Patents
Literature
11640 results about "Waste gas" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Healthcare workers in a variety of settings can be exposed to the anesthetic gases that are released or leak out during medical procedures. These gases and vapours are known as waste anesthetic gases (WAGs).
Isolation and characterization of novel clostridial species
InactiveUS7704723B2High yieldReadily availableBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsSyngasAcetic acid
A novel clostridia bacterial species (Clostridium ragsdalei, ATCC BAA-622, “P11”) is provided. P11 is capable of synthesizing, from waste gases, products which are useful as biofuel. In particular, P11 can convert CO to ethanol. Thus, this novel bacterium transforms waste gases (e.g. syngas and refinery wastes) into useful products. P11 also catalyzes the production of acetate.
Owner:BOARD OF REGENTS FOR OKLAHOMA STATE UNIVERSITY +1
Plant and a method for increased oil recovery
Owner:DEN NORSKE STATS OLJESELSKAP AS
Single-machine single-pump electric drive fracturing semitrailer
PendingCN110656919AOptimize layoutNo emission pollutionPositive displacement pump componentsFluid removalExhaust gas emissionsElectric drive
The invention discloses a single-machine single-pump electric drive fracturing semitrailer. A traditional power supply semitrailer and a fracturing semitrailer are integrated in an optimized manner torealize a semitrailer simultaneously having power supply and fracturing functions; the power supply semitrailer and the fracturing semitrailer do not need to be used in a matched manner so that the single-machine single-pump electric drive fracturing semitrailer is more flexible in actual use and the oil and gas field well site layout is greatly optimized; the transportation is convenient; a working state can be reached only by using one group of high voltage cables to be connected with high voltage power supply so that the wiring mounting is faster; compared with diesel oil drive fracturing,electric drive fracturing has the advantages of small noise and no waste gas exhaust pollution; and as a driving source is electric power, compared with the diesel oil, the electric power has the advantage of lower use cost.
Owner:YANTAI JEREH PETROLEUM EQUIP & TECH CO LTD
Weight-optimized portable oxygen concentrator
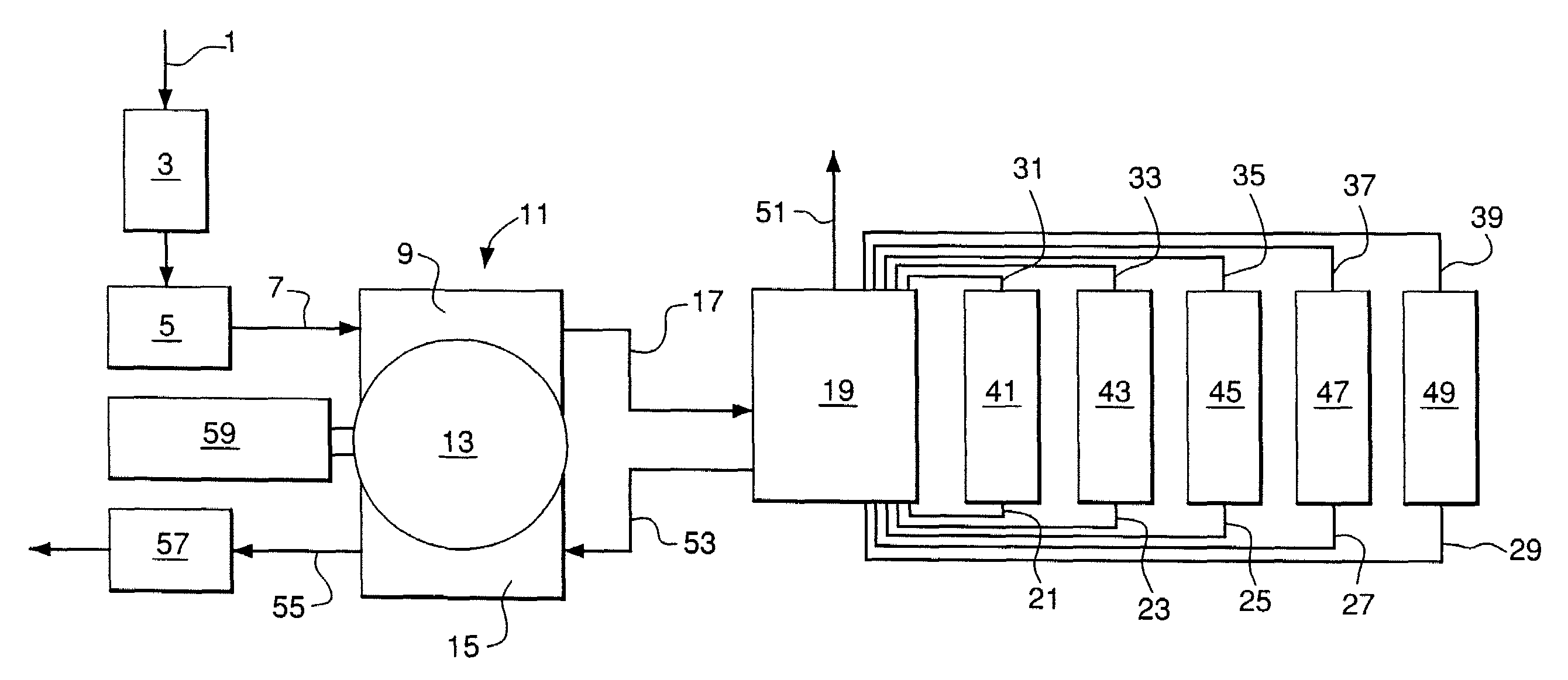
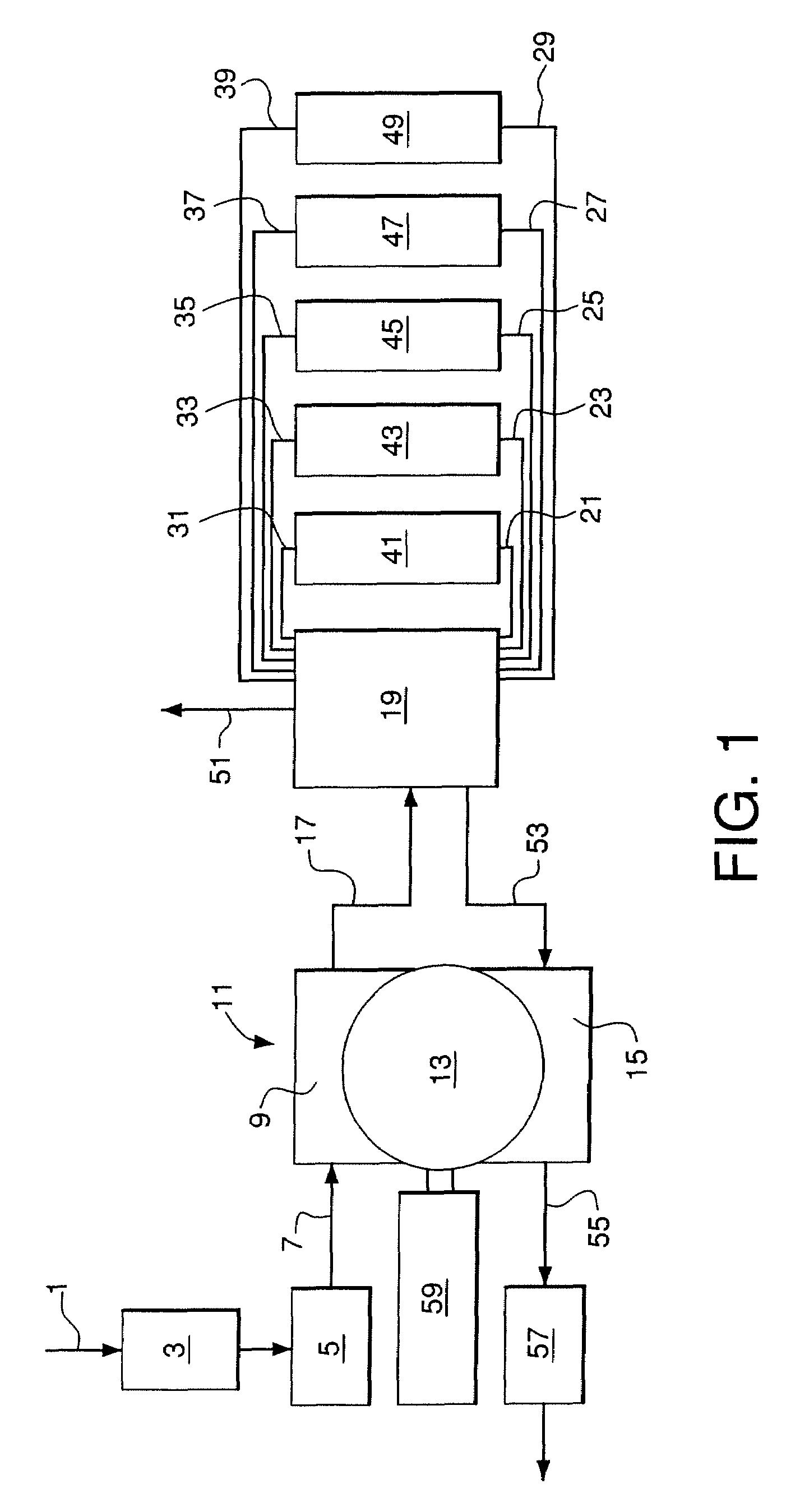
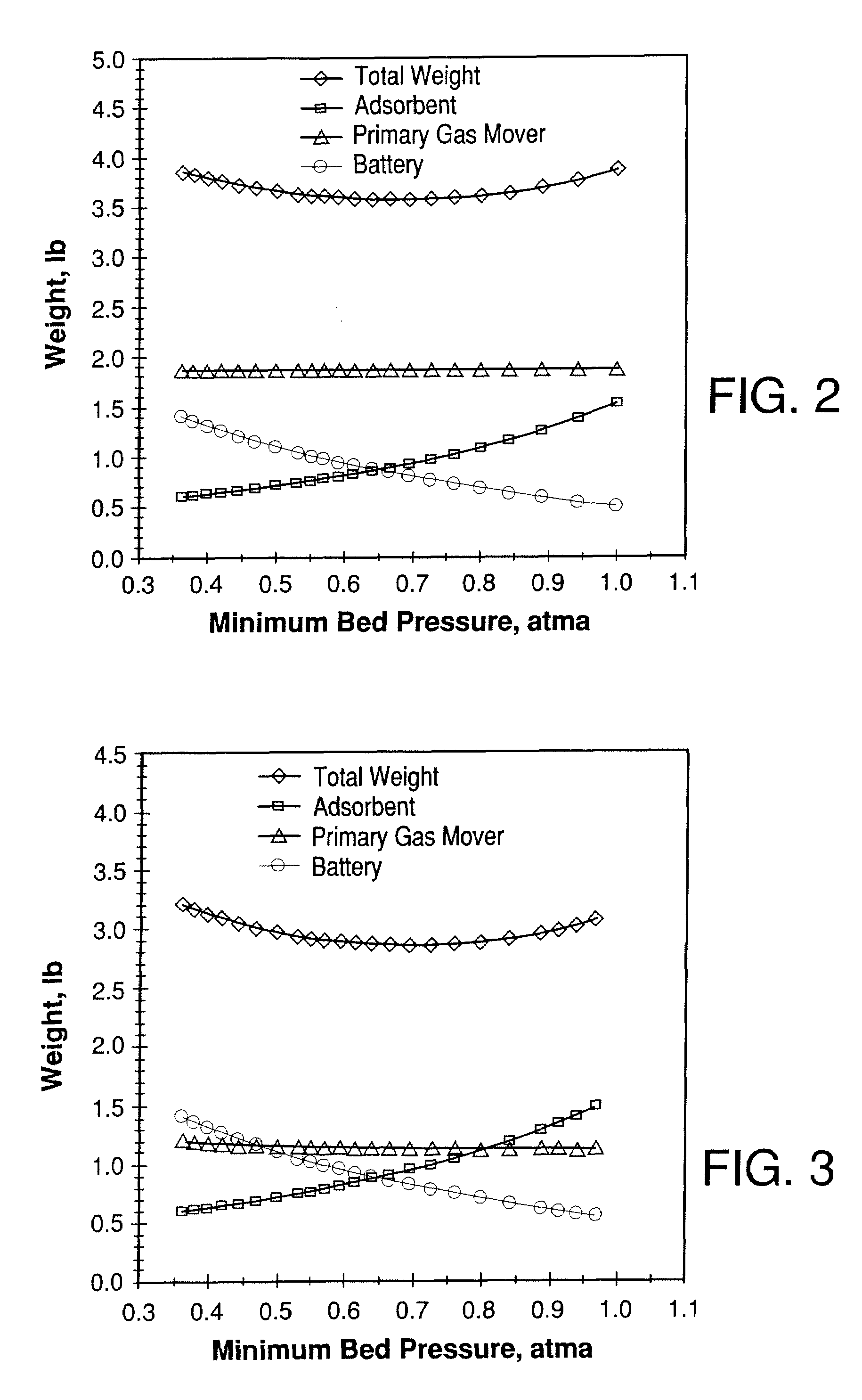
System for producing an oxygen-rich gas comprising (a) a primary gas mover including a first and a second compressor, wherein the primary gas mover is characterized by a weight Wp; (b) a drive motor adapted to drive the first and second compressors; (c) a rechargeable power supply characterized by a weight, Wb; and (d) a pressure / vacuum swing adsorption unit adapted to separate the pressurized feed air into an oxygen-rich product at a product flow rate Fp and an oxygen-depleted waste gas, wherein the adsorption unit comprises a plurality of adsorber beds containing an adsorbent and characterized by a total adsorbent weight Wa; and wherein the combined weight, Wt, of the adsorbent, the primary gas mover, and the rechargeable power supply is characterized by the expression0.75 Fp<Wt<2.02 Fpwhere Fp is in liters per min (at 23° C. and 1 atma pressure), and Wa, Wp, and Wb are in pounds.
Owner:INOGEN INC
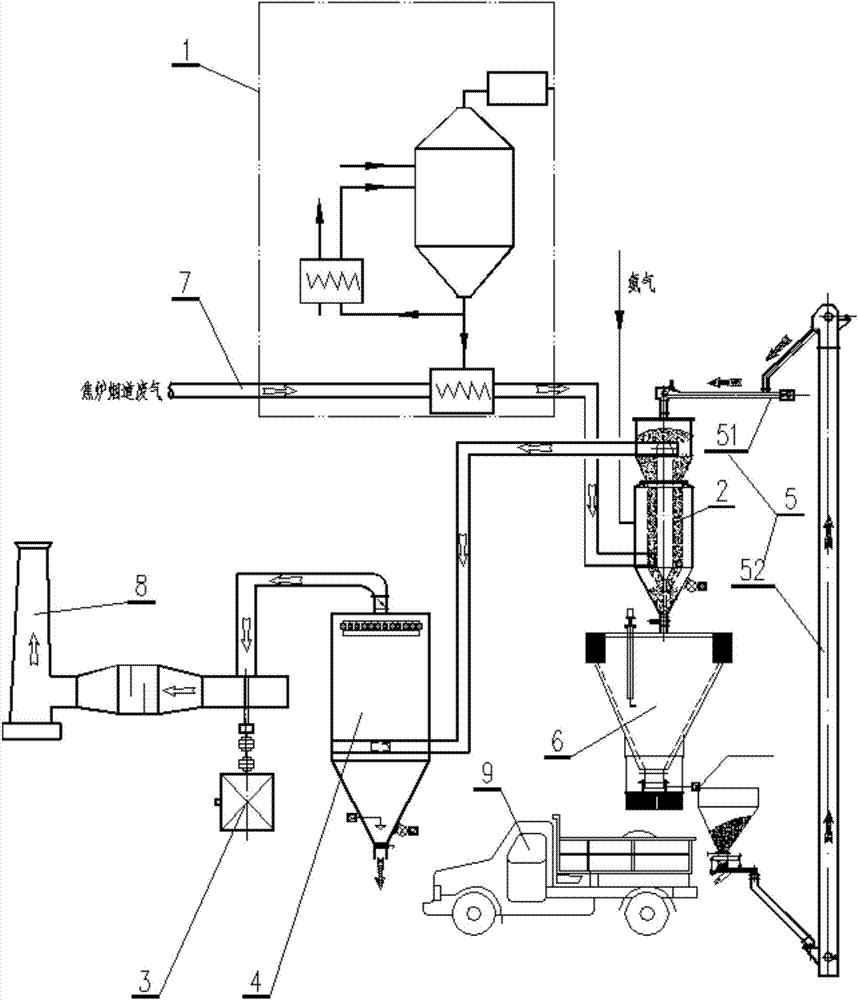
Coke oven flue gas waste heat utilization and purification method
ActiveCN103877856AReduce consumptionEfficient governanceDispersed particle separationPurification methodsCoking plant
The invention relates to the technical field of coke oven flue gas integrated utilization and pollution treatment and in particular relates to a coke oven flue gas waste heat utilization and purification method. The method is characterized in that flue gas waste heat is recovered by utilizing a flue gas waste heat recovery device, the temperature of the flue waste gas is reduced, and integrated desulfurization and denitration of the flue waste gas is realized by utilizing the activated adsorption capacity and low-temperature denitration catalytic capability of the coke. Compared with an existing process, the method has the beneficial effects that the flue waste gas desulfurization and denitration is performed under low-temperature working conditions, an additional heating system is not needed, and the energy consumption is reduced. In order to realize the desulfurization and denitration under low-temperature working conditions, the flue waste gas is cooled through the waste heat recovery device, so that the waste heat of the flue waste gas is fully utilized. The coke serves as a main catalyst for desulfurization and denitration and comes from a coking plant, the source is sufficient, and waste loss is avoided. The method disclosed by the invention can be widely applied to pollution treatment and integrated utilization of coke oven heated flue waste gas in coking production enterprises.
Owner:ACRE COKING & REFRACTORY ENG CONSULTING CORP DALIAN MCC
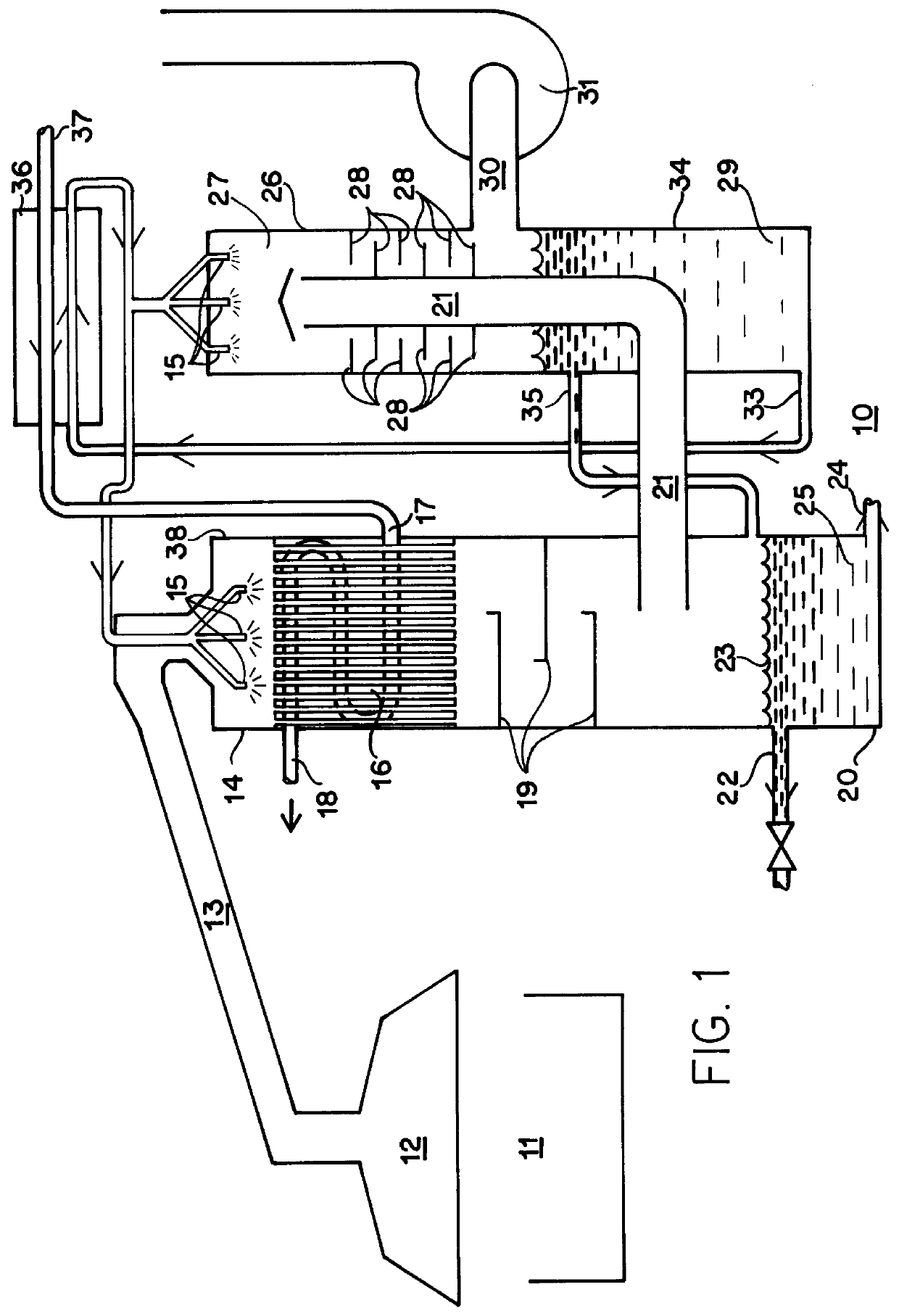
Apparatus and method for extracting heat from contaminated waste steam
InactiveUS6019819ALess energyHotter cooling water temperatureCombination devicesAuxillary pretreatmentAtmospheric airEngineering
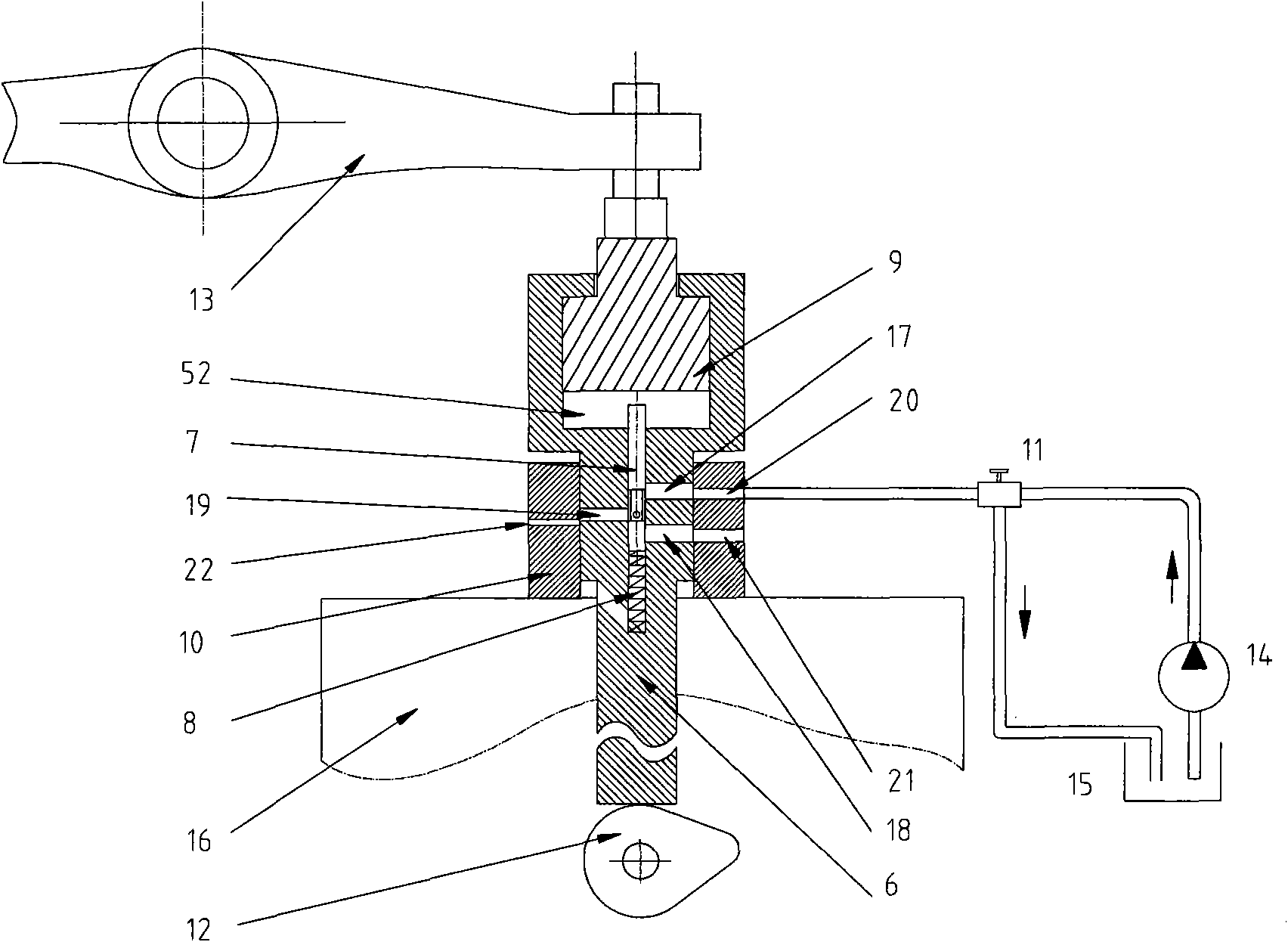
Disclosed is a contaminated waste steam heat recovery apparatus 10 and method therefore which includes a primary condensing unit 38, a low pressure water washing unit 26, a liquid to liquid heat exchanger 36 and a vent fan 31. Waste gas is ducted from fryer 11 to a de-super-heating chamber 14 wherein superheated steam is converted to saturated steam by spraying water into the steam using spray nozzles 15. The gas is then introduced into a vertically disposed air to liquid heat exchanger 16 and is drafted downward therethrough. As heat is removed from the waste gas, water vapor in the steam condenses and in the process, collects some of the oil and hydrocarbons present. A plurality of condensate trays 19 are disposed below the bottom end of heat exchanger 16 in a cascading fashion to collect hold the condensate in the airflow path such that it will absorb some of the heat still present in the remaining waste gas. An oil outlet 22 is provided at the top of collection basin 22 for drawing off concentrated oil 23. The waste gas is pulled into a low pressure water washer 26 where it is washed by a second set of spray nozzles 15. Waste gas and water are sucked downward through a set of turbulence inducing baffles 28. The remaining waste gas is sucked out though exhaust tube 30, using vent fan 31, and vented to the atmosphere.
Owner:ALPHA ENGINEERS
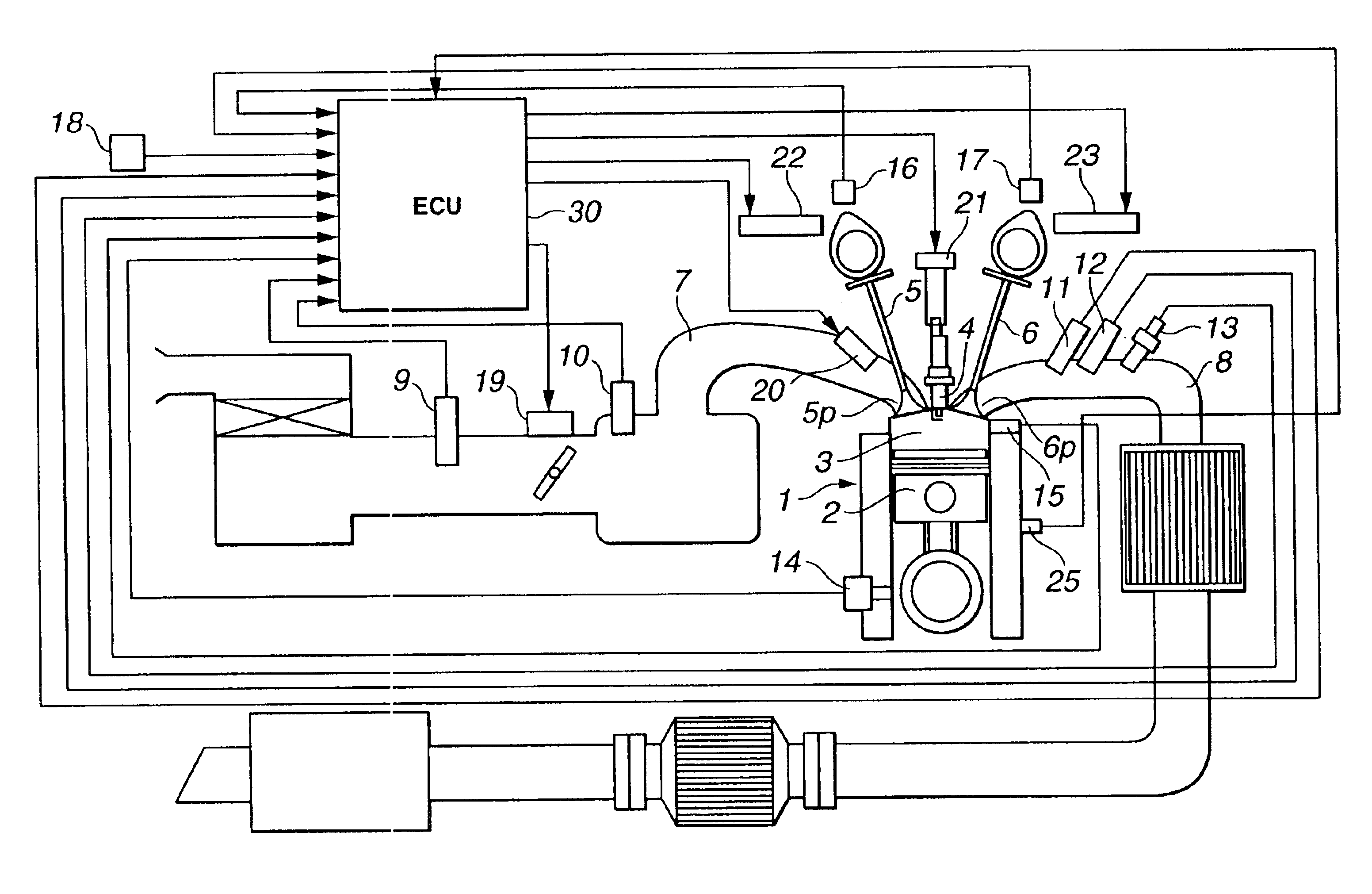
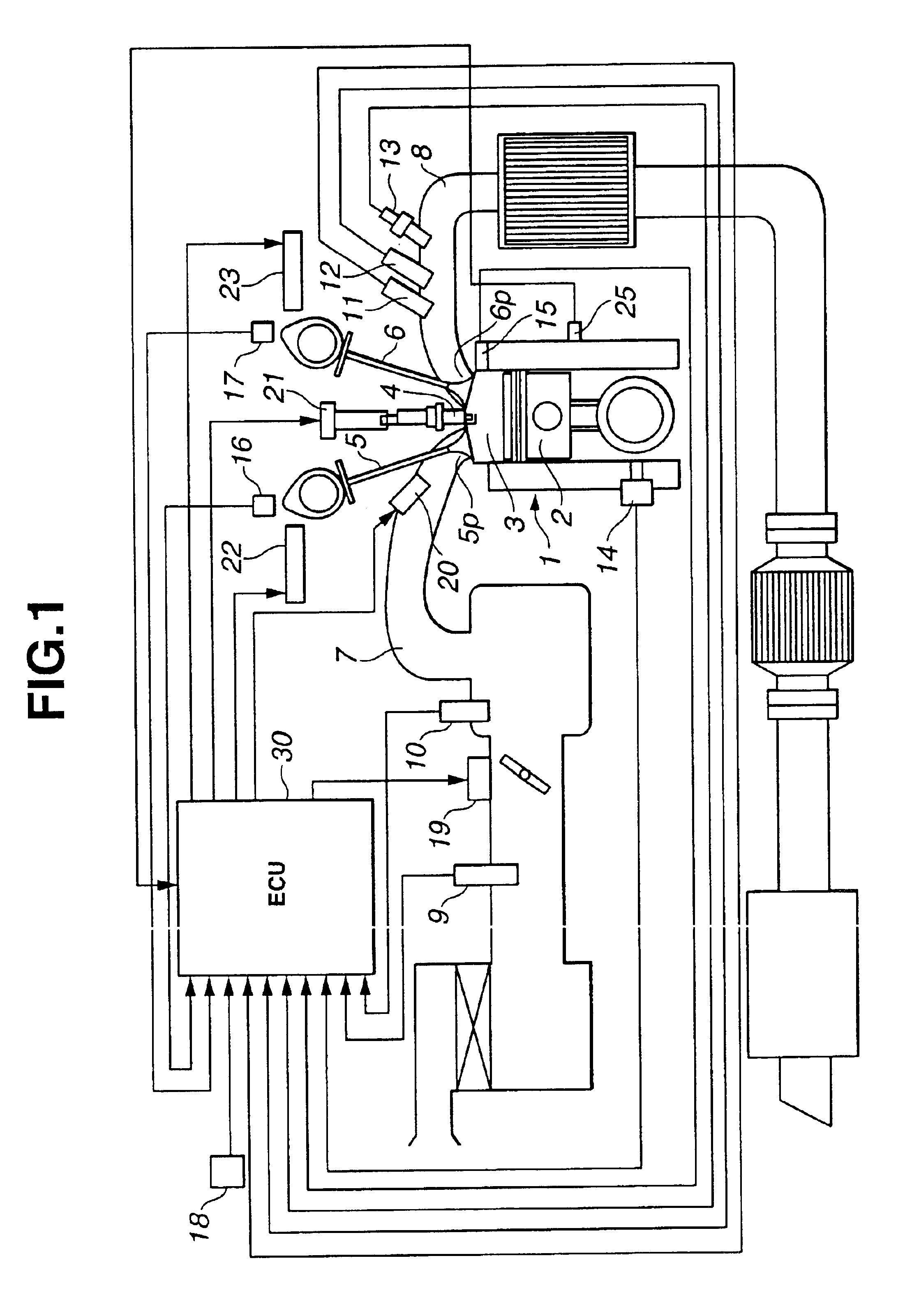
Internal exhaust gas recirculation amount estimation system of internal combustion engines
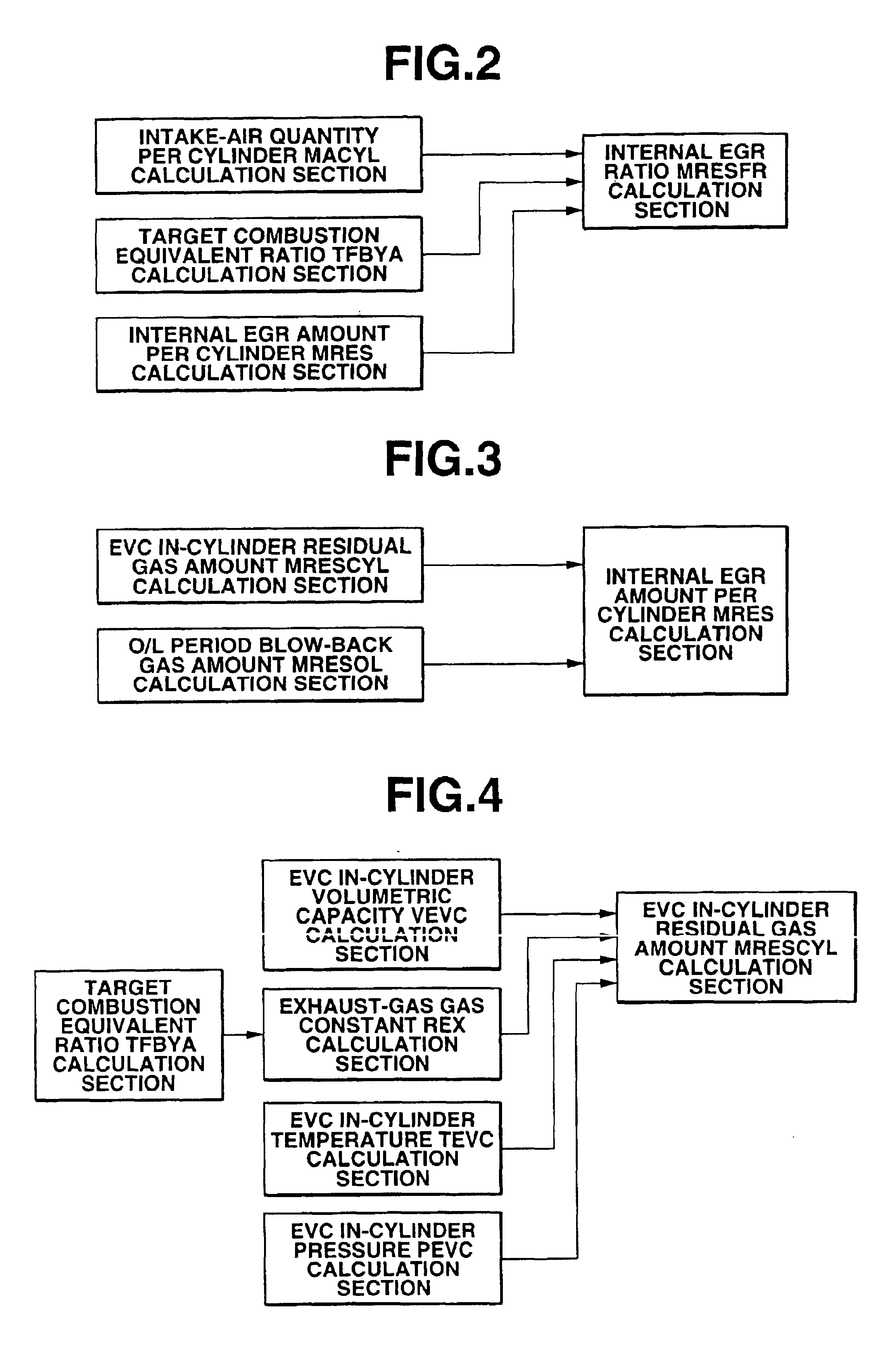
ActiveUS6840235B2Accurate estimateThe right amountValve arrangementsElectrical controlExhaust fumesGas constant
An internal exhaust gas recirculation amount estimation system calculates an in-cylinder temperature at an exhaust valve closure timing, an in-cylinder pressure at the exhaust valve closure timing, and a gas constant corresponding to a change in a composition of exhaust gas, based on an air-fuel mixture ratio. An exhaust valve closure timing in-cylinder residual gas amount is calculated based on at least the in-cylinder temperature, the in-cylinder pressure, and the gas constant. Also calculated is a valve overlap period blow-back gas amount, which is defined as a quantity of gas flow from one of intake and exhaust ports via a combustion chamber to the other port during a valve overlap period. An internal exhaust gas recirculation amount is calculated based on the exhaust valve closure timing in-cylinder residual gas amount and the valve overlap period blow-back gas amount.
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD
Barometric thermal trap and collection apparatus and method thereof for combining multiple exhaust streams into one
InactiveUS20090042070A1Controllable and more efficientIncrease contentFuel cell heat exchangeGas turbine plantsScrubberCogeneration
A device that, in any situation where multiple streams of hot or very hot gases or exhaust are generated, can collect gases into one stream and divert the stream efficiently to any manner of reformers, treatment devices, scrubbers, exchangers, etc. The exhaust flow from multiple fuel cell stacks are mixed in a single stream within the invention. This must be done carefully so that the exhaust stack pressure is approximately atmospheric at a variety of operating conditions. The mixing occurs in a device (the invention) called a Barometric Thermal Trap (BaTT). The fuel cell exhaust has a fairly high steam and CO2 content. The steam represents a potentially significant source of latent heat. Typical fuel cell heat recovery units avoid capturing the latent heat due to its relatively low condensing temperature (140 degrees Fahrenheit) and the resultant acidic level of the condensate due to the presence of CO2, which forms carbonic acid. By combining the exhausts into one stream, the BaTT system makes these problems manageable and more cost effective. Design calculations indicate that a Combined Heat and Power (CHP) efficiency of 82% is possible, which is much higher than provided by standard heat recovery designs.
Owner:UNIV INC AT CALIFORNIA STATE UNIV NORTHRIDGE THE
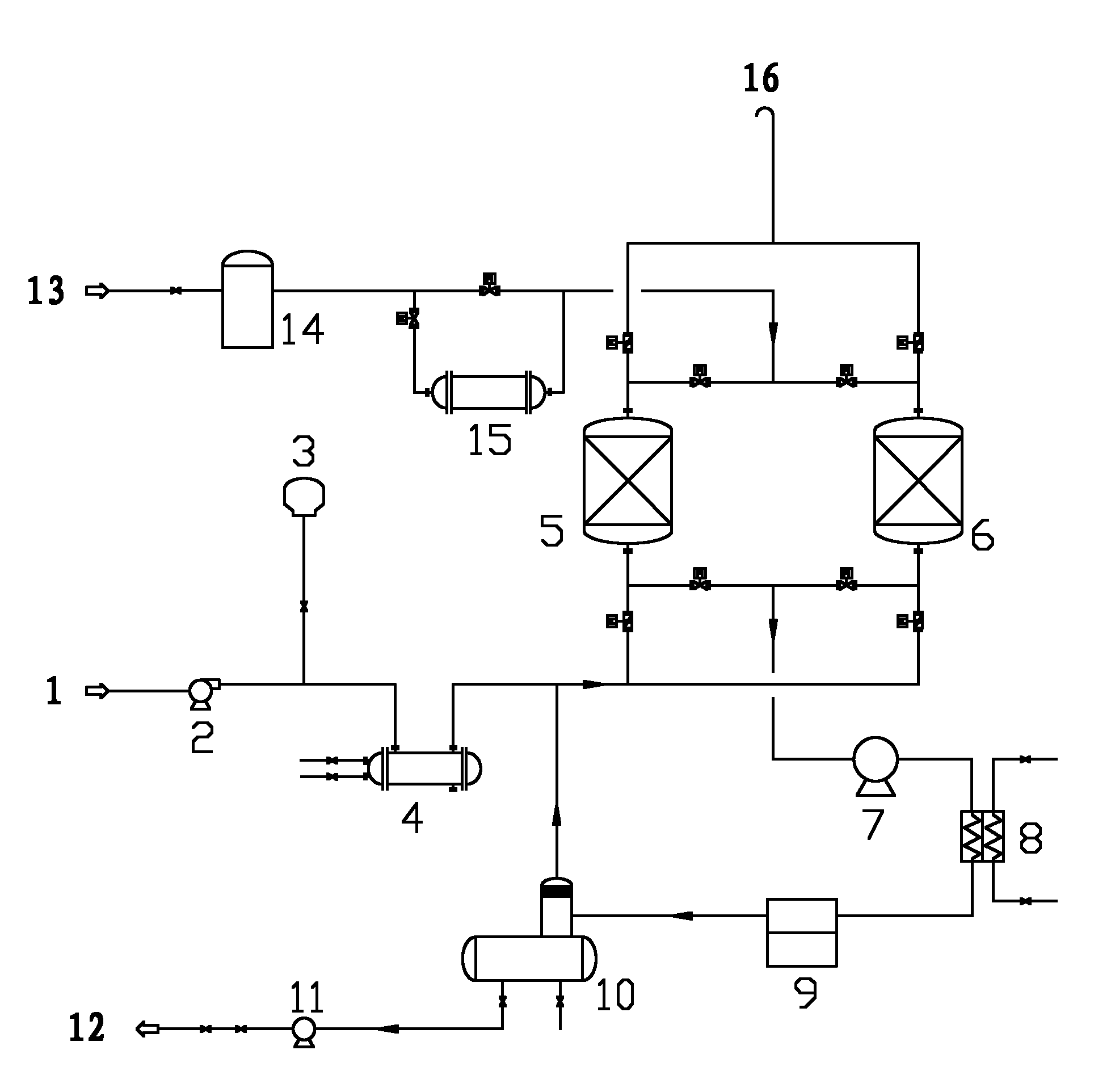
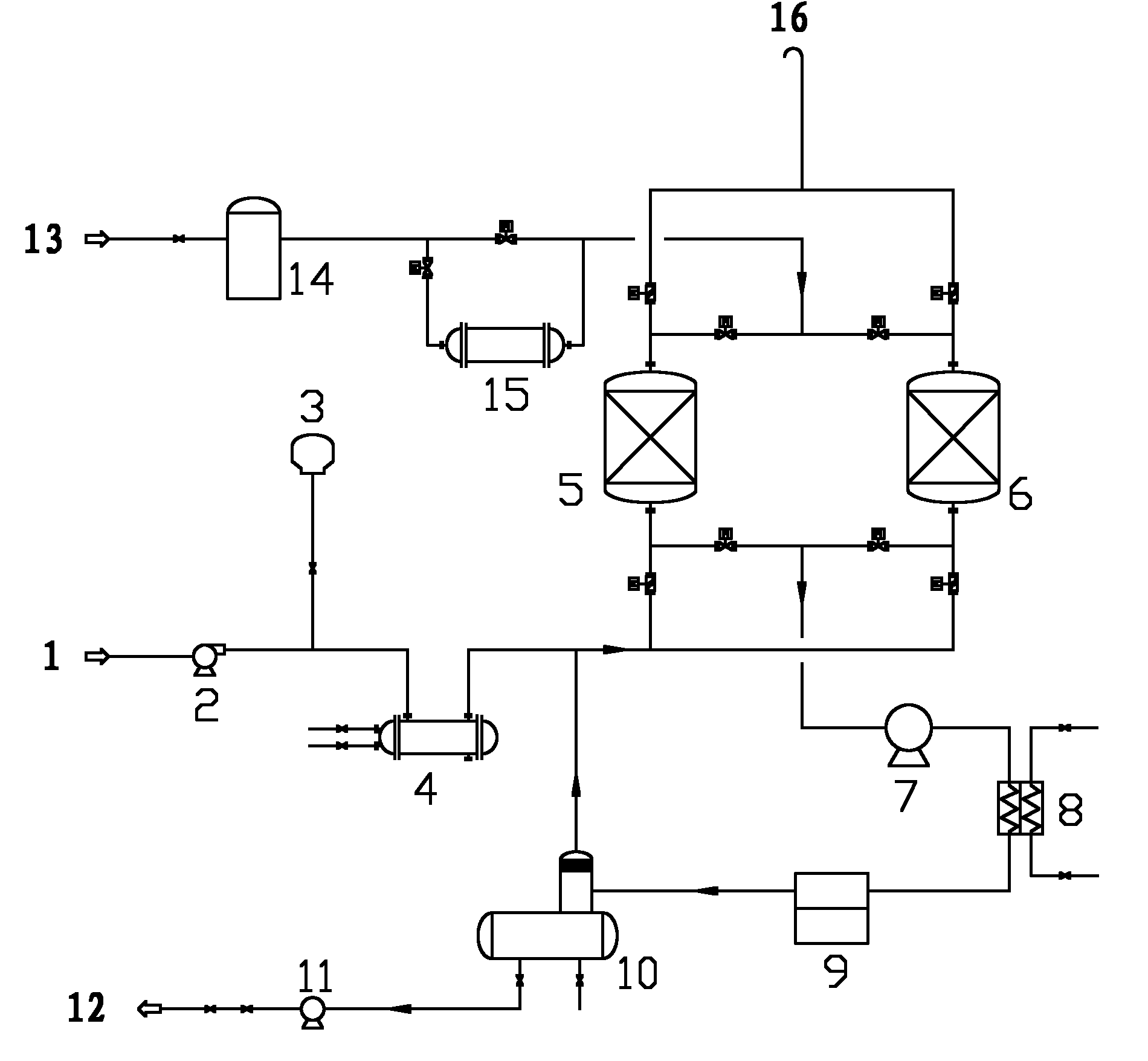
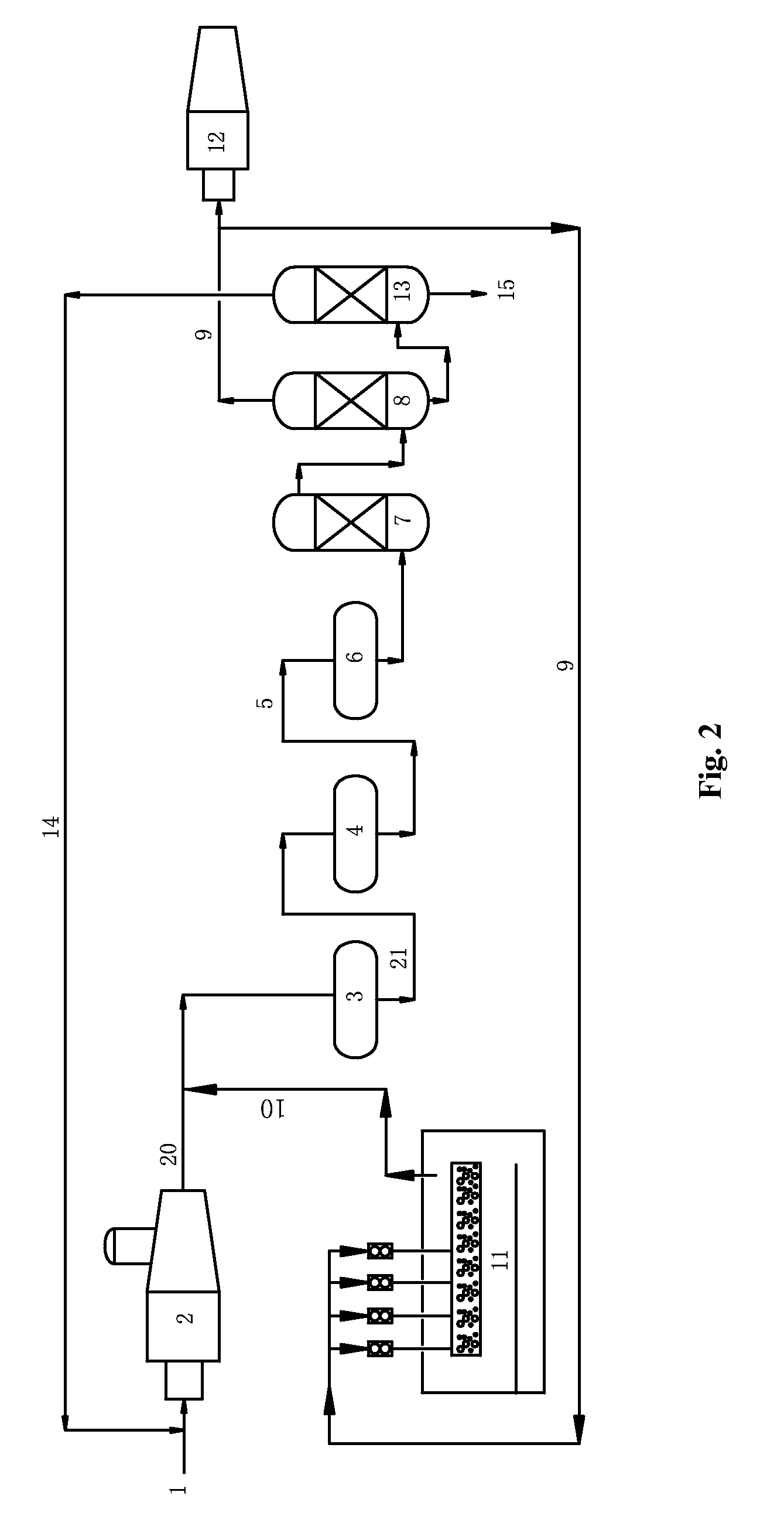
Treatment process for absorbed condensate waste gas
ActiveCN102179129ASo as not to damageShorten heating timeDispersed particle separationVapor condensationNitrogenEnvironmental engineering
The invention provides a treatment process for absorbed condensate waste gas, wherein two active carbon absorbing tanks alternately absorb waste gas; when one active carbon absorbing tank carries out waste gas absorption work, the other active carbon absorbing tank carries out carbon bed reproduction work, wherein the absorbed waste gas in waste gas absorption work is cooled; the carbon bed reproduction work comprises a step of vacuum de-sorption and a step of nitrogen de-sorption in sequence; the step of nitrogen de-sorption comprises flowing heated nitrogen at the temperature of 60-80 DEG Cthrough the carbon bed from top to bottom so that the carbon bed is deeply desorbed, and finally cooling the carbon bed by using unheated cold nitrogen so as to recover adsorptive capacity. The process is simple without providing absorbent on the spot; and the treatment process has high treatment efficiency, and can obtain pure recovery product without causing secondary pollution.
Owner:BAY ENVIRONMENTAL TECH BEIJING
Noise muffler for oxygen concentrator
A noise muffler for the exhaust of waste gases from apparatus such as an oxygen concentrator, including a muffler core with an inlet to receive the waste gases and a plurality of bores in the core first to direct the waste gases through a filter material and a cap enclosing the filter material and forming a plurality of outlets to direct the waste gases out of the muffler, the bores and outlets positioned to cause the waste gases to change their direction of flow multiple times before exiting the muffler.
Owner:CAIRE
Cleaning treatment method and apparatus for malodorous gas
InactiveCN101366966AStrong oxidation abilityImprove processing efficiencyGaseous substancesDeodrantsAdditive ingredientUltraviolet lights
The invention relates to a method for performing purification treatment on malodorous gases and a device carrying out the same. The ultraviolet light catalysis and ozone oxygenation technologies are optimally integrated to adapt to the treatment of the obnoxious gases with different concentrations and ingredients. Waste gas enters a spraying system to be washed by water or drugs, then is filtered and dried by a demisting device, enters an ultraviolet light catalysis and ozone oxygenation system, and finally is discharged at the top. The method for performing purification treatment on the malodorous gases and the device carrying out the same have the characteristics of less investment, low operation cost, small occupied area, high treatment efficiency, wide application scope and simple operation and management.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Heat exchanger
ActiveUS20100089548A1Improve sealingFirmly connectedInternal combustion piston enginesRecuperative heat exchangersPlate heat exchangerBiomedical engineering
A heat exchanger, particularly a charge air heat exchanger or exhaust gas heat exchanger, is provided for the heat exchange between a first fluid, particularly a charge air, or an exhaust gas, and a second fluid, particularly a coolant, comprising the following: heat exchanging guides for the first and second fluids, the guides being separated from each other in the core, the core having a plurality of flow channels through which the first fluid flows, and a housing that receives the flow channels and through which the second fluid flows at least one compartment lid, which is flow-connected to the flow channels, and a base that is attached to the compartment lid and that is equipped with one or more passage openings for flow channels. In order to achieve an advantageous connection of the compartment lid to the base, particularly in case the compartment lid and the base are made of different materials, the invention provides that the compartment lid is attached to the base via one or more connections as a bolted connection and / or a slotted crimping.
Owner:MAHLE BEHR GMBH & CO
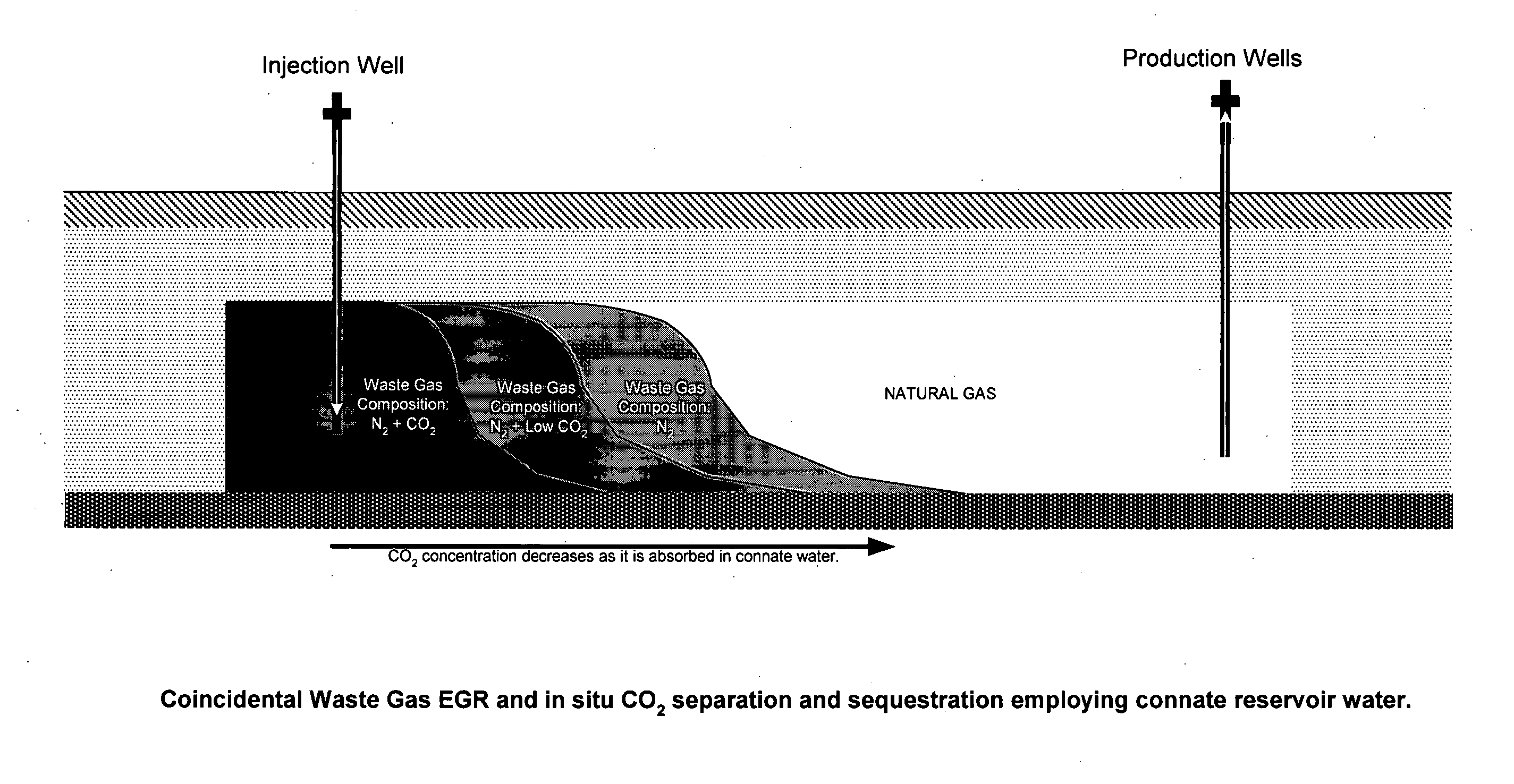
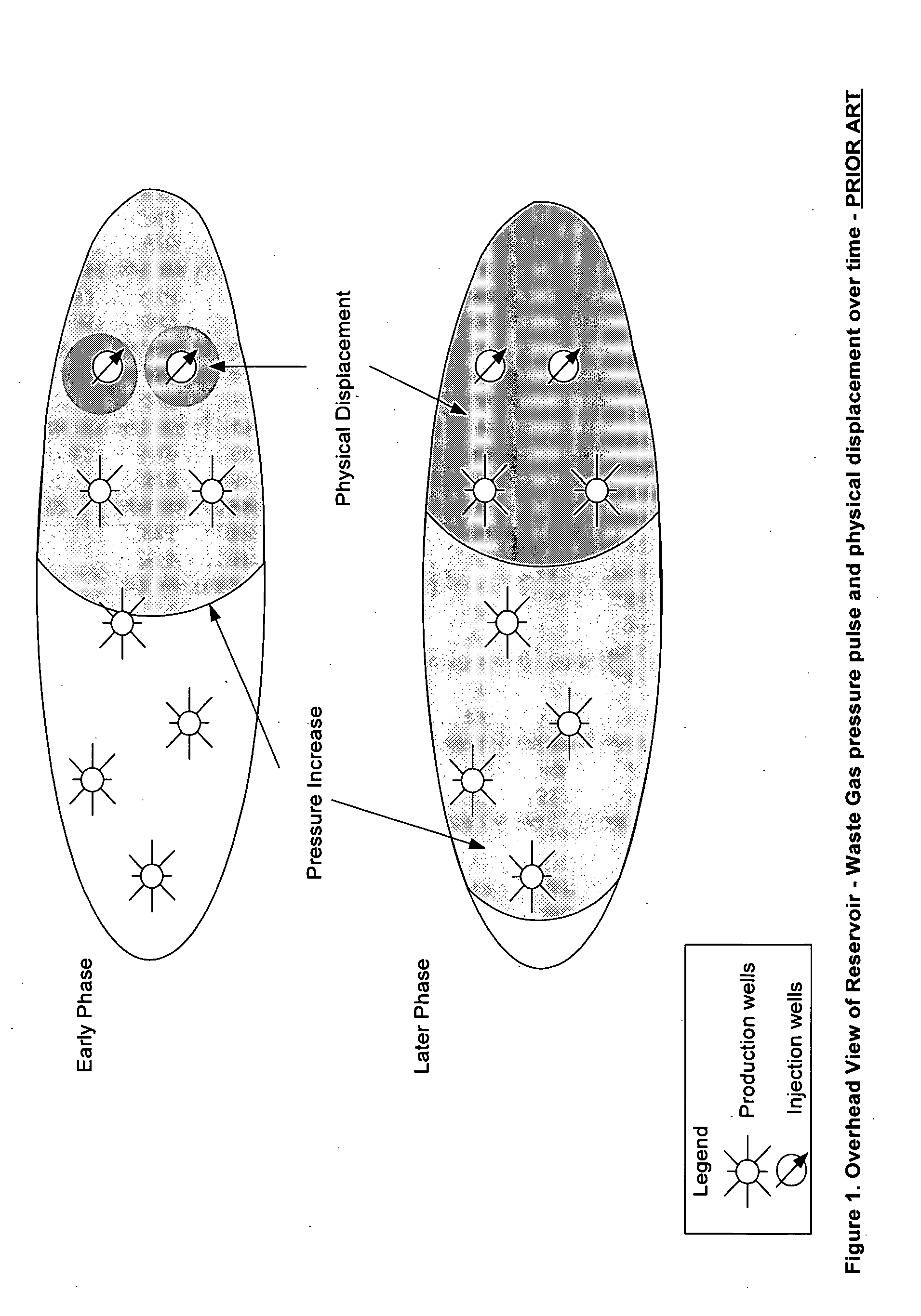
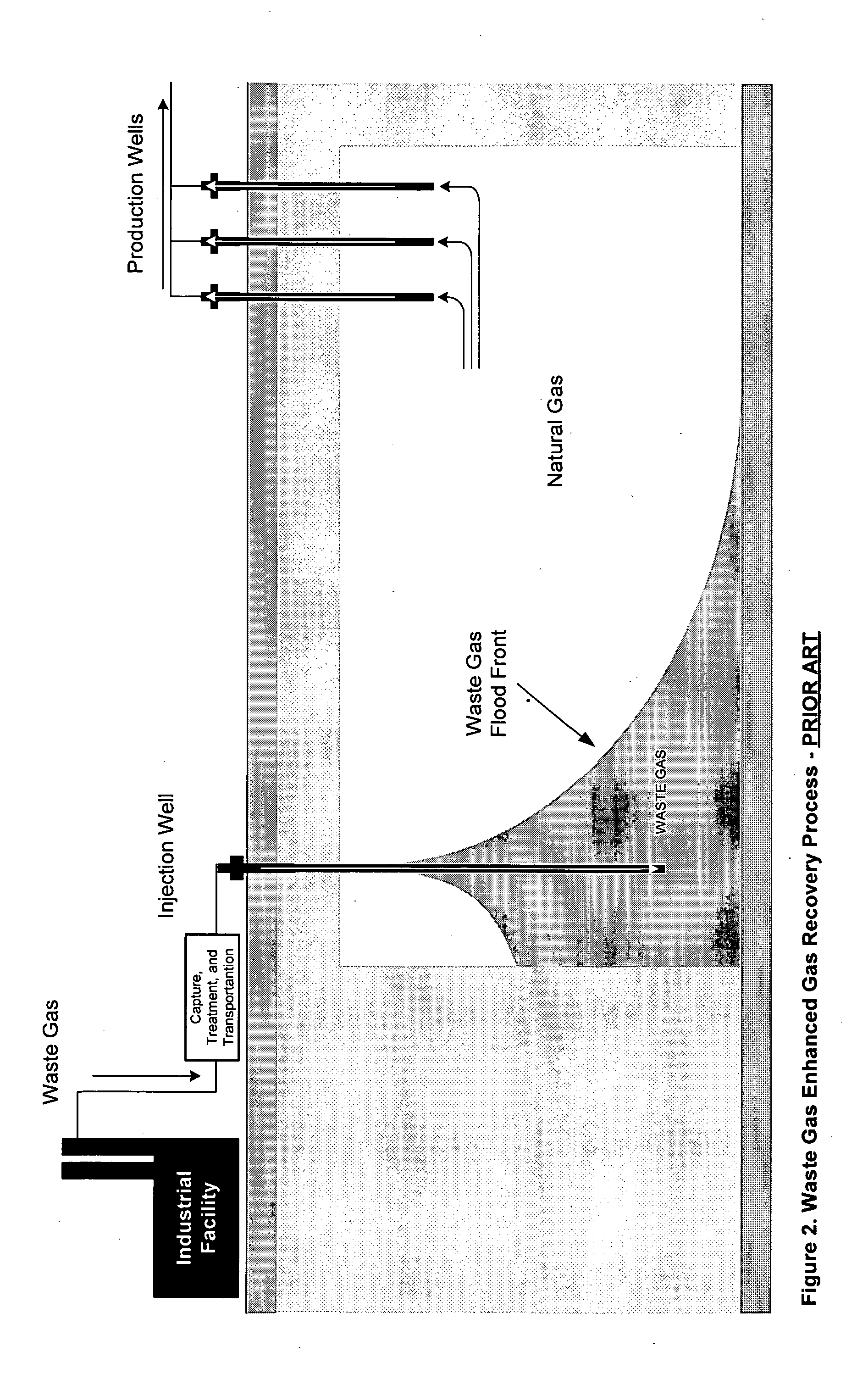
Applications of waste gas injection into natural gas reservoirs
InactiveUS20050167103A1Improve liquidityLow viscosityOther gas emission reduction technologiesFluid removalGreenhouseEnvironmental engineering
Natural gas is produced from a reservoir above a bitumen reserve with minimal or no impact on concurrent or subsequent production of bitumen recovery techniques including SAGD. Greenhouse benefits over and above the benefits of coincidental recovery are available through the injection of waste gas containing carbon dioxide for maintaining pressure in the gas reservoir while producing natural gas. Carbon dioxide separates out of the waste gas through preferential absorption in connate or aquifer water, with the result that carbon dioxide is thereby both retarded from flowing to the natural gas production well and effectively sequestered in the reservoir water. Additional advantage is achieved wherein water influx at production wells can be managed and trapped gas can be recovered.
Owner:BEAUVERT GAS SERVICES
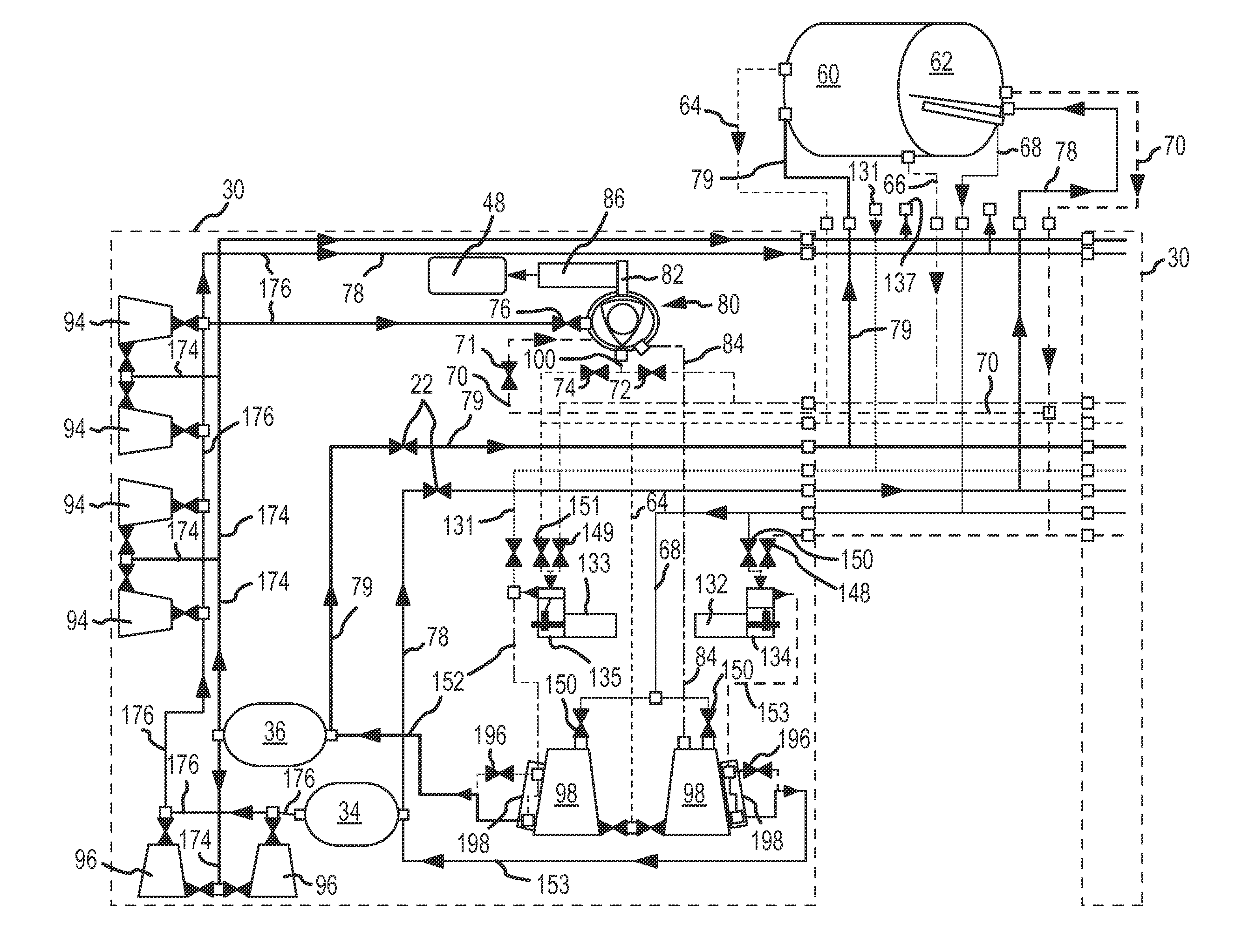
Integrated vehicle fluids
ActiveUS20120227374A1Reduce peak pressureIncrease in temperatureLaunch systemsCosmonautic propulsion system apparatusSpace vehicleModularity
A system and methods are provided for combining systems of an upper stage space launch vehicle for enhancing the operation of the space vehicle. Hydrogen and oxygen already on board as propellant for the upper stage rockets is also used for other upper stage functions to include propellant tank pressurization, attitude control, vehicle settling, and electrical requirements. Specifically, gases from the propellant tanks, instead of being dumped overboard, are used as fuel and oxidizer to power an internal combustion engine that produces mechanical power for driving other elements including a starter / generator for generation of electrical current, mechanical power for fluid pumps, and other uses. The exhaust gas from the internal combustion engine is also used directly in one or more vehicle settling thrusters. Accumulators which store the waste ullage gases are pressurized and provide pressurization control for the propellant tanks. The system is constructed in a modular configuration in which two redundant integrated fluid modules may be mounted to the vehicle, each of the modules capable of supporting the upper stage functions.
Owner:UNITED LAUNCH ALLIANCE
System and method for treating waste acid gas
ActiveCN102910593ANo emissionsLower requirementEnergy inputSulfur preparation/purificationLiquid wasteSulfur
Owner:美景(北京)环保科技有限公司
Production method for manganese sulfate by using biological cellulose and low-grade manganese ores
The invention discloses a production method for manganese sulfate by using low-grade manganese ores. According to the method, manganese sulfate with high purity can be produced by using waste low-grade manganese ores with manganese content of 10% to 20%, manganese tailing or manganese-containing solid waste residue. The method comprises the steps of preparation of raw materials, a slaking reaction, a leaching reaction, neutralization and purification of leachate, etc. According to the invention, production of manganese sulfate is not restricted by the grade of manganese ores, and low-grade manganese oxide ores with a grade greater than 10%, manganese tailing or manganese-containing solid waste residue can be fully utilized; produced manganese sulfate has high yield and high purity and is a very important industrial fundamental product; almost no external heat supply is needed, low energy consumption is achieved, production cost is low, it does not need to turn over and mix materials in the process of the reactions, the reactions are smooth, no toxic gas is generated, and no environmental pollution is produced; discharge of three wastes (waste gas, waste water and industrial residue) reaches national discharge standards for environmental protection, and there is no dust pollution in a workshop.
Owner:陈昆先 +1
Control flows and forces in vtol vehicles
ActiveUS20110049306A1Easy constructionDifferent functionsVertical landing/take-off aircraftsRotocraftOperation modeBlade pitch
The present application relates to VTOL vehicles with multi-function capabilities and, specifically to ducted fan arrangements that facilitate the control of forces and flows of air to control movement of the vehicle in six degrees of freedom in both primary and secondary modes of operation. Also disclosed are pitch control mechanisms for the lift propellers of VTOL vehicles: drive and transmission arrangements; a specially configured exhaust duct for directing exhaust gases from such vehicles along an upper surface of the vehicle; and shock absorbing components for the landing gear of such vehicles.
Owner:URBAN AERONAUTICS
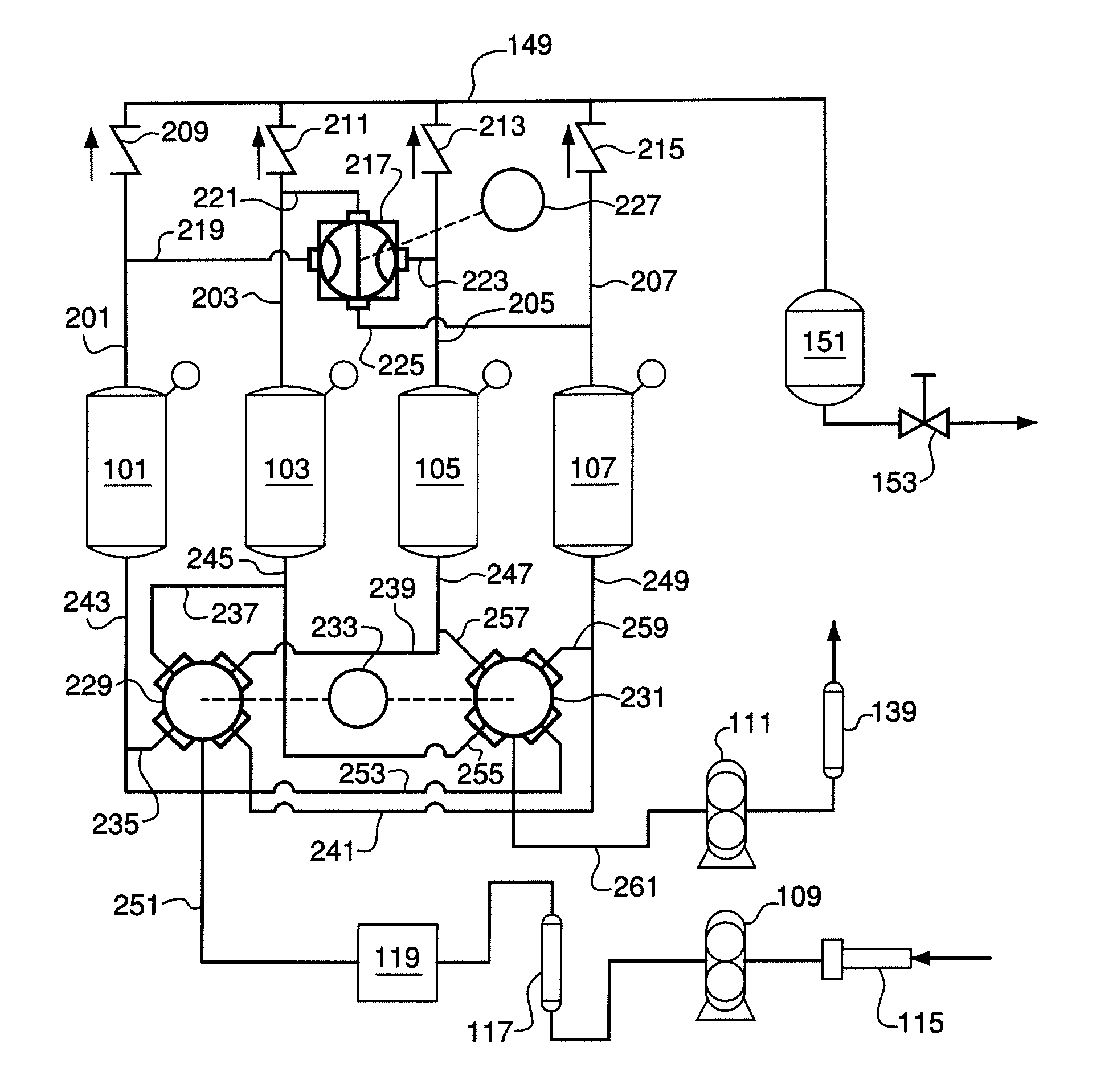
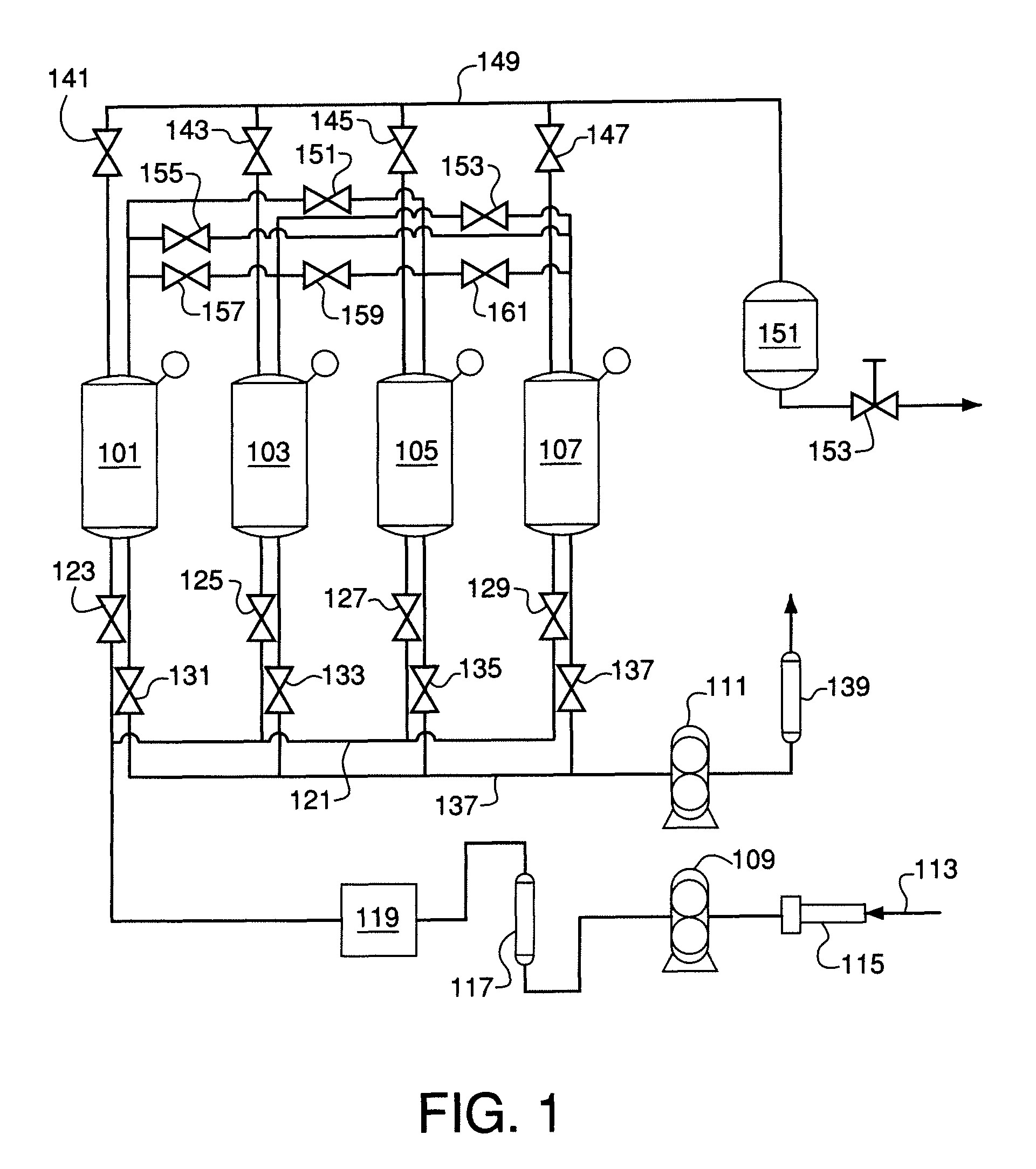
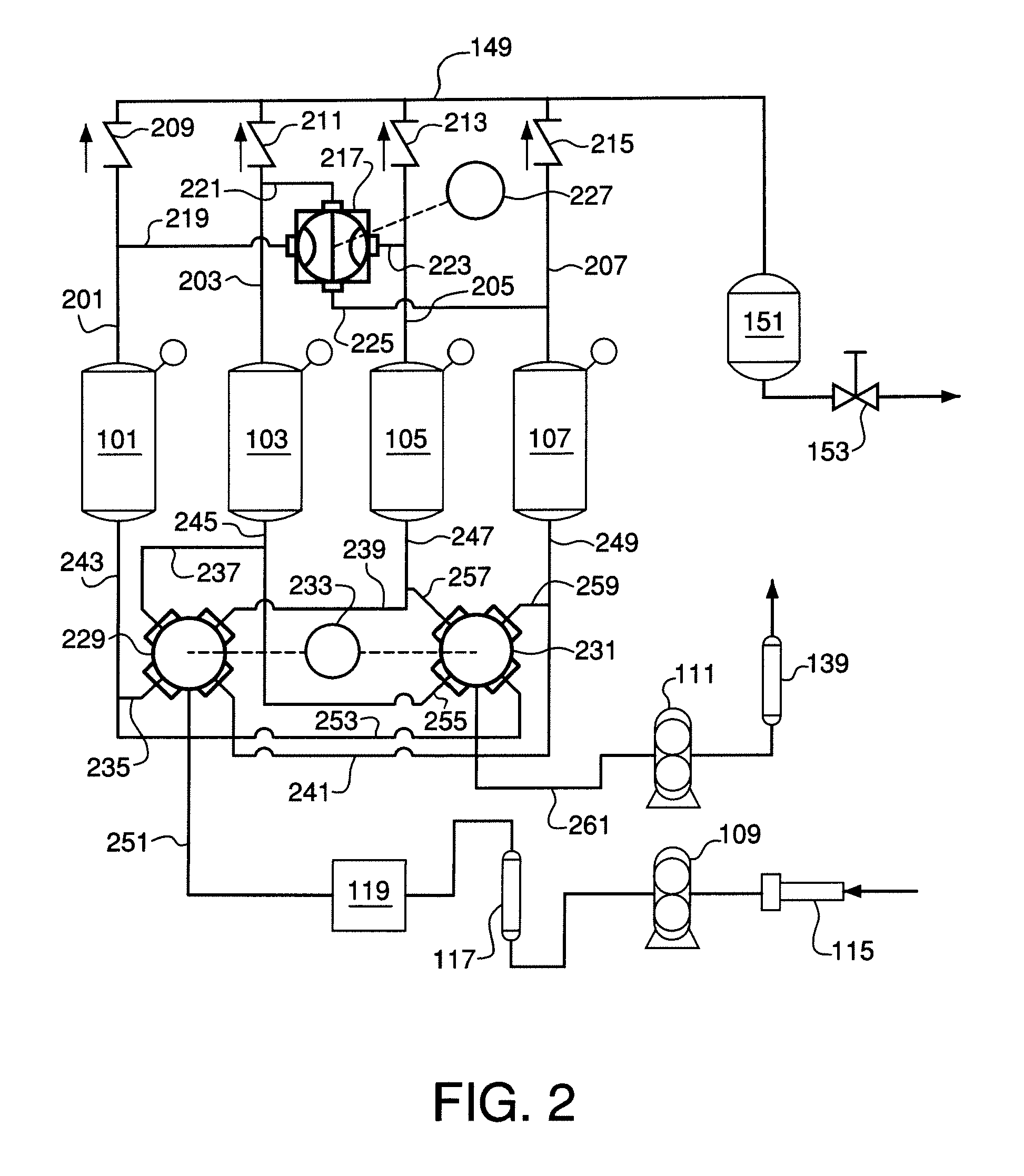
Pressure swing adsorption system with indexed rotatable multi-port valves
Pressure swing adsorption system comprising two or more vessels, each having a feed end, a product end, and adsorbent material adapted to adsorb one or more components from a multi-component feed gas mixture; piping adapted to (1) introduce the feed gas mixture into the feed ends, withdraw a product gas from the product ends, and withdraw a waste gas from the feed ends of the vessels, and (2) place the product ends of any pair of vessels in flow communication; a feed pipe adapted to supply the feed gas mixture to the system; a product pipe adapted to withdraw the product gas from the system; and a waste gas pipe adapted to withdraw the waste gas from the system. An indexed rotatable multi-port valve is adapted to place the product end of each vessel in sequential flow communication with the product end of each of the other vessels.
Owner:AIR PROD & CHEM INC
Hazardous waste treatment method and apparatus
A method and apparatus for heat treating of hazardous waste by heating the waste in a pyrolyzing chamber and forming an off-gas, heating the off-gas for a sufficient time to destroy dioxins and furans, then reducing and cooling the off-gas in a secondary treating chamber having a graphite stack and recovering metallics by distillation.
Owner:GENERAL FORNI
Exhaust gas waste heat recovery
InactiveUS7921640B2Faster engine warm upImprove economyInternal combustion piston enginesExhaust apparatusPower flowEngineering
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Process for reducing sulfur emission of sulfur plant
ActiveUS8871176B2Small investmentReduce operating costsSulfur preparation/purificationSulfurWaste gas
The present invention provides a process for reducing sulfur emission of a sulfur plant, wherein the sulfur plant includes a thermal reaction unit, a catalytic reaction unit and a tail-gas purification unit, the process is characterized in that the waste-gas from the degassing of the liquid sulfur in the liquid sulfur tank is introduced into the catalytic reaction unit, and / or the waste-gas from the degassing of the liquid sulfur in the liquid sulfur tank is introduced into the tail-gas purification unit. In present invention, the H2S in purified tail-gas can be reduced to no more than 10 ppm(v) and the SO2 emission concentration of the sulfur plant can be reduced to no more than 100 mg / m3.
Owner:CHINA PETROCHEMICAL CORP
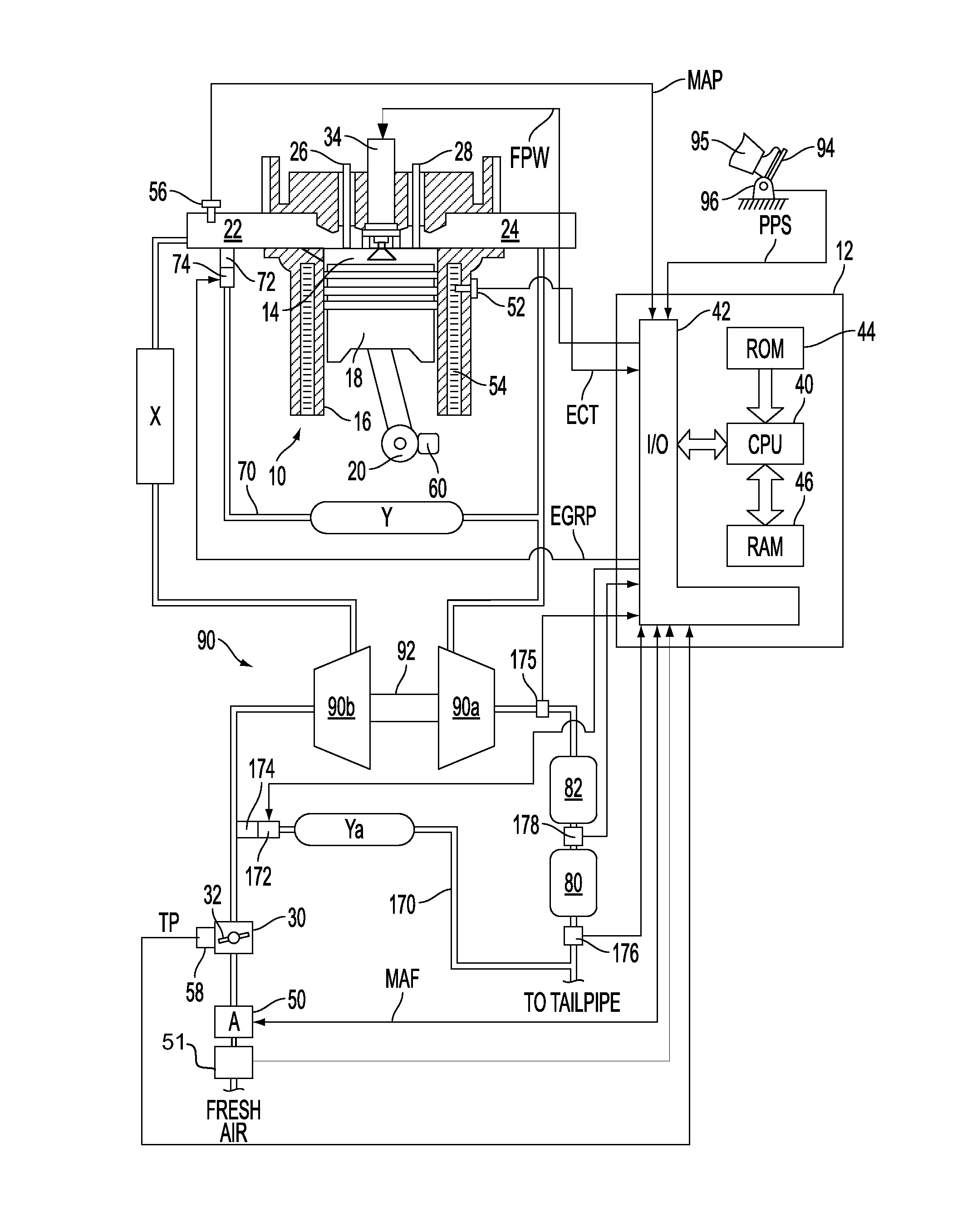
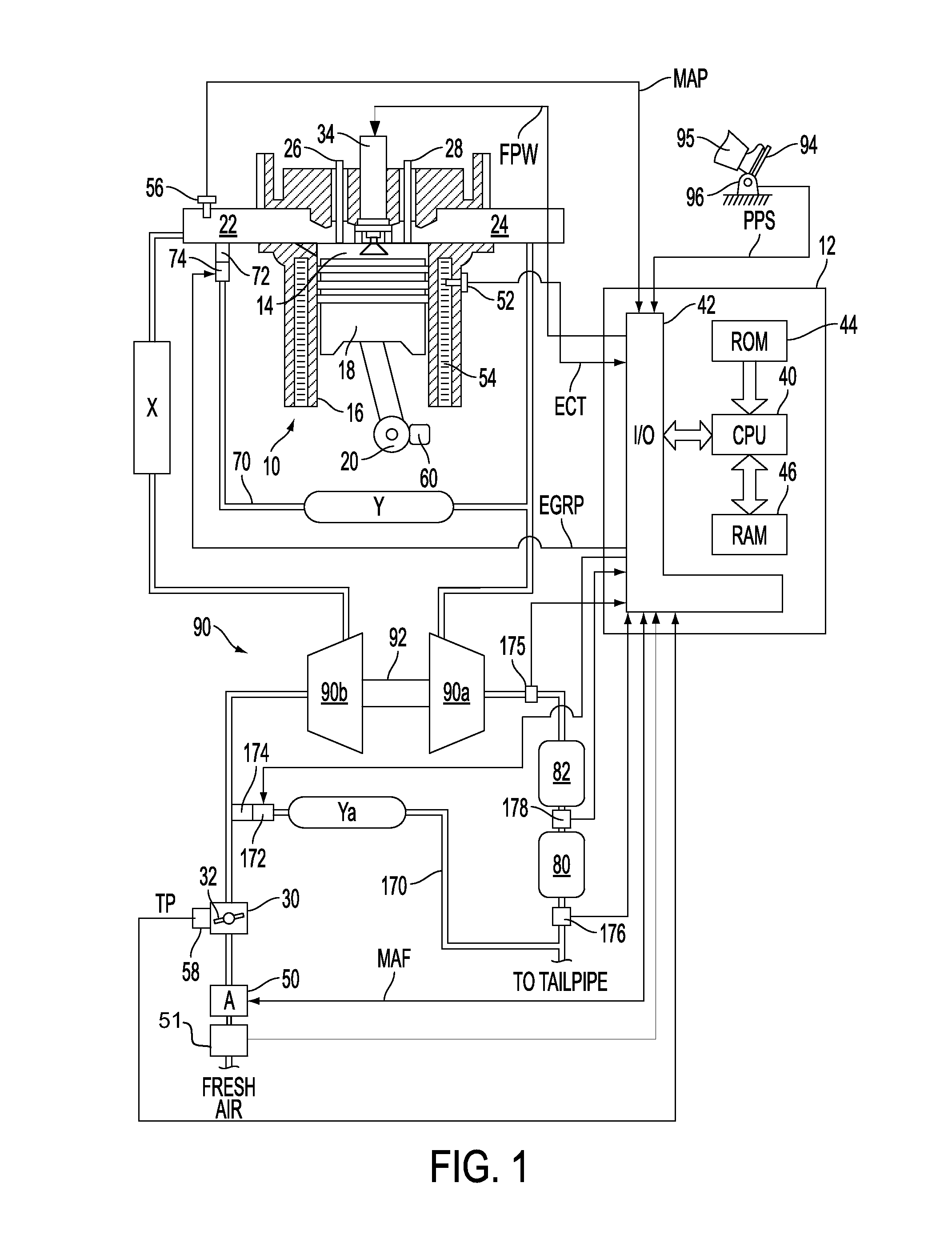
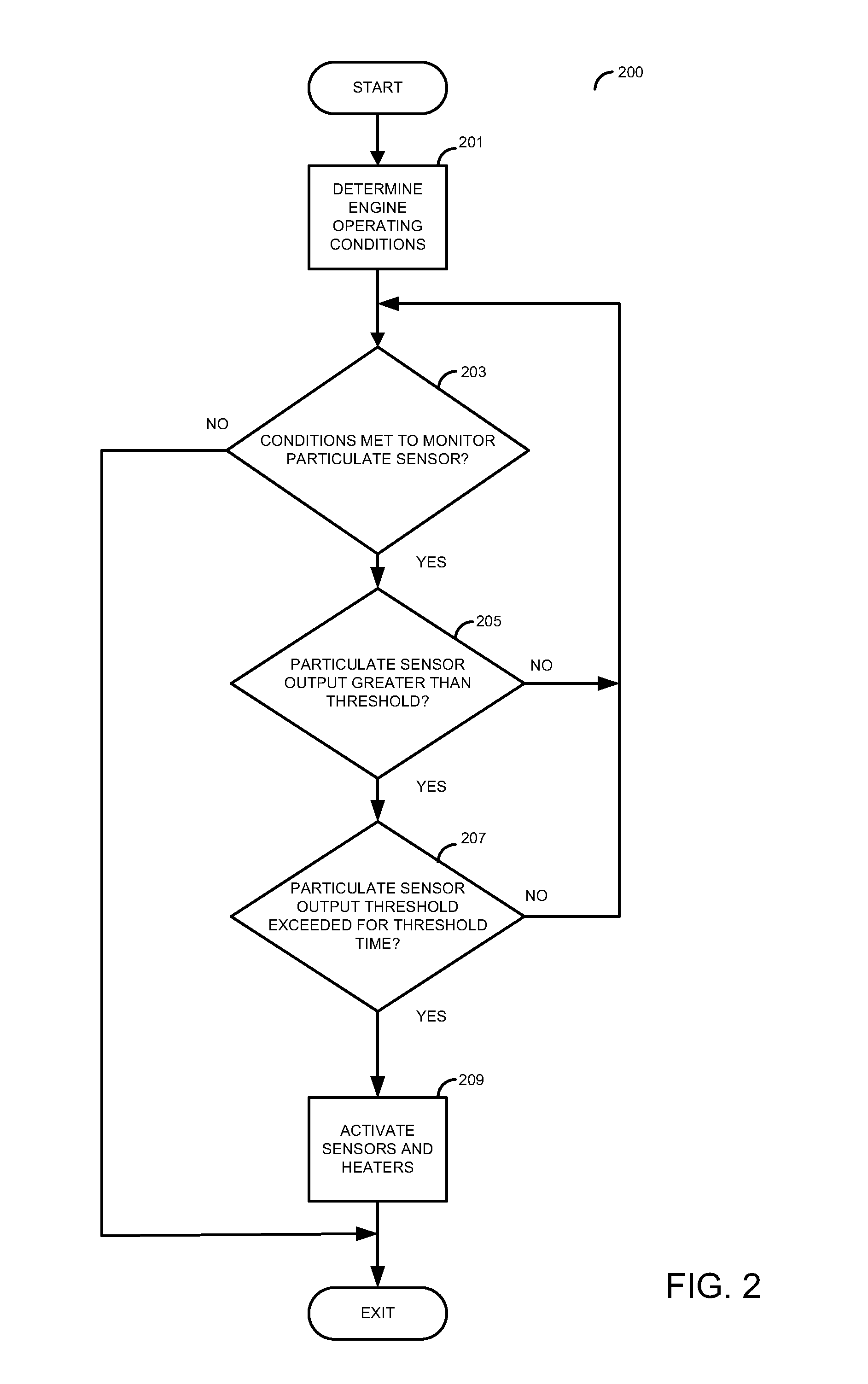
System for an engine having a particulate matter sensor
ActiveUS20110047985A1Easy to controlPerformance of oxygen degradeElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesParticulatesWater vapor
A system for improving operation of an engine having a particulate matter sensor is presented. The system may be used to improve engine operation during cold starts especially under conditions where water vapor or entrained water droplets are present in vehicle exhaust gases. In one embodiment, an engine controller that activates a heater of an exhaust gas sensor after an output of a particulate matter sensor exceeds a threshold value after an engine is started.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Double-cavity excitation enhanced microwave plasma torch generation device
PendingCN107087339AIncrease maximum powerStanding wave enhancementPlasma techniqueSurface modificationMicrowave plasma torch
The invention relates to a double-cavity excitation enhanced microwave plasma torch generation device, and belongs to the technical field of microwave plasma. The device comprises a microwave magnetron, a circulator, a directional coupler, a microwave plasma coupling waveguide, a cylindrical waveguide, an igniter and a discharge tube. After the microwave magnetron, the circulator and the directional coupler are sequentially connected in series, the directional coupler is connected with the microwave plasma coupling waveguide. The cylindrical waveguide chamber is additionally arranged in the axial direction of the discharge tube perpendicular to a compression rectangular waveguide; a thermal resistance waveguide in the microwave plasma coupling waveguide effectively isolates the influence of thermal release of plasma discharge on a whole system; the igniter makes the whole system operated by a single person to complete a series of processes of ignition, excitation and maintenance, and the ignition success rate is close to 100% under the condition that the no-load output of a microwave source is low. Plasma torch afterglow with a larger volume action area can be obtained by increasing the maximum power of a plasma torch, so that the device can operate stably and reliably for a long time, and can be used in various relevant fields such as combustion assistance, nano material synthesis, waste gas treatment and high-temperature-resistant material surface modification.
Owner:李容毅
Electronic control method of variable gas inlet and exhaust system of compression ignition engine
InactiveCN101526042AImprove performanceImprove reliabilityElectrical controlMachines/enginesTurbochargerControl system
The invention relates to an electronic control method of a variable gas inlet and exhaust system of a compression ignition engine, comprising a pressurization system, a waste gas recycle system, a gas intake valve late-closing mechanism and an electronic control system. The pressurization system adopts a two-level turbocharger; the waste gas recycle system comprises a high-pressure part and a low-pressure part; the gas intake late-closing mechanism is a gas intake valve push rod which is capable of adjusting the telescopic length in a self-adapting hydraulic control mode based on self motion position, and the gas intake late-closing mechanism consists of a hydraulic push rod assembly and a hydraulic auxiliary mechanism, wherein the hydraulic push rod assembly is fixed at the upper end of an internal-combustion engine cylinder head; a hydraulic oil pump is fixed on an internal-combustion engine body; an electronic control system is controlled by an electronic control unit; and the electronic control unit judges and controls the density of intake gas in real time through a pressure sensor, a temperature sensor, a rotate speed sensor, and the like in the system. The invention can control the density of intake gas in real time, improves the performance of the internal-combustion engine, greatly reduces discharged harmful product and enhances the reliability.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Apparatus and methods for improving the energy efficiency of dryer appliances
InactiveUS20090100702A1Improve efficiencyReduce operating costsDrying solid materials with heatDrying gas arrangementsResidenceProcess engineering
Apparatus for improving the efficiency of dryer appliances that utilize heated air for drying and are disposed within a residence or other closed conditioned space includes an intake air duct connected between the dryer appliance and a source of intake air outside the conditioned space, an exhaust outlet diverter valve to receive exhaust air from the dryer and direct the exhaust air for release within the conditioned space or alternatively outside the conditioned space. Alternative embodiments provide for drawing intake air from more than one source, with and without heat exchange, for releasing heated air to more than one location, including into a heating system return air duct, either directly or through a heat exchanger. A method of controlling the operation of the apparatus is also provided.
Owner:FAIR ROBERT WOOD
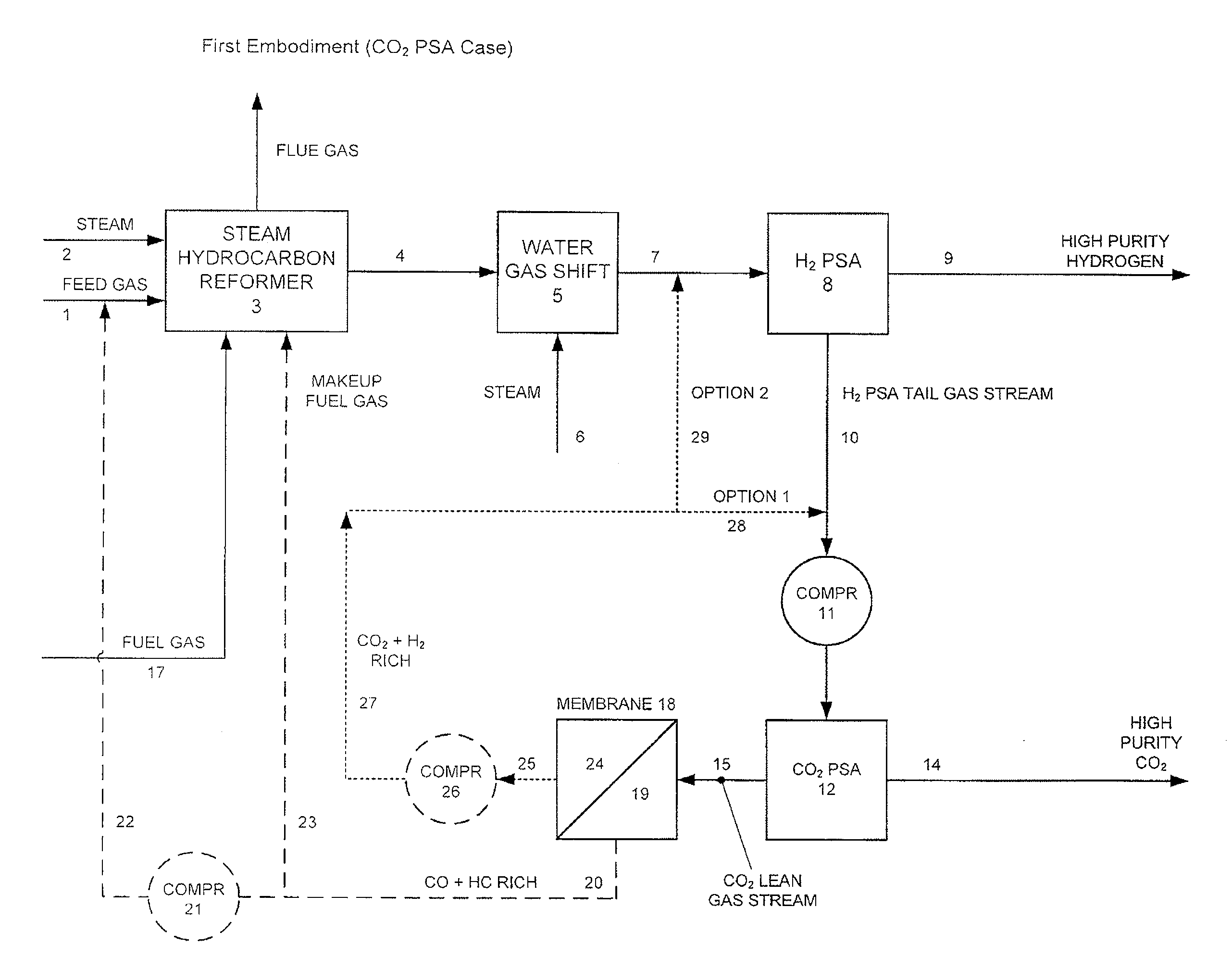
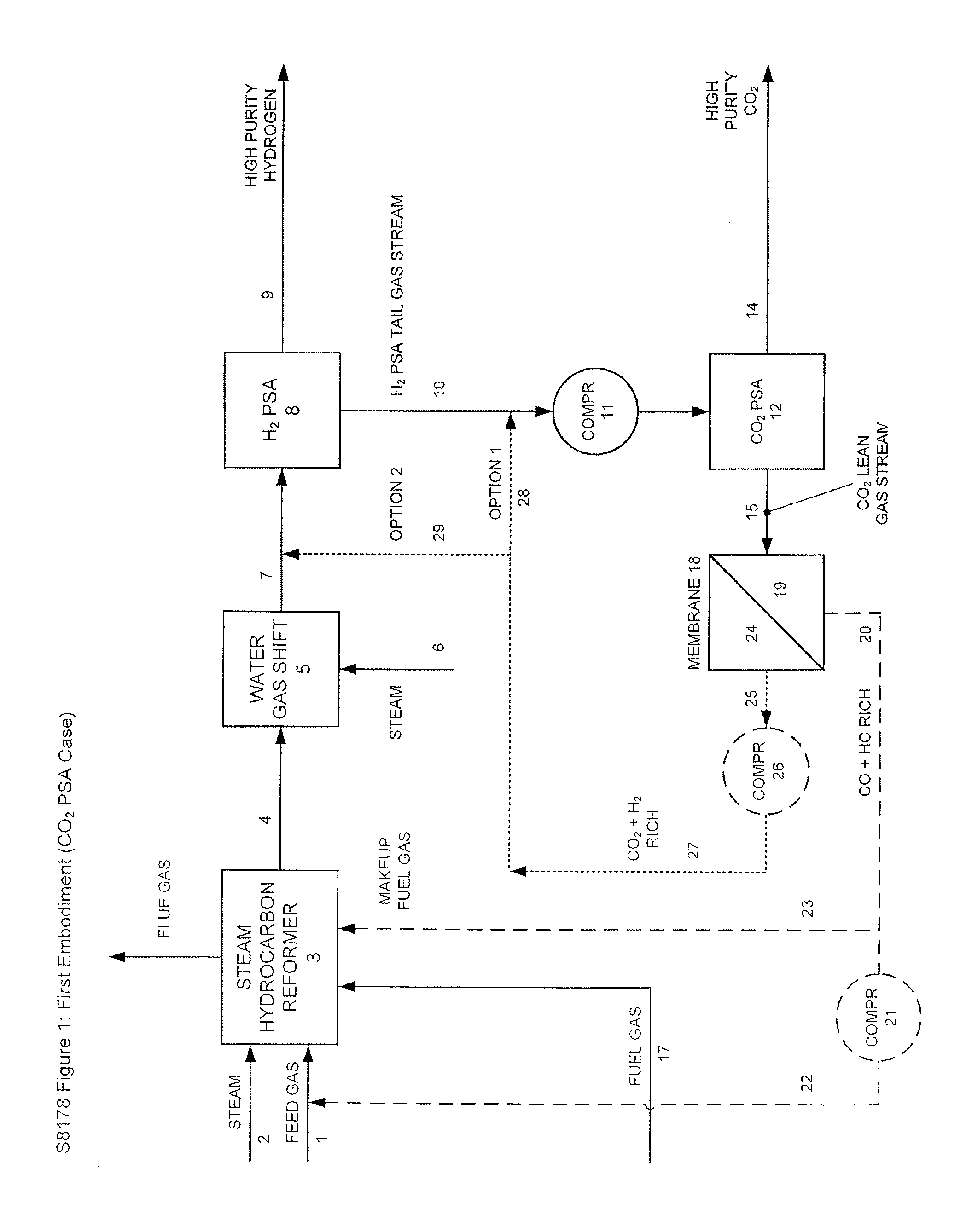
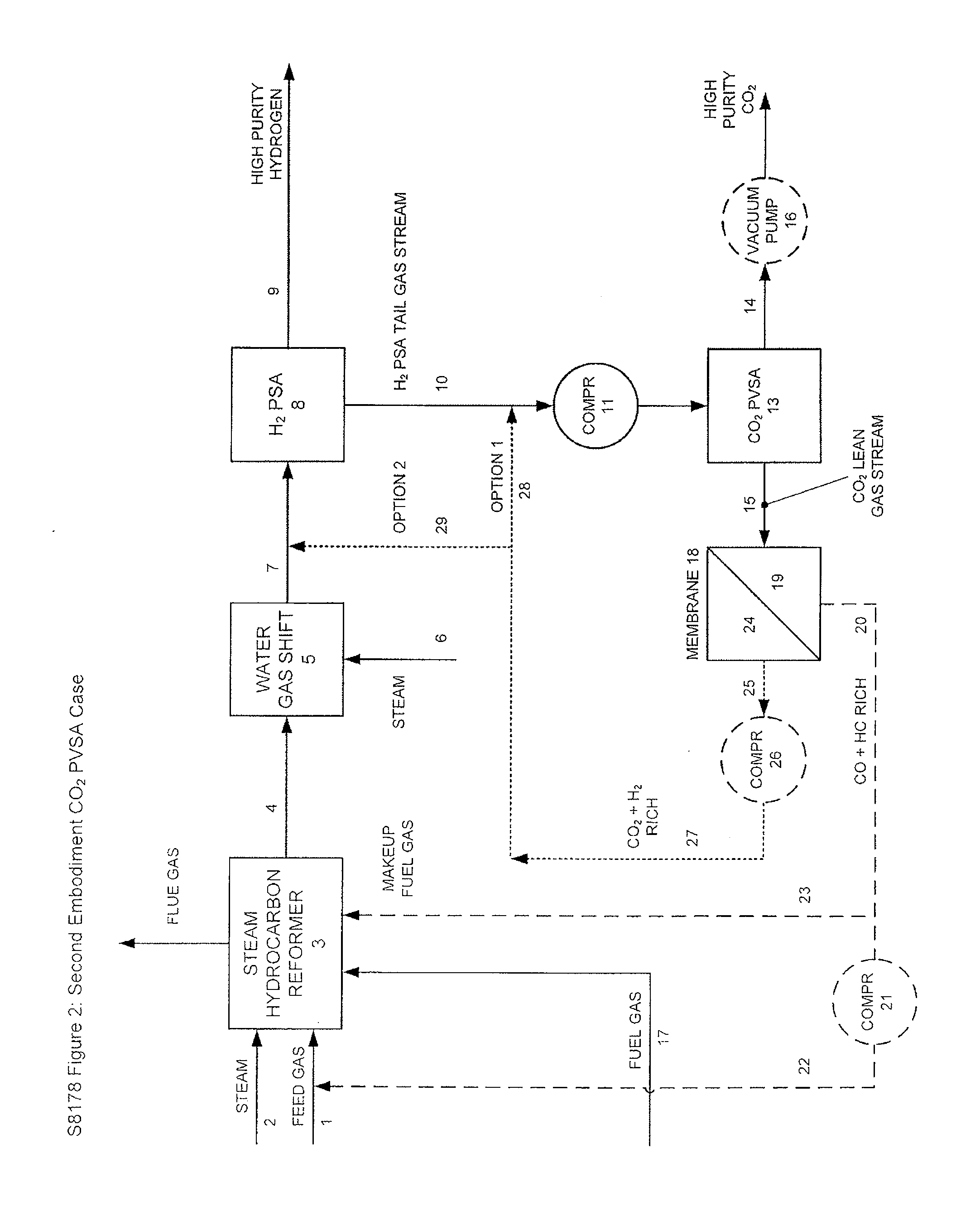
Processes For The Recovery Of High Purity Hydrogen And High Purity Carbon Dioxide
The present invention provides for various processes for recovering high purity gaseous hydrogen and high purity gaseous carbon dioxide from the gas stream produced using steam hydrocarbon reforming, especially steam methane reforming, utilizing a H2 pressure swing adsorption unit in combination with either a CO2 pressure swing adsorption unit in combination with a membrane separation unit or a CO2 pressure vacuum swing adsorption unit in combination with a membrane separation unit. The present invention further relates to a process for optimizing the recovery of carbon dioxide from waste gas streams produced during the hydrogen purification step of a steam hydrocarbon reforming / water gas shift reactor / H2 pressure swing adsorption unit utilizing either a CO2 pressure swing adsorption unit in combination with a membrane separation unit or a CO2 pressure vacuum swing adsorption unit in combination with a membrane separation unit. The present invention even further relates to the apparatus necessary to carry out the various processes of the present invention.
Owner:AIR LIQUIDE IND US LP +1
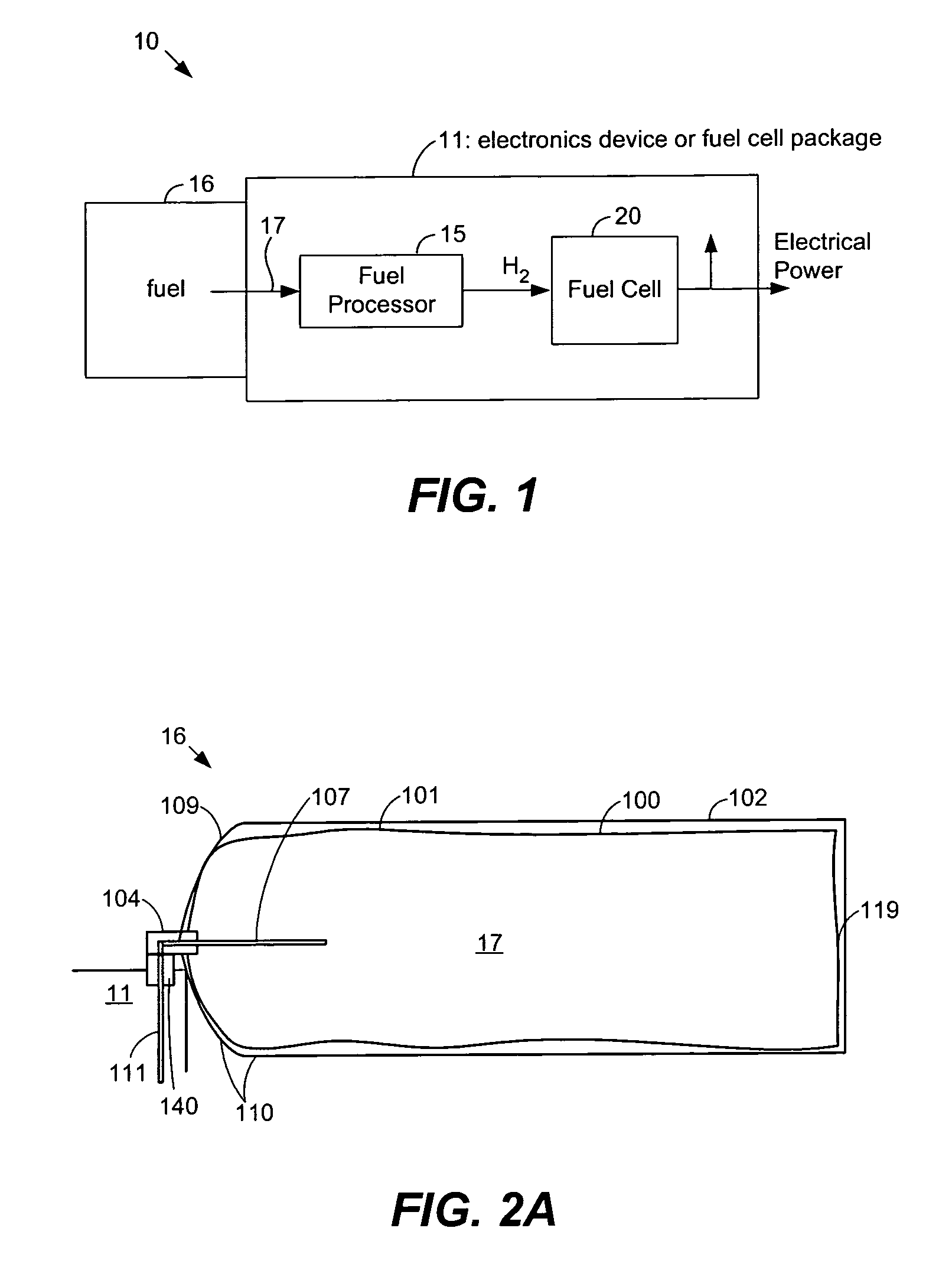
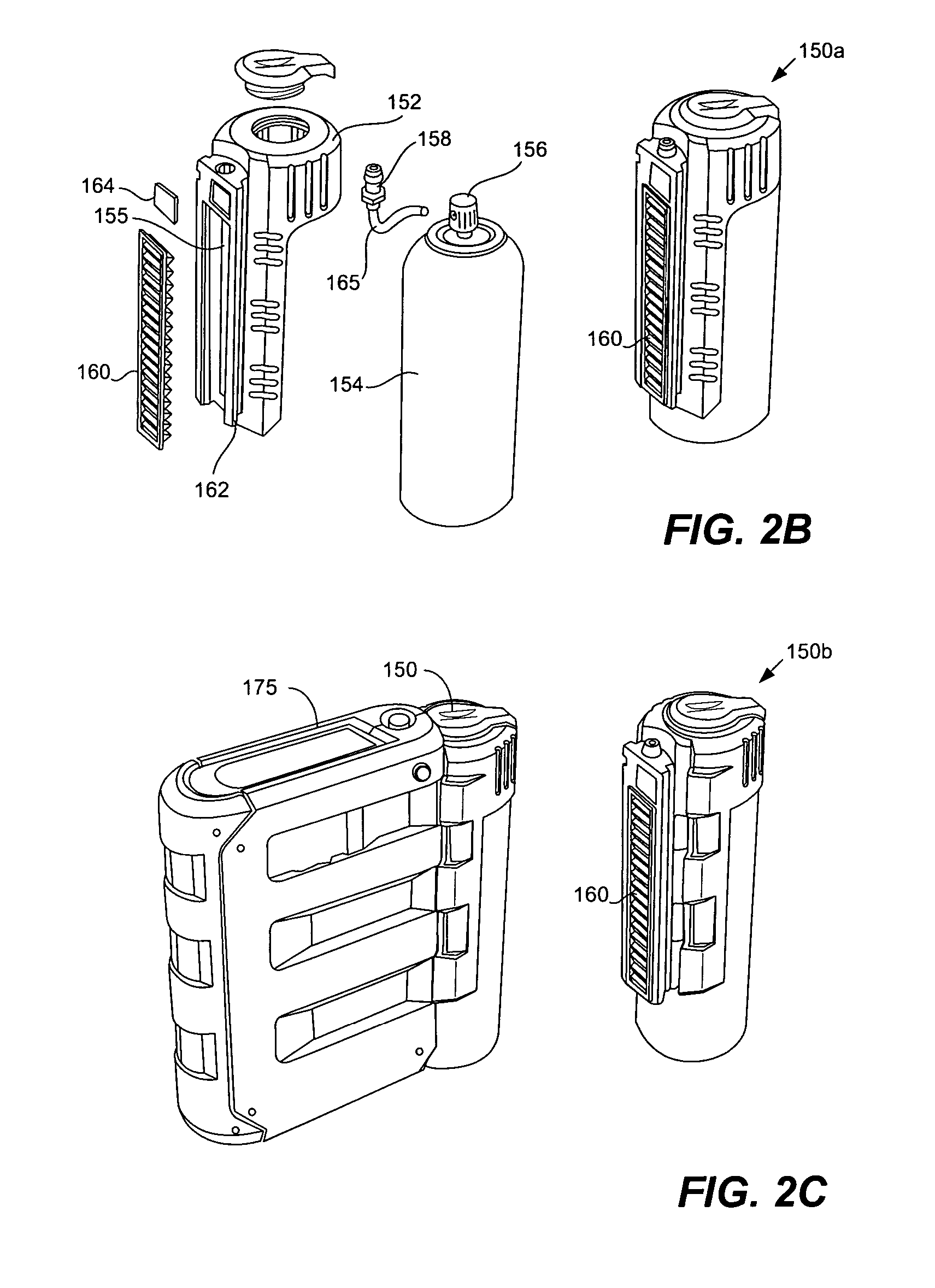
Disposable component on a fuel cartridge and for use with a portable fuel cell system
A portable cartridge that stores a fuel for use with a fuel cell system includes one or more disposable components for use by the fuel cell system. The disposable component may be included on a fuel cartridge, but used by a fuel cell system when the cartridge and a package that includes the system are coupled together. The disposable component may include: an inlet filter that regulates passage of gases and liquids into the fuel system, an outlet filter that cleans fuel cell system exhaust gases, a sensor on the inlet air stream to the fuel cell system; a sensor on the exhaust; a desiccant that sinks moisture from within the fuel cell system package; or a fuel absorbent that soaks fuel between connectors on the fuel cartridge and the fuel cell system.
Owner:ADVENT TECH LLC
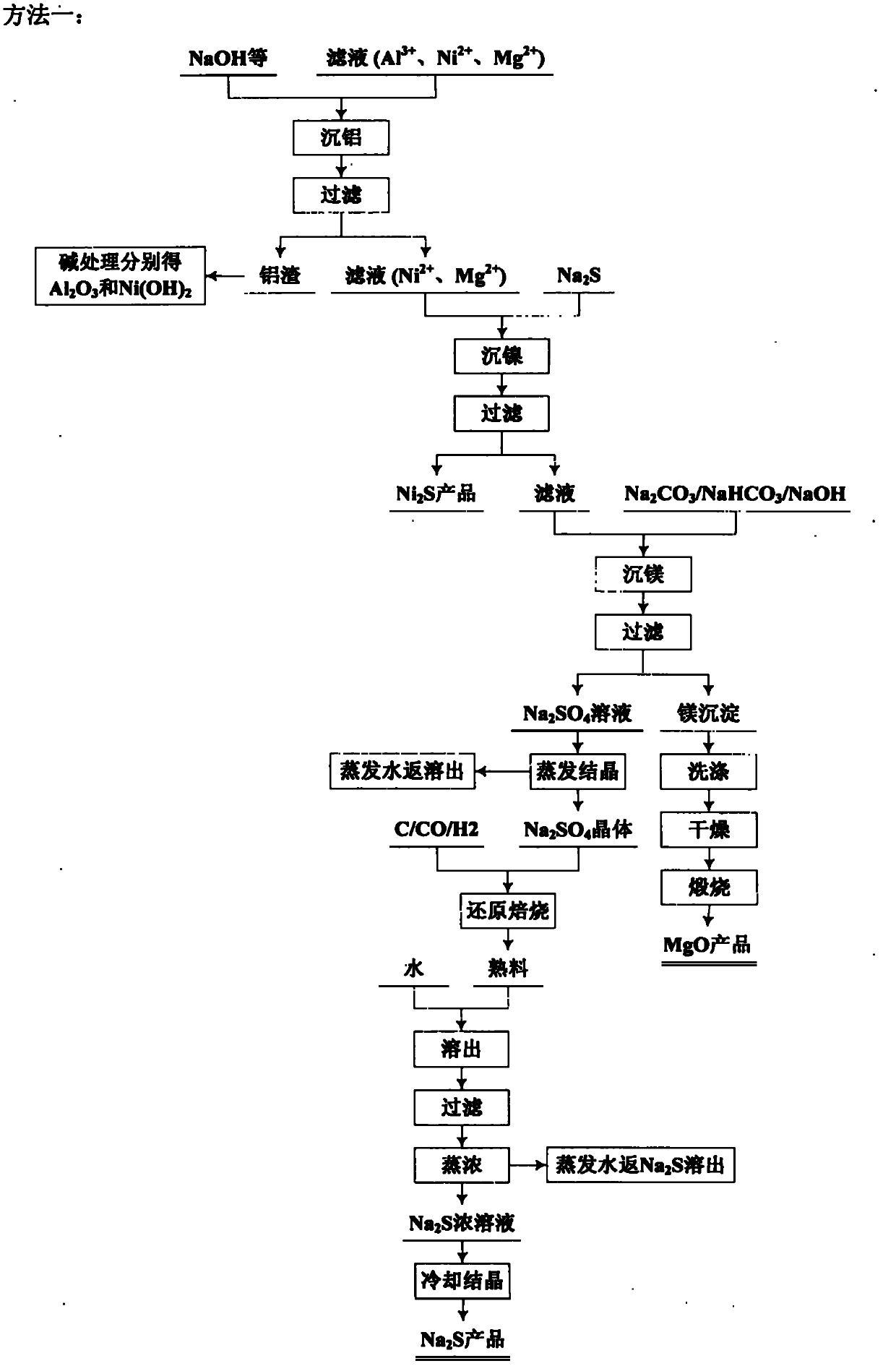
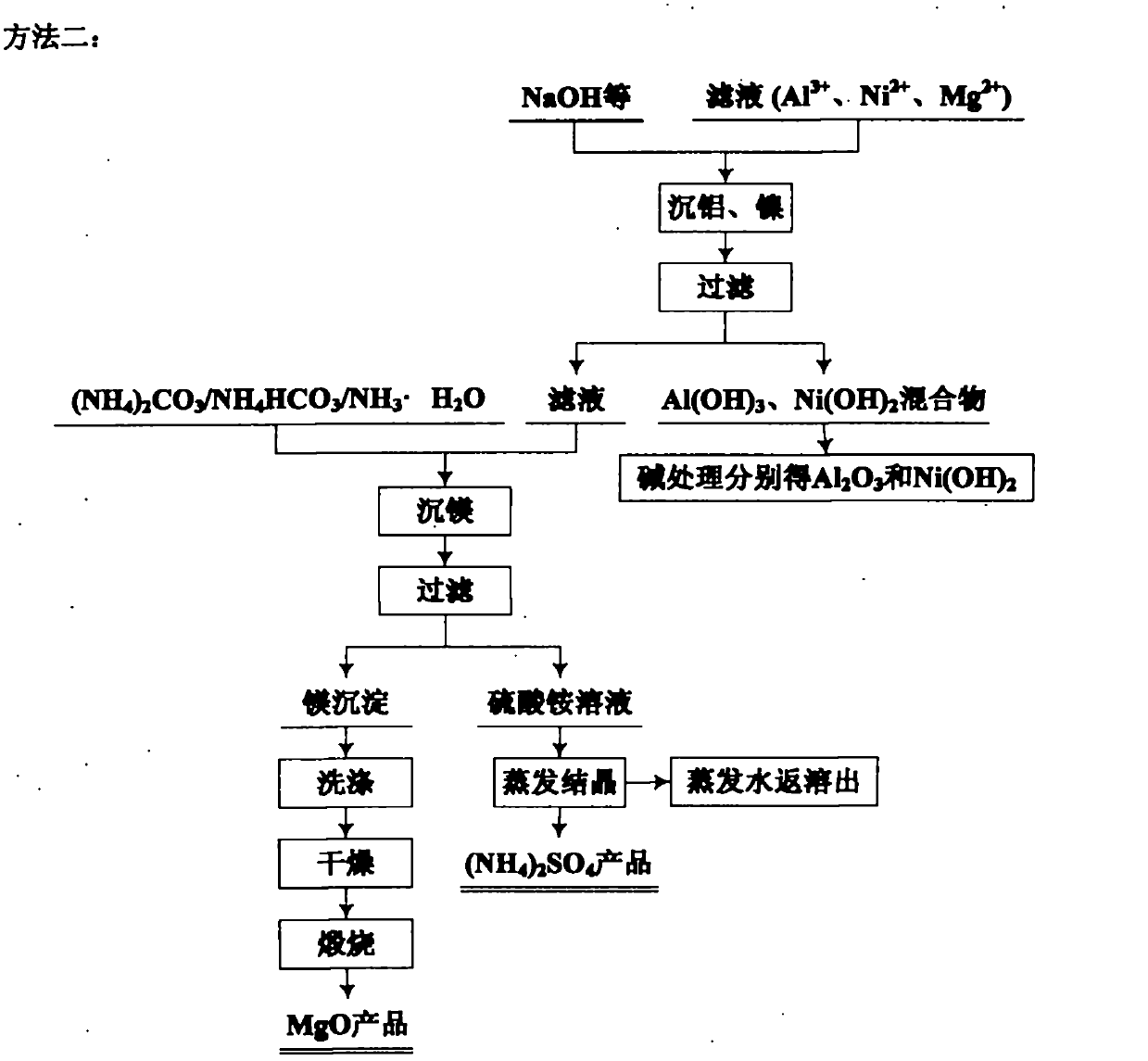
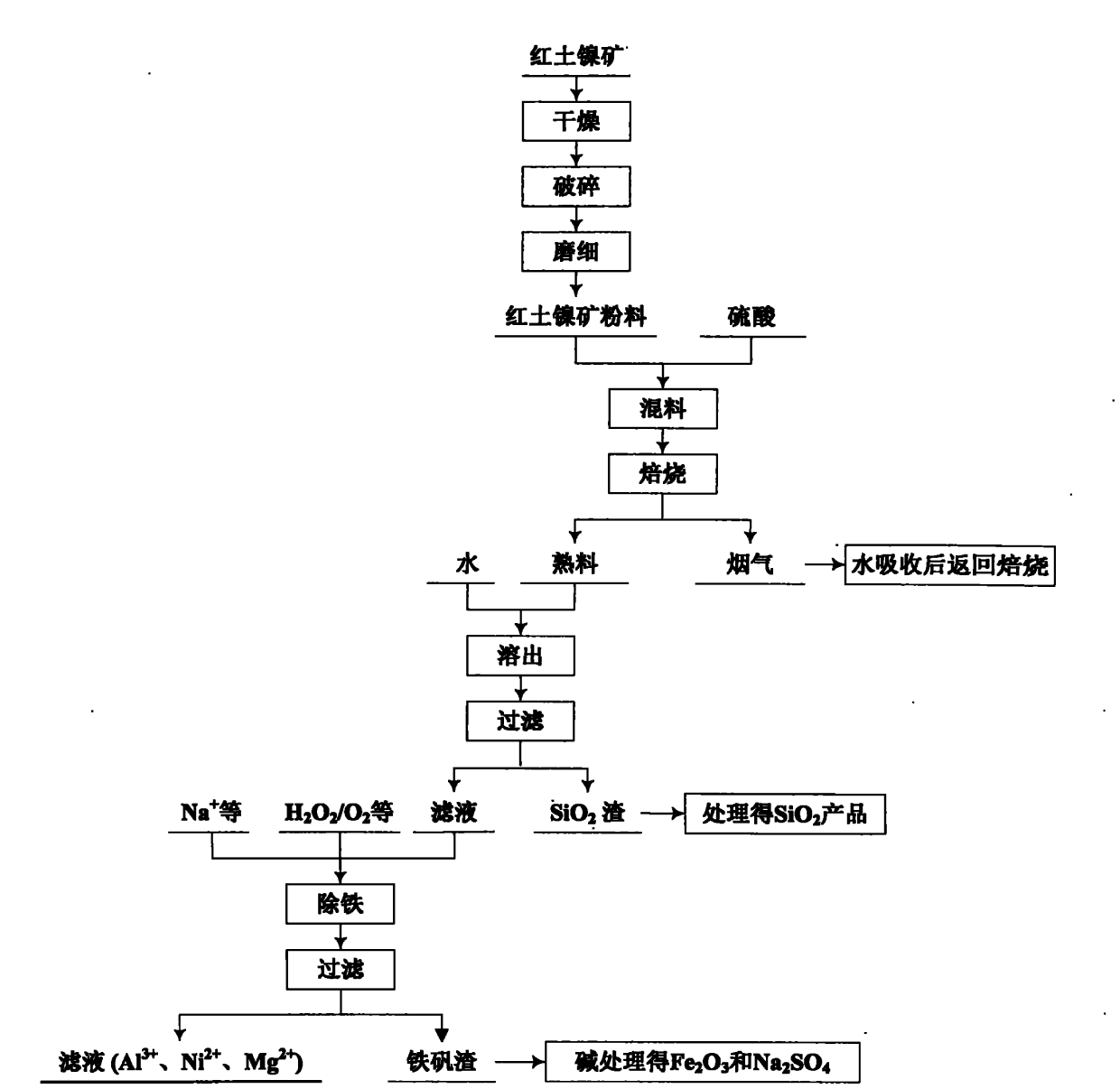
Comprehensive utilization method for laterite-nickel ore
The invention relates to an environmental-friendly comprehensive utilization method for a laterite-nickel ore, which comprises the following steps of: (1) grinding the laterite-nickel ore, mixing with sulfuric acid, roasting, dissolving out roasted clinker and filtering to obtain silicon dioxide and dissolution liquid; (2) deironing the dissolution liquid to obtain liquid No.2 and filter residue (iron compounds), wherein the liquid No.2 comprises aluminum, nickel and magnesium and can be treated by the step (3) or (4); (3) precipitating the aluminum in the liquid No.2 by using alkali, filtering, precipitating the nickel in filtrate by using sodium sulfide, filtering, precipitating the magnesium by using the alkali, and treating filter residue to obtain aluminum oxide, nickel hydroxide, nickel sulfide and magnesium oxide respectively; and (4) precipitating the aluminum and the nickel in the liquid No.2 by using the alkali, treating mixed slag containing the aluminum and the nickel by using the alkali to obtain aluminum hydroxide and nickel hydroxide products, and precipitating the magnesium in filtrate subjected to aluminum and nickel precipitation by using ammonia or ammonium saltto obtain a magnesium oxide product. The method is suitable for treating various laterite-nickel ores, three wastes (waste gas, waste water and waste residue) are not generated, and valuable components magnesium, nickel, iron, aluminum and silicon in the laterite-nickel ore are separated and extracted.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
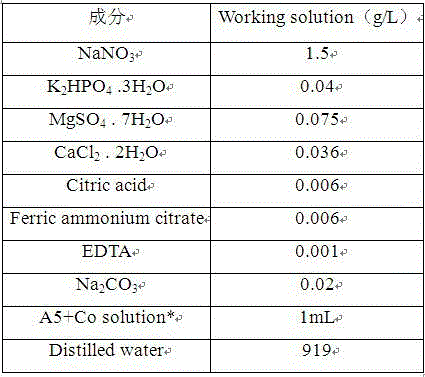
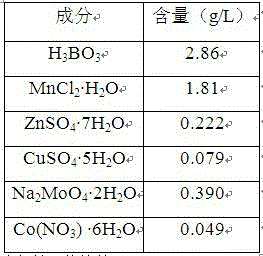
Highly oil-containing monoraphidium and culture and application thereof
The invention provides a highly oil-containing monoraphidium and culture and application thereof, the monoraphidium strain is SS-B1, the classification and nomenclature of the monoraphidium is monoraphidium sp, the monoraphidium is preserved in CGMCC (China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center) on April 15, 2013, and the preservation number is CGMCC No.7479. The monoraphidium strain is able to tolerate high concentrations of CO2 and SO2, highly oil-containing biological matters can be obtained by light autotrophic growth by use of CO2 and SO2 containing waste gas or flue gas, the carbon fixation efficiency is high, cell total lipid content accounts for more than 40% of dry cell weight, and biodiesel can be produced.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
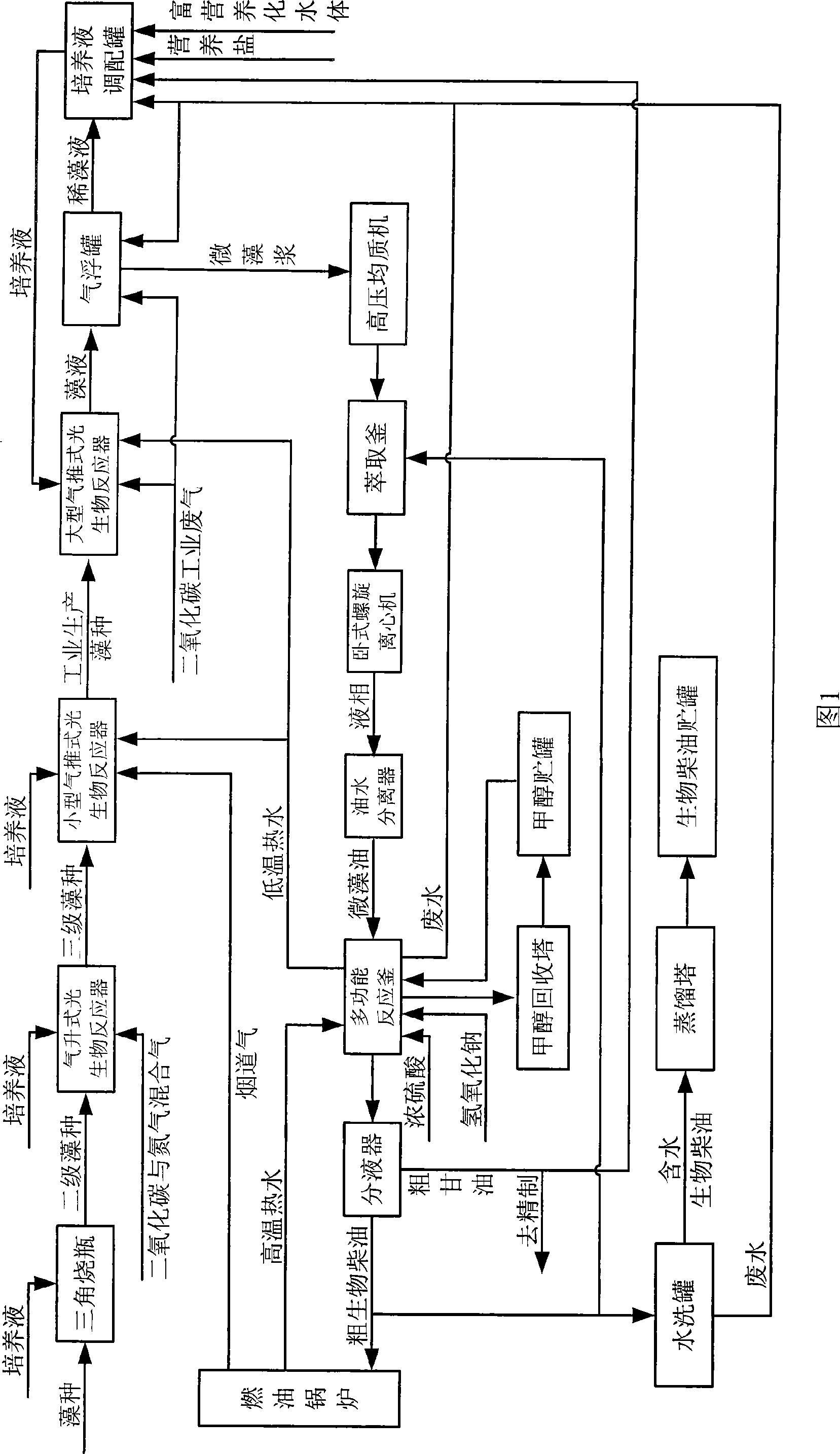
Process for preparing fine algae cultivation coupling biological diesel oil refining
The invention relates to the fields of microalgae culturing project, biodiesel refining and environment protection, in particular to a production method for refining the biodiesel through microalgae culturing and coupling. In the method, carbon dioxide industrial waste water and eutrophicated surface water or industrial waste water is used as main material to extensively culture the microalgae containing oil, and microalgae oil is used as the material to refine the biodiesel and simultaneously realize the drainage reducing of carbon dioxide, the control of polluted water and the cleaning production of biodiesel. The method is characterized in that the waste gas of carbon dioxide and the eutrophicated water are firstly used to culture and collect the microalgae; and then extraction, pre-processing and interchange esterification reaction of microalgae is carried out. In the invention, the two processing of culturing the microalgae and refining the biodiesel are coupled together; the ''three wastes'' and waste heat generated during the reefing process of the biodiesel and the unsalable outgrowth of crude glycerine are used as the materials and the heat source for culturing the microalgae; therefore, not only the production cost is reduced, but also the discharge of the ''three wastes'' is eliminated.
Owner:王彤
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com