Image display apparatus
An image display device and image signal technology, which can be used in projection devices, image communication, and image reproducers using projection devices, etc., and can solve problems such as changes in white balance of display screens
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
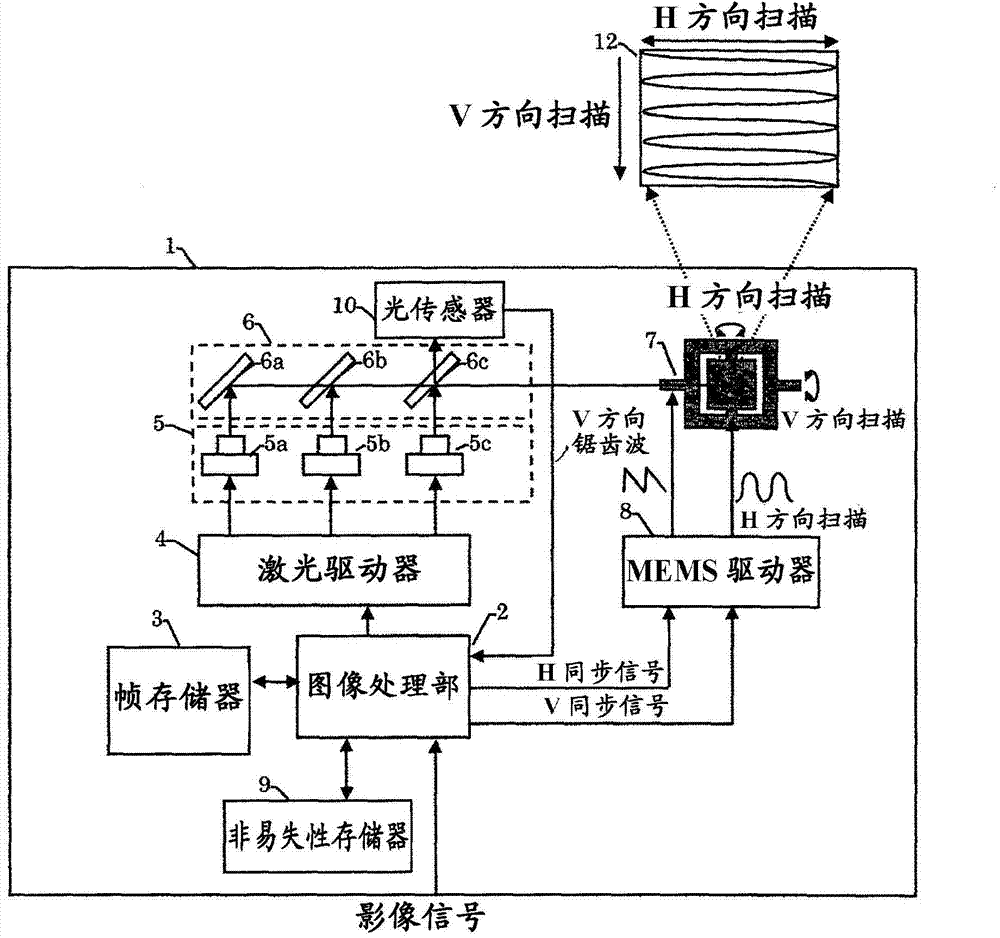
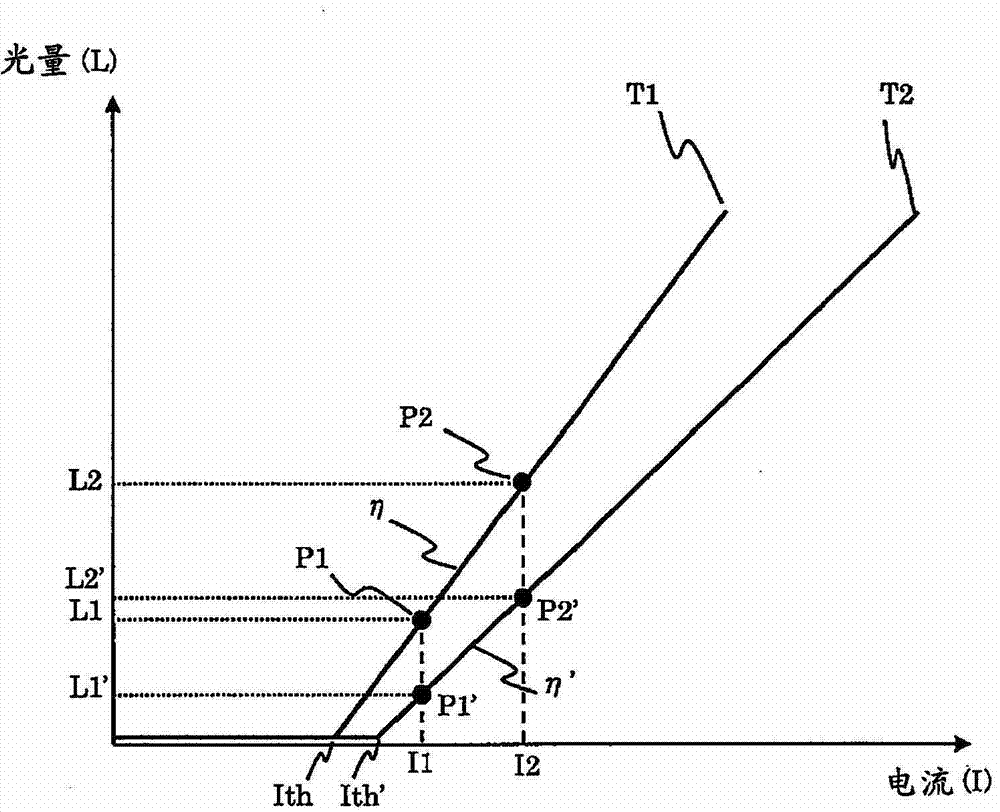
[0025] figure 1 A configuration example of a projection projector using MEMS in this embodiment is shown. The projection projector 1 includes an image processing unit 2, a frame memory 3, a laser driver 4, a laser 5, a mirror 6, MEMS 7, a MEMS driver 8, a nonvolatile memory 9, an optical sensor 10, a temperature sensor 11, and a display image 12 . The image processing unit 2 generates an image signal to which various corrections have been applied to an externally input video signal, and generates a horizontal synchronization signal and a vertical synchronization signal synchronized therewith. In addition, the image signal to the laser driver 4 is controlled based on the amount of light acquired from the optical sensor 10, and the white balance is adjusted so as to be constant. The details will be described later. Here, various corrections refer to correction of image distortion due to scanning of the MEMS 7 and the like. In detail, image distortion occurs due to difference...
Embodiment 2
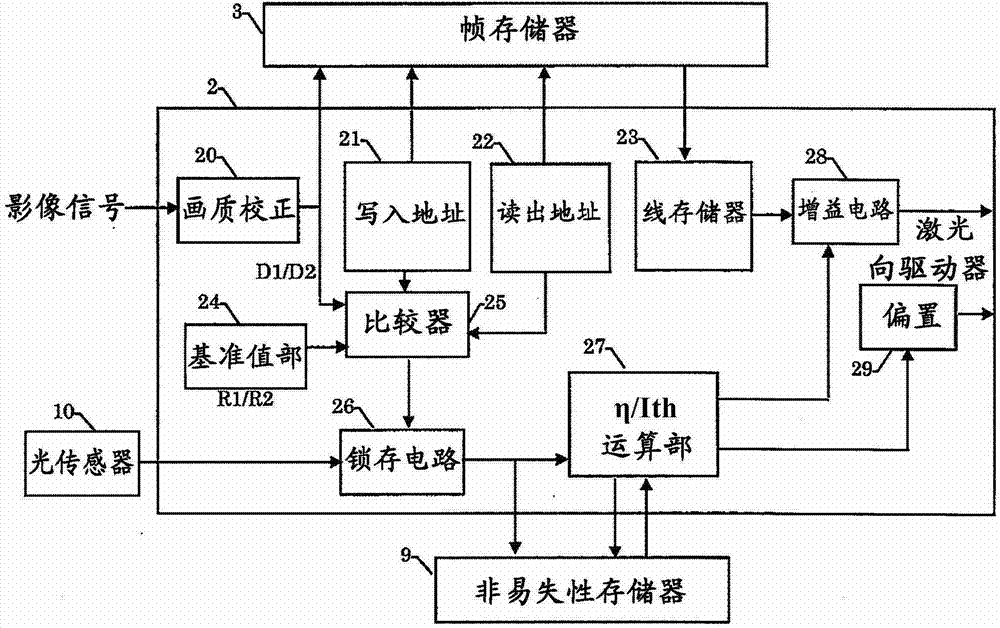
[0050] Next, Example 2 in the present invention will be described. Figure 8 It is a figure which shows the operation example of this embodiment. The difference from the first embodiment is the setting method of the reference value in the reference value unit 24. Other than that, it is the same as that of the first embodiment, so detailed description is omitted.
[0051] In the first embodiment, the reference values stored in the reference value unit 24 are two points of R1 and R2. When the reference value is only 2, the input image data ( D1 , D2 ) equal to the reference value may infrequently enter, and the correctable timing may be limited. Therefore, in the second embodiment, all of the input image data entering between R1 and R2 is used for the reference value. That is, if Figure 8 Like F1 of F1, all write addresses A1~An corresponding to the input image data D1 to Dn (n is an integer) between the entry reference values R1 and R2 are obtained, and the output image...
Embodiment 3
[0054] Next, Example 3 in the present invention will be described. Figure 9 It is a figure which shows the operation example of this embodiment. The difference from Example 1 and Example 2 is that the image data is positively superimposed on the image data on the assumption that the range of the reference value part 24 does not enter the image data, and other than that of Example 1 and Example 2. are the same, so detailed description is omitted.
[0055] In Example 2, the range of the reference value in the reference value unit 24 is between R1 and R2. There is also a possibility that the input image data does not frequently fall between the reference values, and there is a possibility that the correctable timing is limited. Therefore, in the third embodiment, if the reference value does not fall between R1 and R2 within a certain period of time, the reference values D1 and D2 are superimposed on the input image data D3. That is, if Figure 9 Like the F1 and F2 of F1 an...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com