Patents
Literature
34 results about "Brucella abortus" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Brucella abortus is a Gram-negative alpha-proteobacterium in the family Brucellaceae and is one of the causative agents of brucellosis. The rod-shaped pathogen is classified under the domain Bacteria. The prokaryotic B. abortus is non-spore-forming, non-motile and aerobic.
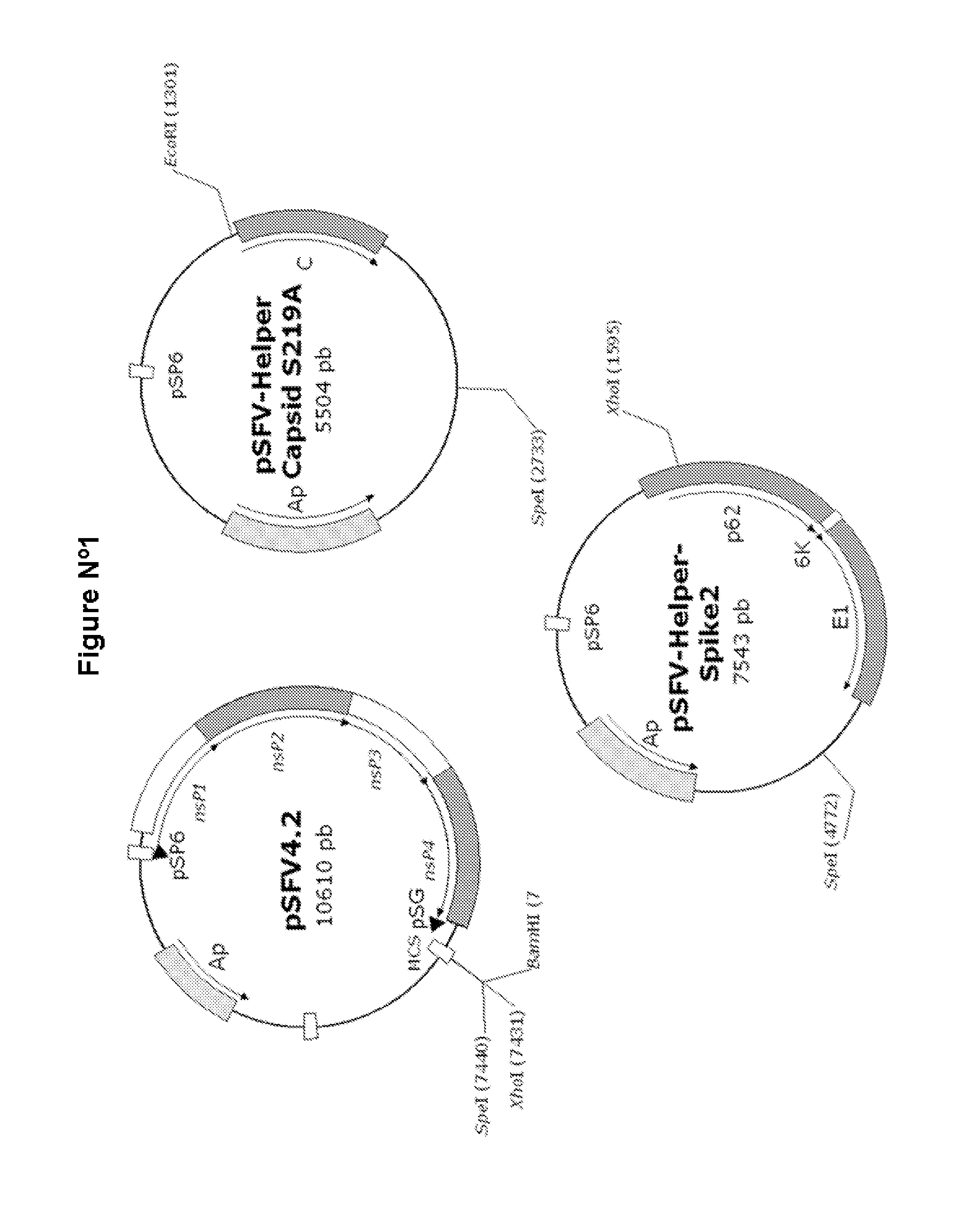
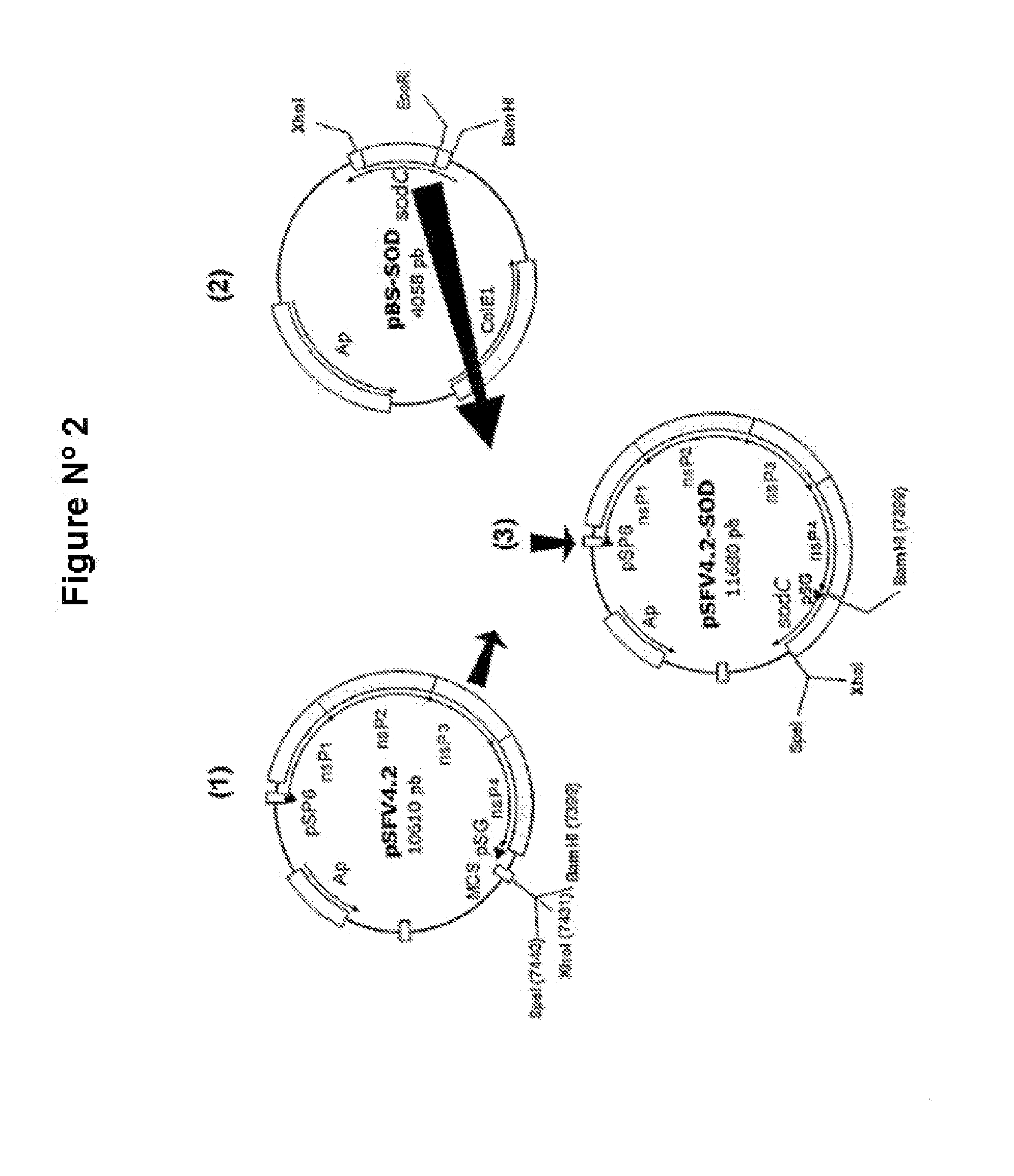
Veterinary pharmaceutical formulacion that comprises an RNA recombinant particle that encodes for a cu/zn superoxide dismutase protein of ruminant pathogenic bacteria and at least one RNA alphavirus belonging to the semliki forest virus family
InactiveUS20110200667A1Improve efficacyProtective efficacyAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsBrucella abortusZn superoxide dismutase
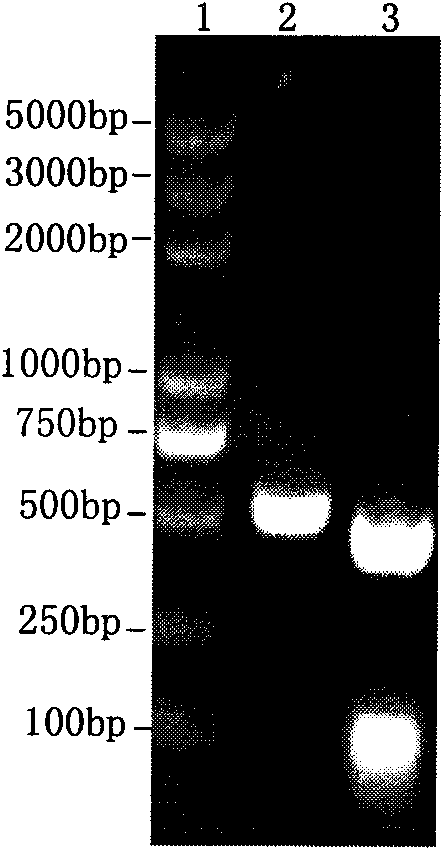
The technology is a veterinary pharmaceutical formulation of two vaccines, one from an RNA viral vector system constituted by an RNA recombinant particle that codifies for a Cu / Zn superoxide dismutase protein of Brucella abortus, and the other based on naked RNA constituted by a recombinant molecule of naked RNA that carries a sequence for the synthesis of at least one recombinant Cu / Zn superoxide dismutase protein of Brucella abortus and some Semliki Forest virus genes. An expression system based on the Semliki Forest virus and a use of this system, in addition to a method for the preparation of the pharmaceutical formulations.
Owner:UNIV DE CONCEPCION
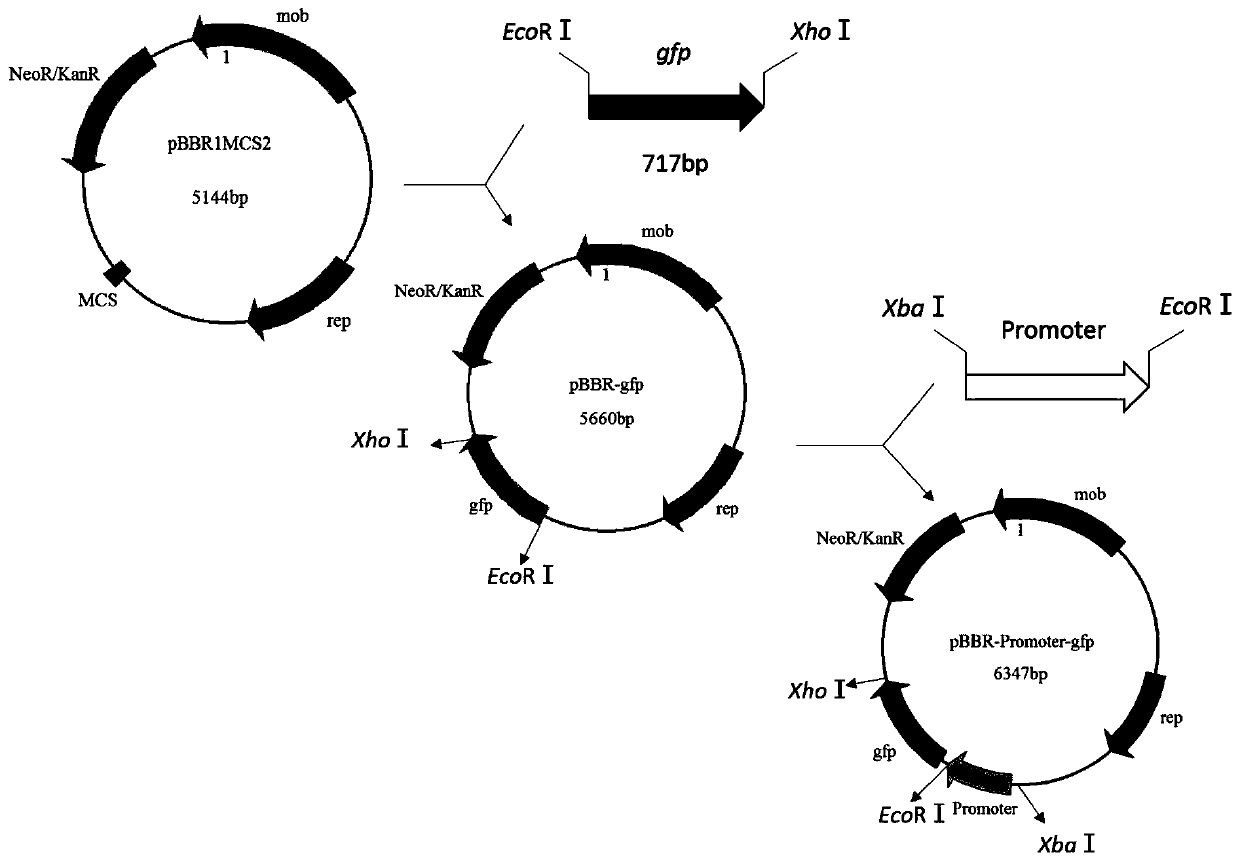
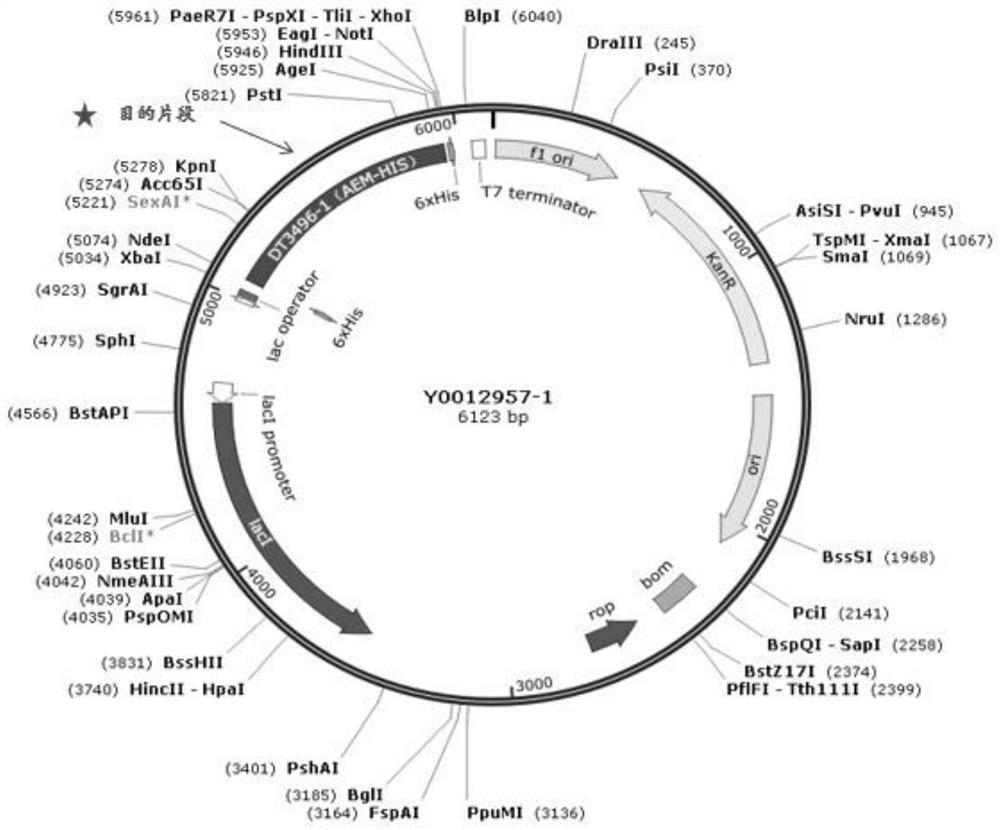
Strong promoter and plasmid vector containing strong promoter and application of strong promoter and plasmid vector
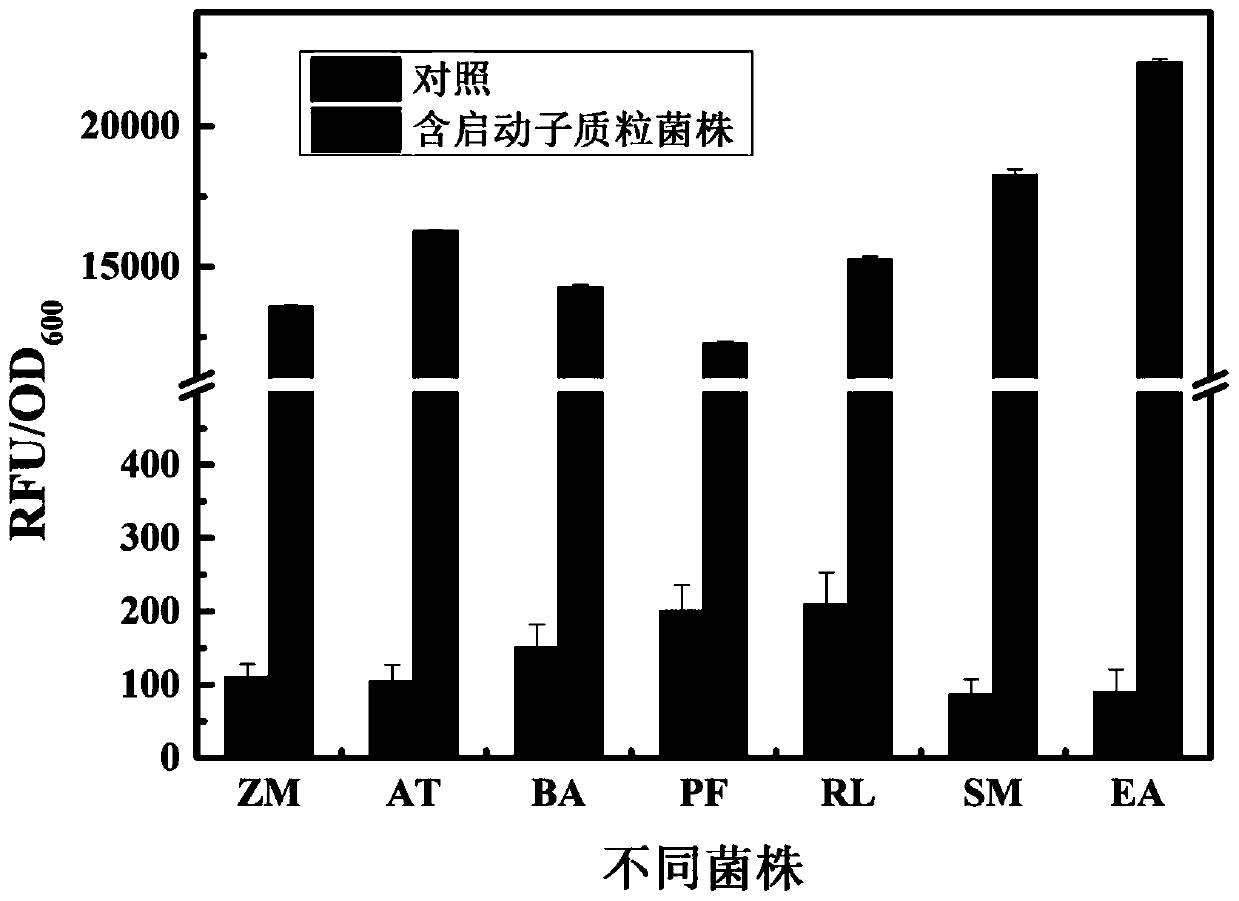
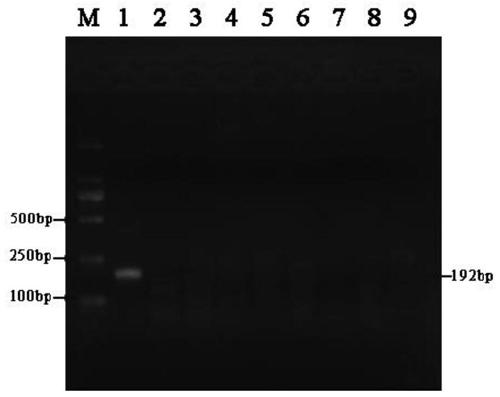
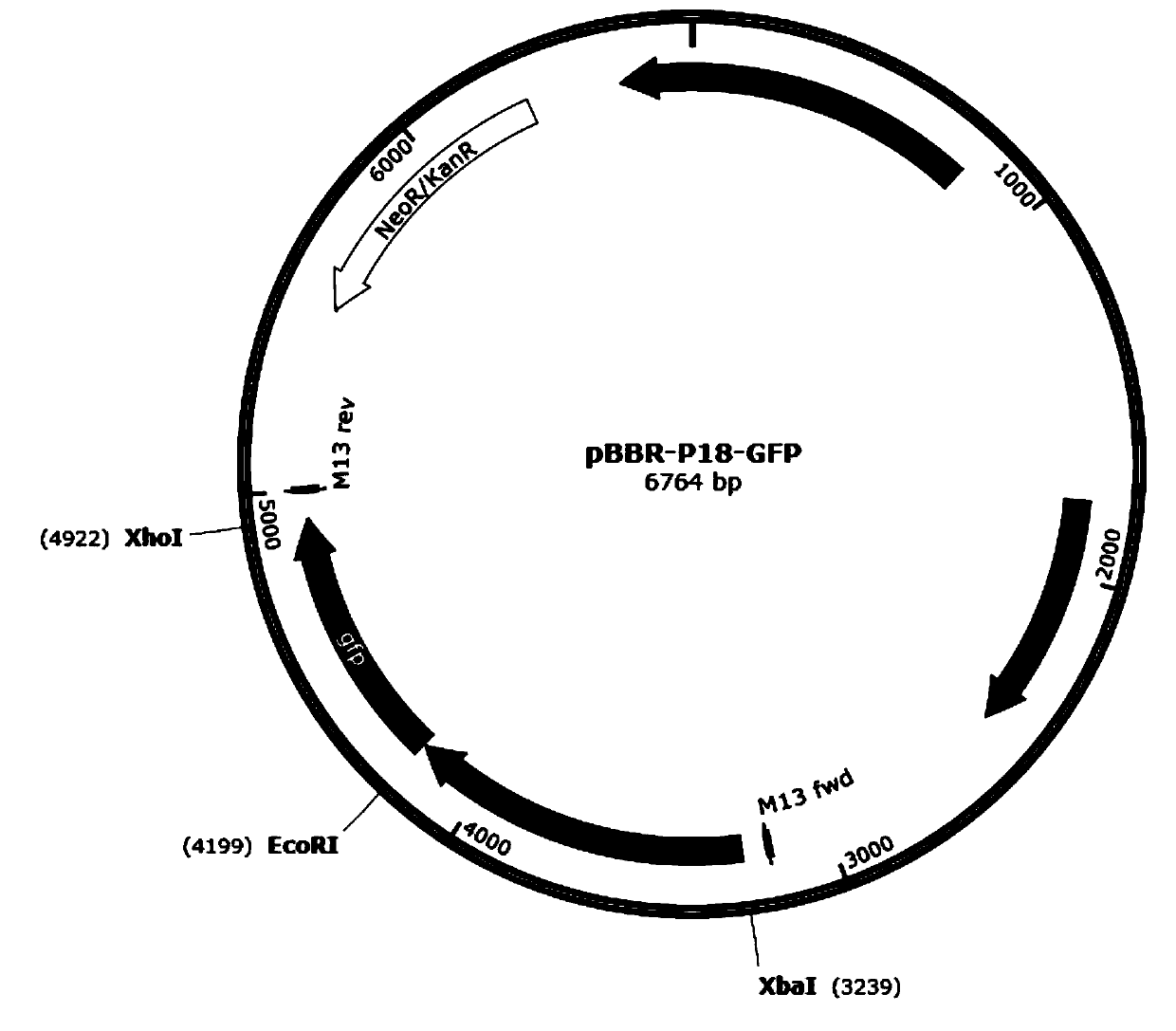
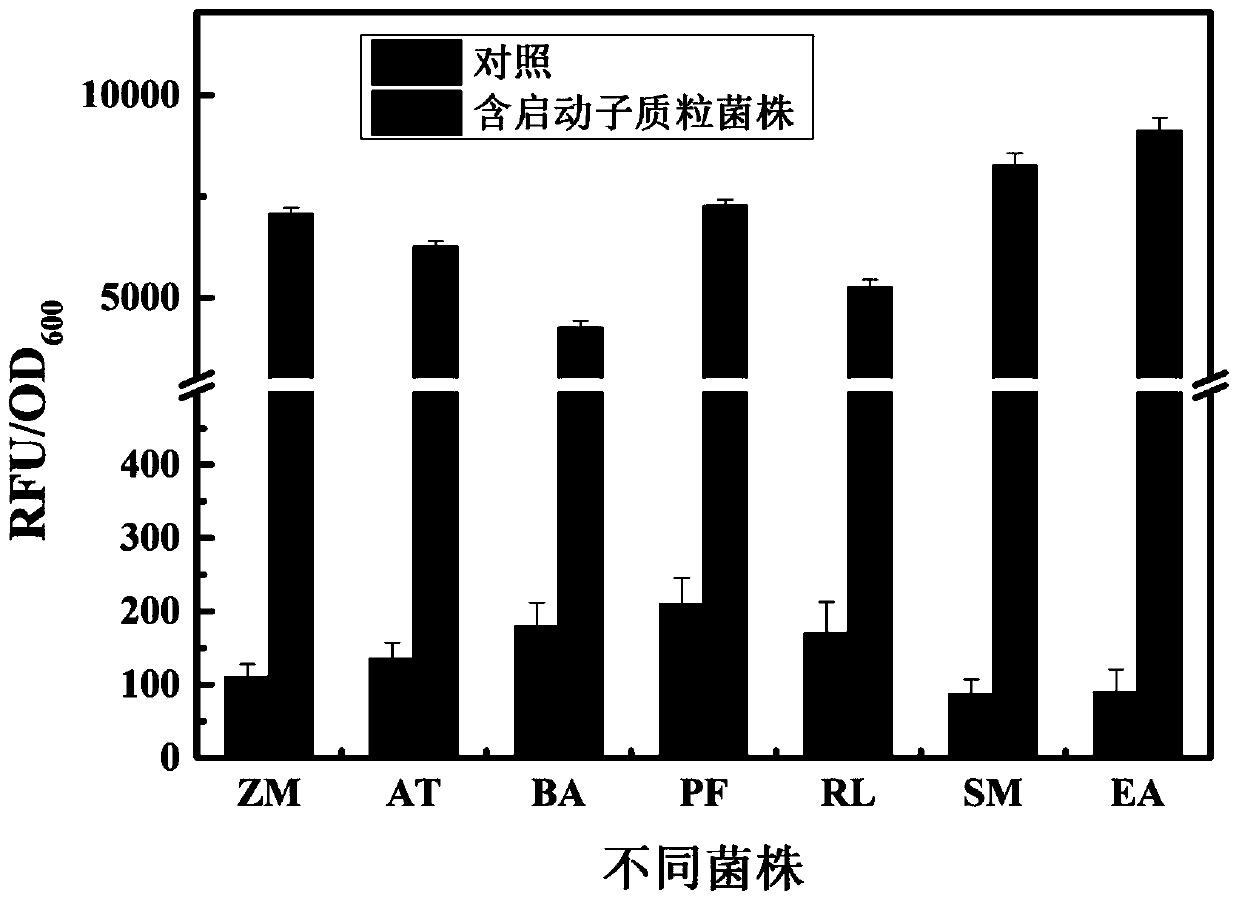
According to the invention, through amplifying a strong promoter in Ensifer adhaerens and carrying out bioinformatics analysis and functional verification, a strong promoter is obtained, and the strong promoter can be widely used for gene expression, genetic manipulation and strain improvement in Sinorhizobium meliloti, Zymomonas mobilis, Caulobacter crescentus, Pseudomonas denitrificans, Agrobacterium tumefaciens, Brucella abortus, Pseudomonas fluorescens, Rhizobium leguminosarum, Ensifer adhaerens and other alpha-proteobacteria and has a nucleotide sequence of SEQ ID NO: 1. The invention also relates to a plasmid vector containing the strong promoter, a method for constructing a genetic engineering strain by using the strong promoter, and an application of the corresponding strain and ahost cell in starting expression of a target gene.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
PCR kit for simultaneously detecting Brucella abortus, Brucella melitensis, Brucella suis and Brucella canis as well as preparation method and using method thereof
InactiveCN103409520APracticalStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementBrucella abortusBiology
A PCR kit for simultaneously detecting Brucella abortus, Brucella melitensis, Brucella suis and Brucella canis as well as a preparation method and a using method thereof, and belongs to the field of gene detection of anthropozoonosis pathogens. The PCR kit comprises a PCR liquid reactant, DNA polymerase, positive quality control standard substances and negative quality control standard substances; the PCR liquid reactant comprises four pairs of primers for identifying Brucella abortus, Brucella melitensis, Brucella suis and Brucella canis and a PCR buffer solution containing dNTPs, Mg<2+> and double distilled water. The PCR kit has high practicability, can be used for directly detecting the type of Brucella in a contaminated sample, has high detection speed, high sensitivity (10<2>cfu / ml), high specificity and good repeatability, is safe, reliable, quick, simple and convenient, can be used for qualitative detection of the type of Brucella in the sample, and can replace traditional etiological and serological methods.
Owner:MILITARY VETERINARY RES INST PLA MILITARY MEDICAL ACAD OF SCI
Recombinant bacterium of brucella abortus with immunity labeling and use thereof
InactiveCN101386831ALow toxicityImprove purification effectAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsBrucella abortusAnimal use
The invention discloses a recombinant strain for Brucella abortus provided with an immune label. The recombinant strain for the Brucella melitensis provided with the immune label is a strain obtained by killing encoding genes of perosamine synthetase in the Brucella abortus. Compared with an original strain, the obtained strain has lower virulence, and can be used as a vaccine to immunize animals without killing the genes. By utilization of the strain to immunize a mouse, immunoreaction states different from those of the standard strain and the prior vaccine strain can be generated in the body of the mouse, and sicken animals can be identified from immune animal groups by immunological detection of serum of the animals. The modification of the brucelliasis vaccine and the research of a diagnosis and identification agent have important significance in developing a brucelliasis gene deletion marker vaccine and a matched diagnosis and identification agent and promoting the elimination and purification of brucelliasis of the animals all over the world.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Controlled release vaccines and methods for treating brucella diseases and disorders
Methods and compositions for the treatment of Brucella induced diseases and disorders are disclosed herein. In preferred embodiments, the invention relates to vaccines. In additional embodiments, the invention relates to formulations capable of releasing said vaccines at a controlled rate of release in vivo. In further embodiments, the invention relates to modified strains of the bacteria Brucella melitensis and Brucella abortus. In still further embodiments, the invention relates to compositions that do not induce clinical symptoms or splenomegaly in a subject receiving said compositions.
Owner:TEXAS A&M UNIVERSITY
Mycobacterium bovis and brucella abortus dual detection card and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN106706906AHigh compliance rateStrong specificityMaterial analysisBrucella abortusQuality control
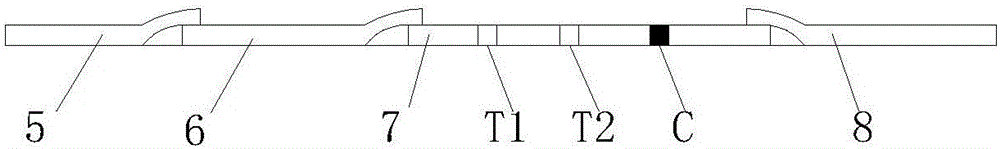
The invention discloses a mycobacterium bovis and brucella abortus dual detection card and a preparation method thereof and aims to provide a detection card which is capable of simultaneously detecting mycobacterium bovis and brucella abortus in a bovine serum specimen, is short in detection time, high in stability, simple in operation and intuitive and reliable in result judgment and does not need other instruments or professional personnel. According to the technical key points, the detection card comprises a shell (1), wherein a sample adding hole (2) and an observation window (3) are formed in the shell (1); and a colloidal gold test strip is arranged in the shell (1). The detection card is characterized in that the colloidal gold test strip comprises a bottom plate (4); a sample pad (5), a gold label pad (6), a coating membrane (7) and an absorbent pad (8) are sequentially connected onto the bottom plate (4); a mycobacterium bovis membrane protein MPB70-MPB83 detection line T1, a brucella abortus LPS detection line T2 and a goat anti-rabbit polyclonal antibody quality control line C are formed in the coating membrane (7); and the three lines are arranged in parallel. The detection card belongs to the technical field of biology.
Owner:深圳市绿诗源生物技术有限公司
Brucella Abortus Proteins and Methods of Use Thereof
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF WYOMING
Brucella abortus fluorescent quantum point coupling antibody detection method
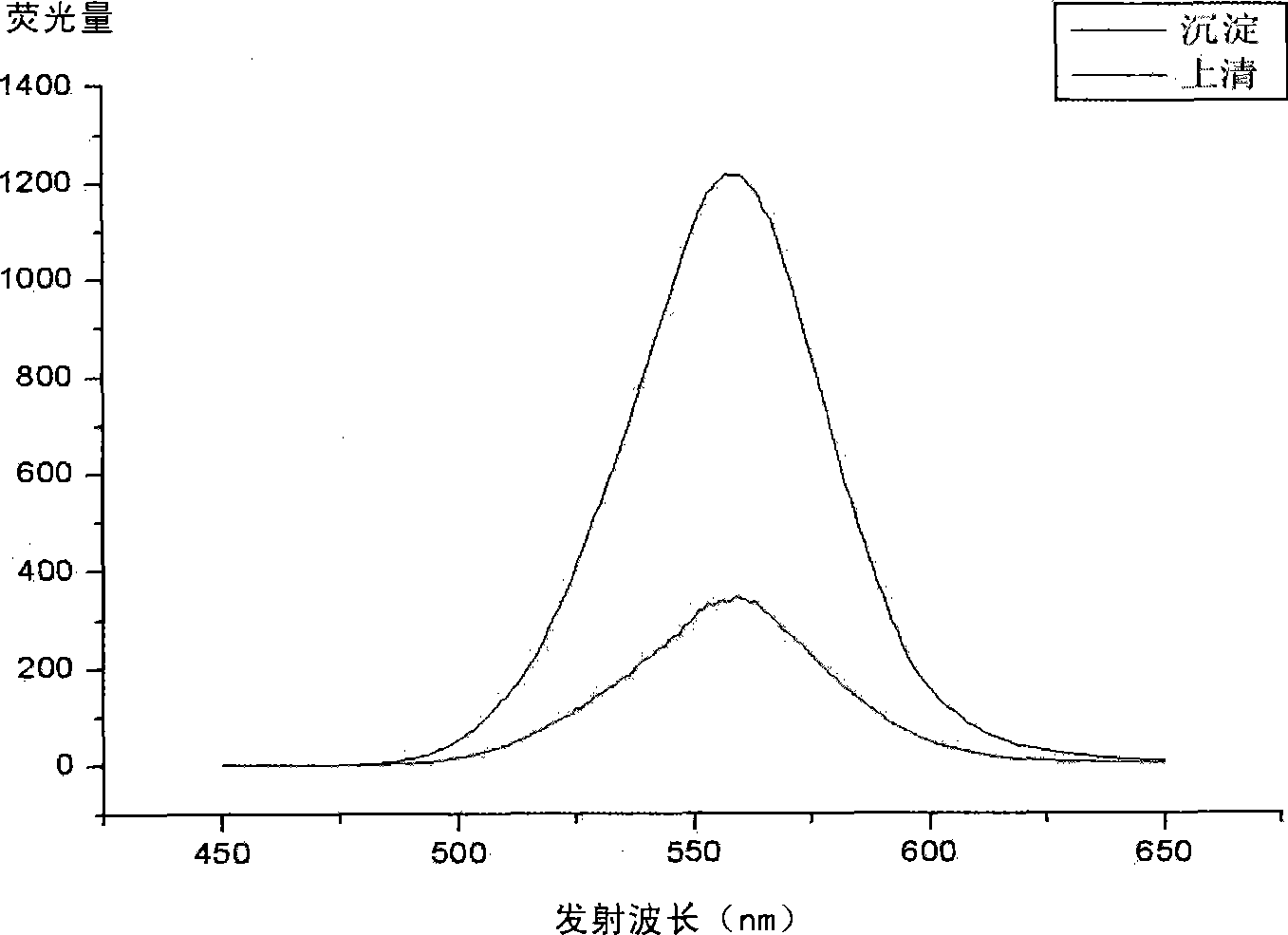
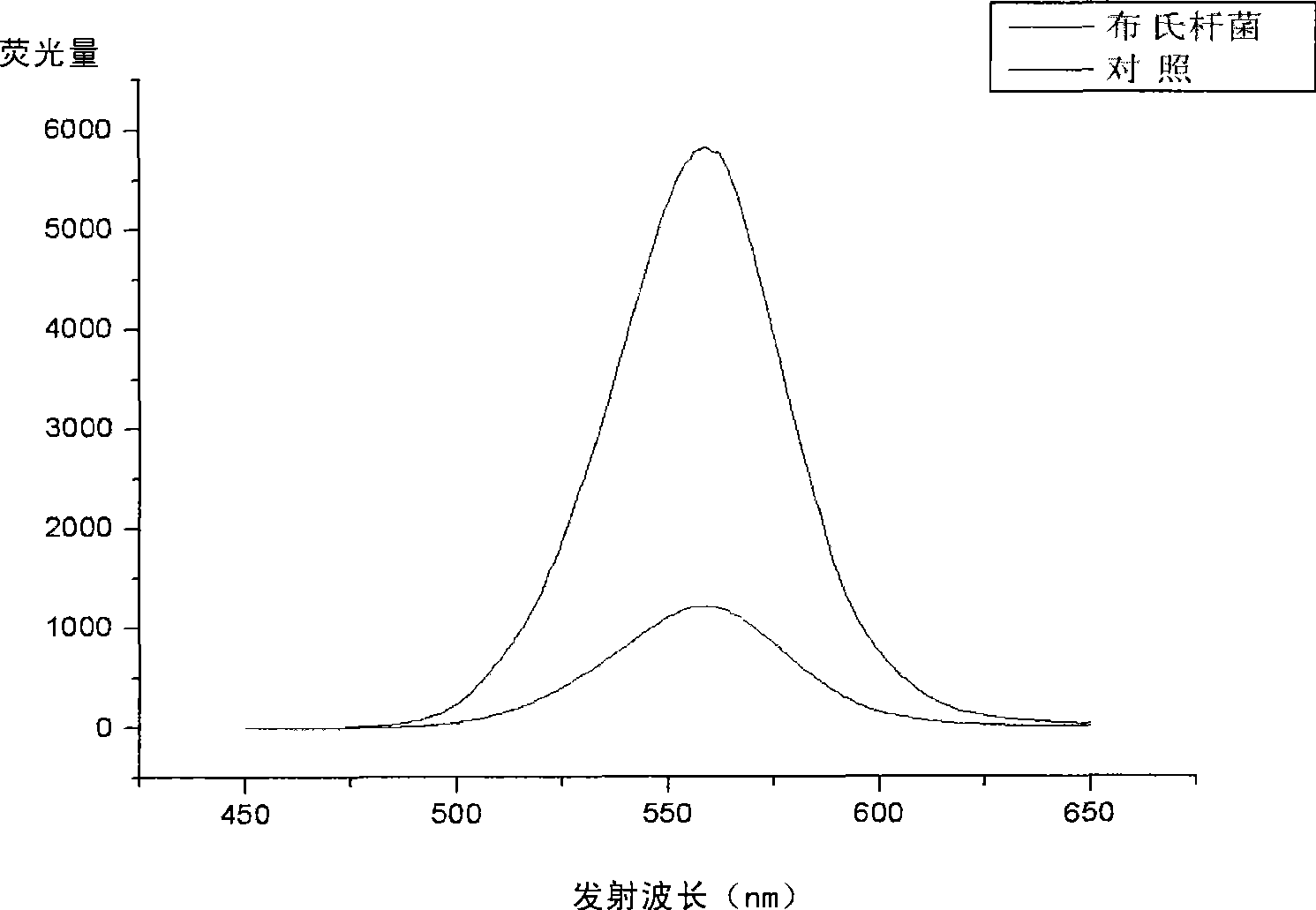
InactiveCN101430331AQuick checkLow detection limitBiological testingFluorescence/phosphorescenceFluorescenceAdditive ingredient
Owner:PEOPLES REPUBLIC OF CHINA BEIJING ENTRY EXIT INSPECTION & QUARANTINE BUREAU
Brucella abortus recombinant strain and application thereof
InactiveCN101629159ALow toxicityImprove purification effectAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsBrucella abortusImmunity
The invention discloses a brucella abortus recombinant strain and the application thereof, and the brucella abortus is obtained by inactivating glycosyltransferase SLT subunit protein gene in strain 2308. Compared with the original strain, the strain obtained in the invention has little strain toxicity, good immunity protecting effect and potential differential diagnosis mark, and can be used for research and development of attenuated vaccine. The invention is beneficial to the reformation of brucellosis vaccine, the research and the preparation of differential diagnosis reagent and the development of the brucellosis vaccine and the differential diagnosis reagent matched with the vaccine, and has very important significance on promoting the elimination of brucellosis of the animals all over the world.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Brucella abortus proteins and methods of use thereof
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF WYOMING
Brucella melitensis mutants and methods
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Controlled release vaccines and methods for treating Brucella diseases and disorders
Methods and compositions for the treatment of Brucella induced diseases and disorders are disclosed herein. In preferred embodiments, the invention relates to vaccines. In additional embodiments, the invention relates to formulations capable of releasing said vaccines at a controlled rate of release in vivo. In further embodiments, the invention relates to modified strains of the bacteria Brucella melitensis and Brucella abortus. In still further embodiments, the invention relates to compositions that do not induce clinical symptoms or splenomegaly in a subject receiving said compositions.
Owner:TEXAS A&M UNIVERSITY
Primer for identifying brucellosis vaccine strain and wild strain, probe and test kit
PendingCN111778342AStrong specificityQuick checkMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesNucleotideBrucella abortus
The invention provides a primer for identifying a brucellosis vaccine strain and a brucellosis wild strain, a probe and a test kit, the nucleotide sequences of the primer are shown as SEQ ID NO.1-2, the nucleotide sequence of the probe is shown as SEQ ID NO.3, and the test kit comprises the primer and the probe. Pure brucella nucleic acid DNA can be identified, trace brucella nucleic acid DNA suchas tissue samples and the like can also be identified, and brucella abortus A19-delta VirB12 molecular marker vaccine immune samples are distinguished from brucella existing vaccine immune samples and wild strain infection samples. The method has the advantages of being high in safety, convenient to operate, high in sensitivity, high in specificity and the like, can detect a large number of samples at the same time, and has practical application value on prevention and control and diagnosis of brucellosis.
Owner:VETERINARY INST XINJINAG ACADEMY OF ANIMAL SCI CLINIC MEDICAL SCI RES CENT XINJIANG ACADEMY OF ANIMAL HUSBANDRY SCI
Brucella deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) vaccine as well as construction method and application thereof
InactiveCN102772793AAvoid defectsEasy to makeAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsCompetent cellBrucella abortus
The invention discloses a Brucella deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) vaccine and a construction method thereof as well as the application of the vaccine. The Brucella DNA vaccine disclosed by the invention contains Brucella P39 and 18KD genes which can also be co-expressed in eukaryotic cells by internal ribosome entry site (IRES) mediation. The Brucella DNA vaccine disclosed by the invention has an SEQ1 gene sequence. According to the Brucella DNA vaccine and the construction method thereof, which are disclosed by the invention, the total DNA of Brucella abortus 2 type CVCC 12 is taken as a template, a polymerase chain reaction is carried out by using P39S primers SEQ2 and SEQ3 and 18KDS primers SEQ4 and SEQ5 respectively so as to obtain a target gene, and then the target gene is converted into a JM109 competent cell after being cleaved so as to obtain positive plasmid named as pQC-P39 / 18KD. Then, the pQC-P39 / 18KD and pcDNA3.1 plasmid are connected by using a T4DNA ligase after being cleaved, and afterwards are converted into E.coli DH5 alpha so as to obtain pcDNA-P39 / 18KD recombinant plasmid.
Owner:LANZHOU INST OF VETERINARY SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Brucella abortus reference serum bank
The invention relates to a Brucella abortus reference serum bank. The Brucella abortus reference serum bank has the following meanings: (1) the Brucella abortus reference serum bank with a certain size is established for the first time internationally; (2) reference substances are provided for scientific assessment of a brucellosis diagnostic method; (3) substance basis is provided for development of various brucellosis diagnostic methods for cattle.
Owner:CHINA INST OF VETERINARY DRUG CONTROL
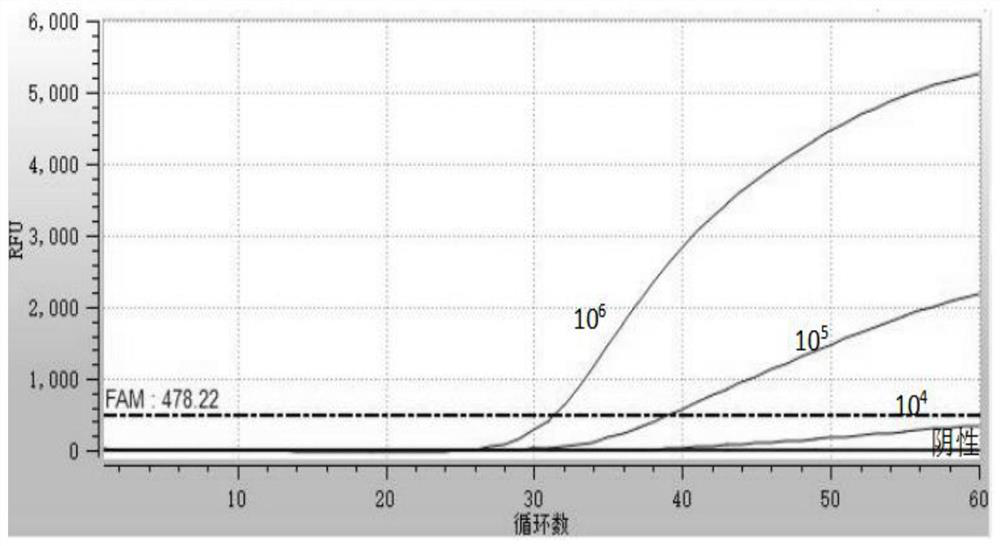
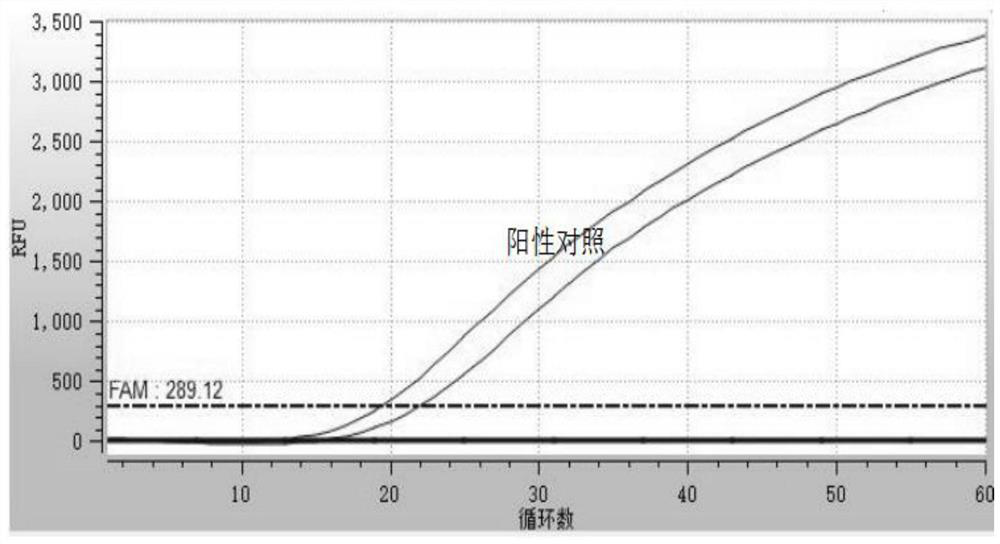
Primer sets and kits for multiple RPA detection of brucella abortus, brucella melitensis and brucella suis
ActiveCN111206109ARealize simultaneous detection and identificationHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesBrucella abortusNucleotide
The invention provides primer sets and kits for the multiple RPA detection of brucella abortus, brucella melitensis and brucella suis, and belongs to the technical field of brucella detection. The primer sets include B107F, B107R, B192F, B192R, B285F and B285R; and the nucleotide sequences of the B107F, B107R, B192F, B192R, B285F and B285R are successively shown as SEQ ID No. 1- SEQ ID No. 6. Multiple RPA detection can be performed on samples through the specific primer sets, the detection sensitivity of the brucella abortus is 10 pg / [mu]L, and the detection sensitivities of the brucella melitensis and brucella suis are 1 pg / [mu]L; and the provided primer sets and kits can respectively detect three spiked samples which are manually set serum, beef and milk, and compared with a brucella Bruce-Ladder detection method of national standard GB / T 18646-2018 diagnostic techniques for animal brucellosis, results are consistent.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Strong promoter from ensifer adhaerens as well as plasmid vector and application of strong promoter
The invention discloses a strong promoter from ensifer adhaerens as well as a plasmid vector and an application of the strong promoter. Function verification is performed by amplifying one strong promoter in ensifer adhaerens, and the strong promoter which can be widely applied to gene expression, gene operation and strain improvement of alpha-proteobacteria such as sinorhizobium meliloti, zymomonas mobilis, caulobacter crescentus, pseudomonas denitrificans, agrobacterium tumefaciens, brucella abortus, pseudomonas fluorescens, rhizobium leguminosarum and ensifer adhaerens is obtained and has the nucleotide sequence being SEQ ID NO:1. The invention also relates to the plasmid vector containing the strong promoter, a method for constructing a gene engineering strain by use of the promoter, the corresponding strain and an application of a host cell in starting target gene expression.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
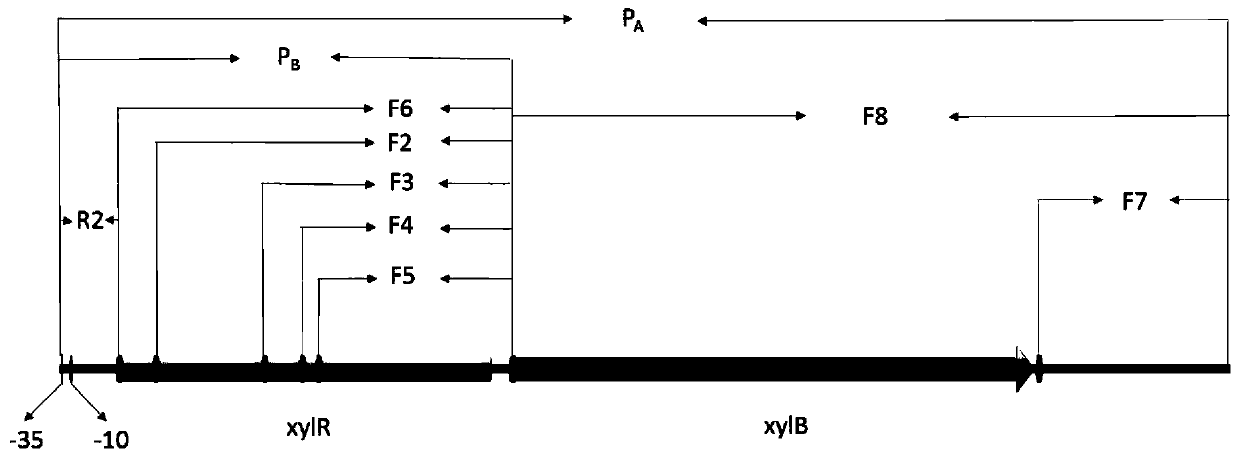
Xylose-induced promoter and plasmid vector and application thereof
The invention discloses a xylose-induced promoter. By amplifying a xylose-induced promoter in sinorhizobium meliloti, bioinformatics analysis and function verification are carried out, the xylose-induced promoter which can be widely applied to gene expression, genetic gene operation and strain improvement in alpha-proteobacteria such as Sinorhizobium meliloti, Zymomonas mobilis, Caulobacter crescentus, Pseudomonas denitrificans, Agrobacterium tumefaciens, Brucella abortus, Pseudomonas fluorescens, Rhizobium leguminosarum and Sinorhizobium adhaerens is obtained, and the nucleotide sequence of the promoter is SEQ ID NO: 1 or SEQ ID NO: 2. The invention also relates to a plasmid vector containing the xylose-induced promoter, a method for constructing a genetic engineering strain by using thepromoter, a corresponding strain, and application of a host cell to induction and starting of expression of a target gene under xylose inducible conditions.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Method for detecting brucella abortus attenuated vaccine strain S19
InactiveCN108048586AStrong specificityStrong throughputMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesWater bathsBrucella abortus
The invention provides a method for detecting a brucella abortus attenuated vaccine strain S19 and a primer group used for detection, wherein the sequence of the adopted primer group is SEQ ID NO: 1-4. The primer group and method have advantages that 1) the primer group and method are efficient and sensitive, amplification can be completed in 30 min, and the lowest detection limit of an amplification template is 1.0*10<-3> ng / [mu]l; 2) the primer group and method are high in specificity, and two pairs of PRA primer groups specifically identify and detect S19 and don't cause any cross reactionwith brucellin of other species and biological types, brucellin vaccine strains and common non-brucellin strains; 3) the primer group and method are simple to operate, the prepared RPA reaction systemundergoes a reaction in a 39-degree constant-temperature condition to undergo a reaction, and a PCR instrument is not required; and 4) the primer group and method are high in flux, a large amount ofsamples can be detected in one time in a water bath or a constant-temperature incubator, and are not limited by the quantity of test holes of the PCR instrument.
Owner:CHINA ANIMAL HEALTH & EPIDEMIOLOGY CENT
Chinese herbal medicine feed capable of preventing brucella abortus
InactiveCN107772082AStir wellReduce morbidityFood processingAnimal feeding stuffDiseaseAnimal science
The invention relates to a feed capable of preventing brucella abortus. The feed comprises the following raw materials in parts by weight: 55-60 parts of corn, 20-35 parts of sorghum straw, 10-15 parts of semen cassiae, 15-20 parts of cortex lycii, 8-10 parts of tree peony bark, 10-15 parts of rhizoma anemarrhenae, 12-14 parts of honeysuckle flowers, 9-12 parts of common selfheal fruit-spike, 12-15 parts of dandelions, and 1-2 parts of a fermenting agent. The Chinese herbal medicine feed disclosed by the invention has obvious effect of preventing brucella abortus, has the efficacy of strengthening disease resistance of cattle, and is high in security coefficient. All of the raw materials are cheap and easy to obtain, so that economic losses caused by the brucella abortus can be greatly reduced.
Owner:董洪民
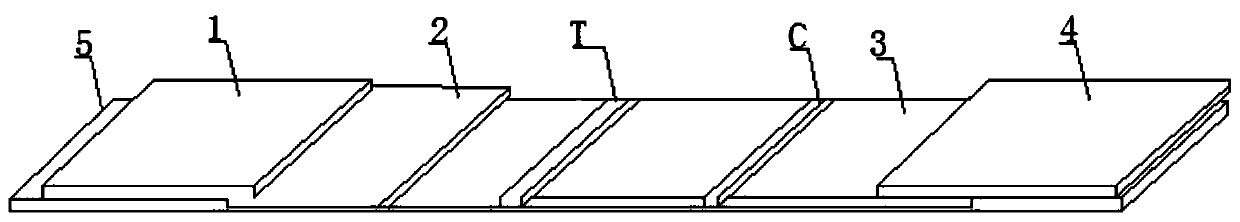
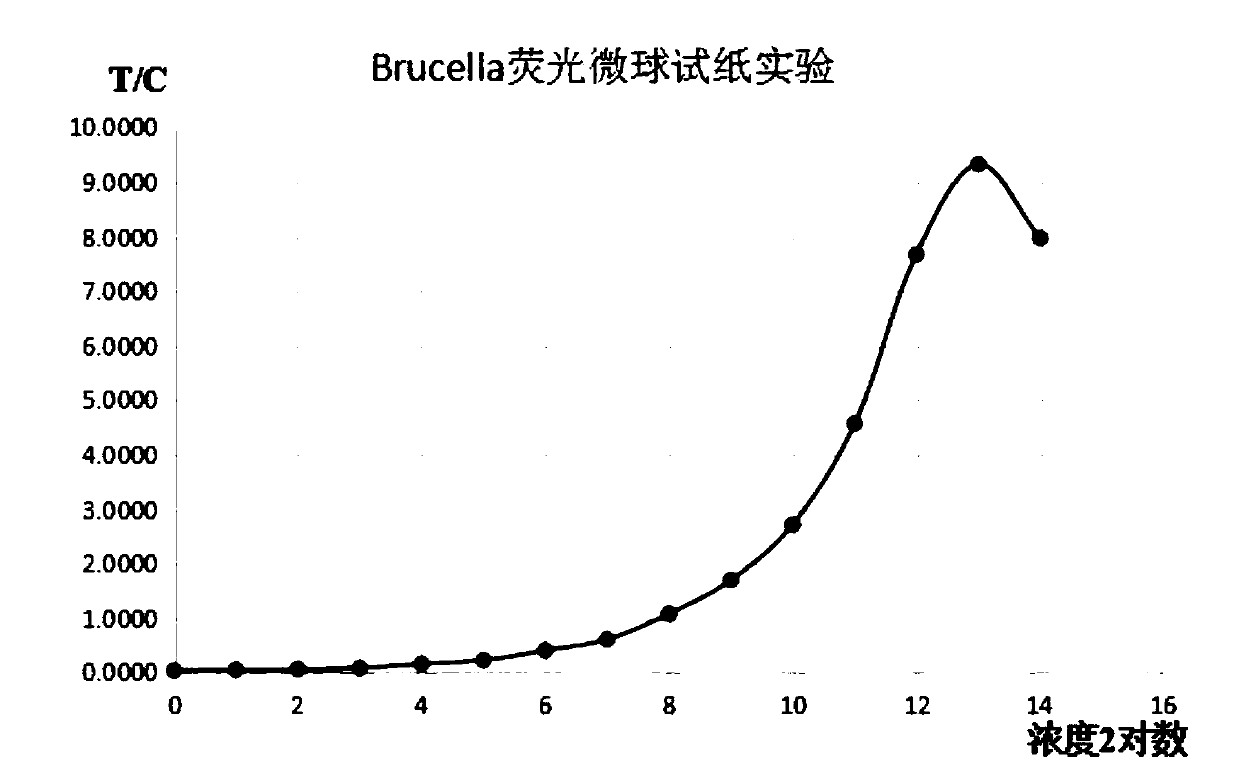
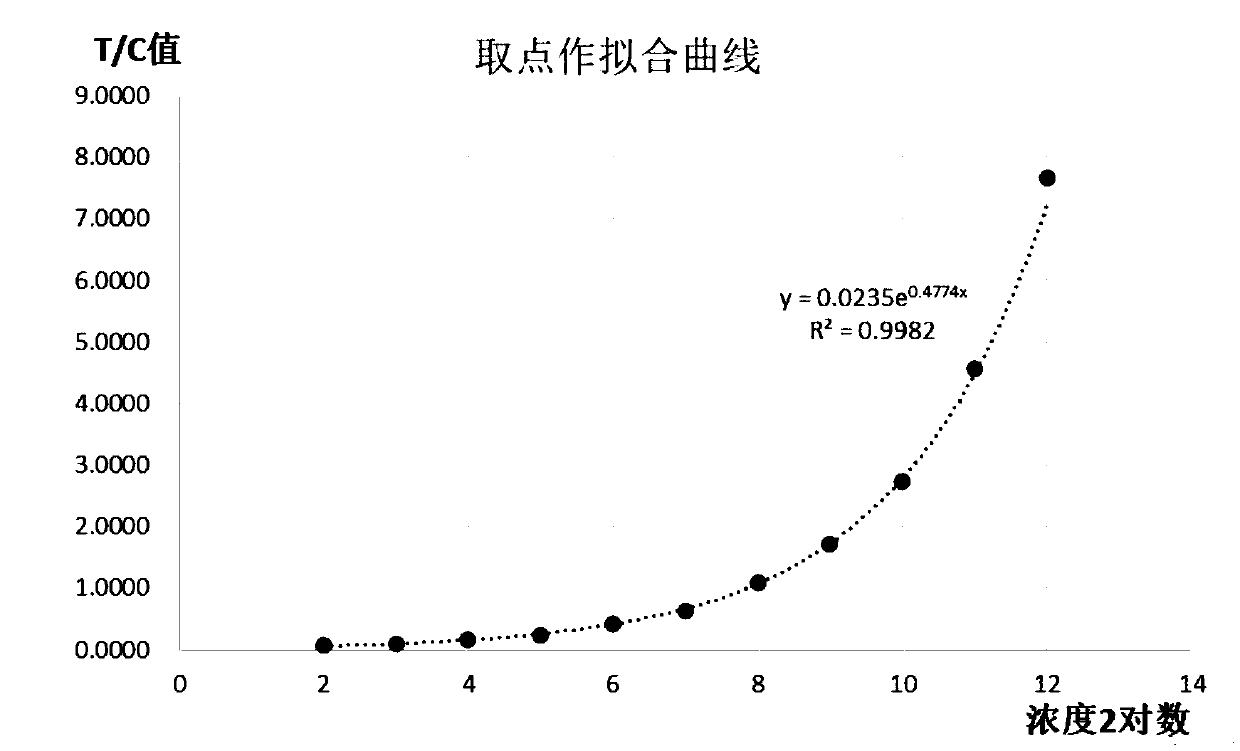
Brucella abortus virus fluorescent microsphere immunochromatography test paper and preparation method and detection method thereof
InactiveCN109655614AHigh detection sensitivitySimplified operational requirementsMaterial analysisBrucella abortusQualitative analysis
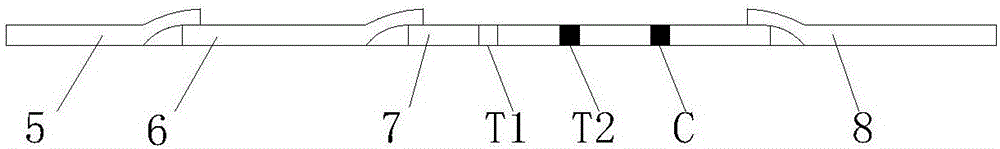
The invention discloses brucella abortus virus fluorescent microsphere immunochromatography test paper and a preparation method and detection method thereof. The invention aims to provide the brucellaabortus virus fluorescent microsphere immunochromatography test paper which has strong specificity, high sensitivity and good repeatability and can be used for quantitative and qualitative analysis.According to the technical scheme, the brucella abortus virus fluorescent microsphere immunochromatography test paper comprises a bottom plate, the bottom plate is sequentially connected with a samplepad, a combination pad, a chromatographic membrane and a water absorption pad, a line C and a line T are arranged on the chromatographic membrane, and the combination pad is sprayed with fluorescentmicrospheres labeled with a BrG11 antibody; a BrF11 antibody is sprayed on the line T; and the line C is painted with A goat anti-mouse IgG antibody. The invention belongs to the field of pathogen detection of experimental animals.
Owner:GUANGZHOU VETERINARY BIOTECH CO LTD
Use of cross-protection to identify novel vaccine candidates for infectious agents
InactiveUS7323180B2Antibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsHigh concentrationEnzyme digestion
This invention discloses methods for identifying Francisella tularensis vaccine candidates. It enables identification of novel vaccine candidates and quality assurance for vaccine batches, assessment of protection in vaccinates and identification of the infecting agent in vaccinates. Mice were first vaccinated with Brucella abortus O-polysaccharide (OPS) vaccine. These animals were then given 10 LD50s of F. tularensis live vaccine strain (LVS). Sixty percent (60%) of the vaccinated mice survived the multiple lethal doses. Sera were collected from these surviving mice and the antibodies were used to probe supernatant and cell lysates of live F. tularensis LVS cultures. Several F. tularensis components were identified only by the noted “survivor” antisera. Of these identified proteins, enzyme digestions and chemical oxidation suggest post-translational modifications of some proteins e.g. a 52 kDa glycoprotein, a 45 kDa lipoprotein and a 19 kDa nucleoprotein. The 52 kDa component caused nitrous oxide induction in tissue cultures at low concentrations, cell death at high concentrations. Vaccination with this gave partial protection while addition of other components acted synergistically to give enhanced protection from 250 LD50s of F. tularensis LVS.
Owner:HER MAJESTY THE QUEEN AS REPRESENTED BY THE MINIST OF NAT DEFENCE OF HER MAJESTYS CANADIAN GOVERNMENT
Establishment method of indirect ELISA (enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay) for detection of Brucella abortus HSP70
The invention discloses an establishment method of indirect ELISA (enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay) for detection of Brucella abortus HSP70. The establishment method includes the steps of preparinga fusion protein of Brucella abortus HSP70, and purifying the fusion protein to obtain a purified protein; using the purified protein as an antigen to detect a Brucella serum sample, and determining antigen coating concentration, serum dilution, confining liquid type, secondary antibody diluted concentration and color rendering time; determining a critical value of indirect ELISA; determining an ELISA results judging standard; analyzing sensitivity and specificity of an indirect ELISA method. HSP70 is subjected to prokaryotic expression to obtain the purified protein; the purified protein is used as the antigen to establish the indirect ELISA method for detection of Brucella abortus; the important method is provided for the serological test of brucellosis.
Owner:HEBEI NORMAL UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Use of cross-protection to identify novel vaccine candidates for infectious agents
This invention discloses methods for identifying Francisella tularensis vaccine candidates. It enables identification of novel vaccine candidates and quality assurance for vaccine batches, assessment of protection in vaccinates and identification of the infecting agent in vaccinates. Mice were first vaccinated with Brucella abortus O-polysaccharide (OPS) vaccine. These animals were then given 10 LD50s of F. tularensis live vaccine strain (LVS). Sixty percent (60%) of the vaccinated mice survived the multiple lethal doses. Sera were collected from these surviving mice and the antibodies were used to probe supernatant and cell lysates of live F. tularensis LVS cultures. Several F. tularensis components were identified only by the noted “survivor” antisera. Of these identified proteins, enzyme digestions and chemical oxidation suggest post-translational modifications of some proteins e.g. a 52 kDa glycoprotein, a 45 kDa lipoprotein and a 19 kDa nucleoprotein. The 52 kDa component caused nitrous oxide induction in tissue cultures at low concentrations, cell death at high concentrations. Vaccination with this gave partial protection while addition of other components acted synergistically to give enhanced protection from 250 LD50s of F. tularensis LVS.
Owner:HER MAJESTY THE QUEEN AS REPRESENTED BY THE MINIST OF NAT DEFENCE OF HER MAJESTYS CANADIAN GOVERNMENT
PCR kit for simultaneously detecting Brucella abortus, Brucella melitensis, Brucella suis and Brucella canis as well as preparation method and using method thereof
InactiveCN103409520BPracticalStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementBrucella abortusBiology
A PCR kit for simultaneously detecting Brucella abortus, Brucella melitensis, Brucella suis and Brucella canis as well as a preparation method and a using method thereof, and belongs to the field of gene detection of anthropozoonosis pathogens. The PCR kit comprises a PCR liquid reactant, DNA polymerase, positive quality control standard substances and negative quality control standard substances; the PCR liquid reactant comprises four pairs of primers for identifying Brucella abortus, Brucella melitensis, Brucella suis and Brucella canis and a PCR buffer solution containing dNTPs, Mg<2+> and double distilled water. The PCR kit has high practicability, can be used for directly detecting the type of Brucella in a contaminated sample, has high detection speed, high sensitivity (10<2>cfu / ml), high specificity and good repeatability, is safe, reliable, quick, simple and convenient, can be used for qualitative detection of the type of Brucella in the sample, and can replace traditional etiological and serological methods.
Owner:MILITARY VETERINARY RES INST PLA MILITARY MEDICAL ACAD OF SCI
Molecular marker capable of distinguishing Brucella abortus from Brucella melitensis and detection method
PendingCN114790490AMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesBrucella abortusNucleotide
The invention provides a molecular marker capable of distinguishing Brucella abortus and Brucella melitensis and a detection method. The sequence of a specific nucleotide fragment capable of identifying all Brucella is SEQ ID NO: 1; the nucleotide sequence of the specific molecular marker for detecting Brucella abortus is SEQ ID NO: 5; the nucleotide sequence of the specific molecular marker for detecting Brucella melitensis is SEQ ID NO: 9. The invention also provides a primer pair and a probe for detecting the specific accounting fragment. The BSCP primer and the probe prepared by the invention have universality and can detect all Brucella, and the primer and the probe not only can be independently used, but also can be prepared into a triple real-time fluorescent quantitative PCR method for identifying the Brucella. The detected samples can be separated strains and can also be clinically collected abortion substances, milk, swabs, tissues and other samples, and the kit has the characteristics of high sensitivity, high specificity and the like.
Owner:CHINA ANIMAL HEALTH & EPIDEMIOLOGY CENT
Detection method for diagnosing Brucella abortus by using recombinant overlapping peptide
InactiveCN113244414AHigh purityQuality improvementAntibacterial agentsCompounds screening/testingEscherichia coliProtein detection
The invention provides a detection method for diagnosing Brucella abortus by using a recombinant overlapping peptide, and relates to the technical field of veterinary drugs and detection of zoonosis. The detection method for diagnosing the Brucella abortus by using the recombinant overlapping peptide (ROP-OMP31) comprises the following steps: screening an antigen protein, namely screening the antigen protein OMP31 from Brucella abortus outer mold proteins; vaccine design, namely designing ROP-OMP31 by using a recombinant overlapping peptide technology; artificially synthesizing, namely constructing a vector, performing prokaryotic expression and performing HPLC identification; performing escherichia coli transformation and protein purification; performing activity detection on ROP-OMP31, namely feeding the mouse for 3 weeks after nasal drip, and carrying out staining to detect the activity by using acid-fast staining; performing a guinea pig skin test, establishing a guinea pig model, and performing the skin test after feeding for 45 days; and performing a bovine skin test, establishing a bovine brucellosis model, and performing out the skin test. According to the present invention, the OMP31-ROP design comprises more antigen T cell epitopes; the protein detection purity is higher, and the corresponding quality is better; and meanwhile, compared with a PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) technology and an Elisa, the method is easy to operate, safer and lower in cost.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIV
Primer and probe for RNA-isothermal-amplification detection on brucella abortus, kit and detection method
PendingCN111647675AEfficient detectionStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesSpecific detectionBrucella abortus
The invention discloses a primer-probe for RNA-isothermal-amplification detection on brucella abortus, a kit and a detection method. The specific detection primer-probe, the detection kit containing the detection primer-probe and the detection method employing RNA isothermal amplification by utilizing the detection kit have the characteristics of high sensitivity, high specificity, low pollution (an amplification product RNA is easy to degrade in a natural environment) and rapidness, have low requirements on instruments and are simple in operation process.
Owner:张家口富熙生物科技有限公司
Brucella Melitensis Mutants and Methods
Certain attenuated mutants of Brucella, especially B. melitensis, B. abortus, B. suis and B. ovis, when administered to a human or animal trigger a protective immune response such that subsequent challenge with virulent Brucella of the same species does not result in disease or results in much less severe symptoms. Functional inactivation of galE, a virB gene or the operon (ORFs 1087-1090) comprising the gene encoding β-hexosaminidase (BMEI1087) and a lytic murein transglycosylase gene (BMEI1088). A specific example of the attenuated galE mutant which produces a protective immune response is B. melitensis GR024. The specific example of an inactivated ORF1087-1090 operon is B. melitensis GR026; it has an insertion mutation in the promoter region upstream of ORF 1090. Vaccination with live cells of either or both of these mutants results in a T cell response which protects the human or animal against challenge with virulent B. melitensis. Similar strategies for protective immunity using live attenuated mutants are useful for B. abortus, B. suis and B. ovis as well.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Multiplex pcr detection kit for pathogens of common bacterial diseases in cattle
ActiveCN110656190BAvoid detectionAvoid wasting materialMicrobiological testing/measurementMultiplexBrucella abortus
Based on the genes of Brucella abortus, Mycobacterium bovis and Chlamydia abortus, the present invention designs three pairs of specific amplification primers for the three pathogens, cooperates with the PCR reaction components, and establishes a multiplex PCR method for detecting and distinguishing the three kinds of cattle Single or mixed infection of common pathogens, and packaging of detection kits for the detection and differentiation of Brucella bovis, Mycobacterium bovis and Chlamydia bovis.
Owner:LANZHOU INST OF VETERINARY SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com