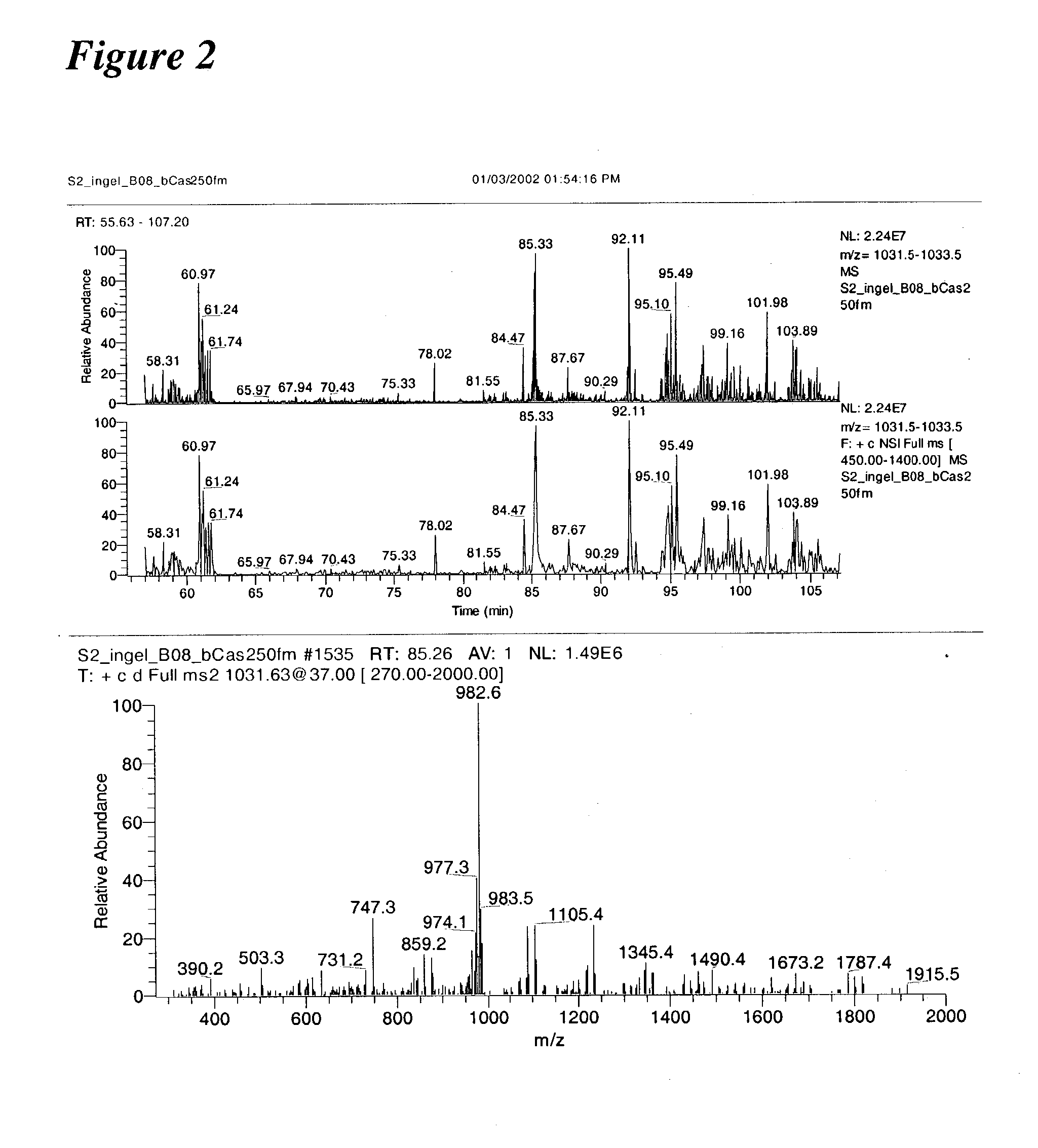
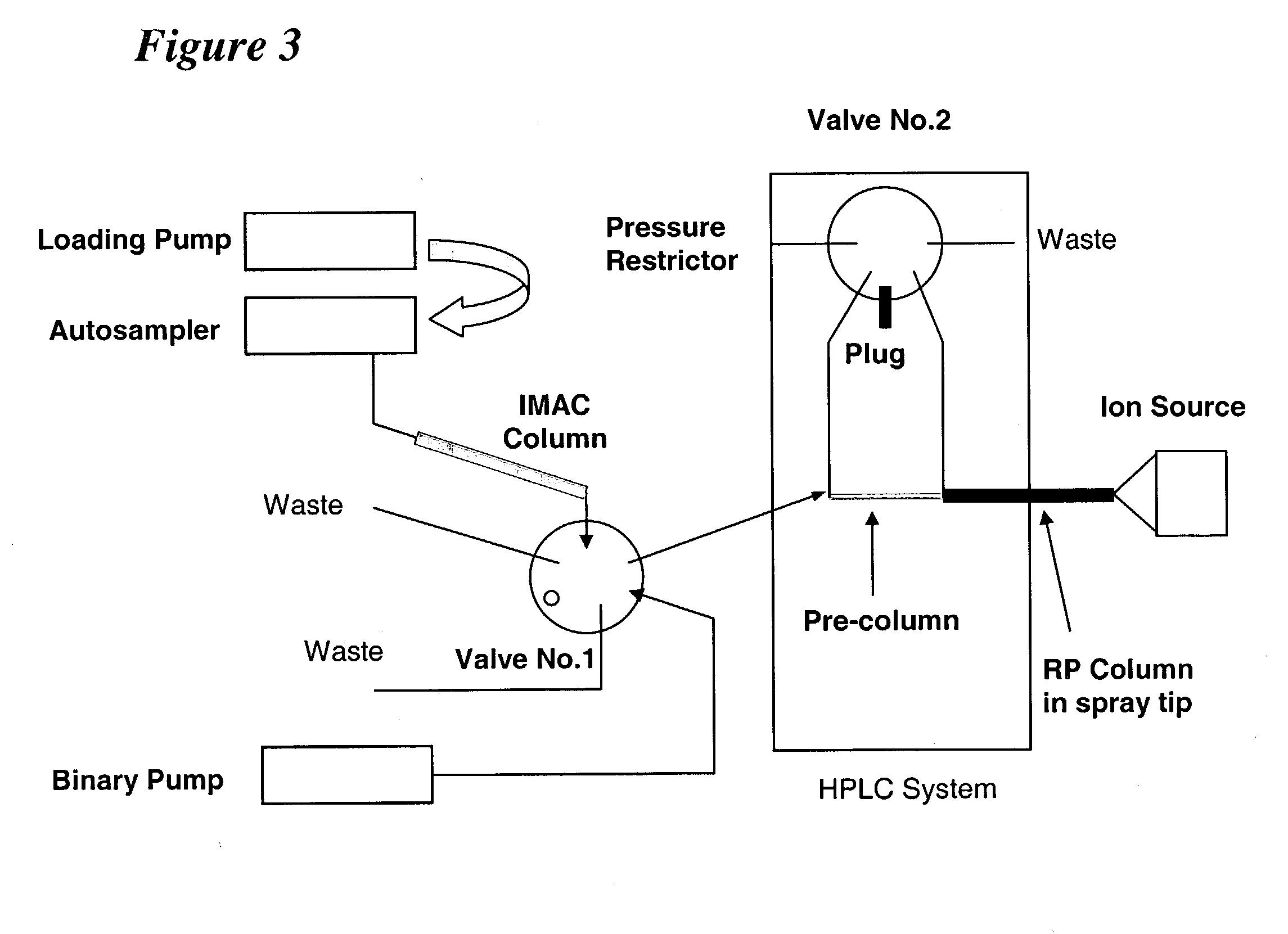
Patents
Literature
92 results about "Amino acid analysis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
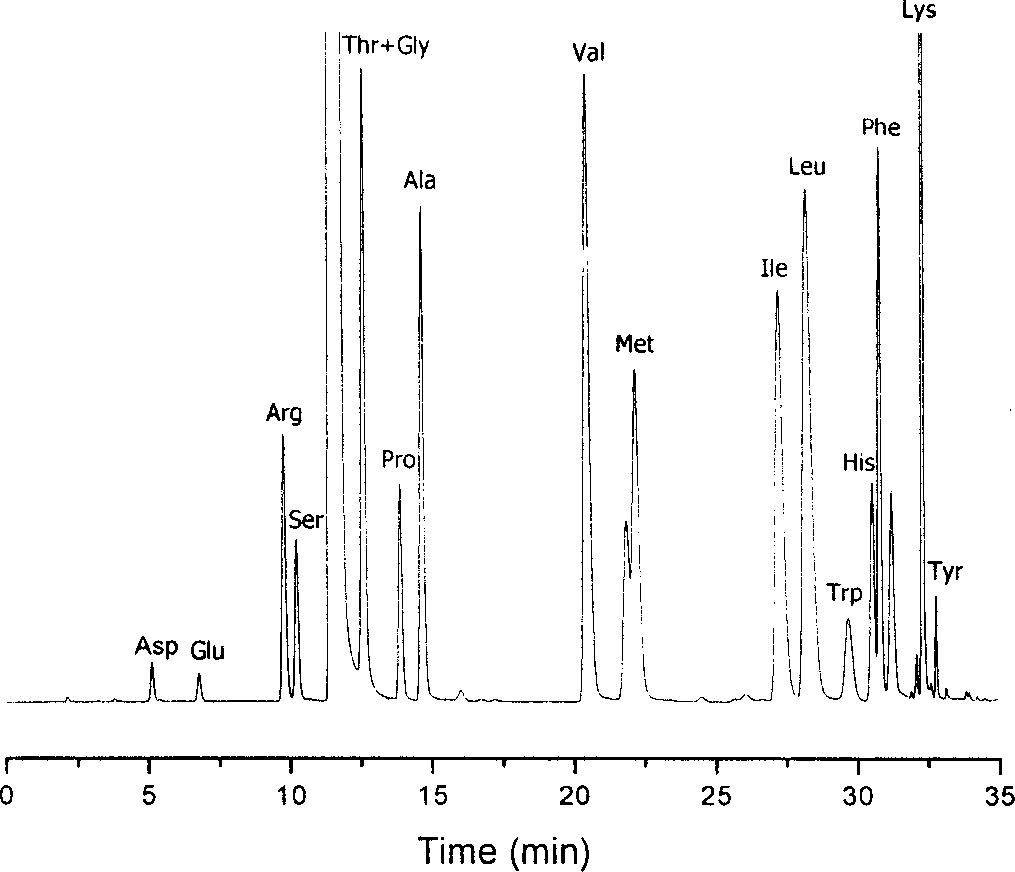
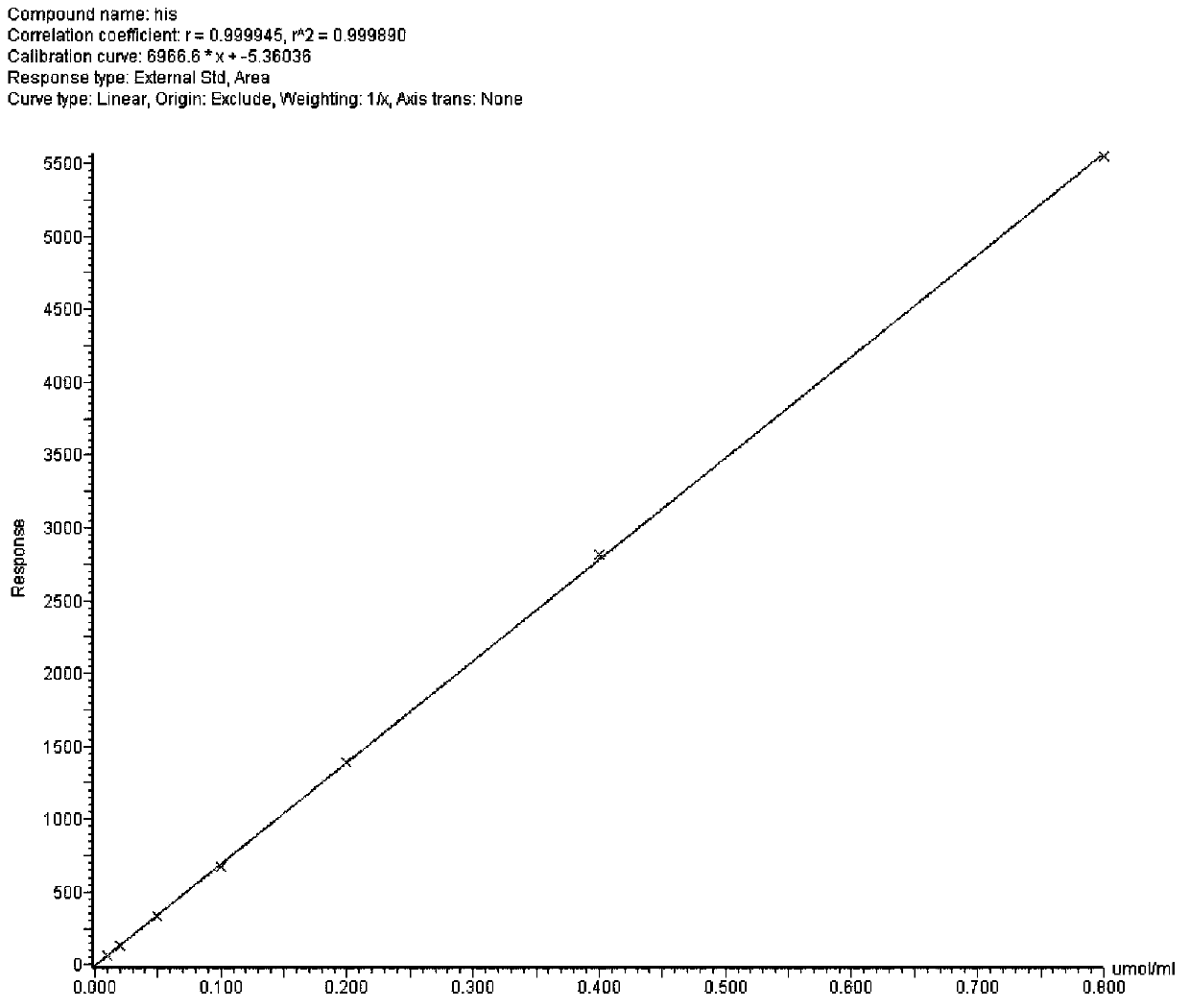
Amino acid analysis is a technique based on ion exchange liquid chromatography, used in a wide range of application areas to provide qualitative and quantitative compositional analysis.
Method and system for rapid biomolecular recognition of amino acids and protein sequencing
InactiveUS6846638B2Low costHigh sensitivityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsProtein Sequence DeterminationDigestion
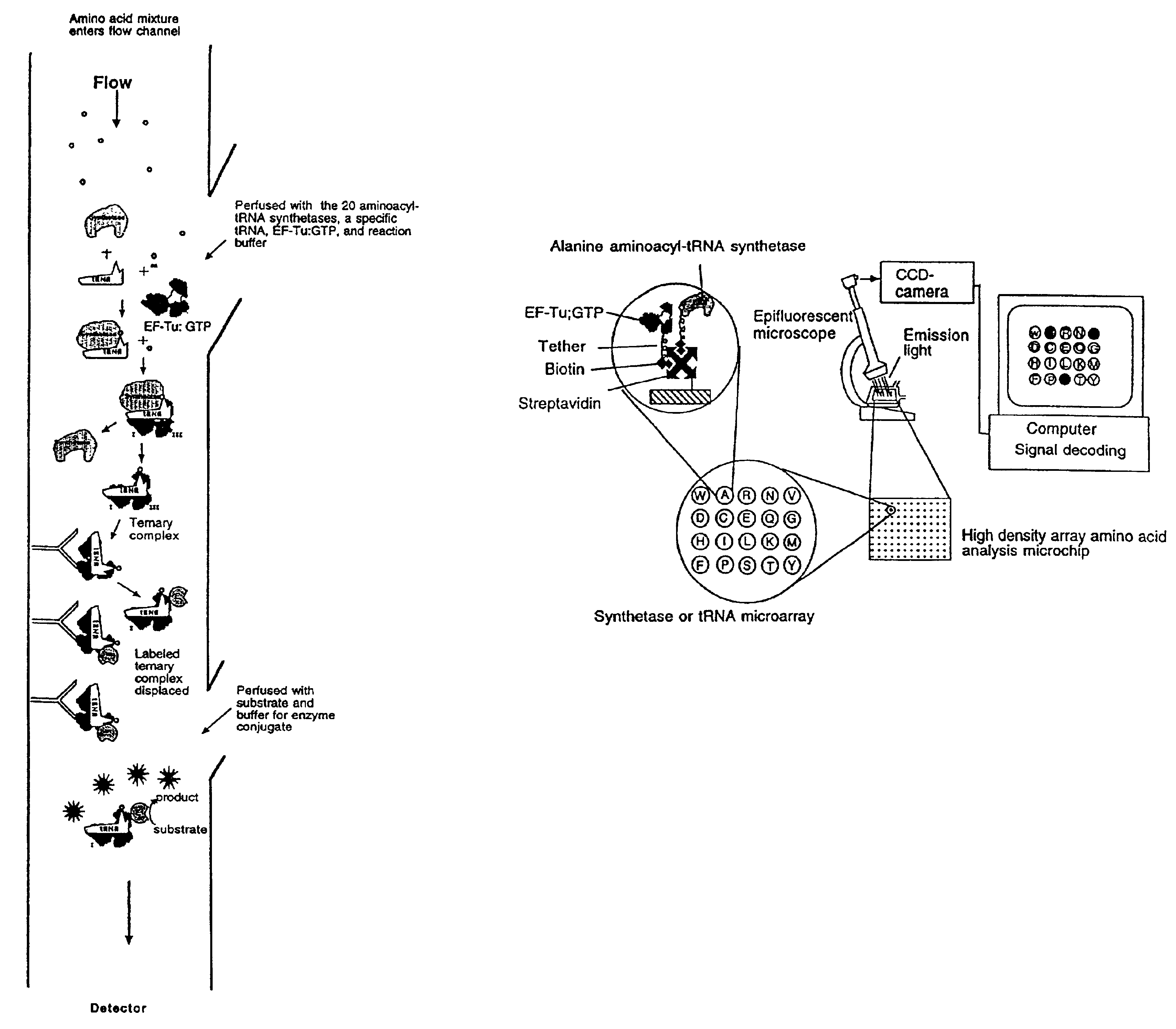
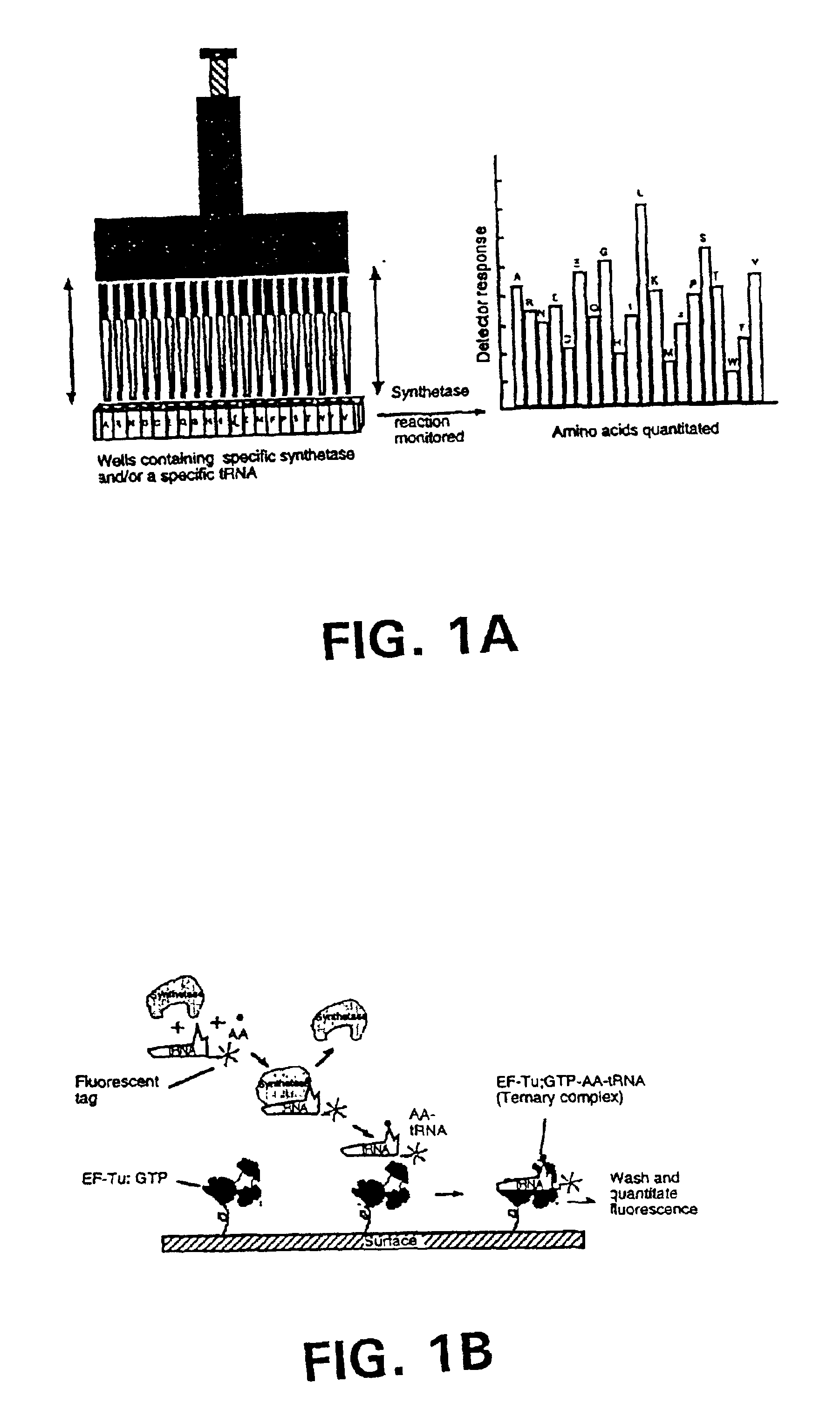
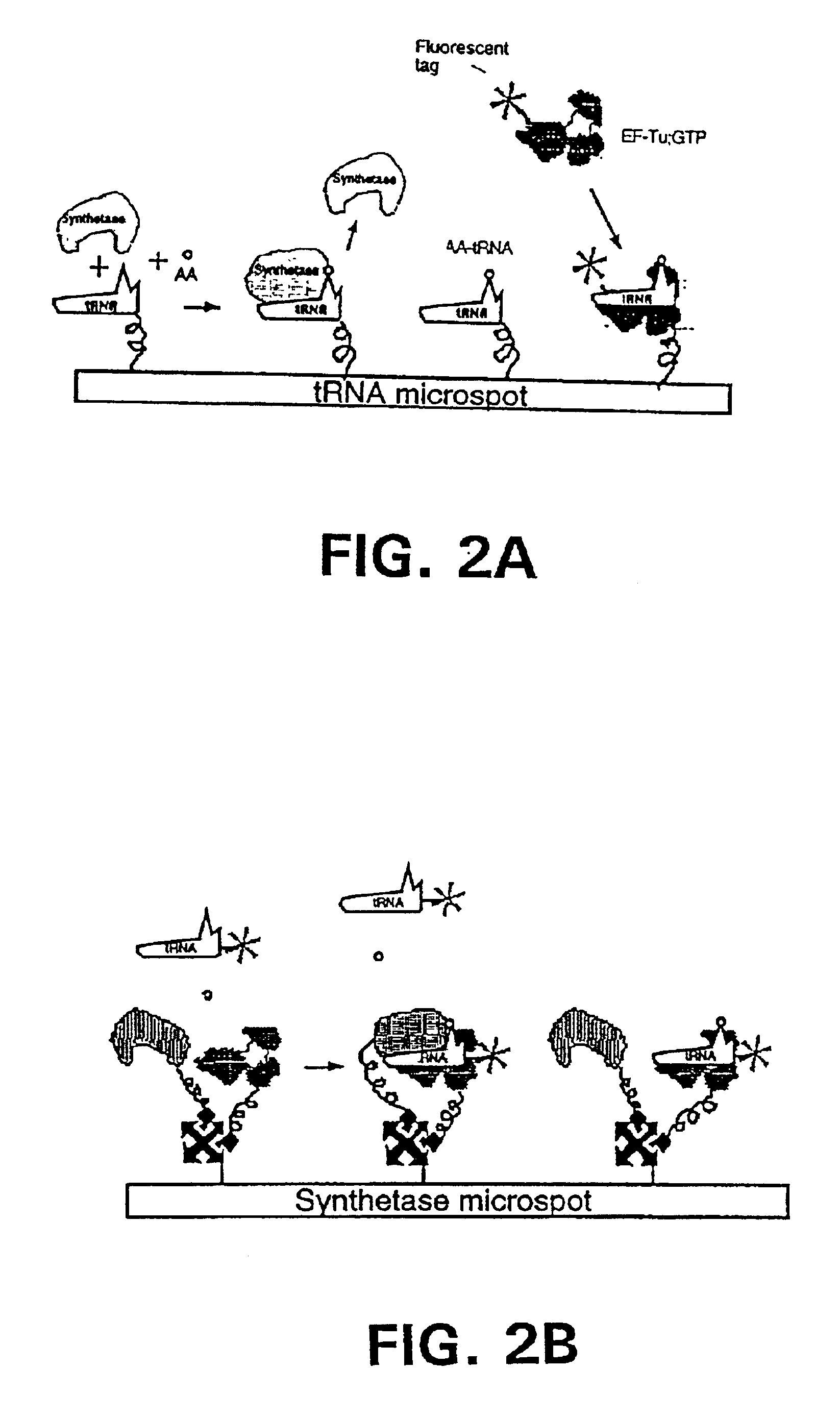
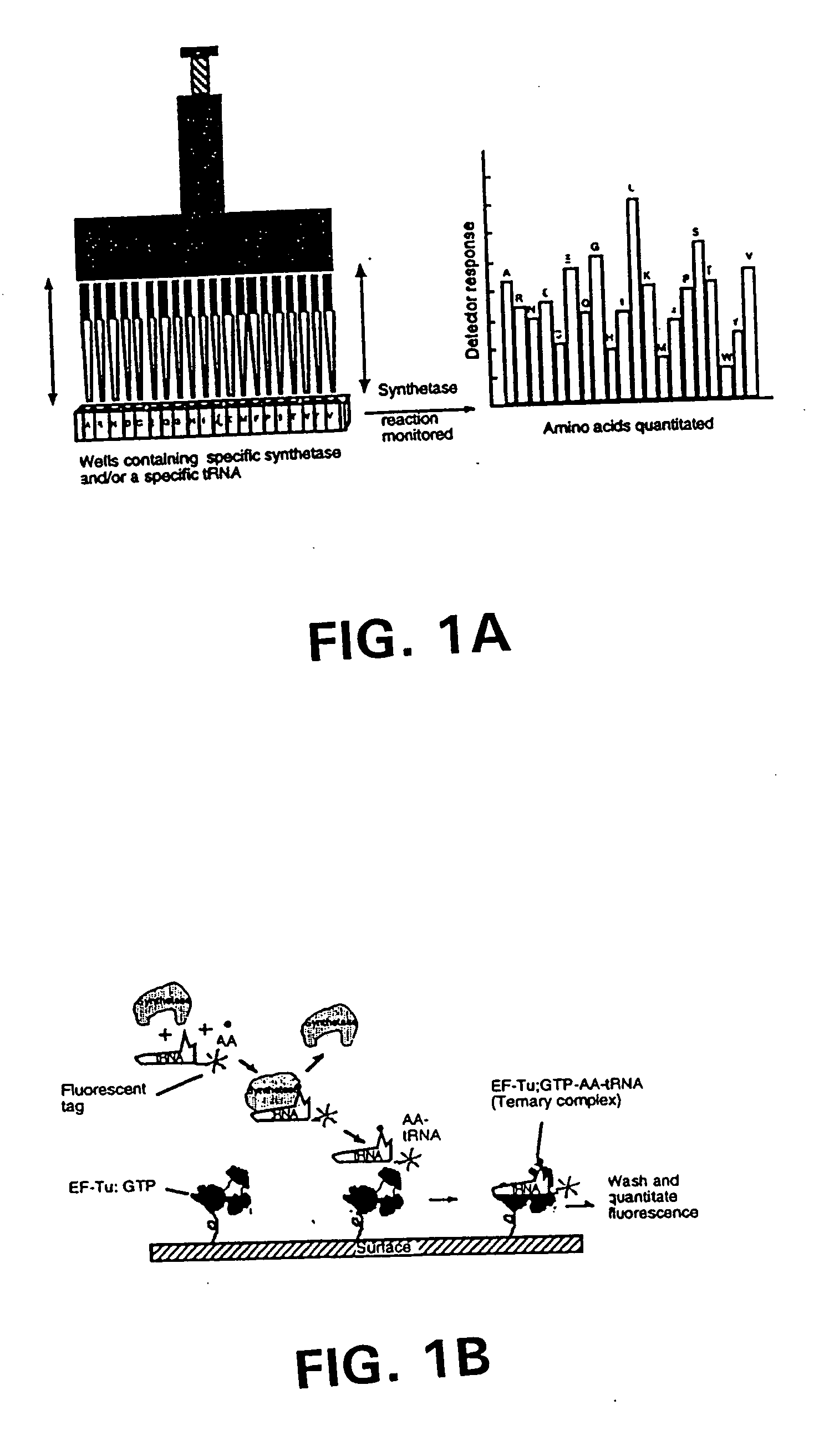
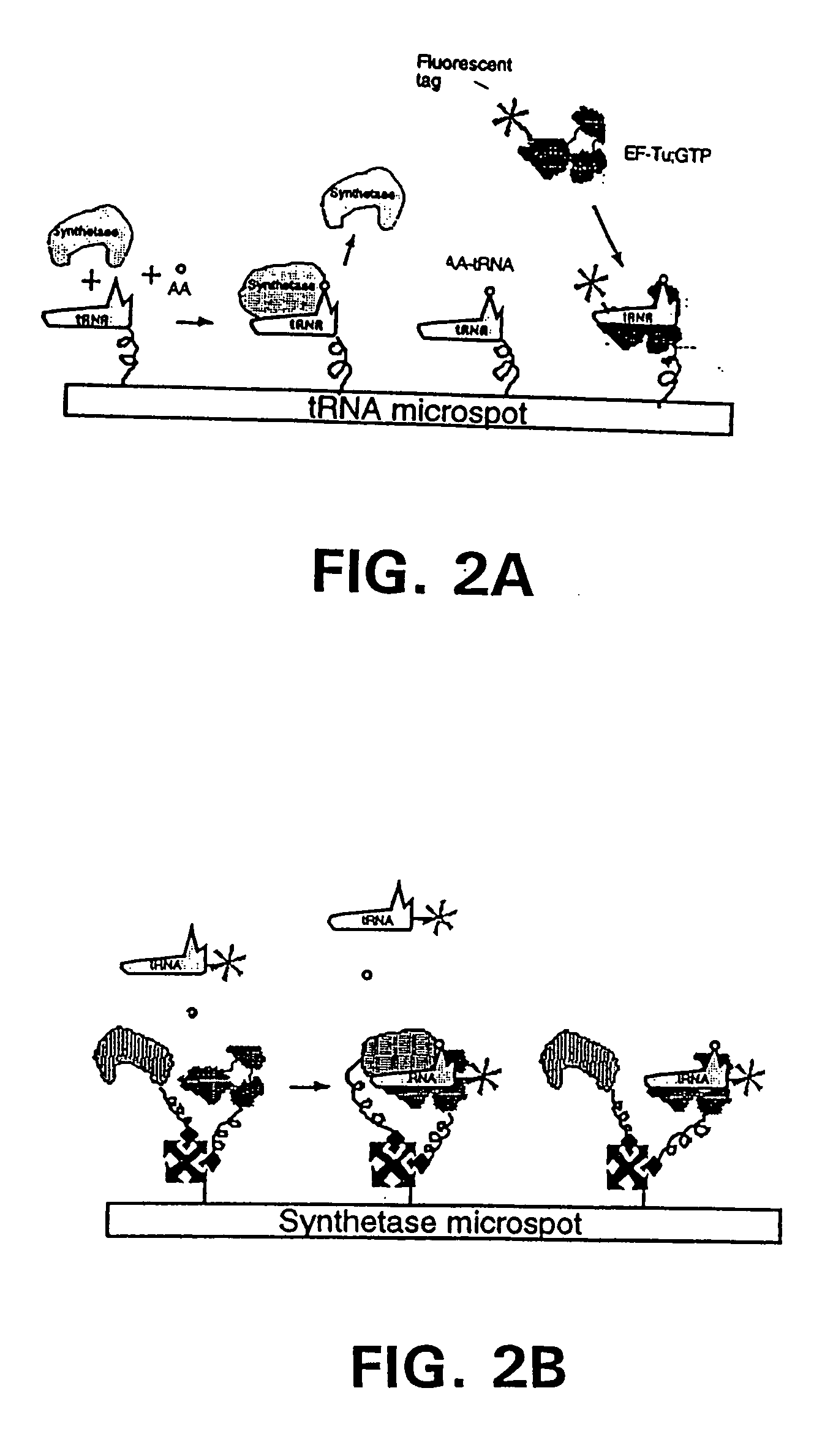
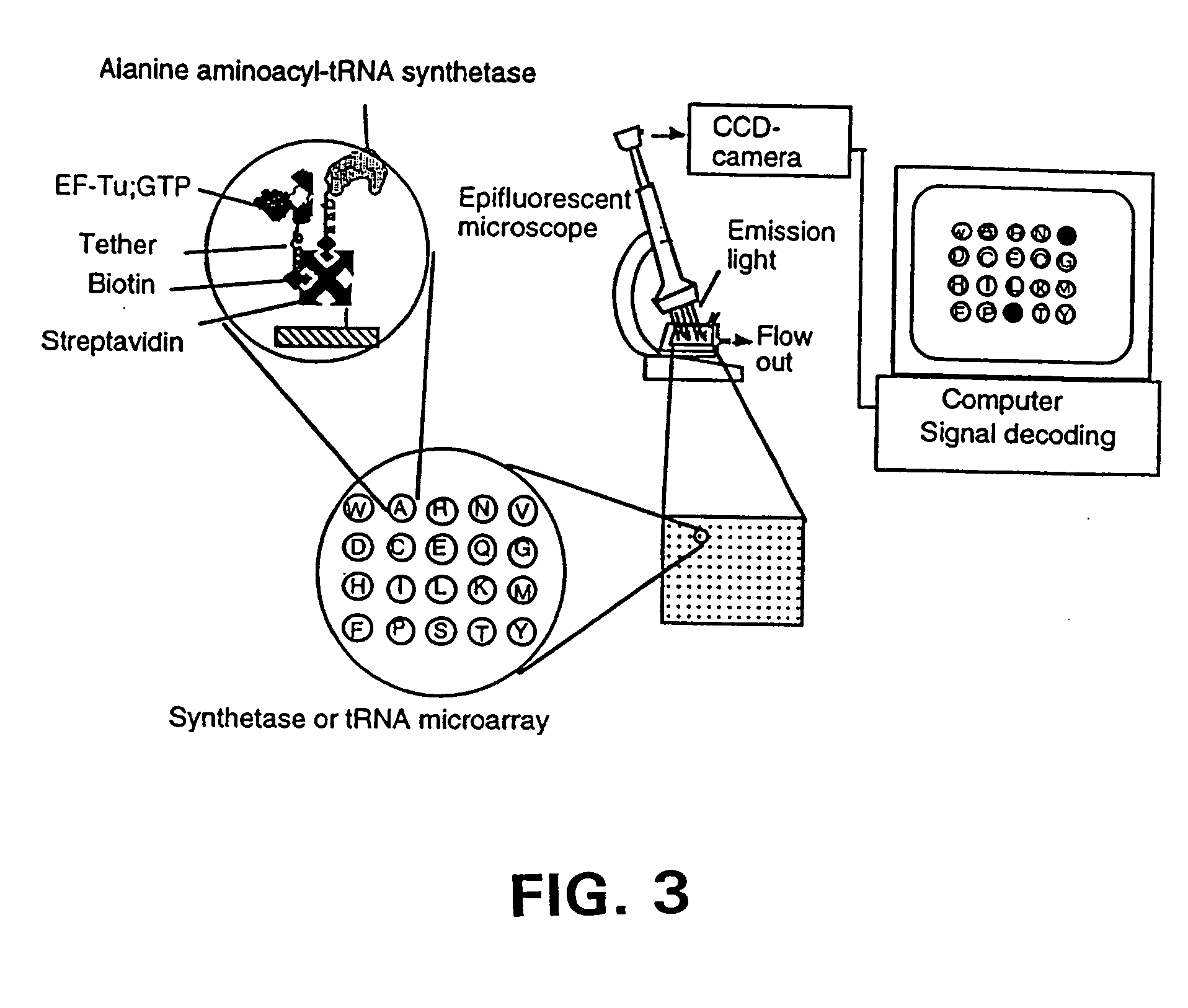
Methods, compositions, kits, and apparatus are provided wherein the aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase system is used to analyze amino acids. The method allows very small devices for quantitative or semi-quantitative analysis of the amino acids in samples or in sequential or complete proteolytic digestions. The methods can be readily applied to the detection and / or quantitation of one or more primary amino acids by using cognate aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase and cognate tRNA. The basis of the method is that each of the 20 synthetases and / or a tRNA specific for a different amino acid is separated spatially or differentially labeled. The reactions catalyzed by all 20 synthetases may be monitored simultaneously, or nearly simultaneously, or in parallel. Each separately positioned synthetase or tRNA will signal its cognate amino acid. The synthetase reactions can be monitored using continuous spectroscopic assays. Alternatively, since elongation factor Tu:GTP (EF-Tu:GTP) specifically binds all AA-tRNAs, the aminoacylation reactions catalyzed by the synthetases can be monitored using ligand assays. Microarrays and microsensors for amino acid analysis are provided. Additionally, amino acid analysis devices are integrated with protease digestions to produce miniaturized enzymatic sequenators capable of generating either N- or C-terminal sequence and composition data for a protein or peptide. The possibility of parallel processing of many samples in an automated manner is discussed.
Owner:NANOBIODYNAMICS
Automated systems and methods for analysis of protein post-translational modification
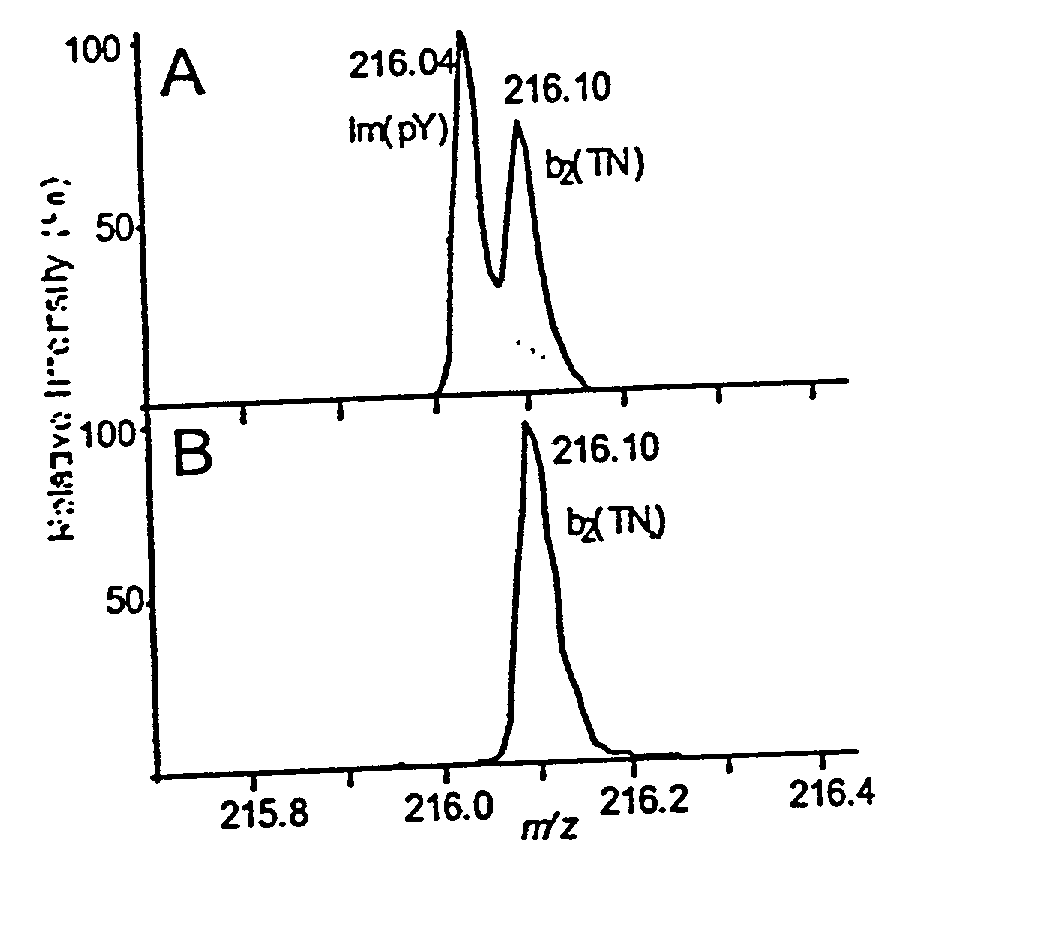
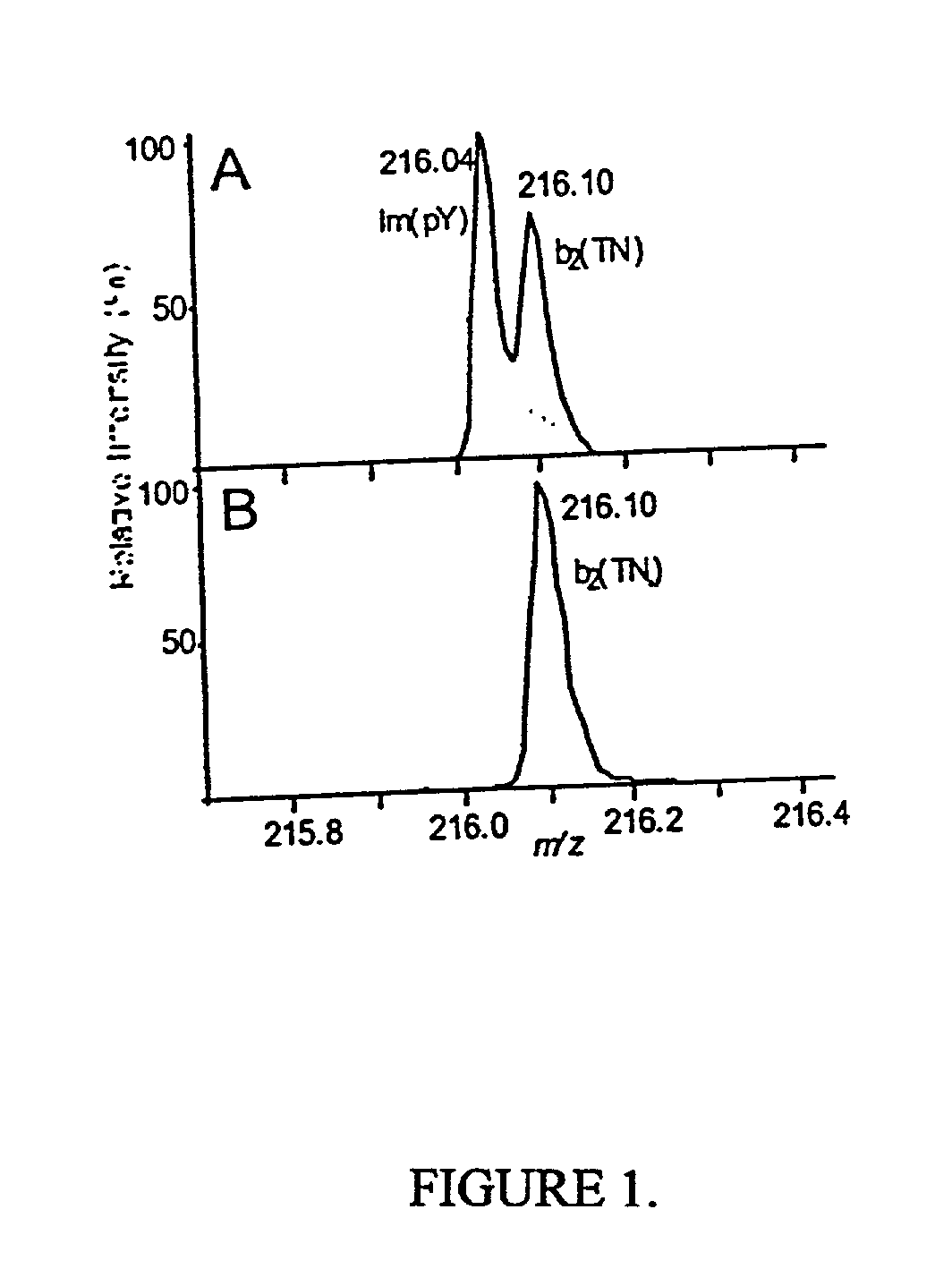
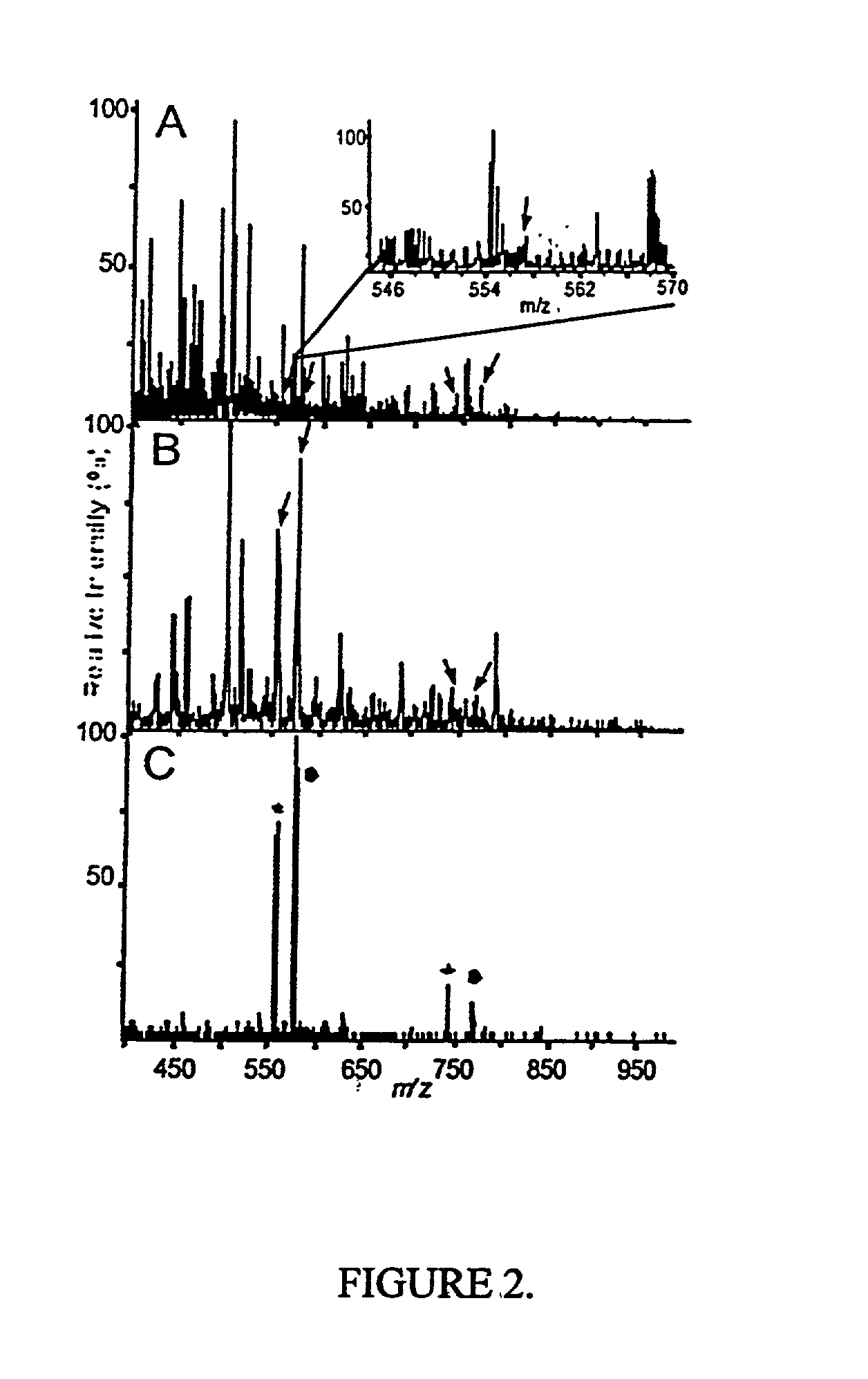
InactiveUS20030153007A1Peptide librariesParticle separator tubesPhosphorylationMass Spectrometry-Mass Spectrometry
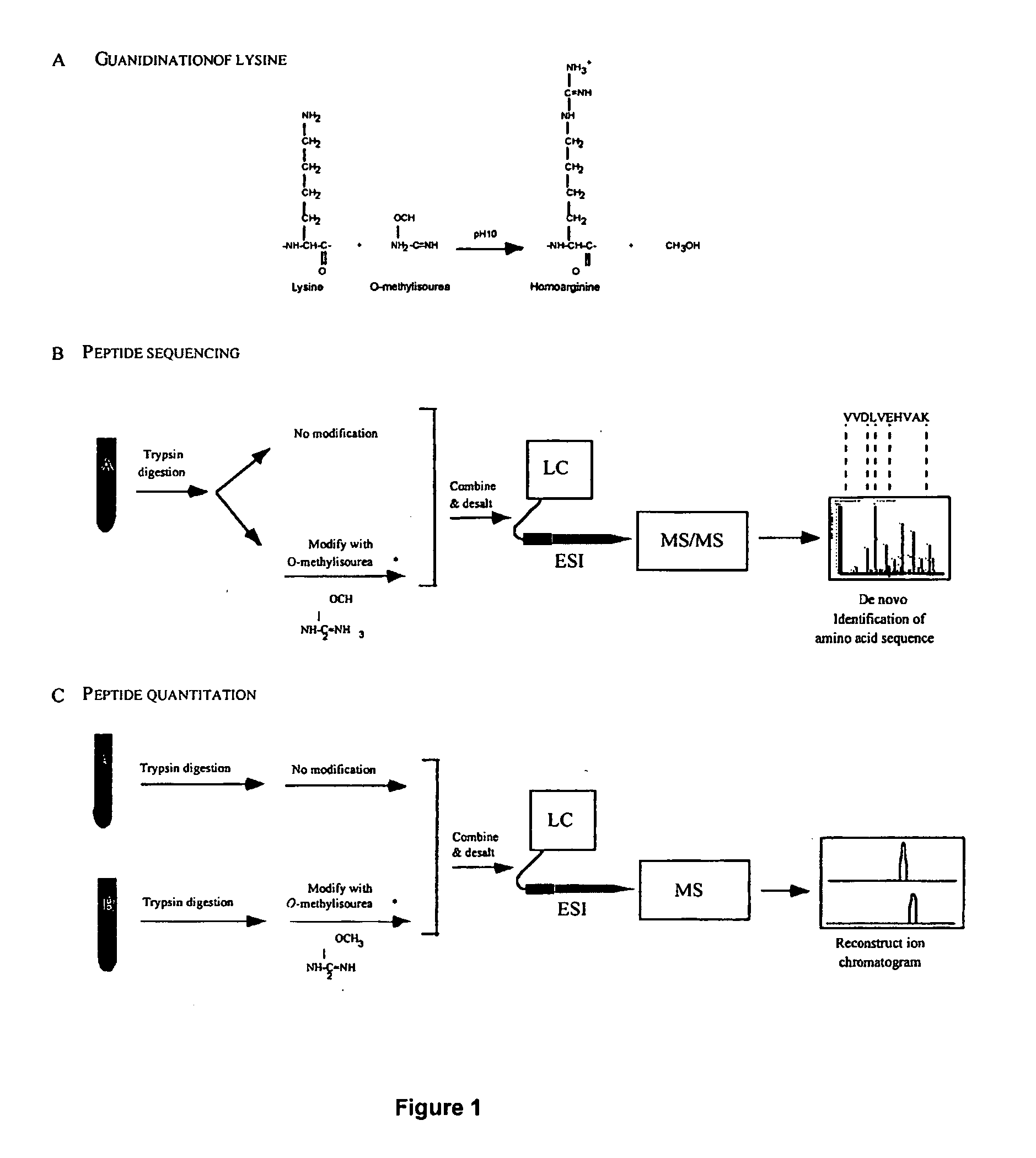
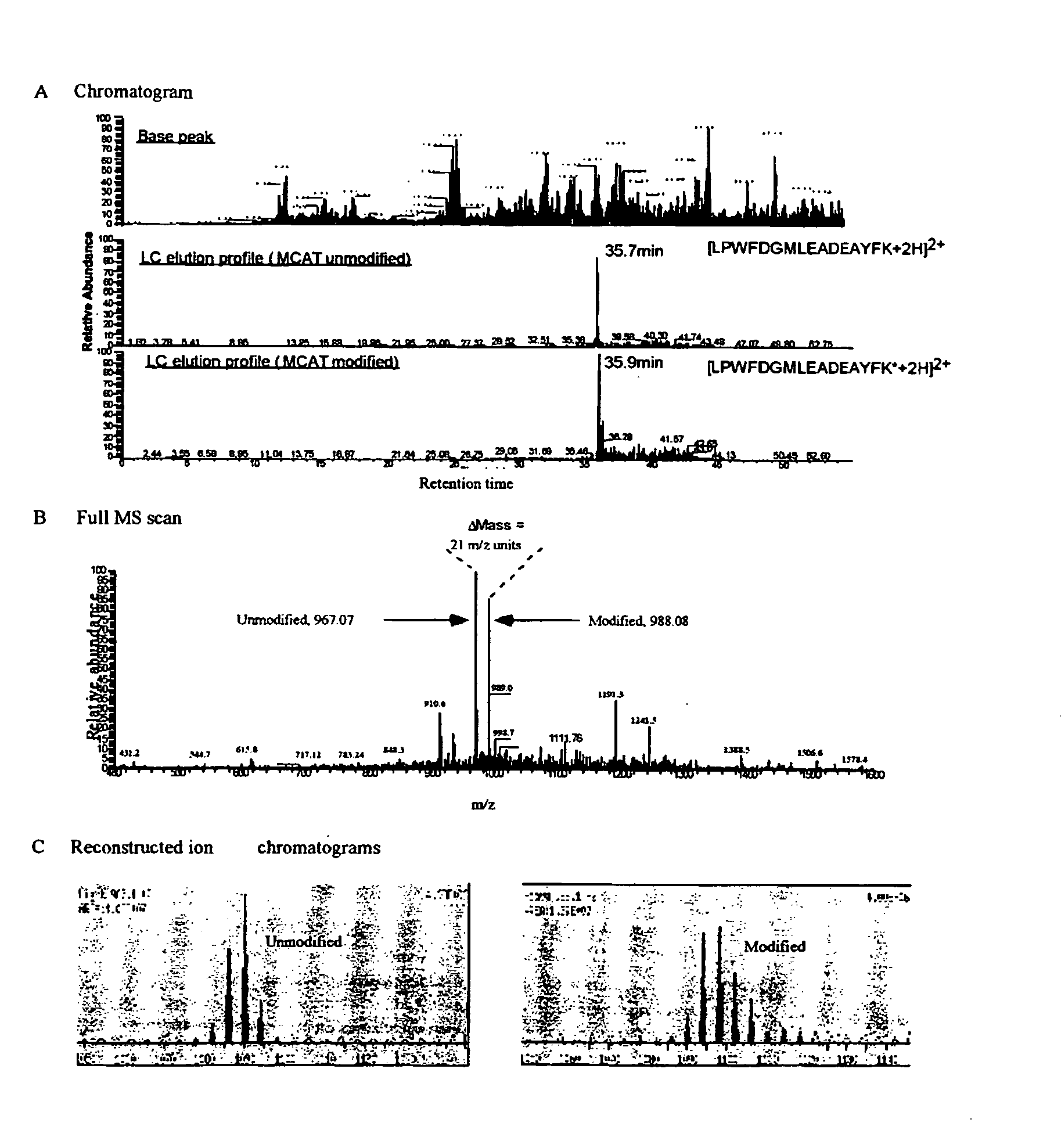
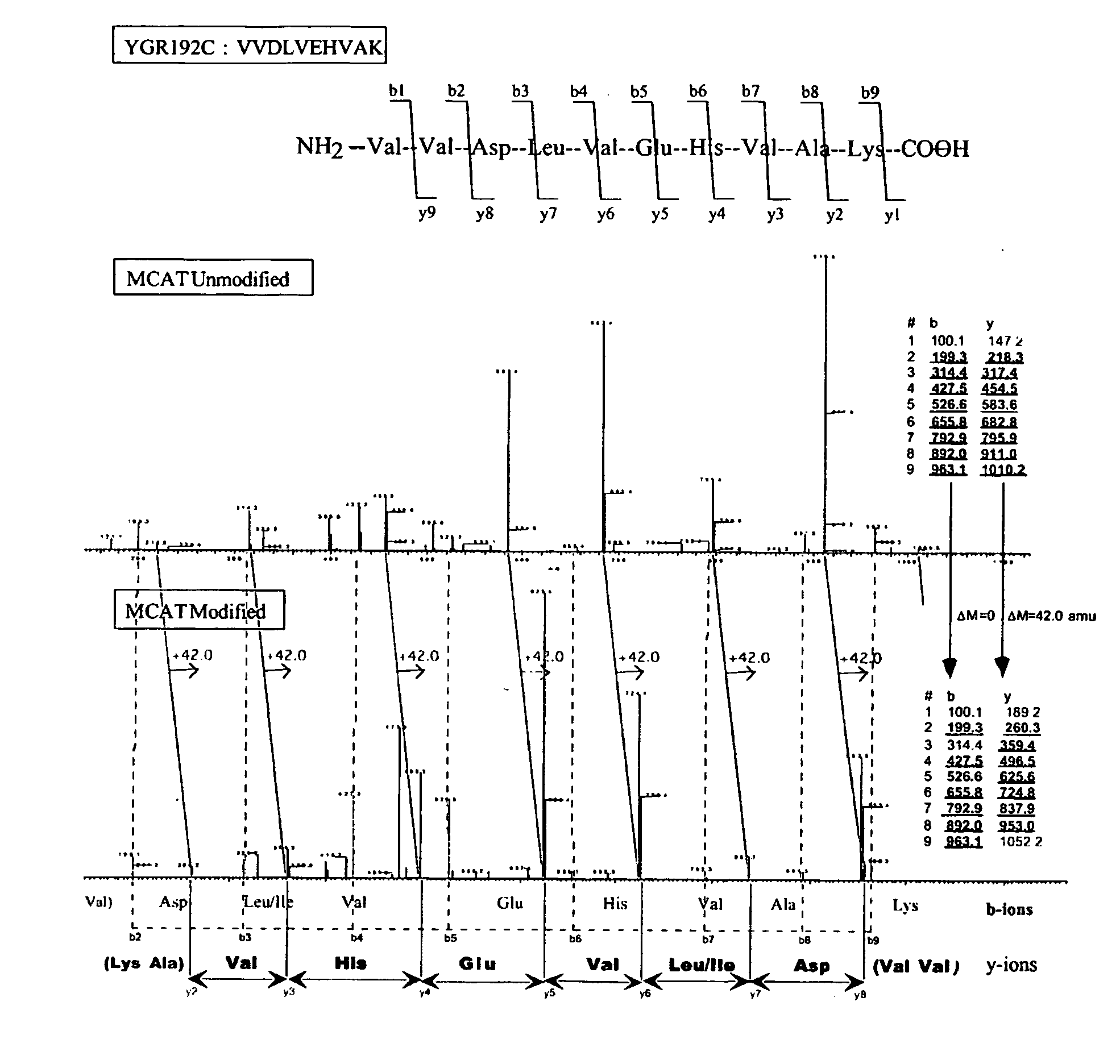
Methods and systems of applying mass spectrometry to the analysis of peptides and amino acids, especially in the proteome setting. More particularly, the invention relates to a mass spectrometry-based method for detection of amino acid modifications, such as phosphorylation.
Owner:PROTANA
Method and system for rapid biomolecular recognition of amino acids and protein sequencing
InactiveUS20050164264A1Quick analysisBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsProtein Sequence DeterminationDigestion
Methods, compositions, kits, and apparatus are provided wherein the aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase system is used to analyze amino acids. The method allows very small devices for quantitative or semi-quantitative analysis of the amino acids in samples or in sequential or complete proteolytic digestions. The methods can be readily applied to the detection and / or quantitation of one or more primary amino acids by using cognate aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase and cognate tRNA. The basis of the method is that each of the 20 synthetases and / or a tRNA specific for a different amino acid is separated spatially or differentially labeled. The reactions catalyzed by all 20 synthetases may be monitored simultaneously, or nearly simultaneously, or in parallel. Each separately positioned synthetase or tRNA will signal its cognate amino acid. The synthetase reactions can be monitored using continuous spectroscopic assays. Alternatively, since elongation factor Tu:GTP (EF-Tu:GTP) specifically binds all AA−tRNAs, the aminoacylation reactions catalyzed by the synthetases can be monitored using ligand assays. Microarrays and microsensors for amino acid analysis are provided. Additionally, amino acid analysis devices are integrated with protease digestions to produce miniaturized enzymatic sequenators capable of generating either N- or C-terminal sequence and composition data for a protein or peptide. The possibility of parallel processing of many samples in an automated manner is discussed.
Owner:NANOBIODYNAMICS
Protein expression profile database
InactiveUS20050048564A1Peptide librariesLibrary screeningSequence databaseProtein expression profile
This invention describes the use of peptide profiling to identify, characterize, and classify biological samples. In complex samples, many thousands of different peptides will be present at varying concentrations. The invention uses liquid chromatography and similar methods to separate peptides, which are then identified and quantified using mass spectrometry. By identification it is meant that the correct sequence of the peptide is established through comparisons with genome sequence databases, since the majority of peptides and proteins are unannotated and have no ascribed name or function. Quantification means an estimate of the absolute or relative abundance of the peptide species using mass spectrometry and related techniques including, but not limited to, pre- or post-experimental stable or unstable isotope incorporation, molecular mass tagging, differential mass tagging, and amino acid analysis.
Owner:EMILI ANDREW +1
Method for discriminating fermentation quality of congou black tea based on near-infrared-spectroscopy-combined amino acid analysis technology
InactiveCN104020129ADiscrimination scienceAccurate discriminationMaterial analysis by optical meansBlack teaAmino acid content
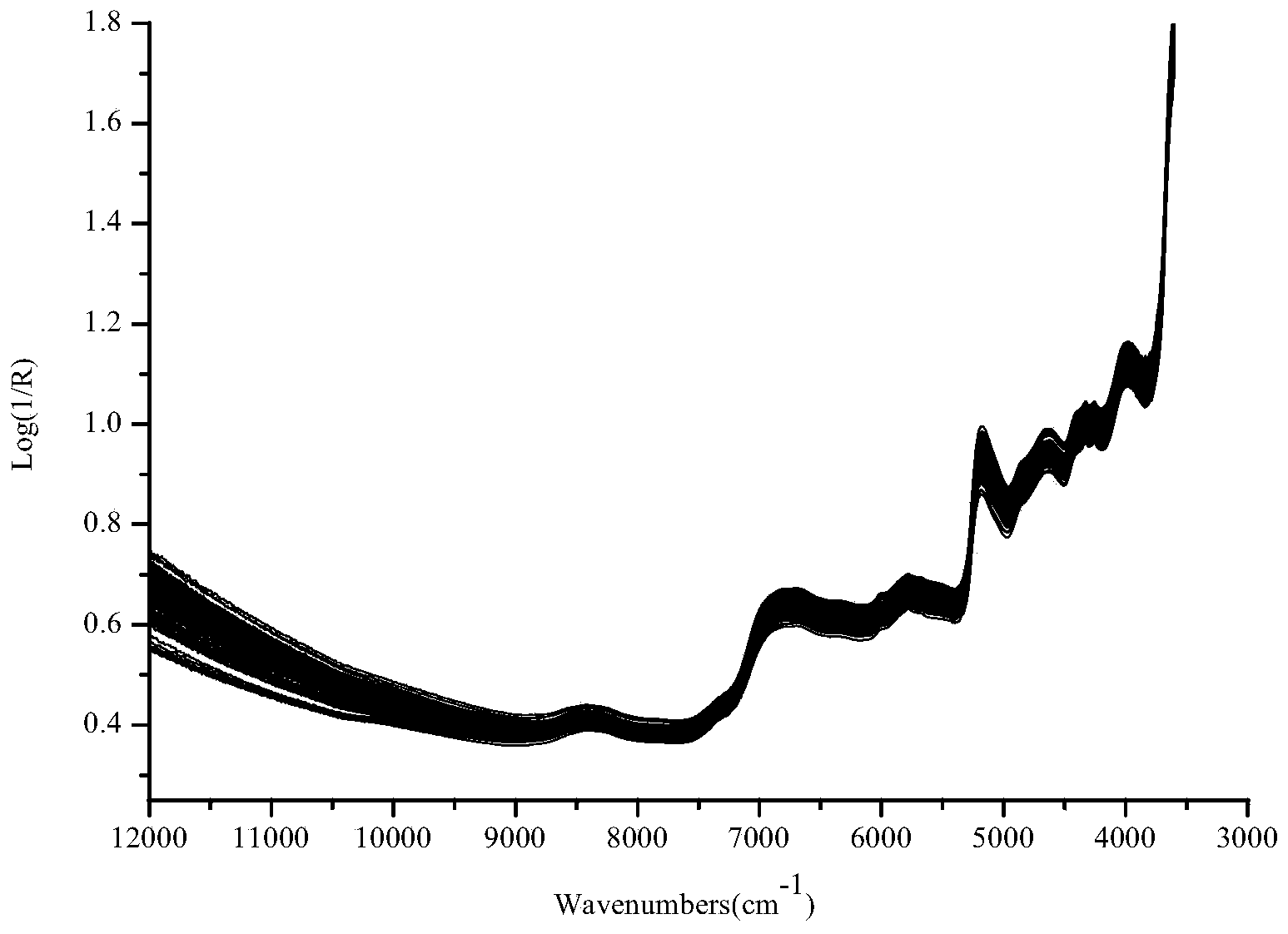
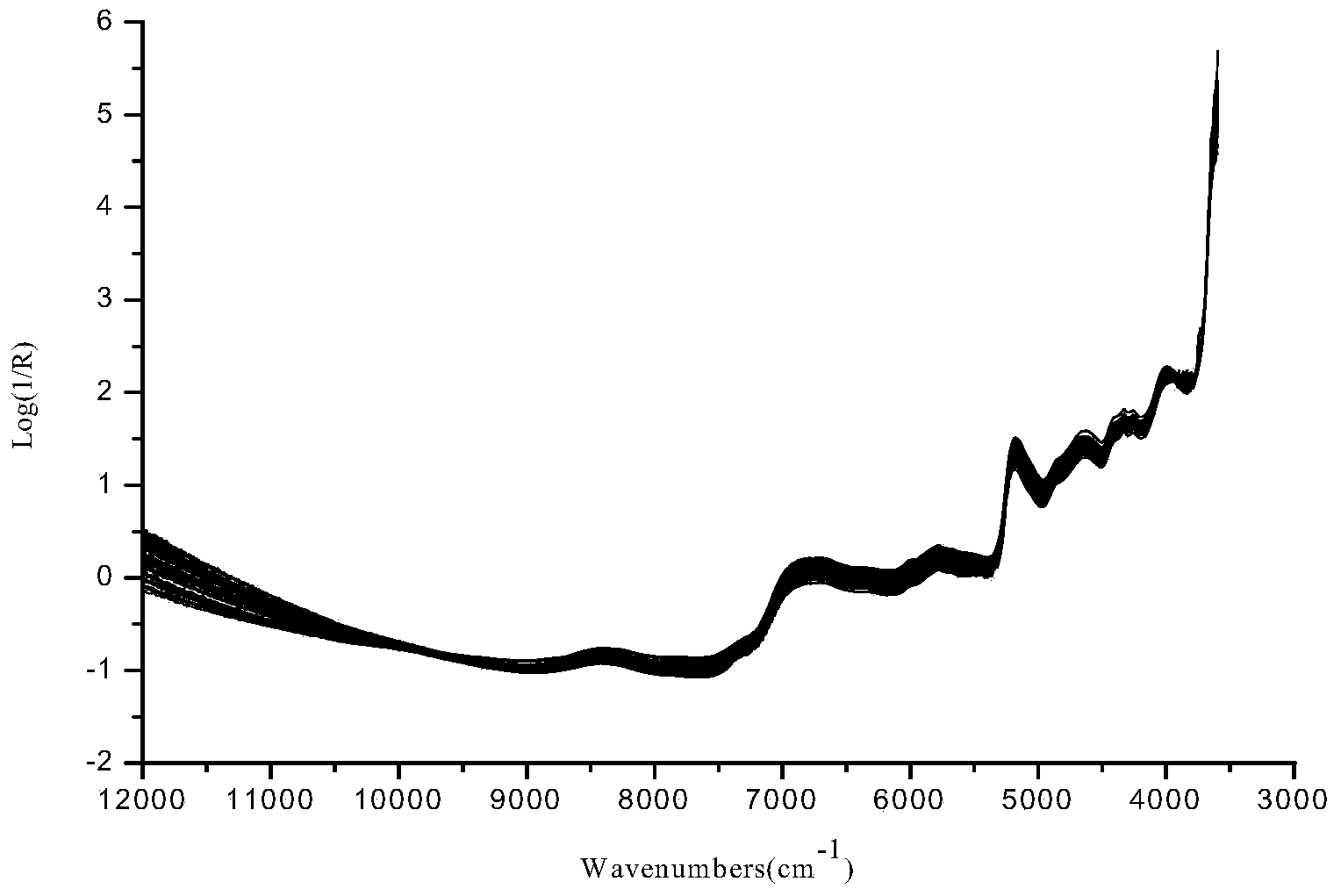
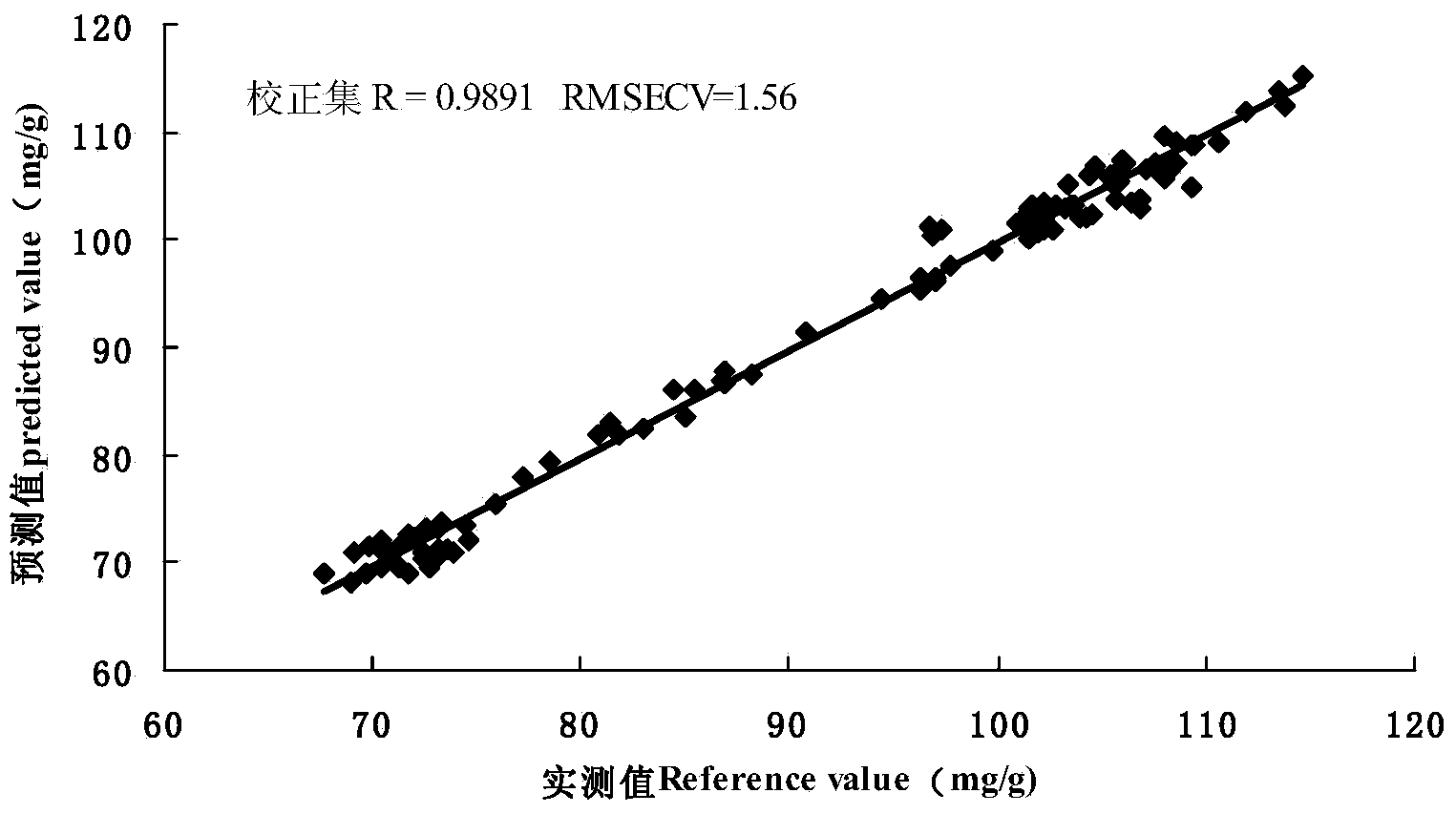
The invention discloses a method for discriminating fermentation quality of congou black tea based on a near-infrared-spectroscopy-combined amino acid analysis technology. The method comprises: selecting a sample and performing pre-processing; using high performance liquid chromatograph to determine the content of amino acids in the sample; acquiring the spectrum of the sample, utilizing synergy interval partial least square to establish a near-infrared-spectroscopy quantitative discrimination model for amino acids, finding amino acid variation distribution, and discriminating the fermentation quality of congou black tea. According to the method for discriminating the fermentation quality of congou black tea based on the near-infrared-spectroscopy-combined amino acid analysis technology, pretreatment is performed on an acquired original spectrum by utilizing standard normal variable transformation (SNVT), and the amino acid near-infrared discrimination model is constructed by employing synergy interval partial least square (SiPLS). The invention provides the quantitative determining method for scientifically accurately discriminating the fermentation quality congou black tea.
Owner:ANHUI AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Detection of modified amino acids by mass spectrometry
InactiveUS20020192708A1Particle separator tubesIsotope separationPhosphorylationMass Spectrometry-Mass Spectrometry
Methods and systems of applying mass spectrometry to the analysis of peptides and amino acids, especially in the proteome setting. More particularly, the invention relates to a mass spectrometry-based method for detection of amino acid modifications, such as phosphorylation.
Owner:STEEN HANNO +2
Brain protein hydrolysate and production process of its freeze dried preparation
InactiveCN1857711ANo pollution in the processReduce investmentPowder deliveryNervous disorderFreeze-dryingNitrogen
The present invention relates to a kind of brain protein hydrolysate and the production process of its freeze dried preparation. The brain protein hydrolysate for injection is prepared with pig brain and through the steps of homogenating in a colloid mill to collect slurry, hydrolyzing with pepsase and pancreatin to collect supernatant, filtering with filer paper to collect filtrate, separating and purifying the filtrate with hydroxyapetite column, regulating peptide map and collecting object, ultrafiltering with membrane of intercepting molecular weight 8 KD to collecting filtrate, nitrogen and amino acid analysis and adding amino acid in the required amount, and fine filtering with 0.22 micron filtering membrane. The brain protein hydrolysate for injection may be further freeze dried to obtain freeze dried brain protein hydrolysate preparation. The production process is environment friendly, high in yield and low in cost.
Owner:HAINAN JINXING PHARMA
Method for preparing bonito stick protein hydrolysate with effect of reducing uric acid
ActiveCN104337836AGood effectHigh purityHydrolysed protein ingredientsSkeletal disorderSerum uric acidArginine
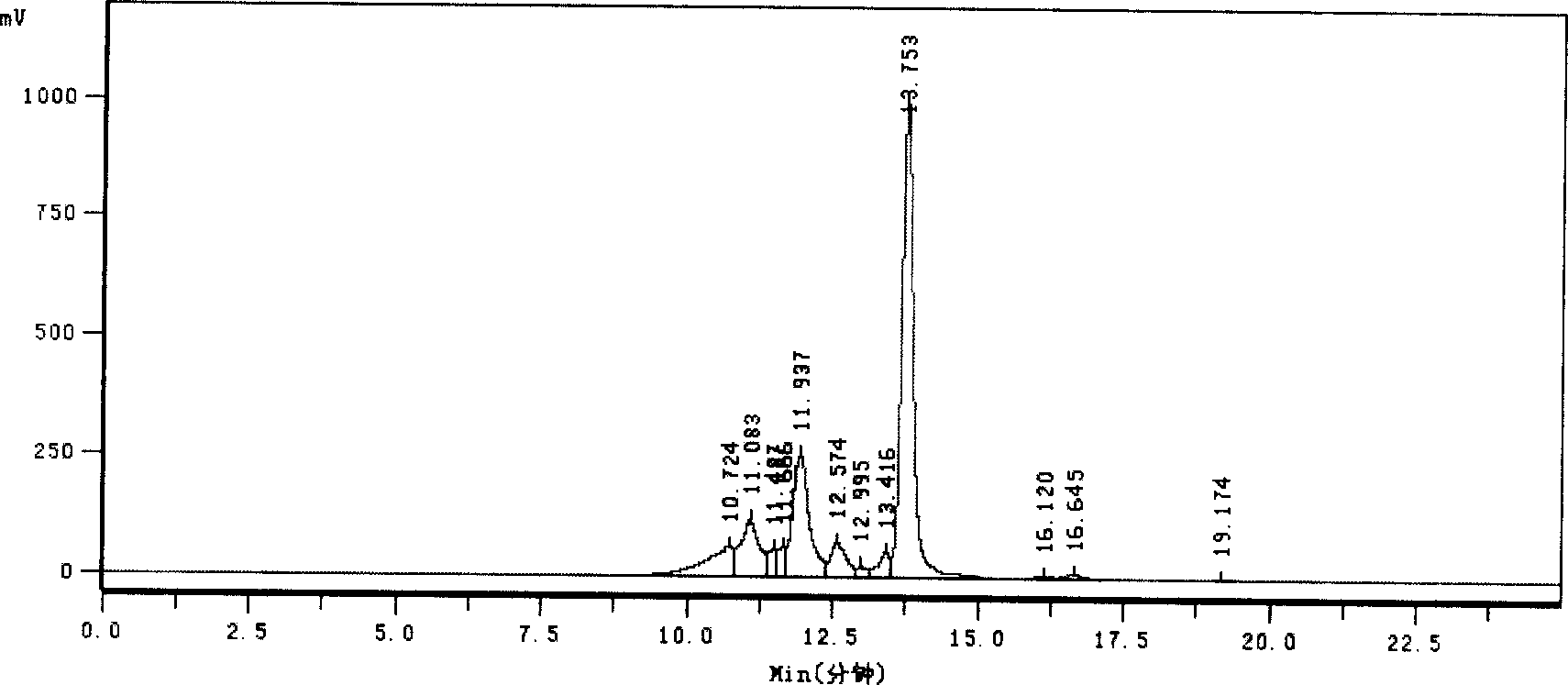
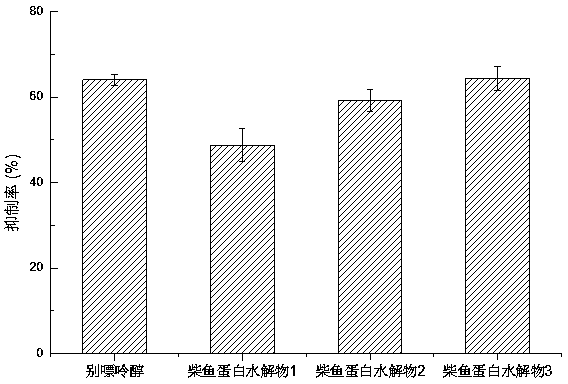
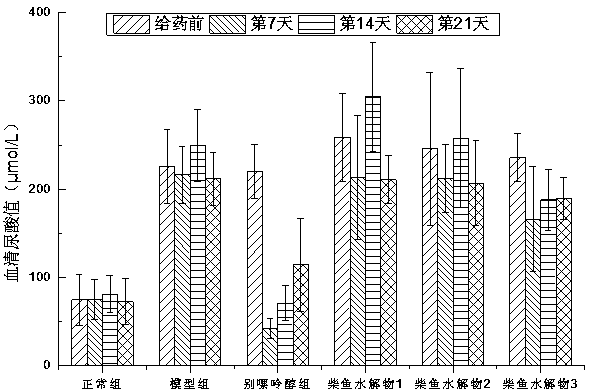
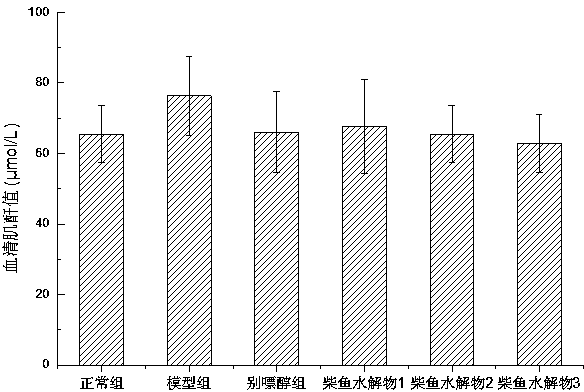
The invention relates to a method for preparing bonito stick protein hydrolysate with an effect of reducing uric acid. The method comprises the following main steps of raw material heat treatment, restriction digestion, membrane separation-anion exchange chromatography-gel filtration chromatography separation, concentration and spray drying so as to obtain the bonito stick protein hydrolysate with an effect of reducing uric acid. The amino acid analysis indicates that the zymolyte peptide fragment primary amino acid sequence contains four amino acids, namely histidine, arginine, lysine and threonine, the total mass content of the four amino acids is 70 percent of the total amino acid content of zymolyte. MALDI-TOF-MS mass spectrum determines that the molecular weight of the main peptide effective ingredient is less than 700Da. In-vitro uric acid reduction experiments prove that the bonito stick protein hydrolysate has a remarkable effect of inhibiting generation of uric acid, and has an inhibition rate over 50 percent; an oteracil potassium molded hyperuricemic rat animal model indicates that the bonito stick protein hydrolysate can be used for remarkably reducing the level of serum uric acid and serum creatinine of rats, and shows a relatively good kidney protecting effect.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Method for detecting free amino acids in tea by using reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography
InactiveCN104678044AEasy to handleLow costComponent separationChromatographic separationAmino acid synthesis
The invention relates to a method for detecting free amino acids in tea by using the reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography. The method comprises the following steps: drying and grinding fresh tea, and adding boiling water for digestion; after supernatant liquor is collected, repeatedly extracting and merging the supernatant liquor; after the supernatant liquor is sucked and filtered, carrying out precolumn derivatization for a tea soup sample with an AccQ.Tag derivatization reagent; optimizing chromatographic separation and detection conditions with HPLC and AccQ.Tag C18 special amino acid analysis columns, and finally separating and detecting 19 kinds of free amino acids such as glutamine. The method can simultaneously determine the contents of 19 kinds of free amino acids such as glutamine in the tea, makes up the vacancy that glutamine in the tea cannot be quickly and accurately analyzed based on the high-performance liquid chromatography qualitatively and quantitatively at present, and provides a new idea for researching the synthesis path of amino acids in the tea.
Owner:ANHUI AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Stenotrophomonas maltophilia for generating keratinase and application of stenotrophomonas maltophilia
ActiveCN102329751AEfficient degradationEasy to handleBacteriaBiochemical fibre treatmentStenotrophomonas maltophiliaNitrogen source
The invention discloses stenotrophomonas maltophilia for generating keratinase and an application of stenotrophomonas maltophilia. A strain for generating keratinase can efficiently degrade feathers within 24 hours, the activity of the keratinase subjected to fermentation and primary optimization can reach 150U / mL. Multiple kinds of amino acids can be produced after the degraded feathers are subjected to amino acid analysis, and the degraded feathers can replace grain crops such as soybeans and the like to be used as a main nitrogen source of feeds. Meanwhile, a fermenting enzyme solution of the stenotrophomonas maltophilia has a better treatment effect on wool. The stenotrophomonas maltophilia for generating the keratinase, screened in the invention, has better application prospects in the industries of feeds and textiles.
Owner:XINYI HANLING BIO ENG
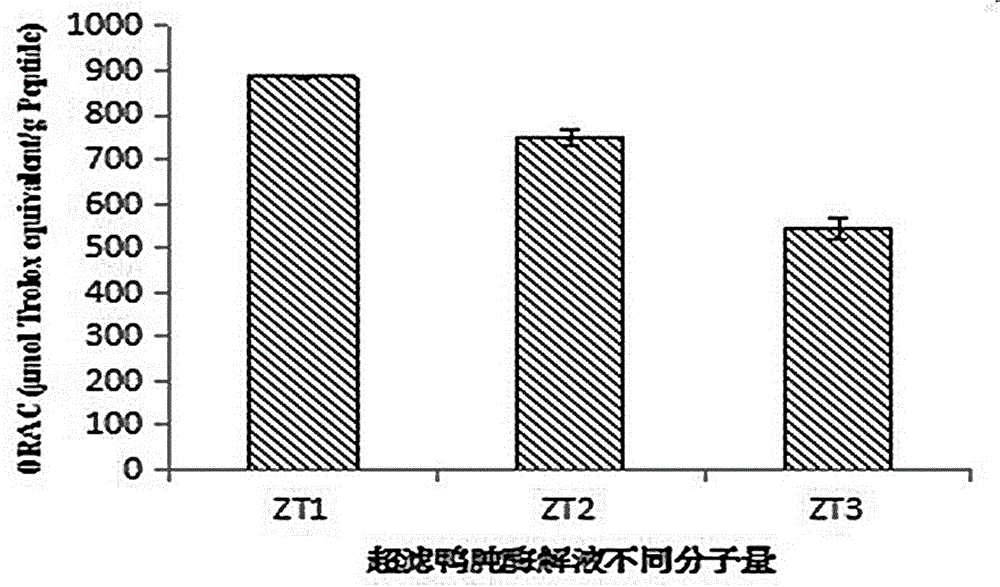
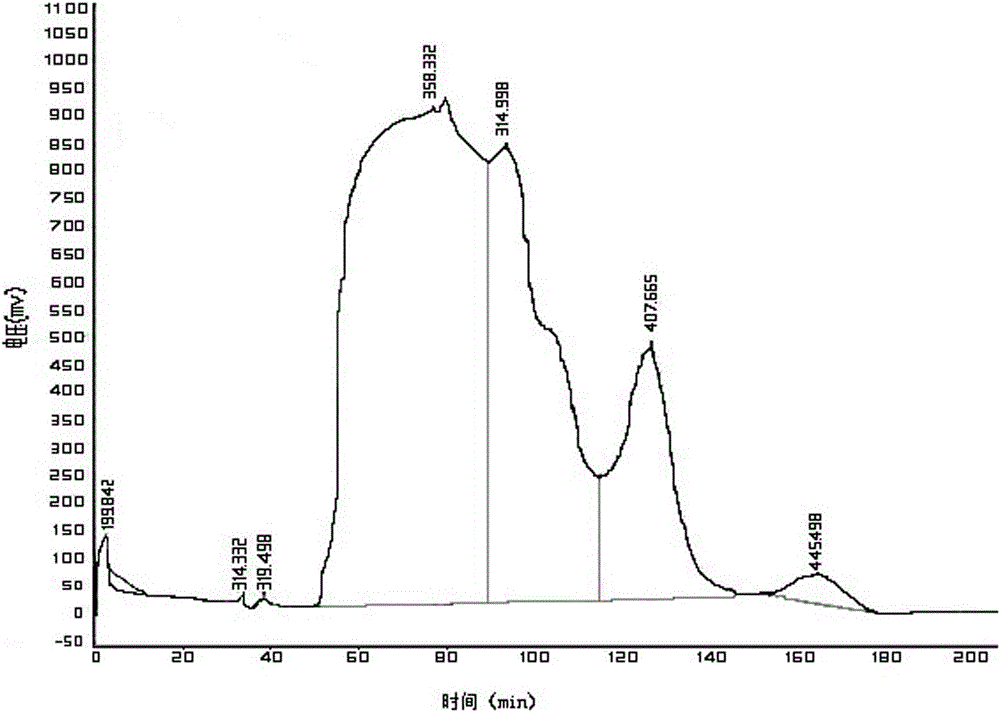
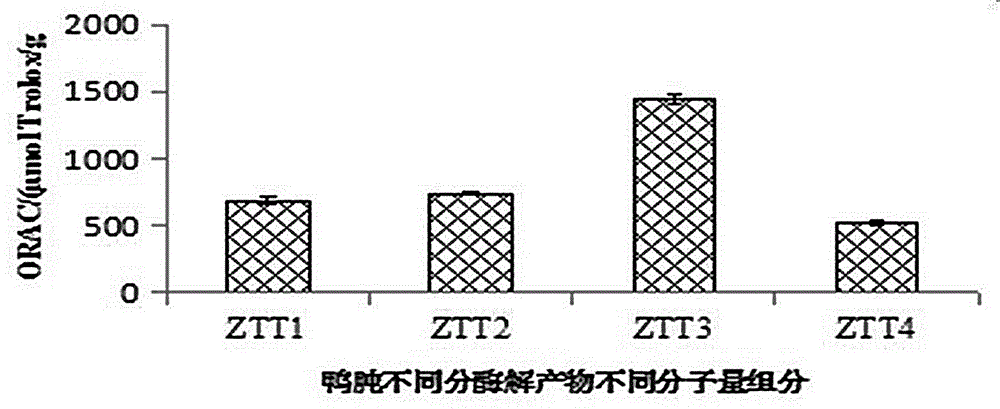
Duck gizzard duck's gizzard antioxidative peptide and application thereof
InactiveCN105820229AWide variety of sourcesHigh activityPeptide/protein ingredientsAntinoxious agentsChemical synthesisSide effect
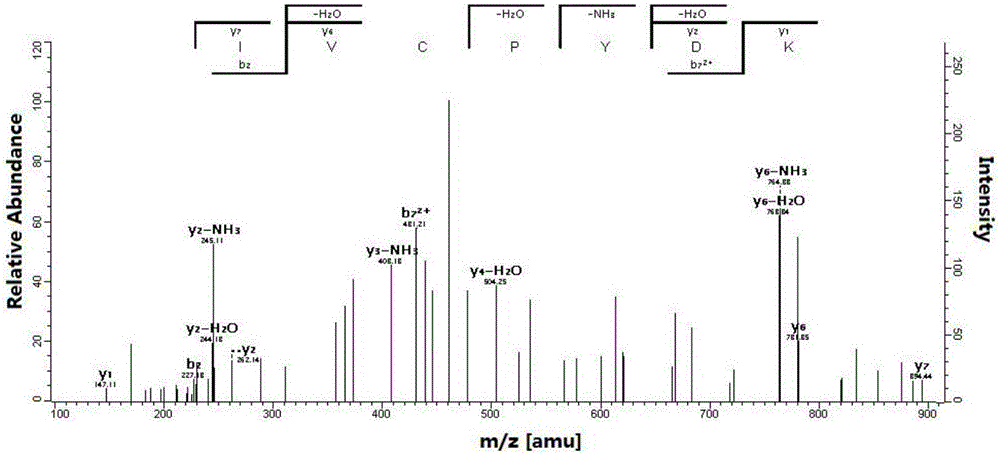
The invention discloses duck gizzard duck's gizzard antioxidative peptide and application thereof. The amino acid sequence of the duck gizzard duck's gizzard antioxidative peptide is as shown in Asn-Ly-Phe-Ile-Leu-Lys (a component DKFILK), and the monoisotopic peak of a parent ion of the sequence is m / z 382.2376 Da. The preparation process comprises the following steps: degreasing duck gizzard, performing enzymolysis, performing ultrafiltration on an enzymolysis product, performing gel filtration chromatography, performing reverse high performance liquid chromatography purification, and performing mass spectrum together with amino acid analysis, thereby obtaining the antioxidative peptide. The duck gizzard duck's gizzard antioxidative peptide is wide and cheap in raw material source and scientific and reasonable in process; by virtue of an enzymolysis technique and together with purification through ultrafiltration grading and chromatographic analysis, the prepared antioxidative peptide has relatively high activity; compared with an antioxidant prepared through chemical synthesis, the antioxidative peptide disclosed by the invention has the advantages of security, no toxic or side effect, good antioxidation property, easiness in digestion and absorption, and the like, and can be used as medicines, functional food and the like.
Owner:GUIZHOU UNIV
Microfluidic nucleic acid analysis
ActiveUS8871446B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCells isolationCDNA library
Nucleic acid from cells and viruses sampled from a variety of environments may purified and expressed utilizing microfluidic techniques. In accordance with one embodiment of the present invention, individual or small groups of cells or viruses may be isolated in microfluidic chambers by dilution, sorting, and / or segmentation. The isolated cells or viruses may be lysed directly in the microfluidic chamber, and the resulting nucleic acid purified by exposure to affinity beads. Subsequent elution of the purified nucleic acid may be followed by ligation and cell transformation, all within the same microfluidic chip. In one specific application, cell isolation, lysis, and nucleic acid purification may be performed utilizing a highly parallelized microfluidic architecture to construct gDNA and cDNA libraries.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Method for analysizing amino acid
ActiveCN1749748AThe result is accurateGood reproducibilityComponent separationChromatographic separationColumn temperature
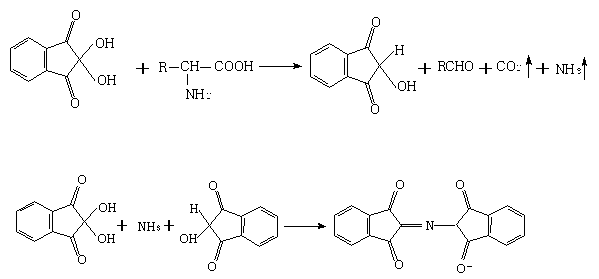
The amino acid analyzing method includes high efficiency liquid phase chromatographic separation of the 2, 4-dinitro fluoro benzene derivative of amino acid in C18 column with pH 2-3 or pH 6-7 TEAP / ACN as flowing phase; and 360nm ultraviolet detection at column temperature 35deg c. The present invention has raised separation result reproducibility, optional water phase buffering area and trimmed pH value for analysis of chromatographic column and sample, and accurate analysis result. The present invention is suitable for common HPLC analysis lab and the application range includes various amino acid analysis, indirect analysis of other matter capable of being converted into amino acid, and other matter capable of taking quantitative deriving reaction with DNFB.
Owner:TIANJIN PHARMA GROUP CORP
Multi-functional pretreatment device used for amino acid analysis
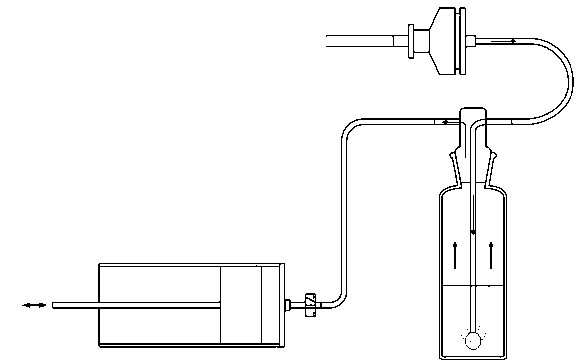
ActiveCN103063785ASimple structureIngenious designComponent separationPretreatment methodBiochemical engineering
The present invention discloses a multi-functional pretreatment device used for amino acid analysis, and a pretreatment method by using the pretreatment device. This amino acid pre-treatment device is simple in structure and is cleverly designed, and integrates a variety of pretreatment functions in one, basically has all pretreatment functions for the amino acid analysis, and is convenient and simple in operation. The pretreatment device is simple in manufacturing process and low in manufacturing cost, and has a variety of advantages as it was, so the pretreatment device is particularly suitable for popularization and application in the current art, and has a very broad market prospect. Compared with the conventional methods, the amino acid pretreatment method provided by the present invention has relative excellent repeatability, and high stability and accuracy, as well as relative good sensitivity.
Owner:DALIAN ELITE ANALYTICAL INSTR
Fmoc amino acid analysis method
InactiveCN109115899AHigh sensitivityGood repeatabilityComponent separationColumn temperatureGradient elution
The invention belongs to the technical field of amino acid analysis, and particularly relates to an Fmoc amino acid analysis method, which comprises: 1, dissolving Fmoc-Arg(Pbf)-OH in acetonitrile, wherein the concentration of the Fmoc-Arg(Pbf)-OH is 2-10 mg / mL; and 2, carrying out high performance liquid chromatography analysis by using the Fmoc-Arg(Pbf)-OH solution prepared in the step 1 as a sample, wherein the chromatographic conditions of the high performance liquid chromatography are that octadecylsilane bonded silica gel is used as a filler, Sinochrom ODS-BP is used as a a chromatographic column, gradient elution is used, the flow rate is 1.0-2.0 ml / min, the column temperature is room temperature, and the detection wavelength is 220 nm. According to the present invention, with the method, the Fmoc amino acid Fmoc-Arg(Pbf)-OH can be precisely analyzed, and the method has advantages of high sensitivity, low detection limit, simple detection method, good stability and high repeatability.
Owner:南京肽业生物科技有限公司
Amino acid analysis method
InactiveCN101915819AEasy to handleHigh detection sensitivityComponent separationWater bathsMicrofiltration membrane
The invention relates to an amino acid analysis method. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) centrifuging a proper amount of sample solution at a speed of 4,000 revolutions per minute for 10 to 30 minutes; adding a proper amount of trichloroacetic acid into supernatant and standing at the temperature of between 0 and 10 DEG C for 0.5 to 2 hours; and performing centrifugal treatment again, and filtering a proper amount of supernatant by using a 0.2 to 0.45-micron microfiltration membrane; (2) adding 1 to 3 parts of DTDPA solution into one part of sample treatment solution obtained by the step (1), mixing uniformly, and heating the mixture in a 60 to 100 DEG C water bath for 0.5 to 2 hours; and (3) absorbing one part of protection liquid obtained by the step (2), absorbing 1 to 3 parts of OPA and mixing; absorbing 1 to 3 parts of FMOC and mixing; absorbing 50 to 100 parts of water and mixing to obtain pre-column derivatization treatment liquid; and performing gradient elution and detection.
Owner:TIANJIN CHUNFA BIO TECH GRP
Detection method for protein adulteration of milk products
ActiveCN103399091AComprehensive adulteration identification methodAccurate adulteration identification methodComponent separationHigh pressureAnalytical technique
The invention provides a detection method for protein adulteration of milk products. The detection method comprises the following steps of: utilizing a liquid chromatogram detection and analysis technique to obtain amino acid high pressure liquid chromatogram fingerprint chromatogram information of standard milk sample proteins; establishing a characteristic amino acid fingerprint chromatogram database to form quality evaluation standards of the proteins of raw milk; and judging whether the proteins in a sample to be detected are adulterated or not. According to the detection method provided by the invention, amino acid analysis is introduced into research, the comprehensive and accurate protein adulteration identification method is obtained by a super-high pressure liquid chromatogram analysis method, and the recognition rate is high.
Owner:BEIJING SANYUAN FOOD
Modified tobacco mosaic virus particles as scaffolds for display of protein antigens for vaccine applications
InactiveUS20090053261A1Many of characteristicSsRNA viruses positive-senseAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsVaccinationADAMTS Proteins
Display of peptides or proteins in an ordered, repetitive array, such as on the surface of a virus-like particle, is known to induce an enhanced immune response relative to vaccination with the “free” protein antigen. The 2100 coat proteins comprising the rod-shaped capsid of Tobacco mosaic virus (TMV) can accommodate short peptide insertions into the primary sequence, but the display of larger protein moieties on the virion surface by genetic fusions to the capsid protein has not been possible. Since TMV lacks surface exposed residues compatible with commonly available linker chemistries, we employed a randomized library approach to introduce a reactive lysine at the externally located at the amino-terminus of the coat protein. We found that we could easily control the extent of virion conjugation and demonstrated stoichiometric biotinylation of the introduced lysine. To characterize this modular platform for the display of heterologous proteins, we bound a model antigen (streptavidin (SA)-green fluorescent protein (GFP), expressed and purified from plants) to the surface of TMV, creating a GFP-SA decorated virus particle. Rapid and quantitative determination of the level of TMV capsid decoration was accomplished by subjecting the complex to amino acid analysis and solving the family of linear equations relating the pmoles of each residue to the known amino acid composition of the complex components. We obtained a GFP-SA tetramer loading of 26%, which corresponds to display of approximately 2200 GFP moieties per intact virion. We evaluated the immunogenicity of GFP decorated virions in both mice and guinea pigs, and found augmented humoral IgG titers in both species, relative to unbound GFP-SA tetramer. In mice, we observed a detectable humoral immune response after only a single immunization with the TMV-protein complex. By demonstrating the presentation of whole proteins, this study expands the utility of TMV as a vaccine scaffold beyond that which is possible by genetic manipulation.
Owner:KENTUCKY BIOPROCESSING
Separation, identification and function analysis for tenebrio-molitor natural anti-oxidation octapeptide
ActiveCN106084007AHigh purityRich sourcesAccessory food factorsPeptide preparation methodsUltrafiltrationMass spectrometry
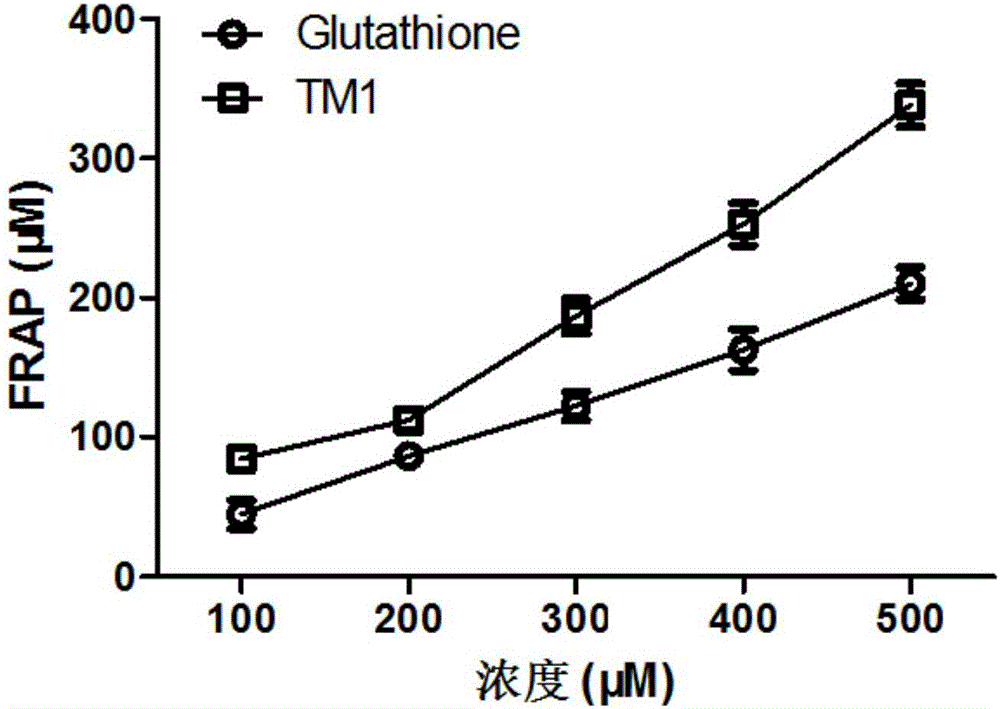
The invention relates to a separation, identification and function analysis method for tenebrio-molitor peptide. The ultrasonic treatment technology, the technology screening technology, the ultrafiltration molecule flow intercepting technology, the molecular sieve technology, the reverse-phase high pressure liquid chromatography (HPLC) column chromatography technology, the mass spectrum technology, the amino acid analysis technology and the like are adopted, and octapeptide is separated from induced tenebrio molitor, wherein the amino acid sequence of the octapeptide is SEQ ID NO:1; the anti-oxidation activity of the octapeptide is further verified, it is verified that the anti-oxidation function of the octapeptide is higher than that of glutathione, and the basis is established for development and application of natural anti-oxidation octapeptide products.
Owner:QINGDAO AGRI UNIV
Silk cultural relic fiber material identification method based on amino acid analysis
The invention discloses a silk cultural relic fiber material identification method based on amino acid analysis. The method comprises the following steps: (A) weighing 0.3-0.5mg of silk cultural relic sample in microgramme grade, putting the silk cultural relic sample in a hydrolysis test tube, dissolving the silk cultural relic sample in 0.5-1.5ml of 6NHCl, vacuumizing while sealing a test tube opening, hydrolyzing the sample for 22-24 hours at 110 DEG C; (B) drying the hydrolyzed sample by using a nitrogen blowing instrument, redissolving in 1.5-2.5ml of 10.1N HCl, freezing, drying and preserving at minus 20 DEG C till the chromatographic analysis is implemented; (C) performing ammonic acid separation and detection by using an AQC amino acid analysis packet and 2695HPLC of Waters company of America; (D) processing data, representing the content of each amino acid by utilizing relative mol percentage, when the mol ratio of the glycine to alanine to serine is 4: 3: 1, deducing that the fiber material of the silk culture relic is mulberry silk, when the mol ratio of the glycine to alanine to serine is 3: 4: 1, deducing that the fiber material of the silk culture relic is tussah silk. The variety and the content of the amino acid can be flexibly detected, and the culture relic cannot be greatly damaged since the sample quantity demand is few. The method disclosed by the invention is suitable for the identification of the silk cultural relic fiber material.
Owner:CHINA NAT SILK MUSEUM
Method for measuring main stream smoke of cigarettes by using amino acid analyzer
The invention discloses a method for measuring main stream smoke of cigarettes by using an amino acid analyzer. The analytical method which is used for measuring ammonia in the main stream smoke of cigarettes by using the amino acid analyzer and a post column derivation device thereof is established according to the selection specificity of color development reaction of ammonia and ninhydrin and by using the design principle of the amino acid analyzer and improving an amino acid analysis method, and the problem of sodion interference puzzled by ion chromatography is successfully avoided; and the method disclosed by the invention is simple, convenient, rapid and accurate and is suitable for actual analysis and detection of a cigarette smoke sample.
Owner:GUIZHOU TOBACCO SCI INST
Method for simultaneously determining active peptide and free amino acid
ActiveCN106468695ARapid determinationEfficient determinationComponent separationElutionTime-Consuming
The invention belongs to the field of analytical chemistry, which relates to a method for determining nutrients, and discloses a method for simultaneously determining active peptide and free amino acid. By adjusting the composition of a buffer, elution process and elution temperature during an amino acid analysis determinator standard determination process, a plurality of amino acid peaks and active peptide peaks are separated, and an amino acid automatic analyzer can perform one-step determination on the free amino acid and the active peptide, a method for preparing the amino acid and peptide simultaneously is established, and the disadvantages that the active peptide and a plurality of free amino acids cannot be separated, and the time consuming for testing is long by a traditional amino acid analyzer method are overcome.
Owner:SHANGHAI OCEAN UNIV
Preparation method of tobacco raffinate used for amino acid analysis
ActiveCN101344508AGood peak shapeOptimum chromatographic run timeComponent separationPost column derivatizationMass Spectrometry-Mass Spectrometry
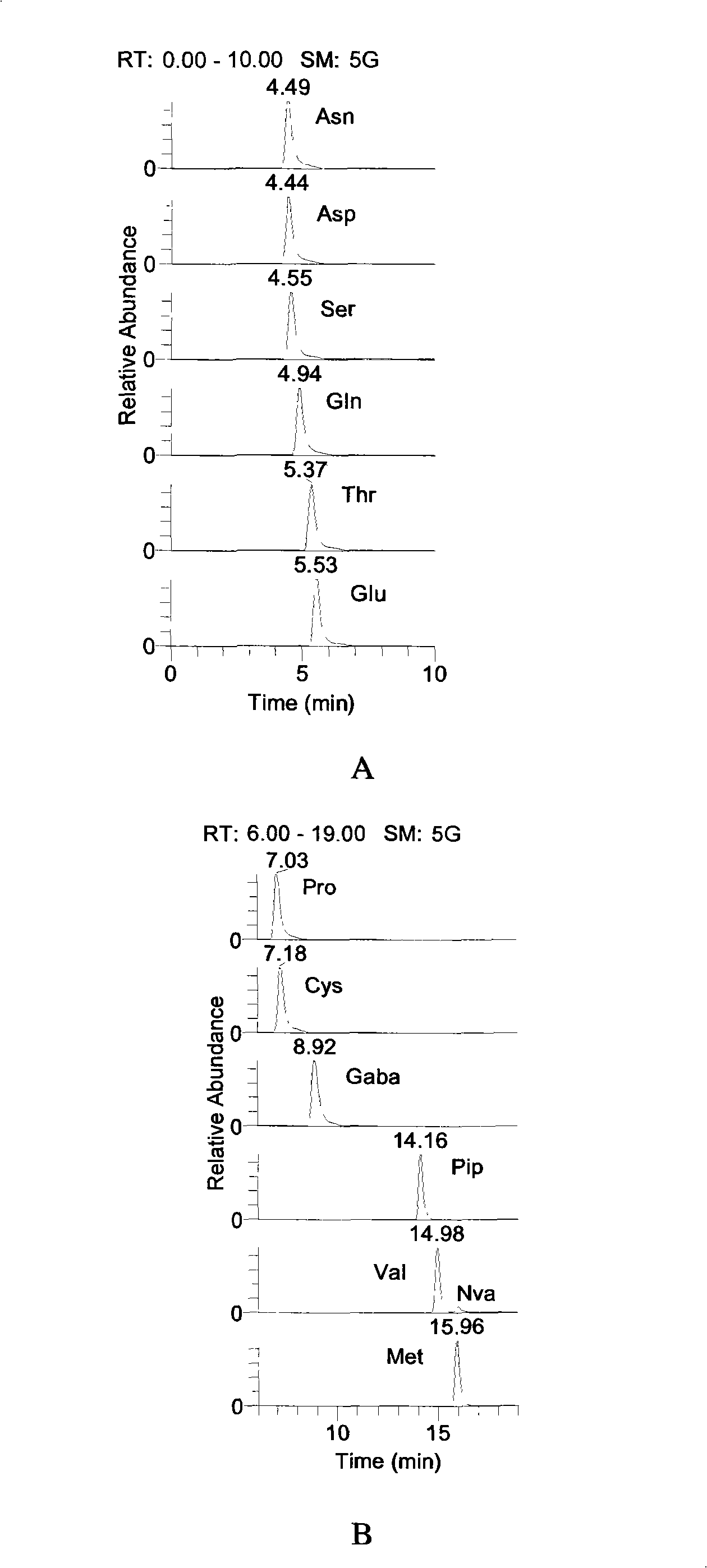
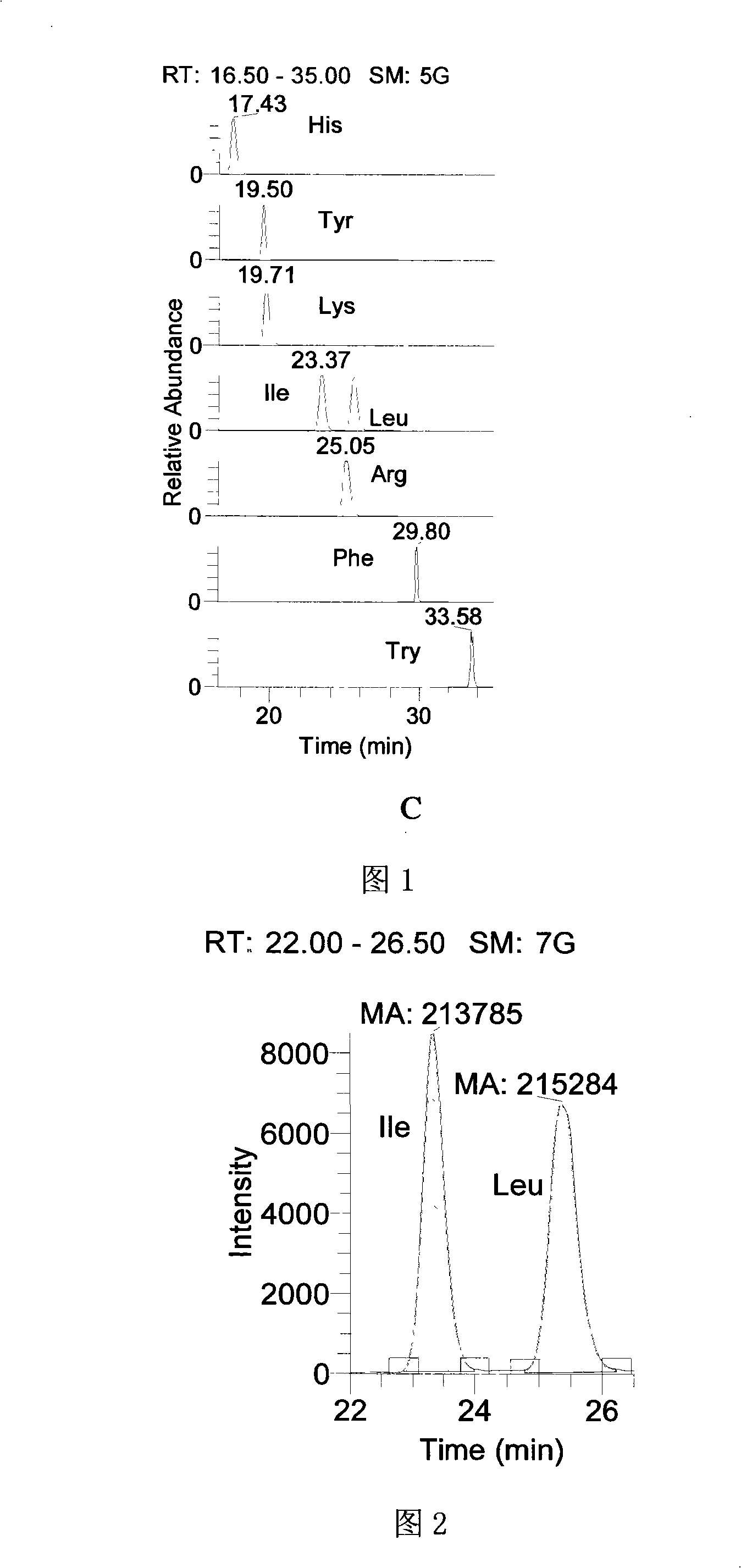
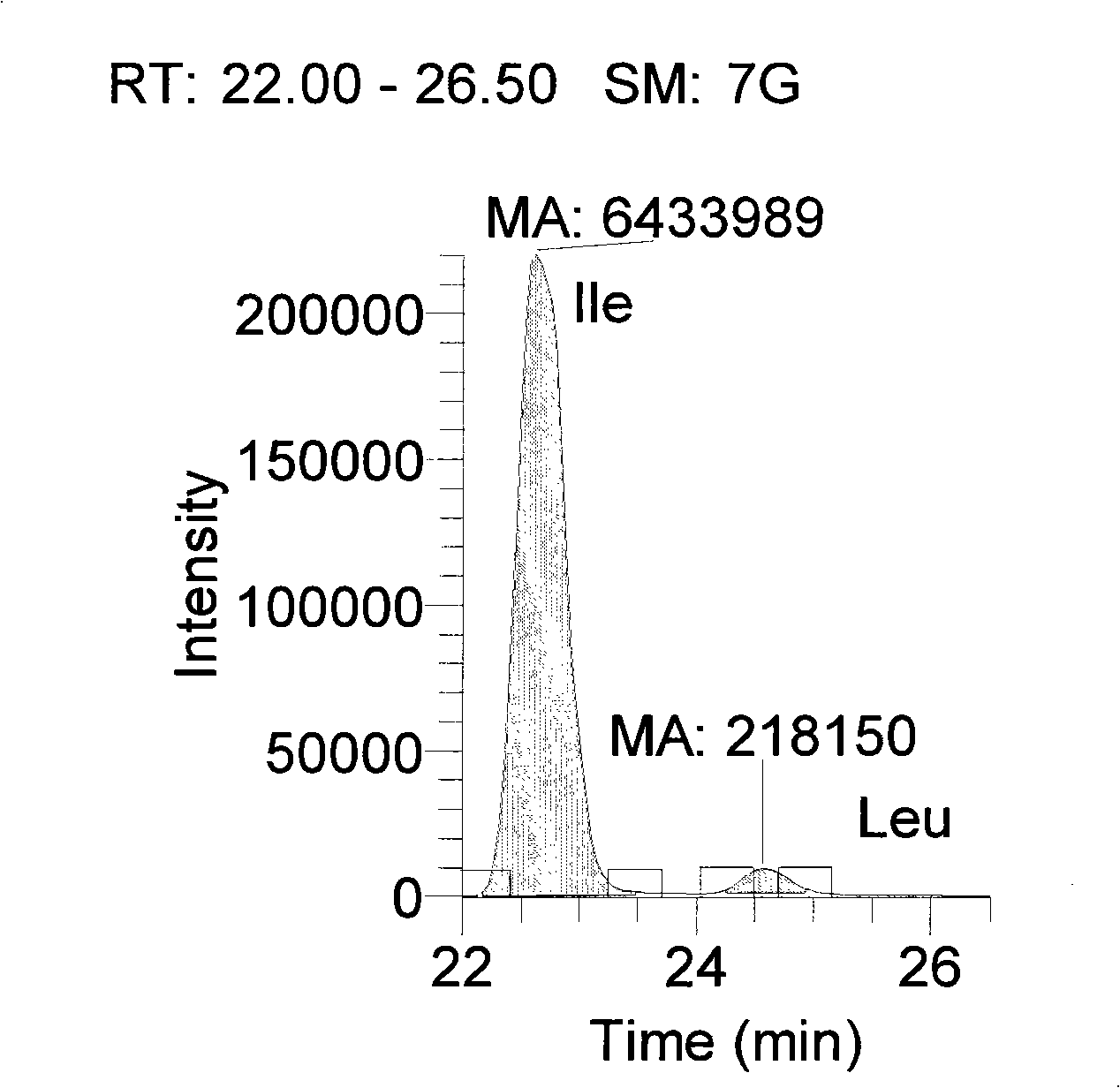
The invention discloses a preparation method of a tobacco extracting solution that is used for amino acid analysis, takes HCl solution that contains norvaline as extracting solution, extracts tobacco ashes under ultrasonic oscillation, and obtains the extracting solution by filtering. The extracting solution is combined with a coupling technique of a liquid chromatogram and an electrospray tandom mass spectrometry, thus providing a complete experimental proposal which avoids fuzzy pre-column and post-column derivatization operations of tobacco samples, obtains good chromatogram peak form and proper chromatogram running time in the experiment, further leads the isomerides Leu and Ile to reach baseline separation, and consequently obtains accurate analyzing result.
Owner:CHINA TOBACCO GUANGDONG IND
Method for determining content of binding-state glutamine in protein or protein hydrolysate
The invention discloses a method for determining the content of binding-state glutamine in protein or protein hydrolysate, belonging to the analysis technology field. In the conventional amino acid analysis, glutamine in protein or peptide molecule is converted into glutamic acid after being hydrolyzed by hydrochloric acid, only the total content of glutamic acid is displayed in an analysis result, but the content of the glutamine in the protein cannot be displayed. Based on the characteristic that binding-state glutamine in protein or peptide molecule cannot be hydrolyzed by hydrochloric acid after reaction with a special reagent (bis(trifluoacetoxy) iodobenzene) (BTI), the method is characterized in that the content of glutamic acid is determined through acid hydrolysis under the protection of the BTI reagent, and finally the content of the binding-state glutamine in protein or peptide molecule can be worked out according to the difference between the content of glutamic acid in the sample under BTI protection and the content of glutamic acid in a sample without BTI protection. The method comprises the steps of preparation of a sample to be tested, BTI protection treatment, acidolysis, derivation, amino acid chromatographic column separation, control sample preparation, and content determination. The method is simple and rapid, has high sensitivity and can timely guide the proteolysis industrial production.
Owner:郑州新威营养技术有限公司
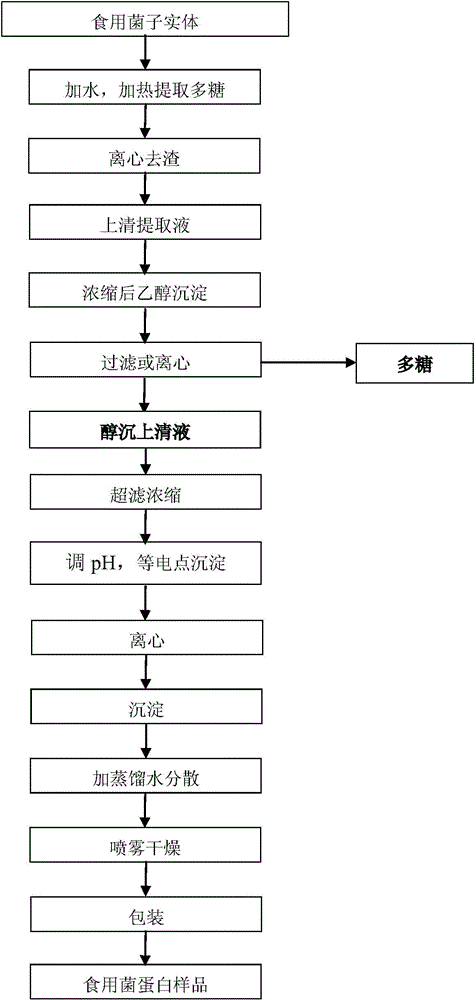
Method for recycling protein from supernatant obtained from edible fungus through polysaccharide extraction and alcohol precipitation
InactiveCN104402970AFull of nutritionReduce processing costsPeptide preparation methodsAlcoholUltrafiltration
The invention discloses a method for recycling protein from supernatant obtained from edible fungus through polysaccharide extraction and alcohol precipitation. The method comprises the following steps: taking the supernatant which is obtained from sporocarp of the edible fungus through the polysaccharide extraction and the alcohol precipitation; performing pressurization and ultrafiltration by adopting an ultrafiltration membrane with the cut-off molecular weight of 3-8 KD, wherein the pressure of the pressurization is 3-5 bar; performing the ultrafiltration to get a concentrated solution; adjusting the pH value to 4.0 to 5.0; mixing and performing the isoelectric precipitation; centrifuging; adding distilled water into the obtained protein precipitate, mixing, dispersing, spraying and drying, so as to obtain the recycled protein of the edible fungus. According to the method, the recycling rate of the protein is more than 70%, the content of the protein in samples is more than 70%, and the total sugar content is about 20%. Through the amino acid analysis, the nutrition of the recycled protein is rich. The treating cost of the waste alcohol precipitation liquid is effectively reduced when the edible fungus are processed through the polysaccharide extraction, and the benefit is increased through the integrated utilization.
Owner:庆元县金源真菌多糖制品有限责任公司
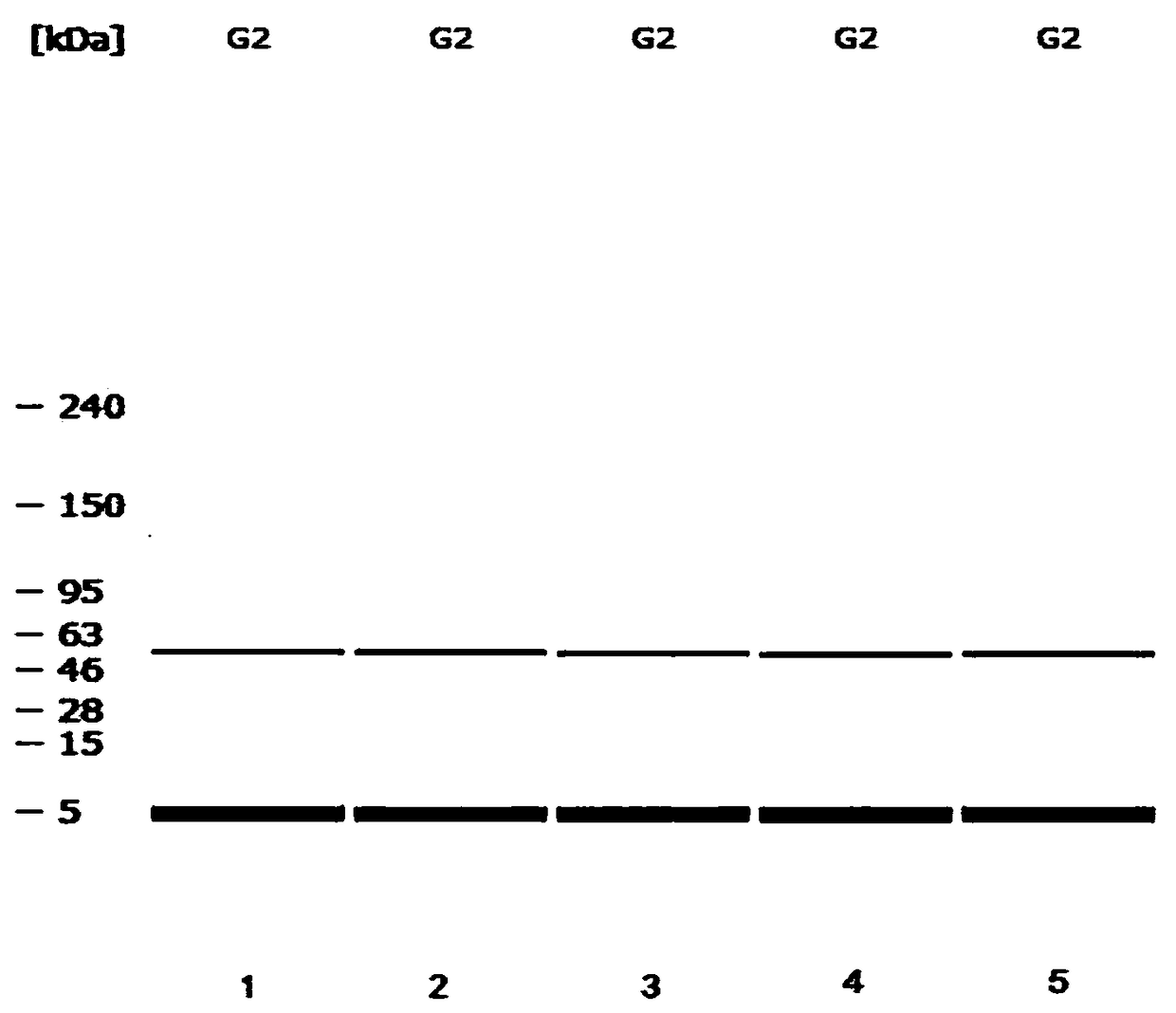
Method for fixing value of standard substance of G2 EPSPS protein solution
InactiveCN108614104AGuaranteed accuracyGuaranteed traceabilityBiological material analysisBiological testingProtein solutionGenetically modified crops
The invention discloses a method for fixing the value of a standard substance of a G2 EPSPS protein solution. The method comprises the following steps: accurately testing the content of a pure G2 EPSPS protein product by using an isotope dilution spectrum method and an amino acid analysis method, finally preparing a G2 EPSPS protein solution standard substance by using a gravimetric method-volumetric method, carrying out value measuring verification by using an ELISA (Enzyme Lined Immunosorbent Assay) method, carrying out uniformity and stability inspection, and carrying out preservation stability verification by putting a stabilizer into the standard substance. The G2 EPSPS protein standard substance prepared by using the method is particularly significant for detecting whether the G2 EPSPS protein in a glyphosate tolerant transgenic crop is reasonably expressed or not. The invention provides the method for fixing the value of the standard substance in the G2 EPSPS protein solution, and the method has good reliability, accuracy and traceability.
Owner:THE INST OF BIOTECHNOLOGY OF THE CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Regeneration method of cation exchange resin for amino acid analysis
InactiveCN104368402AReduce lossesStable conditionsIon-exchanger regenerationAqueous sodium hydroxideSodium hydroxide
The invention provides a regeneration method of a cation exchange resin for amino acid analysis. The regeneration method comprises steps of washing the cation exchange resin by ultrapure water, acetone, ultrapure water, waterless ethanol, ultrapure water, a water solution of hydrochloric acid, ultrapure water, a water solution of sodium hydroxide, and ultrapure water in sequence through an ultrasonic mode, and the supernate is discarded in each step of ultrasonic washing. When a cation exchange resin, which is regenerated by the provided method, is applied to amino acid analysis, the analyzing performance of the resin is prominently improved, and thus a good regeneration effect is achieved.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA MENGNIU DAIRY IND (GRP) CO LTD
Cell culture medium for producing anti-PD-1 monoclonal antibody and optimizing method thereof
InactiveCN106479982AHigh expressionPromote growthCulture processImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntibody expressionCell culture media
The invention provides a cell culture medium for producing anti-PD-1 monoclonal antibody and an optimizing method thereof; by applying an amino acid analysis technology, key amino acid influencing on cell growth and antibody expression is determined; on this basis, the culture medium type is determined, amino acid type and addition of the culture medium are optimized, so that the cell growth, maintenance and antibody expression effect are optimized.
Owner:深圳万乐药业有限公司
Application of phthalic acid in amino acid analysis
ActiveCN104215721AHigh detection sensitivityGood chromatographic separation performanceComponent separationChromatographic separationChromatographic column
The invention discloses application of phthalic acid in amino acid analysis. The application comprises adding the phthalic acid in a mobile phase for performing amino acid liquid chromatography-mass spectrum combined analysis, wherein concentration of the added phthalic acid is 0.005-0.1mmol / L. According to the application of phthalic acid in amino acid analysis, detection sensitivity of the amino acid can be significantly improved, and meanwhile chromatography separating effect can be improved; the application is convenient that only adding proper amount of the phthalic acid into the mobile phase is needed, and thereby analysis result of the amino acid can be significantly improved without changing other analysis conditions; in addition, experiments show that a chromatographic column and a mass spectrum ion source are prevented from being seriously damaged by using the mobile phase added with the phthalic acid for a long time, reproducibility is good, and quantitative analysis is easy to implement, and good application and promotion values are provided.
Owner:国科新研国际技术转移有限公司
Systems and methods for the analysis of protein phosphorylation
InactiveUS20030224967A1Organic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsMass Spectrometry-Mass SpectrometryProtein phosphorylation
Methods and systems of applying mass spectrometry to the analysis of peptides and amino acids, especially in the proteome setting. More particularly, the invention relates to a mass spectrometry-based method for detection of amino acid phosphorylation.
Owner:PROTANA +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com