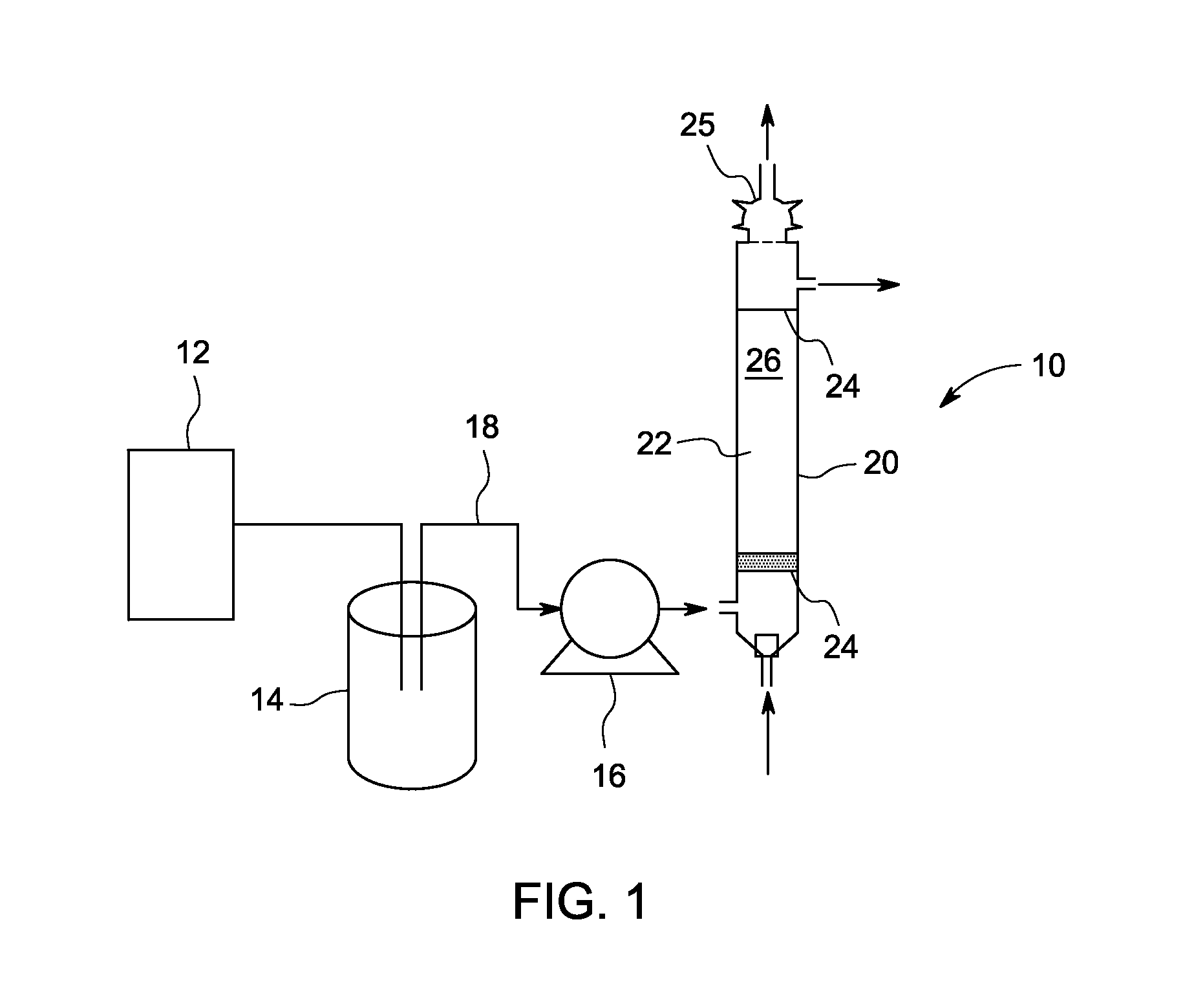
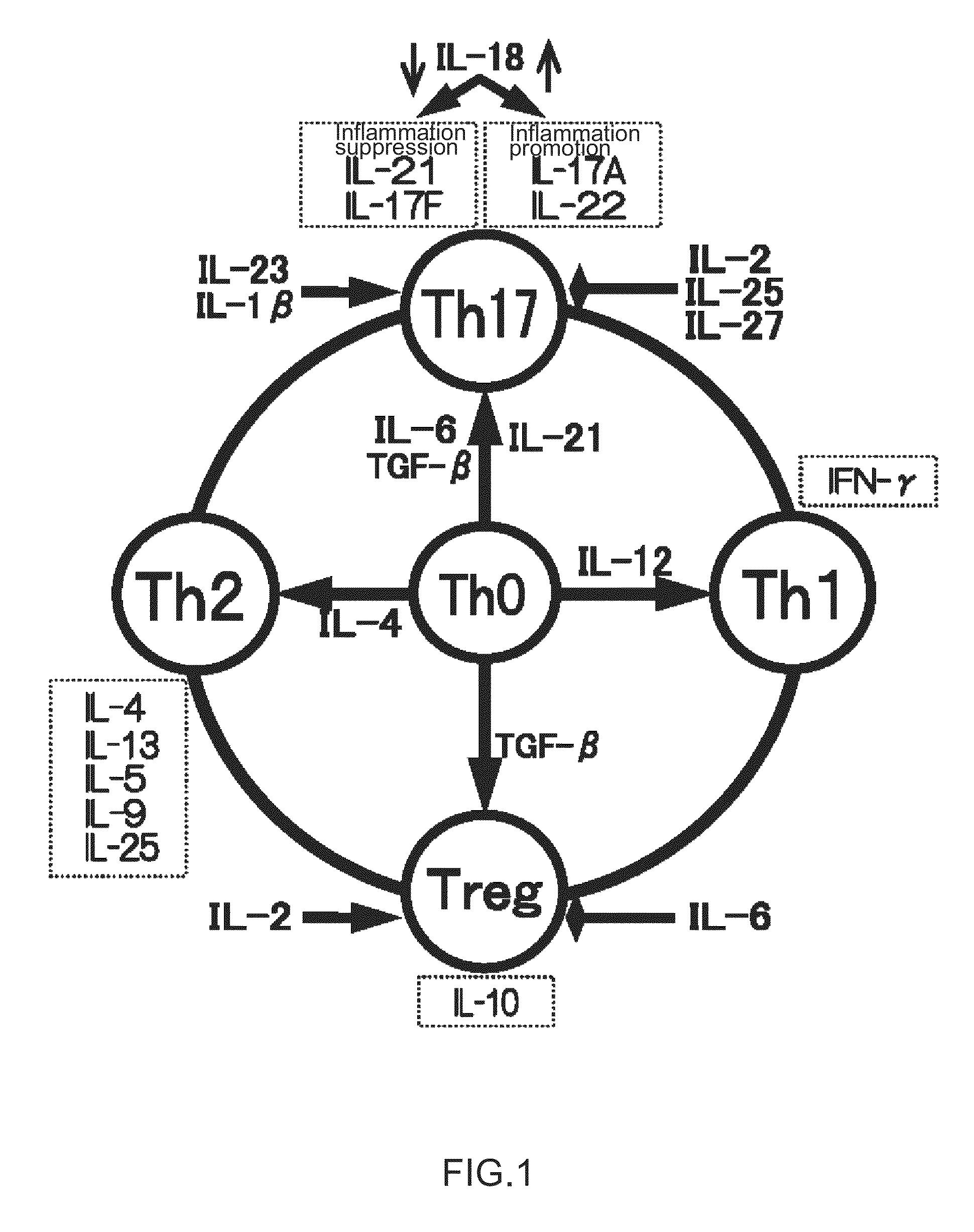
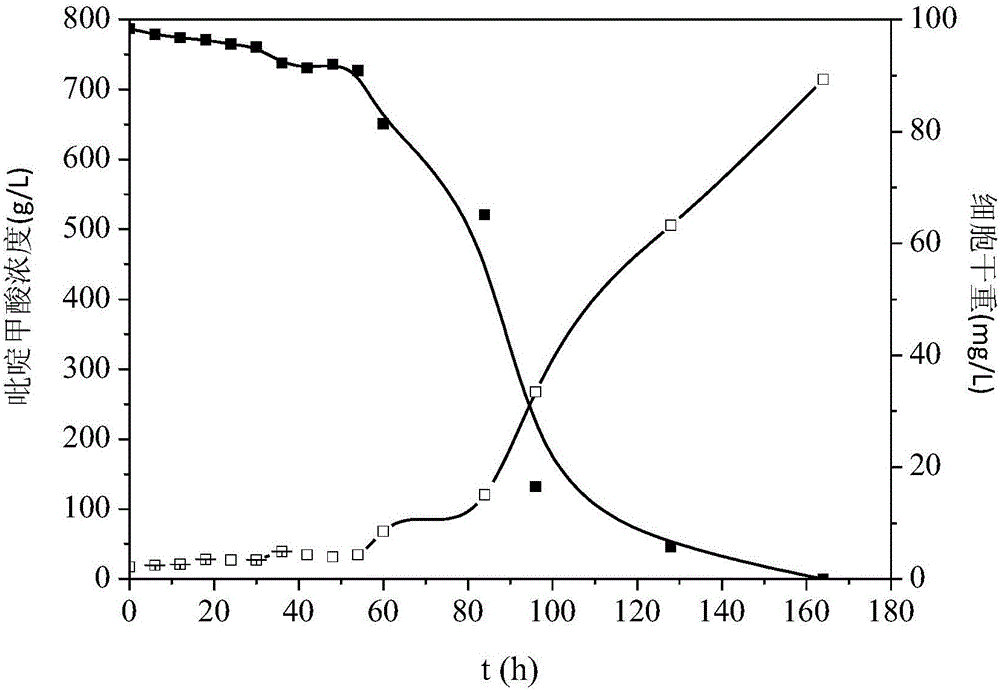
Patents
Literature
46 results about "Comamonas" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Comamonas is a genus of Proteobacteria . Like all Proteobacteria, they are Gram-negative bacteria. Comamonas species are aerobic organisms and motile using bipolar or polar tufts of one to five flagella.
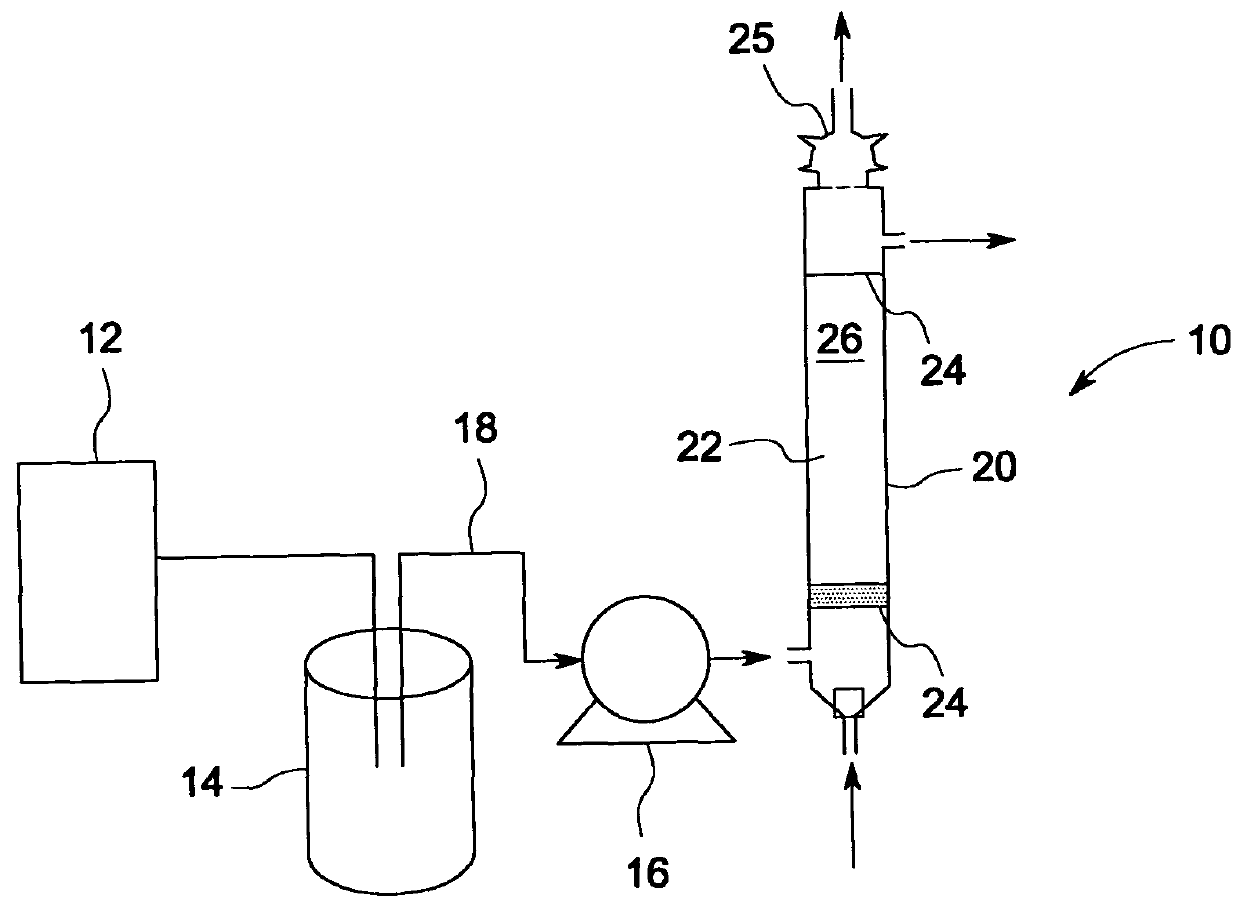
Bioreactor for remediation of pollutants with butane utilizing bacteria
InactiveUS6051130AReduce and eliminate hydrocarbon pollutantEasy to transportGas treatmentBacteriaBacteroidesComamonas
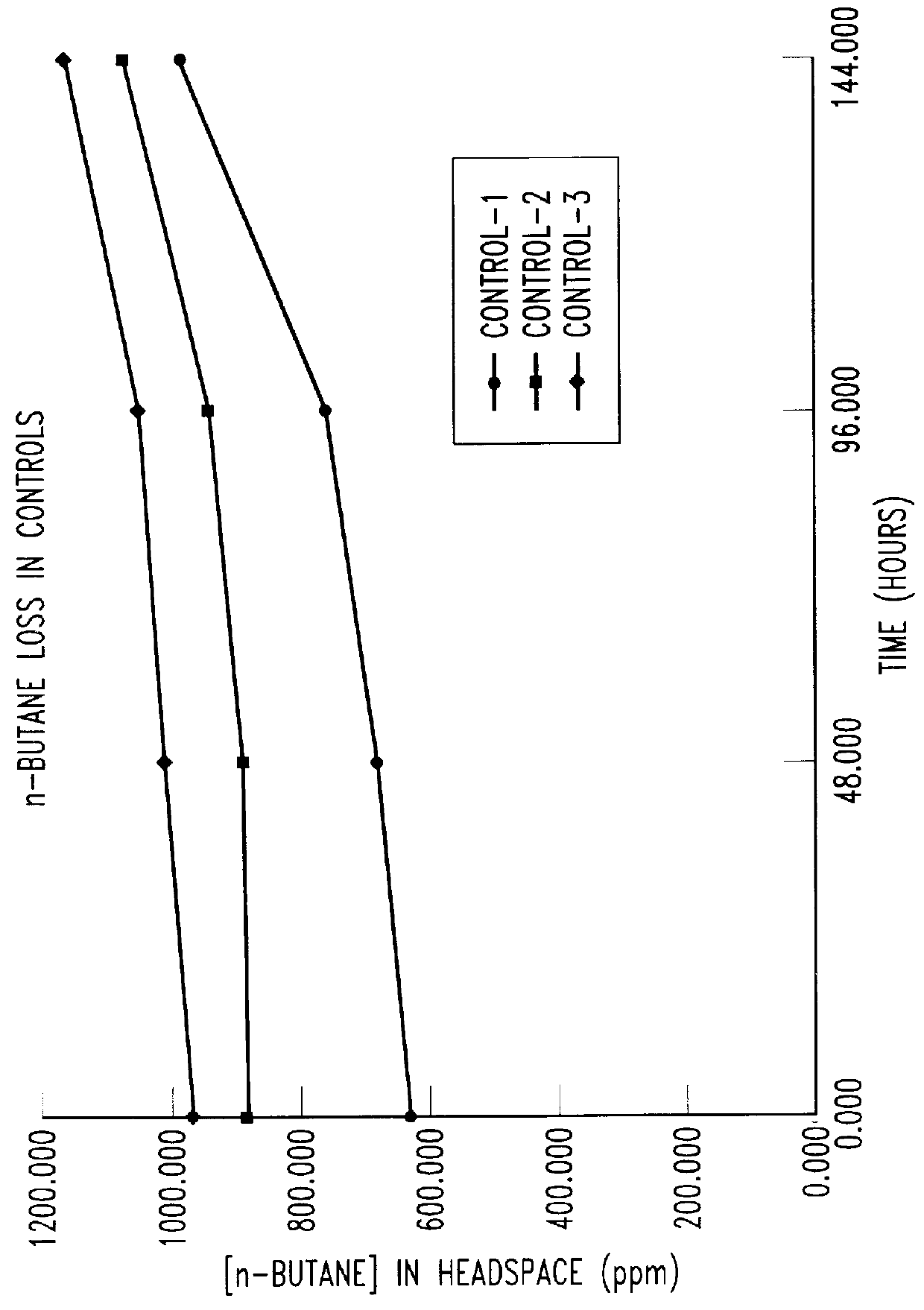
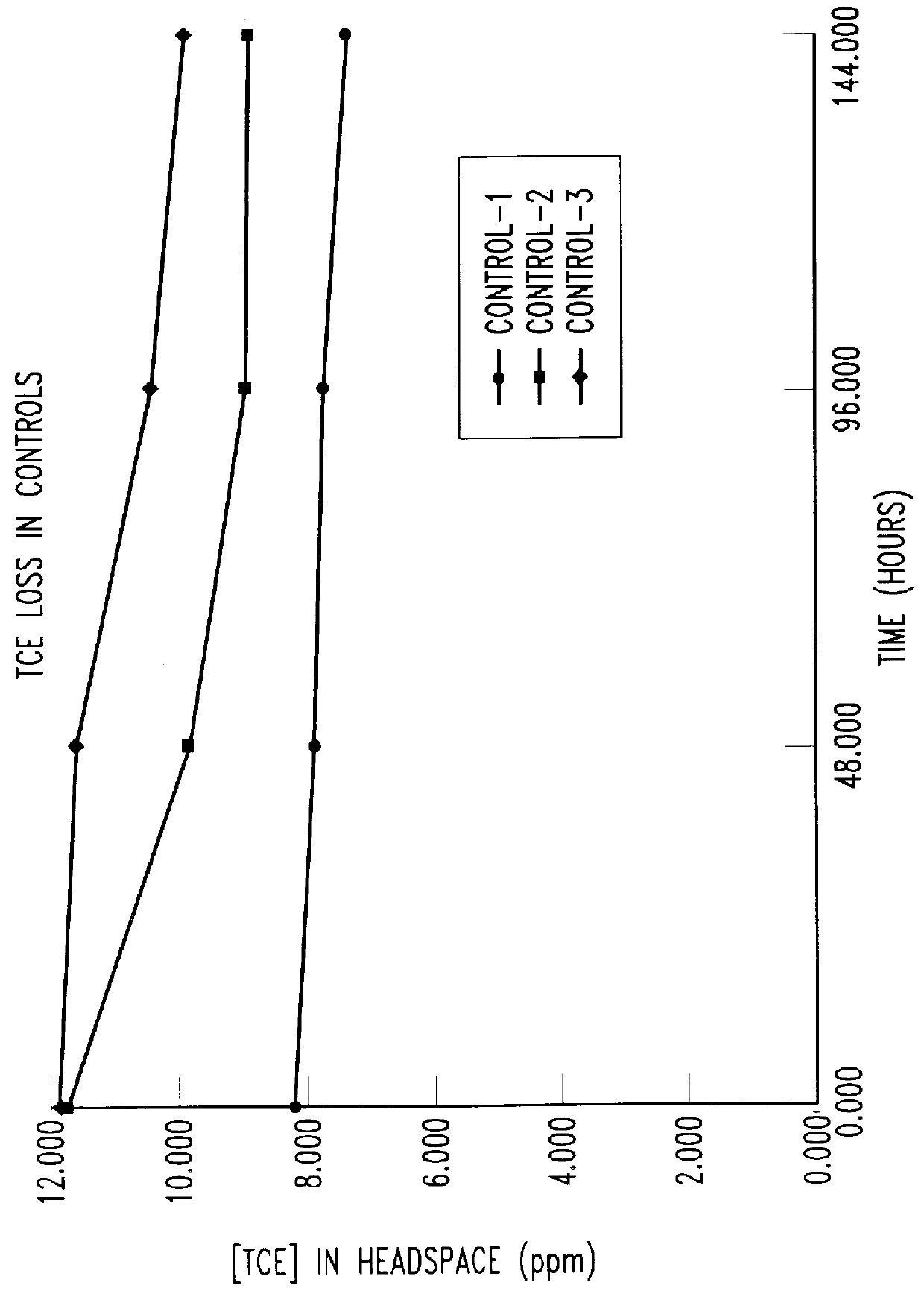
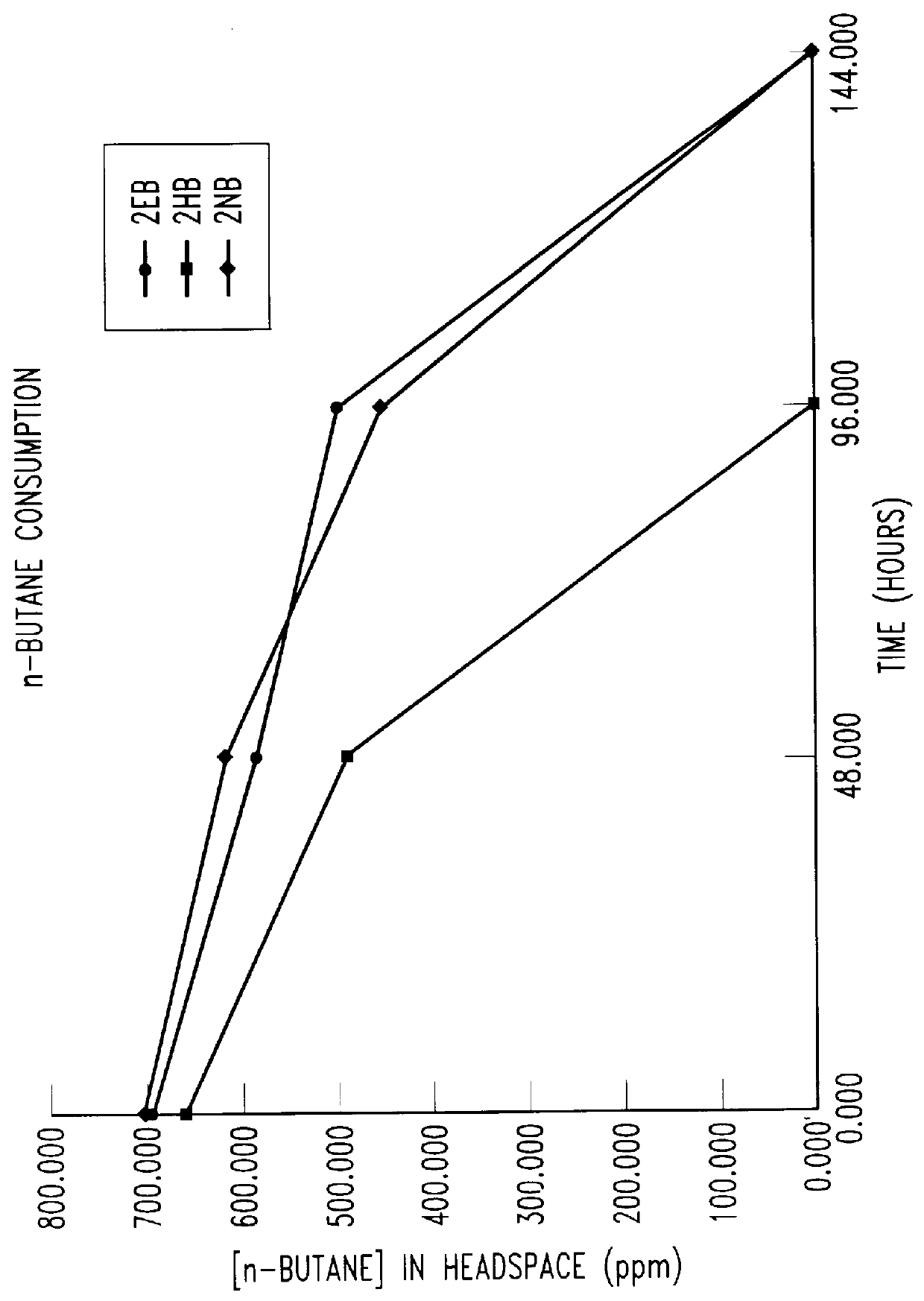
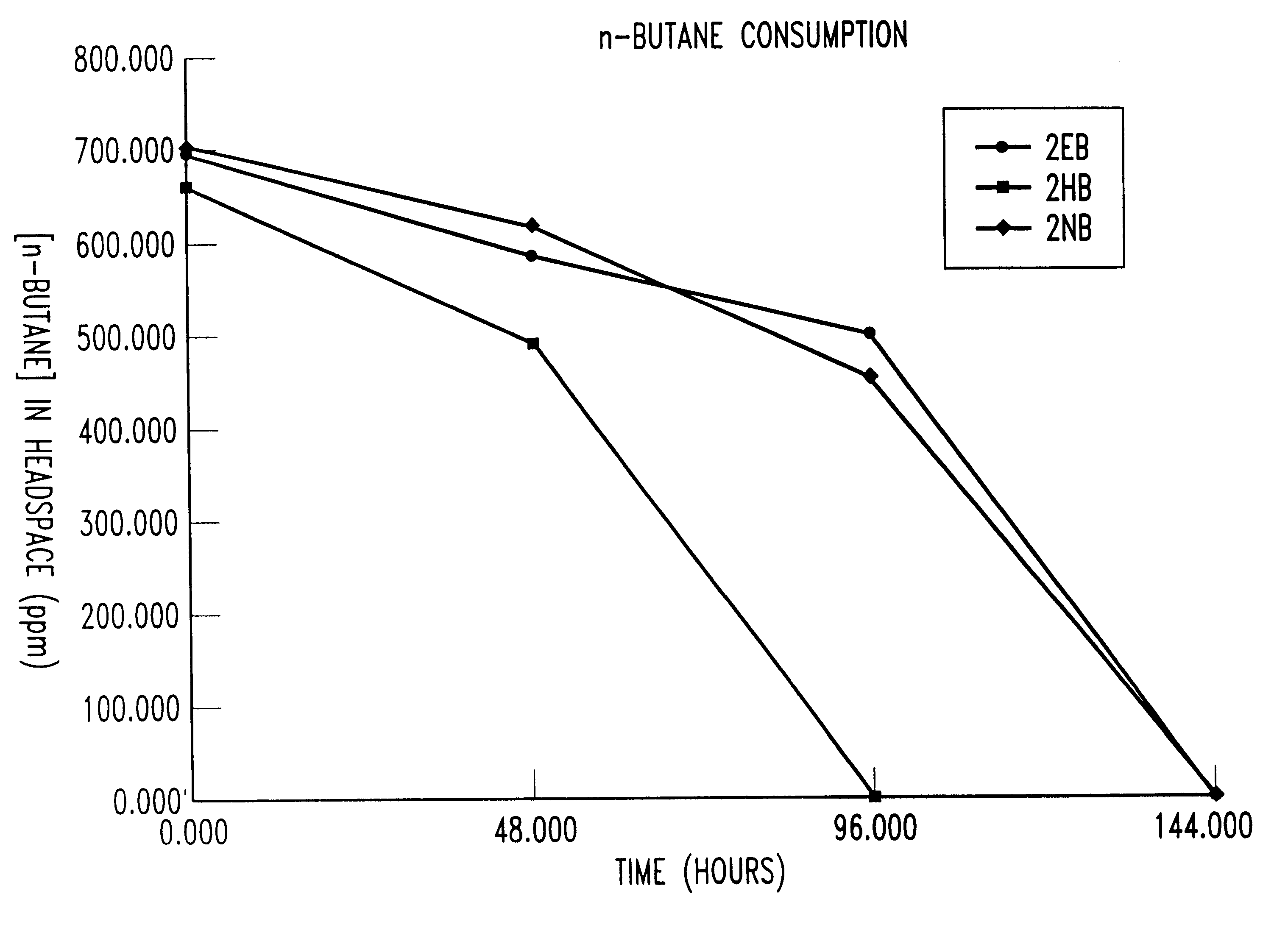
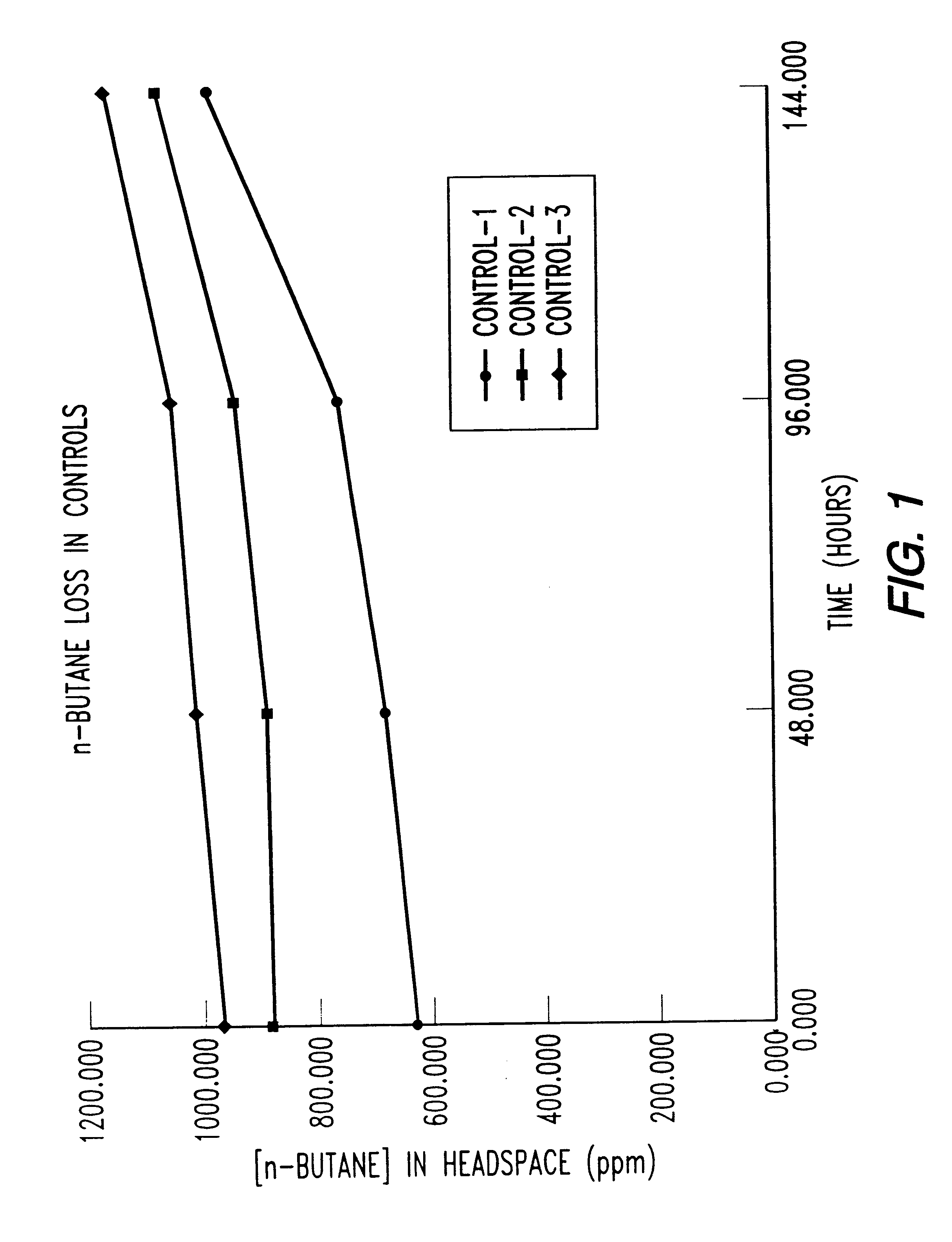
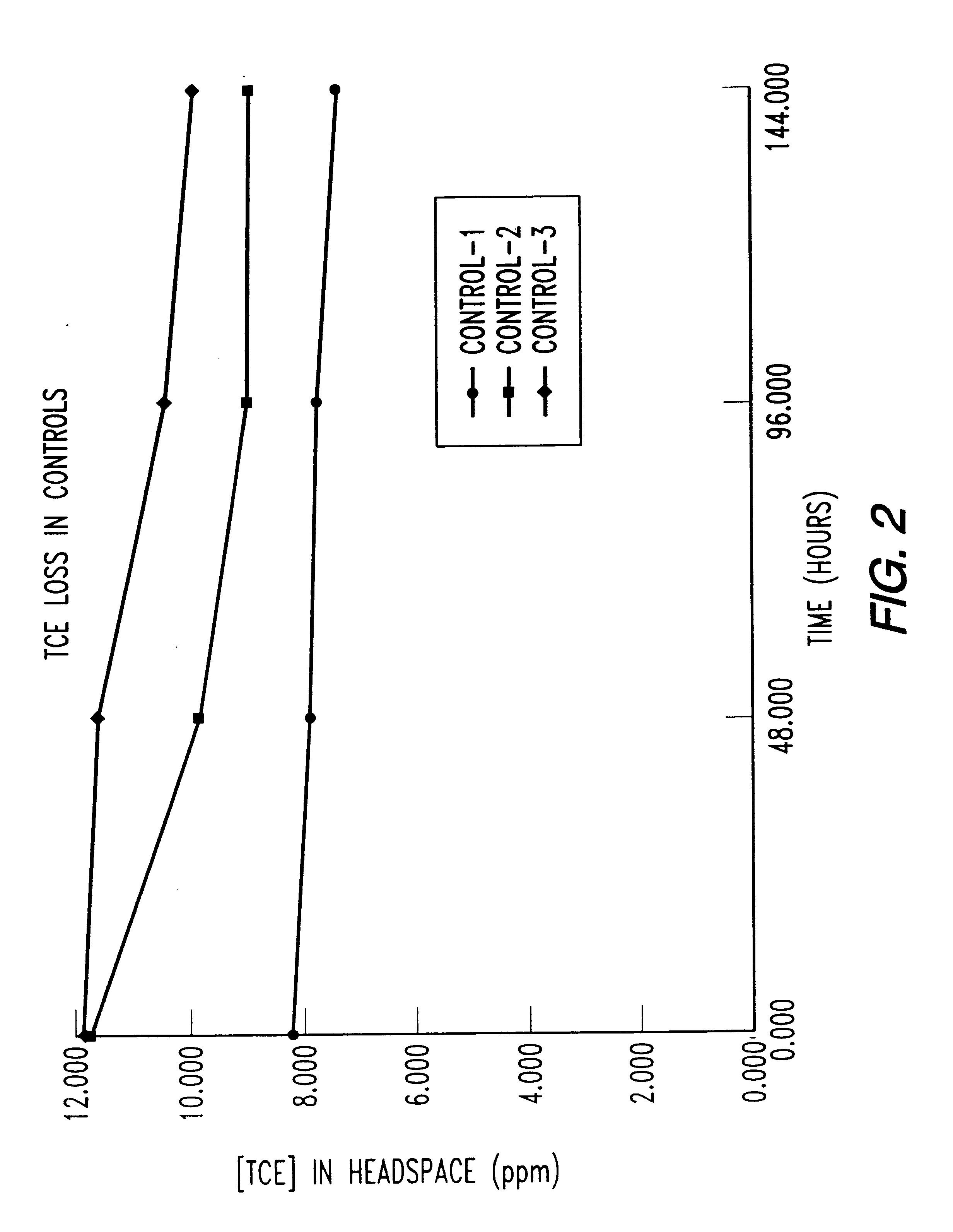
Butane-utilizing bacteria are used to degrade hydrocarbon pollutants such as trichloroethene (TCE). In-situ or ex-situ techniques may be used to reduce or eliminate hydrocarbon pollutants from liquid, gas and solid sources. In a preferred embodiment, TCE concentrations in various aqueous environments are reduced by contacting a contaminated water source with butane-utilizing bacteria in the presence of oxygen to degrade the TCE by cometabolism or direct metabolism. Suitable butane-utilizing bacteria include Pseudomonas, Variovorax, Nocardia, Chryseobacterium, Comamonas, Acidovorax, Rhodococcus, Aureobacterium, Micrococcus, Aeromonas, Stenotrophomonas, Sphingobacterium, Shewanella, Phyllobacterium, Clavibacter, Alcaligenes, Gordona, Corynebacterium and Cytophaga. The butane-utilizing bacteria have relatively low TCE toxicity in comparison with conventional methane-utilizing bacteria, and demonstrate an improved ability to degrade TCE.
Owner:GLOBAL BIOSCI
Microbial agent for repairing petroleum-polluted saline alkali soil and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102994431AEasy to makeImprove stabilityBacteriaContaminated soil reclamationEcological environmentAlkali soil
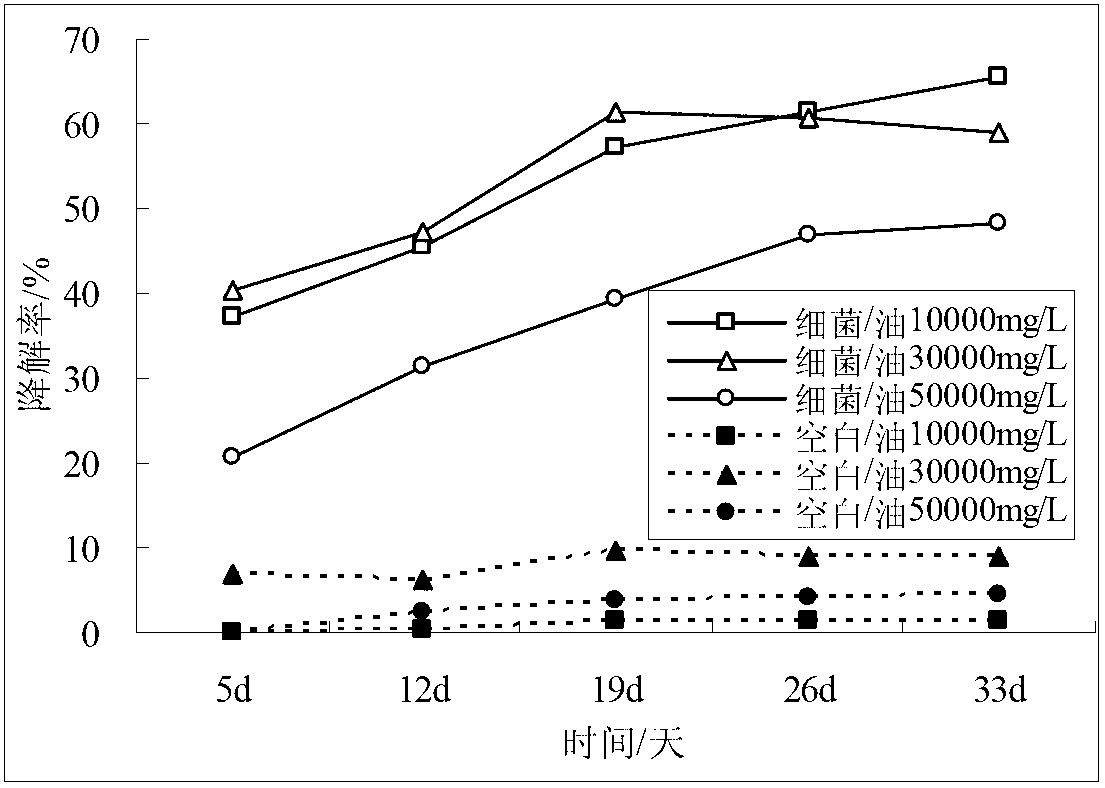
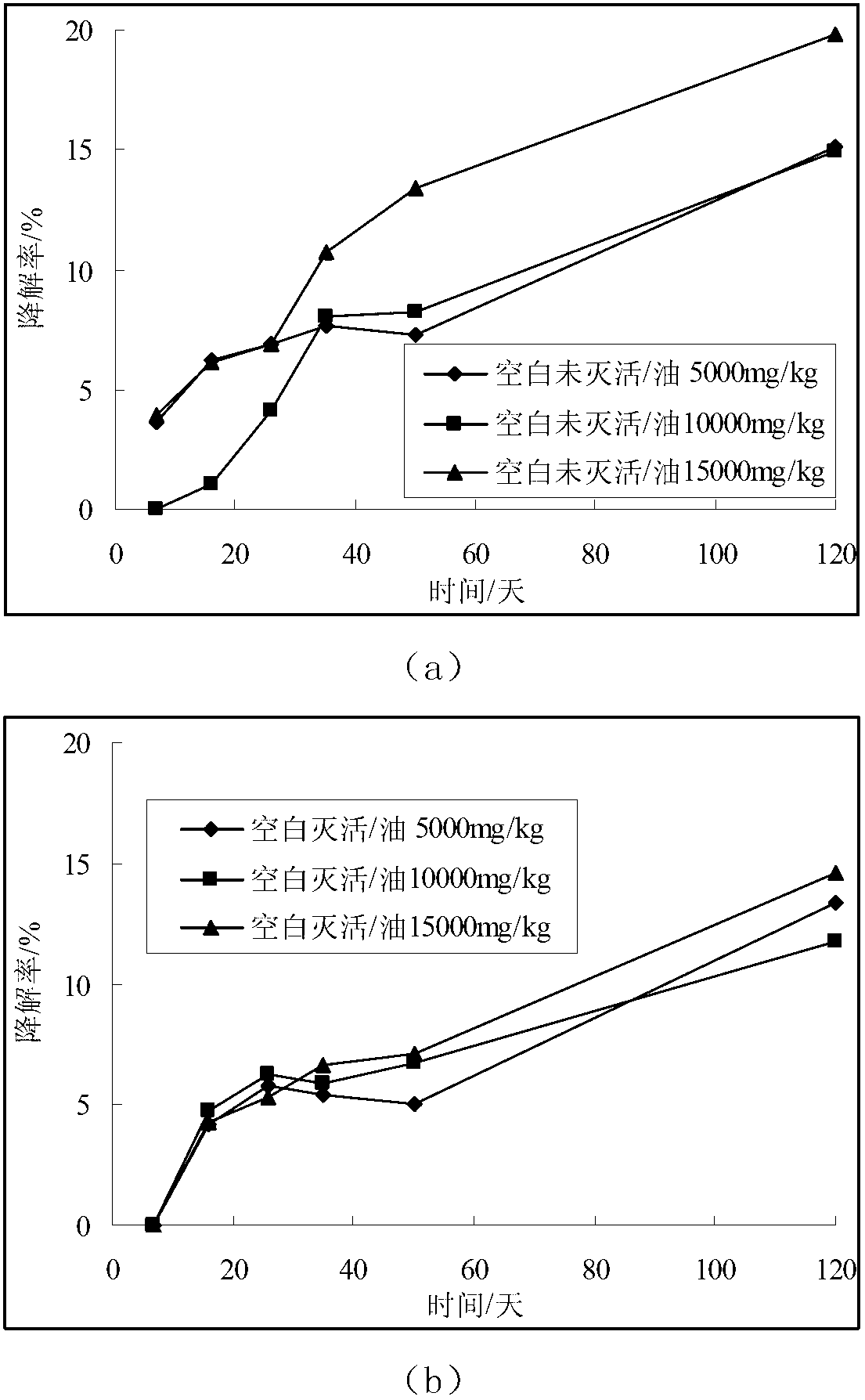
The invention relates to a microbial agent for repairing petroleum-polluted saline alkali soil and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of resource environment. According to a principle of microbial ecology, microbial community is extracted and screened from soils with high salt and alkali and high petroleum pollution to prepare the microbial agent, wherein obligate petroleum degrading bacteria can be sphingolipid bacteria, comamonas, chitin autophagy bacteria and bacillus. According to culture medium and soil environment experiments, the microbial agent can guarantee that the extracted microorganism can be survived in the soils with the salt content of 5,000mg / kg, and meanwhile, the degradation capability to the polluted soils with the petroleum content of 10-50g / kg can reach 80%. The microbial agent has the advantages of simple process, rich microorganisms, obvious dominant bacteria, good stability and capability of facilitating obligate petroleum degrading bacteria to adapt to a new pollution environment, increasing and improving the micro-ecological environment quality of the soils and avoiding secondary pollution to the environment, and can obviously improve the degradation efficiency of petroleum hydrocarbon in the saline alkali soil.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Bioremediation of pollutants with butane-utilizing bacteria
InactiveUS6210579B1Reduce and eliminate hydrocarbon pollutantEasy to transportGas treatmentTreatment using aerobic processesBacteroidesComamonas
Butane-utilizing bacteria are used to degrade hydrocarbon pollutants such as trichloroethene (TCE). In-situ or ex-situ techniques may be used to reduce or eliminate hydrocarbon pollutants from liquid, gas and solid sources. In a preferred embodiment, TCE concentrations in various aqueous environments are reduced by contacting a contaminated water source with butane-utilizing bacteria in the presence of oxygen to degrade the TCE by cometabolism or direct metabolism. Suitable butane-utilizing bacteria include Pseudomonas, Variovorax, Nocardia, Chryseobacterium, Comamonas, Acidovorax, Rhodococcus, Aureobacterium, Micrococcus, Aeromonas, Stenotrophomonas, Sphingobacterium, Shewanella, Phyllobacterium, Clavibacter, Alcaligenes, Gordona, Corynebacterium and Cytophaga. The butane-utilizing bacteria have relatively low TCE toxicity in comparison with conventional methane-utilizing bacteria, and demonstrate an improved ability to degrade TCE.
Owner:GLOBAL BIOSCI
Degradation strain JN6 for petroleum hydrocarbons in oily sludge and application thereof
ActiveCN108048375APromote degradationOptimize the microbial systemBacteriaWater treatment compoundsSludgePetroleum
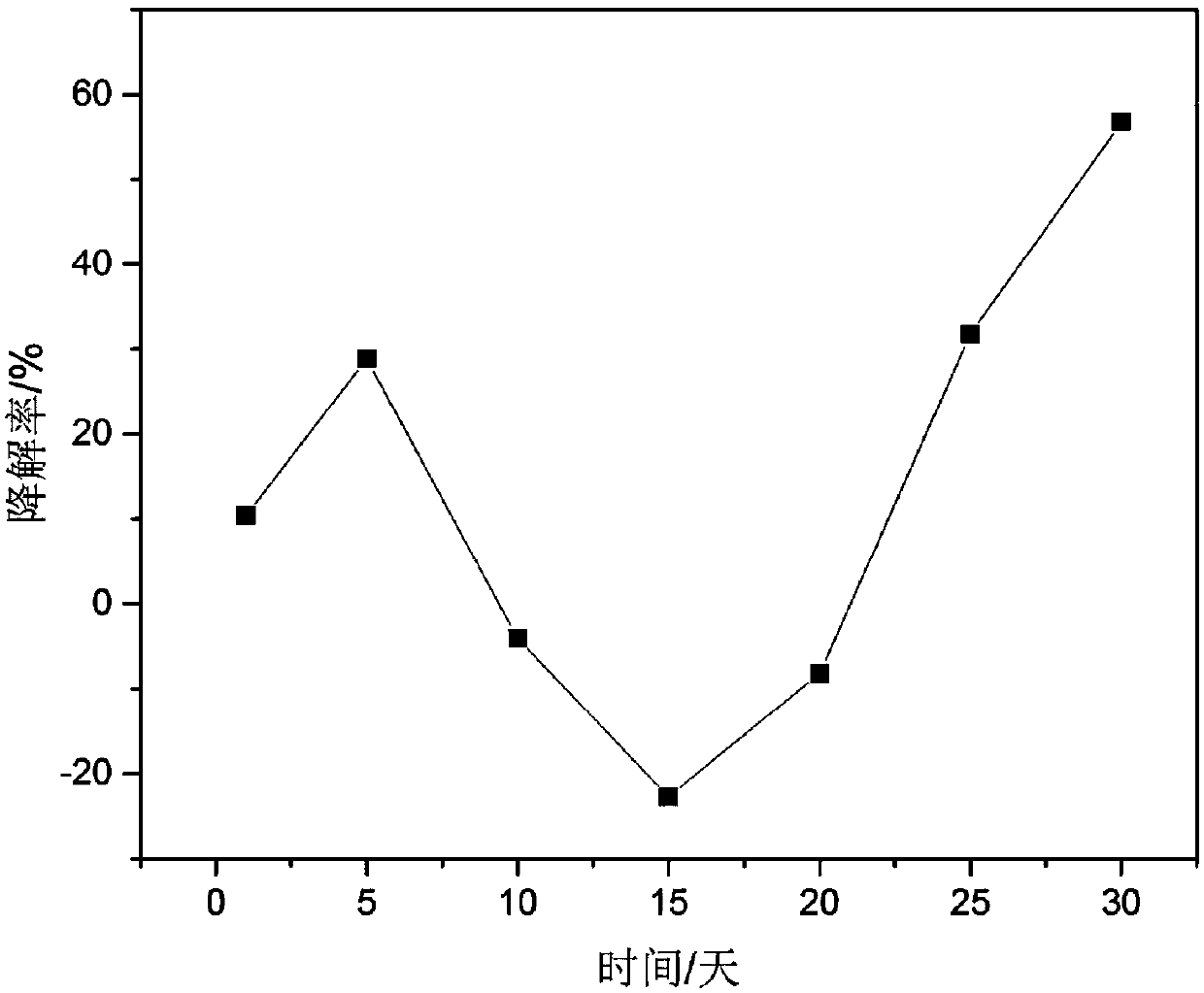
The invention discloses a highly effective degradation strain JN6 for petroleum hydrocarbons in oily sludge and application thereof, which belong to the technical field of bioremediation. The degradation strain JN6 is preserved in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center, the preservation number is CGMCC NO. 14977, and the classification number is Comamonas sp. The strain JN6 with a petroleum hydrocarbon degradation function which is disclosed by the invention is applied to treatment of oily sludge by degrading petroleum hydrocarbons, the degradation rate of the single strain of bacteria on total petroleum hydrocarbon (TPH) in oily sludge is 62.16 percent within 30 days, and the optimum degradation conditions of the bacteria on petroleum pollutants are 15 DEGC to 40 DEGC and the pH value of 7 to 11. The biological method is used in oily sludge remediation technology, and has the advantages of high effectiveness, low cost, environment-friendliness and the like.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Comamonas testosterone engineering bacteria and use thereof
The invention relates to a Comamonas testosteroni engineering bacterium. Directional regulation is adjusted and controlled to Comamonas testosterone through a DNA recombination technology, so as to produce Comamonas testosteroni AMCa 3 (CGMCC No.2364) having the capability of efficiently degrading steroid compounds. The engineering bacterium can effectively degrade testosterone, cholesterol and other steroid compounds, has good degradation effect to soils and livestock-poultry excreta seriously polluted by steroid compounds, and can be used for the treatment of livestock-poultry excreta, producing low-cholesterol food in food industry, and transforming steroid substances in the production of feed additives and dairy products for producing pollution-free food. The engineering bacterium has important significance in environmental remediation and agricultural application.
Owner:FUJIAN AGRI & FORESTRY UNIV
Method of removing recalcitrant organic pollutants
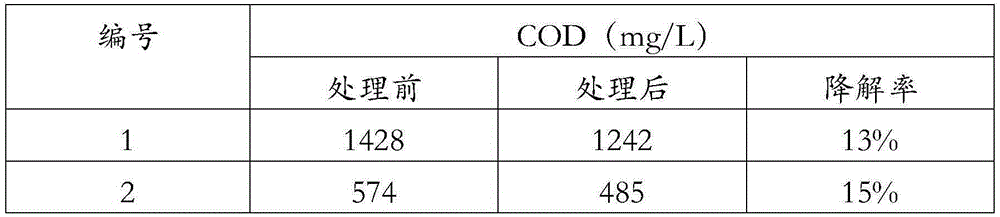
InactiveUS20130334135A1Efficient biodegradationReducing the recalcitrant chemical oxygen demand (COD)Treatment using aerobic processesBacteriaChemical oxygen demandComamonas
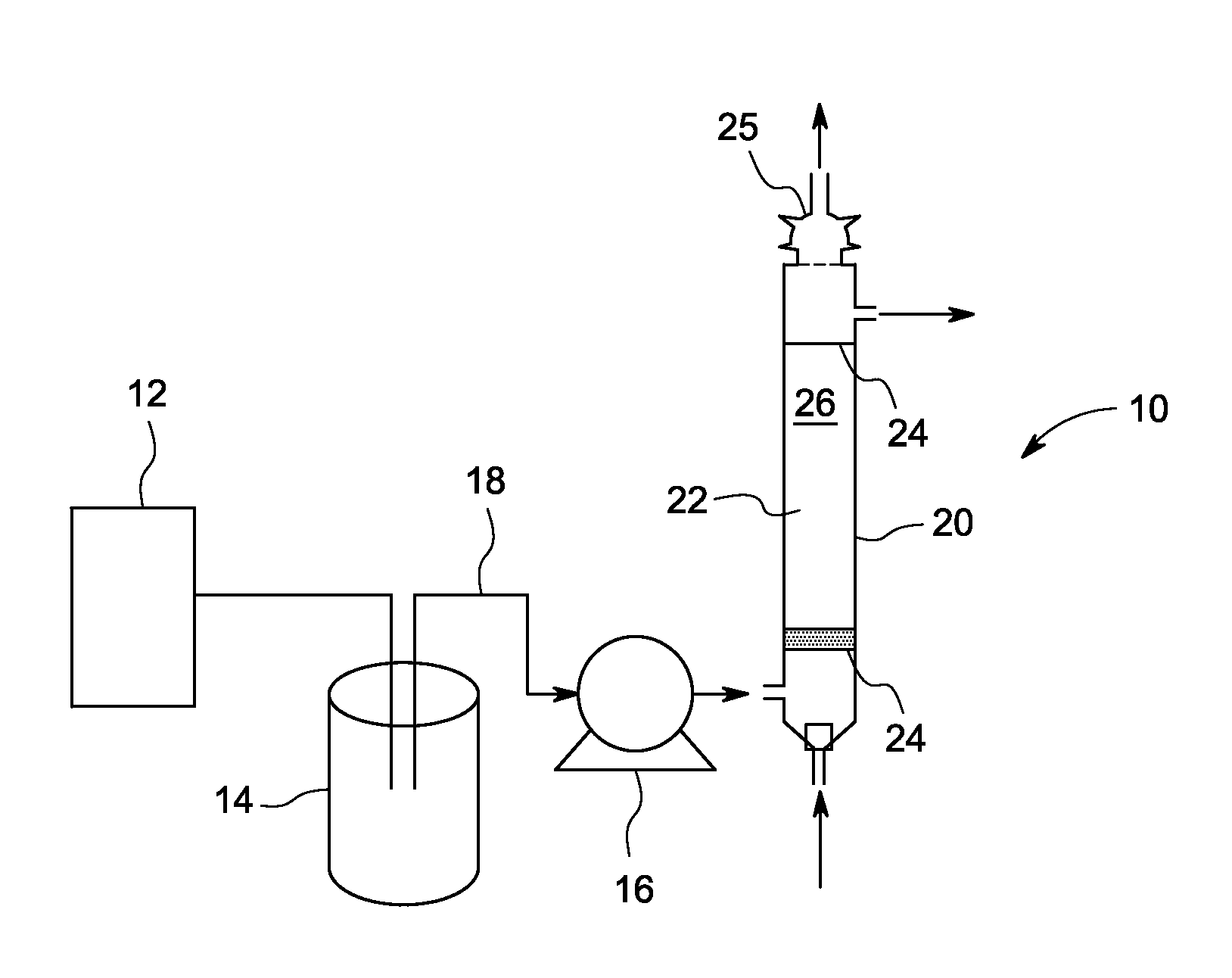
Recalcitrant chemical oxygen demand (COD) of a liquid is reduced in a water treatment system. The method includes pretreating the liquid in a pretreatment unit to remove indigenous bacteria or microbes to a population level below which the indigenous organisms can interfere with the screened and externally introduced microorganisms. The liquid is then provided to a reactor that has a filter bed formed with a carrier material. Special microbes are screened and used to colonize the carrier material to remove recalcitrant COD. A biofilm is cultured on the surface of the carrier material to immobilize the screened microbes in the reactor. The method further includes percolating the liquid from the pretreatment unit through the filter bed colonized with the screened microbes to degrade at least part of the recalcitrant COD under aerobic conditions. In one embodiment, the filter is formed with biological granular activated carbon (GAC) as the carrier material and the screened microbes comprise at least one microbial species selected from the group consisting of Bacillus, Comamonas, Arthrobacter, Micrococcus, Pseudomonas, Pediococcus, Achromobacter, Flavobacterium, Mycobacterium, Rhodanobacter, Stenotrophomonas and Yeast.
Owner:BL TECH INC
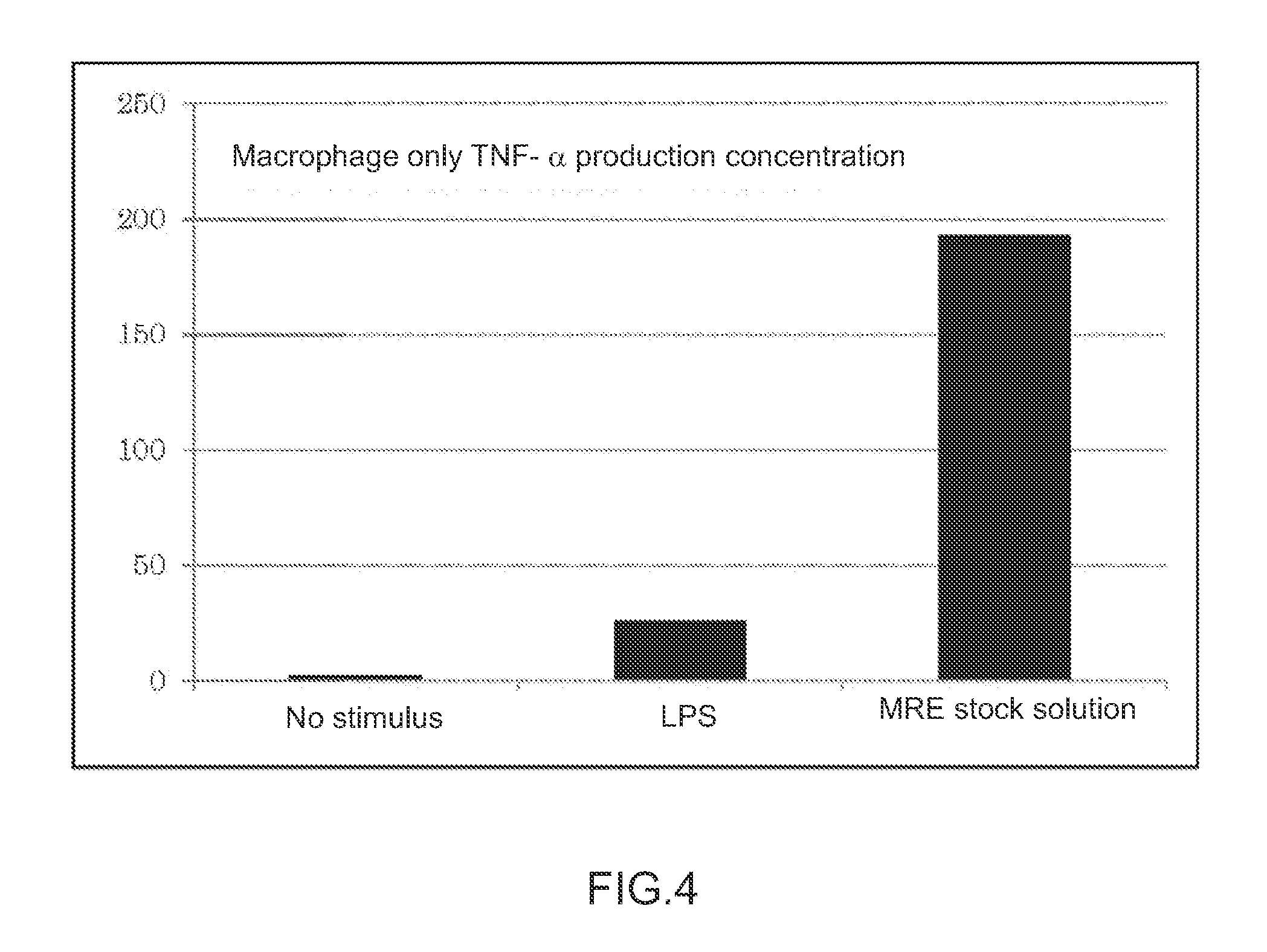
Immunopotentiating composition and process for producing same
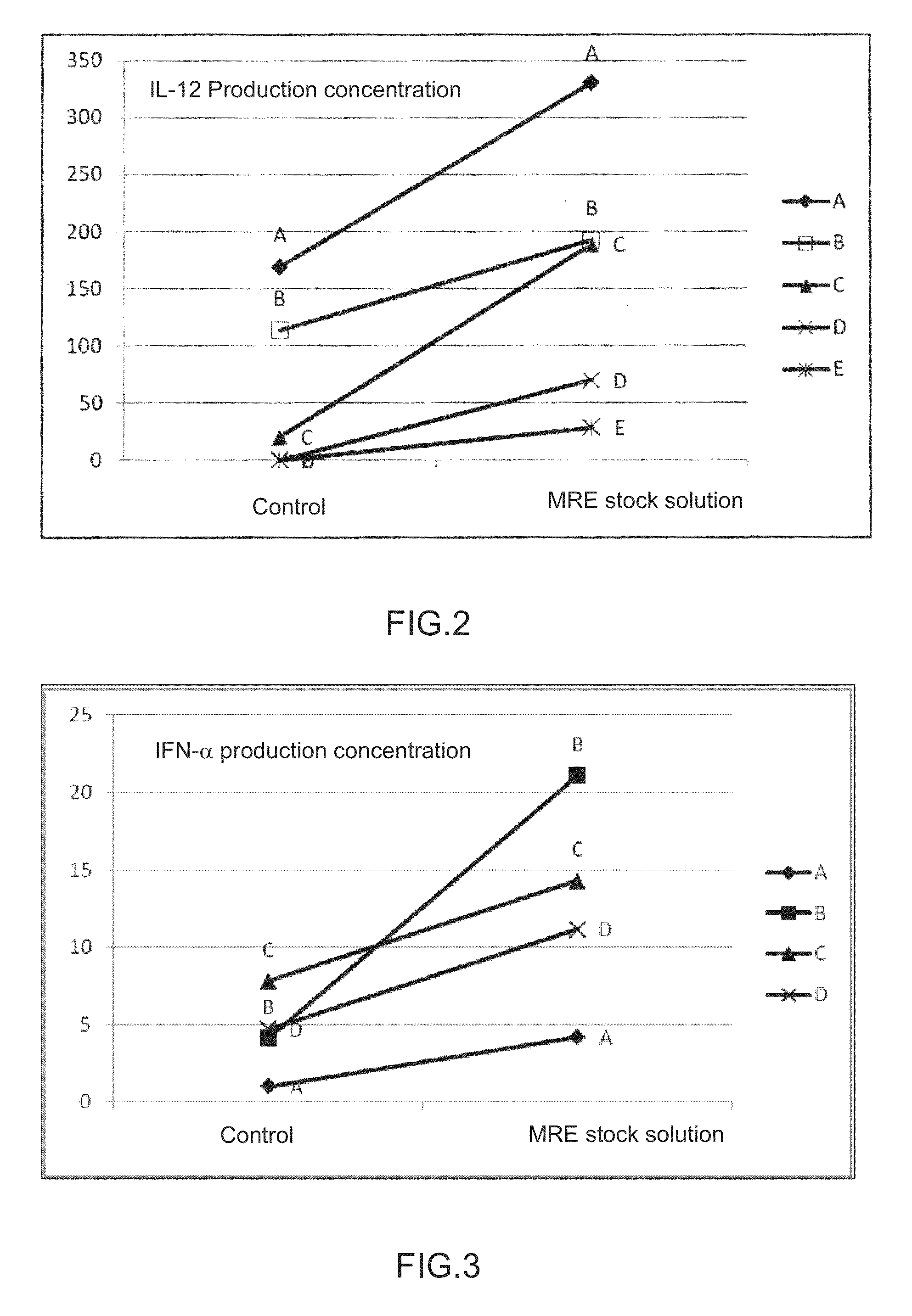
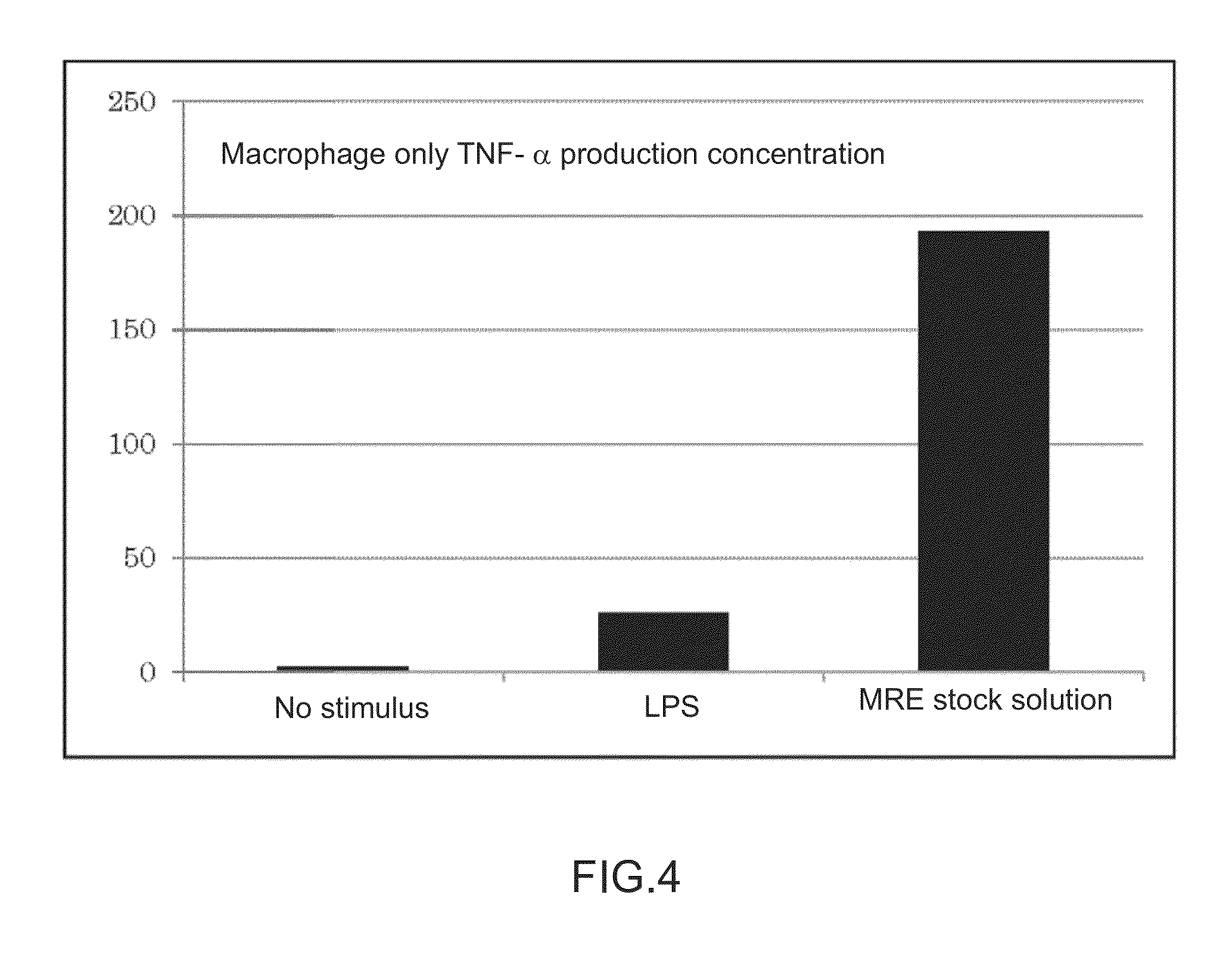
Disclosed is an immunopotentiating composition comprising an effective immunostimulating substance which can activate natural immunity and a subsequent immunity mediated by lymphocytes without causing any damage to cells. Specifically disclosed is an immunopotentiating composition which is characterized by comprising, as an active ingredient, an immunostimulating substance produced by decomposing at least one bacterium selected from an MRE symbiotic bacteria group consisting of Bacillus sp. (FERM BP-11209), Lysinibacillus fusiformis (FERM BP-11206), Bacillus sonorensis, Lysinibacillus sp. (FERM BP-11207) and Comamonas sp. (FERM BP-11208).
Owner:MEISHO
Constitutive expression genetically engineered bacterium and application thereof to produce L-alanine
InactiveCN105018405ALow costEasy to produceBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyEscherichia coli
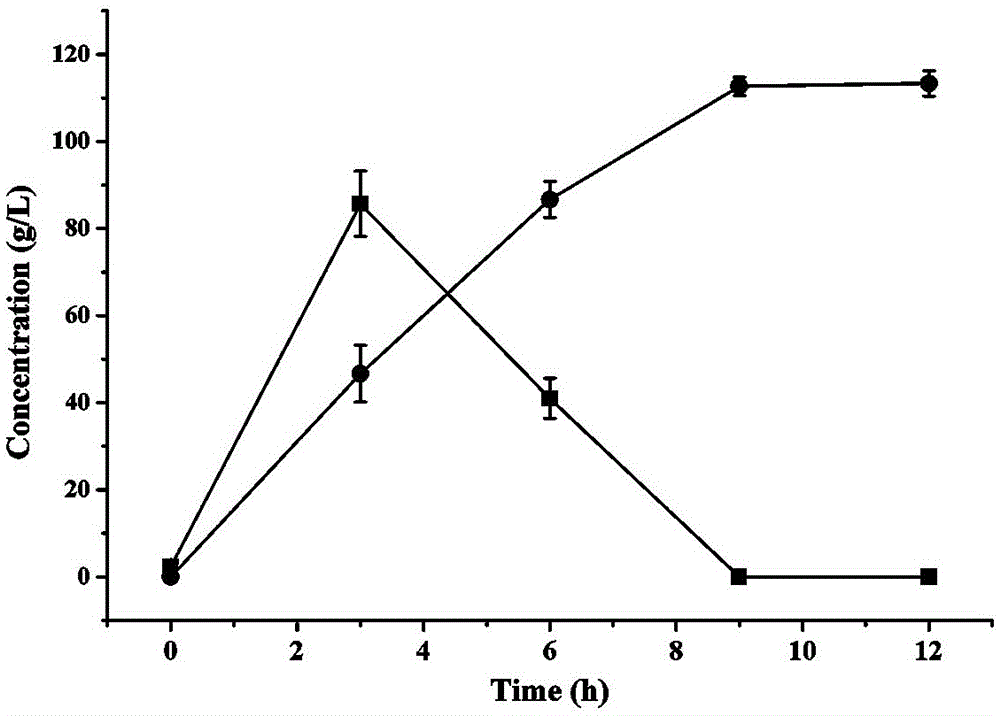
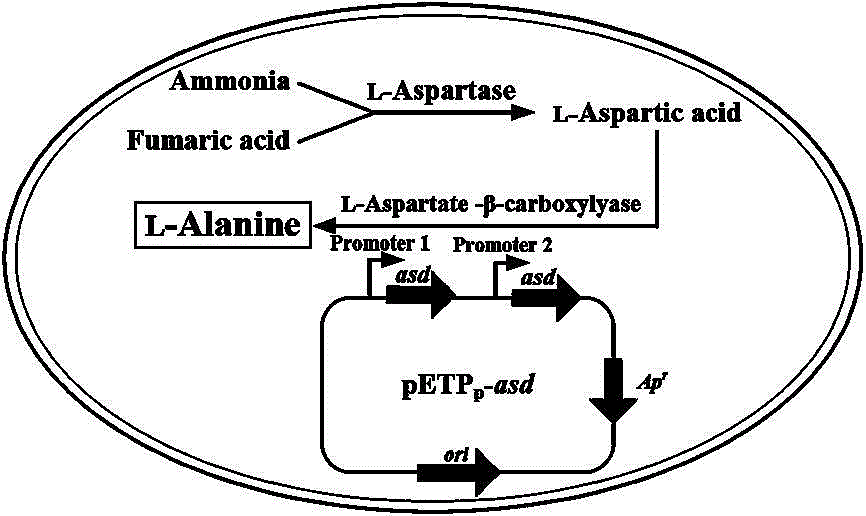
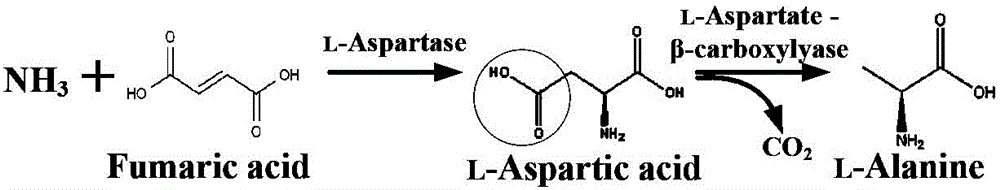
The invention relates to a constitutive expression genetically engineered bacterium Escherichia coli CICC 11032S for producing L-alanine. The host is escherichia coli CICC 11022S (same as CGMCC No. 5450) producing L-aspartase, and contains L-aspartate beta-decarboxylase gene of comamonas testosterone CICC 11023S (same as CGMCC No. 6083). By utilizing the constructed engineered bacterium for whole-cell high-density catalysis, fumaric acid and ammonia water can be efficiently conversed for producing L-alanine, the output is 112.7 g / L, the production rate is 12.5 g / (L*h), and the conversion rate is 93.9%. The substrates are cheap, the production process is simple, by-products are less, the production cost is effectively reduced, and extremely good application value is provided.
Owner:CHINA NAT RES INST OF FOOD & FERMENTATION IND CO LTD +1
Mixed bacterium for efficiently degrading atrazine and fermental culture method
ActiveCN105802874APromote growthStrong Atrazine DegradabilityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesSaccharumBurkholderia glathei
Owner:山东鲁虹智慧农业研究院
Iron-reducing comamonas and application thereof
InactiveCN101586092AUtilize a broad spectrumHas restoreBacteriaMicroorganism based processesReduction ActivitySucrose
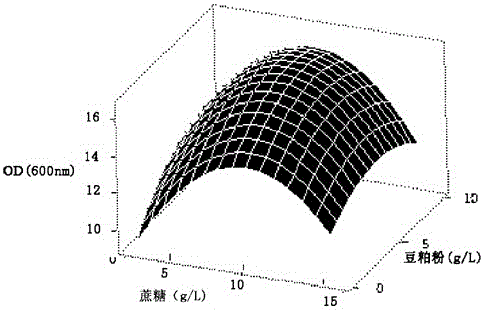
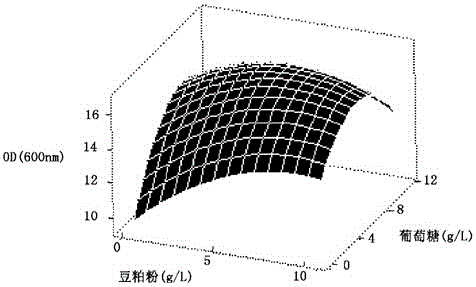
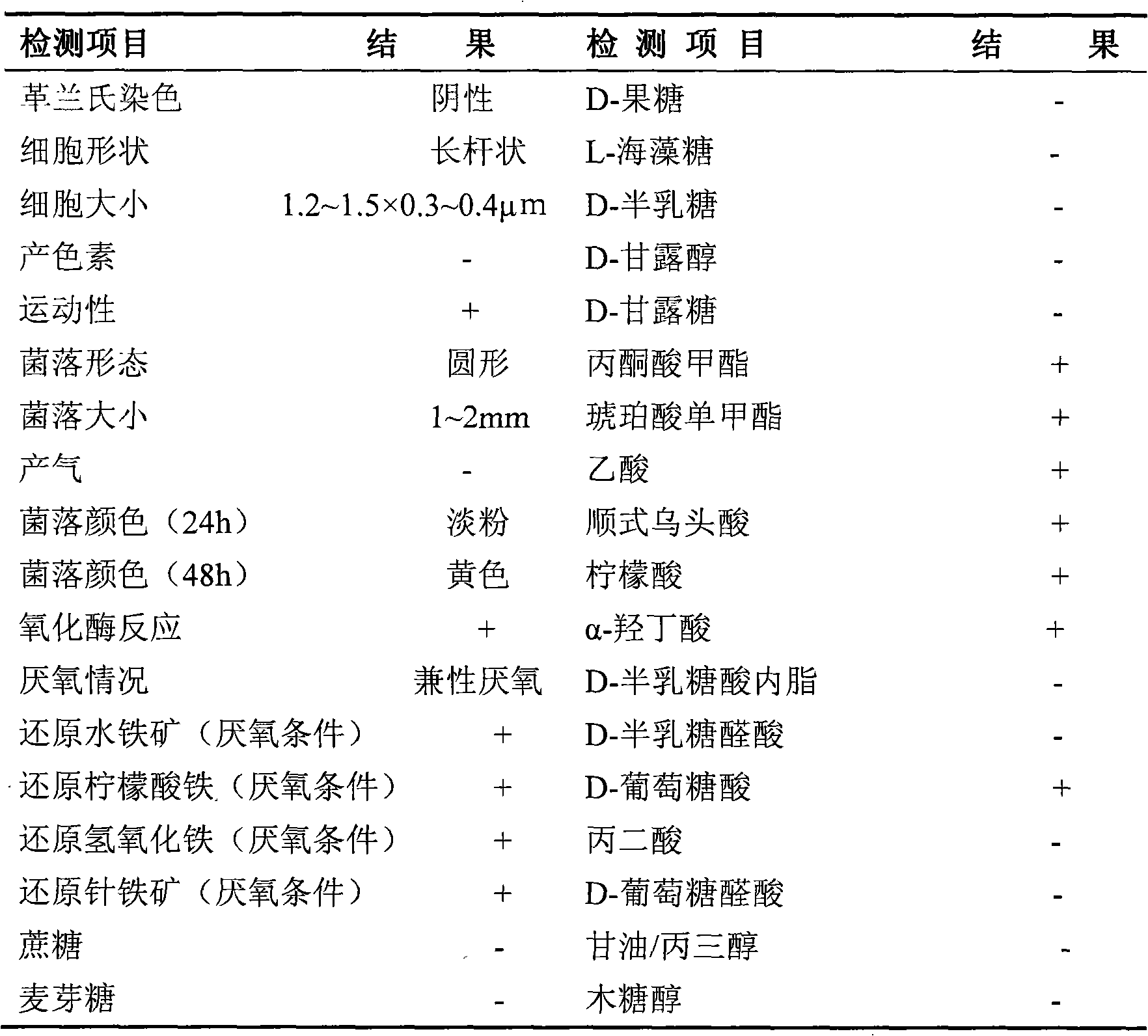
The invention discloses an iron-reducing comamonas and an application thereof. The inventor screens the iron-reducing comamonas with the humus reduction activity and the iron reduction activity by a great deal of experiments. The bacteria can reduce the ferric iron such as ironic citrate, iron hydroxide, ferrihydrite and goethite; and reduce the humus and the humic model AQDS (anthraquinone-2, 6-disulfonic acid). The iron-reducing comamonas is the facultative anaerobe, has wide electro donor spectrum. The electro donors which can be oxidized by the bacteria in the anaerobic condition are glycerine, glucose and sucrose.
Owner:GUANGDONG INST OF ECO ENVIRONMENT & SOIL SCI
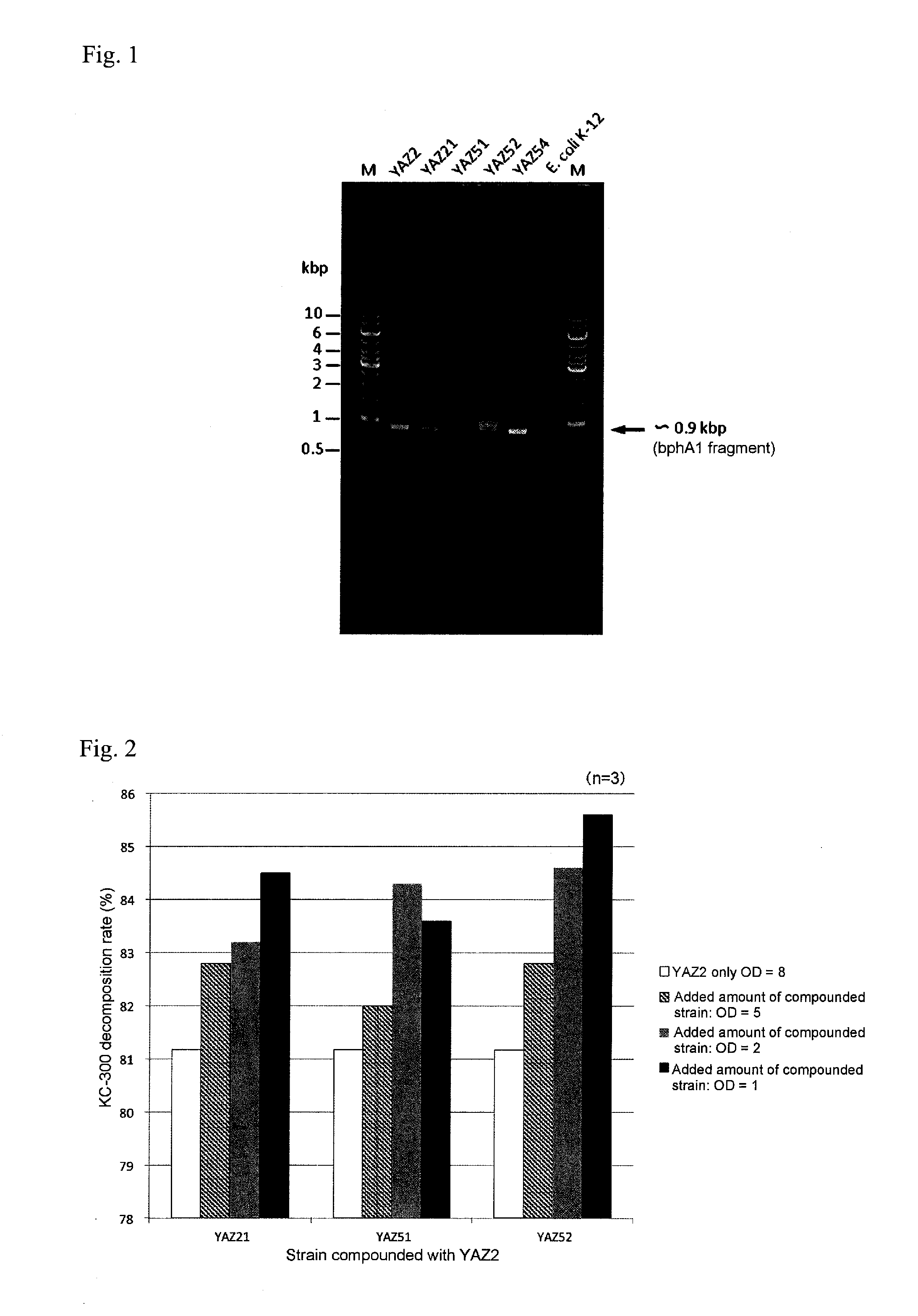
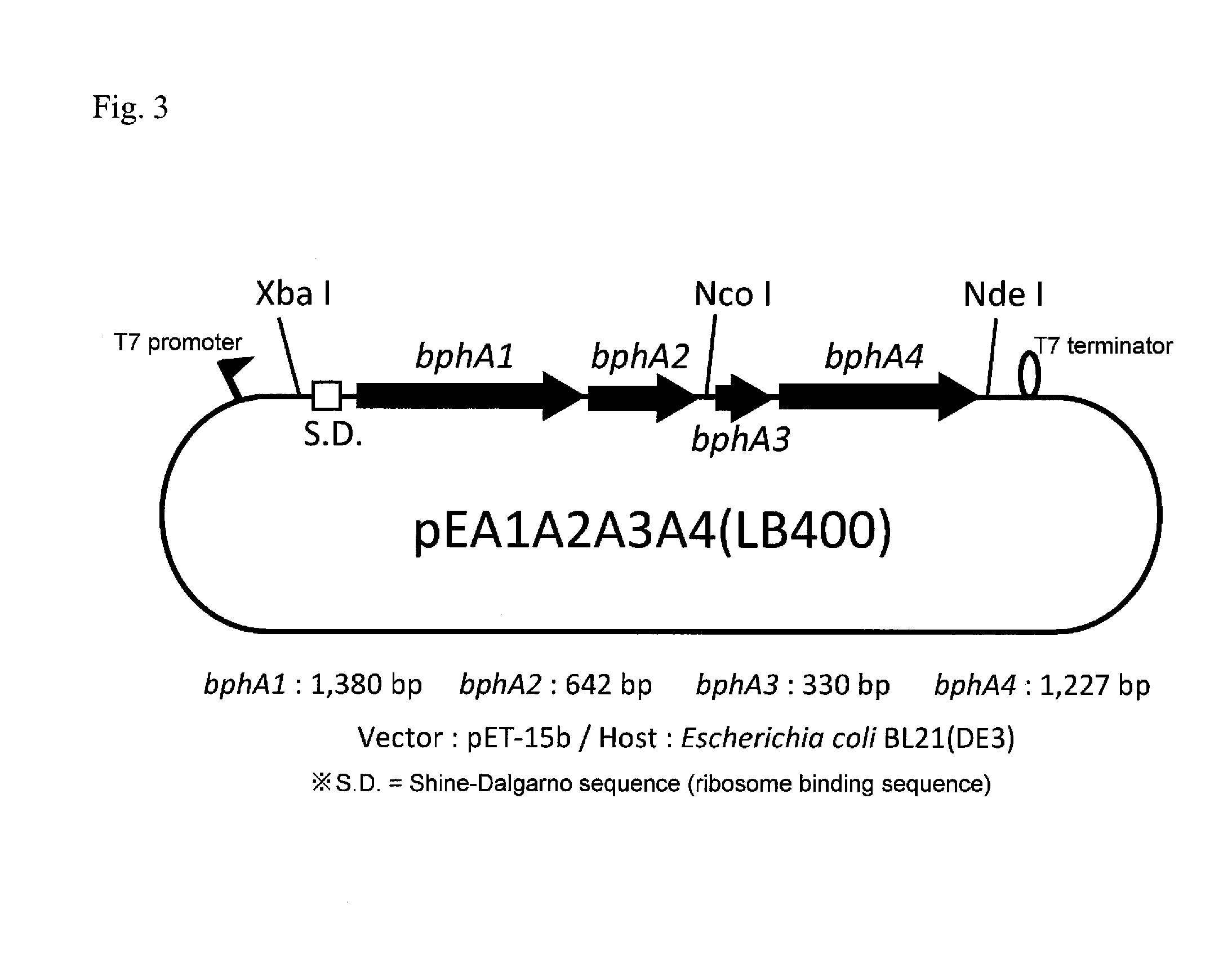
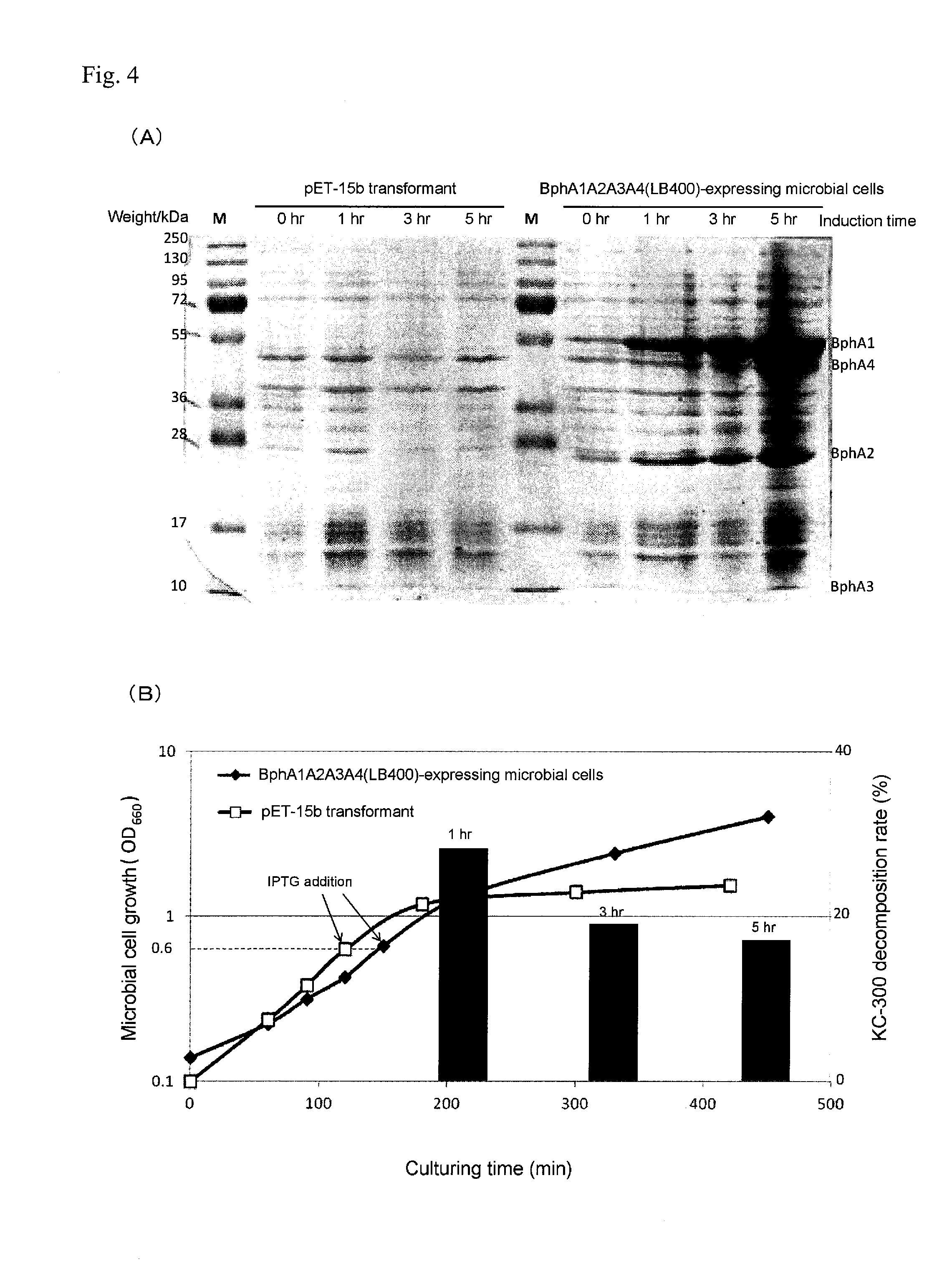
Polychlorinated biphenyl detoxifying complex composition and method for manufacturing same
InactiveUS20160279456A1High PCB decomposition activityGood transportabilityBacteriaOxidoreductasesGenus AchromobacterMicroorganism
Provided is a polychlorinated biphenyl-decomposing composition obtained according to a method comprising respectively culturing at least one main microbial strain belonging to Comamonas species and having biphenyl dioxygenase, and at least one complementary microbial strain selected from the group consisting of Pseudomonas species, Achromobacter species, Rhodococcus species and Stenotrophomonas species and having biphenyl dioxygenase, and mixing at least two types of microbial cells recovered from each of the culture media. A composition containing these compounded microorganisms is useful for efficiently decomposing or detoxifying comparatively low concentrations of PCBs present in large amounts in waste products contaminated with polychlorinated biphenyls.
Owner:YAMAGATA UNIVERSITY
Comamonas capable of effectively degrading picolinic acid and application of comamonas
The invention provides comamonas capable of effectively degrading picolinic acid and an application of the comamonas, and belongs to the technical field of bioengineering. According to the invention, a picolinic acid degrading bacterium, namely comamonas, is separated and screened out, and the comamonas is classified and named as comamonas sp., which is preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center with preservation number of CGMCC NO.10700. The comamonas disclosed by the invention has the advantages that the comamonas is capable of effectively degrading the picolinic acid within a relatively wide pH value range, in particular under the circumstance of relatively high alkalinity; and the comamonas, as a biological enhancing preparation, can be applied to aerobic biological treatment of picolinic acid wastewater in weak base and weak acid environments; therefore, the comamonas has a broad application prospect.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Compound microorganism water purifying agent and application thereof
InactiveCN108624531AHigh activityImprove processing efficiencyFungiBacteriaChemical oxygen demandDecomposition
The invention belongs to the technical field of sewage treatment, and discloses a compound microorganism water purifying agent and an application thereof. The compound microorganism water purifying agent comprises a microorganism and a carrier, the microorganism comprises clostridium, saccharomycetes, micrococcus, acidobacteria, bacteroid, rhizobia, burkholderia cenocepacia, thiobacillus, opitutae, hydrogenophilales, lysobacter, brevundimonas, xanthomonas, comamonas, rhodocyclus and rhodospirillum, and the microorganism is fixed onto the carrier. The compound microorganism water purifying agent has high activity and is high in treatment efficiency, long-time domestication and selection is omitted, a short stable period is achieved in a treatment system, strains in the compound microorganism water purifying agent are cooperatively interact, utilization and metabolic decomposition of nutrient substances in water by the microorganism are facilitated, and COD (chemical oxygen demand) and ammonia nitrogen are efficiently reduced.
Owner:BEIJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Selenium-resistant strain Comamonas testosterone GX-A1 and application thereof
The invention belongs to the technical field of microbiology, and particularly relates to a selenium-resistant strain Comamonas testosteroni GX-A1 and an application of the same. The taxonomic name of the selenium-resistant strain Comamonas testosterone GX-A1 is Comamonas testosterone; the selenium-resistant strain Comamonas testosterone GX-A1 is preserved in Guangdong Microbial Culture Collection Center on December 10, 2020, and the preservation number is GDMCC No.61357. The selenium-resistant strain Comamonas testosterone GX-A1 disclosed by the invention has the advantages that the removal rate of the selenium in the soil is up to 37.44% at most under the condition that the selenium concentration is 2000 mu g / mL. The result can provide strain resources for bioremediation of selenium-polluted areas and provide reference for development and utilization of selenium resources.
Owner:南宁市博发科技有限公司
Microorganism blender, preparation and application of preparation thereof
InactiveCN109679865AEfficient removalHas sediment digestion effectFungiBacteriaMicroorganismEutrophication
The invention discloses a microorganism blender, a preparation and an application of the preparation thereof and relates to the technical field of environmental governance. The microorganism blender comprises the following components by weight percent: 5-15% of photosynthetic bacteria, 12-25% of lactic acid bacteria, 5-15% of saccharomycetes, 20-35% of bacillus, 8-20% of nitrifying bacteria, 8-20%of denitrifying bacteria, 0-10% of filamentous bacteria, 0-10% of phosphate-solubilizing bacteria and 0-10% of comamonas. According to the invention, after the blender is added into water or sludge,eutrophication materials in water or sludge can be effectively removed and a certain effect of digesting bottom mud can be achieved.
Owner:ANHUI JIAMING ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION TECHCO
Aquatic comamonas and culture method and application thereof
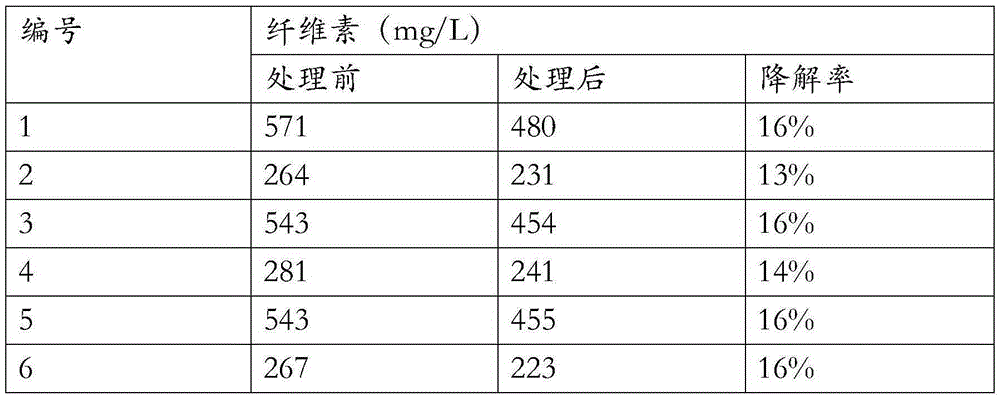
ActiveCN105420170AReduce CODGood economic valueBacteriaMicroorganism based processesCelluloseComamonas
The invention provides aquatic comamonas and a culture method and application thereof. The aquatic comamonas is KY-02, and the preservation number is CGMCC No.11866. The aquatic comamonas KY-02 can degrade cellulose with the content of 1500 mg / L in sewage, so that the COD of sewage is lowered, the degradation onset time is short, and the degradation rate can reach about 15% on the second day. Compared with physical and chemical methods, the aquatic comamonas has the advantages of being low in cost, free of secondary pollution and the like, and has the wide application prospect and the good economic value in the field of papermaking sewage treatment.
Owner:TIANJIN CARING TECH DEV
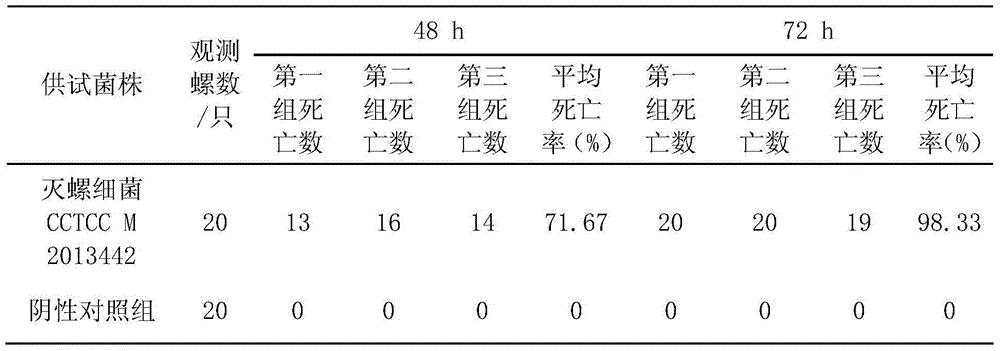
Oncomelania killing bacteria and application thereof
The invention discloses an oncomelania killing bacteria. The biological collection number of the oncomelania killing bacteria (comamonas sp.X3) is CCTCC M 2013442; and the oncomelania killing bacteria CCTCC M 2013442 is comamonas bacteria which is screened from moribund negative oncomelania and can quickly and effectively kill oncomelania. The bacteria provided by the invention is capable of killing oncomelania and can be directly used as a biological molluscacide; by comparing the biological molluscacide prepared from the oncomelania killing bacteria CCTCC M 2013442 with the traditional chemical molluscacide, the preparation method is simple and environment-friendly while the cost is low.
Owner:ANHUI AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Degradation bacterium capable of efficiently degrading propyzamide and application thereof
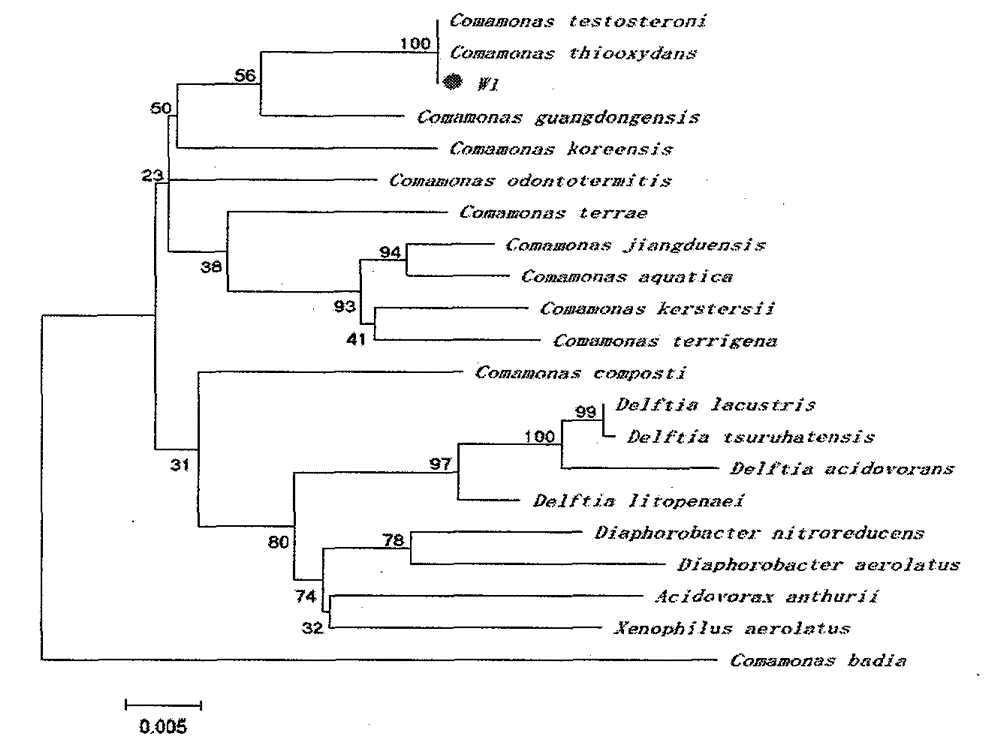
The invention belongs to the field of microorganisms, relates to a degradation bacterium W1 for propyzamide, and belongs to comamonas; the degradation bacterium is preserved in China Center for Type Culture Collection on October 11th, 2013, the preservation number is CCTCC NO. M2013464, and the registered number of 16S rRNA in Genebank is 1680505. The bacterium can degrade 90% of 100mg / L of propyzamide within 8 hours. The degradation bacterium is used for degrading herbicide propyzamide, and is used for biological purification of water, soil and agriculture products polluted by the propyzamide.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Mixed bactericide capable of being applied to monitoring pollution of biodegradable organic matters and microorganisms in water and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104450587AShort timeImprove timelinessBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementChemistryWater quality
The invention discloses a mixed bactericide capable of being applied to monitoring pollution caused by biodegradable organic matters and microorganisms in water and a preparation method thereof. The active ingredients of the bactericide is 10-100 parts of one or more of Klebsiella, aeromonas, comamonas, stenotrophomonas, acinetobacter, microbacteria and shewanella spp. The bactericide disclosed by the invention can be applied to determining biodegradable organic matters in surface water, ground water, source water and micro-polluted water and predicting microorganism pollution and plays an important role in monitoring environment water quality.
Owner:INST OF URBAN ENVIRONMENT CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Immunopotentiating composition and process for producing same
Disclosed is an immunopotentiating composition comprising an effective immunostimulating substance which can activate natural immunity and a subsequent immunity mediated by lymphocytes without causing any damage to cells. Specifically disclosed is an immunopotentiating composition which is characterized by comprising, as an active ingredient, an immunostimulating substance produced by decomposing at least one bacterium selected from an MRE symbiotic bacteria group consisting of Bacillus sp. (FERM BP-11209), Lysinibacillus fusiformis (FERM BP-11206), Bacillus sonorensis, Lysinibacillus sp. (FERM BP-11207) and Comamonas sp. (FERM BP-11208).
Owner:MEISHO
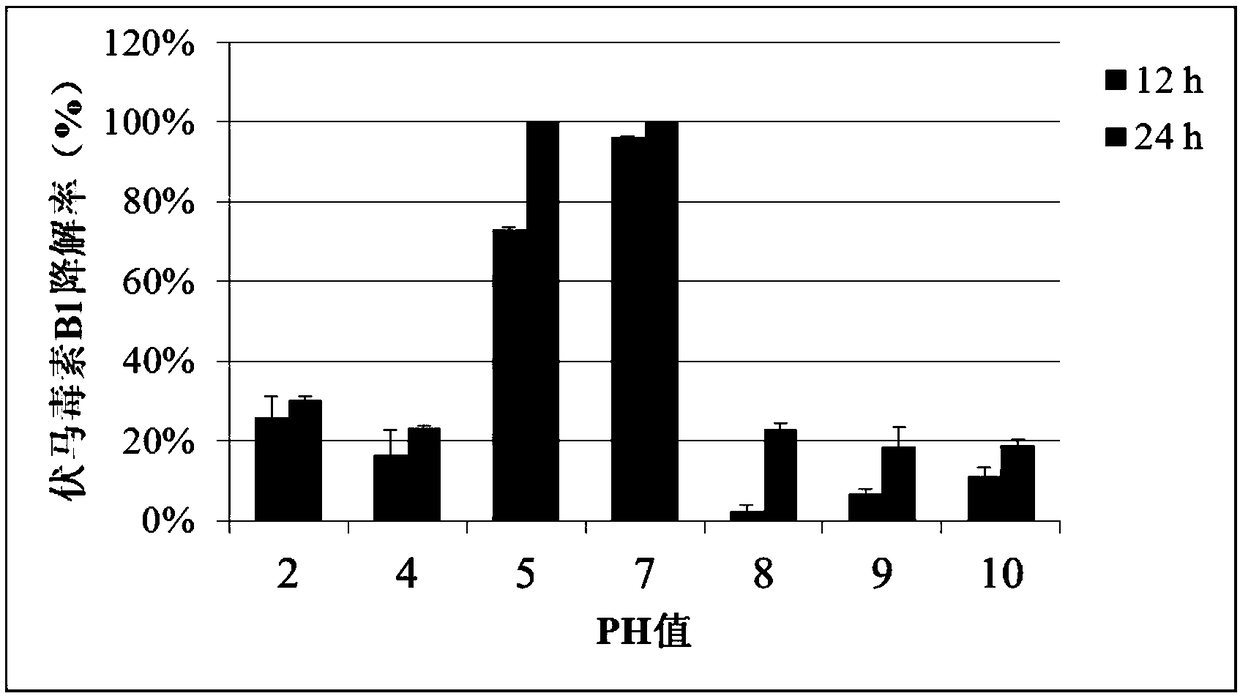
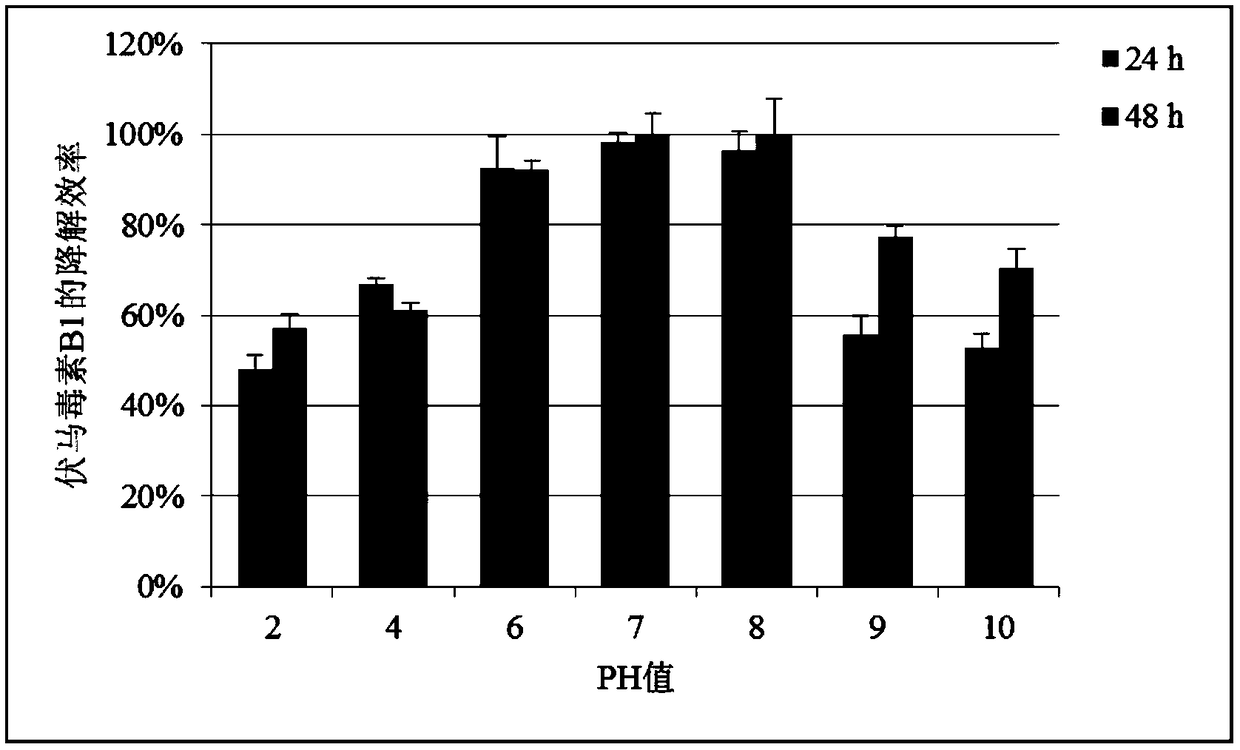
Mixed bacterial flora for degrading fumonisin B1 and crude enzyme preparation thereof
InactiveCN109234196AImprove degradation rateImprove degradation efficiencyBacteriaMicroorganism based processesSucroseSaccharum
The invention discloses a mixed bacterial flora for degrading fumonisin B1 and a crude enzyme preparation thereof. The mixed bacterial flora for degrading fumonisin B1 comprises the following components: Pseudomonas (Pseudomonas), Chaetomonas (Comamonas) and Sphingobacterium (sphingobacterium), wherein the total effective viable number of the mixed microflora accounts for more than 90% of the total number of the mixed microflora. The mixed bacterial flora degrading fumonisin B1 of the invention is amplified and cultured in MM culture medium containing sucrose, the bacterial body obtained by centrifugation is broken by ultrasonic wave, and the supernatant is lyophilized to obtain crude enzyme preparation. The mixed bacterial flora degrading fumonisin B1 of the invention is amplified and cultured in MM culture medium containing sucrose. The fumonisin B1 degradation rate of the mixed microflora and the crude enzyme preparation thereof obtained by the invention is above 90% in 24 hours. The mixed microbial flora and its crude enzyme preparation have the characteristics of simple fermentation and low production cost, and have broad application prospects for detoxification of fumonisin B1 in feedstuffs.
Owner:SHANGHAI ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Method of removing recalcitrant organic pollutants
InactiveUS9994470B2Reducing the recalcitrant chemical oxygen demand (COD)Efficient biodegradationBacteriaTreatment using aerobic processesChemical oxygen demandComamonas
Recalcitrant chemical oxygen demand (COD) of a liquid is reduced in a water treatment system. The method includes pretreating the liquid in a pretreatment unit to remove indigenous bacteria or microbes to a population level below which the indigenous organisms can interfere with the screened and externally introduced microorganisms. The liquid is then provided to a reactor that has a filter bed formed with a carrier material. Special microbes are screened and used to colonize the carrier material to remove recalcitrant COD. A biofilm is cultured on the surface of the carrier material to immobilize the screened microbes in the reactor. The method further includes percolating the liquid from the pretreatment unit through the filter bed colonized with the screened microbes to degrade at least part of the recalcitrant COD under aerobic conditions. In one embodiment, the filter is formed with biological granular activated carbon (GAC) as the carrier material and the screened microbes comprise at least one microbial species selected from the group consisting of Bacillus, Comamonas, Arthrobacter, Micrococcus, Pseudomonas, Pediococcus, Achromobacter, Flavobacterium, Mycobacterium, Rhodanobacter, Stenotrophomonas and Yeast.
Owner:BL TECH INC
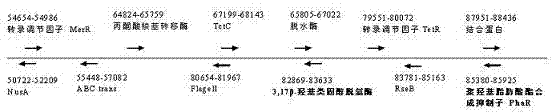
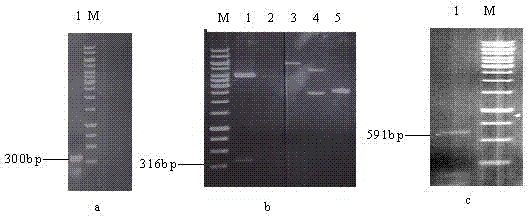
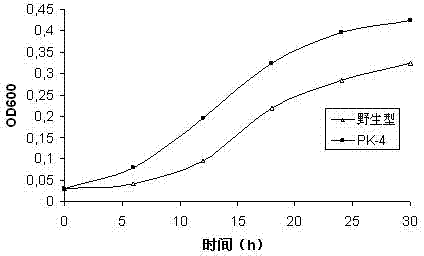
Genetically engineered bacterium for rapidly degrading methyltestosterone and application thereof
InactiveCN103087957APromote degradationEfficient degradationBacteriaWater contaminantsBiotechnologyComamonas
The invention provides a genetically engineered bacterium for rapidly degrading methyltestosterone and an application thereof. The process comprises the steps of knocking a PhaR gene of testosterone comamonas to obtain a high-expression engineering strain PK-4 capable of generating 3,17 beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase by a gene homologous recombination technology; preparing bacterial suspension from the engineering strain PK-4, inoculating into waste water generated by livestock and poultry and aquatic product cultivation containing testosterone pollutant; cultivating for 48 hours when the temperature is 25 DEG C and the rotating speed is 150rpm, wherein the degradation rate of the methyltestosterone is 78.36-90.23%; the pH value is 6-8 in the waste water of which the methyltestosterone concentration is 1mg / L; the temperature is 15-25 DEG C; and cultivating for 48 hours at 150rpm in an oscillating manner, so that the degradation rate of the methyltestosterone can achieve 60.15%-90.23%. The genetically engineered bacterium has the beneficial effects that the engineering strain PK-4 of removed testosterone comamonas of the PhaR gene is obtained for the first time; and the genetically engineered bacterium is strong in adaptive capacity in swine wastewater, and fast in removal speed of the methyltestosterone, and has a great application value in the aspects of treatment and disposal of breeding waste and bioremediation of environmental pollution.
Owner:JILIN AGRICULTURAL UNIV
Anode photosynthetic solar fuel cell system additionally provided with degrading strain and application thereof
InactiveCN111430766AAchieve absorptionDual useContaminated soil reclamationBiochemical fuel cellsComamonasCell system
The invention discloses an anode photosynthetic solar fuel cell system additionally provided with degradation strains and application thereof. According to the anode photosynthetic solar fuel cell system, at least one of additionally added degrading bacteria, namely comamonas or bacillus, is added, and the abundance of electrochemical active microorganisms in soil is improved in a manner of externally connecting the degrading strain so that the capability of degrading surrounding environmental pollutants is improved, and the system has a good application prospect in treating Cr and NO3-N pollution in the soil.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH +1
Composite microbial agent capable of degrading agricultural wastes
ActiveCN106834170AAvoid hardening and other problemsImprove physical and chemical propertiesBacteriaFood processingMicrobial agentComamonas
The invention discloses a composite microbial agent capable of degrading agricultural wastes and belongs to the technical field of microbes. The active ingredients of the agent refer to the following strains separated from environments such as termite guts, composted straws and sediments of South China Sea: enterobacterium (Enterobacter sp.)YC105C, comamonas (Comamonas serinivorans) C35, rhodococcus (Rhodococcus sp.) L17 and bacillus (Bacillus ligniniphilus) L1. The composite microbial agent contains the concentrated bacterium powder of the following components in percentage by mass: 20-30% of enterobacterium, 30-40% of comamonas, 10-20% of rhodococcus and 20-40% of bacillus. The composite microbial agent is capable of degrading the agricultural wastes such as wheat straws, maize straws and green soybean straws, the quantity of the straws returned to the field is increased, and the cultivated land quality is improved, so that the growth of crops is promoted.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Probe composition group for detecting Pseudomonas bacteria
ActiveCN105734115AStrong specificityImprove detection accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationEscherichia coliBacteroides
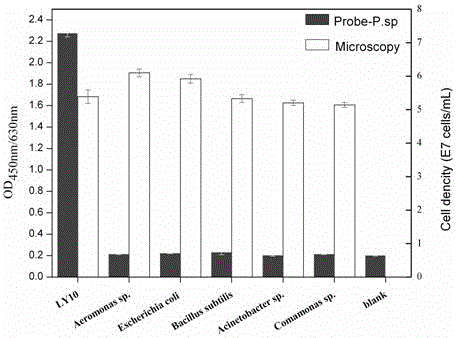
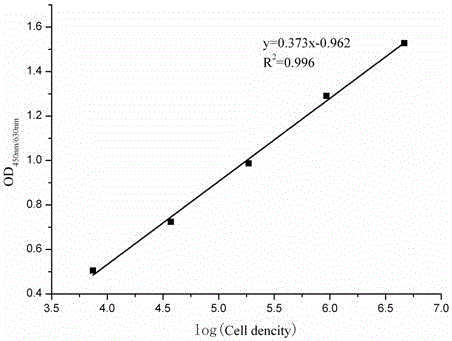
A probe composition group for detecting Pseudomonas bacteria belongs to the technical field of nucleic acid detection. The probe composition is composed of three oligonucleotide probes. An analysis probe has as a nucleotide sequence shown in SEQ ID NO:1; a capture probe has a nucleotide sequence shown in SEQ ID NO:2, and has biotin label at the 3' terminal; a signal probe has a nucleotide sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 3, and has isothiocyanic acid label (FITC) at the 5' terminal. The probe composition has bioinformatics specificity, is able to distinguish Pseudomonas, Comamonas, Aeromonas, Acinetobacter, Bacillus subtilis and Escherichia coli; the probe has quantitative linear range of 7.08*10<3> -6.31*10<6> cells / mL, and the linear equations are as below: y=0.373x-0.962, R<2>=0.996. The probe composition can be used for qualitative and quantitative analysis of Pseudomonas bacteria.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
A kind of compound bacteria capable of rapidly degrading 17β-estradiol and its preparation method and application
InactiveCN107523513BGood synergyEfficient degradationBacteriaContaminated soil reclamationBiotechnologyInorganic salts
The invention discloses a compound bacterium capable of rapidly degrading 17β-estradiol and its preparation method and application. The compound bacterium consists of Rhodococcus DSH with a preservation number of CGMCC No. 12392 and testosterone with a preservation number of CGMCC No. 15223. The composition of Comamonas QYY, the 16S rDNA sequences of Rhodococcus DSH and Comamonas testosteroni QYY are respectively shown in SEQ ID NO: 1 and SEQ ID NO: 2 in the sequence listing. The strain DSH and the strain QYY were respectively inoculated into the inorganic salt medium to obtain the DSH bacterial liquid and the QYY bacterial liquid, and the volume ratio of the two bacterial liquids of DSH and QYY was 1.5:1, and the efficient degradation of 17β-estradiol was obtained. Complex bacteria. The composite bacterium provided by the invention has high-efficiency degradation performance on 17β-estradiol, and has strong ability to adapt to the external environment. Cultivate the complex bacteria in the inorganic salt medium with 17β-estradiol as the only carbon source for continuous culture for 72 hours, and can quickly and efficiently degrade 17β-estradiol with a concentration lower than 50mg / L, and the degradation rate can reach more than 98%. .
Owner:NORTHEAST NORMAL UNIVERSITY
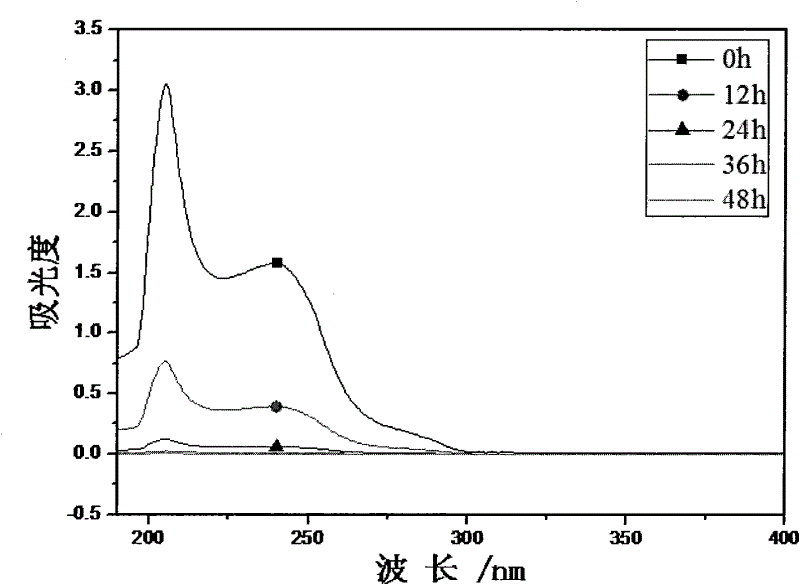
Method for degrading polyethylene terephathalate
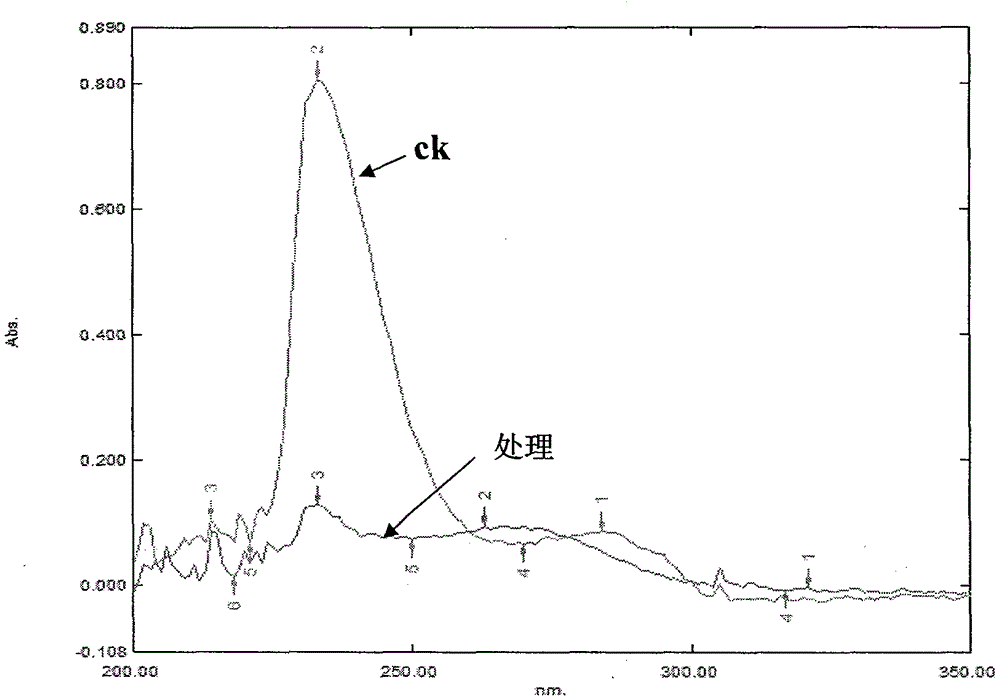
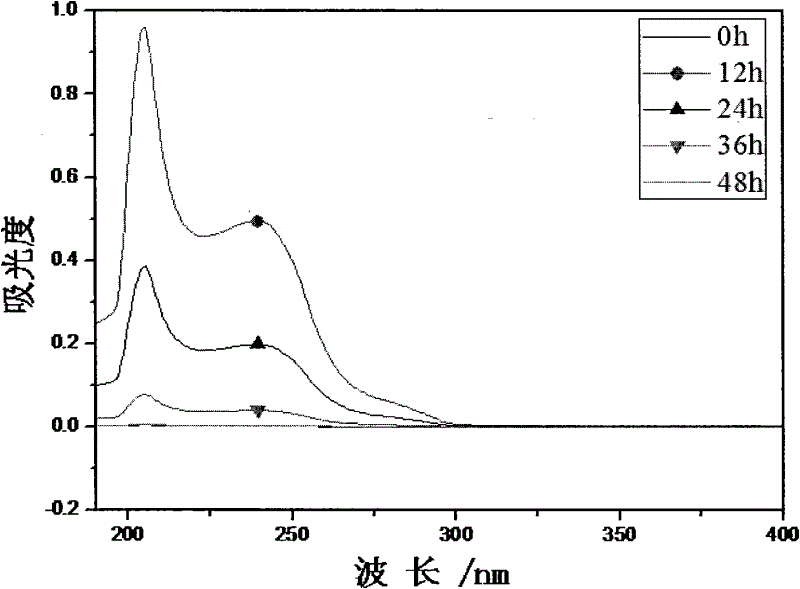
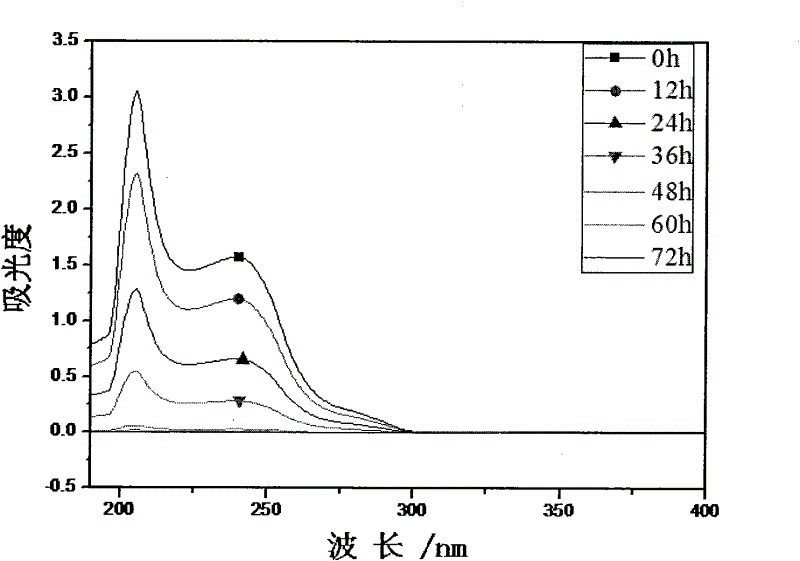
The invention discloses a method for degrading polyethylene terephathalate. The method mainly includes the following steps: 1, strain culture: comamonas testoseroni strain is cultured for 12-18h in a solid medium with inclined surface at 30-37 DEG C; 2, substrate solution preparation: 5-9 parts of substrate solution with the concentration of 1-5g / L are prepared, each part is 50ml and is respectively placed into a 150ml conical flask, and packing up and sterilizing for 25min are carried out at 121 DEG C; 3, substrate degradation: the strain in the step 1 is inoculated into the substrate solution in the step 2, so as to obtain degradation liquor, and shake culture is carried out at the rotating speed of 200r / min and at the temperature of 30-37 DEG C, so as to catalyze degradation on the substrate; 4, substrate degradation ratio detection: 400-190nm wavelength scanning is adopted, and variation of substrate content is judged according to absorption peak at 240nm; 5, substrate degradationproduct detection: 400-190nm wavelength scanning is adopted, and variation of degradation intermediate product content is judged.
Owner:TIANJIN POLYTECHNIC UNIV
Synergistic removal of sulfate and zn(ii) wastewater by sponge iron and microorganisms
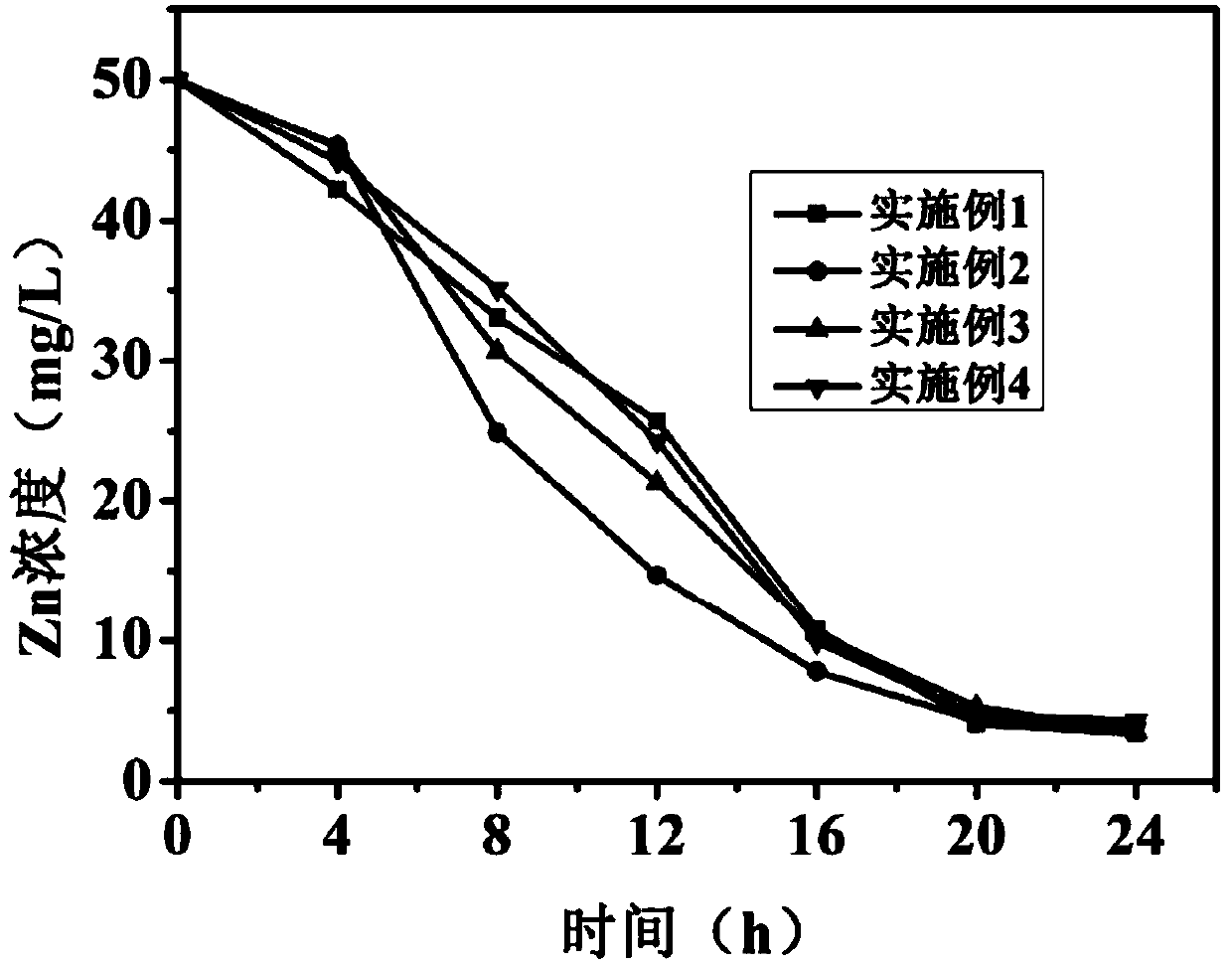
ActiveCN106007001BLarge specific surface areaHigh specific surface energyTreatment with anaerobic digestion processesComamonasSolid phases
The invention relates to a method for removing sulfate and Zn(II) wastewater by virtue of synergism of spongy iron and microorganisms. The method comprises the following steps of: mixing a spongy iron solution A, a bacterial suspension B of sulphate reducing bacteria and a bacterial suspension C of ferric reducing comamonas at a volume ratio of (1:1:1) to (1:3:4), aging the mixture for 40-60 minutes, repeatedly washing with deoxidization deionized water after reaction is finished, and soaking a product in a stroke-physiological saline solution, thereby obtaining a mixture of spongy iron and sulphate reducing bacteria / iron-reducing bacteria; mixing the mixture of spongy iron and sulphate reducing bacteria / iron-reducing bacteria with the sulfate and the Zn(II) wastewater, performing reaction at a room temperature for 20 hours or more, and purifying the wastewater sulfate and the Zn(II) at the same time. The method is capable of achieving the Zn(II) removal rate not less than 91%, required equipment is simple, the operation is convenient, reaction is finished at the normal temperature and a normal pressure, products are in a solid phase, the reaction system is in a liquid phase, the products are easy to separate, and the method is suitable for large-scale industrial production.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Method for promoting anaerobic digestion sludge heavy metal stability
PendingCN109626771AQuick fixSpeed up the digestion processWater contaminantsBiological sludge treatmentK pneumoniaeComamonas
The invention discloses a method for promoting anaerobic digestion sludge heavy metal stability. The method comprises the steps that iron reducing bacteria are added in anaerobic digestion sludge, andanaerobic digestion is conducted for 20-60 days at 25-37 DEG C; the iron reducing bacteria are selected from at least one of humus reductive corynebacterium, iron reducing comamonas and klebsiella pneumoniae. According to the method, heavy metal can form stable minerals, and then rapid fixation of the heavy metal is achieved. In the iron reducing bacteria iron reduction process, mineralization oforganic matter is coupled, and meanwhile the sludge digestion process is directly accelerated.
Owner:GUANGDONG INST OF ECO ENVIRONMENT & SOIL SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com