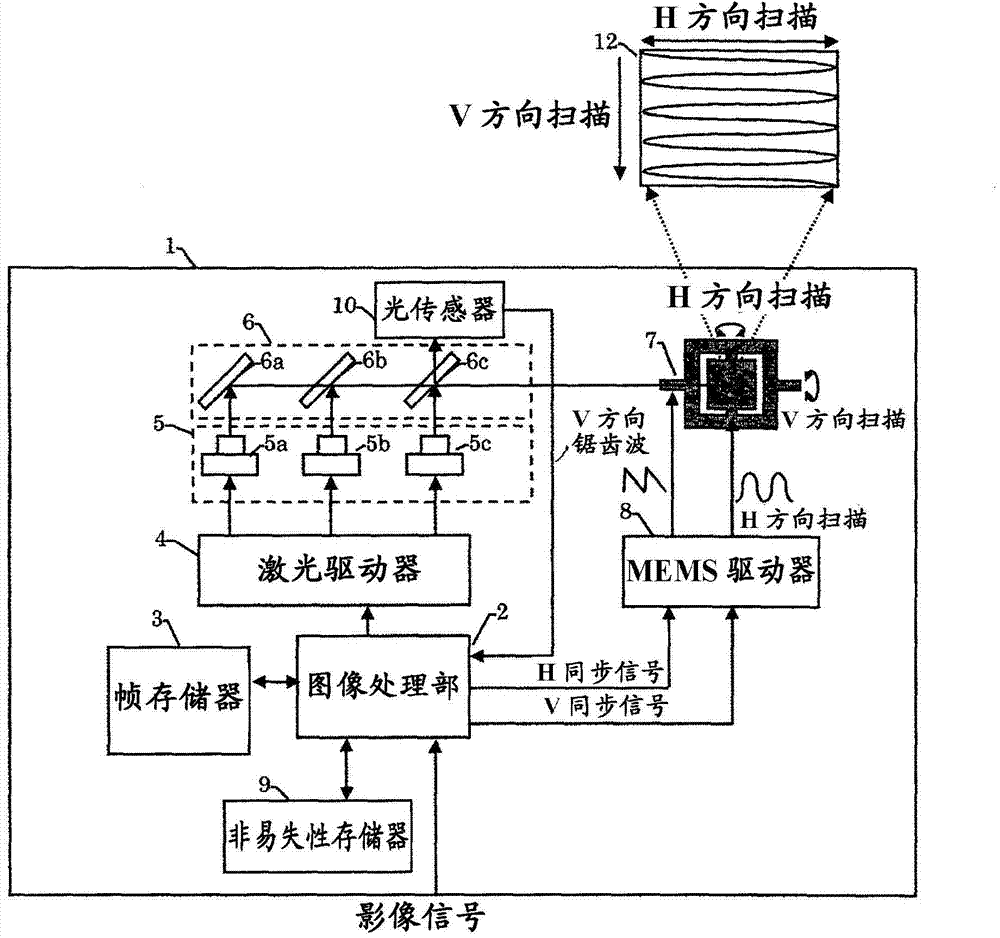
Image display apparatus
InactiveUS20130207950A1Maintaining white balance constantColor television detailsCathode-ray tube indicatorsThreshold currentImage signal
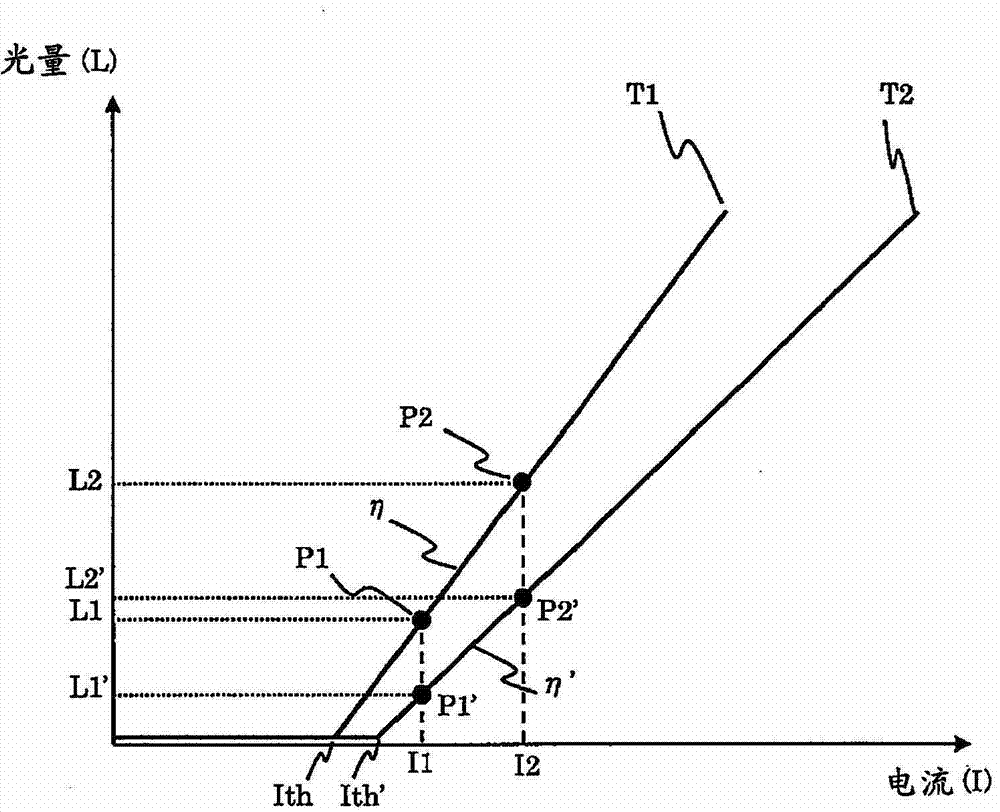
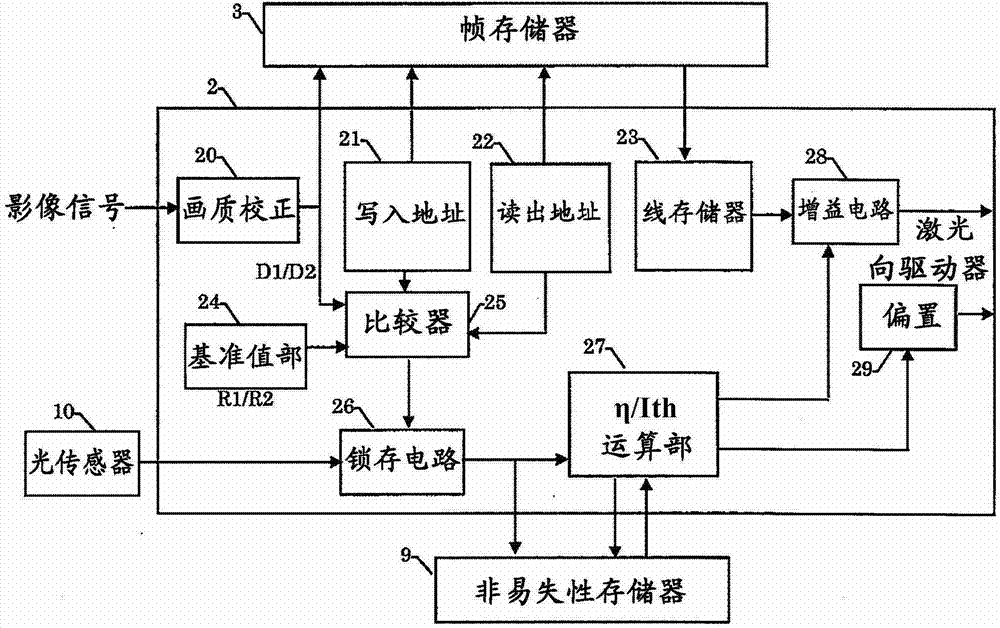
In an image display apparatus which projects and displays an image by scanning emitted light from light sources by a reflective mirror, a correction unit calculates a threshold value and a slope efficiency of a light amount vs. current characteristic of each of the plurality of light sources, from a first light amount value obtained by measuring a light amount when an input image signal agrees with a first reference signal level and a second light amount value obtained by measuring a light amount when the input image signal agrees with a second reference signal level; and corrects, when a calculation result of the threshold value and the slope efficiency varied after a predetermined time, a threshold current and also make a correction so that a light amount ratio of the light sources becomes the same as an initial value of a slope efficiency ratio.
Owner:HITACHI-LG DATA STORAGE
Method and apparatus for providing light having a selected polarization with an optical fiber
ActiveUS7724422B2Increases bend lossIncreased bend lossOptical fibre with polarisationLaser using scattering effectsRare earthLength wave
Optical apparatus (110, 500, 600, 800, 1000) for providing light having a selected linear polarization having a polarization ratio, the apparatus (110, 500, 600, 800, 1000) comprising a length of optical fiber (120, 504, 604, 804, 1001) comprising a rare earth for providing light having a first wavelength responsive to receiving pump light having a second wavelength that is different than said first wavelength, wherein if the length of optical fiber (120, 504, 604, 804, 1004) were placed in a first position between the length of fiber (120, 504, 604, 804, 1004) is substantially linearly oriented (20) the fiber (120, 504, 604, 804, 1004) could propagate at the first wavelength a fundamental mode and a plurality of higher order modes and the apparatus (110, 500, 600, 800, 1000) could provide light having a first polarization ratio for the selected linear polarization and an M2 parameter, and wherein the length of fiber (120, 504, 604, 804, 1004) is positioned in a second position that increases the bend loss of the fiber relative to the first position such that, responsive to the increased bend loss, the apparatus (110, 500, 600, 800, 1000) can provide light having a reduced M2 parameter as well as a second polarization ratio for the selected polarization that is increased relative to the first polarization ratio, the increase being at least 6 dB greater than the first polarization ratio, and wherein when the length of fiber (120, 504, 604, 804, 1004) is in the second position the apparatus (110, 500, 600, 800, 1000) can provide a slope efficiency that is at least 50% of the ratio of the second wavelength to the first wavelength.
Owner:NUFERN
Rare earth doped optical fiber
InactiveUS20080080823A1High gainImprove efficiencyLaser detailsOptical fibre with polarisationRare earthRefractive index
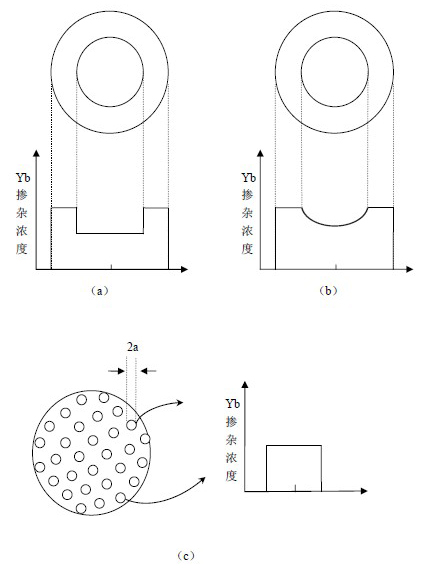
An optical fiber including: (i) a silica based, Yb doped core having a first index of refraction n1, said core comprising more than 1 wt % of Yb, said core having less than 5 dB / km loss at a wavelength situated between 1150 nm and 1350 nm and less than 20 dB / km loss at the wavelength of 1380 nm and slope efficiency of over 0.8; and (ii) at least one silica based cladding surrounding the core and having a second index of refraction n2, such that n1>n2.
Owner:CORNING INC
Multi-active zone epitaxial structure, semiconductor laser adopting same and manufacturing method of multi-active zone epitaxial structure
InactiveCN105429004AIncreased cooling burdenReduce power densityLaser detailsSemiconductor lasersSemiconductor packageDivergence angle
The invention relates to a tunnel cascaded multi-active region epitaxial structure. The tunnel cascaded multi-active region epitaxial structure includes a substrate and a plurality of heterostructure active regions which are limited respectively; the plurality of active regions are formed on the substrate sequentially; and the plurality of active regions are connected with each other through reversely-biased PN junctions. The invention also provides a semiconductor laser adopting the epitaxial structure. According to the laser, a buffer layer and an electrode contact layer are sequentially grown on the uppermost active region; and follow-up laser fabrication is completed through using a standard wide-surfaced strip-shaped laser fabrication process. The number of active regions in the epitaxial structure can be adjusted between 2 to 4 according to needs. With the tunnel cascaded multi-active region epitaxial structure and the laser adopting the same adopted, output power and slope efficiency can be improved, and a vertical divergence angle can be greatly reduced.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Random fiber laser with tunable wavelength
InactiveCN102437500AImprove slope efficiencyWavelength tunableLaser using scattering effectsActive medium shape and constructionRandom laserSeeds source
The invention discloses a random fiber laser system with tunable wavelength, belonging to the laser device field. According to the system, first pump source laser with tunable wavelength and a series of low energy seed source laser are injected into a fiber, through a series of Raman amplification effects, distributed Raman amplification light is generated in a transmission fiber, and distributedRayleigh backward diffusion light forms random laser after Raman amplification. A random laser in the invention can realize continuous tunable wavelength. In a selectable scheme, after first Raman amplification, residual energy of a first pump source or a first seed source is fed back to the fiber for reuse, and slope efficiency of a finally formed random laser is raised. The system can control aRaman gain and a shape of a Raman gain spectrum through additional seed light, reduce a threshold of the laser, and raise output power.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Method for controlling optical power and extinction ratio over entire temperature range
ActiveUS20130230314A1Efficient use ofMinimal costTransmission monitoringTransmission monitoring/testing/fault-measurement systemsFiberTransceiver
The present invention is to provide a method applicable to a fiber-optic transceiver including a transmitter optical subassembly (TOSA) provided therein with a laser diode, but without a monitoring photodiode, a laser driver controlled by a controller IC for driving the laser diode to generate a laser beam, and a thermal sensor for sensing temperature of the laser diode. The method includes executing an approximation process to characteristic data, i.e. threshold currents of the laser diode at a plurality of specific temperatures and corresponding slope efficiencies (SE), provided by manufacturer for obtaining relationship therebetween over entire temperature range, manually adjusting operation parameters (such as bias current and modulation current) of the laser diode for generating expected optical power and extinction ratio at a normal temperature and for subsequently determining the operation parameters over the entire temperature range, and writing the relationship and operation parameters thus obtained into the controller IC.
Owner:ALPHA NETWORKS INC
Watt-grade broadband super-fluorescence light source with ytterbium doped photonic crystal fiber
InactiveCN1844732AImprove coupling efficiencyImprove slope efficiencyLaser detailsCladded optical fibreOptical tomographyFluorescence
The invention relates to an ultra-fluorescence optical fiber light source, which uses Yb-doped photon crystal optical fiber as gain medium, to attain low time interference and high space interference, belonging to the technique of wide-band optical fiber light source and optical fiber sensing. Wherein, the pump semi-conductor laser, lens coupling system, dichroic mirror, Yb-doped large mode-area dual-envelope photo crystal optical fiber and collimation lens are arranged to form dual-range forward or backward output device; compared to general high-power optical fiber ultra-fluorescence light source, the invention has simple structure, better time stability, high incline efficiency, high output power, flat spectrum, and wider band width. The invention can be used in optical fiber sensing, optical fiber top, and optical tomography, etc.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Random fiber laser
InactiveCN102801091AImprove stabilityImprove efficiencyActive medium shape and constructionRayleigh scatteringRefractive index
The invention discloses a random fiber laser system. According to the system, an optical fiber serves as a laser medium, and a fiber laser comprising a crystal fiber laser, a nonlinear fiber laser, a rare earth doped fiber laser and a plastic fiber laser serves as pump light to be coupled into the optical fiber. Because the refractive index of the optical fiber has non-uniformity and is randomly distributed along the optical fiber, so that the photon is subjected to rayleigh scattering during transmission in the optical fiber; and moreover, the pump light provides gain for the backward scattered light along the optical fiber, when the overall gain is greater than the total loss, the backward scattered light is amplified to form random laser. A discrete optical component is not arranged in the light path of the system, so that all-fiber connection is realized. In the system, the residual pump light is returned to the optical fiber, and the distributed weak scattered light is amplified, and therefore, according to the random fiber laser system, the threshold power of the pump light can be reduced, the utilization rate of the pump light can be improved, and the slope efficiency of the laser is improved.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Image display apparatus
Owner:HITACHI-LG DATA STORAGE
Glass ceramics whispering gallery mode resonant cavity capable of outputting single mode high-performance laser and preparation method thereof
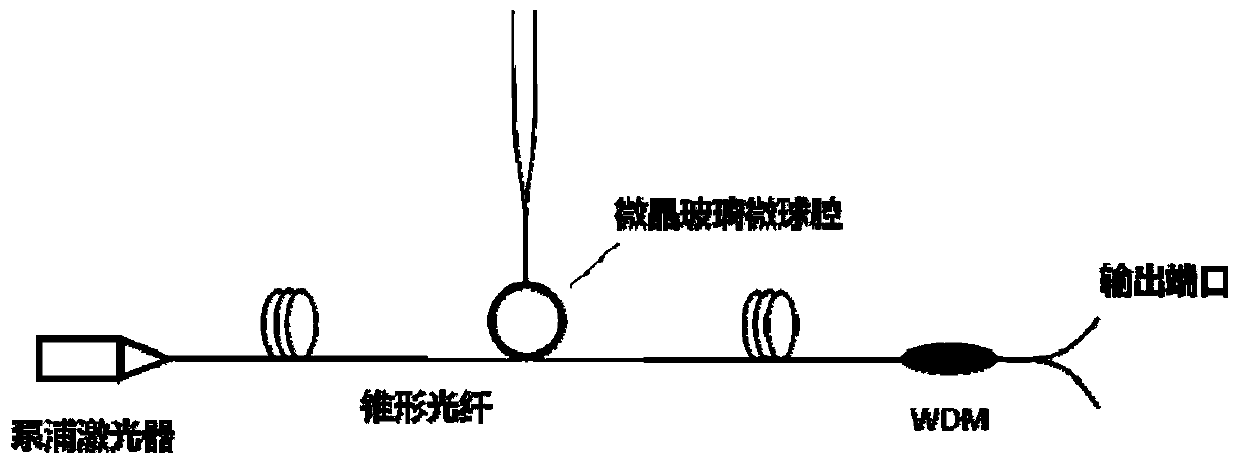
ActiveCN109809685ALower the thresholdImprove slope efficiencyGlass making apparatusOptical resonator shape and constructionFiberWhispering gallery
The invention discloses a glass ceramics whispering gallery mode resonant cavity capable of outputting single mode high-performance laser and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the field ofoptical devices. The method comprises the following steps: firstly mixing raw materials for preparing the glass resonant cavity with rear earth active ion raw materials sufficiently, then carrying outmelting and rod winding to obtain active fiberglass; drawing the active fiberglass to tapered fiber by melt extraction, and truncating the tapered fiber in the middle to obtain single taper fibers; melting the thin ends of the single taper fibers through a heating source, and forming a microsphere cavity by utilizing the action of surface tension; carrying out heat treatment or laser-induced treatment on the microsphere cavity to obtain a glass ceramics microsphere cavity, and carrying out coupling with the tapered fiber and packaging to obtain the glass ceramics whispering gallery mode resonant cavity. According to the invention, the preparation process is simple, the prepared glass ceramics microsphere cavity has relatively high quality factor, the influence on active ion gain propertyof amorphous state and relatively high phonon energy of glass is improved by the separation of microcrystal, and laser output with lower threshold value and higher slope efficiency can be realized.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
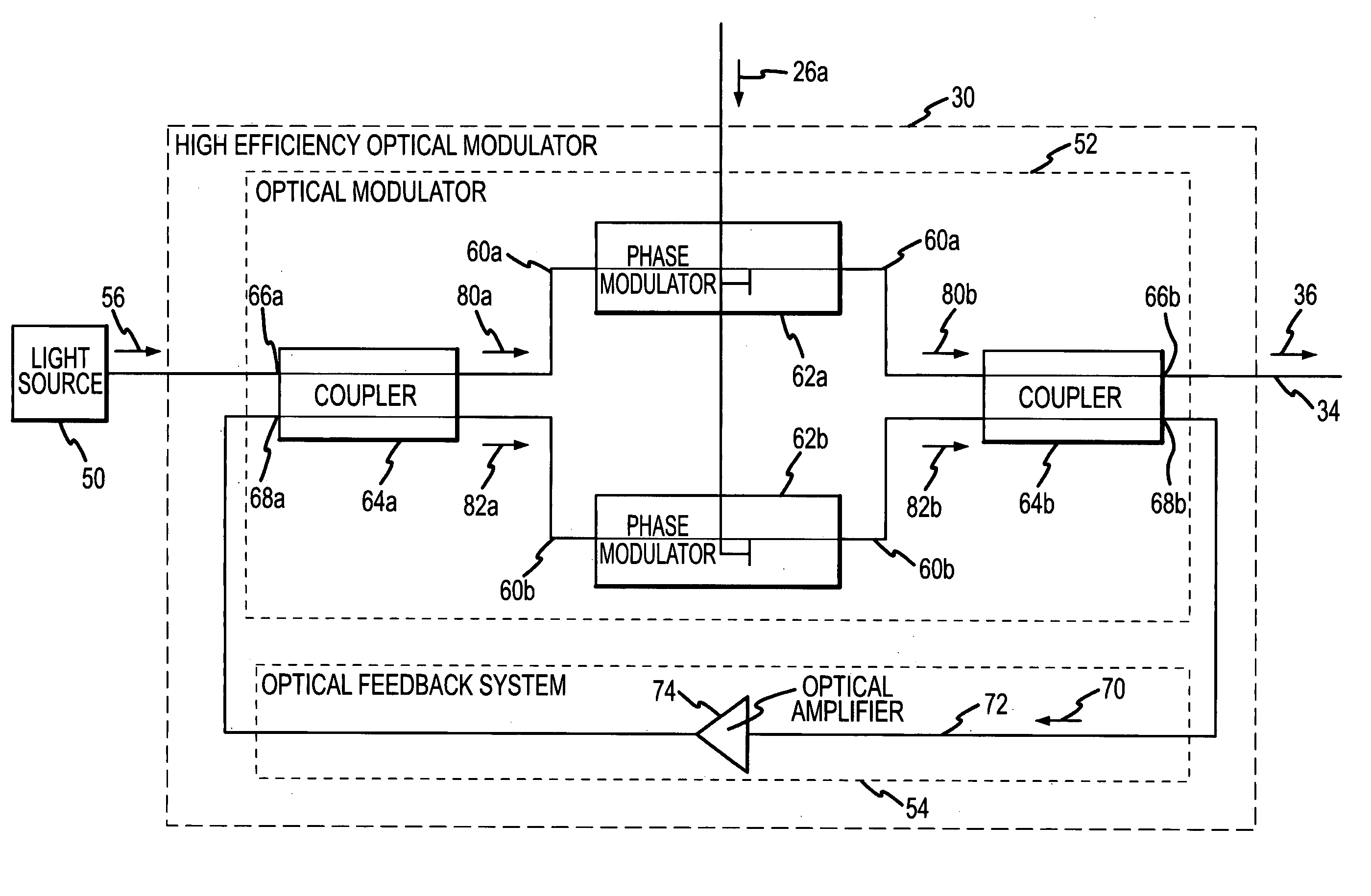
High efficiency optical feedback modulator and method of operation
InactiveUS7065302B1Easily be retrofitted into existing fiber optic systemImprove performanceElectromagnetic transmittersLight beamEngineering
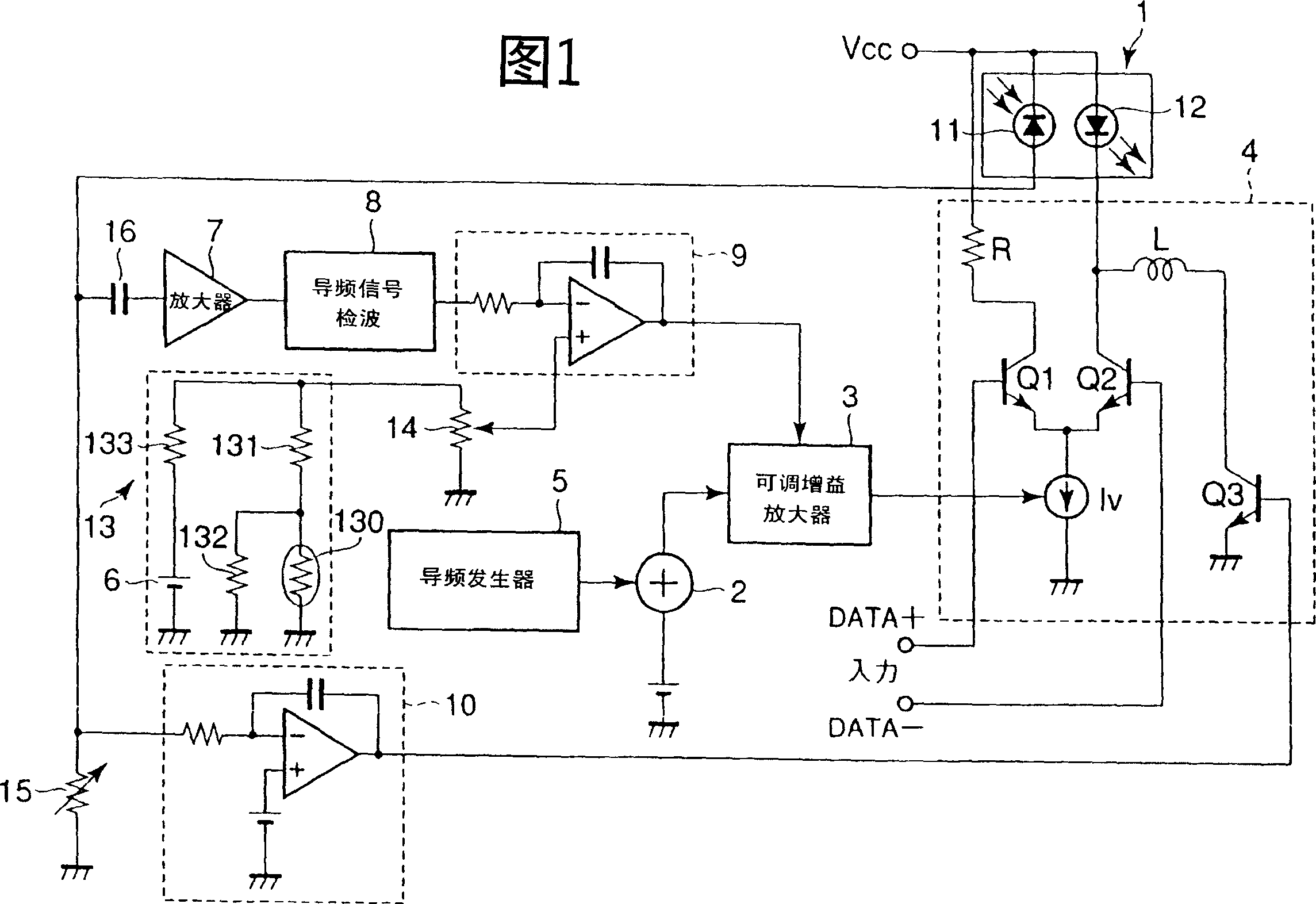
A high efficiency optical feedback modulator and method of operation are provided. The high efficiency optical feedback modulator (30) includes an optical modulator (52) and an optical feedback system (54). The optical modulator (52) includes first and second optical inputs (66a, 68a) and first and second optical outputs (66b, 68b). The optical feedback system (54) is coupled between the second optical output (68b) and the second optical input (68a). The second optical input (68a) receives an optical feedback signal (70) from the optical feedback system (54). The first optical input (66a) receives an input light beam (56). The input light beam (56) and the optical feedback signal (70) are modulated with an electronic input signal (26a) to produce a high modulation depth optical signal (36) output from the first optical output (66b). The high efficiency optical feedback modulator (30) achieves a slope efficiency that is an order of magnitude better than conventional optical modulators, corresponding to an RF link gain improvement of 100 times better than conventional optical modulators.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Method for controlling optical power and extinction ratio over entire temperature range
ActiveUS8855484B2Efficient use ofMinimal costTransmission monitoringTransmission monitoring/testing/fault-measurement systemsTransceiverOptical power
The present invention is to provide a method applicable to a fiber-optic transceiver including a transmitter optical subassembly (TOSA) provided therein with a laser diode, but without a monitoring photodiode, a laser driver controlled by a controller IC for driving the laser diode to generate a laser beam, and a thermal sensor for sensing temperature of the laser diode. The method includes executing an approximation process to characteristic data, i.e. threshold currents of the laser diode at a plurality of specific temperatures and corresponding slope efficiencies (SE), provided by manufacturer for obtaining relationship therebetween over entire temperature range, manually adjusting operation parameters (such as bias current and modulation current) of the laser diode for generating expected optical power and extinction ratio at a normal temperature and for subsequently determining the operation parameters over the entire temperature range, and writing the relationship and operation parameters thus obtained into the controller IC.
Owner:ALPHA NETWORKS INC
Calculation of laser slope efficiency in an optical transceiver module
Systems and methods are provided for determining and compensating for the laser slope efficiency of a light source positioned in an optical transmitter in order to properly set a modulation current for the light source. In one embodiment, a method for setting a modulation current for the laser of an optical transmitter is disclosed, wherein data relating to the laser transmit power and laser bias current at a plurality of laser bias current levels are sensed. A processor is then employed to calculate a slope efficiency of the laser using the data. The processor then determines a desired modulation current for the laser using the slope efficiency. Then if needed, the modulation current of the laser is modified to match the desired modulation current.
Owner:II VI DELAWARE INC
Method of monitoring and controlling a laser diode
A method of controlling a laser diode measures an average light output power of the laser diode and compares the average light output power to a desired average light output power within a target range. If the average light output power is not within the target range, the slope efficiency is determined by measuring two light output powers at two different bias conditions. Each of the two light output powers is greater than a selected minimum light output power, which insures that each measurement occurs within the slope efficiency portion of the laser diode curve. A new bias current for the laser diode is calculated based on the measured slope efficiency so as to produce a new average light output power within the target range.
Owner:AVAGO TECHNOLOGIED FIBER IP SINGAPORE PTE LTD
Control method and control circuit for laser diode, and optical transmitter using the same
A control method for a laser diode is conducted such that optical output and OMA (optical modulation amplitude) or extinction ratio of the laser diode are controlled while modulating the optical output of the laser diode by applying a bias current and a modulation current to the laser diode. The method has: a first step of measuring the optical output of the laser diode; a second step of measuring a slope efficiency or a corresponding value of the slope efficiency while conducting APC (automatic power control) to adjust the bias current such that the optical output coincides with a predetermined value; and a third step of adjusting the modulation current by AAC (automatic amplitude control) according to the slope efficiency or the corresponding value of the slope efficiency such that the OMA or extinction ratio coincides with a predetermined value.
Owner:APRESIA SYST LTD
Preparation method of doped polarization-maintaining optical fiber
InactiveCN106082628AImprove flatnessHigh Laser Slope EfficiencyGlass shaping apparatusCoatingsPolarization-maintaining optical fiberSolid particle
The invention discloses a preparation method of a doped polarization-maintaining optical fiber. The method includes the following specific steps of adding nanopore silicon dioxide powder to a rare earth and co-doped ion inorganic salt solution to form a suspension, centrifugally separating solid particles and liquid at high speed, conducting drying, dewatering and granulating to form ion adsorption silicon dioxide particles, conducting isostatic compaction and the like to obtain a cylindrical rare earth doped silicon oxide core bar, conducting drilling, grinding and polishing, and establishing a uniform porous silicon dioxide thin film layer on the inner wall of a core bar tube through a nanometer assembling technology. Silicon dioxide nanometer particles and doping ions are mixed in a solution, the uniformity of the doping ions in the radial direction and the axial direction of the core bar is quite high, the fiber core refraction rate profile has high flatness, the fiber core numerical value aperture precision can be adjusted, the optical fiber has high laser slope efficiency, the stress area of the rare earth ion doped optical fiber prefabricated bar in the ultrasonic drilling process can be effectively reduced by means of a multi-drilling method, and machining precision is high.
Owner:YANSHAN UNIV
Semiconductor laser light output stabilizing circuit and light transmitting module
InactiveCN1499683AHelp miniaturizationImprove performanceLaser detailsSemiconductor lasersDriving currentOperating temperature range
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
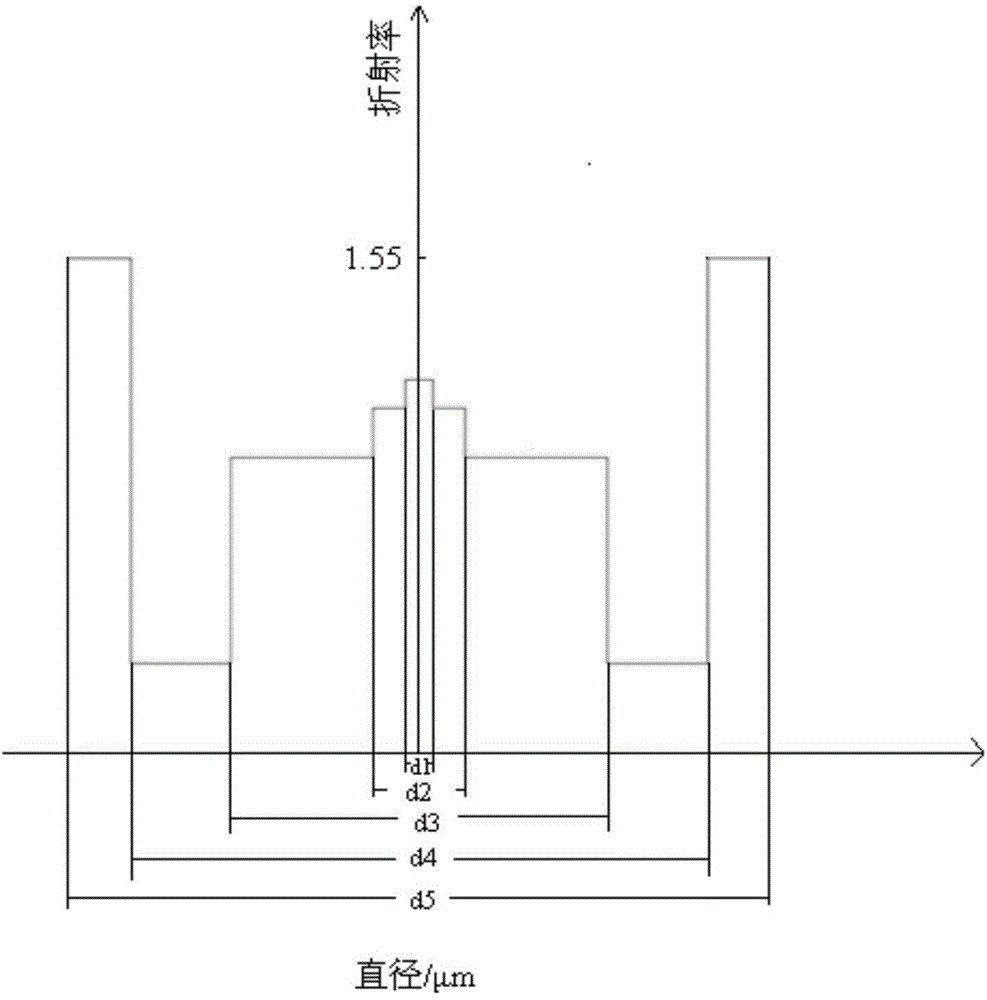
Three-wrapping-layer thulium-doped optical fiber and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104932054AReduce numerical apertureImprove efficiencyOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingFiberDopant
The invention provides a three-wrapping-layer thulium-doped optical fiber and a preparation method thereof. The three-wrapping-layer thulium-doped optical fiber comprises a fiber core, an inner wrapping layer, an outer wrapping layer and a resin layer. The fiber core comprises silicon dioxide, thulium oxide, aluminum oxide and phosphorus pentoxide, wherein the molar content of the thulium oxide is 0.2-0.8%, the molar content of the phosphorus pentoxide is 0.5-1.0%, and the molar ratio of the aluminum oxide to the thulium oxide is larger than or equal to 8; the diameter d1 of the fiber core ranges from 10 microns to 30 microns. The surface of the fiber core is sleeved with the inner wrapping layer. The inner wrapping layer comprises doping agents and silicon dioxide. The diameter of the inner wrapping layer is d2 which meet the relational expression: 2.5d1<=d2<=4d1. The surface of the inner wrapping layer is sleeved with the outer wrapping layer. The outer wrapping layer comprises silicon dioxide. The surface of the outer wrapping layer is sleeved with the resin layer. According to the three-wrapping-layer thulium-doped optical fiber, the numerical aperture of the fiber core is reduced by controlling the components in the inner wrapping layer, the content of the components in the fiber core, the diameter of the fiber core and the diameter of the inner wrapping layer, and the slope efficiency and the beam quality of output lasers are improved.
Owner:SHENZHEN XINAOKE CABLE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com