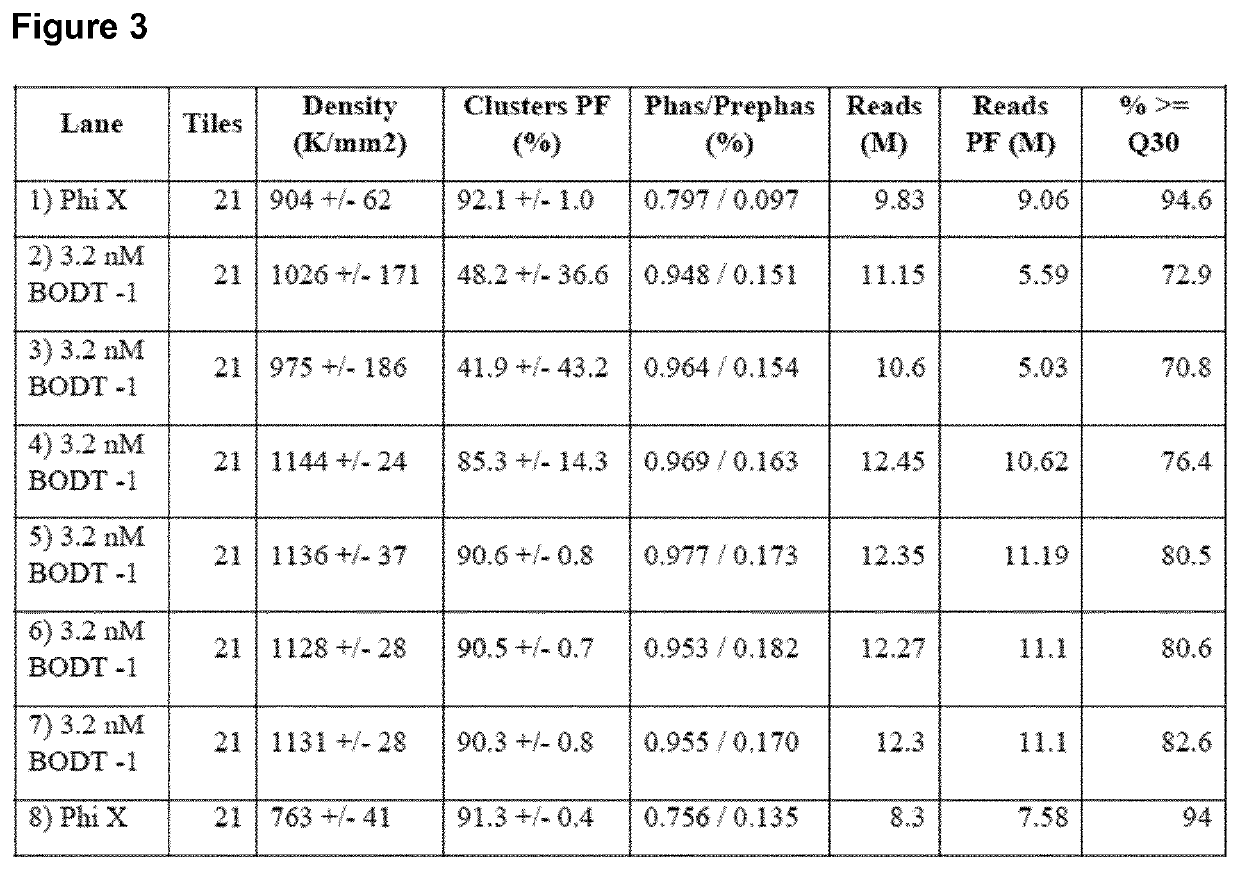
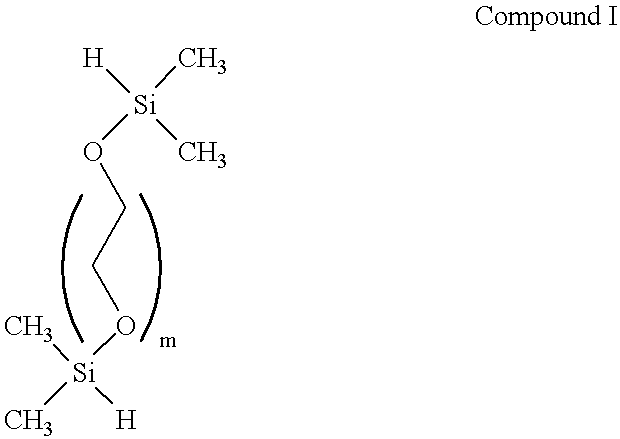
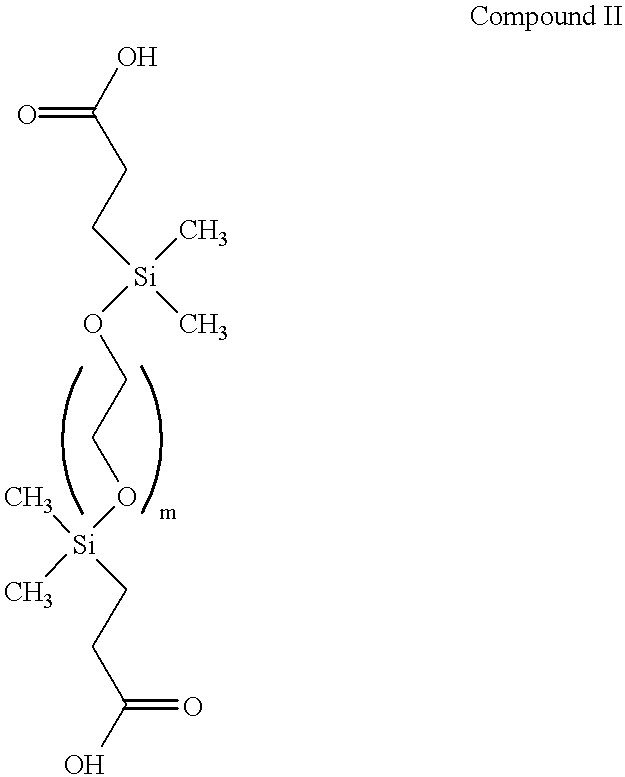
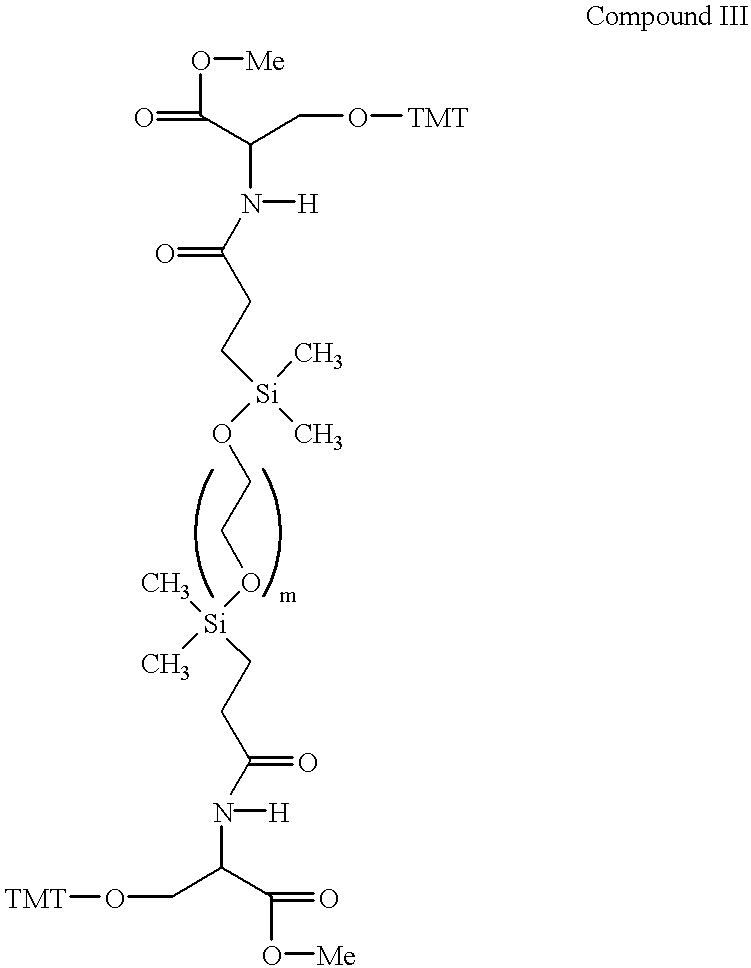
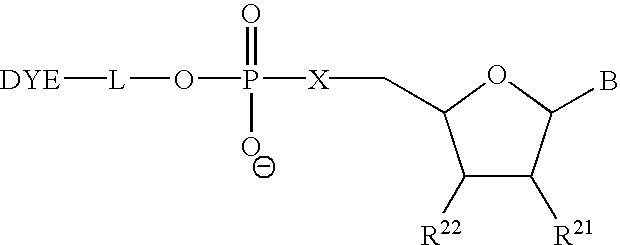
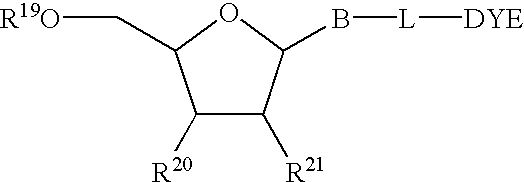
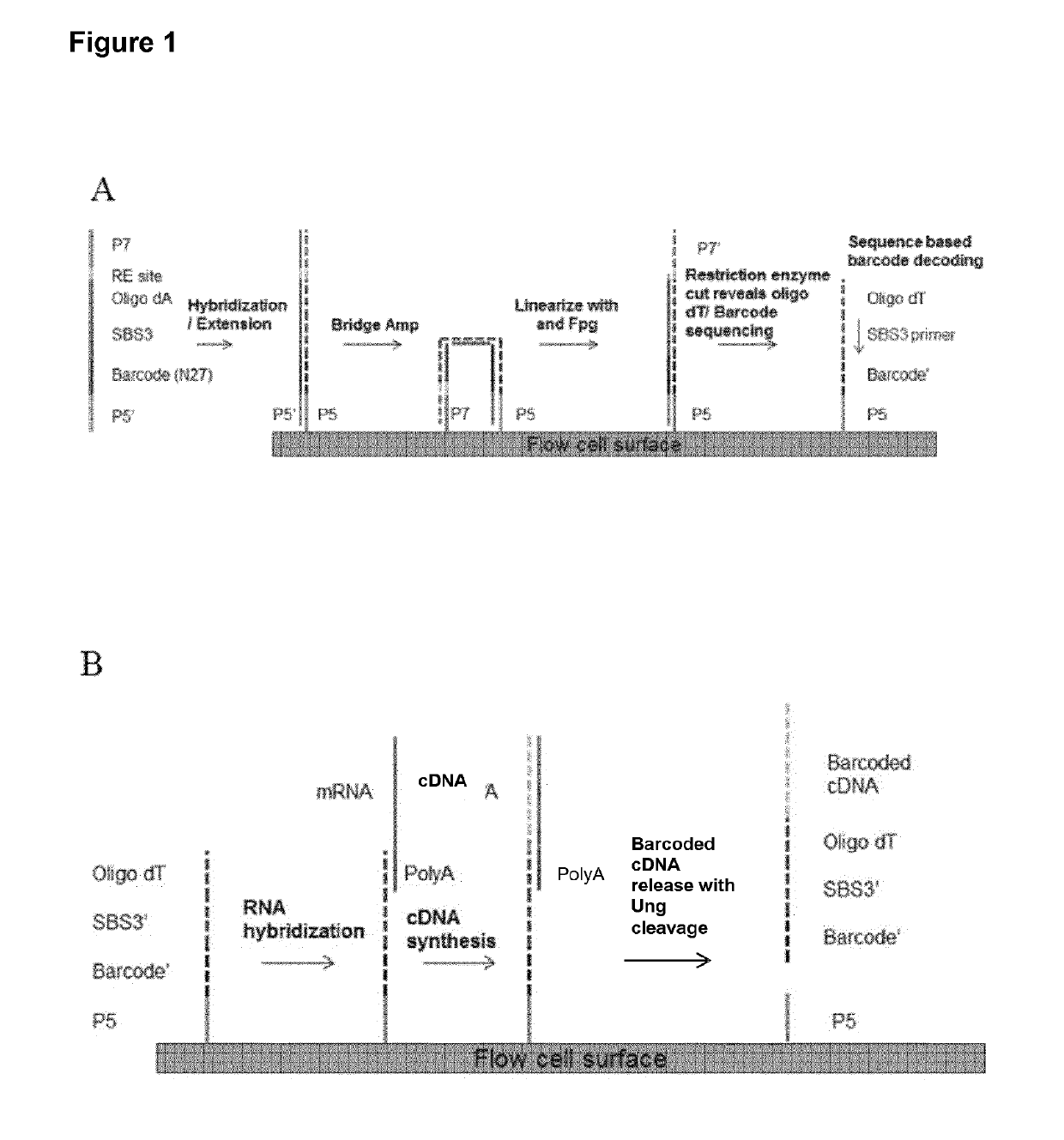
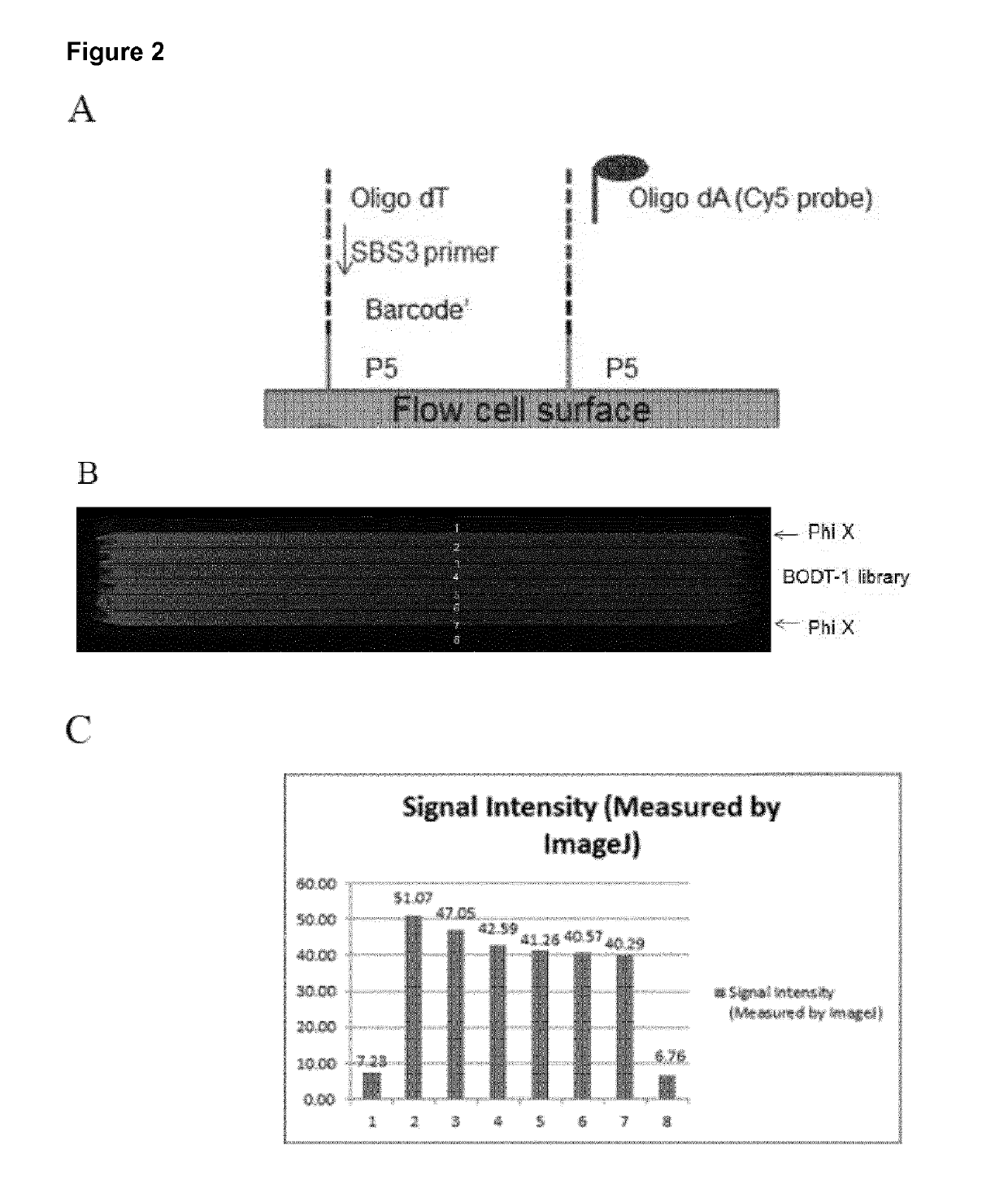
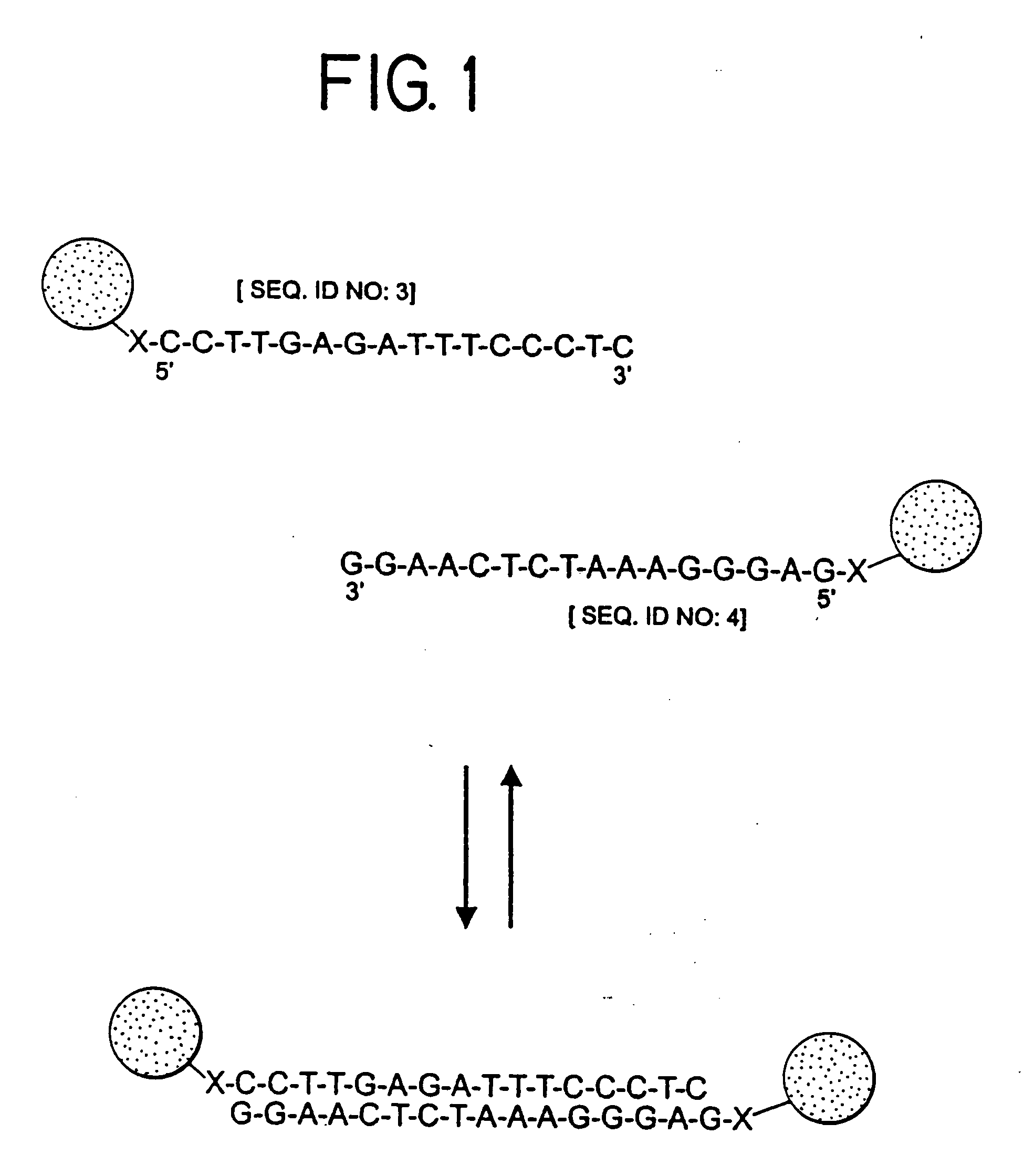
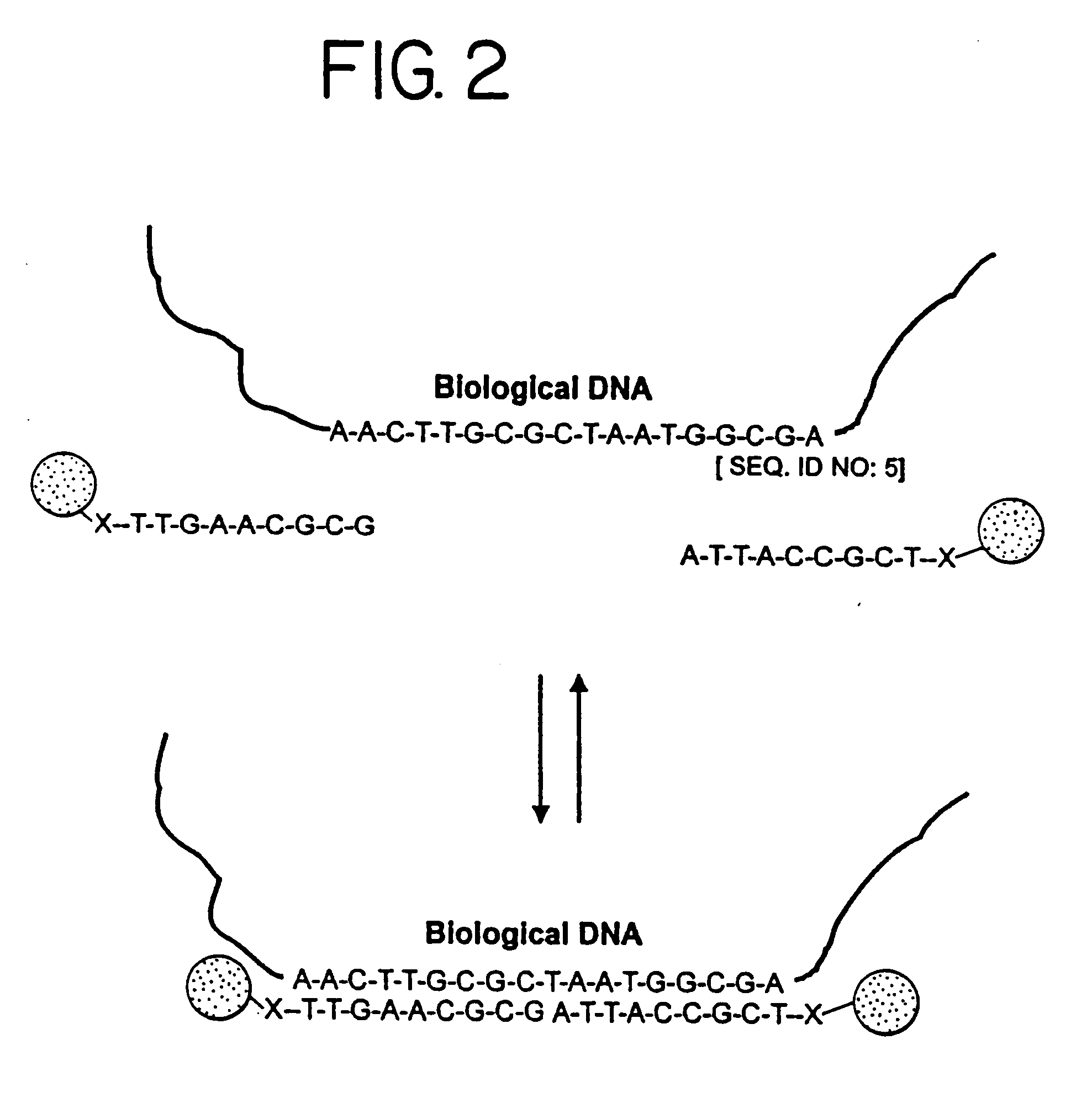
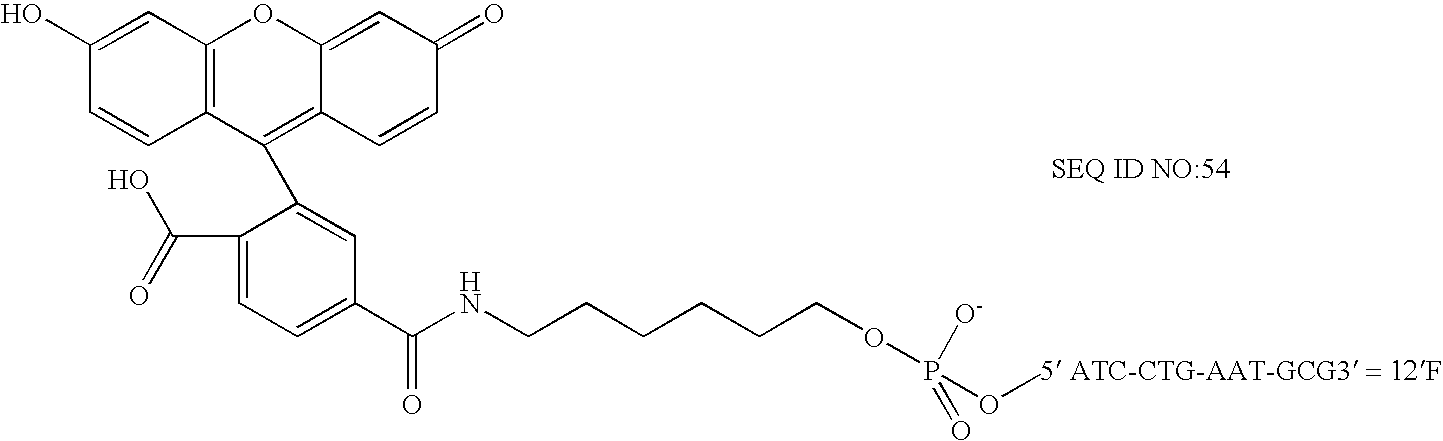
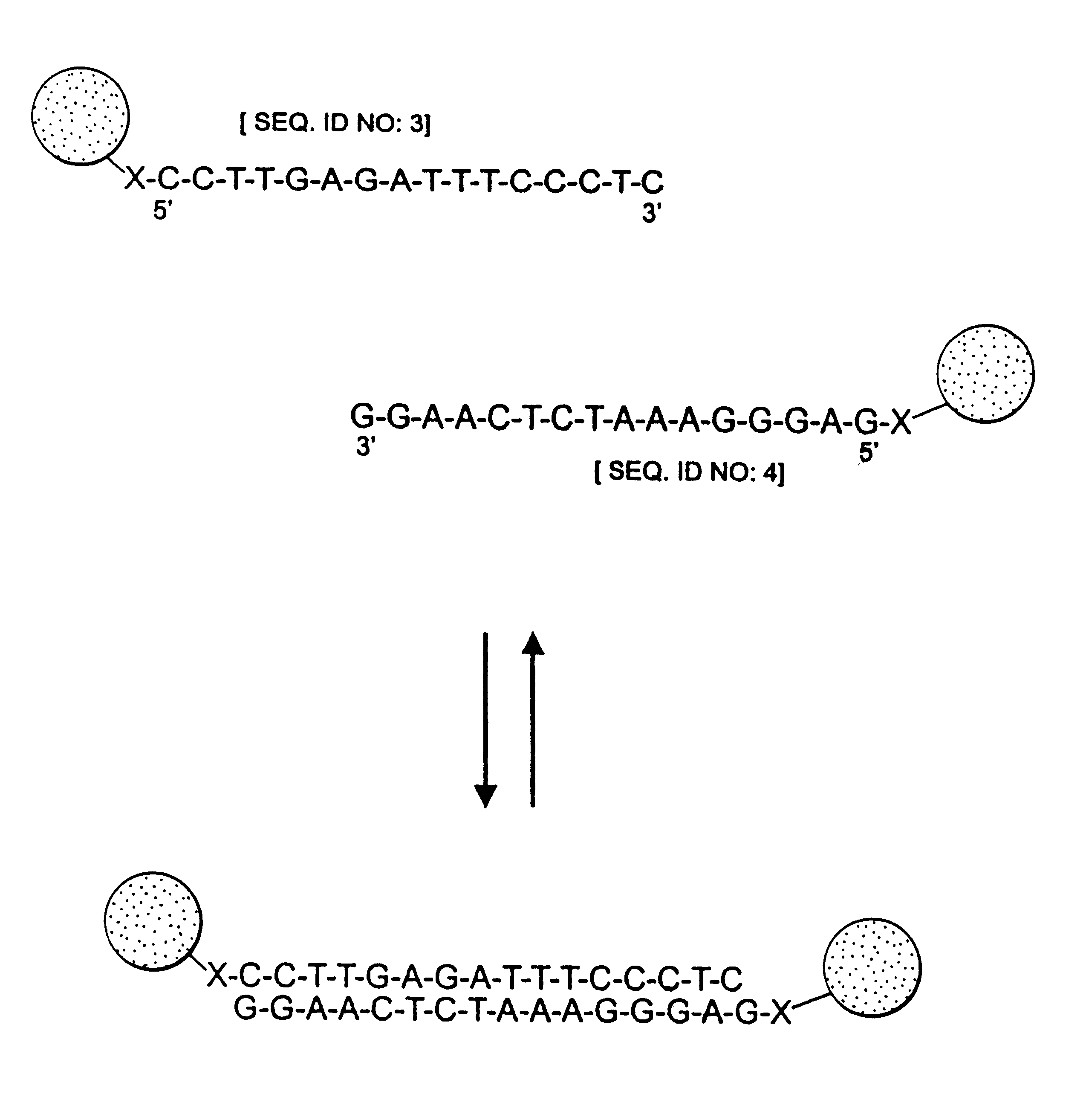Patents
Literature
371 results about "Nucleic acid hybridisation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
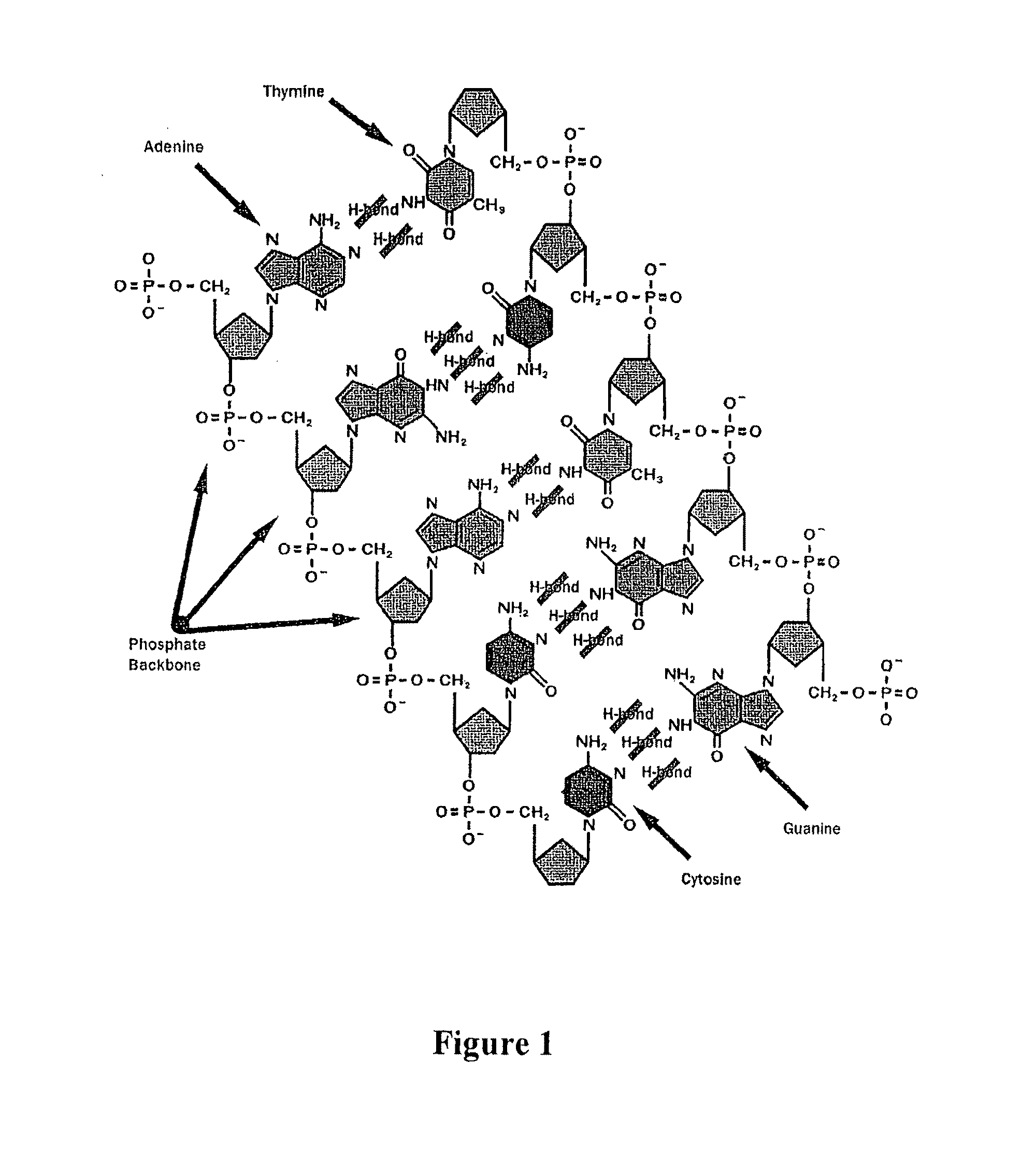
Nucleic acid hybridization: A technique in which single-stranded nucleic acids (DNA or RNA) are allowed to interact so that complexes called hybrids are formed by molecules with similar, complementary sequences.
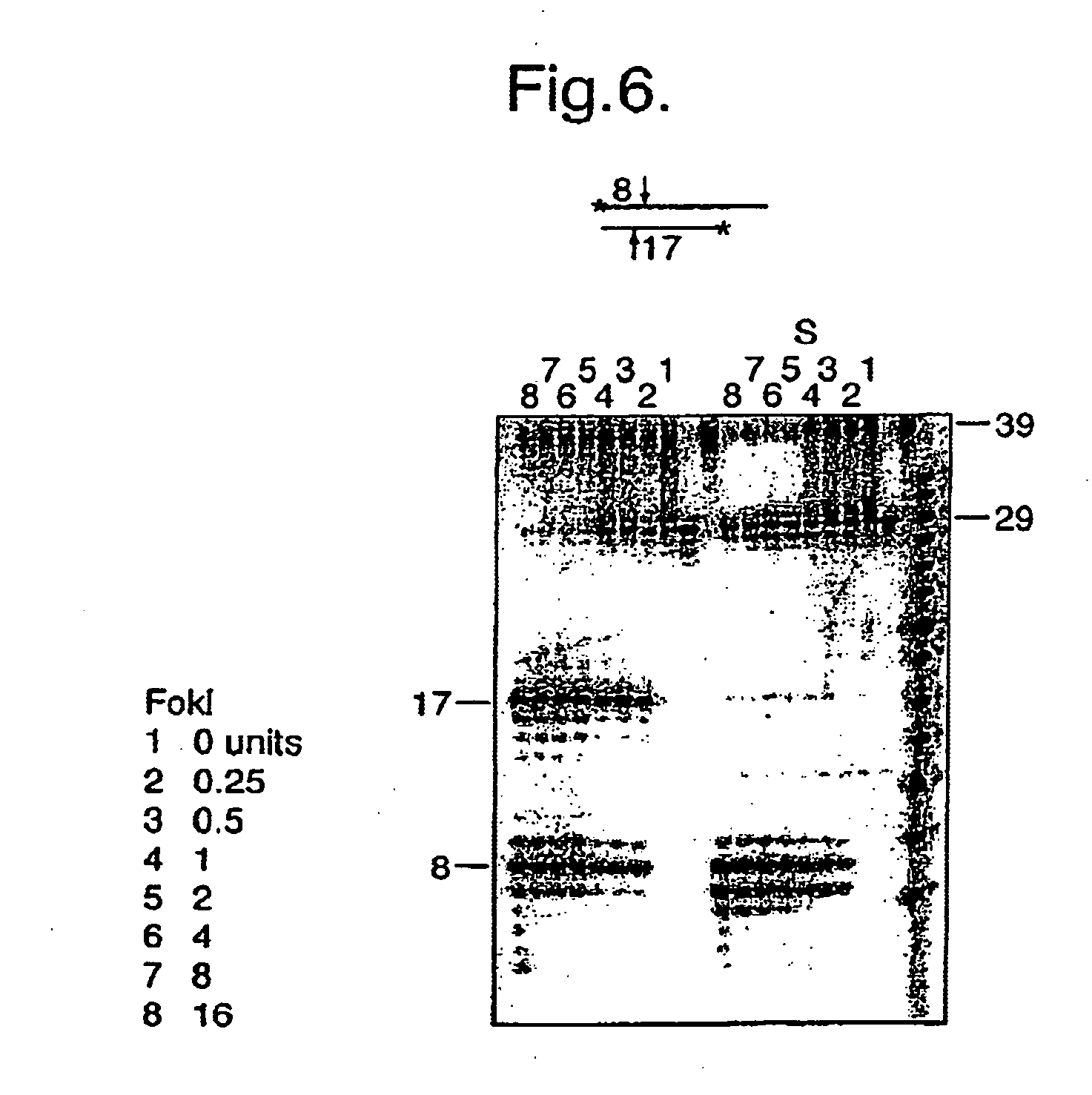
Rolling circle replication of padlock probes
InactiveUS6558928B1Avoid splittingStrong specificitySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic acid hybridisationOligonucleotide
Rolling circle replication of a padlock primer is inhibited when it is hybridized to a target nucleic acid that is long or circular. The invention provides methods of addressing this problem including cutting the target nucleic acid near or preferably at the site which hybridizes with the padlock probe, whereby a 3'-end of the cut target nucleic acid acts as a primer for rolling circle replication of the padlock probe. Also included is a method of assaying for a polyepitopic target by the use of two affinity probes each carrying an oligonucleotide tag and of a padlock probe for rolling circle replication in association with the two affinity probes
Owner:SIGMA ALDRICH CO LLC
Systems and methods for nucleic acid sequencing
ActiveUS20110267457A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic Acid ProbesNucleic acid sequencing
The present invention relates to systems and methods for sequencing nucleic acids, including sequencing nucleic acids in fluidic droplets. In one set of embodiments, the method employs sequencing by hybridization using droplets such as microfluidic droplets. In some embodiments, droplets are formed which include a target nucleic acid, a nucleic acid probe, and at least one identification element, such as a fluorescent particle. The nucleic acid probes that hybridize to the target nucleic acid are determined, in some instances, by determining the at least one identification element. The nucleic acid probes that hybridize to the target nucleic acid may be used to determine the sequence of the target nucleic acid. In certain instances, the microfluidic droplets are provided with reagents that modify the nucleic acid probe. In some cases, a droplet, such as those described above, is deformed such that the components of the droplets individually pass a target area.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Spatially distinguished, multiplex nucleic acid analysis of biological specimens
A method for spatially tagging nucleic acids of a biological specimen, including steps of (a) providing a solid support comprising different nucleic acid probes that are randomly located on the solid support, wherein the different nucleic acid probes each includes a barcode sequence that differs from the barcode sequence of other randomly located probes on the solid support; (b) performing a nucleic acid detection reaction on the solid support to locate the barcode sequences on the solid support; (c) contacting a biological specimen with the solid support that has the randomly located probes; (d) hybridizing the randomly located probes to target nucleic acids from portions of the biological specimen; and (e) modifying the randomly located probes that are hybridized to the target nucleic acids, thereby producing modified probes that include the barcode sequences and a target specific modification, thereby spatially tagging the nucleic acids of the biological specimen.
Owner:X GENOMICS SWEDEN AB +1
Optical disk-based assay devices and methods
InactiveUS6342349B1Strong specificityReduce nonspecific bindingSequential/parallel process reactionsSugar derivativesAnalyteLaser light
Optical disk-based assay devices and methods are described, in which analyte-specific signal elements are disposed on an optical disk substrate. In preferred embodiments, the analyte-specific signal elements are disposed readably with the disk's tracking features. Also described are cleavable signal elements particularly suitable for use in the assay device and methods. Binding of the chosen analyte simultaneously to a first and a second analyte-specific side member of the cleavable signal element tethers the signal-responsive moiety to the signal element's substrate-attaching end, despite subsequent cleavage at the cleavage site that lies intermediate the first and second side members. The signal responsive moiety reflects, absorbs, or refracts incident laser light. Described are nucleic acid hybridization assays, nucleic acid sequencing, immunoassays, cell counting assays, and chemical detection. Adaptation of the assay device substrate to function as an optical waveguide permits assay geometries suitable for continuous monitoring applications.
Owner:VINDUR TECH
Pyrophosphorolysis and incorporation of nucleotide method for nucleic acid detection
InactiveUS7090975B2Useful in detectionSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementDepolymerizationNucleic acid detection
Processes are disclosed using the depolymerization of a nucleic acid hybrid and incorporation of a suitable nucleotide to qualitatively and quantitatively analyze for the presence of predetermined nucleic acid target sequences. Applications of those processes include the detection of single nucleotide polymorphisms, identification of single base changes, genotyping, medical marker diagnostics, mirosequencing, and.
Owner:PROMEGA
Methods and compositions for analyzing nucleic acids
InactiveUS20060078894A1Minimizes problemReduce capacityMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationHybridization probeNucleic acid sequencing
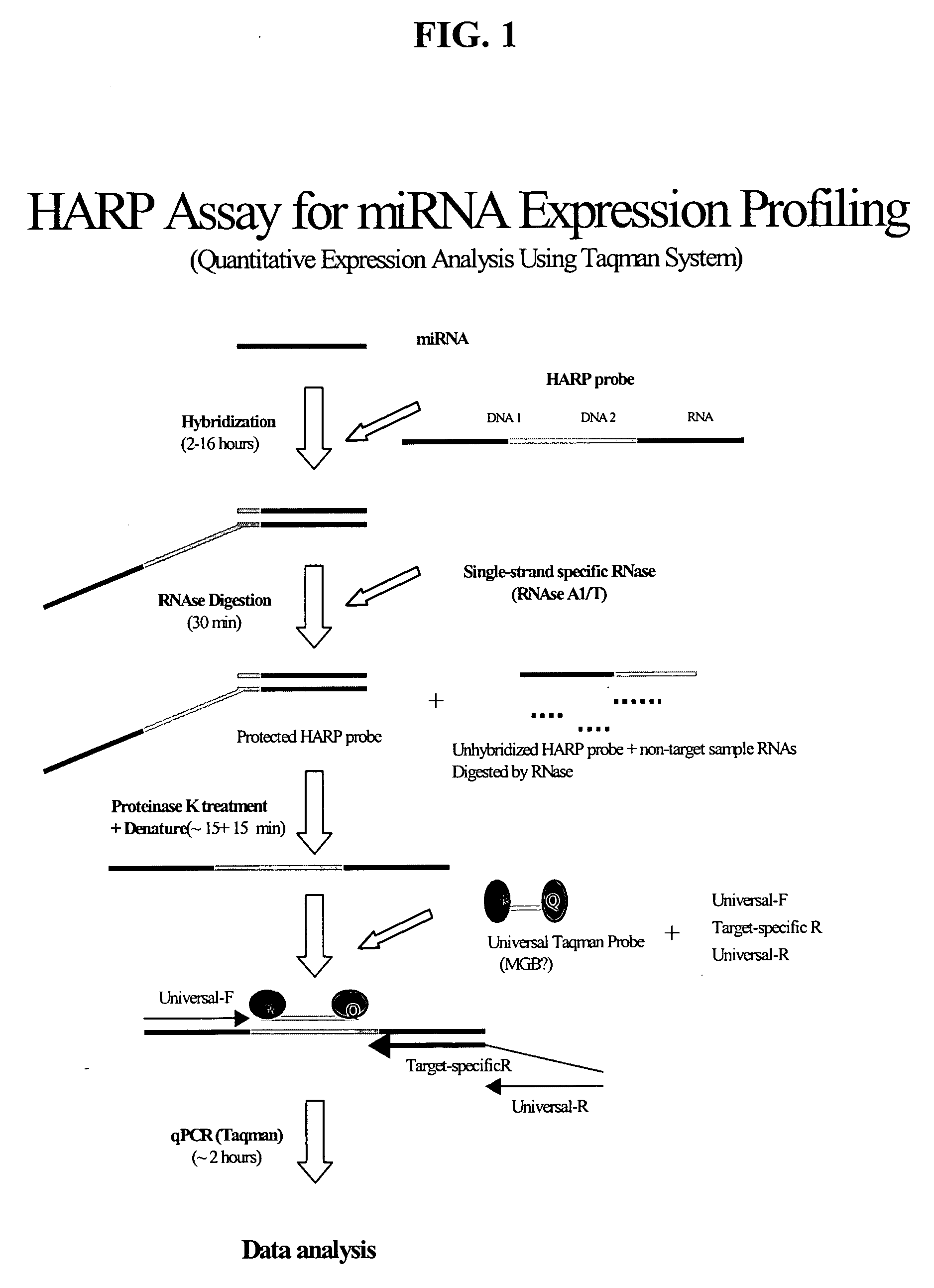
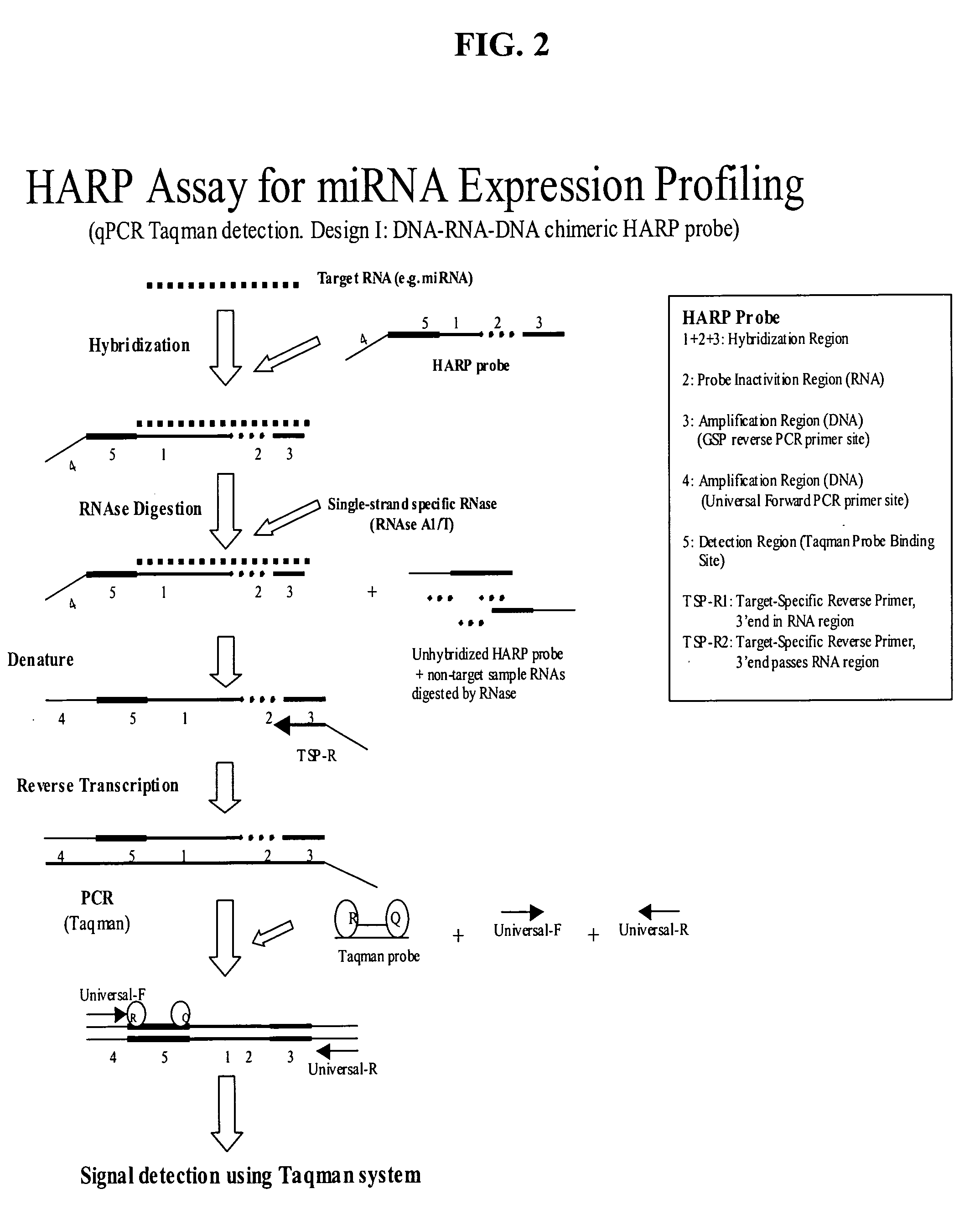
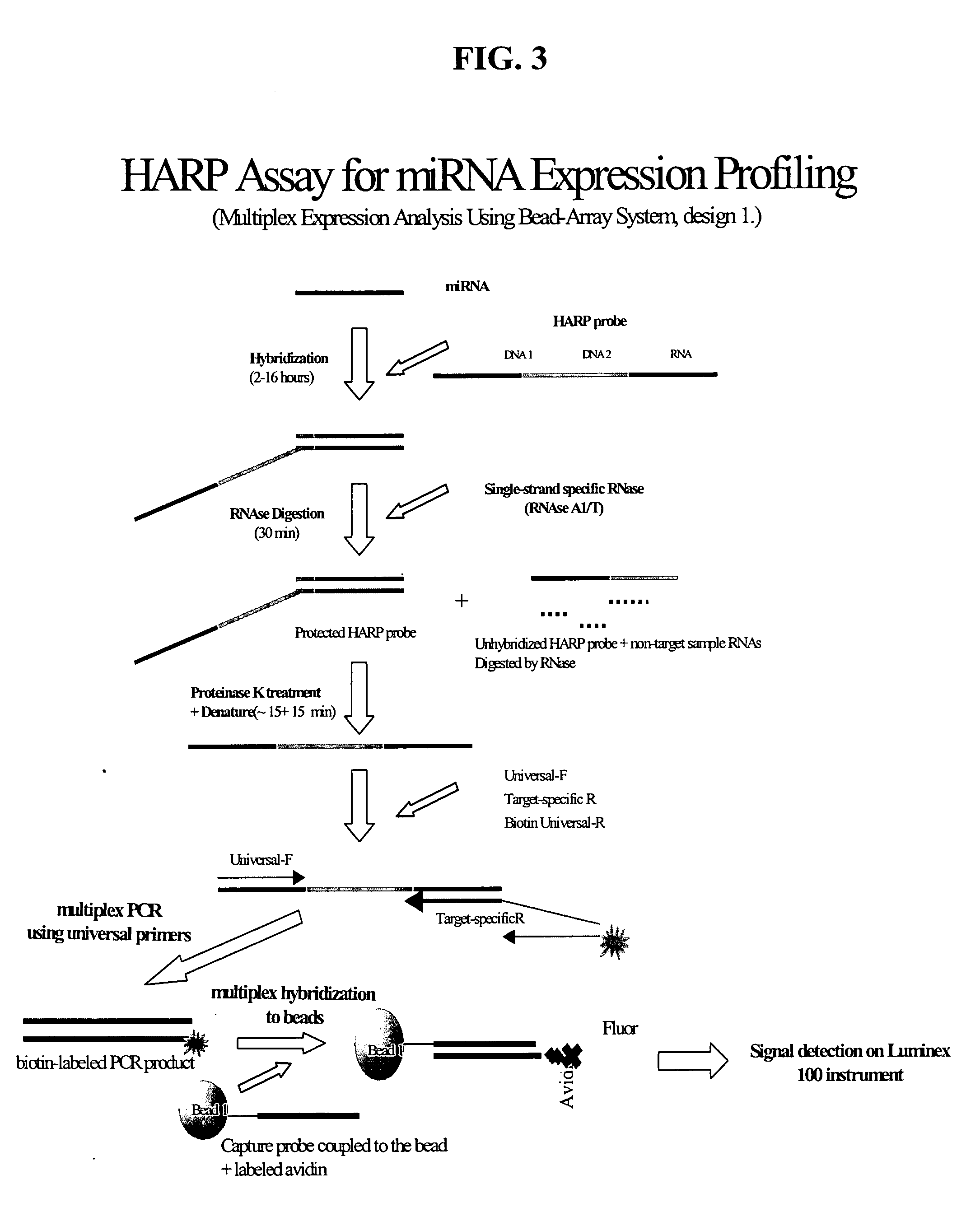
Methods and compositions for probe amplification to detect, identify, quantitate, and / or analyze a targeted nucleic acid sequence. After hybridization between a probe and the targeted nucleic acid, the probe is modified to distinguish hybridized probe from unhybridized probe. Thereafter, the probe is amplified. Moreover, in specific embodiments, the present invention involves a chimeric probe that is particularly effective when the targeted nucleic acid sequence is short and / or has a relatively low concentration, such as with an miRNA molecule.
Owner:ASURAGEN
Multipartite high-affinity nucleic acid probes
InactiveUS6451588B1Accurately determineBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsHybridization probeNucleic Acid Probes
The invention provides a collection of probes useful for hybridizing to a target nucleic acid. The probes associate with each other, binding with high affinity to the target nucleic acid, to form three-way junctions and other complexes. At least one of the probes in each collection includes a nucleic acid analog. Methods using the probes in hybridization and as primers are also provided.
Owner:APPL BIOSYSTEMS INC
Streptococcus pneumoniae 37-kDa surface adhesin a protein
The invention provides a nucleic acid encoding the 37-kDa protein from Streptococcus pneumoniae. Also provided are isolated nucleic acids comprising a unique fragment of at least 10 nucleotides of the 37-kDa protein. The invention also provides purified polypeptides encoded by the nucleic acid encoding the 37-kDa protein from and the nucleic acids comprising a unique fragment of at least 10 nucleotides of the 37-kDa protein. Also provided are antibodies which selectively binds the polypeptides encoded by the nucleic acid encoding the 37-kDa protein and the nucleic acids comprising a unique fragment of at least 10 nucleotides of the 37-kDa protein. Also provided are vaccines comprising immunogenic polypeptides encoded by the nucleic acid encoding the 37-kDa protein and the nucleic acids comprising a unique fragment of at least 10 nucleotides of the 37-kDa protein. Further provided is a method of detecting the presence of Streptococcus pneumoniae in a sample comprising the steps of contacting a sample suspected of containing Streptococcus pneumoniae with nucleic acid primers capable of hybridizing to a nucleic acid comprising a portion of the nucleic acid encoding the 37-kDa protein, amplifying the nucleic acid and detecting the presence of an amplification product, the presence of the amplification product indicating the presence of Streptococcus pneumoniae in the sample. Further provided are methods of detecting the presence of Streptococcus pneumoniae in a sample using antibodies or antigens, methods of preventing and treating Streptococcus pneumoniae infection in a subject.
Owner:US DEPT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES
Spatially distinguished, multiplex nucleic acid analysis of biological specimens
ActiveUS20190203275A1Microbiological testing/measurementDNA preparationNucleic acid detectionNucleic Acid Probes
A method for spatially tagging nucleic acids of a biological specimen, including steps of (a) providing a solid support comprising different nucleic acid probes that are randomly located on the solid support, wherein the different nucleic acid probes each includes a barcode sequence that differs from the barcode sequence of other randomly located probes on the solid support; (b) performing a nucleic acid detection reaction on the solid support to locate the barcode sequences on the solid support; (c) contacting a biological specimen with the solid support that has the randomly located probes; (d) hybridizing the randomly located probes to target nucleic acids from portions of the biological specimen; and (e) modifying the randomly located probes that are hybridized to the target nucleic acids, thereby producing modified probes that include the barcode sequences and a target specific modification, thereby spatially tagging the nucleic acids of the biological specimen.
Owner:SPATIAL TRANSCRIPTOMICS +1
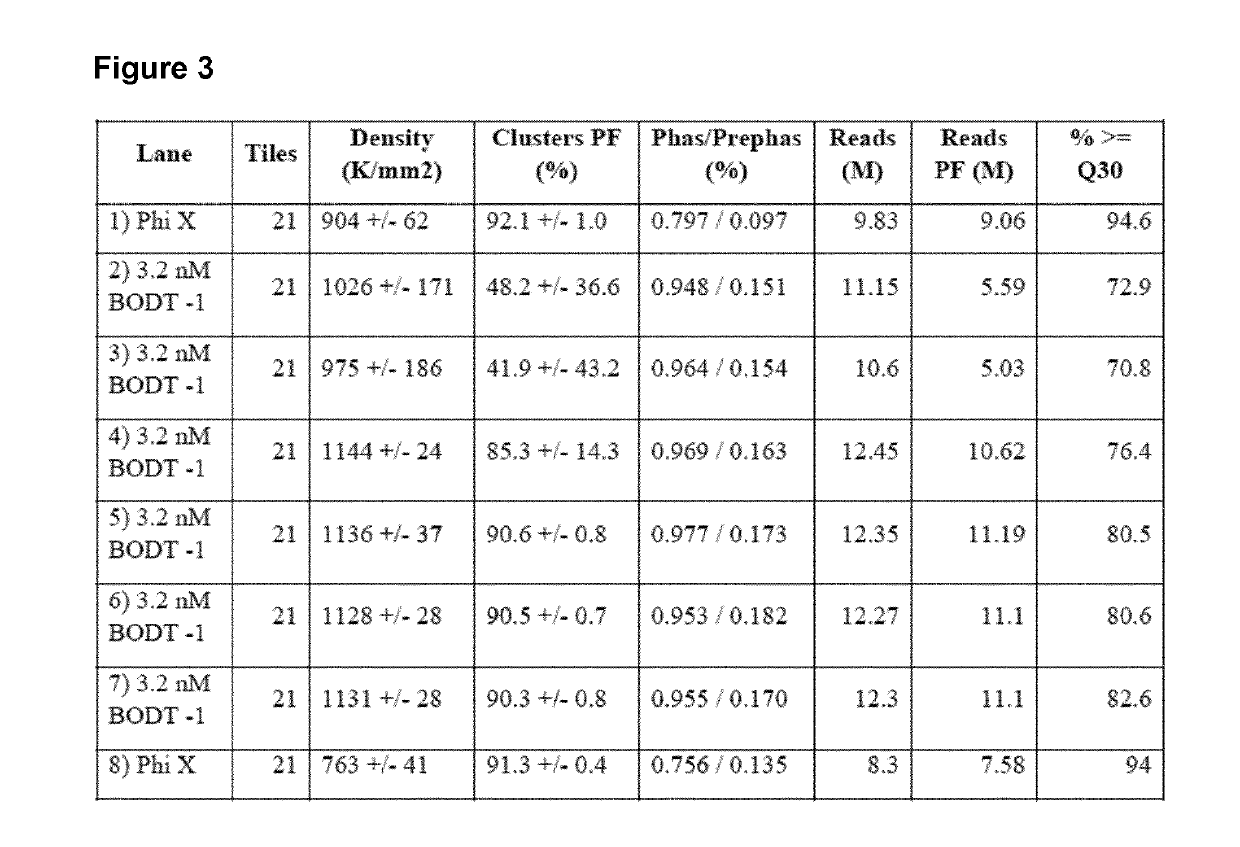
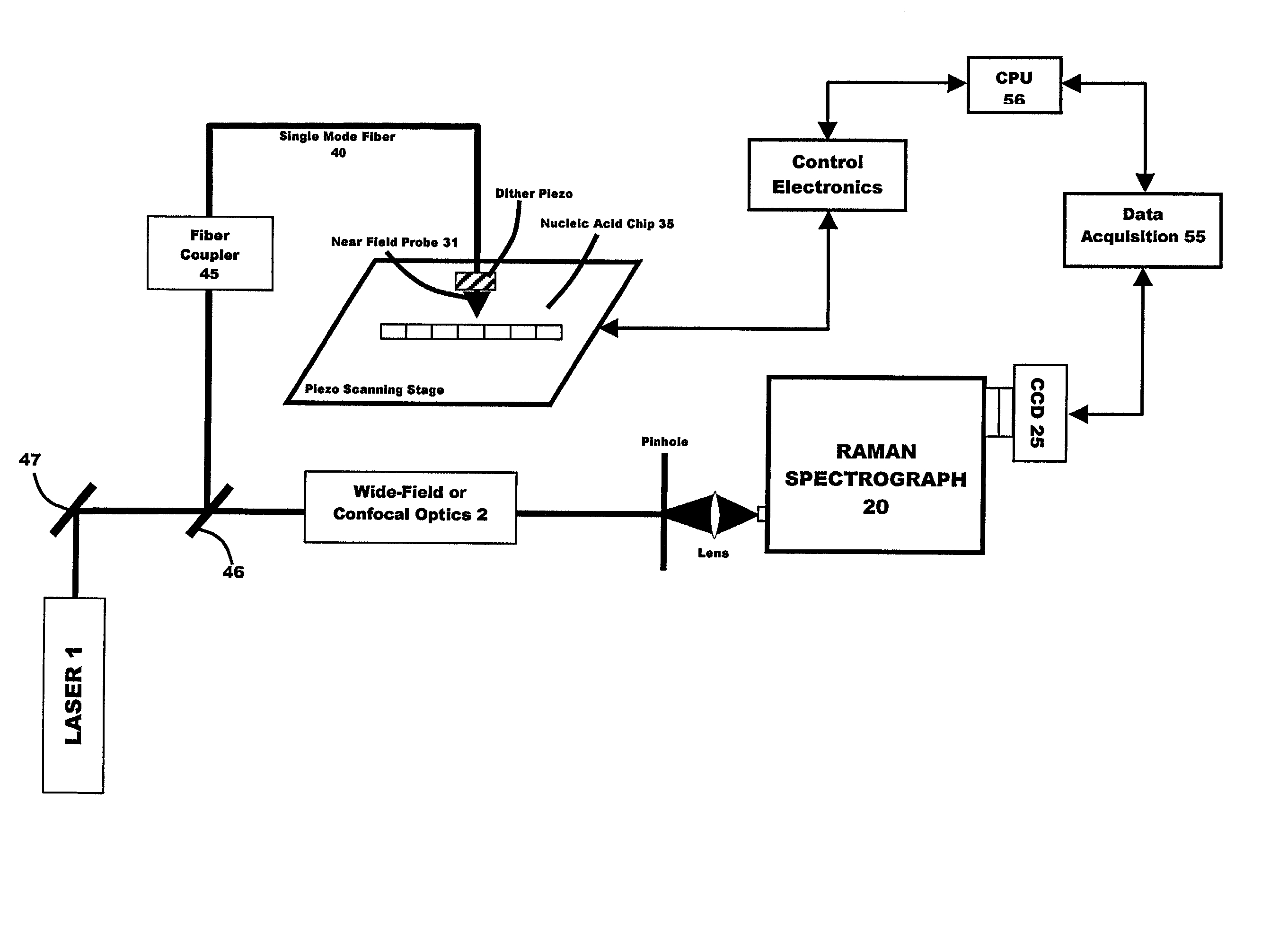
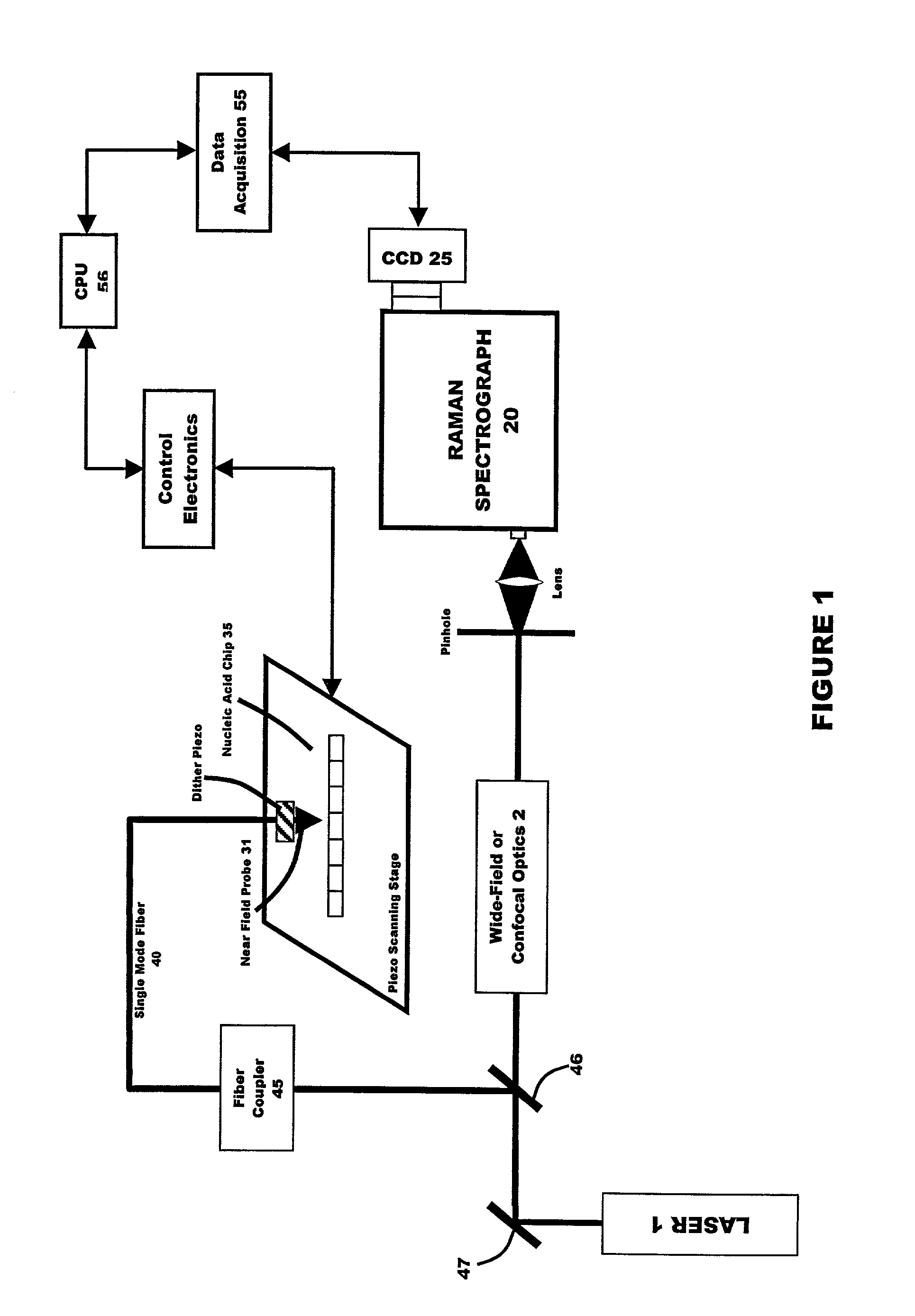
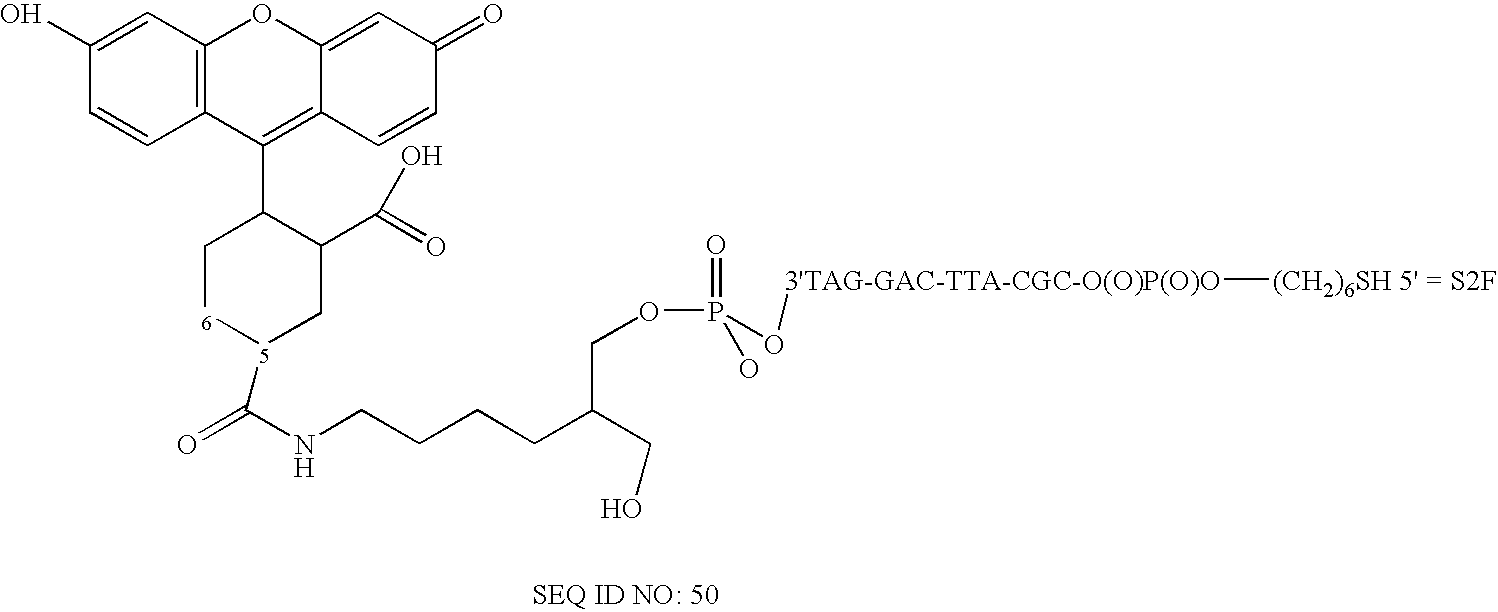
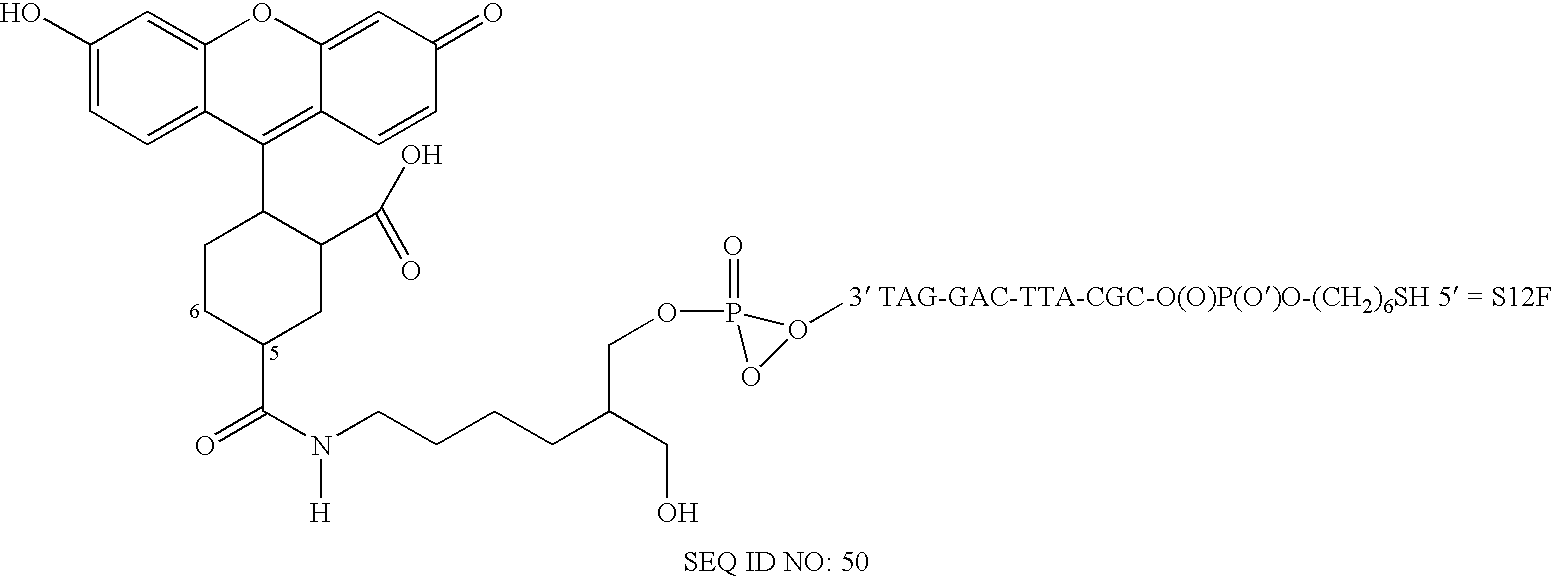
Apparatus and method for analysis of nucleic acids hybridization on high density NA chips.
InactiveUS20020123050A1High sensitivityUseful in detectionBioreactor/fermenter combinationsRadiation pyrometryHigh densityNucleic acid hybridisation
The invention generally relates to a new gene probe biosensor employing near field surface enhanced Raman scattering (NFSERS) for direct spectroscopic detection of hybridized molecules (such as hybridized DNA) without the need for labels, and the invention also relates to methods for using the biosensor.
Owner:POPONIN VLADIMIR
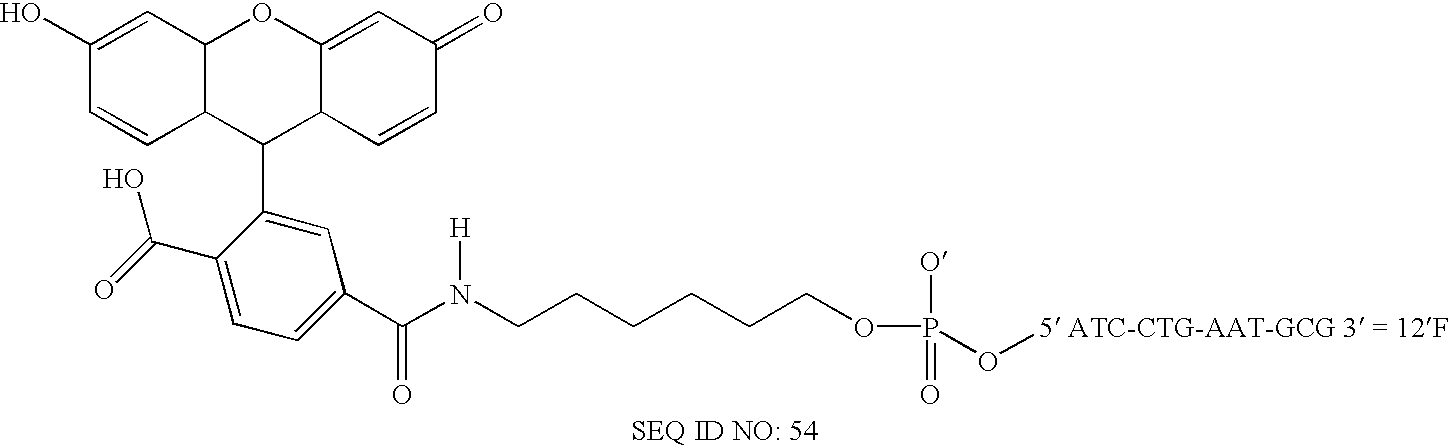
Methods and compositions for the detection of ovarian disease
InactiveUS20090081685A1Easy diagnosisIncrease chanceMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisDiseaseComplement system
Methods and compositions for identifying ovarian cancer in a patient sample are provided. The methods of the invention comprise detecting overexpression of at least one biomarker in a body sample, wherein the biomarker is selectively overexpressed in ovarian cancer. In preferred embodiments, the body sample is a serum sample. The biomarkers of the invention include any genes or proteins that are selectively overexpressed in ovarian cancer, including, for example, acute phase reactants, lipoproteins, proteins involved in the regulation of the complement system, regulators of apoptosis, proteins that bind hemoglobin, heme, or iron, cytostructural proteins, enzymes that detoxify metabolic byproducts, growth factors, and hormone transporters. In some aspects of the invention, overexpression of a biomarker of interest is detected at the protein level using biomarker-specific antibodies or at the nucleic acid level using nucleic acid hybridization techniques. Kits for practicing the methods of the invention are further provided.
Owner:TRIPATH IMAGING INC
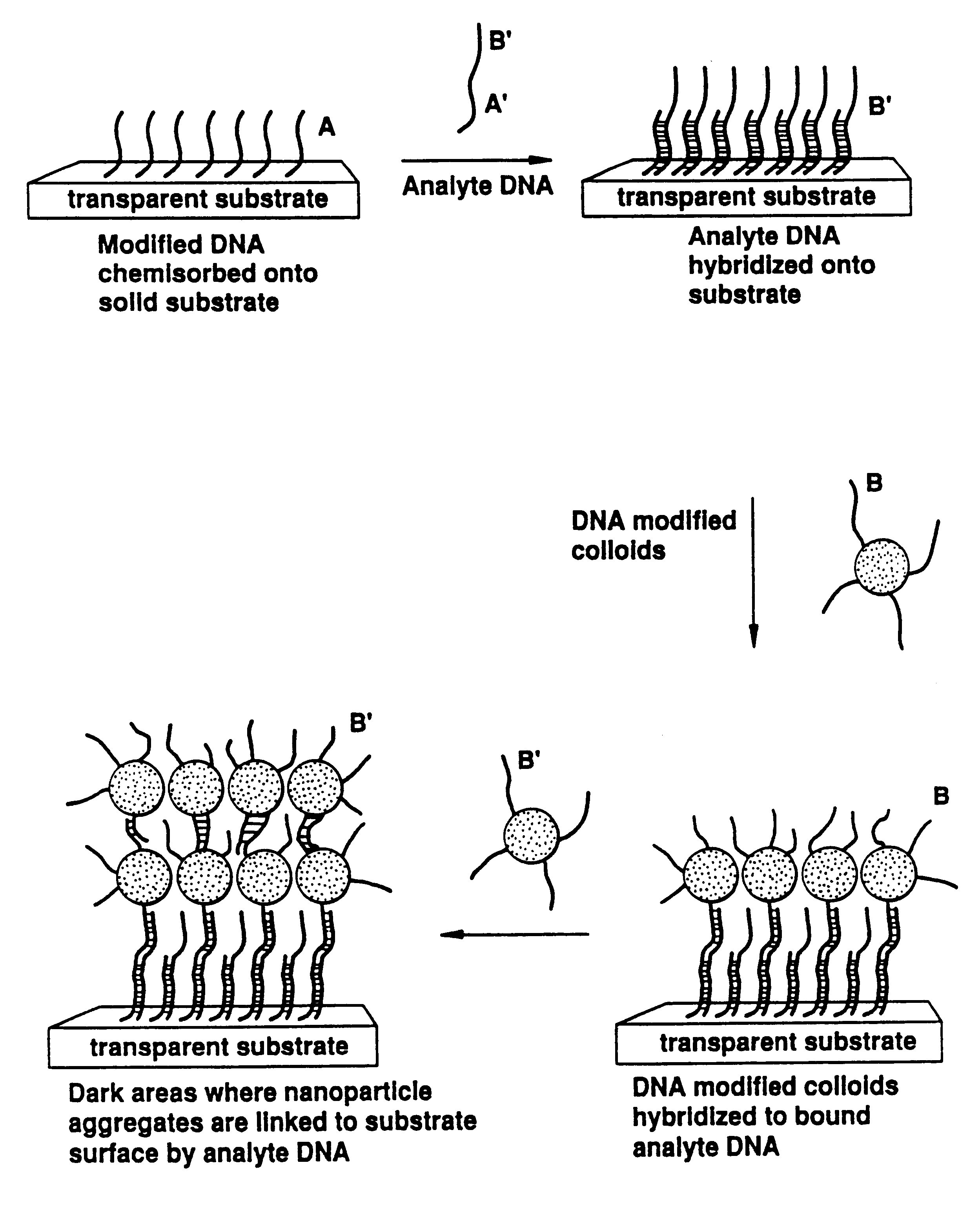
Nanoparticles having oligonucleotides attached thereto and uses therefor
InactiveUS20060068378A1Additional movementImprove bindingMaterial nanotechnologySugar derivativesNanoparticleColor changes
The invention provides methods of detecting a nucleic acid. The methods comprise contacting the nucleic acid with one or more types of particles having oligonucleotides attached thereto. In one embodiment of the method, the oligonucleotides are attached to nanoparticles and have sequences complementary to portions of the sequence of the nucleic acid. A detectable change (preferably a color change) is brought about as a result of the hybridization of the oligonucleotides on the nanoparticles to the nucleic acid. The invention also provides compositions and kits comprising particles. The invention further provides methods of synthesizing unique nanoparticle-oligonucleotide conjugates, the conjugates produced by the methods, and methods of using the conjugates. In addition, the invention provides nanomaterials and nanostructures comprising nanoparticles and methods of nanofabrication utilizing nanoparticles. Finally, the invention provides a method of separating a selected nucleic acid from other nucleic acids.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN UNIV +1
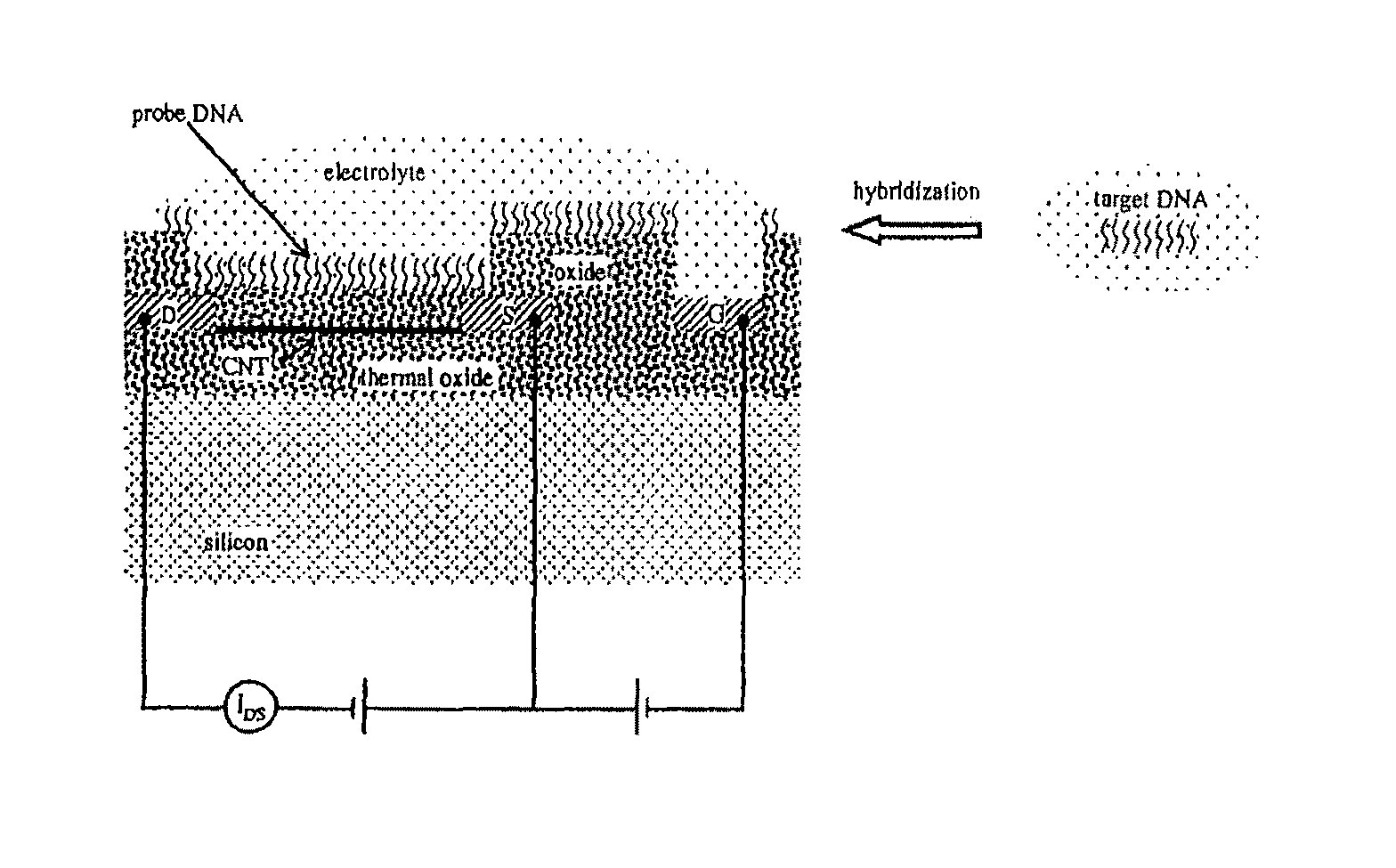
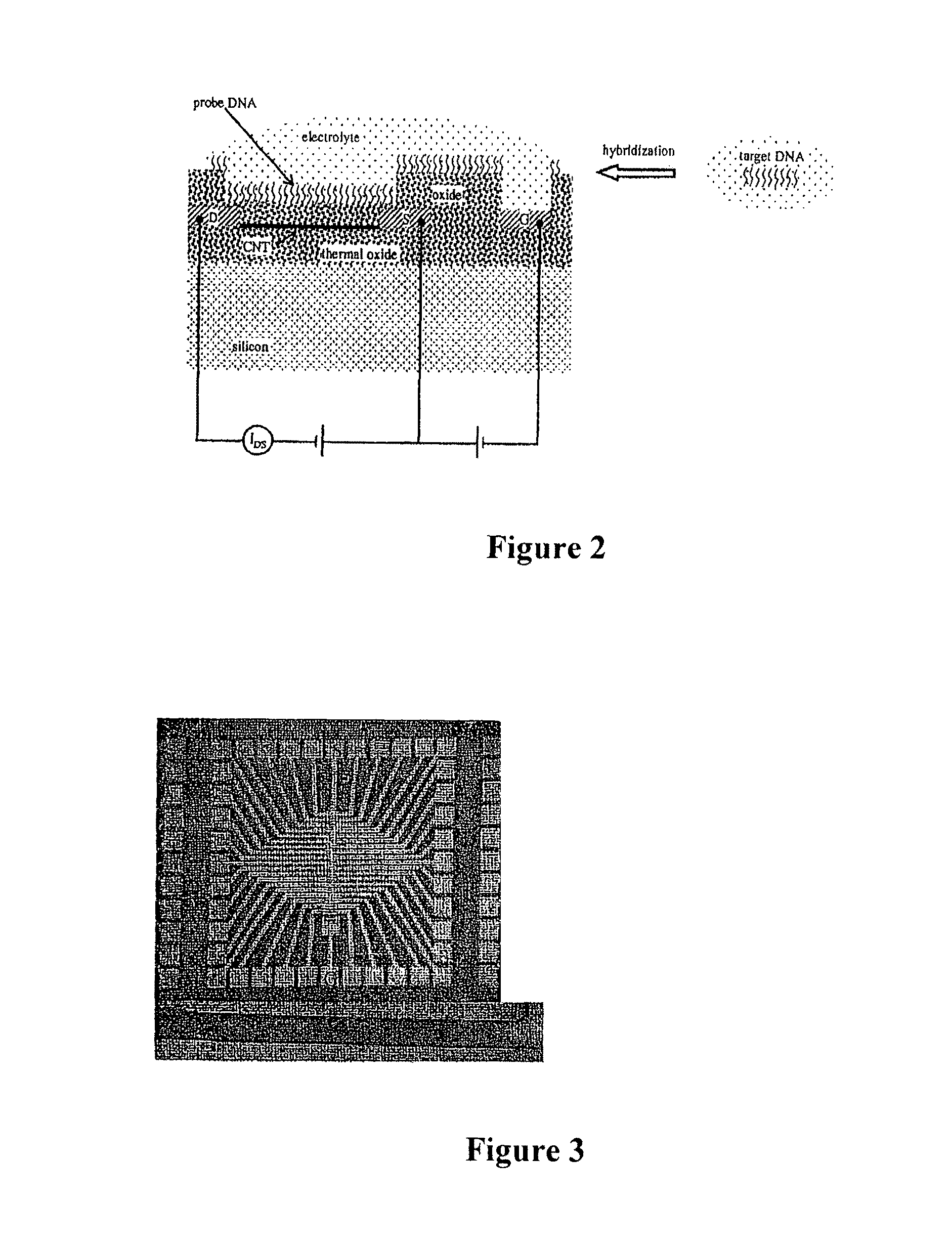
Apparatus for microarray binding sensors having biological probe materials using carbon nanotube transistors
InactiveUS8017938B2Immobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsCarbon nanotubeMiniaturization
A microarray apparatus is provided which contains at least one chip having source and drain electrodes positioned on an array of carbon nanotube transistors which allows for electronic detection of nucleic acid hybridizations, thereby affording both increased sensitivity and the capability of miniaturization.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND +1
Oligomeric compounds comprising bicyclic nucleotides and uses thereof
The present invention provides oligomeric compounds. Certain such oligomeric compounds are useful for hybridizing to a complementary nucleic acid, including but not limited, to nucleic acids in a cell. In certain embodiments, hybridization results in modulation of the amount activity or expression of the target nucleic acid in a cell.
Owner:IONIS PHARMA INC
Determination of methylated DNA
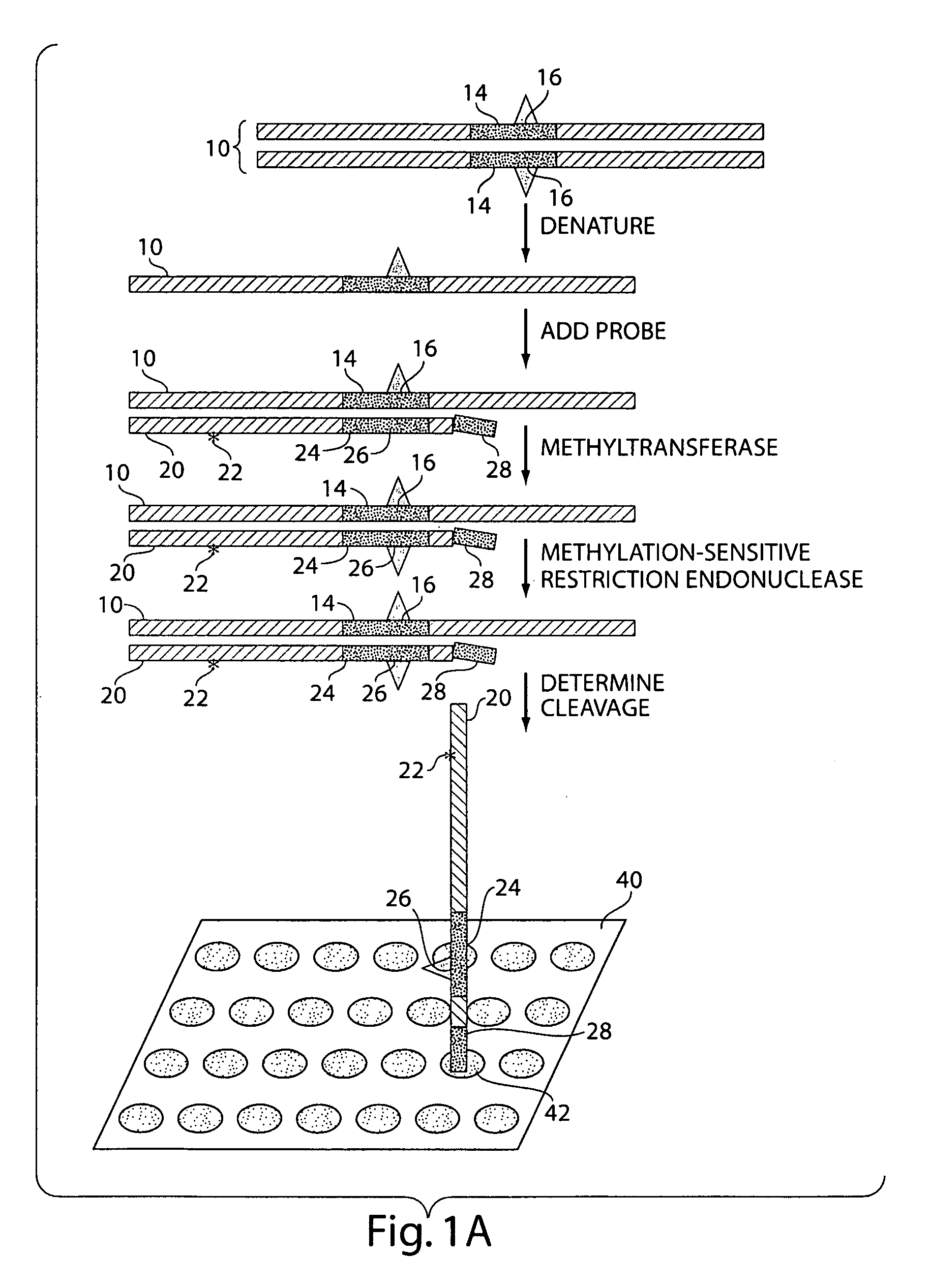
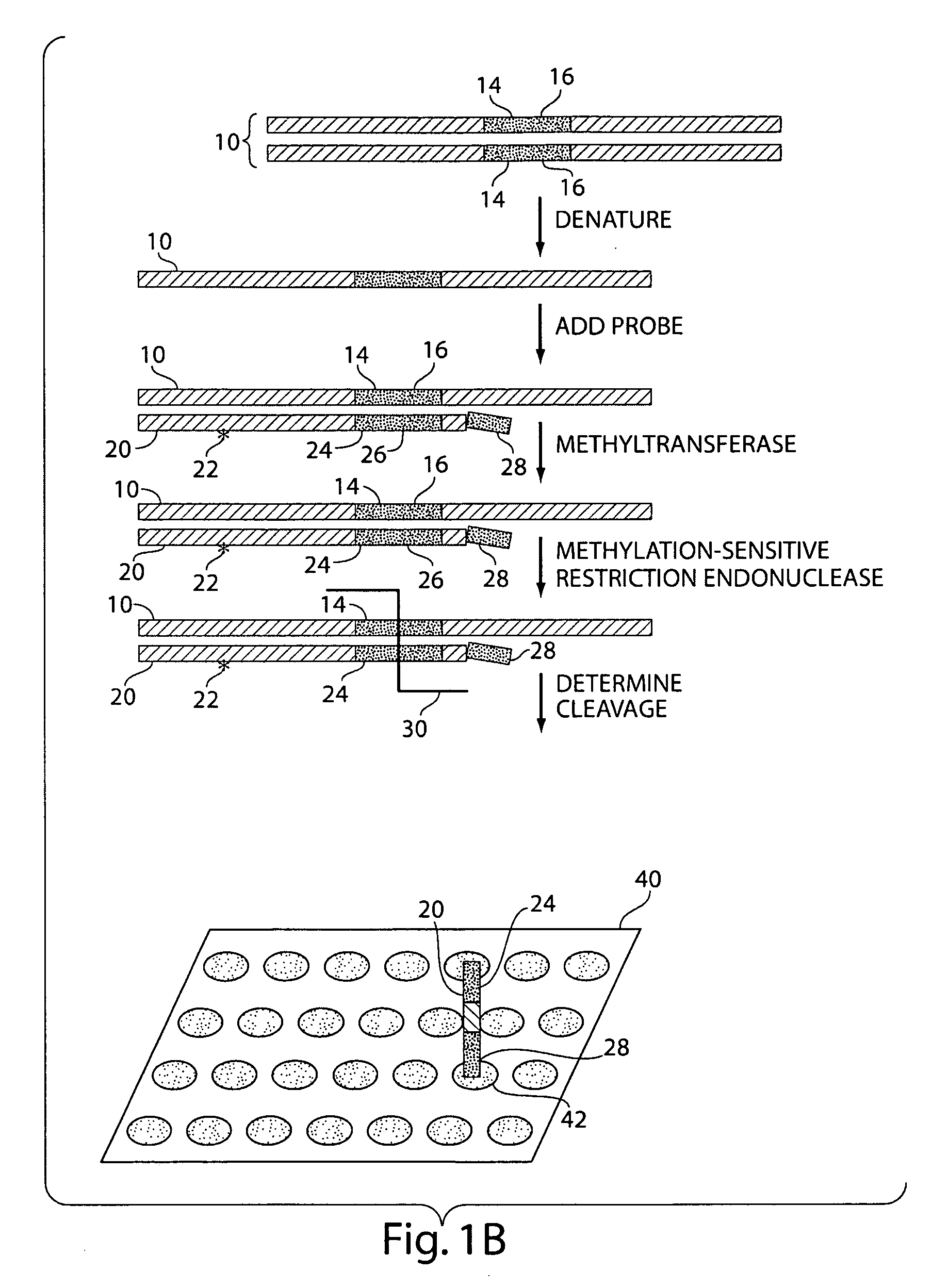
InactiveUS20070231800A1Microbiological testing/measurementFermentationNucleic Acid ProbesNucleic acid hybridisation
The present invention generally relates to the determination of the state of one or more locations within a nucleic acid and, in particular, to the determination of the methylation state of one or more methylation sites within a nucleic acid such as DNA. In one aspect of the invention, a nucleic acid, such as DNA, that is suspected of being methylated is exposed to a nucleic acid probe able to hybridize the nucleic acid at or near the methylation site. After hybridization, the nucleic acid-probe hybrid is exposed to a methylation-sensitive restriction endonuclease able to bind at or near the methylation site. The restriction endonuclease is not able to cleave the nucleic acid-probe hybrid if the DNA is methylated at the methylation site, but is able to cleave the nucleic acid-probe hybrid if the nucleic acid is not methylated at the methylation site. Determination of the cleavage state of the probe can thus be used to determine the state of the methylation site.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Nanoparticles having oligonucleotides attached thereto and uses therefor
InactiveUS20020127574A1Detect changeMaterial nanotechnologySugar derivativesNanoparticleColor changes
The invention provides methods of detecting a nucleic acid. The methods comprise contacting the nucleic acid with one or more types of particles having oligonucleotides attached thereto. In one embodiment of the method, the oligonucleotides are attached to nanoparticles and have sequences complementary to portions of the sequence of the nucleic acid. A detectable change (preferably a color change) is brought about as a result of the hybridization of the oligonucleotides on the nanoparticles to the nucleic acid. The invention also provides compositions and kits comprising particles. The invention further provides methods of synthesizing unique nanoparticle-oligonucleotide conjugates, the conjugates produced by the methods, and methods of using the conjugates. In addition, the invention provides nanomaterials and nanostructures comprising nanoparticles and methods of nanofabrication utilizing nanoparticles. Finally, the invention provides a method of separating a selected nucleic acid from other nucleic acids.
Owner:NANOSPHERE INC
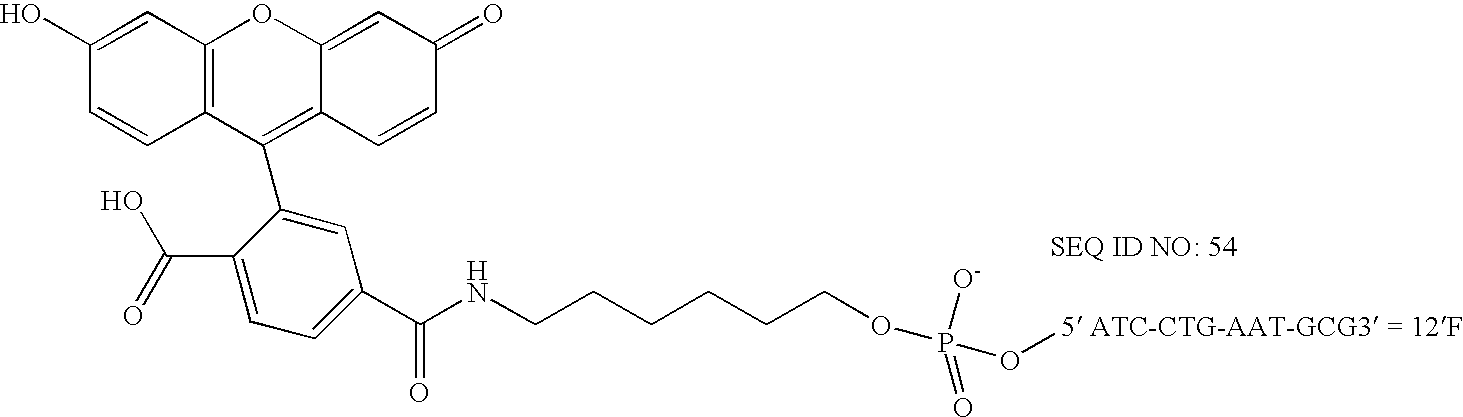
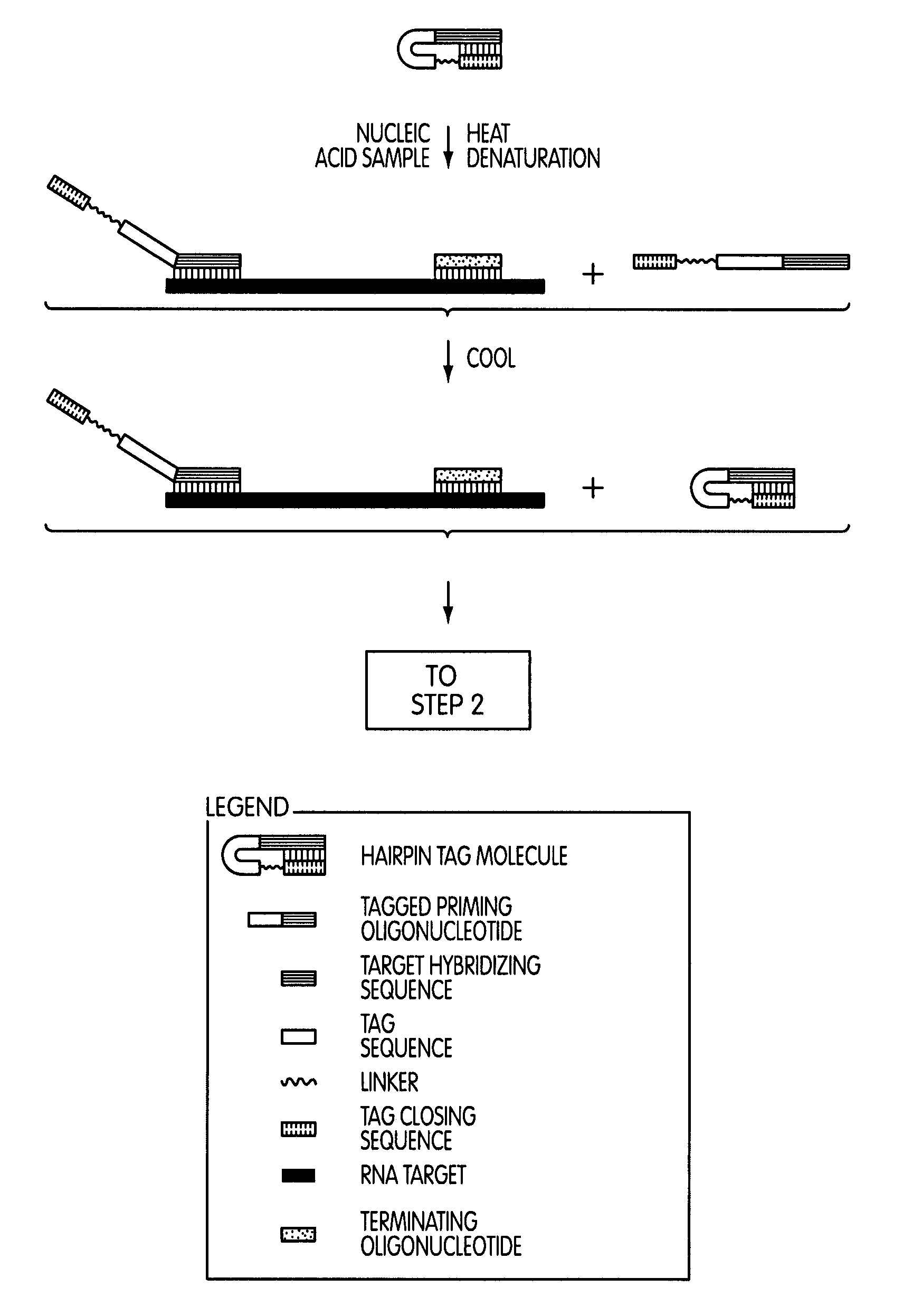
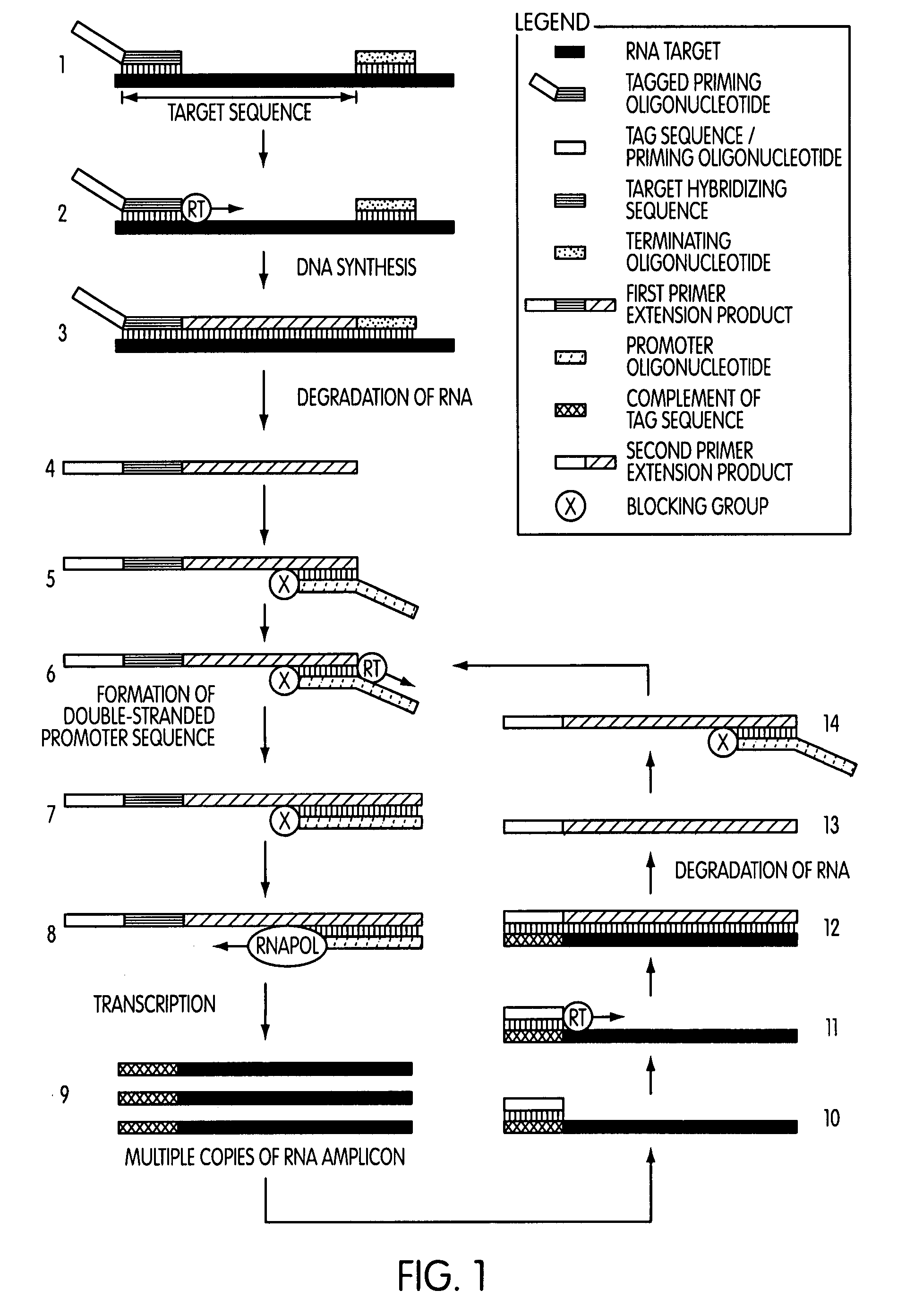
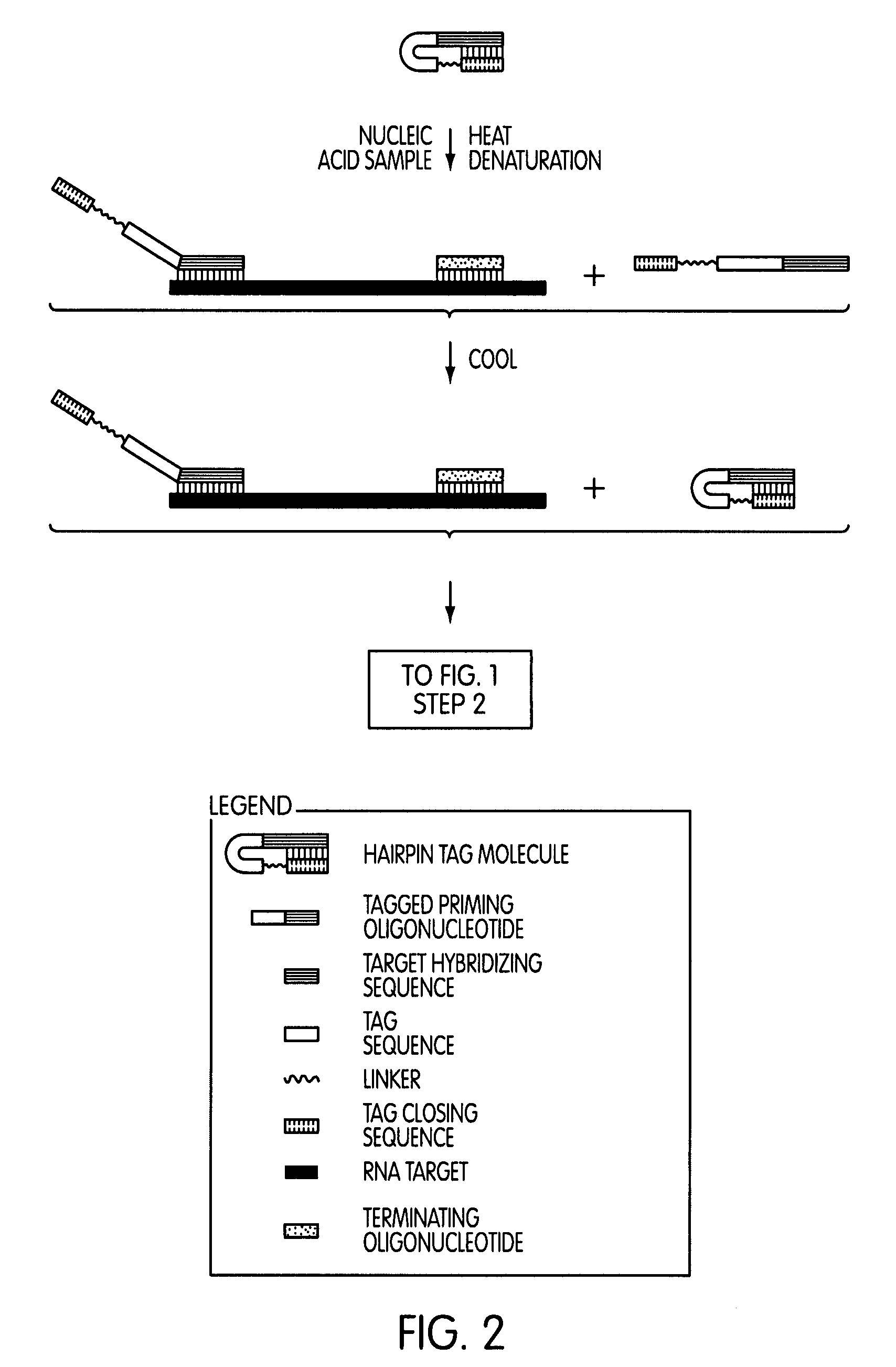
Tagged oligonucleotides and their use in nucleic acid amplification methods
ActiveUS7833716B2Reduce or eliminate false positive amplification signalsLess purificationMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationNucleic acid sequencingNucleic acid hybridisation
A method for selective amplification of at least one target nucleic acid sequence, comprising the steps of: treating a sample with a tagged oligonucleotide comprising a target hybridizing sequence that hybridizes to a 3′-end of the target nucleic acid sequence, and a tag sequence situated 5′ to the target hybridizing sequence that does not stably hybridize to a target nucleic acid, wherein tagged oligonucleotide hybridized to target nucleic acids form tagged target nucleic acids; prior to initiating a primer extension reaction, reducing the effective concentration of unhybridized tagged oligonucleotide having an active form; initiating an extension reaction to produce a primer extension product; separating the primer extension product from the target nucleic acid; and producing amplification products therefrom using an oligonucleotide that hybridizes to the complement of the tag sequence.
Owner:GEN PROBE INC
Nanoparticles having oligonucleotides attached thereto and uses therefor
InactiveUS7250499B2Material nanotechnologyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsNanoparticleNucleic acid sequencing
The invention provides methods of detecting a nucleic acid. The methods comprise contacting the nucleic acid with one or more types of particles having oligonucleotides attached thereto. In one embodiment of the method, the oligonucleotides are attached to nanoparticles and have sequences complementary to portions of the sequence of the nucleic acid. A detectable change (preferably a color change) is brought about as a result of the hybridization of the oligonucleotides on the nanoparticles to the nucleic acid. The invention also provides compositions and kits comprising particles. The invention further provides methods of synthesizing unique nanoparticle-oligonucleotide conjugates, the conjugates produced by the methods, and methods of using the conjugates. In addition, the invention provides nanomaterials and nanostructures comprising nanoparticles and methods of nanofabrication utilizing nanoparticles. Finally, the invention provides a method of separating a selected nucleic acid from other nucleic acids.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN UNIV +1
Methods and compositions for evaluating breast cancer prognosis
InactiveUS20060063190A1Accurate assessmentImproved prognosisMicrobiological testing/measurementProteomicsLymphatic SpreadNucleic acid hybridisation
Methods and compositions for evaluating the prognosis of a breast cancer patient, particularly an early-stage breast cancer patient, are provided. The methods of the invention comprise detecting expression of at least one, more particularly at least two, biomarker(s) in a body sample, wherein overexpression of the biomarker or a combination of biomarkers is indicative of breast cancer prognosis. In some embodiments, the body sample is a breast tissue sample, particularly a primary breast tumor sample. The biomarkers of the invention are proteins and / or genes whose overexpression is indicative of either a good or bad cancer prognosis. Biomarkers of interest include proteins and genes involved in cell cycle regulation, DNA replication, transcription, signal transduction, cell proliferation, invasion, proteolysis, or metastasis. In some aspects of the invention, overexpression of a biomarker of interest is detected at the protein level using biomarker-specific antibodies or at the nucleic acid level using nucleic acid hybridization techniques.
Owner:TRIPATH IMAGING INC
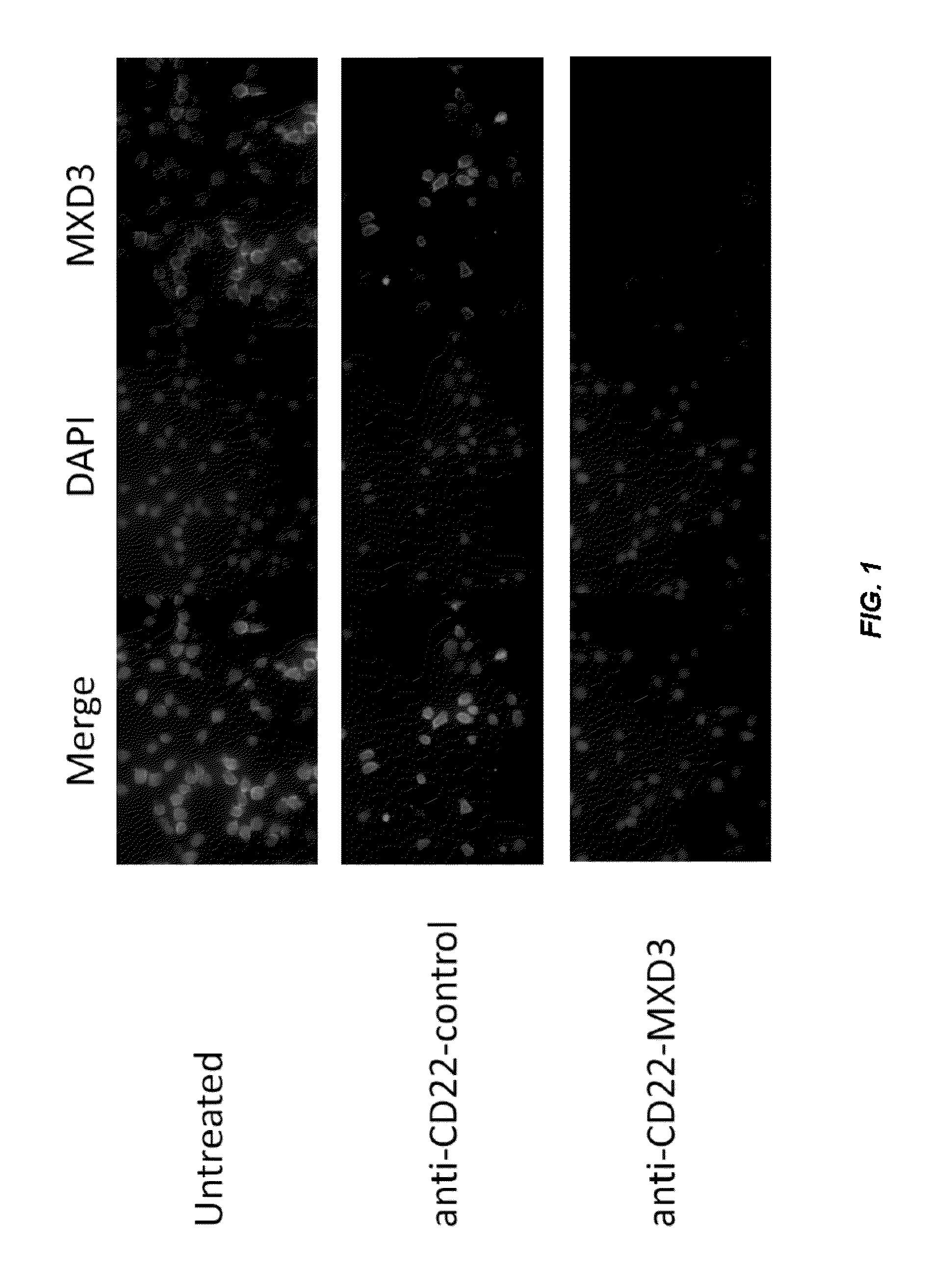
Antisense compounds and uses thereof
ActiveUS20160090598A1Reduce expressionOrganic active ingredientsSpecial deliveryNucleic acid hybridisationOligonucleotide
The present disclosure provides compounds comprising modified oligonucleotides and anti-CD22 antibodies. Certain such modified oligonucleotides conjugated to anti-CD22 antibodies are useful for hybridizing to a complementary nucleic acid, including but not limited, to nucleic acids in a cell. In certain embodiments, hybridization results in modulation of the amount activity or expression of the target nucleic acid in a cell.
Owner:IONIS PHARMA INC +1
Oligomeric compounds comprising bicyclic nucleosides and uses thereof
The present invention provides oligomeric compounds. Certain such oligomeric compounds are useful for hybridizing to a complementary nucleic acid, including but not limited, to nucleic acids in a cell. In certain embodiments, hybridization results in modulation of the amount activity or expression of the target nucleic acid in a cell. In certain embodiments, the present invention provides compounds comprising oligonucleotides. In certain embodiments, such oligonucleotides comprise a region having a gapmer sugar motif. In certain embodiments, oligonucleotides comprise one or more type of modified sugar moieties and / or naturally occurring sugar moieties arranged along an oligonucleotide or region thereof in a defined pattern or sugar modification motif.
Owner:IONIS PHARMA INC
Nanoparticles having oligonucleotides attached thereto and uses therefor
InactiveUS6984491B2Easy to moveImprove bindingMaterial nanotechnologySugar derivativesNanoparticleColor changes
The invention provides methods of detecting a nucleic acid. The methods comprise contacting the nucleic acid with one or more types of particles having oligonucleotides attached thereto. In one embodiment of the method, the oligonucleotides are attached to nanoparticles and have sequences complementary to portions of the sequence of the nucleic acid. A detectable change (preferably a color change) is brought about as a result of the hybridization of the oligonucleotides on the nanoparticles to the nucleic acid. The invention also provides compositions and kits comprising particles. The invention further provides methods of synthesizing unique nanoparticle-oligonucleotide conjugates, the conjugates produced by the methods, and methods of using the conjugates. In addition, the invention provides nanomaterials and nanostructures comprising nanoparticles and methods of nanofabrication utilizing nanoparticles. Finally, the invention provides a method of separating a selected nucleic acid from other nucleic acids.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN UNIV +1
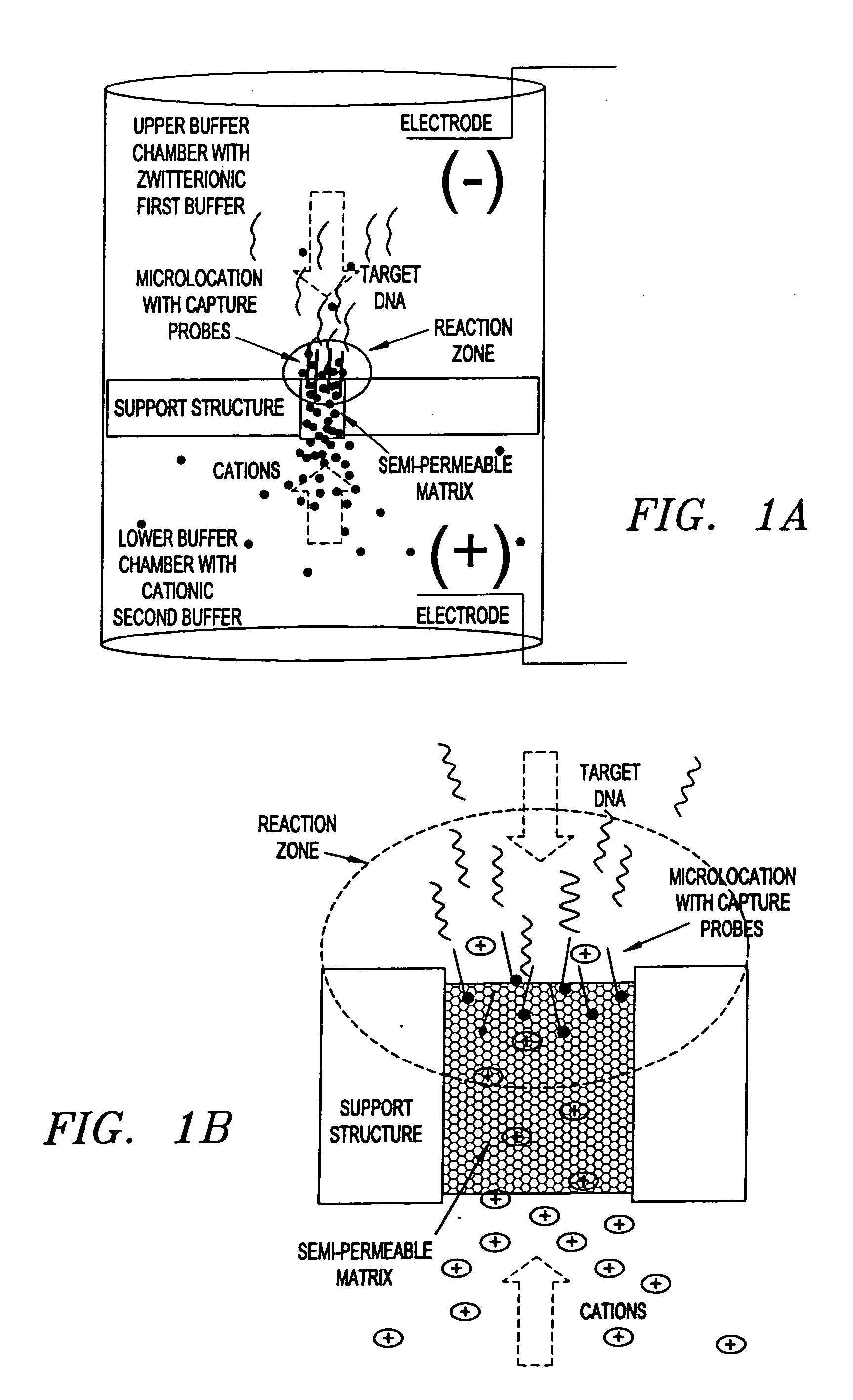
Electronic systems and component devices for macroscopic and microscopic molecular biological reaction, analyses, and diagnostics
InactiveUS20050026202A1Favorable zoneImprove responseBioreactor/fermenter combinationsMaterial nanotechnologyMultiplexBiopolymer
This invention pertains to the design, fabrication, and uses of an electronic system which can actively carry out and control multi-step and multiplex reactions in macroscopic or microscopic formats. In particular, these reactions include molecular biological reactions, such as nucleic acid hybridizations, nucleic acid amplification, sample preparation, antibody / antigen reactions, clinical diagnostics, combinatorial chemistry and selection, drug screening, oligonucleotide and nucleic acid synthesis, peptide synthesis, biopolymer synthesis, and catalytic reactions. A key feature of the present invention is the ability to control the localized concentration of two or more reaction-dependant molecules and their reaction environment in order to greatly enhance the rate and specificity of the molecular biological reaction
Owner:ADOR DIAGNOSTICS SRL
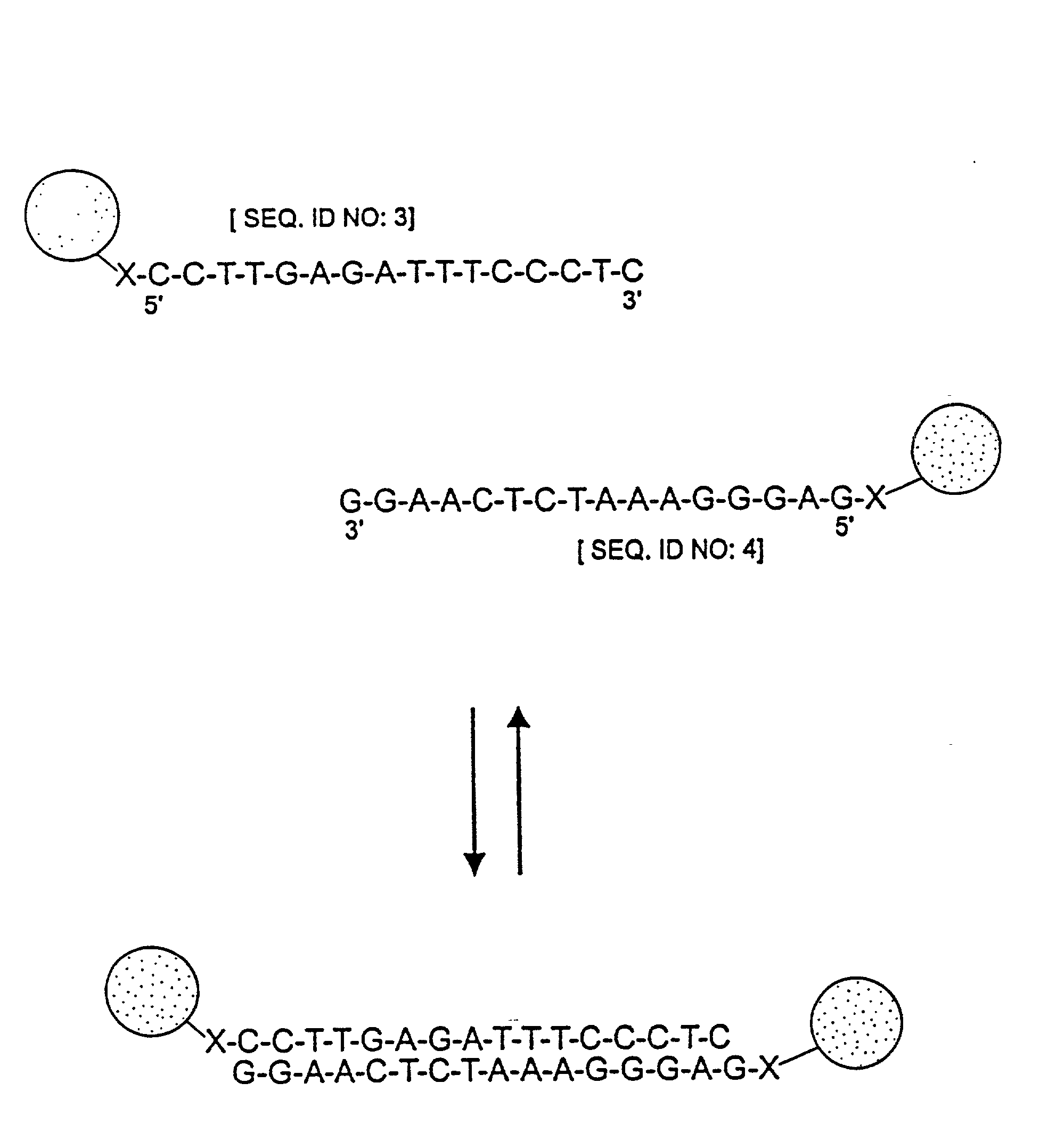
Rolling circle replication of padlock probes
InactiveUS20050282158A1Limited amplificationInhibition of replicationMicrobiological testing/measurementRecombinant DNA-technologyOligonucleotideRolling circle replication
Rolling circle replication of a padlock primer is inhibited when it is hybridised to a target nucleic acid that is long or circular. The invention provides methods of addressing this problem including cutting the target nucleic acid near or preferably at the site which hybridises with the padlock probe, whereby a 3′-end of the cut target nucleic acid acts as a primer for rolling circle replication of the padlock probe. Also included is a method for assaying for a polyepitopic target by the use of two affinity probes each carrying an oligonucleotide tag and of padlock probe for rolling circle replication in association with the two affinity probes.
Owner:SIGMA ALDRICH CO LLC
Nanoparticles having oligonucleotides attached thereto and uses therefor
The invention provides methods of detecting a nucleic acid. The methods comprise contacting the nucleic acid with one or more types of particles having oligonucleotides attached thereto. In one embodiment of the method, the oligonucleotides are attached to nanoparticles and have sequences complementary to portions of the sequence of the nucleic acid. A detectable change (preferably a color change) is brought about as a result of the hybridization of the oligonucleotides on the nanoparticles to the nucleic acid. The invention also provides compositions and kits comprising particles. The invention further provides methods of synthesizing unique nanoparticle-oligonucleotide conjugates, the conjugates produced by the methods, and methods of using the conjugates. In addition, the invention provides nanomaterials and nanostructures comprising nanoparticles and methods of nanofabrication utilizing nanoparticles. Finally, the invention provides a method of separating a selected nucleic acid from other nucleic acids.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN UNIV +1
Nanoparticles having oligonucleotides attached thereto and uses therefor
InactiveUS20020155442A1Detect changeMaterial nanotechnologyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsNucleotideNucleic acid hybridisation
The invention provides methods of detecting a nucleic acid. The methods comprise contacting the nucleic acid with one or more types of particles having oligonucleotides attached thereto. In one embodiment of the method, the oligonucleotides are attached to nanoparticles and have sequences complementary to portions of the sequence of the nucleic acid. A detectable change (preferably a color change) is brought about as a result of the hybridization of the oligonucleotides on the nanoparticles to the nucleic acid. The invention also provides compositions and kits comprising particles. The invention further provides methods of synthesizing unique nanoparticle-oligonucleotide conjugates, the conjugates produced by the methods, and methods of using the conjugates. In addition, the invention provides nanomaterials and nanostructures comprising nanoparticles and methods of nanofabrication utilizing nanoparticles. Finally, the invention provides a method of separating a selected nucleic acid from other nucleic acids.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN UNIV +6
Nanoparticles having oligonucleotides attached thereto and uses therefor
Owner:NANOSPHERE INC
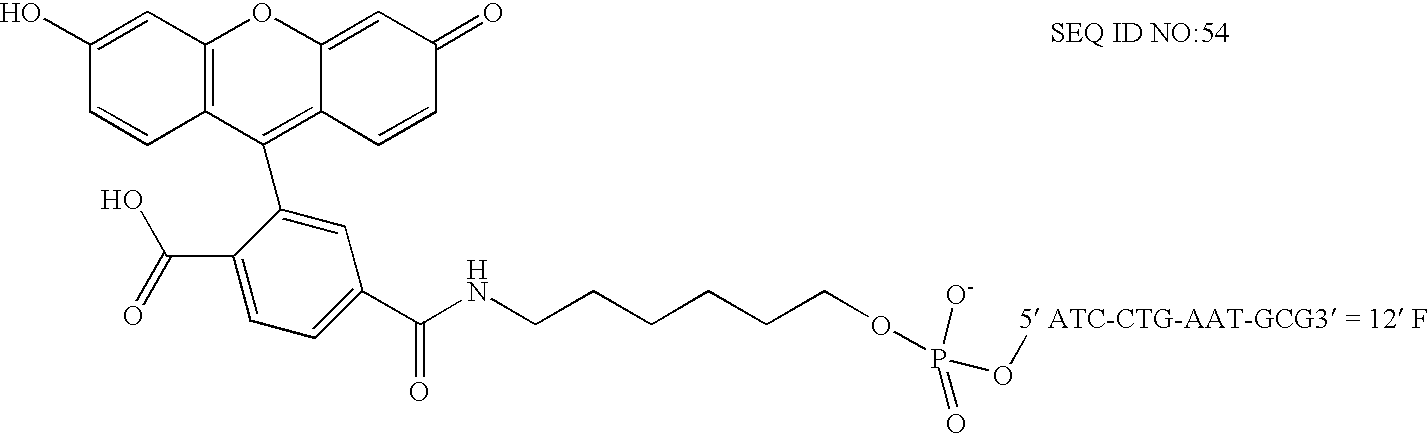
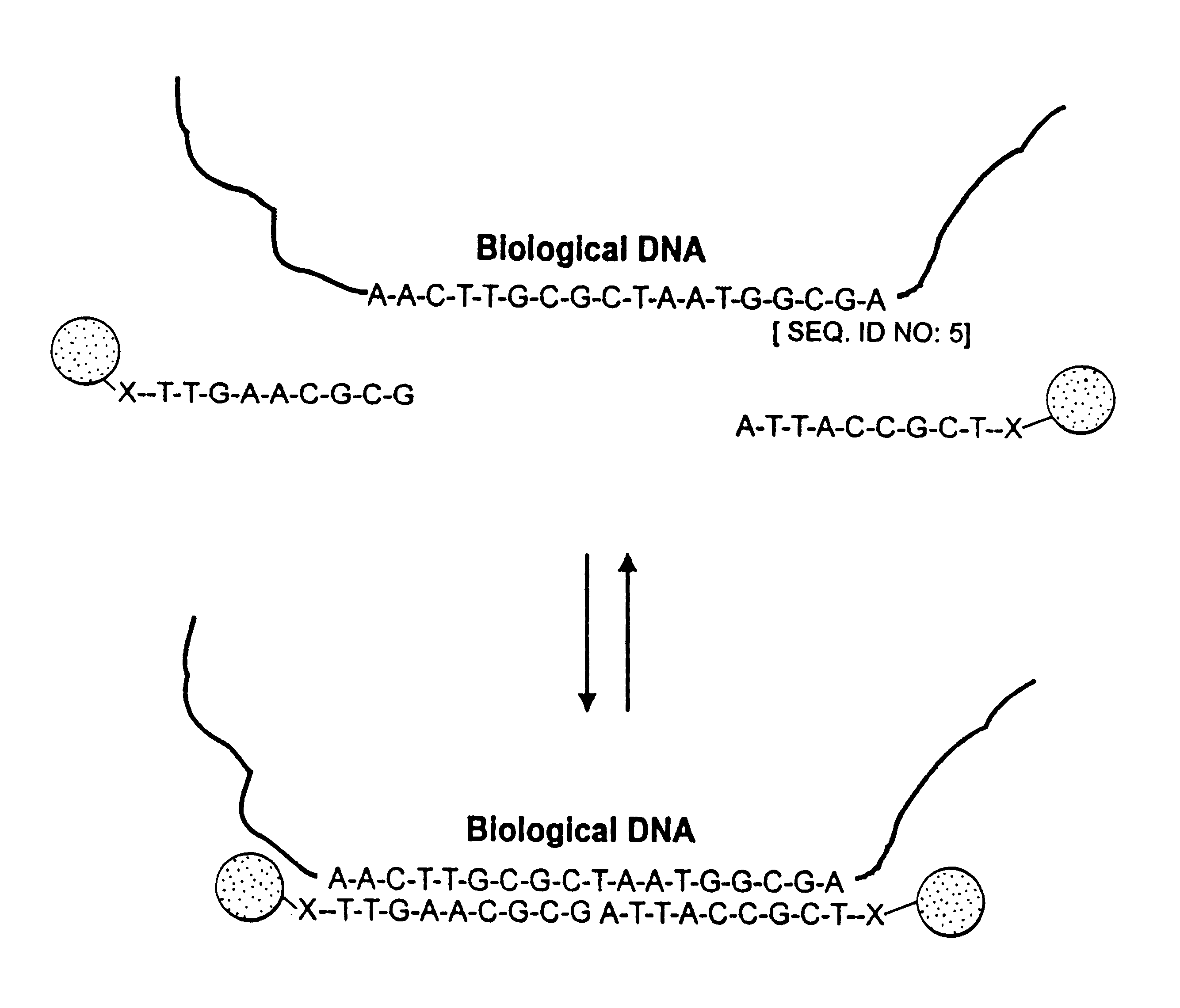
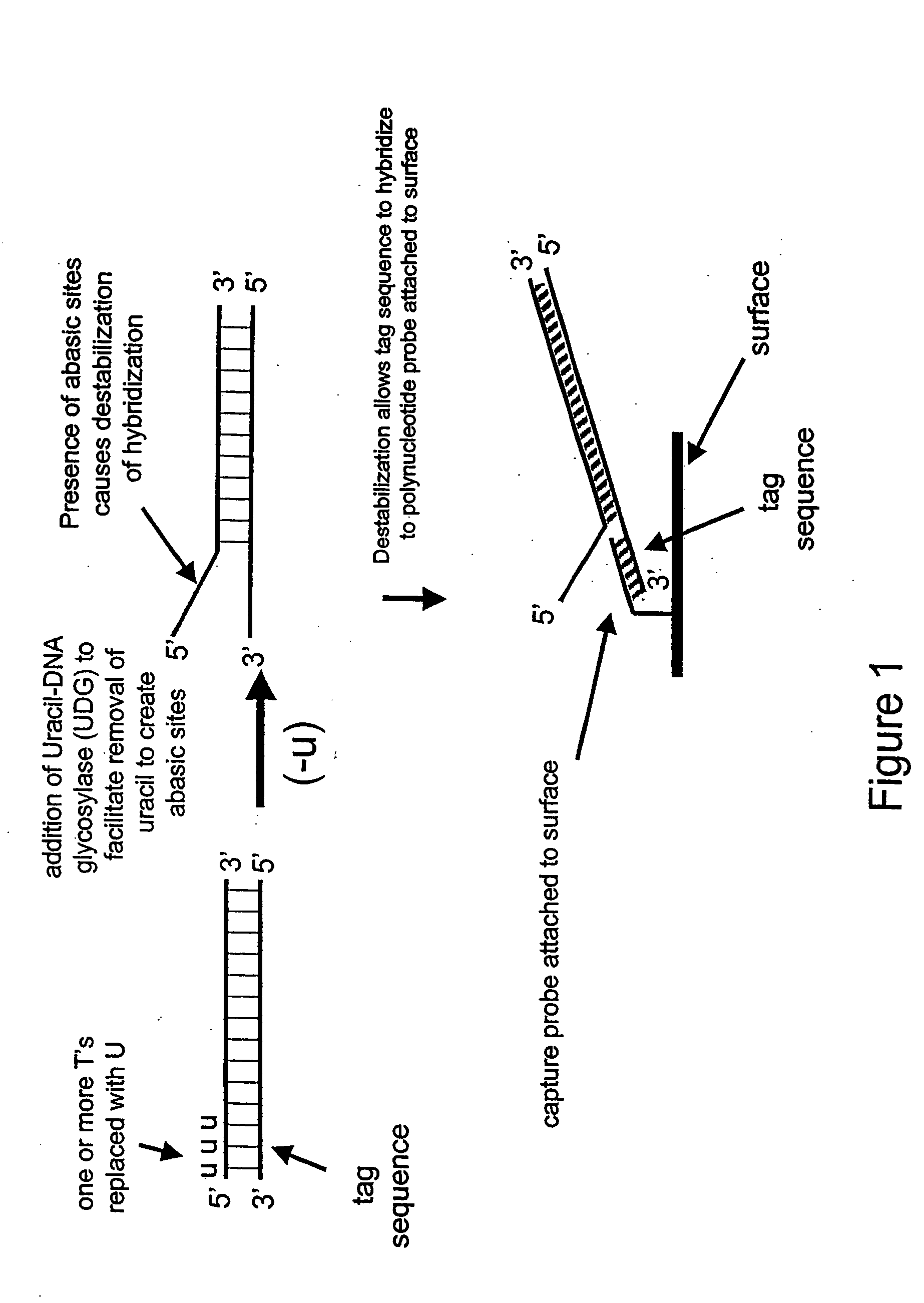
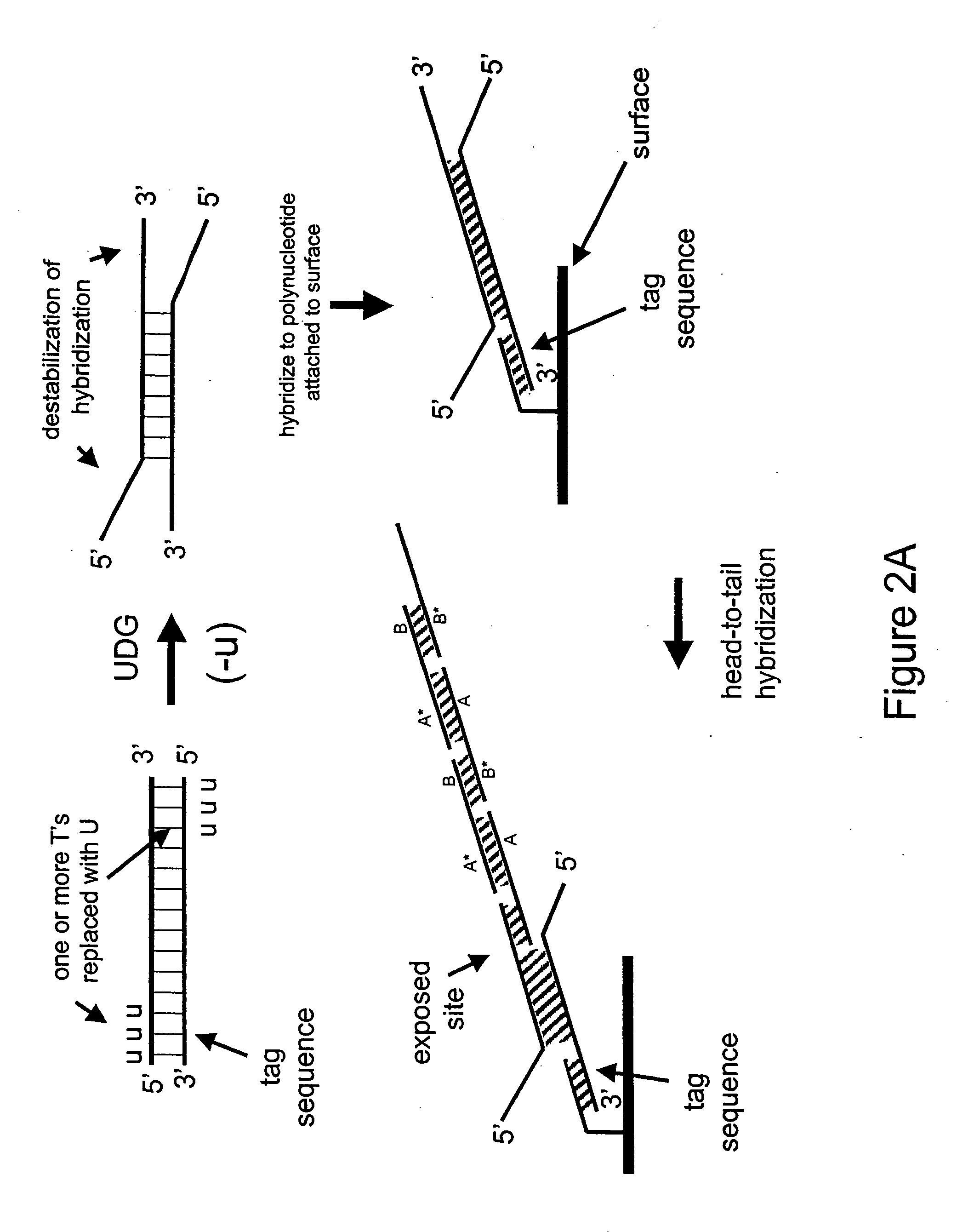
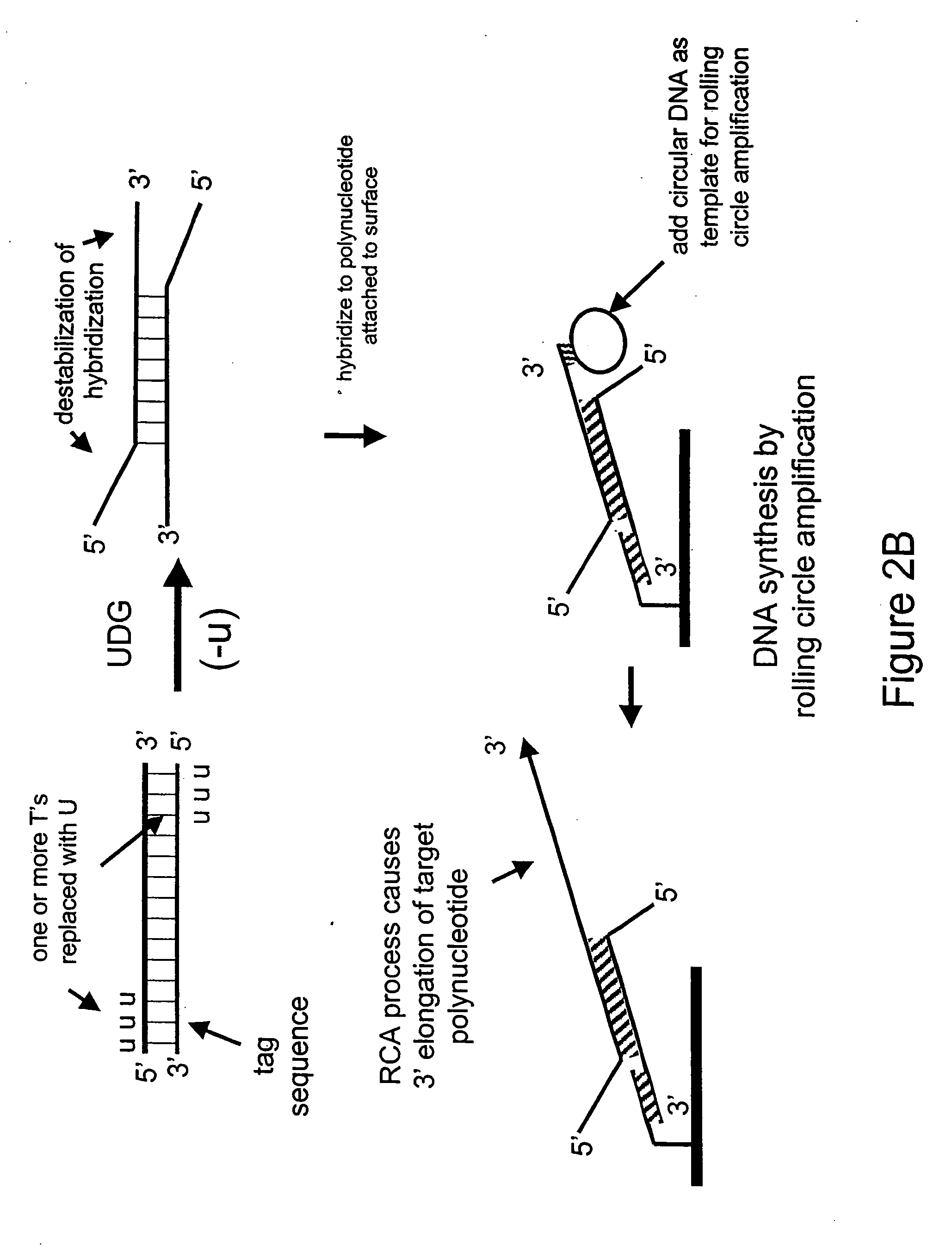
Nucleic acid hybridization methods
Disclosed herein are methods of destabilizing double-stranded nucleic acid hybridization using an enzyme comprising DNA N-glycosylase activity. Also disclosed herein is the detection of a double-stranded target DNA wherein the hybridization of duplex strands has been at least partially disrupted thereby permitting invasion of a probe strand. Also disclosed herein are methods of using an enzyme comprising DNA N-glycosylase activity to generate single-stranded circular nucleic acids.
Owner:GENEOHM SCI INC
Competitive oligonucleotides
InactiveUS20070238104A1Microbiological testing/measurementBiological testingComparative genomic hybridizationGenomic DNA
The present invention generally relates to competitive oligonucleotides and, in some embodiments, to competitive oligonucleotides for use in comparative genomic hybridization (CGH) and related techniques. One aspect is generally directed to a blocking composition constructed and arranged to be used in an assay of a nucleic acid. The blocking composition may comprise oligonucleotides comprising sequences selected to hybridize to the nucleic acid used in the assay. Another aspect is generally directed to performing CGH assays and similar techniques on genomic DNA, in the absence of a Cot-1 fraction, such that the genomic DNA does not substantially cross-hybridize. Yet other aspects of the invention are directed to devices or kits for making or using competitive oligonucleotides, methods of promoting such competitive oligonucleotides, or the like.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Nanoparticles having oligonucleotides attached thereto and uses therefor
The invention provides methods of detecting a nucleic acid. The methods comprise contacting the nucleic acid with one or more types of particles having oligonucleotides attached thereto. In one embodiment of the method, the oligonucleotides are attached to nanoparticles and have sequences complementary to portions of the sequence of the nucleic acid. A detectable change (preferably a color change) is brought about as a result of the hybridization of the oligonucleotides on the nanoparticles to the nucleic acid. The invention also provides compositions and kits comprising particles. The invention further provides methods of synthesizing unique nanoparticle-oligonucleotide conjugates, the conjugates produced by the methods, and methods of using the conjugates. In addition, the invention provides nanomaterials and nanostructures comprising nanoparticles and methods of nanofabrication utilizing nanoparticles. Finally, the invention provides a method of separating a selected nucleic acid from other nucleic acids.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com