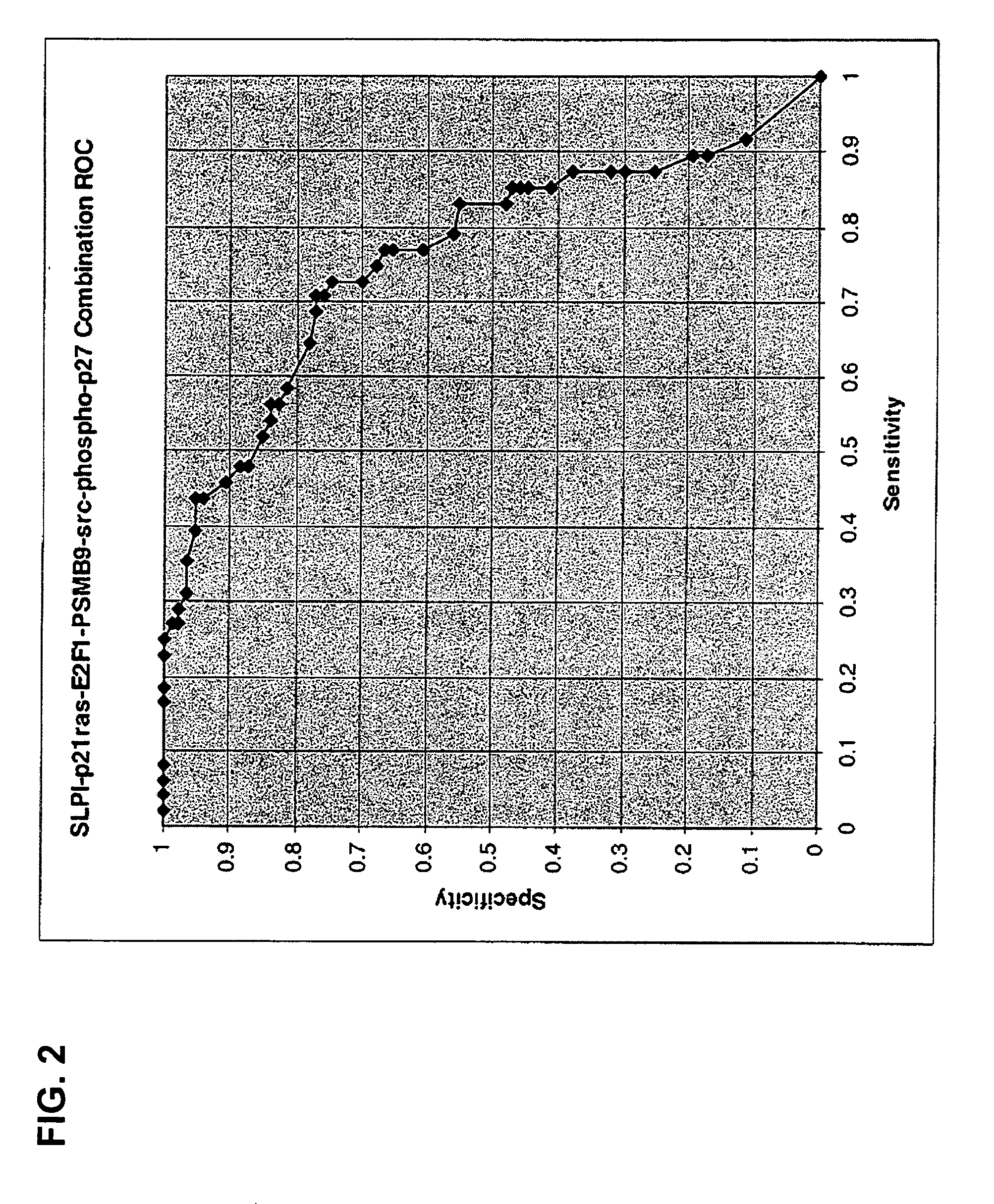
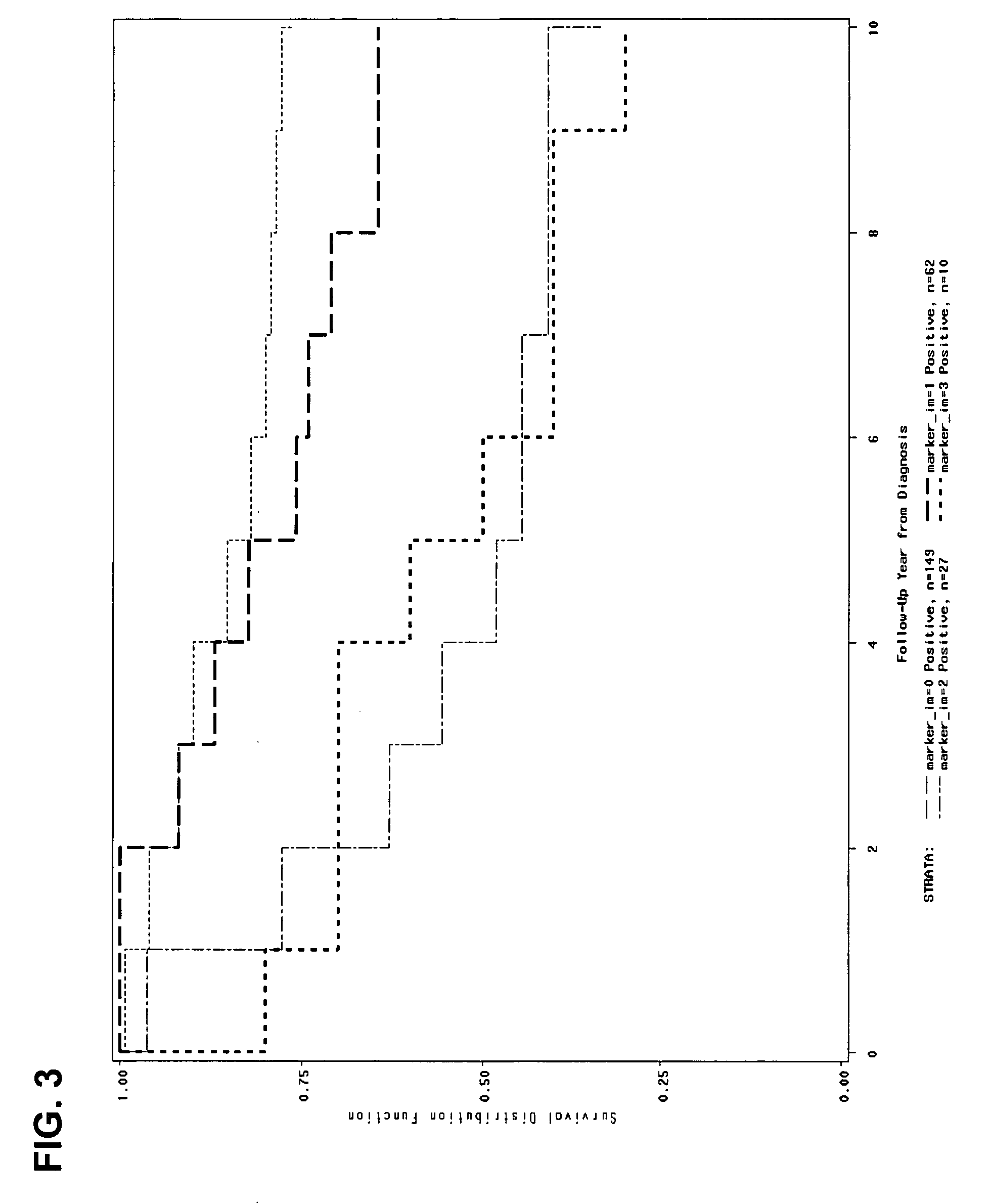
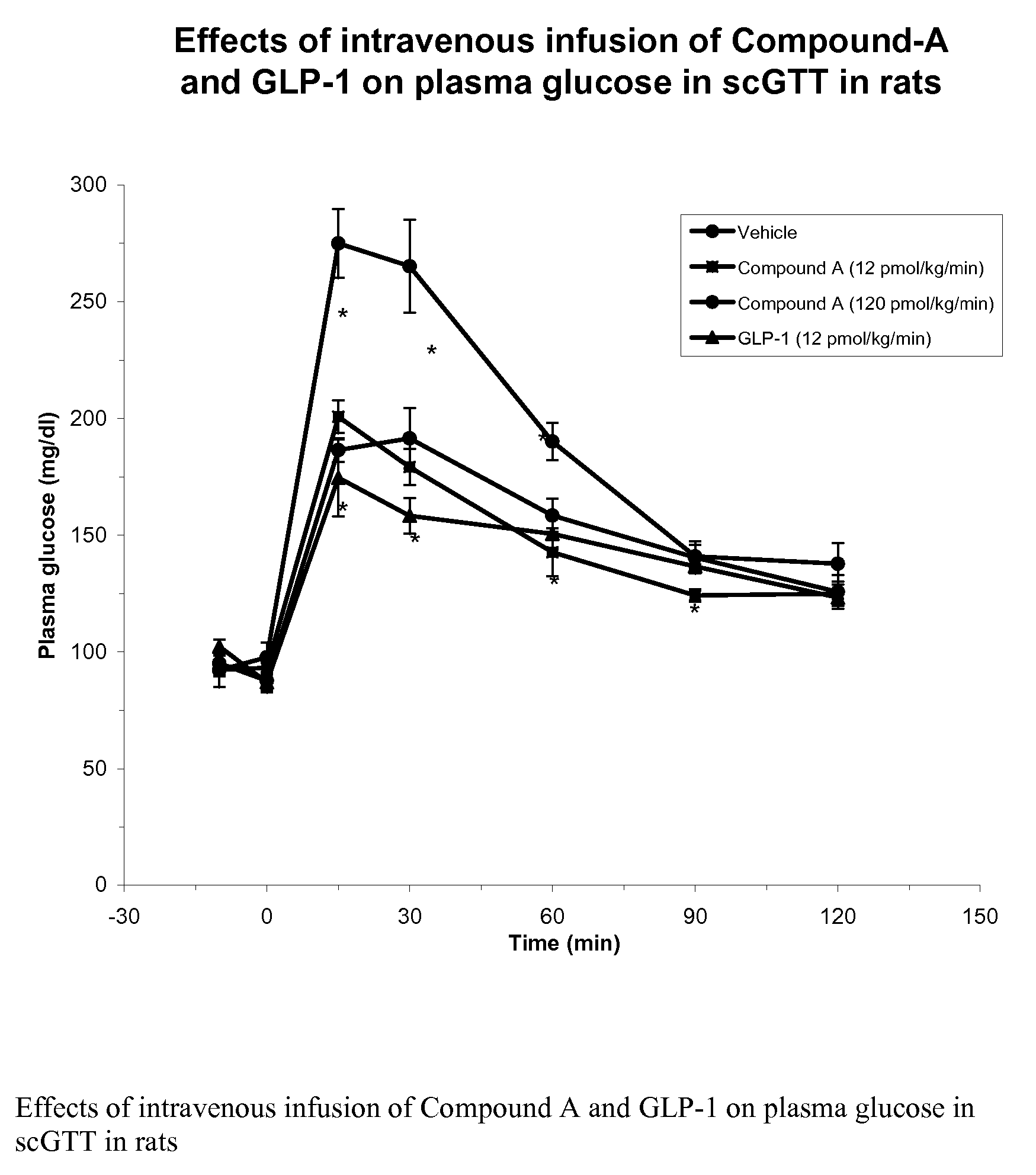
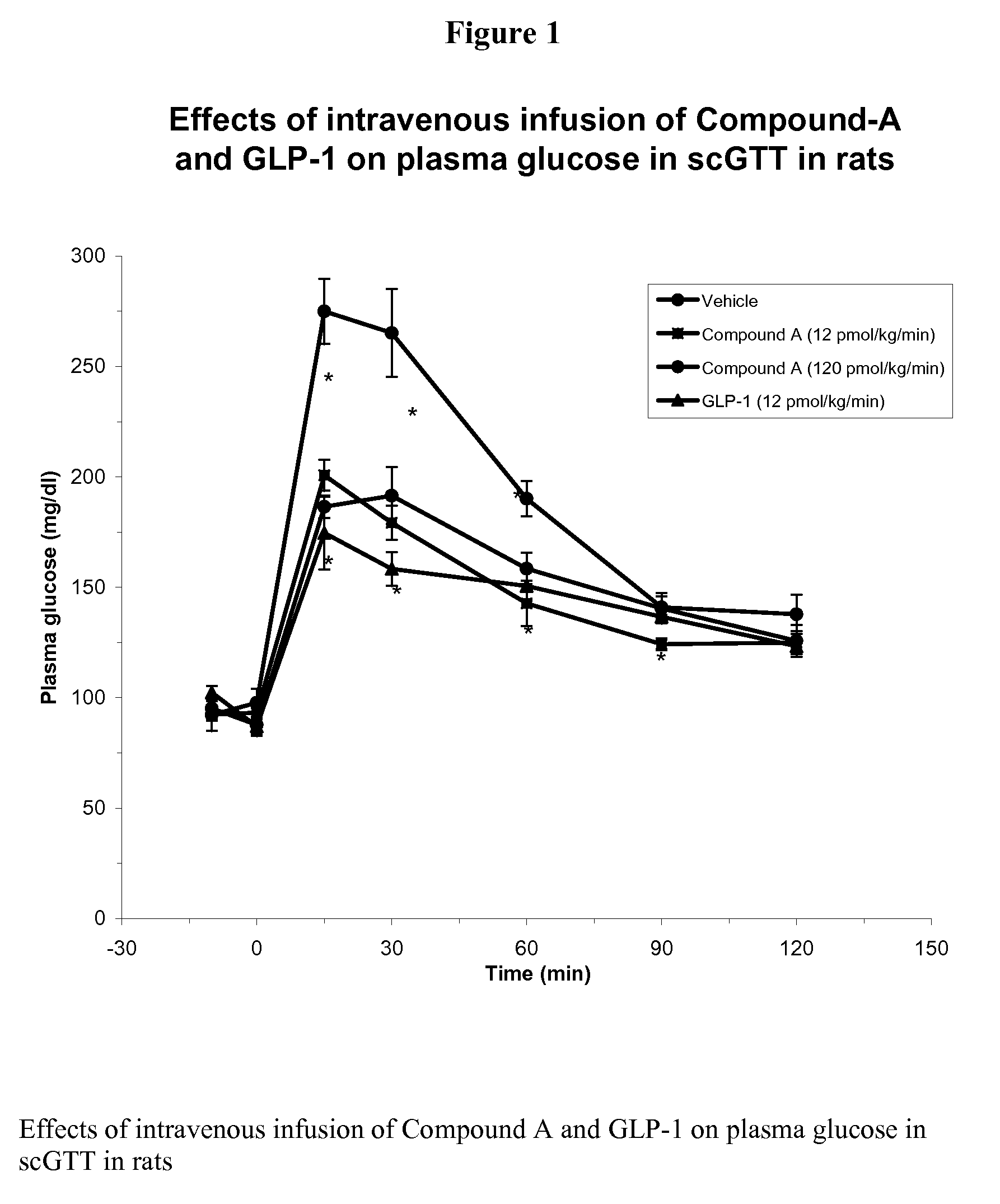
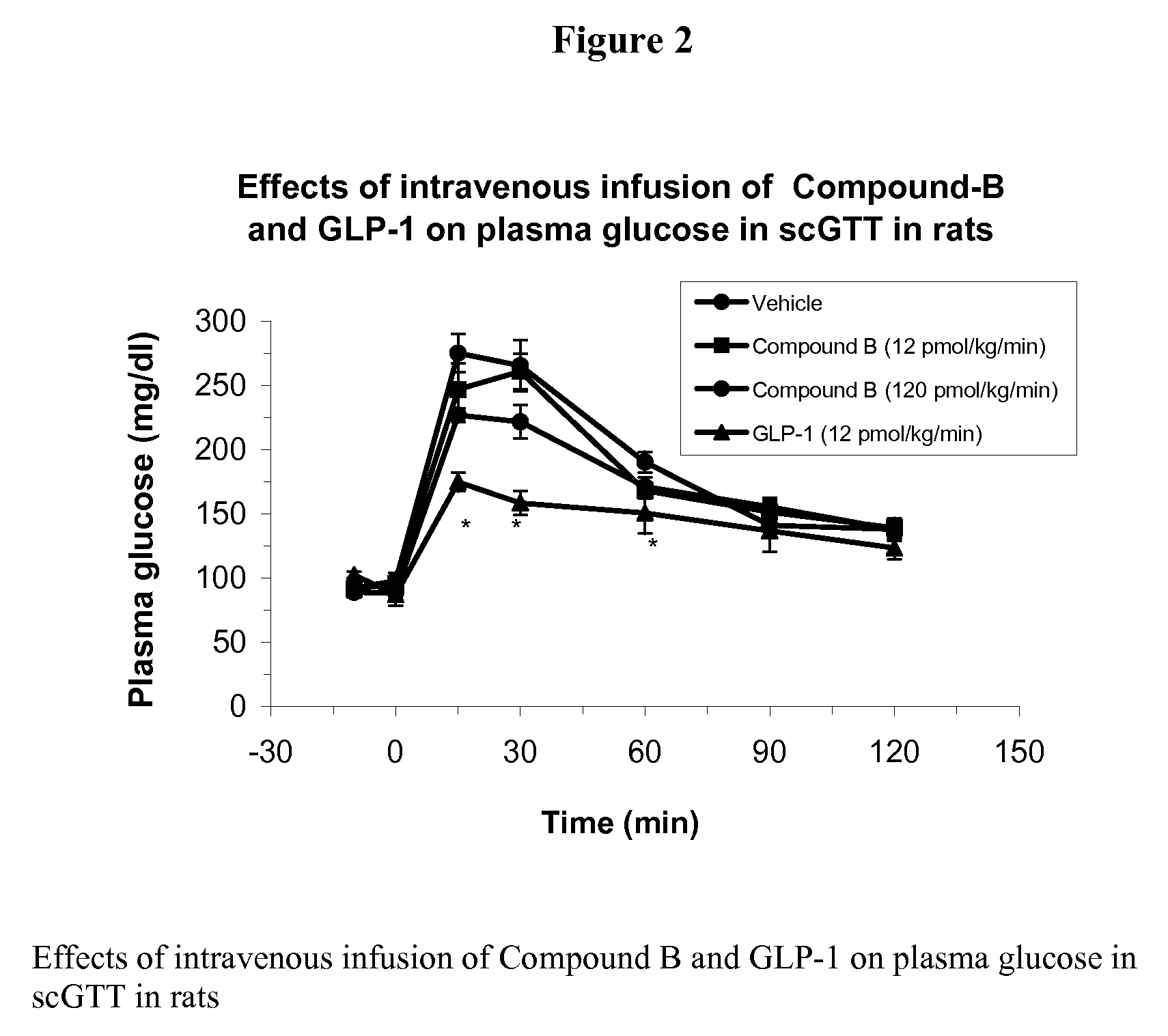
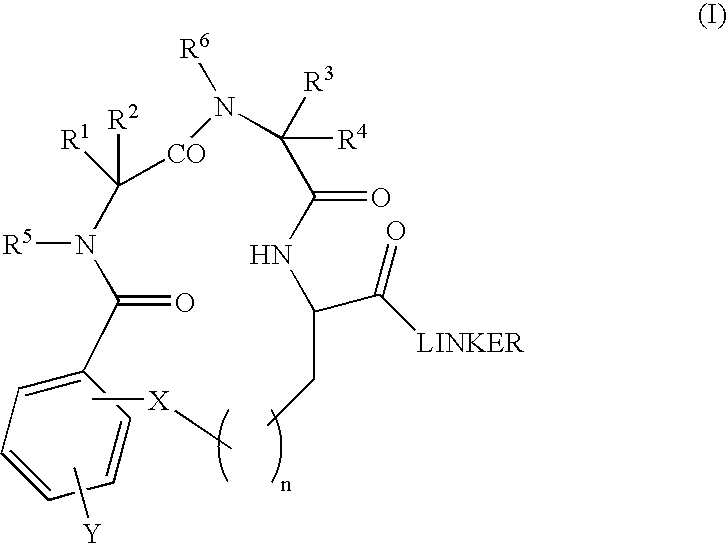
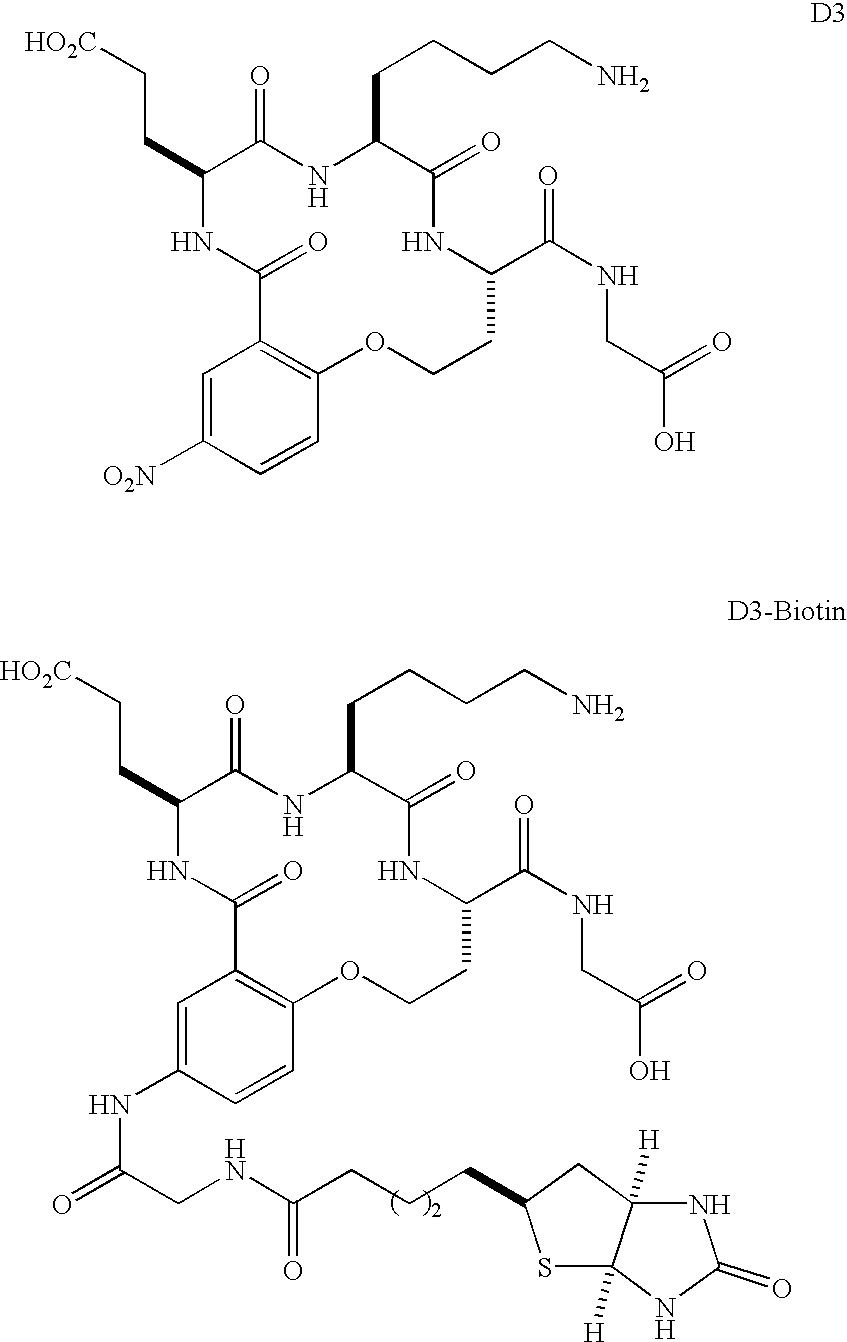
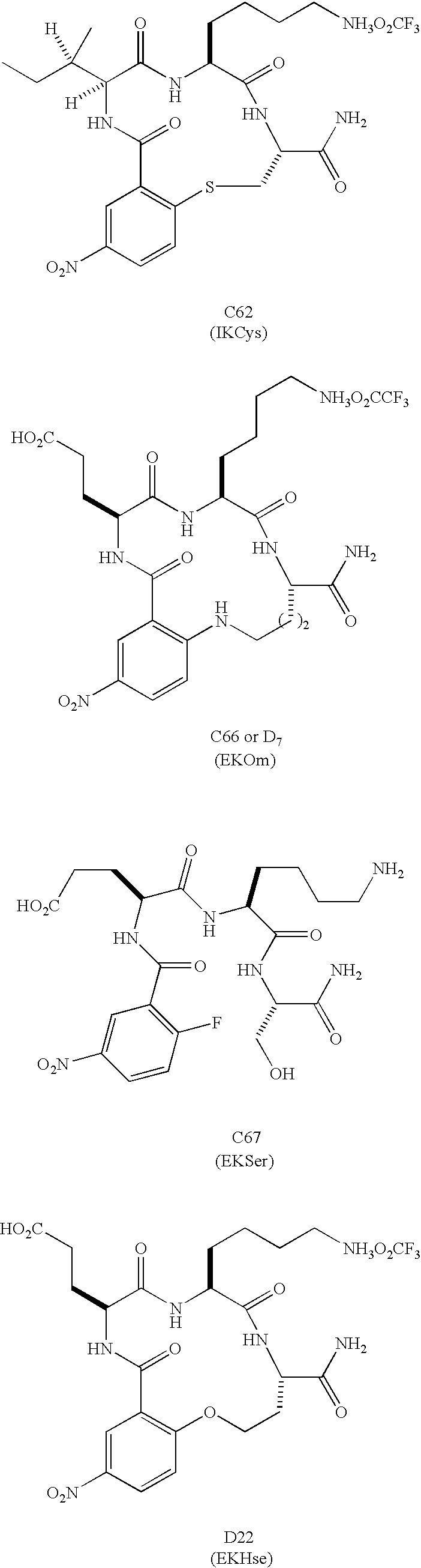
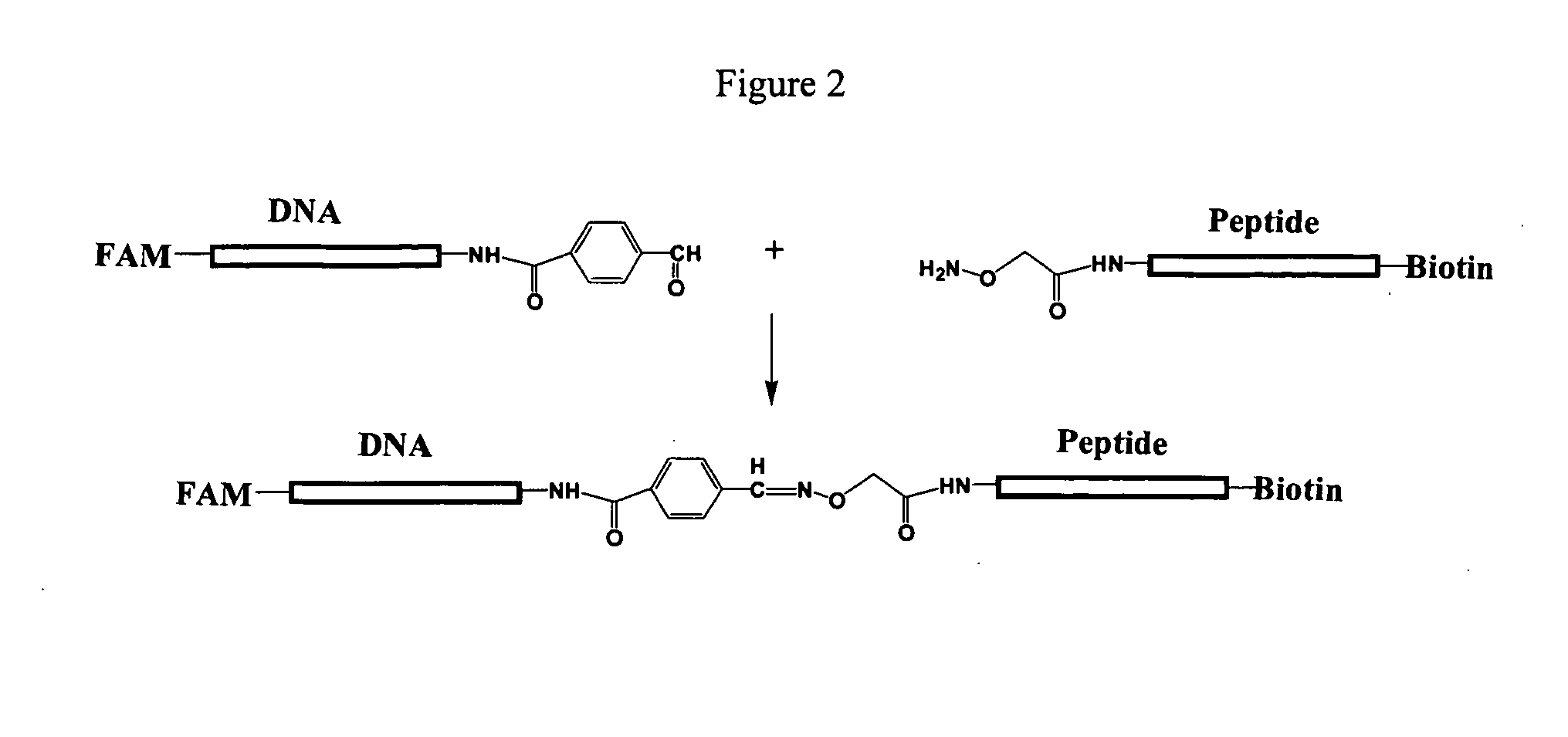
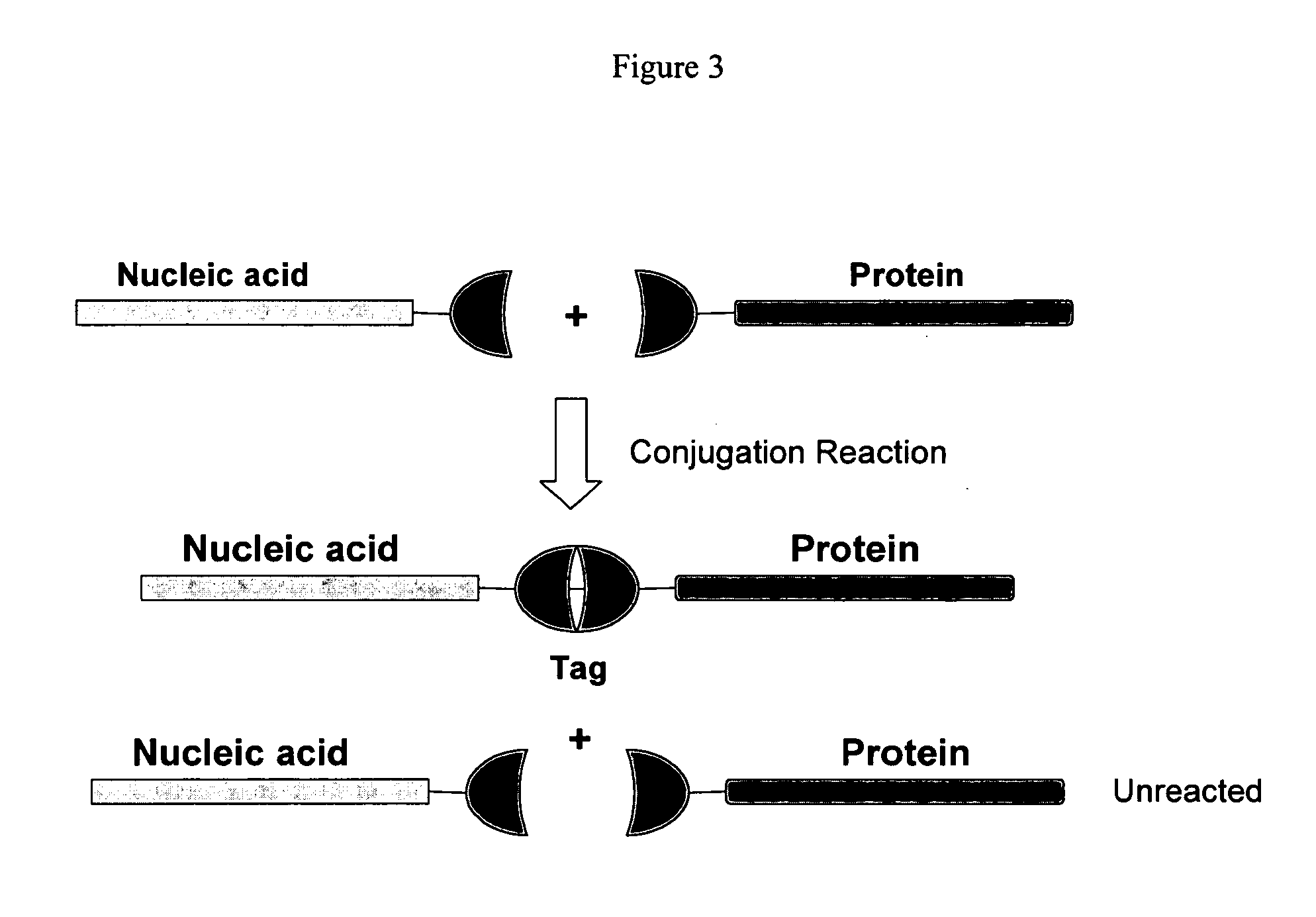
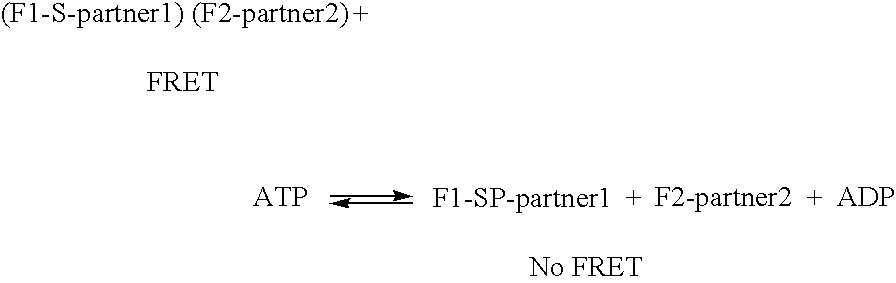Patents
Literature
1322 results about "Proteolysis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Proteolysis is the breakdown of proteins into smaller polypeptides or amino acids. Uncatalysed, the hydrolysis of peptide bonds is extremely slow, taking hundreds of years. Proteolysis is typically catalysed by cellular enzymes called proteases, but may also occur by intra-molecular digestion. Low pH or high temperatures can also cause proteolysis non-enzymatically.
Method and system for rapid biomolecular recognition of amino acids and protein sequencing
InactiveUS6846638B2Low costHigh sensitivityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsProtein Sequence DeterminationDigestion
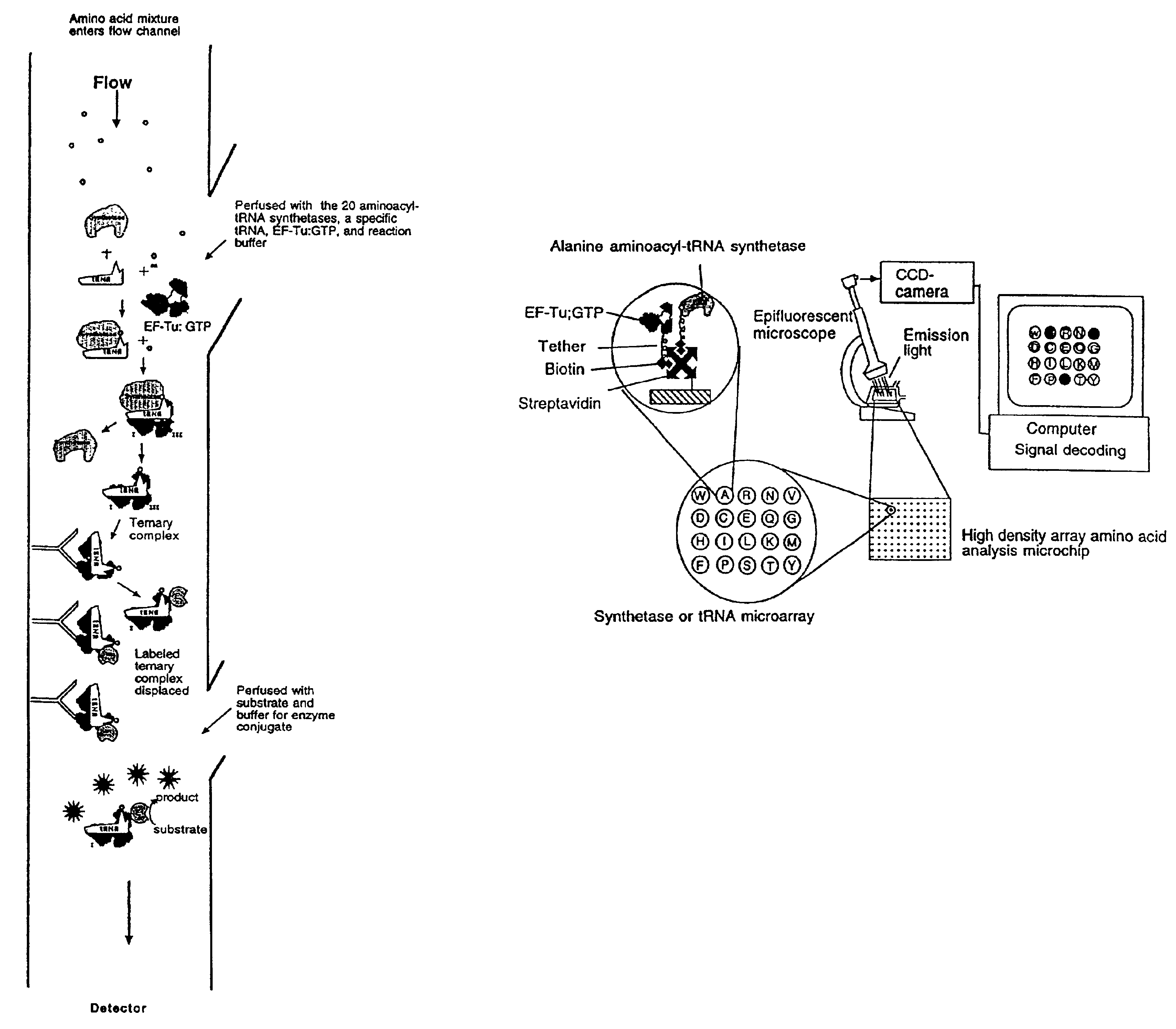
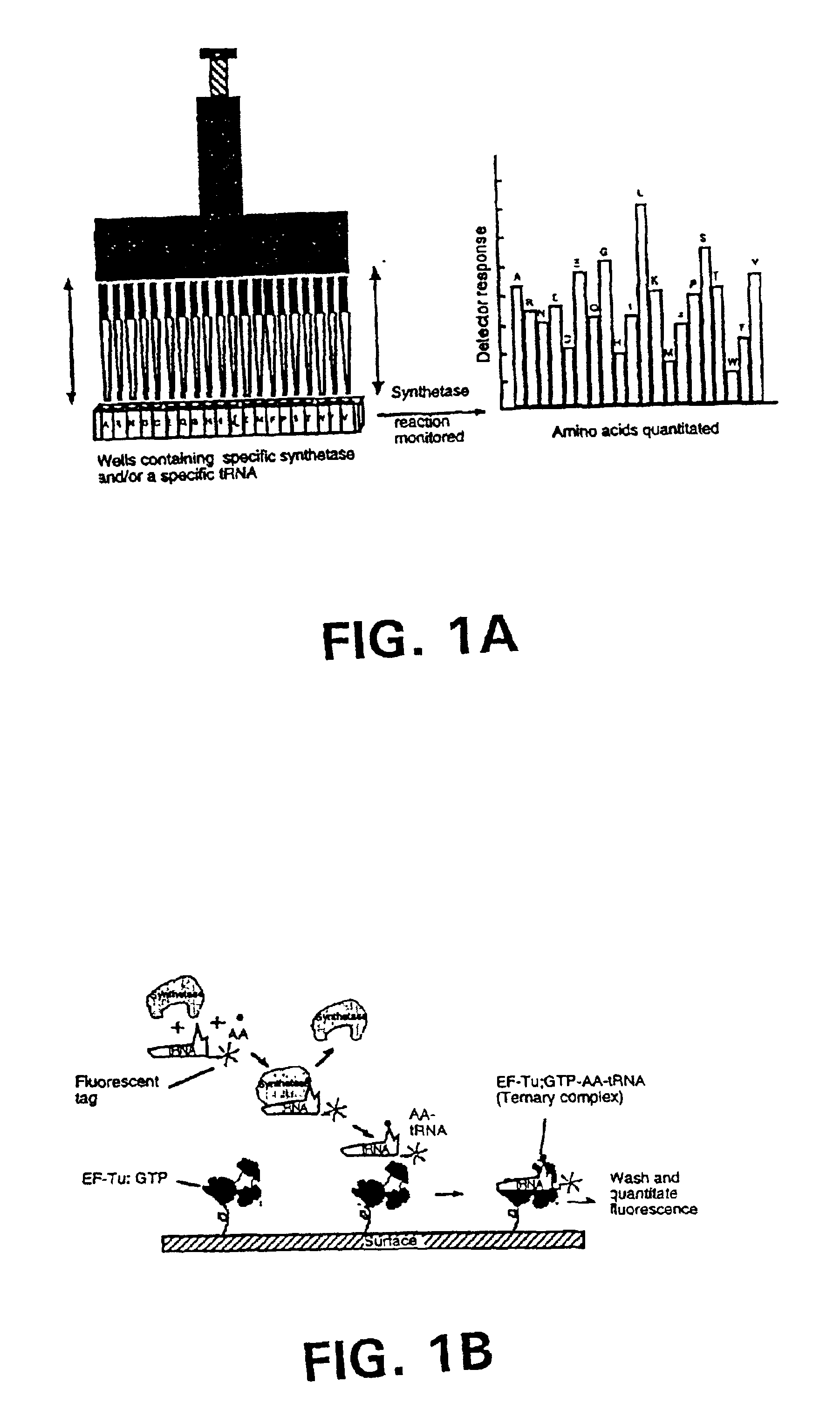
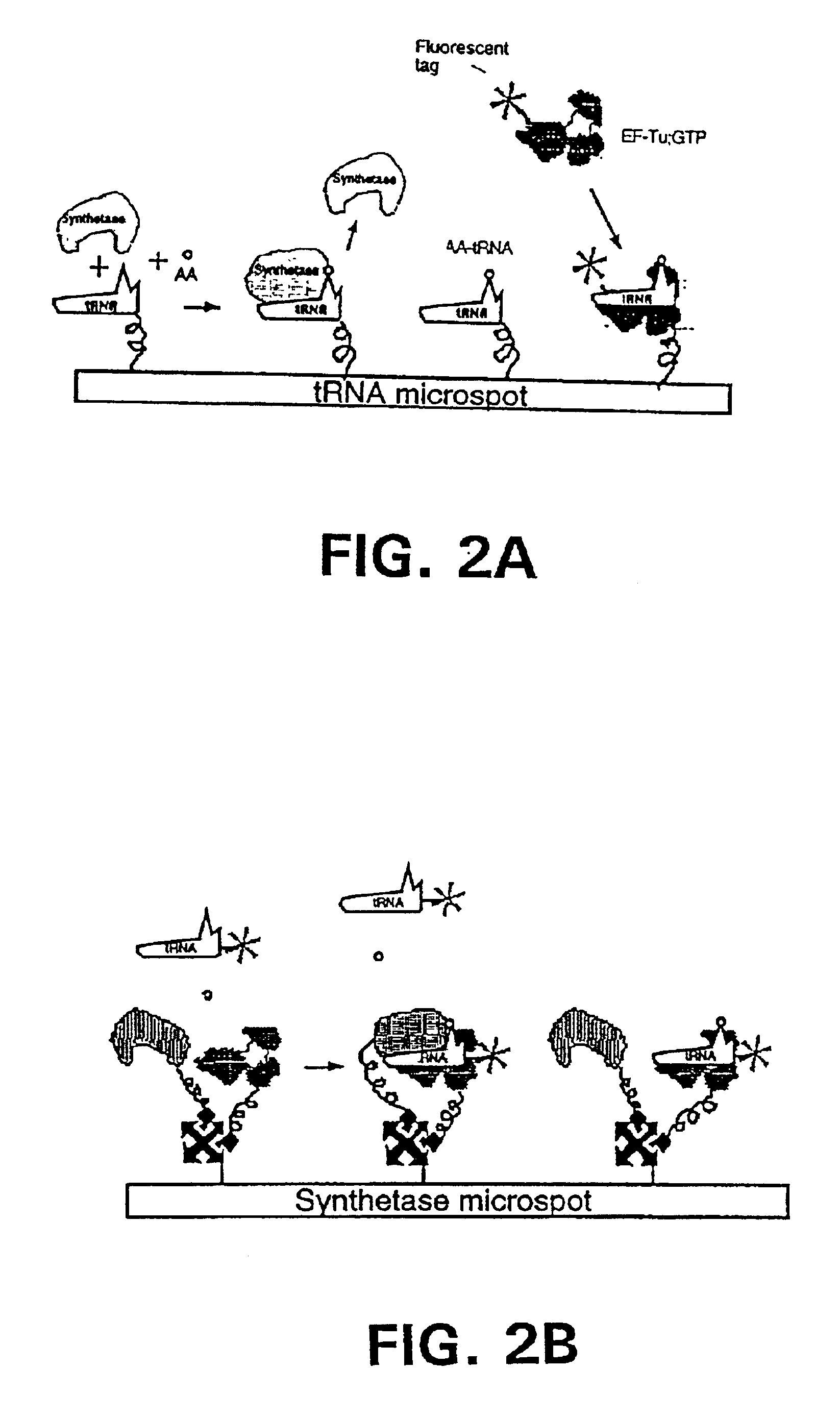
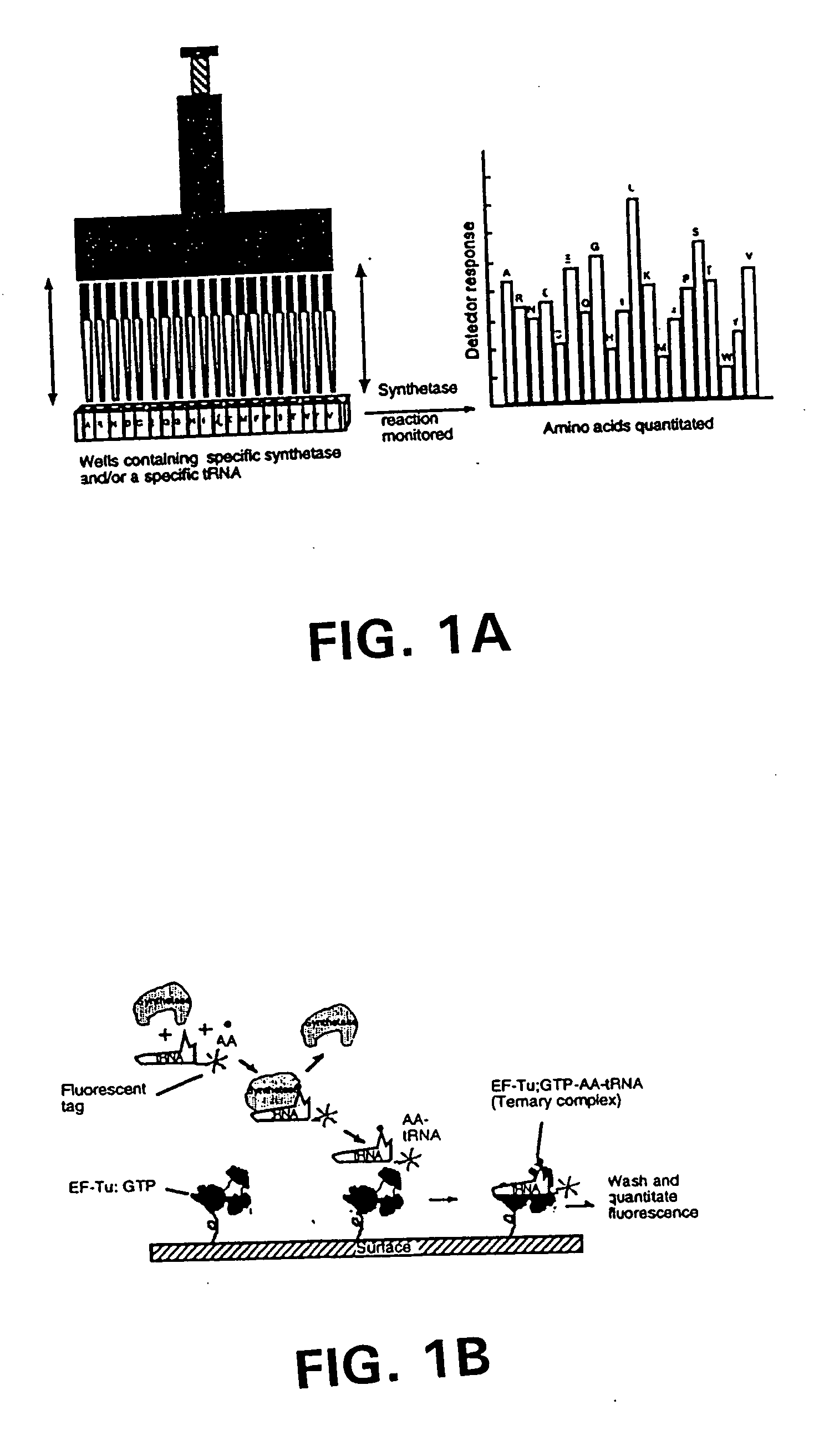
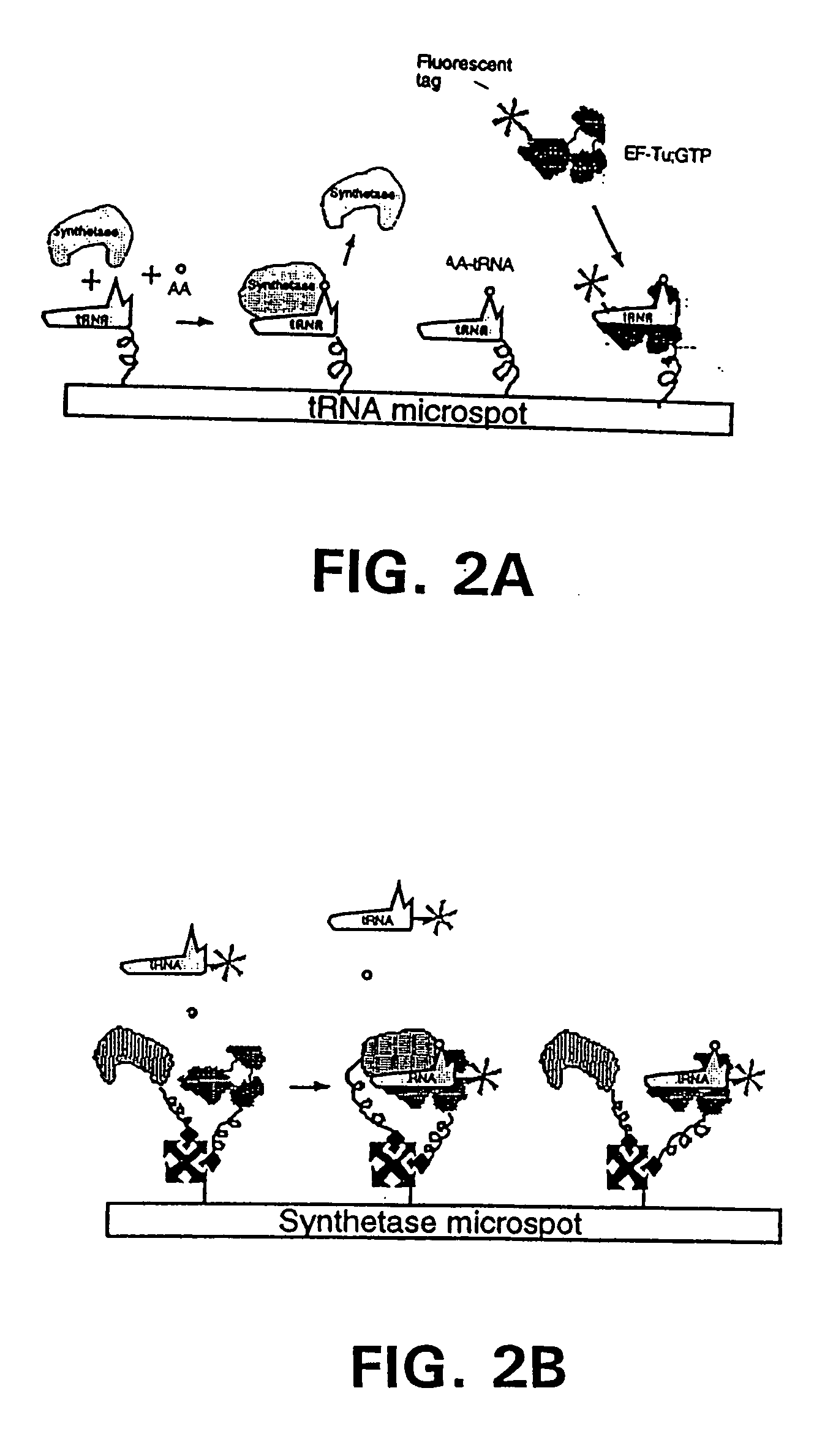
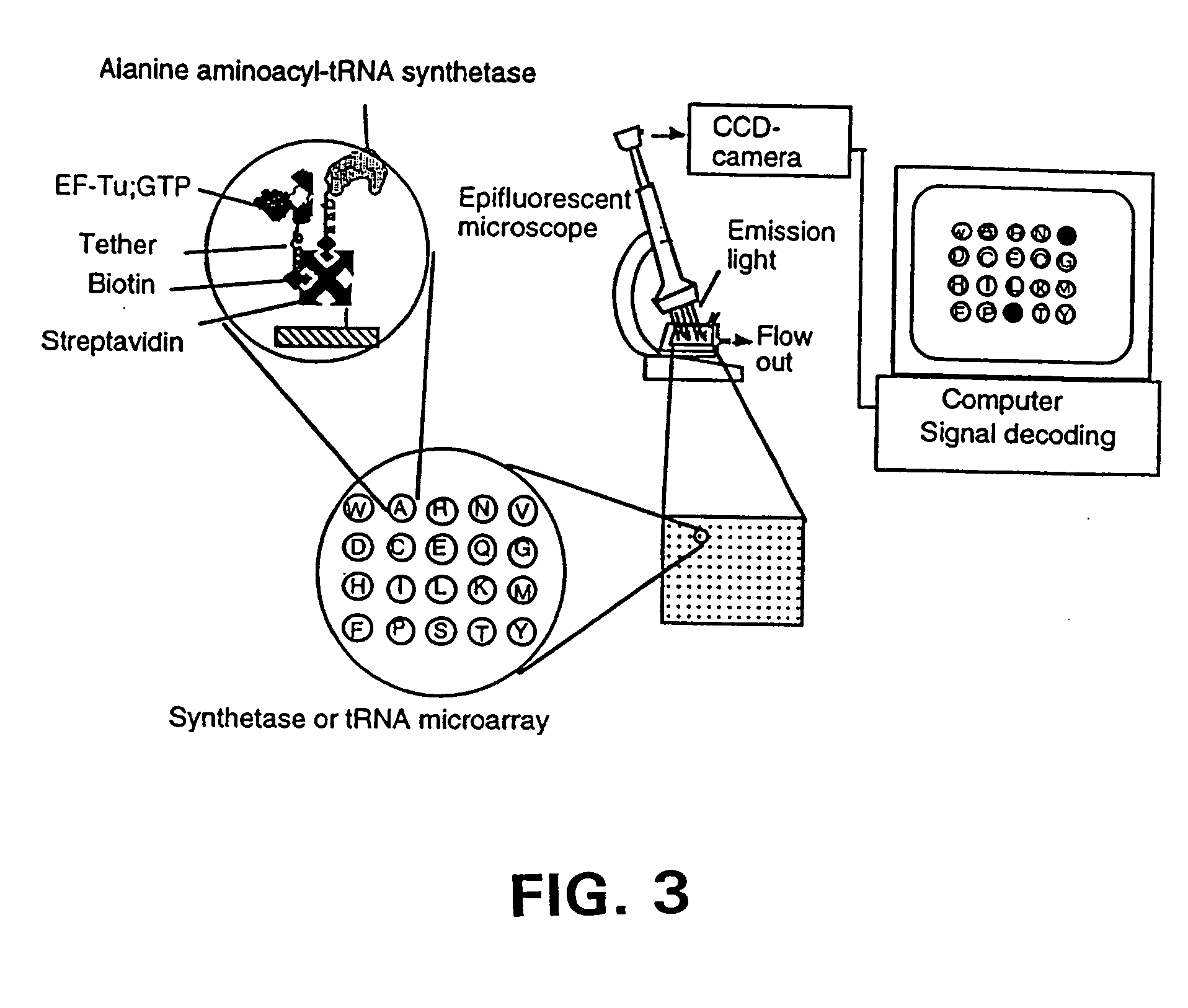
Methods, compositions, kits, and apparatus are provided wherein the aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase system is used to analyze amino acids. The method allows very small devices for quantitative or semi-quantitative analysis of the amino acids in samples or in sequential or complete proteolytic digestions. The methods can be readily applied to the detection and / or quantitation of one or more primary amino acids by using cognate aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase and cognate tRNA. The basis of the method is that each of the 20 synthetases and / or a tRNA specific for a different amino acid is separated spatially or differentially labeled. The reactions catalyzed by all 20 synthetases may be monitored simultaneously, or nearly simultaneously, or in parallel. Each separately positioned synthetase or tRNA will signal its cognate amino acid. The synthetase reactions can be monitored using continuous spectroscopic assays. Alternatively, since elongation factor Tu:GTP (EF-Tu:GTP) specifically binds all AA-tRNAs, the aminoacylation reactions catalyzed by the synthetases can be monitored using ligand assays. Microarrays and microsensors for amino acid analysis are provided. Additionally, amino acid analysis devices are integrated with protease digestions to produce miniaturized enzymatic sequenators capable of generating either N- or C-terminal sequence and composition data for a protein or peptide. The possibility of parallel processing of many samples in an automated manner is discussed.
Owner:NANOBIODYNAMICS
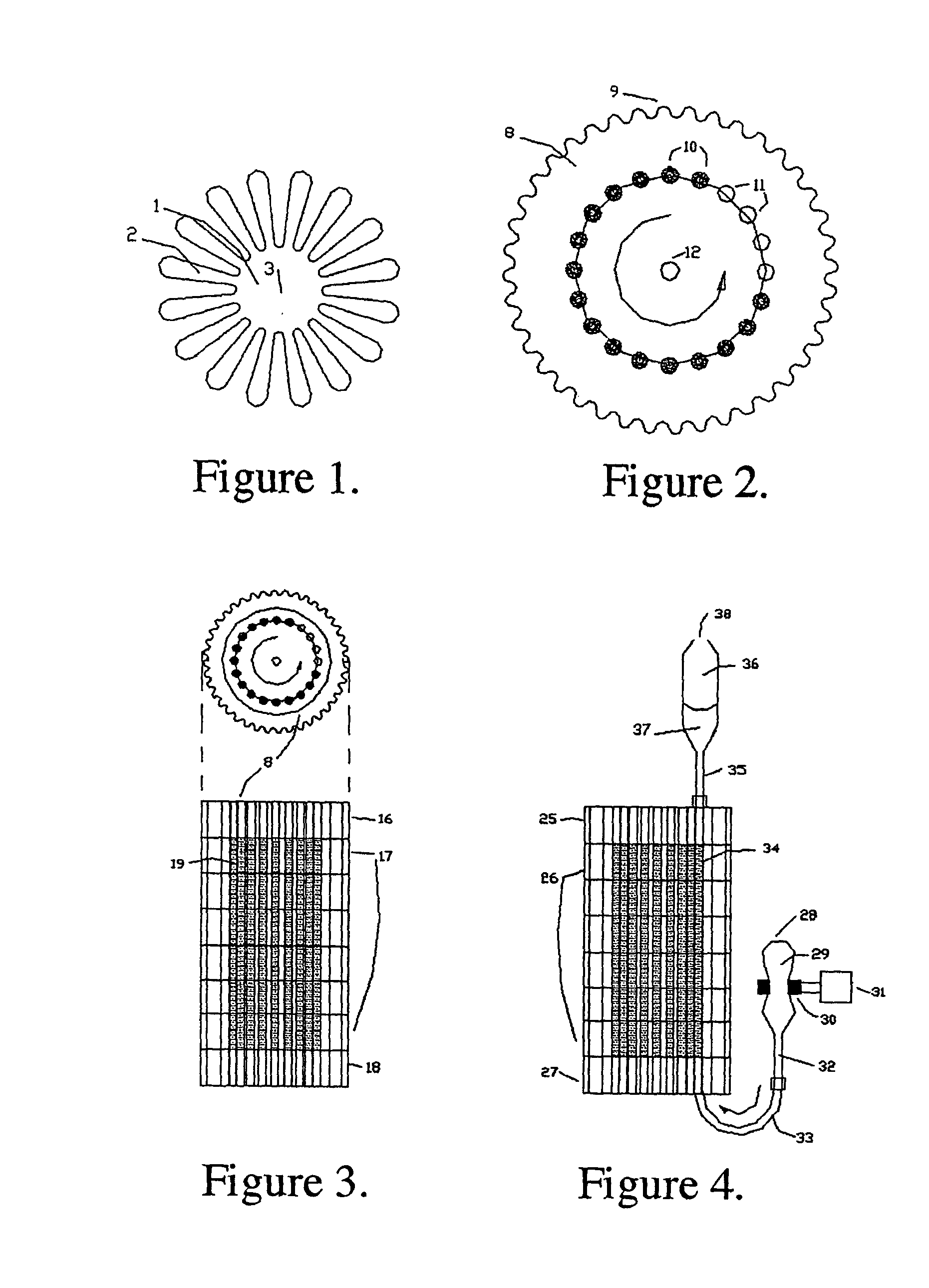
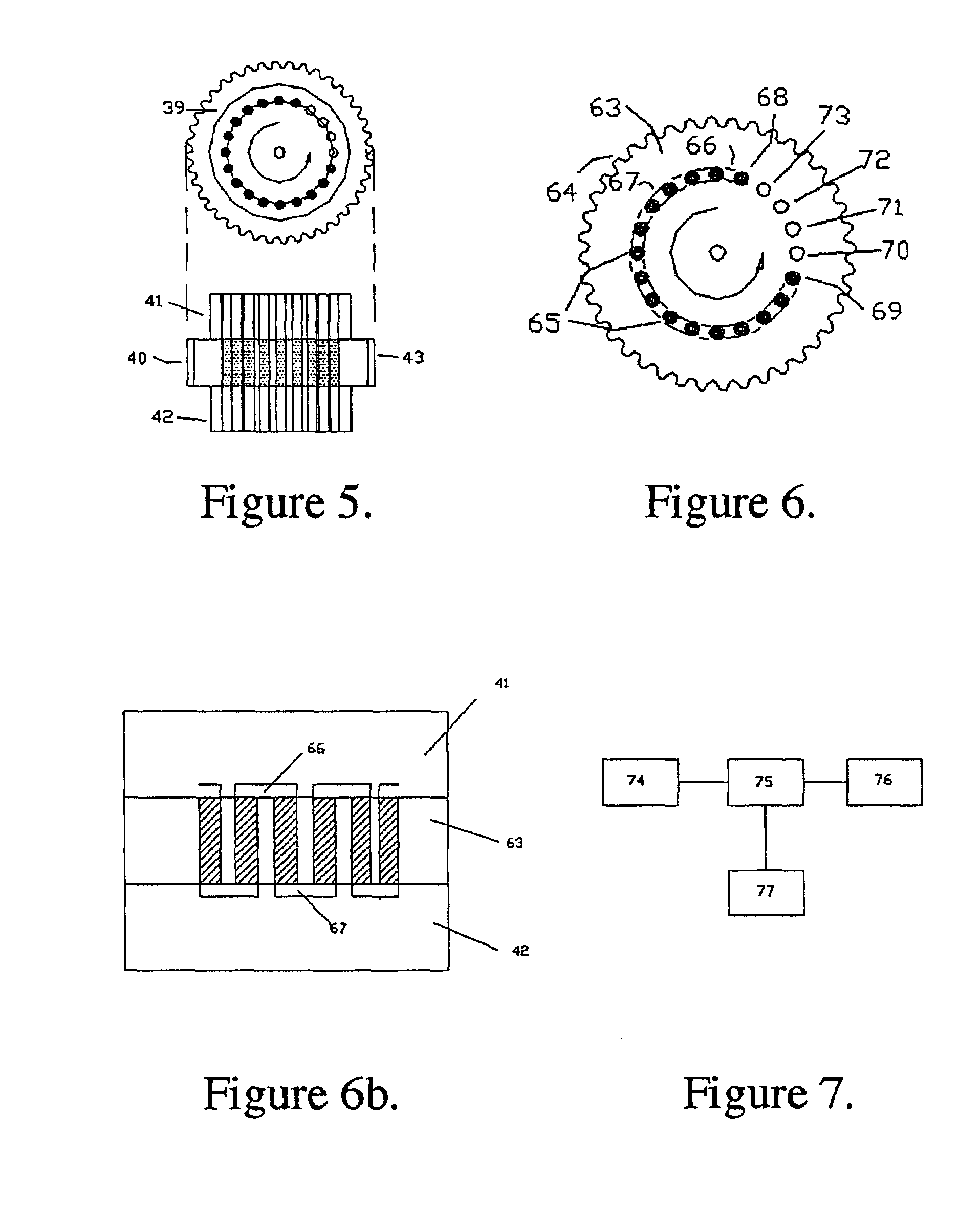
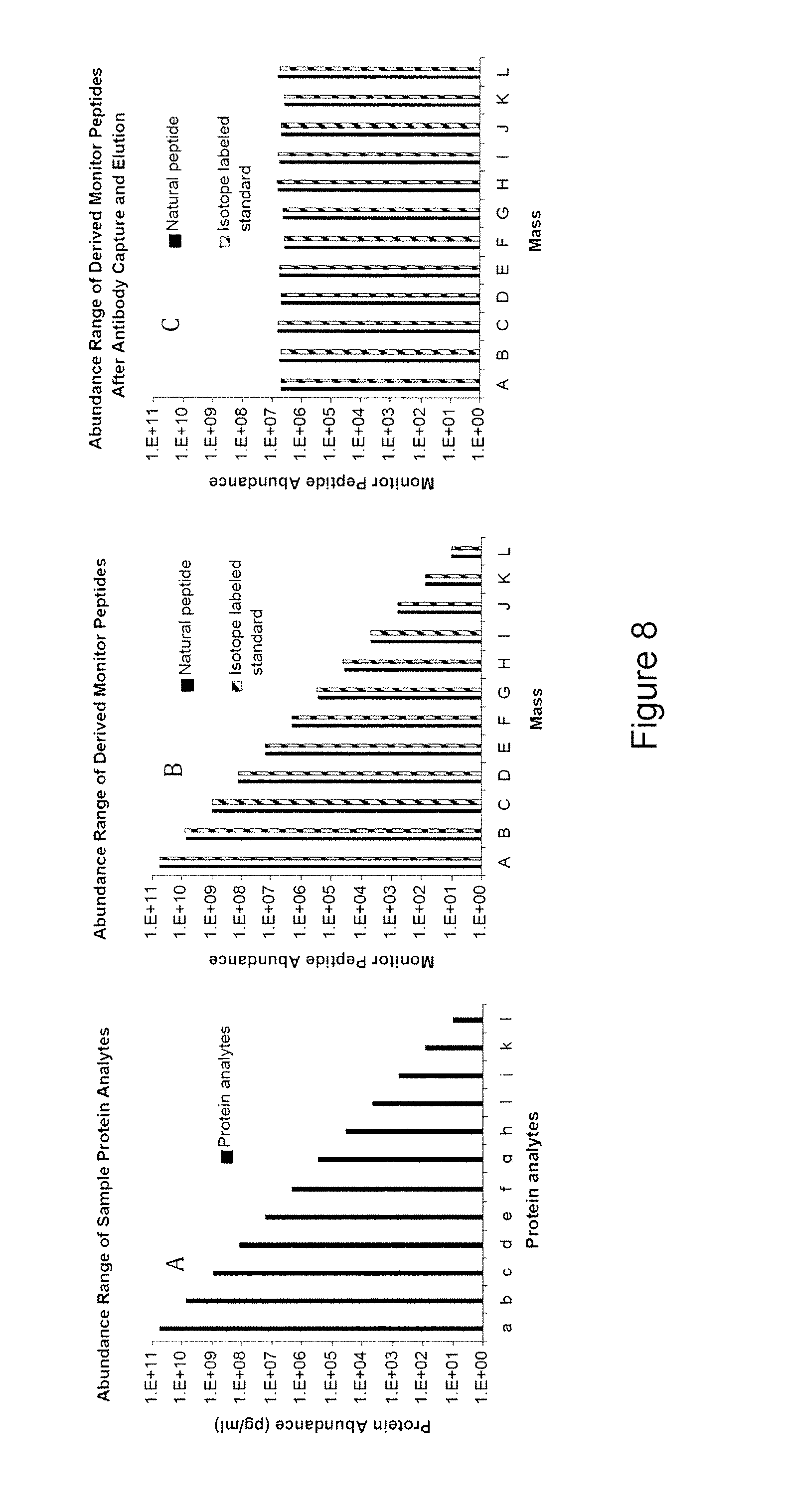
High sensitivity quantitation of peptides by mass spectrometry
InactiveUS20040072251A1Loss of substantial specific binding capacityReduce complexitySamplingComponent separationChemical structureProtein target
The instant invention provides an economical flow-through method for determining amount of target proteins in a sample. An antibody preparation (whether polyclonal or monoclonal, or any equivalent specific binding agent) is used to capture and thus enrich a specific monitor peptide (a specific peptide fragment of a protein to be quantitated in a proteolytic digest of a complex protein sample) and an internal standard peptide (the same chemical structure but including stable isotope labels). Upon elution into a suitable mass spectrometer, the natural (sample derived) and internal standard (isotope labeled) peptides are quantitated, and their measured abundance ratio used to calculate the abundance of the monitor peptide, and its parent protein, in the initial sample
Owner:ANDERSON FORSCHUNG GROUP
Genes encoding plant protease-resistant pesticidal proteins and method of their use
InactiveUS7462760B2High expressionImprove the immunitySugar derivativesClimate change adaptationProteinase activityPlant cell
Compositions and methods for protecting a plant from an insect pest are provided. The invention provides mutagenized nucleic acids that have been engineered to encode pesticidal polypeptides having increased resistance to proteolytic degradation by a plant protease. In particular, nucleic acid sequences encoding pesticidal polypeptides modified to comprise a proteolytic protection site that confers resistance to degradation or proteolytic inactivation by a plant protease are provided. Particular embodiments of the invention provide expression cassettes and transformed plants, plant cells, and seeds. These compositions find use in methods for protecting a plant from a pest.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Compositions and methods for monitoring the modification of modification dependent binding partner polypeptides
InactiveUS7060506B2Promote lowerPromote digestionMicrobiological testing/measurementAnalysis by subjecting material to chemical reactionDigestionProteolysis
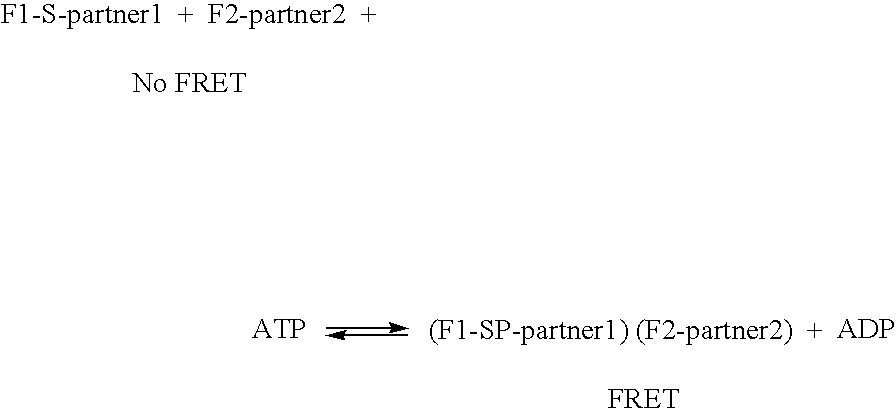
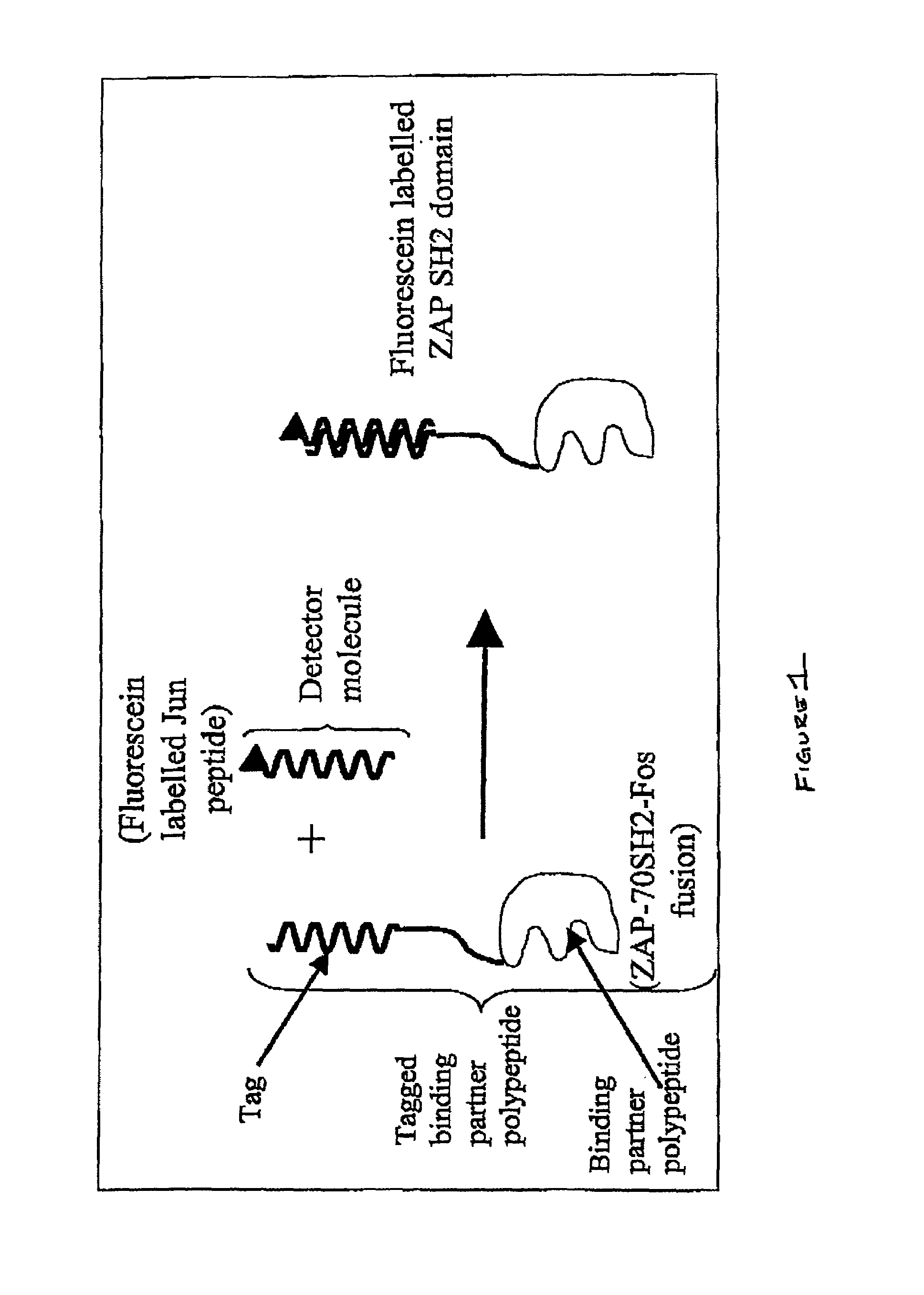
The invention provides methods and compositions for monitoring enzymatic activity as a function of the interaction of modification dependant binding partner polypeptides. Association or dissociation of the binding partner polypeptides is dependant upon the addition or removal of a moiety to or from one or both of the binding partner polypeptides or upon proteolytic digestion of one or both of the binding partner polypeptides by a modifying enzyme.
Owner:CYCLACEL
Chemotherapy treatment
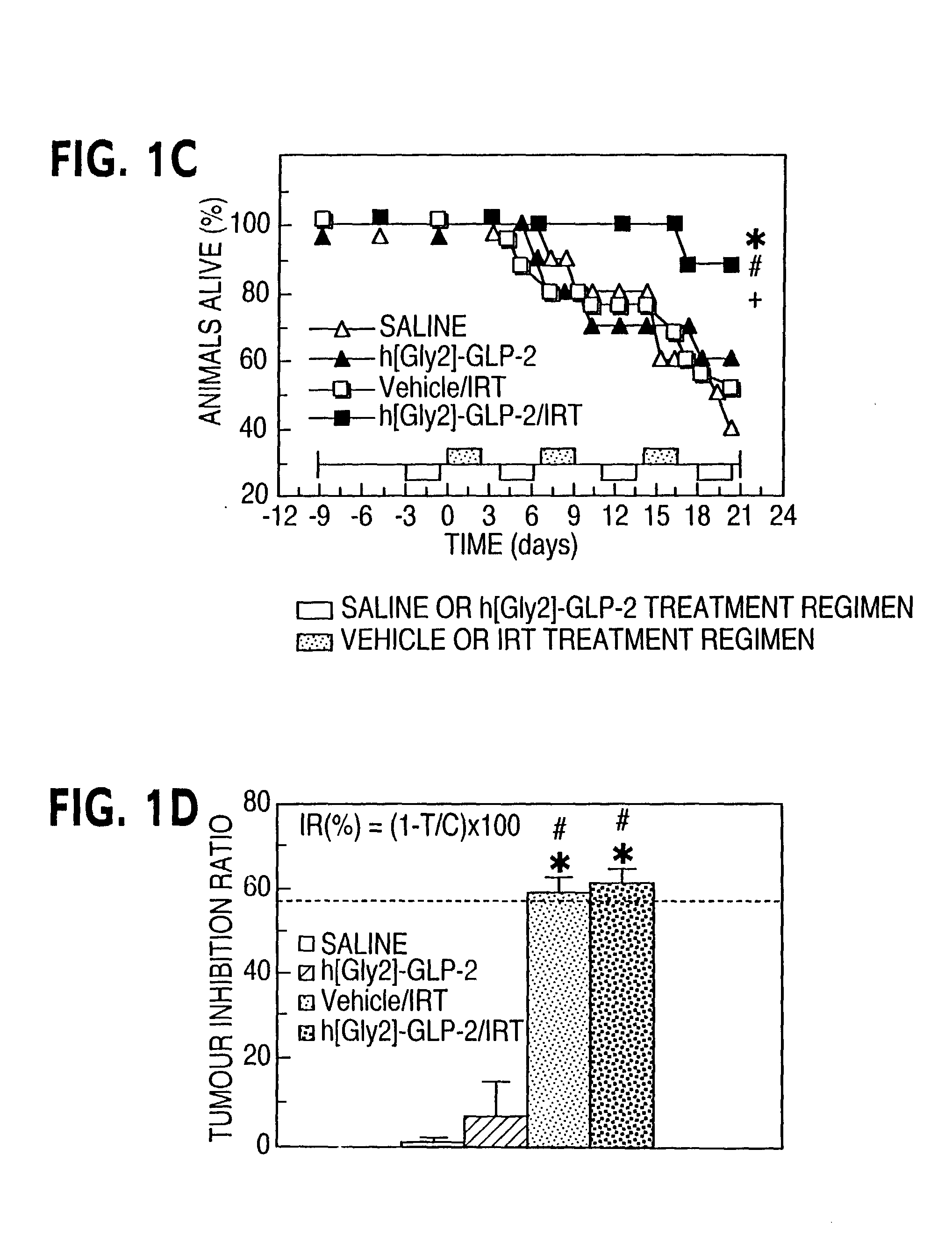
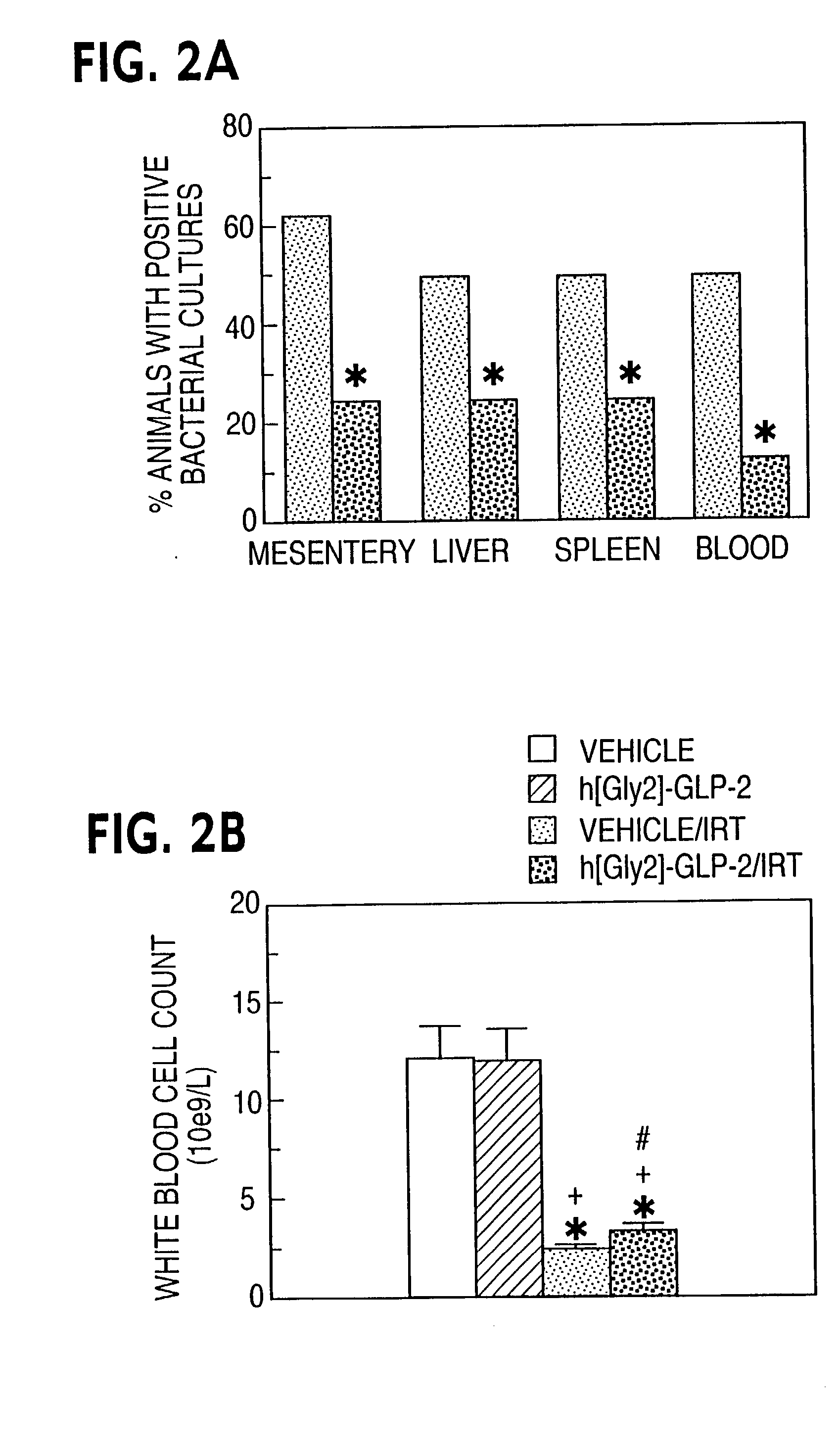
InactiveUS20030040478A1Improve welfareImprove survivalBiocideOrganic active ingredientsRegimenApoptosis
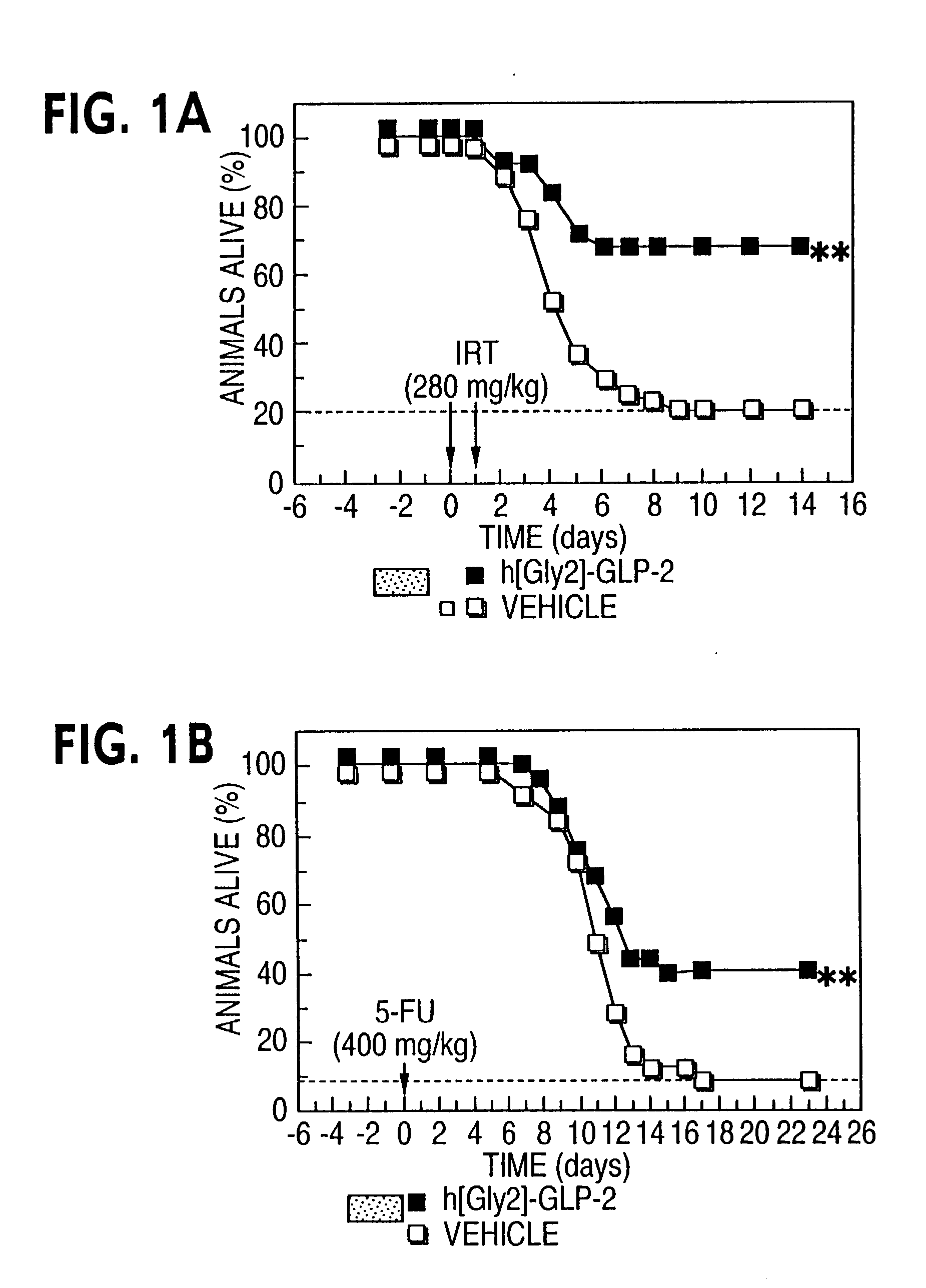
This invention provides a treatment regimen that is effective in inhibiting chemotherapy-induced apoptosis and promoting cell survival. The invention also relates to a treatment regimen that confers resistance to caspase activation, thereby inhibiting caspase-mediated, proteolytic cleavage of functional cellular enzymes. Specifically, subjects undergoing chemotherapy are first exposed to a pretreatment regimen. Under this regimen, a GLP-2 receptor activator, such as h[GLY2]-GLP2, is administered each day for a predetermined beneficial period, e.g., three consecutive days. Approximately about 1 week following pretreatment, the subjects are exposed to an appropriate chemotherapy treatment regimen. Pretreatment with a GLP-2 receptor activator followed by administration of chemotherapeutic agents improves cell survival, reduces bacteremia, attenuates epithelial injury, and inhibits cellular apoptosis. Moreover, it does not impair the effectiveness of chemotherapy nor result in weight loss. The anti-apoptotic effects of GLP-2 may be useful in the reduction of cytoxicity and bacterial infection induced by chemotherapeutic agents.
Owner:1149336 ONTARIO
Compositions and methods for detecting protease activity
ActiveUS7229769B2Microbiological testing/measurementFungi medical ingredientsProteinase activityProtein anabolism
The invention provides a method of determining activity of a protease. The method can include the steps of (a) providing a protease substrate including a protein moiety attached to a nucleic acid moiety and a ligand moiety; (b) contacting the protease substrate with a protease under conditions wherein the protease catalyzes cleavage of the protein moiety, thereby producing a proteolytic product wherein the nucleic acid moiety is separated from at least a portion of the protein moiety and the ligand moiety; (c) contacting the proteolytic product with a receptor under conditions wherein the ligand moiety binds to the receptor to form a complex; (d) separating the complex from the nucleic acid moiety, thereby forming a separation product including the nucleic acid moiety; (e) contacting the separation product with a probe nucleic acid under conditions wherein the nucleic acid moiety hybridizes to a complementary sequence of the probe; and (f) detecting hybridization of the separation product to the probe, thereby determining activity of the protease.
Owner:MURPHY JOHN T
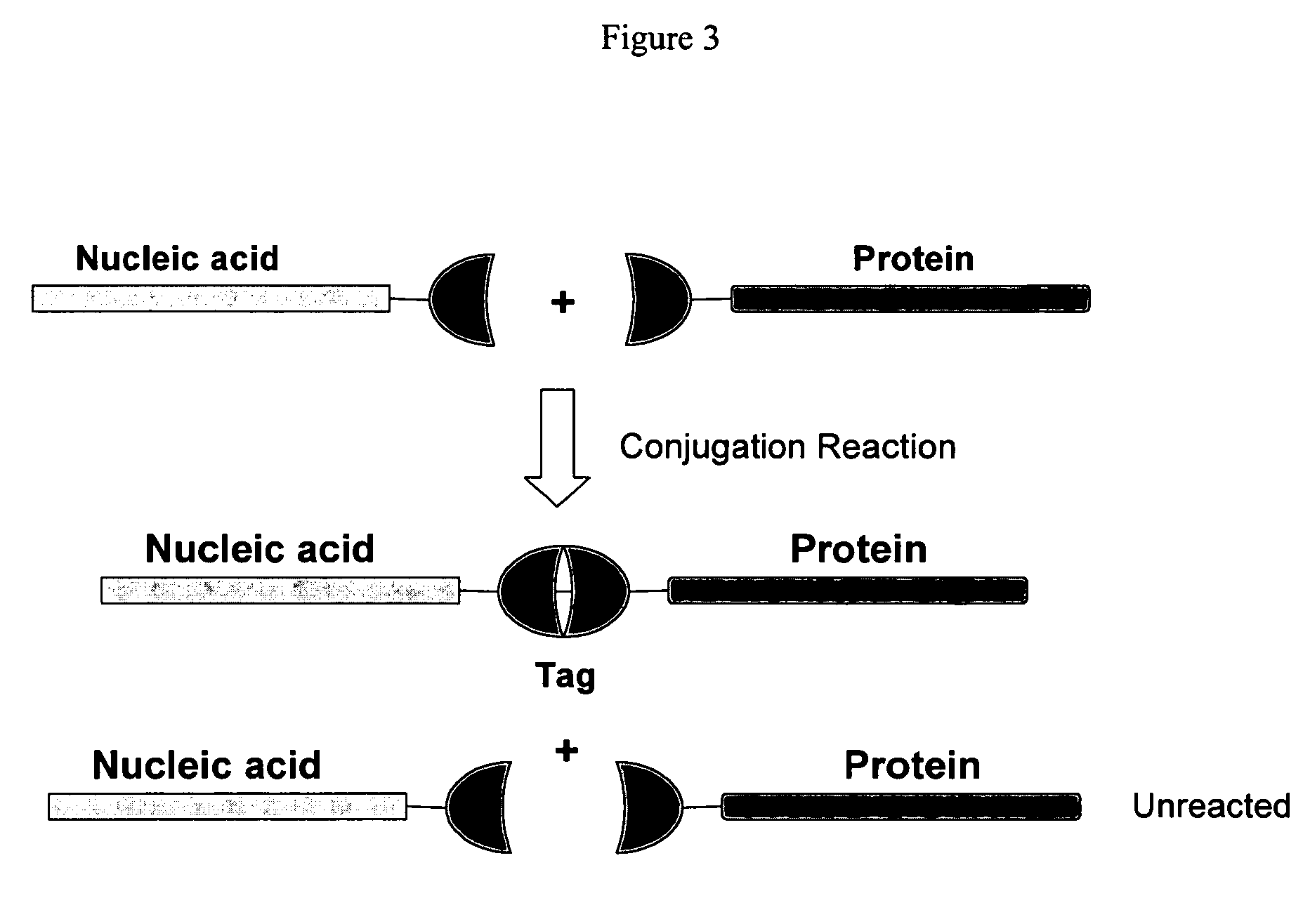
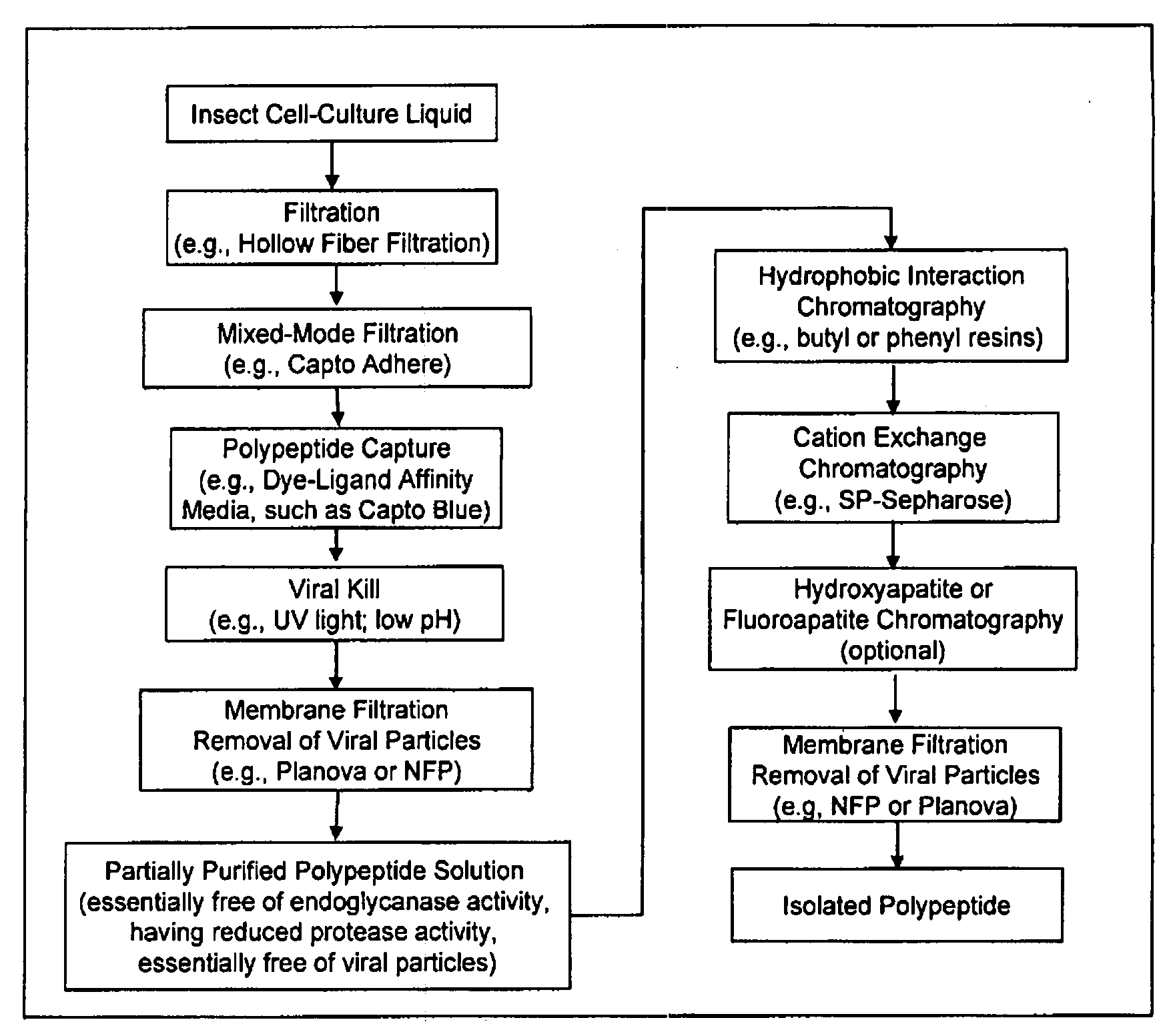
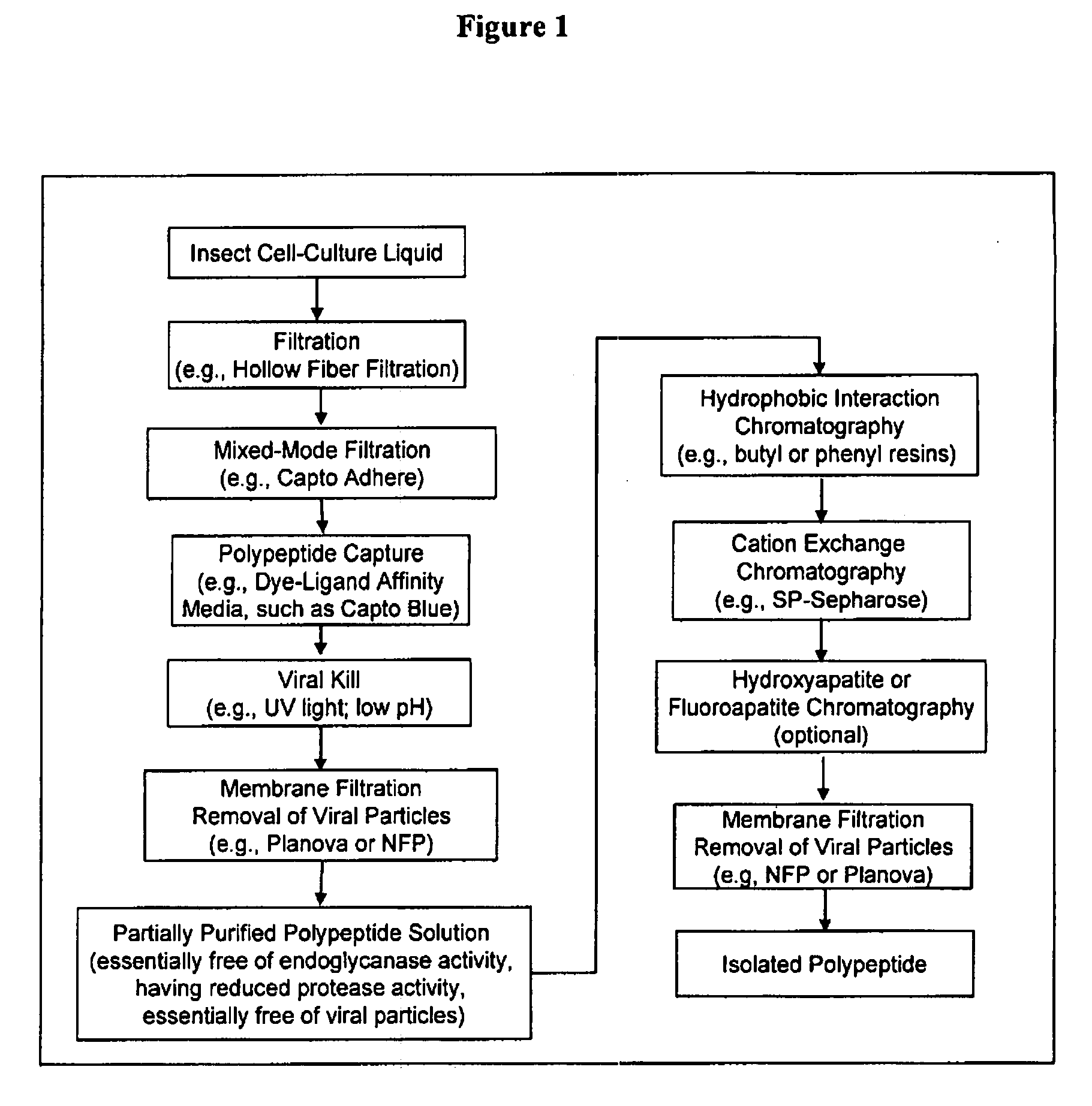
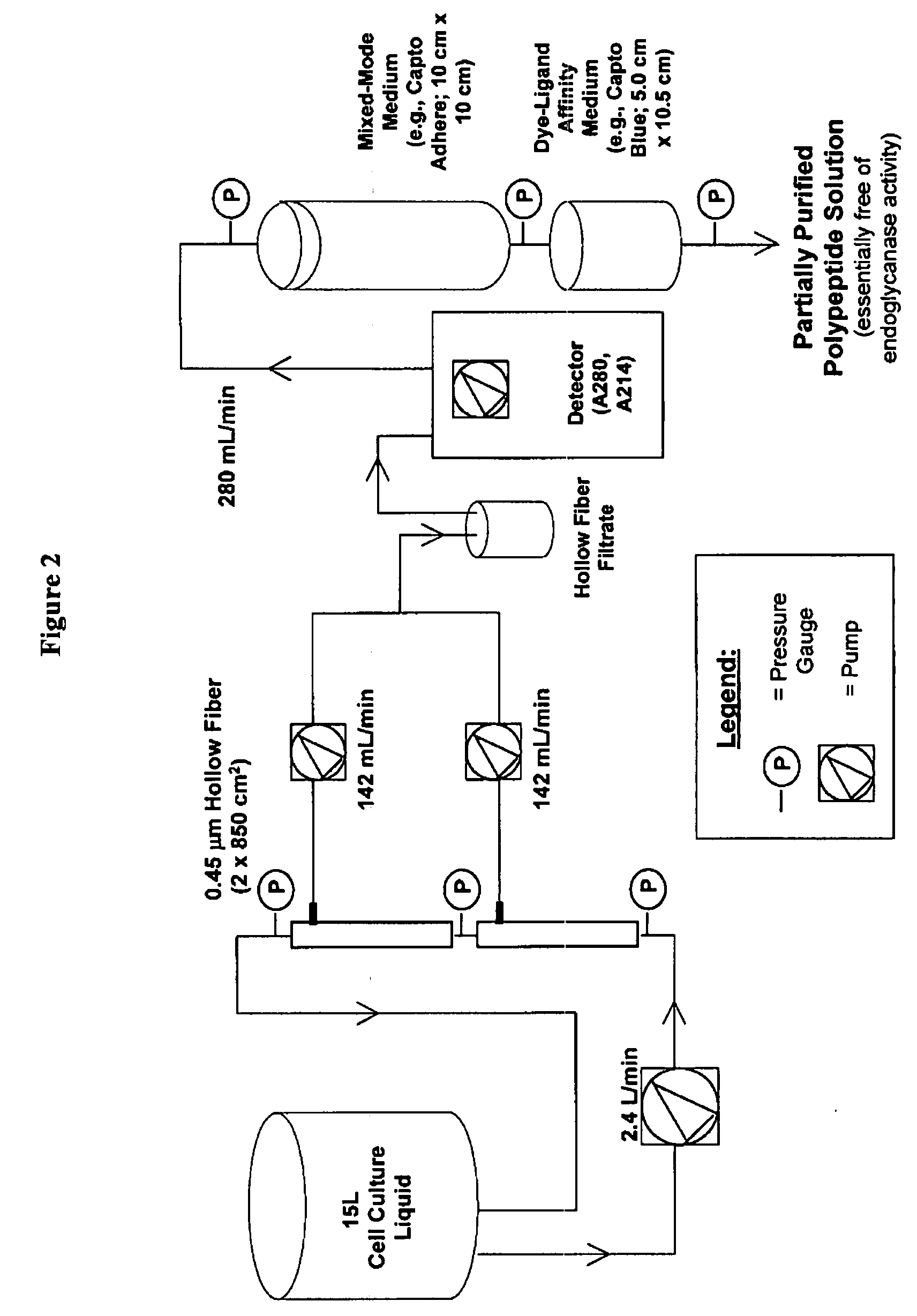
Manufacturing process for the production of polypeptides expressed in insect cell-lines
InactiveUS20080207487A1Promote recoveryReduce manufacturing costPeptide/protein ingredientsDepsipeptidesFiberCulture fluid
The present invention provides a manufacturing method for polypeptides that are produced in insect cells using a baculoviral expression system. In one example, the insect cell culture is supplemented with a lipid mixture immediately prior to infection (e.g., one hour prior to infection). The polypeptides are isolated from the insect cell culture using a method that employs anion exchange or mixed-mode chromatography early in the purification process. This process step is useful to remove insect-cell derived endoglycanases and proteases and thus reduces the loss of desired polypeptide due to enzymatic degradation. In another example, mixed-mode chromatography is combined with dye-ligand affinity chromatography in a continuous-flow manner to allow for rapid processing of the insect-cell culture liquid and capture of the polypeptide. In yet another example, a polypeptide is isolated from an insect cell culture liquid using a process that combines hollow fiber filtration, mixed-mode chromatography and dye-ligand affinity in a single unit operation producing a polypeptide solution that is essentially free of endoglycanase and proteolytic activities. In a further example, the isolated polypeptides are glycopeptides having an insect specific glycosylation pattern, which are optionally conjugated to a modifying group, such as a polymer (e.g., PEG) using a glycosyltransferase and a modified nucleotide sugar.
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS
Compositions and methods for enhancing structural and functional nervous system reorganization and recovery
InactiveUS20060104969A1Improve the degradation problemSimple structurePeptide/protein ingredientsInorganic phosphorous active ingredientsNervous systemDelivery vehicle
The present invention provides methods and compositions for enhancing recovery in a subject suffering from damage to the nervous system. In particular, the invention includes a method for promoting recovery and / or reorganization in the nervous system of a subject in need of enhancement of recovery and / or reorganization of the nervous system as a result of ischemic, hemorrhagic, neoplastic, degenerative, or traumatic damage by focally administering a composition comprising a proteolysis-enhancing agent such as tissue plasminogen activator (tPA), plasmin, or a PAI inhibitor to the nervous system of the subject. In some embodiments an additional active agent is also administered. The composition can be delivered using a variety of techniques including injection, via infusion pump, from an implantable microchip, or using a polymeric delivery vehicle. The composition can be administered, for example, to one or more subdivisions or areas of the brain, the spinal cord, or to one or more nerves or nerve tracts innervating diverse regions of the body. The invention also includes a drug delivery device for implantation into the nervous system to promote nervous system reorganization and / or recovery following ischemic, hemorrhagic, neoplastic, traumatic or degenerative damage, the drug delivery device comprising a biocompatible polymer and a proteolysis-enhancing agent such as tissue plasminogen activator (tPA), plasmin, or a PAI inhibitor, wherein the proteolysis-enhancing agent is released from the polymer in an amount effective to promote structural reorganization of the nervous system. In some embodiments the biocompatible polymer is a hydrogel.
Owner:THE BRIGHAM & WOMEN S HOSPITAL INC +1
Methods and compositions for evaluating breast cancer prognosis
InactiveUS20060063190A1Accurate assessmentImproved prognosisMicrobiological testing/measurementProteomicsLymphatic SpreadNucleic acid hybridisation
Methods and compositions for evaluating the prognosis of a breast cancer patient, particularly an early-stage breast cancer patient, are provided. The methods of the invention comprise detecting expression of at least one, more particularly at least two, biomarker(s) in a body sample, wherein overexpression of the biomarker or a combination of biomarkers is indicative of breast cancer prognosis. In some embodiments, the body sample is a breast tissue sample, particularly a primary breast tumor sample. The biomarkers of the invention are proteins and / or genes whose overexpression is indicative of either a good or bad cancer prognosis. Biomarkers of interest include proteins and genes involved in cell cycle regulation, DNA replication, transcription, signal transduction, cell proliferation, invasion, proteolysis, or metastasis. In some aspects of the invention, overexpression of a biomarker of interest is detected at the protein level using biomarker-specific antibodies or at the nucleic acid level using nucleic acid hybridization techniques.
Owner:TRIPATH IMAGING INC
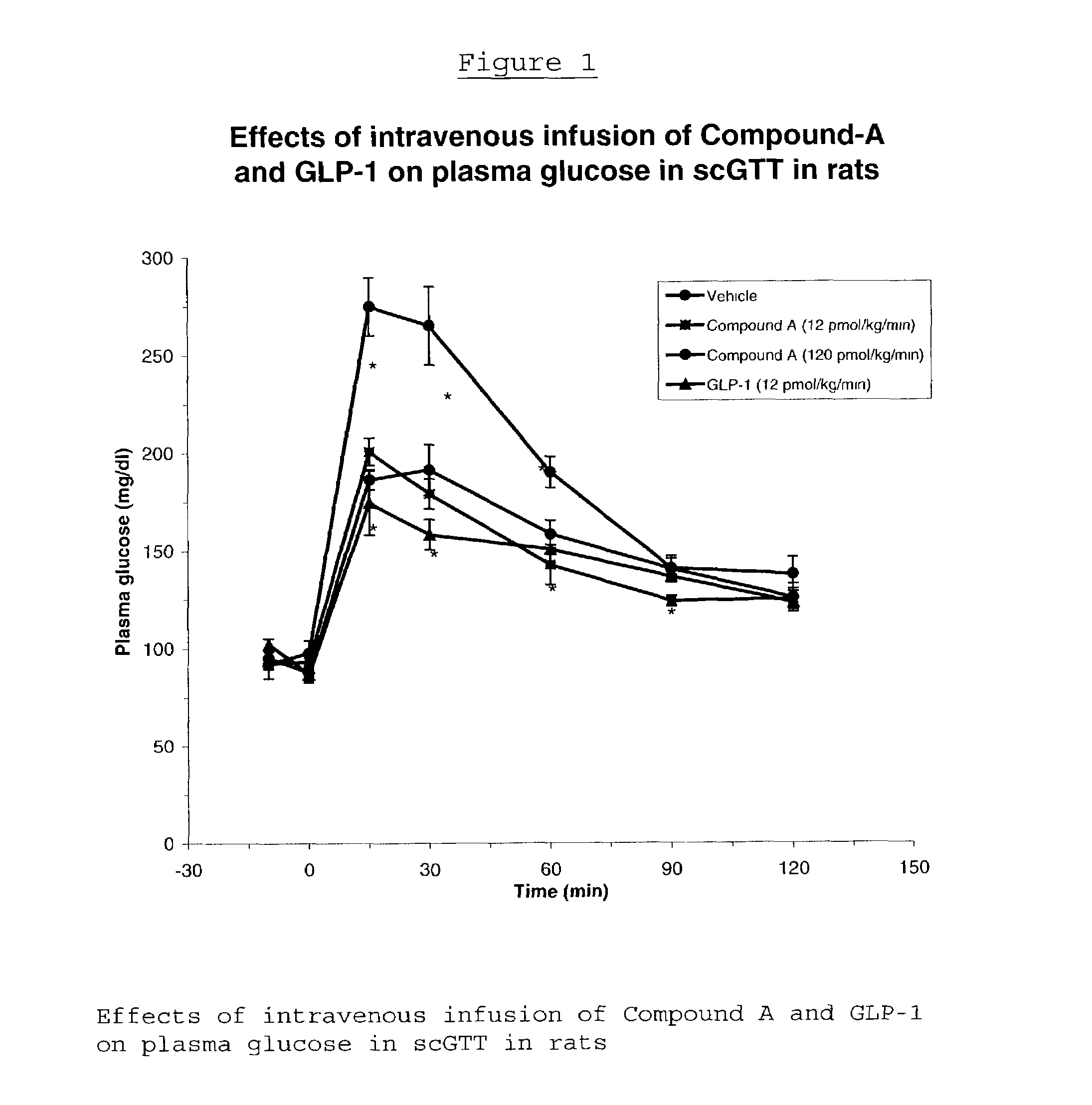
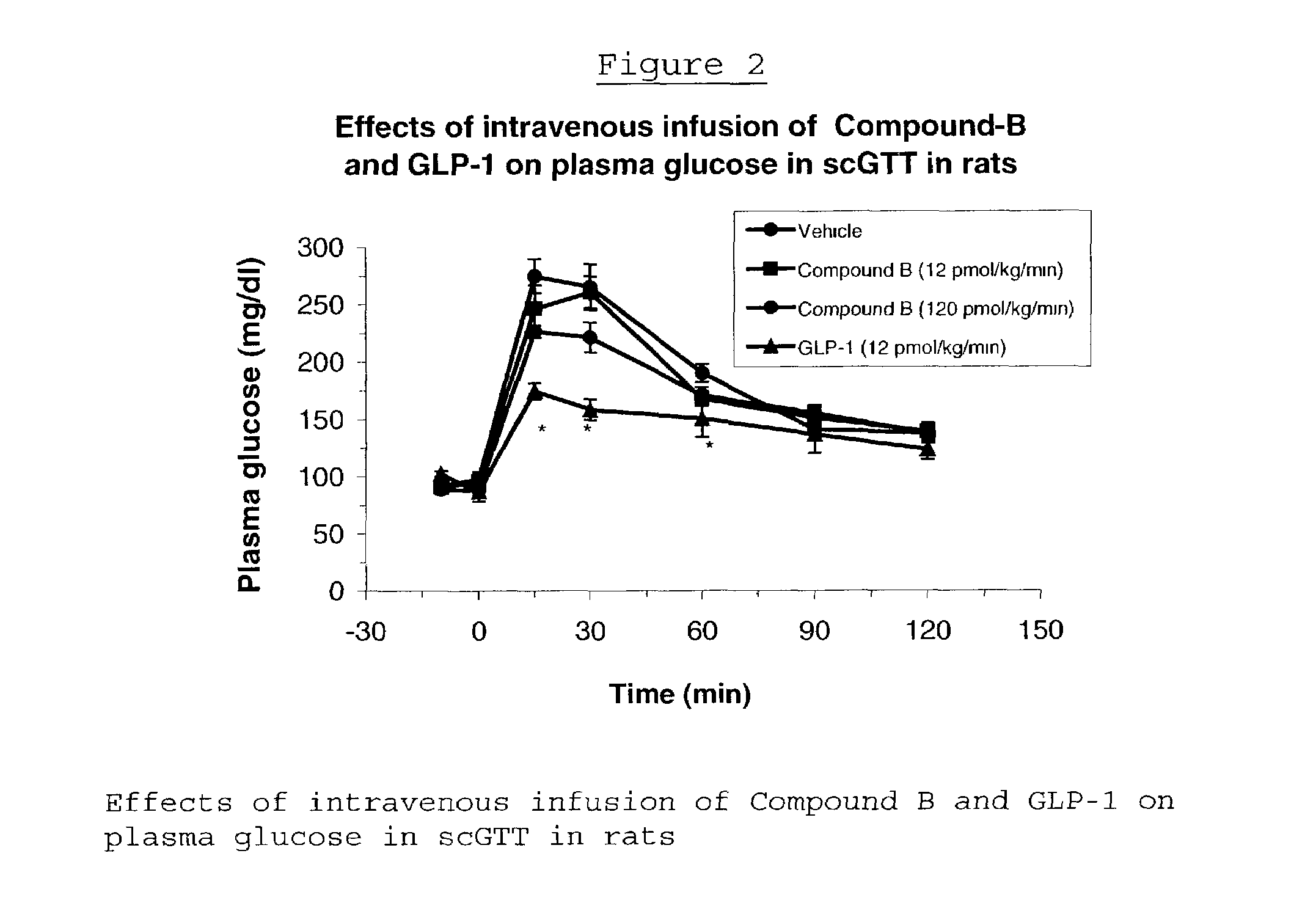
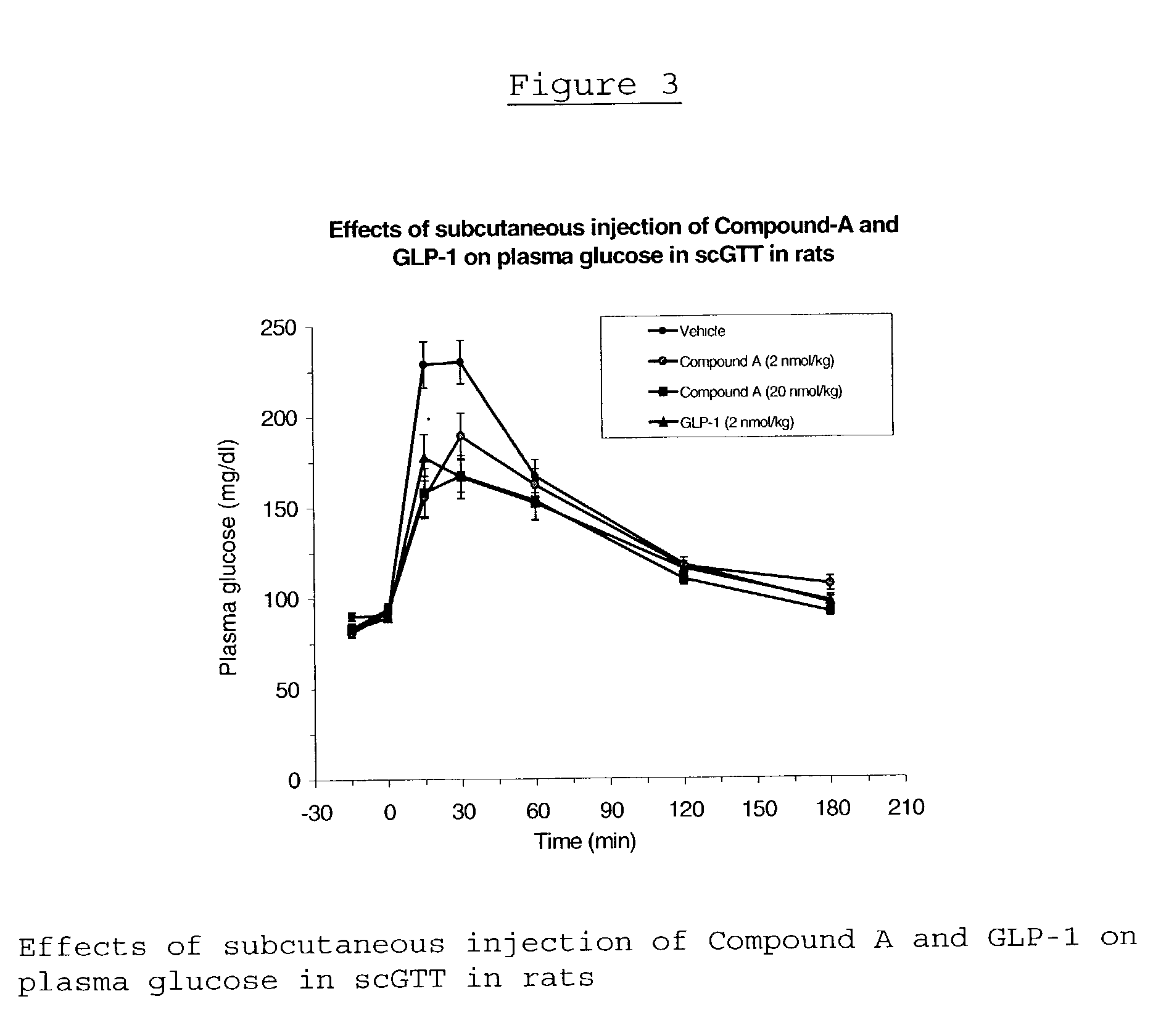
Human glucagon-like peptide-1 mimics and their use in the treatment of diabetes and related conditions
InactiveUS20070287670A1Improve the level ofSenses disorderNervous disorderGlucagon-like peptide-1Drug biological activity
The present invention provides novel human glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) peptide mimics that mimic the biological activity of the native GLP-1 peptide and thus are useful for the treatment or prevention of diseases or disorders associated with GLP activity. Further, the present invention provides novel, chemically modified peptides that not only stimulate insulin secretion in type II diabetics, but also produce other beneficial insulinotropic responses. These synthetic peptide GLP-1 mimics exhibit increased stability to proteolytic cleavage making them ideal therapeutic candidates for oral or parenteral administration.
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB CO
Β-turn peptidomimetic cyclic compounds
InactiveUS6881719B2Easy to manageReduce deliveryOrganic active ingredientsTetrapeptide ingredientsDiseaseNeurotrophin Receptor p75
Proteolytically stable small molecule β-turn peptidomimetic compounds have been identified as agonists or antagonists of neurotrophin receptors, such as TrkA. A compound of particular interest binds the immunoglobulin-like C2 region of the extracellular domain of TrkA, competes the binding of another TrkA ligand, affords selective trophic protection to TrkA-expressing cell lines and neuronal primary cultures, and induces the differentiation of primary neuronal cultures. The small β-turn peptidomimetic compounds of the invention can activate a tyrosine kinase neurotrophin receptor that normally binds a relatively large protein ligand. Such compounds that bind the extracellular domain of Trk receptors are useful pharmacological agents to address disorders where Trk receptors play a role, by targeting populations selectively.
Owner:TEXAS A&M UNIVERSITY +1
High sensitivity quantitation of peptides by mass spectrometry
InactiveUS7632686B2Reduce complexityOverwhelm resolutionSamplingComponent separationChemical structureProtein target
The instant invention provides an economical flow-through method for determining amount of target proteins in a sample. An antibody preparation (whether polyclonal or monoclonal, or any equivalent specific binding agent) is used to capture and thus enrich a specific monitor peptide (a specific peptide fragment of a protein to be quantitated in a proteolytic digest of a complex protein sample) and an internal standard peptide (the same chemical structure but including stable isotope labels). Upon elution into a suitable mass spectrometer, the natural (sample derived) and internal standard (isotope labeled) peptides are quantitated, and their measured abundance ratio used to calculate the abundance of the monitor peptide, and its parent protein, in the initial sample.
Owner:ANDERSON FORSCHUNG GROUP
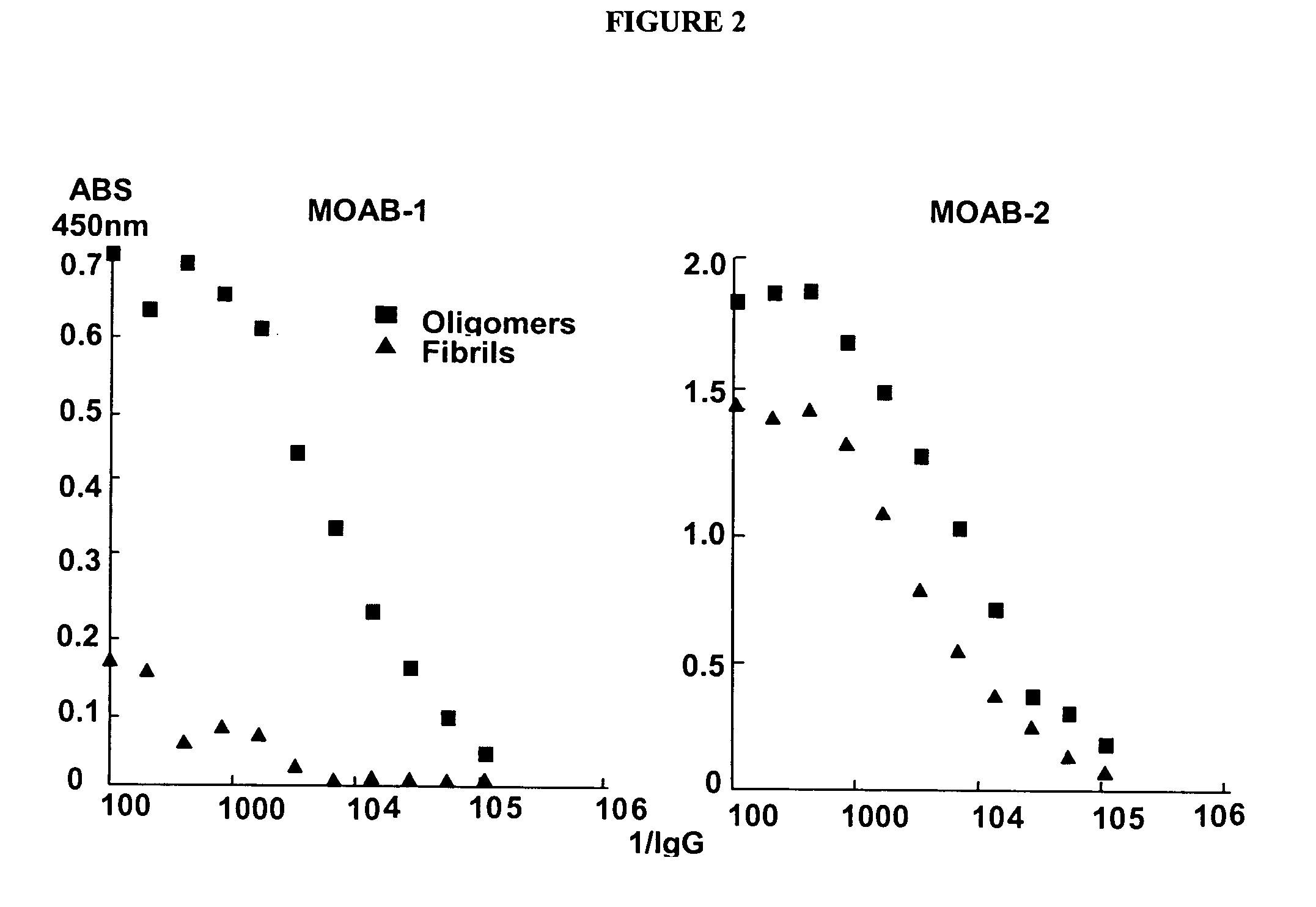
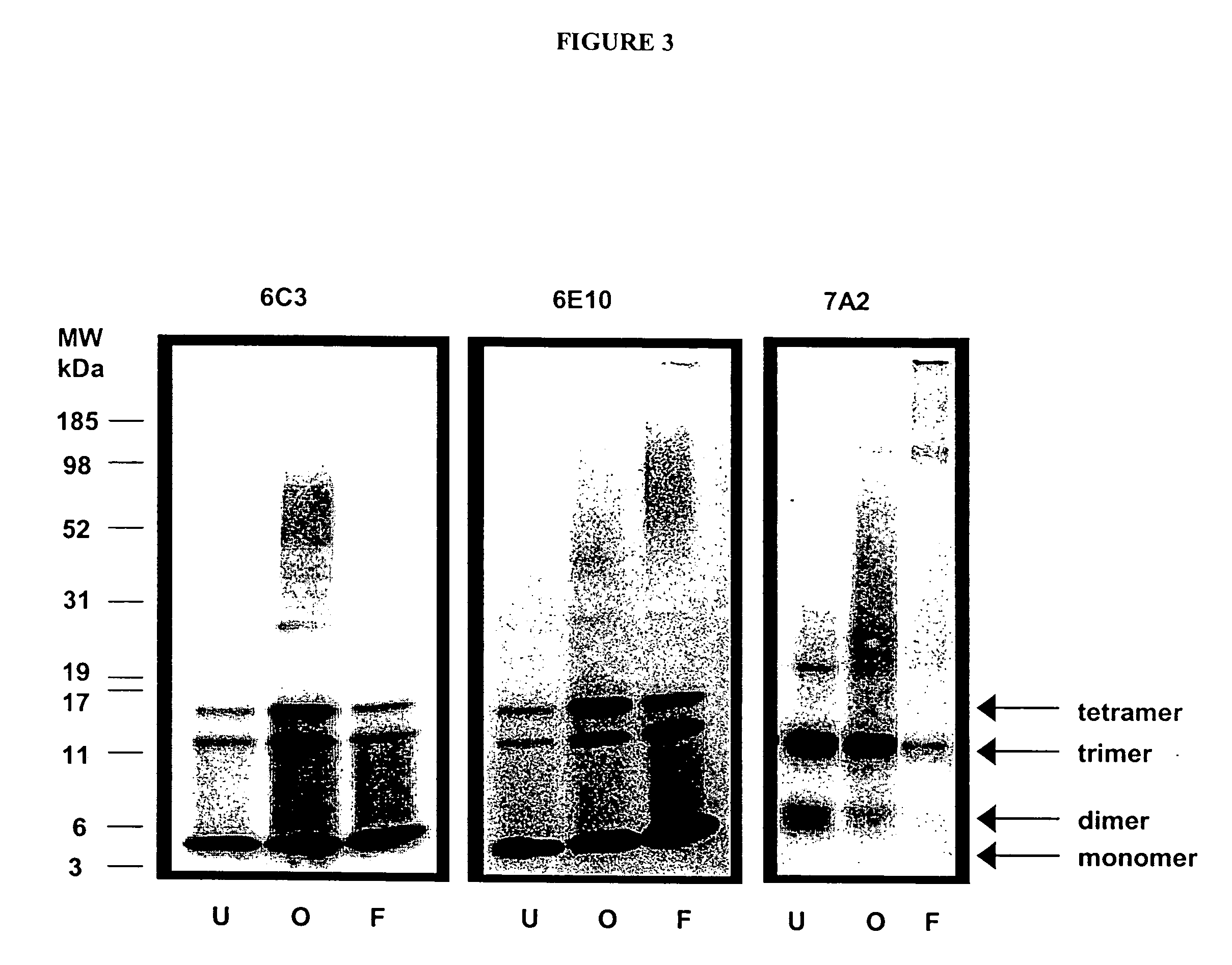
Antibodies specific for toxic amyloid beta protein oligomers
InactiveUS20050124016A1Animal cellsImmunoglobulins against animals/humansOligomerMonoclonal antibody
The present invention provides compositions and methods for diagnosing Alzheimer's disease (AD). In particular, the present invention provides monoclonal antibodies that specifically bind to soluble, non-fibrillar oligomeric amyloid β protein assemblies proteolytically derived from the transmembrane amyloid precursor protein (APP) while not reacting with fibrillar amyloid β protein assemblies, monoclonal antibodies that specifically bind to fibrillar amyloid β protein assemblies that do not react with soluble, non-fibrillar oligomeric amyloid β protein assemblies, and methods of use of these compositions in the diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease, as well as methods to monitor treatment and / or disease progression of AD in patients.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN UNIV +1
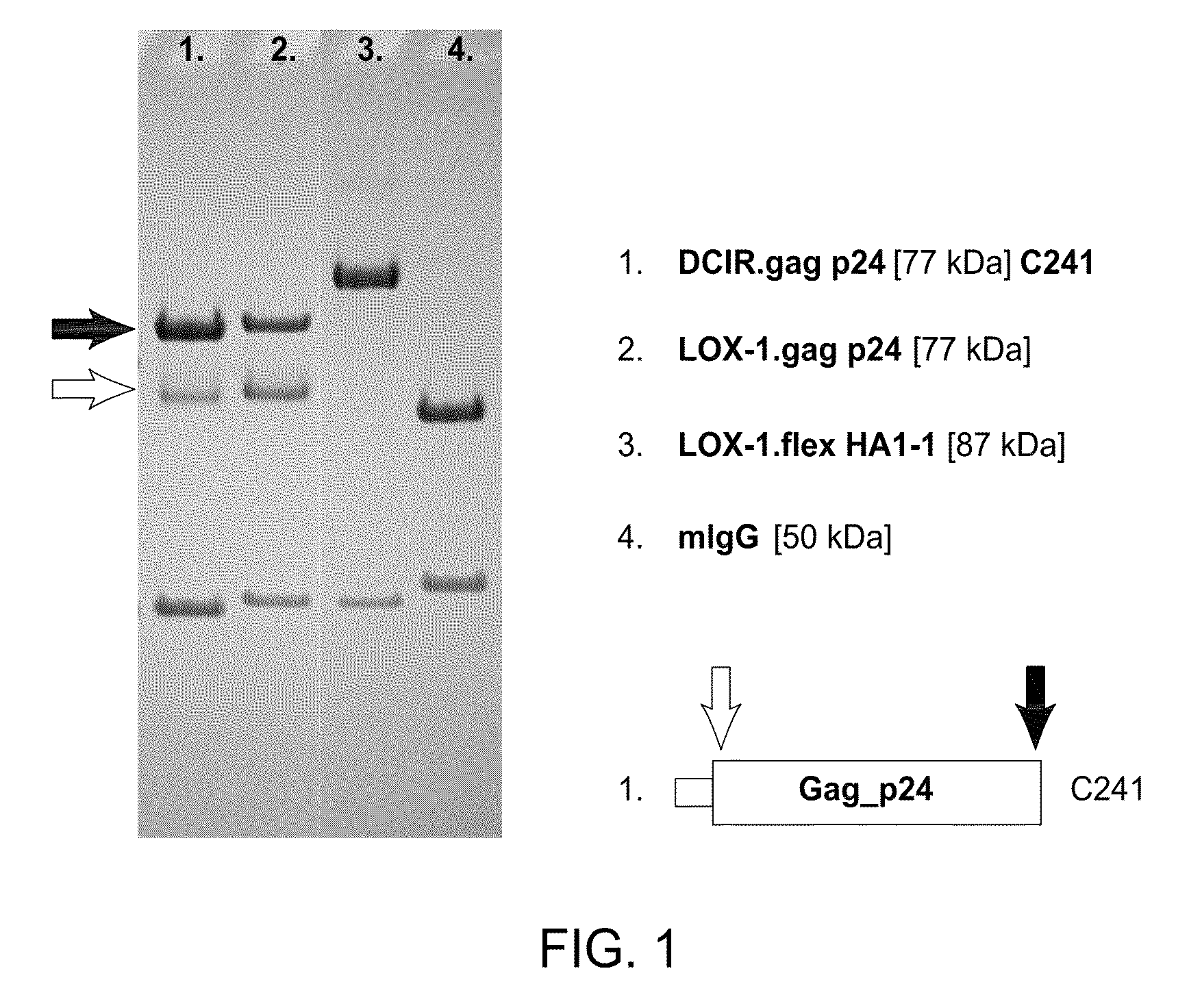
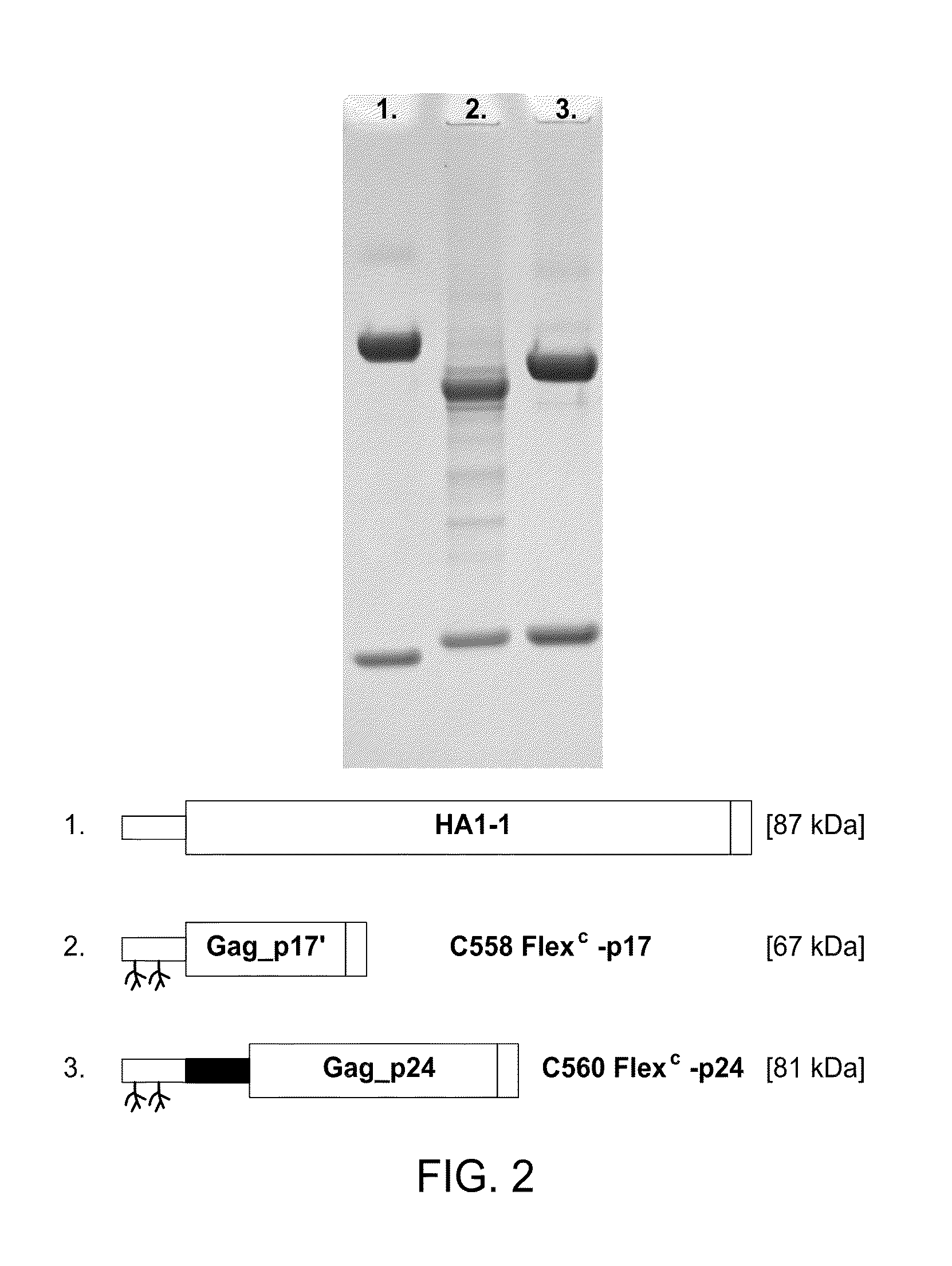
HIV vaccine based on targeting maximized gag and nef to dendritic cells
ActiveUS20100135994A1Improve efficiencyIncrease flexibilityBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsCyclin D1Dendritic cell
The present invention includes compositions and methods for making and using a vaccine that includes a DC-specific antibody or fragment thereof to which an engineered Gag antigen is attached to form an antibody-antigen complex, wherein the Gag antigen is less susceptible to proteolytic degradation by eliminating one or more proteolytic sites or a DC-specific antibody or fragment thereof to which an engineered Nef antigen is attached to form an antibody-antigen complex, wherein the Nef antigen comprises one or more codon usage optimization that increase antibody-antigen complex secretion, or both, wherein the vaccine is able to elicit an HIV-specific T cell immune response to Gag p17, Gag p24, Nef and / or Cyclin D1.
Owner:BAYLOR RES INST
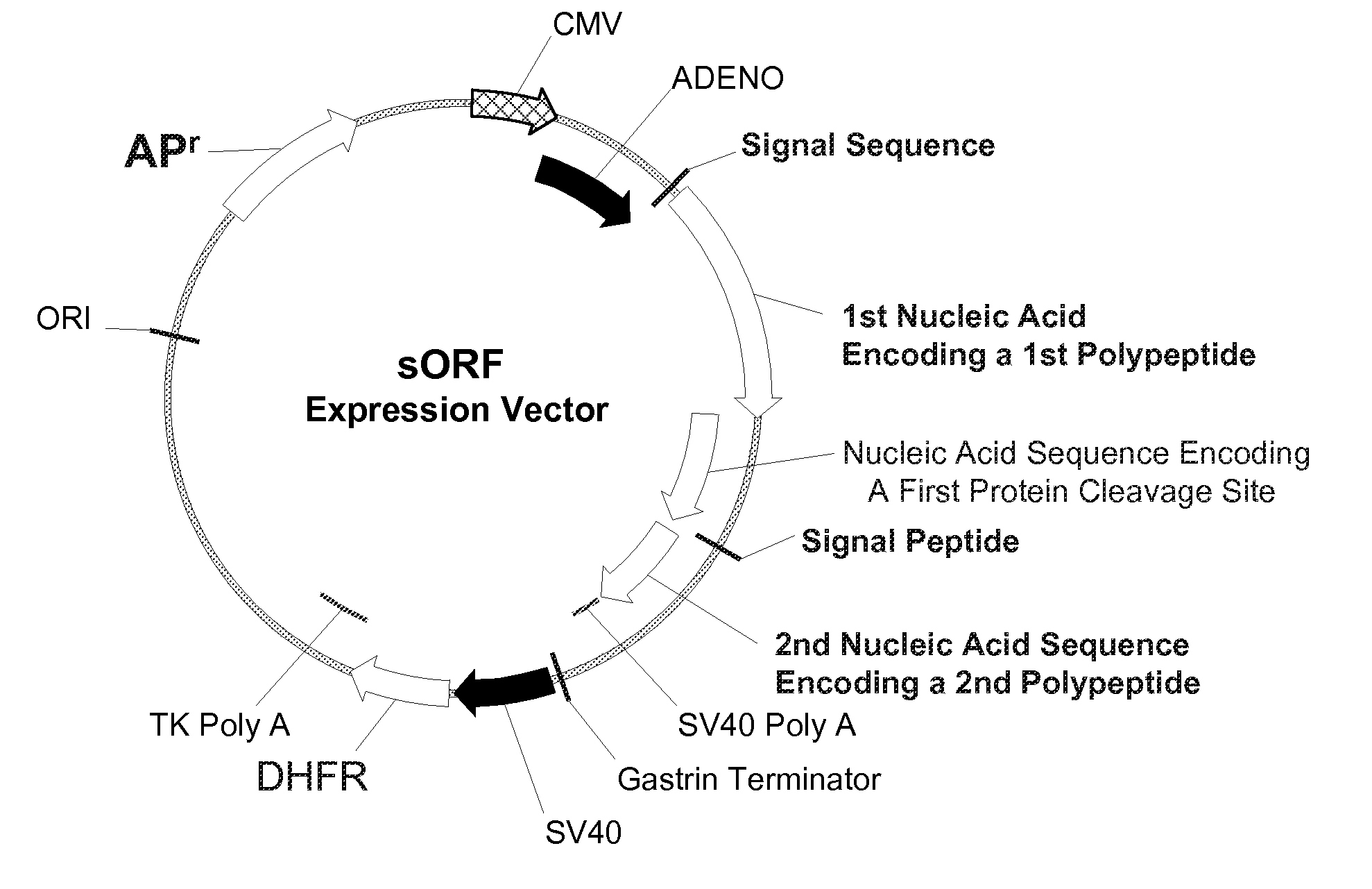
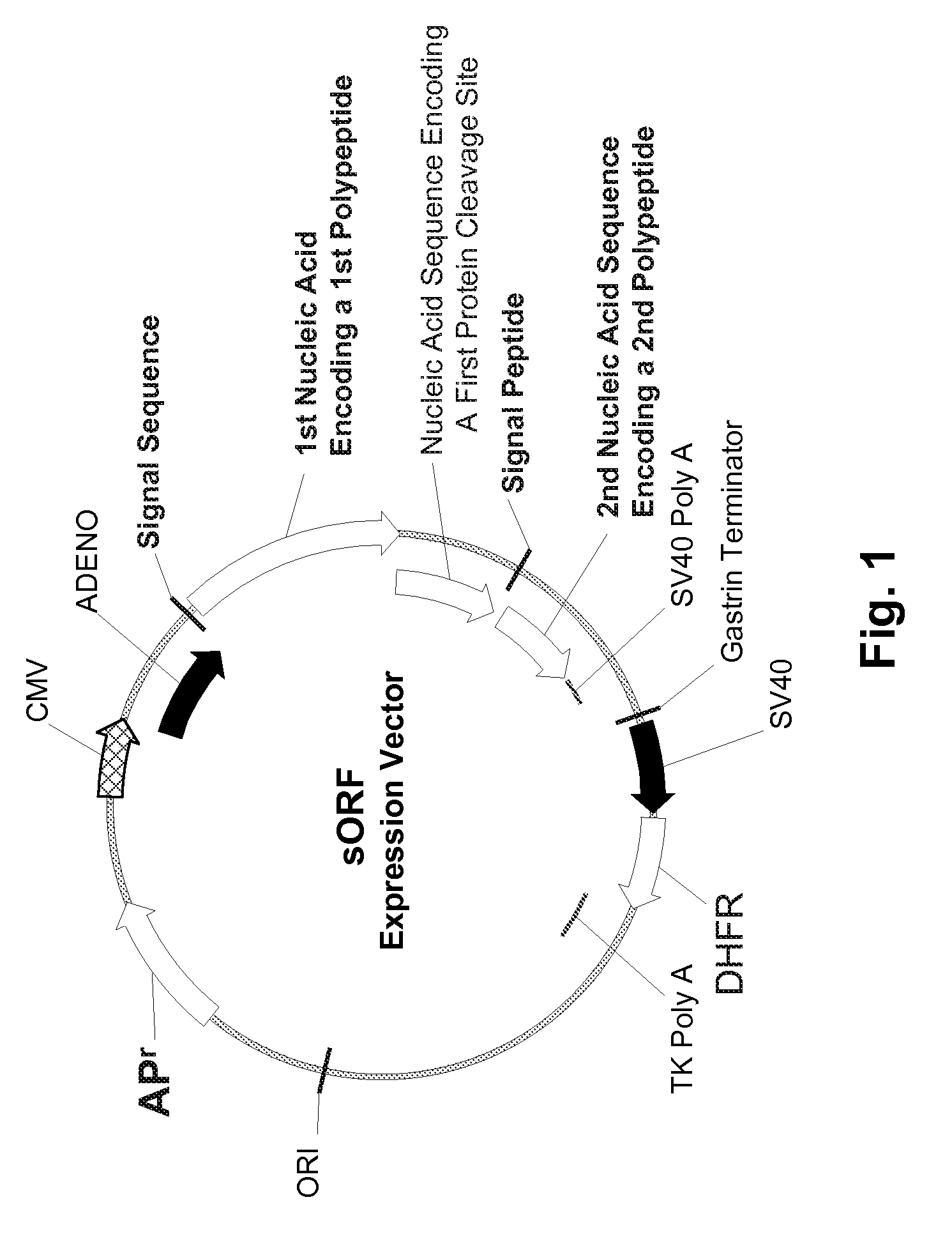
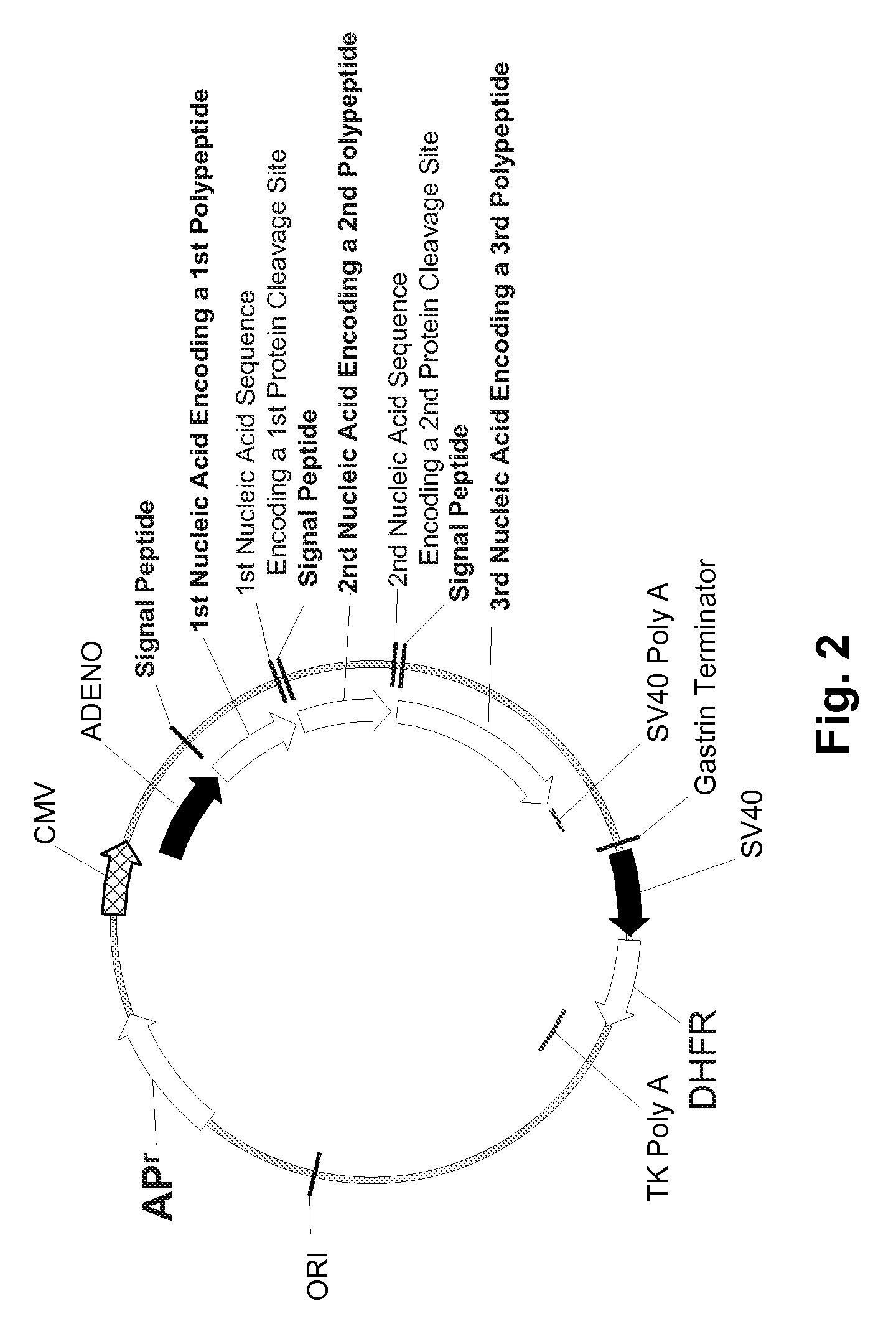
Multiple Gene Expression including sORF Constructs and Methods with Polyproteins, Pro-Proteins, and Proteolysis
InactiveUS20070065912A1Efficient expressionImprove economyFungiFusion with post-translational modification motifOpen reading frameADAMTS Proteins
Disclosed are useful constructs and methods for the expression of proteins using primary translation products that are processed within a recombinant host cell. Constructs comprising a single open reading frame (sORF) are described for protein expression including expression of multiple polypeptides. A primary translation product (a pro-protein or a polyprotein) contains polypeptides such as inteins or hedgehog family auto-processing domains, or variants thereof, inserted in frame between multiple protein subunits of interest. The primary product can also contain cleavage sequences such as other proteolytic cleavage or protease recognition sites, or signal peptides which contain recognition sequences for signal peptidases, separating at least two of the multiple protein subunits. The sequences of the inserted auto-processing polypeptides or cleavage sites can be manipulated to enhance the efficiency of expression of the separate multiple protein subunits. Also disclosed are independent aspects of conducting efficient expression, secretion, and / or multimeric assembly of proteins such as immunoglobulins. Where the polyprotein contains immunoglobulin heavy and light chain segments or fragments capable of antigen recognition, in an embodiment a selectable stoichiometric ratio is at least two copies of a light chain segment per heavy chain segment, with the result that the production of properly folded and assembled functional antibody is made. Modified signal peptides, including such from immunoglobulin light chains, are described.
Owner:ABBOTT LAB INC
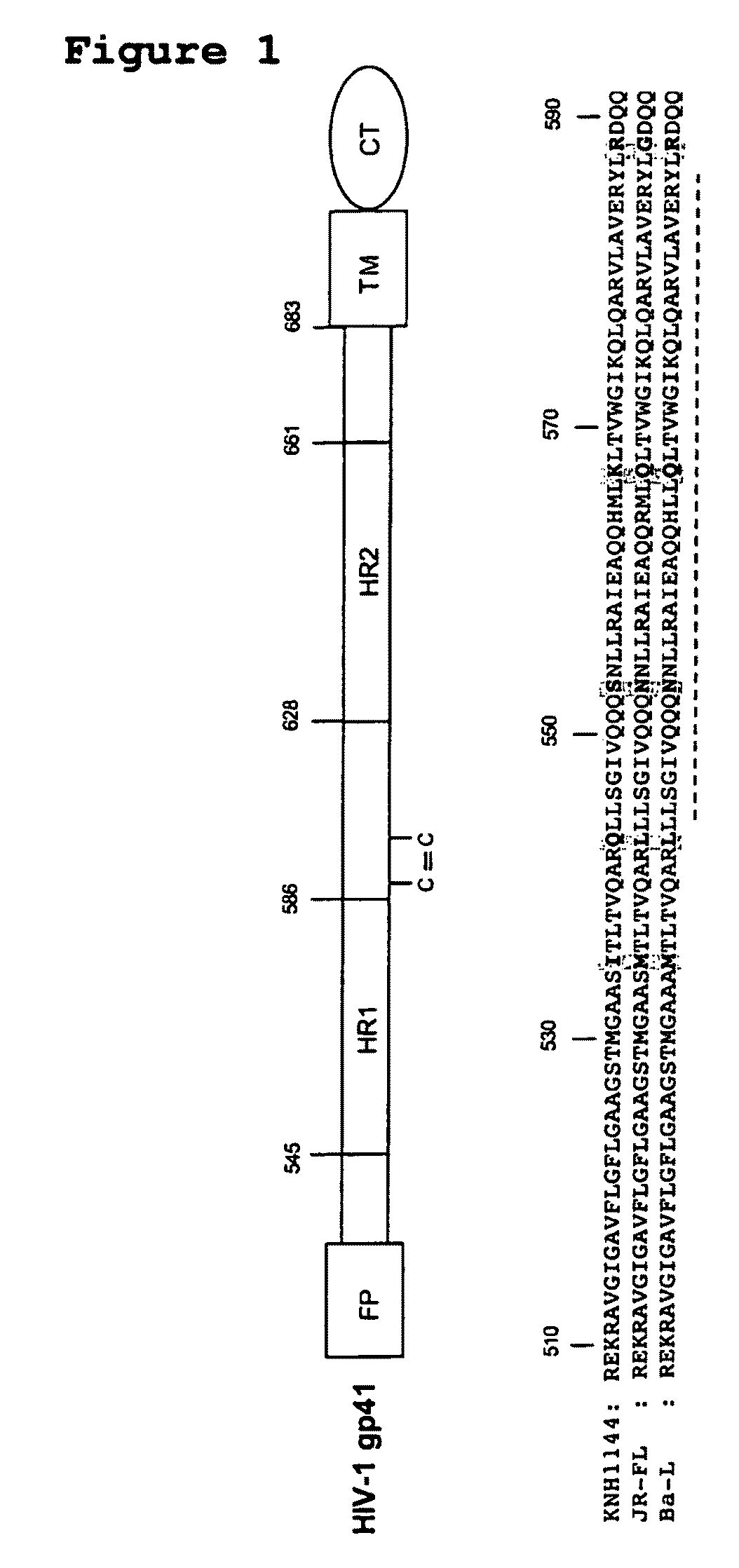
Soluble, stabilized, proteolytically cleaved, trimeric HIV-1 gp140 proteins comprising modifications in the N-terminus of the gp41 ectodomain
InactiveUS7939083B2Improve stabilityOverall antigenic structure of the trimer not adversely affectedViral antigen ingredientsVirus peptidesArginineGlutamine
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC +1
Thiepane compounds
Tri- and tetra substituted thiepane compositions having use as immunogens, therapeutics, diagnostics and for other industrial purposes are disclosed. The compositions inhibit proteolytic activity of viral enzymes and are useful for the inhibition of such enzymes as well as in assays for the detection of such enzymes. Embodiments in which antigenic polypeptides are bonded to the compositions are useful in raising antibodies against the thiepane haptens or the polypeptide. Labeled thiepanes of this invention are useful as diagnostic reagents.
Owner:GILEAD SCI INC
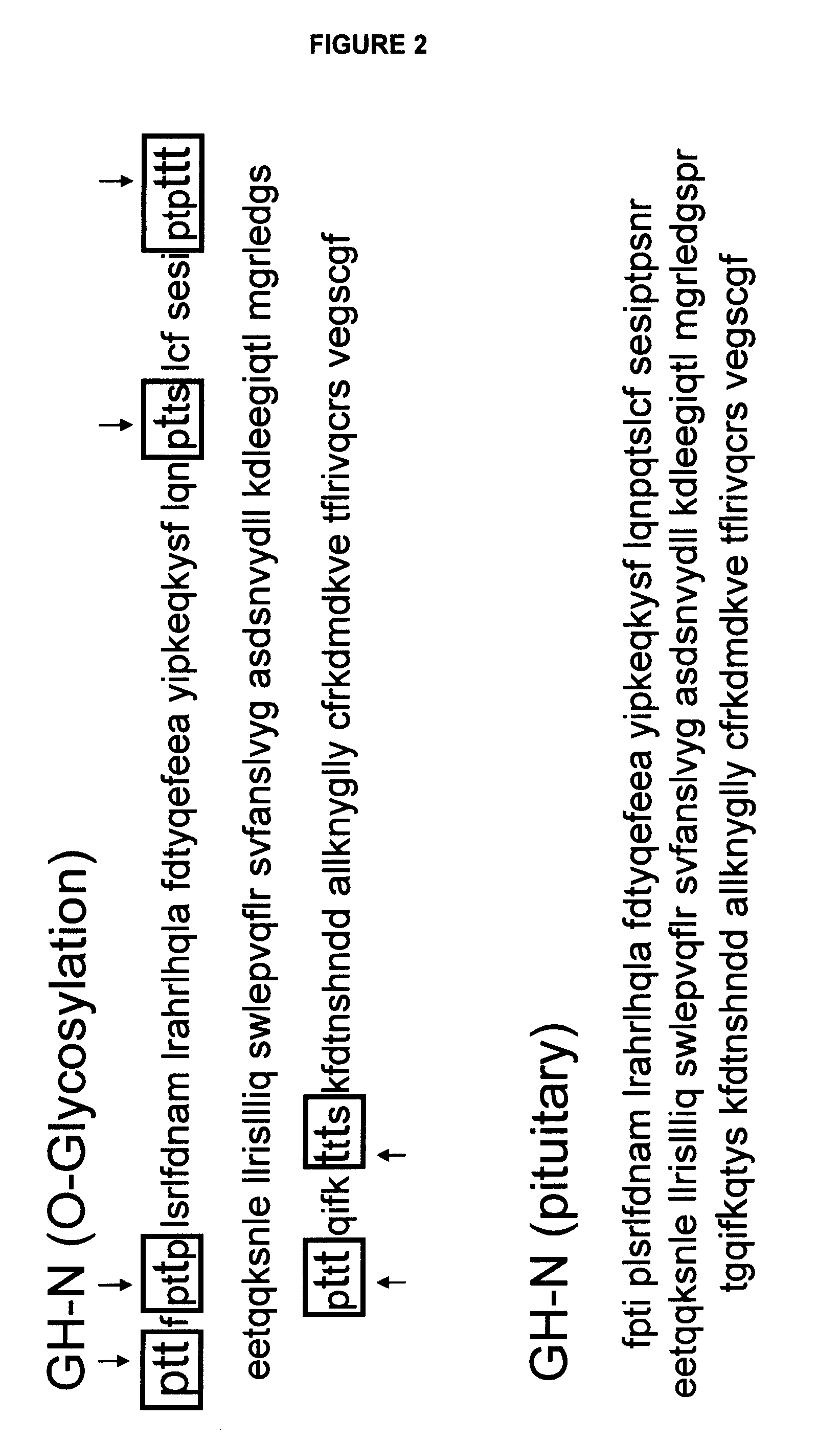
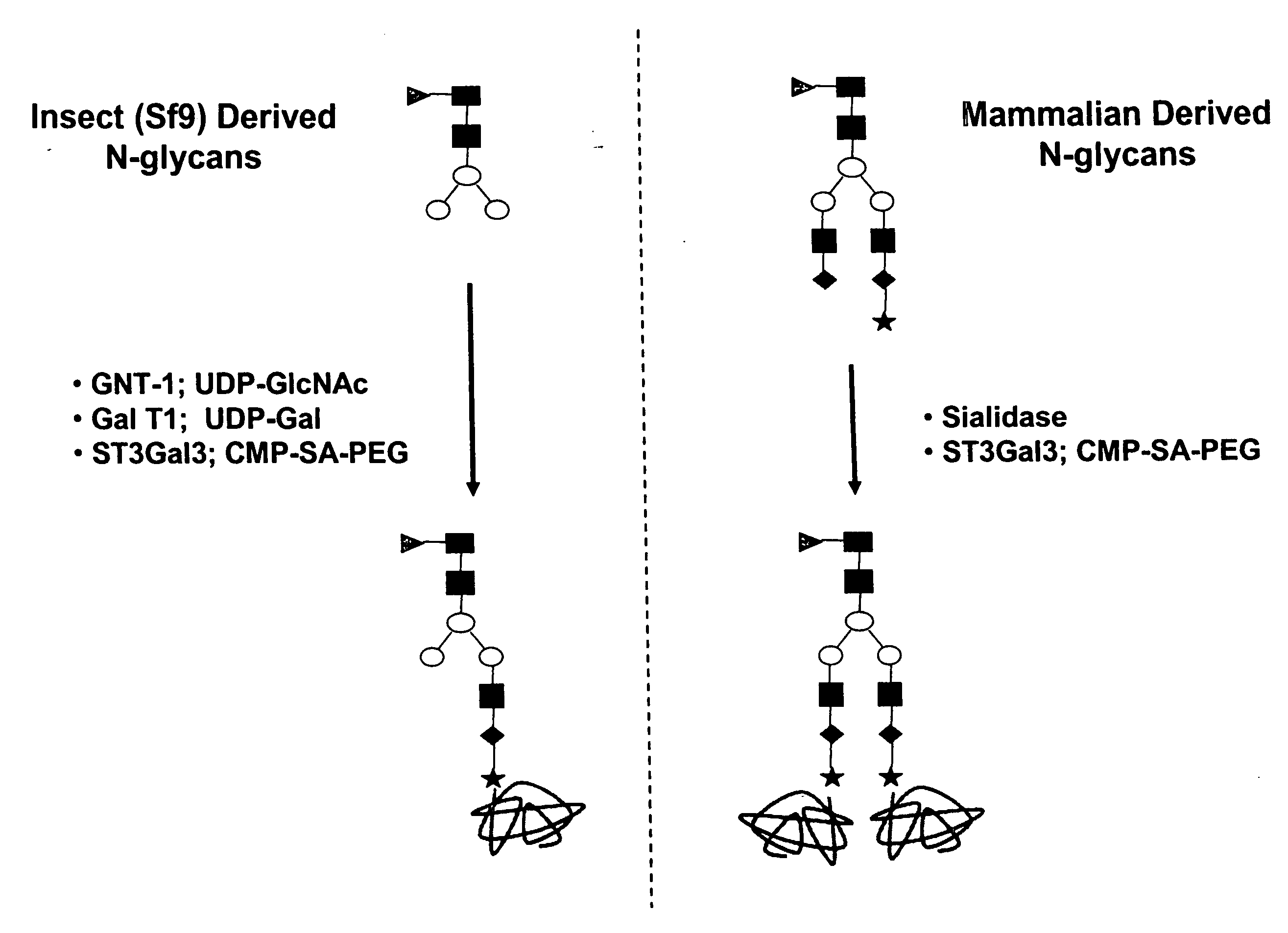
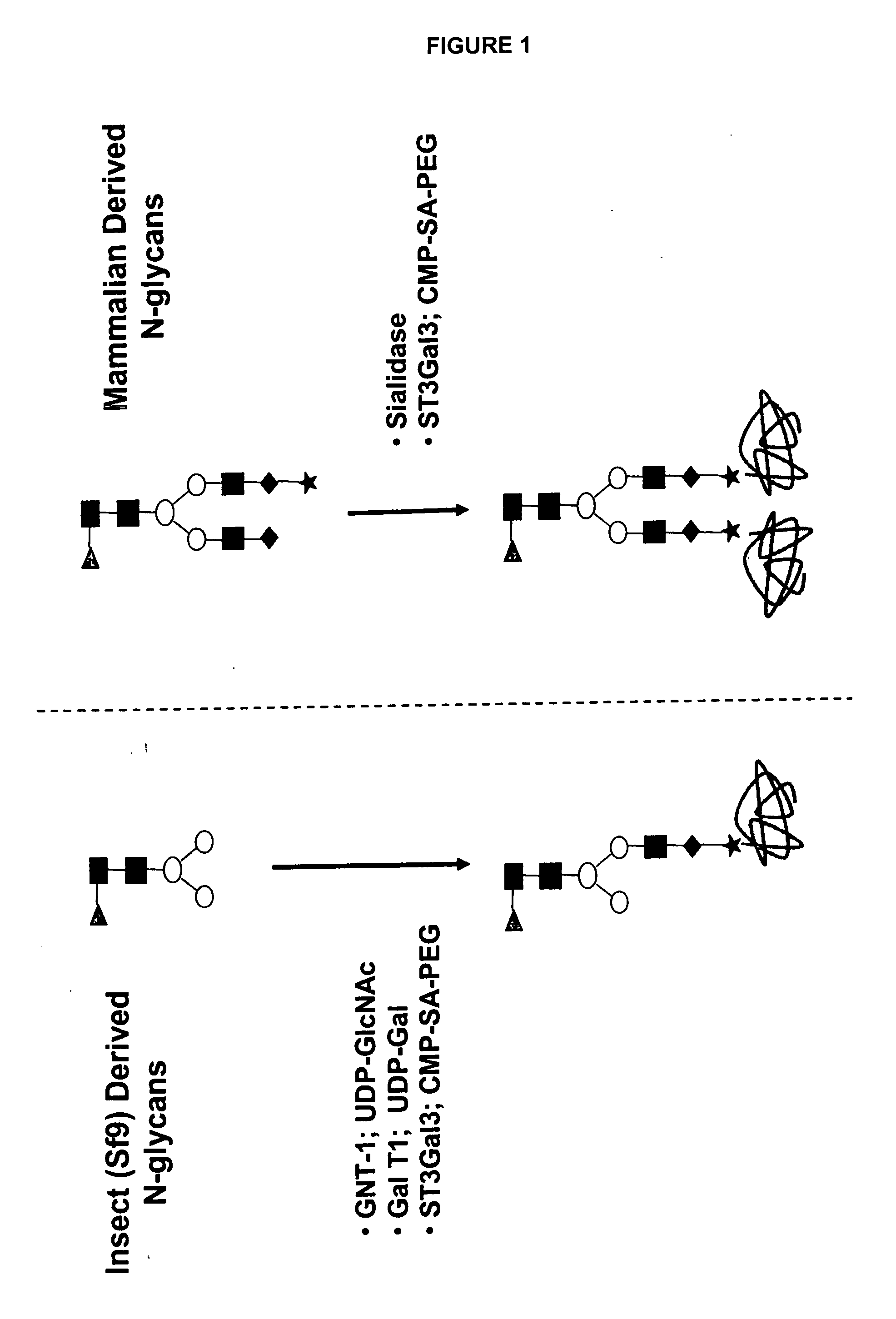
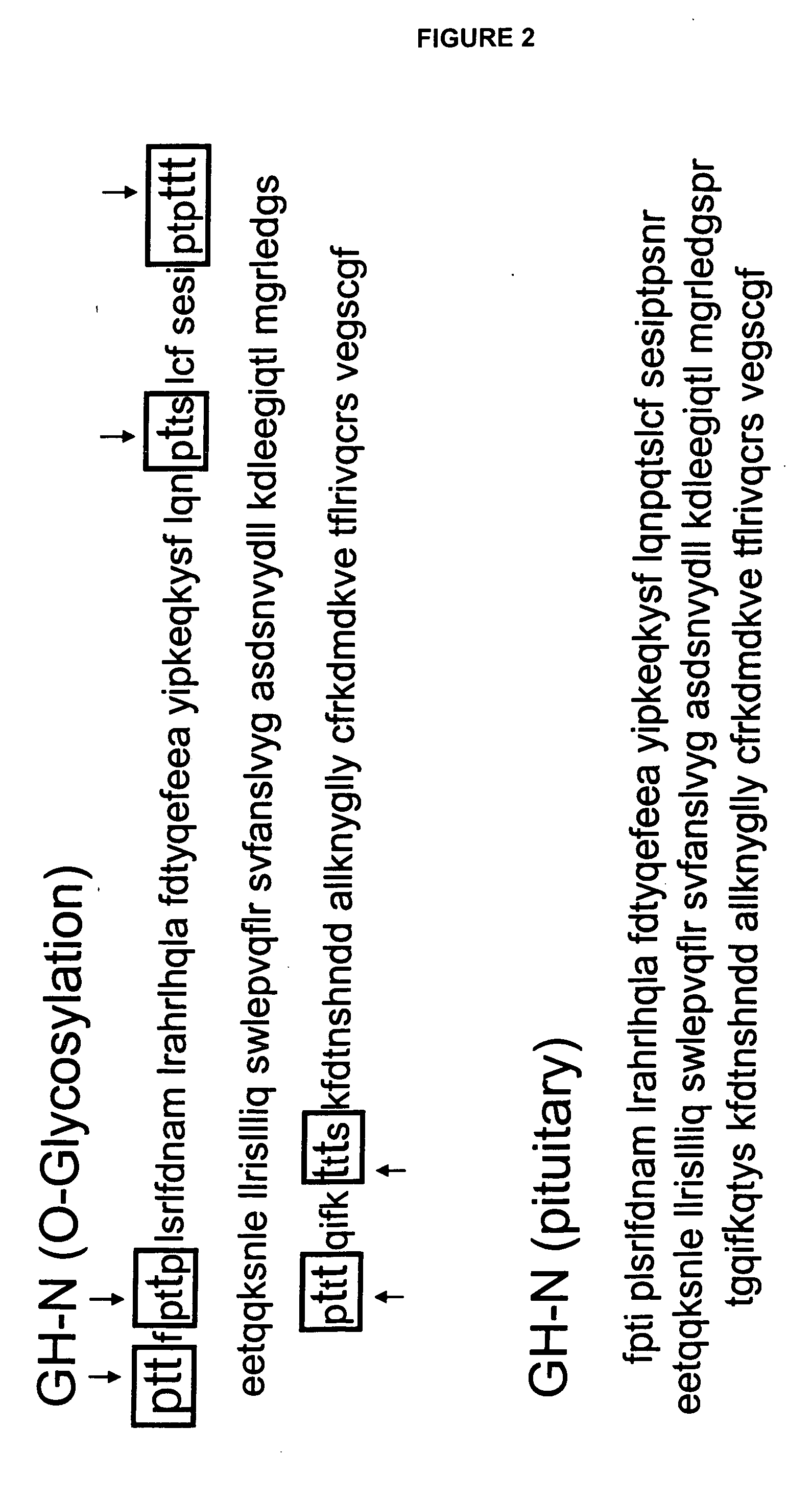
Compositions and methods for the preparation of protease resistant human growth hormone glycosylation mutants
The present invention relates to protease resistant mutants of human growth hormone, which contain newly introduced proteolysis resistant mutations and N-linked or O-linked glycosylation site(s), such that these recombinantly produced polypeptides have glycosylation patterns distinctly different from that of the naturally occurring human growth hormone. The polynucleotide coding sequences for the mutants, expression cassettes comprising the coding sequences, cells expressing the mutants, and methods for producing the mutants are also disclosed. Further disclosed are pharmaceutical compositions comprising the mutants and method for using the mutants.
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS +1
Method and system for rapid biomolecular recognition of amino acids and protein sequencing
InactiveUS20050164264A1Quick analysisBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsProtein Sequence DeterminationDigestion
Methods, compositions, kits, and apparatus are provided wherein the aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase system is used to analyze amino acids. The method allows very small devices for quantitative or semi-quantitative analysis of the amino acids in samples or in sequential or complete proteolytic digestions. The methods can be readily applied to the detection and / or quantitation of one or more primary amino acids by using cognate aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase and cognate tRNA. The basis of the method is that each of the 20 synthetases and / or a tRNA specific for a different amino acid is separated spatially or differentially labeled. The reactions catalyzed by all 20 synthetases may be monitored simultaneously, or nearly simultaneously, or in parallel. Each separately positioned synthetase or tRNA will signal its cognate amino acid. The synthetase reactions can be monitored using continuous spectroscopic assays. Alternatively, since elongation factor Tu:GTP (EF-Tu:GTP) specifically binds all AA−tRNAs, the aminoacylation reactions catalyzed by the synthetases can be monitored using ligand assays. Microarrays and microsensors for amino acid analysis are provided. Additionally, amino acid analysis devices are integrated with protease digestions to produce miniaturized enzymatic sequenators capable of generating either N- or C-terminal sequence and composition data for a protein or peptide. The possibility of parallel processing of many samples in an automated manner is discussed.
Owner:NANOBIODYNAMICS
Tumor activated prodrugs
InactiveUS7635682B2Improve featuresImprove anti-tumor efficacyPeptide/protein ingredientsImmunoglobulinsMedicineProstate-specific antigen
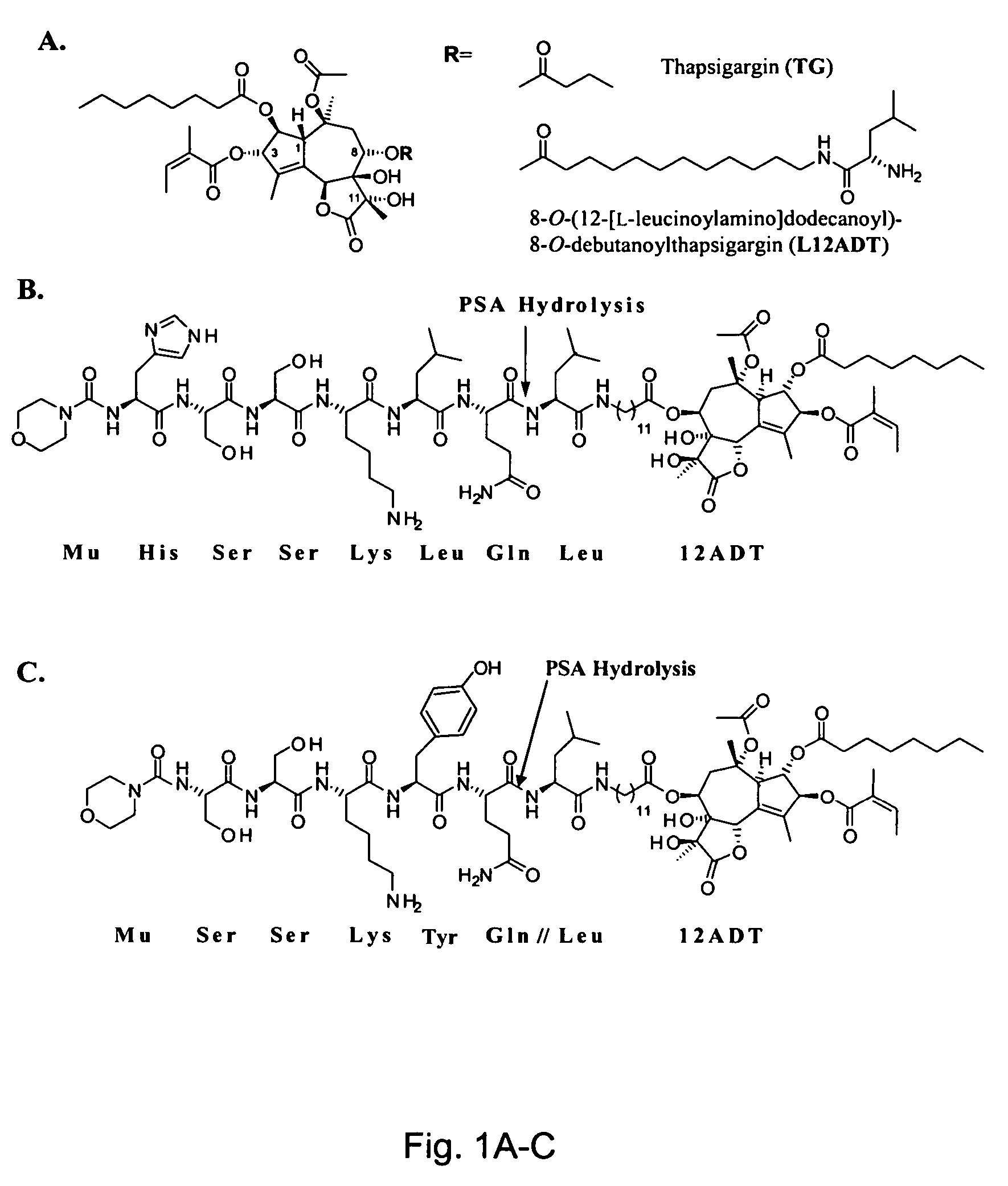
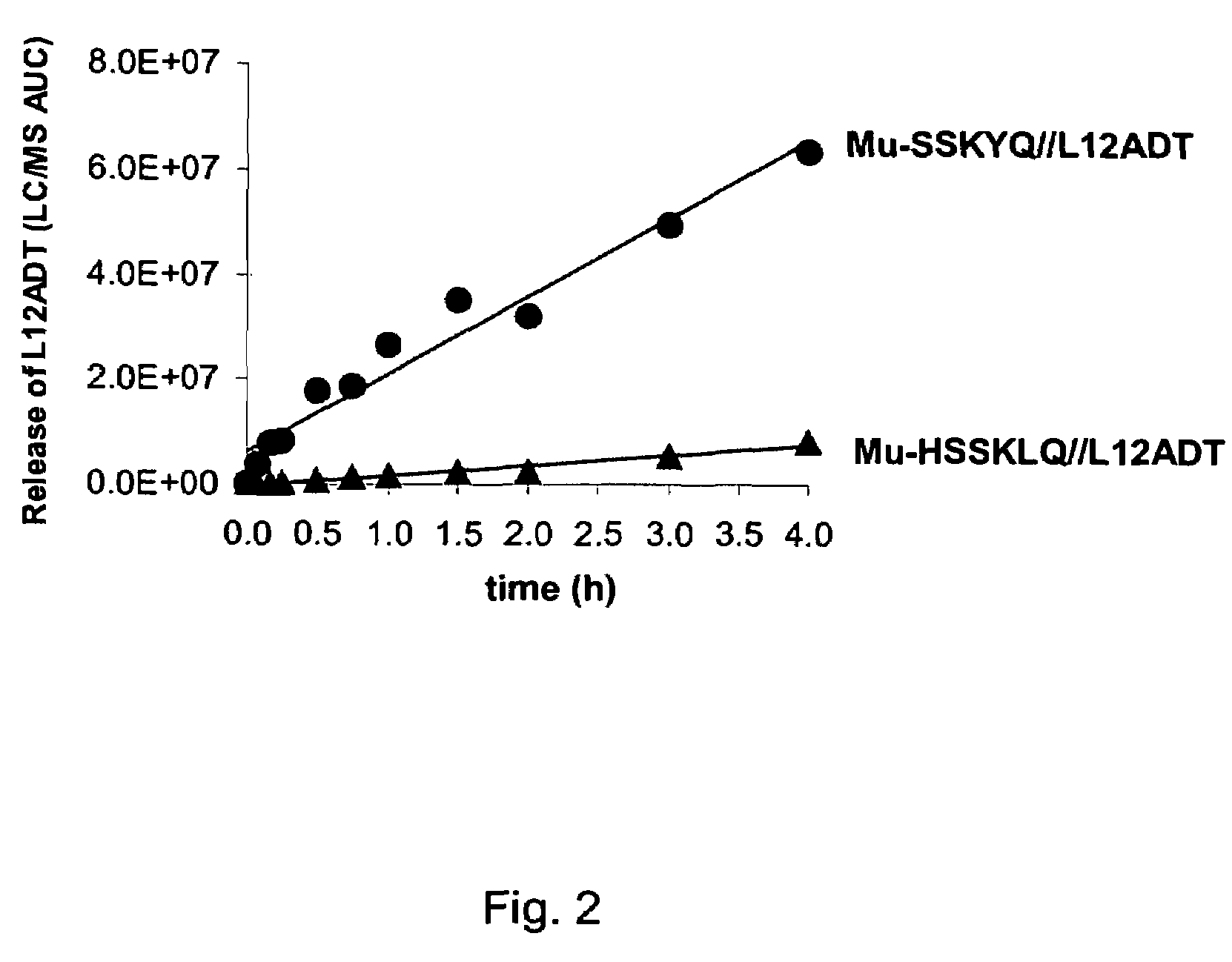
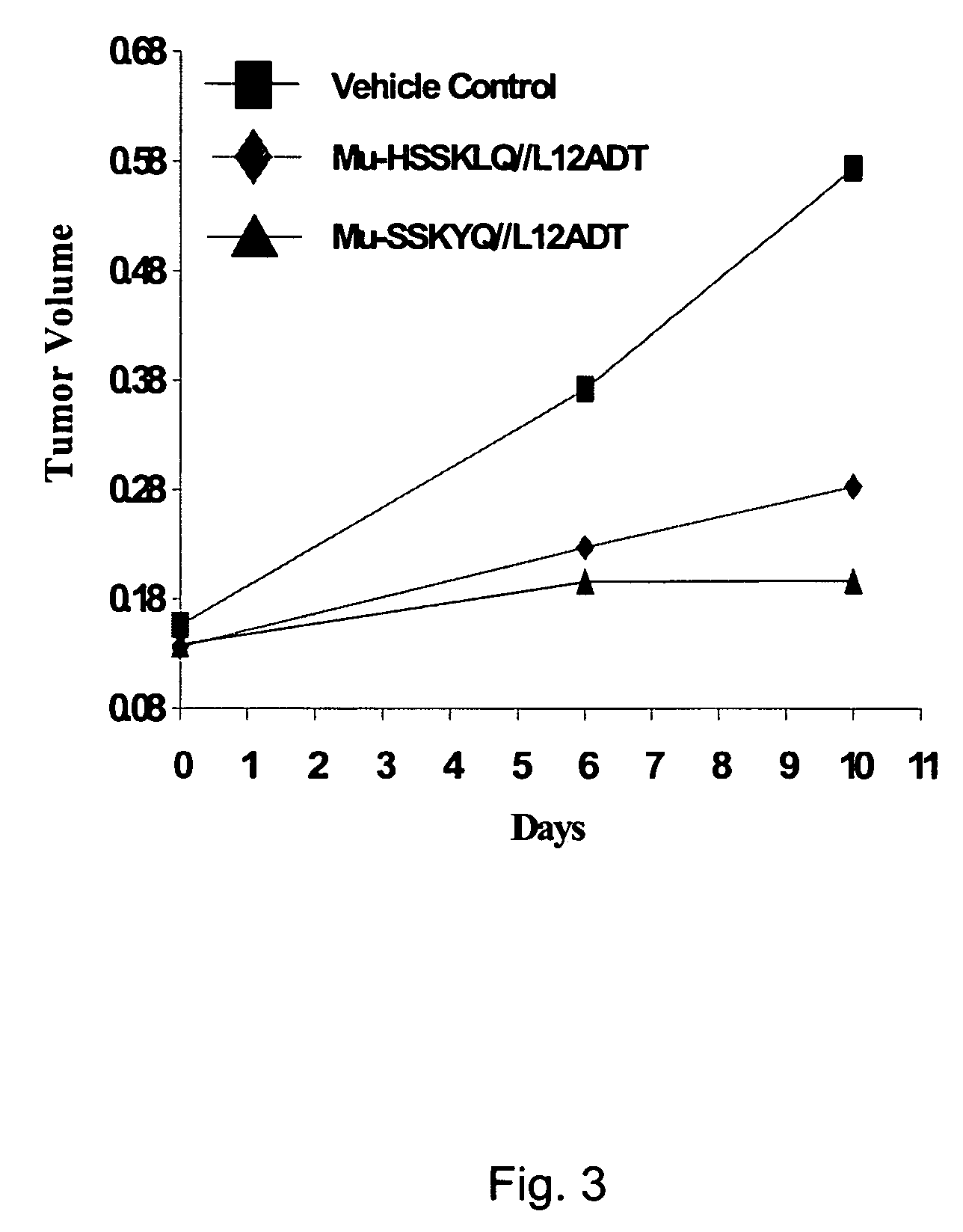
The instant invention provides compositions comprising a prodrug, the prodrug comprising a therapeutically active drug; and a peptide selected from the group consisting of the sequences: Ser-Ser-Lys-Tyr-Gln (SEQ ID NO:1);Gly-Lys-Ser-Gln-Tyr-Gln (SEQ ID NO:2); and Gly-Ser-Ala-Lys-Tyr-Gln (SEQ ID NO:3) wherein the peptide is linked to the therapeutically active drug to inhibit the therapeutic activity of the drug, and wherein the therapeutically active drug is cleaved from the peptide upon proteolysis by an enzyme having a proteolytic activity of prostate specific antigen (PSA). The invention further provides methods of making and using the claimed compositions.
Owner:INSPYR THERAPEUTICS INC
Compositions and methods for detecting protease activity
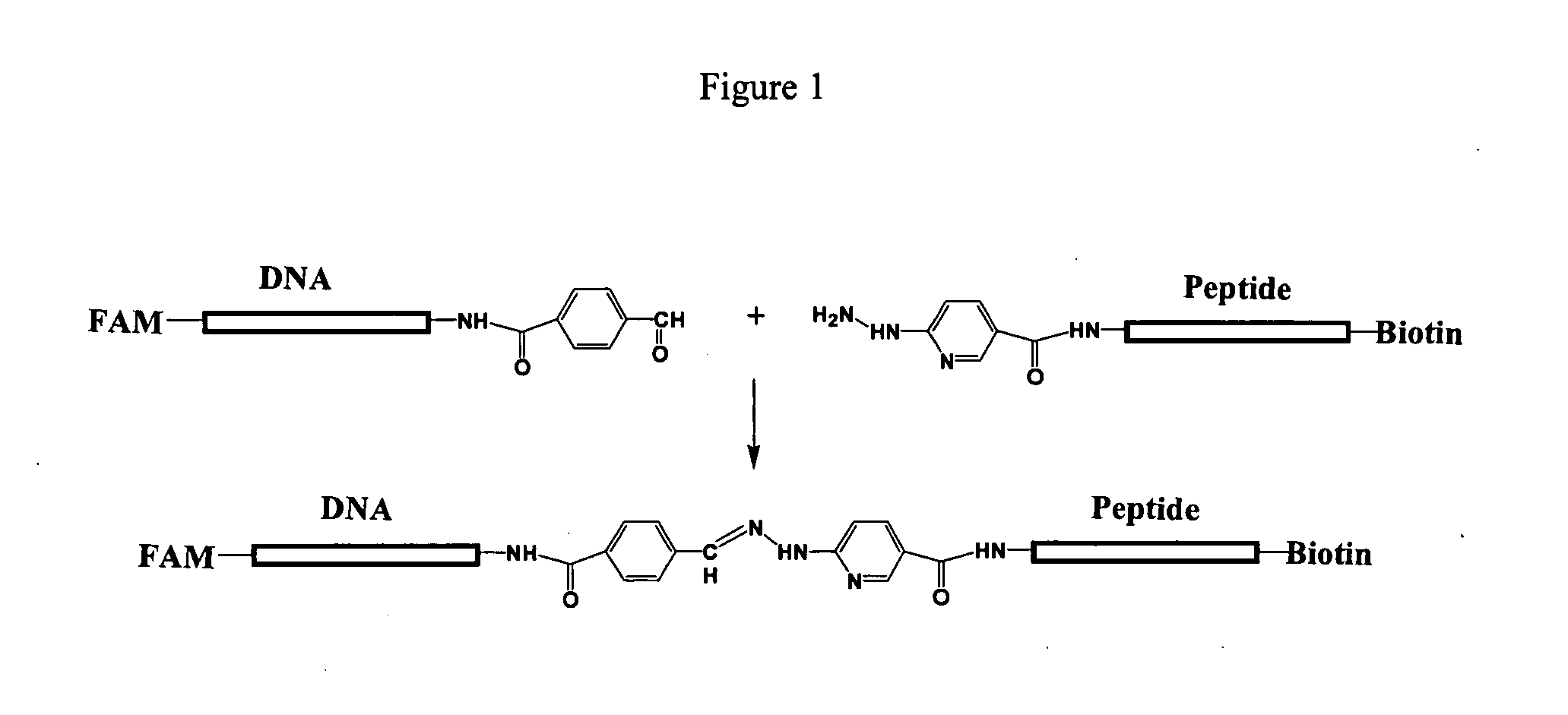
The invention provides a method of determining activity of a protease. The method can include the steps of (a) providing a protease substrate including a protein moiety attached to a nucleic acid moiety and a ligand moiety; (b) contacting the protease substrate with a protease under conditions wherein the protease catalyzes cleavage of the protein moiety, thereby producing a proteolytic product wherein the nucleic acid moiety is separated from at least a portion of the protein moiety and the ligand moiety; (c) contacting the proteolytic product with a receptor under conditions wherein the ligand moiety binds to the receptor to form a complex; (d) separating the complex from the nucleic acid moiety, thereby forming a separation product including the nucleic acid moiety; (e) contacting the separation product with a probe nucleic acid under conditions wherein the nucleic acid moiety hybridizes to a complementary sequence of the probe; and (f) detecting hybridization of the separation product to the probe, thereby determining activity of the protease.
Owner:MURPHY JOHN T
lAP E3 LIGASE DIRECTED PROTEOLYSIS TARGETING CHIMERIC MOLECULES
The present invention relates to compounds, compositions, combinations and medicaments containing said compounds and processes for their preparation. The invention also relates to the use of said compounds, combinations, compositions and medicaments, for example as inhibitors of the activity of RIP2 kinase, including degrading RIP2 kinase, the treatment of diseases and conditions mediated by the RIP2 kinase, in particular for the treatment of inflammatory diseases or conditions.
Owner:GLAXOSMITHKLINE INTPROP DEV LTD
Protease variants and compositions
The present invention relates to enzymes produced by mutating the genes for a number of subtilases and expressing the mutated genes in suitable hosts are presented. The enzymes exhibit improved autoproteolytic stability in comparison to their wild type parent enzymes.
Owner:NOVOZYMES AS
Serum-free medium for MDCK cell large-scale adherent culture and single-cell suspension culture
ActiveCN101760442ASupports adherent growthReduce the burden of separation and purification in the later stageVertebrate cellsArtificial cell constructsLipid formationSerum free media
The invention relates to the culture medium research and development technical field of modern biological technology and provides a serum-free medium for MDCK cell large-scale adherent culture and single-cell suspension culture, which comprises 21 amino acids, 6 vitamins, 8 salts, 8 lipids, 4 trace elements, 2 buffers, 1 protein hydrolysate, 1 acid-base indicator and 6 other additives. The serum-free medium can be prepared by the conventional preparation method, and an application method thereof is the conventional method. The serum-free medium has the beneficial effects that: the serum-free medium does not contain serum, has clear components, is beneficial for separating and purifying the product and improves the product quality; the serum-free medium supports long-term subculture of MDCK cells and does not require long-term and complex adaptation process; and the serum-free medium can well support the adherent growth and single-cell suspension growth of the MDCK cells, has clear components and easy preparation and utilization, and is suitable for mass production of biological products.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Protein hydrolysates produced with the use of cod proteases
InactiveUS7070953B1Increase contentCosmetic preparationsHydrolysed protein ingredientsProtein materialsFood flavor
The invention relates to a method for enzymatically obtaining protein hydrolysates for human consumption, animal feed and cosmetics. The process involves the use of a proteolytic composition derived from fish, such as Cod (Gadus morhua), to obtain hydrolysates which have a non-bitter taste and retain the flavor and aroma of the protein-containing material which is hydrolyzed: e.g. when hydrolyzing protein-containing material from marine organisms or parts thereof, such as fish, shrimp, lobster or other seafood according to the invention, a protein hydrolysate is produced that has a characteristic natural flavor of the organism Also provided are food products comprising the hydrolysates of the invention, such as soup, sauce, cheese, HVP, meat extract and flavoring agent, broth, paté, mousse, frying dough, orly dough, and pastries.
Owner:NORDUR EHF
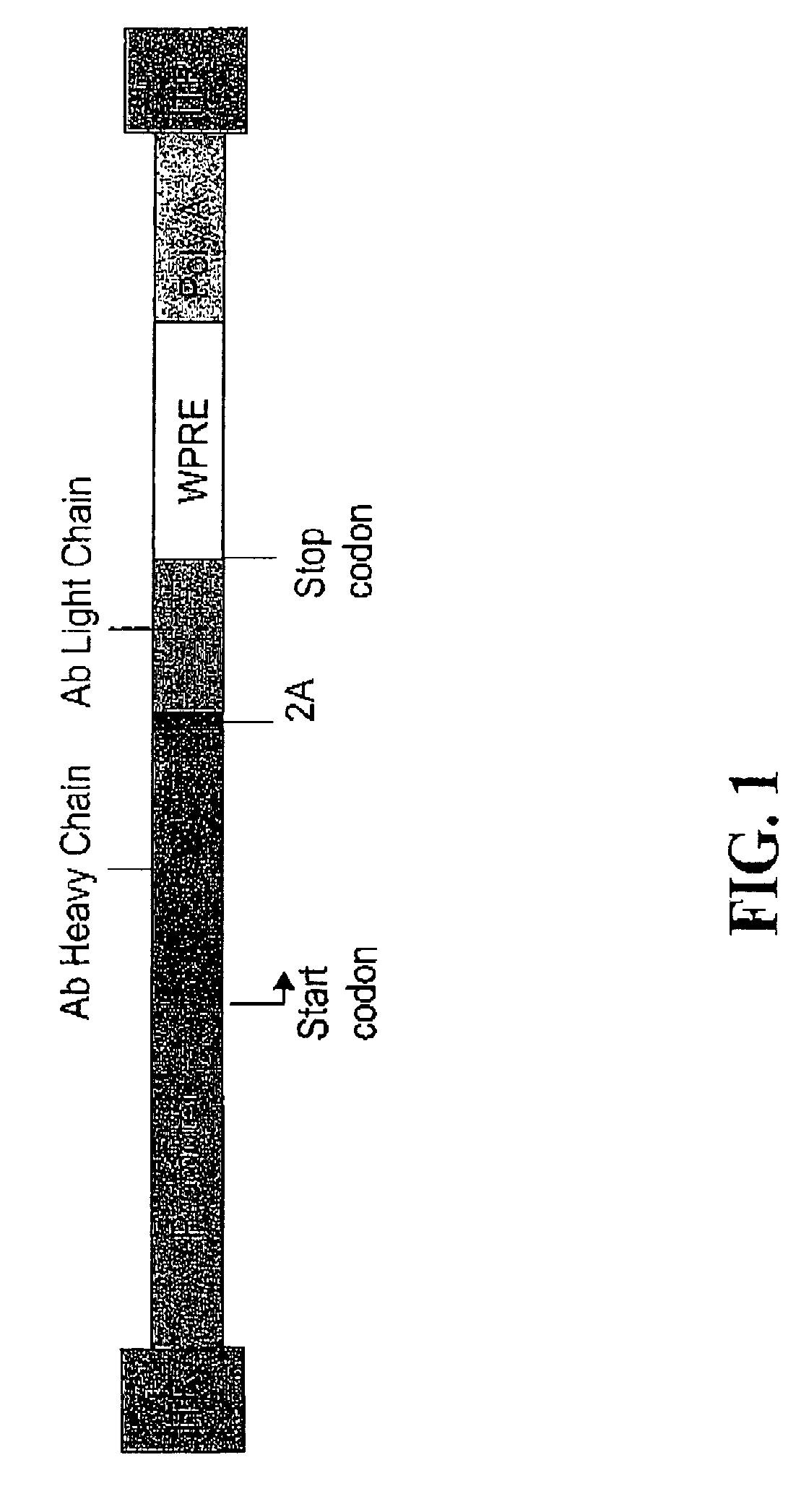
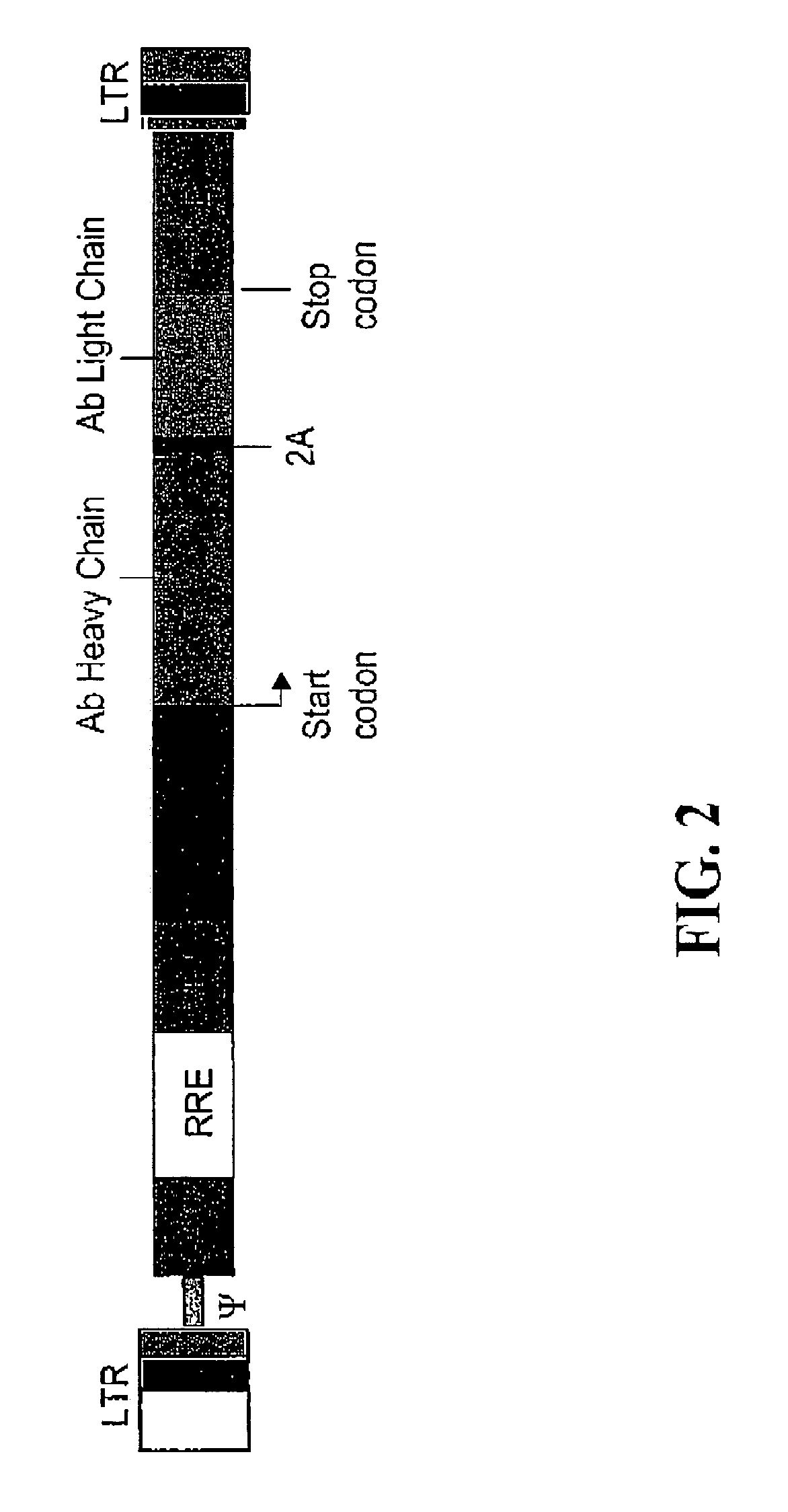
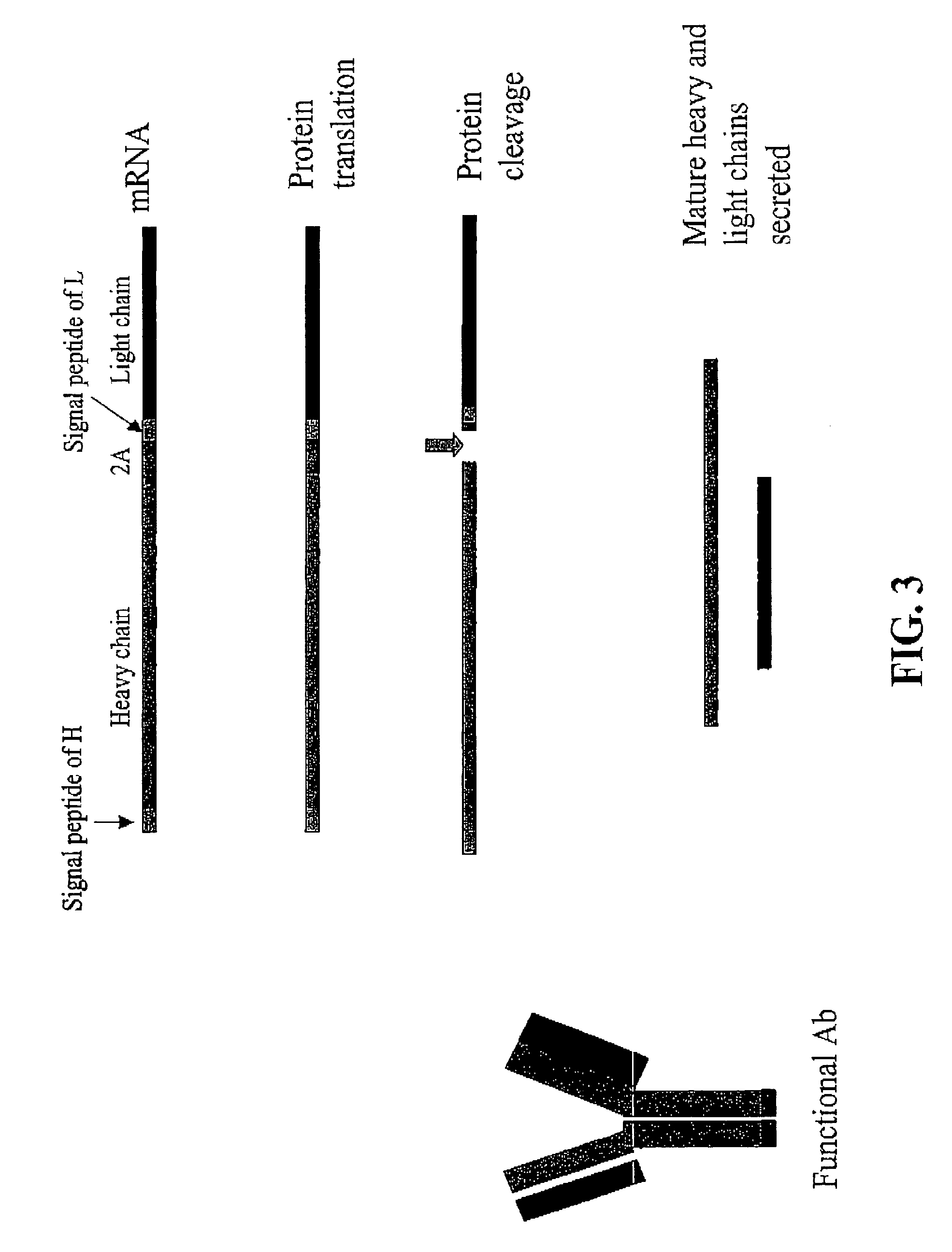
Compositions and methods for enhanced expression of immunoglobulins from a single vector using a peptide cleavage site
Single vector constructs for expression of an immunoglobulin molecule or fragment thereof and methods of making and using the same are described. The vectors comprise a self-processing cleavage sequence between a first and second immunoglobulin coding sequence allowing for expression of a functional antibody molecule using a single promoter. The vector constructs include the coding sequence for a self-processing cleavage site and may further include an additional proteolytic cleavage sequence which provides a means to remove the self processing peptide sequence from an expressed immunoglobulin molecule or fragment thereof. The vector constructs find utility in methods for enhanced production of biologically active immunoglobulins or fragments thereof in vitro or in vivo.
Owner:BIOSANTE PHARMA
Compositions and methods for the preparation of protease resistant human growth hormone glycosylation mutants
InactiveUS20070154992A1Sugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsHuman growth hormoneProtease resistant
The present invention relates to protease resistant mutants of human growth hormone, which contain newly introduced proteolysis resistant mutations and N-linked or O-linked glycosylation site(s), such that these recombinantly produced polypeptides have glycosylation patterns distinctly different from that of the naturally occurring human growth hormone. The polynucleotide coding sequences for the mutants, expression cassettes comprising the coding sequences, cells expressing the mutants, and methods for producing the mutants are also disclosed. Further disclosed are pharmaceutical compositions comprising the mutants and method for using the mutants.
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS
Human glucagon-like-peptide-1 mimics and their use in the treatment of diabetes and related conditions
InactiveUS7238670B2Increased blood levelsImprove the level ofSenses disorderNervous disorderProteolysisGLP-1 Mimetics
The present invention provides novel human glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) peptide mimics that mimic the biological activity of the native GLP-1 peptide and thus are useful for the treatment or prevention of diseases or disorders associated with GLP activity. Further, the present invention provides novel, chemically modified peptides that not only stimulate insulin secretion in type II diabetics, but also produce other beneficial insulinotropic responses. These synthetic peptide GLP-1 mimics exhibit increased stability to proteolytic cleavage making them ideal therapeutic candidates for oral or parenteral administration.
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB CO
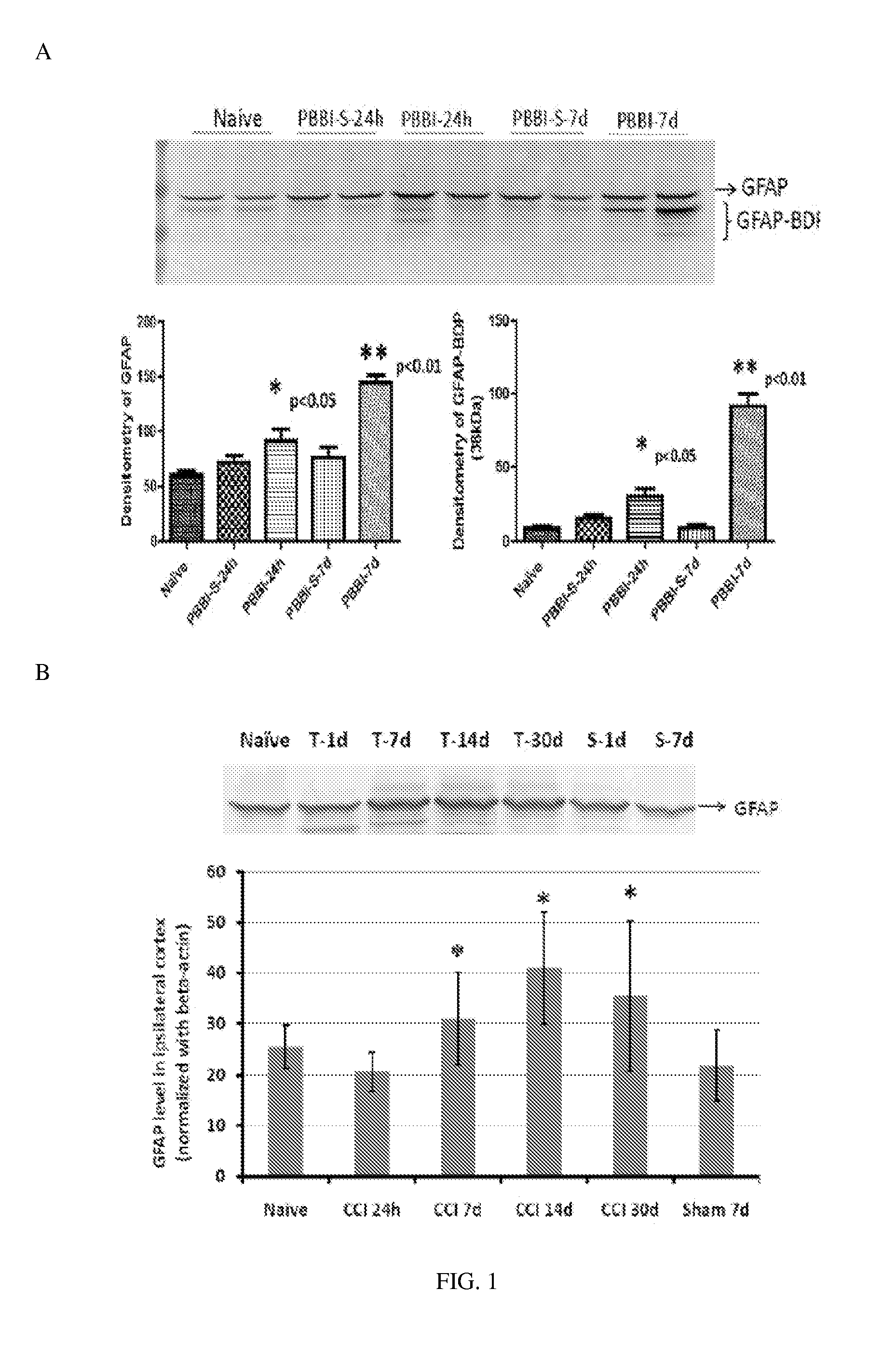
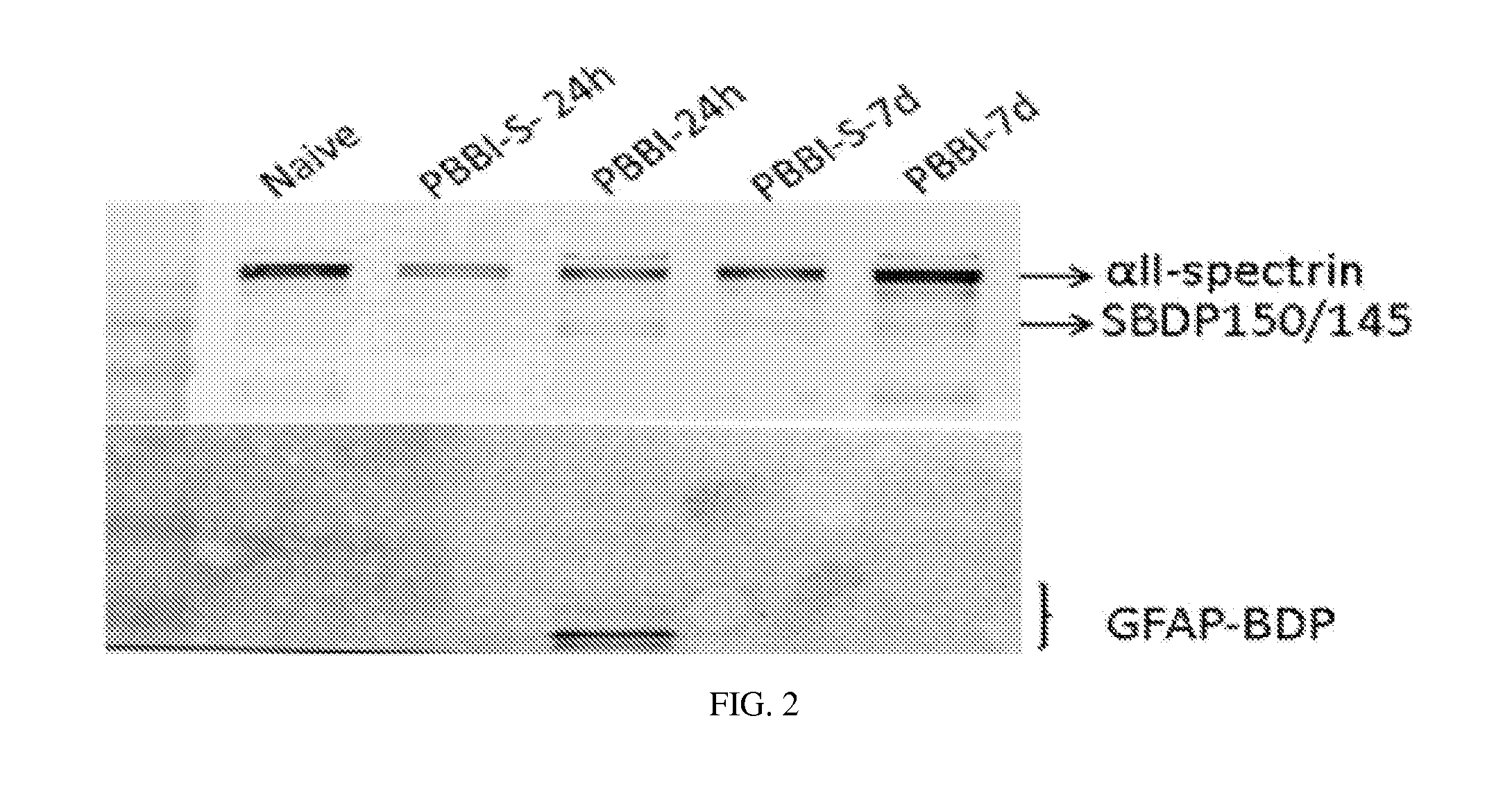
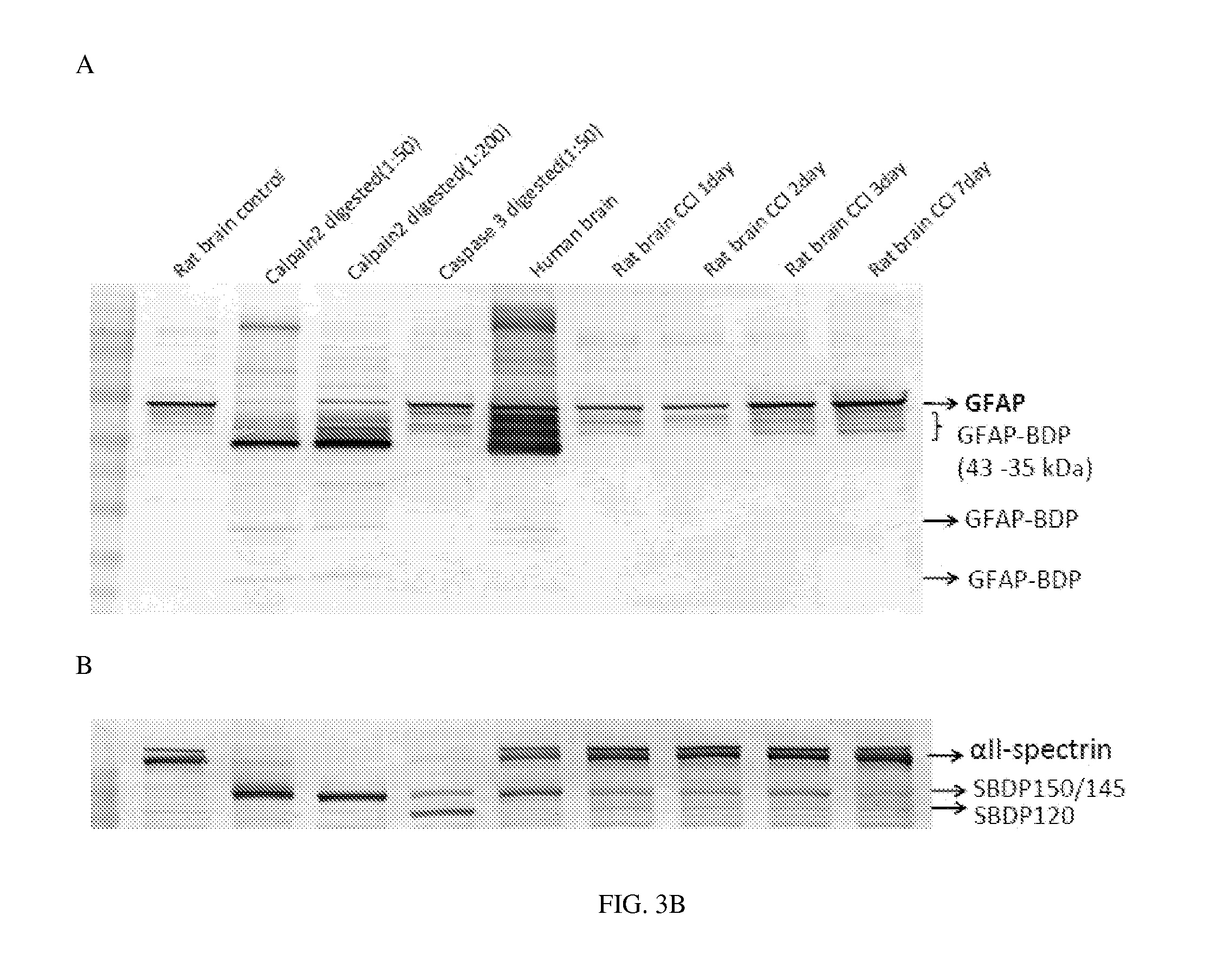
Micro-RNA, autoantibody and protein markers for diagnosis of neuronal injury
InactiveUS20130022982A1Microbiological testing/measurementImmunoglobulins against animals/humansProtein markersInjury brain
Processes and materials are provided for the detection, diagnosis, or determination of the severity of a neurological injury or condition, including traumatic brain injury, multiple-organ injury, stroke, Alzeimer's disease, Pakinson disease and Chronic Traumatic Encephalopathy (CTE). The processes and materials include biomarkers detected or measured in a biological sample such as whole blood, serum, plasma, or CSF. Such biomarkers include Tau and GFAP proteins, their proteolytic breakdown products, brain specific or enriched micro-RNA, and brain specific or enriched protein directed autoantibodies. The processes and materials are operable to detect the presence of absence of acute, subacute or chronic brain injuries and predict outcome for the brain injury.
Owner:BANYAN BIOMARKERS INC
Compounds with growth hormone releasing properties
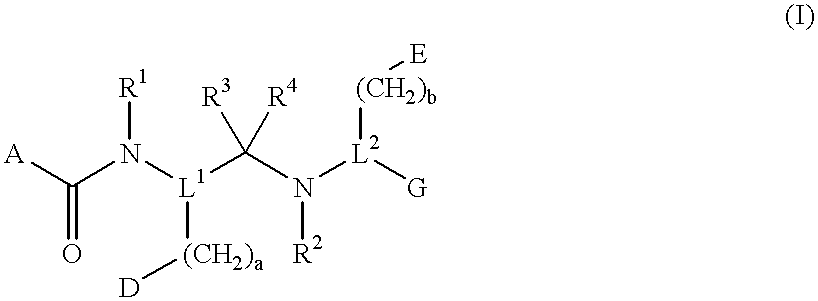
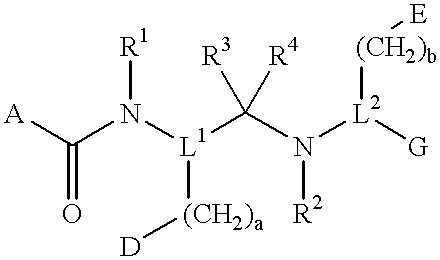
InactiveUS6274584B1Promote growthIncrease ratingsPowder deliveryBiocideMedical disorderBioavailability
Novel peptide derivatives, compositions containing them, and their use for treating medical disorders resulting from a deficiency in growth hormone are disclosed. The peptides have the formula (1):wherein a, b, A, R1, L1, D, R3, R4, R2, L2, E and G are as defined in the specification. These peptides exhibit improved resistance to proteolytic degradation, and hence, improved bioavailability.
Owner:HELSINN THERAPEUTICS (US) INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com