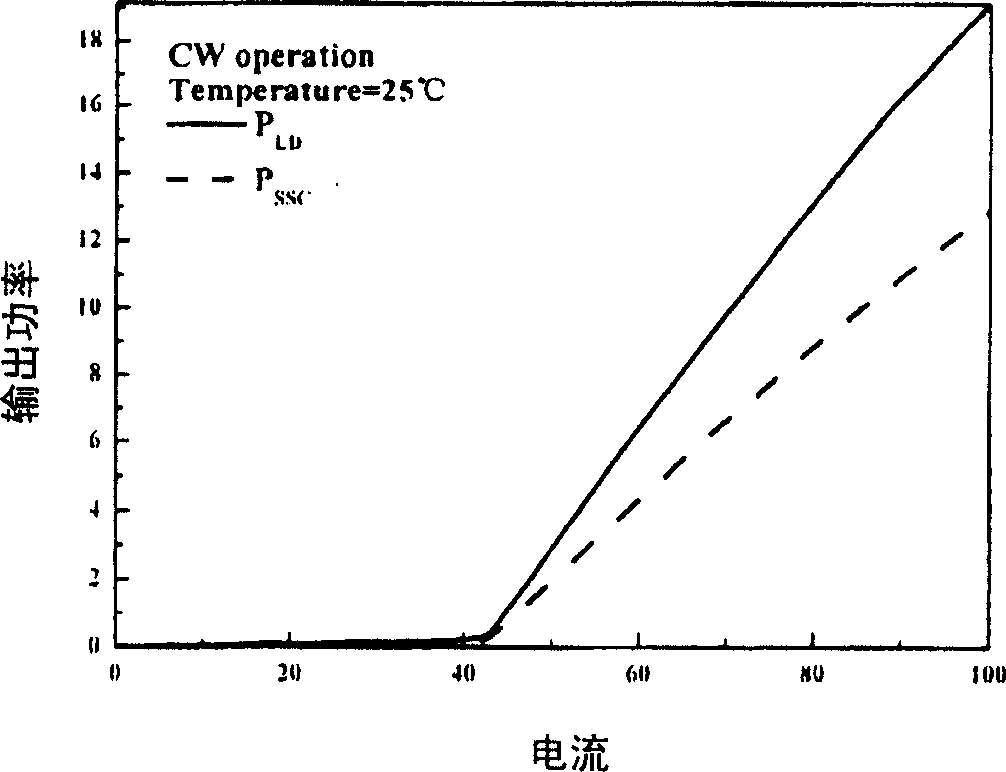
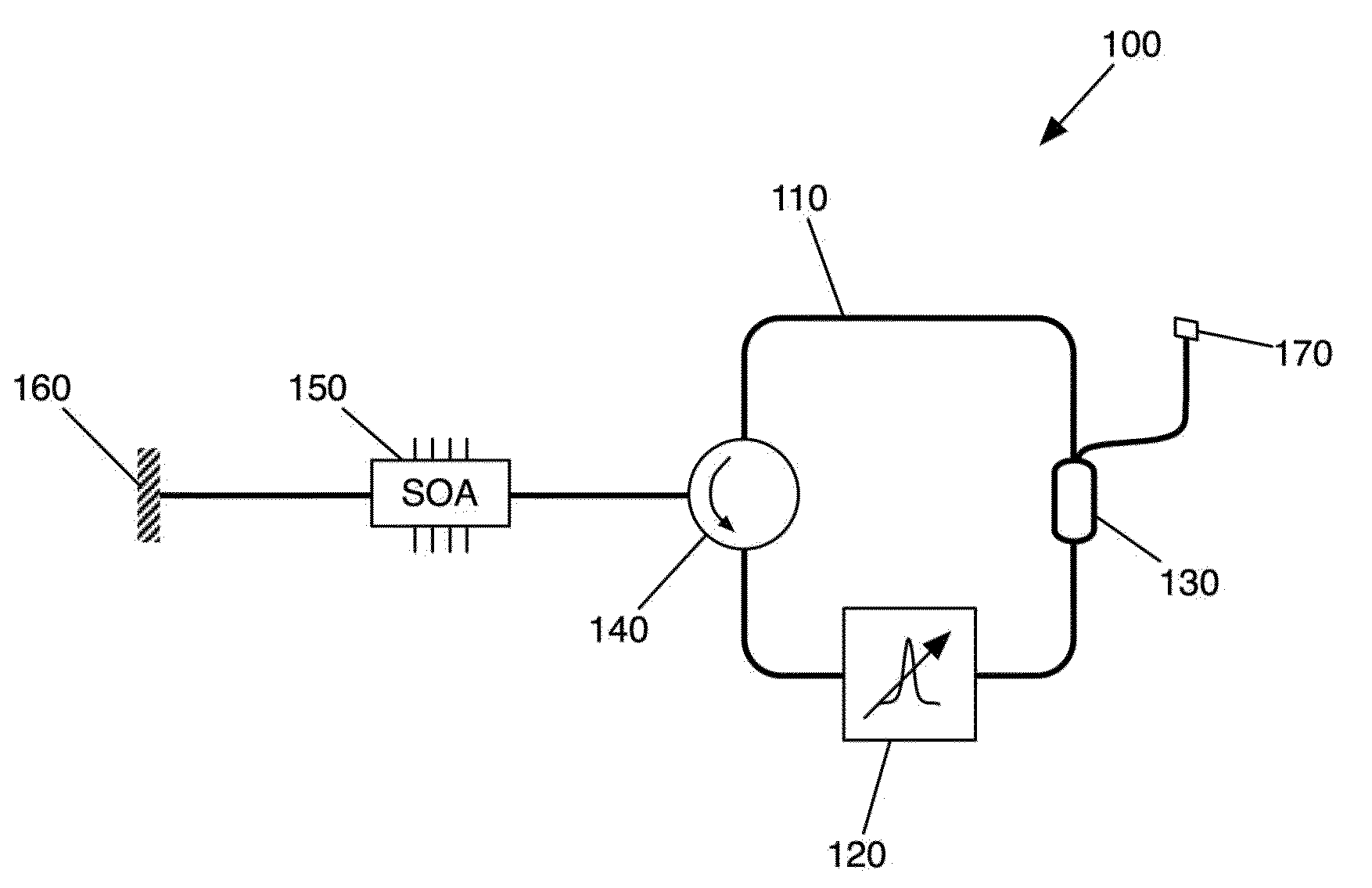
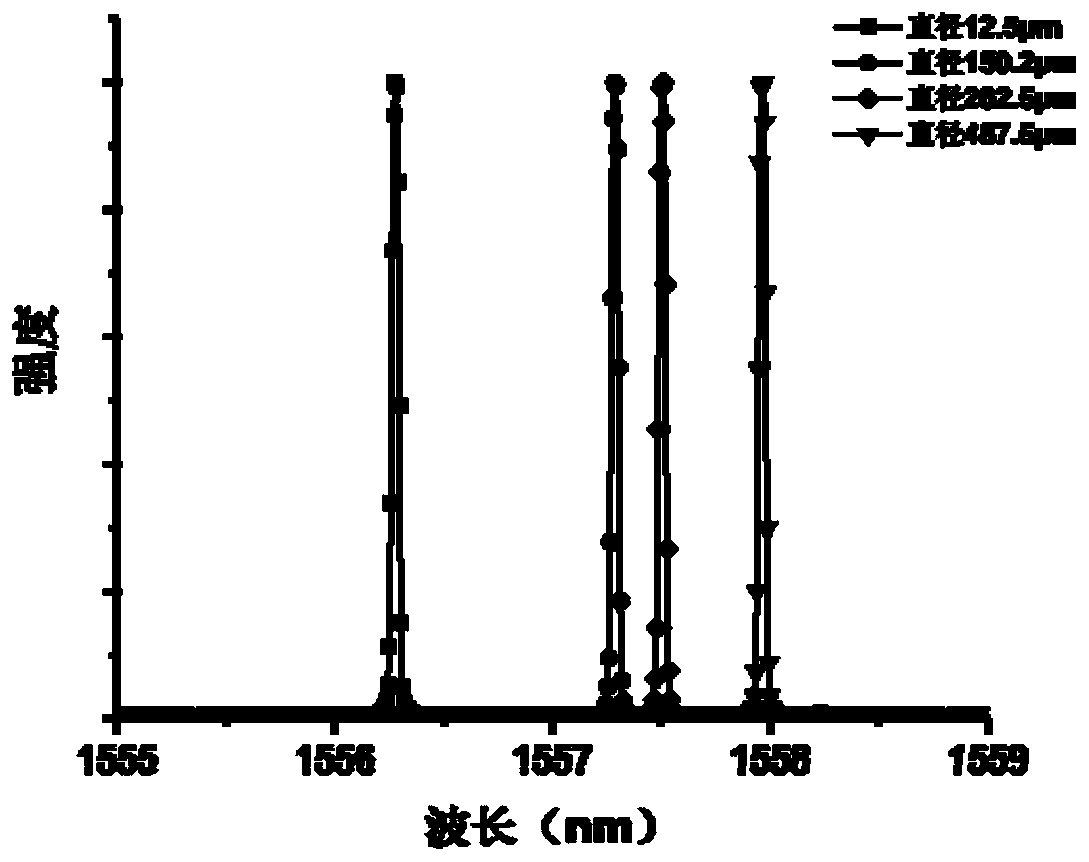
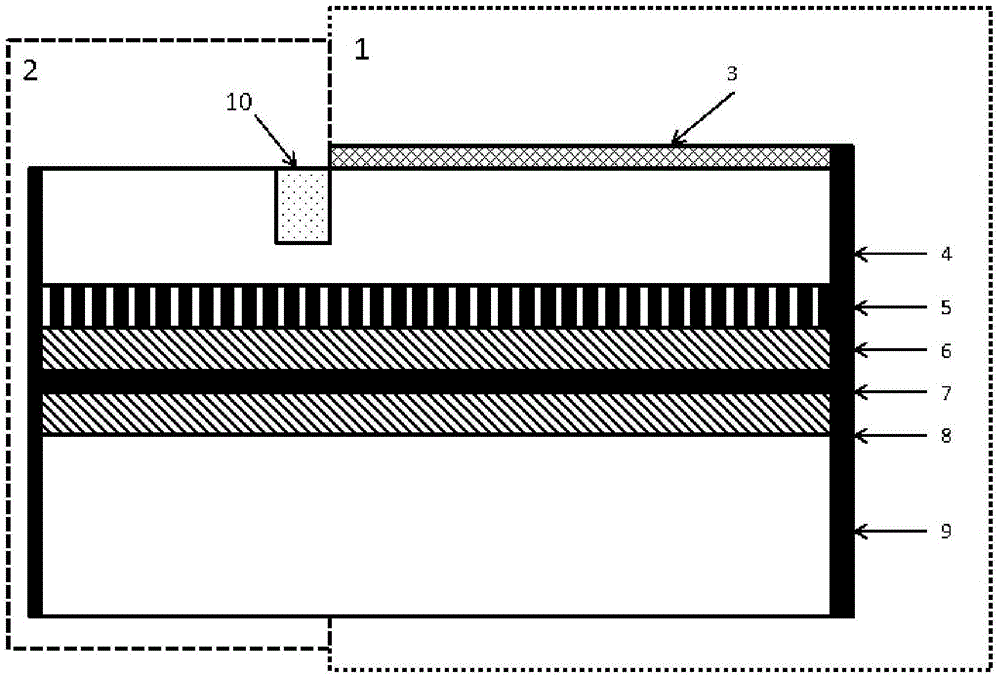
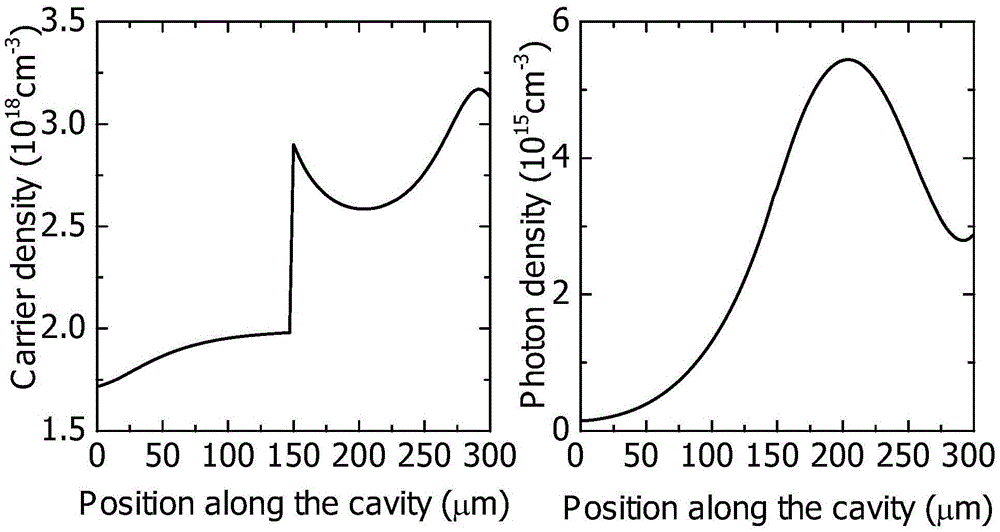
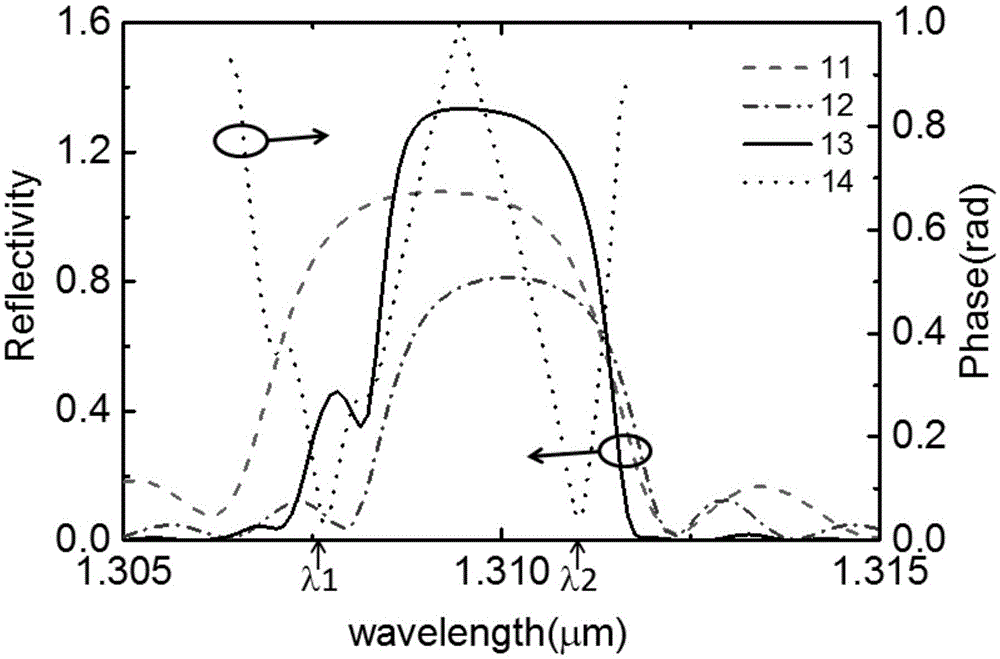
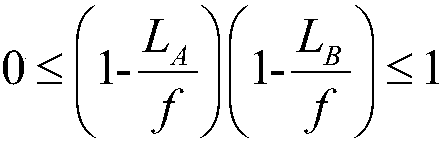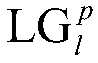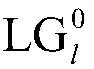Patents
Literature
58results about How to "Improve slope efficiency" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
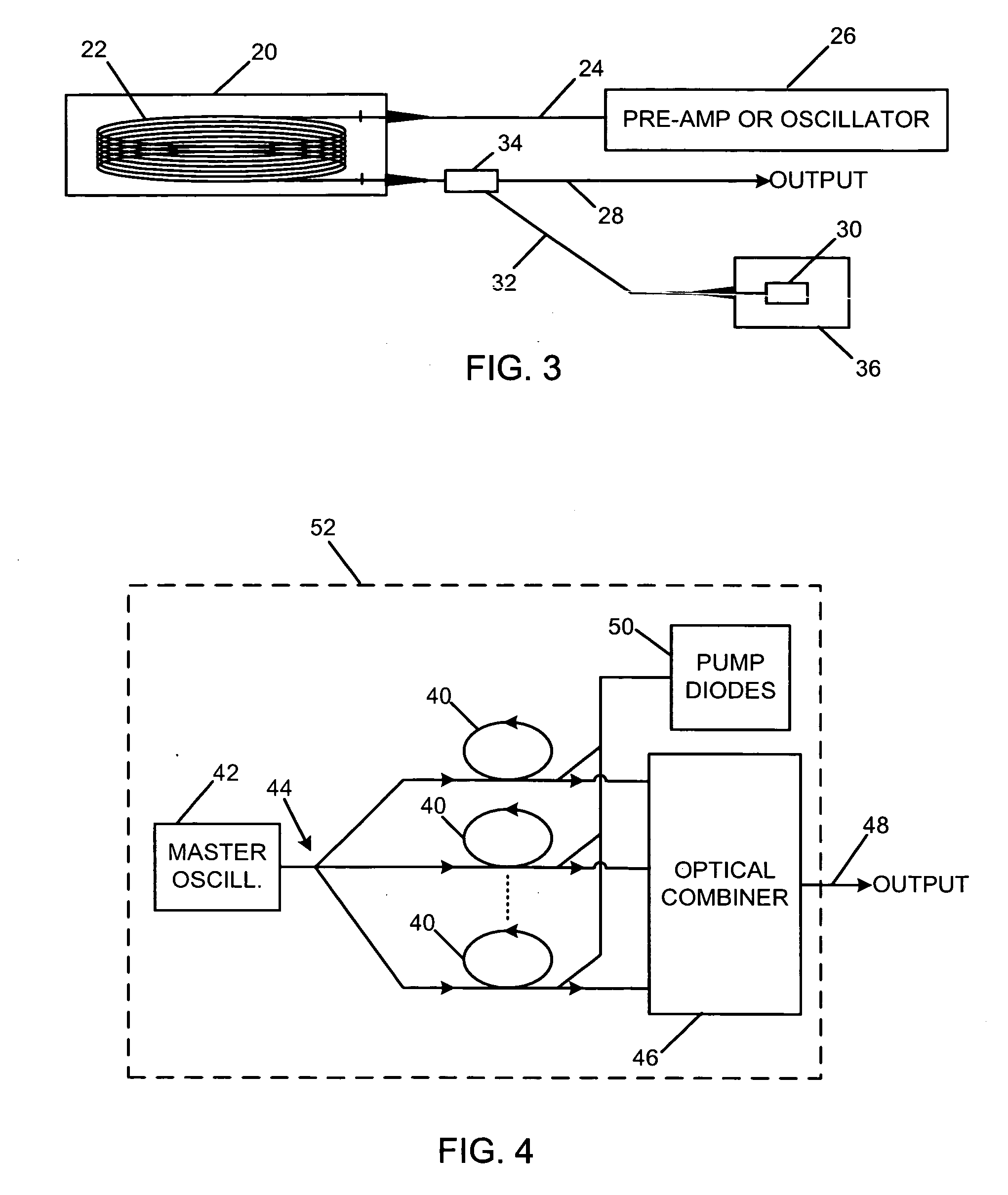
Stable solid state raman laser and method of operating same
InactiveUS20040028090A1Effective approachLimited scalabilityLaser using scattering effectsOptical resonator shape and constructionSolid massInstability
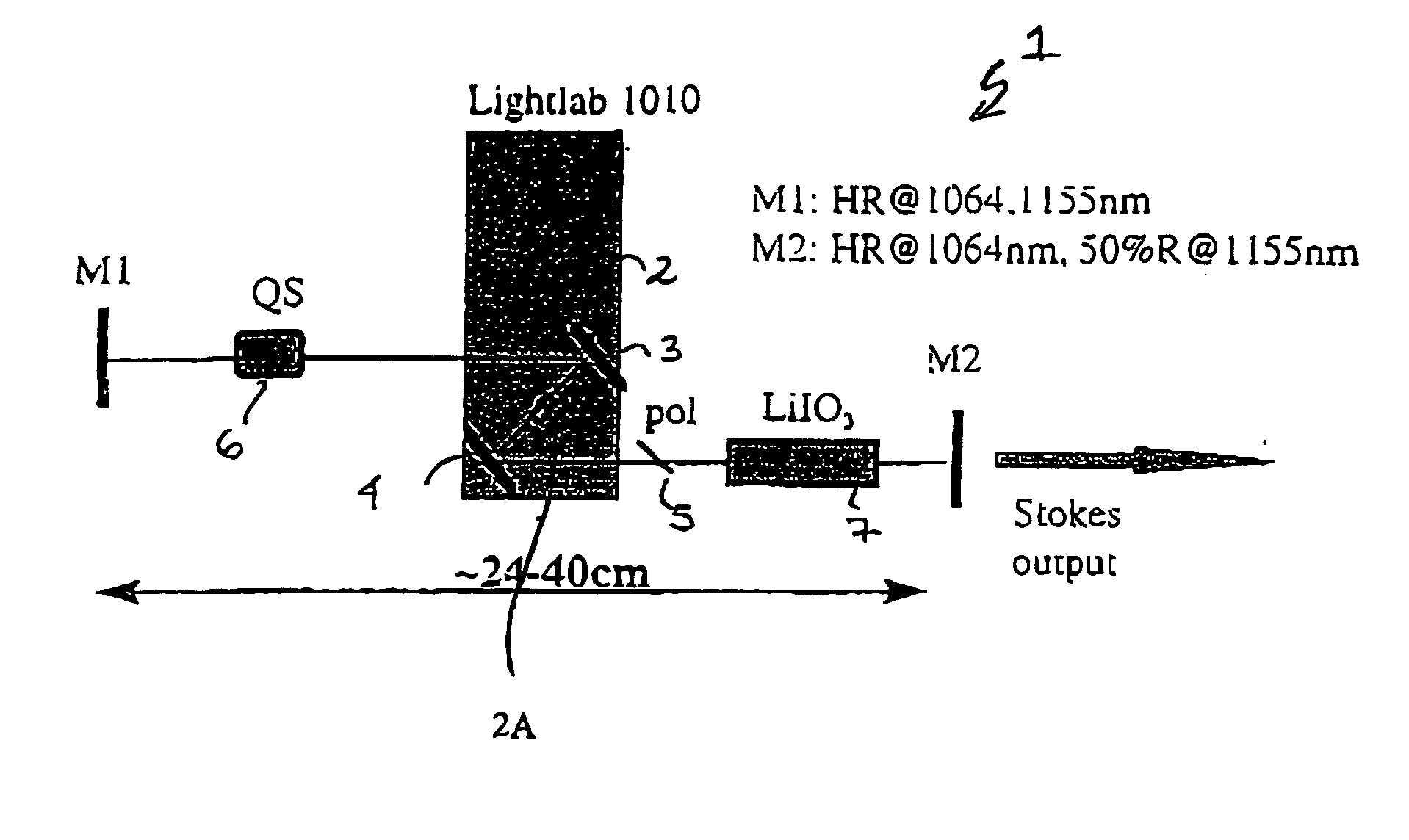
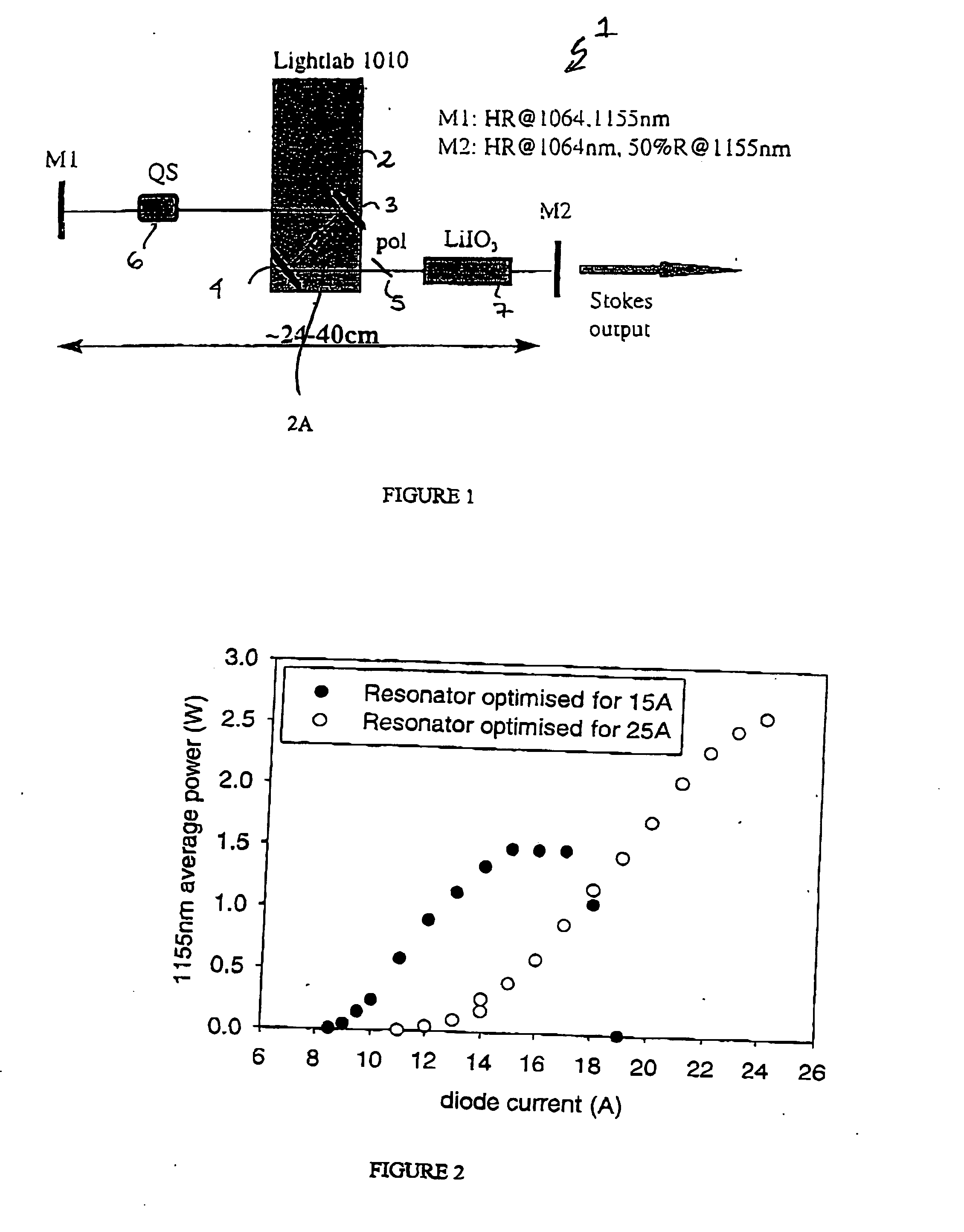
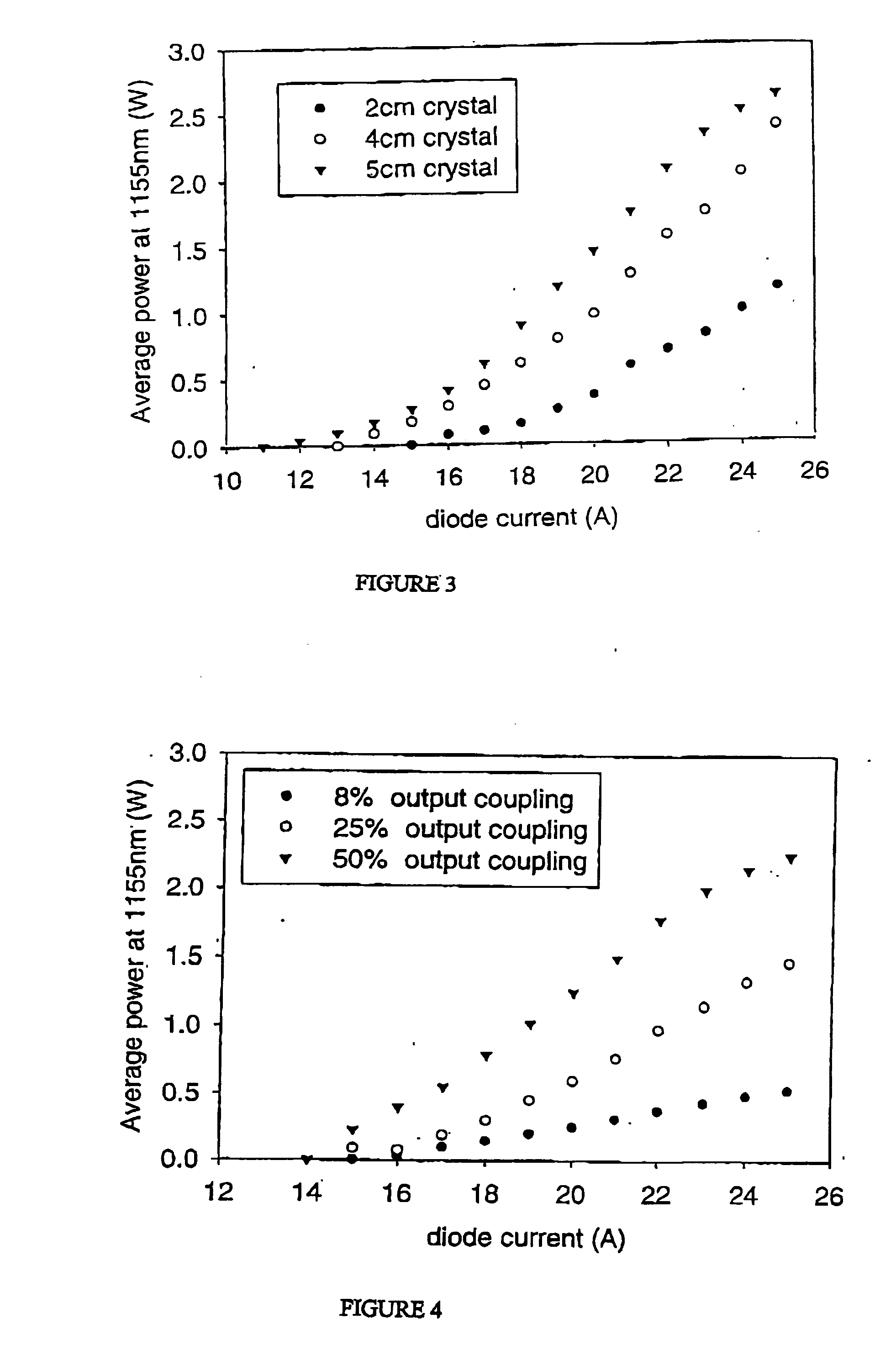
The present invention relates to a stable solid-state Raman laser (1), the solid-state Raman laser including: (a) a resonator cavity defined by at least two reflectors (M1 and M2), (b) a laser material (2A) located in the resonator cavity and capable of generating a cavity laser beam which propagates within the resonator cavity, (c) a solid Raman medium (7) located in the resonator cavity for shifting the frequency of the cavity laser beam to produce a Raman laser beam which propagates within the resonator cavity; and (d) an output coupler (M2) for coupling and outputting the Raman laser beam from the resonator cavity, wherein at least one parameter selected from the group consisting of (i) the position of the laser material (2A) relative to the position of the Raman medium (7) in the cavity, (ii) the length of the cavity and (iii) the curvature of at least one of the reflectors (M1 or M2), is selected such that changes in the focal lengths of both the laser material (2A) and the Raman medium (7) as a result of thermal effects in the laser material (2A) and the Raman medium (7) during operation of the laser do not substantially cause instability in the power of the output Raman laser beam. A method of maintaining stable operation of a solid state Raman laser is also described.
Owner:MACQUARIE UNIV
Method and device for measuring light frequency through high-power optical fiber optics frequency comb
ActiveCN103794980AAvoid complex adjustmentsSuppresses the phenomenon of jitter enhancementLaser detailsMode-lockingCarrier signal
The invention discloses a method and device for measuring the light frequency through a high-power optical fiber optics frequency comb. A mode locking pulse laser serves as an optics frequency comb seed resource to set up the high-power optical fiber optics frequency comb, and a carrier envelope phase signal of the optics frequency comb is locked at the zero frequency; the beat frequency is carried out on the output light of the optics frequency comb and continuous lasers to be tested, the repeated frequencies of the pulse of the optics frequency comb seed resource are finely adjusted through an externally loaded modulation signal, a plurality of sets of beat frequency signals corresponding to different repeated frequencies are obtained, and therefore the accurate measuring of the frequency of the continuous lasers to be tested can be achieved. The method and device have the advantages that the device is stable in structure, the measuring process is easy, and the application is flexible.
Owner:CHONGQING HUAPU INFORMATION TECH CO LTD
Semiconductor laser device
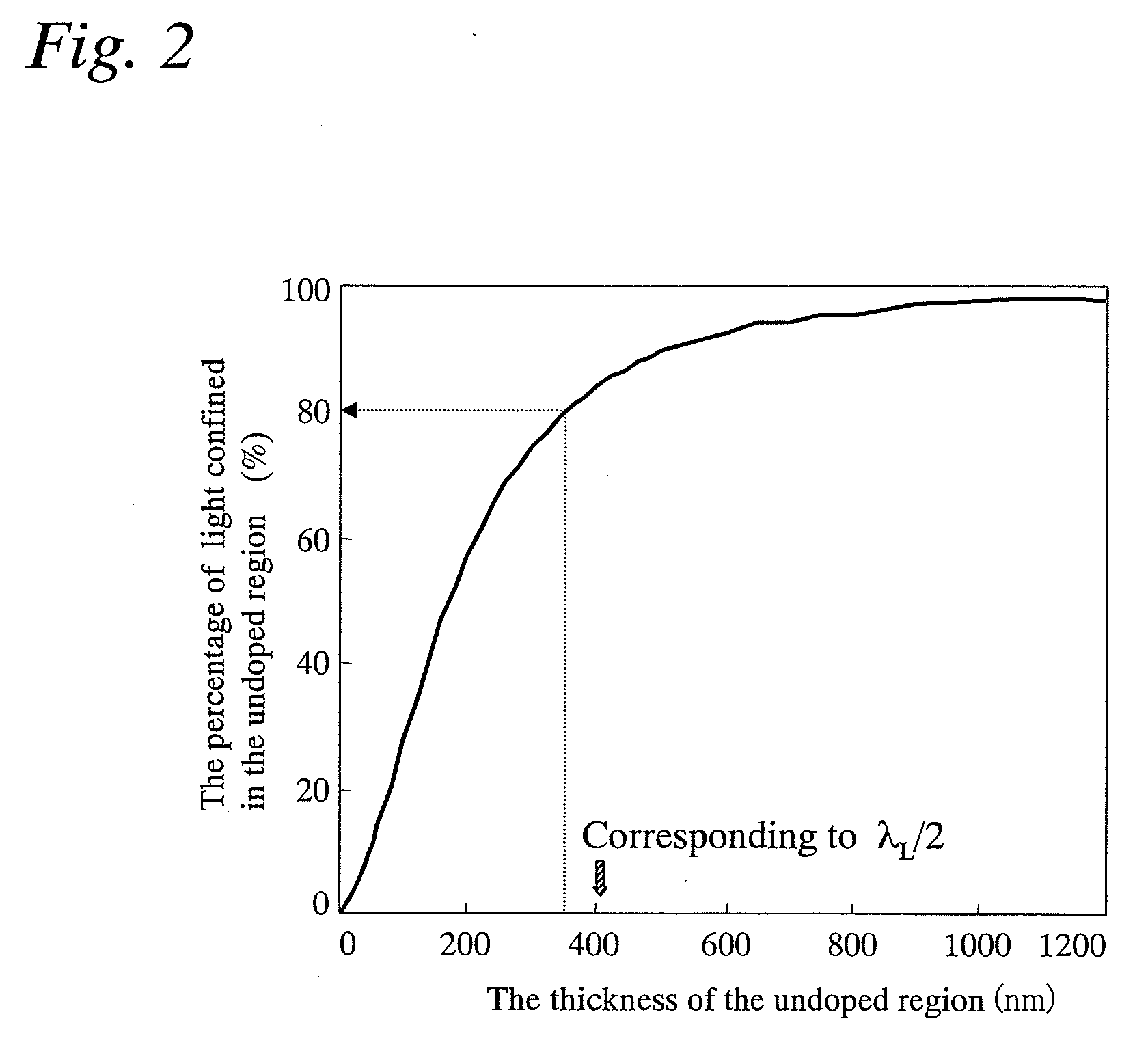
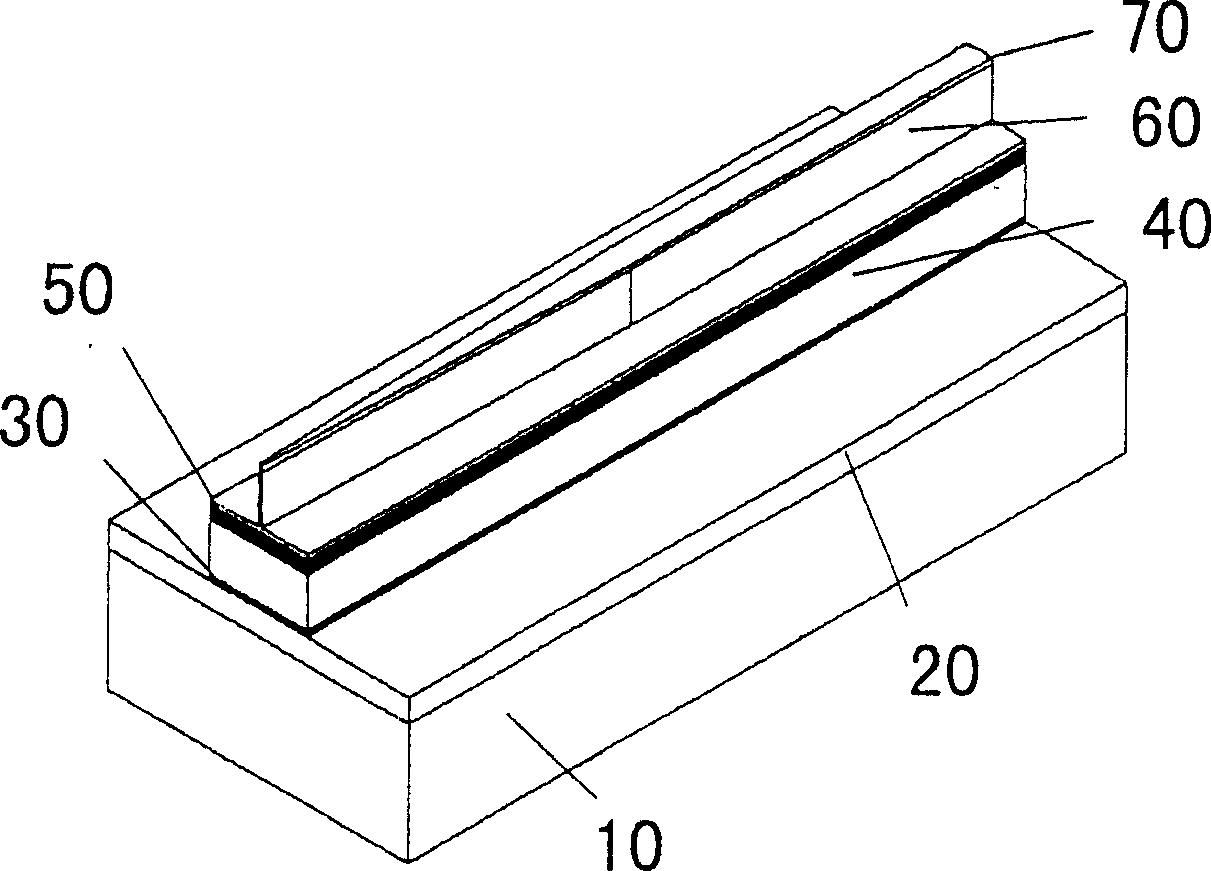
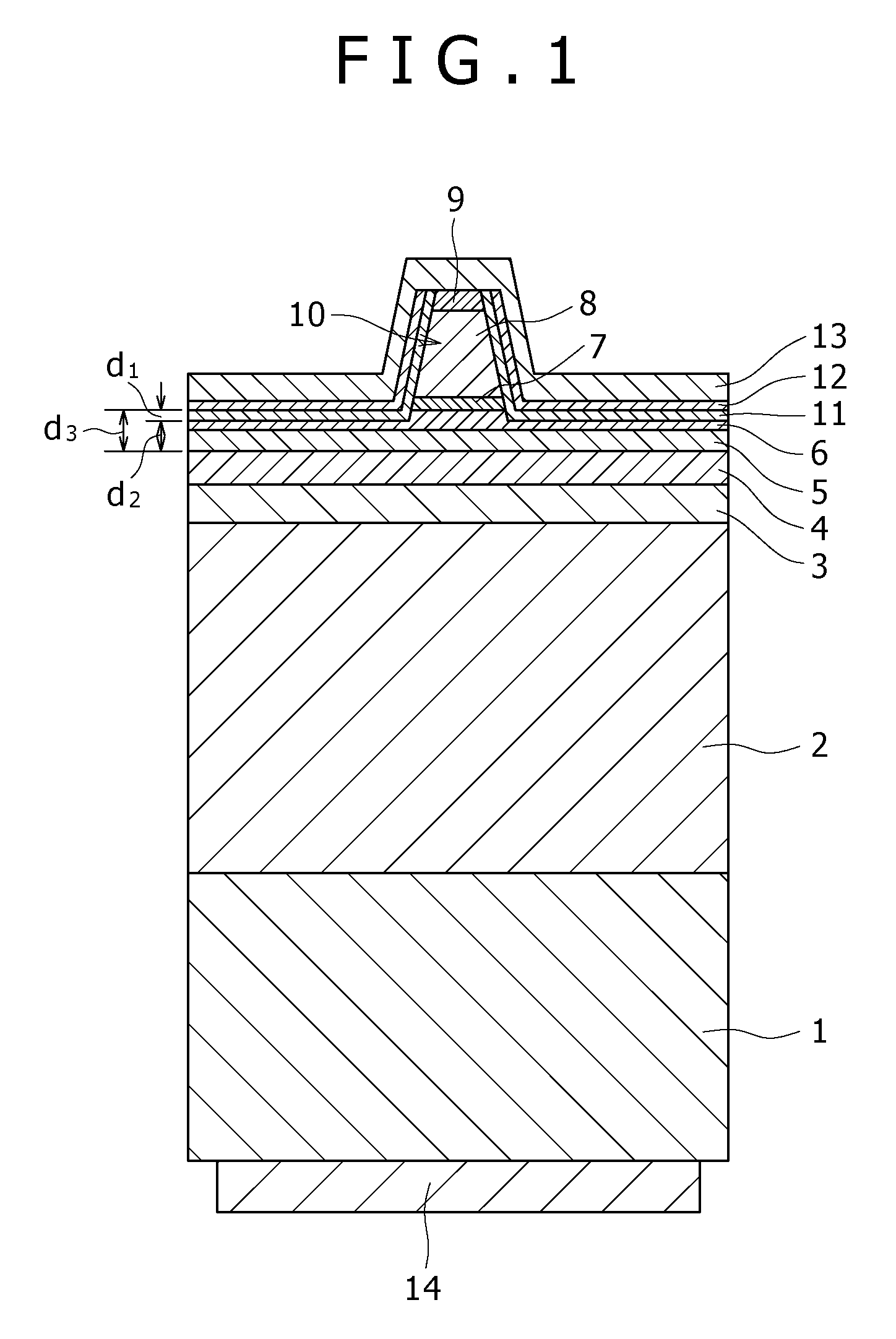
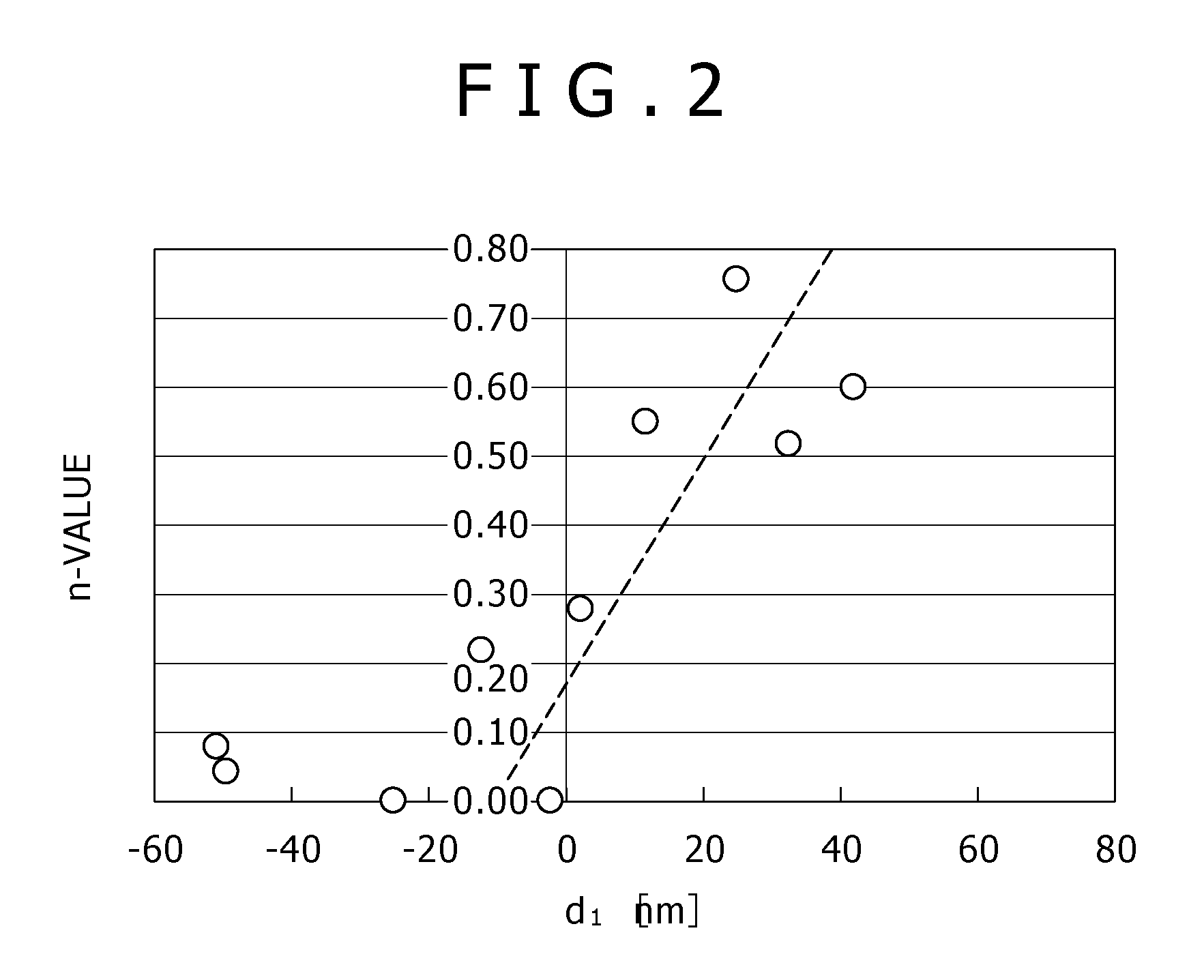
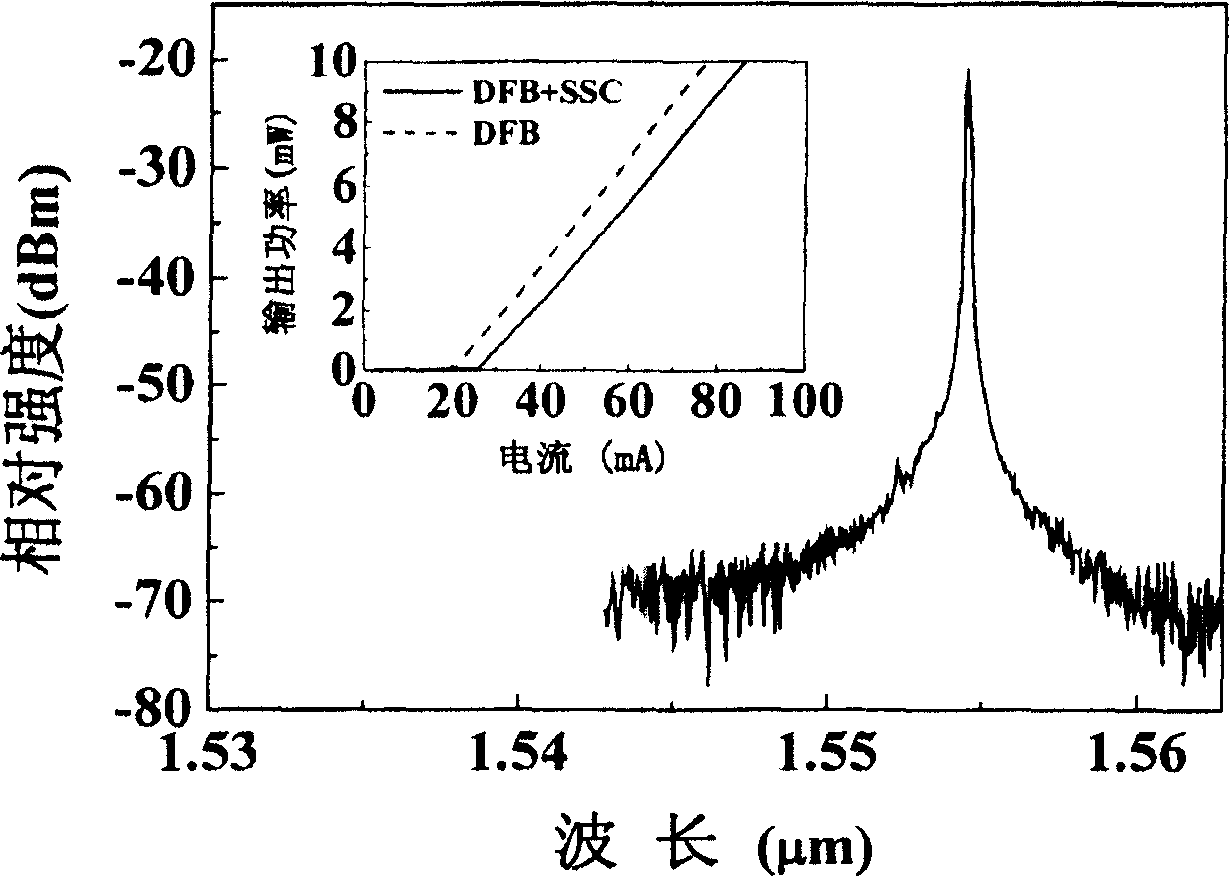
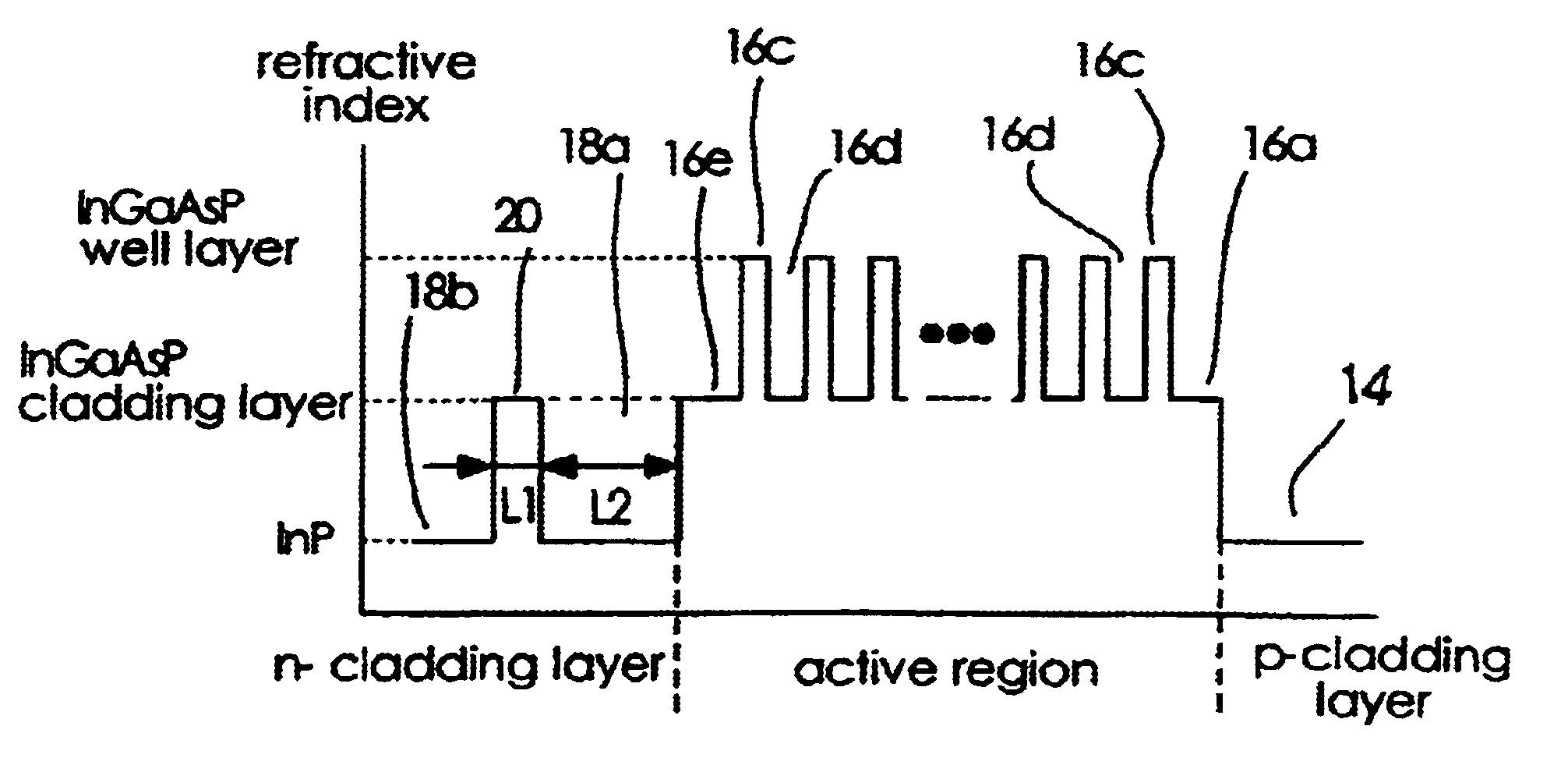
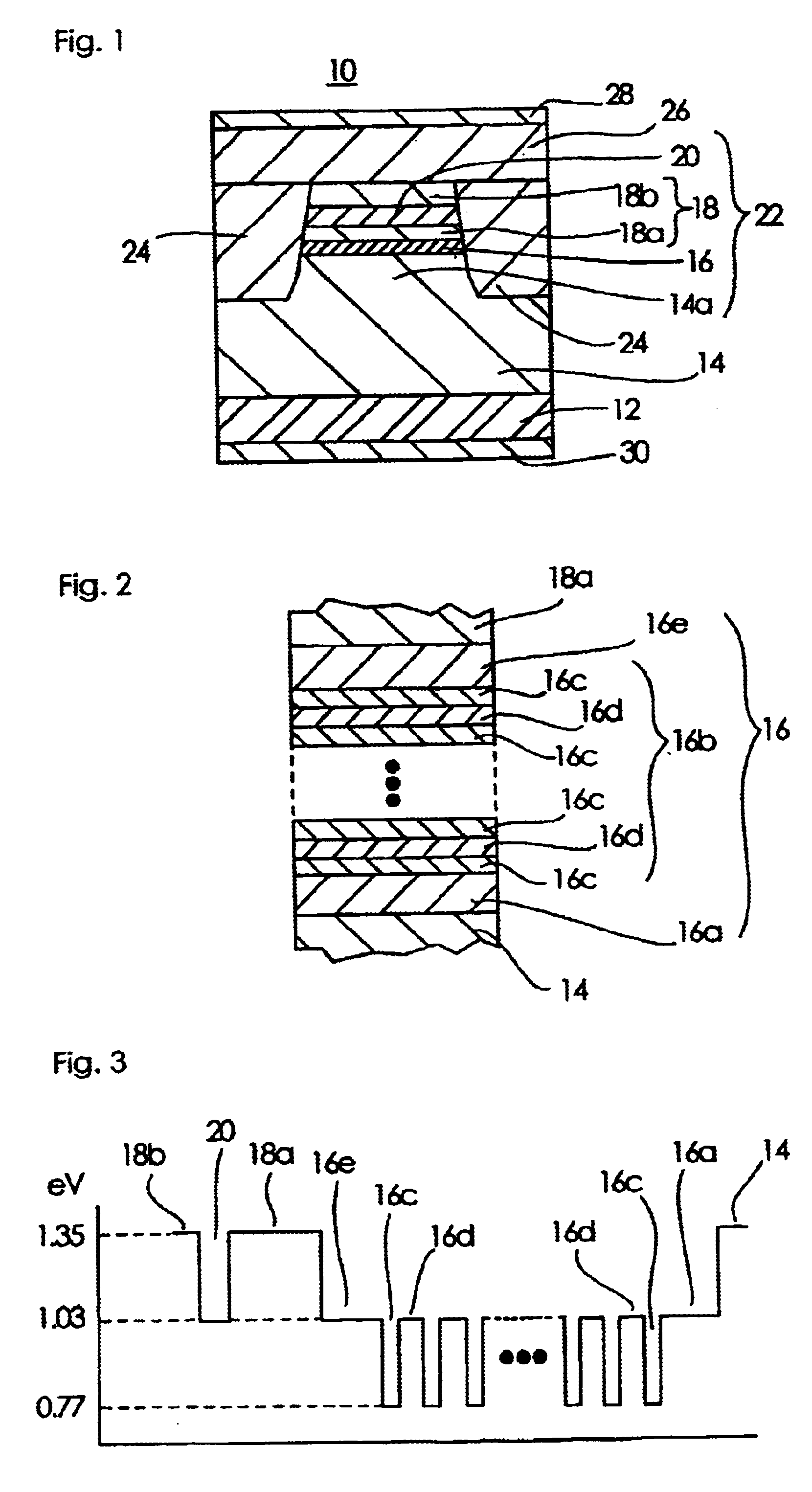
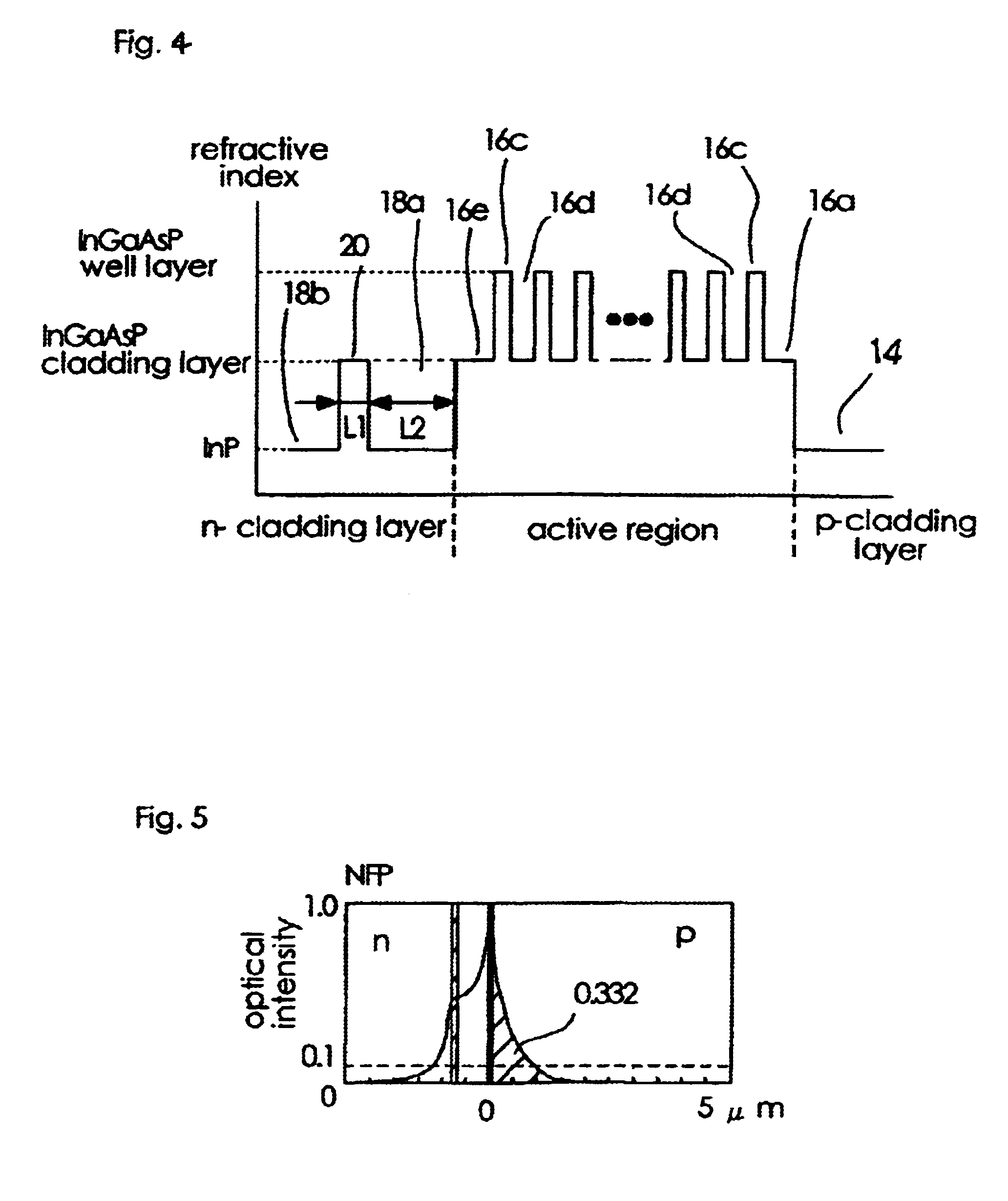
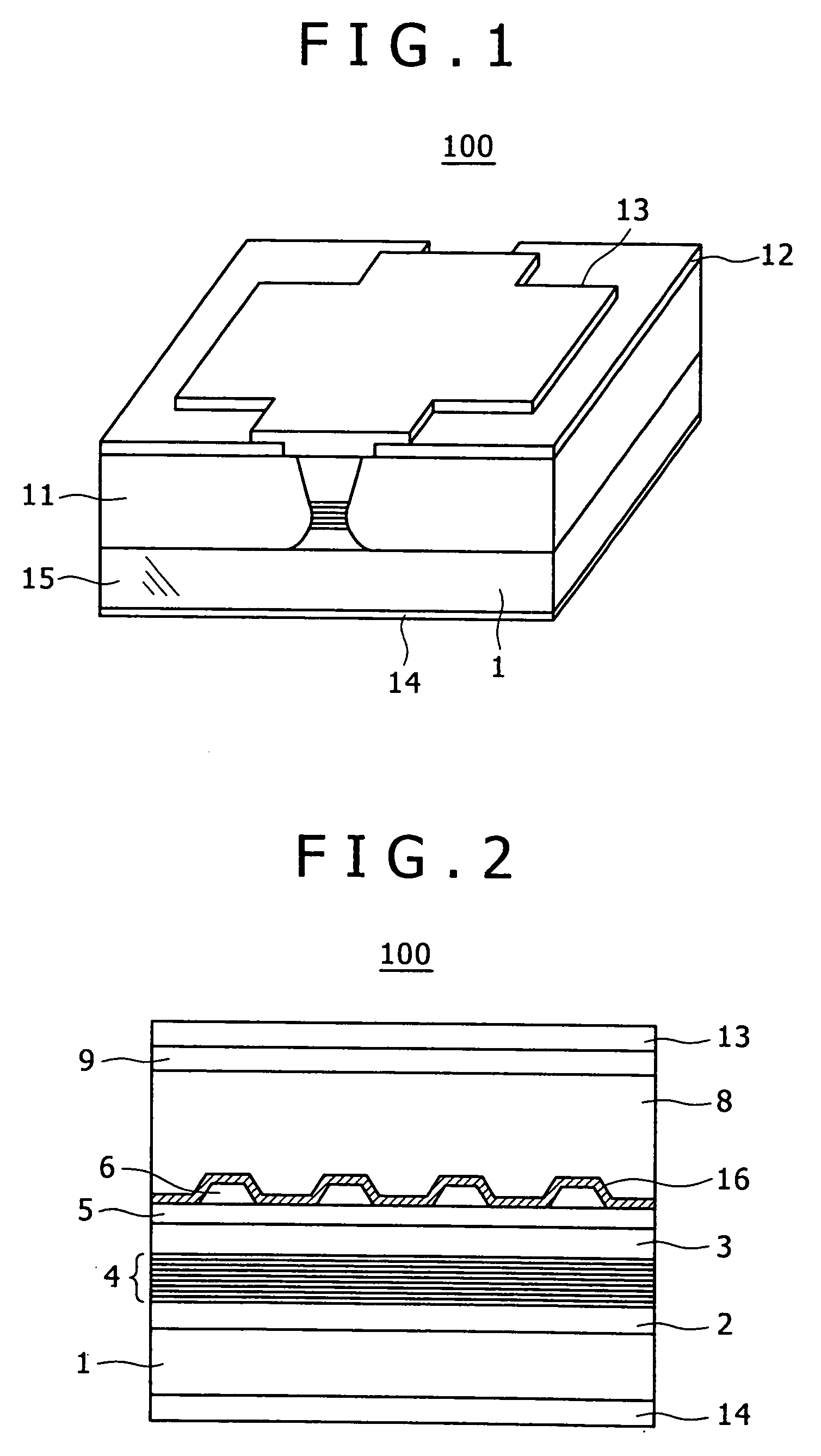
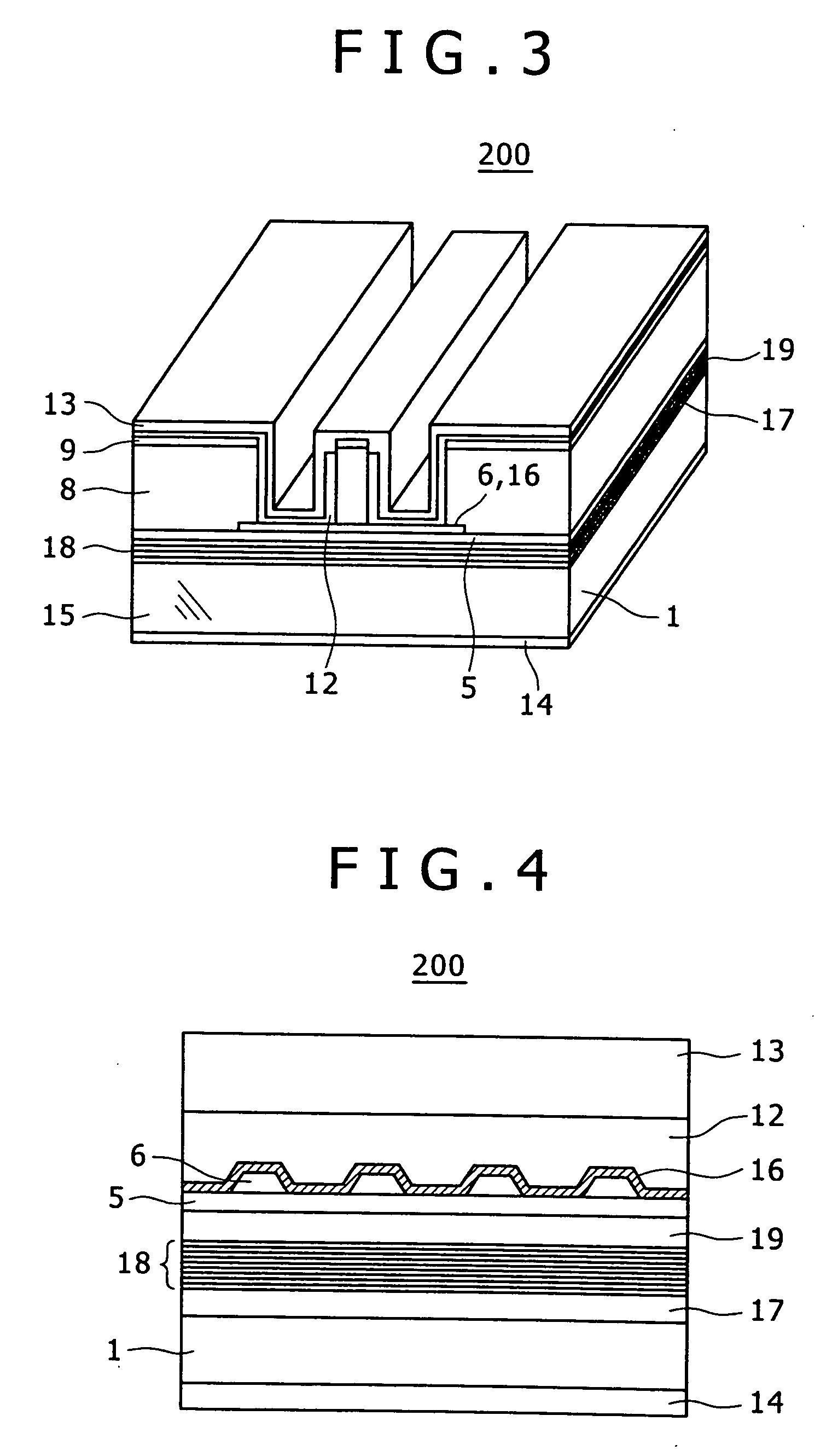
InactiveUS20100103970A1Reduce power consumptionImprove slope efficiencyOptical wave guidanceLaser detailsRefractive indexLasing wavelength
A semiconductor laser device includes: an n-type cladding layer, a p-type cladding layer, an active layer located between the n-type cladding layer and the p-type cladding layer, an n-side guiding layer located on the same side of the active layer as the n-type cladding layer, and a p-side guiding layer located on the same side of the active layer as the p-type cladding layer. The n-side guiding layer, the active layer, and the p-side guiding layer are undoped or substantially undoped. The sum of the thicknesses of the n-side guiding layer, the active layer, and the p-side guiding layer is not less than 0.5 times the lasing wavelength of the semiconductor laser device and is not more than 2 μm. The p-side guiding layer is thinner and has a lower refractive index than the n-side guiding layer.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Distributed feedback laser with short cavity length
InactiveCN104993375AImprove direct modulation bandwidthImprove slope efficiencyOptical wave guidanceLaser detailsDistributed feedback laserGrating
The invention relates to the technical field of semiconductor lasers, and provides a distributed feedback laser with a short cavity length. The laser contains two parts, i.e., a gain region and a reflection region; a metal electrode exists in the gain region, current needs to be injected to provide a gain for the laser; a grating layer of the gain region is a distributed feedback Bragg grating containing a lambda / 4 phase shift region; one end of the gain region is the reflection region which contains a core layer structure which is the same as that of the gain region, i.e., a waveguide transmission layer is also an active quantum well material, but current is not injected to the region; a grating layer of the reflection region is formed by evenly distributed Bragg gratings; an outer end face of the reflection region is plated with an antireflection film or adopts an antireflection structure to reduce reflection; and the other end of the gain region is an output end face of the laser, and the end face is plated with an antireflection film to reduce reflection. The scheme of the laser can enable the laser to still have a relatively low threshold gain and a good side-mode suppression ratio when the cavity length is relatively short, and the laser has the characteristic of small manufacture difficulty at the same time.
Owner:宁波元芯光电子科技有限公司
Random fiber laser with tunable wavelength
InactiveCN102437500AImprove slope efficiencyWavelength tunableLaser using scattering effectsActive medium shape and constructionRandom laserSeeds source
The invention discloses a random fiber laser system with tunable wavelength, belonging to the laser device field. According to the system, first pump source laser with tunable wavelength and a series of low energy seed source laser are injected into a fiber, through a series of Raman amplification effects, distributed Raman amplification light is generated in a transmission fiber, and distributedRayleigh backward diffusion light forms random laser after Raman amplification. A random laser in the invention can realize continuous tunable wavelength. In a selectable scheme, after first Raman amplification, residual energy of a first pump source or a first seed source is fed back to the fiber for reuse, and slope efficiency of a finally formed random laser is raised. The system can control aRaman gain and a shape of a Raman gain spectrum through additional seed light, reduce a threshold of the laser, and raise output power.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Watt-grade broadband super-fluorescence light source with ytterbium doped photonic crystal fiber
InactiveCN1844732AImprove coupling efficiencyImprove slope efficiencyLaser detailsCladded optical fibreOptical tomographyFluorescence
The invention relates to an ultra-fluorescence optical fiber light source, which uses Yb-doped photon crystal optical fiber as gain medium, to attain low time interference and high space interference, belonging to the technique of wide-band optical fiber light source and optical fiber sensing. Wherein, the pump semi-conductor laser, lens coupling system, dichroic mirror, Yb-doped large mode-area dual-envelope photo crystal optical fiber and collimation lens are arranged to form dual-range forward or backward output device; compared to general high-power optical fiber ultra-fluorescence light source, the invention has simple structure, better time stability, high incline efficiency, high output power, flat spectrum, and wider band width. The invention can be used in optical fiber sensing, optical fiber top, and optical tomography, etc.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Method for forming semiconductor laser and spot-size converter by once epitaxy
InactiveCN1756008AReduce pollutionLow costLaser detailsSemiconductor lasersTime extensionSemiconductor package
Disclosed a method for one time extension forming the semiconductor laser and mode spot switch comprises following steps: (1), on the N type indium phosphide substrate, extending growing the N type indium phosphide breaker, a lower waveguide layer, a 2.4 ª–m indium phosphide space layer, a lower light-limited layer of active region, a compression strain quanta active region, a upper light-limited layer, a P type indium phosphide envelope, and a high doping P type indium gallium arsenide ohmic electrode contract layer; (2), utilizing the wet corrosion process to etch the upper carinate shape of laser and mode spot switch; (3) utilizing the auto-alignment process to etch the lower carinate shape; (4), growing the SiO2 insulating layer and opening a electrode window; (5) decreasing the substrate of extended plate to 100 ª–m, and manufacturing P / N electrodes to be scribed into the tube core of 250í‡600ª–m.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
High gain resonant modulator system and method
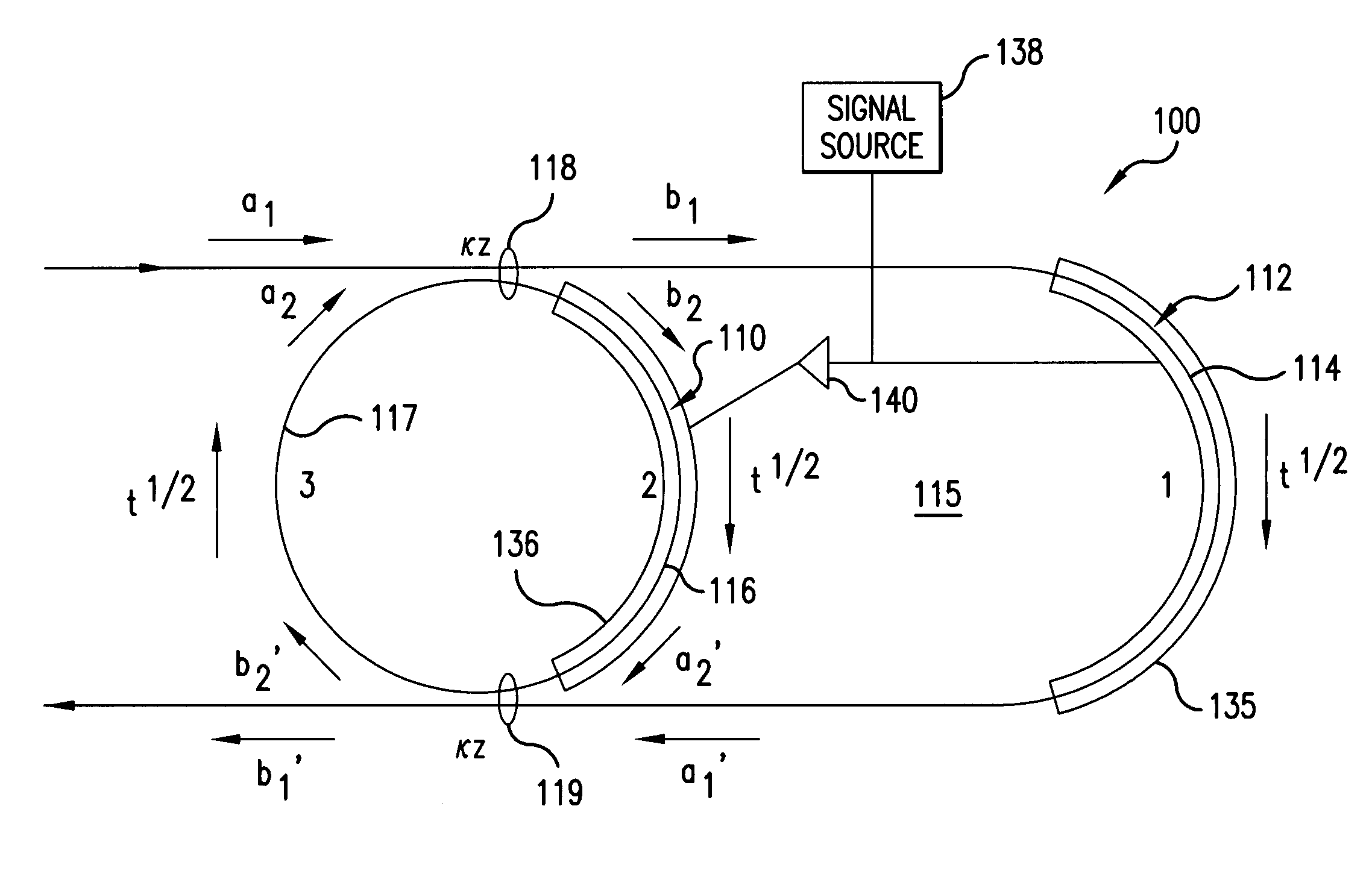
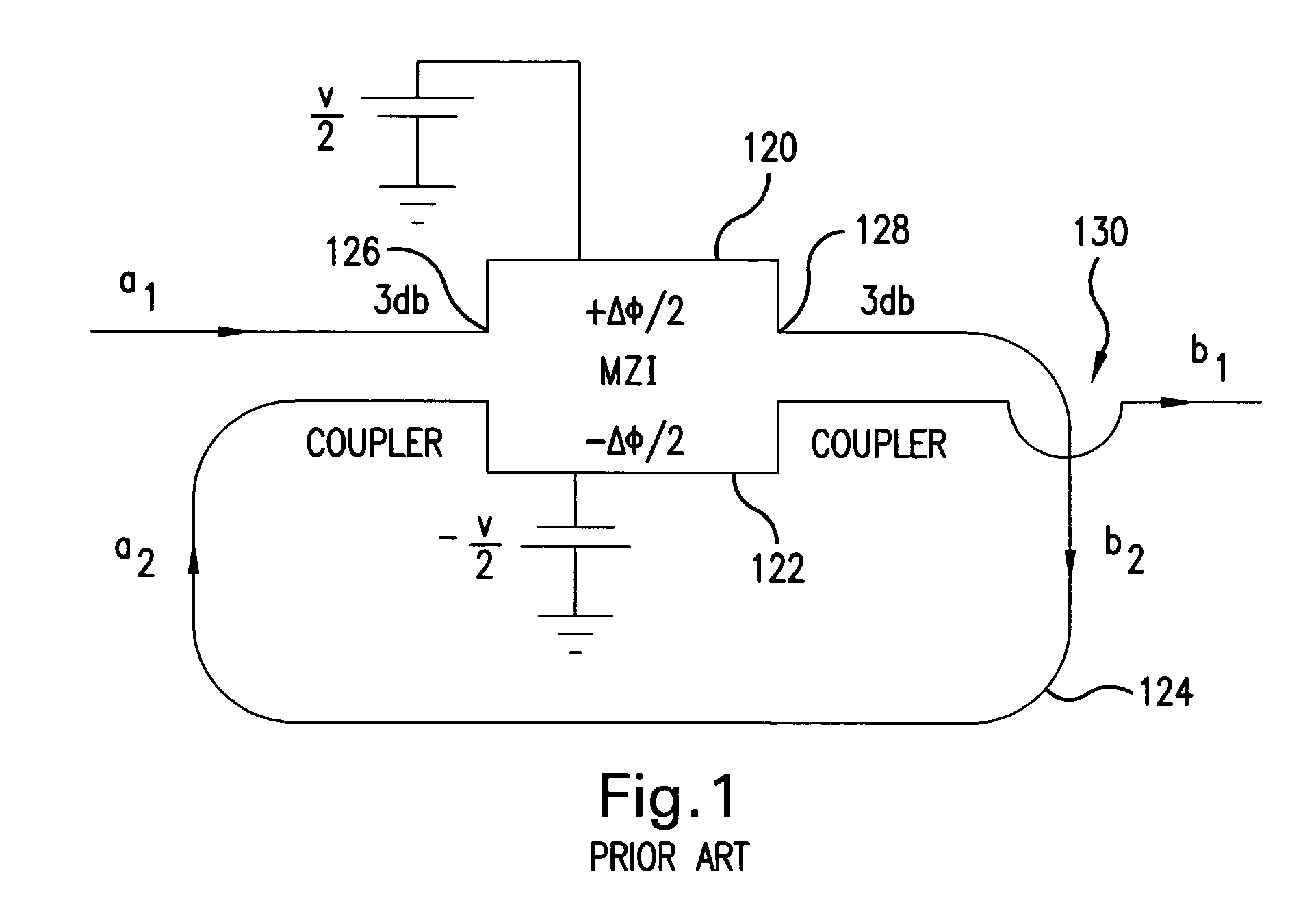
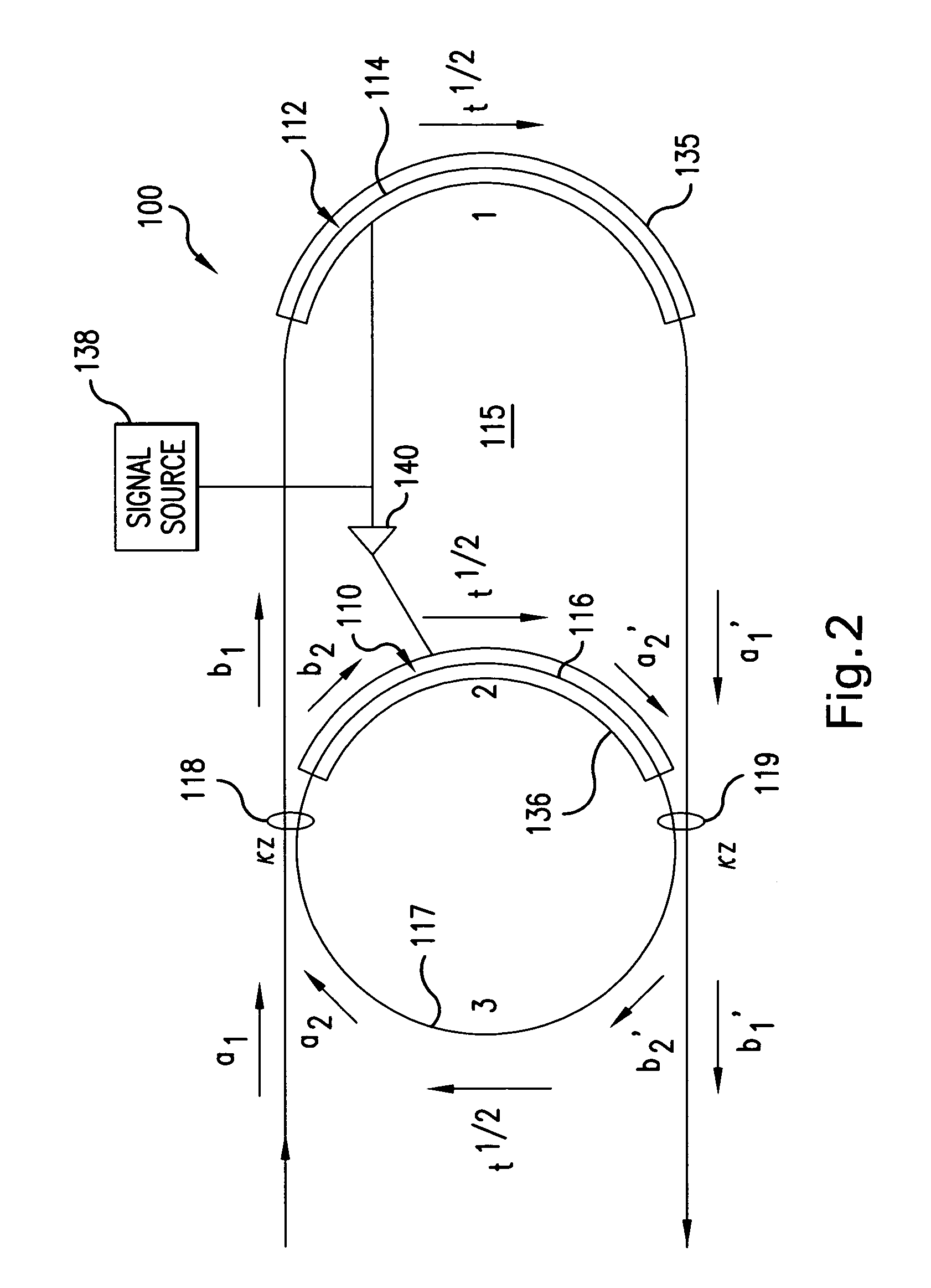
InactiveUS7262902B2High gainImprove slope efficiencyLaser using scattering effectsOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingMach–Zehnder interferometerHelical resonator
An optical resonant modulator includes an optical ring resonator and an optical loop that is coupled to the optical ring resonator by two couplers. The optical ring resonator can have a hybrid design in which the ring resonator is formed on an electro-optically passive material and the optical loop is formed on an electro-optically active material. An amplification section can be inserted between the electro-optically passive and the electro-optically active sections. In analog applications, an optical resonator includes a Mach Zehnder interferometer section having an input and an output, with a feedback path coupling the output to the input. Applications of the optical modulator of the invention, and a method for modulating an optical signal also are disclosed.
Owner:PHOTONICSYST INC
Method for making semiconductor laser and spot-size converter by double waveguide technology
InactiveCN1756009AReduce the number of growthLow costLaser detailsSemiconductor lasersSemiconductor packageIntrinsics
Disclosed a method for utilizing the dual-waveguide technology to manufacture the semiconductor laser and mode spot switch comprises following steps: on the N type indium phosphide substrate, sequentially extending growing the N type indium phosphide breaker, a lower waveguide layer, a space layer, a active region, and a thinner indium phosphide intrinsic layer, wherein, the indium phosphide intrinsic layer can prevent the oxidation of active region; removing the highest indium phosphide intrinsic layer, partly covering the laser with SiO2, and utilizing the wet corrosion process to etch the upper carinate shape of mode spot switch; utilizing the auto-alignment process to etch the lower carinate shape which comprises a lower waveguide layer, a space layer, a second growth P type indium phosphide coating layer, and a high doping P type indium gallium arsenide ohmic electrode contract layer; utilizing the SiO2 to partly cover the mode spot switch and etching the upper and lower carnate shapes again while the upper carinate shape comprises a active region, a P type indium phosphide coating layer and a high doping P type indium gallium arsenide ohmic electrode contract layer; and decreasing the substrate of extended plate to 100 ª–m, and manufacturing P / N electrodes to be scribed into the tube core of 250í‡500ª–m.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Swept fiber laser source for optical coherence tomography
InactiveUS20110069722A1Easy to reach deep saturationLarge tuning rangeLaser using scattering effectsSemiconductor lasersAudio power amplifierLength wave
The present invention provides a swept fiber optic laser source for optical coherence tomography emitting around ˜1060 nm wavelength, with tuning range higher than 50 nm, sweep repetition rate from DC to 40 kHz, instantaneous linewidth shorter than 50 pm (FWHM), and providing an average output around 1 mW (or 20 mW with output optical booster amplifier). The fiber laser source is based on a proper linear-cavity fiber laser configuration, with an intra-cavity half-symmetrical confocal Fabry-Perot tunable fiber (FP-TFF) filter and semiconductor optical amplifier (SOA), a device combination that gives a very robust and vibration-resistant laser configuration.
Owner:MULTIWAVE PHOTONICS
Single-mode laser based on high-order surface gratings
ActiveCN105826813AReduce lossLower Threshold GainLaser detailsSemiconductor lasersRadiation lossGroove width
The invention discloses a single-mode laser based on high-order surface gratings. The laser is of a ridge waveguide structure, and comprises a covering layer, a core layer and a substrate in a transverse direction. Narrow-groove-width high-order Bragg gratings are etched on a front segment ridge waveguide surface close to the output end of the laser, the etching depth of the group of gratings does not penetrate through the core layer, and optical feedback of the laser at the output end is provided; and a rear segment ridge waveguide of the other end of the laser does not contain gratings, an end face of the end is a deeply-etched interface, and optical feedback of the laser at the end is provided. The single-mode laser does not need secondary epitaxial growth of a material, and the manufacturing process is simple and convenient, thereby reducing the manufacturing cost of a device, and improving the reliability of the device; through introduction of the narrow-groove-width high-order surface gratings, radiation loss of the gratings is reduced, and laser performance is improved; and the laser rear end face formed by a deep etching method is easy to accurately position, the problem that the cavity length is indeterminate which is generated due to cleavage of an end face is avoided, and the laser is guaranteed to have good single-mode characteristics.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Semiconductor laser, method of manufacturing semiconductor laser, optical pickup and optical disk system
ActiveUS20080117945A1Avoid damageImprove reliabilityOptical wave guidanceLaser detailsOptical pickupElectron blocking layer
A semiconductor laser using a nitride type Group III-V compound semiconductor includes: an n-side clad layer; an n-side optical waveguide layer over the n-side clad layer; an active layer over the n-side optical waveguide layer; a p-side optical waveguide layer over the active layer; an electron barrier layer over the p-side optical waveguide layer; and a p-side clad layer over the electron barrier layer. A ridge stripe is formed at an upper part of the p-side optical waveguide layer, the electron barrier layer and the p-side clad layer, and the distance between the electron barrier layer and a bottom surface in areas on both sides of the ridge stripe is not less than 10 nm.
Owner:SONY CORP
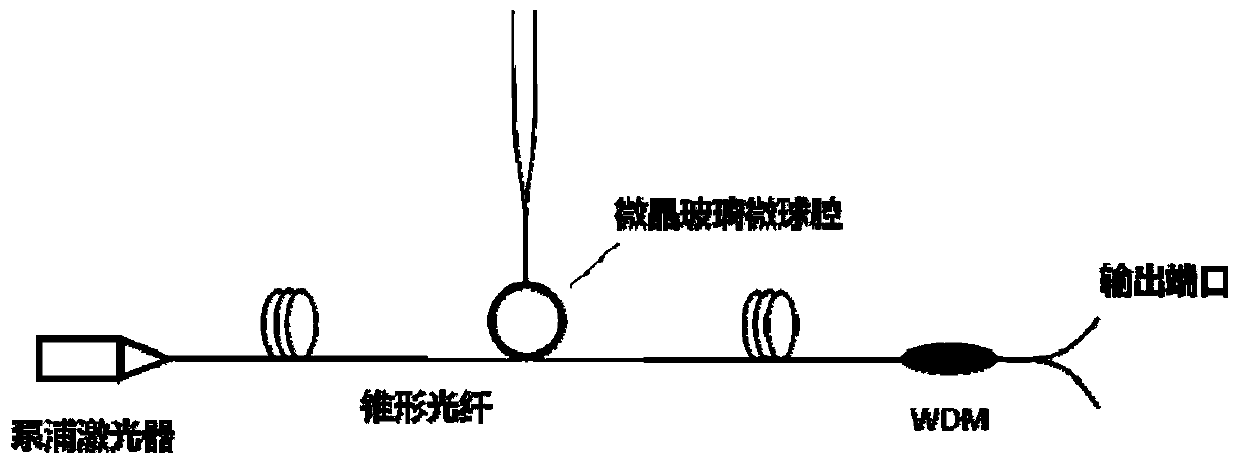
Glass ceramics whispering gallery mode resonant cavity capable of outputting single mode high-performance laser and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN109809685ALower the thresholdImprove slope efficiencyGlass making apparatusOptical resonator shape and constructionFiberWhispering gallery
The invention discloses a glass ceramics whispering gallery mode resonant cavity capable of outputting single mode high-performance laser and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the field ofoptical devices. The method comprises the following steps: firstly mixing raw materials for preparing the glass resonant cavity with rear earth active ion raw materials sufficiently, then carrying outmelting and rod winding to obtain active fiberglass; drawing the active fiberglass to tapered fiber by melt extraction, and truncating the tapered fiber in the middle to obtain single taper fibers; melting the thin ends of the single taper fibers through a heating source, and forming a microsphere cavity by utilizing the action of surface tension; carrying out heat treatment or laser-induced treatment on the microsphere cavity to obtain a glass ceramics microsphere cavity, and carrying out coupling with the tapered fiber and packaging to obtain the glass ceramics whispering gallery mode resonant cavity. According to the invention, the preparation process is simple, the prepared glass ceramics microsphere cavity has relatively high quality factor, the influence on active ion gain propertyof amorphous state and relatively high phonon energy of glass is improved by the separation of microcrystal, and laser output with lower threshold value and higher slope efficiency can be realized.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
1.5-1.6ª–m wave band laser using erbium and ytterbium ion doped boro-ahuminate crystal as gain medium
InactiveCN101165978AHigh phonon energyHigh thermal conductivityOptical resonator shape and constructionActive medium materialIonYb element
This invention relates to a 1.5-1.6mum wave band laser with ErxYbR(1-x-y)Al3(BO3)4 as the gain medium, in which, x=0.05-5.00mol%, y=1.0-40.0mol%, R is Sc, Y, La, Gd or Lu or combination of several of them, and 0.93-1.00mum wave band infrared light is applied for pumping to realize 1.5-1.6mum laser output of high efficiency (higher than 20% slope efficiency) and high power ( higher than 1.5W of laser output power)at the same time.
Owner:FUJIAN INST OF RES ON THE STRUCTURE OF MATTER CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Laser device outputting 1064nm tunable Laguerre-Gaussian beams
ActiveCN107565352AReduce in quantityReduce lossOptical resonator shape and constructionLaser cooling arrangementsResonant cavityGaussian beam
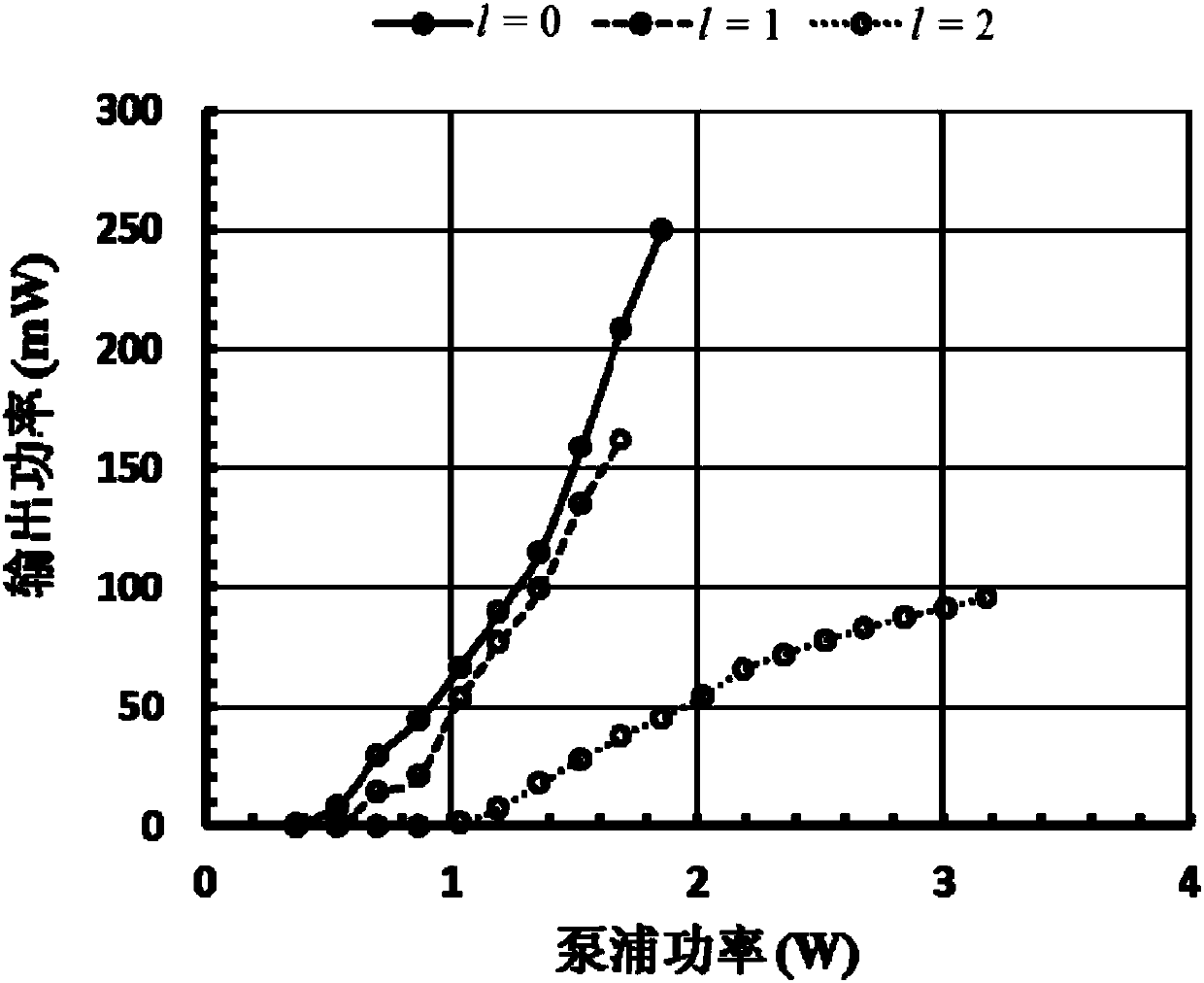
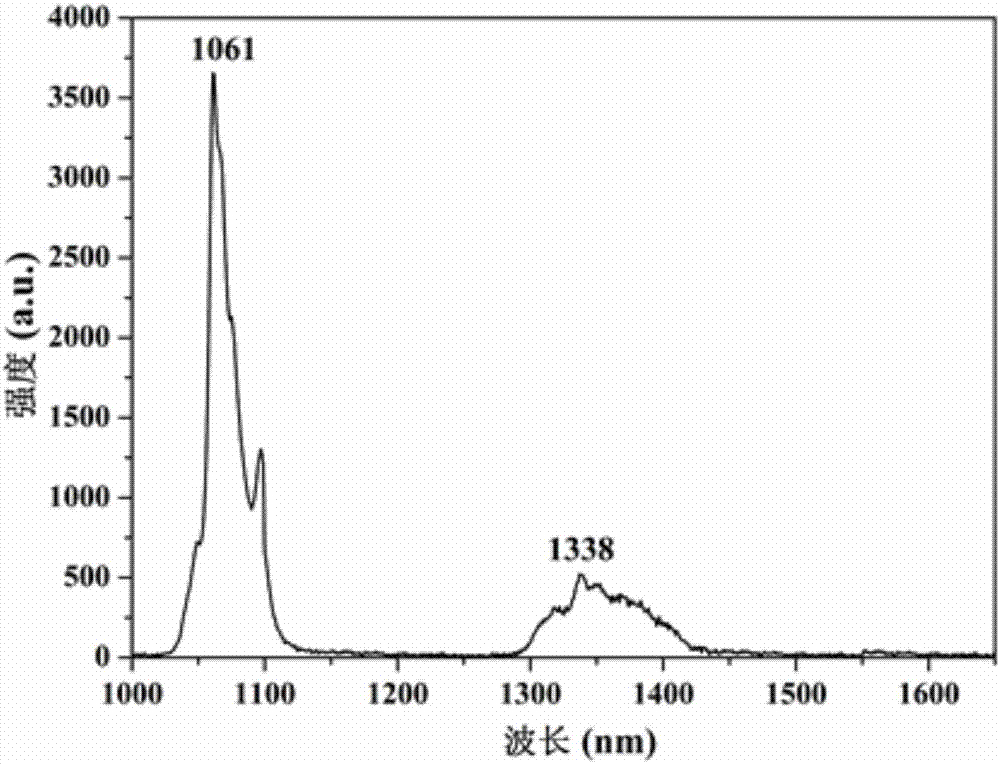
The invention discloses a laser device outputting 1064nm tunable Laguerre-Gaussian beams. The laser device outputting the 1064nm tunable Laguerre-Gaussian beams comprises a 808nm laser diode, an optical fiber coupler, a film coated endoscope, a gain crystal, a heat dissipation device, a polarizing element, a scroll half wave plate and a pinhole, which are arranged along the direction of light propagation; and the film coated endoscope comprises a film coated front endoscope, a film coated focusing lens and a film coated back endoscope, which form a resonant cavity. By means of the laser deviceoutputting the 1064nm tunable Laguerre-Gaussian beams, the output of the 1064nm tunable Laguerre-Gaussian beams with low threshold, high skew efficiency, high purity and tunable angular Index l is realized.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Transition-metal-doped zinc sulfide or zinc selenide planar waveguide material and preparation method
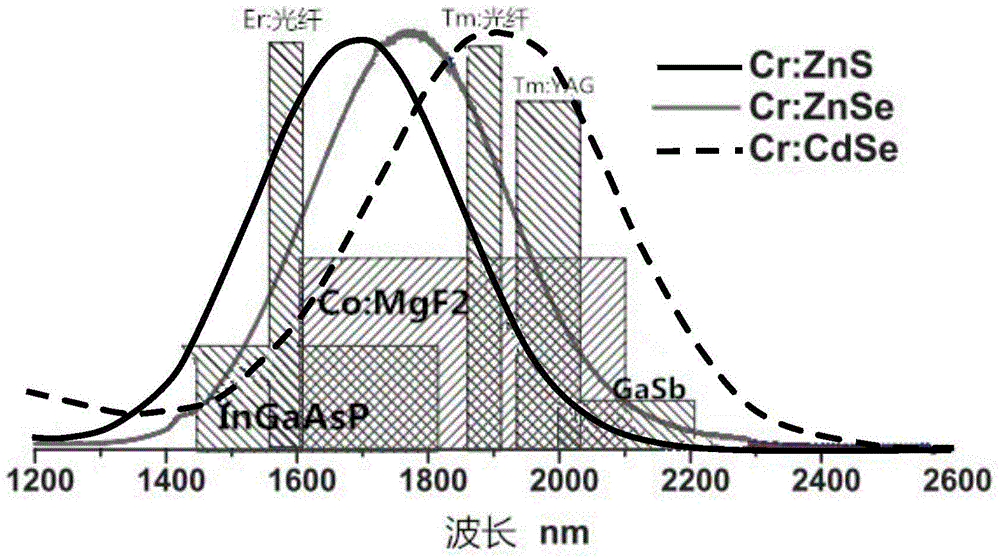
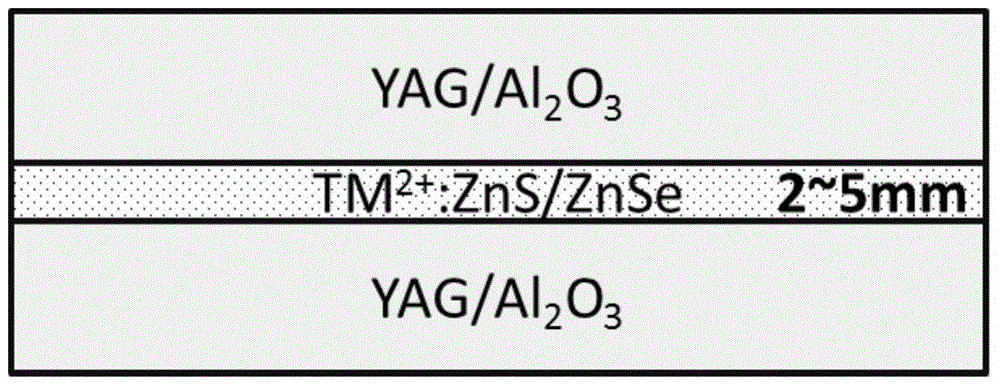
ActiveCN104441849ALower pumping thresholdImprove cooling effectCeramic layered productsZinc selenideHigh power lasers
The invention relates to a transition-metal-doped zinc sulfide or zinc selenide planar waveguide material and a preparation method. The transition-metal-doped zinc sulfide or zinc selenide planar waveguide material is characterized in that a YAG (yttrium aluminum garnet) or Al2O3 lath is respectively combined to two sides of transition-metal-ion-doped zinc sulfide or zinc selenide ceramic to form a sandwich planar waveguide structure, so that a heat-mirror effect of laser can be effectively controlled, and the intermediate infrared waveguide laser output is realized. By adopting the transition-metal-doped zinc sulfide or zinc selenide planar waveguide material, not only can the heat management be effectively realized by virtue of the sandwich composite structure, but also the mass production can be realized, and important significance on the development of a high-power laser technology and integrated optics can be realized.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Polarization continuously adjustable cylindrical vector optical solid-state laser
ActiveCN107681426ALower the thresholdImprove slope efficiencyLaser detailsHalf waveOptical polarization
The invention discloses a polarization continuously adjustable cylindrical vector optical solid-state laser. The laser comprises a laser diode, an optical fiber coupling unit, a film-coating cavity mirror, a gain medium, a polarized element, a vortex half wave plate and a pin hole; the film-coating cavity mirror comprises a film-coating front cavity mirror, a film-coating focusing lens and a film-coating back cavity mirror which form a resonant cavity; the polarization state orientation in different positions in the space is controlled by using a polarization beam splitter, a 1 / 2 wave plate and the vortex half wave plate in the cavity; and cylindrical vector beams in different polarization state distribution are output. By virtue of the laser, the intra-cavity loss is lower, the active mode is higher in flexibility, and the output cylindrical vector beams are higher in quality.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Crystal material, preparation method thereof and application as laser crystal
InactiveCN107419334AEnhanced fluorescence emissionSolution to short lifePolycrystalline material growthBy pulling from meltTetragonal crystal systemSpace group
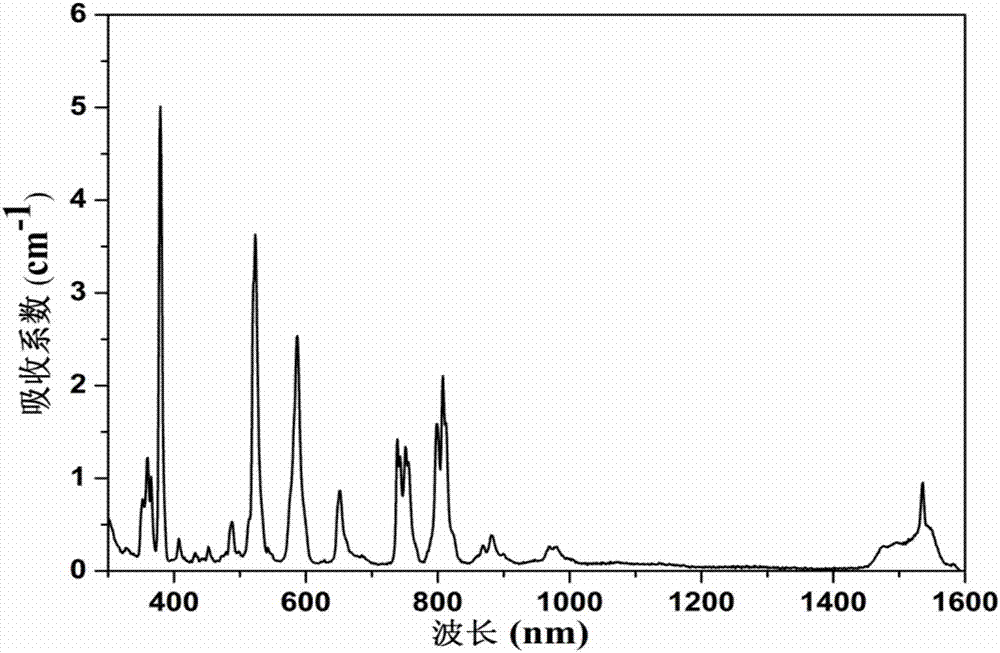
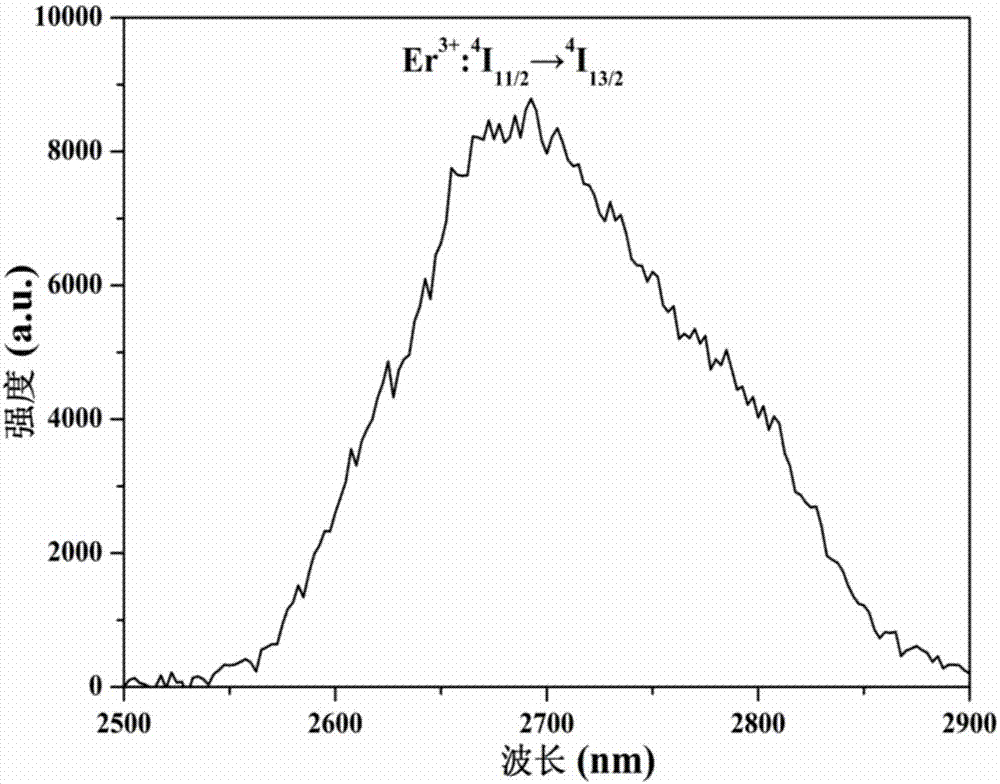
The invention discloses a crystal material, which is characterized in that the chemical formula of the crystal material is CaNdxEryLa(1-x-y)Ga3O7, wherein x is greater than or equal to 0.01 and less than or equal to 0.05, and y is greater than or equal to 0.1 and less than or equal to 0.3; the crystal material belongs to a tetragonal system and a space group shown in the description; the crystal material is formed into a laminated electronegative skeleton structure formed by a GaO4 tetrahedron, and Nd<3+>, Er<3+>, Ca2<+> and La<3+> are distributed among layers and have an unordered crystal structure. An Nd<+> ion is doped in Er<+3> activated CaLaGa3O7 crystal to greatly enhance the adsorption efficiency of the crystal for pump light, the efficient laser output of the -2.7mu m waveband of LD pumping is realized, the fluorescence emission of the crystal in an intermediate infrared waveband is enhanced, the service life and the particle number of 4I13 / 2 are greatly decreased, a self-final state bottleneck effect is inhibited, high gain is kept by laser media in an oscillation process, and the slope efficiency of the laser output is improved.
Owner:FUJIAN INST OF RES ON THE STRUCTURE OF MATTER CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Distributed feedback laser
InactiveCN105490164AImprove direct modulation bandwidthImprove slope efficiencyLaser detailsLaser output parameters controlDistributed feedback laserGrating
The invention relates to the technical field of a semiconductor laser, and provides a novel distributed feedback laser adopting uniform optical grating and capable of realizing single modes. The laser comprises an active region and a reflecting region; current is injected to the active region for providing gain for the laser; the outer end plane of the reflecting region is plated with an antireflection film or provided with an anti-reflection structure for reducing reflection; and the other end of the active region is the output end plane of the laser, and the end plane is plated with the anti-reflection film for reducing reflection. The optical grating in the reflecting region can increase the feedback of the laser and reduce threshold value gain under a short cavity length; the optical grating in the active region and the reflecting region is continuously and uniformly distributed feedback Bragg grating; the optical grating periods of the active region and the reflecting region are equivalent; and an effective refractivity difference between the active region and the reflecting region is realized through current injection for performing mode selection. According to the distributed feedback laser with uniform optical grating, the single mode is realized; the distributed feedback laser has a relatively low threshold value gain under the short cavity length; and meanwhile, the distributed feedback laser is low in manufacturing difficulty.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Porous channel hollow micro-knot echo wall mode resonant cavity and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN108899750AEvenly dispersedSimple preparation processOptical resonator shape and constructionActive medium shape and constructionFiberResonant cavity
The invention belongs to the optical device field, and discloses a porous channel hollow micro-knot echo wall mode resonant cavity and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method of the porous channel hollow micro-knot echo wall mode resonant cavity includes the steps: drawing the middle portion of a porous glass capillary tube into a hollow micro-nano fiber having an outer diameter of 0.5 to 10 mu m through a melt drawing method, and then forming a hollow micro-knot cavity by micro-operation knotting; and injecting a liquid gain medium into a fiber pore channel of the hollow micro-knot cavity by means of a mode of capillary force suction or external force injection, and then coupling with the tapered fiber, and packaging to obtain a porous channel hollow micro-knot echo wall moderesonant cavity. The preparation process of the preparation method is simple, and the prepared hollow micro-knot cavity can be injected with various liquid gain media by capillary force suction or external force injection, and the obtained porous channel hollow micro-knot echo wall mode resonant cavity has multiple gain channels, thus realizing low threshold and high slope efficiency, and high power echo wall laser output.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
High efficiency, high power cryogenic laser system
InactiveUS20070201518A1Enhanced optical slope efficiencyImprove efficiencyLaser using scattering effectsSemiconductor lasersAudio power amplifierErbium doping
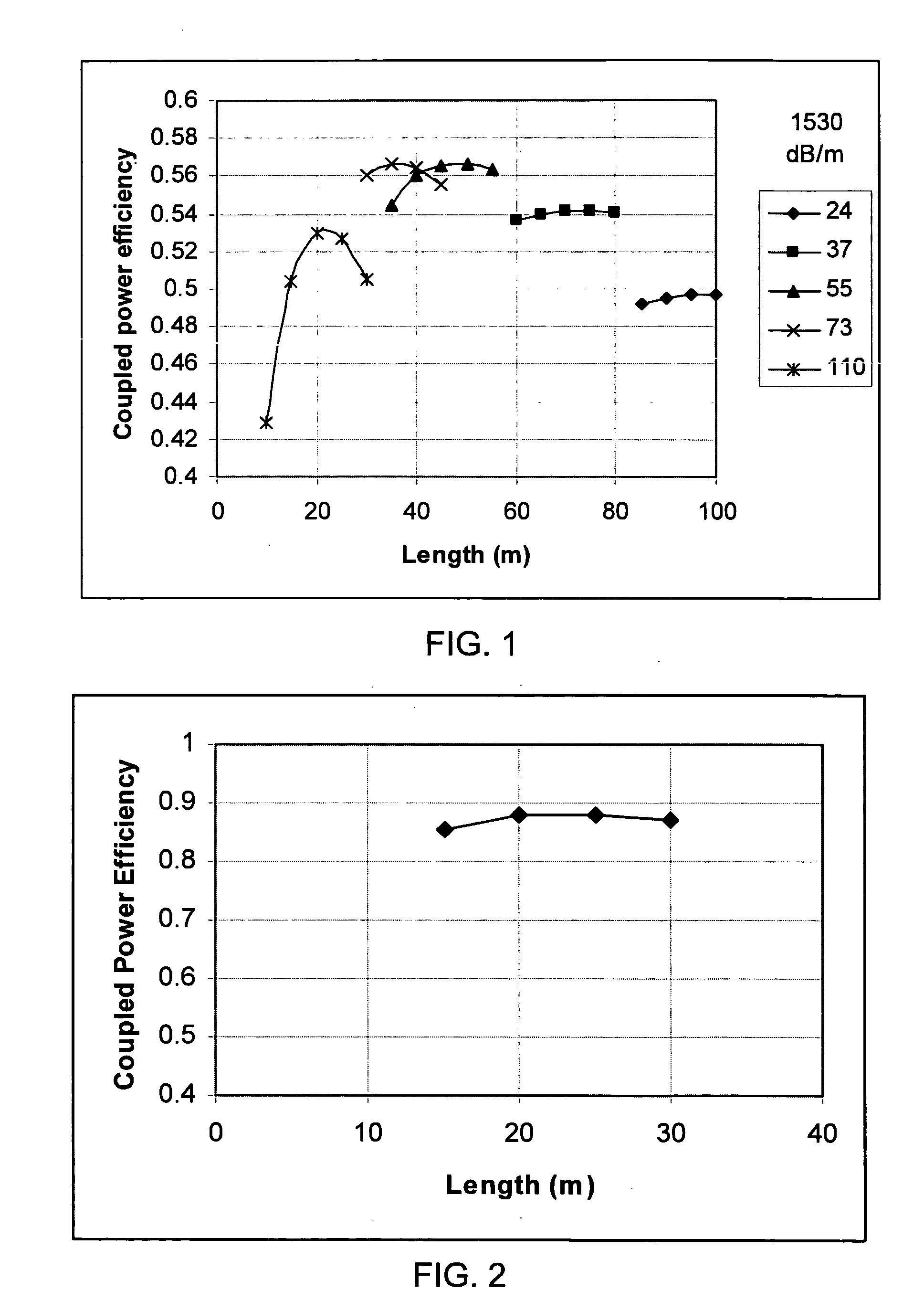
A fiber laser system and a related method for its use, in which one or more fiber laser amplifiers are cryogenically cooled and optimized to operate at a desirably high efficiency. Versions of the laser system using either thulium or erbium doped fibers are disclosed. In a high power version of the system, the outputs of multiple fiber lasers are coherently combined. Cooling by a selected liquefied gas, such as nitrogen, is applied to the fiber laser amplifiers and, optionally, to pump diodes and to optical elements used to combine the outputs of the fiber laser amplifiers.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
Preparation method of Nd-YVO4 transparent laser ceramic material
InactiveCN101659552AWide variety of sourcesIncrease the doping concentrationRare earthMetallic materials
The invention relates to a transparent laser ceramic material, in particular to a preparation method of Nd:YVO4 transparent laser ceramic material, belonging to the technical field of an inorganic non-metallic material. The method comprises the following steps of: mixing the raw materials for preparing neodymium-doped yttrium vanadate laser material according to the proportion, grinding, sieving by 200 meshes after drying processing, pressing into bisque; carrying out vacuum sintering to the bisque with the vacuum degree of less than 10<-3>Pa, temperature-rising speed of 2 to 10 DEG C for every minute, sintering temperature of 1500 to 2000 DEG C and insulating time of 4 to 50 hours; and sintering ingot blanks, cooling with a furnace, annealing, carrying out planar processing after being taken out, and obtaining the transparent laser Nd:YVO4 ceramics after precisely polishing. The invention can improve the content of the rare soil element in the material, can prepare transparent ceramic with larger size, has shorter preparing period and lower cost, and better solves the problems that the doping concentration of single-crystal material is hard to be improved, the preparation with larger size is difficult and the like, thus leading the comprehensive performance of the material to be improved.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for making modular spot converting distributed-feedback Prague laser by using quantum trap confounding
InactiveCN1909310AReduce the number of growthHas an effectOptical wave guidanceLaser detailsGratingPhosphate
The invention relates to a method for using quantum well mixing to produce mode speckle conversion distributed feedback Bragg lasers, which comprises: growing n-type indium phosphate buffer layer on the substrate; using silica dioxide to mask the distributed feedback Bragg lasers, and generating point corrosion on the characteristic indium phosphate pour buffer layer at the mode speckle converter; corroding the silica dioxide protective layer; heating chip, keeping warm and annealing; corroding the protective layer; grating the whole chip; corroding the characteristic indium phosphate pour buffer layer; etching the upper and lower ridge pilot structures on the converter; cleaning the chip; growing p-type indium phosphate layer, indium gallium arsenic phosphate etching stopping layer, p-type indium phosphate package and high-doping p-type indium gallium arsenic ohm electrode contact layer; growing silica dioxide insulated layer on the whose chip; opening electrode window at the laser, and splashing p electrode; extending the substrate; boiling n electrode at the back; slicing the sample into tubular core.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Semiconductor laser device
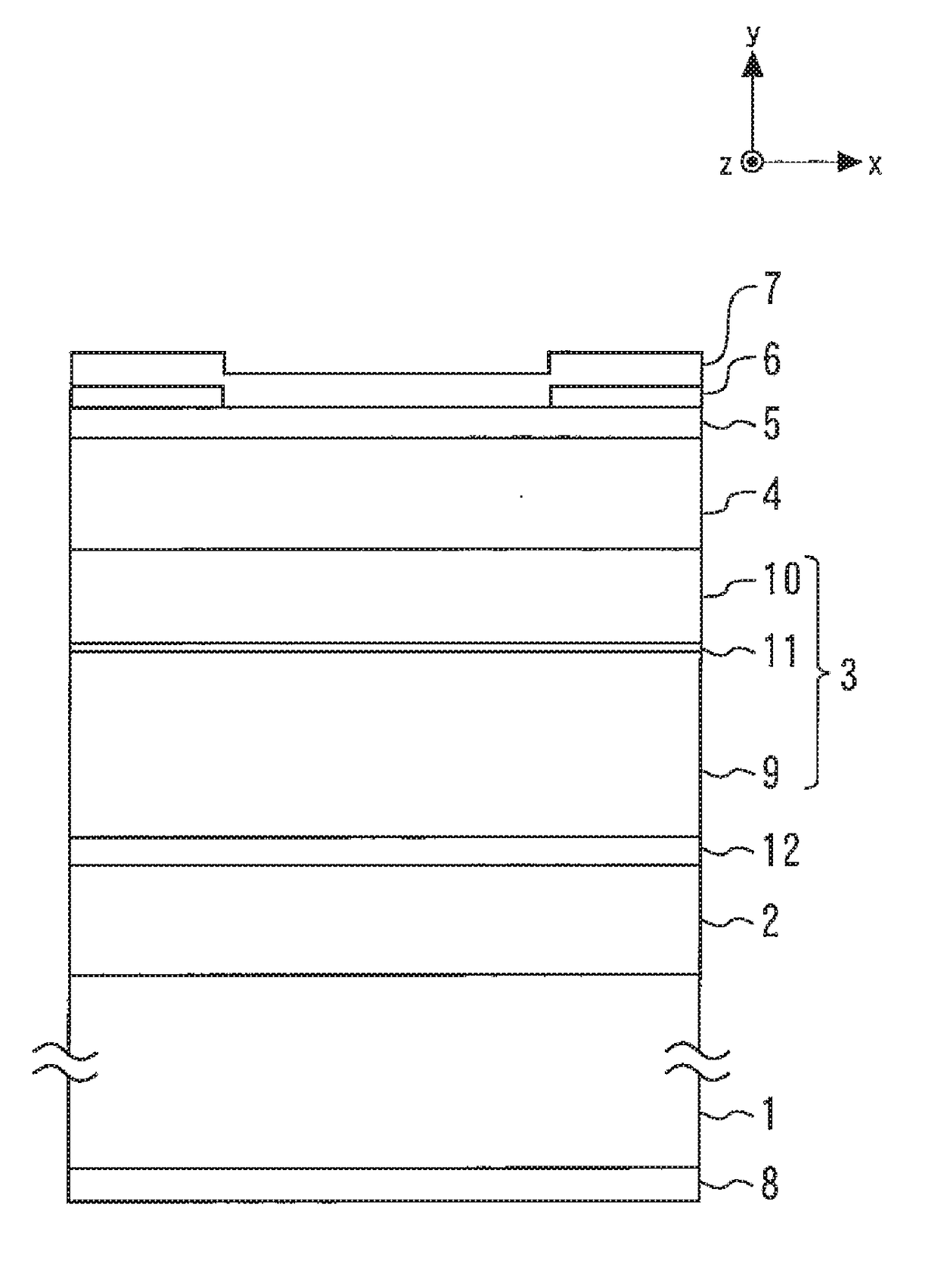
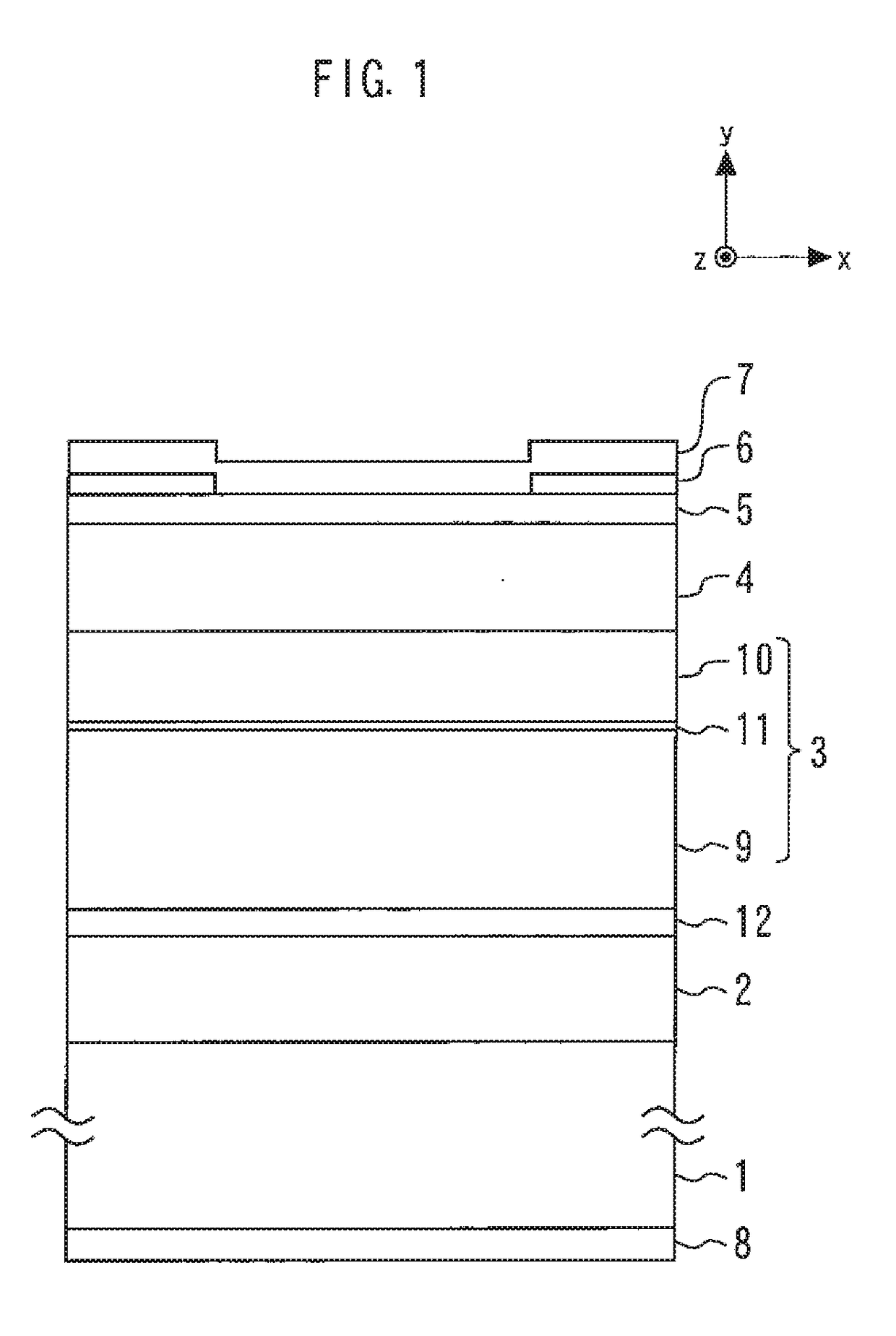
InactiveUS6947461B2Solve the large outputImprove efficiencyOptical wave guidanceLaser detailsLaser lightField pattern
A semiconductor laser device includes a p-InP cladding layer, an active region, a first n-InP cladding layer, a second n-InP cladding layer, and an n-InGaAsP cladding layer with a thickness between 0.05 μm and 0.3 μm, sandwiched by the first and second n-laP cladding layers and laminated at a position closer to the active region than a position at which optical intensity of a near-field pattern of laser light emitted from the active region becomes substantially zero. The semiconductor laser device exhibits a small reduction in the optical output even when a large current flows, and has a high slope efficiency without changing the near-field pattern a great deal.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
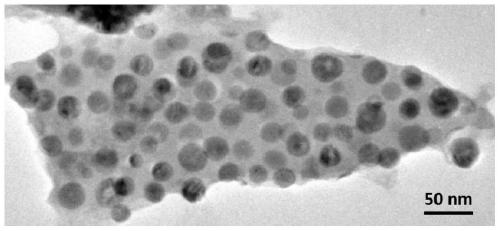
Double-doped quantum dot active region epitaxial structure and preparation method and application thereof
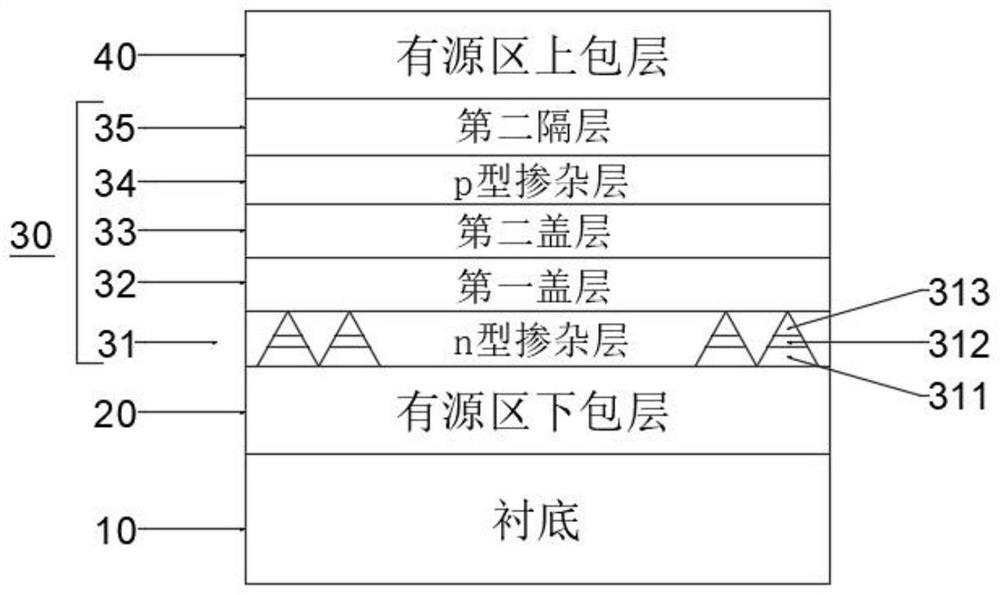
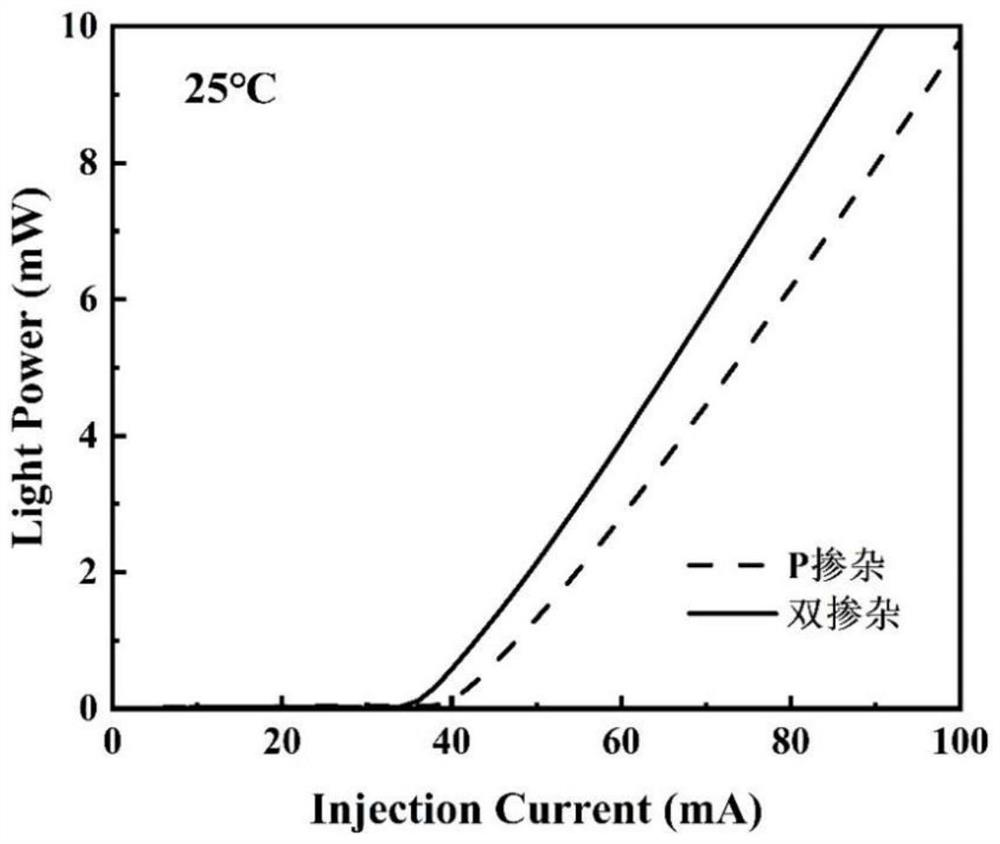
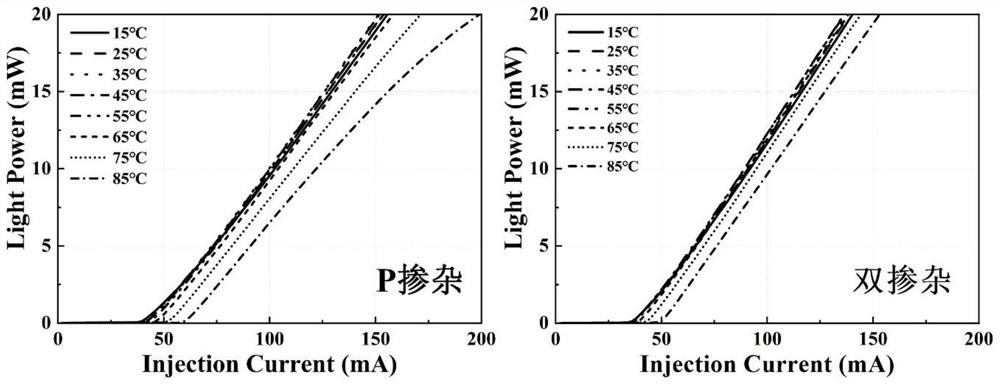
PendingCN114421283AEffective passivationReduce lossLaser detailsLaser active region structureValence bandConduction band
The invention discloses a double-doped quantum dot active region epitaxial structure and a preparation method and application thereof, a quantum dot active region of the double-doped quantum dot active region epitaxial structure is configured as a periodic double-doped quantum dot laminated structure, and the quantum dot active region comprises an n-type doped layer and a p-type doped layer which are periodically arranged; wherein the p-type doped layer and the n-type doped layer generate a synergistic effect, and the first interlayer is arranged between the n-type doped layer and the p-type doped layer which are periodically arranged; the second interlayer is arranged on the other side of the p-type doped layer, and the other side of the second interlayer is different from the side where the first interlayer is located; the first interlayer or the second interlayer is used for providing stress regulation or stress relief, and through a spatially separated alternate doping structure, the loss of current carriers is reduced, and the optical quality of the material is improved; the asymmetry of quasi-Fermi level movement of conduction bands and valence bands of the quantum dots is improved, and the peak gain and differential gain of the material are improved.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Optical semiconductor element, method of manufacturing optical semiconductor element and optical module
InactiveUS20060222032A1Improve solid solubilityStable optical output powerLaser detailsLaser optical resonator constructionDopantOptical Module
An InGaAsP thin film layer having the same index of refraction as a diffraction grating is inserted between a p-type InP clad layer and the diffraction grating composed of an InGaAsP layer. In this structure, the InGaAsP layer is present over an active layer, and the amount of thermal diffusion of dopant to the vicinity of the active layer does not depend on an aperture width or the presence or absence of the diffraction grating when the p-type InP clad layer is grown, thereby obtaining a stable optical output, a threshold current, and slope efficiency.
Owner:OPNEXT JAPAN INC
Semiconductor laser device
ActiveUS20170117685A1Improve power conversion efficiencyIncrease output powerOptical wave guidanceLight guideRefractive index
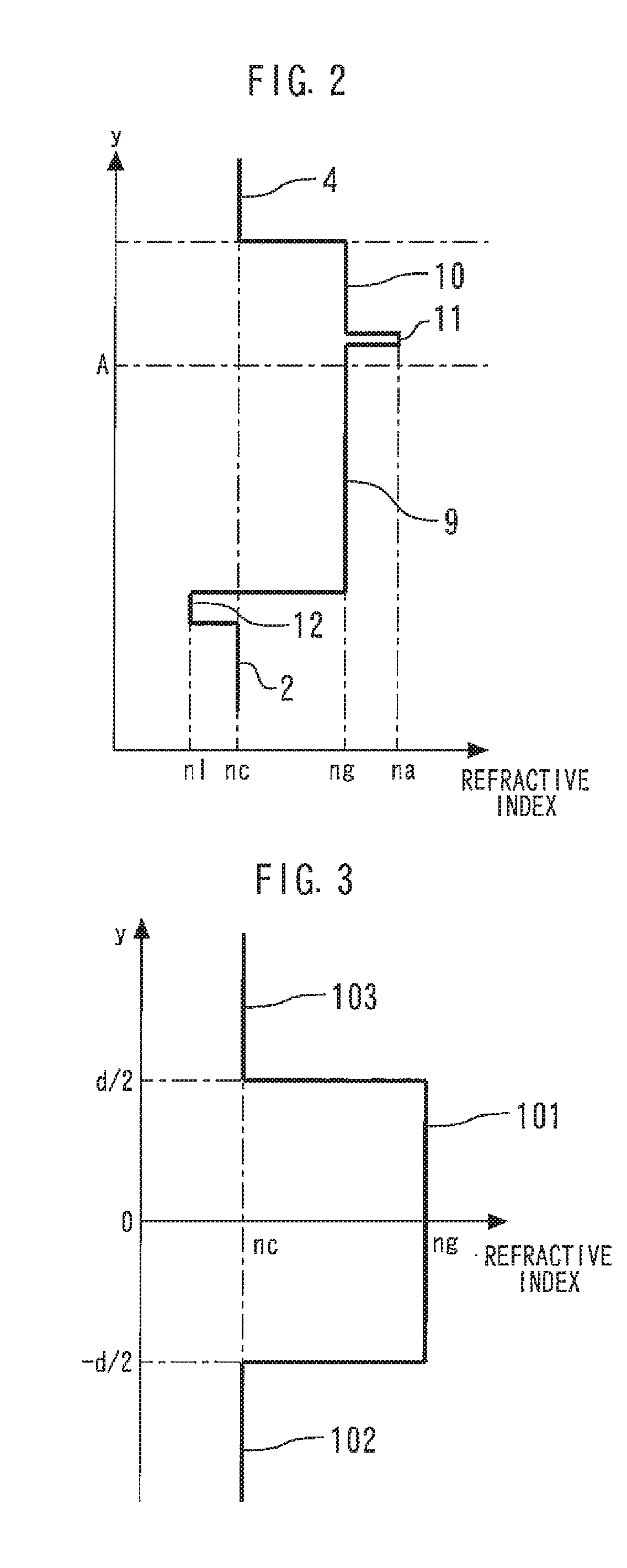
An active layer is provided on a side closer to the second conductivity type cladding layer than a center of the light guide layer in the light guide layer. A first conductivity type low-refractive-index layer is formed between the first conductivity type cladding layer and the light guide layer and has a refractive index which is lower than a refractive index of the first conductivity type cladding layer. A layer thickness d of the light guide layer is a value at which a high-order mode equal to or higher than a first-order mode is permissible in a crystal growing direction by satisfying2πλng2-nc2d2≧π2.The active layer is disposed at a position where a light confinement of the active layer becomes smaller compared to a case in which the active layer is disposed at a center of the light guide layer while there is not the first conductivity type low-refractive-index layer.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
High-efficiency single-frequency thulium-doped fiber laser based on in-band pumping
PendingCN113675720AImprove slope efficiencyHigh absorption coefficientActive medium shape and constructionLine widthThulium
The invention discloses a high-efficiency single-frequency thulium-doped fiber laser based on in-band pumping. Laser with the wavelength of 1650 nm is adopted as a pumping thulium-doped fiber laser, the pumping wavelength corresponds to the vicinity of the peak value of a pumping absorption spectrum in a thulium-doped fiber ribbon, the high absorption cross section is achieved, the small quantum loss is achieved, the efficiency of the laser can be greatly improved, and the noise and line width characteristics of the laser are improved. High-efficiency and high-power 1650 nm laser output can be obtained in a stimulated Raman scattering mode, and a foundation is laid for obtaining a high-power single-frequency fiber laser.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Semiconductor laser device
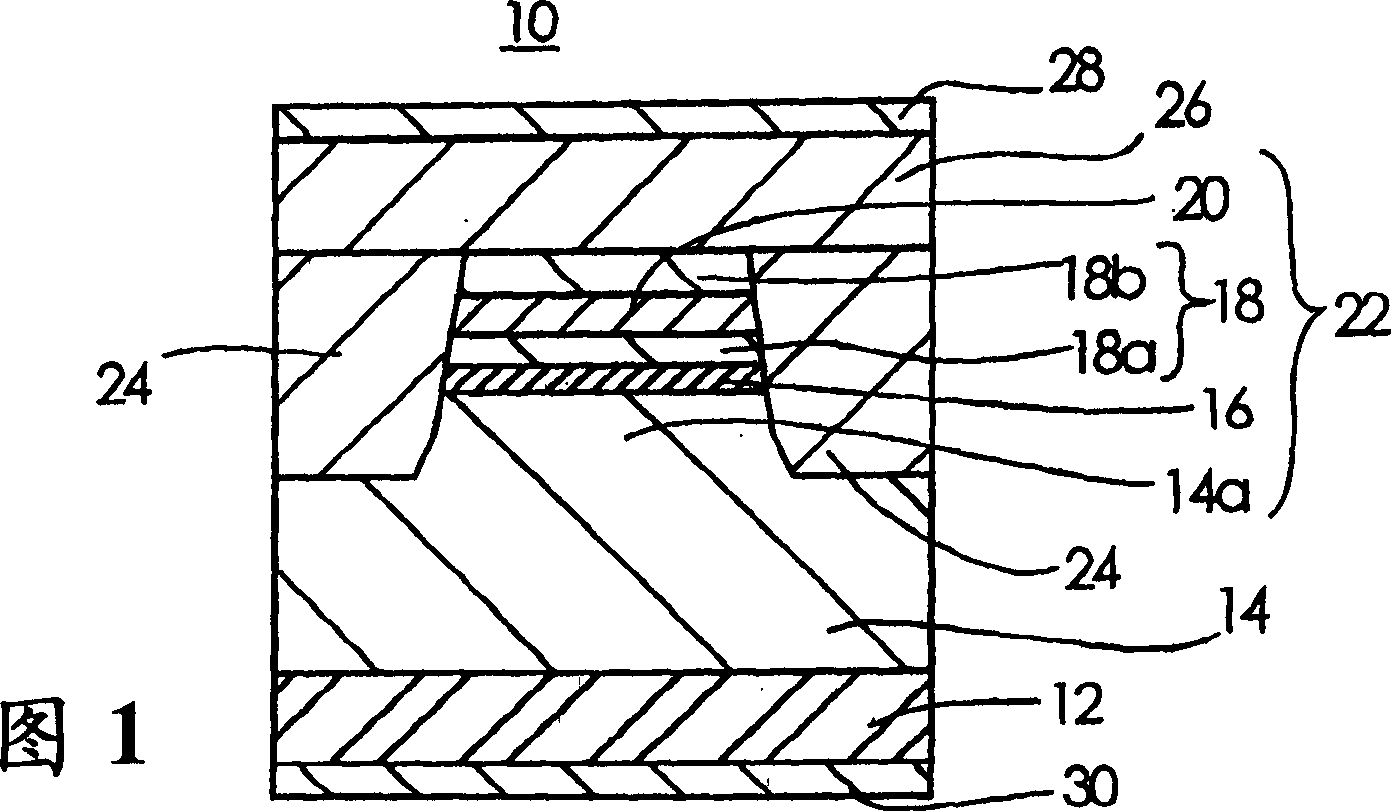
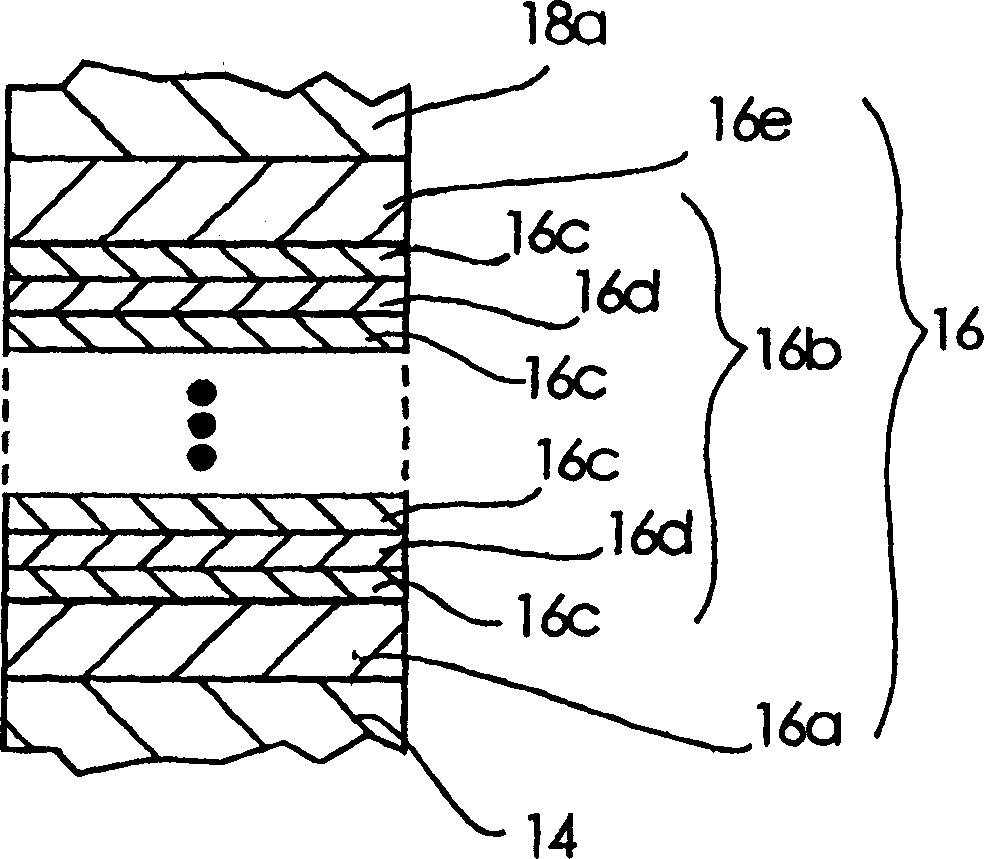
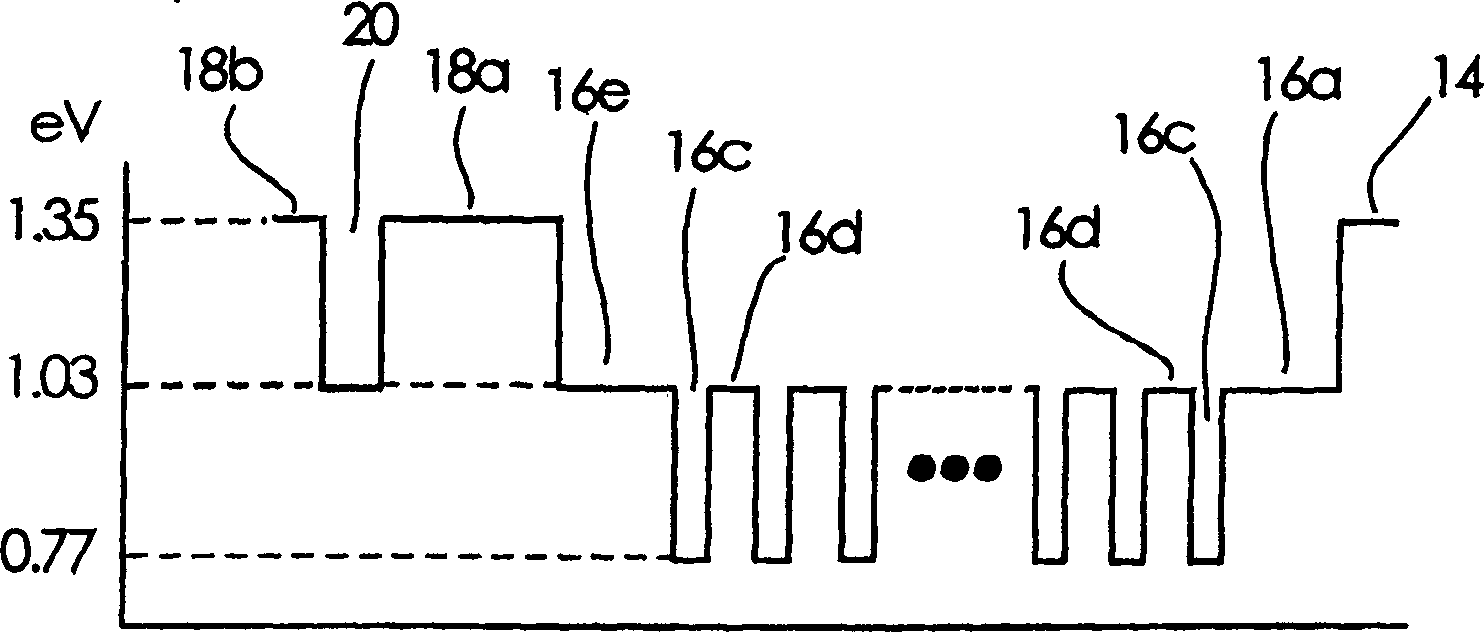
InactiveCN1484350AReduce light absorptionImprove slope efficiencyOptical wave guidanceLaser detailsLaser lightField pattern
A semiconductor laser device according to the present invention comprises a p-InP cladding layer 14, an active region 16, an n-InP cladding layer 18a, an n-InP cladding layer 18b, and an n-InGaAsP cladding layer 20 with a thickness of between 0.05 mum and 0.3 mum sandwiched by the n-InP cladding layers 18a and 18b and laminated at a position closer to the active region 16 than a position at which an optical intensity of a near-field pattern of laser light emitted from the active region 16 becomes substantially zero. The semiconductor laser device exhibits small reduction in the optical output even when a large current flows, and has a high slope efficiency without changing the near-field pattern a great deal.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Phase shift optical grating of symmetric structure and DFB semiconductor laser device
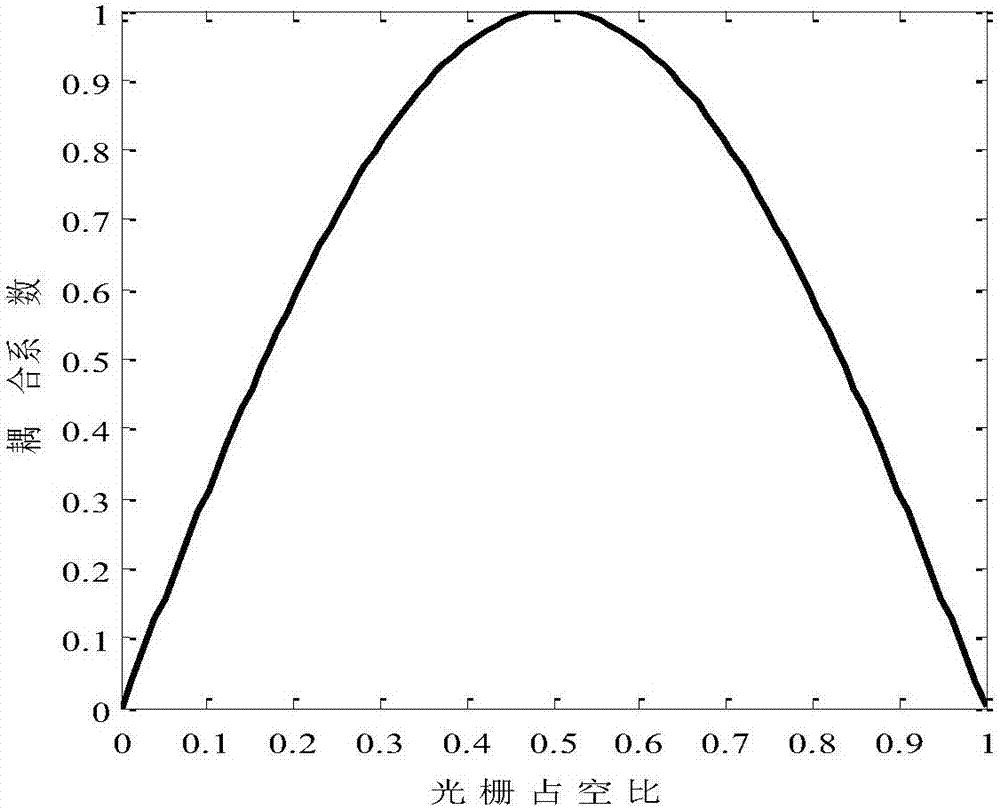
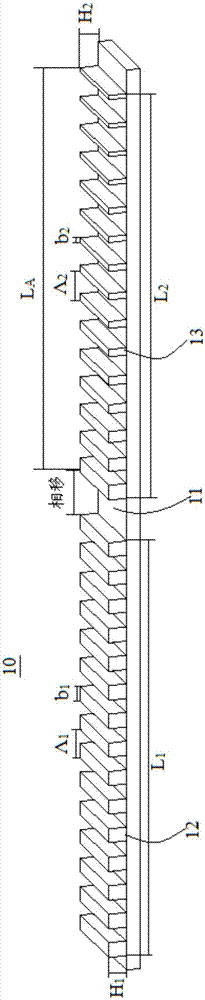
InactiveCN107516817AImprove slope efficiencyImprove stabilityLaser detailsLaser optical resonator constructionPhase shiftedGrating coupling
The application discloses a phase shift optical grating of a symmetric structure and a DFB semiconductor laser device. The phase shift optical grating comprises a phase shift structure arranged at a central position of the phase shift optical grating and a first optical grating and a second optical grating positioned at two sides of the phase shift structure; the first optical grating and the second optical grating are the same in length, etching depth and optical grating period; the first optical grating is constantly invariant in duty ratio, the second optical grating comprises an apodized optical grating, the duty ratio of the apodized optical grating gradually changes along an axial direction of the optical grating, and the second optical grating is weaker than the first optical grating in refractive index modulation intensity. In the DFB semiconductor laser device based on the phase shift optical grating of the symmetric structure disclosed in the invention, the apodized optical grating is introduced in the second optical grating in a condition that the optical gratings at the two sides of the phase shift structure remain unchanged in terms of length, etching depth and period; asymmetry of phase shift optical grating coupling factors at the two sides can be realized, asymmetry of output light power can be realized via the DFB semiconductor laser device, and effective output light power of the laser device can be increased.
Owner:INNOLIGHT TECHNOLOGY (SUZHOU) LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com