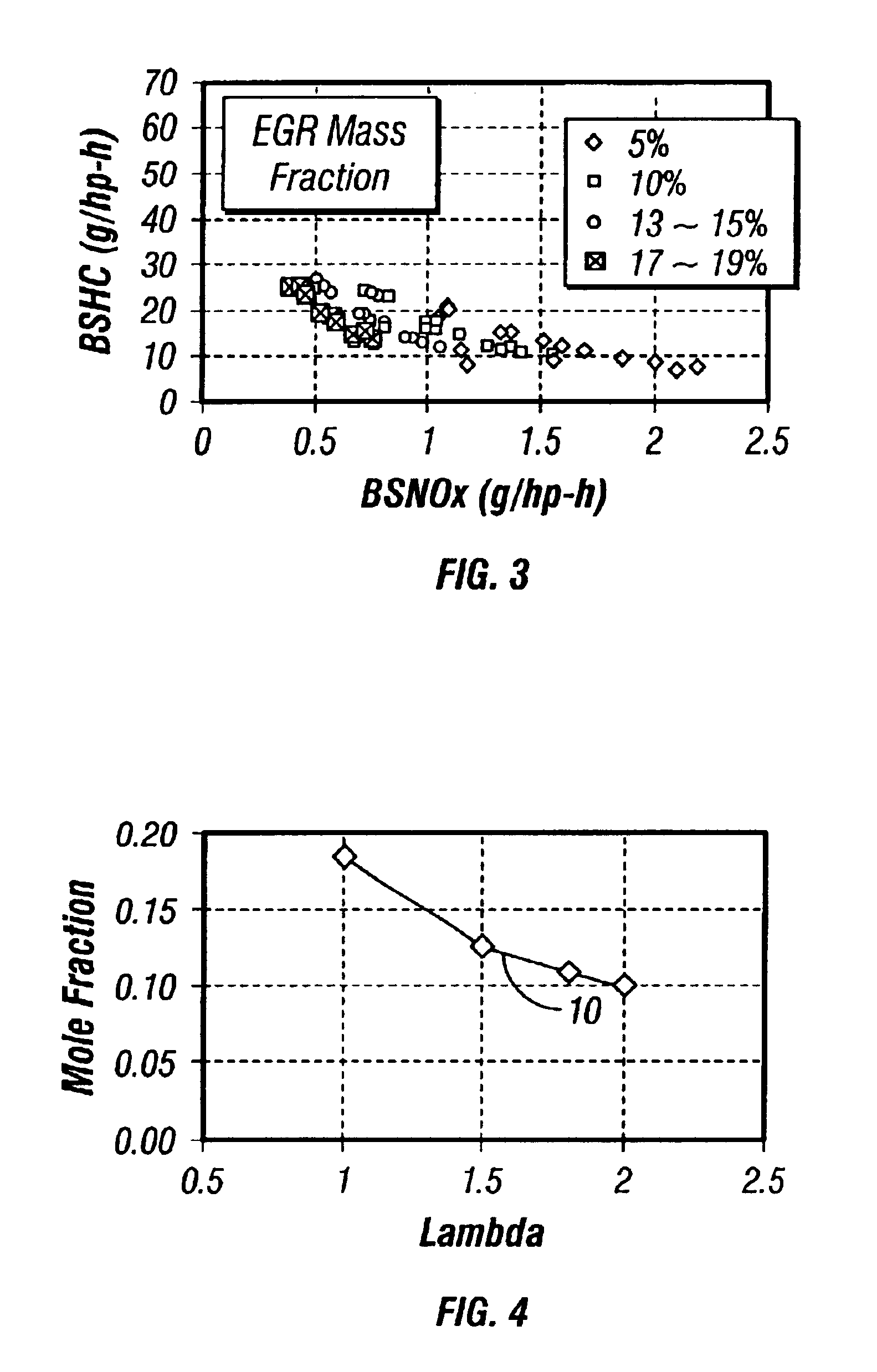
Patents
Literature
8536results about "Exhaust gas recirculation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
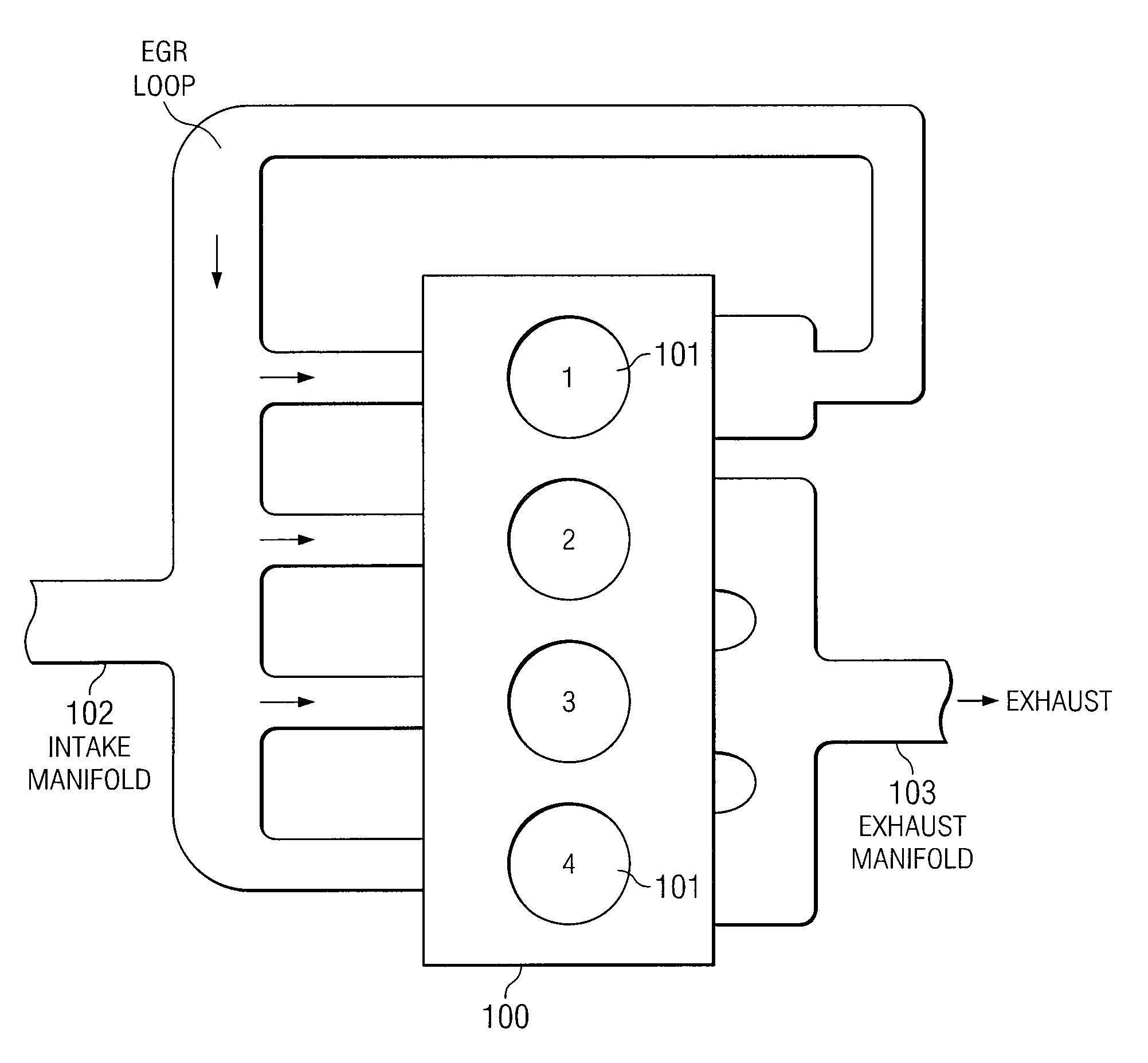
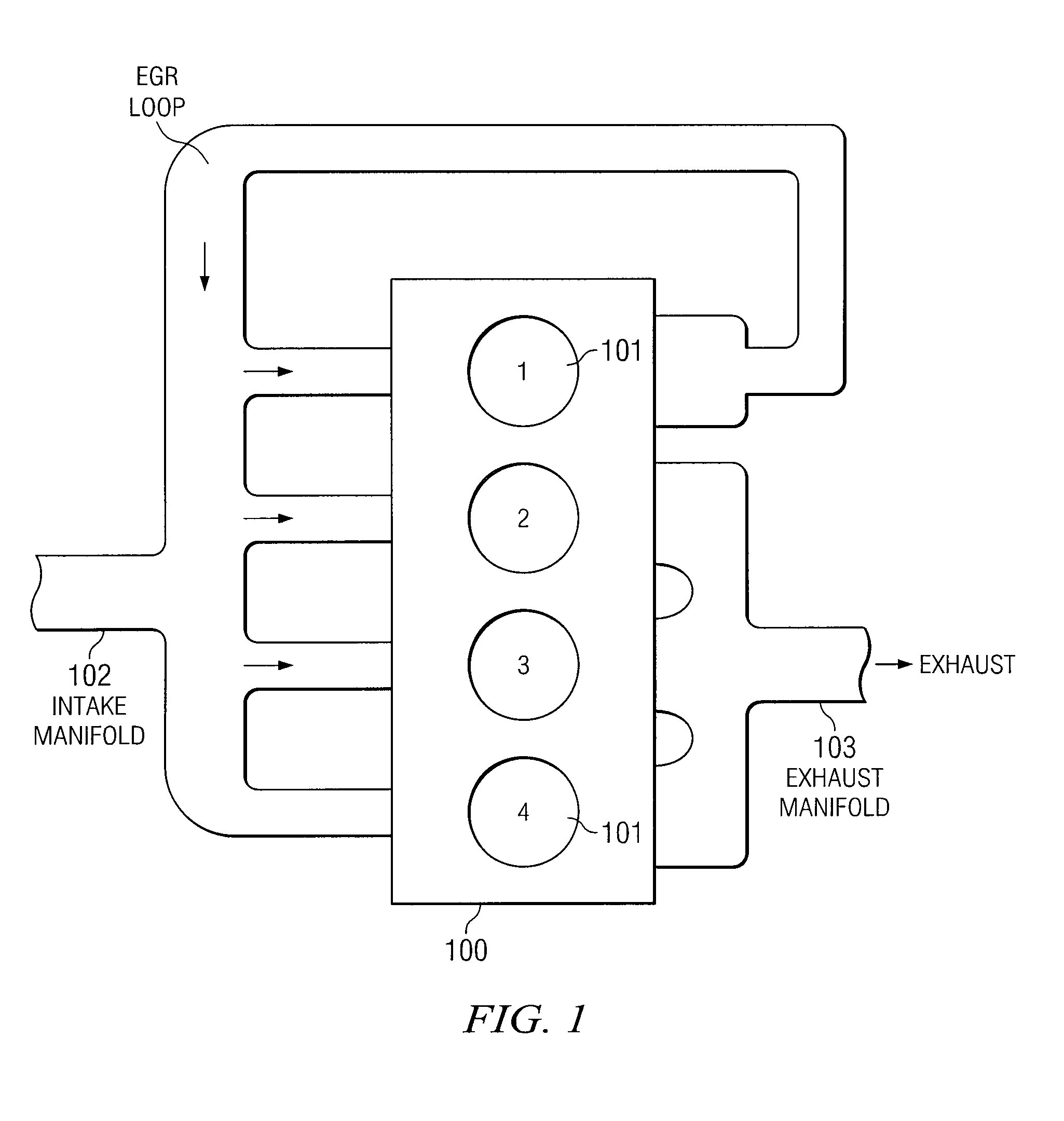
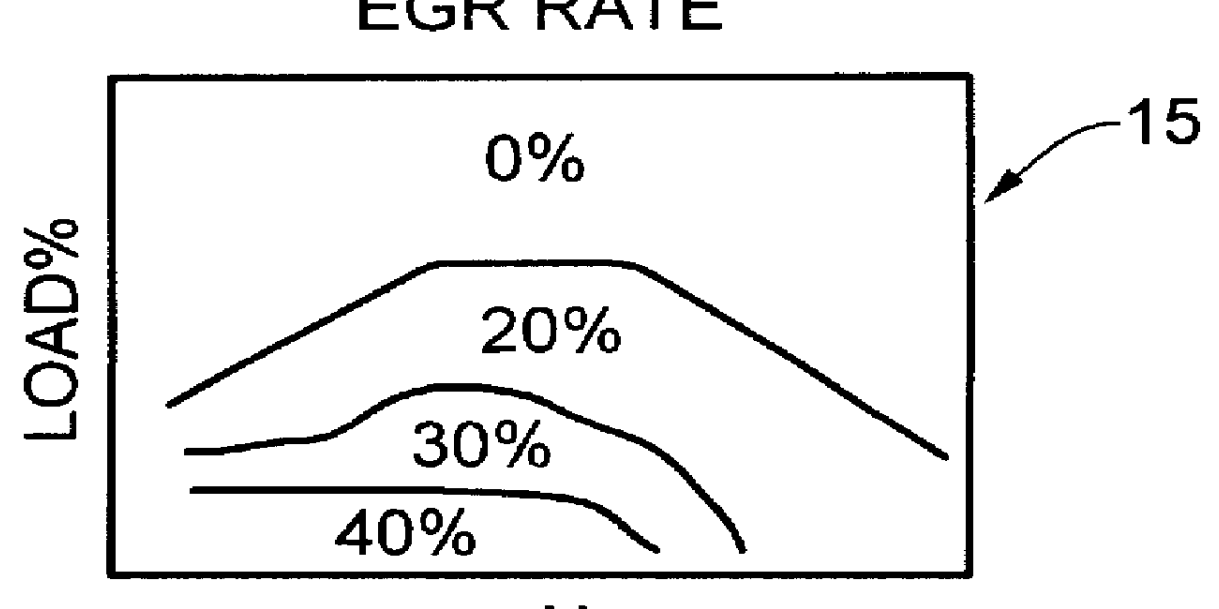
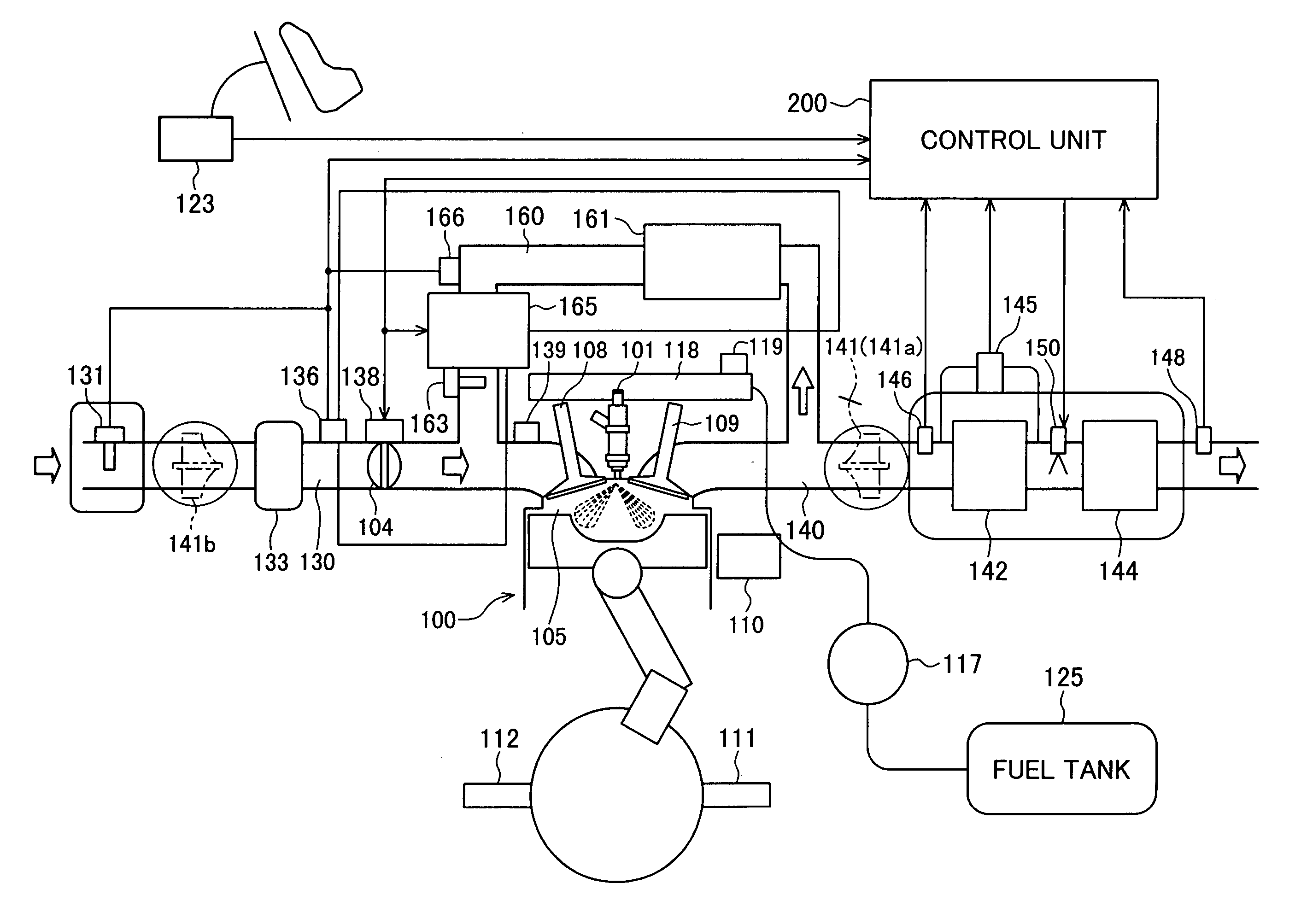
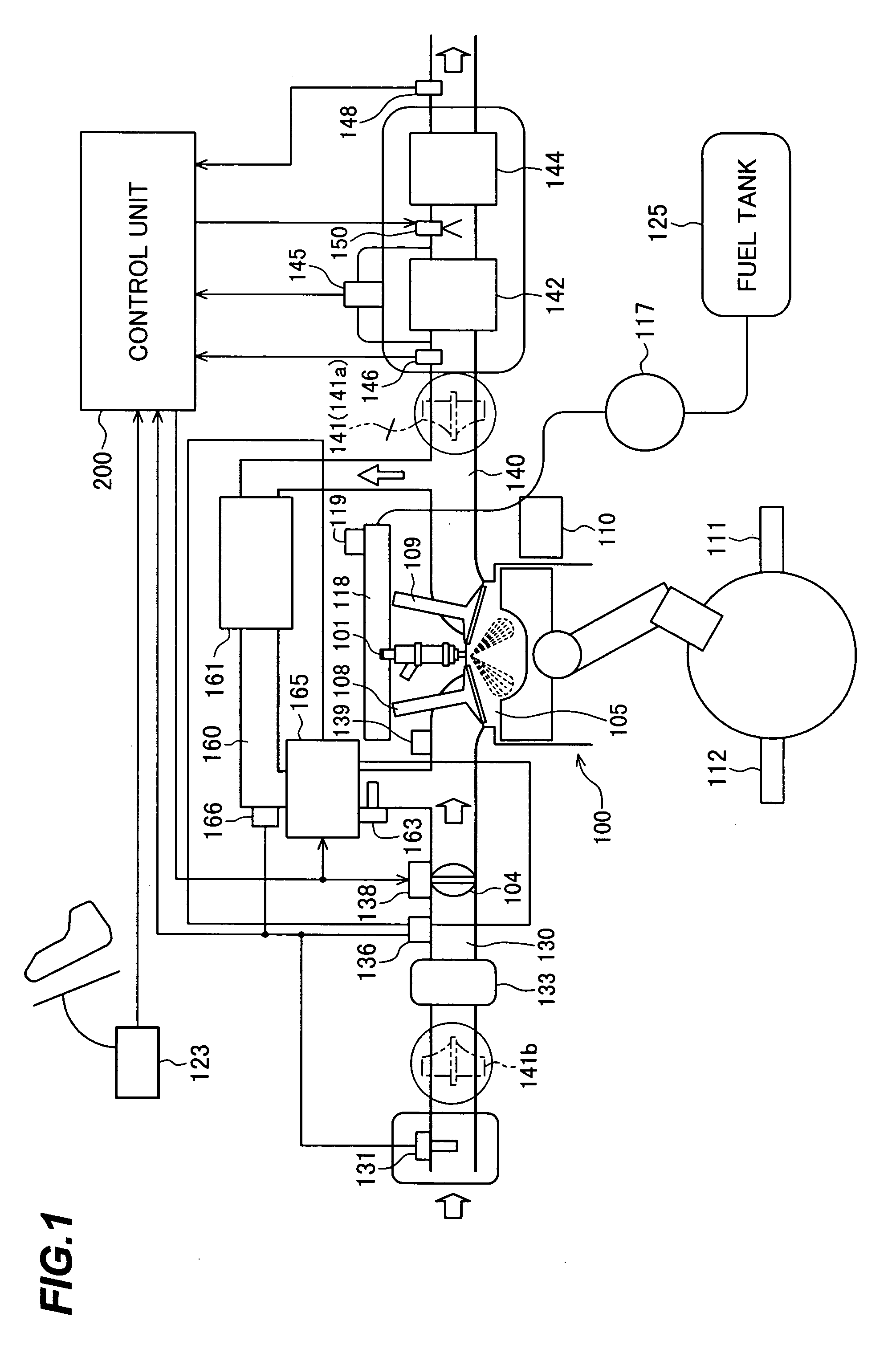
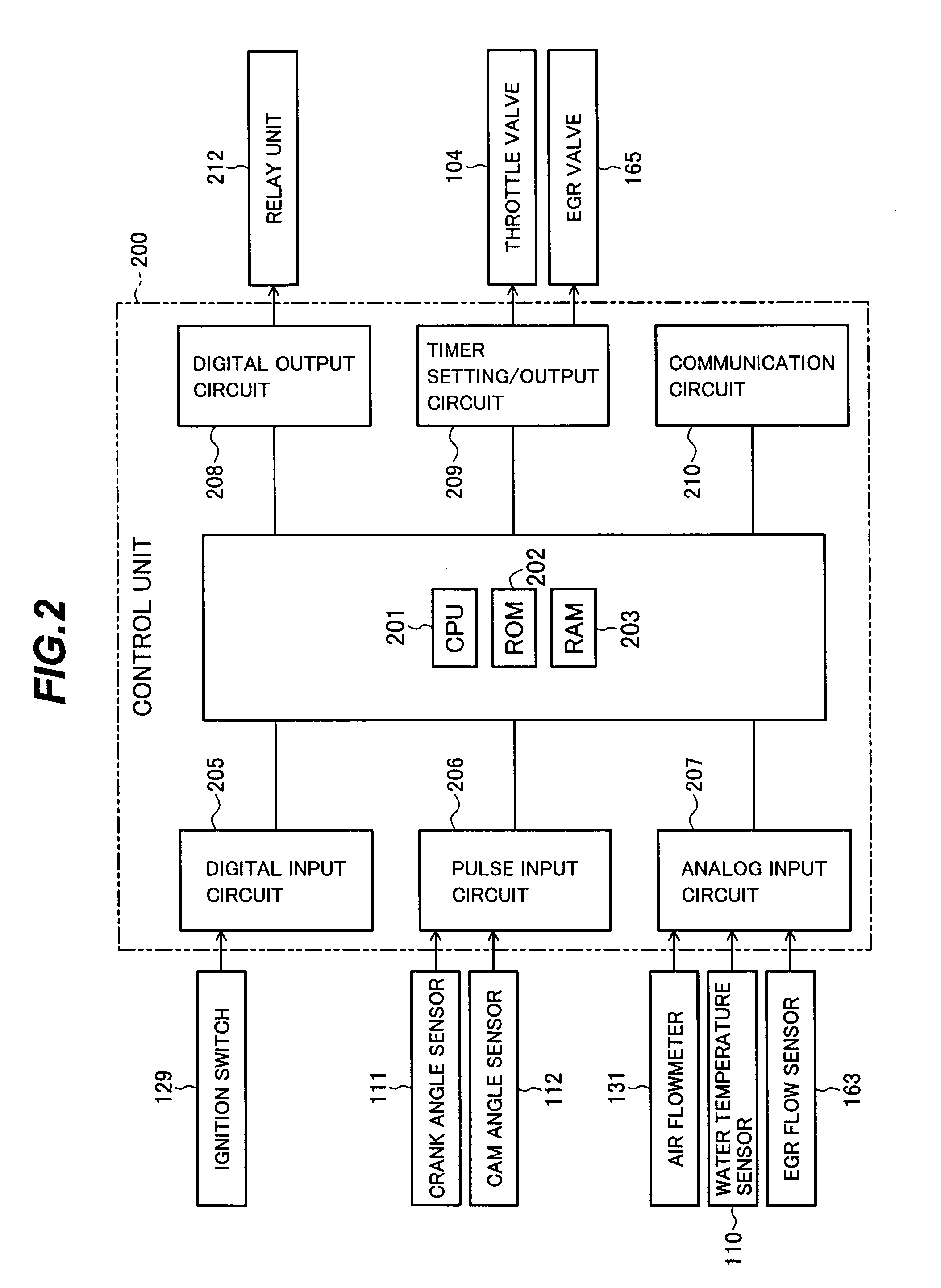
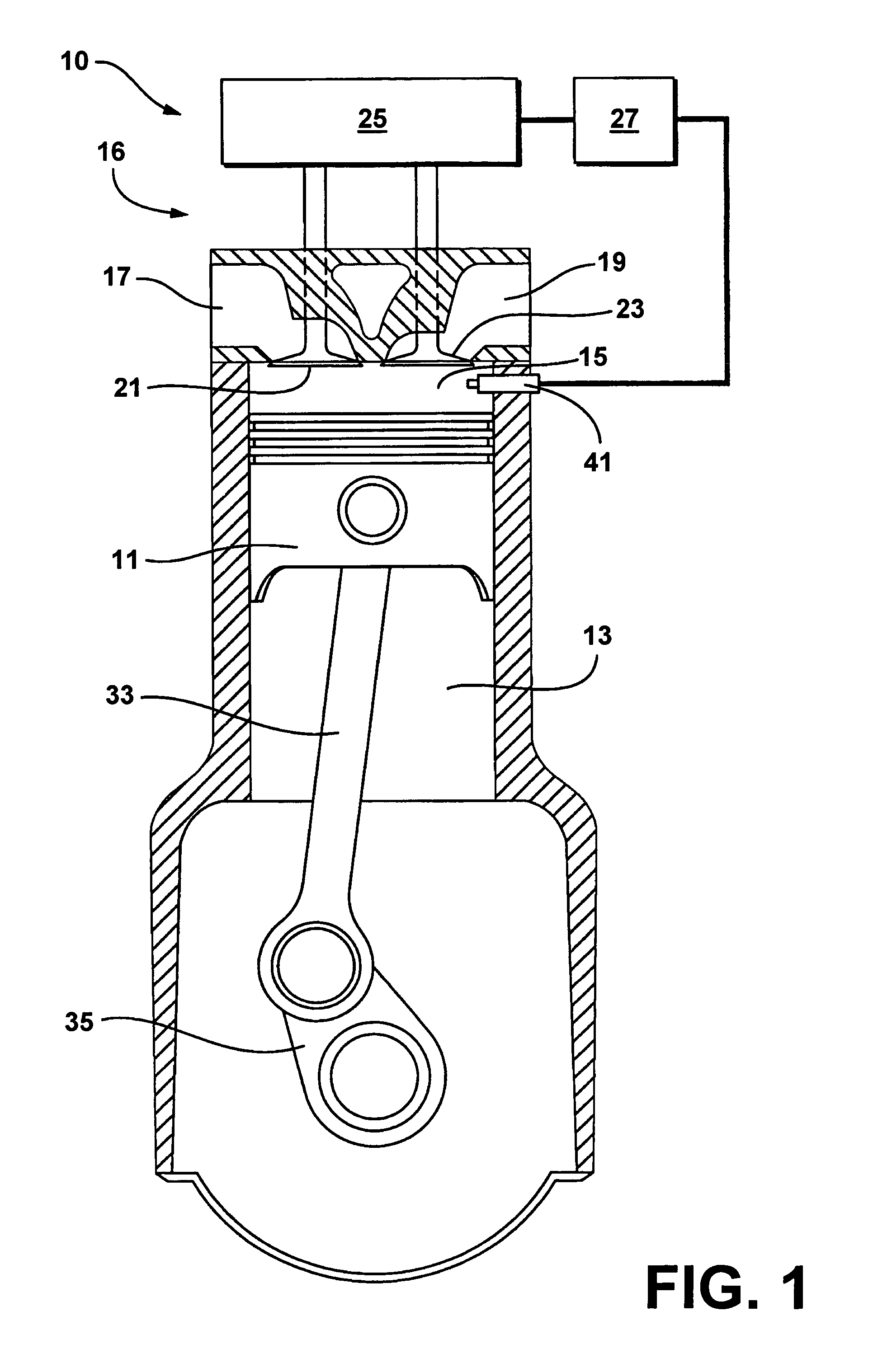
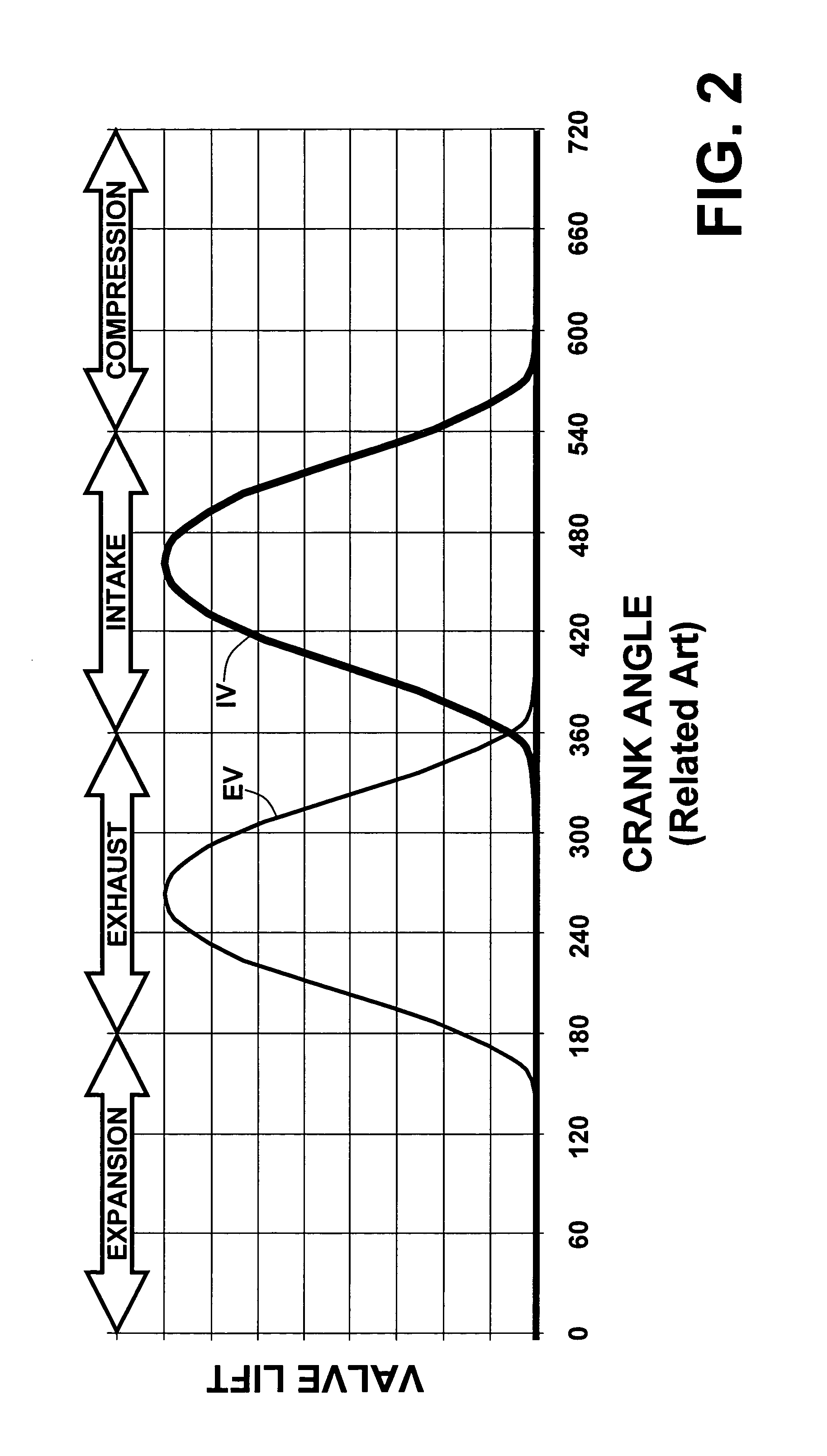
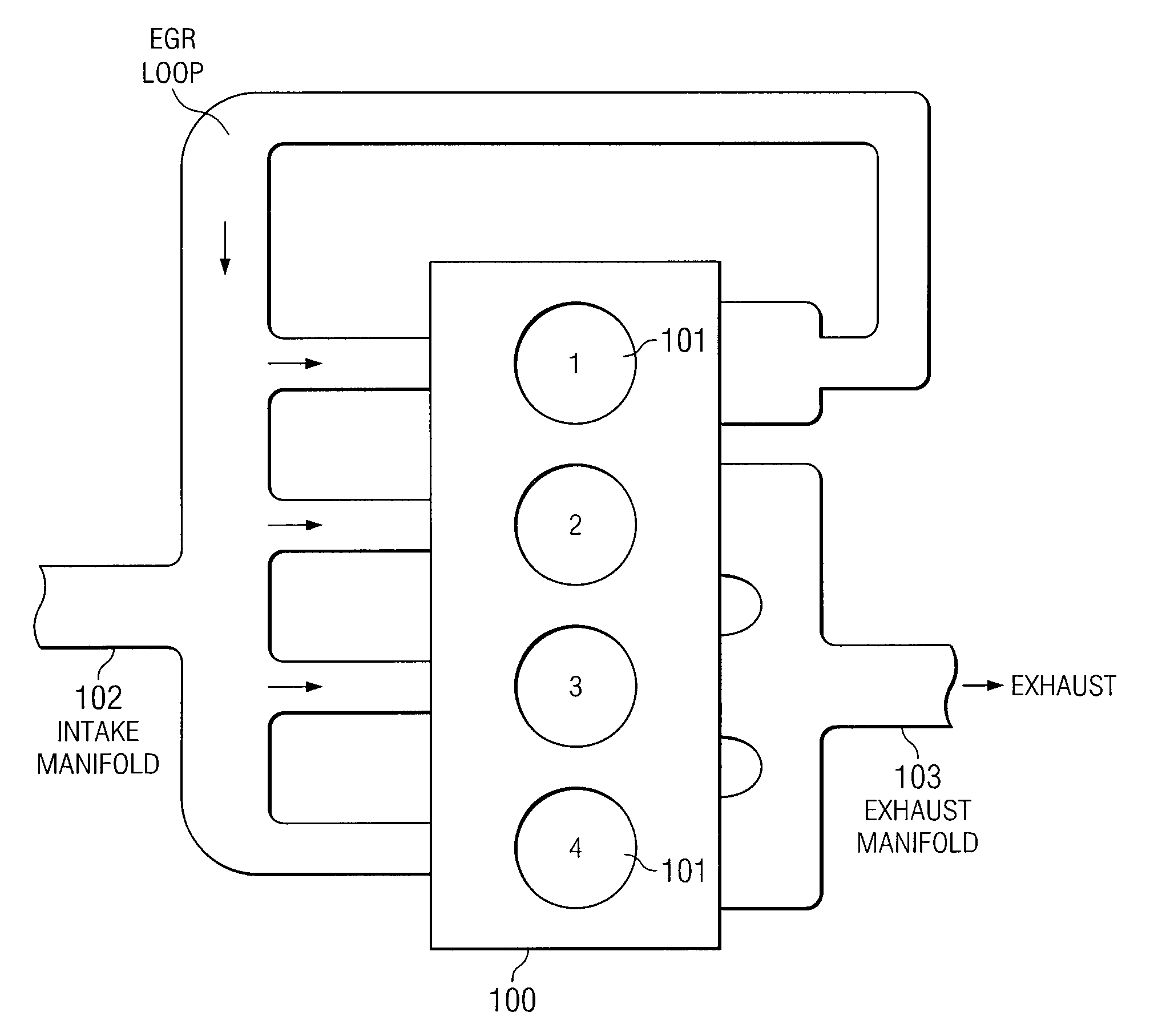
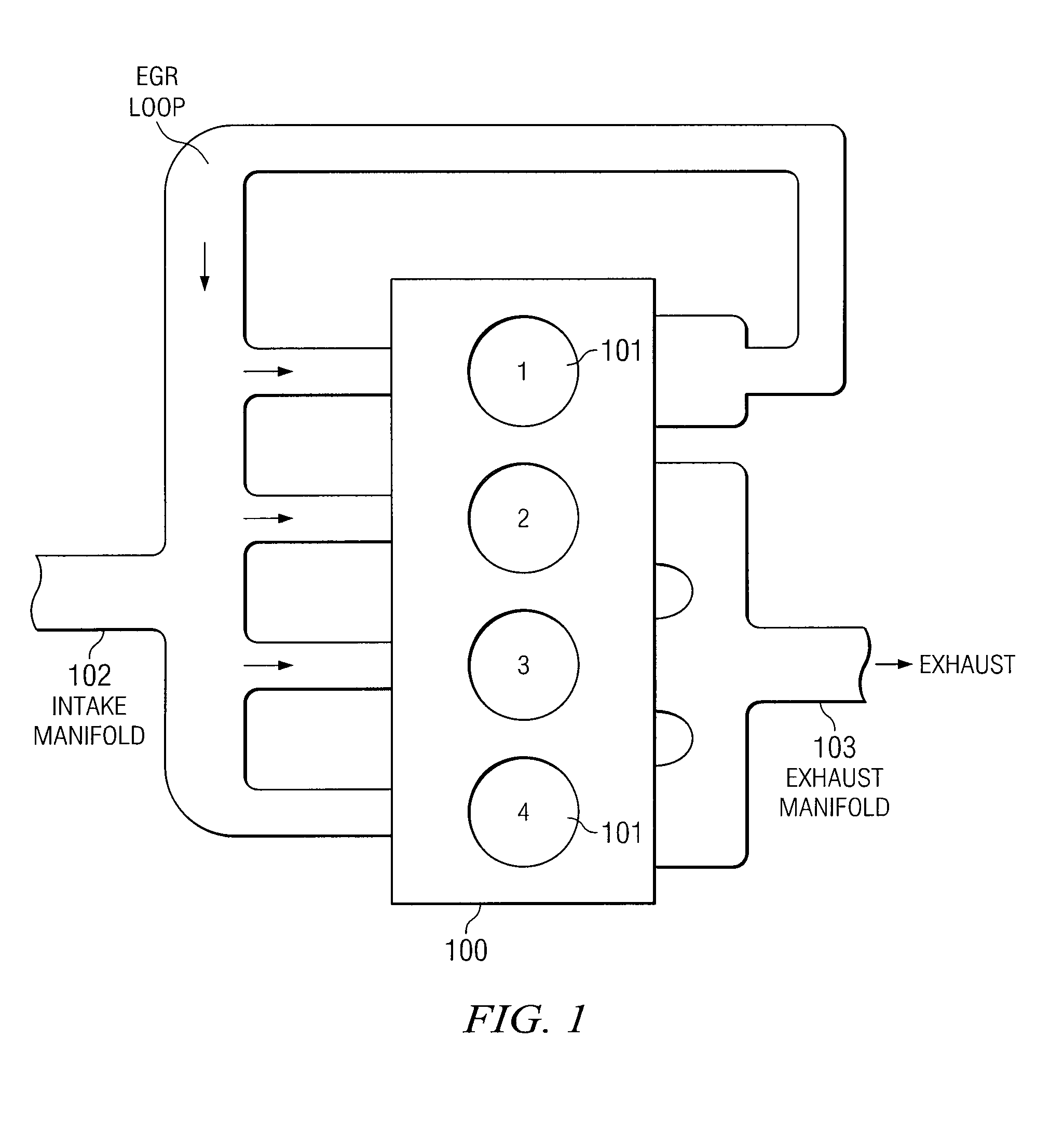
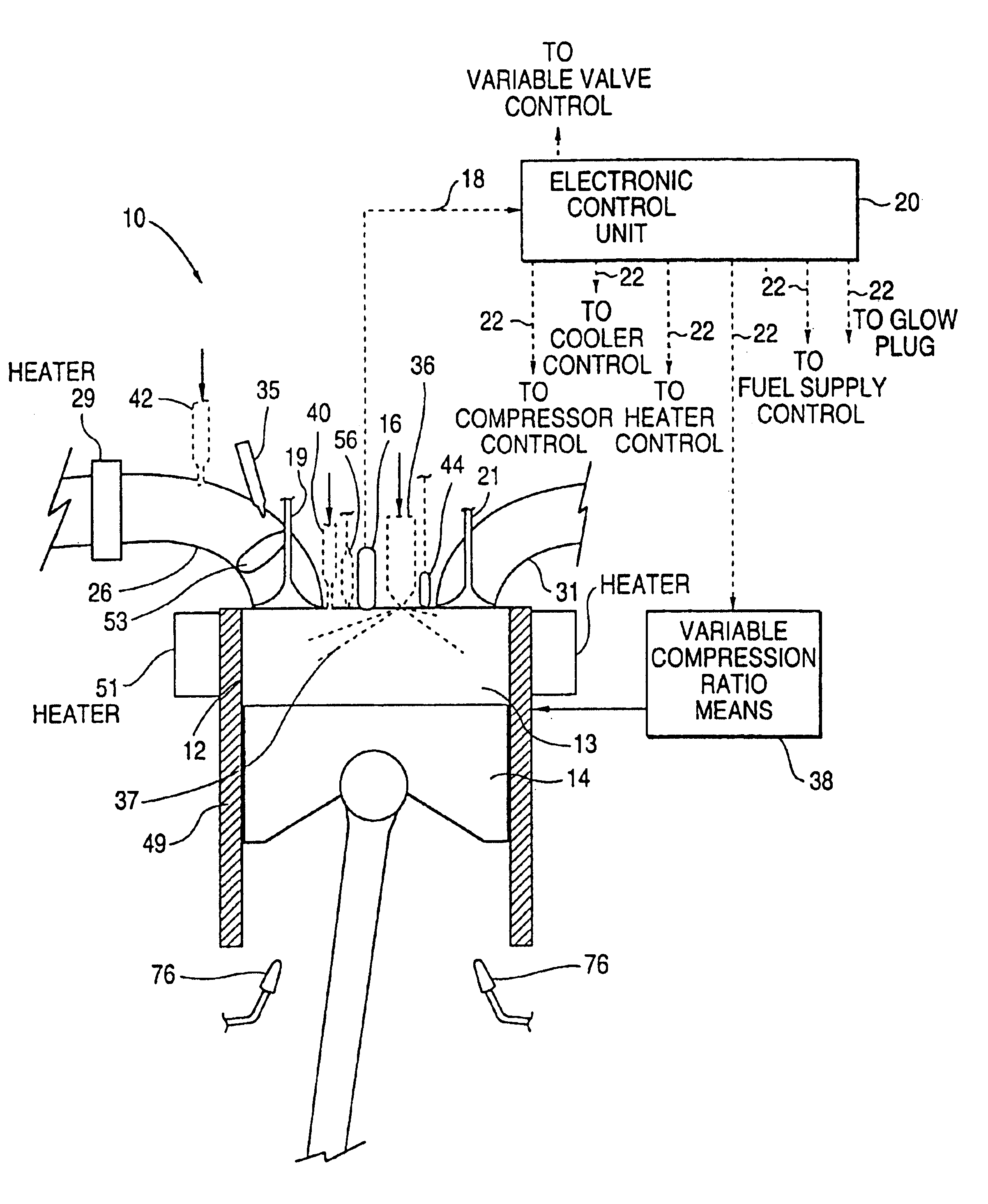
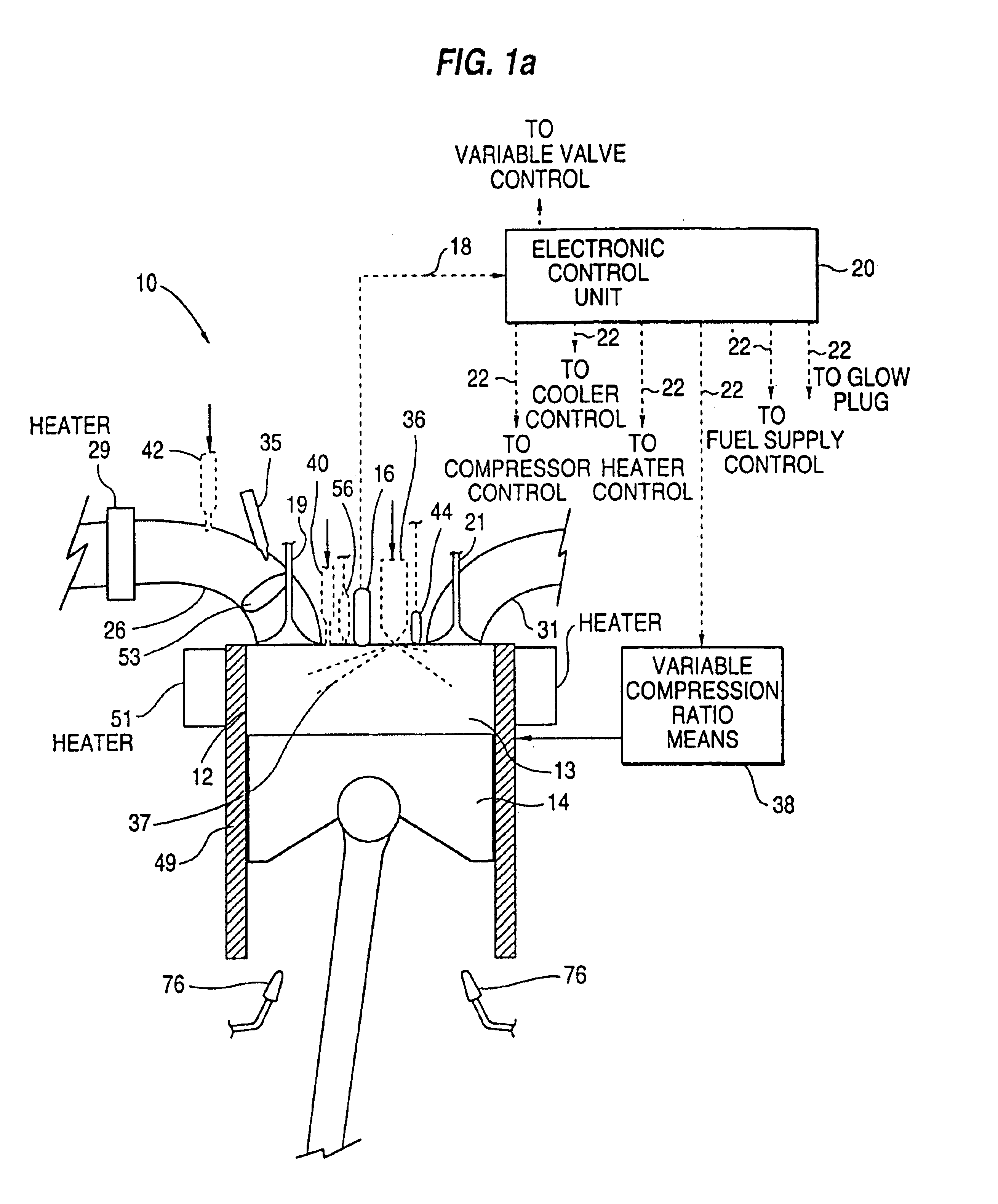
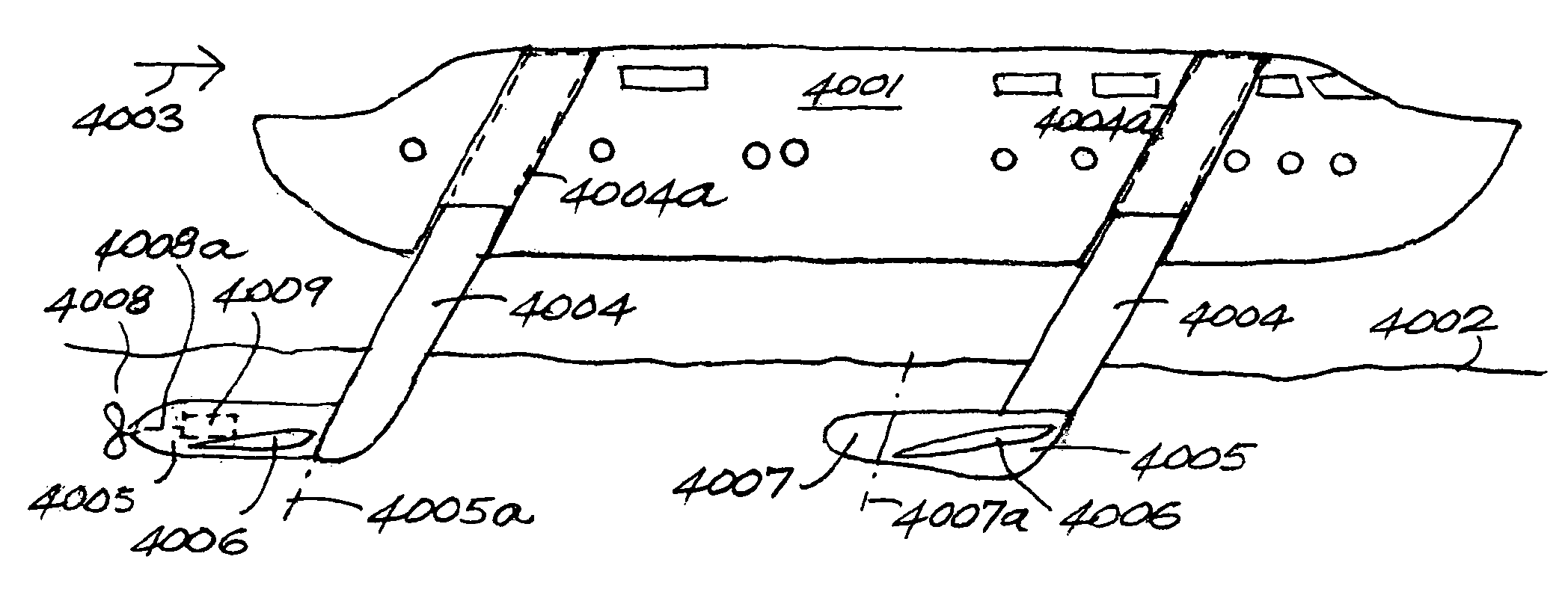
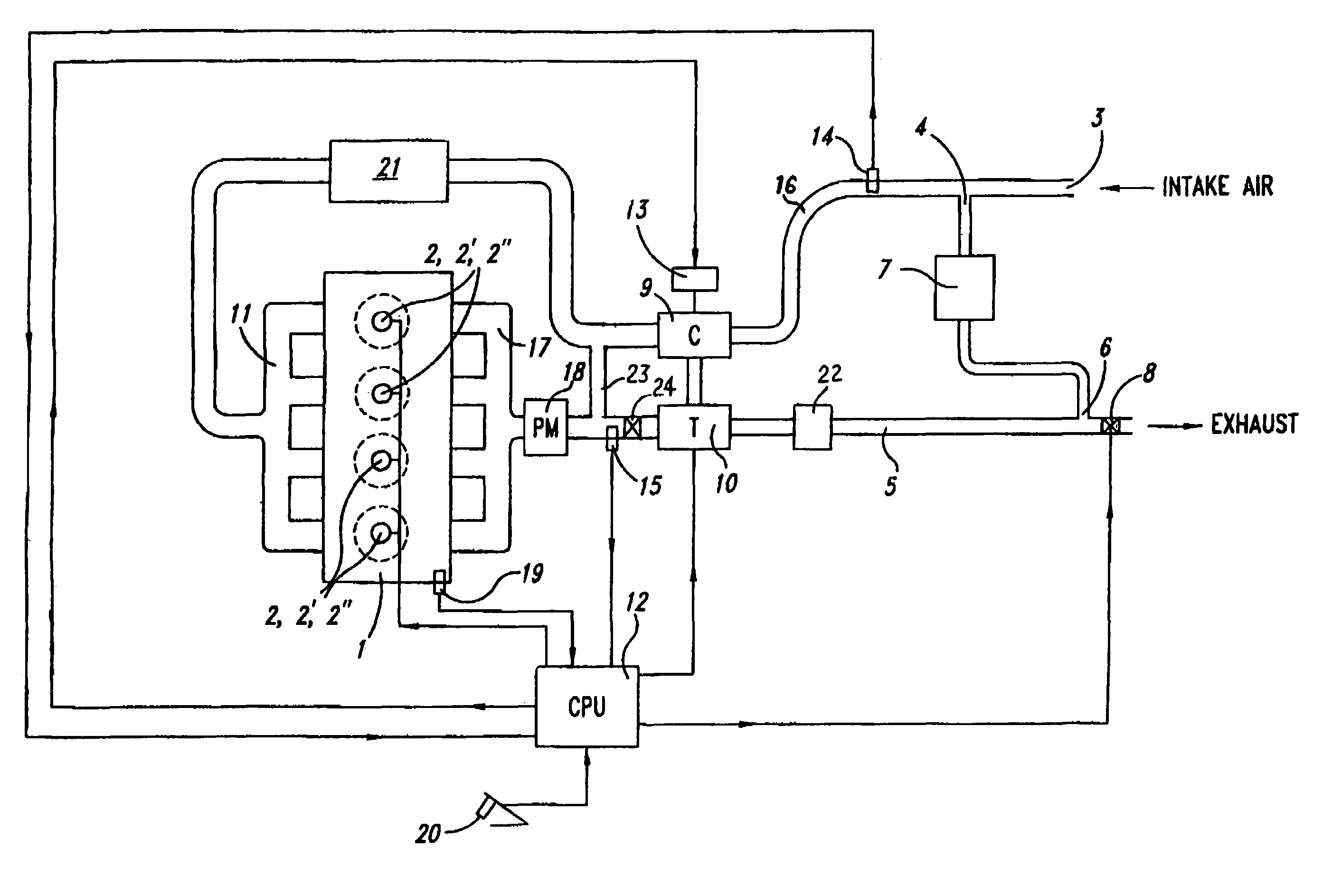
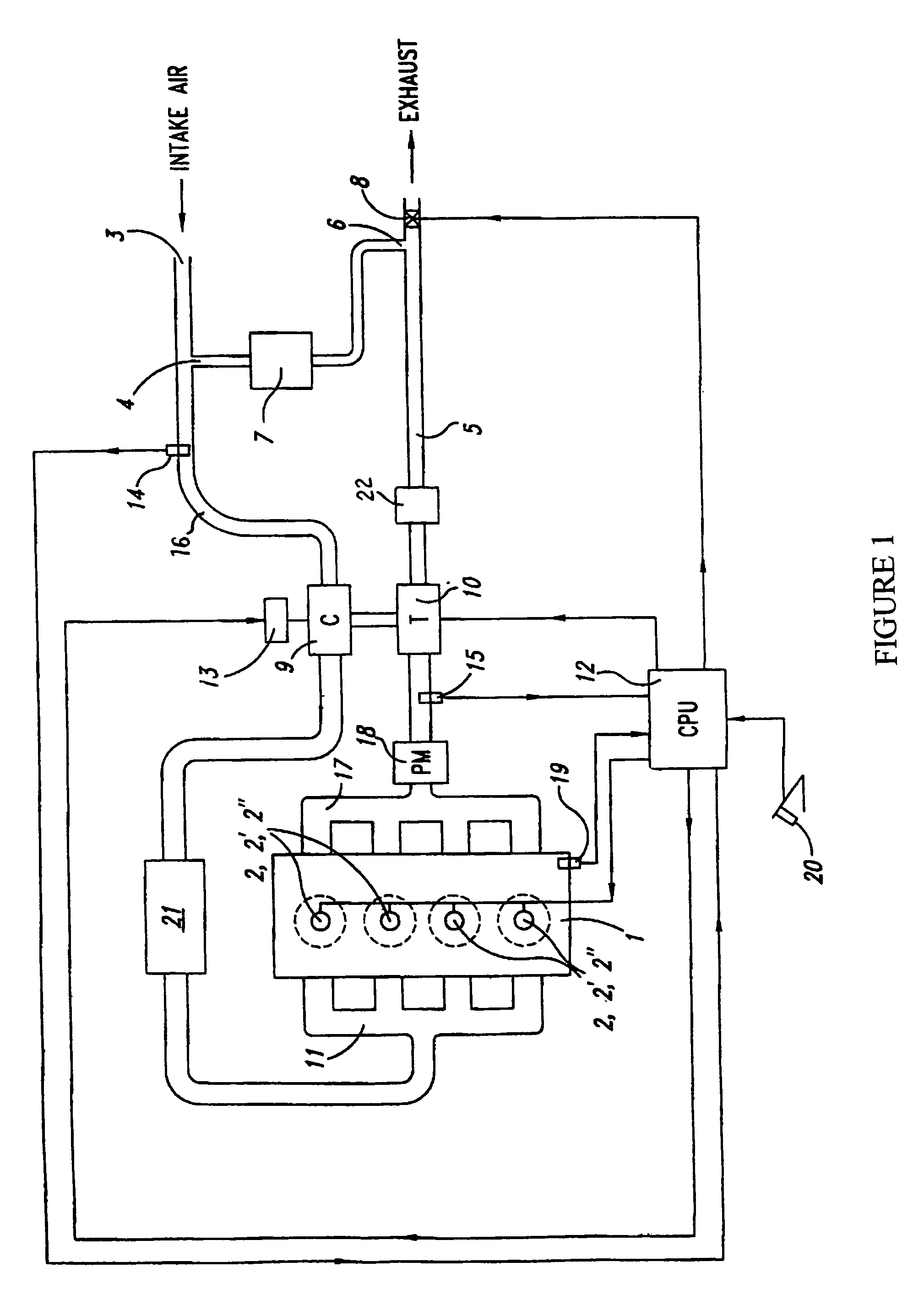
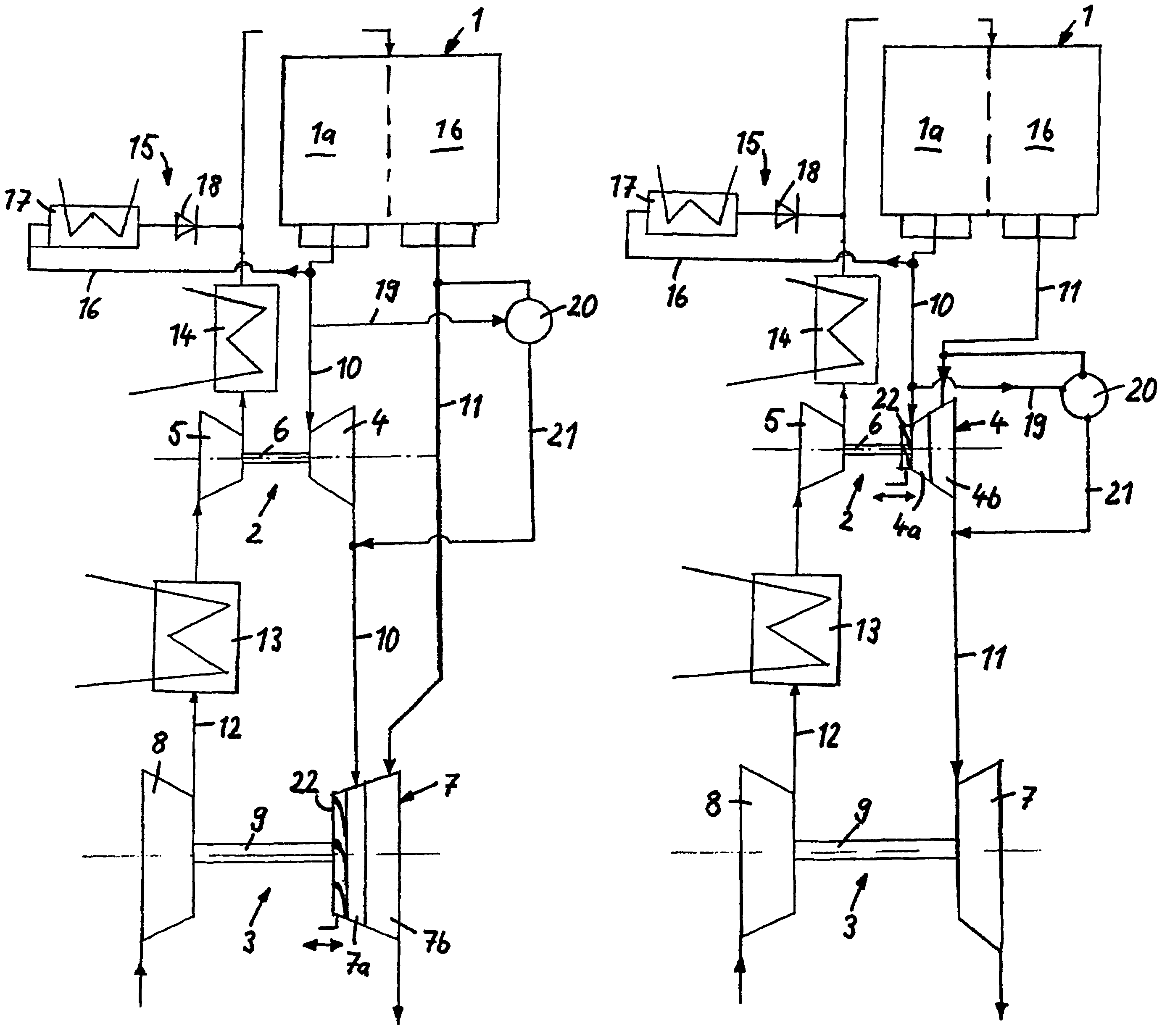
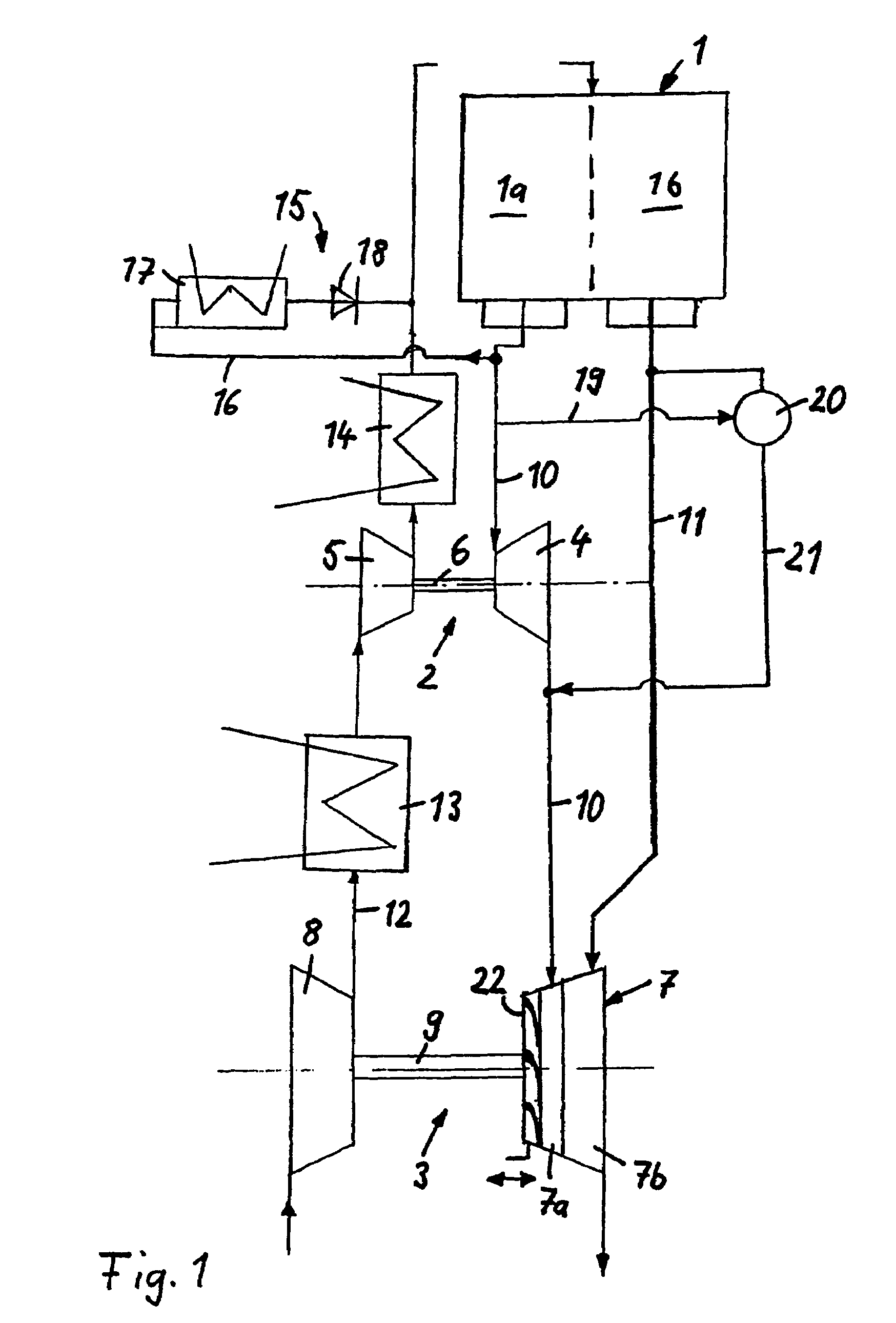
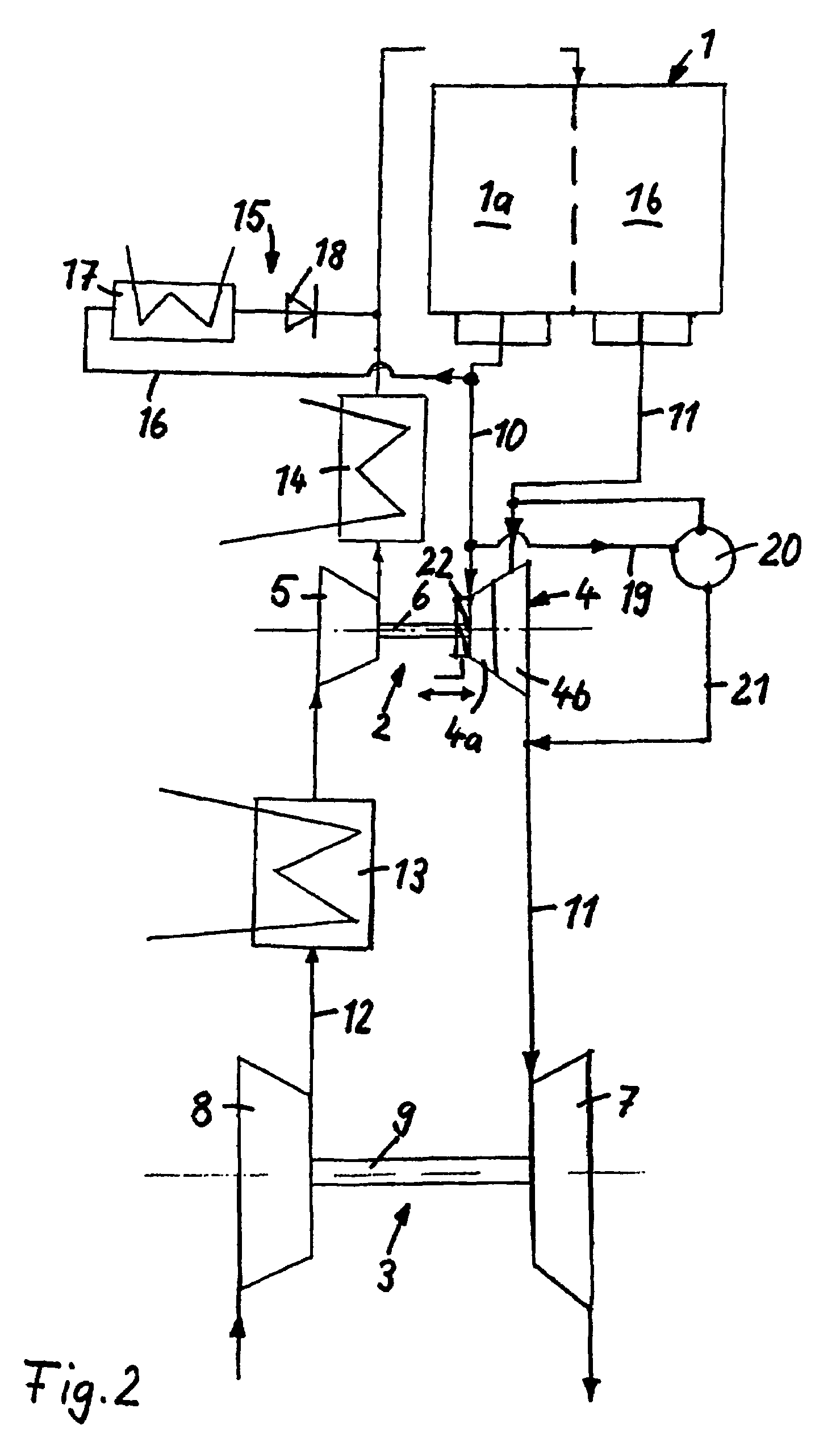
Egr system with dedicated egr cylinders
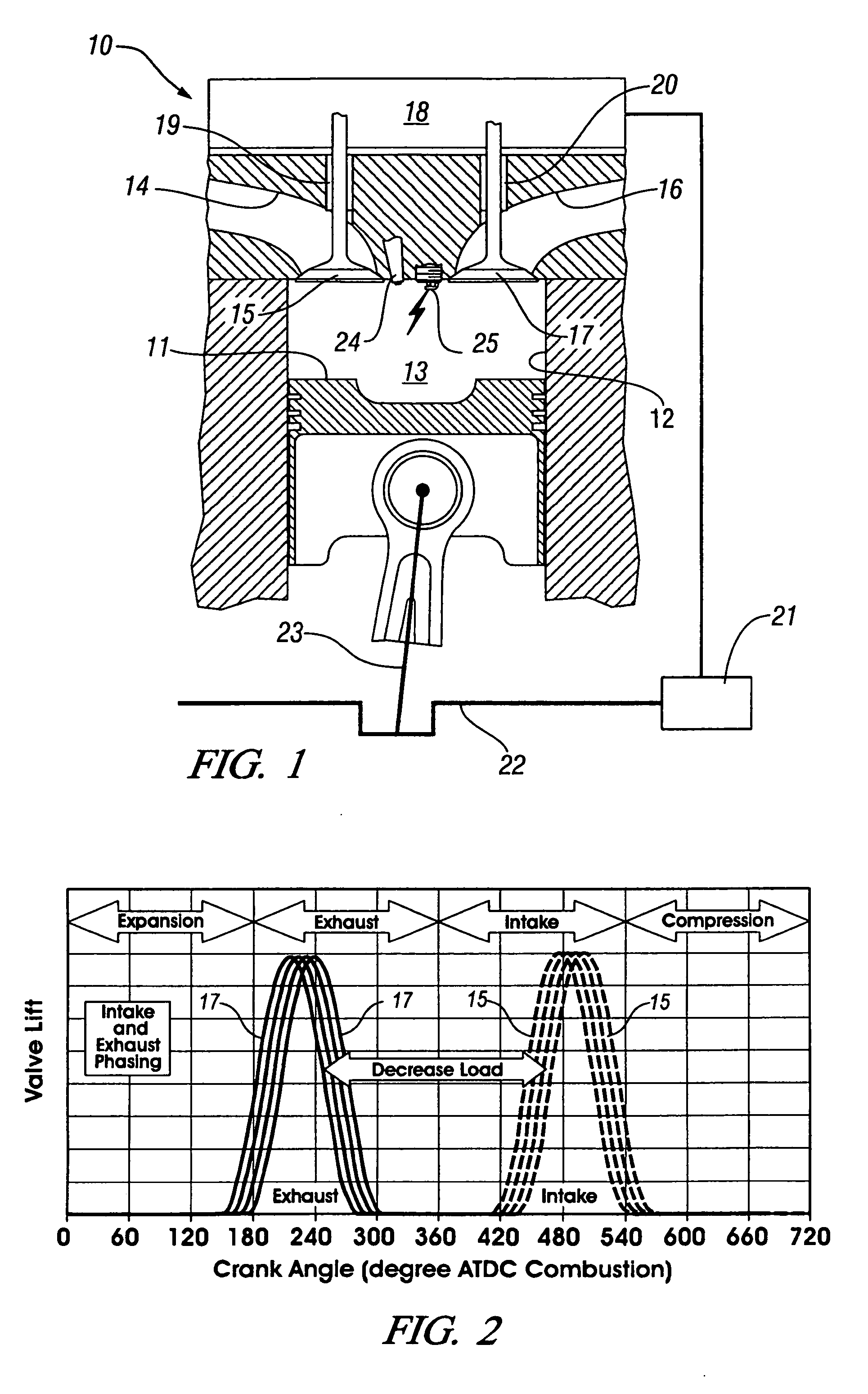
Improved exhaust gas recirculation system and methods that use one or more of the engine's cylinders as dedicated EGR cylinders. All of the exhaust from the dedicated EGR cylinders is recirculated back to the engine intake. Thus, the EGR rate is constant, but the EGR mass flow may be controlled by adjusting the air-fuel ratio of the dedicated EGR cylinders or by using various variable valve timing techniques.
Owner:SOUTHWEST RES INST
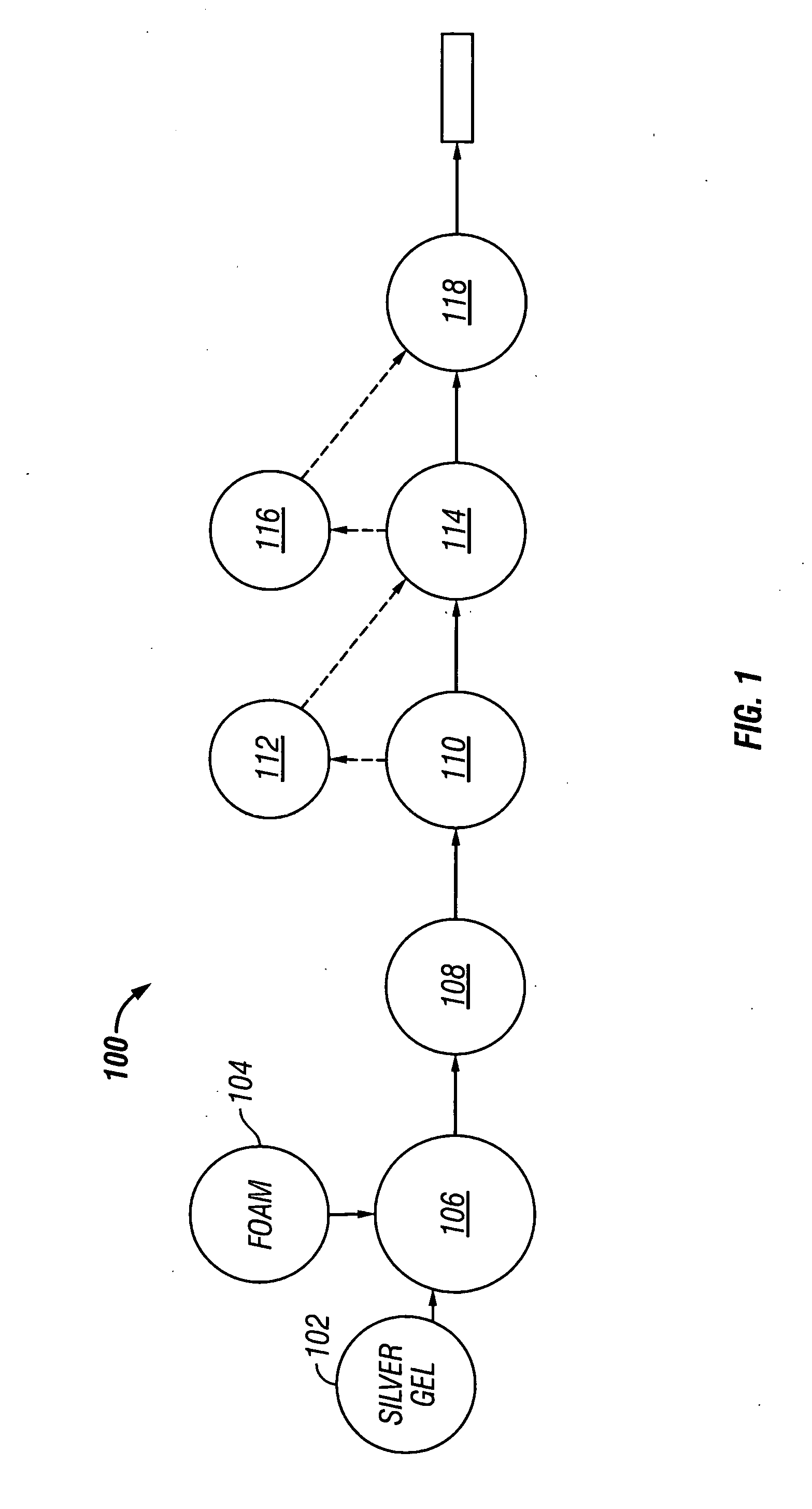
Method for coating substrate with antimicrobial agent and product formed thereby
A method for uniformly coating a foam or dressing with antimicrobial polymer incorporating agents, such as silver, and a foam or dressing formed by this process. Such foam or dressing is particularly useful in combination with negative pressure wound therapy.
Owner:KCI LICENSING INC
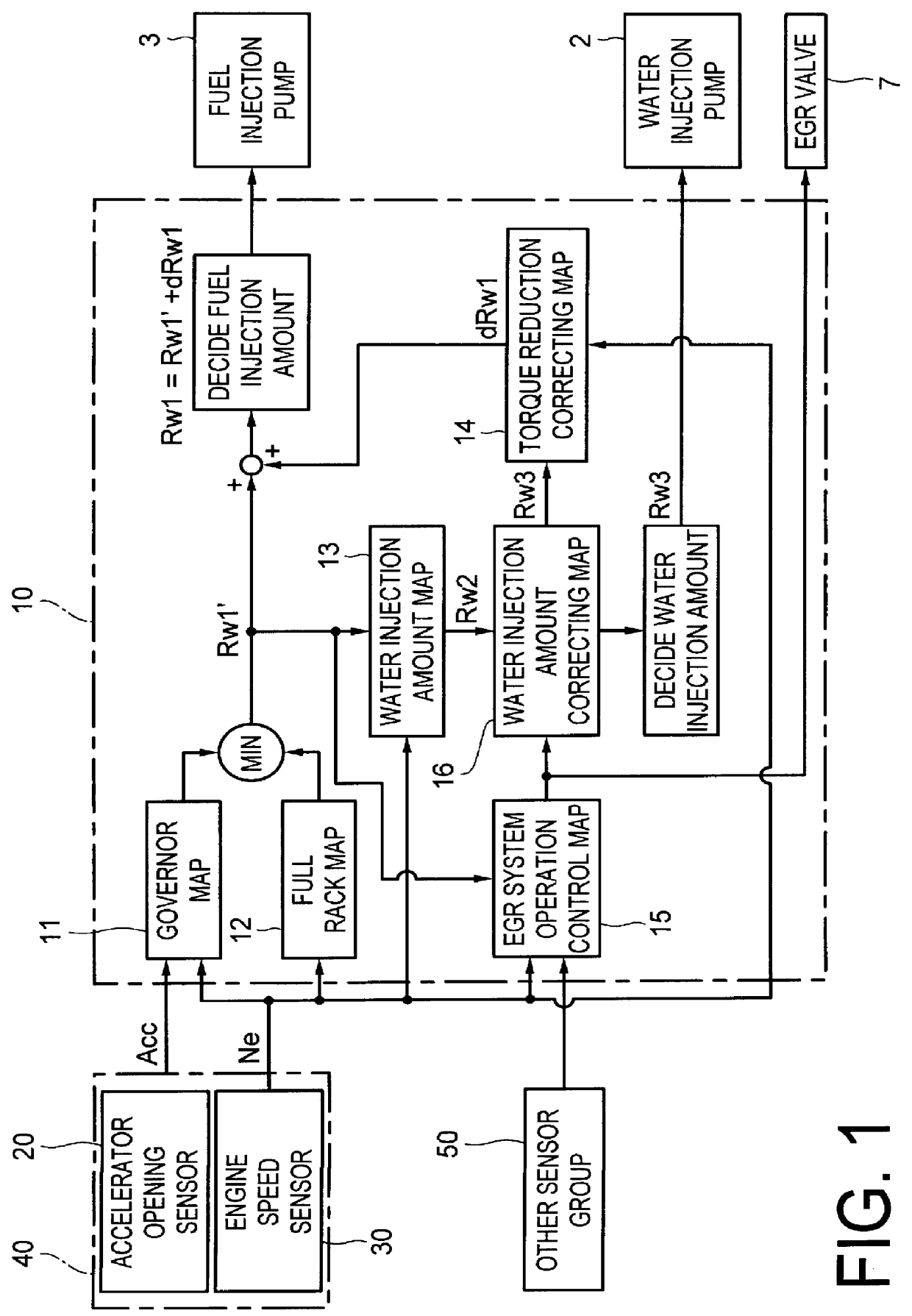
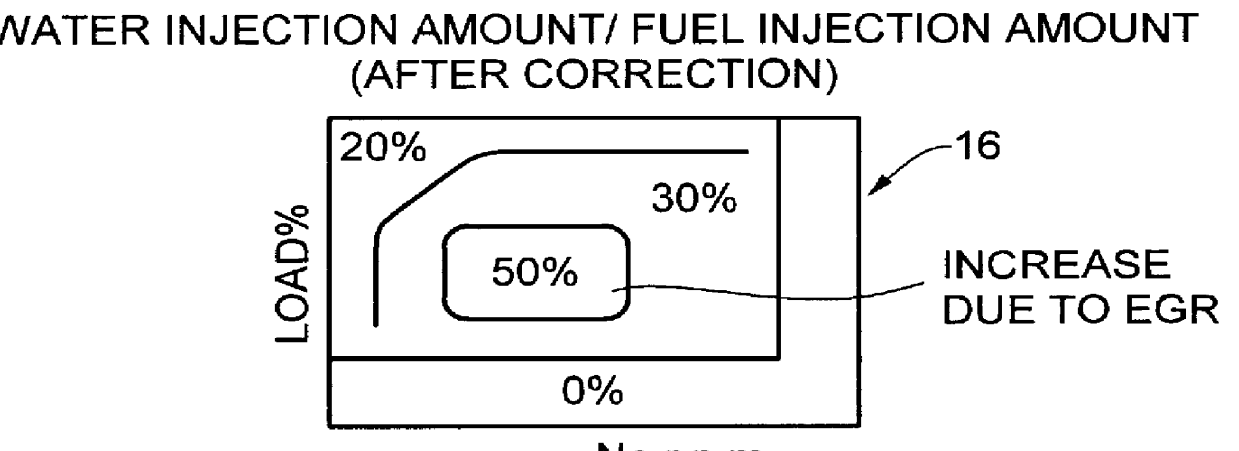
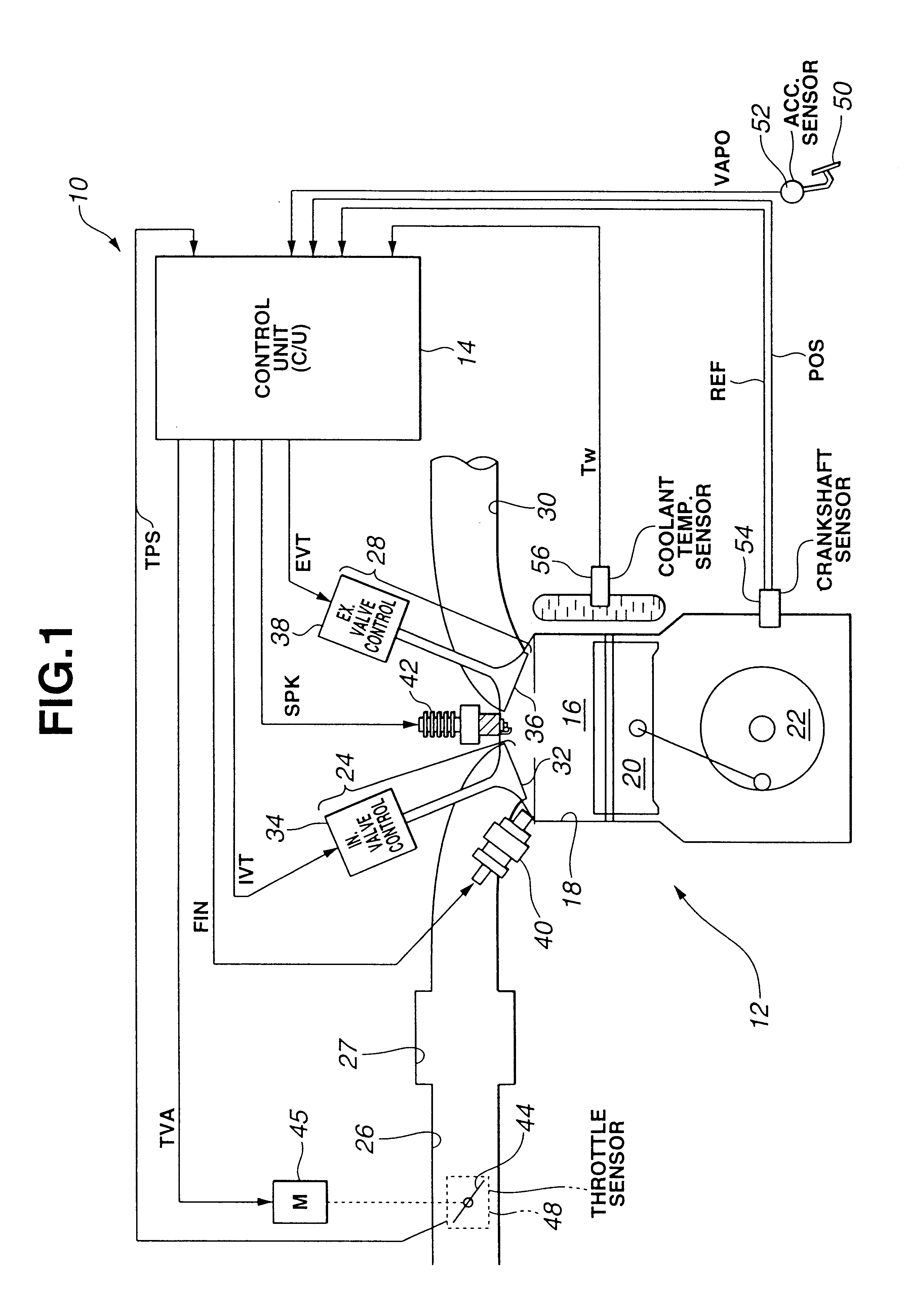
Water injection amount control system for fuel and water injection engine
InactiveUS6112705AEnhance NOx reducing effectImprove reducibilityElectrical controlNon-fuel substance addition to fuelCombustion chamberControl system
A water injection amount control system for a fuel and water injection engine, comprises running state detecting unit for detecting the running state of the engine; an EGR system for recirculating part of exhaust gas of the engine to a combustion chamber of the engine; EGR system operating state detecting unit for detecting or estimating the operating state of the EGR system; water injection amount regulating unit for regulating an amount of water to be injected to the combustion chamber of the engine; and control unit for controlling the operation of the water injection amount regulating unit: wherein the system is arranged to have water injection amount setting unit for deciding a water injection amount based on information from the running state detecting unit and on the operating state of the EGR system detected by the EGR system operating state detecting unit, so that the control unit controls the operation of the water injection amount regulating unit based on the water injection amount decided by the water injection amount setting unit.
Owner:MITSUBISHI FUSO TRUCK AND BUS CORPORATION
Reciprocating devices
ActiveUS20080141921A1Improve power densityImprove efficiencyHybrid vehiclesInternal combustion piston enginesExternal combustion engineEnergy absorption
The disclosure relates to fluid working devices including reciprocating internal combustion engines, compressors and pumps. A number of arrangements for pistons and cylinders of unconventional configuration are described, mostly intended for use in reciprocating internal combustion IC engines operating without cooling. Included are toroidal combustion or working chambers, some with fluid flow through the core of the toroid, pistons reciprocating between pairs of working chambers, tensile valve actuation, tensile links between piston and crankshaft, energy absorbing piston-crank links, crankshafts supported on gas bearings, cylinders rotating in housings, injectors having components reciprocate or rotate during fuel delivery. In some embodiments pistons mare rotate while reciprocating. High temperature exhaust emissions systems are described, including those containing filamentary material, as are procedures for reducing emissions during cold start by means of valves at reaction volume exit. Compound engines having the new engines as a reciprocating stage are described. Improved vehicles, aircraft, marine craft and transmissions adapted to receive or be linked to the improved IV engines are also disclosed.
Owner:HINDERKS MITJA VICTOR
System and method for auto-ignition of gasoline internal combustion engine
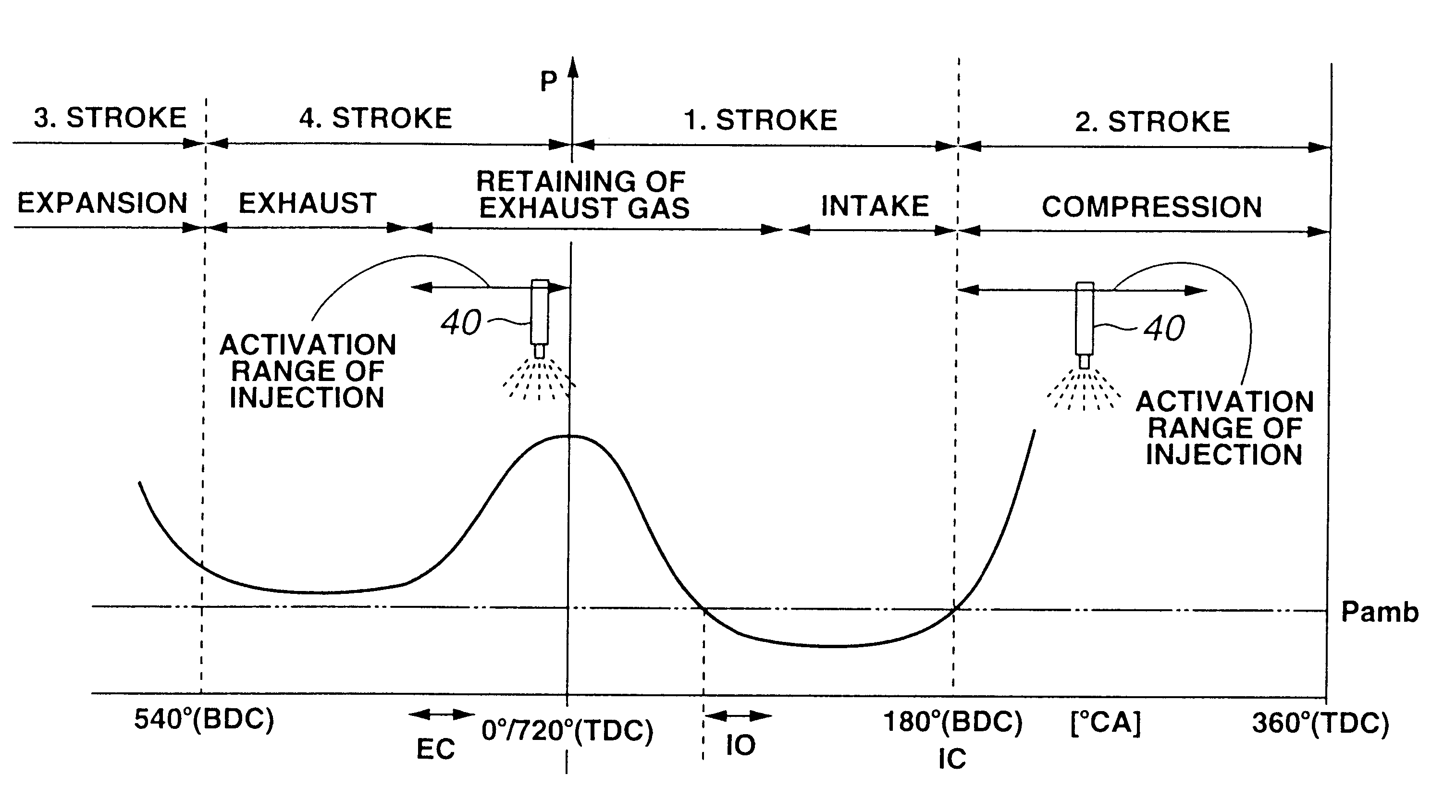
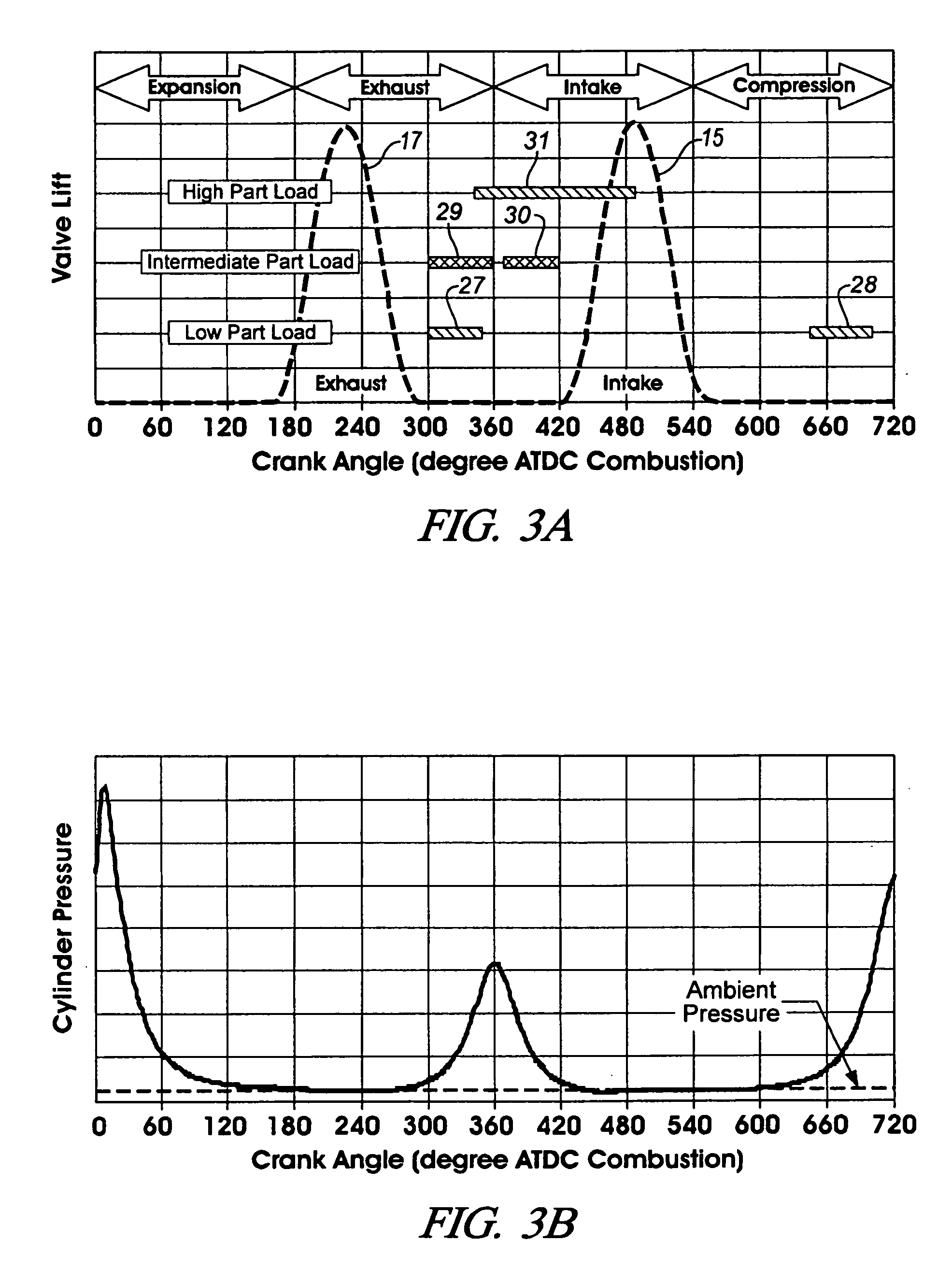
During operation with part load, a gasoline internal combustion engine is operated with a lean air / fuel mixture by auto-ignition. During operation with full load, spark-ignition is used to operate the engine. The internal combustion engine is operated in three auto-ignition combustion modes depending upon magnitude of a predetermined operating parameter. The operating parameter is indicative of the engine load or the engine speed. The three auto-ignition combustion modes are a gasoline reform auto-ignition combustion mode, an auto-ignition stratified charge combustion mode, and an auto-ignition homogeneous charge combustion mode. In the gasoline reform auto-ignition combustion mode that may be selected during operation with low part load, a first fuel injection during an exhaust gas retaining phase produces sufficient amount of active fuel radicals for promotion of auto-ignition of air / fuel mixture produced by a second fuel injection during the subsequent compression phase. In the auto-ignition stratified charge combustion mode that may be selected during operation with intermediate part load, a fuel injection during compression phase supports auto-ignition. In the auto-ignition homogeneous charge combustion mode that may be selected during operation with high part load, a fuel injection during intake phase supports auto-ignition.
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD
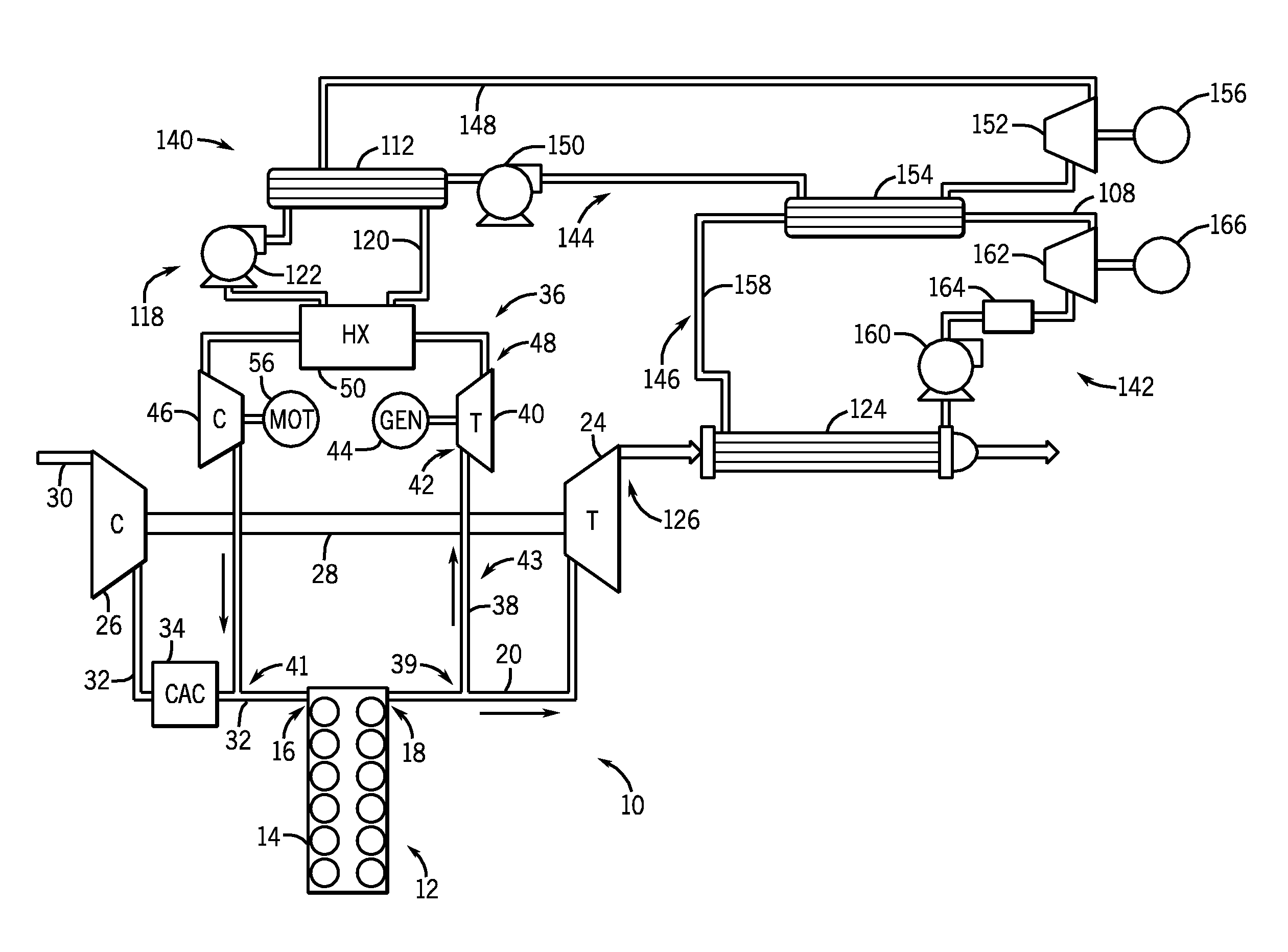
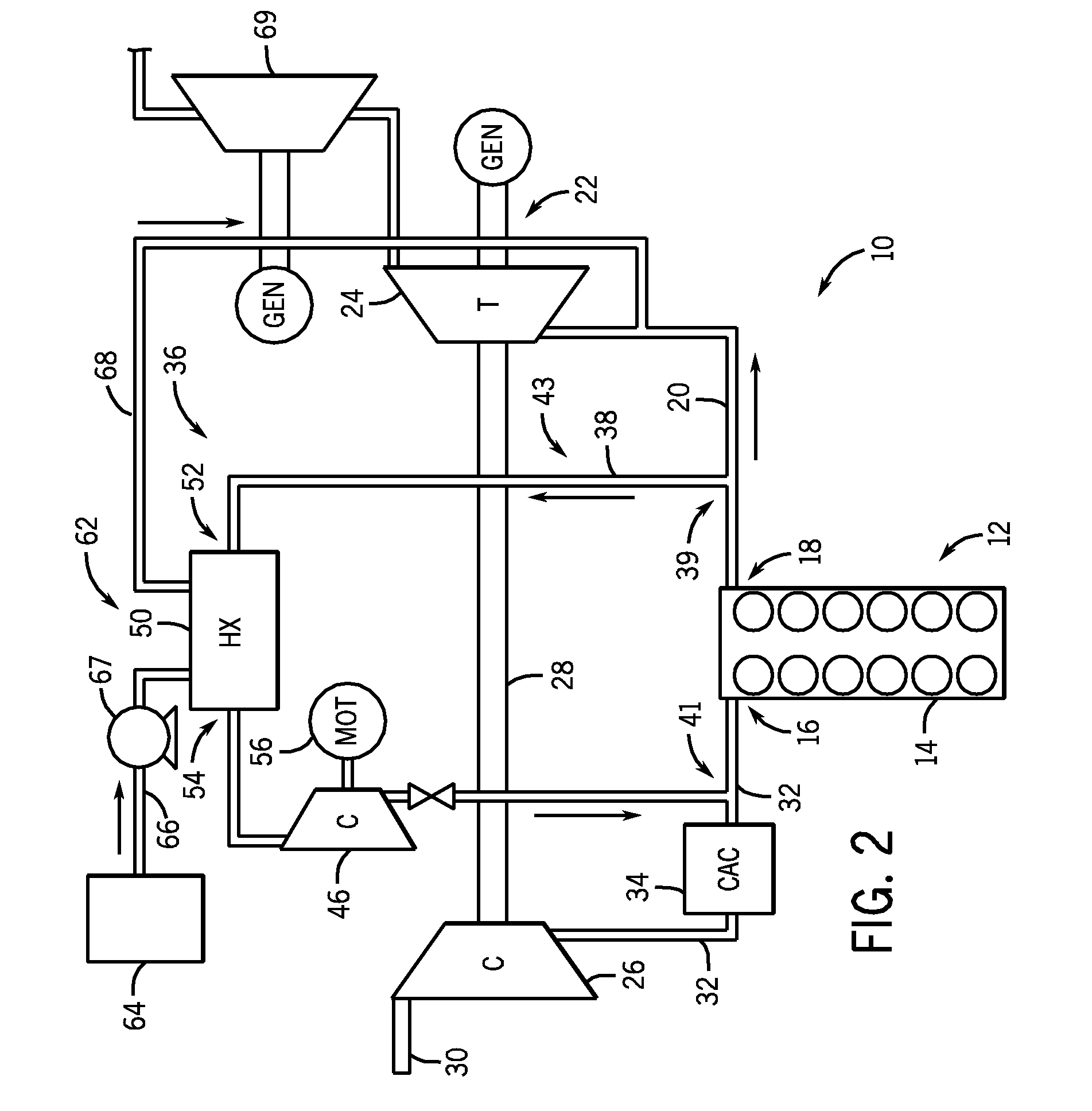
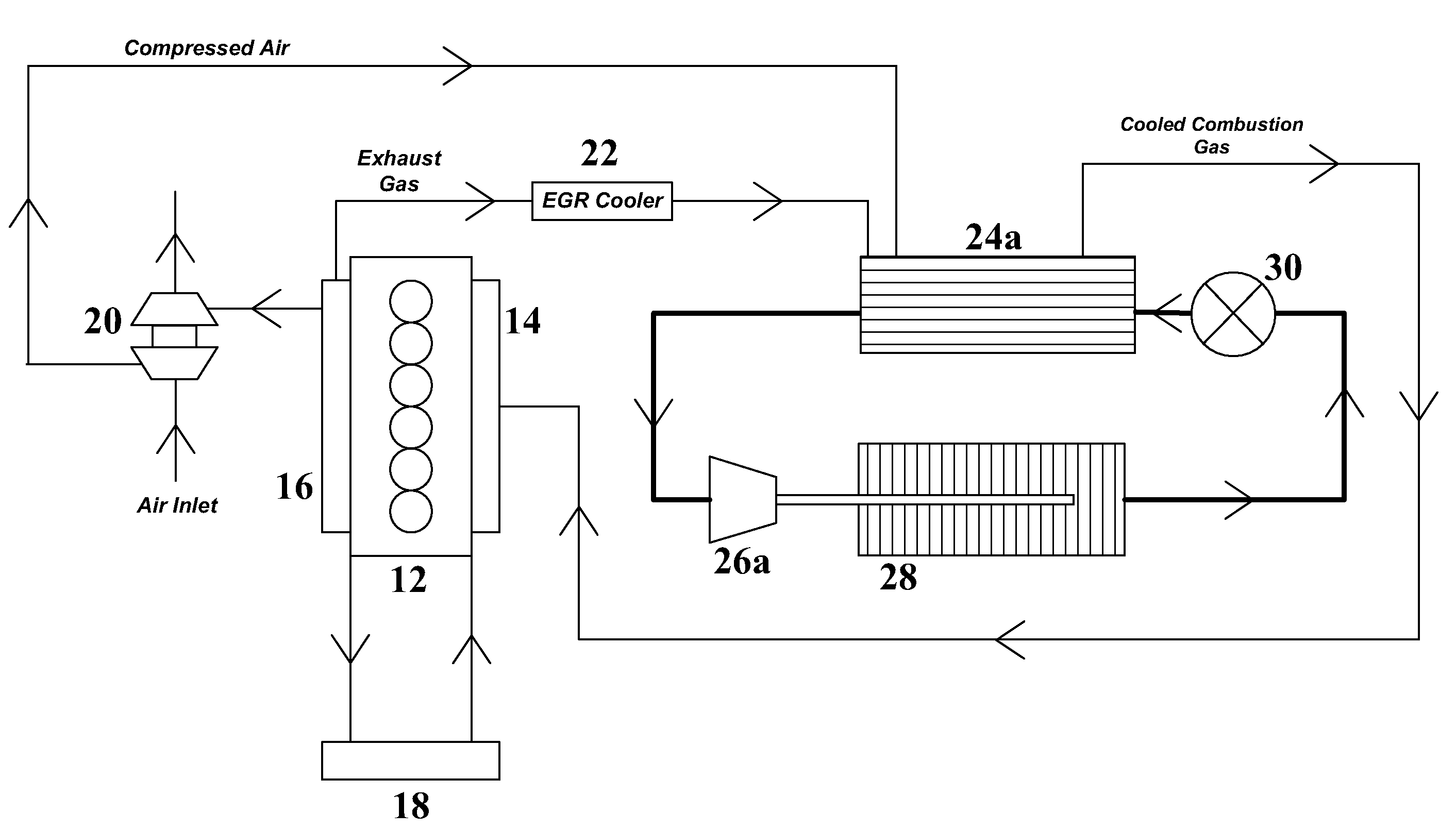
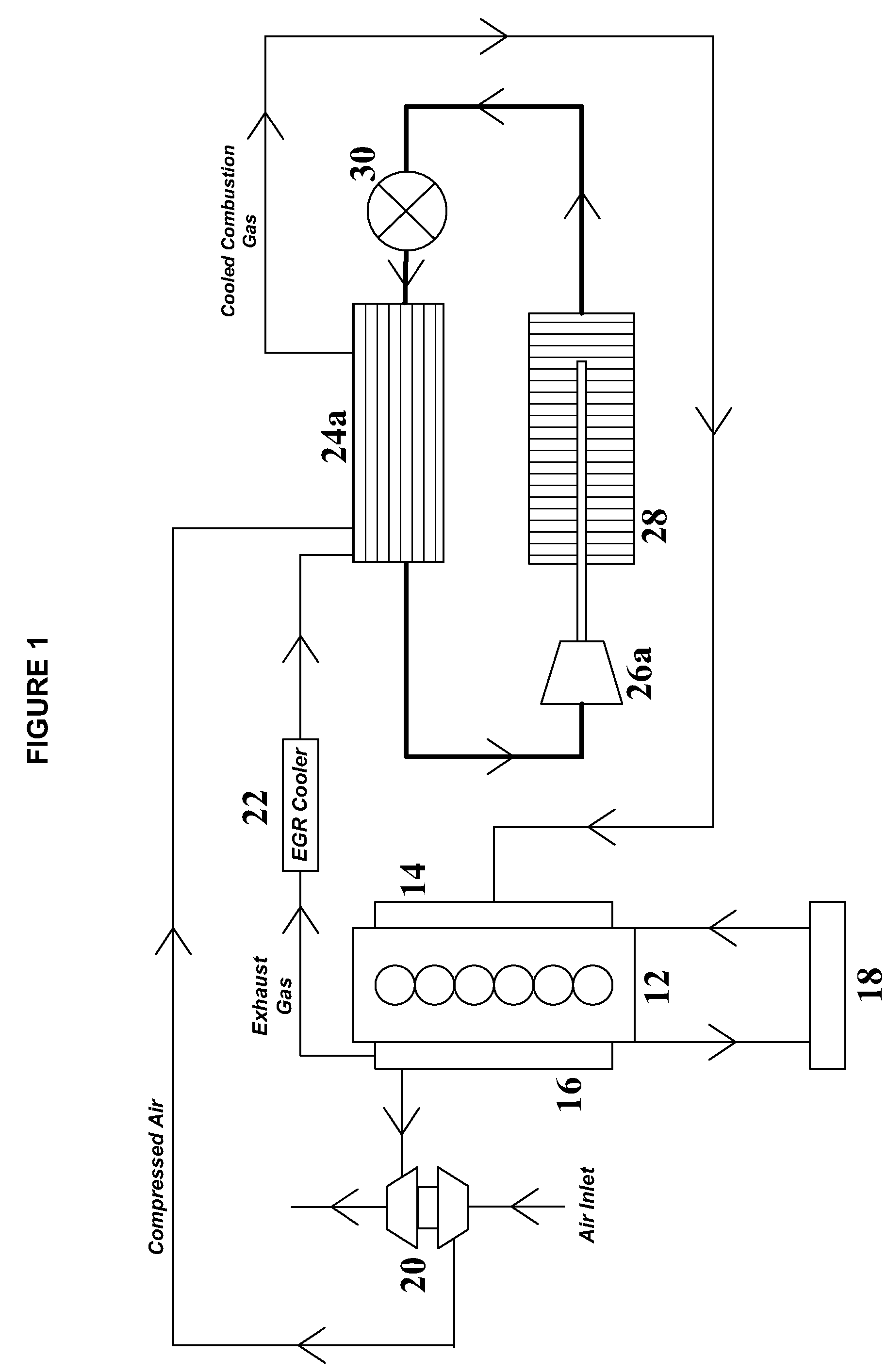
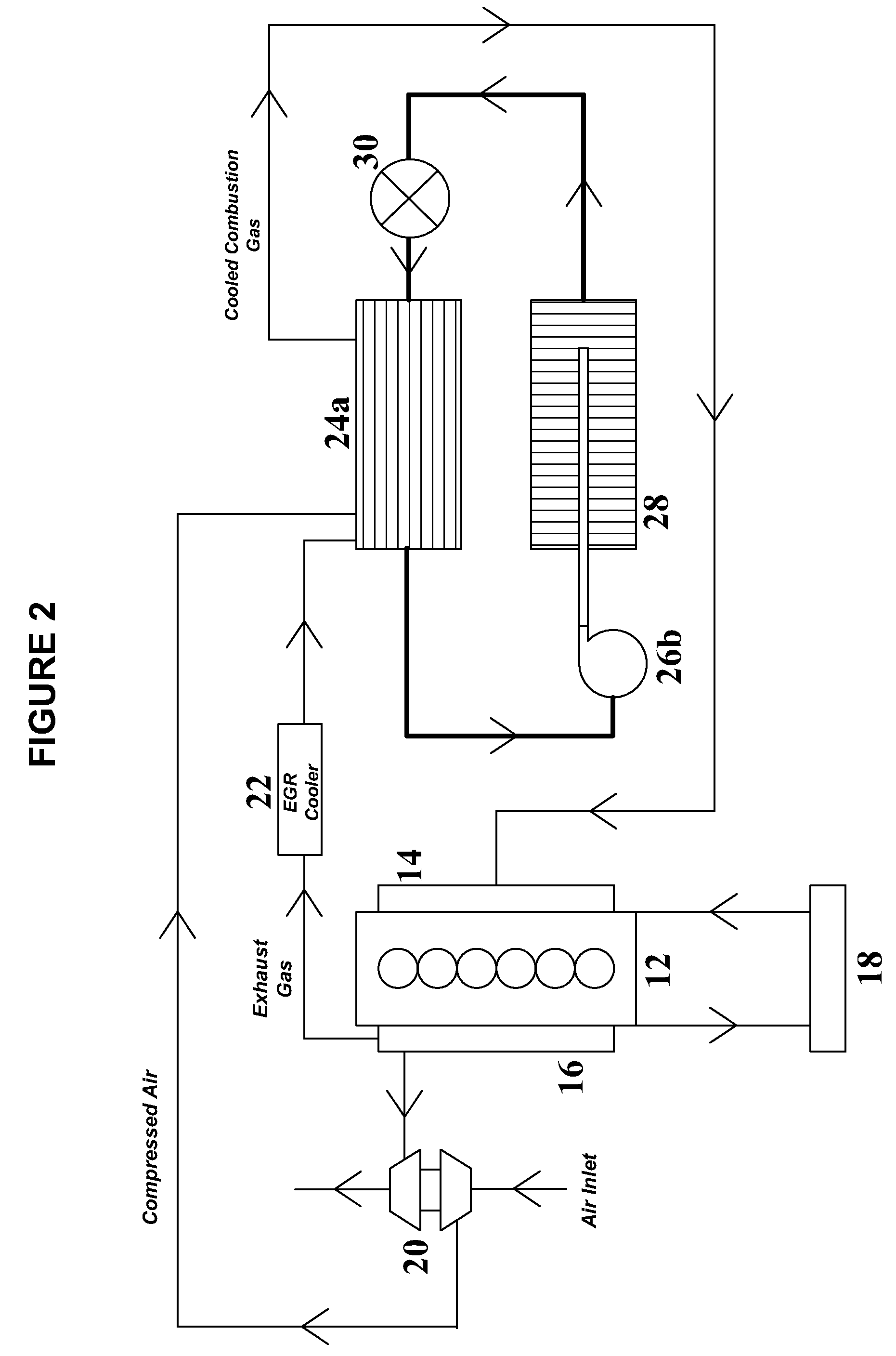
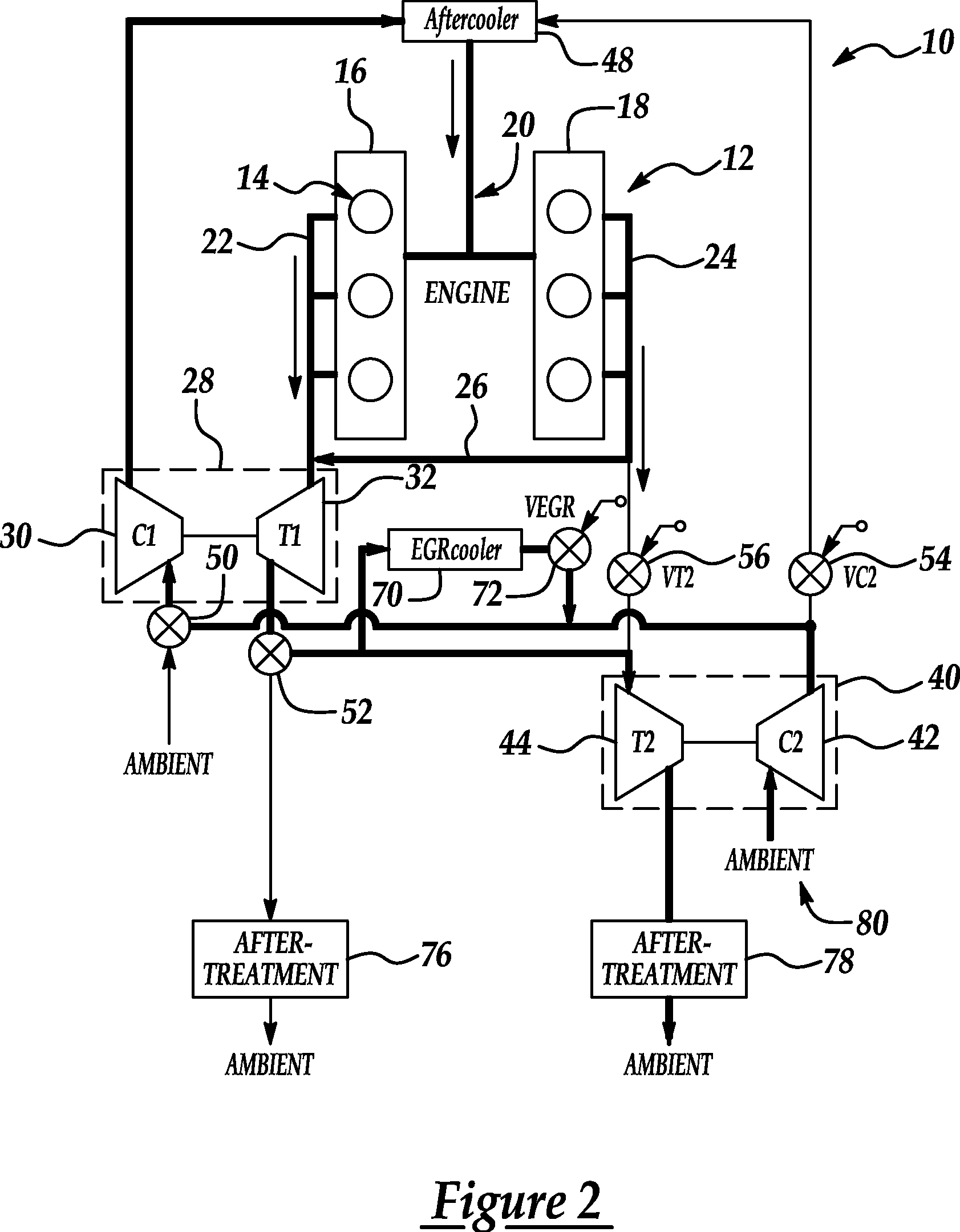
System and method for waste heat recovery in exhaust gas recirculation
InactiveUS20110209473A1Liquid degasificationInternal combustion piston enginesTurbochargerExhaust fumes
A system and method for waste heat recovery in exhaust gas recirculation is disclosed. The system includes an engine having an intake manifold and an exhaust manifold, an exhaust conduit connected to the exhaust manifold, and a turbocharger having a turbine and a compressor, the turbine being connected to the exhaust conduit to receive a portion of the exhaust gas from the exhaust manifold. The system also includes an EGR system connected to the exhaust conduit to receive a portion of the exhaust gas, with the EGR system including an EGR conduit that is connected to the exhaust conduit to receive a portion of the exhaust gas, a heat exchanger connected to the EGR conduit and being configured to extract heat from the exhaust gas, and a waste heat recovery system connected to the heat exchanger and configured to capture the heat extracted by the heat exchanger.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Optimized combustion control of an internal combustion engine equipped with exhaust gas recirculation
InactiveUS6948475B1Avoid condensationImprove concentrationElectrical controlNon-fuel substance addition to fuelExhaust fumesExhaust gas recirculation
An EGR equipped internal combustion engine is controlled to maximize the beneficial effects and minimize the detrimental effects of EGR on engine operation. Specifically, at least one parameter indicative of the O2 concentration in the intake mixture and / or at least one parameter indicative of the H2O concentration in the intake mixture is monitored, and the monitored parameter is relied on to control one or more aspects of engine operation by open loop adjustment of other control strategies and / or by a separate closed loop control strategy. These controls are applicable to virtually any engine, and are particularly beneficial to lean burn engines such as diesel (compression ignition) engines, spark ignited natural gas engines, and dual fuel or other compression ignited natural gas engines. The engine may be equipped with either actively controllable EGR or passive and uncontrolled EGR.
Owner:CLEAN AIR POWER
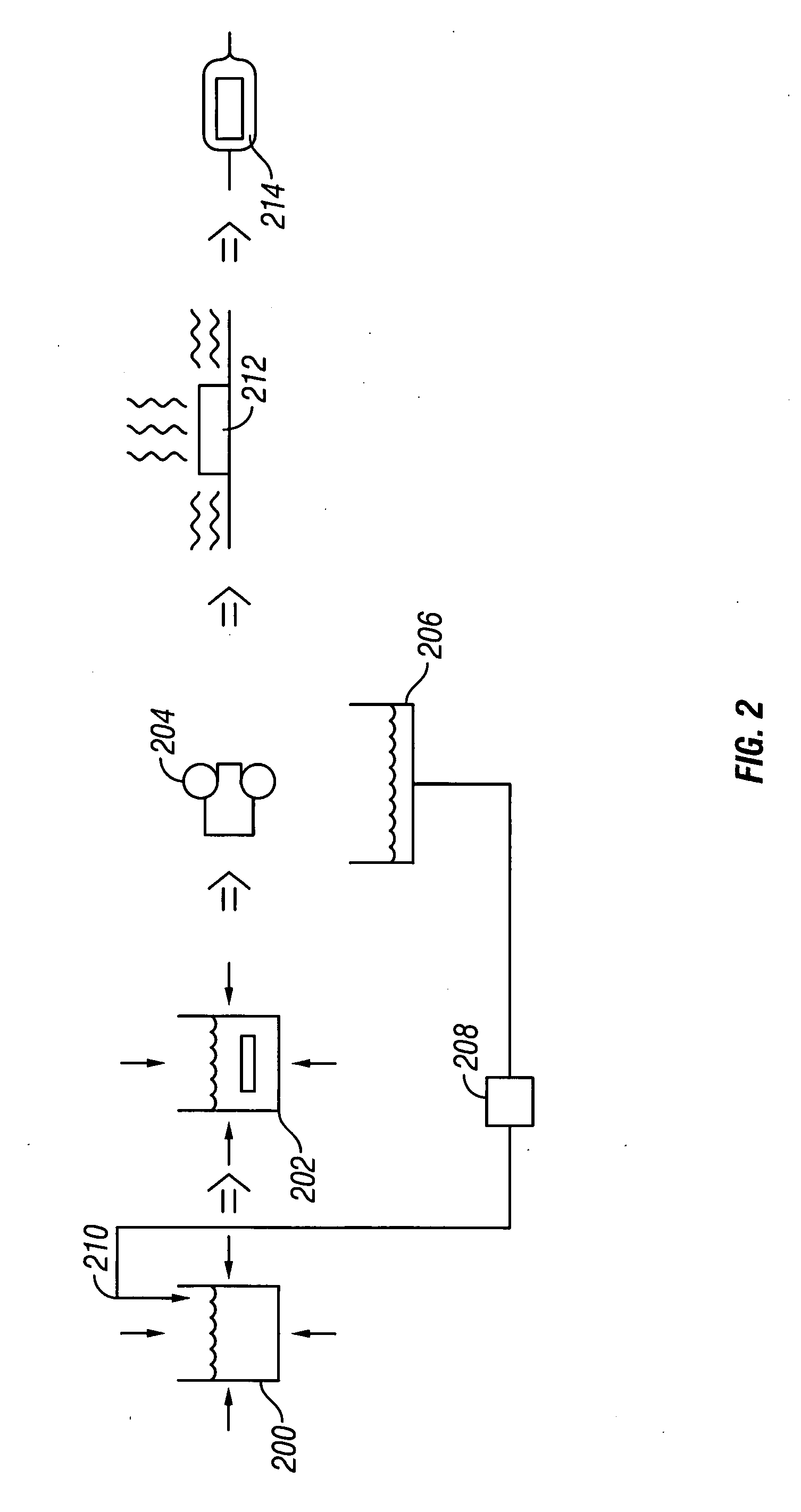
Thermoelectric generating device
InactiveUS7100369B2Maximum electricityLiquid coolingCoolant flow controlElectricityThermoelectric element
A thermoelectric generating device has a thermoelectric element which utilizes an exhaust gas from an engine as a high temperature heat source and an engine coolant as a low temperature heat source in order to generate electricity. An introducing passage introduces a part of the exhaust gas passed through the thermoelectric element into an intake of the engine. An introducing valve opens and closes the introducing passage. A controller controls an opening degree of the introducing valve according to a load of the engine.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Engine exhaust gas cleaning method and system
InactiveUS20060086080A1Emission reductionReduce cleaning rateElectrical controlNon-fuel substance addition to fuelExhaust fumesEnvironmental engineering
An engine exhaust gas cleaning method and system, which can effectively reduce emission amounts of particular components, such as NOx, contained in exhaust gas by adding an additive, such as urea water or light oil, into an exhaust passage, which is adaptable for a reduction of the cleaning rate caused by deterioration of a catalyst, which can always maintain a high cleaning rate during acceleration and deceleration as well, and which can minimize environmental pollution with use of the additive in the least necessary amount. The engine exhaust gas cleaning system comprises a catalyst for removing a particular component, represented by NOx, contained in exhaust gas of an engine, an additive adding unit for adding, to the exhaust gas, an additive for reducing the particular component represented by NOx, and an EGR amount adjusting unit for adjusting an EGR amount. An addition amount of the additive and the EGR amount are set depending on an operating state and deterioration of the catalyst with time. The catalyst is regenerated when a cleaning capability of the catalyst has reduced to a predetermined value or below.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
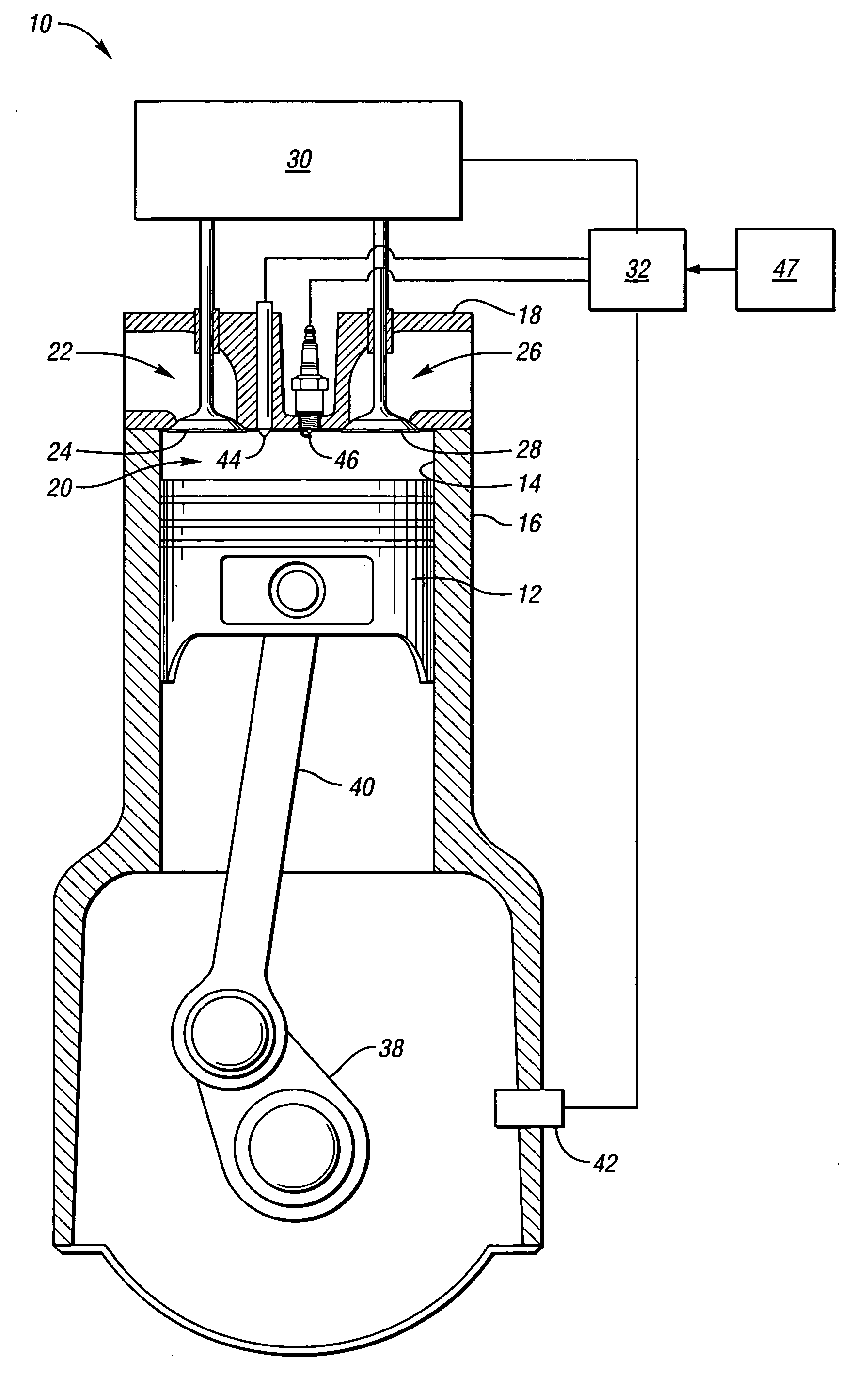
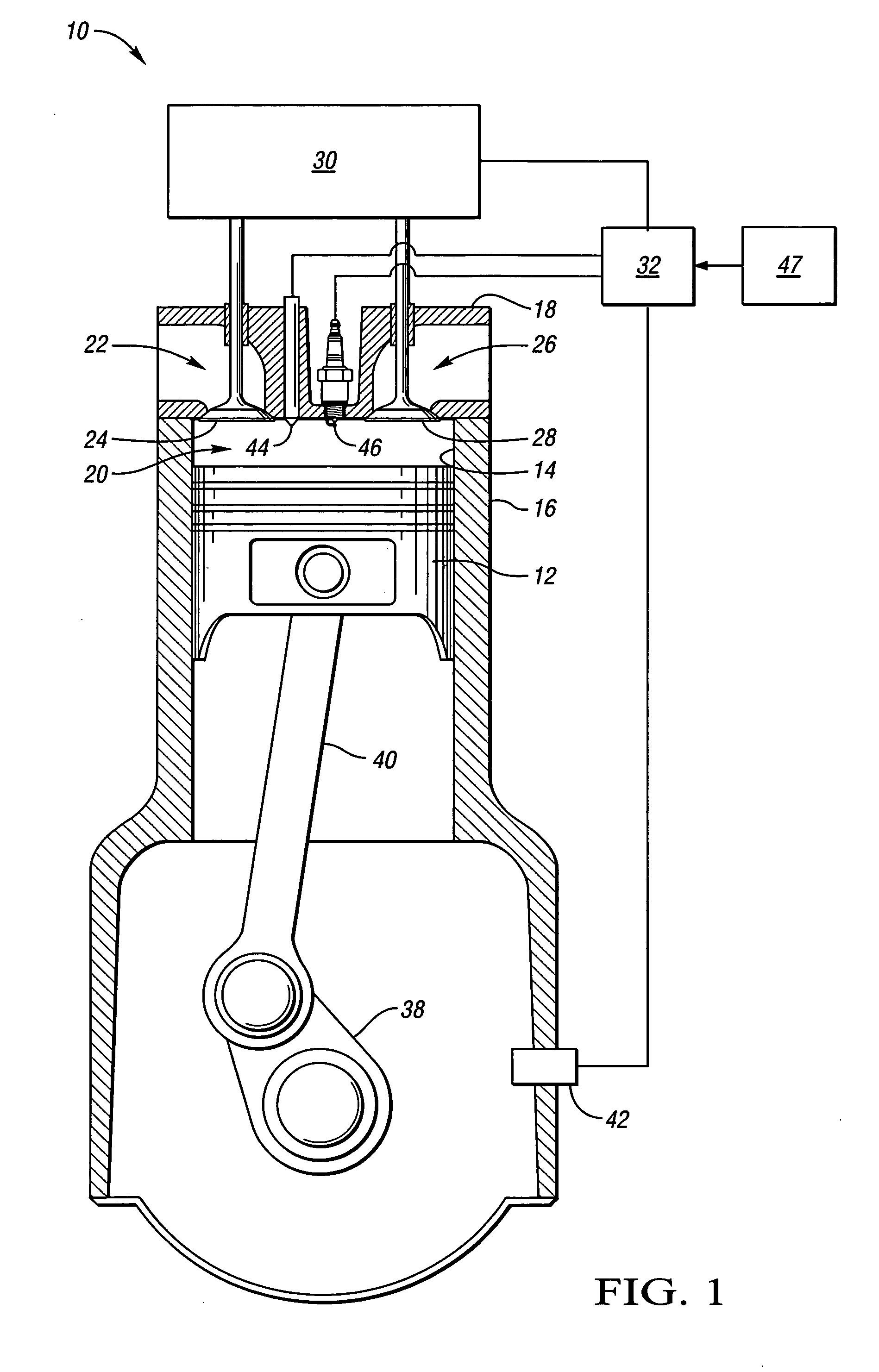
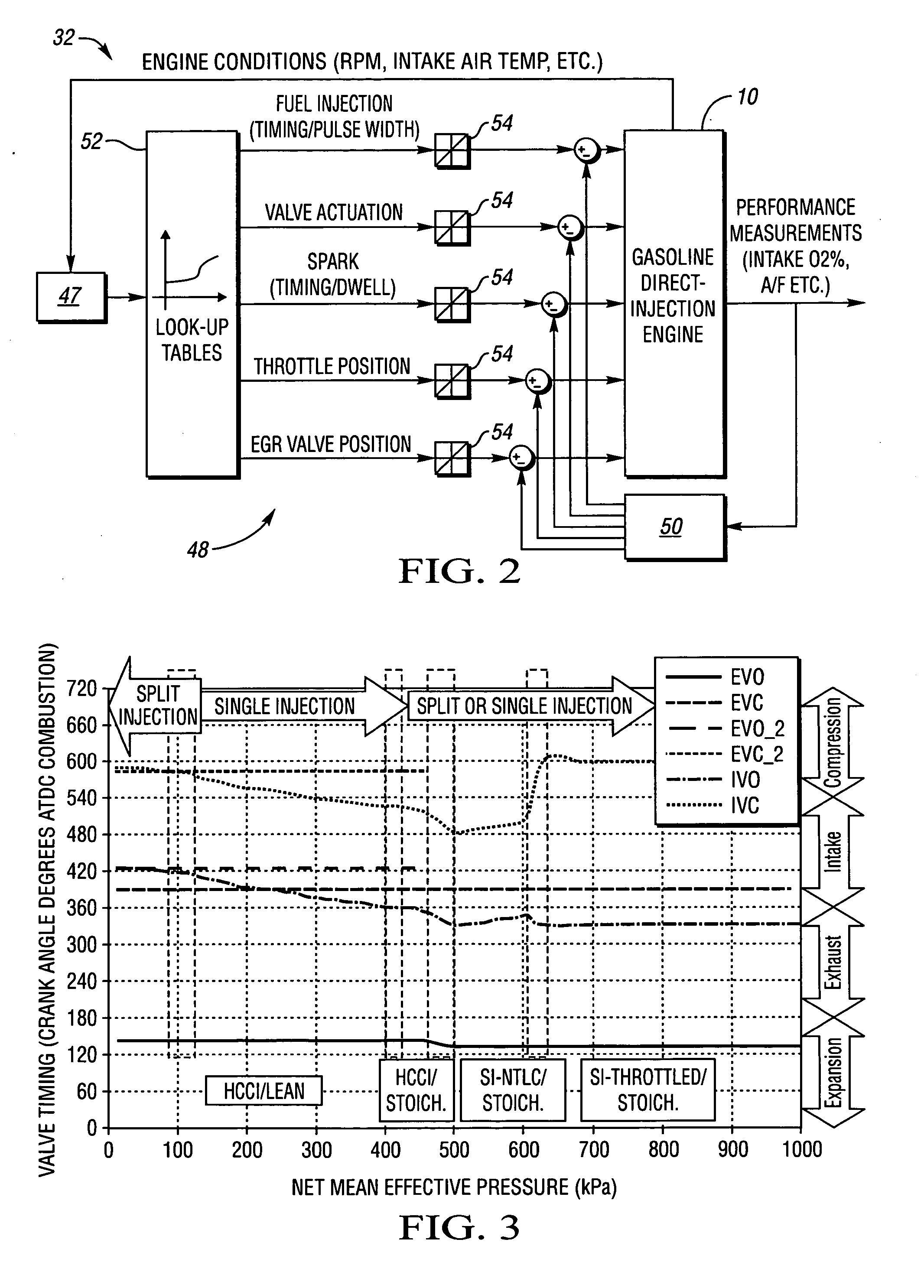
Valve and fueling strategy for operating a controlled auto-ignition four-stroke internal combustion engine
ActiveUS7021277B2Improve abilitiesReduce decreaseValve arrangementsElectrical controlCombustionOperating point
Part load operating point for a controlled auto-ignition four-stroke internal combustion engine is reduced without compromising combustion stability through load dependent valve controls and fueling strategies. Optimal fuel economy is achieved by employing negative valve overlap to trap and re-compress combusted gases below a predetermined engine load and employing exhaust gas re-breathing above the predetermined engine load. Split-injection fuel controls are implemented during low and intermediate part load operation whereas a single-injection fuel control is implemented during high part load operation. Split-injections are characterized by lean fuel / air ratios and single-injections are characterized by either lean or stoichiometric fuel / air ratios. Controlled autoignition is thereby enabled through an extended range of engine loads while maintaining acceptable combustion stability and emissions at optimal fuel economy.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
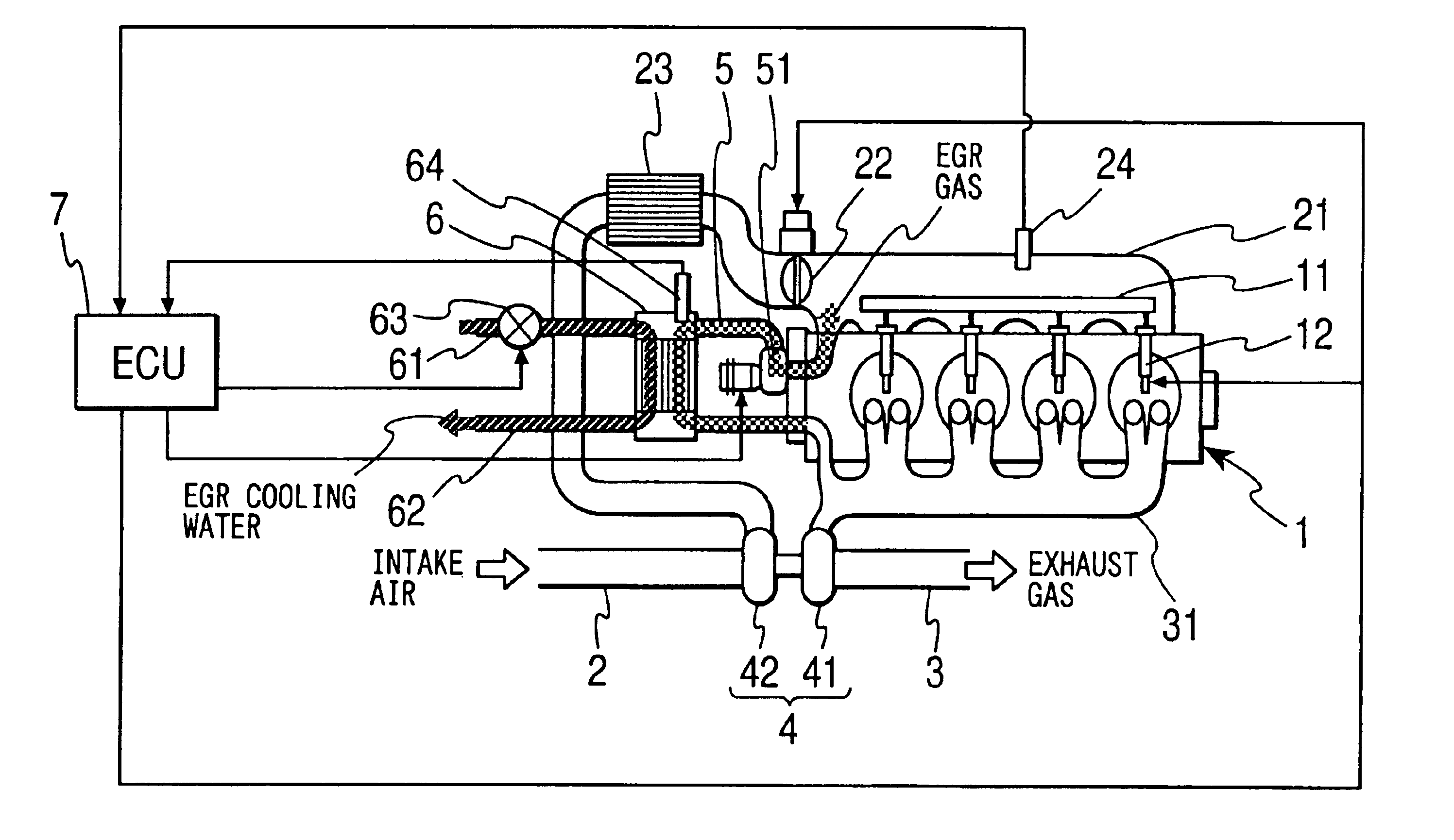
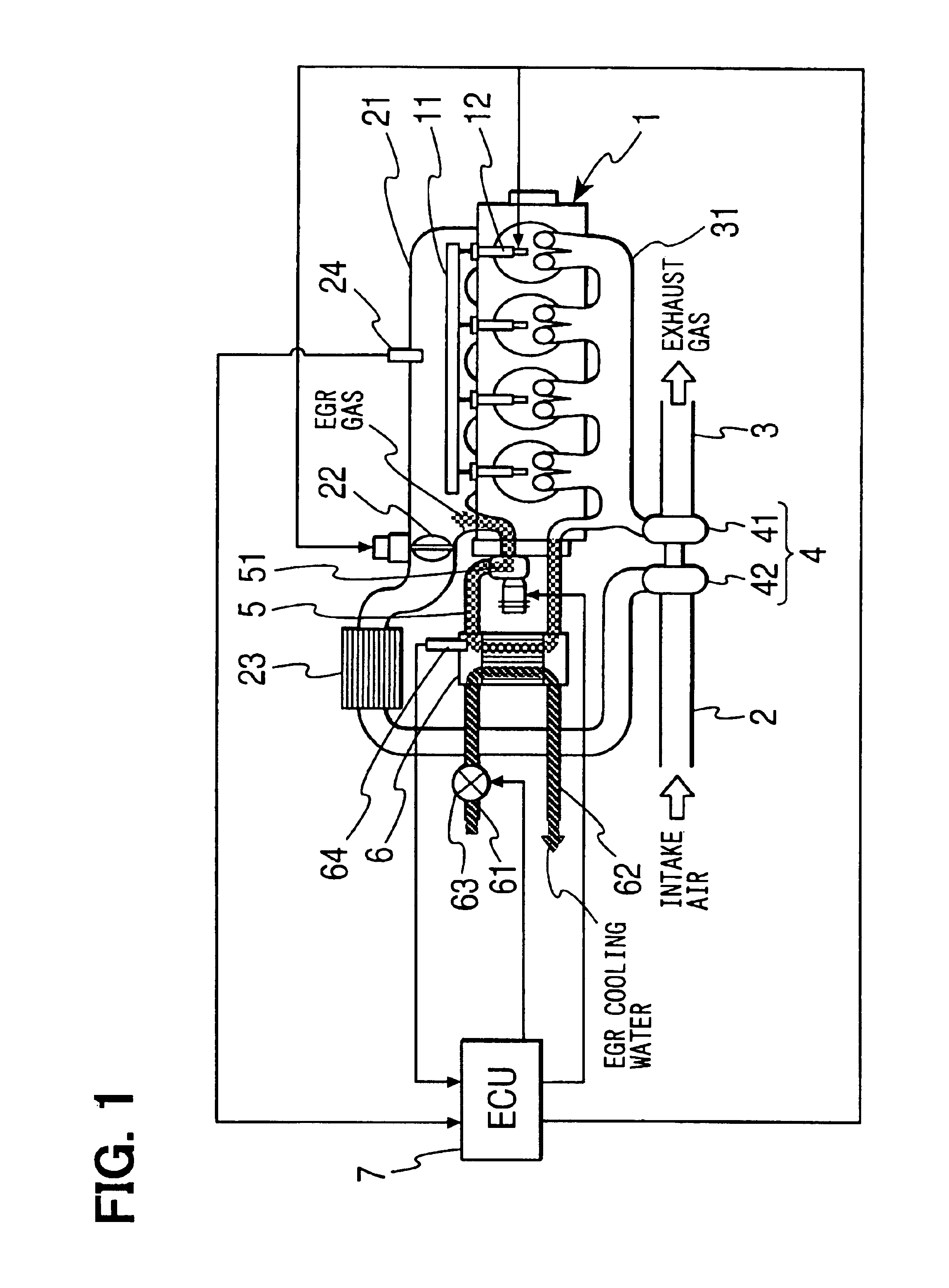
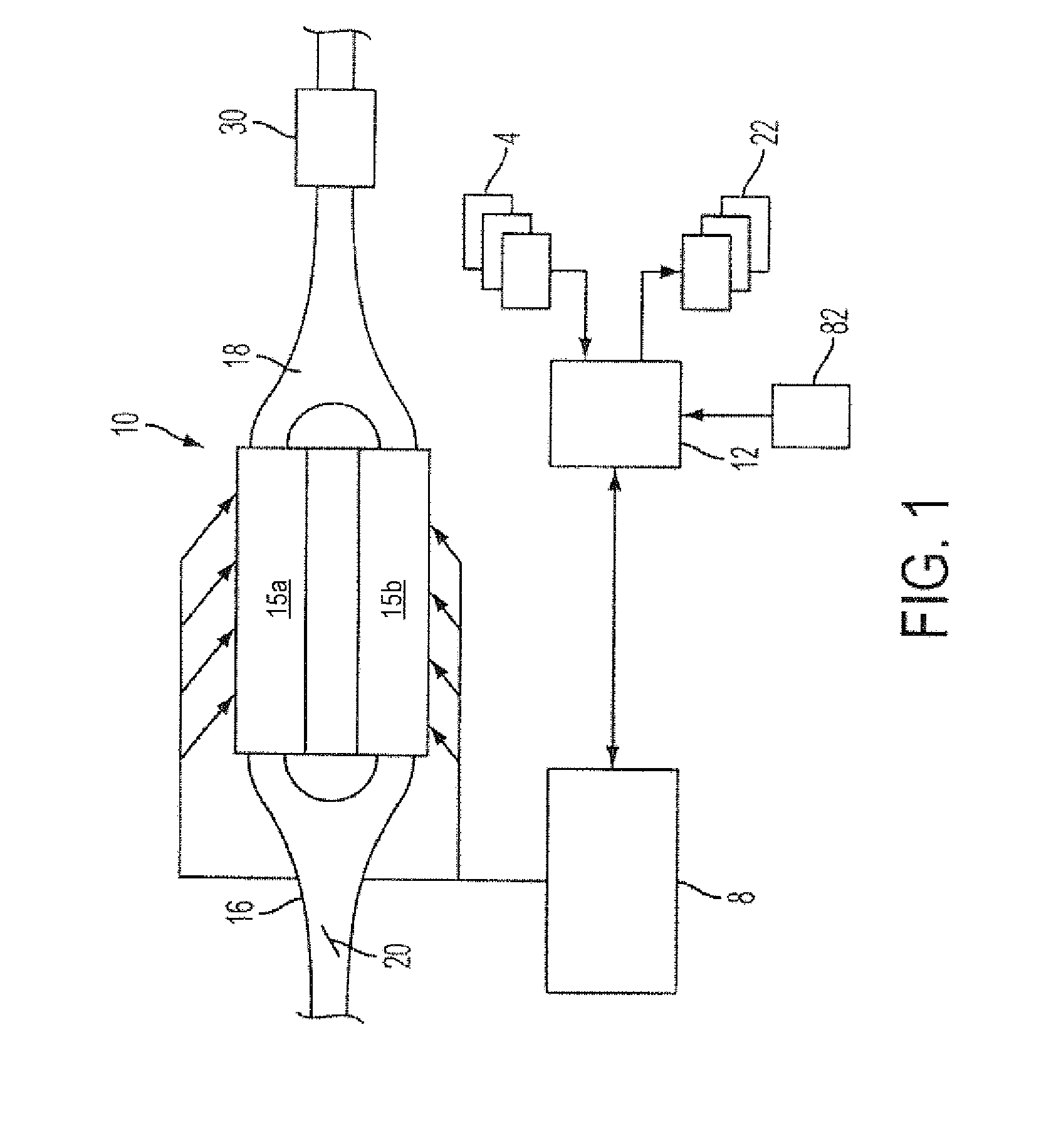
Exhaust gas recirculation system having cooler
InactiveUS6826903B2Improve heat transfer effectElectrical controlNon-fuel substance addition to fuelExhaust fumesExhaust gas recirculation
An exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) system of an internal combustion engine has an EGR cooler in an EGR passage connecting an exhaust manifold with an intake manifold. The EGR cooler cools EGR gas recirculated through the EGR passage. Cooling performance detecting means included in an electronic control unit (ECU) determines that cooling performance of the EGR cooler is degraded when intake pressure measured by an intake pressure sensor is lower than a normal intake pressure by at least a predetermined value. When the degradation of the cooling performance is detected, cooling performance regeneration controlling means included in the ECU increases the temperature inside the EGR cooler by heating the exhaust gas to eliminate soot or unburned hydrocarbon by oxidization. Thus, the cooling performance of the EGR cooler is regenerated.
Owner:DENSO CORP
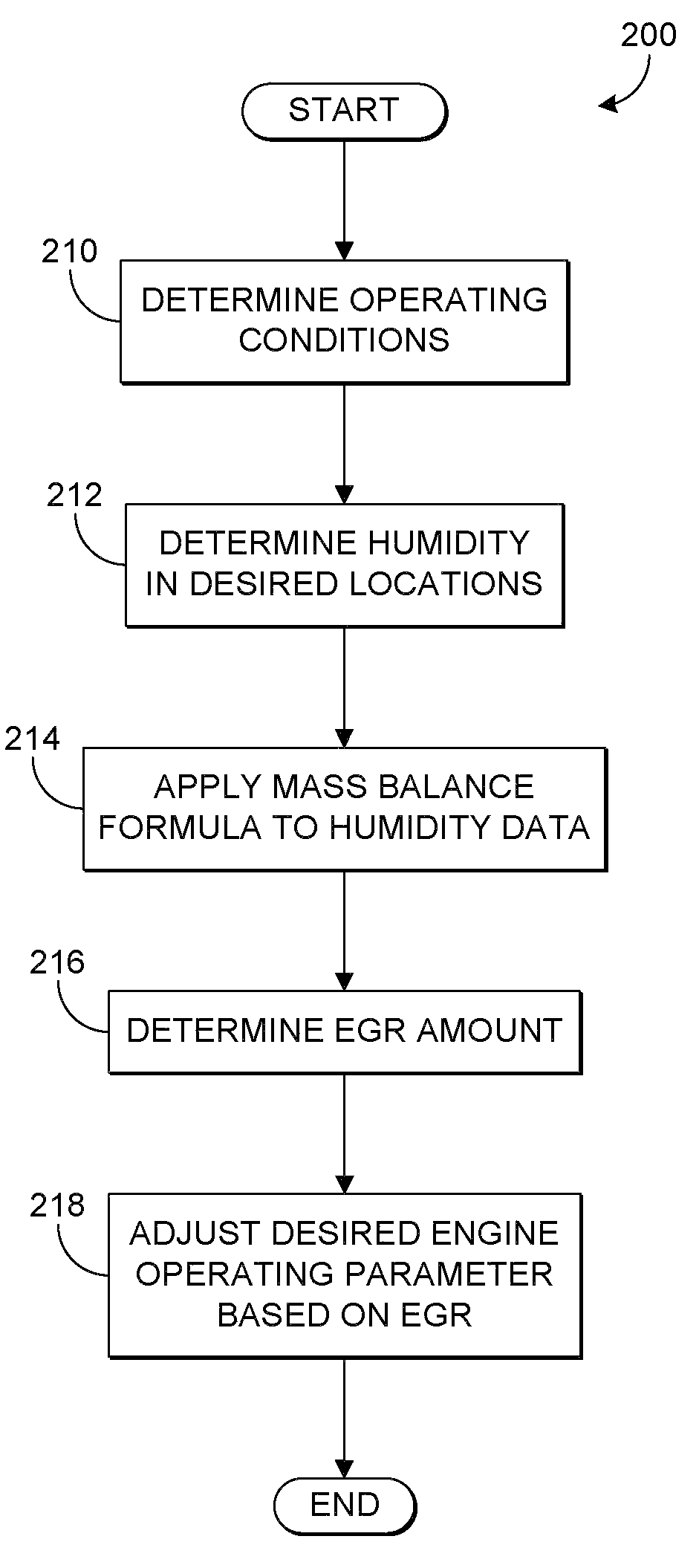
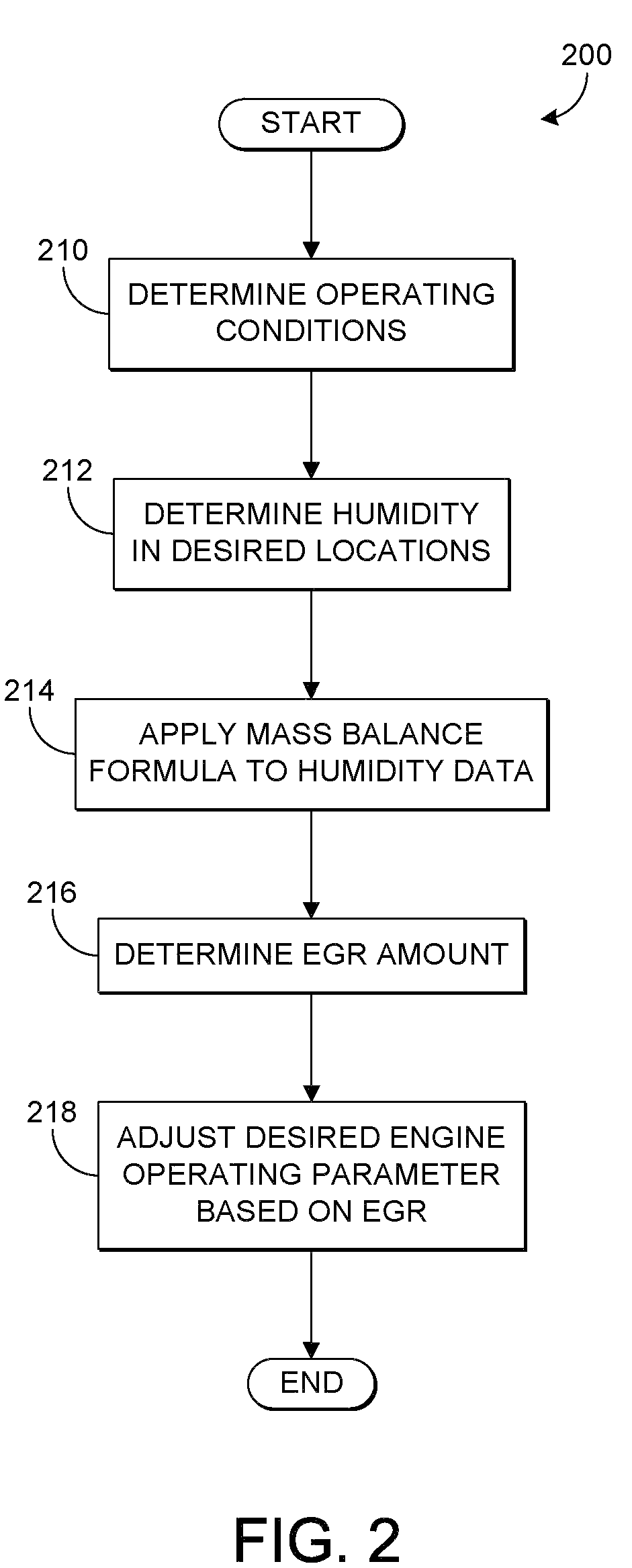
EGR detection via humidity detection
InactiveUS7715976B1Amount of EGRAccurately determineElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesExhaust gas recirculationMoisture sensor
Various systems and methods are described for controlling an engine in a vehicle which includes an exhaust passage and an exhaust gas recirculation system. One example method comprises adjusting an engine operating parameter based on an exhaust gas recirculation amount, the exhaust gas recirculation amount based on a first humidity and a second humidity, the first humidity generated from a first humidity sensor at a first location and the second humidity generated from a second humidity sensor located in the exhaust passage of the engine.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
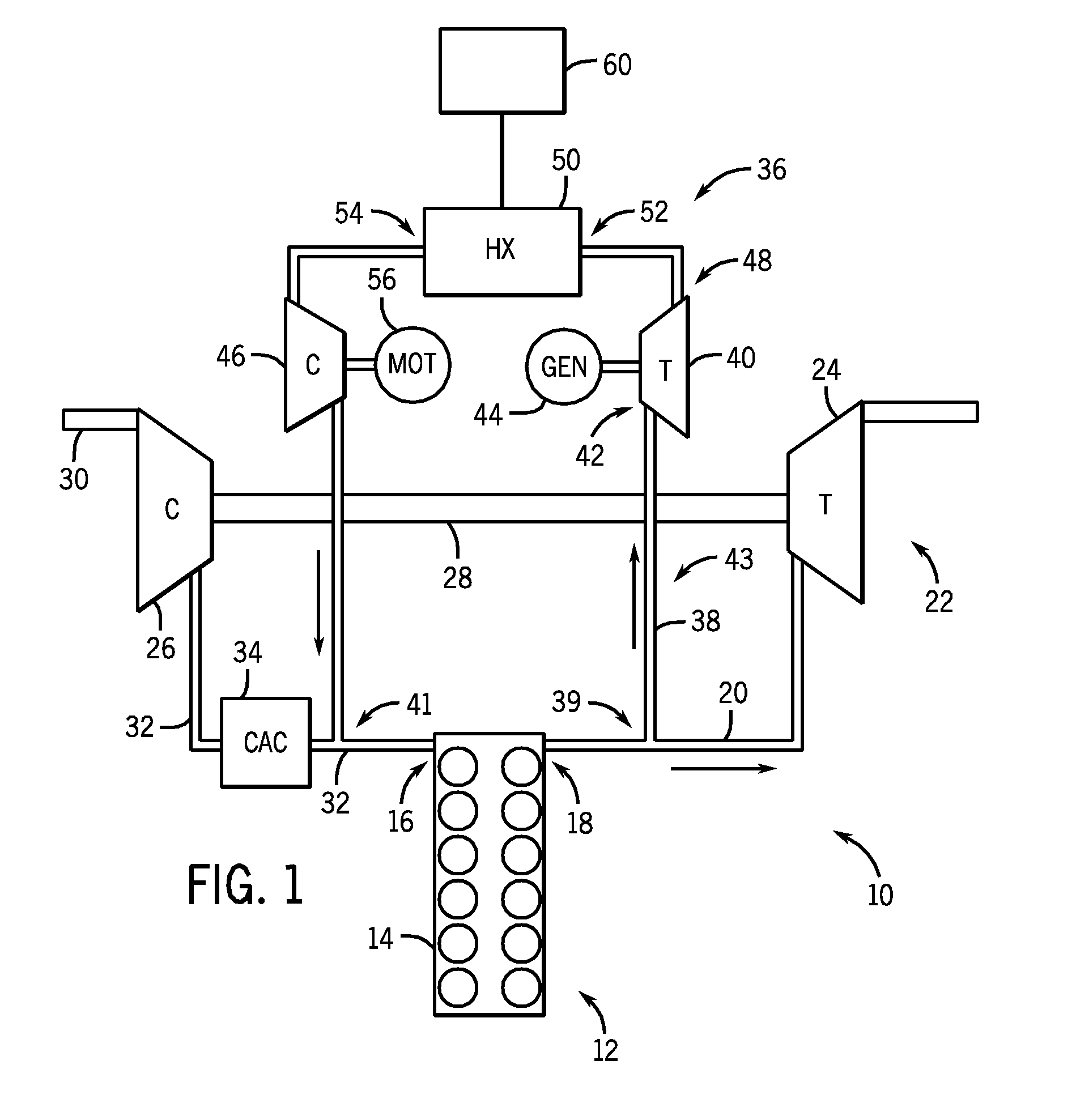
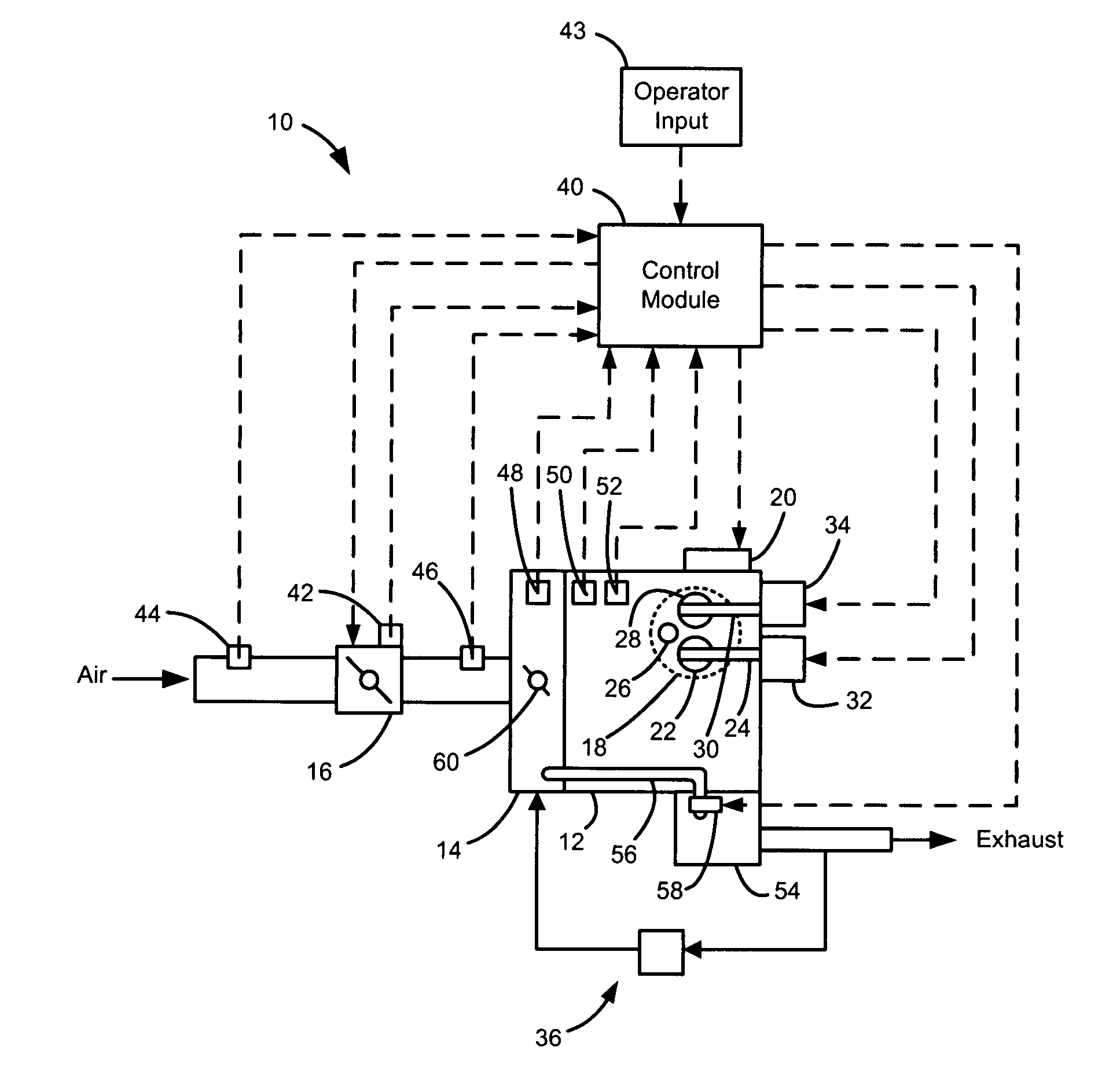
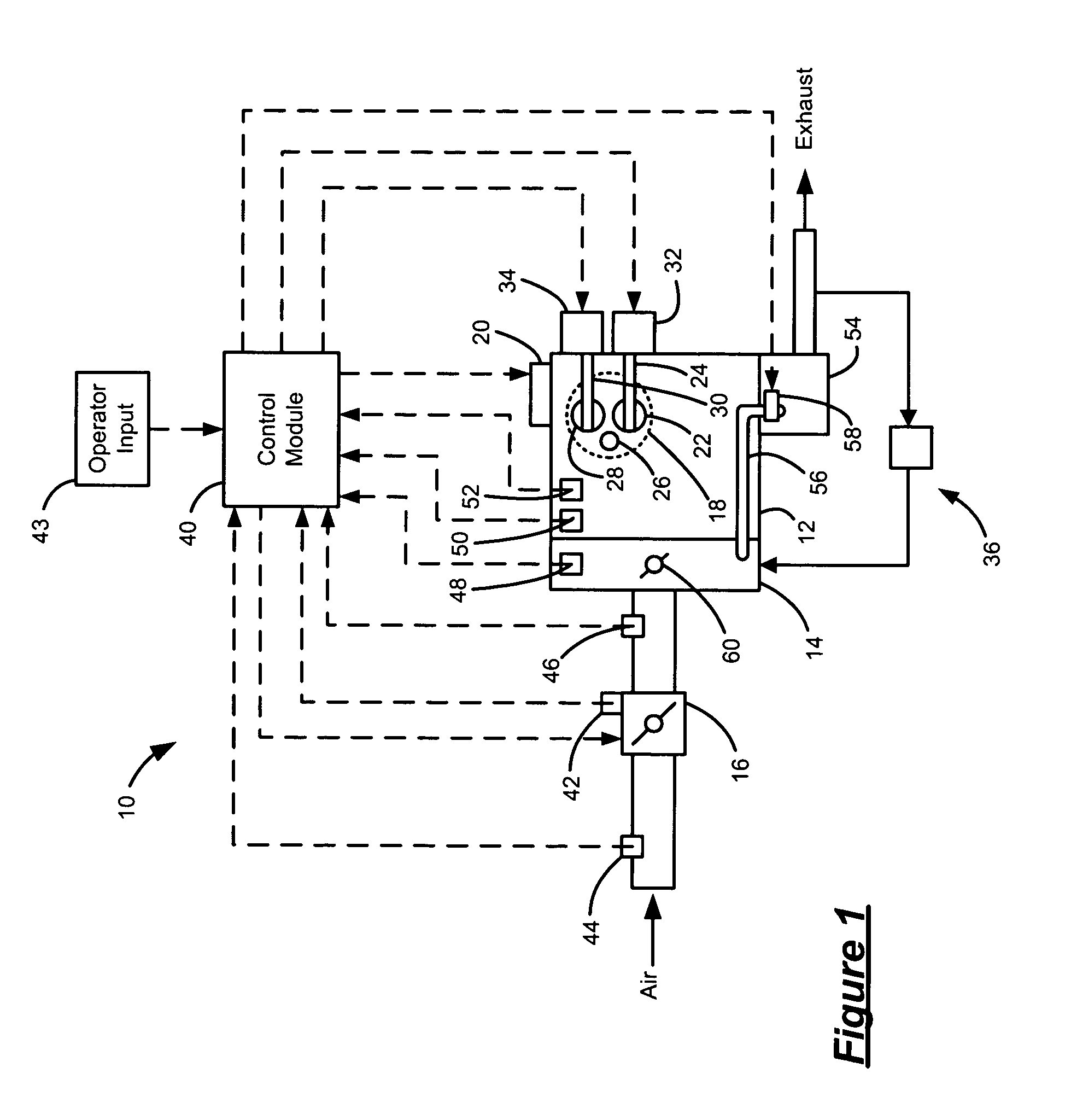
EGR system with dedicated EGR cylinders
Improved exhaust gas recirculation system and methods that use one or more of the engine's cylinders as dedicated EGR cylinders. All of the exhaust from the dedicated EGR cylinders is recirculated back to the engine intake. Thus, the EGR rate is constant, but the EGR mass flow may be controlled by adjusting the air-fuel ratio of the dedicated EGR cylinders or by using various variable valve timing techniques.
Owner:SOUTHWEST RES INST
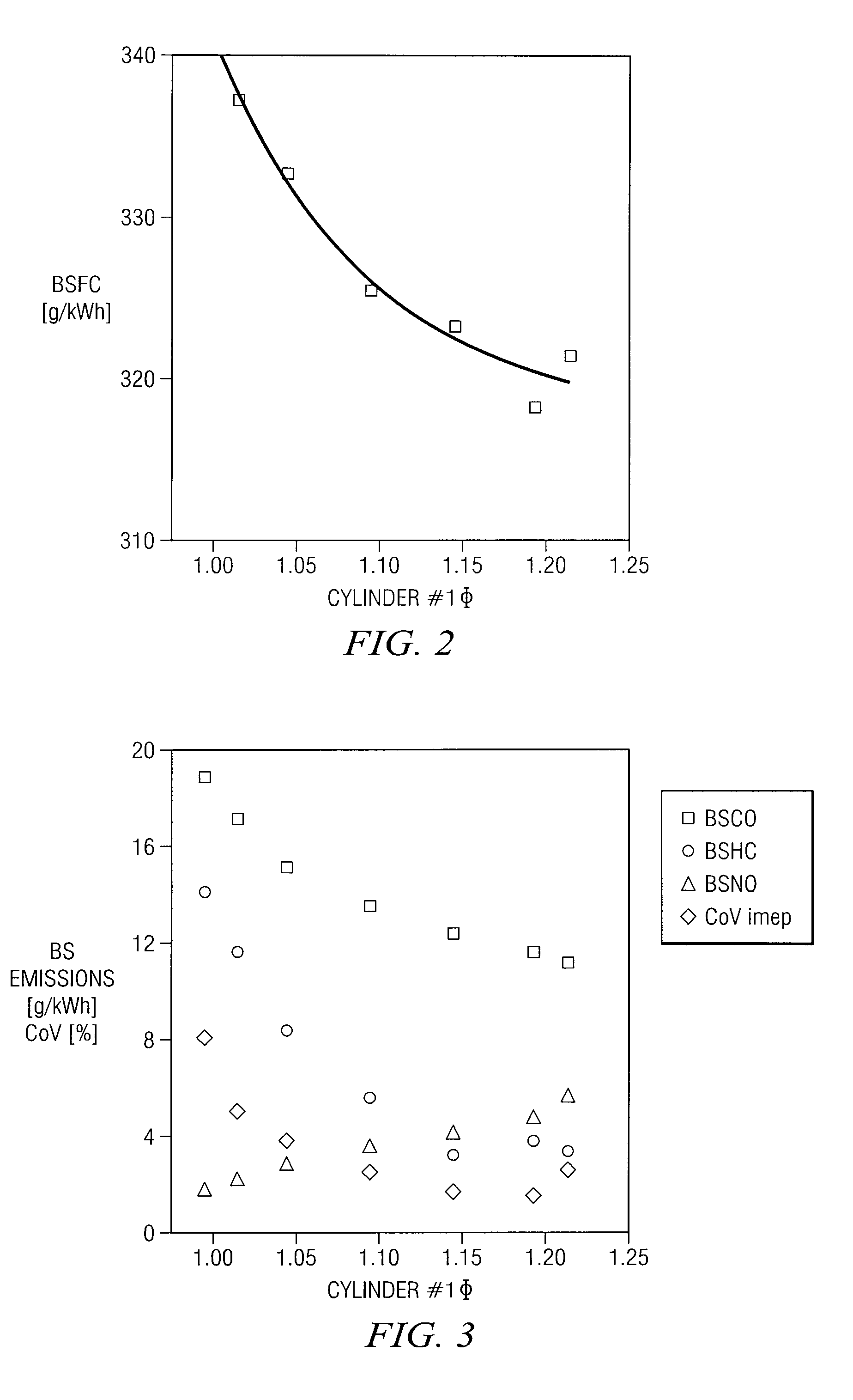
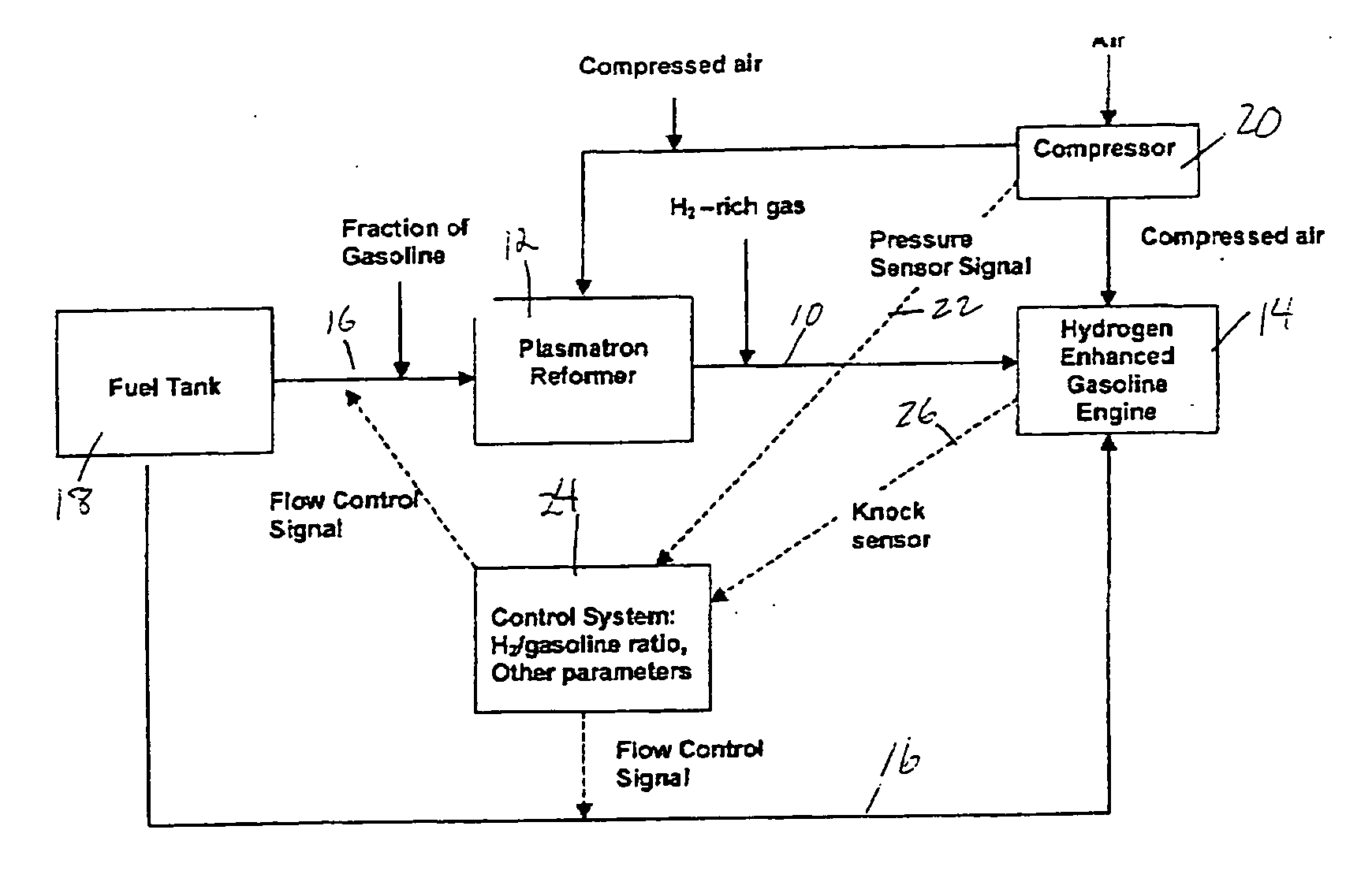
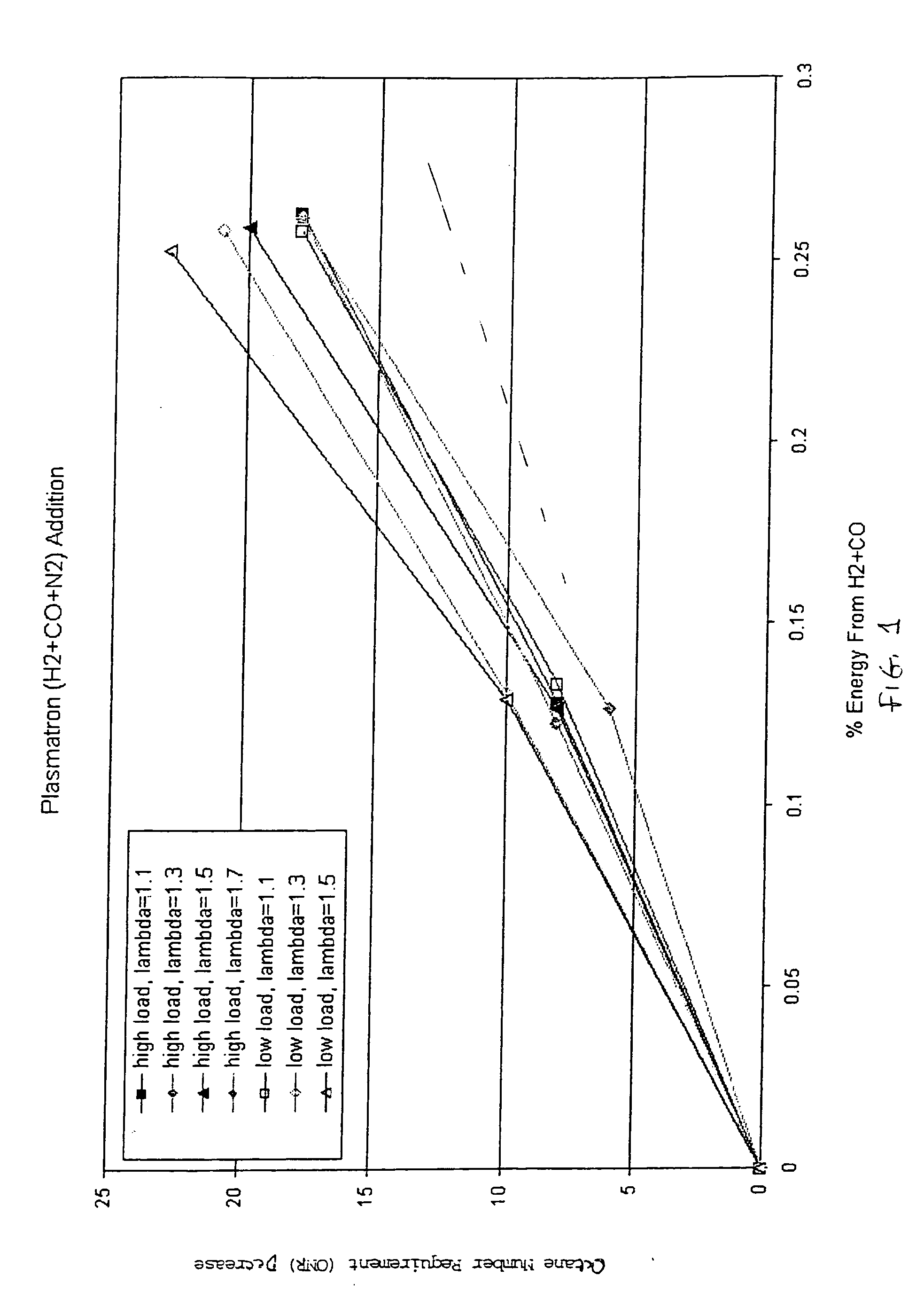
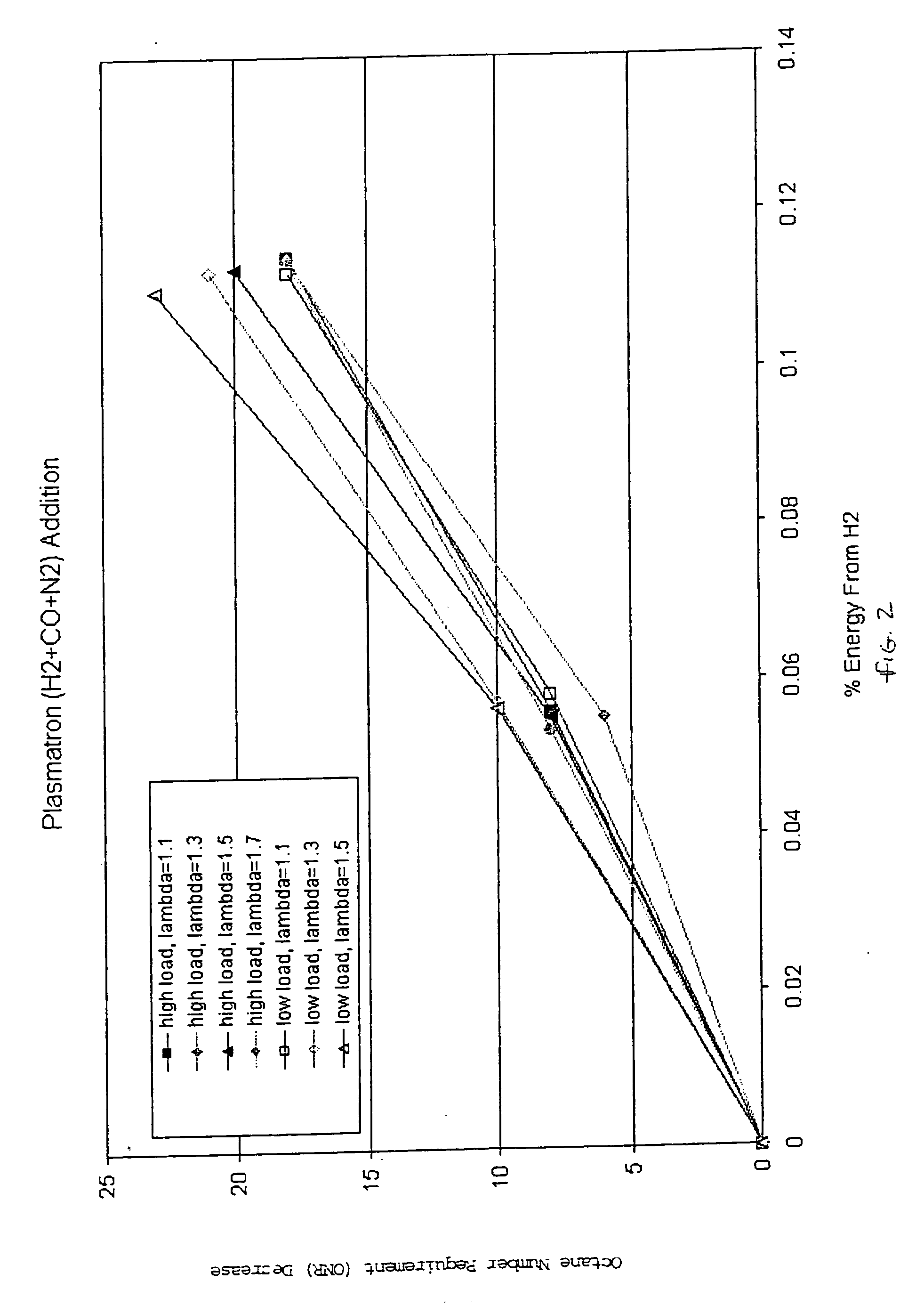
Hydrogen and carbon monoxide enhanced knock resistance in spark ignition gasoline engines
InactiveUS20060075991A1Good anti-knock performanceGreater spark retardElectrical controlNon-fuel substance addition to fuelHydrogenCombustion
A method for reducing required octane number and a spark ignition gasoline engine system with hydrogen-enhanced knock resistance. The method for reducing required octane number of gasoline needed to prevent knock includes the addition of hydrogen or hydrogen-rich gas containing carbon monoxide to gasoline. Octane number can be improved by 5 or more for a hydrogen energy fraction of 10%. The spark ignition gasoline engine system includes a spark ignition gasoline engine and a source of gasoline and hydrogen or hydrogen-rich gas. Apparatus is provided to supply the gasoline and the hydrogen or hydrogen-rich gas to the engine at a varying hydrogen or hydrogen-rich gas to gasoline ratio selected both to prevent knock and to ensure a desired level of combustion stability throughout a full range of engine operation. The engine system may be normally aspirated or boosted; the compression ratio may be high such as greater than 11 or below 11, and EGR may be added. The hydrogen or hydrogen-rich gas to gasoline ratio may be controlled as a function of boost pressure, torque, engine speed, or air / fuel mixture ratio.
Owner:HEYWOOD JOHN B +4
Premixed charge compression ignition engine with optimal combustion control
InactiveUS6915776B2Operate efficiently and effectivelyOvercome deficienciesElectrical controlNon-fuel substance addition to fuelCombustion noiseControl signal
A premixed charge compression ignition engine, and a control system, is provided which effectively initiates combustion by compression ignition and maintains stable combustion while achieving extremely low nitrous oxide emissions, good overall efficiency and acceptable combustion noise and cylinder pressures. The present engine and control system effectively controls the combustion history, that is, the time at which combustion occurs, the rate of combustion, the duration of combustion and / or the completeness of combustion, by controlling the operation of certain control variables providing temperature control, pressure control, control of the mixture's autoignition properties and equivalence ratio control. The combustion control system provides active feedback control of the combustion event and includes a sensor, e.g. pressure sensor, for detecting an engine operating condition indicative of the combustion history, e.g. the start of combustion, and generating an associated engine operating condition signal. A processor receives the signal and generates control signals based on the engine operating condition signal for controlling various engine components to control the temperature, pressure, equivalence ratio and / or autoignition properties so as to variably control the combustion history of future combustion events to achieve stable, low emission combustion in each cylinder and combustion balancing between the cylinders.
Owner:CUMMINS INC
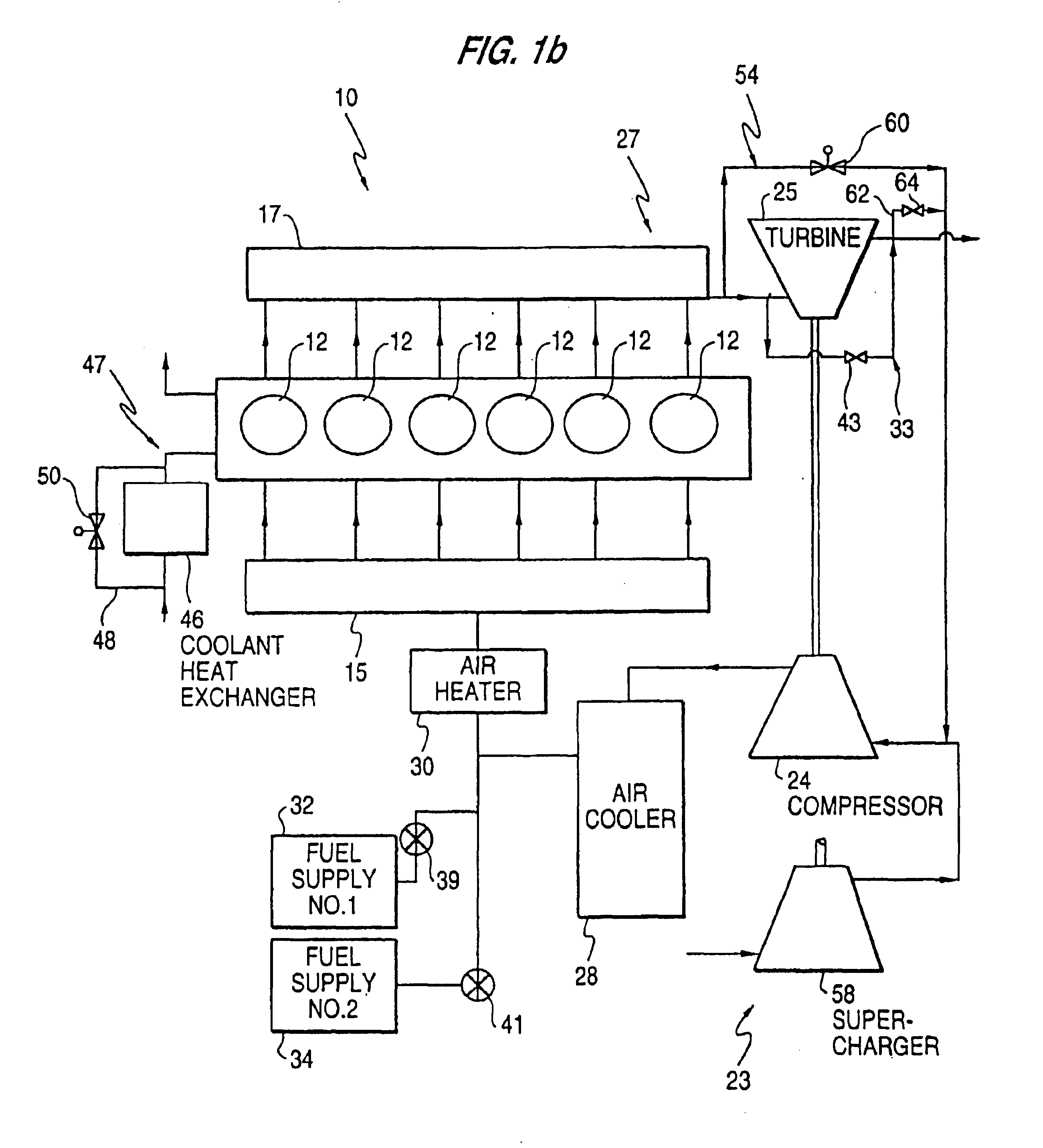
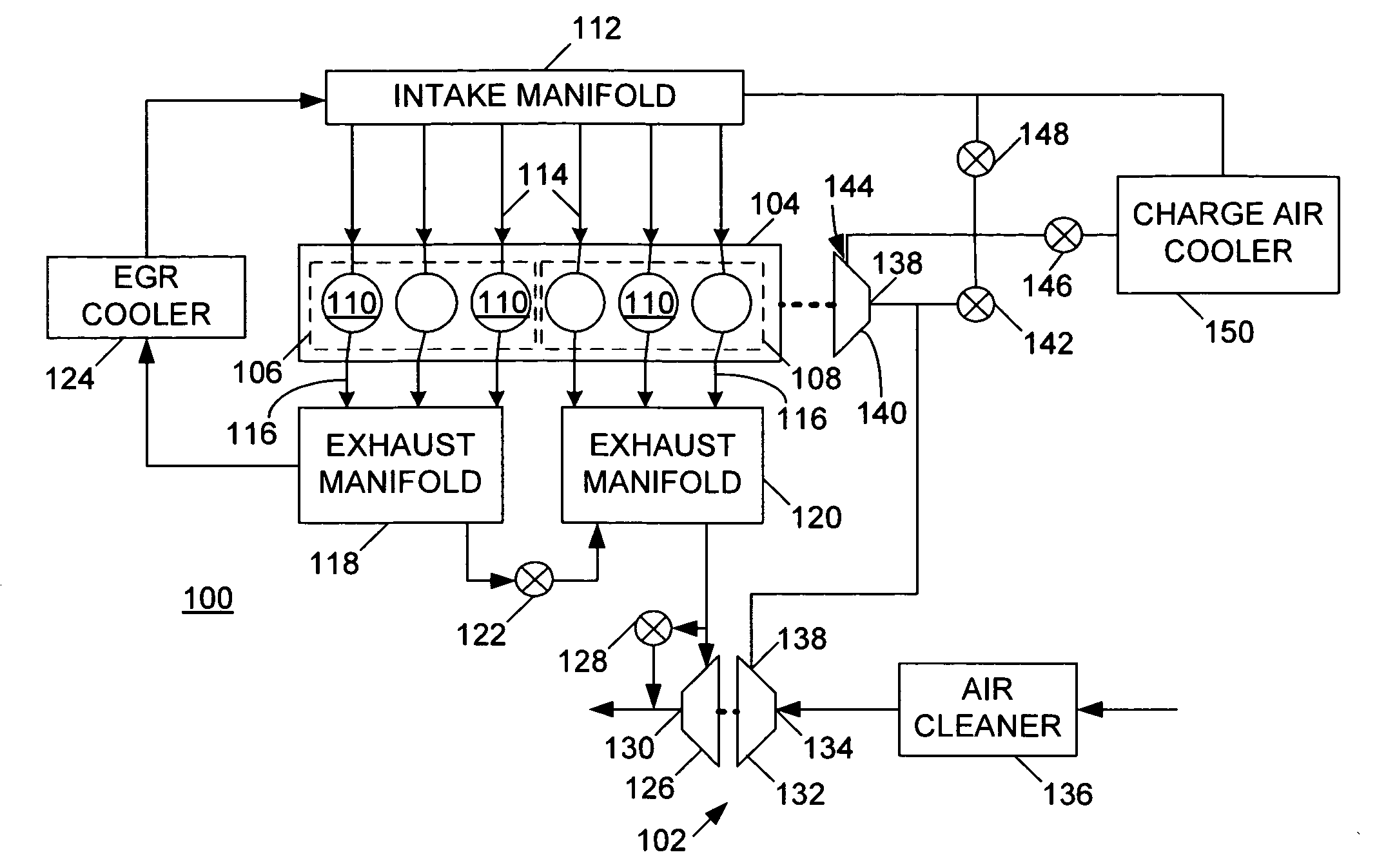
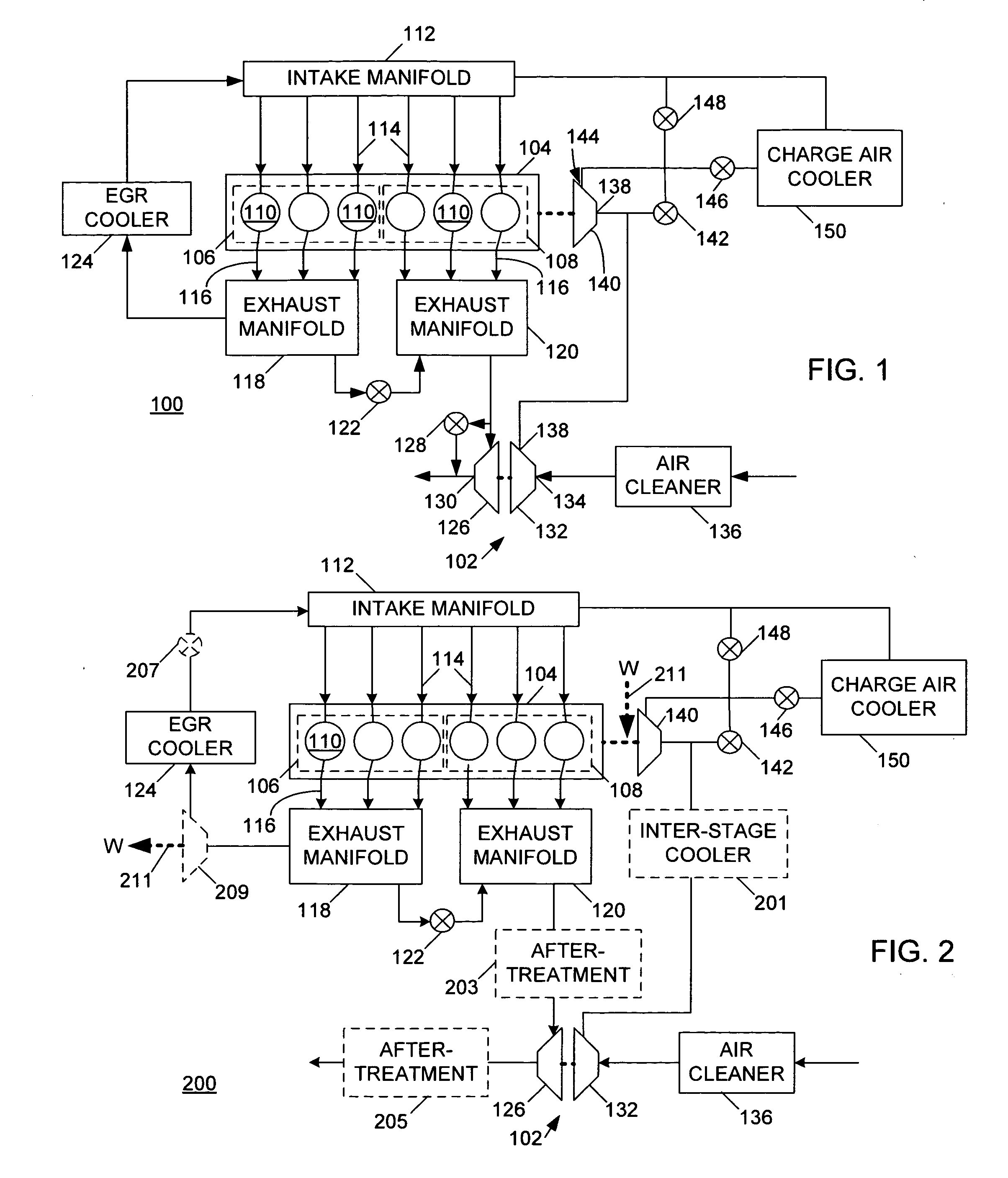
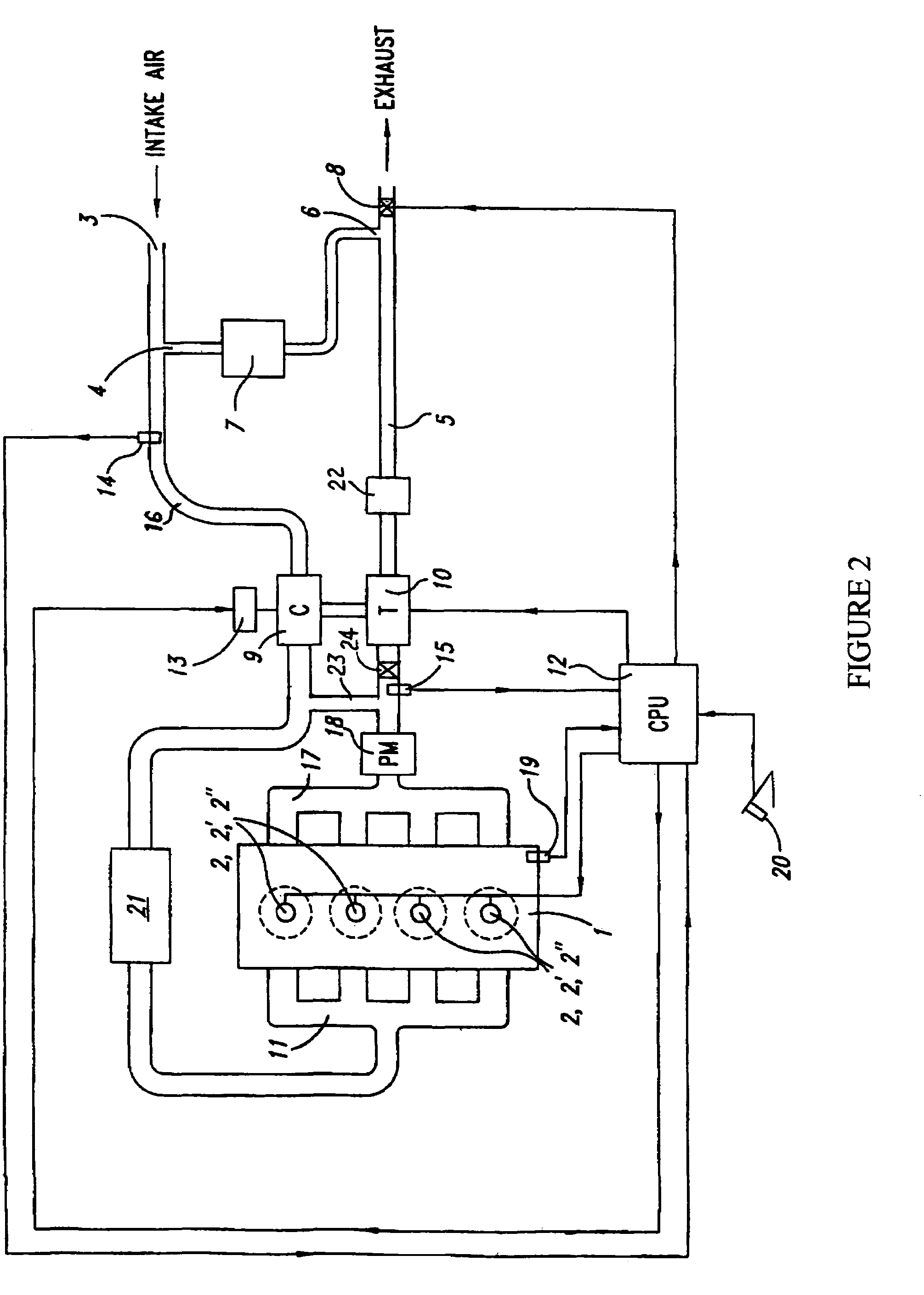
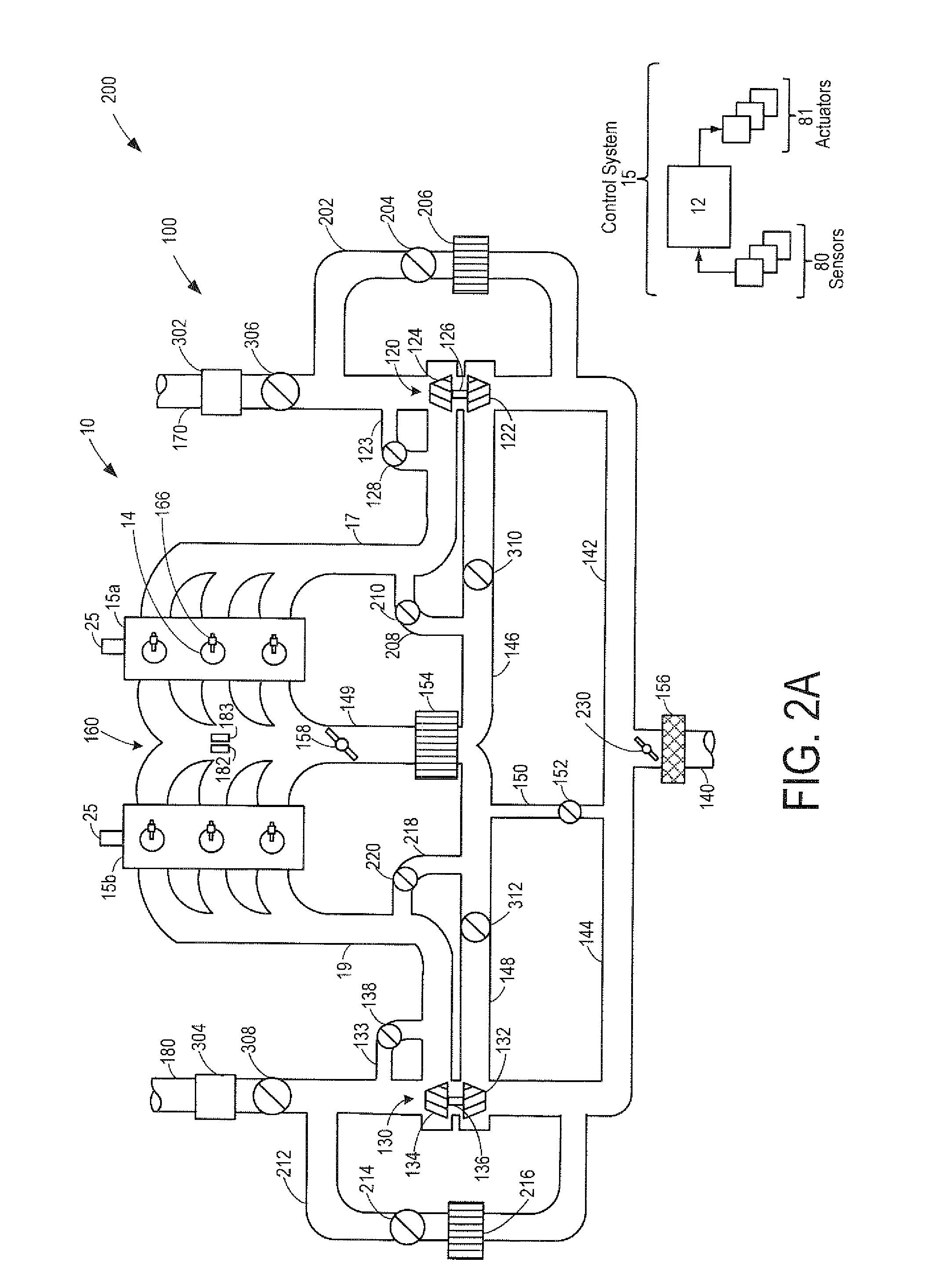
Constant EGR rate engine and method
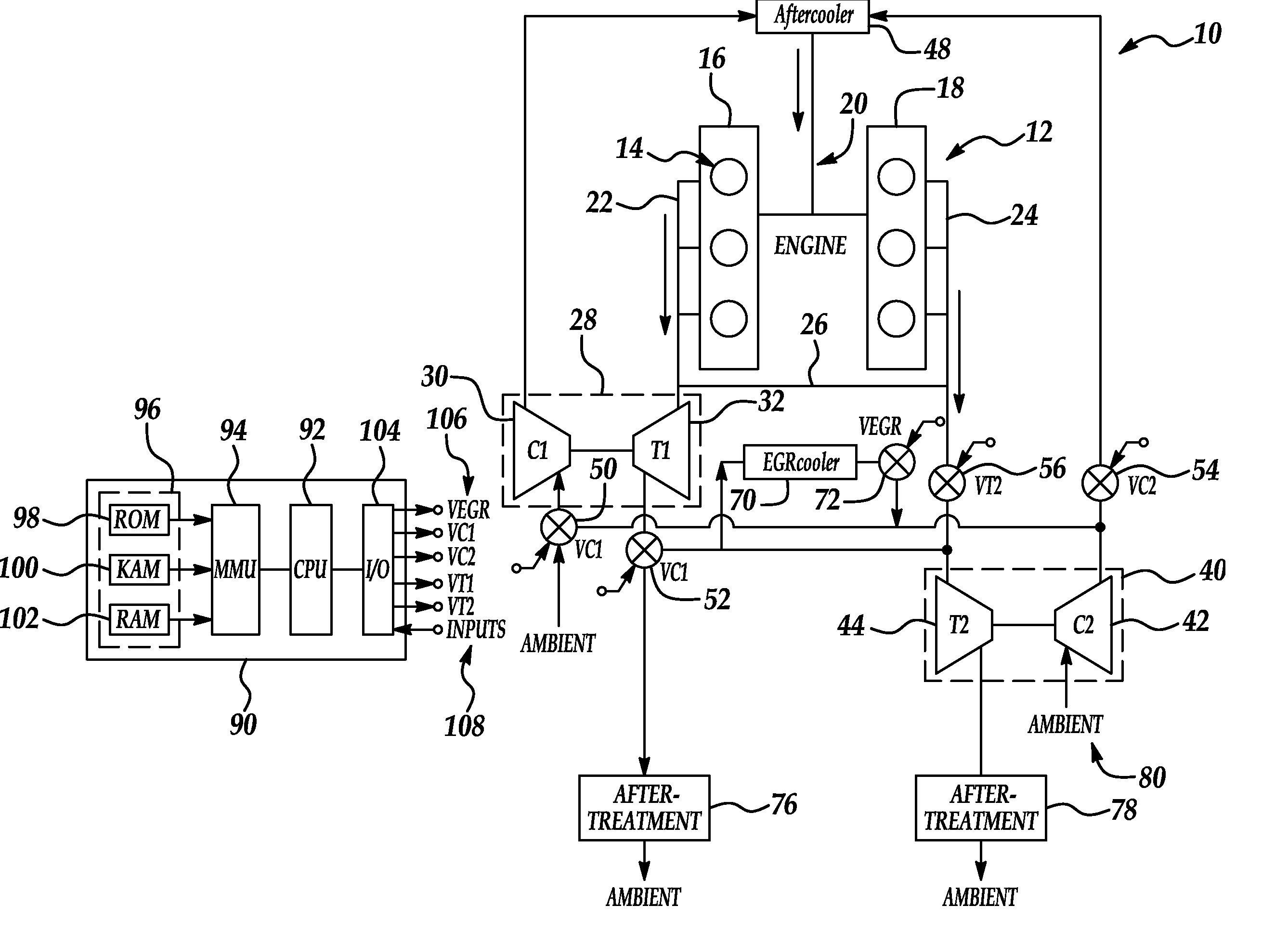
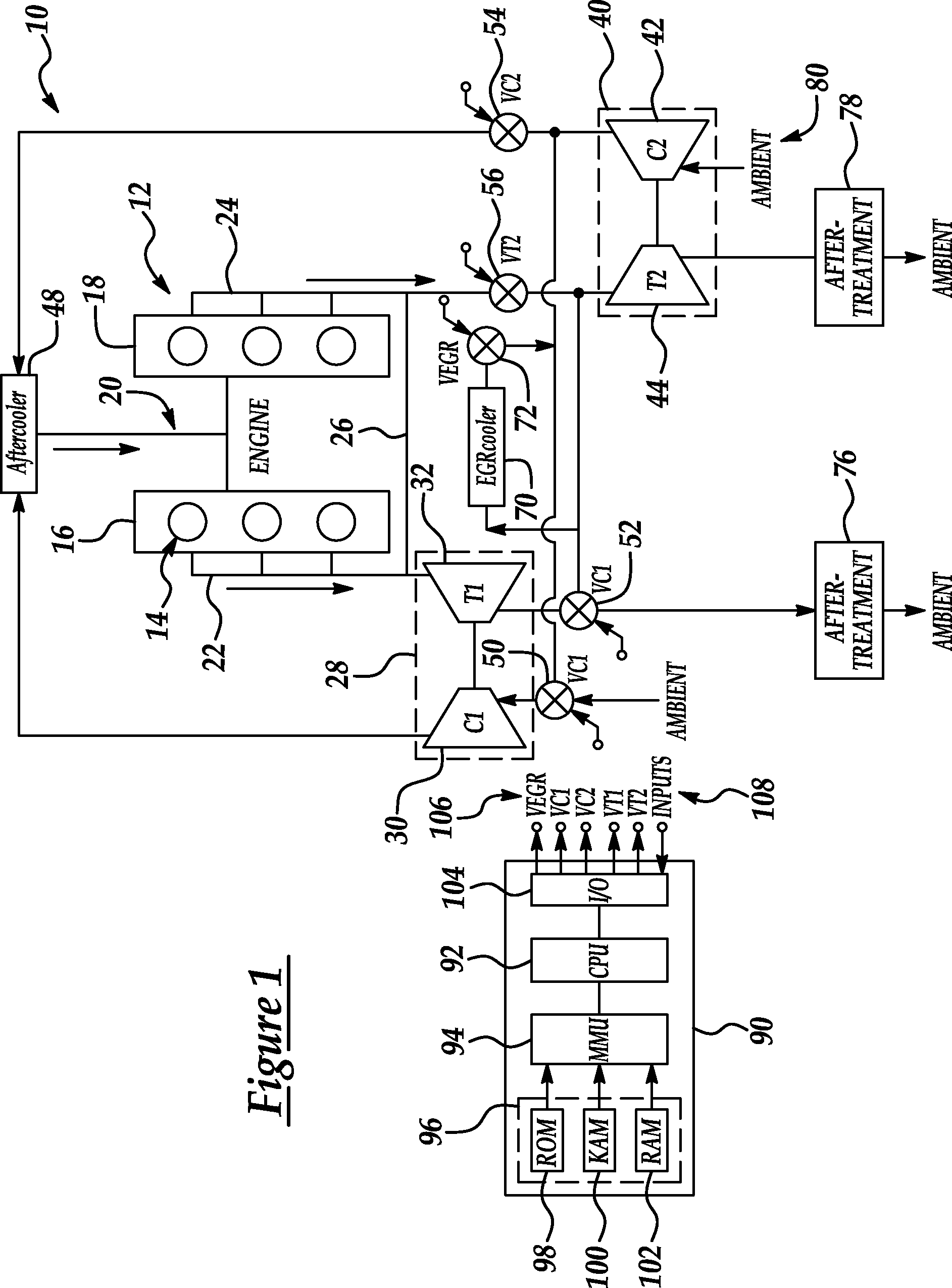
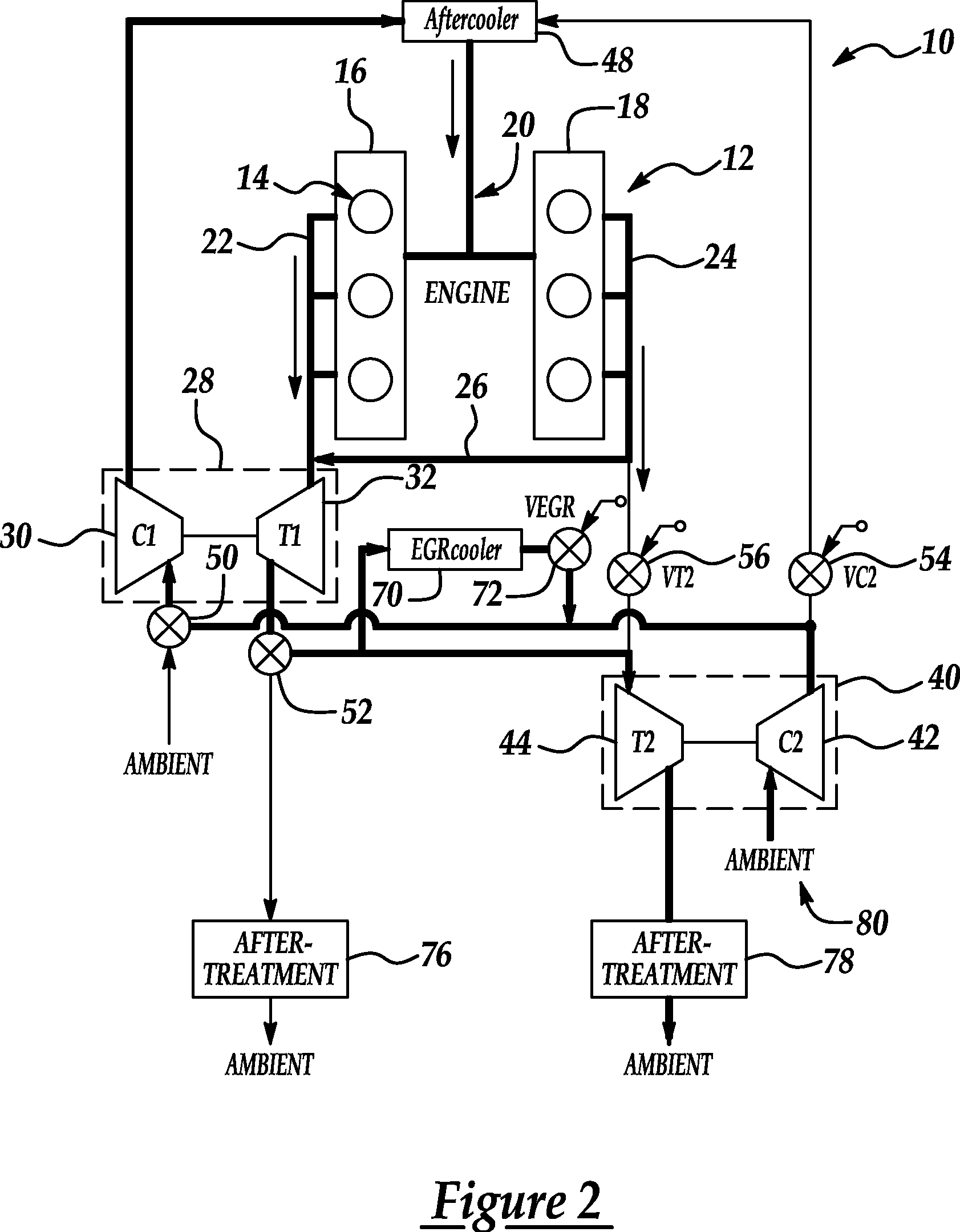
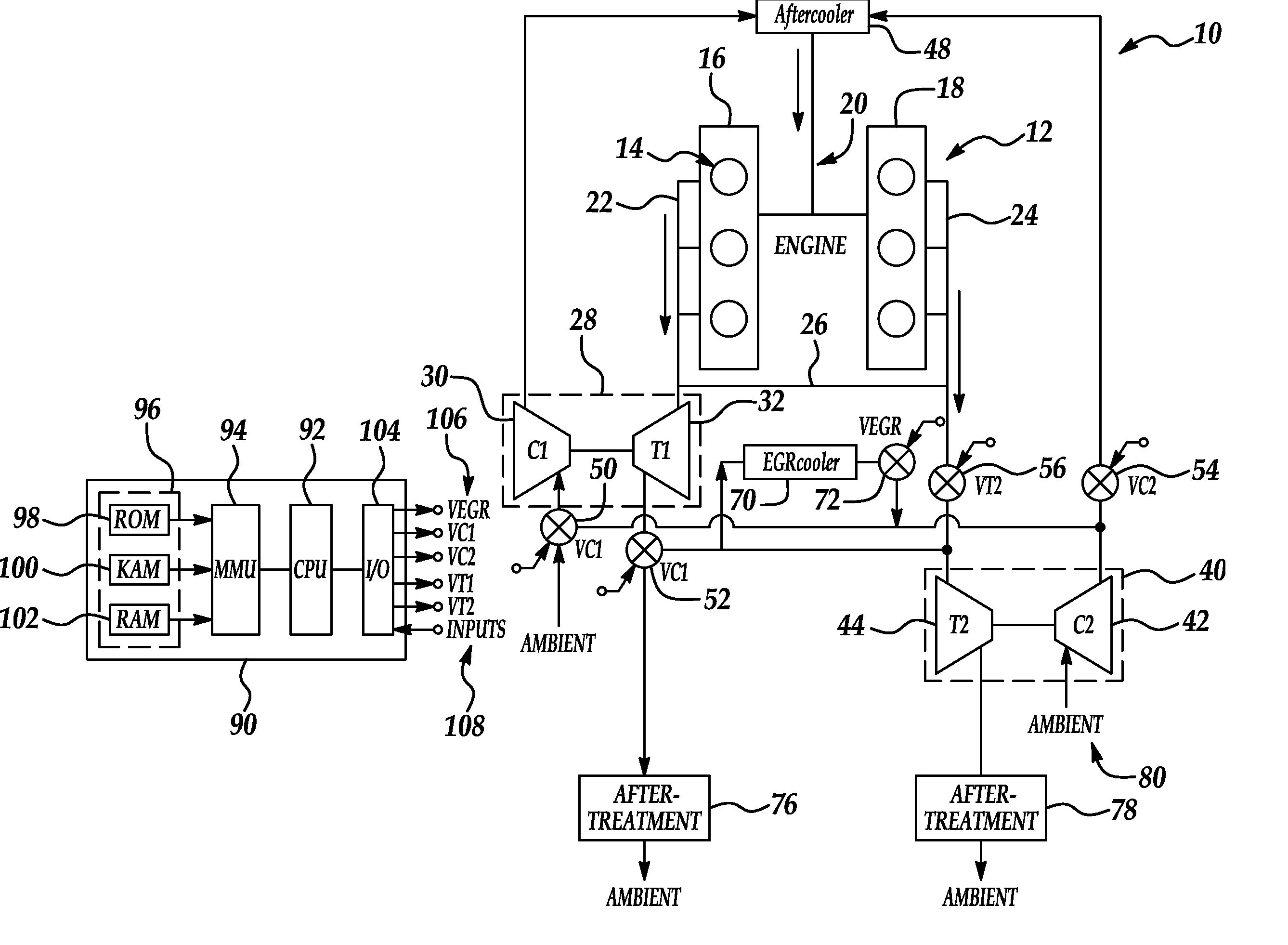
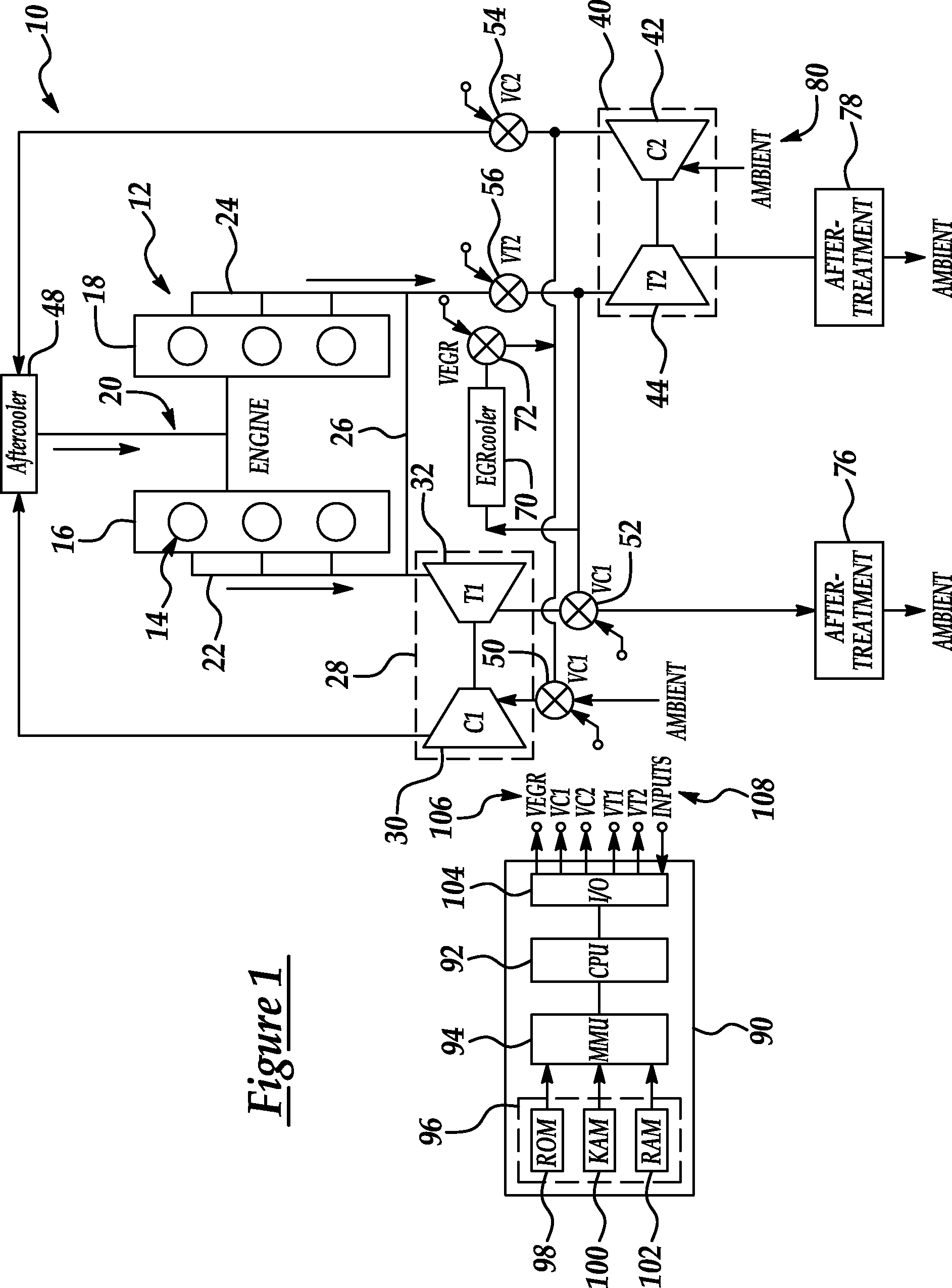
ActiveUS20070175215A1Non-fuel substance addition to fuelInternal combustion piston enginesExhaust valveTurbocharger
An internal combustion engine (100) includes a first exhaust manifold (120), and a second exhaust manifold (118) fluidly connected to the first exhaust manifold (120) through an exhaust valve (122). An exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) cooler (124) constantly fluidly connects the second exhaust manifold (118) with an intake manifold (112). A turbocharger (102) has a turbine (126) in fluid communication with the first exhaust manifold (120), and a compressor (132) in fluid communication with a supercharger (140). A charge air cooler (150) fluidly connects the supercharger (140) with the intake manifold (112).
Owner:INT ENGINE INTPROP CO LLC
Marine hulls and drives
InactiveUS7984684B2Improve power densityNo coolingHybrid vehiclesInternal combustion piston enginesTravel modeCombustion
Owner:HINDERKS MITJA VICTOR
System and method for cooling a combustion gas charge
ActiveUS7721543B2Non-fuel substance addition to fuelInternal combustion piston enginesCombustionExhaust fumes
The present invention relates to a system and method for cooling a combustion gas charge prior. The combustion gas charge may include compressed intake air, exhaust gas, or a mixture thereof. An evaporator is provided that may then receive a relatively high temperature combustion gas charge and discharge at a relatively lower temperature. The evaporator may be configured to operate with refrigeration cycle components and / or to receive a fluid below atmospheric pressure as the phase-change cooling medium.
Owner:SOUTHWEST RES INST
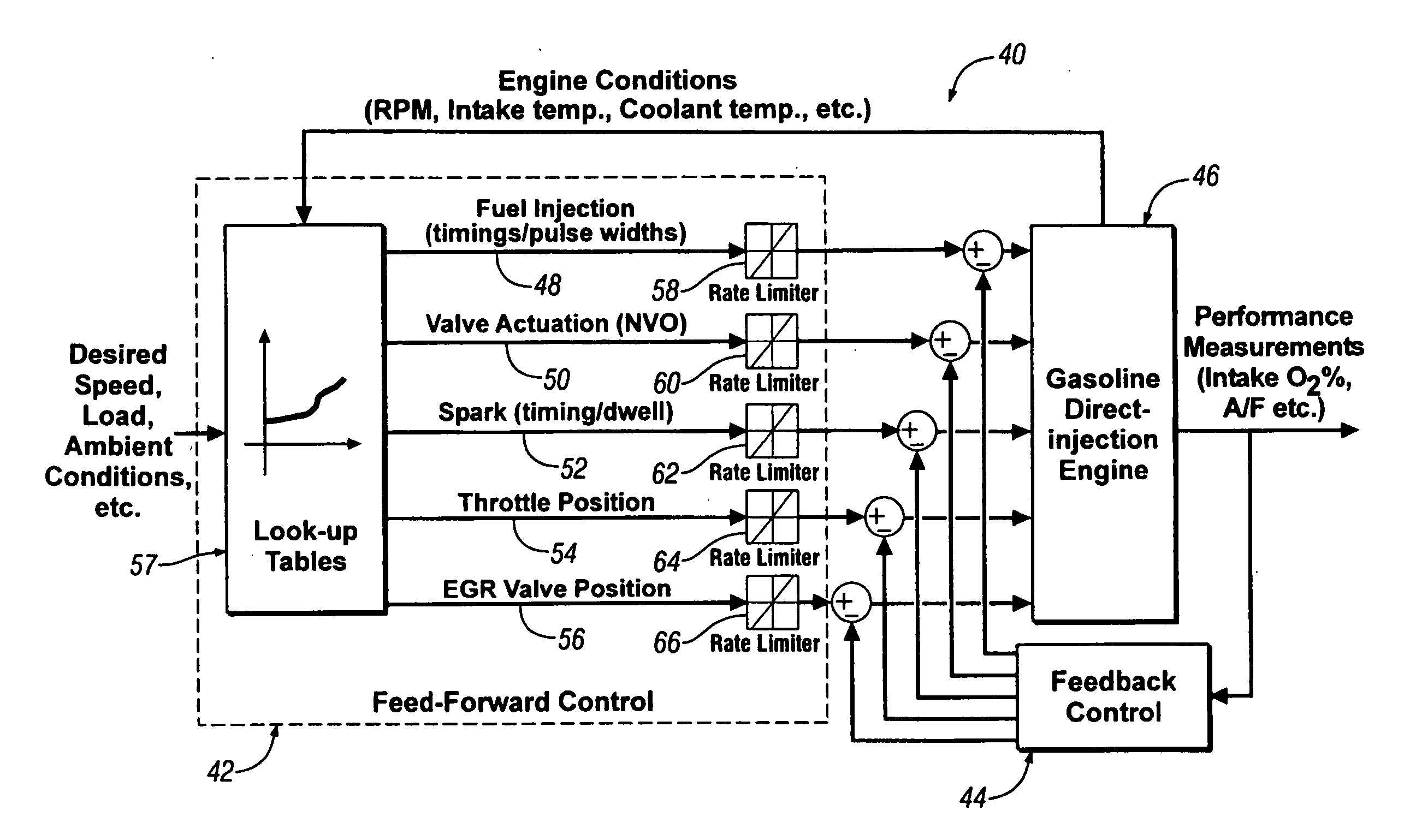
Method of HCCI and SI combustion control for a direct injection internal combustion engine
InactiveUS20060243241A1Improve fuel economyRobust controlValve arrangementsElectrical controlHomogeneous charge compression ignitionGasoline direct injection
The present invention relates to methods for robust controlled auto-ignition and spark ignited combustion controls in gasoline direct-injection engines, including transients, using either exhaust re-breathing or a combination of exhaust re-compression and re-breathing valve strategy. These methods are capable of enabling engine operation with either lean of stoichiometric or stoichiometric air / fuel ratio for oxides of nitrogen (NOx) control, with varying exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) rates and throttle valve positions for knock control, and with a combination of homogeneous charge compression ignition (HCCI) and spark ignition (SI) combustion modes to optimize fuel economy over a wide range of engine operating conditions.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Series/parallel turbochargers and switchable high/low pressure EGR for internal combustion engines
InactiveUS20060021347A1Promote generationSufficient handling capacityElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesTurbochargerHigh pressure
Systems and methods for turbocharging an internal combustion engine include operating two turbochargers in a series configuration for a first operating region and a parallel configuration for a second operating region. Systems and methods for controlling exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) in a turbocharged internal combustion engine provide low pressure EGR upstream of a compressor inlet for a first operating region and high pressure EGR downstream of a compressor outlet for a second operating range to further improve turbocharger operating margin and overall efficiency.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Control methods for low emission internal combustion system
InactiveUS7681394B2Cost-effectiveMaintaining NOx emissionsElectrical controlNon-fuel substance addition to fuelCombustion systemEngineering
Owner:US EPA OFFICE OF GENERAL COUNSEL UNITED STATES OF AMERICA THE
Method for load transient control between lean and stoichiometric combustion modes of direct-injection engines with controlled auto-ignition combustion
InactiveUS20060196469A1Electrical controlNon-fuel substance addition to fuelStable stateHomogeneous charge compression ignition
A method is provided for control of a direct-injection engine operated with controlled auto-ignition (HCCI) during load transient operations between modes of lean combustion low load (HCCI / Lean) and stiochiometric combustion medium load (HCCI / Stoich.). The method includes 1) operating the engine at steady state, within a homogeneous charge compression-ignition (HCCI) load range, with fuel-air-exhaust gas mixtures at predetermined conditions, for each speed and load, and controlling the engine during changes of operating mode between one to another of the HCCI / Stoich. medium load mode and the HCCI / Lean lower load mode by synchronizing change rates of predetermined controlled inputs to the current engine fueling change rate.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Series/parallel turbochargers and switchable high/low pressure EGR for internal combustion engines
InactiveUS7165403B2Promote generationImproved vehicle launchElectrical controlNon-fuel substance addition to fuelTurbochargerExternal combustion engine
Systems and methods for turbocharging an internal combustion engine include operating two turbochargers in a series configuration for a first operating region and a parallel configuration for a second operating region. Systems and methods for controlling exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) in a turbocharged internal combustion engine provide low pressure EGR upstream of a compressor inlet for a first operating region and high pressure EGR downstream of a compressor outlet for a second operating range to further improve turbocharger operating margin and overall efficiency.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
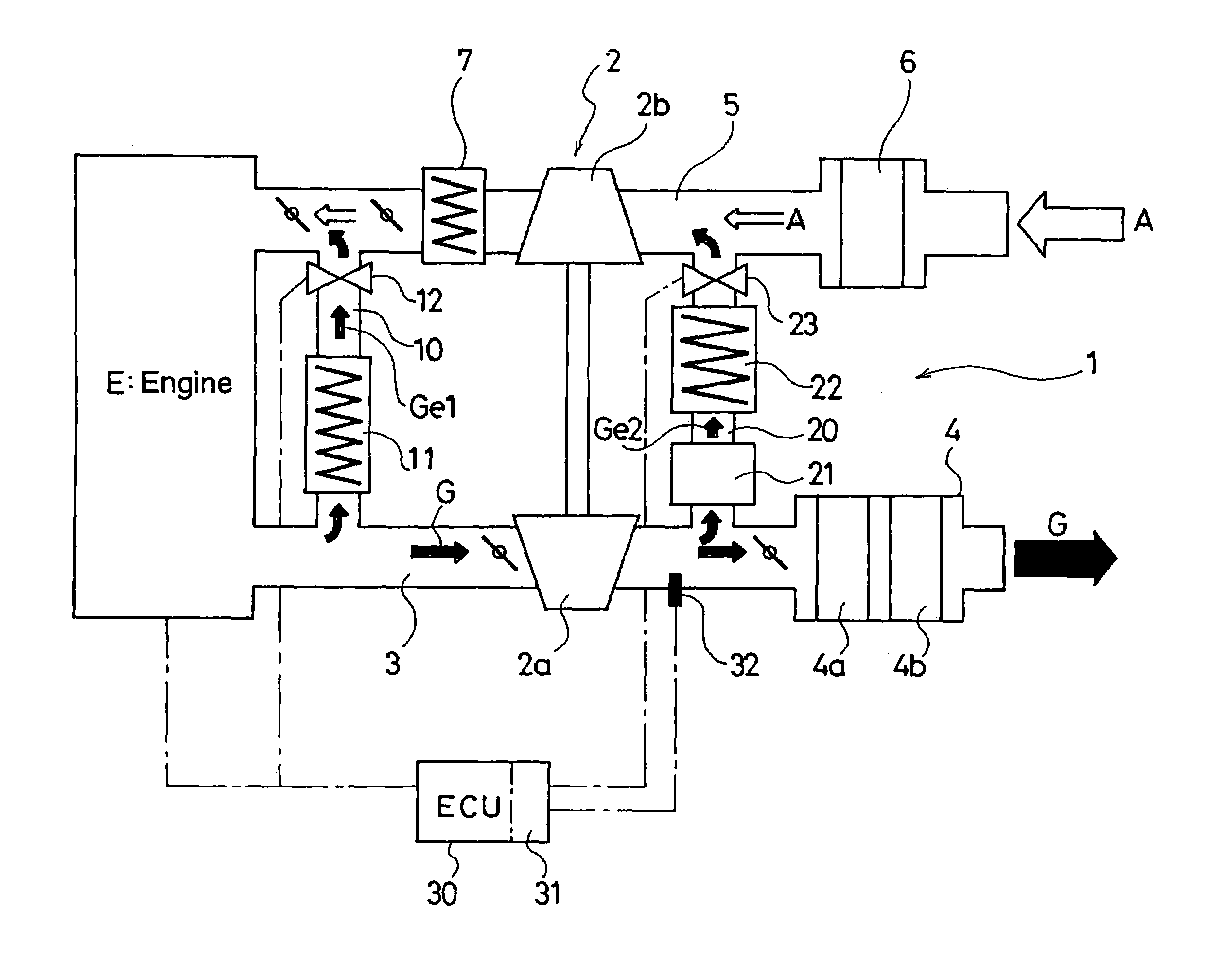
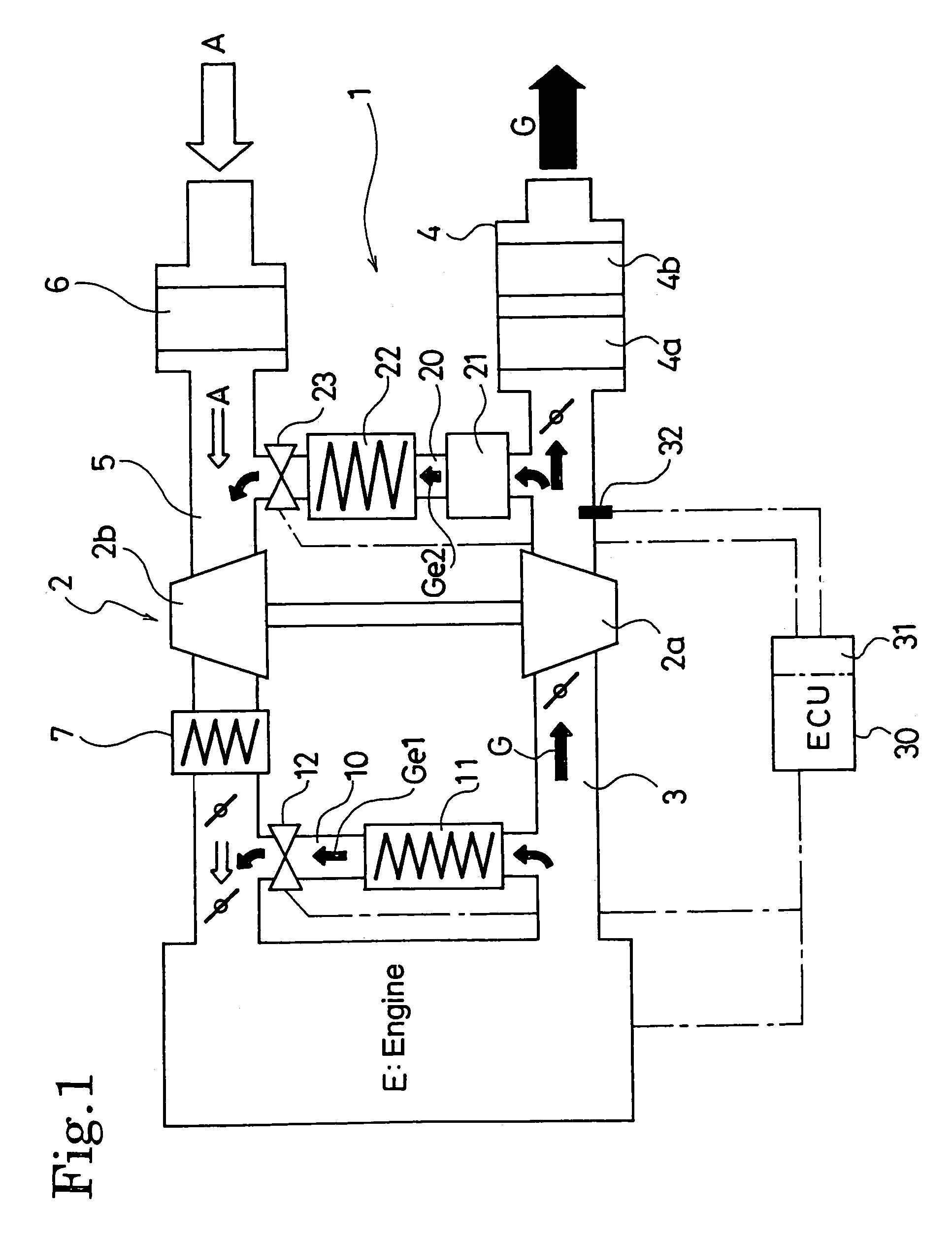
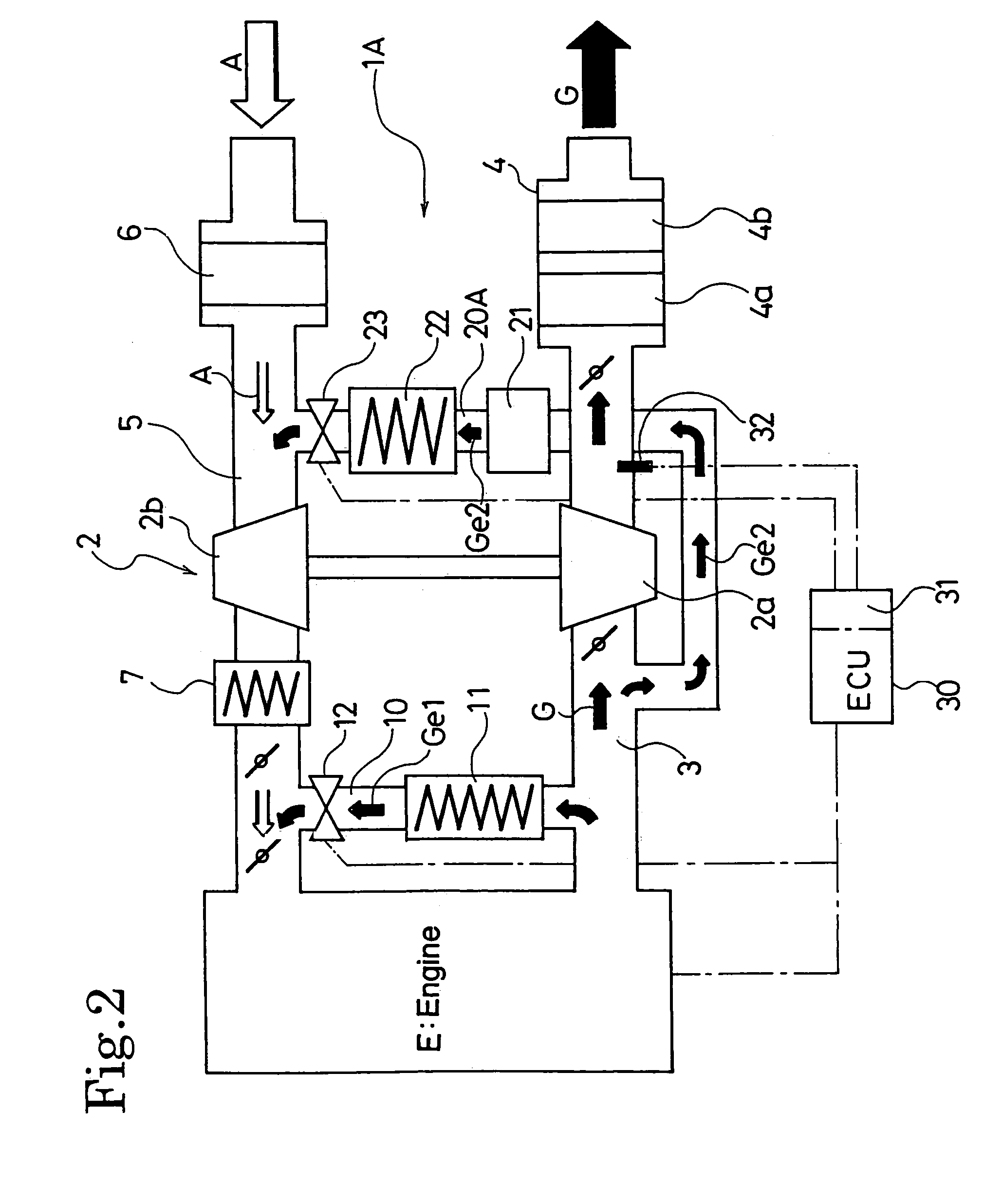
EGR system for internal combustion engine provided with a turbo-charger
InactiveUS7043914B2High EGR rateEfficiently reduce NOxElectrical controlNon-fuel substance addition to fuelTurbochargerInternal combustion engine
An EGR system for an internal combustion engine provided with a first EGR passage for recirculating EGR gas to the downstream side of a compressor from the upstream side of a turbine of a turbo-charger is provided with a second EGR passage for recirculating EGR gas from the downstream side of the turbine to the upstream side of the EGR gas, and provided also with a DPF in the second EGR passage, while the exhaust gas flow in the first EGR passage and the second EGR passage is controlled based on the exhaust gas temperature detected by an exhaust gas temperature sensor arranged in the exhaust gas passage.
Owner:ISUZU MOTORS LTD
Coordinated engine torque control
ActiveUS7021282B1Electrical controlNon-fuel substance addition to fuelThrottle controlControl system
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
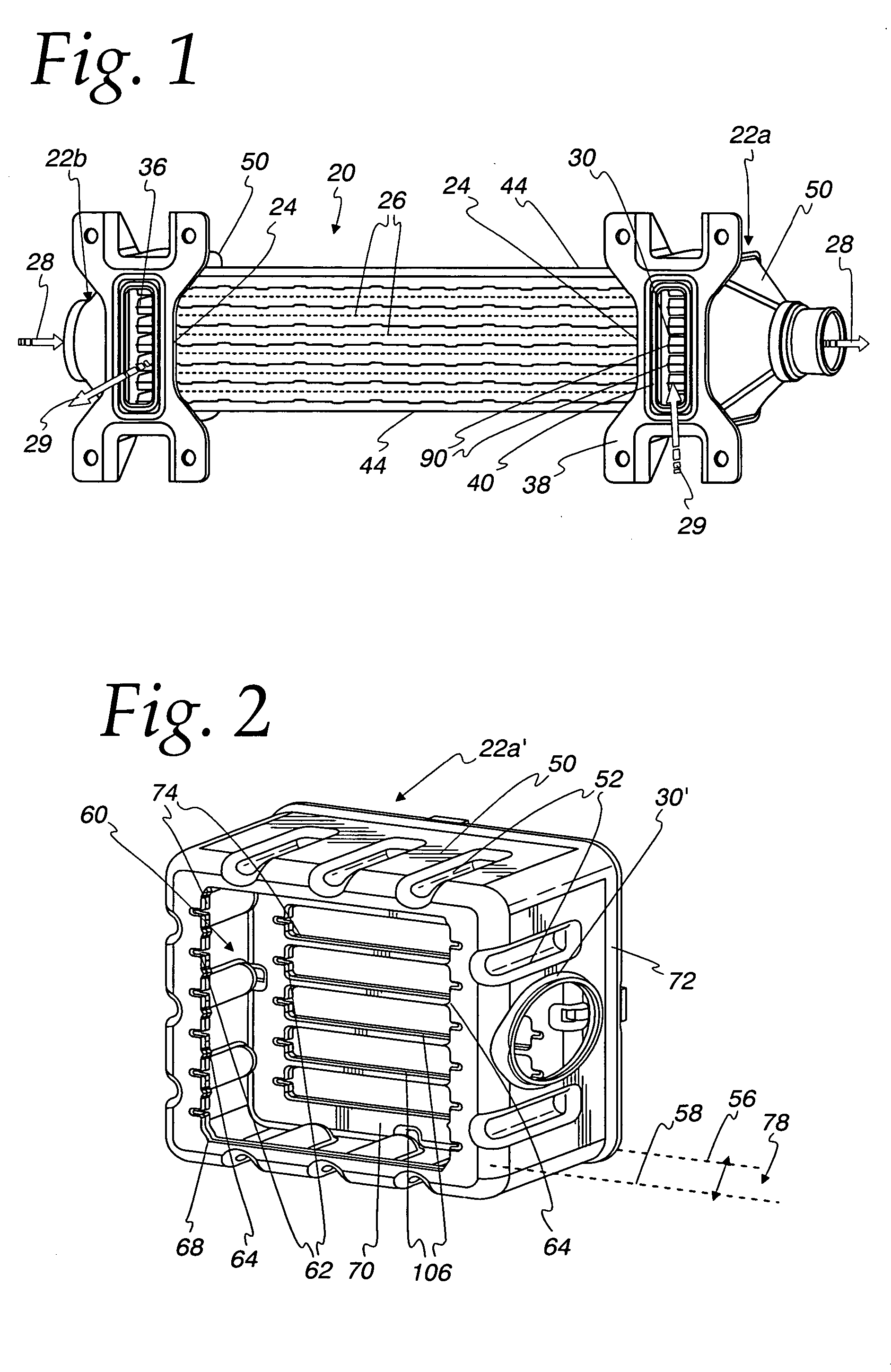
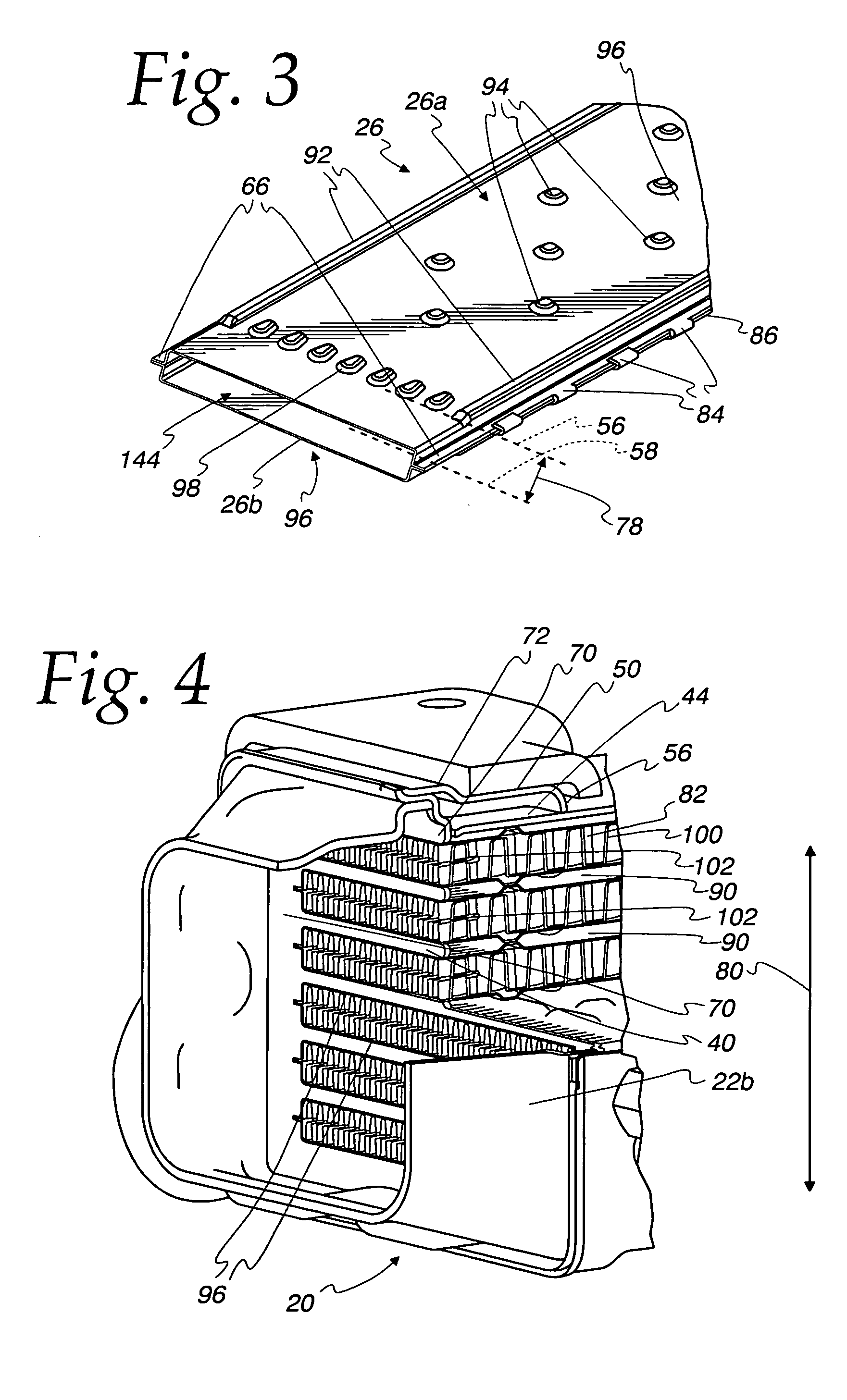
Heat exchanger with flat tubes
ActiveUS20050161206A1Reinforcing meansInternal combustion piston enginesElectrical and Electronics engineeringHeat exchanger
A heat exchanger with a plurality of stacked flat tubes and a collecting tank having a wall extending around the entire periphery of, and connected to, the end of the stacked flat tubes. A first medium may be distributed through the collecting tank and flat tubes. Internal inserts are in the flat tubes, with the inserts being bonded between the broad sides of the tubes and, in the region of connection of the tubes to the collecting tank, being configured to compensate for length changes in the stacking direction caused by temperature changes, as by recesses in connectors such as wave flanks or by corrugated wave flanks. The flat tubes with inserts such as described may be separately provided for use in manufacture of heat exchangers.
Owner:MODINE MFG CO
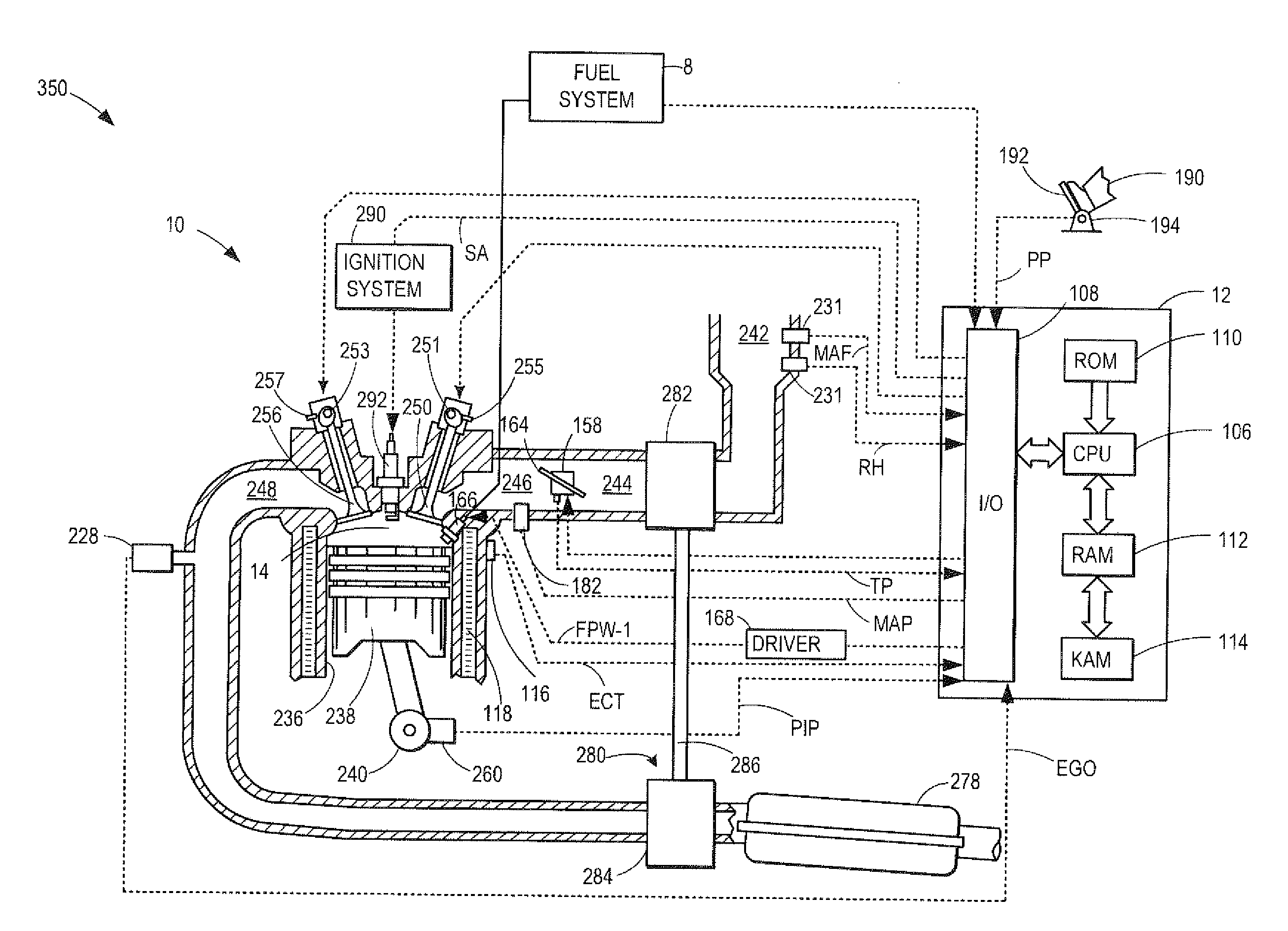
Methods and Systems for Variable Displacement Engine Control
ActiveUS20110265454A1Control flowHigh catalytic efficiencyInternal combustion piston enginesNon-fuel substance addition to fuelEngineeringThrottle
Methods and systems are provided for selecting a group of cylinders for selective deactivation, in a variable displacement engine system, based at least on a regeneration state of an exhaust catalyst. The position of one or more valves and throttles may be adjusted based on the selective deactivation to reduce back-flow through the disabled cylinders while also maintaining conditions of a downstream exhaust catalyst. Pre-ignition and knock detection windows and thresholds may also be adjusted based on the deactivation to improve the efficiency of knock and pre-ignition detection.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Control device for spark-ignition engine
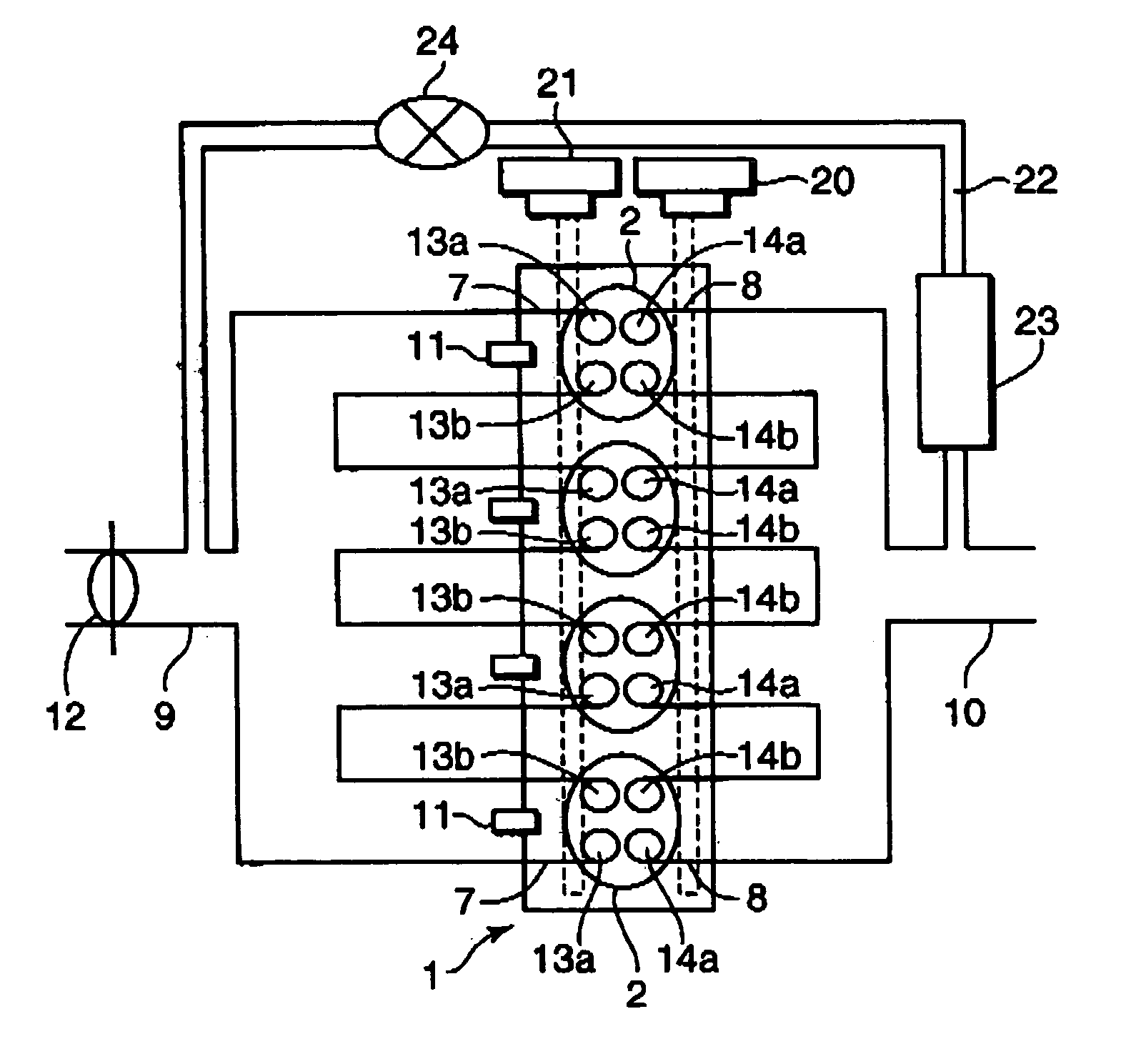
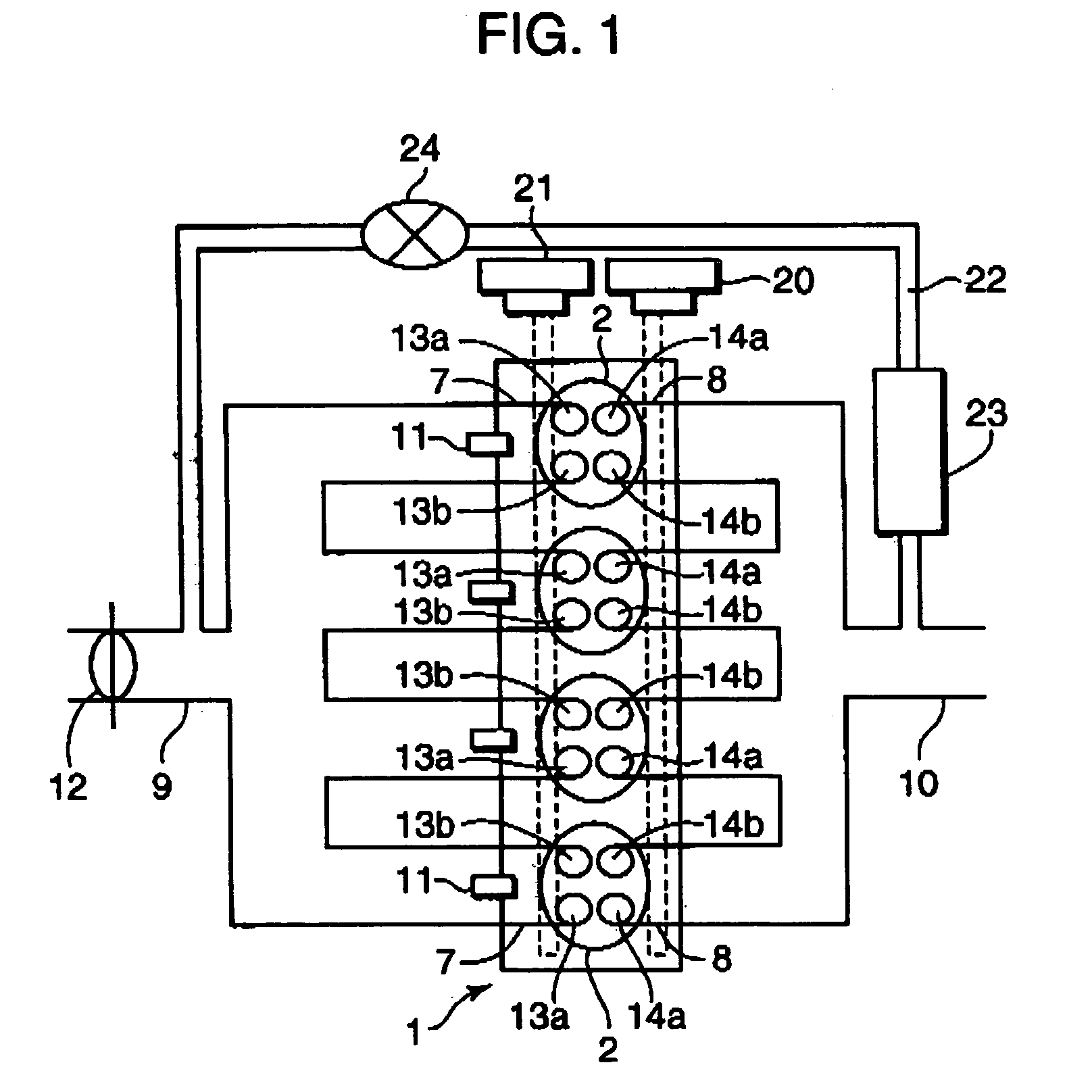
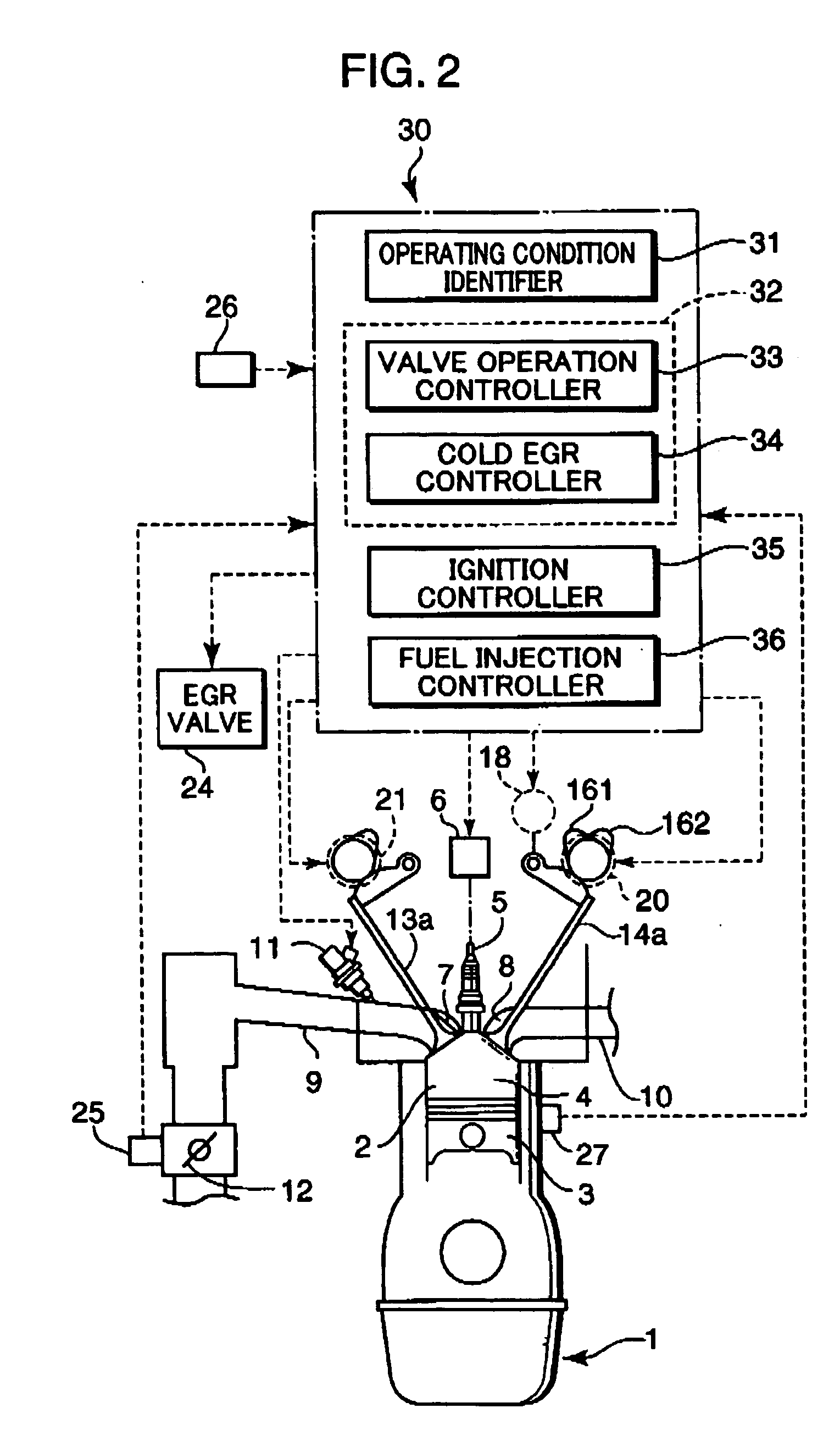
InactiveUS20050016496A1Increase rangeEfficiently prevent knockingValve arrangementsElectrical controlCombustion chamberLow speed
A control device for a spark-ignition engine, in which a mixture in a combustion chamber is fired by compression ignition in a part-load range under warm-running conditions, includes an EGR controller incorporating a valve operation controller for controlling internal EGR of hot burned gas and a cold EGR controller for controlling external EGR of cold burned gas. The EGR controller performs EGR control operation to leave the hot EGR gas in the combustion chamber in a lower-load, lower-speed region within a compression ignition combustion range and to introduce the cold EGR gas into the combustion chamber in a higher-load, higher-speed region within the compression ignition combustion range. The control device further includes a firing assist unit for inducing the compression ignition at least when ignitability of the mixture decreases due to introduction of the cold EGR gas in the compression ignition combustion range.
Owner:MAZDA MOTOR CORP
Internal combustion engine having two exhaust gas turbocharger
InactiveUS7540150B2Simple meansNon-fuel substance addition to fuelInternal combustion piston enginesExhaust valveTurbocharger
In an internal combustion engine provided with two exhaust gas turbochargers which each comprise a turbine in an exhaust line and one compressor in an intake section of the engine, two exhaust lines are provided which are each assigned to at least one of the exhaust gas turbines, an exhaust gas recirculation device being arranged between an exhaust line upstream of an exhaust gas turbine and the intake section downstream of a compressor and the two exhaust lines including bypass lines with a control valve for selectively permitting the exhaust gas to bypass the turbine closer to the engine.
Owner:DAIMLER AG
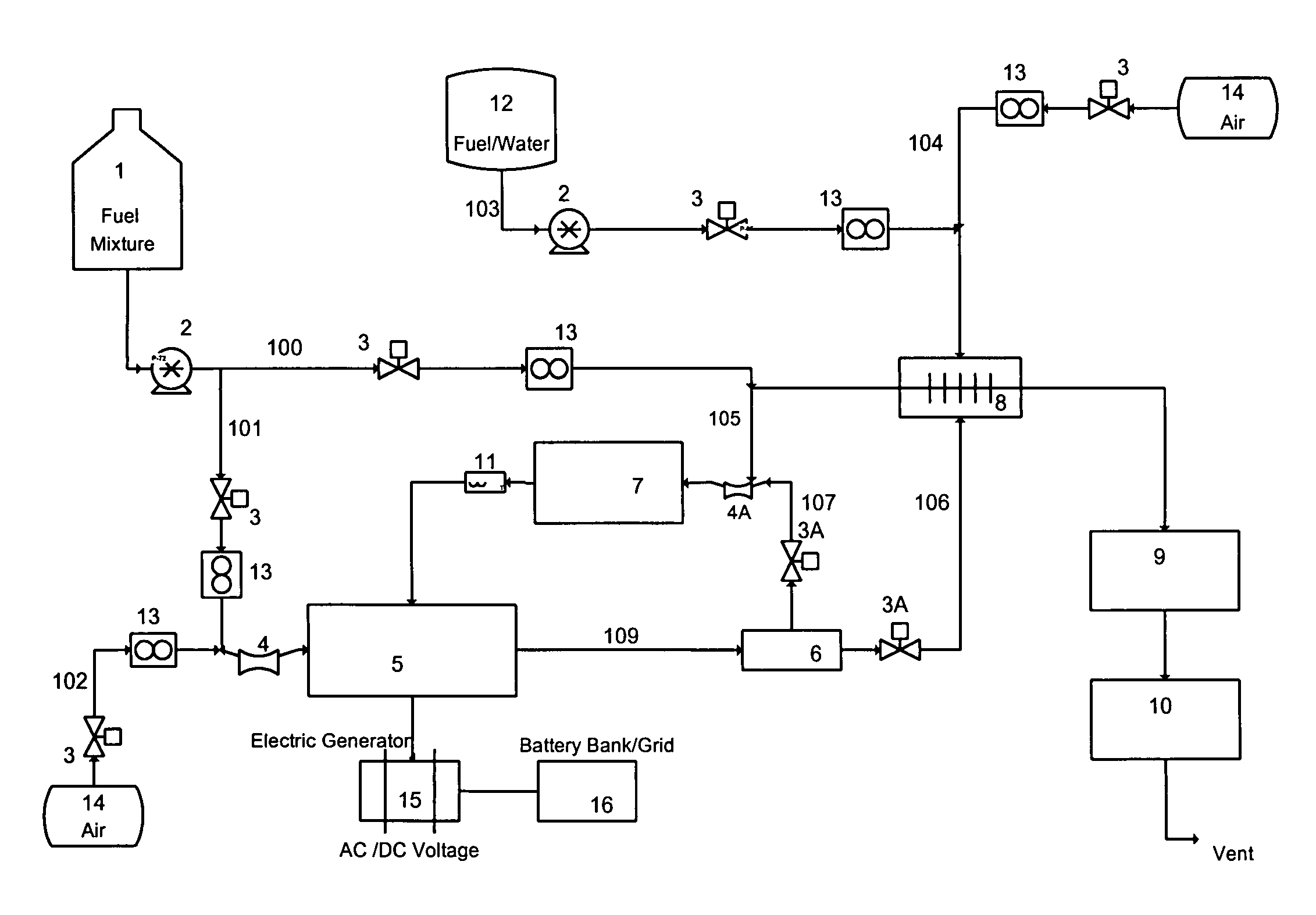
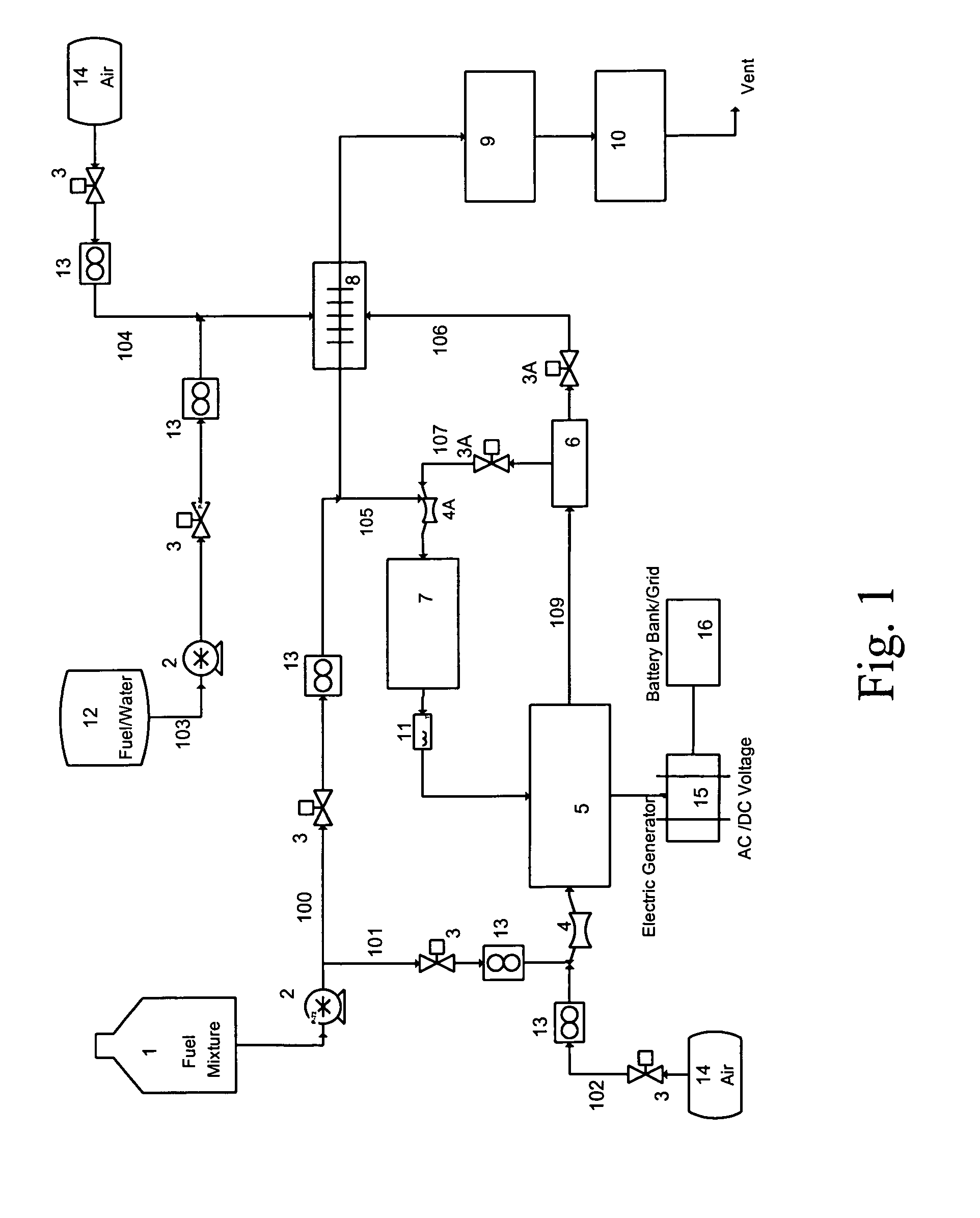
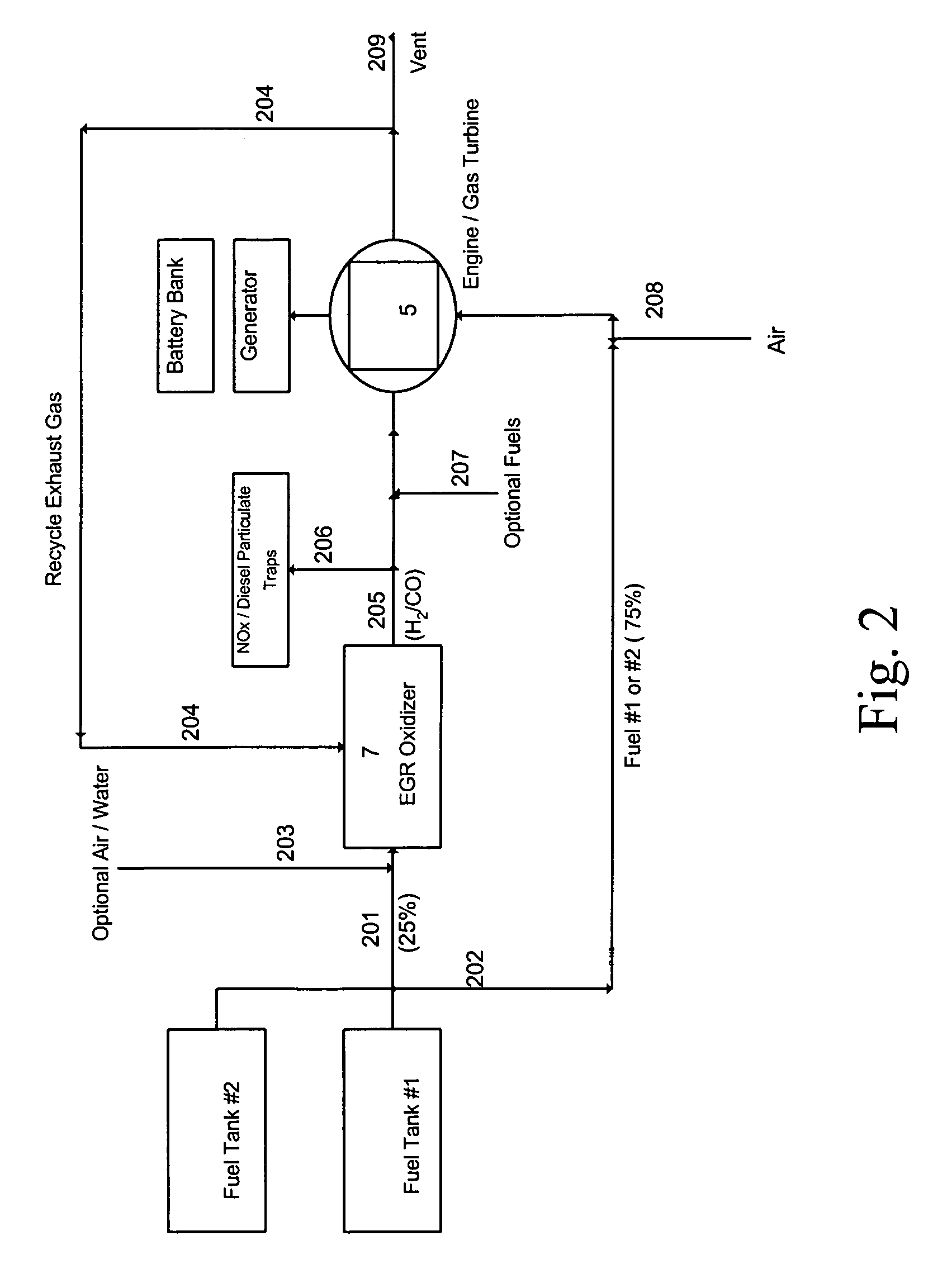
Catalytic EGR oxidizer for IC engines and gas turbines
InactiveUS8061120B2Increased durabilityProlong lifeCombination devicesInternal combustion piston enginesElectricityPartial oxidation
By using catalytic partial oxidation or autothermal reforming process, a catalytic oxidizer installed in the engine's Exhaust Gas Recycle (EGR) line can be used to produce from fossil fuels or bio-fuels a reformate gas containing H2 and CO for an IC engine or a gas turbine. Thus, a system consisting of an EGR Oxidizer and an IC engine / gas turbine can be used by itself as a driving device, or can be combined with an electric generator and a battery bank to produce, store and transmit electricity to be used in stationary or mobile power generation, transportation and utility etc.The Oxidizer can also be used to provide reducing gases to regenerate the NOx or diesel particulate traps, so that the traps can continuously be used for reducing emissions from IC engine, diesel truck, gas turbine, power plant etc.
Owner:HWANG HERNG SHINN
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com