Apparatus and method for analysis of nucleic acids hybridization on high density NA chips.
a nucleic acid hybridization and high density technology, applied in the field of new gene probe biosensors, can solve the problems of short shelf life of common labels and the safety hazards associated with the use of radioactive compounds, and achieve the effect of improving spectral sensitivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
third embodiment
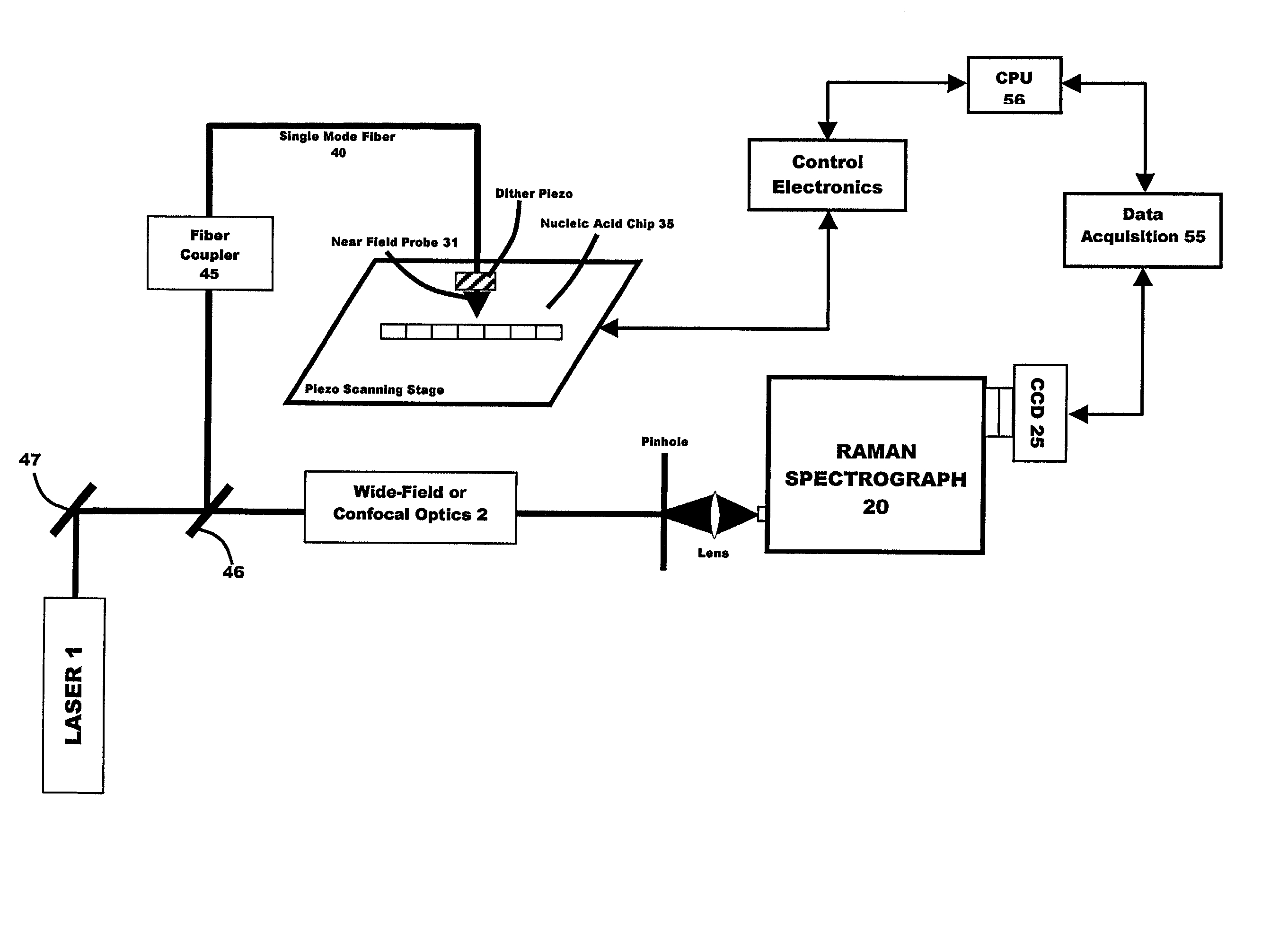
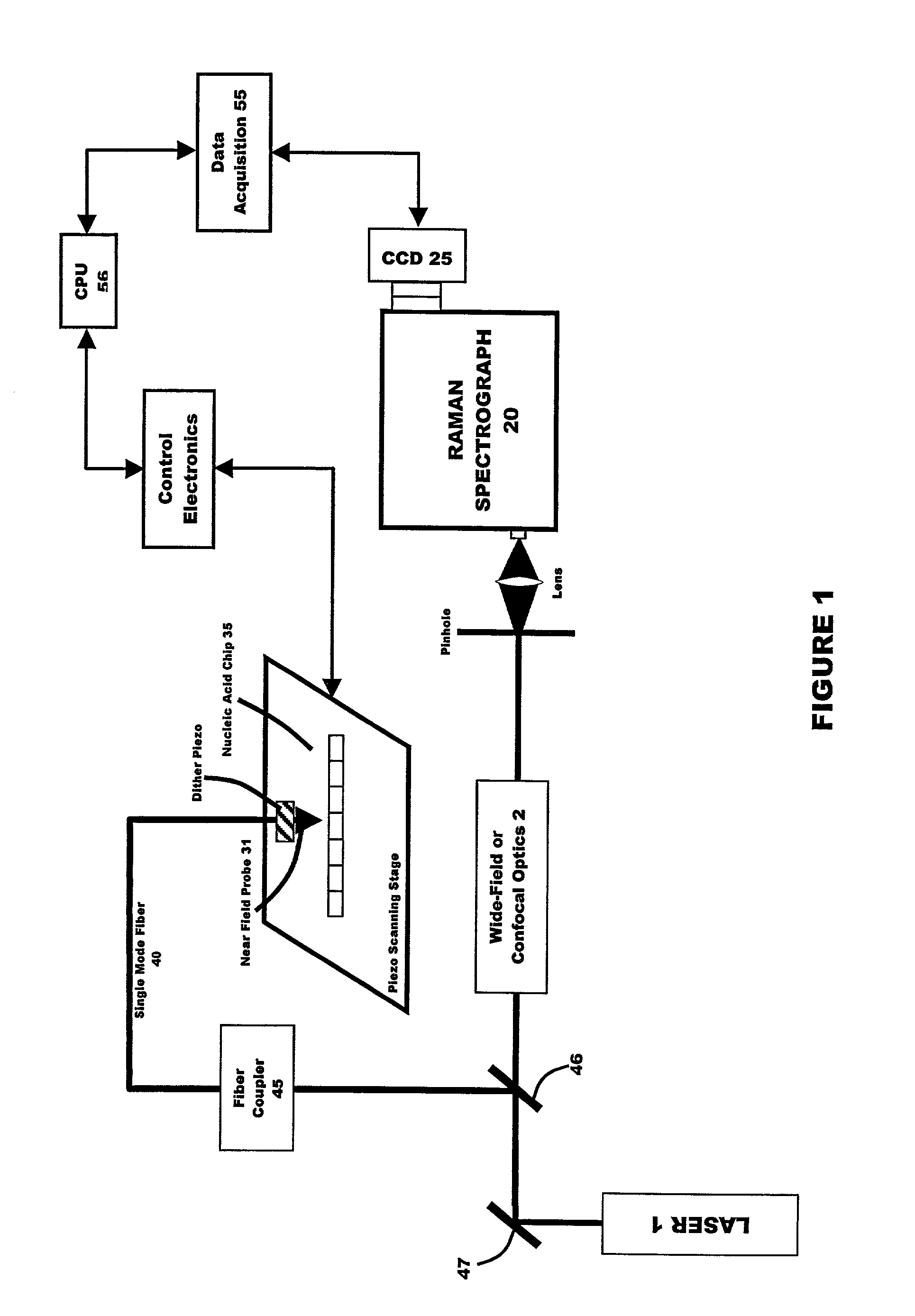
[0041] In a third embodiment, random array technology may be used in combination with a fiber optic sensor (e.g., a sensor arrangement of the type disclosed in U.S. Pat. Nos. 5,244,636 and 5,244,813 ). In this embodiment, ultimate spatial resolution is 5 microns per pixel, enabling the speed at which the chip can be read to be reduced to microseconds. Optical IR fiber employed in the practice of the present invention may be single-mode fiber or a multi-mode fiber bundle. Multi-mode fiber bundles, which commonly have up to 2000 fibers in one bundle, may be used in multichannel recording.
[0042] A fiber coupler may be used to transfer illuminating and scattered optical signals into large aperture beams and vice versa. A splitter can be used to send reflected light through wide-field or confocal optics into the Raman spectrograph.
[0043] The preferred source of illuminating radiation is an argon ion laser, although other suitable radiation sources may be usefully employed in the general ...
first embodiment
[0045] Where the SNOM is employed (first embodiment above), a signal from the piezo scanning device 30 is transferred to the control electronics system.
[0046] The spectral range of Raman spectra used in the near field SERS molecular hybridization detection system of the present invention is preferably in the range of about 0 to about 1700 sm.sup.-1 with the preferred spectral interval ranging from about 0 to about 300 sm.sup.-1. It is anticipated that the best results will be in a spectral interval which ranges from 10 to about 150 sm.sup.-1.
[0047] The present invention also provides a method for detecting hybridization of molecules using the near field SERS technology of the present invention. The method is enabled by the fundamental property that single stranded and double stranded fragments of nucleic acids have different characteristic frequencies in Raman spectra. In fact, each complimentary fragment of DNA from a set of double stranded DNA fragments has an intrinsic low freque...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com