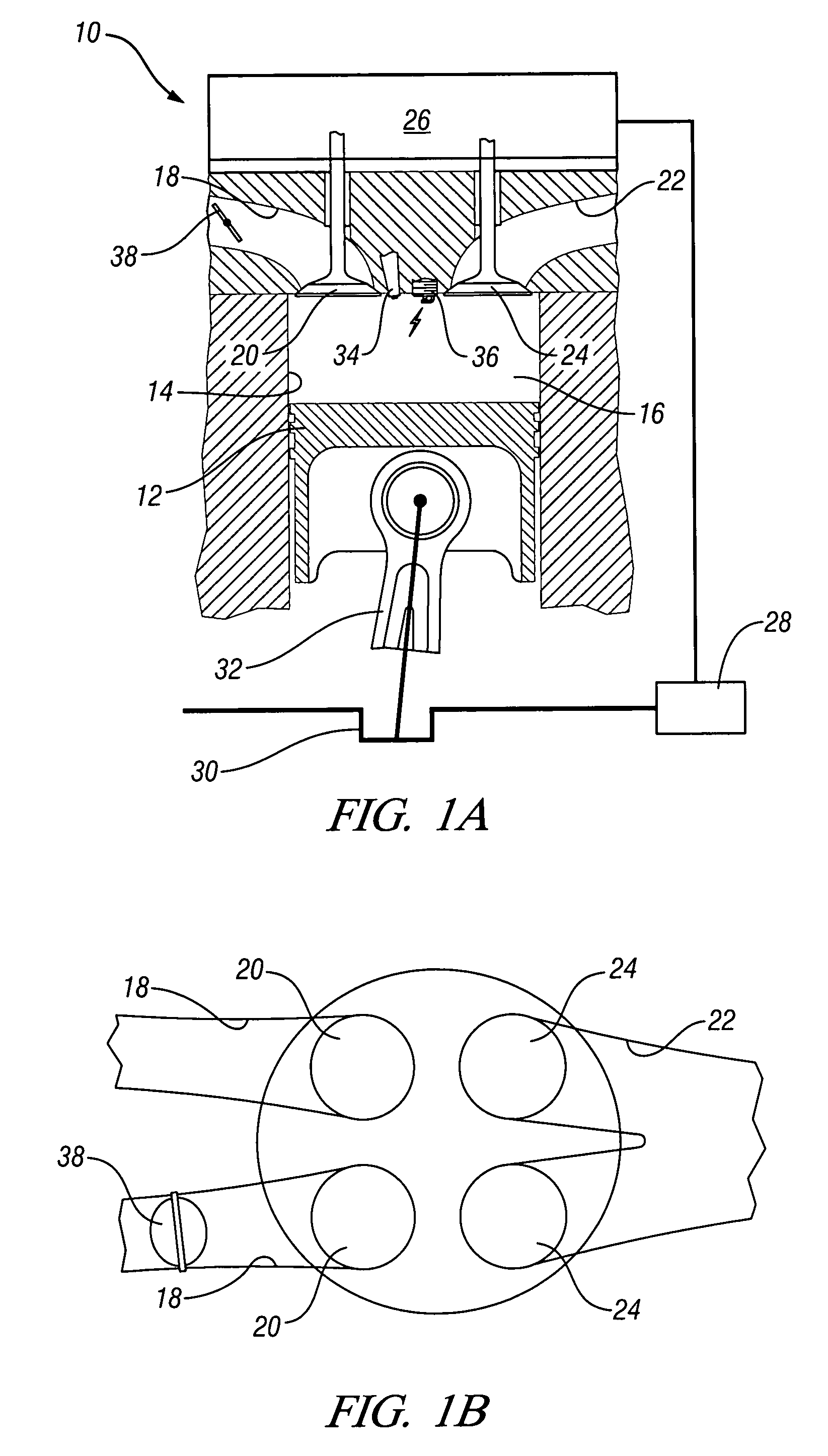
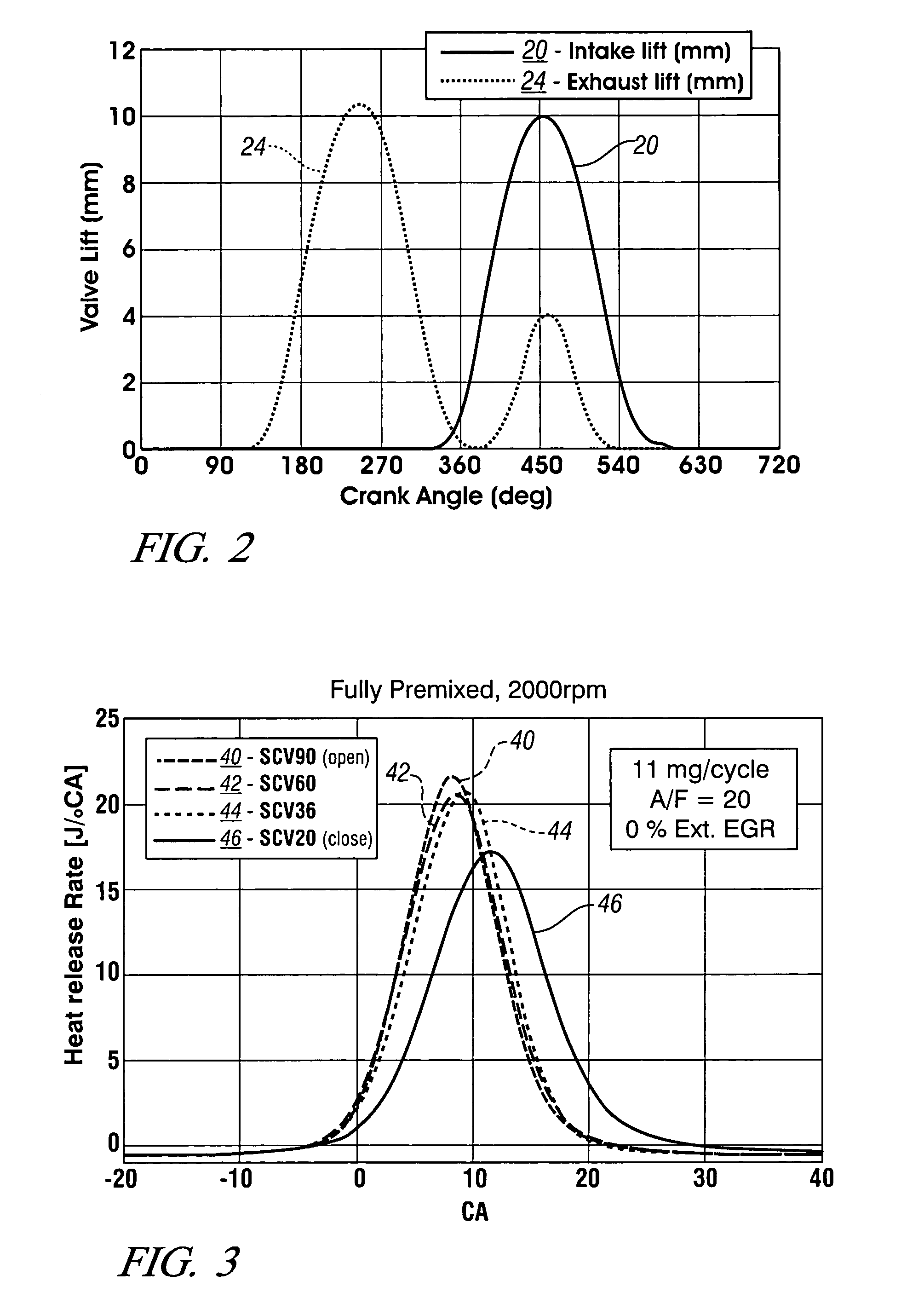
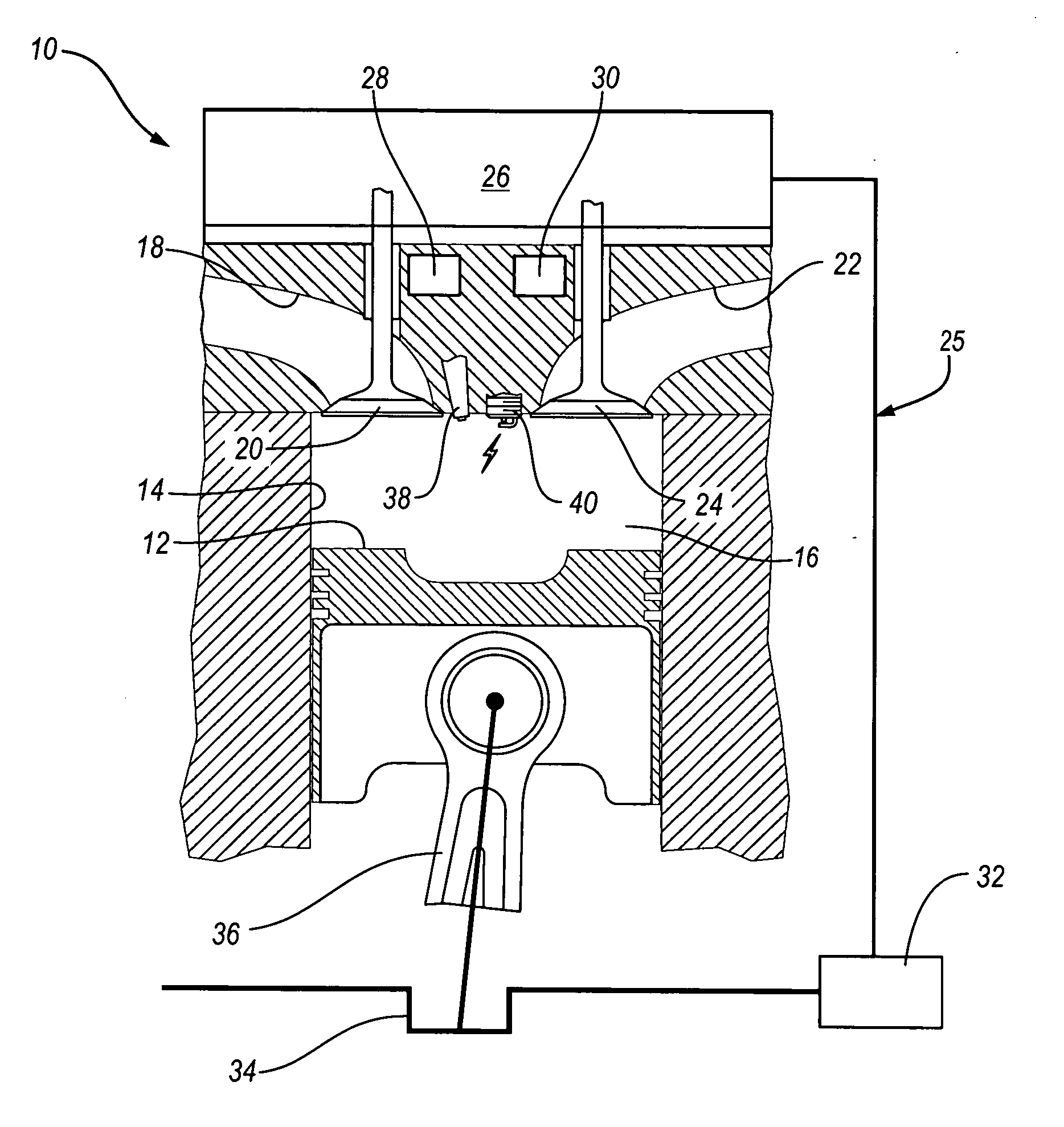
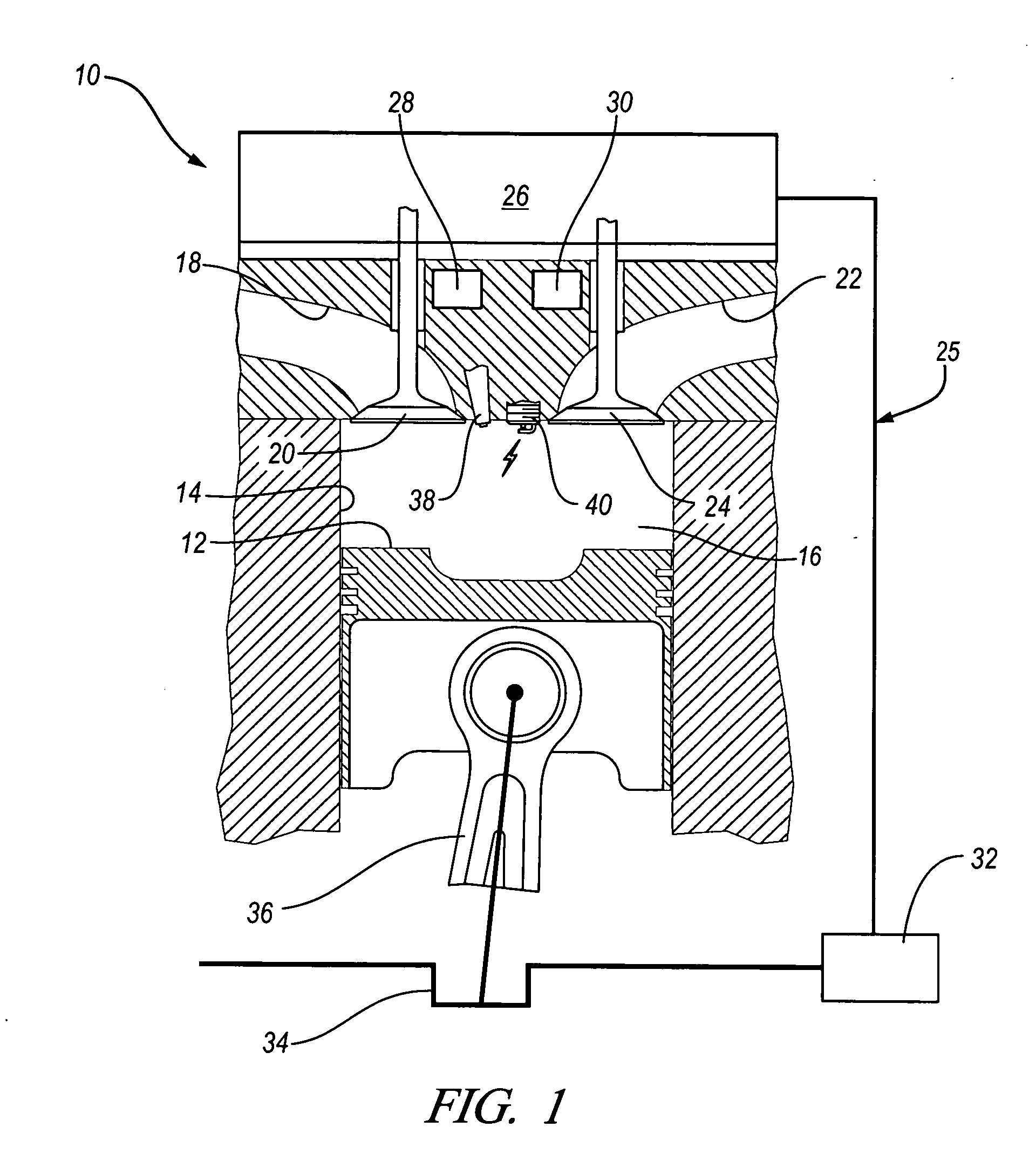
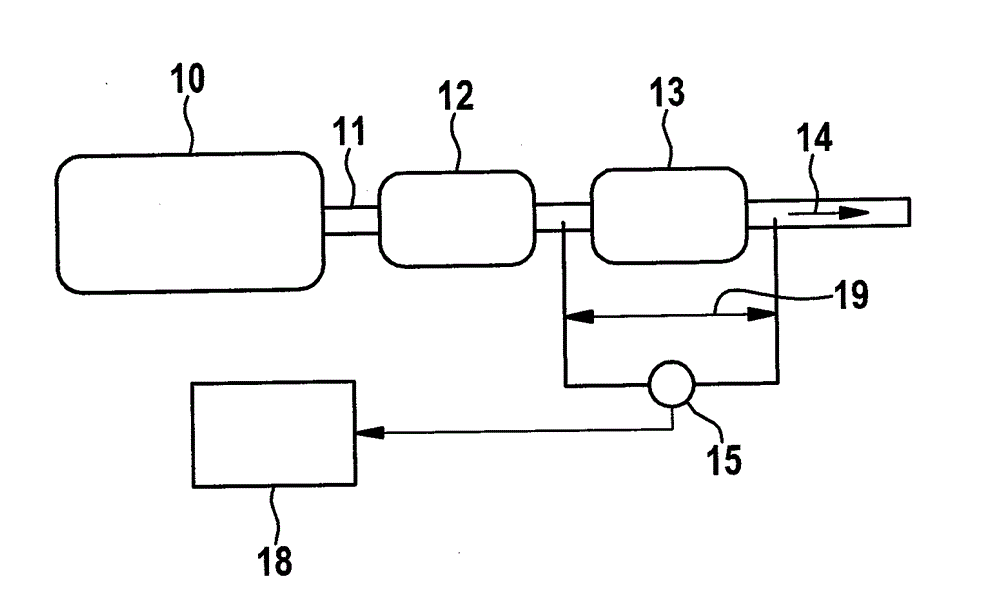
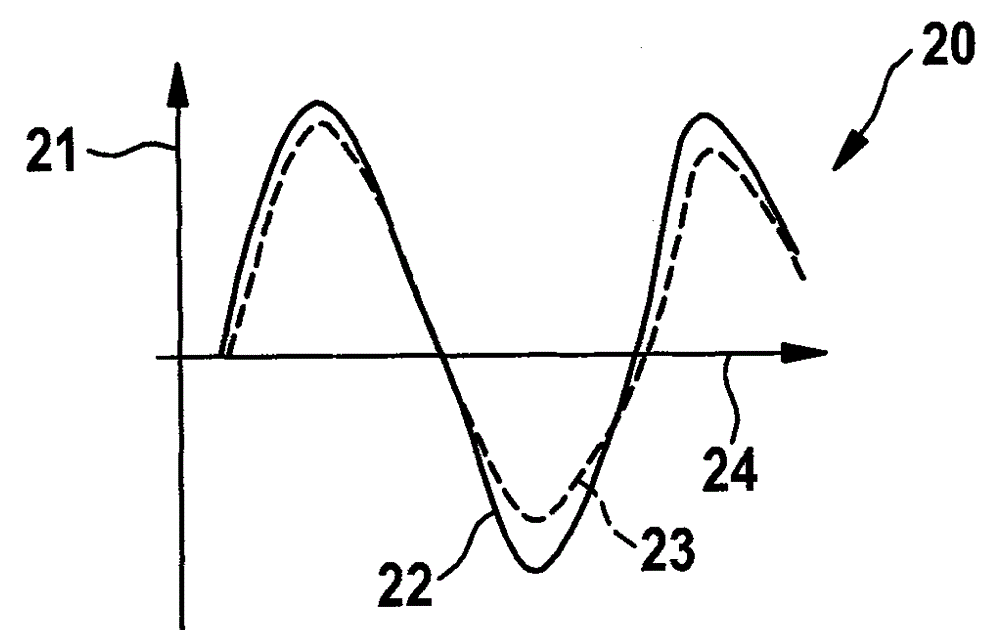
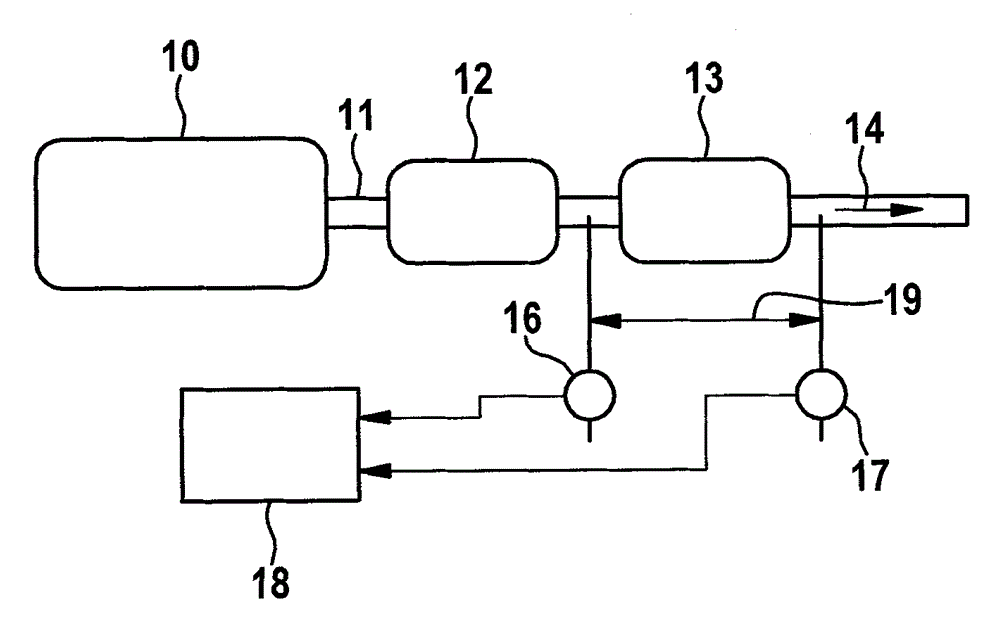
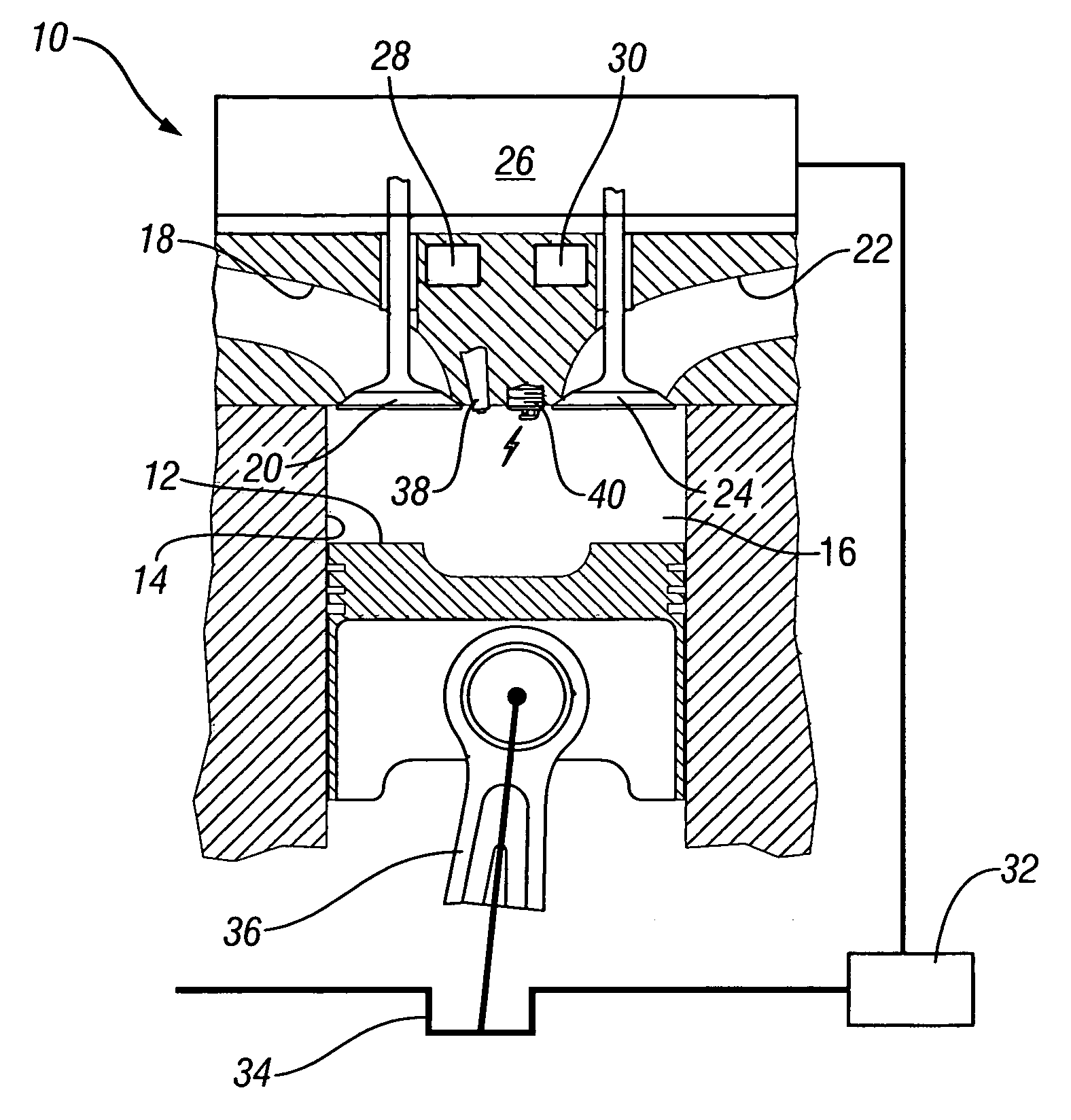
Patents
Literature
216 results about "Gasoline direct injection" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
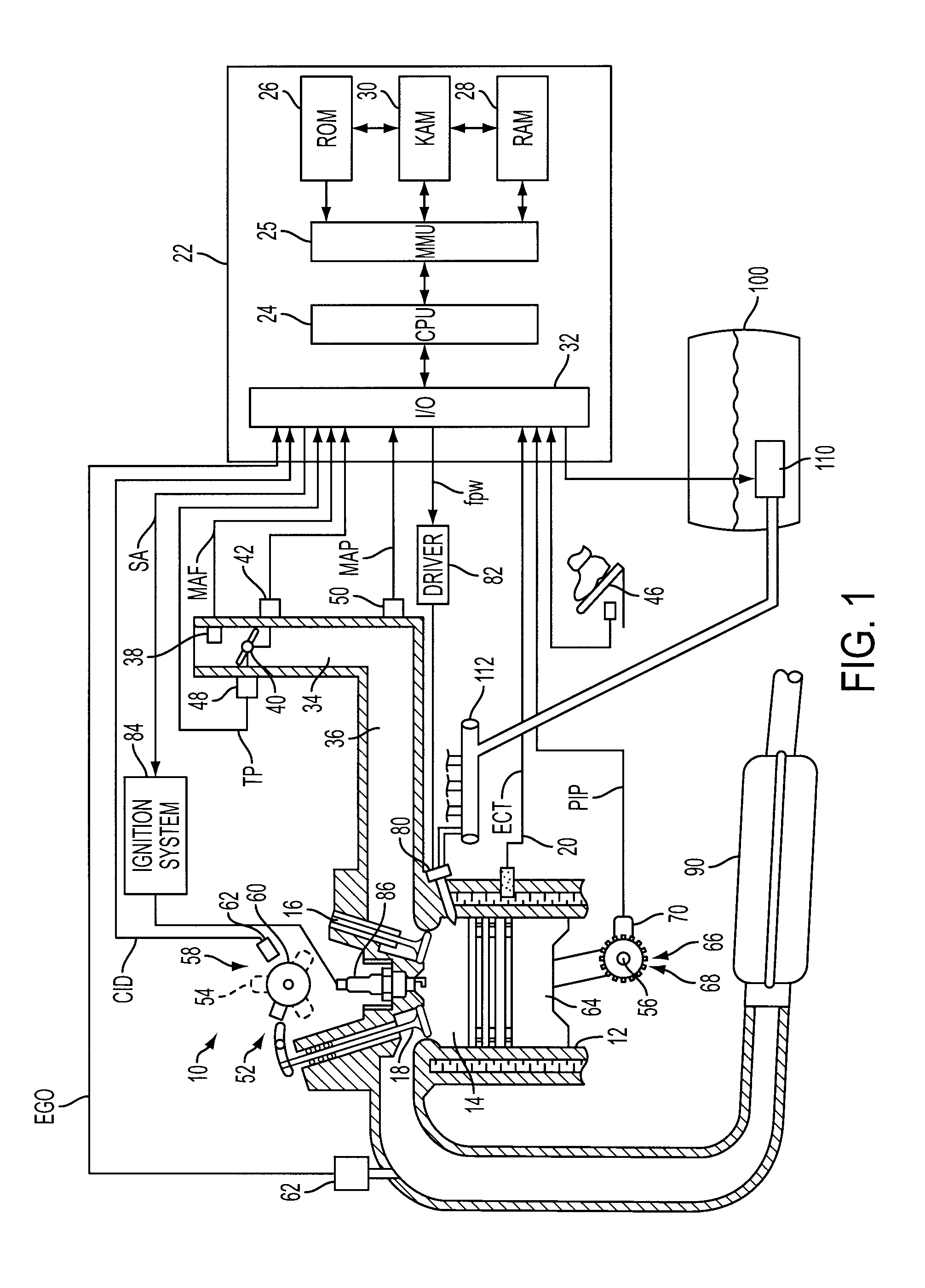
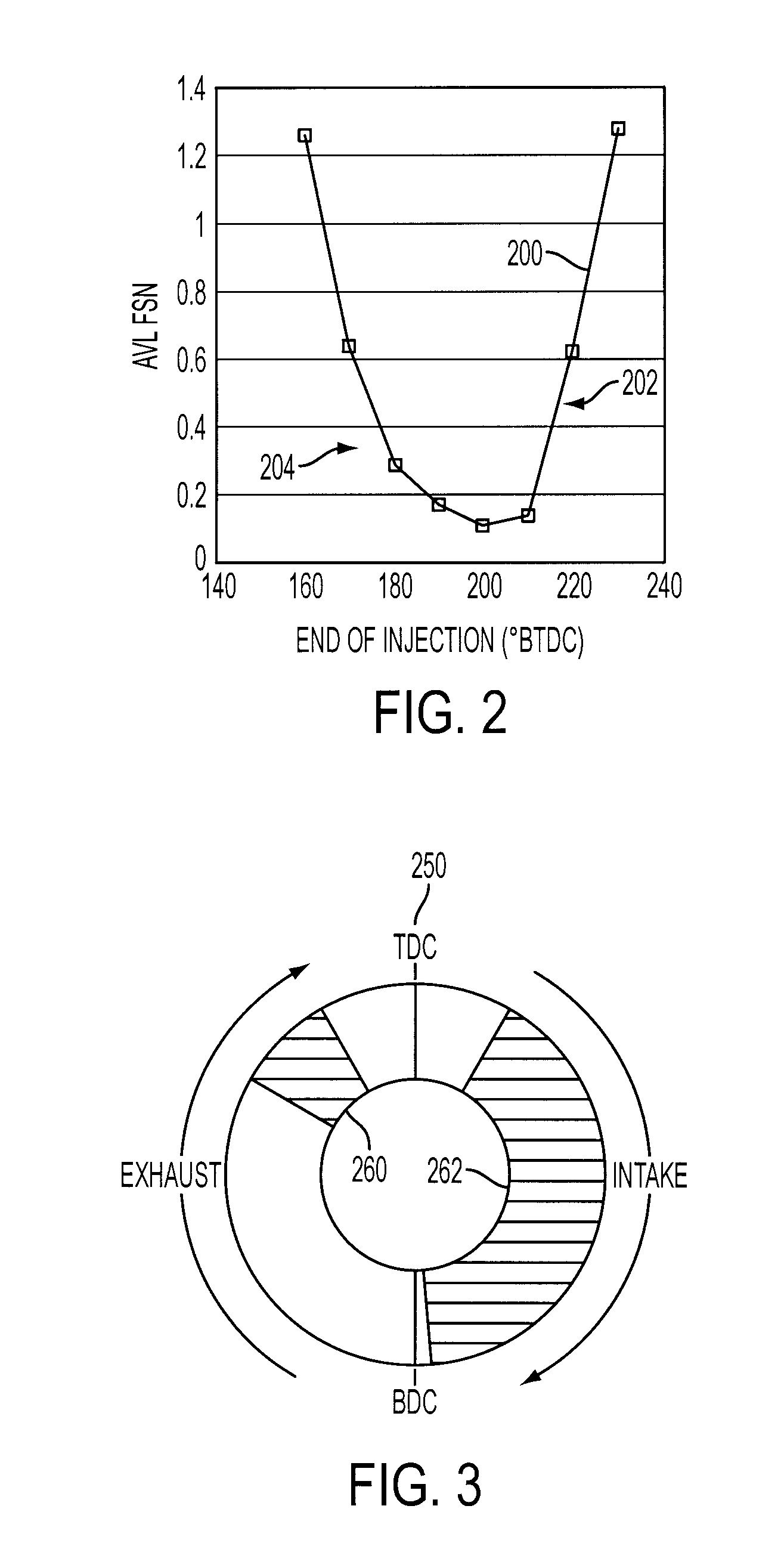
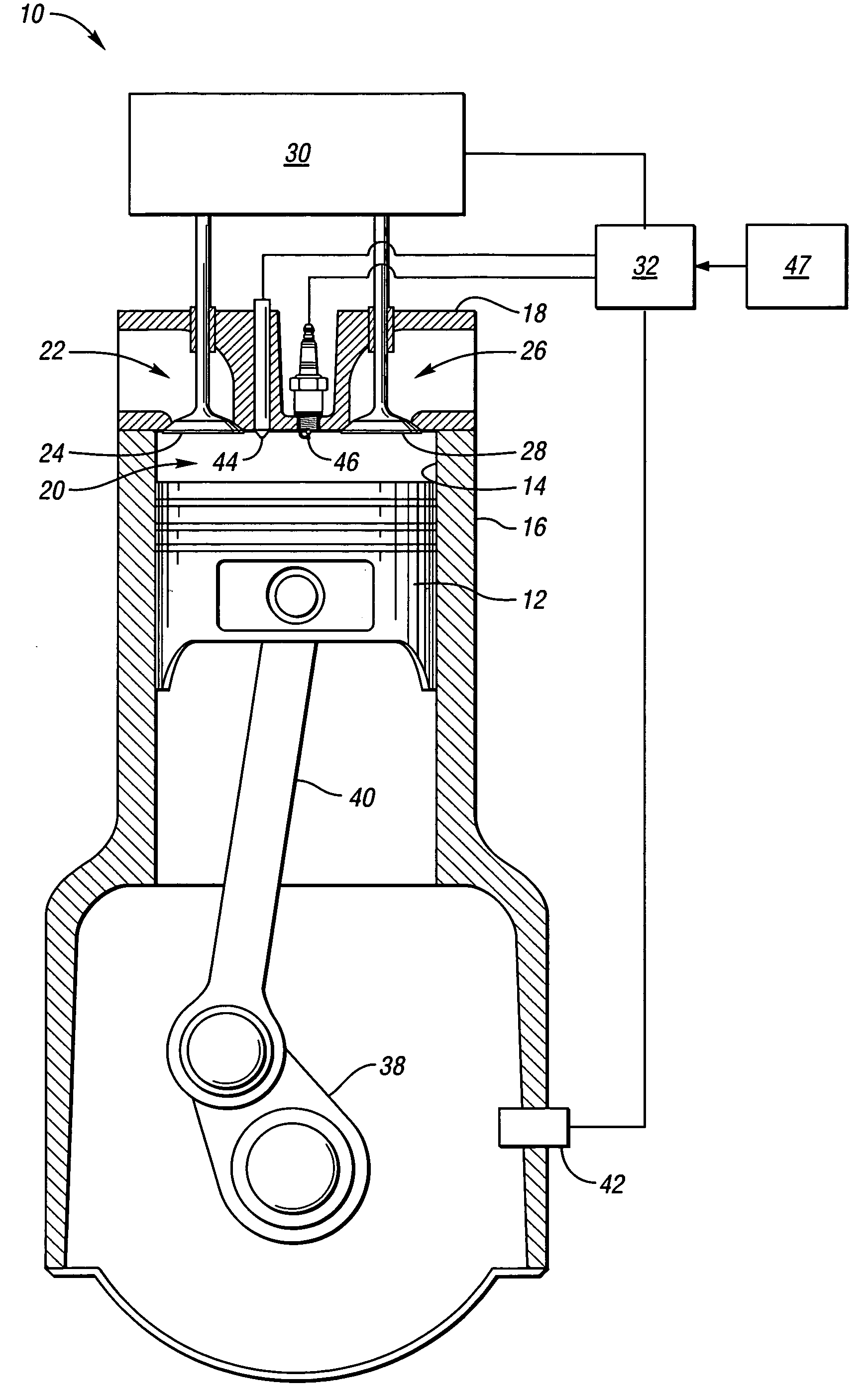
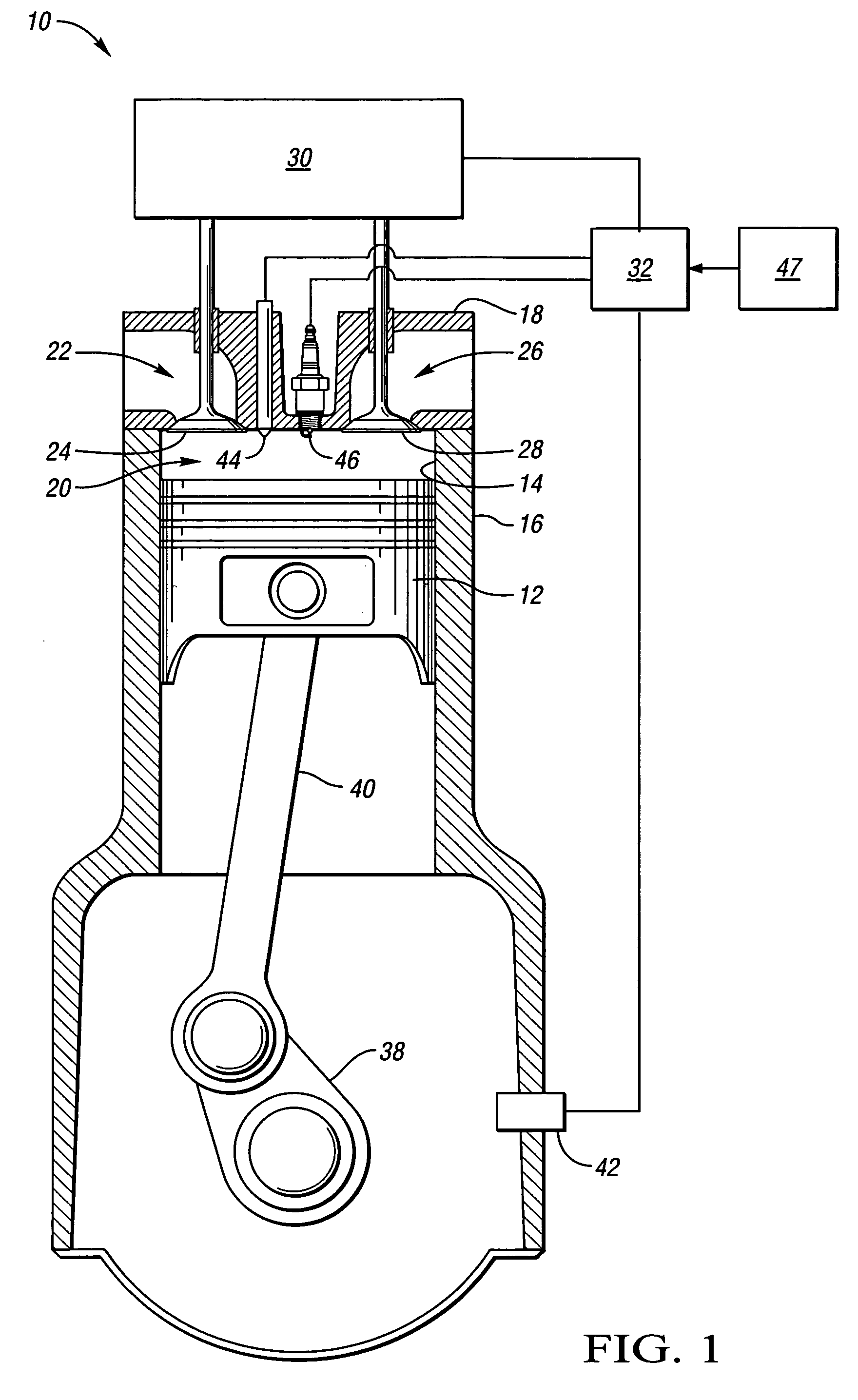
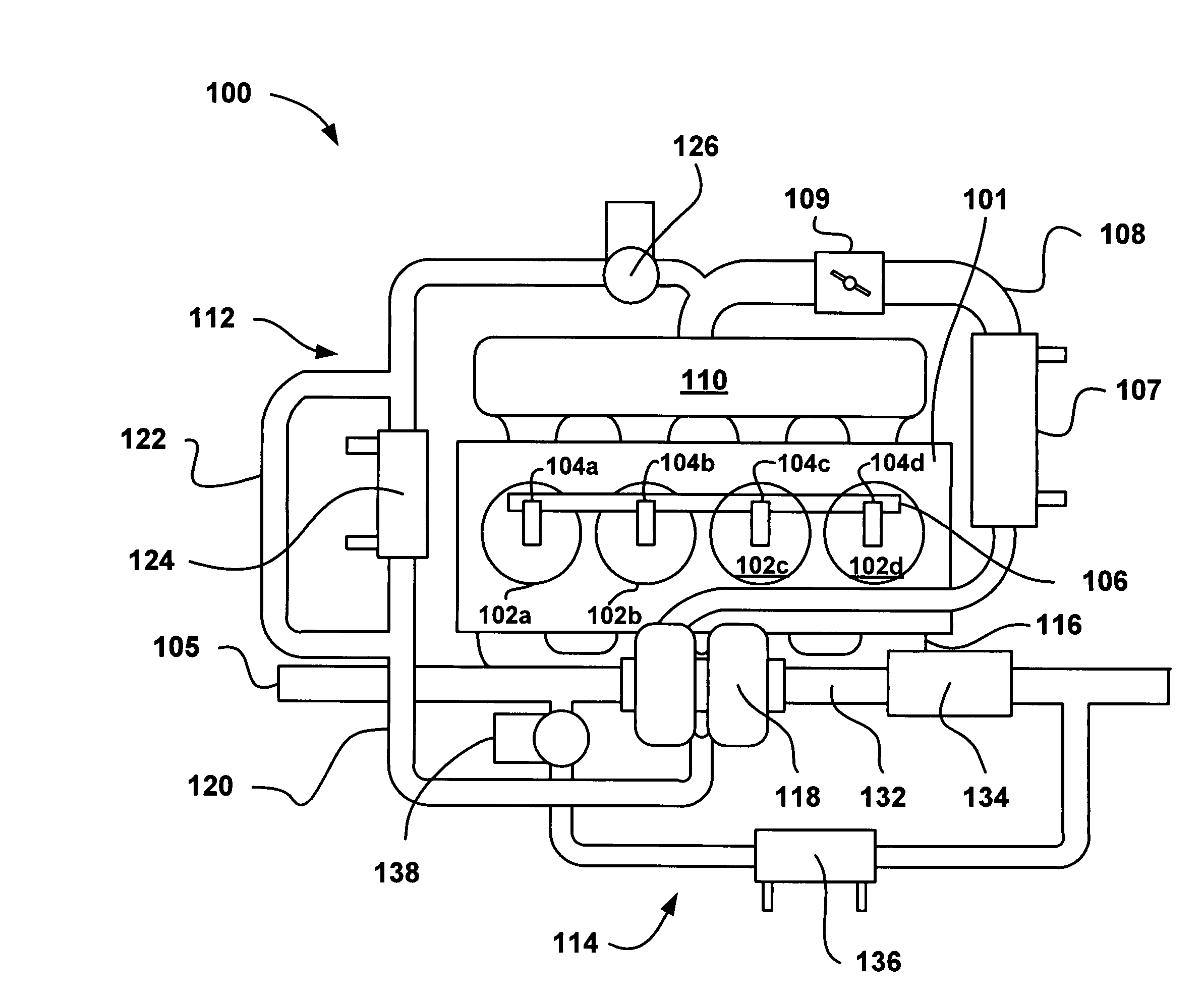
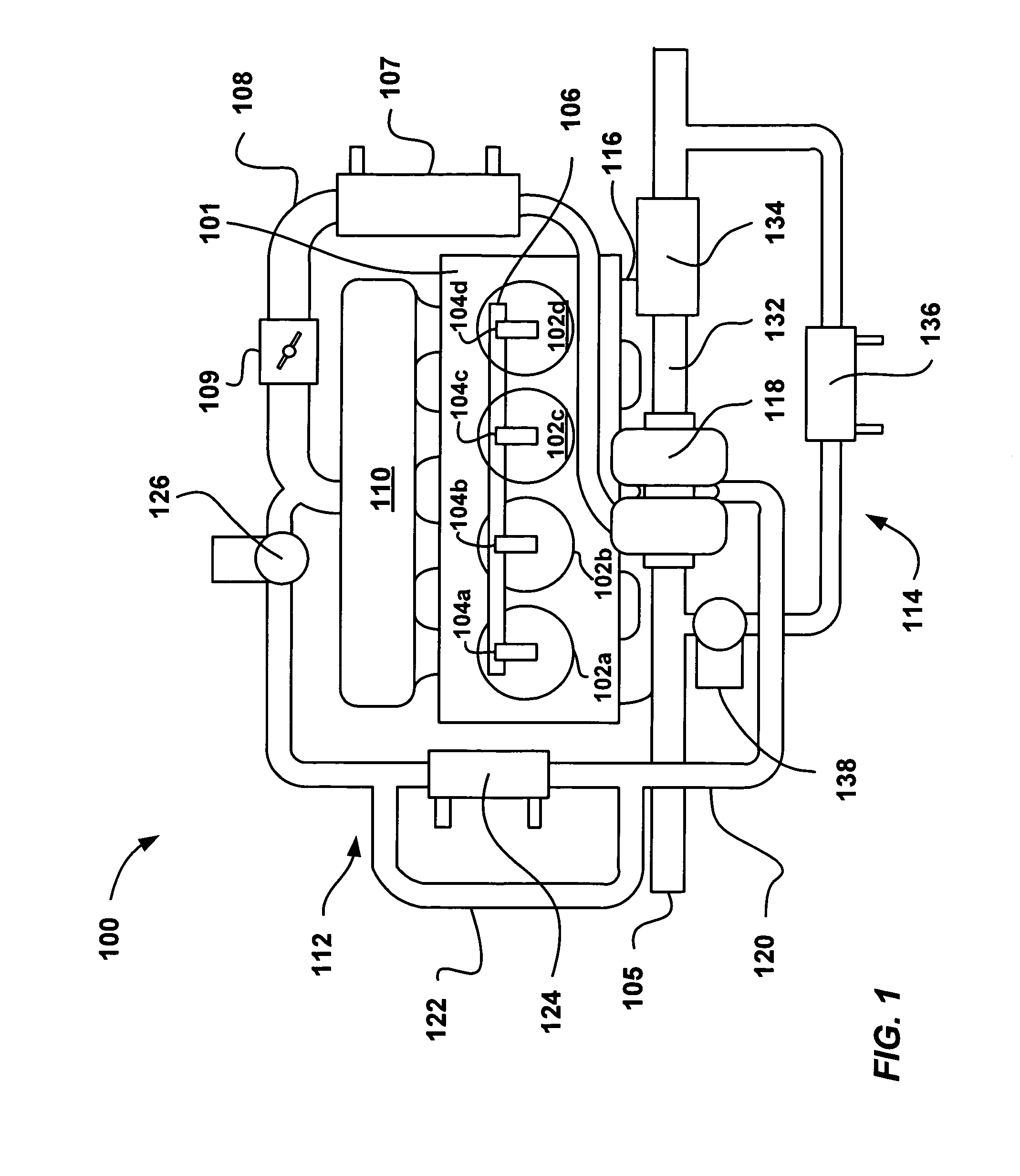
Gasoline direct injection (GDI) (also known as petrol direct injection, direct petrol injection, spark-ignited direct injection (SIDI) and fuel-stratified injection (FSI)), is a form of fuel injection employed in modern two-stroke and four-stroke gasoline engines. The gasoline is highly pressurized, and injected via a common rail fuel line directly into the combustion chamber of each cylinder, as opposed to conventional multipoint fuel injection that injects fuel into the intake tract or cylinder port. Directly injecting fuel into the combustion chamber requires high-pressure injection, whereas low pressure is used injecting into the intake tract or cylinder port.
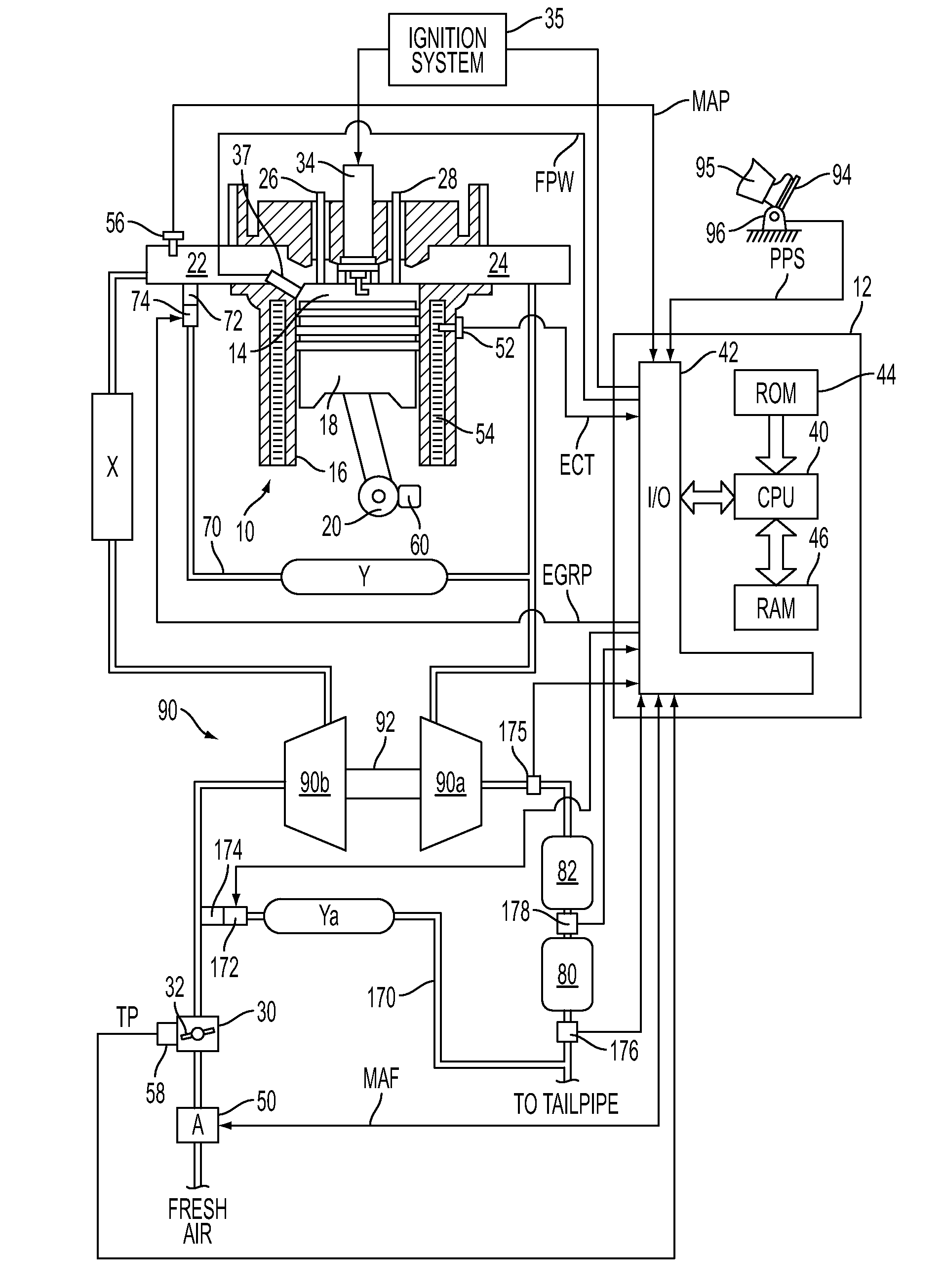
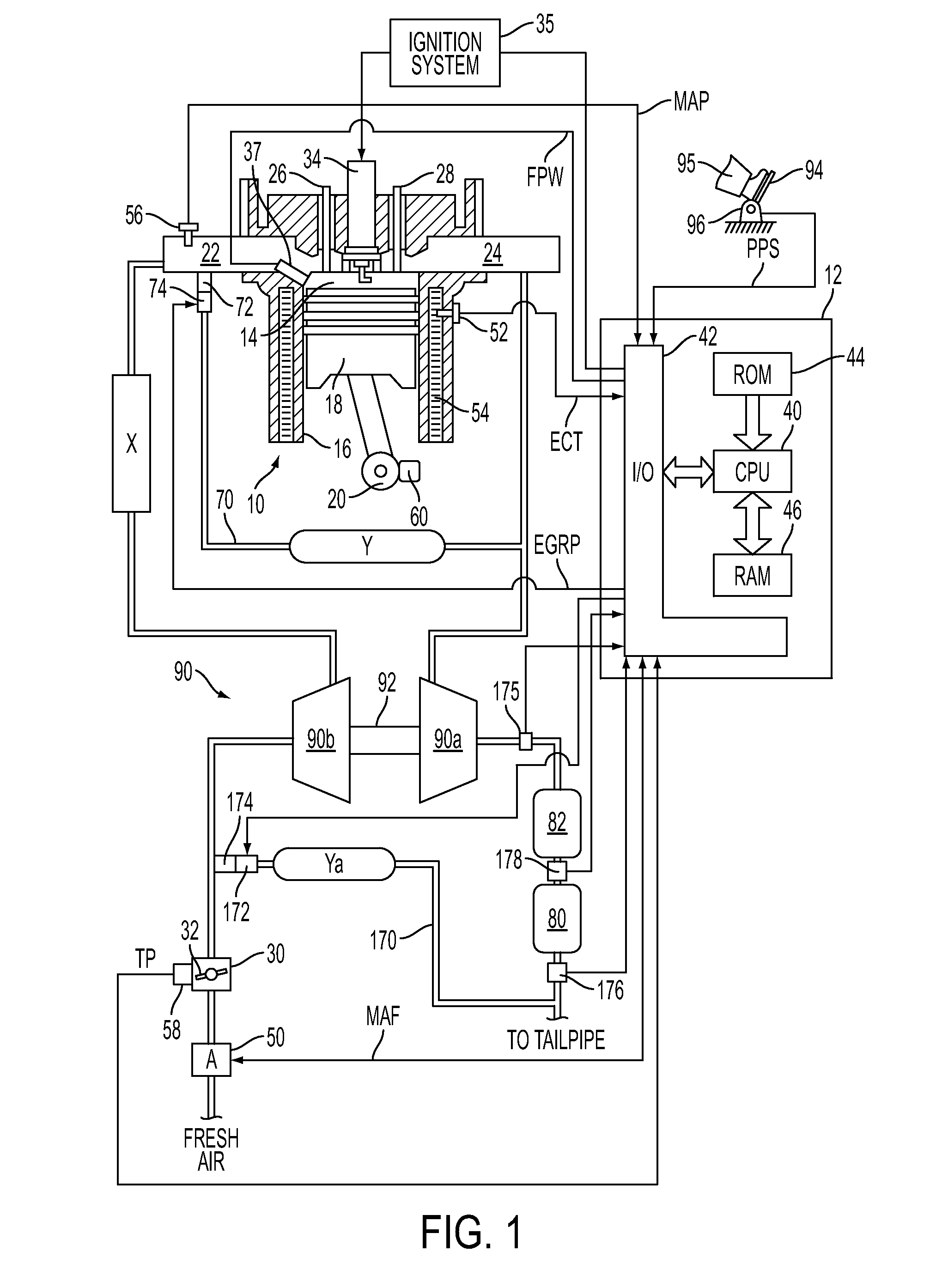
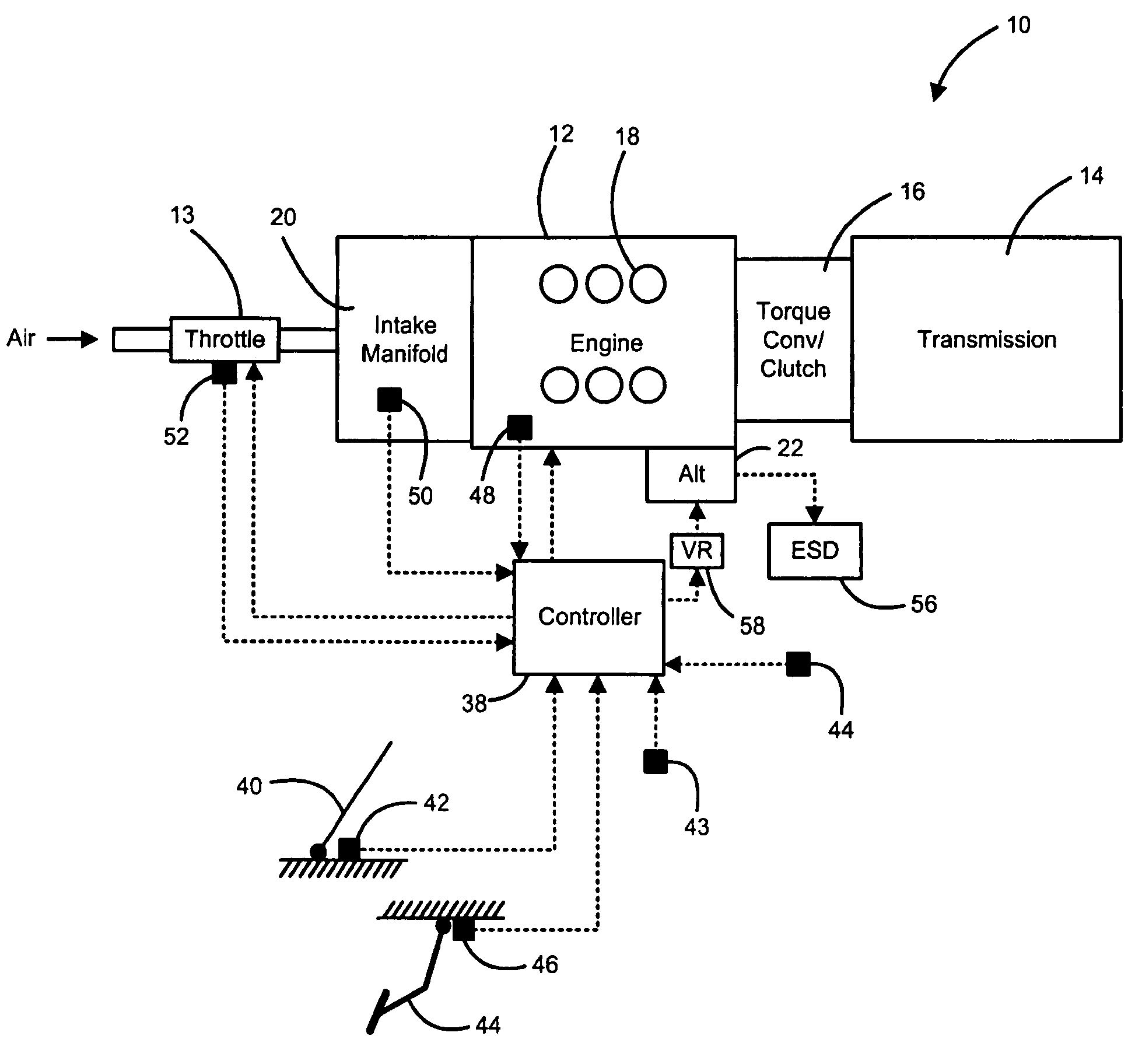
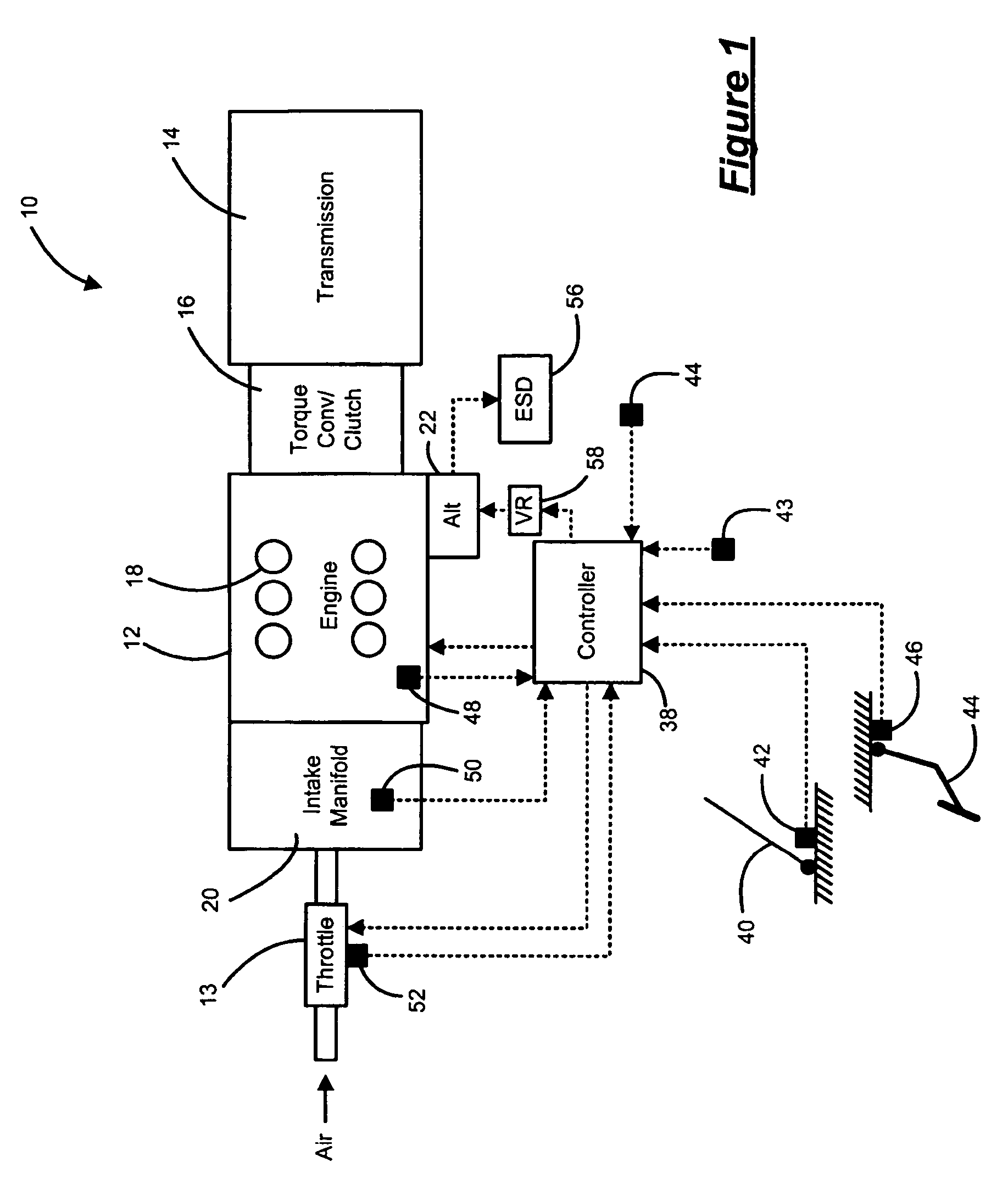
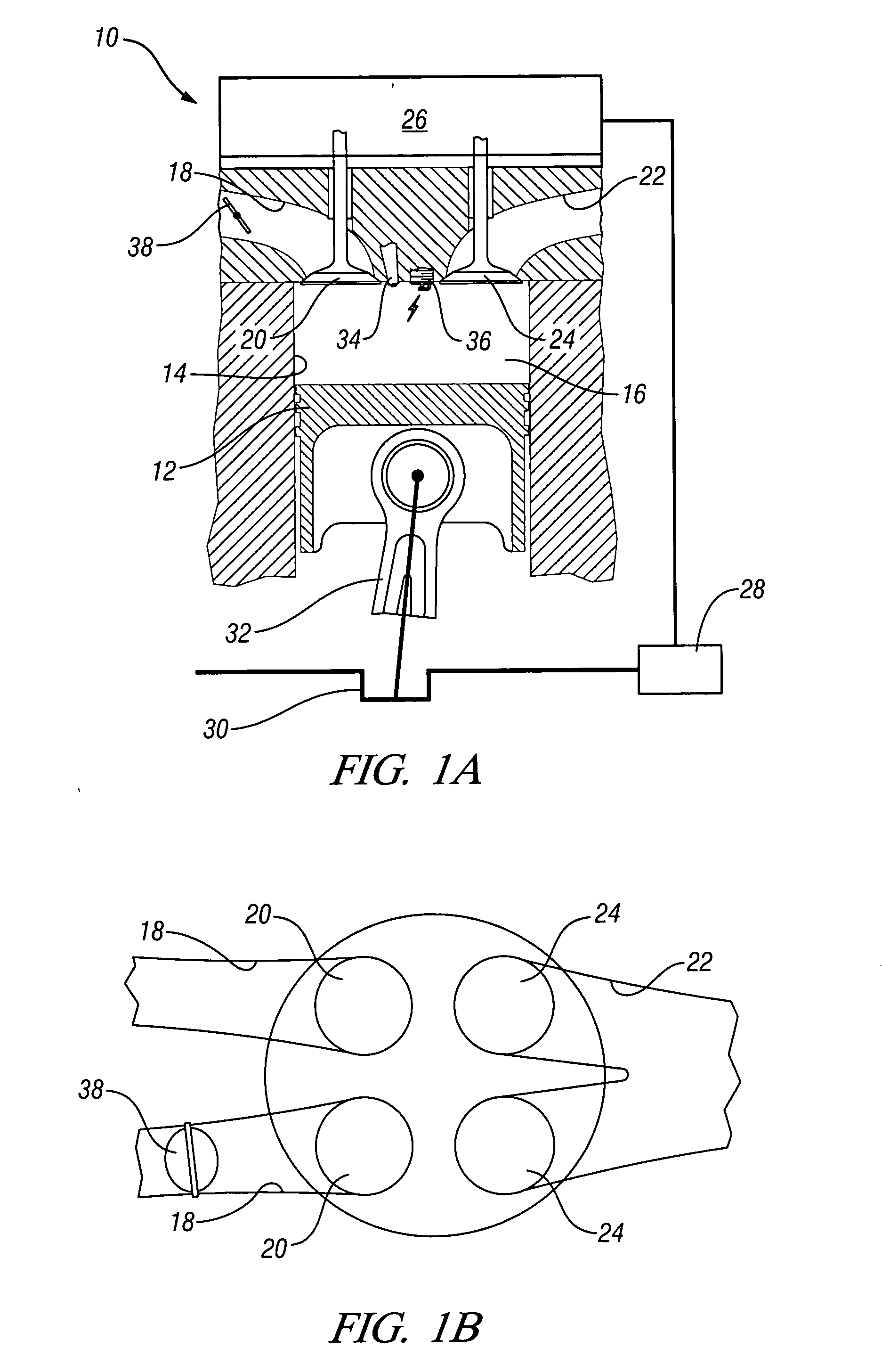
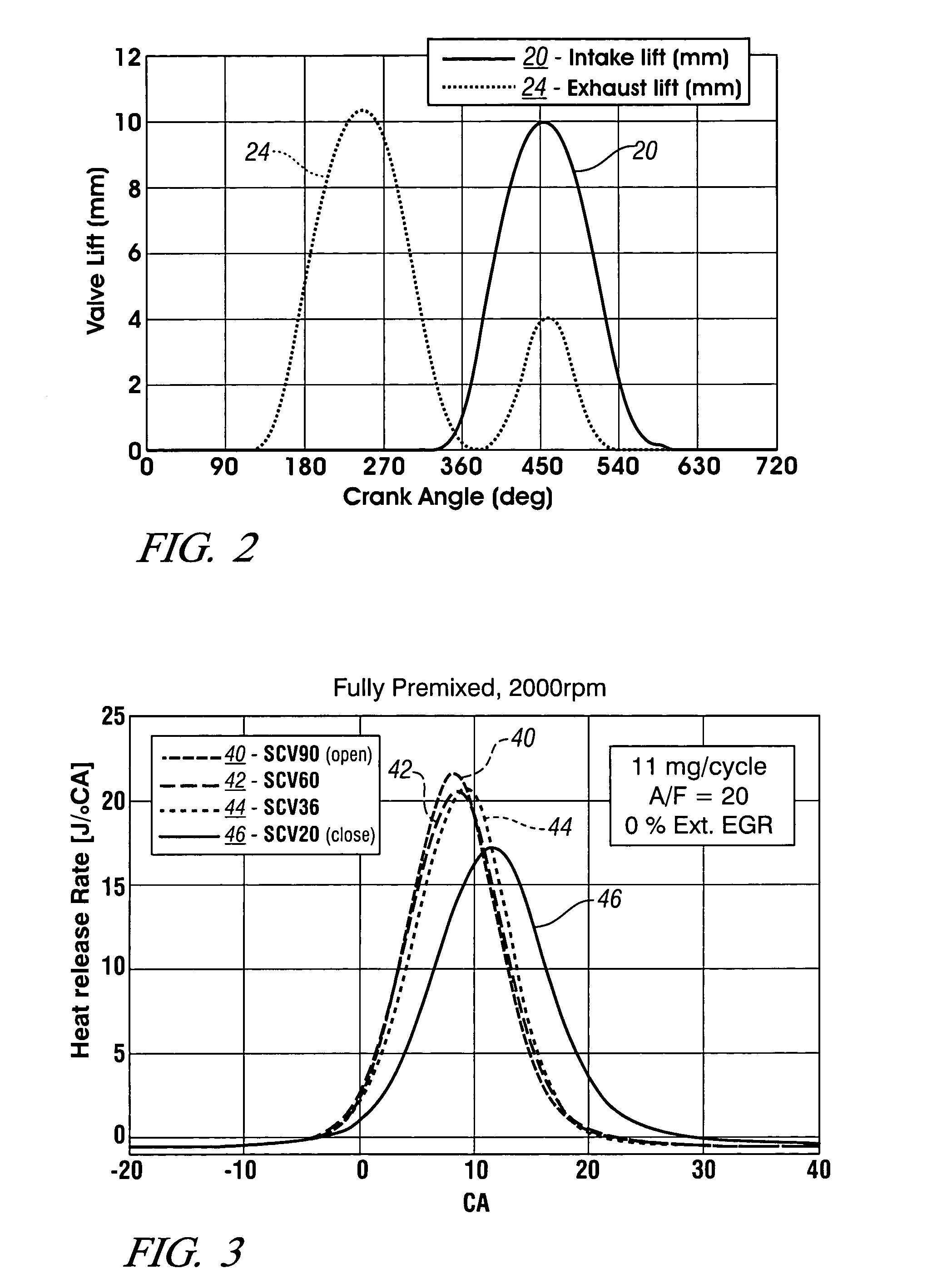
Method of HCCI and SI combustion control for a direct injection internal combustion engine
InactiveUS20060243241A1Improve fuel economyRobust controlValve arrangementsElectrical controlHomogeneous charge compression ignitionGasoline direct injection
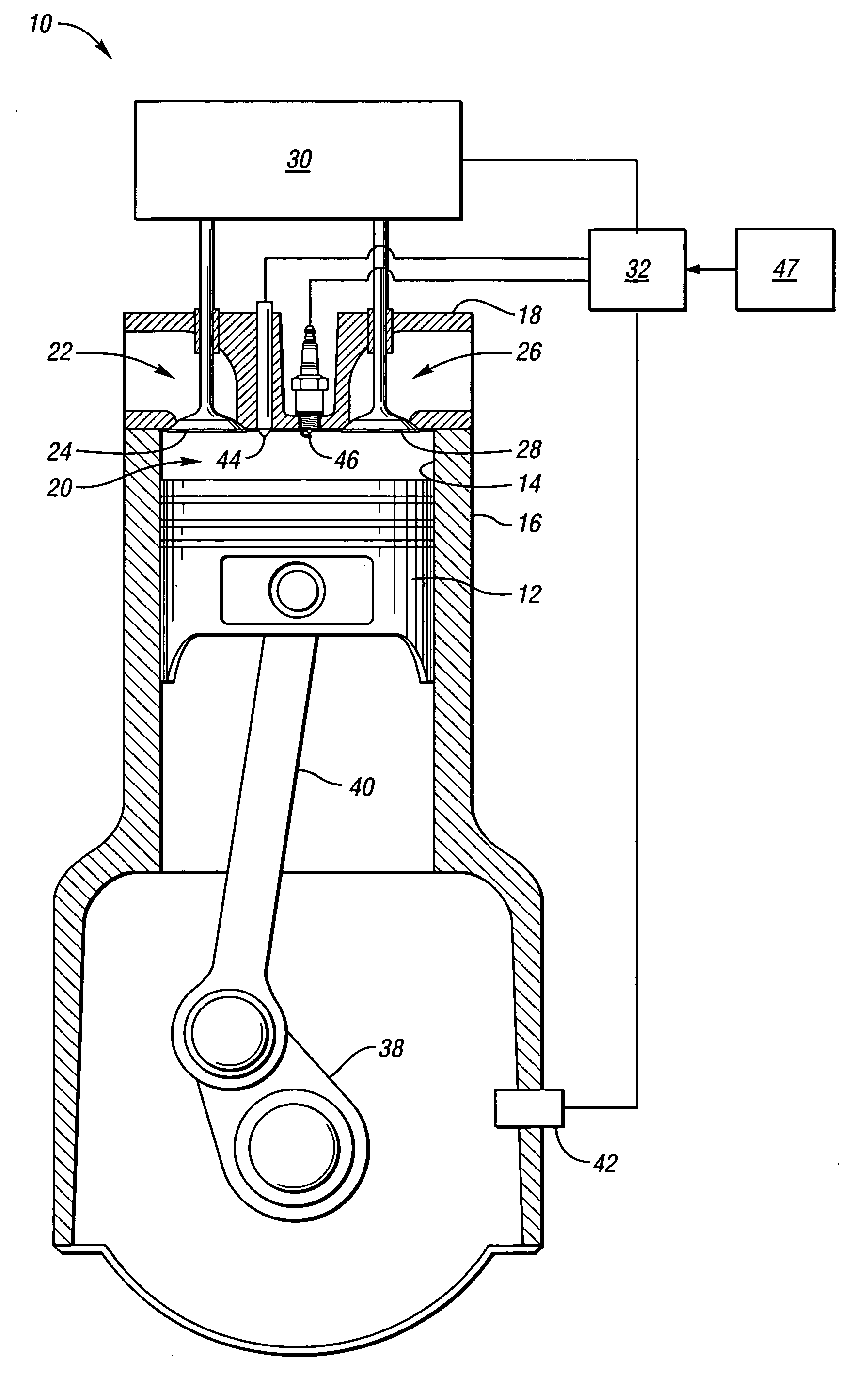
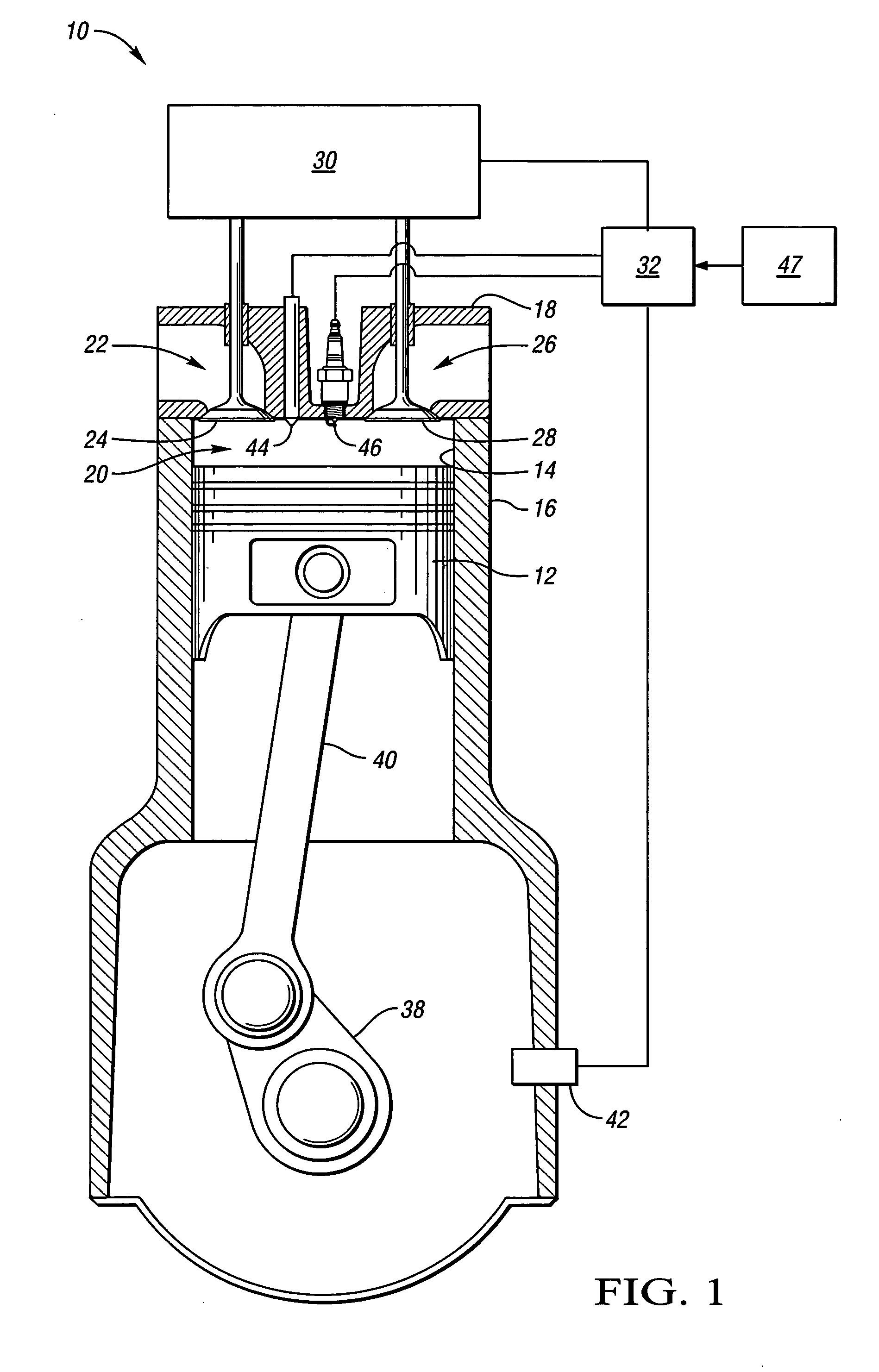
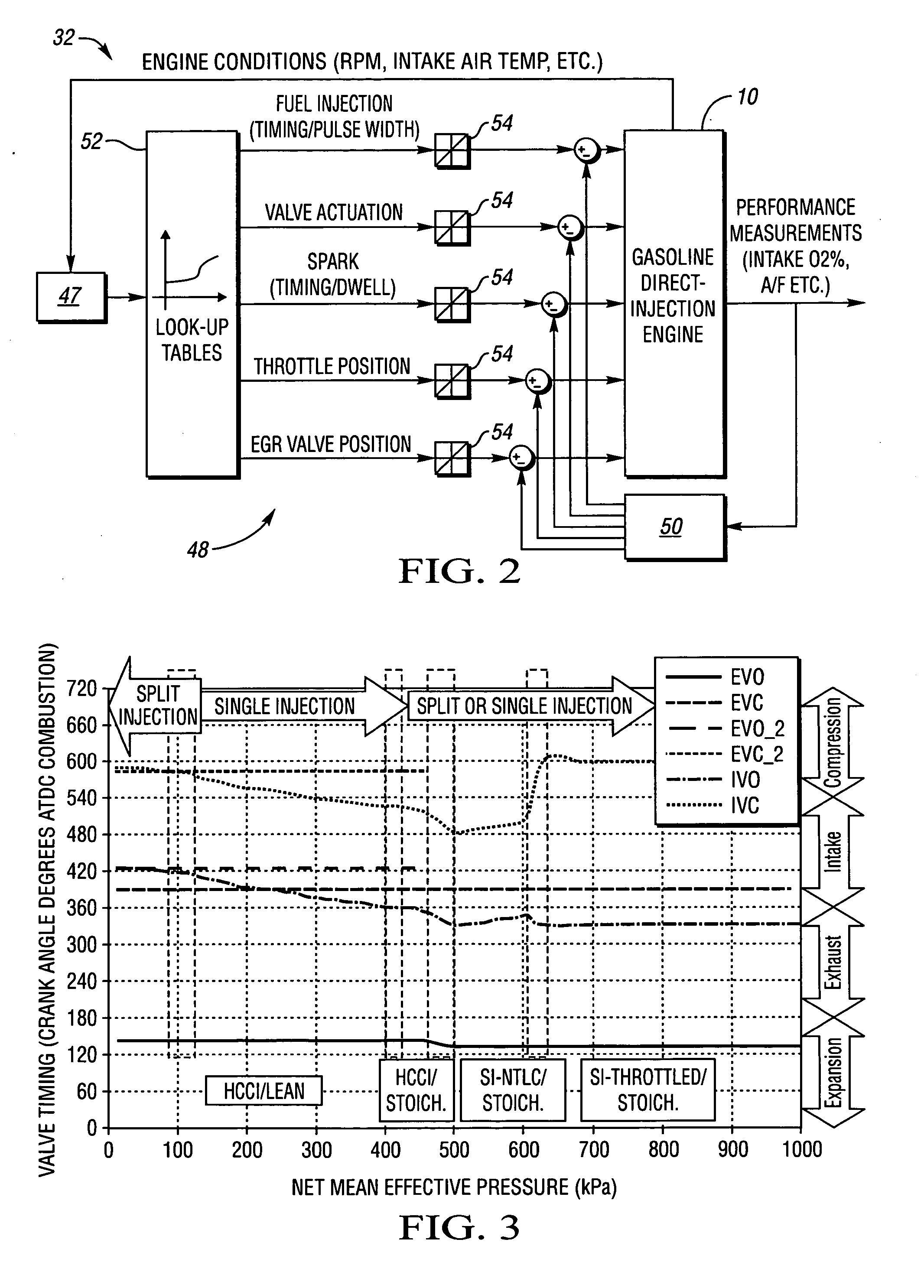
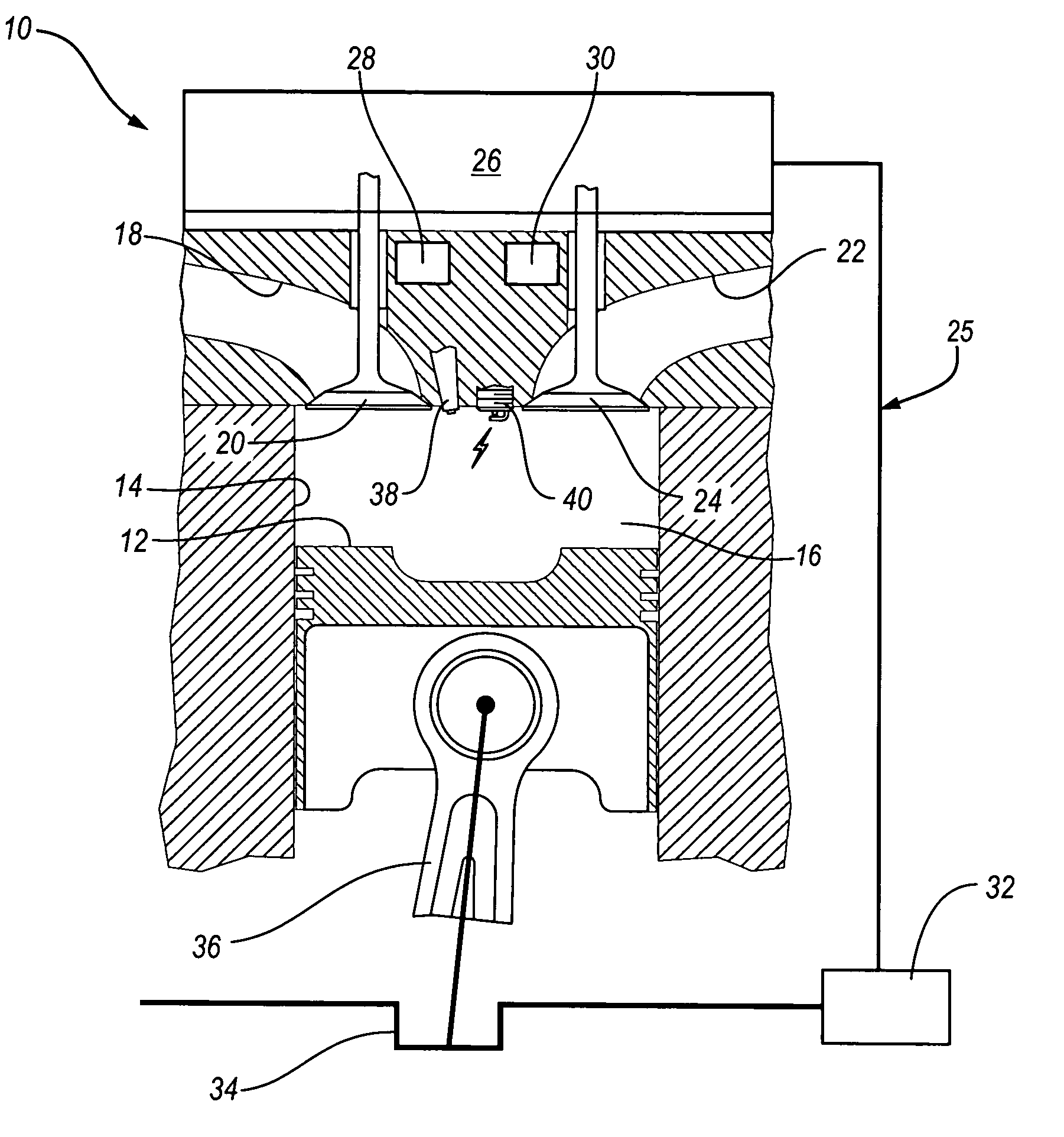
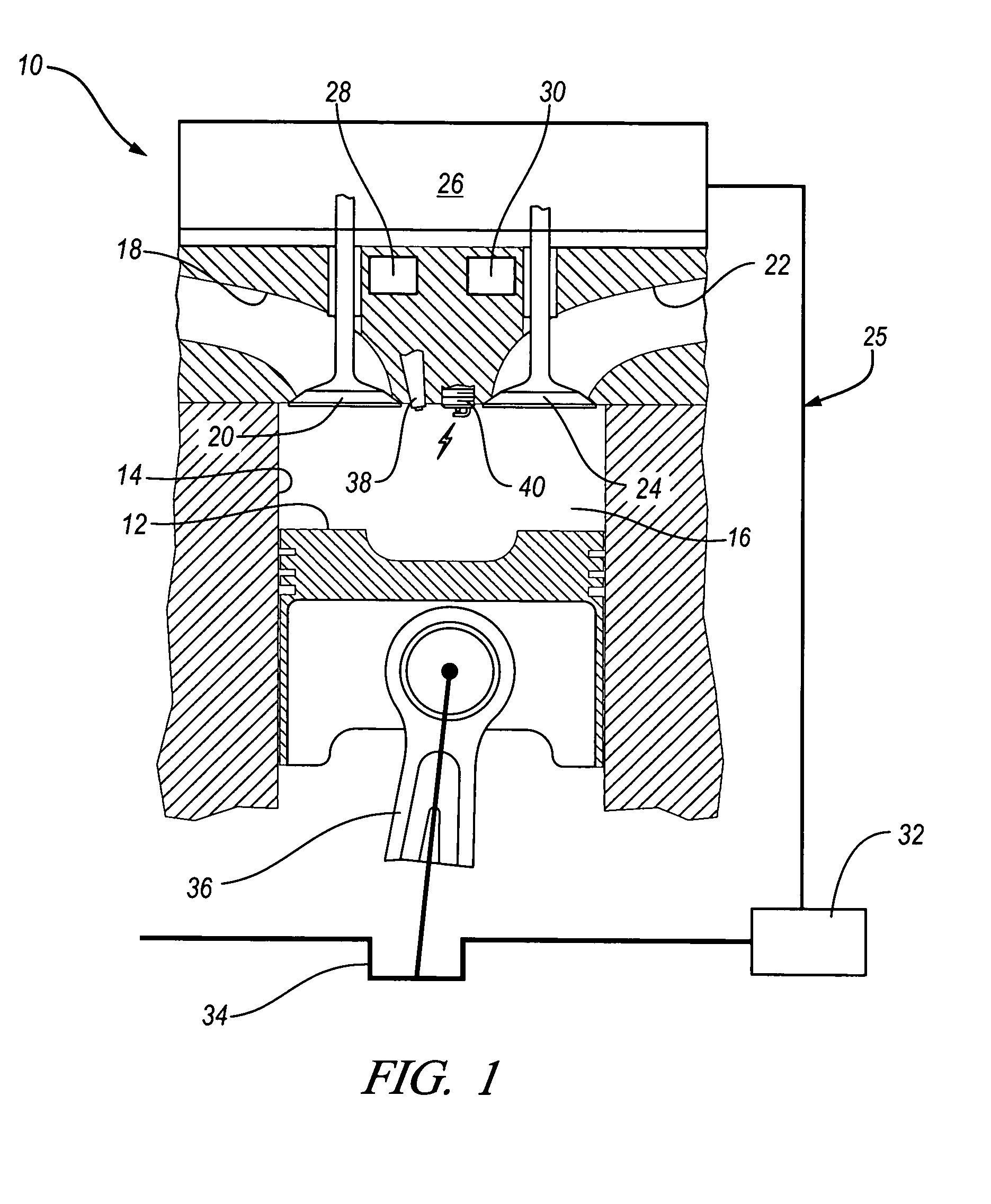
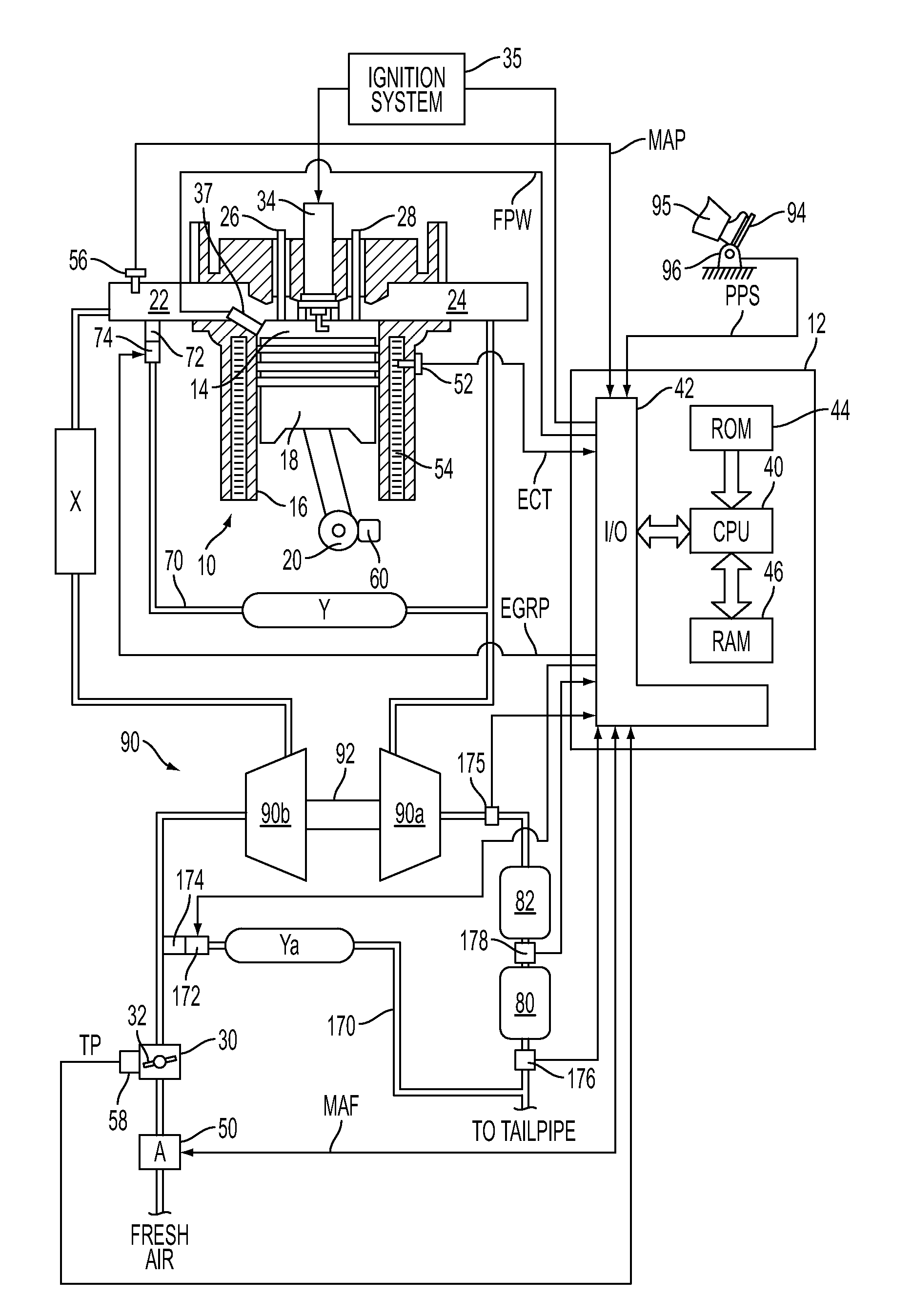
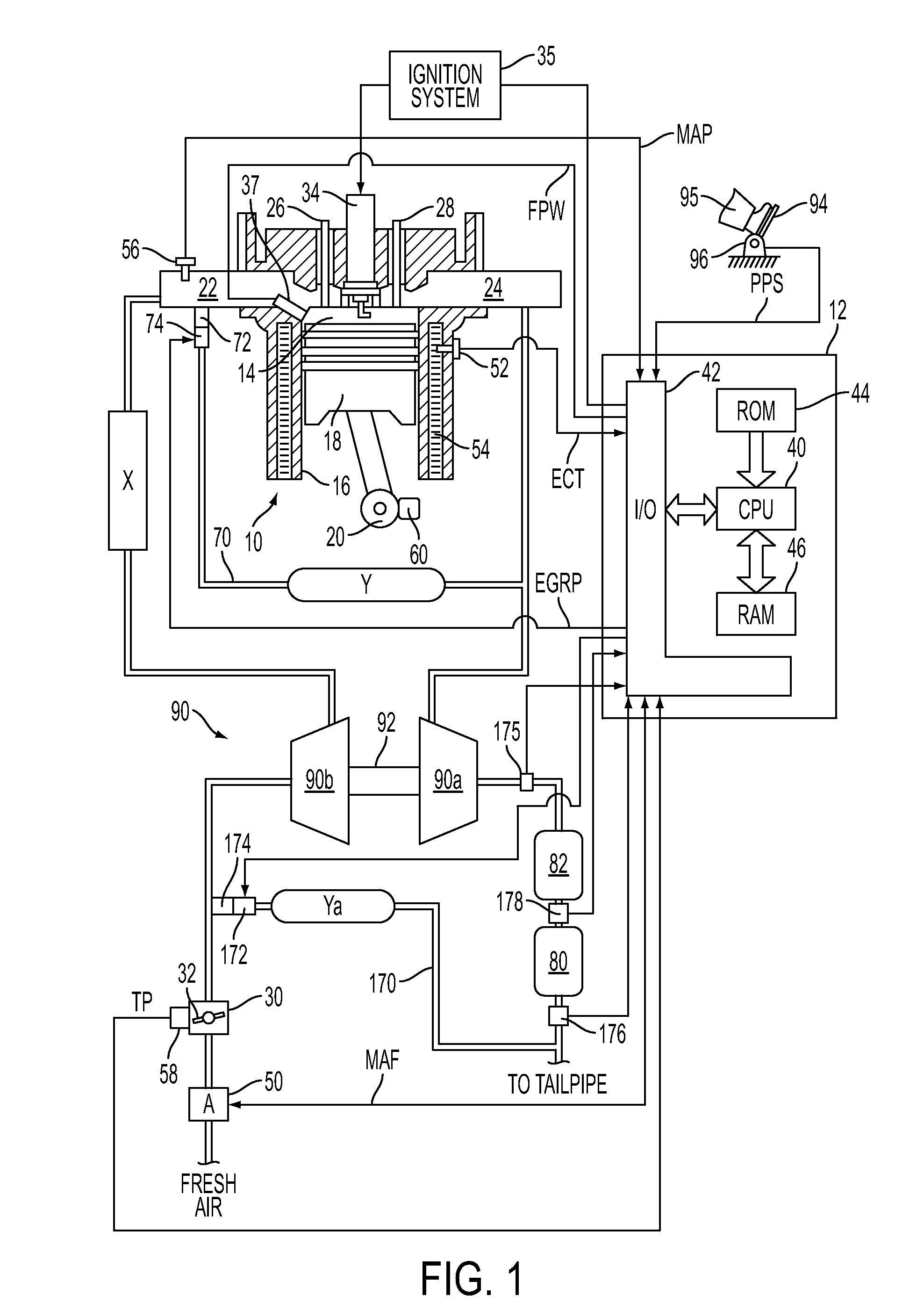
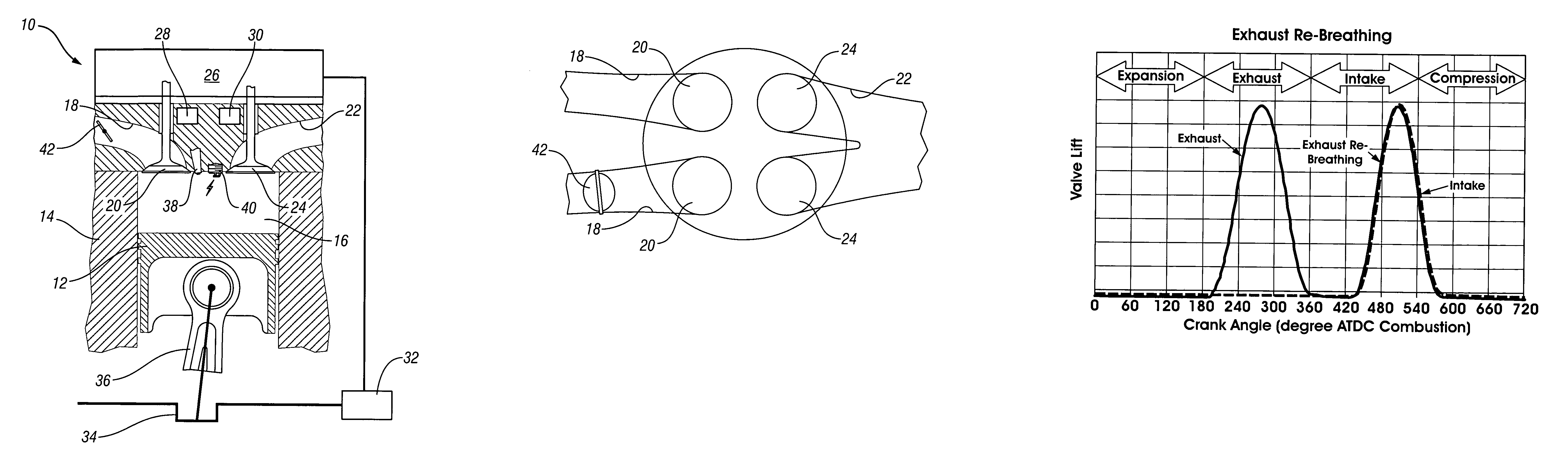
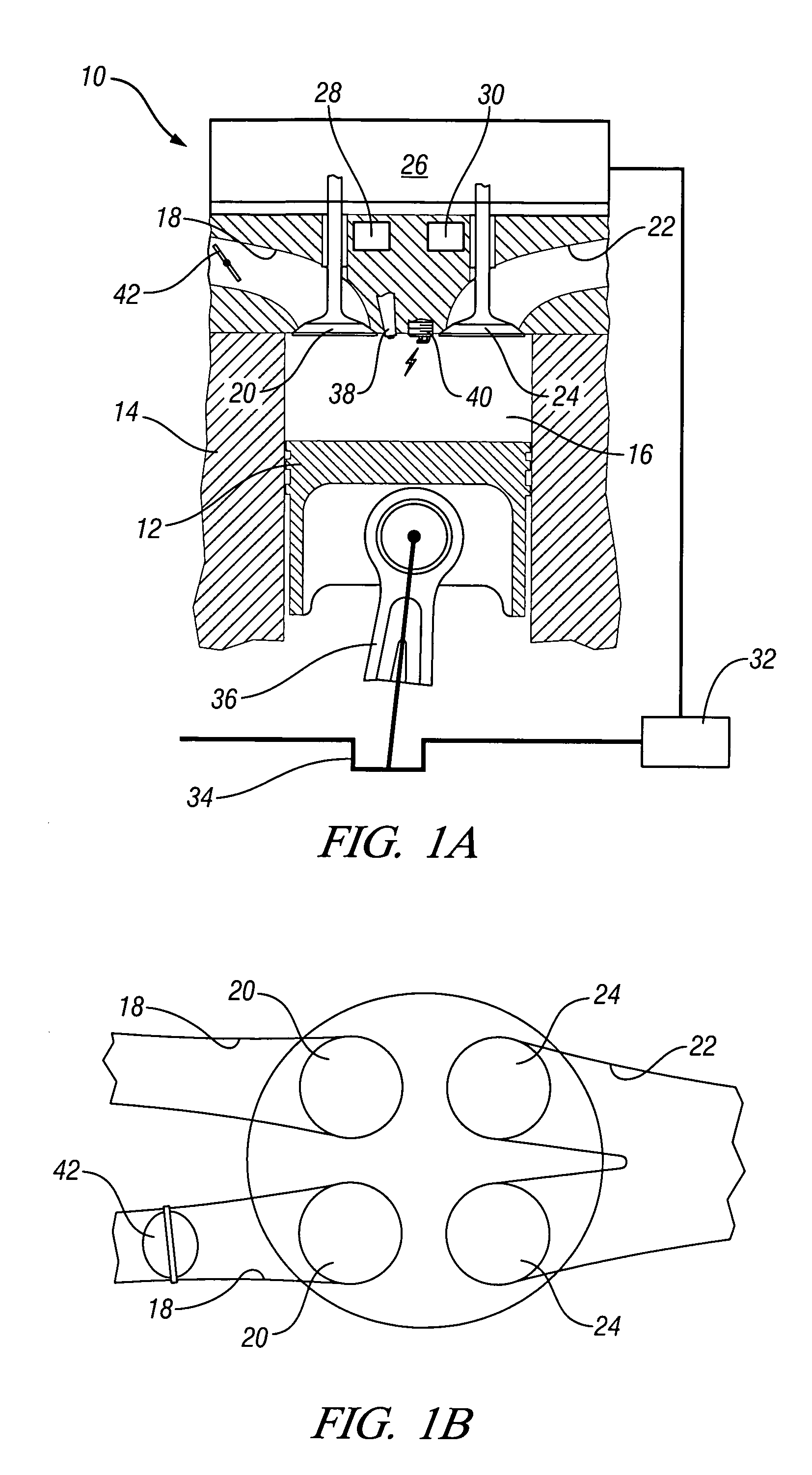
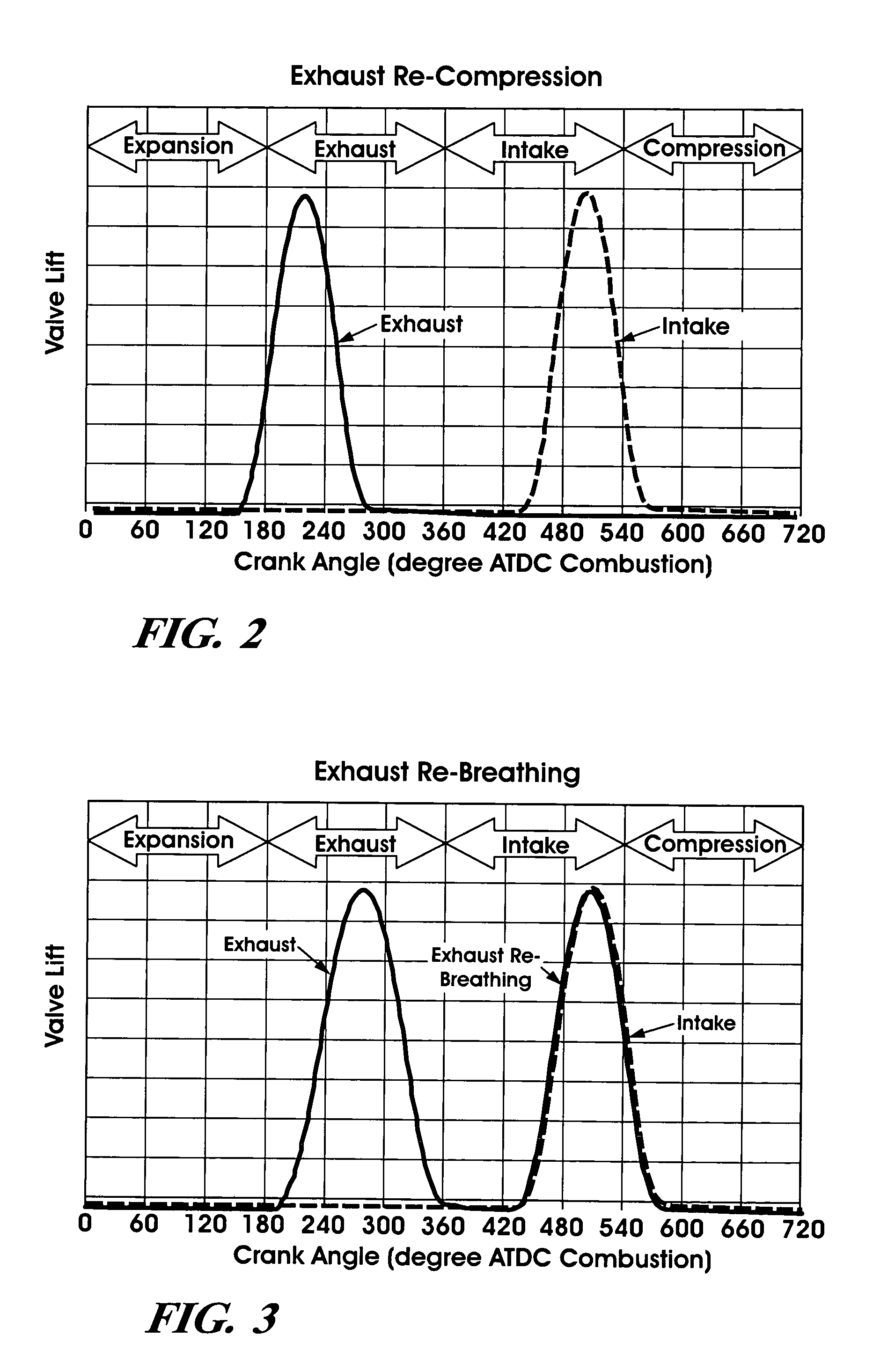
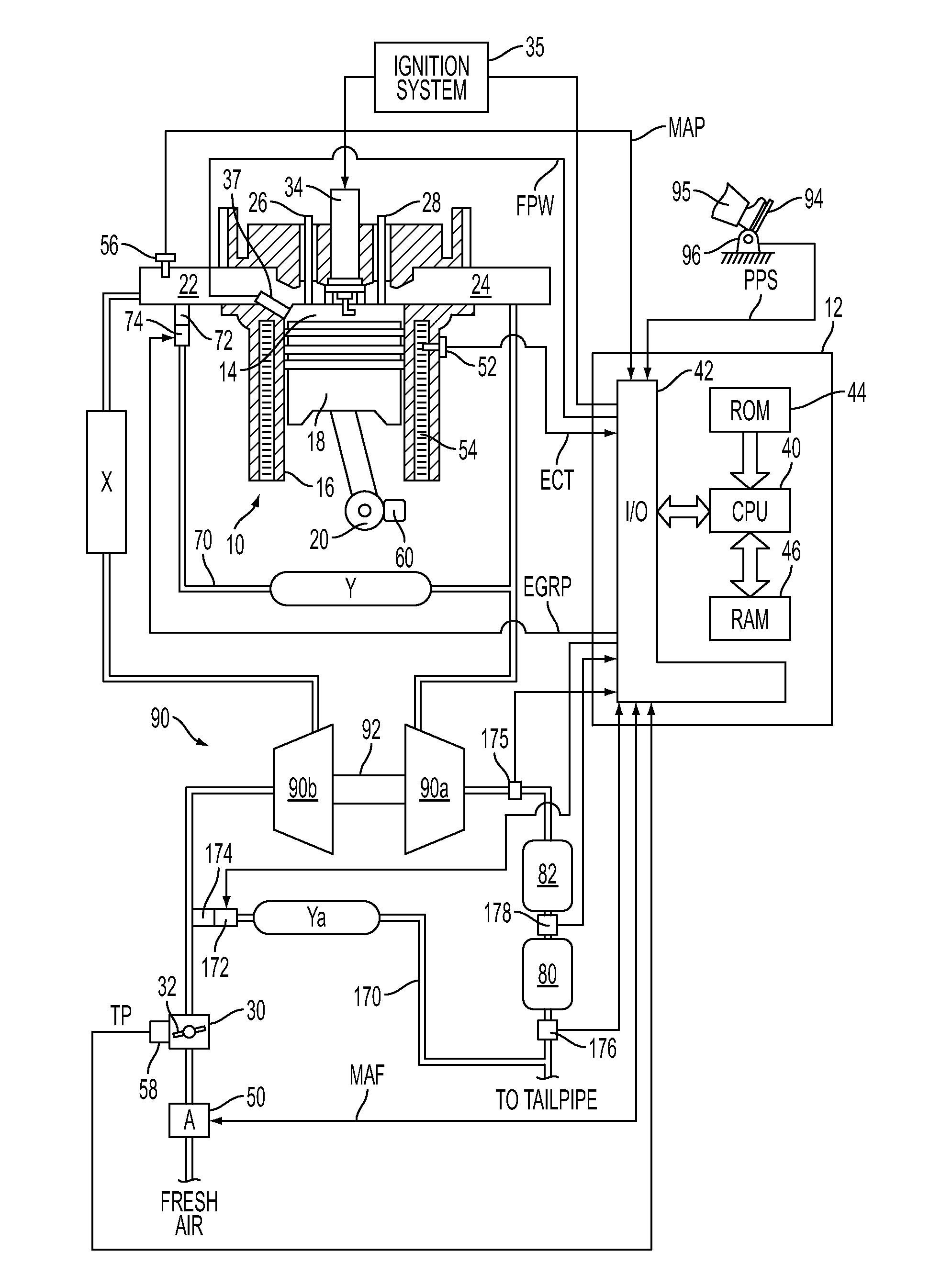
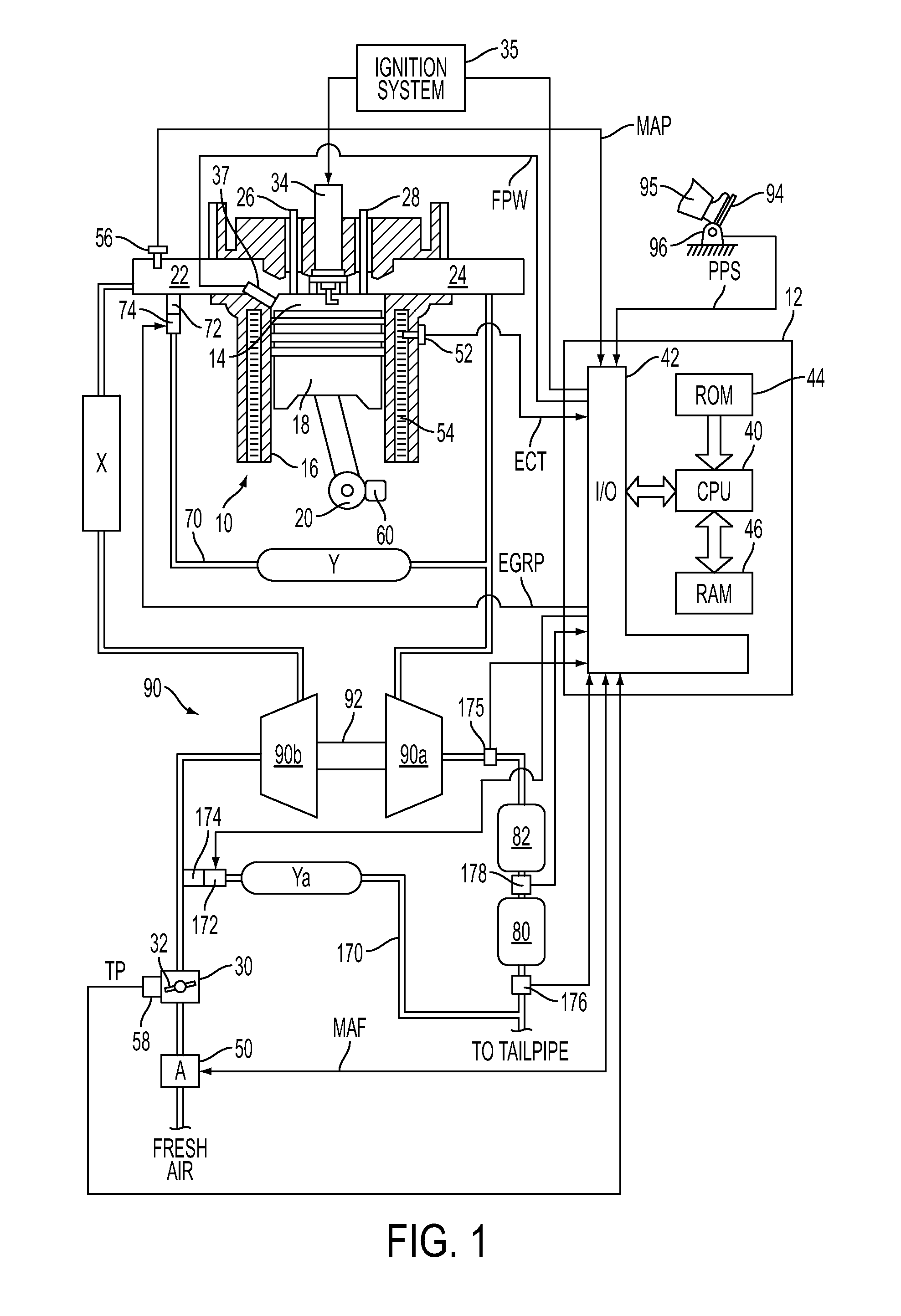
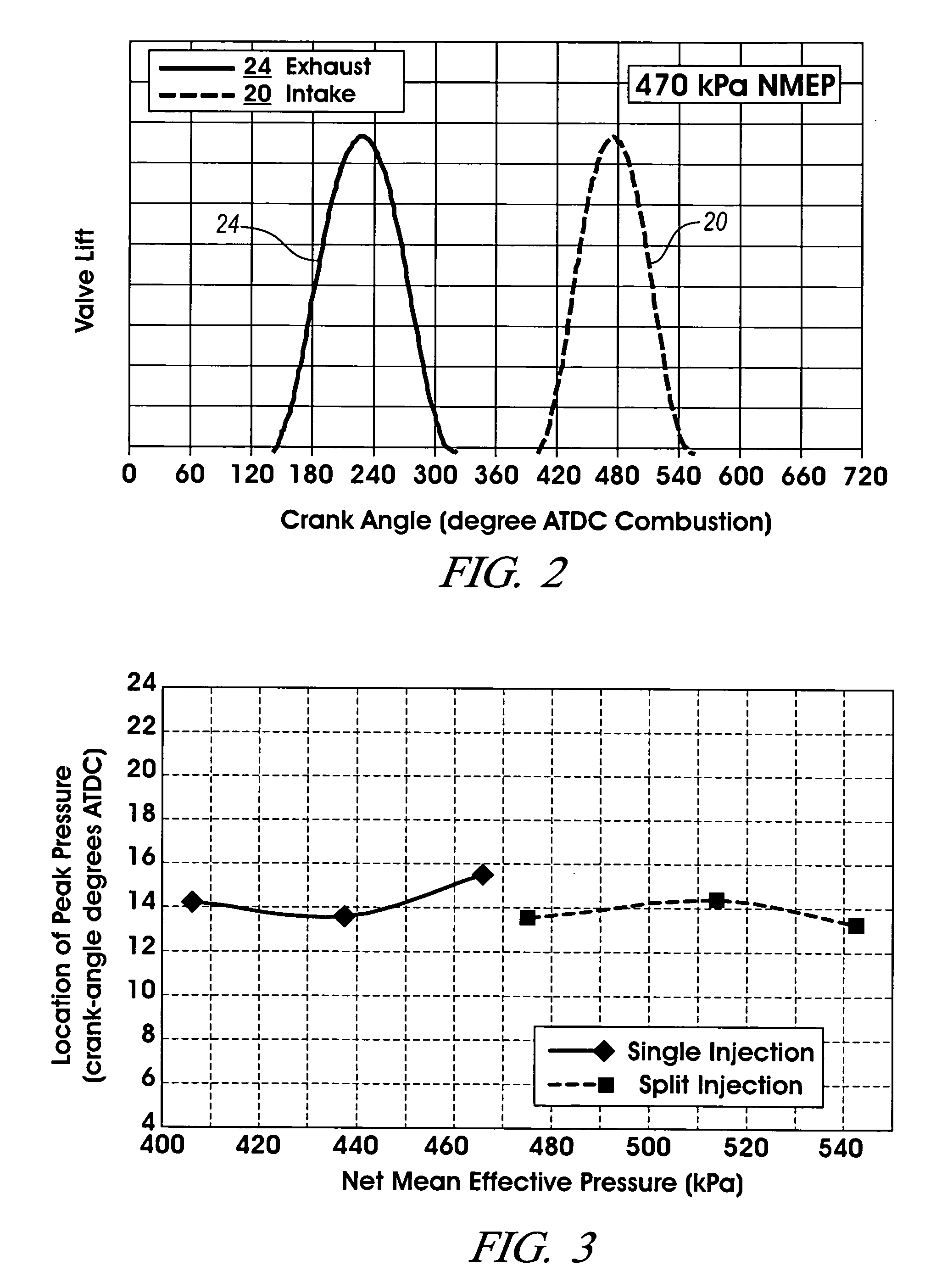
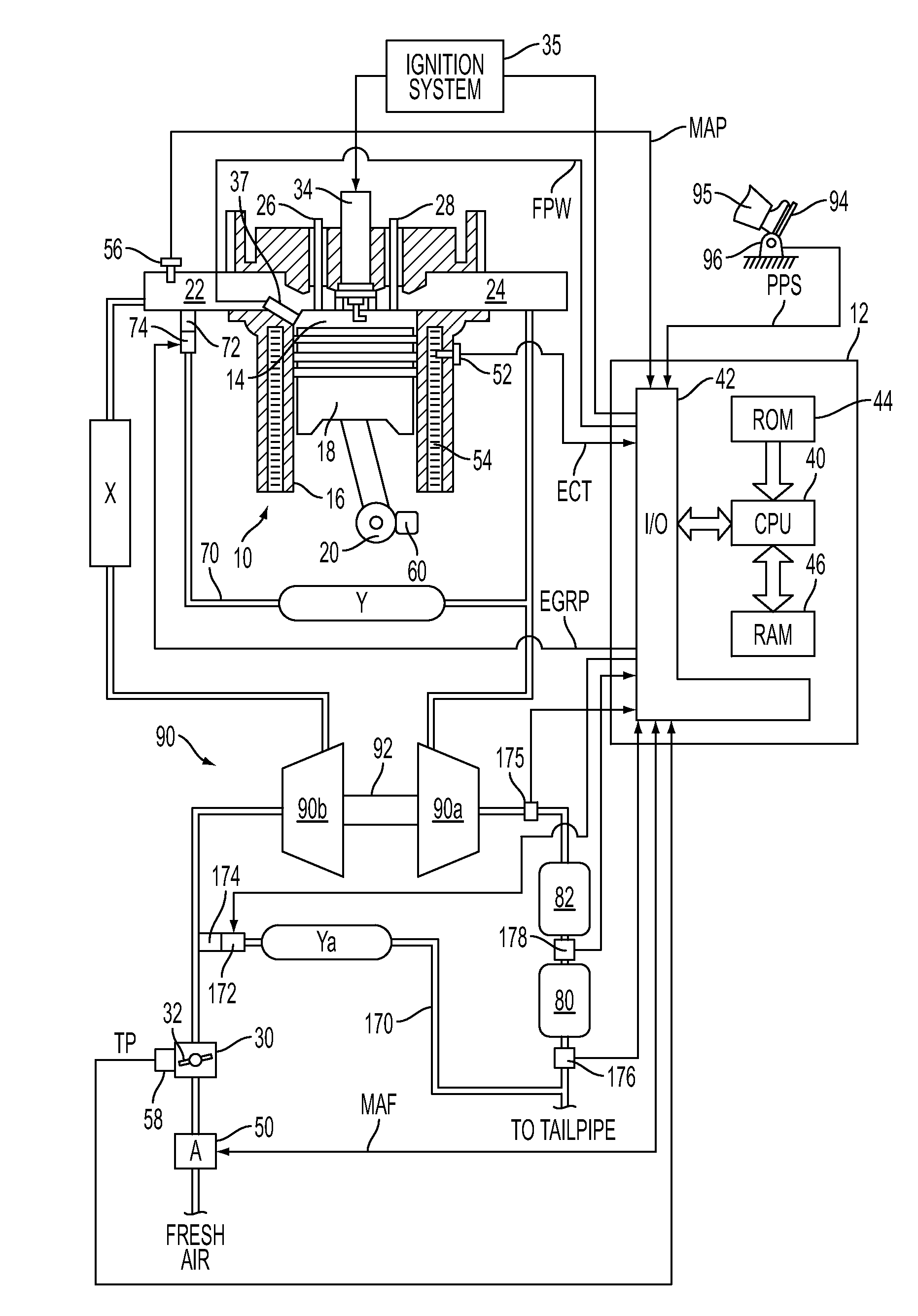
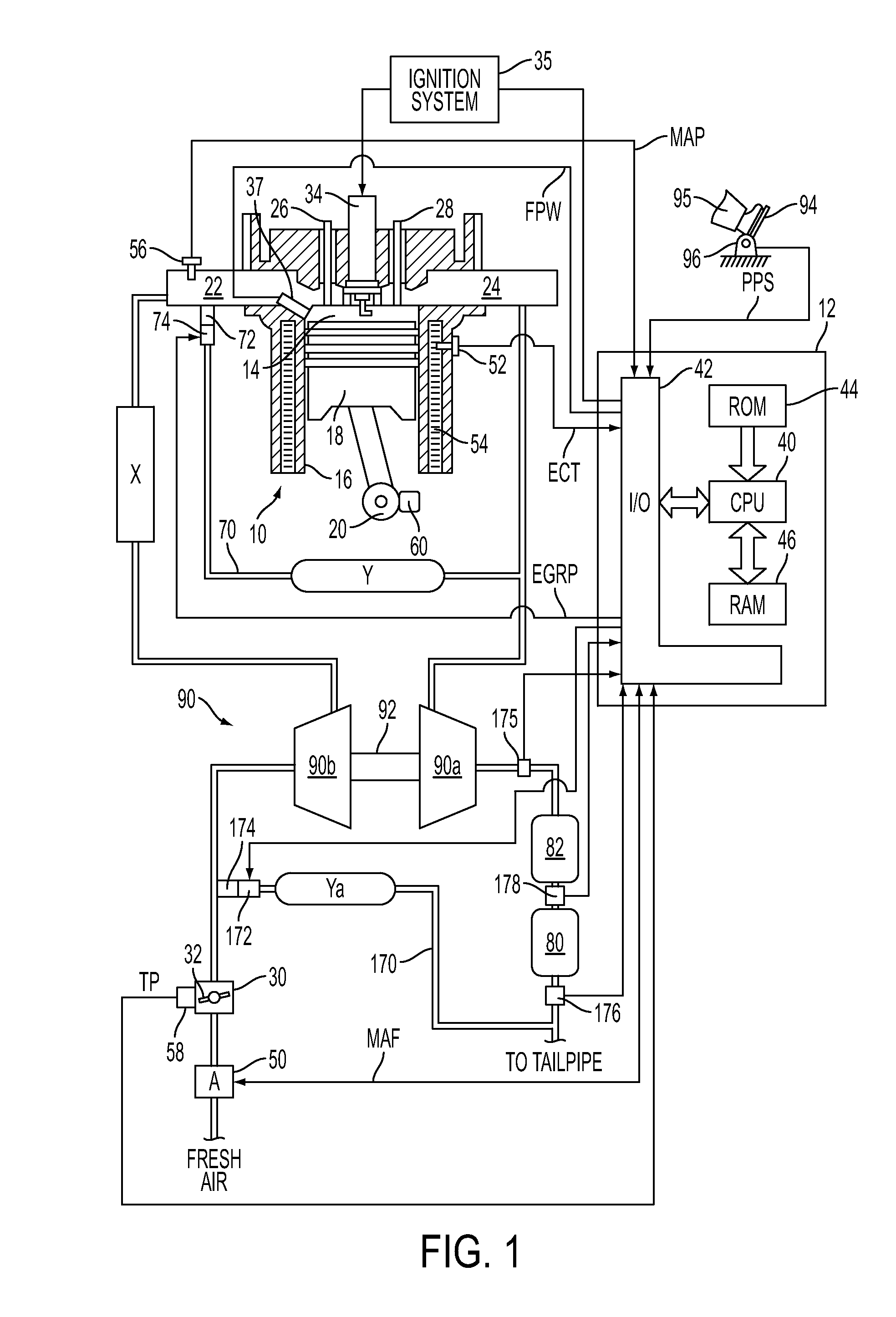
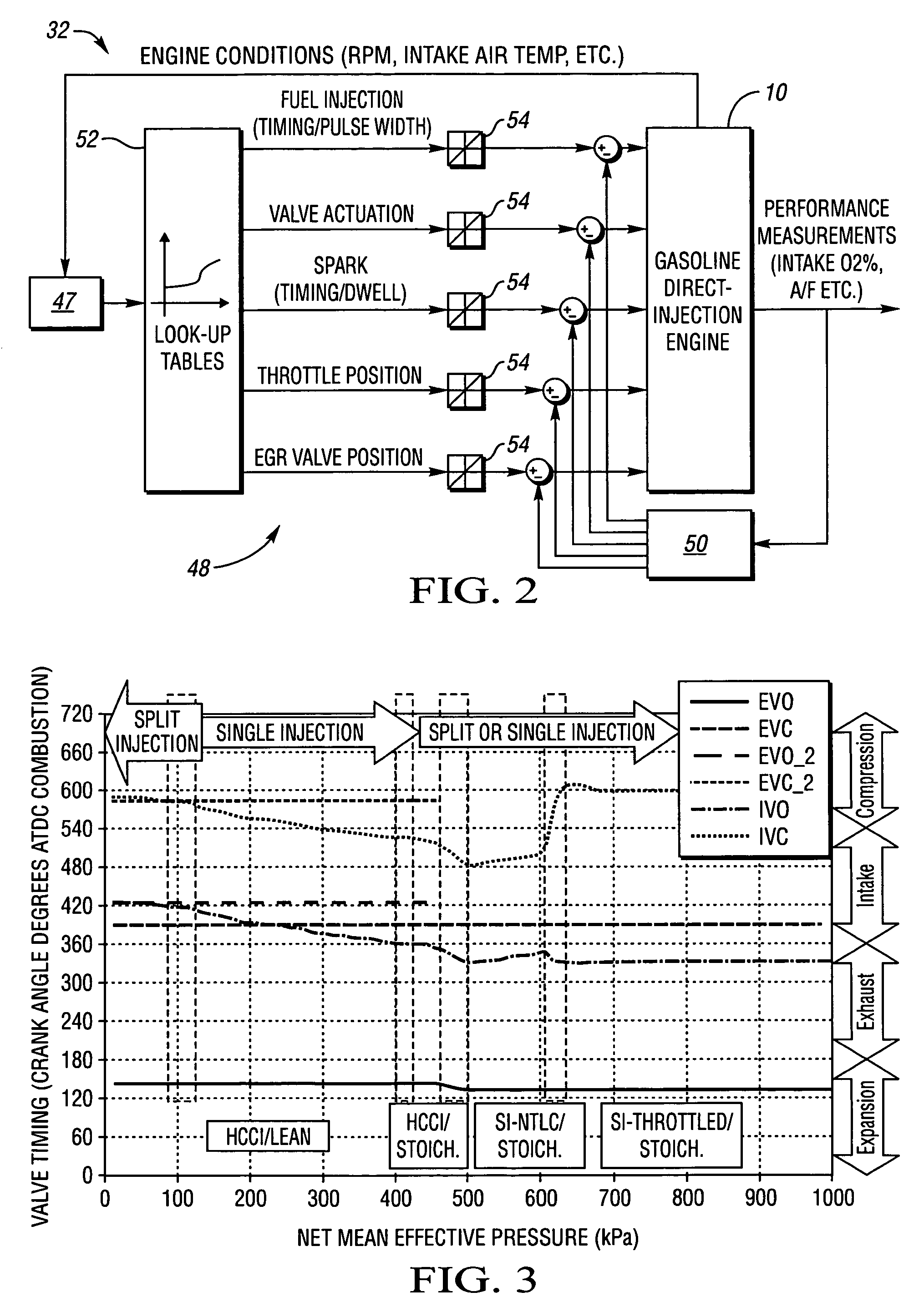
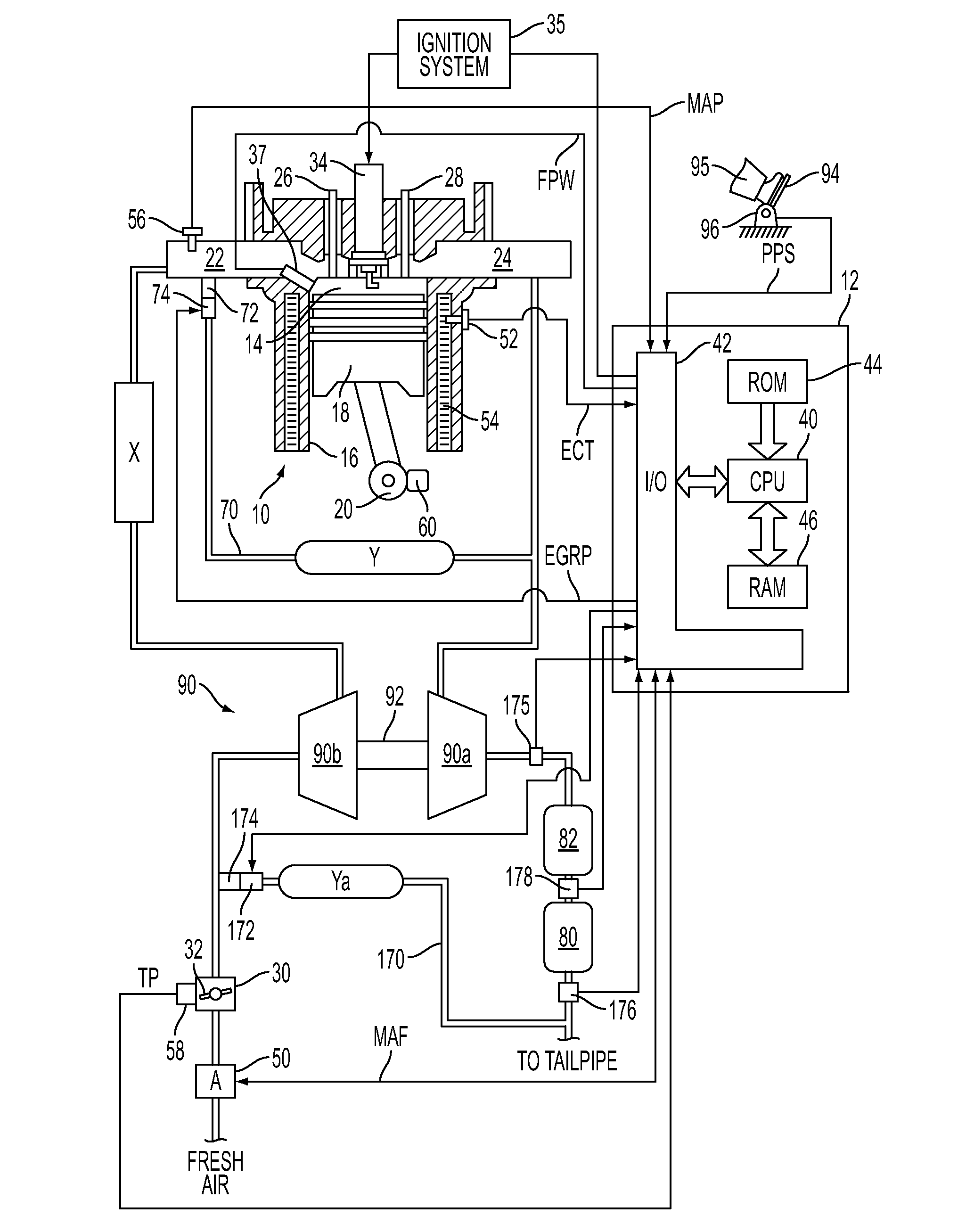
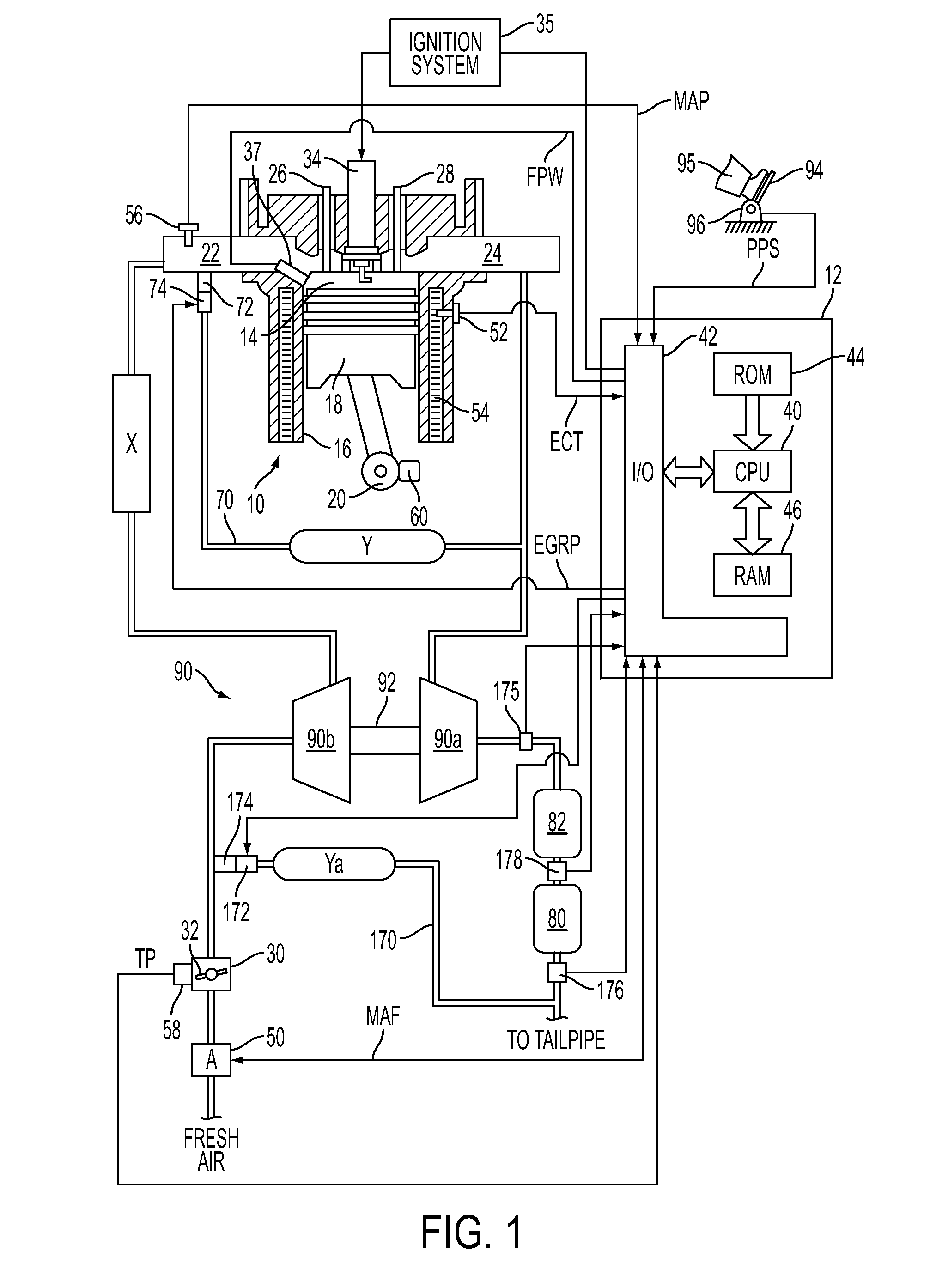
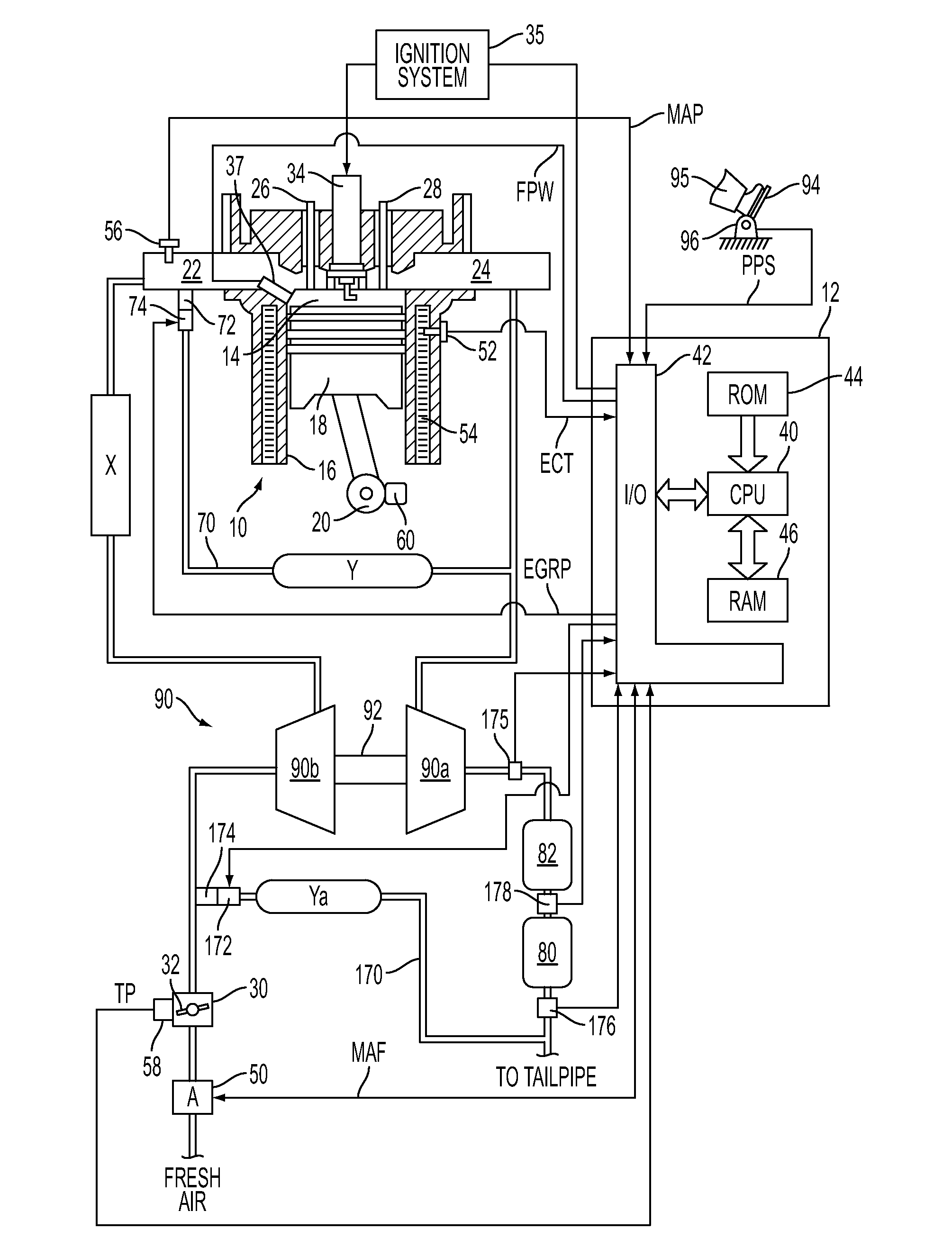
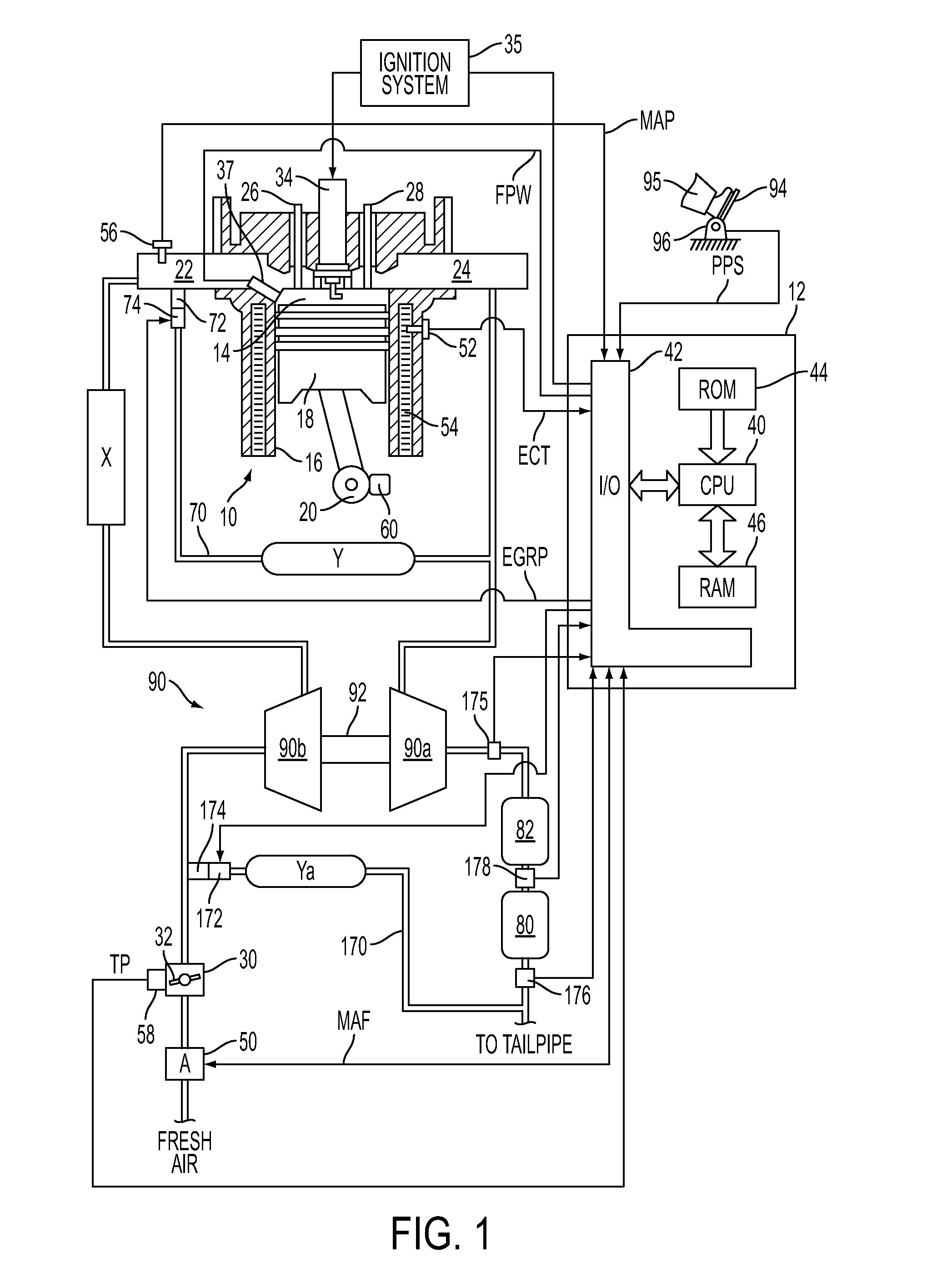
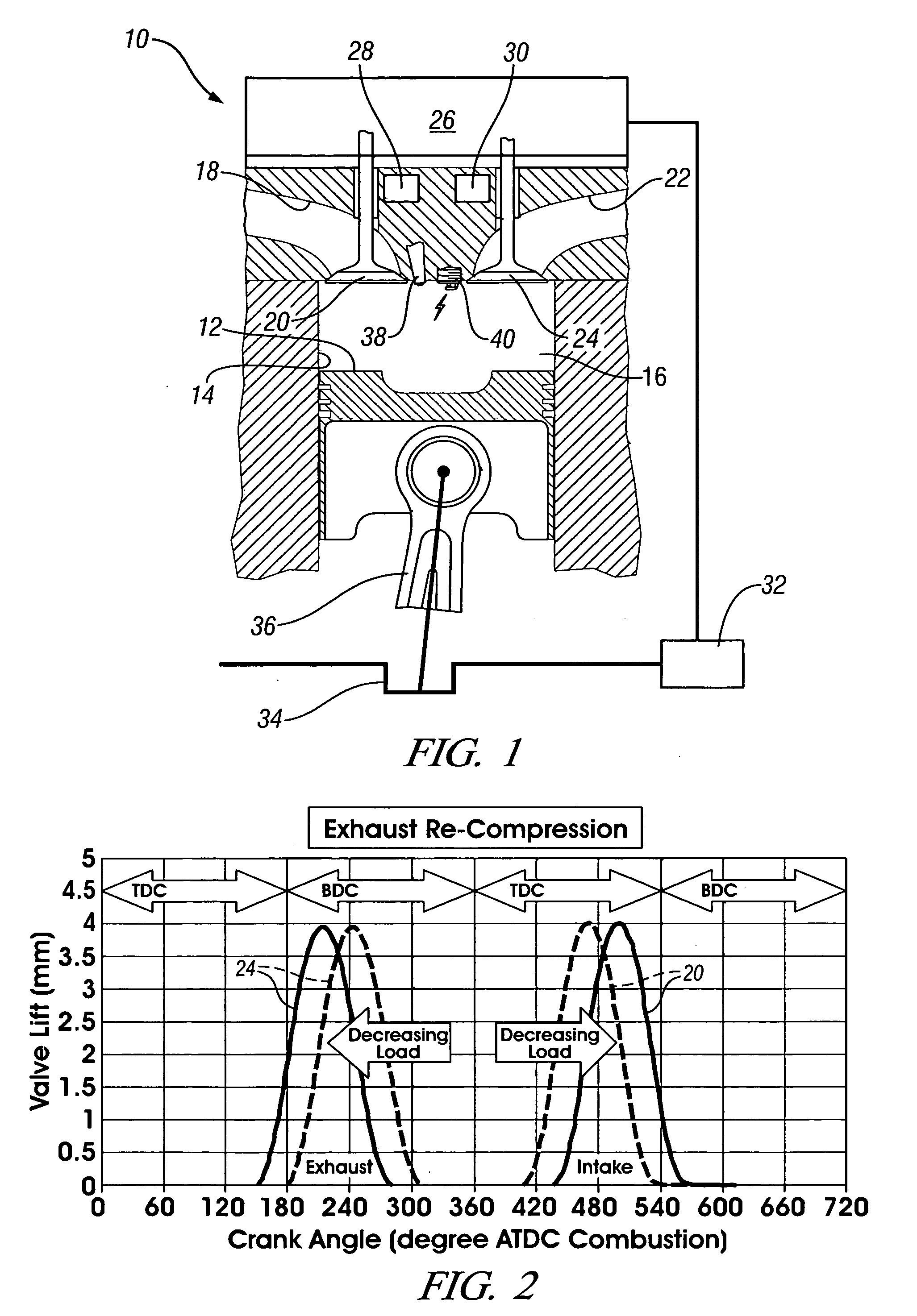
The present invention relates to methods for robust controlled auto-ignition and spark ignited combustion controls in gasoline direct-injection engines, including transients, using either exhaust re-breathing or a combination of exhaust re-compression and re-breathing valve strategy. These methods are capable of enabling engine operation with either lean of stoichiometric or stoichiometric air / fuel ratio for oxides of nitrogen (NOx) control, with varying exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) rates and throttle valve positions for knock control, and with a combination of homogeneous charge compression ignition (HCCI) and spark ignition (SI) combustion modes to optimize fuel economy over a wide range of engine operating conditions.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Method for mid load operation of auto-ignition combustion
ActiveUS6994072B2Electrical controlNon-fuel substance addition to fuelPressure riseMultiple injection
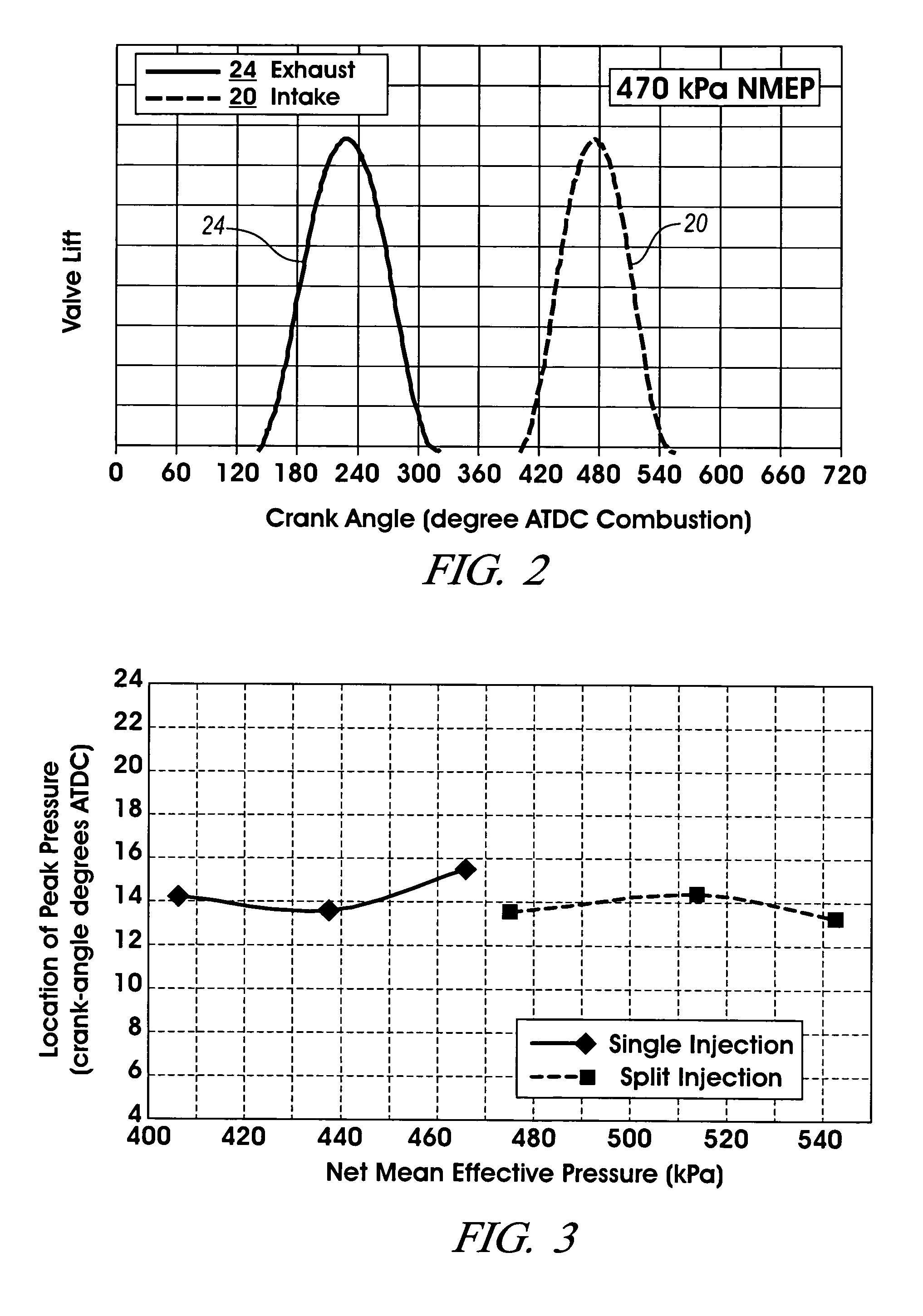
A method is disclosed for expanding the mid load operation limit in a four-stroke gasoline direct-injection controlled auto-ignition combustion engine. A system is employed for variably actuating the intake and exhaust valves and for operating the valves with an exhaust re-compression or exhaust re-breathing valve strategy. A spark plug is provided. A fuel injector having multiple injection capability is employed. A first fuel charge is injected into the combustion chamber to form a lean air-fuel mixture. A second fuel charge is injected into the combustion chamber to form a stratified air-fuel mixture having an ignitable mixture located near the spark plug. The ignitable mixture is ignited at the spark gap, thereby causing spark-ignition combustion that causes a sufficient increase in chamber pressure and temperature to trigger auto-ignition of the lean air-fuel mixture, resulting in the obtaining of a higher engine load before a pressure rise rate in the combustion chamber exceeds a prescribed threshold value.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Method for controlling fuel of a spark ignited engine while regenerating a particulate filter
ActiveUS20110073088A1Improve efficiencyLower charging temperatureElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesGasoline direct injectionExhaust fumes
A system for filtering and oxidizing particulate matter produced by a gasoline direct injection engine is disclosed. In one embodiment, engine cylinder air-fuel is adjusted to allow soot to oxidize at an upstream particulate filter while exhaust gases are efficiently processed in a downstream catalyst.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Method for auto-ignition combustion control
ActiveUS7080613B2Lower ratioIncrease ratingsElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesExhaust valveCombustion chamber
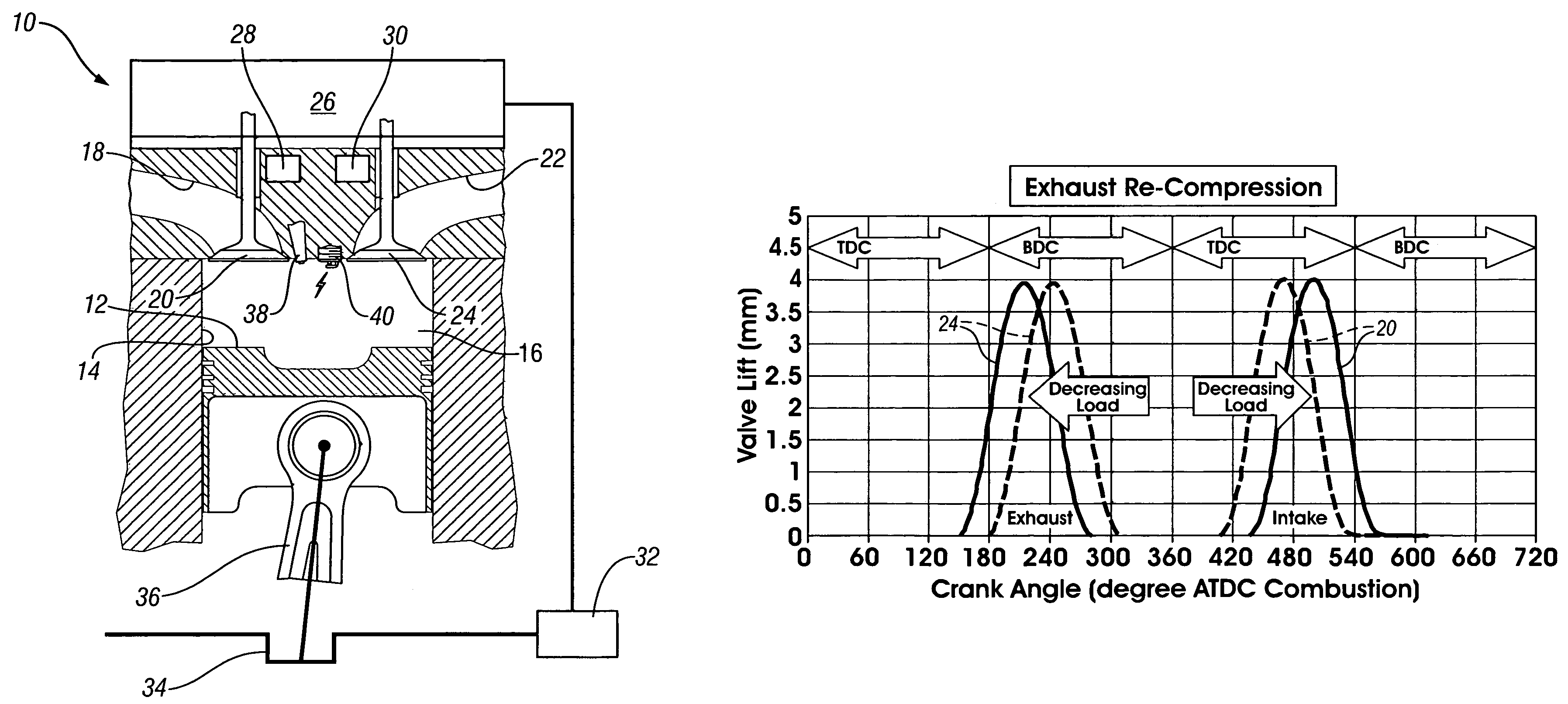
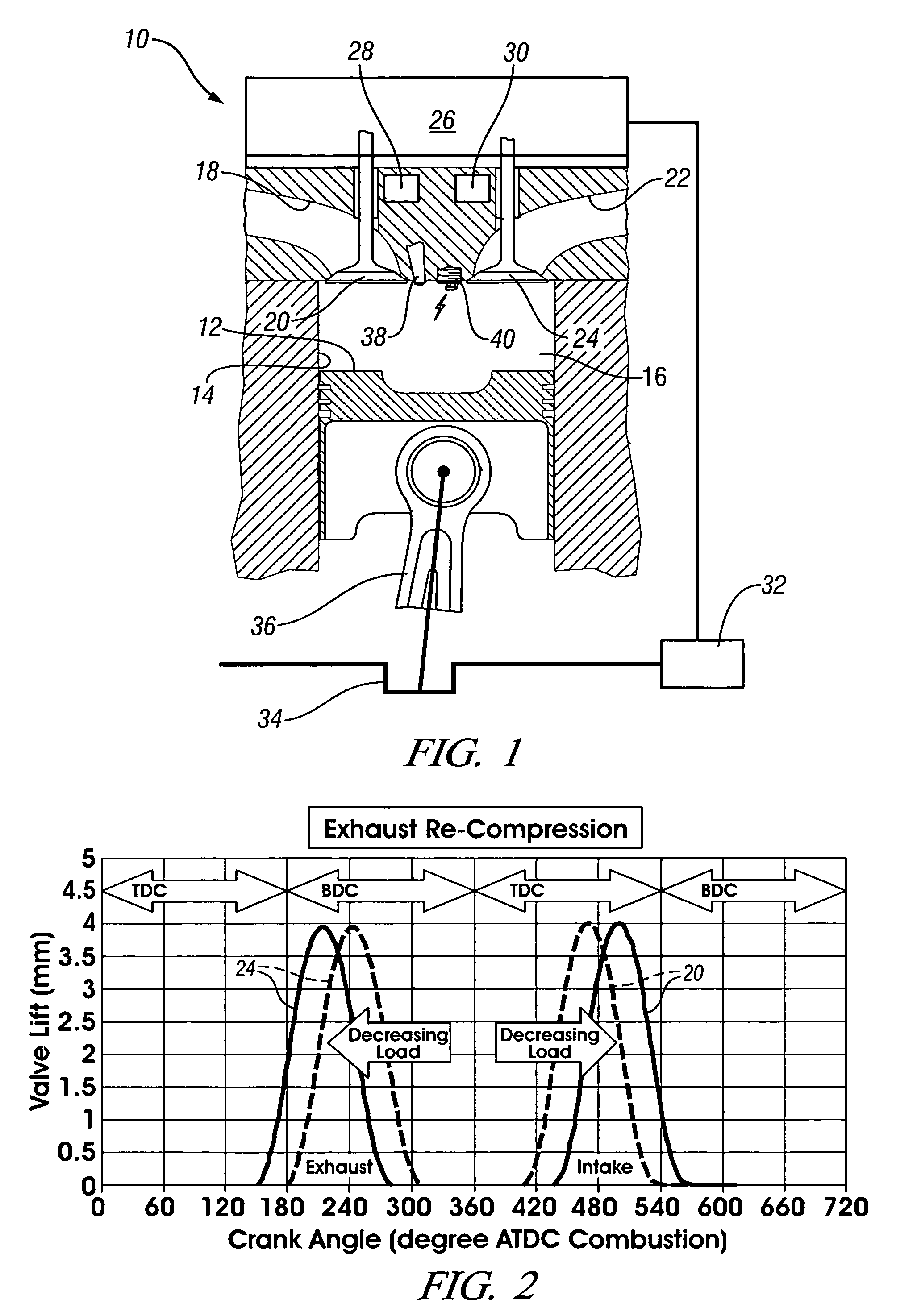
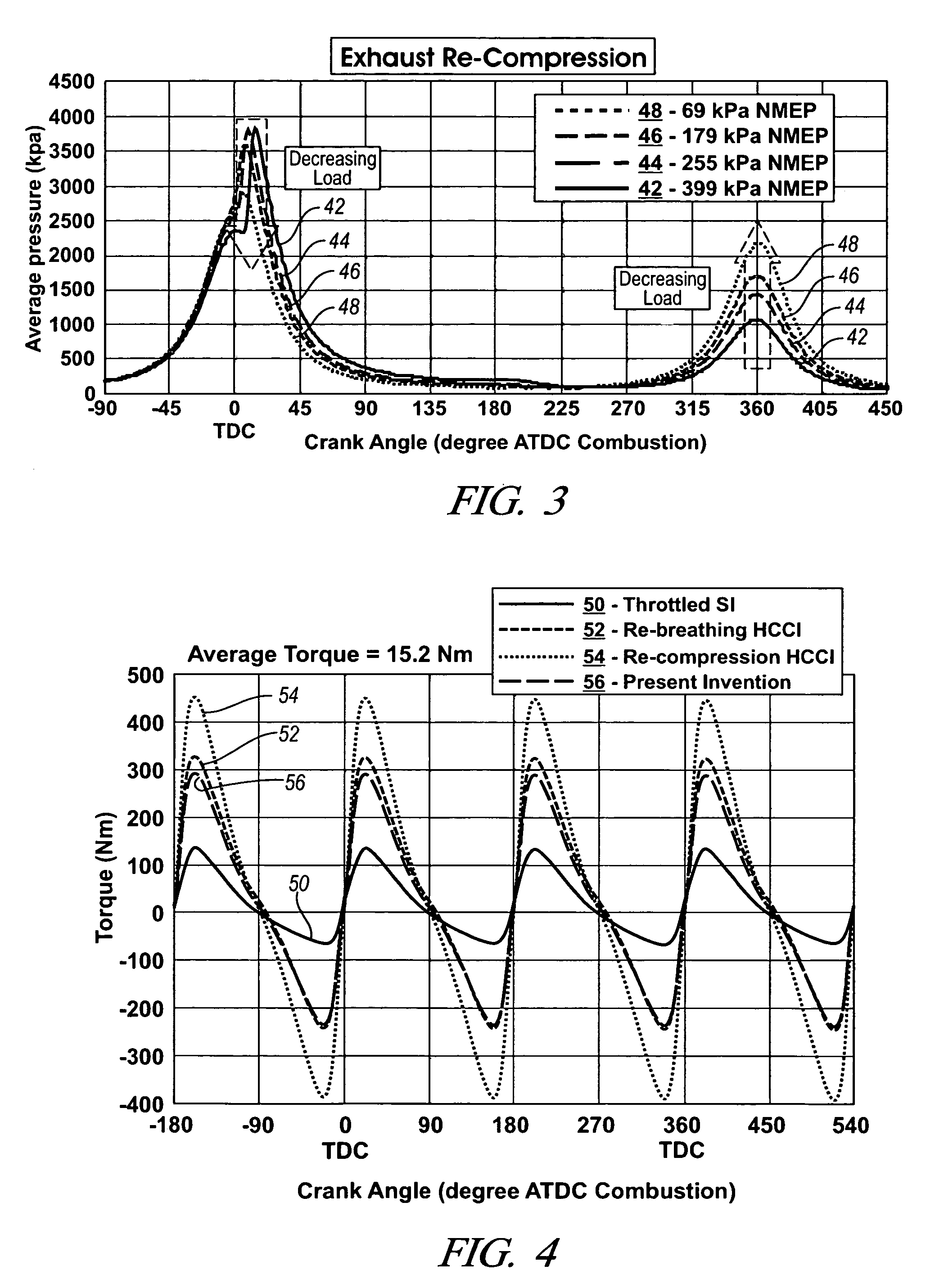
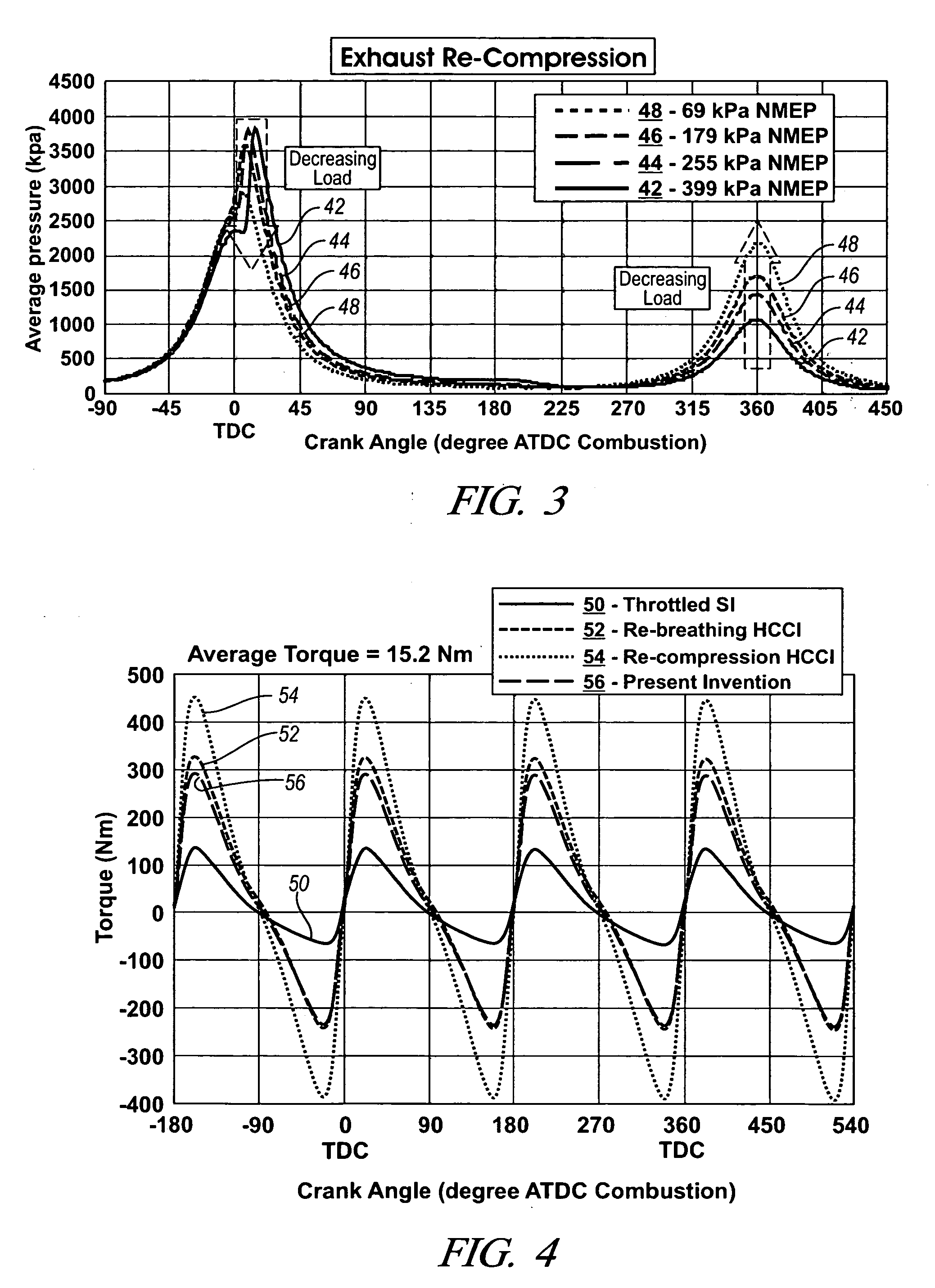
A method is disclosed for controlling the air-fuel ratio in a four-stroke gasoline direct-injection controlled auto-ignition combustion. The engine is operated with two sequential pairs of expansion and contraction strokes during two revolutions of the engine crank, the two revolutions defining a combustion cycle. A system is employed for variably actuating the intake and exhaust valves and adjusting the flow of air and burned gases entering the combustion chamber. Adjusting the flow affects the resulting air-fuel ratio in the combustion chamber. The valve actuating system is employable to operate the intake and exhaust valves with an exhaust re-compression or an exhaust re-breathing valve strategy. Either valve strategy affects the air-fuel ratio in the cylinder and causes a proportion of burned gases from previous combustion cycles to be retained in the cylinder to provide the necessary conditions for auto-ignition of the air-fuel mixture.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Fuel control for spark ignited engine having a particulate filter system
ActiveUS20110072787A1Improve efficiencyLess tendencyElectrical controlNon-fuel substance addition to fuelGasoline direct injectionFilter system
A system for filtering and oxidizing particulate matter produced by a gasoline direct injection engine is disclosed. In one embodiment, engine cylinder air-fuel is adjusted to allow soot to oxidize at an upstream particulate filter while exhaust gases are efficiently processed in a downstream catalyst.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Method for mid load operation of auto-ignition combustion
Owner:MICHIGAN UNIV OF OFFICE OF TECH TRANSFER +1
Method for mid load operation of auto-ignition combustion
ActiveUS20060005804A1Easy loadingElectrical controlNon-fuel substance addition to fuelPressure riseMultiple injection
A method is disclosed for expanding the mid load operation limit in a four-stroke gasoline direct-injection controlled auto-ignition combustion engine. A system is employed for variably actuating the intake and exhaust valves and for operating the valves with an exhaust re-compression or exhaust re-breathing valve strategy. A spark plug is provided. A fuel injector having multiple injection capability is employed. A first fuel charge is injected into the combustion chamber to form a lean air-fuel mixture. A second fuel charge is injected into the combustion chamber to form a stratified air-fuel mixture having an ignitable mixture located near the spark plug. The ignitable mixture is ignited at the spark gap, thereby causing spark-ignition combustion that causes a sufficient increase in chamber pressure and temperature to trigger auto-ignition of the lean air-fuel mixture, resulting in the obtaining of a higher engine load before a pressure rise rate in the combustion chamber exceeds a prescribed threshold value.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Four stroke engine auto-ignition combustion
ActiveUS7059281B2Electrical controlNon-fuel substance addition to fuelExhaust valveGasoline direct injection
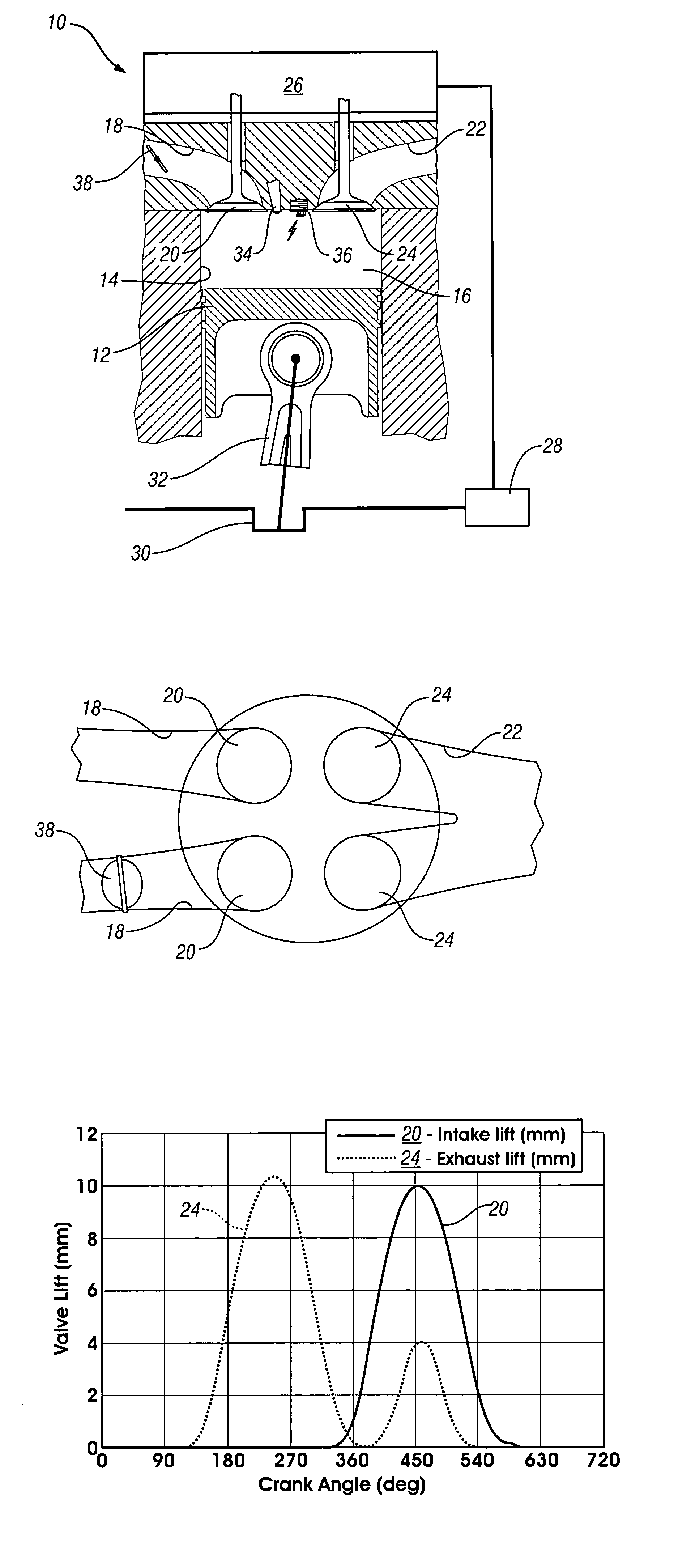
A method of operating a four-stroke gasoline direct-injection controlled auto-ignition combustion engine includes opening both the intake and exhaust valves during terminal portions of the expansion strokes and initial portions of the contraction strokes, injecting fuel directly into the combustion chamber for mixing with retained gases and igniting the fuel near the ends of the contraction strokes. In the process, combustion gases are expanded to produce power during major portions of the expansion strokes, combusted gases are blown down into the exhaust outlet and the air inlet and are partially redrawn into the cylinder with fresh air during the terminal portions of the expansion strokes so the air charges are heated by the hot exhaust gases. Portions of the charges re-expelled and the remaining portions of the charges and injected fuel are compressed for ignition of the dilute fuel / air and exhaust gas mixture. Substantial reductions of NOx emissions result from the method.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
System and method for regenerating a particulate filter accompanied by a catalyst
ActiveUS20110072783A1Improve efficiencyLess tendencyElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesGasoline direct injectionExhaust fumes
A system for filtering and oxidizing particulate matter produced by a gasoline direct injection engine is disclosed. In one embodiment, engine cylinder air-fuel is adjusted to allow soot to oxidize at an upstream particulate filter while exhaust gases are efficiently processed in a downstream catalyst.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
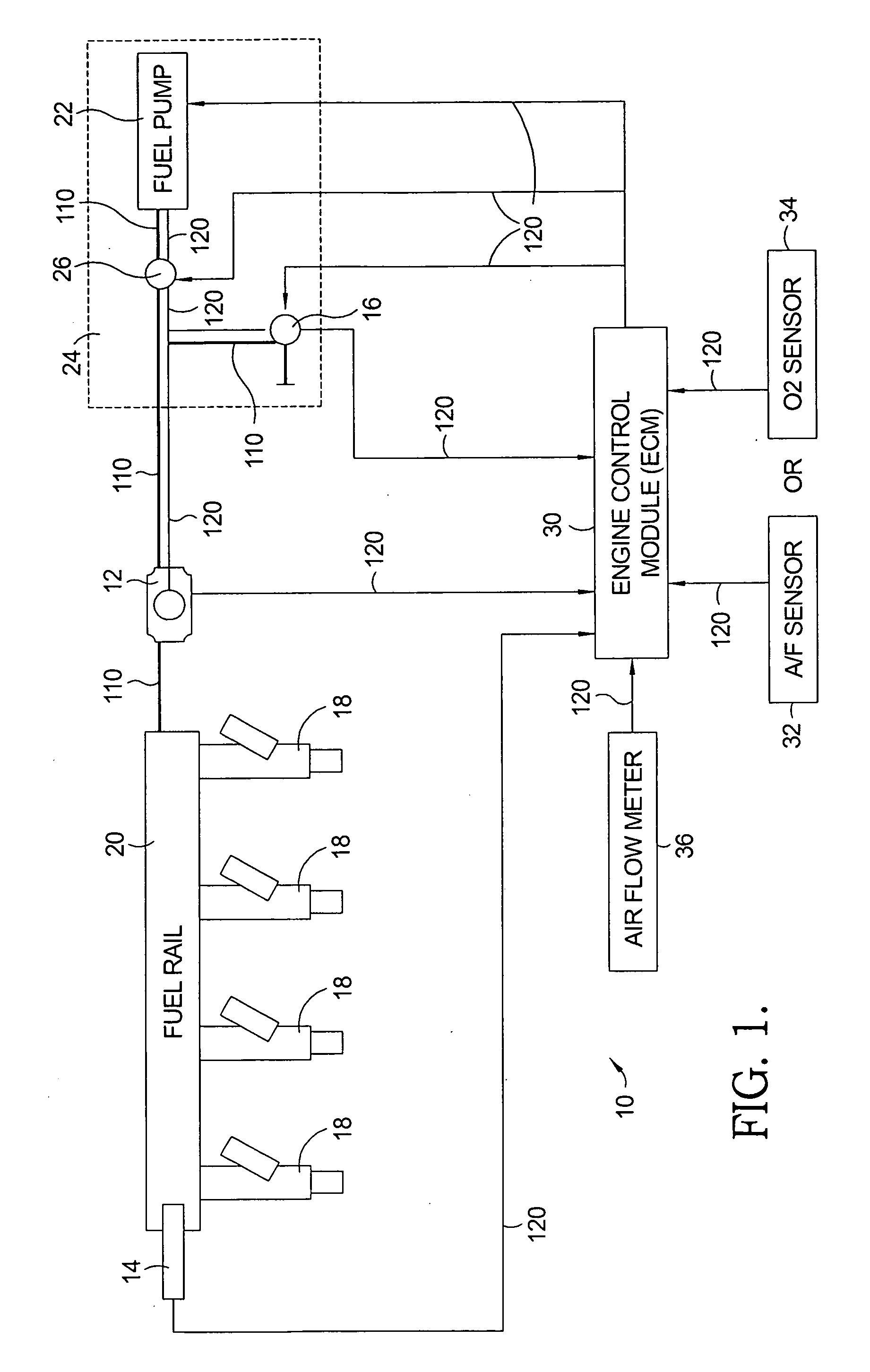
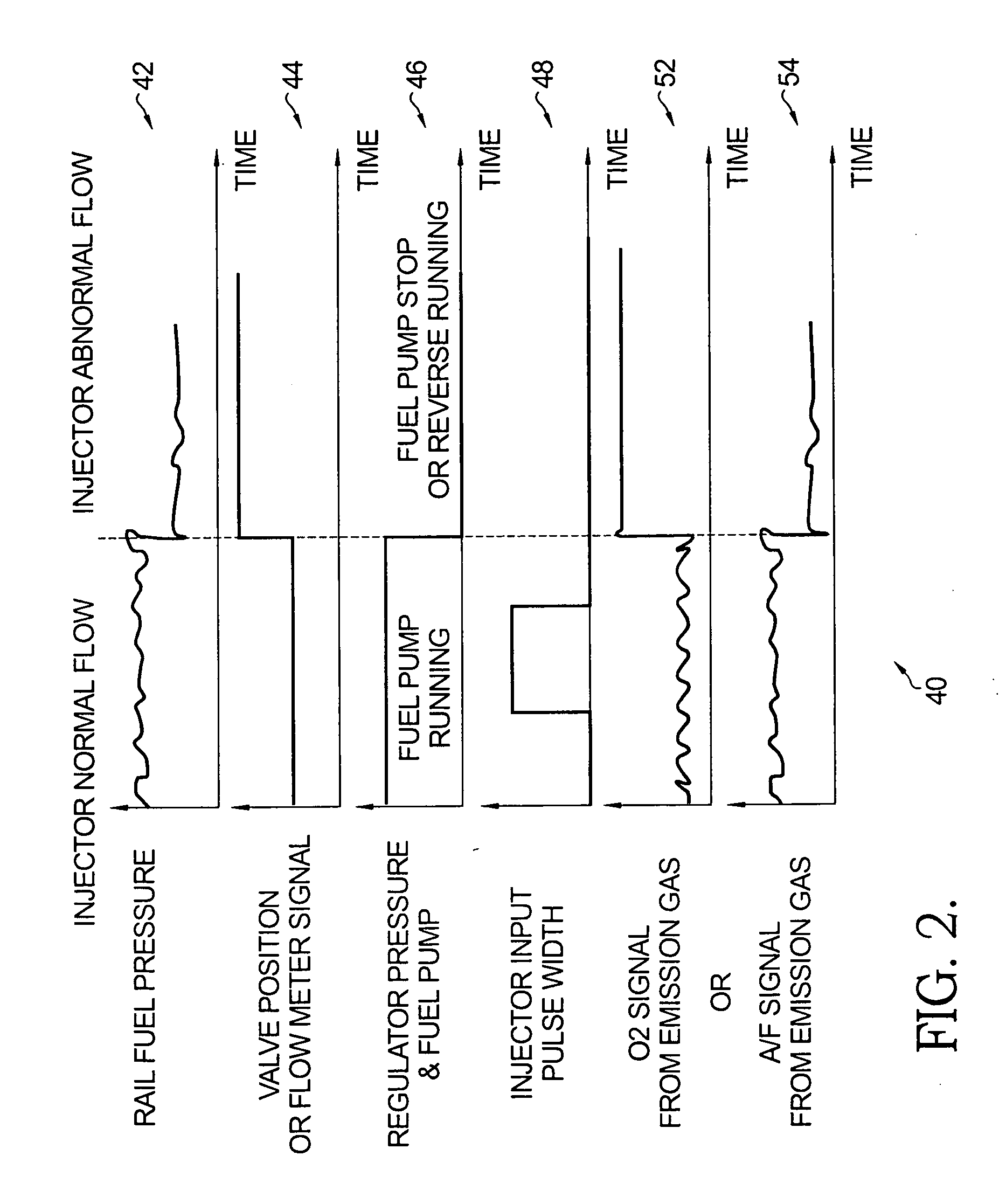
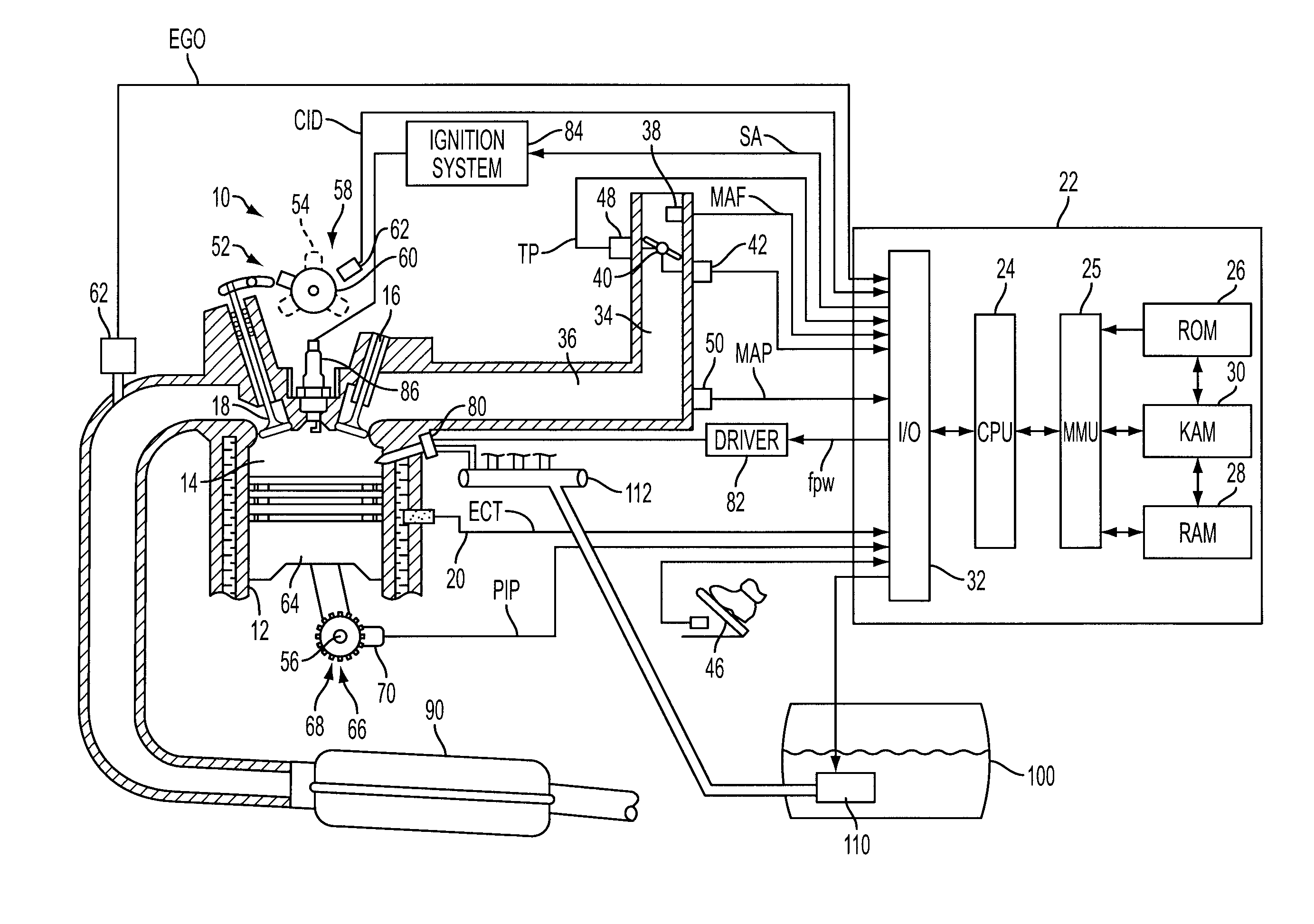
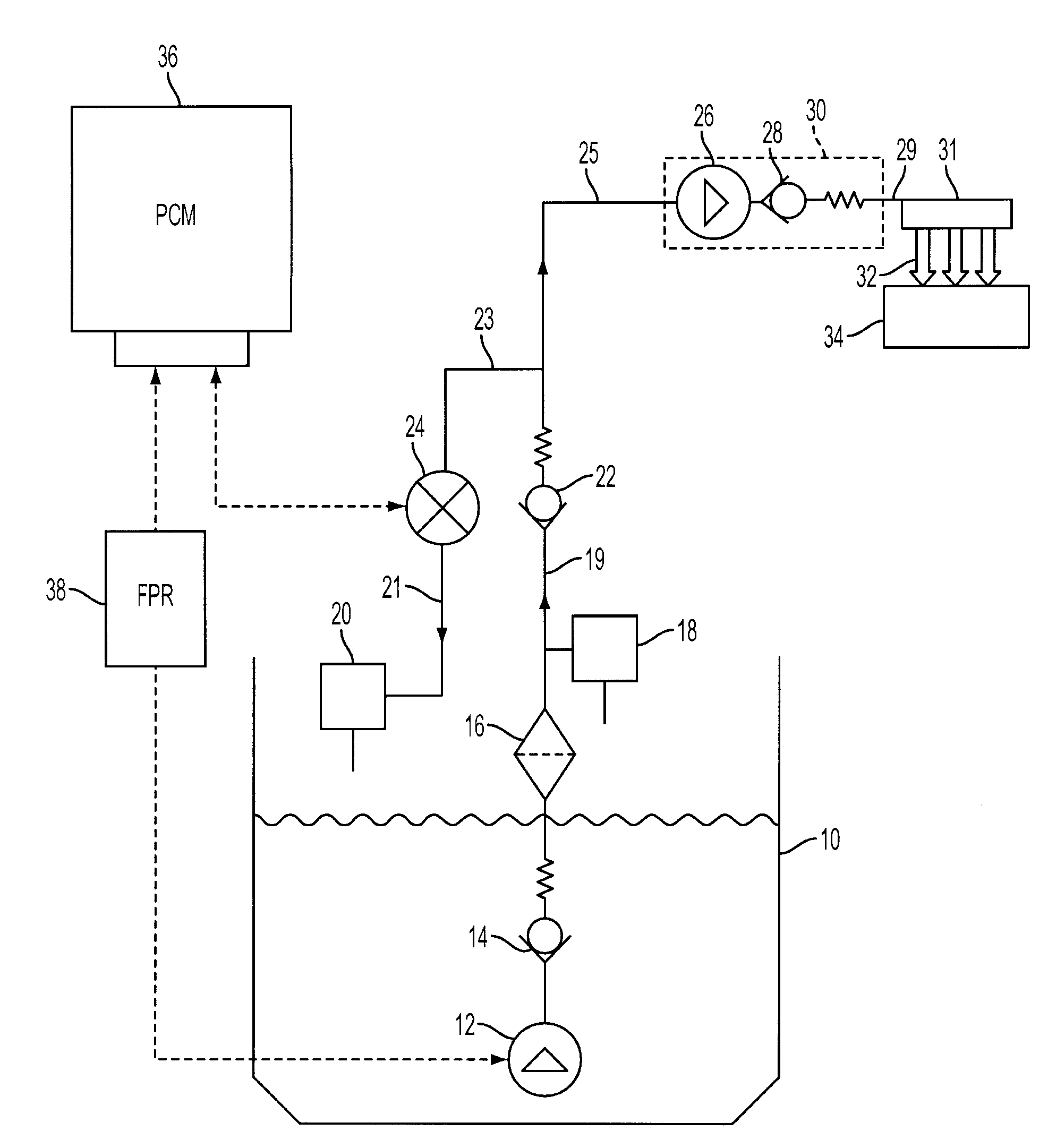
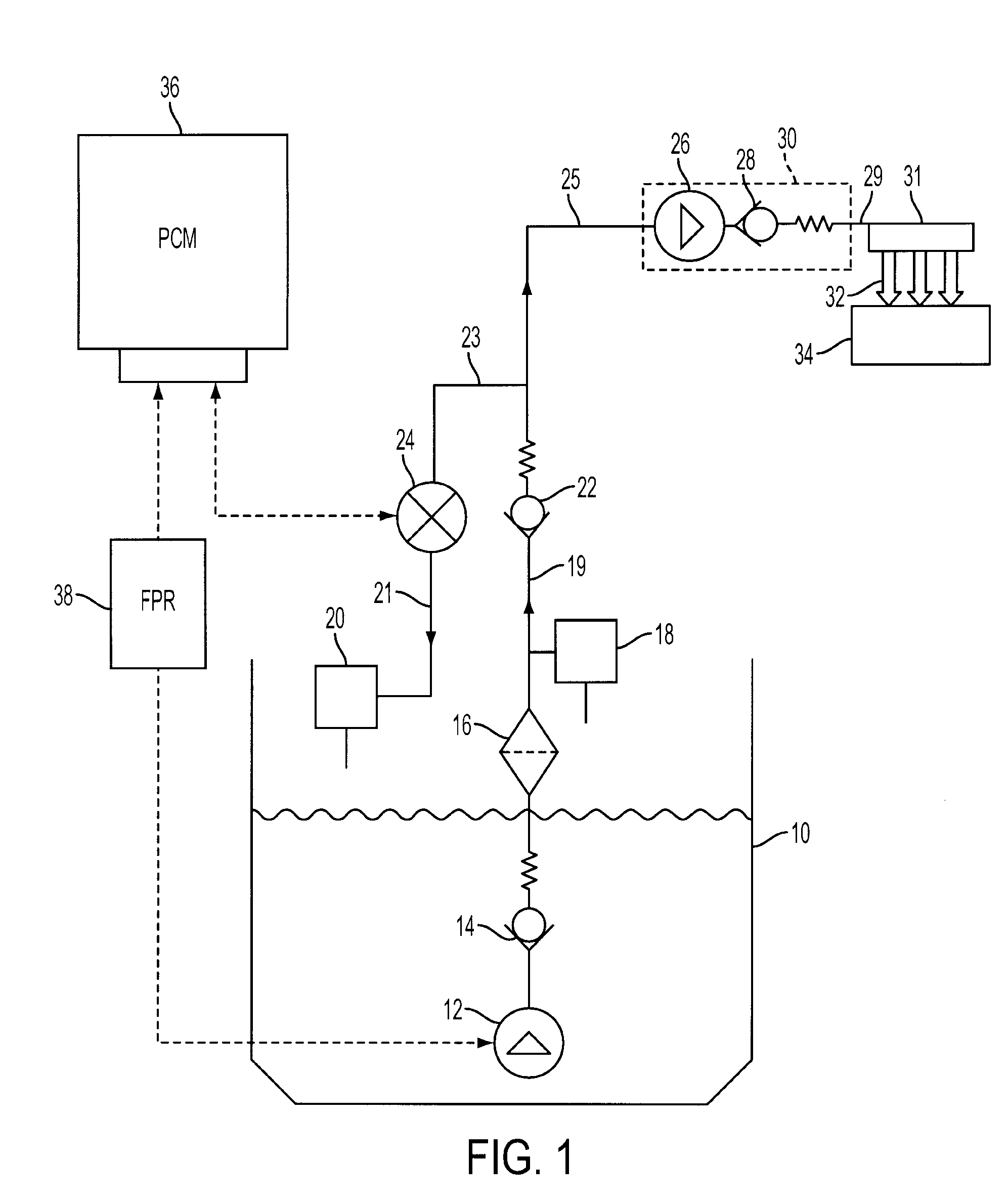
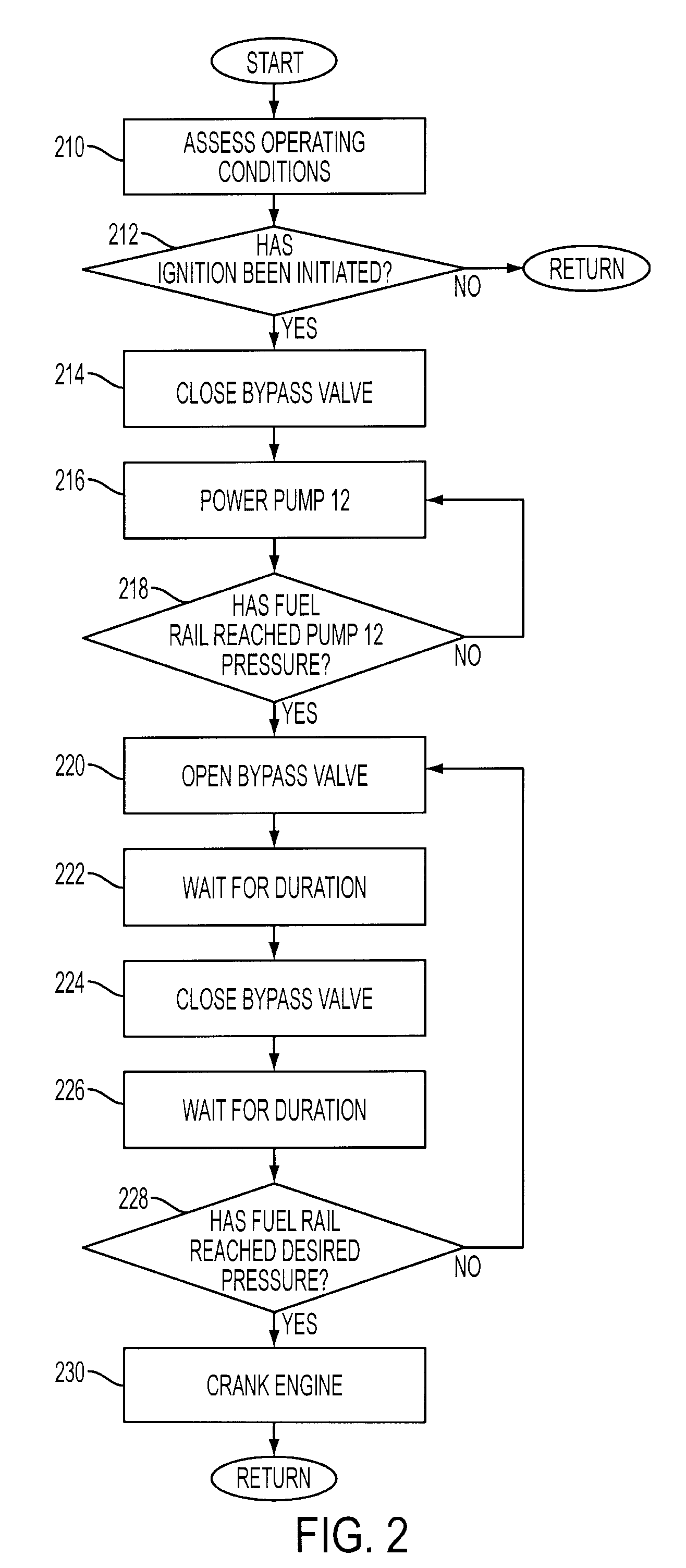
Flow sensing fuel system
InactiveUS20090250038A1Prevent fuel leakagePrevent leakageAnalogue computers for vehiclesElectrical controlGasoline direct injectionPort fuel injection
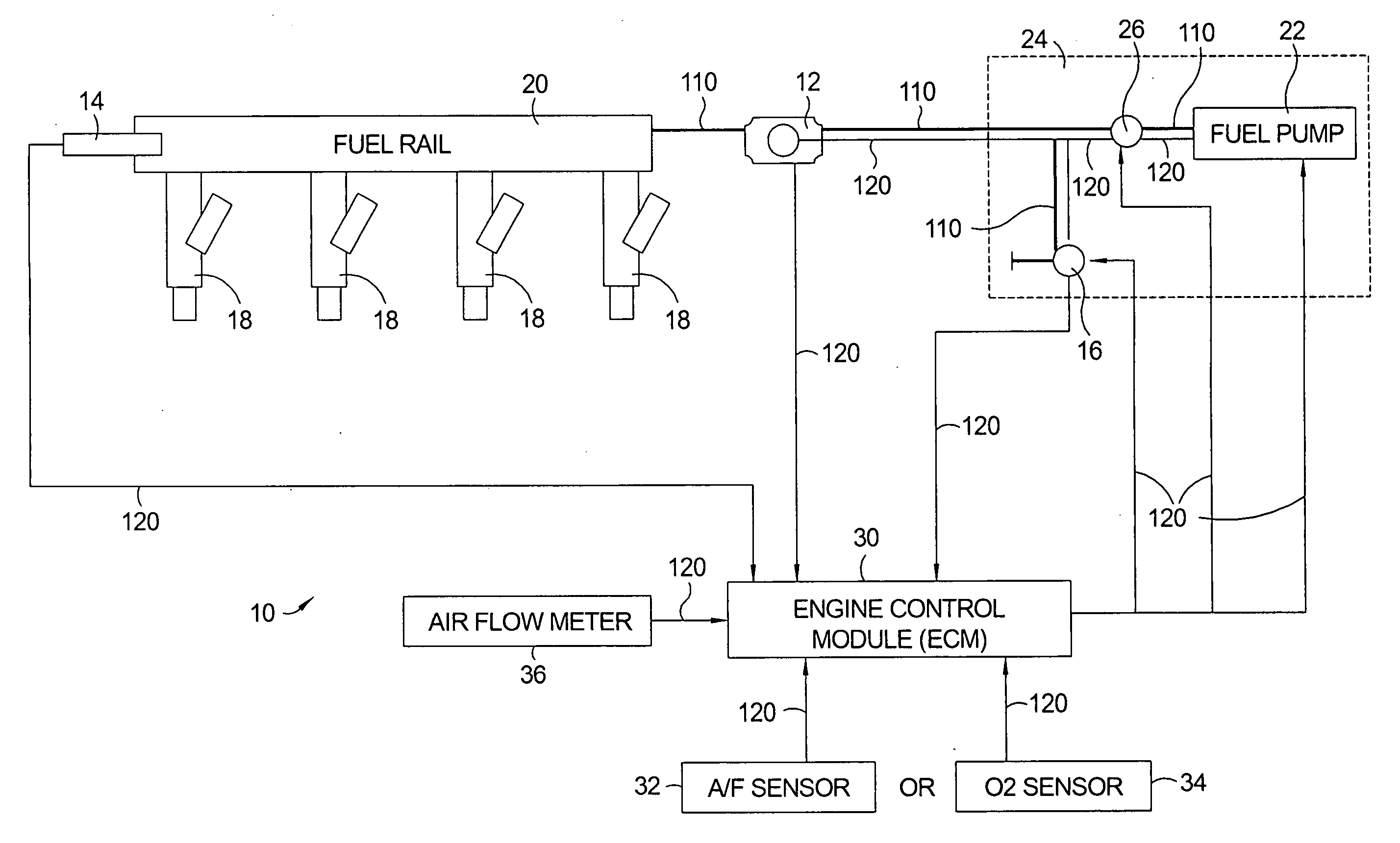
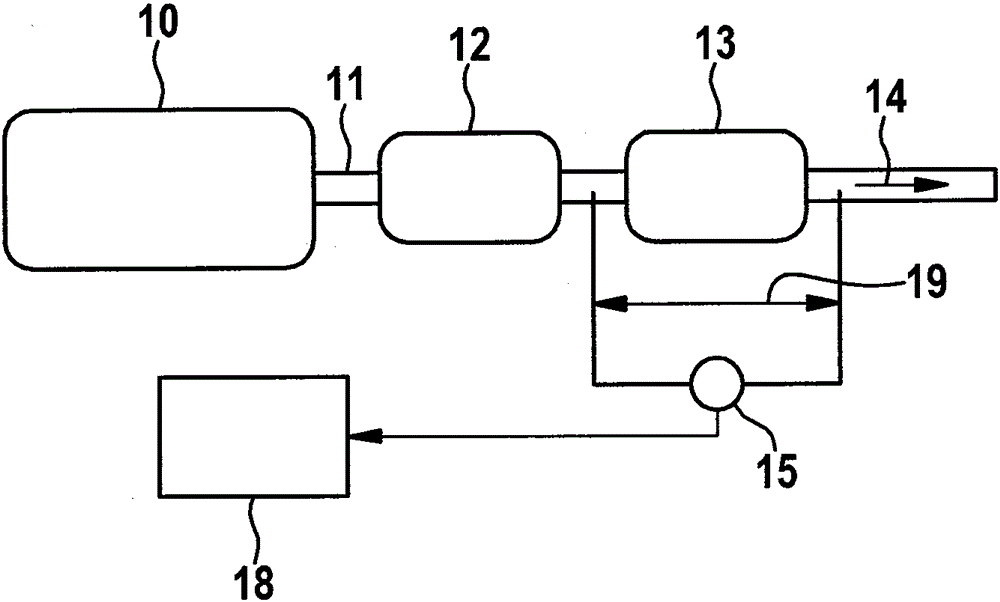
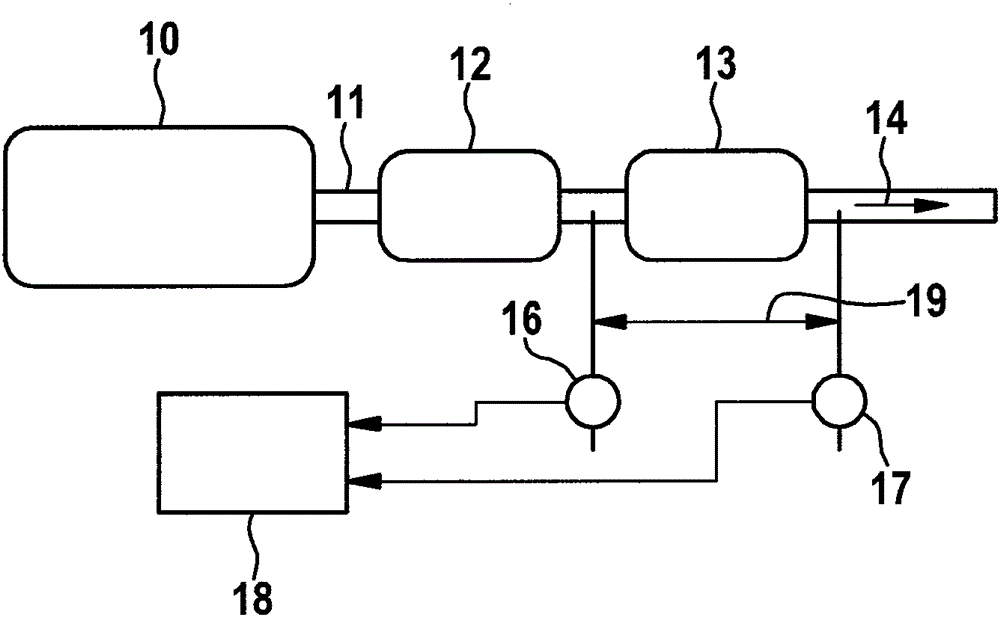
A flow sensing fuel system for multiple port fuel injection gasoline engines, gasoline direct injection engines, or common rail diesel engines include a flow monitoring device positioned in a fuel flow passage between a fuel pump and a fuel rail, a fuel pressure sensor in fluid communication with said fuel rail, and a controllable pressure regulator closing to a fuel tank. By integrating flow monitoring device, fuel pressure sensor, and controllable pressure regulator in existing fuel systems, a flow sensing fuel system is provided that protects the engine and limits the fuel leaking into the environment in case of a stuck open condition or sealing problem of one or more injectors or in case of a leak in the fuel rail assembly. The flow sensing fuel system enables monitoring the fuel flow during engine start-up, during engine operation, and after engine shut down.
Owner:DELPHI TECH INC
System and method for regenerating a particulate filter
ActiveUS20110072784A1Improve efficiencyLess tendencyElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesGasoline direct injectionEnvironmental engineering
A system for filtering and oxidizing particulate matter produced by a gasoline direct injection engine is disclosed. In one embodiment, engine cylinder air-fuel is adjusted to allow soot to oxidize at an upstream particulate filter while exhaust gases are efficiently processed in a downstream catalyst.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
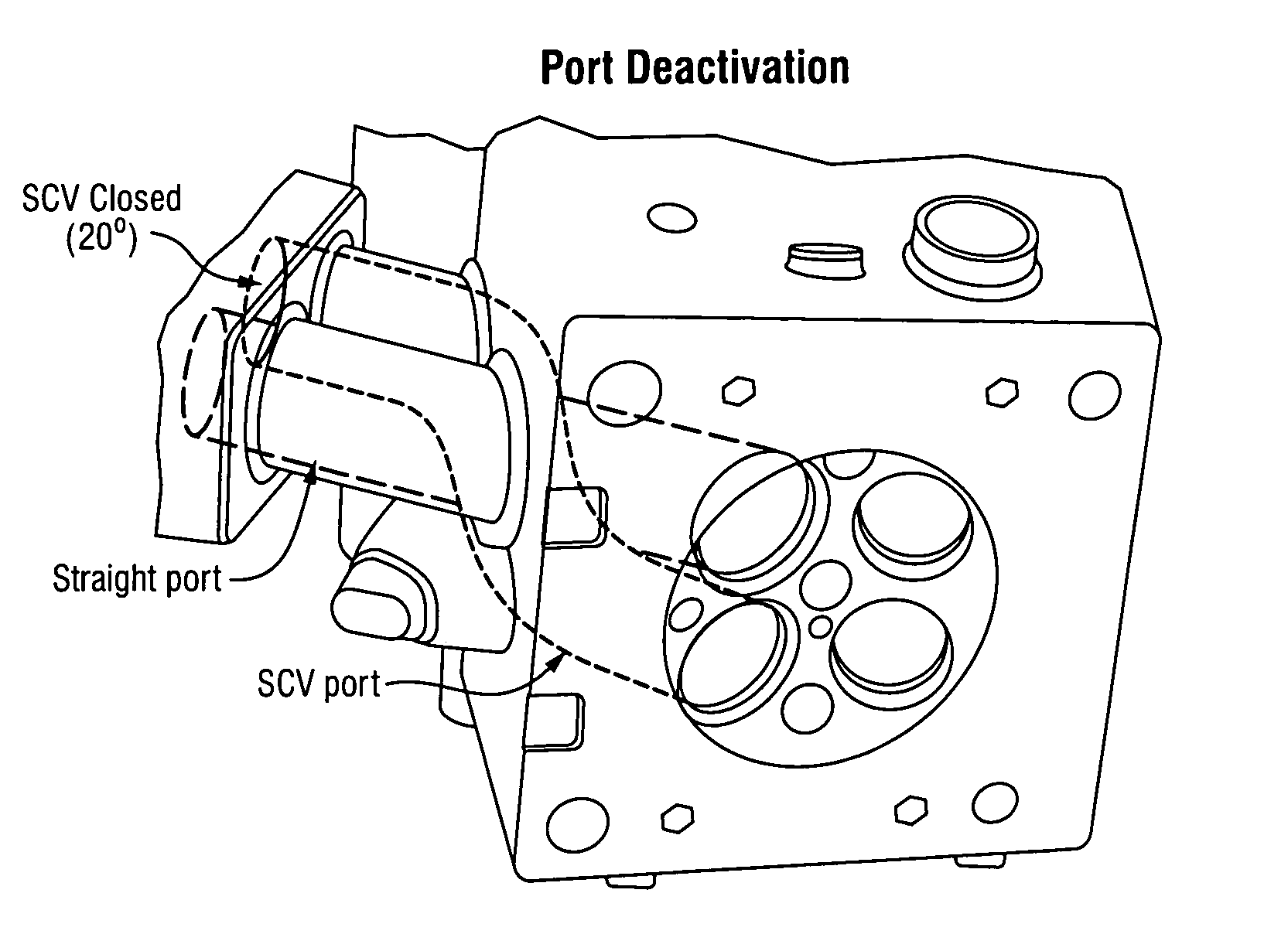
Cold start strategy and system for gasoline direct injection compression ignition engine
InactiveUS20150114339A1Increase temperatureIncrease pressureMechanical controlValve arrangementsExhaust valveGasoline direct injection
A method for starting a compression ignition engine having at least one cylinder with a reciprocating piston located therein, an intake valve configured to control the intake of air to an intake port of the cylinder and an exhaust valve configured to control the expulsion of gas from an exhaust port of the cylinder. The method includes the steps of: cranking the engine, conditioning intake air at the intake port of the cylinder to raise the temperature of air in the cylinder, controlling a valve timing the intake valve and / or the exhaust valve to allow the piston to compress the air within the cylinder, thereby increasing the temperature of the air within the cylinder, and injecting fuel into the cylinder when the air within the cylinder has been heated to a temperature sufficient to support compression ignition of a gasoline and air mixture within the cylinder.
Owner:DELPHI TECH IP LTD
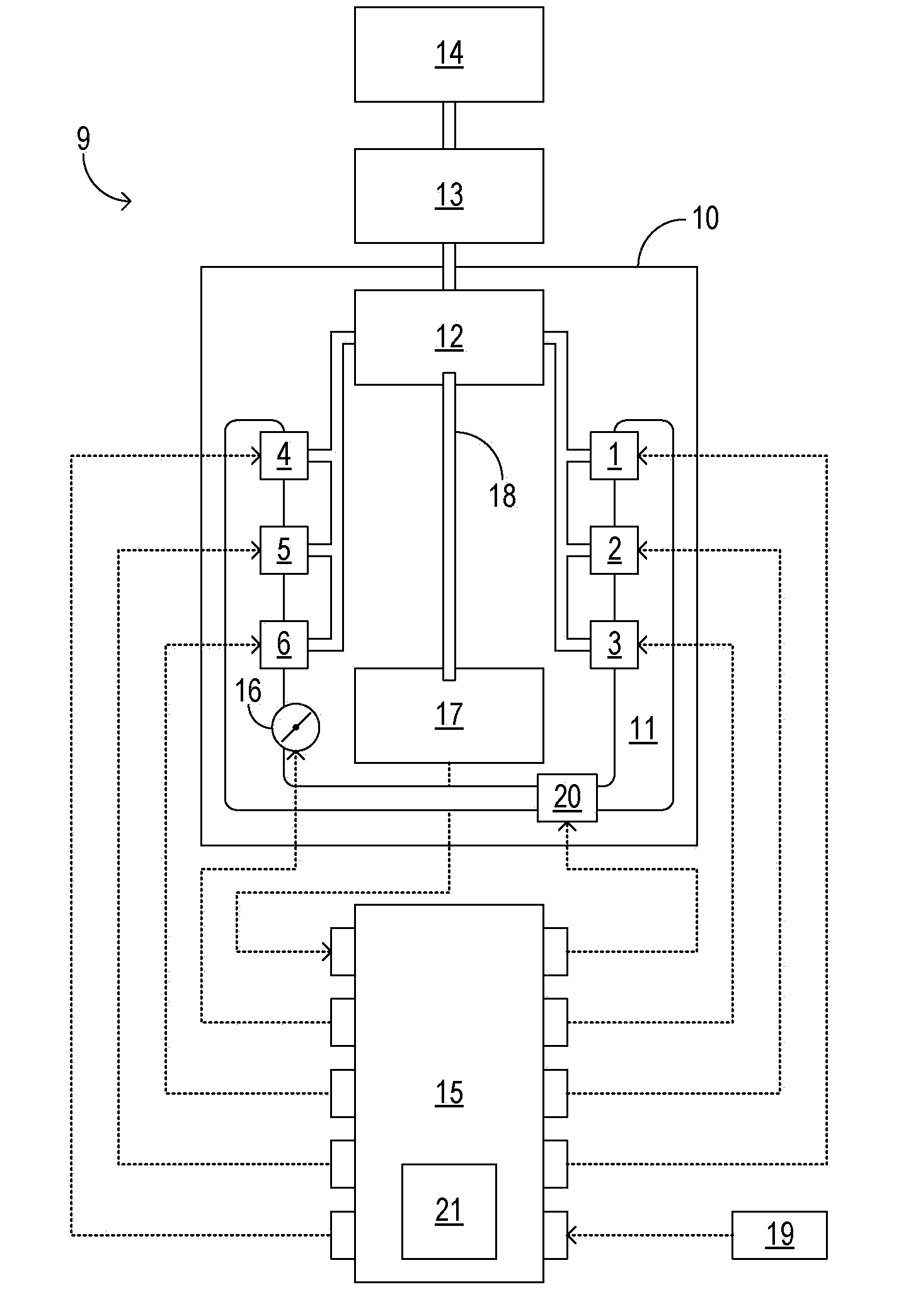
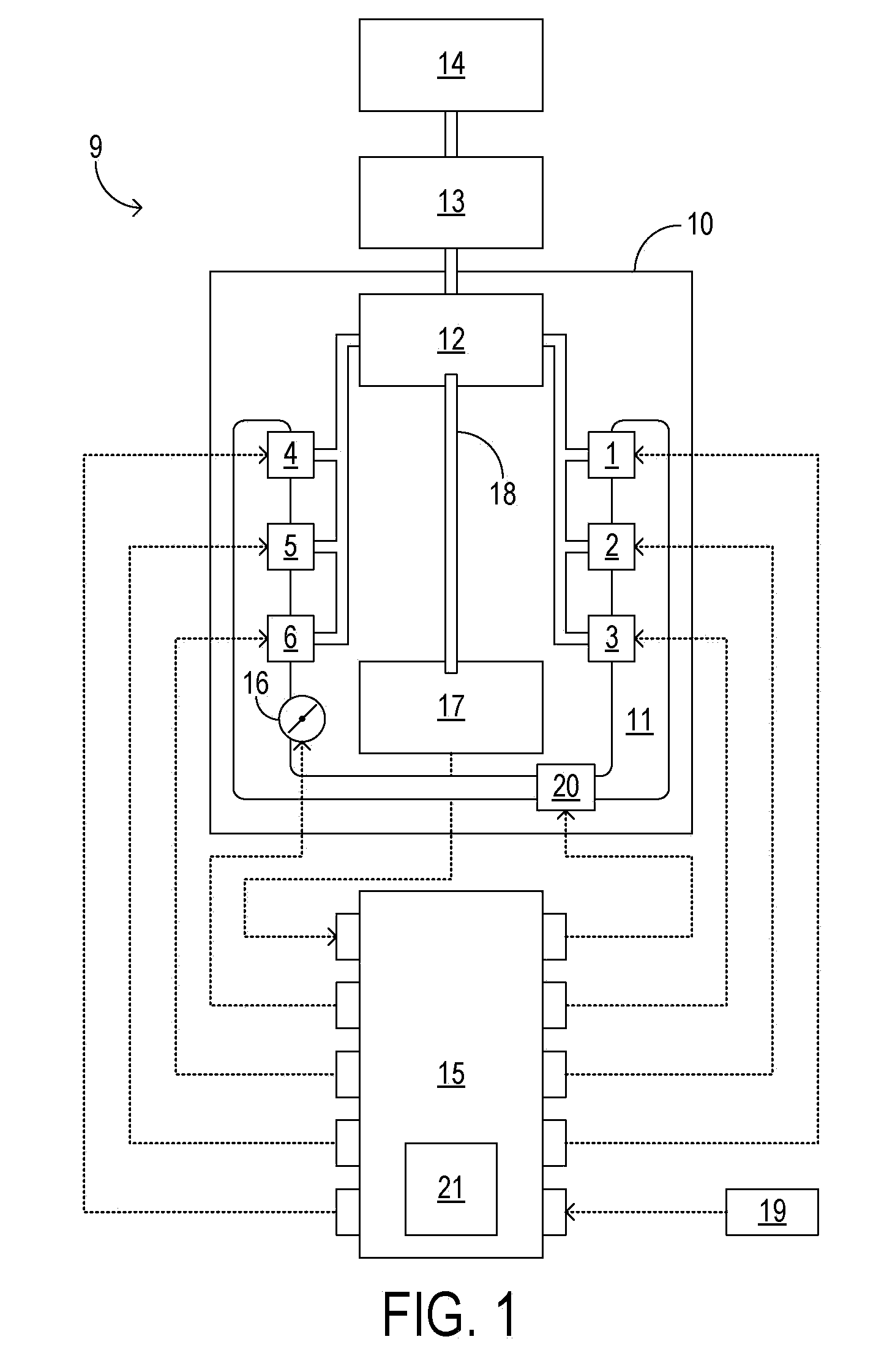
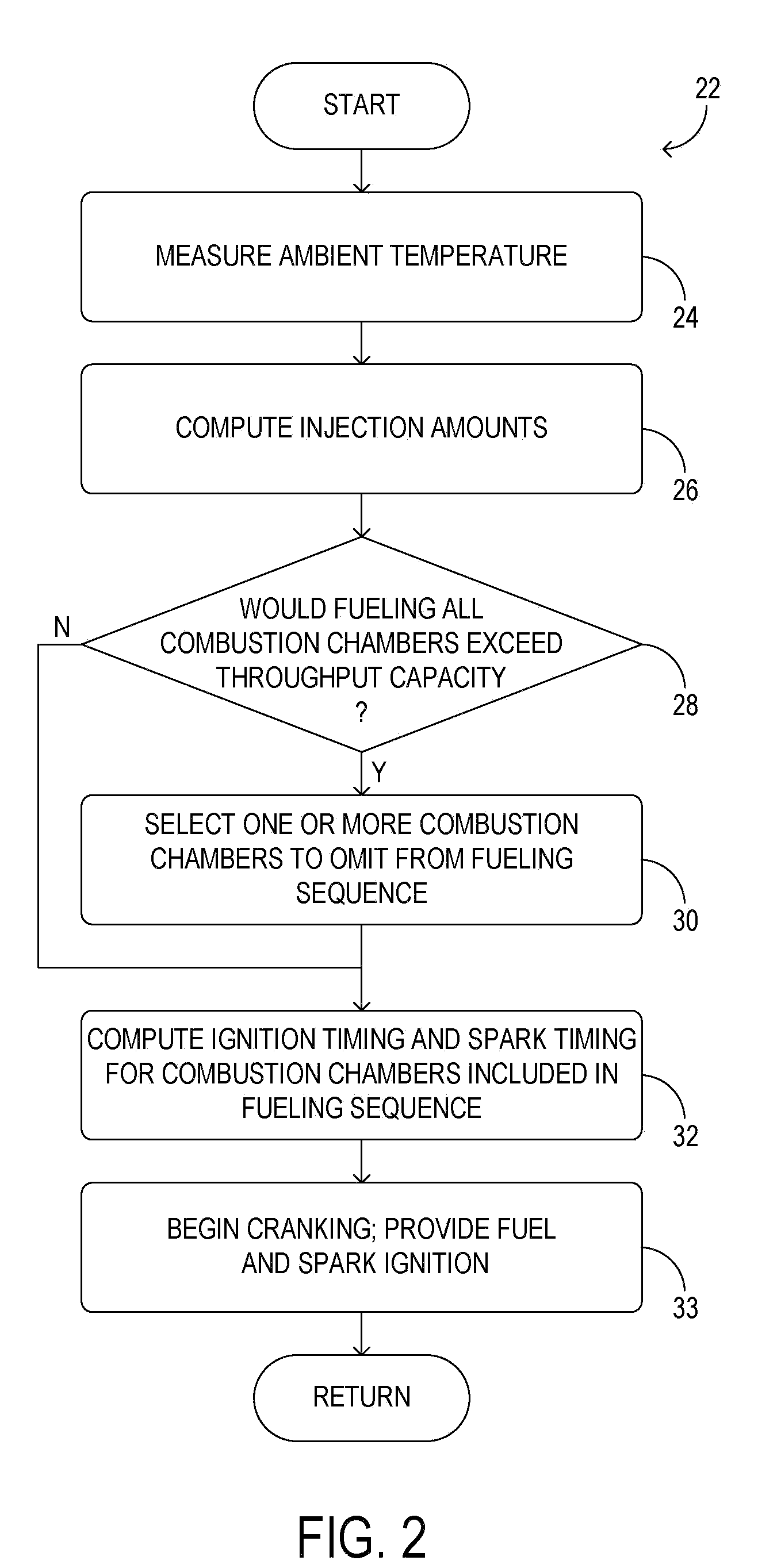
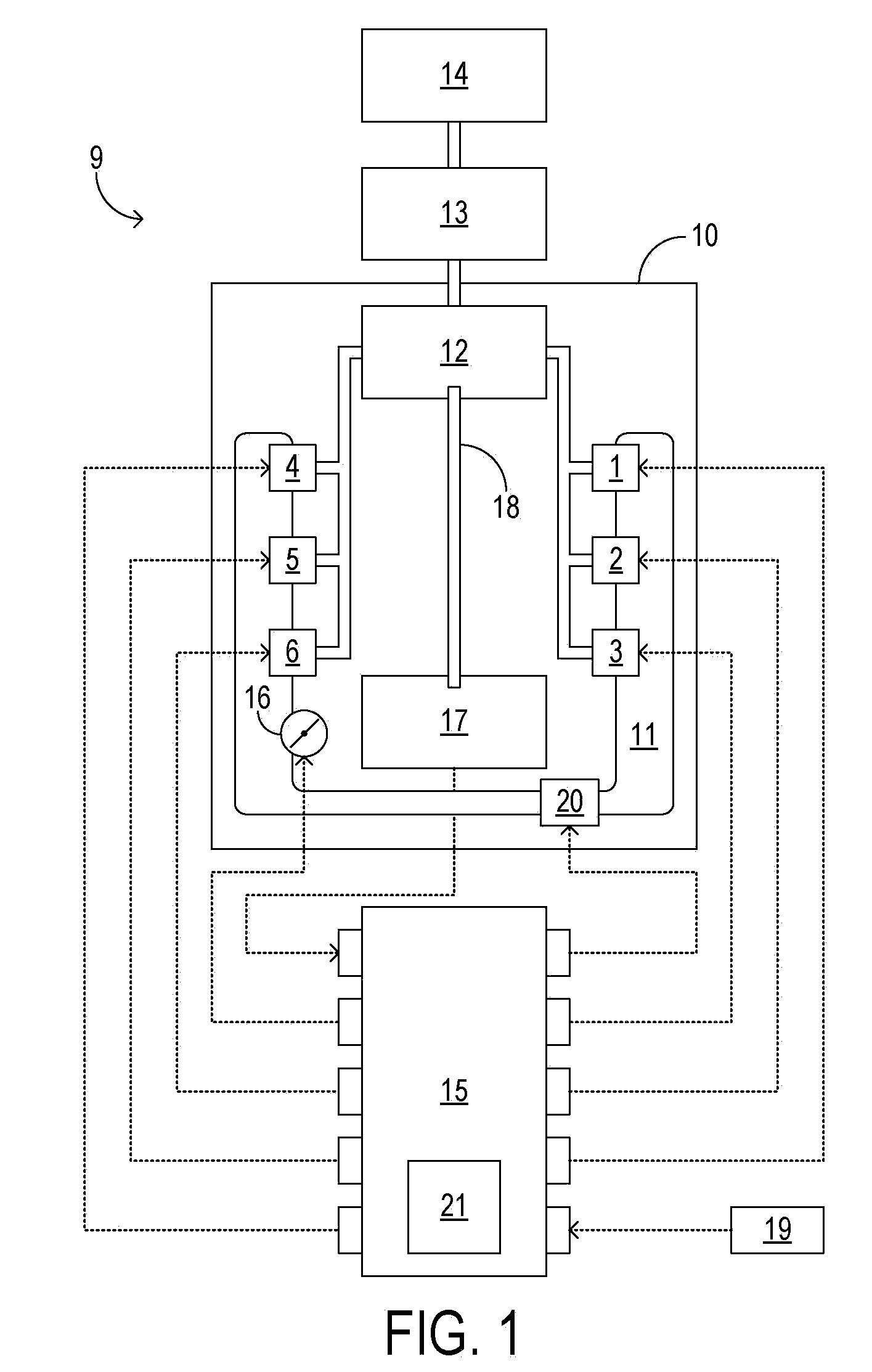
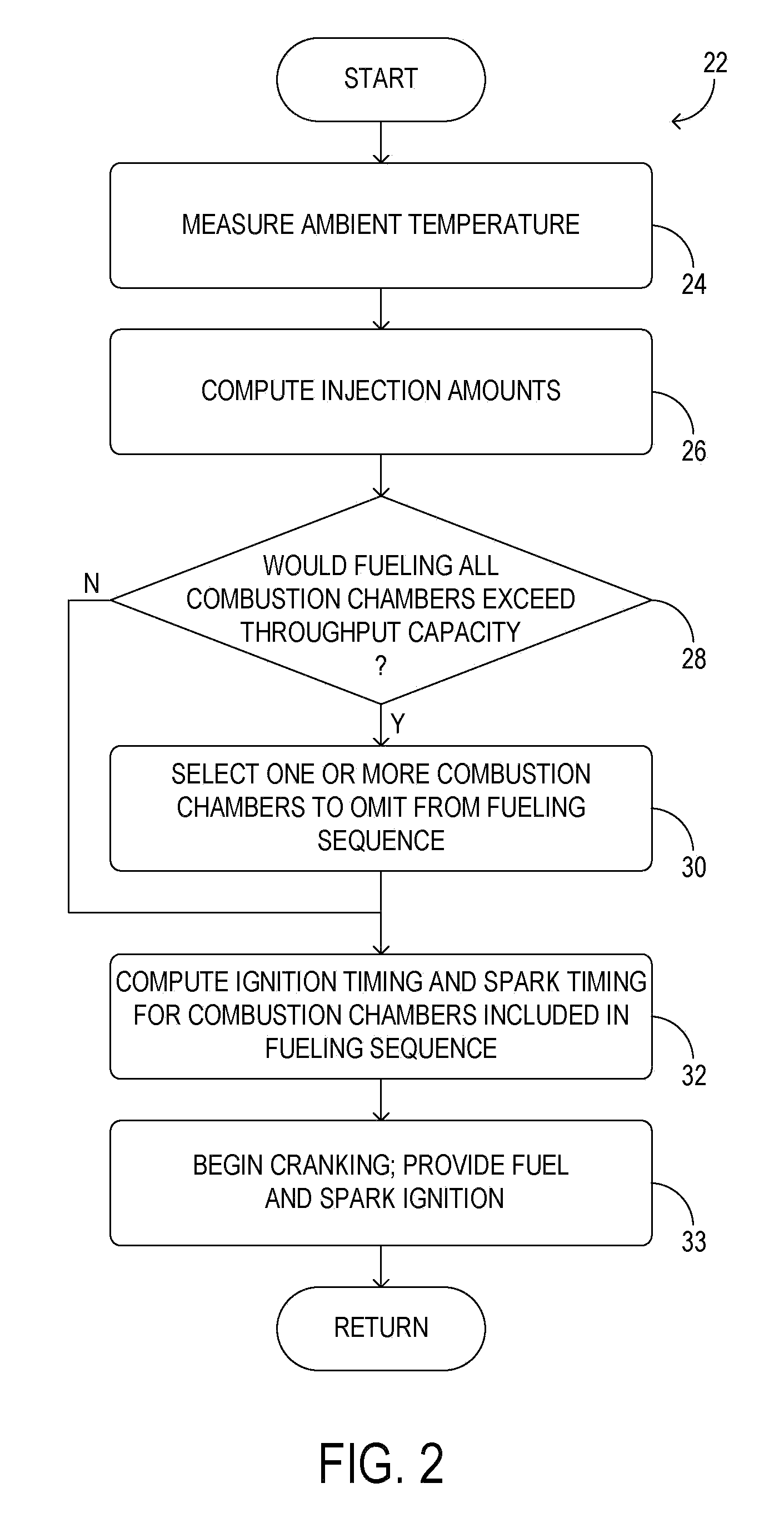
Cold-start reliability and reducing hydrocarbon emissions in a gasoline direct injection engine
InactiveUS20100175657A1Simple introductionIncreasing fractionAnalogue computers for vehiclesElectrical controlCombustion chamberGasoline direct injection
A method for starting an engine of a motor vehicle under varying temperature conditions, the engine having a plurality of combustion chambers and a pump for pressurizing fuel for delivery to the combustion chambers, the method comprising during a first, higher-temperature, starting condition, directly injecting fuel into all of the combustion chambers during at least an initial fueled cycle of the engine, and spark igniting the fuel to increase a rotation speed of the engine, the initial fueled cycle comprising two rotations of a crankshaft of the engine during which at least some fuel is injected for a first time since the engine was brought from rest; and during a second, lower-temperature, starting condition, directly injecting fuel into less than all of the combustion chambers during at least the initial fueled cycle of the engine, and spark igniting the fuel to increase the rotation speed of the engine.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Fuel Injection Strategy For Gasoline Direct Injection Engine During High Speed/Load Operation
InactiveUS20090088945A1Increase torqueReduce sootElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesGasoline direct injectionCombustion chamber
A system and method for controlling operation of a multiple cylinder direct injection internal combustion engine include injecting fuel directly into the combustion chamber during the exhaust stroke at high engine speeds and loads to reduce the effect of intake airflow on the injection spray and improve fuel-air mixture homogeneity.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Method of HCCI and SI combustion control for a direct injection internal combustion engine
InactiveUS7275514B2Improve fuel economyValve arrangementsElectrical controlHomogeneous charge compression ignitionGasoline direct injection
The present invention relates to methods for robust controlled auto-ignition and spark ignited combustion controls in gasoline direct-injection engines, including transients, using either exhaust re-breathing or a combination of exhaust re-compression and re-breathing valve strategy. These methods are capable of enabling engine operation with either lean of stoichiometric or stoichiometric air / fuel ratio for oxides of nitrogen (NOx) control, with varying exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) rates and throttle valve positions for knock control, and with a combination of homogeneous charge compression ignition (HCCI) and spark ignition (SI) combustion modes to optimize fuel economy over a wide range of engine operating conditions.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
System and method for regenerating a particulate filter
ActiveUS8341947B2Improve efficiencyLower charging temperatureElectrical controlNon-fuel substance addition to fuelGasoline direct injectionExhaust fumes
A system for filtering and oxidizing particulate matter produced by a gasoline direct injection engine is disclosed. In one embodiment, engine cylinder air-fuel is adjusted to allow soot to oxidize at an upstream particulate filter while exhaust gases are efficiently processed in a downstream catalyst.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Extending fuel economy operating range in gasoline direct injection (GDI) engines
InactiveUS7245038B2Motor/generator/converter stoppersElectrical controlAlternatorGasoline direct injection
An engine control system for controlling engine operation in high-output (HO) and fuel-economy (FE) modes in a gasoline direct injection (GDI) engine includes an alternator that is driven by the engine and that is regulated by a load control signal. An alternator load control module generates the load control signal based on an engine torque to regulate a load of the alternator on the engine to maintain the engine torque below a threshold level and maintain engine operation in the FE mode.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Lean oil direct injection and mixing low-pollution combustion chamber
ActiveCN107543201AGuarantee job stabilityReduce the temperatureContinuous combustion chamberSpontaneous combustionGasoline direct injection
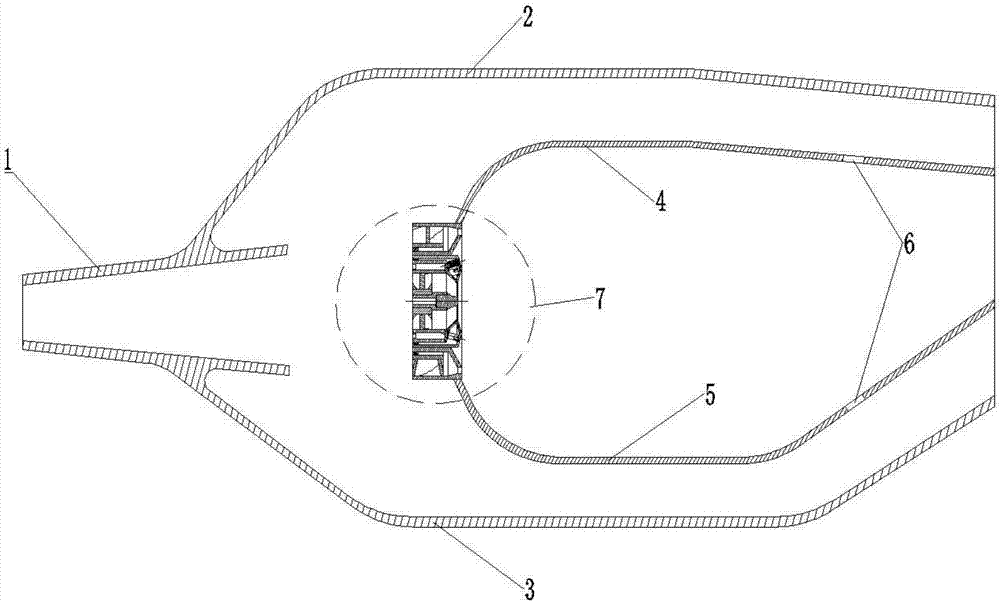
The invention relates to a lean oil direct injection and mixing low-pollution combustion chamber. The lean oil direct injection and mixing low-pollution combustion chamber is composed of a diffuser, acombustion chamber outer case, a combustion chamber inner case, a combustion chamber head, a flame tube outer wall and a flame tube inner wall, wherein combustion air all enters a flame tube from thecombustion chamber head; the combustion chamber head is divided into an on-duty grade and a main combustion grade through a grading and partitioning combustion strategy; the on-duty grade and the main combustion grade both adopt a direct injection and mixing combustion method, the phenomena of spontaneous combustion and tempering are effectively avoided, and the risk of occurrence of oscillationcombustion is lowered; the lean oil direct injection and mixing low-pollution combustion chamber only works in an on-duty grade mode under an idling rating state, the designed partial equivalence ratio is higher, and the work stability of the combustion chamber is guaranteed; and with the increase of the work state of the combustion chamber, the main combustion grade is opened gradually, the maincombustion grade and the on-duty grade work simultaneously under a large state, the designed combustion area average equivalence ratio is lower, the average temperature of the combustion area is effectively lowered, and therefore the generation quantity of pollutants is lowered.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Method for controlling spark for particulate filter regenerating
ActiveUS20110073070A1Improve efficiencyLess tendencyElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesGasoline direct injectionEngineering
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Method and apparatus for detecting soot and ash loading of a particle filter
ActiveCN105089757AImprove accuracySuppress signal fluctuationsInternal combustion piston enginesExhaust apparatusParticulatesGasoline direct injection
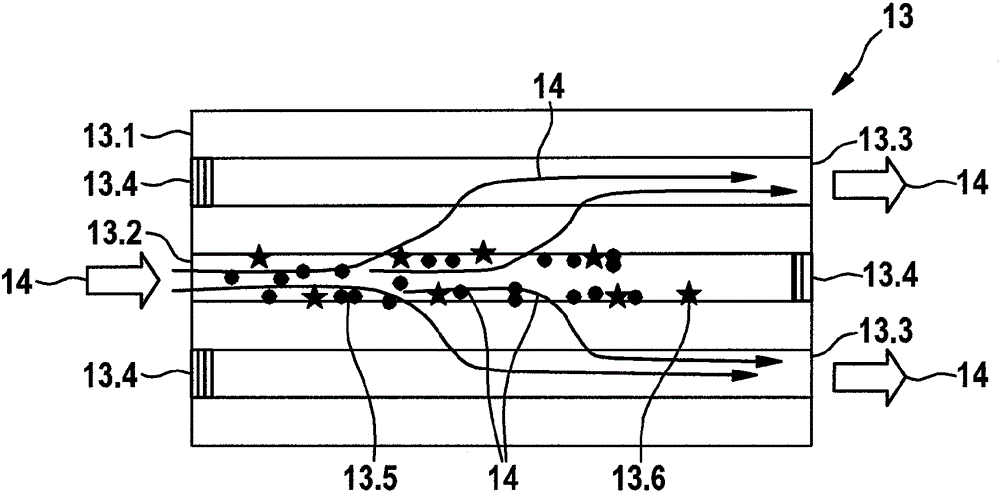
The invention relates to a method for the detection of a soot and ash loading of a particulate filter as a component of an exhaust gas cleaning system in the exhaust line of an internal combustion engine, wherein a differential pressure between the inlet and outlet of the particulate filter is measured for monitoring the particulate filter and this is evaluated in a diagnostic unit. The invention further relates to a device, in particular a diagnostic unit for carrying out the provided method. The invention is characterized in that for determining the soot and ash charge the time gradient of the measured differential pressure is set at the particle filter in correlation with an expected temporal gradient of a differential pressure of an intact and unloaded reference particulate filter and this correlation different temporal trend analysis is subjected. Compared to the prior art, the method has the advantage that, even at very low absolute pressure differences, as in gasoline direct injection engines is the case in particular when the internal combustion engine, a load diagnosis of the particulate filter and distinction between ash and soot loading can be made possible.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
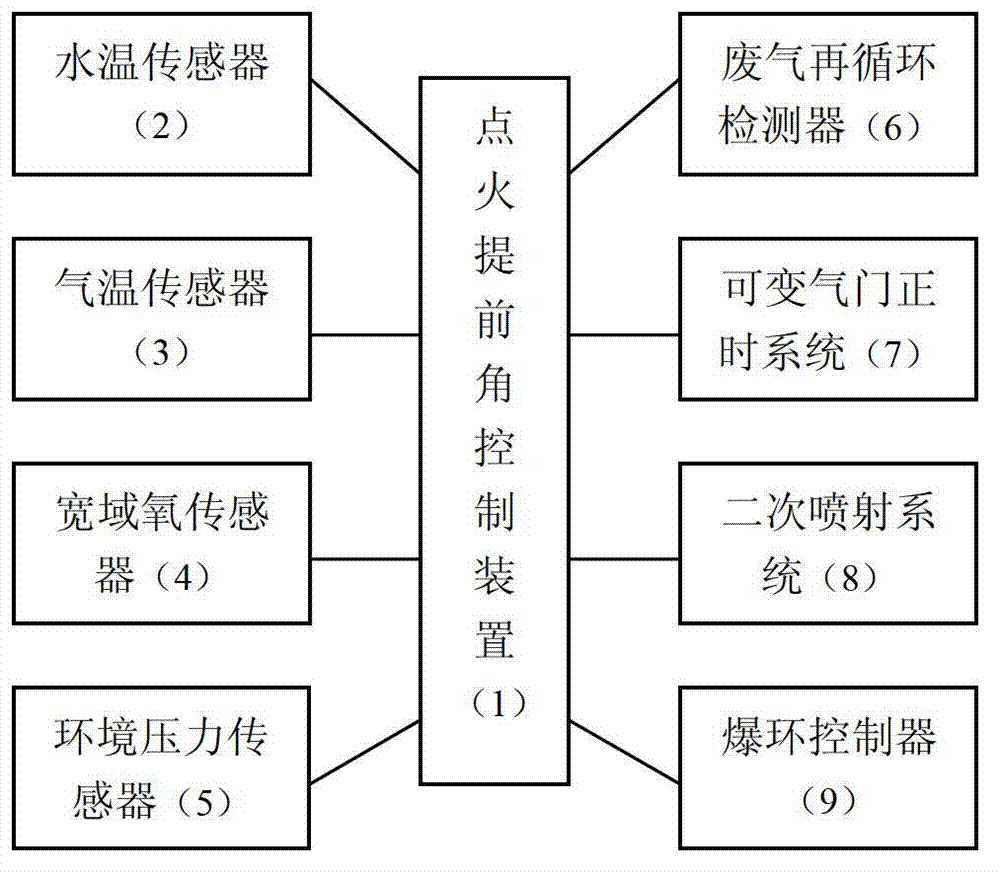
Controlling method of gasoline direct injection engine optimal ignition angular advance
ActiveCN103114951AImprove powerBest economyMachines/enginesIgnition automatic controlGasoline direct injectionVariable valve timing
The invention discloses a controlling method of gasoline direct injection engine optimal ignition angular advance. The process of obtaining the optimal ignition angular advance is that a water inlet and outlet temperature of a motor, an air inlet temperature of a motor, air fuel ratio of a motor, altitude of an automobile, waste gas recirculation rate, variable air valve timing opening, a spraying mode and knocking controlling are logically operated after a base ignition angular advance is set. The base ignition angular advance is calculated and revised according to influences of the eight factors in sequence. The base ignition angular advance is revised through the influence of each factor, the ignition angular advance is controlled at the best time all the time no matter the motor is operated under any working condition and any environment, power performance, economy and discharging time of the motor are at the best state.
Owner:ZHEJIANG GEELY POWERTRAIN CO LTD +2
Method for mid load operation of auto-ignition combustion
ActiveUS20060005818A1Reduce the probability of burningExtended durationElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesCombustion chamberExhaust valve
A method is disclosed for expanding the mid load range of a four-stroke gasoline direct-injection controlled auto-ignition combustion engine. The engine includes at least one cylinder containing a piston reciprocably connected with a crank and defining a variable volume combustion chamber including an intake valve controlling communication with an air intake and an exhaust valve controlling communication with an exhaust outlet. A system is employed for variably actuating the intake and exhaust valves. The valve actuating system is employable to operate the intake and exhaust valves with an exhaust re-compression or an exhaust re-breathing valve strategy. A reservoir chamber in communication with the combustion chamber is provided for temporary holding of residual burned gas. Residual burned gas in the combustion chamber and the exhaust outlet enters into the reservoir chamber and then loses thermal energy while in the reservoir chamber before being drawn back into the combustion chamber.
Owner:MICHIGAN UNIV OF OFFICE OF TECH TRANSFER +1
Method and apparatus for diagnosing particulate filter
ActiveCN105089761ASuppress signal fluctuationsImprove diagnostic qualityInternal combustion piston enginesExhaust apparatusParticulatesGasoline direct injection
The invention relates to a method for diagnosing a particulate filter as part of an exhaust gas cleaning system in the exhaust system of an internal combustion engine. In order to monitor the particulate filter, a differential pressure between the inlet and outlet of the particulate filter is measured and is evaluated in a diagnostic unit. The invention further relates to a device, in particular a diagnostic unit. According to the invention, in order to identify the detachment of the particle filter or a damaged particle filter, the time gradient of the measured differential pressure set at the particulate filter is in correlation with an expected temporal gradient of a differential pressure of a reference particulate filter with normal functions and the correlation is evaluated. Compared with the prior art, the method has the advantage that even at very low absolute pressure differences, and under the condition that the gasoline direct injection is used as the internal combustion engine, the detachment diagnosis is realized without the need for the extra active intervention, e.g. the mass flow is improved or a throttle turn plate is opened during the inertia driving.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Four stroke engine auto-ignition combustion
ActiveUS20060005788A1Electrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesExhaust valveGasoline direct injection
A method of operating a four-stroke gasoline direct-injection controlled auto-ignition combustion engine includes opening both the intake and exhaust valves during terminal portions of the expansion strokes and initial portions of the contraction strokes, injecting fuel directly into the combustion chamber for mixing with retained gases and igniting the fuel near the ends of the contraction strokes. In the process, combustion gases are expanded to produce power during major portions of the expansion strokes, combusted gases are blown down into the exhaust outlet and the air inlet and are partially redrawn into the cylinder with fresh air during the terminal portions of the expansion strokes so the air charges are heated by the hot exhaust gases. Portions of the charges re-expelled and the remaining portions of the charges and injected fuel are compressed for ignition of the dilute fuel / air and exhaust gas mixture. Substantial reductions of NOx emissions result from the method.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
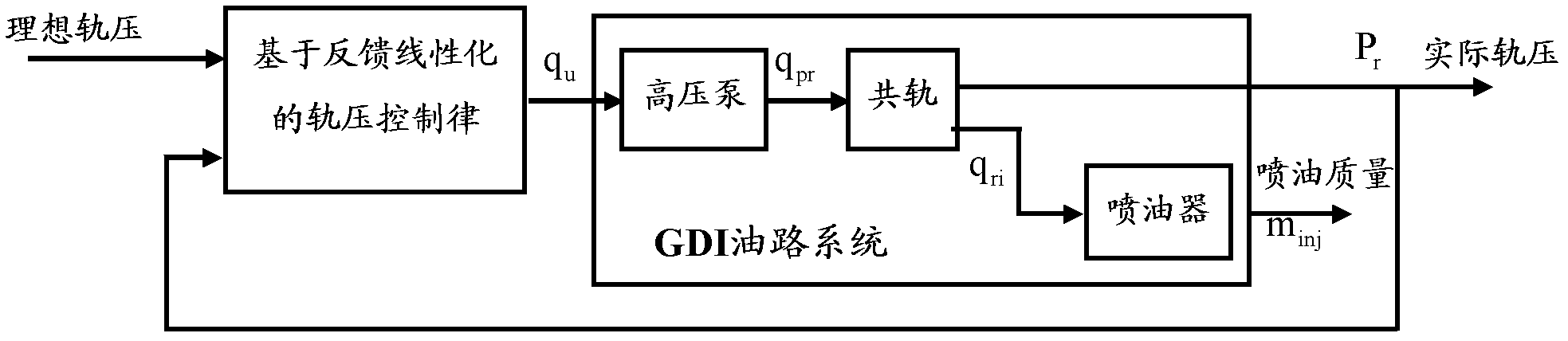
Rail pressure control method for gasoline direct injection engine common rail fuel system
ActiveCN102562336AGuaranteed stabilityImprove robustnessElectrical controlMachines/enginesRail pressureMathematical model
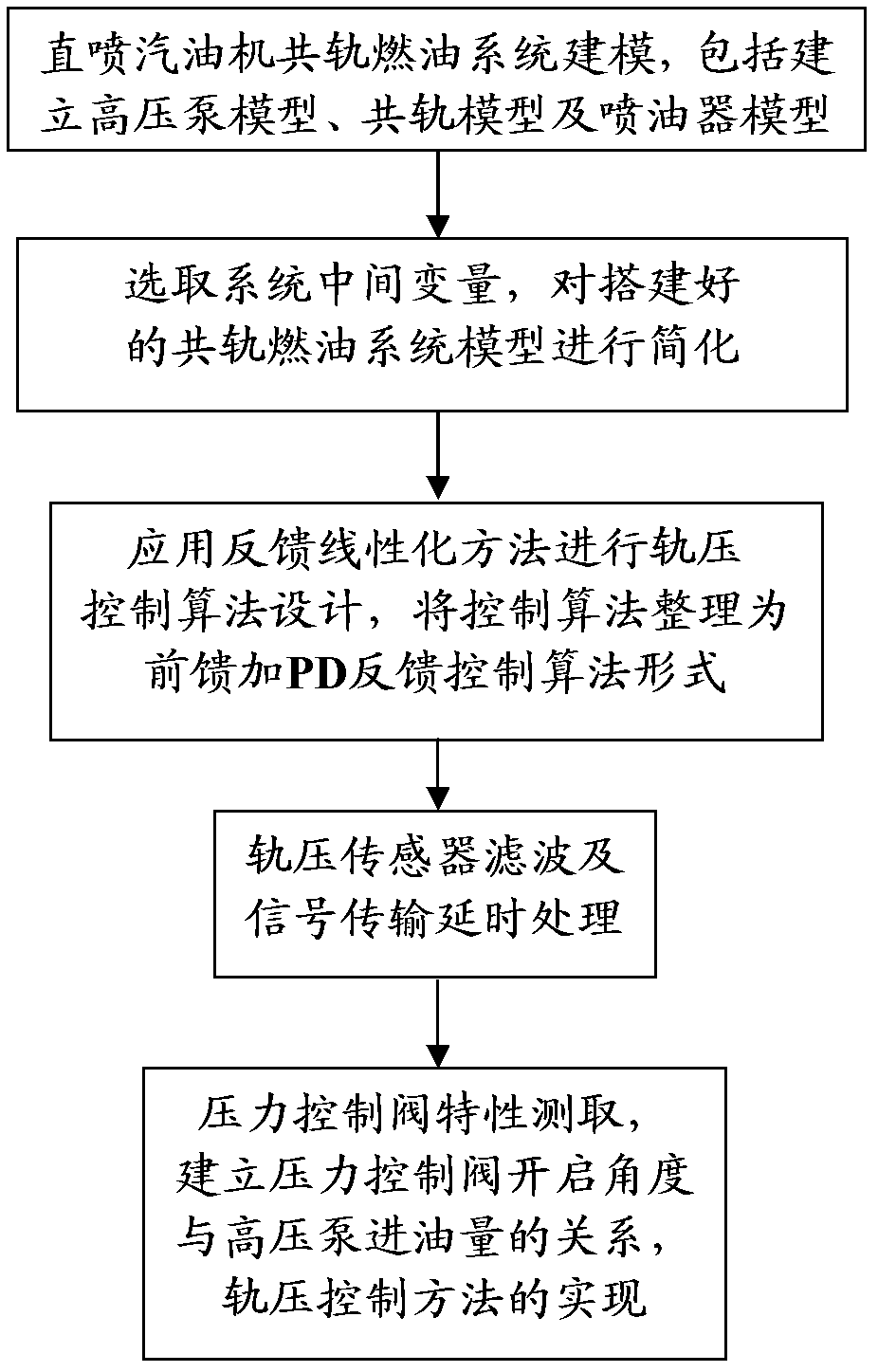
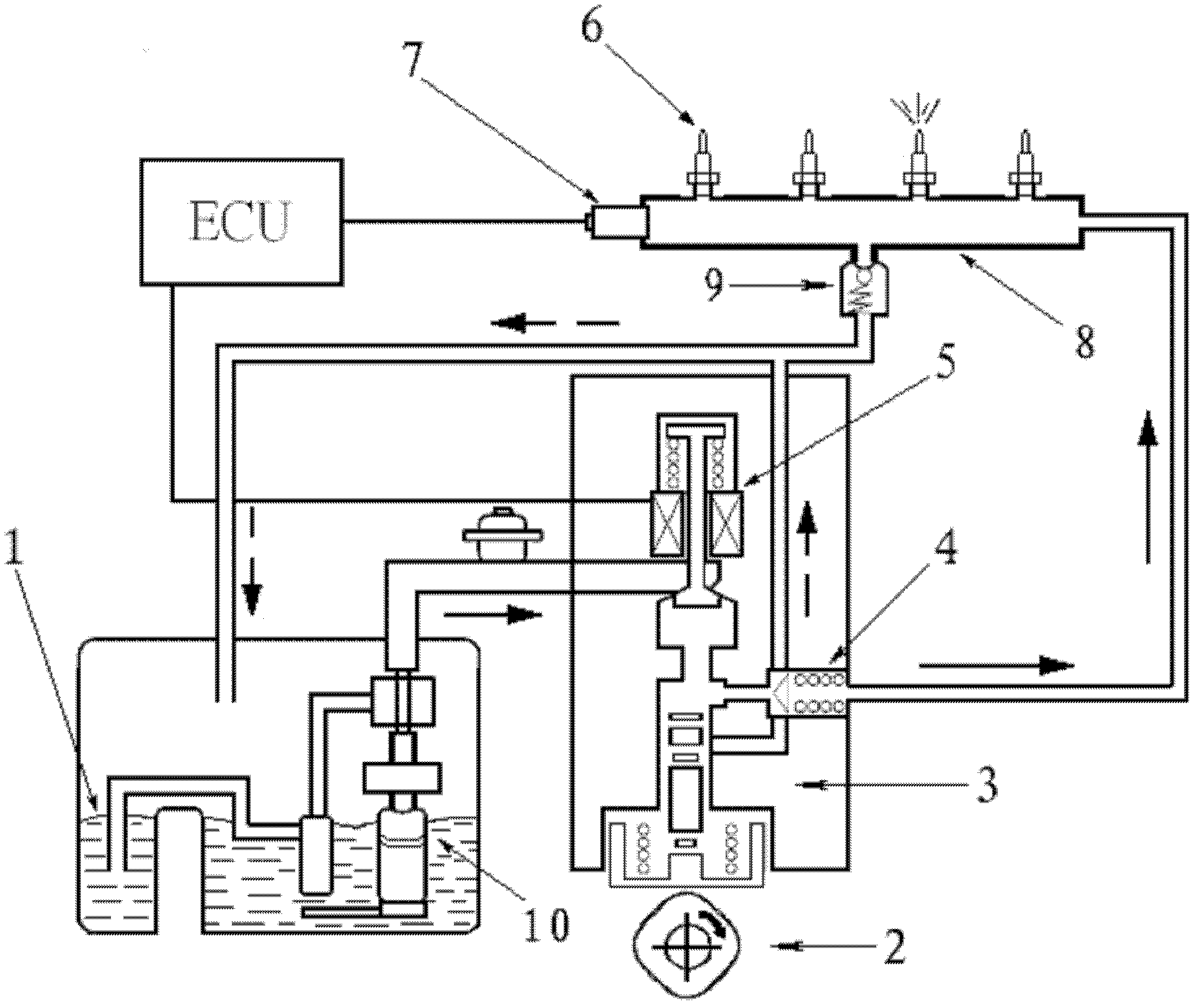
The invention discloses a rail pressure control method for a gasoline direct injection engine common rail fuel system, which includes: the first step, building a mathematical model of the gasoline direct injection engine common rail fuel system, namely building a mathematical model of a high-pressure pump, then building a common rail mathematical model and finally building a mathematical model of a fuel injector; the second step, simplifying the mathematical model of the common rail fuel system; the third step, designing the control algorithm and regulating the form of the control algorithm on the basis of the mathematical model of the common rail fuel system; the fourth step, filtering by a rail pressure sensor and delaying signal transmission, namely acquiring rail pressure signals by an AD (analog-digital) passage of a single-chip microcomputer and removing individual error points and signal interference by the filter algorithm, and then designing signal tests for the rail pressure sensor (7); the fifth step, testing characteristics of a pressure control valve, converting the output of the control algorithm into action time of the pressure control valve, namely testing the characteristics of the pressure control valve (5) to acquire relation between the switching delay of the pressure control valve (5) and voltage of a vehicular storage battery and then building the relation between the opening angle of the pressure control valve (5) and the flow of the high-pressure pump (3).
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Direct injection fuel system utilizing water hammer effect
InactiveUS7448361B1Improve power efficiencyIncrease rangeElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesGasoline direct injectionInternal combustion engine
A method is described for operating a fuel system during start up, the system utilizing gasoline direct injection for an internal combustion engine including a first pump and second pump, an electromechanical valve, and a check valve fluidly coupled downstream of the first pump. The fuel system further includes a fuel rail downstream of the check valve and direct fuel injectors coupled to the engine. The method includes generating a flow of fuel in the fuel system via the first pump during an engine start before ignition of the engine; actuating the valve during the fuel flow to generate a pressure wave that travels through the fuel system past the check valve; and injecting fuel via the direct fuel injectors at an increased pressure generated by the pressure wave and held in the fuel rail via the check valve.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Stratified Charge Gasoline Direct Injection Systems Using Exhaust Gas Recirculation
ActiveUS20090266344A1Emission reductionImproving knock-toleranceInternal combustion piston enginesNon-fuel substance addition to fuelGasoline direct injectionCombustion chamber
An aspect of the present disclosure relates to a method and system for reducing emissions and improving knock-tolerance in an engine. Air, including exhaust gas present at levels greater than 20% by total air mass, may be introduced into a combustion chamber having a volume including a piston and a cylinder head. A first amount of fuel and a second amount of fuel may be directly injected into the combustion chamber at various points during the cycle, wherein the ratio of the air, including the exhaust gas, to the first and second amounts of fuel is 14.0:1 to 15.0:1. The first and second amounts of fuel may then be ignited. An electronic control unit may be utilized to time the injections and control the introduction of exhaust gas.
Owner:SOUTHWEST RES INST
Cold-start reliability and reducing hydrocarbon emissions in a gasoline direct injection engine
InactiveUS20100179743A1Increasing fractionLower requirementAnalogue computers for vehiclesElectrical controlCombustion chamberGasoline direct injection
A method for starting an engine of a motor vehicle, the engine having an intake manifold, an intake throttle controlling admission of air into the intake manifold, and a plurality of combustion chambers communicating with the intake manifold, the method comprising providing a reduced pressure of air in the intake manifold prior to delivering fuel or spark to the engine, the reduced pressure of air responsive to a temperature of the engine; delivering fuel to one or more of the plurality of combustion chambers in an amount based on the reduced pressure of air; and delivering spark to the one or more combustion chambers to start the engine.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
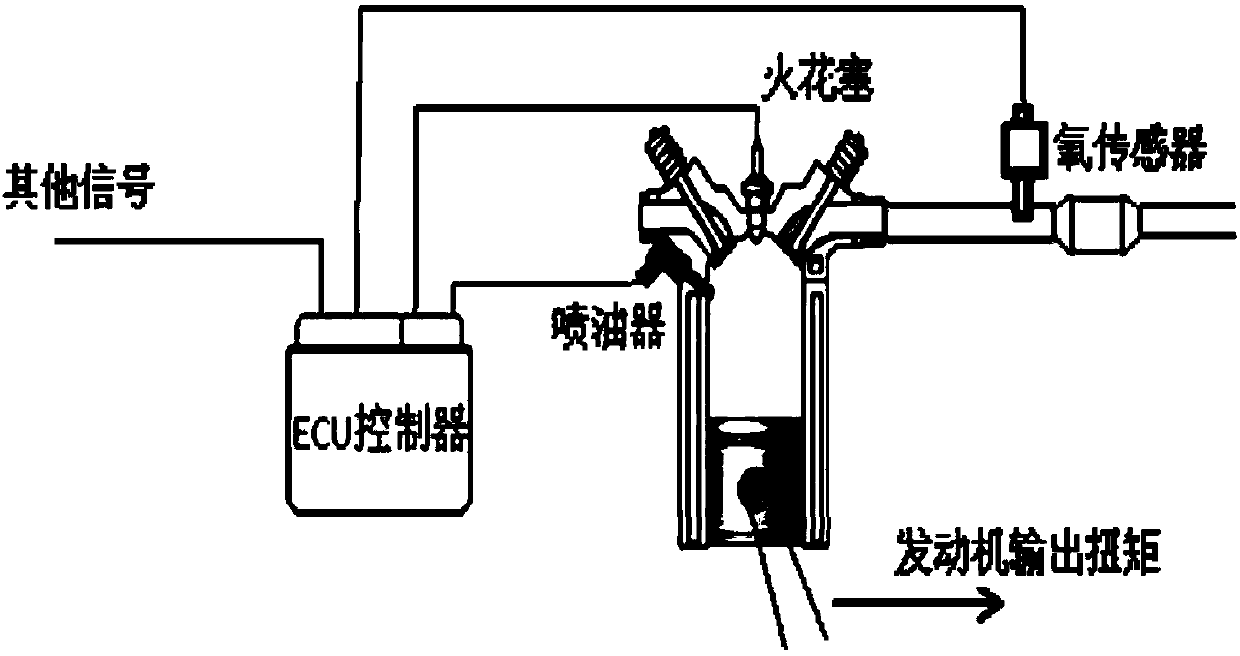
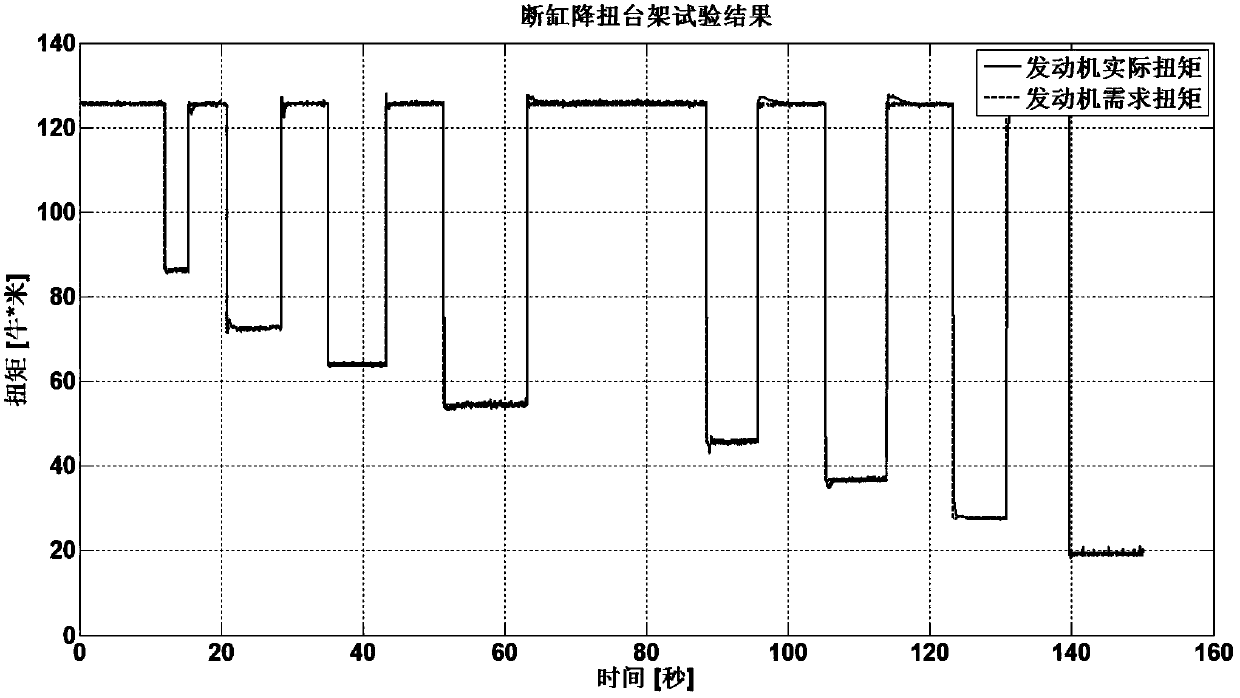
Method for shutting off cylinders and reducing torsion of gasoline engines
ActiveCN107795395AImproved torque reduction accuracyImproved torque reductionElectrical controlMachines/enginesGasoline direct injectionClosed loop
The invention relates to a method for shutting off cylinders and reducing torsion of gasoline engines. The method is applied to gasoline engines with three or more cylinders. The method is characterized by adding mixed gas self-adaption control function through special control software for mixed gas self-adaption on the basis of general gasoline direct injection engine air-fuel ratio closed-loop function; two engine operation cycles are used as a cylinder shutoff control period for sending gasoline injection commands of gasoline injectors; through combination of adjustment of ignition angles,the more accurate torsion reduction requirement can be achieved. The method specifically comprises eight steps. The method has the beneficial effects that the functions of calculating torsion reduction efficiency, coordinating torsion reduction, making cylinder shutoff strategy, executing cylinder shutoff and correcting ignition are added into ECU control strategy under the premise of not adding engine mechanical structures and electronic device hardware cost; finally, the engine torsion reduction accuracy is more than doubled; the engine torsion reduction effect of the vehicle during shiftinggears is effectively improved; the gear shifting smoothness of the vehicle is improved.
Owner:CHINA FIRST AUTOMOBILE
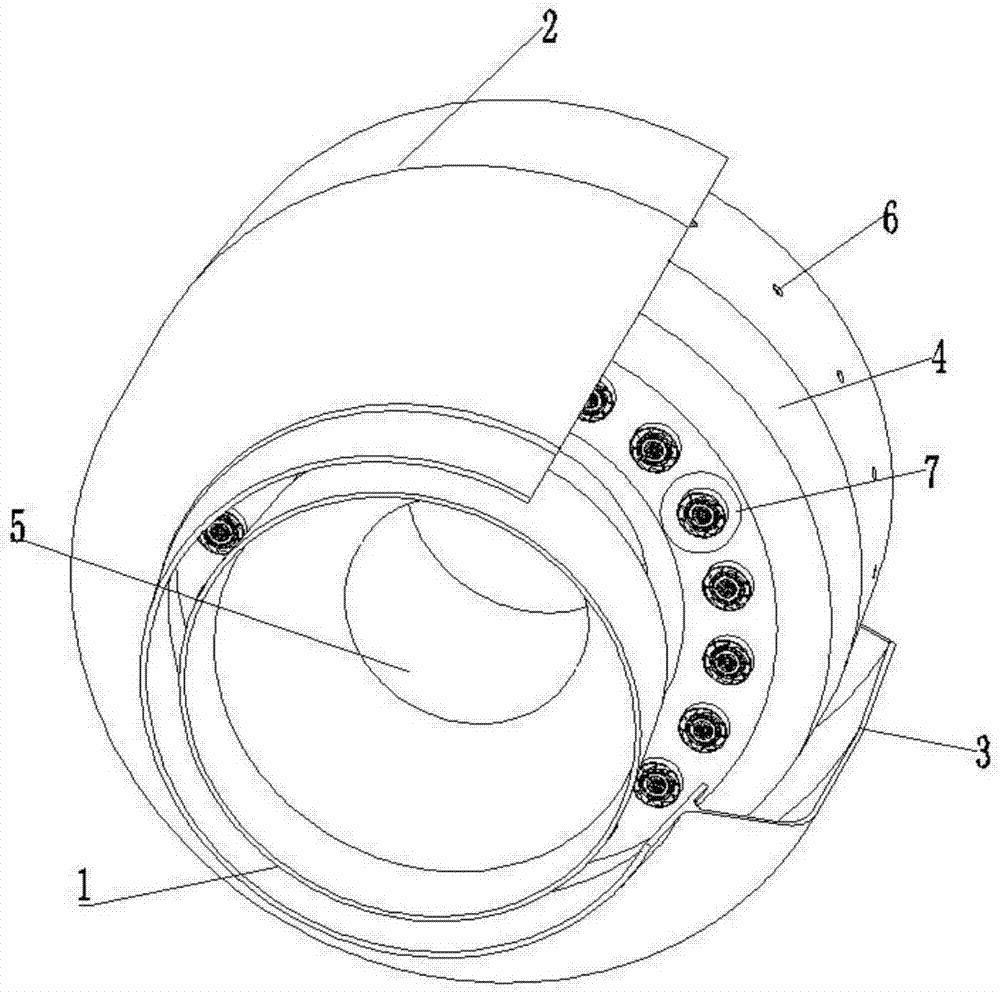
Piston of gasoline direct injection engine
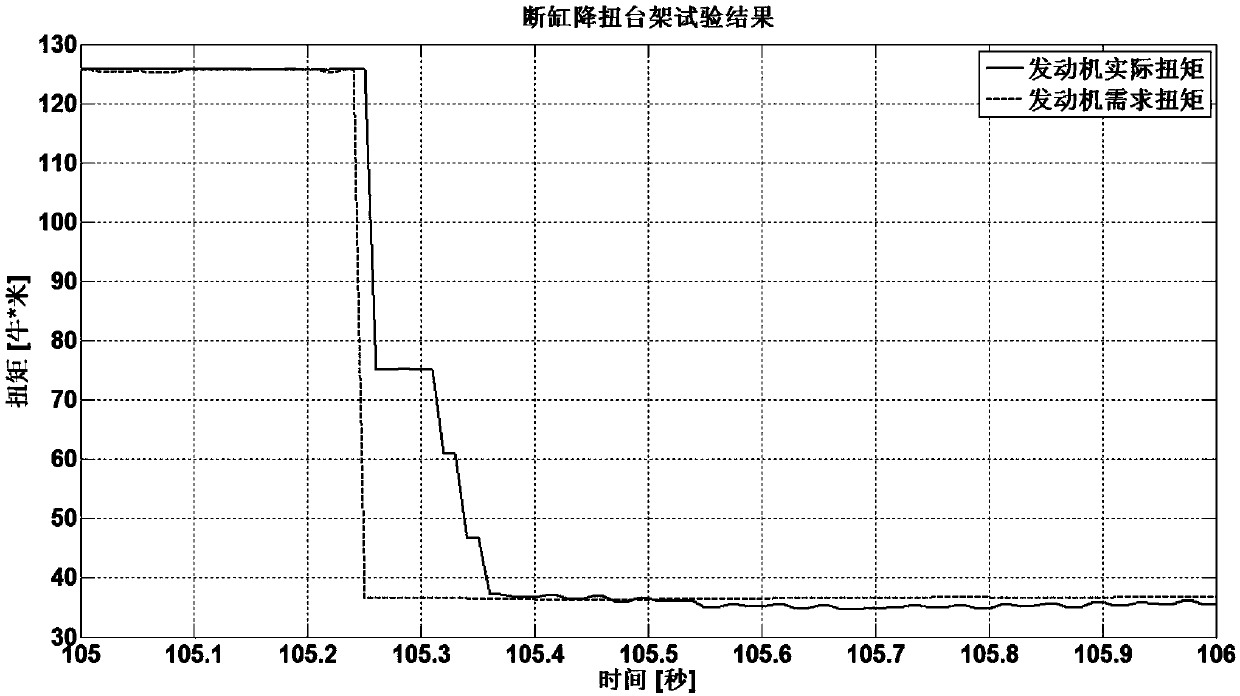
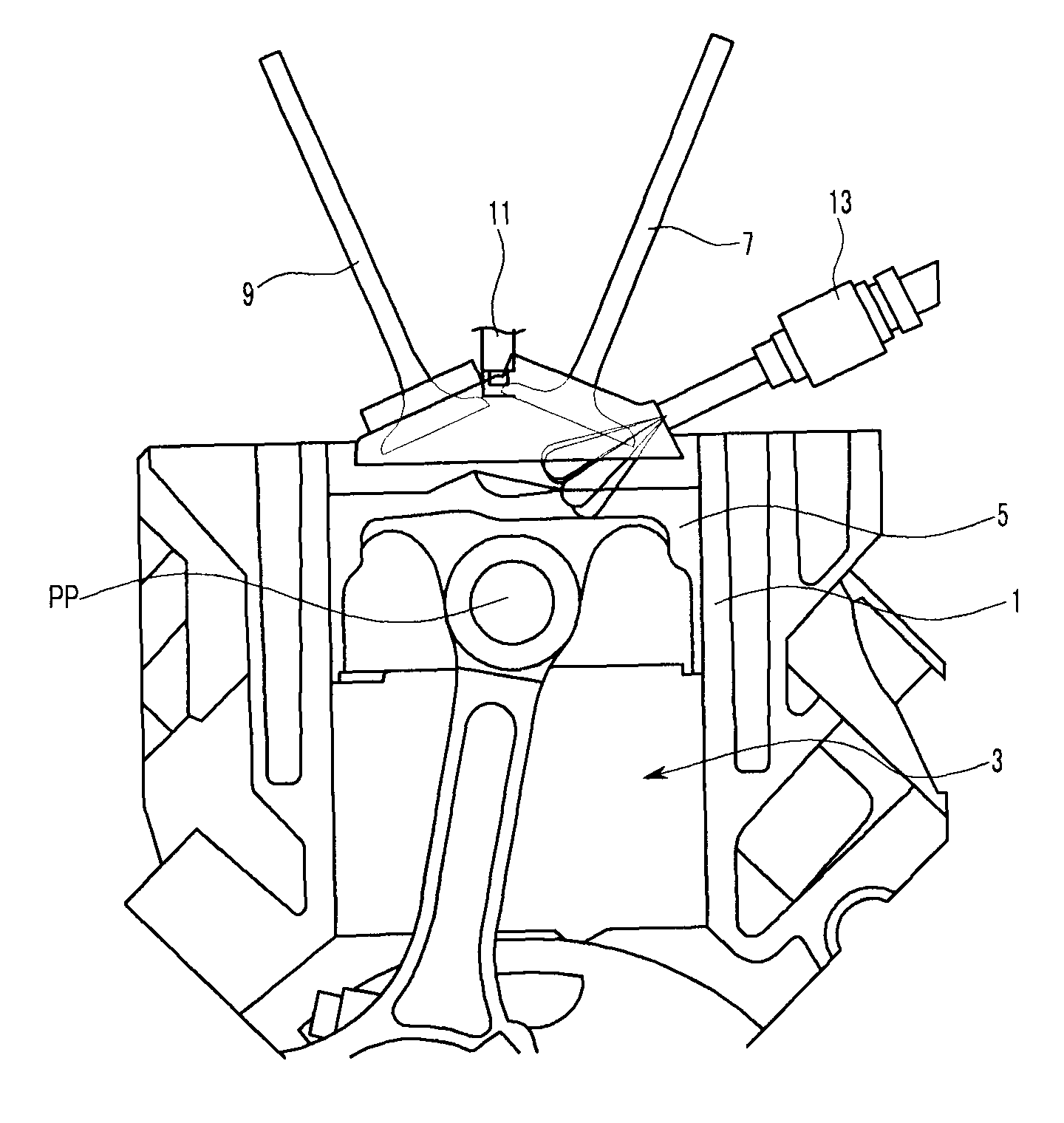
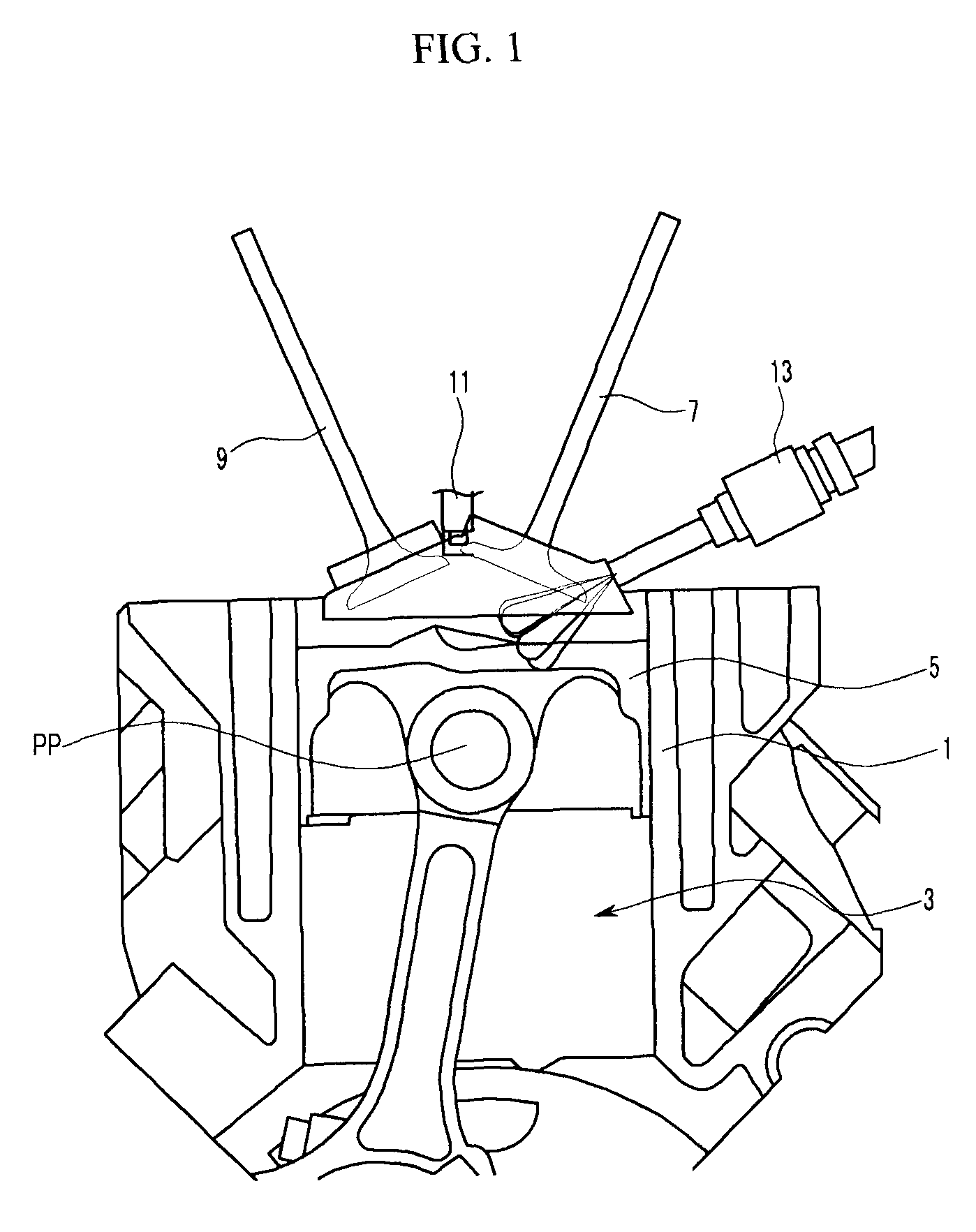
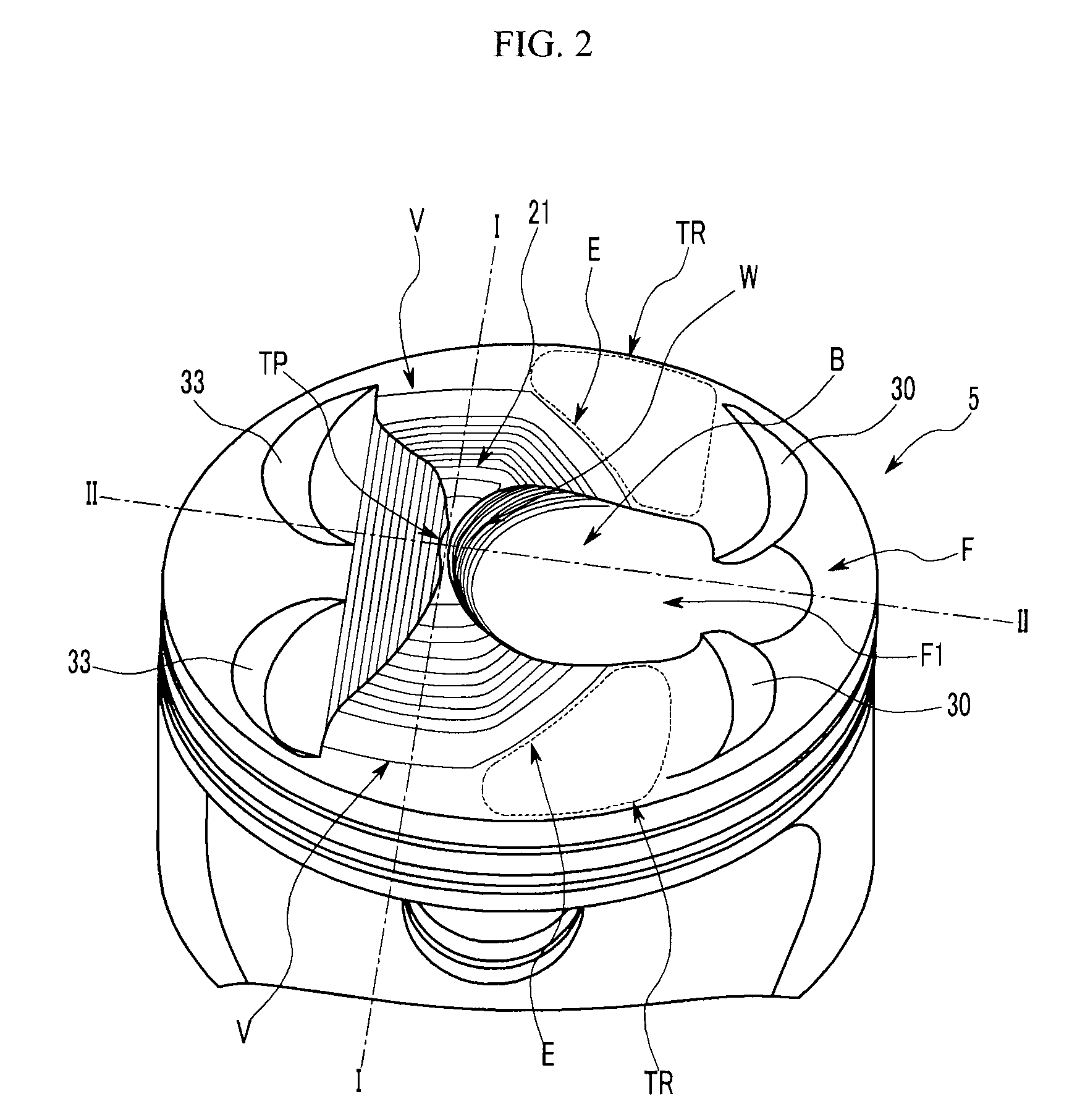
ActiveUS7971568B2Minimise concentrationReduce pollutantsInternal combustion piston enginesPistonsGasoline direct injectionSlope angle
A piston of a gasoline direct engine may include a protuberance portion protruding along a circular arc shape having a radius (R1) equal to the piston diameter to have a predetermined height (T) from the upper surface thereof, and the edge of the protuberance portion is rounded to be connected with the upper surface; a bowl (B) having a bottom surface (F1) having an asymmetrical ellipse shape from the center of the protuberance portion to the intake side direction thereof, wherein the bottom surface thereof becomes deeper in the exhaust side direction to have a predetermined slope angle (θ1), and the inner wall portion thereof has a circular arc shape to form a predetermined rising angle (θ2) at the upper part thereof; and trumpet portions (TR) of which edge ends (E) thereof are expanded in the intake side direction of the protuberance portion to be connected to the bowl (B).
Owner:HYUNDAI MOTOR CO LTD +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com