Patents
Literature
931results about "Pressure relieving devices on sealing faces" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
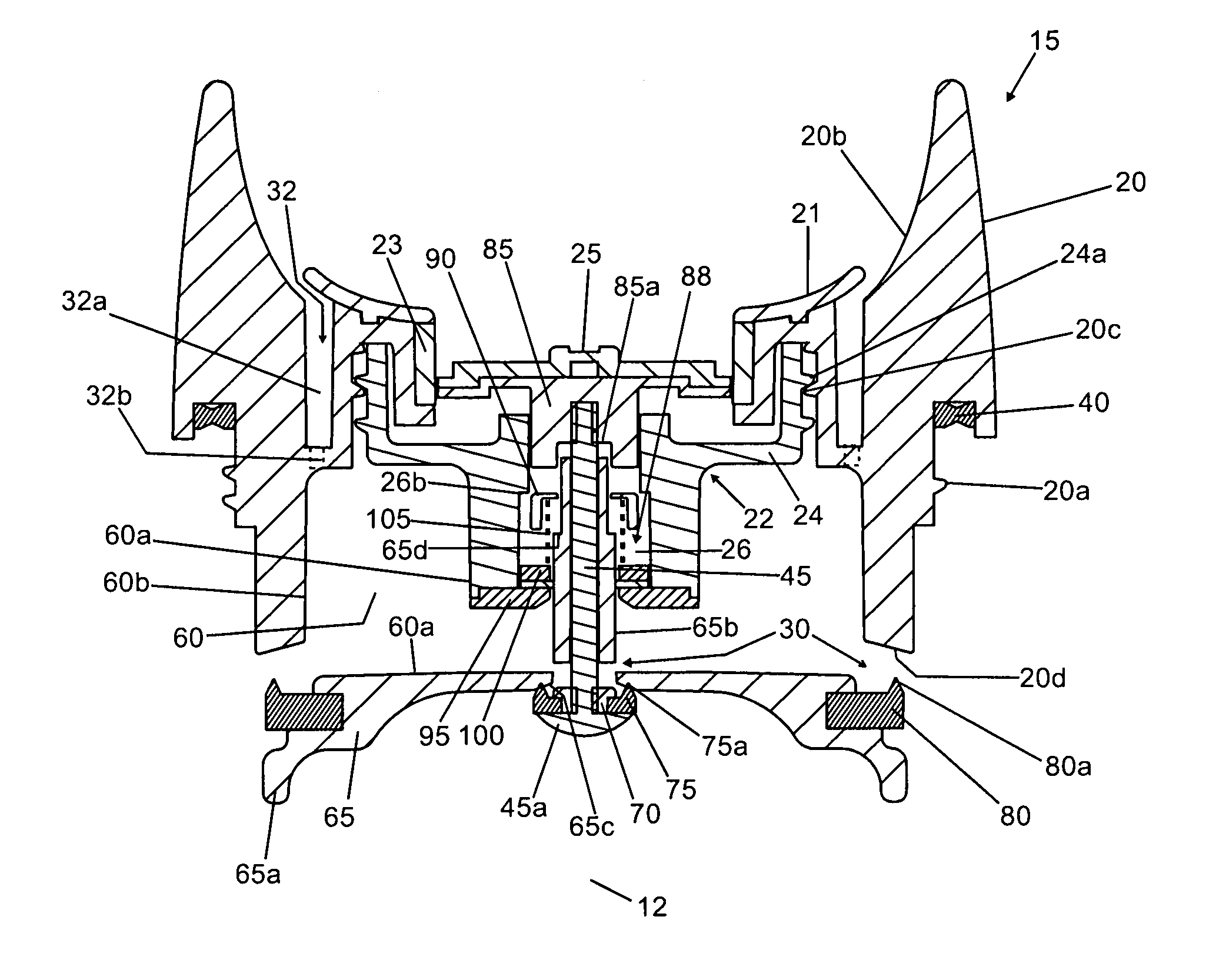
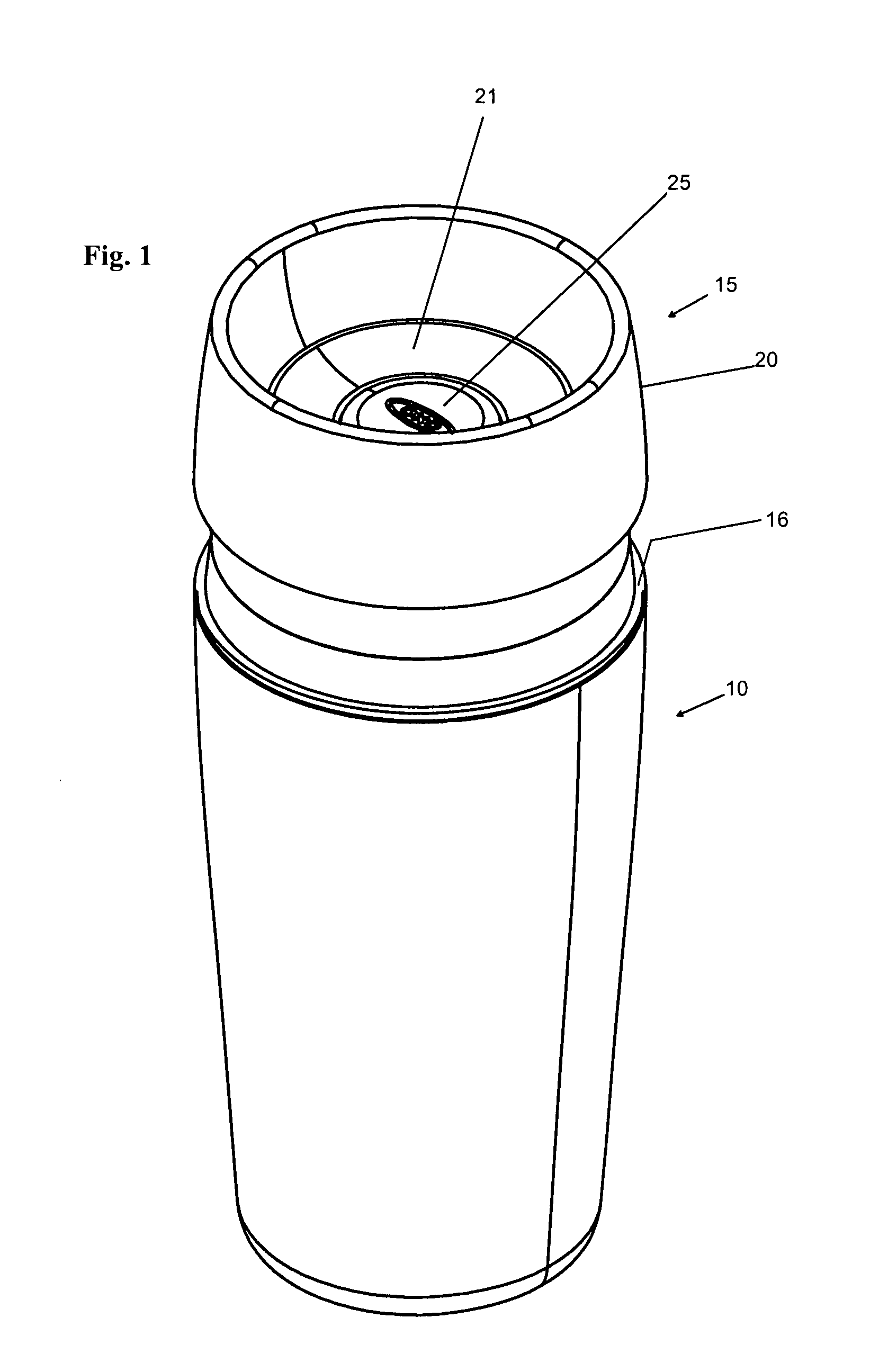
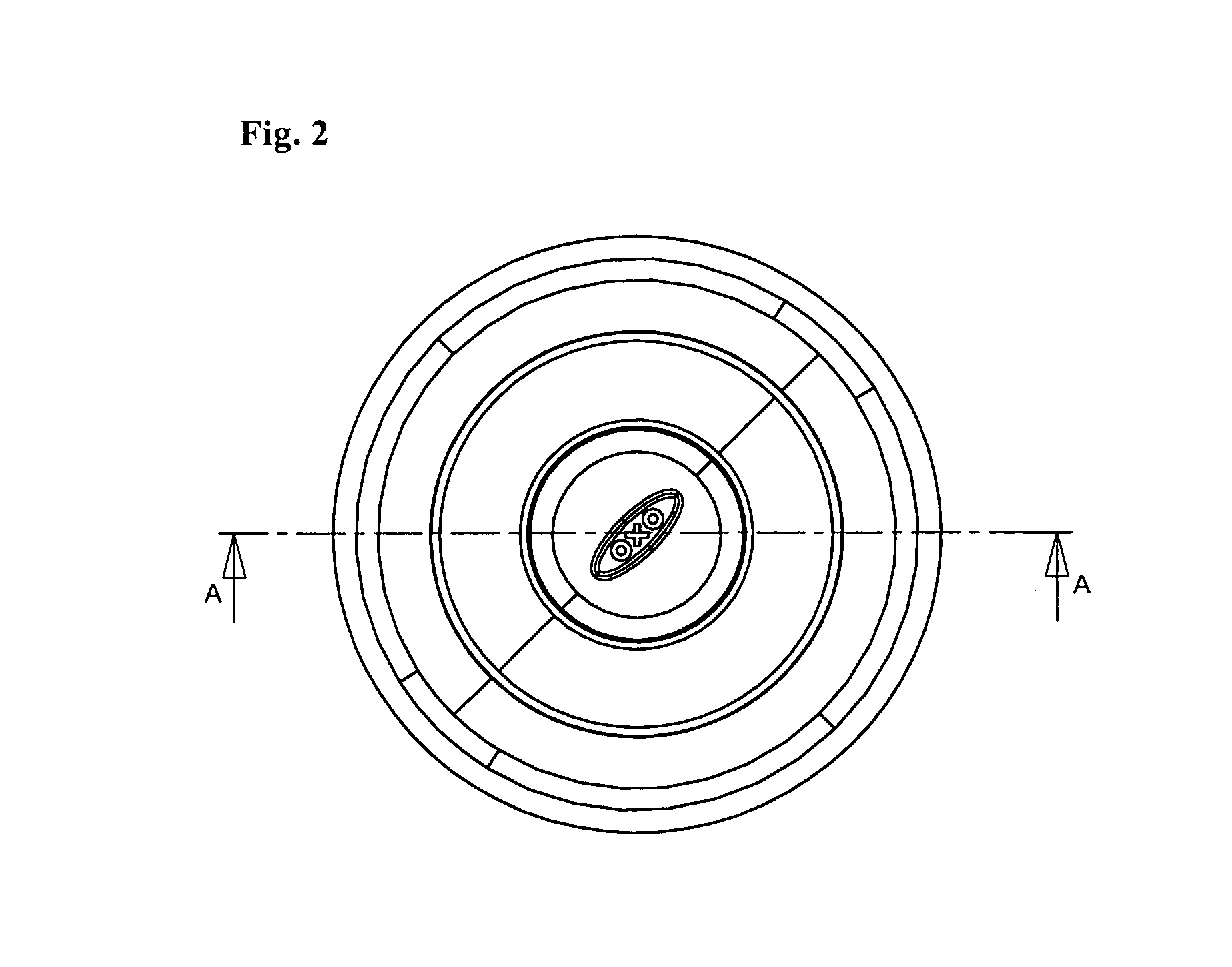
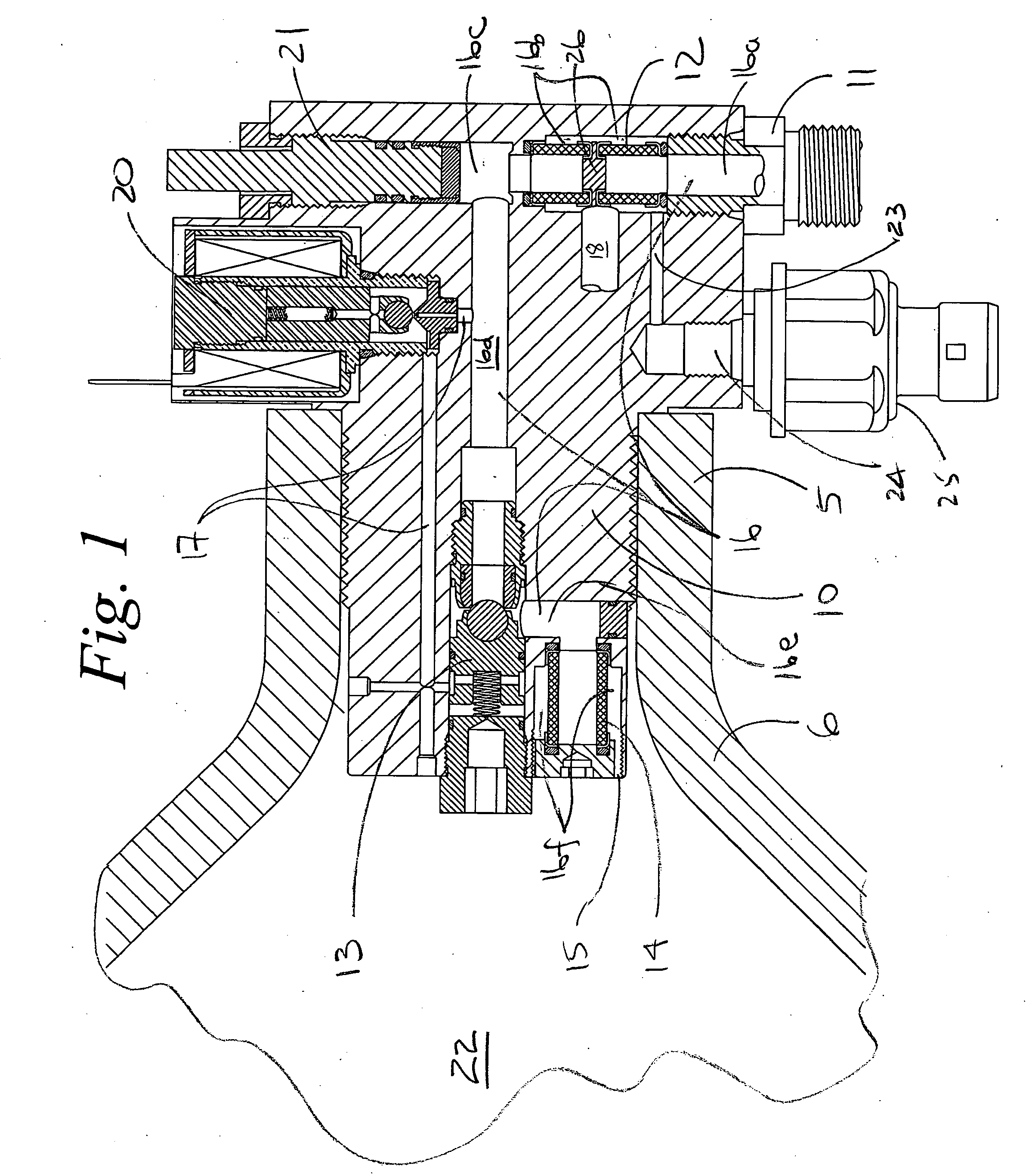
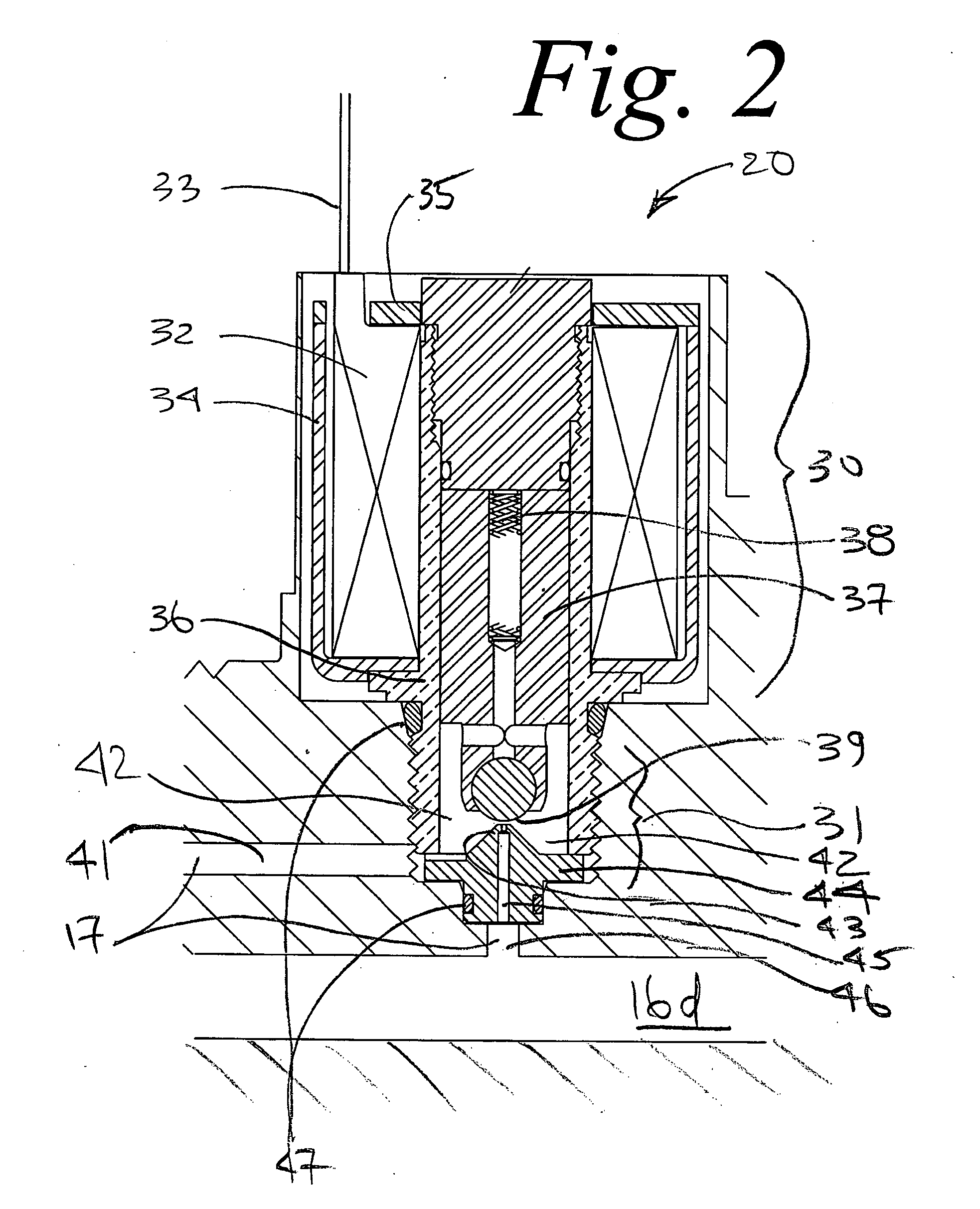
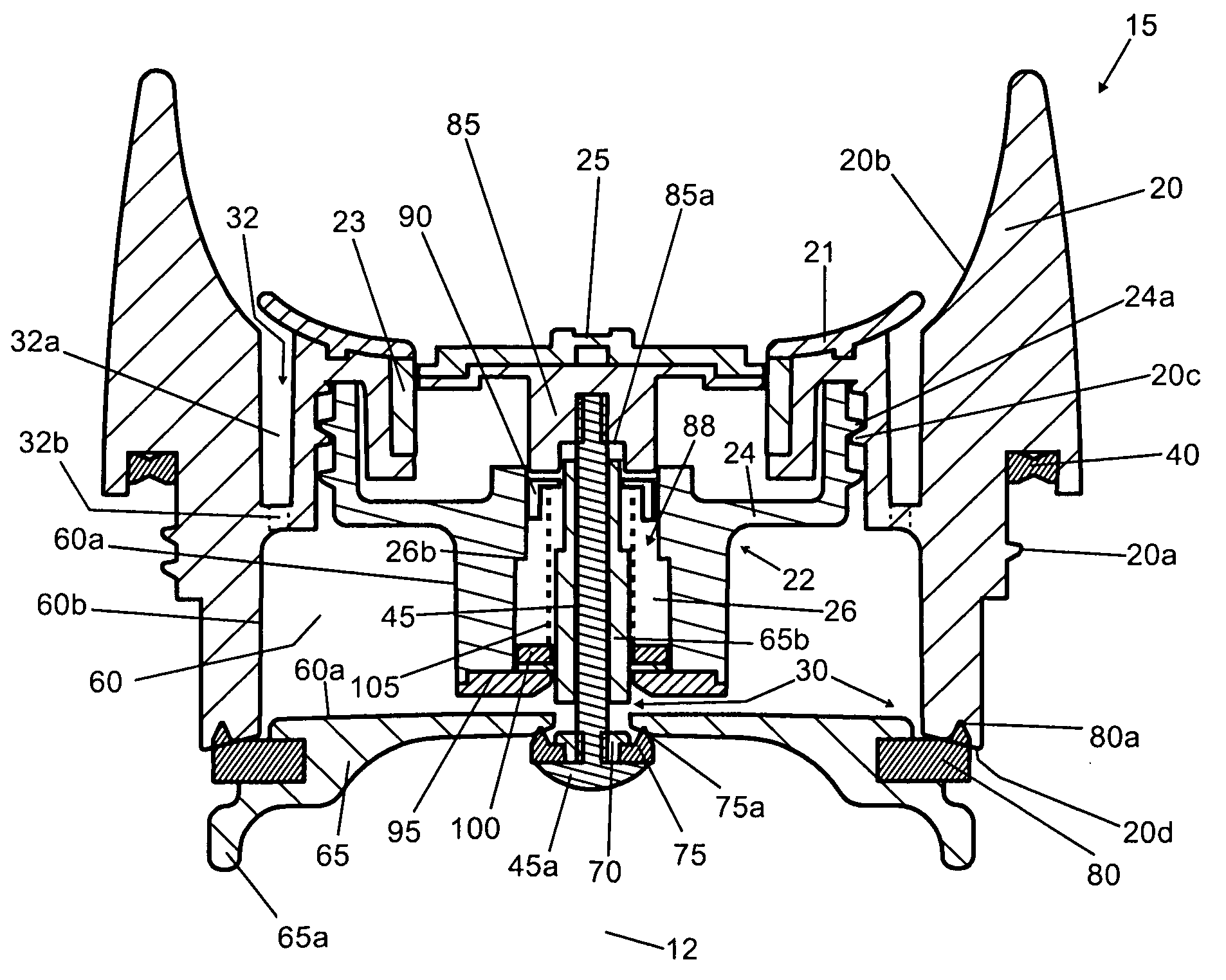
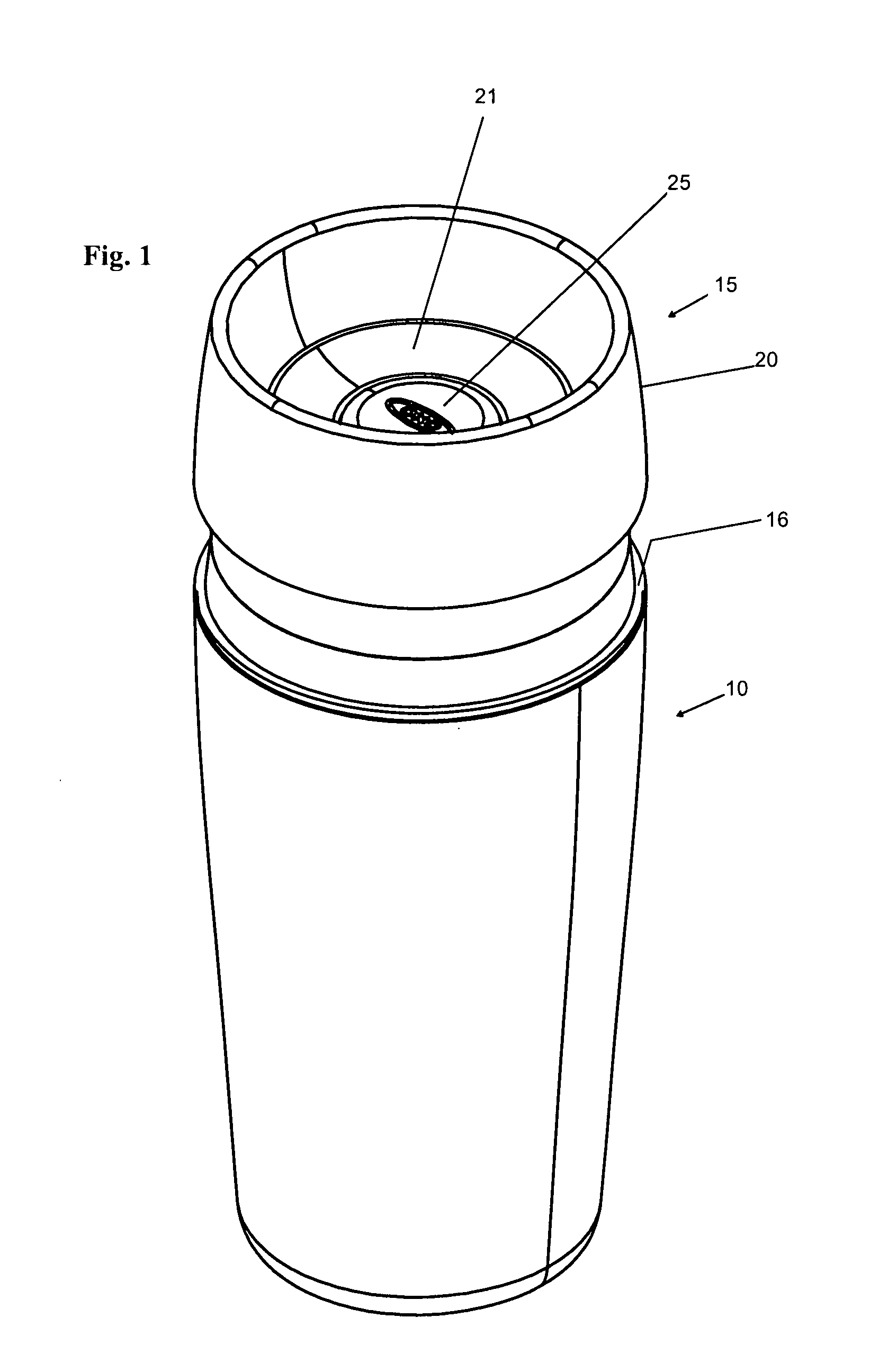
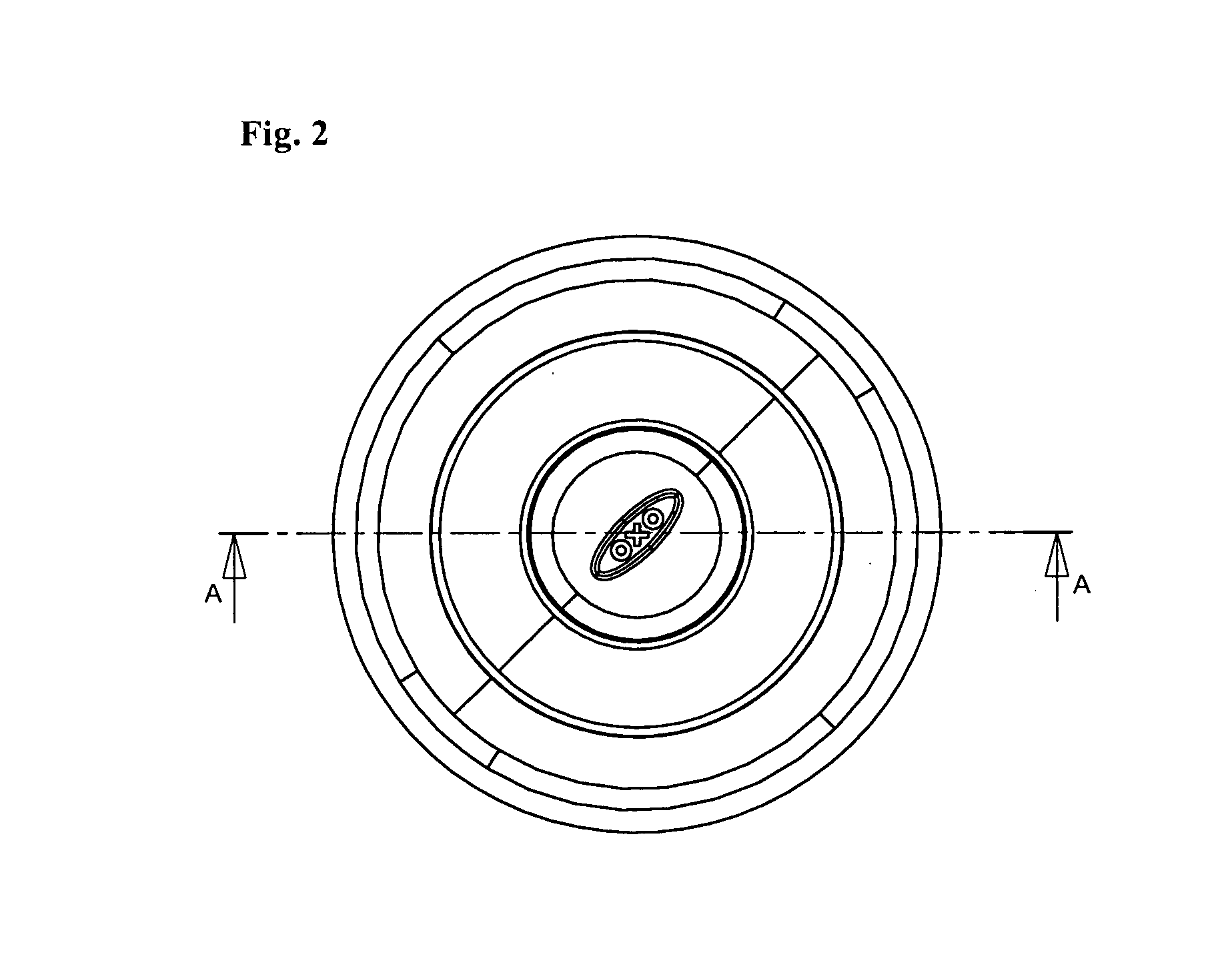
Beverage container lid
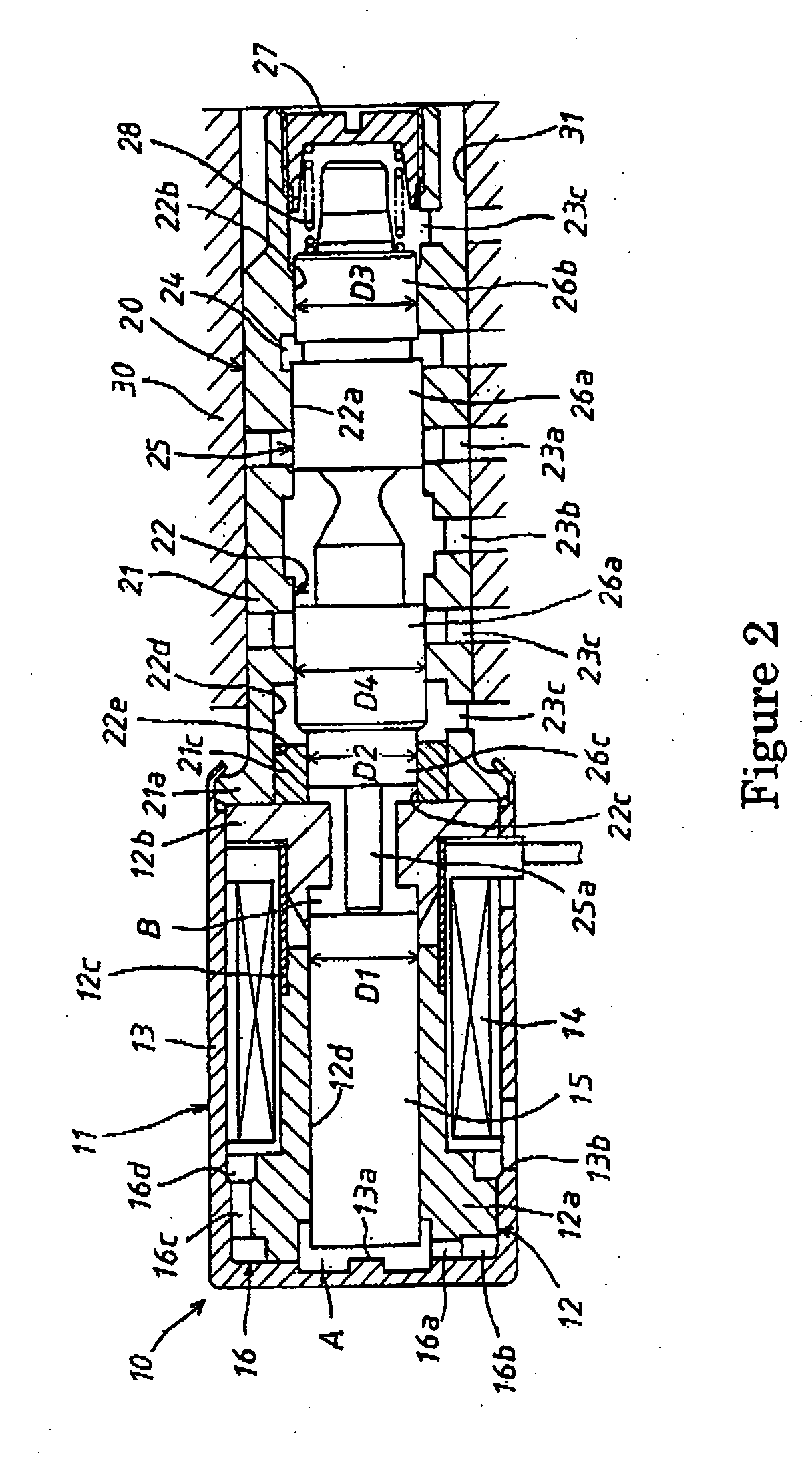
ActiveUS8272532B2Enhanced advantageAvoid disadvantagesCapsPressure relieving devices on sealing facesEngineeringMechanical engineering
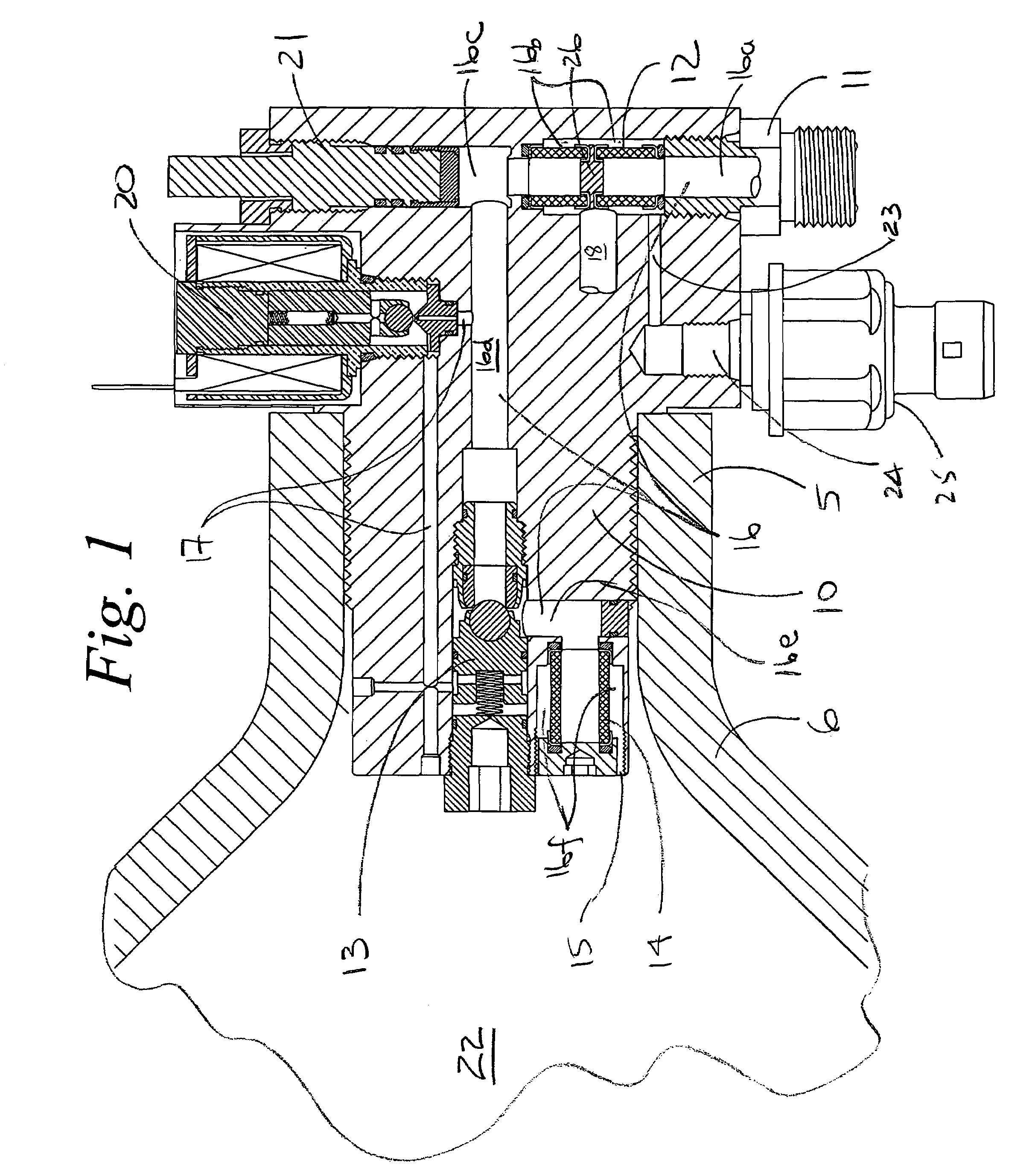
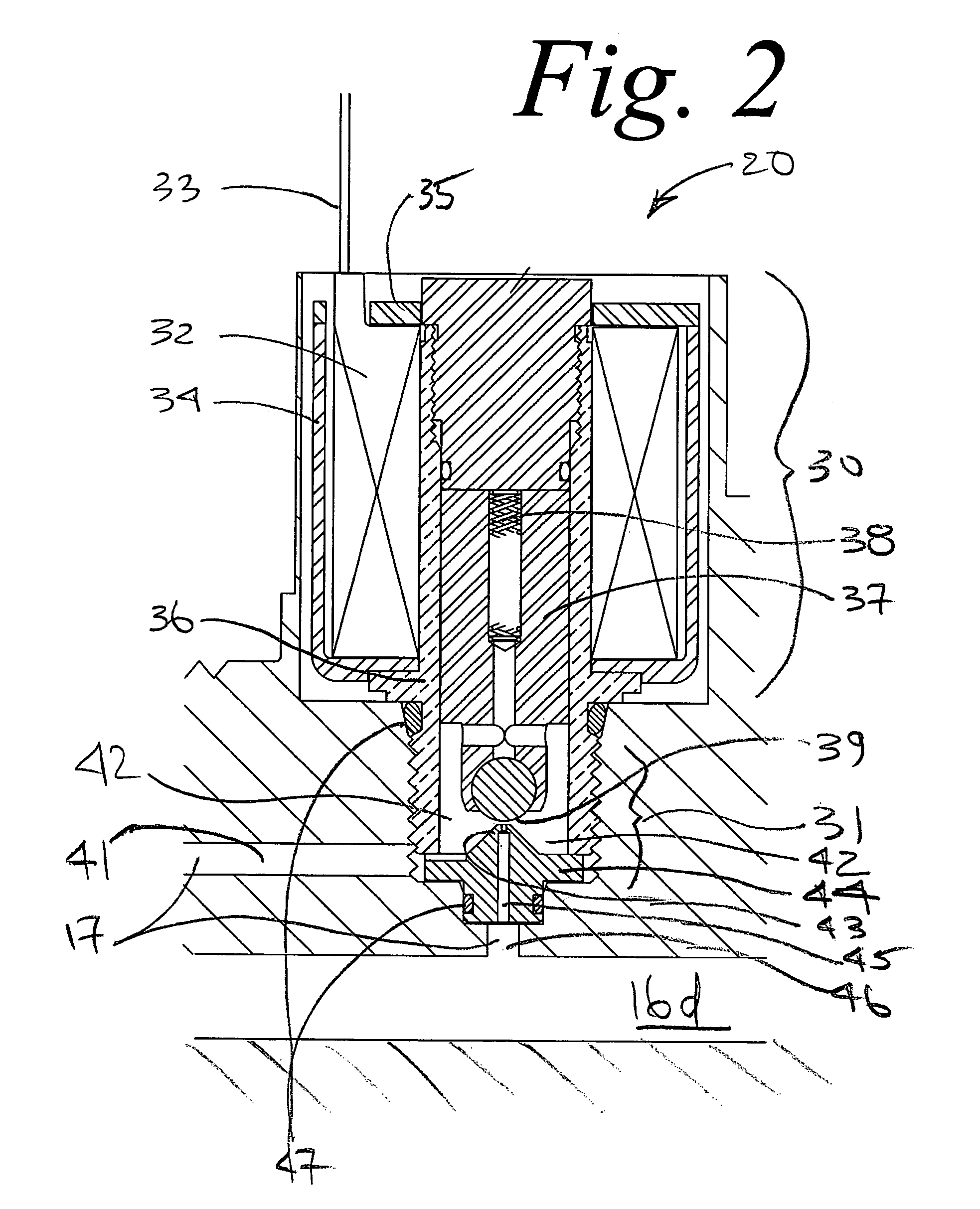
A beverage container lid for a container base having a reservoir, the lid comprising a shell removably mountable on the base comprising a first drink passage that extends through the shell and communicates with ambient and a cartridge removably engageable to the shell. A second drink passage is in communication with the first drink passage and is formed between an outer surface of the cartridge and inner surface of the shell. The cartridge comprises a valve that is moveable between an open condition and closed condition to control communication between the reservoir and second drink passage.
Owner:HELEN OF TROY LTD
High bandwidth rotary servo valves
InactiveUS20060096644A1Pressure relieving devices on sealing facesValve members for absorbing fluid energyHigh bandwidthEngineering
A valve includes a rotating, substantially pressure-balanced spool that selectively aligns openings within the spool with openings within a sleeve to selectively connect ports of a manifold for gas or liquid routing. A valve may also include a stem, a needle coupled to the stem. a seat configured to receive the needle, a reservoir, an outlet coupled to the reservoir, and a servo motor coupled to the stem. The servo motor rotates the stem to raise or lower the needle relative to the seat to variably restrict or allow matter flowing from the reservoir to the outlet.
Owner:VANDERBILT UNIV
Solenoid valve
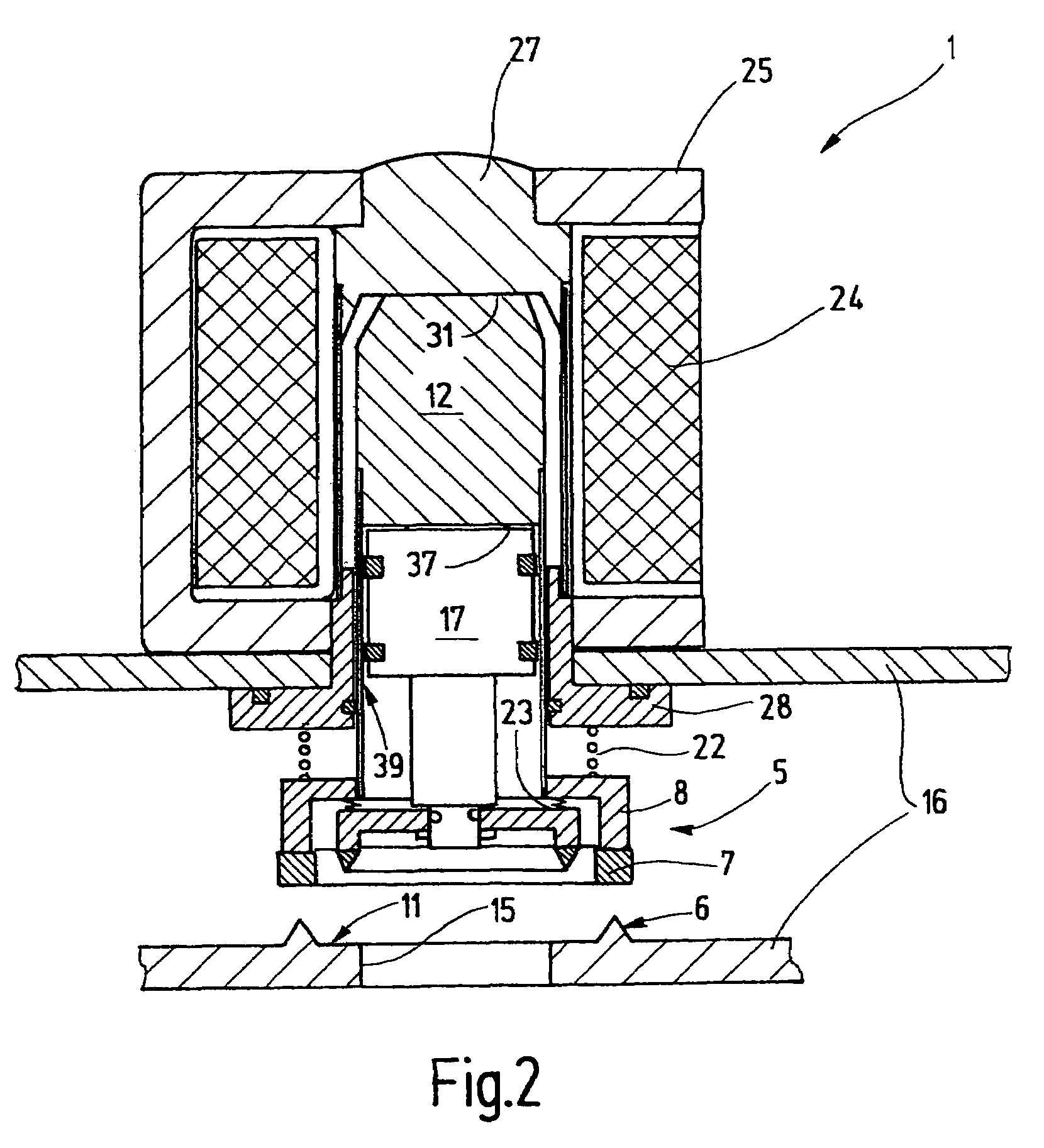
ActiveUS7347221B2Easy to moveMinimal gap widthFuel supply regulationGaseous fuel feeder/distributionPower flowSolenoid valve
A valve assembly comprises two valves and a single solenoid actuator with only one magnetizing coil that controls both valves. The corresponding magnetic circuit comprises a yoke with only two pole pieces. The valves are arranged concentric to one another. The valve closing element of the outer valve is connected to an armature by means of a sleeve. The cup thus formed receives the armature that is connected to the valve closing element of the inner valve. The pole piece and the armature form a transmission air gap through which the sleeve extends. A coupling air gap is formed between the armatures. The armature and the pole piece form a working air gap. The valves are opened collectively and are able to close independently of one another when the coil is rendered currentless.
Owner:KARL DUNGS
Solenoid valve
InactiveUS6505812B1Simple designEasily assembled togetherSpindle sealingsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesSolenoid valveEngineering
A valve assembly including a body having an inlet port, an outlet port, and a valve seat having a passageway. An electrical solenoid assembly moves a valve member upon being energized to control fluid flow between the inlet and the outlet ports. The valve assembly also includes a fluid-tight bellows positioned to apply a force to the valve member, and a pressure balancing passageway connects the inlet port to the bellows. The valve assembly further includes a housing received over the solenoid assembly and having a flange received against the valve body. A seal is positioned between the flange of the housing and the valve body, and a collar is secured in a continuous manner to the valve body over the housing flange, thereby securing the housing to the valve body and applying a sealing force to the seal in a substantially even manner.
Owner:MKS INSTR INC
Solenoid valve
ActiveUS20050166979A1Easy to moveMinimal gap widthFuel supply regulationGaseous fuel feeder/distributionSolenoid valveEngineering
A valve assembly comprises two valves and a single solenoid actuator with only one magnetizing coil that controls both valves. The corresponding magnetic circuit comprises a yoke with only two pole pieces. The valves are arranged concentric to one another. The valve closing element of the outer valve is connected to an armature by means of a sleeve. The cup thus formed receives the armature that is connected to the valve closing element of the inner valve. The pole piece and the armature form a transmission air gap through which the sleeve extends. A coupling air gap is formed between the armatures. The armature and the pole piece form a working air gap. The valves are opened collectively and are able to close independently of one another when the coil is rendered currentless.
Owner:KARL DUNGS
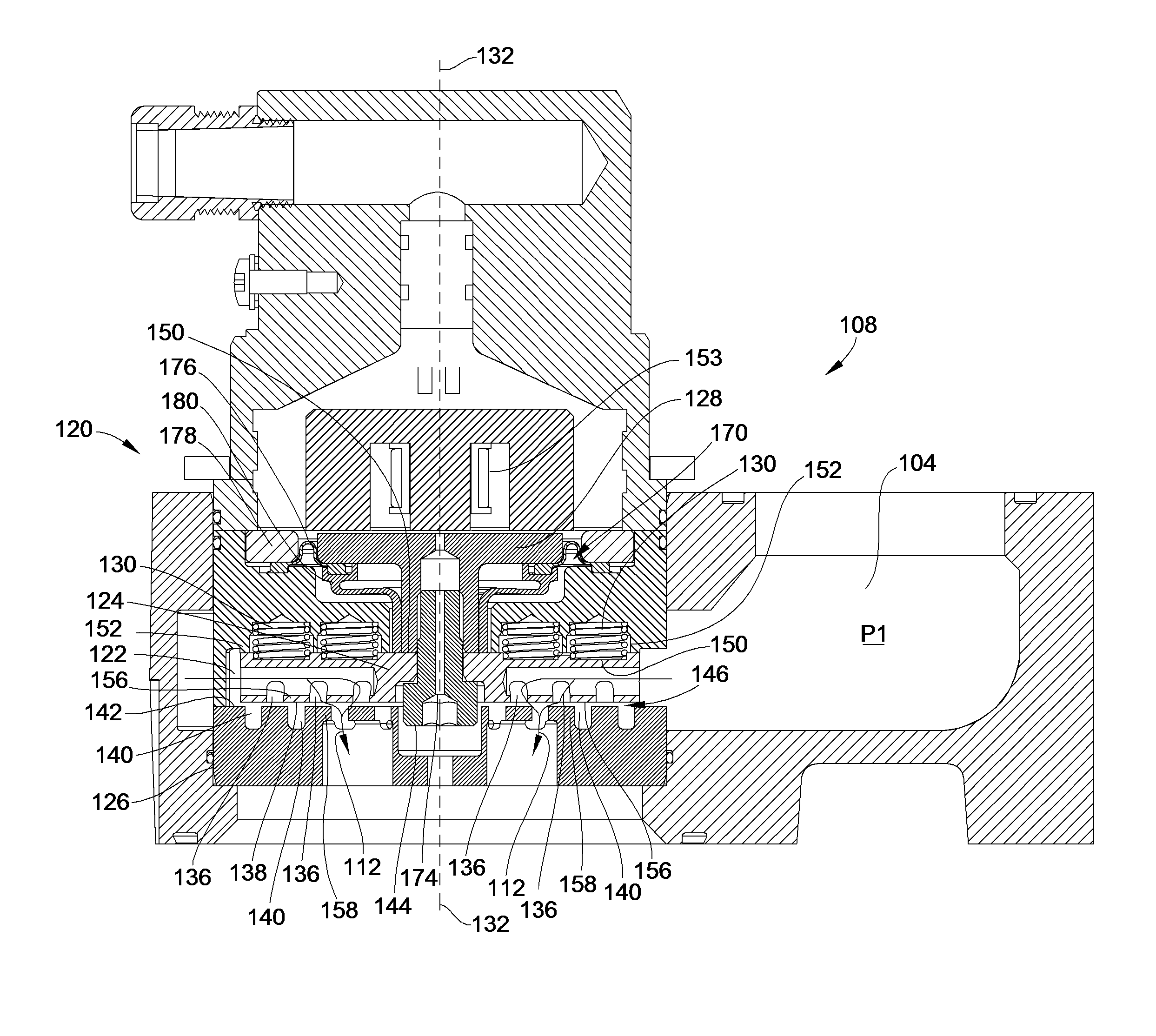
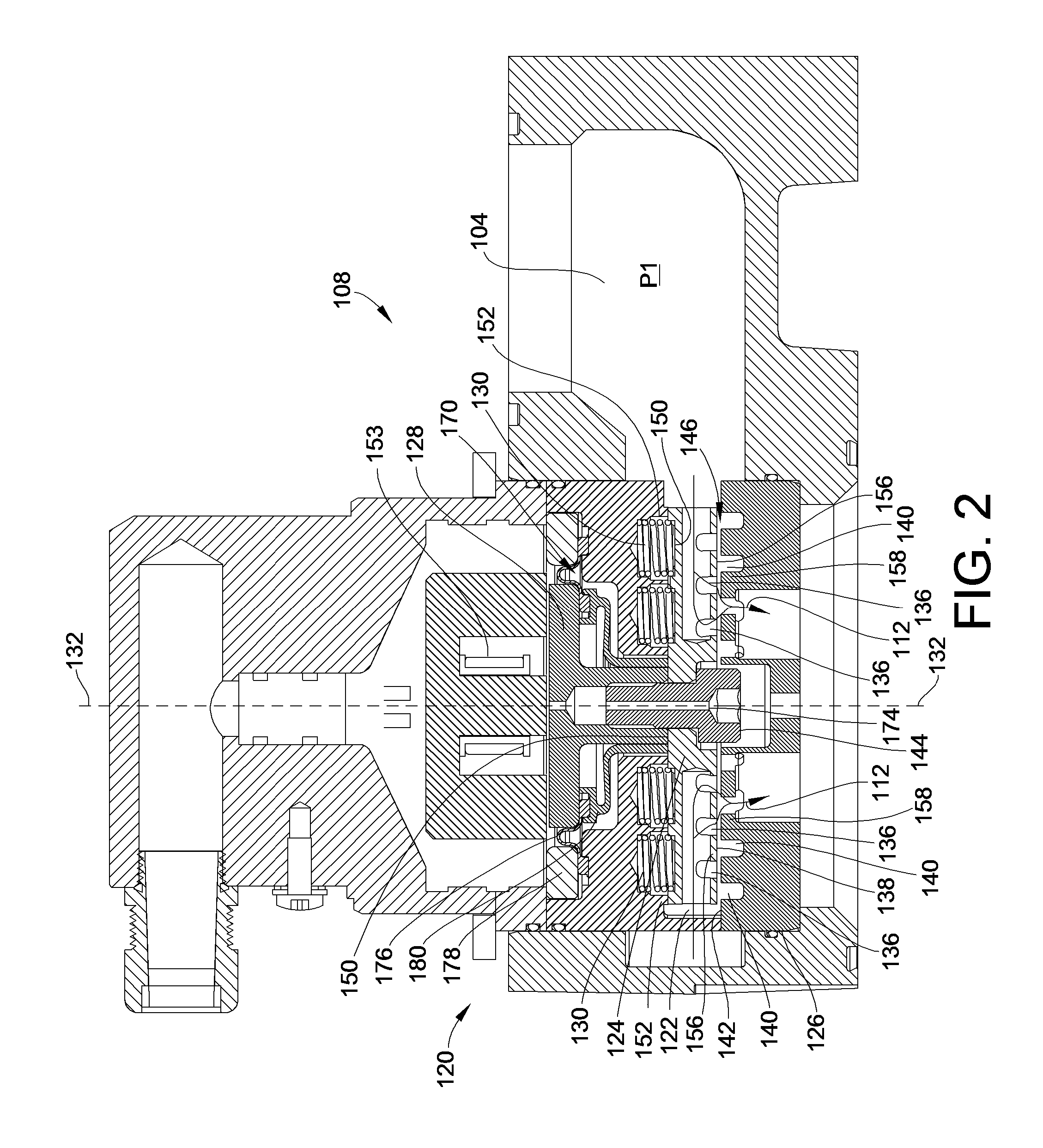
Flow control system for a valve
ActiveUS20050103382A1Vessel mounting detailsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesDifferential pressureControl system
A fluid-flow control system for a valve comprises a valve body and a bi directional main flow passage between a first and second fluid areas. The shuttle piston having a first face in direct communication with the second area and a second face in communication therewith through a bleed orifice. The second face is alternately exposed to the first fluid area through a backpressure passage and second orifice which alters the pressure differential across the shuttle piston. A second valve such as a solenoid operates to either close the second orifice wherein the shuttle piston is operable under differential pressure between the first and second pressure areas, or to close the second orifice wherein the shuttle piston is operable under differential pressure between the second pressure area and the backpressure passage. Filters at the fluid inlet and outlets protect the sealing components therein.
Owner:LUXFER CANADA
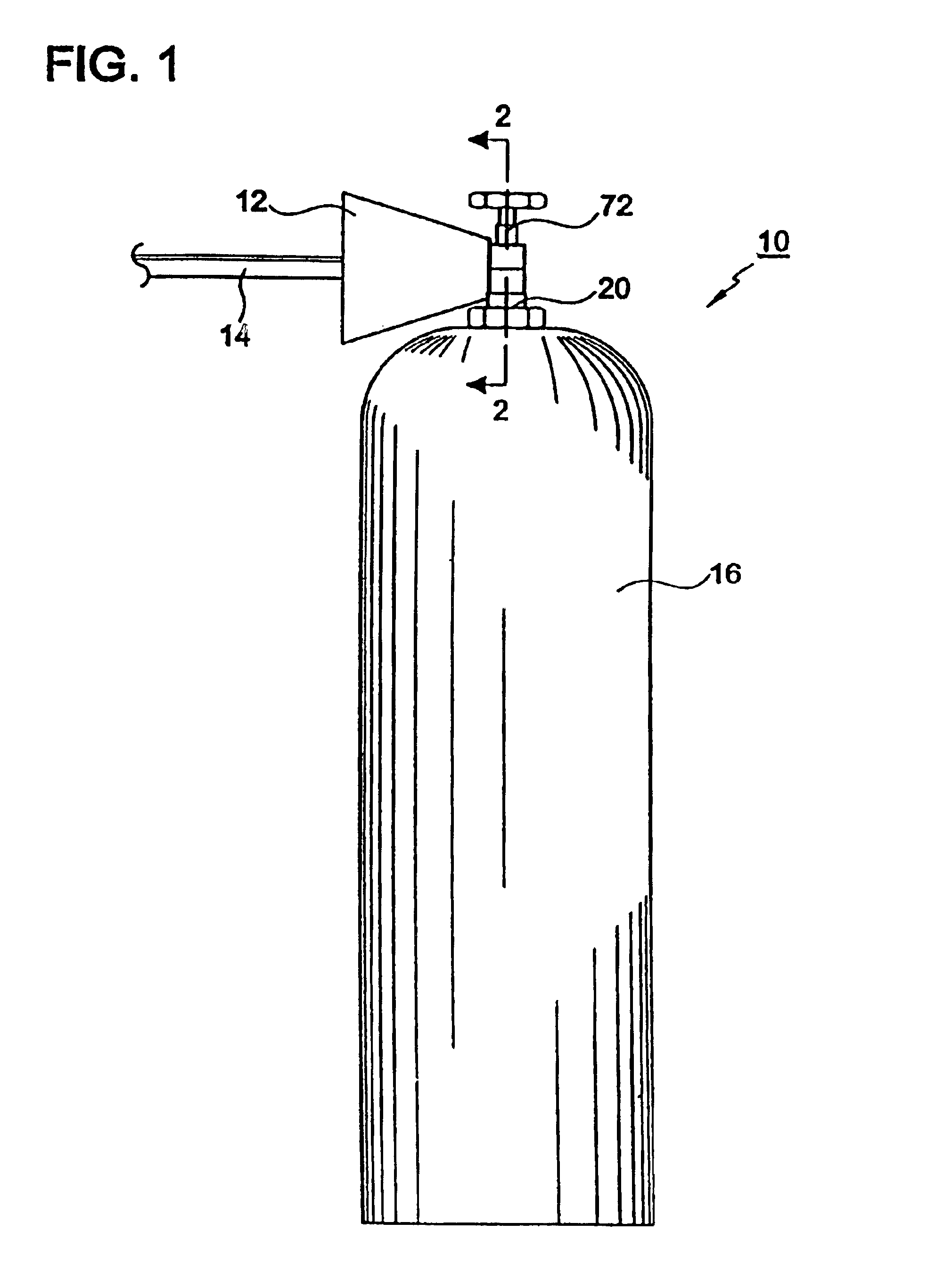
Surge prevention device
InactiveUS6901962B2High trafficIncrease flow rateCircuit elementsContainer filling methodsGas cylinderHigh pressure
A surge prevention valve may be used to prevent the formation of an initial surge of high pressure. The valve may be located, for example, between a high pressure gas cylinder and a medical pressure regulator. The valve is provided with first and second valves located within a housing and integrating a pressurization orifice. The initial opening of the valve in an axial direction enables gas to flow through the pressurization orifice at a first flow rate. The full opening of the valve in the axial direction enables the gas to flow through the second valve at a second flow rate, which is much higher than the first flow rate. The controlled pressurization of the gas through the orifice delays the time during which the gas reaches full recompression.
Owner:ALLIED HEALTHCARE PROD INC
Self-modulating inert gas fire suppression system
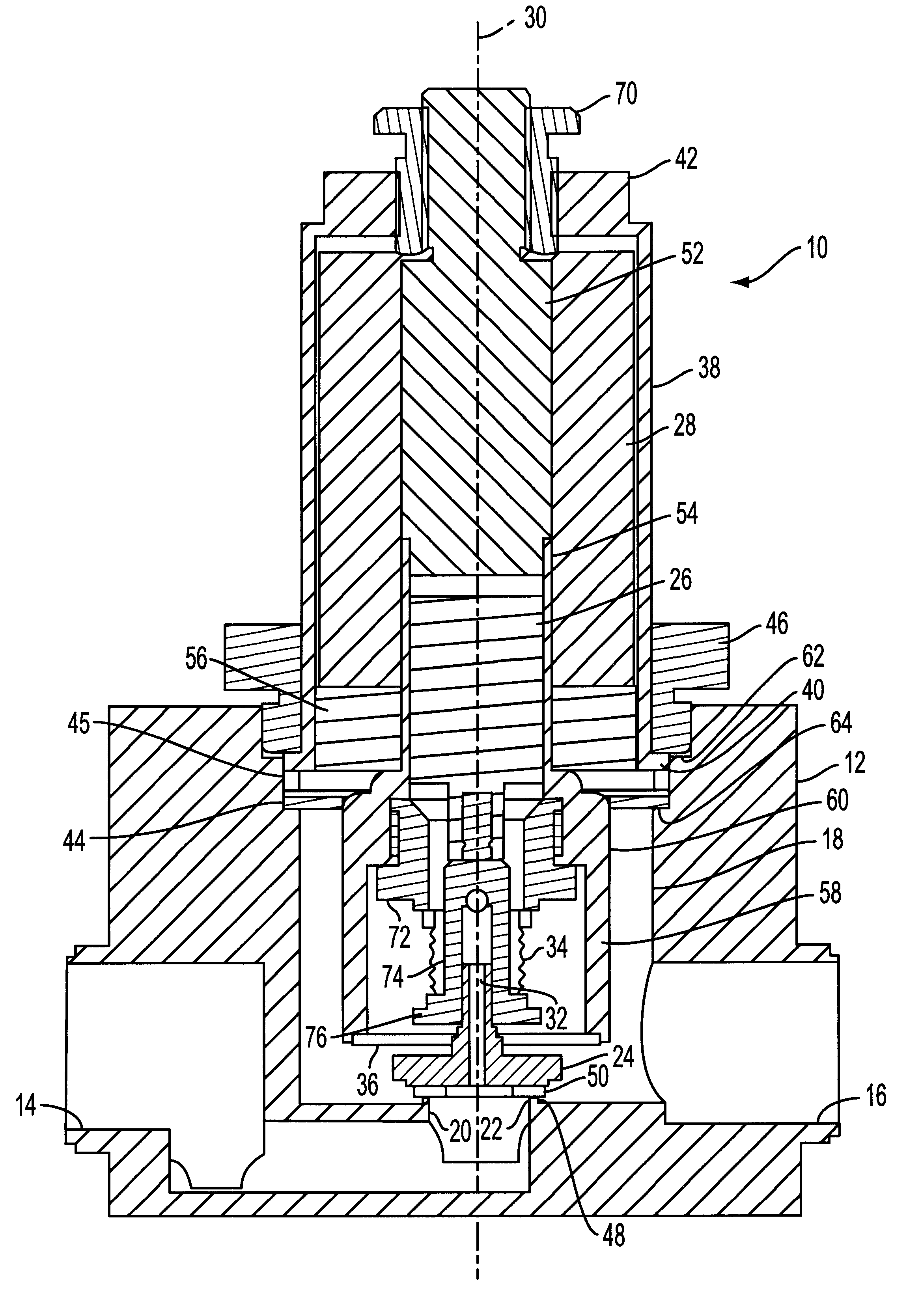
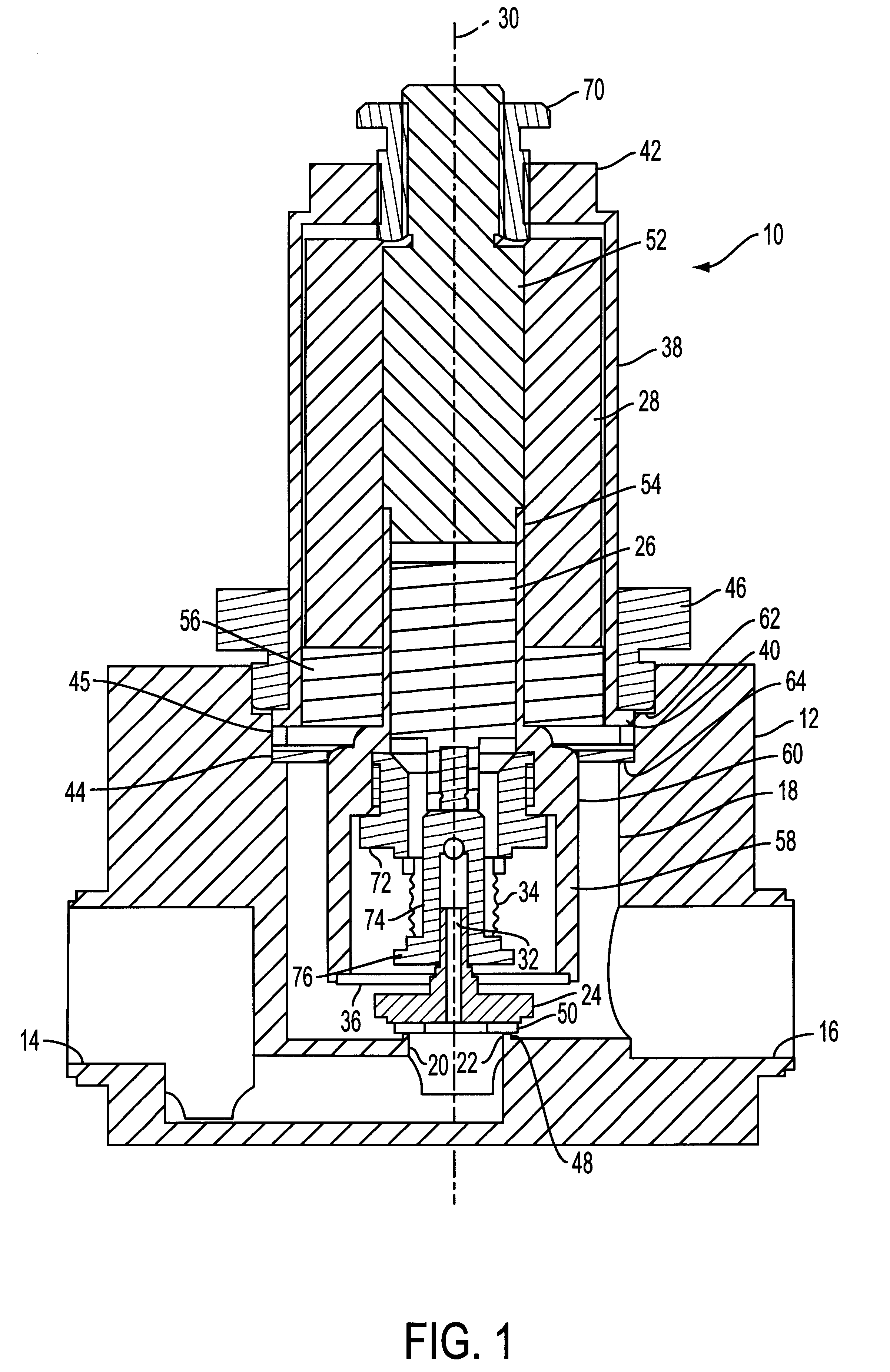
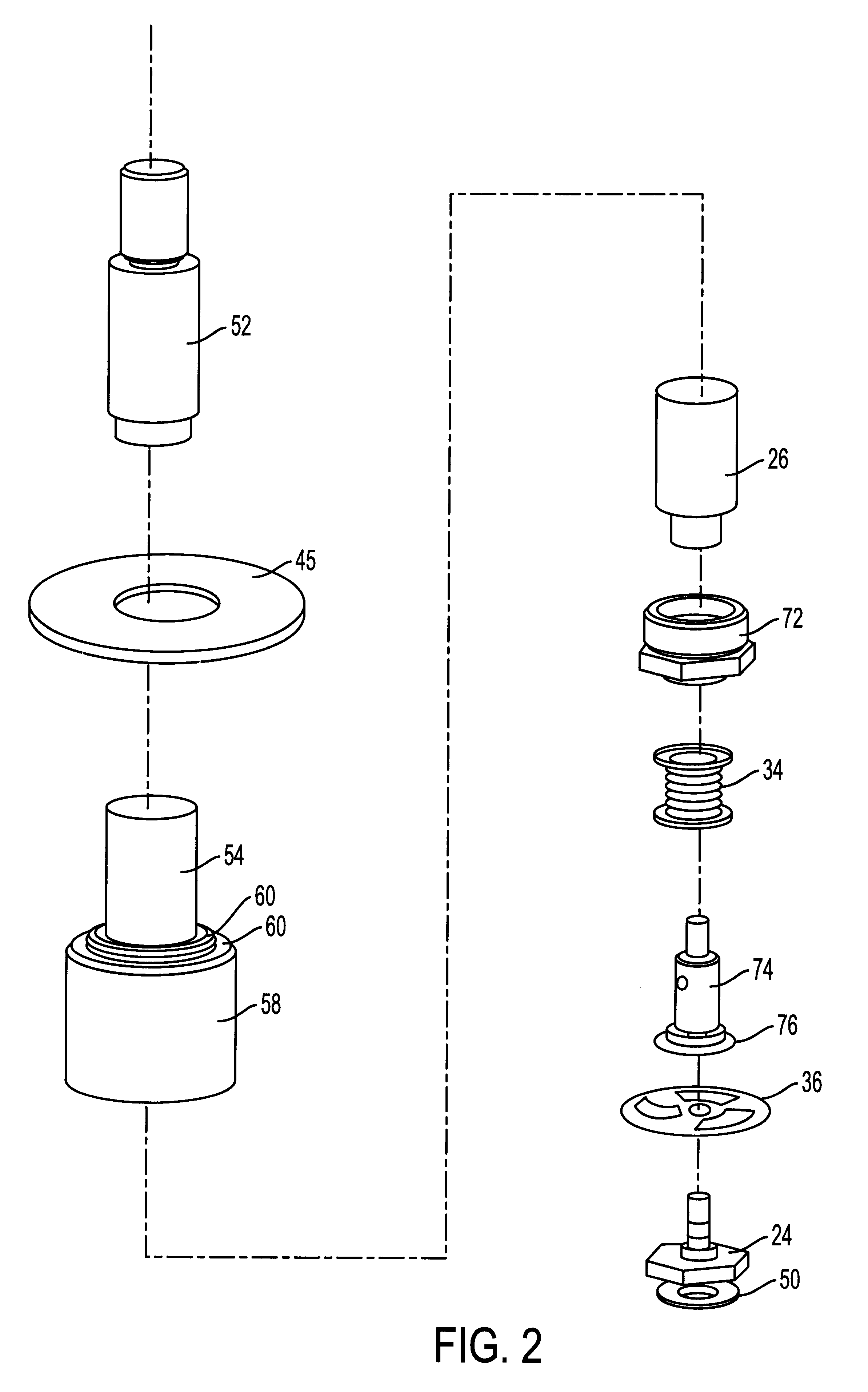
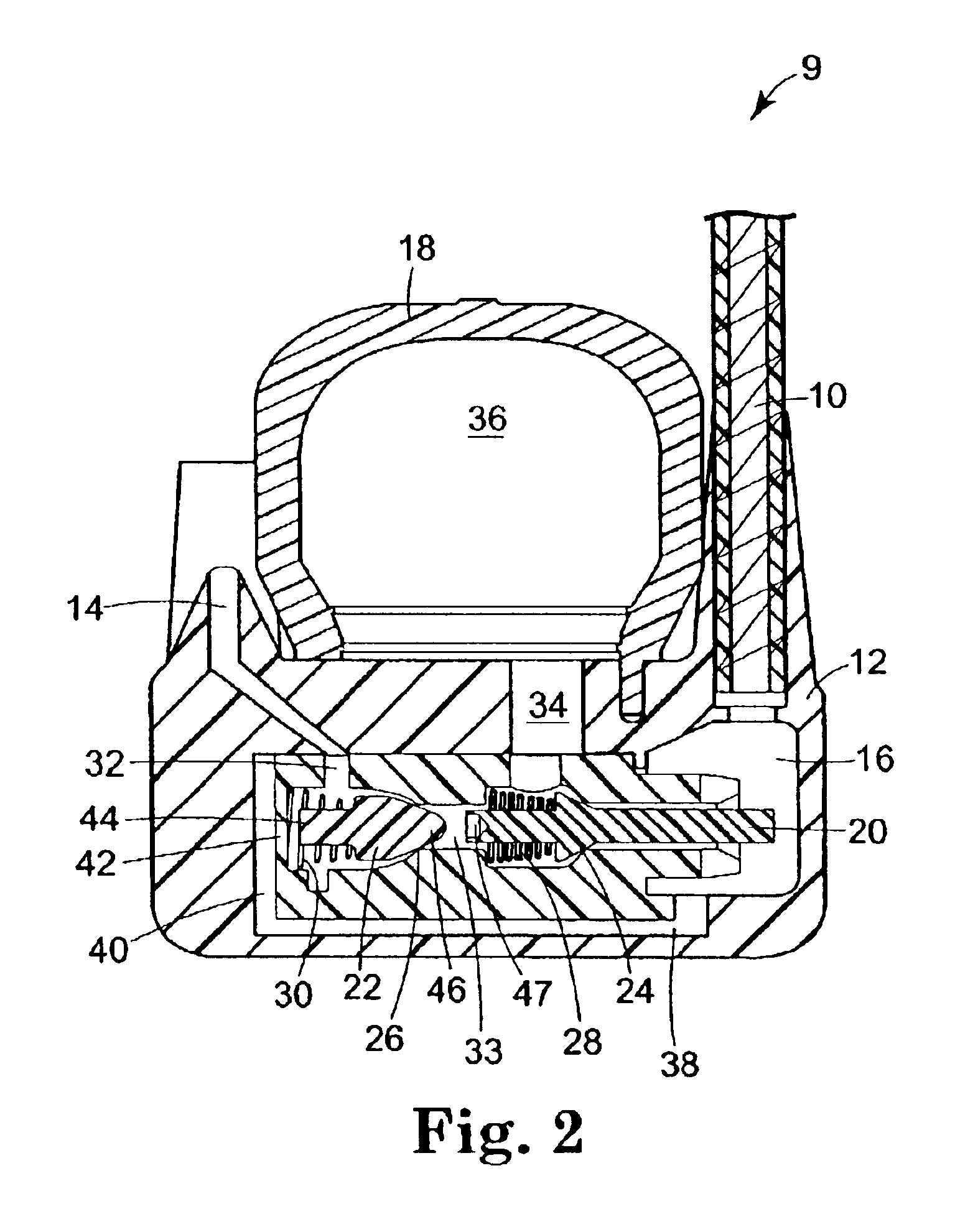
InactiveUS6871802B2Effectively suppressing hazardsConstant flowContainer filling methodsGas handling applicationsEngineeringHigh pressure
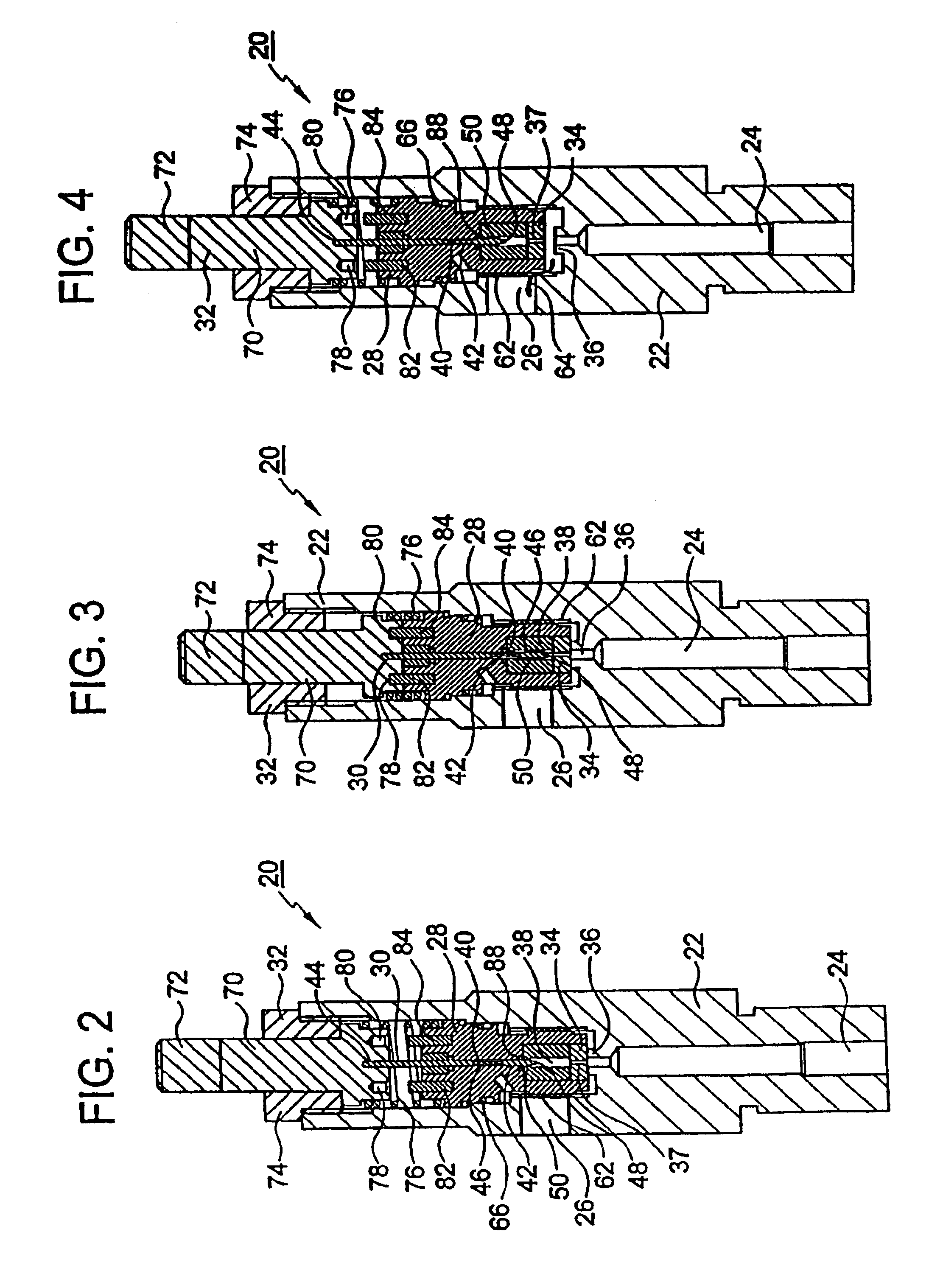
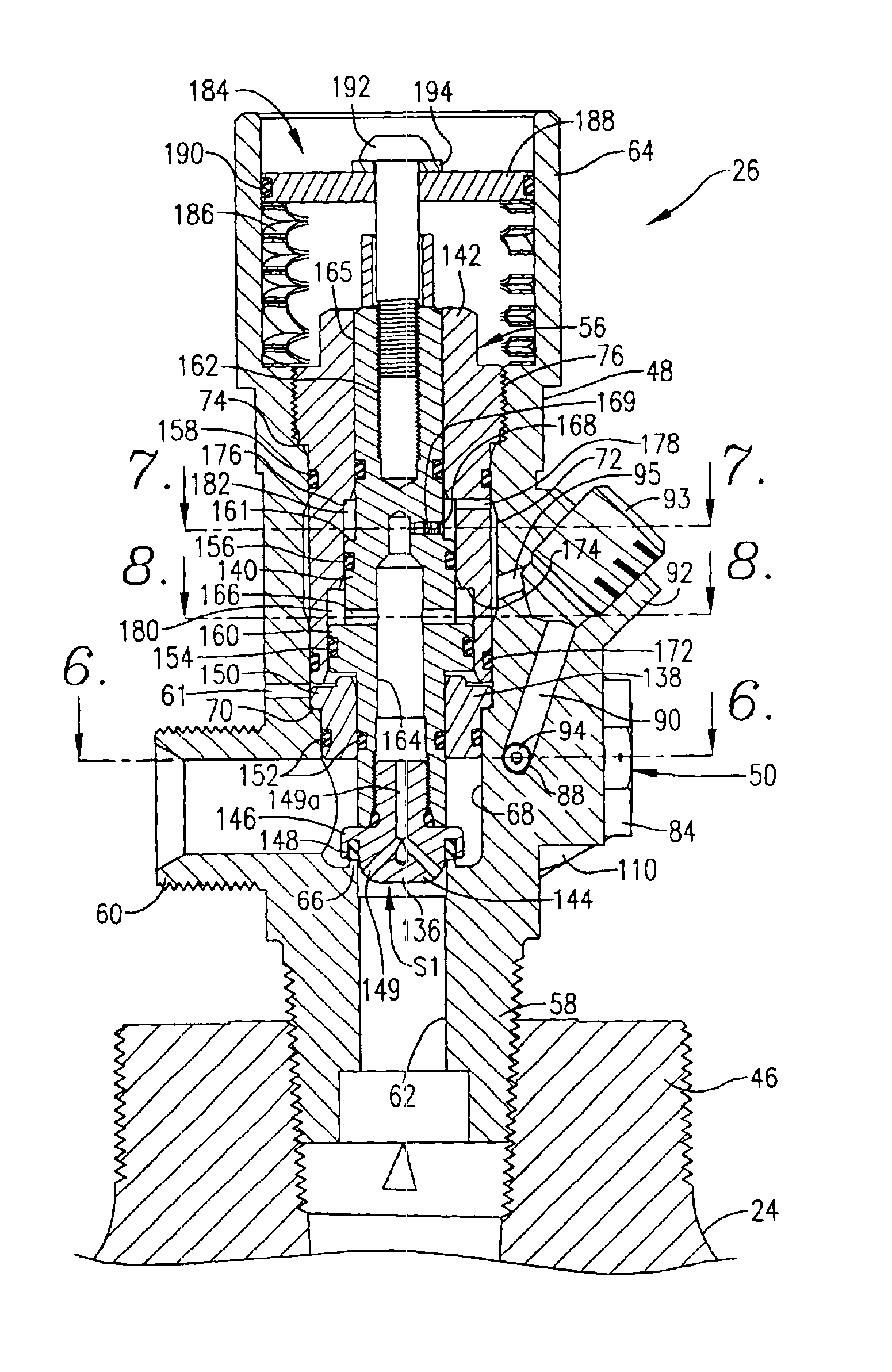
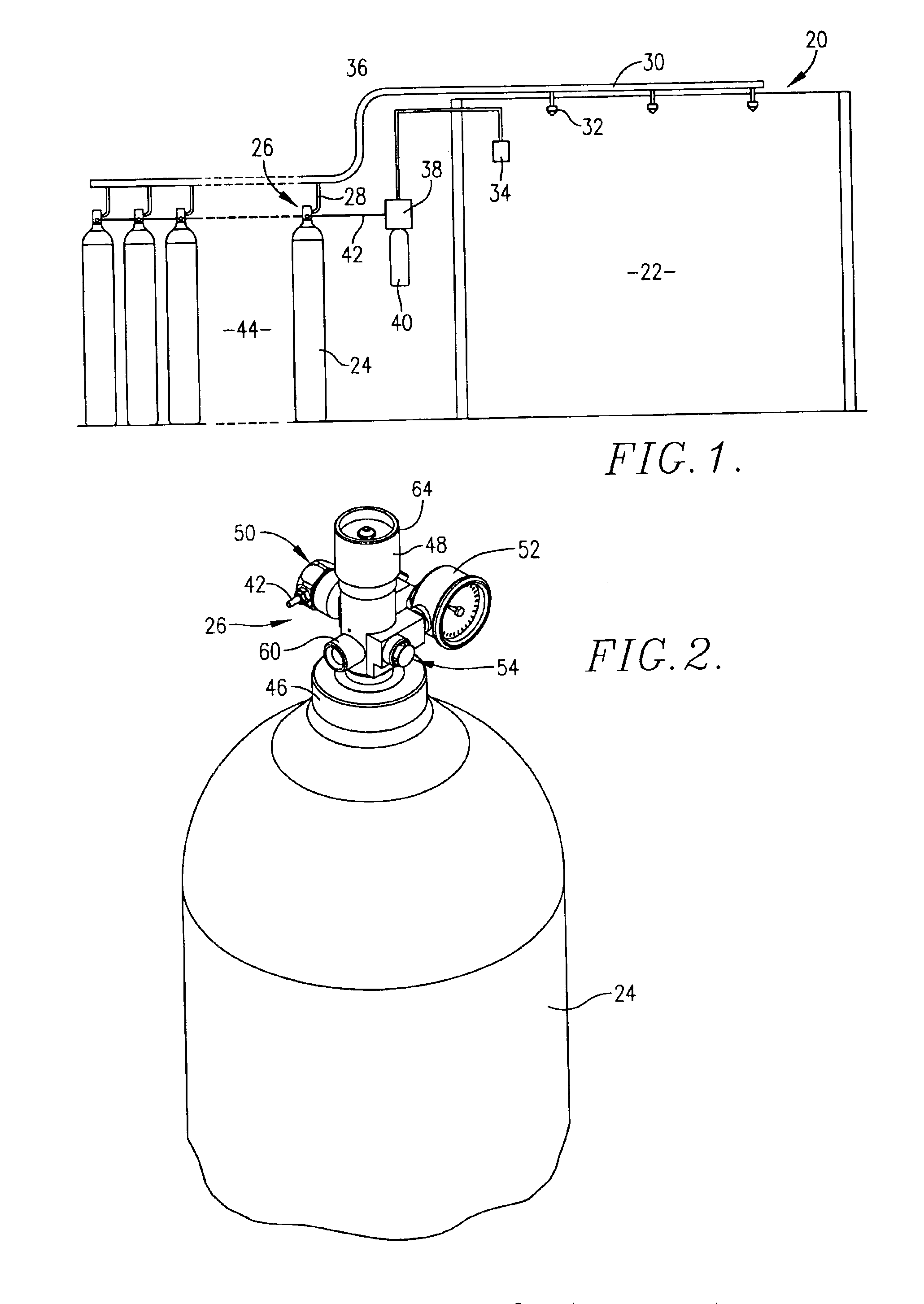
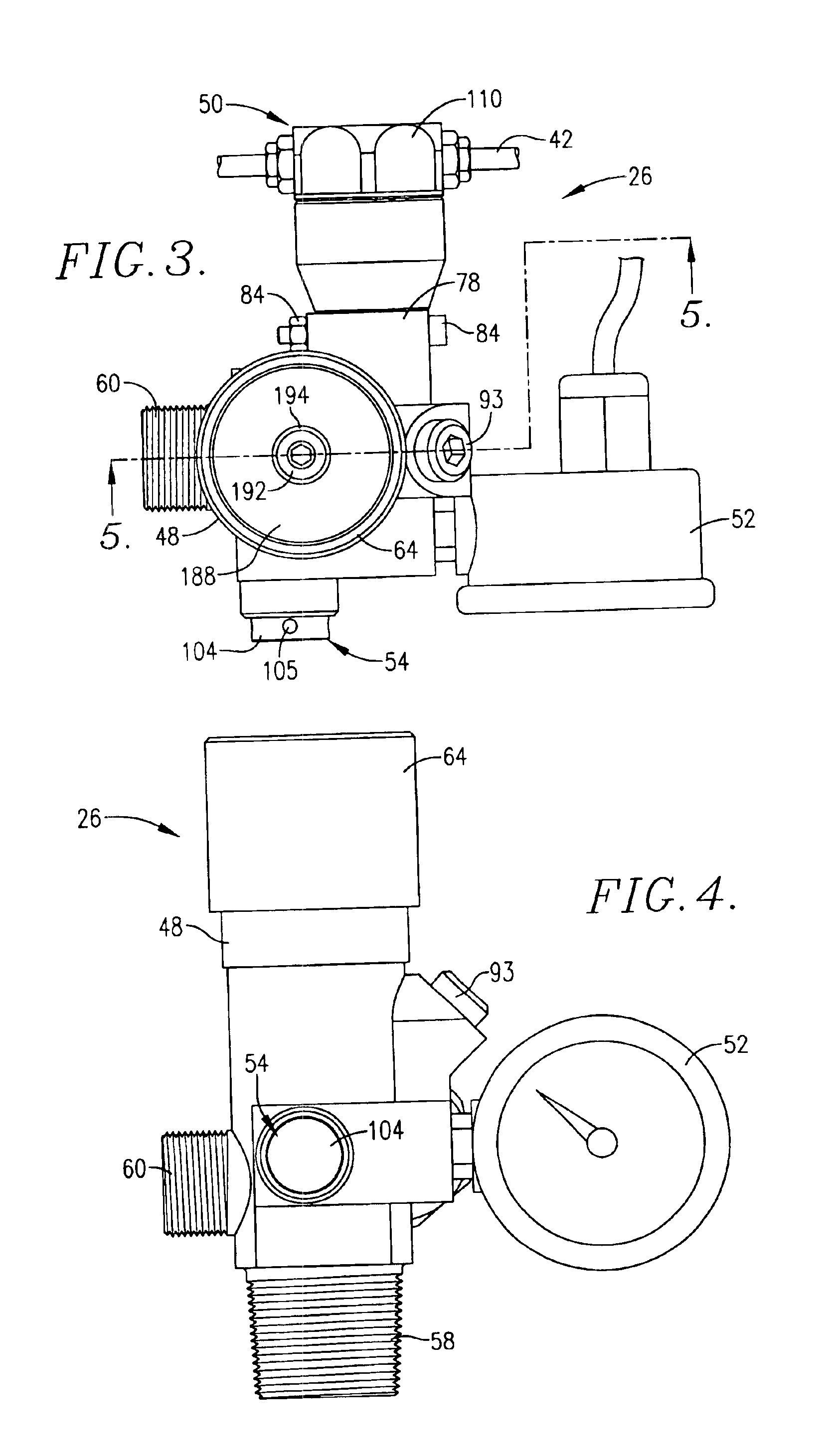
A relatively low pressure inert gas hazard suppression system (20) is provided which is designed to protect a room (22) or the like from the effects of fire or other hazard. The system (20) includes a plurality of pressurized inert gas cylinders (24) each equipped with a valve unit (26); each valve unit (26) is in turn coupled via a conduit (28) to a delivery manifold (30). The respective valve units (26) are operable to deliver gas from the cylinders (24) at a generally constant pressure (usually around 10-100 bar) throughout a substantial portion of the time of gas delivery, to thereby provide effective hazard suppression without the need for expensive high-pressure gas handling and distribution hardware and a reduction in room venting area due to lower room over-pressurization. Each valve unit (26) has a valve body (48) and a shiftable piston-type sealing member (56). Gas pressure from the cylinder (24) and a spring assembly (184) biases the member 56 to the valve open position, this being counterbalanced by gas pressure within equalization and modulation chambers (180, 182) provided in the valve unit (26). When a hazard is detected, the valve units (26) are actuated by draining of gas from the modulation chambers (182), allowing gas flow from the cylinders (24). As gas discharge proceeds, gas flows into and out of the modulation chambers (182) so as to achieve the desired generally constant pressure gas output. Near the end of gas discharge, the spring assembly (184) becomes predominant and holds the valve unit (26) open until all gas is discharged.
Owner:FIKE CORP
Instant-on vented tank valve with manual override and method of operation thereof
An instant-on valve assembly with manual override is designed to be connected to a tank containing high pressure gaseous fuel. The valve assembly and manual override allows the tank to be alternately closed off, vented or allows the gas in the tank to bypass the instant-on valve. The instant-on valve assembly can be repaired or replaced without venting the tank. The instant-on valve assembly has a main valve and a bleed valve The main valve has a secondary plunger that opens and closes a main orifice. The bleed valve has a bleed valve stem that opens and closes a bleed orifice. The main valve is slidably mounted within a housing and has a chamber at one end and a zone at another end. Both the zone and the chamber have access to high pressure gaseous fuel within the tank. High pressure gaseous fluid within the zone can be drained when the bleed valve stem is fully open. The bleed valve stem is connected to a solenoid and opens upon activation of the solenoid. When the pressure within the zone is sufficiently reduced, the pressure within the chamber will cause the main valve to open by sliding into the zone. A spring moves the main valve towards a closed position when the solenoid is deactivated. Since the volume of the zone is relatively small, the main valve opens within one second after the solenoid is activated.
Owner:WESTPORT POWER
Flow control system for a valve
ActiveUS7309113B2Vessel mounting detailsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesDifferential pressureControl system
A fluid-flow control system for a valve comprises a valve body and a bi directional main flow passage between a first and second fluid areas. The shuttle piston having a first face in direct communication with the second area and a second face in communication therewith through a bleed orifice. The second face is alternately exposed to the first fluid area through a backpressure passage and second orifice which alters the pressure differential across the shuttle piston. A second valve such as a solenoid operates to either close the second orifice wherein the shuttle piston is operable under differential pressure between the first and second pressure areas, or to close the second orifice wherein the shuttle piston is operable under differential pressure between the second pressure area and the backpressure passage. Filters at the fluid inlet and outlets protect the sealing components therein.
Owner:LUXFER CANADA
Spontaneous inflation inhibitor for inflatable prosthesis
InactiveUS6935847B2Preventing inflationCheck valvesPharmaceutical delivery mechanismEngineeringPenile implant
A pump assembly for a penile implant is provided having a mechanism which prevents spontaneous inflation of the cylinders implanted within the user. The preventative mechanism uses overpressure generated by the reservoir during unintentional compression to effectively seal the pump assembly from unintended fluid flow. The prevention mechanism itself creates all necessary forces to prevent the undesired fluid flow to the cylinders. This is accomplished by incorporating appropriate mechanisms within the pump itself.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Low emission fluid transfer device
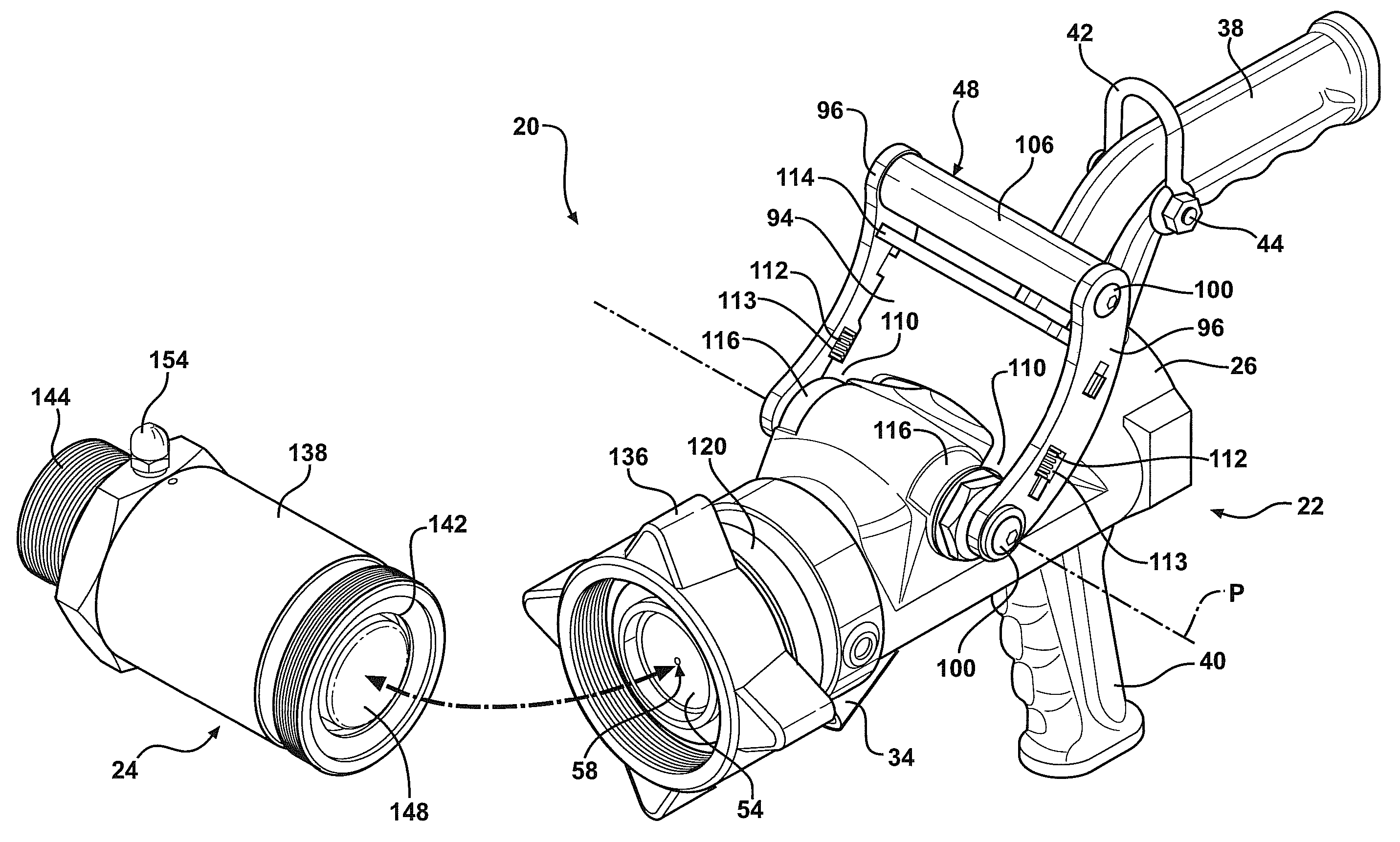
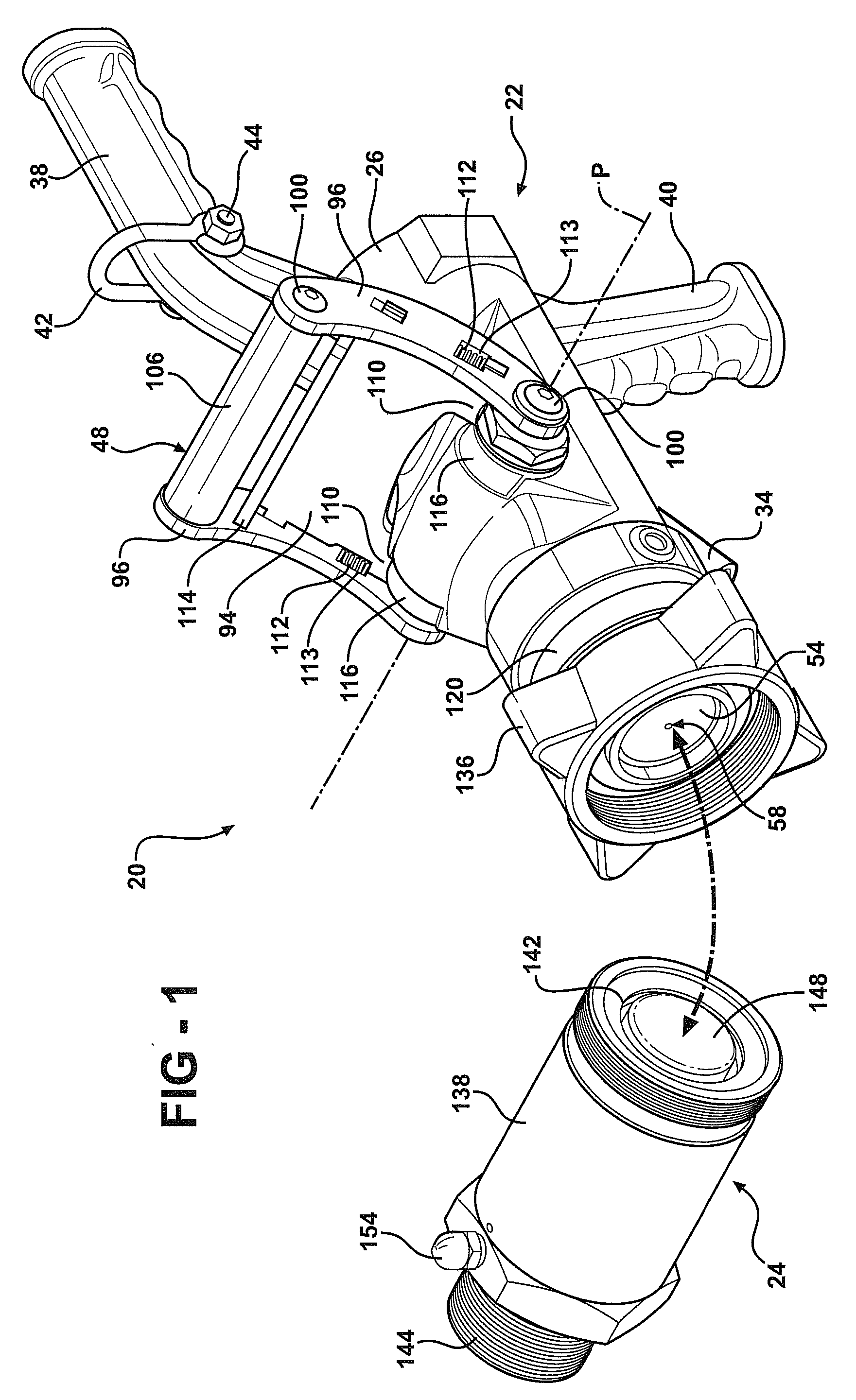
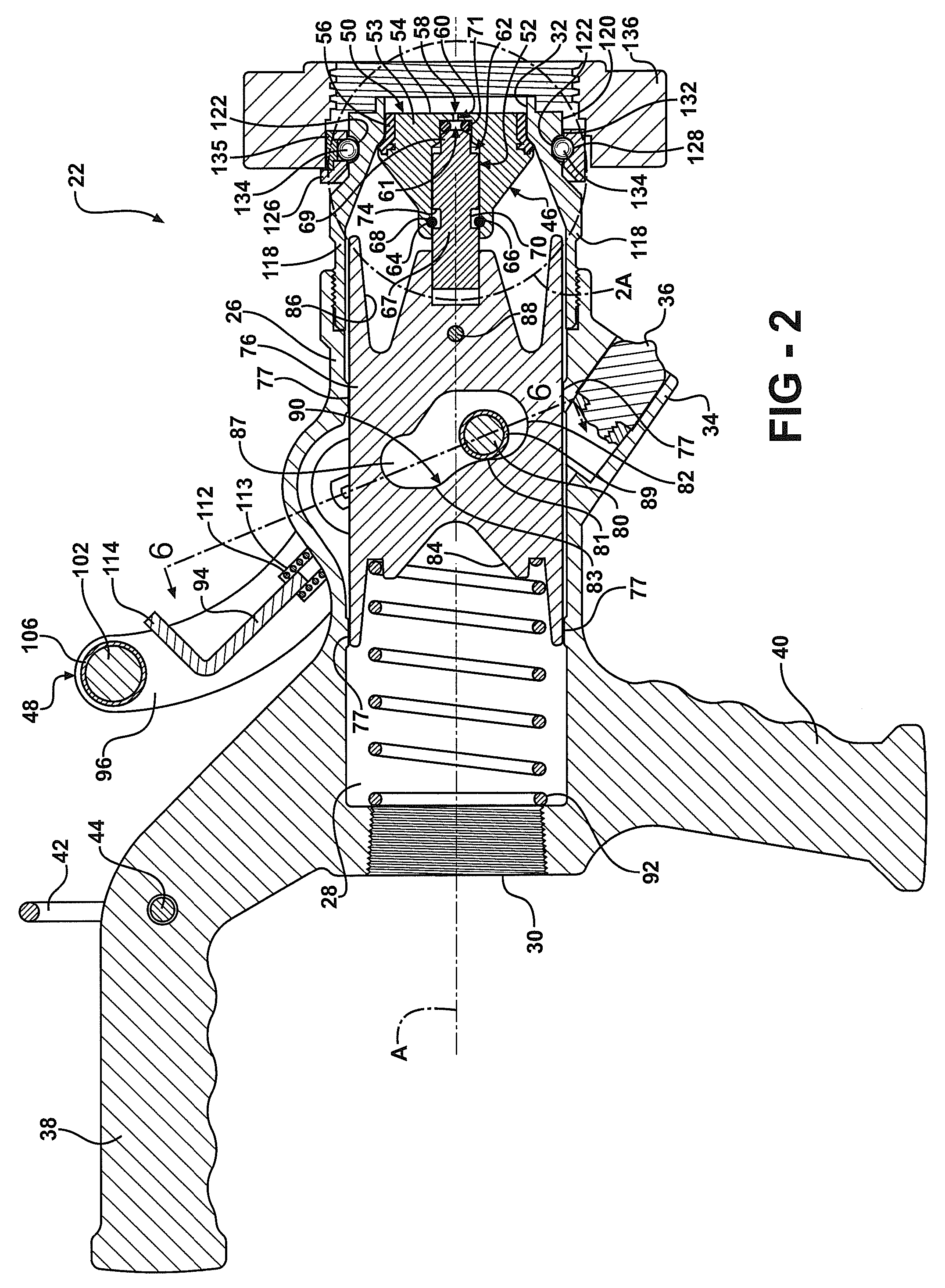
ActiveUS20100024904A1Easy to openEasy to moveServomotor componentsContainer filling methodsTransfer systemEngineering
A fluid transfer system includes a transfer device coupled to a dry break coupler. The transfer device includes a valve assembly moveable between an open and a closed position. The valve assembly includes a main valve and a pilot valve. An actuator controls both the main valve and the pilot valve. A cam plate interconnects the actuator and the valve assembly. The cam plate provides a quick acting shutoff to quickly move the valve assembly to the closed position. A pivotal and rotatable connector couples the transfer device to the dry break coupler. A lock is integrated with the actuator to lock the valve assembly in the closed position.
Owner:MARSHALL EXCELSIOR CO
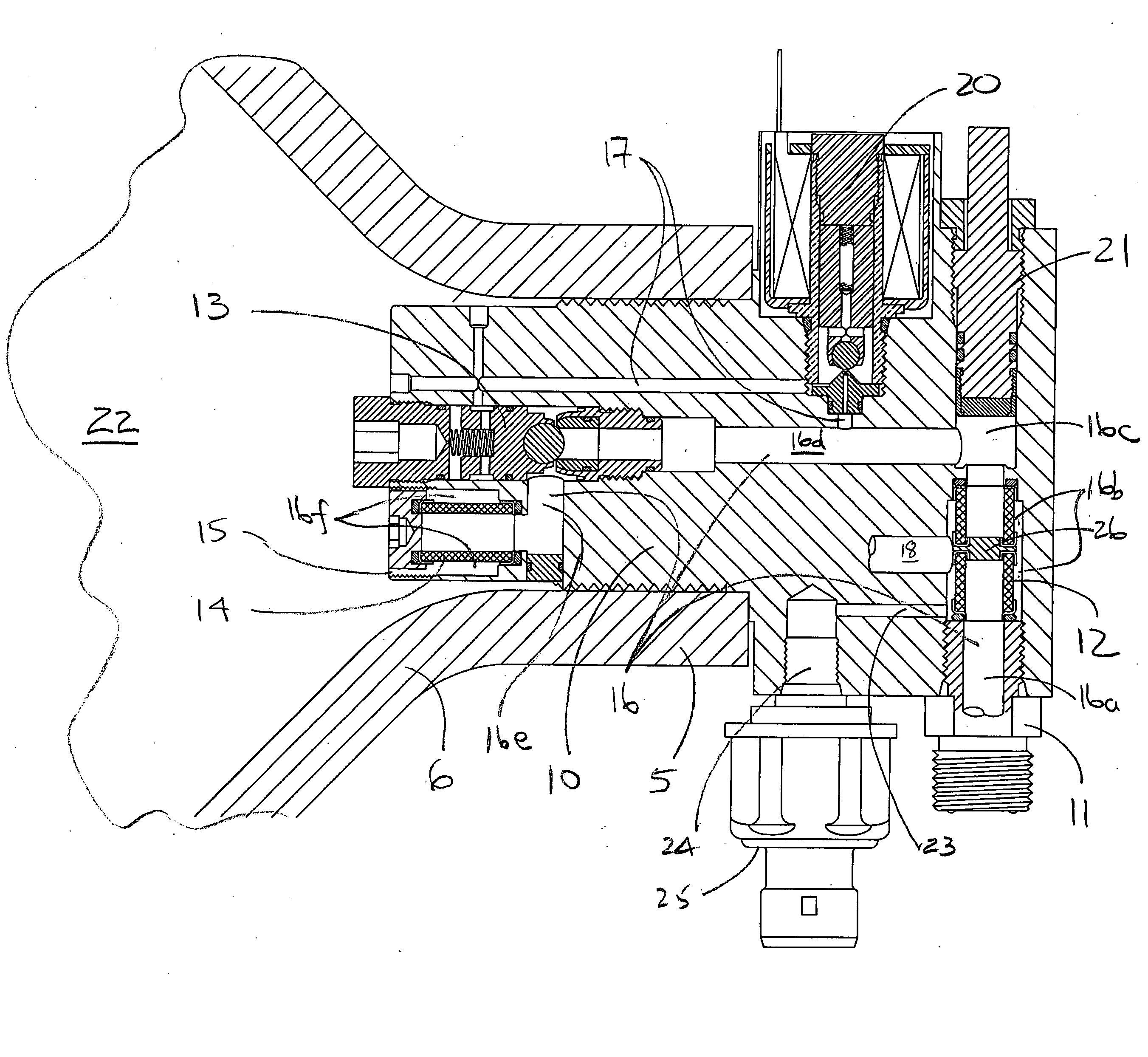
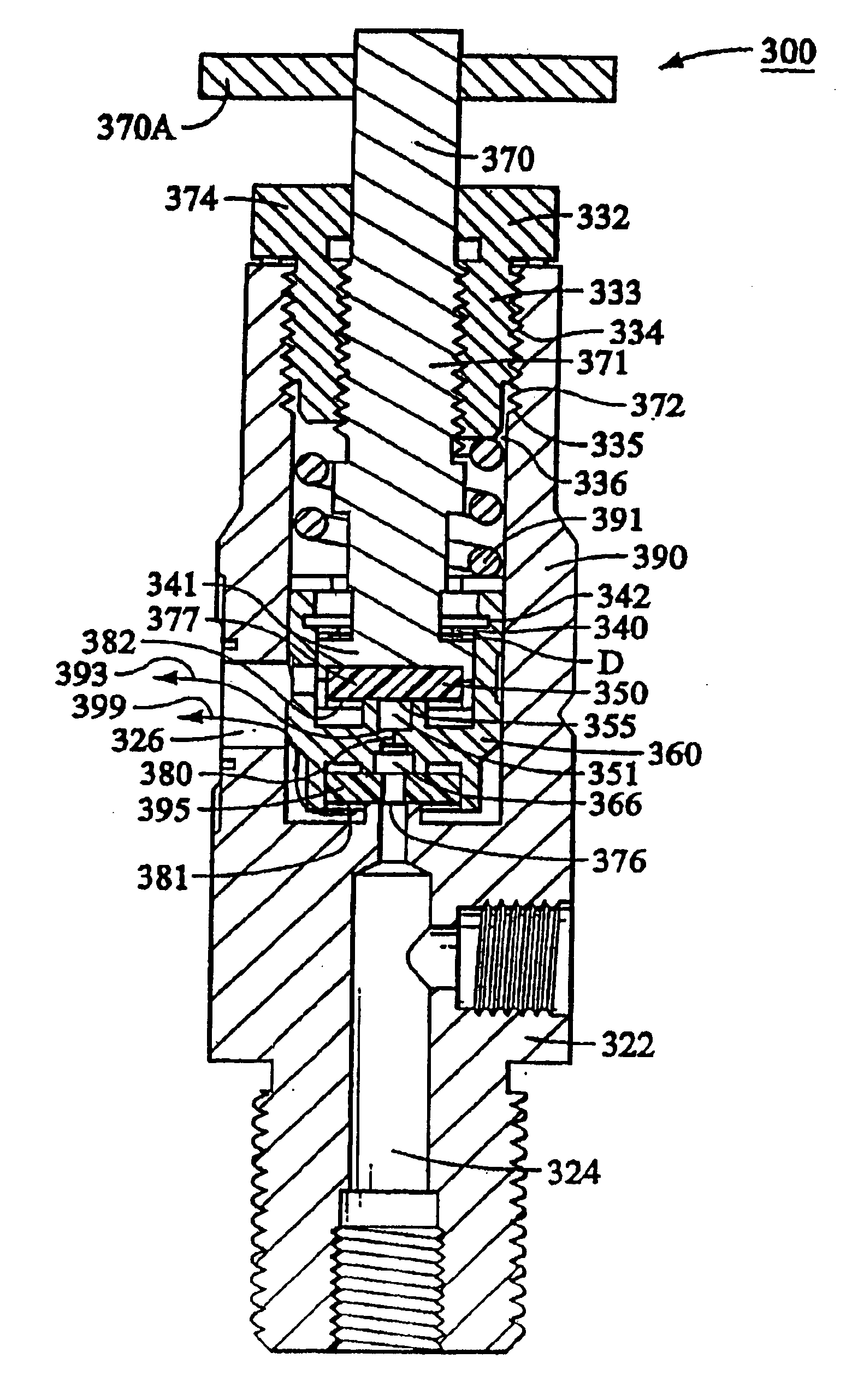
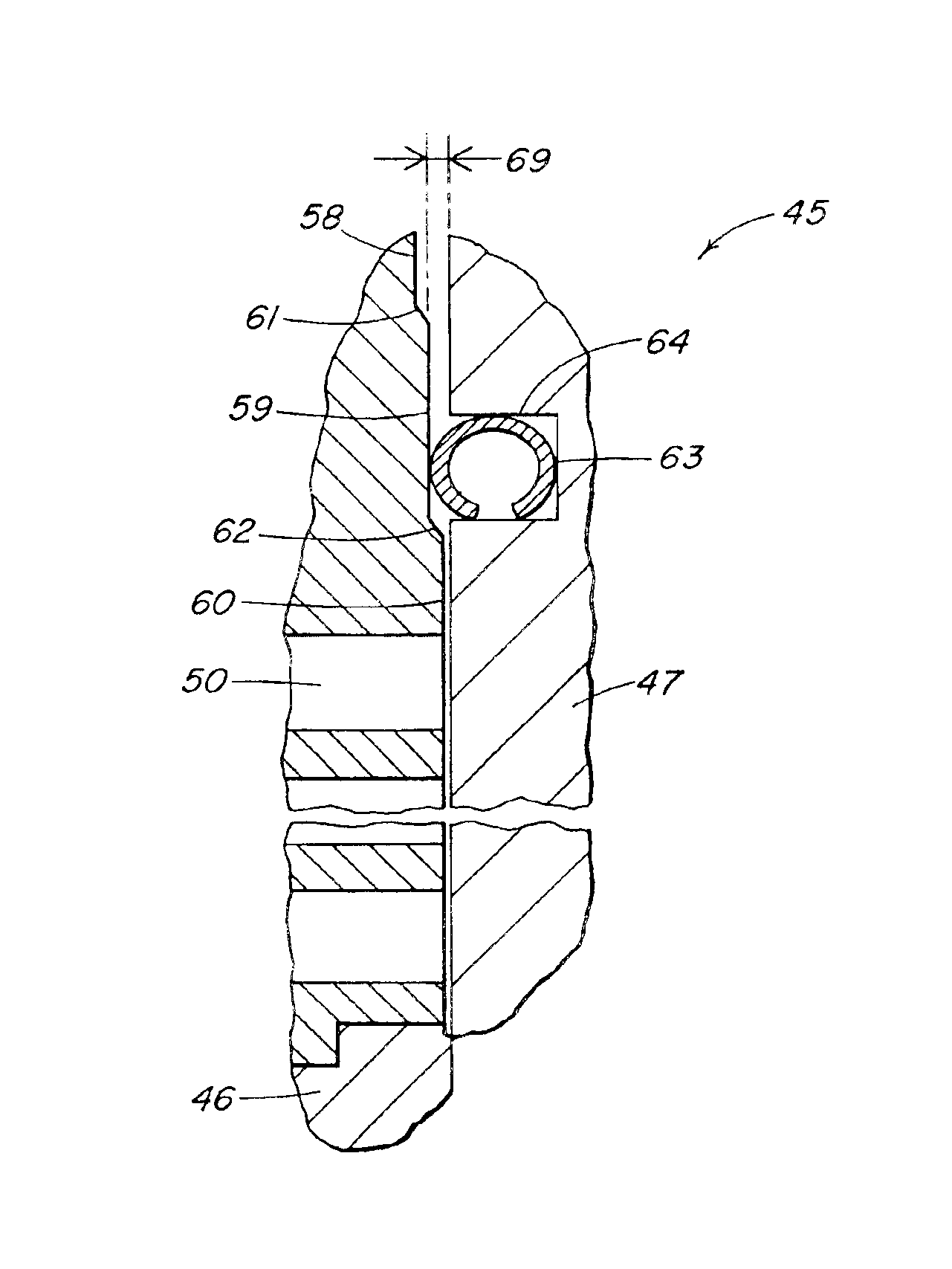
Control valve trim and bore seal
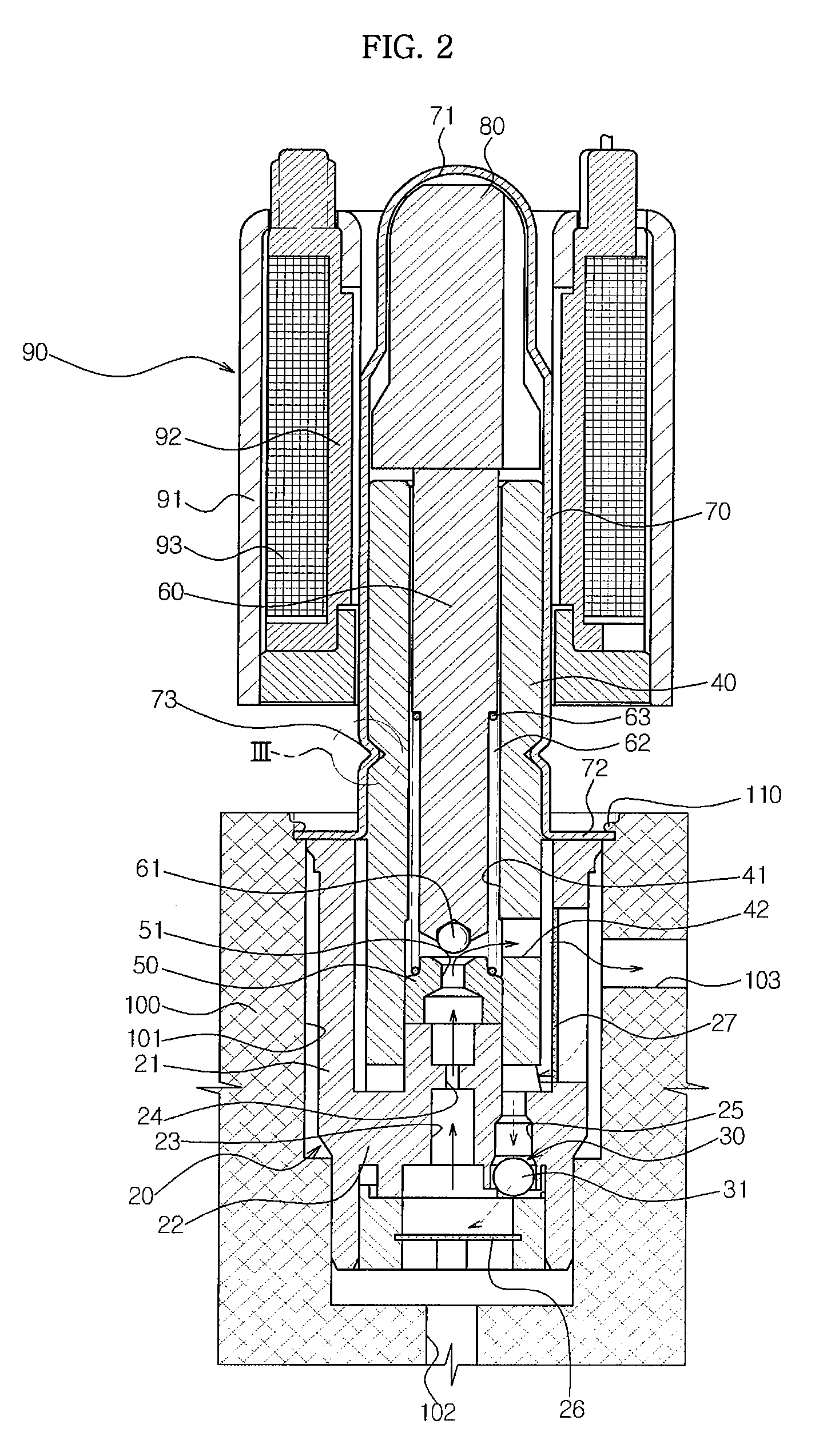
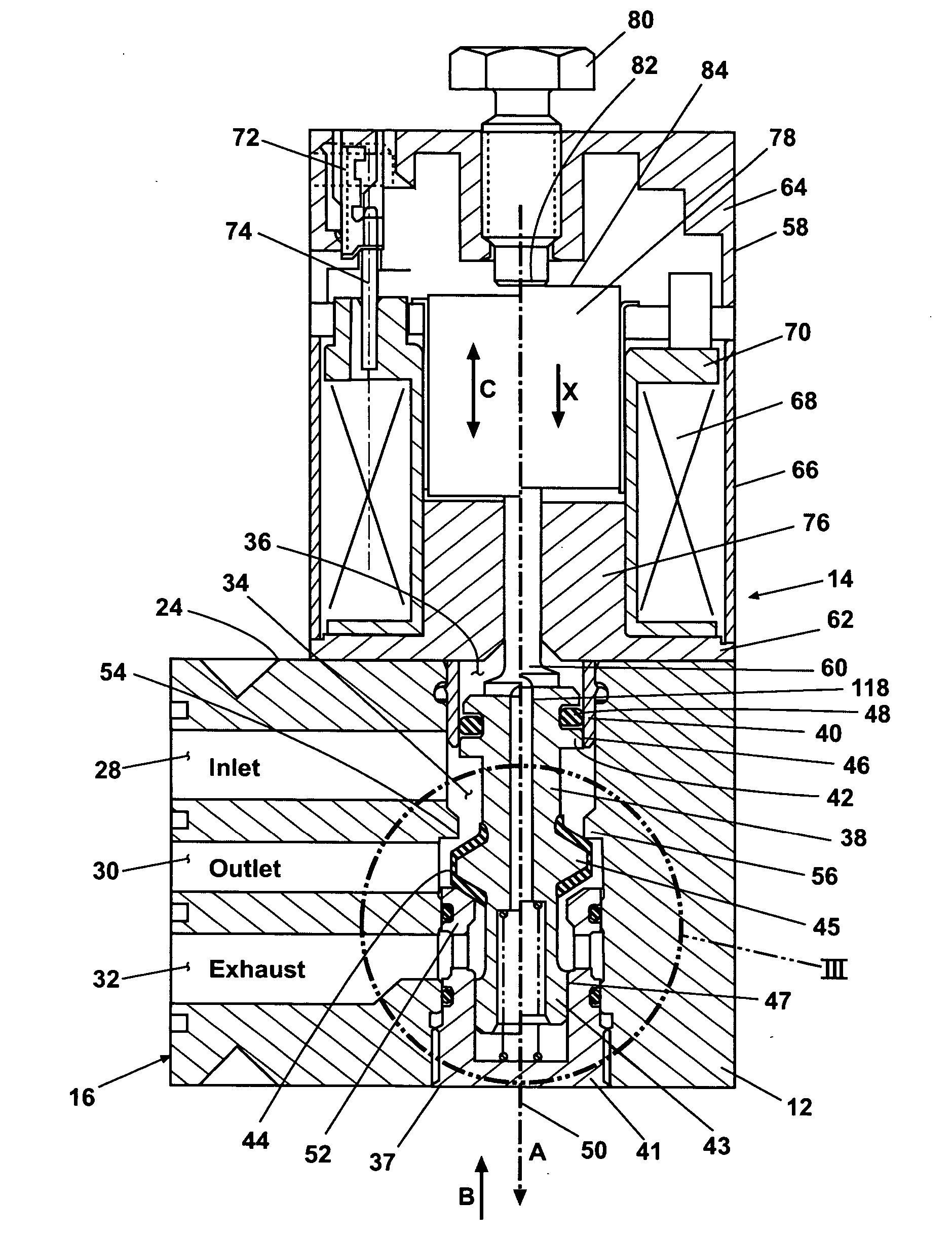
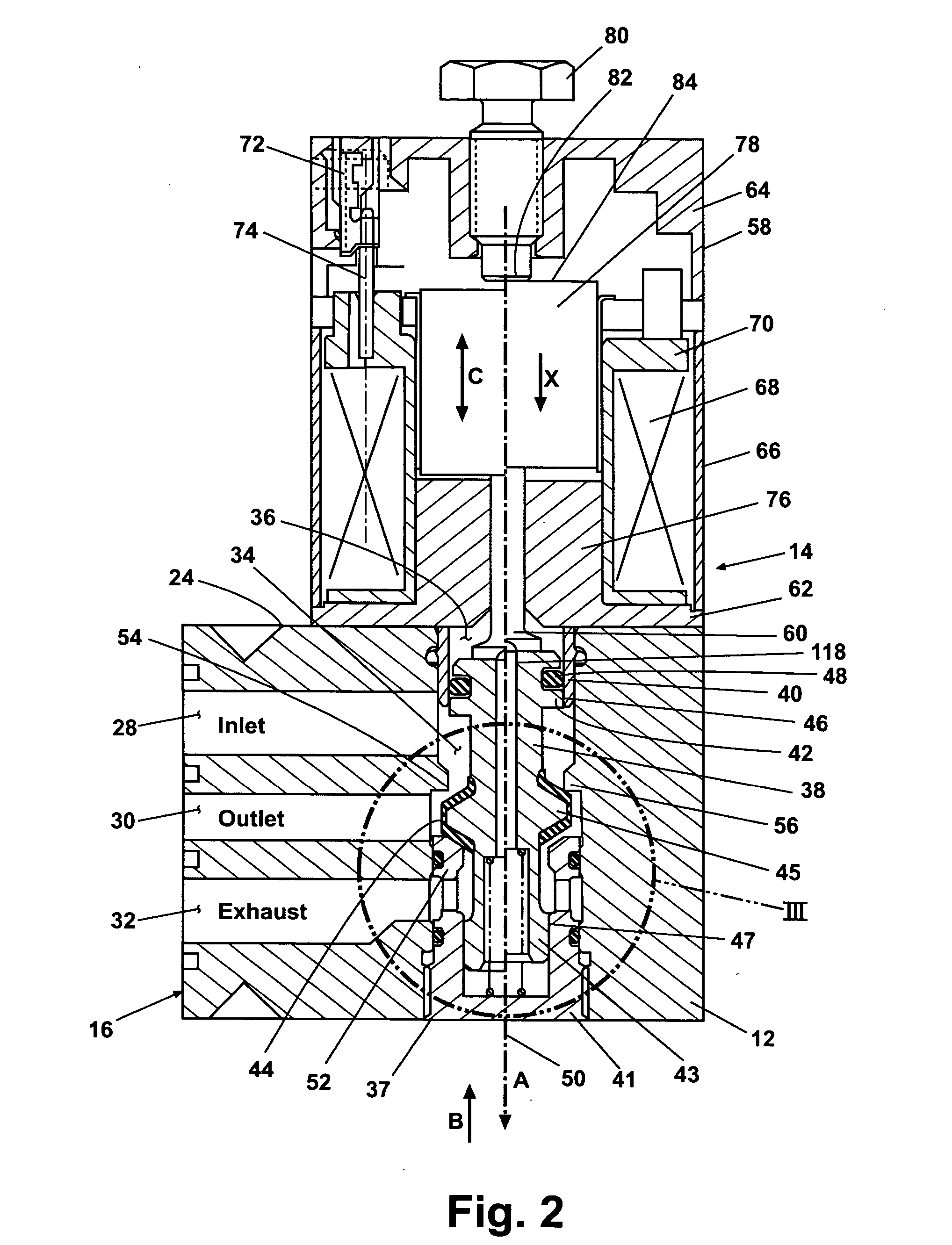
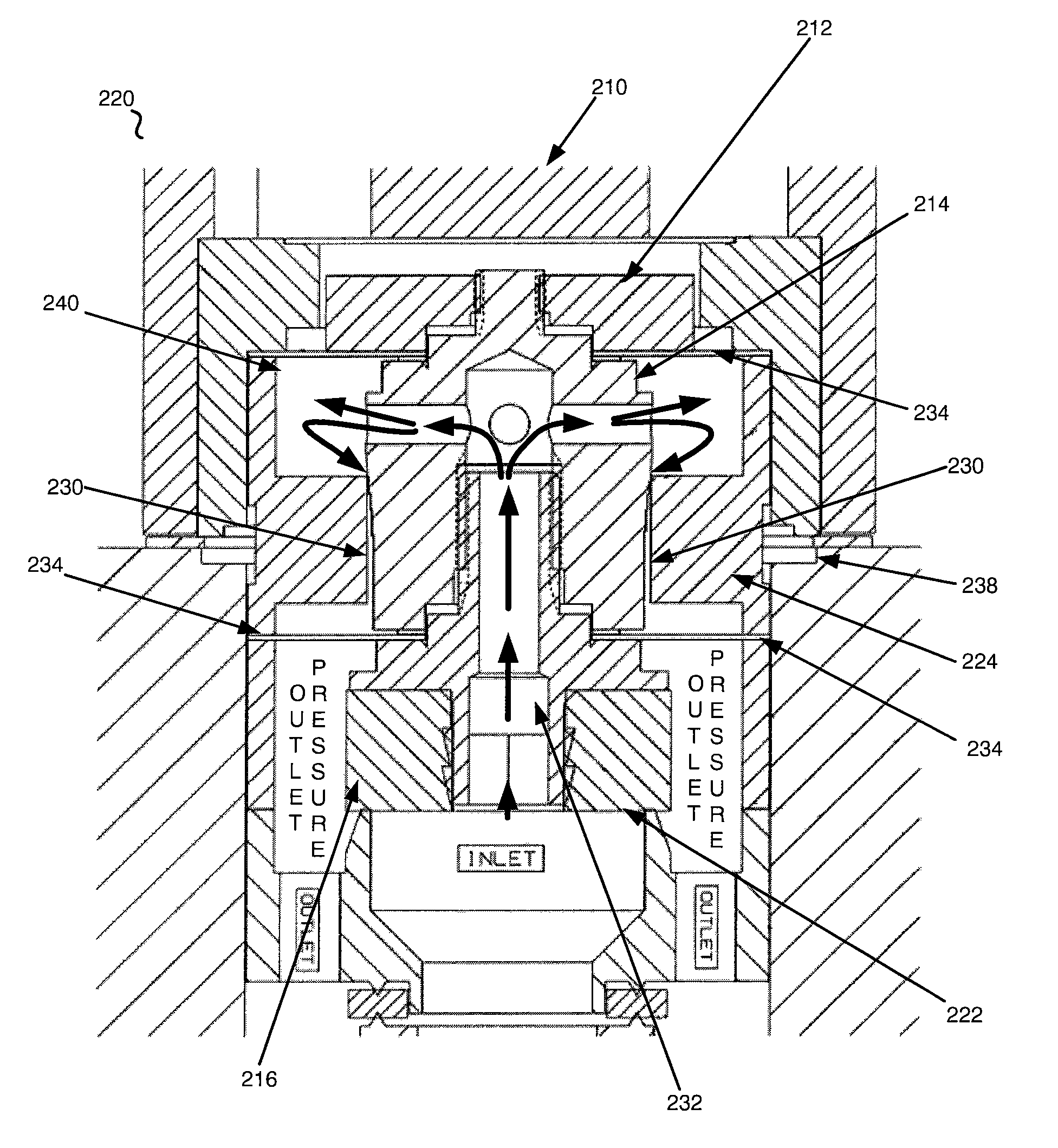
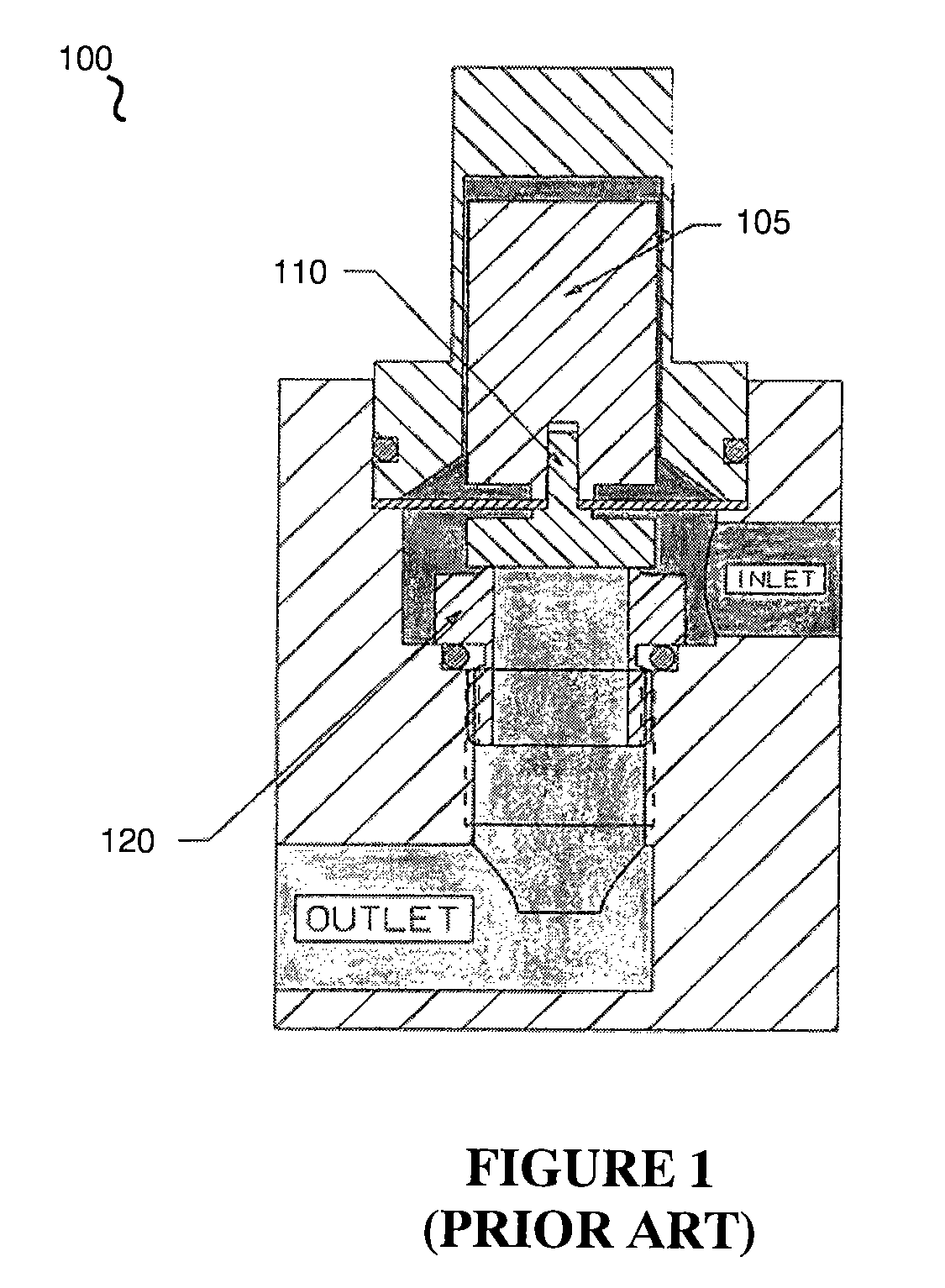
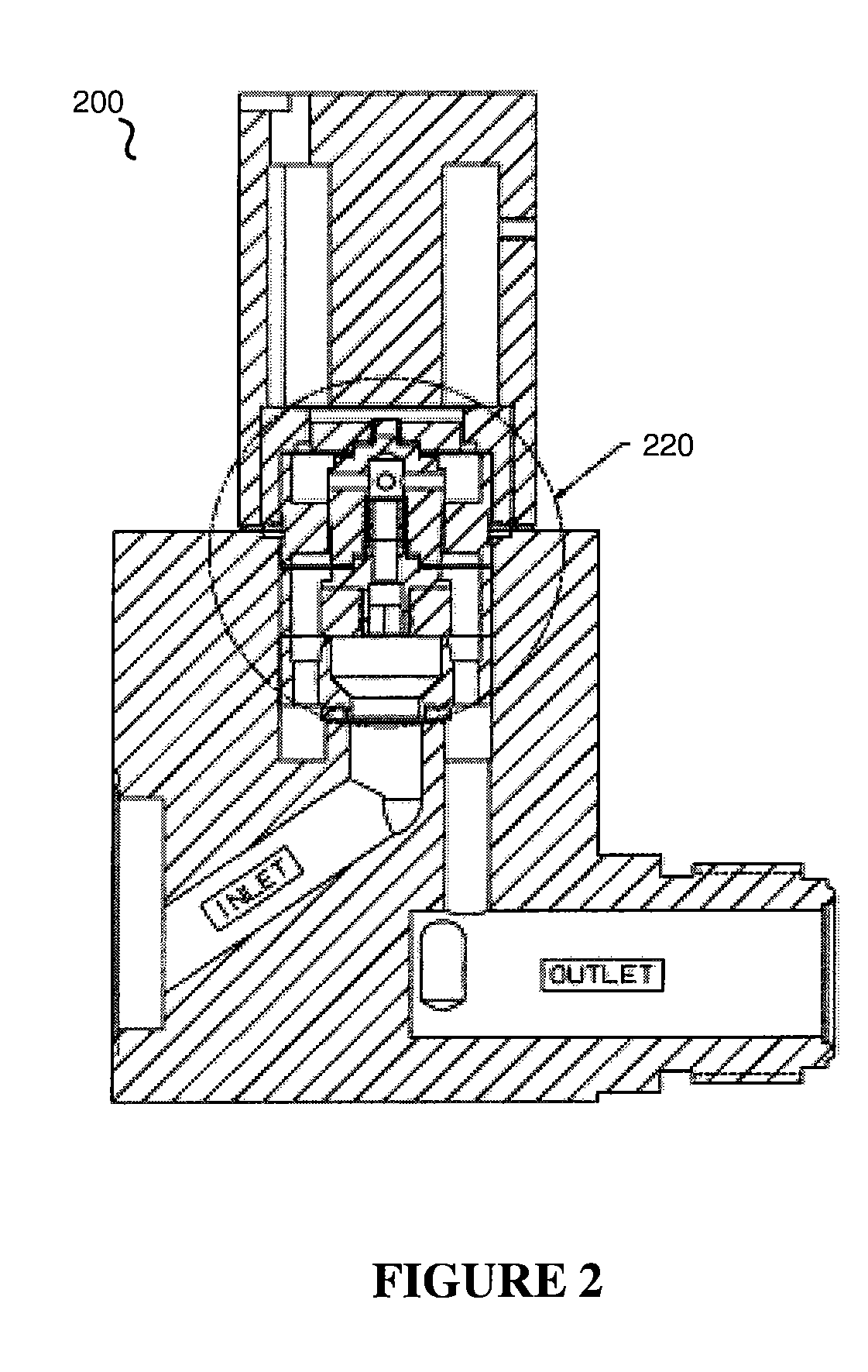
InactiveUS6851658B2Less stringent partReduced actuator forcePressure relieving devices on sealing facesValve members for absorbing fluid energyControl valvesActuator
An ANSI Leakage Class V control valve having consistent shut off characteristics with a reduced actuator force required to open and close the valve is provided. The trim arrangement of the control valve includes a valve cage having a multi-contoured inner surface. The multi-contoured inner surface can include a plurality of surfaces. The multi-contoured surface can include first, second, and third perimeter surfaces, and a first transition surface disposed between and coupling the first and second perimeter surfaces, and a second transition surface disposed between and coupling the second and third perimeter surfaces. The valve also includes a valve plug disposed at one end of a valve stem. The valve plug controls the fluid flow through the valve. The valve plug includes an opening through the plug for equalizing pressure across the valve plug. An annular channel is formed within a wall of the valve plug and is sized to accommodate a sealing ring. The sealing ring engages the second perimeter surface to form a fluid seal that substantially hinders fluid leakage through the valve.
Owner:FISHER CONTROLS INT LLC
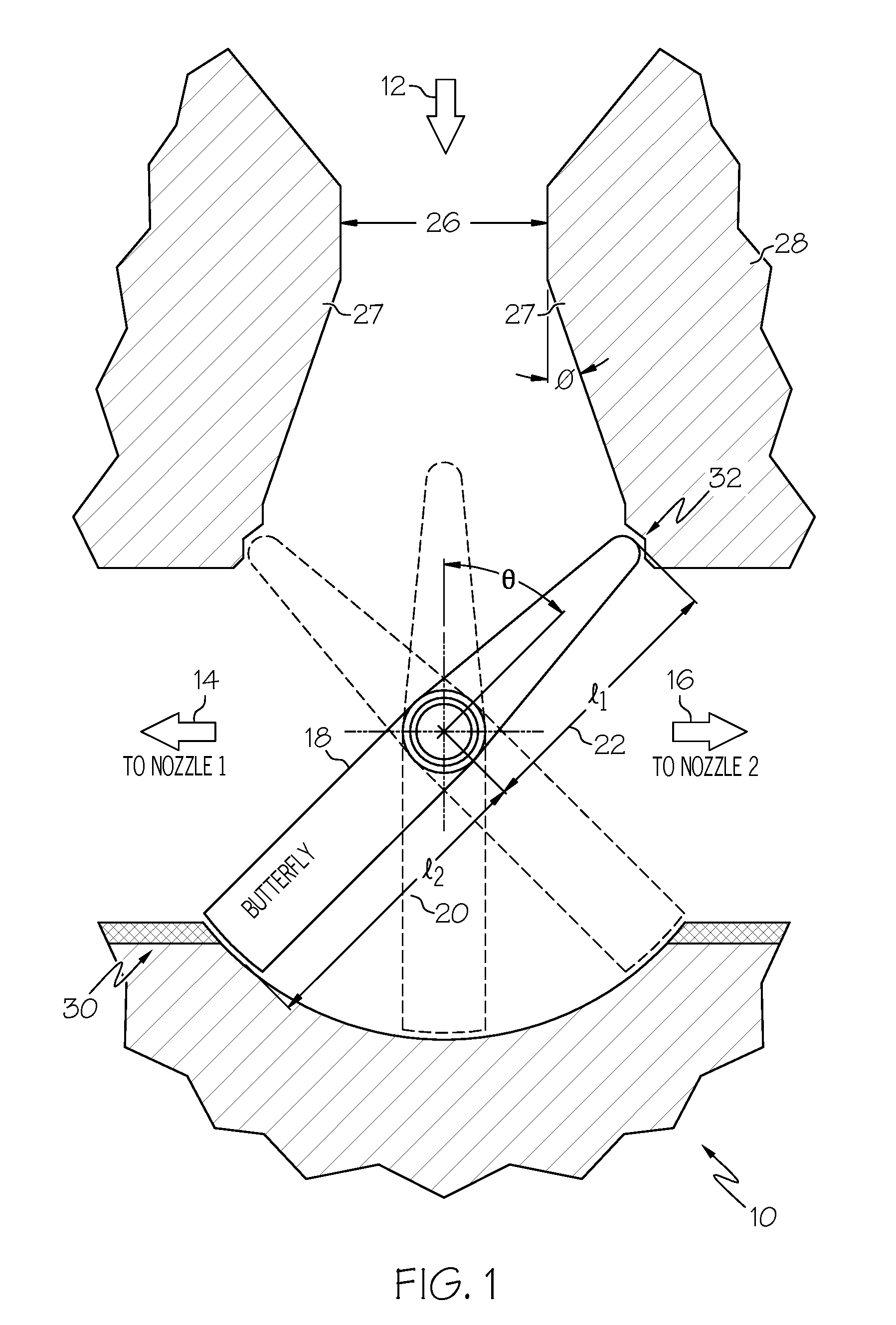
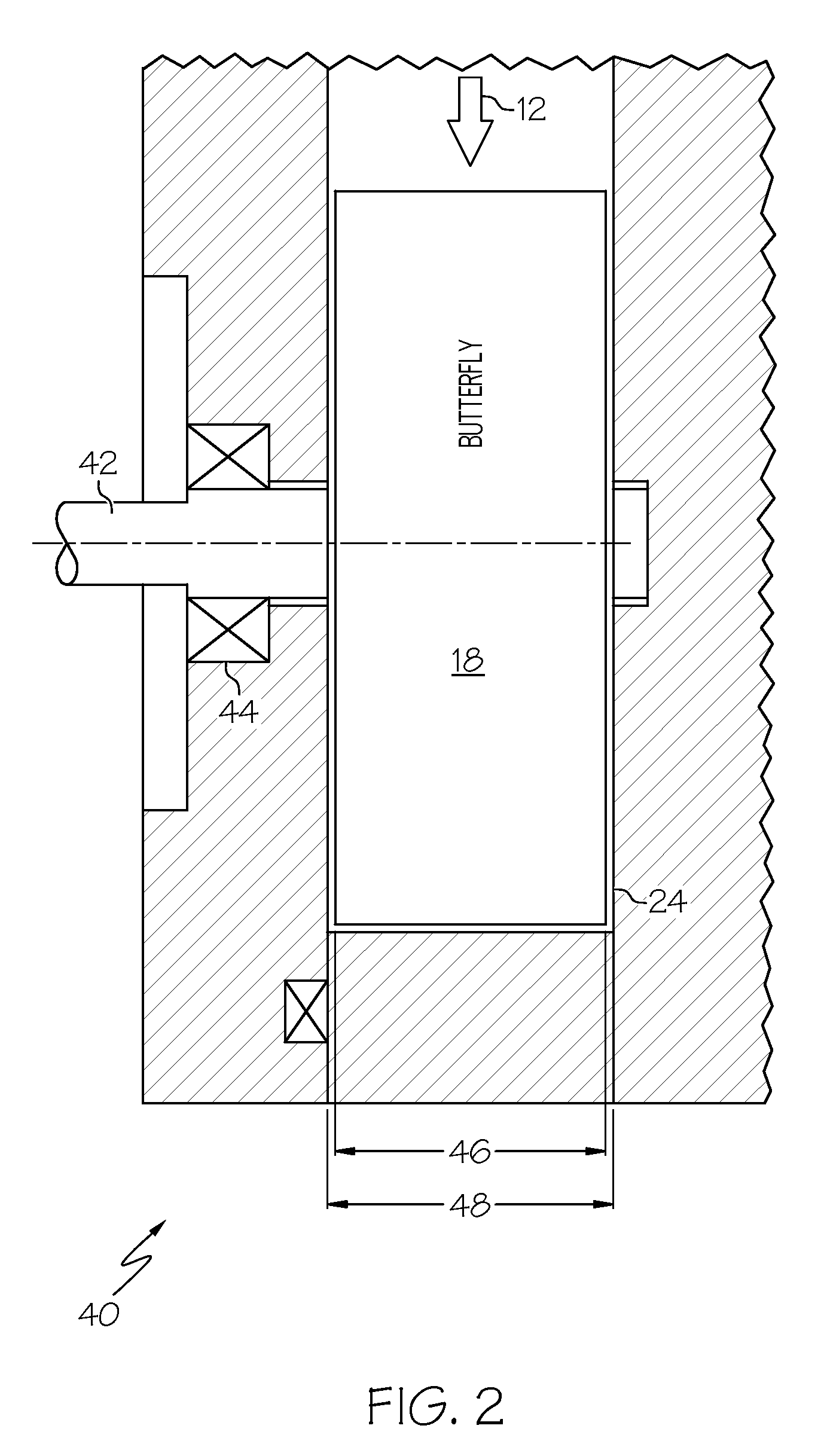
Force balanced butterfly proportional hot gas valve
InactiveUS20080302991A1Cosmonautic vehiclesPressure relieving devices on sealing facesEngineeringVALVE PORT
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
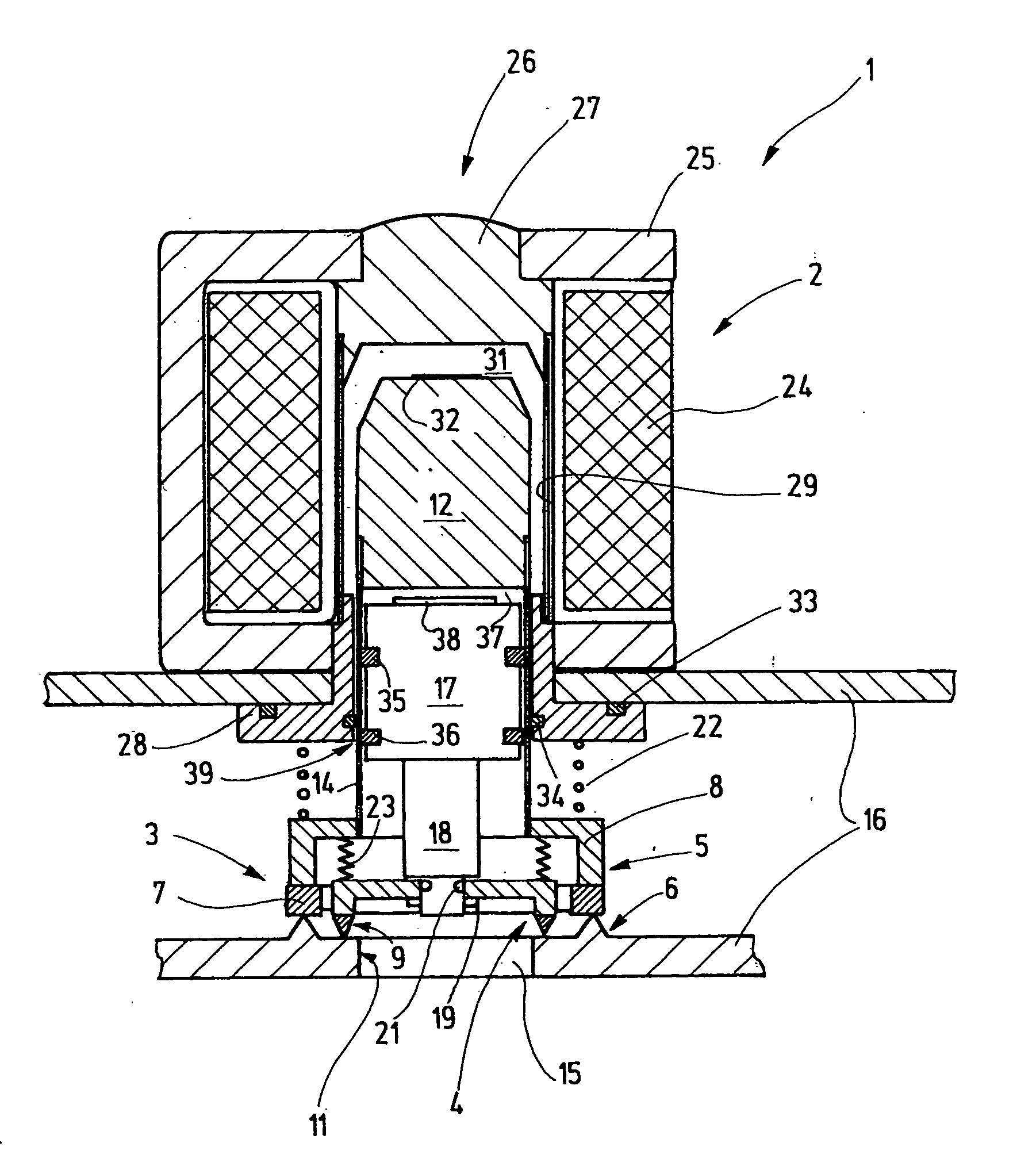
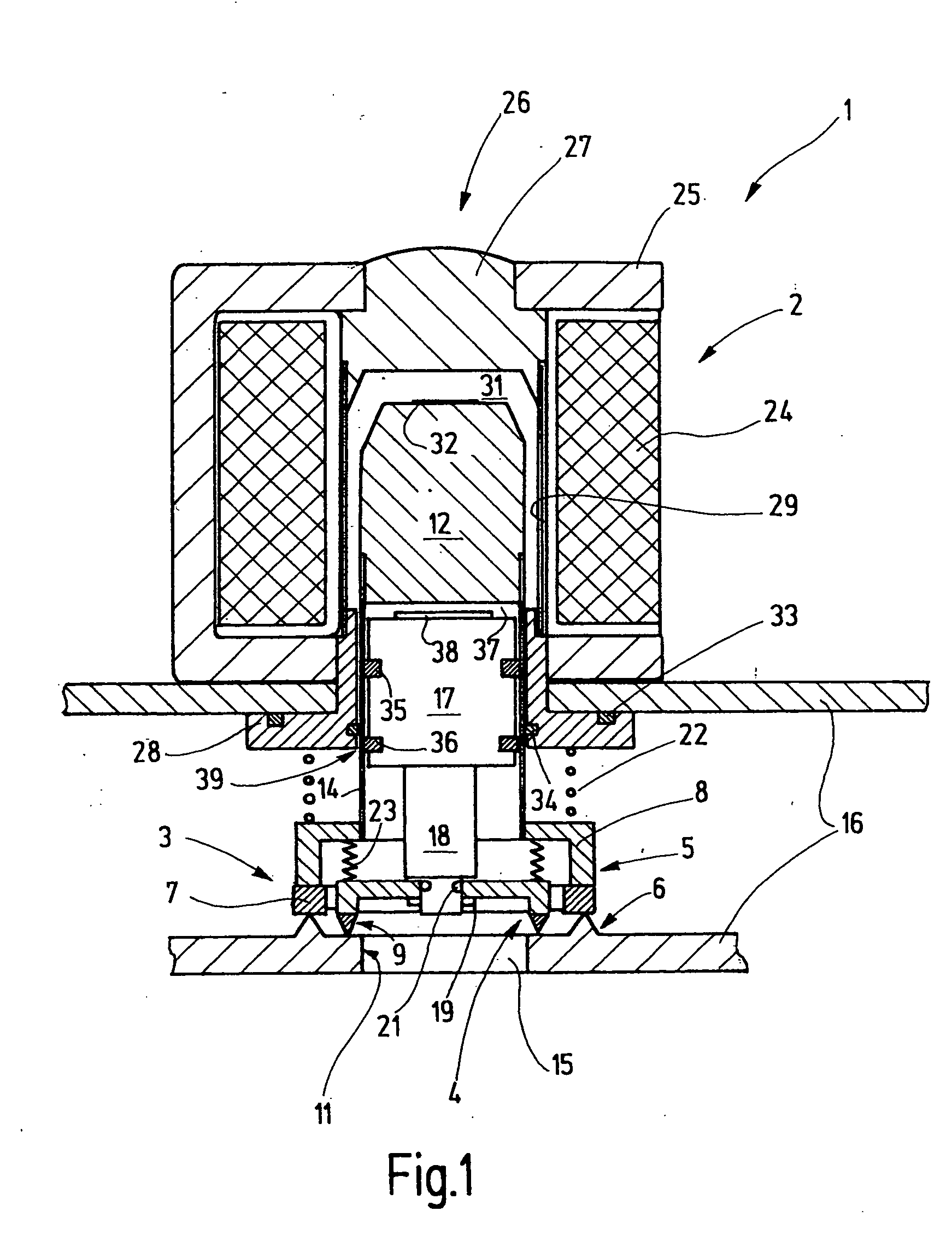
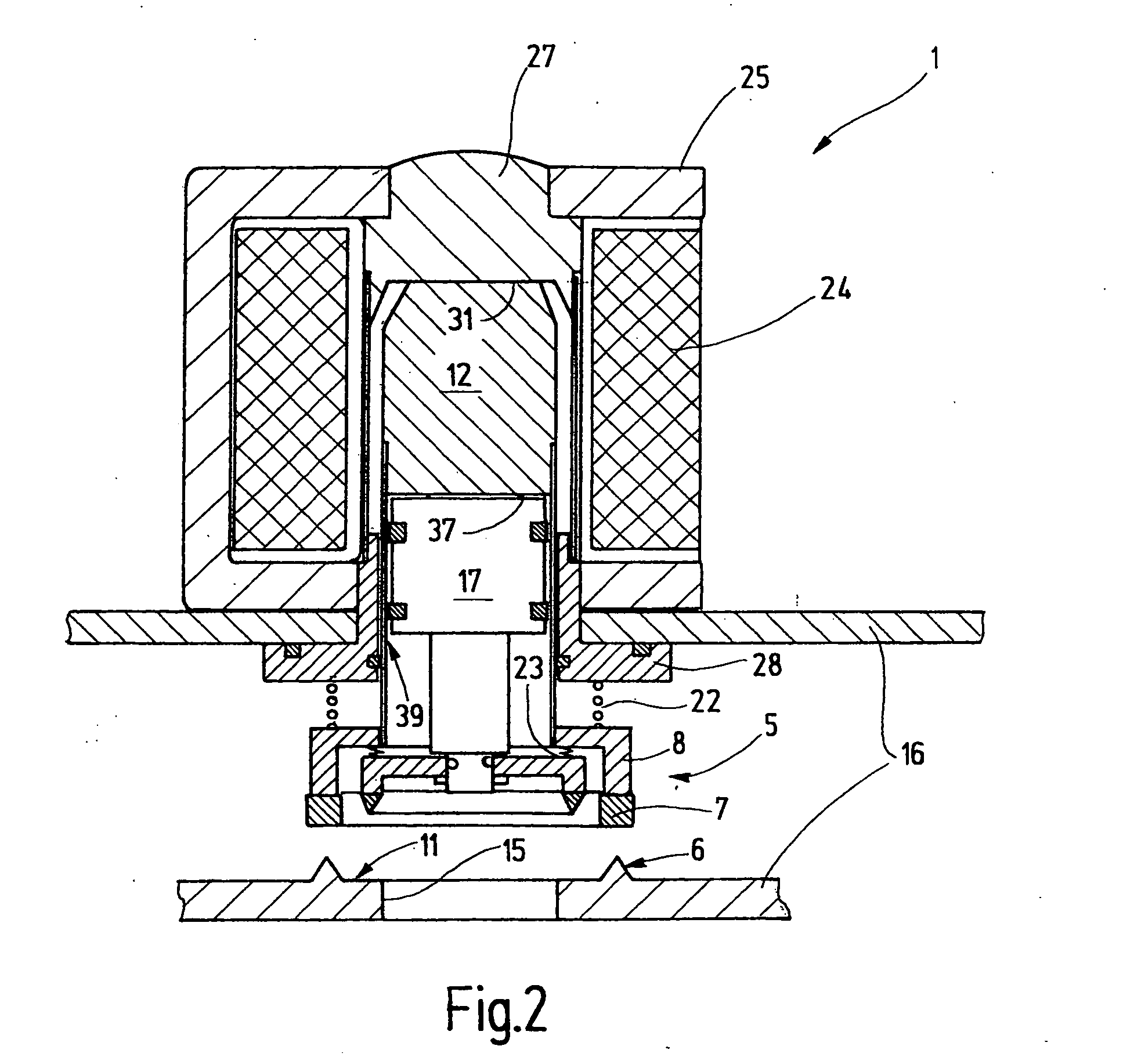
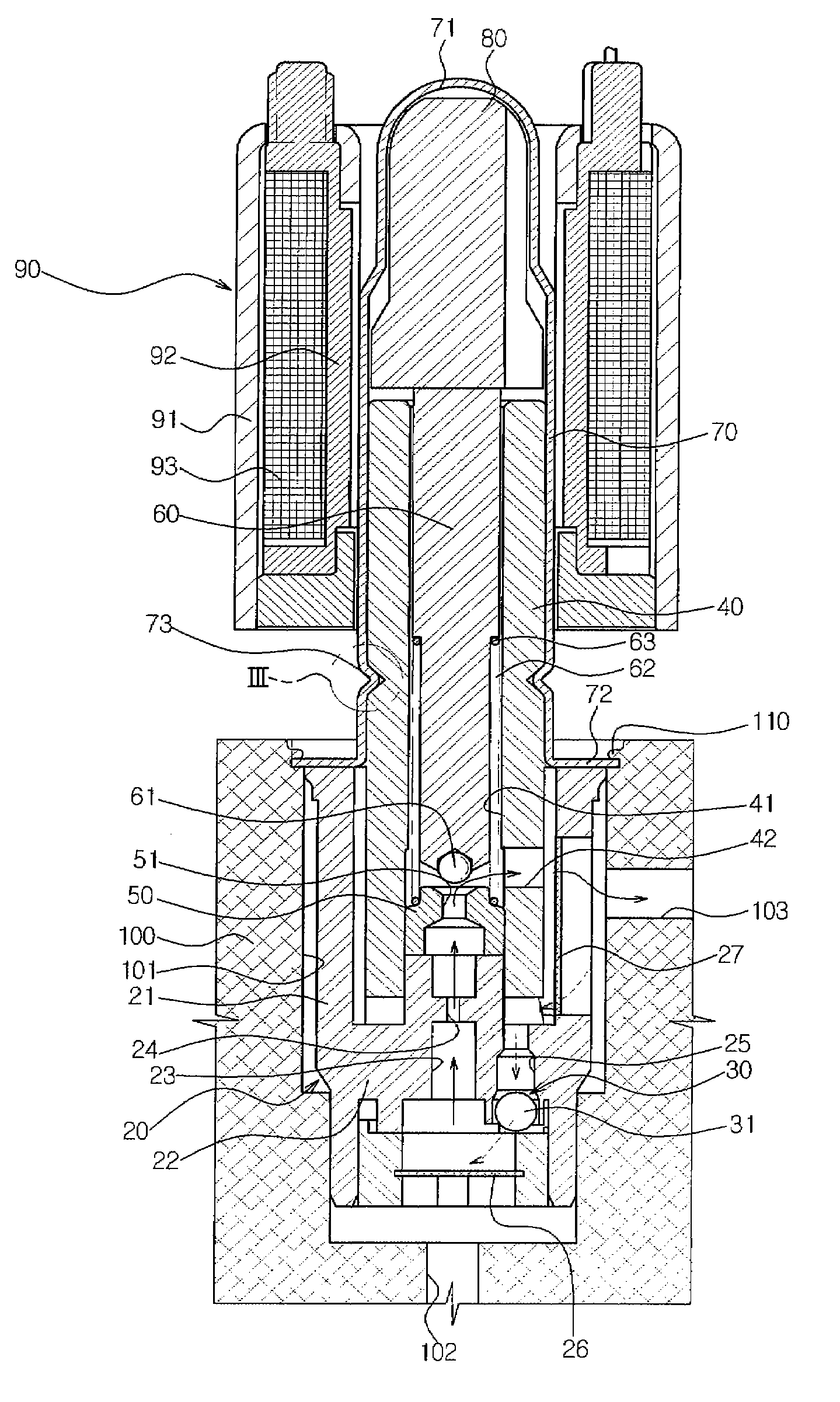
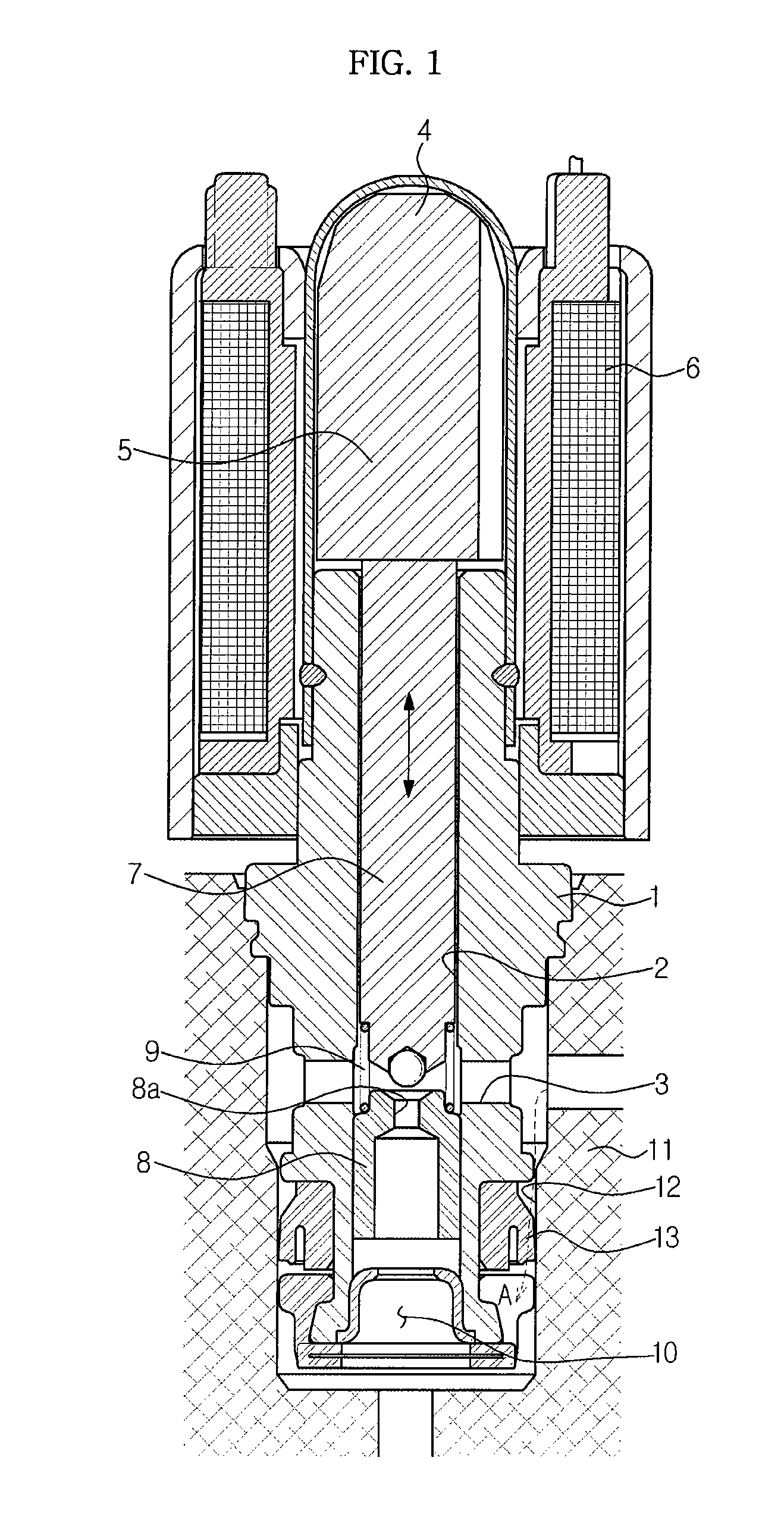
Solenoid valve for brake system
ActiveUS20090121541A1Simple constitutionEasy to manufactureOperating means/releasing devices for valvesPressure relieving devices on sealing facesSolenoid valveEngineering
A solenoid valve for a brake system, which has a simple constitution and can be easily manufactured with reduced manufacturing costs, is disclosed. A valve core is formed in a cylindrical shape, and has a through-hole formed in a longitudinal direction of the valve core and a fluid passage formed in a radial direction of the valve core so as to communicate with the through-hole. A sleeve is coupled to an outer surface of the valve core. The sleeve has a dome-shaped shielding portion at one end, and a flange portion to be fixed to a modulator block at the other end. An armature is slidably mounted in the sleeve. An exciting coil is provided to move the armature. A valve seat is fixed in the valve core, and has a first orifice. A plunger is mounted in the valve core. The plunger moves by movement of the armature to open or close the first orifice. A restoring spring is provided to press the plunger toward the armature. A filter member is coupled to the valve core to surround an outer surface and an end portion of the valve core, which are to be received in a bore of the modulator block. The filter member includes a filtering part to filter oil, a second orifice to rectify oil flow, and a check valve to permit oil to flow back when braking operation is released.
Owner:HL MANDO CORP
Directly operated pneumatic valve having a differential assist return
ActiveUS20060065315A1Eliminates bypass flowMove quickly and efficientlyOperating means/releasing devices for valvesServomotor componentsFluid controlNet return
A fluid control valve includes a valve body having both fluid inlet and discharge ports. A flow passage axially extending within the valve body communicates with the inlet and discharge ports. A valve member within the flow passage is movable by an actuator force in a first direction to direct a pressurized fluid from the inlet to the discharge port. The valve member includes first and second valve heads having different diameters and a valve seating member. The valve seating member engages first and second sealing diameters of the flow passage, the second sealing diameter being smaller than the first. Fluid pressure acting on the different diameters of the first valve head and valve seating member in contact with the second sealing diameter creates a net return force directing the valve member in a second direction opposite to the first direction upon removal of the actuator force.
Owner:MAC VALVES INC
Modular actuator system for valves and chokes
ActiveUS6883614B2Rapidly and safely and efficiently interchangedSimple and easyOperating means/releasing devices for valvesDrilling rodsLinear motionCoupling
The invention contemplates a simple coupling means for interfacing linear acting actuator shafts with valves or hydraulic chokes. The coupling means of the present invention allows either an actuator or an interconnected valve or choke to be rapidly, safely, and efficiently interchanged with a replacement part. The present invention is broadly applicable to a wide variety of actuator types having rectilinear motion outputs and to a large variety of valve and choke types which are operated by linear motions, including gate valves with or without balanced stems.
Owner:ADS SERVICES LLC
Balanced rotary servovalve
InactiveUS6470913B1Operating means/releasing devices for valvesServomotor componentsIn planePower flow
A rotory servovalve is constructed with a cylindrical annular housing and a cylindrical valve element rotatable therewithin. The valve housing has at least two inlet orifices, at least two outlet orifices, at least two first fluid transfer control orifices, and at least two second fluid transfer control orifices. At least two orifices of each type are located on opposite sides of the valve housing from each other. Preferably there is a first end orifice, a central orifice, and a second end orifice of each type. The end orifices of each type are angularly and longitudinally aligned with each other and are angularly offset 180 degrees from a central orifice of the same type. The end orifices of each type have an area equal to one-half the area of the central orifice of the same type and are equally spaced in opposite longitudinal directions from the central orifice of the same type. An imbalance of fluid forces within the servovalve mechanism is thereby avoided, both in a direction perpendicular to the valve axis and in planes passing through and containing the valve axis. By eliminating force imbalances within the valve in high-pressure applications the electrical current requirement and the mass of the components required for the driving motor or rotory solenoid that operates the valve are reduced.
Owner:WOODWORTH RAYMOND D
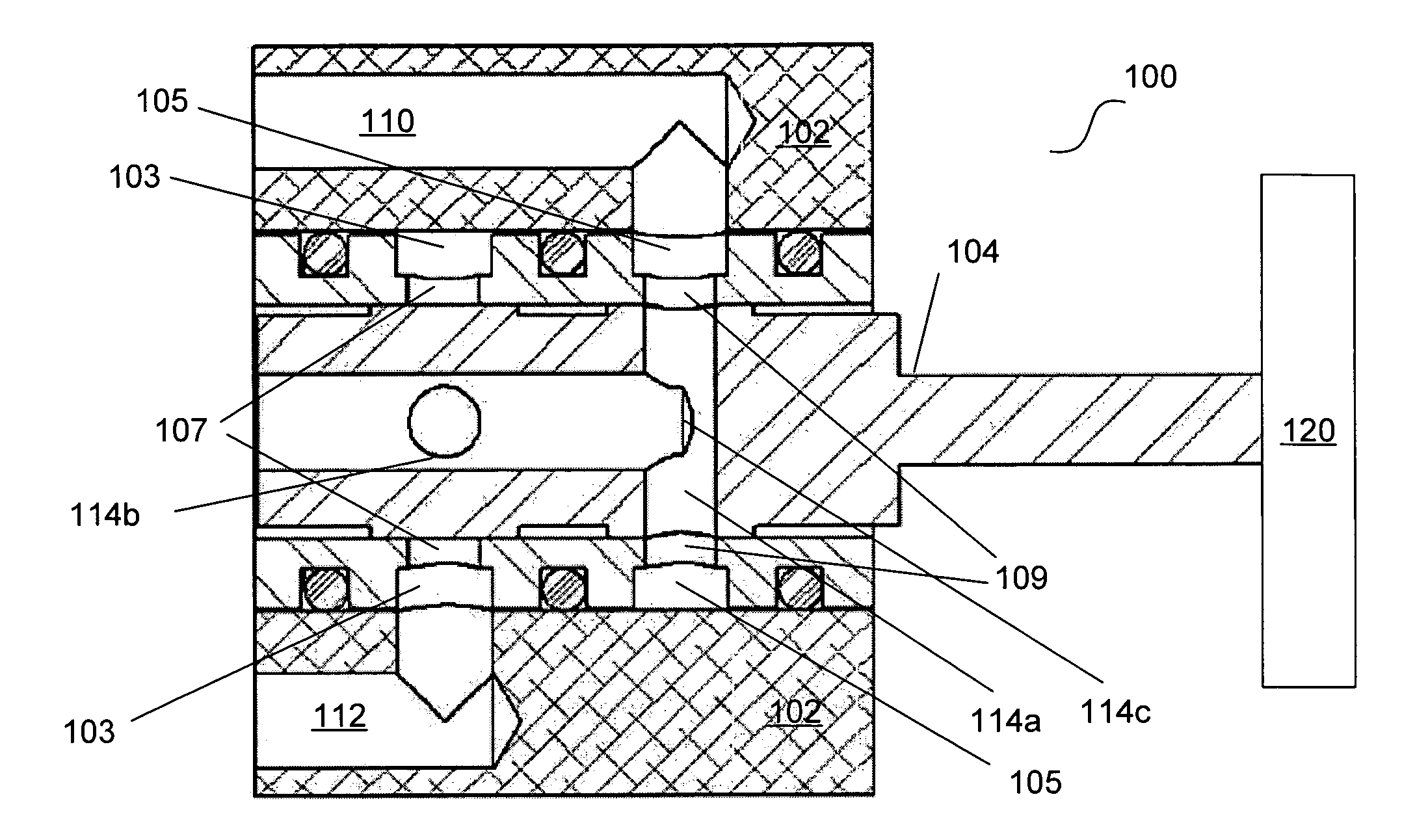
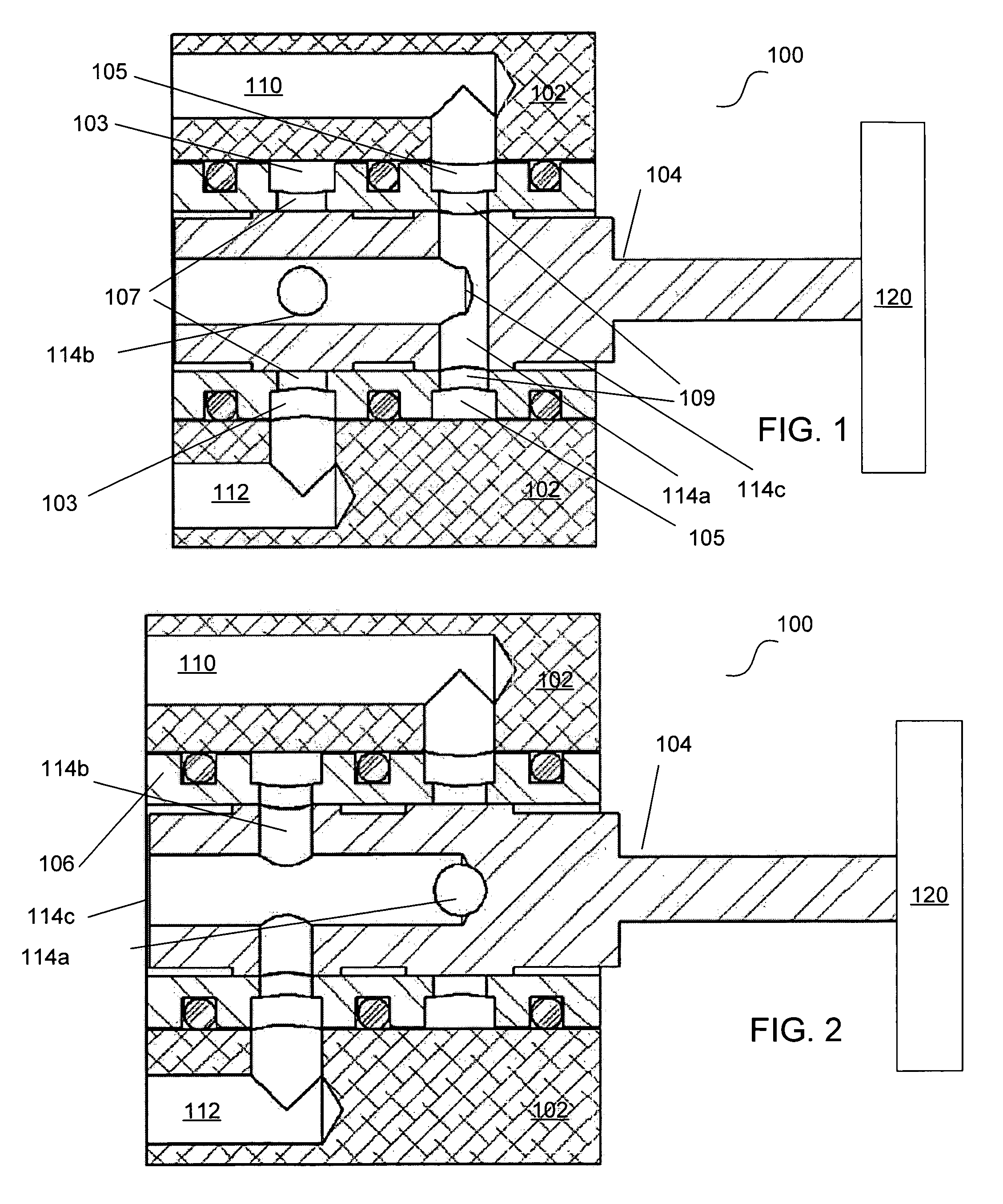
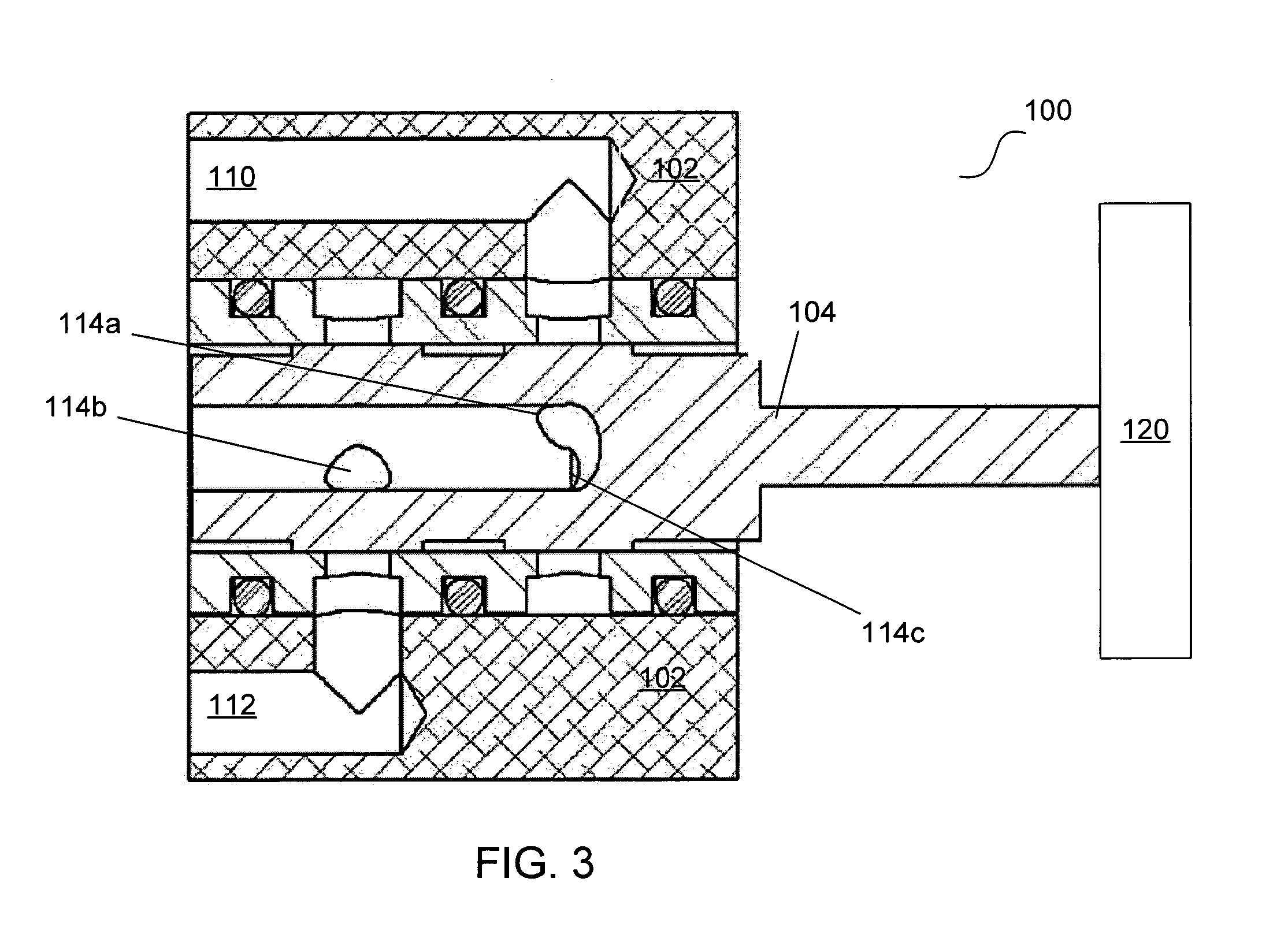
Solenoid valve
InactiveUS20050217740A1Constant volumeOperating means/releasing devices for valvesServomotor componentsSolenoid valveEngineering
A solenoid valve comprises a solenoid portion 10 and a valve portion 20. The solenoid portion 10 is constructed by a stator core 12, an electromagnetic coil 14 and a plunger 15. The valve portion 20 is constructed by a valve sleeve 21 and a spool 25 axially forming plural lands 26a-26c in series. The plunger 15 is axially moved by electromagnetic attraction and drives the spool 25. There are formed the same pressurized areas at the plunger 15 and the land of the spool 25 closest to the plunger 15. Therefore, the volume in an intermediate space B between the plunger 15 and the spool 25 is constant and contaminants in the oil are not sucked into the intermediate space B.
Owner:JTEKT CORP
High bandwidth rotary servo valves
InactiveUS7322375B2Pressure relieving devices on sealing facesValve members for absorbing fluid energyHigh bandwidthEngineering
Owner:VANDERBILT UNIV
Electronic expansion valve
ActiveCN103388694AReduce shockAvoid eccentricityOperating means/releasing devices for valvesPressure relieving devices on sealing facesCoolant flowEngineering
The invention discloses an electronic expansion valve, which is characterized in that a sleeve (4) is fixed in a main valve cavity (11), the lower end part of the sleeve (4) is supported by a valve seat (1), the lower end part of the sleeve (4) wraps a main valve port (441), a valve core seat (2) is axially movably arranged in the sleeve (4), the lower part of a valve needle part (3) extends into the sleeve (4) for opening and closing a valve core valve port (21), and a first communicating hole (41) close to the main valve port (441) and a second communicating port (42) far away from the main valve port (441) are formed in the periphery side wall of the sleeve (4). When a coolant flows forwards, overlarge impact of the coolant on the valve core seat can be avoided due to the structural design of the electronic expansion valve, the valve core seat is prevented from being eccentric, internal leaking is avoided and the work reliability of the system is ensured.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SANHUA INTELLIGENT CONTROLS CO LTD
Pressure balanced fluid control device
ActiveUS20050173667A1Avoid enteringOperating means/releasing devices for valvesPressure relieving devices on sealing facesWorking fluidFluid control
The present invention is directed to a pressure balanced fluid control device. In one illustrative embodiment, the device comprises a body, a bonnet coupled to the body, a valve stem operatively coupled to a gate positioned in the body, a valve stem seal positioned between the valve stem and the bonnet, wherein a sealed cavity exists above the valve stem seal, and an opening through the bonnet that is adapted to allow a pressure of a working fluid flowing through the valve to be exerted in the sealed cavity above the valve stem seal. In another illustrative embodiment, the device comprises a body, a bonnet coupled to the body, a valve stem operatively coupled to a gate positioned in the body, a valve stem seal positioned between the valve stem and the bonnet, wherein a sealed cavity exists above the valve stem seal, and an opening through the bonnet, the opening being in fluid communication with the sealed cavity and an interior region of the body. In a further illustrative embodiment, the device comprises a body, a bonnet coupled to the body, a valve stem operatively coupled to a gate positioned in the body, a valve stem seal positioned between the valve stem and the bonnet, wherein a sealed cavity exists above the valve stem seal, a piston chamber formed in the bonnet, the piston chamber being in fluid communication with the sealed cavity and an interior region of the body, and a piston positioned in the piston chamber.
Owner:FMC TECH INC
Low emission fluid transfer device
ActiveUS8113240B2Easy to openEasy to moveContainer filling methodsCouplingsTransfer systemEngineering
A fluid transfer system includes a transfer device coupled to a dry break coupler. The transfer device includes a valve assembly moveable between an open and a closed position. The valve assembly includes a main valve and a pilot valve. An actuator controls both the main valve and the pilot valve. A cam plate interconnects the actuator and the valve assembly. The cam plate provides a quick acting shutoff to quickly move the valve assembly to the closed position. A pivotal and rotatable connector couples the transfer device to the dry break coupler. A lock is integrated with the actuator to lock the valve assembly in the closed position.
Owner:MARSHALL EXCELSIOR CO
Fluid control devices
ActiveUS7357151B2Operating means/releasing devices for valvesPressure relieving devices on sealing facesFluid controlDifferential pressure
Owner:EXXONMOBIL UPSTREAM RES CO
Beverage container lid
ActiveUS20090159595A1Enhanced advantageAvoid disadvantagesCapsPressure relieving devices on sealing facesEngineeringMechanical engineering
A beverage container lid for a container base having a reservoir, the lid comprising a shell removably mountable on the base comprising a first drink passage that extends through the shell and communicates with ambient and a cartridge removably engageable to the shell. A second drink passage is in communication with the first drink passage and is formed between an outer surface of the cartridge and inner surface of the shell. The cartridge comprises a valve that is moveable between an open condition and closed condition to control communication between the reservoir and second drink passage.
Owner:HELEN OF TROY LIMITED
Wastegate valve and associated method
InactiveUS20060289072A1Operating means/releasing devices for valvesInternal combustion piston enginesWastegateProduct gas
A wastegate valve and associated method for controlling a flow of gas, such as a flow of exhaust gas from an exhaust inlet of a turbocharger, are provided. The wastegate valve includes multiple bypass ports that are selectively opened and closed by poppets, which are controlled by a linkage. The poppets are configured so that the pressure of the gas in the exhaust inlet biases one of the poppets to the open position and one of the poppets to the closed position. Thus, the forces resulting from the pressure of the gas on the poppets are offset, thereby reducing the force required for adjusting or maintaining the position of the linkage and the poppets.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Multi-stage Pressure Equalization Valve Assembly for Subterranean Valves
ActiveUS20110079394A1Avoid enteringOperating means/releasing devices for valvesConstructionsDifferential pressureControl system
A downhole valve that operates on turning of a member having a passage through it with a control system also features a passage from above an uphole seat for the member which communicates to the isolated passage within the member when the valve is closed. The passage features a check valve assembly that preferably has redundant sealing features and filters to prevent debris entry. Pressure applied from above the closed member gets through the check valve assembly to equalize the higher pressure below the ball with the pressure raised in the ball from pressure application at the surface. Removal of the applied pressure reseats the check valve or valves to allow the hydraulic system to rotate the member while the member is no longer subject to a high differential pressure.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
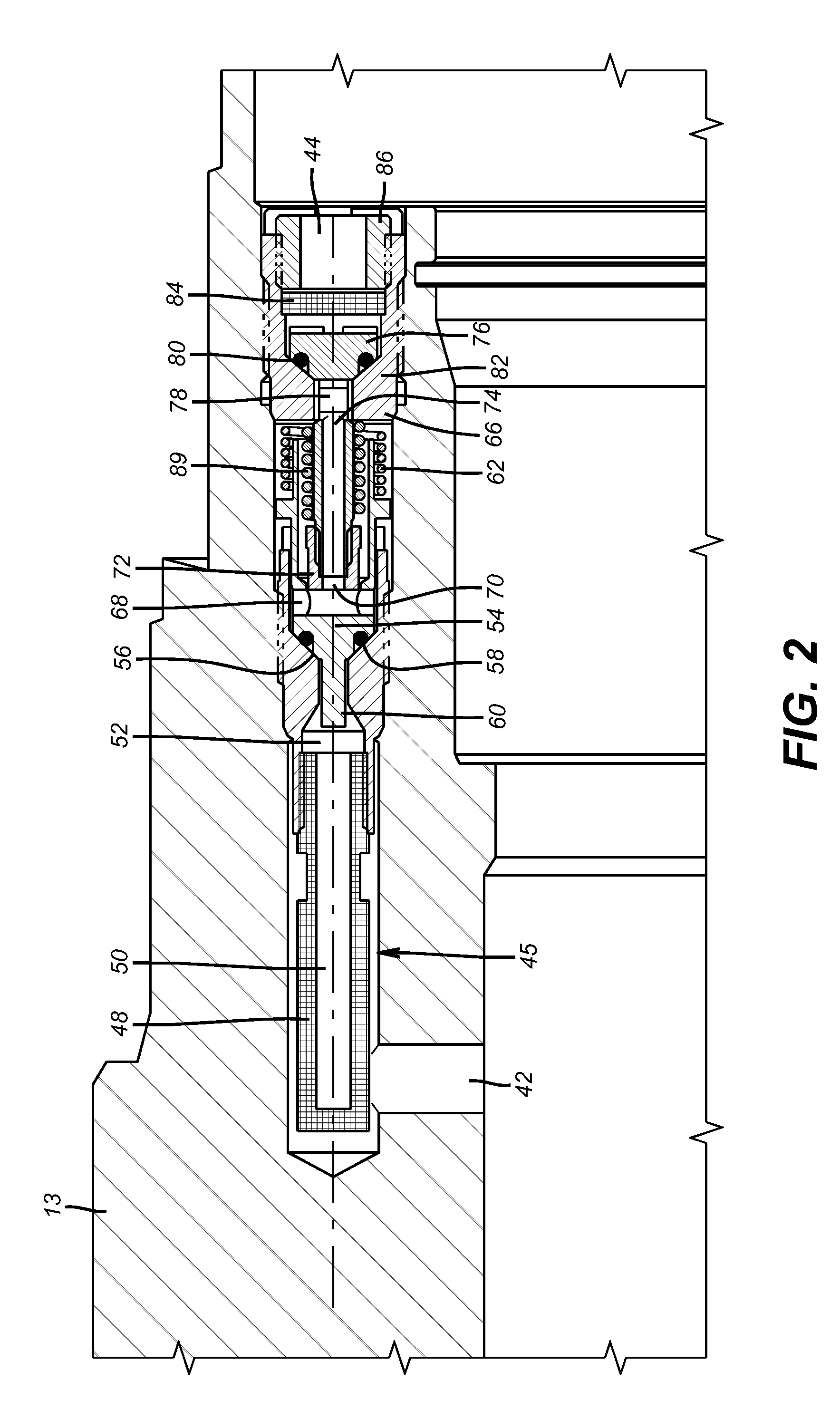
Fluid admission system for providing a pressure-balanced valve
ActiveUS8272399B2Eliminates valve lock-upLittle strengthInternal combustion piston enginesEngine diaphragmsEngineeringMechanical engineering
Owner:WOODWARD GOVERNOR CO
Pressure balanced valve
ActiveUS20120323379A1Operating means/releasing devices for valvesPressure relieving devices on sealing facesEngineeringPressure balance
The disclosed embodiments include a pressure balance valve that solves one or more problems associated with existing designs. For example, in one embodiment, a pressure balancing valve assembly is disclosed that provides a low cost frictionless assembly that is constructed to not seal the leak path between an inlet port and an outlet port. Instead, this leak path is minimized with small angle tapered plunger and a precision bored annulus to provide a defined area for the pressure drop to occur and to limit the flow from the inlet to the outlet.
Owner:BROOKS INSTRUMENT
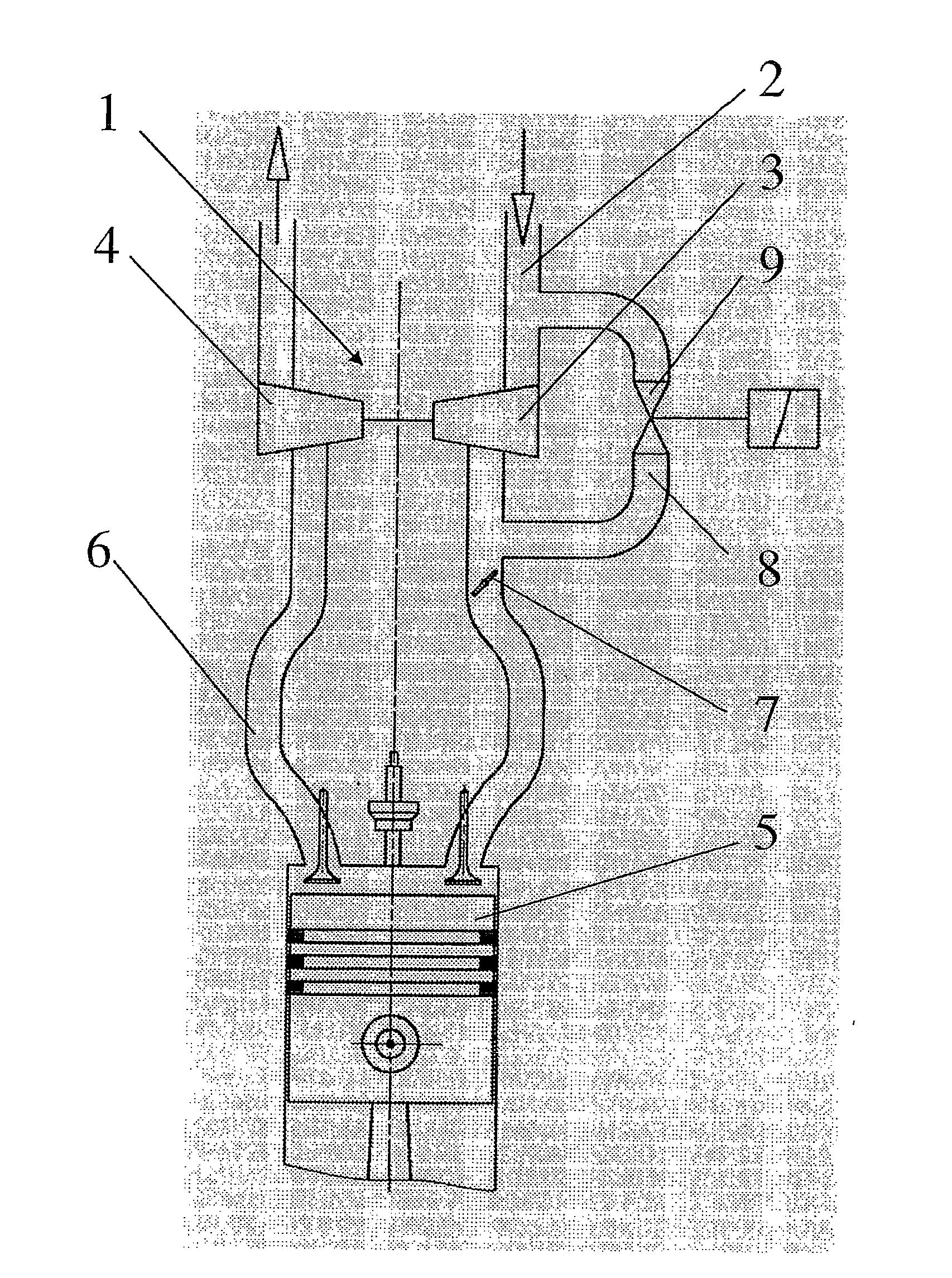
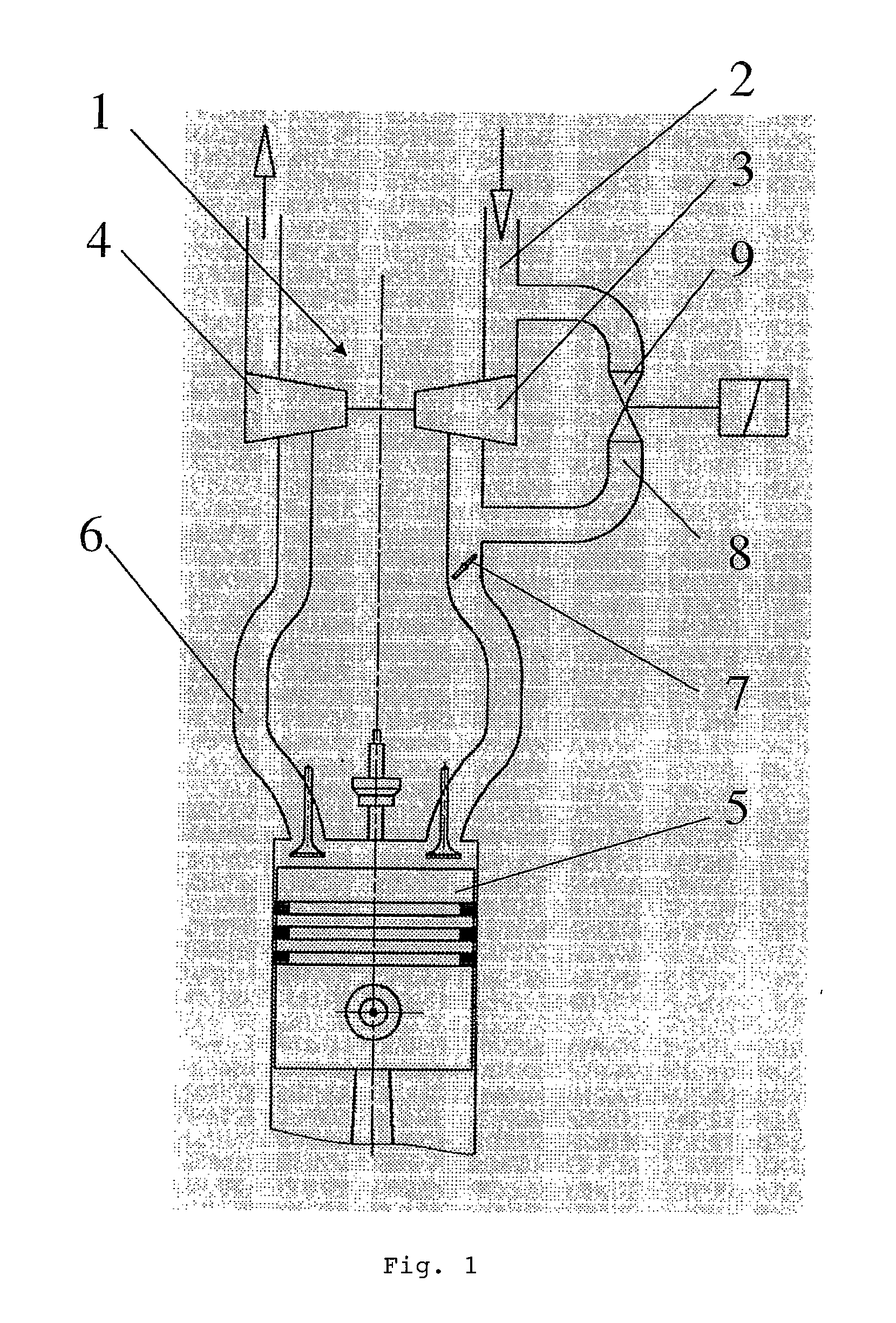
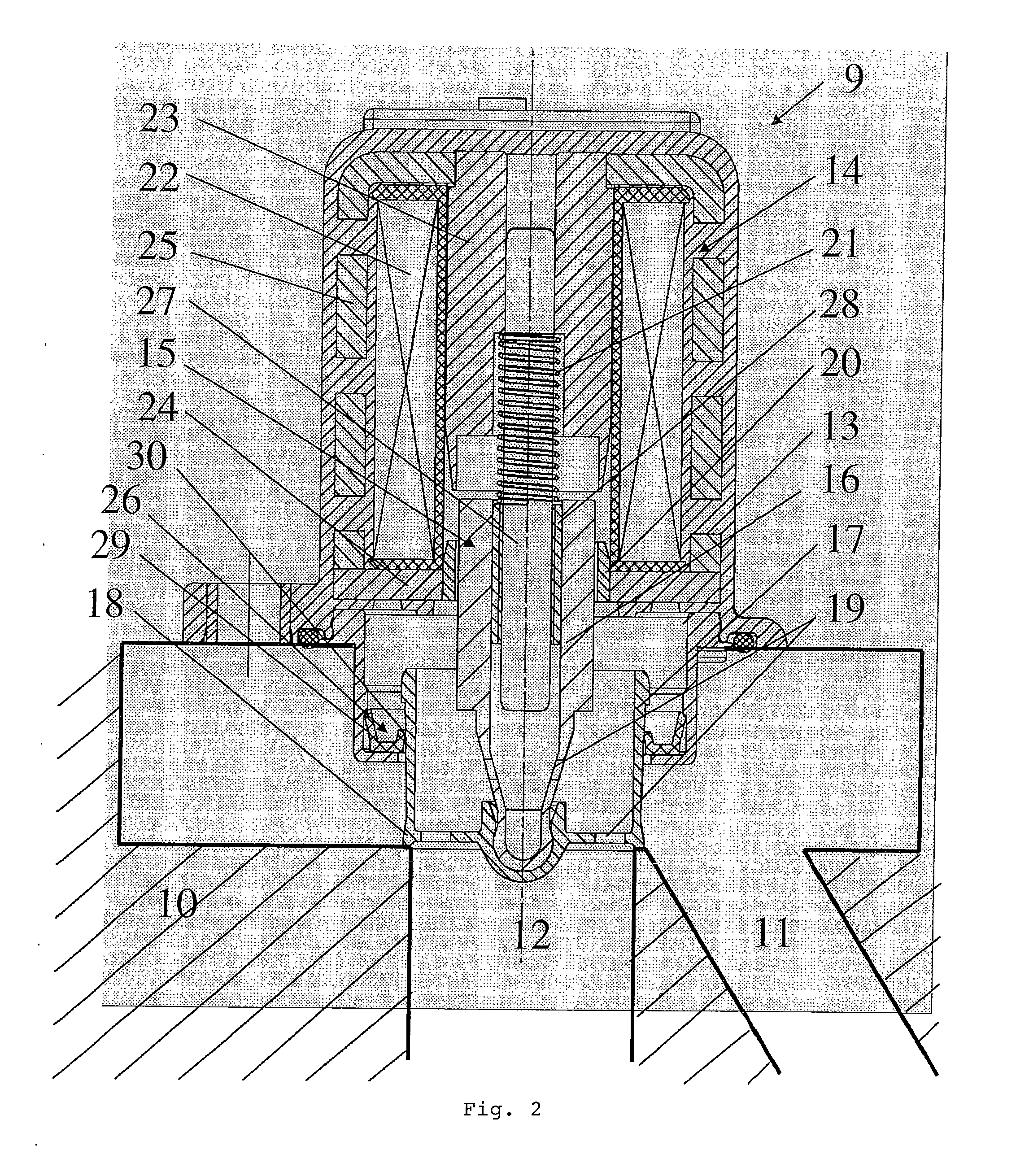
Ambient-air pulsed valve for internal combustion engines equipped with a turbocharger
InactiveUS20090301081A1Easy to manufactureSimple and inexpensive sealingOperating means/releasing devices for valvesInternal combustion piston enginesCombustionExternal combustion engine
The invention relates to an air control valve for internal combustion engines comprising a turbocharger, the air control valve being placed inside a bypass channel between a pressure side and an intake side of a boost pressure pump of the turbocharger, a housing which comprises an electromagnetic drive unit and a valve unit movable in said housing, said valve unit essentially comprising a valve rod and a valve closing body attached thereto and having a circular sealing element, wherein means are provided that keep the moving valve unit in a closed position when no current is supplied to said valve unit, wherein at least one pressure compensation opening is provided at the moving valve unit, wherein the valve closing body has a cylindrical lateral surface which cooperates with means in such a manner that a housing interior is sealed towards the pressure side or the intake side.
Owner:PIERBURG GMBH & CO KG NEUSS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com