Patents
Literature
139 results about "Stress regulation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Stress regulation means learning to control the levels of stress you are feeling and bring them back down to healthy levels. There are various methods available for lowering underlying stress levels, such as breathing meditation, HRV training and mindfulness. Learning to regulate stress is also about how you respond...
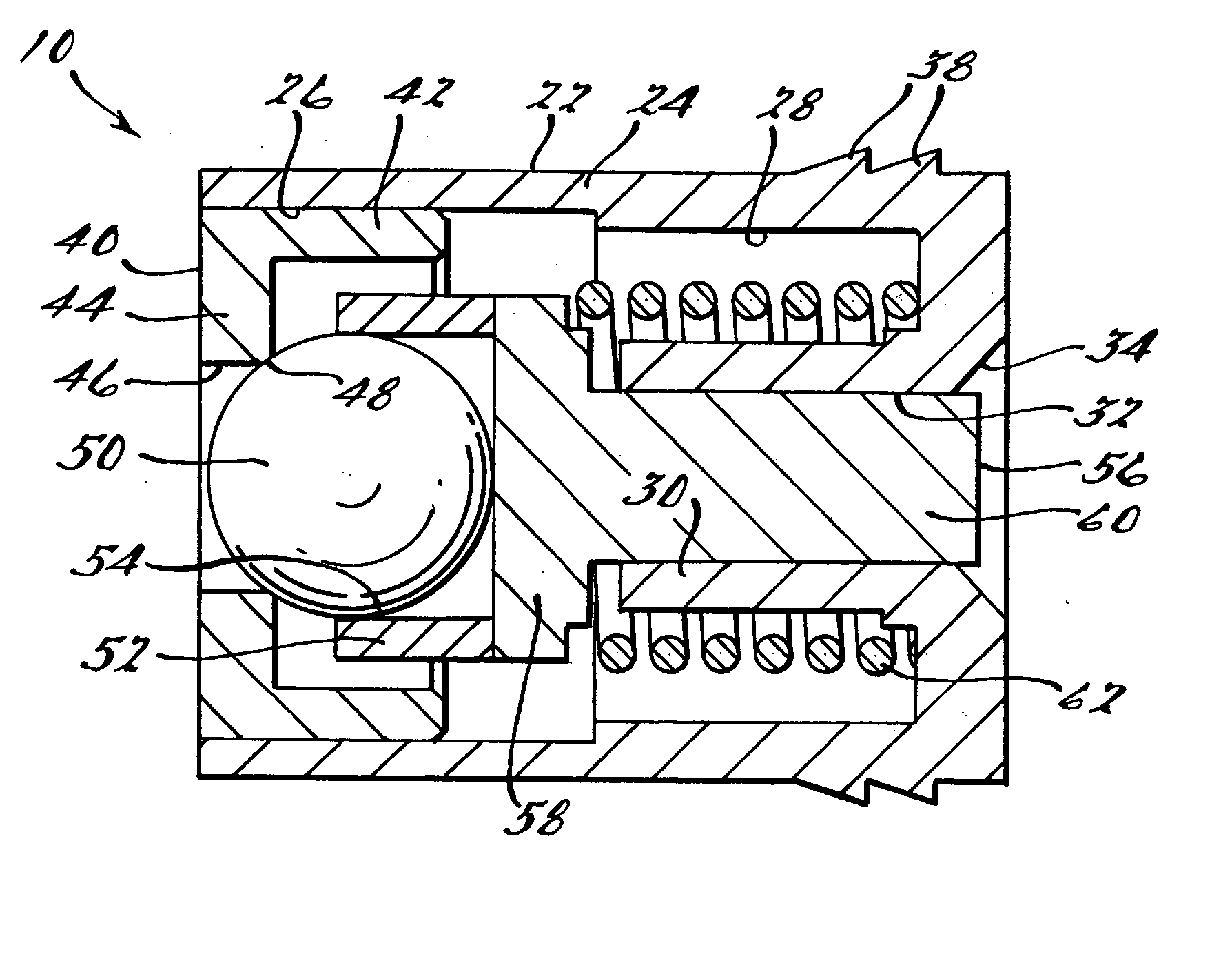
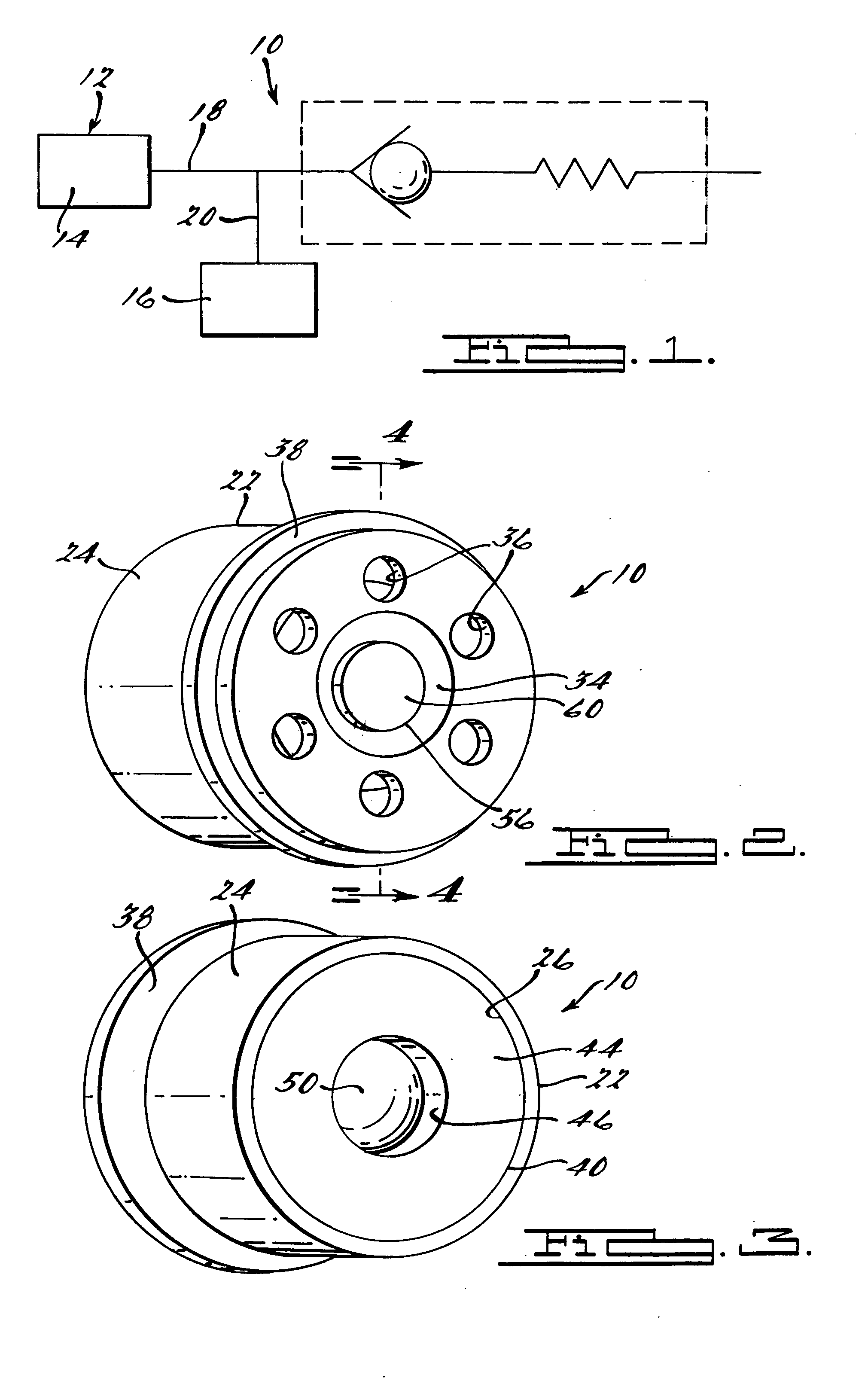
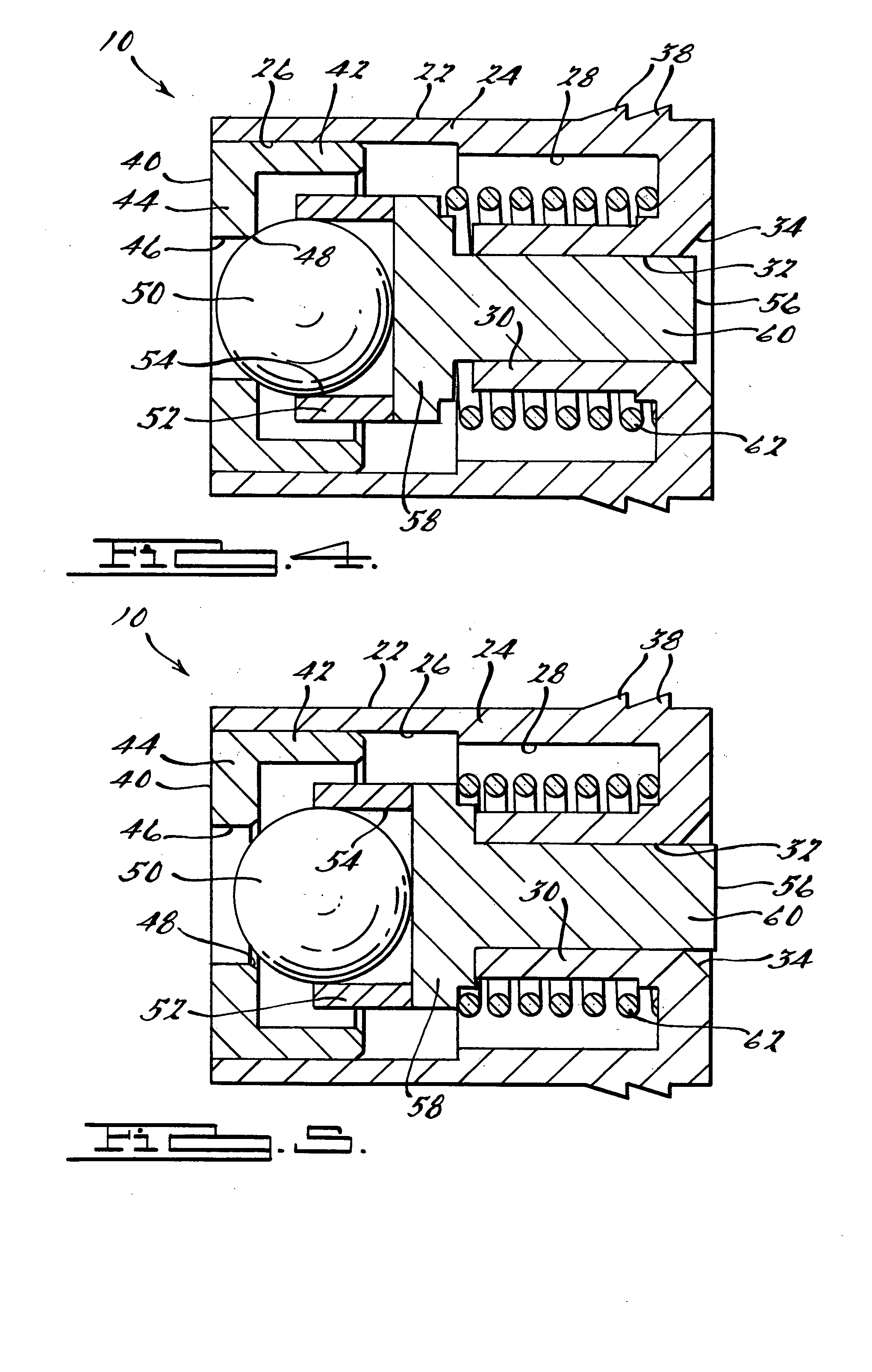
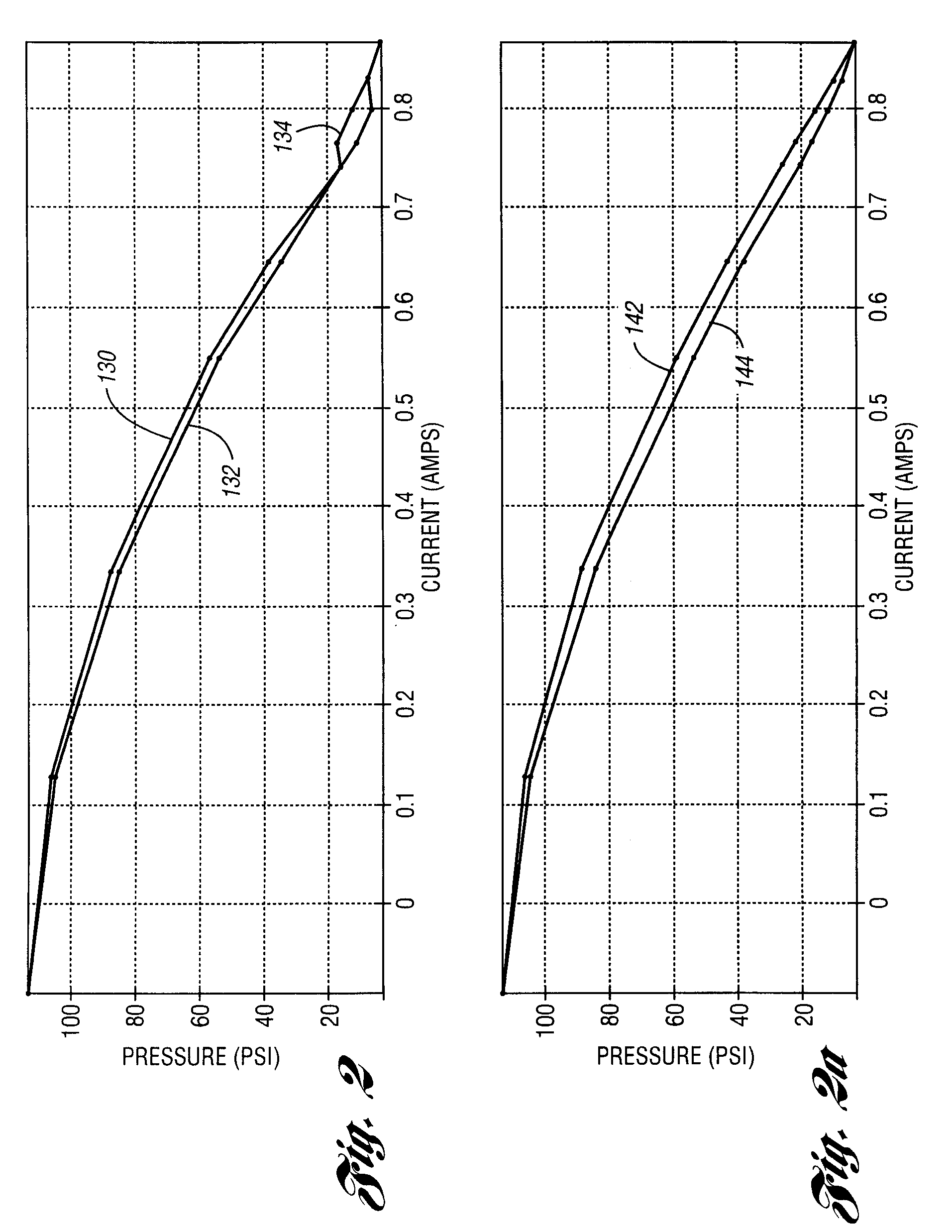
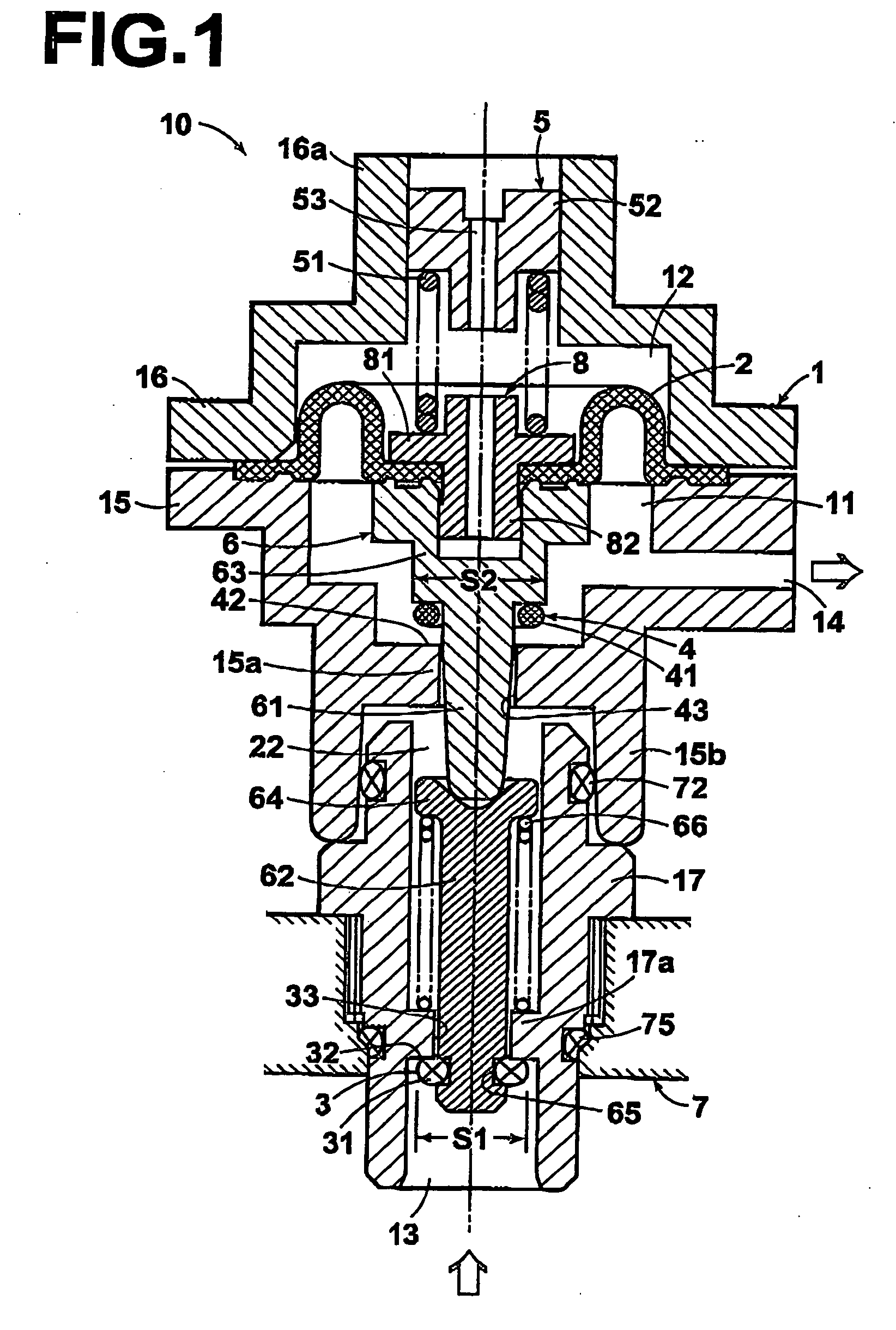
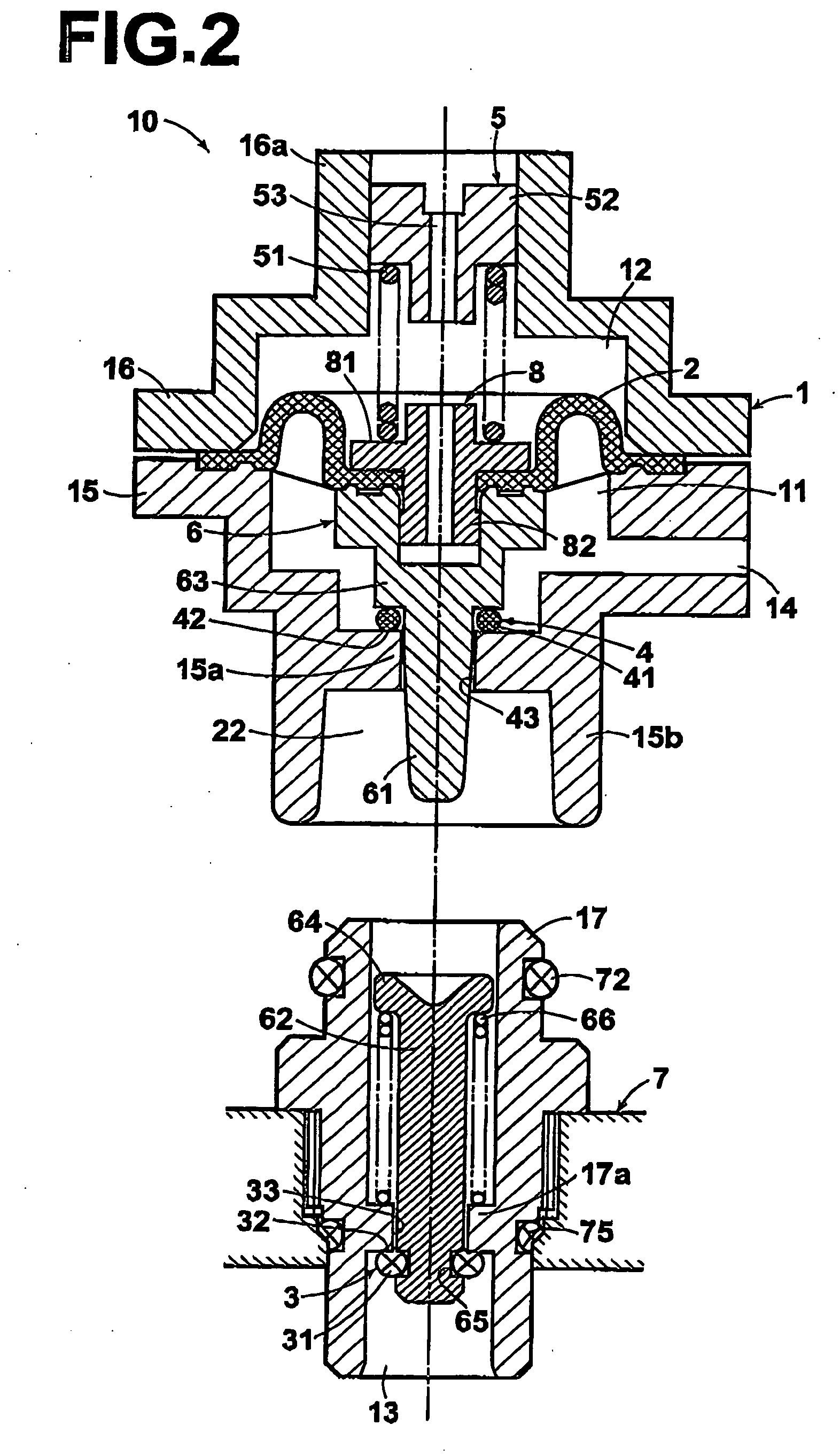
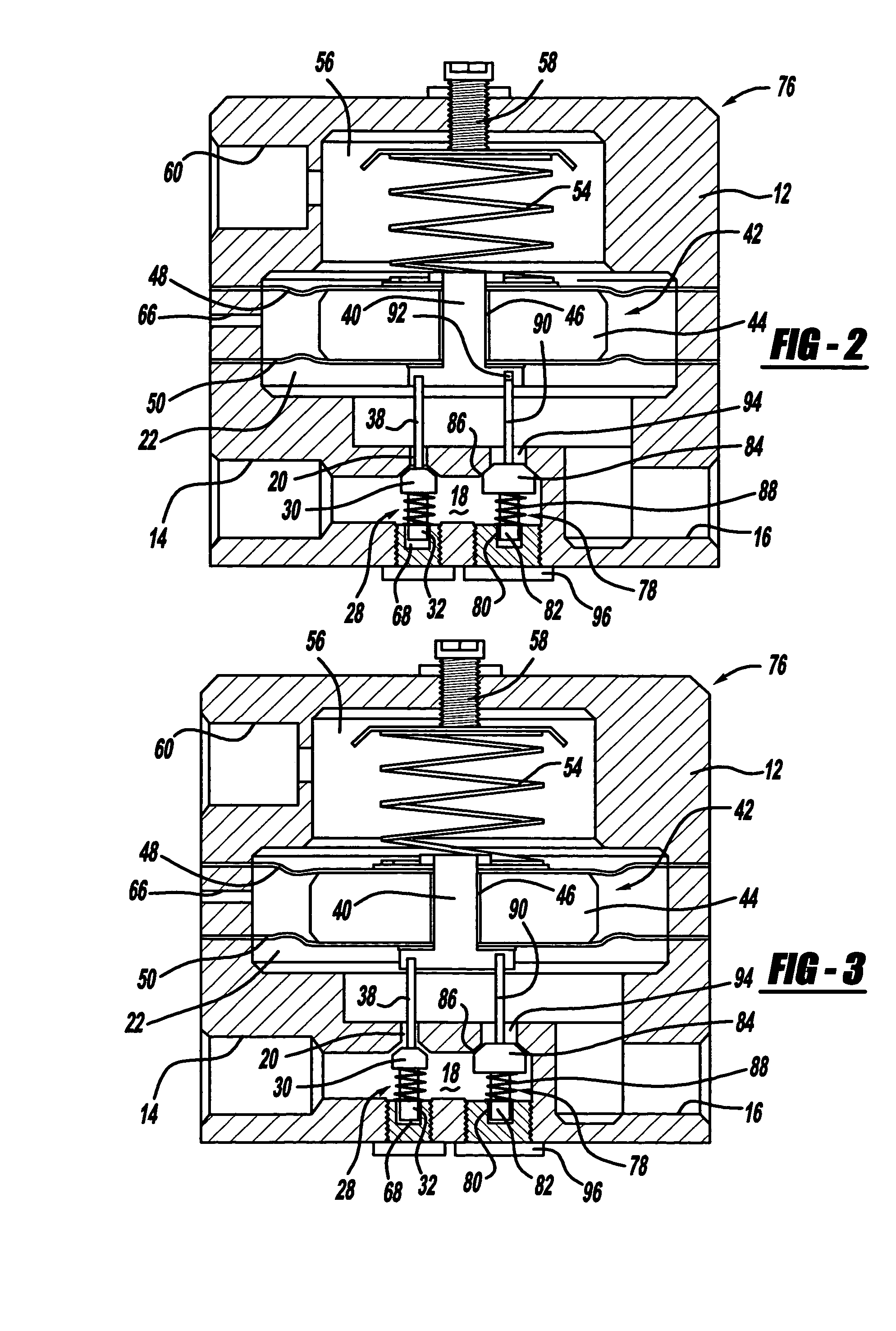
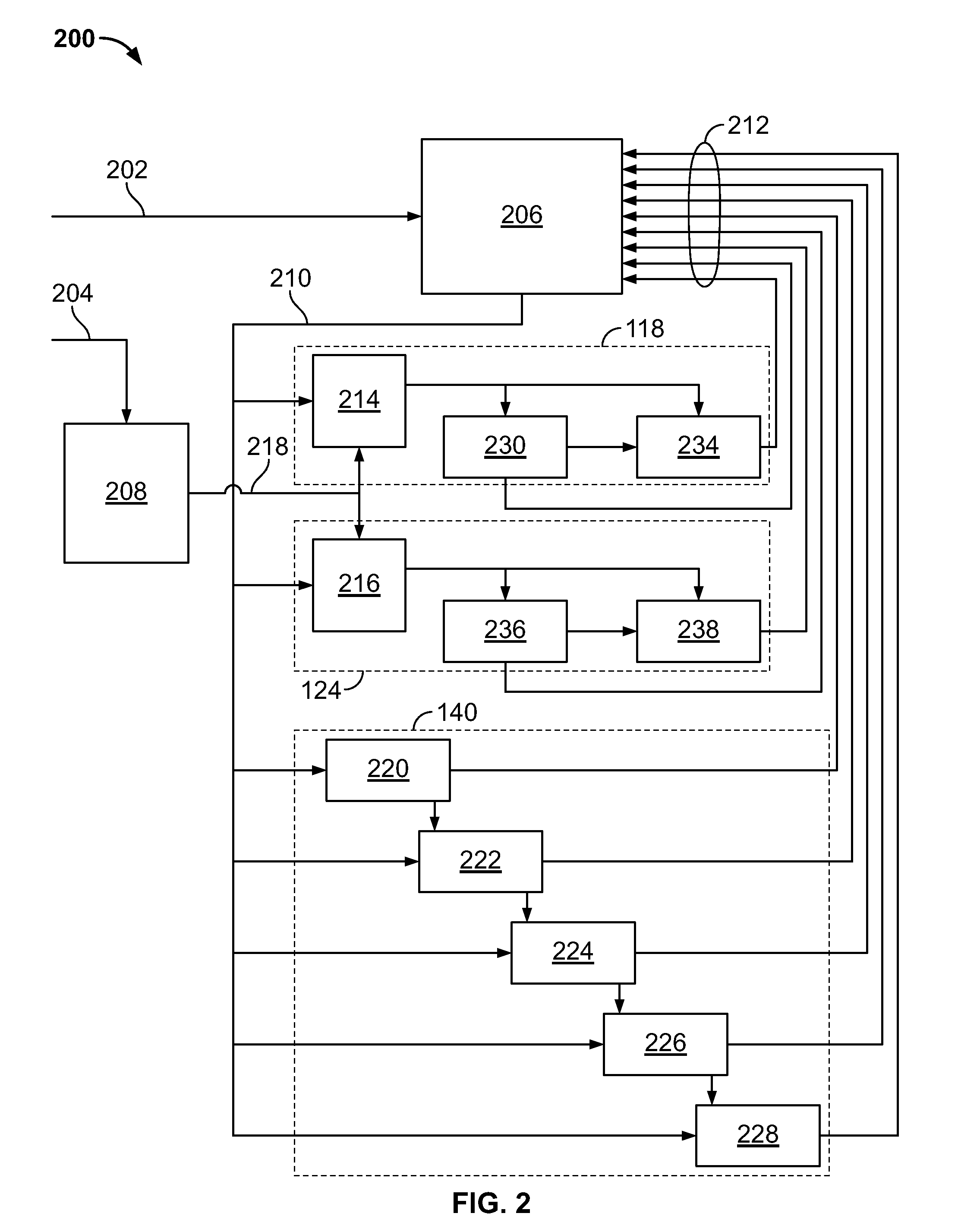
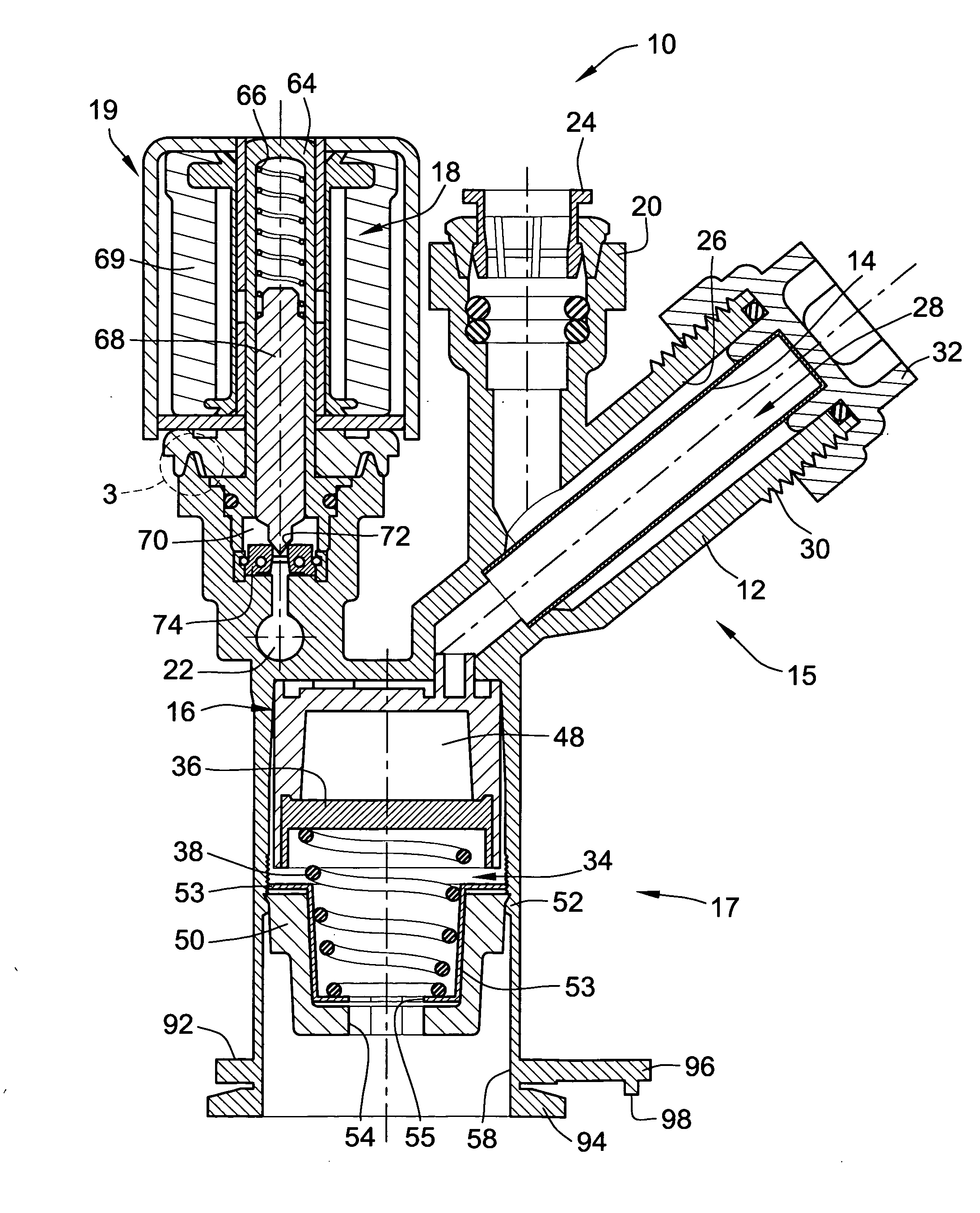
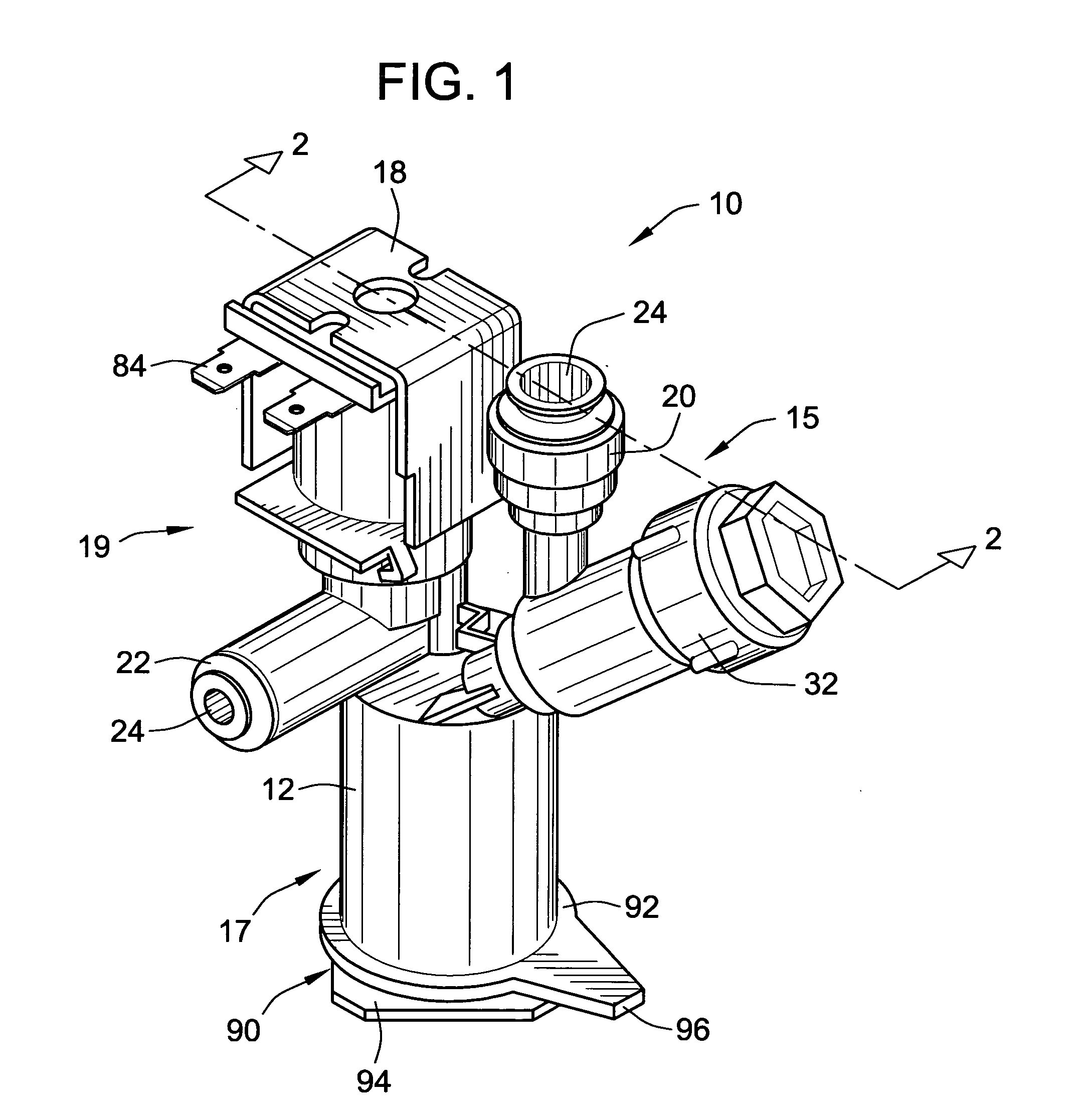
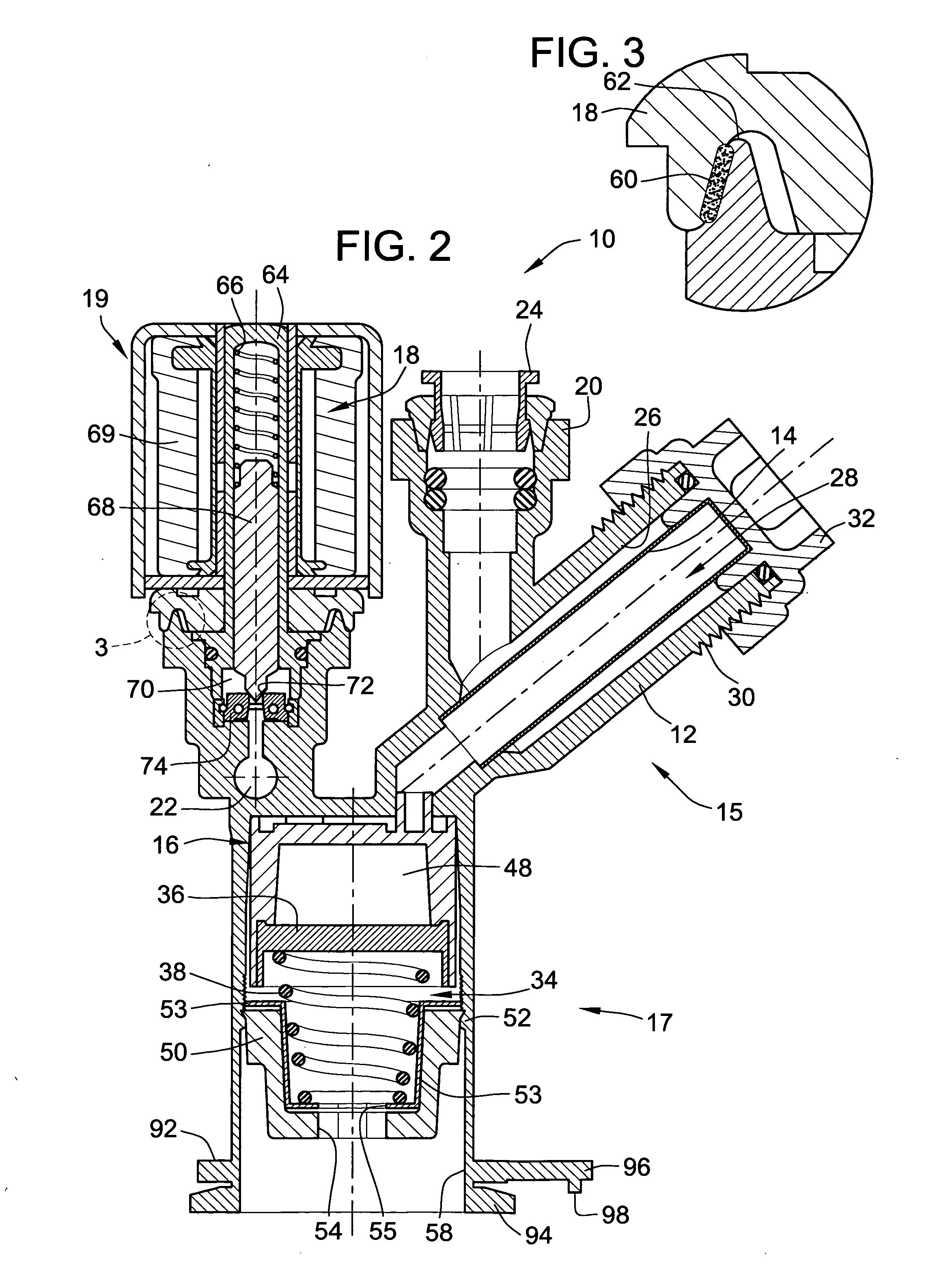
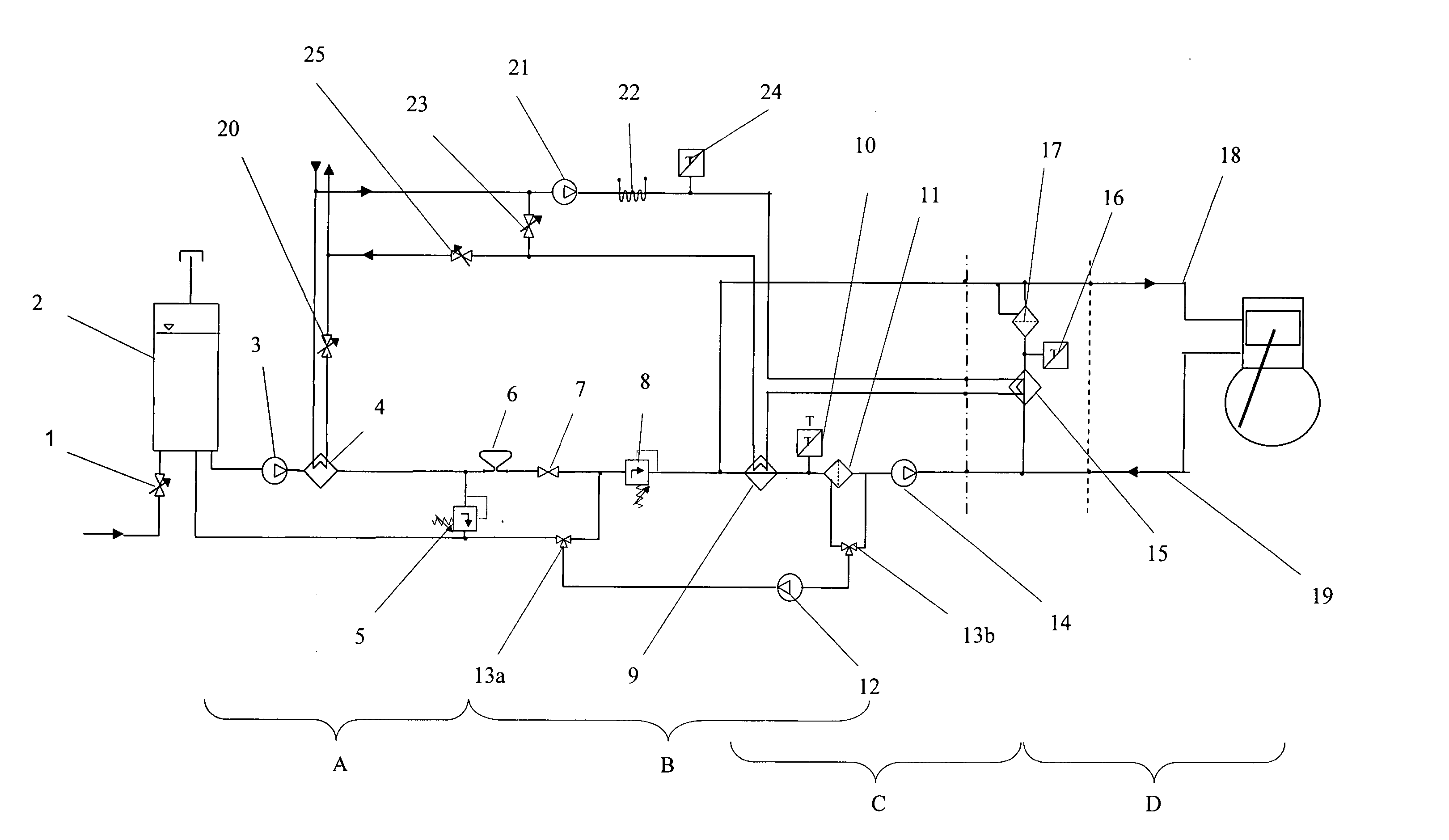
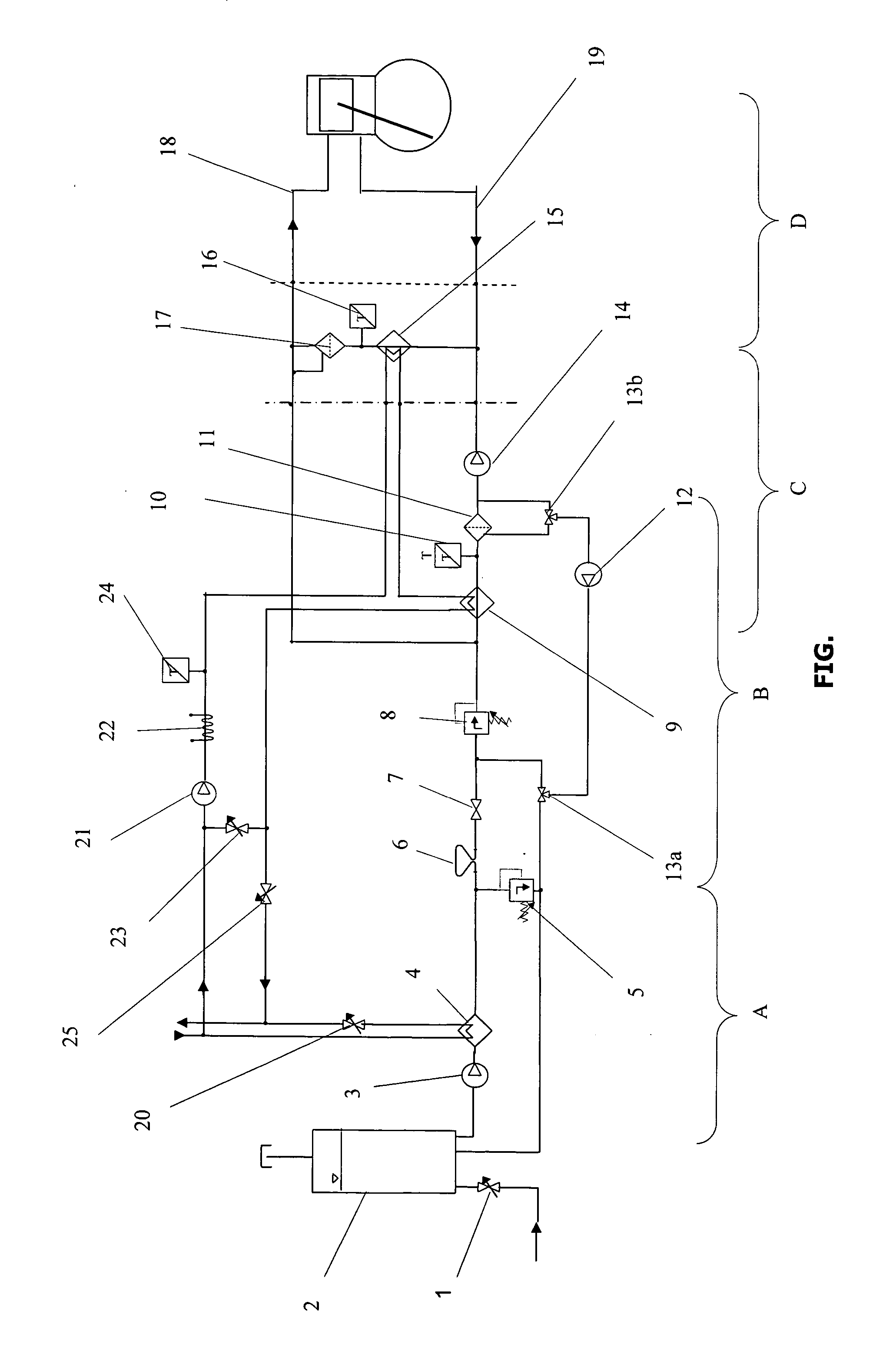
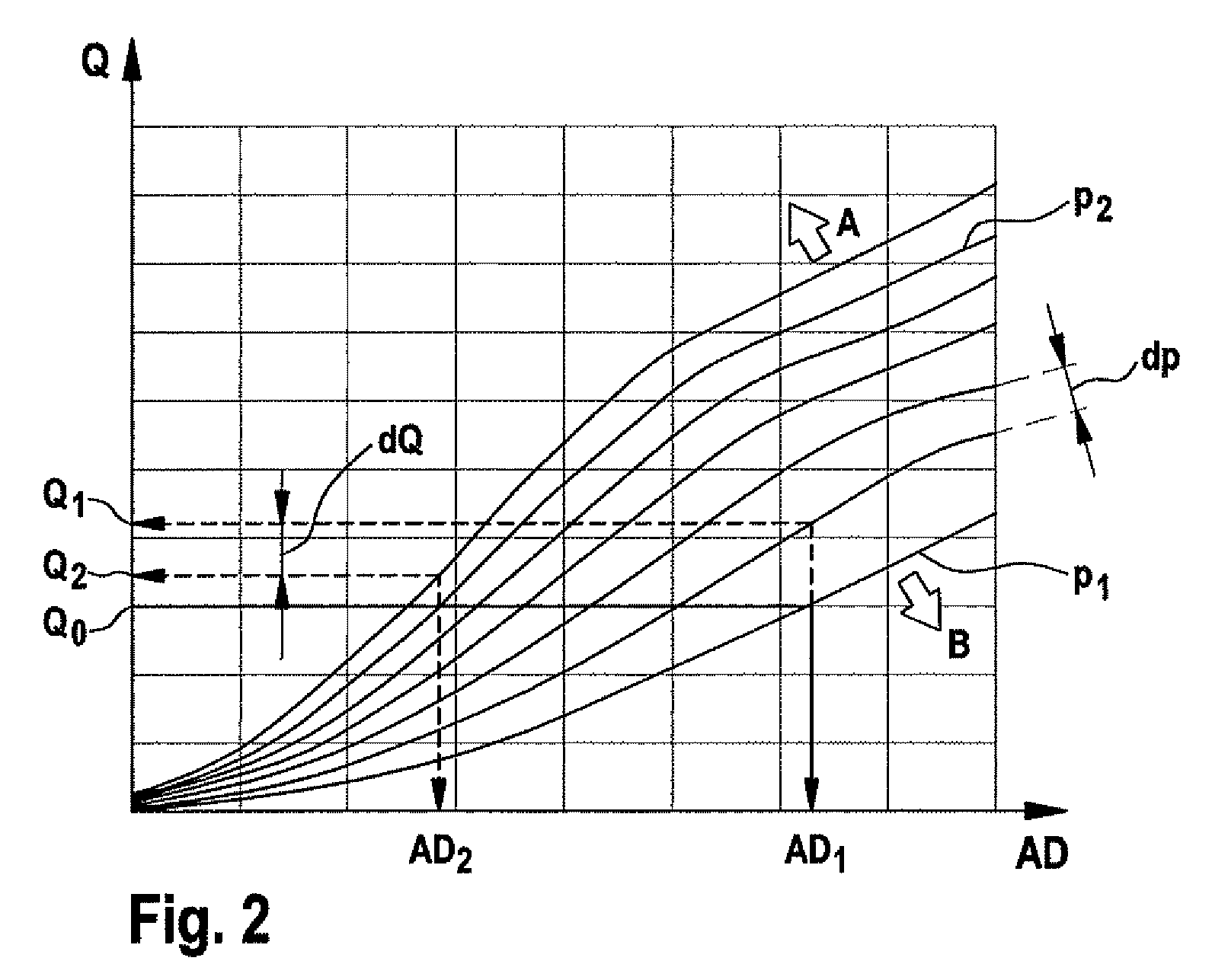
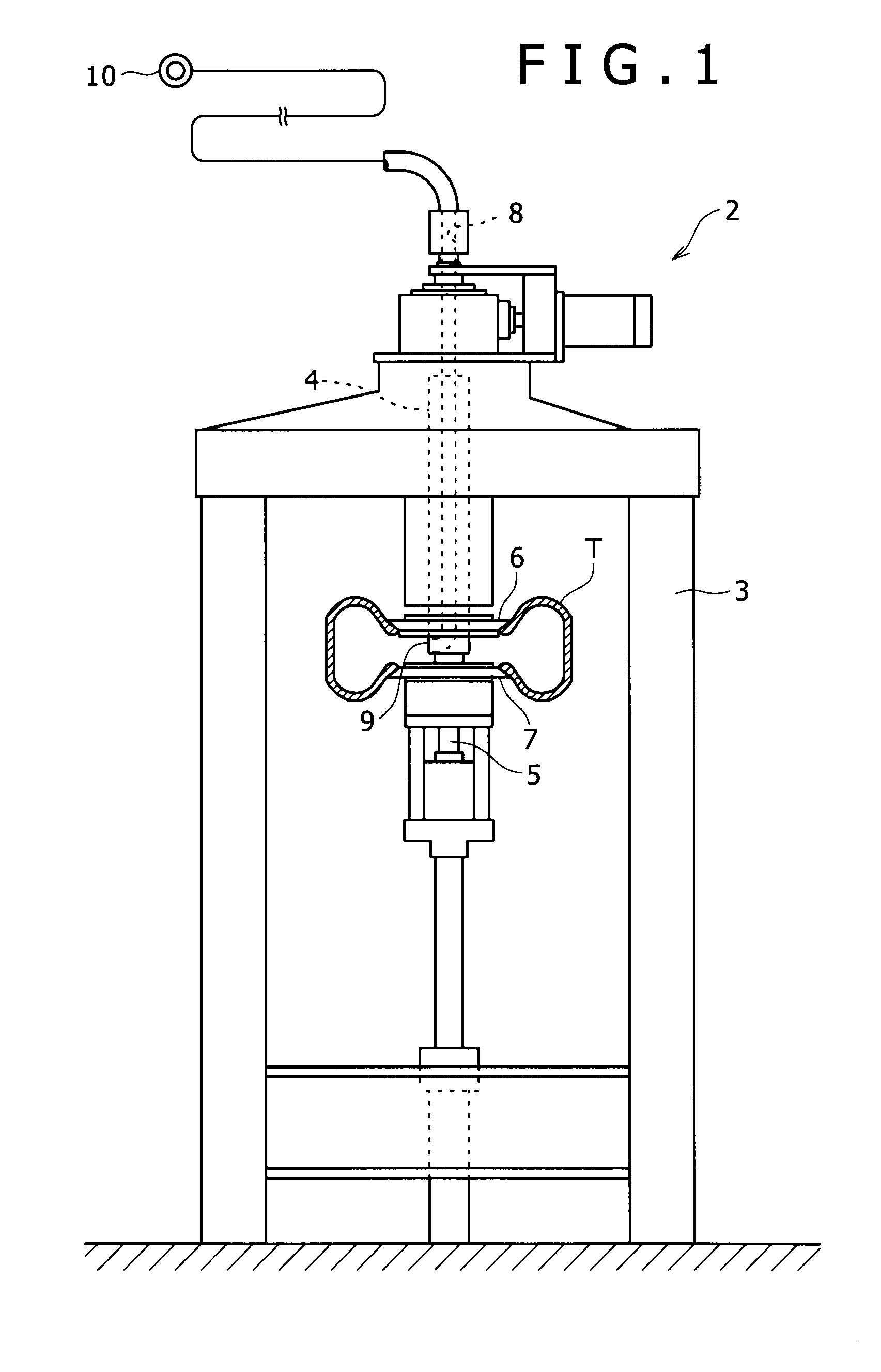
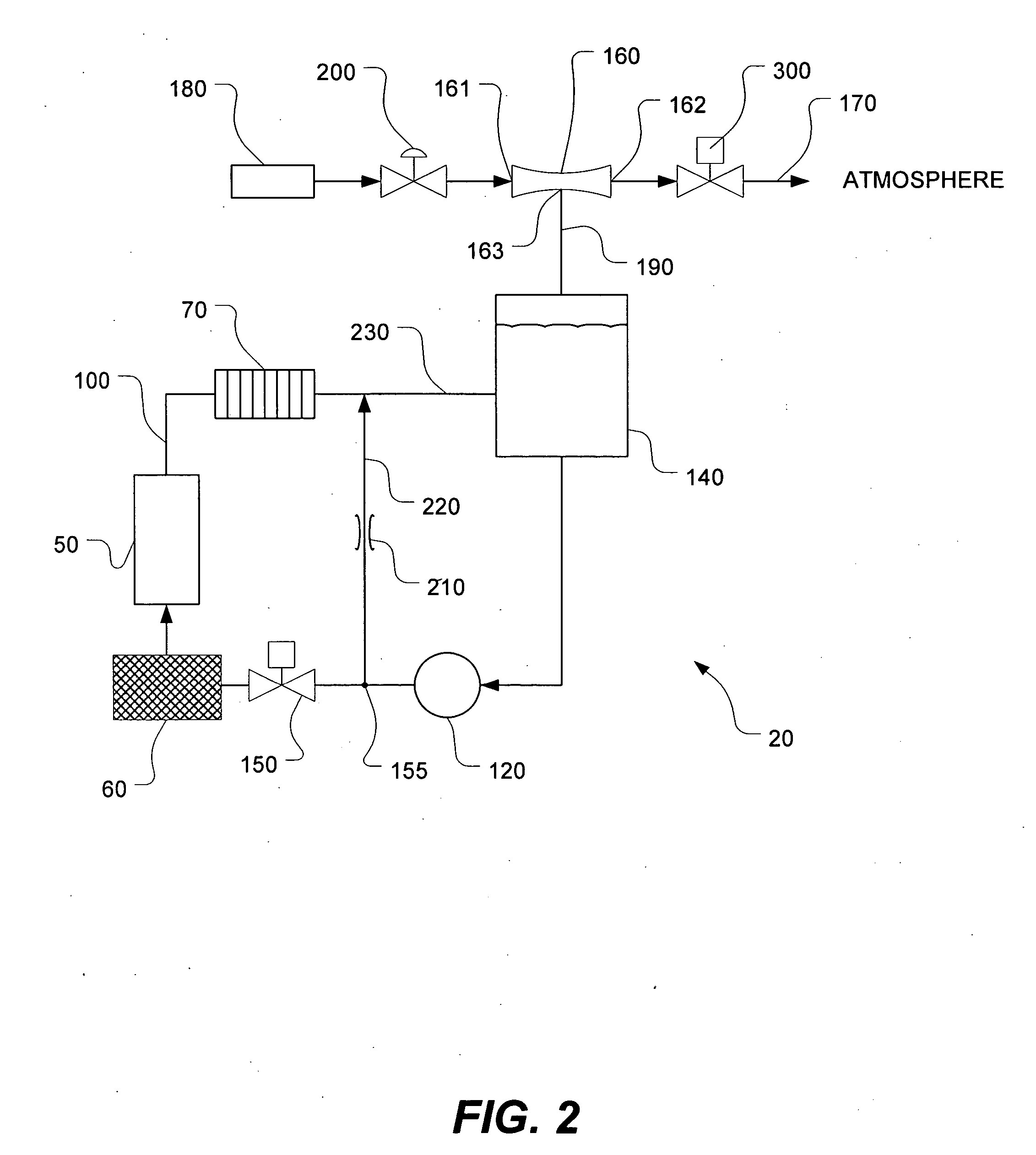
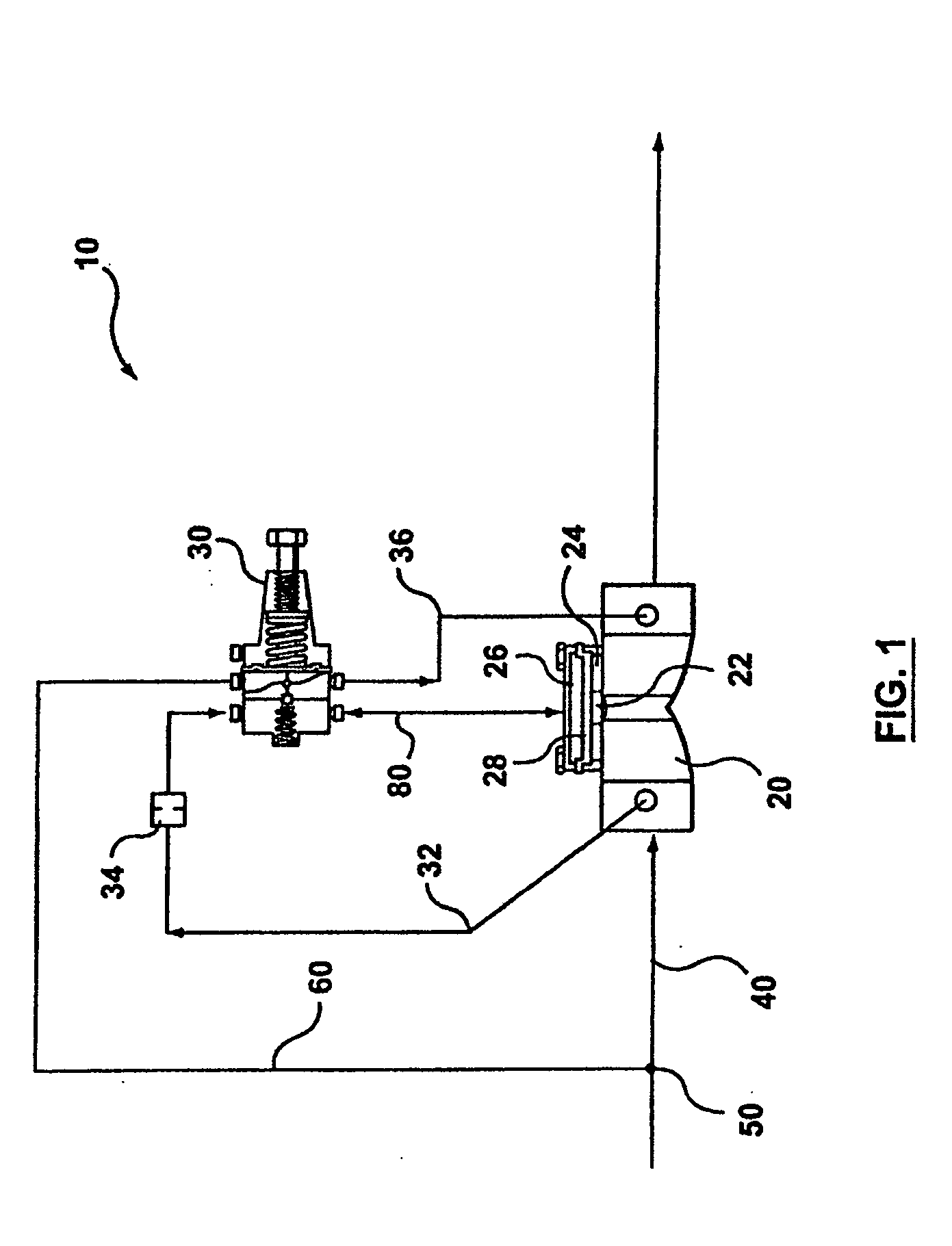
Pressure regulator assembly
InactiveUS20050061372A1Reduce in quantityLow costCheck valvesLow pressure fuel injectionEngineeringCavity pressure
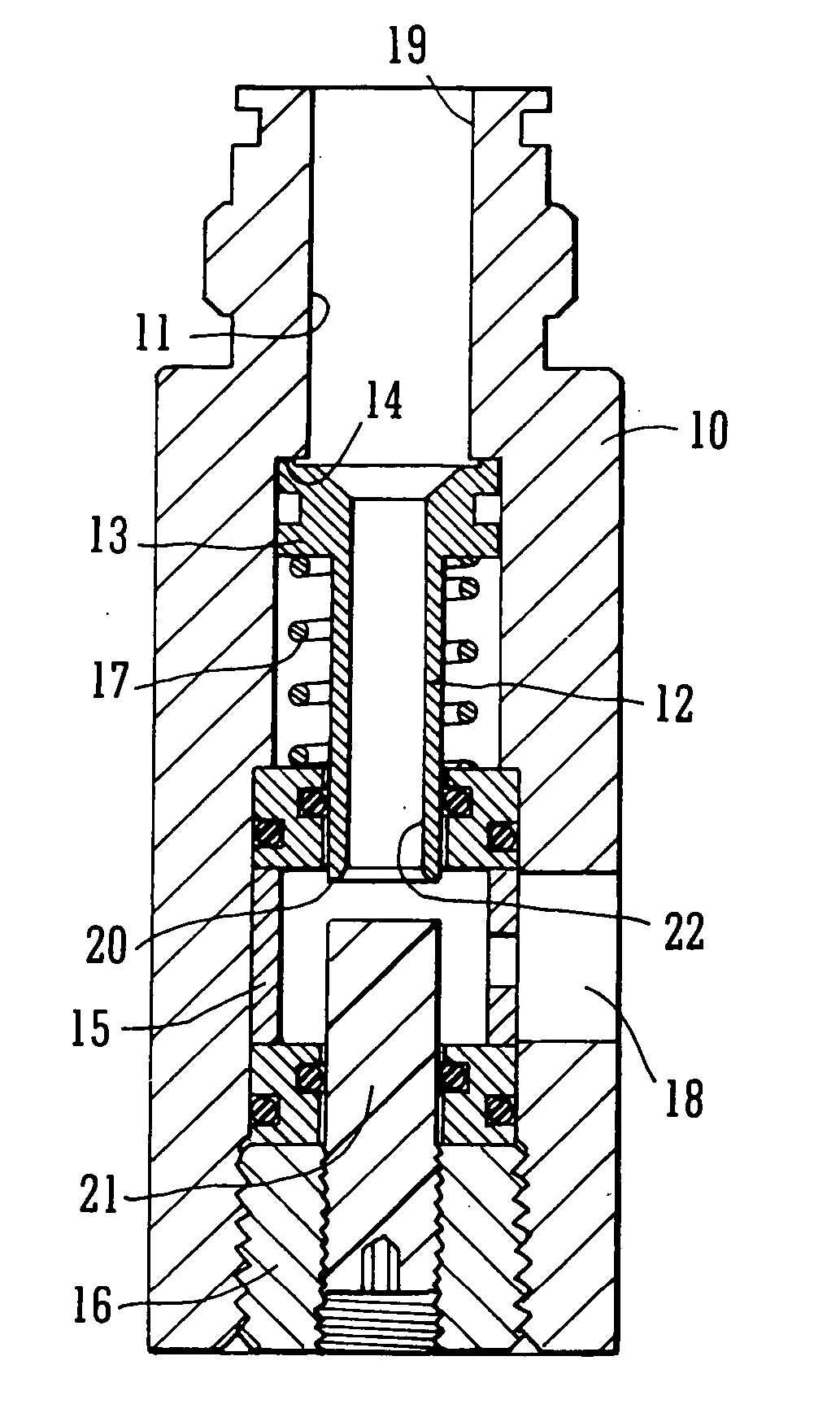
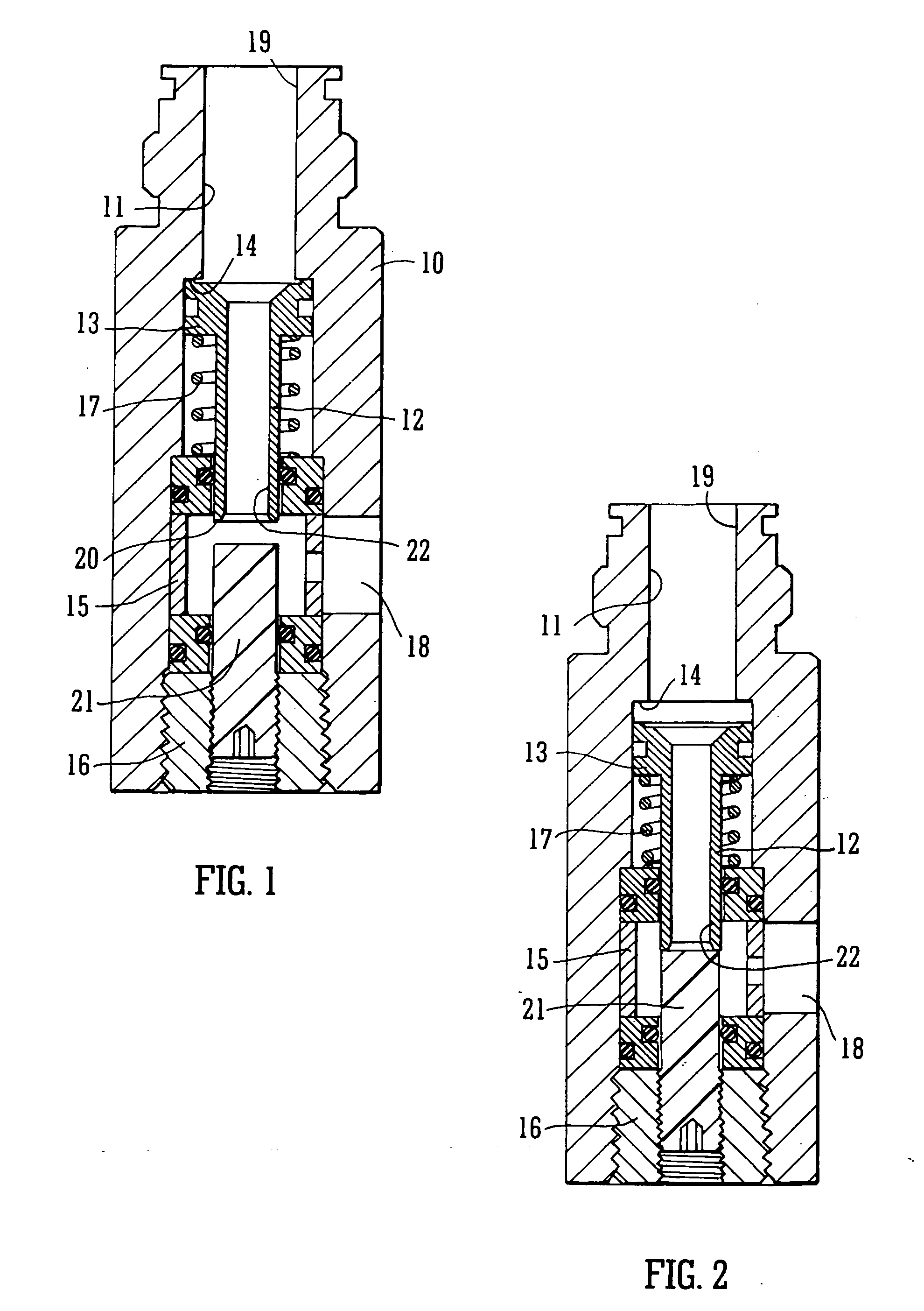
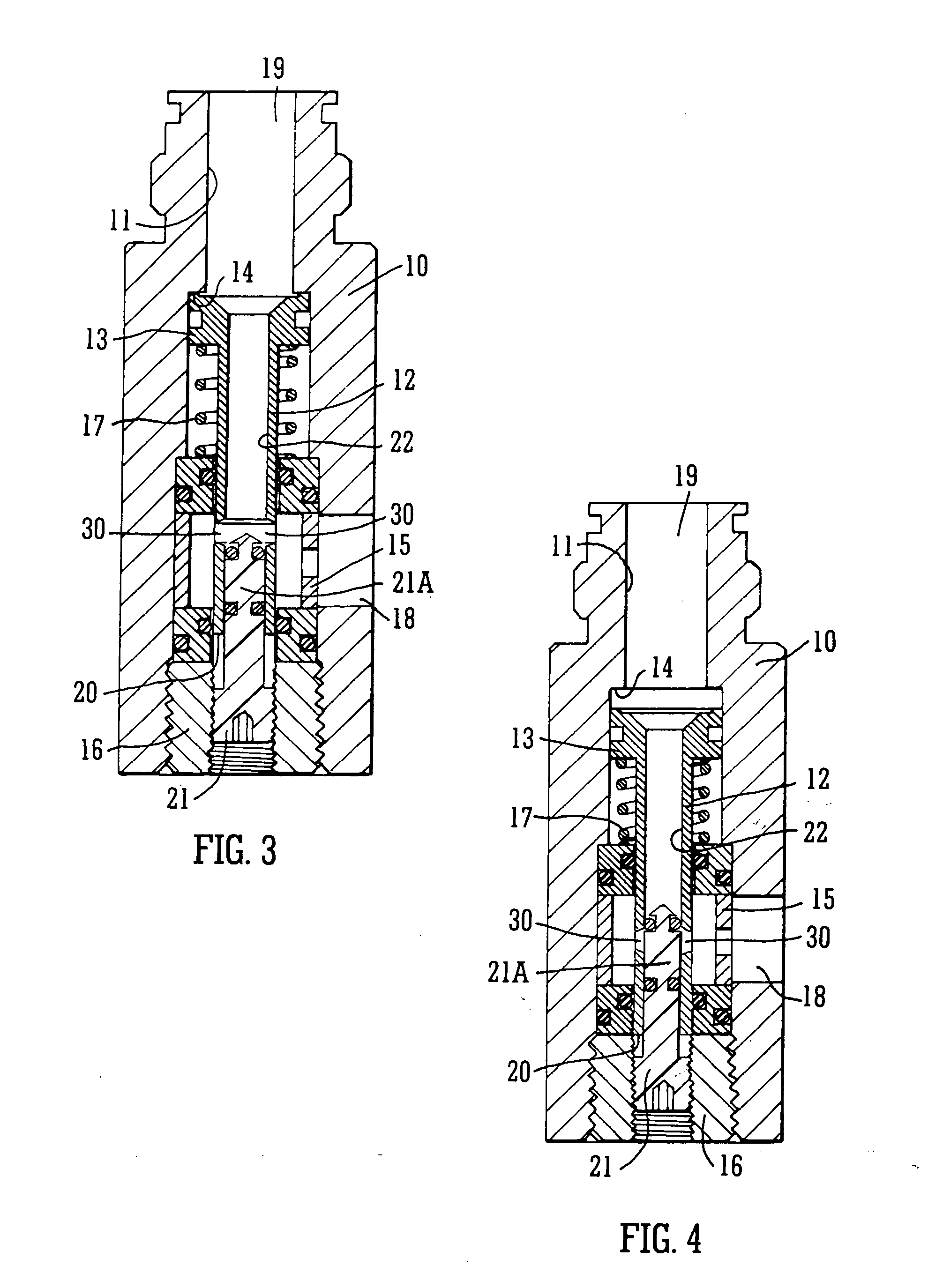
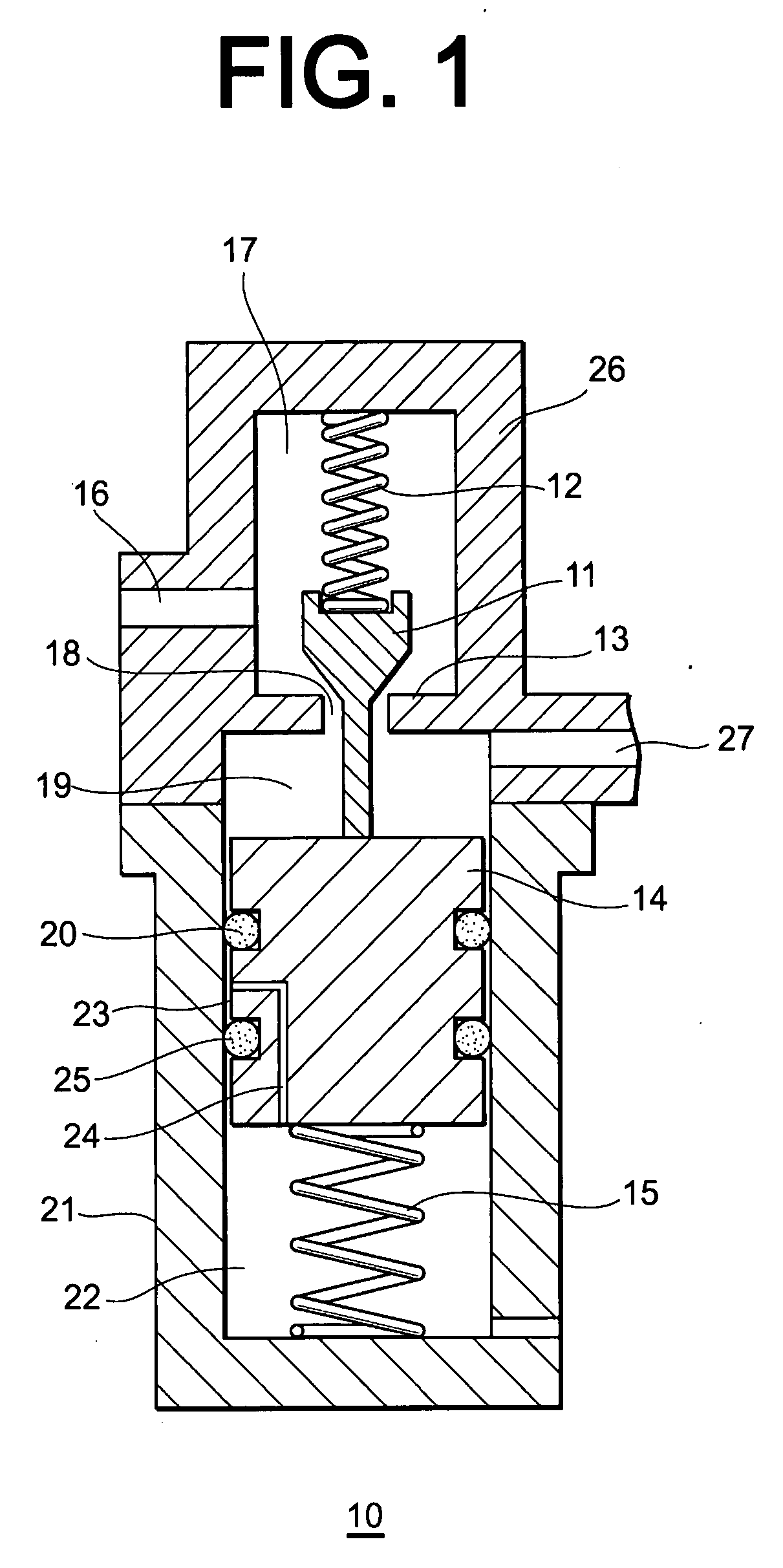
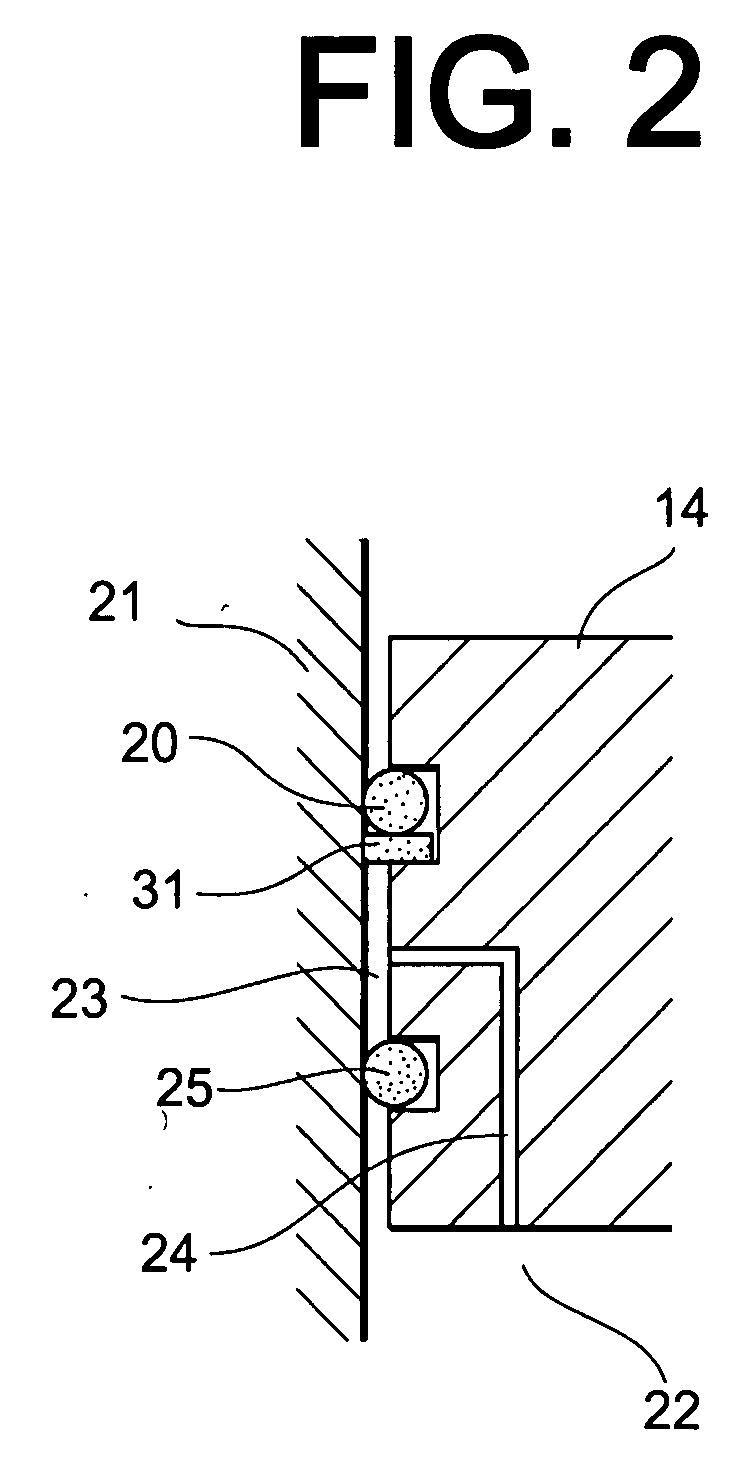
A pressure regulator assembly for a fluid system includes a housing having at least one cavity therein and a valve seat disposed in the at least one cavity and having an aperture extending therethrough. The pressure regulator assembly also includes a movable valve member disposed in the at least one cavity of the housing. The valve member has a closed position to engage the valve seat to prevent fluid from flowing into the at least one cavity and an open position to disengage the valve seat to allow fluid to flow into the at least one cavity. The pressure regulator assembly further includes a biasing mechanism disposed in the at least one cavity to bias the valve member toward the valve seat to close the aperture. The valve seat and the valve member and the biasing mechanism are aligned linearly along an axis of the valve housing.
Owner:MCGRATH DENNIS P +3
Method and apparatus for monitoring and controlling pressure in an inflatable device
ActiveUS20070227594A1Improve the level ofStuffed mattressesLiquid fillingEngineeringStress regulation
In one aspect, the invention provides a method for a user to adjust a pressure in an inflatable device. The method includes acts of adjusting the pressure in the inflatable device with a control device to a pressure preferred by the user, where the pressure preferred by the user has a first value, and establishing a first setting corresponding to the pressure preferred by the user with the control device, and automatically establishing a second setting corresponding to a second pressure having a second value once the first setting is established, where the second value differs from the first value by a predetermined amount.
Owner:CHAFFEE ROBERT B
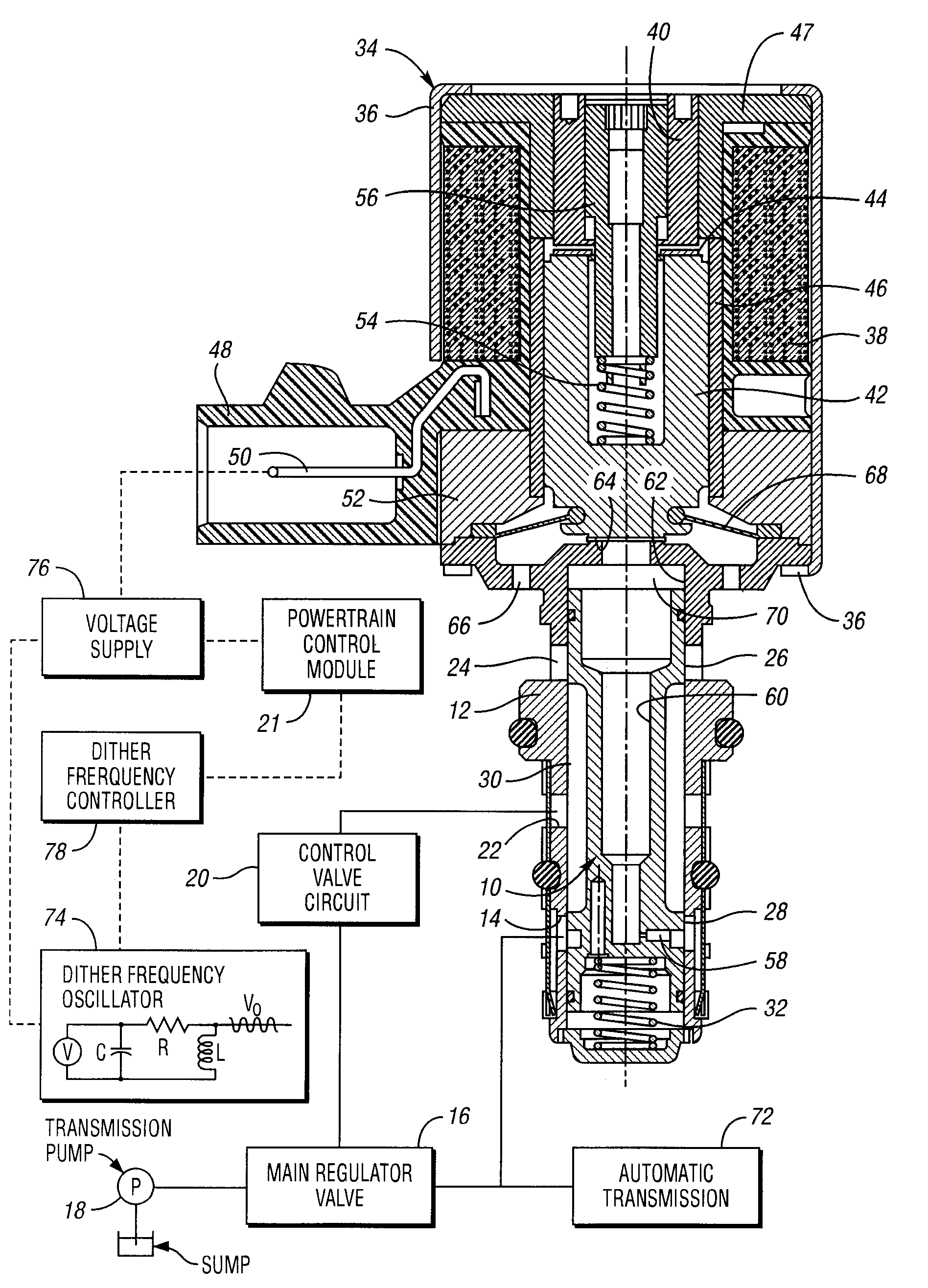
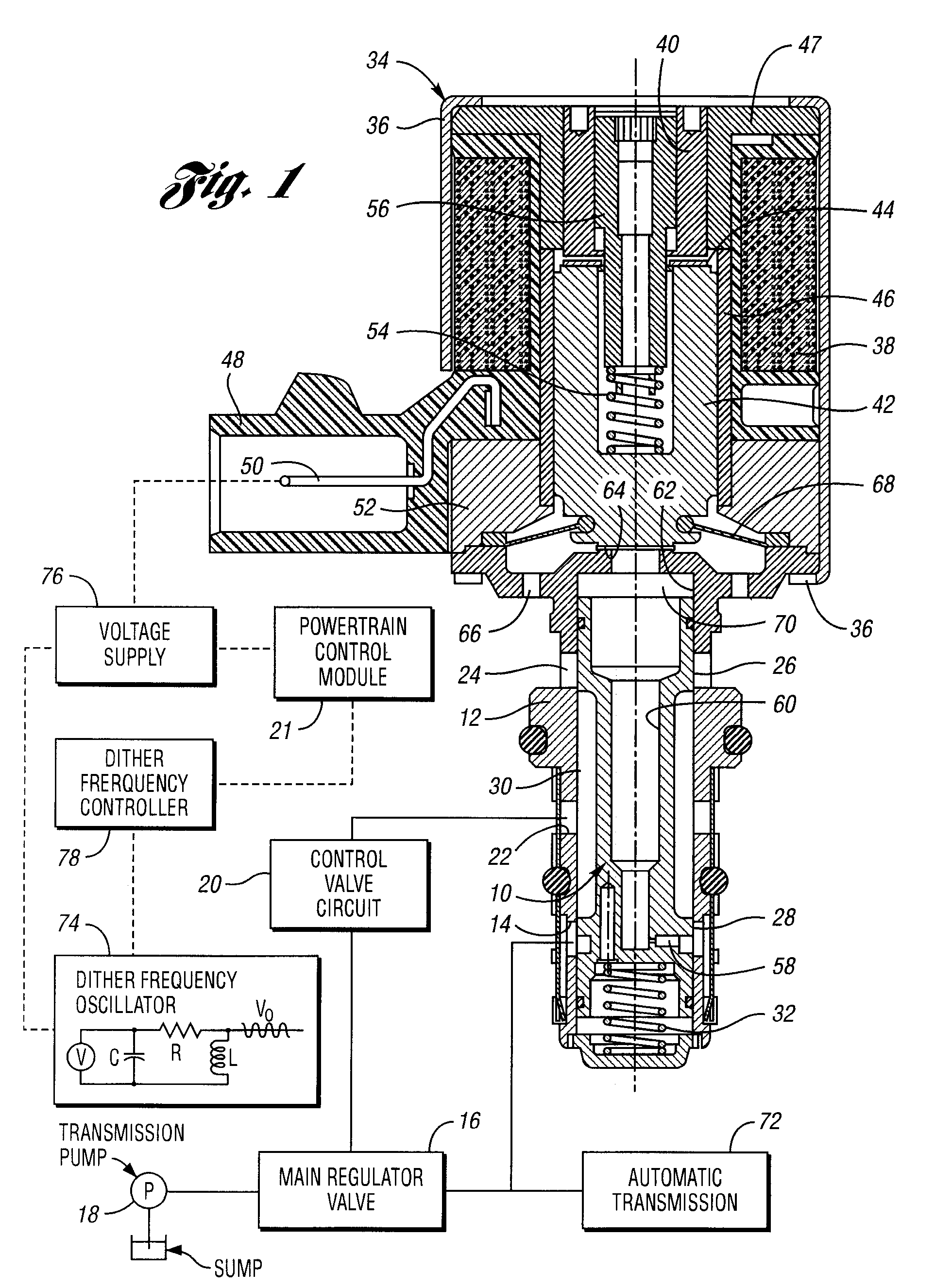
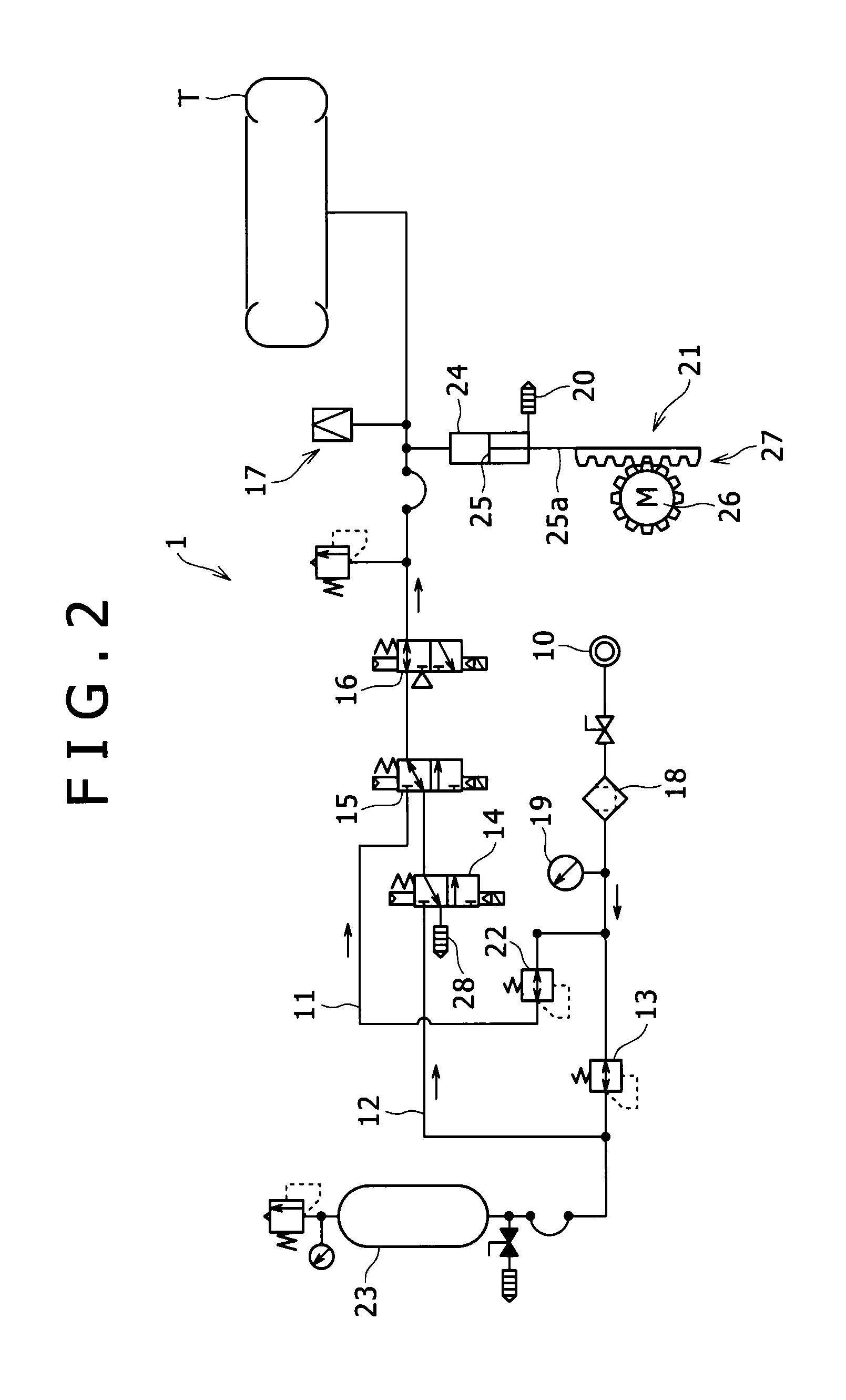
A control method and controller for a solenoid-operated electrohydraulic control valve
ActiveUS20060011878A1Reduce and to avoid undesirable transmission pressure control variationGreat pressure control accuracyOperating means/releasing devices for valvesThin material handlingInstabilityControl valves
A method and system for controlling a solenoid-operated pressure regulator valve to achieve high compliance with respect to a commanded current in accordance with a precalibrated transfer function. A dither frequency imposed on applied current is changed at precalibrated regulated pressure values to avoid dynamic instability.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
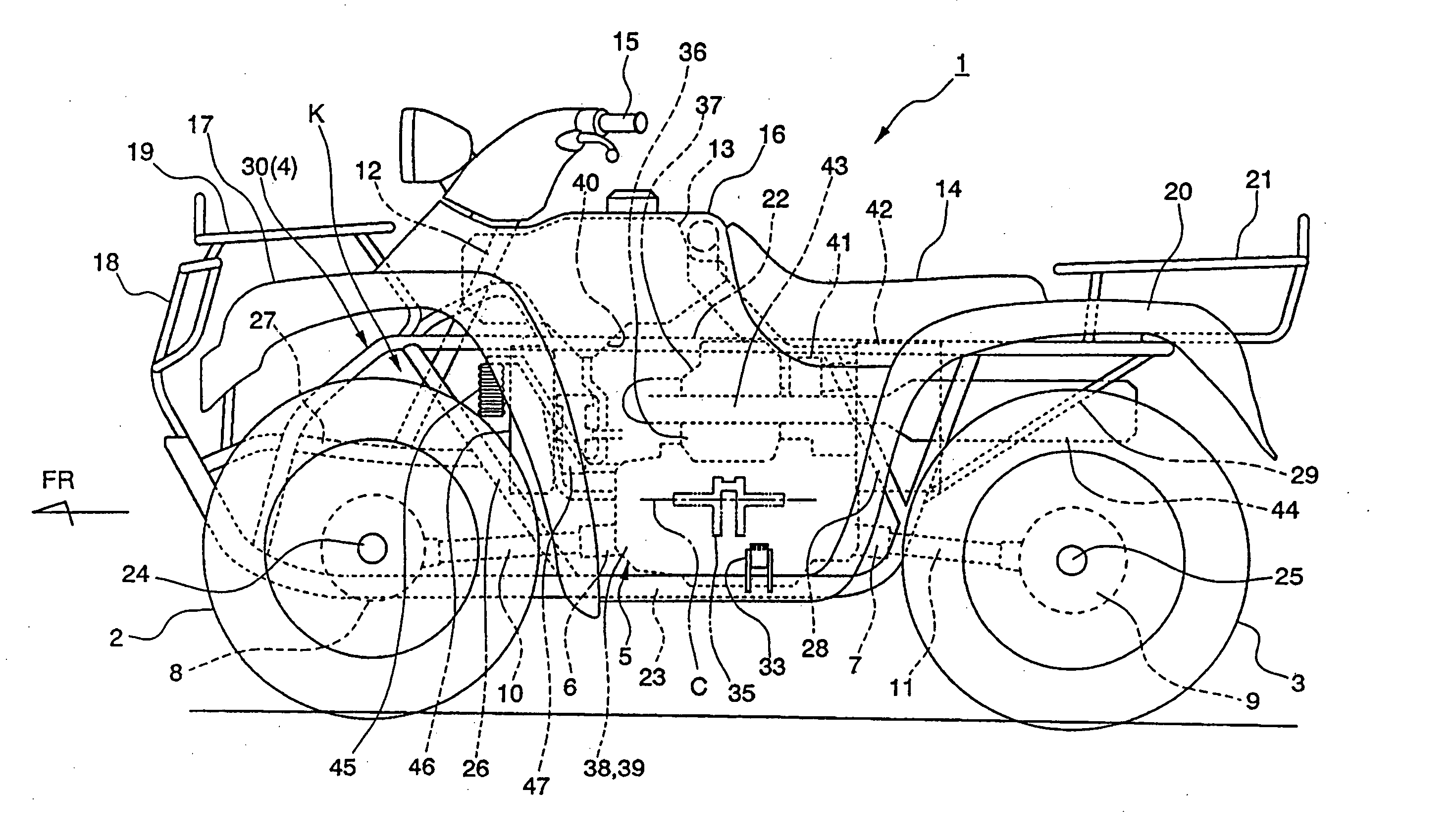
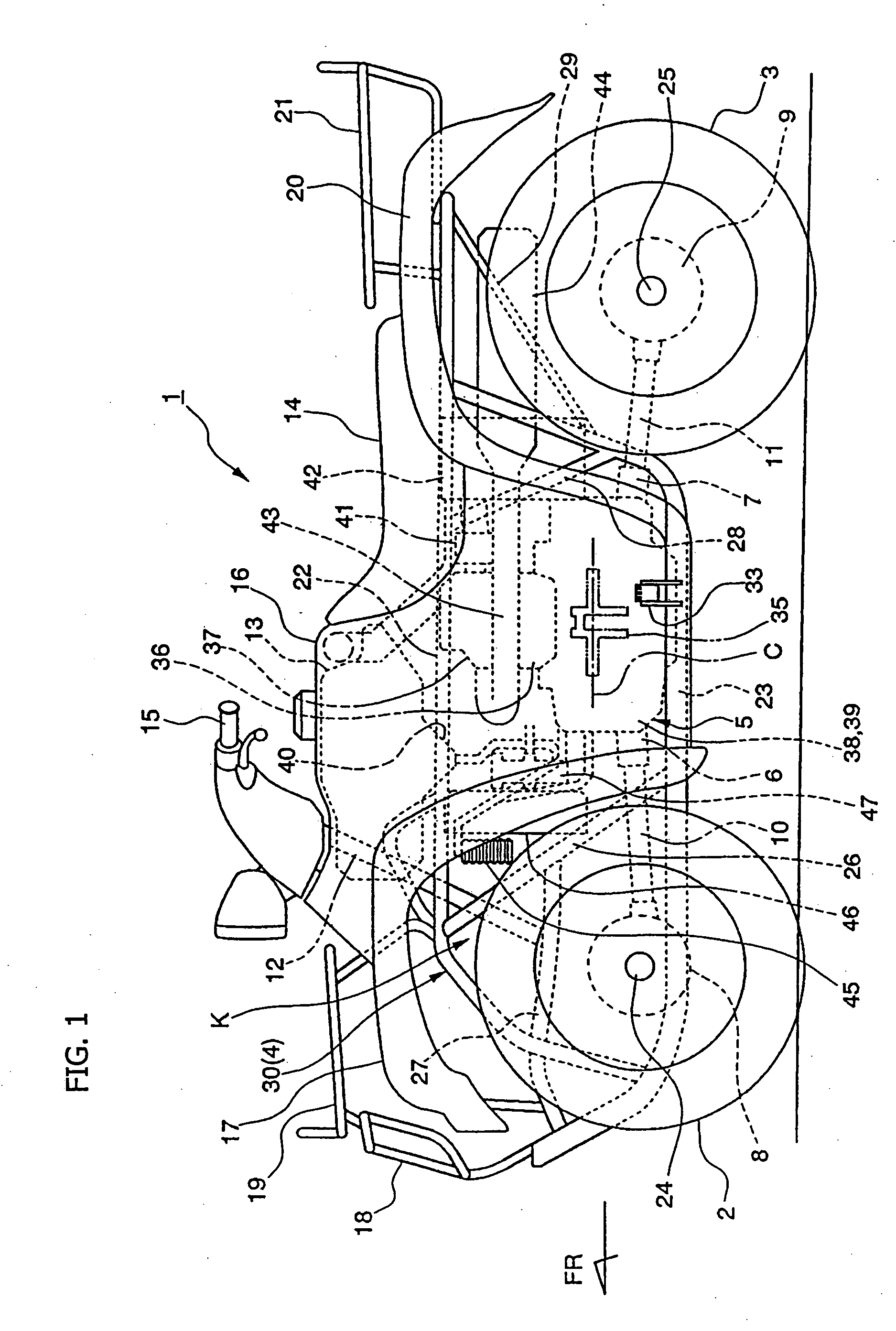
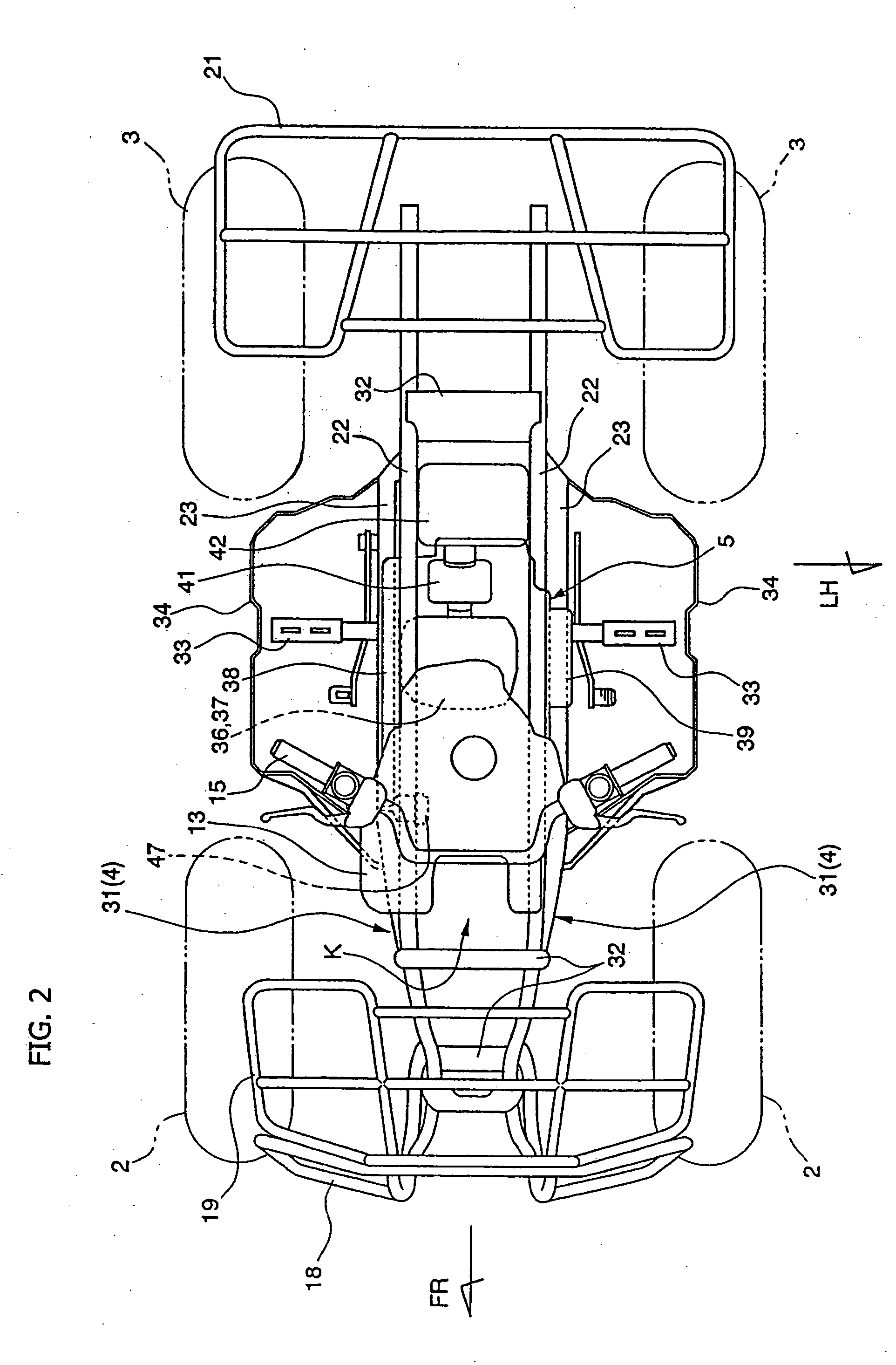
Fuel injection system and related structure for a four-wheeled saddle-type vehicle
InactiveUS20050150706A1Less likely to draw mudLess likely to dustElectric propulsion mountingGas pressure propulsion mountingTerrainCylinder head
A saddle riding type four-wheeled vehicle, suitable for rough terrain running, includes an engine having an electronically controlled fuel injection system. The vehicle also includes a throttle body disposed in back of a cylinder head of the engine. This configuration substantially protects the engine from drawing in mud, dust, and the like, and also eliminates the need for a protector of a throttle body. The fuel pump unit of the fuel injection system integrates the fuel pump, the fuel filter, and the pressure regulator into a single housing, to simplify the fuel piping required to connect different parts of the fuel supply system, as compared with conventional structures. This facilitates procedures of removing and installing the fuel tank and the fuel pump unit. The feature also reduces pumping loss of the fuel pump as well as parts cost.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Gas pressure regulator
InactiveUS20060137745A1Operating means/releasing devices for valvesEqualizing valvesEngineeringAtmospheric pressure
A gas pressure regulator of the kind in which a valve member is spring biased to the valve-open position and is moved to the valve-closed position when upstream pressure at an outlet overcomes the spring is arranged such that gas pressure at an inlet end of the valve member 12 does not influence it in the valve-opening direction. In the embodiment of FIGS. 3 and 4 a bottom end of the valve member receives a piston-like plug. Openings in the wall of the valve member are occluded when the valve is closed. In the open position of the valve-member pressure is equal all round each opening. In another embodiment of the invention a spool is provided having one enlarged end within the valve member and another outside it. Pressure on the combined surfaces of the end and the end of the valve member is equal to the pressure on the end of the spool.
Owner:EIP MANAGEMENT
Pressure regulator
InactiveUS20050263189A1Simple structureOptimization mechanismOperating means/releasing devices for valvesFluid pressure control without auxillary powerDecreased pressureEngineering
A pressure regulator include a fluid introducing port; a primary regulating valve for reducing the primary pressure to a secondary pressure; a pressure regulating chamber receiving the fluid from the first pressure regulating valve; a diaphragm which is being displaced in response to the secondary pressure; a shift for drivingly connecting the diaphragm and the primary regulating valve; a pressure-setting section for adjusting a displacement magnitude of the diaphragm; and a discharging port through which the fluid of secondary pressure is discharged. The shaft includes a secondary regulating valve operatively associated with the primary regulating valve so as to further regulate the fluid from the primary regulating valve by opening-closing operations in reverse to those of the primary regulating valve. Hence, the pressure regulation characteristic of the secondary regulating valve against the fluctuations in the primary pressure become reverse to that of the primary regulating valve.
Owner:TOKAI
Multi-stage pressure regulator
ActiveUS20060260692A1Large adjustment ratioReduce flow rateOperating means/releasing devices for valvesMultiple way valvesFuel cellsEngineering
A pressure regulator that has particular application for an anode input side of a fuel cell system to provide the desired large turn-down ratio. The pressure regulator includes at least two valves positioned in parallel where the first valve is smaller than the second valve. The first valve is opened and closed and the second valve is maintained closed at low flow rates. Once the flow rate is high enough, the first valve is maintained completely open, and the second valve is opened and closed to control the flow at high flow rates.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Pressure regulating valve
InactiveUS20050247354A1Service lifeConstantOperating means/releasing devices for valvesNon-fuel substance addition to fuelSpring forceEngineering
Known pressure regulating valves have a valve closing body, which cooperates with a valve seat, and a restoring spring, which acts on a valve closing body in the direction facing away from the valve seat. It is disadvantageous that the restoring spring is disposed in a pressure chamber, which has the valve seat and through which aggressive blowby gases flow out of the crankcase. The blowby gases for instance have a corrosive, etching effect on the material of the restoring spring, shortening the service life and lessening the spring force of the restoring spring. This has a highly adverse effect on the regulation of the pressure in the crankcase. In the pressure regulating valve of the invention, the service life of the restoring spring is increased. According to the invention, the restoring spring (31) is embodied as a tension spring and is located on the side of the valve closing body (15) facing away from the valve seat (12).
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Control apparatus for continuously-variable transmission of vehicle
InactiveUS20070142142A1Improve responseResponse of shifting can be enhancedGearingGear lubrication/coolingAutomatic transmissionPressure sense
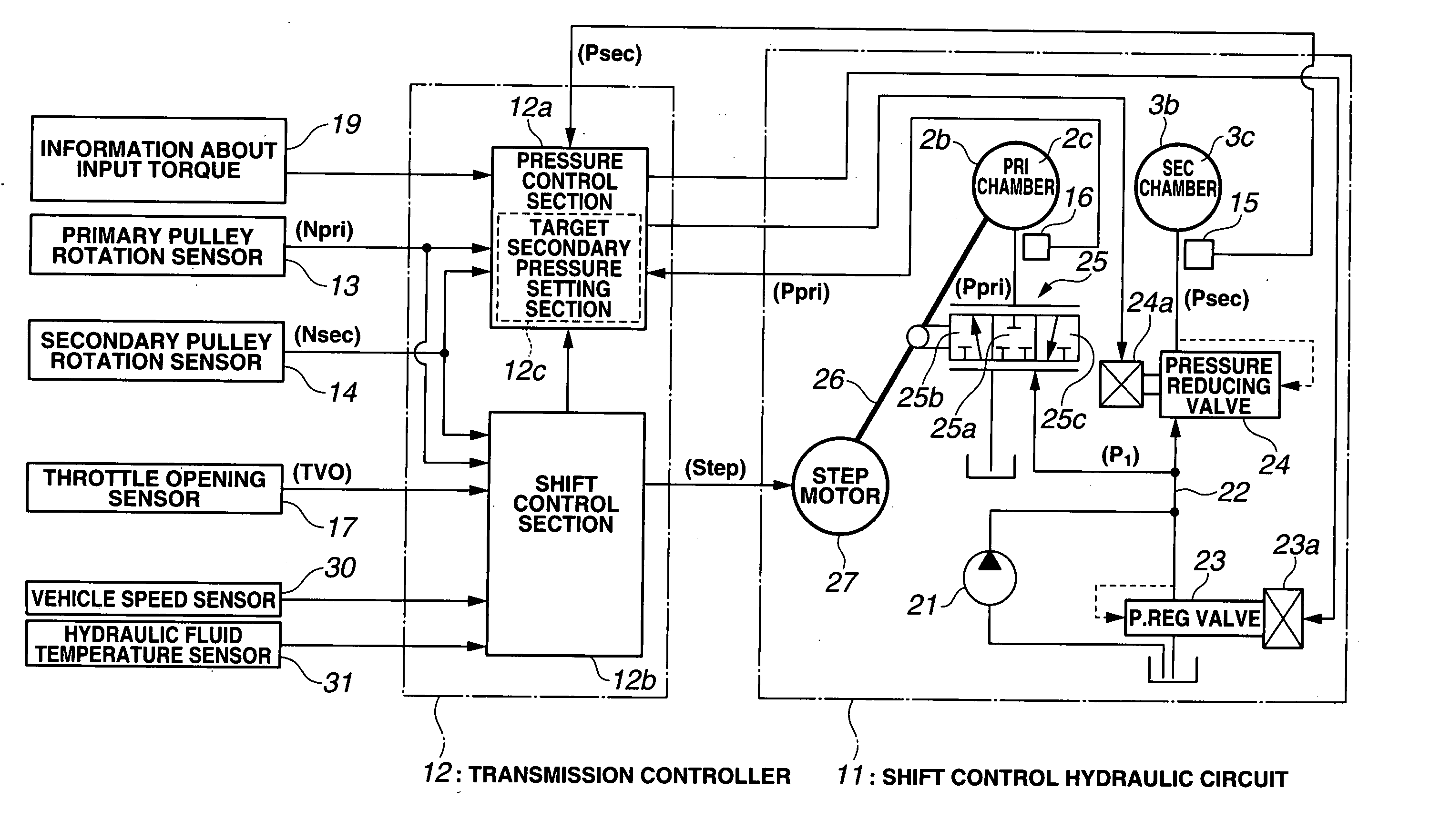
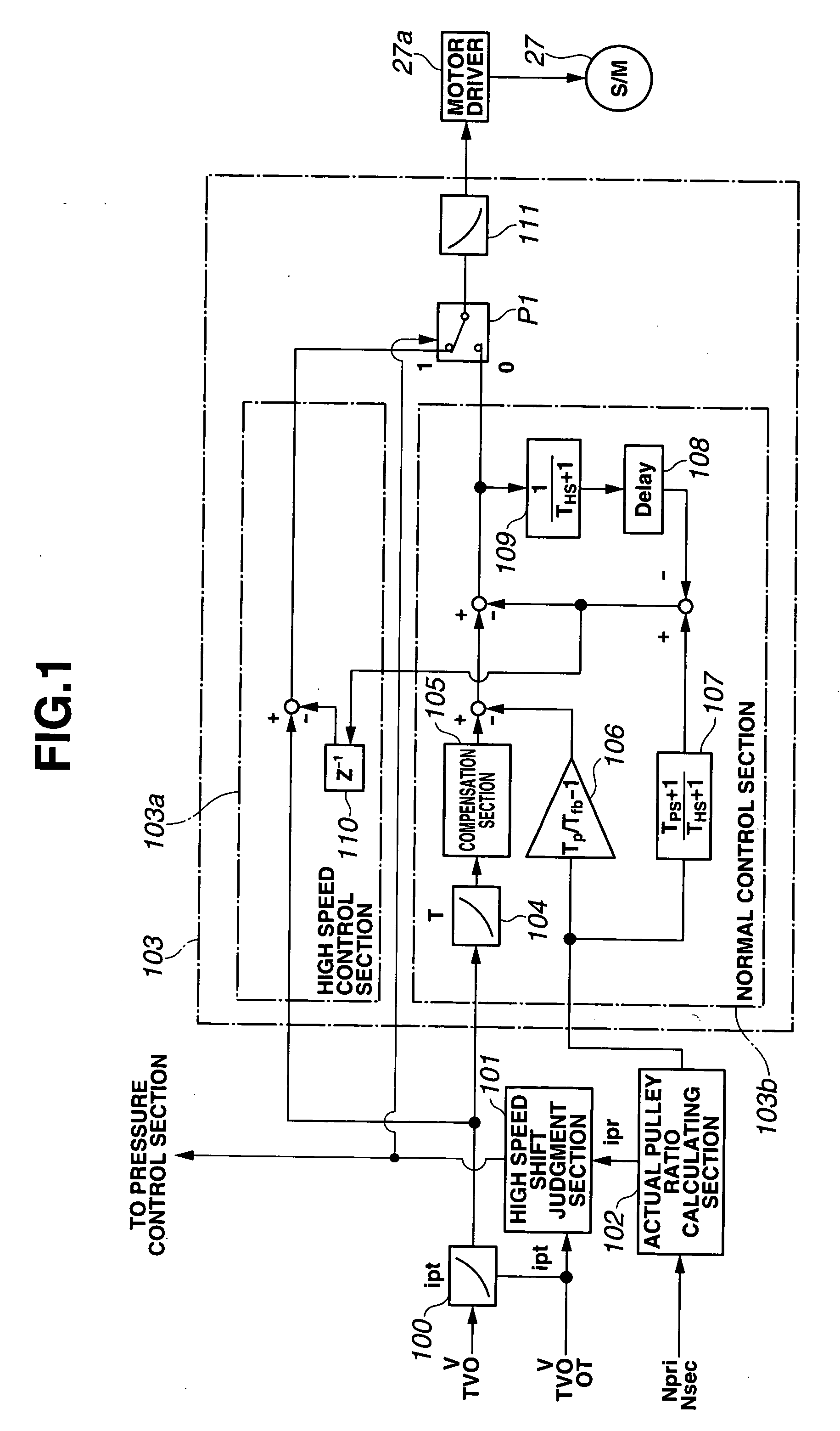
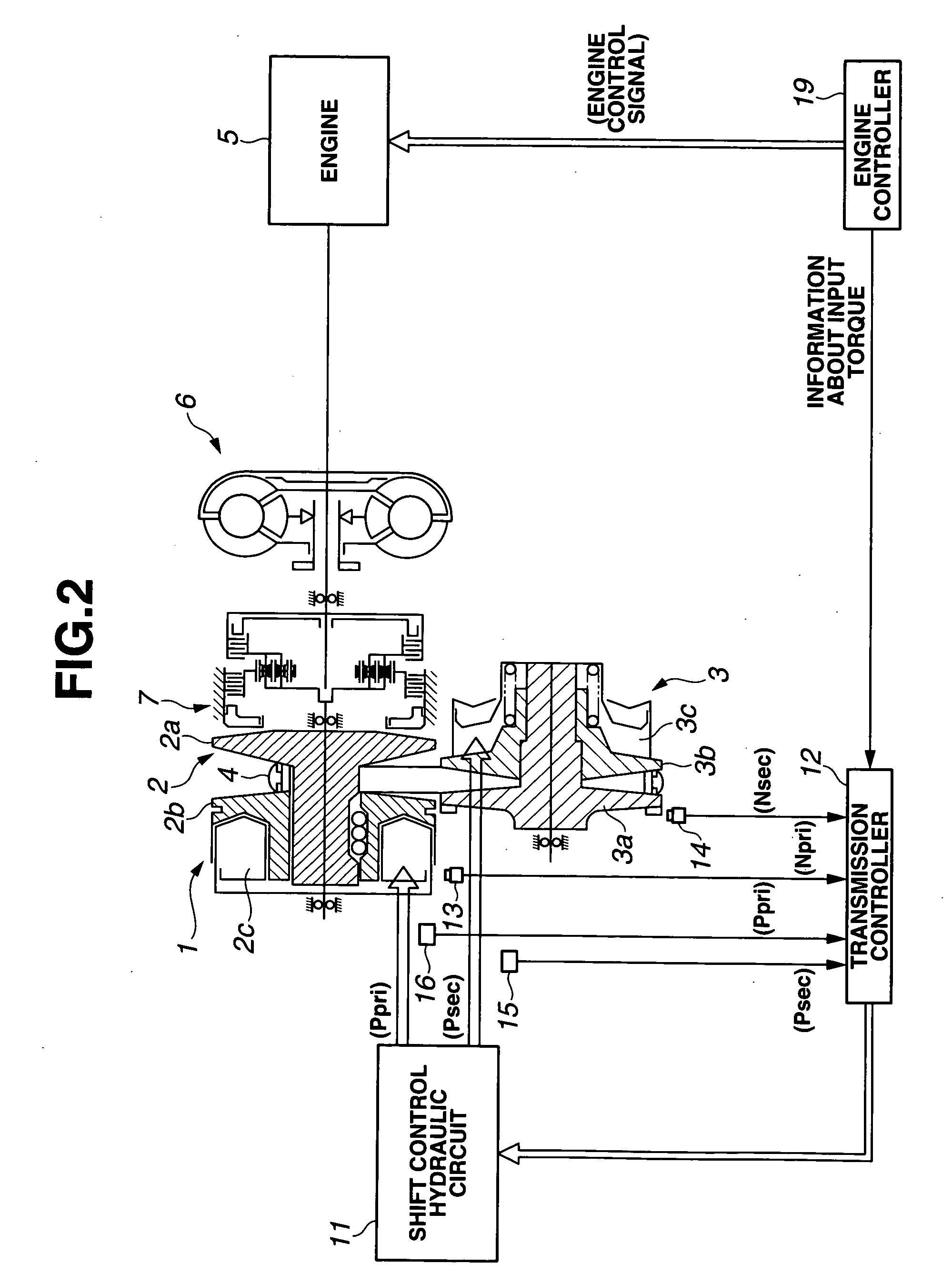
A control apparatus for an automatic transmission includes a control section having a target secondary pressure setting section configured to set a target secondary pressure within a strength limit of the belt, and an operation switching section configured to switch a shift operation from a normal speed to a high speed higher than the normal speed when a predetermined condition is satisfied. The control section is configured to control the secondary pressure regulating valve by a feedback control based on the target secondary pressure and the actual secondary pressure sensed by the hydraulic pressure sensor. The target secondary pressure setting section is configured to modify the target secondary pressure by adding a predetermined quantity when a correction initiation condition is satisfied, the condition initiation including a first condition that the shift operation is performed at a high speed by switching of the operation switching section.
Owner:JATCO LTD +1
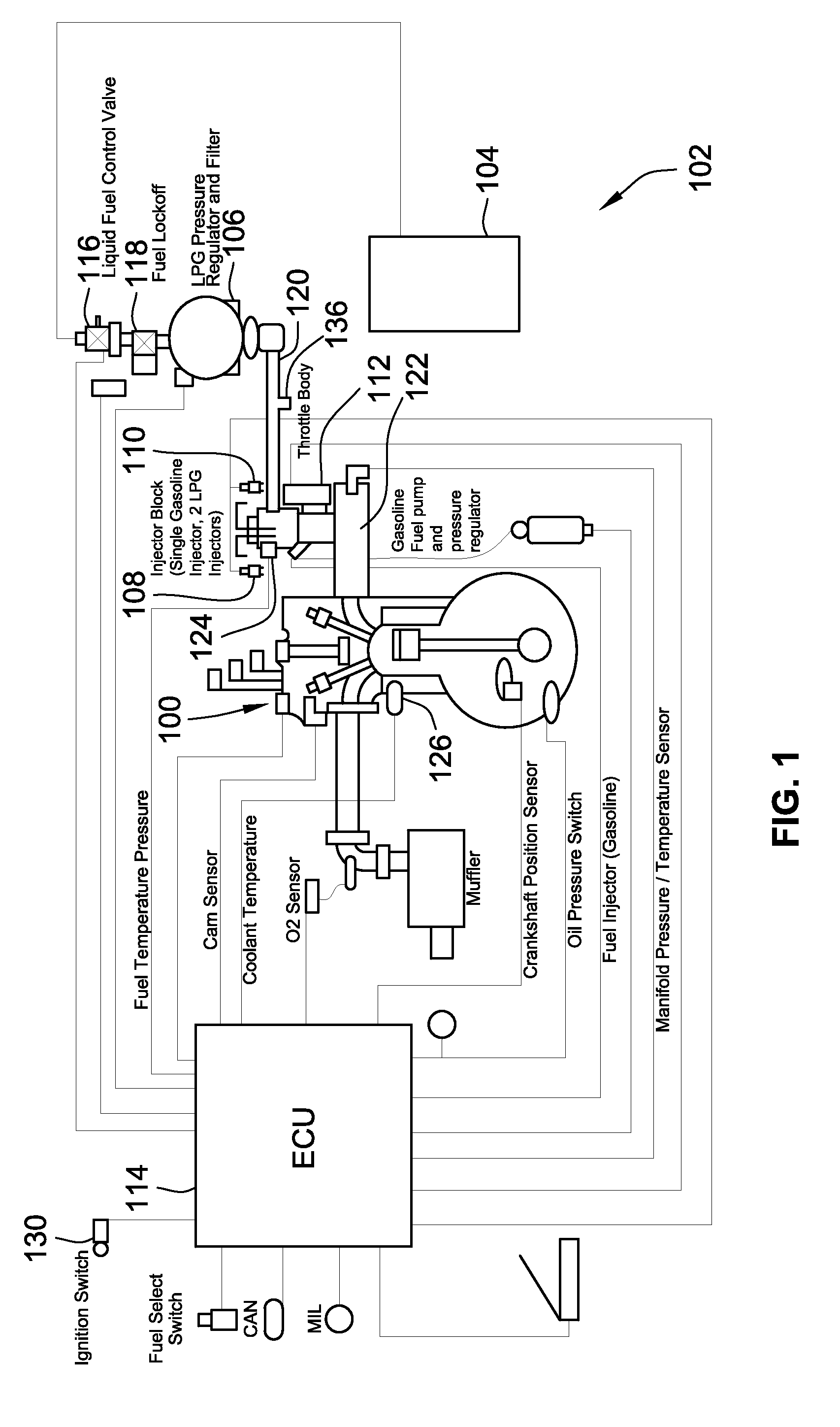
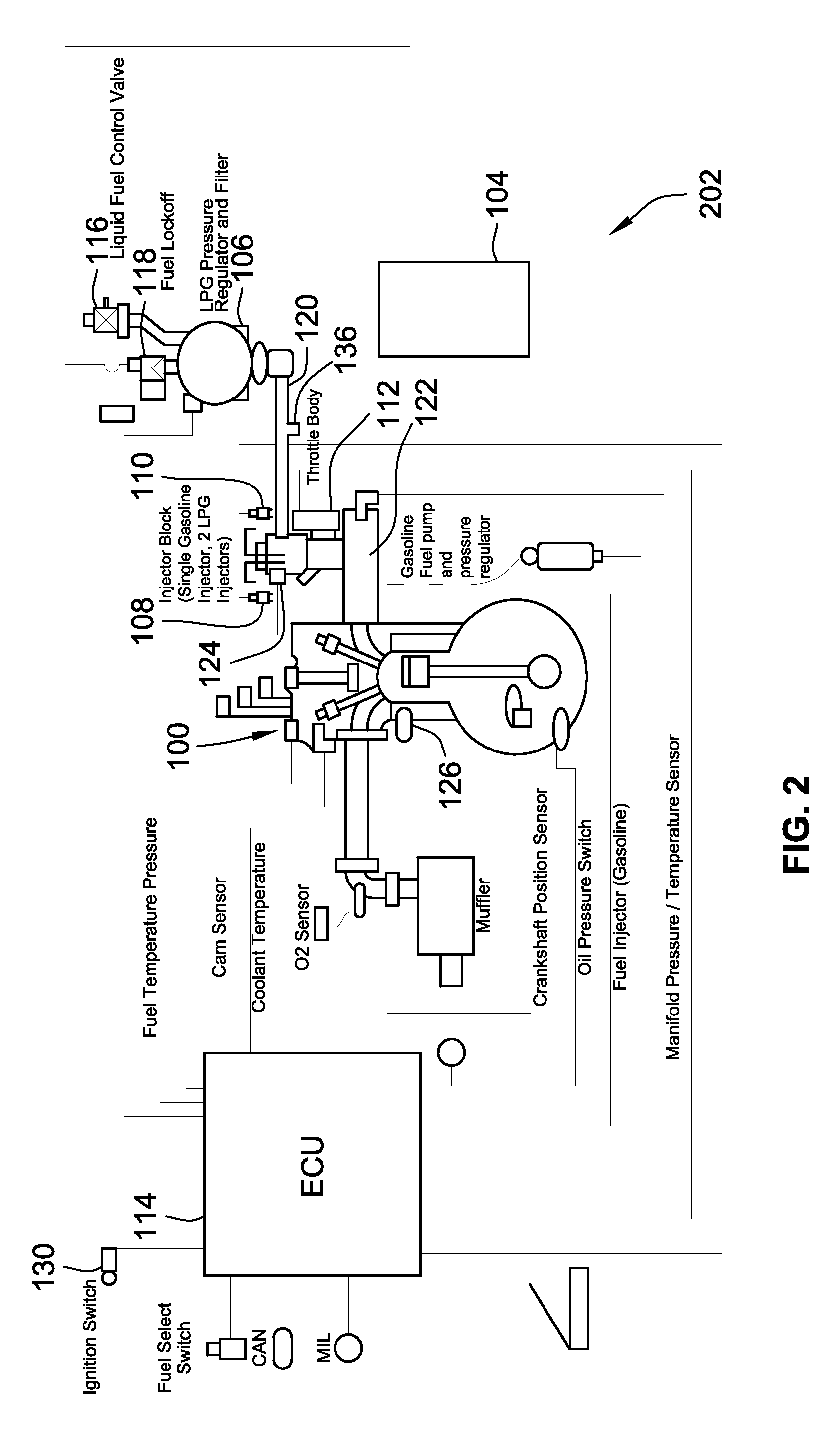
Cold-Start Fuel Control System
InactiveUS20110214644A1Easy to operatePrevent floodingElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesControl systemEngineering
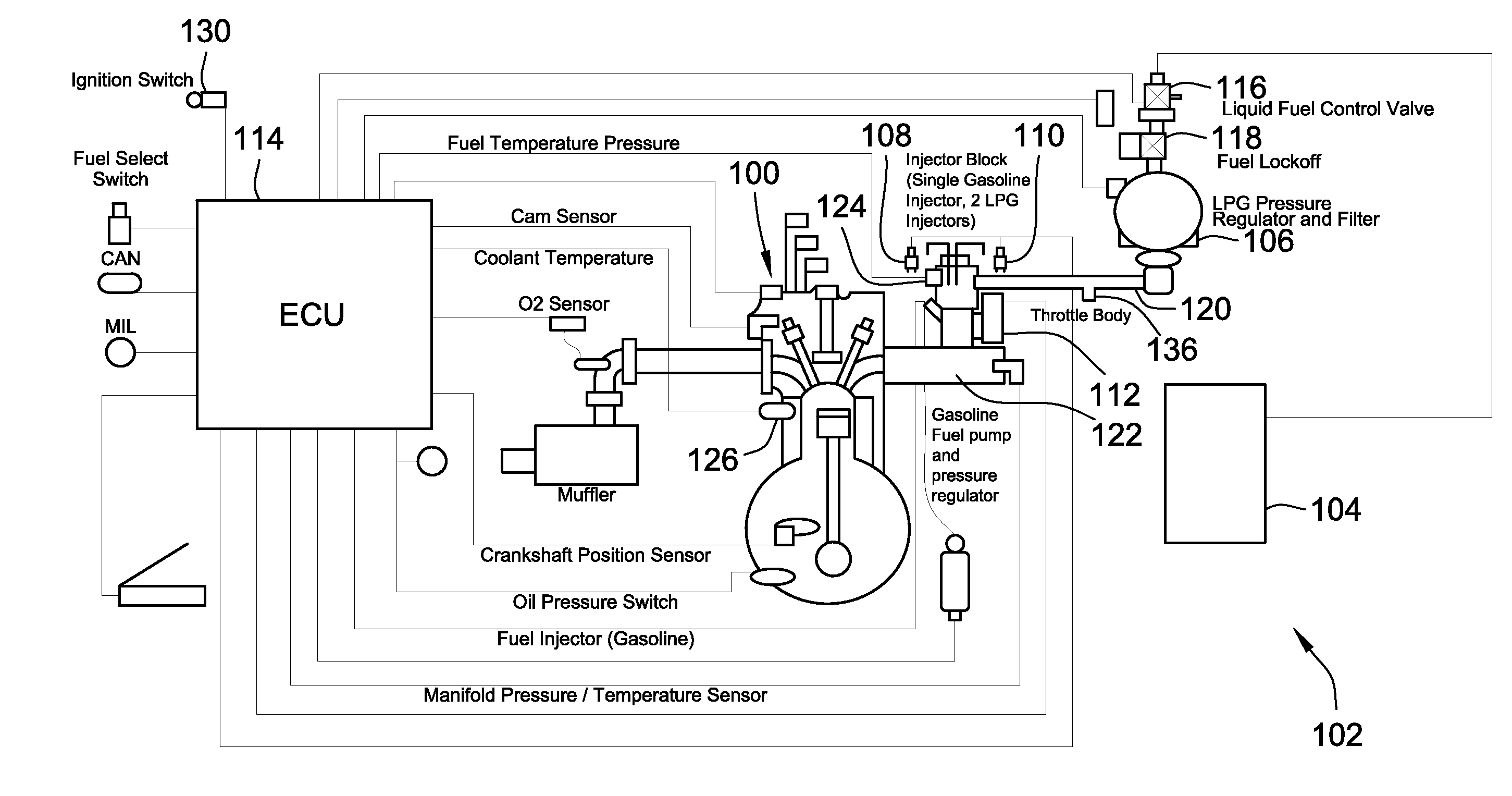
A fuel control system for controlling the supply of liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) to injectors of a fuel supply system during a cold start is provided. The fuel control system includes a LPG pressure regulator and a cold-start fuel control valve for throttling fuel to the injectors when the pressure of the LPG is below a nominal set point pressure of the pressure regulator. The cold-start fuel control valve may be in parallel or series with a fuel lock-off valve. The system is configured to supply limited discrete amounts of LPG to the injectors when the pressure of the LPG is below the nominal set point pressure to allow the LPG to vaporize prior to being injected, by the injector, into an engine. Operation of the cold-start fuel control valve during non-cold starts and normal operation are also provided.
Owner:WOODWARD GOVERNOR CO
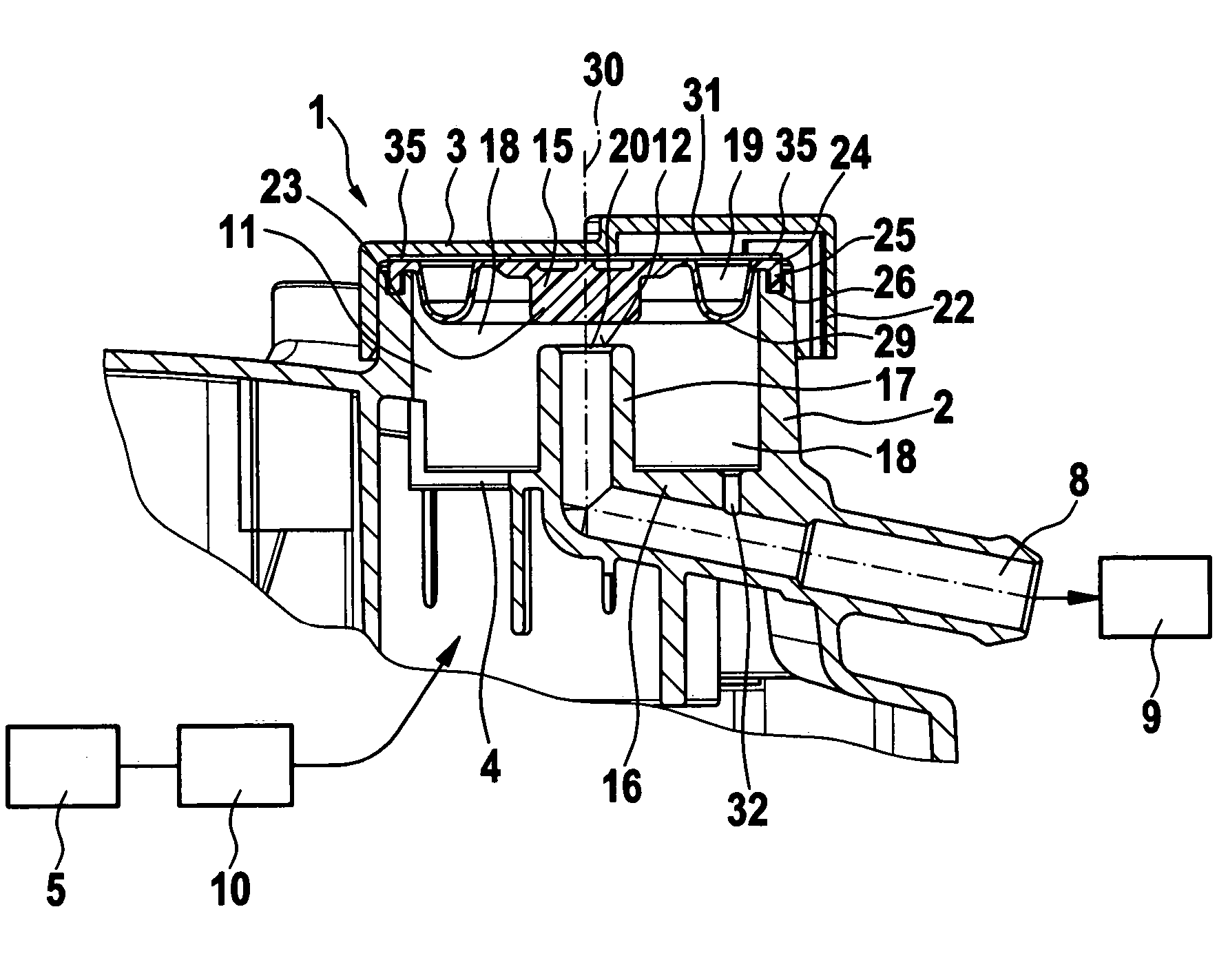
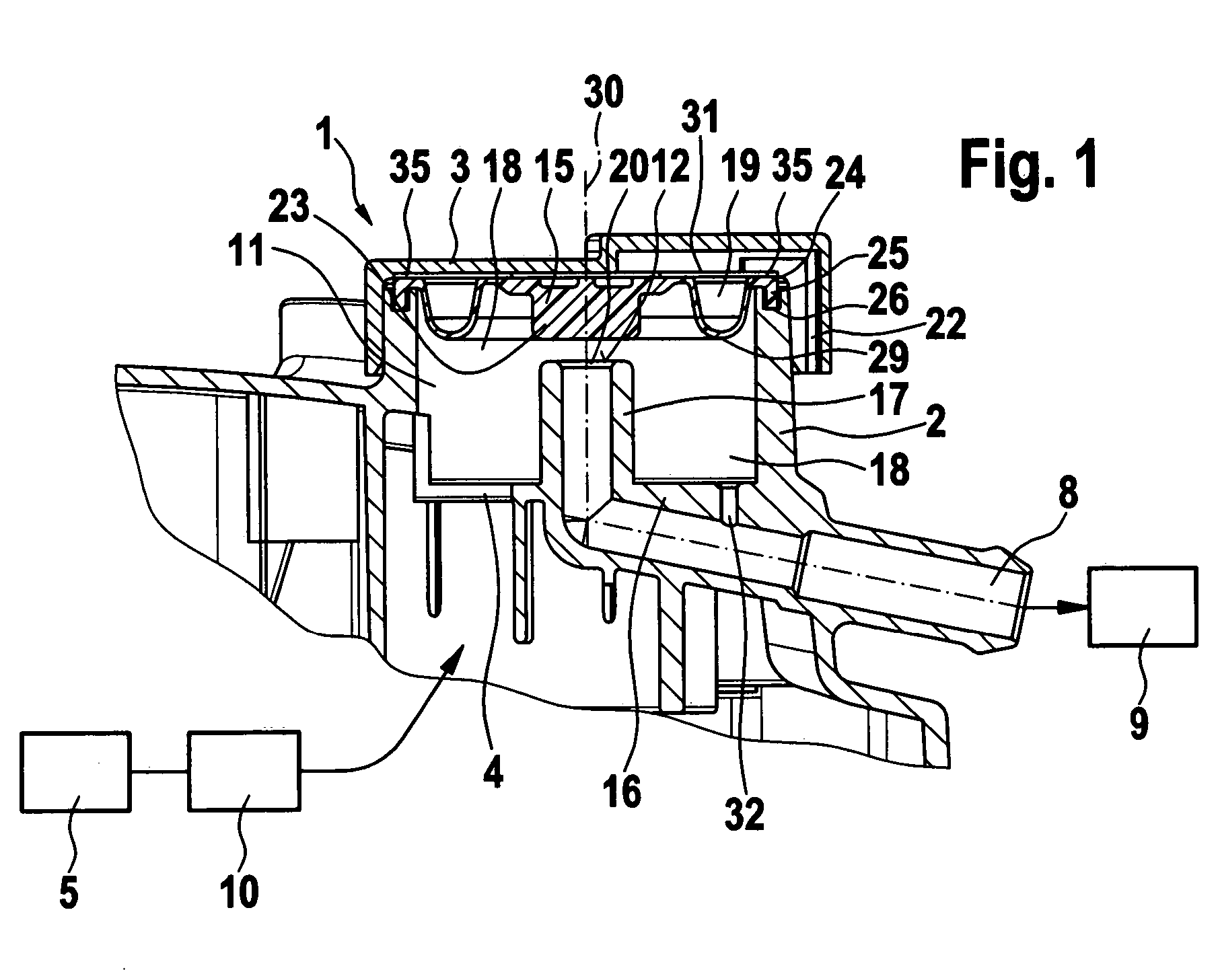
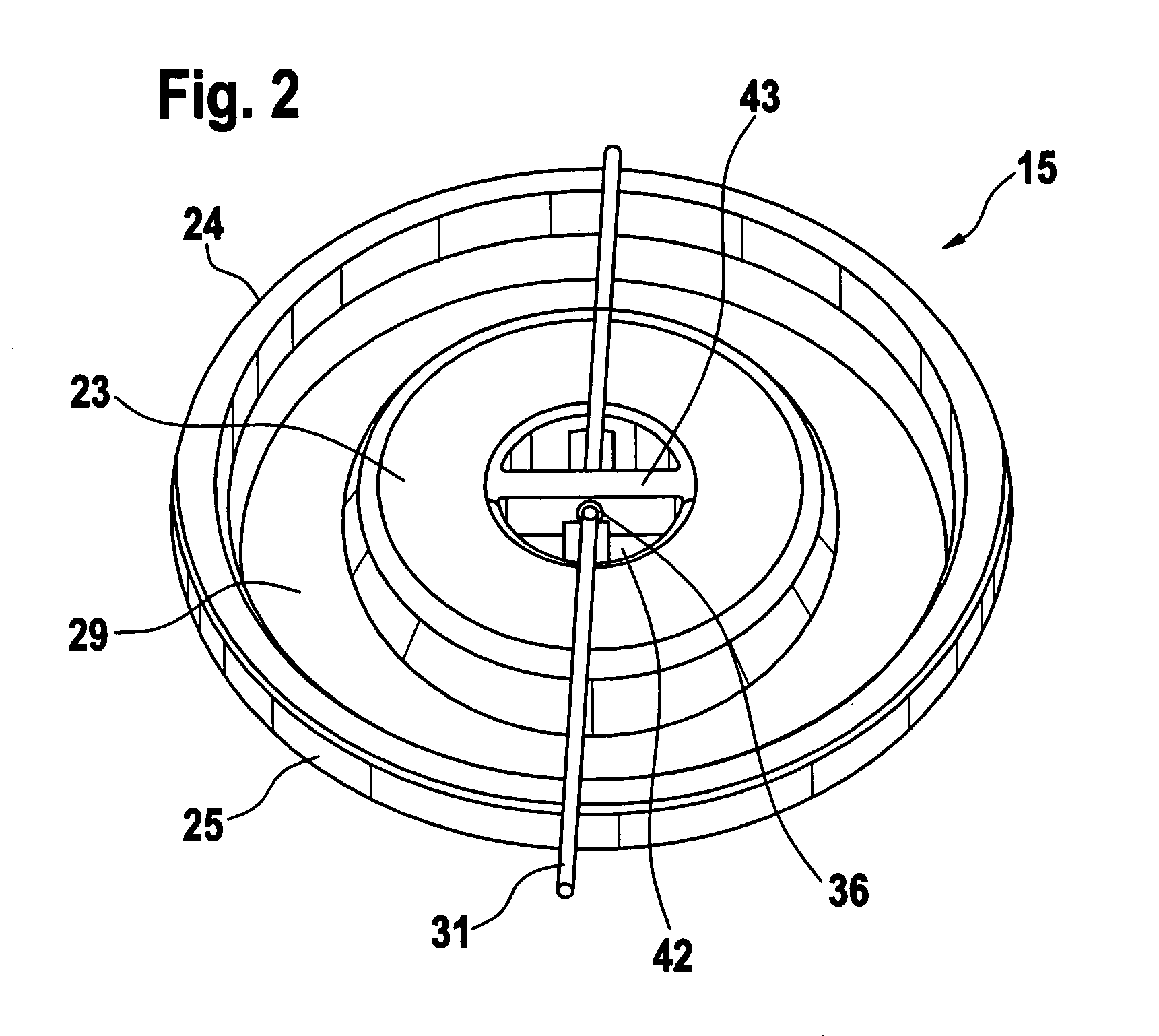
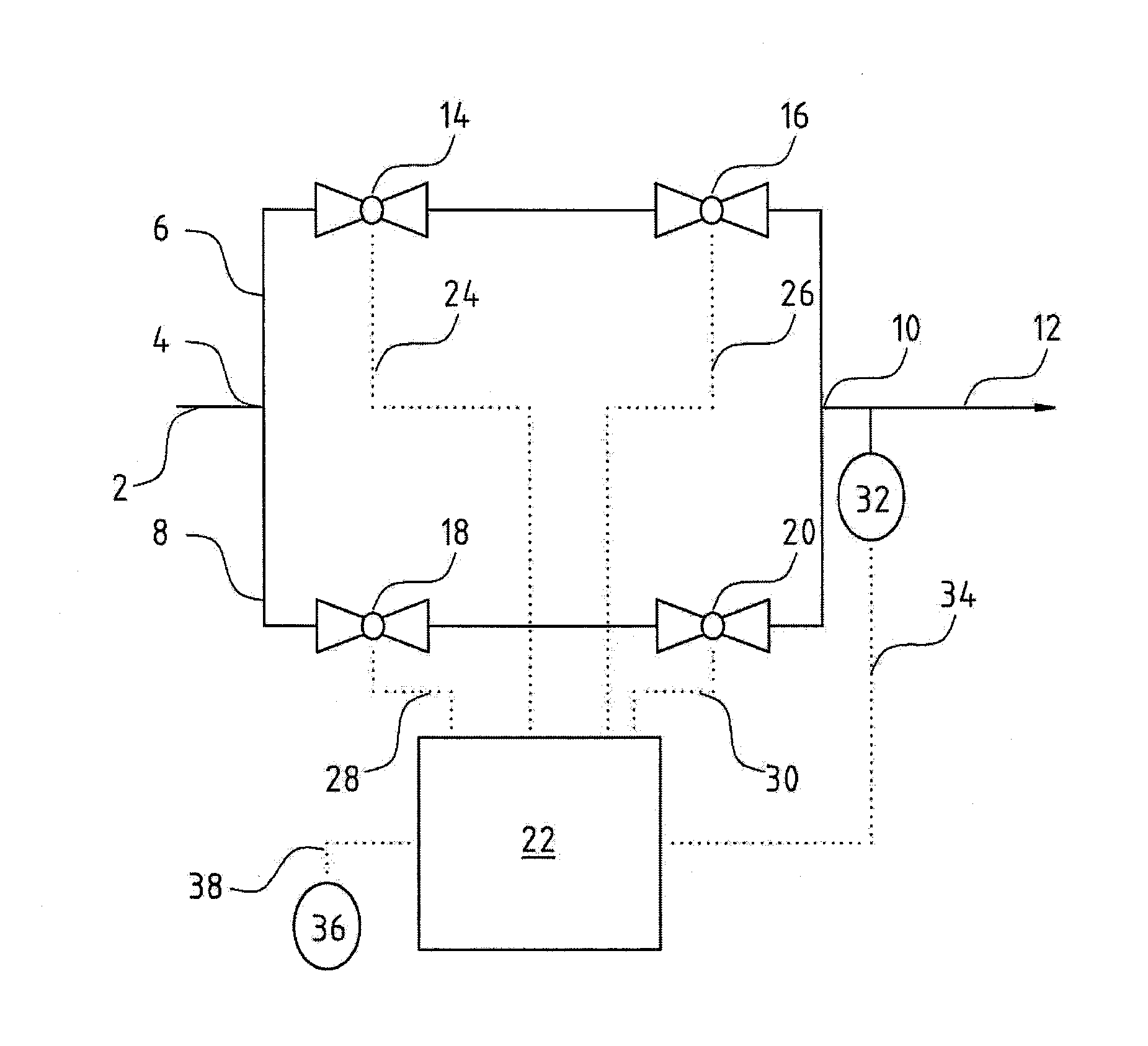
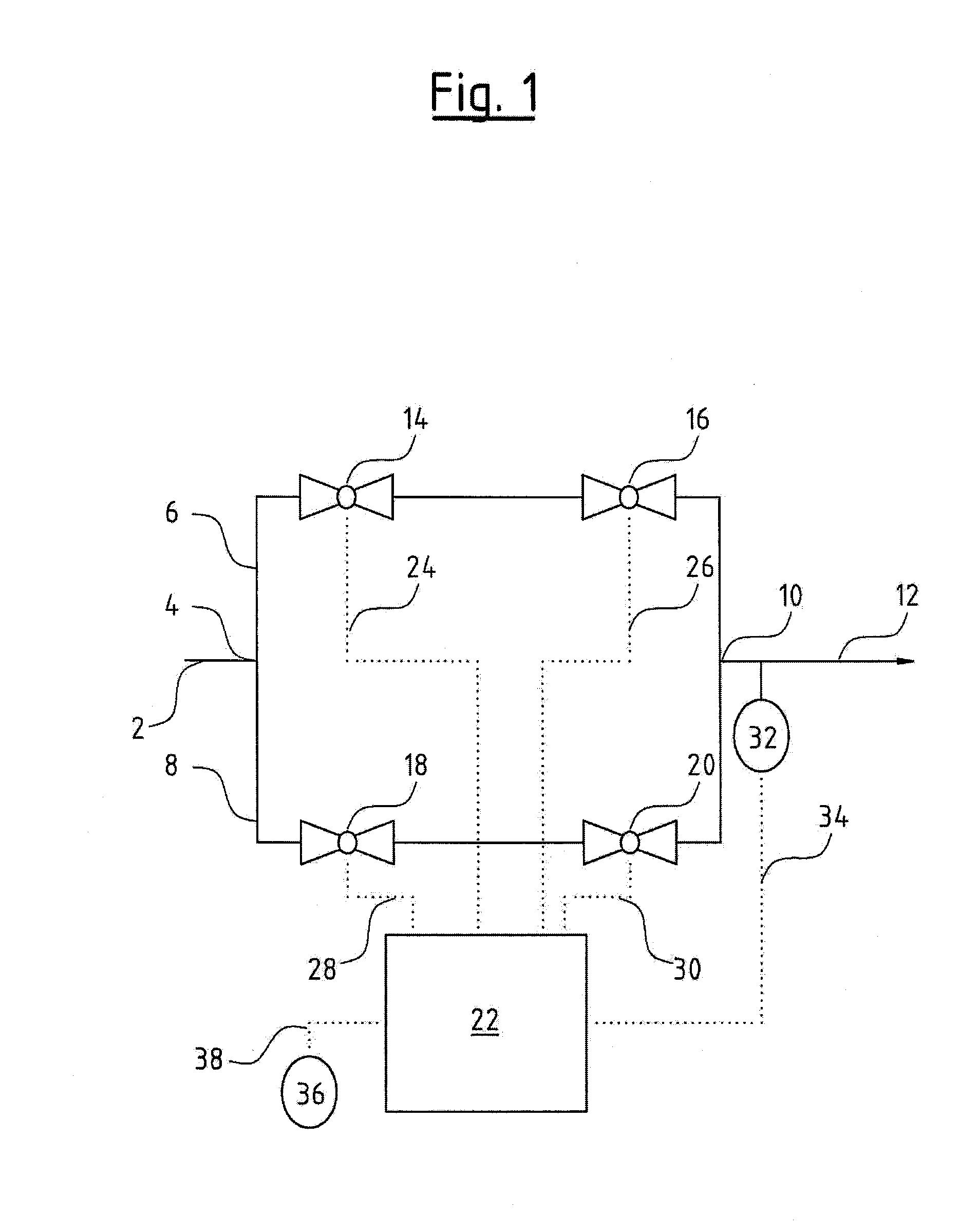
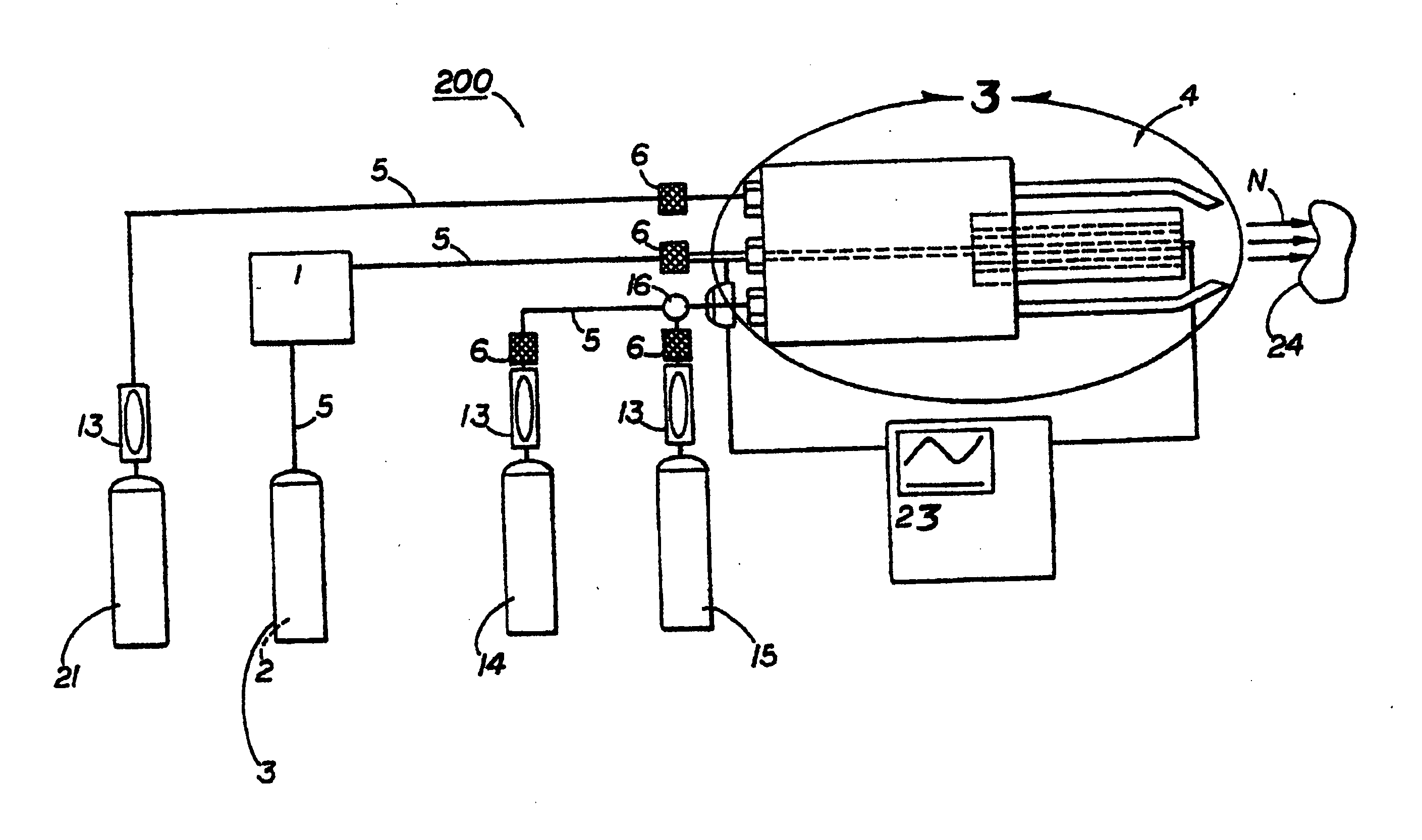
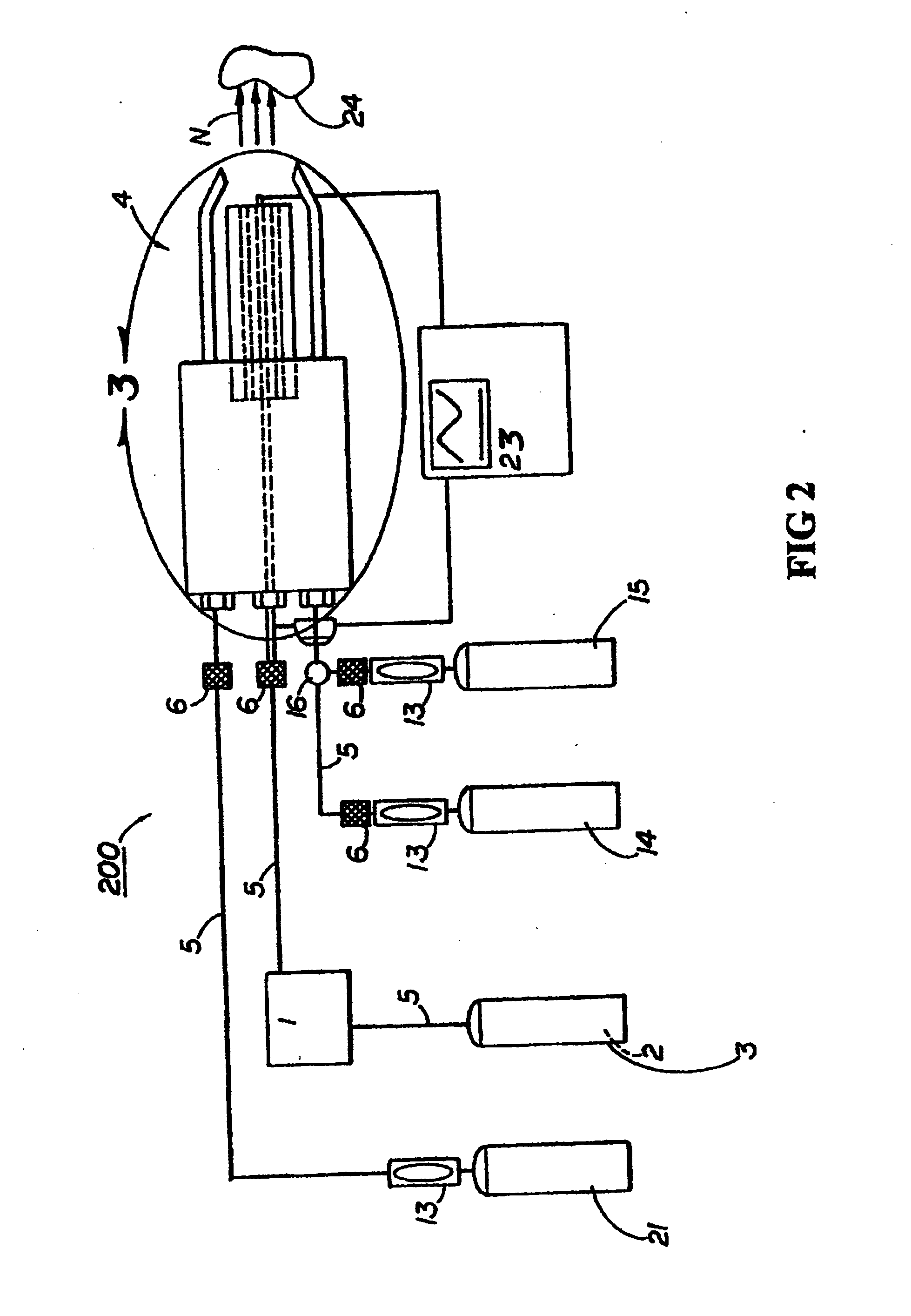
Pressure regulation device, in particular for an oxygen emergency supply system in an aircraft
InactiveUS20080053541A1Simple and inexpensive designImprove reliabilityOperating means/releasing devices for valvesFlying suitsEmergency SupplyEngineering
A pressure regulation device is provided, in particular for an oxygen emergency supply system in an aircraft. The device includes at least two parallel conduits in each of which at least two controllable valves are arranged in series. Further, a pressure sensor is arranged on the exit side of the valve arrangement, for the detection of the actual pressure value, and a controller is provided, which is signal-connected to the pressure sensor and controls the valves.
Owner:DAE SYST
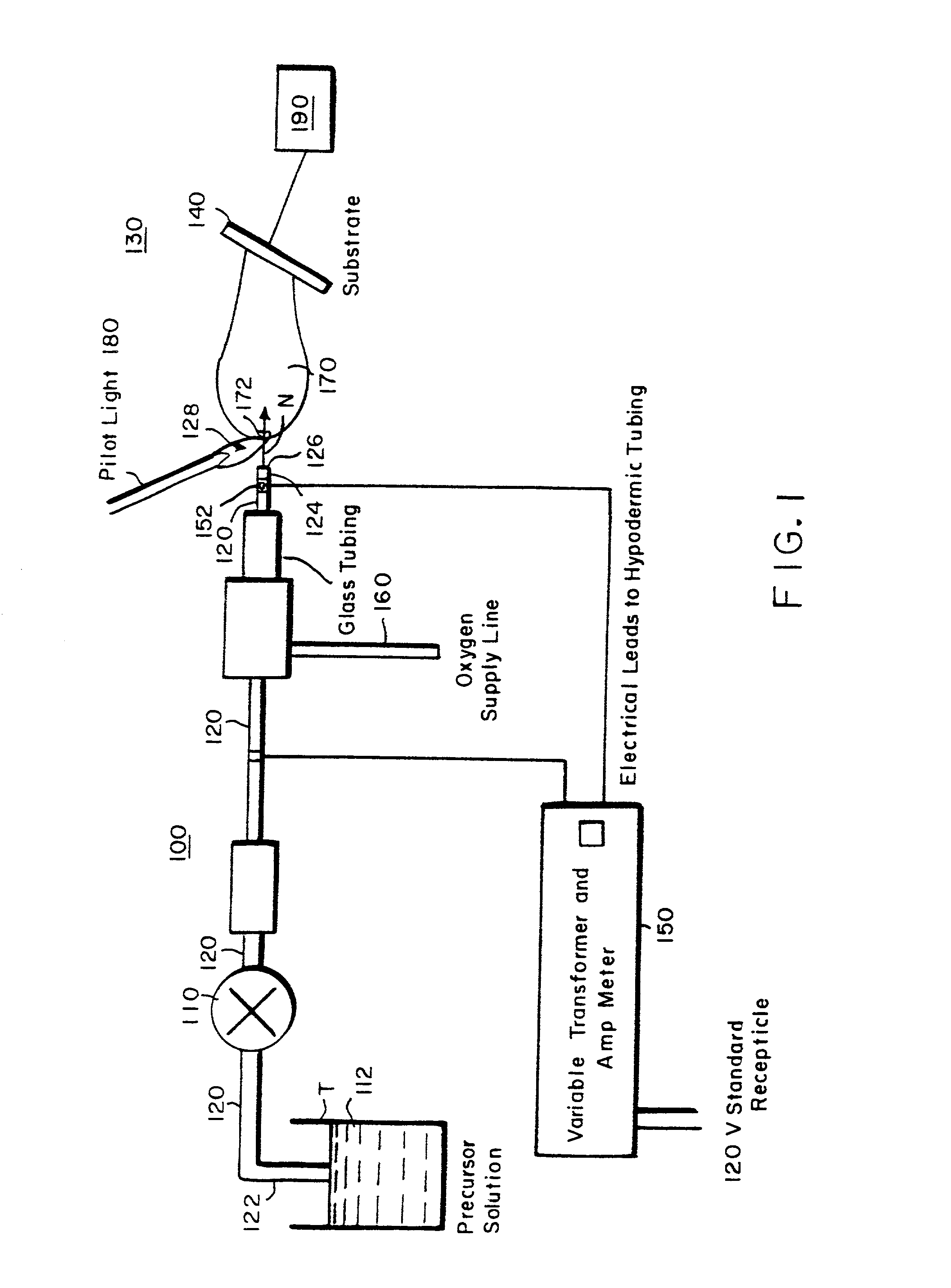
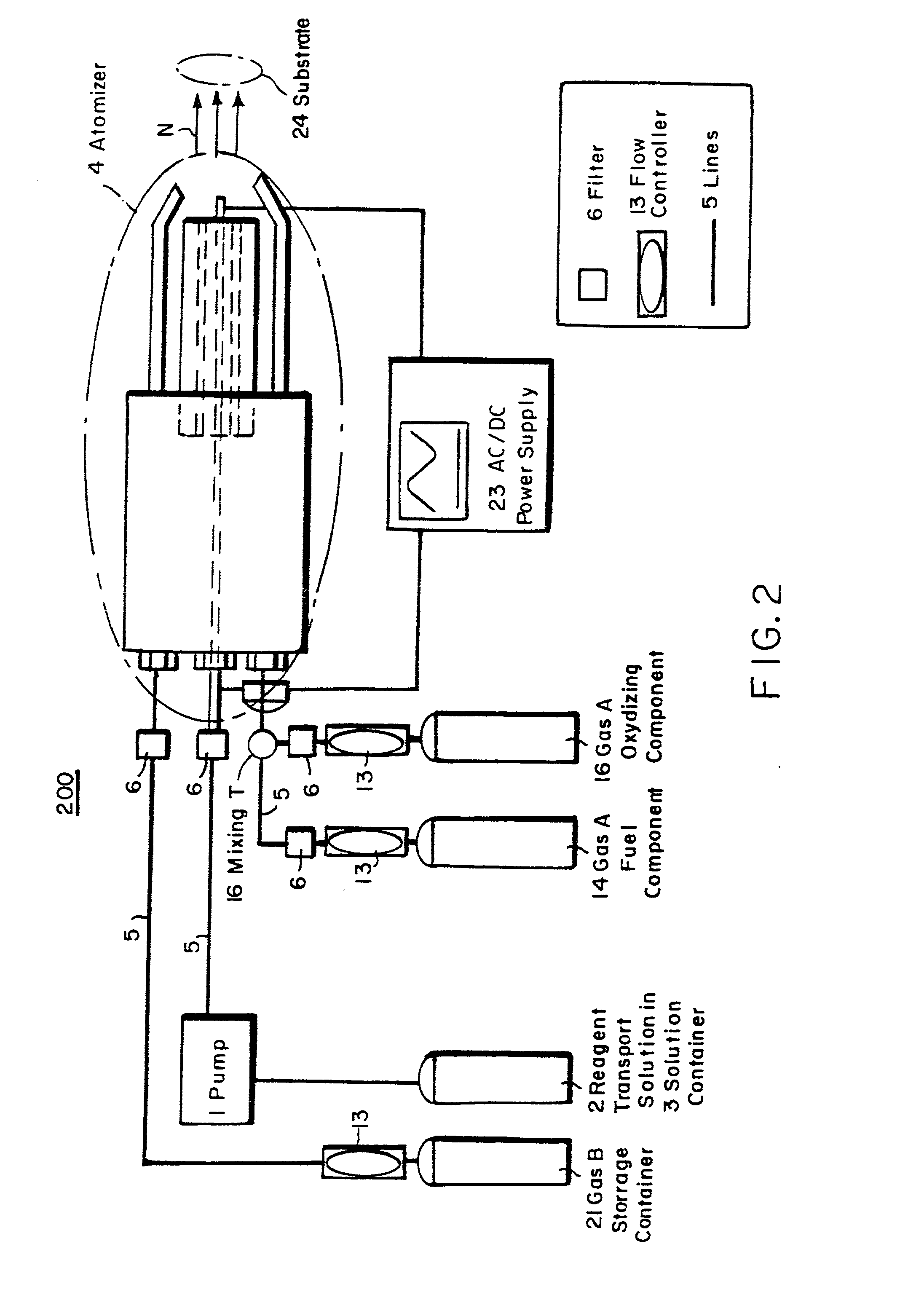
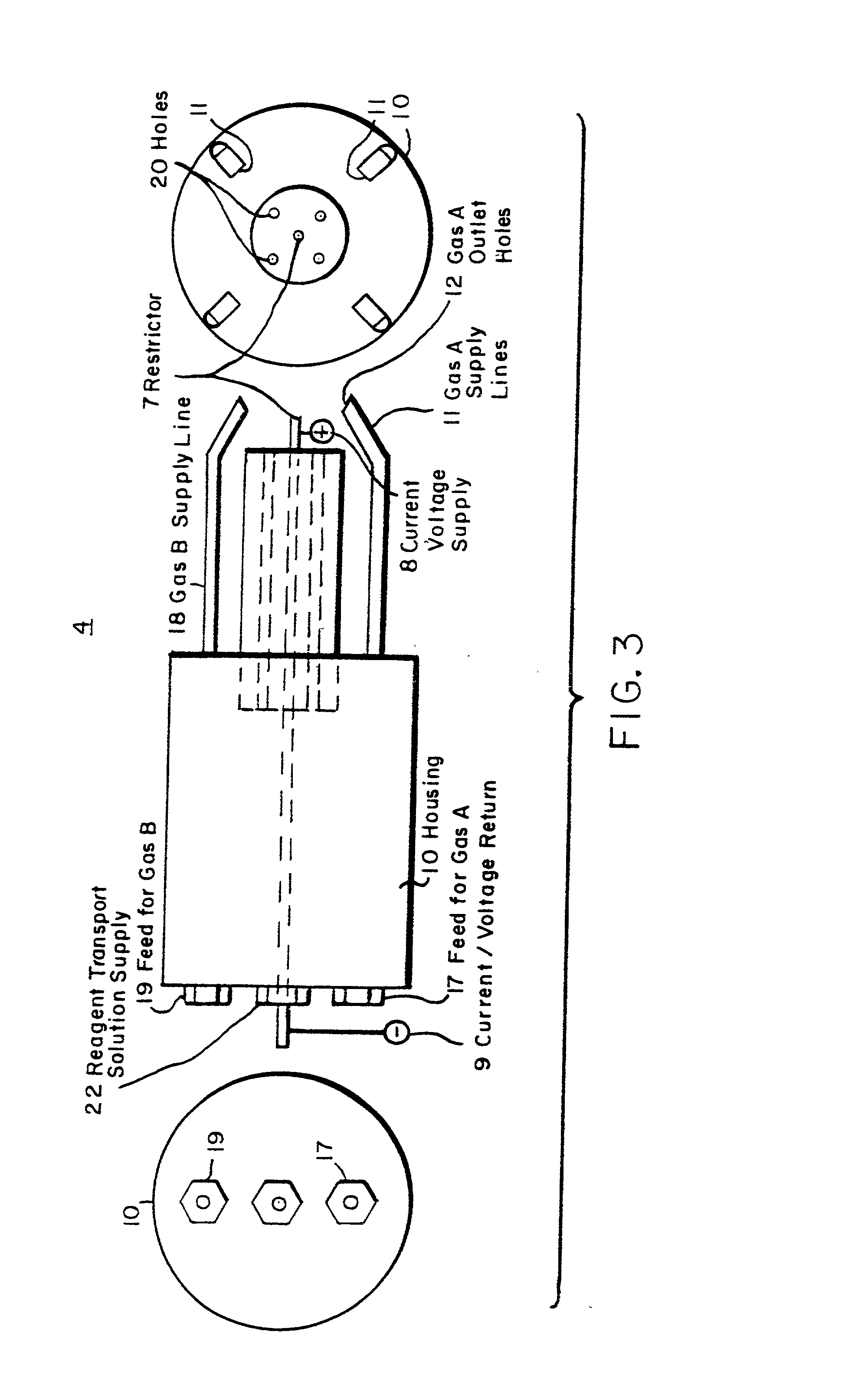
Chemical vapor deposition and powder formation using thermal spray
InactiveUS20010039919A1Promote formationMinimize occurrenceOxygen/ozone/oxide/hydroxideLiquid surface applicatorsThermal sprayingGas phase
A method for chemical vapor deposition using a very fine atomization or vaporization of a reagent containing liquid or liquid-like fluid near its supercritical temperature, where the resulting atomized or vaporized solution is entered into a flame or a plasma torch, and a powder is formed or a coating is deposited onto a substrate. The combustion flame can be stable from 10 torr to multiple atmospheres, and provides the energetic environment in which the reagent contained within the fluid can be reacted to form the desired powder or coating material on a substrate. The plasma torch likewise produces the required energy environment, but, unlike the flame, no oxidizer is needed so materials stable in only very low oxygen partial pressures can be formed. Using either the plasma torch or the combustion plasma, coatings can be deposited and powders formed in the open atmosphere without the necessity of a reaction chamber, but a chamber may be used for various reasons including process separation from the environment and pressure regulation.
Owner:HUNT ANDREW T +1
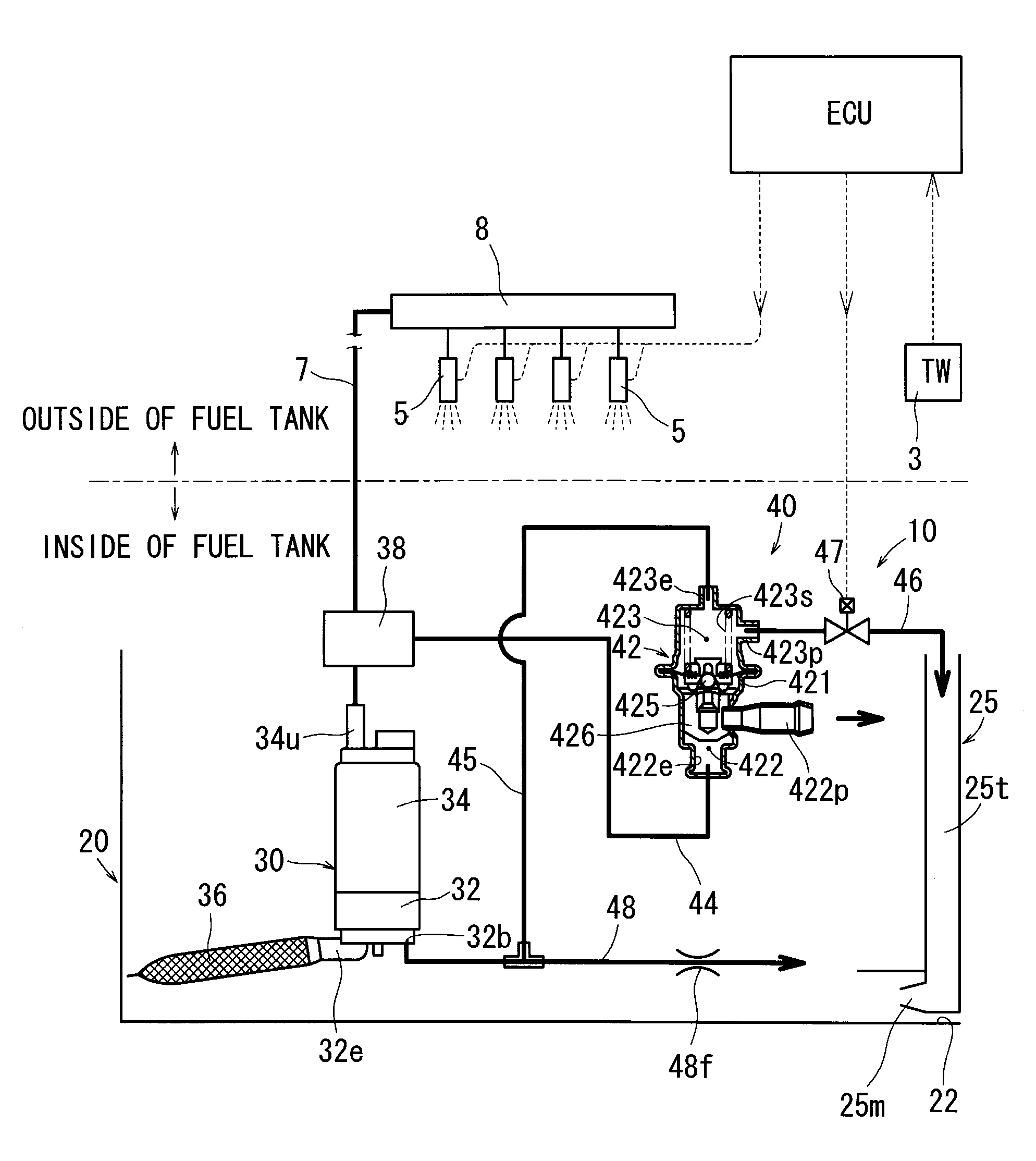
Fuel supply apparatuses
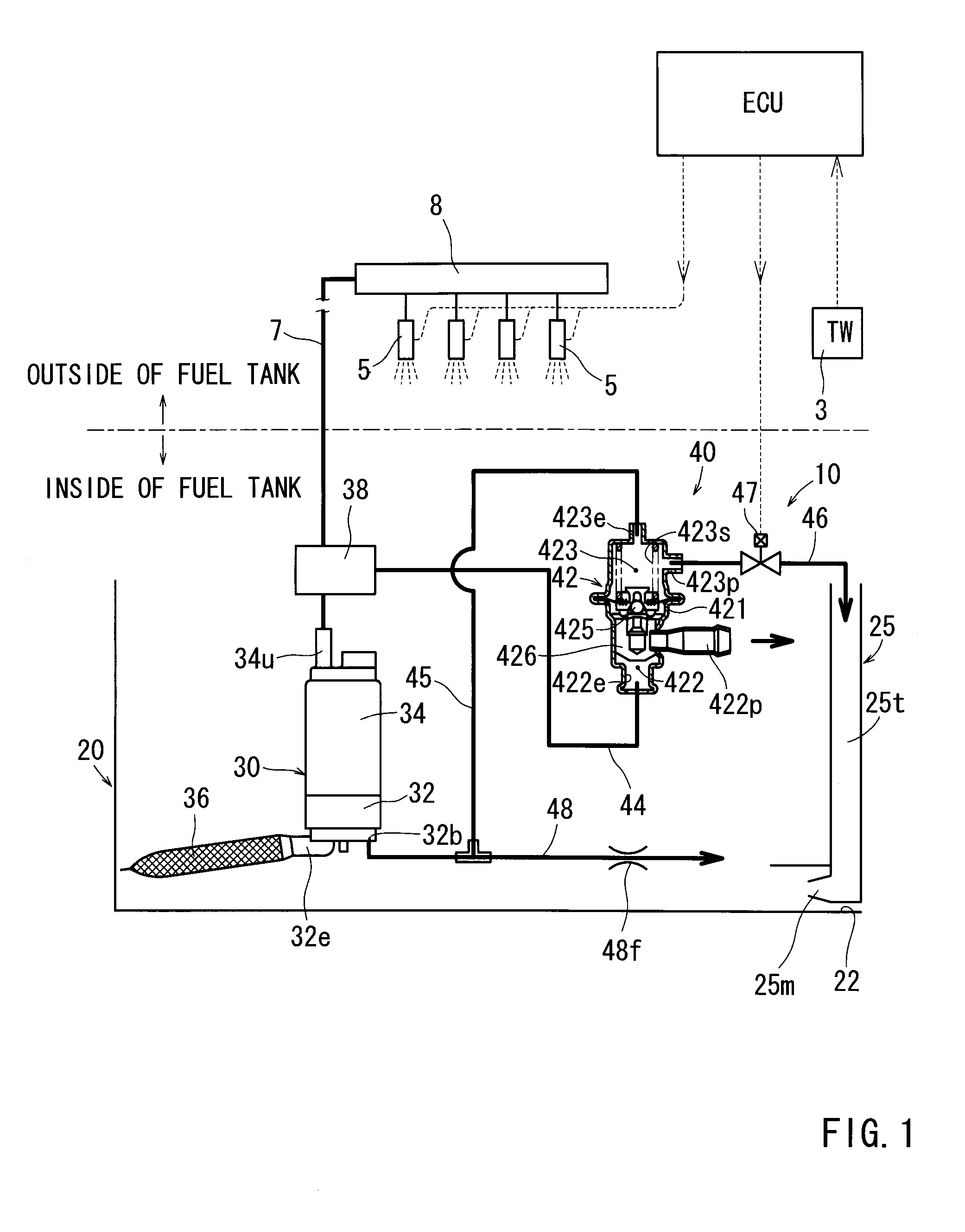
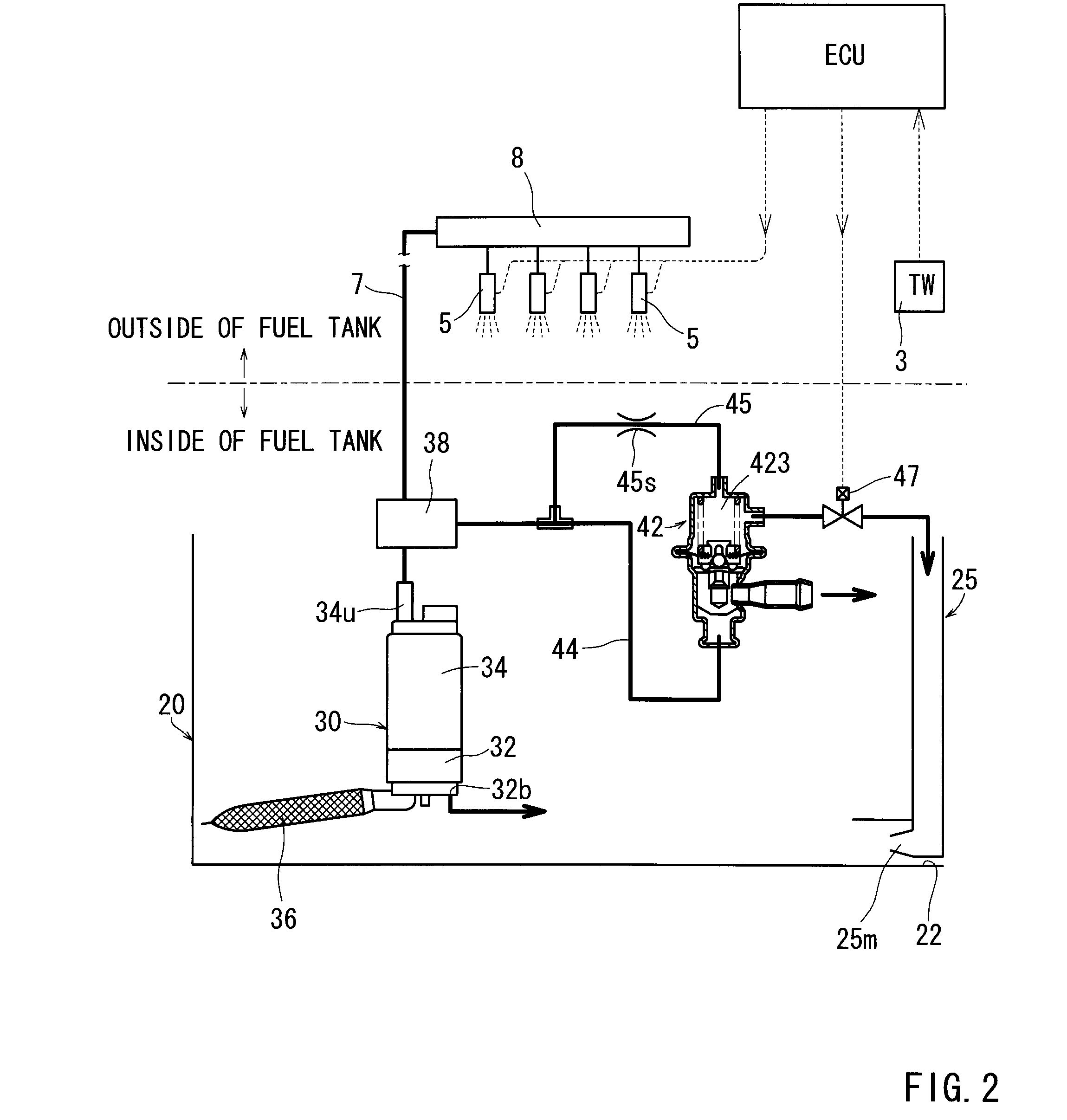
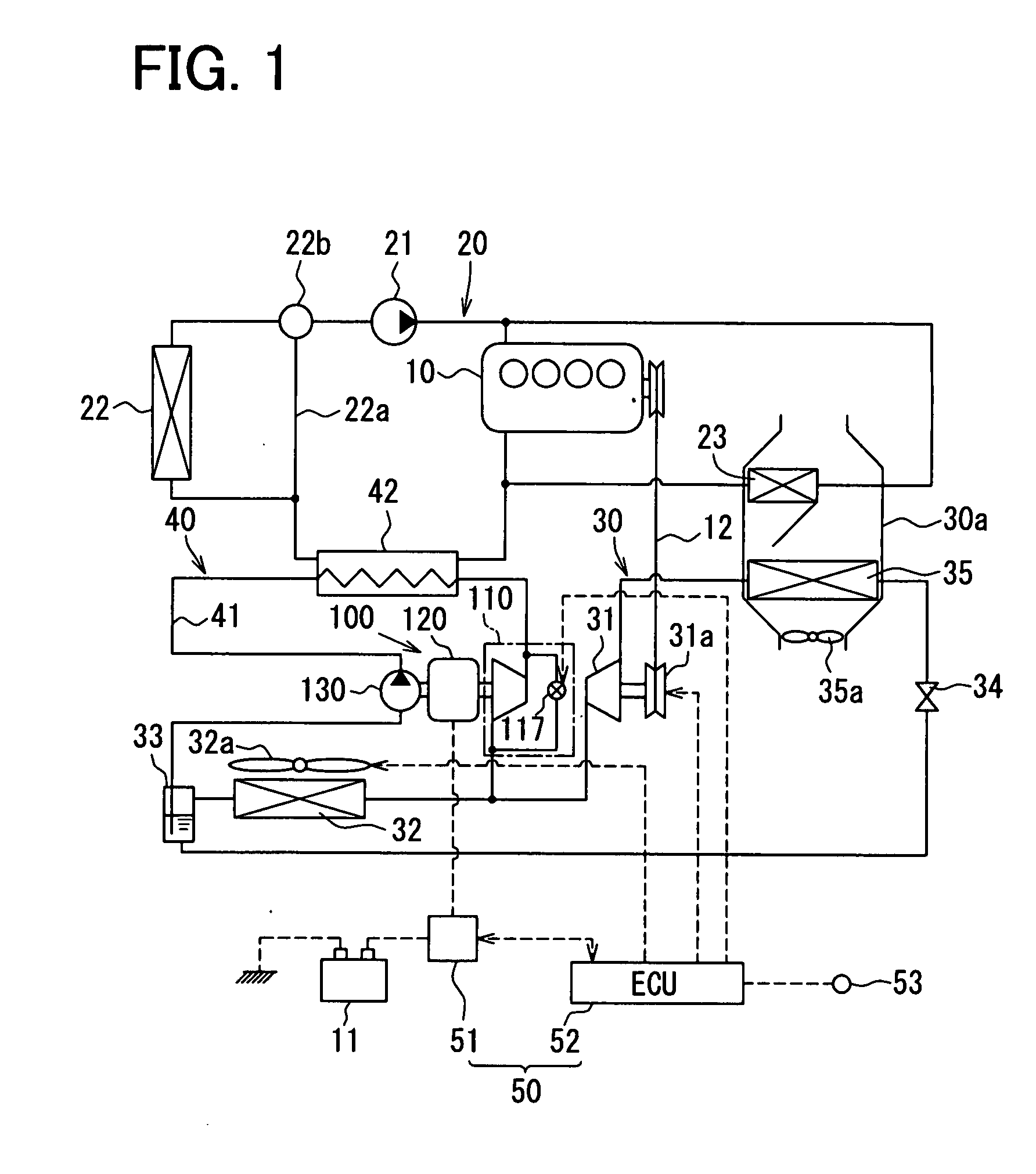
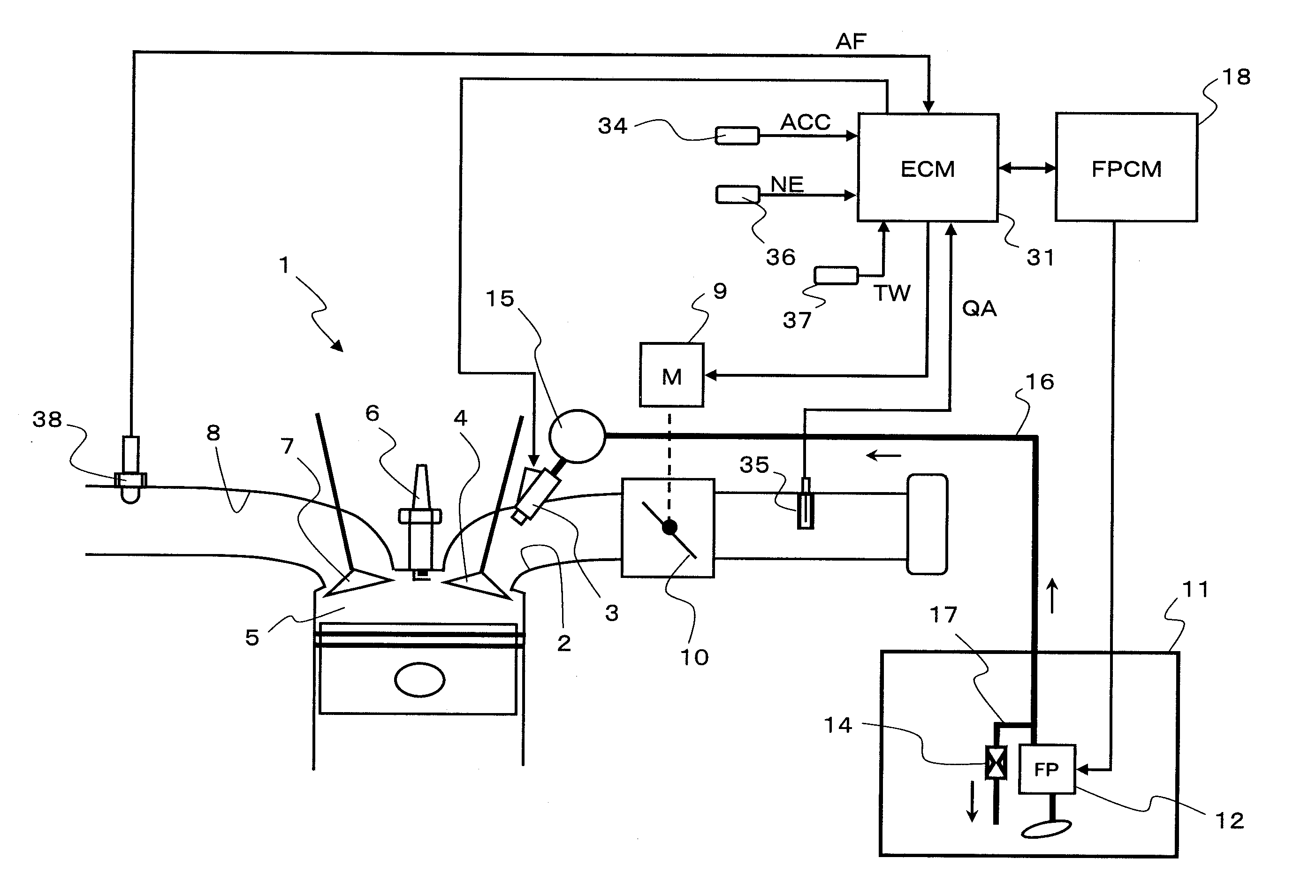
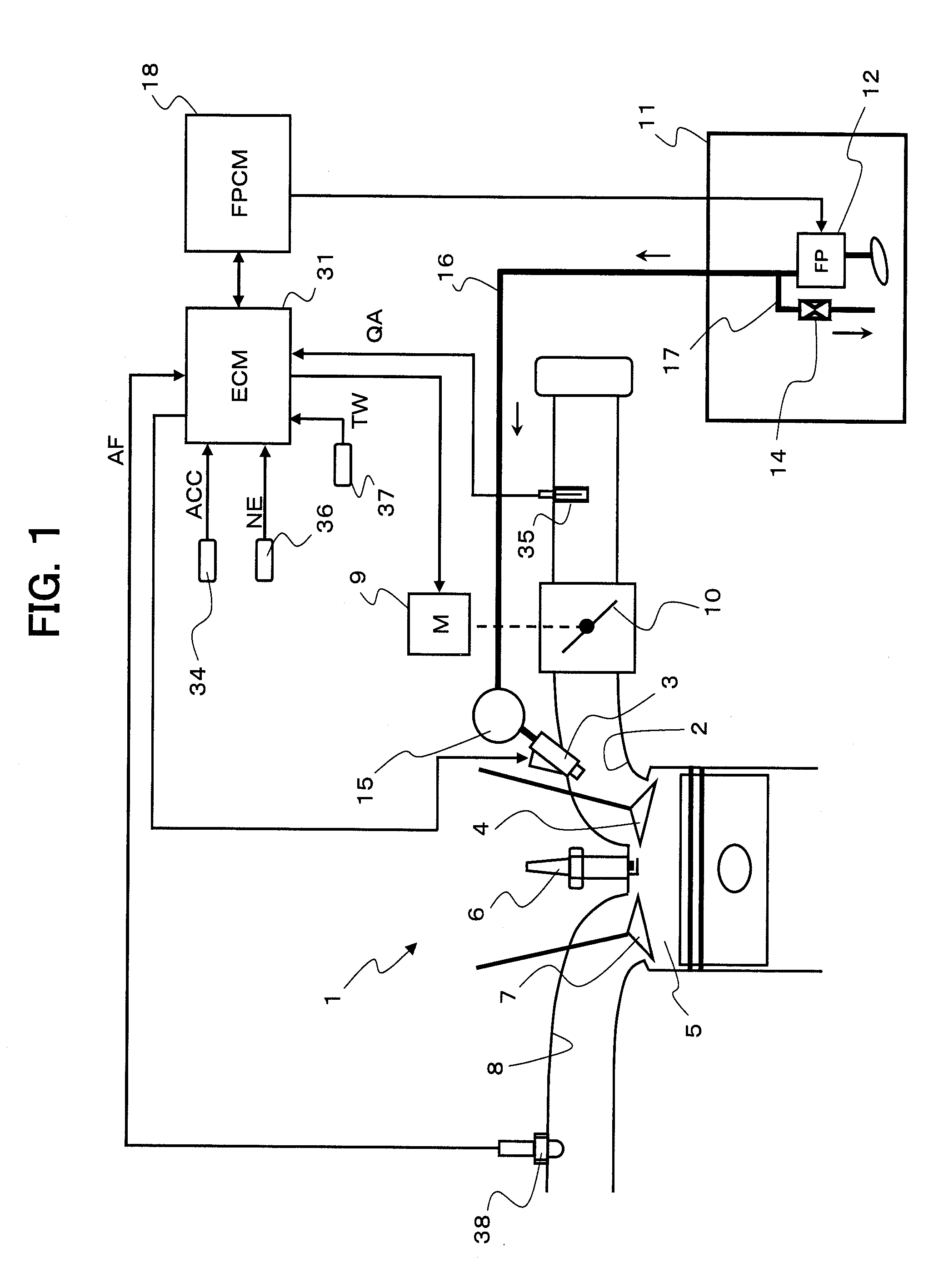
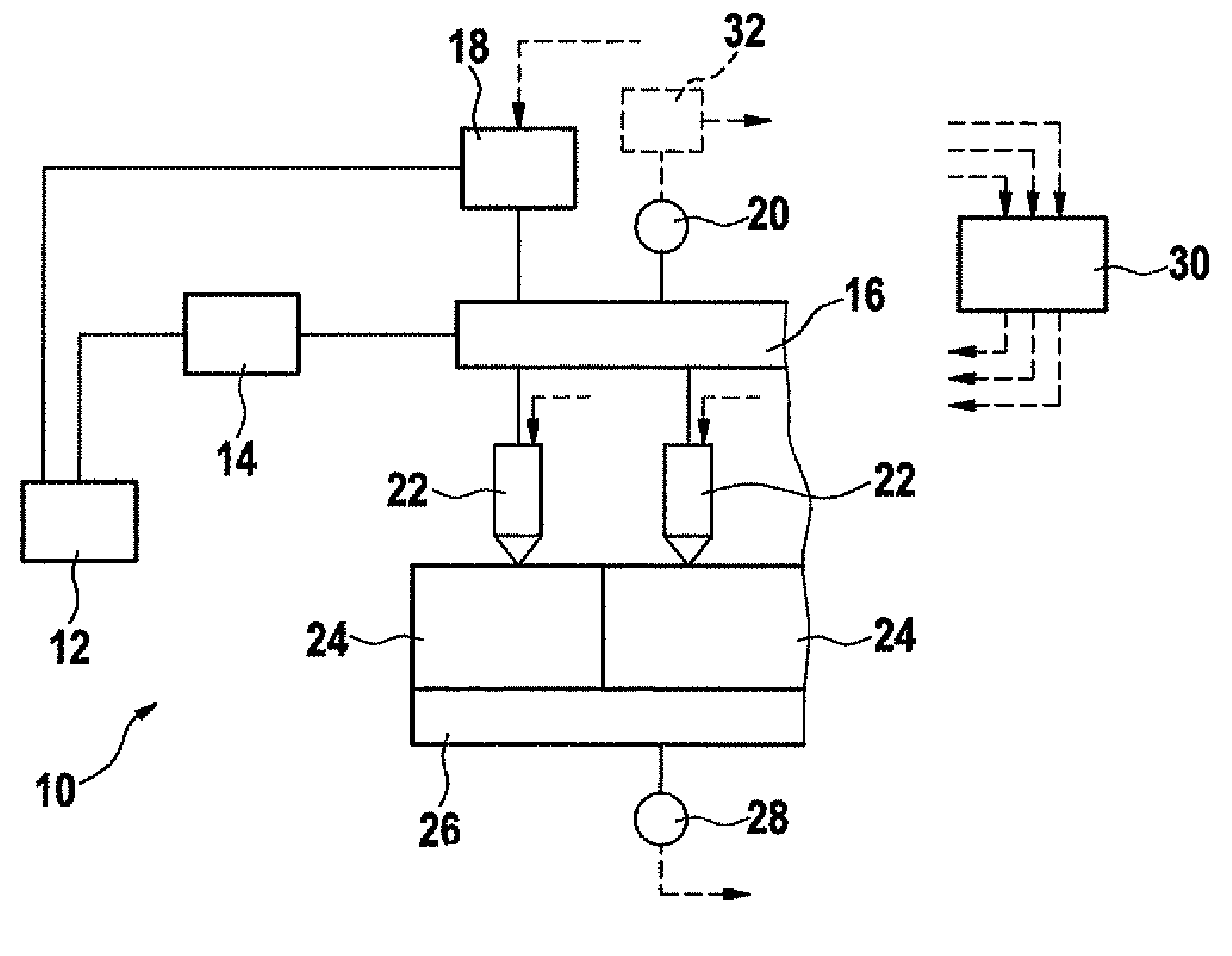
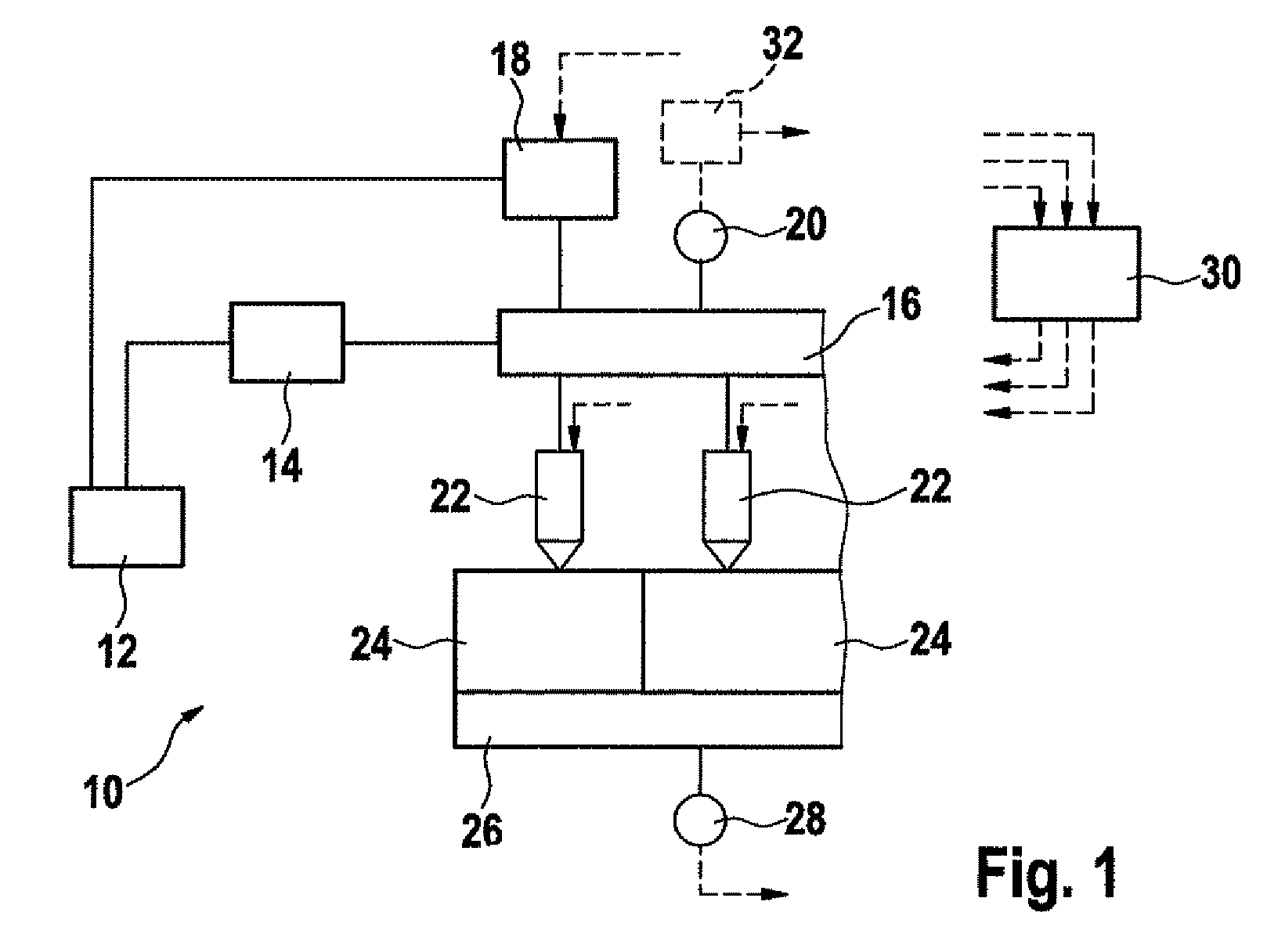
InactiveUS20090071444A1Adjustable performanceAvoid volatilityElectrical controlLow pressure fuel injectionStress regulationSteam generation
It is an object of the present invention to inhibit production of vapor within fuel when an engine is at a high temperature and to inhibit change of amount of the fuel injected from an injector.A fuel supply apparatus according to the present invention includes vapor production determining means (3) for determining whether or not the vapor of the fuel is producible, and control means (ECU) for operating a passage resistance adjusting means (47) of a pressure adjusting mechanism (40) to cause increase of the pressure of the fuel supplied to an injector (5) insomuch as the production of the vapor is inhibited when the vapor production determining means (3) has determined a vapor producible condition.
Owner:AISAN IND CO LTD
Managing Treatment of Subterranean Zones
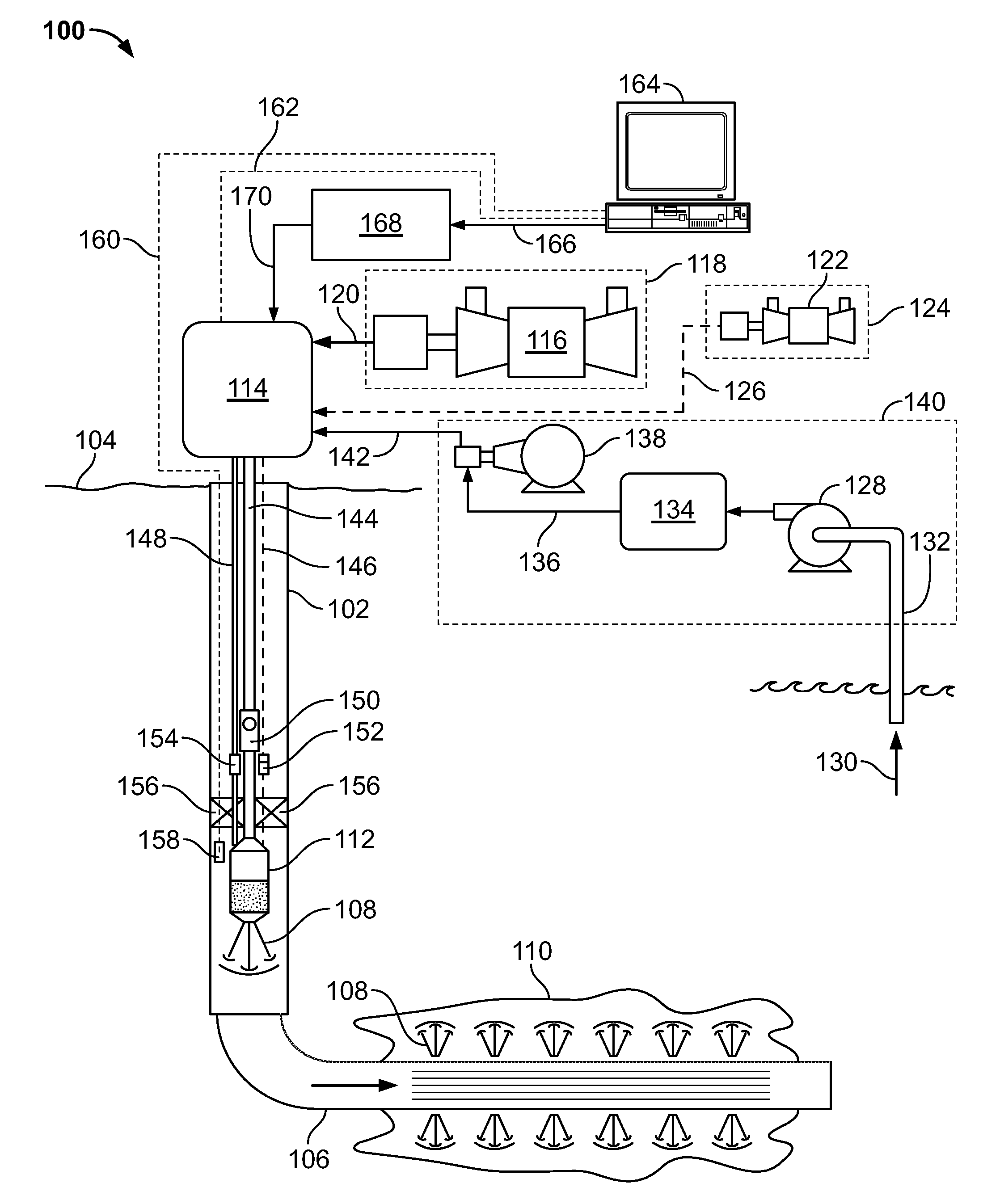
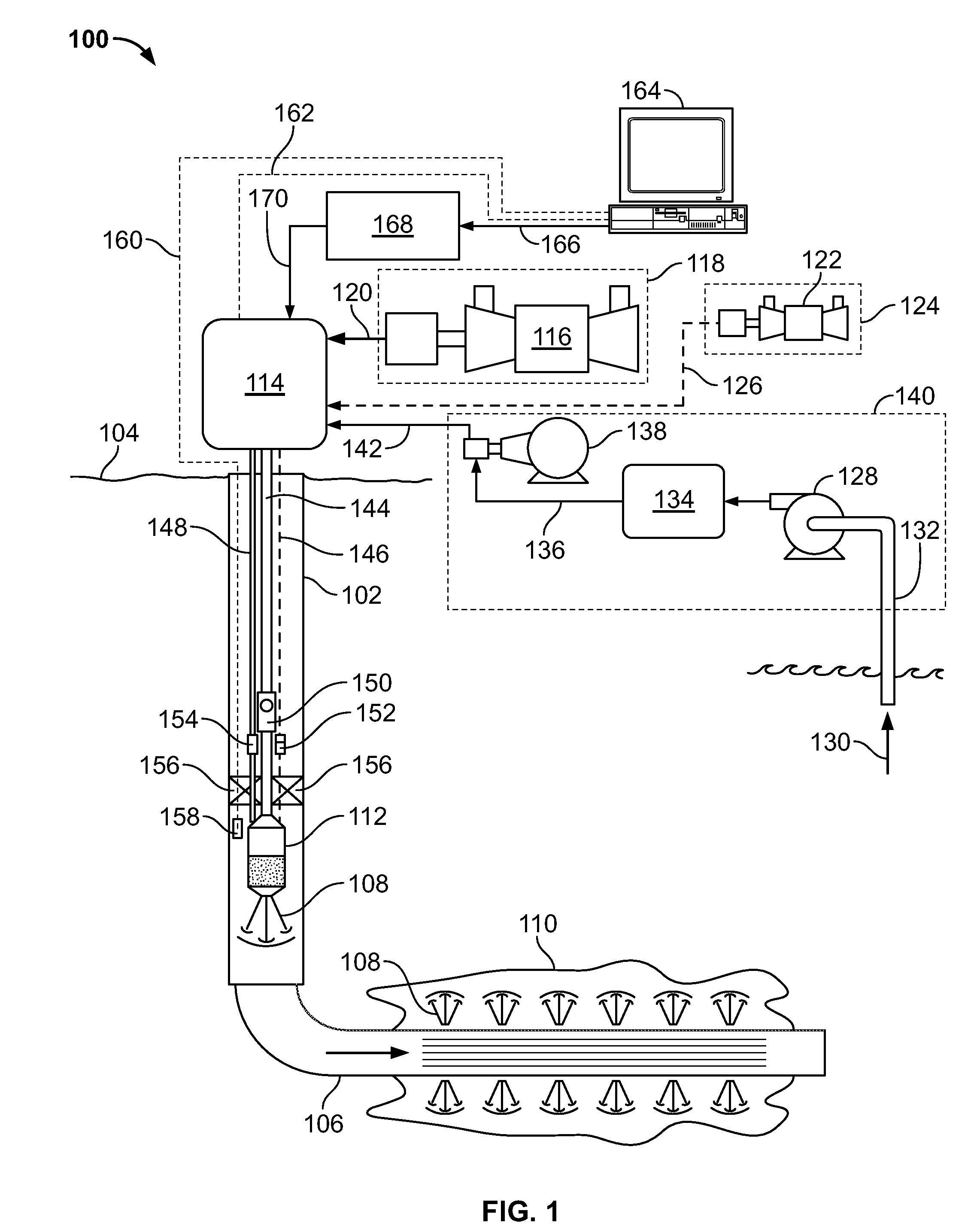
InactiveUS20120318526A1Efficient responseReduce waste heat and lost energyFlexible member pumpsInsulationCombustorEngineering
A downhole heated fluid generation system includes: a compressor-valve assembly having a compressor and a valve, the assembly operable to compress and regulate a fluid used in generating a heated treatment fluid; a combustor fluidly coupled to the compressor-valve assembly, the combustor operable to provide the heated treatment fluid into a wellbore; and a controller communicably coupled to the compressor-valve assembly, the controller operable to: determine an input indicative of a desired position of the valve; determine a value indicative of an actual position of the valve; determine a desired operating condition of the compressor based, at least in part, on the input indicative of the desired position of the valve and the value indicative of an actual position of the valve; and adjust an operating parameter of the compressor based on the desired operating pressure to compress a fluid flowing through the compressor and the valve.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Chemical vapor deposition and powder formation using thermal spray
InactiveUS20050019551A1Promote formationMinimize occurrenceMolten spray coatingLayered productsThermal sprayingGas phase
A method for chemical vapor deposition using a very fine atomization or vaporization of a reagent containing liquid or liquid-like fluid near its supercritical temperature, where the resulting atomized or vaporized solution is entered into a flame or a plasma torch, and a powder is formed or a coating is deposited onto a substrate. The combustion flame can be stable from 10 torr to multiple atmospheres, and provides the energetic environment in which the reagent contained within the fluid can be reacted to form the desired powder or coating material on a substrate. The plasma torch likewise produces the required energy environment, but, unlike the flame, no oxidizer is needed so materials stable in only very low oxygen partial pressures can be formed. Using either the plasma torch or the combustion plasma, coatings can be deposited and powders formed in the open atmosphere without the necessity of a reaction chamber, but a chamber may be used for various reasons including process separation from the environment and pressure regulation.
Owner:HUNT ANDREW T +1
Pressure-temperature control for a cryoablation catheter system
InactiveUS20050198972A1Great pressure dropMore resistantDomestic cooling apparatusCompression machines with non-reversible cycleEngineeringStress regulation
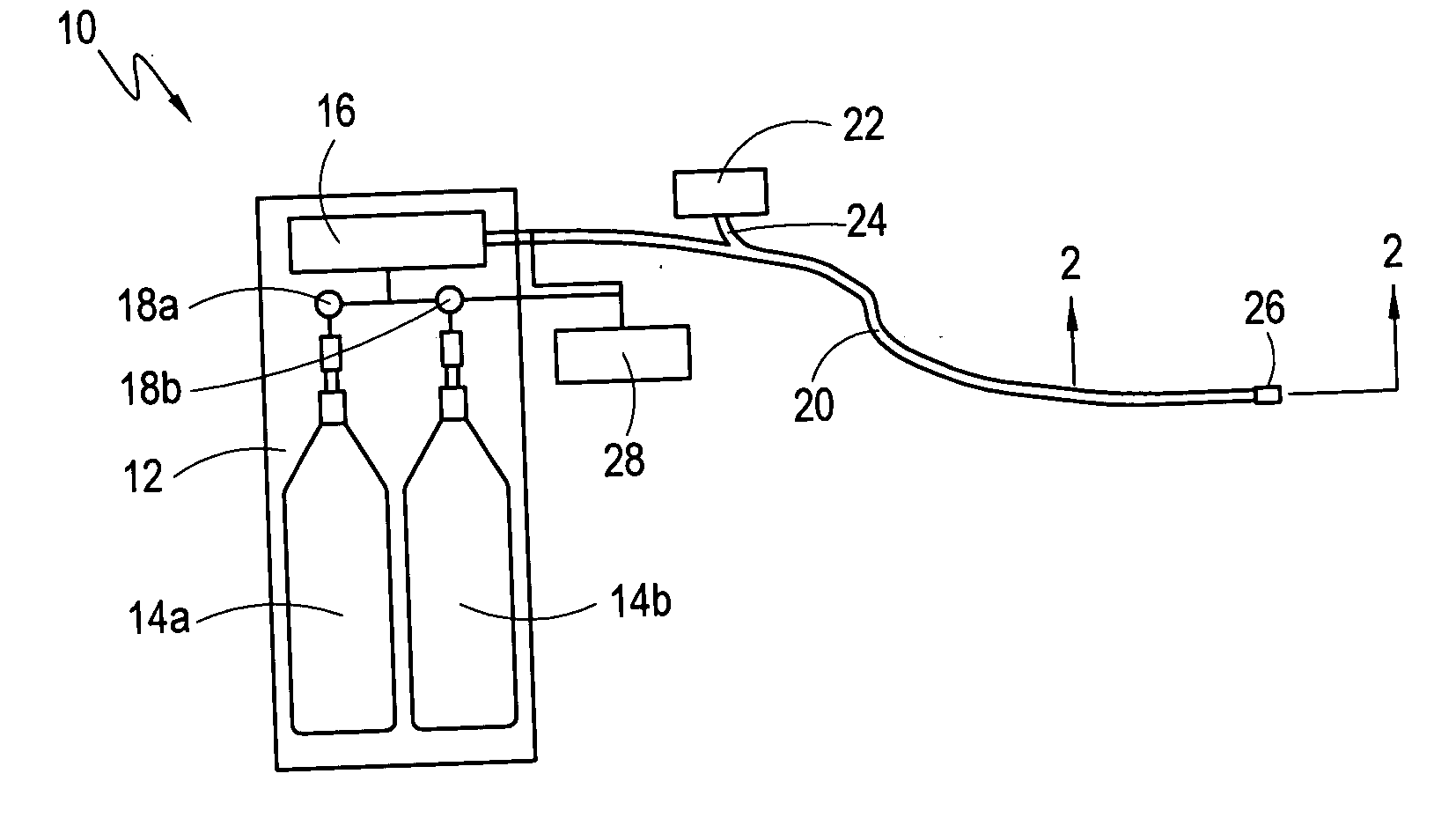
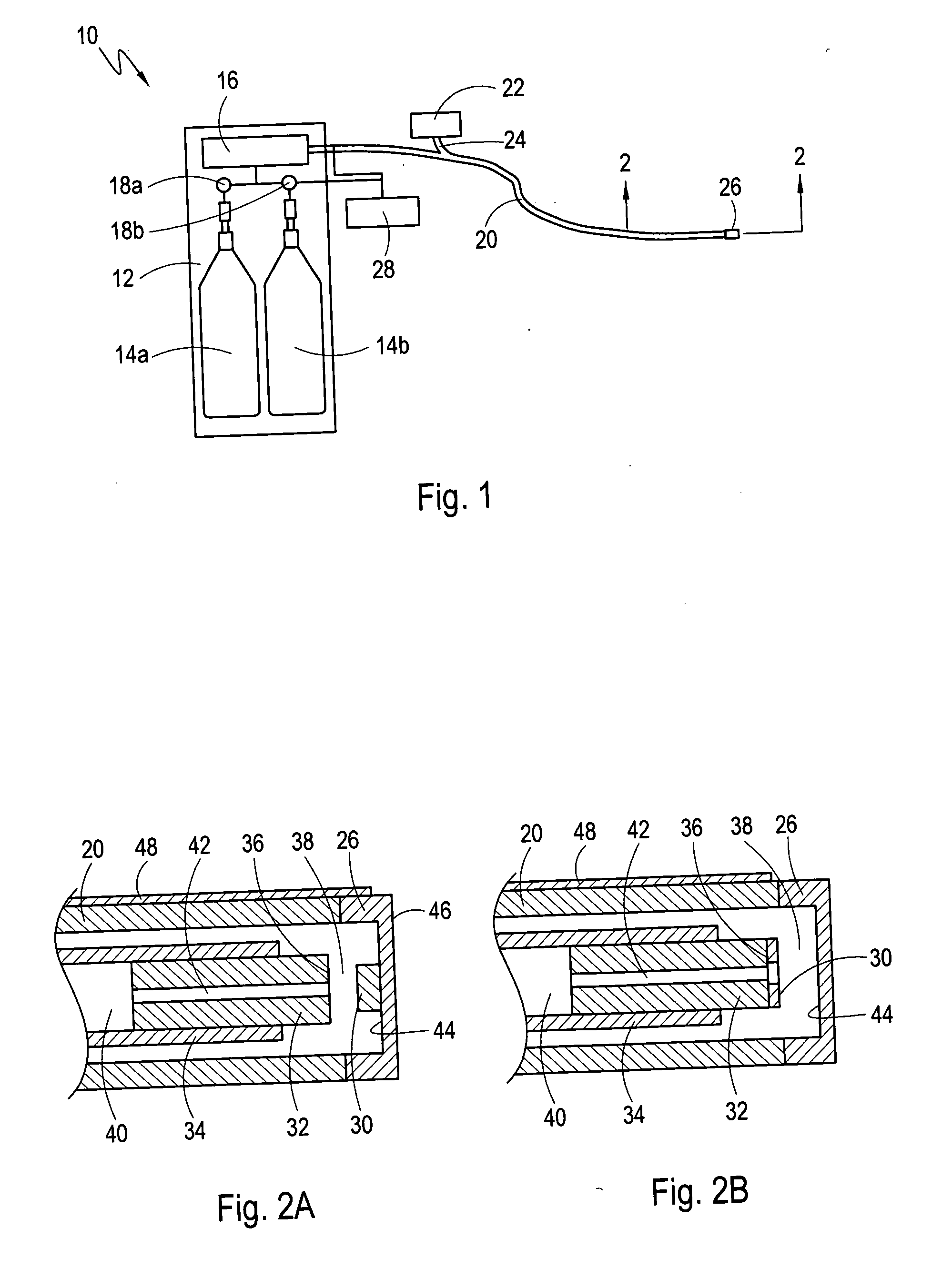
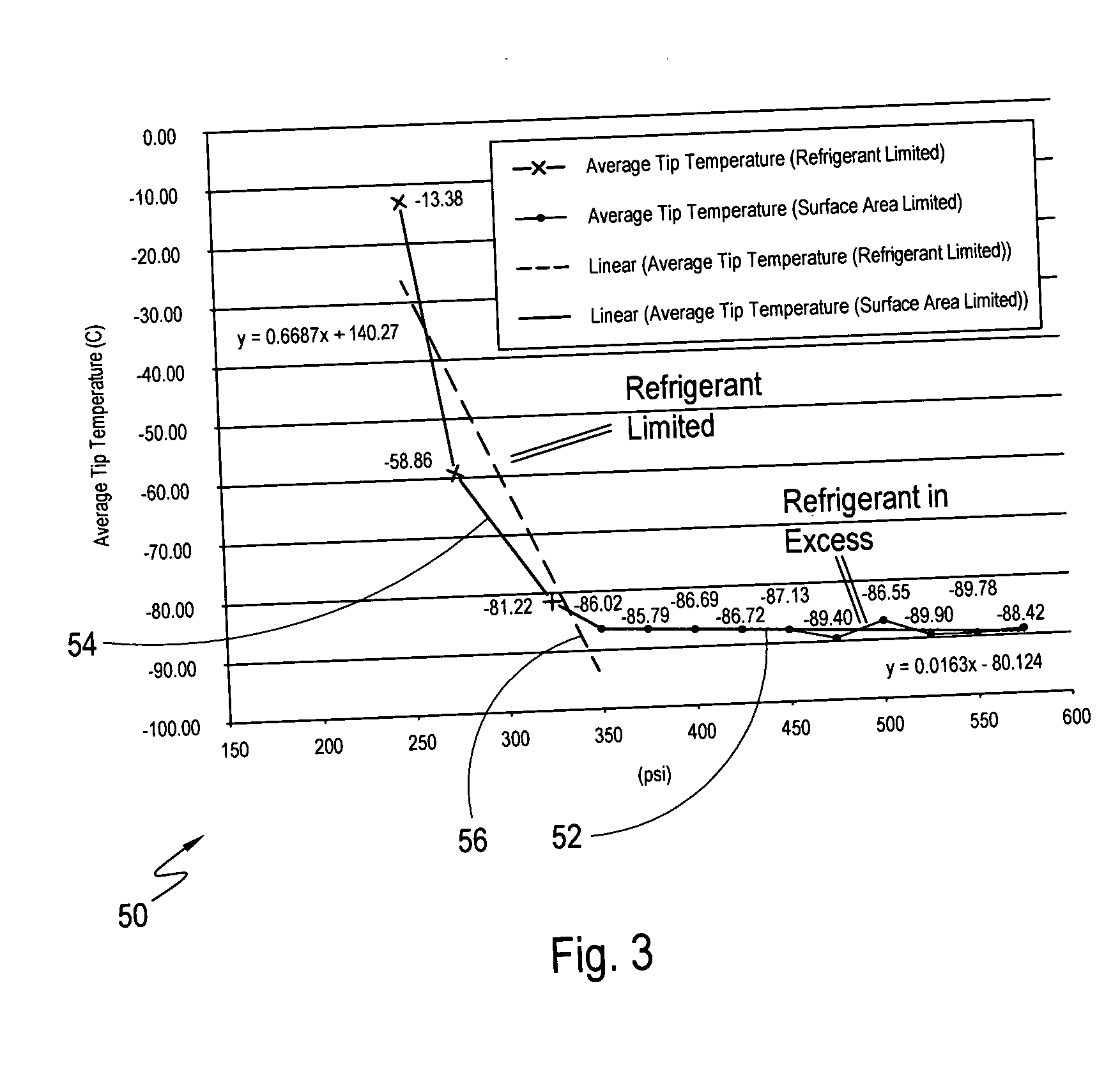
A heat transfer system and method for cryoablation includes a cryo-catheter with a tip, and a temperature sensor mounted at the distal end of the cryo-catheter. A system controller is in electronic communication with both a pressure regulator and the temperature sensor. The system takes advantage of the transfer of latent heat to minimize the tip temperature at the distal end of the cryo-catheter. More specifically, after measuring the temperature at the distal end of the cryo-catheter, and comparing the temperature data and input pressure to a known pressure-temperature curve, the input pressure of the liquid fluid refrigerant may be adjusted. At the correct pressure setting, the liquid fluid refrigerant will begin to boil at the distal end of the cryo-catheter, and the tip temperature will be at a minimum.
Owner:CRYOCOR
Fluid machine, rankine cycle and control method
InactiveUS20070245732A1Simple structureEngine of arcuate-engagement typeOscillating piston enginesWorking fluidGas phase
A fluid machine includes a fluidization portion for compressing or expanding a working fluid which is heated to be brought into a vapor phase state after circulating in a cycle, an oil storage portion for storing therein lubricant oil for lubricating a sliding surface of the fluidization portion, a lubricant oil feed passage for guiding the lubricant oil stored in the oil storage portion to a sliding portion of the fluidization portion by a flow of the working fluid, and a sliding surface pressure adjustment portion that is controlled to adjust a sliding surface pressure of the sliding portion. The working fluid flows inside the machine with the sliding surface pressure of the sliding portion decreased as compared with that in a normal operation of the fluidization portion by the sliding surface pressure adjustment portion, and thereafter the decreasing of the sliding surface pressure by the sliding surface pressure adjustment portion is released.
Owner:DENSO CORP +1
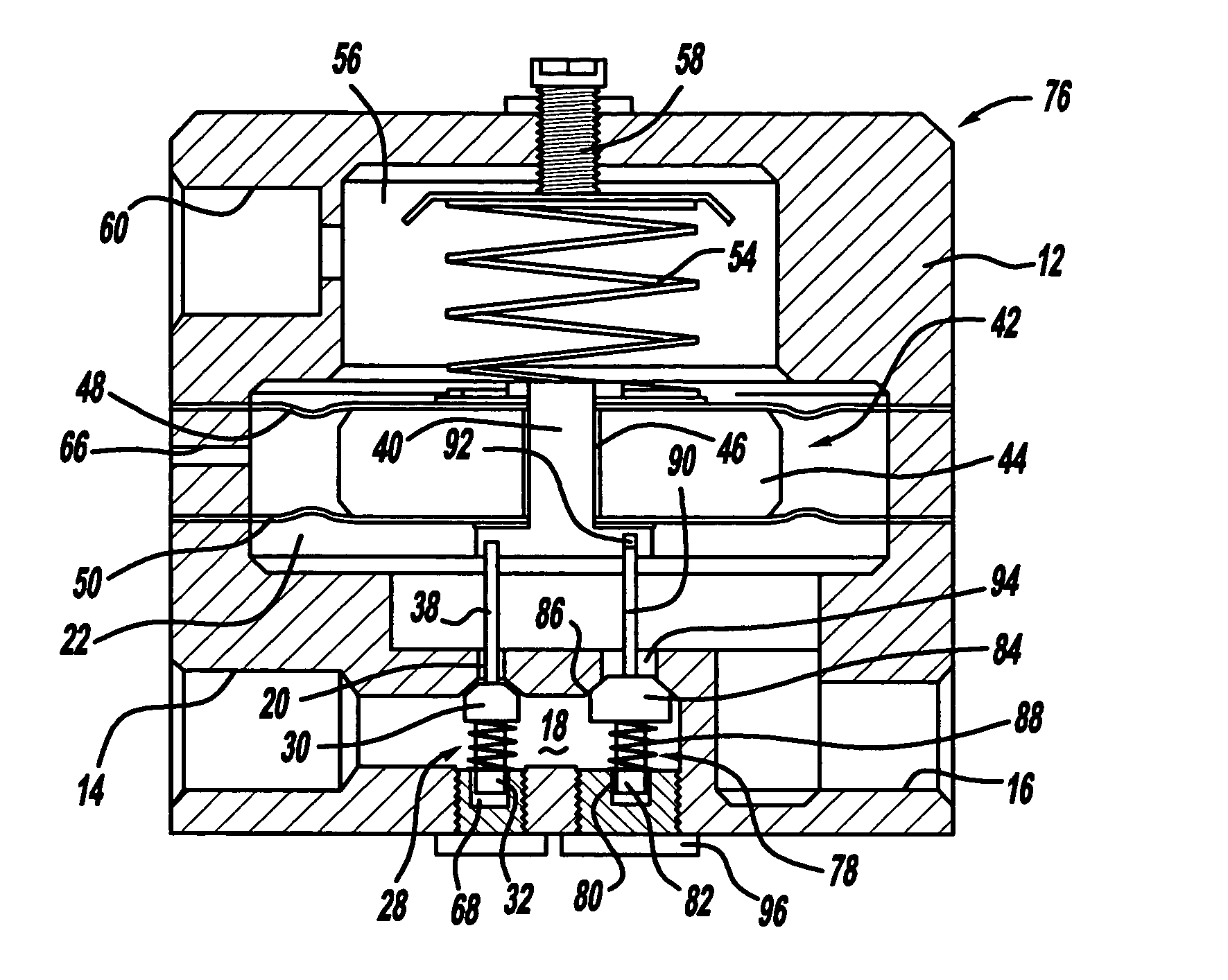
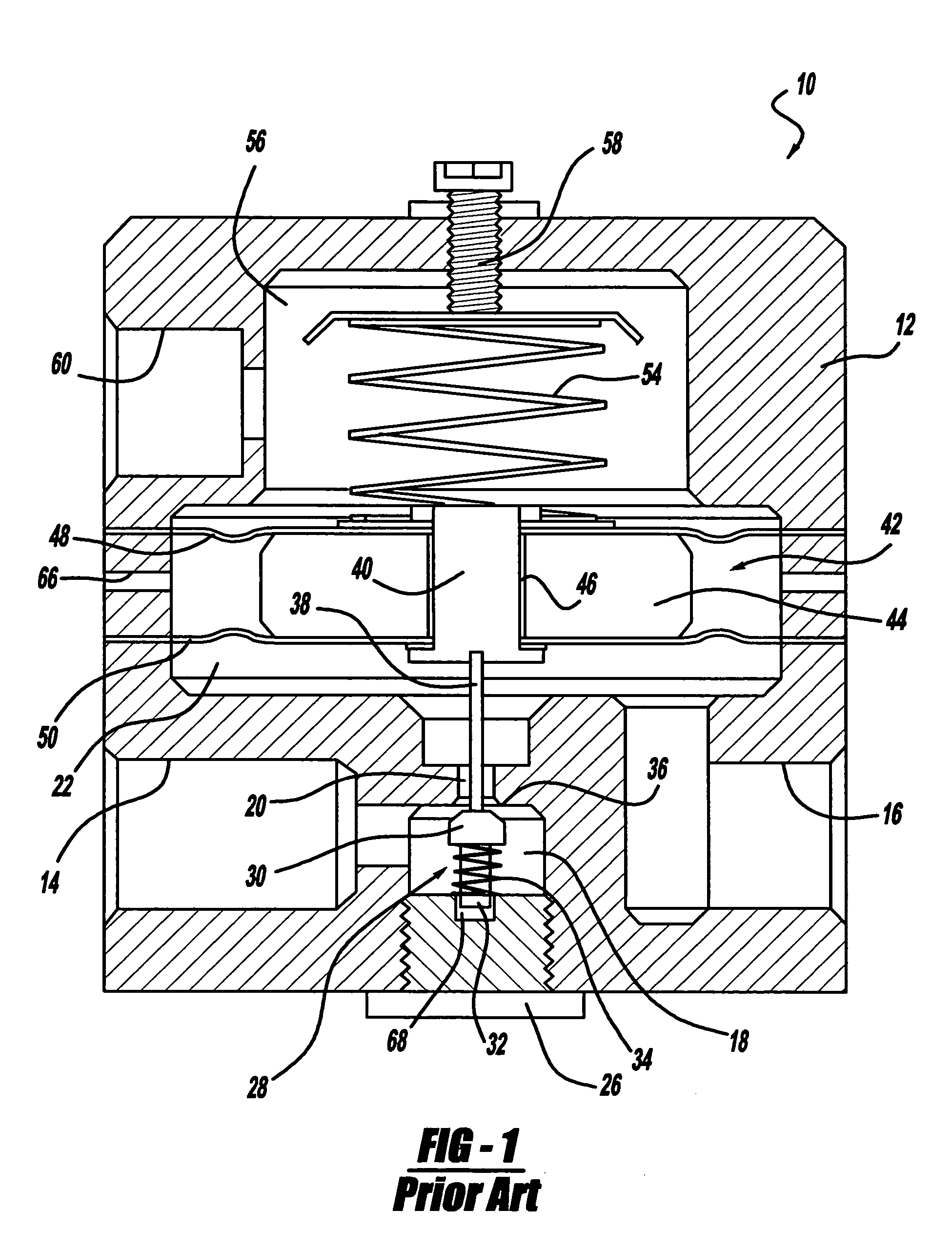
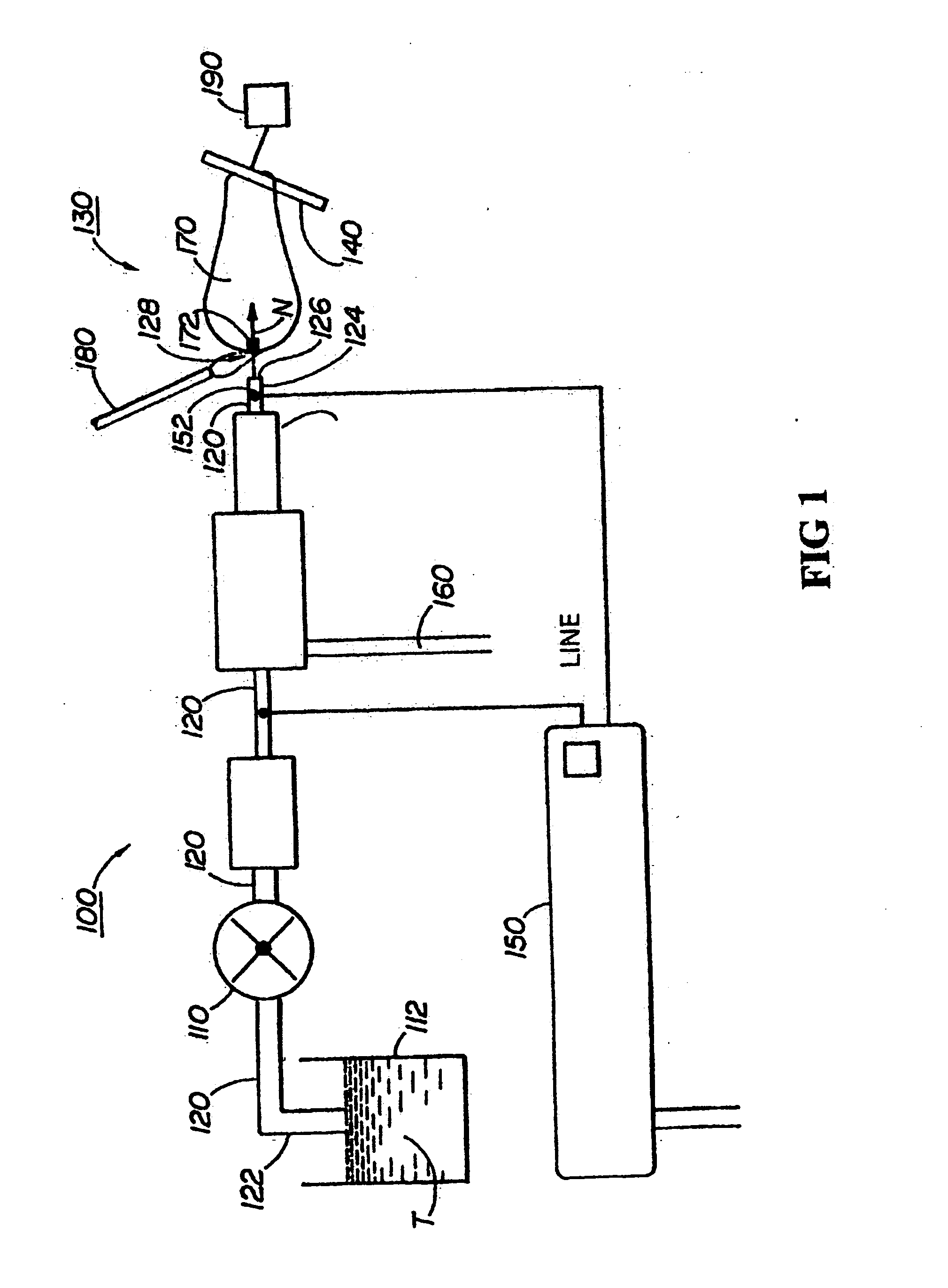
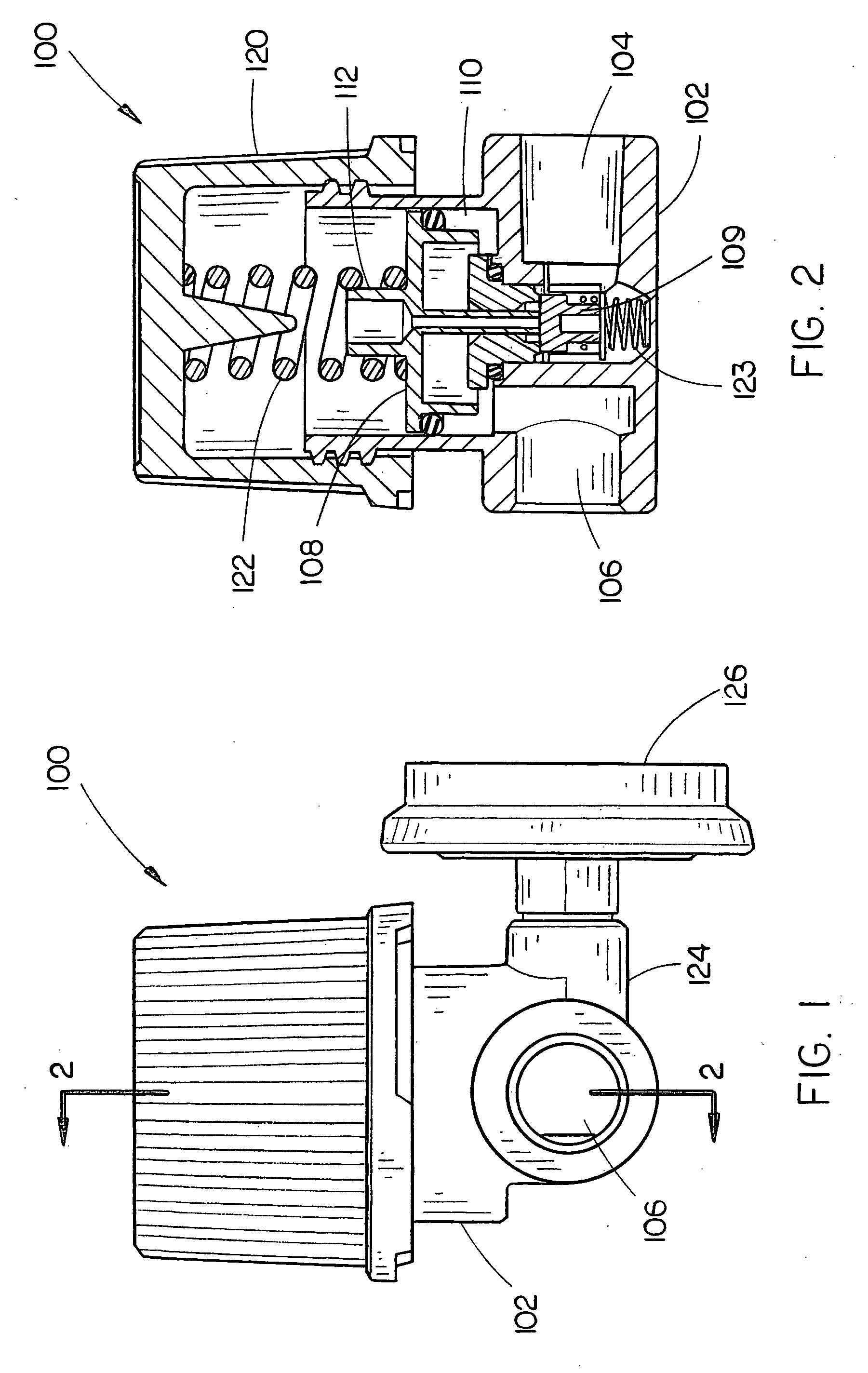
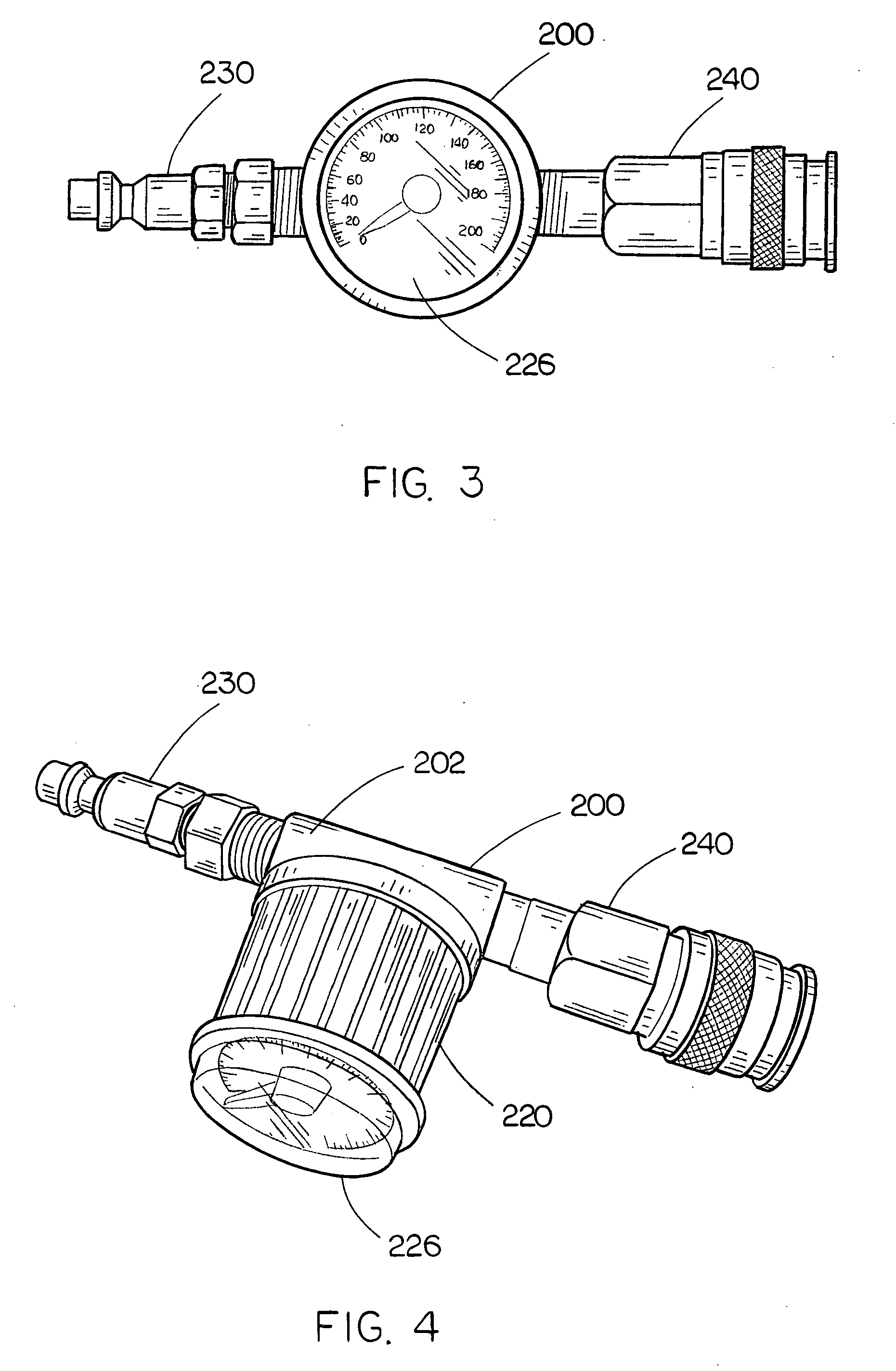
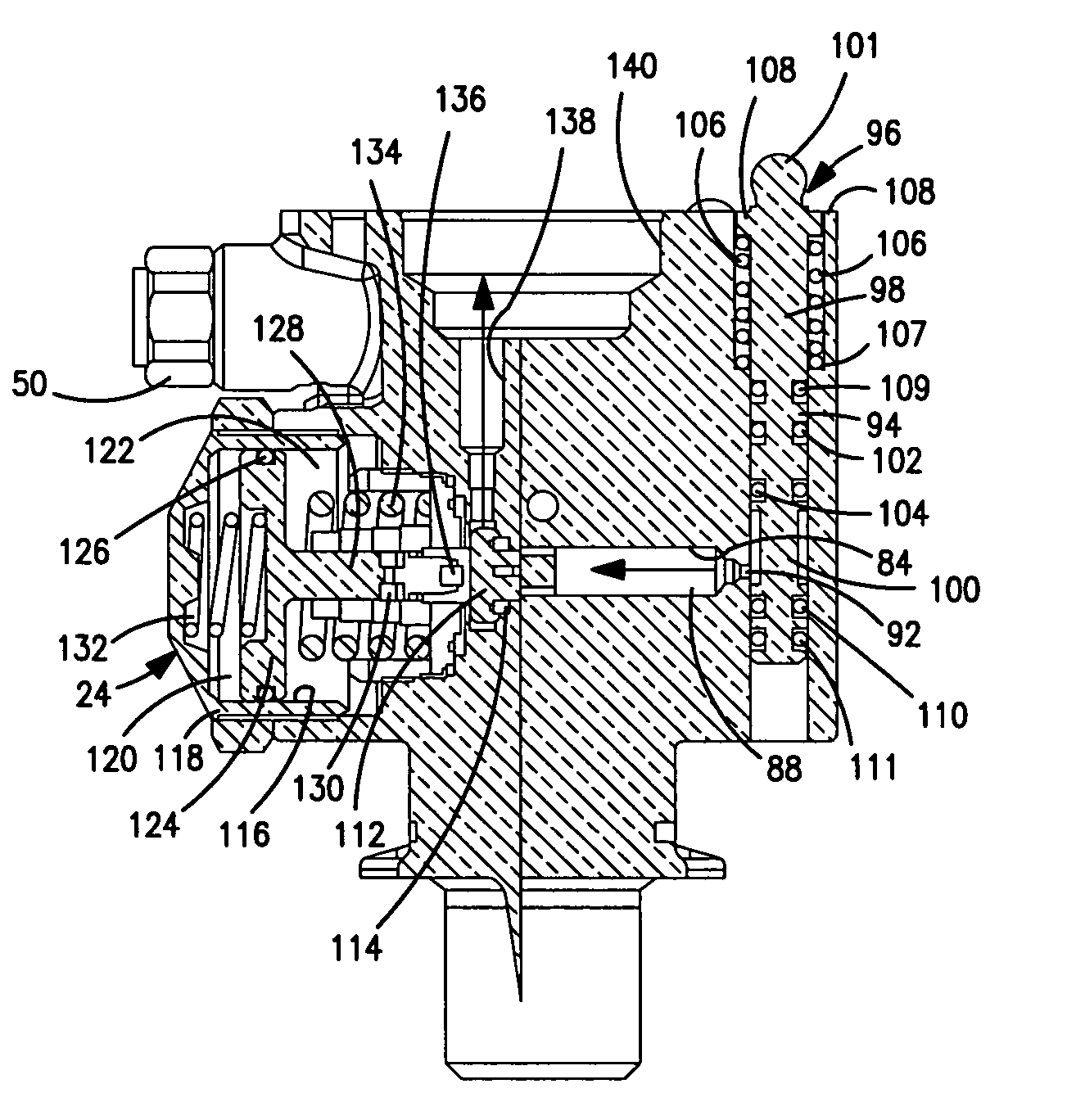
Integrated pressure regulator and pressure gauge
An integrated pressure regulator and pressure gauge employs a pressure gauge in a biasing assembly, e.g. integrated into a knob. The integrated pressure regulator and pressure gauge includes an adapter body; a plunger which forms a seal to retain a regulated pressure and includes a bleed off passageway, a tap into the regulated pressure, and a post including an O-ring seal; a knob threadably connected to the adapter body; a spring compressed between the knob and the plunger; and a pressure gauge connected to the post.
Owner:BLACK & DECKER INC
Pressure regulated solenoid valve having integral mounting structure
InactiveUS20060219302A1Avoid expulsionOperating means/releasing devices for valvesService pipe systemsSolenoid valveEngineering
A regulator valve for managing a fluid in an appliance is provided. The regulator valve comprises a housing having an inlet and an outlet, a filter, a pressure regulator, a solenoid valve, a mounting structure, and a locking tab depending from the mounting structure. The inlet and outlet utilize quick connect adaptors. The pressure regulator maintains the fluid in the housing within a desired pressure range and the solenoid valve alternatively permits and prevents expulsion of the fluid from the outlet. The twist mount is inserted through a twist mount aperture on, e.g., a drinking fountain and rotated until a portion of the twist mount engages with a portion of the drinking fountain and the locking tab rests in a tab aperture on the drinking fountain. Therefore, the regulator valve is secured to the drinking fountain and can clean, regulate, and manage the fluid.
Owner:ROBERTSHAW CONTROLS CO
Method for continuous measurement of dynamic fluid consumption
InactiveUS20060277982A1Faulty measurements based on the thermal expansion of the fluid are reduced or avoidedEngine testingWork measurementContinuous measurementFlow transducer
A method for continuous measurement of the dynamic fluid consumption of a consumer by means of a two-way flow sensor, particularly the measurement of gaseous or liquid fuel, and possibly a conditioning device, whereby the pressure is reduced to a constant exit pressure downstream from the flow sensor. A minimum quantity of fluid is fed through the pressure regulator (8) at any desired time whereby fluid is continuously returned in variable quantities from the region of constant exit pressure to the region between the flow sensor (6) and the pressure regulator (8) to make possible a continuous, accurate and timely highly defined consumption measurement with controlled exit pressure for the fluids be means of an open system, which is able even at highly dynamic consumption changes to maintain pressures in the entire line system and which does not allow the formation of a multiphase flow. The device for to carrying out the method is provided with a pressure control device (8) downstream from the flow sensor (6) and a connecting line with a pump (12) leading from the region behind the pressure control device (8) to the region between the flow sensor (6) and the pressure control device (8).
Owner:AVL LIST GMBH
Fuel supply control apparatus for internal combustion engine and fuel supply control method thereof
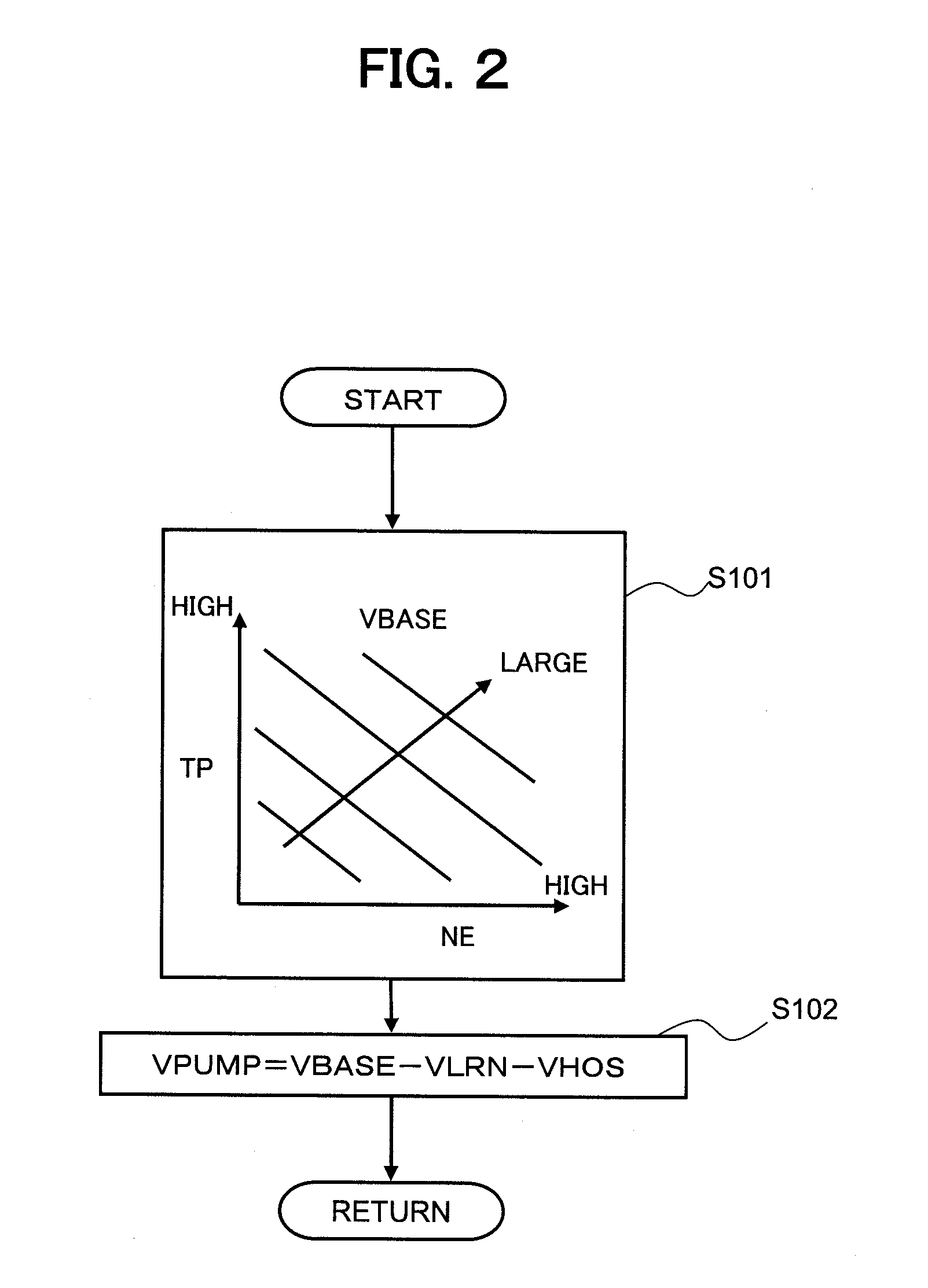
ActiveUS20110238282A1More flow amountImprove accuracyElectrical controlDigital data processing detailsStress regulationFuel supply
The present invention relates to a fuel supply control apparatus and a fuel supply control method for controlling an electric fuel pump, in an internal combustion engine provided with the electric fuel pump for pumping fuel to a fuel injection valve and a pressure regulator for regulating fuel pressure at set pressure. When a learning condition of a drive voltage for the electric fuel pump is established, the drive voltage is temporarily reduced and a change amount ΔAF of an air-fuel ratio at the time is detected. Then, if the change amount ΔAF is within a first threshold ΔAF1, the drive voltage is reduced, whereas, if the change amount ΔAF is greater than a second threshold ΔAF2 which is equal to or greater than the first threshold ΔAF1, the drive voltage is increased.
Owner:HITACHI ASTEMO LTD
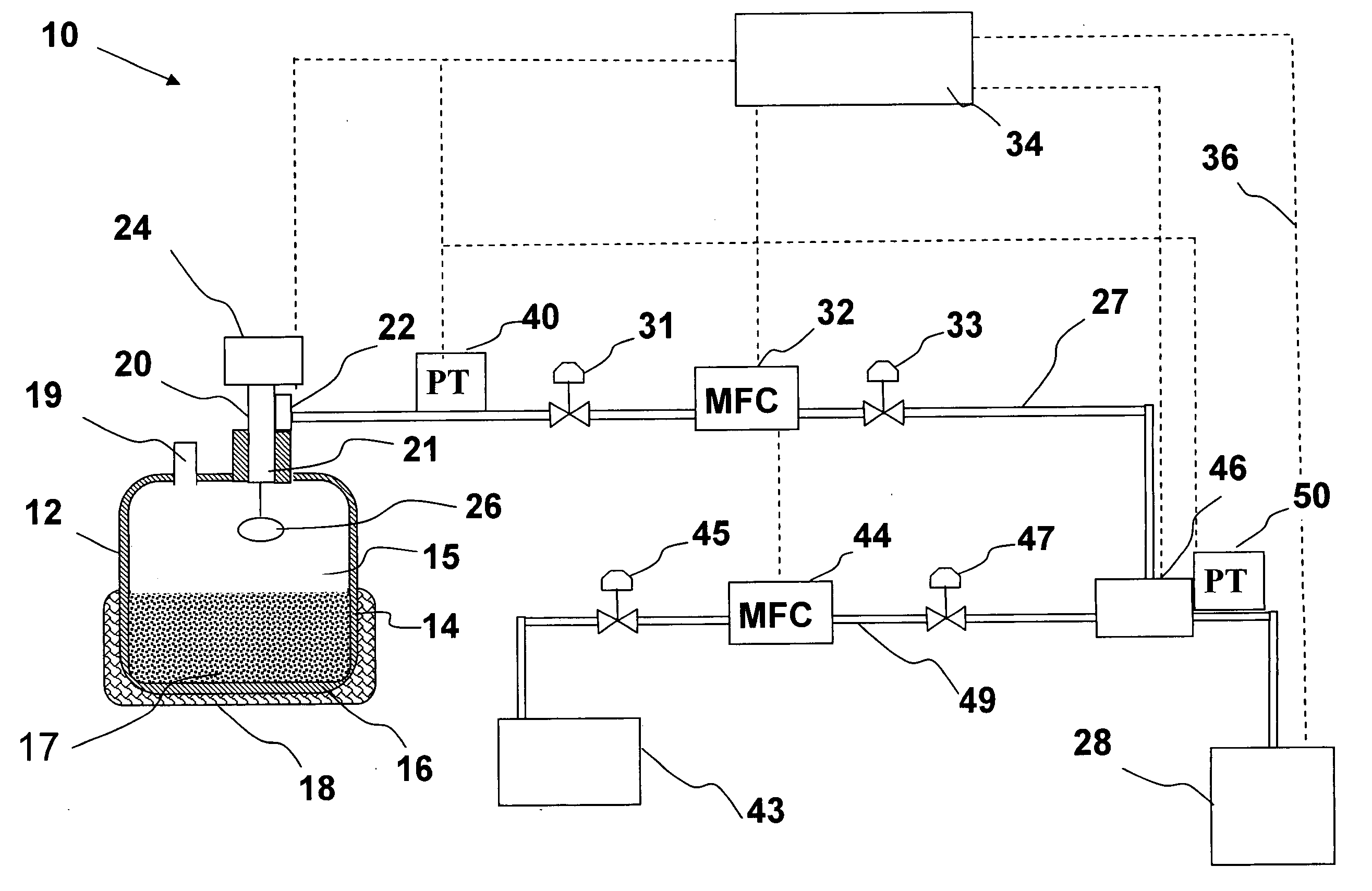
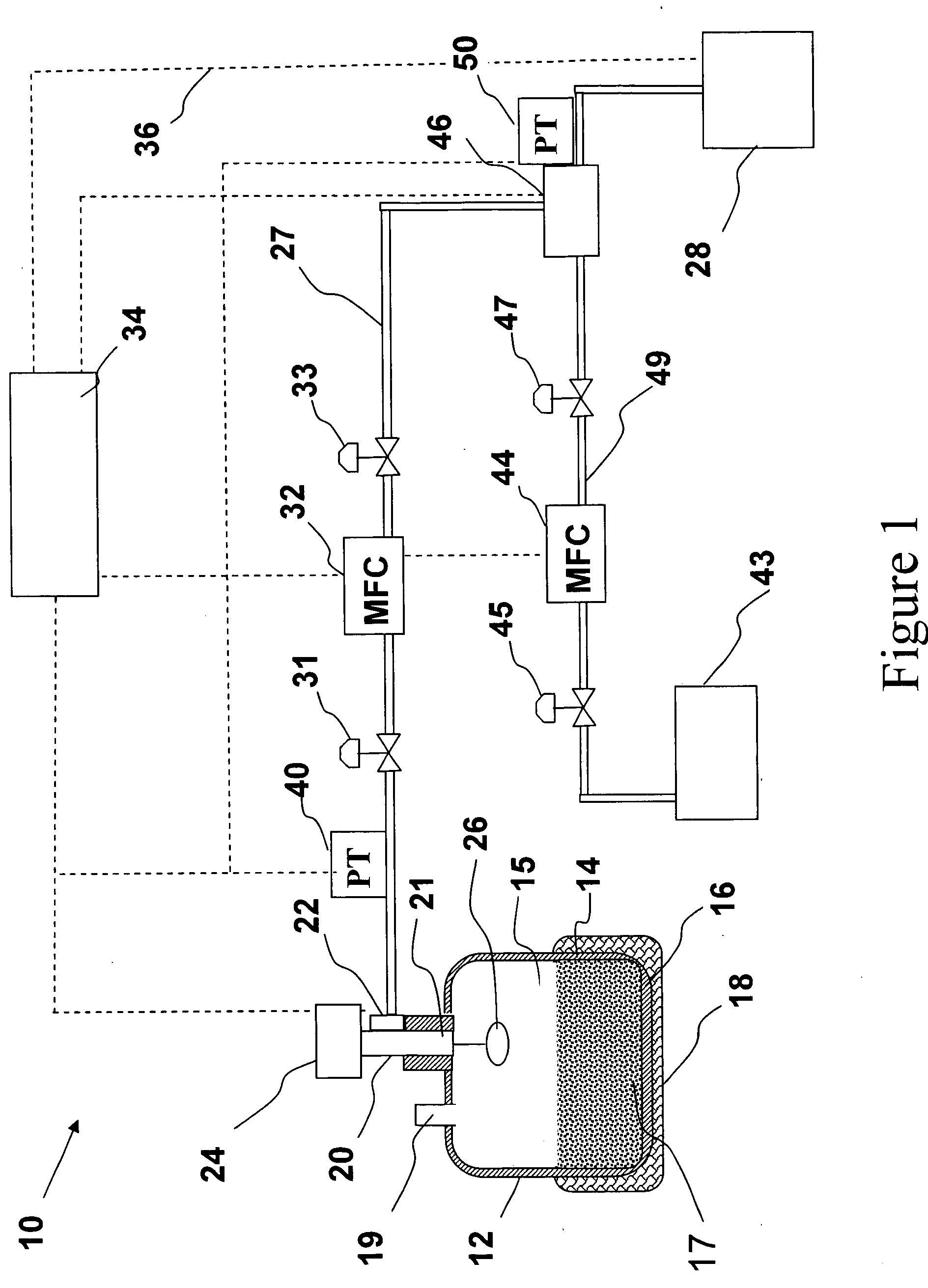
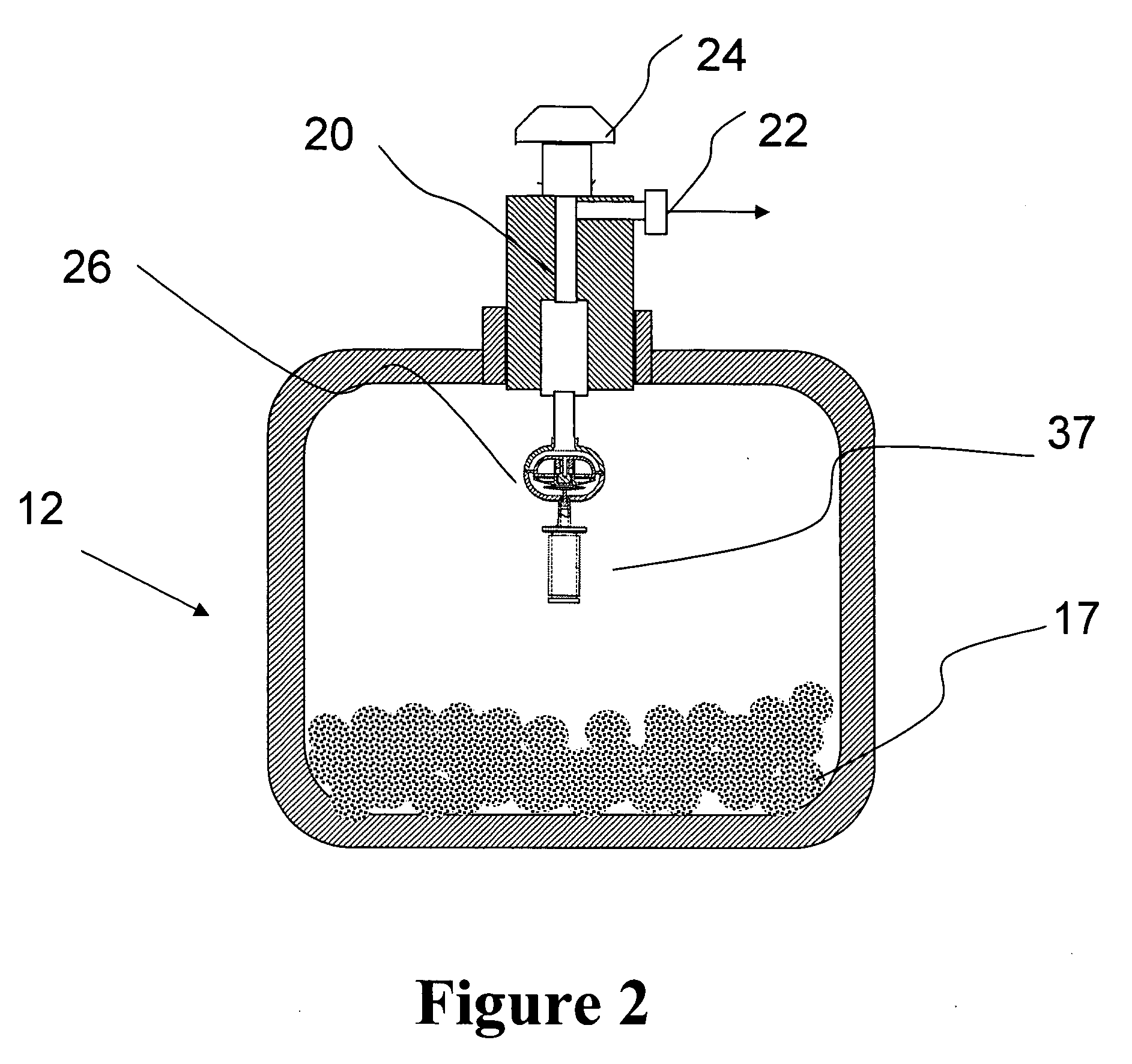
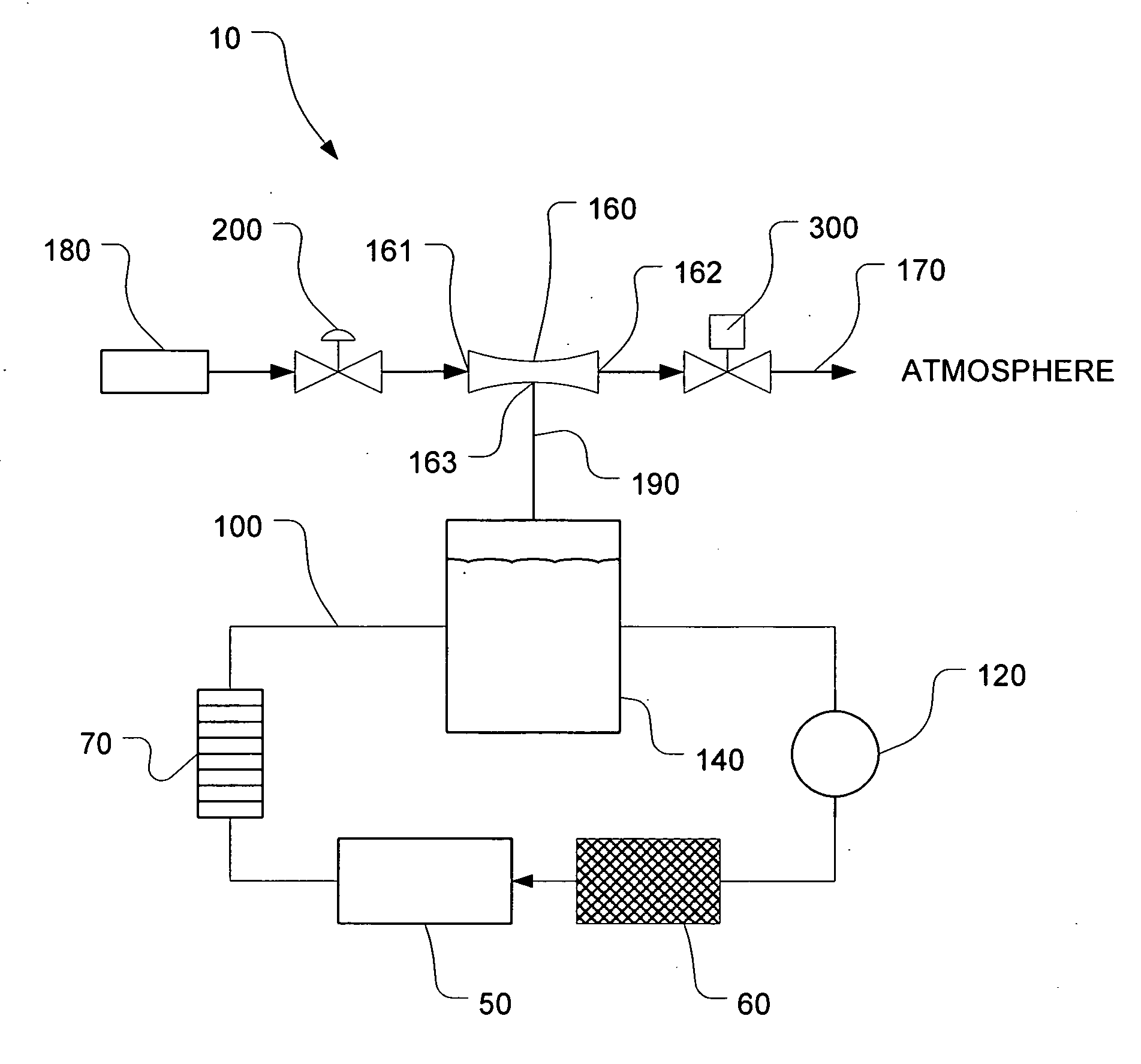
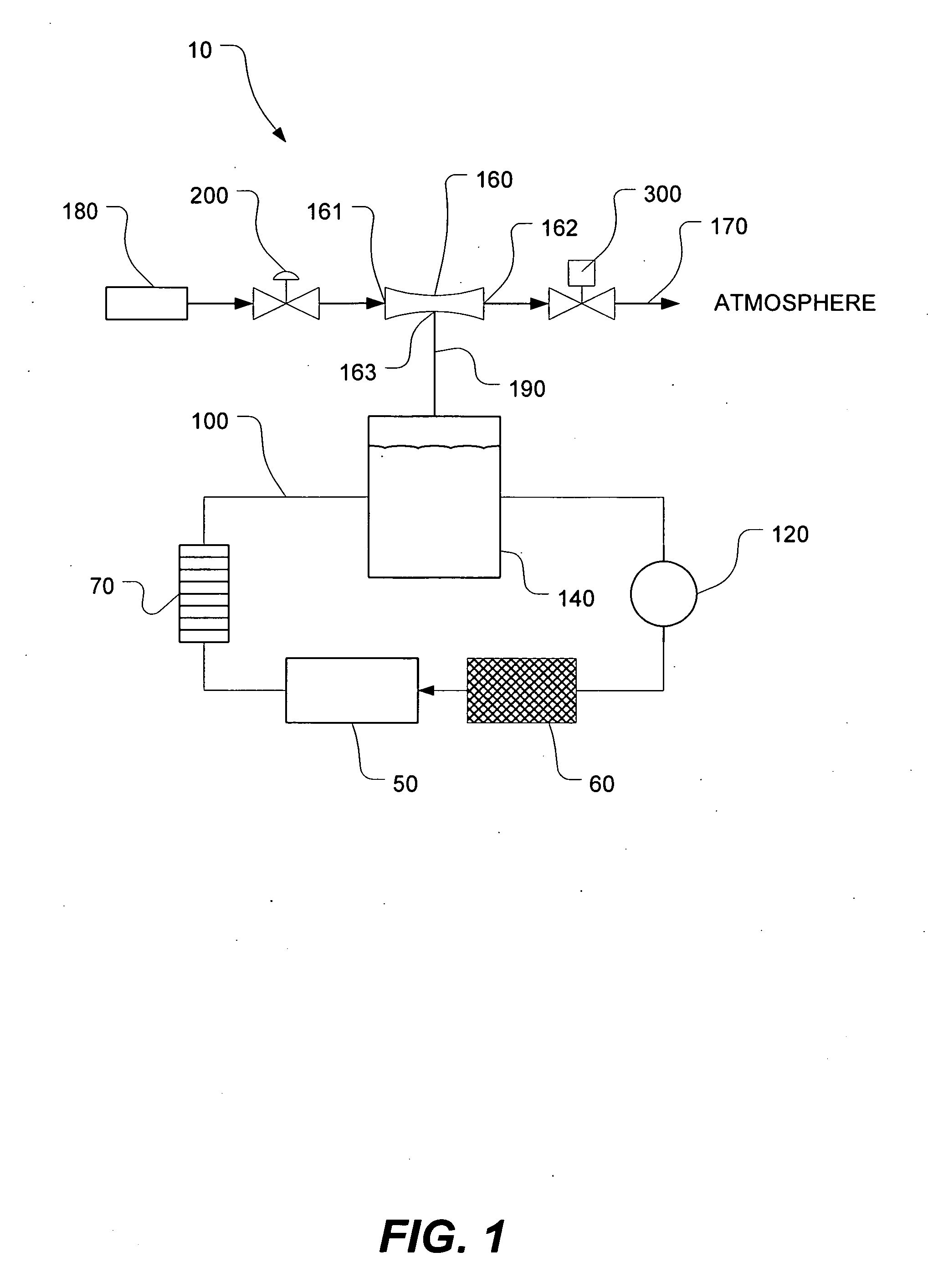
Sub-atmospheric pressure delivery of liquids, solids and low vapor pressure gases
InactiveUS20050181129A1Reduce pressureReducing inherent problemVessel mounting detailsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSource materialStream flow
A delivery system and method for vaporizing and delivery of vaporized solid and liquid precursor materials at sub-atmospheric pressures between a heatable vaporization vessel and a processing tool. The system includes a pressure regulator internally positioned within the vaporization vessel and in fluid communication with a downstream mass flow controller to maintain a consistent flow of vaporized source material. The system further comprises introducing a carrier / diluent gas for diluting the vaporized source material before entry into the processing tool. A venturi is positioned directly upstream of the processing tool and provides for mixing of the carrier gas with the vaporized source material while providing the negative pressure required to open the gas pressure regulator within the vaporization vessel.
Owner:OLANDER W KARL
Flow restricted seat ring for pressure regulators
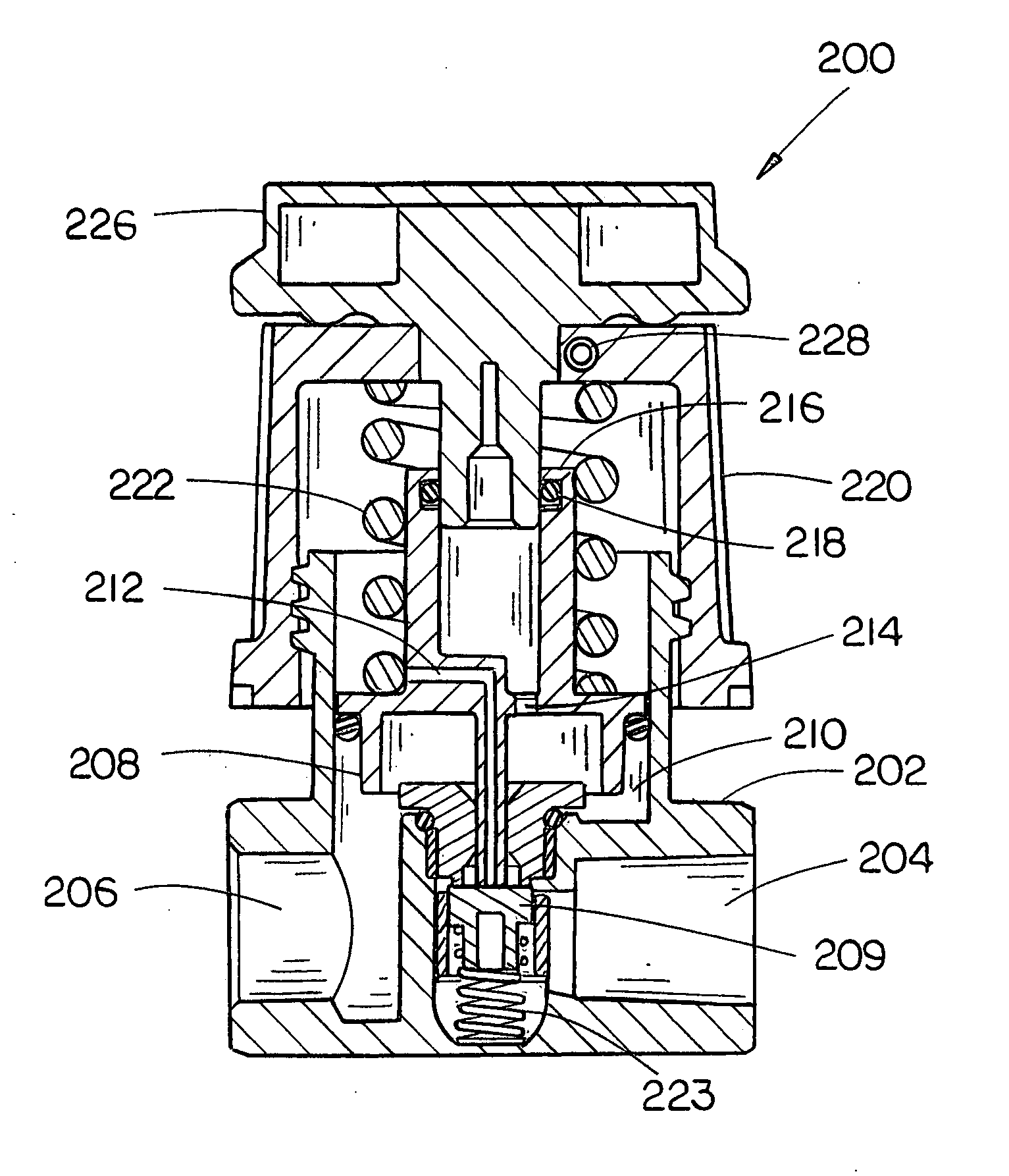
ActiveUS7896028B2Operating means/releasing devices for valvesPressure relieving devices on sealing facesEngineeringActuator
A control device includes a valve body, a seat ring, and an actuator. The valve body defines a flow-path for a fluid. The seat ring is disposed within the flow-path. The actuator is coupled to the valve body and includes a control member. The control member is adapted for displacement relative to the seat ring for regulating a flow of the fluid through the flow-path. The control member includes a scaling disk adapted to sealingly engage the seat ring and close the flow-path. The seat ring includes an orifice disposed within the flow-path such that the seat ring prevents at least a portion of the flow of the fluid from substantially perpendicularly impacting the sealing disk.
Owner:FISHER CONTROLS INT LLC
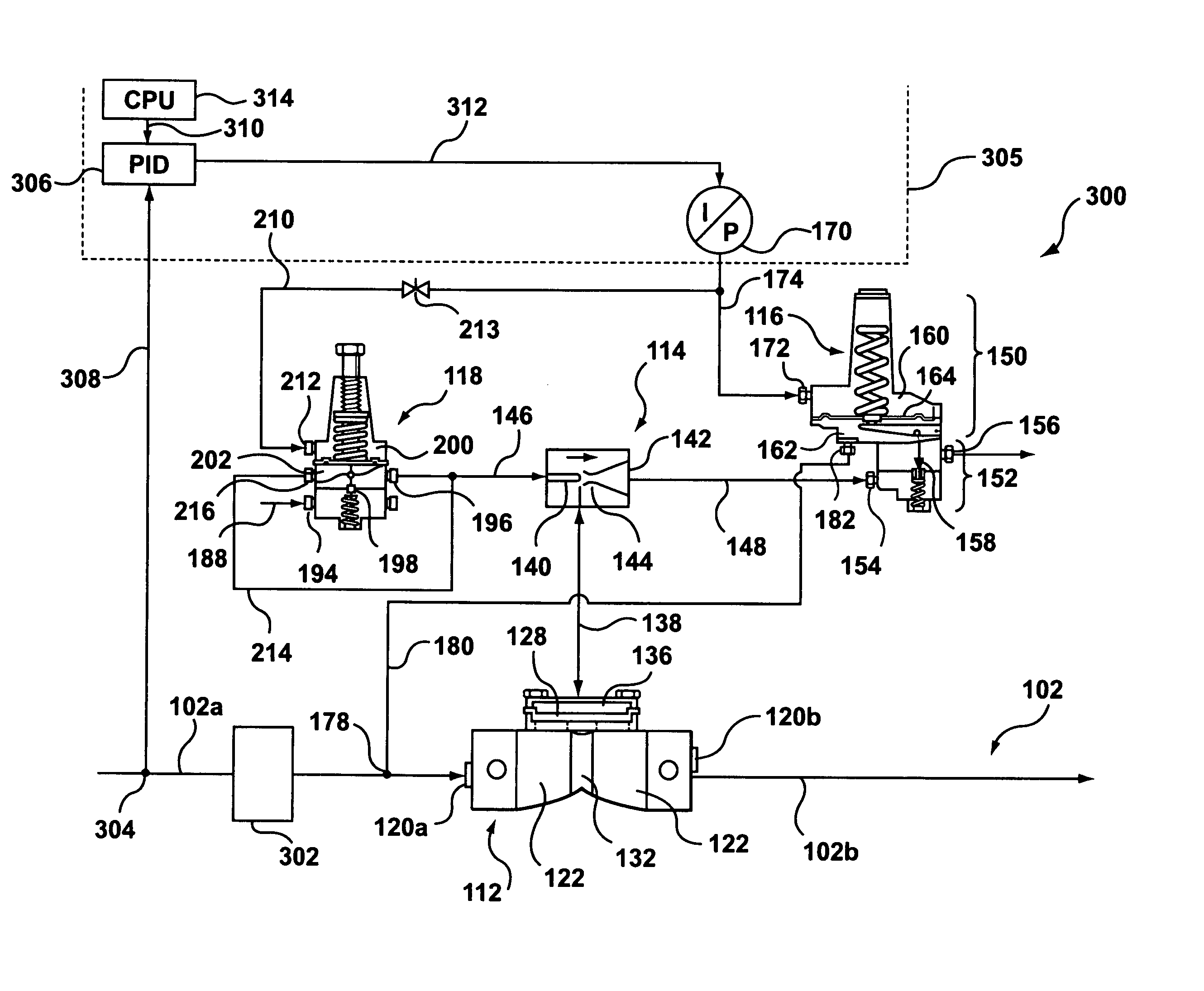
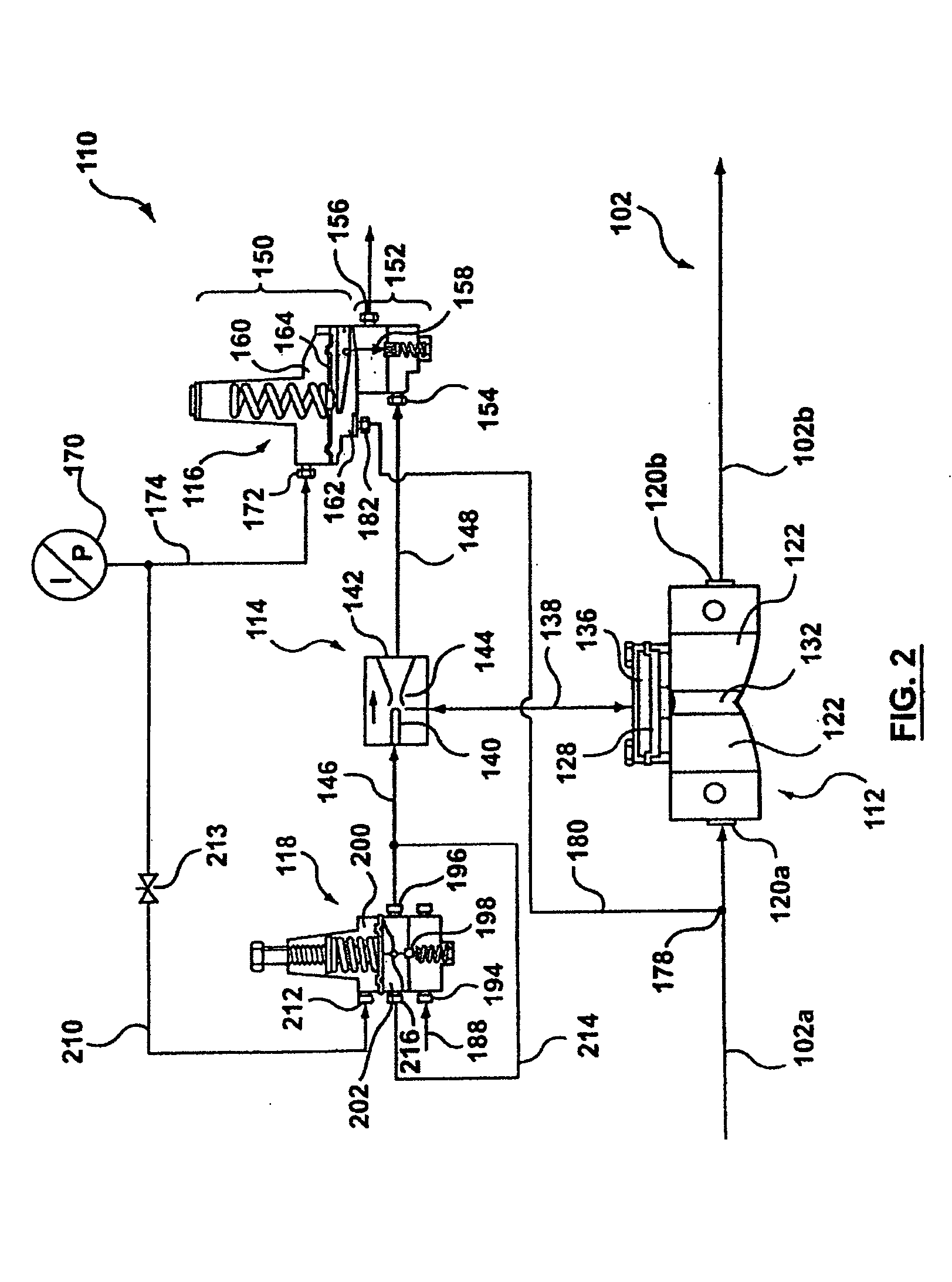
Pressure Regulating Valve
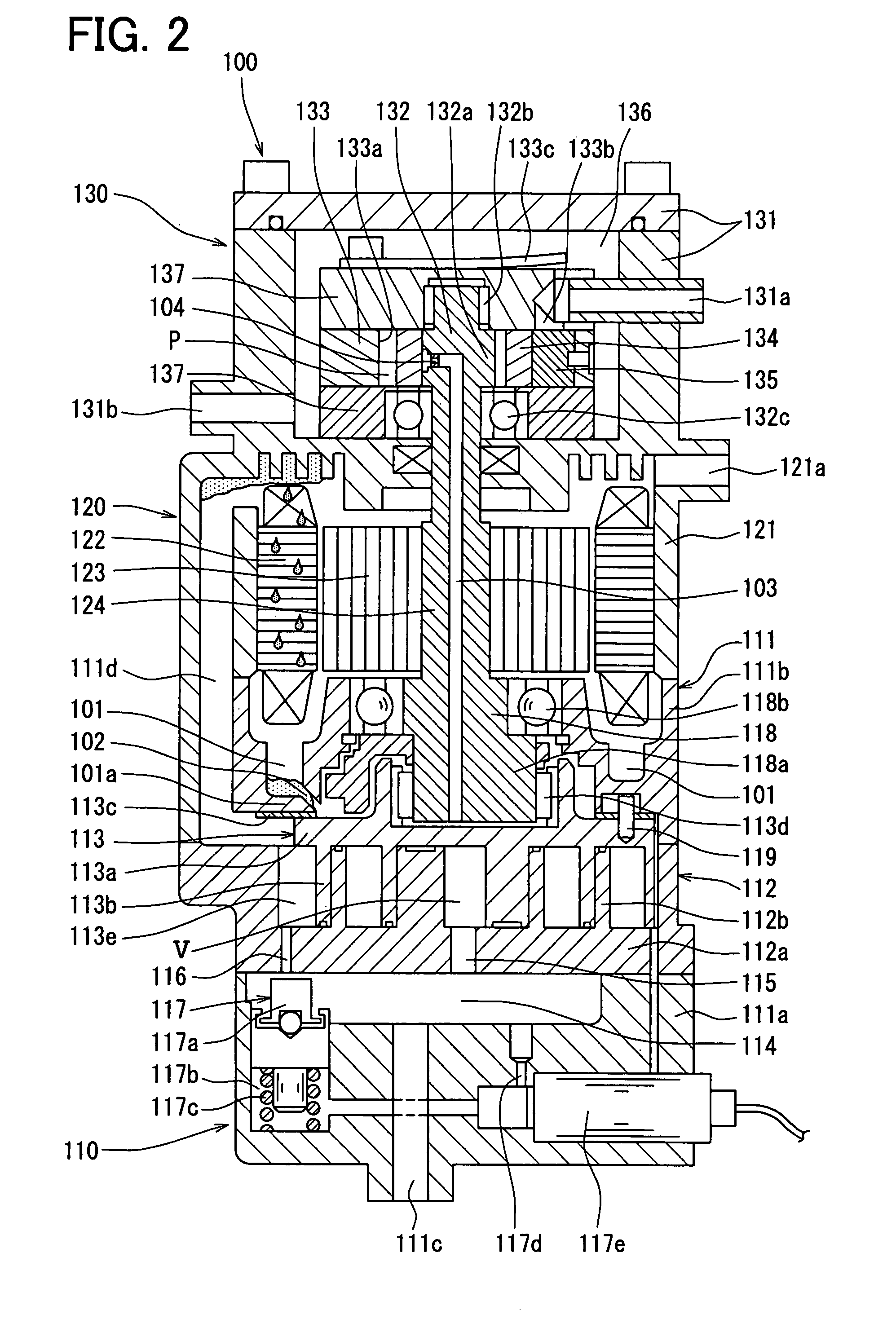
InactiveUS20070289638A1Provide durabilityReduce vibrationOperating means/releasing devices for valvesCheck valvesEngineeringStress regulation
In order to achieve seal durability and bring about a damping action for a piston-type pressure regulating valve, a pressure regulating valve (10) of the present invention is characterized by a valve moving member (11, 14) moving in such a manner as to cause communication or block communication between a primary chamber (17) and a secondary chamber (19) within a case (21, 26), wherein a plurality of central members (20, 25) are arranged between the case and the valve moving member and the plurality of central members are taken to be different materials. It is then possible to bring about both a damping action and seal durability using the central members by providing central members of different materials.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Method for operating a fuel system
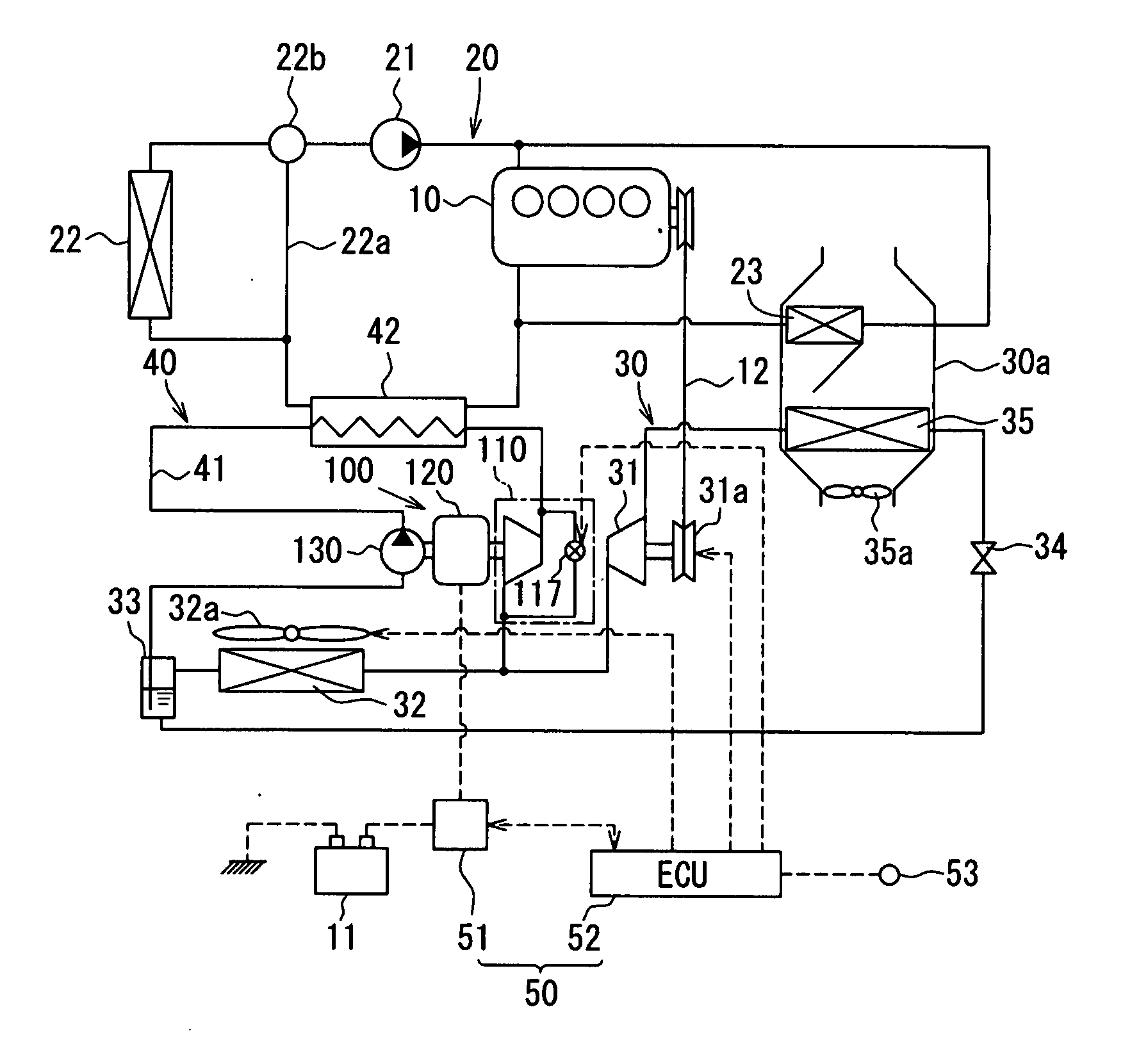
InactiveUS7991538B2Analogue computers for vehiclesElectrical controlCombustion chamberInternal combustion engine
In a fuel system of an internal combustion engine, the fuel quantity injected into a combustion chamber is a function of an activation period, during which a fuel injection device is activated. A pressure sensor detects the pressure in the fuel rail and provides a signal. The pressure in the fuel rail may be regulated to a setpoint pressure using a setting unit and employing the signal provided by the pressure sensor. The following method is provided for testing the fuel system:(a) establishing a test fuel quantity to be injected;(b) operating the internal combustion engine using a first setpoint pressure and a first activation period corresponding thereto and to the test fuel quantity to be injected;(c) detecting a speed- or torque-dependent variable characterizing the operating state;(d) operating the internal combustion engine using a second setpoint pressure and a second activation period corresponding thereto and to the test fuel quantity to be injected;(e) detecting a speed- or torque-dependent variable characterizing the operating state;(f) implementing an action if the variables detected in (c) and (e) differ by more than a limit value.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
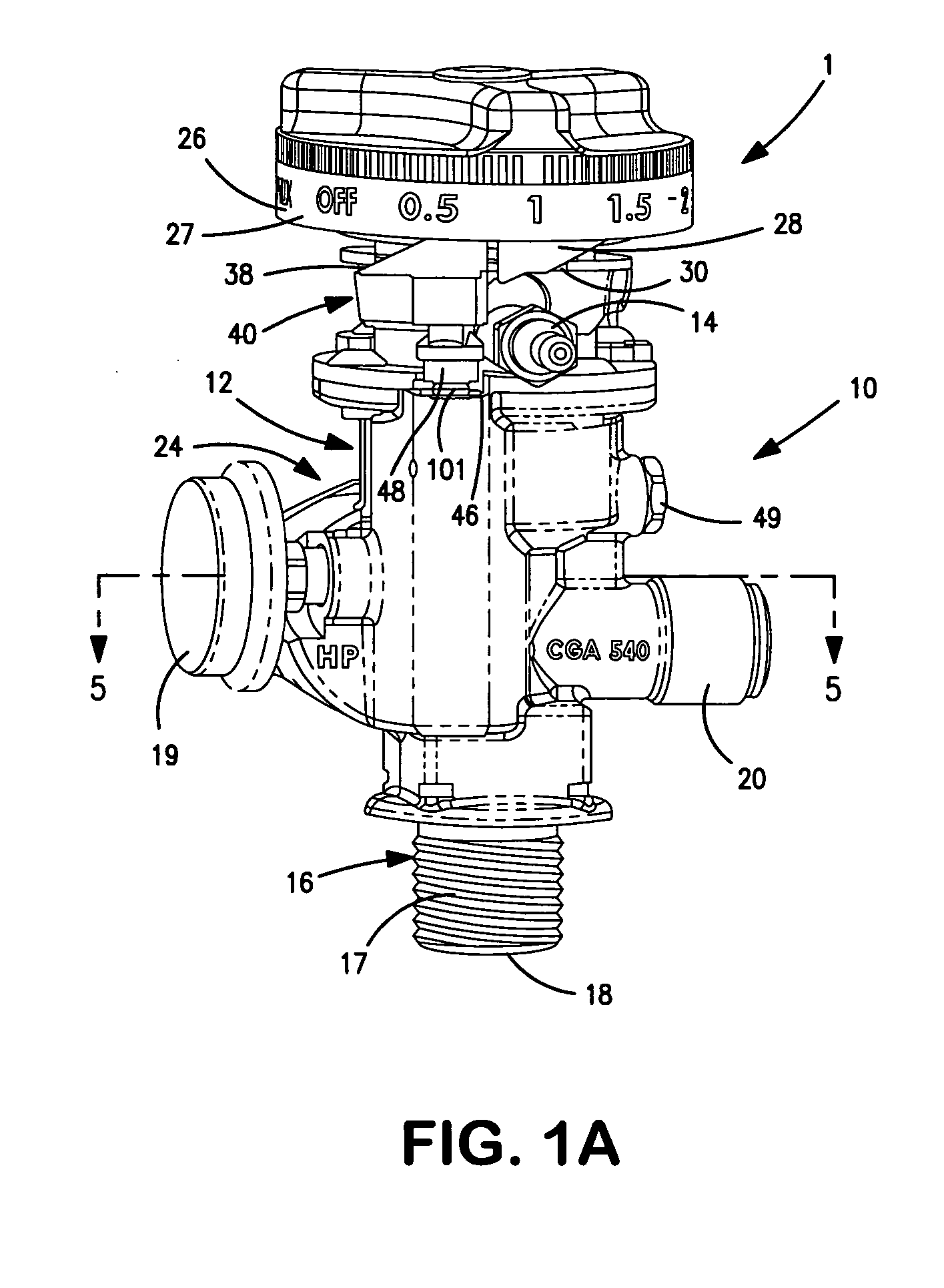
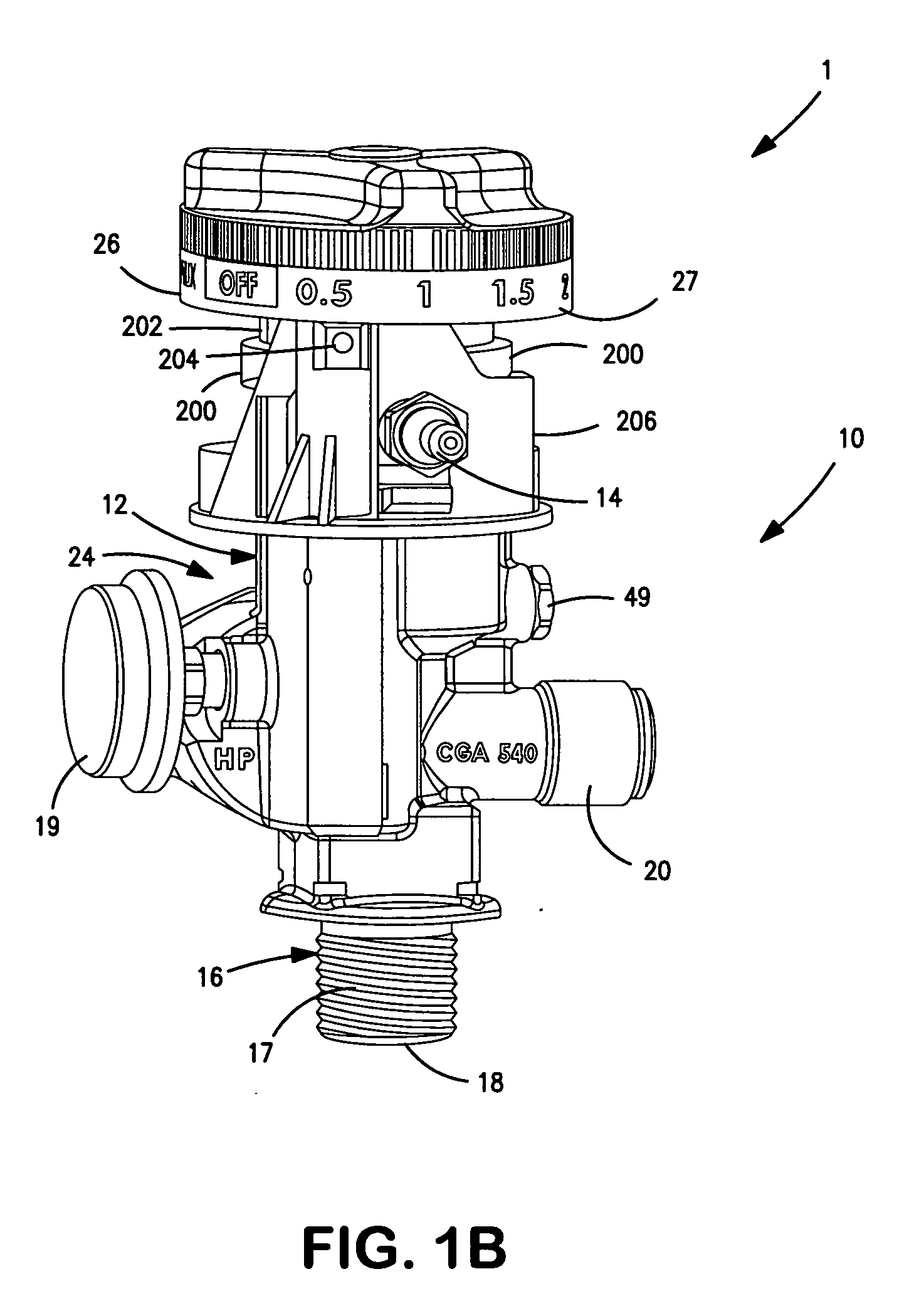
Gas cyclinder dispensing valve
ActiveUS20070062585A1Easy to operateFlow adjustableContainer filling methodsEqualizing valvesIsolation valveGas cylinder
A gas cylinder dispensing valve having an internal flow path provided with a pressure regulator. An isolation valve is provided within the flow path between the pressure regulator and a gas inlet of the valve and a flow control valve is provided within the flow path between the pressure regulator and a gas outlet to discharge the gas. Both isolation valve and the flow control valve can be manipulated by a single control knob which when set in an off position closes the isolation valve. The control knob can be rotated from the off position to select discrete, calibrated flow rates or an auxiliary position in which gas may be dispensed at a regulated pressure from an auxiliary outlet port.
Owner:PRAXAIR TECH INC
Pressure swing CVI/CVD
InactiveUS7959973B2Increase ratingsReduce in quantityChemical vapor deposition coatingCarbon fibersPorous carbon
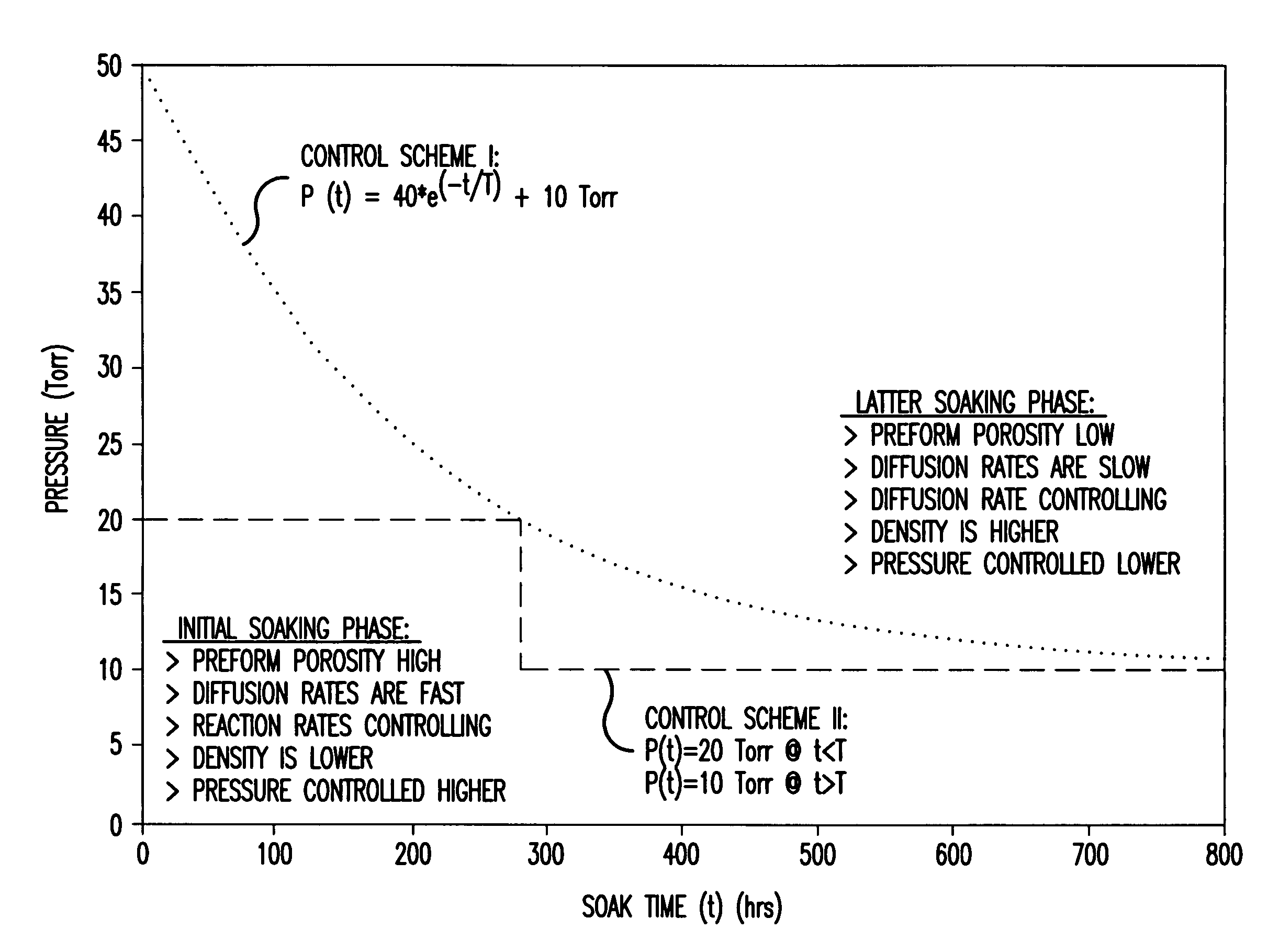
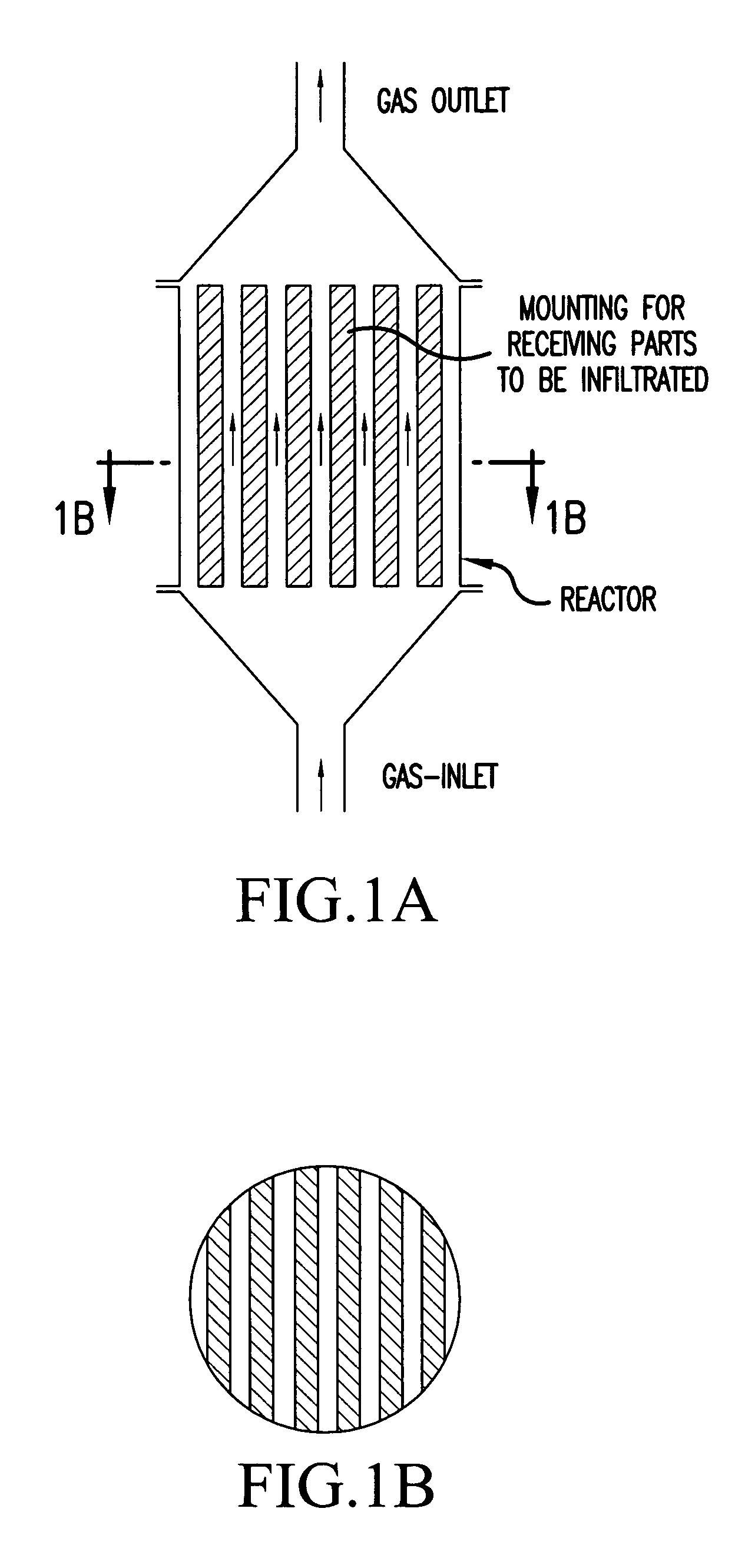
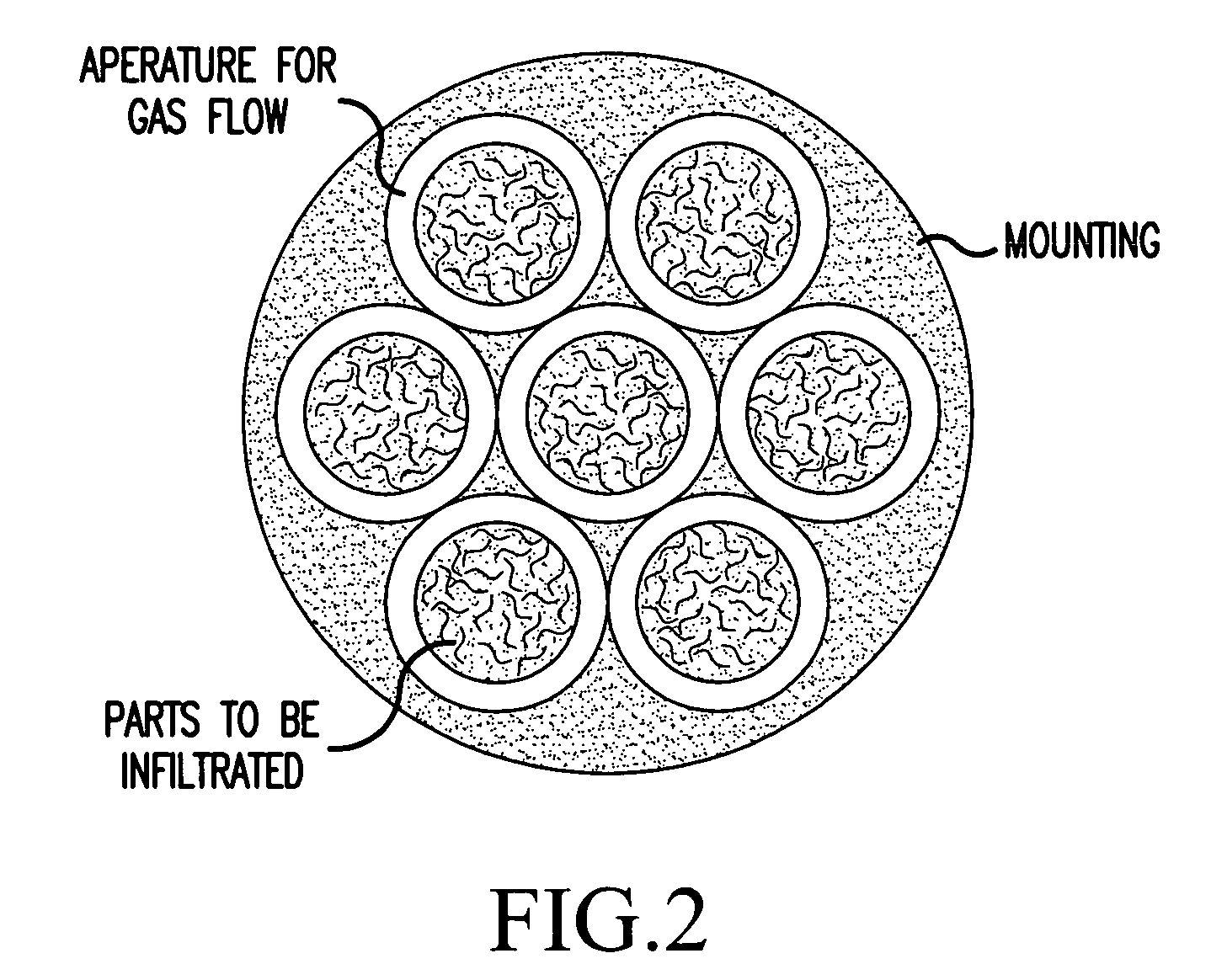
Method of chemical vapor infiltration of a deposable carbon material into a porous carbon fiber preform in order to densify the carbon fiber preform. The method includes the steps of: situating the porous carbon fiber preform in the reaction zone; providing a linear flow of a reactant gas comprising deposable carbon material in the reaction zone at an initial reaction pressure of at most 50 torr to produce deposition of the deposable carbon material into the preform; and adjusting the pressure of the gas to reaction pressures lower than said initial reaction pressure while deposable carbon material continues to be deposited into the porous carbon fiber preform. This method enables attainment of a target increased density in a carbon fiber preform much more quickly than known processes. A programmed pressure swing throughout the CVI / CVD run may be set in order to provide a linear increase in density. Alternatively, step changes in pressure during the course of the densification process may be made to enhance the rate of densification. This method reduces the number of cycles and the required intermediate machining steps necessary to densify preforms.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Pneumatic circuit for tire testing device, tire testing device, and tire testing method
ActiveUS20120085158A1Inspection is accurateLow costCheck valvesTyre measurementsPneumatic circuitEngineering
A pneumatic circuit whereby small amounts of variations in pneumatic pressure in a tire occurring during tire testing can be adjusted in a short time. The pneumatic circuit includes an air supply source which generates compressed air to be supplied to a tire retained in a tire testing device; a pressure regulating valve which regulates the pressure of the compressed air generated; a discharge / supply valve provided downstream of the pressure regulating valve and by which compressed air is supplied to, or discharged from, the tire; a pressure detection unit provided downstream of the discharge / supply valve and which detects the tire pressure inside the tire; and a volume adjustment mechanism provided between the pressure regulating valve and the tire and which increases or decreases the volume of compressed air in an airflow path between the tire and the pressure regulating valve, as well as in the tire.
Owner:KOBE STEEL LTD
Electrochemical cell cooling system
InactiveUS20050120731A1Simple and efficient coolingEfficient and cost-effective coolingDomestic cooling apparatusFuel cell auxillariesPositive pressureClosed loop
An electrochemical cell cooling system includes a closed loop for circulating coolant through an electrochemical cell. The loop includes a pump for pumping the coolant from a container through a filter and a heat exchanger. Pressure in the container and loop is selectively adjusted upwardly for a positive pressure condition or downwardly for a negative pressure condition using a pressure-adjusting flow line. The flow line includes a venturi in fluid communication with the container and a shut-off valve downstream of the venturi which is opened to induce depressurization of the loop or closed to cause pressurization. A variable-flow valve upstream of the venturi enables fine adjustment of the pressurization or depressurization. Alternatively, a flow-restricted bypass and a second variable-flow valve can be introduced to facilitate coolant temperature control.
Owner:GREENLIGHT POWER TECH
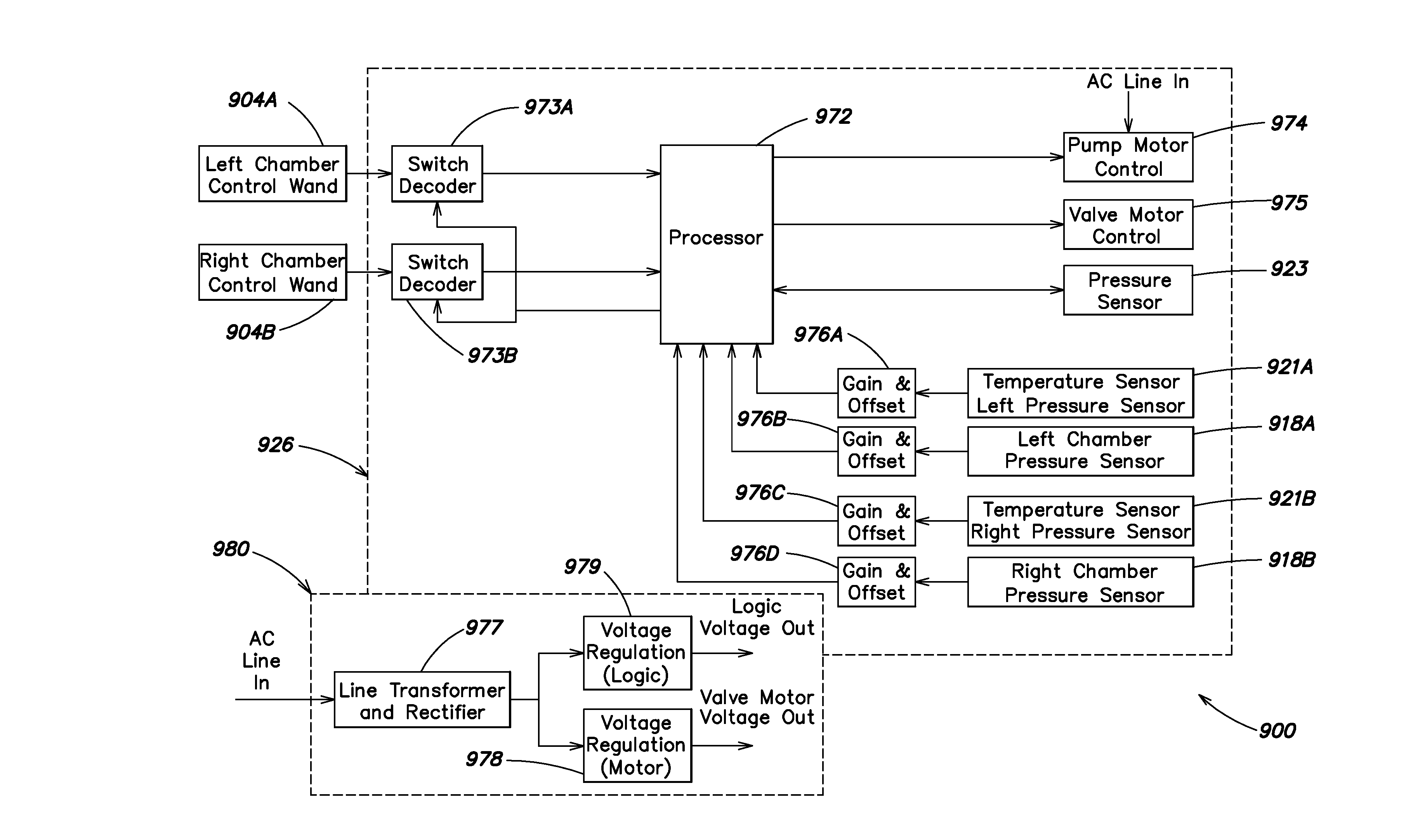
Pressure control system for low pressure high flow operation
InactiveUS20050268968A1Operating means/releasing devices for valvesFluid pressure control with auxillary non-electric powerInspiratorAutomatic control
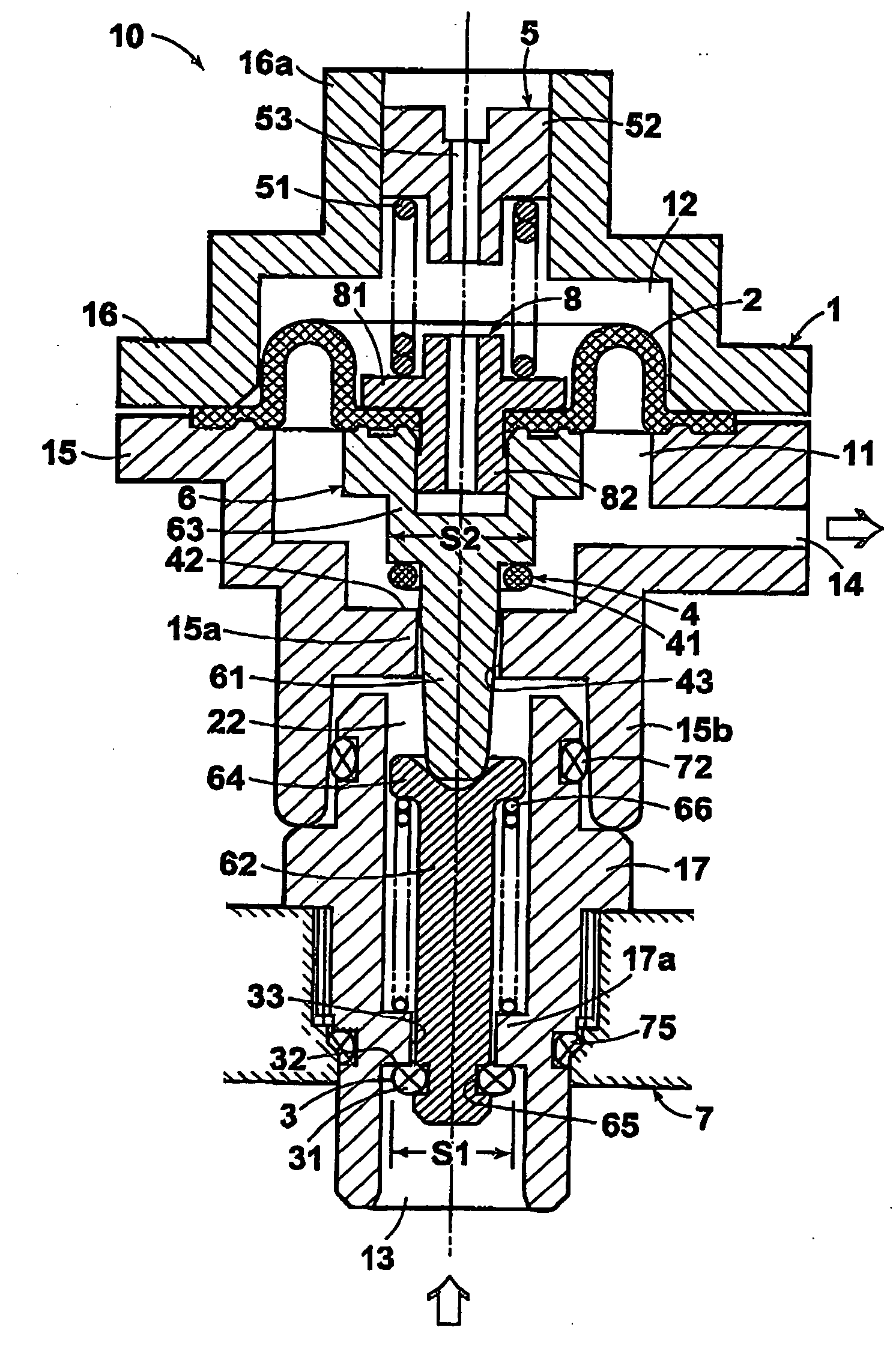
A pressure control system for controlling the pressure of a process fluid stream at a certain location, comprising: a pressure regulator disposed in the process fluid stream, through which the process fluid stream flows; a first pilot controller adapted to sense the pressure of the process fluid at the said location and receive a control pressure from a control source; a second pilot controller adapted to receive same control pressure from the control source and provide added pressure; an inspirator adapted to receive the added pressure from the second pilot controller and generate a differential pressure; wherein the differential pressure is used to control the pressure of the process fluid stream within the pressure regulator. The pressure regulator comprises a first chamber and a second chamber therein separated by a flexible element and a divider is disposed in the first chamber and operative to abut against the flexible element to divide the first chamber into separate spaces. Preferably, the pressure regulator is disposed such that the flexible element extends substantially in vertical direction and the divider extends substantially in horizontal direction. The pressure control system further comprises an automatic control system including an electronic proportional-integral-derivative controller adapted to control the process fluid pressure based on pressure measurements received from a pressure transducer.
Owner:HYDROGENICS CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com