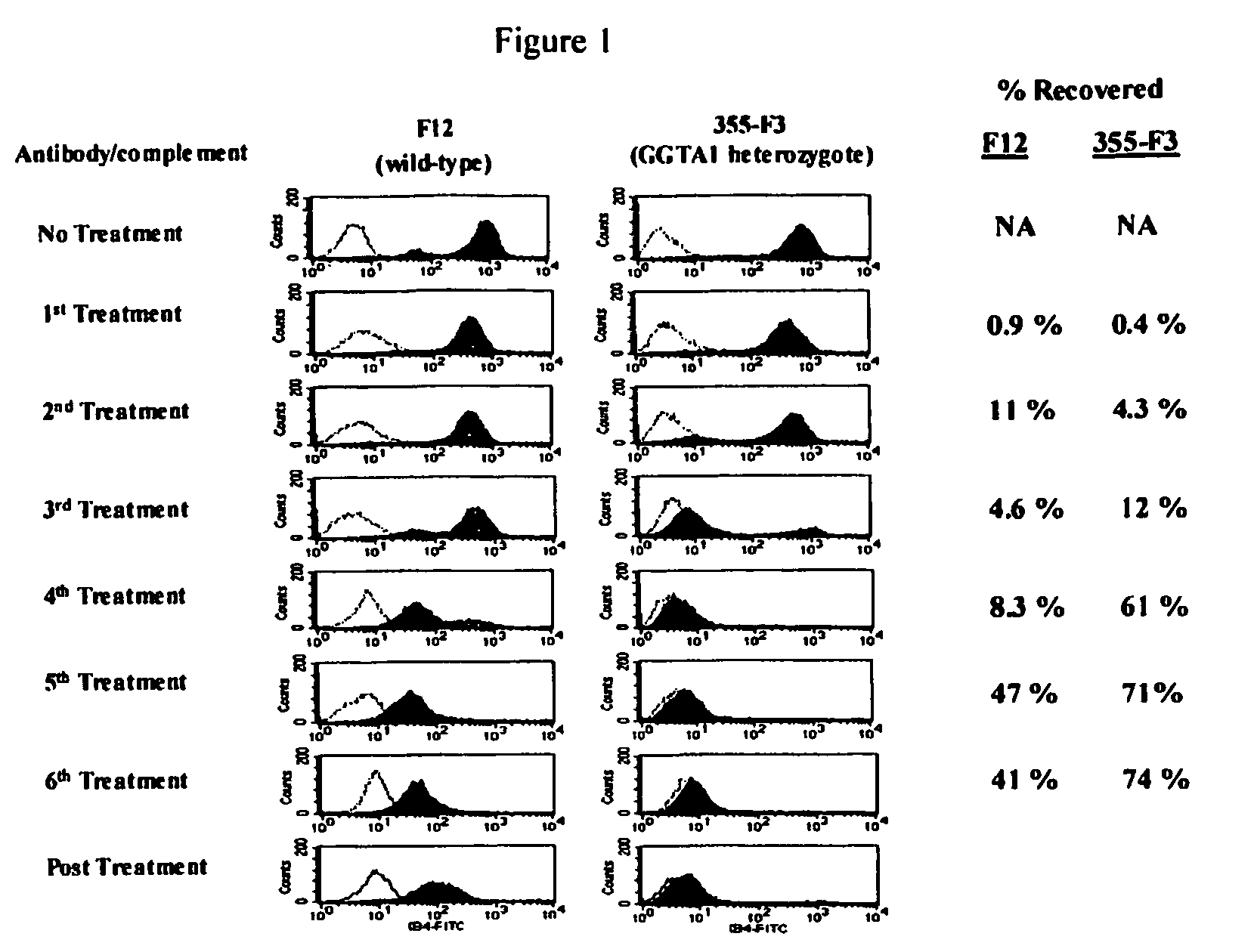
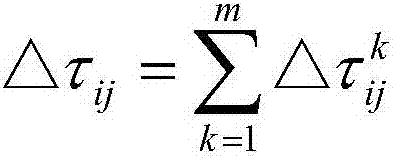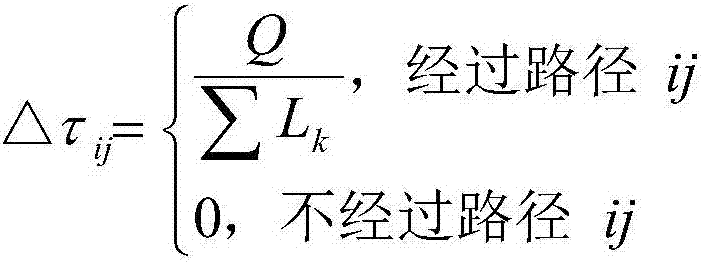Patents
Literature
244 results about "Genetics manipulation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Encapsulation of discrete quanta of fluorescent particles
InactiveUS20030132538A1Individual particle analysisGlass/slag layered productsGenetics manipulationFlow cytometry
The present invention provides novel encapsulation compositions and methods. In particular, the invention relates to fluorescent capsule compositions, which consists of a layer of a polymer shell enclosing one or more fluorescent materials such as fluorescent microspheres and which are capable of emitting at least two distinct fluorescent signals. Also provided are methods for their preparation. The compositions and methods of this invention are useful in a variety of applications, including preparation of multiplexed arrays for industrial, chemical, immunological, and genetic manipulation and analysis especially as related but not limited to flow cytometry.
Owner:LUMINEX
Transgenic dunaliella salina as a bioreactor
Disclosed is a method for making a bioreactor comprising a foreign target gene, special selectable markers and Dunaliella Salina as host. It is prepared by the genetic transformation techniques that include introducing a foreign target gene into the cells of Dunaliella Salina and screening the transformed cells of Dunaliella Salina. The bioreactor of the present invention can be used as a safe and cheap production system for proteins of pharmaceutical interest including vaccines, especially oral products, in a large scale, because the cells of Dunaliella Salina are easy of genetic manipulation in preparation of the bioreactor, nontoxic and edible for humans and animals, and harmless to the environment.
Owner:XUE LEXUN +1
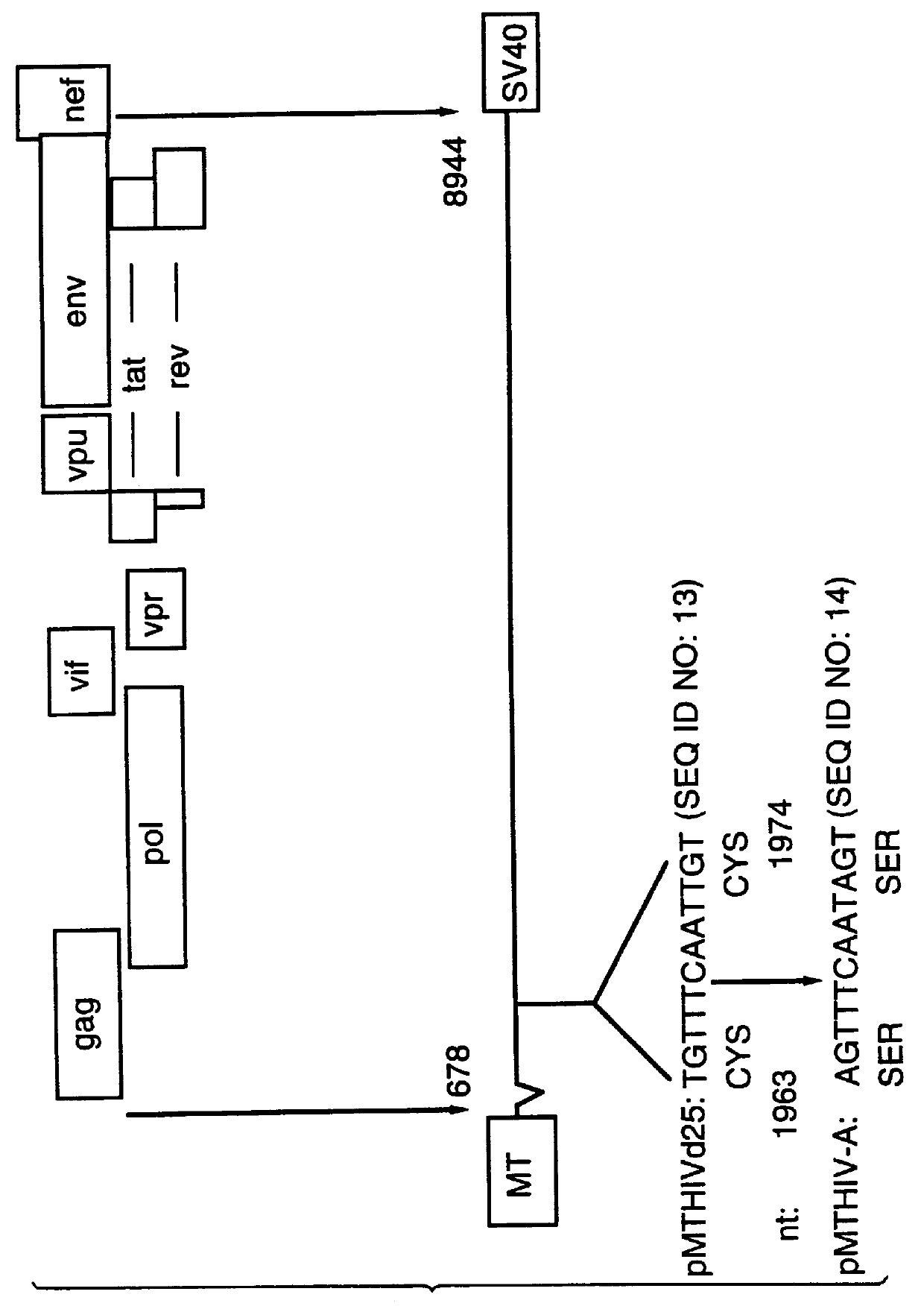
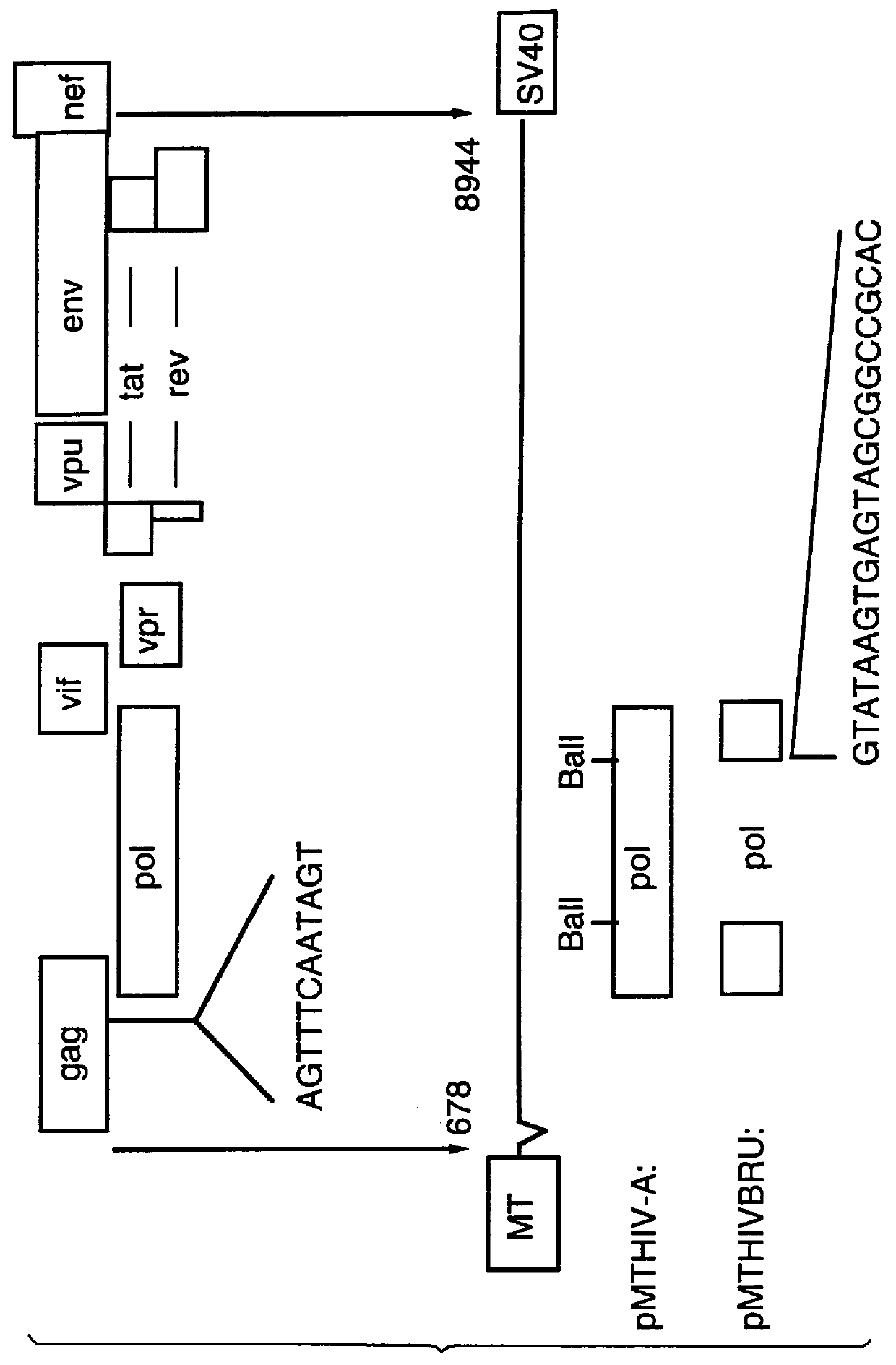
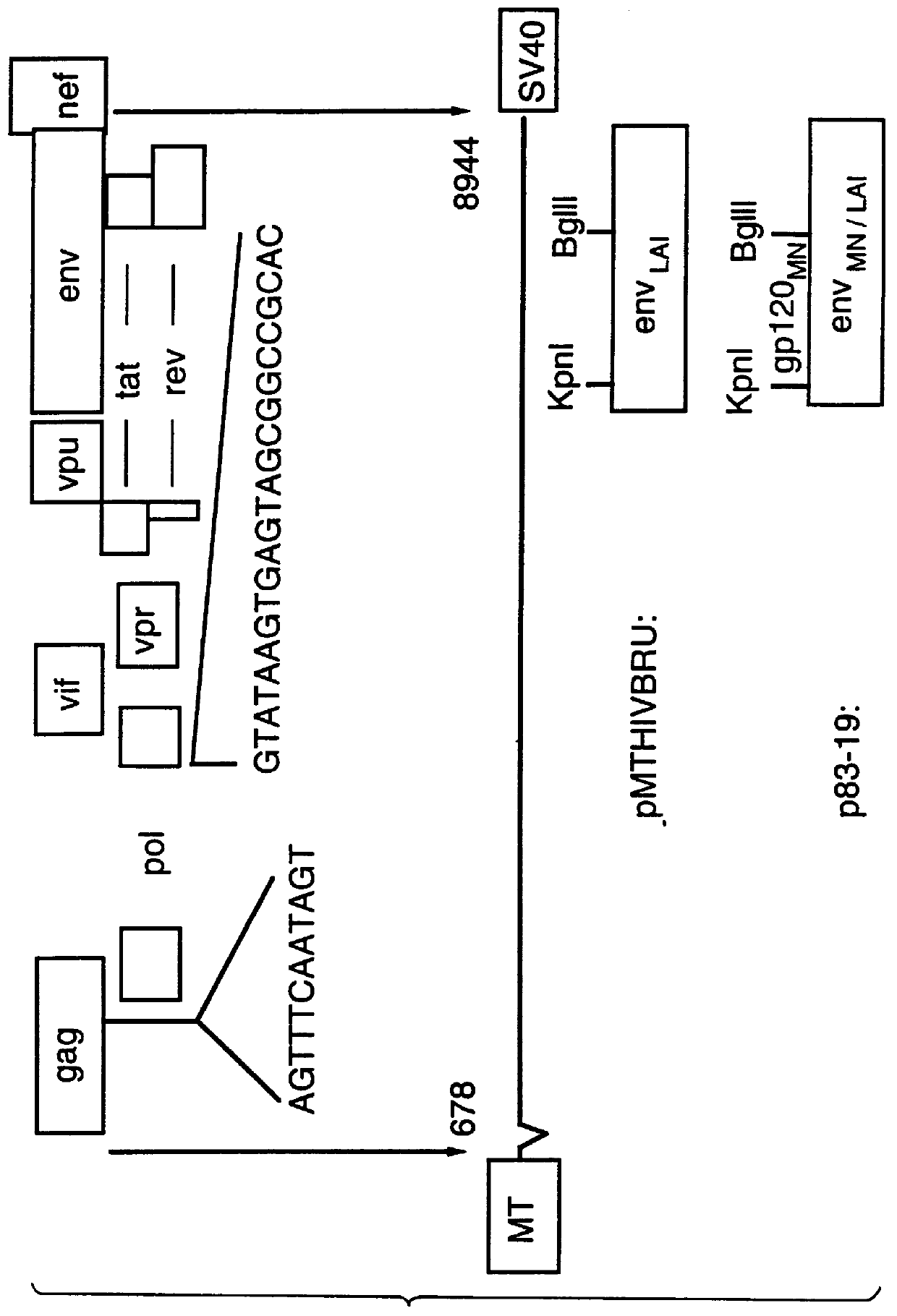
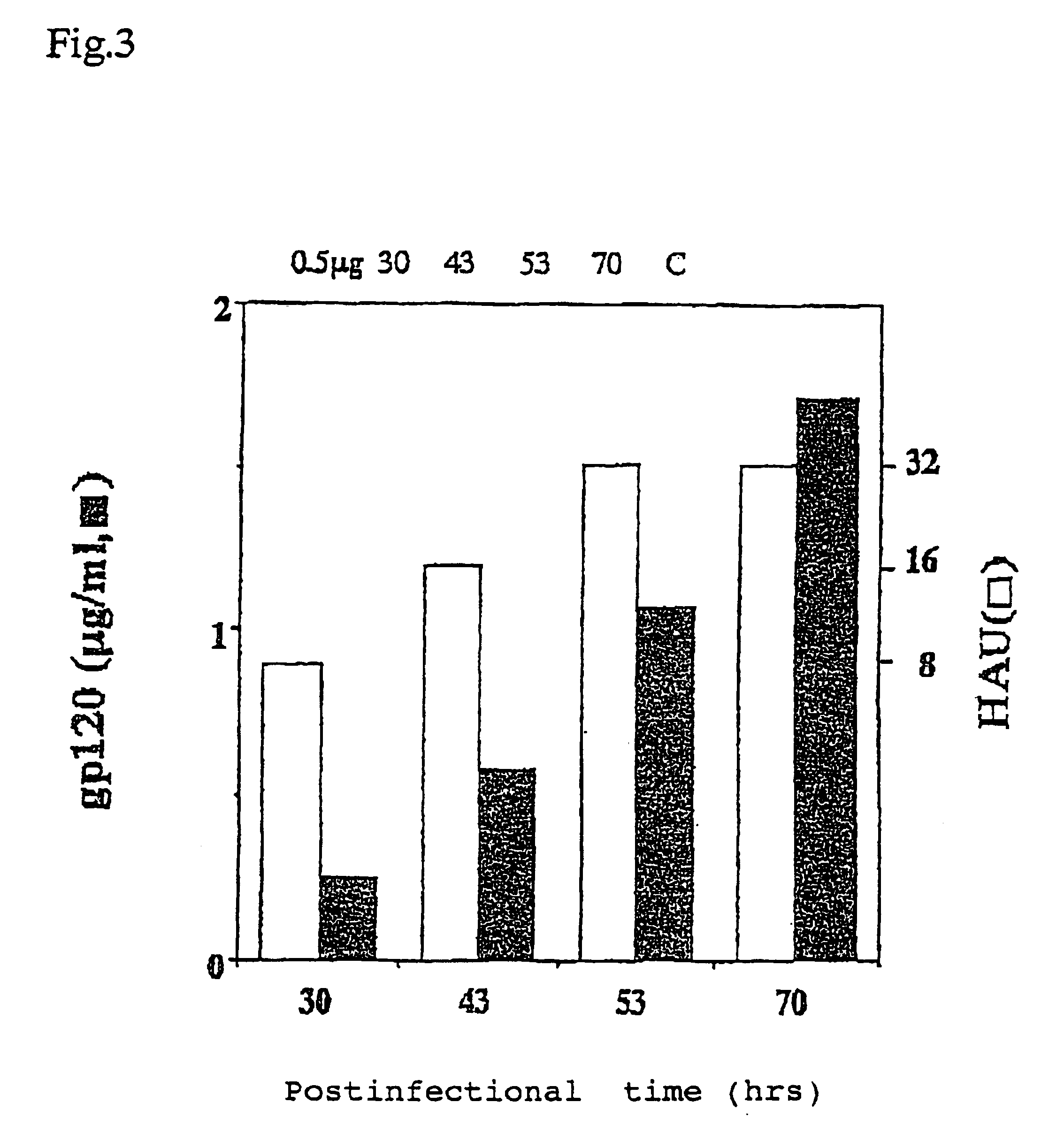
Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 nucleic acids devoid of long terminal repeats capable of encoding for non-infectious, immunogenic, retrovirus-like particles
InactiveUS6080408AImprove efficiencyLow backgroundSugar derivativesViral antigen ingredientsPol genesReverse transcriptase activity
Non-infectious, retrovirus-like particles contain mutations to reduce gag-dependent RNA-packaging of the gag gene product, eliminate reverse transcriptase activity of the pol gene product, eliminate integrase activity of the pol gene product and eliminate RNase H activity of the pol gene product through genetic manipulation of the gag and pol genes. The corresponding nucleic acid molecules are described. The non-infectious, retrovirus-like particles have utility in diagnosis.
Owner:CONNAUGHT LAB
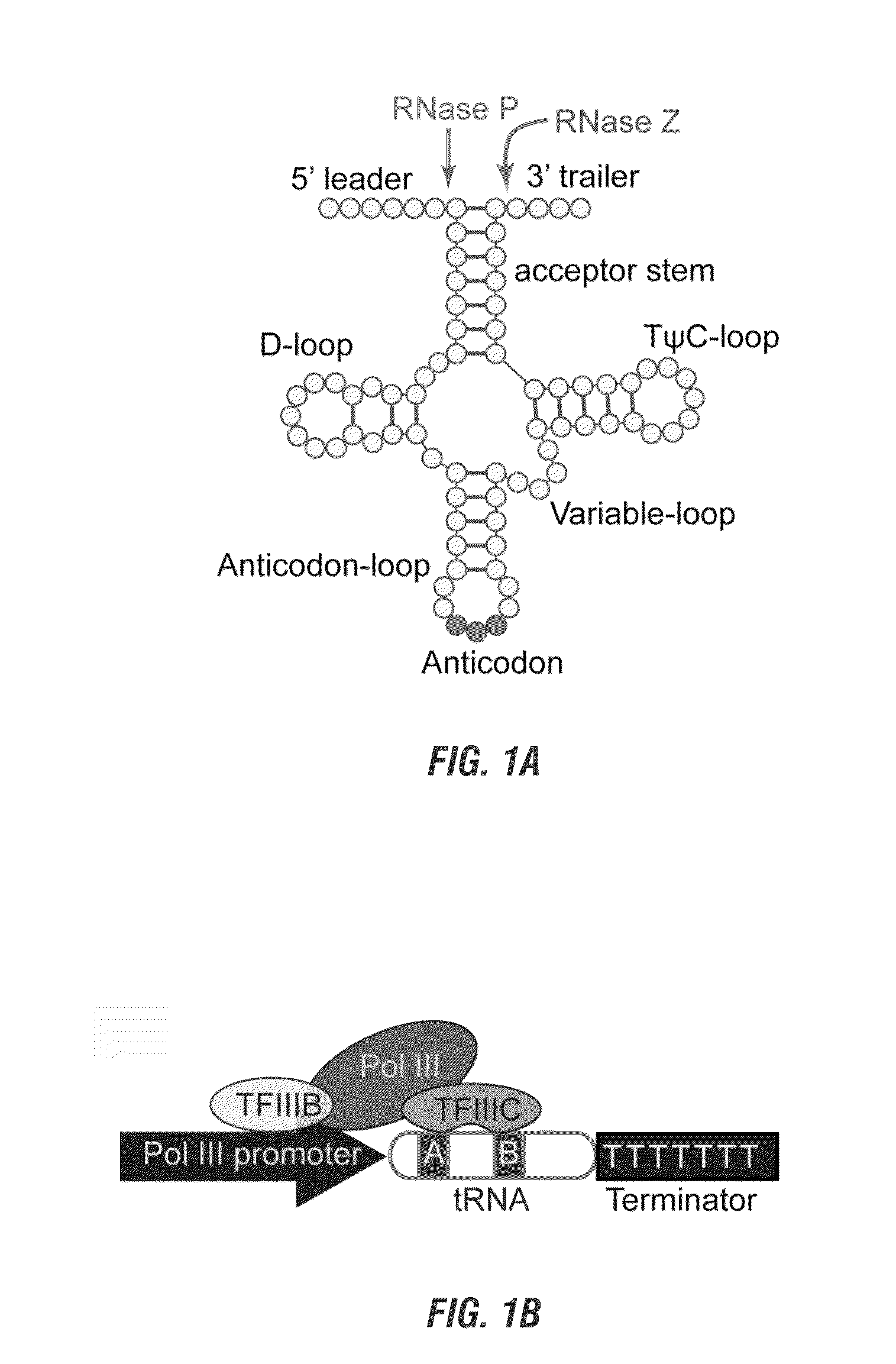
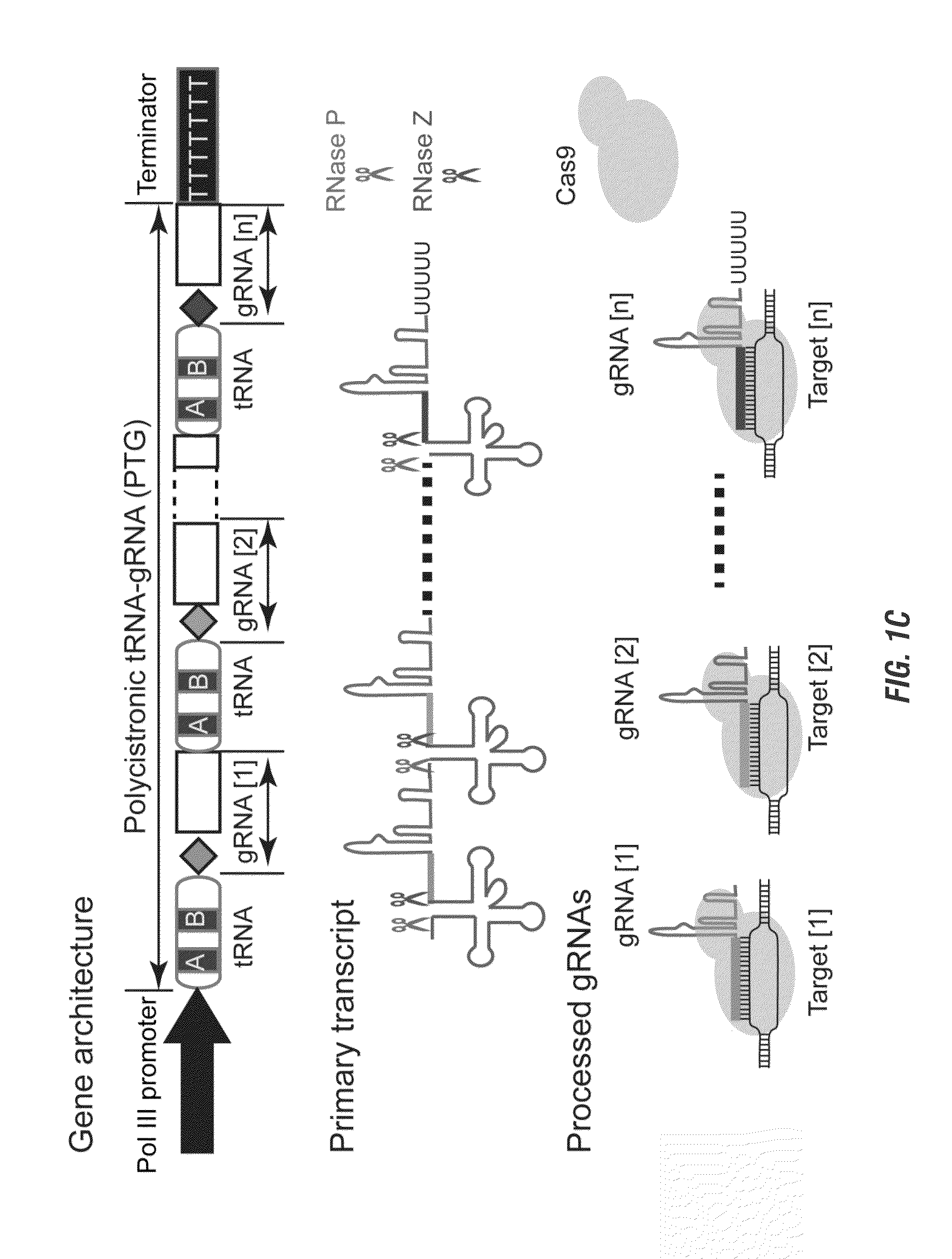
Methods and compositions for multiplex RNA guided genome editing and other RNA technologies
ActiveUS20160264981A1Facilitate RNA-guided multiplex genome editingVector-based foreign material introductionDNA/RNA fragmentationGenome editingGene silencing
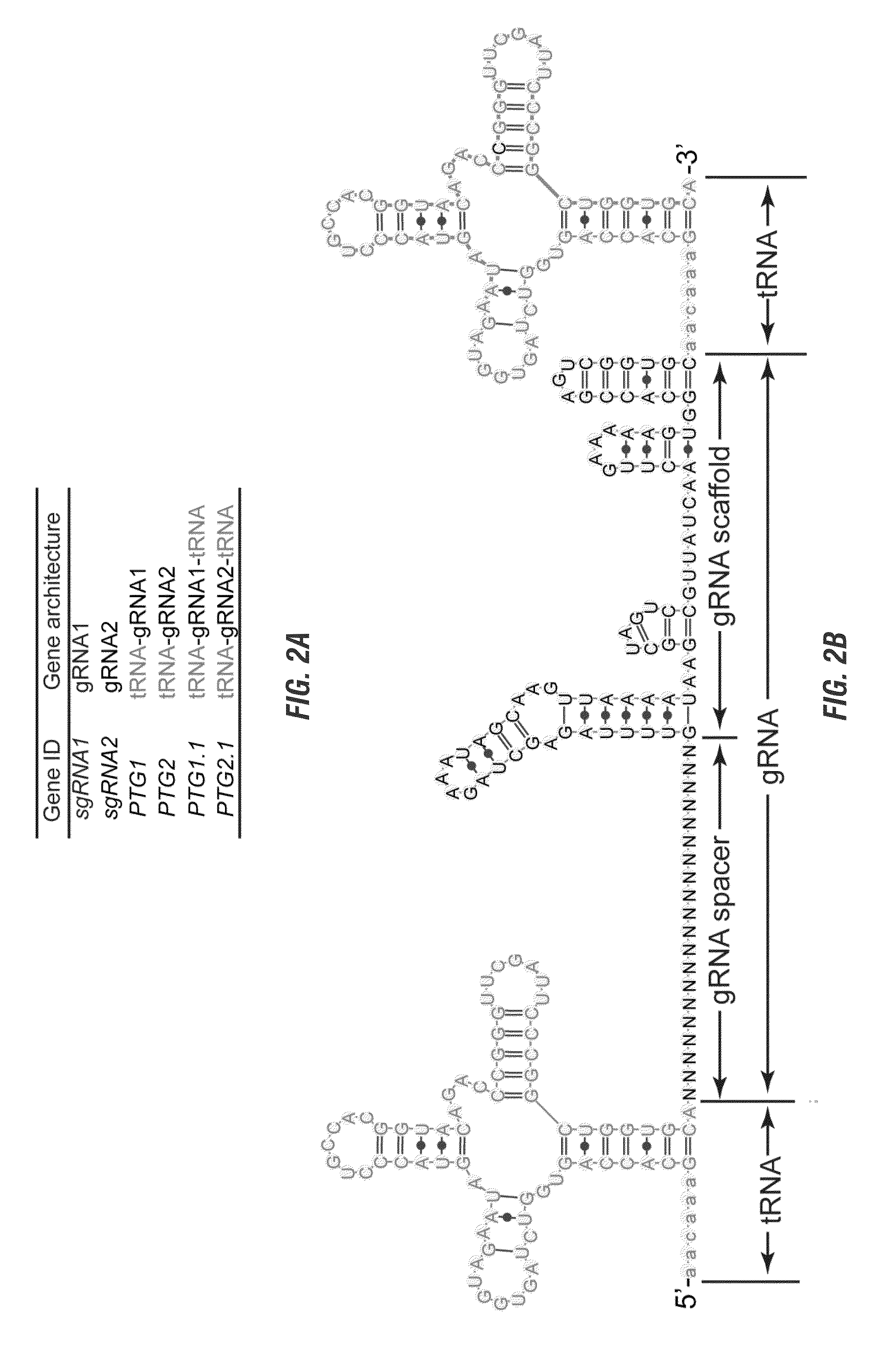
The invention includes materials and methods to generate numerous small RNAs from one polynucleotide construct (synthetic gene) to facilitate RNA-guided multiplex genome editing, modification, inhibition of expression and other RNA-based technologies. The synthetic gene / polynucleotide construct encodes polycistronic RNA components separated by tRNAs, and preferably also includes regulatory components such as a promoter or terminator to form an expression cassette. Once transcribed in a cell, the transcript is processed by the cell to multiple RNA molecules by the endogenous tRNA processing system. The system can be used for any RNA based gene manipulation method including RNA-mediated genome editing, artificial microRNA mediated gene silencing, small RNA mediated genetic manipulation, double-stranded RNA mediated gene silencing, antisense mechanisms and the like.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND
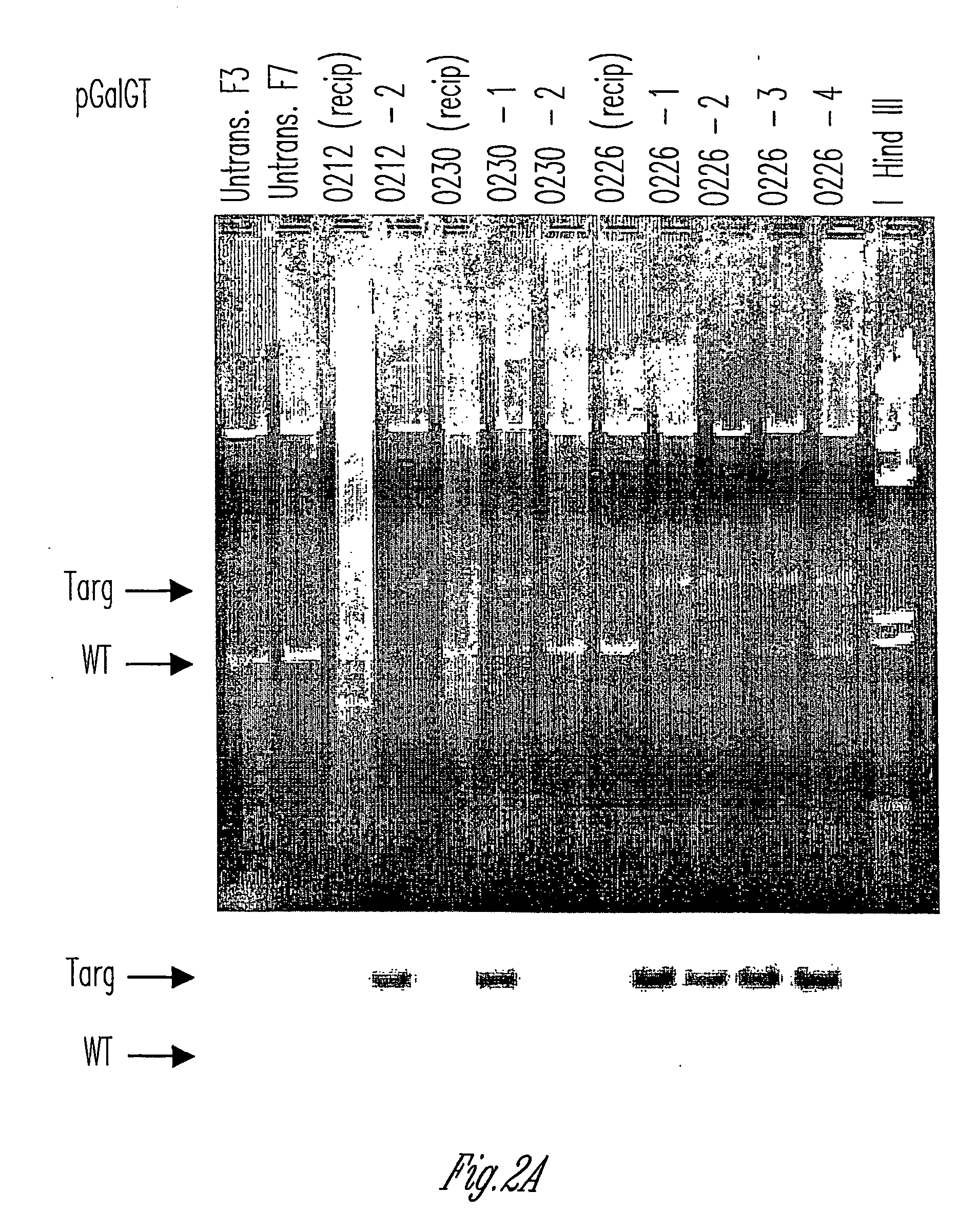
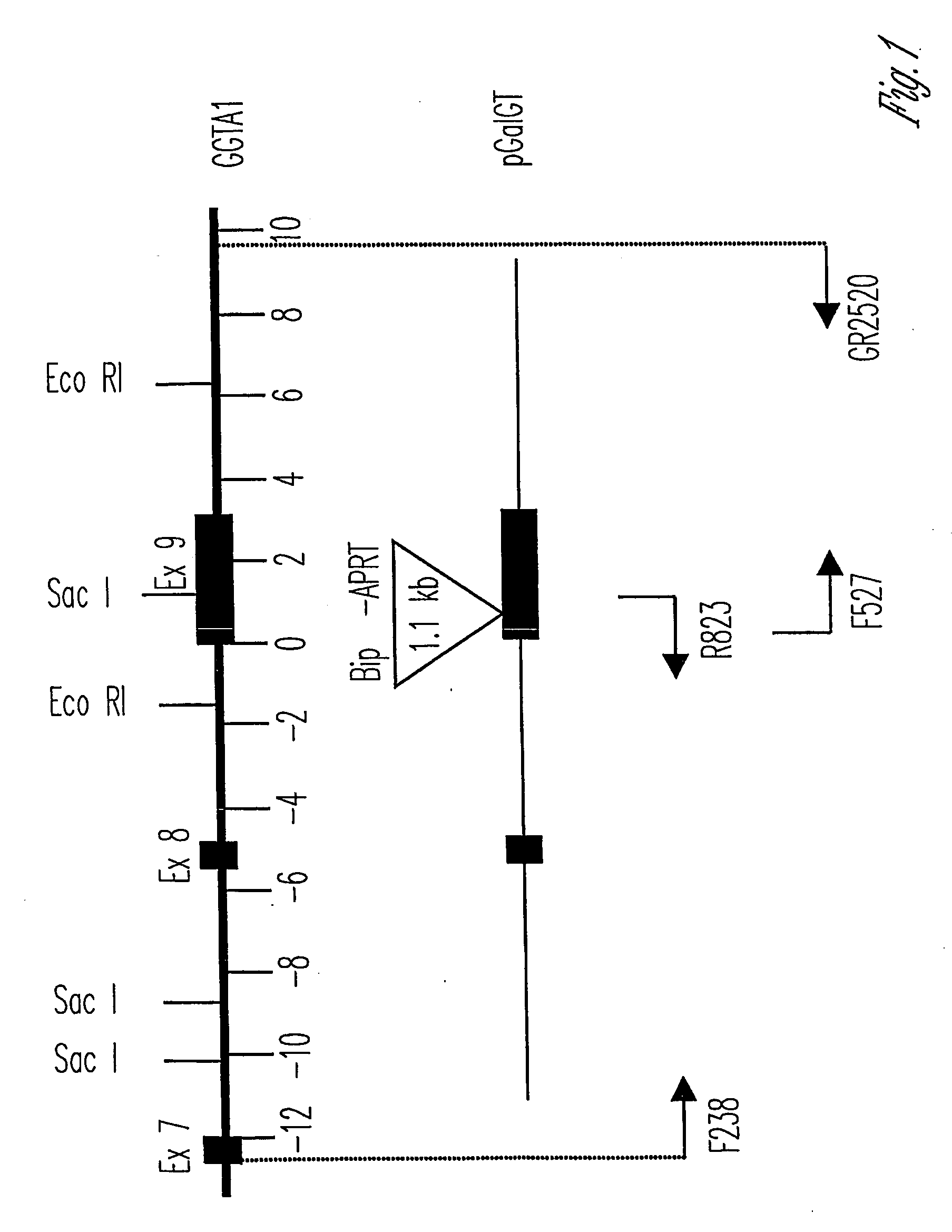
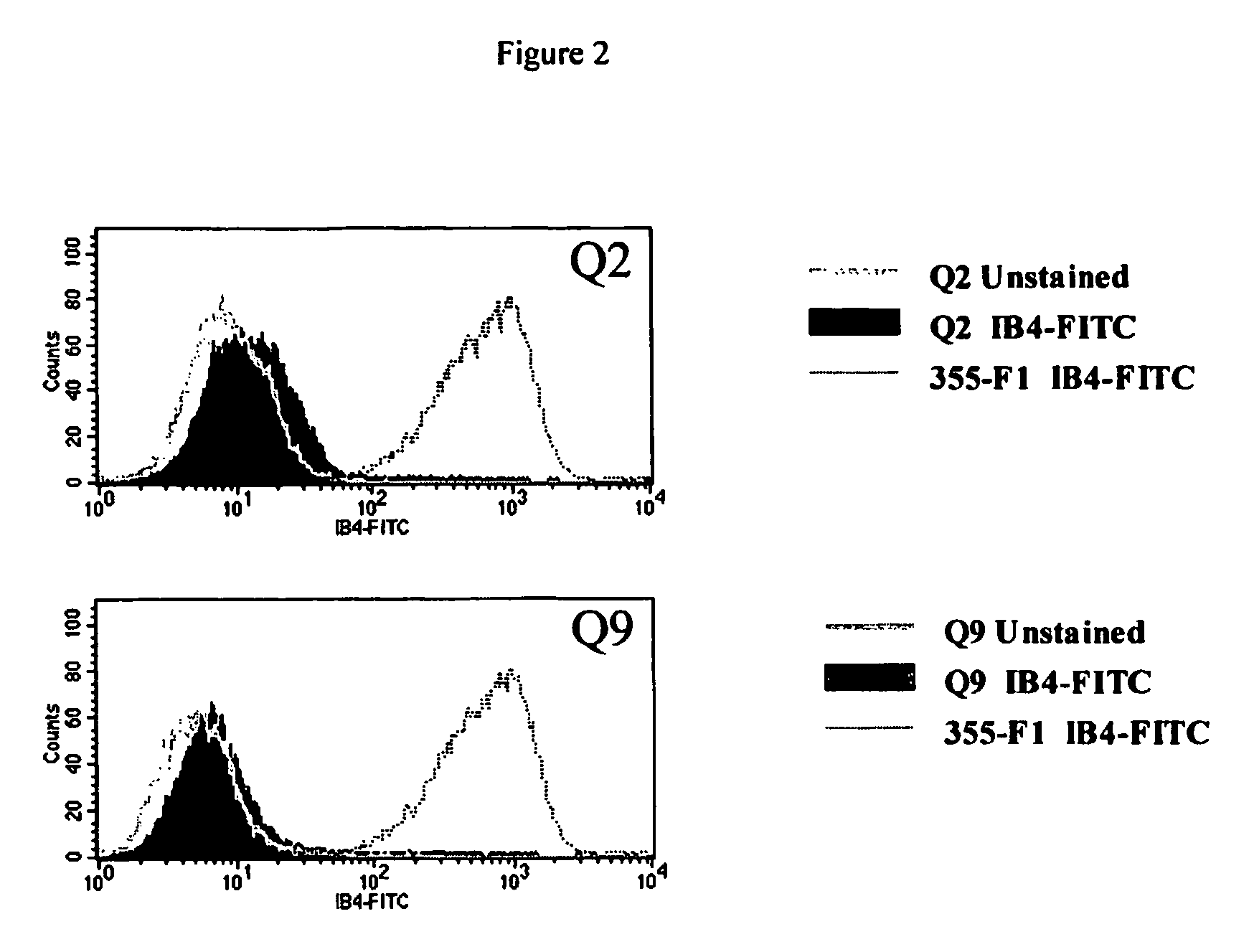
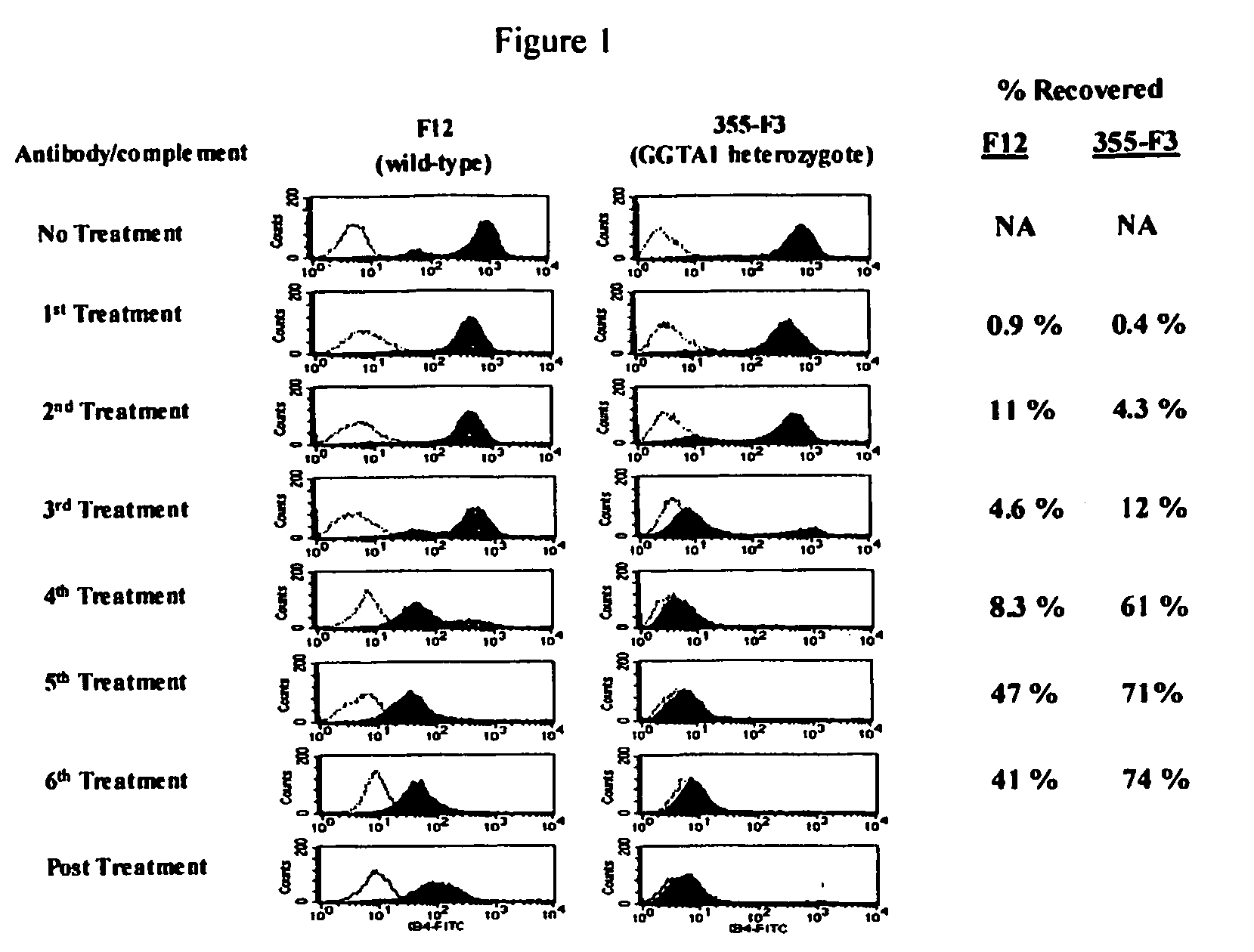
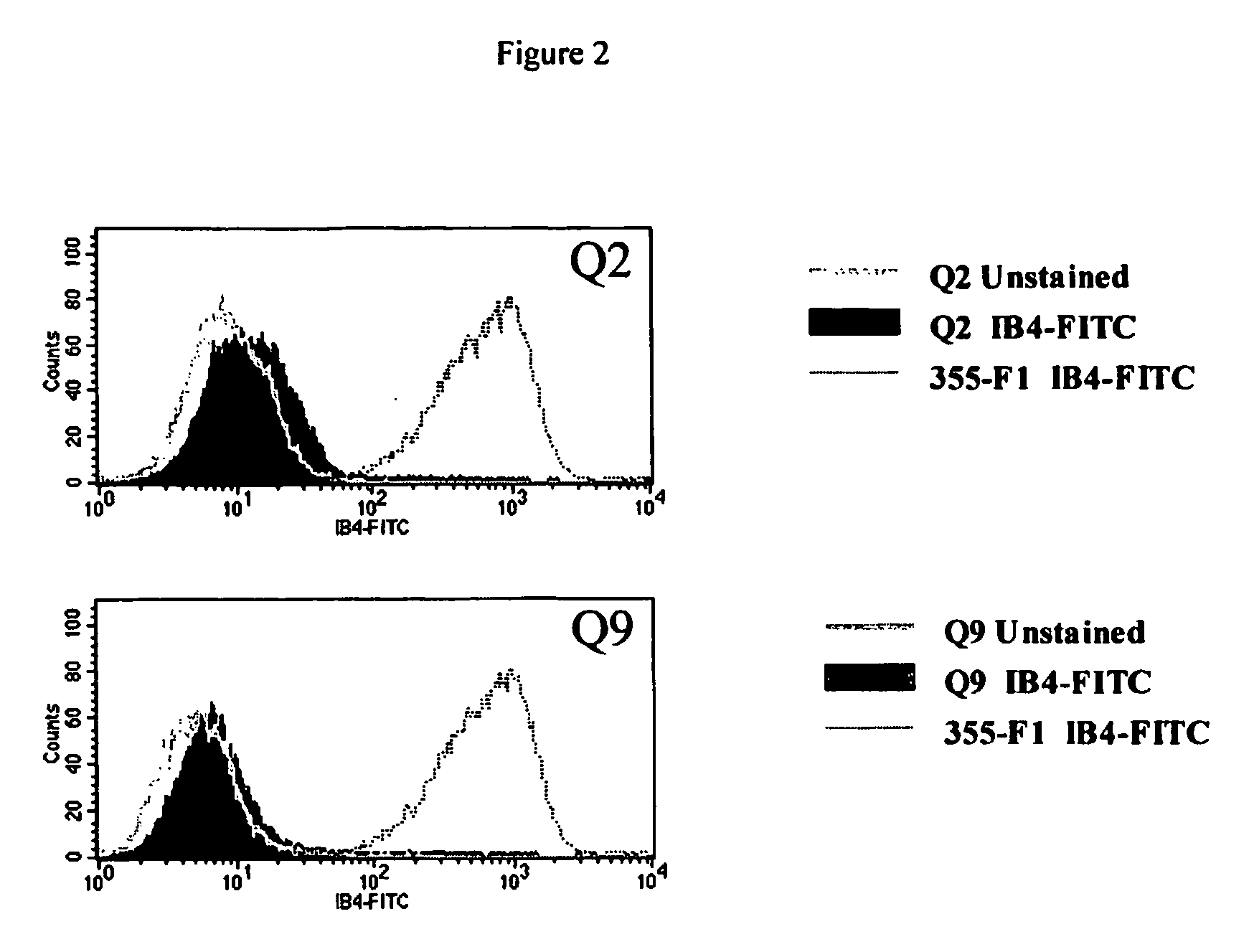
Alpha(1,3)-galactosyltransferase knockout swine, tissues and organs
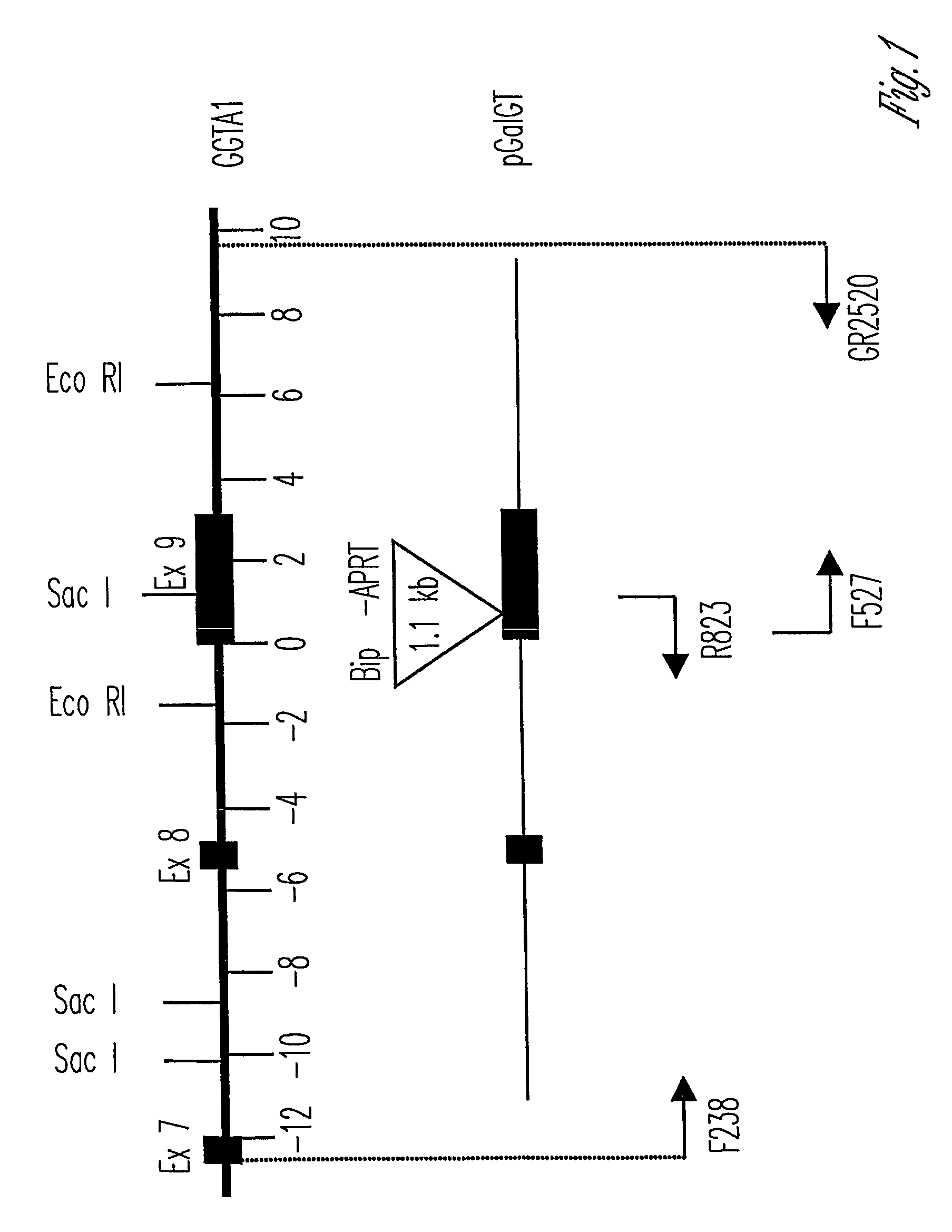
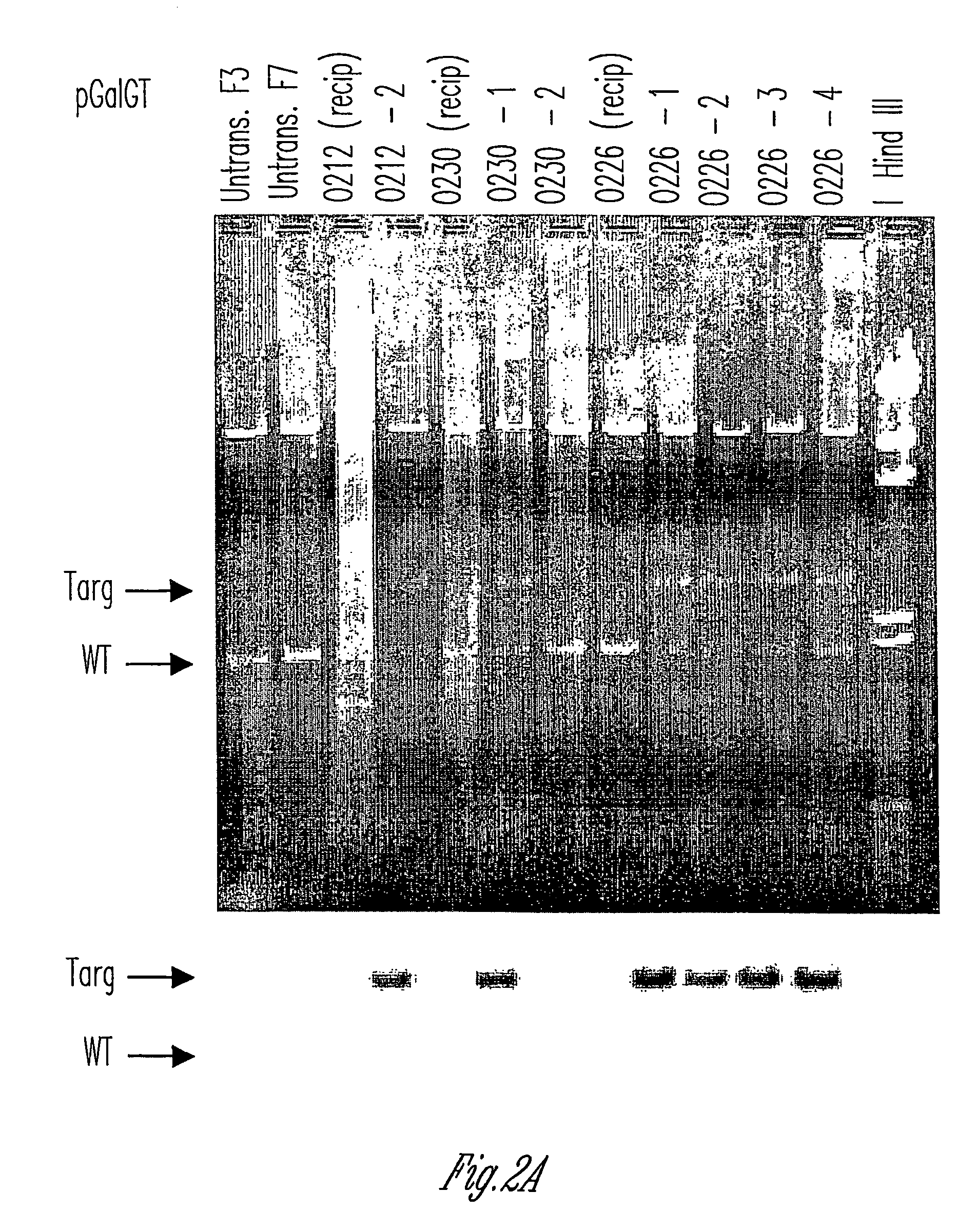
The invention relates to the genetic manipulation of non-human animals. More particularly, the invention relates to genetic manipulation of non-human animals to be used for xenotransplantation. The invention provides viable gene knockout swine including swine in which the α(1,3)-galactosyltransferase gene has been disrupted, methods for making such swine, and methods of using the tissues and organs of such swine for xenotransplantation.
Owner:IMMERGE BIOTHERAPEUTICS +1
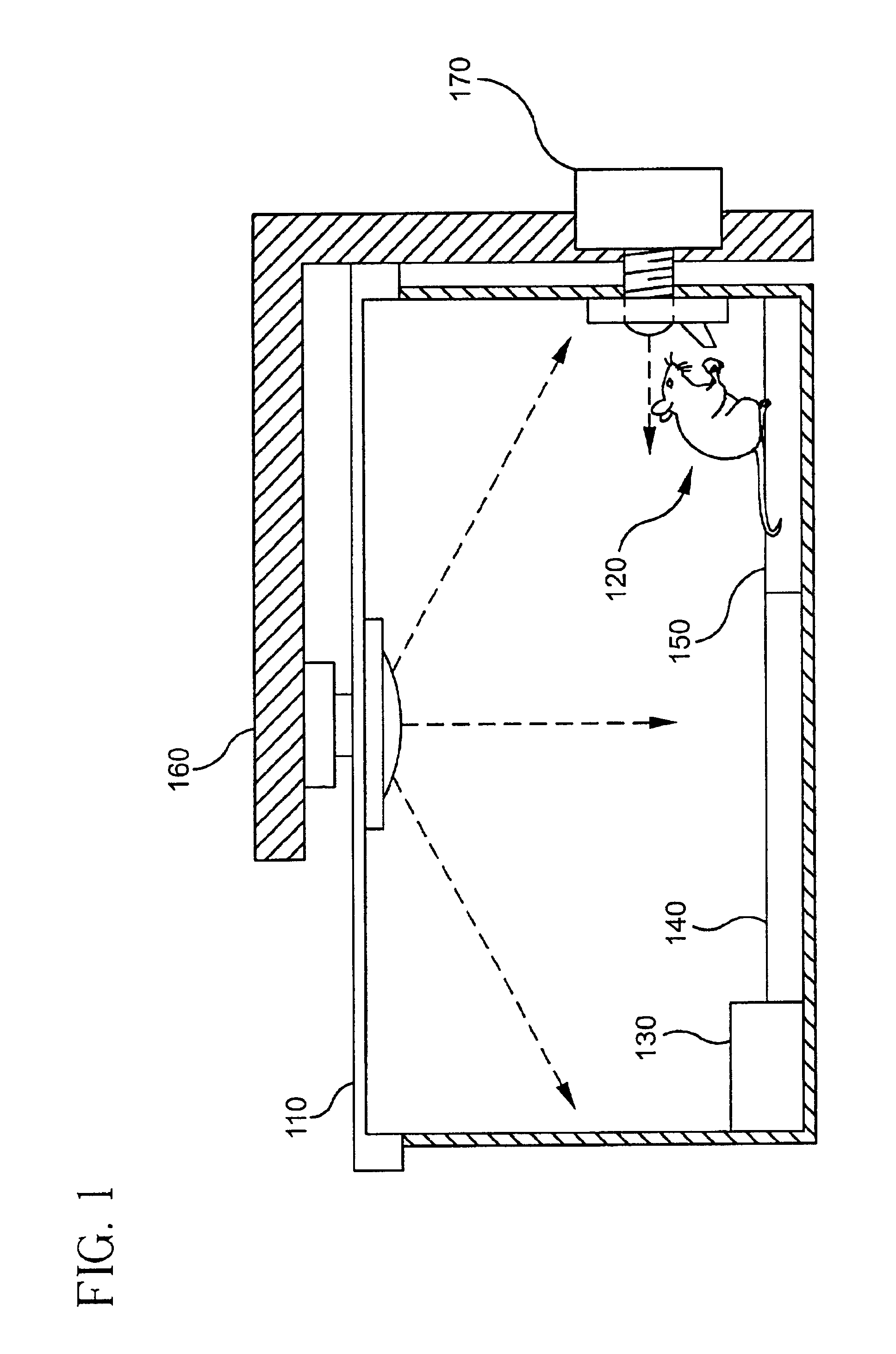
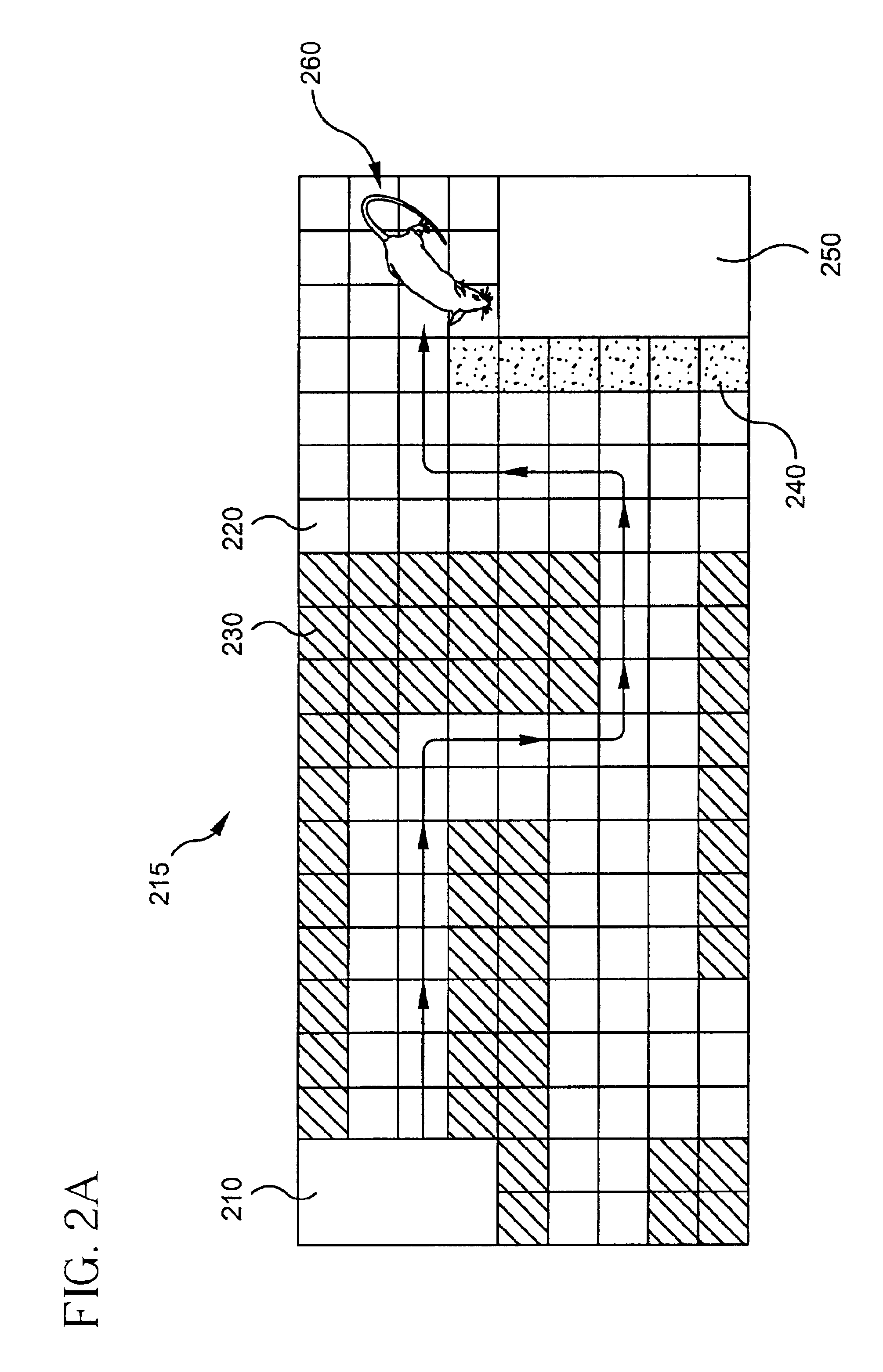
Programmable electronic maze for use in the assessment of animal behavior
InactiveUS6837184B2Efficient, user-independent, and cost-effectiveBuilding roofsPeptide/protein ingredientsAnimal behaviorExperimental drug
A system and method for studying a test subject includes monitoring the test subject as it traverses through a programmable maze. The test subject may be under the influence of experimental drugs or genetic manipulation. The dynamic maze can be changed automatically or manually to test the abilities of the test subject. The dynamic maze comprises of a starting point, an ending point, and an electronically programmable floor capable of constructing various obstacles and passageways. The programmable floor may be programmed by a human user using an interface, or it may be programmed by an automated control system that programs the maze in accordance with the ability of the test subject to traverse the maze. Various devices are incorporated with the use of the maze to monitor the activities and welfare of the test subject.
Owner:PSYCHOGENICS
Knockout swine and methods for making the same
The invention relates to the genetic manipulation of non-human animals. More particularly, the invention relates to genetic manipulation of non-human animals to be used for xenotransplantation. The invention provides viable gene knockout swine including swine in which the α(1,3)-galactosyltransferase gene has been disrupted, methods for making such swine, and methods of using the tissues and organs of such swine for xenotransplantation.
Owner:IMMERGE BIOTHERAPEUTICS +1
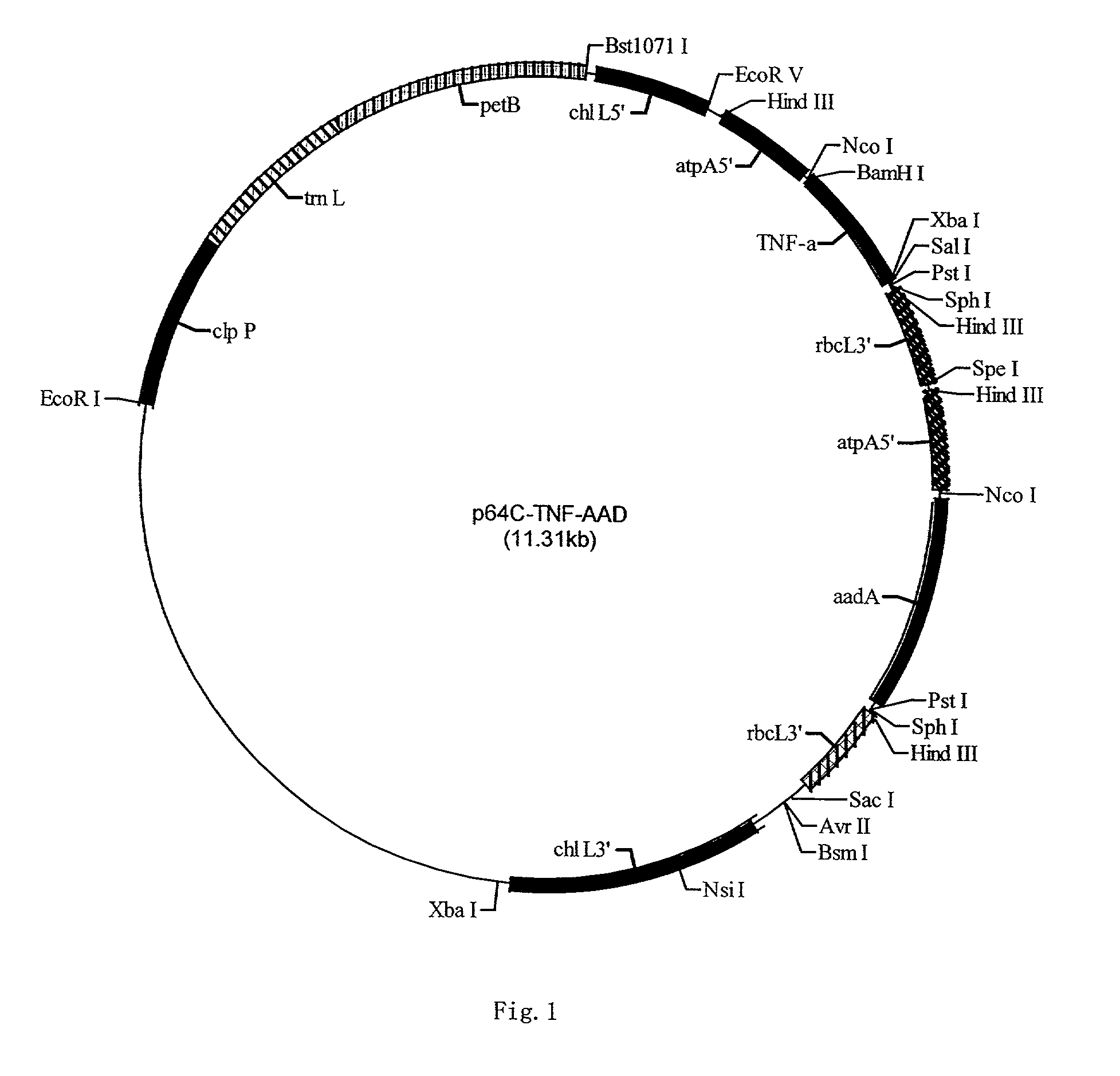
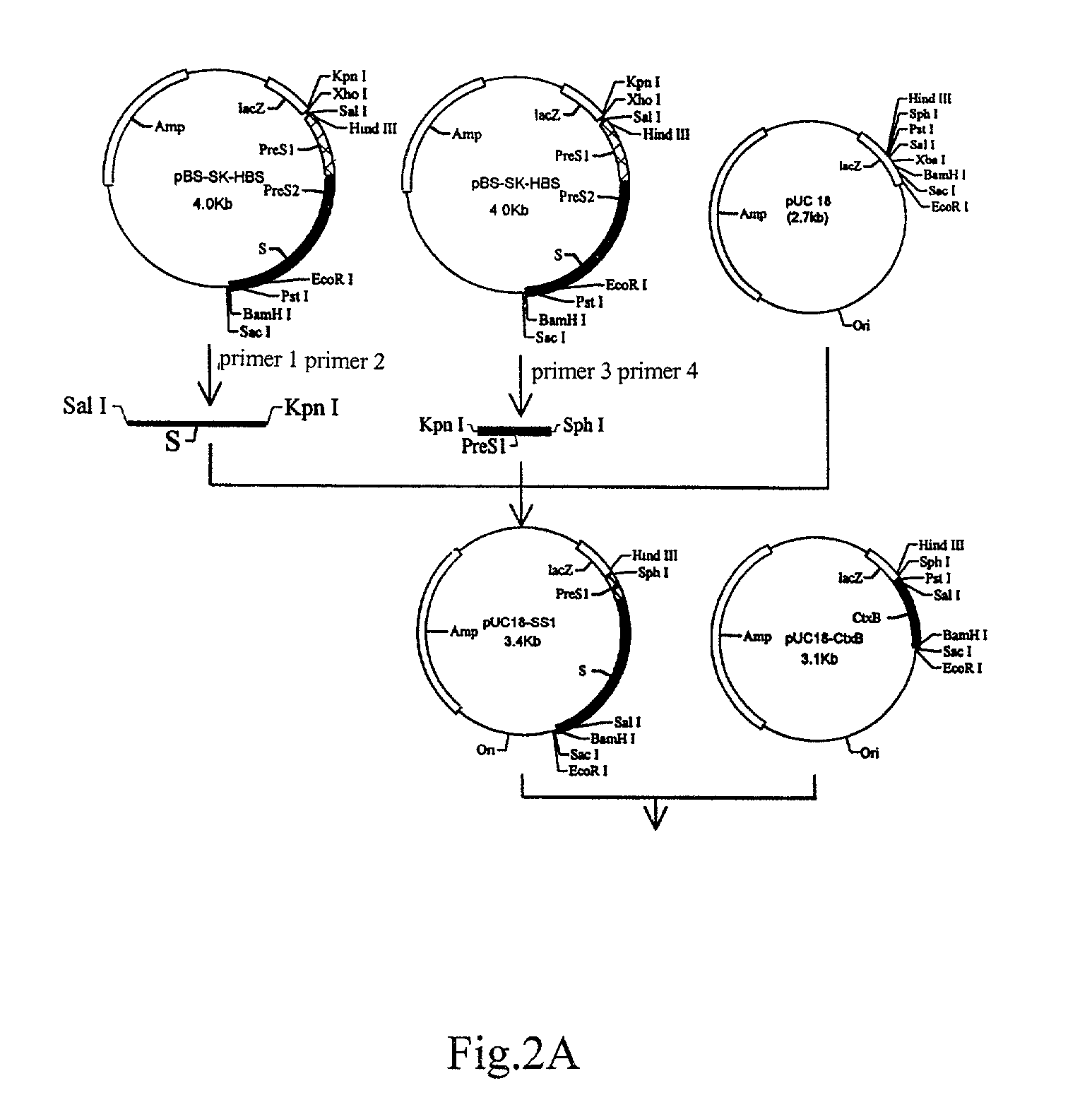
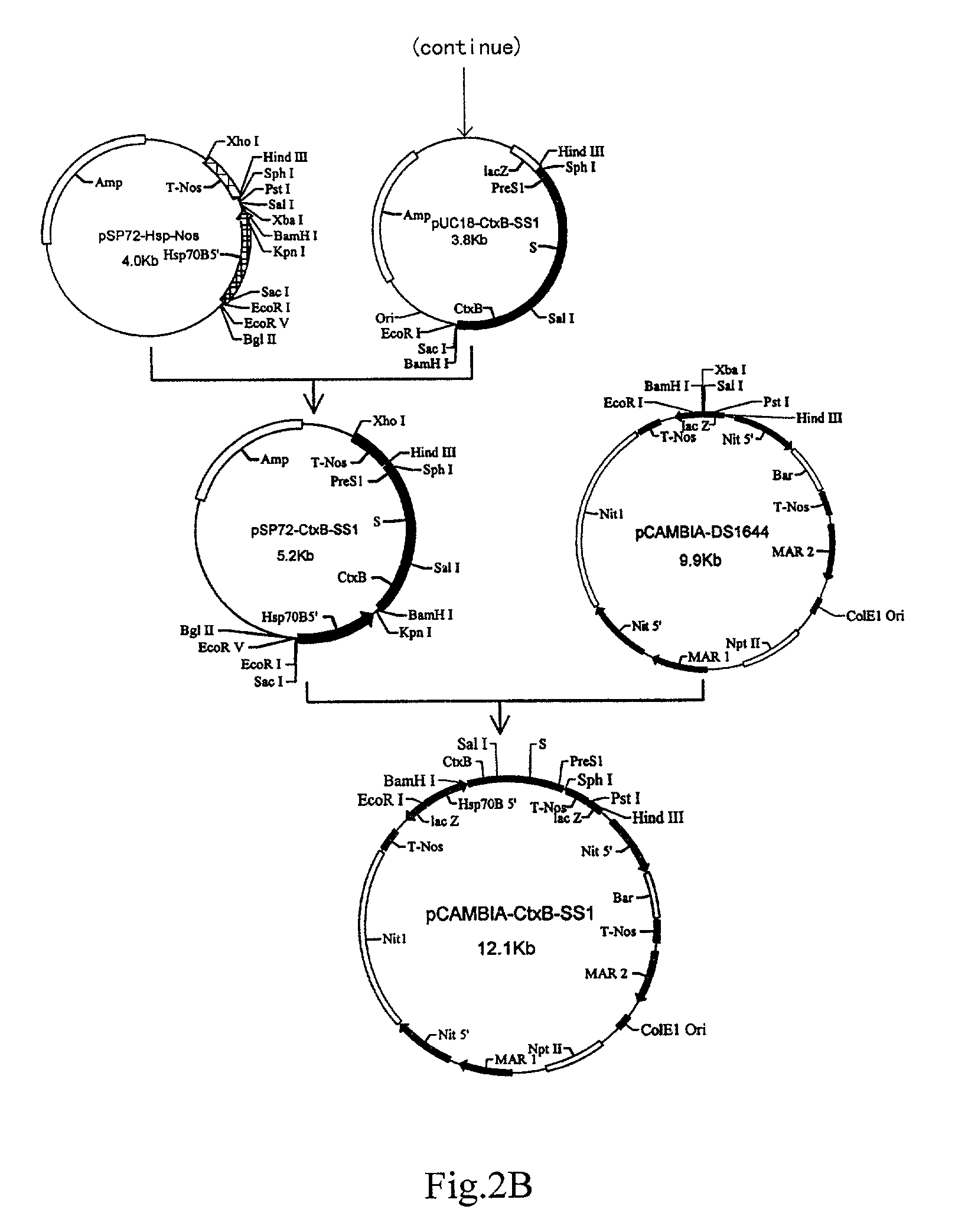
Pharmaceutical proteins, human therapeutics, human serum albumin, insulin, native cholera toxic b submitted on transgenic plastids
InactiveUS20030204864A1Eliminate needLarge biomassBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsEscherichia coliInsulin-like growth factor
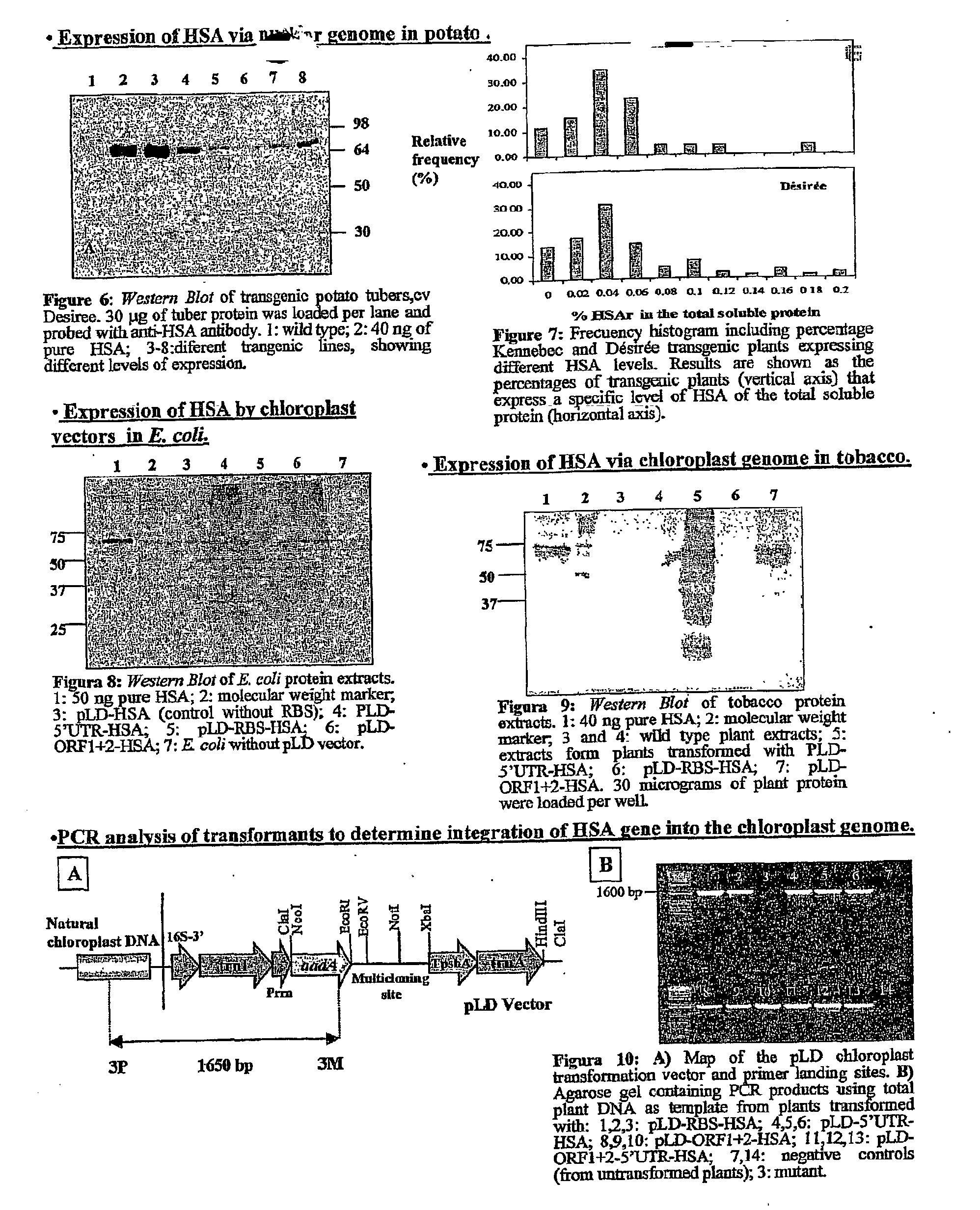
Transgenic chloroplast technology could provide a viable solution to the production of Insulin-like Growth Factor I (IGF-I), Human Serum Albumin (HSA), or interferons (IFN) because of hyper-expression capabilities, ability to fold and process eukaryotic proteins with disulfide bridges (thereby eliminating the need for expensive post-purification processing). Tobacco is an ideal choice because of its large biomass, ease of scale-up (million seeds per plant), genetic manipulation and impending need to explore alternate uses for this hazardous crop. Therefore, all three human proteins will be expressed as follows: a) Develop recombinant DNA vectors for enhanced expression via tobacco chloroplast genomes b) generate transgenic plants c) characterize transgenic expression of proteins or fusion proteins using molecular and biochemical methods d) large scale purification of therapeutic proteins from transgenic tobacco and comparison of current purification / processing methods in E. coli or yeast e) Characterization and comparison of therapeutic proteins (yield, purity, functionality) produced in yeast or E. coli with transgenic tobacco f) animal testing and pre-clinical trials for effectiveness of the therapeutic proteins. Mass production of affordable vaccines can be achieved by genetically engineering plants to produce recombinant proteins that are candidate vaccine antigens. The B subunits of Enteroxigenic E. coli (LTB) and cholera toxin of Vibrio cholerae (CTB) are examples of such antigens. When the native LTB gene was expressed via the tobacco nuclear genome, LTB accumulated at levels less than 0.01% of the total soluble leaf protein. Production of effective levels of LTB in plants, required extensive codon modification. Amplification of an unmodified CTB coding sequence in chloroplasts, up to 10,000 copies per cell, resulted in the accumulation of up to 4.1% of total soluble tobacco leaf protein as oligomers (about 410 fold higher expression levels than that of the unmodified LTB gene). PCR and Southern blot analyses confirmed stable integration of the CTB gene into the chloroplast genome. Western blot analysis showed that chloroplast synthesized CTB assembled into oligomers and was antigenically identical to purified native CTB. Also, GM1,-ganglioside binding assays confirmed that chloroplast synthesized CTB binds to the intestinal membrane receptor of cholera toxin, indicating correct folding and disulfide bond formation within the chloroplast. In contrast to stunted nuclear transgenic plants, chloroplast transgenic plants were morphologically indistinguishable from untransformed plants, when CTB was constitutively expressed. The introduced gene was stably inherited in the subsequent generation as confirmed by PCR and Southern blot analyses. Incrased production of an efficient transmucosal carrier molecule and delivery system, like CTB, in transgenic chloroplasts makes plant based oral vaccines and fusion proteins with CTB needing oral administration a much more practical approach.
Owner:AUBURN UNIV +1
Tailor-made pluripotent stem cell and use of the same
InactiveUS20080003560A1Lower Level RequirementsTransplantation rejection reaction could be significantly reducedGenetically modified cellsHybrid cell preparationEgg cellSomatic cell
An object of the present invention is to efficiently establish cells, tissues, and organs capable of serving as donors for treating diseases, without eliciting immune rejection reactions, without starting with an egg cell. This object was achieved by providing a pluripotent stem cell having a desired genome. The cell was produced by treating with a reprogramming agent, producing a fusion cell of an MHC deficient stem cell with a somatic cell, or after producing a fusion cell of a stem cell with a somatic cell, removing a gene derived from the stem cell by performing genetic manipulation with a retrovirus.
Owner:REPROCELL
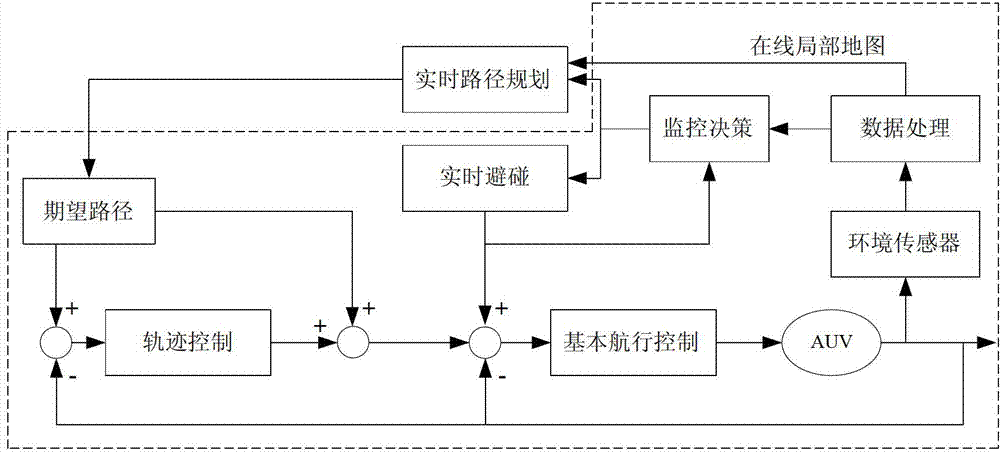
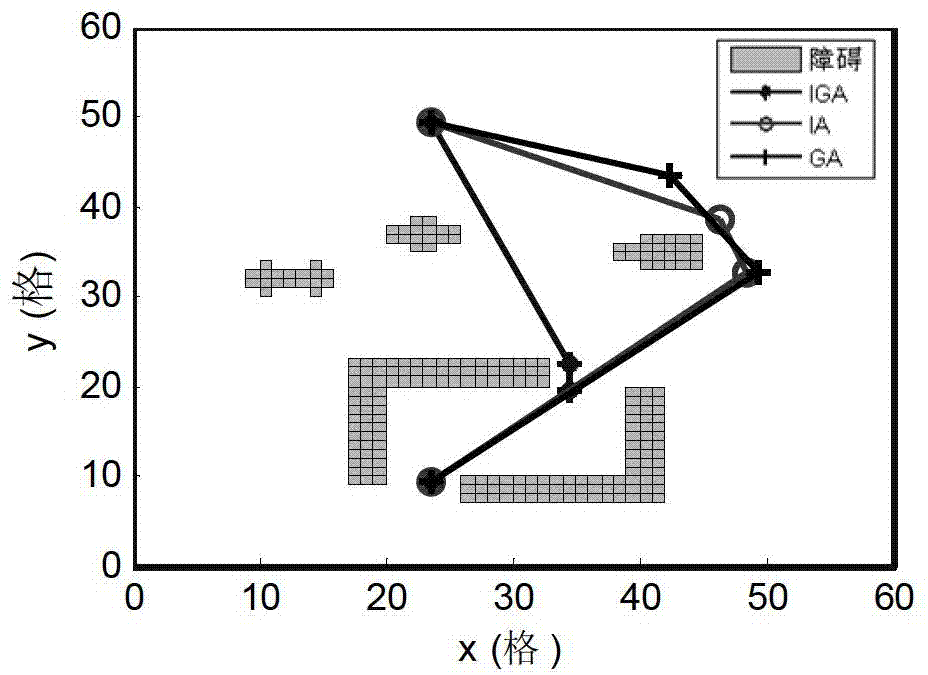
Immune genetic algorithm for AUV (Autonomous Underwater Vehicle) real-time path planning
ActiveCN103077425AAvoid premature convergenceAchieve global optimizationGenetic modelsImmune genetic algorithmVaccination
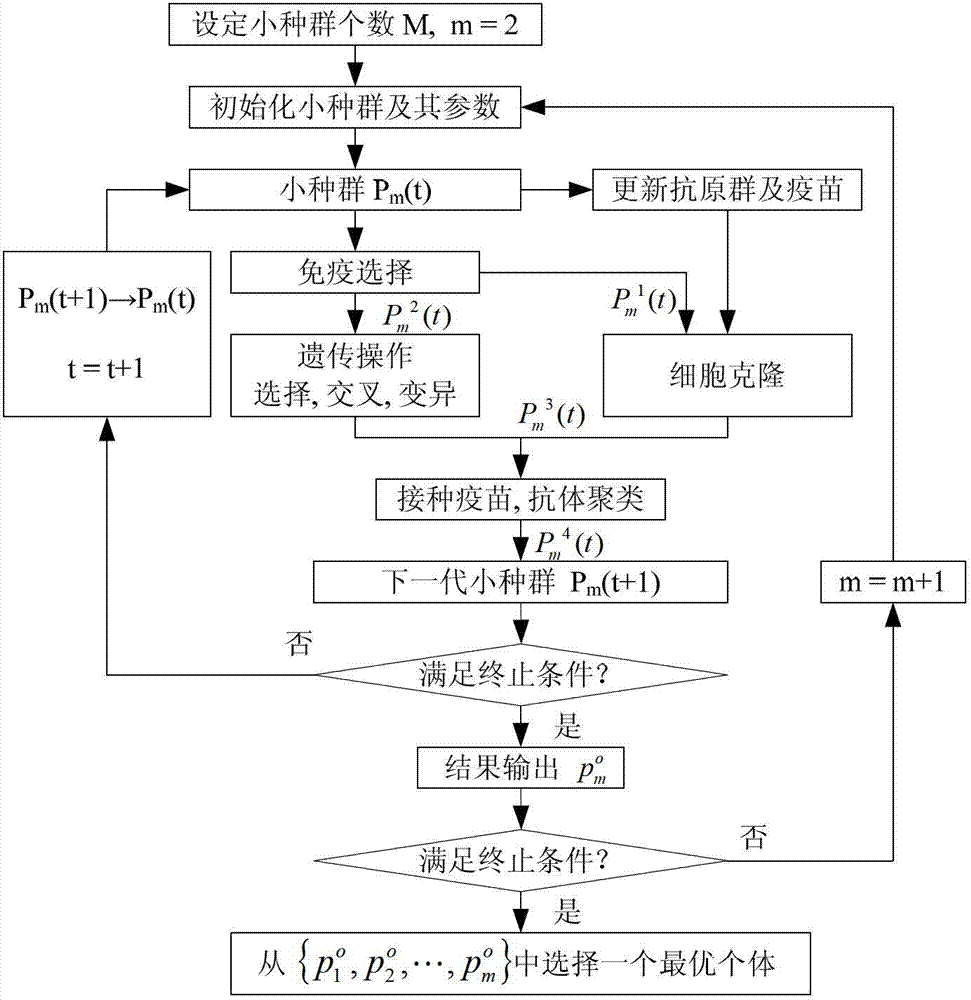
The invention relates to a real-time path planning method of AUV (Autonomous Underwater Vehicle), in particular to a method for carrying out online, real-time local path planning according to an online map in an AUV real-time collision preventation process. The method comprises the steps of: setting the quantity of small populations according to the quantity of path points of the AUV, initializing; carrying out immune selection on each small population to obtain subgroups; carrying out genetic manipulation on one subgroup, carrying out cell cloning on the other subgroup; then clustering through a vaccination and an antibody to form the next generation of small population, judging whether the next generation of small population meets the conditions or not; if yes, selecting optimal individuals of the small populations; and selecting the optimal individuals from the set consisting of all optimal individuals to be used as a planning path. According to the invention, the diversity of the population is maintained by using an antibody clustering principle, the premature convergence of an algorithm is avoided, and the global optimization is facilitated. The established immune genetic algorithm is used for clustering and analyzing generated filial generations by adopting a self-regulating mechanism, and the diversity of the population is ensured.
Owner:SHENYANG INST OF AUTOMATION - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
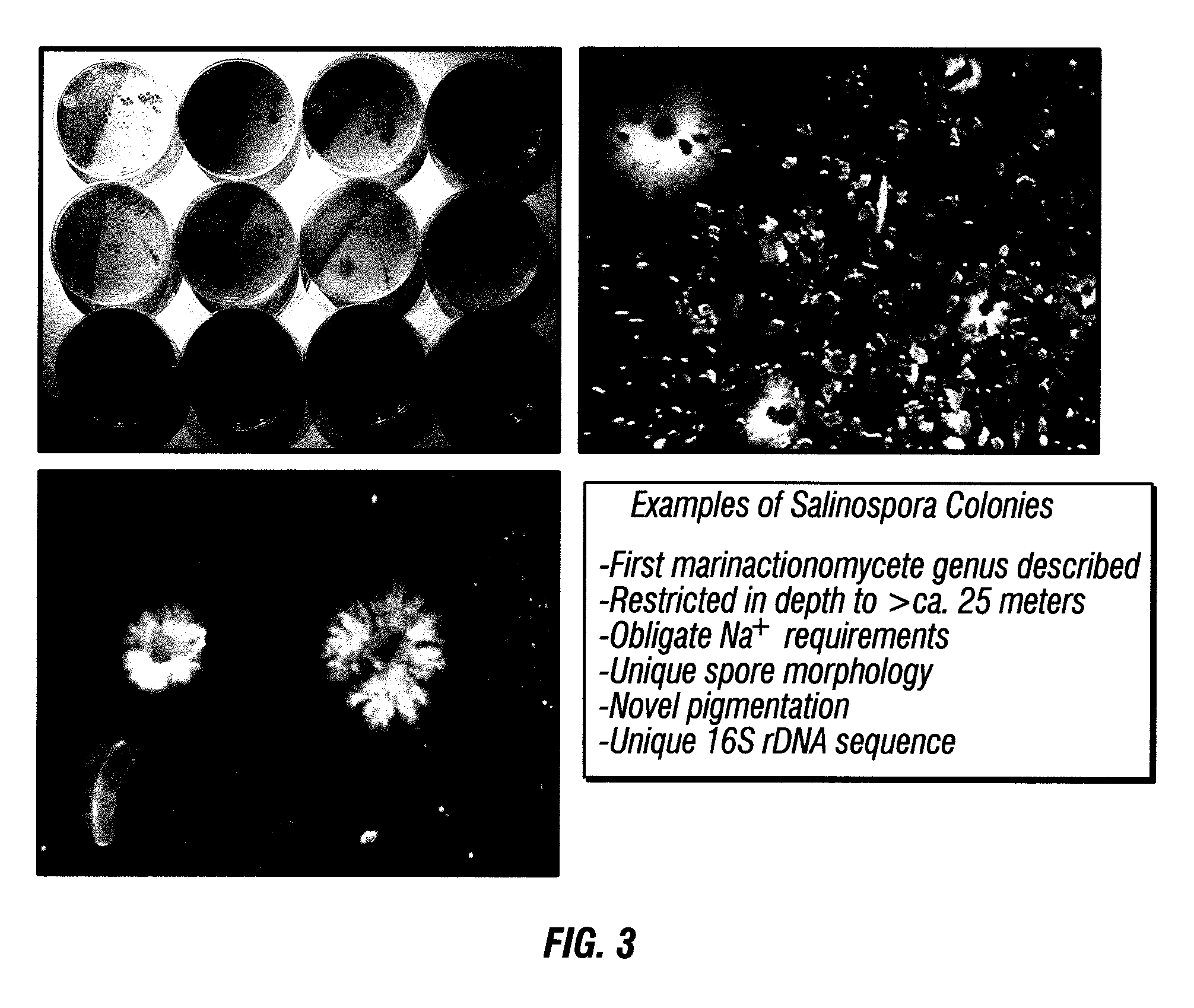
Biosyntheses of salinosporamide A and its analogs and related methods of making salinosporamide A and its analogs
Disclosed are methods of modulating biosynthesis of Salinosporamide A and its analogs, which are useful in treating cancer, inflammatory conditions, and / or infectious disease. The methods involve, for example, genetic manipulation, selection of reagents in the fermentation feedstock, and selection of fermentation conditions.
Owner:TRIPHASE RES & DEV I
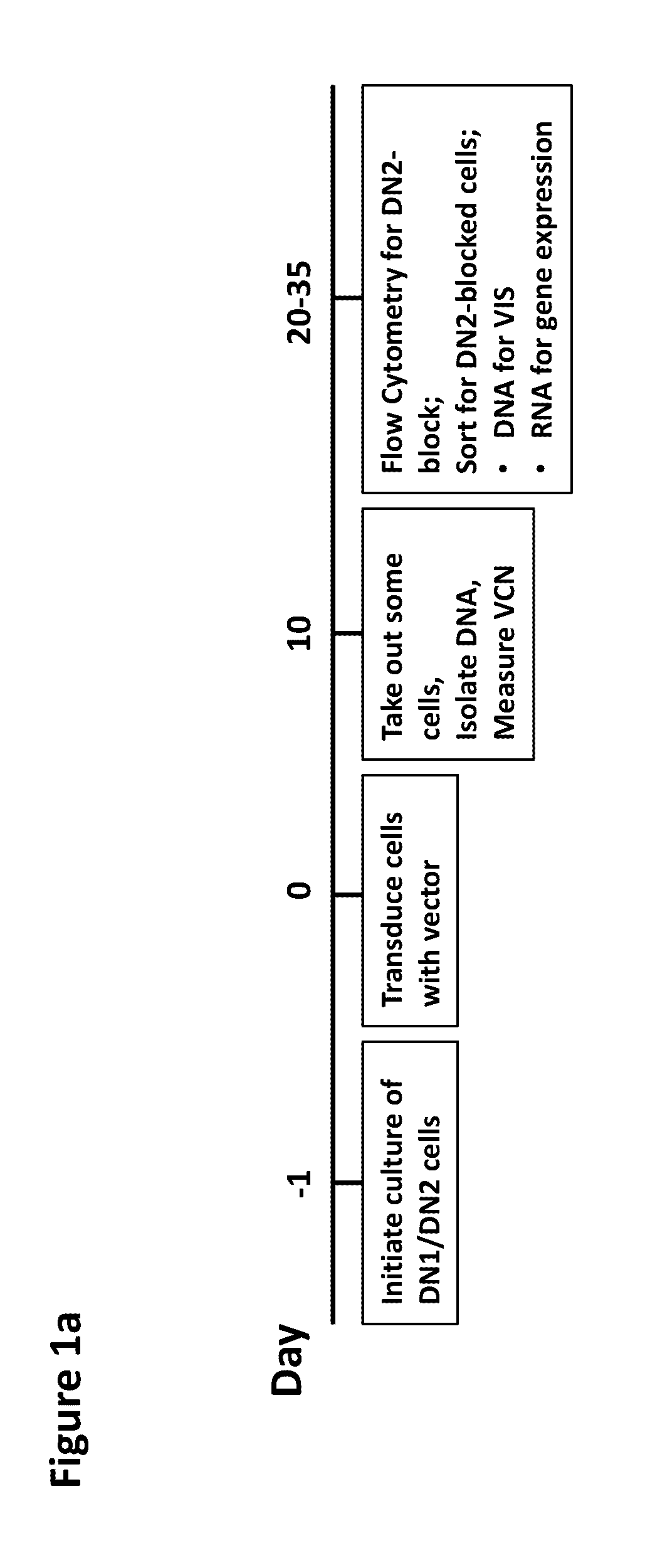
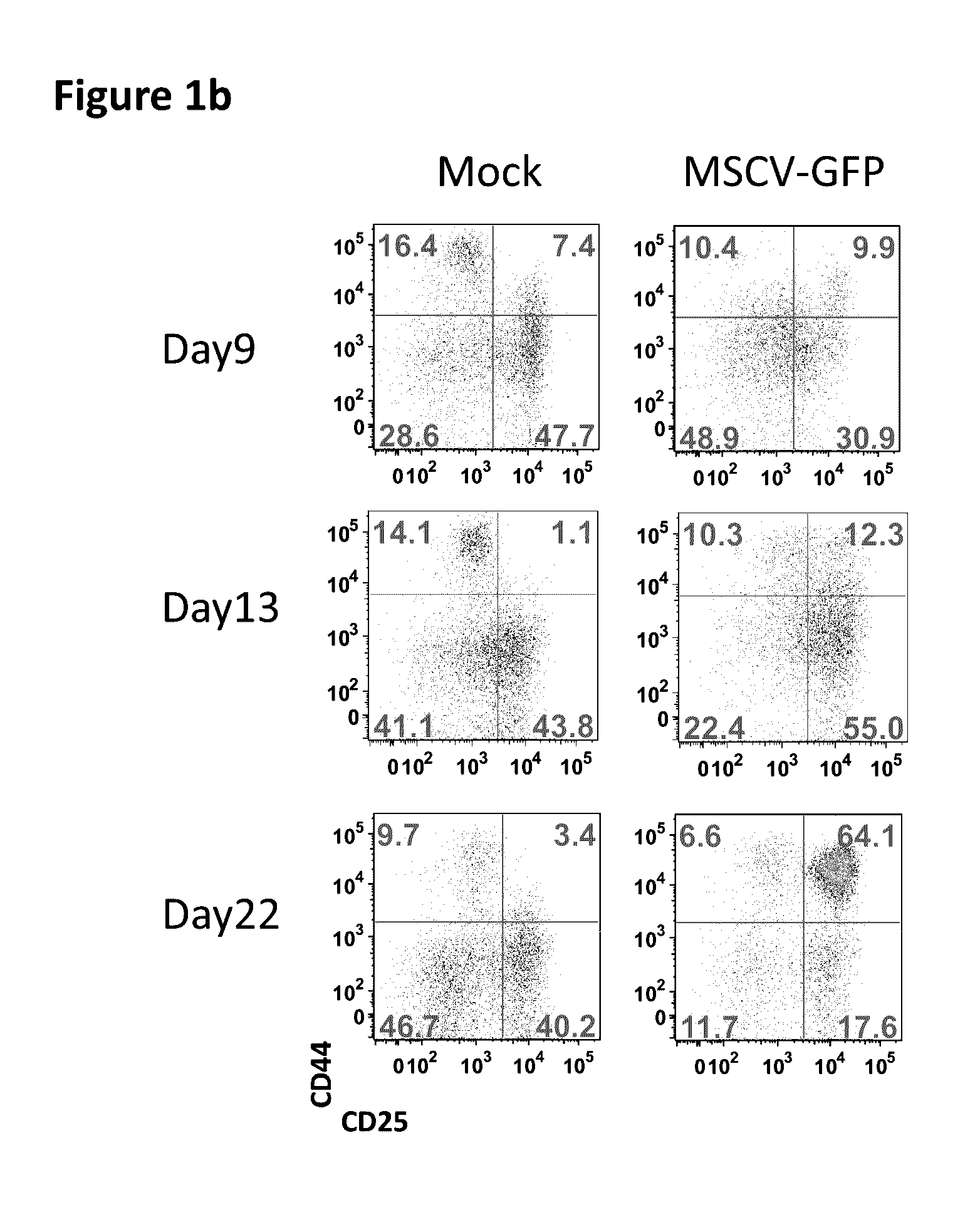
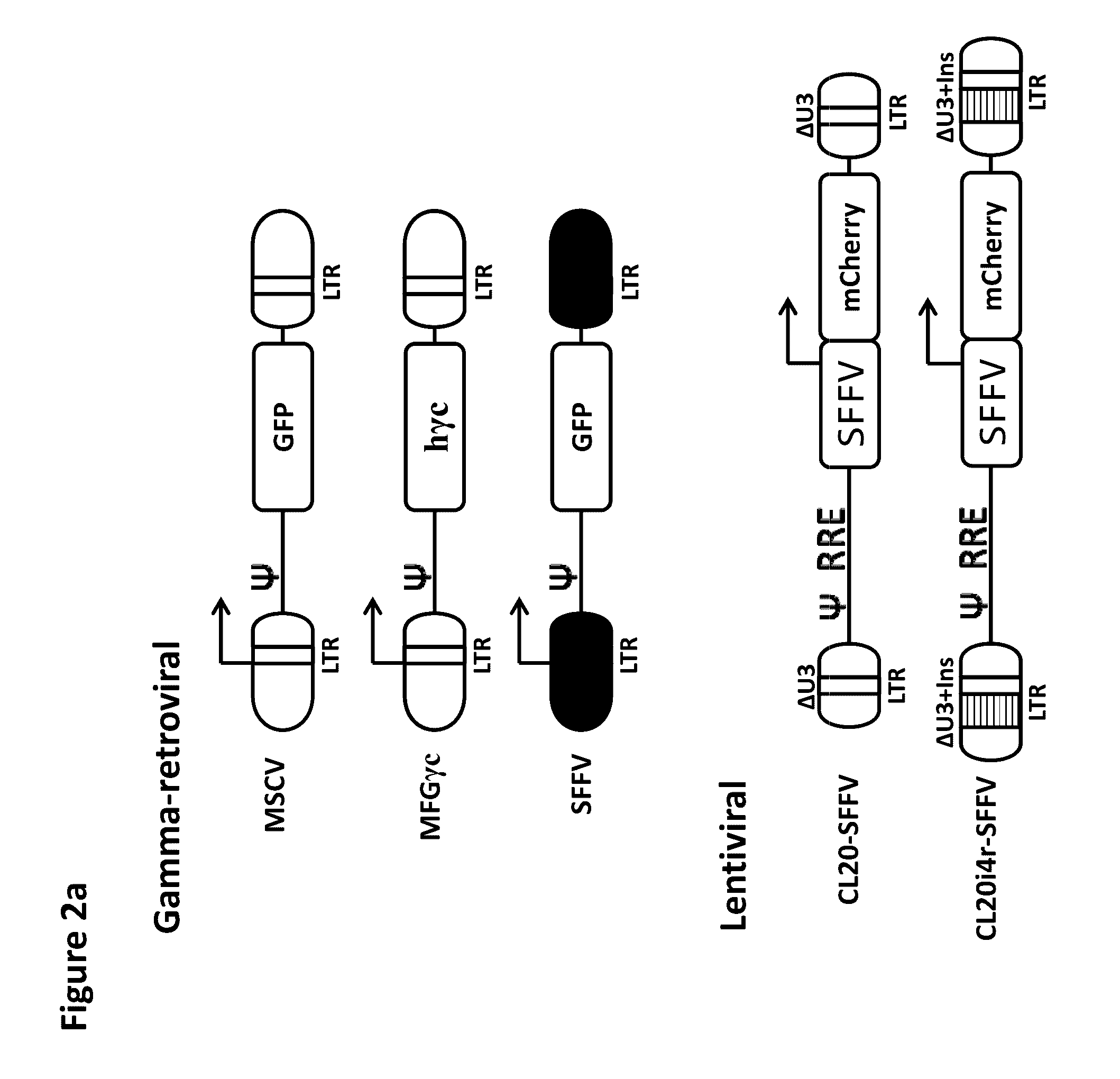
Assay for safety assessment of therapeutic genetic manipulations, gene therapy vectors and compounds
ActiveUS20160312304A1Microbiological testing/measurementGenome editingHematopoietic progenitor cells
The invention is directed to methods of assessing the safety of therapeutic compounds and therapeutic genetic manipulations, including integrating gene therapy vectors and genome editing. In particular, the invention provides a method, wherein the oncogenic potential of therapeutic compounds and therapeutic genetic manipulations, including integrating gene therapy vectors and genome editing, is determined by determining the percentage of differentiation blocked hematopoietic progenitor cells.
Owner:ST JUDE CHILDRENS RES HOSPITAL INC
T cell anergy is reversed by active Ras and regulated by diacylglycerol kinase
ActiveUS20050266510A1Wide applicationMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingWestern blotIl 2 production
T cell anergy has been correlated with defective Ras signaling. However, neither a causal relationship nor the mechanism of Ras hypoactivation have been established. Using adenoviral transduction of CAR Tg T cells to enable genetic manipulation in nonproliferating cells, we show that Ras61L restores IL-2 production and MAP kinase signaling in T cells anergized in vitro or in vivo. A gene array screen revealed upregulated diacylglycerol kinase (DGK) in the anergic state, which was confirmed by RT-PCR and Western blot analysis. A DGK inhibitor significantly restored IL-2 production by anergic cells. Our data support a causal role for DGK and defective Ras signaling in T cell anergy.
Owner:CHICAGO UNIV OF THE
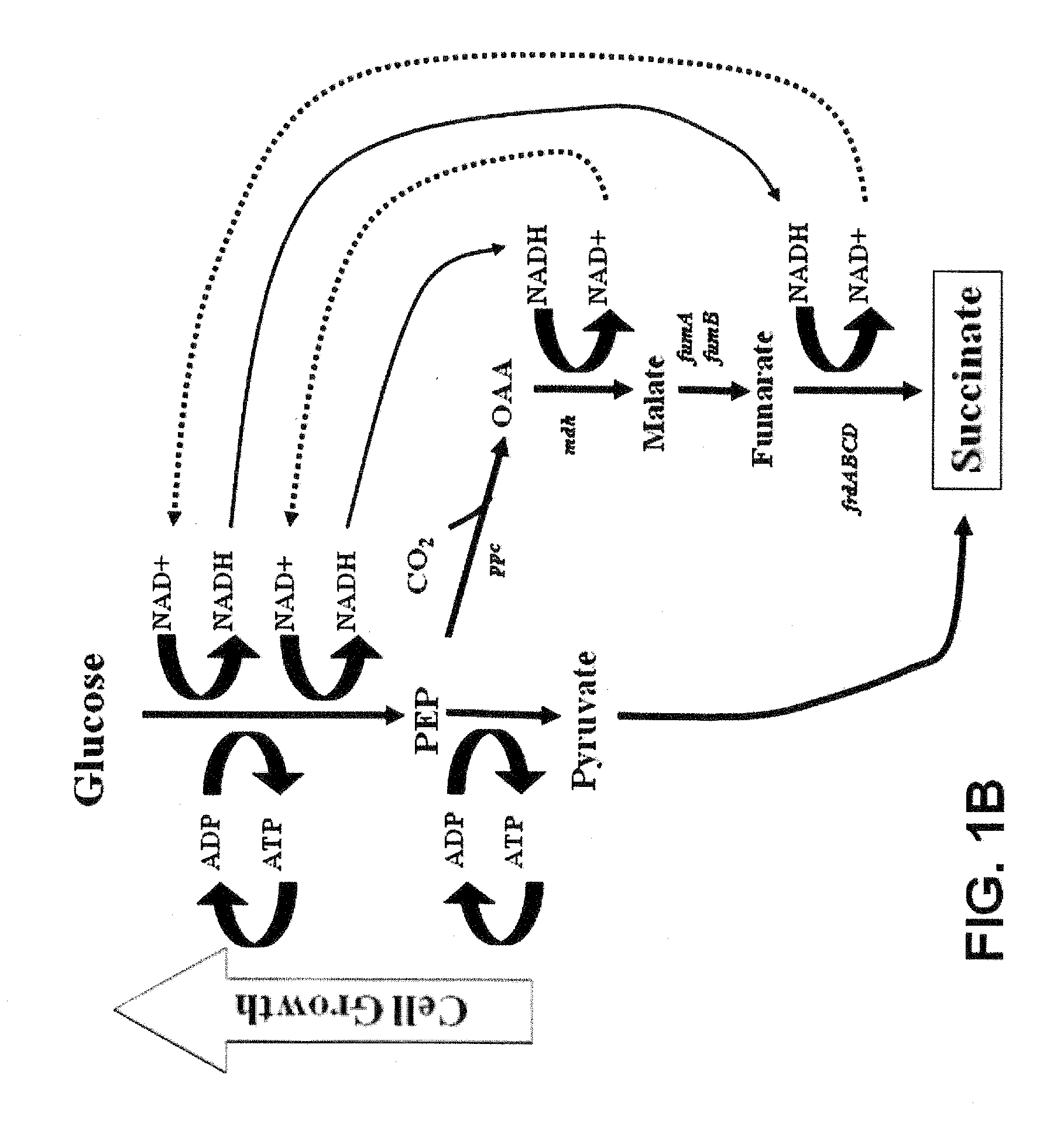
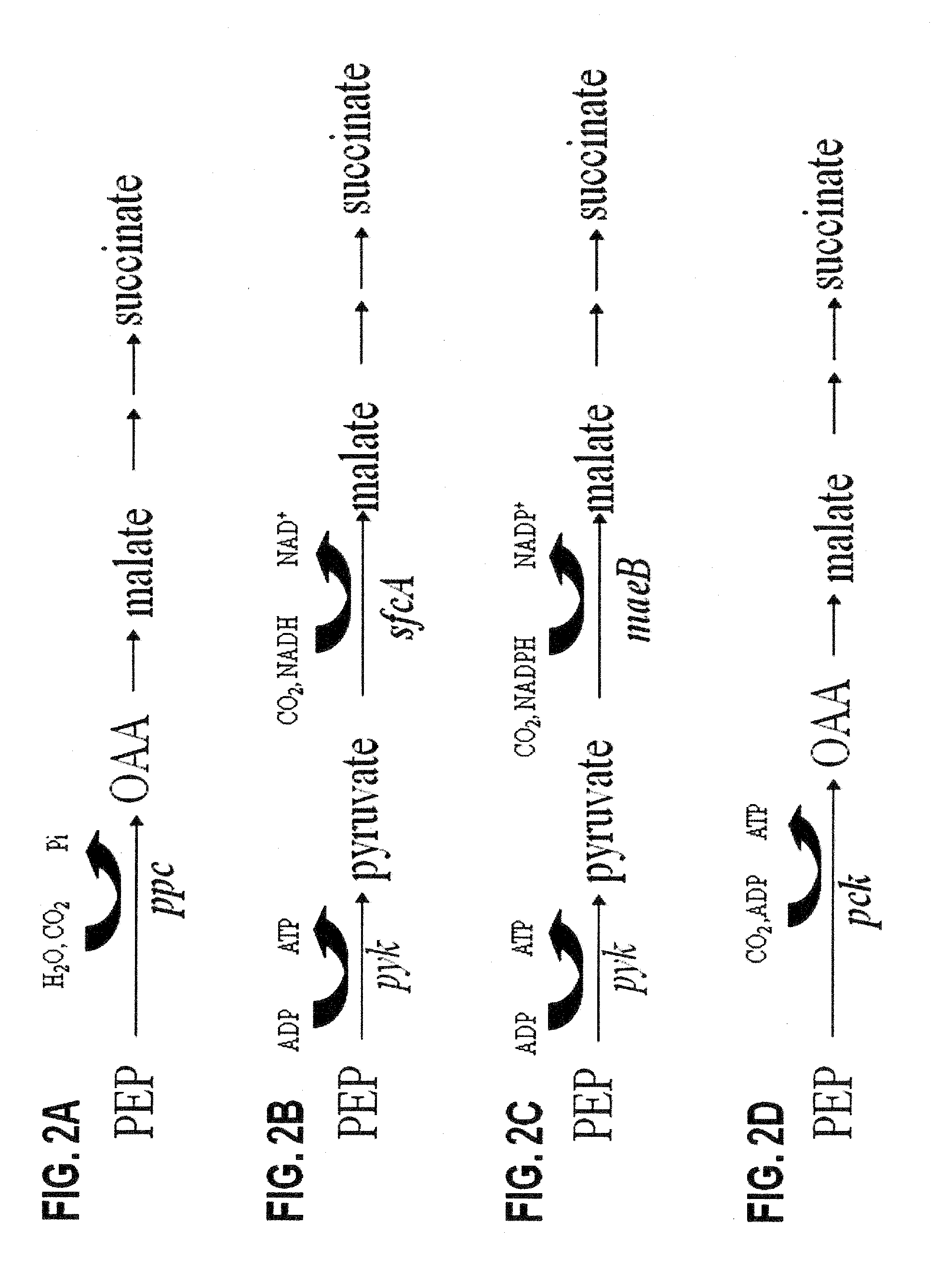
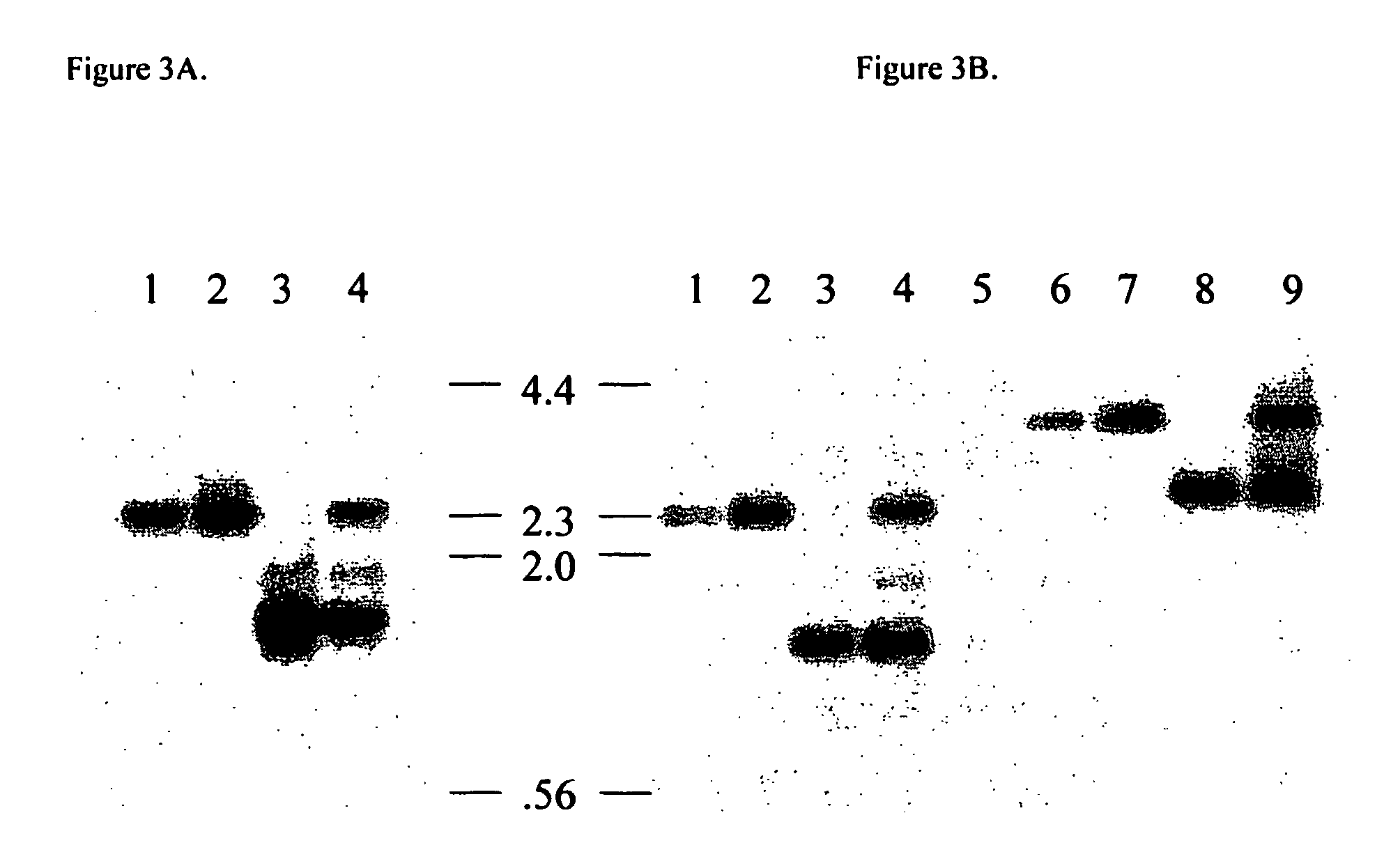
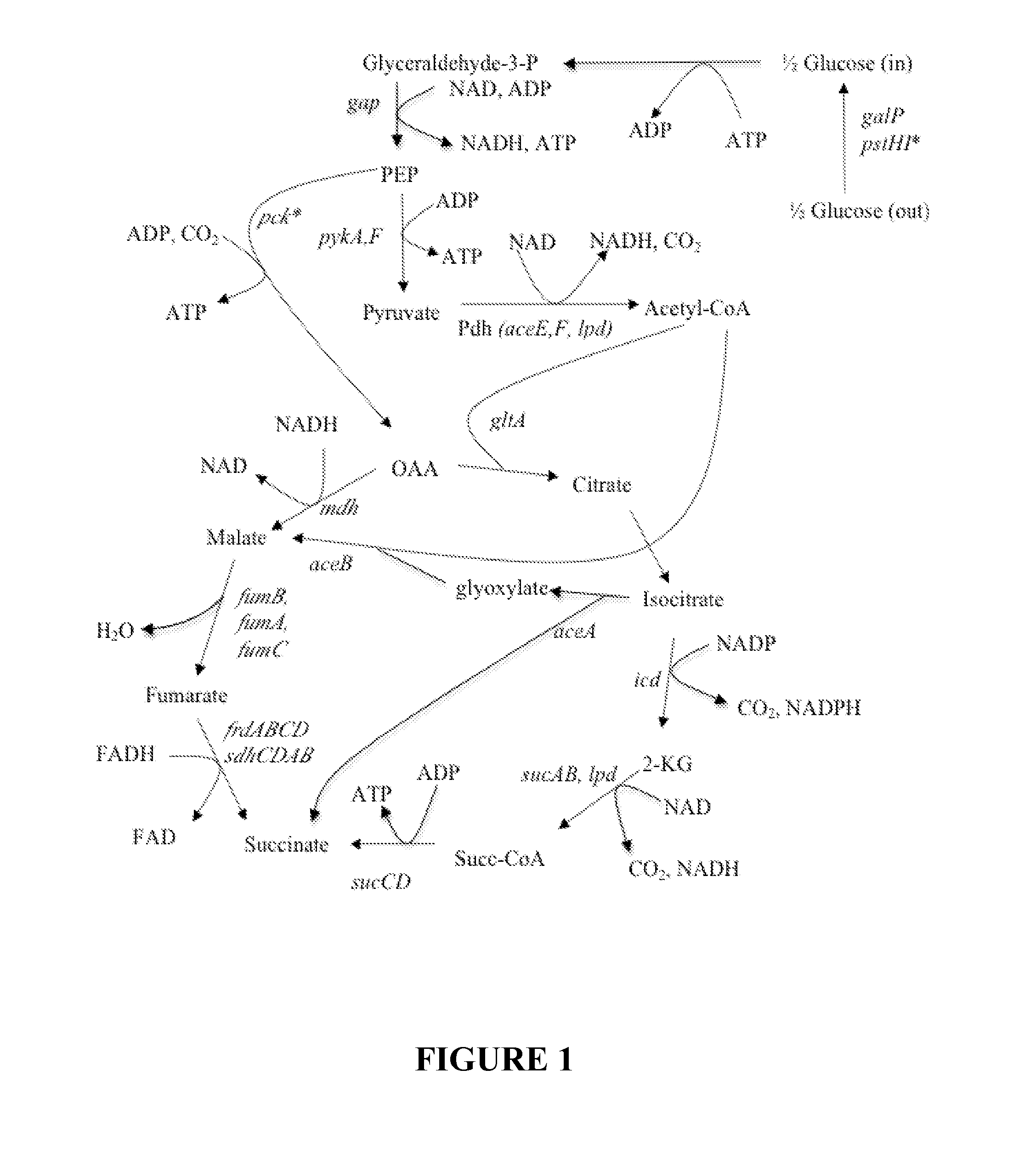
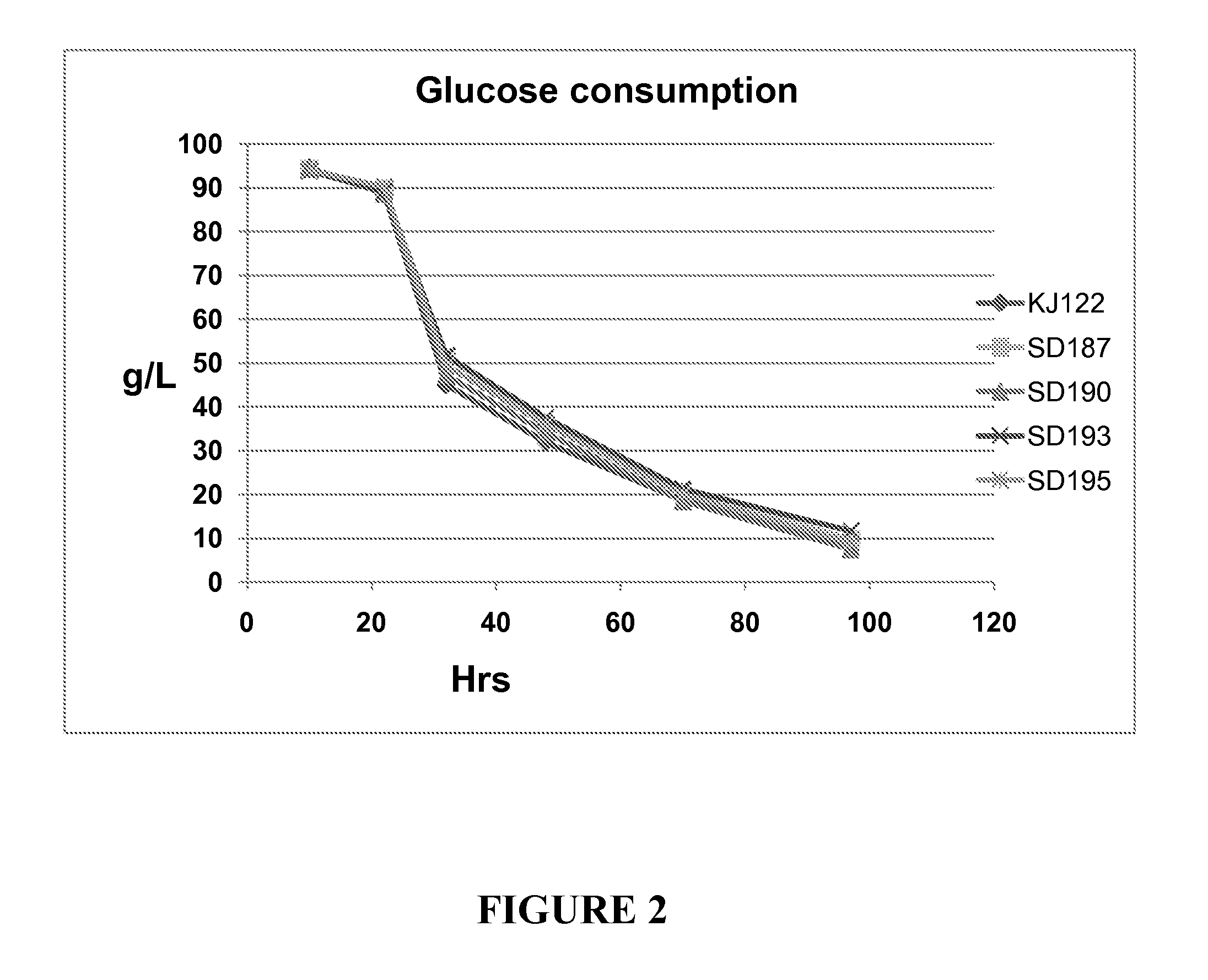
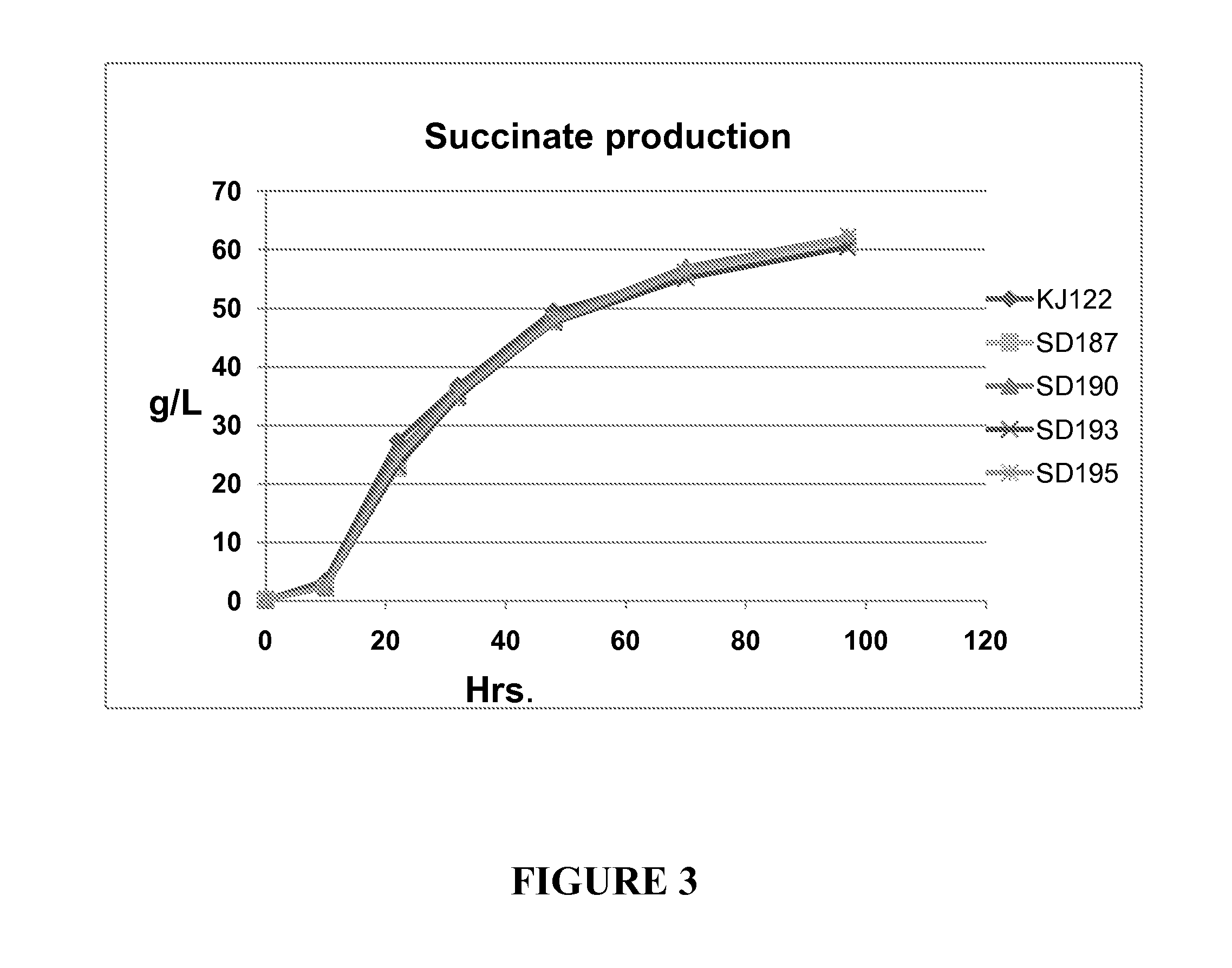
Engineering the pathway for succinate production
InactiveUS20120058530A1Increase overall carbon flowHigh expressionVectorsBacteriaMannheimiaPh control
This invention relates to the biocatalysts for the efficient production of succinic acid and / or other products from renewable biological feedstocks. The biocatalysts have a very high efficiency for the growth-coupled production of succinic acid and / or other products from carbohydrate feed stocks as a result of both genetic manipulations and metabolic evolution. More specifically, certain biocatalysts of the present invention produce succinic acid at high titers and yield in mineral salts media during simple pH-controlled, batch fermentation without the addition of any exogenous genetic material. The genetic manipulations of the present invention are concerned with the energy-conserving strategies coupled with the elimination of alternative routes for NADH oxidation other than the routes for succinic acid production. The biocatalysts contain glucose-repressed gluconeogenic phosphoenol pyruvate carboxykinase (pck) depressed by genetic modifications and a genetically-inactivated phosphotransferase system. In terms of succinic acid production efficiency, the biocatalysts of the present invention are functionally equivalent to succinate producing rumen bacteria such as Actinobacillus succinogens and Mannheimia succiniproducens with one difference that the biocatalysts are able to achieve this high level of succinic acid production in a minimal salt medium with carbohydrate source as opposed to the requirement for a rich media for succinic acid production by rumen bacteria.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
Therapeutic composition with a botulinum neurotoxin
ActiveUS7879341B2Low immunogenicityImprove stabilityCosmetic preparationsSenses disorderGenetics manipulationHuman serum albumin
The present invention pertains to pharmaceutical compositions which comprise a botulinum neurotoxin from Clostridium botulinum, the neurotoxin being free of the complexing proteins naturally present in the botulinum neurotoxin complex or being chemically modified or being modified by genetic manipulation. Moreover the pharmaceutical compositions of the instant invention have good stability and are advantageously formulated free of human serum albumin.
Owner:MERZ PHARMA GMBH & CO KGAA
Crustacean Expression Vector
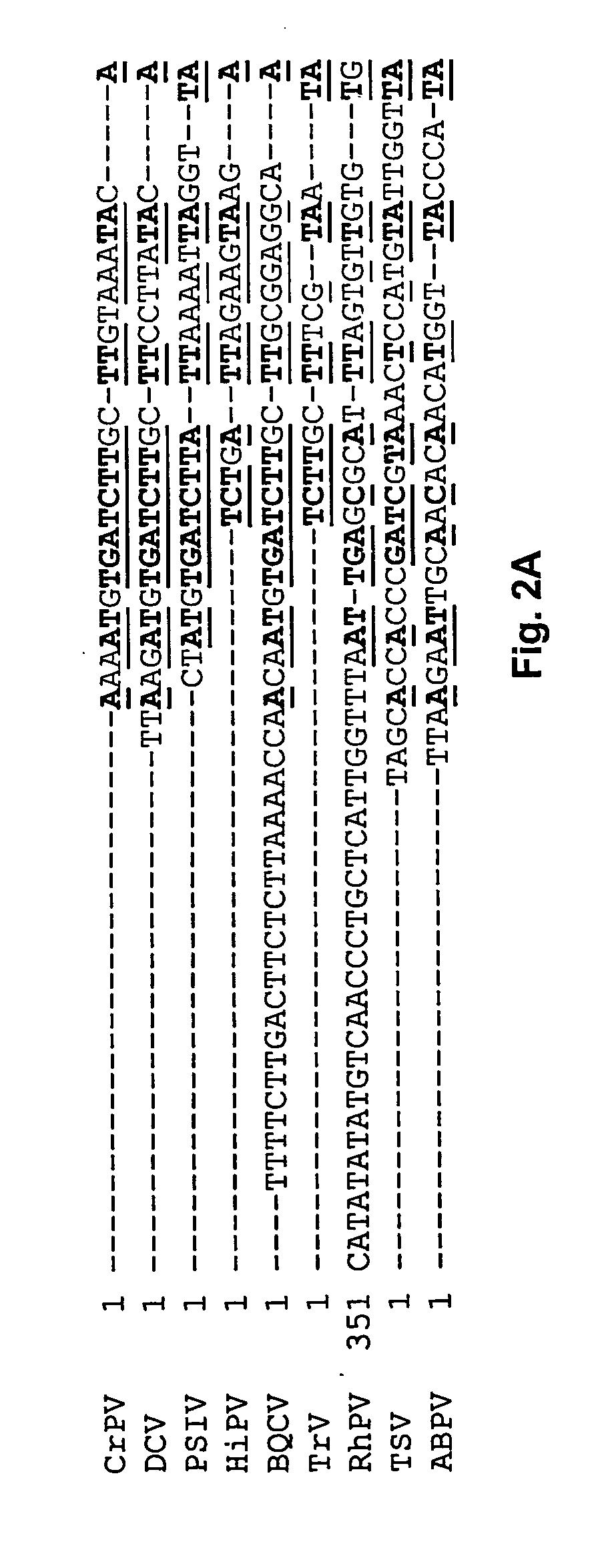
Methods and constructs for genetic manipulation of one or more of shrimp, shellfish, mollusks, and fish are disclosed. The nucleic acid construct includes a promoter and an internal ribosome entry site of an insect picomavirus, such as a cricket paralysis-like picomavirus. One or more open reading frames can be operably associated with one or both of the promoter and the internal ribosome entry site, and one or more proteins or protein subunits can be expressed upon introduction of the construct into a host cell, such as into a shrimp. Method for producing immortalized crustacean cell lines using enhancer elements derived from shrimp and / or shrimp viruses are also described.
Owner:INTERVET INC
Process for the purification of marigold xanthophylls
Owner:POBLETE VIDAL ALFONSO MR
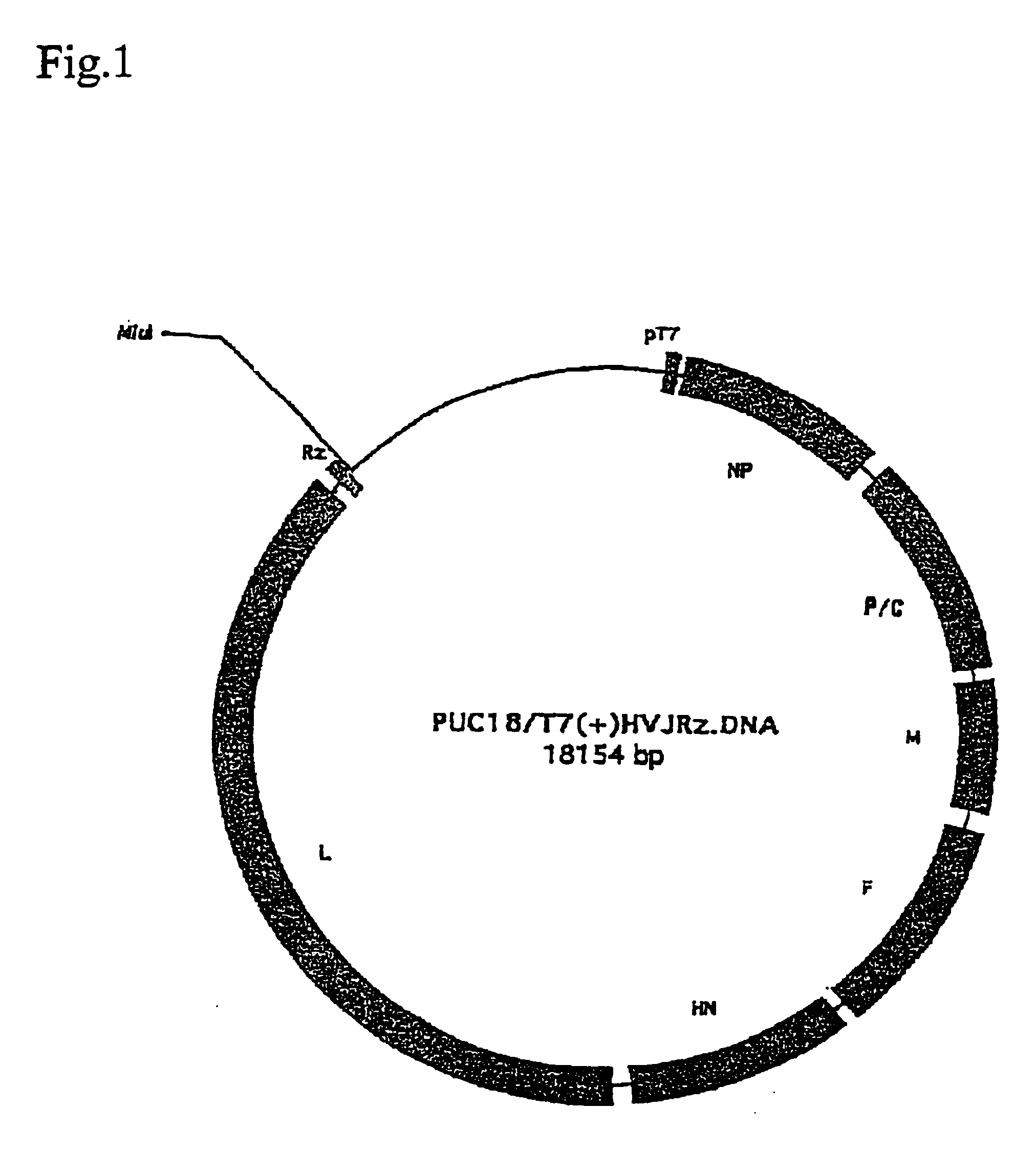
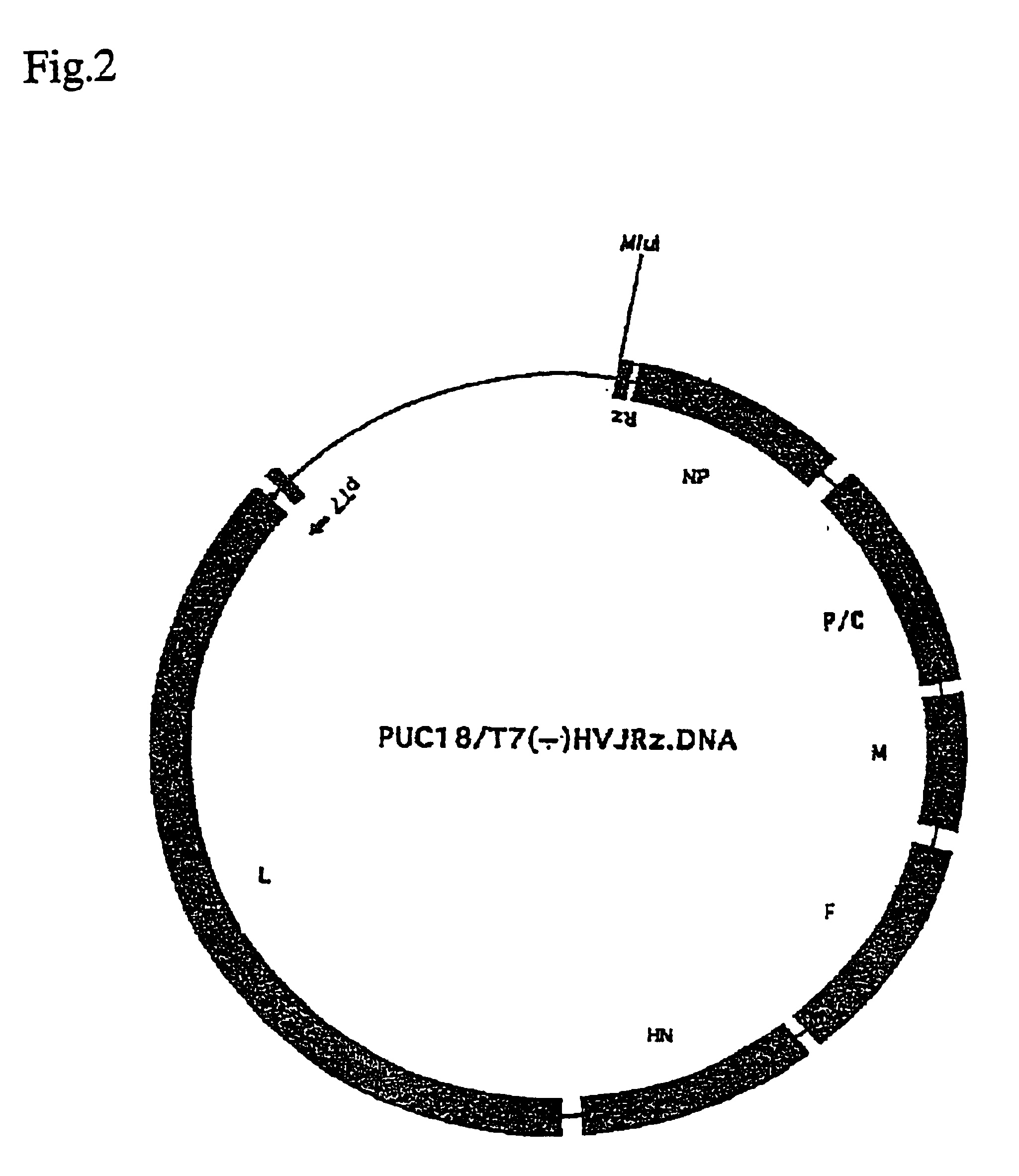
Recombinant sendai virus
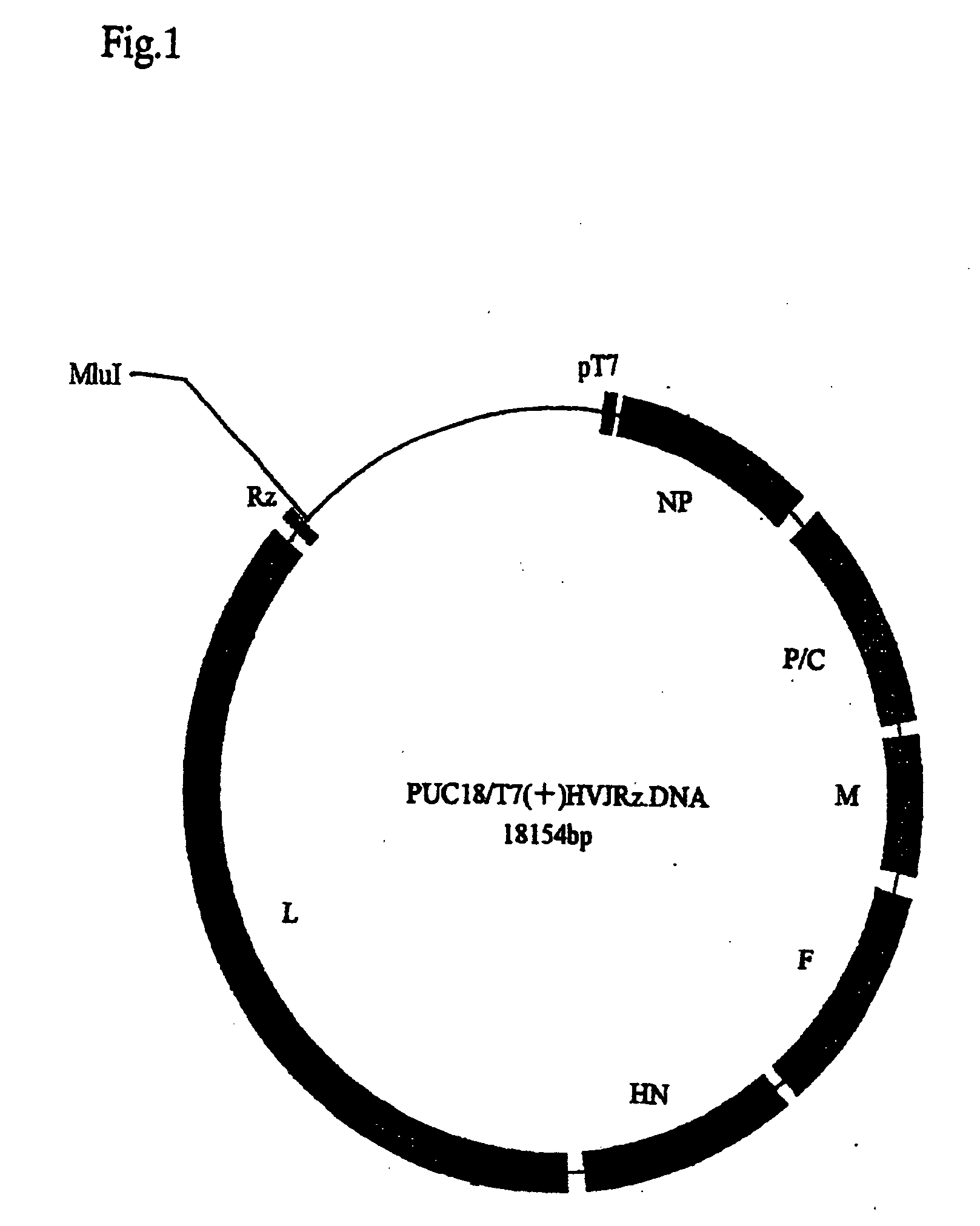
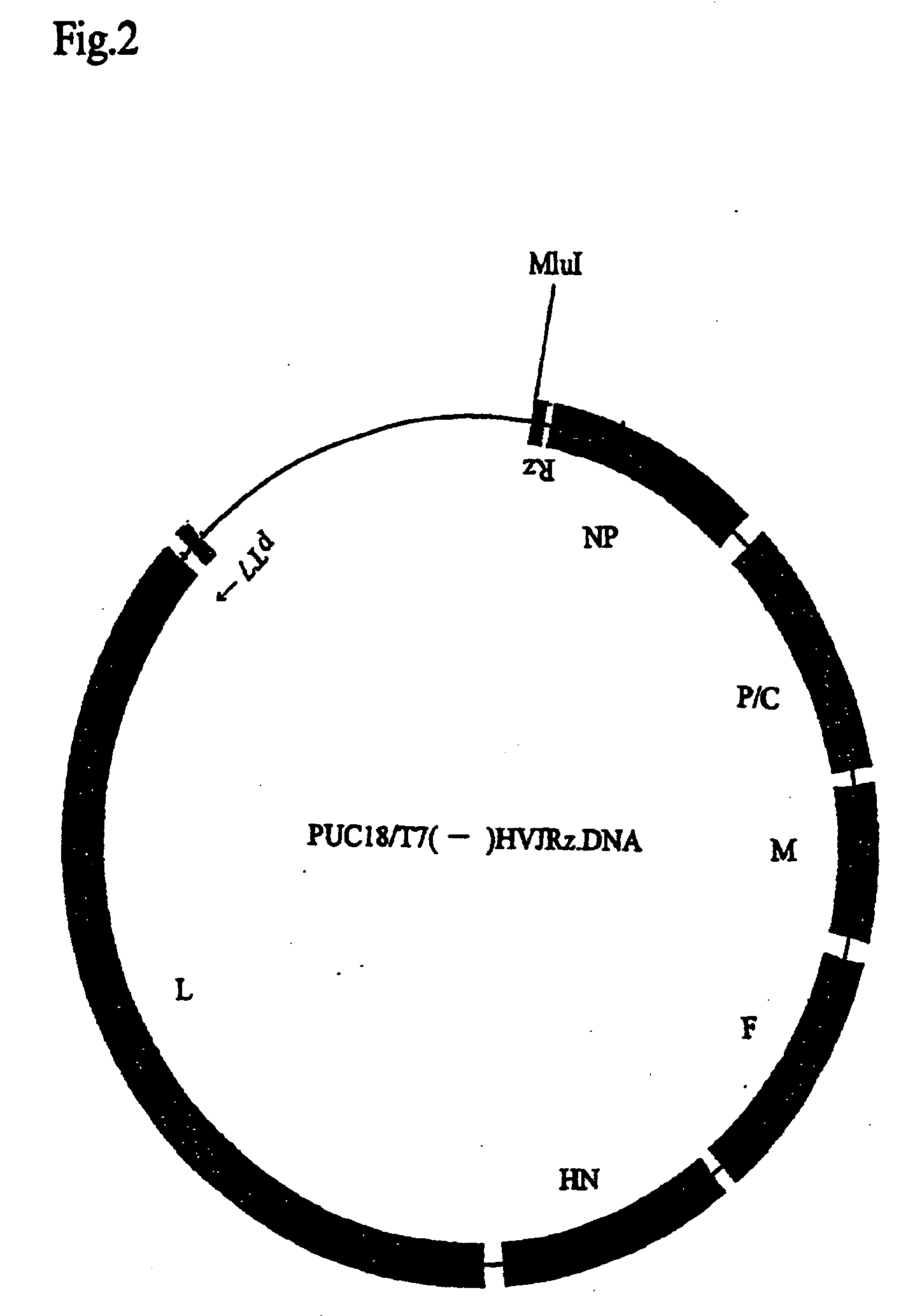
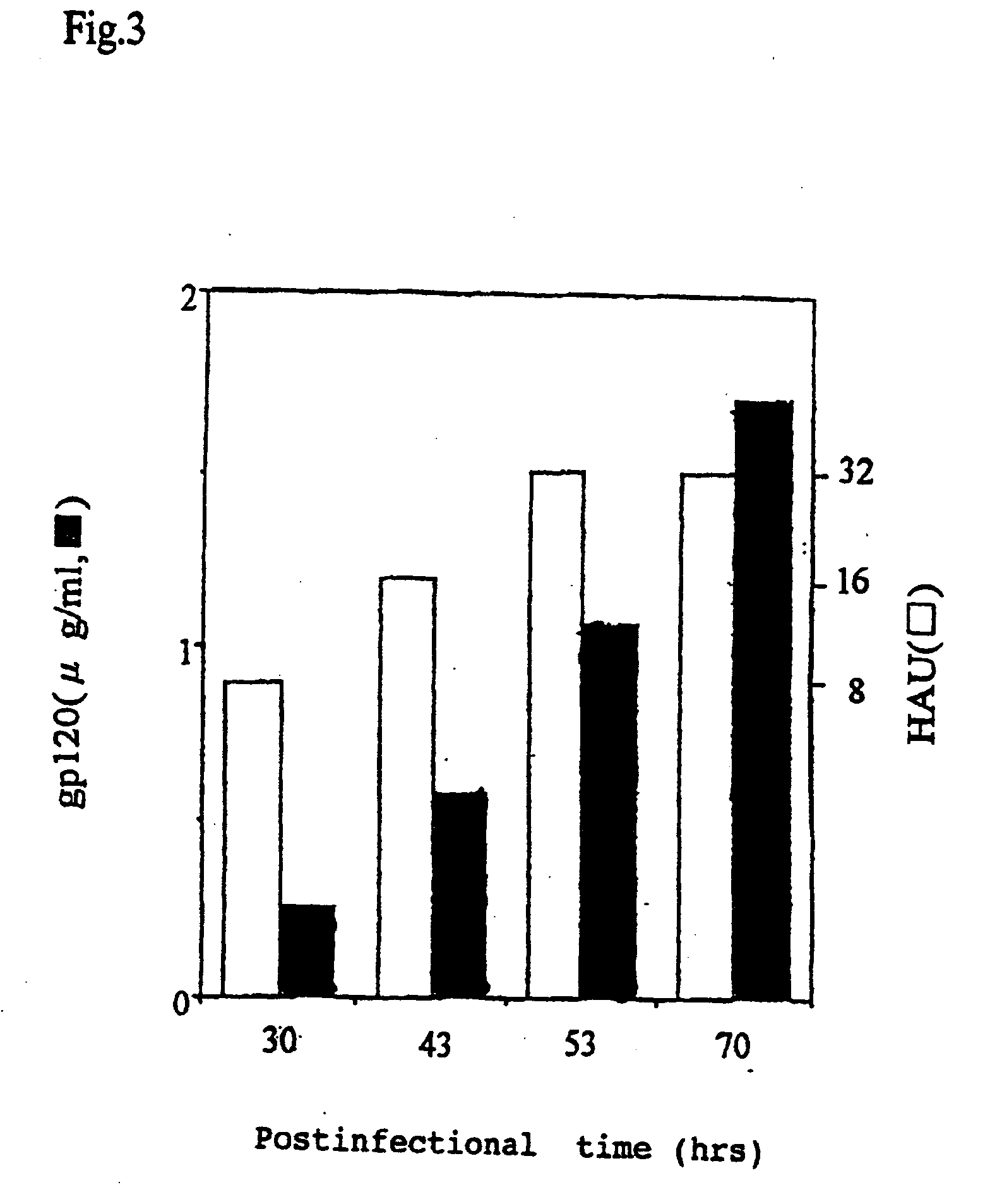
InactiveUS20050266566A1Efficient systemSsRNA viruses negative-senseSugar derivativesViral replicationGenetics manipulation
A method for regenerating Sendai virus particles by transfecting the Sendai virus genome to a host expressing all genes for the initial viral replication has been developed, enabling the genetic manipulation of Sendai virus and effective utilization of said virus as the vector.
Owner:DNAVEC RES
Cascade hydropower station multi-object optimal scheduling mixed searching method coupling peak shaving and navigation demands
ActiveCN104036334AReasonable cascade operation planImprove search and solution efficiencyForecastingTemporal couplingCounter regulation
The invention relates to the field of comprehensive development and utilization and optimized scheduling of water resources, in particular to a cascade hydropower station multi-object optimal scheduling mixed searching method coupling peak shaving and navigation demands. The function of a navigation counter regulation power station can be fully performed, the peak shaving of a power grid and river channel navigation application requirements are taken into account, and a cascade operation plan which is practical and more reasonable in scheduling is obtained. According to the technical scheme, the minimum of the maximum value of the redundant loads of the power grid and the minimum of the variance of the counter regulation power station downstream river channel water level process are adopted as objects, in the NSGA-II searching process, for the complex constrains of the climbing upper limit, the output fluctuation control limit, the machine starting and shutting down minimum lasting time, the term end water level control and the like, time coupling constraint handling strategies, end water level correction strategies and improved genetic manipulation operators are put forward, so that the searching and solving efficiency of the method can be improved, a calculating result meeting engineering application request is obtained, and the method is suitable for being adopted and popularized in the scheduling operation of a cascade hydropower station with navigation requests.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Method to enrich for alpha(1,3)-galactosyltransferase null pig cells
The invention relates to the genetic manipulation of non-human animals. More particularly, the invention relates to genetic manipulation of non-human animals to be used for xenotransplantation. The invention provides a method of selecting GGTA 1 null cells, a viable GGTA 1 null swine, methods for making such swine, and methods of using cells, tissues and organs of such swine for xenotransplantation.
Owner:IMMERGE BIOTHERAPEUTICS
Method for generating immune-compatible cells and tissues using nuclear transfer techniques
InactiveUS6808704B1High incidenceImprove the level ofCompounds screening/testingBiocideNuclear transferTransgene
This invention relates to methods for making immune compatible tissues and cells for the purpose of transplantation and tissue engineering, using the techniques of nuclear transfer and cloning. Also encompassed are methods for determining the effect on immune compatibility of expressed transgenes and other genetic manipulations of the engineered cells and tissues.
Owner:ADVANCED CELL TECH INC
Alpha(1,3)-galactosyltransferase null cells, methods of selecting and alpha(1,3)-galactosyl transferase null swine produced therefrom
ActiveUS20060242722A1New breed animal cellsMicrobiological testing/measurementHuman animalCell selection
The invention relates to the genetic manipulation of non-human animals. More particularly, the invention relates to genetic manipulation of non-human animals to be used for xenotransplantation. The invention provides a method of selecting GGTA 1 null cells, a viable GGTA 1 null swine, methods for making such swine, and methods of using cells, tissues and organs of such swine for xenotransplantation.
Owner:IMMERGE BIOTHERAPEUTICS
Organic acid production in microorganisms by combined reductive and oxidative tricaboxylic acid cylce pathways
This invention relates to succinic acid production from renewable feedstock using microbial biocatalysts genetically modified to produce succinic acid in commercially significant quantities. More specifically, this invention relates to the genetic manipulations in the pathway of carbon from renewable feedstock to succinic acid.
Owner:PTT GLOBAL CHEMICAL PUBLIC COMPANY LIMITED
Expressed sequences of arabidopsis thaliana
Isolated nucleotide compositions and sequences are provided for Arabidopsis thaliana genes. The nucleic acid compositions find use in identifying homologous or related genes; in producing compositions that modulate the expression or function of its encoded protein, mapping functional regions of the protein; and in studying associated physiological pathways. The genetic sequences may also be used for the genetic manipulation of cells, particularly of plant cells. The encoded gene products and modified organisms are useful for screening of biologically active agents, e.g. fungicides, insecticides, etc.; for elucidating biochemical pathways; and the like.
Owner:PARADIGM GENETICS
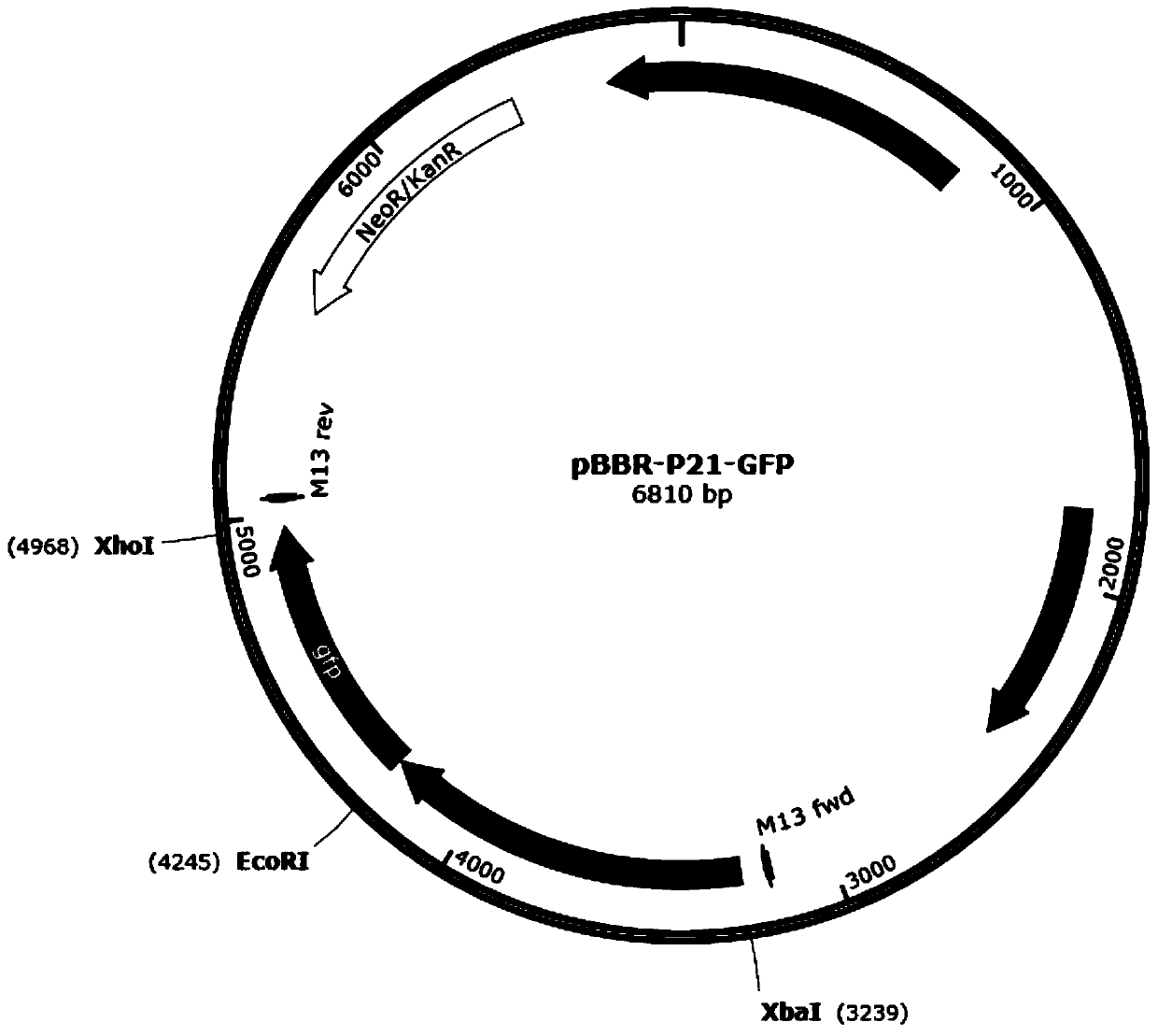
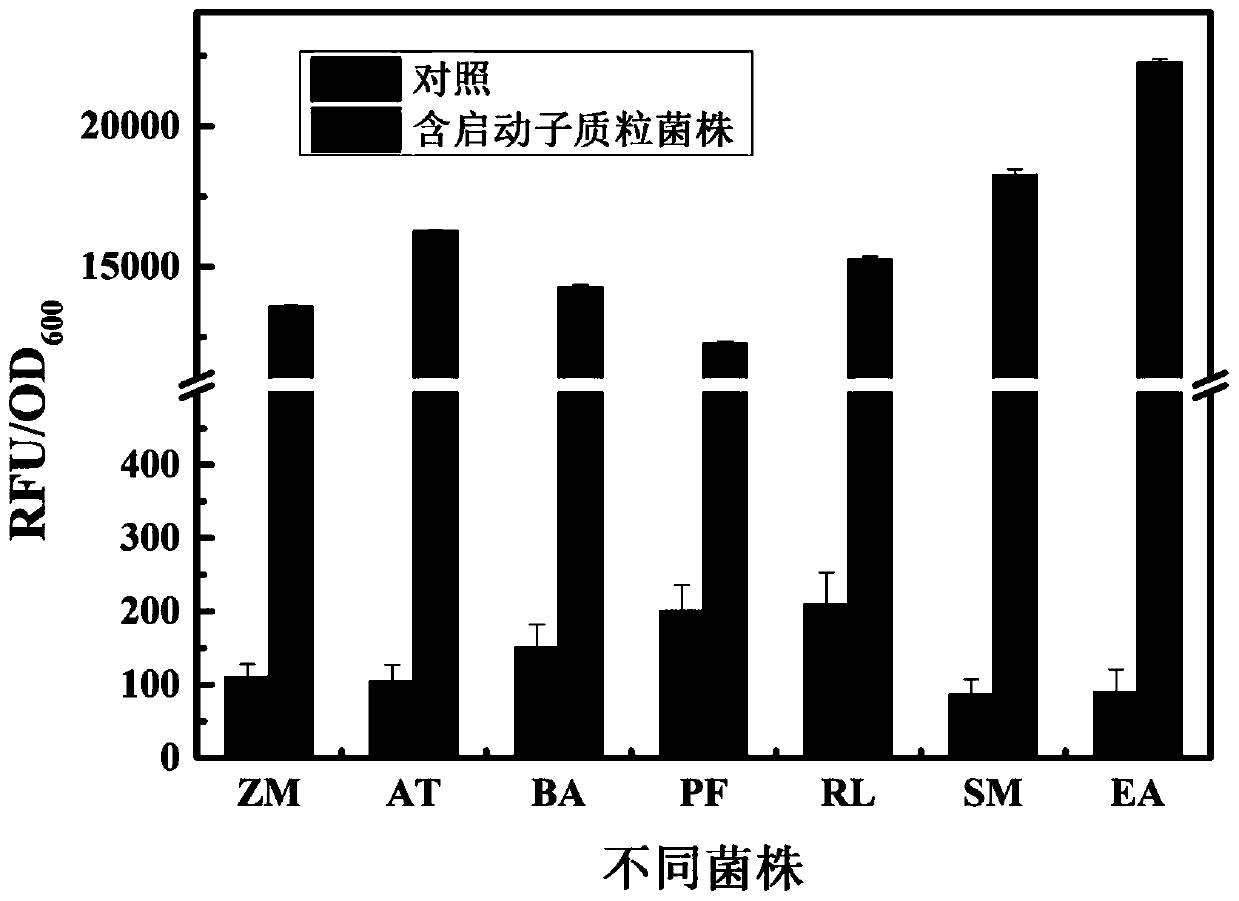
Strong promoter and plasmid vector containing strong promoter and application of strong promoter and plasmid vector
According to the invention, through amplifying a strong promoter in Ensifer adhaerens and carrying out bioinformatics analysis and functional verification, a strong promoter is obtained, and the strong promoter can be widely used for gene expression, genetic manipulation and strain improvement in Sinorhizobium meliloti, Zymomonas mobilis, Caulobacter crescentus, Pseudomonas denitrificans, Agrobacterium tumefaciens, Brucella abortus, Pseudomonas fluorescens, Rhizobium leguminosarum, Ensifer adhaerens and other alpha-proteobacteria and has a nucleotide sequence of SEQ ID NO: 1. The invention also relates to a plasmid vector containing the strong promoter, a method for constructing a genetic engineering strain by using the strong promoter, and an application of the corresponding strain and ahost cell in starting expression of a target gene.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
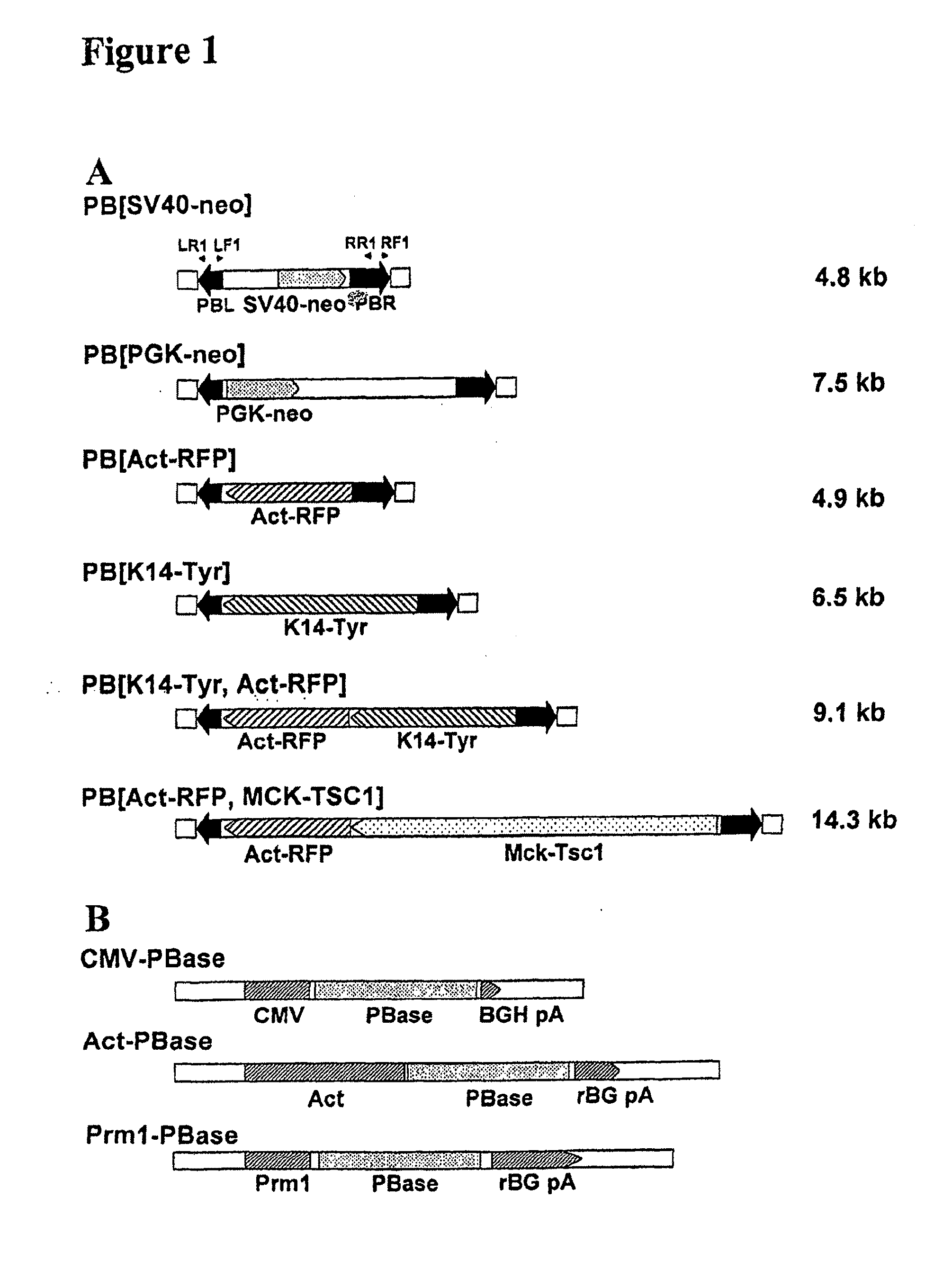
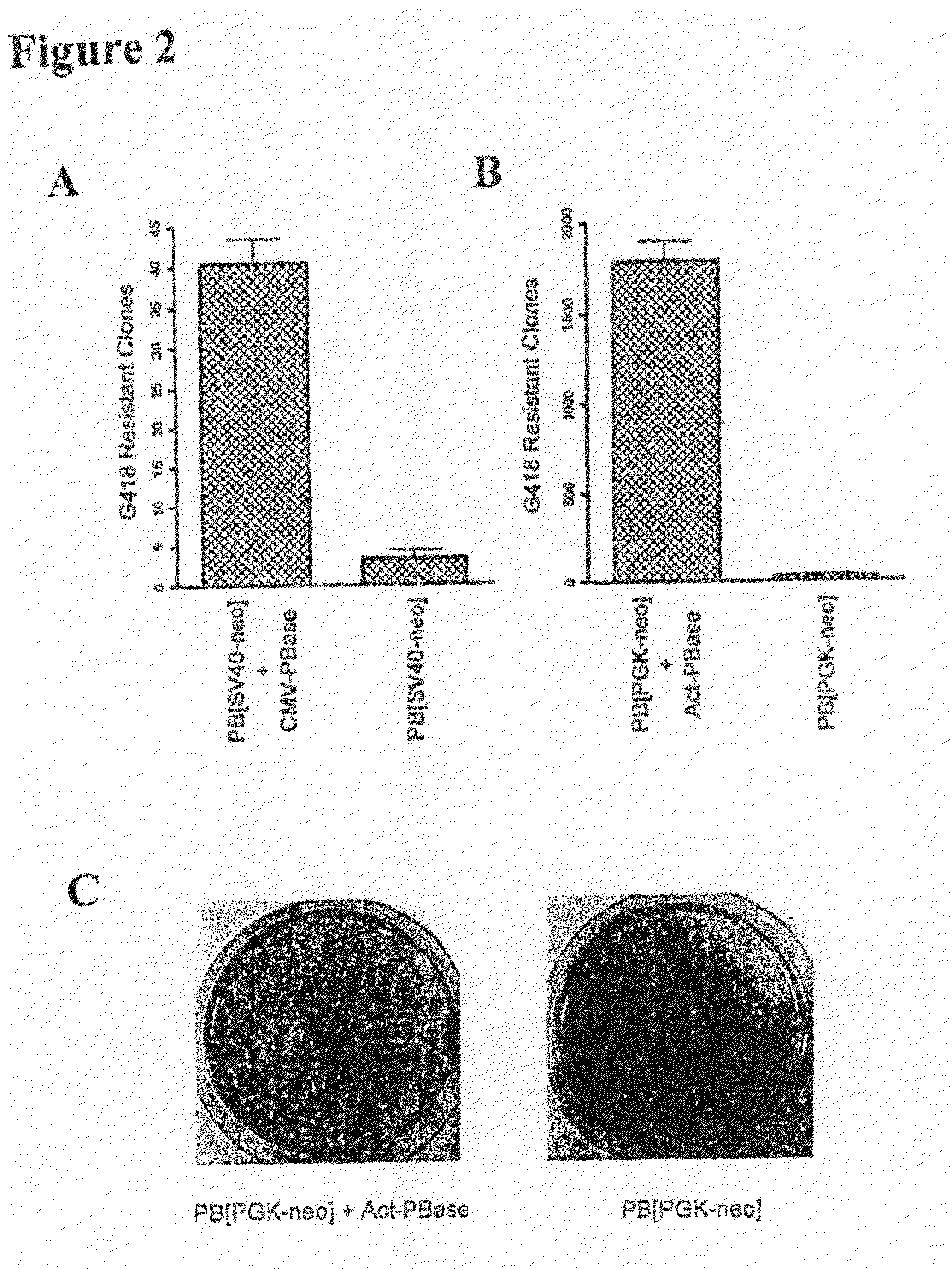
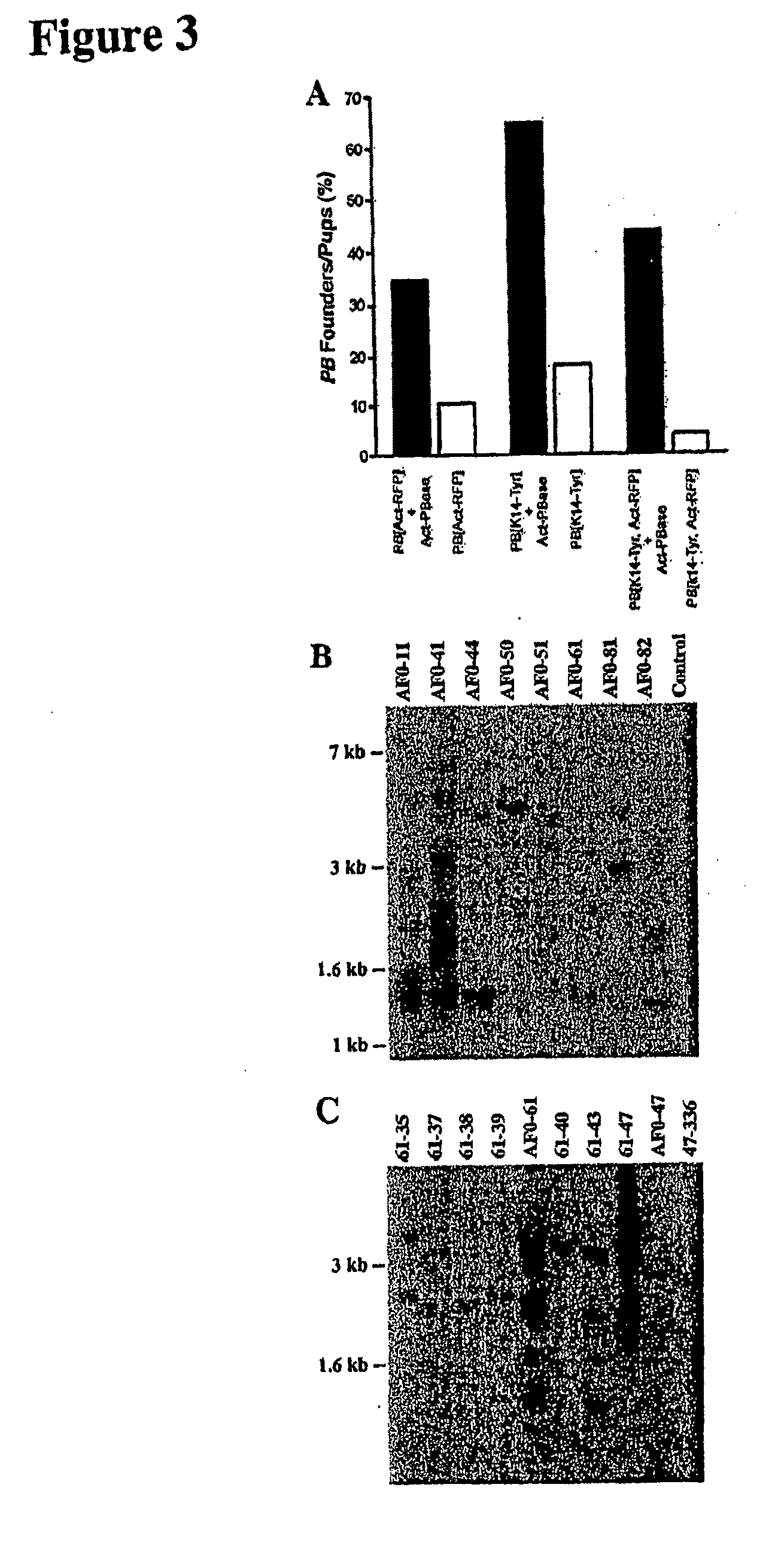
PiggyBac as a Tool for Genetic Manipulation and Analysis in Vertebrates
InactiveUS20100154070A1Efficient analysisEfficient genetic manipulationSugar derivativesArtificial cell constructsMammalGenetics manipulation
The present invention relates to transgenic vertebrate, including mammalian, cells, whose genomes comprise one or more elements of the piggyBac family transposon system. Transgenic non-human vertebrates, including transgenic non-human mammals, whose genomes comprise one or more elements of the piggyBac family transposon system, are also provided. Methods of making and using the cells and animals of the invention, including applications in the medical, veterinary, and agricultural fields, are additionally provided. The present invention also relates to kits useful for practicing such methods.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
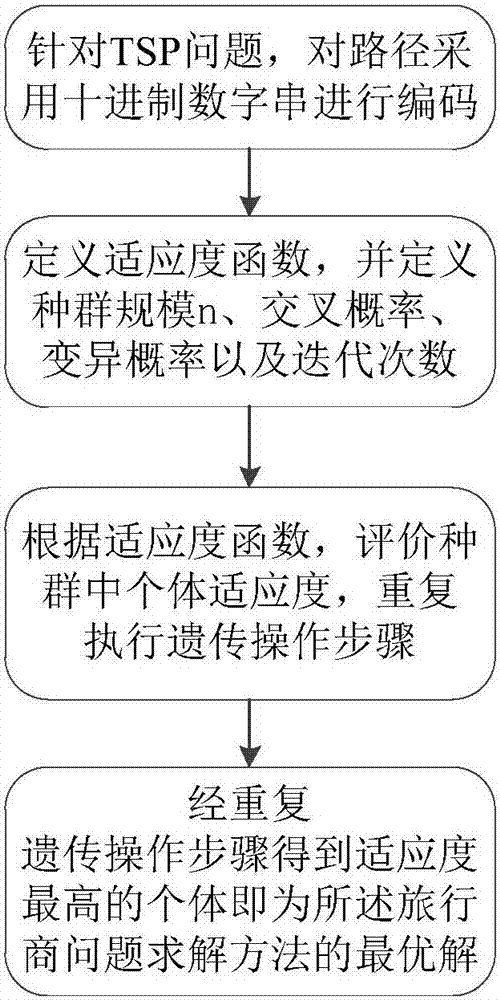
Improved genetic algorithm-based traveling salesman problem solving method
InactiveCN107122843ASolving NP-hard problemsImprove efficiencyForecastingGenetic algorithmsMutation probabilityImproved algorithm
The invention discloses a method for solving the traveling salesman problem based on an improved genetic algorithm. The steps include: aiming at the TSP problem, encoding the path using a decimal number string; calculating the total length, and then judging the total length; after encoding On the search space U of the decimal number string path, define the fitness function f(x), and define the population size n, the crossover probability Pc, the mutation probability Pm and the number of iterations T; in the search space U, randomly generate n individuals s1, s2, s3, ..., sn, constitute the initial population S0 = {s1, s2, s3, ..., sn}, set the current iteration number t = 0; according to the fitness function f(x), evaluate the individual fitness in the population , if t<T, then end the step, otherwise perform the genetic operation step; the individual with the highest fitness obtained through the genetic operation step is the optimal solution of the traveling salesman problem solving method. Based on the traditional genetic algorithm, the present invention optimizes the traveling salesman problem to achieve the purpose of improving the shortcoming that the algorithm is prone to premature convergence and optimizing the search efficiency.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Method for generating immune-compatible cells and tissues using nuclear transfer techniques
InactiveUS20020046410A1Easily propagatableEasily transfectedCompounds screening/testingNew breed animal cellsNuclear transferTransgene
This invention relates to methods for making immune compatible tissues and cells for the purpose of transplantation and tissue engineering, using the techniques of nuclear transfer and cloning. Also encompassed are methods for determining the effect on immune compatibility of expressed transgenes and other genetic manipulations of the engineered cells and tissues.
Owner:LANZA ROBERT +1
Recombinant Sendai virus
InactiveUS7101685B2Improve expression levelReduce distanceSsRNA viruses negative-senseSugar derivativesViral replicationGenetics manipulation
A method for generating Sendai virus particles by transfecting the Sendai virus genome to a host expressing all genes for the initial viral replication has been developed, enabling the genetic manipulation of Sendai virus and effective utilization of said virus as the vector.
Owner:DNAVEC RES
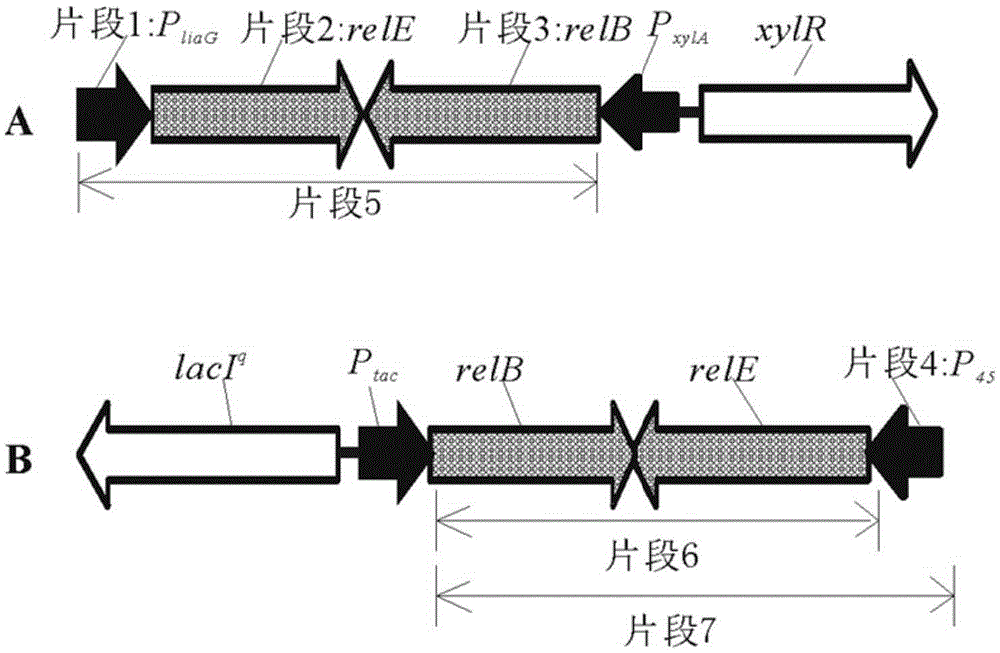
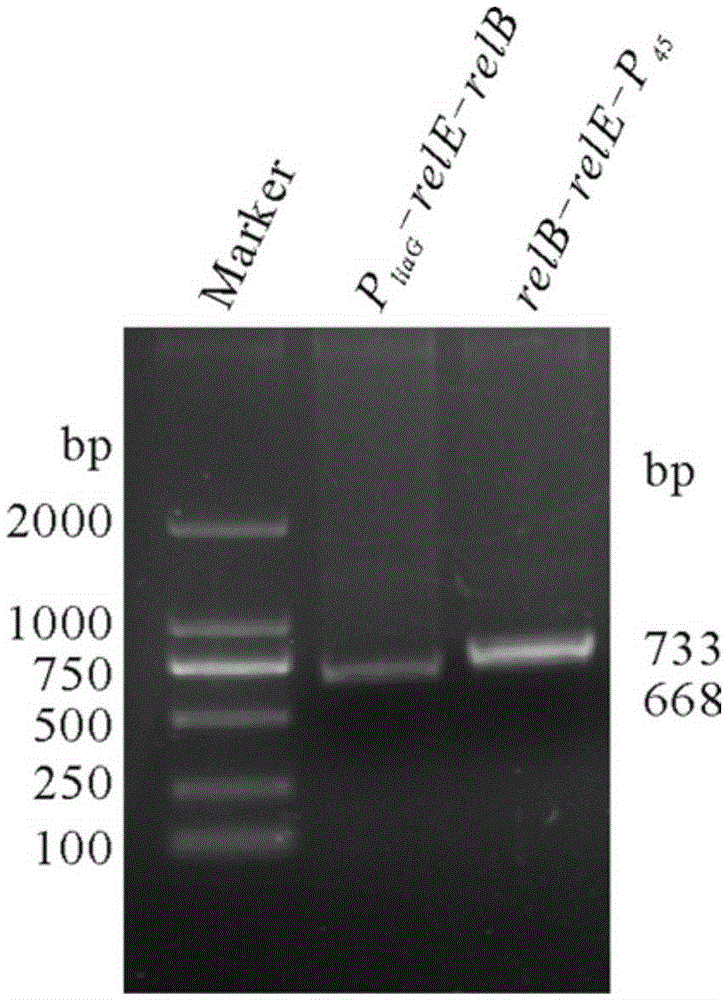
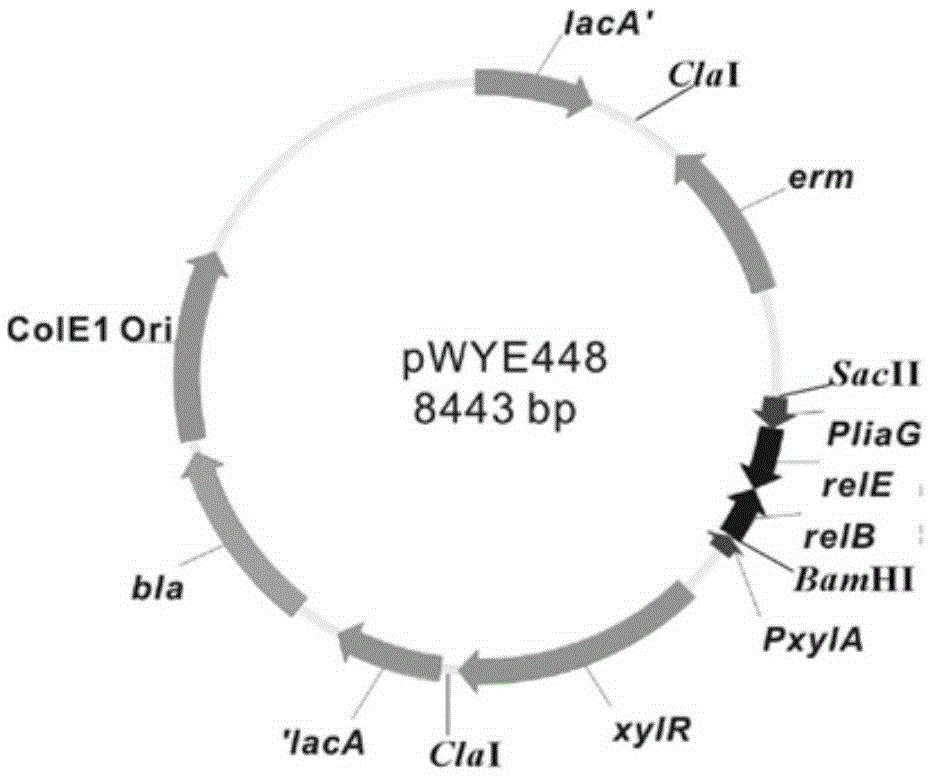
Bacterial traceless genetic manipulation vector and construction method and application thereof
ActiveCN106676119AAvoid toxicityImprove function and effectBacteriaVector-based foreign material introductionAntibiotic YToxin protein
The invention provides a bacterial traceless genetic manipulation vector. The vector contains a toxin inverse-screening element controlled by an antitoxin switch and an antibiotics resistance gene. The invention also provides a construction method of the vector and a method for application of the vector in bacterial traceless gene knock-out, knock-in, replacement, point mutation and insertion and deletion of large DNA fragments (larger than 194kb). By the utilization of a constitutive promoter for continuous expression of toxin protein and by the utilization of an inducible promoter for inducible expression of antitoxin protein, the toxin inverse-screening element (TCCRAS) controlled by the antitoxin switch is established, and the problem that specificity of existing genetic manipulation systems of gram-positive bacterium is not high, the systems are instable and screening is difficult is solved.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com