Patents
Literature
243 results about "Lipid content" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
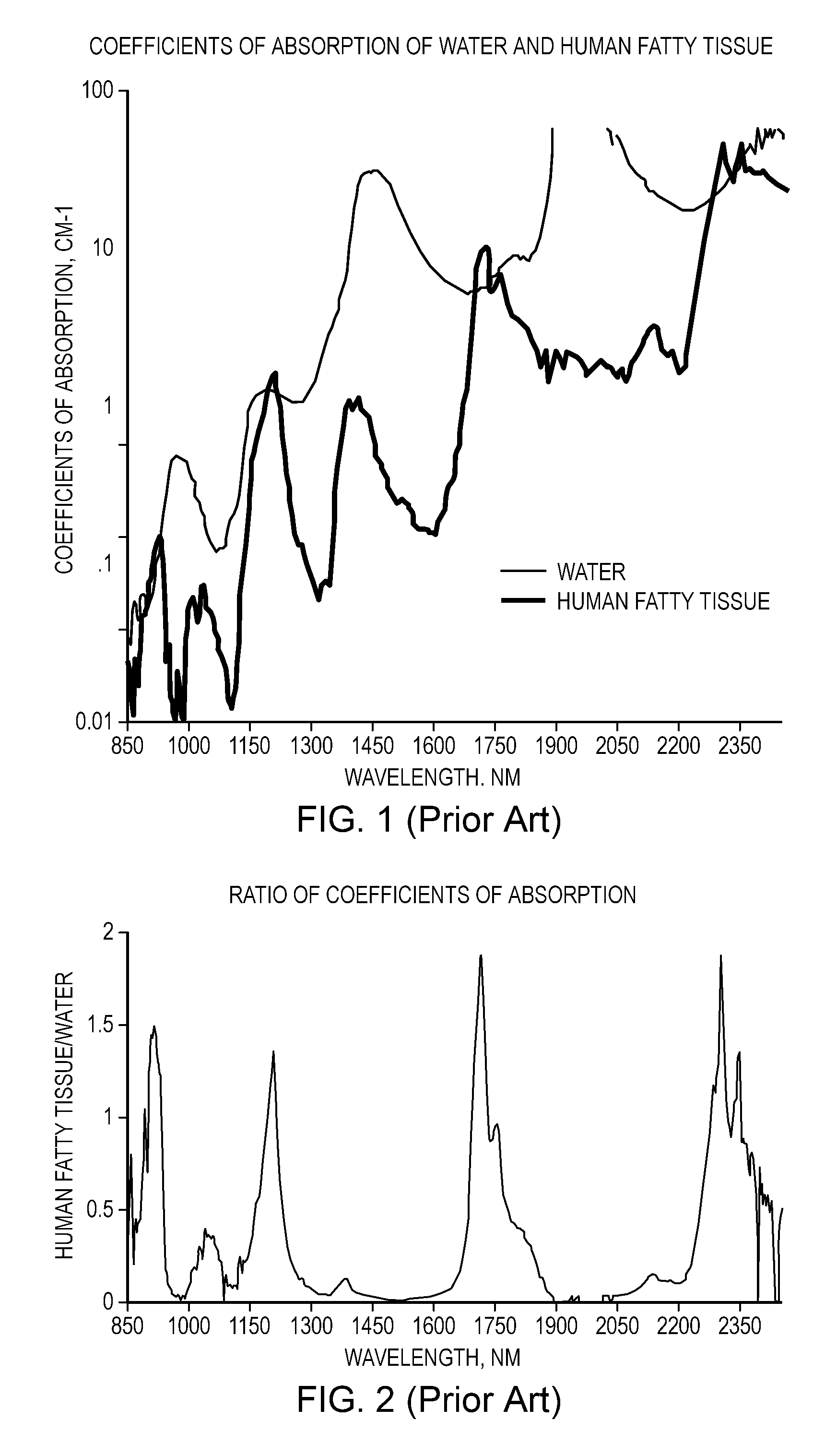
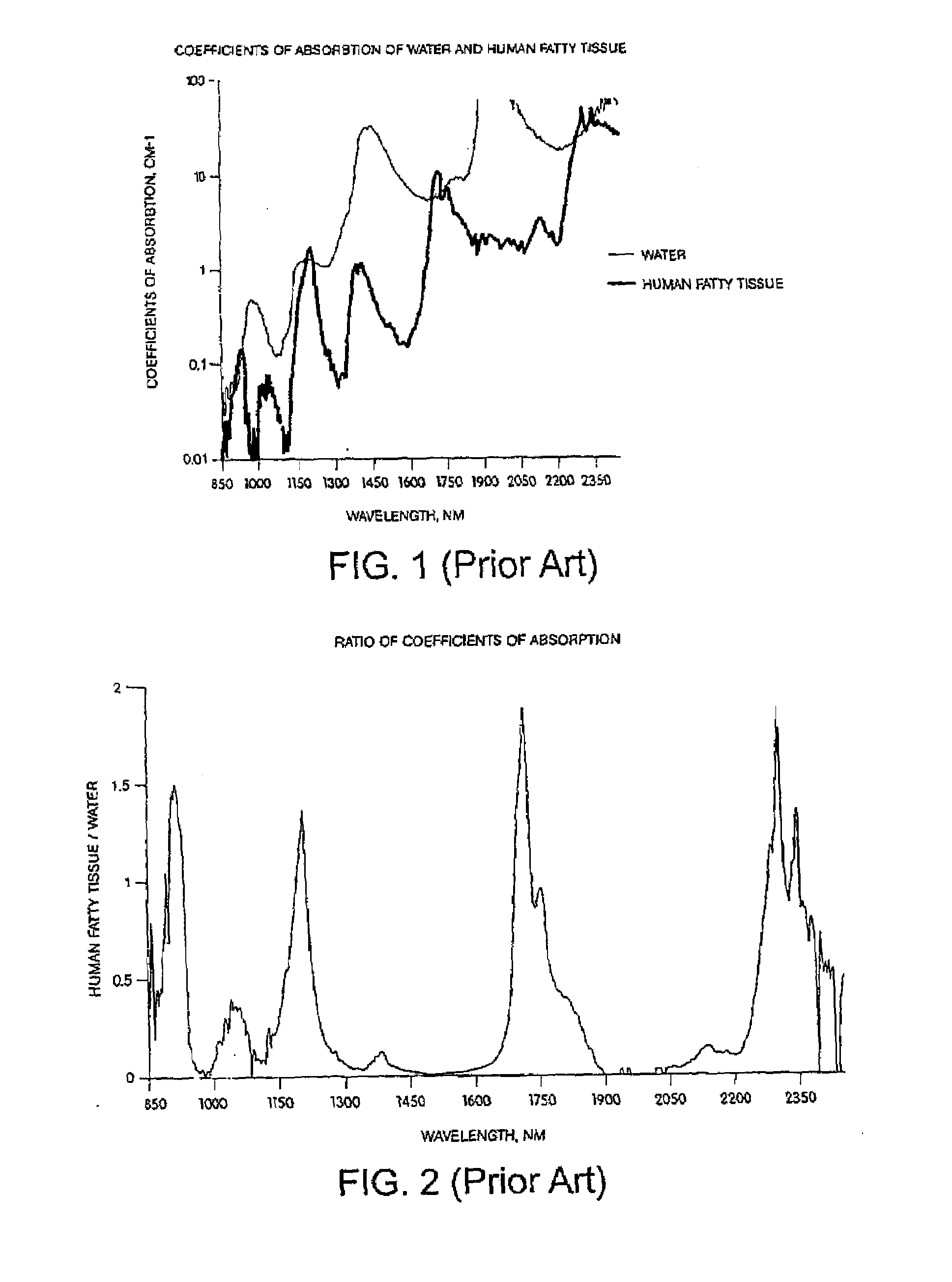
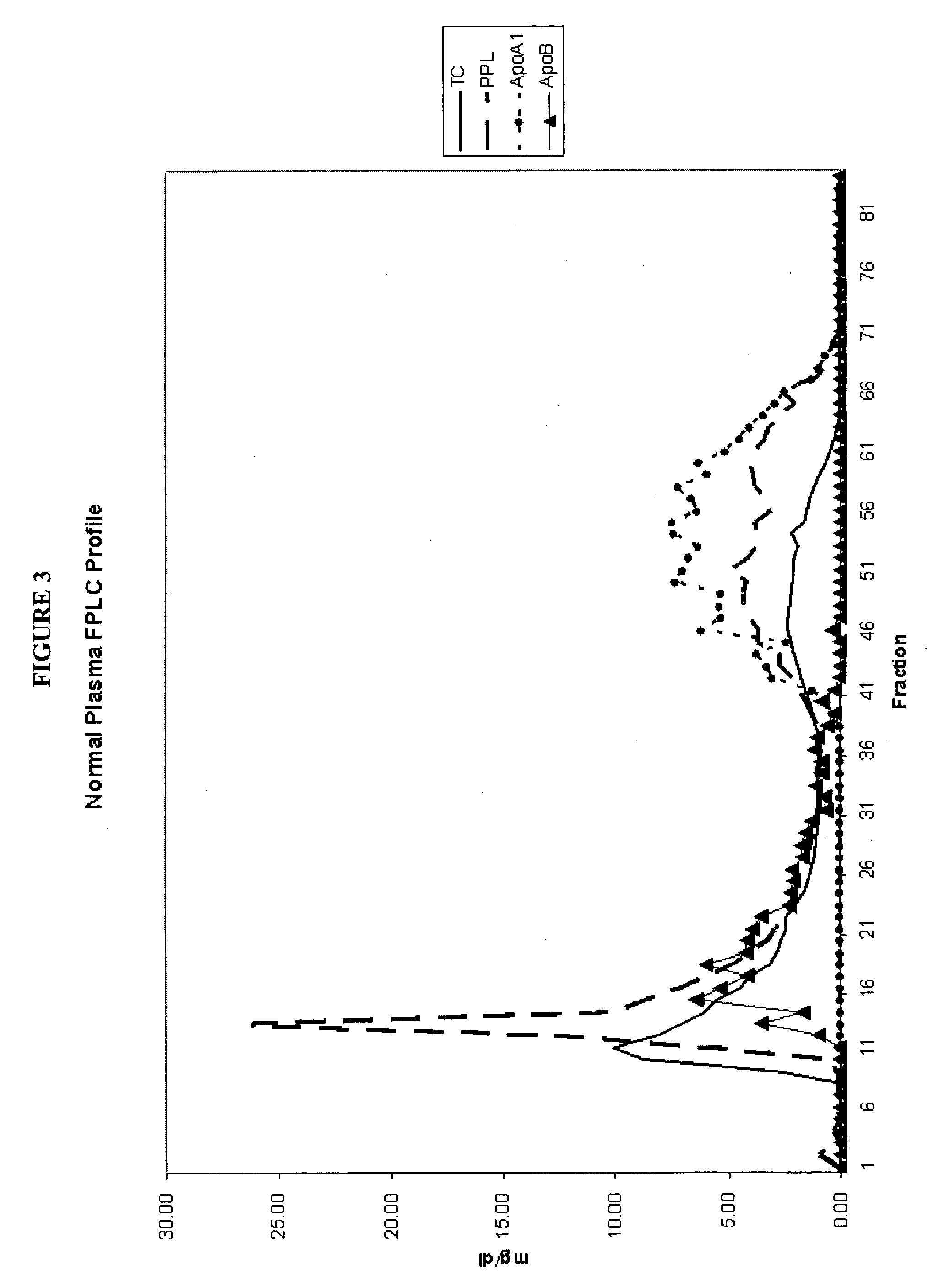
The normal concentrations of lipids in serum are total, 400 to 800 mg/dl; cholesterol, 150 to 250 mg/dl; fatty acids, 9 to 15 mM/L; phospholipids, 150 to 380 mg/dl; phospholipid as phosphorus, 9 to 16 mg/dl; and triglycerides, 10 to 190 mg/dl.
Lipid particles on the basis of mixtures of liquid and solid lipids and method for producing same
InactiveUS8663692B1Promote formationImprove stabilityPowder deliveryCosmetic preparationsLipid particleSolid content
The invention relates to drug-free or drug-loaded lipid particles of a mixed matrix made of solid and liquid lipids, and to a method for producing highly concentrated lipid particle dispersions of solid-liquid particles having a lipid content of from 30% to 95% or a solids content of from 30% to 95% (lipid and stabilizer), which in contrast to biamphipileic cremes are integer particles, and / or which upon dilution of the highly concentrated particle dispersions with the outer phase result in free-flowable particle dispersions.
Owner:PHARMASOL
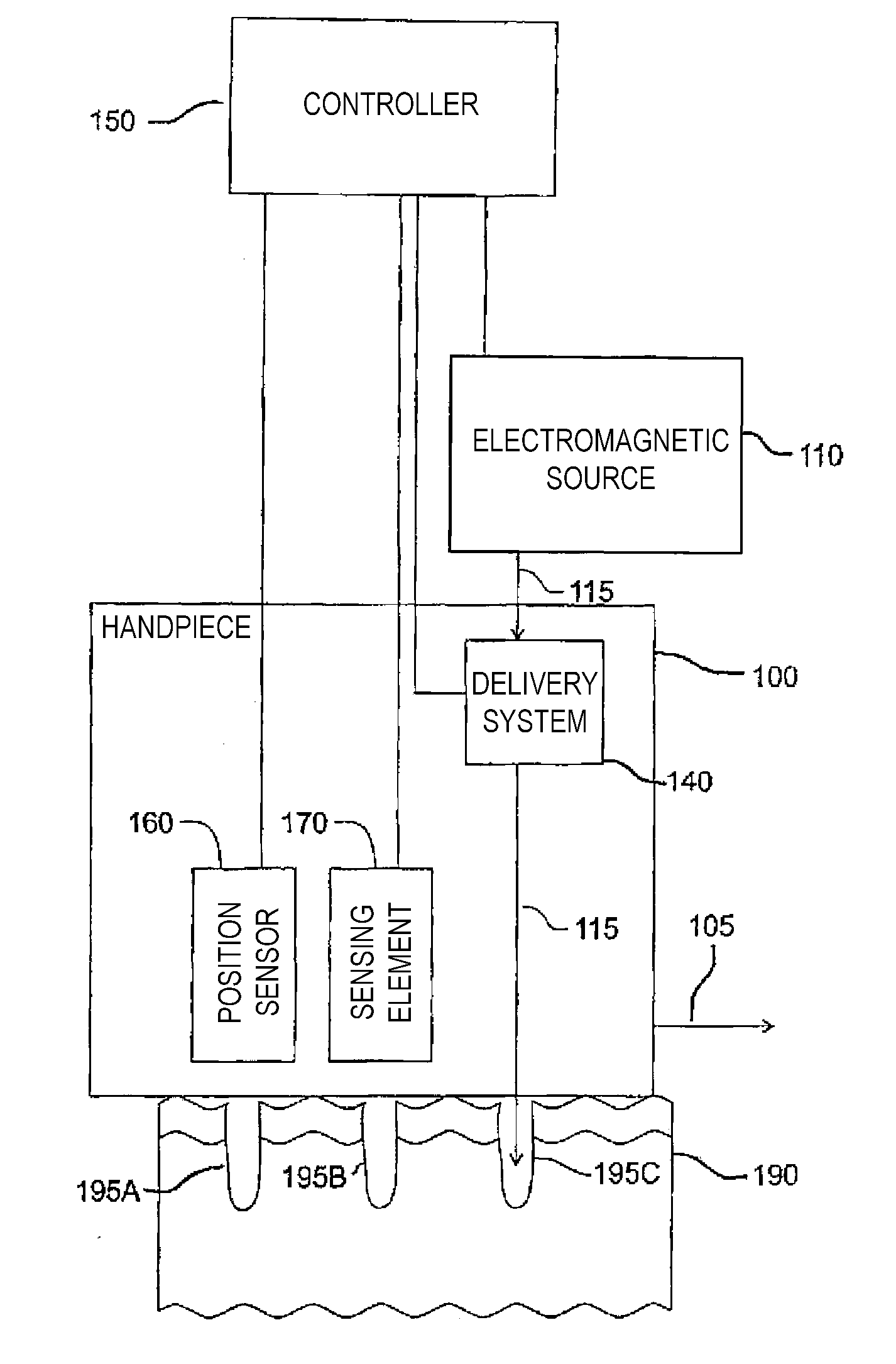
Apparatus and method for ablation-related dermatological treatment of selected targets
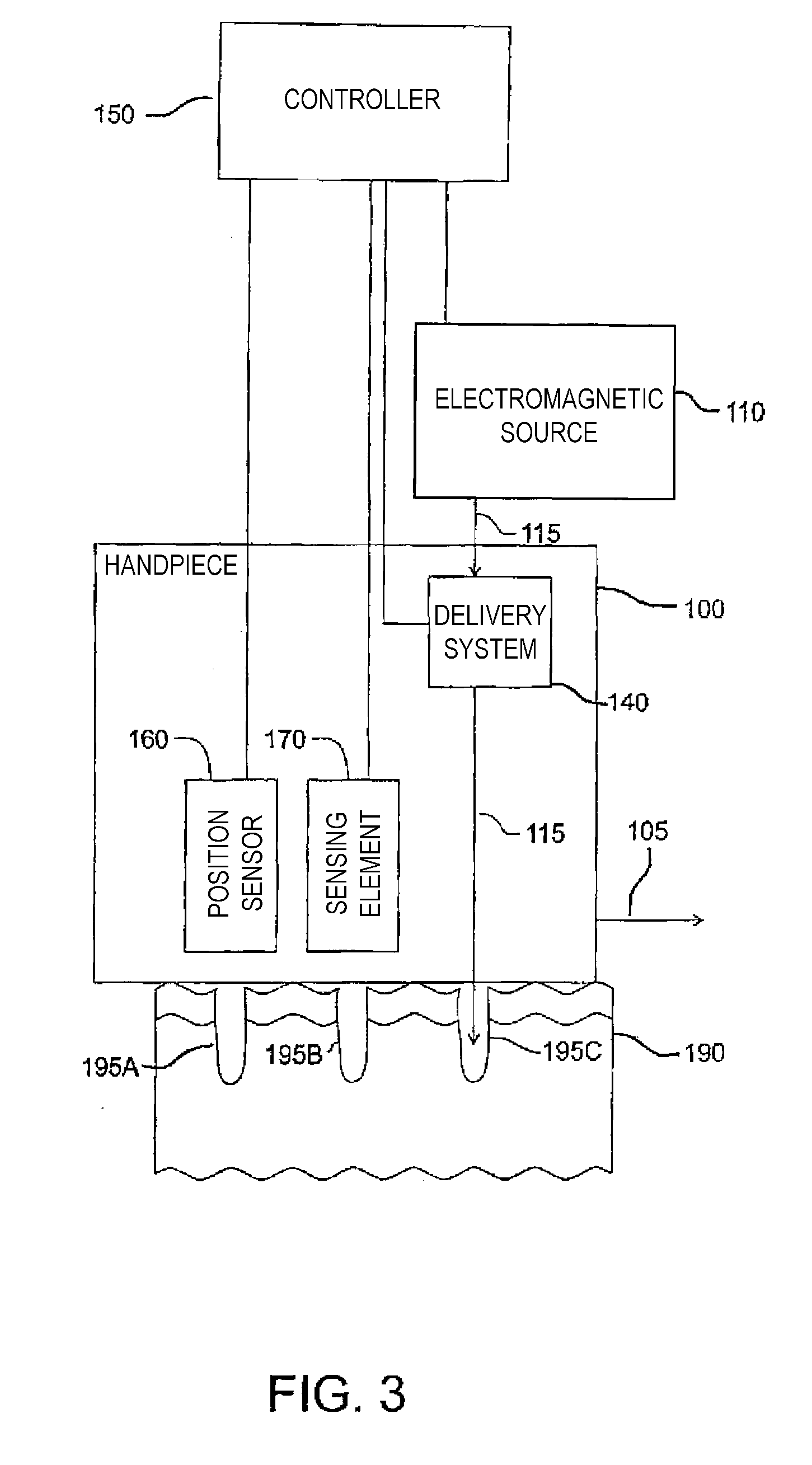
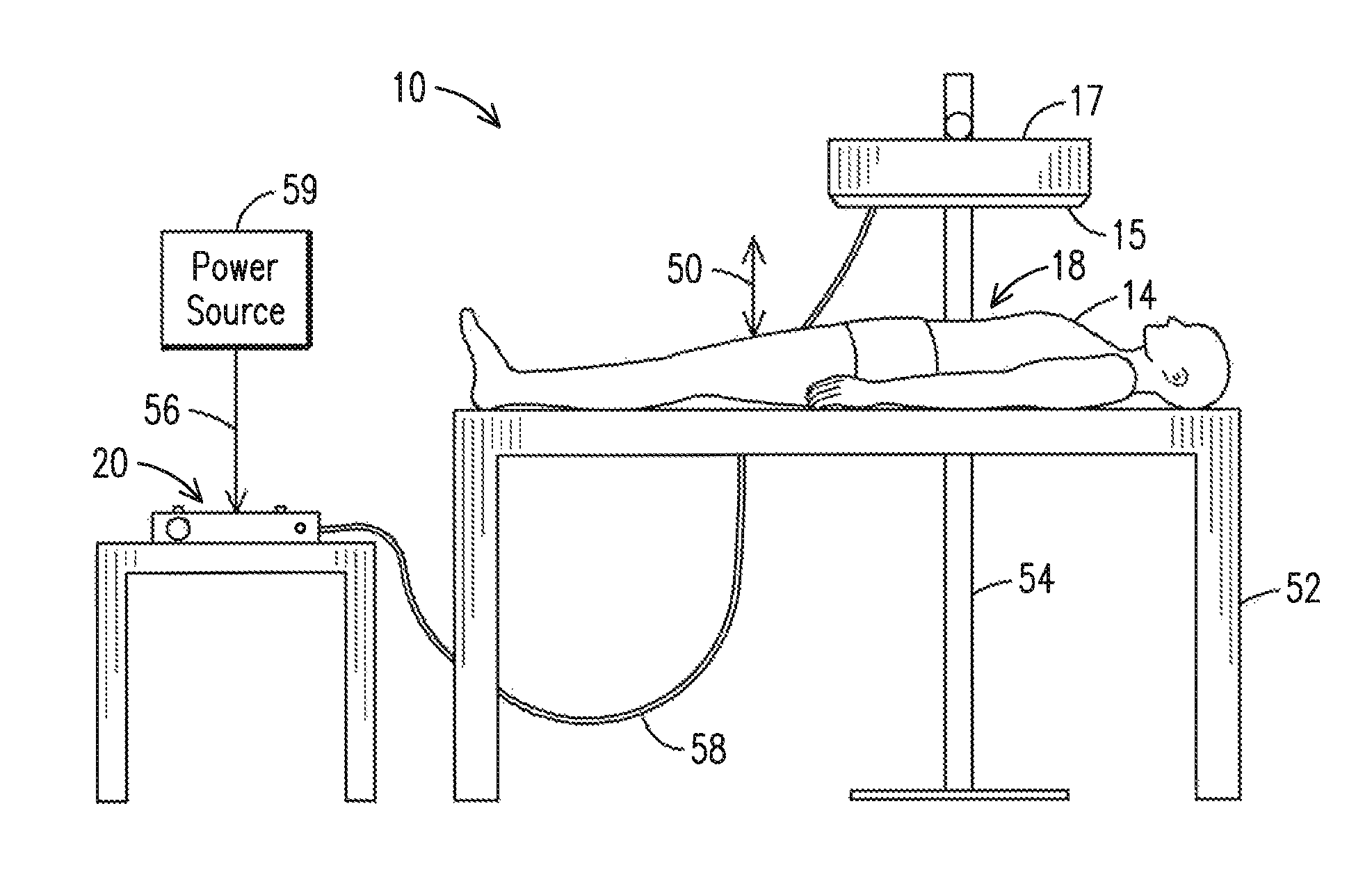
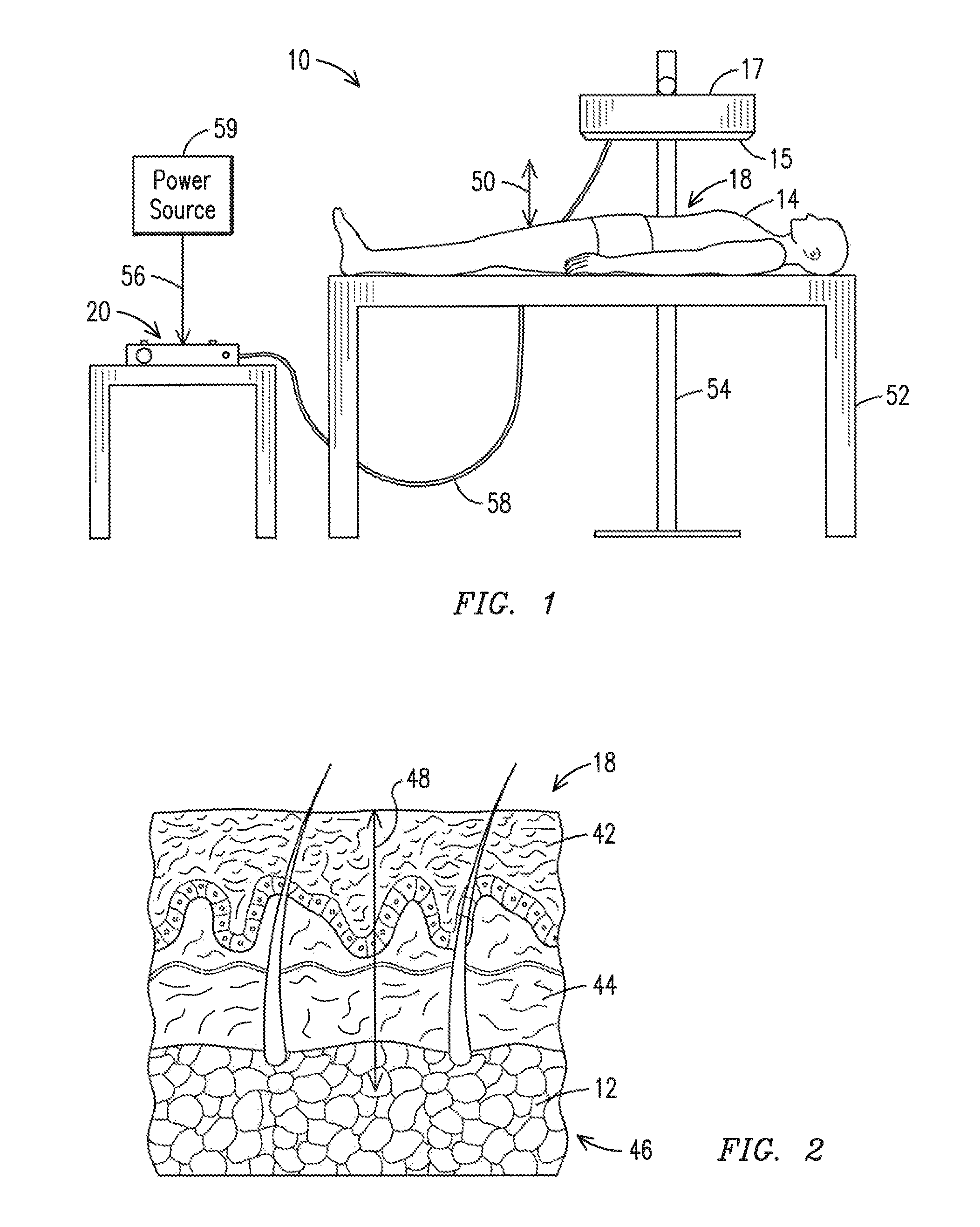
InactiveUS20090318909A1Convenient treatmentOvercome limitationsDiagnosticsControlling energy of instrumentSkin treatmentsLipid content
The invention describes a treatment for skin containing selected targets that provides feedback in response to a measurement enabled by the ablation of holes. The inventive apparatus includes an electromagnetic source configured to emit ablative electromagnetic energy, a delivery system, a sensing element, and a controller. The delivery system can be configured to receive ablative energy from the electromagnetic source and deliver it to multiple discrete locations at the selected region to form a pattern of discrete holes in epidermal and dermal tissue of the skin. The lipid content a portion of the tissue can be evaluated using a sensing element. At least one pulse of electromagnetic energy is delivered to the skin under control of a controller in response to the result of a measurement by the sensing element. The apparatus may include a positional sensor to provide additional dosage control, particularly when the inventive method is used with a continuously movable handpiece.
Owner:BARCLAYS BANK PLC AS SUCCESSOR AGENT
Method for producing biodiesel from an alga
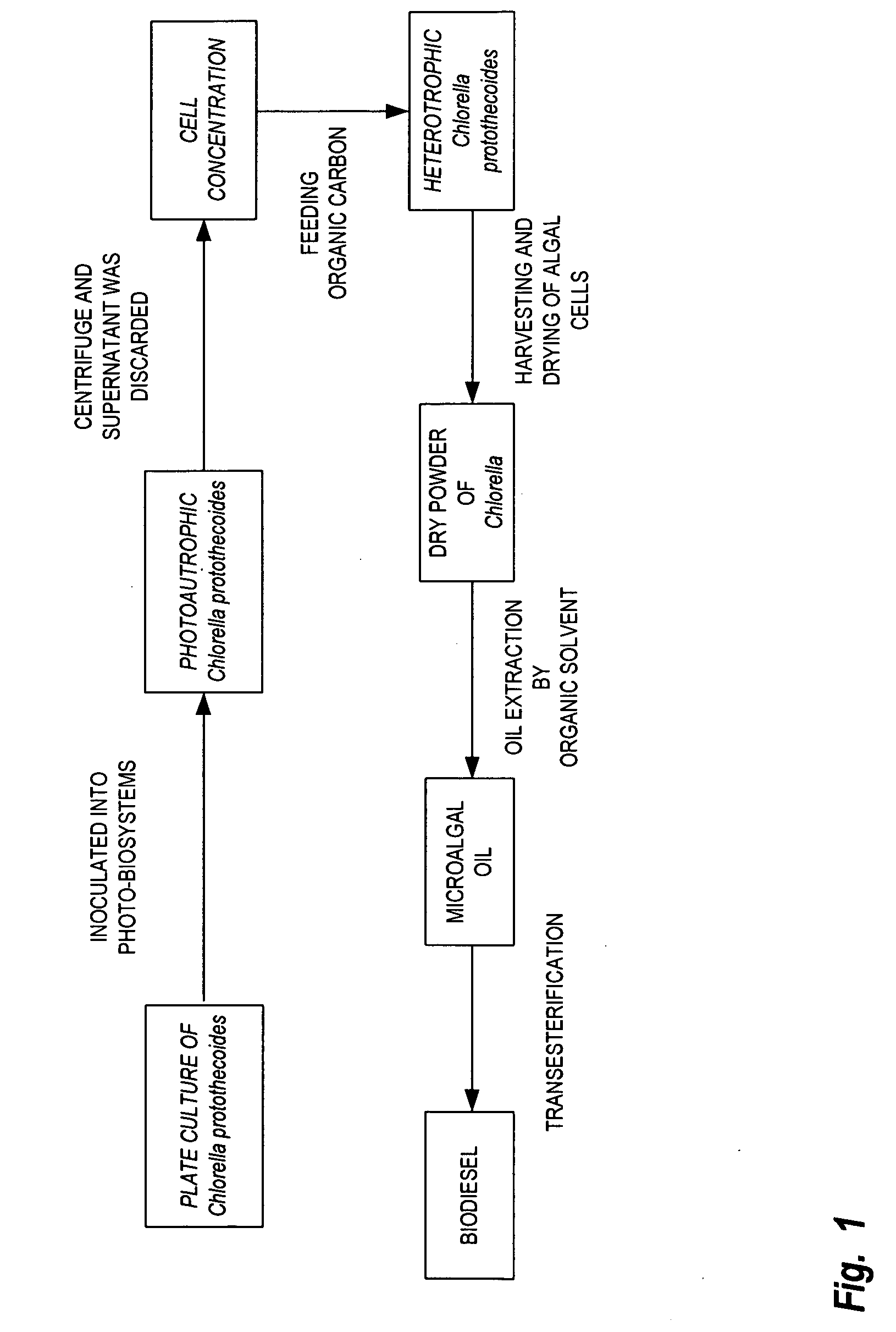
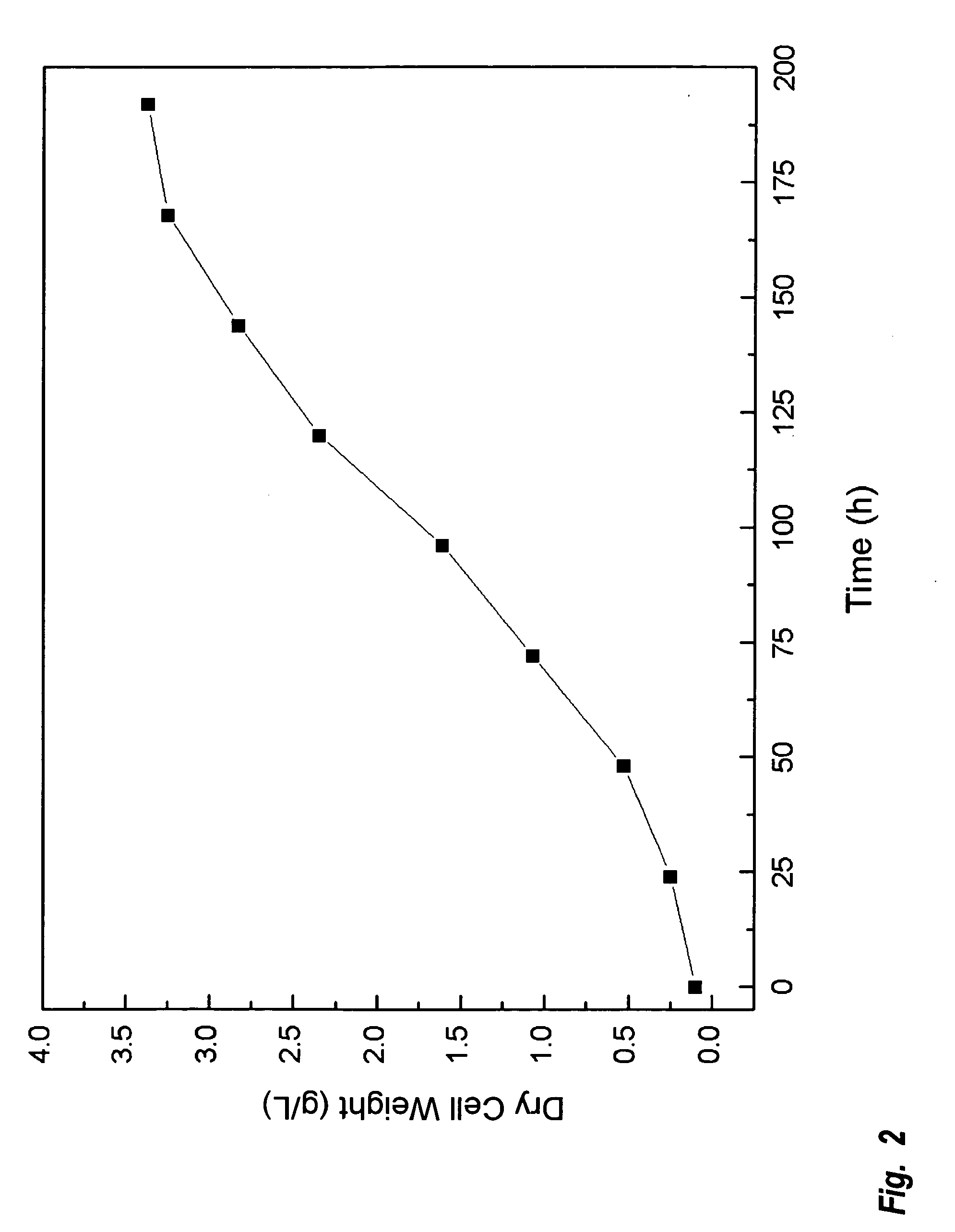
InactiveUS20090298159A1Avoid Microbial ContaminationOrganic chemistryFatty acid esterificationMembrane lipid metabolismOrganism
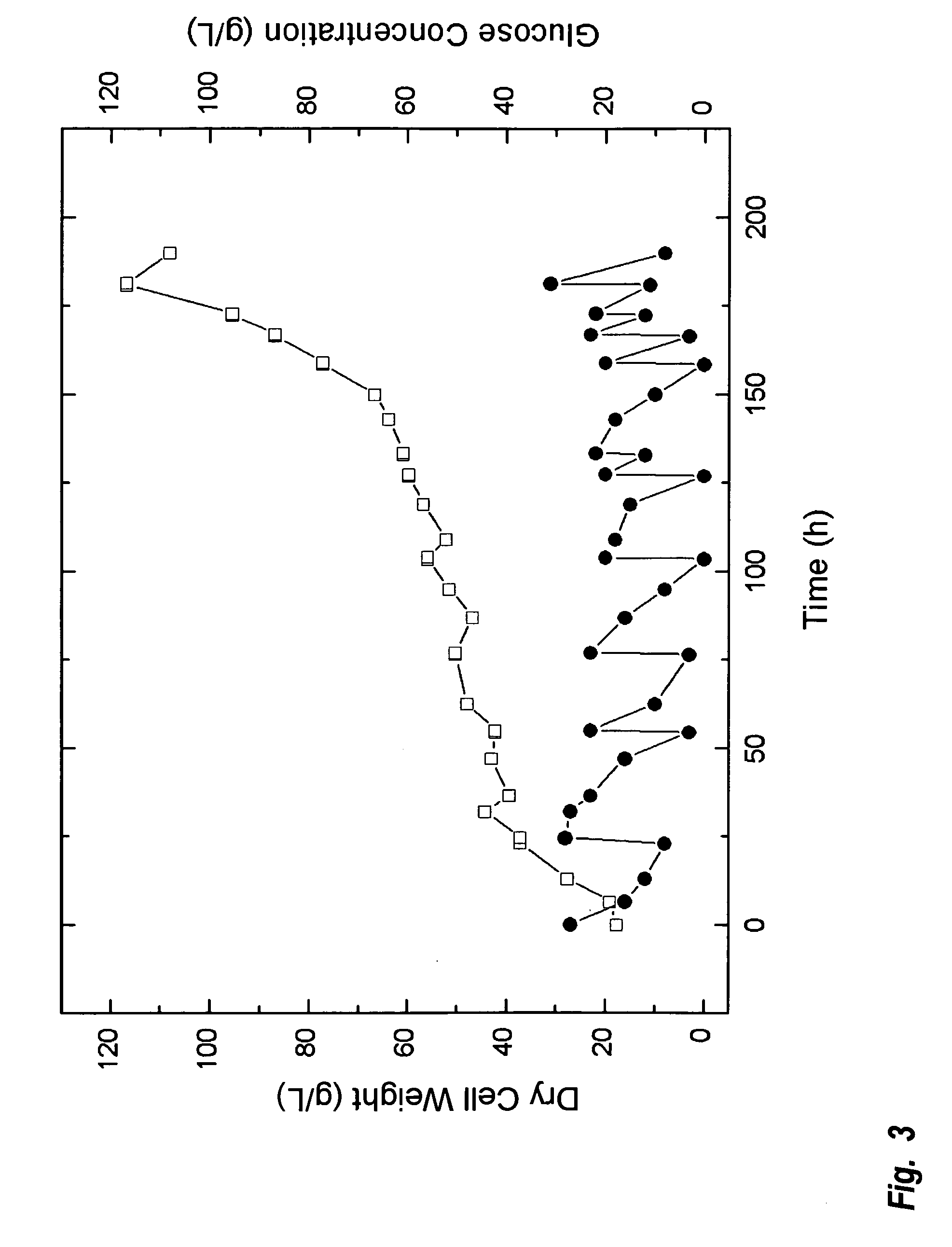
A method is provided to produce biodiesel from algae using a two-stage, autotrophic and heterotrophic cultivations of chlorella for biodiesel production. This method includes a sequence of procedures: cultivating photoautotrophic algae, concentrating cells and then transferring them to a fermentor for heterotrophic cultivation. During the photoautotrophic cultivation stage, the culture is exposed to a light source, such as sunlight with carbon dioxide obtained from a carbon dioxide source or from air. antibacterial agents may be added to prevent contamination from undesired microorganisms. Organic carbons are added during heterotrophic cultivation stage. Fermentation conditions are optimized for maximizing lipid synthesis. High biomass is achieved to about 108 g / L with lipid content reaching about 52% of dry cell weight. After cultivation, biodiesel is made through extraction and transesterification of algae lipids.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Enrichment of process feedstock
InactiveUS20110124034A1Fit for consumptionUnicellular algaeBiomass after-treatmentMicroorganismBiofuel
The subject invention relates to novel methods for treating microbial biomass and uses thereof. In particular, this invention provides methods for production of lipids using ionic liquid solutions, and subsequent uses of biomass components in food, biofuels, and as chemical precursors. Further, this invention provides methods for recovering the ionic liquids using an antisolvent, thus enables subsequent reuse of the ionic liquids In addition, this invention provides practical methods for determining the lipid content of a biomass and screening potential lipid-producing microbial classes. This invention also provides a method of chemical dewatering the lipid-rich algae cells by ionic liquids with its subsequent reuse.
Owner:KUEHNLE AGROSYST
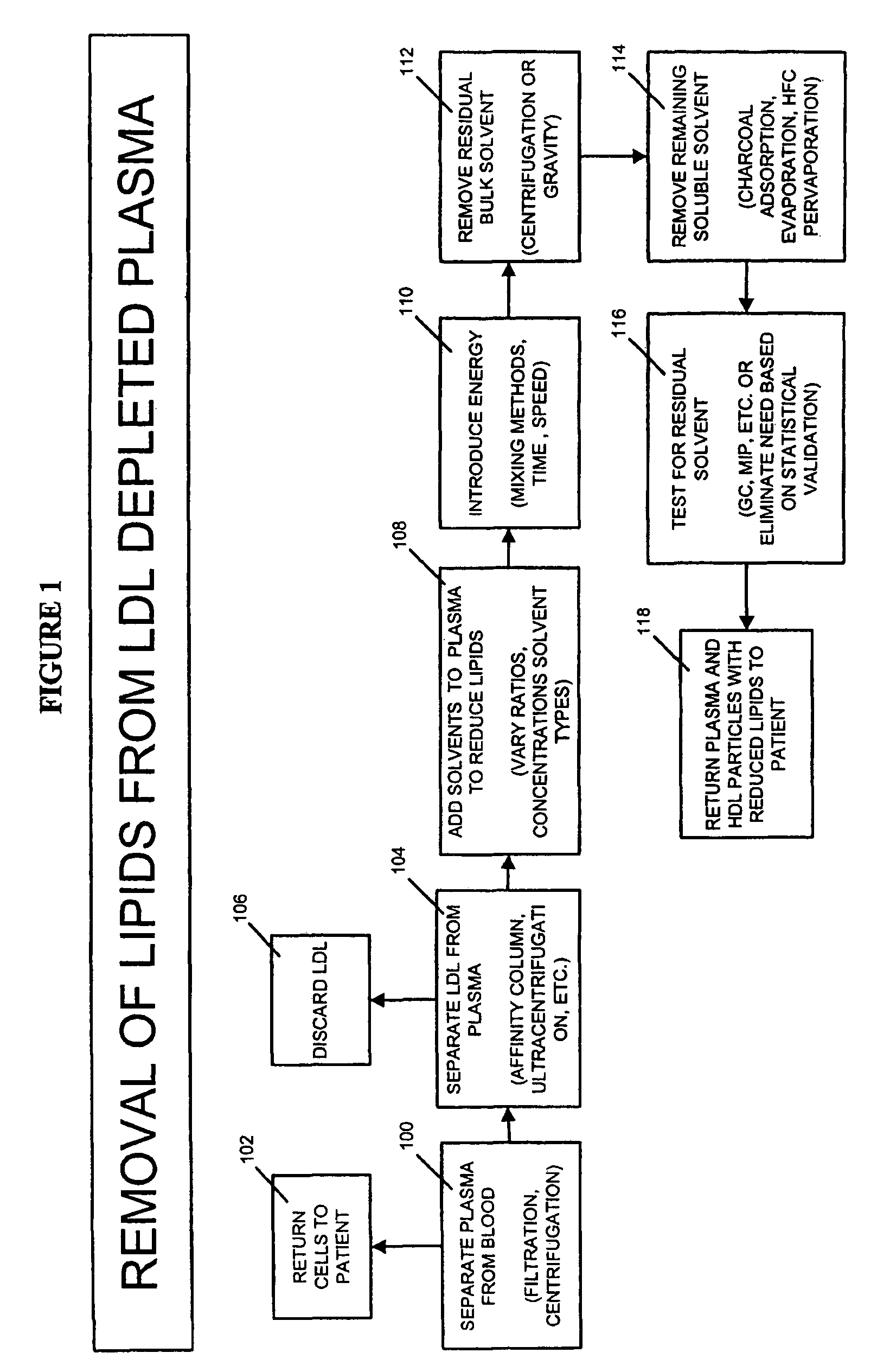
System and method for reducing lipid content of adipocytes in a body
ActiveUS9044595B2Low in lipidsPromote lipolysisSurgical instrument detailsLight therapyCellular lipidLipid content
A system is provided for reducing lipid content of adipocytes in a body. The system includes an optical device configured to illuminate a region of the body at a selective peak wavelength and at a selective power density for a selective time period. The system also includes a controller connected to the optical device to determine the selective wavelength, the selective power density and the selective time period to stimulate lipolysis in the adipocytes. A system is also provided for reducing pain in the body. A method is also provided for reducing lipid content of adipocytes in the body.
Owner:BLUE WATER INNOVATIONS L L C
Aerated confectionery material
ActiveUS20180064127A1Assemble firmlyResisting bubble shrinkageFrozen sweetsConfectioneryPorosityMonoglyceride
The present invention relates generally to the field of aerated fat-based confectionery material. One aspect of the invention provides an aerated fat-based confectionery material having a continuous lipid phase and a porosity of between 1 and 80%, wherein, at a temperature at which the lipid phase has a solid lipid content between 0.1 and 80, the fat-based confectionery material comprises gas bubbles having at least 50% of their surface occupied by crystals, the crystals comprising a glyceride selected from the group consisting of monoglycerides, diglycerides, triglycerides, esters of monoglycerides, esters of diglycerides and combinations of these. Further aspects of the invention are a confectionery product comprising an aerated fat-based confectionery material and a process for forming an aerated fat-based confectionery material.
Owner:SOC DES PROD NESTLE SA
Apparatus and Method for Ablation-Related Dermatological Treatment of Selected Targets
InactiveUS20070264625A1Convenient treatmentOvercome limitationsMicrobiological testing/measurementControlling energy of instrumentSkin treatmentsLipid content
The invention describes a treatment for skin containing selected targets that provides feedback in response to a measurement enabled by the ablation of holes. The inventive apparatus includes an electromagnetic source configured to emit ablative electromagnetic energy, a delivery system, a sensing element, and a controller. The delivery system can be configured to receive ablative energy from the electromagnetic source and deliver it to multiple discrete locations at the selected region to form a pattern of discrete holes in epidermal and dermal tissue of the skin. The lipid content a portion of the tissue can be evaluated using a sensing element. At least one pulse of electromagnetic energy is delivered to the skin under control of a controller in response to the result of a measurement by the sensing element. The apparatus may include a positional sensor to provide additional dosage control, particularly when the inventive method is used with a continuously movable handpiece.
Owner:RELIANT TECH INC
Method for preparing low-fluorine Euphausia superba protein base materials
InactiveCN101690538AHigh nutritional valueThe method is simple and effectiveProtein composition from fishLipid contentAcid washing
The invention provides a method for preparing low-fluorine Euphausia superba protein base materials. The method is characterized by freezing and grinding the Euphausia superba, extracting proteins under alkali condition, precipitating and separating the proteins under acid condition and acid-washing the precipitated proteins for defluorination, thus preparing the products. The water contents of the products are 82-87% and the fluorine contents of the products are lower than 2mu g / g wet basis. The method is simple and effective, can ensure the recovery rate of the crude protein of the Euphausia superba to be 39-46%, the recovery rate of the crude lipid to be 38-42%, the content of the crude protein to be 66-71g / 100g wet basis, the content of the crude lipid to be 27-30g / 100g wet basis and the content of phospholipid to be 380-420mg / g lipid and ensure the products to have high nutritional values. The method is suitable for industrial application and the prepared products are wide in use and can serve as the accessories or base materials for preparing the Euphausia superba protein powder and other food.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Method for making reduced calorie cultured cheese products
A method is disclosed for making reduced calorie cultured cheeses whereby the natural lipid content of milk is replaced with colloidal forms of synthetic or chemically structured lipids displaying low to no human digestibility. The colloidal dispersion of modified lipids contained within the milk base is initially stabilized by preferred combinations of polymeric and particulate hydrocolloidal materials such as structurally expanded cellulose. Such stabilization is important during formation of the curd to ensure homogeneous distribution and maintenance of the lipid dispersion throughout the coagulum yet allow effective concentration of the coagulum solids by means of ordinary water removal methods commonly used in the manufacture of conventional cultured cheeses. The coagulum is then processed by means similar to that employed for naturally fermented cheeses. The resulting cultured cheese is a reduced calorie product with low to no metabolizable fat content yet possesses organoleptic properties similar to a full fat product.
Owner:WEIBEL MICHAEL K
Cultivation of dha-rich prey organisms for aquatic species
InactiveUS6789502B2Increase successClimate change adaptationAnimal feeding stuffAquatic speciesOrganism
A method is provided for producing prey organisms such as Artermia and rotifers, for feeding aquacultural organisms in particular at the larval stage. The method comprises cultivating the prey organisms during at least part of their life cycle in an aqueous medium comprising at least one lipid component having a DHA content of at least 30 wt %. The enriched prey organisms preferably have a DHA content of at least 12 wt % of their total lipid content. The prey organisms are suitable feed for larvae of fish including halibut, turbot, bass, and flounder, and crustaceans and molluscs.
Owner:EPAX NORWAY
Peroxisome biogenesis factor protein (PEX) disruptions for altering polyunsaturated fatty acids and total lipid content in oleaginous eukaryotic organisms
InactiveUS20090117253A1Lipid content in PEX-disrupted can be increased and decreasedFungiNervous disorderBiotechnologyOrganism
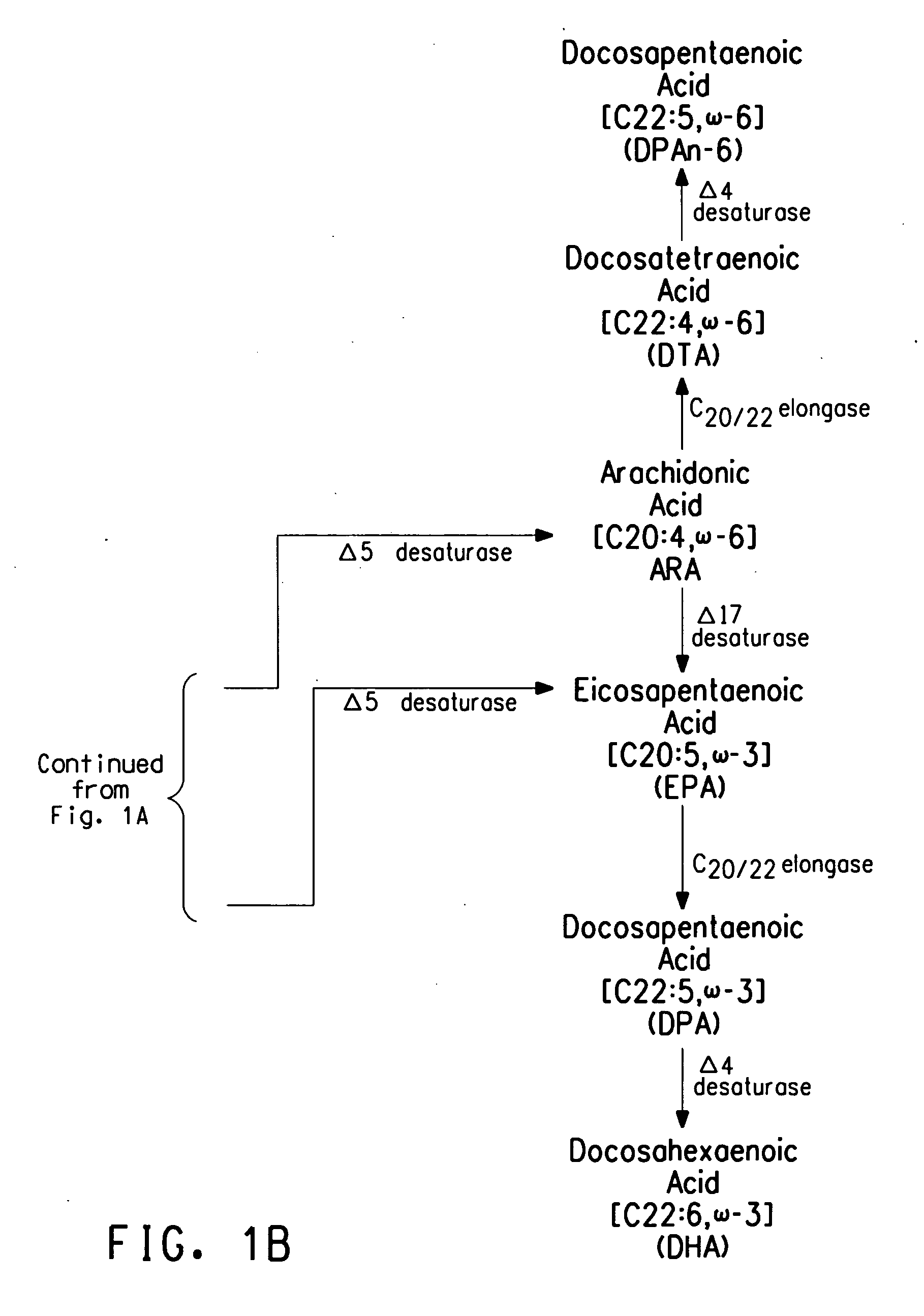
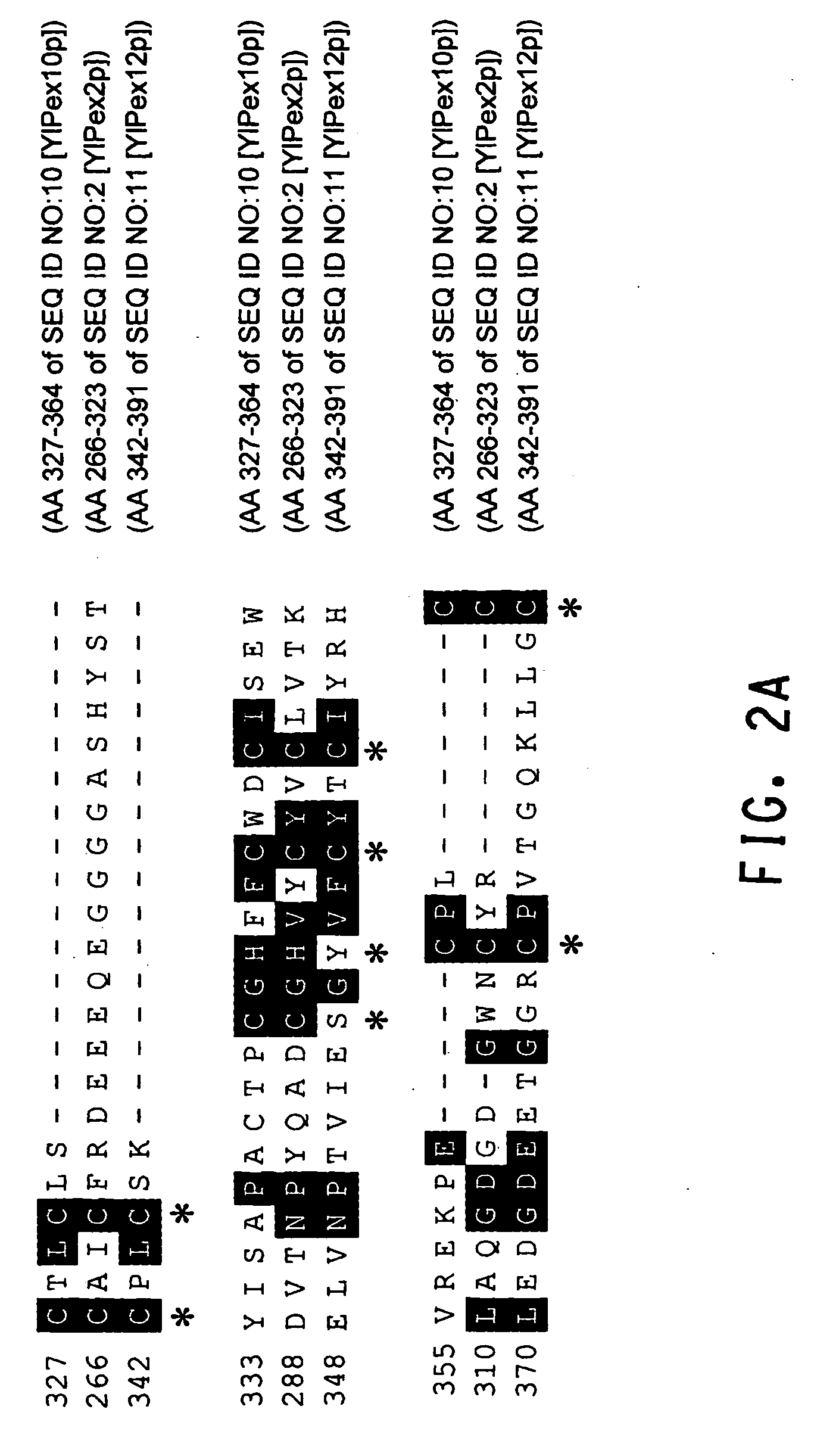
Methods of increasing the amount of polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) in the total lipid fraction and in the oil fraction of PUFA-producing, oleaginous eukaryotes, accomplished by modifying the activity of peroxisome biogenesis factor (Pex) proteins. Disruptions of a chromosomal Pex3 gene, Pex10p gene or Pex16p gene in a PUFA-producing, oleaginous eukaryotic strain resulted in an increased amount of PUFAs, as a percent of total fatty acids and as a percent of dry cell weight, in the total lipid fraction and in the oil fraction of the strain, as compared to the parental strain whose native Pex protein was not disrupted.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
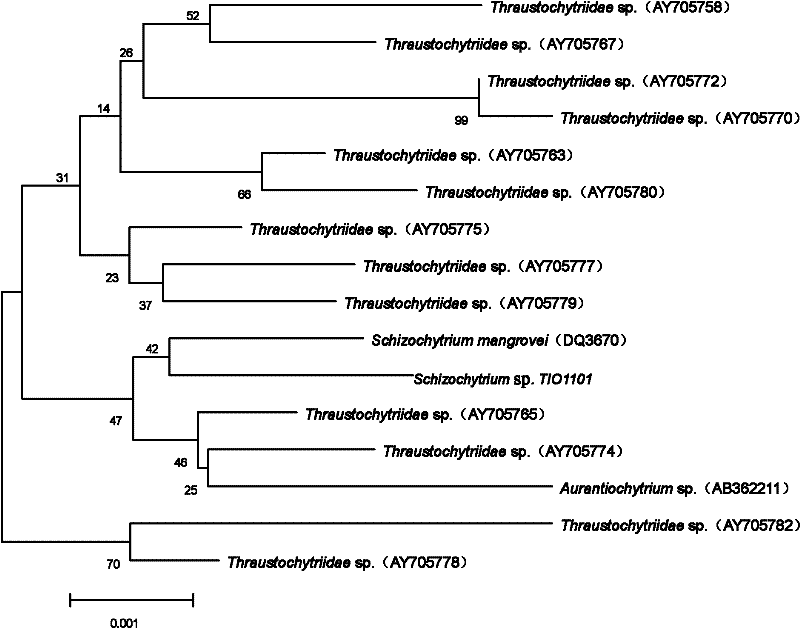
Schizochytrium sp.TIO1101 strain with high-yield DHA (docosahexaenoic acid) and fermentation method thereof
InactiveCN102199541AHigh in DHASimple ingredientsUnicellular algaeMicroorganism based processesHigh densityLipid content
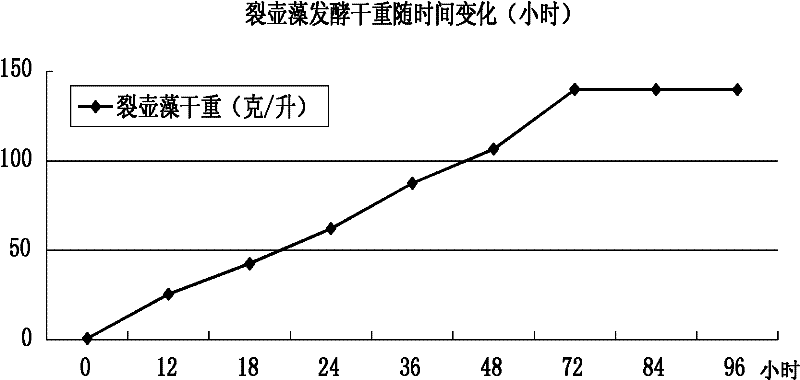
The invention discloses a Schizochytrium sp.TIO1101 strain with high-yield DHA (docosahexaenoic acid) and a fermentation method thereof. The Schizochytrium sp.TIO1101 strain provided by the invention has a preservation number of CGMCC (China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center) No.4603. After the Schizochytrium sp.TIO1101 is subjected to high-density heterotrophic fermentation for 72h, the biomass liveweight, the lipid content and the DHA are respectively 120g / L, 54.3% and 51.4% of the content of total lipid, therefore the Schizochytrium sp.TIO1101 has development and application values extremely. The Schizochytrium sp.TIO1101 disclosed by the invention has the advantages that: the Schizochytrium sp.TIO1101is obtained through separation; the high-density heterotrophic fermentation of the Schizochytrium sp.TIO1101 is realized; and the lipid extracted from the Schizochytrium sp.TIO1101 cells obtained under the fermentation condition has high DHA content and purer components.
Owner:THIRD INST OF OCEANOGRAPHY STATE OCEANIC ADMINISTATION +1
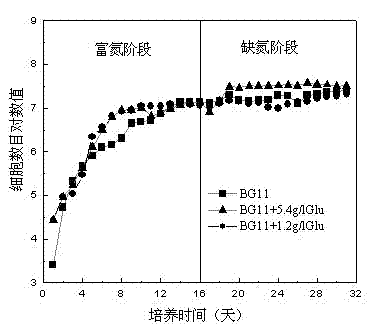
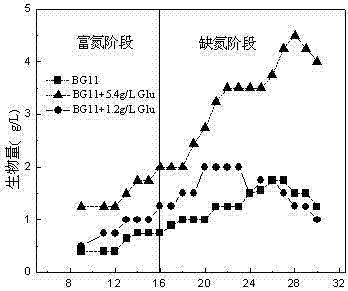
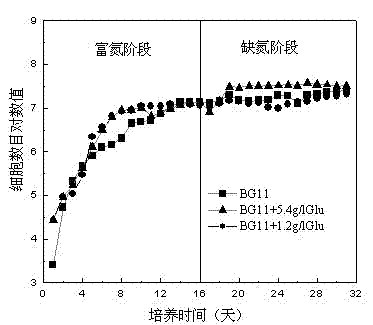
A method for improving the biomass and oil accumulation of oleaginous microalgae using a two-stage culture strategy of admixture and nitrogen-enrichment-nitrogen deficiency
InactiveCN102268377APromote accumulationUnicellular algaeMicroorganism based processesOil and greaseConcentrations glucose
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method for detecting oil content of microalgae
InactiveCN102565012AEasy to detectThe process is simple and convenientUsing optical meansIndividual particle analysisLipid formationMicrobial oil
The invention relates to lipid producing microalgae, in particular relates to a method for detecting the oil content of microalgae, comprising the following steps of: 1) taking microalgae-cultivated algae liquid, and computing the quantity concentration C of microalgae cells; 2) observing the lipid of the microalgae: adopting a BODIPY (boron-dipyrromethene) 505 / 515 staining fluorescent recording method; staining for 1-2min by adopting dye use liquid with concentration of 1-2mM, and observing and recording accumulation change conditions of single-celled lipid in a photographing way by using excitation light with wave length of 488nm under a fluorescence microscope; recording the number (n) of single-celled oil drop grains according to a photograph, detecting the diameter (d) of each oil drop, and computing the volume of each oil drop according to a ball volume formula, wherein the content of each cell lipid is the sum of the volume of all the oil drops; and computing the lipid content of the algae liquid in unit volume according to the quantity concentration C of the microalgae and the lipid content of a single cell: Vt=CV, wherein C is the concentration of tetraselmis cells, V is the lipid volume of the single cell, and Vt is the lipid content in the unit volume.
Owner:YELLOW SEA FISHERIES RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERIES SCI
Method for cultivating oleaginous microalgae by using fecal sewage
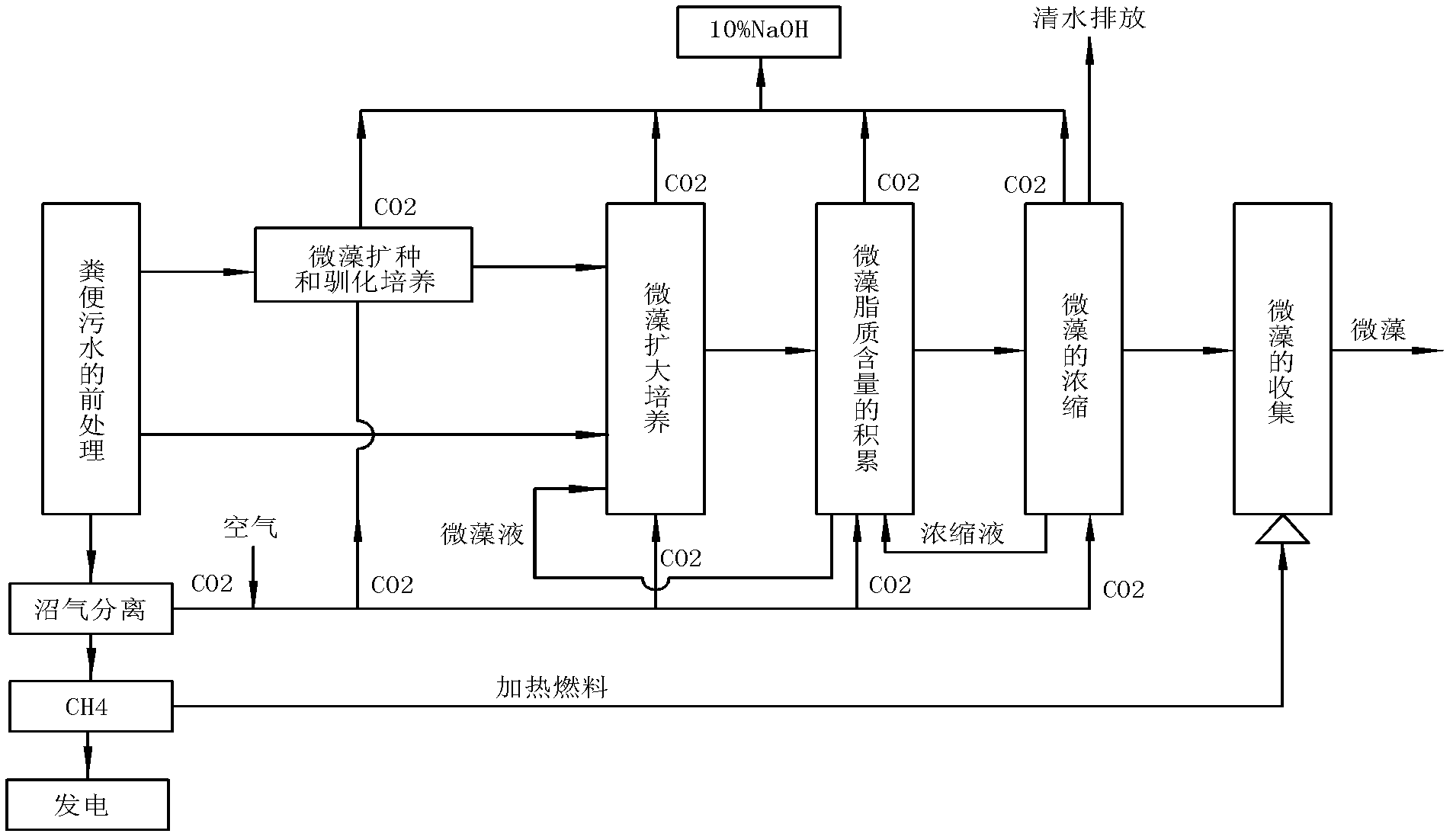
ActiveCN102618446AReagent savingLow costUnicellular algaeBiological water/sewage treatmentBiodieselFeces
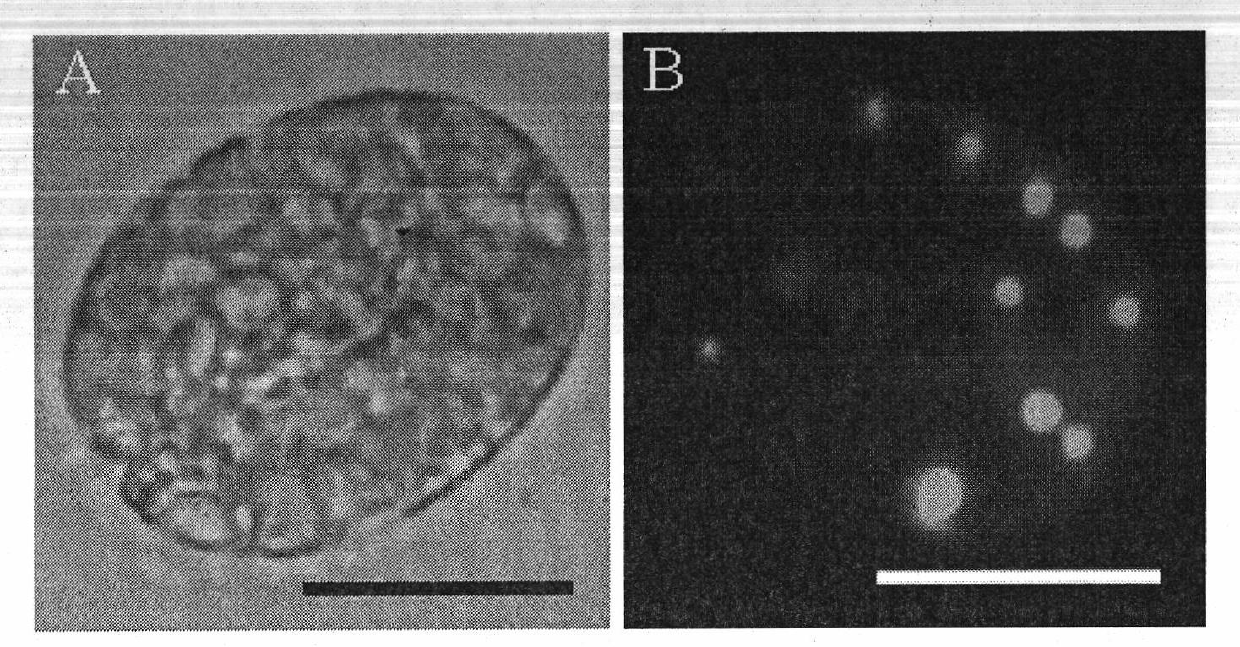
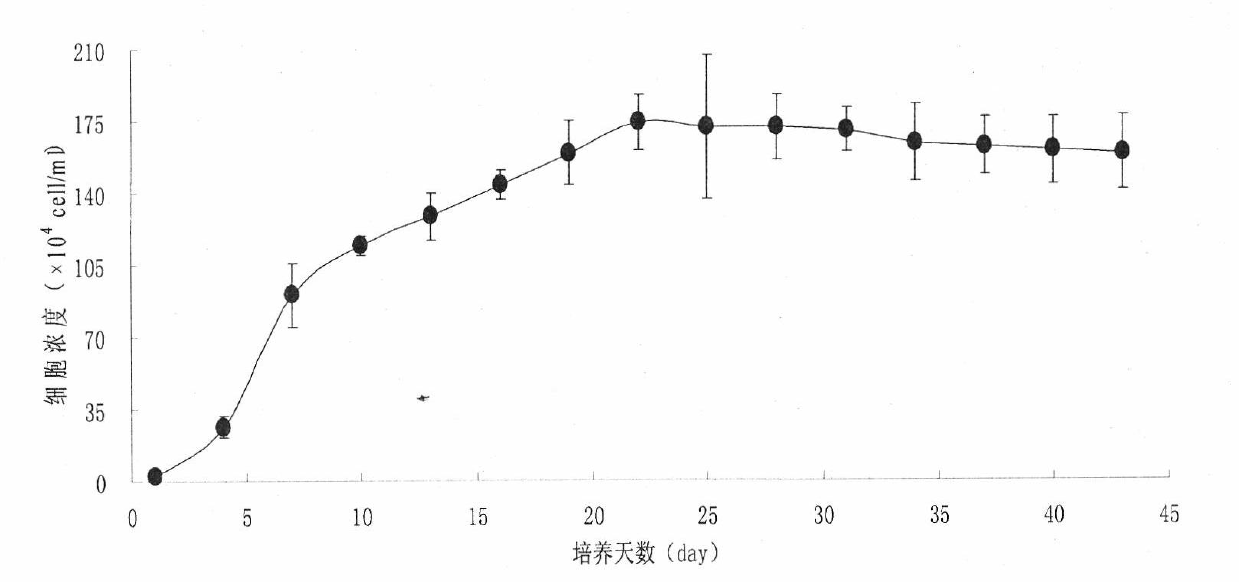
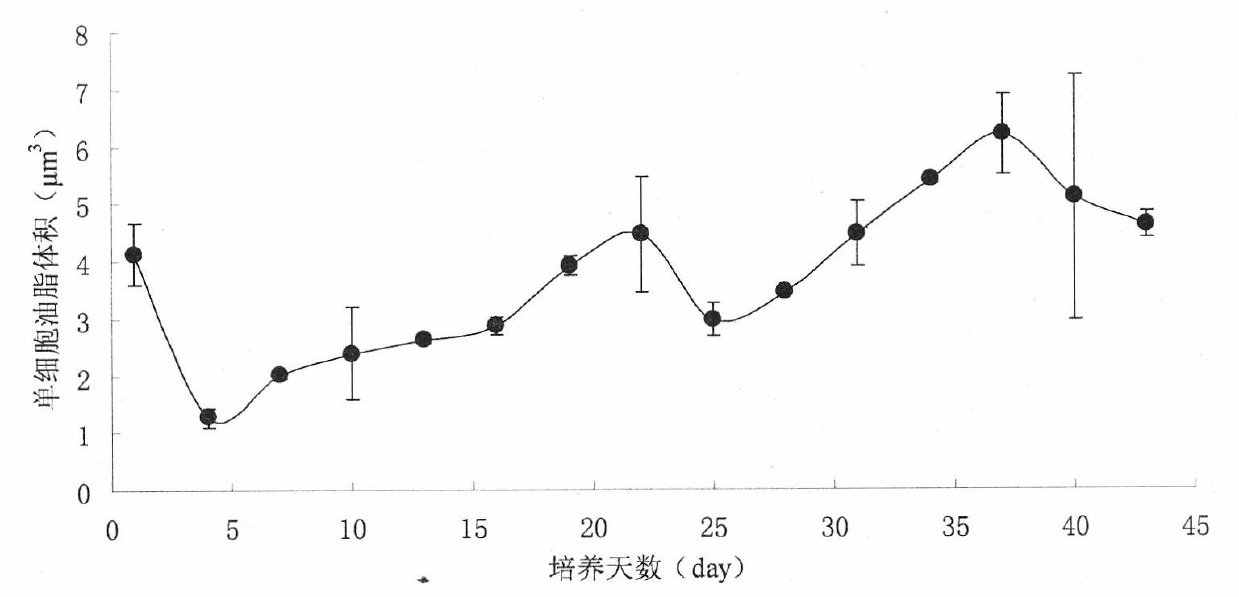
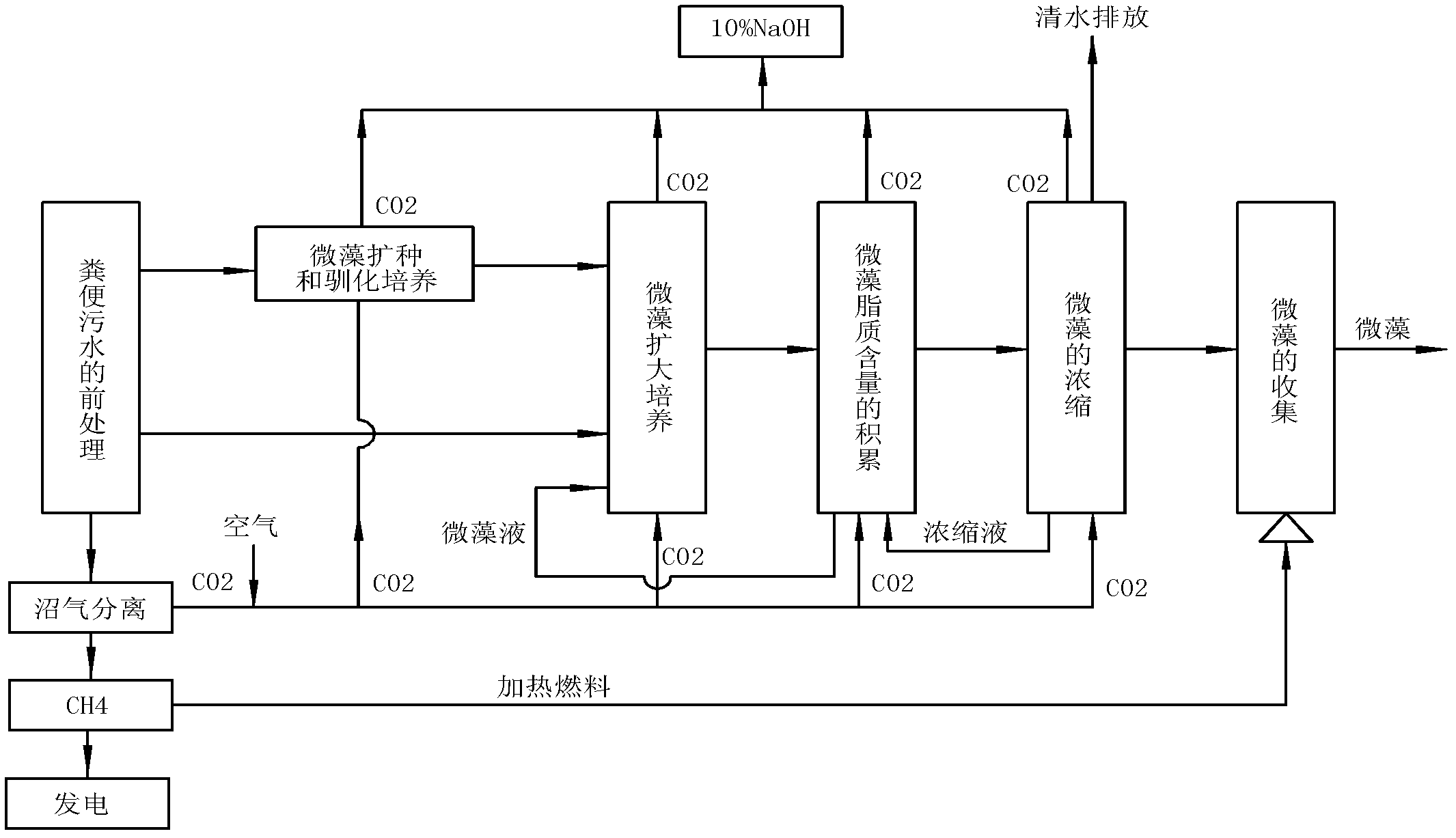
The invention relates to a method for cultivating oleaginous microalgae by using fecal sewage, which comprises the steps of pretreatment of the fecal sewage, inoculation activation and acclimated cultivation of microalgae, amplification cultivation of the microalgae, accumulation of lipid content of the microalgae, concentration of the microalgae and collection of the microalgae. According to themethod, a liquid which is discharged during the process of feces recycling treatment and conforms to the emission standard is used for cultivating the microalgae so that cultivation water and reagents are saved during the microalgae cultivation, simultaneously, the microalgae can be used without being sterilized, the production process is reduced, the cost of obtaining microalgae biodiesel is reduced, nitrogen and phosphorus in the liquid serve as nutrient materials during the microalgae cultivation, various indexes in the sewage are further reduced, and water quality of the sewage is improved. Besides, biogas produced during the process of feces recycling treatment serve as a heating fuel, carbon dioxide (CO2) separated during biogas purification serve as a carbon source for the microalgae cultivation, the microalgae cultivation and the feces recycling treatment are organically coupled, and energy conservation and emission reduction are promoted while the cost is reduced.
Owner:北京昊业怡生科技有限公司
Methods for modifying plant responses to stress and correspondingly derived plants
InactiveUS7615681B2Improve plant resistanceImprove the immunityHydrolasesImmunoglobulinsGrowth plantStress conditions
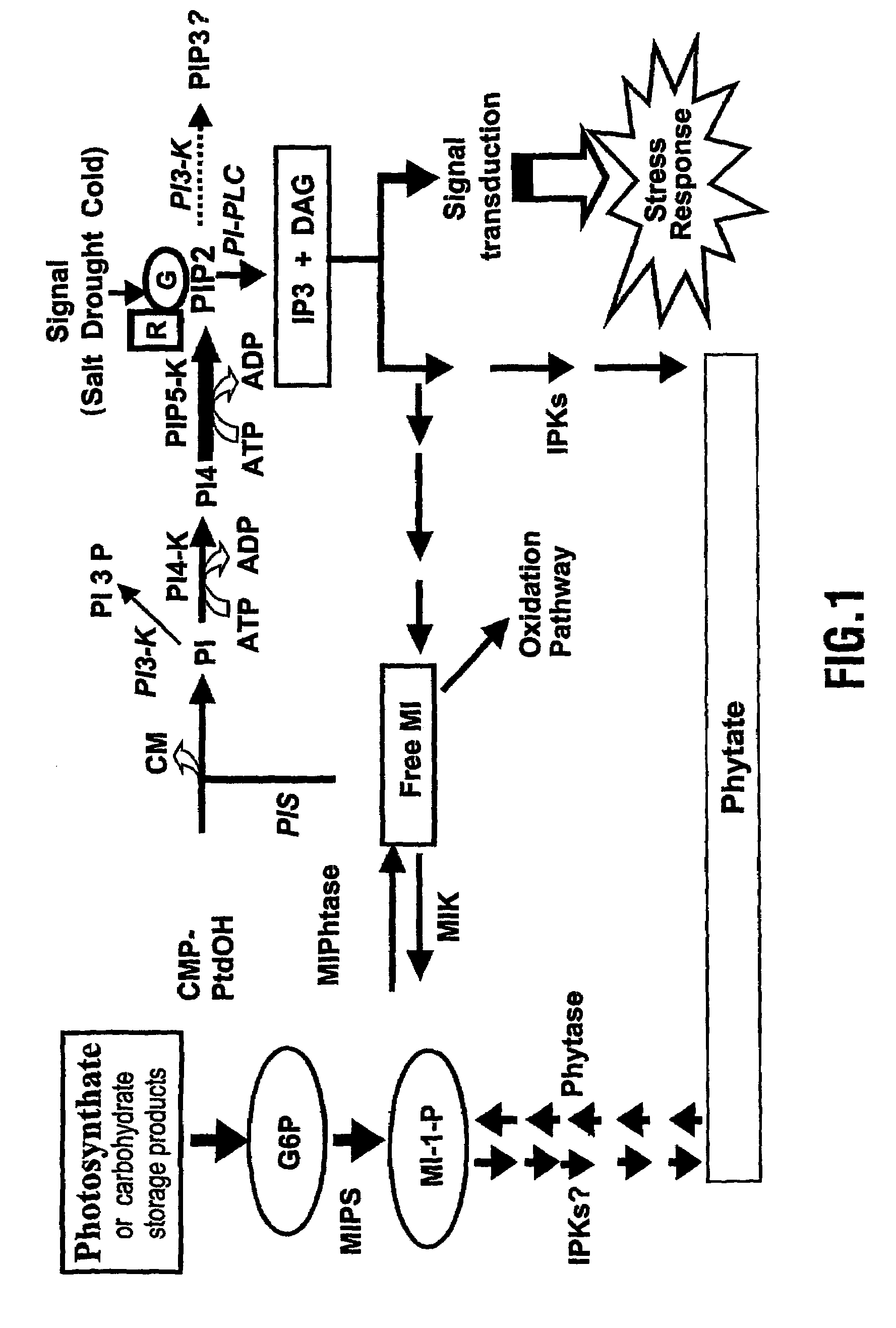
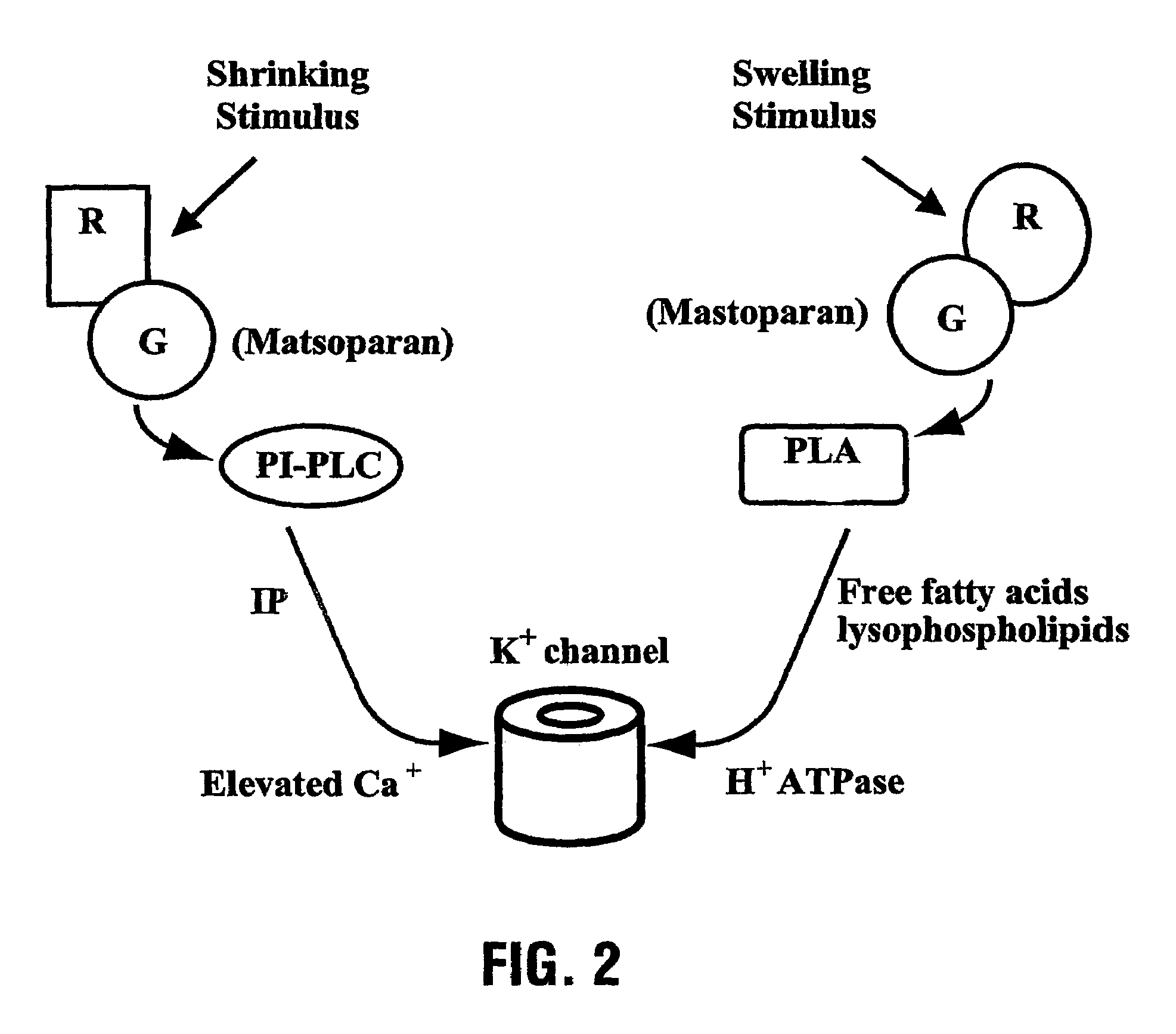
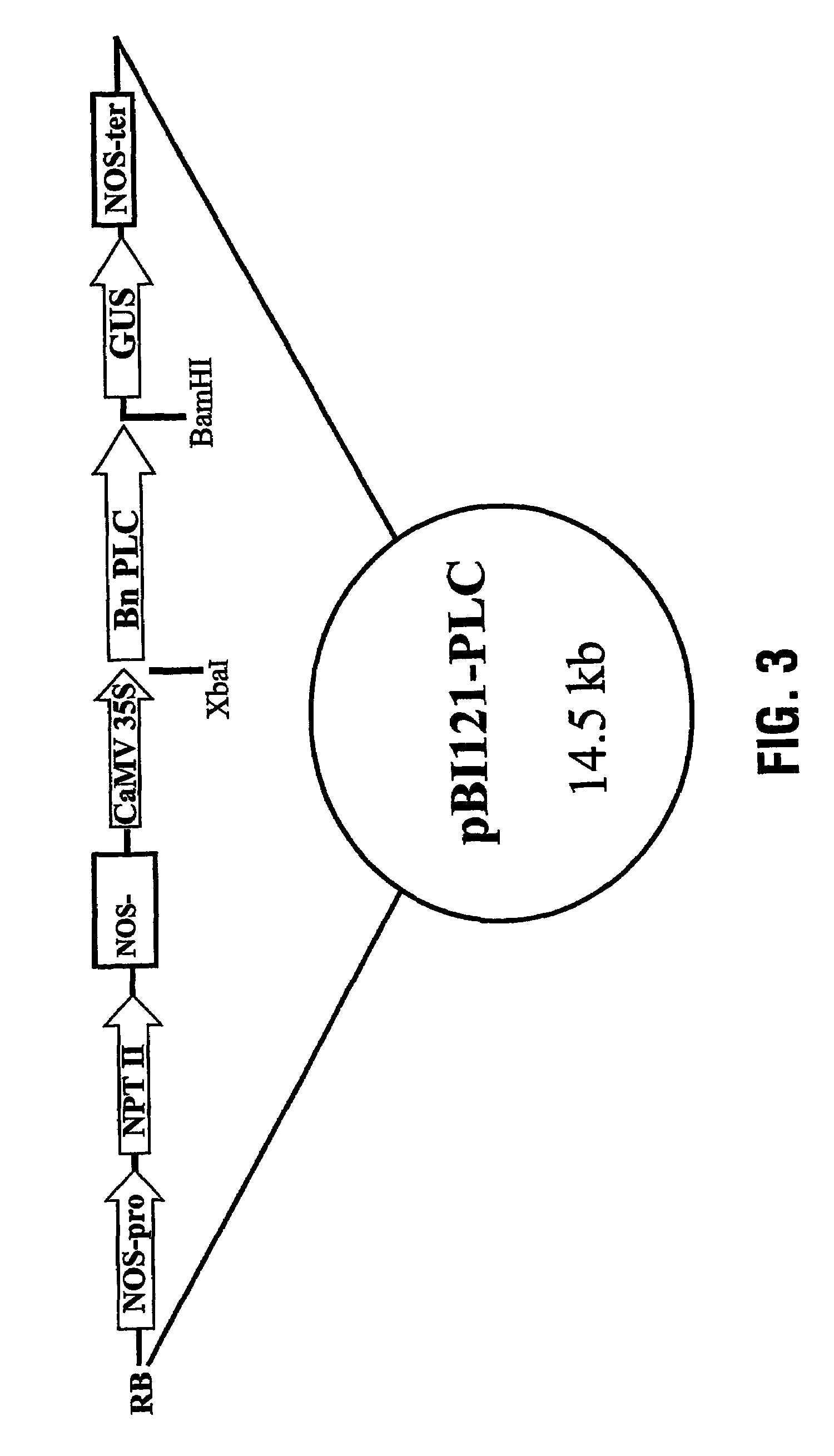
Plant stresses such as pest drought, and excessive temperatures can lead to significant losses of crops each year. There is a continuing need to develop novel plant varieties that are less susceptible to damage or loss by such stresses. The present invention provides a system and method for generating plants having an increased resistance to plant stresses such as drought or adverse temperatures. Transgenic plants expressing a phosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C (PI-PLC) gene can show an unexpected and dramatic improvement in their capacity to tolerate a variety of stress conditions. Moreover, increased PI-PLC expression can further lead to marked increase in plant growth rates, maturation, and lipid content. The present invention encompasses transgenic plants having modifications with regard to PI-PLC pathways, such as altered PI-PLC levels, and plant products thereof.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
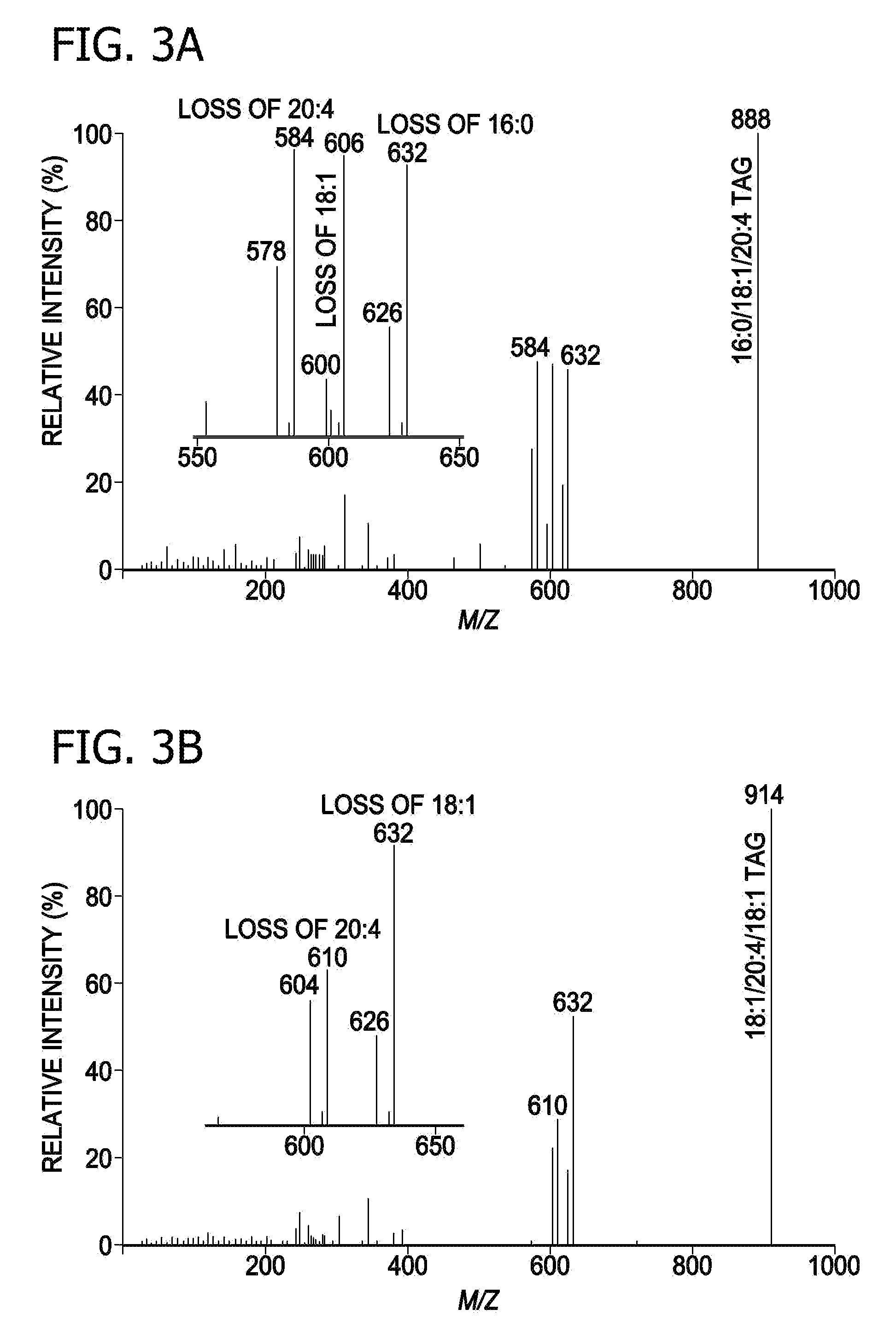
Multidimensional mass spectrometry of serum and cellular lipids directly from biologic extracts
InactiveUS7510880B2Enhanced interactionRespond effectivelyParticle separator tubesFuel testingLipid formationElectrospray
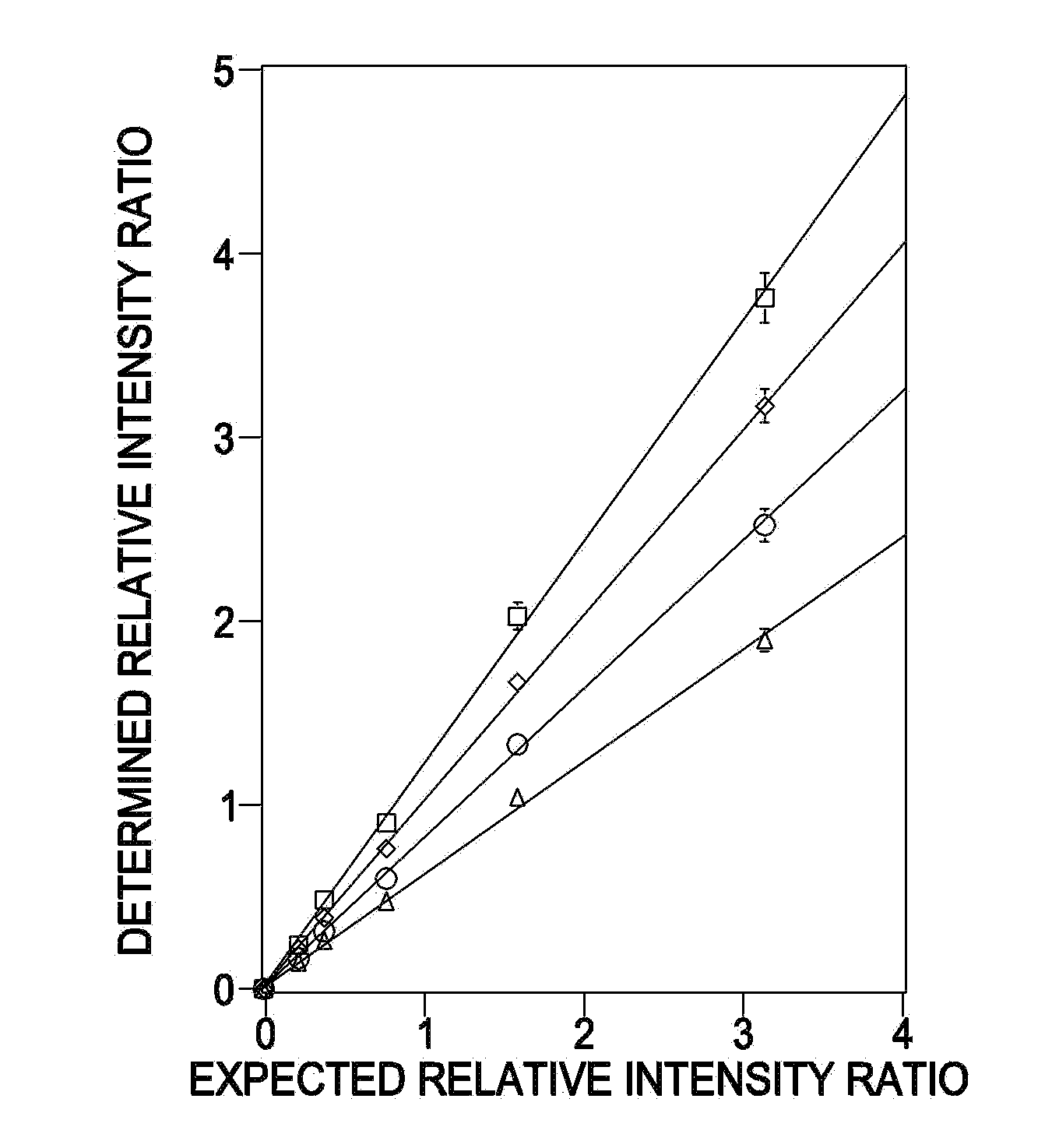
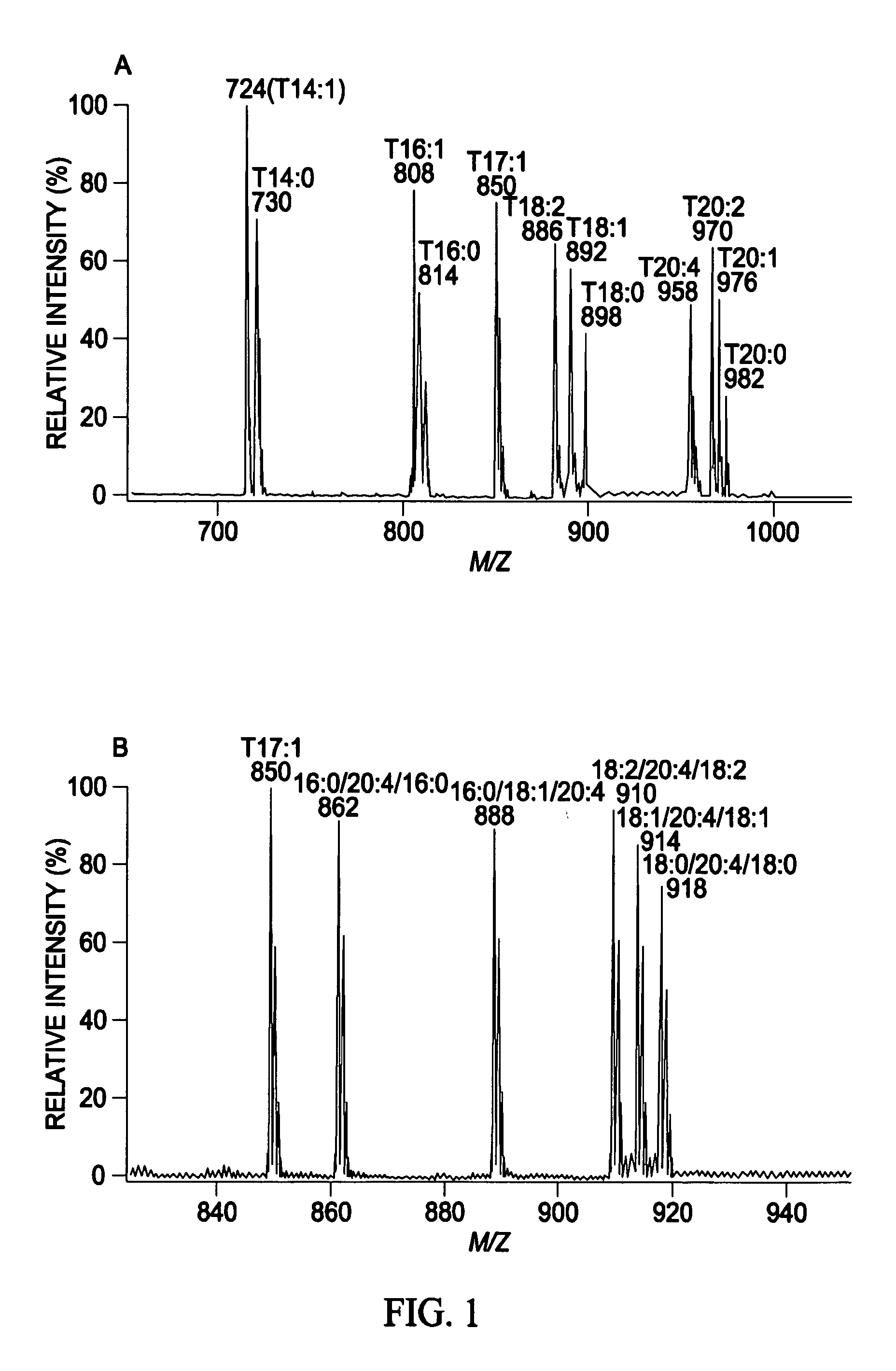
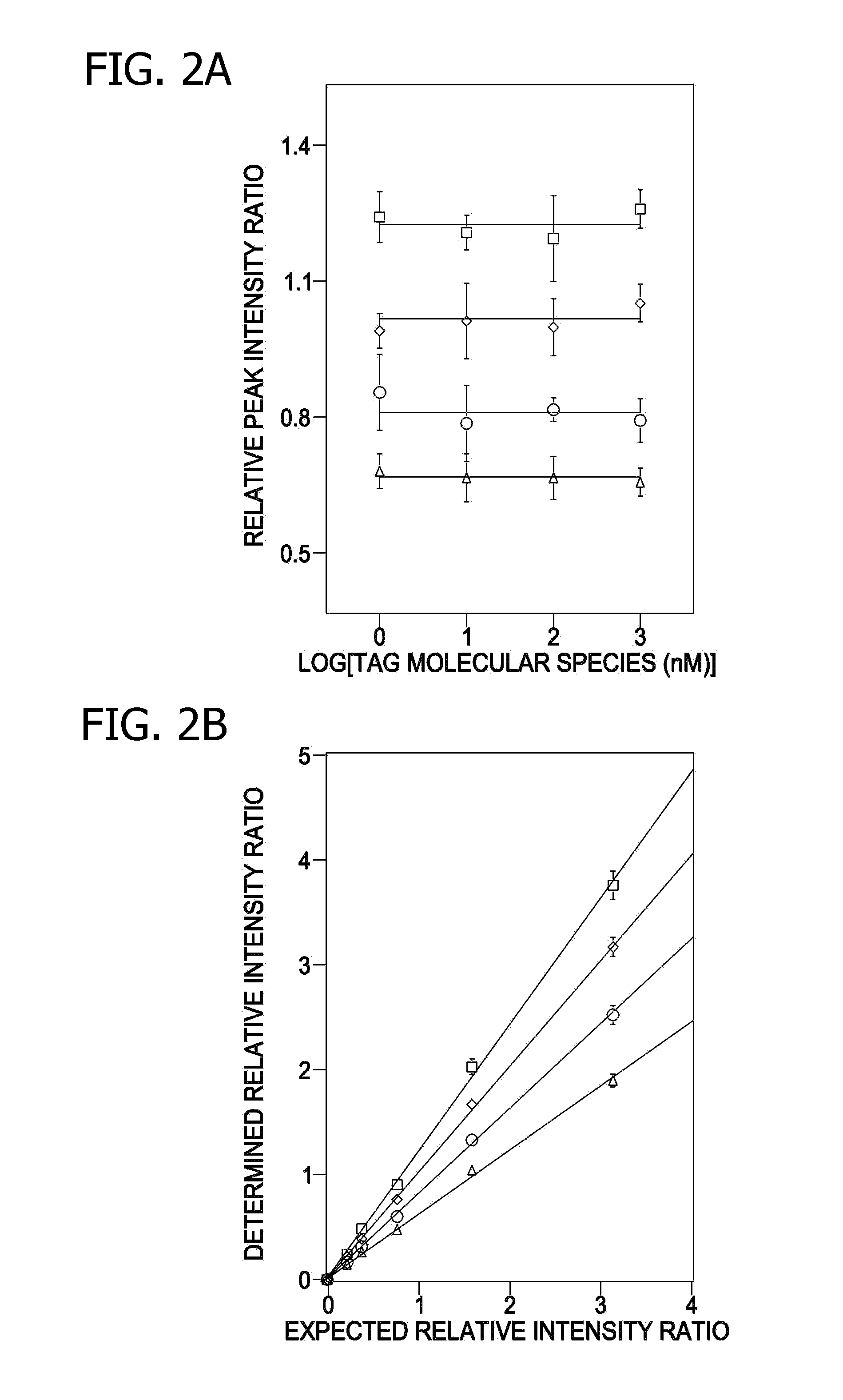
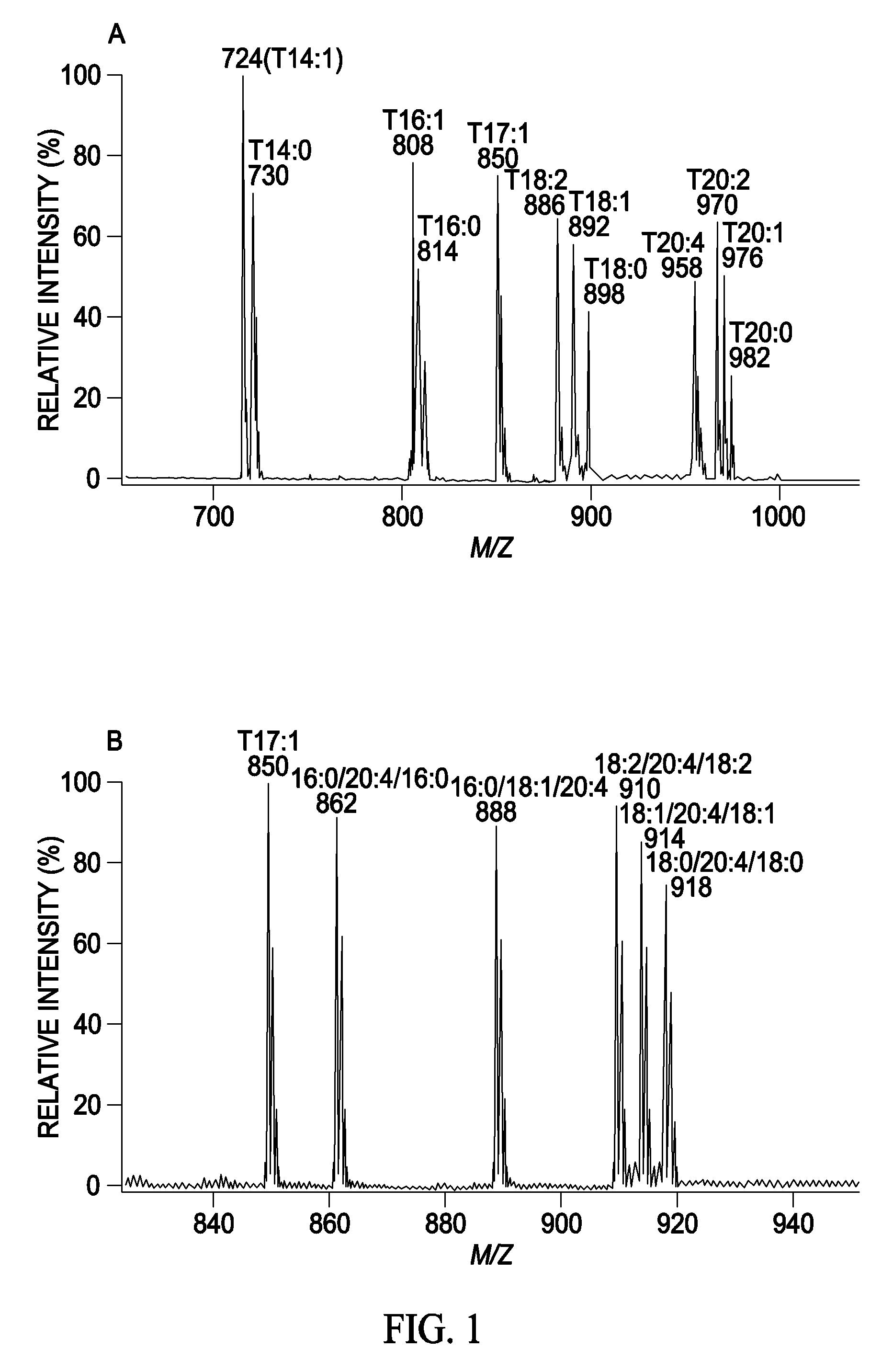
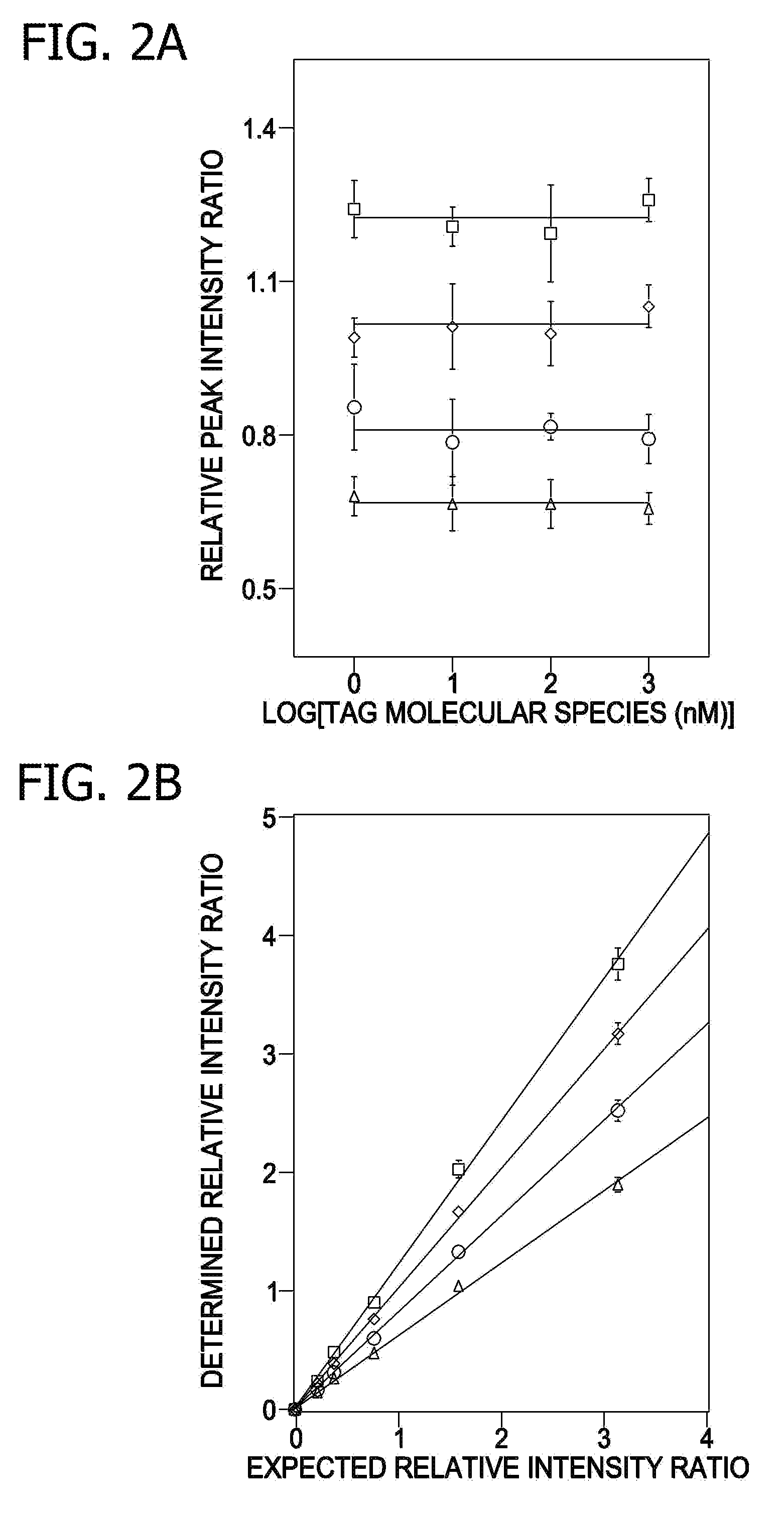
A method for determination of at least one of the lipid species in a biological sample comprising subjecting the sample to lipid extraction to obtain a lipid extract and subjecting the resulting lipid extract to multidimensional electrospray ionization mass spectrometry using either precursor ion or neutral loss scanning (or both) of all naturally occurring aliphatic chains, lipid fragments and precursor ions leading to observed fragments to generate a multidimensional matrix whose contour densities provides structural and quantitative information directly without chromatography. A method for determination of lipid content and / or lipid molecular species composition and quantity directly from lipid extracts of a biological sample comprising subjecting said lipid extract to electrospray ionization multidimensional mass spectrometry by comparisons to standards and algorithms described herein.
Owner:GROSS RICHARD W +1
Compositions and methods for increasing cellular far and bleaching skin
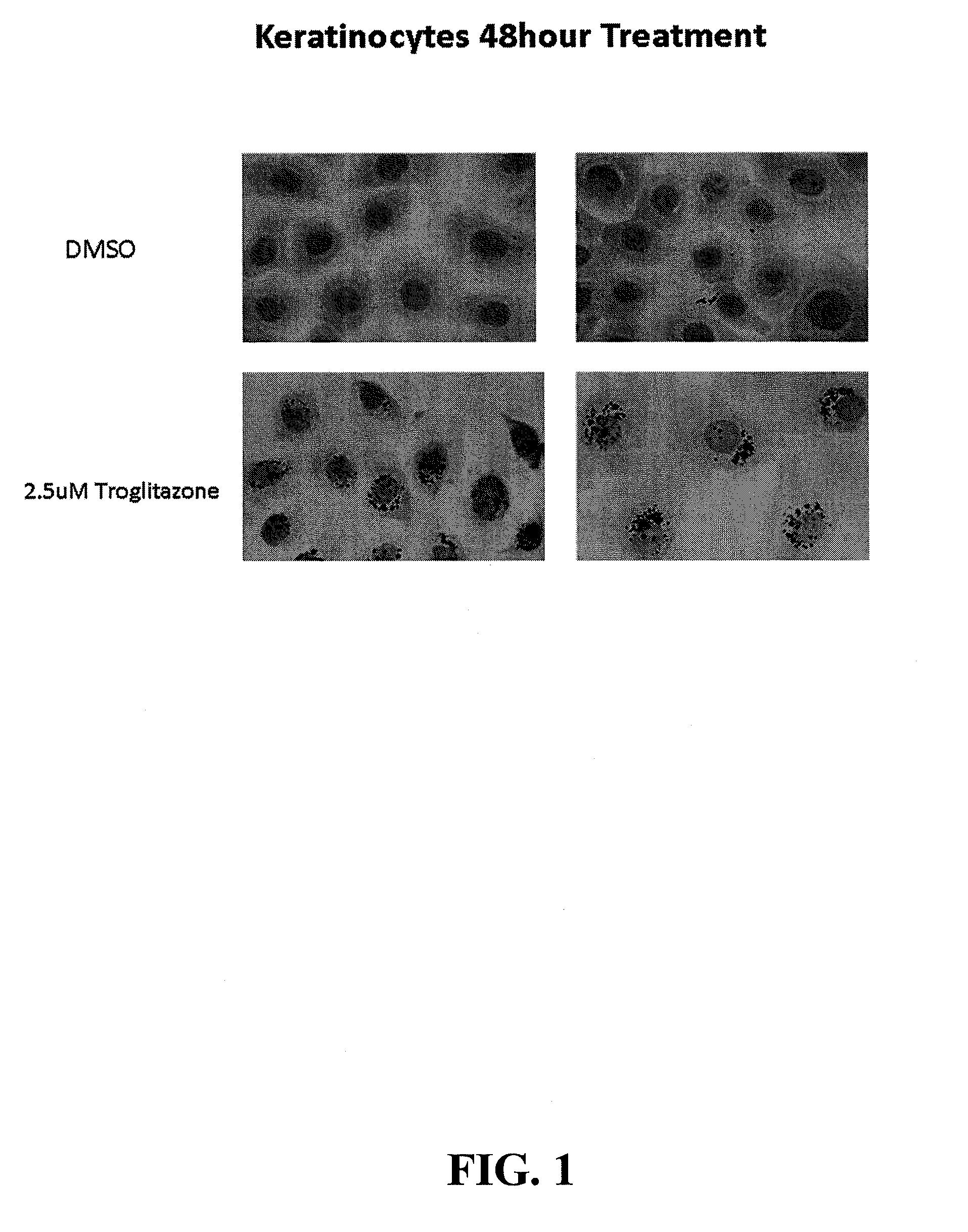
InactiveUS20110150798A1Reduce tissue damageCut skinOrganic active ingredientsCosmetic preparationsLipid contentPharmacology
Compositions and methods are disclosed for the treatment of cells, such as keratinocytes and adipocytes, to increase their lipid content and compositions and methods are disclosed for treatment of skin cells to diminish the appearance of blemishes.
Owner:0901911 B C UNLIMITED LIABILITY
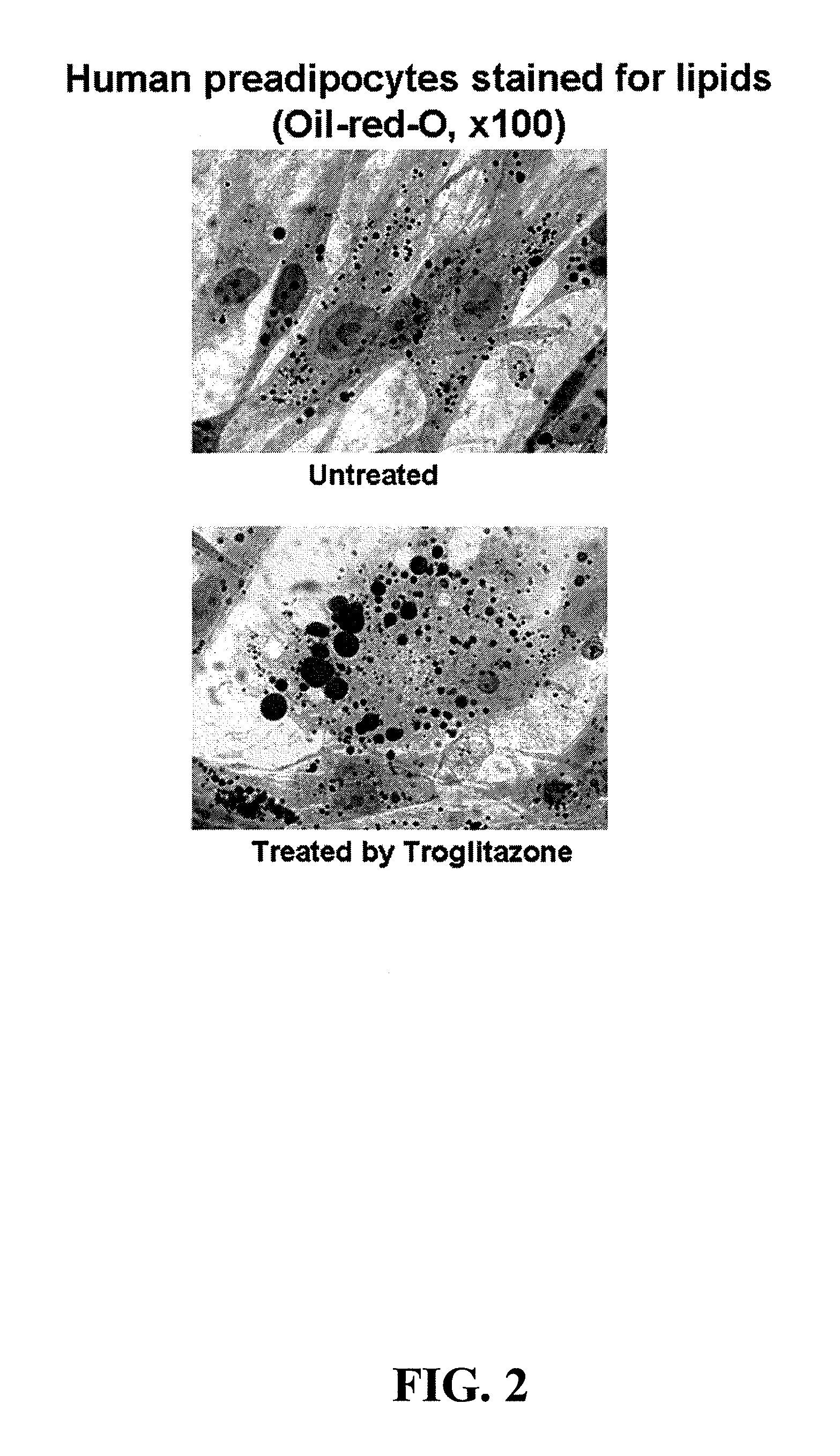
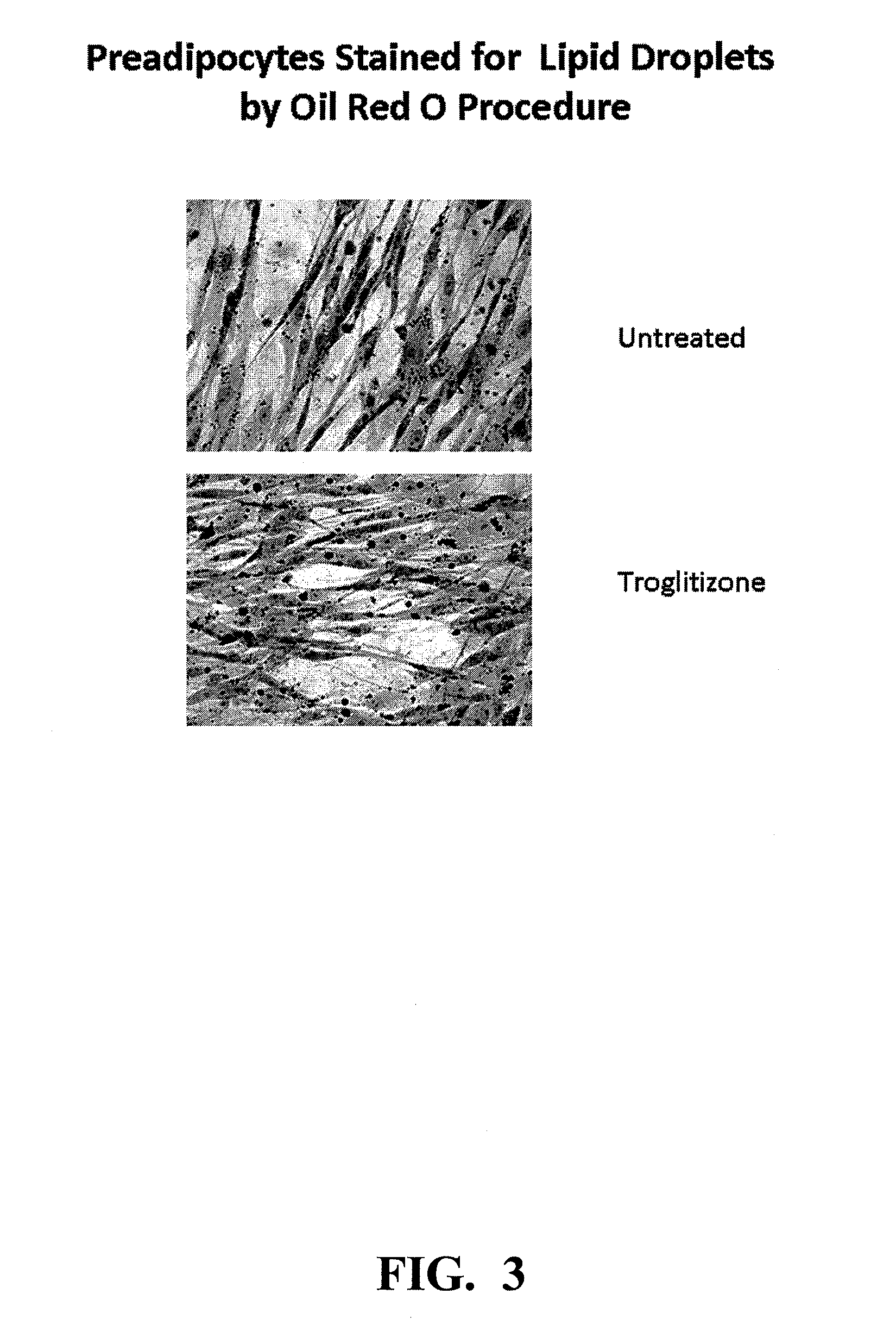
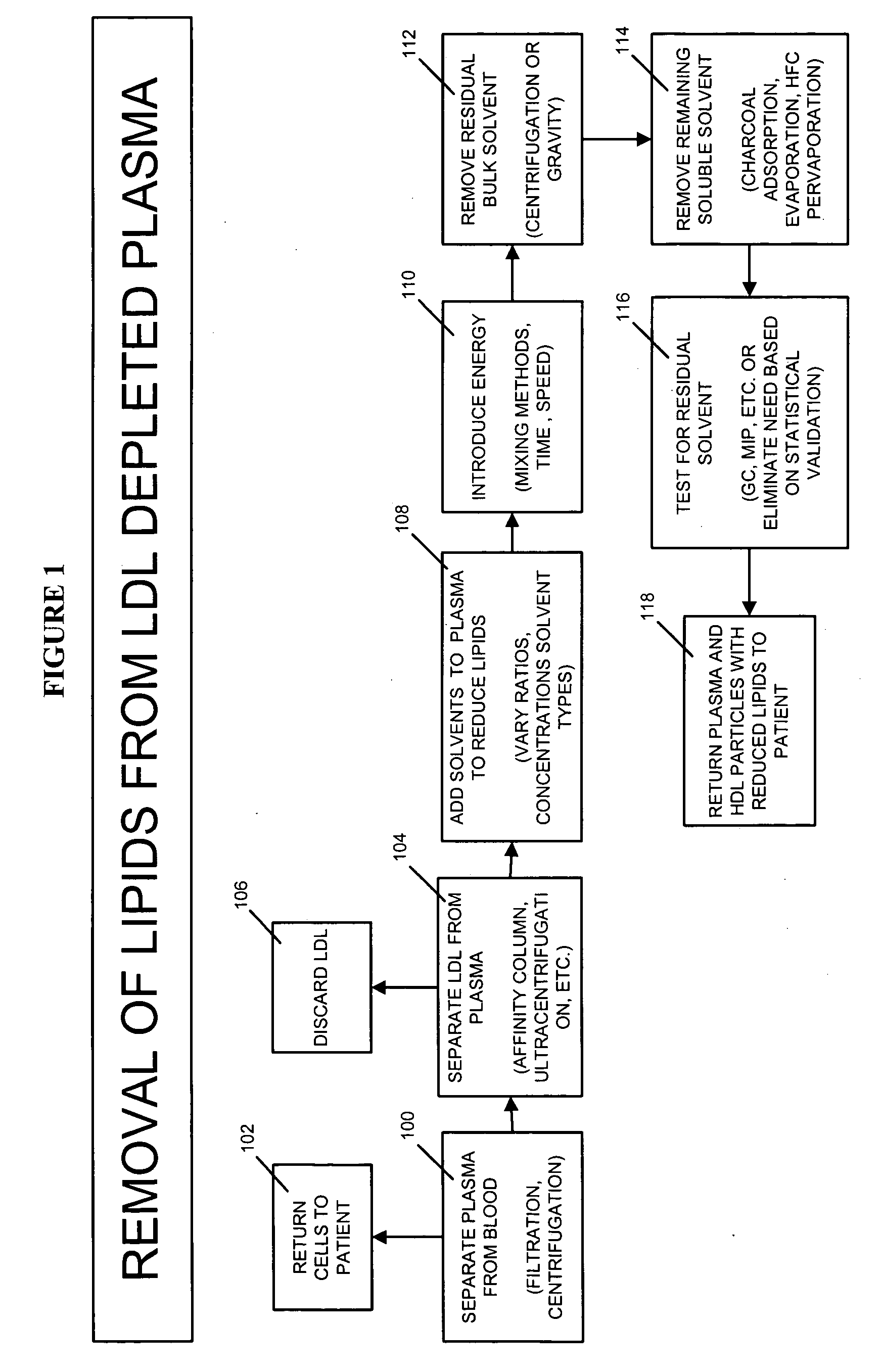
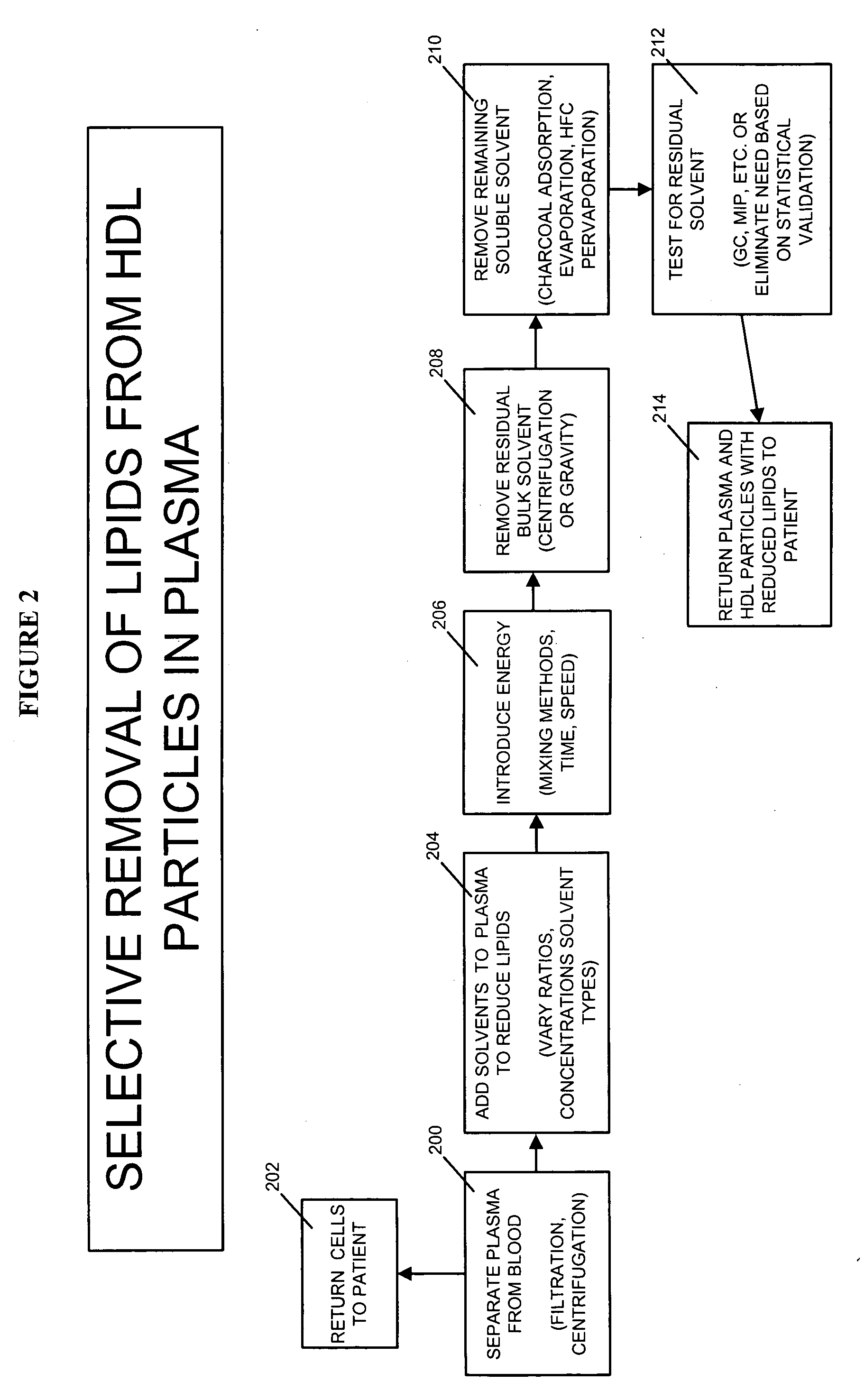
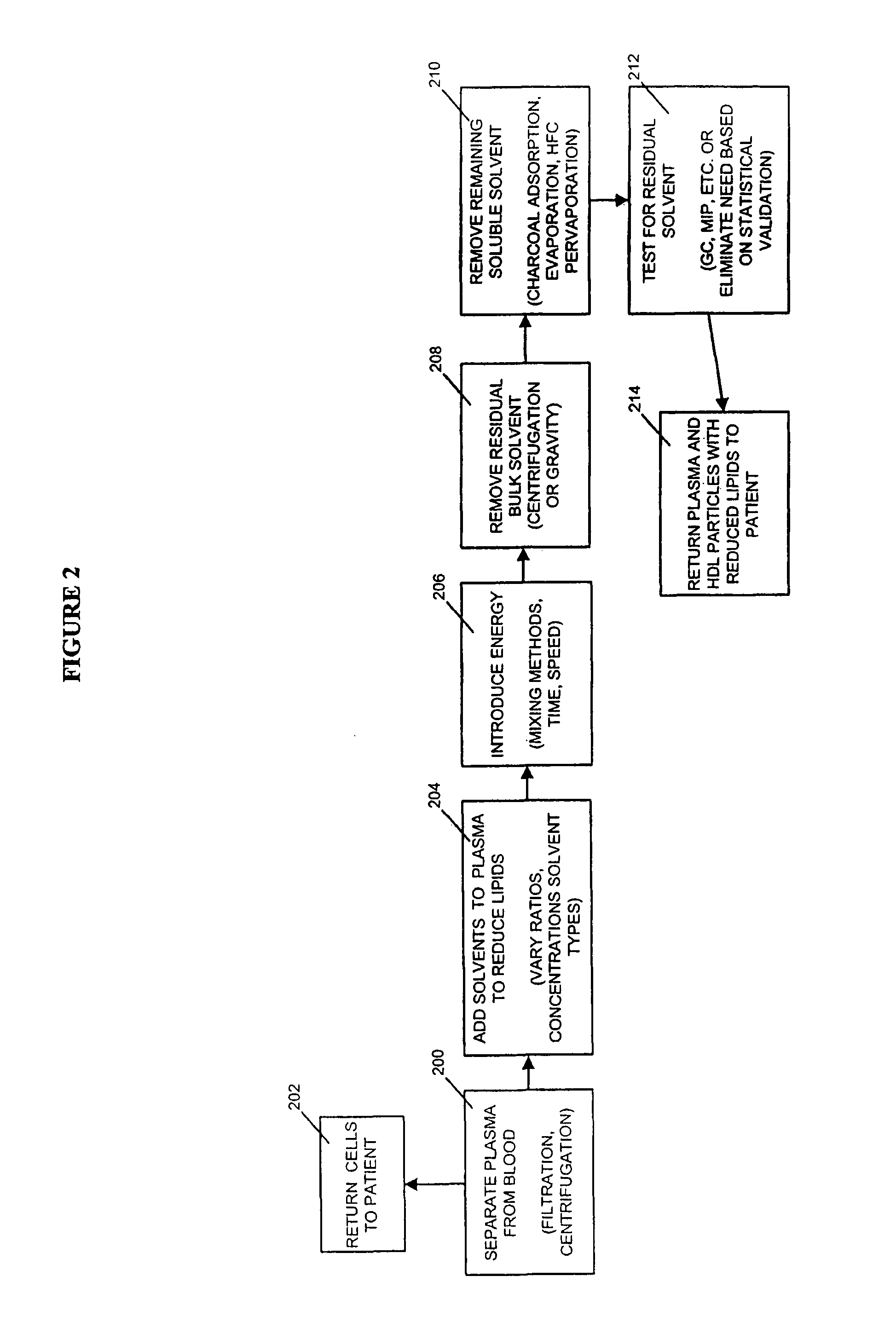
Methods and apparatus for creating particle derivatives of HDL with reduced lipid content
ActiveUS20050004004A1Low in lipidsEnhancing cellular cholesterol effluxNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsPresent methodCellular cholesterol
The present invention is directed to systems, apparatus and methods for creating derivatives of at least one form of HDL without substantially affecting LDL. These derivatives of HDL are particles with reduced lipid content, particularly reduced cholesterol content. These particles have the capacity to bind cholesterol and are administered to a patient to enhance cellular cholesterol efflux and reduce cholesterol levels in cells, tissues, organs, and blood vessels. The present method is useful for treating atherogenic vascular disease and may be combined with other therapies such as statins, inhibitors of cholesterol absorption, niacin, anti-inflammatories, exercise and dietary restriction.
Owner:LIPID SCI +1
Lipid-rich chlorella and culture application thereof
ActiveCN109576158AImprove fixation efficiencyReduce the greenhouse effectGas treatmentUnicellular algaeMicroorganismHigh concentration
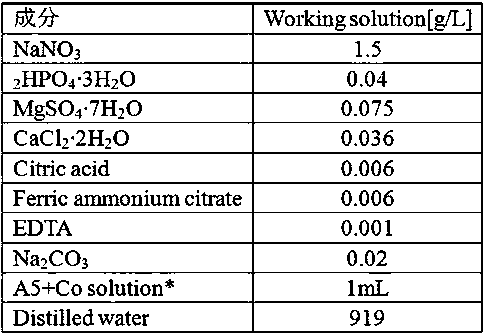
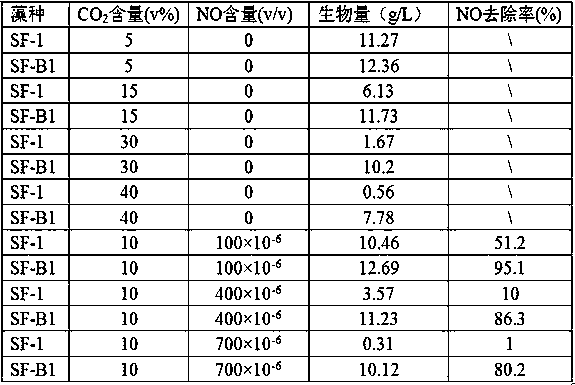
The invention relates to lipid-rich chlorella and culture application thereof. The strain is SF-B1, is classified and named as Chlorella sp., and has been preserved in the General Microbiological Center of the China Microbiological Culture Collection Management Committee on July 6, 2015, and the preservation number is CGMCC No. 11005. The chlorella can tolerate high-concentration CO2 and NOx, thecarbon fixation efficiency is high, and the total lipid content of cells in obtained biomass is 45% or above of the dry weight of the cells.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Cosmetic compositions comprising tobacco seed-derived component
Cosmetic compositions are provided that include an extract from a seed of the Nicotiana species, one or more cosmetically acceptable carriers to act as a diluent, dispersant or carrier for the composition, and optionally one or more cosmetic adjuvants. The tobacco seed extract is typically characterized as having a significant lipid content and, thus, finds use as an oil component in a cosmetic composition.
Owner:R J REYNOLDS TOBACCO COMPANY
Method for improving biomass and oil fat yield of microorganisms
ActiveCN106754383AGood yieldMitigate disadvantagesFungiUnicellular algaeDry weightConcentrations glucose
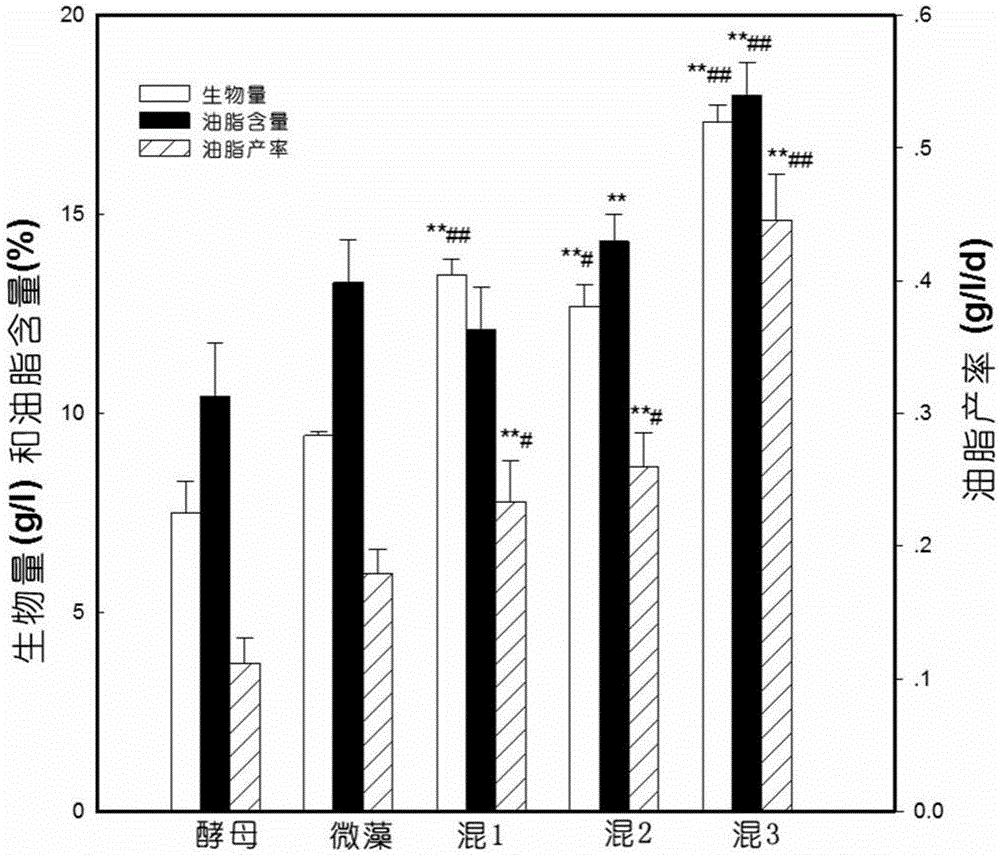
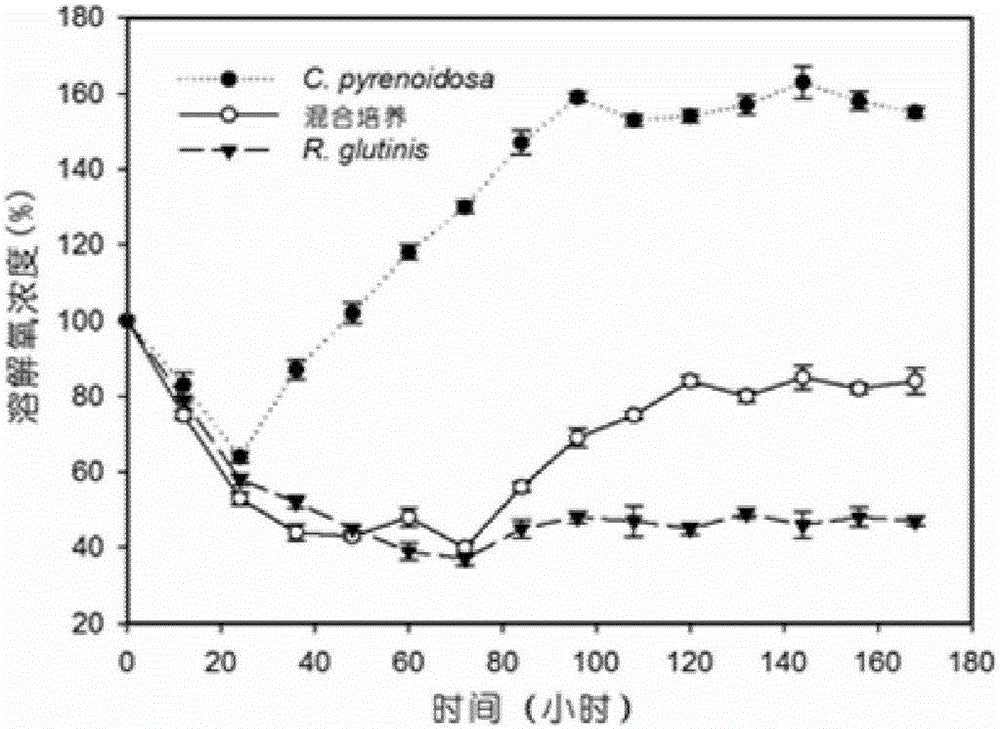
The invention discloses a method for improving the biomass and oil fat yield of microorganisms. The method comprises the following steps: (1) carrying out activated culture: respectively inoculating chlorella pyrenoidosa and rhodotorula glutinis cells into a culture medium, carrying out activated culture to a logarithmic phase, and taking a product as a seed solution; (2) respectively inoculating chlorella pyrenoidosa and rhodotorula glutinis into a shake flask according to different proportions, wherein each shake flask is internally filled with a culture medium, putting the shake flasks into a lighting shaker, and culturing; (3) respectively inoculating chlorella pyrenoidosa and rhodotorula glutinis cells into a BG11 culture medium, wherein the ratio of chlorella pyrenoidosa cell number to the rhodotorula glutinis cell number is equal to 3: 1, and the BG11 culture mediums contain 1.6g / L of yeast extract and have different glucose concentrations; putting the inoculated shake flasks into the lighting shaker, and culturing for 12 days; (4) after the culture is finished, centrifuging microbial cells, washing and carrying out freeze drying to obtain powder; the powder can be used for measuring and evaluating the dry weight concentration, total lipid content, fatty acid content and yield of the biomass. The method has the advantages that the biomass and oil fat yield of the oil-containing microorganisms are remarkably improved by utilizing a mixed culturing mode, and are 3-4 times or more than those of microorganisms cultured under a single culture condition; the method is relatively simple and convenient, and the energy consumption and the production cost are effectively reduced.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
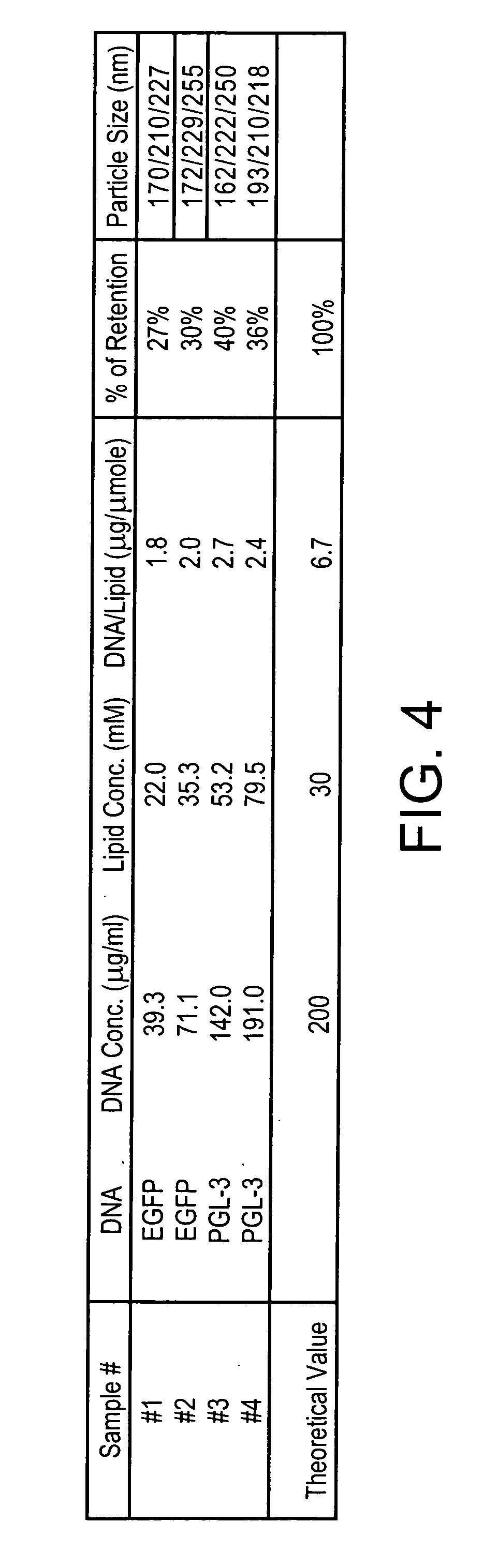
Efficient nucleic acid encapsulation into medium sized liposomes
A method for preparing liposomes containing at least one nucleic acid encapsulated therein comprising the following steps: (A) mixing a gel or a liquid containing gel particles with aqueous medium Z1 to directly form the liposomes containing the at least one nucleic acid encapsulated therein; (B)(i) mixing a gel or a liquid containing gel particles with aqueous medium Z1 to form a curd or curdy substance; and (ii) mixing the curd or curdy substance with aqueous medium Z2 to directly form the liposomes containing the at least one nucleic acid encapsulated therein; or (C)(i) cooling a gel or a liquid containing gel particles to form a waxy substance; and (ii) mixing the waxy substance with aqueous medium Z1 to directly form the liposomes containing the at least one nucleic acid encapsulated therein; wherein said gel or liquid containing gel particles comprises at least one liposome-forming lipid, at least one fusogenic lipid, a water-miscible organic solvent and the at least one nucleic acid; wherein an amount of the at least one fusogenic lipid is at least 20% by weight of a lipid content of the gel or the liquid containing gel particles; and wherein the aqueous media Z1 and Z2 are the same or different.
Owner:TRANSAVE
Rhodotorula glutinis oil genetic engineering strain and construction method and application thereof
ActiveCN102796675AImprove the lubrication effectImprove securityFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyLipid formation
The invention relates to a rhodotorula glutinis oil genetic engineering strain and a construction method and an application thereof. The construction method of the genetic engineering strain is mainly as follows: utilizing rDNA (recombinant deoxyribonucleic acid) of rhodotorula glutinis as a target sequence for homologous integration, using strong promoter genes PGK1 of saccharomyces cerevisiae and malate dehydrogenase genes ME of chaetomium cochloides to construct an expression vector to be introduced into rhodotorula glutinis, and enabling ME genes to obtain high-efficient expression in a rhodotorula glutinis body, wherein the content of lipid in a transformant is improved by 2.5 times in comparison with a wild strain. According to the construction method disclosed by the invention, key enzyme genes and a strong promoter for anabolism of the lipid are introduced on the basis that the anabolism of microbial oil is known, so that the lipid metabolism is regulated and controlled, and the yield of oil is improved. The genetic engineering strain can be applied to production of the microbial oil and development of functional oil related products, such as medicaments, health care products and the like.
Owner:广州溯原生物科技股份有限公司
Treatment for dark adaptation
InactiveUS7470660B2Increasing reverse cholesterol transportReduce accumulationBiocideSenses disorderReverse cholesterol transportCholesterol
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Methods and apparatus for creating particle derivatives of HDL with reduced lipid content
ActiveUS7393826B2Low in lipidsLower blood lipid levelsBiocideOrganic active ingredientsPresent methodCellular cholesterol
The present invention is directed to systems, apparatus and methods for creating derivatives of at least one form of HDL without substantially affecting LDL. These derivatives of HDL are particles with reduced lipid content, particularly reduced cholesterol content. These particles have the capacity to bind cholesterol and are administered to a patient to enhance cellular cholesterol efflux and reduce cholesterol levels in cells, tissues, organs, and blood vessels. The present method is useful for treating atherogenic vascular disease and may be combined with other therapies such as statins, inhibitors of cholesterol absorption, niacin, anti-inflammatories, exercise and dietary restriction.
Owner:HDL THERAPEUTICS +1
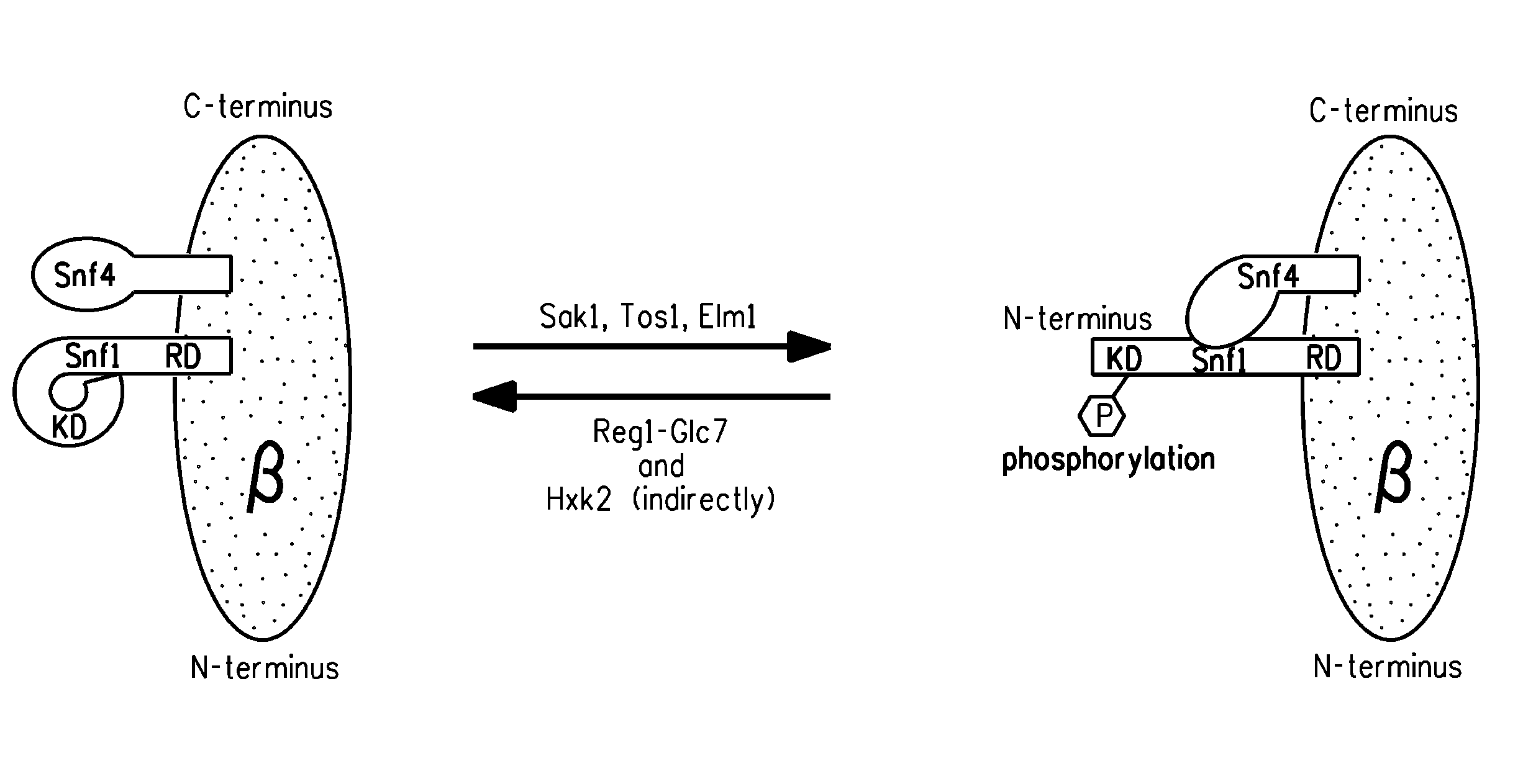
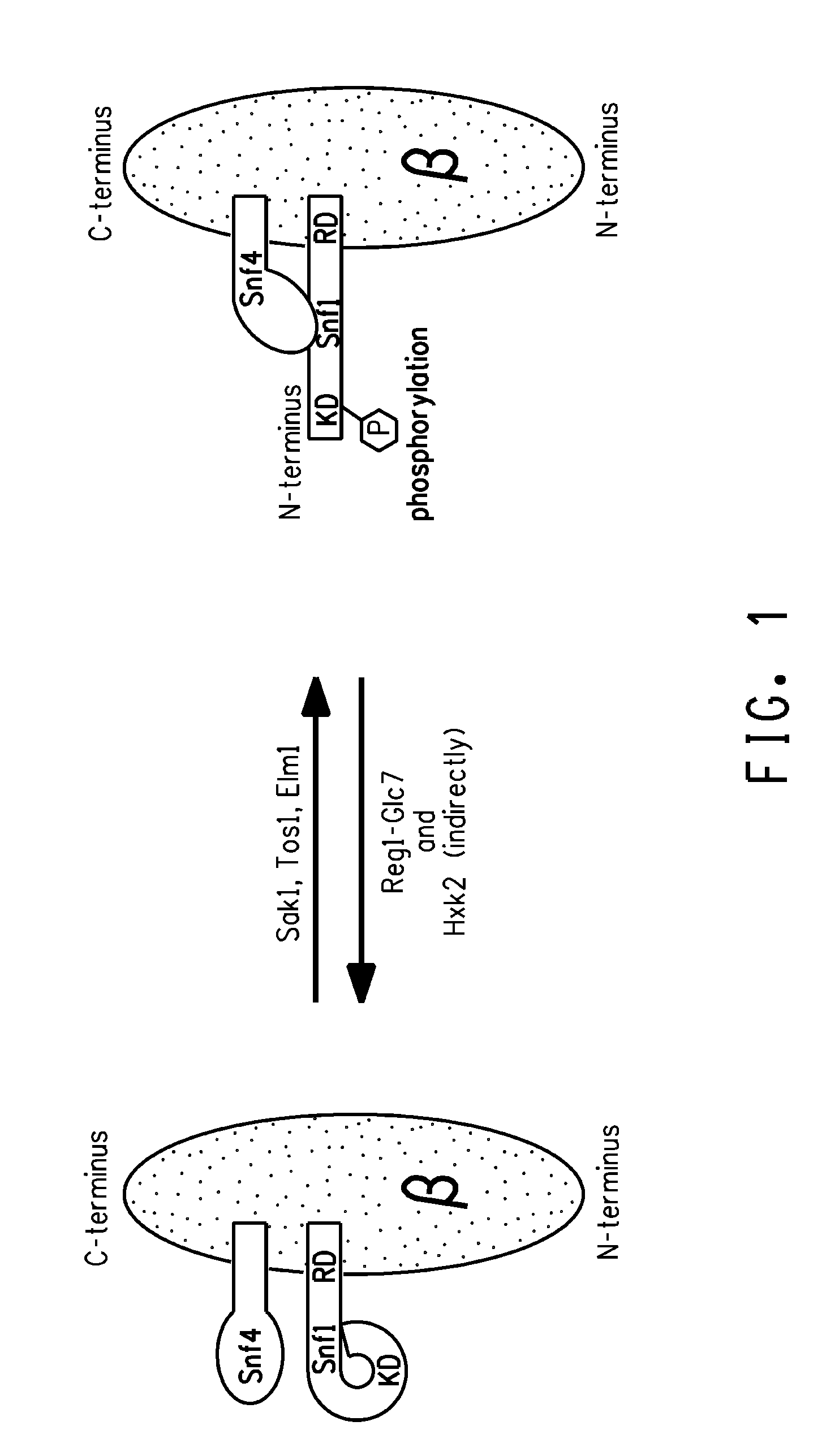
Manipulation of snf1 kinase for altered oil content in oleaginous organisms
ActiveUS20100062502A1Lipid content can be increasedFungiOrganic chemistryHeterologousSaturated fatty acid
Methods of increasing the total lipid content in a eukaryotic cell, the total content of polyunsaturated fatty acids [“PUFAs”], and / or the ratio of desaturated fatty acids to saturated fatty acids by reducing the activity of the heterotrimeric SNF1 protein kinase are disclosed. Preferably, the chromosomal genes encoding the Snf1 α-subunit, Gal83 β-subunit or Snf4 γ-subunit of the SNF1 protein kinase, the upstream regulatory genes encoding Sak1, Hxk2, Glk1 or Reg1, or the downstream genes encoding Rme1, Cbr1 or Snf3 are manipulated in a PUFA-producing strain of the oleaginous yeast Yarrowia lipolytica, resulting in increased total lipid content, as compared to the parent strain comprising the heterotrimeric SNF1 protein kinase not having reduced activity.
Owner:DUPONT US HLDG LLC
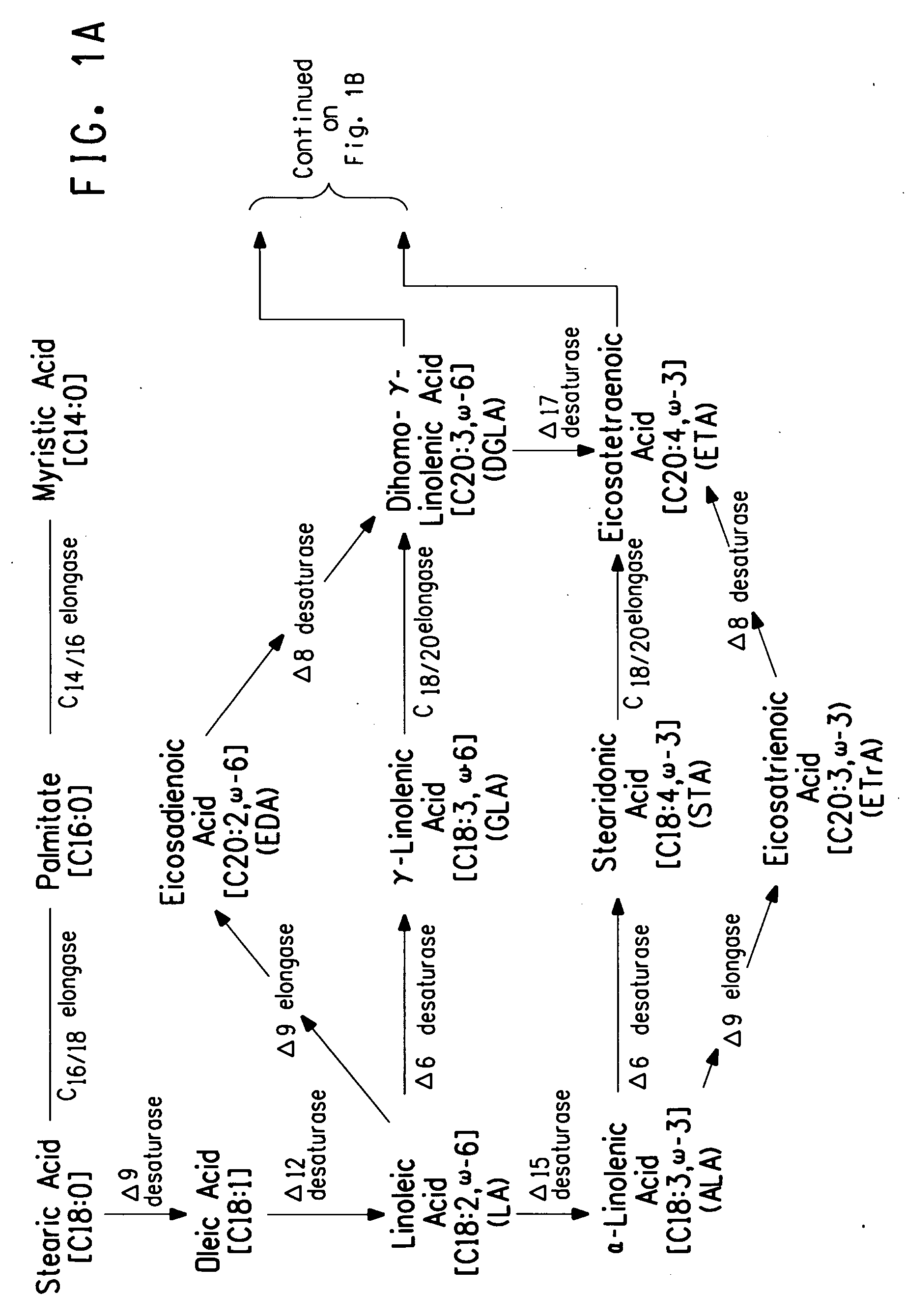
Delta6-desaturases from Primulaceae, expressing plants and PUFA-containing oils
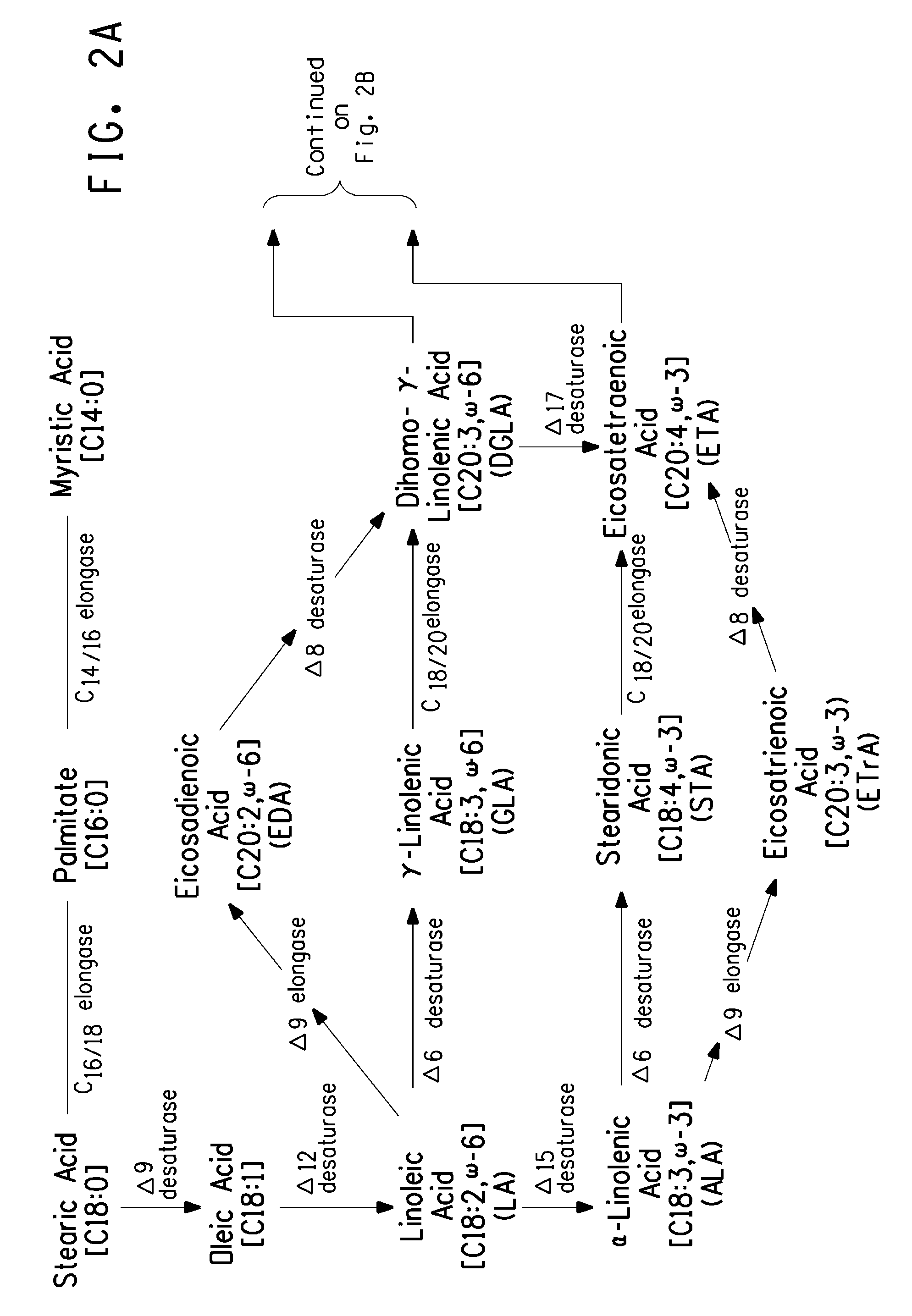
The present invention relates to an improved method for the specific production of unsaturated ω-3 fatty acids and a method for the production of triglycerides having an increased content of unsaturated fatty acids, in particular ω-3 fatty acids having more than three double bonds. The invention relates to the production of a transgenic organism, preferably a transgenic plant or a transgenic microorganism, having an increased content of fatty acids, oils or lipids having Δ6 double bonds due to the expression of a Δ6-desaturase from Primulaceae. The invention additionally relates to expression cassettes containing a nucleic acid sequence, a vector and organisms containing at least one nucleic acid sequence or an expression cassette. The invention further relates to unsaturated fatty acids and triglycerides having an increased content of unsaturated fatty acids and use thereof.
Owner:IACR ROTHAMSTED
Multidimensional mass spectrometry of serum and cellular lipids directly from biologic extracts
InactiveUS20090134323A1Enhanced interactionRespond effectivelyParticle separator tubesIsotope separationLipid formationOrganism
A method for determination of at least one of the lipid species in a biological sample comprising subjecting the sample to lipid extraction to obtain a lipid extract and subjecting the resulting lipid extract to multidimensional electrospray ionization mass spectrometry using either precursor ion or neutral loss scanning (or both) of all naturally occurring aliphatic chains, lipid fragments and precursor ions leading to observed fragments to generate a multidimensional matrix whose contour densities provides structural and quantitative information directly without chromatography. A method for determination of lipid content and / or lipid molecular species composition and quantity directly from lipid extracts of a biological sample comprising subjecting said lipid extract to electrospray ionization multidimensional mass spectrometry by comparisons to standards and algorithms described herein.
Owner:GROSS RICHARD W +1
Oil-producing monoraphidium sp. as well as culture and application thereof
ActiveCN106635807AEfficient growth processStrong low temperature resistanceUnicellular algaeBiofuelsMicroorganismBiodiesel
The invention relates to monoraphidium sp. SHJ-02, with the classification name of Monoraphidium sp. preserved in CGMCC (China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center) of CCCCM (China Committee for Culture Collection of Microorganisms) on April 24, 2015, with the preservation number being CGMCC N0.10763. The strain can grow efficiently under the autotrophy condition to obtain oil-rich biomass; besides, the strain has high environment adaptability, can still grow more quickly at the low temperature, has high oil content, has the cell total lipid content being 40% of the dry cell weight of cells or above and can be applied to production of biodiesel.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com