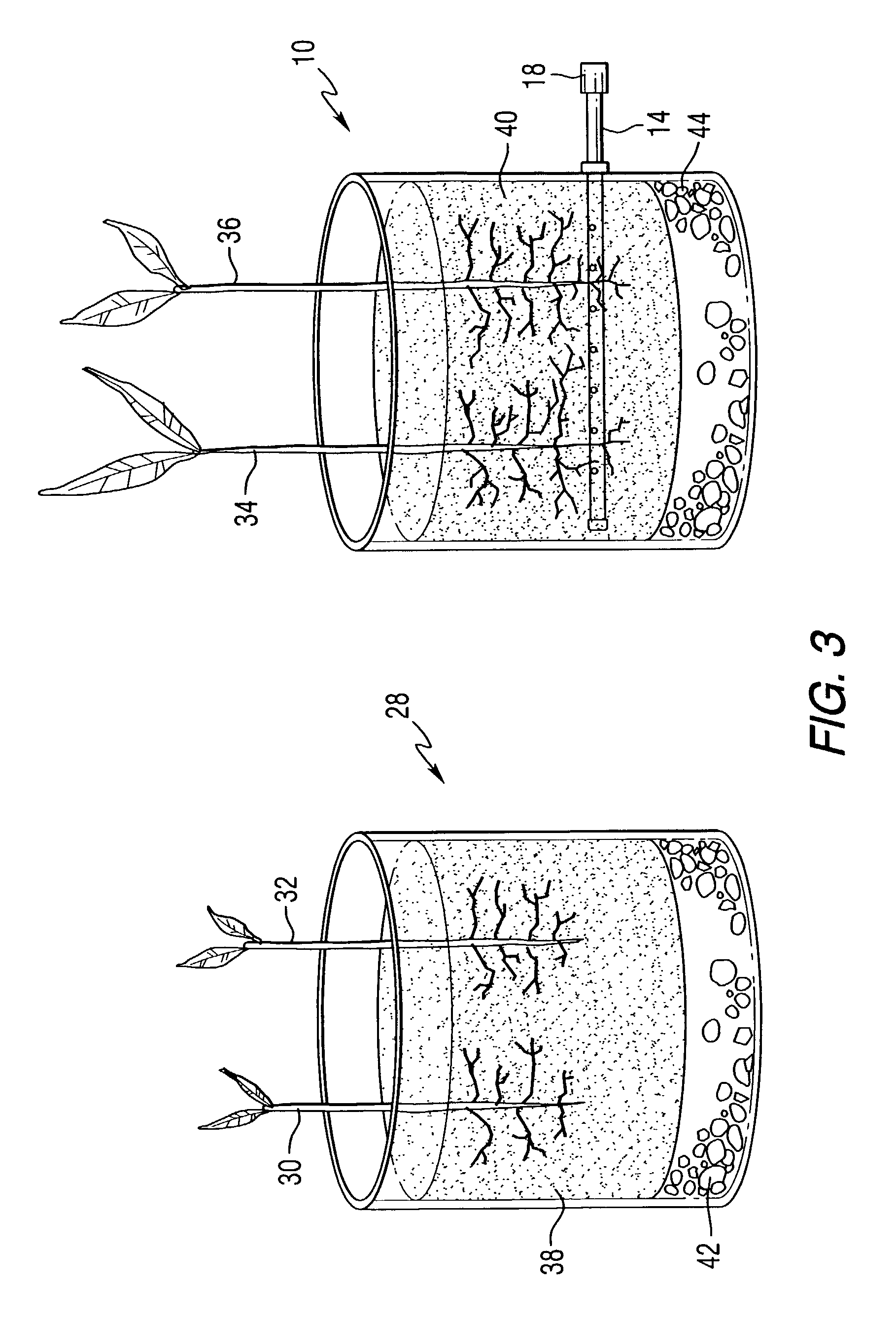
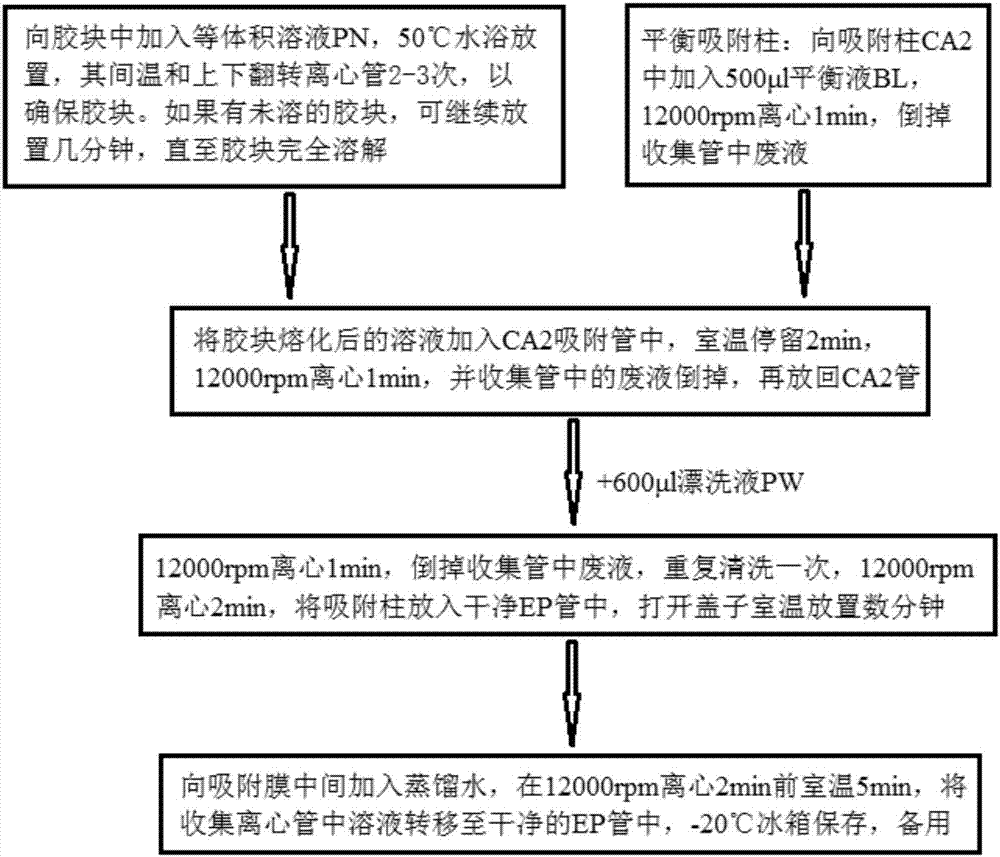
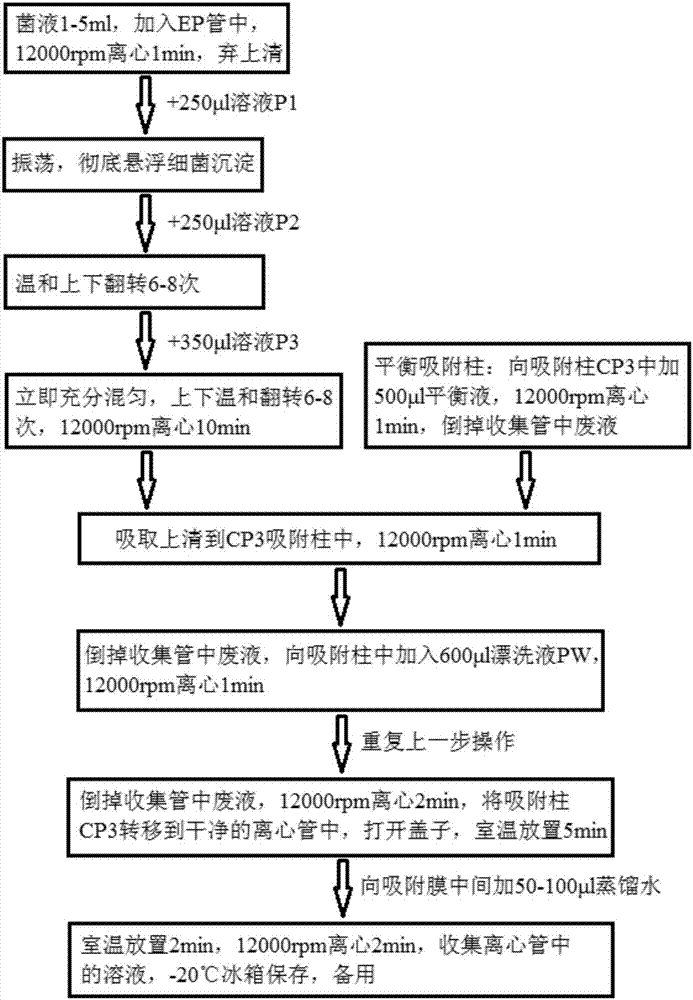
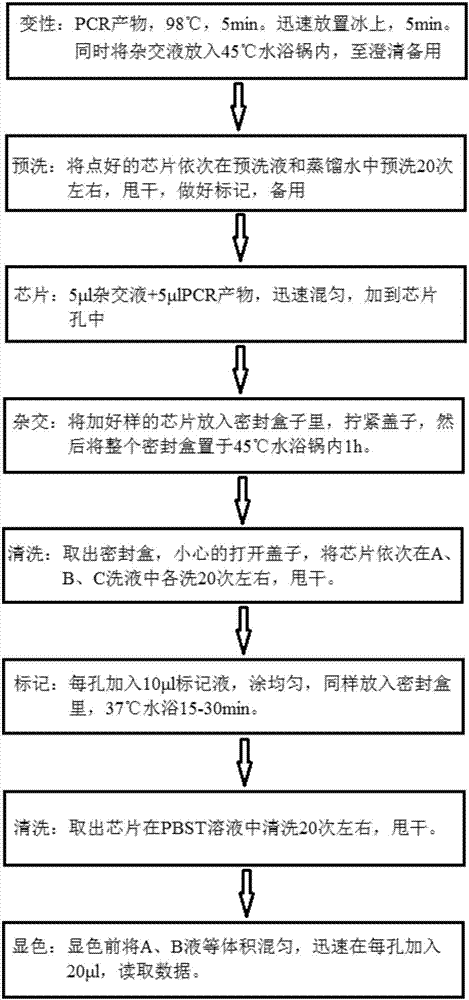
Patents
Literature
191 results about "Stenotrophomonas maltophilia" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
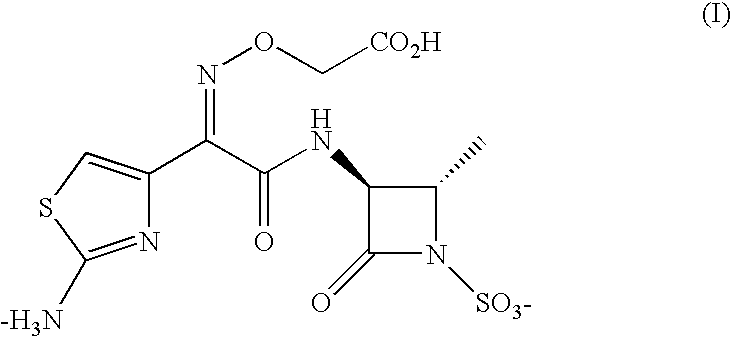
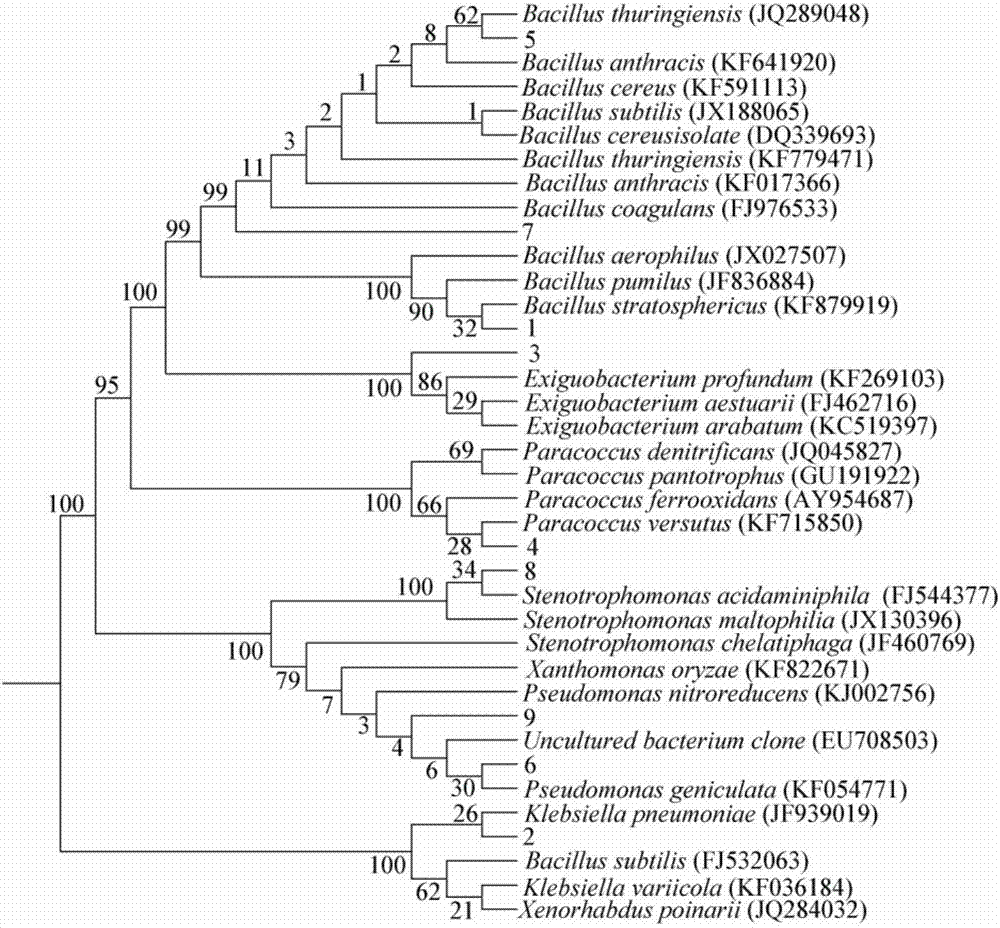
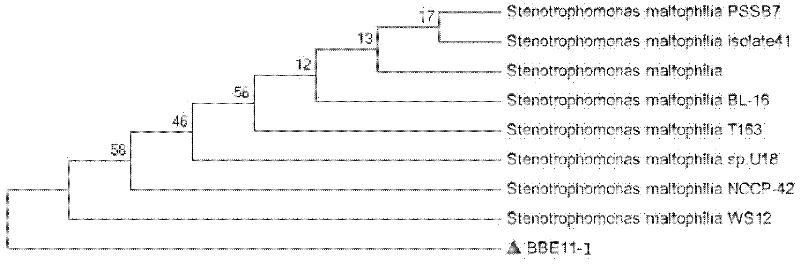
Stenotrophomonas maltophilia is an aerobic, nonfermentative, Gram-negative bacterium. It is an uncommon bacterium and human infection is difficult to treat. Initially classified as Bacterium bookeri, then renamed Pseudomonas maltophilia, S. maltophilia was also grouped in the genus Xanthomonas before eventually becoming the type species of the genus Stenotrophomonas in 1993.
Heterotrophic nitrification microbial preparation, cultivation method and use thereof
ActiveCN101302485AWide range of substratesEasy to trainImmobilised enzymesBacteriaHigh concentrationMicroorganism
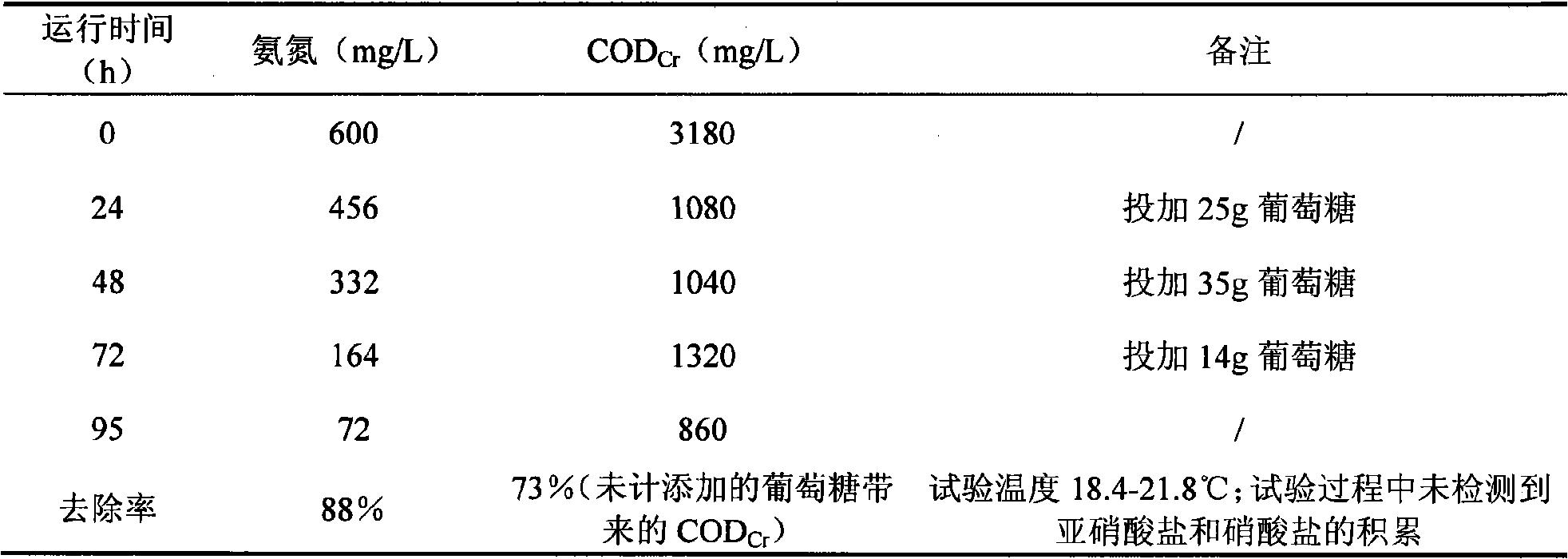
The invention belongs to the environmental microorganism field, and in particular relates to a heterotrophic nitrification microorganism agent, a method for cultivating the same, and a use of the same in culture wastewater treatment. The microorganism agent contains Stenotrophomonas maltophilias strain DN1.1 and Pseudomonas putida strain DN1.2 which have the preservation registration numbers respectively as CCTCC M 207074 and CCTCC M 207075. The microorganism agent can effectively remove ammonia nitrogen and total nitrogen in a water body, accumulates no nitrite or nitrate during denitrification, and can simultaneously remove CODCr in organic wastewater, which is applicable to the treatment of high-concentration culture wastewater. The use of the microorganism agent in treating culture wastewater is simple in process and stable in effect.
Owner:CHENGDU INST OF BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF S
Enhanced plant growth using alkane biostimulation
A method of enhancing plant growth comprises the step of introducing an alkane into a location adjacent to a plant. The alkane can be introduced intermittently, and can be combined with another gas and / or nutrients. The alkane preferably comprises a butane substrate. The butane substrate can stimulate the growth of butane-utilizing bacteria, such as Aeromonas caviae, Stenotrophomonas maltophilia, Micrococcus varians, Aureobacterium esteroaromaticum, Aureobacterium barkeri, Rhodococcus fascians, Nocardia paradoxus, Comamonas acidovorans and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. The alkane can increase the amount of heterotrophic bacteria in the location adjacent to the plant, and thereby accelerate a heterotrophic nitrification process. The butane substrate can also stimulate the growth of butane-utilizing fungi. The method can also enhance the growth protists and / or prokaryotes. A system for enhancing plant growth in accordance with the method is also disclosed.
Owner:GLOBAL BIOSCI
Kit for quickly detecting 15 pneumonia pathogenic bacteria
ActiveCN107338315AMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesBacteroidesStaphylococcus aureus
The invention discloses a kit for quickly detecting 15 pneumonia pathogenic bacteria. The kit can detect streptococcus pneumoniae, staphylococcus aureus, haemophilus influenzae, mycoplasma pneumoniae, pseudomonas aeruginosa, baumanii, enterococcus faecalis, enterococcus faecium, klebsiella pneumoniae, escherichia coli, enterobacter cloacae, stenotrophomonas maltophilia, burkholderia cepacia, legionella pneumophila and chlamydia pneumoniae which cover clinically common pneumonia pathogenic bacteria difficult to culture. 16S rDNA and specific gene sequences corresponding to the pneumonia pathogenic bacteria are detected by combining gene chips with multiple asymmetric PCR reactions, and the categories of the bacteria in a to-be-detected sample are identified in genus and species. The kit makes up for the defect that current clinical detection of pneumonia pathogenic bacteria is not in time or comprehensive and a novel detection means for early diagnosis and early treatment of patients suffering from pneumonia is provided.
Owner:GENERAL HOSPITAL OF PLA +1
Inhalable aztreonam aerosol for treatment and prevention of pulmonary bacterial infections
A method and a composition for treatment of pulmonary bacterial infections caused by gram-negative bacteria suitable for treatment of infection caused by Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Klebsiella oxytoca, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Haemophilus influenzae, Proteus mirabilis, Enterobacter species, Serratia marcescens as well as those caused by Burkholderia cepacia, Stenotrophomonas maltophilia, Alcaligenes xylosoxidans, and multidrug resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa, using a concentrated formulation of aztreonam, or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, delivered as an aerosol or dry powder formulation.
Owner:GILEAD SCI INC
Inhalable aztreonam lysinate formulation for treatment and prevention of pulmonary bacterial infections
InactiveUS7214364B2Improve stabilityHigh purityAntibacterial agentsPowder deliveryK pneumoniaeKlebsiella oxytoca
A method and a composition for treatment of pulmonary bacterial infections caused by gram-negative bacteria suitable for treatment of infection caused by Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Klebsiella oxytoca, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Haemophilus influenzae, Proteus mirabilis, Enterobacter species, Serratia marcescens as well as those caused by Burkholderia cepacia, Stenotrophomonas maltophilia, Alcaligenes xylosoxidans, and multidrug resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa, using a concentrated formulation of aztreonam lysinate delivered as an aerosol or dry powder formulation.
Owner:GILEAD SCI INC
Strain for generating keratinase and application thereof
InactiveCN101580807AExtended biodegradable rangeMild degradation conditionsBacteriaHydrolasesBiotechnologyStenotrophomonas maltophilia
The invention relates to a strain for generating keratinase and an application thereof. The strain is Stenotrophomonas maltophilia) DHHJ CGMCC No.2231 applied to the degradation of soft keratin, such as chicken feathers, pigeon feathers, cow hair, wool, hair and hard keratin, such as ox horns, goat horns, sheep hoofs and nail waste. Compared with other strains for degrading the keratin, the strain has mild fermentation conditions, is convenient to apply and can generate the keratinase with higher enzymatic activity and stability.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
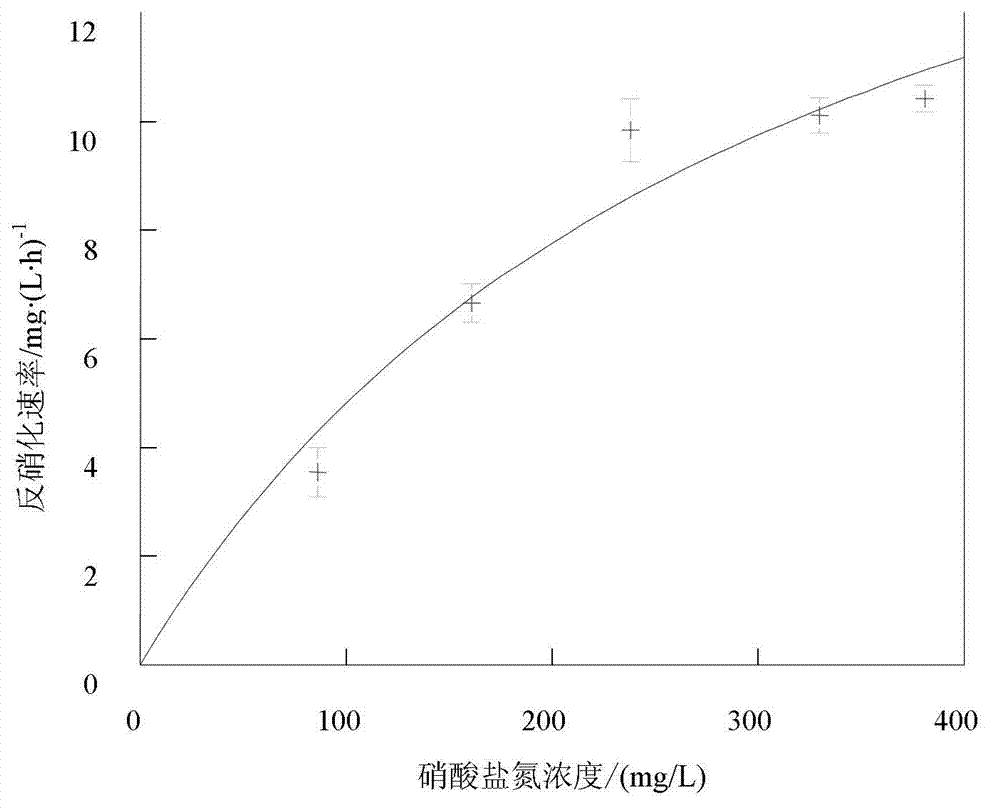
Denitrifying bacterium and application thereof
ActiveCN103074277AImprove denitrification effectImprove denitrification abilityBacteriaWater contaminantsBacteroidesStenotrophomonas maltophilia
The invention discloses a denitrifying bacterium and the application thereof. The denitrifying bacterium is named as Stenotrophomonas maltophilia CM-NRD3, which has be preserved in the China center for type culture collection (CCTCC) in Wuhan university in November 12, 2012, and has the preservation number as CCTCC NO:M2012455. The invention further provides an application of the CCTCC M2012455 to biological denitrificaion in sewage or water. The strain has strong denitrification ability on trate nitrogen and nitrite nitrogen, can remove CODcr in the sewage or the water, is suitable for various nitrogen-polluted water qualities, can also be used for partial nitrification or denitrification process, can be applicable to biological denitrificaion treatment of water with low carbon to nitrogen ratio, and is beneficial to popularization and application.
Owner:浙江至美环境科技有限公司 +2
Heterotrophic nitrification aerobic granule sludge, culture method thereof and use
ActiveCN101306870APre-fixed validCultivate successBacteriaMicroorganism based processesActivated sludgeMicroorganism
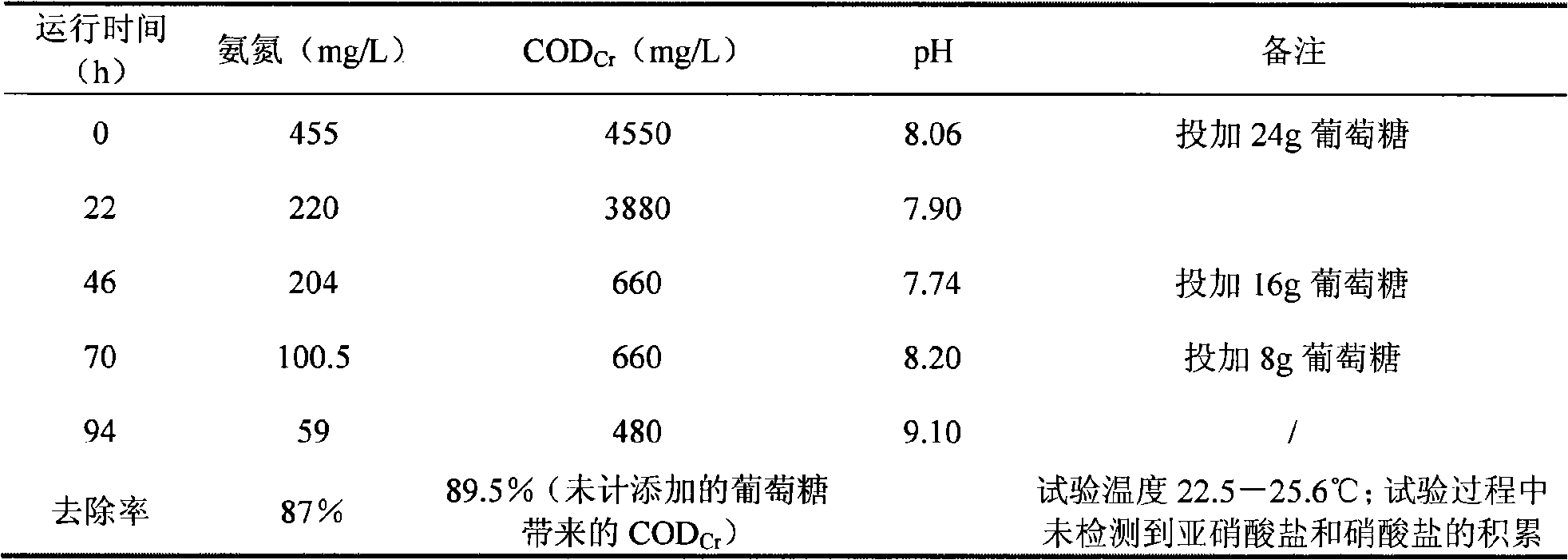
The invention belongs to the environmental microorganism field, in particular relating to heterotrophic nitrification aerobic granular sludge and a cultivation method and an application thereof. An inoculated strain of the aerobic granular sludge is stenotrophomonas maltophilia and pseudomonas putida. Activated carbon is adopted to prefix a functional strain culture, ordinary activated sludge is not inoculated, and the heterotrophic nitrification aerobic granular sludge can be cultivated. The aerobic granular sludge can effectively remove ammonia nitrogen, nitrite nitrogen, nitrate nitrogen and a mixture thereof in a water body, can also simultaneously remove CODCr in organic wastewater, is applicable to the treatment of high concentrated organic nitrogen-containing wastewater and inorganic nitrogen-containing wastewater, and does not produce the accumulation of nitrite and nitrate during the denitrification. The application of the aerobic granular sludge for wastewater treatment has simple process and steady denitrification effect.
Owner:CHENGDU INST OF BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF S
Primer probe combination and kit for combined inspection of 15 kinds of respiratory tract infection pathogens
ActiveCN107937578ARapid combined detectionGuaranteed matchMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesStreptococcus pyogenesStaphylococcus aureus
The invention provides a pathogen inspection reagent, and concretely discloses a primer probe combination and a kit for combined inspection of 15 kinds of respiratory tract infection pathogens. By aiming at specific target sequences of the gene sequence conserved region of klebsiella pneumoniae, haemophilus influenzae, streptococcus pyogenes, staphylococcus aureus, escherichia coli, chlamydia pneumoniae, mycobacterium tuberculosis, stenotrophomonas maltophilia, baumanii, mycoplasma pneumoniae, enterococcus faecalis, ligionella pneumohpillia, streptococcus pneumoniae, bacillus pyocyaneus and mycobacterium abscessus, primers and probes which do not have mutual crossed reaction are designed, so that the problem that detection probes of different pathogens can easily generate mutual influenceor interference is solved; the combination and matching of different primers and probes are ensured; the goal of simultaneously performing efficient specific inspection at the same temperature can also be achieved.
Owner:西安九安生物技术有限公司
Preparation method of polyurethane foam immobilized microbe for treatment of azo dye sewage
InactiveCN104498469AEffectively fixedLarge specific surface areaMicroorganism based processesOn/in organic carrierPolyesterStenotrophomonas maltophilia
The invention relates to a preparation method of a polyurethane foam immobilized microbe for treatment of azo dye sewage. The preparation method comprises the following steps: performing ultrasonic dispersion on polyester polyol, triethanolamine, water, methyl silicone oil, dibutyltin dilaurate and graphite felt powder after grinding together, then adding diphenylmethane diisocyanate (MDI), stirring until whitening, rapidly transferring, naturally foaming to obtain polyurethane foam, washing with distilled water for several times, then drying, preparing a lysogeny broth (LB) culture medium, putting the polyurethane foam into the LB culture medium, sterilizing together, cooling, then inoculating an immobilized microbe, namely a Stenotrophomonas maltophilia strain T-8, performing shaking culture and washing with the distilled water for several times for preparation. The polyurethane foam with the immobilized microbe prepared by the preparation method provided by the invention has a macroporous reticular structure, high specific surface area and hydroxyl and other groups, and can effectively immobilize the microbe and greatly improve the effect of decoloring azo dye.
Owner:SHAANXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Stenotrophomonas maltophilia for generating keratinase and application of stenotrophomonas maltophilia
ActiveCN102329751AEfficient degradationEasy to handleBacteriaBiochemical fibre treatmentStenotrophomonas maltophiliaNitrogen source
The invention discloses stenotrophomonas maltophilia for generating keratinase and an application of stenotrophomonas maltophilia. A strain for generating keratinase can efficiently degrade feathers within 24 hours, the activity of the keratinase subjected to fermentation and primary optimization can reach 150U / mL. Multiple kinds of amino acids can be produced after the degraded feathers are subjected to amino acid analysis, and the degraded feathers can replace grain crops such as soybeans and the like to be used as a main nitrogen source of feeds. Meanwhile, a fermenting enzyme solution of the stenotrophomonas maltophilia has a better treatment effect on wool. The stenotrophomonas maltophilia for generating the keratinase, screened in the invention, has better application prospects in the industries of feeds and textiles.
Owner:XINYI HANLING BIO ENG
Method for preparing levodopa by virtue of enzymic method
ActiveCN104726513ARich sourcesReduce manufacturing costMicroorganism based processesFermentationBiotechnologyStenotrophomonas maltophilia
The invention discloses a method for preparing levodopa by virtue of an enzymic method. The method comprises the following steps: picking up an annular stenotrophomonas maltophilia strain slant for inoculation into a seed culture medium for culturing, thereby obtaining a primary seed liquid; inoculating a fermentation culture medium with the primary seed liquid at the inoculum size of 3-10% for fermentation culturing, centrifuging after the fermentation is ended and collecting bacterial cells; and adding tyrosine and the bacterial cells to a buffer solution to have an enzymatic reaction under the conditions of 18-30 DEG C and the pH of 5.0-6.0, thereby converting the tyrosine into the levodopa. According to the method, due to the resting cell transformation technology, and the preferred intermittent weak ventilation technology, adopted in the transformation process, the catalytic efficiency of the enzyme is improved; the concentration of the levodopa is 27g / L and the molar transformation rate of the tyrosine is above 99%; and besides, the method is mild in conditions, high in enantio-selectivity and free from racemization effect, is more suitable for industrial production, and has remarkable economic benefit and industrial application value.
Owner:SHANDONG YANGCHENG BIOLOGY TECH CO LTD
Nitrogen fixation stenotrophomonas maltophilia C4Y41 strain and application thereof
InactiveCN101781628APromote growthLarge biomassBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMicroorganismPodocarpus
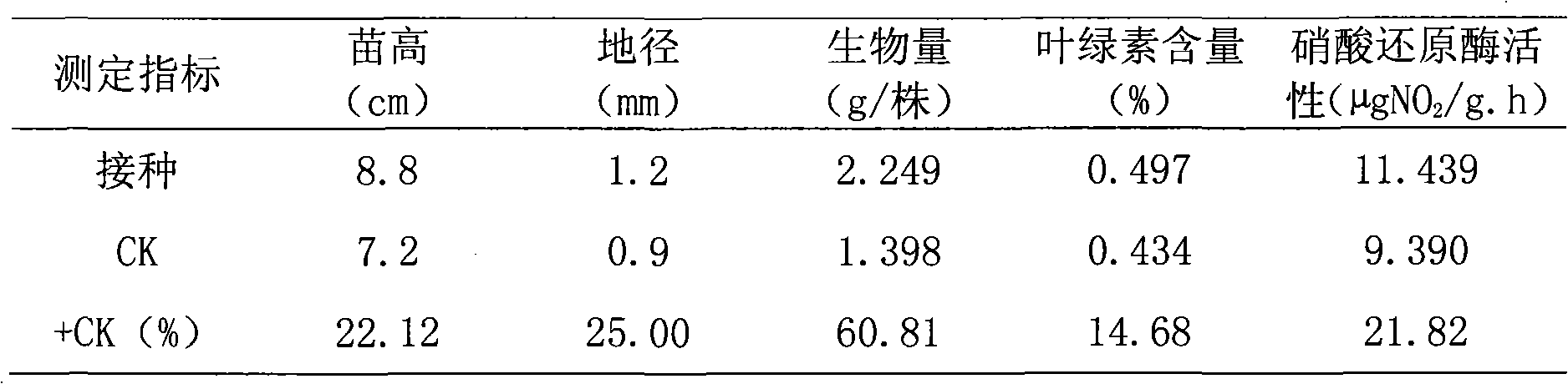
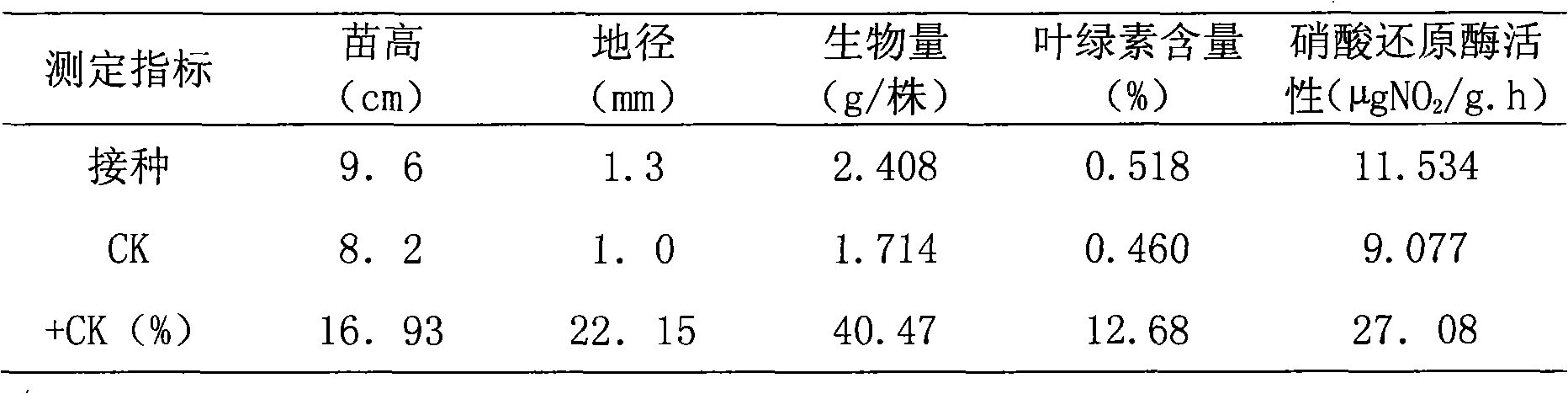
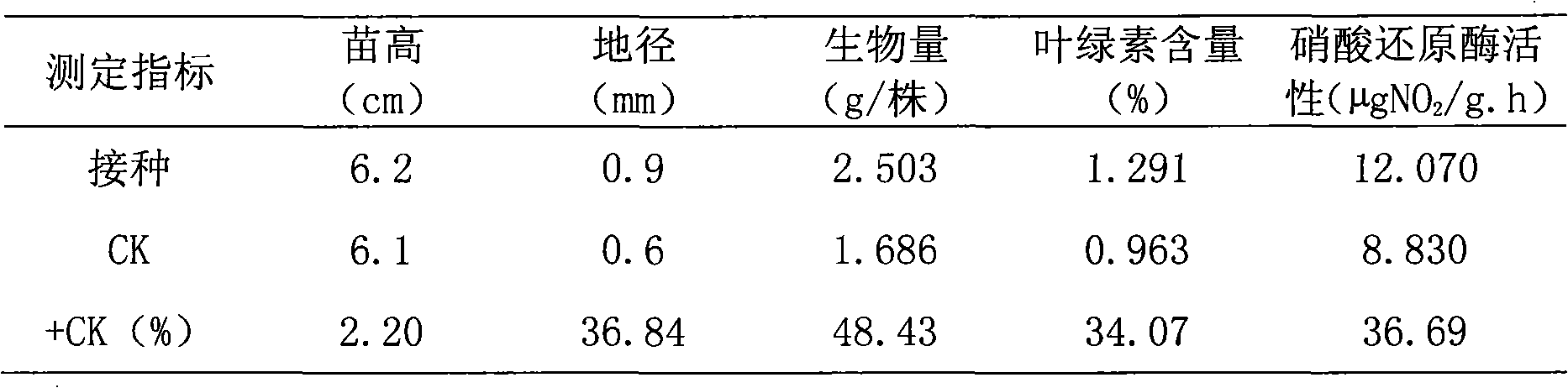
The invention relates to a nitrogen fixation stenotrophomonas maltophilia C4Y41 strain and an application thereof. The strain is stored in the common microorganism center of China microorganism strain management committee and has a storage number of CGMCC No.3349. The strain is a new nitrogen fixation strain obtained by applying a general microorganism-separating and purifying method on podocarpus root nodules, has the nitrogen fixation enzyme activity of 0.019-0.030nmol*g-1*h-1 and enables the height of inoculated eucalyptus seedlings to increase by 2.20-22.12 percent, the ground diameter to increase by 22.15-36.84 percent, the average biomass to increase by 40.47-60.81 percent, the chlorophyll content to increase by 12.68-34.07 percent and the nitrate reductase activity to increase by 21.82-36.69 percent. The strain can be applied as a biological fertilizer for stimulating the growth of the eucalyptus seedlings.
Owner:广西绿满地农资有限公司
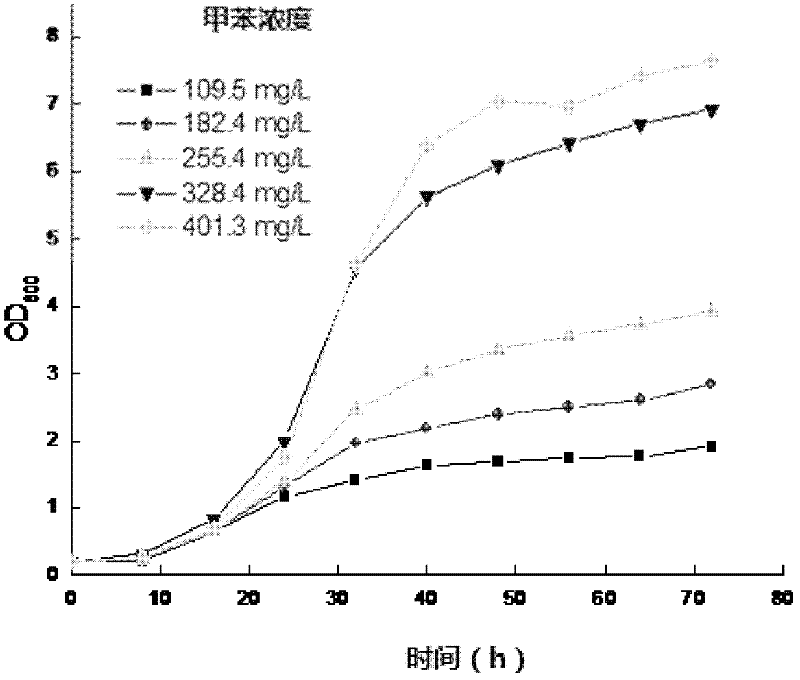
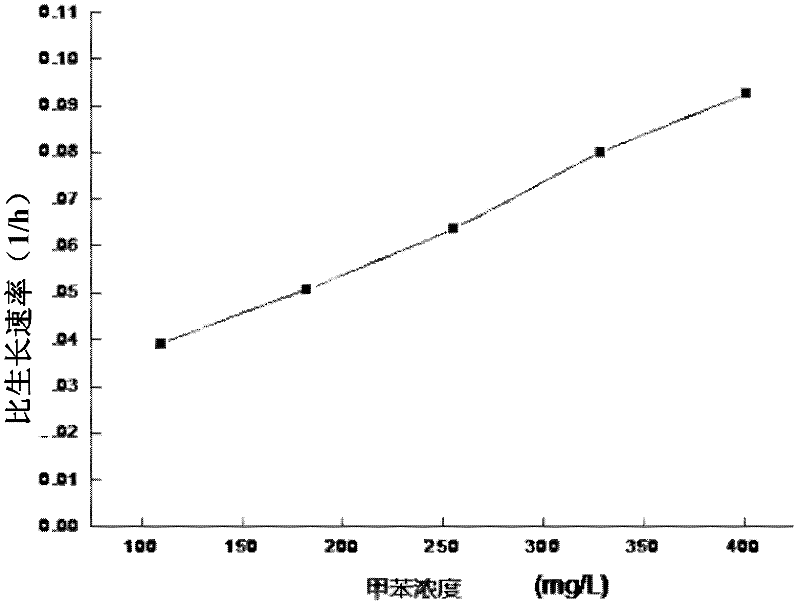
Stenotrophomonas maltophilia for degrading high-concentration methylbenzene and application of stenotrophomonas maltophilia
ActiveCN102250788APromote degradationUse strongBacteriaMicroorganism based processesHigh concentrationStenotrophomonas maltophilia
The invention discloses a Stenotrophomonas maltophilia for degrading high-concentration methylbenzene and application of the Stenotrophomonas maltophilia. The Stenotrophomonas maltophilia is named as the specifications and has the collection number of CGMCC (China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center) No.4839. The invention also discloses a method for degrading methylbenzene by using the Stenotrophomonas maltophilia with the collection number of CGMCC No.4839. The Stenotrophomonas maltophilia with the collection number of CGMCC No.4839 can degrade the methylbenzene at high concentration, can grow by taking the methylbenzene as the unique carbon source and energy, and has high capacity of degrading, utilizing and tolerating the methylbenzene.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Inhalable aztreonam lysinate formulation for treatment and prevention of pulmonary bacterial infections
A method and a composition for treatment of pulmonary bacterial infections caused by gram-negative bacteria suitable for treatment of infection caused by Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Klebsiella oxytoca, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Haemophilus influenzae, Proteus mirabilis, Enterobacter species, Serratia marcescens as well as those caused by Burkholderia cepacia, Stenotrophomonas maltophilia, Alcaligenes xylosoxidans, and multidrug resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa, using a concentrated formulation of aztreonam lysinate delivered as an aerosol or dry powder formulation.
Owner:GILEAD SCI INC
In-situ bioremediation preparation and remediation method for chlorothalonil contaminated soil
ActiveCN106591166ASolve serious dangerAddressing food safetyFungiBacteriaPhotochemical degradationIn situ bioremediation
Relating to the soil remediation field, the invention discloses a preparation for in-situ remediation of chlorothalonil contaminated soil. The preparation contains fungi and / or bacteria with chlorothalonil degradation ability. The fungi can be at least one of Aspergillus niger, rhizomucor variabilis and Cunninghamella bertholletiae, and the bacteria can be at least one of Burkholderia zhejiangensis, pseudomonas aeruginosa and Stenotrophomonas maltophilia. According to the invention, the provided preparation is employed for in-situ bioremediation of chlorothalonil contaminated soil, not only overcomes the problems that photochemical degradation is easily limited by illumination conditions and can easily cause secondary chemical reagent pollution to arable land, at the same time makes full use of fungi and / or bacteria for catabolism of chlorothalonil residual in soil, thus solving the problem that high residual chlorothalonil in soil severely endangers food safety. At the same time, the micro-ecology of soil is improved, so that soil can recover farming ability more rapidly. Also, the method is low in cost, thus having broad application prospects.
Owner:粮华生物科技(北京)有限公司
Fecal deodorizing microorganism combining bacteria and method for producing organic fertilizer using same
InactiveCN101845394AReduce generationGood deodorizing effectFungiBio-organic fraction processingMicroorganismFeces
The invention discloses fecal deodorizing microorganism combining bacteria and a method for producing an organic fertilizer using same. The combining bacteria comprise the following components: Mucor circinelloides (Mucor Circinelloides), Bacillus pumilus (Bacillus Pumilus), and Stenotrophomonas maltophilia (Stenotrophomonas maltophilia), the number ratio of which is 1:0.9-1.2:0.9-1.2. The manure and straws are used as raw materials, and the microorganism combining bacteria are fermented to produce the organic fertilizer. In the process of producing the organic fertilizer by the method, the odor generation can be obviously reduced in the compositing process, and the method has simple process, low cost and easy promotion.
Owner:INST OF ANIMAL HUSBANDRY & VETERINARY MEDICINE ANHUI ACAD OF AGRI SCI +1
Stenotrophomonas maltophilia DS4
InactiveCN102586160AImprove growth abilityEfficient removalBacteriaWater contaminantsHigh concentrationStenotrophomonas maltophilia
The invention discloses Stenotrophomonas maltophilia DS4. The Stenotrophomonas maltophilia DS4 is preserved in China Center for Type Culture Collection, and the preservation number is CCTCC NO:M2010147. The Stenotrophomonas maltophilia DS4 has a strong growing ability and a good ability of removing organic pollutants from saponin wastewater in high-concentration sulfate ion environments; and the strain can remove chemical oxygen demand (COD) at the concentration of 2,930mg / L from the saponin wastewater within 72 hours, and the removal efficiency reaches 62.34 percent. The invention provides auseful bacterial source for degrading high-concentration organic pollutants in the saponin wastewater, broadens the application of functions of Stenotrophomonas maltophilia, and has relatively high application value.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF GEOSCIENCES (WUHAN)
Method for quickly identifying bloodstream infection pathogenic bacteria
InactiveCN102453752ARapid determinationEfficient determinationMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesBacteroidesKlebsiella oxytoca
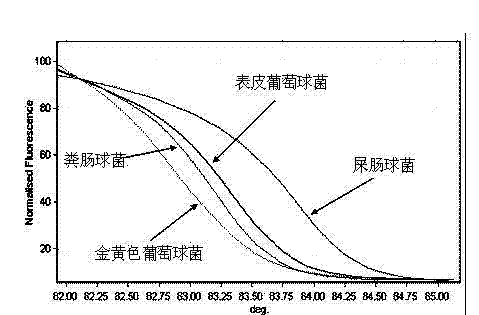
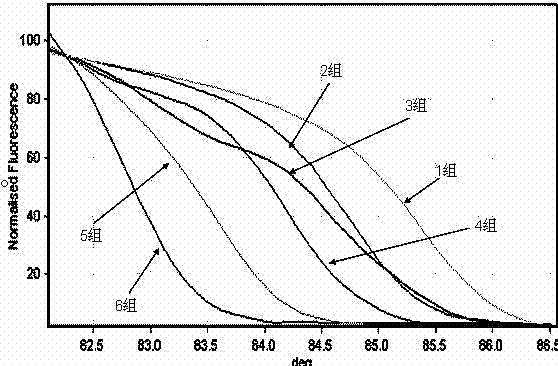
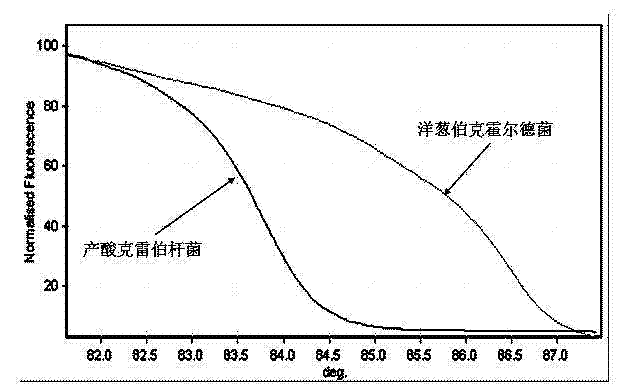
The invention belongs to the field of examination of microorganisms, and relates to a method for quickly identifying bloodstream infection bacteria by a high-resolution fusion curve method. The method comprises the following steps of: performing smear gram staining on a blood culture positive culture flask to distinguish negative bacteria and positive bacteria; selectively amplifying different 16S fragments for the negative bacteria and the positive bacteria; and analyzing by the high-resolution fusion curve method. Common bloodstream infection pathogenic bacteria comprise staphylococcus aureus, staphylococcus epidermidis, enterococcus faecalis, enterococcus faecium, Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, acinetobacter baumannii, pseudomonas aeruginosa, enterobacter cloacae, Serratia marcescens, Klebsiella oxytoca, acinetobacter lwoffii, enterobacter aerogenes, stenotrophomonas maltophilia and burkholderia cepacia. By the method, the common bloodstream infection pathogenic bacteria can be measured quickly, efficiently and accurately, so that strong evidences are provided and precious time is striven for subsequent treatment.
Owner:AFFILIATED HUSN HOSPITAL OF FUDAN UNIV +1
Application of Stenotrophomonas maltophilia DS4 for degrading organic pollutants in saponin waste water
InactiveCN102583780AImprove growth abilityEfficient removalNature of treatment waterBiological water/sewage treatmentHigh concentrationChemical oxygen demand
The invention discloses the application of Stenotrophomonas maltophilia Hilia DS4 for degrading organic pollutants in saponin waste water. The Stenotrophomonas maltophilia Hilia DS4 strain is preserved in China Center for Type Culture Collection with preservation number CCTCC No. M2010147. The Stenotrophomonas maltophilia Hilia DS4 strain has strong capability of growing in high-concentration sulfate ion environments and good ability of removing organic pollutants from saponin waste water. The strain can reduce the COD (chemical oxygen demand) of the saponin waste water by 2930 mg / L within 72 hours, with high removal efficiency up to 62.34%. The invention provides a useful bacterial source for degrading high-concentration organic pollutants in saponin waste water, increases the application range of Stenotrophomonas maltophilia Hilia, and has a high application value.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF GEOSCIENCES (WUHAN)
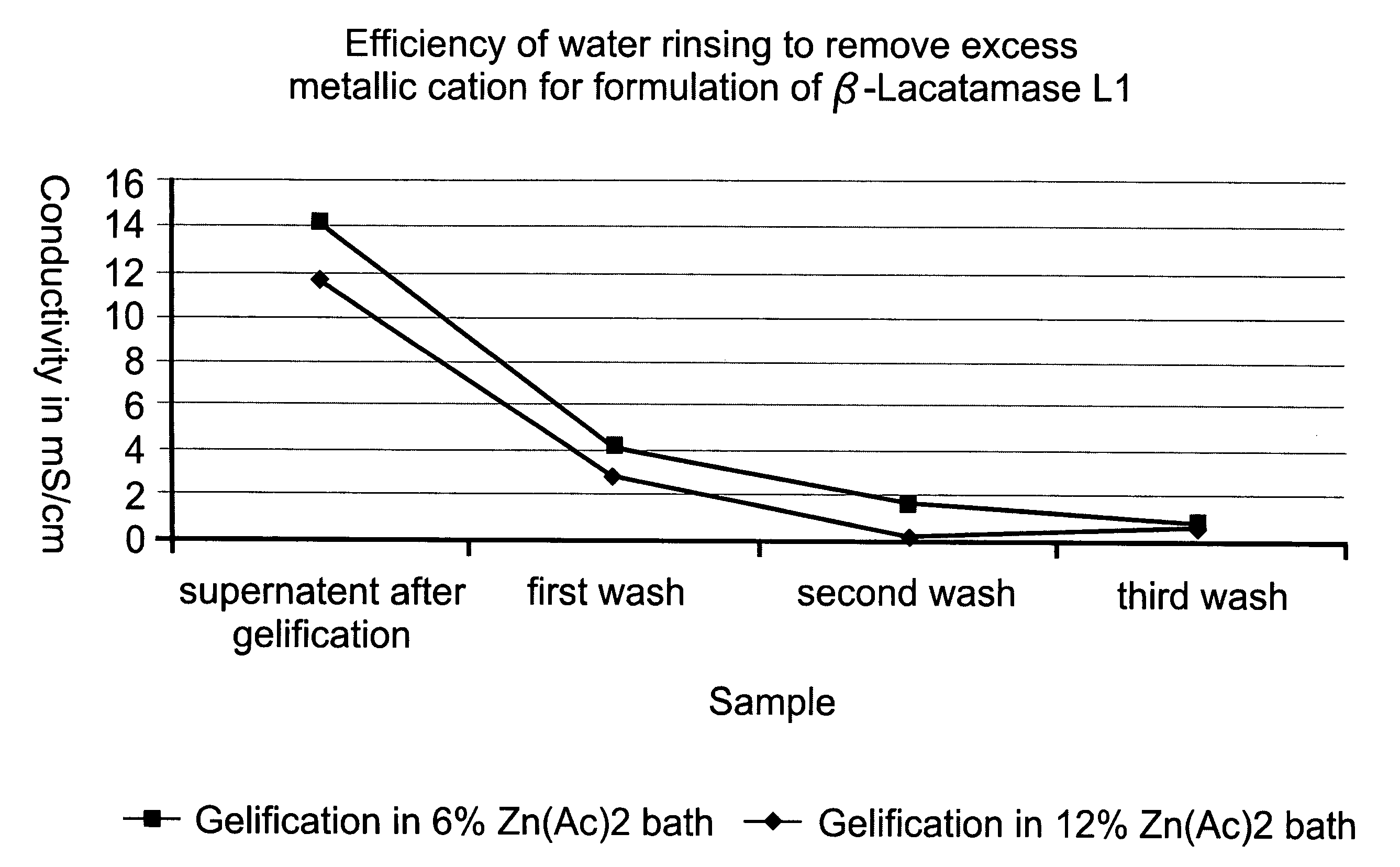
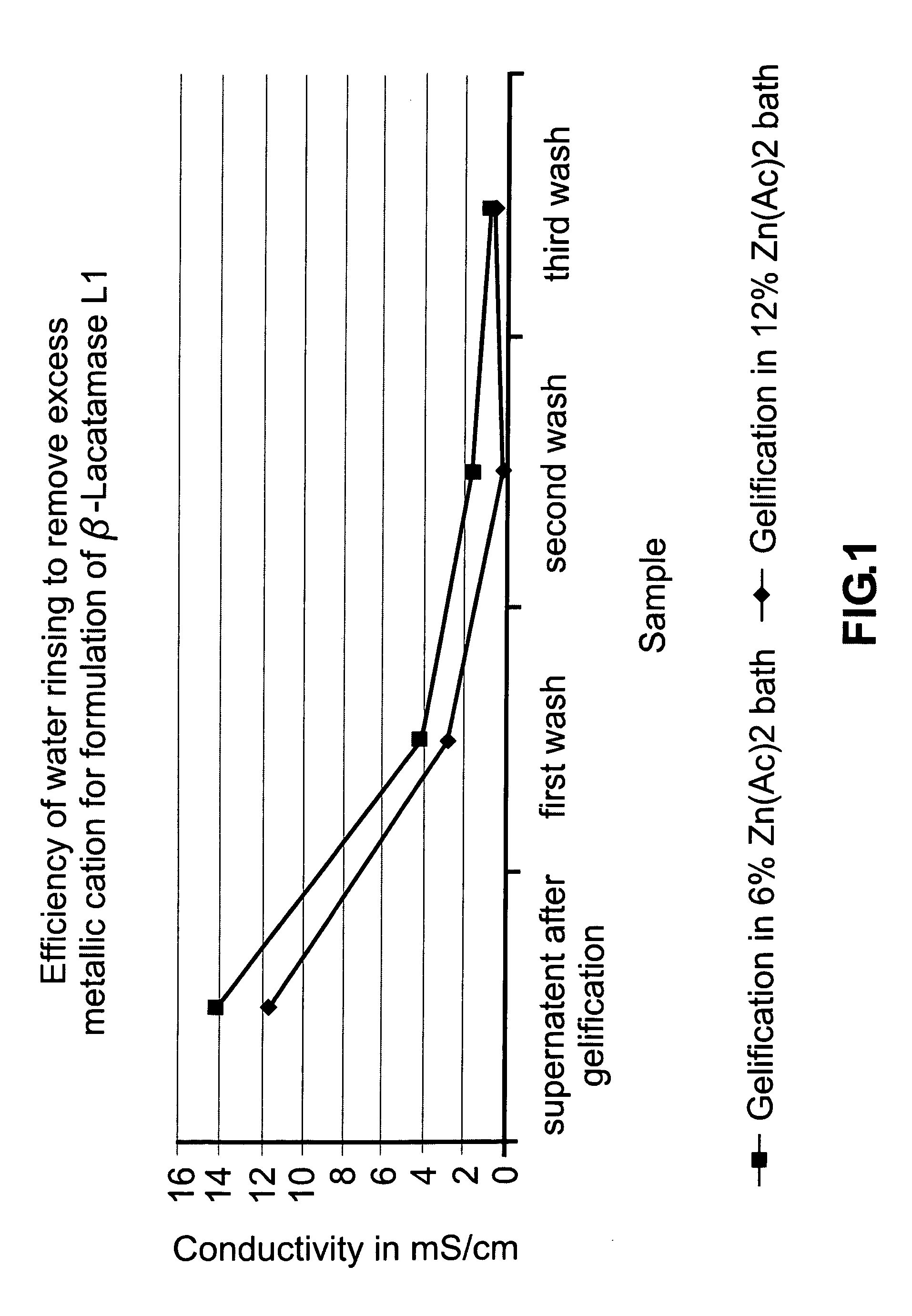
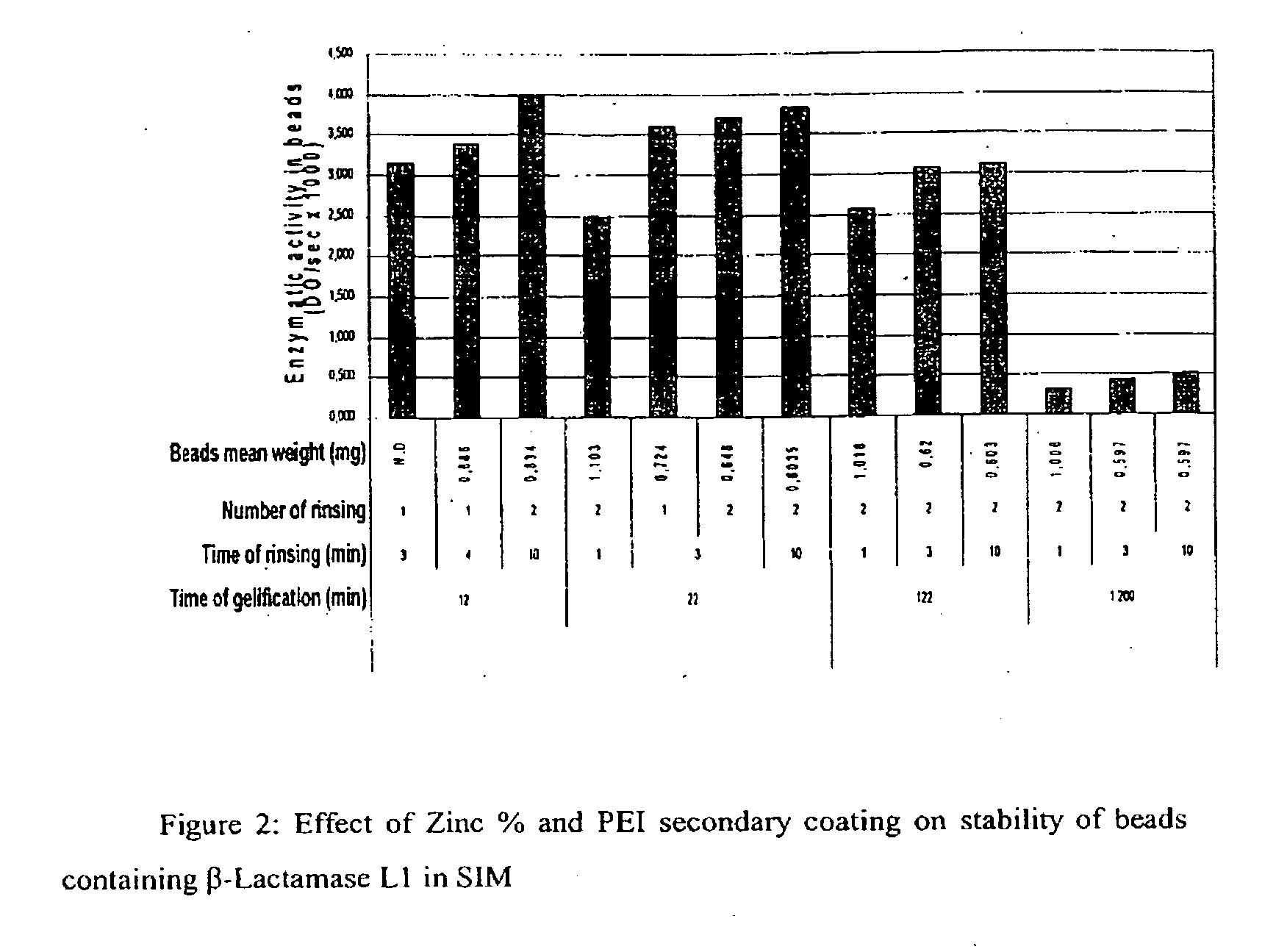
Colonic delivery of metallo-dependent enzymes
Drug delivery systems for delivering agents capable of reducing the quantity of residual antibiotics reaching the colon following oral or parenteral antibiotic therapy, and for delivering metallo-dependent enzymes, and methods of using the drug delivery systems, are disclosed. The drug delivery systems include pectin beads that encapsulate the active agent (which can be a metallo-dependent enzyme), where the pectin is crosslinked with zinc or any divalent cation of interest and the pectin beads are coated with Eudragit®-type polymers. The drug delivery systems are orally administrable, but can deliver the active agents to the colon. In some embodiments, they can administer the agents to various positions in the gastro-intestinal tract, including the colon. One metallo-dependent enzyme is the β-lactamase L1 from Stenotrophomonas maltophilia, and agents that inactivate macrolide, quinolone, fluoroquinolone or glycopeptide antibiotics can also be used. The delivery of the active agent can be modulated to occur at various pre-selected sites of delivery within the intestinal tract by gelling / crosslinking a mixture of the active agent, such as a metallo-dependent enzyme, and pectin, with divalent metallic cations such as Ca+2 or Zn+2. A stable metallo-dependent enzyme formulation can be delivered to the lower intestine or colon. The use of zinc cations to crosslink the pectin is particularly preferred when specific metallo-dependent enzymes, which are Zn2+ dependent, could interact with other cationic species if they were used to gel the pectin beads and thus adversely affect the activity of such metallo-dependent enzymes.
Owner:ASSISTANCE PUBLIQUE HOPITAUX DE PARIS +2
Stenotrophomonas maltophilia and application thereof
ActiveCN107523518AImprove diffusivityStrong green fragranceTobacco treatmentBacteriaMicroorganism preservationMicroorganism
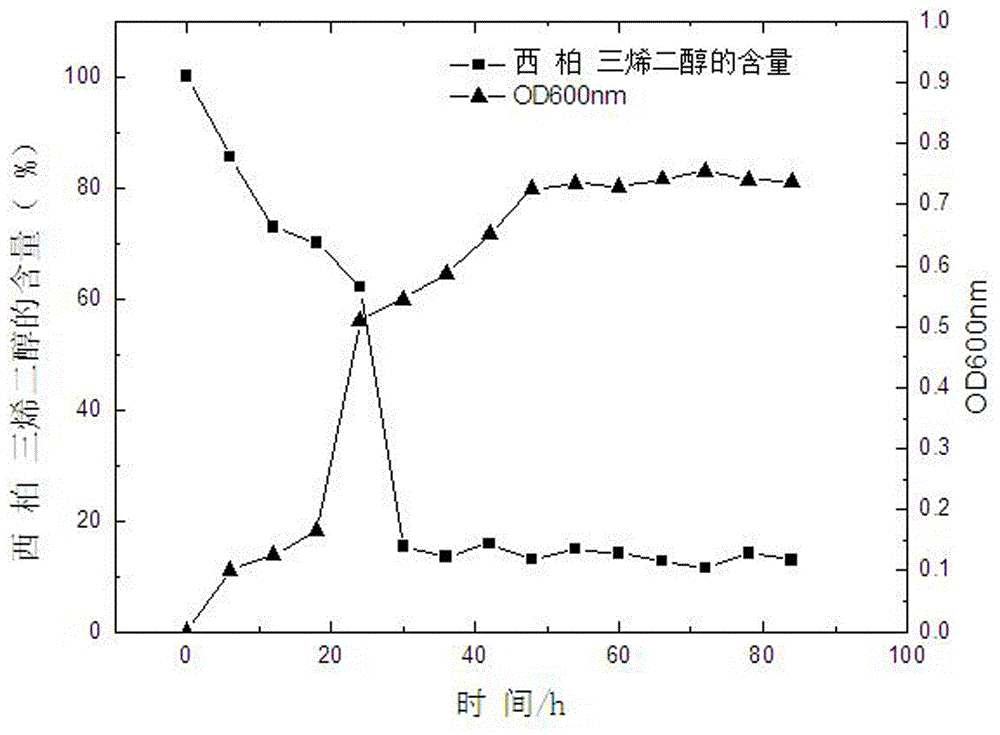
The invention belongs to the field of biological engineering and relates to a strain, in particular to a stenotrophomonas maltophilia and an application thereof. The stenotrophomonas maltophilia is preserved in the general microbiological center of Chinese microorganism preservation management committee on Mar. 20th, 2017 with the preservation number of CGMCC No. 13905. The stenotrophomonas maltophilia is used for degrading 2,7,11-westpac triene-4,6-diol and is applied in fermentation of a reconstituted-tobacco concentrate. During aging of tobacco leaves, the stenotrophomonas maltophilia can degrade 2,7,11-westpac triene-4,6-dialcohols into aromatic substances, and tobacco aroma is increased; in application of the reconstituted-tobacco concentrate, taste of reconstituted tobacco can be improved by improving aroma quality after conversion, increasing volume of aroma and reducing stimulation.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIVERSITY OF LIGHT INDUSTRY
Bacterial agent capable of killing nematode and application thereof
The invention relates to nematocide and its appliances thereof, belonging to the field of biological pesticide technique. Said nematocide is acquired through the sequence of culturing preparing strain in test tube, fluid enlargement culture and extracting nematocide active component, and said preparing strain is as follows: germinated barley-acceptable single cell bacteria stenotrophomonas maltophilia G6 which is preserved in microbe bacterial preservation management commission common microbe center of China with preservation data: 2005-10-31 and preservation registration number CGMCC No: 1522. The main mechanism of action of G6 strain is to break up body wall of worm through producing enzyme and poisoning worm, especially pine beam worm, and could be used to prepare biological nematocide. The production in said invention is characterized on high poison ability, which has better potential utility.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
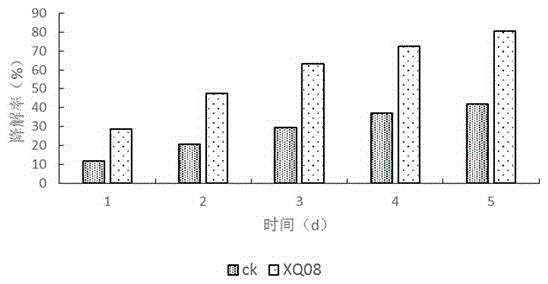
Stenotrophomonas maltophilia XQ08 efficiently degrading deltamethrin and application thereof
InactiveCN105602871AEasy to useReduce manufacturing costBacteriaWater contaminantsInorganic saltsEcological environment
The invention discloses stenotrophomonas maltophilia XQ08 efficiently degrading deltamethrin and application thereof. The strain stenotrophomonas maltophilia XQ08 is preserved in China Center for Type Culture Collection (CCTCC) on December 8th, 2015 at the address of Wuhan University in Wuhan, China and with the preservation number of CCTCC M 2015726. The Bacillus cereus stenotrophomonas maltophilia XQ08 provided by the invention has the advantage that the degradation rate on deltamethrin (50.0mg / L) in an inorganic salt culture medium after 5 days reaches 67.04%, so that the strain can efficiently degrade deltamethrin and can effectively restore deltamethrin-polluted soil and water, the excessive pesticide residue problem in production of agricultural products and environmental pollution problem are solved and ecological environment and human health are protected.
Owner:GUIZHOU UNIV
Primer group and kit for rapidly identifying respiratory tract microorganisms based on nanopore sequencing and application of primer group
ActiveCN112501268APrecise positioningImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesPneumonitisEnterococcus
The invention discloses a primer group for detecting respiratory tract microorganisms based on a nanopore sequencing method. The nucleotide sequences of the primer group are as shown in SEQ ID NO:1-20. The microorganisms are streptococcus pneumoniae, staphylococcus aureus (resisting to methicillin), klebsiella pneumoniae, pseudomonas aeruginosa, acinetobacter baumannii, stenotrophomonas maltophilia, candida albicans, haemophilus influenzae, legionella pneumophila, enterococcus faecium, chlamydia psittaci, cryptococcus gattii, aspergillus fumigatus and pneumocystis jiroveci. According to the invention, sequencing optimization is carried out on different types of samples of the respiratory tract microorganisms, so that the detection method, the kit and the like are suitable for various typesof respiratory tract samples; and a targeted amplification method is adopted, so that the detection requirements of sputum, alveolar lavage and other sample types can be met. In addition, parallel sequencing can be performed, so that the flux of the detected samples is increased, the sequencing time is shortened, and the contradiction between the flux of detected pathogenic species and the cost and time is further relieved.
Owner:GUANGZHOU DARUI BIOTECH
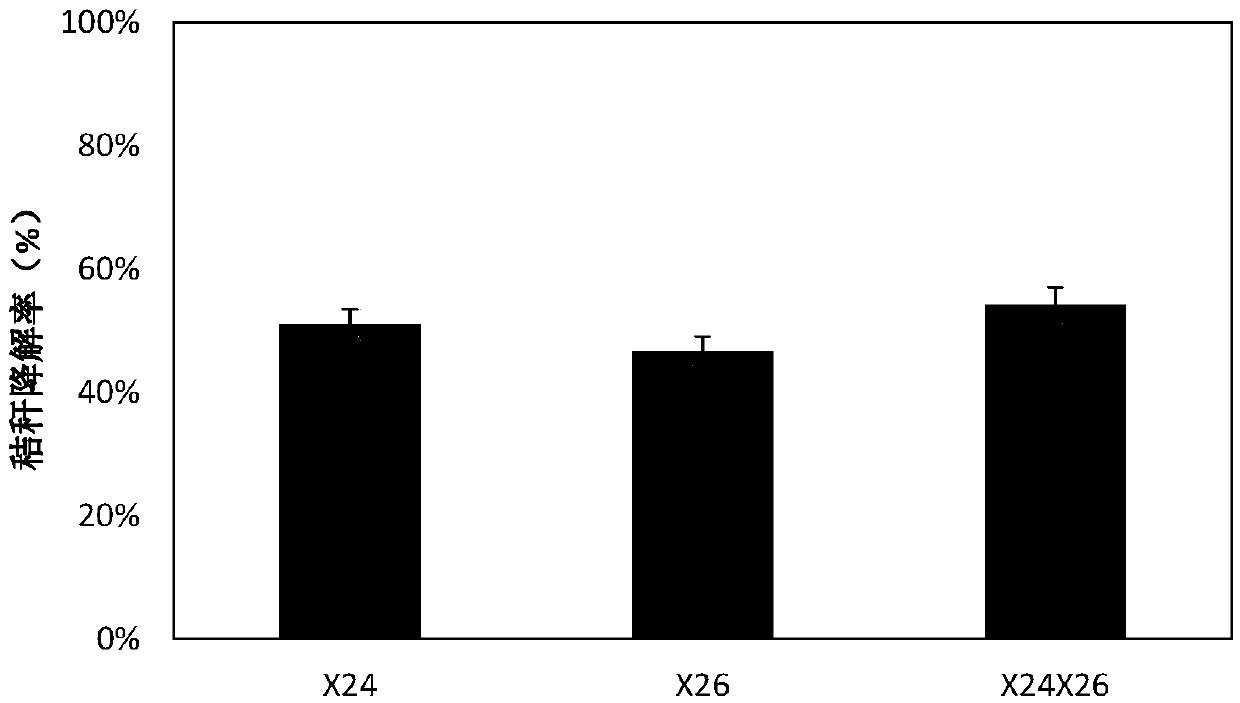
Cellulose degradation composite microbial inoculum with low-temperature resistance as well as preparation method and application of cellulose degradation composite microbial inoculum
PendingCN109593677AEasy to prepareEasy to implementBio-organic fraction processingBacteriaCelluloseIn situ degradation
The invention discloses a cellulose degradation composite microbial inoculum with low-temperature resistance as well as a preparation method and an application of the cellulose composite microbial inoculum. The cellulose degradation composite microbial inoculum with low-temperature resistance comprises effective components of flavobacterium johnsoniae and stenotrophomonas maltophilia in a weight ratio of (0.5-1.51): 1, and the total effective viable count in the cellulose degradation composite microbial inoculum with low-temperature resistance is 3*10<9> CFU / g or more. The cellulose degradation composite microbial inoculum with low-temperature resistance can be further applied to in-situ degradation and returning to the field of t straws due to efficient degradation of cellulose such as crop straws at low temperature. The composite microbial inoculum can solve the problems of low cellulose degradation rate and long period in the low temperature environment in northern China.
Owner:SHENYANG AGRI UNIV
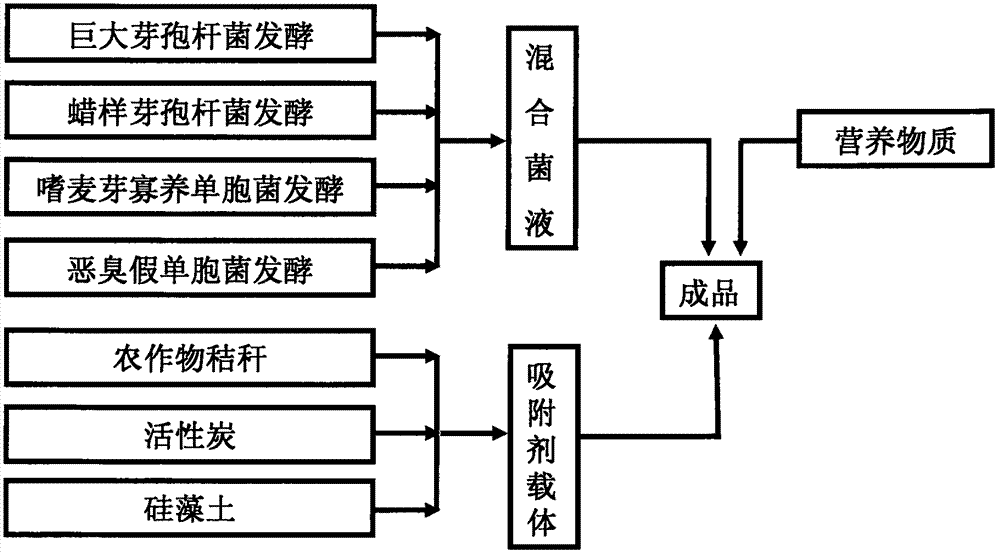
Efficient remediation compound microbial agent for cultivated soil
The invention discloses an efficient remediation compound microbial agent for cultivated soil. The efficient remediation compound microbial agent is prepared from a bacteria solution prepared by fermenting a compound microbial agent, and a compound adsorption carrier, wherein the mass ratio of the bacteria solution to the compound adsorption carrier is (0.01 to 0.2) to (1 to 2); the viable count is 22 to 86 million per gram; the microbial agent is prepared from bacillus megatherium, bacillus cereus, stenotrophomonas maltophilia and pseudomonas putida; the compound adsorption carrier is prepared from crop straw, active carbon and diatomite. Bacteria solutions of the bacillus megatherium, the bacillus cereus and the stenotrophomonas maltophilia are combined together, and the four bacteria facilitate one another, so that remediation of the soil can be finished more efficiently, pollution on soil suffering from heavy metal pollution and organic chemical product pollution can be eliminated rapidly, soil productivity is improved, and the remediation efficiency is increased. By adopting the compound adsorption carrier, the limit of a single carrier is overcome, the service life of a strain is prolonged, and the service cycle of the strain is prolonged.
Owner:BEIJING ZNFY GRP CO LTD
Enhanced plant growth using alkane biostimulation
A method of enhancing plant growth comprises the step of introducing an alkane into a location adjacent to a plant. The alkane can be introduced intermittently, and can be combined with another gas and / or nutrients. The alkane preferably comprises a butane substrate. The butane substrate can stimulate the growth of butane-utilizing bacteria, such as Aeromonas caviae, Stenotrophomonas maltophilia, Micrococcus varians, Aureobacterium esteroaromaticum, Aureobacterium barkeri, Rhodococcus fascians, Nocardia paradoxus, Comamonas acidovorans and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. The alkane can increase the amount of heterotrophic bacteria in the location adjacent to the plant, and thereby accelerate a heterotrophic nitrification process. The butane substrate can also stimulate the growth of butane-utilizing fungi. The method can also enhance the growth protists and / or prokaryotes. A system for enhancing plant growth in accordance with the method is also disclosed.
Owner:GLOBAL BIOSCI
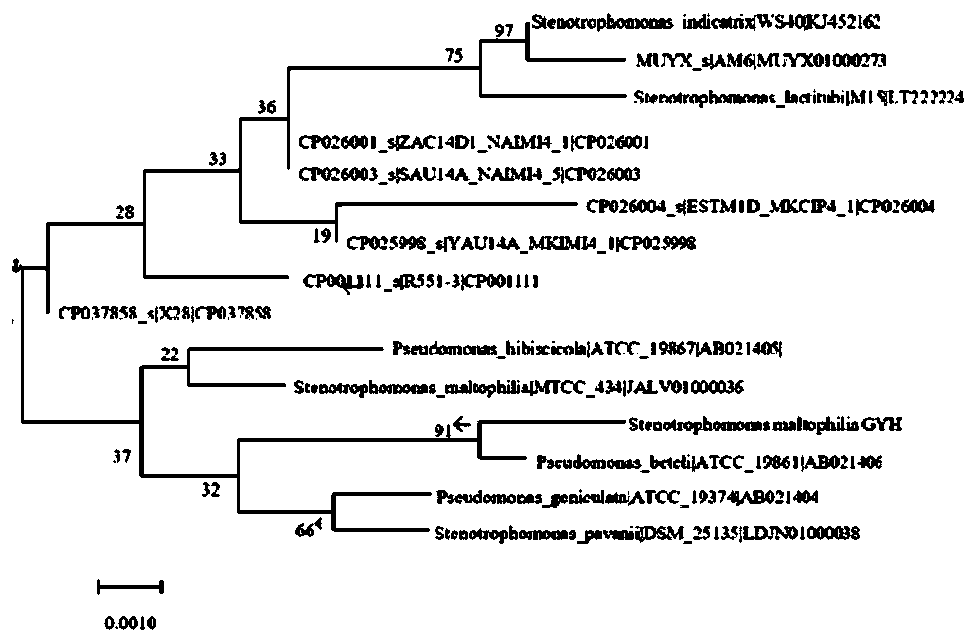
Stenotrophomonas maltophilia GYH and application thereof in degradation of chlorinated hydrocarbon pollutants
ActiveCN111254091APromote degradationEfficient degradation abilityBacteriaWater contaminantsStenotrophomonas maltophiliaEnvironmental engineering
The invention discloses stenotrophomonas maltophilia GYH and application thereof in degradation of chlorinated hydrocarbon pollutants. The application comprises the following steps: adding resting cells obtained by expanding culture of stenotrophomonas maltophilia GYH into an inorganic culture medium with a pH value of 5-8, then adding chlorinated hydrocarbon pollutants, and conducting culturing under the conditions of a temperature of 20-35 DEG C and a rotation speed of 140-180 rpm to realize degradation of the pollutants. The stenotrophomonas maltophilia GYH disclosed by the invention can beused for removing chlorinated hydrocarbon pollutants with concentrations in a range of 2.9 mg / L to 8.93 mg / L. Therefore, the stenotrophomonas maltophilia has efficient degradation capability on industrial similar pollutants, and can bear pollutants with a relatively high concentration.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
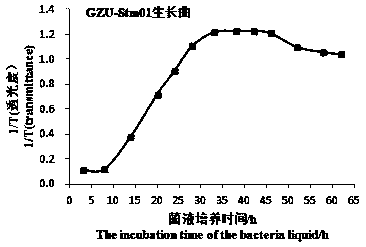
Stenotrophomonas maltophilia strain and application thereof
ActiveCN110982727AGood dissociation effectEfficient decompositionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiologyExchangeable calcium
The invention discloses a stenotrophomonas maltophilia strain and an application thereof. The stenotrophomonas maltophilia strain is stenotrophomonas maltophilia, is named stenotrophomonas maltophiliaGZU-Stm01, and is preserved in China Center for Type Culture Collection on January 21, 2019, wherein the preservation number is CCTCC NO:M2019059. According to the invention, with the stenotrophomonas maltophilia GZU-Stm01, insoluble phosphorus, insoluble potassium, insoluble silicon, insoluble calcium, insoluble sulfur and other components in coal gangue can be effectively dissociated and converted into available phosphorus, available potassium, available silicon, exchangeable calcium, available sulfur and other nutrient components absorbed by plants; particularly, the GZU-Stm01 can be usedfor effectively dissociating insoluble phosphorus in coal gangue, so that insoluble phosphorus becomes available phosphorus, and an available phosphorus resource source is provided; the GZU-Stm01 alsohas a good dissociation effect on other phosphorus-containing minerals; other phosphorus-containing minerals such as low-grade phosphorite can be doped into coal gangue; and the phosphorus content ina mineral microorganism compound fertilizer taking coal gangue as a basic raw material can be further improved.
Owner:GUIZHOU UNIV +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com