Patents
Literature
500 results about "Wastegate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
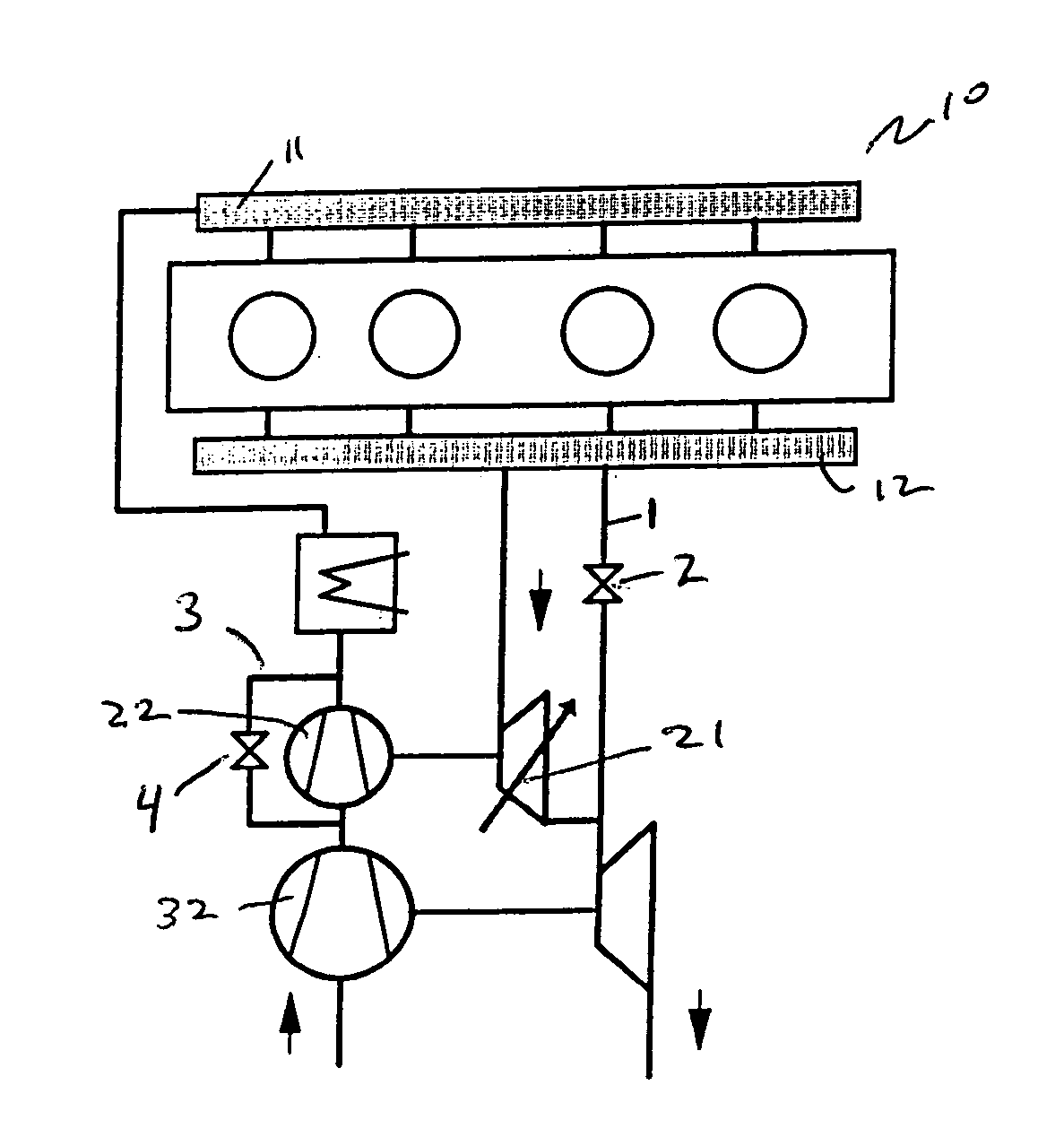
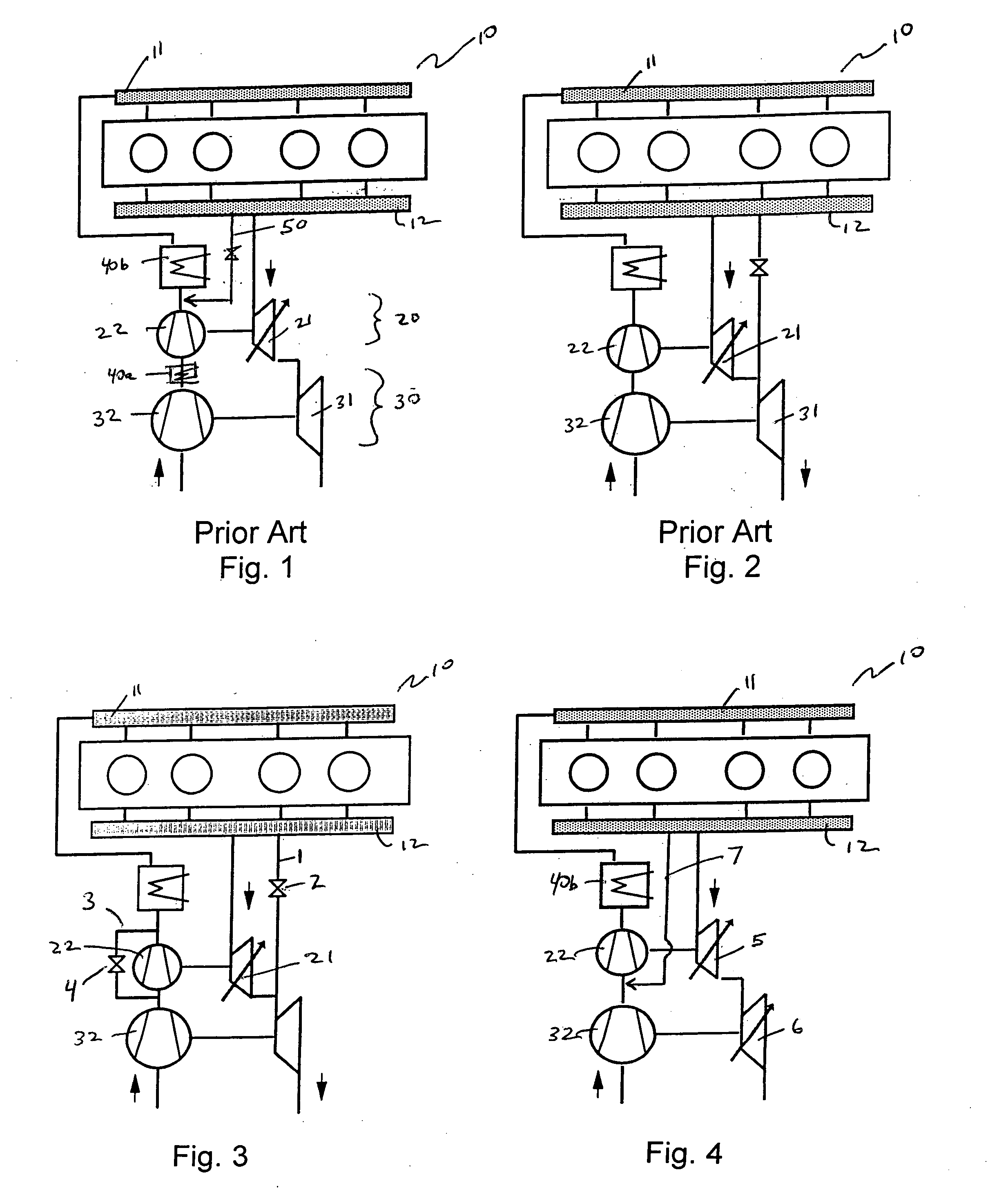
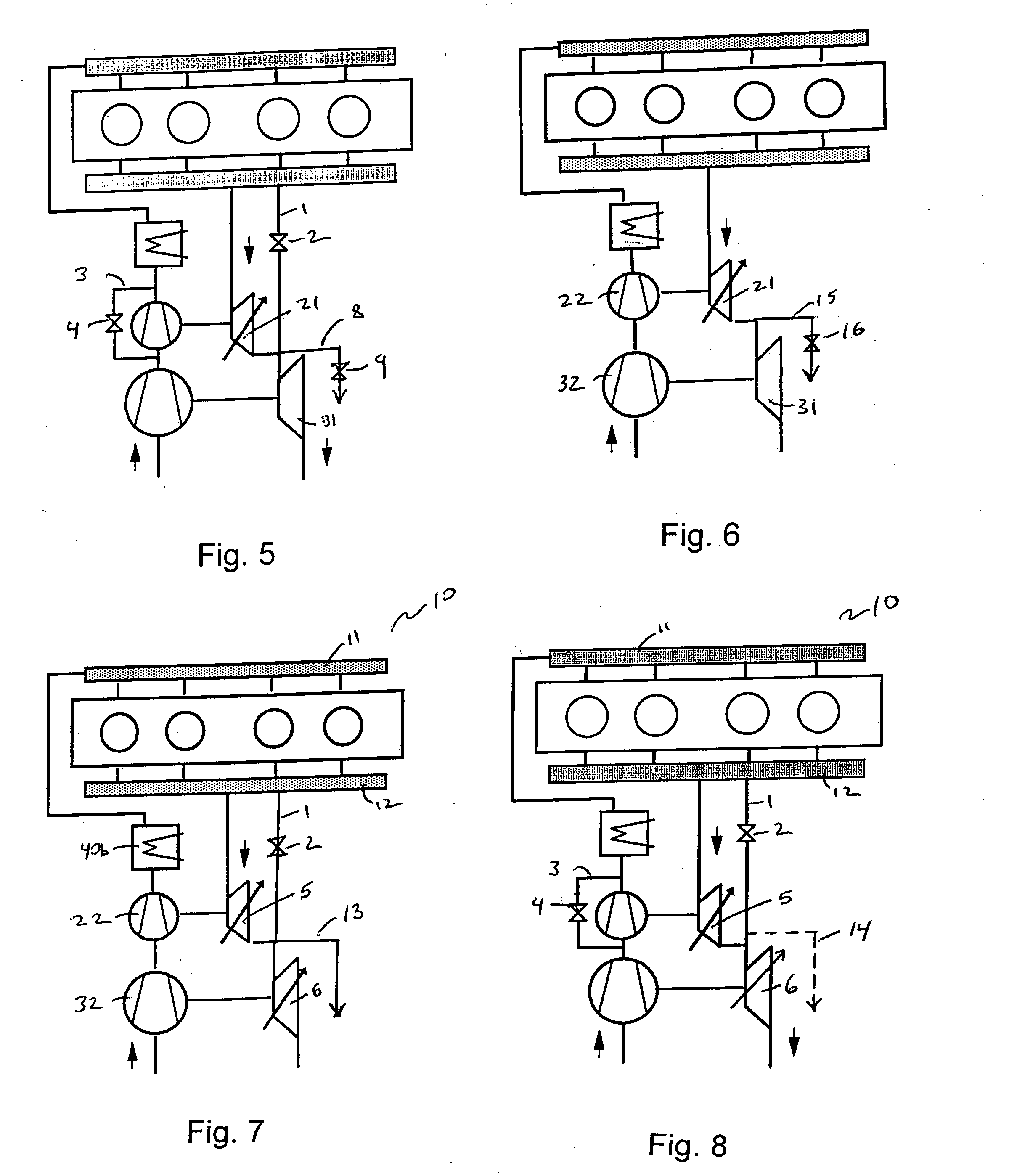
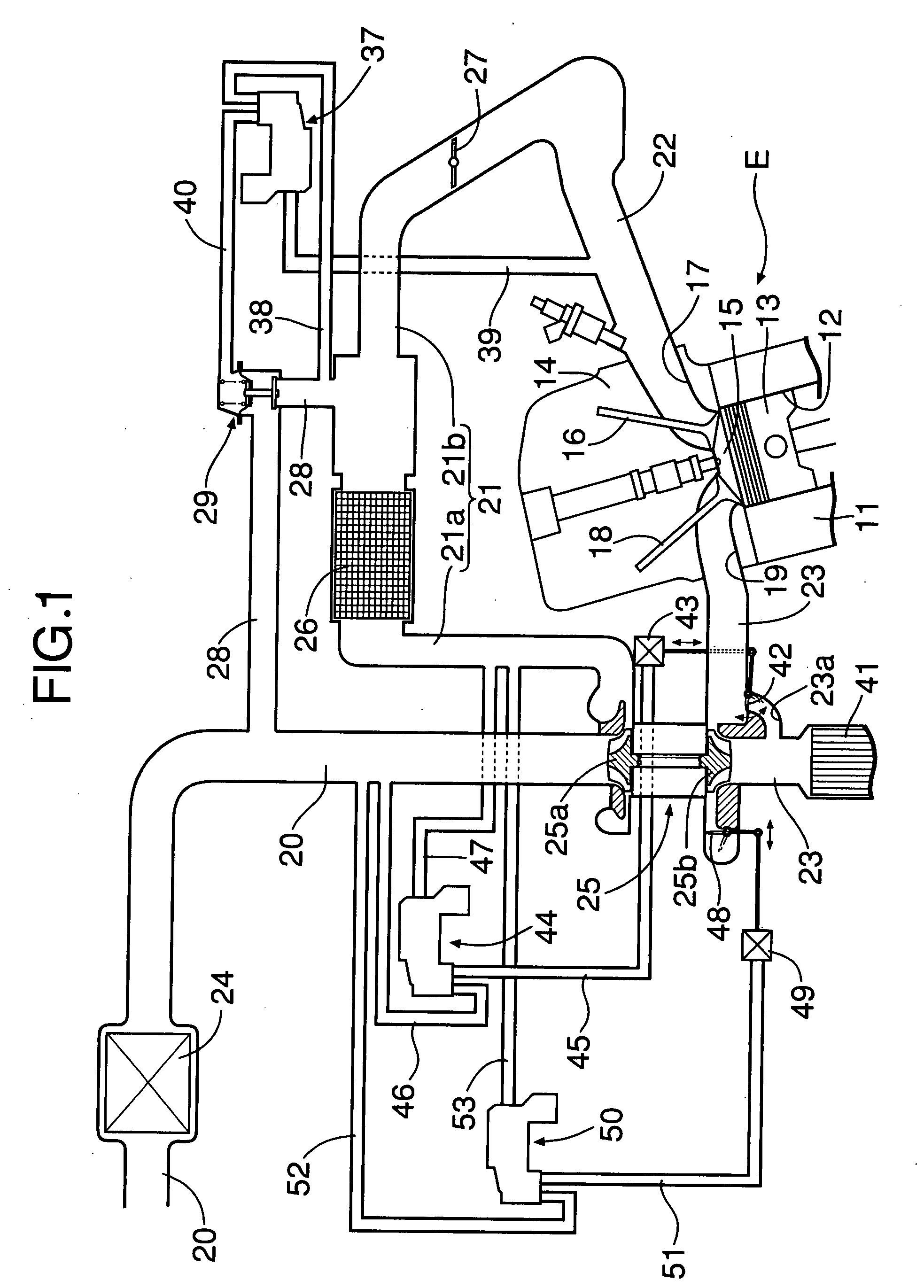
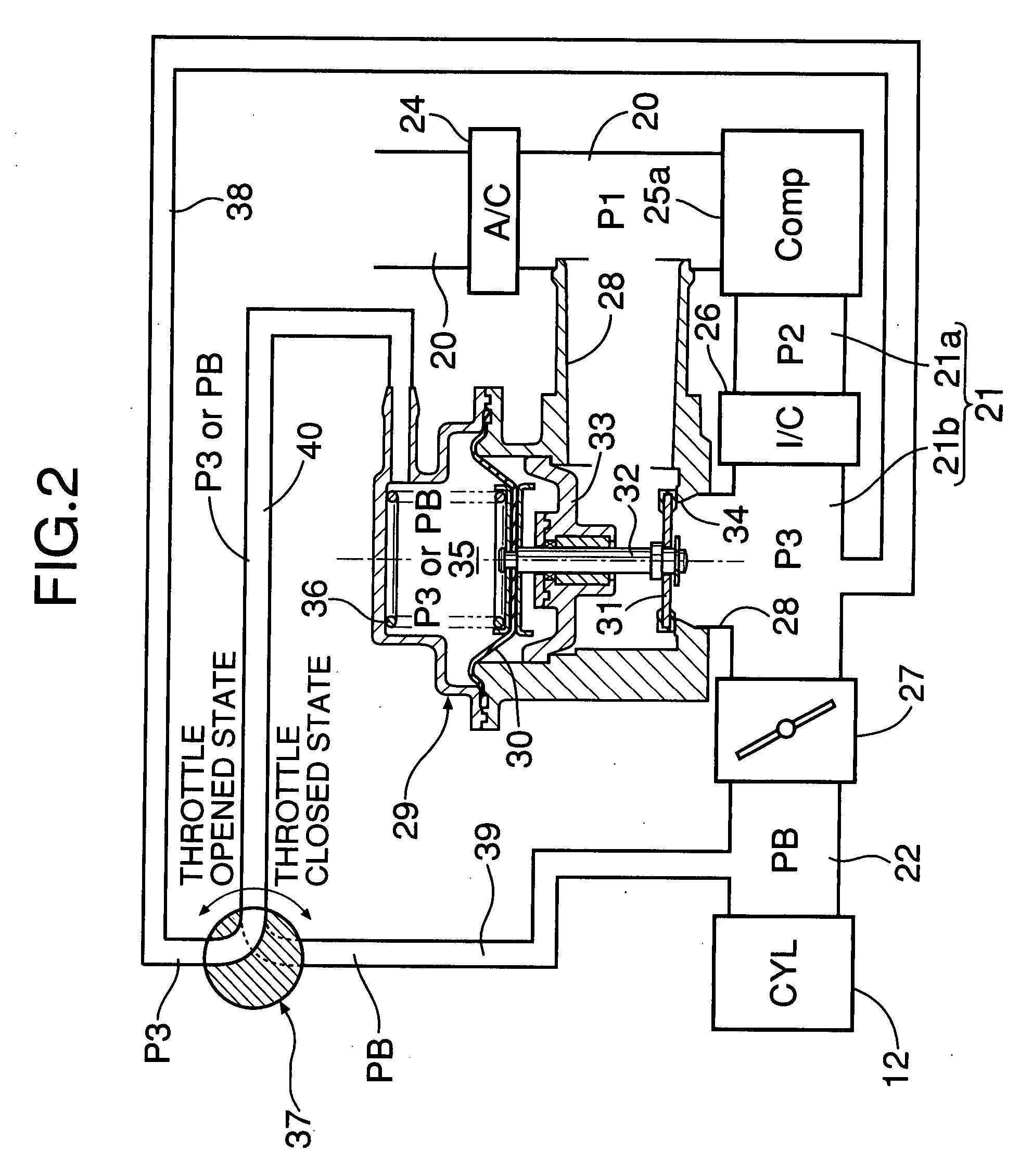
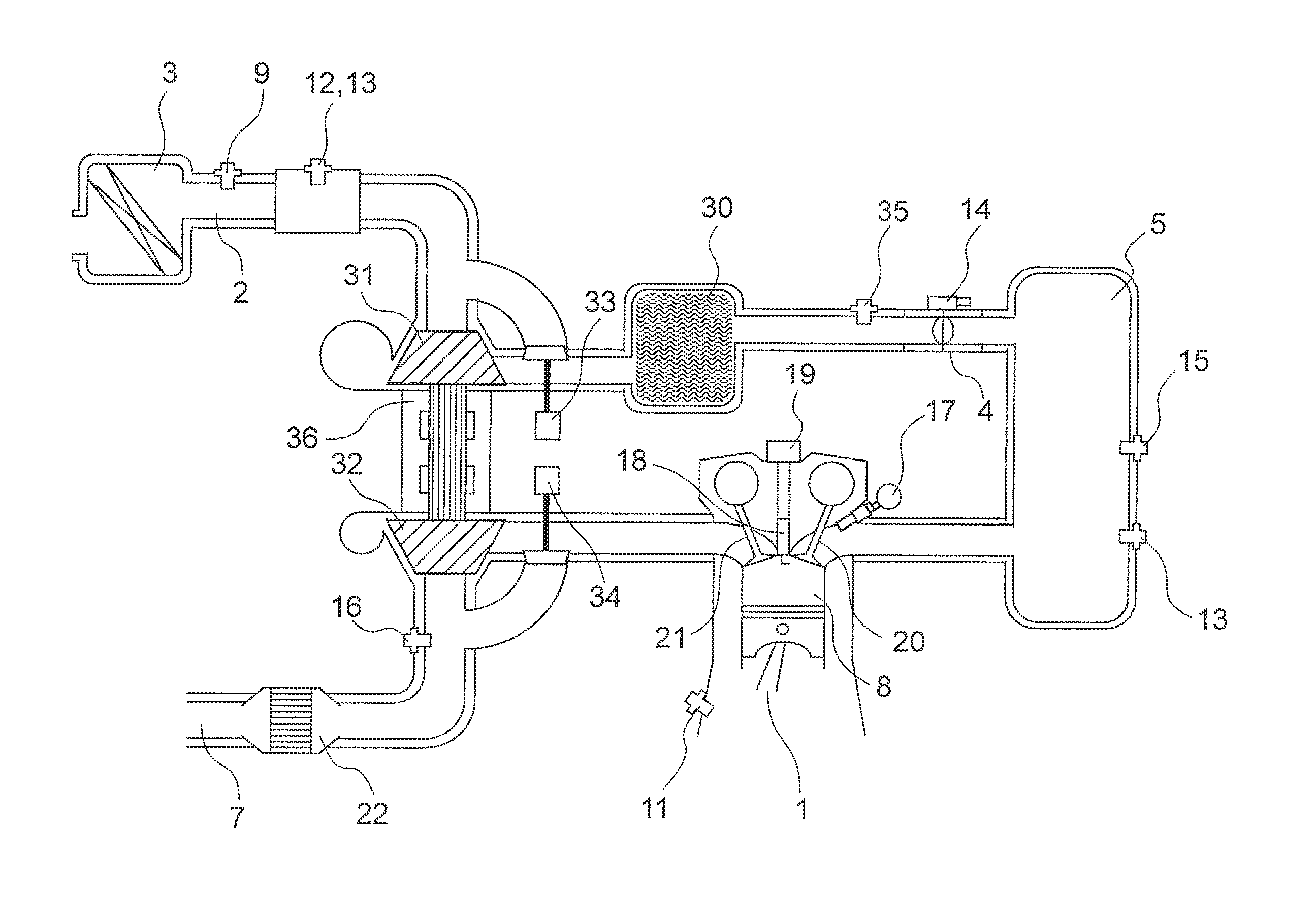
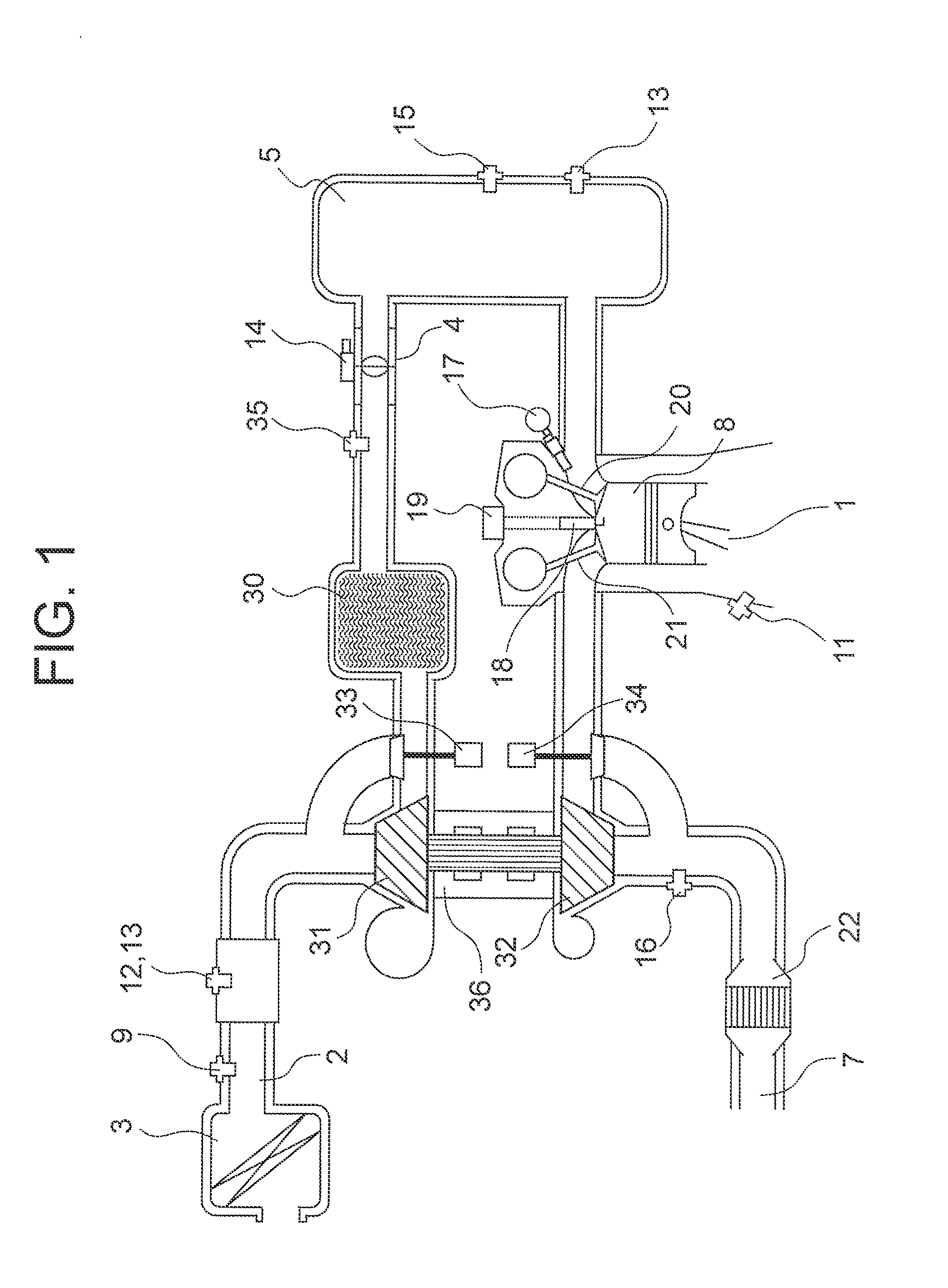
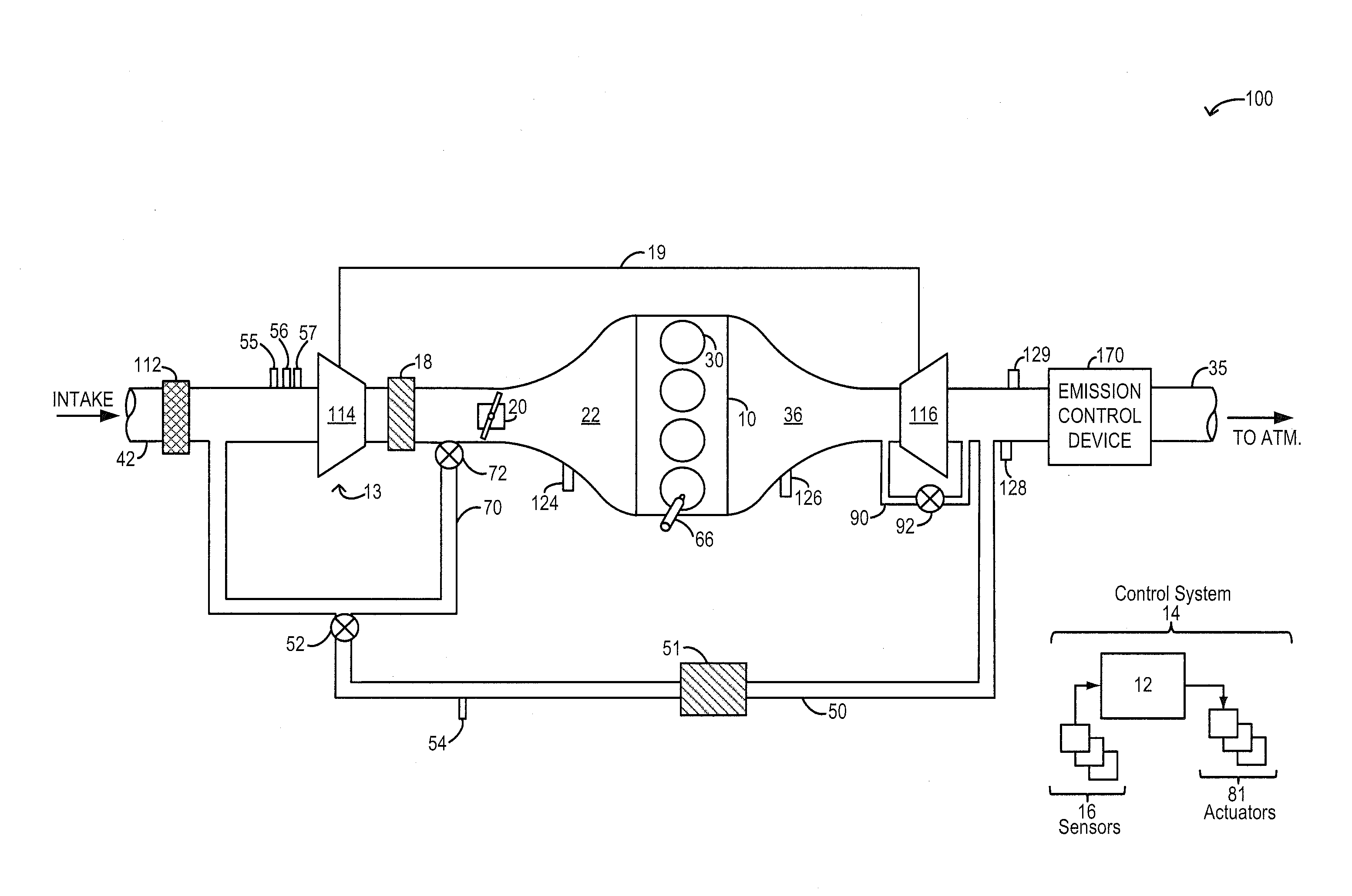
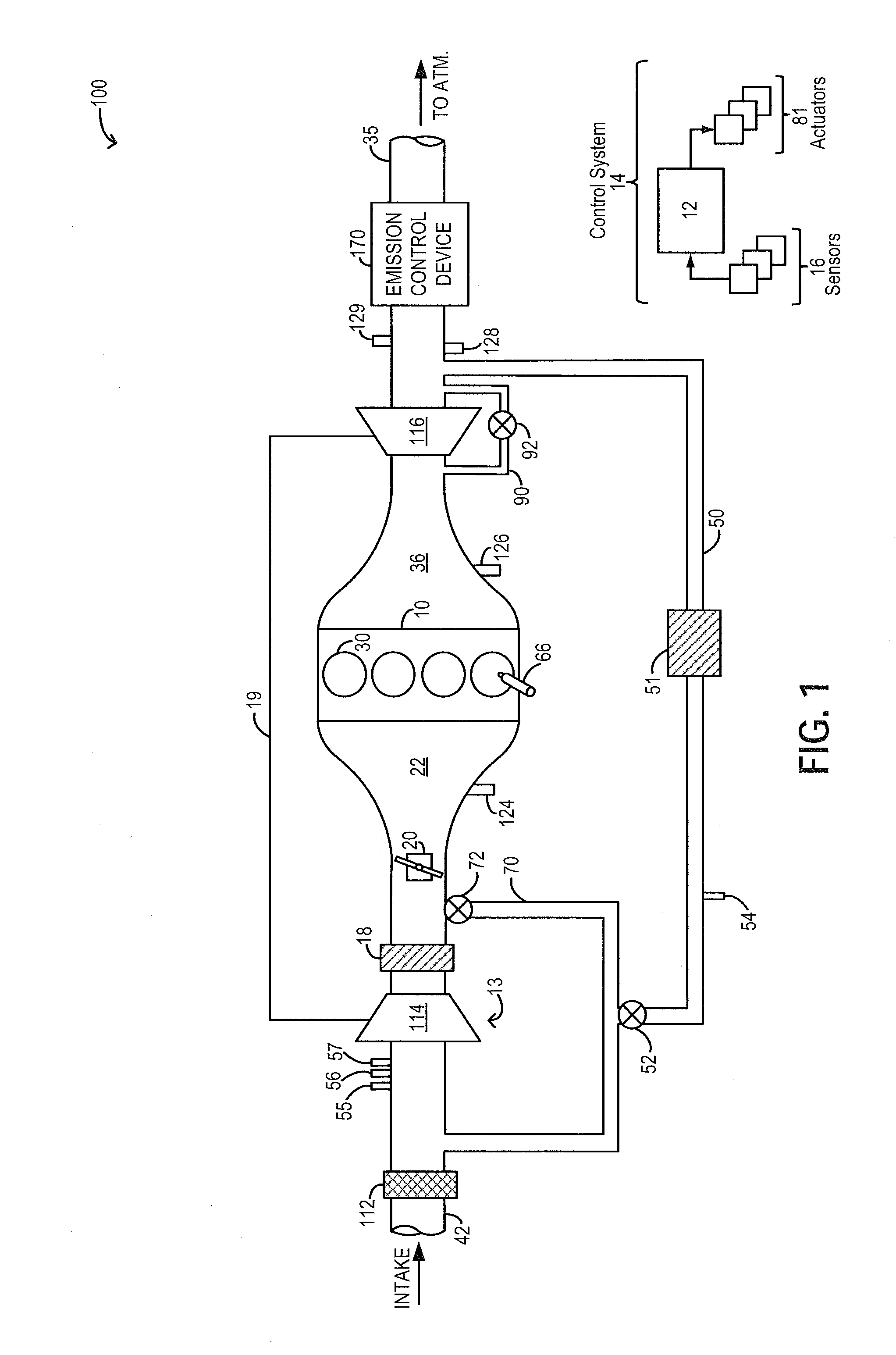
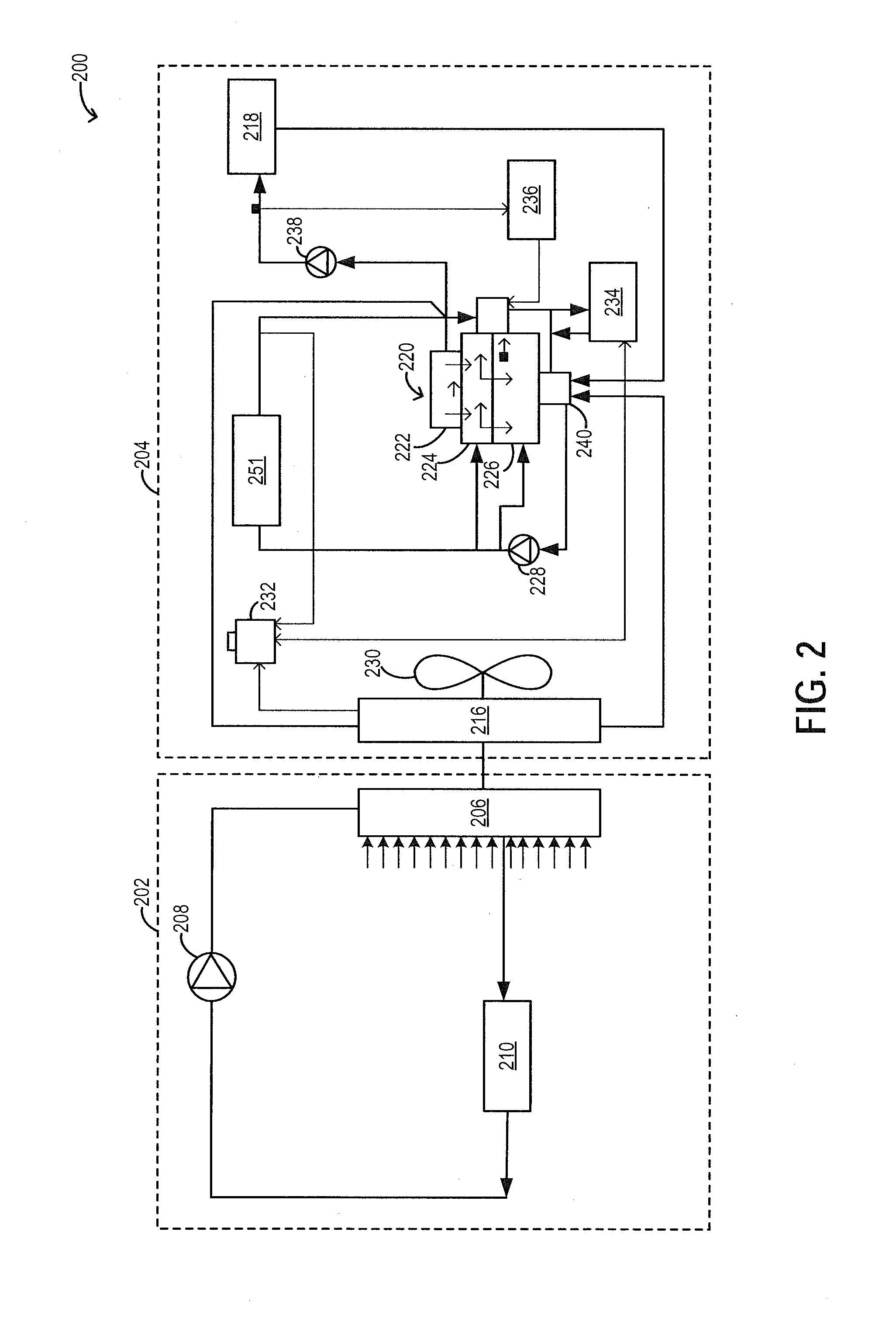
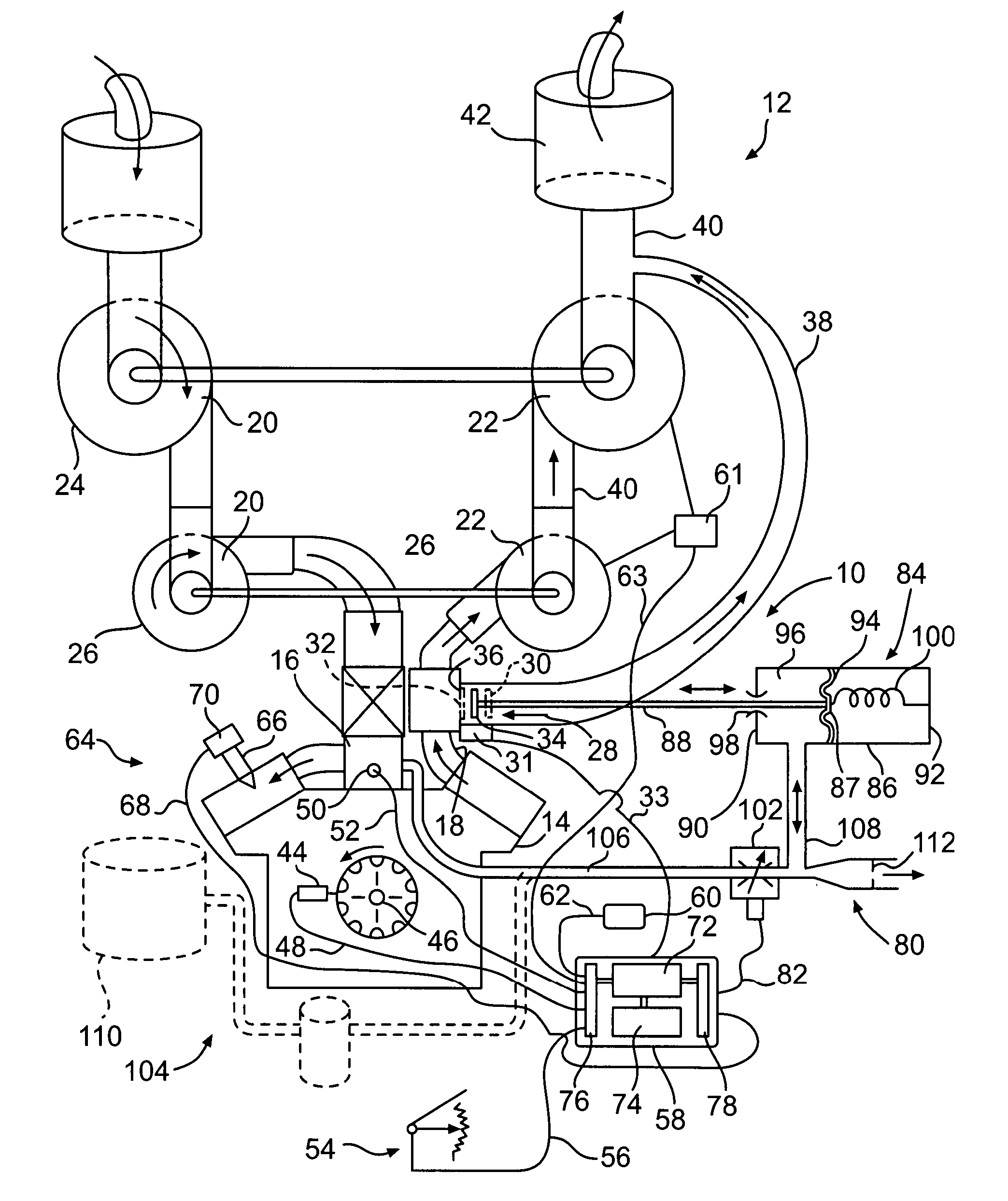
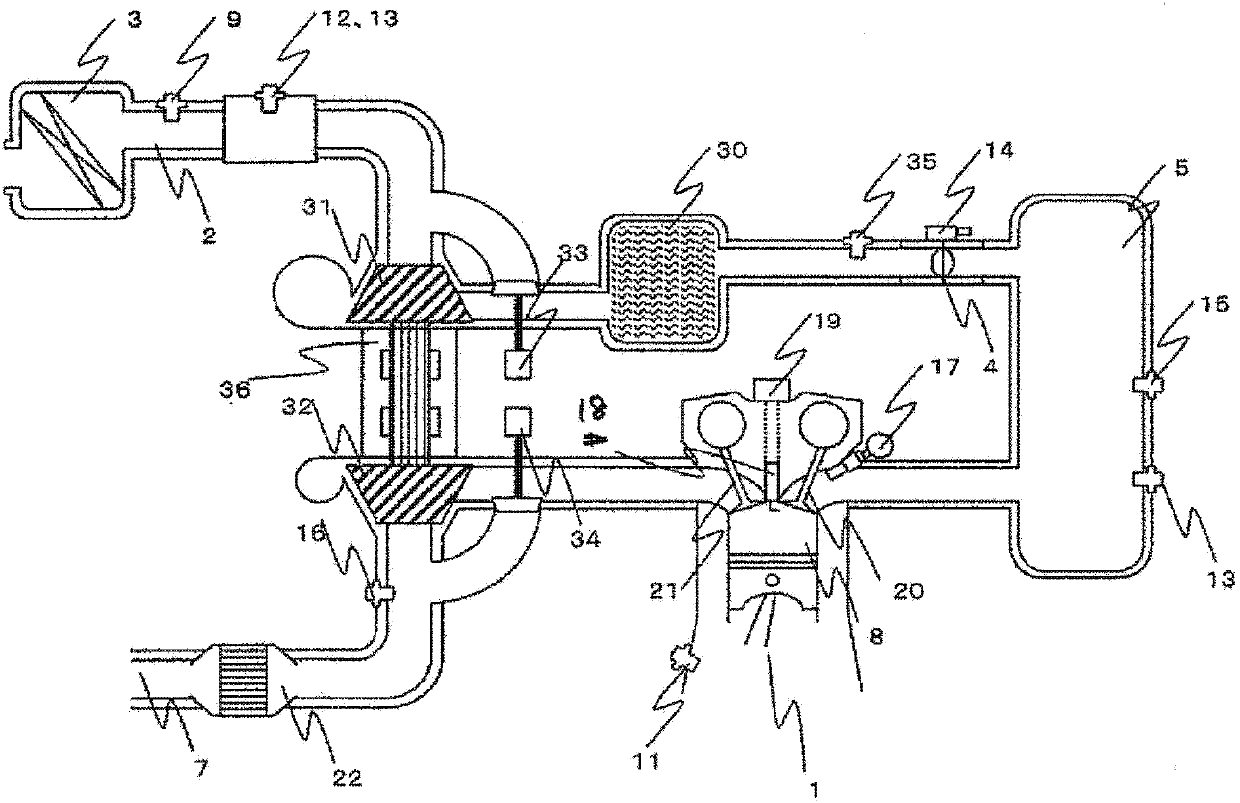
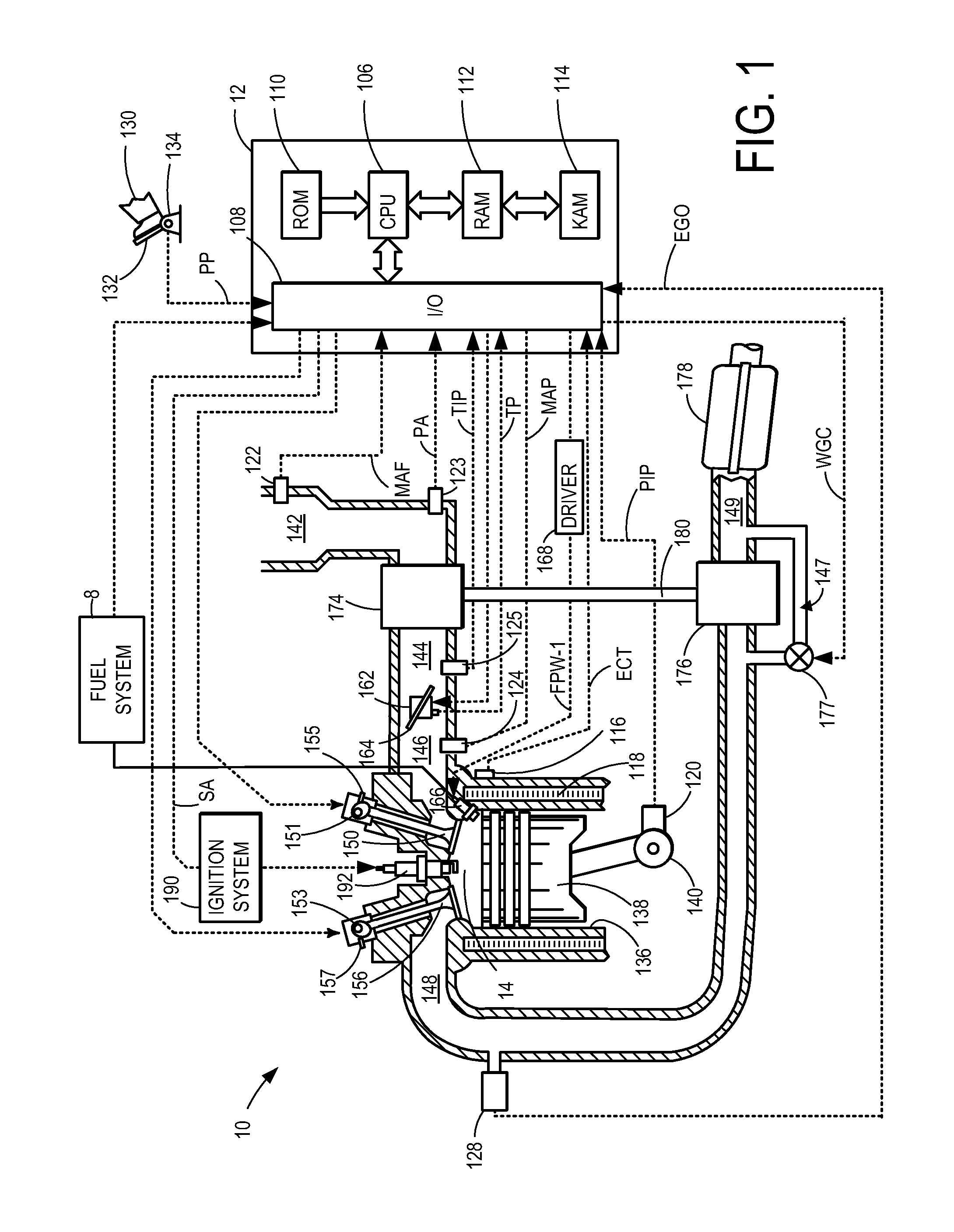
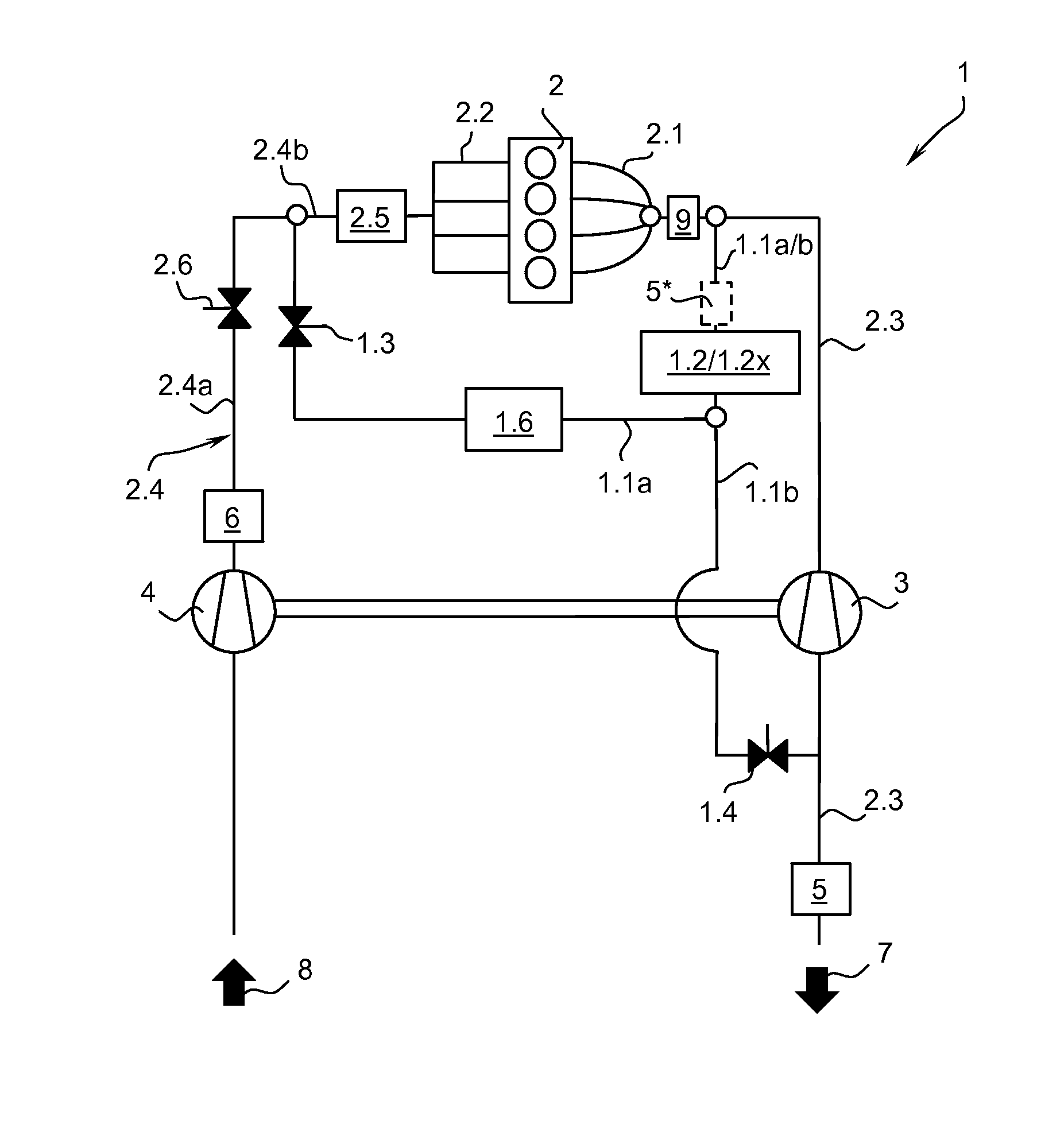
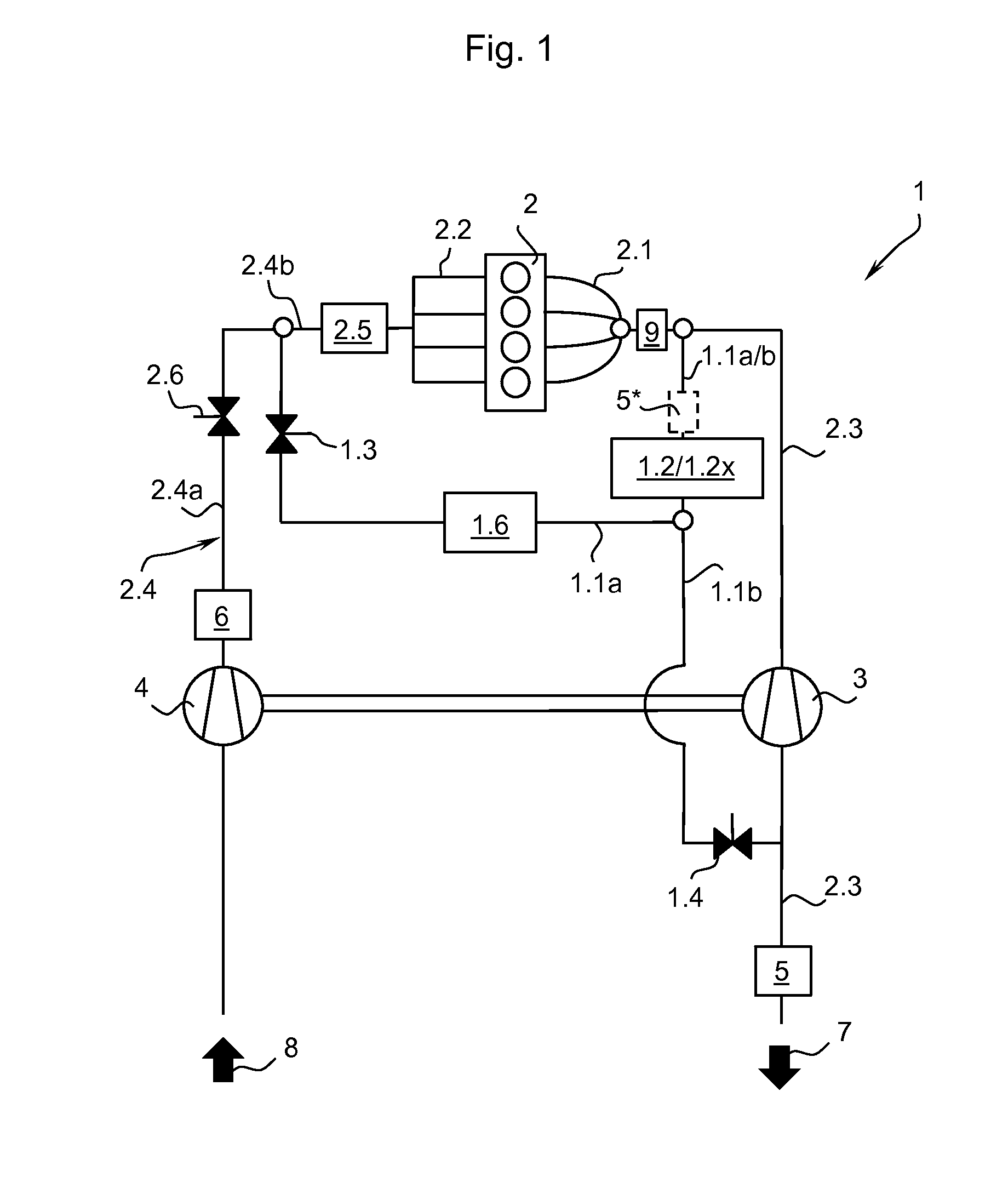
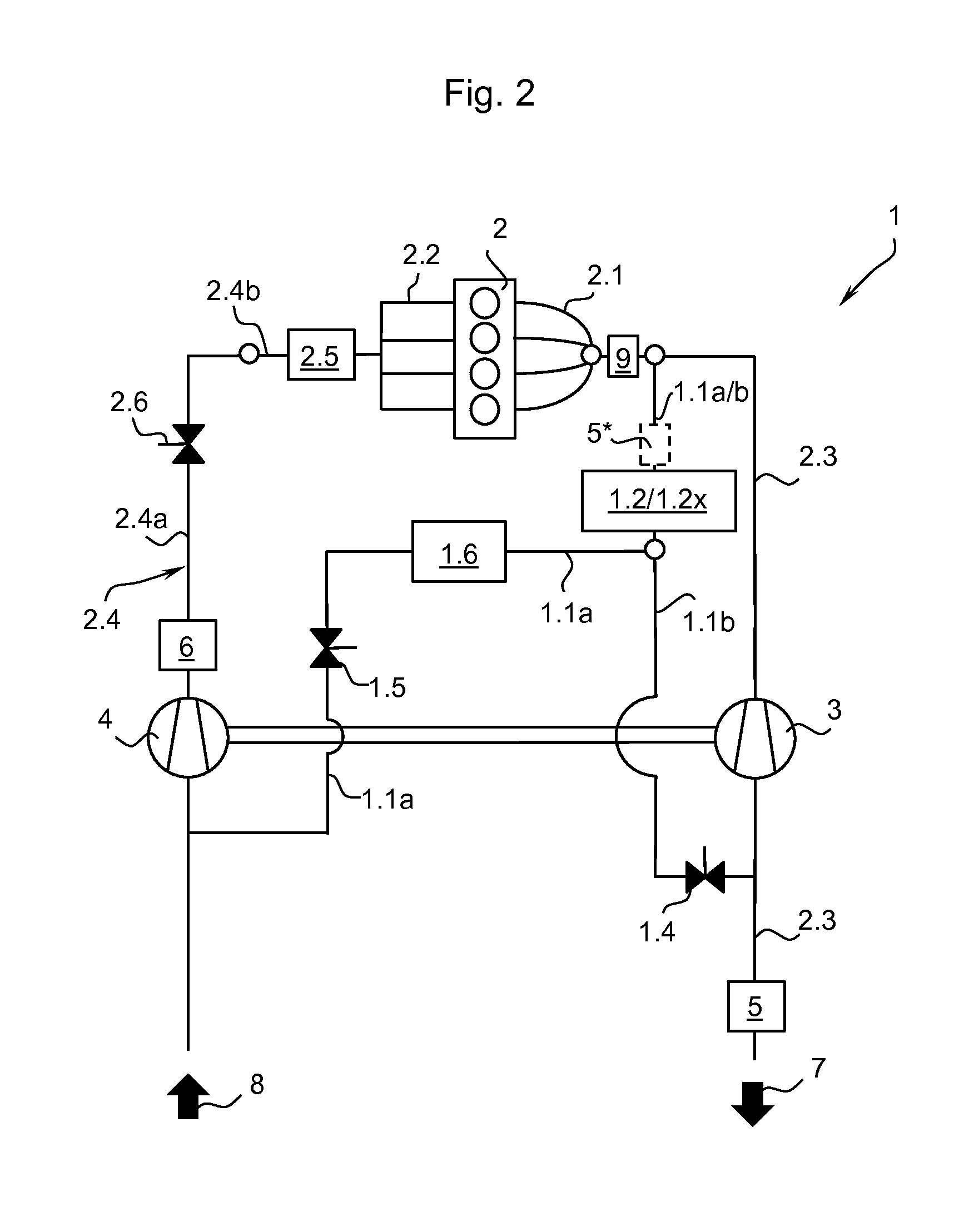
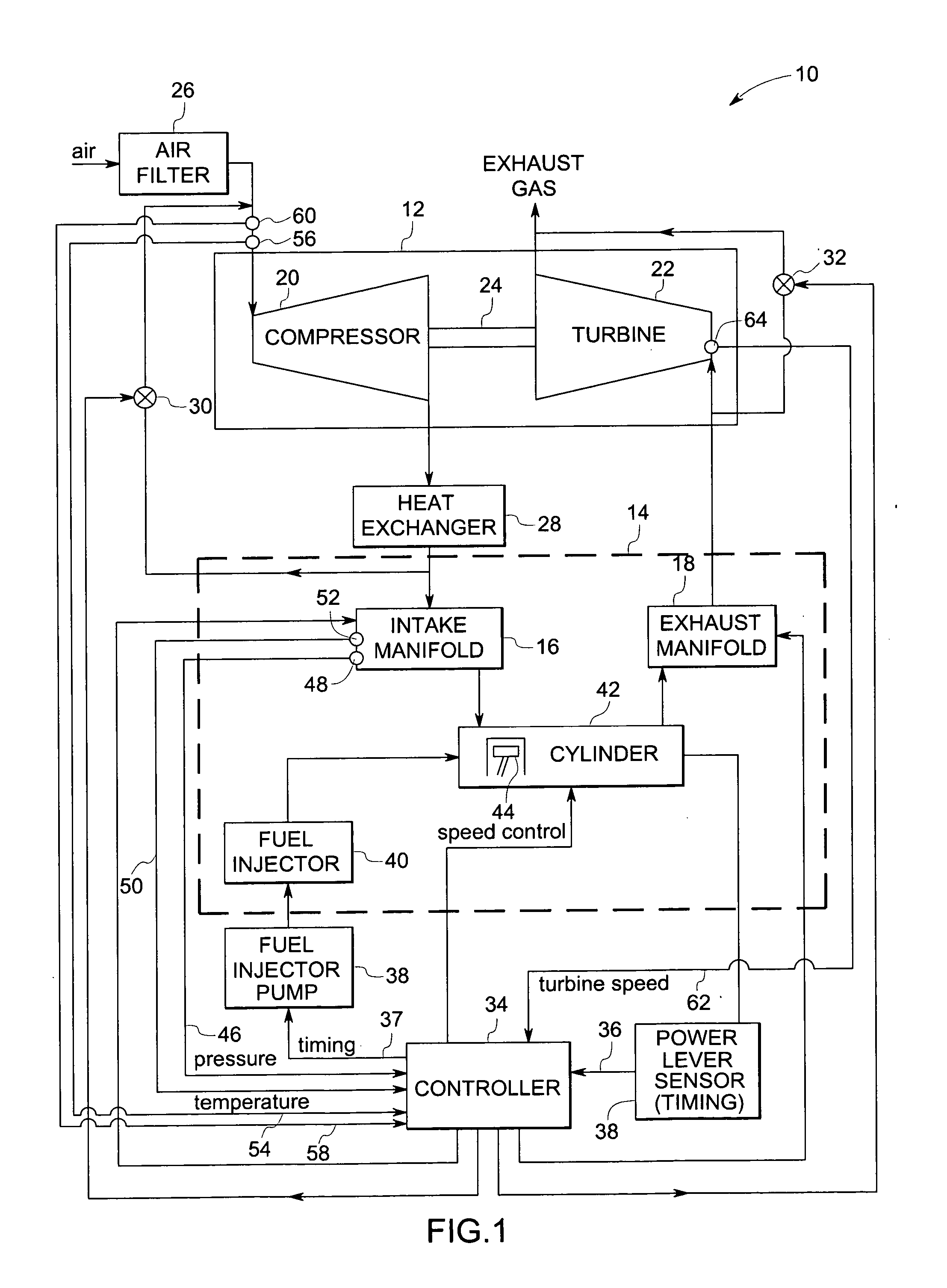
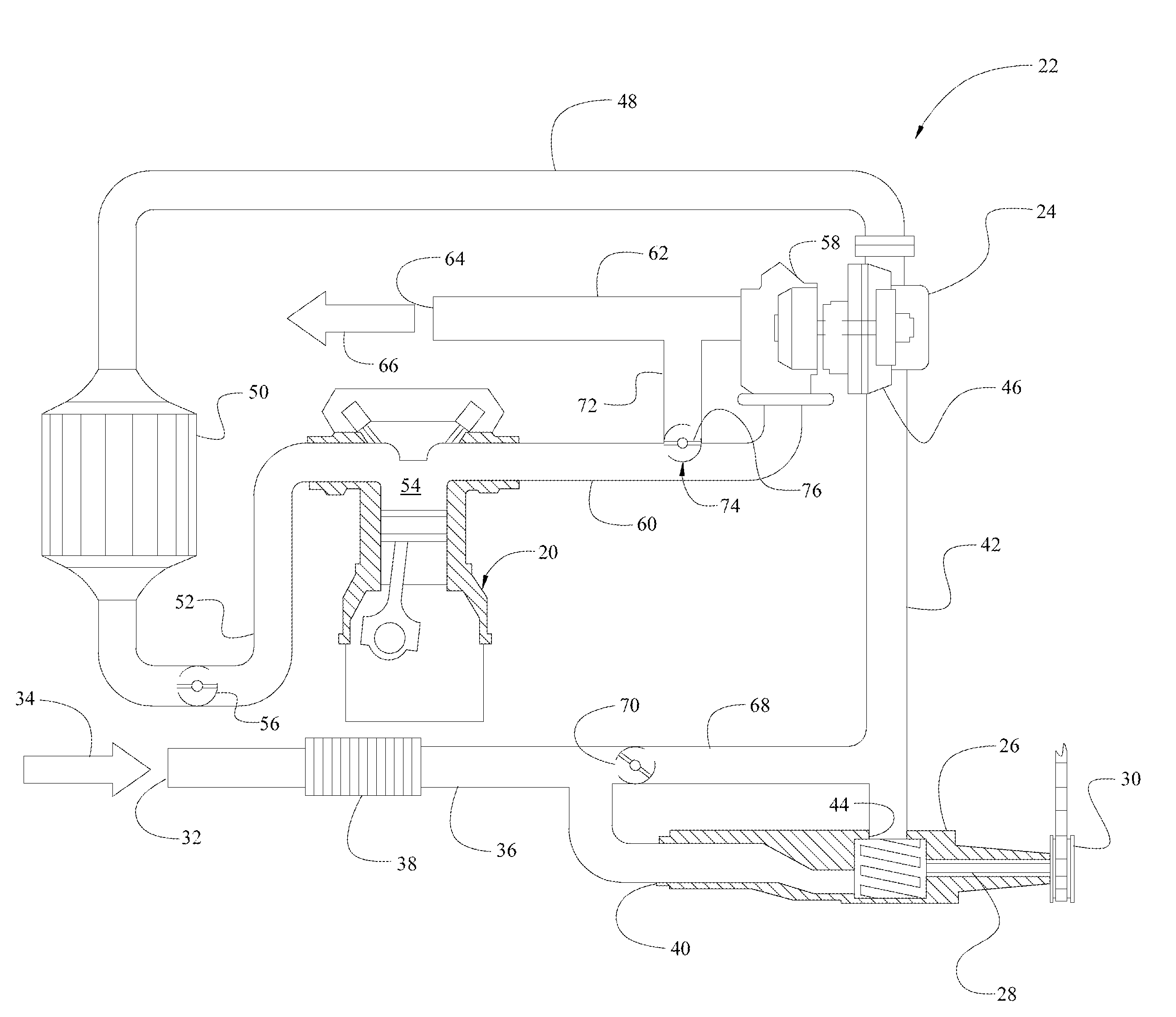
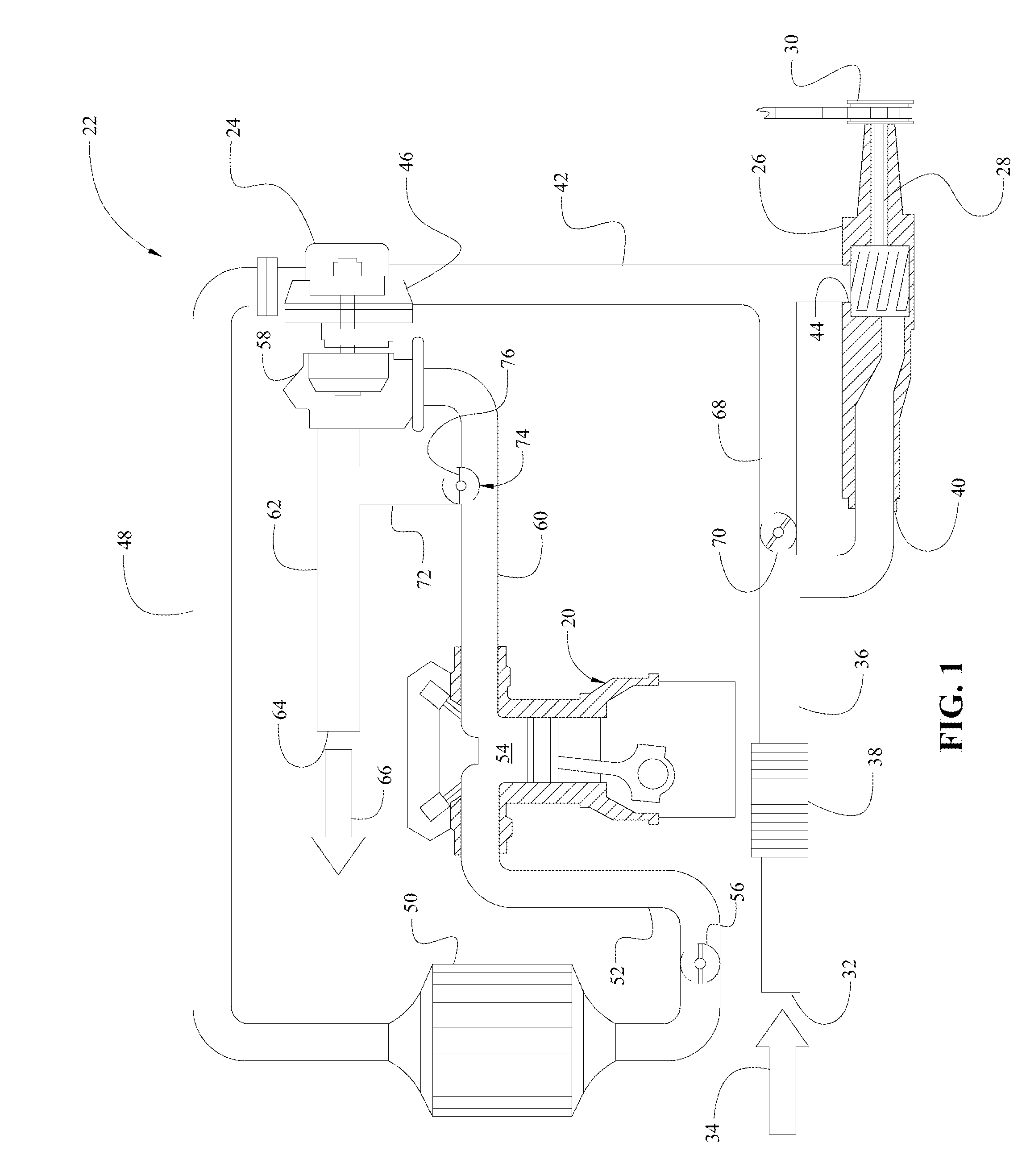
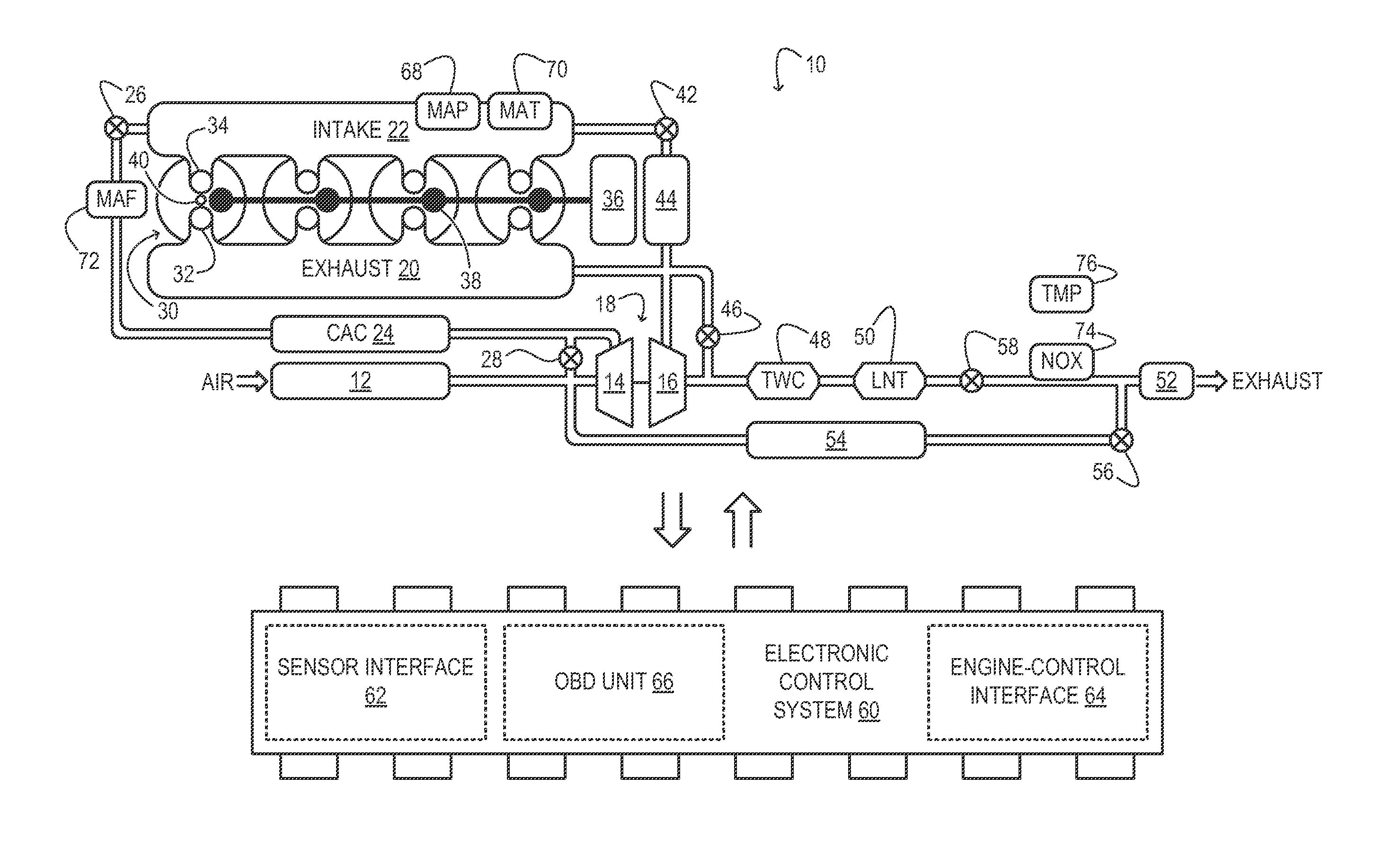
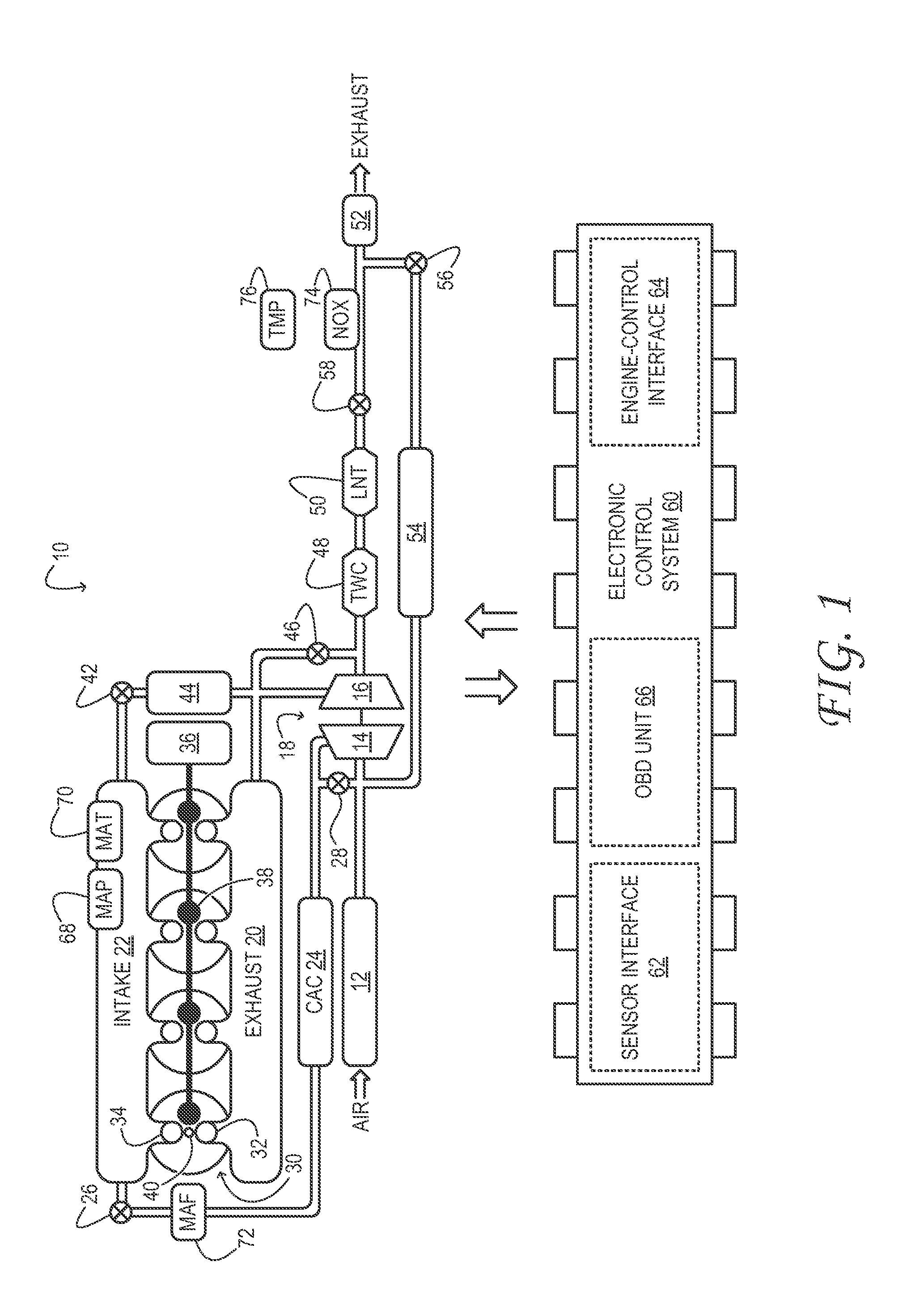
A wastegate is a valve that diverts exhaust gases away from the turbine wheel in a turbocharged engine system. Diversion of exhaust gases regulates the turbine speed, which in turn regulates the rotating speed of the compressor. The primary function of the wastegate is to regulate the maximum boost pressure in turbocharger systems, to protect the engine and the turbocharger. One advantage of installing a remote mount wastegate to a free-float (or non-WG) turbo includes allowance for a smaller A/R turbine housing, resulting in less lag time before the turbo begins to spool and create boost.
Multi-stage turbocharging system utilizing VTG turbine stage(s)
InactiveUS20060070381A1Improve fuel economyEmission reductionInternal combustion piston enginesNon-fuel substance addition to fuelWastegateInternal combustion engine
Multi-stage turbocharging, and more particularly, an advanced multi-stage turbocharging system using the variable turbine power of one or more variable turbine geometry (VTG) turbochargers to adjust compressor boost and exhaust back pressure to engine operating demands. The invention further relates to a turbocharged internal combustion engine, in particular a turbocharged internal combustion engine with at least one high-pressure turbine stage and one downstream low-pressure turbine stage, wherein the high-pressure turbine may be a single-flow or double-flow type, wherein the high pressure or low pressure compressor may be variable geometry, wherein the high pressure or low pressure compressor may be variably bypassed, and wherein the high pressure or low pressure turbine may be provided with an active control variable bypass or wastegate.
Owner:BORGWARNER INC
Failure detecting device for supercharging-pressure control means in supercharging device of engine
InactiveUS20080022679A1Accurate detectionHigh frequencyElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesWastegateResponse delay
When an engine load QC is equal to or larger than a predetermined value, an acceleration-state determiner determines that a turbine is in an acceleration state, and a supercharging-pressure-control-state determiner determines that supercharging-pressure controller (a bypass valve, a wastegate, and a variable flap) of a turbocharger are in a maximum supercharging pressure control state (a closed valve state), i.e., when a delay coefficient α of the turbocharger calculated by a delay-coefficient calculator on the basis of an actual supercharging pressure πc and a convergent value πc* of a supercharging pressure calculated by a convergent-value calculator indicates a value peculiar to the turbocharger, a failure of the supercharging-voltage controller is determined on the basis of the delay coefficient α. Thus, it is possible to secure a high failure detection accuracy, and increase a frequency of performing failure detection even when the engine load QC suddenly changes to cause a delay in a response of the supercharging pressure πc.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Methods and systems for boost control
InactiveUS20140260241A1Fast dynamicsConfound the wastegate control loopElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesWastegateControl theory
Methods and systems are provided for improving boost response. A continuously variable compressor recirculation valve and a wastegate are adjusted in complementary frequency bands to move compressor operation away from a surge limit and reduce boost delivery errors. An intake throttle is also concurrently adjusted to offset manifold air-flow rate errors resulting from the wastegate or recirculation valve adjustments.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Variable flow wastegate
ActiveUS20110173974A1Melt-holding vesselsInternal combustion piston enginesEffective solutionWastegate
A wastegate for a turbocharger wherein the valve is provided with a horn to provide a more progressive, optimally near linear, curve of turbocharger boost-to-valve opening than possible with the typical flat wastegate valve. The addition of a three-dimensional horn in the flow path is a far more cost-effective solution to acquire linear flow than an approach involving very finite, accurate control of the valve position.
Owner:BORGWARNER INC
Control device for internal combustion engine and method for controlling internal combustion engine
ActiveUS20130282256A1Improve efficiencyAnalogue computers for vehiclesElectrical controlWastegateFuel efficiency
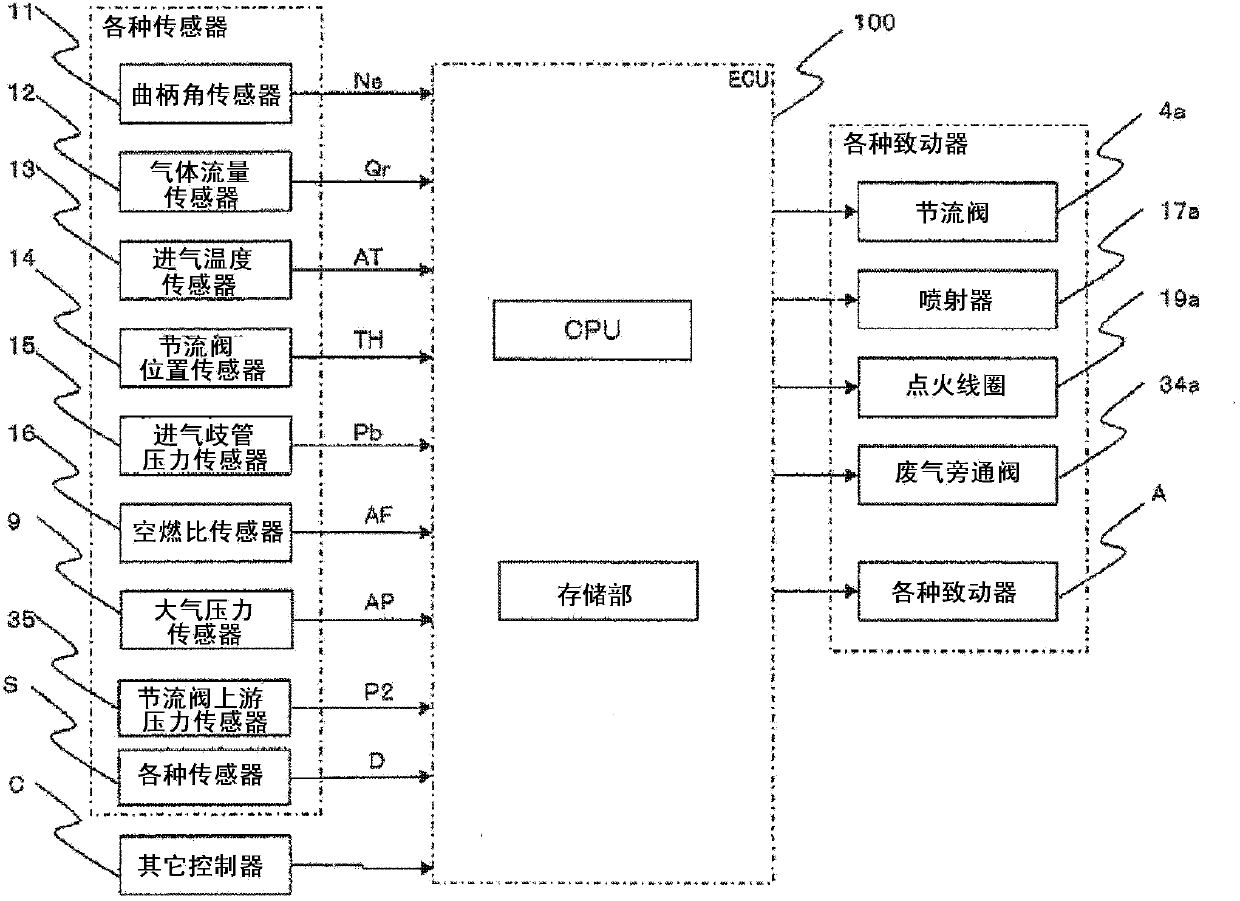
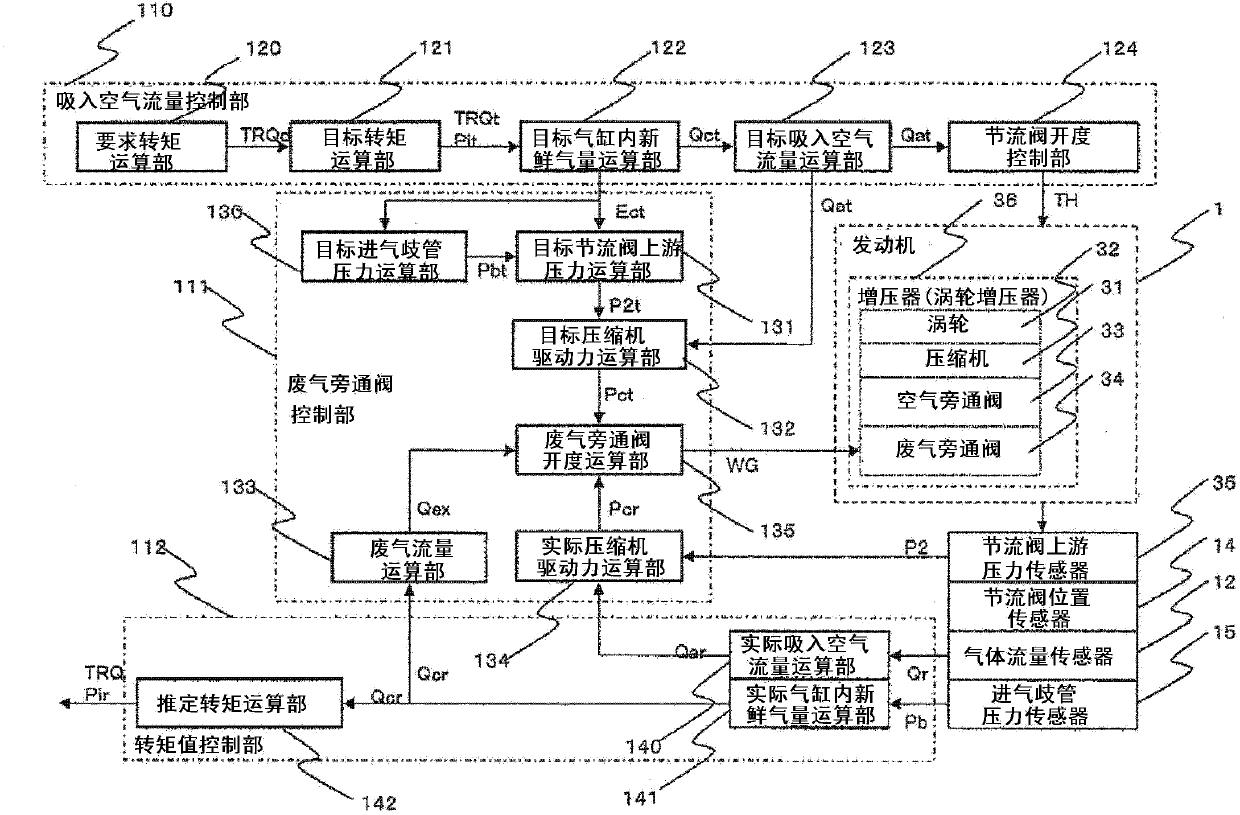
Provided is a control device for an internal combustion engine, capable of controlling acceleration-response characteristics, performing an operation at an optimal fuel-efficiency point, and learning variation factors in an internal combustion engine provided with a supercharger including a wastegate valve. A target throttle-valve upstream pressure is calculated based on a target charging efficiency and a rotation speed. An exhaust-gas flow rate is calculated based on an air / fuel ratio and an intake-airflow rate. A target compressor driving force is calculated based on a target intake-airflow rate and a target throttle-valve upstream pressure. A wastegate-valve control value is calculated from the exhaust-gas flow rate and the target compressor driving force by using the relationship in which the relation expression expressing the characteristics of the exhaust-gas flow rate and the target compressor driving force depends only on the wastegate-valve control value.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
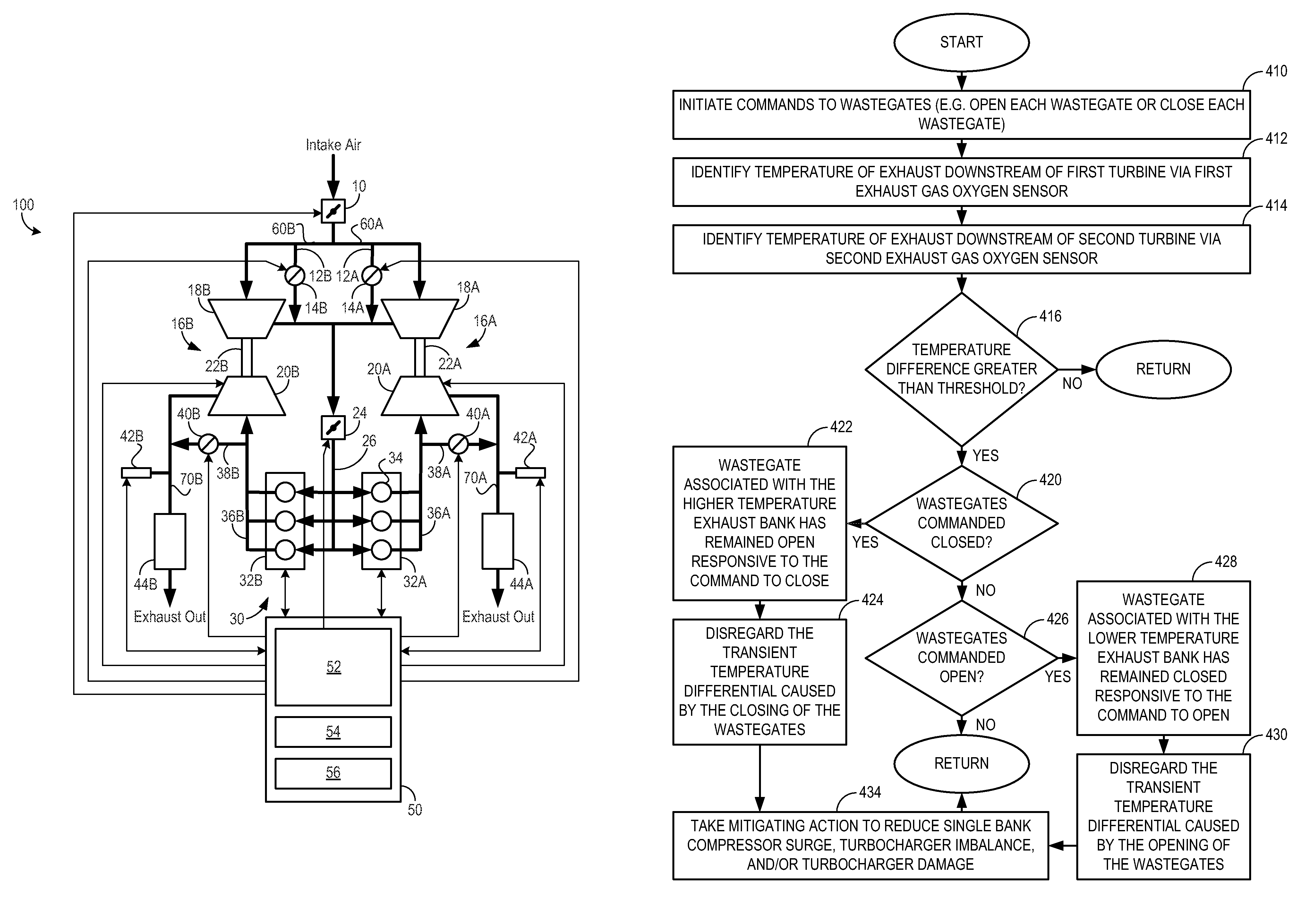
Approach for Identifying and Responding to an Unresponsive Wastegate in a Twin Turbocharged Engine
ActiveUS20090077965A1Reduce turbocharger imbalanceReduce compressor surgeElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesWastegateControl system
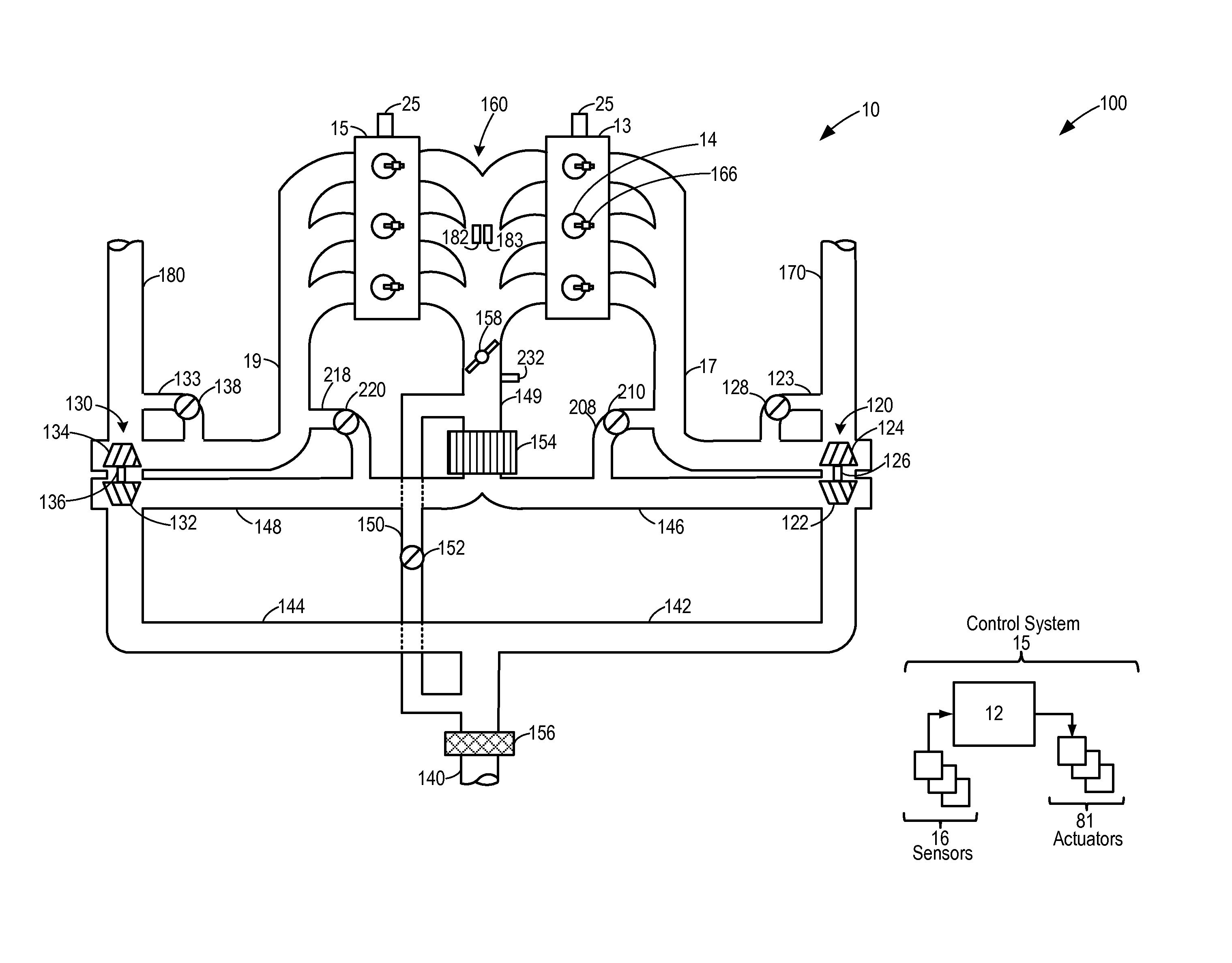
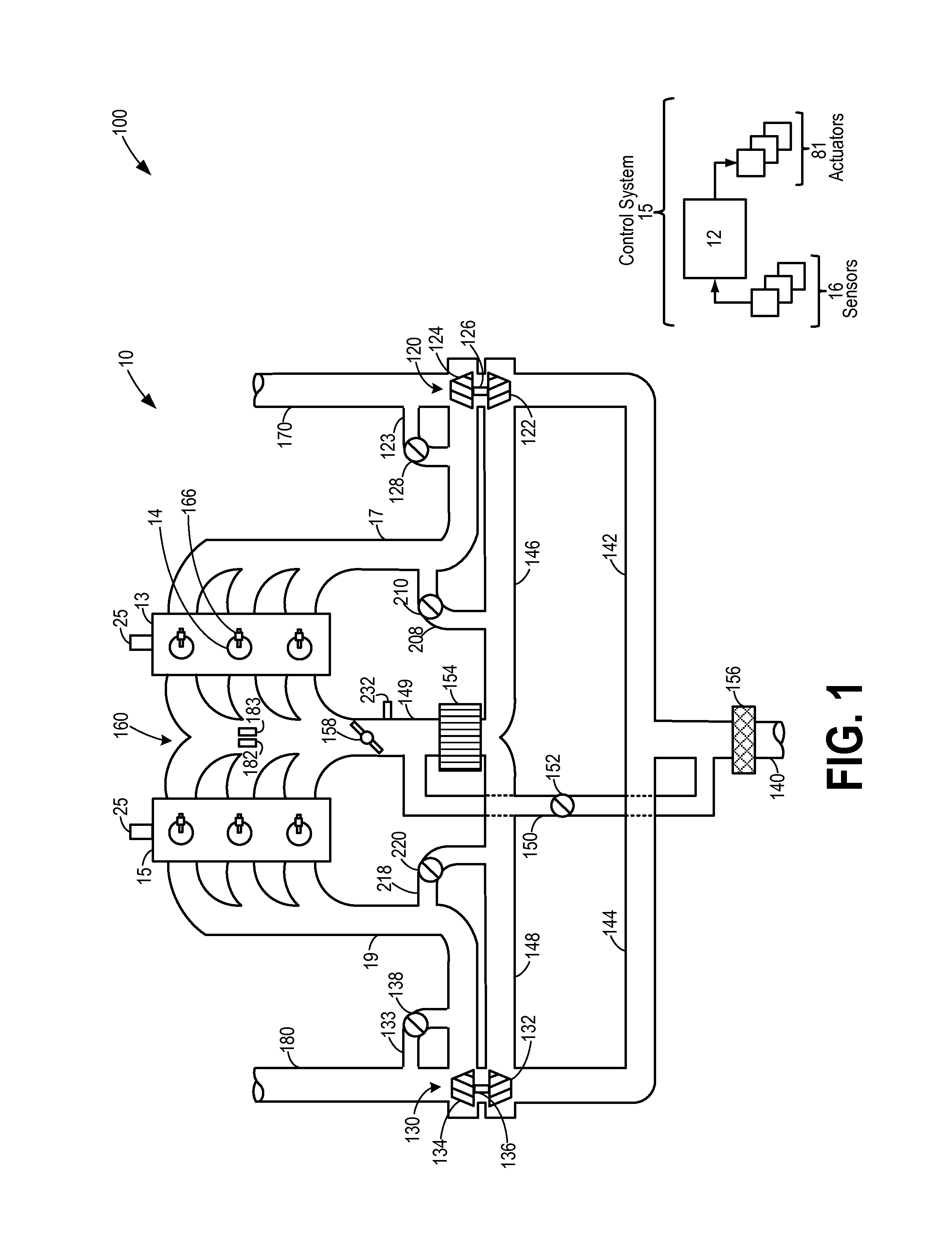
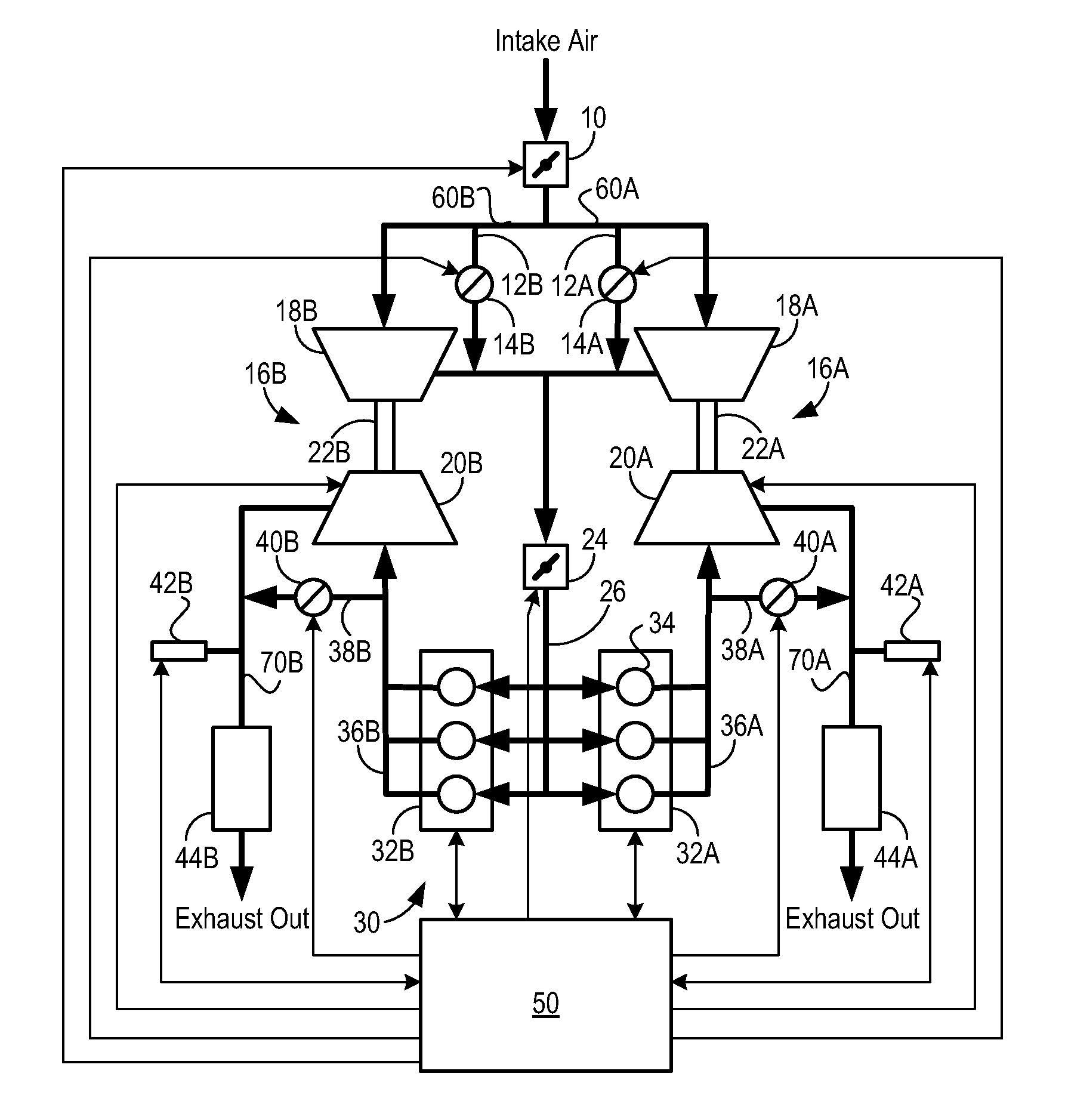
As one example, an engine system for a vehicle is provided, comprising an internal combustion engine including an air intake system and an exhaust system; a first turbocharger including a first compressor arranged along a first branch of the air intake system, a first turbine arranged along a first branch of the exhaust system, and a first turbine bypass passage include a first wastegate; a second turbocharger including a second compressor arranged along a second branch of the air intake system, a second turbine arranged along a second branch of the exhaust system, and a second turbine bypass passage including a second wastegate; a first exhaust gas sensor arranged along the first branch of the exhaust system downstream of the first turbine and first wastegate; a second exhaust gas sensor arranged along the second branch of the exhaust system downstream of the second turbine and the second wastegate; and a control system configured to command both the first wastegate and the second wastegate to a closed position or an opened position and to indicate one of said wastegates as unresponsive to said command in response to a temperature difference between the first and second branches indicated by the first and second exhaust gas sensors.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
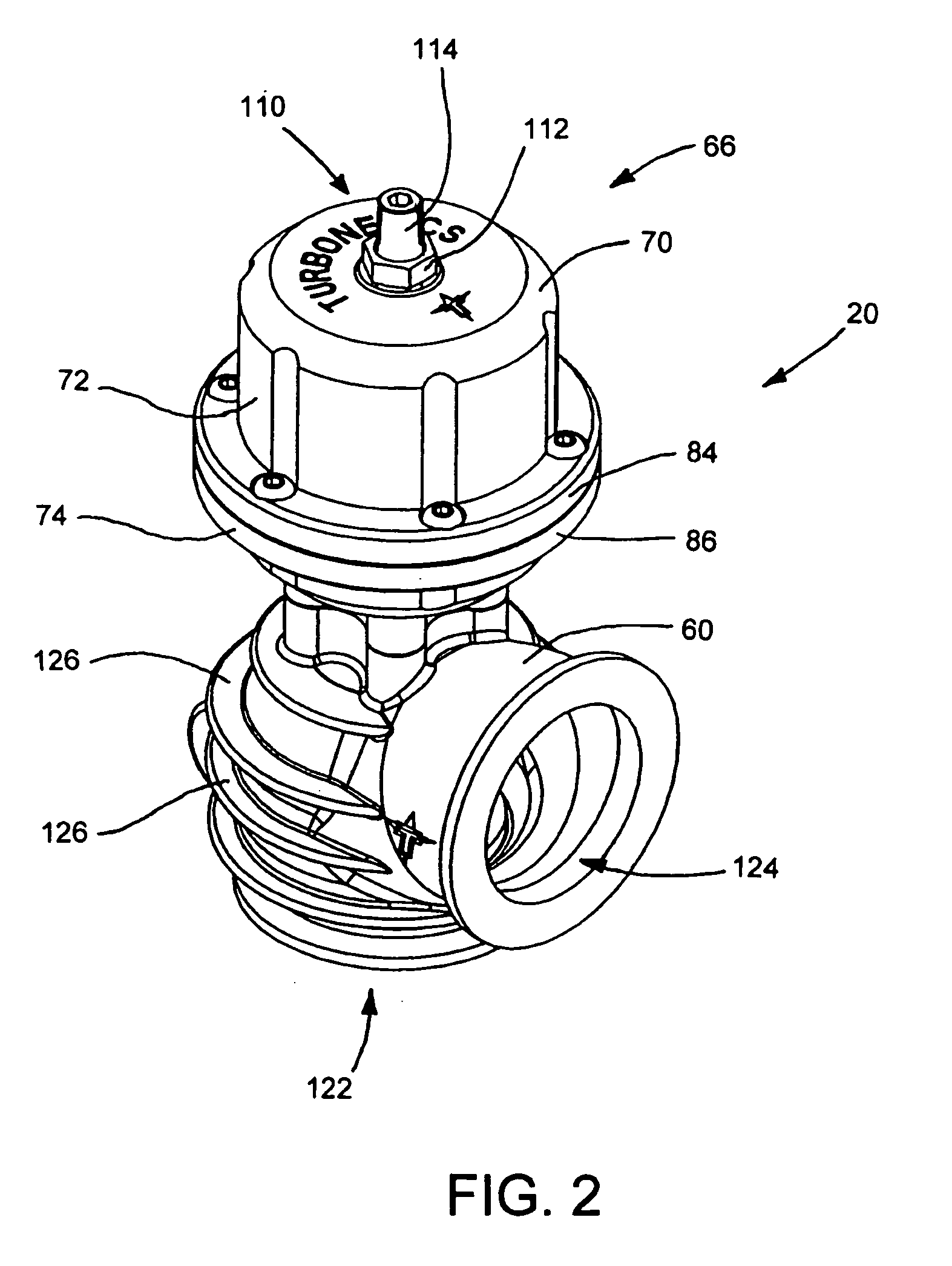
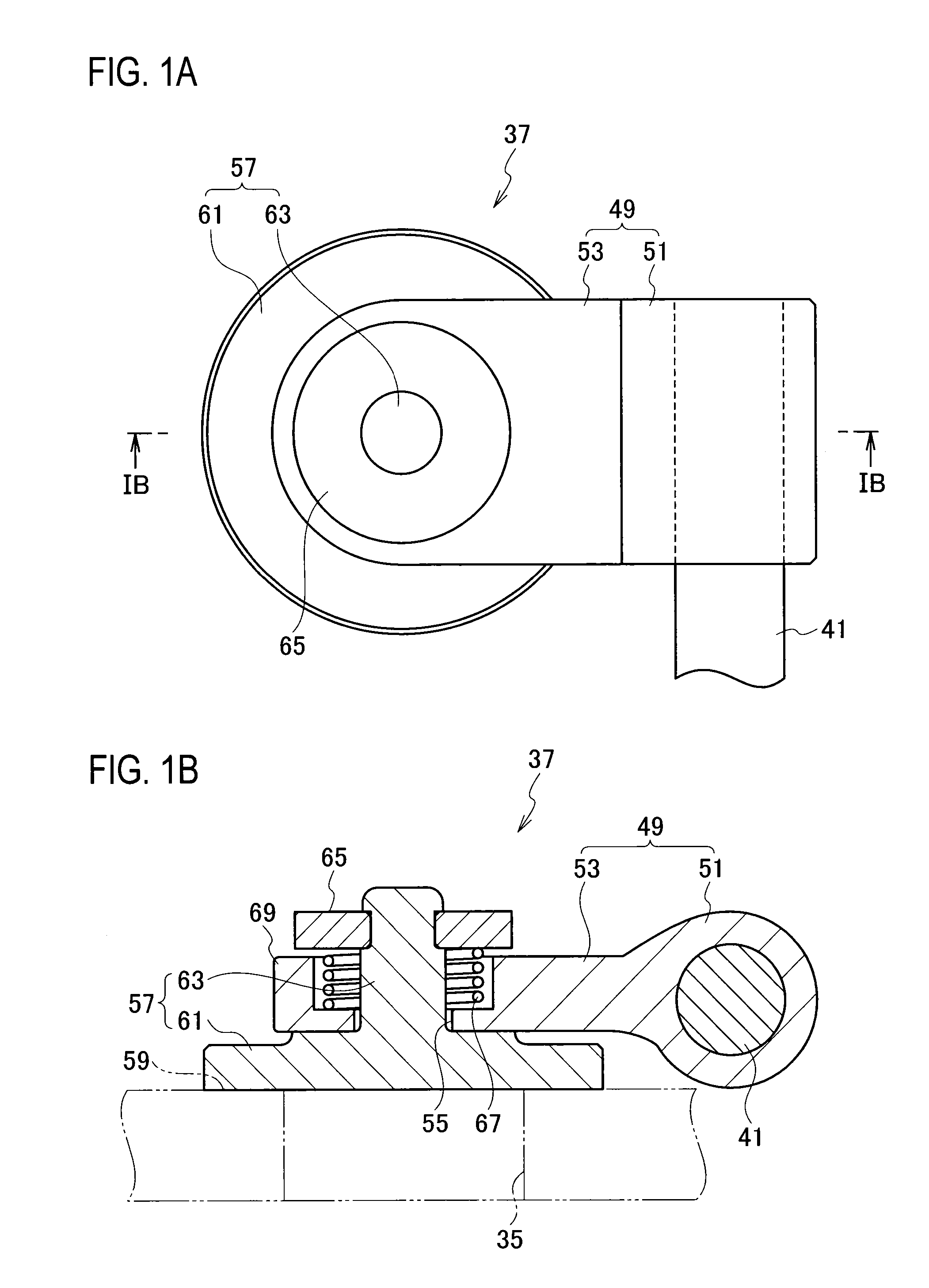
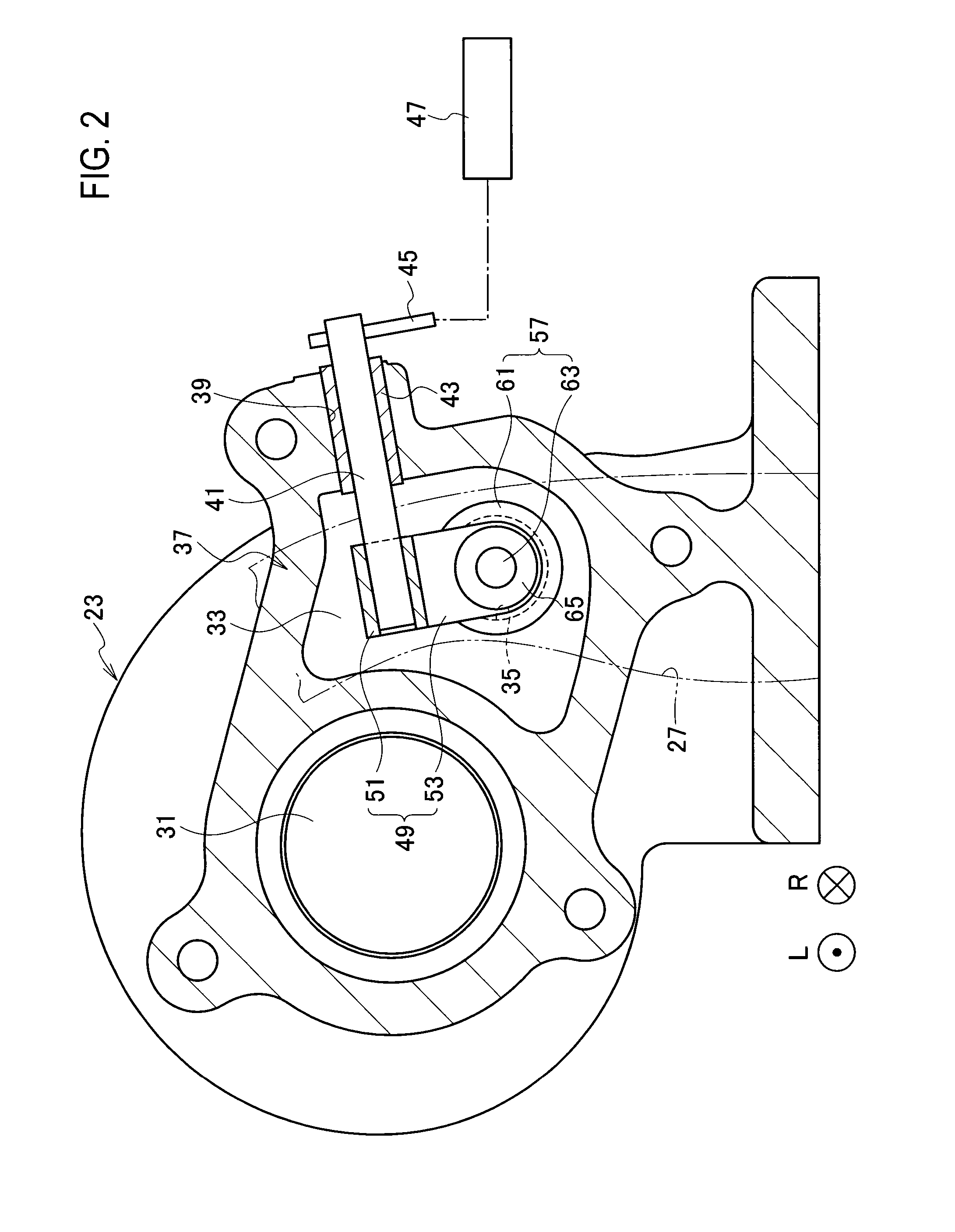
Wastegate for a turbocharged internal combustion engine
InactiveUS6976359B2Easy maintenanceEasy to implementInternal combustion piston enginesEngine controllersWastegateExternal combustion engine
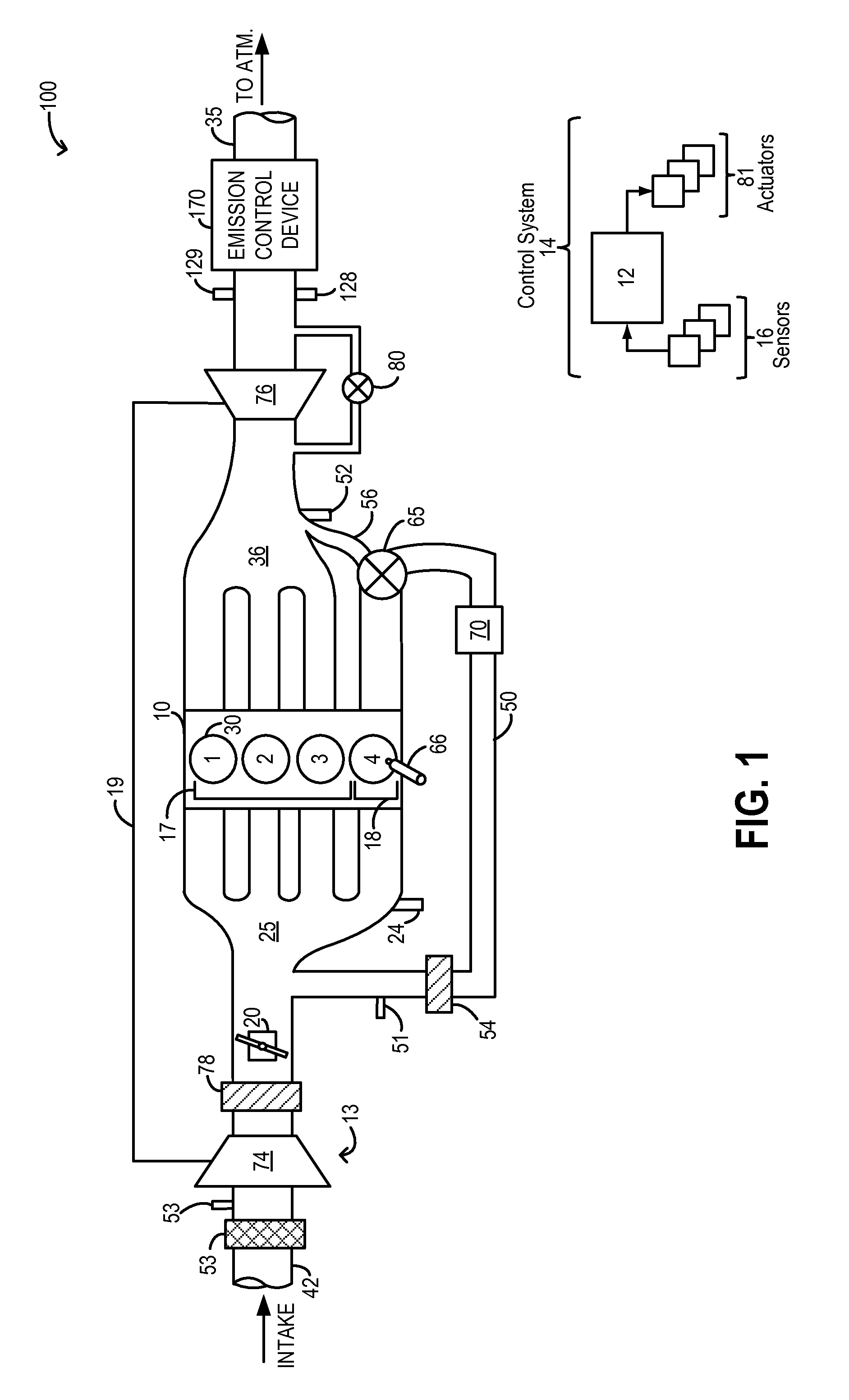
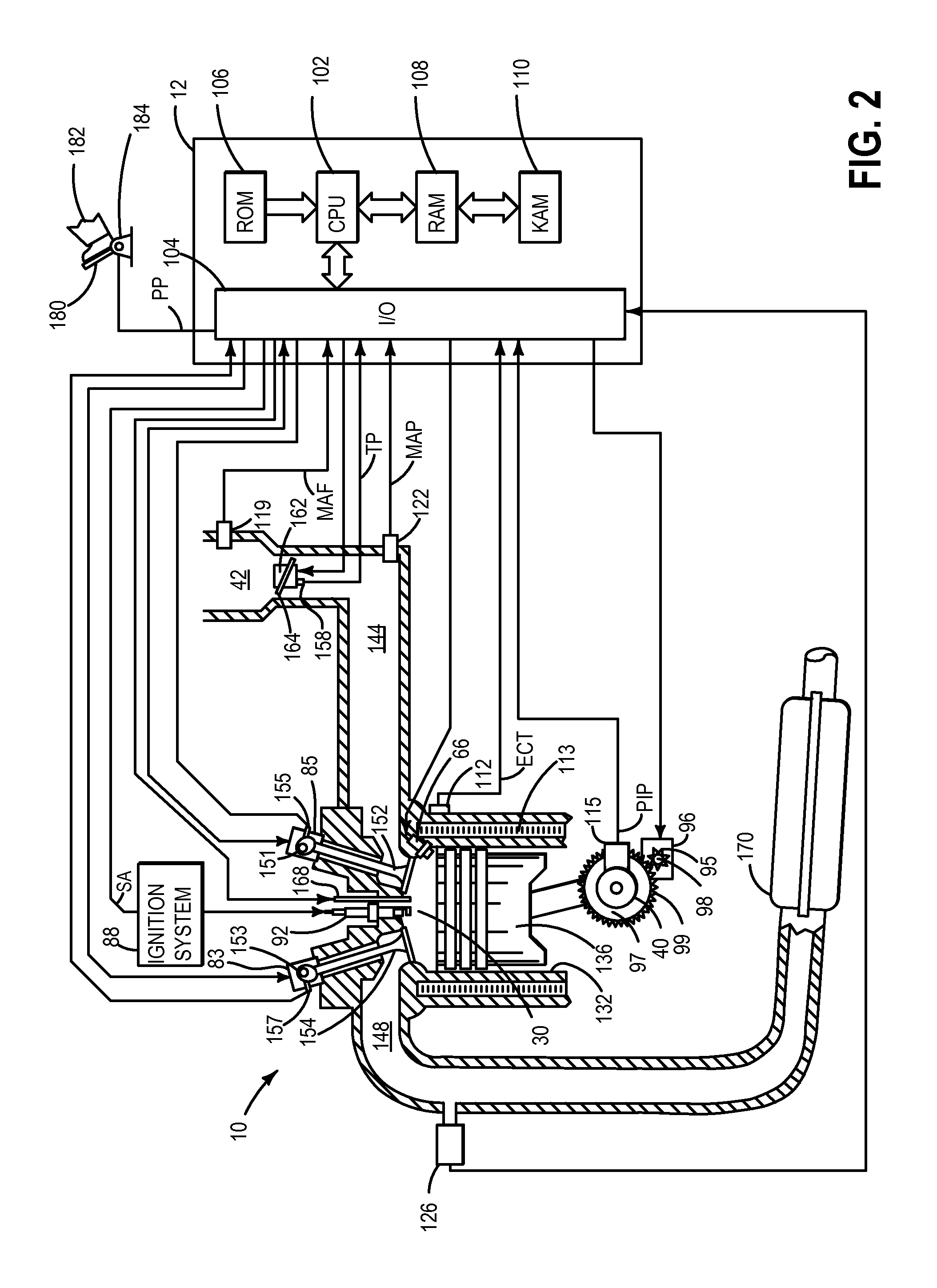
A wastegate valve for a turbocharger that is separate from the turbocharger has an actuator mounted to a valve housing. The valve housing has a passage therethrough and a swing valve that opens and closes the passage. The swing valve has a pivot point that lies outside the path of the exhaust gases. The passage has a recess therein that receives a portion of the swing valve in its open position to improve the flow of exhaust gases through the passage. In an internal combustion engine system, the wastegate valve forms part of a bypass conduit that redirects a portion of the exhaust gases from an engine away from and past the turbocharger.
Owner:TURBONETICS HLDG
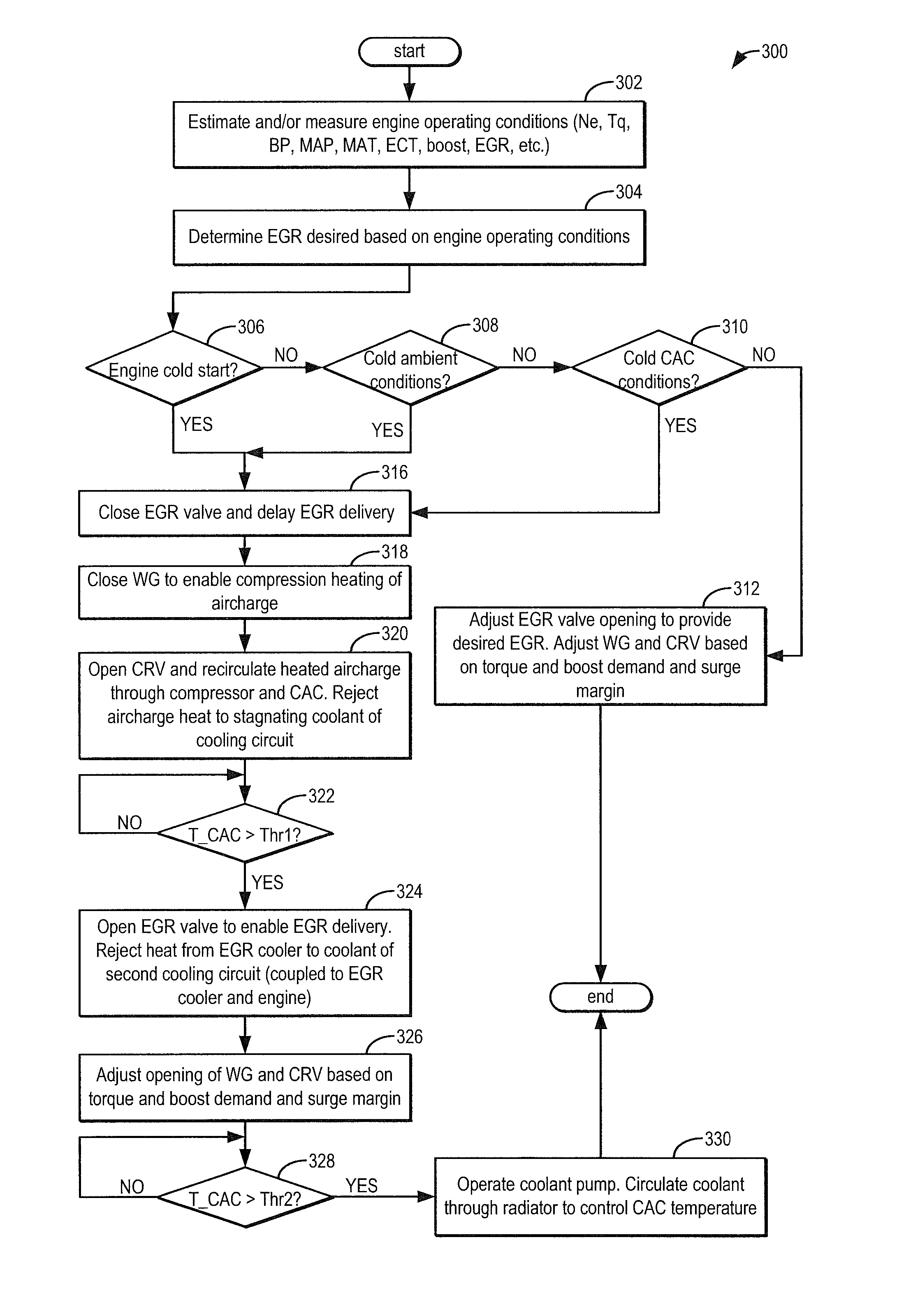
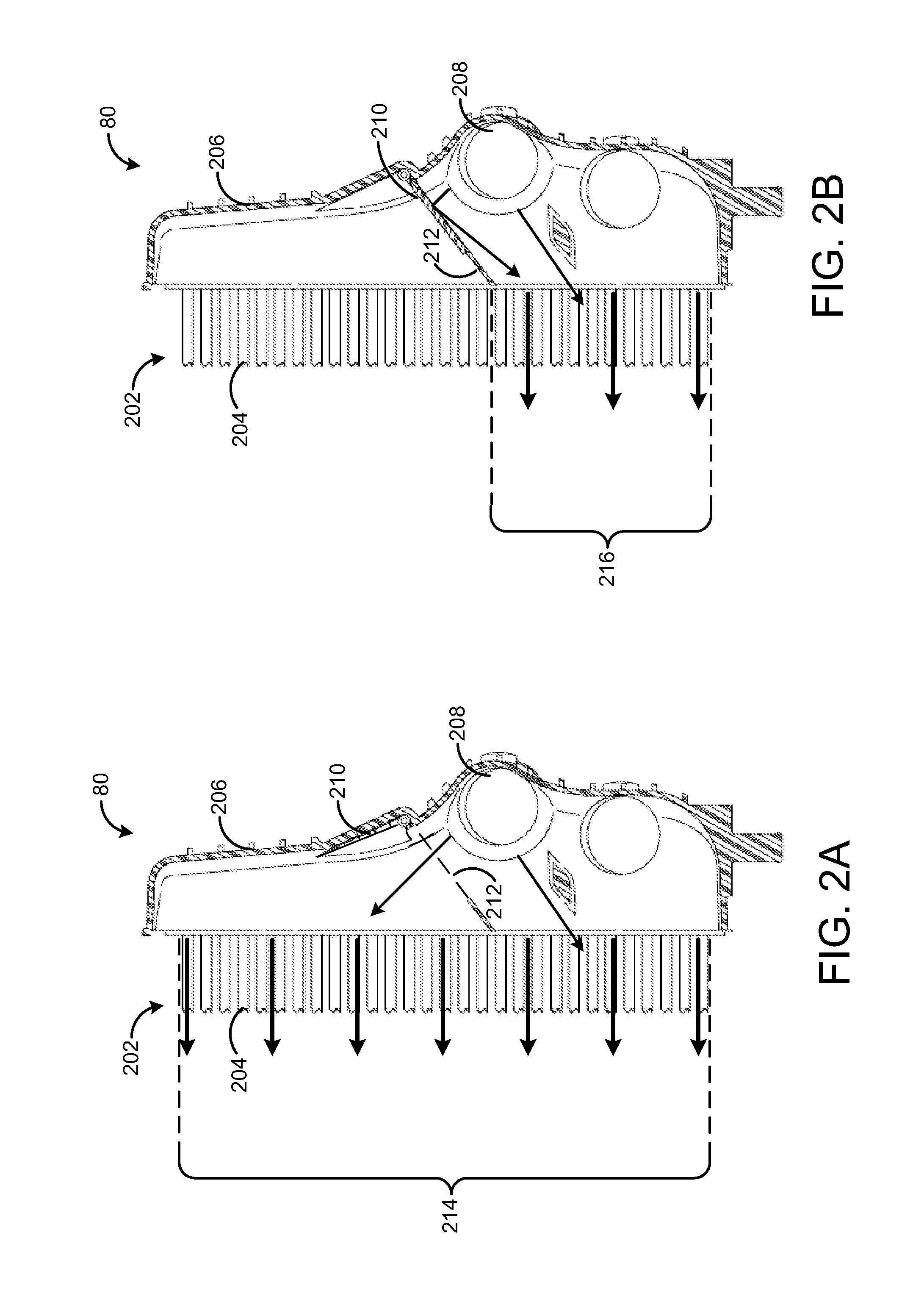
Methods and systems for condensation control
ActiveUS9109505B2Boosted airchargeHigh outputElectrical controlNon-fuel substance addition to fuelWastegateEngineering
Methods and systems are provided for reducing condensate accumulation at a charge air cooler (CAC) during cold ambient conditions. A wastegate may be held closed while a compressor recirculation valve is held open during an engine cold start so as to use compressor heating and increased compressor recirculation to expedite CAC heating. EGR delivery is delayed until the CAC is sufficiently warm to reduce the propensity for condensation.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Methods and systems for condensation control
ActiveUS20150047340A1Improving peak power outputHigh charge densityElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesWastegateEngineering
Methods and systems are provided for reducing condensate accumulation at a charge air cooler (CAC) during cold ambient conditions. A wastegate may be held closed while a compressor recirculation valve is held open during an engine cold start so as to use compressor heating and increased compressor recirculation to expedite CAC heating. EGR delivery is delayed until the CAC is sufficiently warm to reduce the propensity for condensation.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
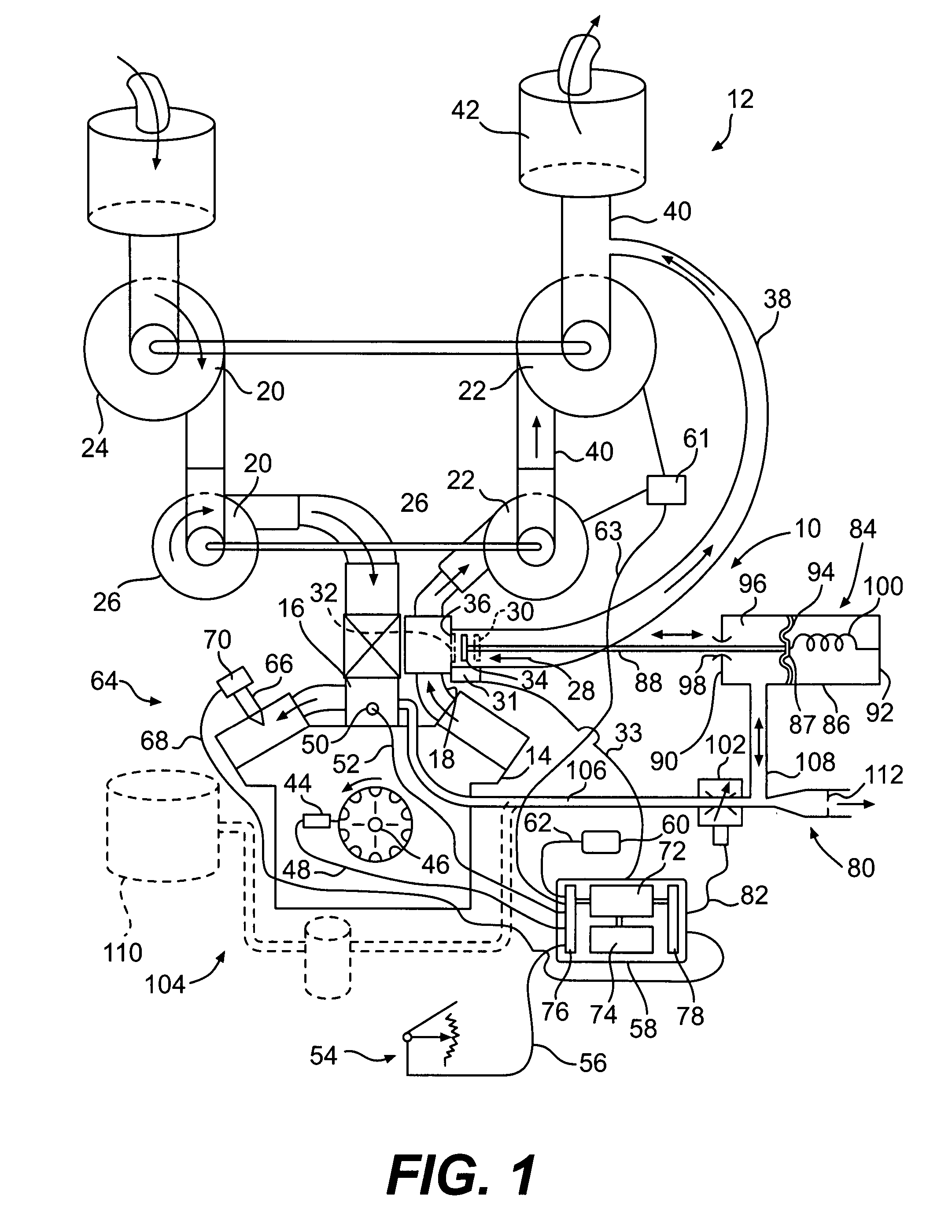
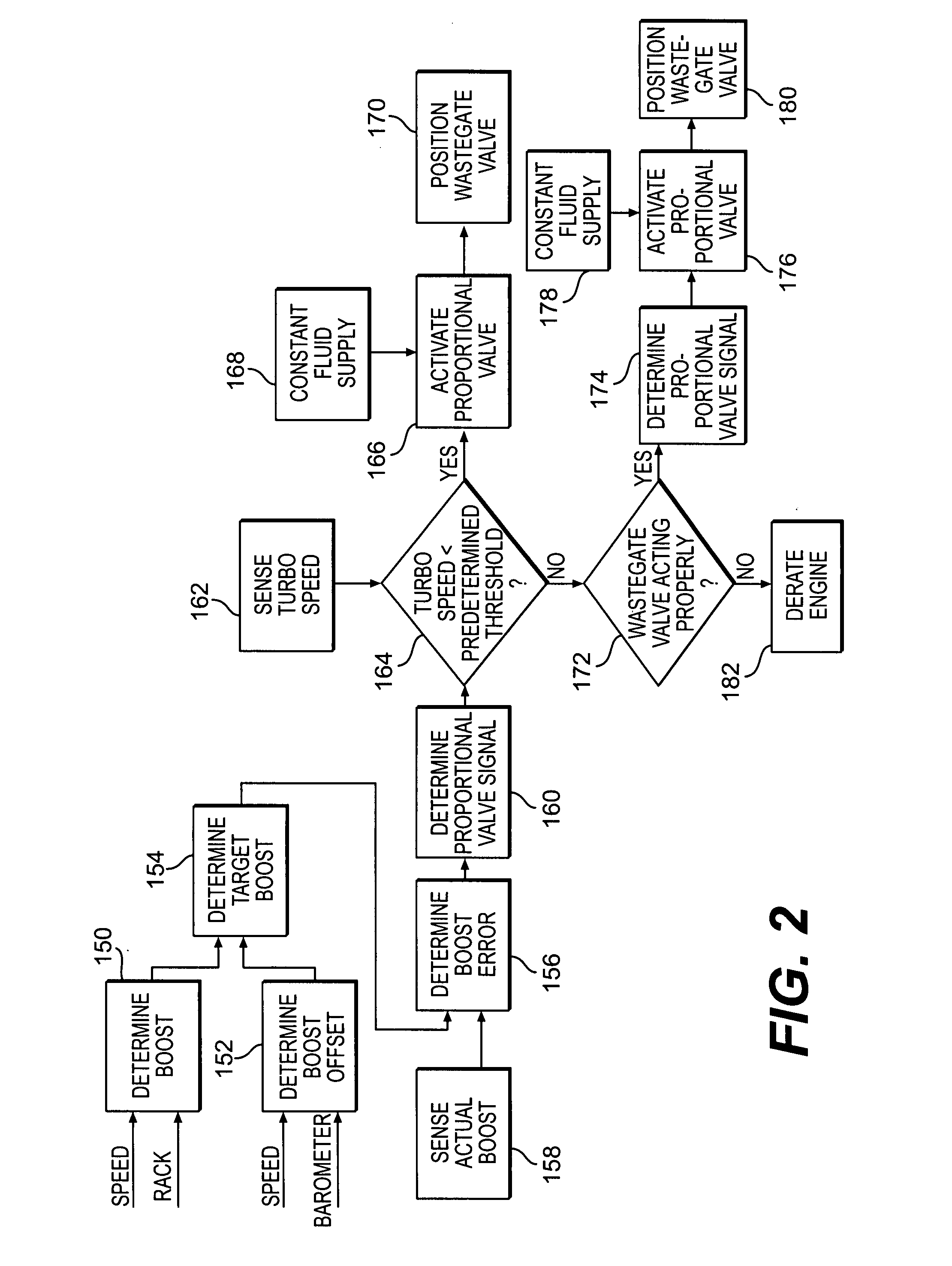
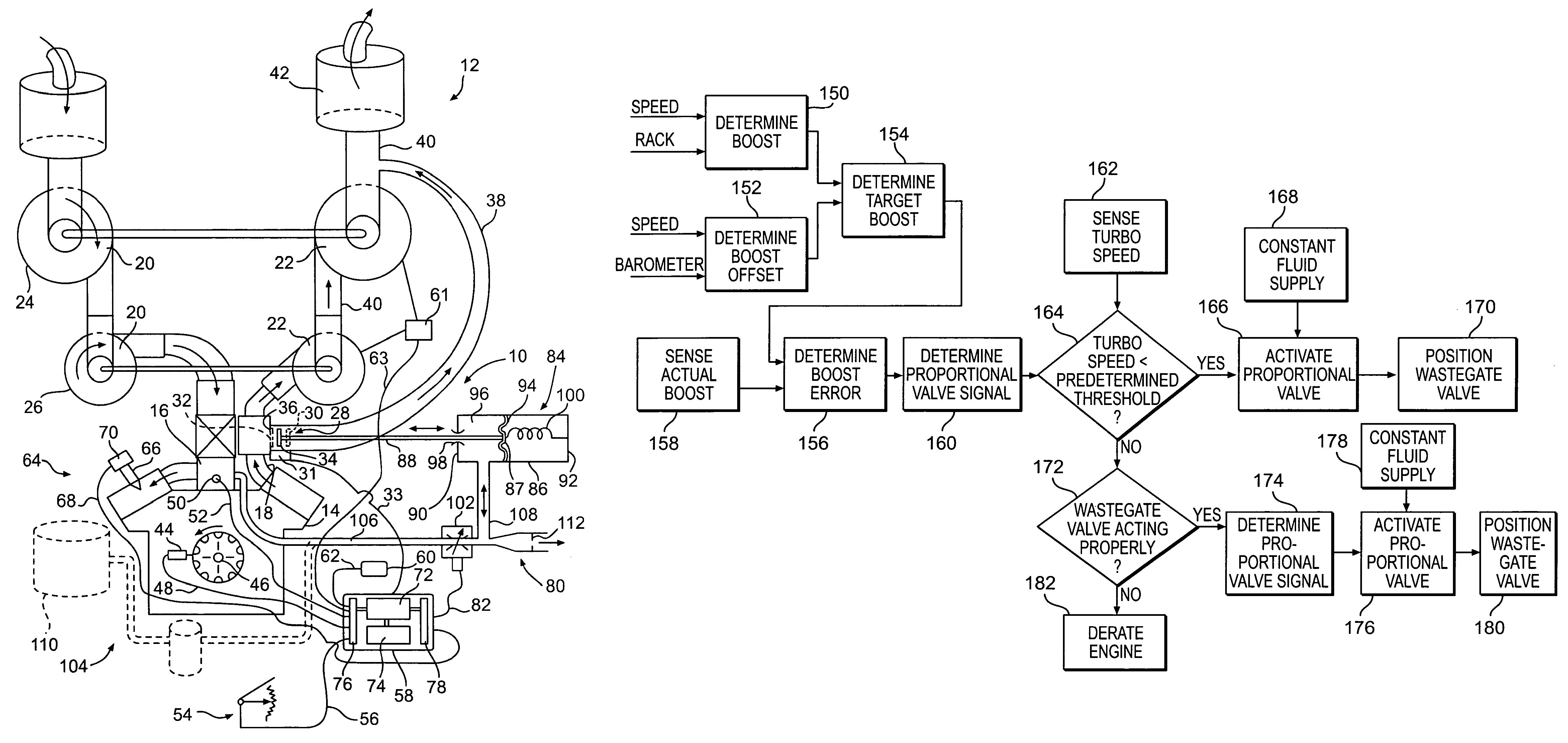
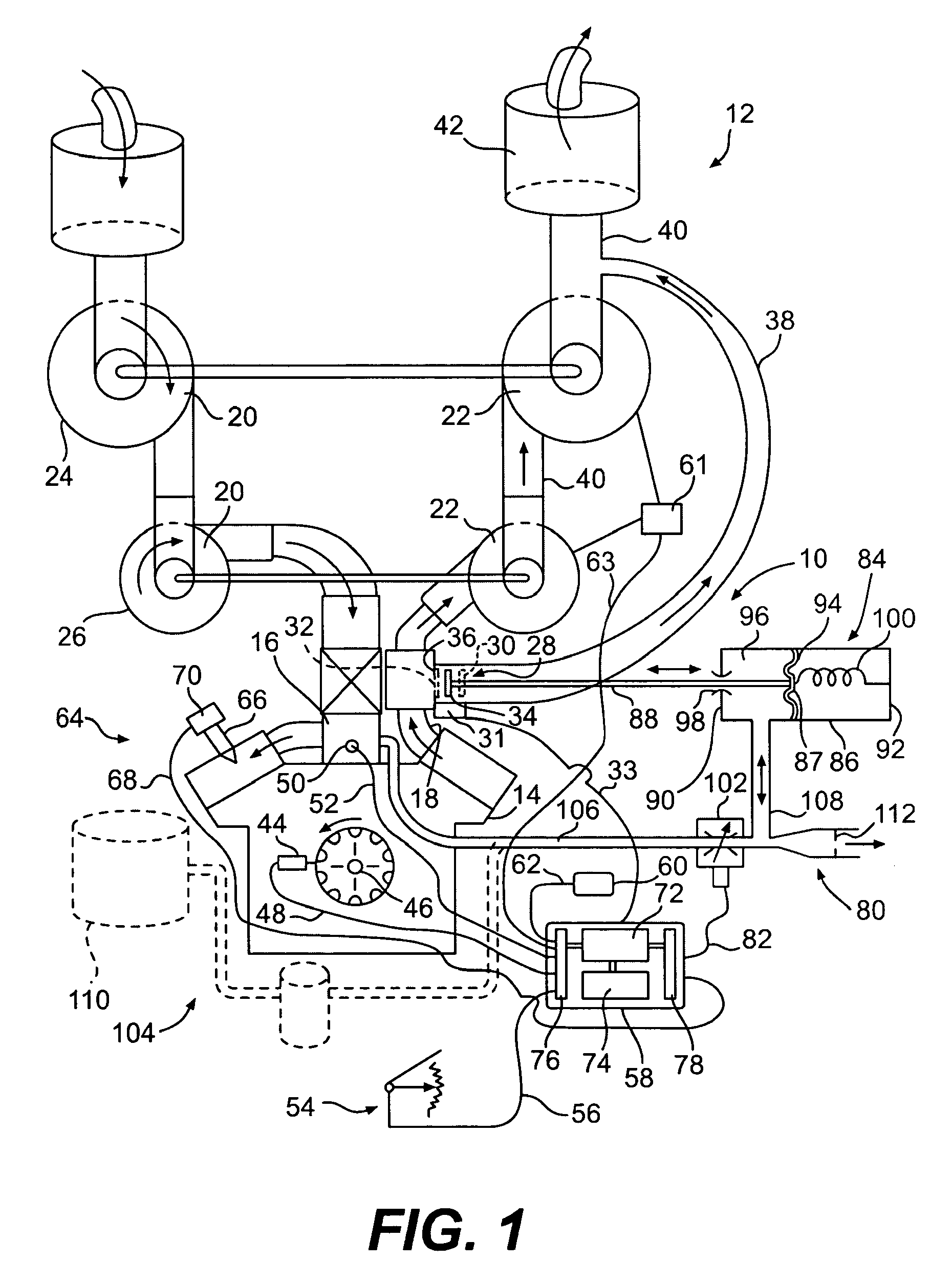
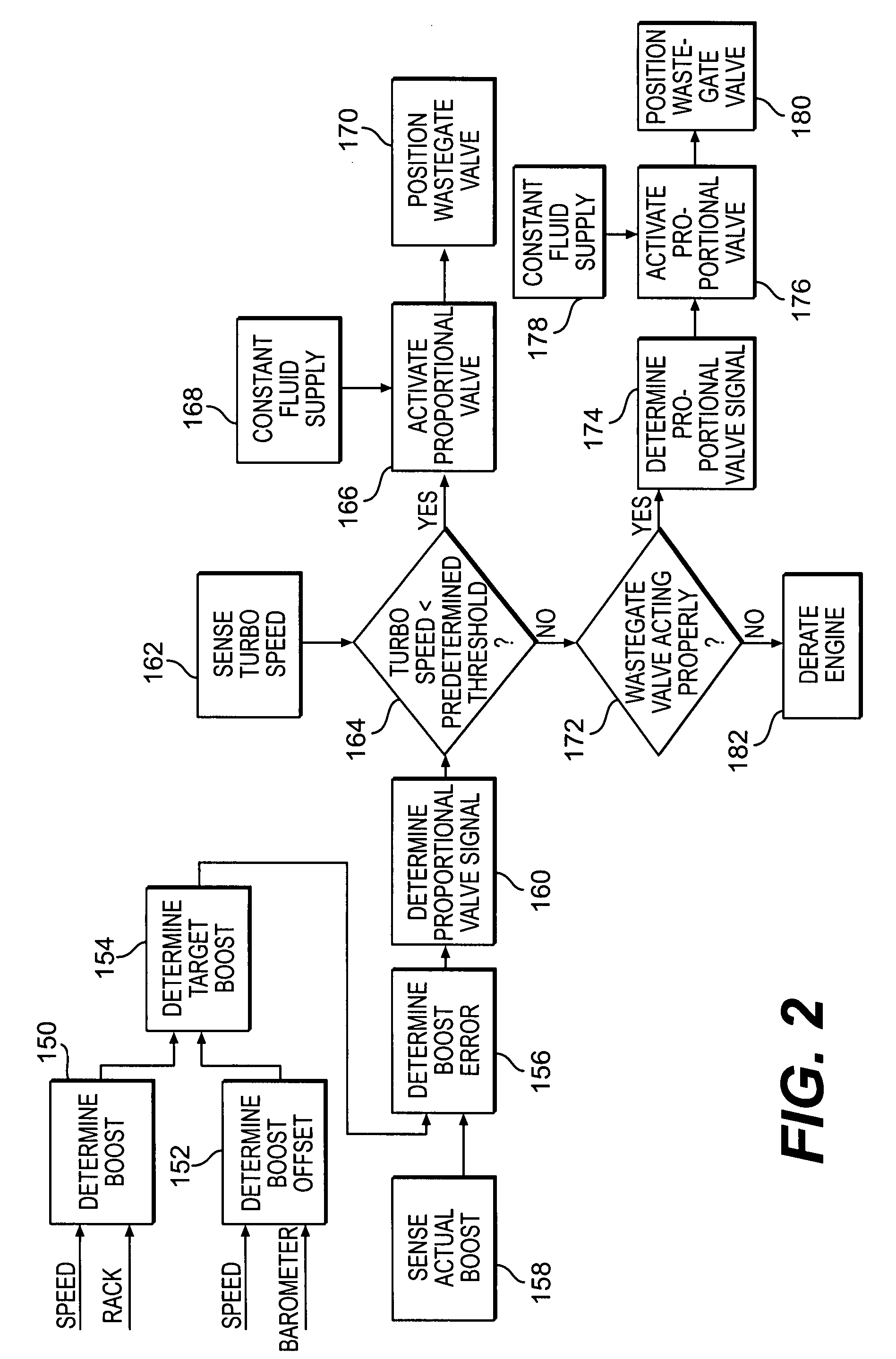
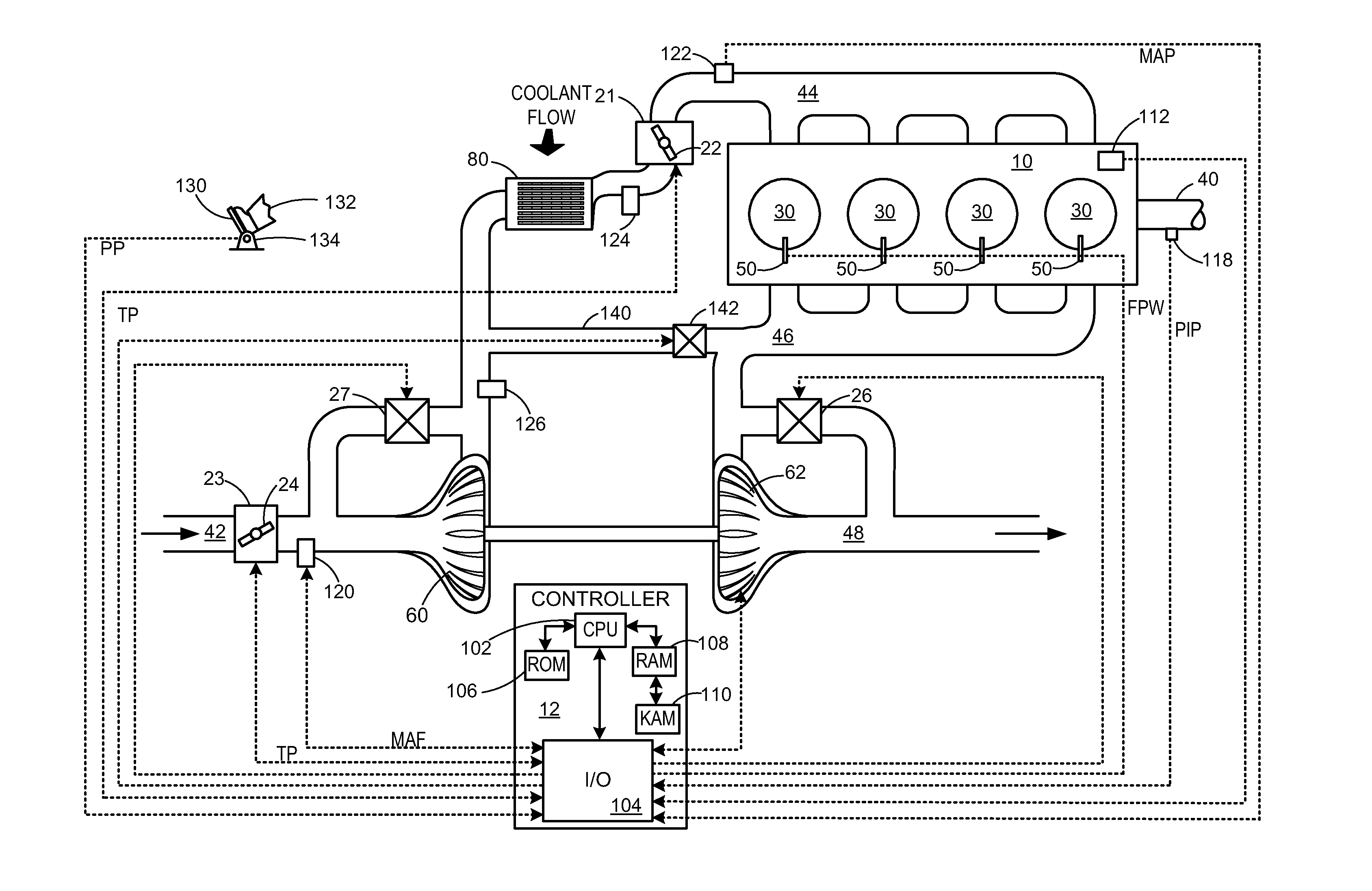
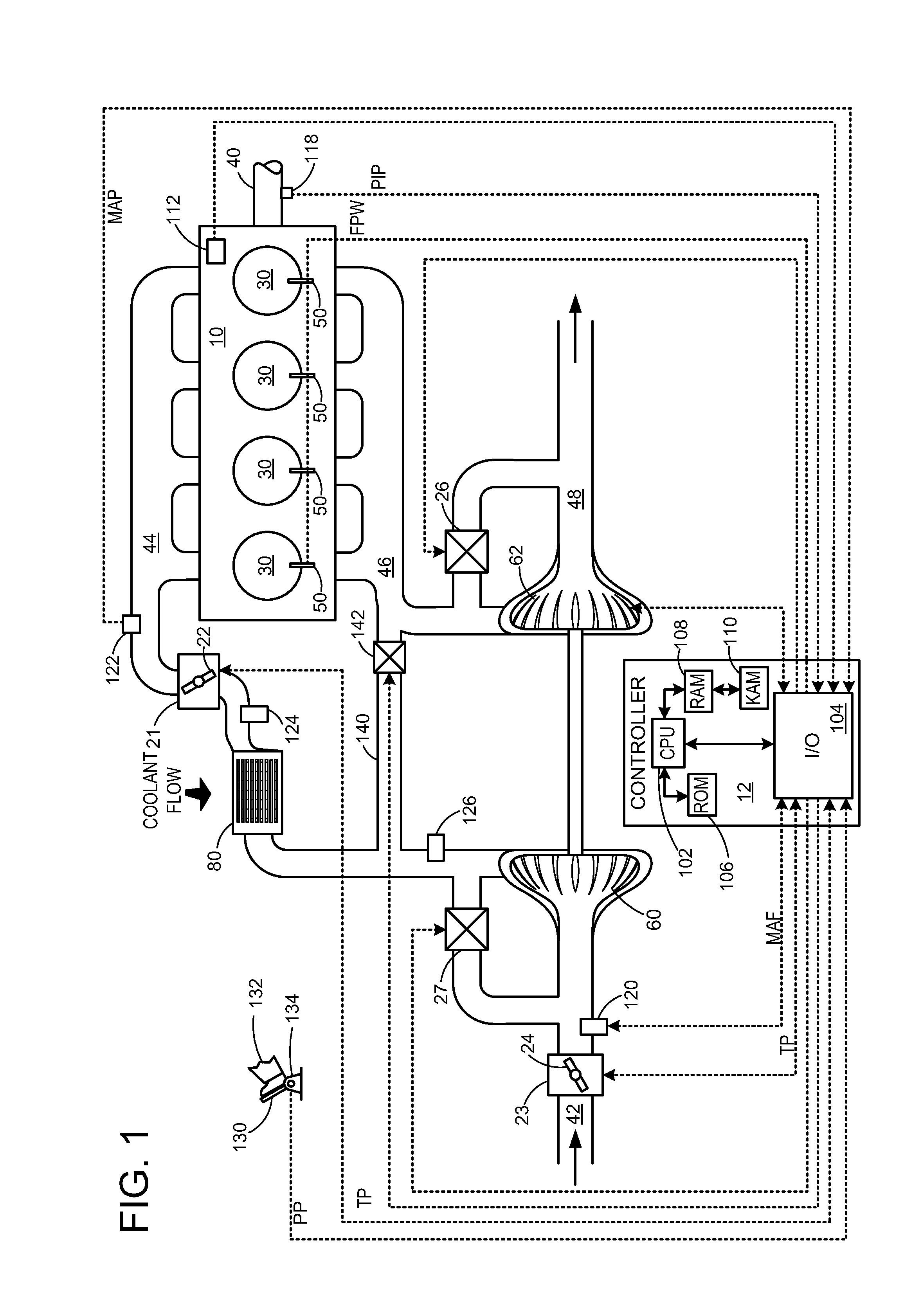
Turbocharger control system
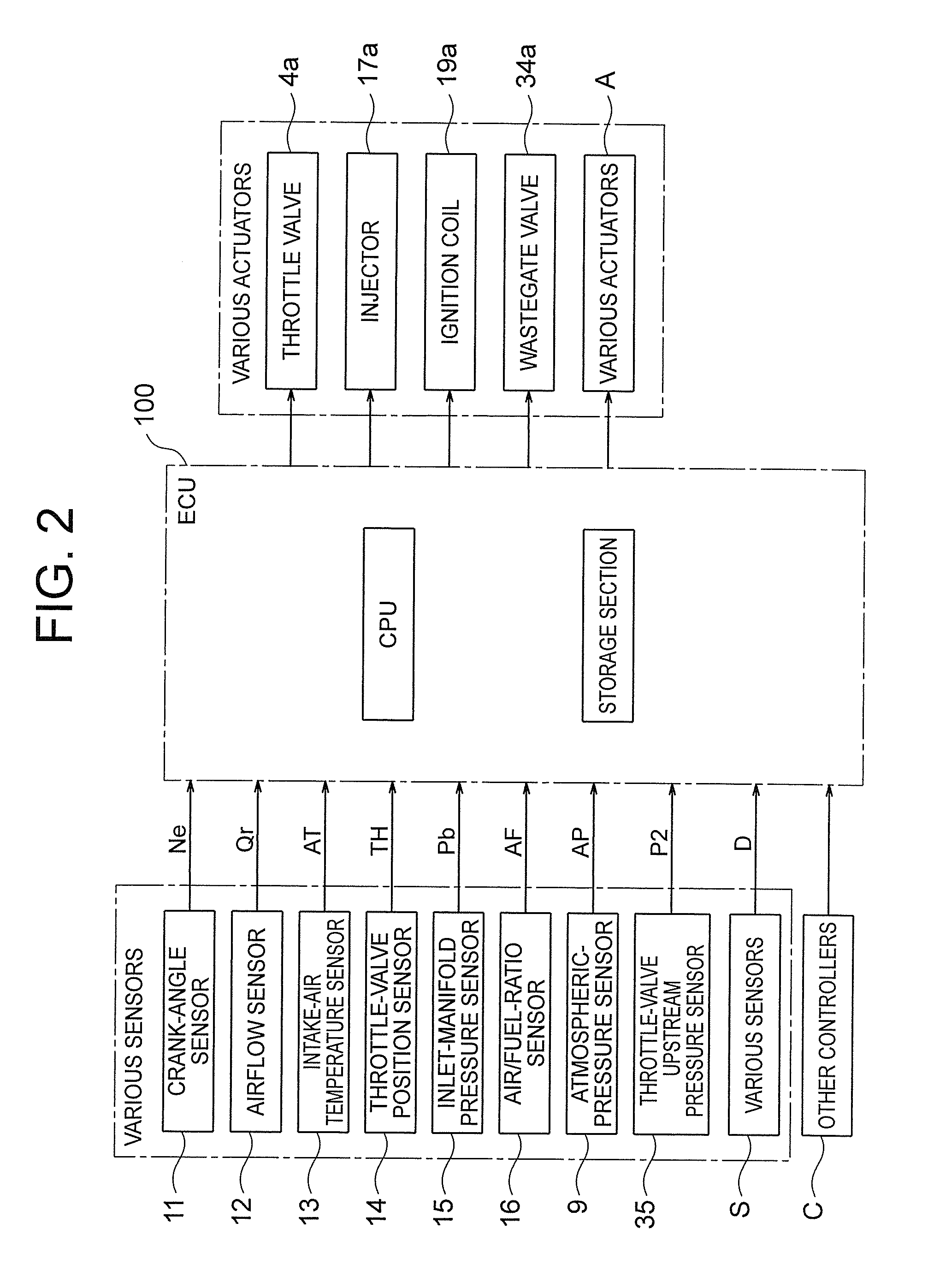
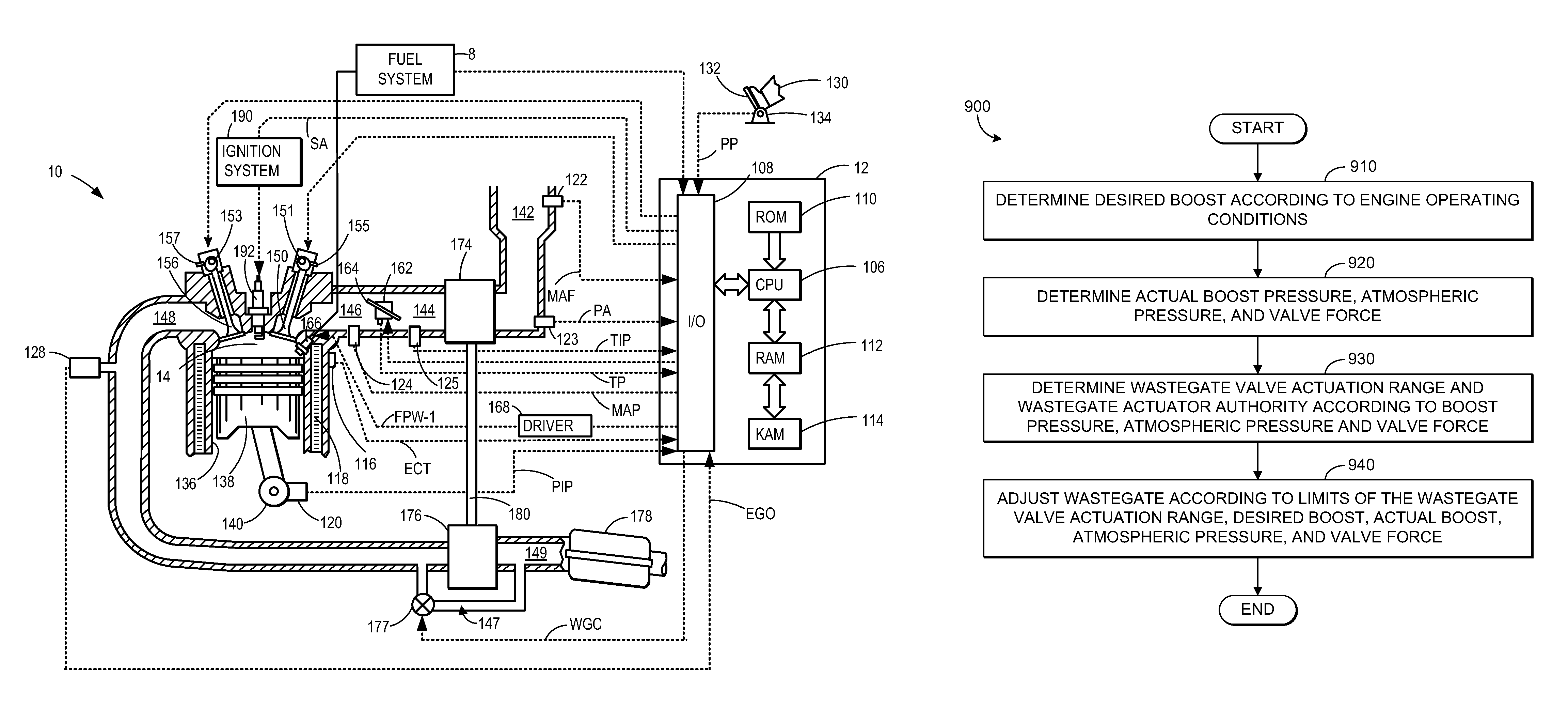
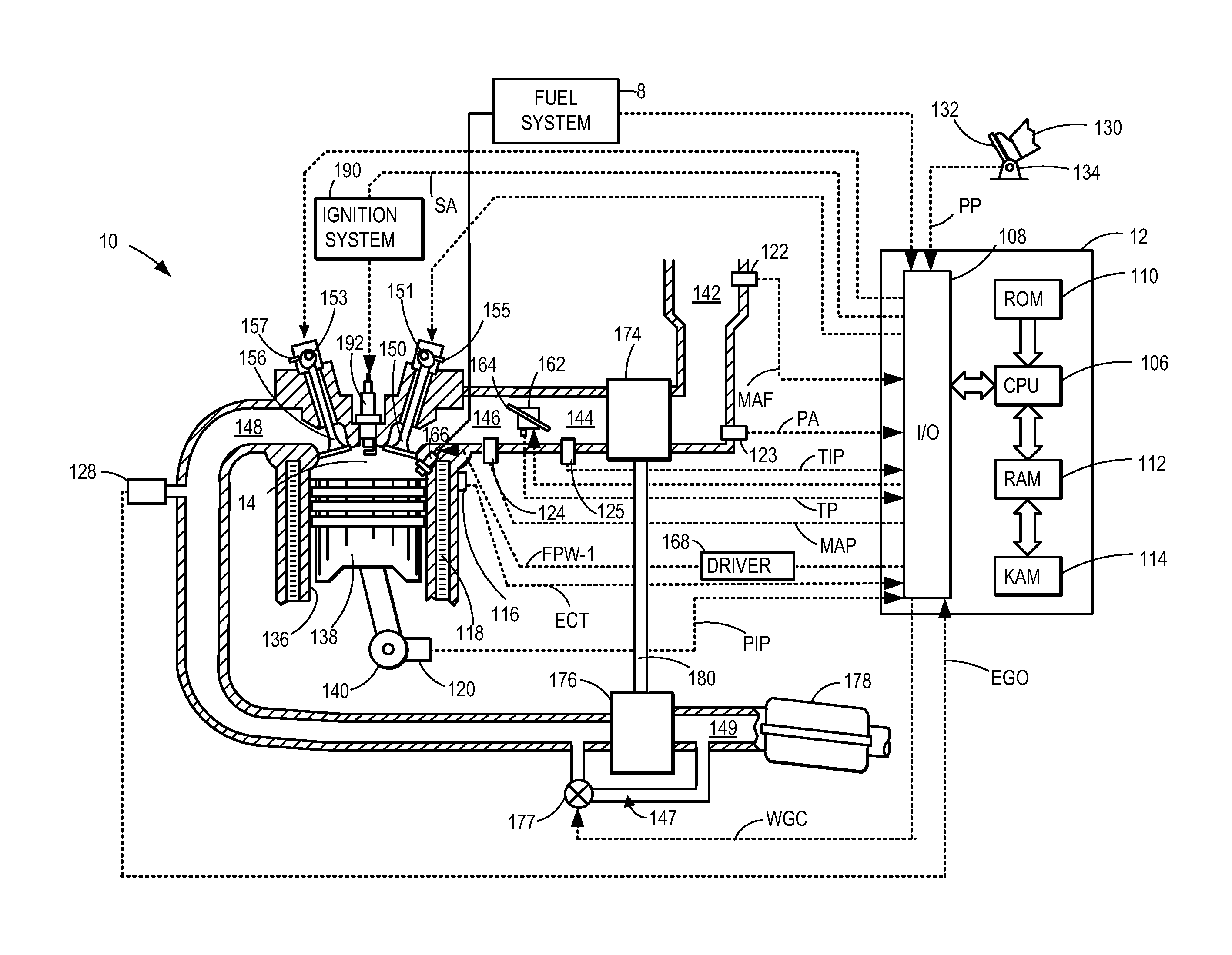
A system for controlling boost pressure at various different altitudes of operation of a turbo charged internal combustion engine includes a wastegate valve, an actuator, and a controller. Signals delivered from an engine speed sensor, a boost pressure transducer, a barometric pressure sensor, and a turbocharger speed sensor are processed in the controller. A control signal delivered from the controller to the actuator controls the position of the wastegate valve, bypass of exhaust gasses, and the speed of the turbocharger. The controller is configured to compare the turbocharger speed to a predetermined threshold value and determine the control signal based on the comparison.
Owner:CATERPILLAR INC
Turbocharger housing with exhaust gas recycling
InactiveUS6381960B1Easy to assembleInternal combustion piston enginesNon-fuel substance addition to fuelWastegateExternal combustion engine
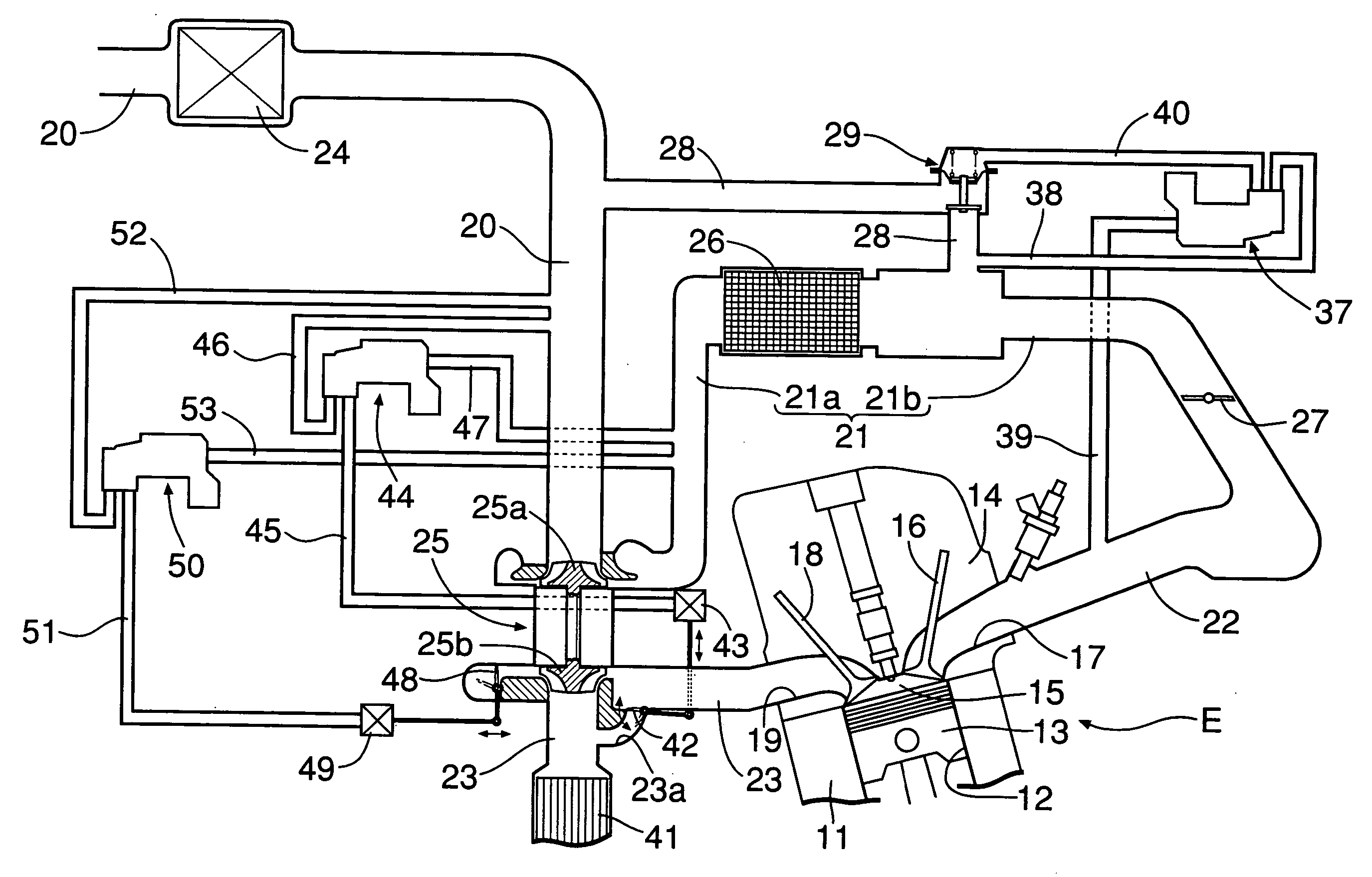
A turbocharger for an internal combustion engine and which has a housing with a turbine housed in a chamber in the housing, and driven by exhaust gases from the engine. The turbocharger has an integral EGR valve and wastegate.
Owner:SCANIA CV AB
Washer for reducing noise and system for reducing noise of wastegate valve apparatus by using the same
ActiveUS20130139502A1Reduce noiseEfficiently reducing noiseOperating means/releasing devices for valvesLinear bearingsBall bearingWastegate
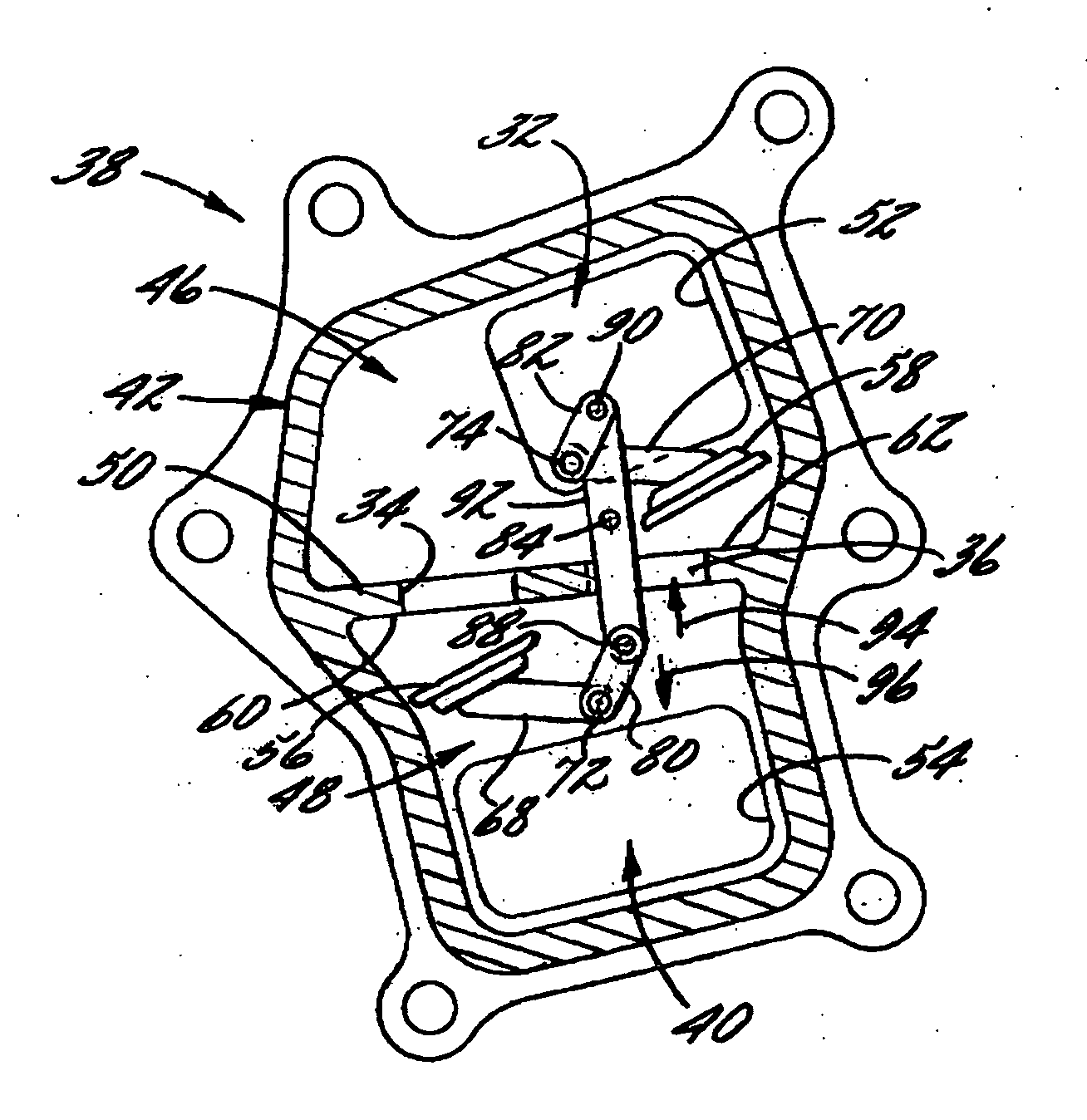
A system for reducing noise of a wastegate valve apparatus including a bypass passage, a wastegate valve, an actuator and a link unit delivering the power of the actuator to the wastegate valve, may have a first link connected to the actuator, a third link connected to the wastegate valve, a second link provided with a rod disposed between the first link and the third link, wherein the second link includes a rod end ball bearing having a penetration hole into which a bolt member is inserted and a ball coupled to the penetration hole, and a joint connecting the rod and the third link, and a first washer disposed between the rod end ball bearing and the first link, wherein the first washer includes a support body, and an elastic member disposed between the first link and the support body.
Owner:HYUNDAI MOTOR CO LTD +1
Approach for identifying and responding to an unresponsive wastegate in a twin turbocharged engine
InactiveUS8001782B2Balance levelLoading can be alteredElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesWastegateControl system
An engine system for a vehicle is provided, comprising an internal combustion engine including an exhaust system; a first turbine including a first wastegate and arranged along a first branch of the exhaust system, a second turbine including a second wastegate and arranged along a second branch of the exhaust system; a first exhaust gas sensor arranged along the first branch of the exhaust system downstream of the first turbine and first wastegate; a second exhaust gas sensor arranged along the second branch of the exhaust system downstream of the second turbine and the second wastegate; and a control system configured to command the first and second wastegates to a closed or open position and to indicate one of said wastegates as unresponsive to said command in response to a temperature difference between the first and second branches indicated by the first and second exhaust gas sensors.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Boost pressure estimation apparatus for internal combustion engine with supercharger
ActiveUS20050172628A1Accurate calculationLow costElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesTurbochargerExhaust fumes
An opening is provided for an exhaust bypass pipe that bypasses an exhaust turbine of an exhaust turbine supercharger. According to the opening, an exhaust gas amount bypassing the exhaust turbine is calculated. An exhaust gas amount supplied to the exhaust turbine is found by subtracting the waste-gate-valve-passing gas amount from an intake air amount (exhaust gas amount) detected by the air flow meter. A rotational speed of the exhaust turbine is calculated from this turbine-supplied gas amount. An estimated boost pressure is calculated from this rotational speed of the exhaust turbine. Consequently, a boost pressure can be accurately estimated without using a boost pressure sensor even under such conditions as to disable detection of boost pressures or degrade the detection accuracy in a system using a conventional boost pressure sensor.
Owner:DENSO CORP
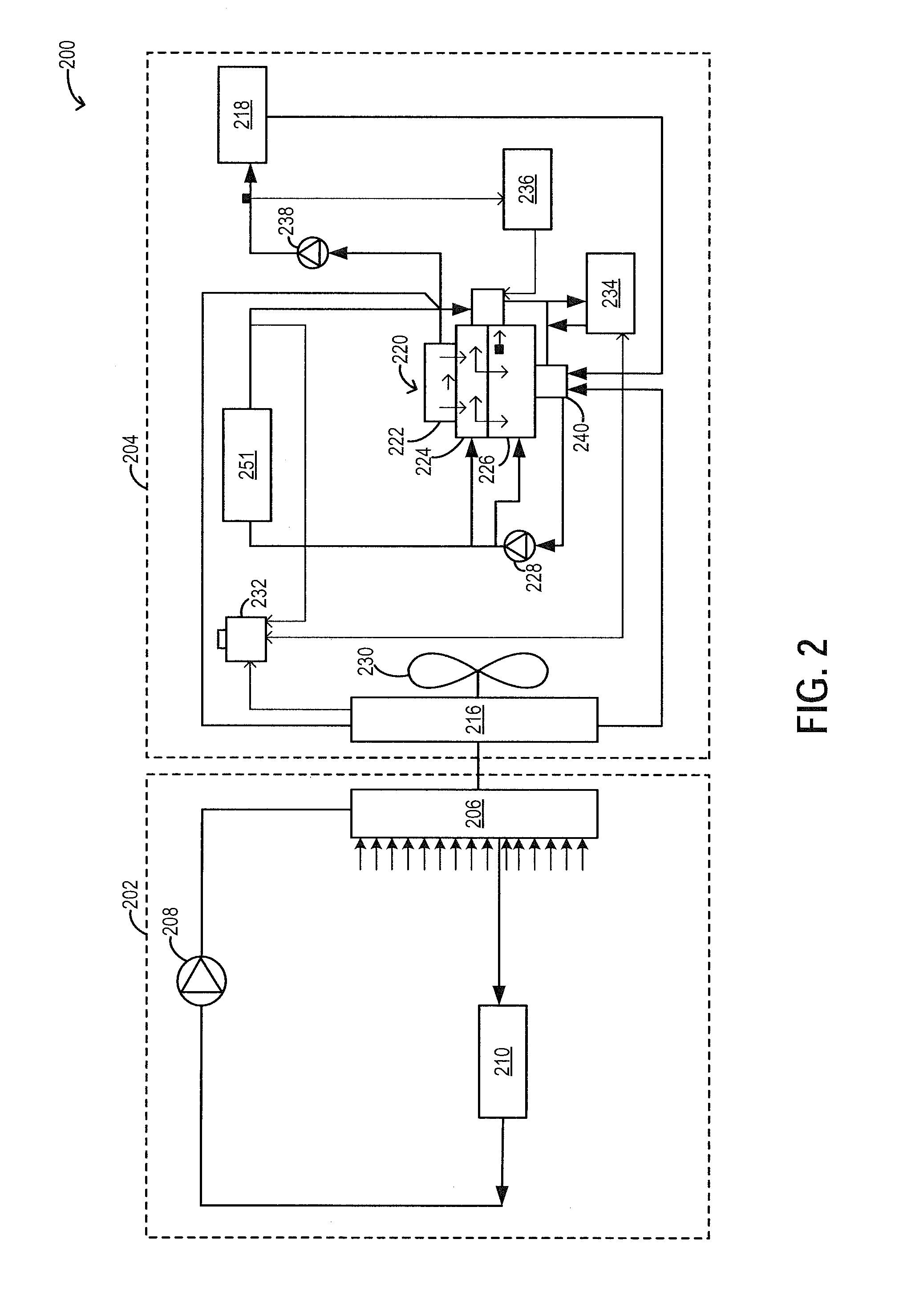
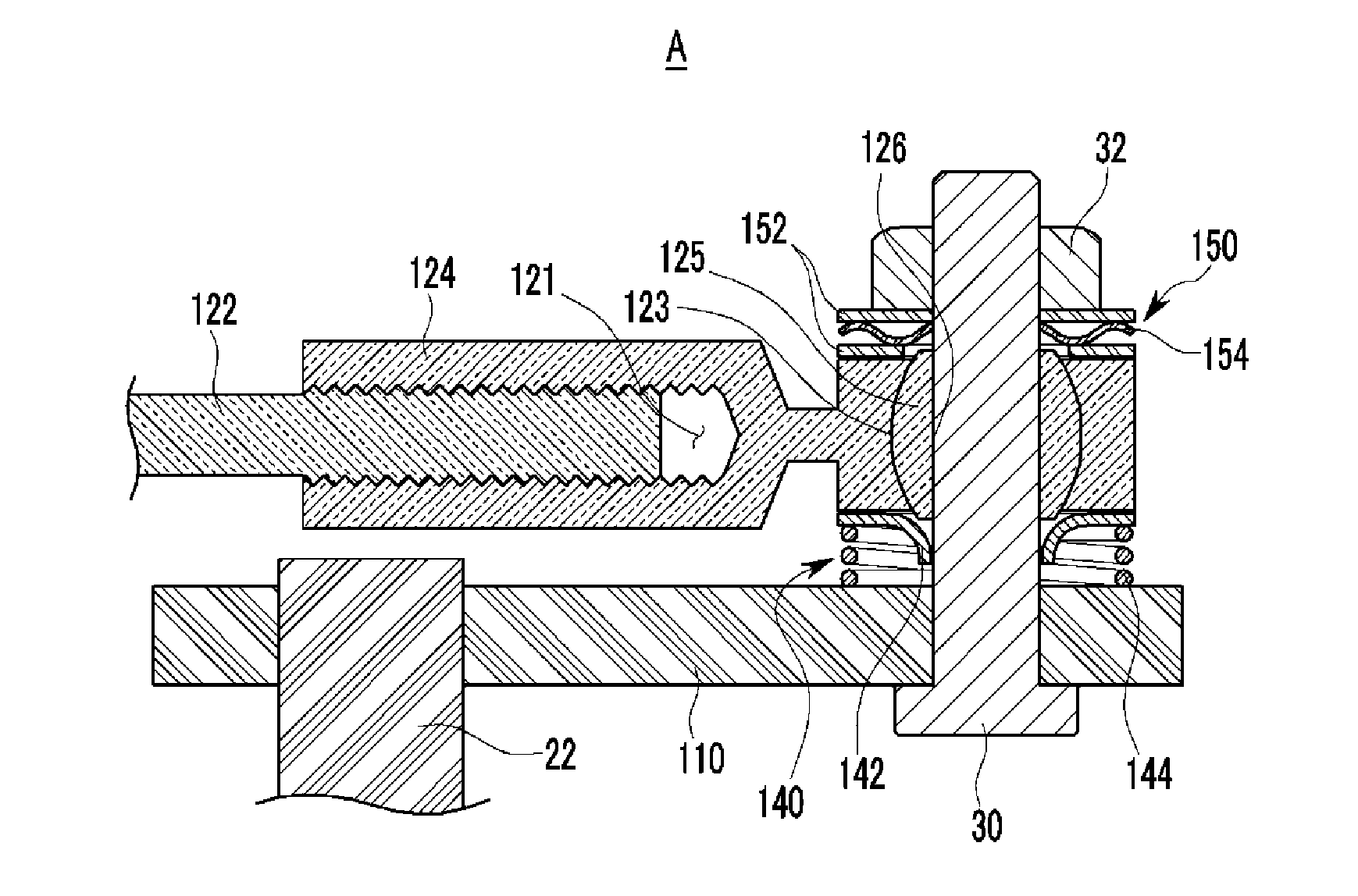
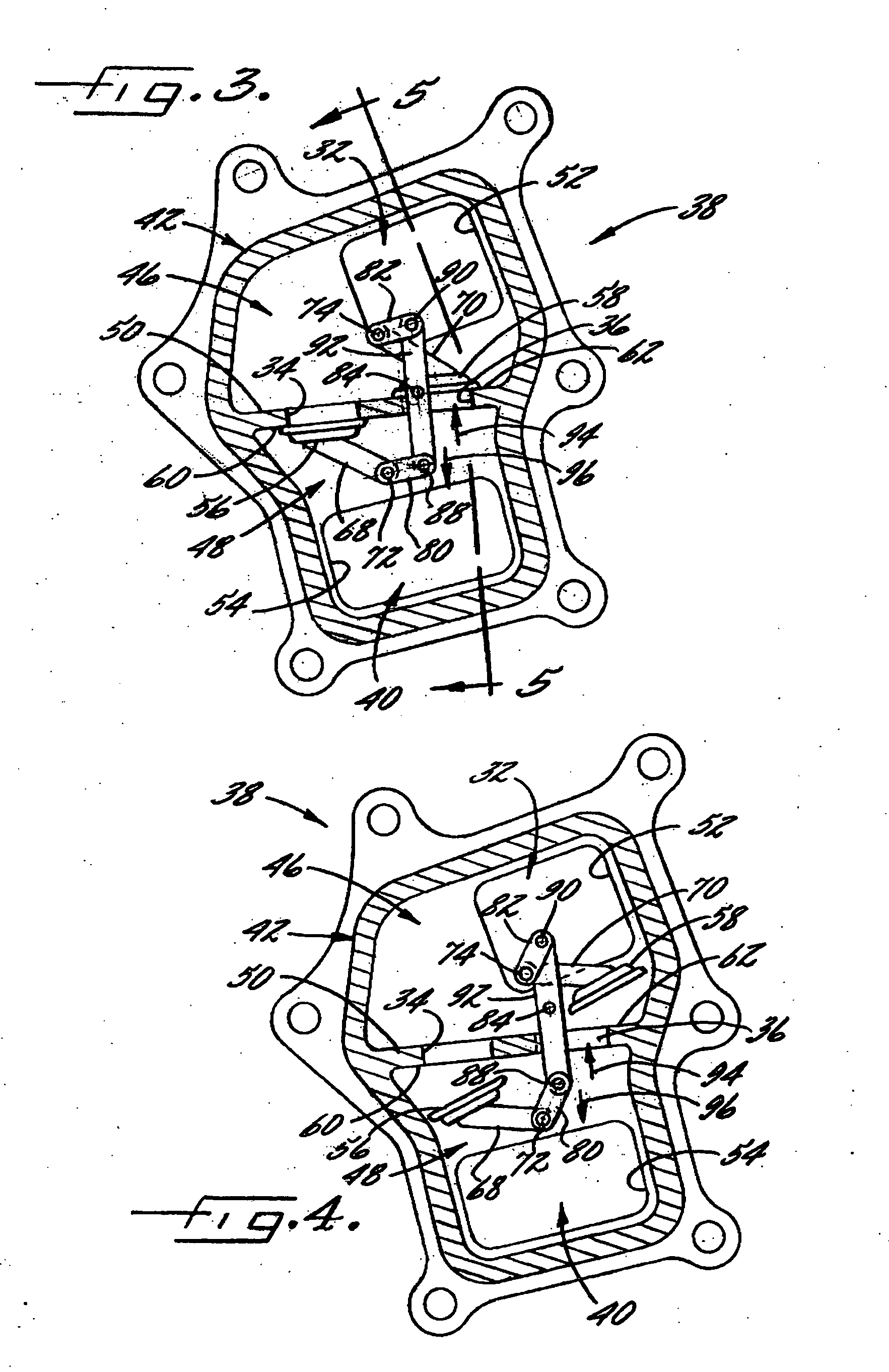
Wastegate assembly
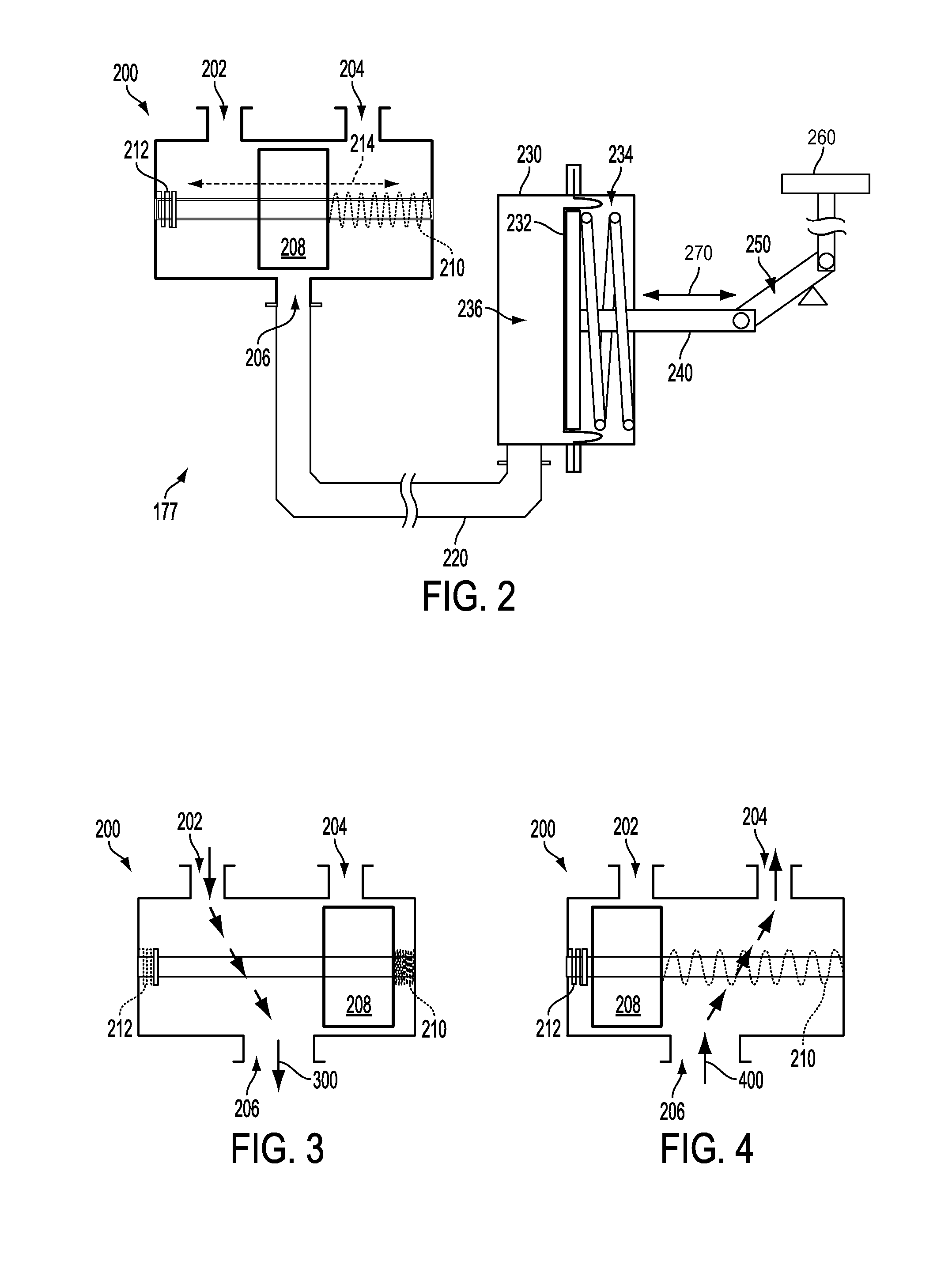
ActiveUS20080298953A1Easy to manufactureCost-effectiveInternal combustion piston enginesWind motor controlWastegateEngineering
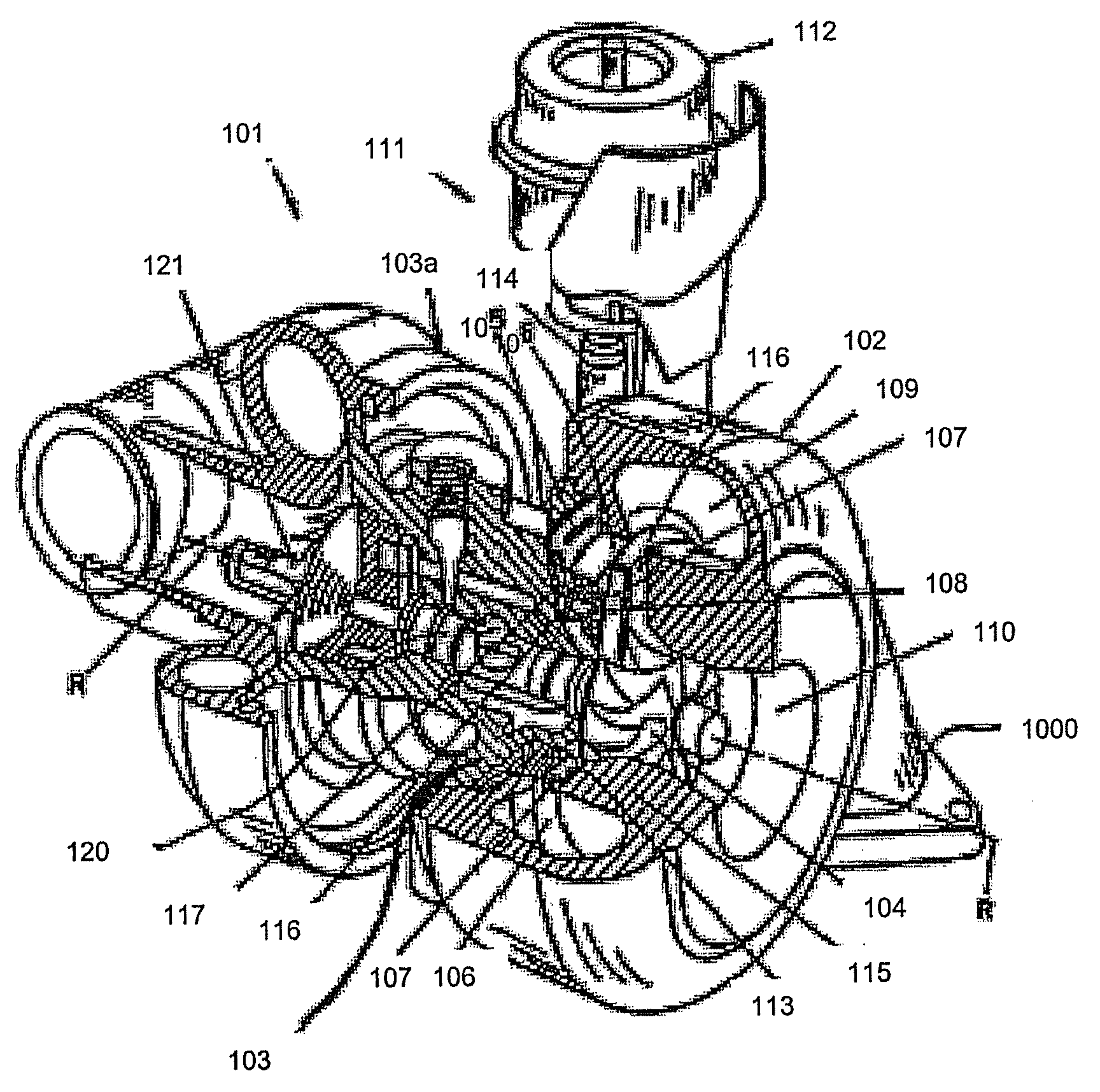
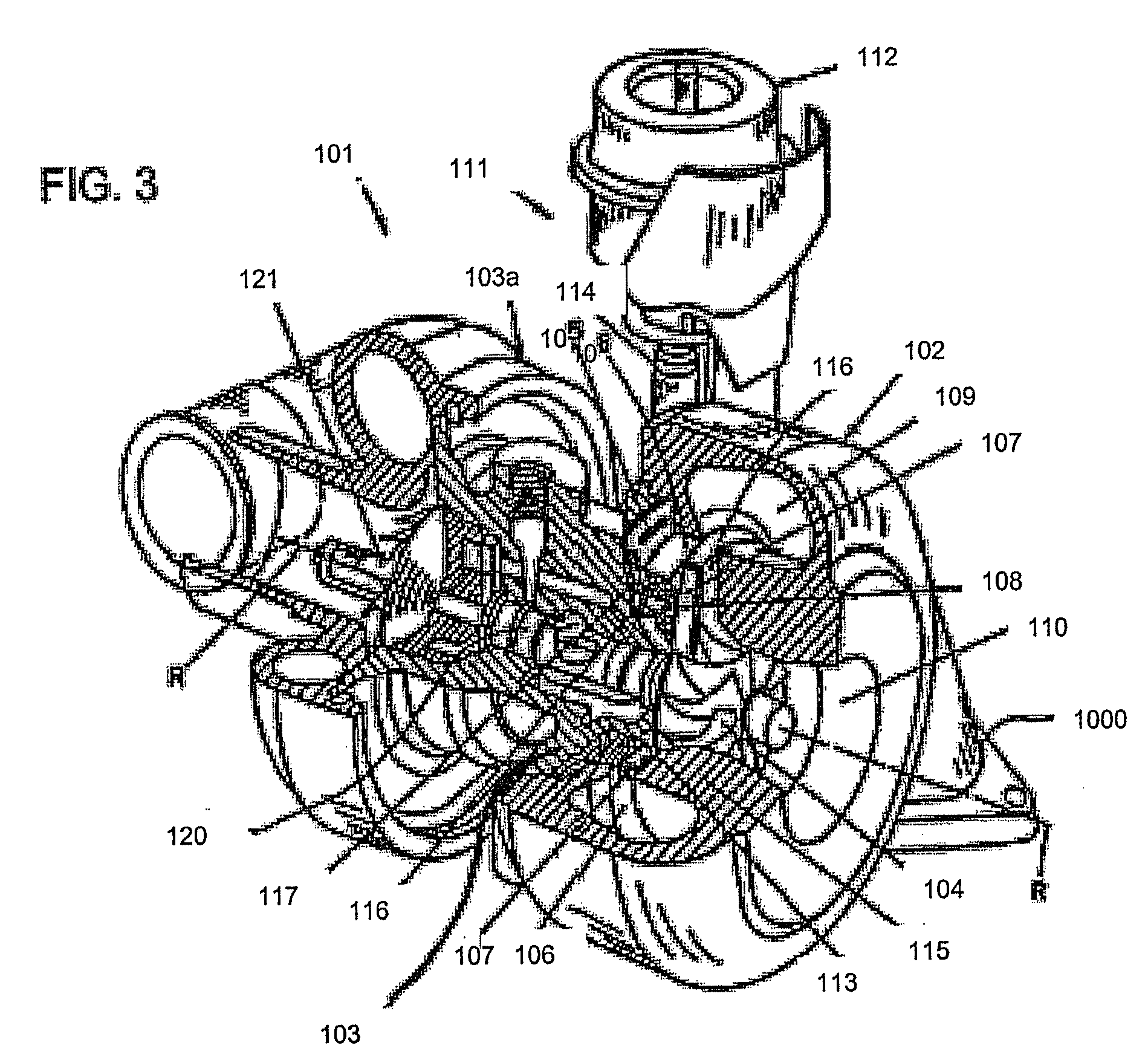
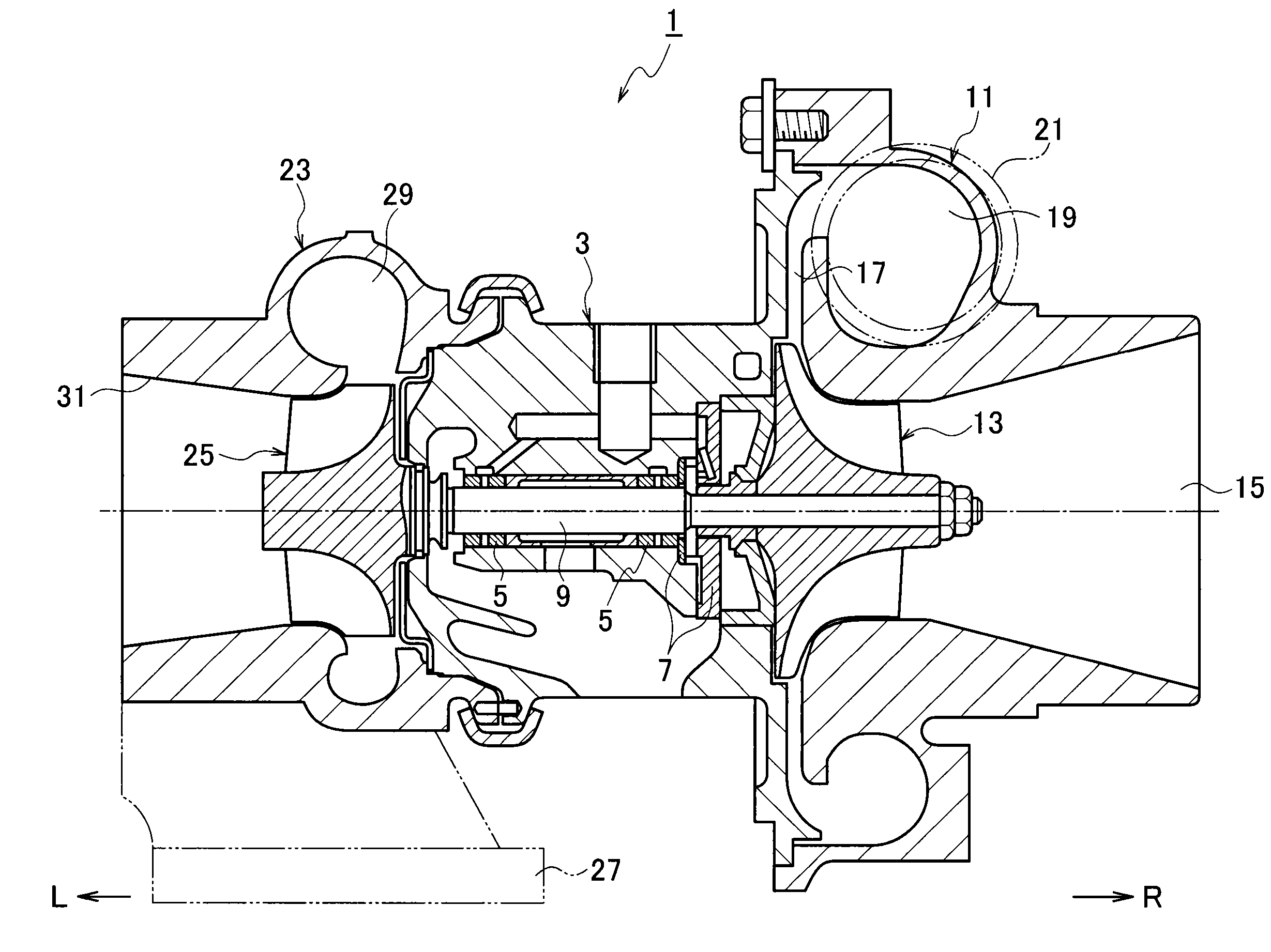
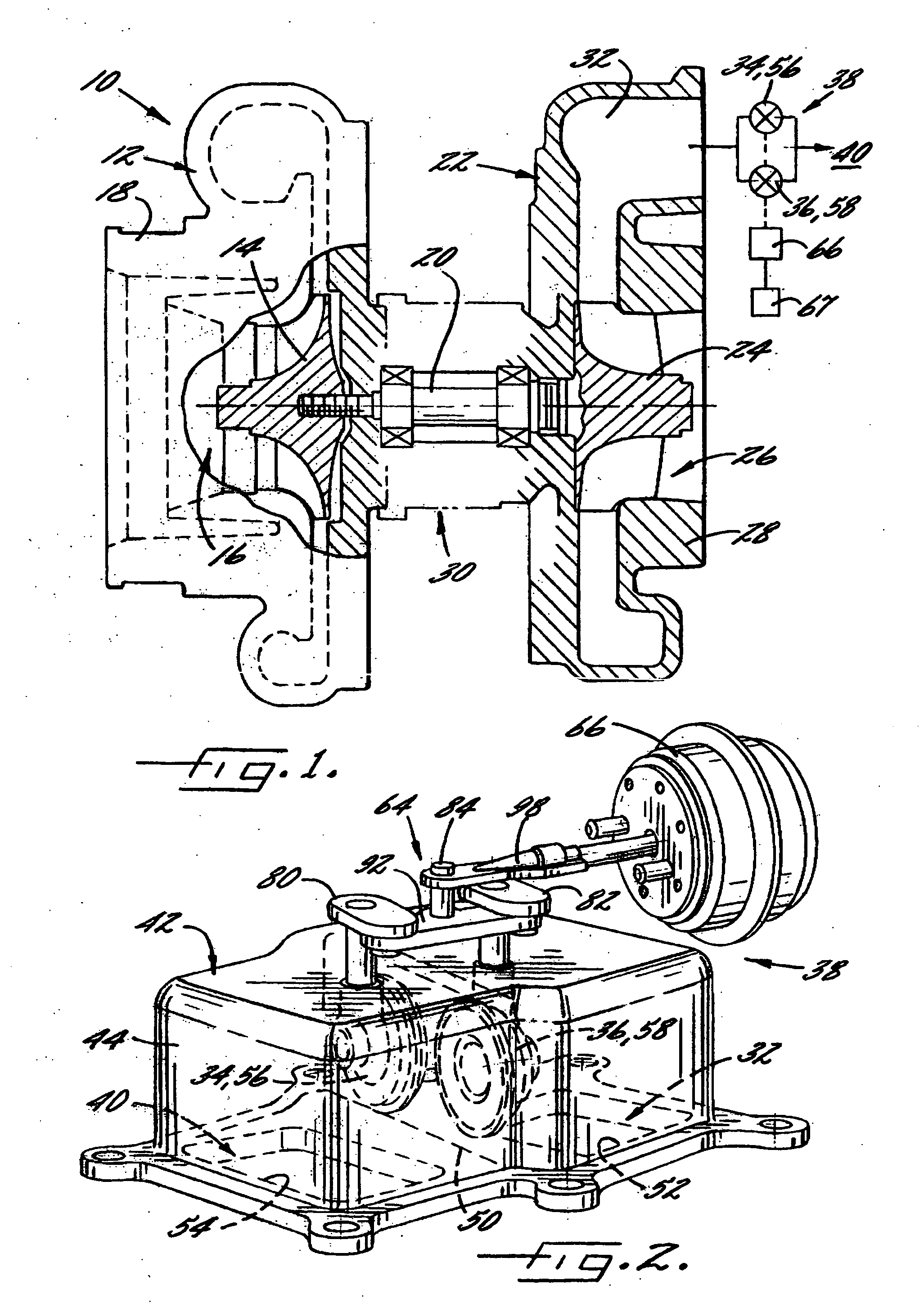
A wastegate assembly (200) for a turbocharger (101) or the like is provided having a support plate (300), an actuator (275), a linkage (250) operably connected to the actuator (275), and a valve plate (225) operably connected to the linkage (250). The linkage (250) translates actuation of the actuator (275) to movement of the valve plate (225) thereby sealing or unsealing the bypass outlet (500). The actuator (275), linkage (250) and valve plate (225) can be pre-assembled to the support plate (300) prior to the support plate (300) being connected to the turbine housing (102). The actuator (275), linkage (250) and valve plate (225) can be calibrated prior to the wastegate assembly (200) being connected to the turbine housing (102). The bypass outlet (500) can be machined via access provided by the wastegate port (400).
Owner:BORGWARNER INC
Control device for internal combustion engine and method for controlling the same
Provided is a control device for an internal combustion engine, capable of controlling acceleration-response characteristics, performing an operation at an optimal fuel-efficiency point, and learning variation factors in an internal combustion engine provided with a supercharger including a wastegate valve. A target throttle-valve upstream pressure is calculated based on a target charging efficiency and a rotation speed. An exhaust-gas flow rate is calculated based on an air / fuel ratio and an intake-airflow rate. A target compressor driving force is calculated based on a target intake-airflow rate and a target throttle-valve upstream pressure. A wastegate-valve control value is calculated from the exhaust-gas flow rate and the target compressor driving force by using the relationship in which the relation expression expressing the characteristics of the exhaust-gas flow rate and the target compressor driving force depends only on the wastegate-valve control value.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Variable flow valve mechanism and vehicle turbocharger
InactiveUS20140366530A1Improve fatigue resistanceReduce vibrationInternal combustion piston enginesOutput powerTurbochargerCoil spring
In a waste gate valve, a coil spring being expandable and contractible in the axial direction of a valve shaft is provided between a washer and an attachment tongue in an axial direction of a valve shaft of a valve. The coil spring is made of a heat-resistant alloy or a ceramic. An annular guard wall is formed on a front surface of the attachment tongue by counter boring in such a way as to surround the coil spring.
Owner:IHI CORP
Turbocharger control
ActiveUS20110225967A1Increase pressureIncrease airflowElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesWastegateAtmospheric air
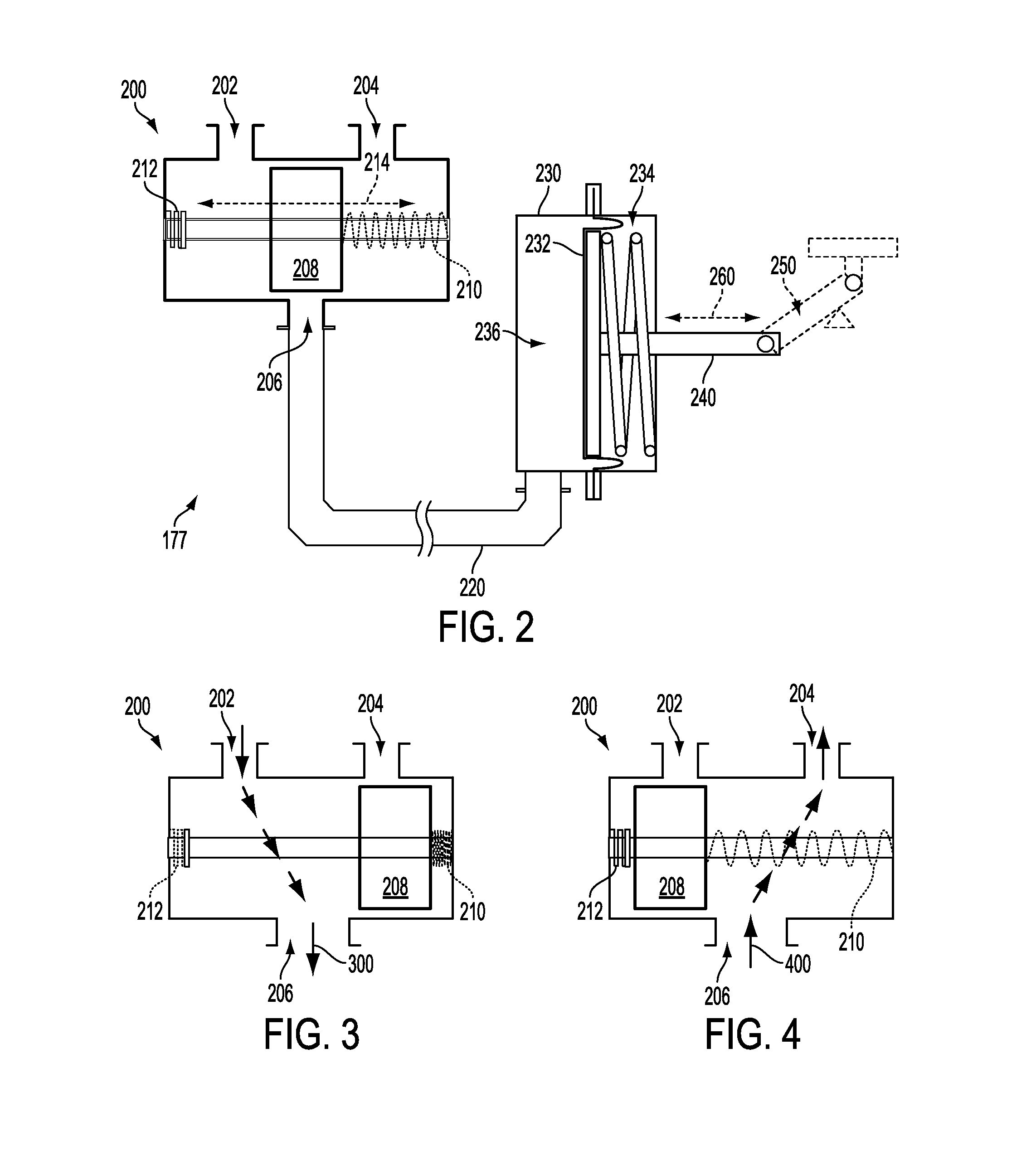
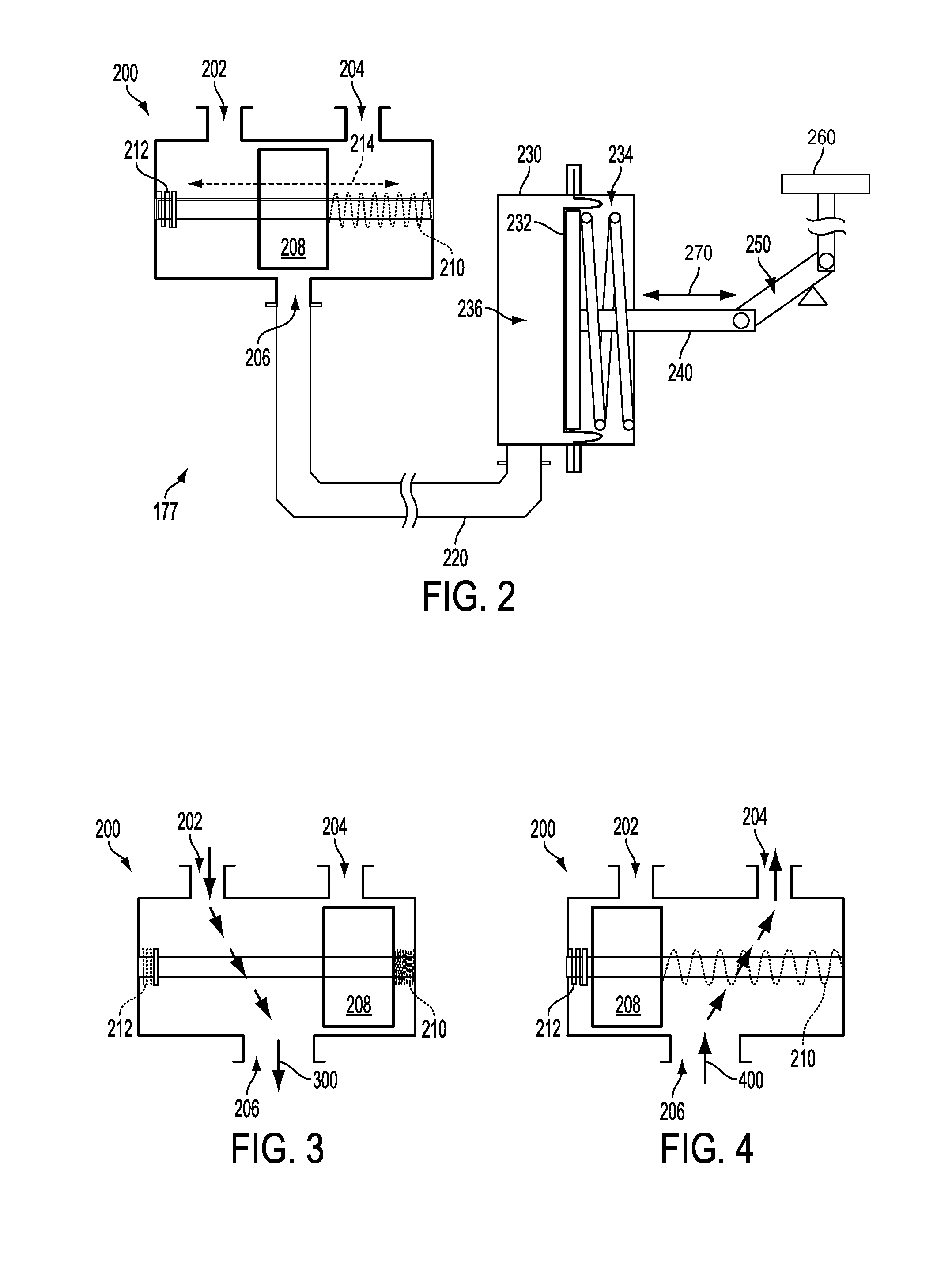
Various systems and methods for controlling a turbocharger of an engine via a wastegate are described. In one example, the wastegate is adjusted according to a difference between the boost pressure and the atmospheric pressure. In this manner, the interdependency between controlling the boost pressure and using the boost pressure to actuate the wastegate in a boost-based wastegate configuration may be reduced.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Turbocharger control
ActiveUS8572961B2Increase pressureIncrease airflowInternal combustion piston enginesEngine controllersWastegateAtmospheric air
Various systems and methods for controlling a turbocharger of an engine via a wastegate are described. In one example, actuation of the wastegate is limited when outside a range, the limits of the range varying with boost pressure, turbine inlet pressure, turbine outlet pressure, and atmospheric pressure. In this manner, a tracking error may be reduced when controlling the boost pressure and using the boost pressure to actuate the wastegate in a boost-based wastegate configuration.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
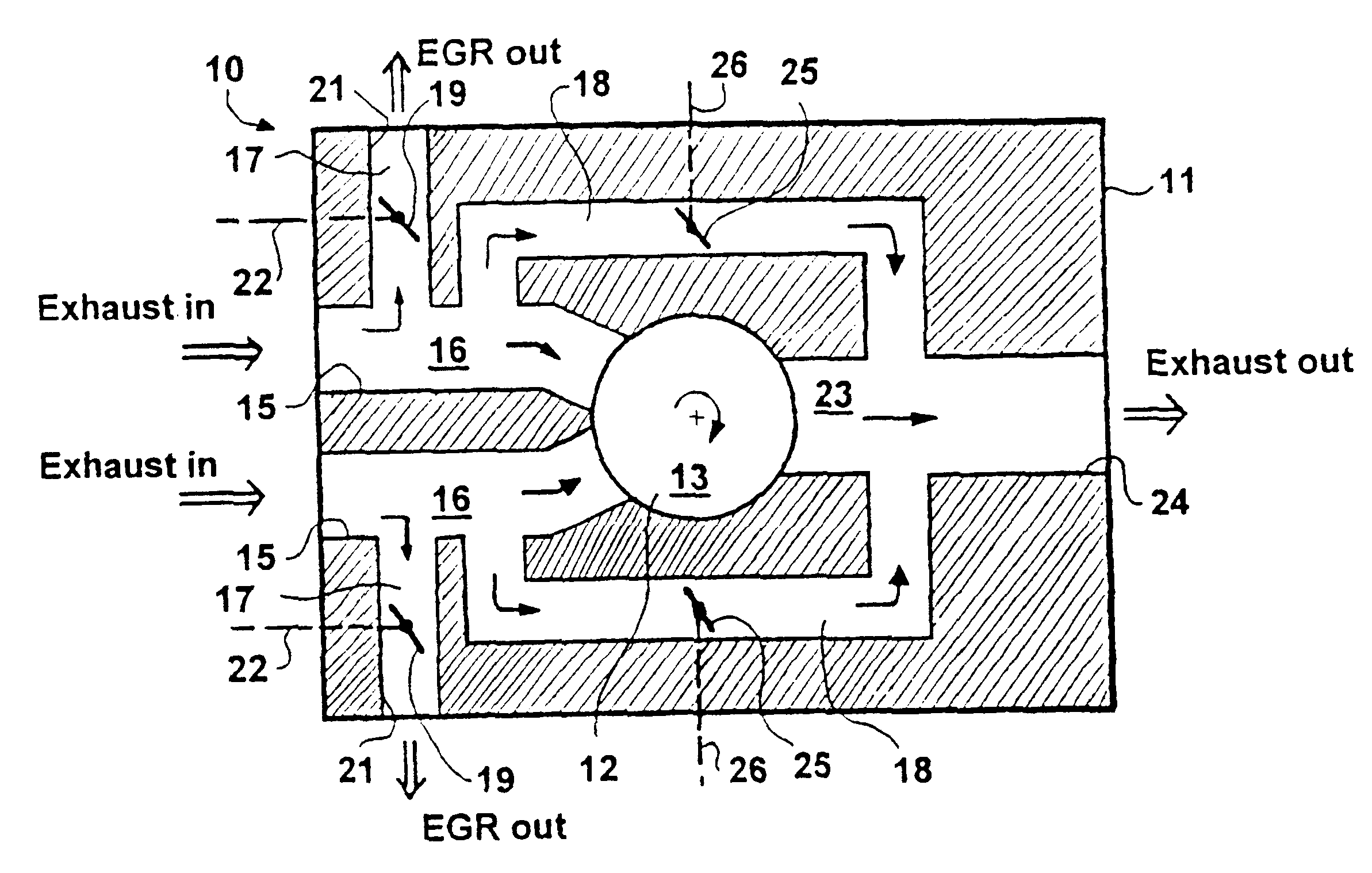
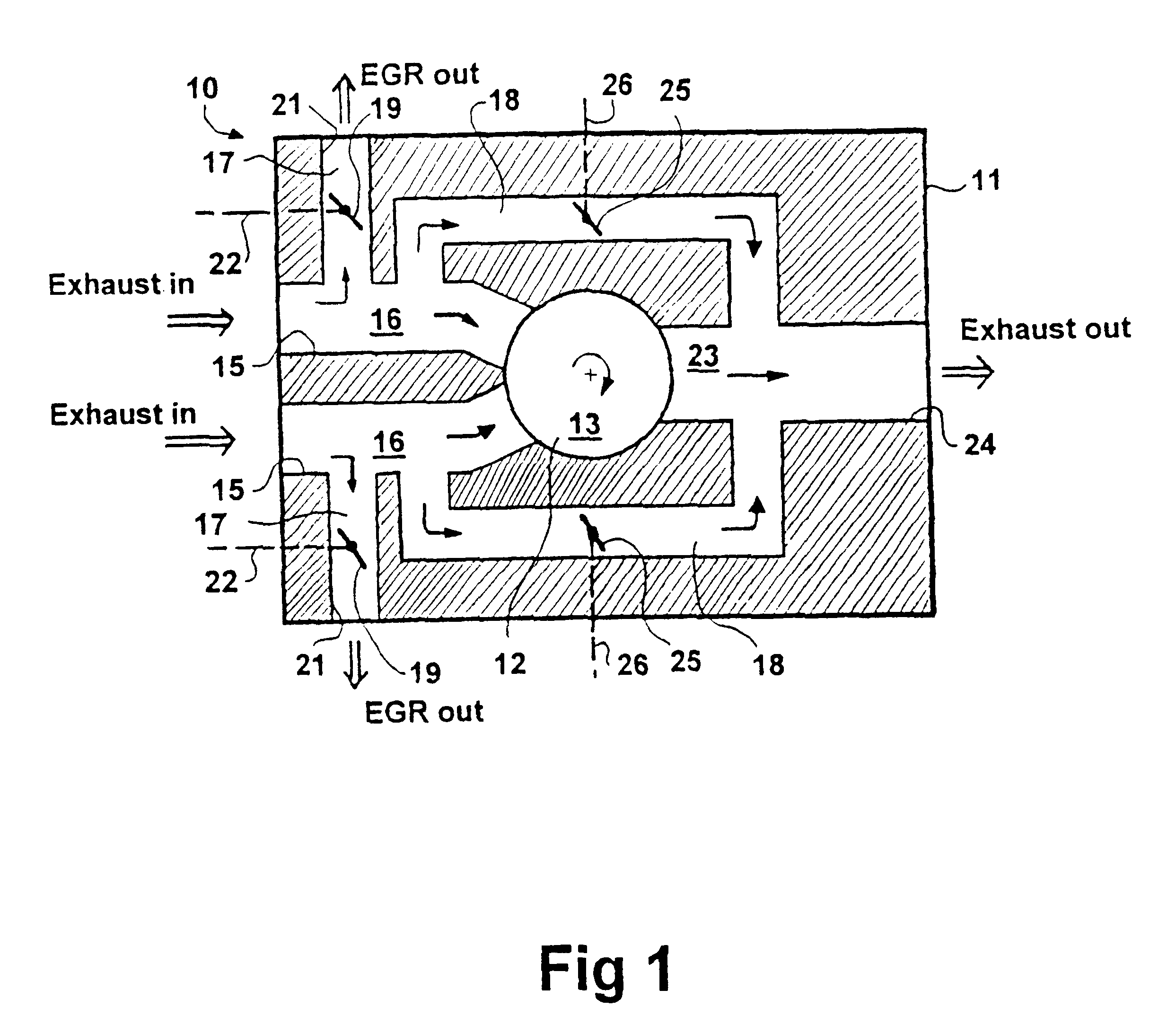
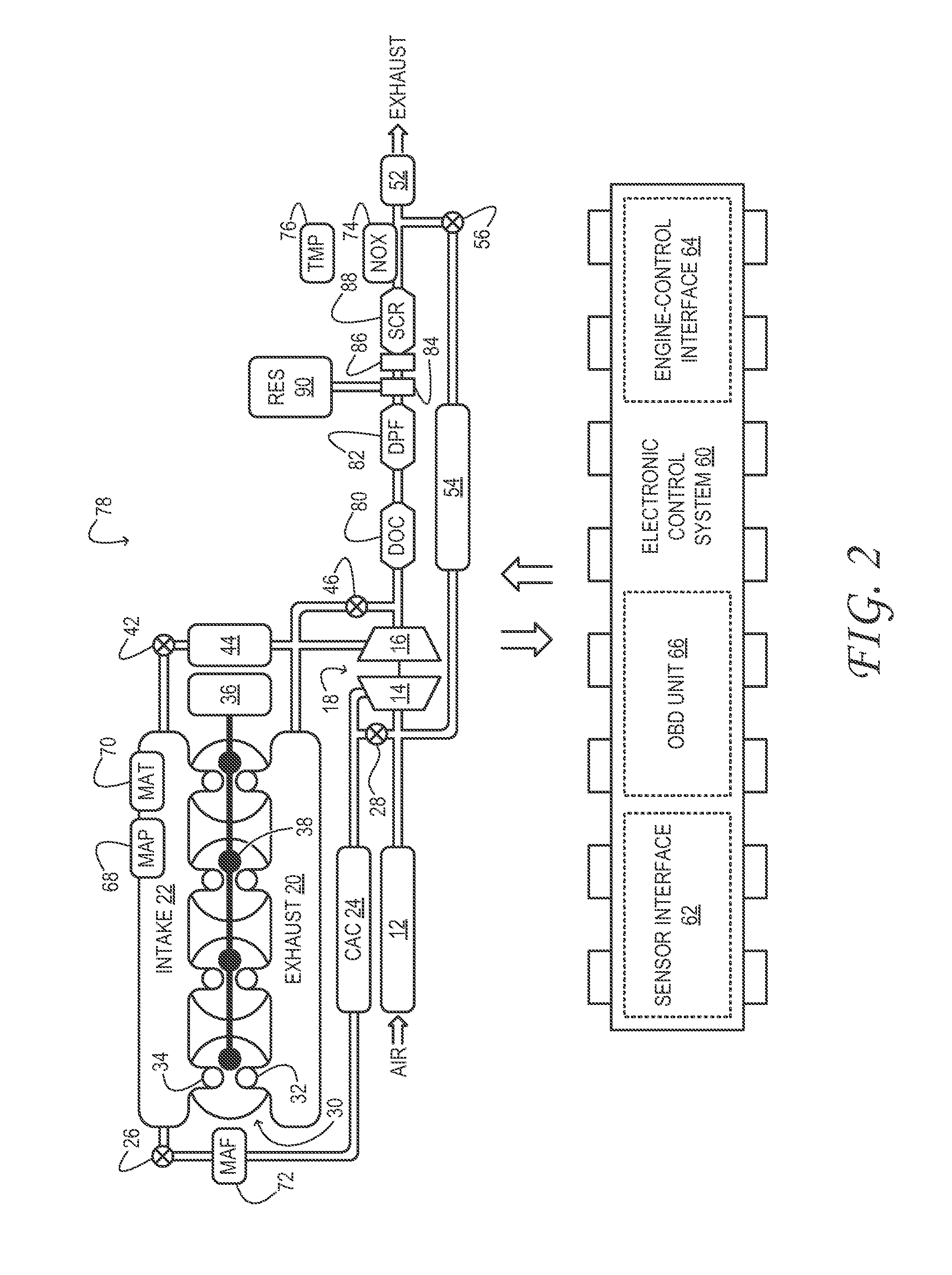
Egr system with particle filter and wastegate
ActiveUS20160348615A1Increase very knock tendencyReduce riskInternal combustion piston enginesExhaust gas recirculationParticulatesWastegate
An emissions control system for a gasoline engine having an exhaust gas conduit which can be connected to an exhaust manifold of the gasoline engine, having an inlet conduit which can be connected to an inlet manifold of the gasoline engine and having a turbine arranged in the exhaust gas conduit. At least one exhaust gas recirculation conduit is provided, which opens into the inlet conduit, and the exhaust gas conduit has at least one bypass conduit, which opens into the exhaust gas conduit downstream of the turbine, wherein a) the exhaust gas recirculation conduit branches off upstream of the turbine and the bypass conduit branches off at the exhaust gas recirculation conduit or b) the bypass conduit branches off upstream of the turbine and the exhaust gas recirculation conduit branches off at the bypass conduit, wherein c) at least one particulate filter, is arranged in the exhaust gas recirculation conduit or in the bypass conduit upstream of the exhaust gas recirculation conduit or in the exhaust gas conduit upstream of the exhaust gas recirculation conduit.
Owner:TENNECO GMBH
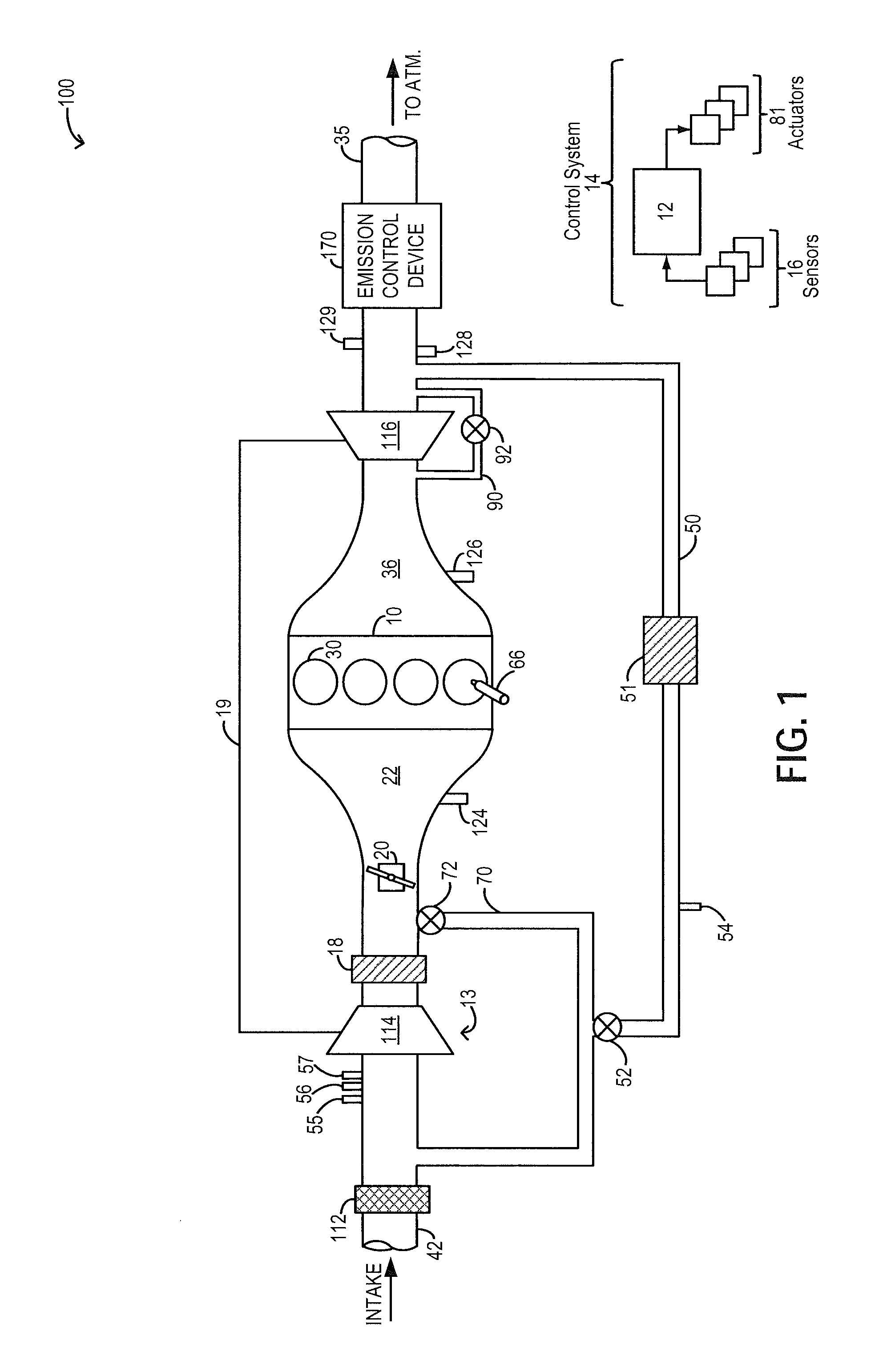
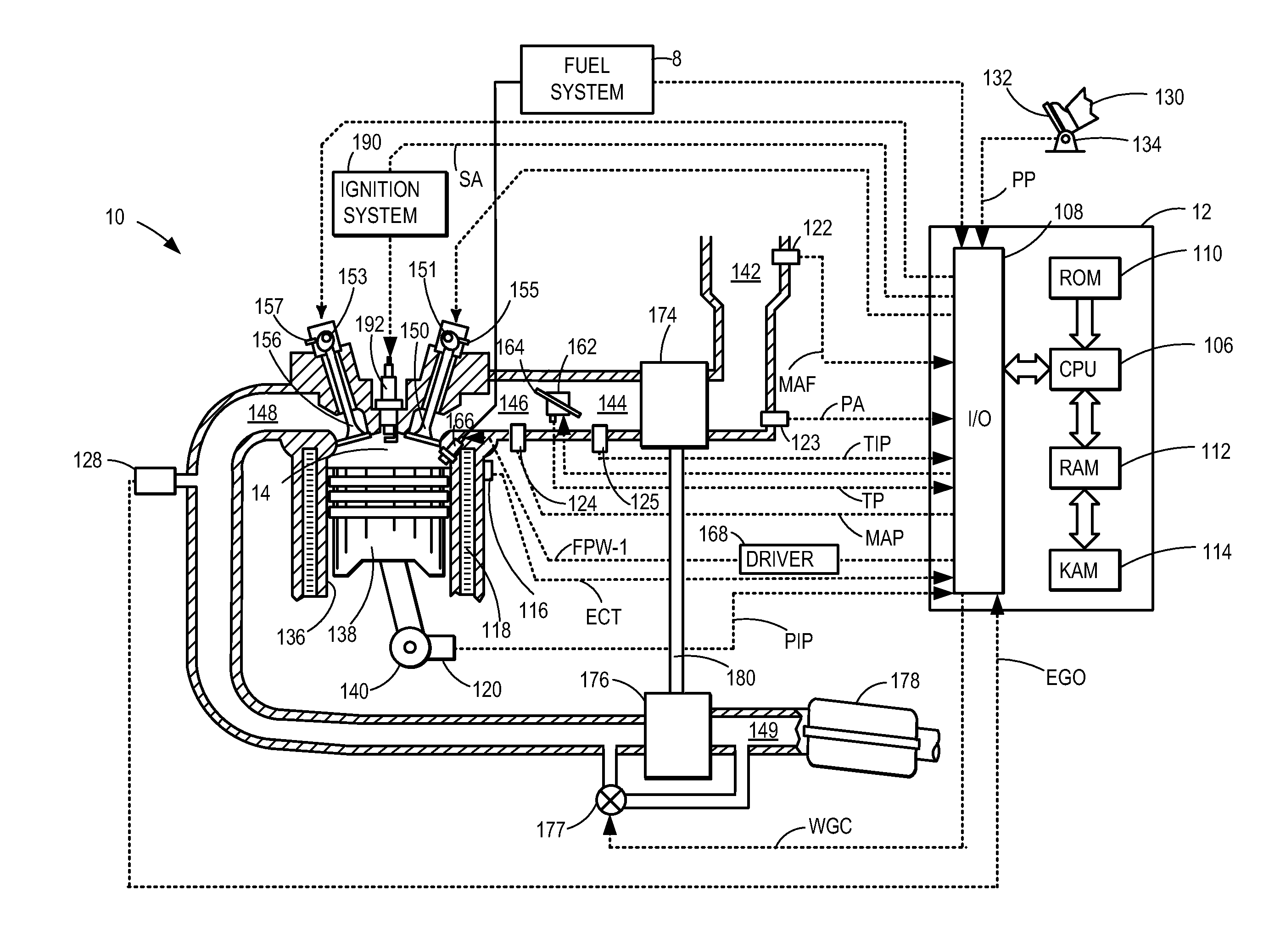
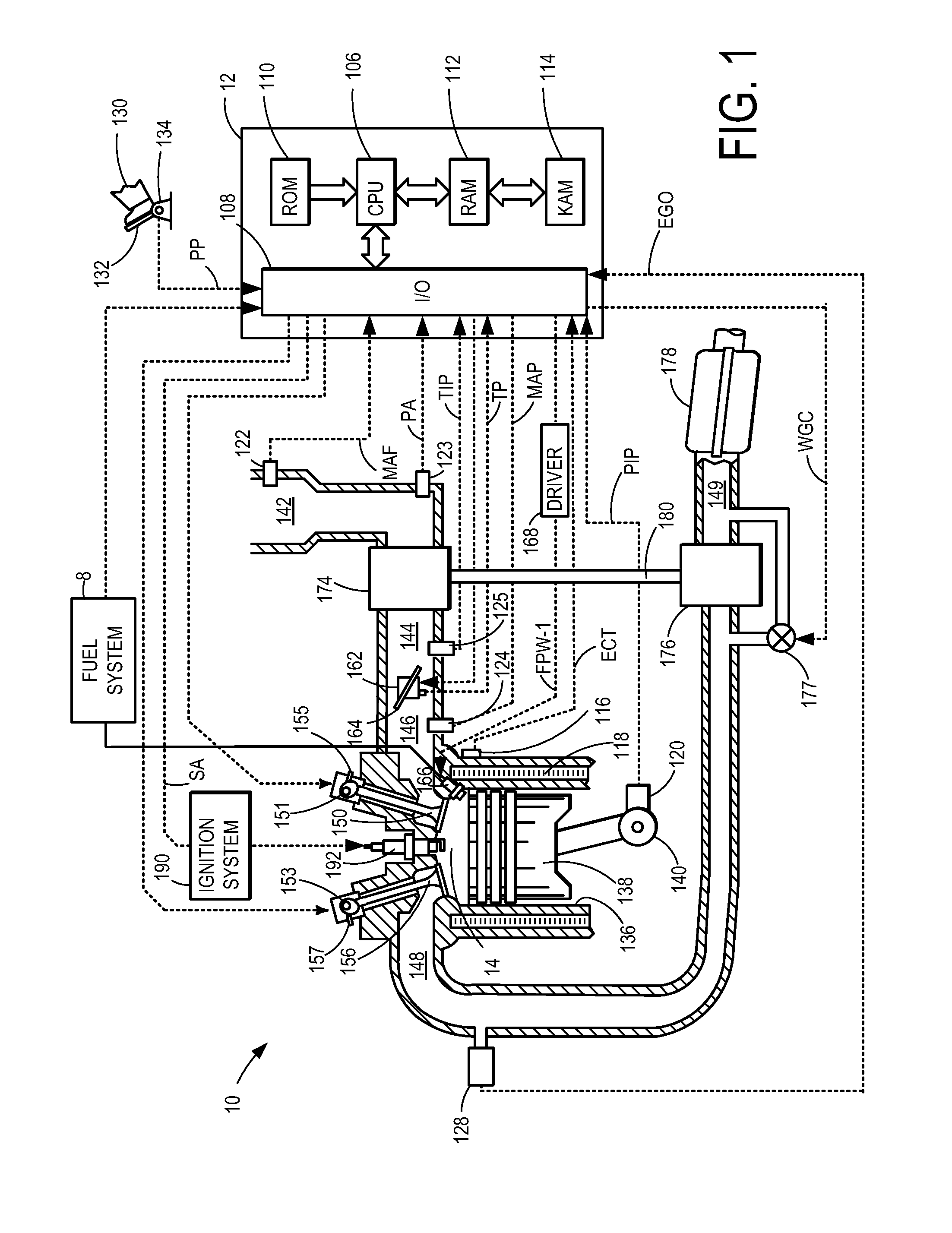
System and method for operating a turbocharged engine
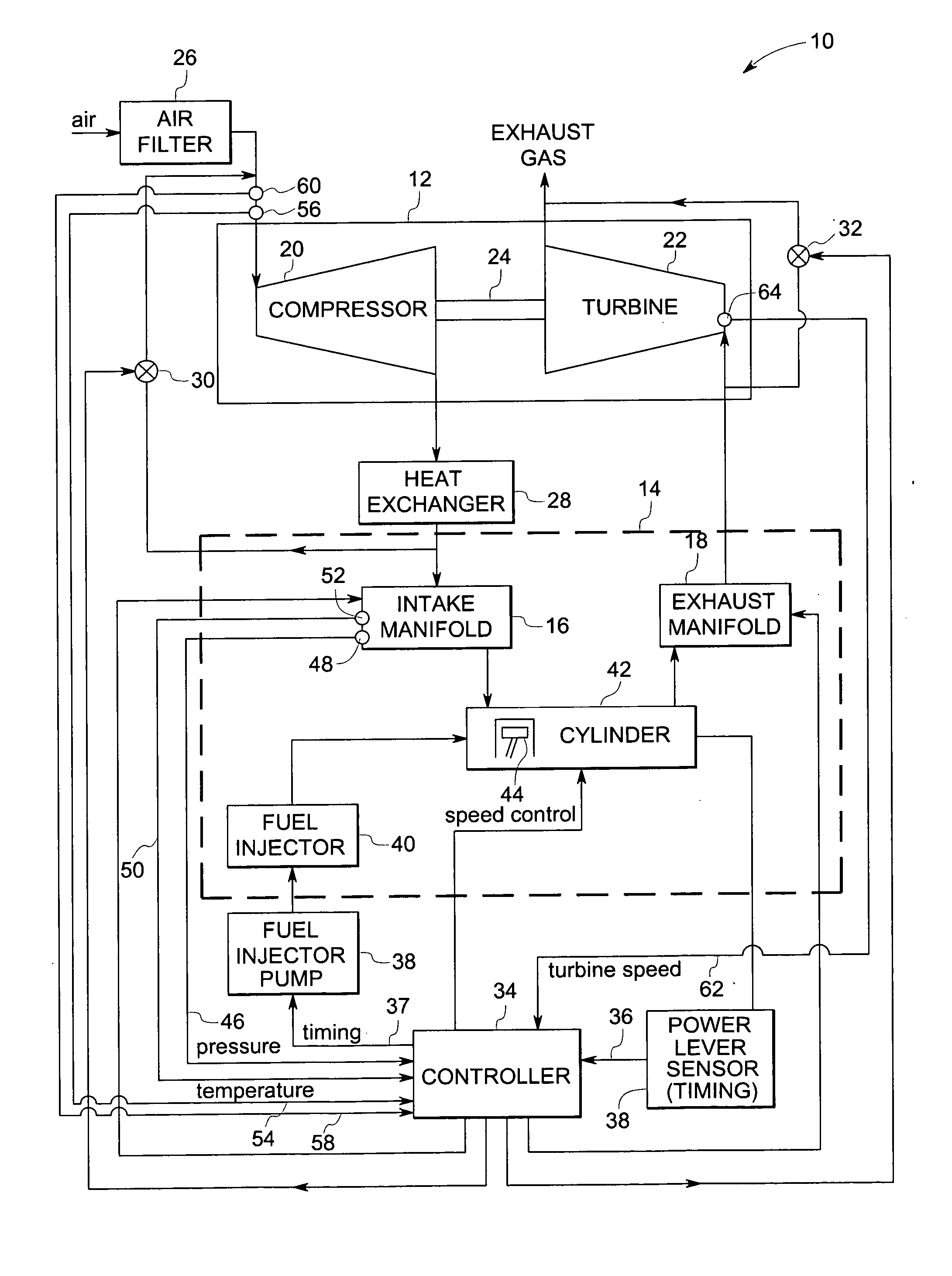
ActiveUS20060288702A1Eliminating chokeControl speedAnalogue computers for vehiclesInternal combustion piston enginesWastegateInlet pressure
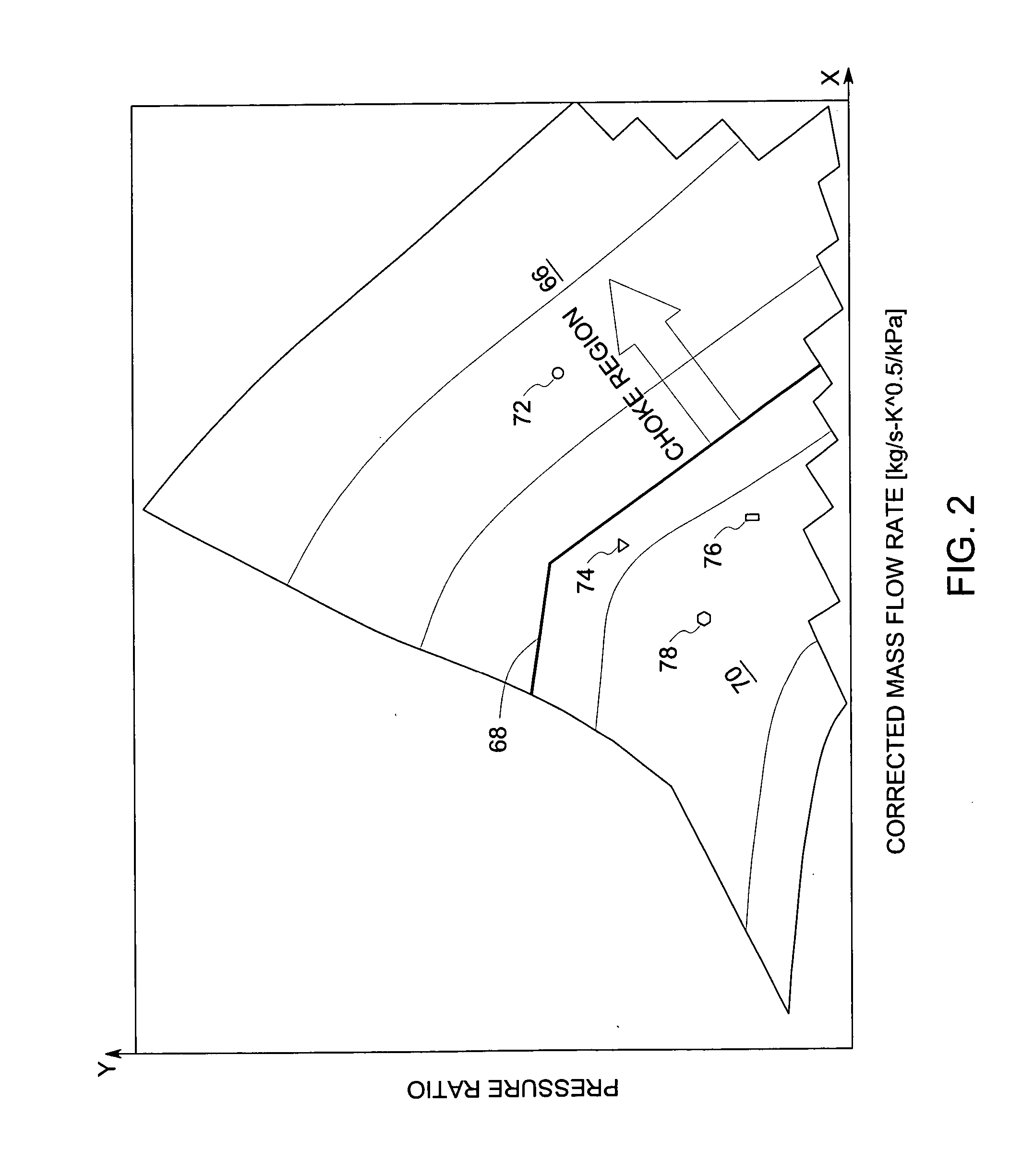
A method of operating a turbocharged system includes controlling speed of a turbocharger and substantially eliminating choke of a compressor coupled to a turbine by adjusting exhaust flow through a turbine wastegate, or by adjusting airflow through a compressor recirculation valve, or by adjusting a combination thereof in response to variance in parameters including compressor inlet temperature, compressor inlet pressure, and turbocharger speed.
Owner:GE GLOBAL SOURCING LLC
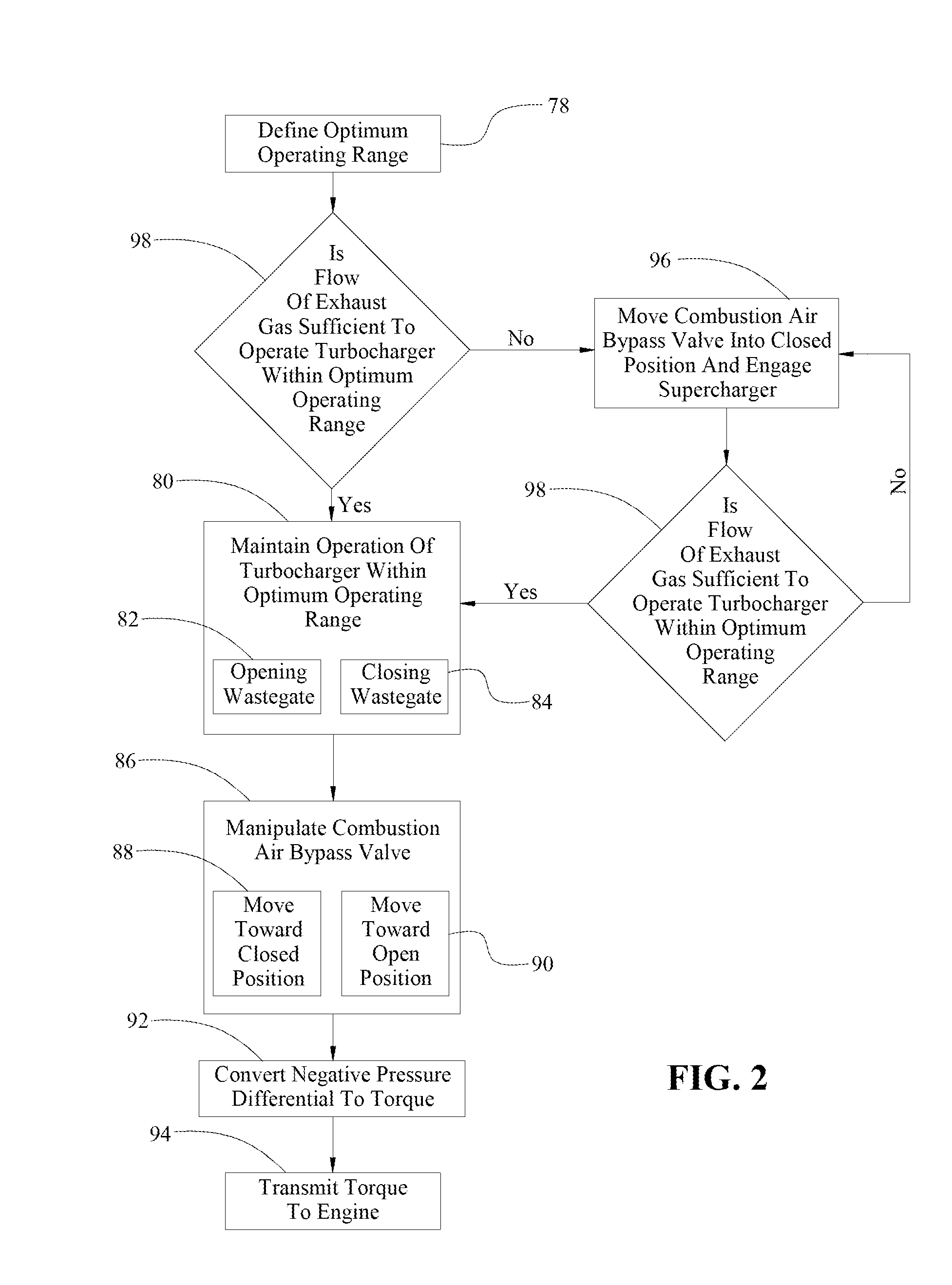
Control Strategy for an Engine
InactiveUS20110094480A1Easy to operateLarge operating rangeElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesWastegateCombustion
A method of controlling an engine includes manipulating a wastegate to maintain the operation of the turbocharger within an optimum operating range. A combustion air bypass valve is manipulated between an open position and a closed position to create a negative pressure differential across a supercharger. The supercharger is sequentially disposed in-line before the turbocharger. The negative pressure differential is converted into a torque by the supercharger and transmitted from the supercharger back to the engine to increase the operating efficiency of the engine.
Owner:EATON INTELLIGENT POWER LTD
Turbocharger control system
Owner:CATERPILLAR INC
Engine System
InactiveUS20120192557A1High power outputEmission reductionInternal combustion piston enginesExhaust apparatusWastegateEngineering
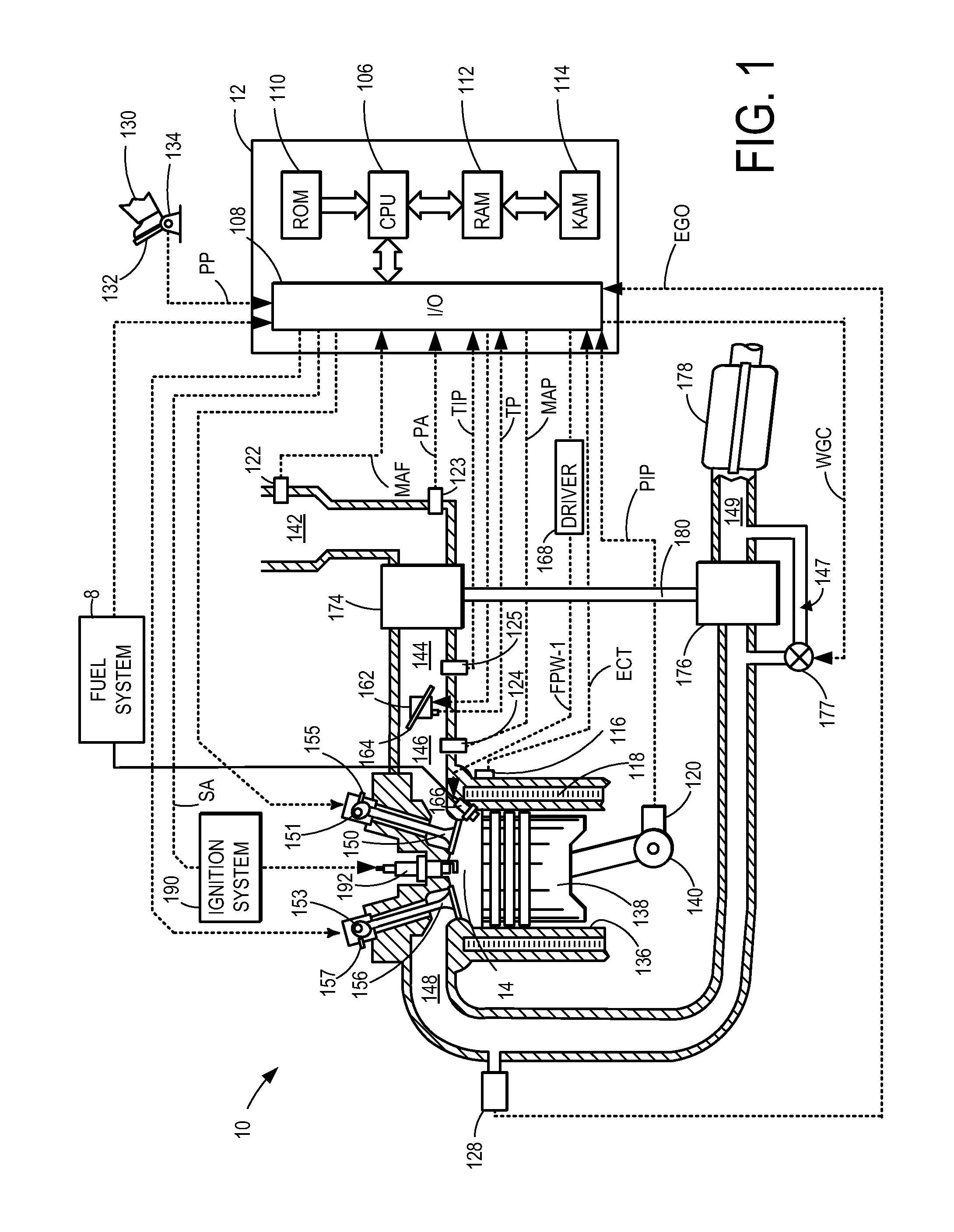
An engine system comprises an internal combustion engine, a turbocharger and an external wastegate valve. The turbocharger includes a housing for an exhaust gas turbine and a separate housing for the wastegate valve. The turbine housing is liquid cooled so as to reduce its operating temperature thereby allowing it to be made from an aluminium alloy so as to save cost and reducing, during use, the radiation of heat therefrom.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Systems and methods for transient control
ActiveUS20160102636A1Improve EGR toleranceEmission reductionElectrical controlNon-fuel substance addition to fuelWastegateCam
Methods and systems are provided for reducing torque transients experienced when a dedicated EGR cylinder is transitioned in to or out of dedicated EGR mode. During a transition, each of an intake throttle and a wastegate is adjusted in opposing directions. Throttle and wastegate adjustments are coordinated with adjustments to spark timing and intake cam timing to provide sufficient torque reserve for the transition.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Wastegate valve and associated method
InactiveUS20060289072A1Operating means/releasing devices for valvesInternal combustion piston enginesWastegateProduct gas
A wastegate valve and associated method for controlling a flow of gas, such as a flow of exhaust gas from an exhaust inlet of a turbocharger, are provided. The wastegate valve includes multiple bypass ports that are selectively opened and closed by poppets, which are controlled by a linkage. The poppets are configured so that the pressure of the gas in the exhaust inlet biases one of the poppets to the open position and one of the poppets to the closed position. Thus, the forces resulting from the pressure of the gas on the poppets are offset, thereby reducing the force required for adjusting or maintaining the position of the linkage and the poppets.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Method for controlling a variable charge air cooler
InactiveUS20140048049A1Inhibition formationElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesWastegateControl theory
Embodiments for a charge air cooler are provided. In one example, an engine method comprises increasing intake air flow velocity through a charge air cooler and coordinately adjusting a position of one or more of an intake manifold throttle and a turbocharger wastegate in response to the increased intake air flow velocity to maintain torque. In this way, intake air flow velocity may be increased while maintaining desired torque.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Spring system to reduce turbocharger wastegate rattle noise
InactiveUS20130189072A1Reduce boost pressureReduce engine backpressureInternal combustion piston enginesWind motor controlWastegateEngineering
A turbocharger for a motor vehicle. The turbocharger includes a compressor mechanically coupled to a turbine. The wastegate of the turbine includes a valve head matched to a valve seat. The valve head is retained at one end of an actuator arm. A resilient spacer is arranged between the valve head and the actuator arm. The resilient spacer is configured to forcibly separate the valve head from the actuator arm when the valve head is unseated.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Turbocharger control
ActiveUS20110314807A1Increase pressureIncrease airflowInternal combustion piston enginesEngine controllersWastegateInlet pressure
Various systems and methods for controlling a turbocharger of an engine via a wastegate are described. In one example, actuation of the wastegate is limited when outside a range, the limits of the range varying with boost pressure, turbine inlet pressure, turbine outlet pressure, and atmospheric pressure. In this manner, a tracking error may be reduced when controlling the boost pressure and using the boost pressure to actuate the wastegate in a boost-based wastegate configuration.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Method and system for binary flow turbine control
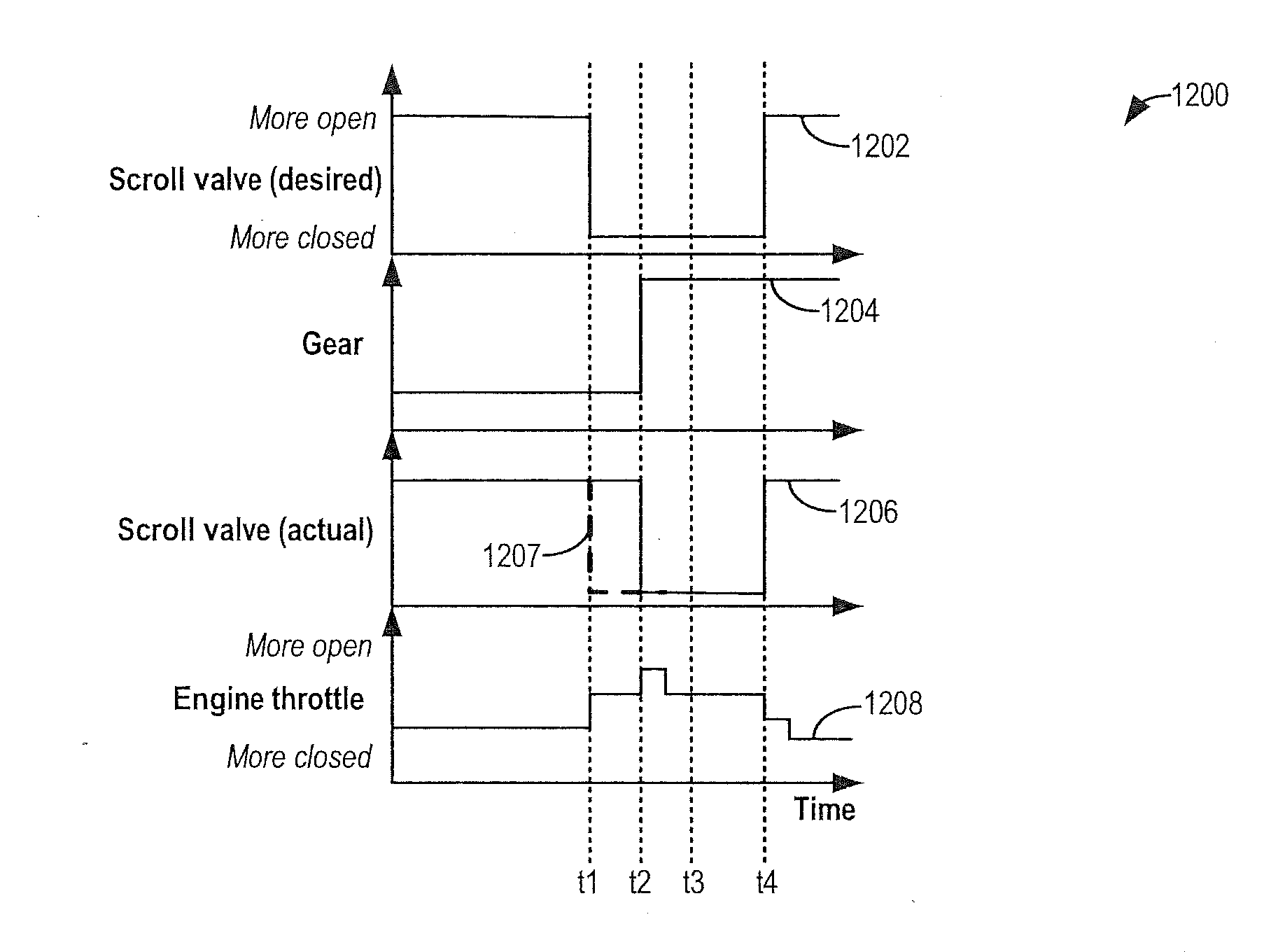
ActiveUS20140360179A1Improve engine performanceAvoid serious impactElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesWastegateTurbine
Methods and systems are provided for adjusting the opening of a scroll valve of a binary flow turbine. Scroll valve adjustments are used at different engine operating conditions to improve engine performance and boost response. Scroll valve adjustments are coordinated with wastegate and EGR valve adjustments for improved engine control.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com