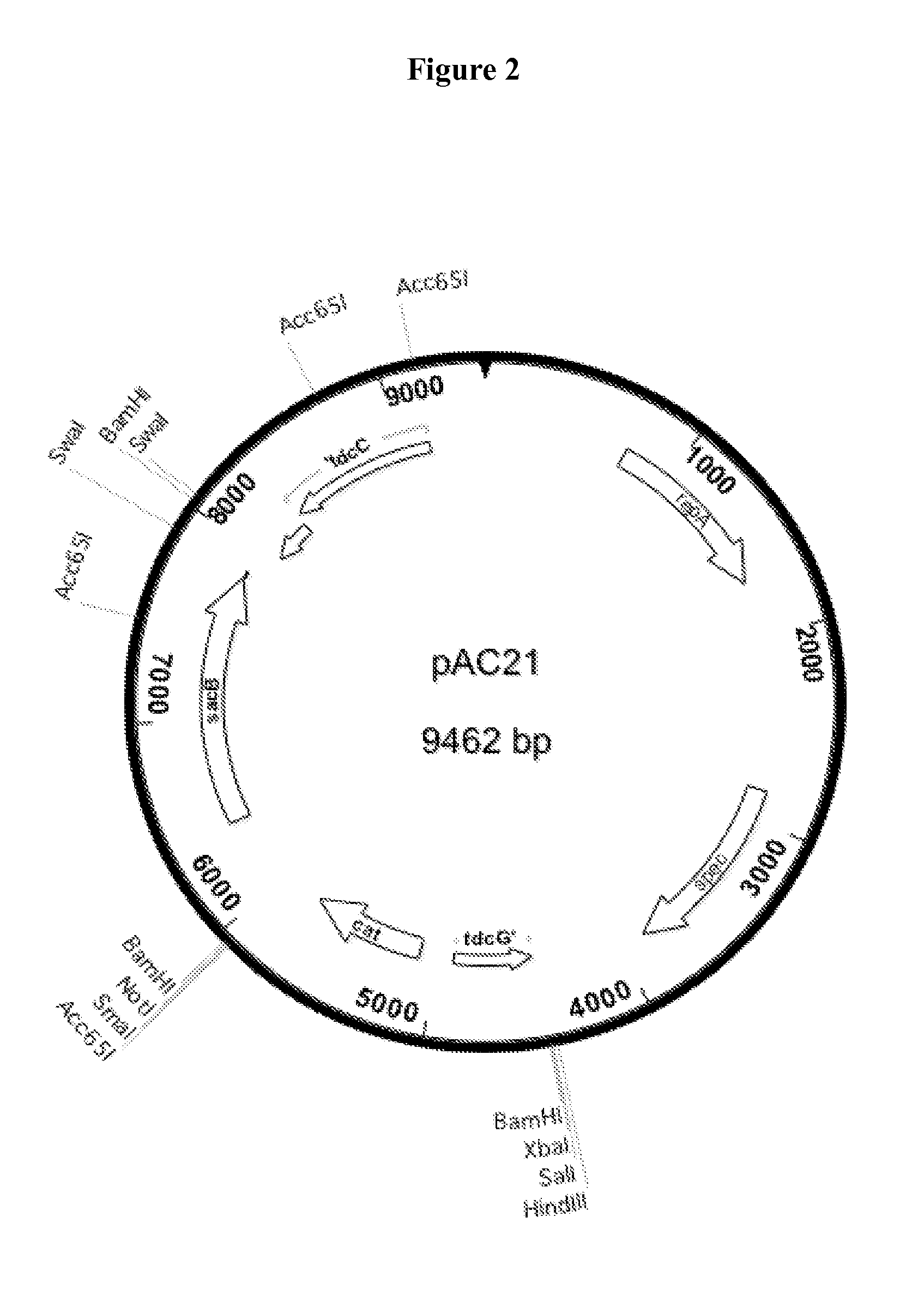
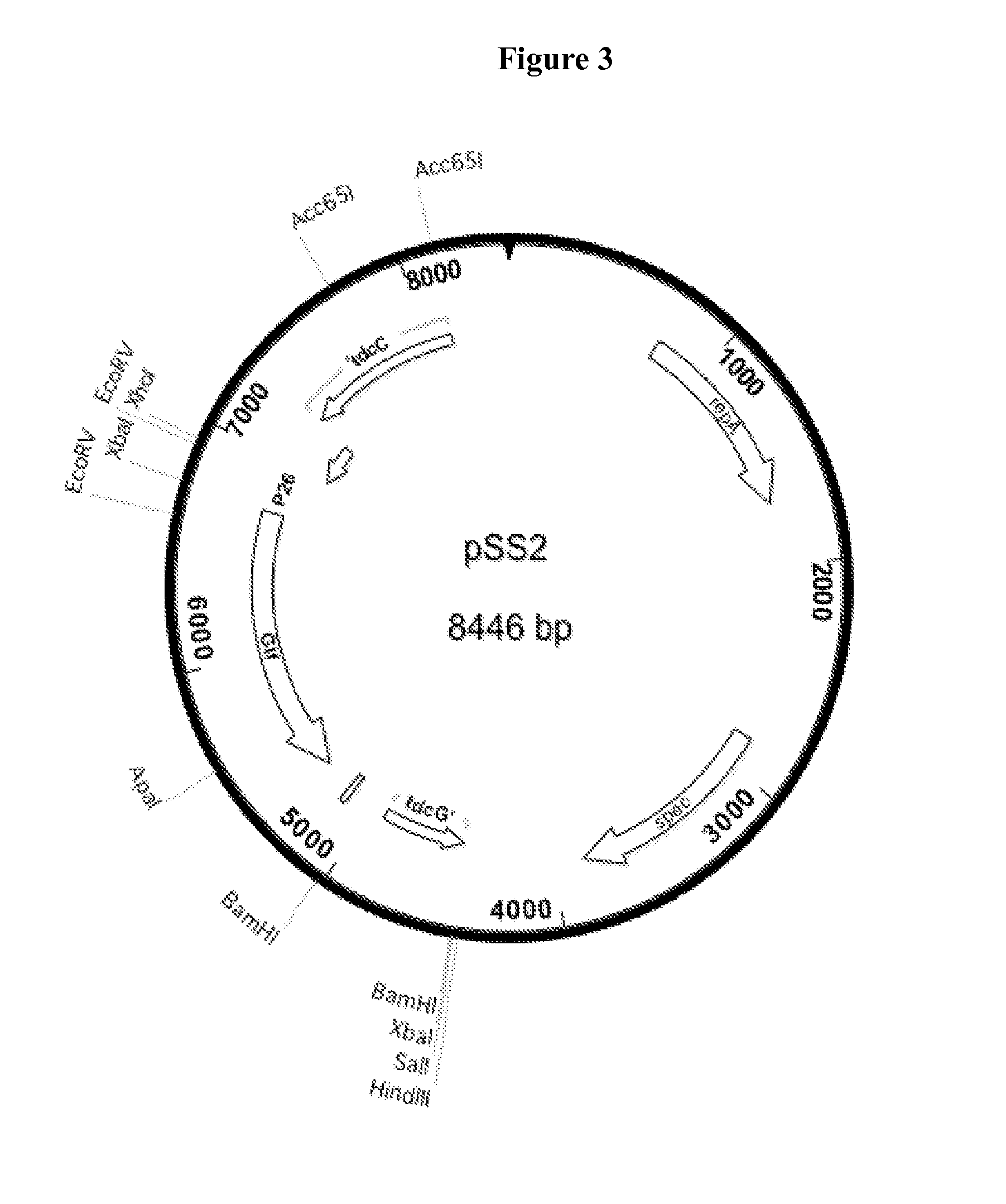
Patents
Literature
45 results about "Parental strain" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
These results suggest that parental strain can compromise a caregiver’s ability to parent effectively by impacting their mental health. Opportunities for intervention include helping caregivers process trauma and mental health problems associated with parental strain.
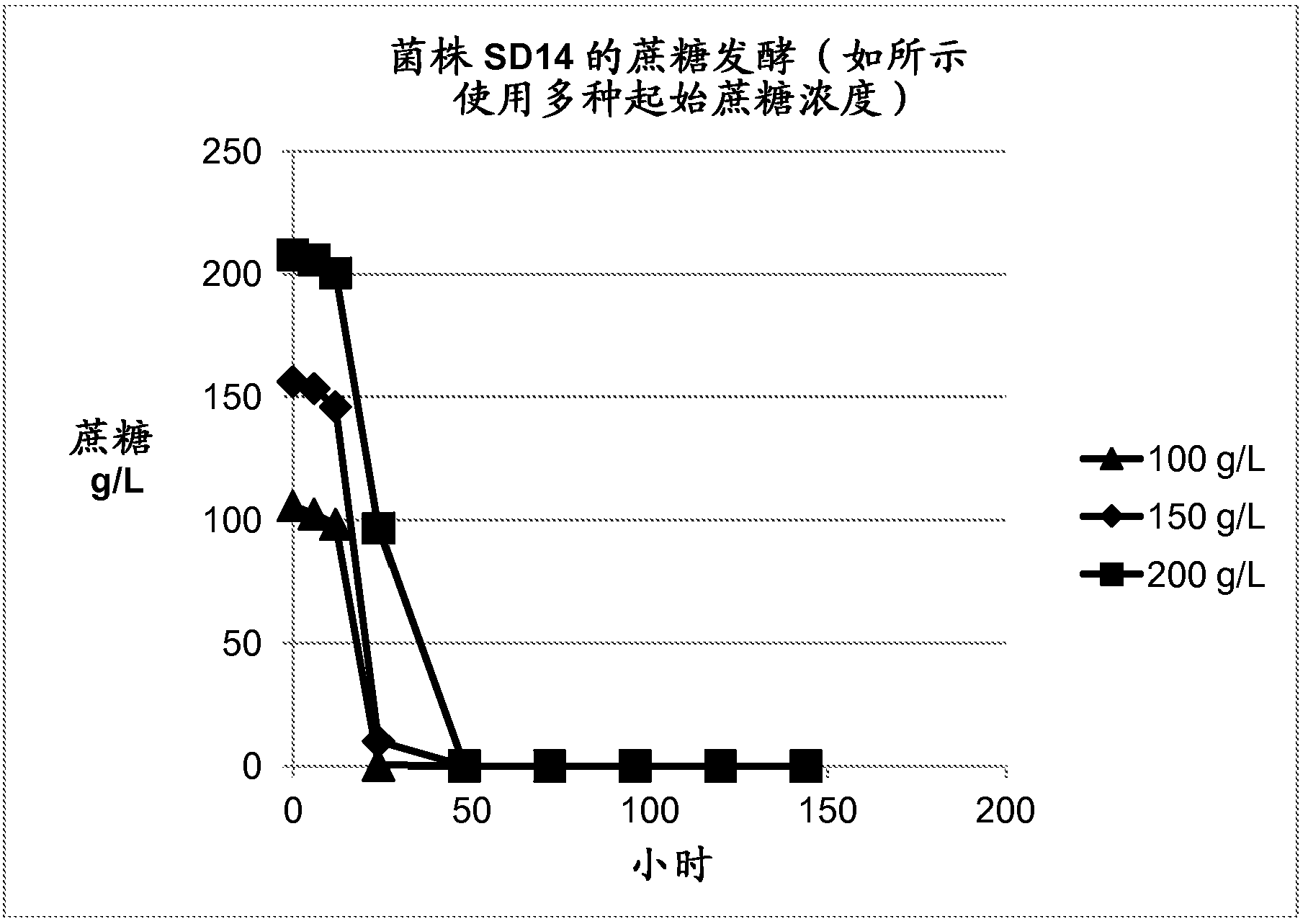
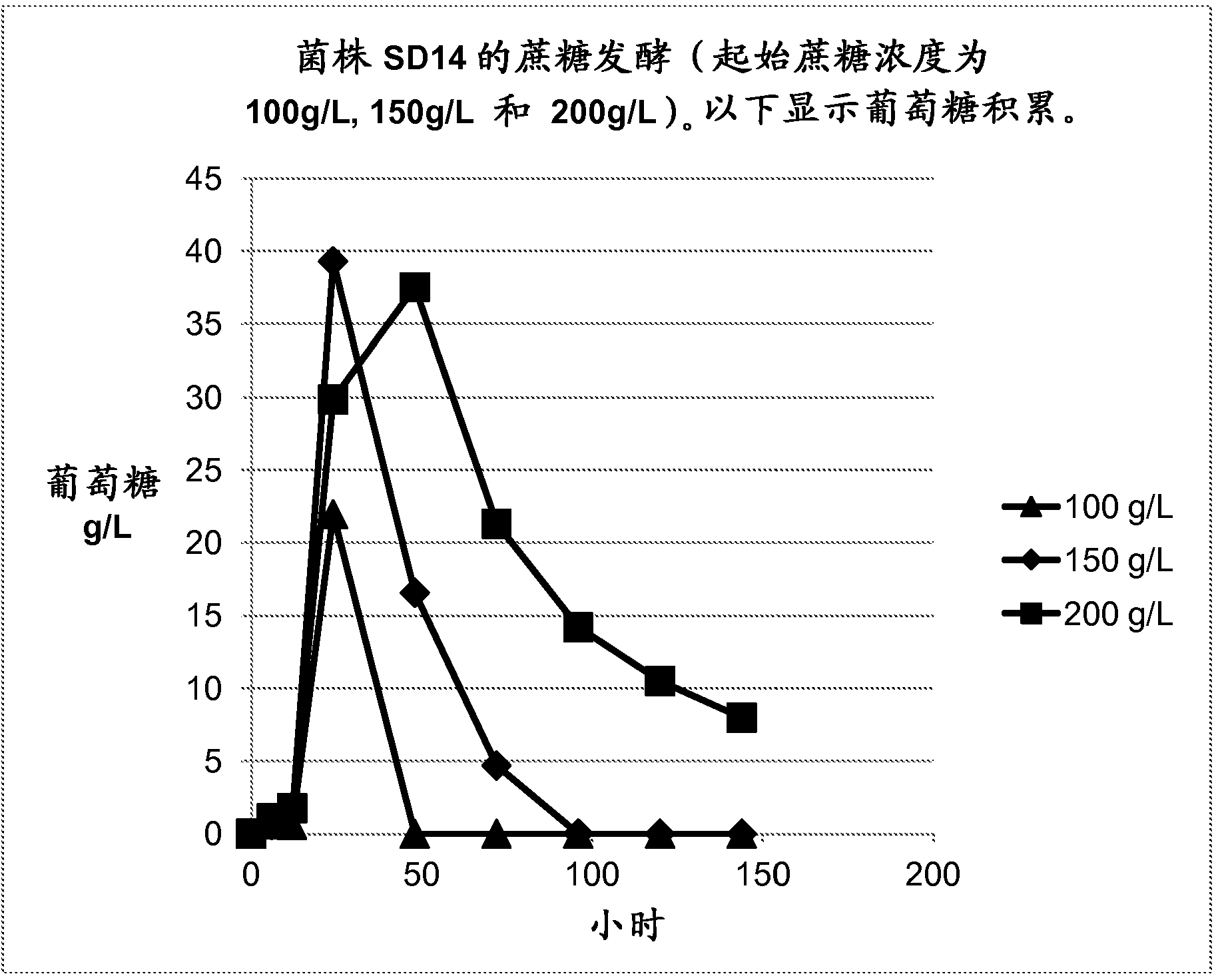
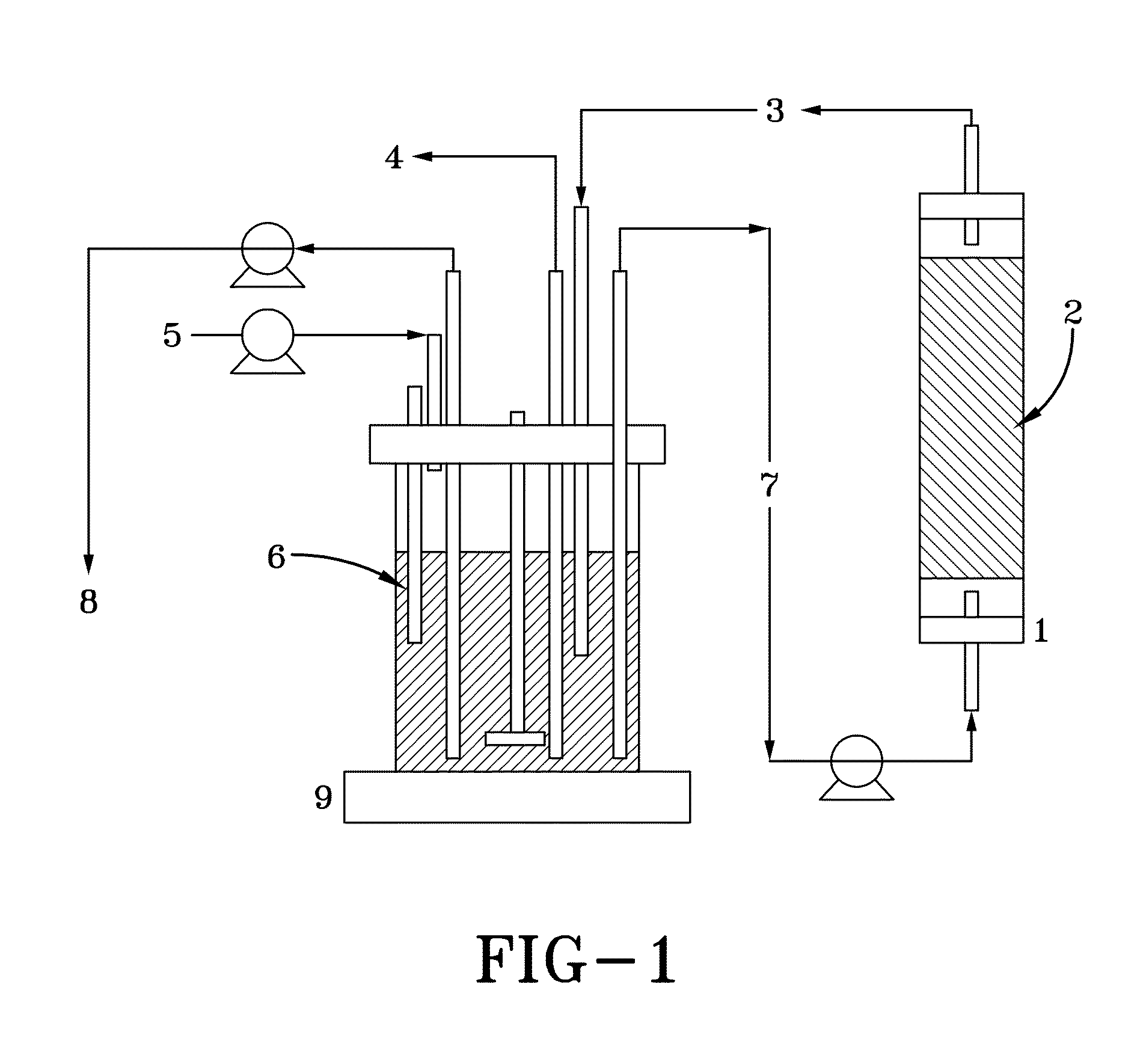
Zymomonas with improved ethanol production in medium containing concentrated sugars and acetate
InactiveUS20090203099A1Improve performanceIncreased acetate toleranceBacteriaBiofuelsAcetic acidSugar
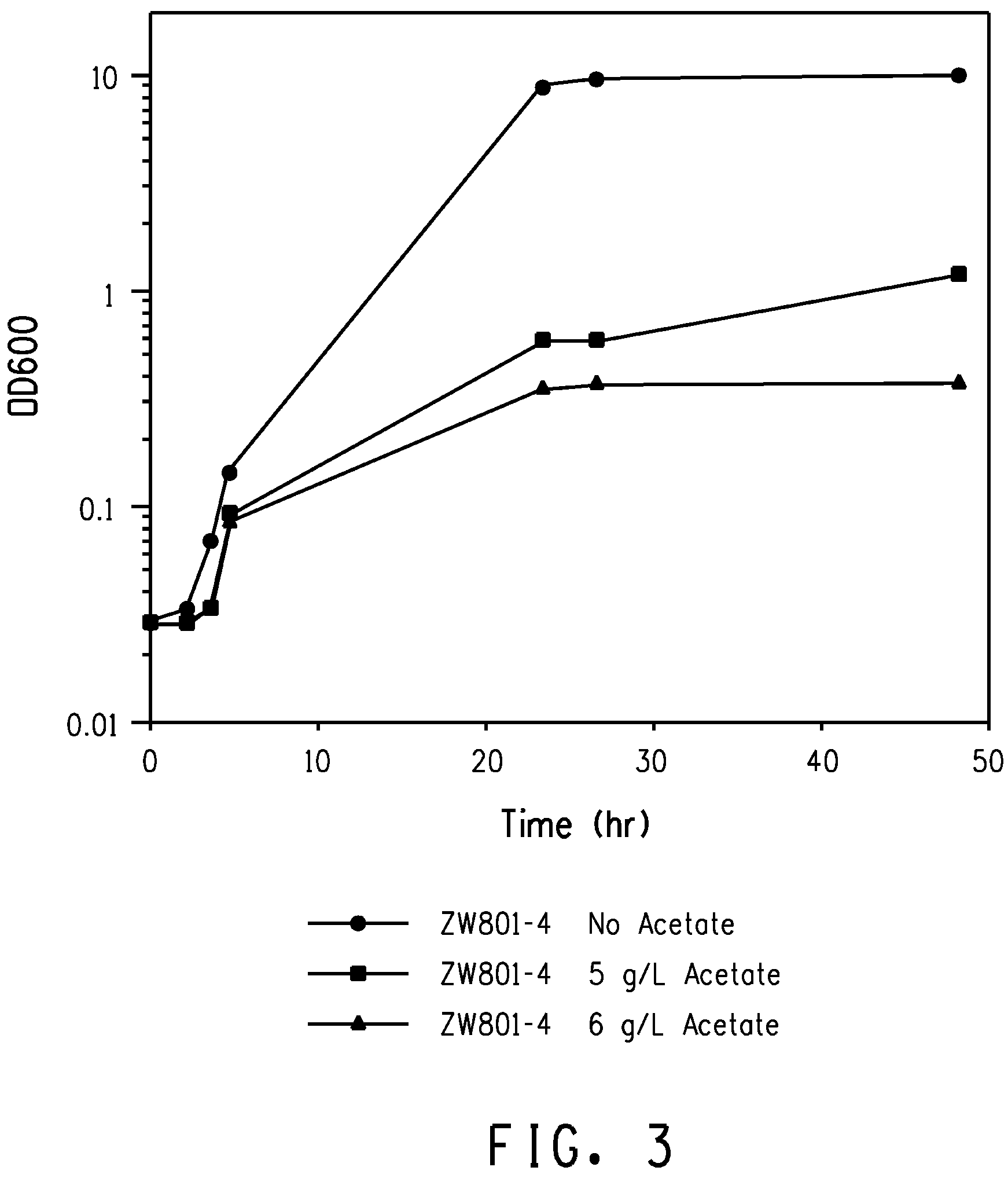
Through screening of a Zymomonas mutant library the himA gene was found to be involved in the inhibitory effect of acetate on Zymomonas performance. Xylose-utilizing Zymomonas strains further engineered to reduce activity of the himA gene were found to have increased ethanol production in comparison to a parental strain, when cultured in mixed-sugars medium comprising xylose, and, in particular, in the presence of acetate.
Owner:ALLIANCE FOR SUSTAINABLE ENERGY +1
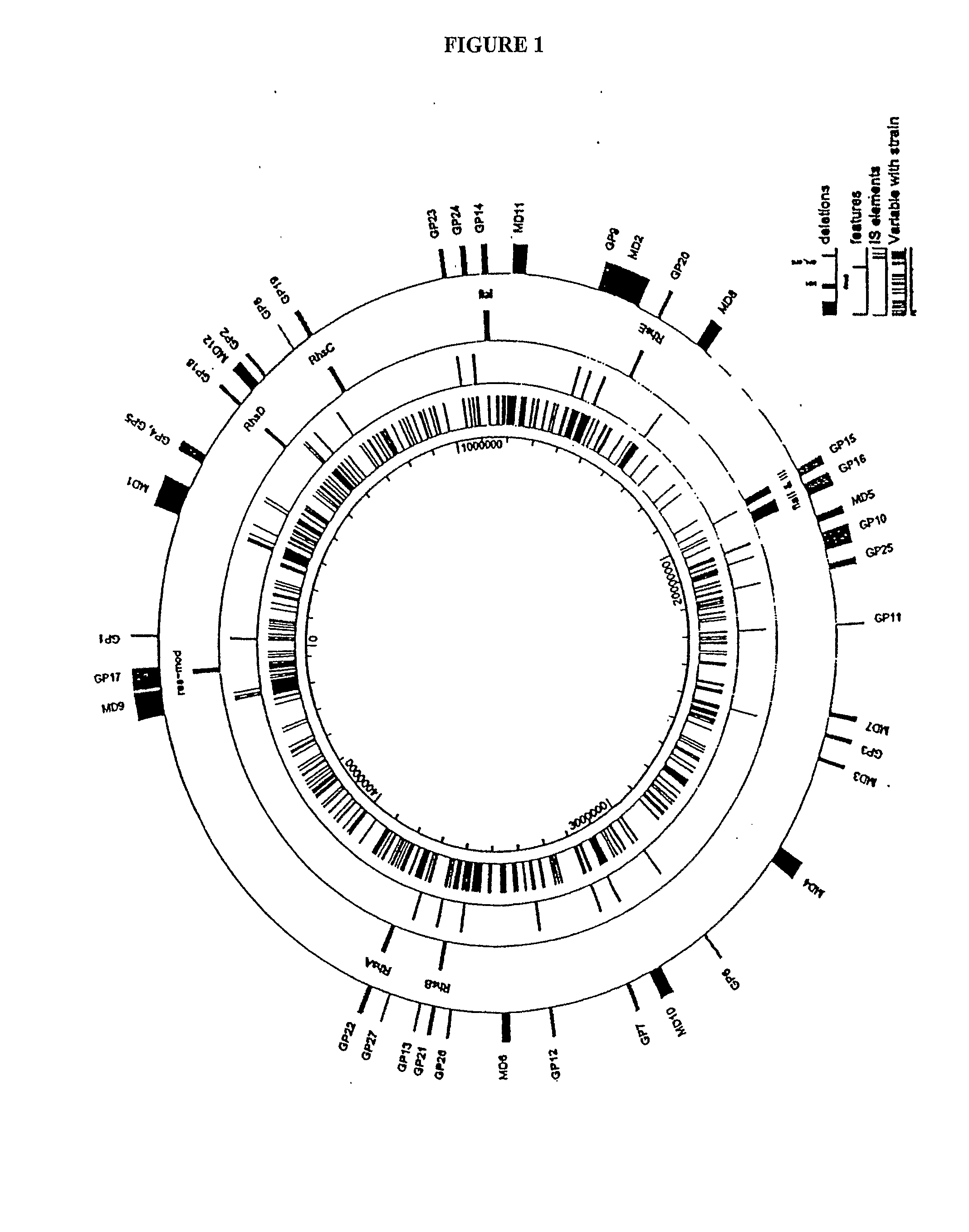
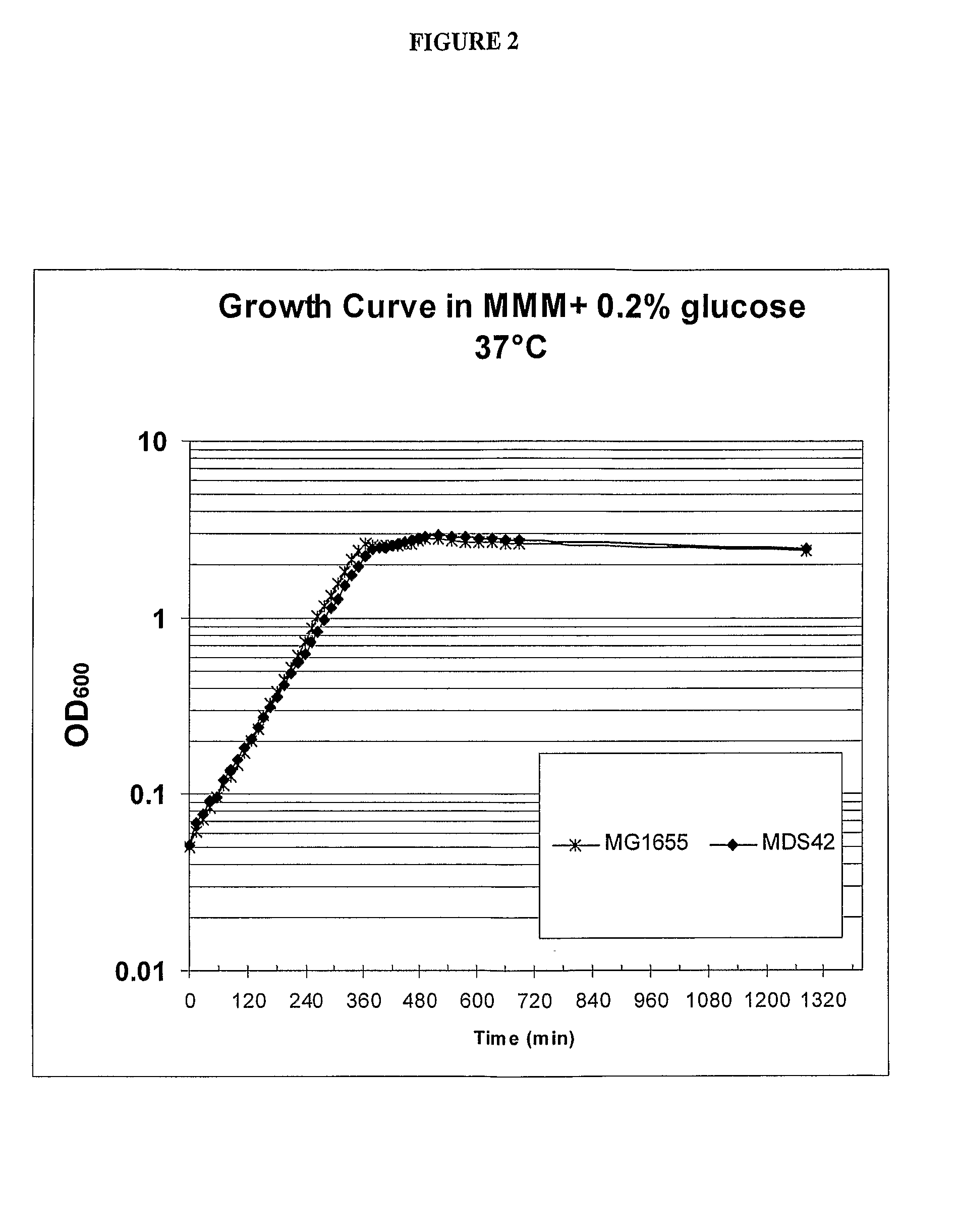
Reduced Genome E. Coli
Reduced genome strains of E. coli MGl 655 are described. In various embodiments, the strains have one or more of equal or improved growth rate, transformation efficiency, protein expression, DNA production, DNA yield and / or DNA quality compared to the parental strain and commercially available strains.
Owner:SCARAB GENOMICS LLC
Reducing byproduction of malonates in a fermentation process
Described are methods of reducing the amount of byproduct organic acids during fermentation of an organism, based on expression of a heterologous malonyl-CoA synthetase. A polyunsaturated fatty acid [“PUFA”]-producing strain of the oleaginous yeast Yarrowia lipolytica was engineered to express a heterologous malonyl-CoA synthetase gene. The expression did not effect the production of PUFAs, but did result in a reduced amount of malonates when compared to the amount of malonates produced in the parental strain not expressing malonyl-CoA synthetase.
Owner:DUPONT US HLDG LLC
Zymomonas with improved ethanol production in medium containing concentrated sugars and acetate
Owner:ALLIANCE FOR SUSTAINABLE ENERGY +1
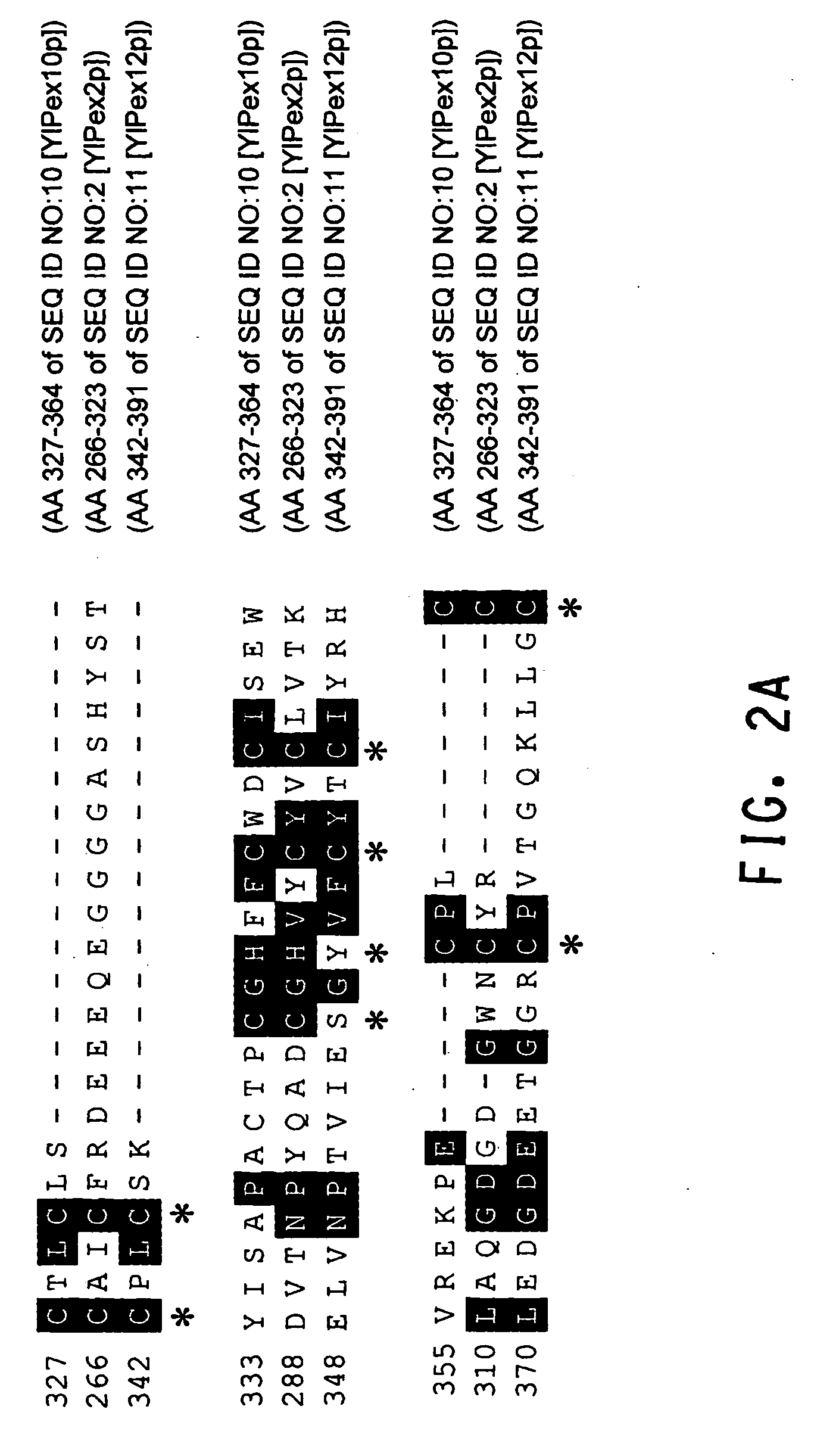
Peroxisome biogenesis factor protein (PEX) disruptions for altering polyunsaturated fatty acids and total lipid content in oleaginous eukaryotic organisms
InactiveUS20090117253A1Lipid content in PEX-disrupted can be increased and decreasedFungiNervous disorderBiotechnologyOrganism
Methods of increasing the amount of polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) in the total lipid fraction and in the oil fraction of PUFA-producing, oleaginous eukaryotes, accomplished by modifying the activity of peroxisome biogenesis factor (Pex) proteins. Disruptions of a chromosomal Pex3 gene, Pex10p gene or Pex16p gene in a PUFA-producing, oleaginous eukaryotic strain resulted in an increased amount of PUFAs, as a percent of total fatty acids and as a percent of dry cell weight, in the total lipid fraction and in the oil fraction of the strain, as compared to the parental strain whose native Pex protein was not disrupted.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
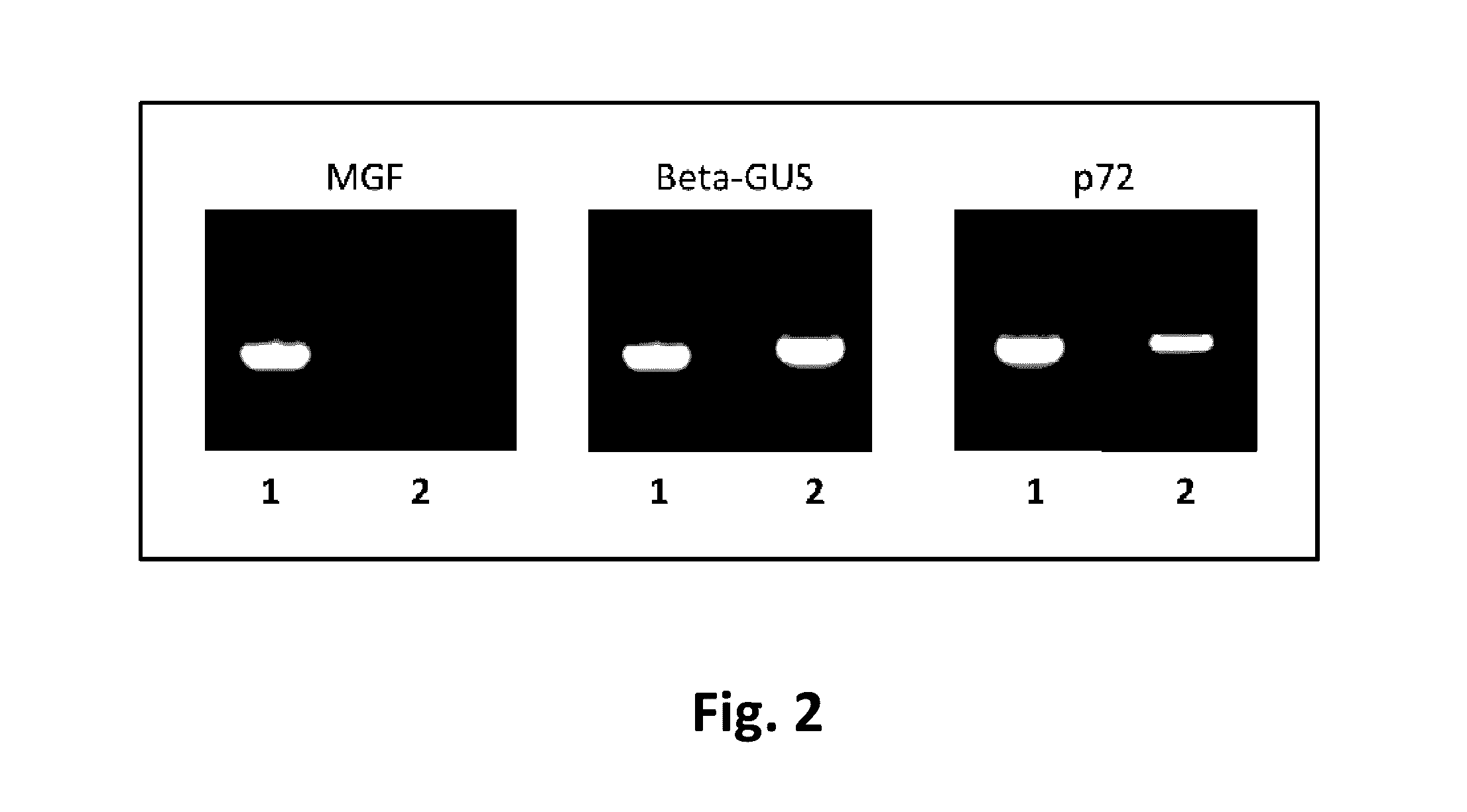
Attenuated African Swine Fever Virus Vaccine Based in the Deletion of MGF Genes
ActiveUS20160130562A1Viral antigen ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementVirulent characteristicsDomestic pig
African swine fever virus (ASFV) is the etiological agent of a contagious and often lethal viral disease of domestic pigs. Control of ASF has been hampered by the unavailability of vaccines. Experimental vaccines have been derived from naturally occurring, cell culture-adapted, or genetically modified live attenuated ASFVs; however, these vaccines are only successful when protecting against homologous viruses. Among viral genes reported to be involved in virulence are components of the multi gene family (MGF). Here we report the construction of a recombinant ΔMGF virus derived from the highly virulent ASFV Georgia 2007 (ASFV-G) isolate. In vivo, ASFV-G ΔMGF administered intramuscularly (IM) to swine at either 102 or 104 HAD50 are completely attenuated; the inoculated animals are completely asymptomatic. Animals infected with 102 or 104 HAD50 of ASFV-G ΔMGF are protected against the presentation of clinical disease when challenged at 28 days post infection with the virulent parental strain Georgia 2007.
Owner:US SEC AGRI +1
Molecular marker method for avirulence gene of rice blast
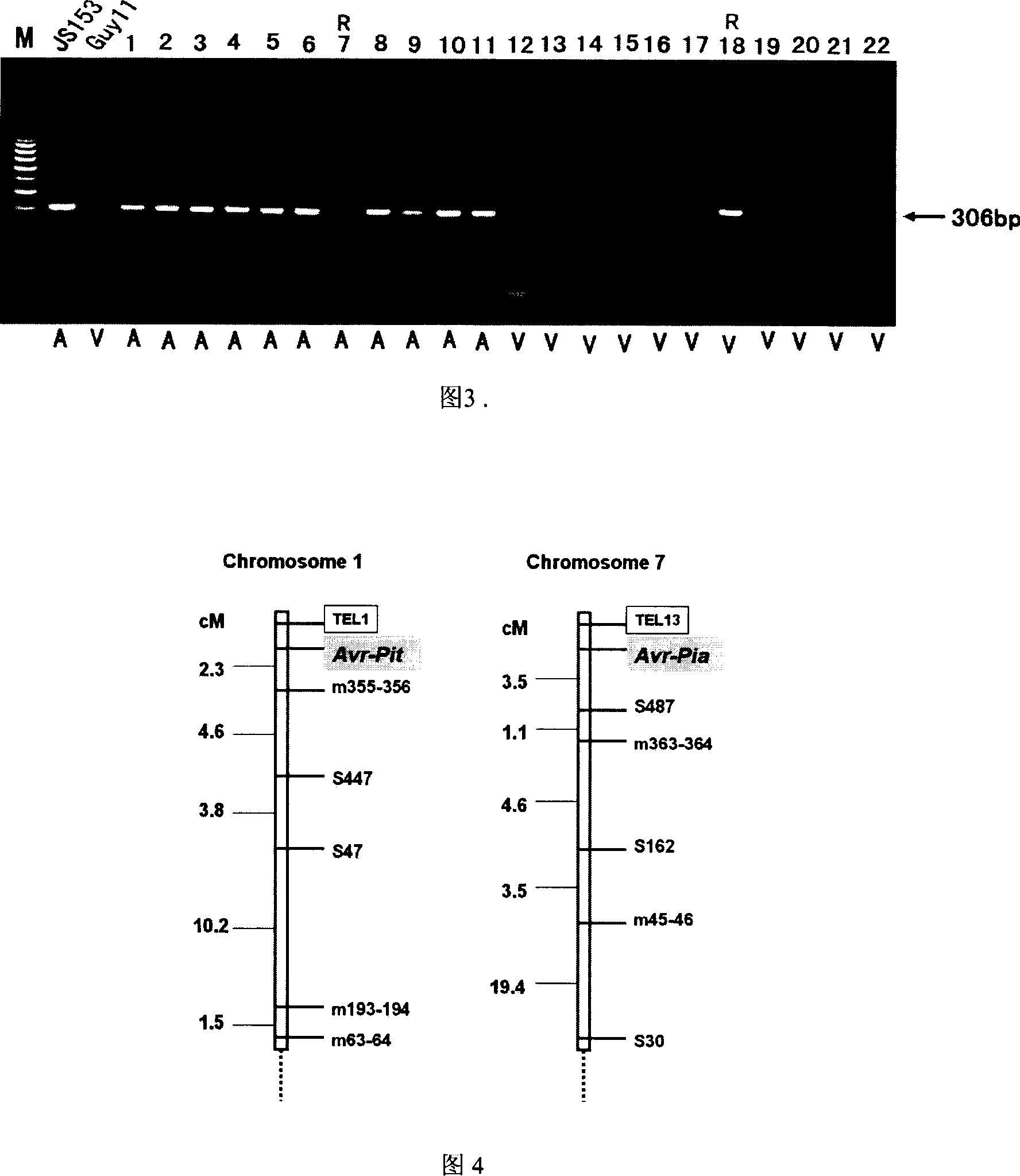
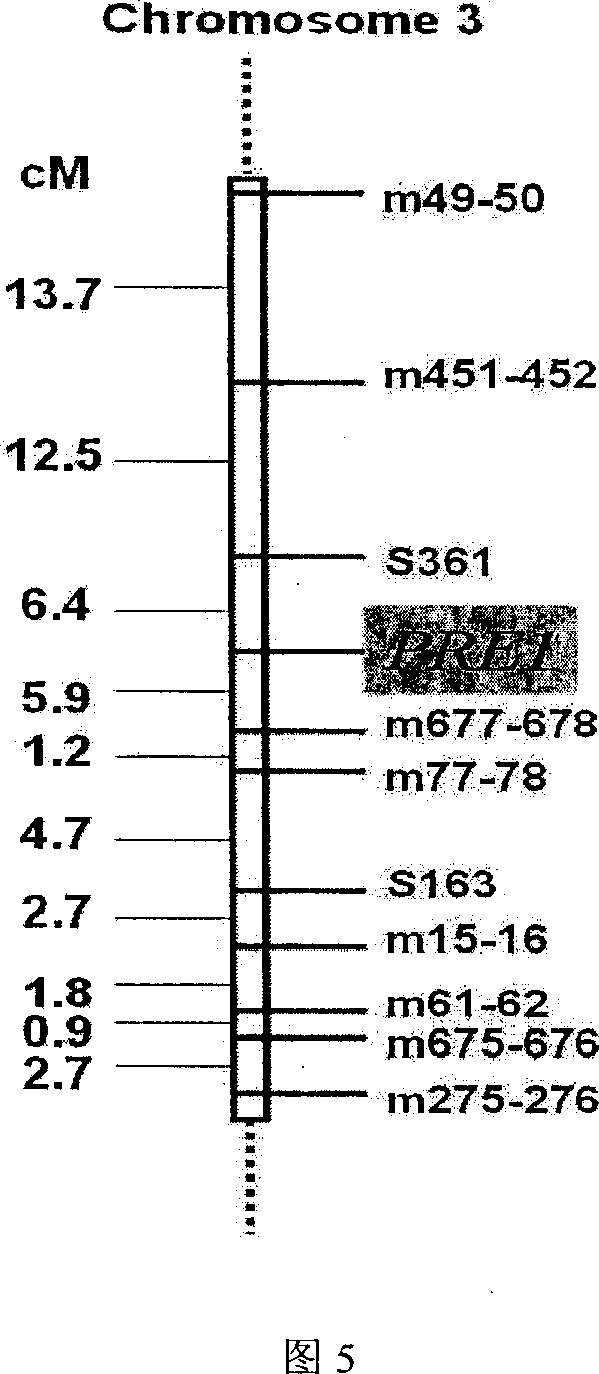
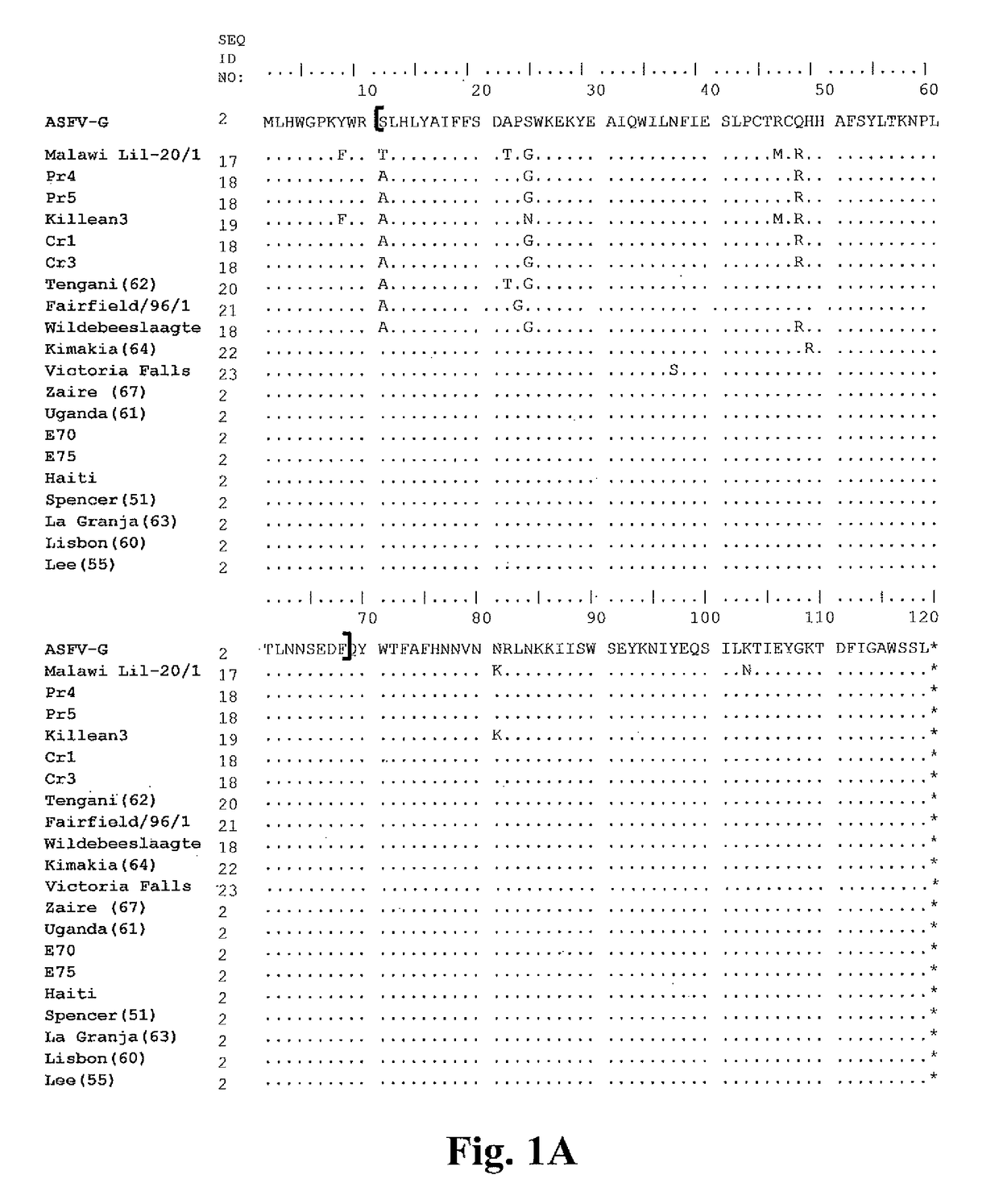
InactiveCN1952177AReveal Toxic ComponentsReveal featuresMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationPyricularia griseaParental strain
The invention of molecular labeling method of Pyricularia grisea avirulent gene belongs to the field of agricultural biotechnology. The molecular labeling technology includes performing molecular labeling to avirulent gene though assessment from two parental strains and filial generation groups of Pyricularia grisea. M355-356 labeled by SSR near NO. 1 chromosome telomere links with avirulent gene Avr-Pit with a genetic distance of 2.3cm; S487 labeled by RAPD located near NO. 7 chromosome telomere links with avirulent gene Avr-Pia with a genetic distance of 3.5cm; S361 labeled by m677-678 and RAPD located at middle of N0. 3 chromosome telomere links with Pyricularia grisea specified avirulent gene PRE1 with genetic distances of 5.9cm and 6.4. The invention can not only make use of the nontoxic gene marker as gene probe, but also set foundations for further clone of the gene through physical mapping.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Rationally developed african swine fever attenuated virus strain protects against challenge with parental virus georgia 2007 isolate
ActiveUS9808520B1Viral antigen ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementAfrican swine feverDomestic pig
African swine fever virus (ASFV) is the etiological agent of a contagious, often lethal viral disease of domestic pigs. The control of African Swine Fever (ASF) has been hampered by the unavailability of vaccines. Experimental vaccines have been derived from naturally occurring, cell culture-adapted, or genetically modified live attenuated ASFVs; however, these vaccines are only successful when protecting against homologous viruses. We have constructed a recombinant Δ9GL / ΔUK virus derived from the highly virulent ASFV Georgia 2007 (ASFV-G) isolate by deleting the specific virulence-associated 9GL (B119L) and the UK (DP96R) genes. In vivo, ASFV-G Δ9GL / ΔUK administered intramuscularly to swine even at relatively high doses (106 HAD50) does not induce disease. Importantly, animals infected with 104 or 106 HAD50 are solidly protected against the presentation of clinical disease when challenged at 28 days post infection with the virulent parental strain Georgia 2007.
Owner:UNIV OF CONNECTICUT +1
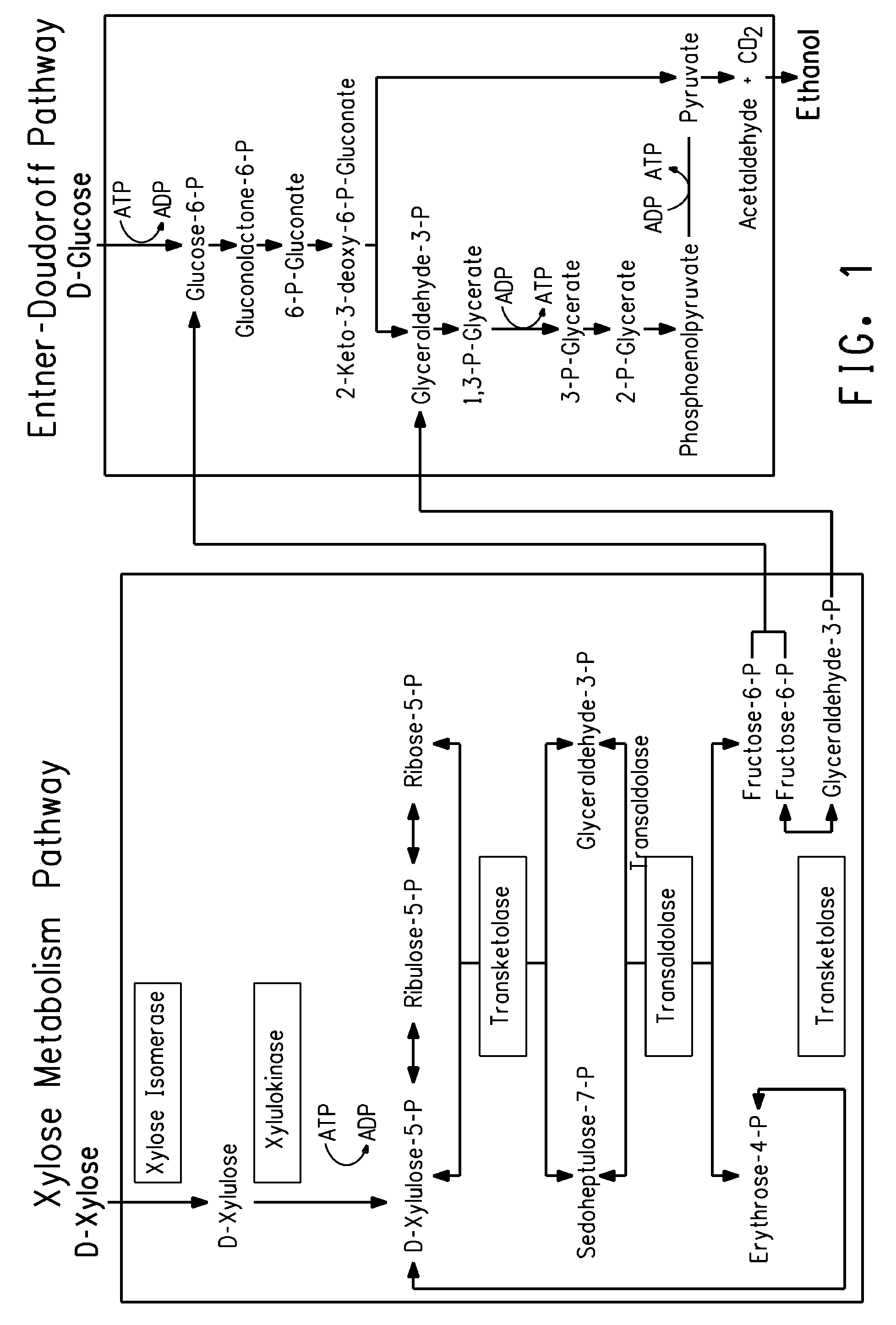
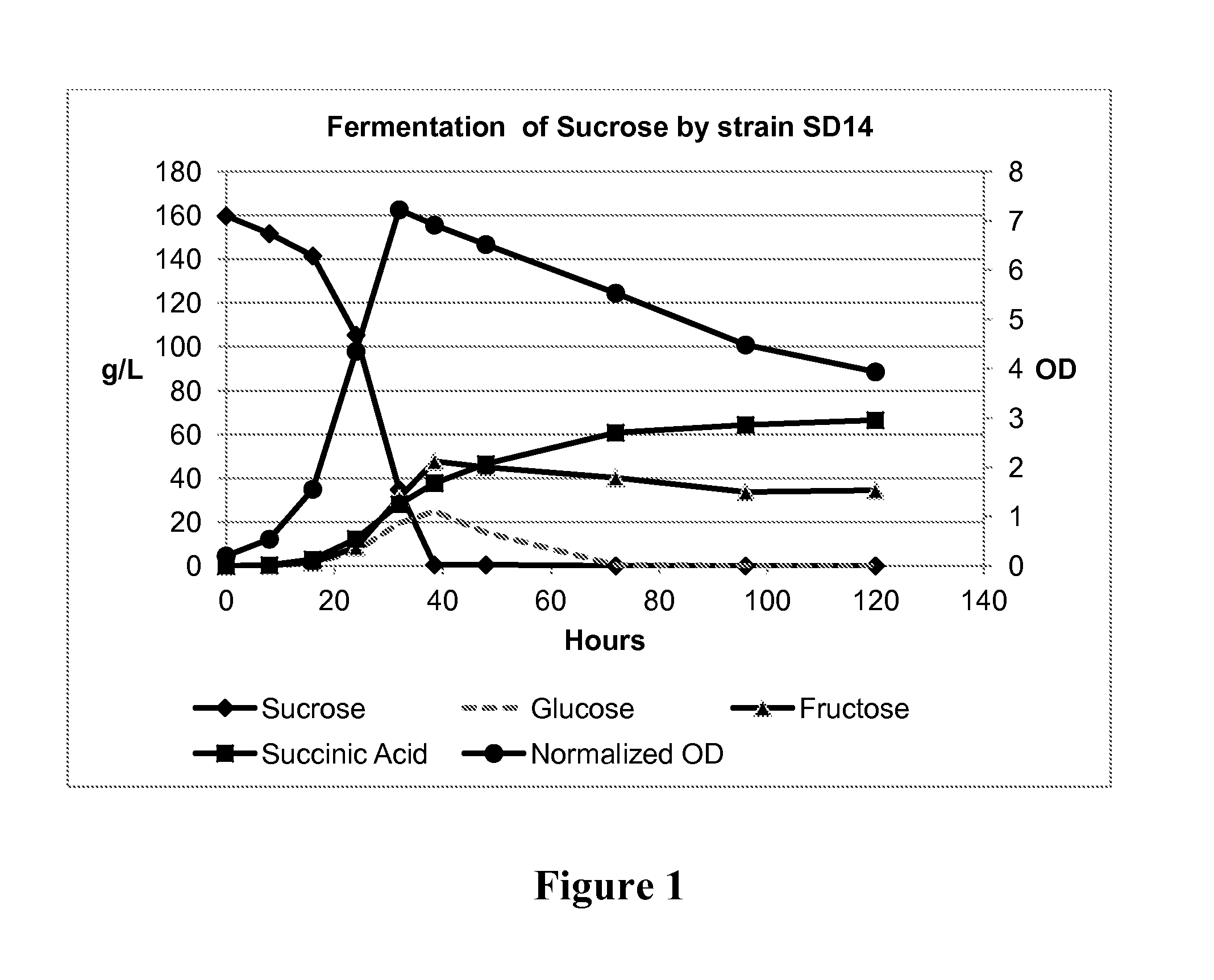
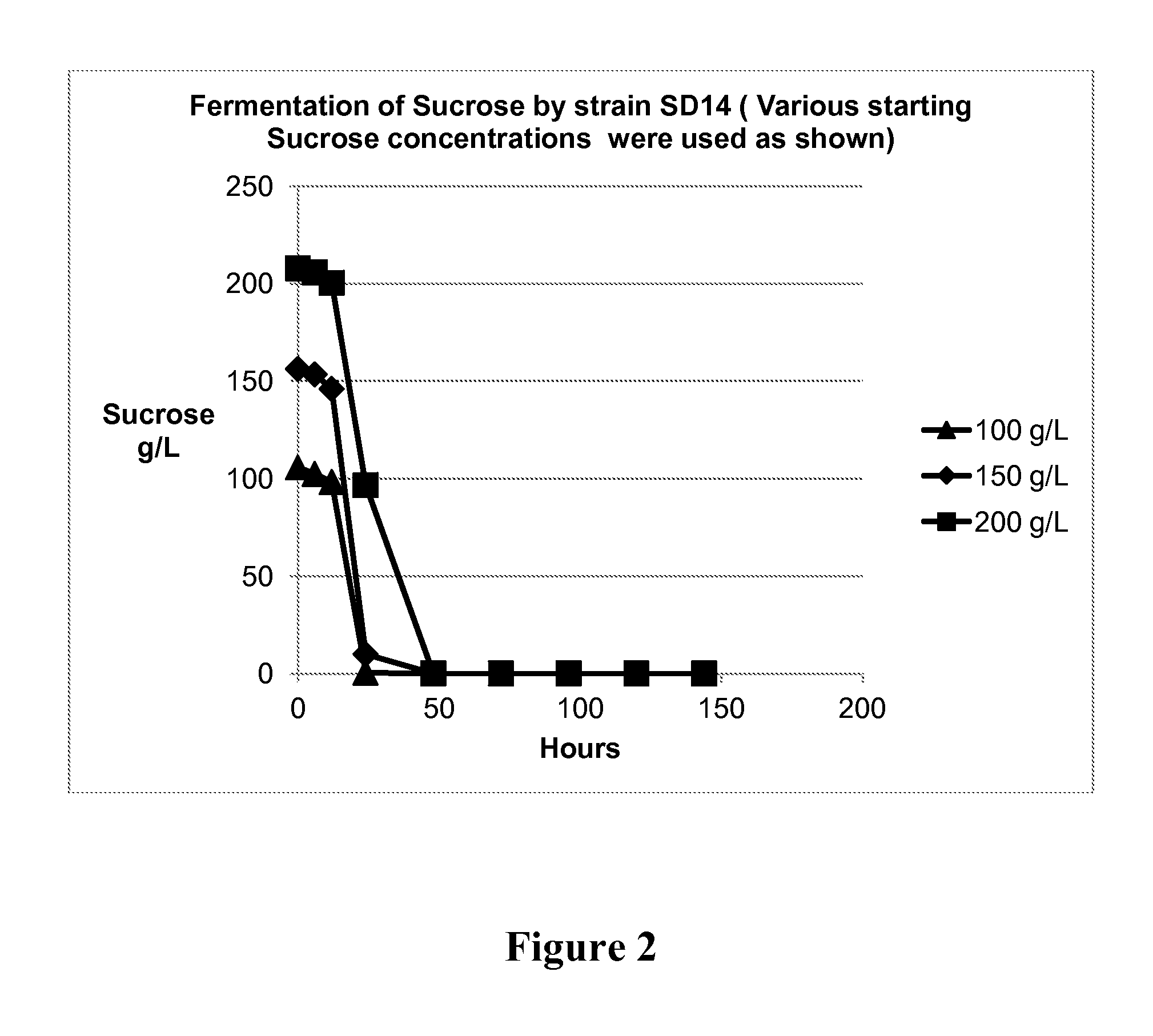
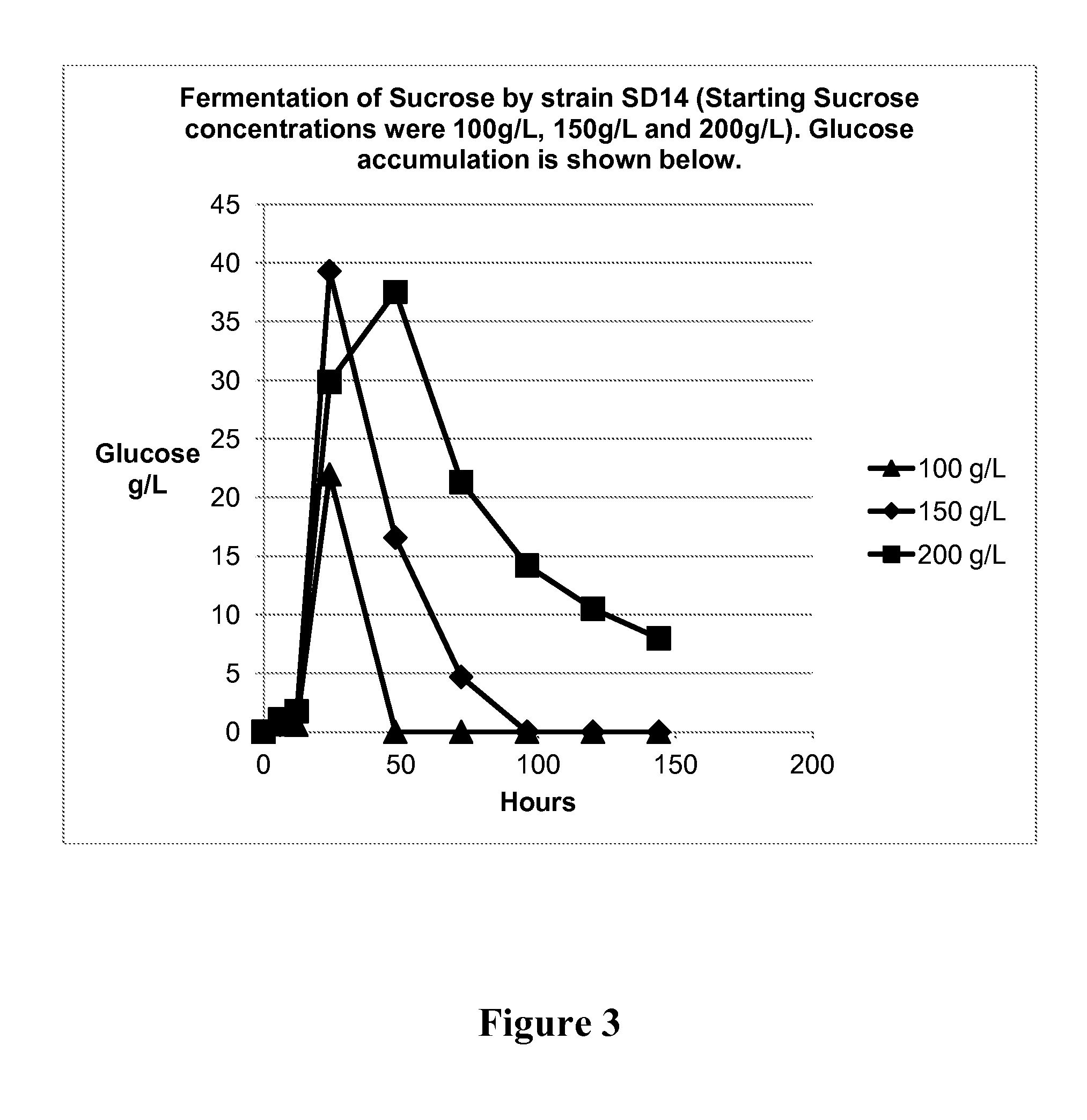
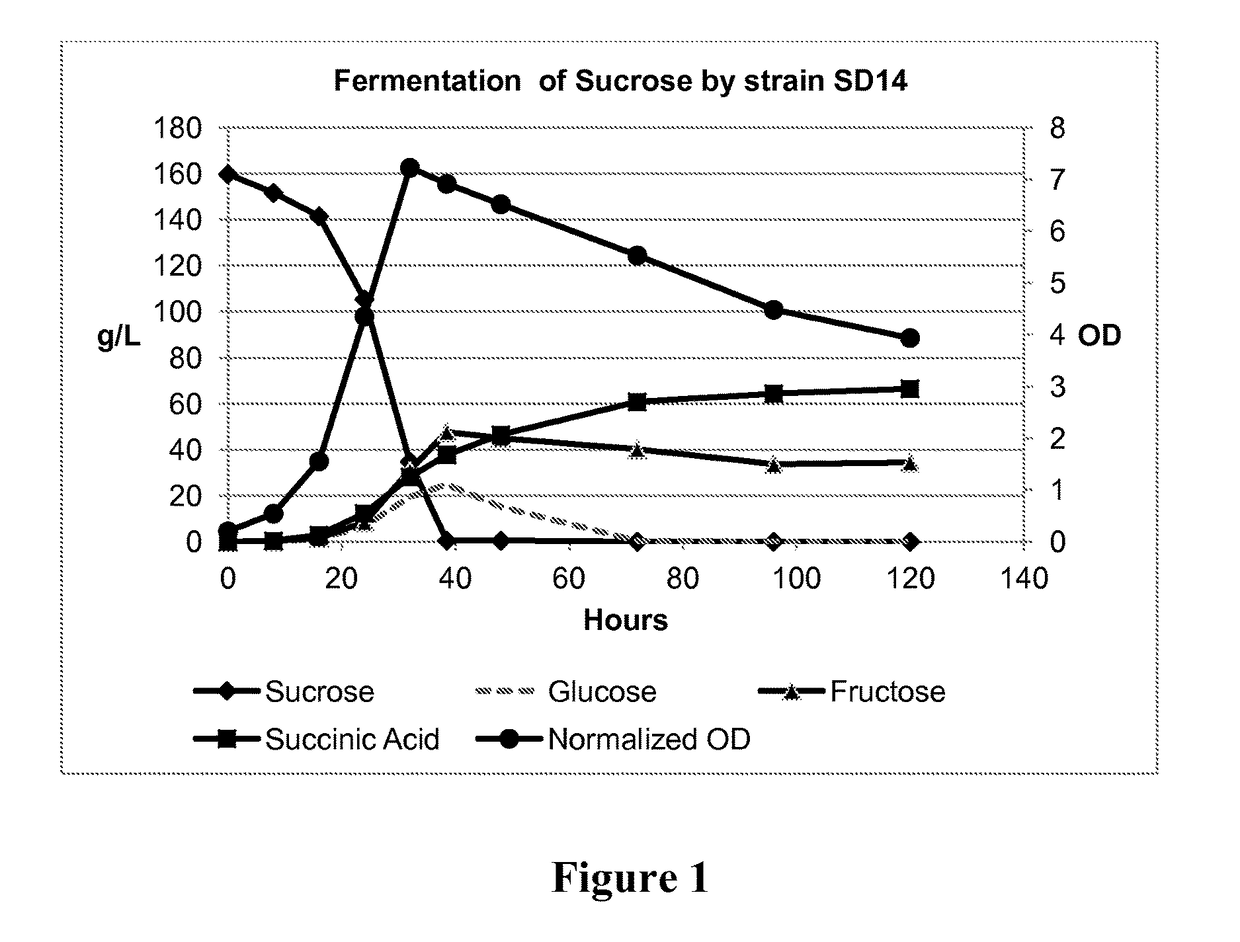
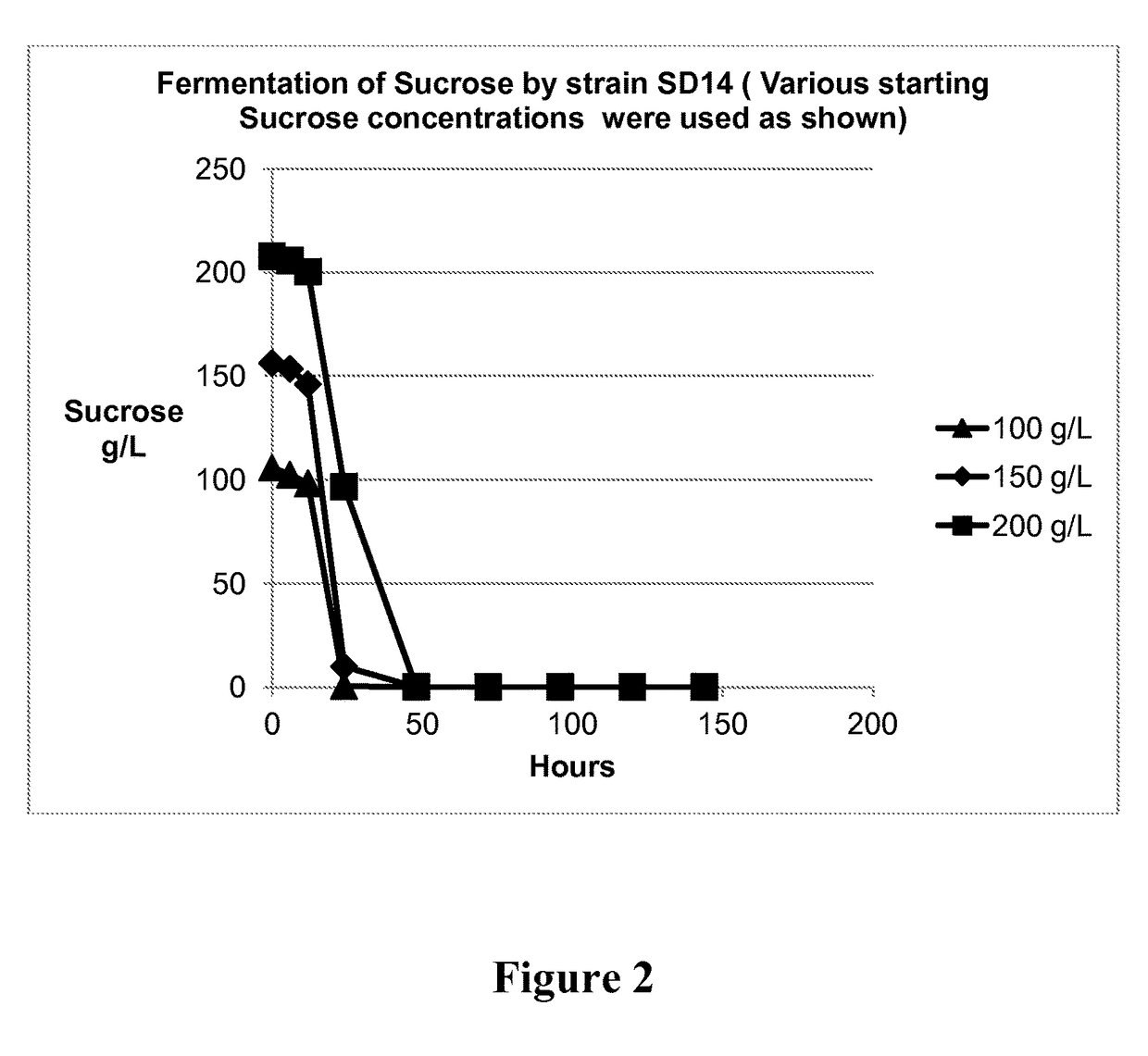
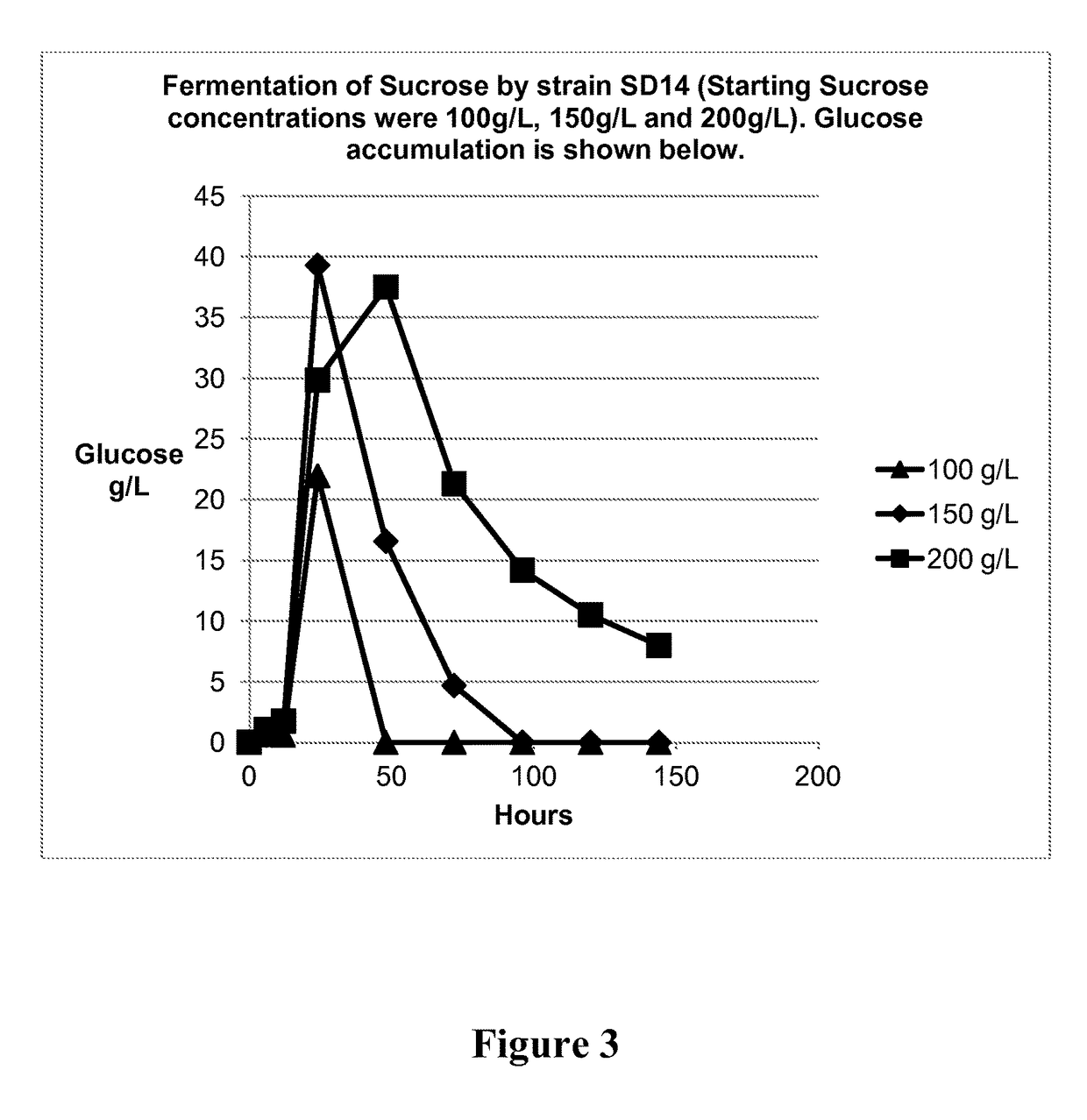
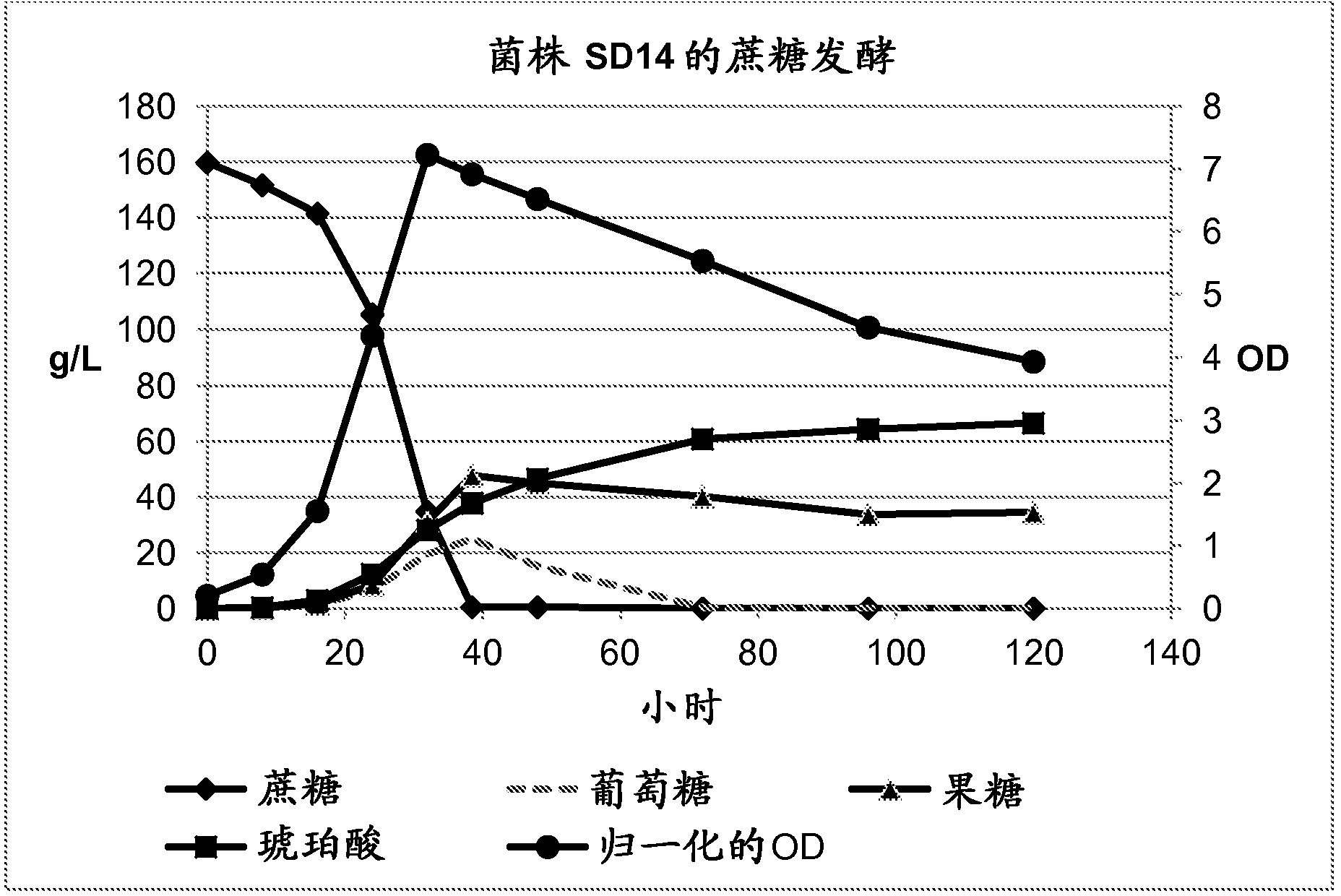
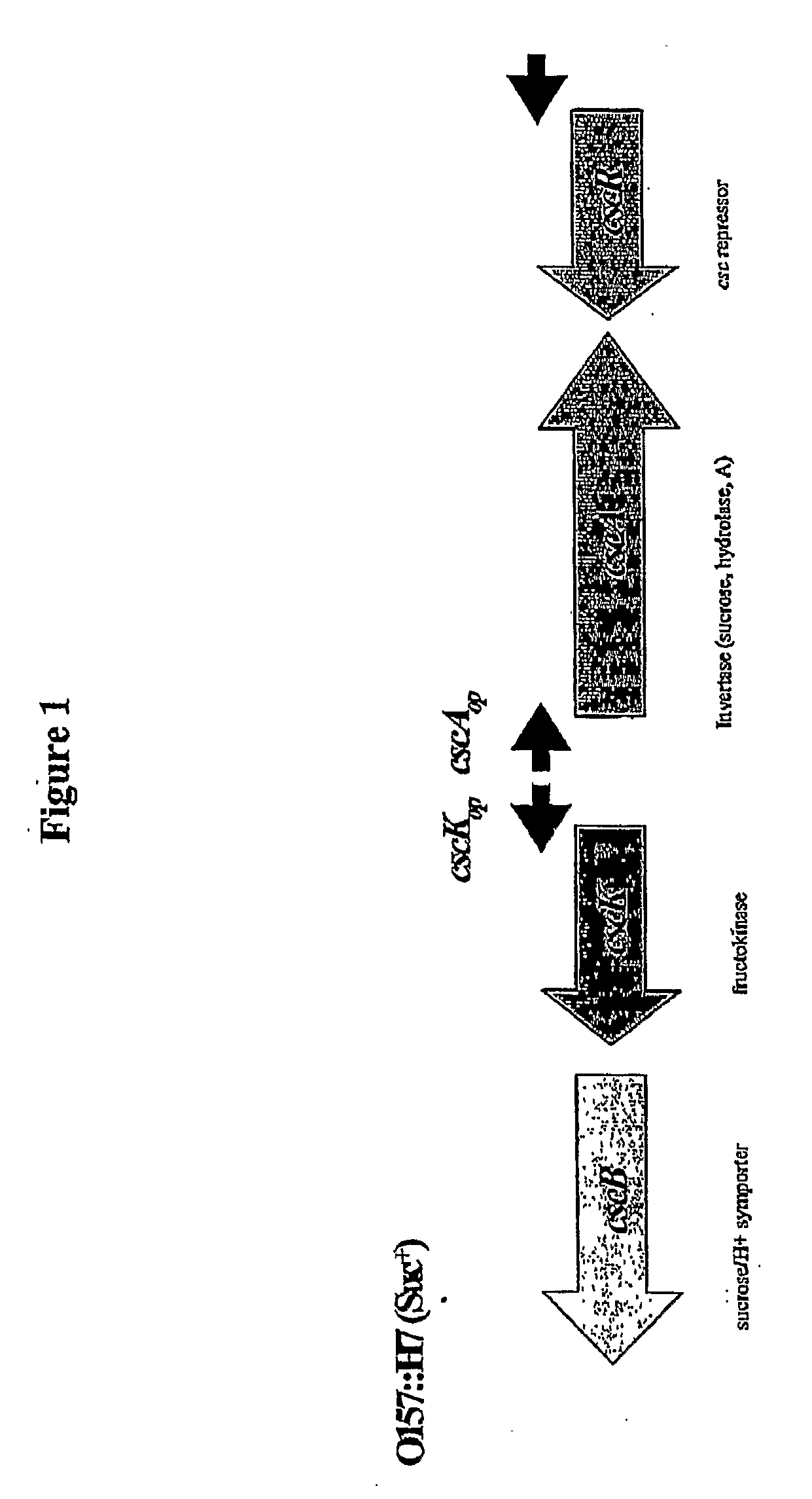
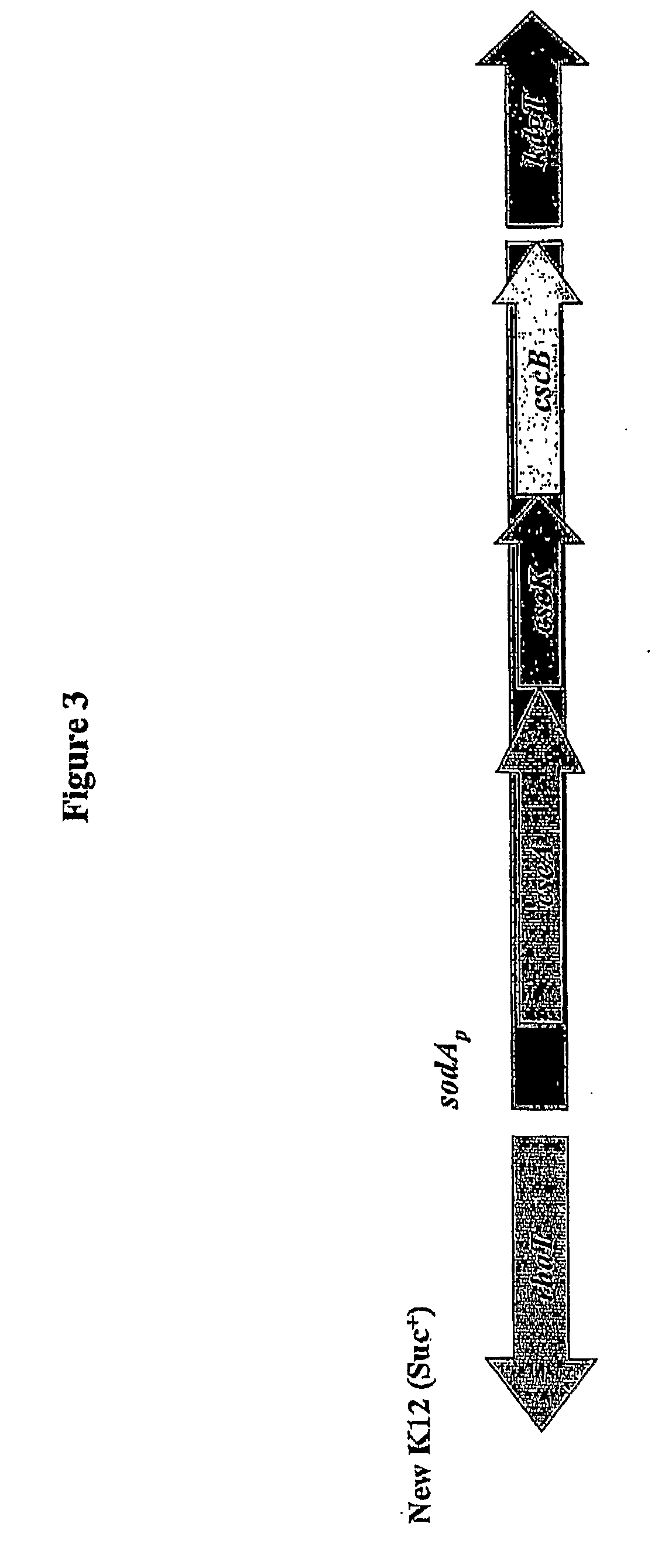
Method of producing succinic acid and other chemicals using sucrose-containing feedstock
ActiveUS20130337519A1Improve abilitiesIncrease productivityBacteriaHydrolasesSuccinic acidGenetics manipulation
This invention relates to the production of chemicals by fermentation with a microorganism in which the fermentation medium contains the sugar sucrose. As a specific example, succinic acid is produced from a sucrose-containing renewable feedstock through fermentation using a biocatalyst. Examples of such a biocatalyst include microorganisms that have been enhanced in their ability to utilize sucrose as a carbon and energy source. The biocatalysts of the present invention are derived from the genetic manipulation of parental strains that were originally constructed with the goal to produce one or more chemicals (for example succinic acid and / or a salt of succinic acid) at a commercial scale using feedstocks other than sucrose. The genetic manipulations of the present invention involve the introduction of exogenous genes involved in the transport and metabolism of sucrose into the parental strains. The genes involved in the transport and metabolism of sucrose can also be introduced into a microorganism prior to developing the organism to produce a particular chemical. The genes involved in the transport and metabolism of sucrose can also be used to augment or improve the sucrose transport and metabolism by strains already known to have some ability for sucrose utilization in biological fermentation.
Owner:PTT GLOBAL CHEMICAL PUBLIC COMPANY LIMITED
Method of producing succinic acid and other chemiclas using facilitated diffusion for sugar import
InactiveUS20160160245A1Facilitated DiffusionImprove filtering effectBacteriaMutant preparationBiotechnologyGlucose utilization
This invention relates to the production of succinic acid and other chemicals derived from phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP) by fermentation with a microorganism in which the fermentation medium contains one or more sugars, and in which one or more of the sugars is imported into the cell by facilitated diffusion. As a specific example, succinic acid is produced from a glucose-containing renewable feedstock through fermentation using a biocatalyst. Examples of such a biocatalyst include microorganisms that have been enhanced in their ability to utilize glucose as a carbon and energy source. The biocatalysts of the present invention are derived from the genetic manipulation of parental strains that were originally constructed with the goal to produce one or more chemicals (for example succinic acid and / or a salt of succinic acid) at a commercial scale using feedstocks that include, for example, glucose, fructose, or sucrose. The genetic manipulations of the present invention involve the introduction of exogenous genes involved in the transport and metabolism of glucose or fructose into the parental strains. The genes involved in the transport and metabolism of glucose or fructose can also be introduced into a microorganism prior to developing the organism to produce a particular chemical. The genes involved in the transport and metabolism of sucrose can also be used to augment or improve the efficiency of sugar transport and metabolism by strains already known to have some ability for glucose utilization in biological fermentations.
Owner:PTT GLOBAL CHEMICAL PUBLIC COMPANY LIMITED
Mutants of paenibacillus and methods for their use
The present invention provides a composition comprising a biologically pure culture of a Paenibacillus sp. strain comprising a mutant DegU lacking a functional receiver domain or a functional DNA binding domain and / or a mutant DegS lacking a functional single binding domain or a functional ATPase domain with decreased viscosity in a liquid culture. Also provided is a method of identifying a Paenibacillus sp. mutant derivative strain with decreased viscosity in a liquid culture compared to a Paenibacillus sp. parental strain with a visual screen for mutant isolates with a non-mucoid morphology.
Owner:BAYER CROPSCI LP
Recombinant equine influenza virus strain, preparation method thereof and vaccine prepared from recombinant equine influenza virus strain
InactiveCN103602638AImproving immunogenicityViral/bacteriophage medical ingredientsMicroorganism based processesCanine kidneyChick embryos
The invention discloses a recombinant equine influenza virus strain, a preparation method thereof and a vaccine prepared from the recombinant equine influenza virus strain. The recombinant influenza virus strain contains genes HA and NA of an equine influenza virus A / equine / xinjiang / 3 / 07 (H3N8) strain and six internal genes PB2, PB1, PA, NP, M and NS of an influenza virus A / Puerto Rico / 8 / 34 / Mount Sinai (H1N1) or A / PR / 8 / 34 (H1N1 short for PR8 virus). The recombinant equine influenza virus strain disclosed by the invention is named as rH3N8-PR and is preserved with the number of CGMCC NO.8161. The invention also discloses a preparation method of the recombinant equine influenza virus strain and a vaccine prepared from the recombinant equine influenza virus strain. Compared with a parental strain, the recombinant equine influenza virus strain disclosed by the invention can generate very high virus titer and blood clotting titer on both chick embryos and MDCK (Madin Darby Canine Kidney) cells, and the pathogenicity of the recombinant equine influenza virus strain to mice is remarkably reduced; experiments prove that the vaccine prepared from the recombinant equine influenza virus strain disclosed by the invention has favorable immunogenicity and protective effect.
Owner:HARBIN VETERINARY RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Preparation method for increasing CK (Compound K) yield of ginsenoside
InactiveCN103509842AIncrease productionImprove permeabilityMutant preparationMicroorganism based processesHigh concentrationMicrobial transformation
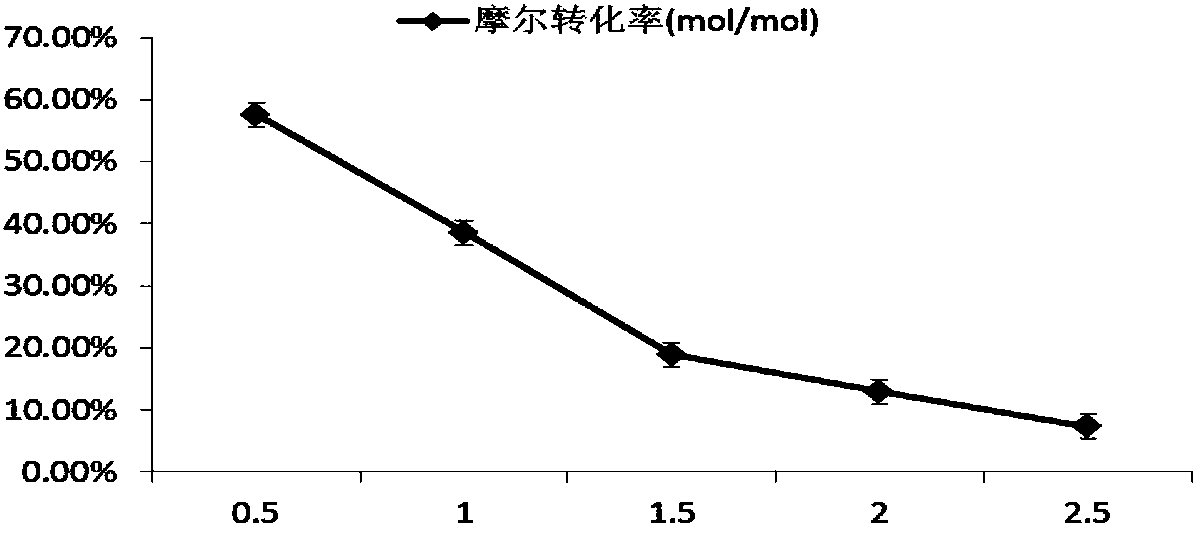
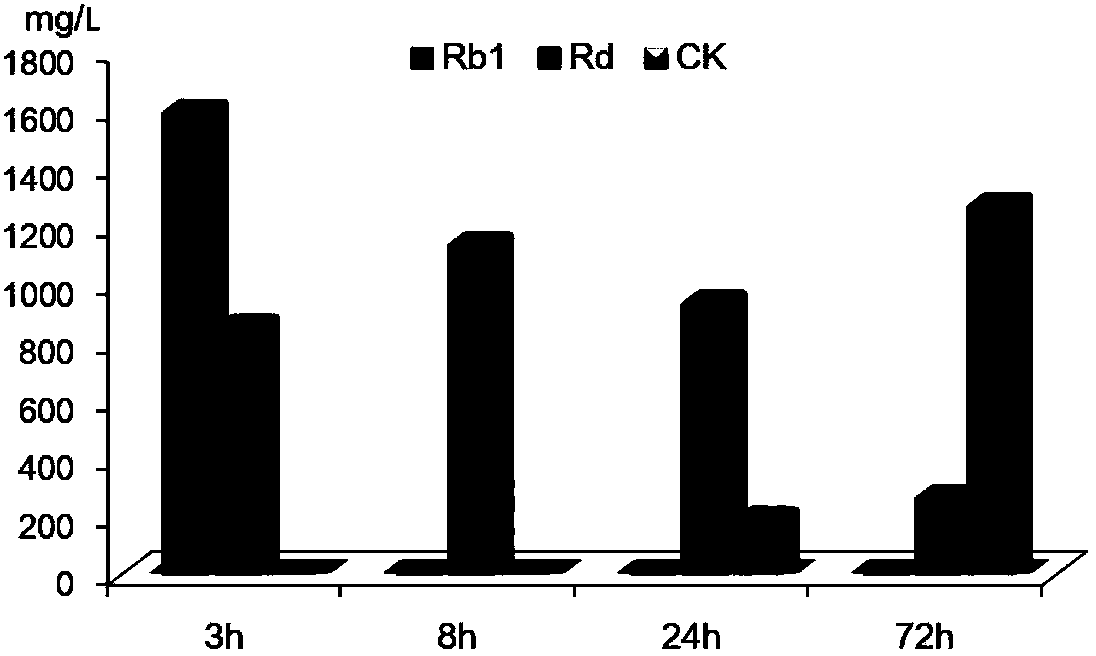
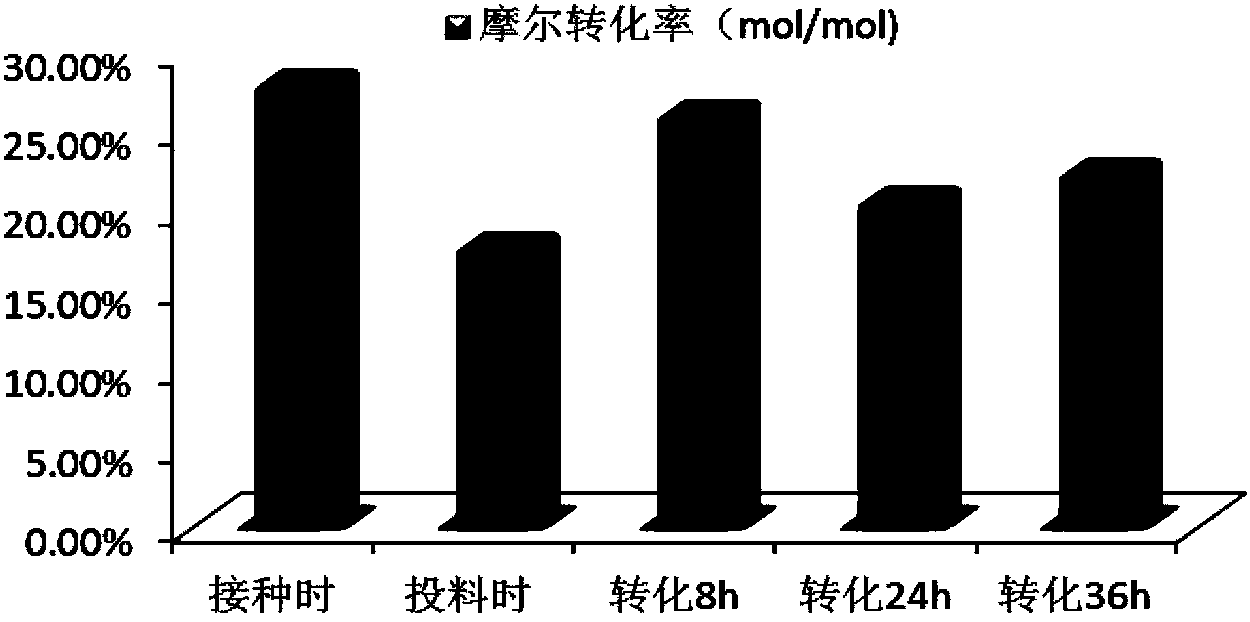
The invention belongs to the technical field of medical technology, relates to a preparation method for increasing CK (Compound K) yield of ginsenoside, and in particular relates to a preparation method for increasing the CK yield of ginsenoside by increasing the yield of a converted product through adjustment and control in a microbial conversion process. According to the preparation method, the yield of the converted product and the concentration of a primer are improved through metabolic regulation. The preparation method comprises the steps of: reconstructing ultraviolet mutagenesis of a parental strain, culturing in a high-concentration pseudo-ginseng stem and leave saponin culture medium, sieving in a directional manner to obtain a strain resisting to 1-5% of the total saponins of the pseudo-ginseng stems and leaves. Through the strain mutagenesis and the metabolic regulation, the concentration of the primer and the yield of the converted product are improved obviously, the final conversion rate is up to 43.63%, and the yield of the Compound K of the ginsenoside is improved by more than 80%. The preparation method for increasing CK yield of ginsenoside has practical significance for the industrial application of the microbial conversion.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Method of producing succinic acid and other chemicals using sucrose-containing feedstock
ActiveUS9845513B2Augment or improve an already existing capacity of the biocatalystsImprove abilitiesBacteriaHydrolasesBiotechnologySuccinic acid
Owner:PTT GLOBAL CHEMICAL PUBLIC COMPANY LIMITED
Attenuated African swine fever virus vaccine based in the deletion of MGF genes
ActiveUS9528094B2Viral antigen ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementVirulent characteristicsDomestic pig
African swine fever virus (ASFV) is the etiological agent of a contagious and often lethal viral disease of domestic pigs. Control of ASF has been hampered by the unavailability of vaccines. Experimental vaccines have been derived from naturally occurring, cell culture-adapted, or genetically modified live attenuated ASFVs; however, these vaccines are only successful when protecting against homologous viruses. Among viral genes reported to be involved in virulence are components of the multi gene family (MGF). Here we report the construction of a recombinant ΔMGF virus derived from the highly virulent ASFV Georgia 2007 (ASFV-G) isolate. In vivo, ASFV-G ΔMGF administered intramuscularly (IM) to swine at either 102 or 104 HAD50 are completely attenuated; the inoculated animals are completely asymptomatic. Animals infected with 102 or 104 HAD50 of ASFV-G ΔMGF are protected against the presentation of clinical disease when challenged at 28 days post infection with the virulent parental strain Georgia 2007.
Owner:US SEC AGRI +1
Porcine parvovirus infectious cloning system stably carrying genetic marker, construction method and application thereof
ActiveCN109706179ASolve the problem of low cloning efficiencyEasy to identifyMicroorganism based processesViruses/bacteriophagesCytopathic effectParental strain
The invention discloses a porcine parvovirus infectious cloning system stably carrying a genetic marker, a construction method and an application thereof. The blunt-end enzyme sites are introduced into an ITR sequence at both ends of a porcine parvovirus (PPV) genome, and an In-Fusion technology is used, and a non-sense mutation is introduced into a PPV intermediate sequence to obtain a PPV full-length infectious cloning plasmid carrying genetic marker and distinguished with a wild strain. The infectiou cloning plasmid constructed by a reverse heredity operation technology is used for transfection of PK15 cells in vitro, can induce the cells to generate the same cytopathic effect as the parental strain after continuous blind passage, and a rescue virus that having a similar growth trend asthe parent strain and carrying genetic marker can be rescued. The cloning system can quickly and conveniently perform base mutations at any position in the genome, and provides a convenient and effective tool for the subsequent development of attenuated vaccines and multiple vaccines of porcine parvovirus.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
Mycobacterial vaccine vectors and methods of using the same
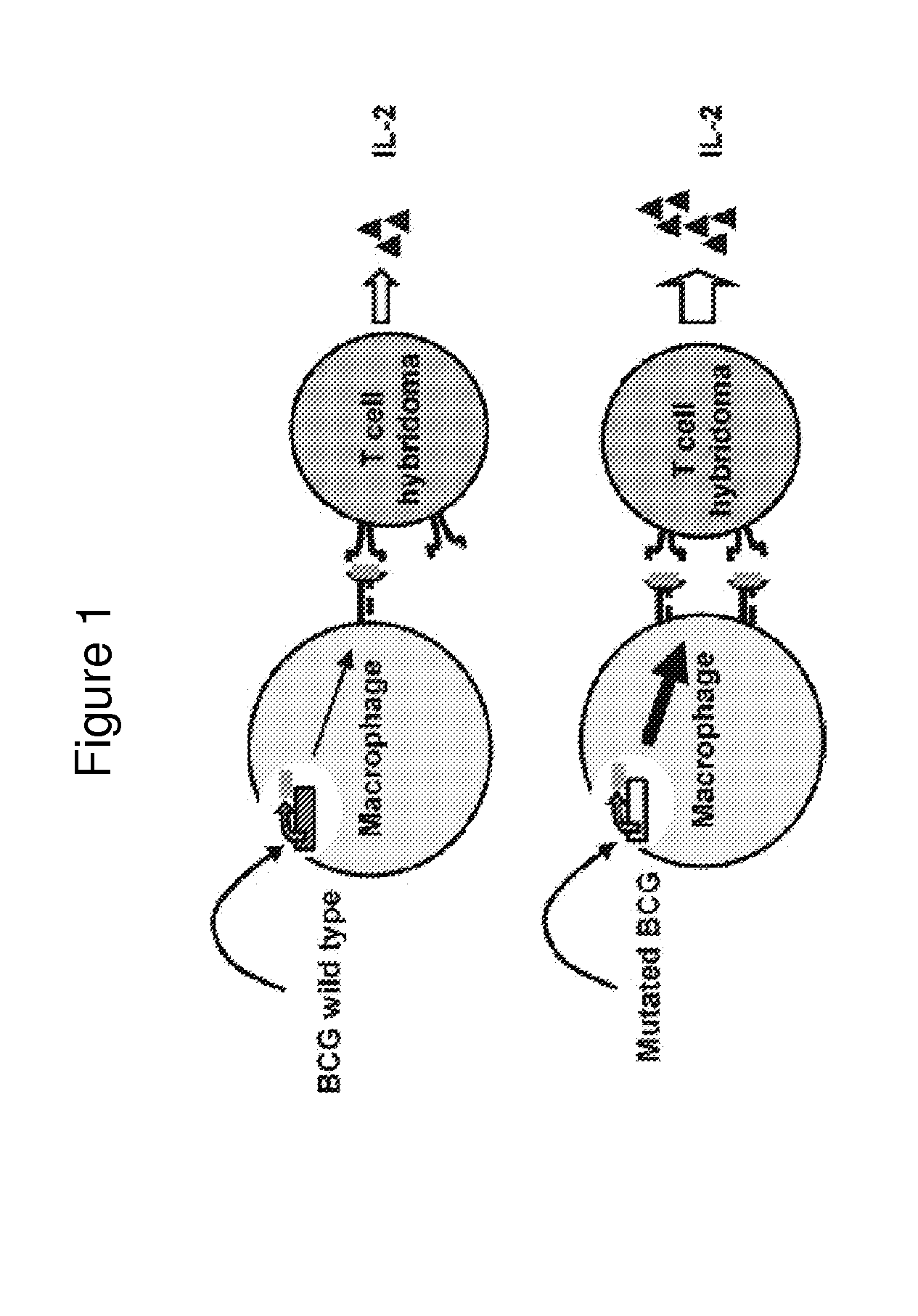
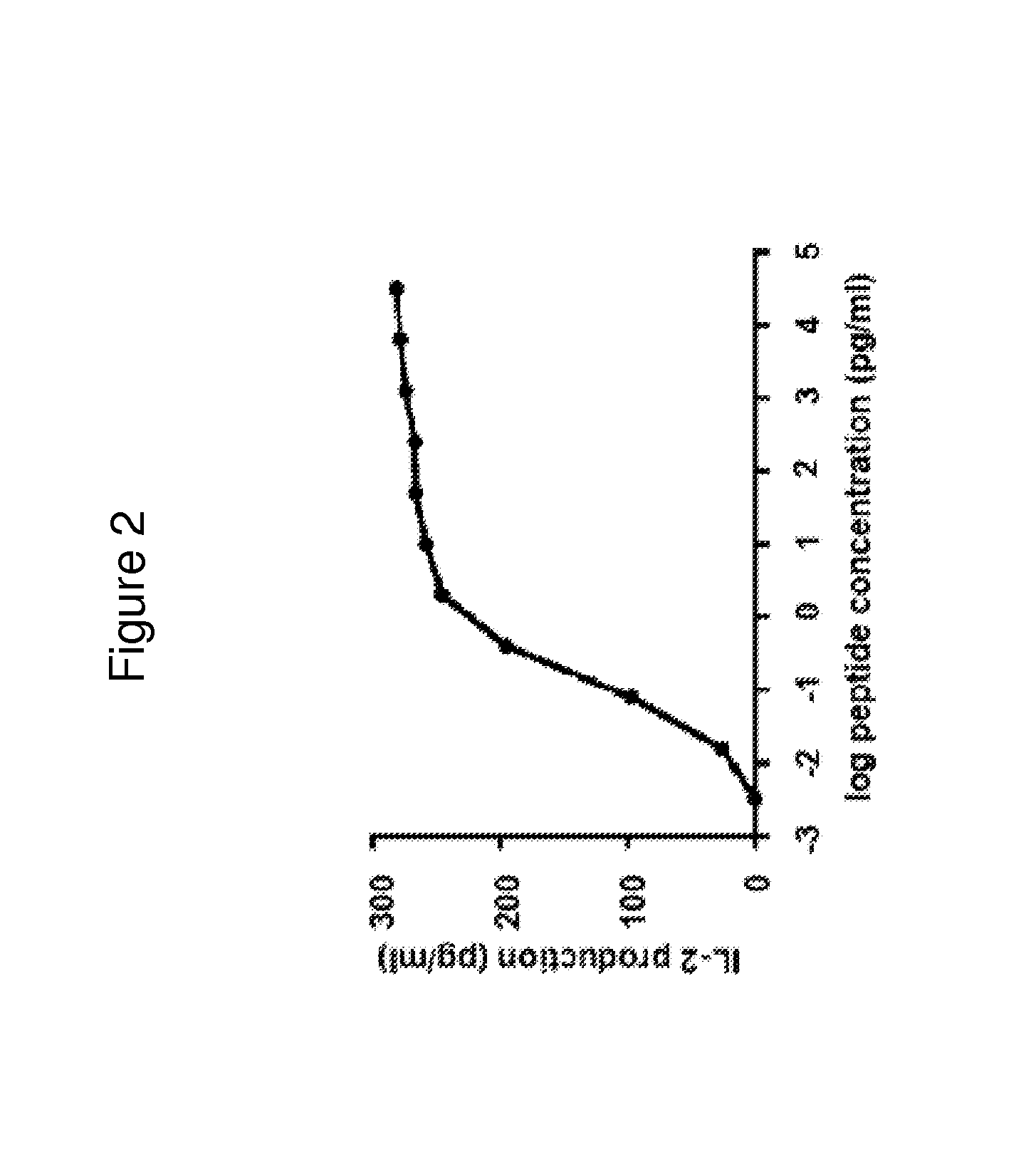
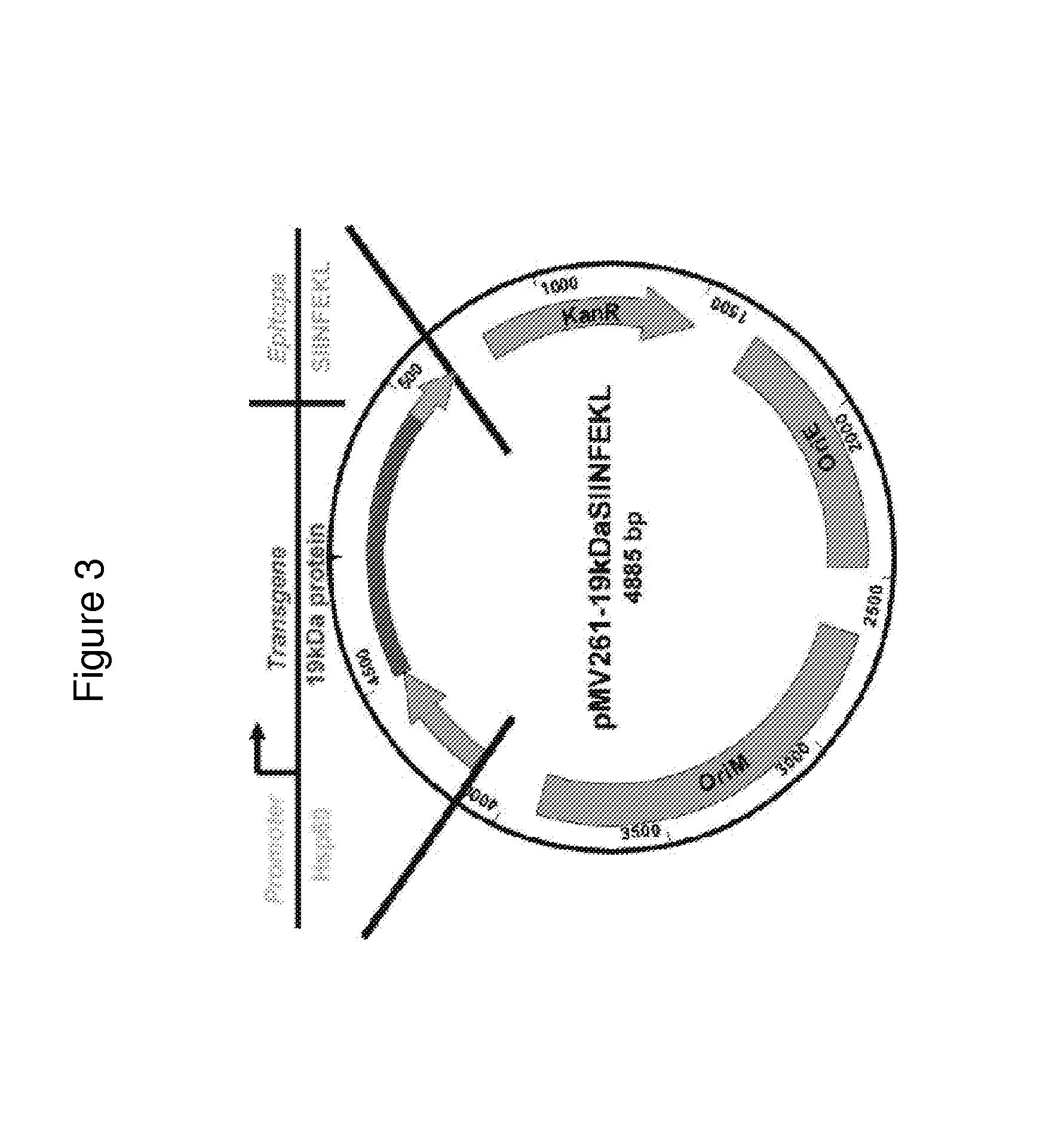
Mycobacterium bovis BCG is a potent stimulator of the cellular immune response and has potential as a recombinant vaccine vector. Disclosed are BCG strains that generate greater MHC class I presentation of a transgenic protein, relative to the unmutated parental strain, and that improve a recipient's CD8+ T cell response against the transgenic protein following vaccination. The mycobacterial constructs and their respective t / ansposon mutant BCG strains exhibit increased immunogenicity that is several times greater than responses generated by the parental strain and other existing modified rBCG strains. Furthermore, upon introducing the SIV gag gene into these novel strains, we observed that these strains primed for increased CD8+ T cell responses in a heterologous prime / boost regimen, comparable to levels generated by plasmid DNA vaccines. Creation of a second generation rBCG vector that may be utilized as a vaccine vector for immunizing against a variety of pathogens.
Owner:BETH ISRAEL DEACONESS MEDICAL CENT INC
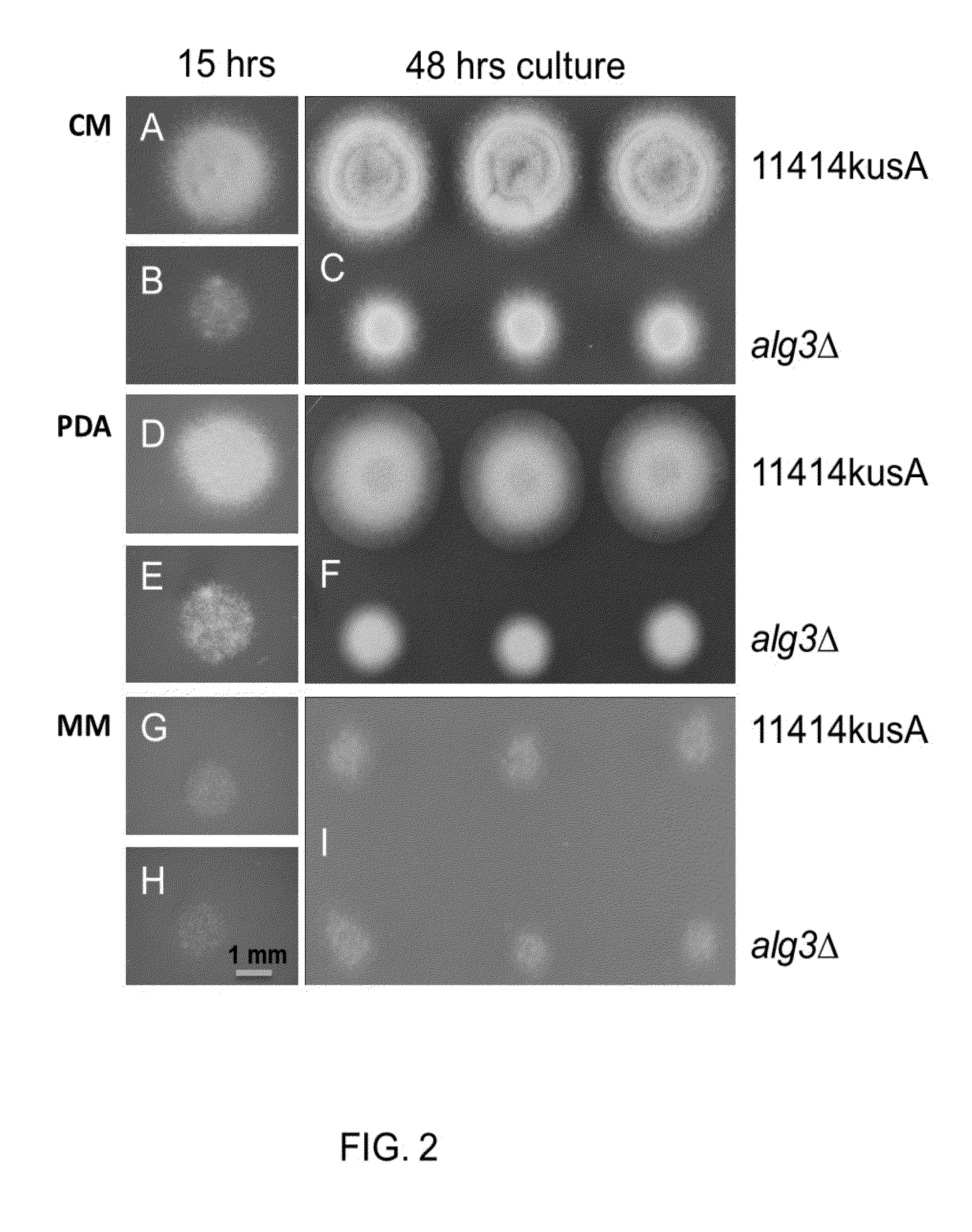
Enhanced citric acid production in aspergillus with inactivated asparagine-linked glycosylation protein 3 (ALG3), and/or increased laea expression
ActiveUS20150232892A1Promote growthSolve the low germination rateFungiDepsipeptidesMannosyltransferaseAscus fungus
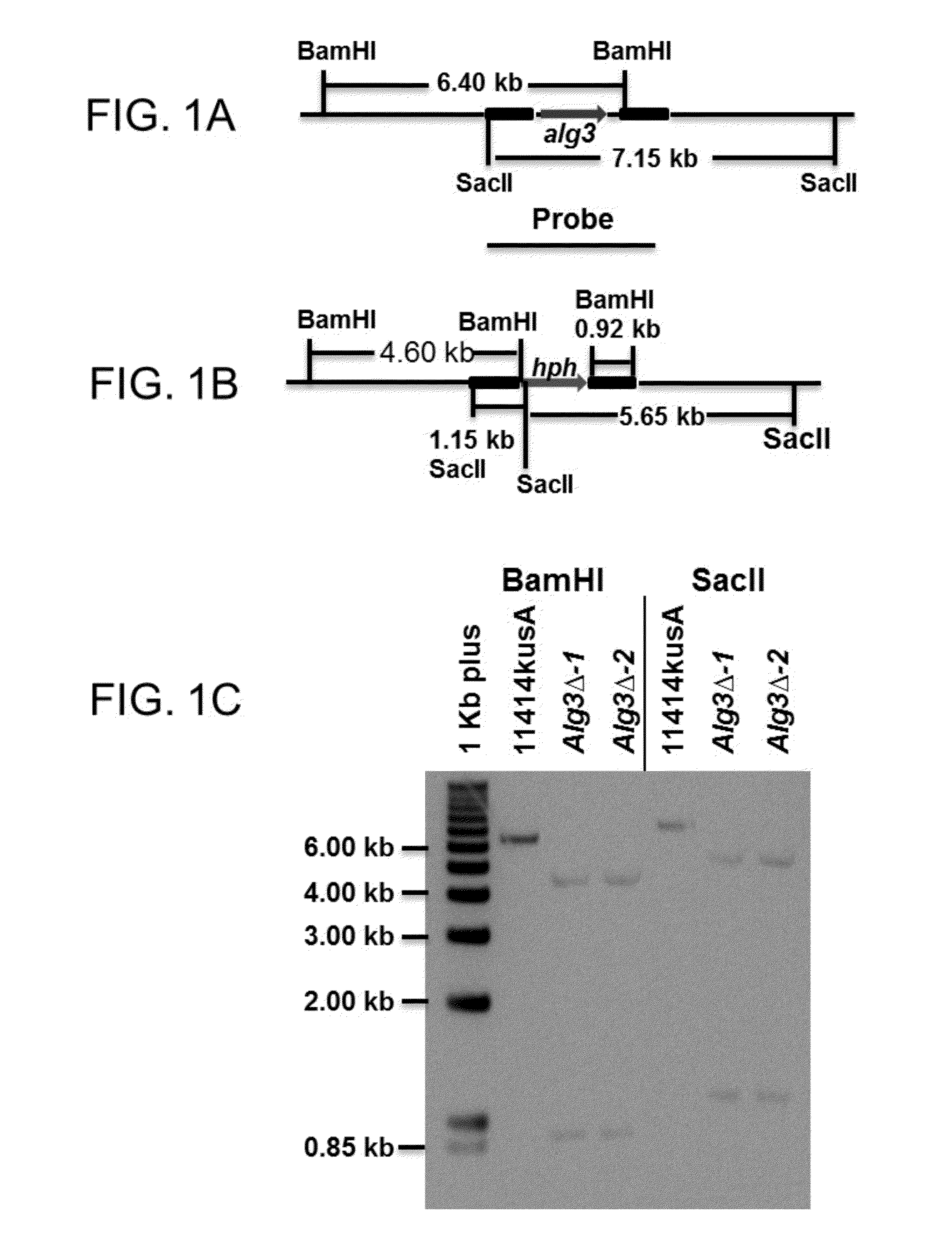
Provided herein are fungi, such as Aspergillus niger, having a dolichyl-P-Man:Man(5)GlcNAc(2)-PP-dolichyl mannosyltransferase (Alg3) gene genetic inactivation, increased expression of a loss of aflR expression A (Lae), or both. In some examples, such mutants have several phenotypes, including an increased production of citric acid relative to the parental strain. Methods of using the disclosed fungi to make citric acid are also provided, as are compositions and kits including the disclosed fungi.
Owner:BATTELLE MEMORIAL INST
Method for breeding selection of insecticidal fungus with relatvely stable pathogenicity
This invention discloses a method for breeding pesticidal fungi with stable pathogenicity. The method comprises: (1) separating monospores of pesticidal fungi, mutagenizing on chlorate potato medium (KPS), punching to separate anti-chlorate mutants, and identifying with basic medium and KPS medium to obtain nitrate-utilization auxotrophic mutants (nit); (2) selecting nit mutants with high vegetative compatibility to obtain parental strains, collecting zygospores, and culturing to obtain heterocaryon; (3) staining the heterocaryon with Hoechest 33258, and observing to identify heterocaryosis. The pesticidal fungi have stable pathogenicity, and can prevent and treat pests in agriculture, forestry and stockbreeding.
Owner:GUIZHOU UNIV
Hericium erinaceus strain and breeding method thereof
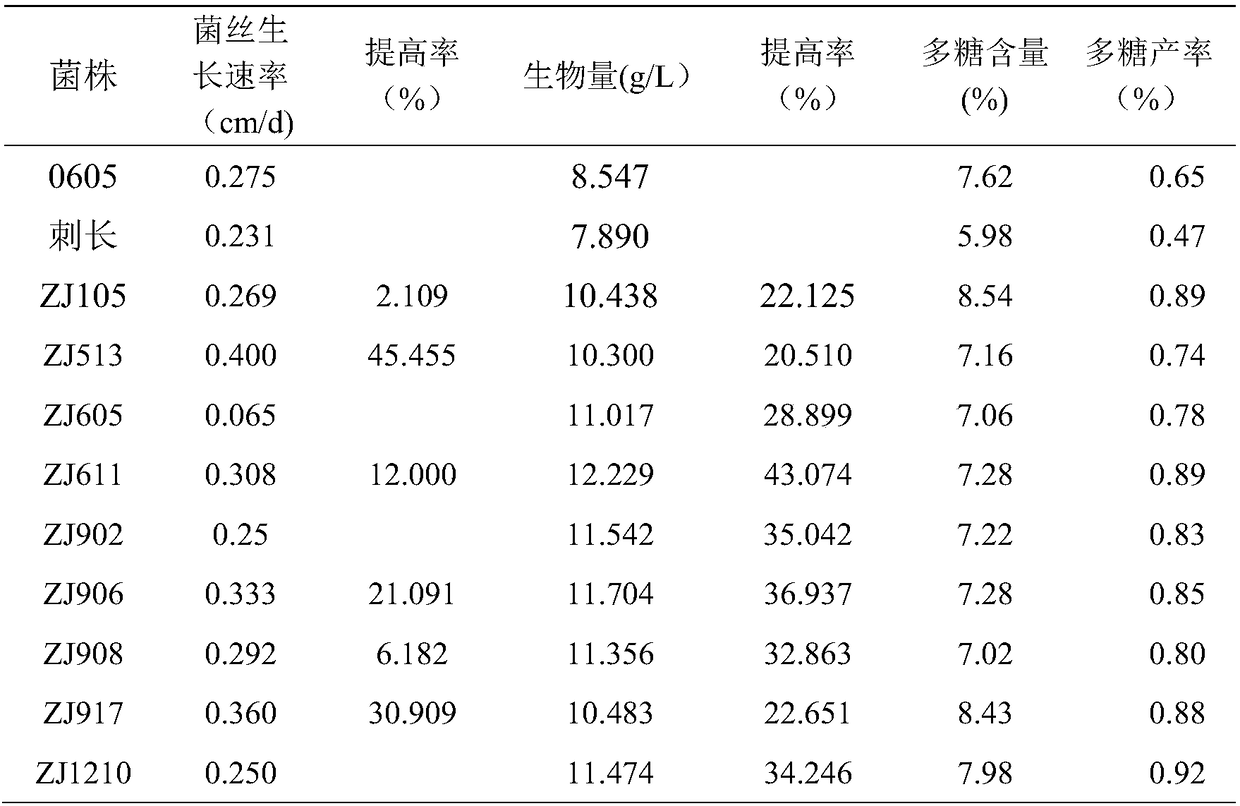
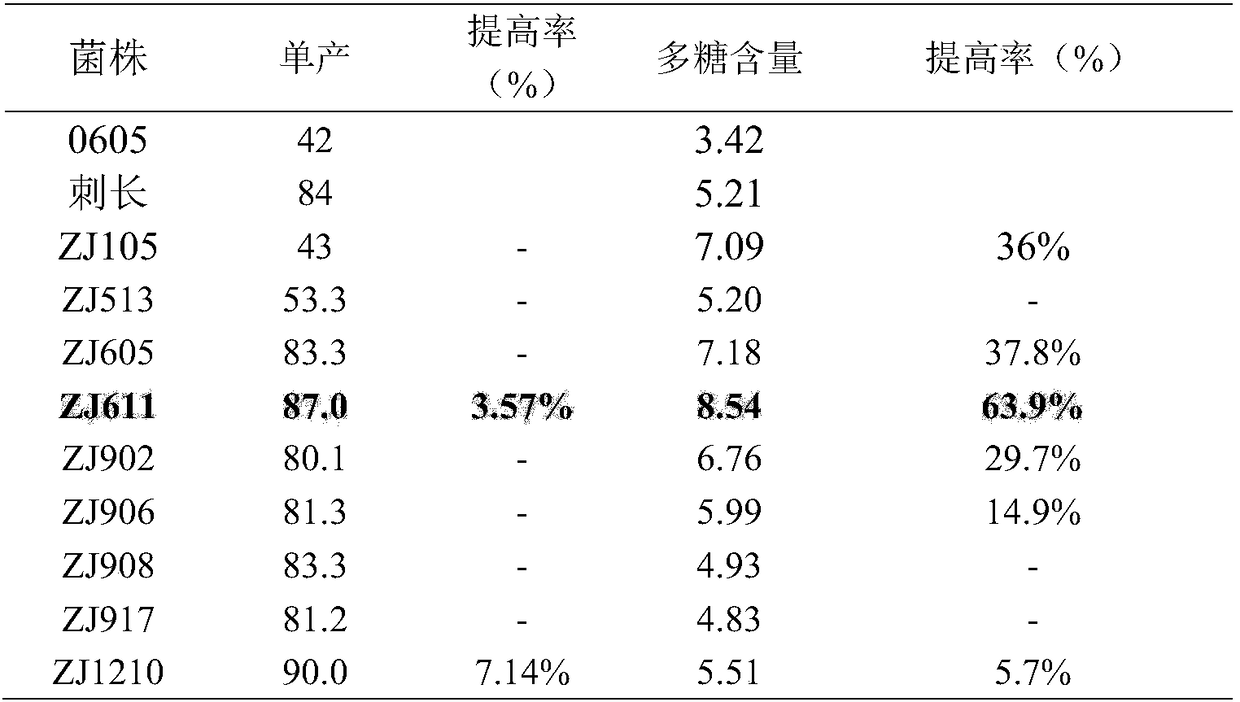
ActiveCN108575556AHigh in polysaccharidesIncreased intracellular polysaccharide contentCultivating equipmentsMushroom cultivationMyceliumHypha
The invention provides a hericium erinaceus strain. A good strain ZJ611 which has high mycelium biomass, stable per unit area yield and high fruiting body polysaccharide content and has the collectionnumber of CGMCC No.14990 is obtained through preparation of parental strain protoplast, selection of mononuclear bodies, identification of hybrid strains, further screening of the hybrid strains andscreening of hybrid strain cultivation fruiting bodies. The growth rate of the hericium erinaceus strain reaches 0.308 cm / d, which is 12% higher than that of parent strains; the shake flask biomass reaches 12.23 g / L, which is 43.07% higher than that of parent strains; the intracellular polysaccharide yield is 0.89 g / L, which is 36% higher than that of parent strains; the per unit area yield of cultivation fruiting bodies reach 87 g / bag; the polysaccharide content reaches 8.54%, which is 63.9% higher than that of parents.
Owner:SHANGHAI ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Method of producing succinic acid and other chemicals using sucrose-containing feedstock
This invention relates to the production of chemicals by fermentation with a microorganism in which the fermentation medium contains the sugar sucrose. As a specific example, succinic acid is produced from a sucrose-containing renewable feedstock through fermentation using a biocatalyst. Examples of such a biocatalyst include microorganisms that have been enhanced in their ability to utilize sucrose as a carbon and energy source. The biocatalysts of the present invention are derived from the genetic manipulation of parental strains that were originally constructed with the goal to produce one or more chemicals (for example succinic acid and / or a salt of succinic acid) at a commercial scale using feedstocks other than sucrose. The genetic manipulations of the present invention involve the introduction of exogenous genes involved in the transport and metabolism of sucrose into the parental strains. The genes involved in the transport and metabolism of sucrose can also be introduced into a microorganism prior to developing the organism to produce a particular chemical. The genes involved in the transport and metabolism of sucrose can also be used to augment or improve the sucrose transport and metabolism by strains already known to have some ability for sucrose utilization in biological fermentation.
Owner:PTT GLOBAL CHEMICAL PUBLIC COMPANY LIMITED
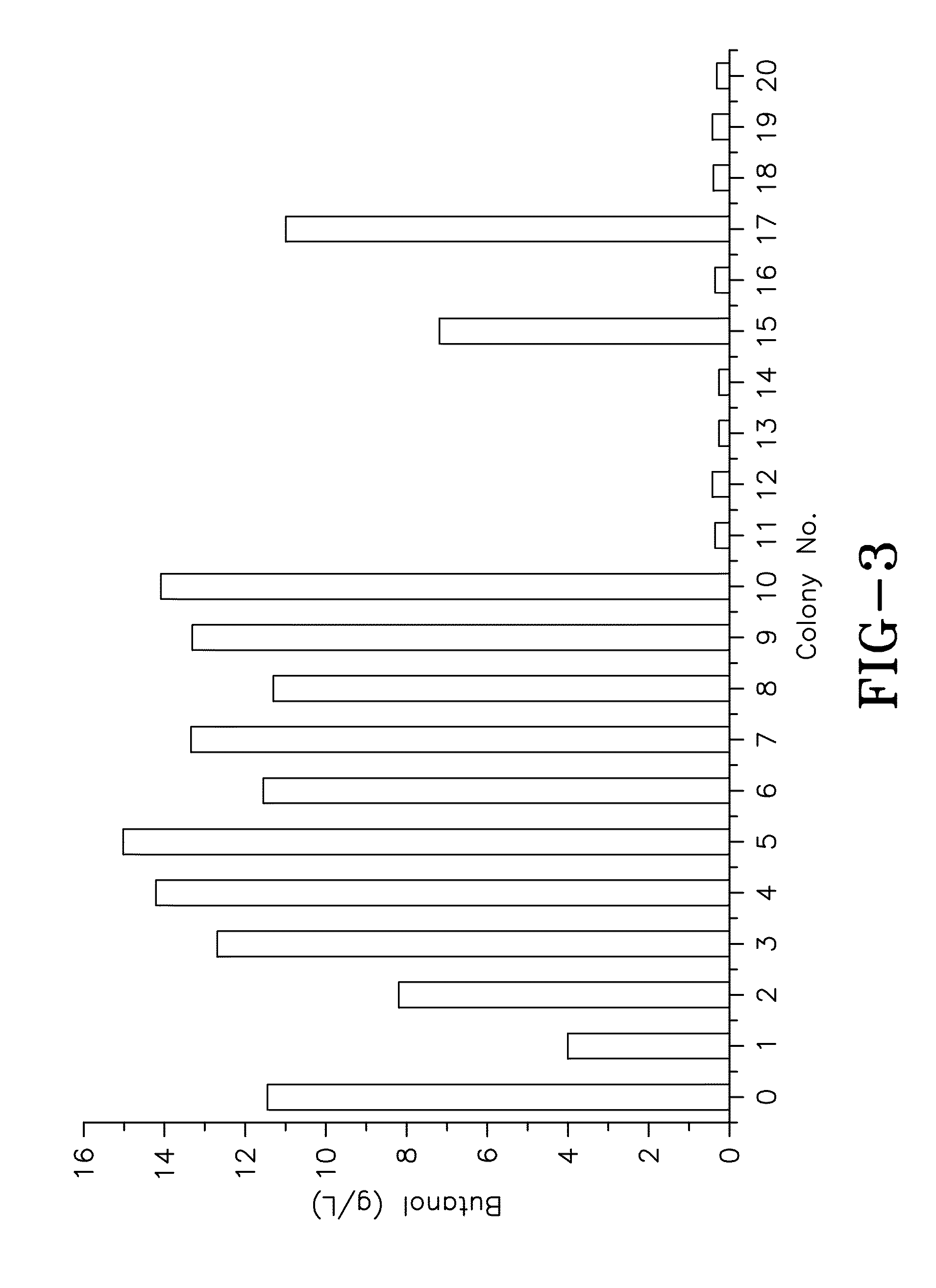
Adaptive engineering of clostridium for increased butanol production
ActiveUS8450093B1Improved production of butanolImprove toleranceBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMicroorganismMutated protein
Adaptive engineering of microorganisms to create mutants exhibiting high butanol tolerance and productivity. Mutant strains are obtained through the fermentation of parental strains in a fibrous bed bioreactor in the presence of butanol. Also provided are methods of producing butanol using mutant strains in ABE fermentation. Butanol production may be furthered by gas stripping and distillation. Also provided are mutant proteins for increasing butanol production in a microorganism.
Owner:THE OHIO STATES UNIV
Uk-2 biosynthetic gene and method for improving uk-2 productivity using the same
ActiveUS20140011203A1High UK- productivityLow costBiocideSugar derivativesBiosynthetic genesGene cluster
The genomic DNA of Streptoverticillium sp. 3-7, which produces UK-2, was analyzed to identify a region expected to be a UK-2 biosynthetic gene cluster. Moreover, by colony hybridization, DNAs in the region were successfully isolated. Further, the DNAs were used to prepare a strain in which the genes present in the region were disrupted. The strain was found not to produce UK-2. It was verified that the genomic region was the UK-2 biosynthetic gene cluster. Furthermore, Streptoverticillium sp. 3-7 was transformed by introduction of a vector in which the isolated UK-2 biosynthetic gene cluster was inserted. It was also found out that the UK-2 productivity by the transformant was improved about 10 to 60 times or more in comparison with that of the parental strain. Moreover, it was revealed that 2 copies of the UK-2 biosynthetic gene cluster were present per cell in these transformants, respectively.
Owner:MMAG CO LTD
Bacillus thuringiensis mutants which produce higher yields of crystal delta-endotoxin than their corresponding parental strains
The invention relates to a mutant of Bacillus thuringiensis which produces a larger amount of crystal delta-endotoxin with a greater pesticidal activity as compared to the corresponding parental strain. The mutant may also have a larger crystal size as compared to the corresponding parental strain. The crystal delta-endotoxin produced by the mutant Bacillus thuringiensis will have an activity directed towards the same pest(s) as its parental Bacillus thuringiensis crystal delta-endotoxin. The invention further relates to a method for producing such a mutant, compositions comprising such a mutant as well as methods for controlling a pest(s) using these compositions.
Owner:VALENT BIOSCIENCES CORP
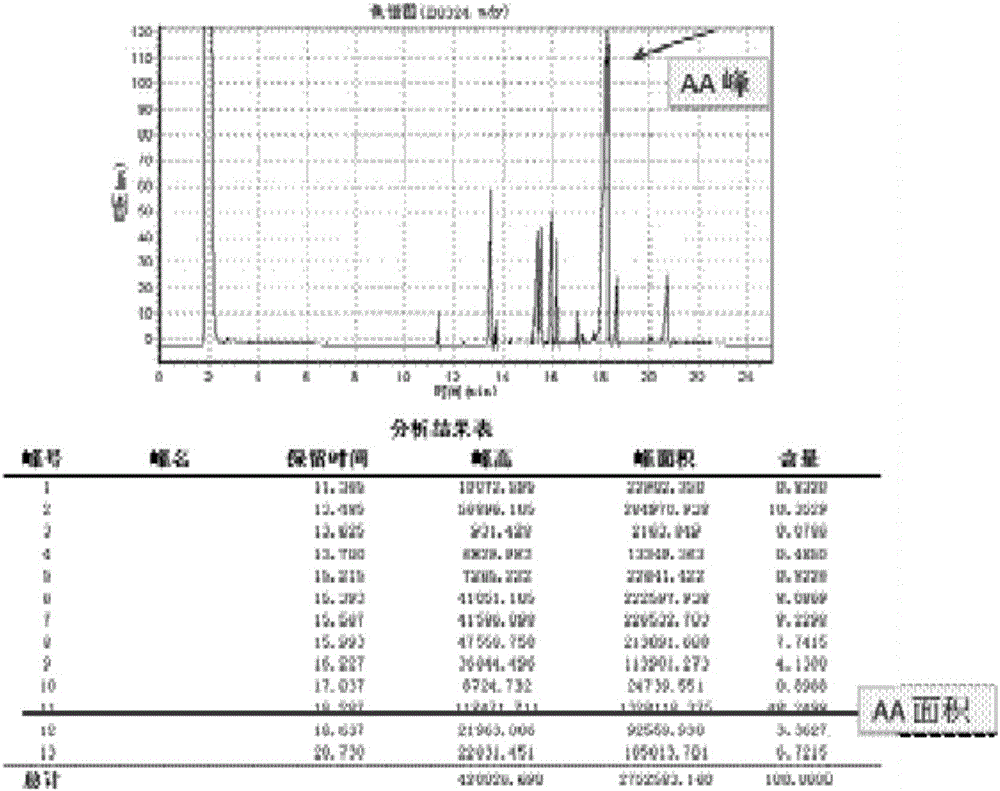
Method for breeding AA-high-producing strains by utilizing protoplast fusion and combining with fusant screening through fluorescence staining
The invention provides a method for breeding AA-high-producing strains by utilizing protoplast fusion and combining with fusant screening through fluorescence staining. In order to obtain mortierella alpina strains with high yield of arachidonic acid, the invention provides the method adopting the following scheme: two mortierella alpina strains with different superior characteristics are subjected to fusion treatment by adopting a protoplast fusion method, and fusants are screened by combining with the fluorescence staining method. The method provided by the invention comprises the following specific steps: culturing two parental strains, preparing protoplasts of the two parental strains, carrying out fluorescence staining on the protoplasts of the two parental strains, fusing the protoplasts of the two parental strains, and screening and verifying the fusants. The method provided by the invention is easy to operate, the process is easy to realize, and the breeding success probability is high. The method can be used for improving the yielding level of arachidonic acid producing strains, optimizing the fat components of the arachidonic acid product, and improving the characters of the strains.
Owner:INST OF PLASMA PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
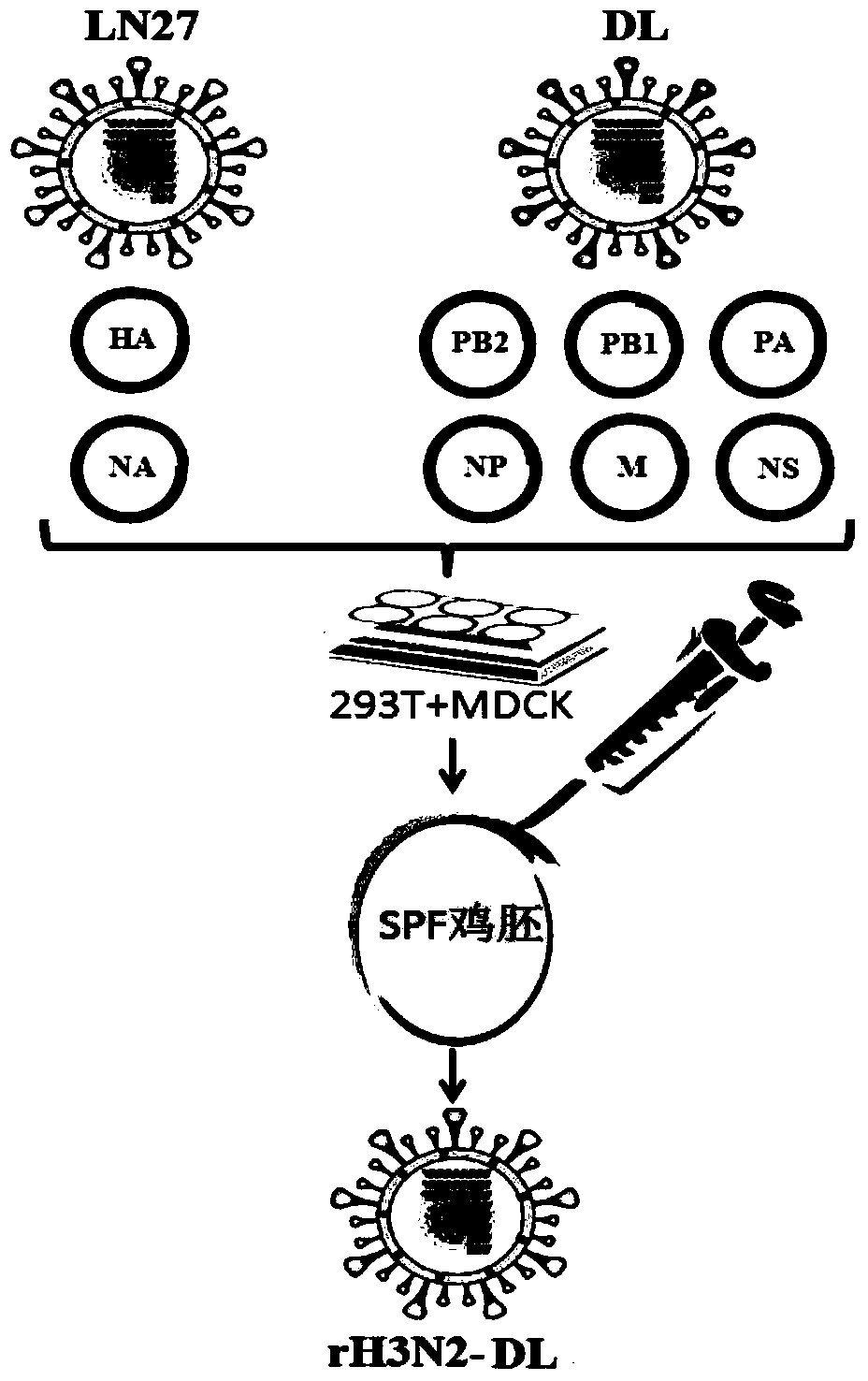
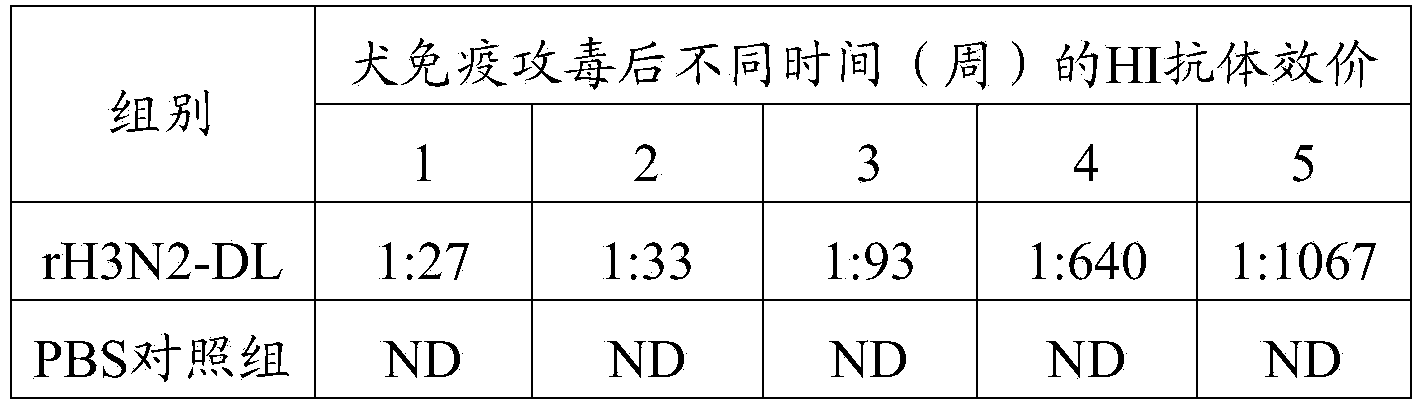
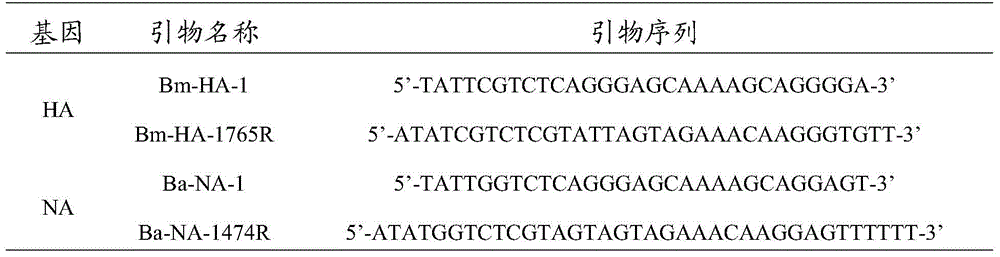
Recombinant canine influenza virus strain and preparation method thereof as well as vaccine prepared from recombinant canine influenza virus strain
InactiveCN103881983AHigh viral titeHigh hemagglutination titerMicroorganism based processesAntiviralsChick embryosAvian influenza virus
The invention discloses a recombinant canine influenza virus strain and a preparation method thereof as well as a vaccine prepared from the recombinant canine influenza virus strain. A recombinant canine influenza virus comprises HA and NA genes of a H3N2 subtype canine influenza virus and six internal genes of a H9N2 avian influenza virus including PB2, PB1, PA, NP, M and NS. The recombinant canine influenza virus strain disclosed by the invention is named after rH3N2-DL. The preservation number of the recombinant canine influenza virus strain disclosed by the invention is CGMCC No.8162. The invention further discloses the preparation method of the recombinant canine influenza virus and the vaccine prepared from the recombinant canine influenza virus. Compared with the parental strain, the recombinant canine influenza virus disclosed by the invention has high virus titer and blood congeal titer both on chick embryos and MDCK cells. Animal experimental results show that the vaccine prepared from the recombinant canine influenza virus has good immunogenicity and protective efficacy.
Owner:HARBIN VETERINARY RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Attenuated african swine fever virus strain induces protection against challenge with homologous virulent parental virus georgia 2007 isolate
ActiveUS9463234B2Viral antigen ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementVirulent characteristicsDomestic pig
African swine fever virus (ASFV) is the etiological agent of a contagious and often lethal viral disease of domestic pigs that has significant economic consequences for swine breeding. Control of ASF has been hampered by the unavailability of vaccines. Recombinant viruses harboring engineered deletions of specific virulence-associated genes induce solid protection against the challenge with parental viruses. Here we report the construction of a recombinant Δ9GL virus derived from the highly virulent ASFV Georgia 2007 (ASFV-G) isolate. In vivo, ASFV-G Δ9GL administered intramuscularly (IM) to swine at relatively high doses (104 HAD50) retains a virulent phenotype practically indistinguishable from the parental virus. Conversely, at low IM doses (102 or 103 HAD50), ASFV-G Δ9GL does not induce disease. Importantly, animals infected with 103 HAD50 are protected against the presentation of clinical disease when challenge at 28 days post infection with the virulent parental strain Georgia 2007.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA +1
Recombinant canine influenza virus strain, its preparation method and vaccine prepared therefrom
InactiveCN103881983BImproving immunogenicityMicroorganism based processesAntiviralsChick embryosAvian influenza virus
The invention discloses a recombinant canine influenza virus strain and a preparation method thereof as well as a vaccine prepared from the recombinant canine influenza virus strain. A recombinant canine influenza virus comprises HA and NA genes of a H3N2 subtype canine influenza virus and six internal genes of a H9N2 avian influenza virus including PB2, PB1, PA, NP, M and NS. The recombinant canine influenza virus strain disclosed by the invention is named after rH3N2-DL. The preservation number of the recombinant canine influenza virus strain disclosed by the invention is CGMCC No.8162. The invention further discloses the preparation method of the recombinant canine influenza virus and the vaccine prepared from the recombinant canine influenza virus. Compared with the parental strain, the recombinant canine influenza virus disclosed by the invention has high virus titer and blood congeal titer both on chick embryos and MDCK cells. Animal experimental results show that the vaccine prepared from the recombinant canine influenza virus has good immunogenicity and protective efficacy.
Owner:HARBIN VETERINARY RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Oxygen-regulated microorganisms
The present invention relates to novel strains of microorganisms with oxygen-regulated metabolism. The microorganisms have higher growth rates and are more efficient than parental strains. The microorganisms may be used to produce a variety of products of interests, such as recombinant proteins, nucleic acids, such as DNA, amino acids, and chemicals.
Owner:SCARAB GENOMICS LLC
A type 3 duck hepatitis A virus mutant gene isa-t1142a and its construction method
ActiveCN110283836BAccelerate cultivationSpeed up the research processSsRNA viruses positive-senseViral antigen ingredientsNucleotideVirus Protein
The invention discloses a type 3 duck hepatitis A virus mutant gene ISA-T1142A and its construction method. The 3403rd nucleotide G of the mutant gene genome is mutated into T, which can be used as a genetic marker for infectious clones and can be used to distinguish rescued strains With the parental strain and the wild strain; the 1142nd nucleotide is mutated from T to A, so that the 164th amino acid of the virus VPO protein is mutated from the tyrosine of the parental strain to asparagine. The mutant gene virus strain has the same antigenicity as the parent strain, and has higher proliferation efficiency and virus titer than the parent strain on duck embryos, and has good immunogenicity and genetic stability. The pathogenicity of the mutant gene virus strain to ducklings has been significantly reduced, which has laid an important foundation for the pathogenic mechanism of the virus and the development of vaccines. In conclusion, the type 3 duck hepatitis A virus mutant gene ISA‑T1142A virus strain can be used as a vaccine candidate or strain and can be used for the study of the attenuation mechanism of type 3 duck hepatitis A virus, with broad application prospects.
Owner:SICHUAN AGRI UNIV
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com