Patents
Literature
113 results about "Post infection" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
POST OPERATIVE INFECTIONS. Post operative infections are a concern following any type of surgery. Since the skin is the body’s largest natural barrier against infection, anything that causes a break in the skin has the potential to lead to an infection. Post operative infections pose a threat to the health and well being of a patient,...
Mycobacterial proteins as early antigens for serodiagnosis and vaccines
In view of the paucity of human material available to study the immunological events occurring after inhalation of virulent bacilli, but prior to development of clinical TB, the present invention is based in part on studies of aerosol infected rabbits. The present inventors reasoned that by 3-5 weeks post-infection, the sera from infected rabbits would contain antibodies to the antigens being expressed by the in vivo bacteria.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
Algorithm for estimating the outcome of inflammation following injury or infection
InactiveUS20030087285A1Medical simulationMicrobiological testing/measurementInterleukin 6Interleukin 10
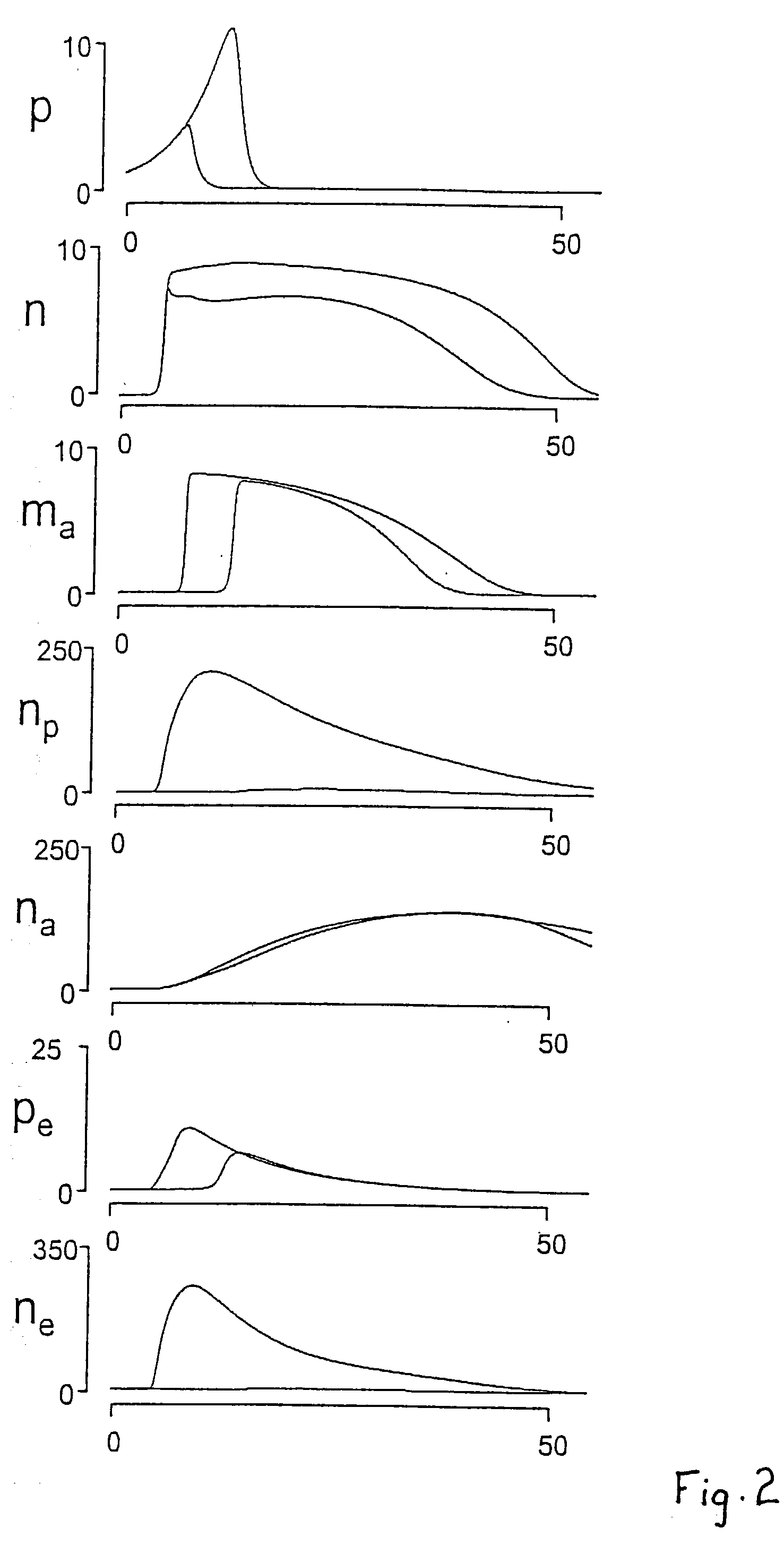
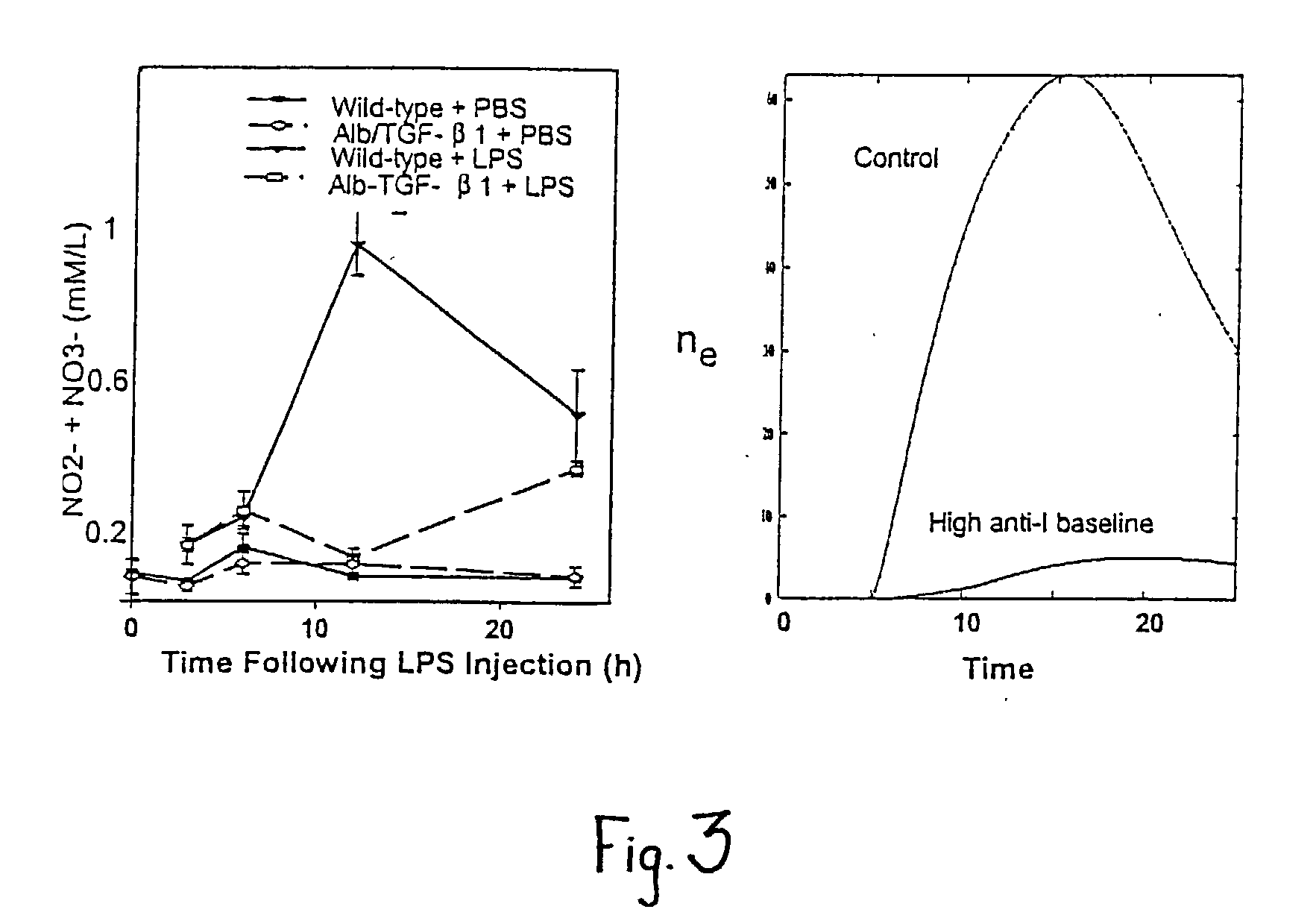
A mathematical prognostic in which changes in a number of physiologically significant factors are measured and interpolated to determine a "damage function" incident to bacterial infection or other serious inflammation. By measuring a large number of physiologically significant factors including, but not limited to, Interleukin 6 (IL6), Interleukin 10 (IL10), Nitric Oxide (NO), and others, it is possible to predict life versus death by the damage function, dD / dt, which measures and interpolates differential data for a plurality of factors. In mammals, an IL6 / NO ratio <8 at 12 hours post infection is highly predictive (60%) of mortality; also in mammals, an IL6 / NO ratio <4 at 24 hours post infection is highly predictive (52%) of mortality; and an IL6 / IL10 ratio in mammals of <7.5 at 24 hours post infection is highly predictive (68%) of mortality.
Owner:PITTSBURGH UNIV OF
Combined therapy for treatment of HIV infection
InactiveUS7094413B2Good curative effectReduce resistanceBiocideSugar derivativesImmunodeficiency virusGastrointestinal complications
The present invention relates to pharmaceutical preparations and methods for treating individuals infected with the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). The pharmaceutical preparations comprise an immunomodulating agent and a anti-retroviral compound. The pharmaceutical preparations are used to treat HIV infected patients, particularly for gastrointestinal complications arising from viral infection. In addition, the pharmaceutical preparations of the present invention have the effect of raising the levels of CD4+ single positive and CD4+ and CD8+ double positive T cells, thus promoting restoration and normalization of the immune system following HIV infection.
Owner:SANGSTAT MEDICAL +1
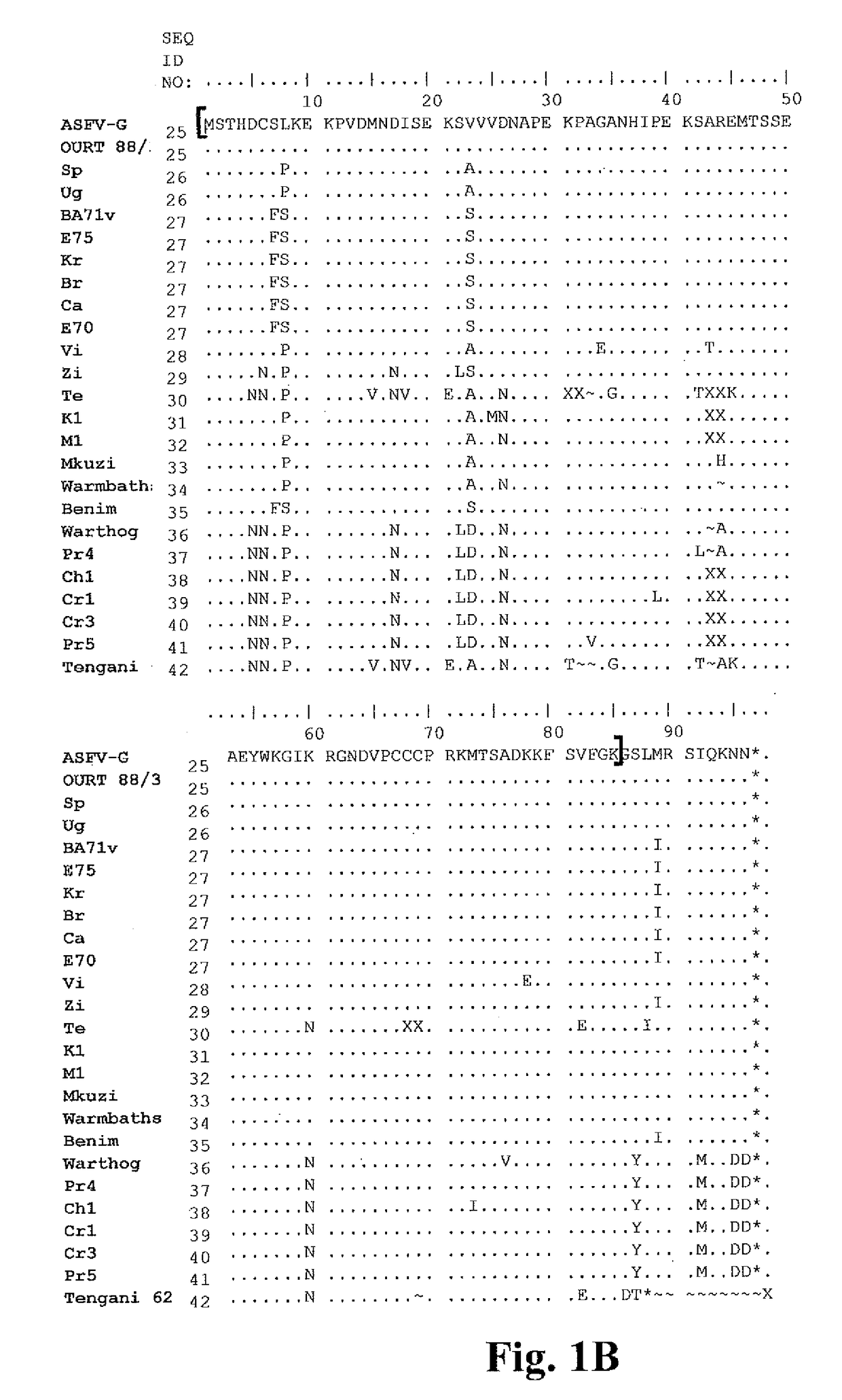
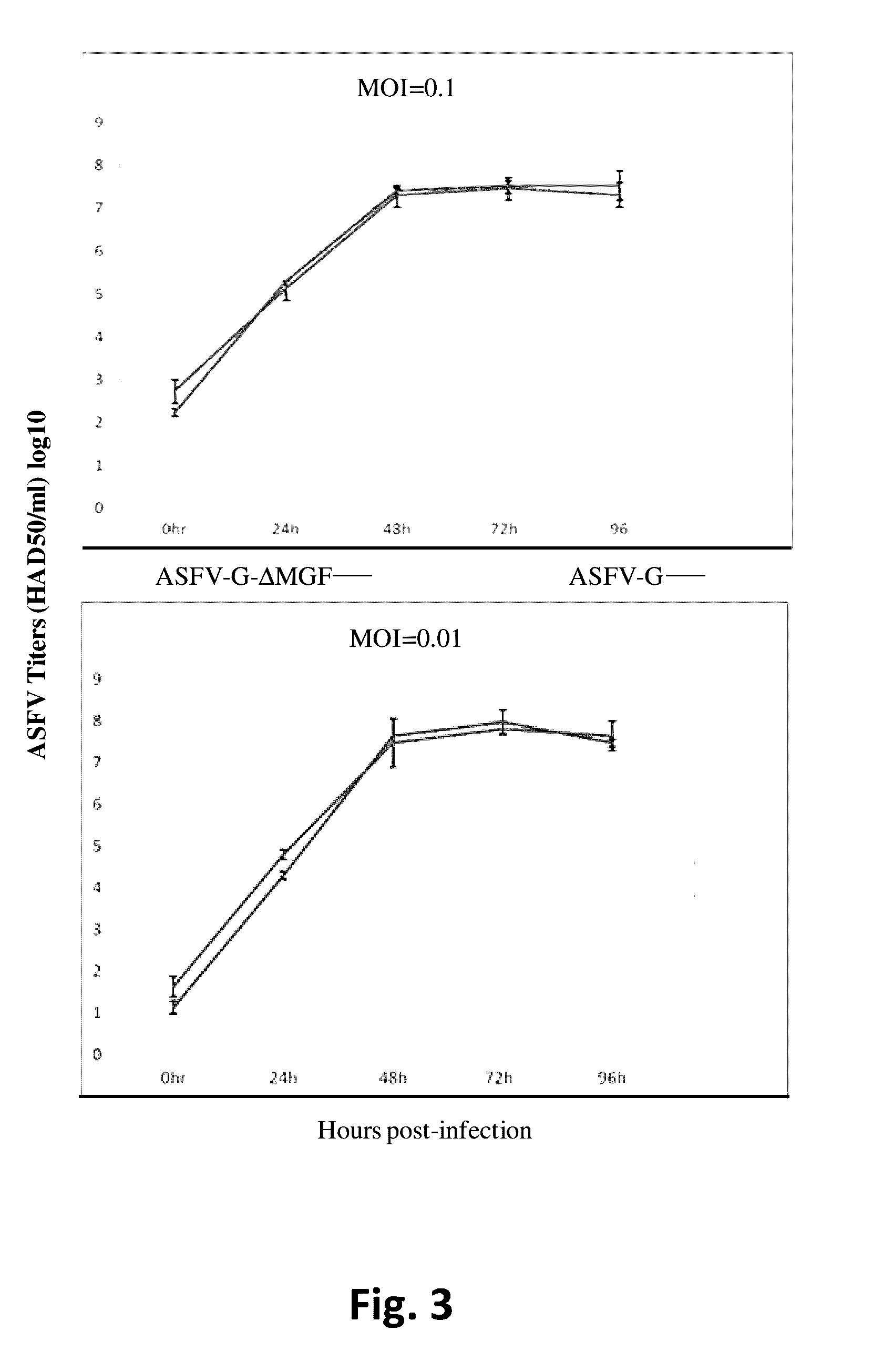
Attenuated African Swine Fever Virus Vaccine Based in the Deletion of MGF Genes
ActiveUS20160130562A1Viral antigen ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementVirulent characteristicsDomestic pig
African swine fever virus (ASFV) is the etiological agent of a contagious and often lethal viral disease of domestic pigs. Control of ASF has been hampered by the unavailability of vaccines. Experimental vaccines have been derived from naturally occurring, cell culture-adapted, or genetically modified live attenuated ASFVs; however, these vaccines are only successful when protecting against homologous viruses. Among viral genes reported to be involved in virulence are components of the multi gene family (MGF). Here we report the construction of a recombinant ΔMGF virus derived from the highly virulent ASFV Georgia 2007 (ASFV-G) isolate. In vivo, ASFV-G ΔMGF administered intramuscularly (IM) to swine at either 102 or 104 HAD50 are completely attenuated; the inoculated animals are completely asymptomatic. Animals infected with 102 or 104 HAD50 of ASFV-G ΔMGF are protected against the presentation of clinical disease when challenged at 28 days post infection with the virulent parental strain Georgia 2007.
Owner:US SEC AGRI +1
Combinant polypeptide for use in the manufacture of vaccines against Campylobacter induced diarrhea and to reduce colonization
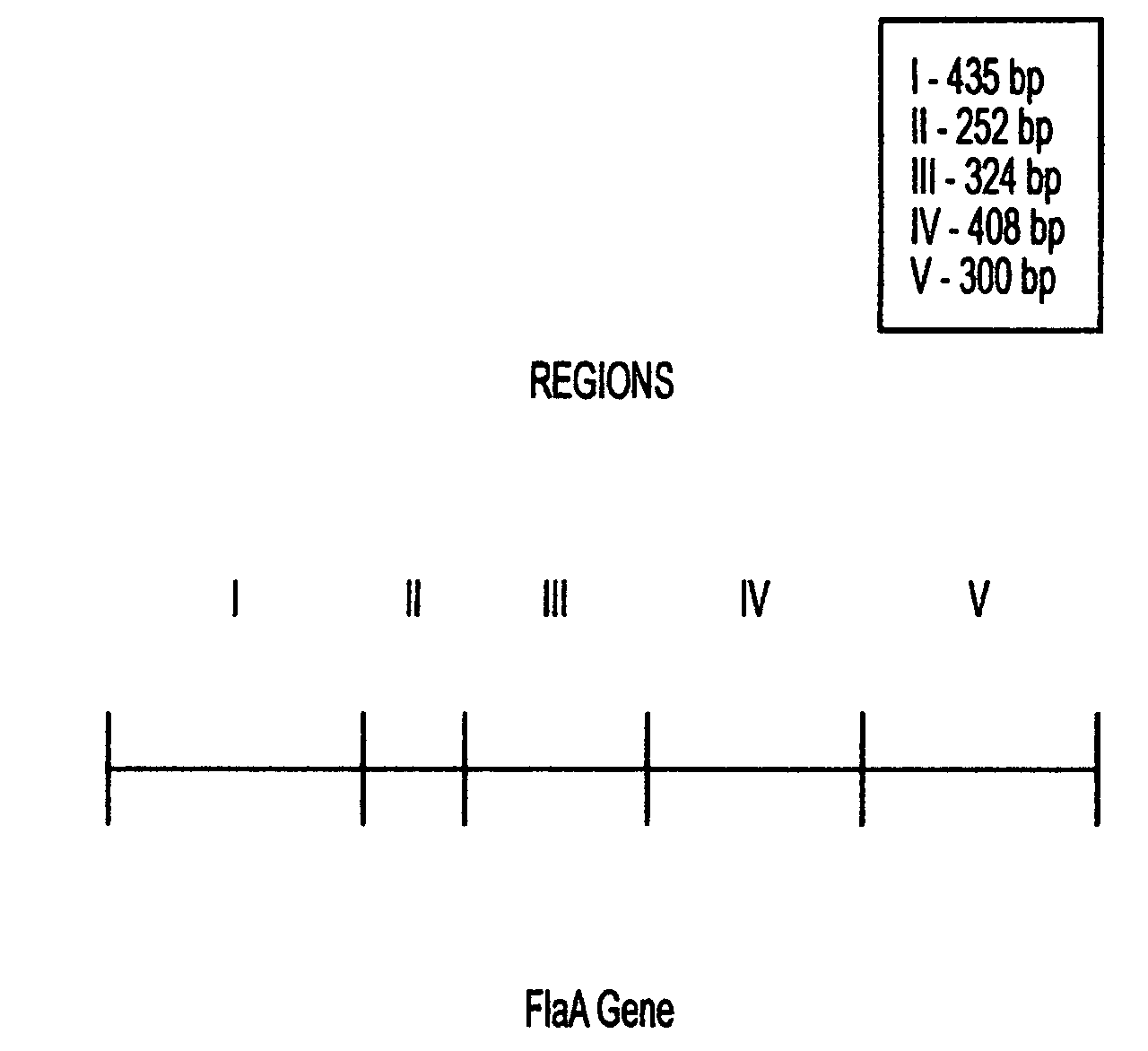
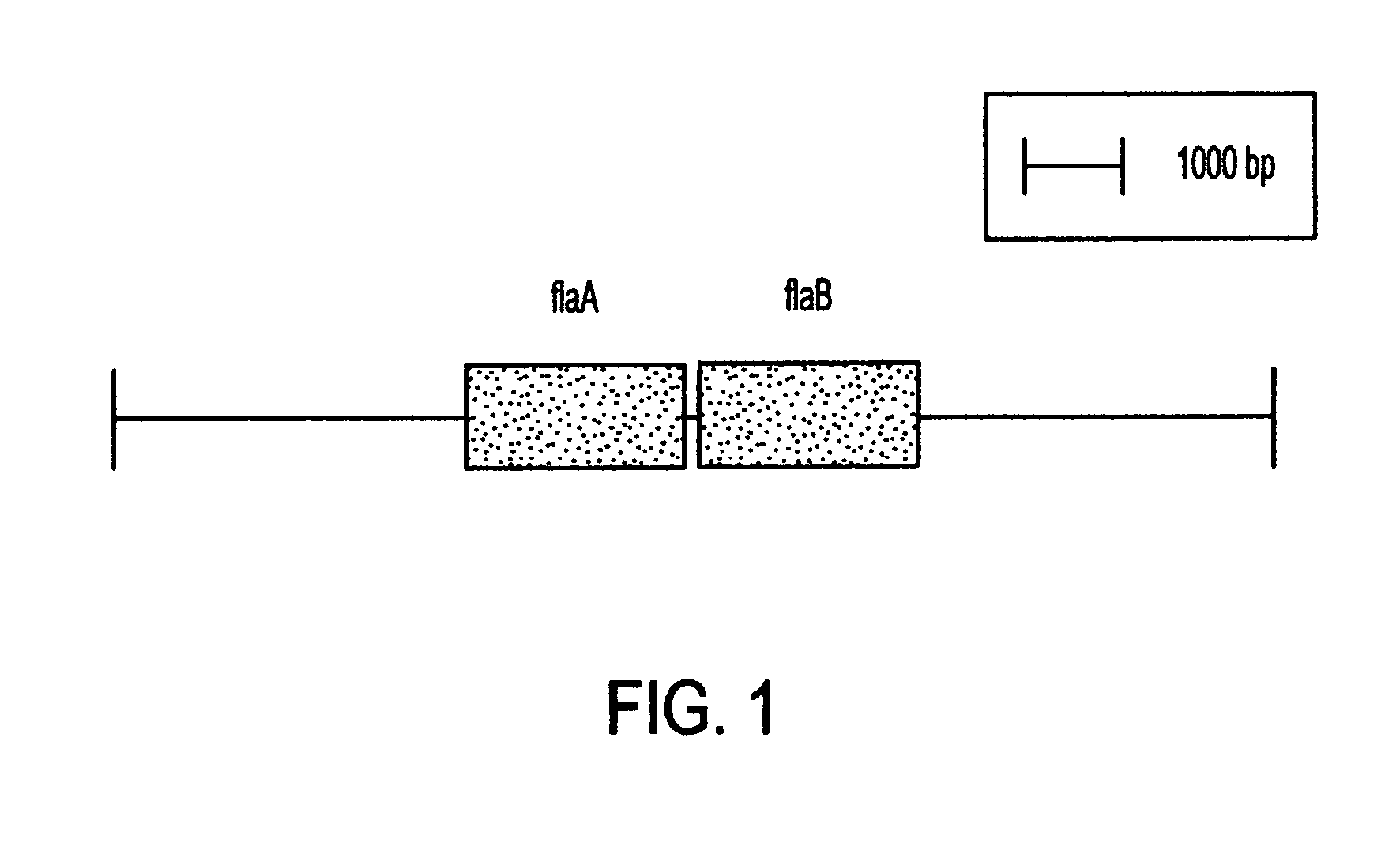
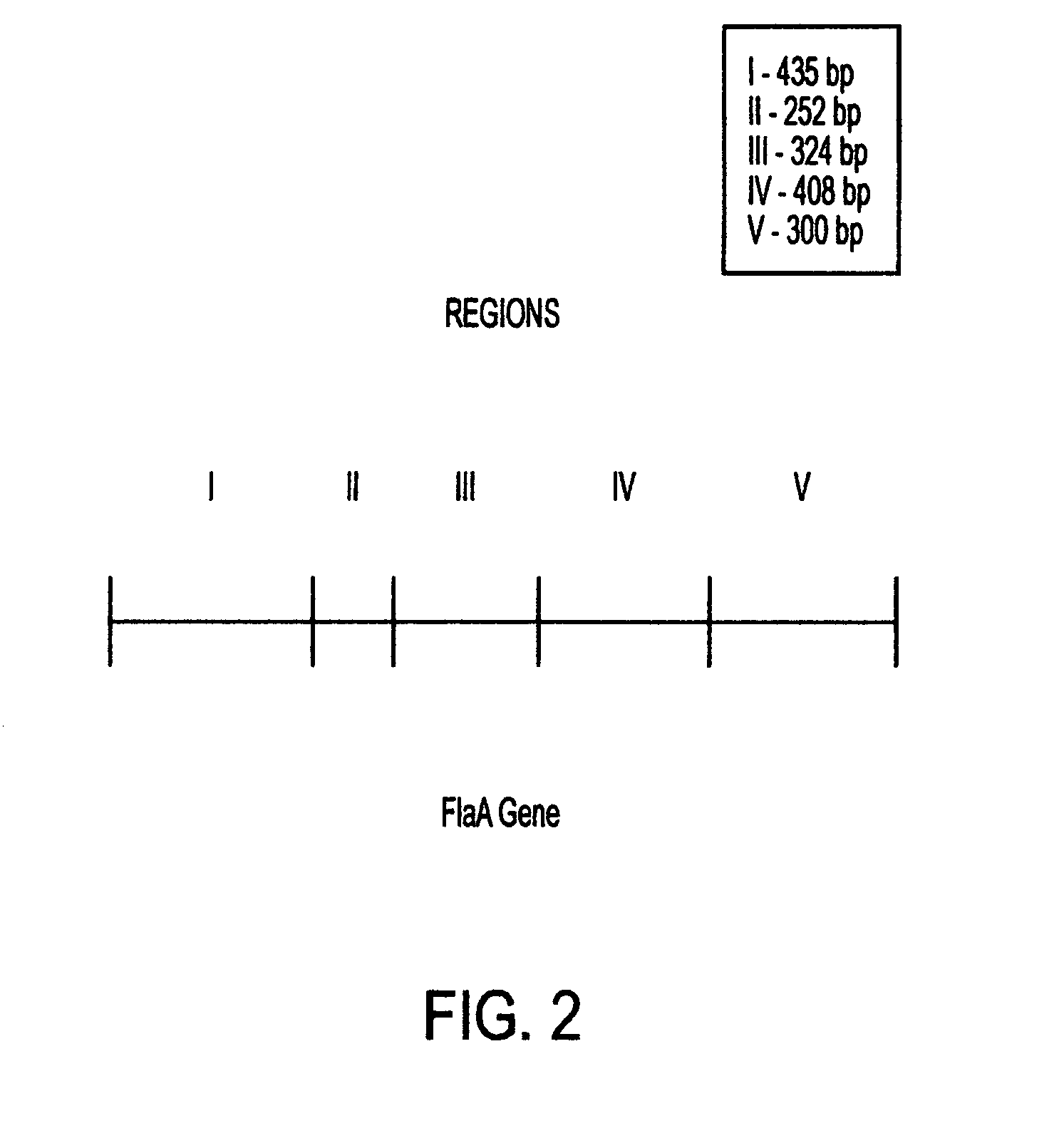
This invention comprises a recombinant protein comprising the maltose binding protein (MBP) of Escherichia coli fused to amino acids 5–337 of the FlaA flagellin of Campylobacter coli VC167 which has provided evidence of immunogenicity and protective efficacy against challenge by a heterologous strain of campylobacter, Campylobacter jejuni 81–176 in mammals. The invention further comprises a recombinant DNA construct encoding the immunodominant region (region I through III) of flagellin from Campylobacter spp. for use as a component of a vaccine against Campylobacter diarrhea. The invention therefore represents an effective treatment against Campylobacter but avoids inducing the autoimmune Guillain Barre Syndrome (GBS), a post-infection polyneuropathy caused by Campylobacter molecular mimicry of human gangliosides which has hampered the development of vaccines heretofore.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
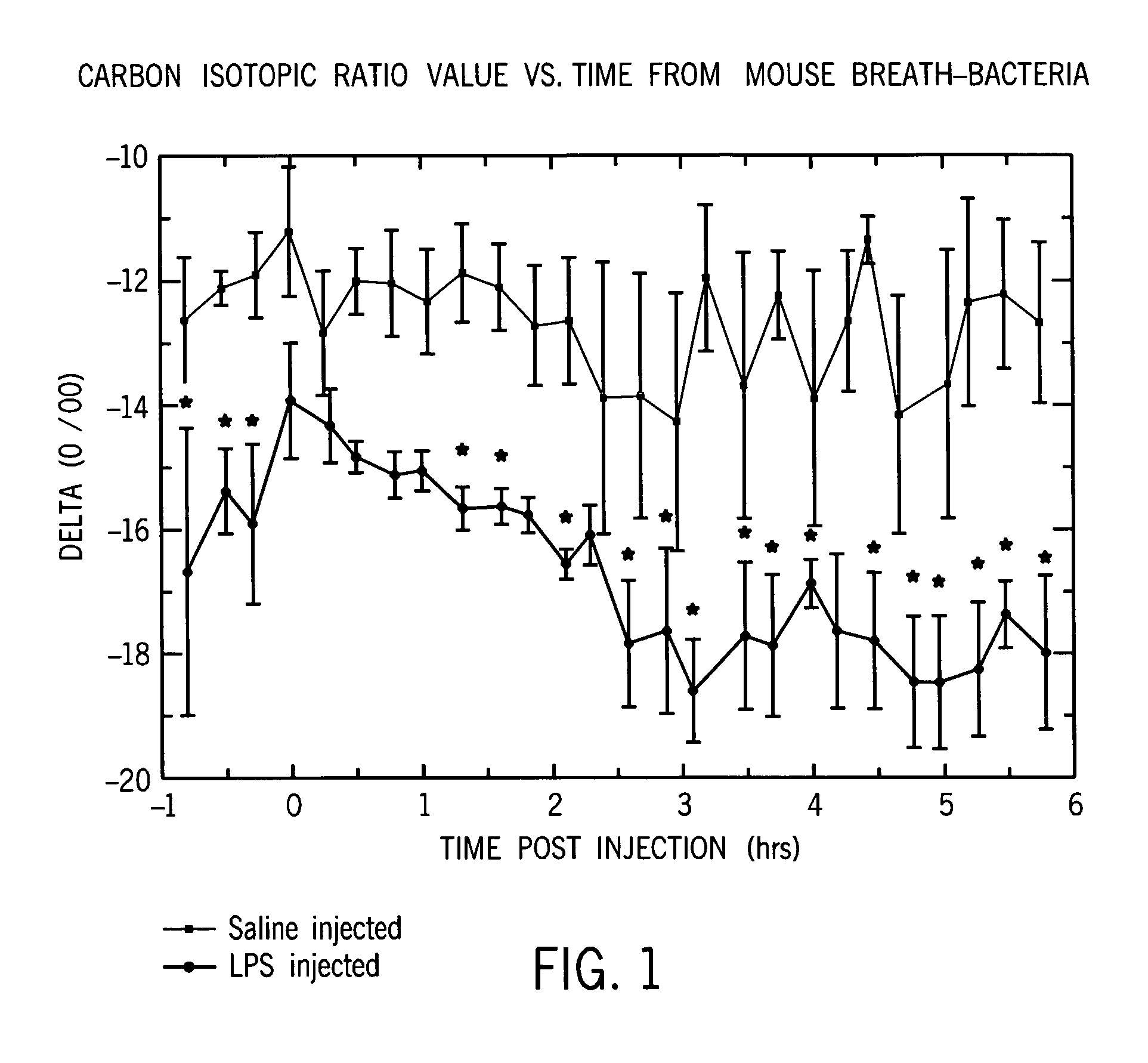
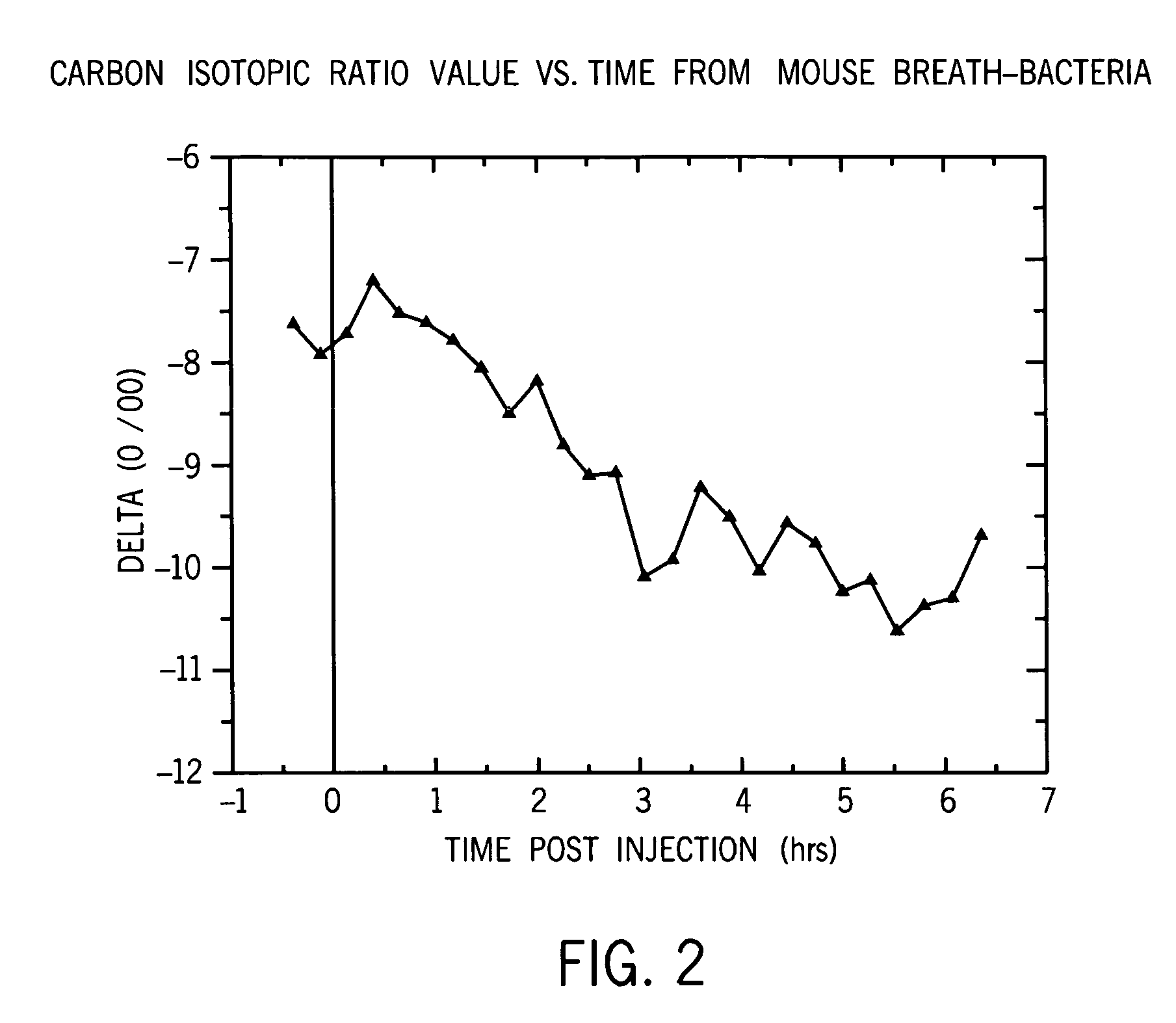
Identification of disease characteristics using isotope ratios in breath
ActiveUS7465276B2Early effective indicatorEasy to detectWithdrawing sample devicesRespiratory organ evaluationTriageIsotope
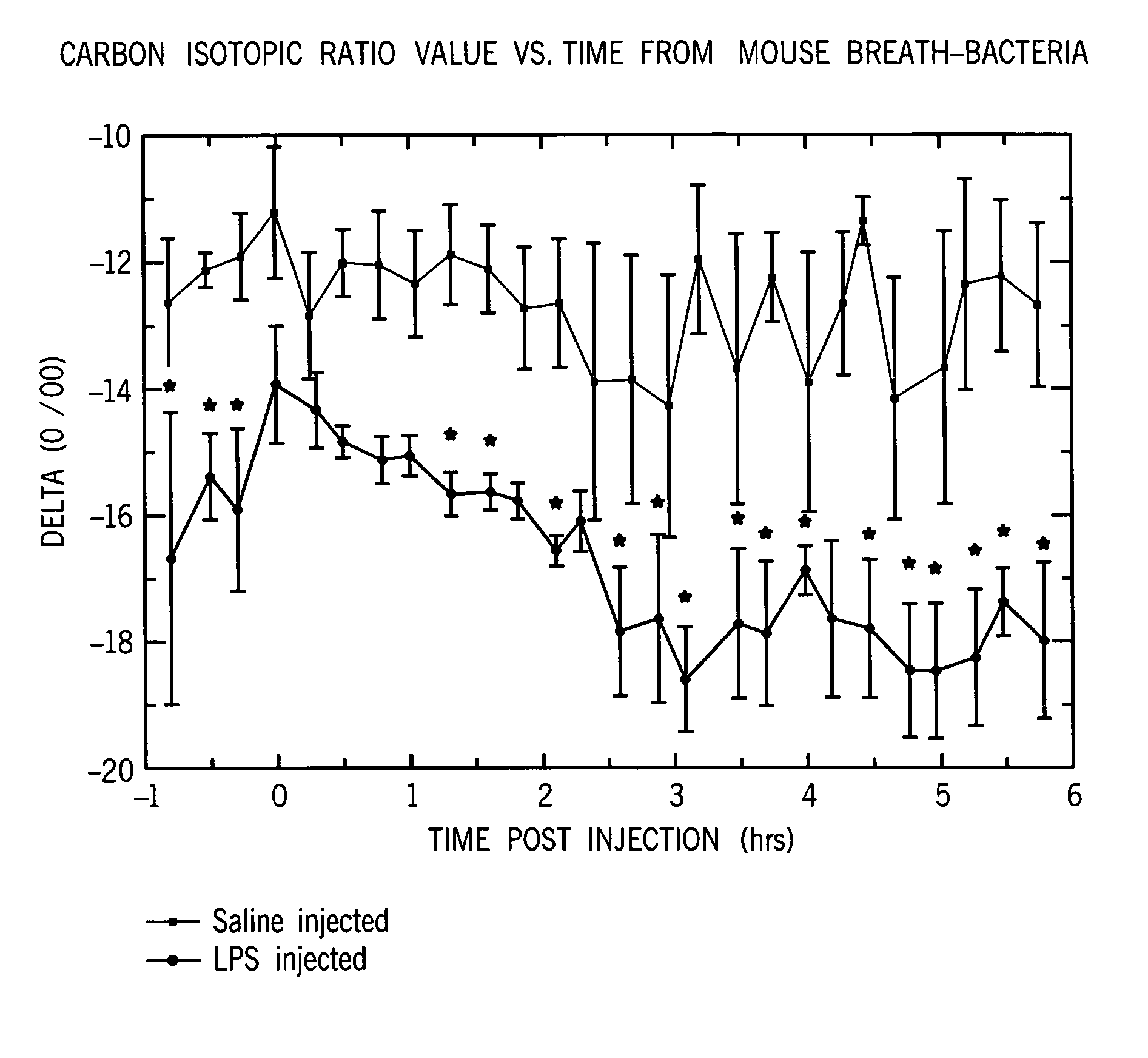
Methods are disclosed for distinguishing whether an animal is experiencing a bacterial infection or a viral infection. One monitors breath taken from the animal over time to measure the relative amount of a first breath stable isotope to a second breath stable isotope therein over time. A quick change in the isotope ratios within several hours from the likely infection is indicative of a bacterial infection. A delayed change in the isotope ratios, followed by periodic repeated alterations in the ratios, is indicative of viral infection. The methods are particularly efficient when using cavity ringdown spectroscopy for the monitoring. They may be used for monitoring a patient already admitted to a hospital, or for monitoring a patient initially complaining of adverse symptoms, or for triage, or for collectively monitoring a population of animals.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
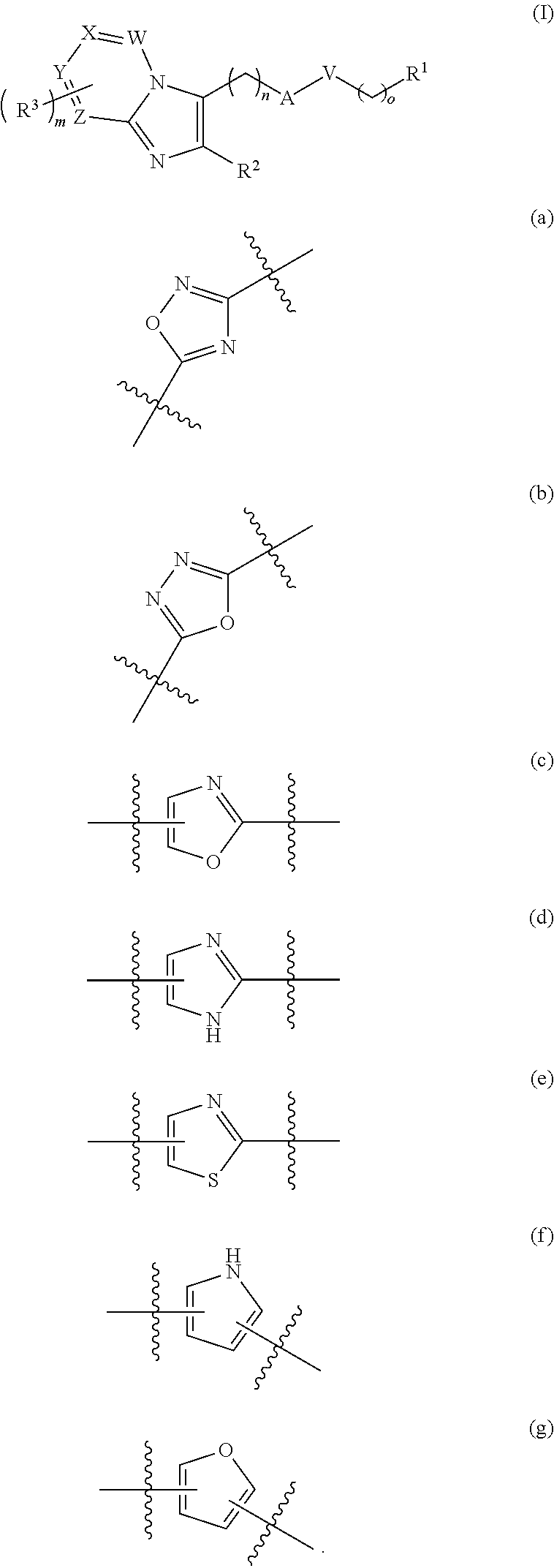
Anti-inflammation compounds
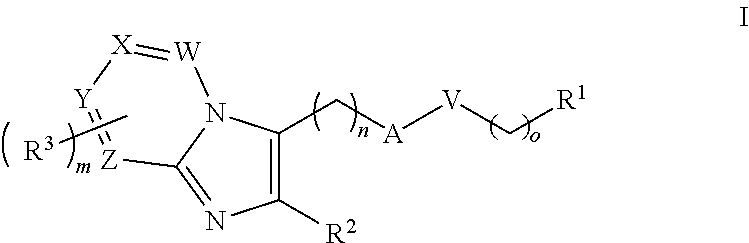
The present invention refers to: a compound having the general formula (I), wherein n is 0, 1, 2 or; m is 0, 1, 2 or 3; o is 0, 1, 2 or 3; W, X, Y and Z are independently selected from CH, N or N-oxide; A is NR4, C═O, C═S, OP(O)(O), P═O, CH2, or a heteroarly selected from the group consisting of (a), (b), (c), (d), (e), (f), (g); V is C═O, O, S, CH2, or NR5; as well as its use in treating inflammatory diseases such as asthma, COPD, inflammation post infection, arthritis, atherosclerosis, pain and dermatitis.
Owner:QURIENT CO LTD +1
Cloud based systems and methods for determining and visualizing security risks of companies, users, and groups
Systems and method implemented through a distributed security system for determining and addressing risk of users, groups of users, locations, and / or companies include obtaining log data from the distributed security system; analyzing the log data to obtain a risk score for an entity associated with the distributed security system, wherein the entity comprises one of a user, a group of users, a location, and a company, and wherein the risk score is a weighted combination of pre-infection behavior, post-infection behavior, and suspicious behavior; performing one or more remedial actions for the entity; and subsequently obtaining updated log data and analyzing the updated log data to obtain an updated risk score to determine efficacy of the one or more remedial actions.
Owner:ZSCALER INC
Live attenuated antigenically marked classical swine fever virus
ActiveUS20080292653A1Effective protectionSsRNA viruses positive-senseAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsEpitopeStructural glycoprotein
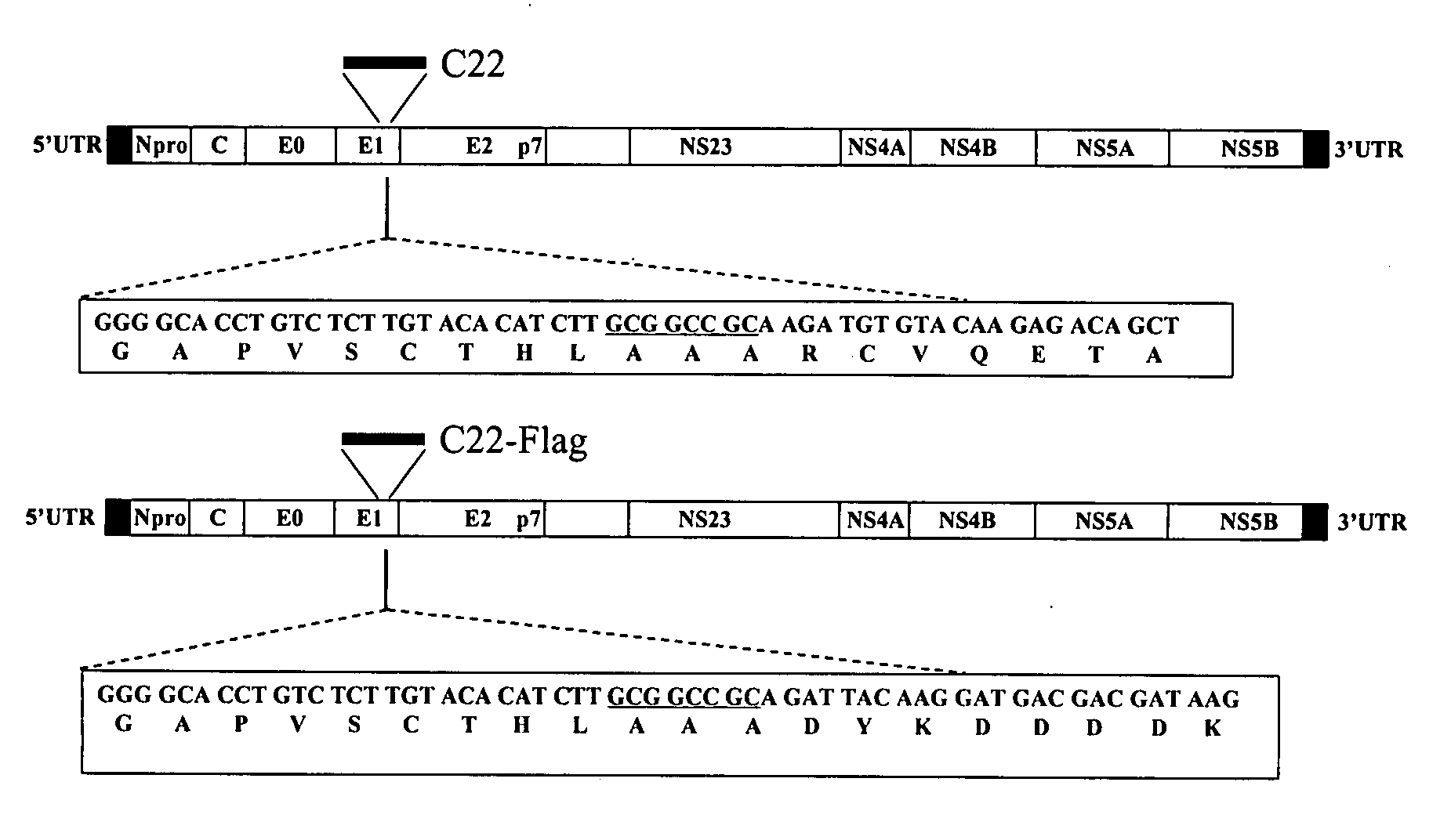
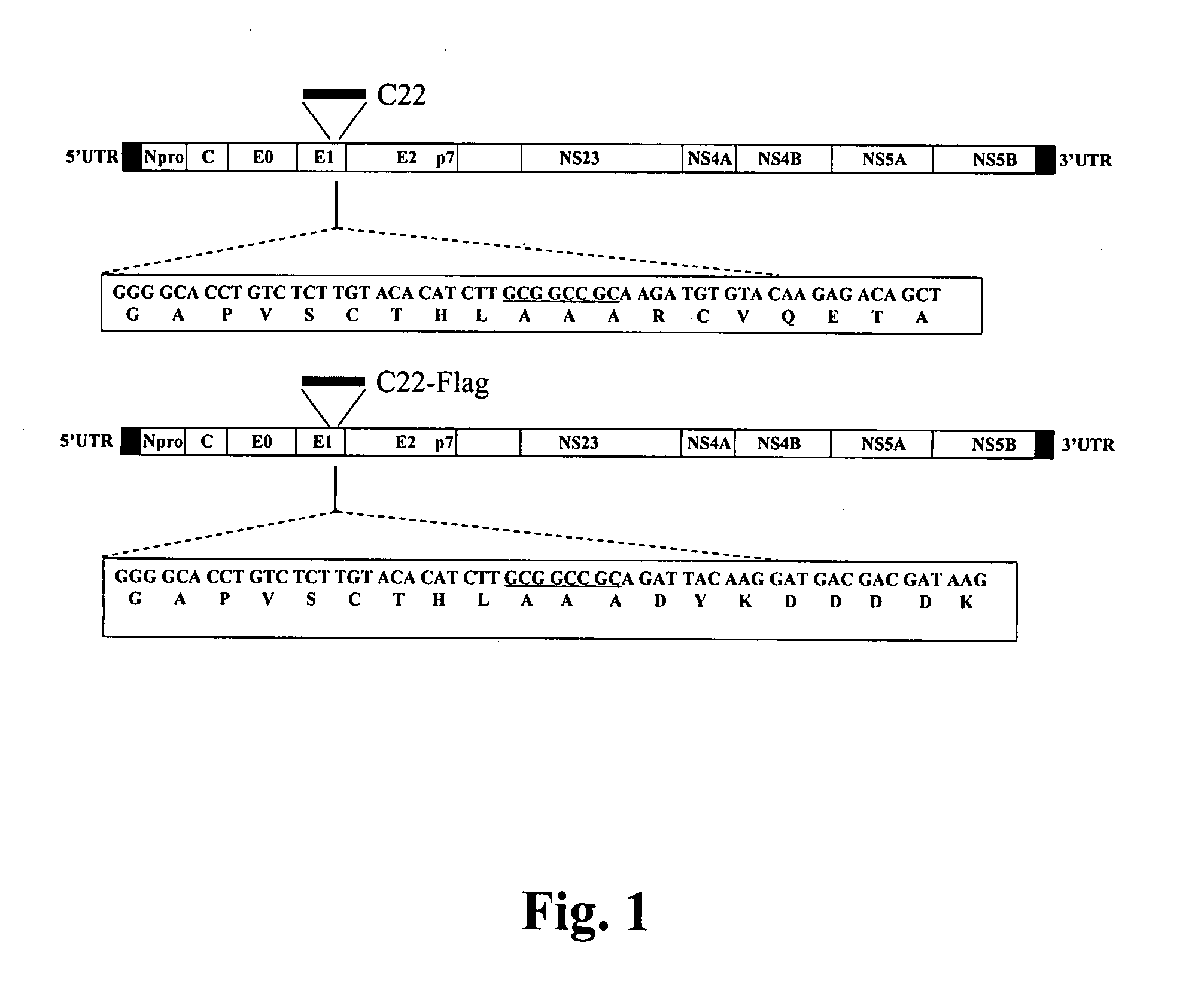
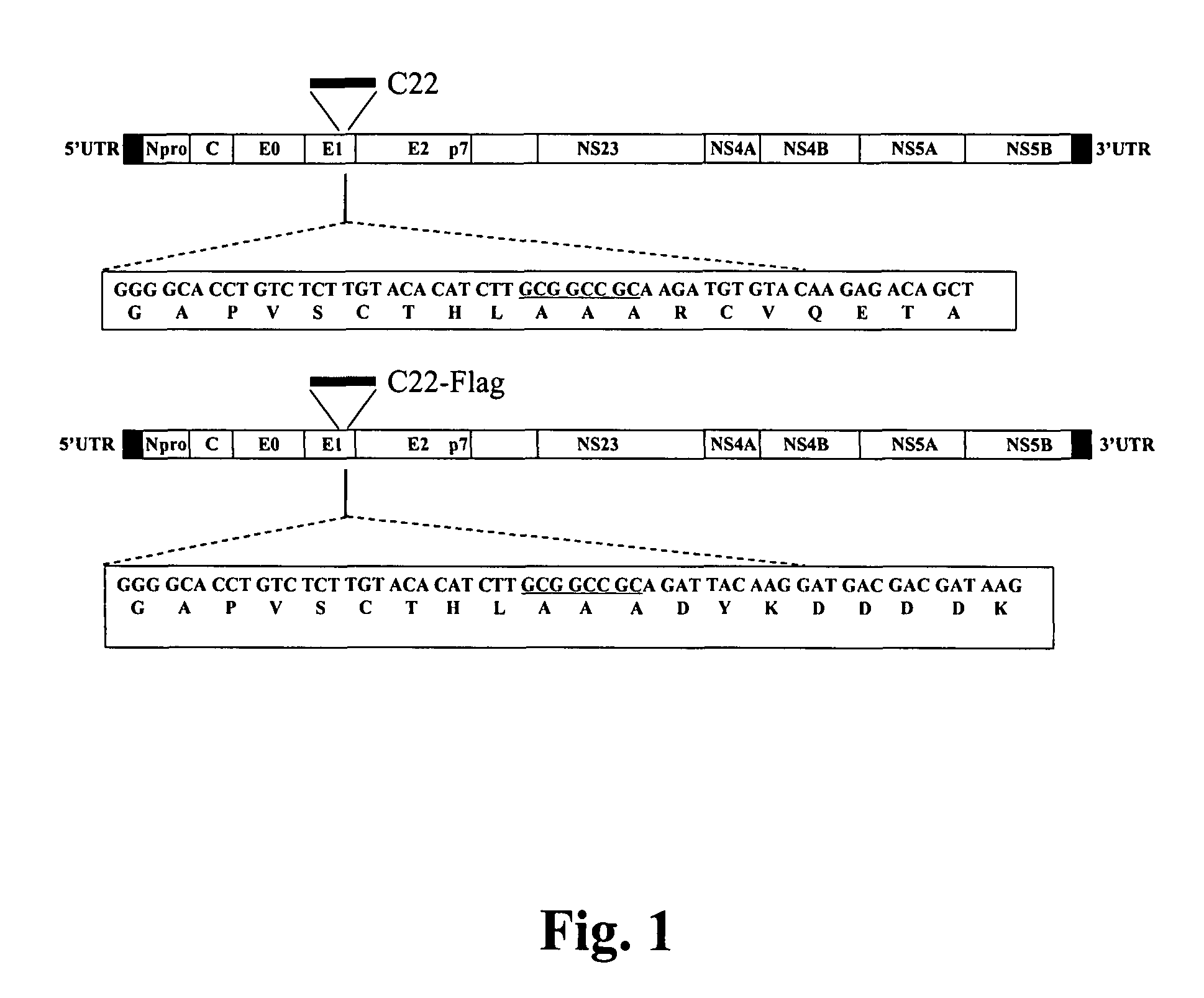
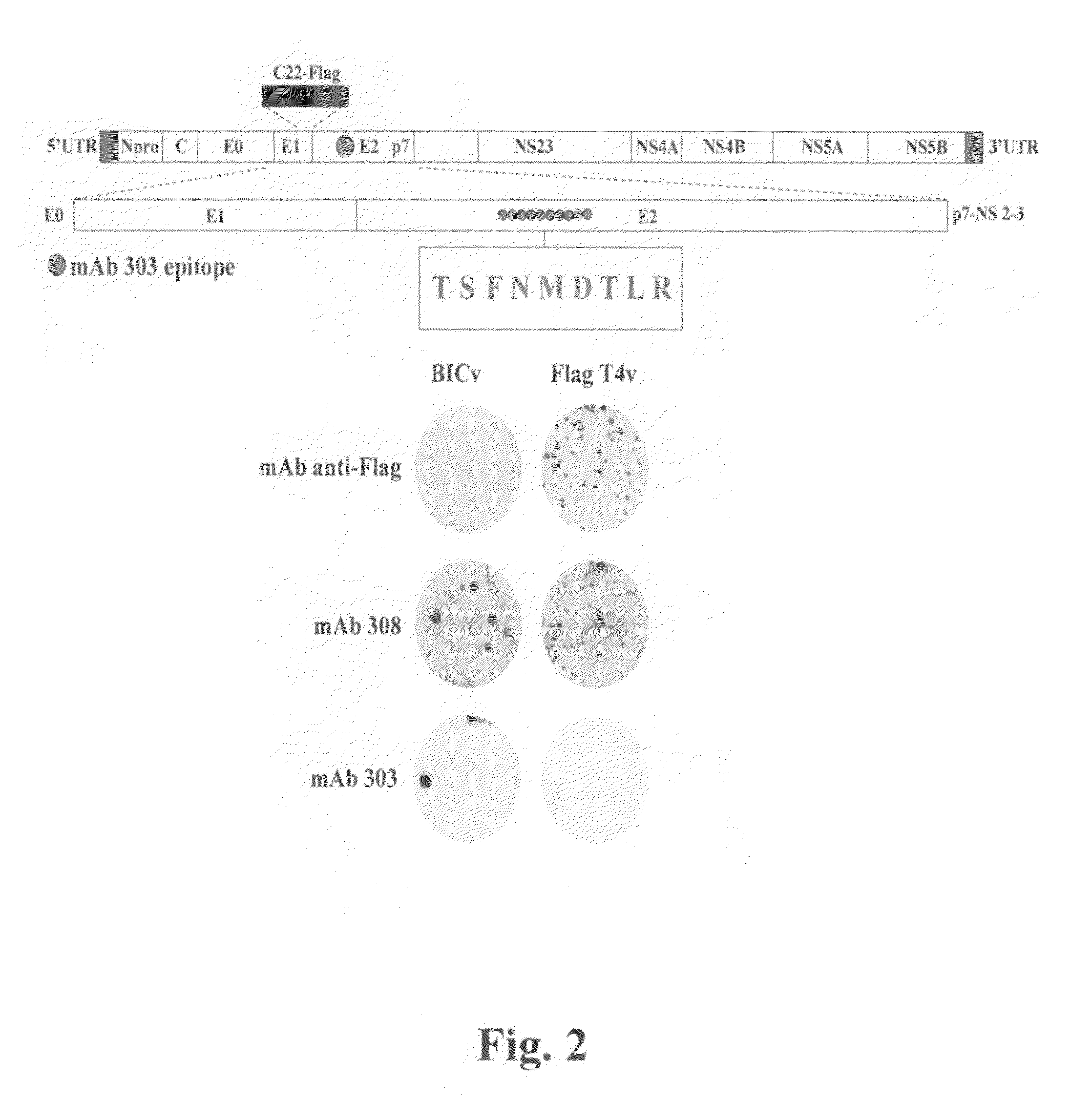
Classical swine fever virus is a world-wide distributed highly-contagious disease affecting swine. The two main strategies for diseases control are prophylactic vaccination and non-vaccination stamping out policies. Marker vaccines are a promising strategy. Here we report the rational development of a doubly antigenic marker CSFV experimental live attenuated candidate strain vaccine (Flag / T4 virus). Flag / T virus (Flag / T4v) is based in the combination of two Brescia derived recombinant attenuated viruses: RB-C22 and T4. RB-C22v contains a 19mer insertion in the structural glycoprotein E1, while T4v posses mutated CSFV amino acid residues 830 to 834 in the structural glycoprotein E2, deleting the highly conserved epitope recognized by monoclonal antibody (mAb) WH303. Flag / T4 virus contains a positive foreign antigenic marker, due to the insertion of the highly antigenic epitope Flag in the 19mer insertion of E1, as well as a negative antigenic marker, the lack of reactivity with mAb WH303. Immunized with Flag / T4v induced a complete protection against the challenge with virulent strain Brescia both at 3 and 28 days post infection when nasally administered and since the second day post infection when intramuscularly administered. These results constitute an example of rational design of a CSFV antigenically marked LAV.
Owner:AGRI UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS RESPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE +1
Rationally developed african swine fever attenuated virus strain protects against challenge with parental virus georgia 2007 isolate
ActiveUS9808520B1Viral antigen ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementAfrican swine feverDomestic pig
African swine fever virus (ASFV) is the etiological agent of a contagious, often lethal viral disease of domestic pigs. The control of African Swine Fever (ASF) has been hampered by the unavailability of vaccines. Experimental vaccines have been derived from naturally occurring, cell culture-adapted, or genetically modified live attenuated ASFVs; however, these vaccines are only successful when protecting against homologous viruses. We have constructed a recombinant Δ9GL / ΔUK virus derived from the highly virulent ASFV Georgia 2007 (ASFV-G) isolate by deleting the specific virulence-associated 9GL (B119L) and the UK (DP96R) genes. In vivo, ASFV-G Δ9GL / ΔUK administered intramuscularly to swine even at relatively high doses (106 HAD50) does not induce disease. Importantly, animals infected with 104 or 106 HAD50 are solidly protected against the presentation of clinical disease when challenged at 28 days post infection with the virulent parental strain Georgia 2007.
Owner:UNIV OF CONNECTICUT +1
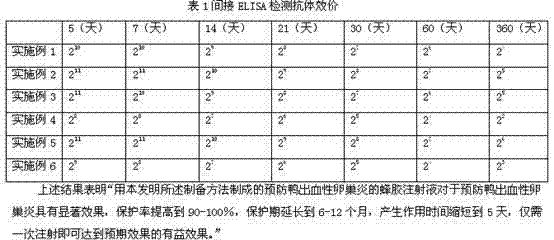
Propolis injection for preventing duck hemorrhagic oophoritis and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102228482AHigh protection rateExtended protection periodAnthropod material medical ingredientsViral antigen ingredientsDiseaseTembusu virus
The invention relates to the field of animal prevention medicine, particularly to a preparation method for an injection for preventing animal epidemic diseases from occurring, wherein the propolis injection for preventing duck hemorrhagic oophoritis is composed of a propolis aqueous solution, a duck embryo homogenated tissue inoculated with duck flavivirus-Tembusu virus and dead by infection, andan inactivation solution; the preparation method comprises the step of adding the inactivation solution in the mixed solution of the duck embryo homogenated tissue and propolis to obtain the propolisinjection for preventing duck hemorrhagic oophoritis; the propolis injection for preventing duck hemorrhagic oophoritis prepared by the preparation method of the invention has a remarkable effect to prevent duck hemorrhagic oophoritis (duck Tembusu virus disease); the protection ratio is increased to 90-100%, the protection period is prolonged to 6-12 months, the action time is shortened to 5 days, and only once injection can achieve an expected effect.
Owner:CHONGQING ACAD OF ANIMAL SCI
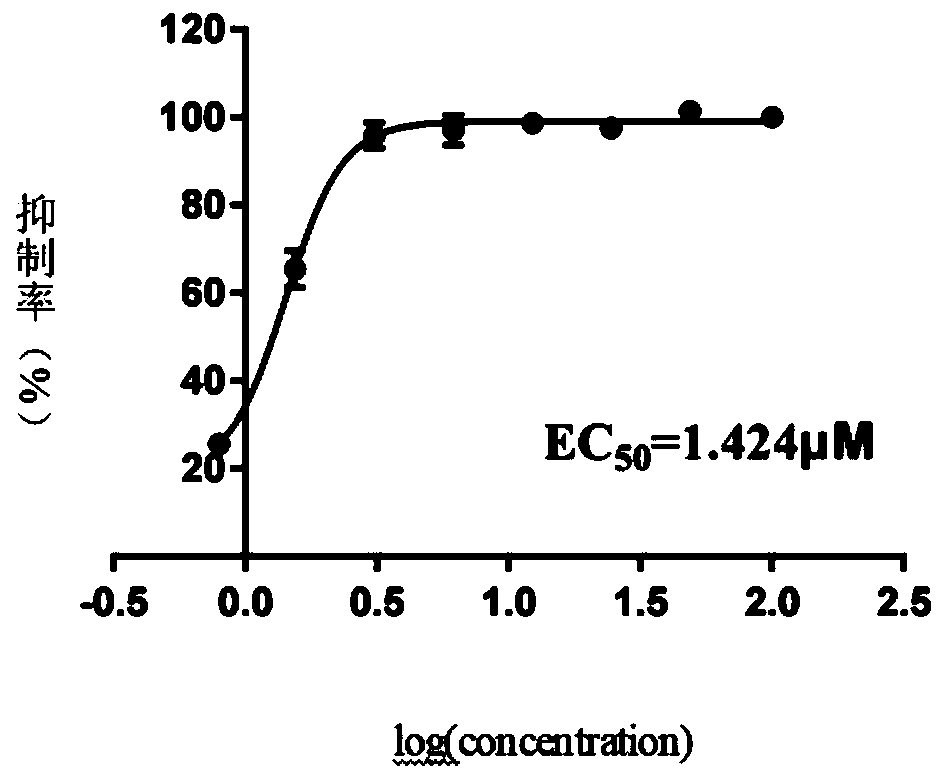
Application of GS-441524 in preparation of novel coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 inhibitor
InactiveCN111135184AImprove securitySmall toxicityOrganic active ingredientsAntiviralsDiseasePost infection
The invention discloses the application of GS-441524 in the preparation of a novel coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 inhibitor. In-vitro cell test results show that the GS-441524 can significantly inhibit the infection of normal cells by SARS-CoV-2, has an inhibition effect on the novel coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 at a cellular level, can significantly reduce the virus titer of the novel coronavirus in cells andinhibit the proliferation of the novel coronavirus in cells, and has dose dependence. Therefore, the GS-441524 can be used as a novel coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 inhibitor, and has the potential of treating COVID-19 pneumonia of human beings caused by infection with the coronavirus or other diseases of animals caused by infection with the coronavirus.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV +1
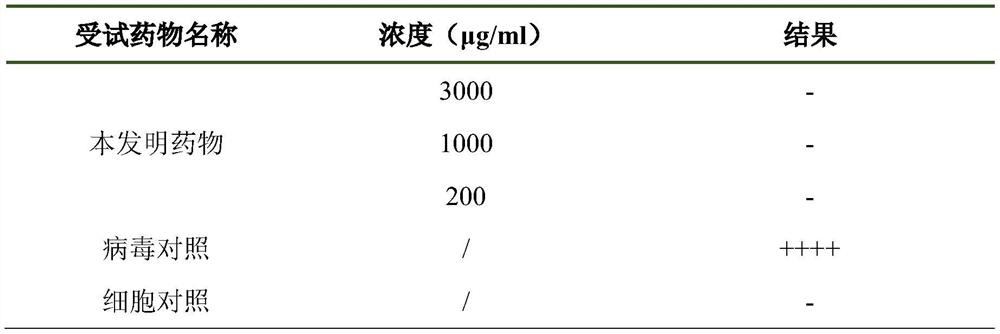
Application of traditional Chinese medicine composition in preparation of medicine for treating or preventing coronavirus infection
ActiveCN111603515ANo diseaseImprove protectionAntiviralsRespiratory disorderBiotechnologyInfected cell
The invention discloses application of a traditional Chinese medicine composition in preparation of a medicine for treating or preventing coronavirus infection. The traditional Chinese medicine composition is characterized by being prepared from 5-30 parts of herba houttuyniae, 5-30 parts of honeysuckle flowers, 5-20 parts of radix paeoniae rubra, 3-15 parts of folium artemisiae argyi and 3-15 parts of herba menthae. According to the invention, the inhibition effect of the traditional Chinese medicine composition on the novel coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 under different concentrations is investigated on Vero cells; experimental results show that under the concentrations of 3000 [mu] g / ml, 1000 [mu] g / ml and 200 [mu] g / ml, the traditional Chinese medicine composition shows a good protective effect on Vero cells infected with SARS-CoV-2 viruses, can inhibit replication of SARS-CoV-2 in cells, and enables infected cells not to have lesions, which indicates that the traditional Chinese medicinecomposition has a good effect of treating or preventing coronavirus-related diseases.
Owner:JIANGSU KANION PHARMA CO LTD
Method for preparing human DNA polymerase delta by using bombyx mori bioreactor
InactiveCN102031263AHigh expressionLow costImmunoglobulins against animals/humansEnzymesEscherichia coliDisease
The invention relates to a method for preparing human DNA polymerase delta by using a bombyx mori bioreactor. The method comprises the following specific steps of: respectively constructing four subunits of the human DNA polymerase delta onto a donor plasmid; carrying out transposition on Tn7 transposons in transformed escherichia coli DH10Bac / BmNPV (Bombyx mori Nuclear Polyhedrosis Virus) and BmNPV DNA and screening out clones with correct subunits; and then preparing recombinant viruses of the four subunits assembled by different combinations in BmN cells; infecting host bombyx mori; performing the expression and assembly of a multi-subunit protein complex in bombys mori; and collecting the body liquid of infected larvas or homogenizing entirely, and finally separating and purifying to obtain the target product. By using the method disclosed in the invention, the DNA polymerase multi-subunit protein complex which has high specific activity and is assembled correctly can be prepared efficiently in large scale with low cost. The method can be widely applied to the field of researches on some important diseases, especially on cancers, and the basic research on DNA replication and injury repair.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Combination therapy for the treatment of influenza
InactiveCN102036658AInhibit or reduce the effective amountOrganic active ingredientsAntiviralsInfected cellImmunomodulating Agent
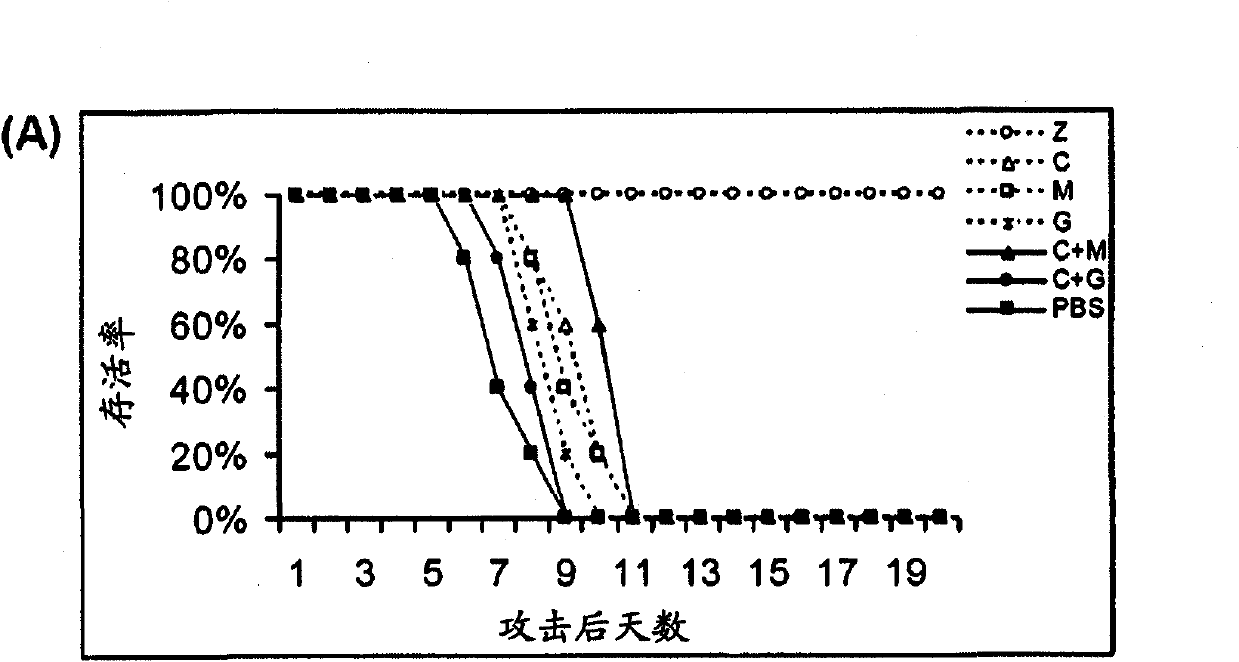
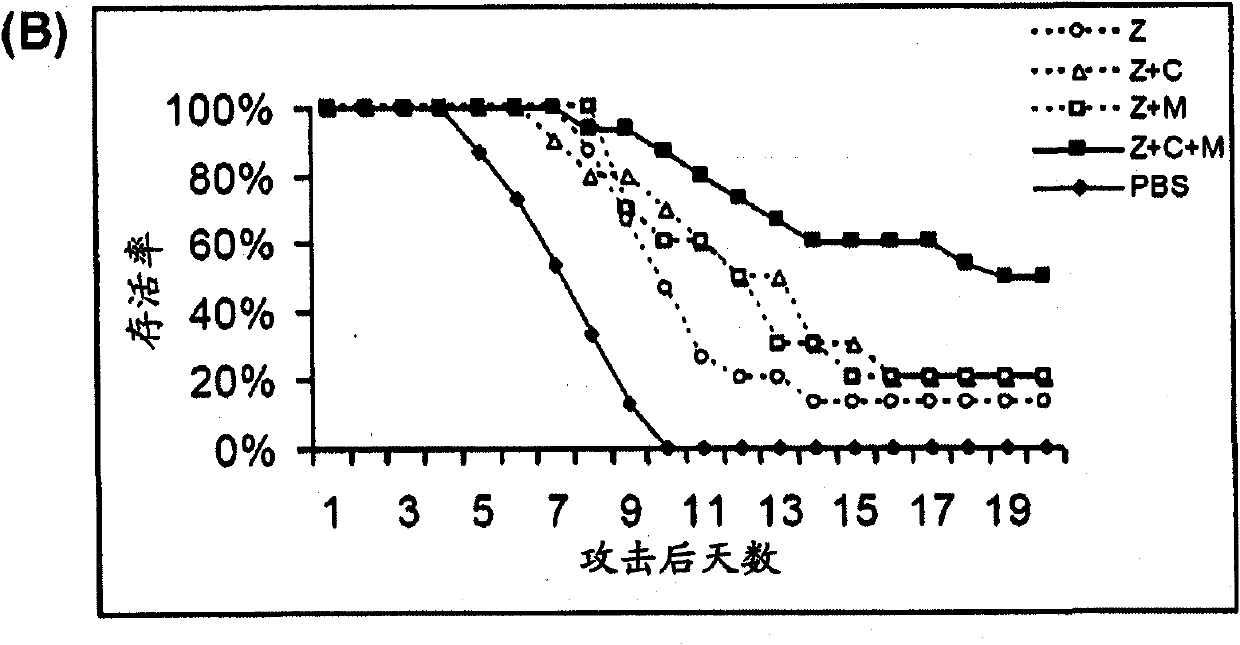
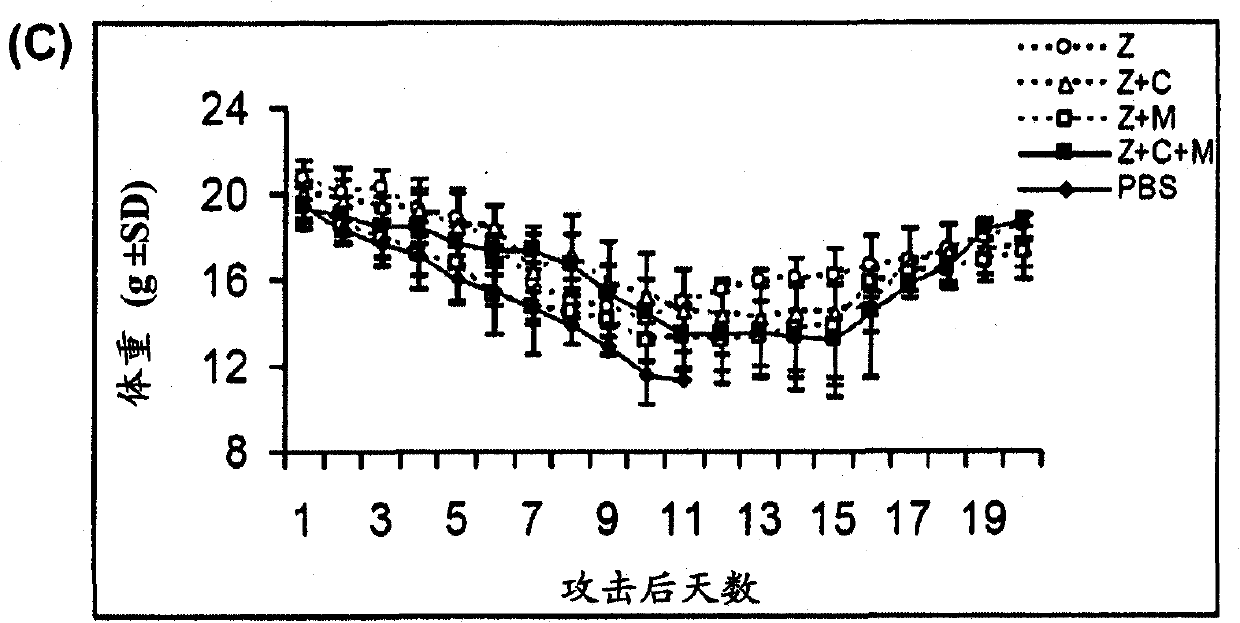
Compositions and methods for treating one or more symptoms of influenza, preferably influenza due to infection with influenza A (H5N1) are provided. It has been discovered that administration of a combination of a neuraminidase inhibitor with two immunomodulators increases survivability in subjects 24, 48, or even 72 hours post infection compared to administration of the neuraminidase inhibitor alone. A preferred neuraminidase inhibitor includes, but is not limited to zanamivir. Preferred immunomodulators include, but are not limited to celecoxib and mesalazine. Another embodiment provides a method for treating influenza, preferably, influenza due to infection with avian influenza A (H5N1) by administering to subject infected with the influenza virus, an effective amount of a neuraminidase inhibitor to inhibit or reduce budding of the influenza virus from infected cells of the subject, and an effective amount of at least two immunomodulators effective to reduce or inhibit one or more symptoms of inflammation in the subject.
Owner:THE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
N-linked glycosylation alteration in E0 and E2 glycoprotein of classical swine fever virus and novel classical swine fever virus vaccine
InactiveUS20100104597A1Slow onsetDelaying severitySsRNA viruses positive-senseSugar derivativesVirulent characteristicsWild type
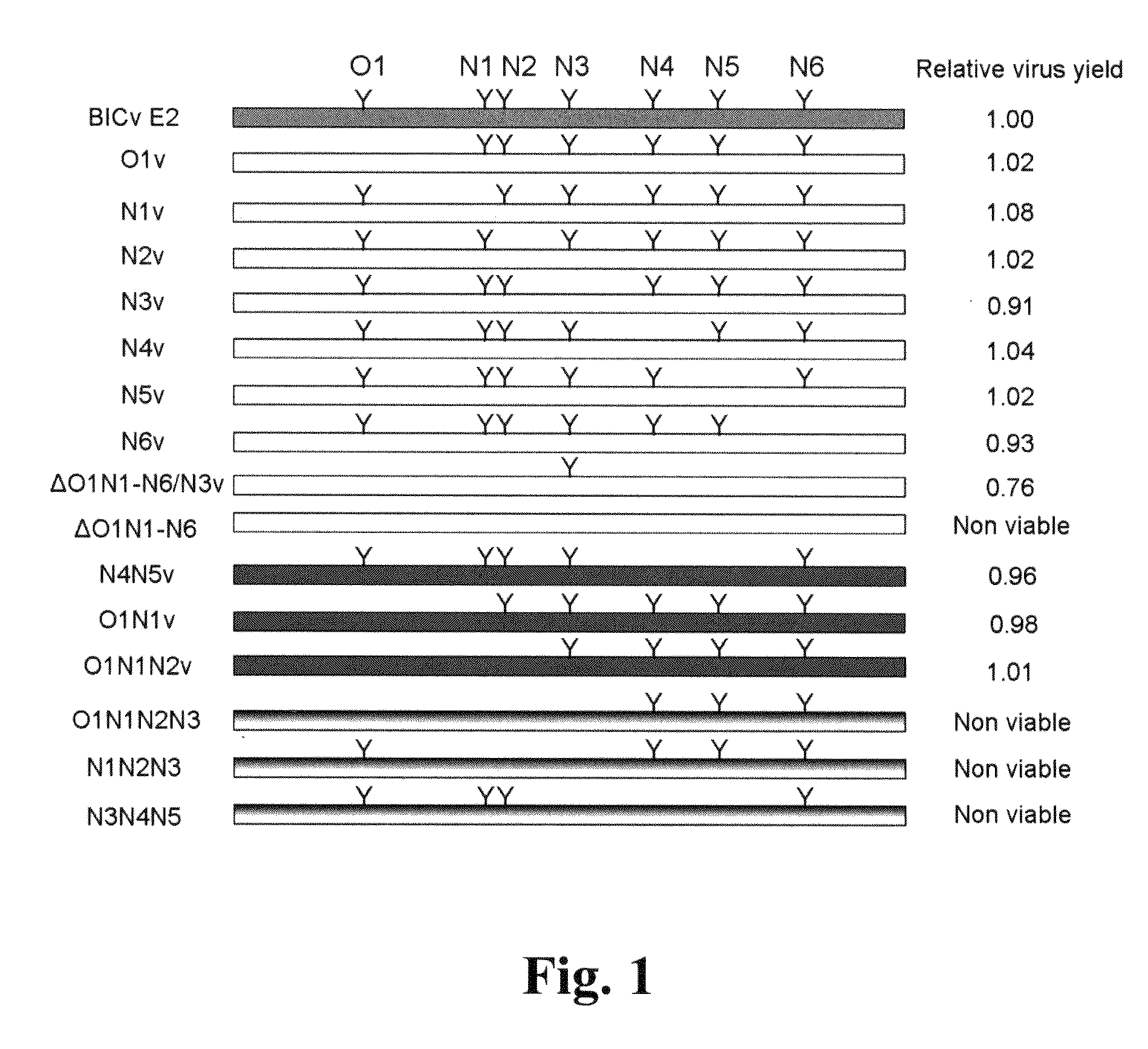
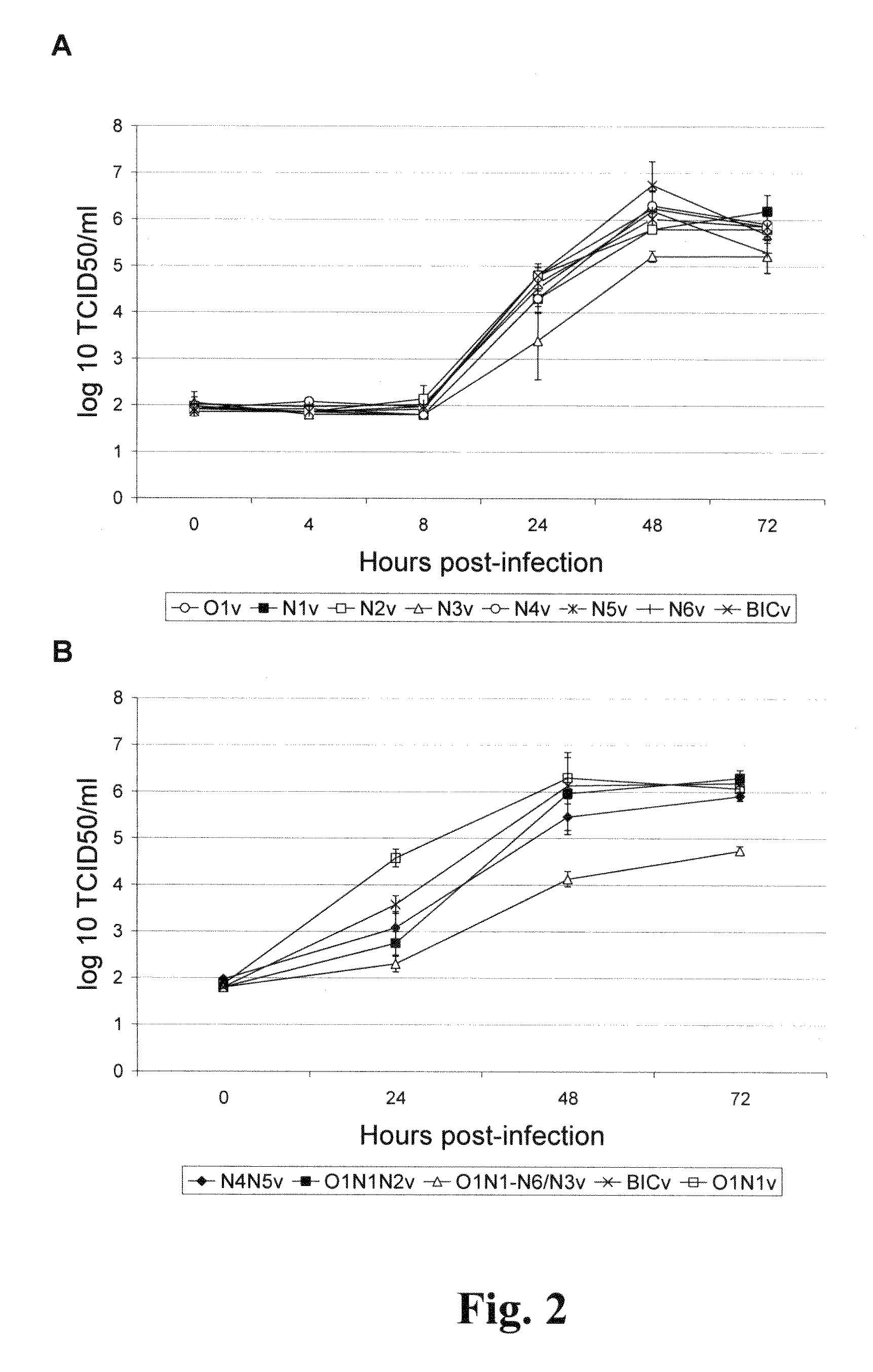
E2 is one of the three envelope glycoproteins of Classical Swine Fever Virus (CSFV). E2 is involved in several functions including virus attachment and entry to target cells, production of antibodies, induction of protective immune response in swine, and virulence. Seven putative glycosylation sites in E2 were modified by site directed mutagenesis of a CSFV Brescia infectious clone (BICv). A panel of virus mutants was obtained and used to investigate whether the removal of putative glycosylation sites in the E2 glycoprotein would affect viral virulence / pathogenesis in swine. We observed that rescue of viable virus was completely impaired by removal of all putative glycosylation sites in E2, but restored when mutation N185A reverted to wild-type asparagine produced viable virus that was attenuated in swine. Single mutations of each of the E2 glycosylation sites showed that amino acid N116 (N1v virus) was responsible for BICv attenuation. N1v efficiently protected swine from challenge with virulent BICv at 3 and 28 days post-infection suggesting that glycosylation of E2 could be modified for development of CSF live-attenuated vaccines. Additionally, a new developed virus, contained deletions of putative glycosylation sites N1 in E2 and N1 in E0 (6b), called N1E0 / 2v, induce a solid protection against the challenge at 3 and 28 days post-inoculation.
Owner:BORCA MANUEL +1
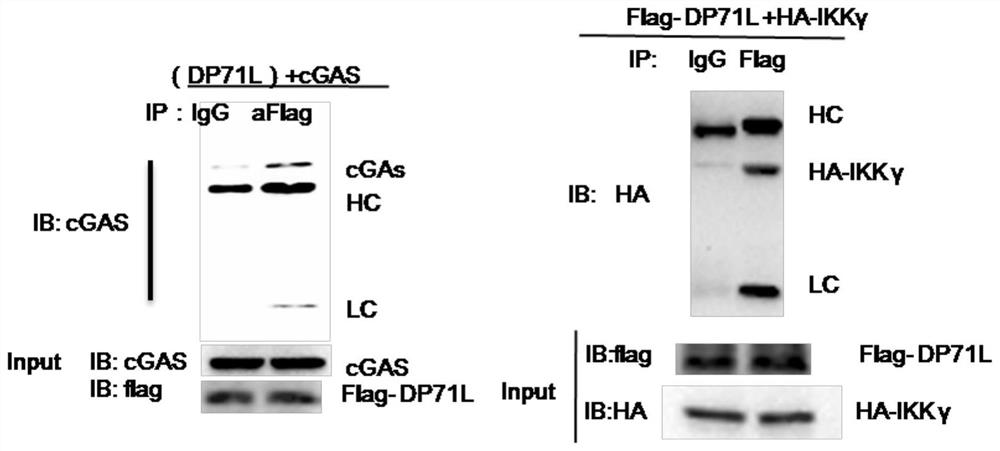
DP71L gene deleted recombinant African swine fever virus and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN111925994ADecreased blood virus levelsViral antigen ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementClassical swine fever virus CSFVInfected cell
The invention belongs to the field of veterinary prevention, and particularly relates to a DP71L gene deleted recombinant African swine fever virus and a preparation method and application thereof. According to the method, the African swine fever virus DP71L protein can inhibit the activity of cGAS + MITA or IFN beta induced by MITA; the invention also provides the DP71L gene deleted recombinant African swine fever virus. The DP71L gene deleted recombinant African swine fever virus is obtained by deleting the DP71L gene of the African swine fever virus. Compared with a wild strain, the gene-deleted African swine fever virus infected cell shows that the toxicity is weakened; after pigs are immunized by the constructed gene-deleted African swine fever virus, clinical symptoms such as death and the like are avoided, the content of blood viruses is remarkably reduced in the later period of infection, and the survival rate is 100 percent so that the recombinant virus is fully weakened and is very safe as a vaccine. Therefore, the DP71L gene deleted recombinant African swine fever virus can be applied to preparation of African swine fever vaccines, and has corresponding social value.
Owner:LANZHOU INST OF VETERINARY SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
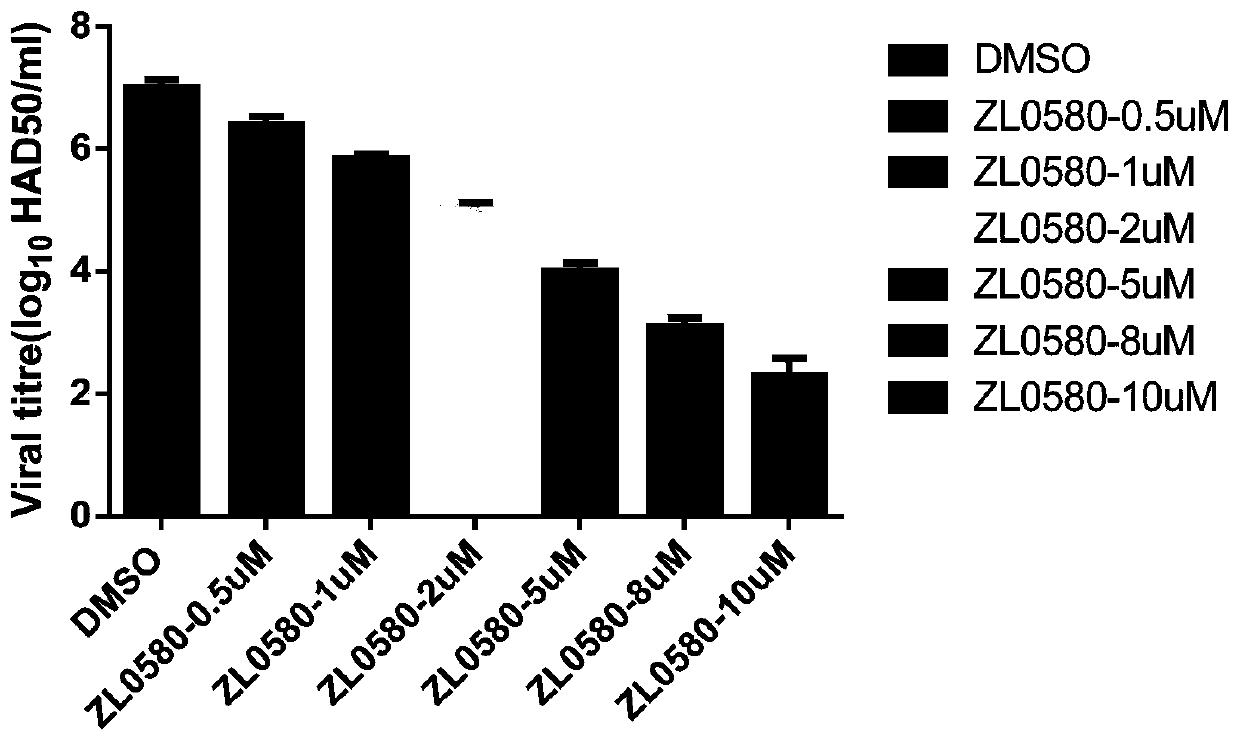
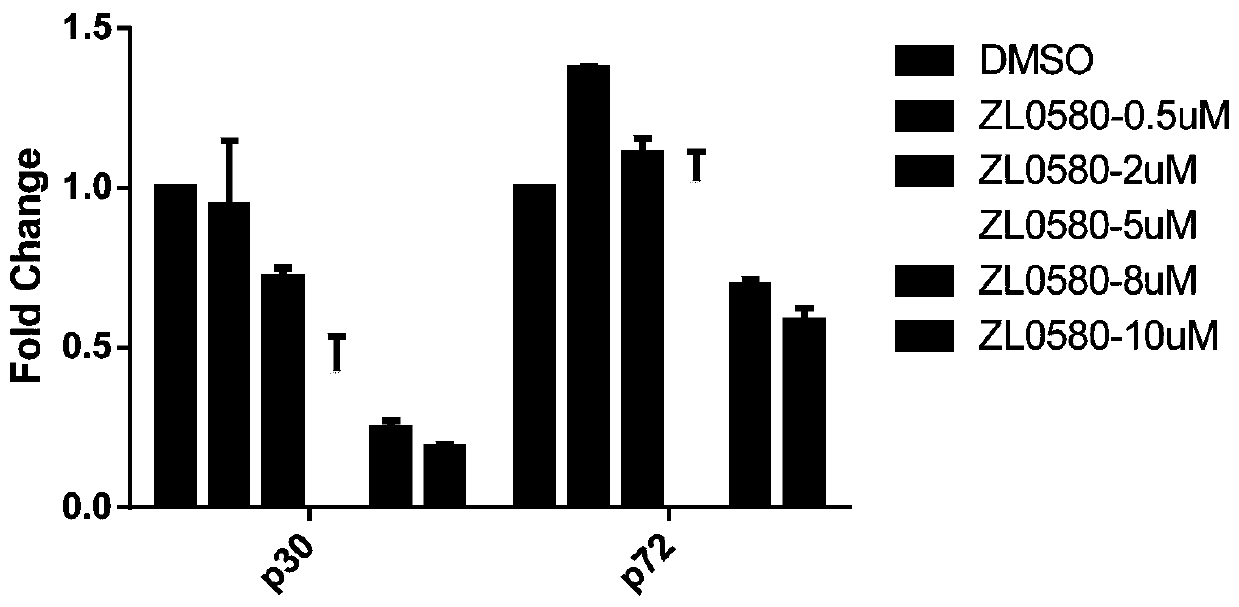
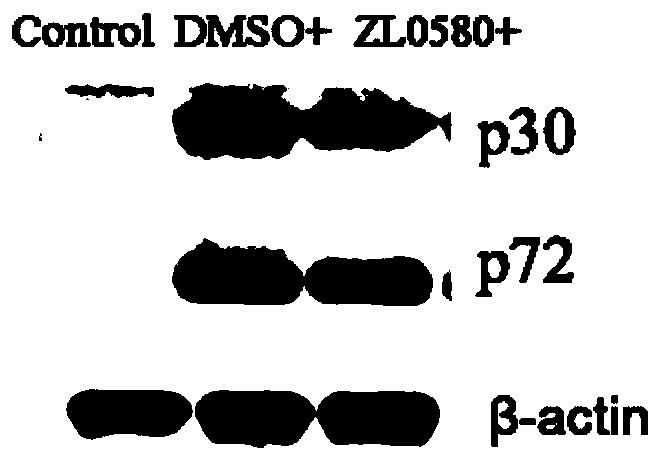
New use of compound ZL0580 for preventing or treating African swine fever
ActiveCN111588721AInhibit early infectionPrevent intrusionOrganic active ingredientsAntiviralsAfrican swine feverChemical compound
The invention belongs to the technical field of African swine fever treatment, and specifically relates to a new use of a compound ZL0580 for preventing or treating African swine fever. The inventionunexpectedly discovers that the compound ZL0580 can significantly inhibit the RNA and protein expression level of p30 and p72 in ASFV, prevents viruses from invading host cells, and can be used to inhibit the early infection of ASFV. The compound ZL0580 can significantly increase expression levels of genes such as TNF-alpha, NF-kappa B, IL-1beta, and IL-8 after ASFV infection, up-regulates transcription levels of TNF-alpha, NF-kappa B, IL-1beta, and IL-8, and enhances the immune response. Therefore, the compound ZL0580 can be used to prevent or treat African swine fever.
Owner:LANZHOU INST OF VETERINARY SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
N-Linked Glycosylation Alteration in E1 Glycoprotein of Classical Swine Fever Virus And Novel Classical Swine Fever Virus Vaccine
ActiveUS20120014992A1Reduce severityAltered glycosylation patternSsRNA viruses positive-senseSugar derivativesPost infectionEnv Glycoproteins
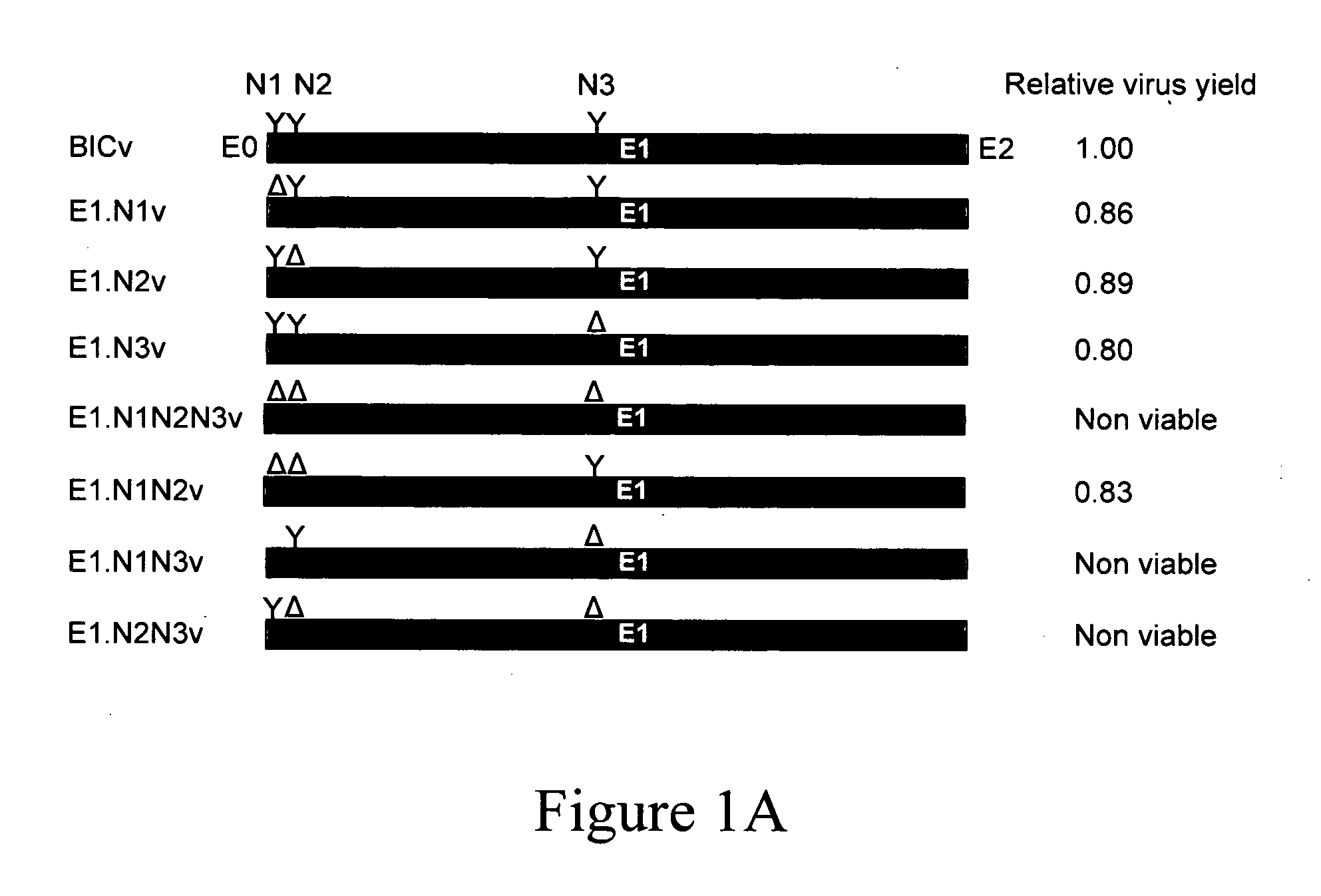
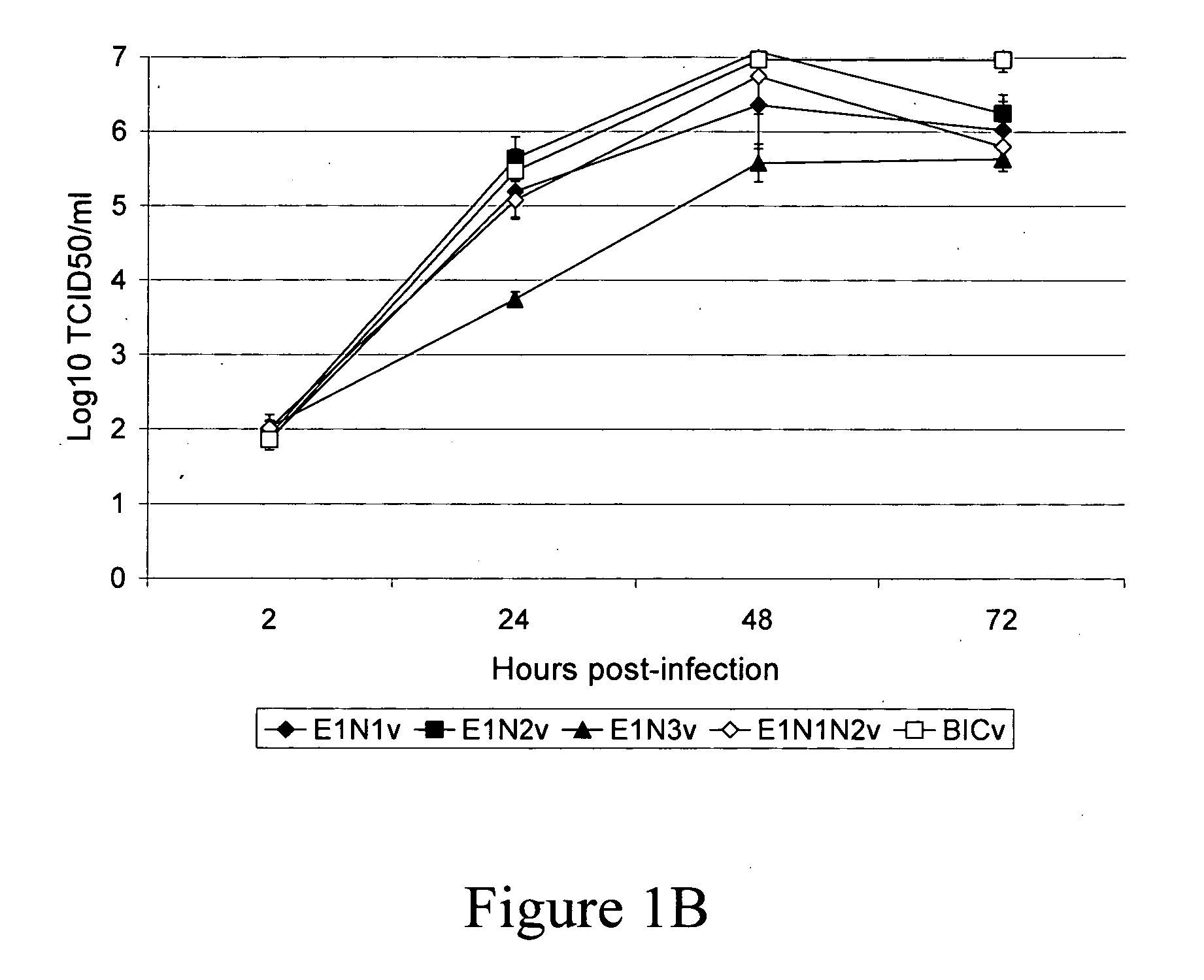
E1, along with Erns and E2 is one of the three envelope glycoproteins of Classical Swine Fever Virus (CSFV). Our previous studies indicated that glycosylation status of either E2 or Erns strongly influence viral virulence in swine. Here, we have investigated the role of E1 glycosylation of highly virulent CSFV strain Brescia during infection in the natural host. The three putative glycosylation sites in E1 were modified by site directed mutagenesis of a CSFV Brescia infectious clone (BICv). A panel of virus mutants was obtained and used to investigate whether the removal of putative glycosylation sites in the E1 glycoprotein would affect viral virulence / pathogenesis in swine. We observed that rescue of viable virus was completely impaired by removal of all three putative glycosylation sites in E1. Single mutations of each of the E1 glycosylation sites showed that CSFV amino acid N594 (E1.N3 virus), as well the combined mutation of N500 and N513 (E1.N1N2 virus) resulted in BICv attenuation. Infection of either E1.N1N2 or E1.N3 viruses were able to efficiently protected swine from challenge with virulent BICv at 3 and 28 days post-infection. These results, along with those demonstrating the role of glycosylation of Erns and E2, suggest that manipulation of the pattern of glycosylation could be a useful tool for development of CSF live-attenuated vaccines.
Owner:US SEC AGRI
N-linked glycosylation alteration in E1 glycoprotein of classical swine fever virus and novel classical swine fever virus vaccine
InactiveUS20090181051A1Slow onsetDelaying severityBiocideSsRNA viruses positive-senseClassical swine fever virus CSFVTGE VACCINE
E1, along with Erns and E2 is one of the three envelope glycoproteins of Classical Swine Fever Virus (CSFV). Our previous studies indicated that glycosylation status of either E2 or Erns strongly influence viral virulence in swine. Here, we have investigated the role of E1 glycosylation of highly virulent CSFV strain Brescia during infection in the natural host. The three putative glycosylation sites in E1 were modified by site directed mutagenesis of a CSFV Brescia infectious clone (BICv). A panel of virus mutants was obtained and used to investigate whether the removal of putative glycosylation sites in the E1 glycoprotein would affect viral virulence / pathogenesis in swine. We observed that rescue of viable virus was completely impaired by removal of all three putative glycosylation sites in E1. Single mutations of each of the E1 glycosylation sites showed that CSFV amino acid N594 (E1.N3 virus), as well the combined mutation of N500 and N513 (E1.N1N2 virus) resulted in BICv attenuation. Infection of either E1.N1N2 or E1.N3 viruses were able to efficiently protected swine from challenge with virulent BICv at 3 and 28 days post-infection. These results, along with those demonstrating the role of glycosylation of Erns and E2, suggest that manipulation of the pattern of glycosylation could be a useful tool for development of CSF live-attenuated vaccines.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
Kit for detecting norovirus I, norovirus II and rotavirus
InactiveCN110305987AFix compatibility issuesSolve pollutionMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationConserved sequenceRotavirus RNA
The invention belongs to the technical field of nucleic acid detection kits (fluorescent PCR (polymerase chain reaction) method) of a norovirus I, a norovirus II and a rotavirus, relates to the fieldof molecular biology, in particular to a kit for detecting the norovirus I, the norovirus II and the rotavirus and a use method of the kit. The kit solves the technical problems that the norovirus I,the norovirus II and the rotavirus belong to main pathogens of diarrhea, transmission routes, post-infection symptoms and the like are exactly similar, and an individual pathogen detection product inthe market cannot rapidly detect and distinguish three pathogens. The technical scheme includes that according to the principle of the fluorescent PCR method and nucleotide sequence characteristics, specific conserved sequences of the three viruses are selected, and corresponding primers, namely, TaqMan fluorescent probes are designed. The kit is mainly used for specimens such as excrement and cloacal swabs or vomituses, and nucleic acid of the three viruses is qualitatively detected.
Owner:张鹏
Live attenuated antigenically marked classical swine fever virus
ActiveUS8133495B2SsRNA viruses positive-senseAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsEpitopeStructural glycoprotein
Owner:AGRI UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS RESPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE +1
Virulent aeromonas vaccines and methods
ActiveUS20200030428A1Bacterial antigen ingredientsMultivalent vaccineHighly pathogenicVaccine antigen
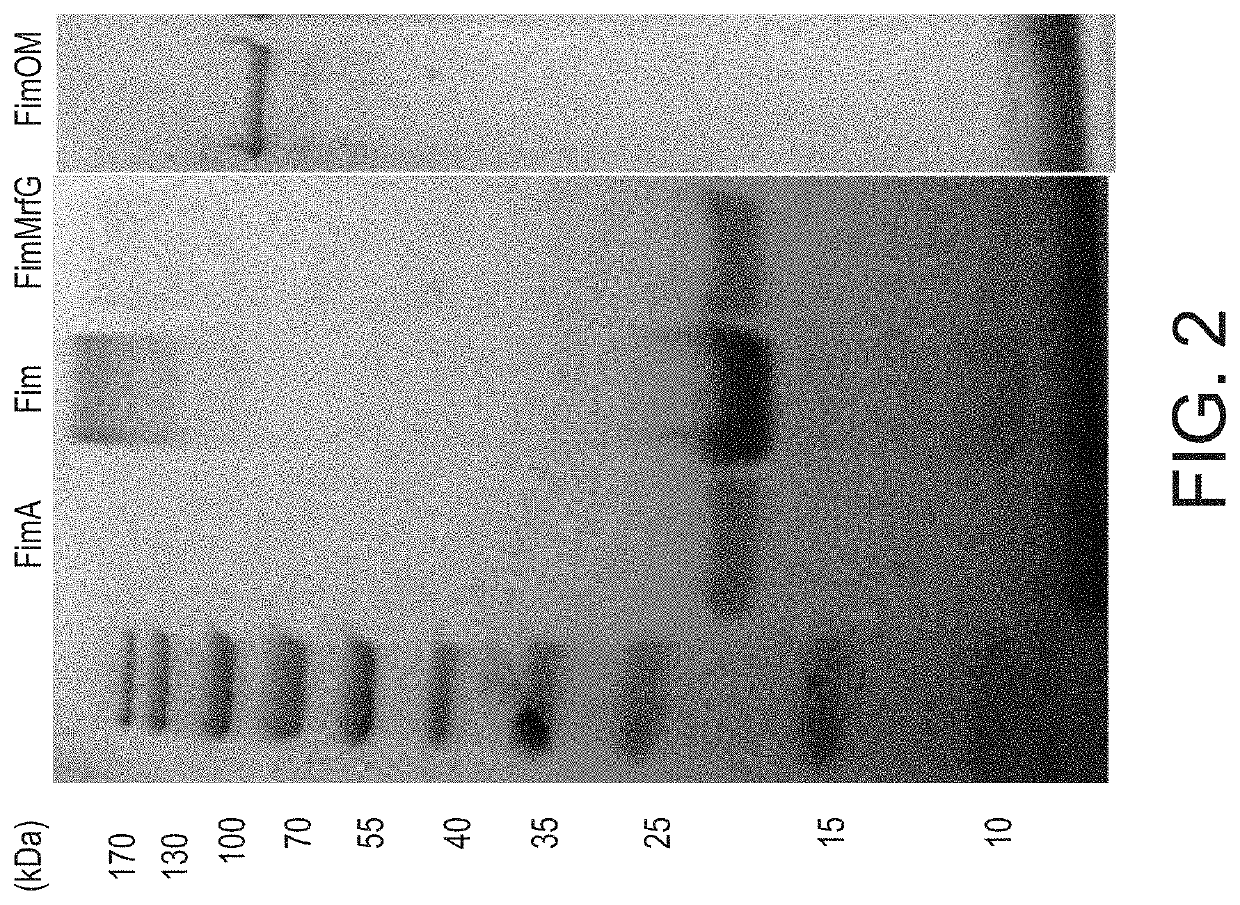
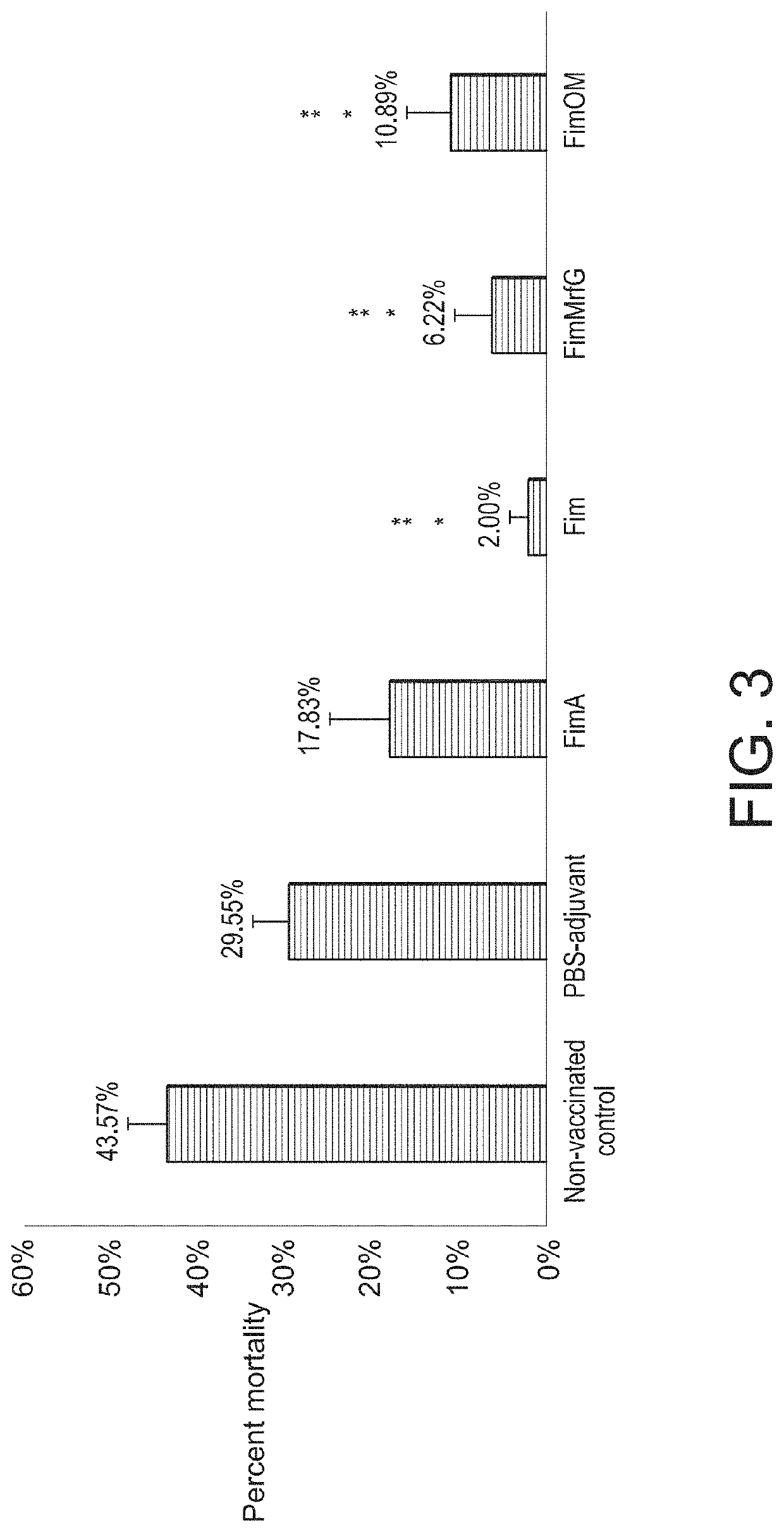
Aeromonas hydrophila is a reemerging pathogen of channel catfish (Ictalurus punctatus); recent outbreaks from 2009 to 2014 have caused the loss of more than 12 million pounds of market size catfish in Alabama and Mississippi. Genome sequencing revealed a clonal group of A. hydrophila isolates with unique genetic and phenotypic features that is highly pathogenic in channel catfish. Comparison of the genome sequence of a representative catfish isolate (ML09-119) from this virulent clonal group with lower virulence A. hydrophila isolates revealed four fimbrial proteins unique to strain ML09-119. In this work, we expressed and purified four A. hydrophila fimbrial proteins (FimA, Fim, MrfG, and FimOM) and assessed their ability to protect and stimulate protective immunity in channel catfish fingerlings against A. hydrophila ML09-119 infection for vaccine development. Our results showed catfish immunized with FimA, Fim, FimMrfG, and FimOM exhibited 59.83%, 95.41%, 85.72%, and 75.01% relative percent survival, respectively, after challenge with A. hydrophila strain ML09-119. Bacterial concentrations in liver, spleen, and anterior kidney were significantly (p<0.05) lower in vaccinated fish compared to the non-vaccinated sham groups at 48 h post-infection. However, only the Fim immunized group showed a significantly higher antibody titer in comparison to the non-vaccinated treatment group (p<0.05) at 21 days post-vaccination. Altogether, Fim and FimMrfG recombinant proteins have potential for vaccine development against virulent A. hydrophila infection. Genomic subtraction revealed three outer membrane proteins present in strain ML09-119 but not in the low virulence reference A. hydrophila strain; the major outer membrane protein OmpAI (OmpA1), TonB-dependent receptor (TonB-DR), and transferrin-binding protein A (TbpA). Here, the genes encoding OmpAI, tonB-DR, and tbpA were cloned from A. hydrophila ML09-119 and were expressed into Escherichia coli. The purified recombinant OmpA, TonB-DR, and TbpA proteins had estimated molecular weights of 37.26, 78.55, and 41.67 kDa, respectively. Catfish fingerlings vaccinated with OmpA1, TonB-DR, and TbpA emulsified with non-mineral oil adjuvant were protected against the subsequent A. hydrophila ML09-119 infection with 98.59%, 95.59%, and 47.89% relative percent survival (RPS), respectively. Furthermore, the mean liver, spleen, and anterior kidney bacterial loads were significantly lower in catfish vaccinated with the OmpA1 and TonB-DR than the non-vaccinated control group. ELISA demonstrated that catfish immunized with OmpA1, TonB-DR, and TbpA produce significant antibody response by 21 days post-immunization. Therefore, data generated during the study suggest that OmpAI and TonB-DR proteins could be used as potential candidates for vaccine development against A. hydrophila epidemic strain infection. However, TbpA protein failed to provide such strong protection. Recombinant ATPase from A. hydrophila also showed promise as a vaccine antigen. A live attenuated vaccine was prepared that combined the advantages of a live attenuated vaccine (ESC-NDKL1 (ΔgcvPΔsdhCΔfrdA) mutant of Edwardsiella ictaluri) against enteric septicemia of catfish (ESC) and three immunogenic recombinant proteins (Fim, FimMrfg, and ATPase) against A. hydrophila infection. Our results showed channel catfish fingerlings immersion-vaccinated with ESC-NDKL1::pETfim, ESC-NDKL1::pETmrfG, and ESC-NDKL1::pETATPase exhibited 100%, 91.67%, and 100% percent survival after challenge with the A. hydrophila ML09-119, which was significantly less than non-vaccinated group (88.89% mortality). In a second study, Catfish immunized with NDKL1::pETfim, ESC-NDKL1::pETmrfG, ESC-NDKL1::pETATPase had significantly (p<0.05) lower mortalities than sham-vaccinated group.
Owner:MISSISSIPPI STATE UNIVERSITY
Medicinal carbohydrates for treatment of respiratory conditions
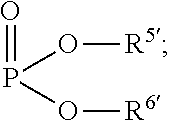
The present invention relates to a method and compounds of Formula (1) and / or (2) or their pharmaceutically acceptable inorganic or organic salt thereof, and their compositions for treating respiratory conditions including post viral / bacterial infections, acute / chronic bronchitis, COPD, cystic fibrosis, and inflammatory conditions. It has been found by the applicants that the compounds of Formula (1) and / or (2) or their pharmaceutically acceptable inorganic or organic salt thereof could speed up the recovery of the viability of damaged respiratory tract cells by restoring sialylglyco-conjugates on their surface.
Owner:AUSTRALIAN BIOMEDICAL CORP LTD
New antimicrobial composition and preparation method and application thereof
PendingCN110302192ASignificant activity against vesicular stomatitis virusAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsInfected cellArginine
The present invention provides an antimicrobial composition, which comprises a lauroyl lauroyl arginate (LAE) ion pair derivative, and the antimicrobial composition is an antiviral agent against an enveloped virus, wherein the enveloped virus is selected from vesicular stomatitis virus of the herpes virus, or the Newcastle disease virus selected from the paramyxovirus. The antiviral agent is the anti-infective agent comprising a condensate derived from fatty acid and esterified binary amino acid, and is capable of acting on Newcastle disease virus and vesicular stomatitis virus in-vitro, and reducing the infection of Newcastle disease virus and vesicular stomatitis virus to cells. The antiviral agent is added to the cultured Newcastle disease virus (NDV) and vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV), or the antiviral agent is added at different times before the virus is infected and after the infection, the infected cells are detected, and the number of viruses is found to be significantly reduced. The antiviral agent can effectively inhibit or kill the virus and can be used to prevent or reduce the ability of the virus to infect cells. The present invention also provides a method of preparing the antimicrobial composition, which has the characteristics of better virucidal effect and lower dosage than that of the original antimicrobial composition containing a LAE compound.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV
Attenuated African swine fever virus vaccine based in the deletion of MGF genes
ActiveUS9528094B2Viral antigen ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementVirulent characteristicsDomestic pig
African swine fever virus (ASFV) is the etiological agent of a contagious and often lethal viral disease of domestic pigs. Control of ASF has been hampered by the unavailability of vaccines. Experimental vaccines have been derived from naturally occurring, cell culture-adapted, or genetically modified live attenuated ASFVs; however, these vaccines are only successful when protecting against homologous viruses. Among viral genes reported to be involved in virulence are components of the multi gene family (MGF). Here we report the construction of a recombinant ΔMGF virus derived from the highly virulent ASFV Georgia 2007 (ASFV-G) isolate. In vivo, ASFV-G ΔMGF administered intramuscularly (IM) to swine at either 102 or 104 HAD50 are completely attenuated; the inoculated animals are completely asymptomatic. Animals infected with 102 or 104 HAD50 of ASFV-G ΔMGF are protected against the presentation of clinical disease when challenged at 28 days post infection with the virulent parental strain Georgia 2007.
Owner:US SEC AGRI +1
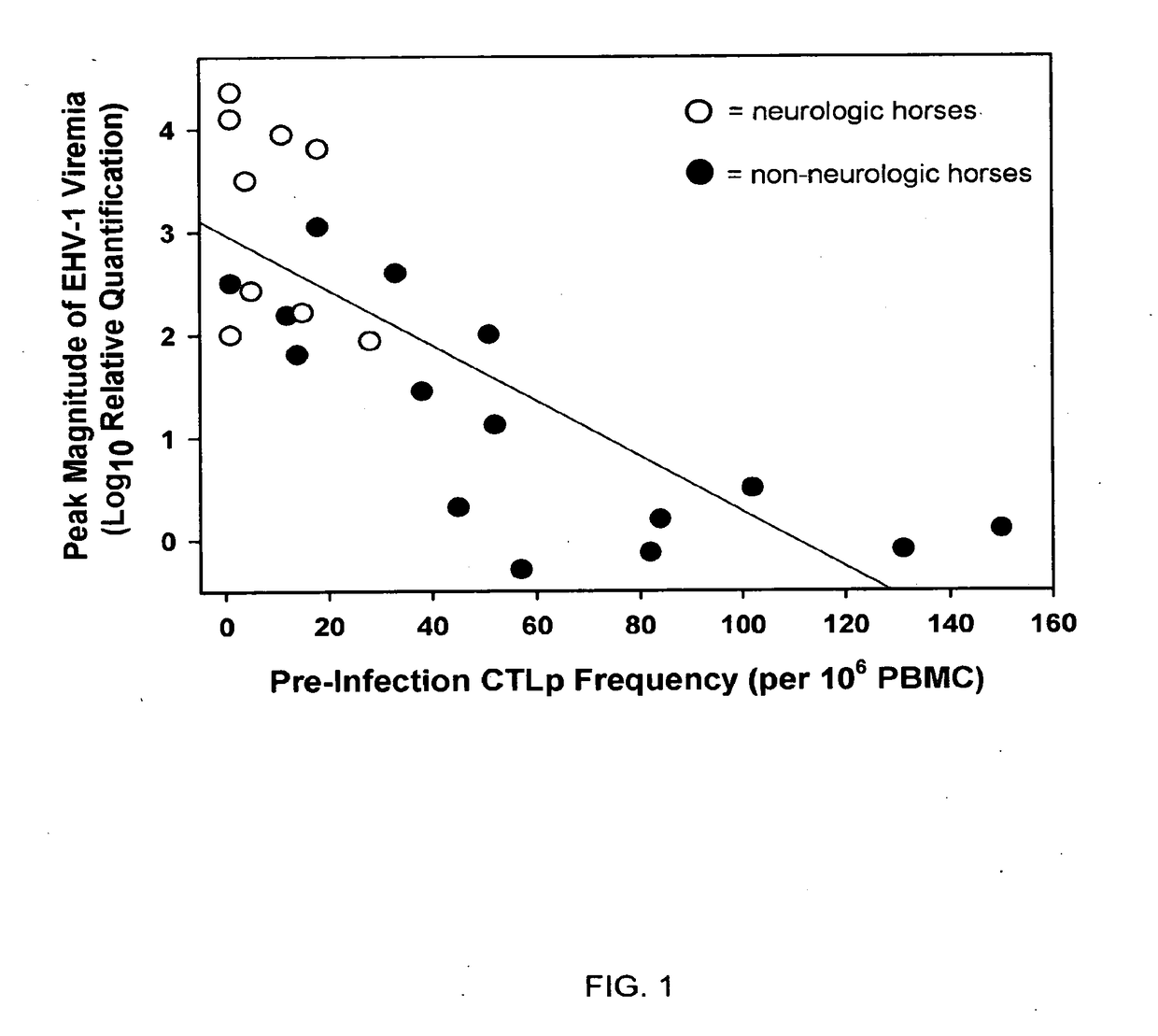
Equine disease model for herpesvirus neurologic disease and uses thereof
InactiveUS20170281751A1Increase chanceProtection levelAntibacterial agentsViral antigen ingredientsNervous systemEquine herpesvirus
The present invention relates to an in vivo equine disease model for equine herpesvirus-1 neurological disease comprising a horse having a low pre-exposure level of herpesvirus-specific CTL precursors and / or is approximately 20 years of age or older wherein the horse is experimentally infected with a neuropathogenic strain of equine herpesvirus or a mutant thereof. The invention includes a method of preparing an in vivo equine disease model for equine herpesvirus-1 neurological disease comprising obtaining a horse that possesses low pre-infection levels of EHV-1 specific CTL precursors and / or is approximately 20 years of age or older and inoculating the horse intranasally with an effective infecting amount of a neuropathogenic strain of EHV-1. A particularly preferred method involves the advanced neurological disease stage when the experimental horse presents clinical signs of myeloencephalopathy. Additionally, the invention concerns a method of quantifying the risk factors and predicting the development of clinical neurologic signs of equine herpesvirus-1 neurological disease in a horse comprising the steps of (a) determining the pre-infection CTLp frequency to be less than approximately 40 EHV-1 specific CTLp per 106 PBMC; and (b) determining the post-infection viremic load following exposure to EHV-1 to be approximately 10-fold or more over the viremic load present in horses following exposure to a non-neuropathogenic strain of EHV-1. Also described in the invention is the determination of the risk of developing the clinical neurologic signs by use of an equation y=a+bx wherein y is the peak viremic load, a=2.97, b=−0.027 and the variable x is the pre-infection CTLp frequency. Lastly, the invention deals with a new live, attenuated vaccine formulation that is effective against neurologic disease due to equine herpesvirus-1.
Owner:UNIV OF KENTUCKY RES FOUND
Application of arbidol hydrochloride in preparation of anti-enterovirus medicines
InactiveCN102440988AInhibition of proliferative abilityInhibit 71Organic active ingredientsAntiviralsAntiviral drugPharmaceutical drug
The invention discloses a new application of arbidol hydrochloride in preparation of anti-enterovirus medicines. The research disclosed in the invention indicates that the arbidol hydrochloride has the function of resisting hand-foot-mouth disease virus (enterovirus 71) in cells and animal bodies, and has effective antiviral actions in the dosage mode before and after the virus infection. When the compound is used as an antiviral drug for directly killing virus and interdicting and preventing virus infected cells, the treatment indexes (TI) are respectively 3.08 (directly killing virus), 23.55 (interdicting virus invasion) and 2.5 (inhibiting multiplication of virus). The invention provides a new effective way for treating hand-foot-mouth disease virus infection, and has practical application value.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
N-Linked Glycosylation Alteration in E0 and E2 Glycoprotein of Classical Swine Fever Virus and Novel Classical Swine Fever Virus Vaccine
InactiveUS20110038886A1Reduce severityAltered glycosylation patternSsRNA viruses positive-senseVirus peptidesClassical swine fever virus CSFVTGE VACCINE
E2 is one of the three envelope glycoproteins of Classical Swine Fever Virus (CSFV). E2 is involved in several functions including virus attachment and entry to target cells, production of antibodies, induction of protective immune response in swine, and virulence. Seven putative glycosylation sites in E2 were modified by site directed mutagenesis of a CSFV Brescia infectious clone (BICv). A panel of virus mutants was obtained and used to investigate whether the removal of putative glycosylation sites in the E2 glycoprotein would affect viral virulence / pathogenesis in swine. We observed that rescue of viable virus was completely impaired by removal of all putative glycosylation sites in E2, but restored when mutation N185A reverted to wild-type asparagine produced viable virus that was attenuated in swine. Single mutations of each of the E2 glycosylation sites showed that amino acid N116 (N1v virus) was responsible for BICv attenuation. N1v efficiently protected swine from challenge with virulent BICv at 3 and 28 days post-infection suggesting that glycosylation of E2 could be modified for development of CSF live-attenuated vaccines. Additionally, a new developed virus, contained deletions of putative glycosylation sites N1 in E2 and N1 in E0 (6b), called N1E0 / 2v, induce a solid protection against the challenge at 3 and 28 days post-inoculation.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA +1
Application of Lanosta-7,9(11),24-trien-3-one 15,26-dihydroxy-sterane triterpene in preparation of medicament for preventing and/or treating EV71 infection
InactiveCN102526072ASmall side effectsEasy to useOrganic active ingredientsAntiviralsPharmacologyPost infection
The invention discloses an application of Lanosta-7,9(11),24-trien-3-one 15,26-dihydroxy in preparation of medicaments for preventing and / or treating enterovirus 71 infection. The invention confirms that the Lanosta-7,9(11),24-trien-3-one 15,26-dihydroxy has good antiviral effect in in-vitro enterovirus 71 (EV 71) infection cell tests. Meanwhile, the Lanosta-7,9(11),24-trien-3-one 15,26-dihydroxyhas certain killing effect on enterovirus 71 (EV 71), can prevent enterovirus 71 (EV 71) infection, has good treating effect on enterovirus 71 (EV 71) infected cells, has good inhibition effect on viral replication, and has more significant effect than a positive control medicament of ribavirin. In addition, the Lanosta-7,9(11),24-trien-3-one 15,26-dihydroxy has good inhibition effect on inflammation responses caused by enterovirus 71 (EV 71), which reveals that the Lanosta-7,9(11),24-trien-3-one 15,26-dihydroxy has the prospect of being developed into anti-enterovirus 71 (EV 71) medicaments.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com