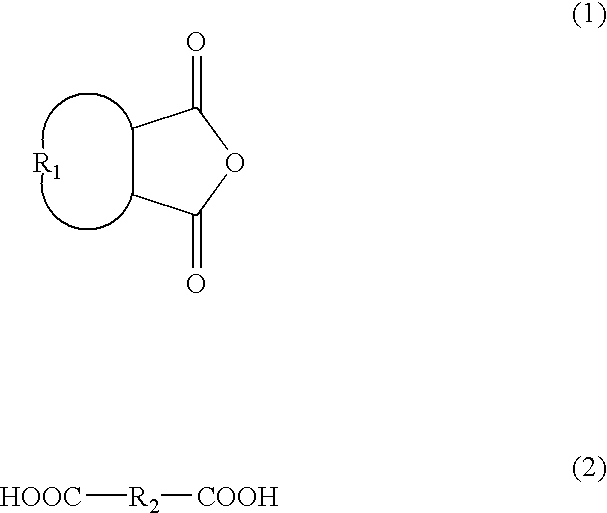
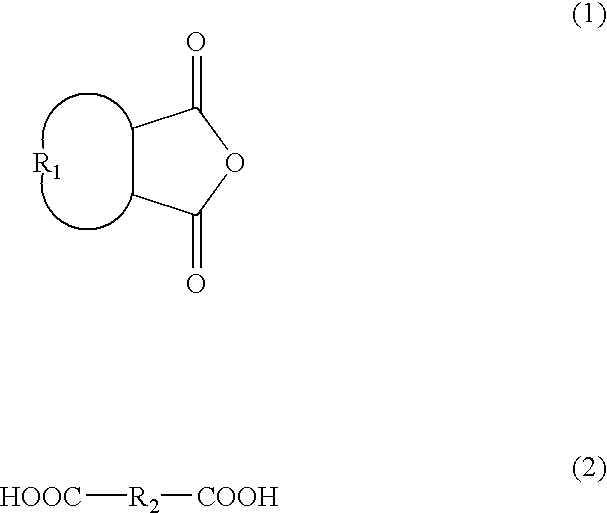
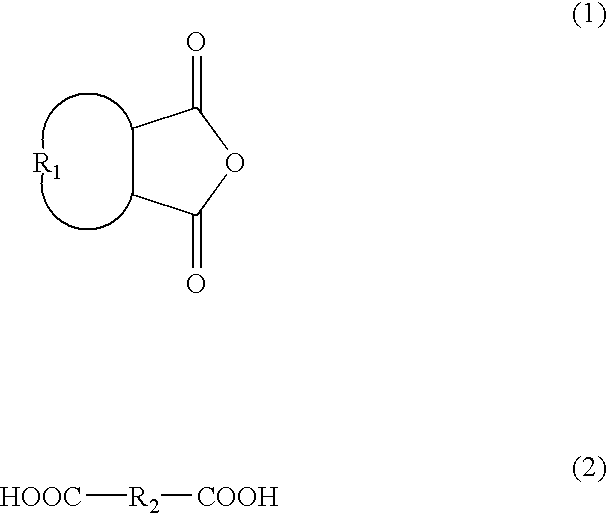
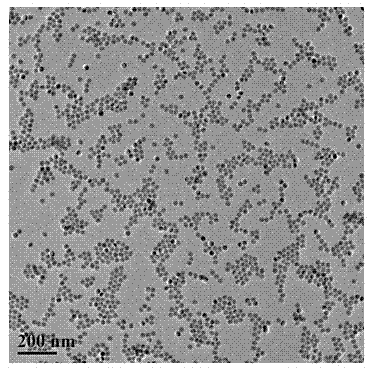
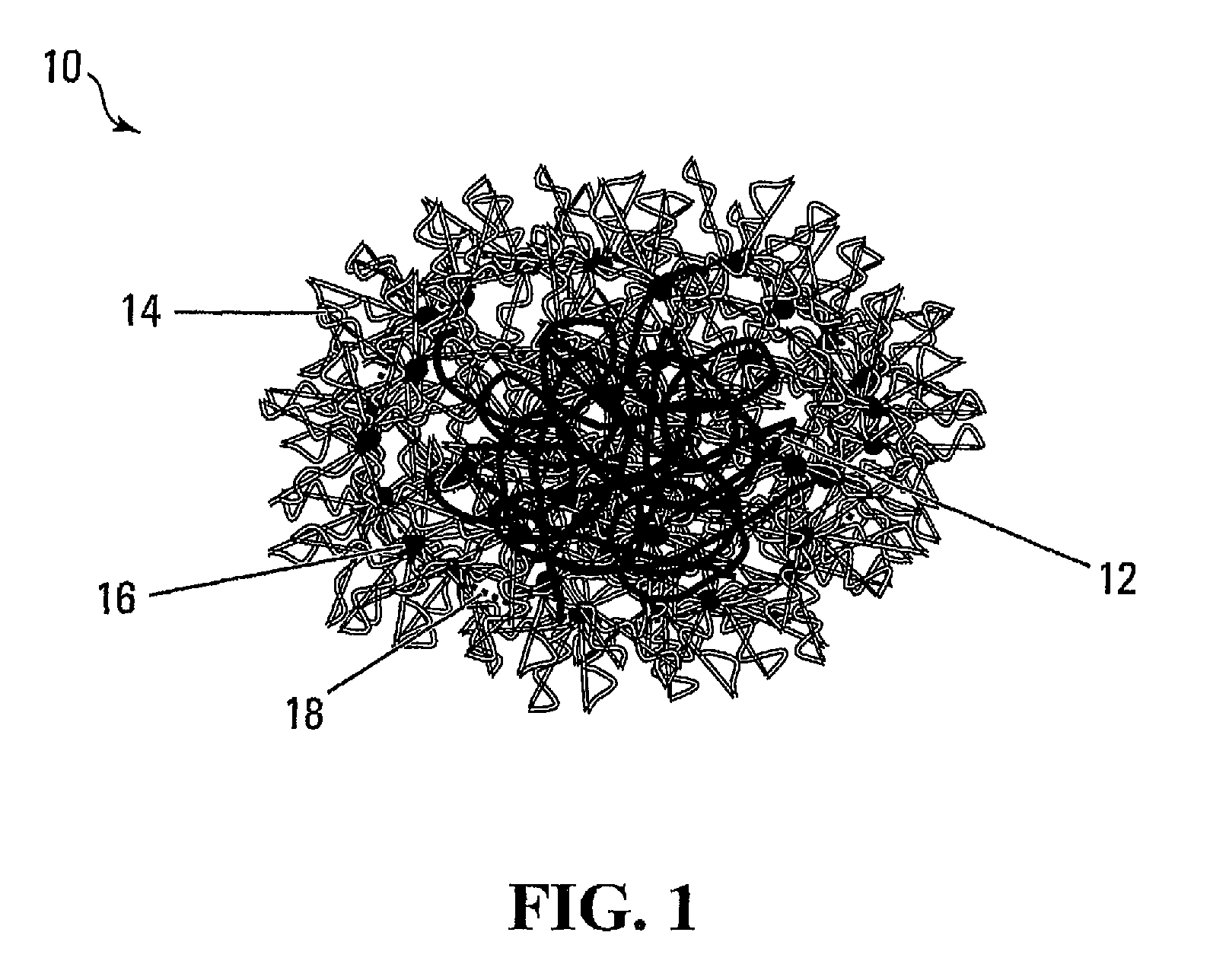
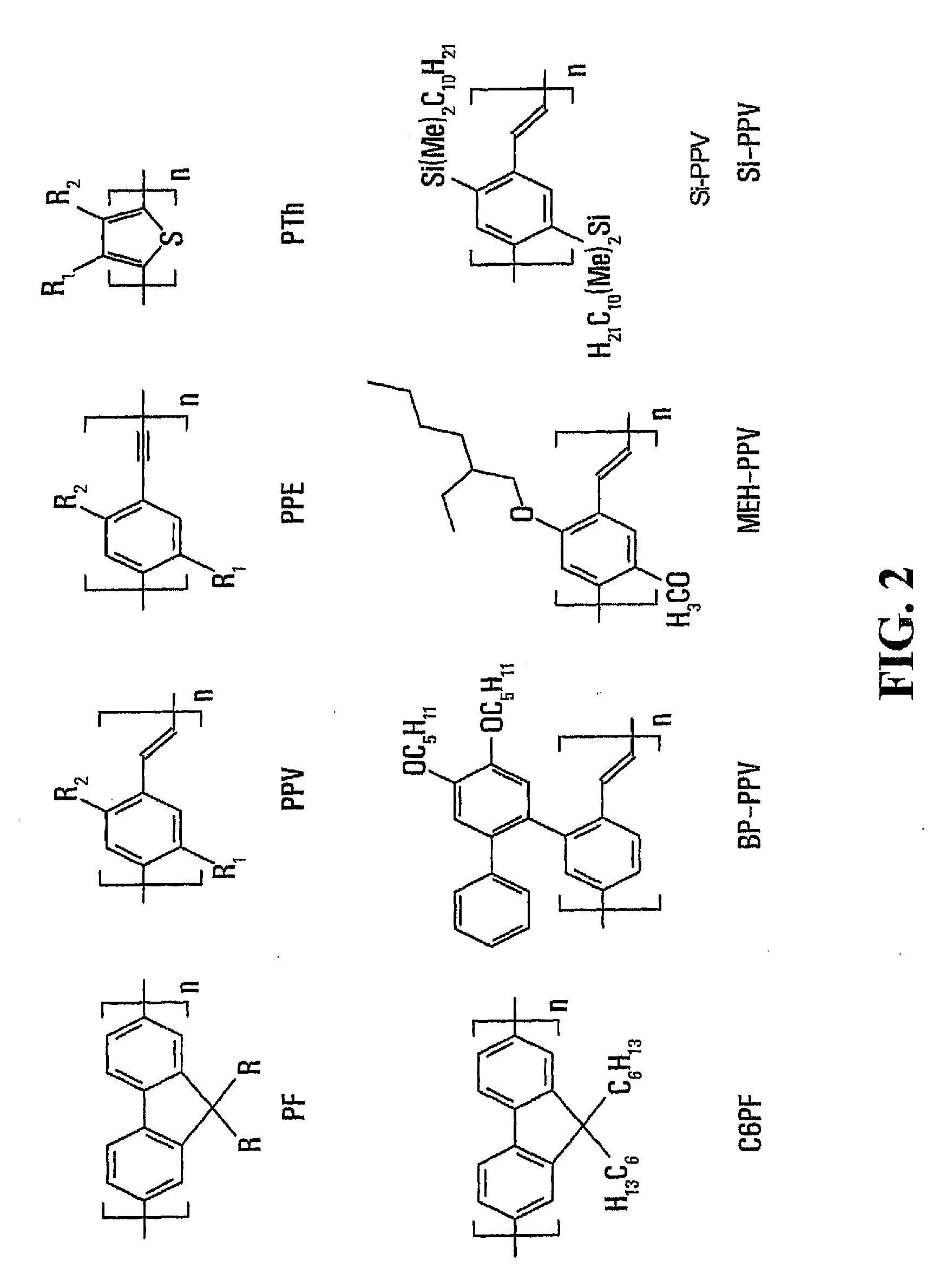
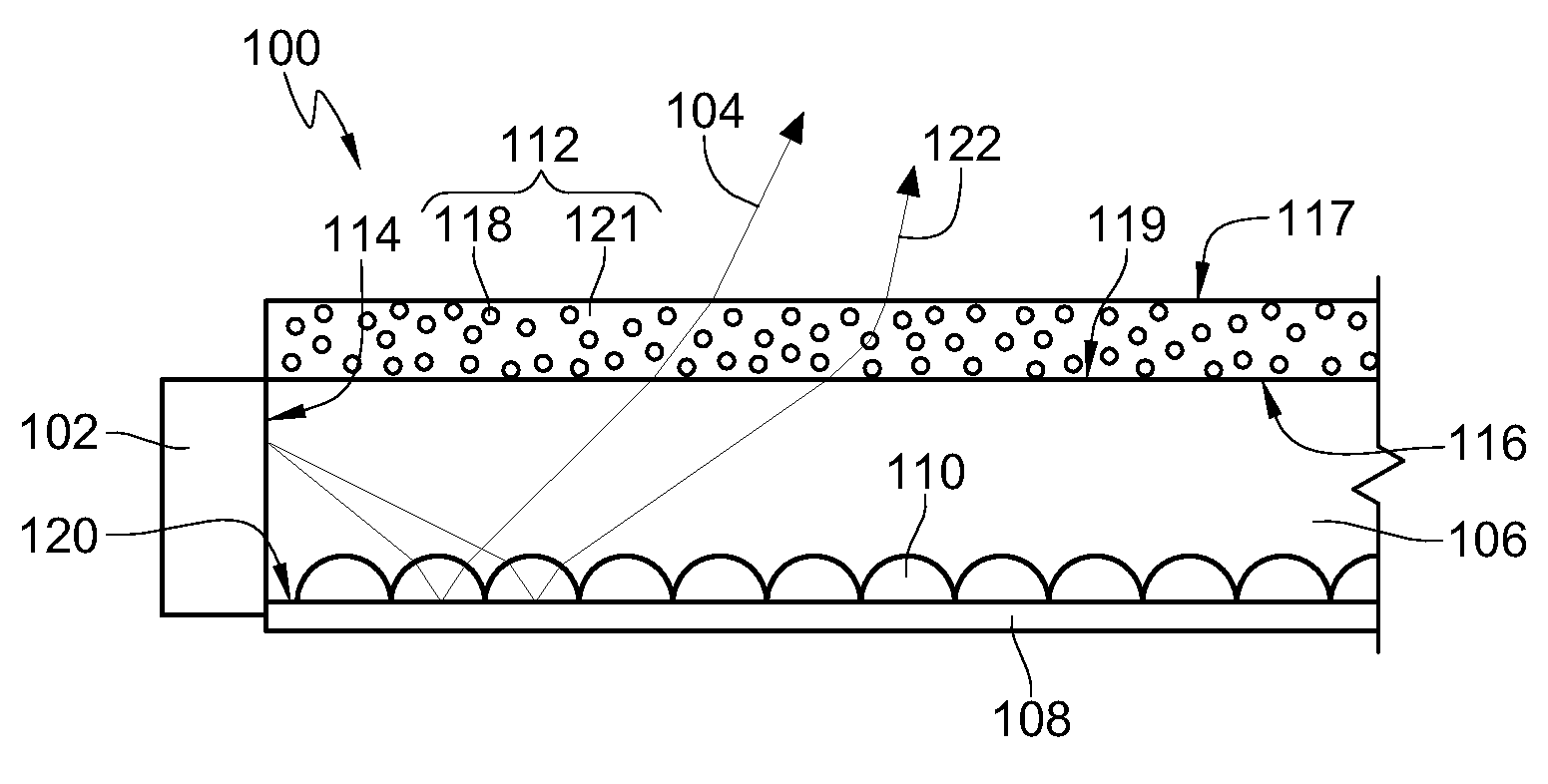
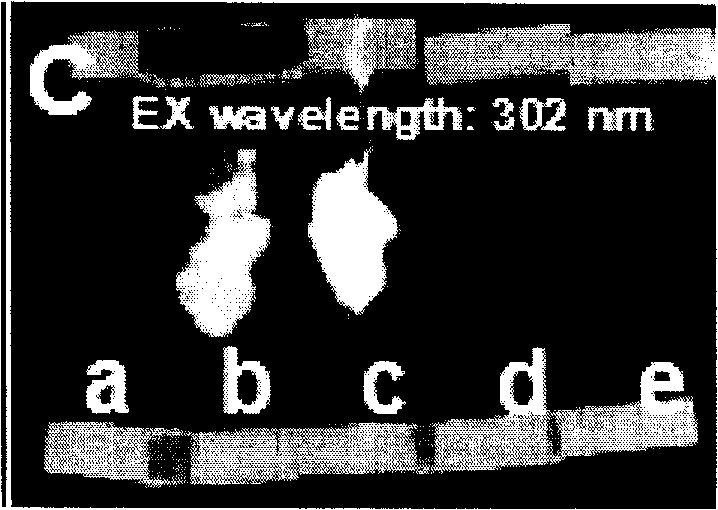Patents
Literature
408 results about "Fluorescent particle" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
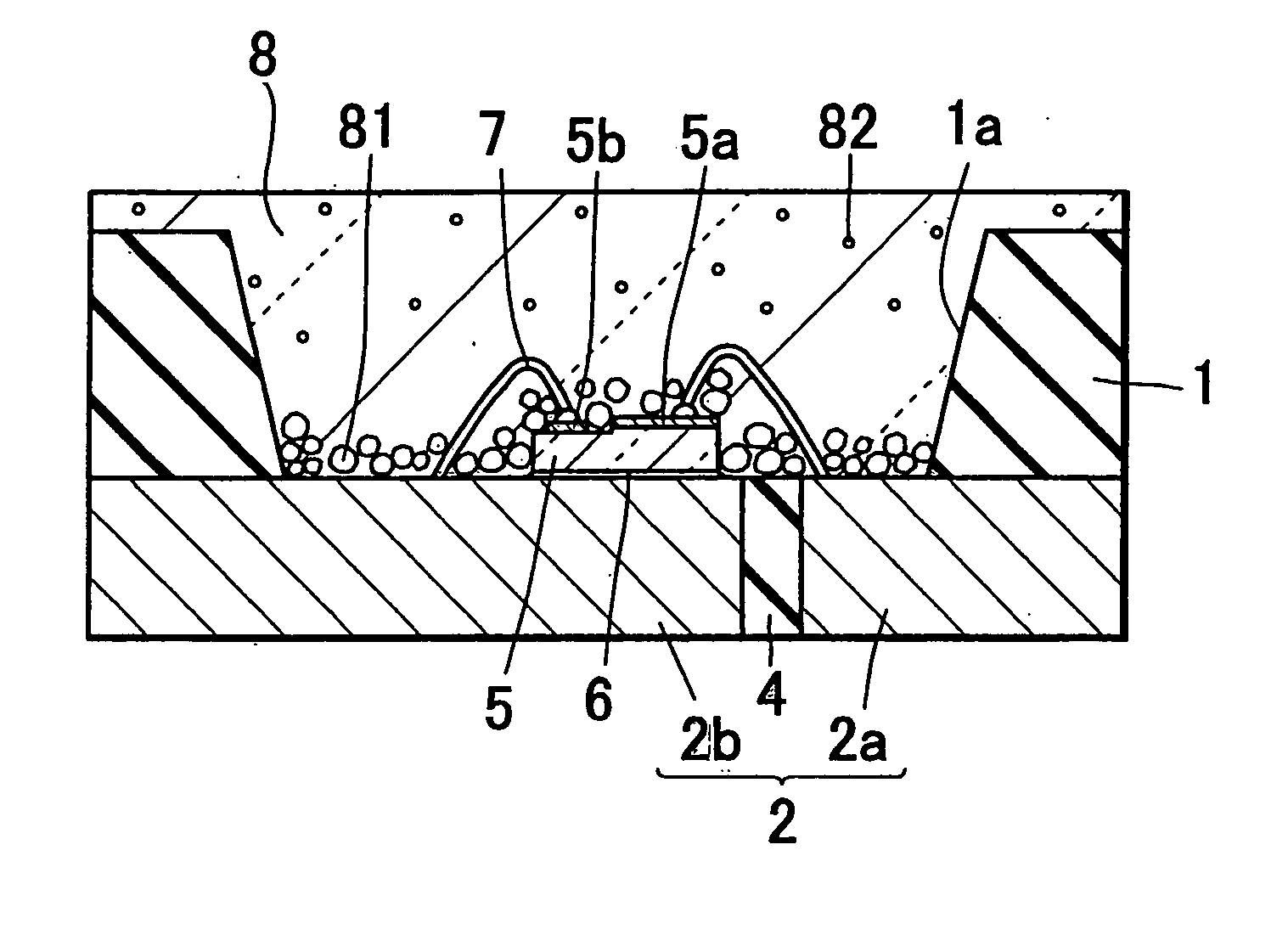
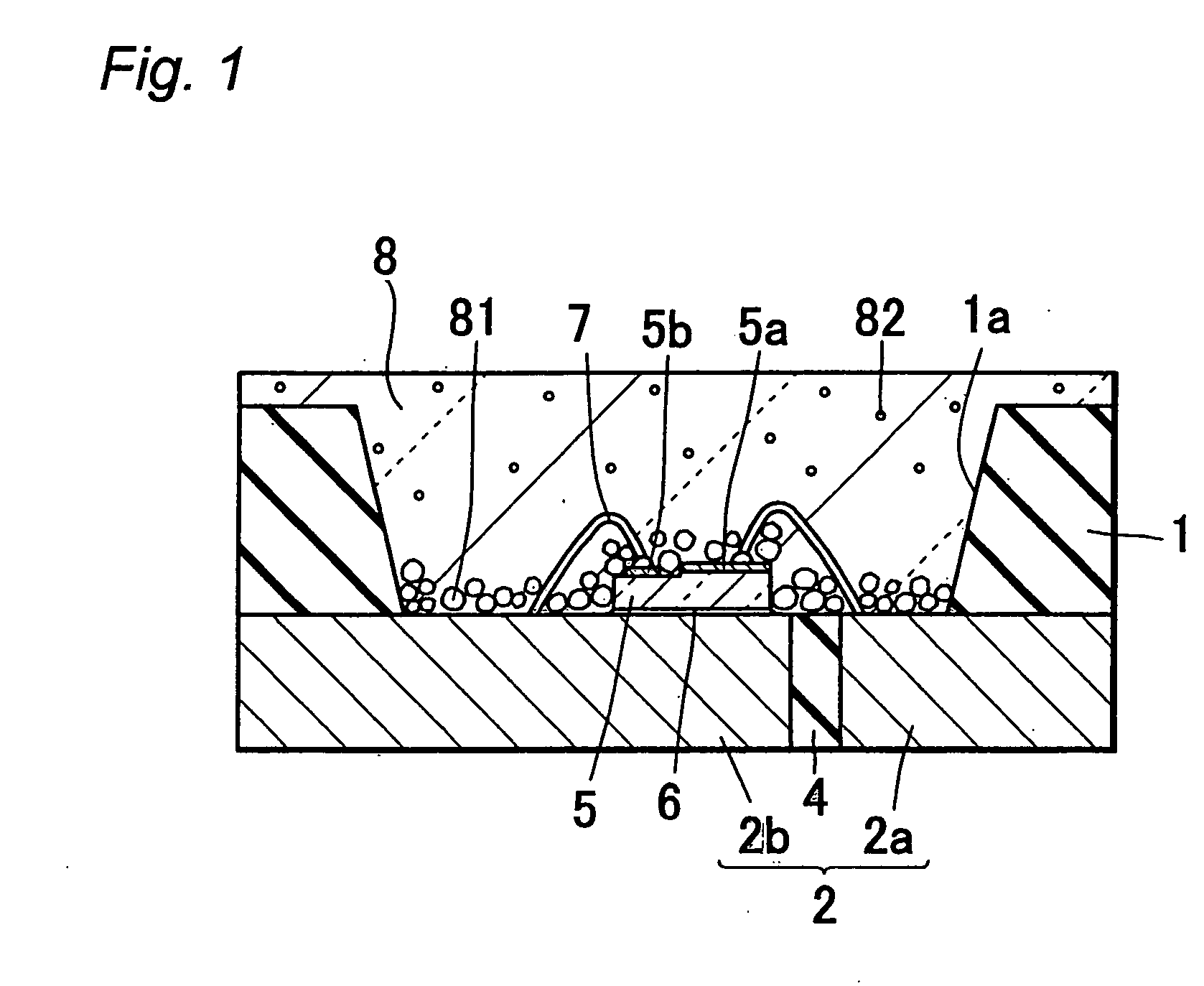
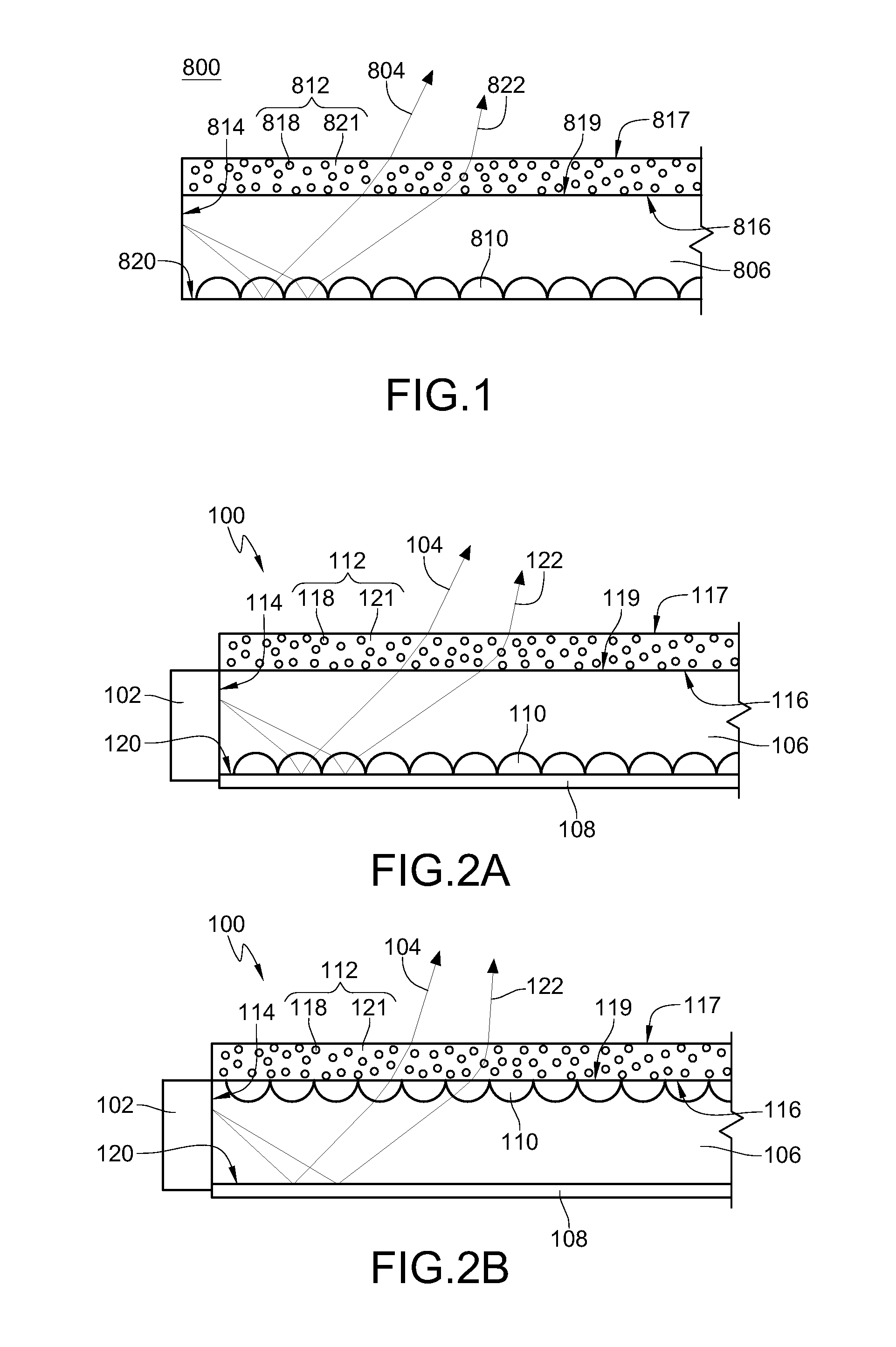
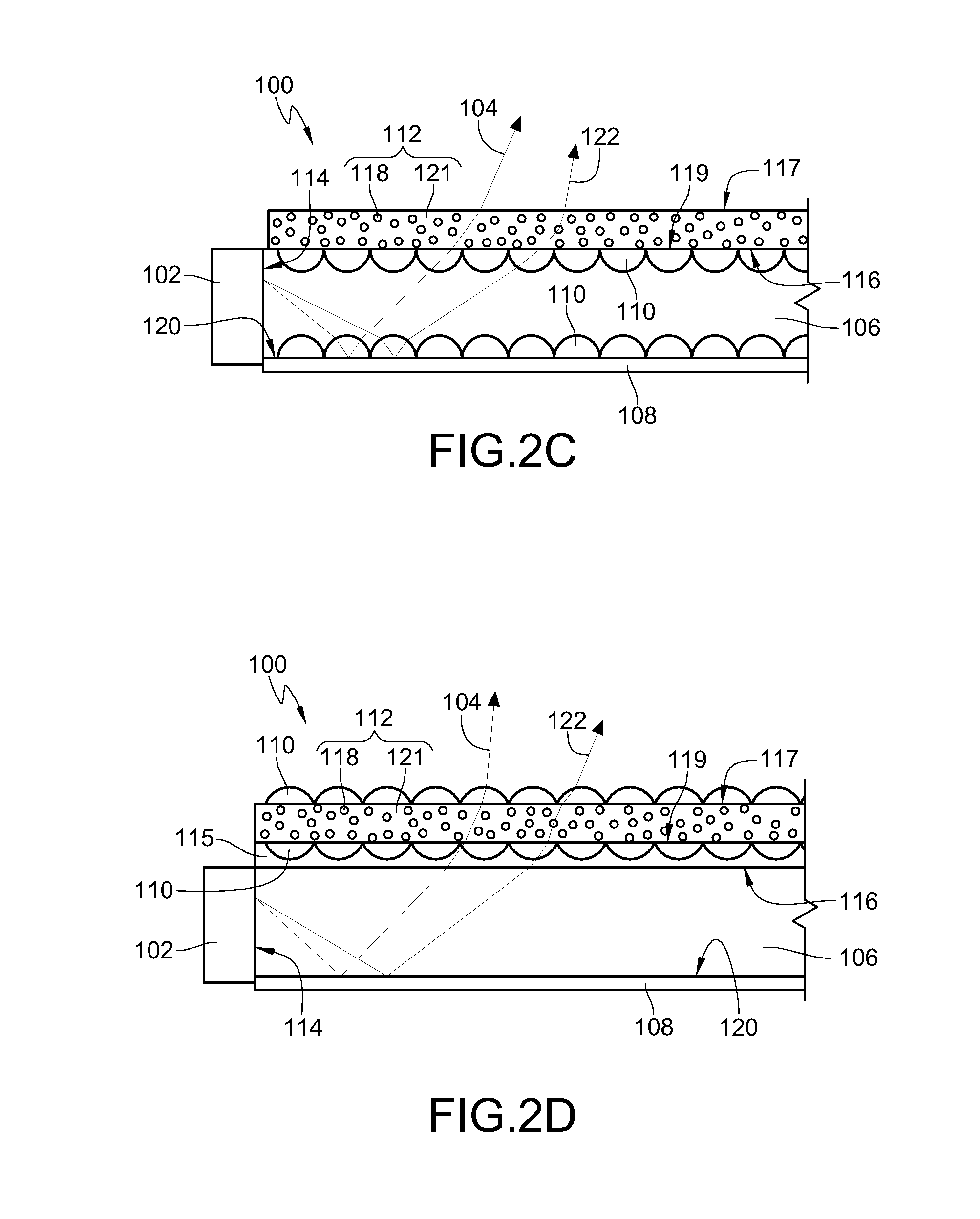
Light emitting diode, optical semiconductor element and epoxy resin composition suitable for optical semiconductor element and production methods therefor
InactiveUS20030080341A1Light emission characteristicSuppress the variation in the chromaticity of the light emittedDischarge tube luminescnet screensLamp detailsEpoxyLight-emitting diode
A light emitting diode comprising an LED chip having a light emitting layer made of a nitride compound semiconductor and a light transmitting resin that includes a fluorescent material which absorbs at least a part of light emitted by the LED chip and emits light of a different wavelength, wherein the fluorescent material includes a fluorescent particles of small particle size and a fluorescent particles of large particle size, the fluorescent particles of large particle size being distributed in the vicinity of the LED chip in the light transmitting resin to form a wavelength converting layer, the fluorescent particles of small particle size being distributed on the outside of the wavelength converting layer in the light transmitting resin.
Owner:NICHIA CORP
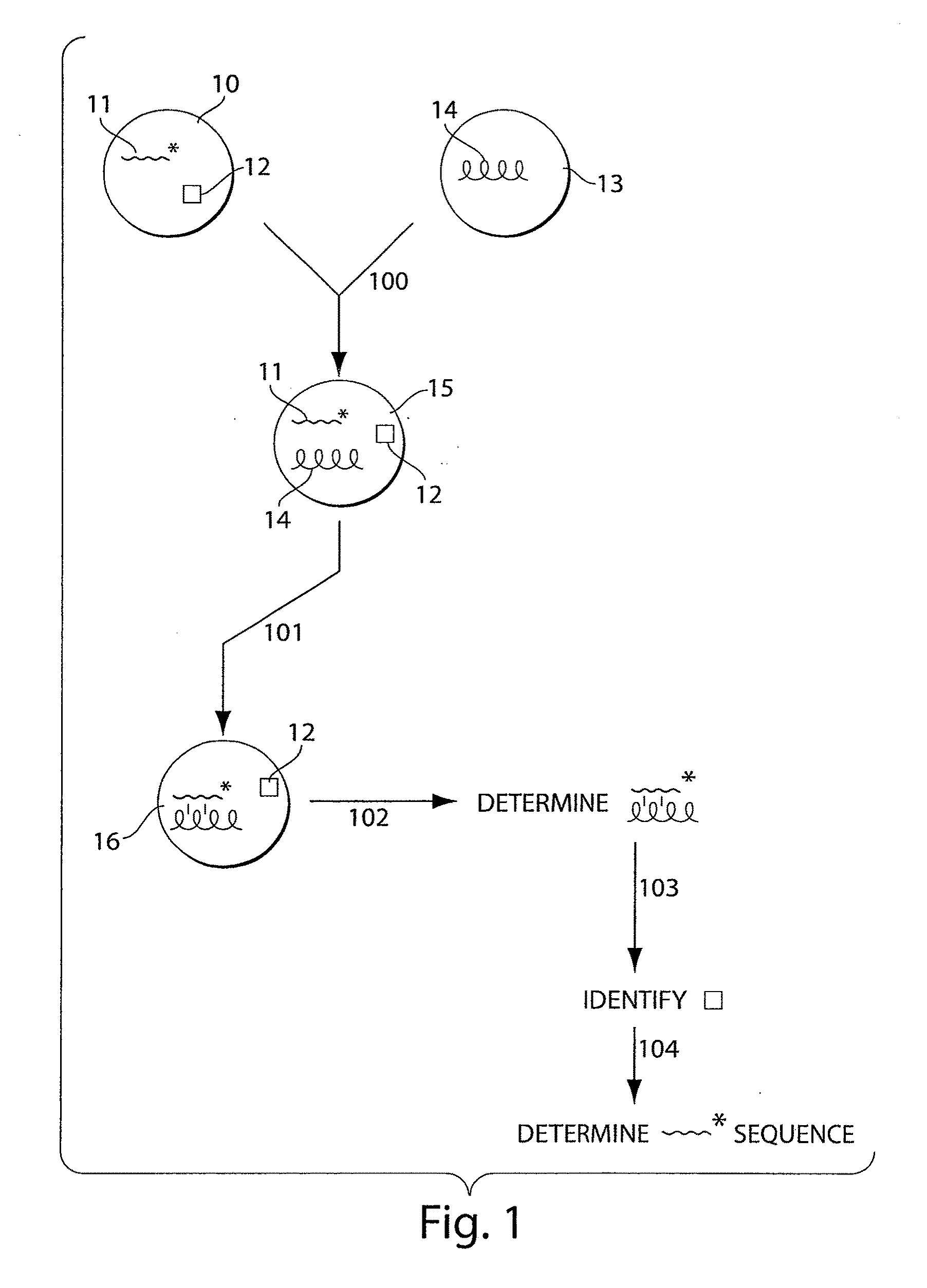
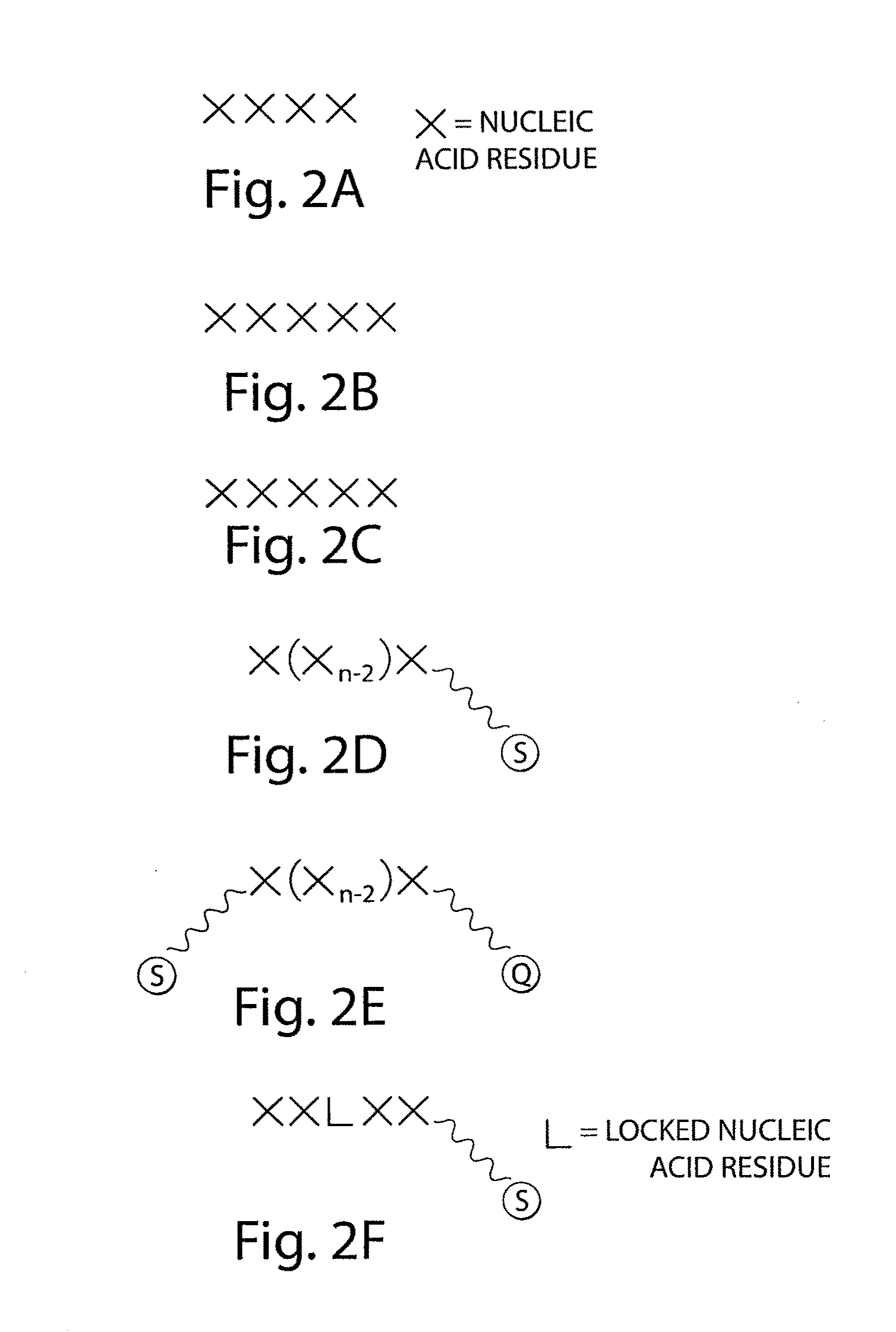
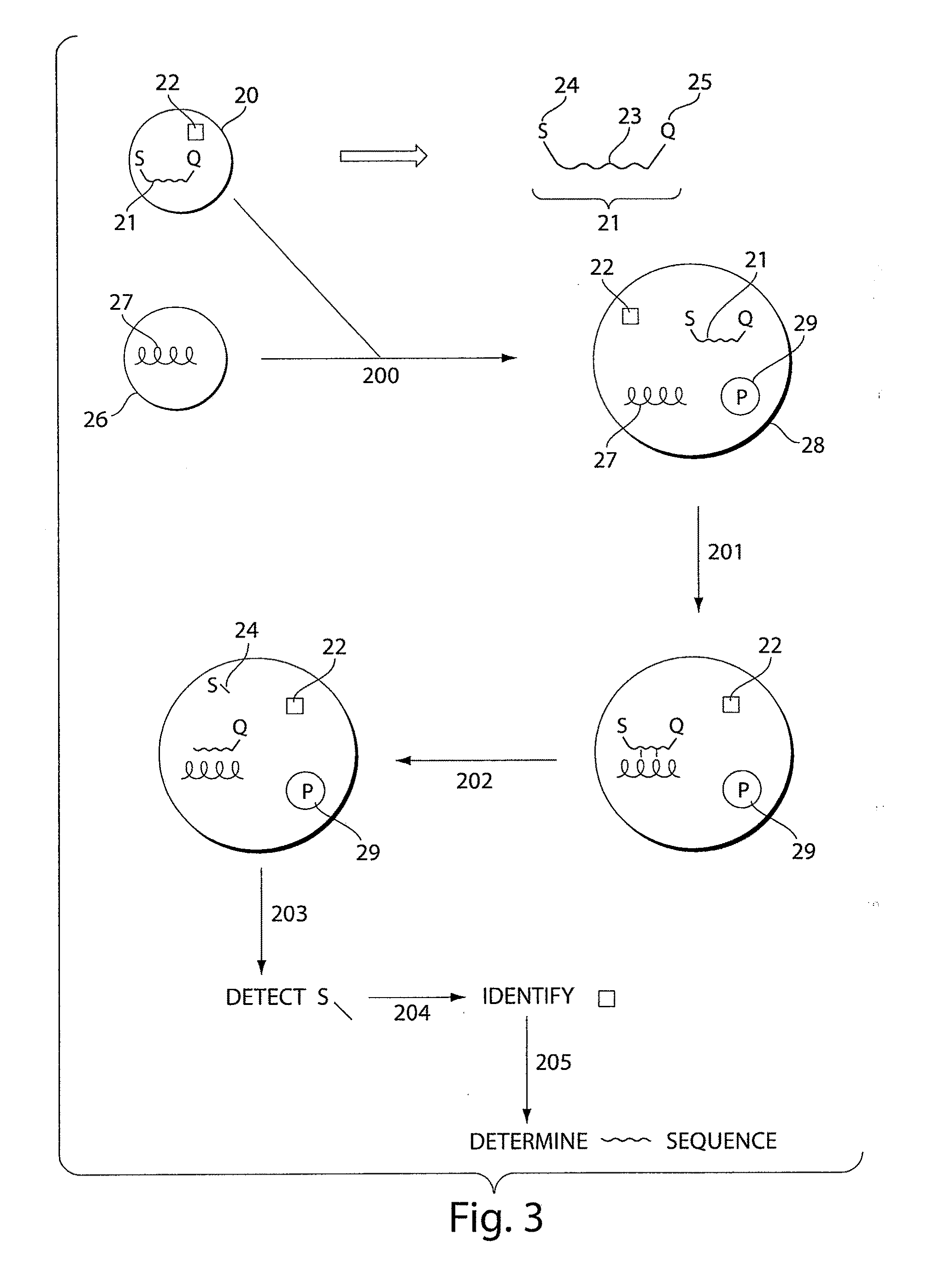
Systems and methods for nucleic acid sequencing
ActiveUS20110267457A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic Acid ProbesNucleic acid sequencing
The present invention relates to systems and methods for sequencing nucleic acids, including sequencing nucleic acids in fluidic droplets. In one set of embodiments, the method employs sequencing by hybridization using droplets such as microfluidic droplets. In some embodiments, droplets are formed which include a target nucleic acid, a nucleic acid probe, and at least one identification element, such as a fluorescent particle. The nucleic acid probes that hybridize to the target nucleic acid are determined, in some instances, by determining the at least one identification element. The nucleic acid probes that hybridize to the target nucleic acid may be used to determine the sequence of the target nucleic acid. In certain instances, the microfluidic droplets are provided with reagents that modify the nucleic acid probe. In some cases, a droplet, such as those described above, is deformed such that the components of the droplets individually pass a target area.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Encapsulation of discrete quanta of fluorescent particles
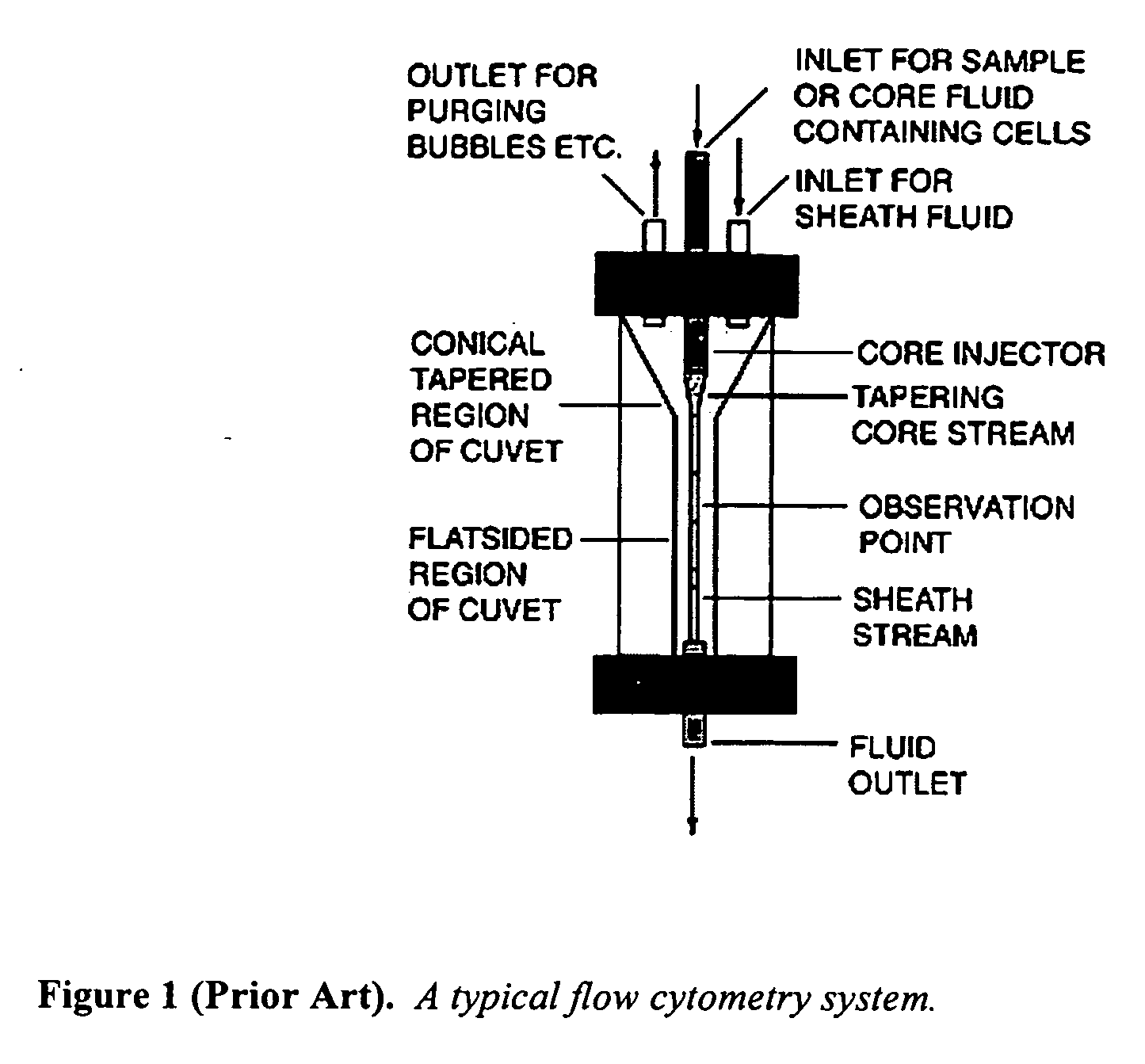
InactiveUS20030132538A1Individual particle analysisGlass/slag layered productsGenetics manipulationFlow cytometry
The present invention provides novel encapsulation compositions and methods. In particular, the invention relates to fluorescent capsule compositions, which consists of a layer of a polymer shell enclosing one or more fluorescent materials such as fluorescent microspheres and which are capable of emitting at least two distinct fluorescent signals. Also provided are methods for their preparation. The compositions and methods of this invention are useful in a variety of applications, including preparation of multiplexed arrays for industrial, chemical, immunological, and genetic manipulation and analysis especially as related but not limited to flow cytometry.
Owner:LUMINEX
Light emitting diode, optical semiconductor device, epoxy resin composition suited for optical semiconductor device, and method for manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20050224821A1Light emission characteristicSuppress the variation in the chromaticity of the light emittedDischarge tube luminescnet screensLamp detailsEpoxyLength wave
A light emitting diode comprising an LED chip having a light emitting layer made of a nitride compound semiconductor and a light transmitting resin that includes a fluorescent material which absorbs at least a part of light emitted by the LED chip and emits light of a different wavelength, wherein the fluorescent material includes a fluorescent particles of small particle size and a fluorescent particles of large particle size, the fluorescent particles of large particle size being distributed in the vicinity of the LED chip in the light transmitting resin to form a wavelength converting layer, the fluorescent particles of small particle size being distributed on the outside of the wavelength converting layer in the light transmitting resin.
Owner:NICHIA CORP
Methods and devices for characterizing particles in clear and turbid media
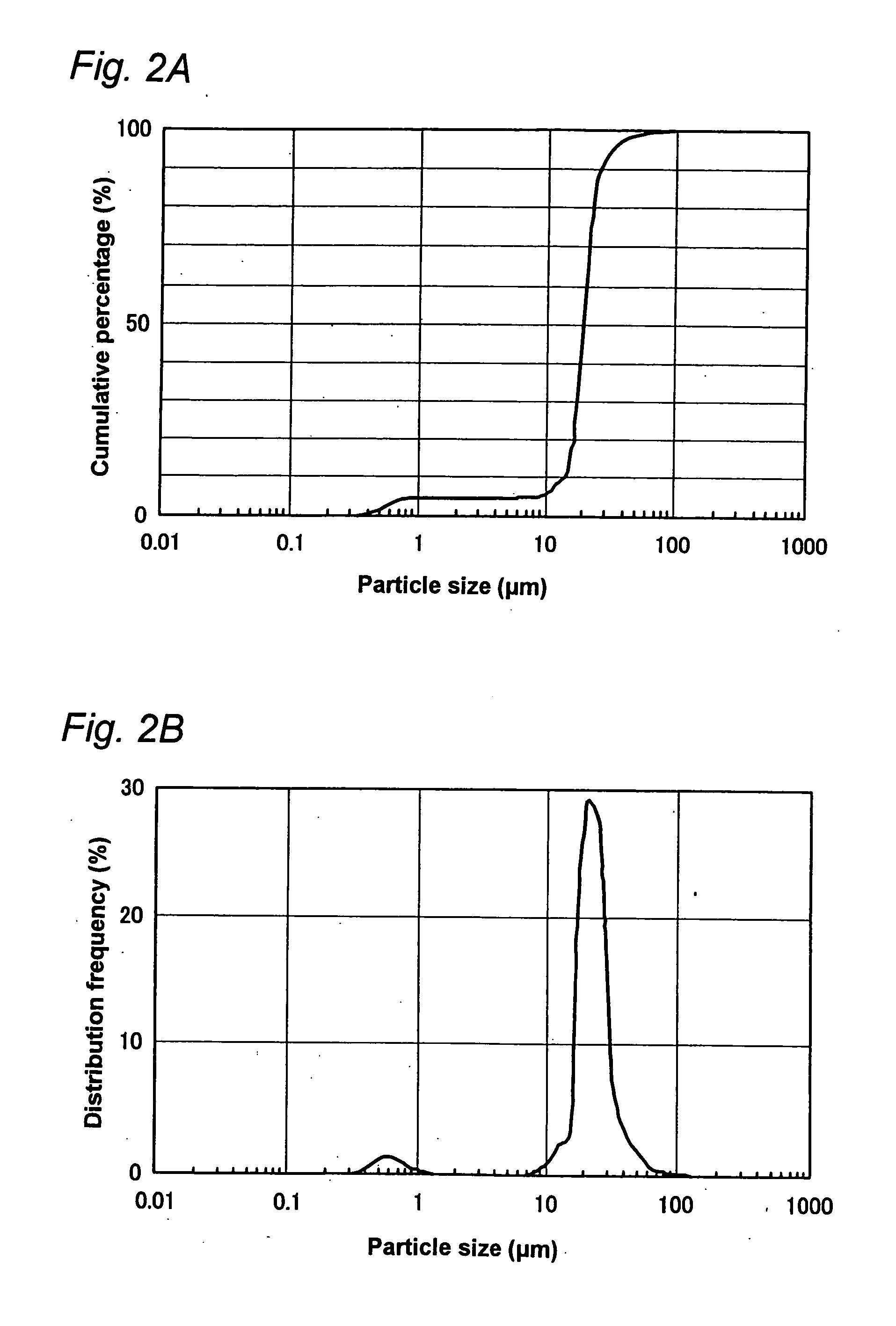
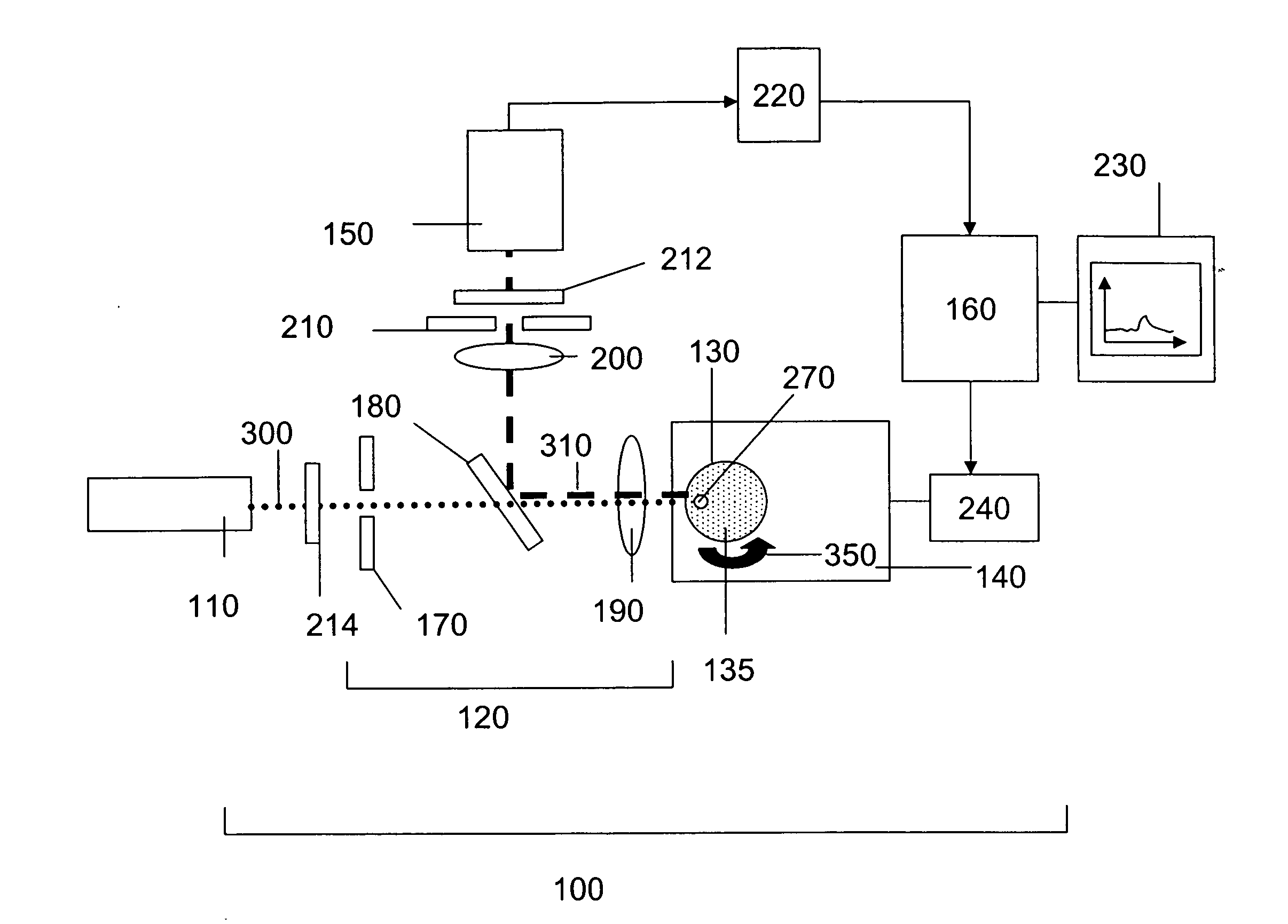
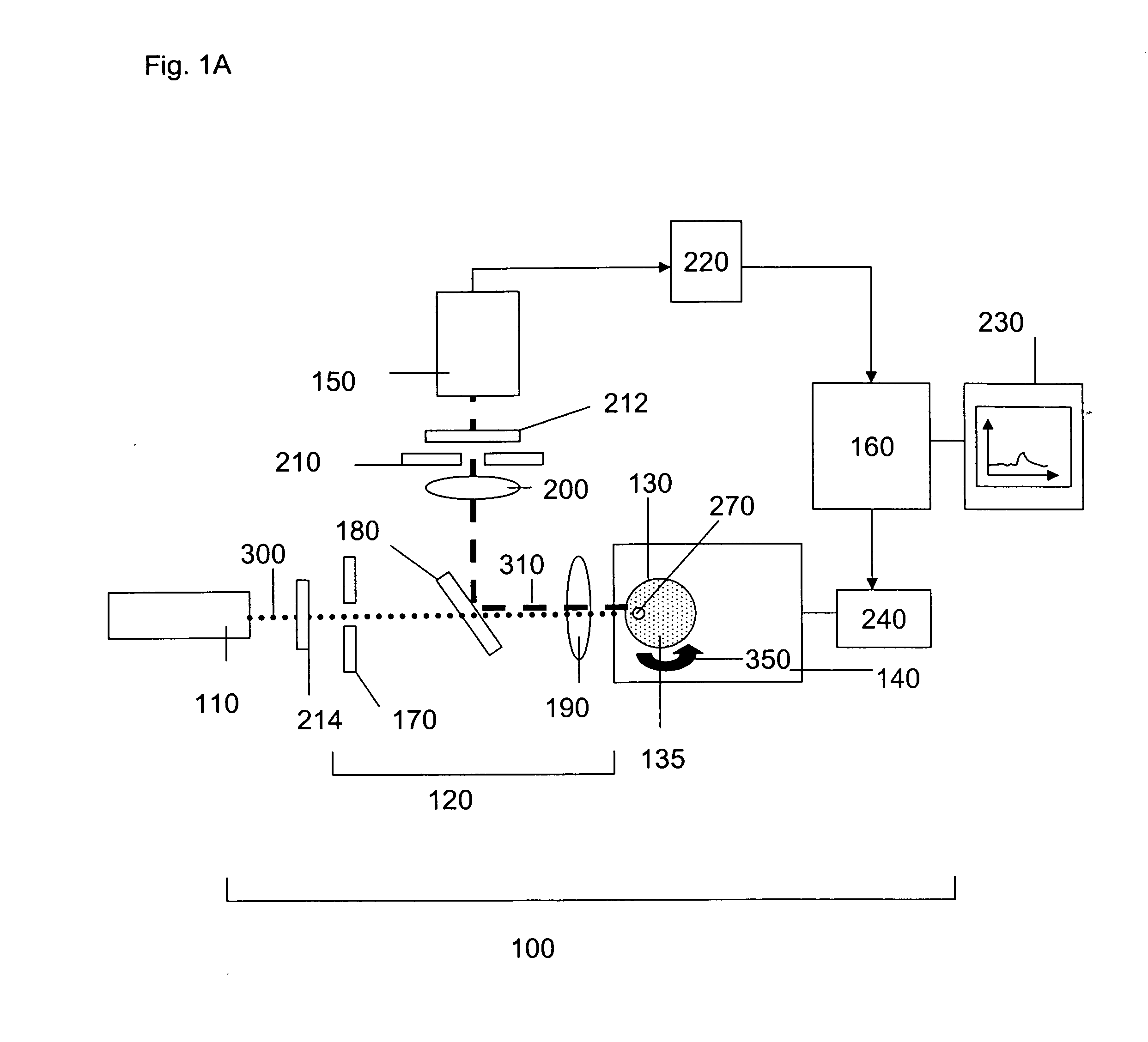
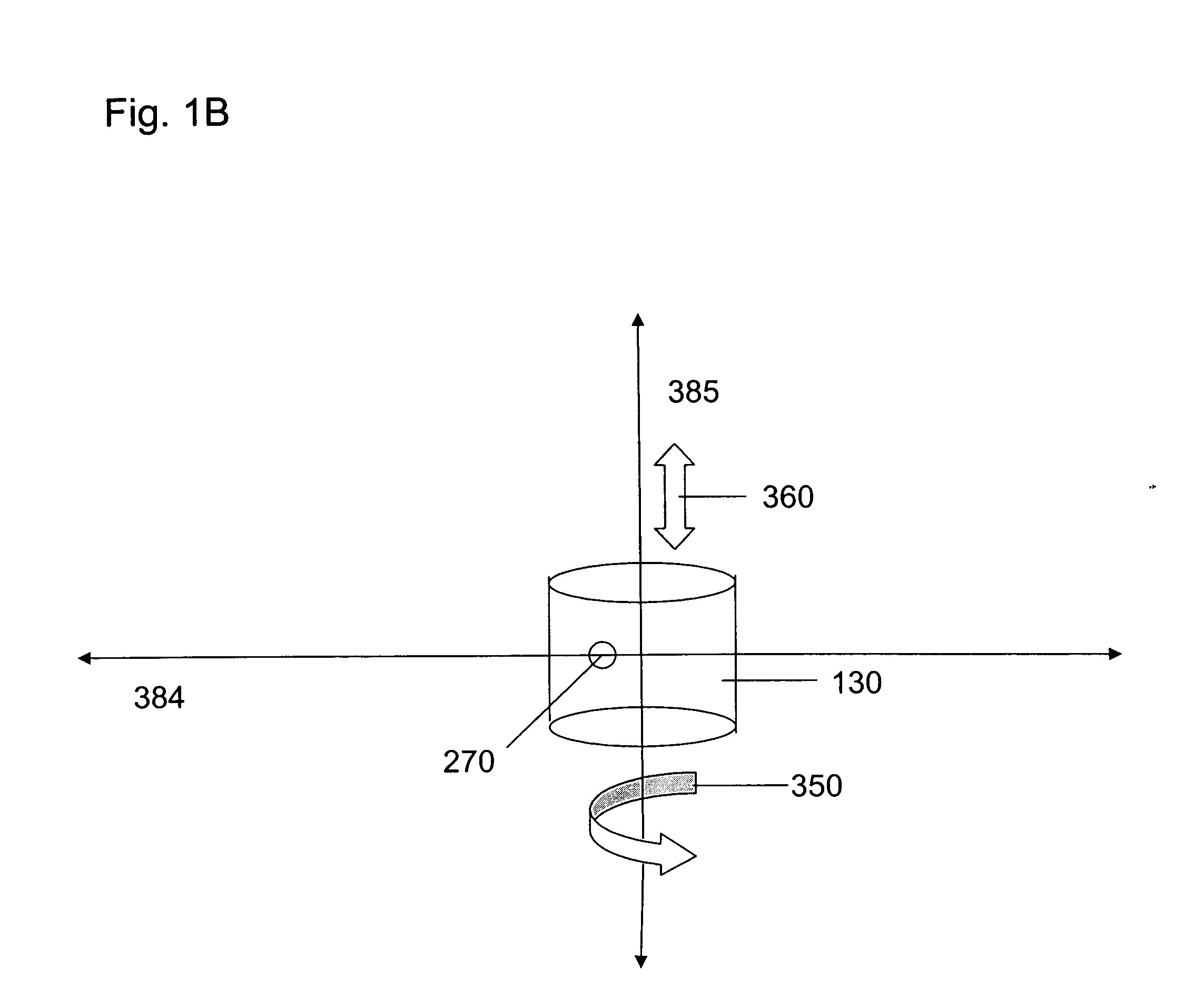
ActiveUS20060256338A1Accurate classificationImprove portabilityColor/spectral properties measurementsFluorescence/phosphorescenceDiffusionAnalytical technique
The invention provides methods and devices for detecting, identifying, classifying and characterizing particles in a fluid sample. Optical analyzers are provided having a rotating and / or translating sample container for measuring the concentrations of fluorescent particles present in very low concentrations and for characterizing fluorescent particles on the basis of size, shape, diffusion constant and / or composition. Scanning optical analyzers are provided using pattern recognitions data analysis techniques and multichannel detection.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
In situ micromachined mixer for microfluidic analytical systems
The present invention relates to an in situ micromachined mixer for microfluidic analytical systems. In a preferred embodiment, a 100 pL mixer for liquids transported by electroosmotic flow (EOF) is described. Mixing was achieved in multiple intersecting channels with a bimodal width distribution and varying lengths. Five .mu.m width channels ran parallel to the direction of flow whereas larger 27 .mu.m width channels ran back and forth through the network at a 45.degree. angle. All channels were approximately 10 .mu.m deep. It was observed that little mixing of confluent streams occurred in the 100 .mu.m wide mixer inlet channel where mixing would be achieved almost exclusively by diffusion. In contrast, mixing was complete after passage through the channel network in the .apprxeq.200 .mu.m length mixer. Solvent composition was altered by varying the voltage on solvent reservoirs. The high efficiency attained in this mixer was attributed to the presence of a 2 pL vortex in the center of the mixer. Video tracking of fluorescent particles with a fluorescence microscope allowed the position and volume of this vortex to be determined.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
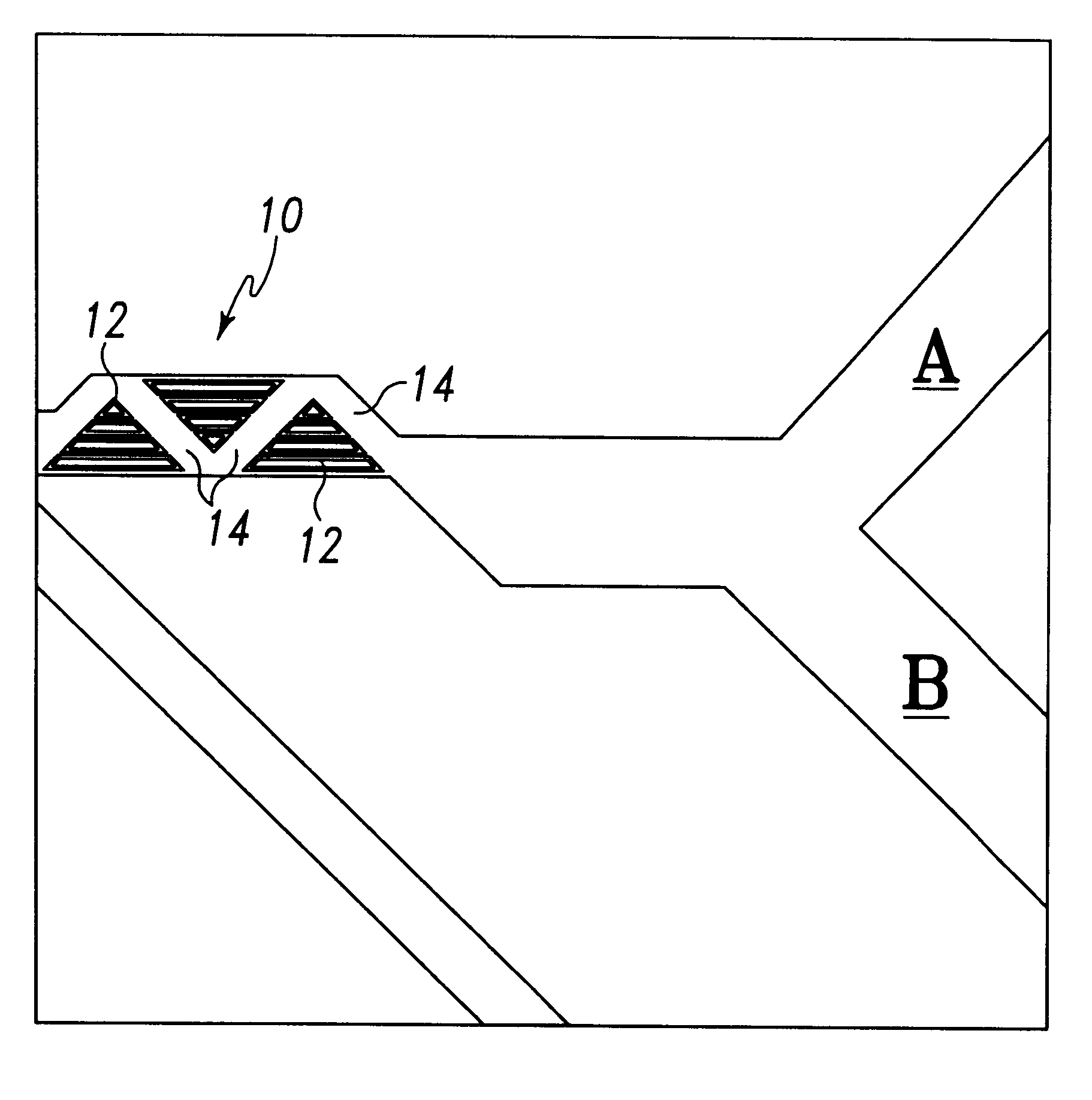
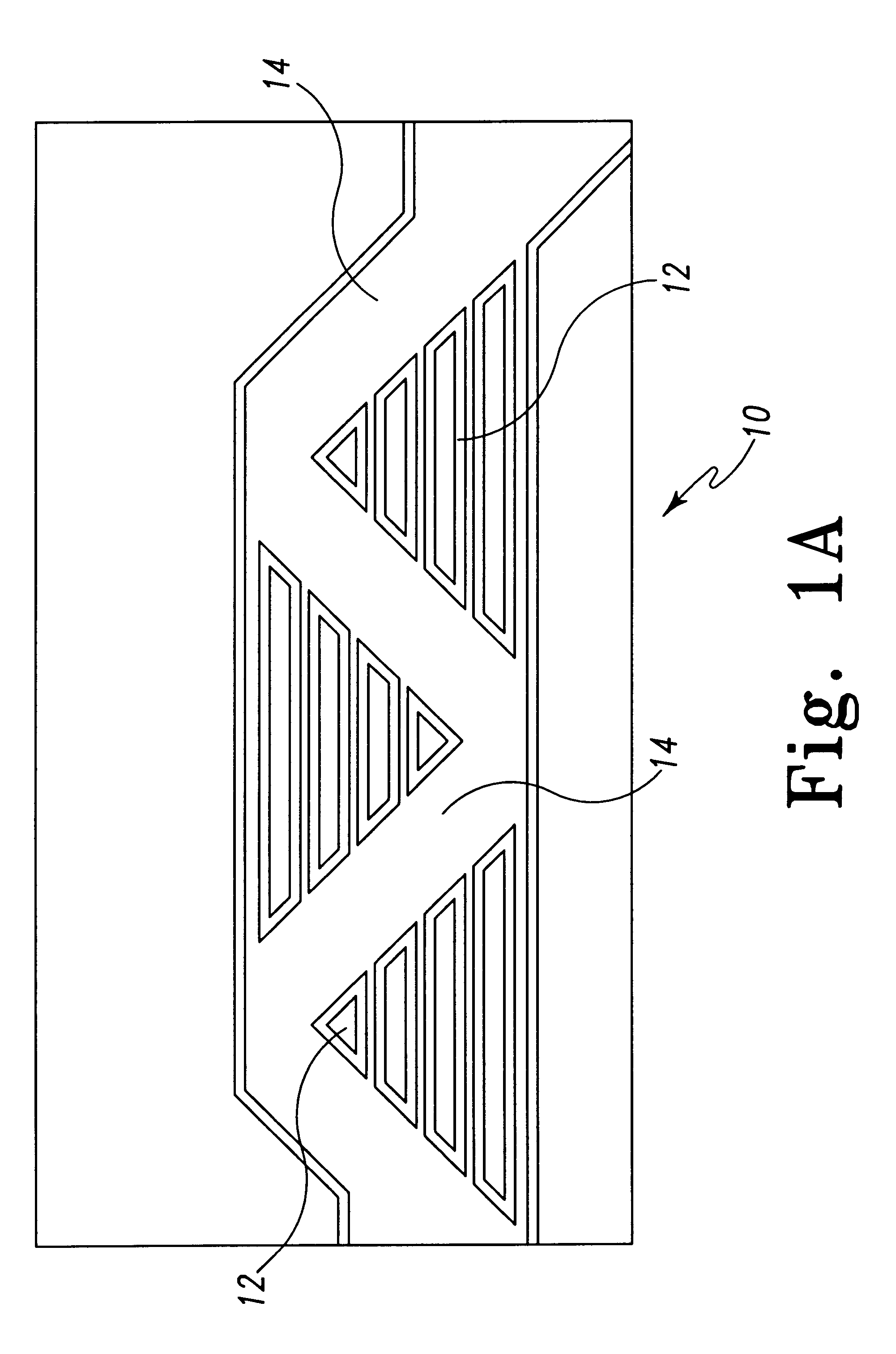
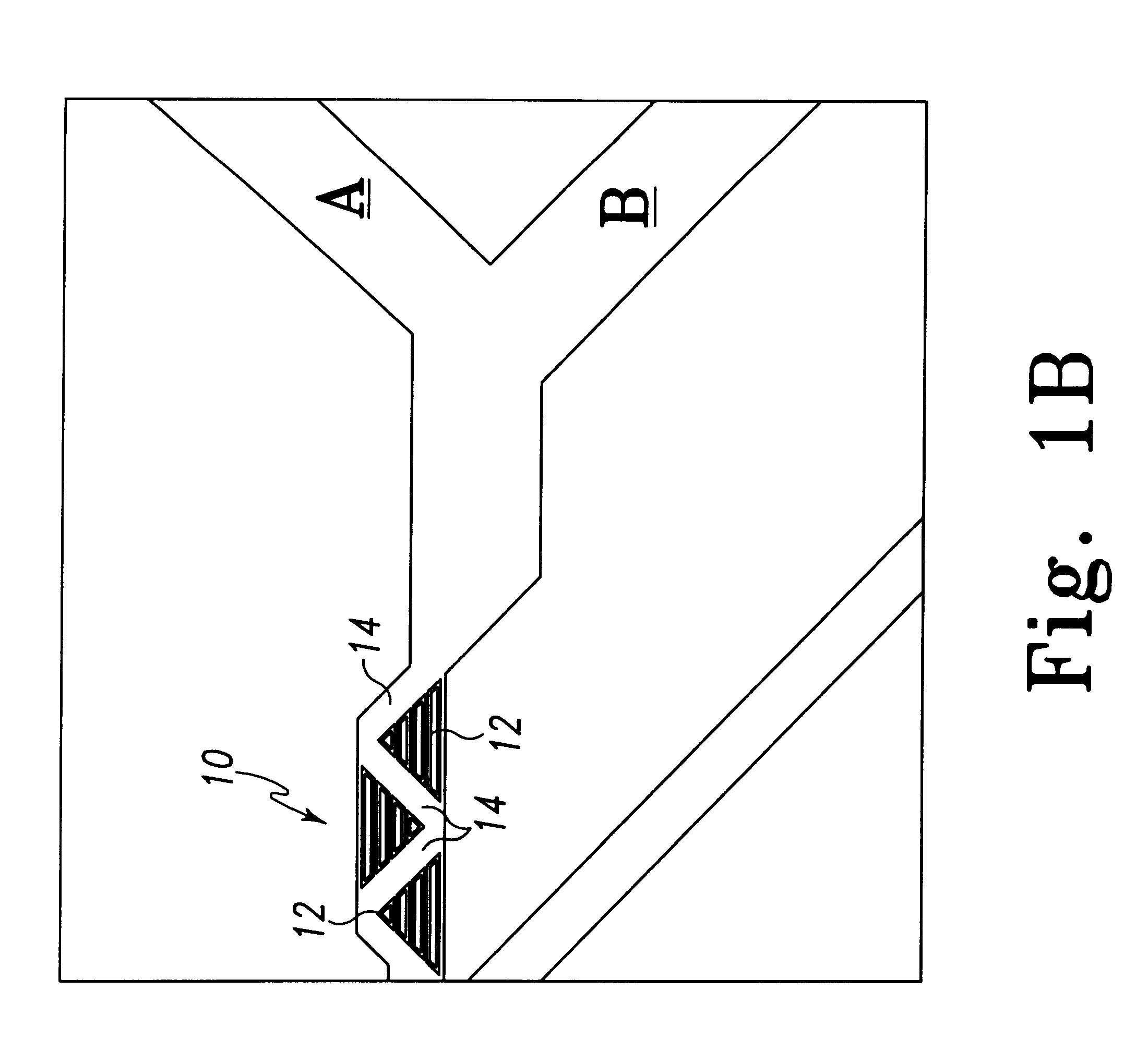
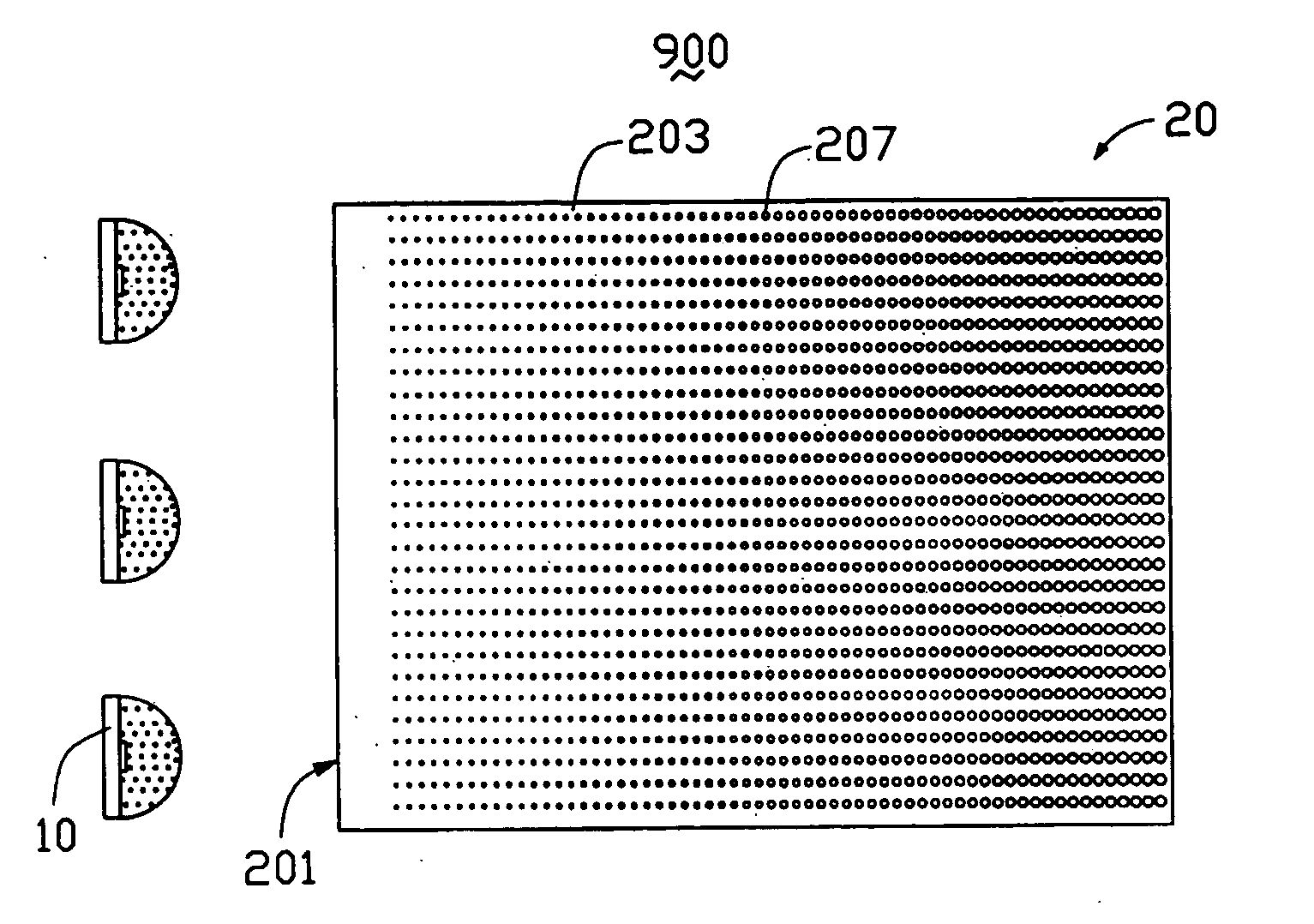
Light-emitting diode and backlight system using the same
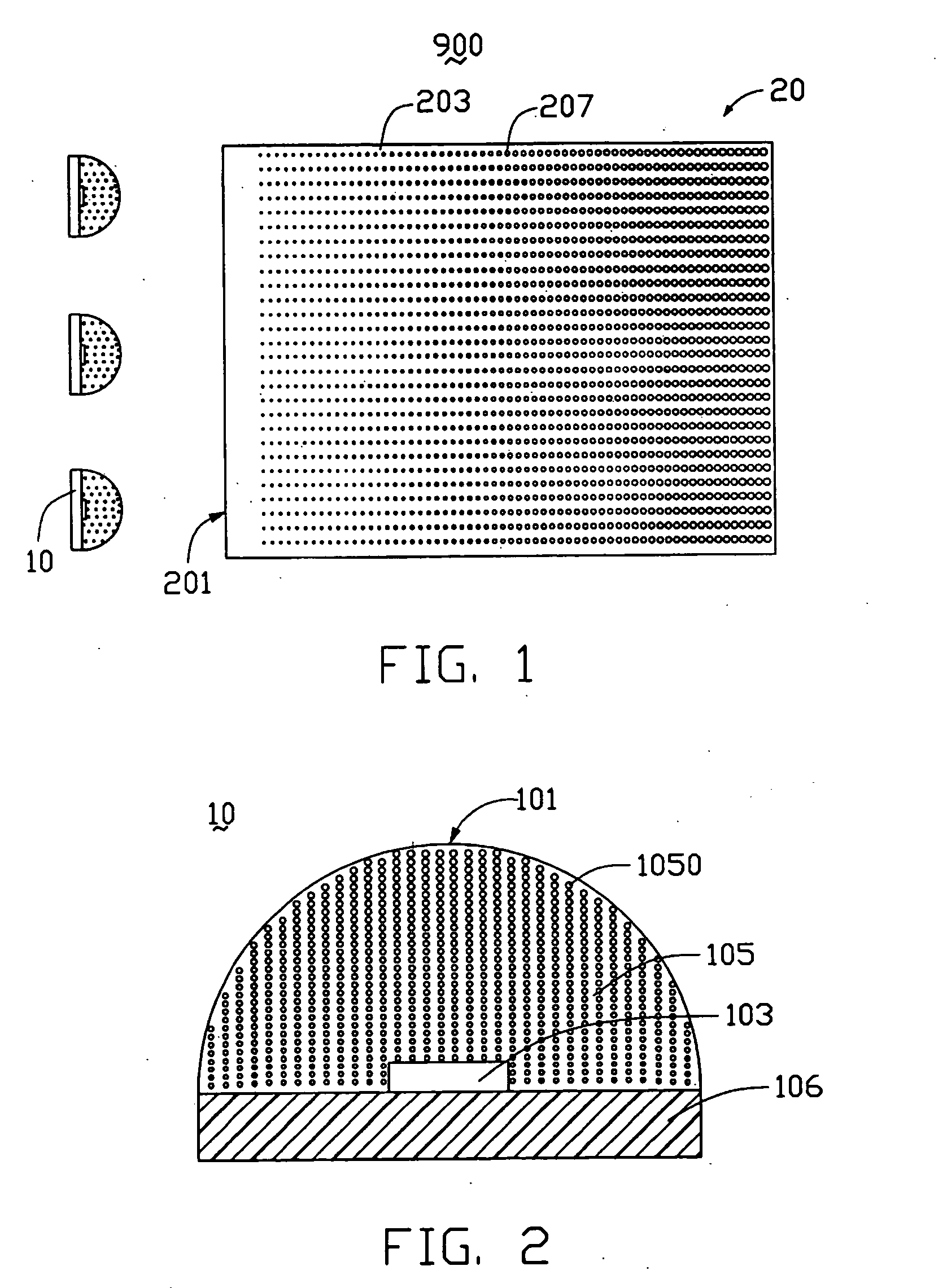
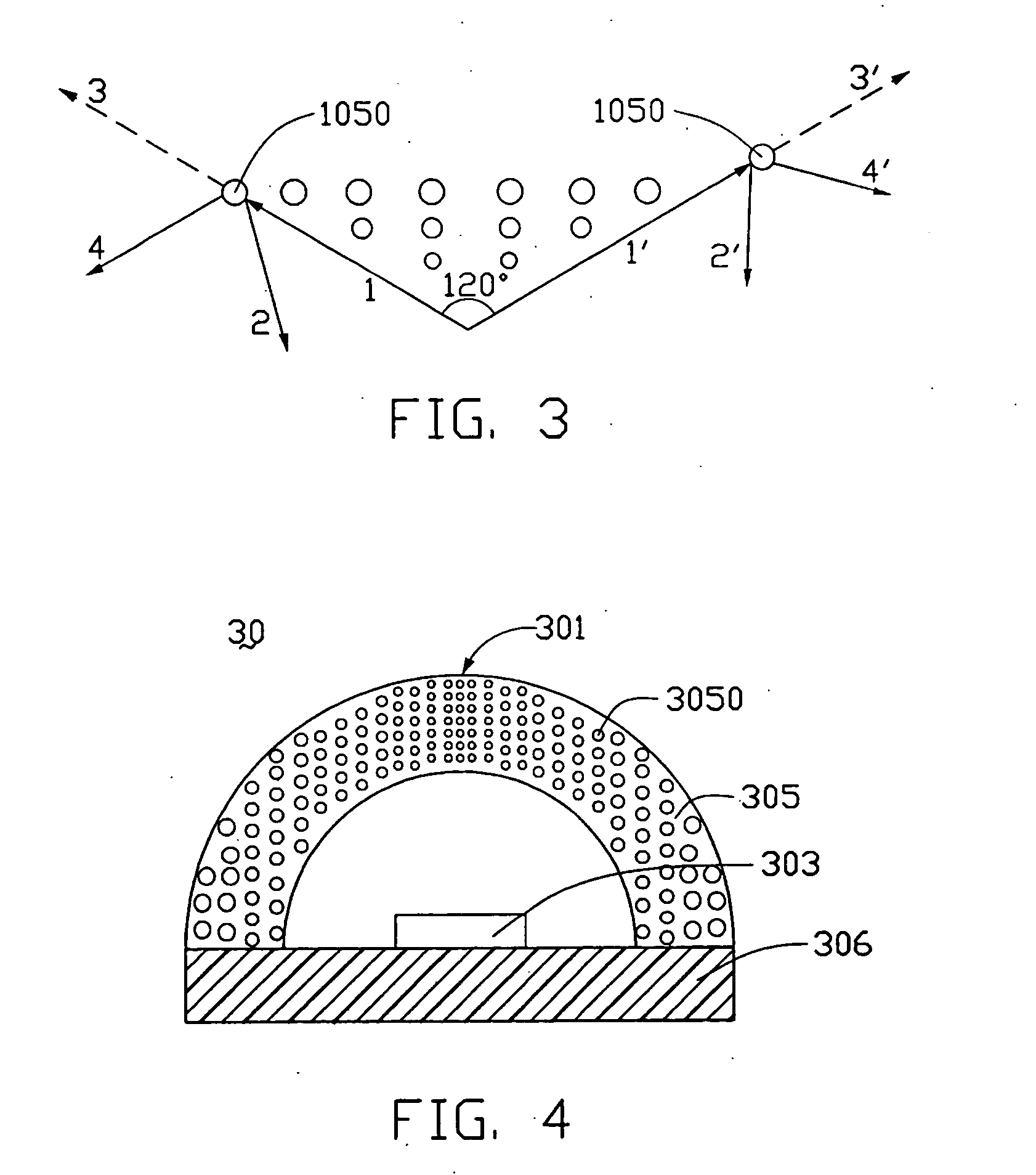
InactiveUS20050117320A1Uniform lightWider radiation angleMechanical apparatusDischarge tube luminescnet screensLight guideLight beam
A light-emitting diode (LED) (10) includes a chip body (103), an encapsulation can (105) surrounding the chip body, and a base (106) supporting the encapsulation can and the chip body thereon. Numerous fluorescent particles (1050) are provided in the encapsulation can. With the fluorescent particles, light beams from the chip body are diffused and attain wider irradiation angles. A backlight system (900) includes a light guide plate (20), and a number of the above-described LEDs disposed adjacent to the light guide plate. Light beams having wide irradiation angles are emitted from the LEDs and enter the light guide plate. This enables a light emitting surface of the light guide plate to have highly uniform brightness.
Owner:GOLD CHARM LTD
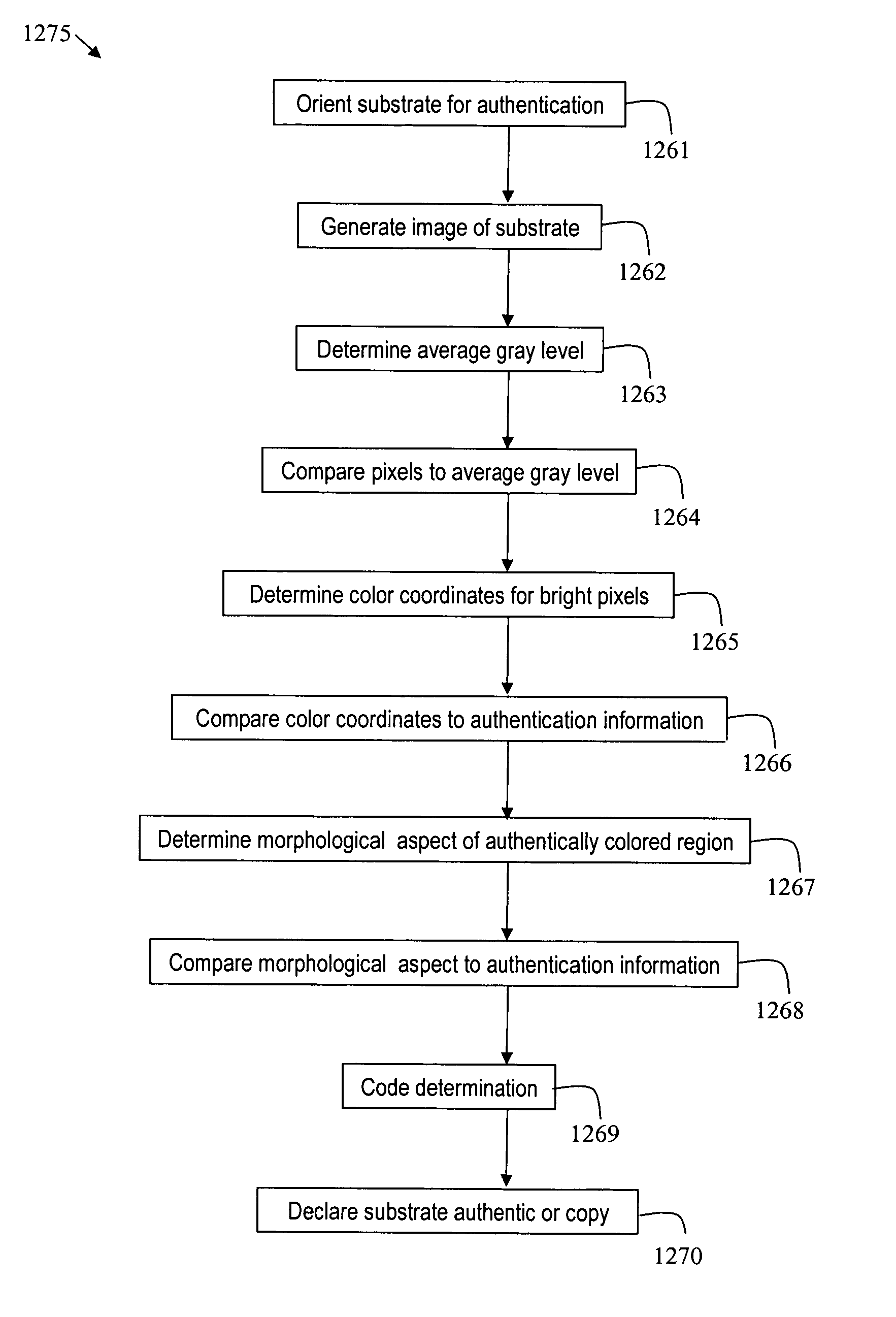
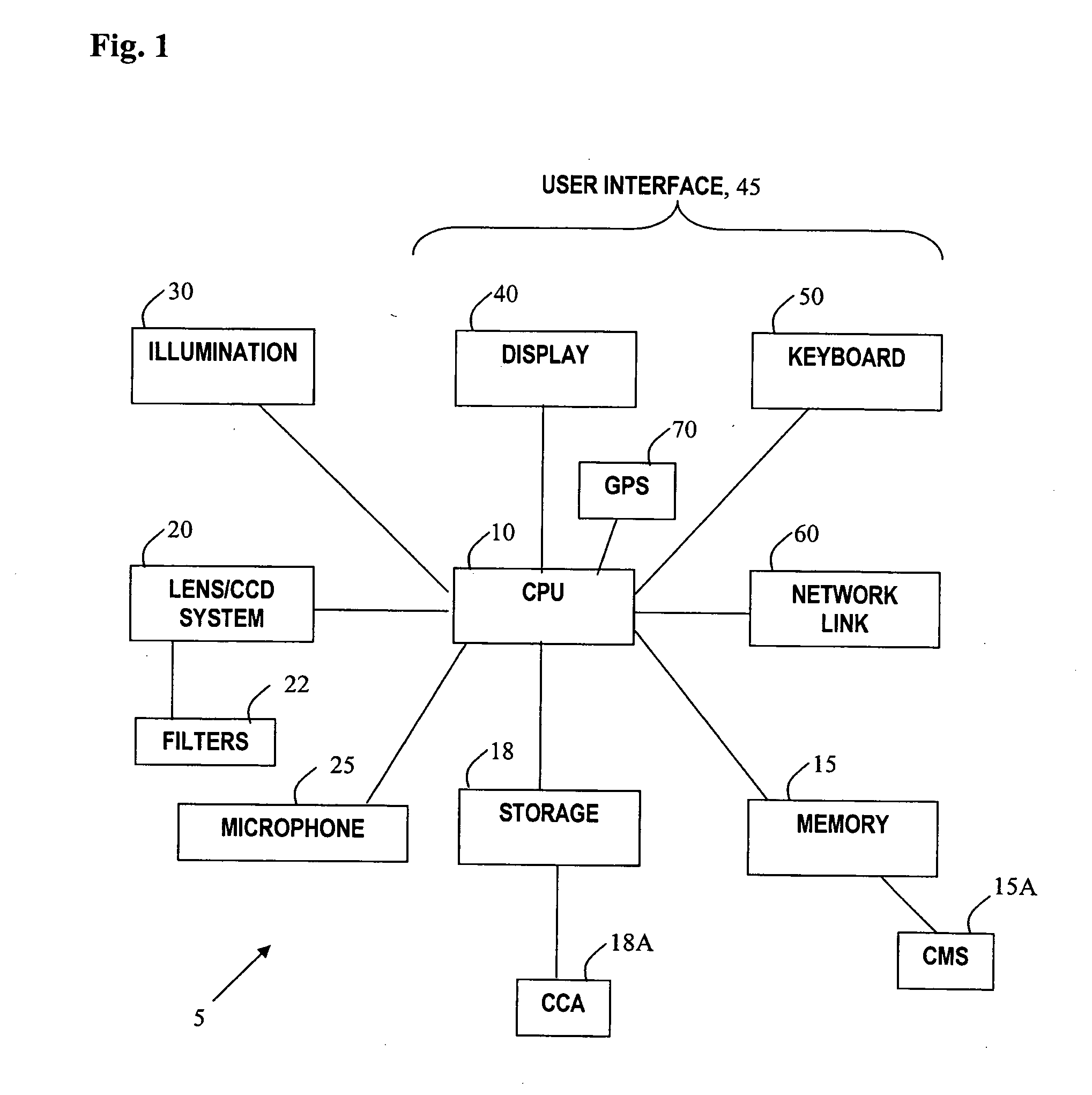
Method and apparatus for detecting fluorescent particles contained in a substrate
Disclosed herein are methods and apparatus for authentication of various substrates, including paper based substrates such as currency. Techniques are disclosed for use of security features to generate security codes. The security codes are deciphered with apparatus including a color recognition sub-system that provides for verification of authenticity of the substrate containing the security features.
Owner:SPECTRA SYST CORP
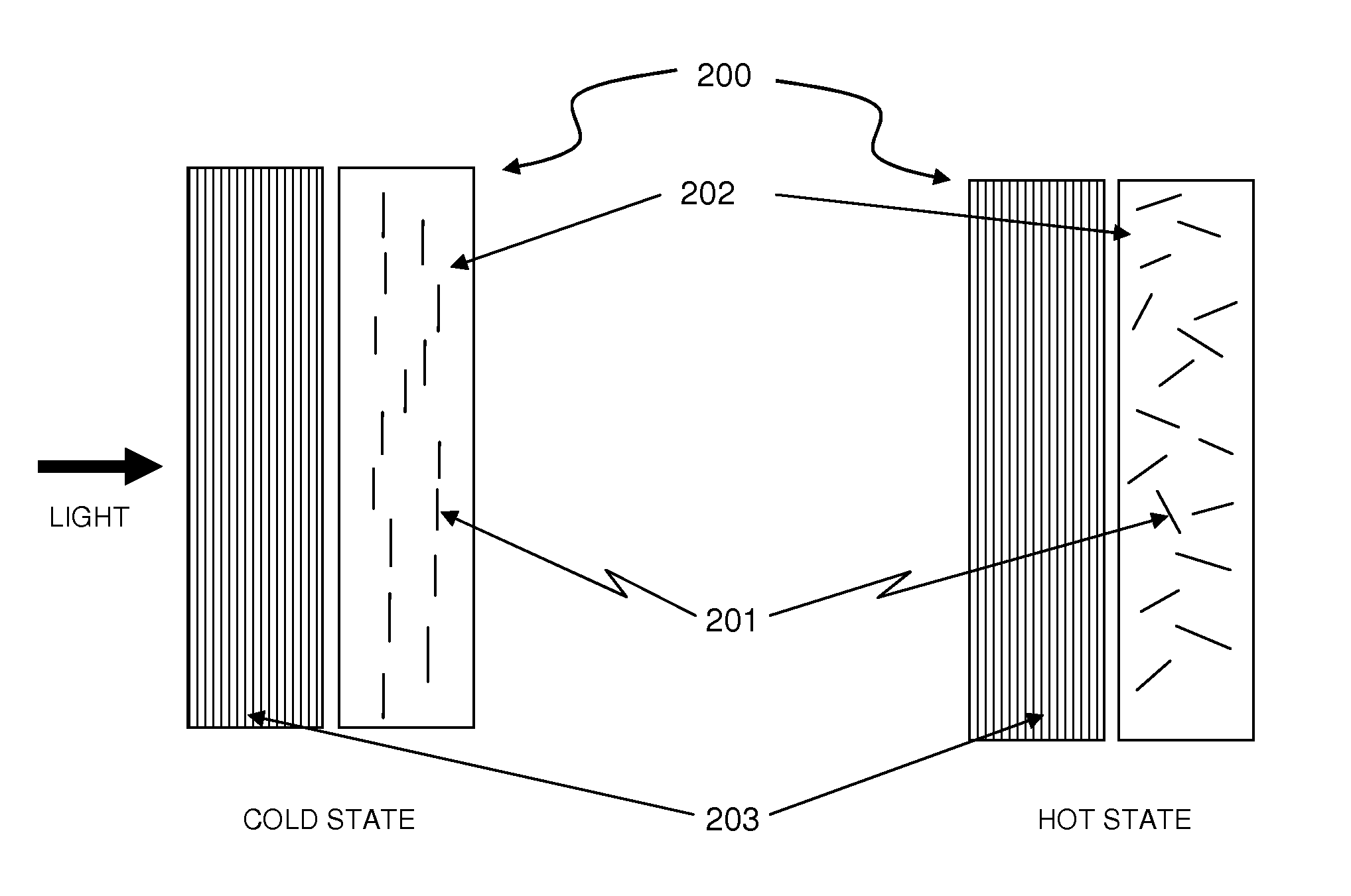
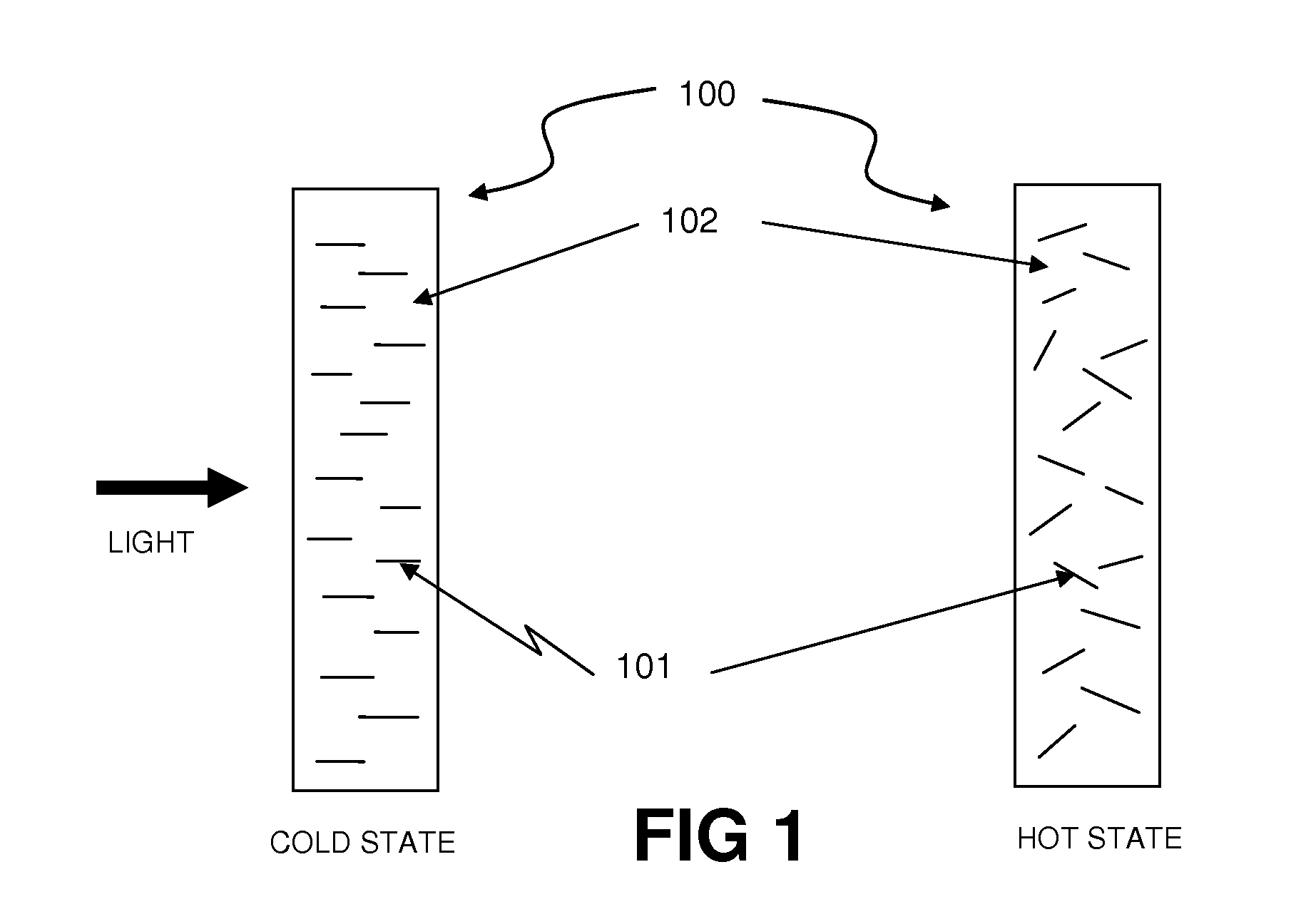
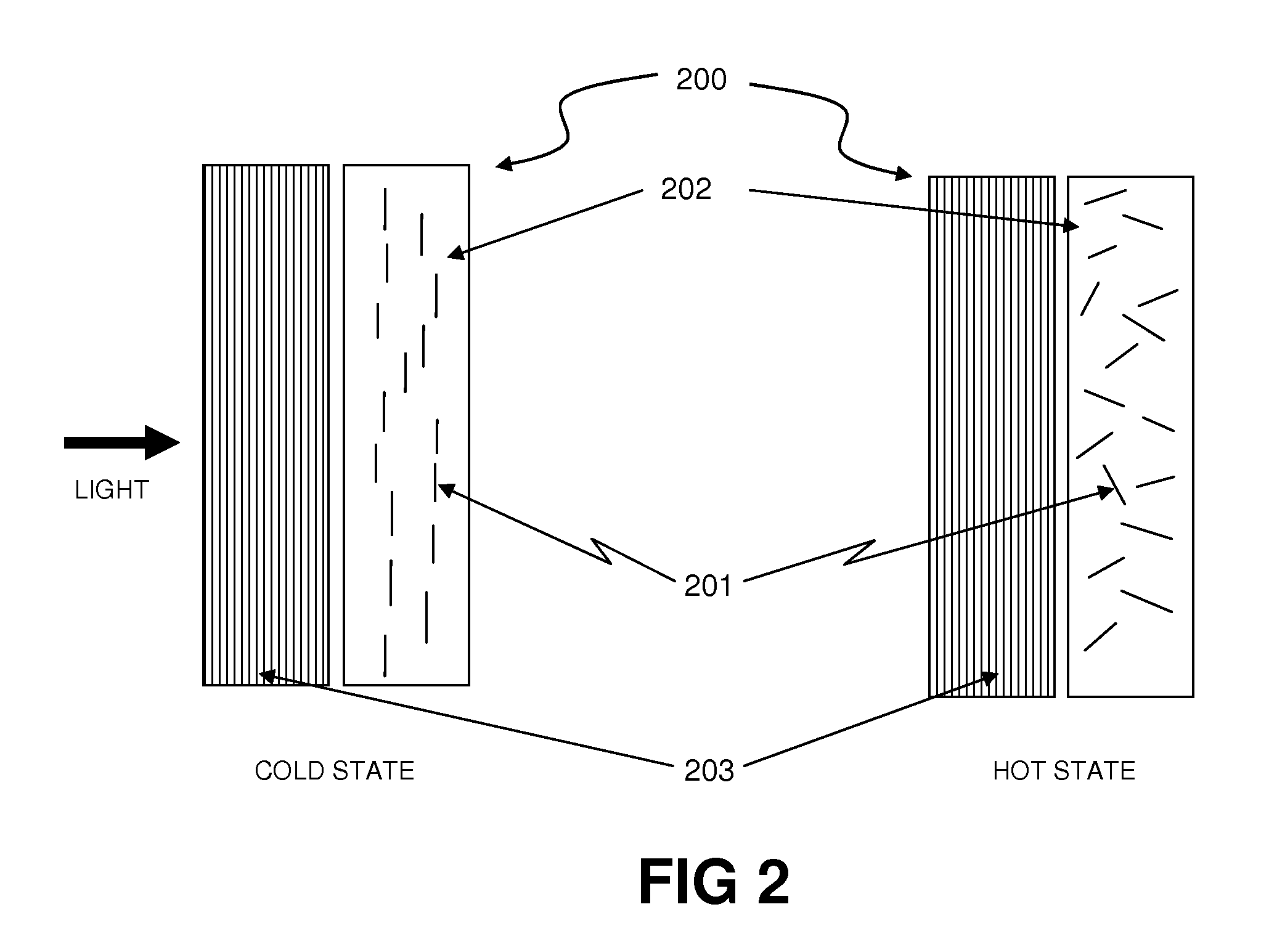
Thermally Switched Optical Filter Incorporating a Guest-Host Architecture
InactiveUS20100259698A1Avoid concentrationLess transmissiveLiquid crystal compositionsStatic indicating devicesLiquid crystallineSelective reflection
Thermochromic filters are constructed using absorptive, reflective, or fluorescent dyes, molecules, polymers, particles, rods, or other orientation-dependent colorants that have their orientation, order, or director influenced by carrier materials, which are themselves influenced by temperature. These order-influencing carrier materials include thermotropic liquid crystals, which provide orientation to dyes and polymers in a Guest-Host system in the liquid-crystalline state at lower temperatures, but do not provide such order in the isotropic state at higher temperatures. The varying degree to which the absorptive, reflective, or fluorescent particles interact with light in the two states can be exploited to make many varieties of thermochromic filters. Thermochromic filters can control the flow of light and radiant heat through selective reflection, transmission, absorption, and / or re-emission. The filters have particular application in passive or active light-regulating and temperature-regulating films, materials, and devices, and particularly as construction materials and building and vehicle surfaces.
Owner:RAVENBRICK
Microparticles with multiple fluorescent signals and methods of using same
This invention provides a novel fluorescent particle including a core or carrier particle having on its surface a plurality of smaller polymeric particles or nanoparticles, which are stained with different fluorescent dyes. When excited by a light source they are capable of giving off multiple fluorescent emissions simultaneously, which is useful for multiplexed analysis of a plurality of analytes in a sample. The coupled complex particles carrying on their surface fluorescent nanoparticles, methods of preparing such polymer particles, and various applications and methods of using such particles are claimed.
Owner:LUMINEX
Fluorescent complex, a fluorescent particle and a fluorescence detection method
The fluorescent complexes of the invention each comprise a magnetic nano-particle; an inorganic phosphor nano-particle; and a linker, wherein the magnetic nano-particles have an average particle diameter of 2 to 100 nm, the inorganic phosphor nano-particles have an average particle diameter of 1 to 50 nm, and the linker links the magnetic nano-particles with the inorganic phosphor nano-particles. The fluorescence detection method of the present invention comprises detecting a target substance in a sample by using the fluorescent complex of the present invention.
Owner:FUJIFILM HLDG CORP +1
Method and system for counting particles in a laminar flow with an imaging device
ActiveUS20070159627A1Reduce noiseDensity is accurateParticle size analysisCounting objects with random distributionComputational physicsParticle density
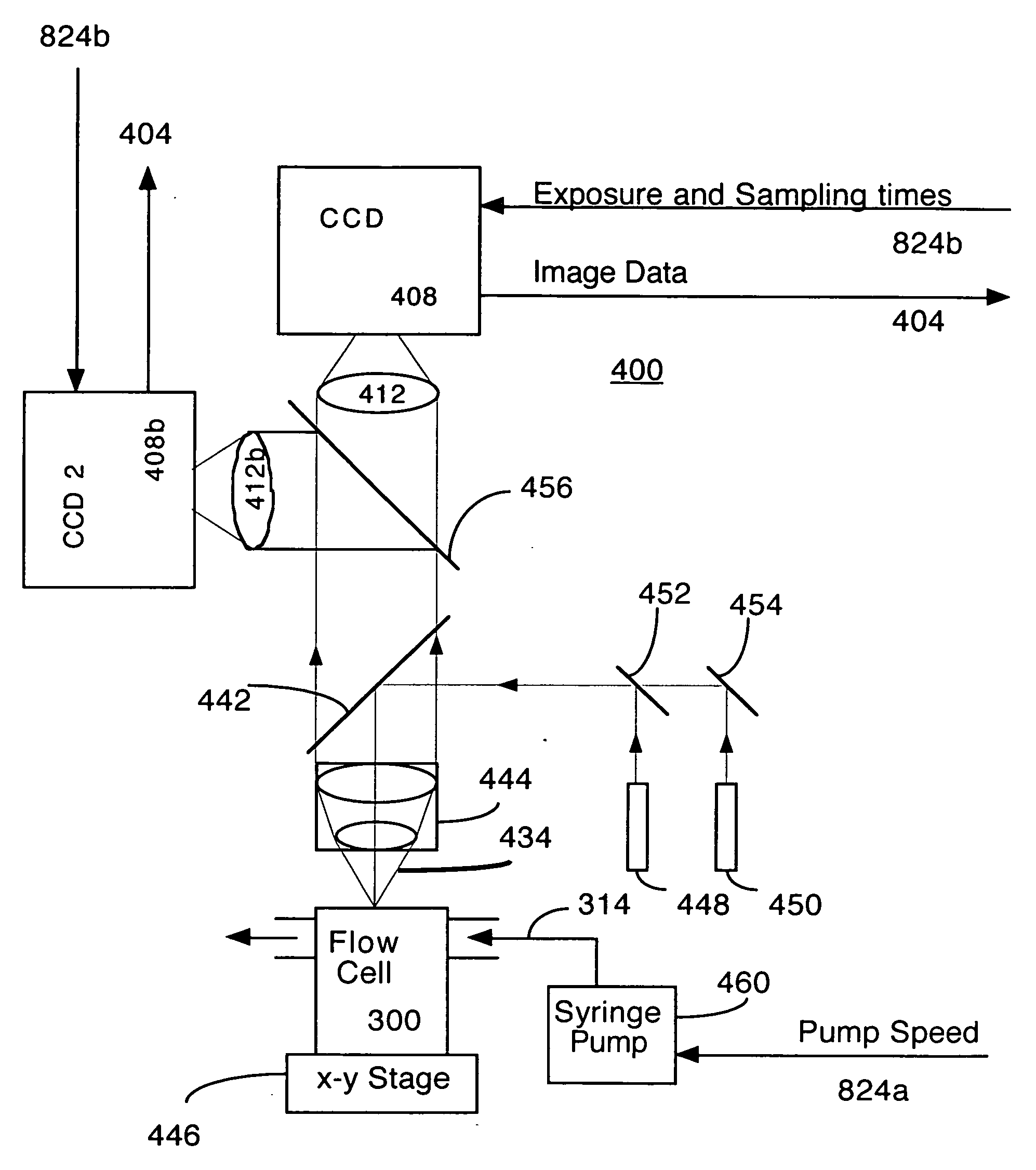
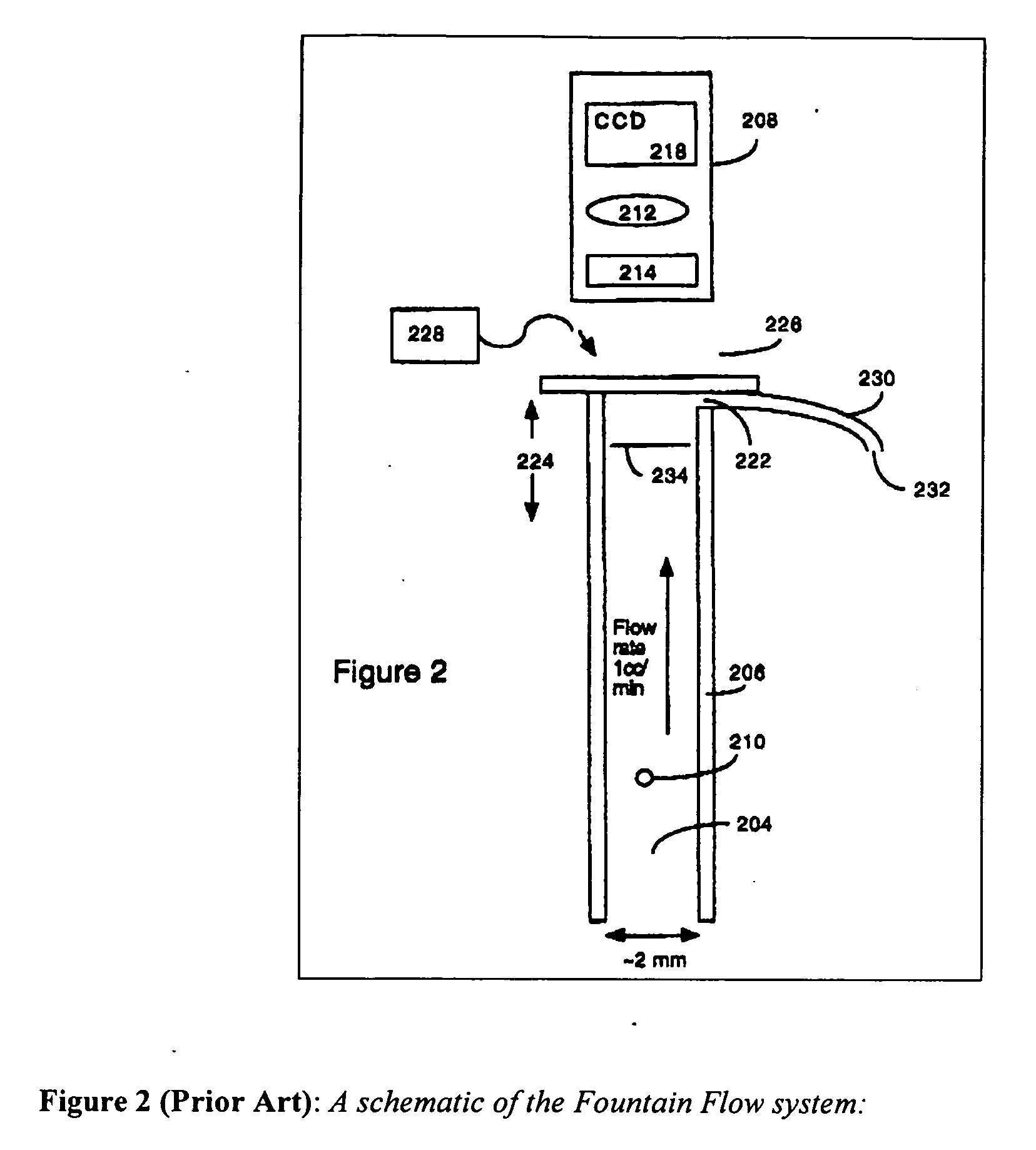
An invention is described which allows measurement of the concentration of fluorescent particles in a flowing (laminar) fluid by imaging the flow with a video camera. A beam of illumination is used to illuminate the target particles. Imaging optics are arranged to view the focal plane to form an image of the multiple fluorescent sample particles in the flow stream; a camera records the image formed by the imaging optics, and a counting algorithm enumerates the particles. Operational parameters of the system are adjusted according to an initial estimate of particle density, for example flow rate, exposure time, and sampling interval. In addition, the counting algorithm is selected according to the estimated particle density.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF WYOMING
Fluorescent quantum dot micro-nano encapsulated composite material structure
InactiveCN105086993AMaintain fluorescence efficiencyReduce reunionMaterial nanotechnologyNanoopticsMicro nanoQuantum dot
Owner:TIANJIN ZHONGHUAN QUANTUM TECH CO LTD
NaYF4-based fluorescent nano particles with double effects and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102391874AUniform and controllable scaleIn-vivo testing preparationsLuminescent compositionsChemical physicsMagnet resonance imaging
The invention relates to NaYF4-based fluorescent nano particles with double effects and a preparation method thereof. The NaYF4-based fluorescent nano particles at least comprise a kernel and a shell, wherein the kernel is NaYF4: Er / Yb / Gd or NaYF4: Er / Yb, and the shell is NaGdF4. By introducing different luminous ion pairs into different layers, the single-excitation multi-color luminescence function of the single fluorescent particles is realized, and the fluorescent particles have magnetic resonance imaging function; and meanwhile, by introducing a wrapping layer, surface defects of the particles are reduced, and the fluorescent strength of the particles is improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF CERAMIC CHEM & TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Water-Soluble Fluorescent Particle Comprising Entangled Fluorescent Polymer and Amphiphilic Molecule
Water-soluble fluorescent particles are formed in a simple process. A mixture comprising a solvent, water, a fluorescent polymer dissolved in the solvent, and an amphiphilic molecule is provided. The fluorescent polymer comprises a hydrophobic segment. The amphiphilic molecule comprises hydrophilic and hydrophobic segments. The solvent is removed from the mixture to allow the fluorescent polymer and the amphiphilic molecule to entangle in the presence of water, thus forming the water-soluble fluorescent particles. In the formed particles, the hydrophilic segments of the amphiphilic molecule are entangled with one another, and the hydrophobic segments of the fluorescent polymer and amphiphilic molecule are entangled with one another. The amphiphilic molecule encapsulates the fluorescent polymer and at least some of the hydrophilic segments are exposed to render the particle soluble in water.
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES
Light mixing module
A mixing light module includes a matrix, a fluorescent film, and a plurality of micro-structures. The matrix includes an incidence surface, an emission surface and a reflective surface. The fluorescent film disposed on or above the emission surface has an upper surface and a lower surface and includes a plurality of fluorescent particles.The matrix receives a first light having a first wavelength, and the reflective surface reflects the first light to make the first light to be emitted from the emission surface. Since the plurality of fluorescent particles receives a part of the first light from the emission surface, the plurality of fluorescent particles is excited to emit a second light having a second wavelength. The second light and the first light are mixed into a predetermined light. The plurality of micro-structures is used to make the first light or the second light uniform.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Preparation for silk with quantum dot nano-particles
A preparing method of fluorescent cocoon fibre assembled with quantum point nano particles, takes the quantum point nano particles as fluorescent particles, takes cocoon fibre as nuclear, adopts an electrostatic absorption method to connect one layer of organic high molecule on the cocoon fibre surface, and then adopts an electrostatic absorption method to connect one layer of quantum point nano particles on the organic high molecule surface, or alternately repeats steps for multitime, and then uses an electrostatic absorption method to connect one layer of organic high molecule on the quantum point nano particles surface, so as to compose a fluorescent cocoon fibre coated by quantum point nano particles once or many times, wherein, the quantum point nano particles surface is coated by organic small molecule and / or organic high molecule. The invention has advantages that the inventive fluorescent cocoon fibre assembled with quantum point nano particle, not only has large superiority in optical aspects such as fluorescent stability, fluorescent strength and fluorescent color kinds, but also can produce in large under low cost conditions with better product character repetitiveness.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Optical sheet and backlight unit having the optical sheet
ActiveUS20150301257A1Increase heatConvenient lightingMechanical apparatusDiffusing elementsOptoelectronicsFluorescent particle
Owner:LMS
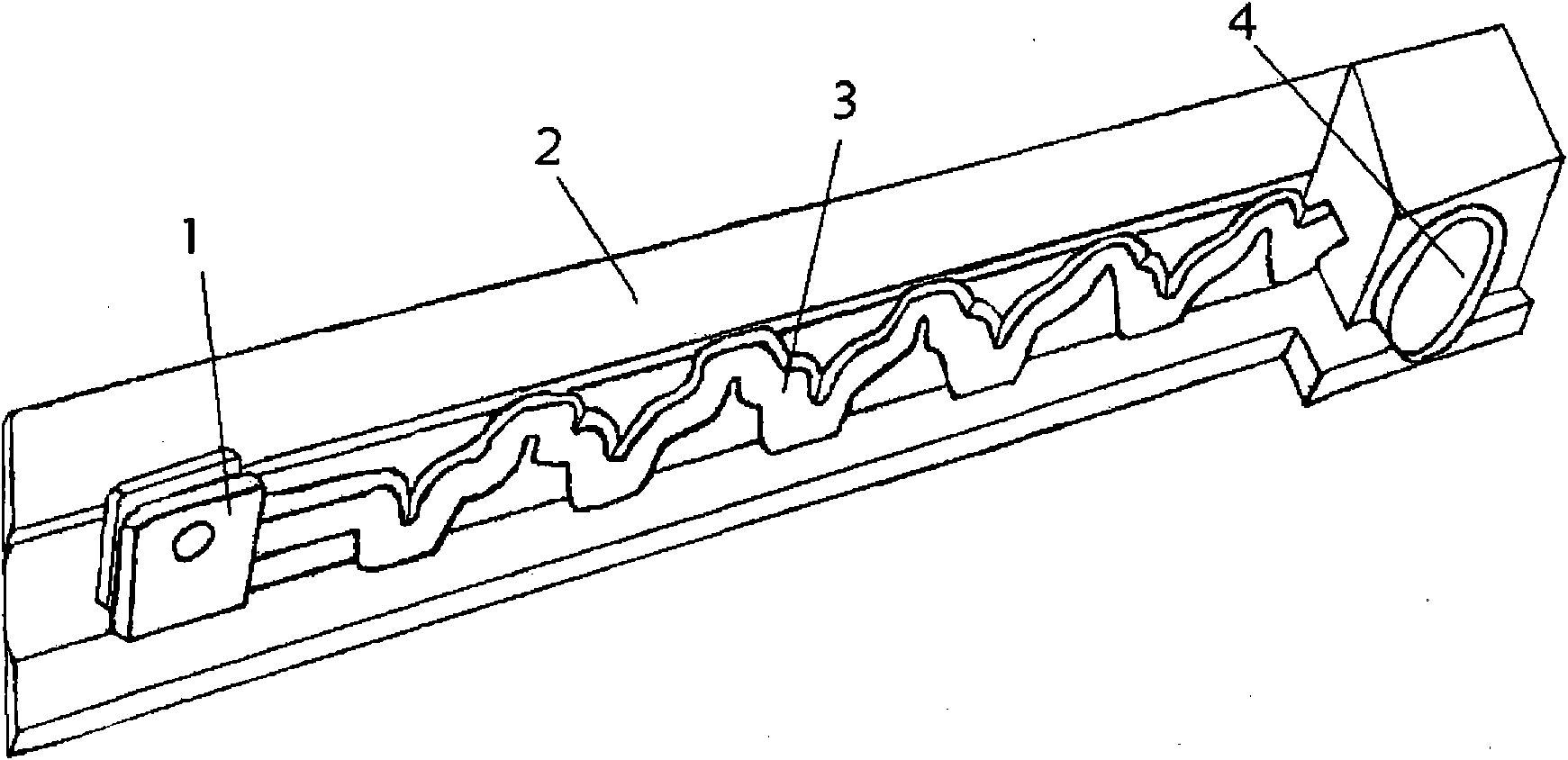
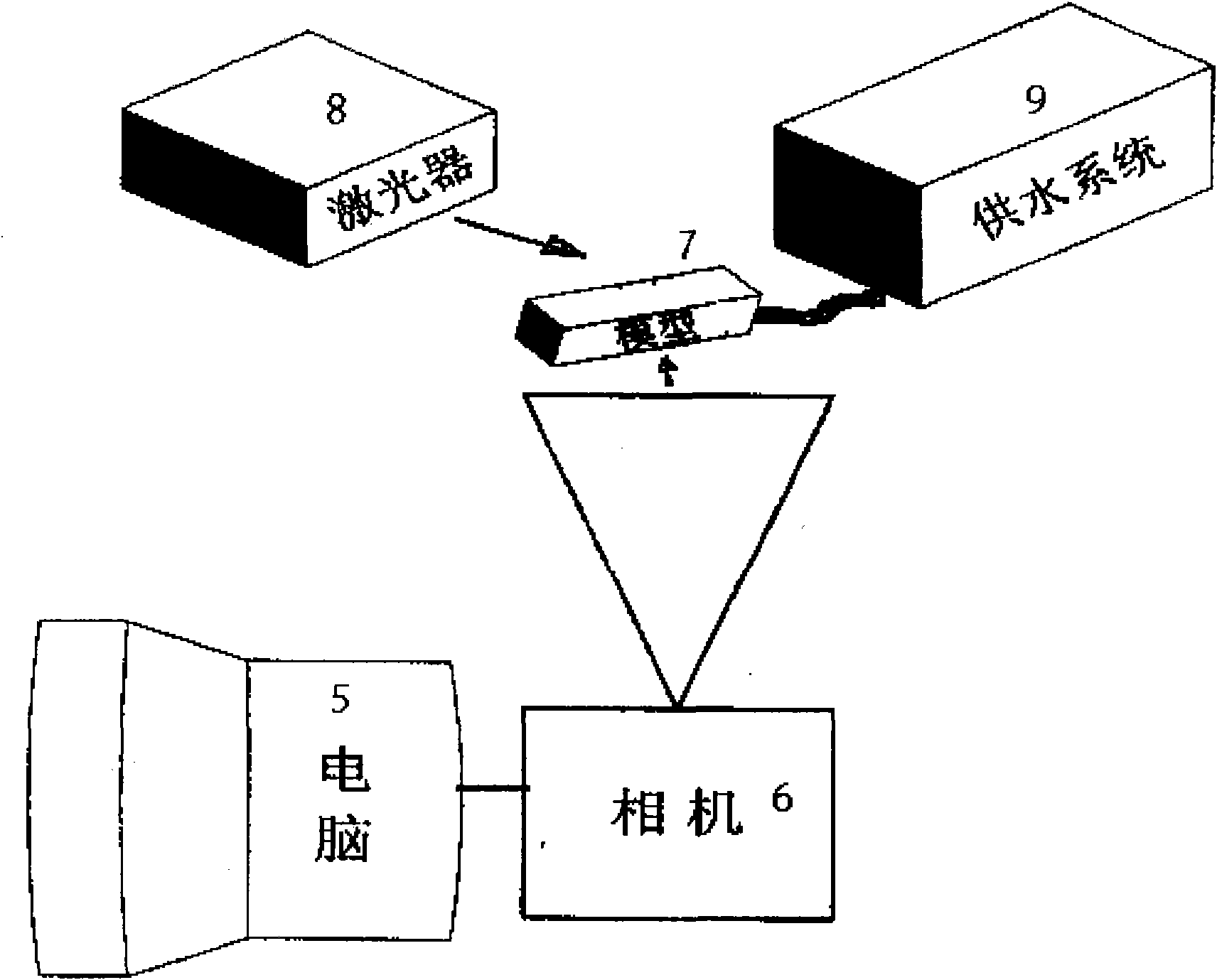
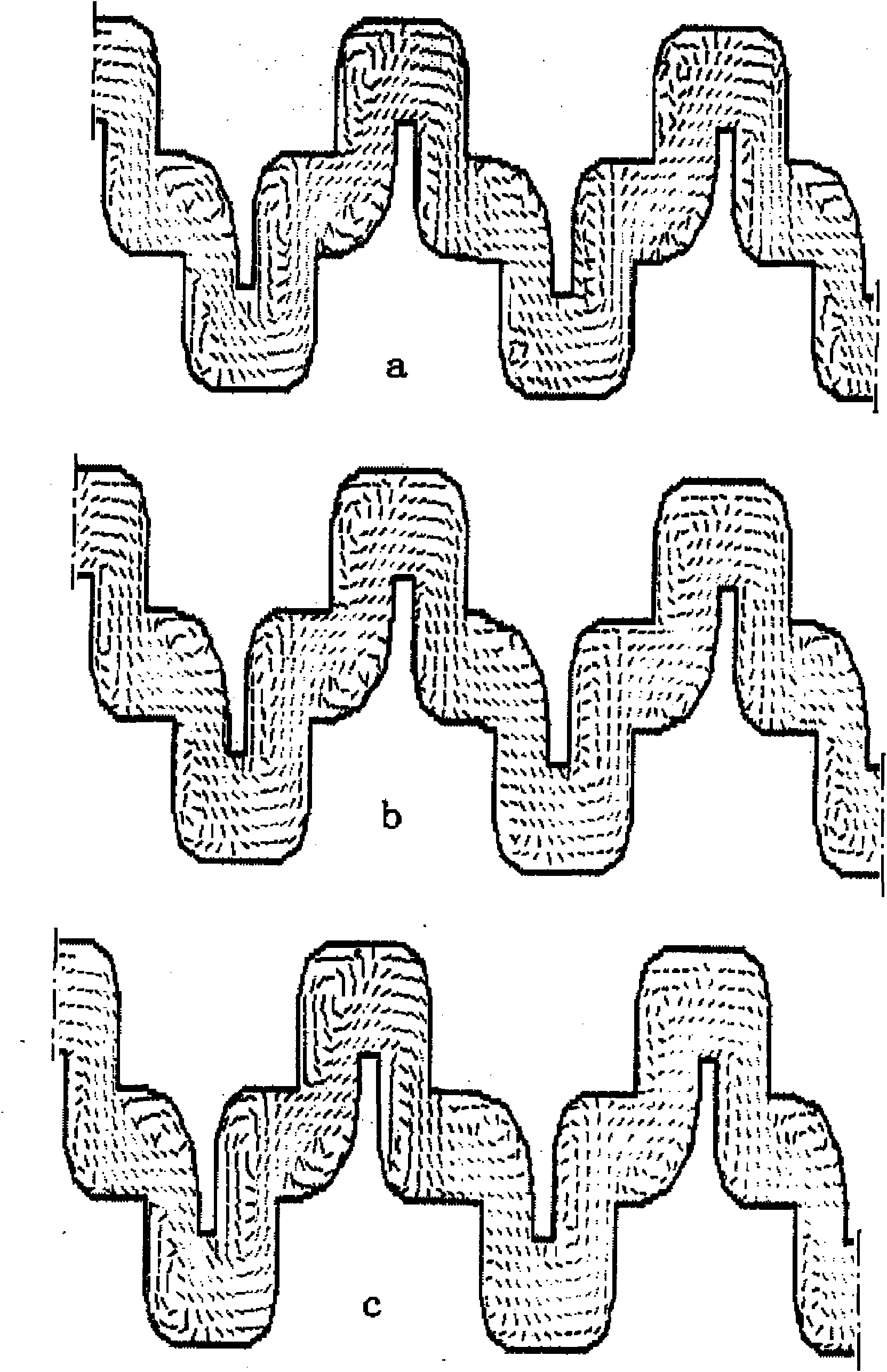
Whole-field testing method for internal flow of drip emitter maze flow channel
ActiveCN101852814ASolve the shooting areaResolve resolutionFluid speed measurementImage resolutionFull field
The invention discloses a whole-field testing method for the internal flow of a drip emitter maze flow channel, which belongs to the technical field of detection. Firstly, a transparent cylindrical drip emitter flow channel model and an internal flow rate testing system of the drip emitter maze flow channel are constructed, and water flow moving action is represented by the following movement of a tracer particle and a DPIV system on the basis of tracer fluorescent particles; and by a laser beam illumination flow field, a CCD camera is used for continuously shooting pictures of the flow field, and related computation is carried out on two continuous frames of particle pictures so as to obtain the characteristic parameters of the speed flow field. The invention utilizes a microscope objective to modify a conventional CCD camera so as to successfully solve the contradiction between the shooting area and the image resolution of the internal fluid flow of the critical scale of the drip emitter flow channel and successfully realize the two-dimensional whole-field and quasi-three-dimensional local undisturbed test of the internal flow field of the drip emitter flow channel. The invention has the flowing characteristics of the maze flow channel and the characteristic of being consistent with the whole-field test result display of the existing numerical simulation and water flow movement.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
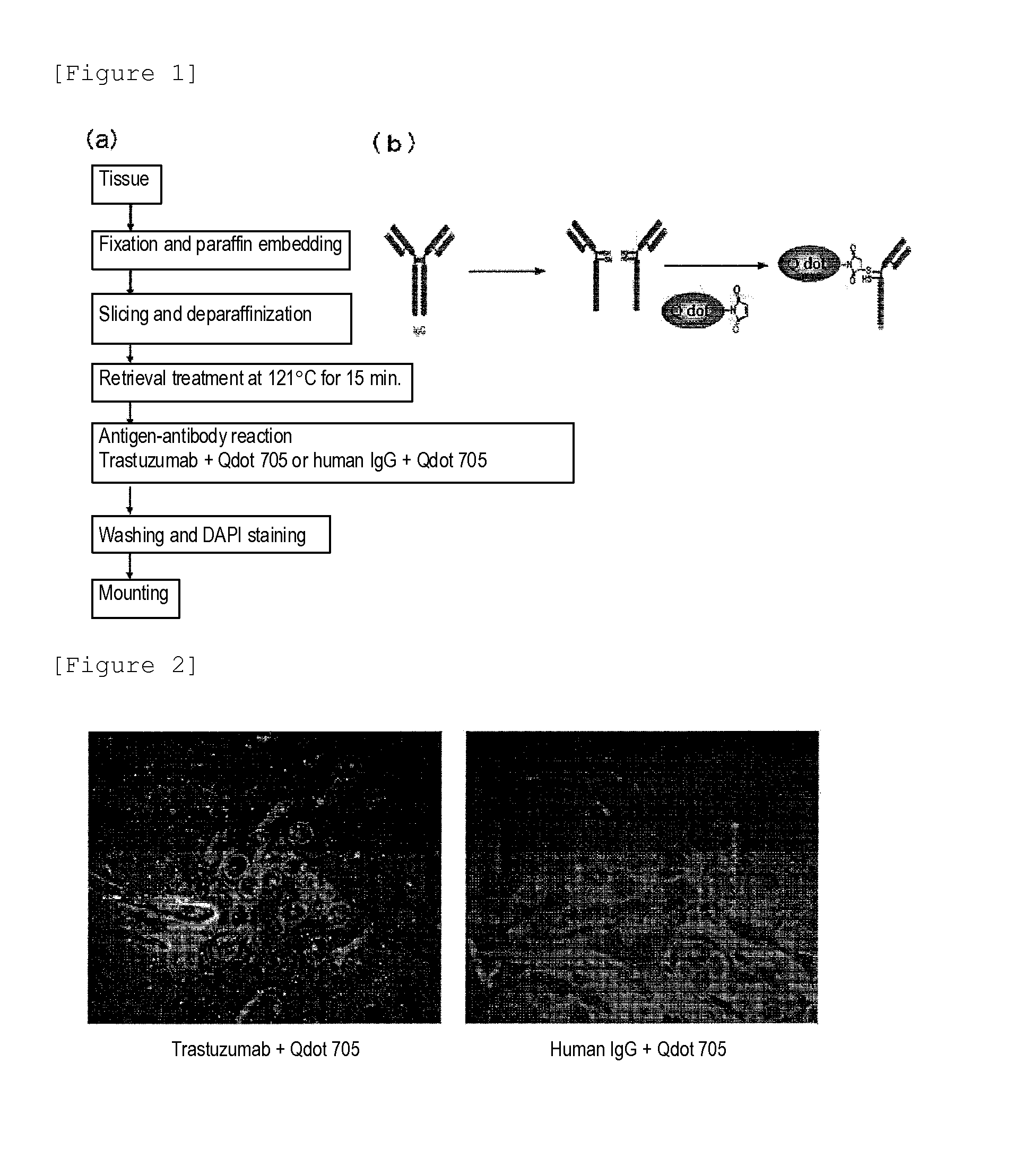
Method for Determining Effectiveness of Medicine Containing Antibody as Component
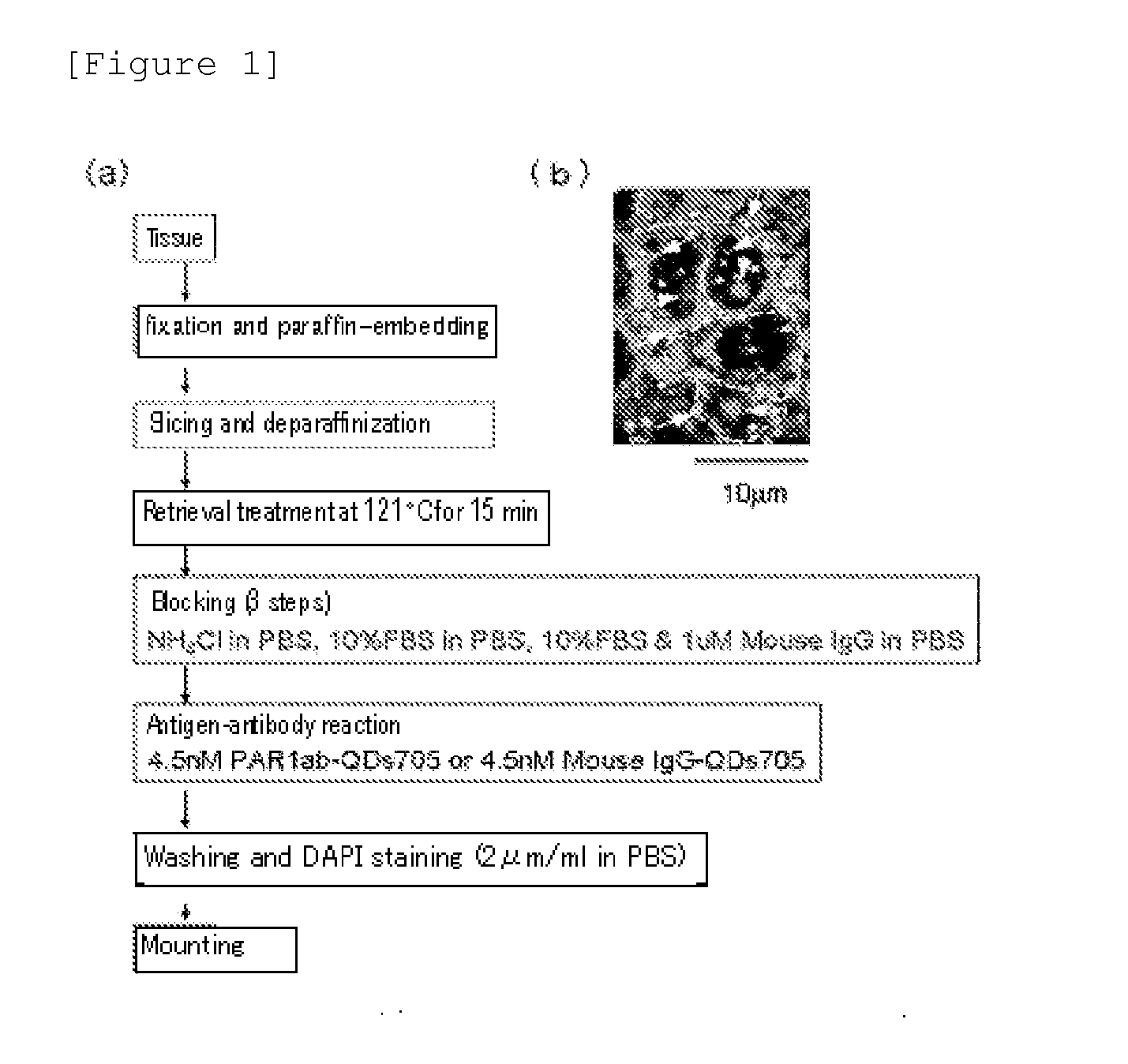
InactiveUS20130230866A1High sensitivityWide rangeBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsTissue stainingTreatment effect
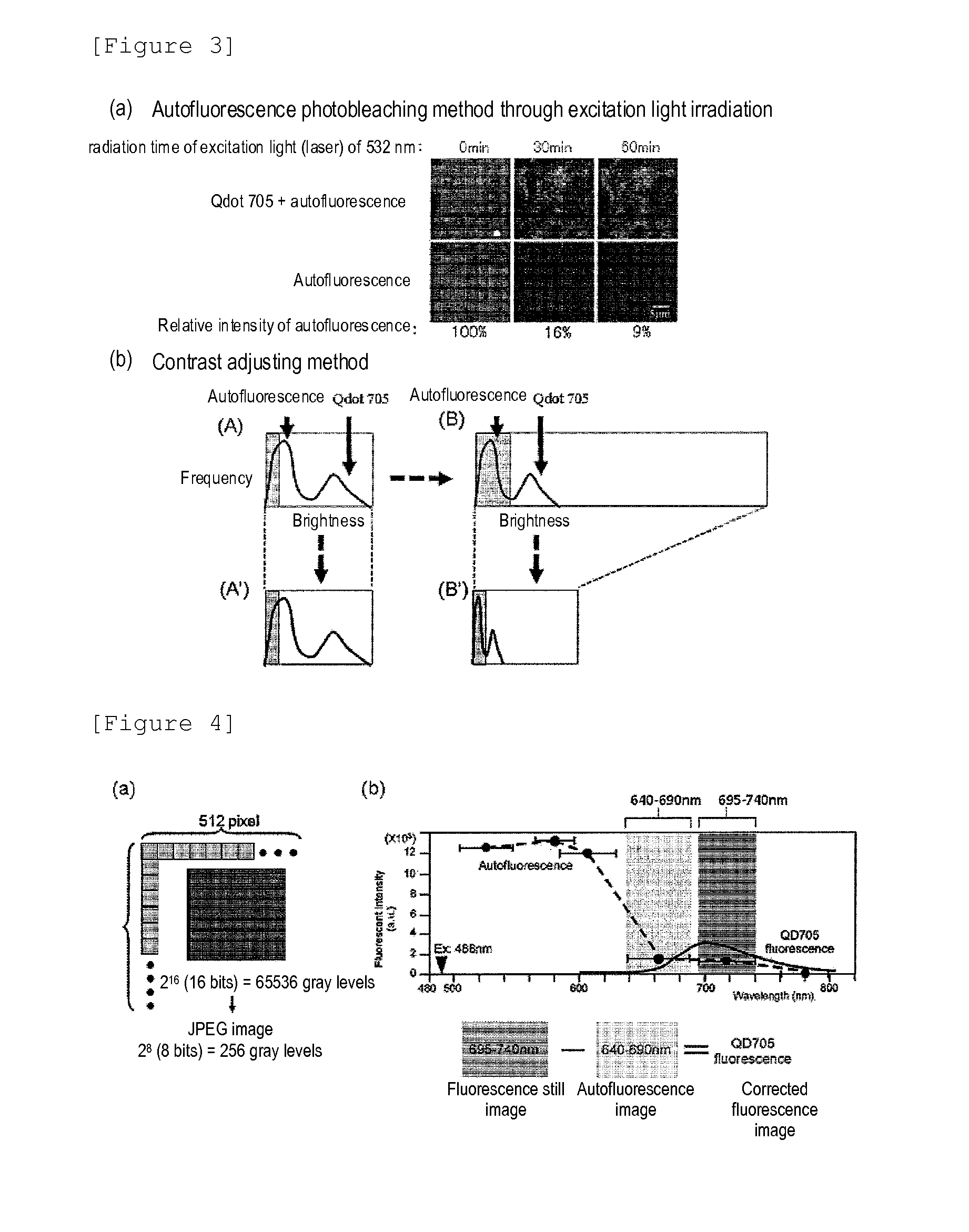
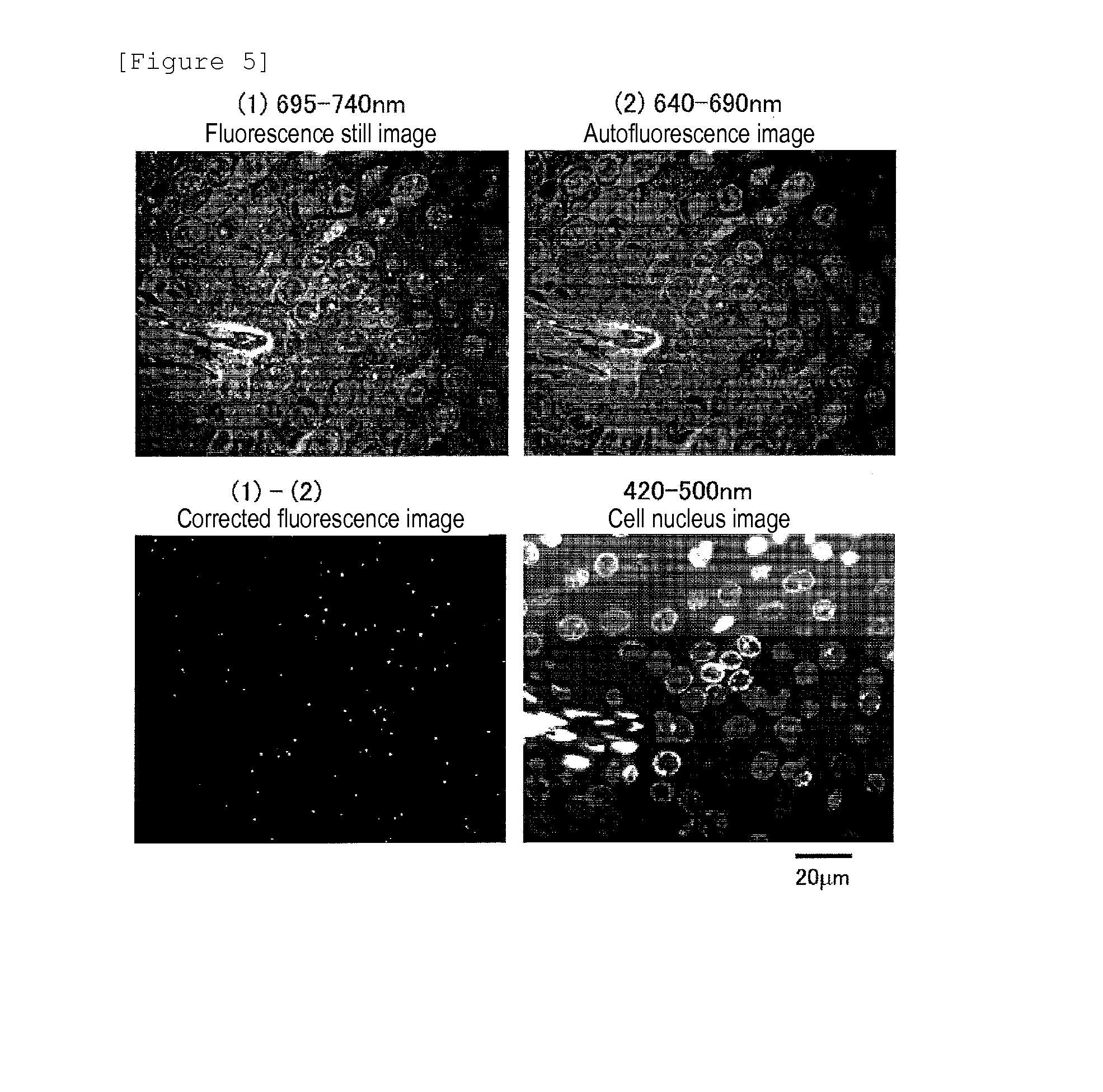
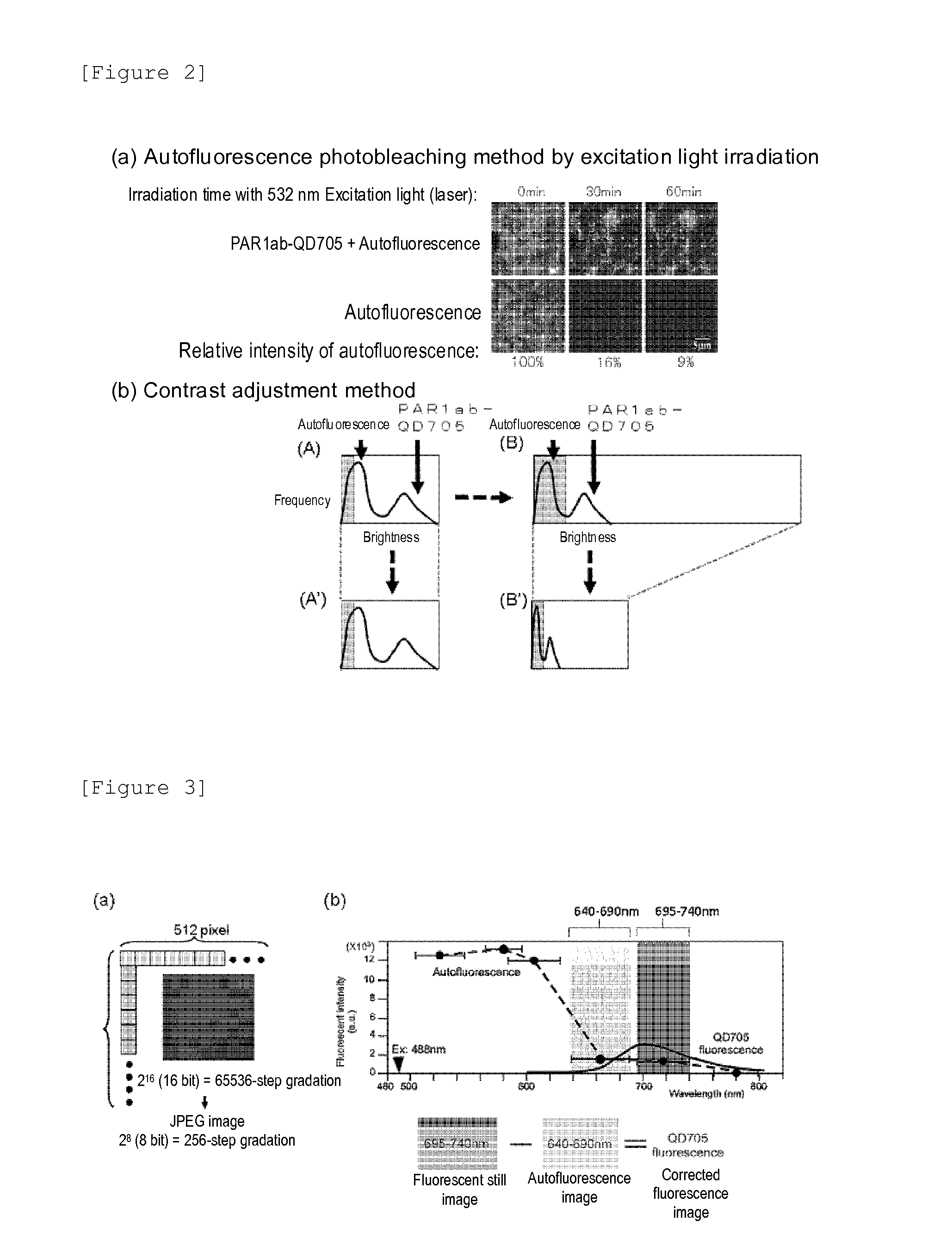
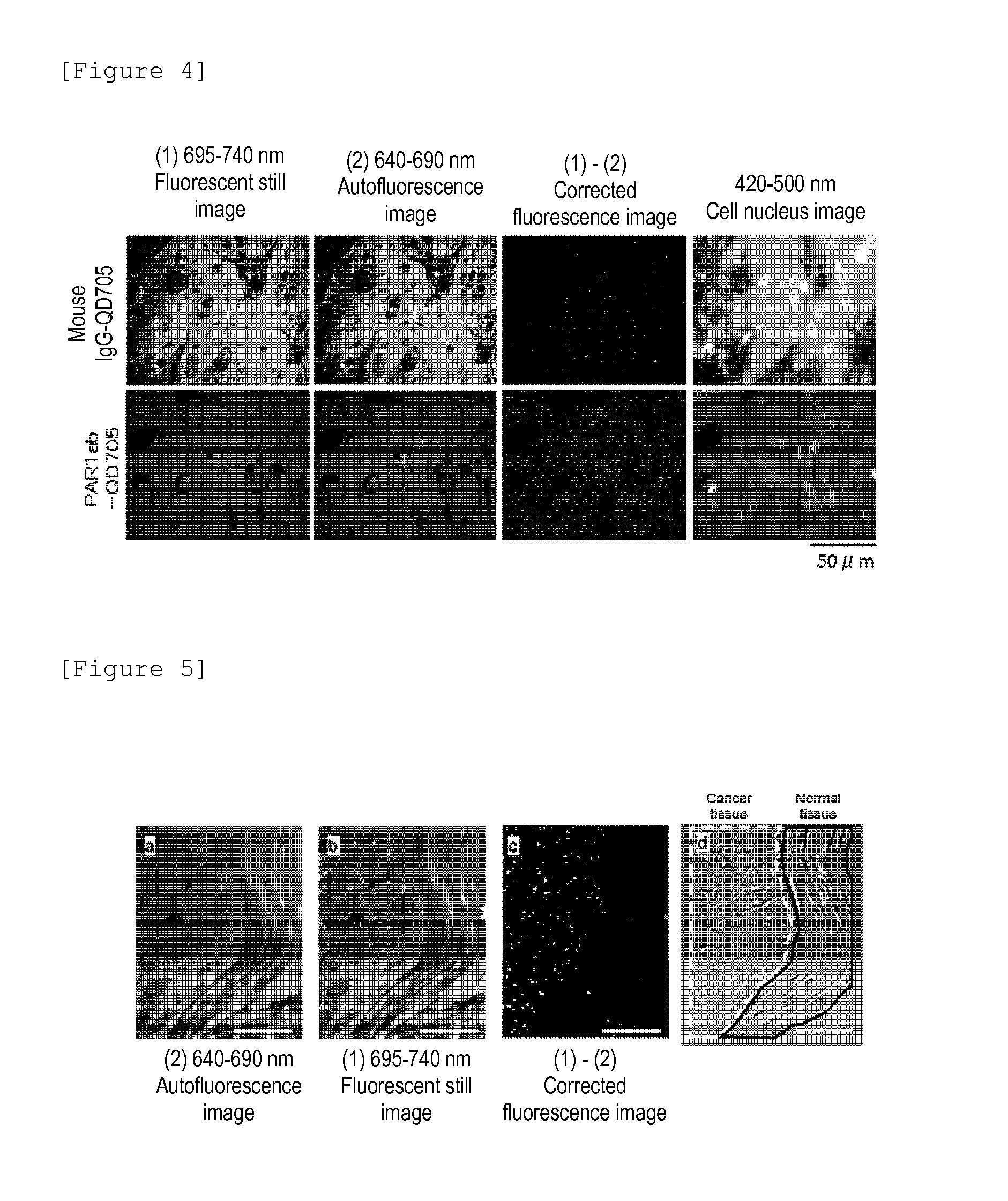
Protein recognized by an antibody used as an active ingredient of an antibody medicine such as trastuzumab or an antibody used for targeting a target site of an active ingredient is highly accurately quantitatively determined by employing a quantitative tissue staining method of biological tissues, thereby providing a method for determining therapeutic effectiveness of a medicine containing such an antibody as a component. The effectiveness of a medicine containing an antibody as a component is determined by employing a tissue staining method comprising the steps of: labeling the antibody in the medicine containing an antibody as a component with a fluorescent material and contacting the thus fluorescence-labeled antibody with a tissue sample; obtaining a fluorescence image by irradiating, with excitation light, a tissue site contacted with the antibody; obtaining an autofluorescence image in the same field of view and at the same focus as in the fluorescence image in a close region on a shorter wavelength side or a longer wavelength side of an acquisition wavelength region of fluorescence emitted by the fluorescent material; obtaining a corrected fluorescence image by performing image processing for removing fluorescence brightness of the autofluorescence image from fluorescence brightness of the fluorescence image; counting the number of cells in the tissue site contacted with the antibody; measuring average fluorescence brightness per fluorescent particle; and calculating the number of fluorescent particles per cell.
Owner:TOHOKU UNIV
Light mixing module
A mixing light module includes a matrix, a fluorescent film, and a plurality of micro-structures. The matrix includes an incidence surface, an emission surface and a reflective surface. The fluorescent film disposed on or above the emission surface has an upper surface and a lower surface and includes a plurality of fluorescent particles. The matrix receives a first light having a first wavelength, and the reflective surface reflects the first light to make the first light to be emitted from the emission surface. Since the plurality of fluorescent particles receives a part of the first light from the emission surface, the plurality of fluorescent particles is excited to emit a second light having a second wavelength. The second light and the first light are mixed into a predetermined light. The plurality of micro-structures is used to make the first light or the second light uniform.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
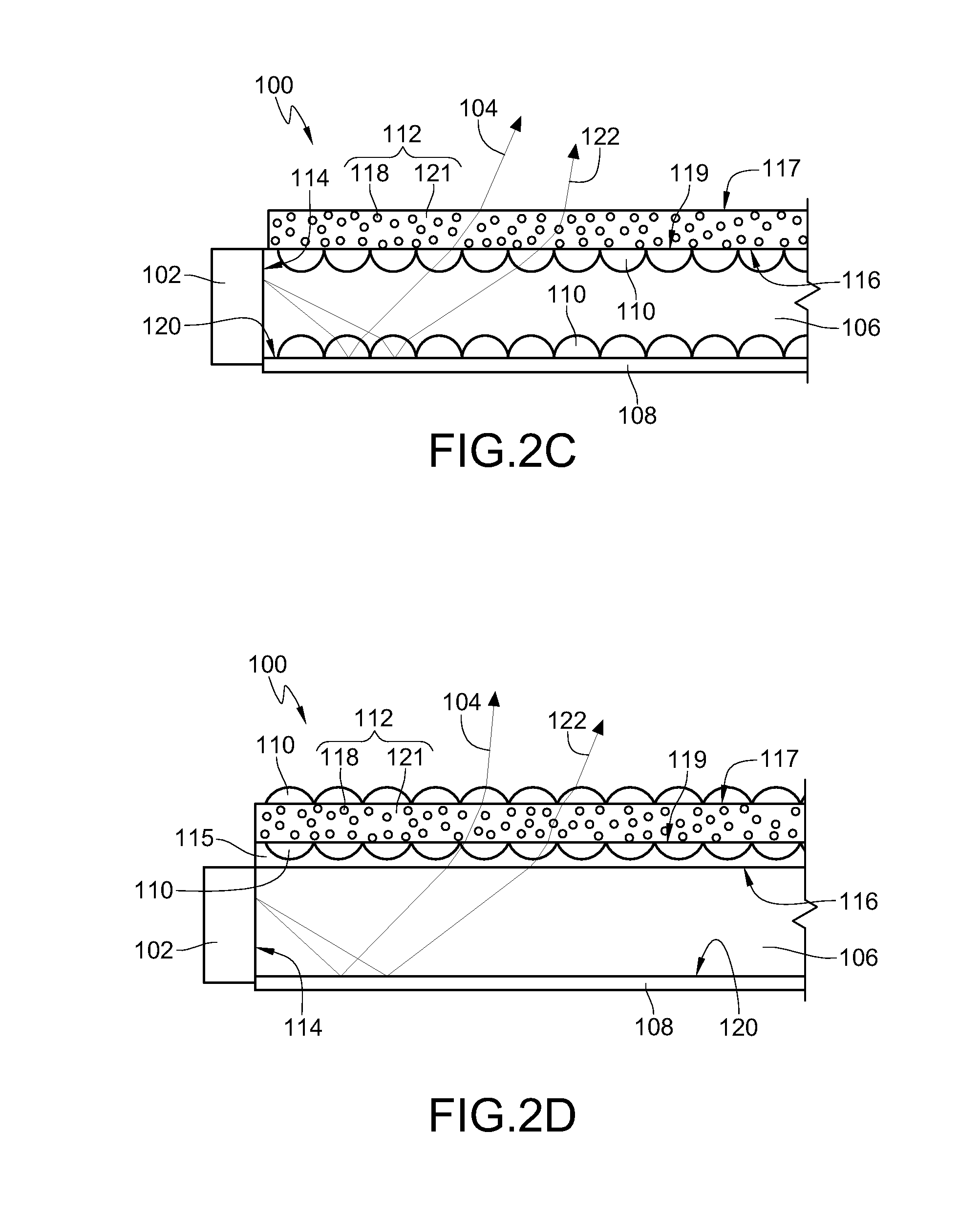
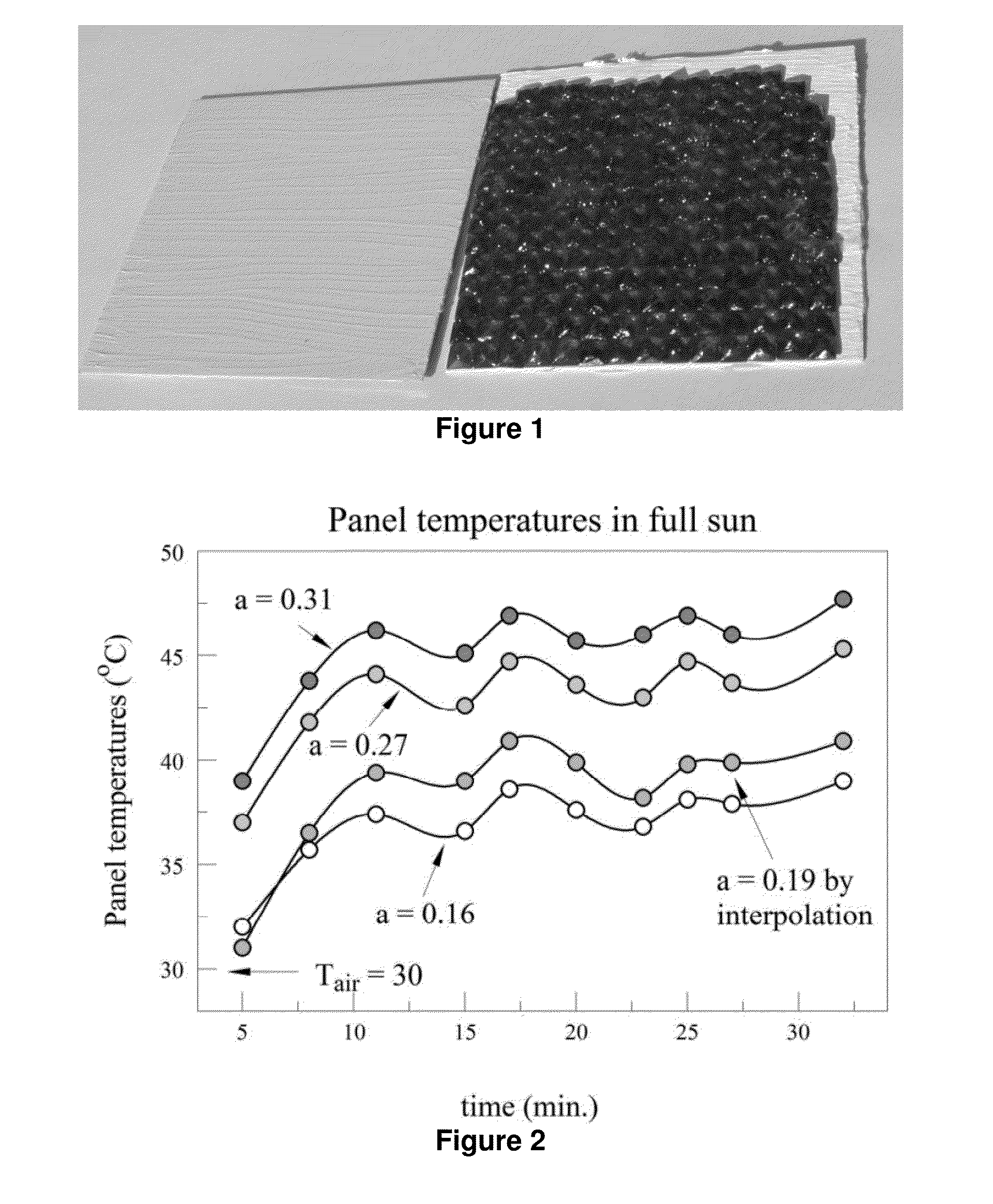
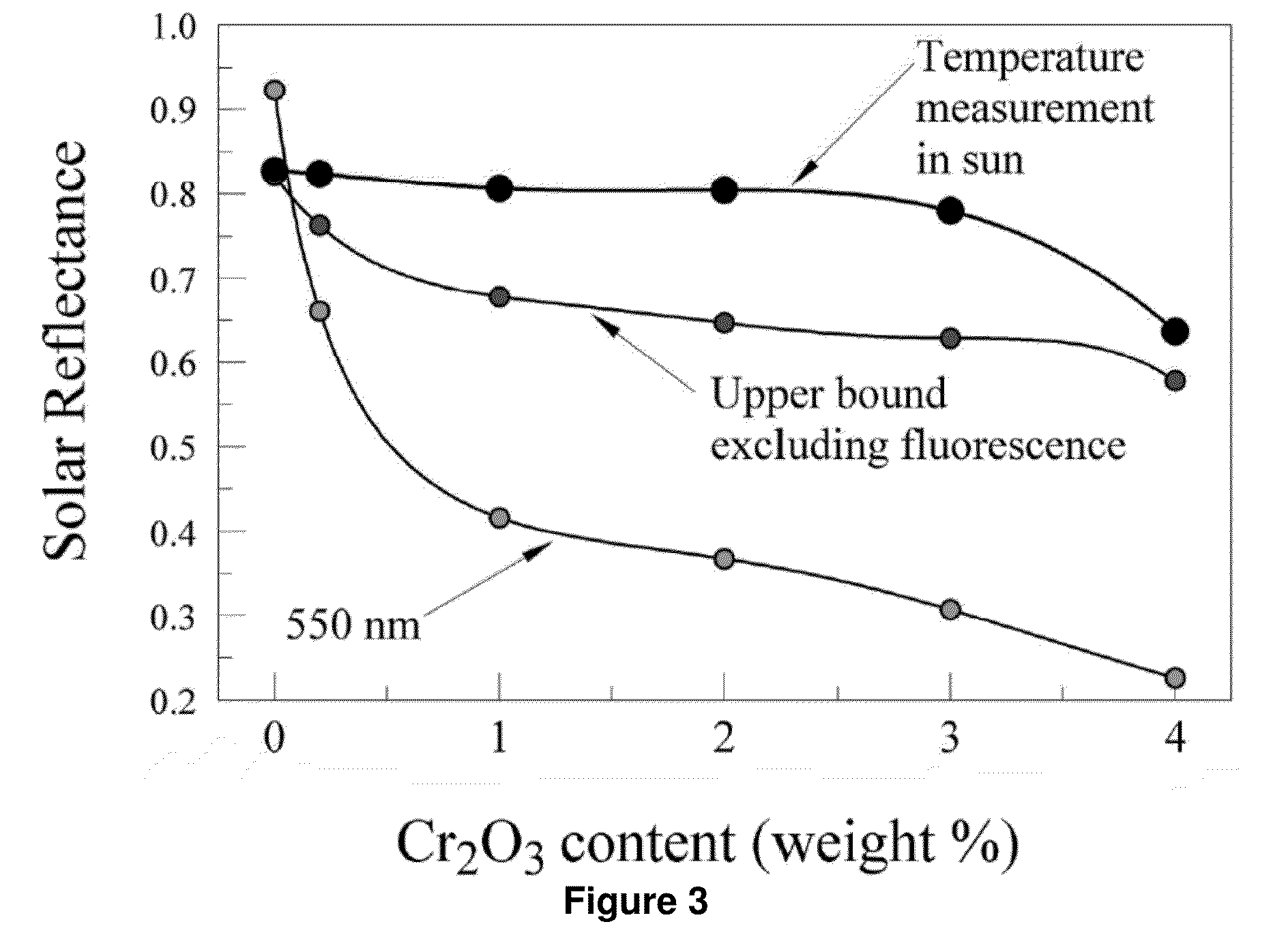
Novel Compositions for Cooling Materials Exposed to the Sun
The present invention provides for a composition comprising a pigment, wherein the composition is suitable for coating a surface that is, or is expected to be, exposed to the sun. The pigment comprises particles that fluoresce in sunlight, thereby remaining cooler in the sun than coatings pigmented with non-fluorescent particles. The particles comprise solids that fluoresce or glow in the visible or near infrared (NIR) spectra, or that fluoresce when doped. Suitable dopants include, but are not limited to, ions of rare earths and transition metals.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES AS REPRESENTED BY THE DEPARTMENT OF ENERGY
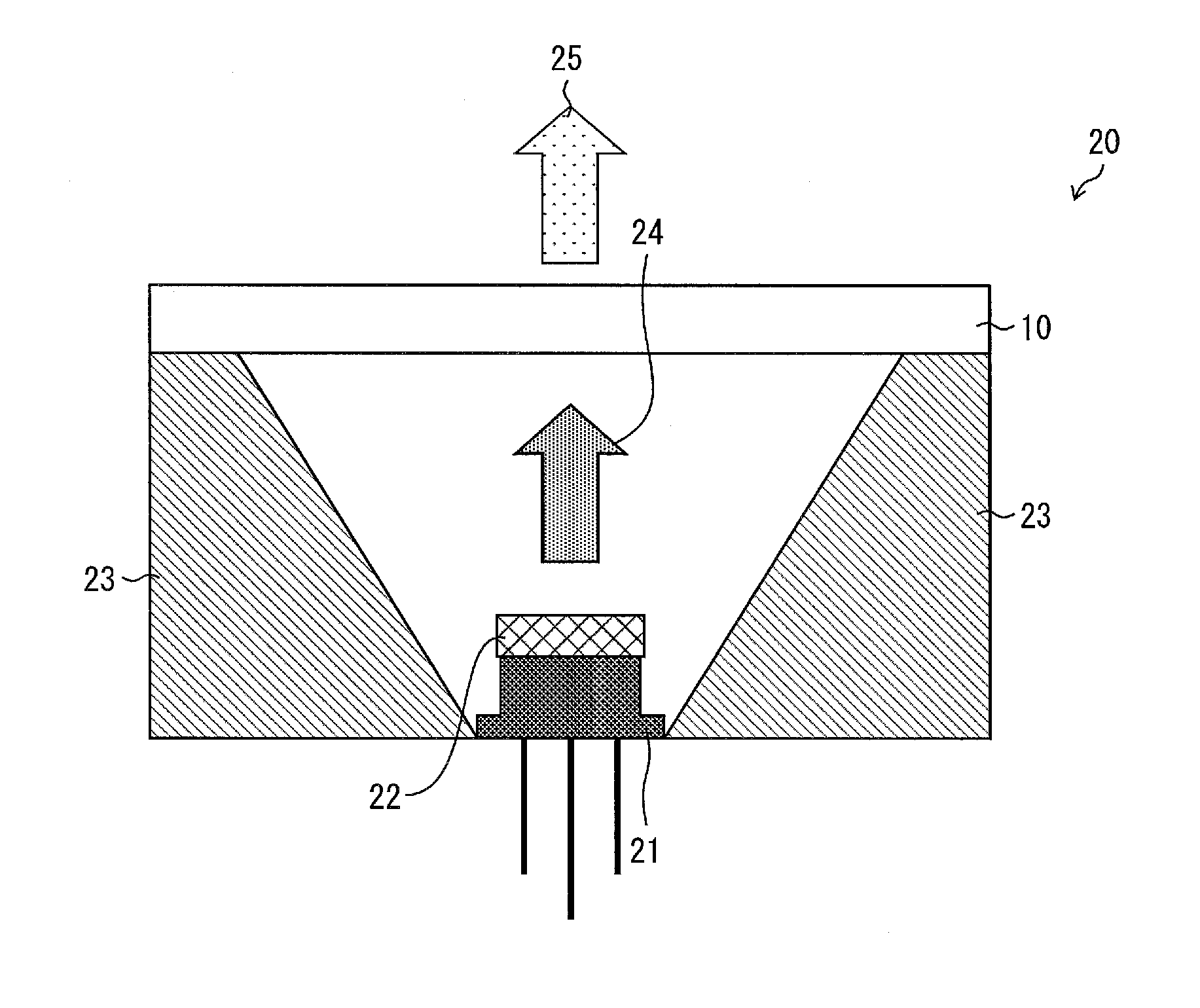
Wavelength conversion member, light-emitting device, and method for producing wavelength conversion member
InactiveUS20150211712A1High mechanical strengthLaser detailsPoint-like light sourceLight emitting deviceWavelength conversion
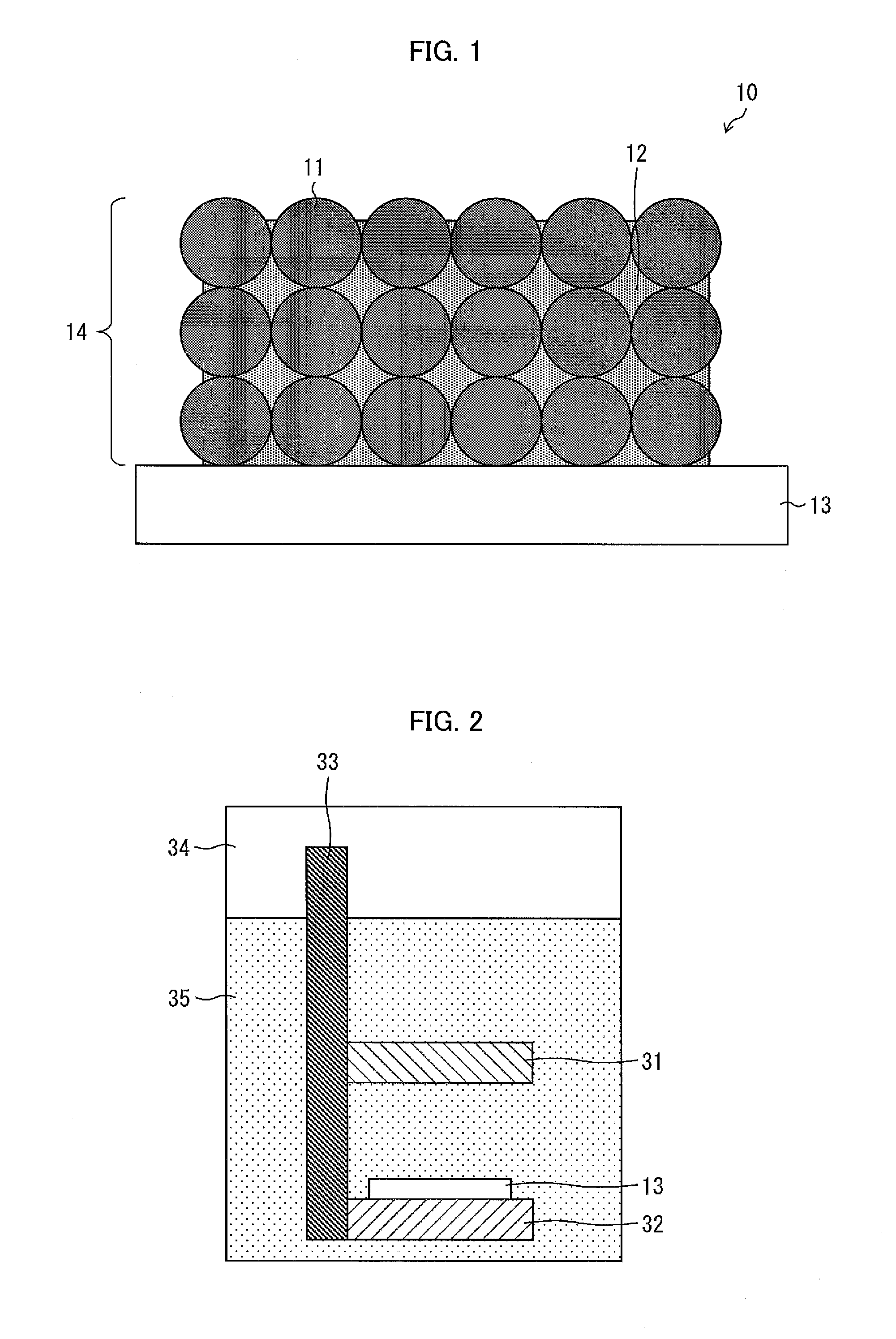
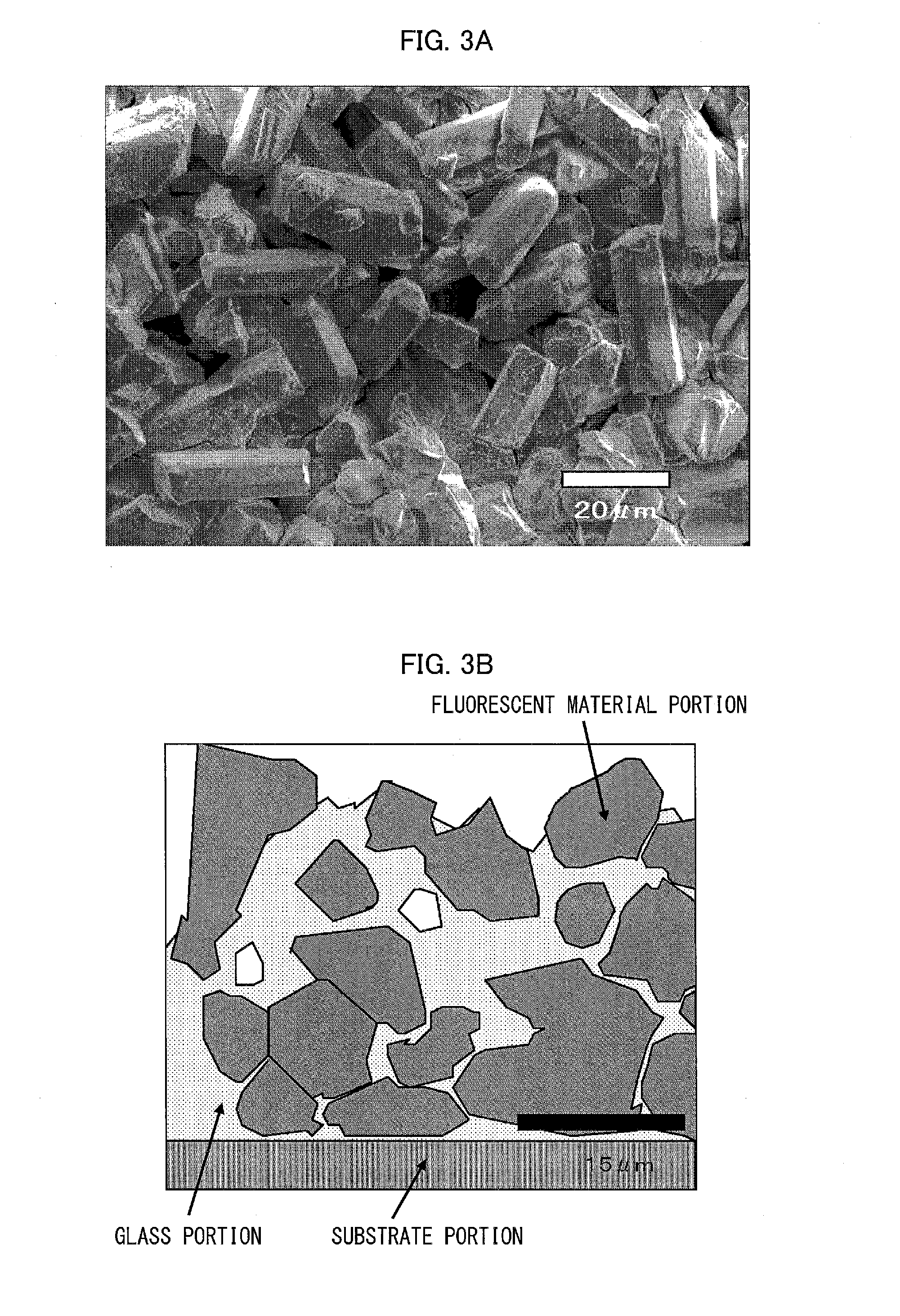
A wavelength conversion member includes a substrate and a fluorescent film that is disposed on the substrate and emits fluorescence upon reception of excitation light, wherein the fluorescent film includes an aggregate of a plurality of fluorescent particles, the aggregate being formed as a result of contact among the fluorescent particles, and a glass material filling gaps between the fluorescent particles in the aggregate, and a total volume of a volume of the glass material and a volume of the fluorescent particles in the fluorescent film is equal to or less than an envelope volume of the aggregate of the fluorescent particles in the fluorescent film.
Owner:SHARP KK +1
Nano fluorescent particles doping with rare-earth ions and relevant application thereof
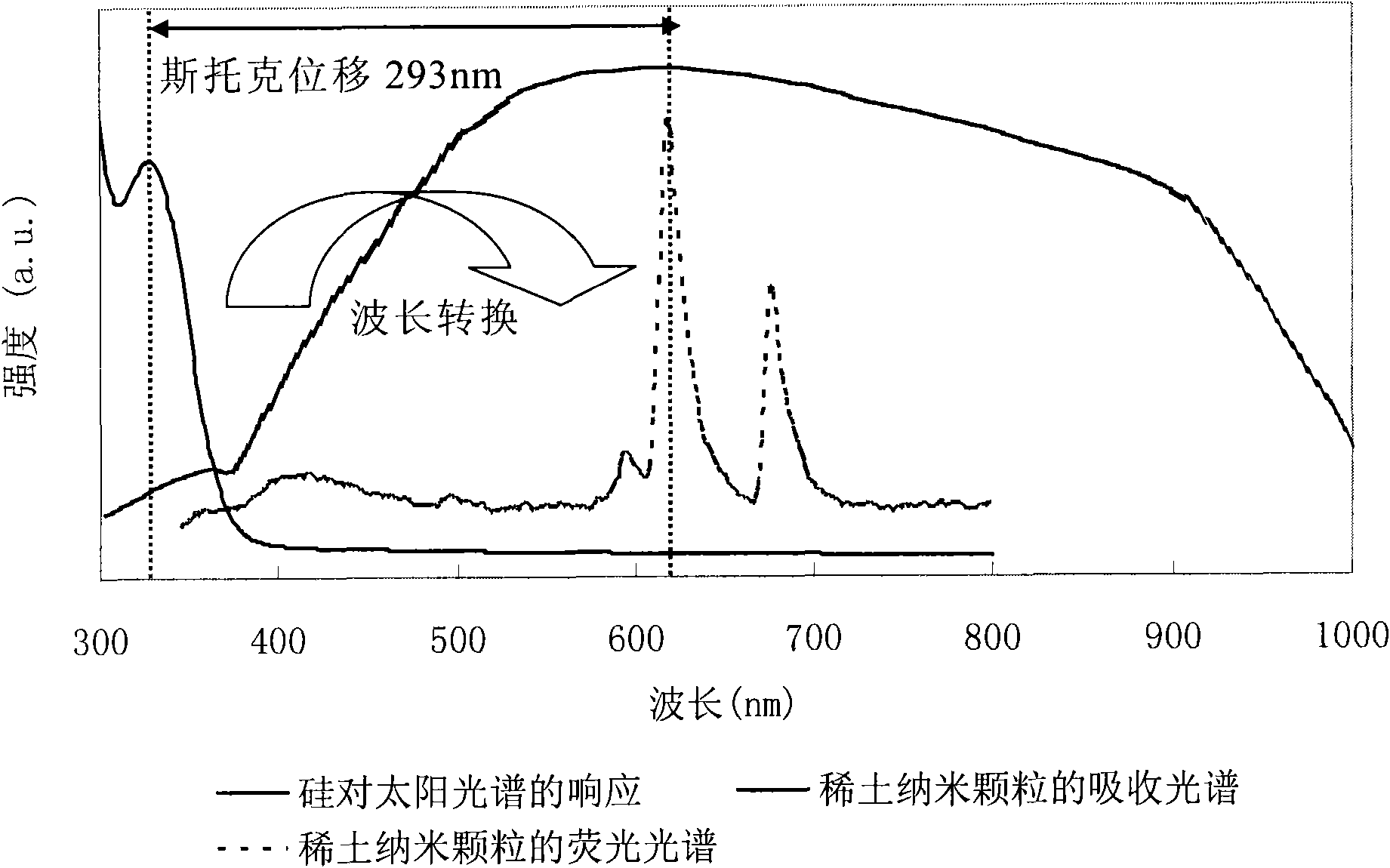
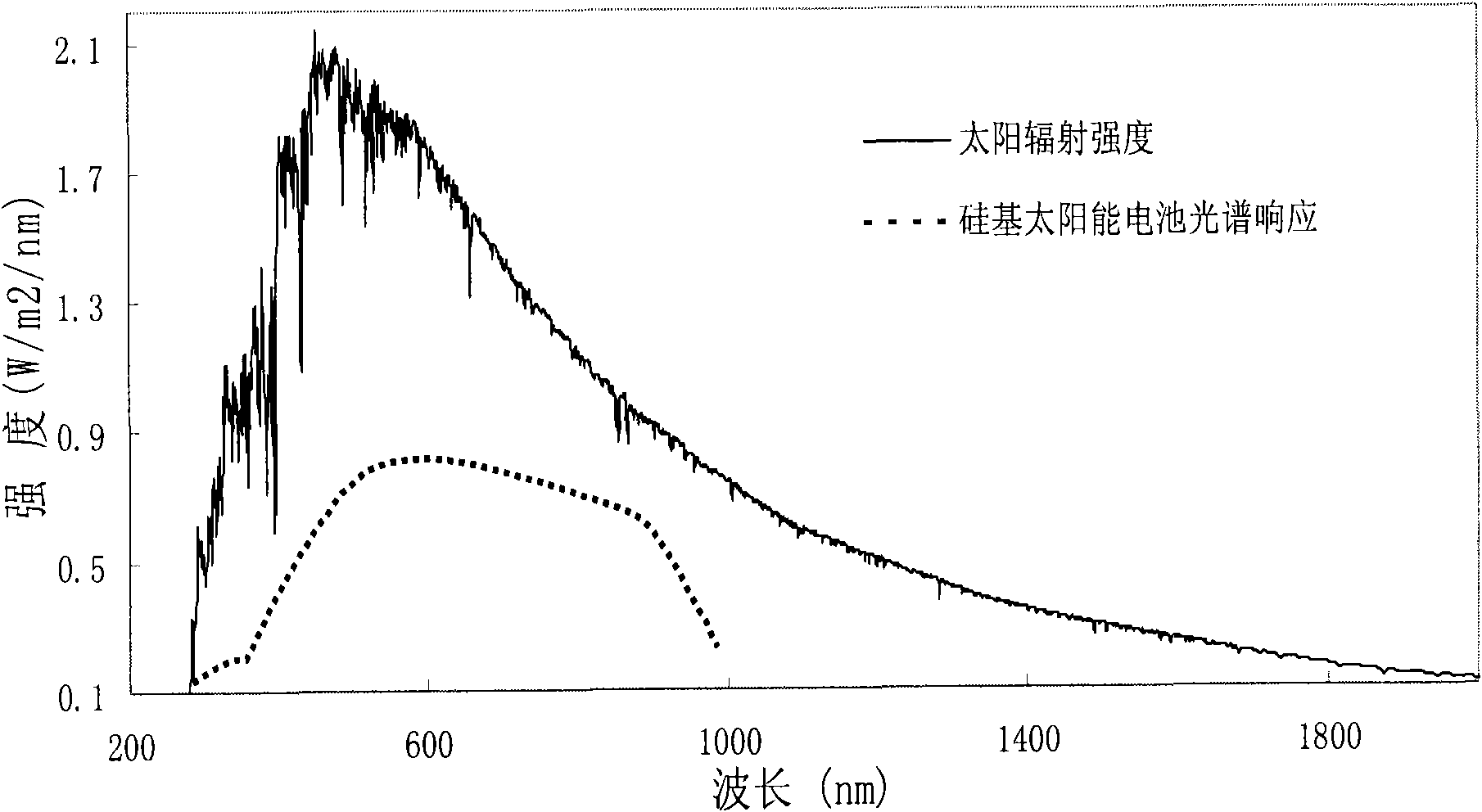
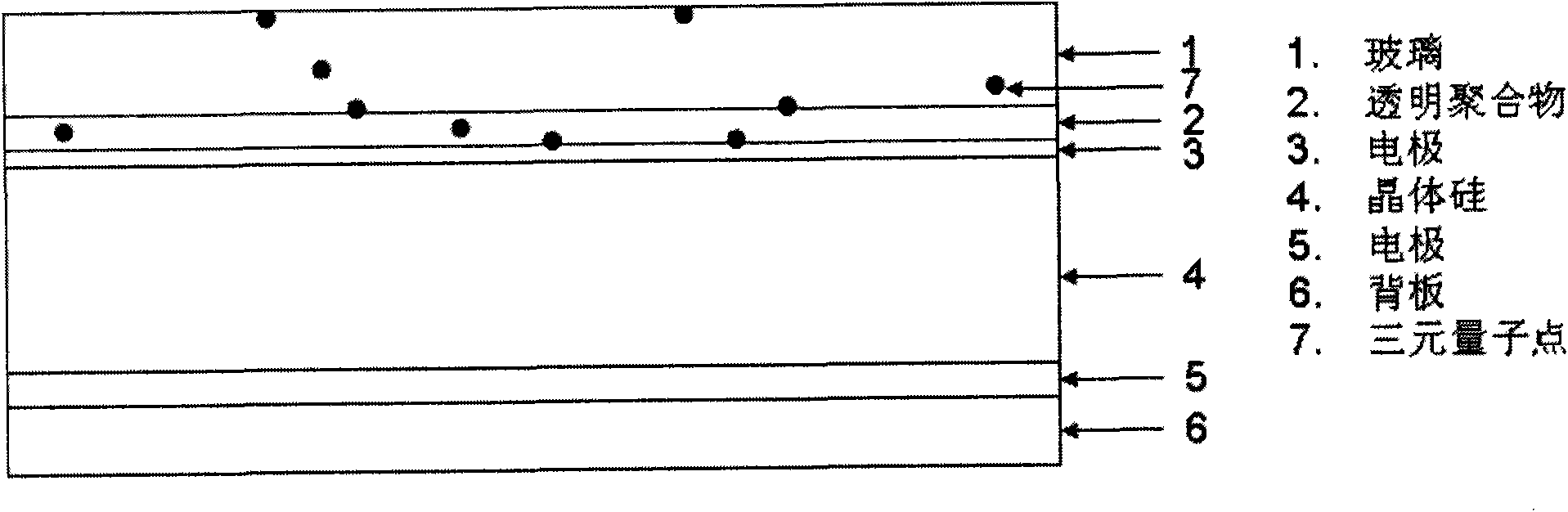
InactiveCN101787272AHigh fluorescence efficiencyEffective absorptionTenebresent compositionsPhotovoltaic energy generationMischmetalRare earth ions
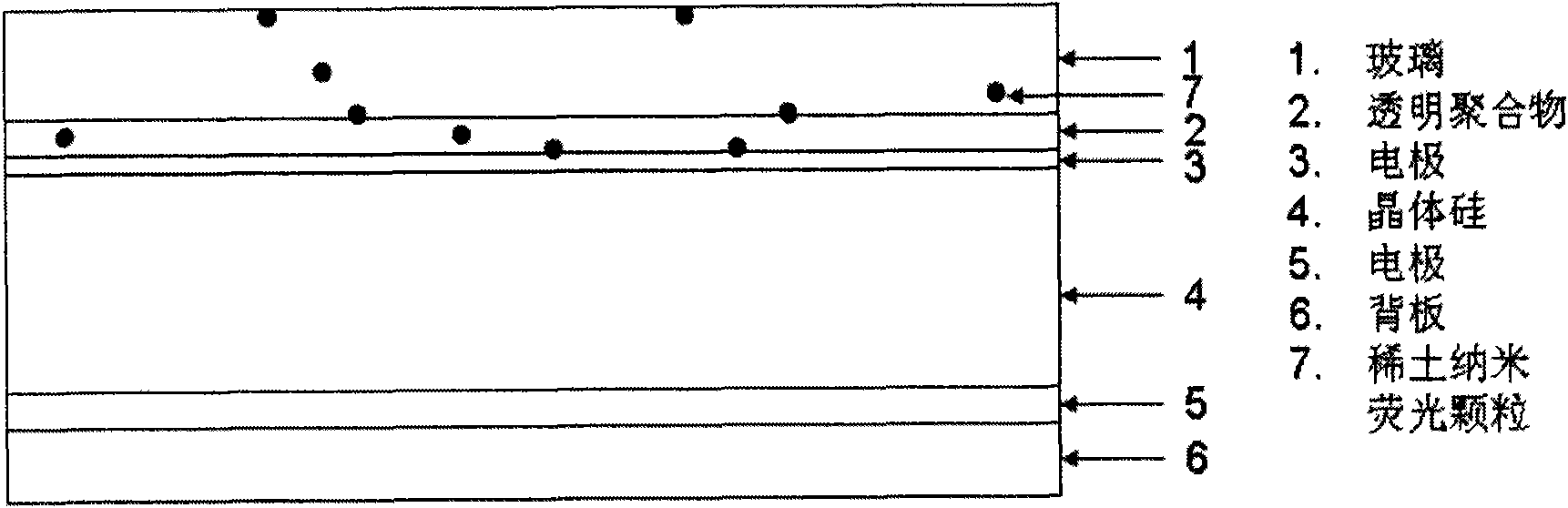
The invention provides nano fluorescent particles doping with rare-earth ions. The grain size of the nano particles is 1-200nm, and the nano particles comprise a nano particle matrix and rare-earth ions. The invention also provides a solar battery containing the nano particles.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Quantum dot optical wavelength converting layer for solar cell
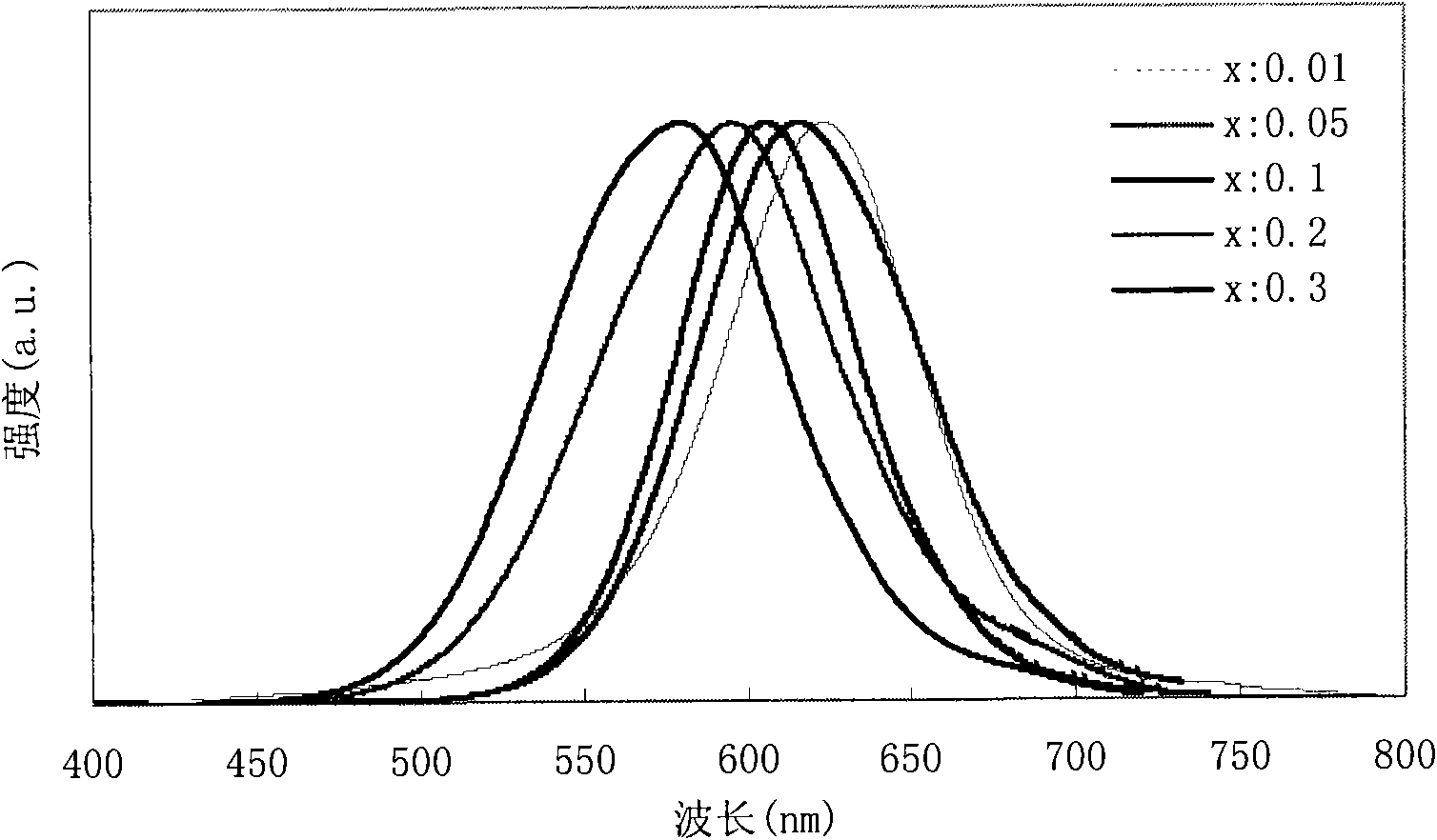
InactiveCN101787271AGood fluorescence stabilityHigh fluorescence efficiencyTenebresent compositionsPhotovoltaic energy generationSolar cellOxygen
The invention provides a quantum dot optical wavelength converting layer for a solar cell. Ternary alloy quantum dot fluorescent particles are provided, wherein the particle size of quantum dots is between 1 and 100nm; the quantum spot can be represented by the following formula: AxByCz, wherein the A is a transition metal element; the B is a transition metal and oxygen group element and / or a nitrogen group element; the C is an oxygen group element and / or a nitrogen group element; the B is different from the C; and the x, the y and the z are greater than 0 and less than 1. The invention also provides the application of the ternary alloy quantum dot fluorescent particles in the solar cell.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Biological substance detection method
A biological substance detection method for detecting a biological substance specifically in a pathological specimen, comprising a step of immunologically staining the pathological specimen using a fluorescent label, a step of staining the pathological specimen with a staining reagent for morphology observation purposes (eosin) to observe the morphology of the pathological specimen, a step of irradiating the stained pathological specimen, with excited light to cause the emission of a fluorescent and detecting the biological substance in the pathological specimen. In the step of immunologically staining the pathological specimen, a special fluorescent particle for which the excitation wavelength appears in a region that is different from the excitation wavelength region of eosin is used as the fluorescent label.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA INC +1
Core-shell structured fluorescence granular material with adjustable luminescence and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101294071ASimple preparation processLuminescence is stable and adjustableLuminescent compositionsGreen-lightLight emission
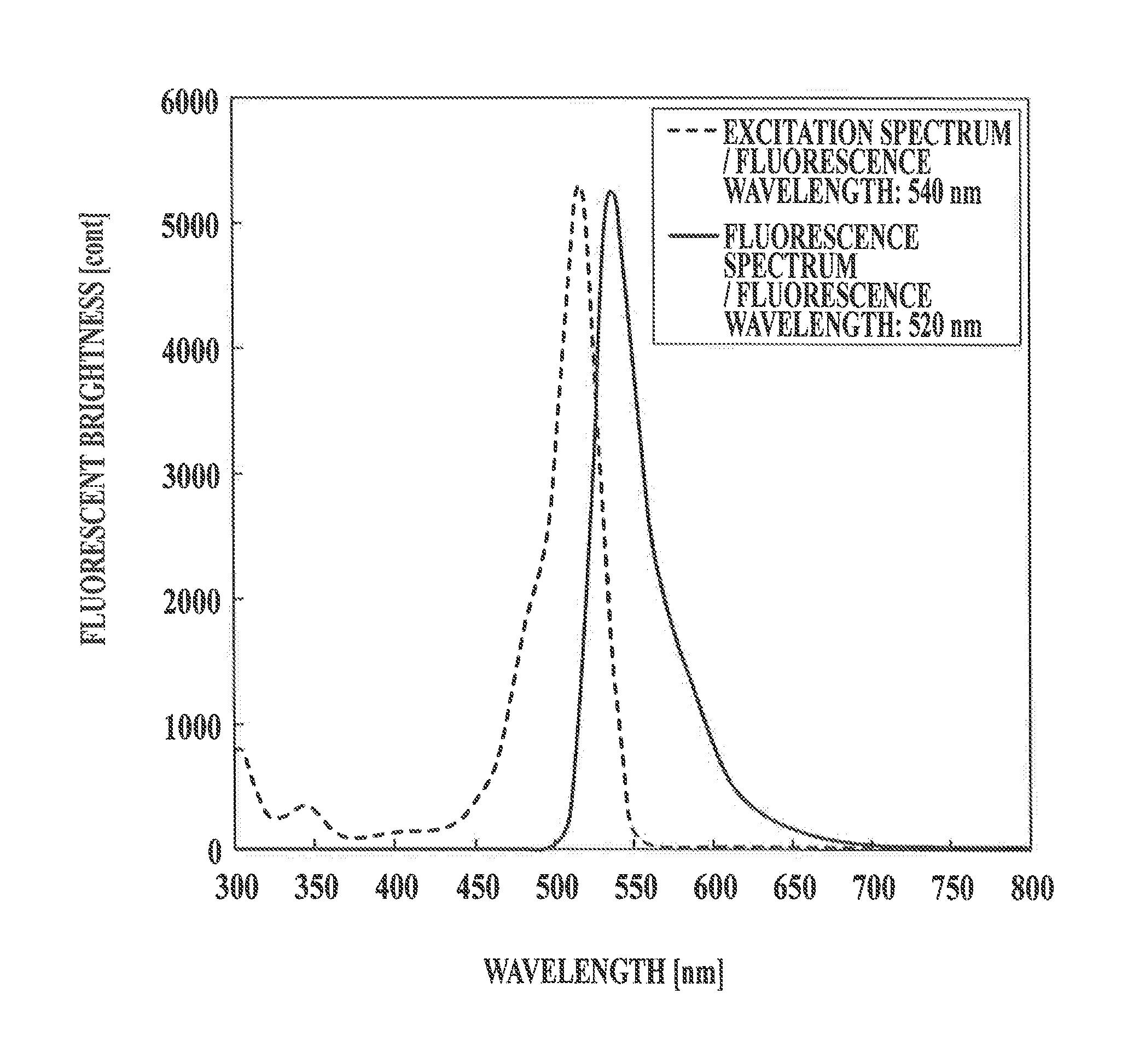
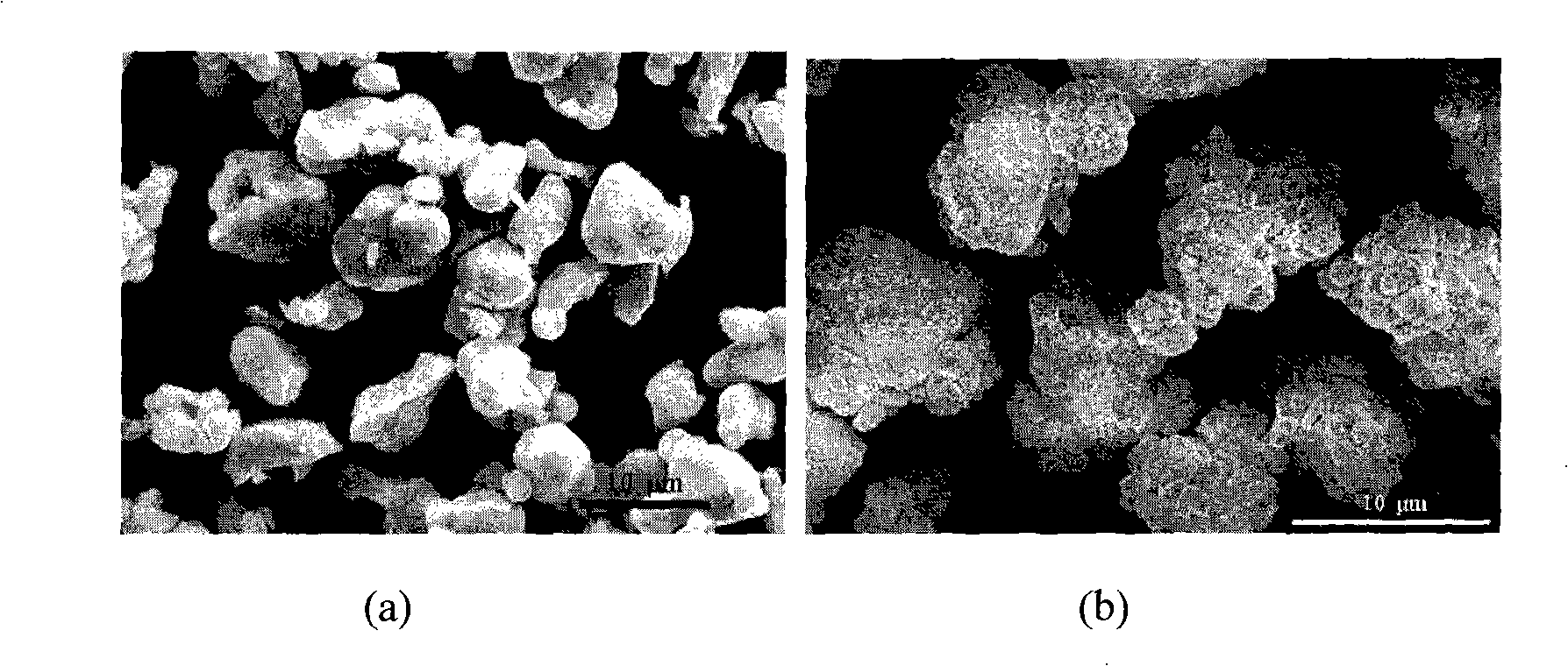
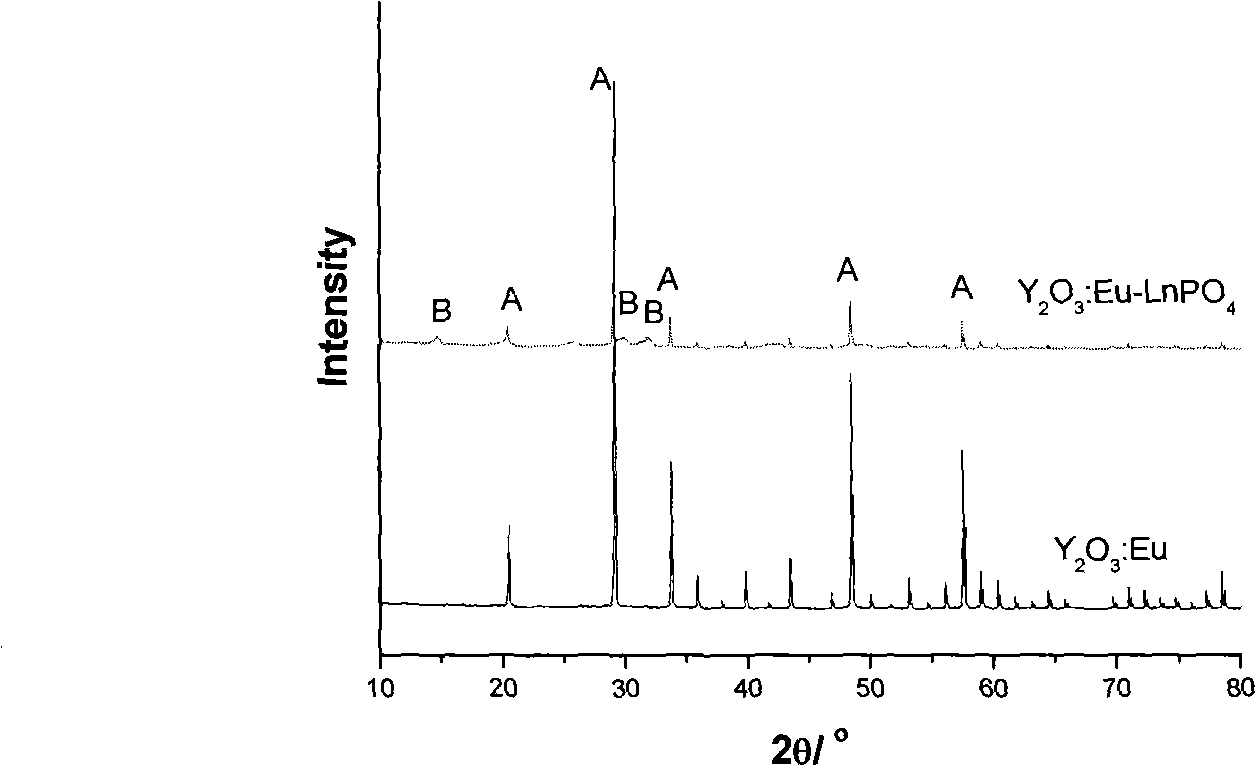
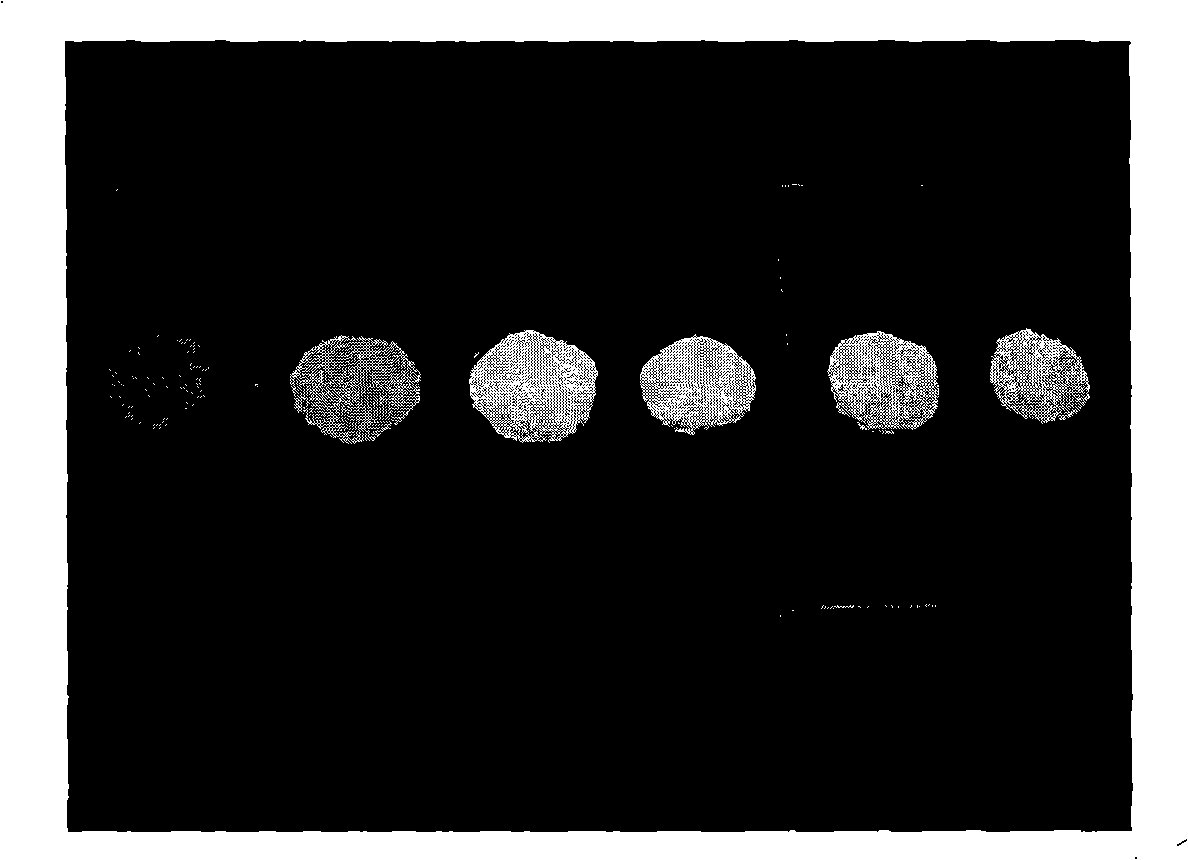
The invention relates to a Y2O3:Eu-LnPO4 fluorescent particle material of kernel-housing structure with adjustable light emission. The kernel material is selected from a Y2O3:Eu fluorescent material capable of emitting red light, and the housing material is selected from an LnPO4 fluorescent material capable of emitting green light, wherein the kernel has a size within 4 to 8 mum, and the molar ratio of the Y2O3:Eu material to the LnPO4 material is 1:0.4 to 1:2. The preparation method comprises the following steps: adding a rear earth ion mixture solution for preparing the housing material into a sodium tripolyphosphate solution dropwise, adding the Y2O3:Eu micrometer particles as the kernel, growing the LnPO4 housing layer on the kernel of the Y2O3:Eu micrometer particles, cooling, filtering, cleaning, vacuum drying and collecting the product. The preparation process is simple, and the Y2O3:Eu-LnPO4 fluorescent particle material has stable and adjustable light emission.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Immuno-chromatography kit for quickly and quantitatively detecting calprotectin in excrement
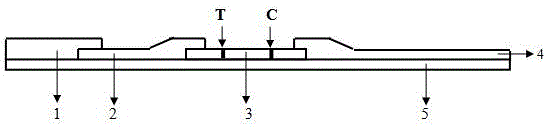
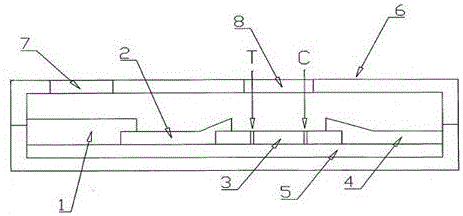
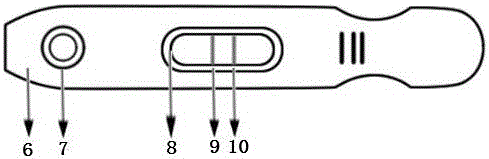
The invention provides an immuno-chromatography kit for quickly and quantitatively detecting calprotectin in excrement and belongs to the technical field of clinical in-vitro diagnosis reagents. The kit includes: a test strip, which includes a substrate, and a sample pad, a marker combination pad, a nitrocellulose membrane and a water absorption pad which are all arranged on the substrate. The marker combination pad is coated with a calprotectin monoclonal antibody A marked by colloidal gold particles, colloidal silver particles, colloidal iron particles, magnetic particles, fuel particles, latex particles or fluorescent particles. The nitrocellulose membrane contains a detection line T and a quality control line C, wherein the detection line T is formed by a calprotectin monoclonal antibody B, and the quality control line C is formed by goat-anti-mouse IgG. The calprotectin monoclonal antibody A and the calprotectin monoclonal antibody B respectively recognize different epitopes of the calprotectin. The kit is convenient and quick, is simple in operation, has accurate result and is suitable for clinical quick detection.
Owner:江苏奥的特生物技术有限公司
Method for determining cancer onset or cancer onset risk
InactiveUS20130203082A1High sensitivityExclude influenceBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsTissue stainingCancer cell
A highly accurate and quantitative method for determining cancer onset or cancer onset risk by a quantitative tissue staining method in biological tissues using an antibody capable of recognizing a cancer growth regulatory factor or cancer metastasis regulatory factor such as PAR1 antibody, which inhibits the cancer cell mobility and infiltration is provided. Cancer onset or cancer onset risk is determined using the tissue staining method comprising the steps of: labeling an antibody which recognizes a cancer growth regulatory factor or cancer metastasis regulatory factor with a fluorescent material, and contacting the fluorescent-labeled antibody with a tissue sample; irradiating a tissue site in contact with the antibody with excitation light to acquire a fluorescence image; acquiring an autofluorescence image in a vicinity region of a short wavelength side or long wavelength side of an acquisition region of fluorescence wavelength emitted by the fluorescent material, in the same field of vision and in the same focal point as those of the fluorescence image; acquiring a corrected fluorescence image by image processing to eliminate a fluorescent brightness of the autofluorescence image from the fluorescent brightness of the fluorescence image; counting the number of cells at the tissue site in contact with the antibody; measuring a mean fluorescent brightness of a single fluorescent particle; and calculating the number of fluorescent particles per cell.
Owner:TOHOKU UNIV
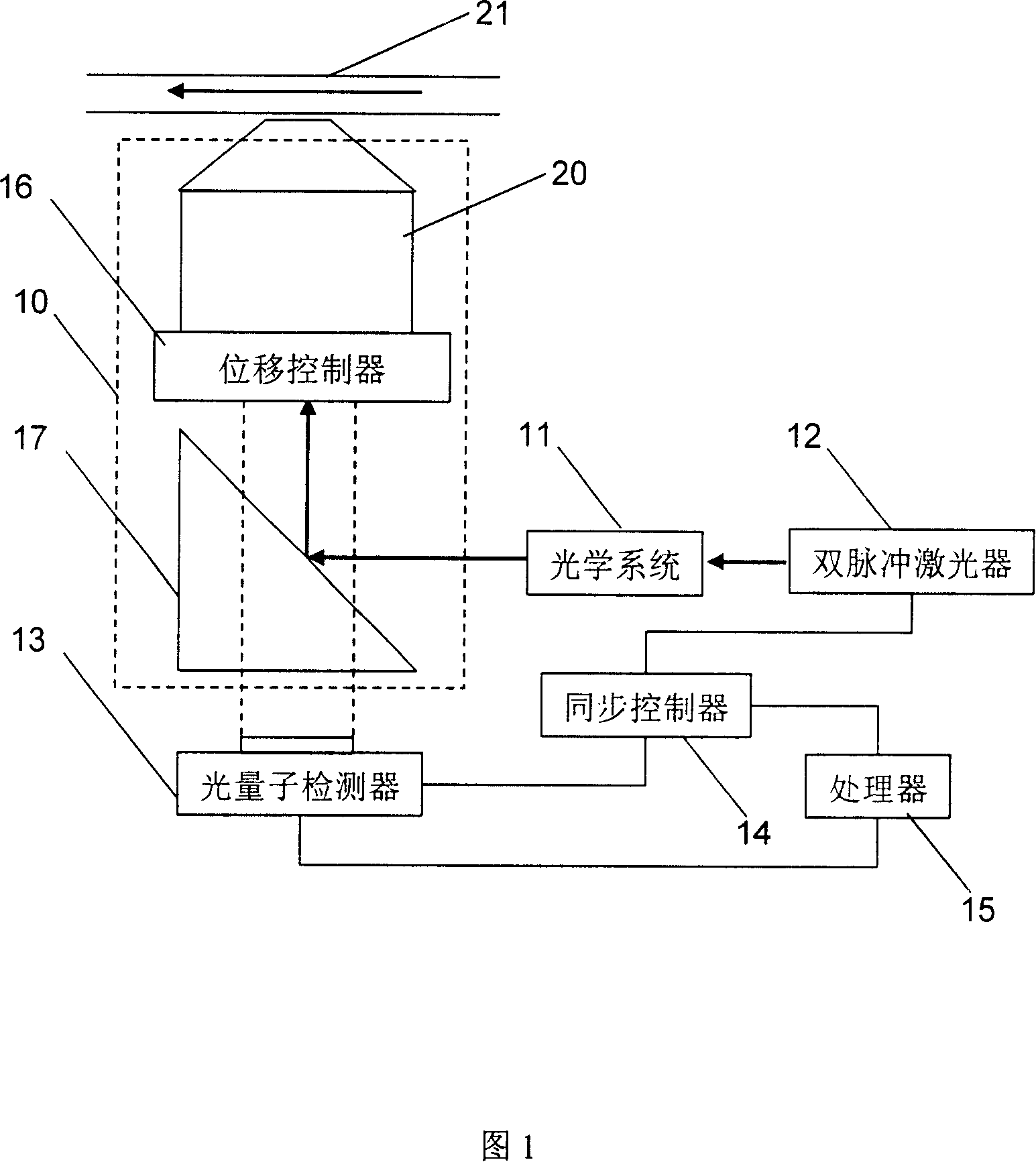
Microchannel speed distribution measuring apparatus and method
InactiveCN101122610AHigh optical detection sensitivityHigh resolutionHydrodynamic testingFluid speed measurementMeasurement deviceLight spot
The invention discloses a measuring device and a measuring method for micro-channel velocity distribution, including a microscope, a double-pulse laser, a photons detector, a synchronous controller and a processor. The method includes the following steps: 1) regulating all instruments to a working state; 2) injecting fluorescent particle solution into micro channel and drive the liquid flowing in the channel; 3) adjusting the vertical position of lens to the clearest imaging position on the bottom surface of the micro channel; 4) the distance between two light spots on the same particle irradiating by the double-pulse laser should be within 20 to 50 pixels; 5) continuously shooting multi-frame images under the irradiation of the double-pulse laser; 6) adjusting the focal plane of lens to a new position and shoot multi-frame images again; 7) repeating the step 6) and shooting images in different positions. The invention has the advantages of high optical sensitivity, high spatial resolution of flow speed detection and high adjustable accuracy of vertical displacement.
Owner:INST OF MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com