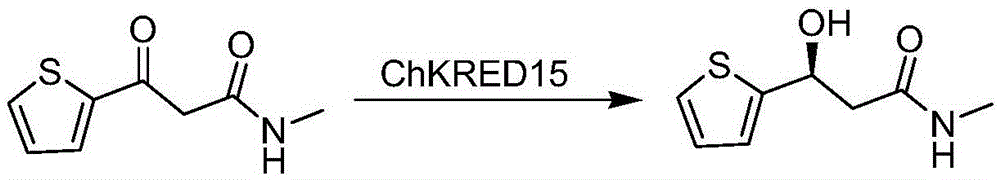Patents
Literature
32 results about "Chryseobacterium" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Chryseobacterium is a genus of Gram-negative bacteria. Chryseobacterium species are chemoorganotrophic, rod shape gram-negative bacteria. Chryseobacterium form typical yellow-orange color colonies due to flexirubin-type pigment. The genus contains more than 100 described species from diverse habitats, including freshwater sources, soil, marine fish, and human hosts.
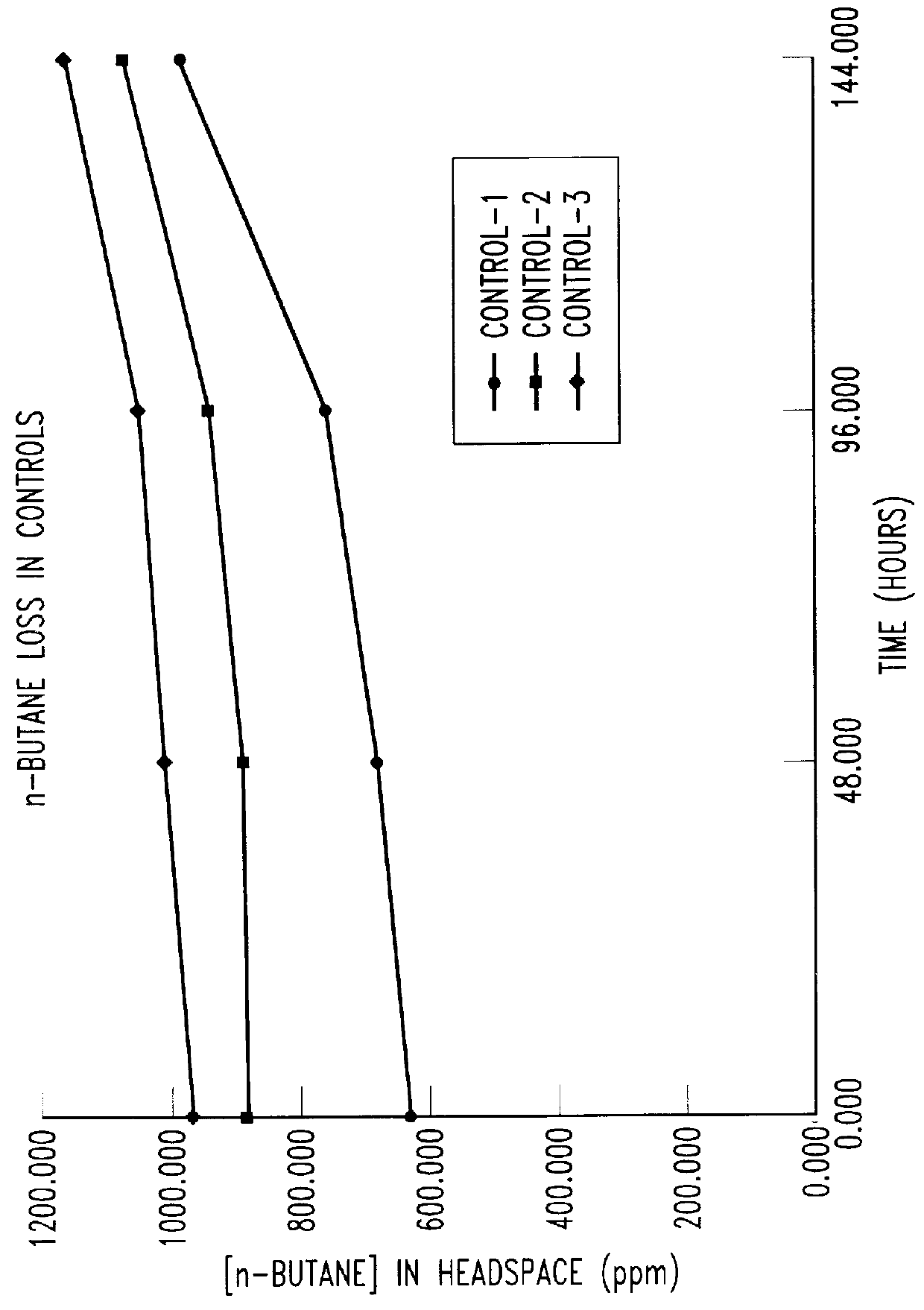
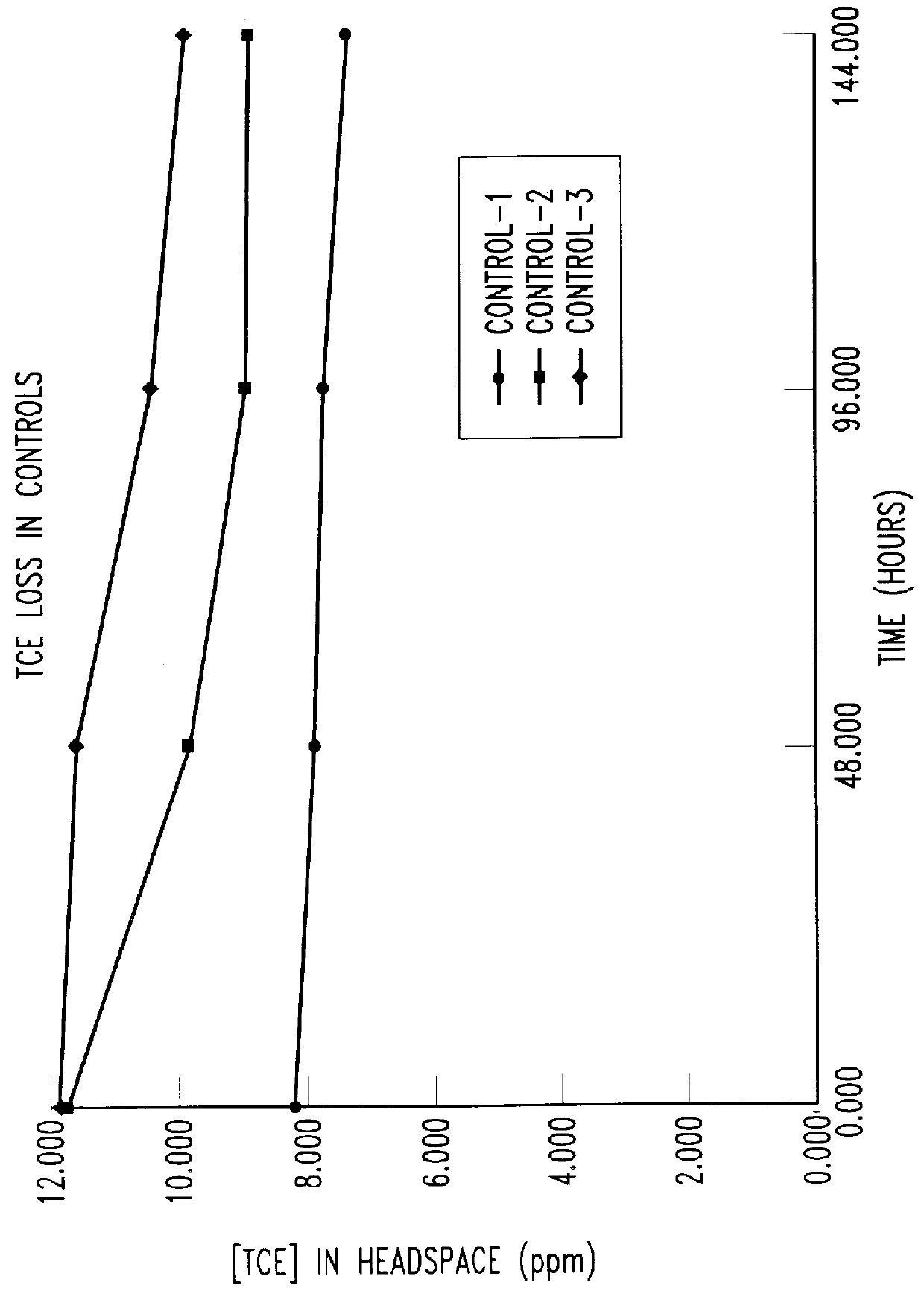
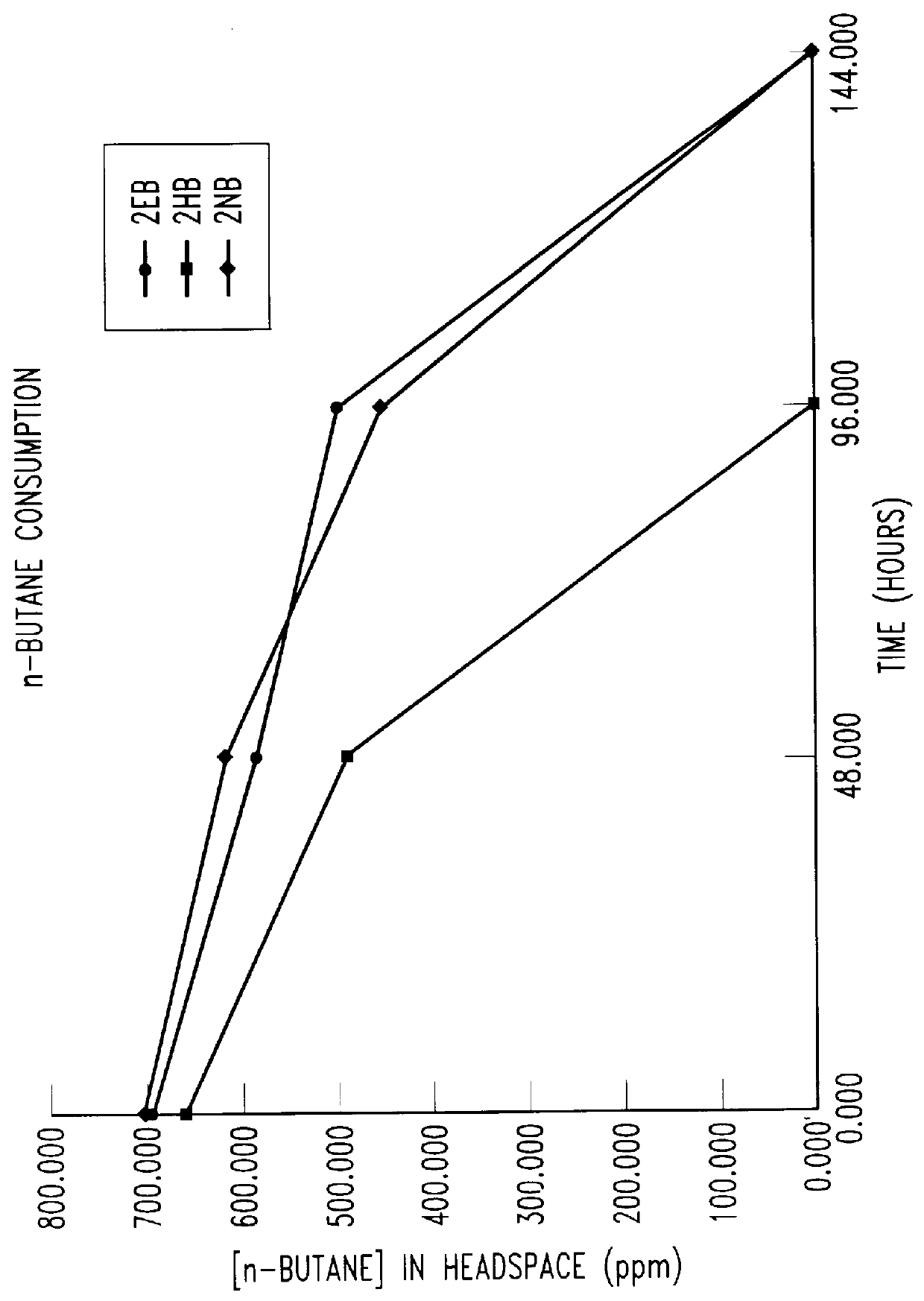
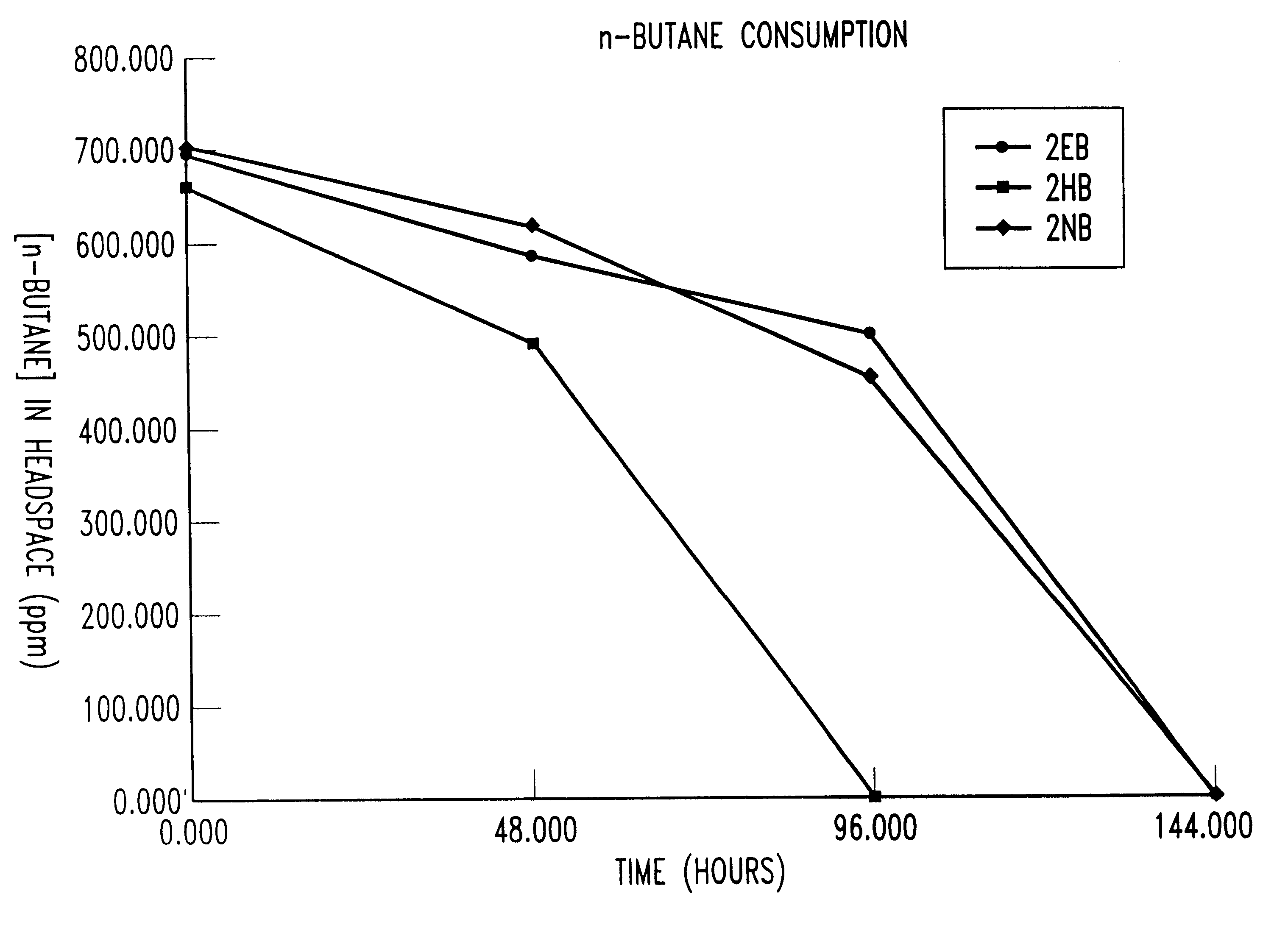
Bioreactor for remediation of pollutants with butane utilizing bacteria
InactiveUS6051130AReduce and eliminate hydrocarbon pollutantEasy to transportGas treatmentBacteriaBacteroidesComamonas
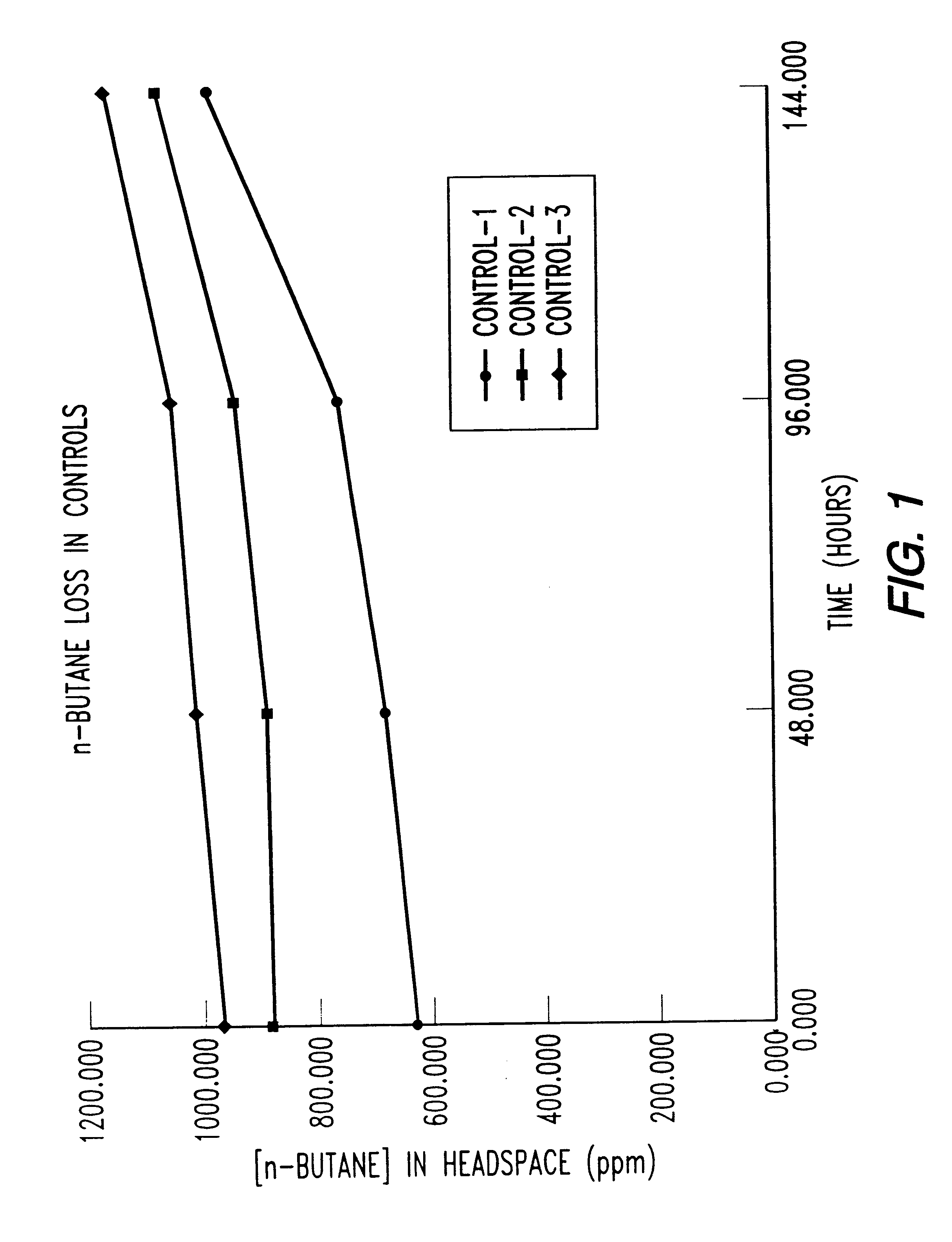
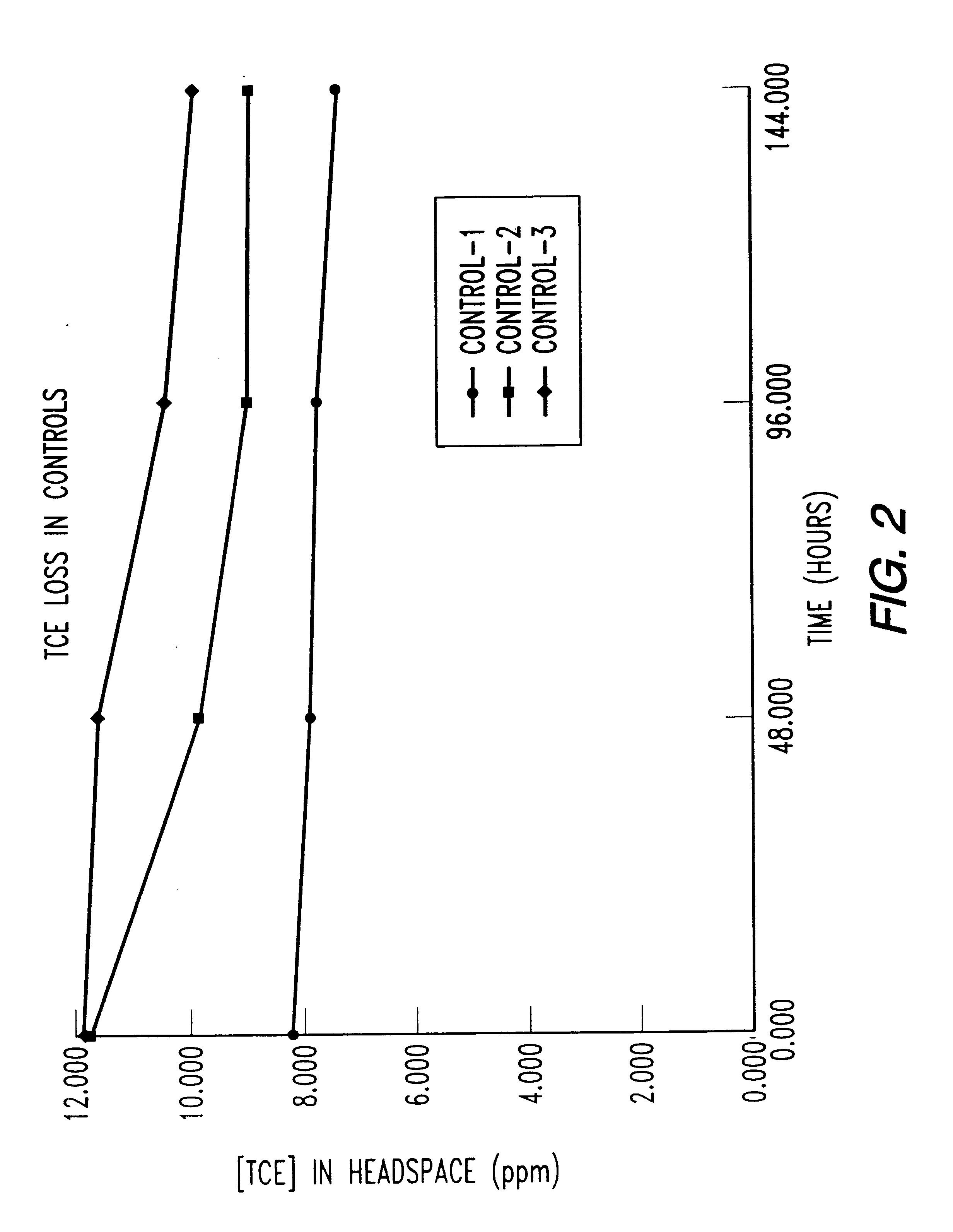
Butane-utilizing bacteria are used to degrade hydrocarbon pollutants such as trichloroethene (TCE). In-situ or ex-situ techniques may be used to reduce or eliminate hydrocarbon pollutants from liquid, gas and solid sources. In a preferred embodiment, TCE concentrations in various aqueous environments are reduced by contacting a contaminated water source with butane-utilizing bacteria in the presence of oxygen to degrade the TCE by cometabolism or direct metabolism. Suitable butane-utilizing bacteria include Pseudomonas, Variovorax, Nocardia, Chryseobacterium, Comamonas, Acidovorax, Rhodococcus, Aureobacterium, Micrococcus, Aeromonas, Stenotrophomonas, Sphingobacterium, Shewanella, Phyllobacterium, Clavibacter, Alcaligenes, Gordona, Corynebacterium and Cytophaga. The butane-utilizing bacteria have relatively low TCE toxicity in comparison with conventional methane-utilizing bacteria, and demonstrate an improved ability to degrade TCE.
Owner:GLOBAL BIOSCI
Bioremediation of pollutants with butane-utilizing bacteria
InactiveUS6210579B1Reduce and eliminate hydrocarbon pollutantEasy to transportGas treatmentTreatment using aerobic processesBacteroidesComamonas
Butane-utilizing bacteria are used to degrade hydrocarbon pollutants such as trichloroethene (TCE). In-situ or ex-situ techniques may be used to reduce or eliminate hydrocarbon pollutants from liquid, gas and solid sources. In a preferred embodiment, TCE concentrations in various aqueous environments are reduced by contacting a contaminated water source with butane-utilizing bacteria in the presence of oxygen to degrade the TCE by cometabolism or direct metabolism. Suitable butane-utilizing bacteria include Pseudomonas, Variovorax, Nocardia, Chryseobacterium, Comamonas, Acidovorax, Rhodococcus, Aureobacterium, Micrococcus, Aeromonas, Stenotrophomonas, Sphingobacterium, Shewanella, Phyllobacterium, Clavibacter, Alcaligenes, Gordona, Corynebacterium and Cytophaga. The butane-utilizing bacteria have relatively low TCE toxicity in comparison with conventional methane-utilizing bacteria, and demonstrate an improved ability to degrade TCE.
Owner:GLOBAL BIOSCI
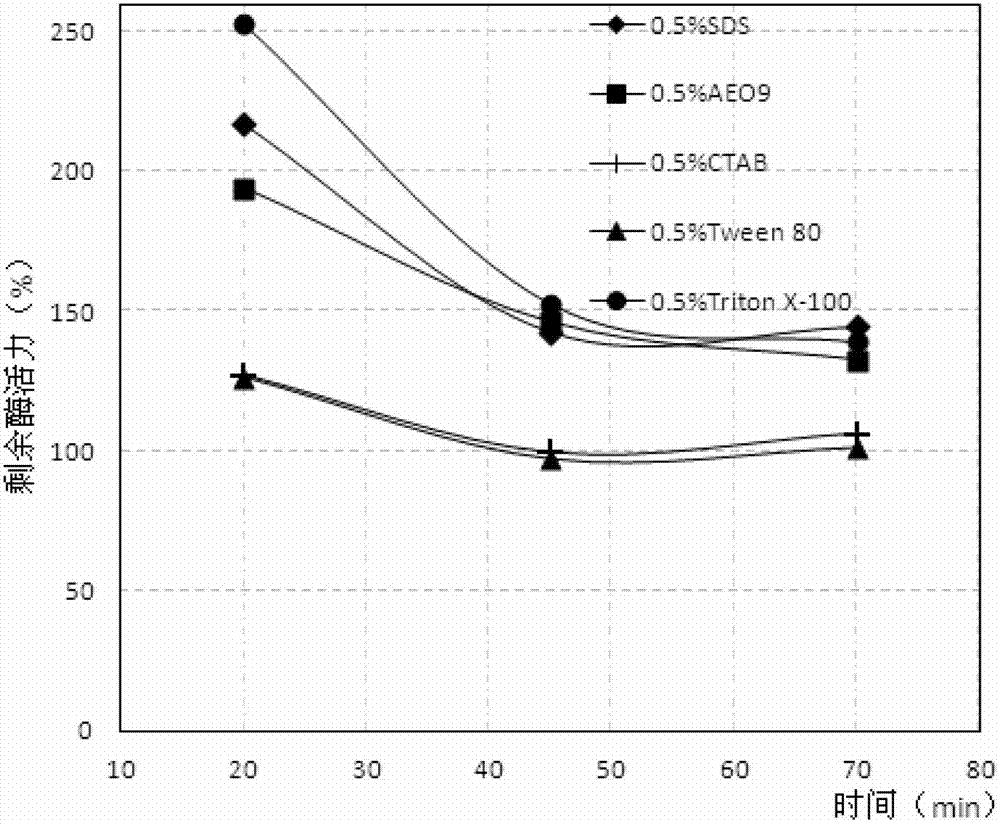
Strain producing surface active agent resistance lipase and surface active agent resistance lipase preparation method
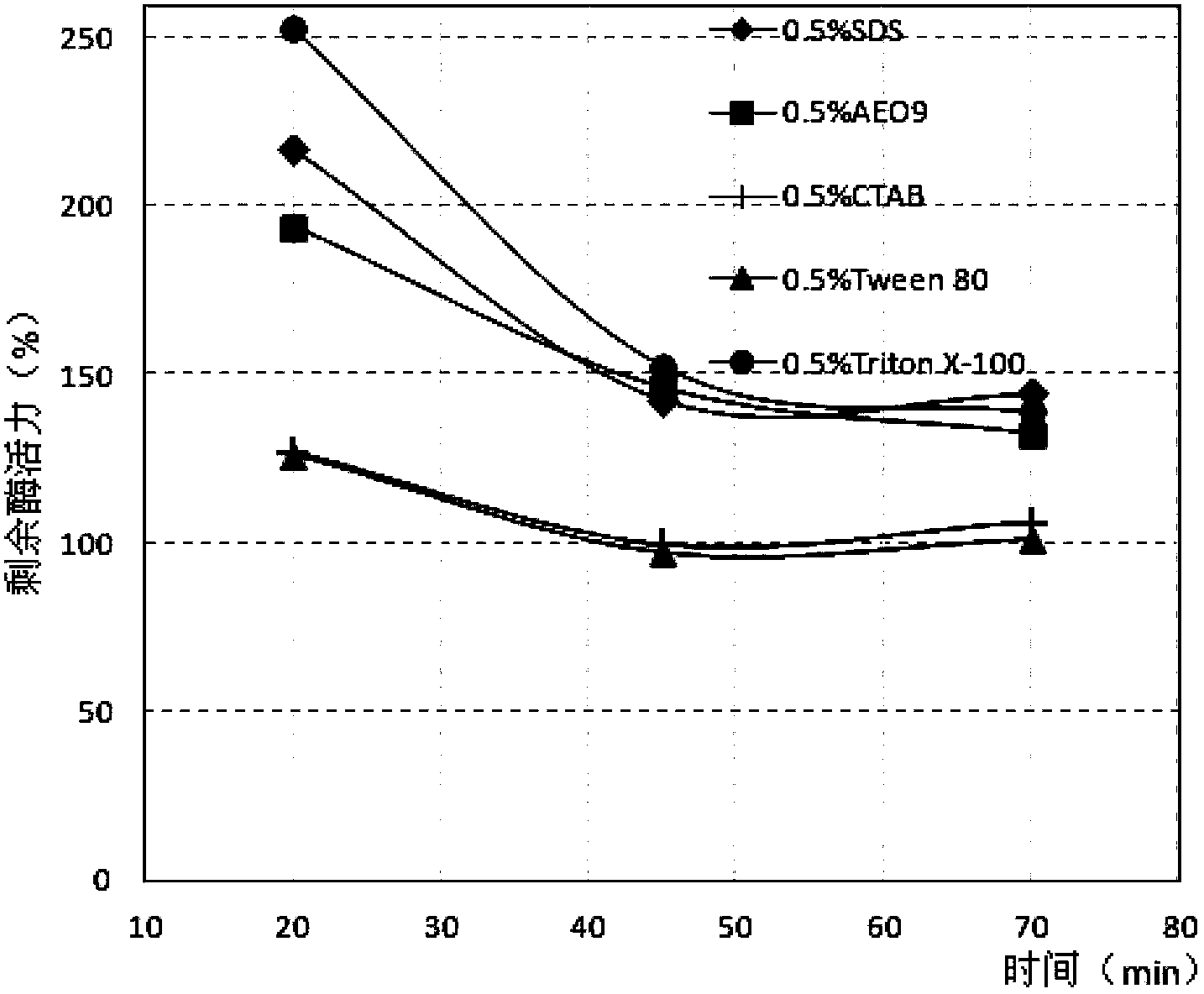
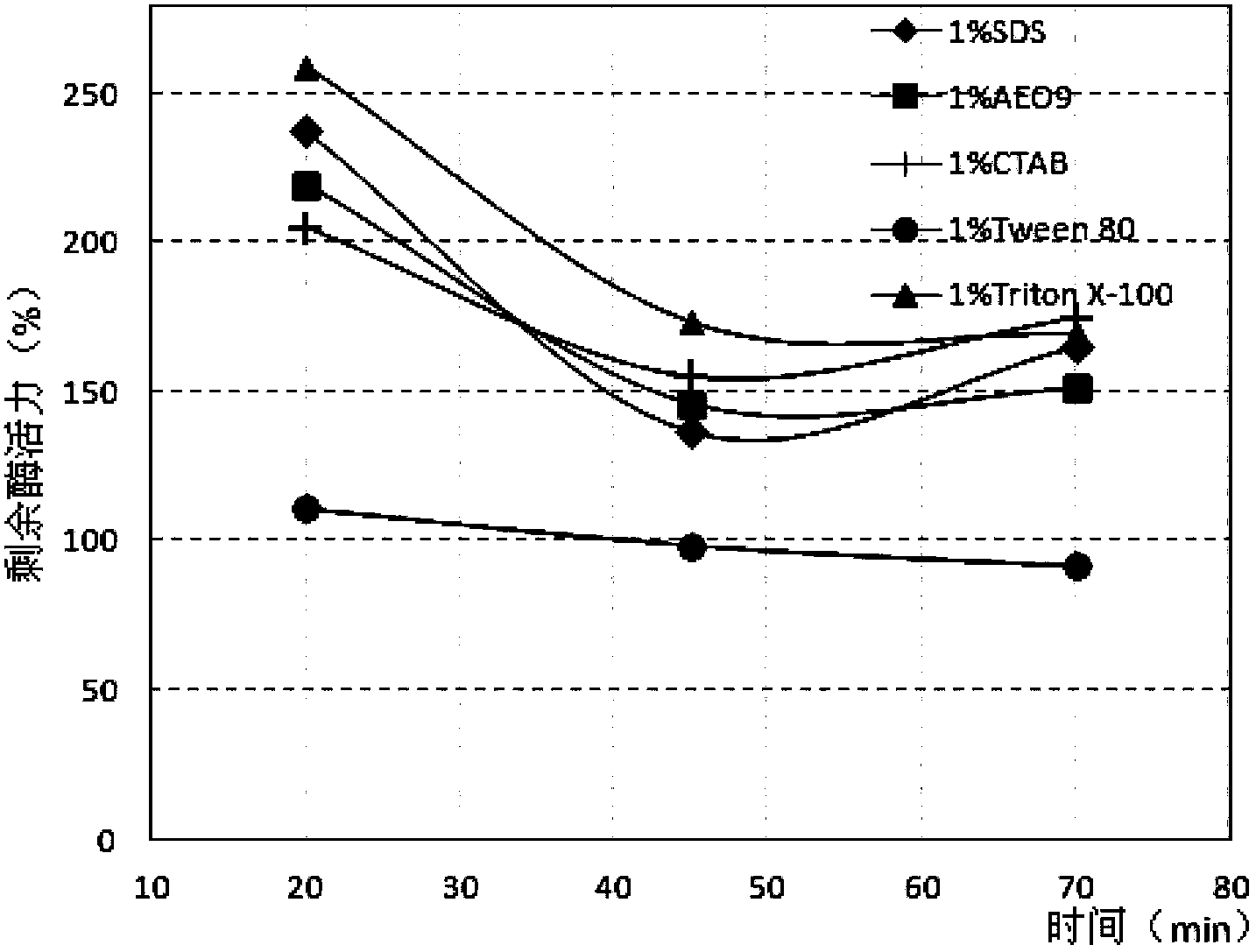
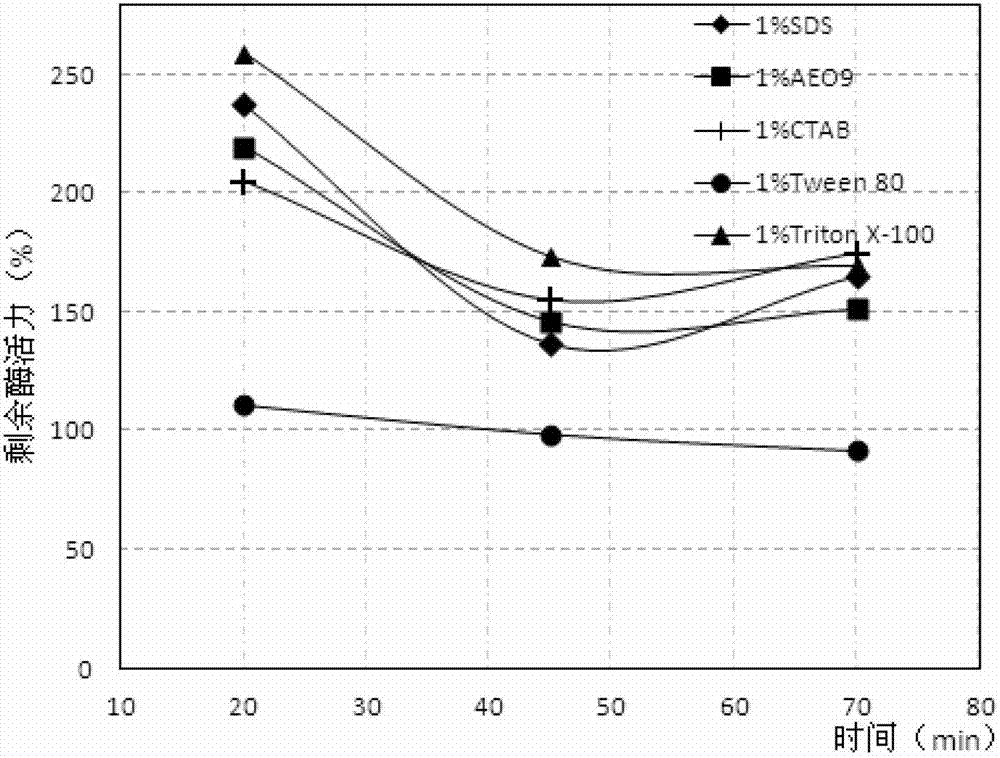
The invention discloses a strain WBRD1.11121501 producing surface active agent resistance lipase and a surface active agent resistance lipase preparation method using the strain. According to the invention, the lipase which is prepared by using the strain and the preparation method has strong stability in an anionic surface active agent SDS, nonionic surface active agents AEO-9 and Triton X-100 and a cationic surface active agent CTAB, and most of the surface active agents can enhance the reaction activity of the lipase. In addition, oxidant hydrogen peroxide can enhance the reaction activity of chryseobacterium lipase provided by the invention.
Owner:WILMAR SHANGHAI BIOTECH RES & DEV CENT
Morchella esculenta nutritional bag prepared by straw fermenting substrates and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN106258478AIncrease productionLow costCalcareous fertilisersBio-organic fraction processingBiotechnologyCorn meal
The invention belongs to the field of cultivation of morchella esculenta, and relates to a nutritional bag prepared by crop wastes needed in a morchella esculenta cultivation process and a preparation method thereof, in particular to a morchella esculenta nutritional bag prepared by straw fermenting substrates and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps of (1) crushing straw; (2) mixing straw chips and wheat bran; (3) mixing a solid mixture in the step (2) and a liquid culture matter of chryseobacterium HT2, and soaking in an opening container; (4) filtering to obtain the straw chips and wheat bran, adding 3 to 5% of quicklime, and 5 to 10% of corn meal, mixing to obtain a mixture, bagging, and sterilizing, so as to obtain the nutritional bag. The preparation method has the advantages that the preparation raw materials of the nutritional bag are changed, the straw is used as the main raw material, the traditional wheat grains are replaced, the agricultural wastes are utilized, the straw is fermented and decomposed by the chryseobacterium HT2, and one part of cellulose and hemicellulose in the straw is converted into saccharides which can be easily utilized by the morchella esculenta; the cost is reduced, the pollution is reduced, and the yield of morchella esculenta is improved.
Owner:四川省食用菌研究所
Carbonyl reductase, gene thereof, and application thereof in preparing Duloxetine chiral intermediates
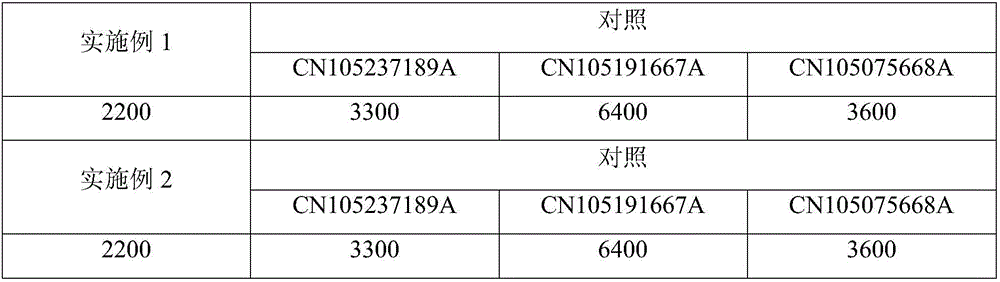
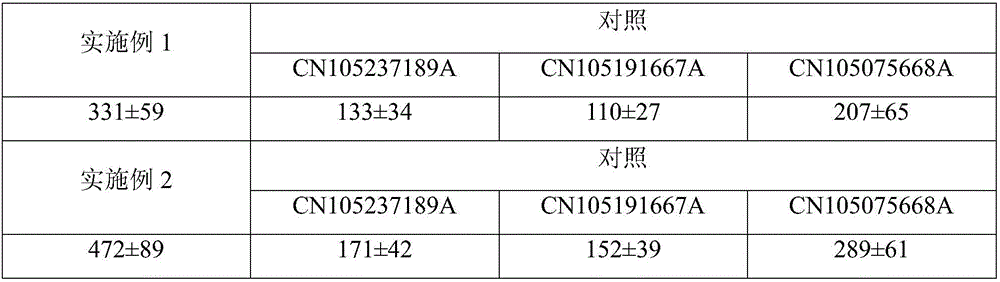
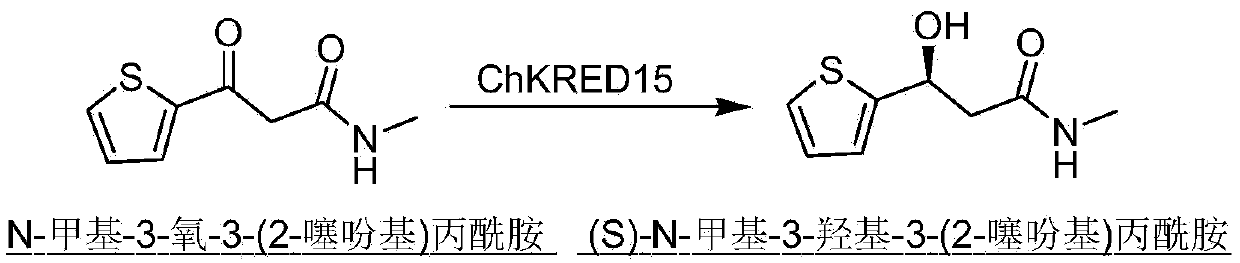
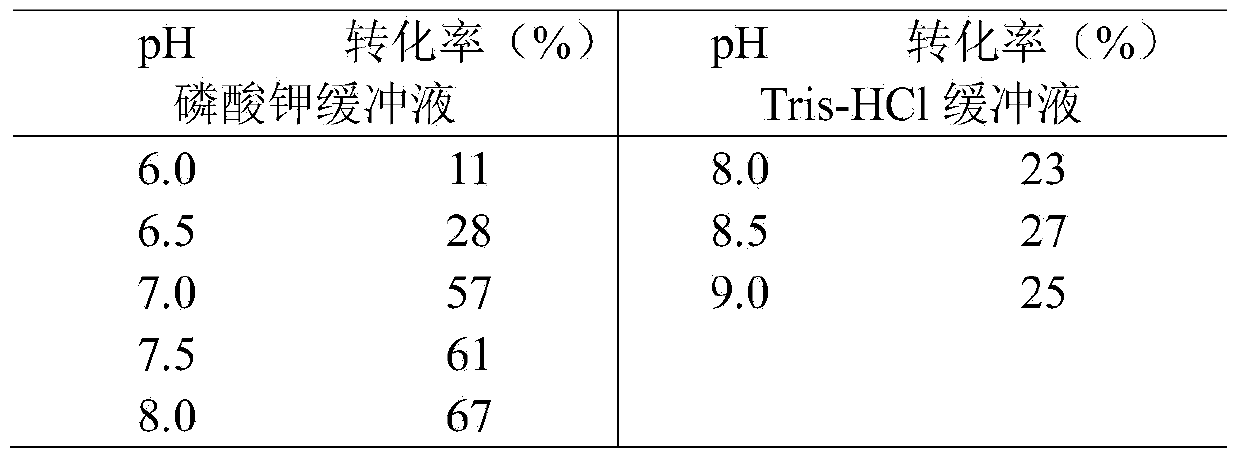
The invention discloses a carbonyl reductase (i)Ch ( / i) KRED15 derived from Chryseobacterium ((i) Chryseobacterium ( / i) (i) ( / i) sp. CA49), and a coding gene thereof; the invention also discloses application of the carbonyl reductase as a biocatalyst in preparing a Duloxetine chiral intermediate ((i) S ( / i))-N-methyl-3-hydroxy-3-(2-thienyl) propanamide. The enantiomer excess of products is greater than 99.9%. 20 g / L of substrate can be catalyzed by Ch( / i) KRED15 crude enzyme (2U / mL), and the conversion rate of over 99% can be obtained in 2 hours; a coenzyme circulation system is simple, and has large industrial application prospect.
Owner:CHENGDU INST OF BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF S
Toadstool nutrition bag prepared by utilizing edible mushroom dregs and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN106187515AIncrease productionLow costCalcareous fertilisersBioloigcal waste fertilisersNutritionPollution
The invention belongs to the field of toadstool cultivation, and in particular relates to a toadstool nutrition bag prepared by utilizing edible mushroom dregs and a preparation method thereof. The invention has the main improvement that the edible mushroom dregs are adopted as main raw materials, and are soaked by utilizing a liquid cultural substance of chryseobacterium HT2. The preparation method comprises the following steps of (1) collecting the mushroom dregs; (2) mixing the mushroom dregs and the liquid cultural substance of the chryseobacterium HT2, and soaking in an open vessel; (3) filtering to obtain the mushroom dregs, adding 1 to 6 percent of unslaked lime and 2 to 10 percent of husk or wheat bran, mixing to obtain a mixture, bagging, and sterilizing to obtain the nutrition bag. According to the method provided by the invention, the preparation raw materials of the nutrition bag are changed, the mushroom dregs remained after cultivating the edible mushrooms are adopted to replace traditional wheat berries and husks, and the chryseobacterium HT2 is utilized to ferment and decompose the mushroom dregs, so that cellulose and hemicellulose in the mushroom dregs are partially turned into saccharides easily utilized by the toadstool; agricultural wastes are utilized, so that the cost is reduced, the pollution is reduced, and the yield of the toadstool is improved.
Owner:四川省食用菌研究所
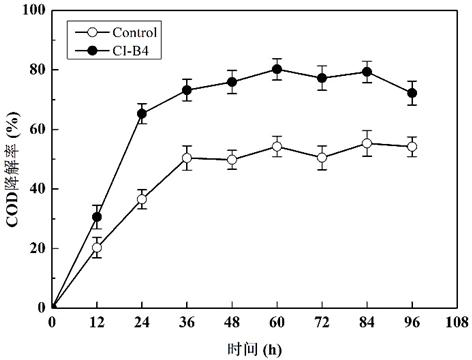
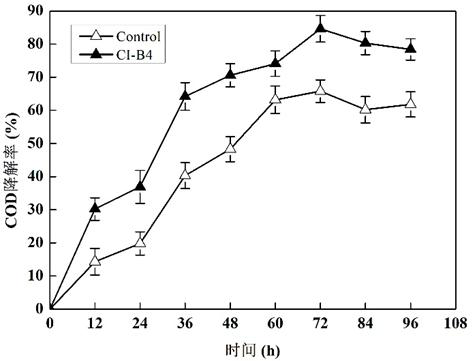
COD (chemical oxygen demand) degrading strain and application thereof
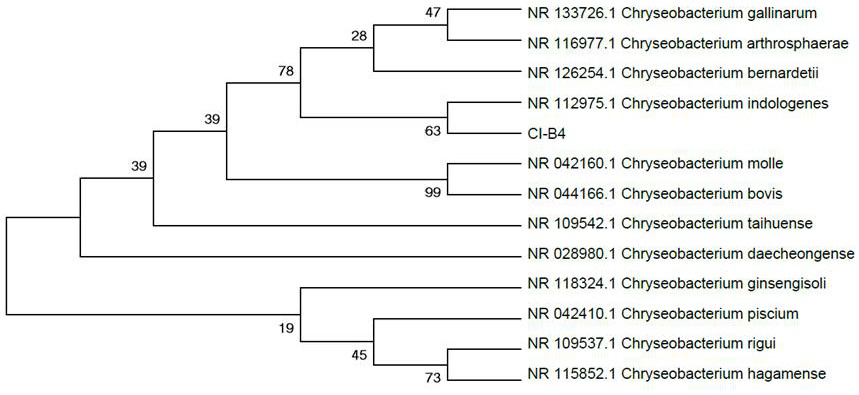
ActiveCN111733113AImprove processing efficiencyEasy to operateWater treatment parameter controlBacteriaChemical oxygen demandChryseobacterium indologenes
The invention relates to the technical field of environmental microorganisms, and particularly relates to a COD (chemical oxygen demand) degrading strain and application thereof. The COD degrading strain is identified as Chryseobacterium indologenes, and the preservation number is CCTCC NO: M 2018651. The Chryseobacterium indologenes CI-B4 is salt-resistant and low-temperature-resistant, and has awide temperature application range (5-40 DEG C); the Chryseobacterium indologenes CI B4 has the capability of efficiently degrading organic pollutants in wastewater, and can improve the effluent quality of organic wastewater; after enlarged culture, the Chryseobacterium indologenes CI-B4 can be applied to biochemical treatment of livestock and poultry breeding wastewater, industrial organic wastewater, black and odorous water bodies of rivers, anaerobic digestion biogas slurry of kitchen waste and the like, and has a high application value; and when the Chryseobacterium indologenes CI-B4 is used for treating organic wastewater, the treatment efficiency is high, the economic benefit is good, the operation is convenient, and pollution is avoided.
Owner:SHANGHAI ADVANCED RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Pastry factory production wastewater treatment agent and wastewater treatment method
InactiveCN105293721AReduce SS contentHigh removal rateWaste water treatment from food industryBiological water/sewage treatmentMicrobial agentEmission standard
The present invention belongs to the field of wastewater treatment of food businesses, in particular relates to a pastry factory wastewater treatment agent, and also relates to a pastry factory production wastewater treatment method. The pastry factory wastewater treatment agent comprises a physical purifying agent, complex microbial agents and an enzyme preparation, the physical purifying agent comprises the following components by weight: 1-5 parts of activated carbon, 1-5 parts of organically modified zeolite and 1-5 parts of polyacrylamide; the complex microbial agents comprise 0.02-0.1 part of saccharomycetes powder, 0.05-0.2 part of flocculating bacteria powder, 0.05-0.2 part of bacillus megatherium powder and 0.04-0.2 part of chryseobacterium powder; the enzyme preparation comprises 0.05-0.1 part of xylanase, 0.04-0.09 part of glucose oxidase and 0.01-0.06 part of amylase. According to the pastry factory production wastewater treatment method, wastewater treatment agent wastewater treatment method, the complex, large particle and difficult-to-degrade organic matters are hydrolyzed into easily-degradable simple organic matters, wastewater SS content is greatly reduced, and the treated wastewater has BOD and COD removal efficiency, and reaches prescribed emission standards.
Owner:JINAN HAOZE ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION TECH CO LTD
Bacteria and its application in absorbing VOCs
InactiveCN107254418AEasy to handleImprove degradation efficiencyGas treatmentBacteriaBacteroidesSynechococcus
The invention discloses a bacteria; the bacteria is prepared from, by weight, 32-56 parts of sarcina, 15-34 parts of spirillum, 20-35 parts of Brevibacillus laterosporus, 23-62 parts of Acinetobacter lwoffii, and 36-68 parts of Chryseobacterium indologenes. When the bacteria is applied to treat the VOCs waste gas, the treatment effect to VOCs is good, and the degrading efficiency is high.
Owner:SCI RES ACADEMY OF GUANGXI ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION
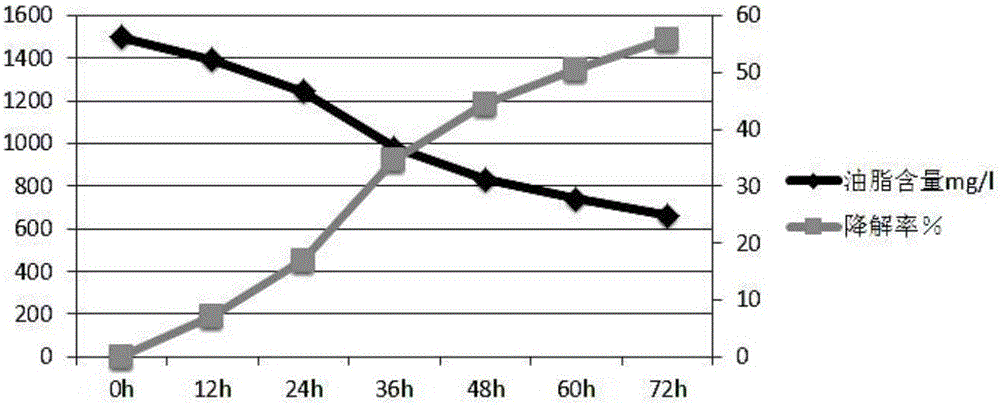
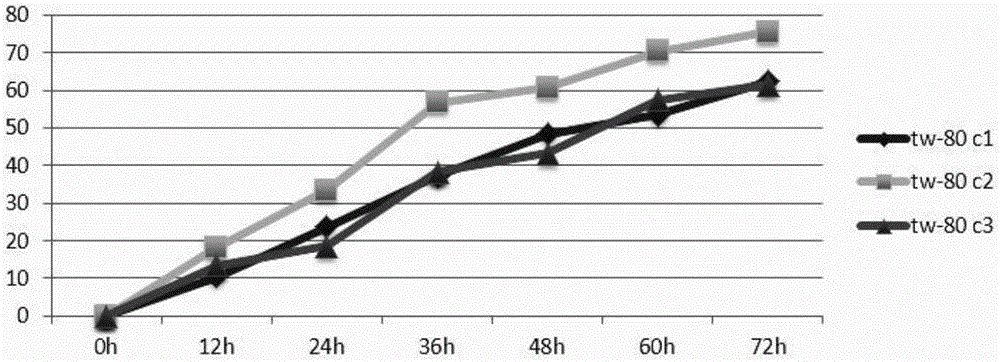
Preparation method and application of grease degrading bacterium community
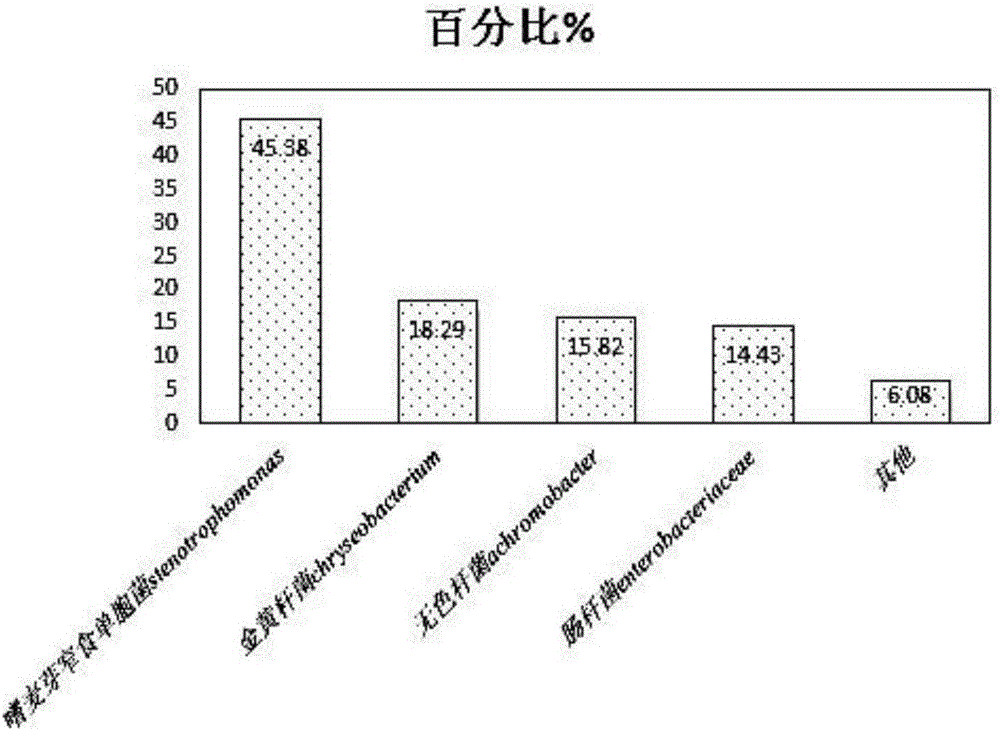
InactiveCN105907666AEfficient degradationLow costBacteriaMicroorganism based processesInorganic saltsStenotrophomonas maltophilia
The invention relates to the technical field of biodegradation treatment, and aims at providing a preparation method and an application of a grease degrading bacterium community. The preparation method of the grease degrading bacterium community comprises the following steps: adding a deposit sample and grease collected from a food waste hogwash grease wastewater zone to an inorganic salt medium, and culturing the deposit sample and grease at 30DEG C under a rotating speed of 150r / min for 5d; repeatedly culturing the obtained material through the same technology 2 times to obtain a final liquid which is a bacterial liquid containing the grease degrading bacterium community; and carrying out DNA sequencing confirmation, wherein the grease degrading bacterium community comprises Stenotrophomonas maltophilia, Chryseobacterium spp, Achromobacter sp and enterobacteria. Onsite sampling (for achieving low cost) is realized, the grease degrading bacterium community is enriched and screened through a simple and convenient process, and grease wastewater in the food waste hogwash grease wastewater zone is effectively degraded; and the degradation efficiency in the treatment of the grease wastewater in the food waste hogwash grease wastewater zone under the action of a surfactant is greatly increased.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Protein glutaminase production strain, screening method and characteristic analysis method
The invention relates to a protein glutaminase production strain, a screening method and a characteristic analysis method. The invention discloses a protein glutaminase high-yield strain, which is named as Chryseobacterium proteolyticumA4142, and is preserved in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center on July 10, 2020, the preservation address is No.3, Yard 1, Beichen West Road, Chaoyang District, Beijing, and the preservation number is CGMCC (China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center) NO.20337. The invention further discloses a preparation method of the protein glutaminase high-yield strain. The bacterial strain is rod-shaped, does not produce spores, is gram negative, has a round bacterial colony, and is full in state, smooth in edge, free of notch and sticky. According to the present invention, the Chryseobacterium prion A4142 strain is subjected to fermentation culture in the culture medium, the enzyme yield is up to 2.15 U / mL, and the Chryseobacterium prion A4142 is the strain subjected to food safety certification; the invention further discloses a screening method of the novel protein glutaminase high-yield strain, and characteristic analysis is carried out on the novel protein glutaminase high-yield strain to determine that the strain is Chryseobacterium prion. The method disclosed by the invention has a good implementation prospect in the aspect of industrial production of the protein glutaminase.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV
Biological preparation containing plant source component and microorganism source component and application of biological preparation in prevention and treatment of plant nematode diseases
ActiveCN113462599APromote growthImprove the ability to resist root-knot nematodeBiocideBacteriaBiotechnologyPlant nematode
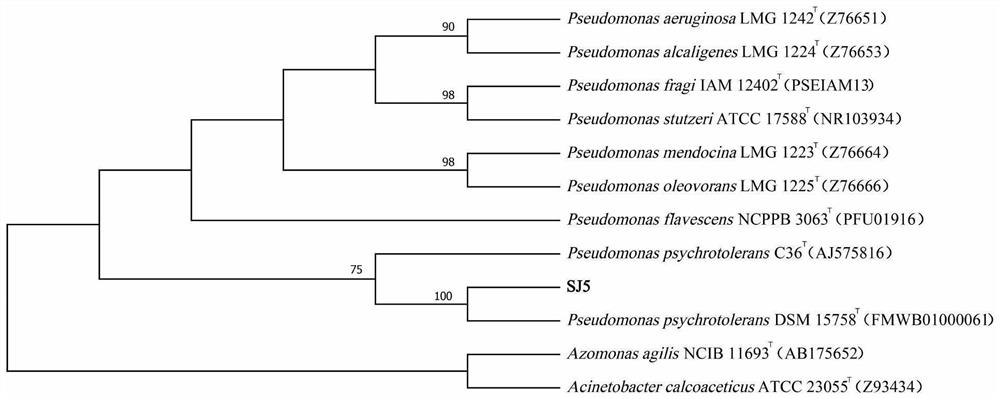
The invention provides a biological preparation containing a plant source component and a microorganism source component and application of the biological preparation in prevention and treatment of root knot nematode diseases, which belongs to the technical field of biological pesticides. The invention provides a cold-resistant pseudomonas strain SJ5 with the preservation number of CCTCC No.M2021375, and the cold-resistant pseudomonas strain SJ5 has a relatively strong killing effect on nematodes. Meanwhile, the invention further provides a biological preparation containing plant source components and microorganism source components. The biological preparation is prepared from sophora flavescens azadirachtin missible oil, fermentation liquor of a cold-resistant pseudomonas strain SJ5, fermentation liquor of Chryseobacterium mucilaginosus and fermentation liquor of bacillus subtilis. The biological agent is used for preventing and treating plant nematode diseases, the biological prevention effect of chemical agents such as fosthiazate and dazomet can be achieved, plant growth can be effectively promoted, and the biological agent has higher application value.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
Application of Amomum tsao-ko oil to preparation of medicament for treating bacterial infectious disease
InactiveCN103394016AHas antibacterial activityGood antibacterial effectAntibacterial agentsAgainst vector-borne diseasesBacteroidesPseudomonas
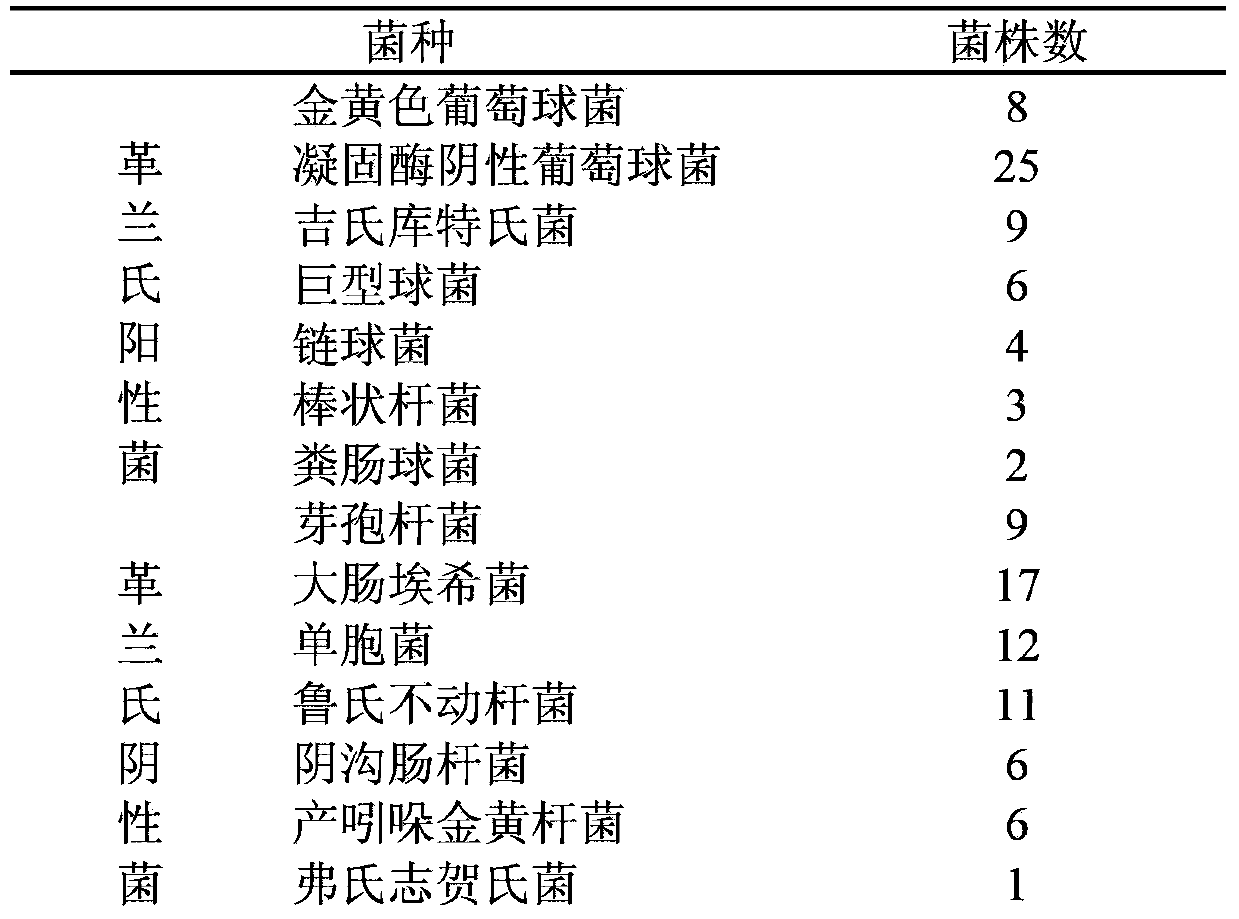
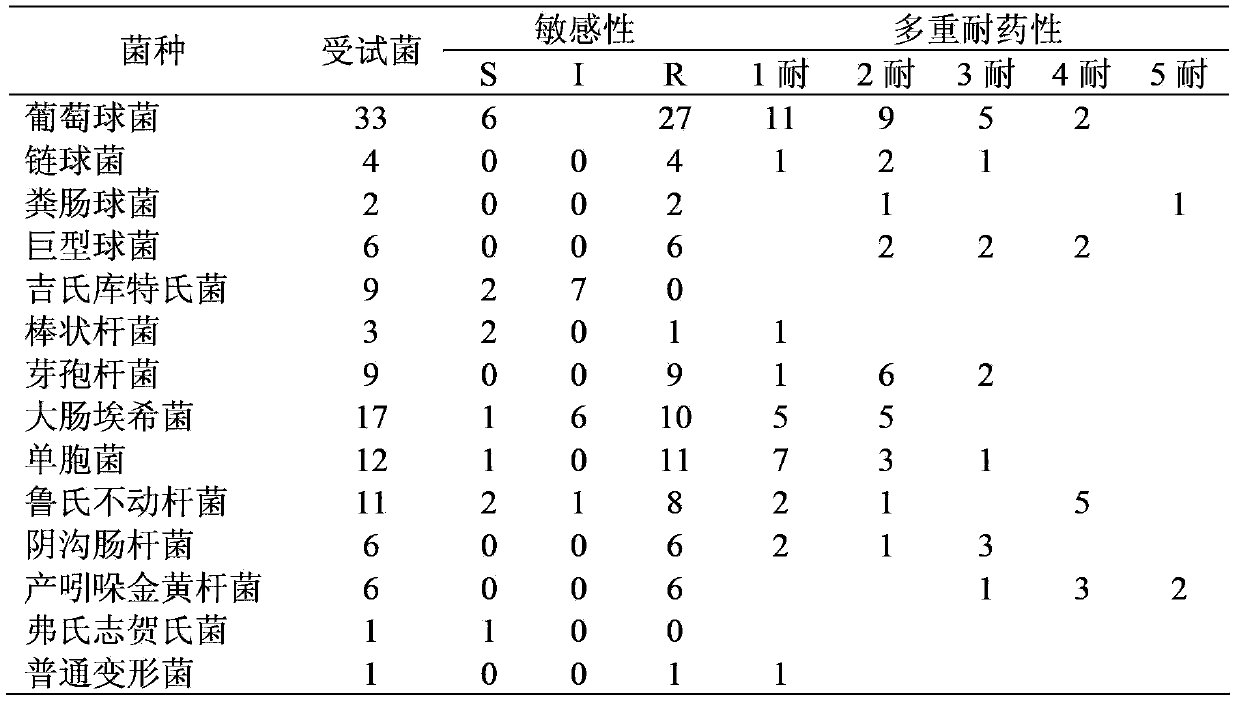
The invention provides application of Amomum tsao-ko oil to preparation of medicaments for treating bacterial infectious diseases. The bacteria is coagulase negative staphylococcus, Kurthia gibsonii, megacoccus, corynebacterium, enterococcus faecalis, bacillus, escherichia coli, Pseudomonas, Acinetobacter lwoffii, Chryseobacterium indologenes, Enterobacter cloacae, S.flexneri or proteus vulgaris. The medicine provided by the invention has antibacterial activity against gram positive bacteria and gram negative bacteria, as well as strong inhibitory effect on the resistant strains, and also has good antibacterial effect in vivo; in addition; and the medicament can effectively treat clinical infectious diseases caused by gram positive and gram negative bacteria of various types, and provides a novel clinical medicine choice.
Owner:CHENGDU UNIV OF TRADITIONAL CHINESE MEDICINE
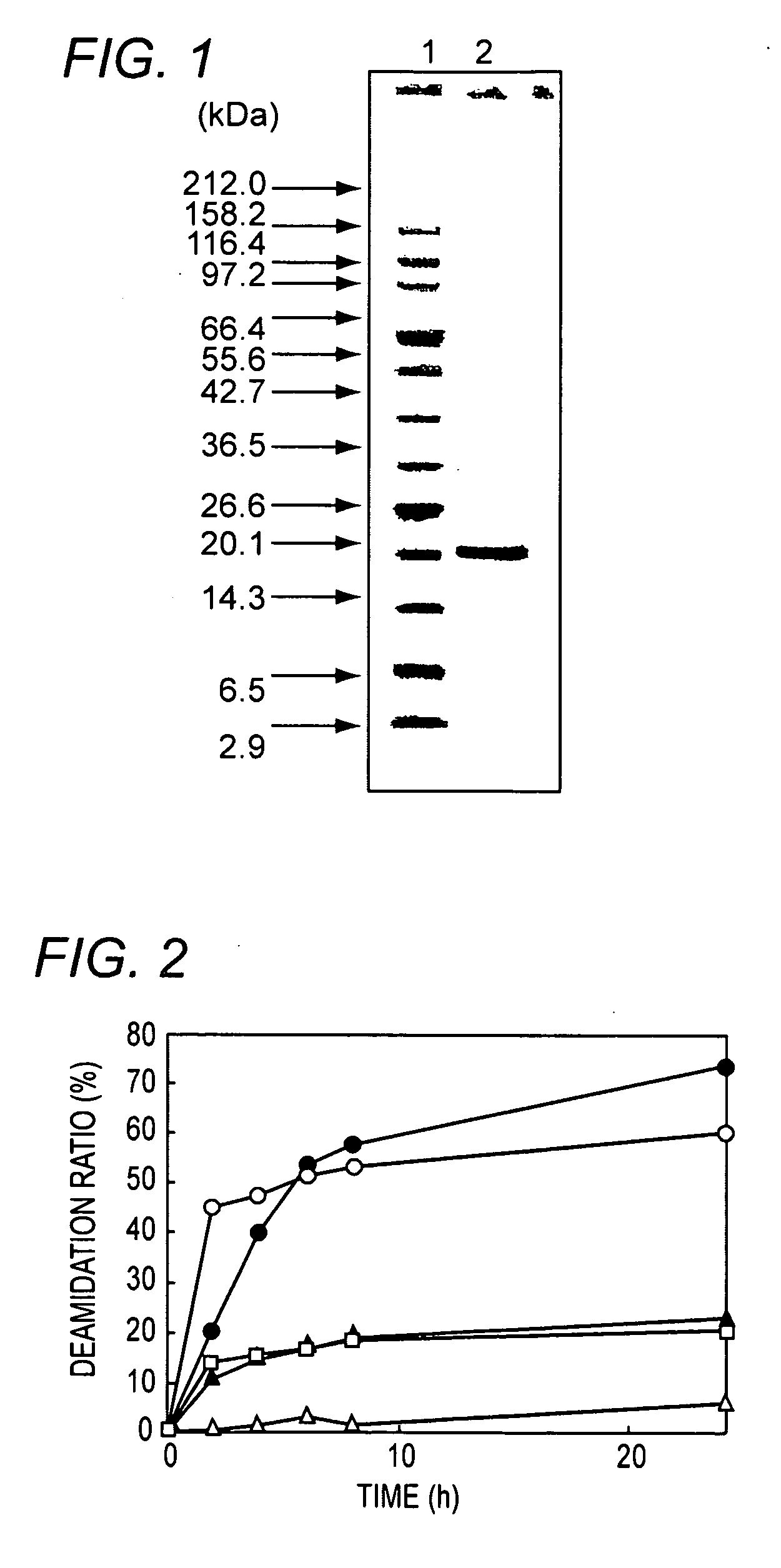
Novel protein-deamidating enzyme, microorganism producing the same, gene encoding the same, production process therefor, and use thereof
InactiveUS20090061500A1Function increaseHydrolasesProtein foodstuffs working-upBacteroidesSide chain
A method for the production of an enzyme, which comprises culturing in a medium a strain that belongs to a bacterium classified into Cytophagales or Actinomycetes, or a new bacterium Chryseobacterium sp. No. 9670 belonging to the genus Chryseobacterium, and has the ability to produce an enzyme having a property to deamidate amido groups in protein, thereby effecting production of the enzyme, and subsequently collecting the enzyme from the culture mixture and a method for the modification of protein making use of a novel enzyme which directly acts upon amido groups in protein, as well as a gene which encodes the enzyme, a recombinant vector which contains the gene, a transformant transformed with the vector and a method in which the transformant is cultured in a medium to effect production of the protein-deamidating enzyme and then the protein-deamidating enzyme is collected from the culture mixture. It is possible to provide a novel protein-deamidating enzyme which has an activity to release side chain carboxyl groups and ammonia from a protein by acting upon side chain amido groups in the protein, a microorganism capable of producing the same, a gene encoding the same, a production process therefor and use thereof.
Owner:AMANO ENZYME INC
Acquisition method of halohydrocarbon degrading flora suitable for bioelectrochemical repair system
InactiveCN112048461AHas the ability to degradeSimple structureBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsHalohydrocarbonGroundwater pollution
The invention relates to the field of groundwater pollution treatment, in particular to an acquisition method of halohydrocarbon degrading flora suitable for a bioelectrochemical repair system. The acquisition method mainly comprises the following steps: constructing an electrochemical bacteria liquid culture device by adopting a culture device, providing O2 and H2 for microorganisms by electrolyzing water, adding an inorganic salt culture medium, a co-metabolism matrix and sediments polluted by halogenated hydrocarbon into to the culture device, and performing subculture by adopting a TCE gradient domestication method with the TCE concentration of 76-608[mu] mol / L in the culture process, so as to finally obtain the halohydrocarbon degrading flora. The main dominant bacteria of the flora comprise Chryseobacterium, Sphingomonas and Microbacterium. The acquisition method of halohydrocarbon degrading flora provides an acquisition method for the flora which can survive in an electrochemical repair system and has certain degradation capacity on halohydrocarbon, and the flora can be used for strengthening the electrochemical in-situ microbial repair effect and has wide engineering application prospects.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF GEOSCIENCES (WUHAN)
Yarn dyeing and weaving wastewater treatment agent
InactiveCN107500418AEasy to handleImprove work efficiencyWaste water treatment from textile industryBiological water/sewage treatmentAlkaneYarn
The present invention provides a yarn dyeing and weaving wastewater treatment agent, wherein the components of the formula comprise 5-8 g of active carbon, 6-9 g of organic modified zeolite, 4-7 g of polyacrylamide, 0.1-0.2 g of Lysinibacillus sphaericus powder, 0.3-0.8 g of Chryseobacterium powder, 0.1-0.15 g of lignan hydroxylase, 0.09-0.19 g of laccase, 2-7 g of epoxy chlorobenzene alkane, 1-3 g of concentrated sulfuric acid, and 3-6 g of hydrogen peroxide. According to the present invention, dyeing and weaving wastewater is subjected to composite treatment with the treatment agent prepared from activated carbon, organic modified zeolite, polyacrylamide, Lysinibacillus sphaericus powder, Chryseobacterium powder, lignan hydroxylase, laccase, epoxy chlorobenzene alkane, concentrated sulfuric acid and hydrogen peroxide so as to improve the dyeing and weaving wastewater treatment effect; and the auxiliary filtration agent and the decolorizing agent are added so as to improve the wastewater treatment efficiency.
Owner:WUHU FUCHUN DYEING & WEAVING
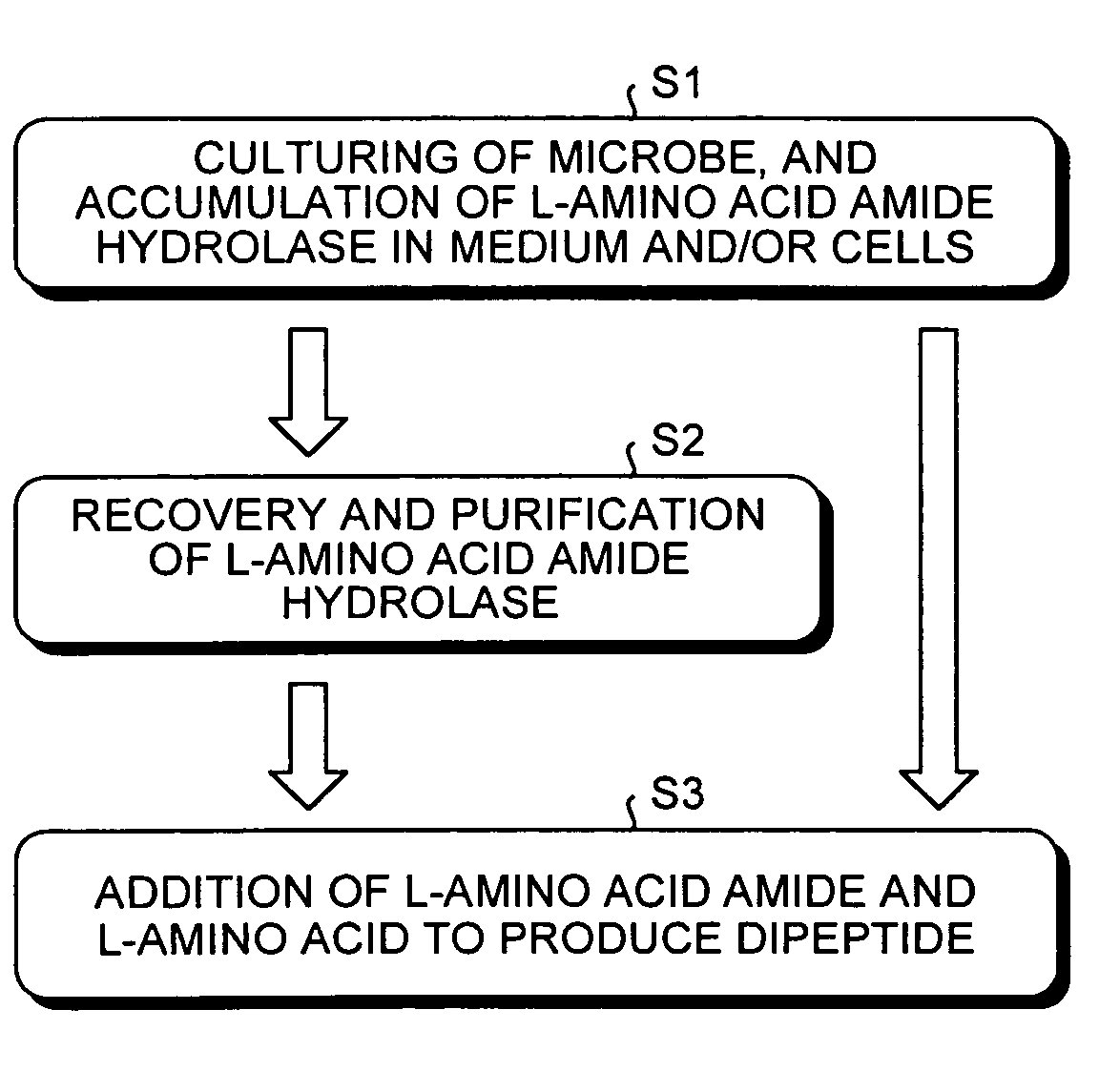
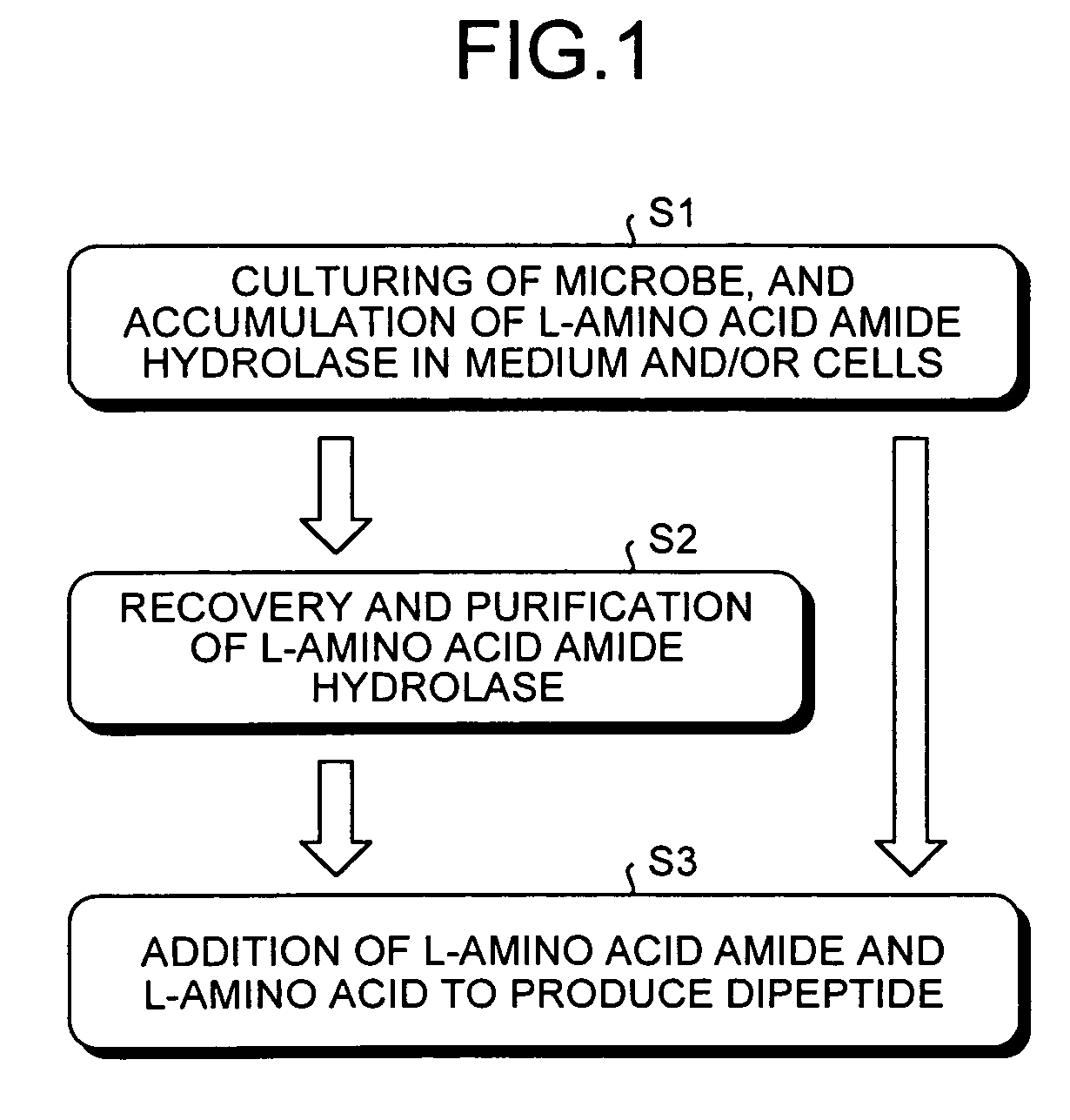
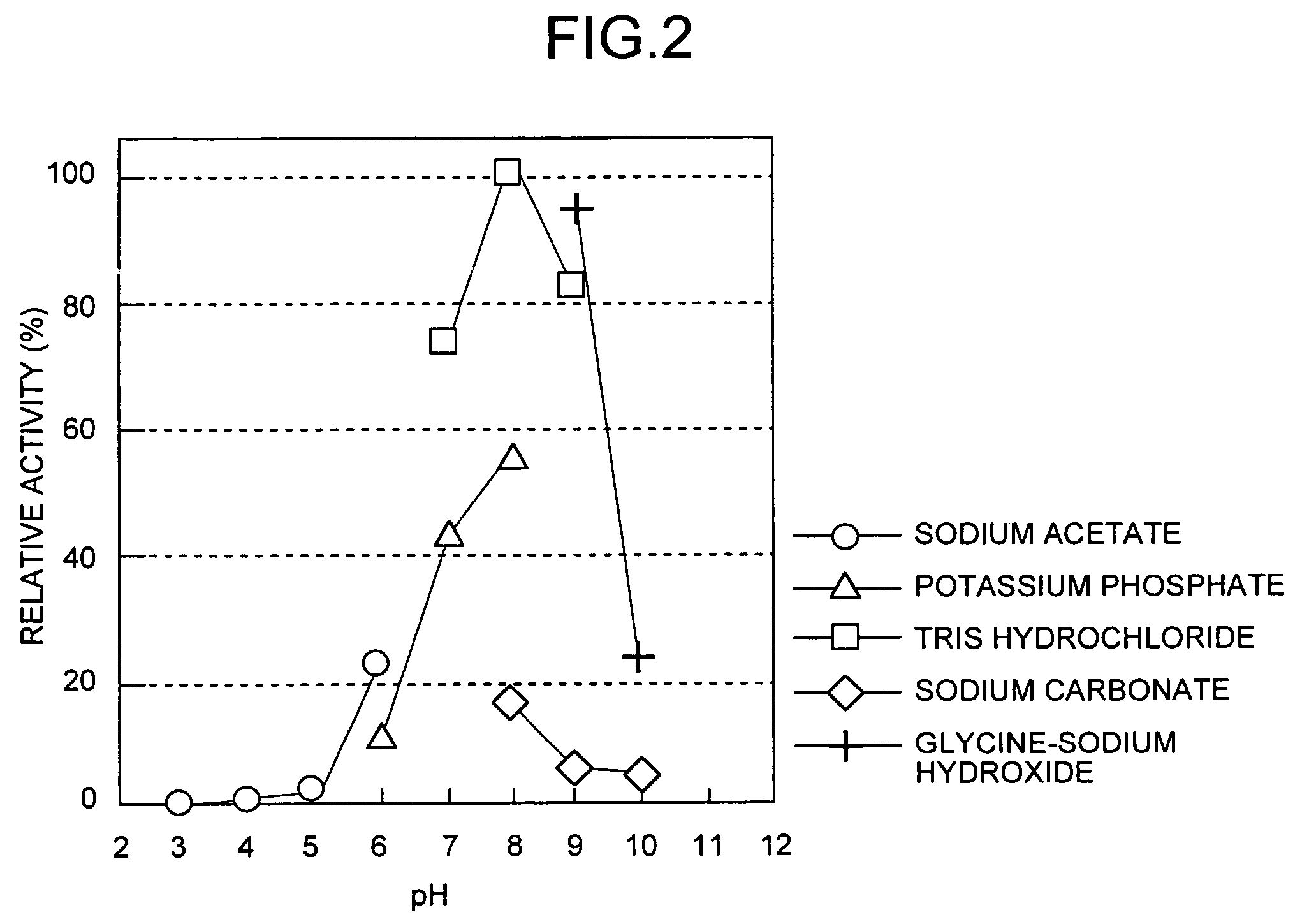
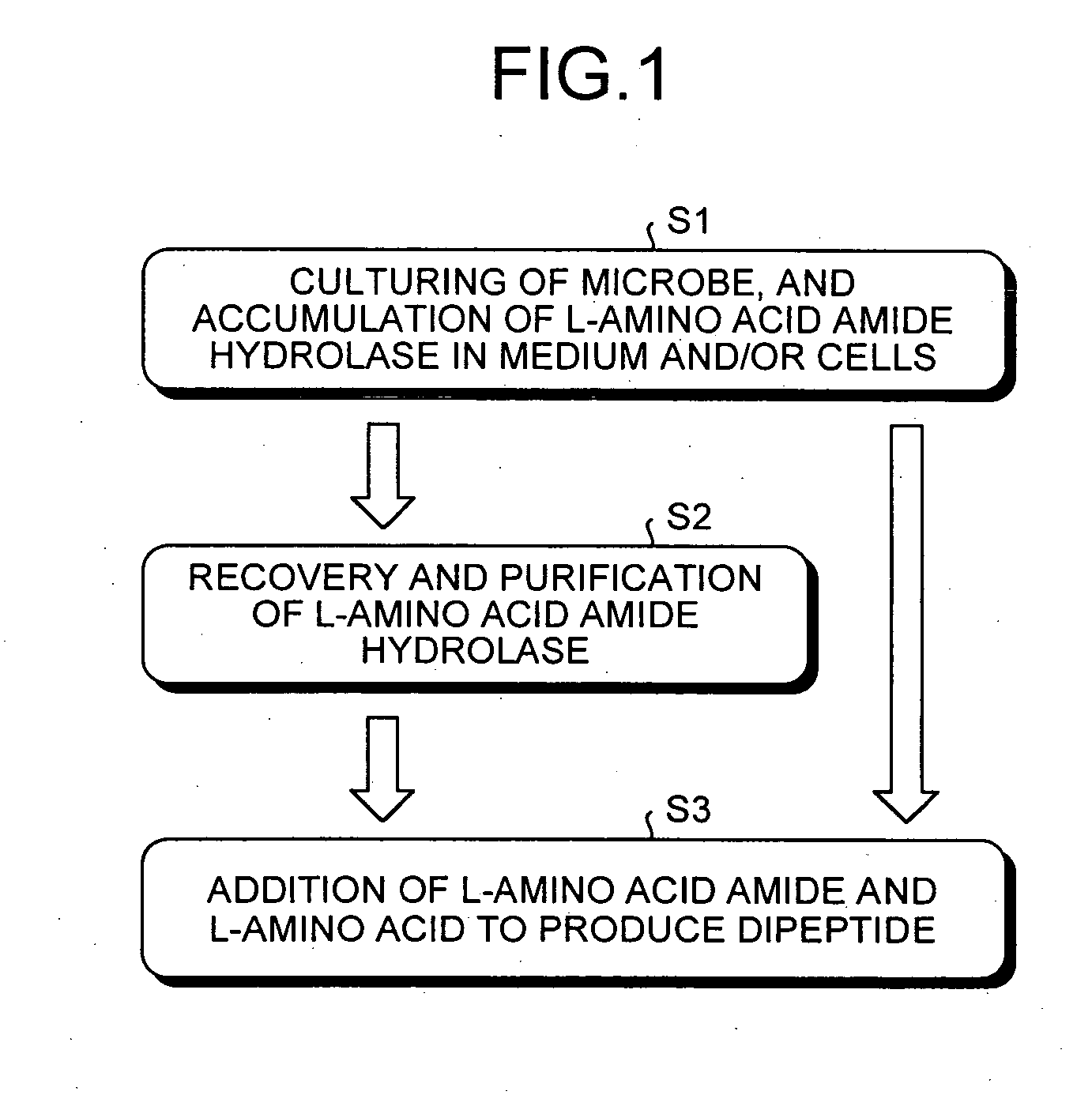
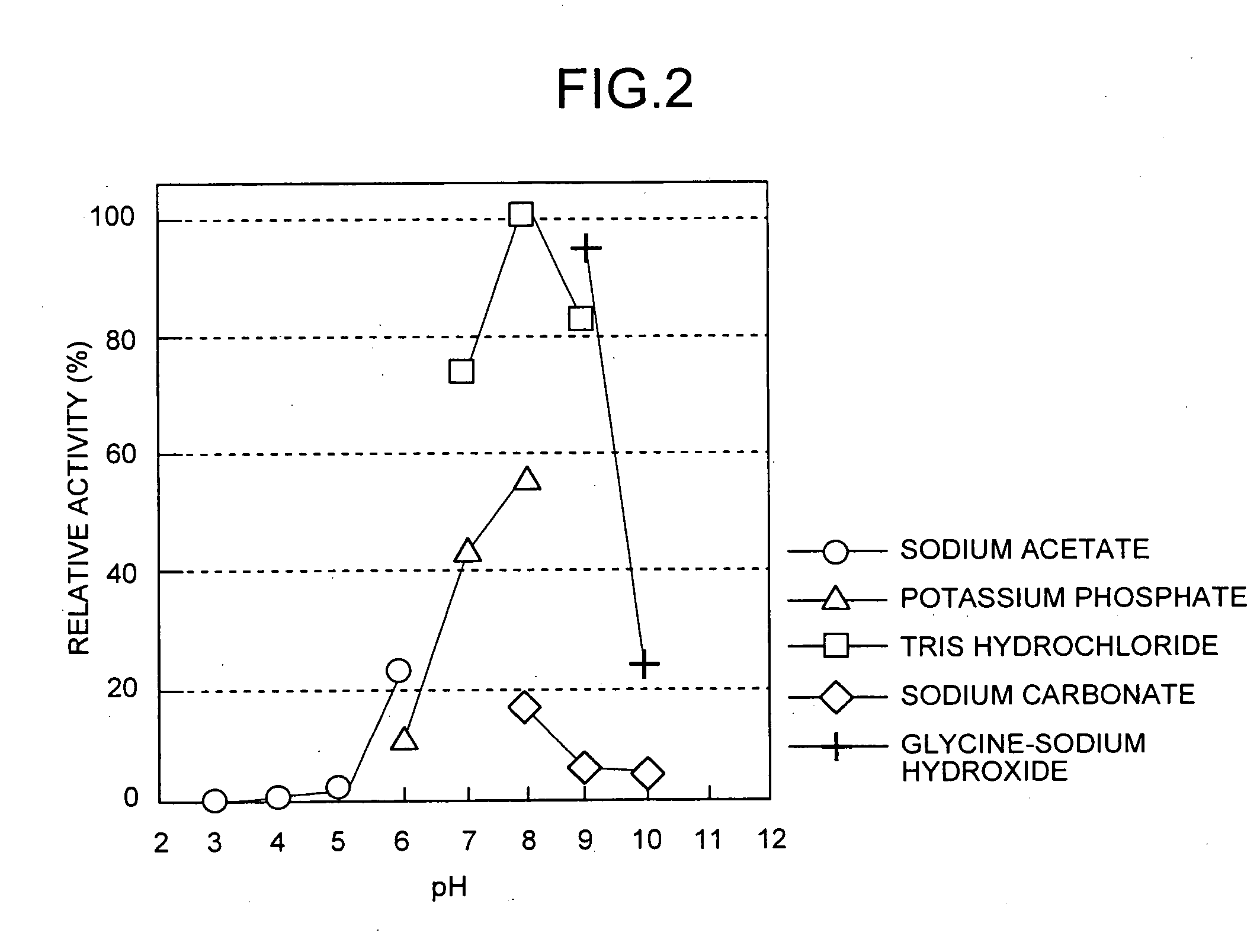
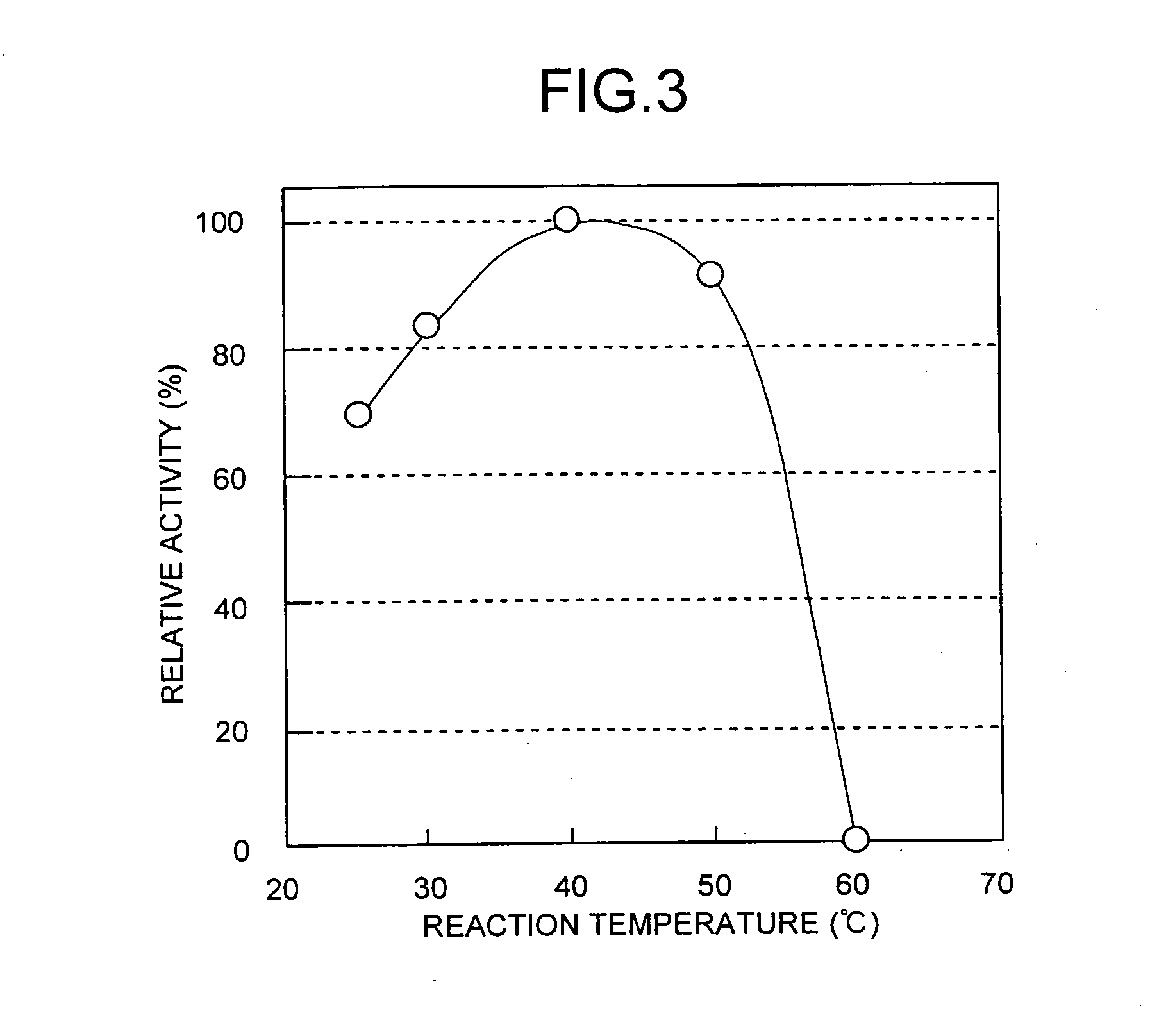
Dipeptide production method, L-amino acid amide hydrolase used therein, and production method of L-amino acid amide hydrolase
InactiveUS7037673B2Inexpensive and easily availableSimple production pathwayFungiBacteriaAmino acid synthesisDipeptide
A process for industrially advantageously producing a dipeptide via a convenient pathway starting with less expensive and easily available materials is provided. A dipeptide is produced from an L-amino acid amide and an L-amino acid by using a culture of a microbe capable of synthesizing the dipeptide from the L-amino acid amide and the L-amino acid, microbial cells separated from the culture or a treated microbial cell product from the microbe. An L-amino acid amide hydrolase is obtained from a microbe belonging to the genus erwinia, genus Rhodococcus, genus Chryseobacterium, genus Micrococcus, genus Cryptococcus, genus Trichosporion, genus Rhodosporidium, genus Sporobolomyces, genus Tremela, genus Torulaspora, genus Sterigmatomyces or genus Rhodotorula. The hydrolase catalyzes a reaction that produces a dipeptide from an L-amino acid amide and an L-amino acid.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Dipeptide production method, L-amino acid amide hydrolase used therein, and production method of L-amino acid amide hydrolase
InactiveUS20070042459A1Inexpensive and easily available starting materialsEasy to manufactureFungiBacteriaAmino acid synthesisBacteroides
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Carbonyl reductase, its gene and its use in the preparation of duloxetine chiral intermediate
ActiveCN103740738BThe conversion process is simpleThe coenzyme cycle system is stableMicroorganism based processesOxidoreductasesDuloxetineMethyl group
The invention discloses a carbonyl reductase (i)Ch ( / i) KRED15 derived from Chryseobacterium ((i) Chryseobacterium ( / i) (i) ( / i) sp. CA49), and a coding gene thereof; the invention also discloses application of the carbonyl reductase as a biocatalyst in preparing a Duloxetine chiral intermediate ((i) S ( / i))-N-methyl-3-hydroxy-3-(2-thienyl) propanamide. The enantiomer excess of products is greater than 99.9%. 20 g / L of substrate can be catalyzed by Ch( / i) KRED15 crude enzyme (2U / mL), and the conversion rate of over 99% can be obtained in 2 hours; a coenzyme circulation system is simple, and has large industrial application prospect.
Owner:CHENGDU INST OF BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF S
Method of treating reclaimed water containing chryseobacterium meningosepticum
ActiveCN110002672AReduce the risk of infectionAchieving flocculationSpecific water treatment objectivesMultistage water/sewage treatmentFlocculationReclaimed water
The invention relates to a method of treating reclaimed water containing chryseobacterium meningosepticum and belongs to the field of water treatment. The method comprises the steps of adding a biological flocculant solution into the reclaimed water containing the chryseobacterium meningosepticum, and adding 103 lethal plasmid donor bacteria per L and nano graphite oxide with a concentration of 50-80mg / L. A lethality rate of the chryseobacterium meningosepticum can reach above 50% after 24h, and above 80% after 36h. The method has the advantages that a biological flocculant secreted from bacillus subtilis is used for efficient flocculation of the chryseobacterium meningosepticum and relevant florae, so that promotion of flora cell flocculation and polymerization is achieved; in addition, the transmission efficiency of pNJR6 plasmids in the florae in a chryseobacterium meningosepticum conjugation process is improved by low-concentration graphite oxide; and the method achieves the purpose of flocculation removal and induction killing to reduce an infection risk of the chryseobacterium meningosepticum in the reclaimed water.
Owner:JILIN INST OF CHEM TECH
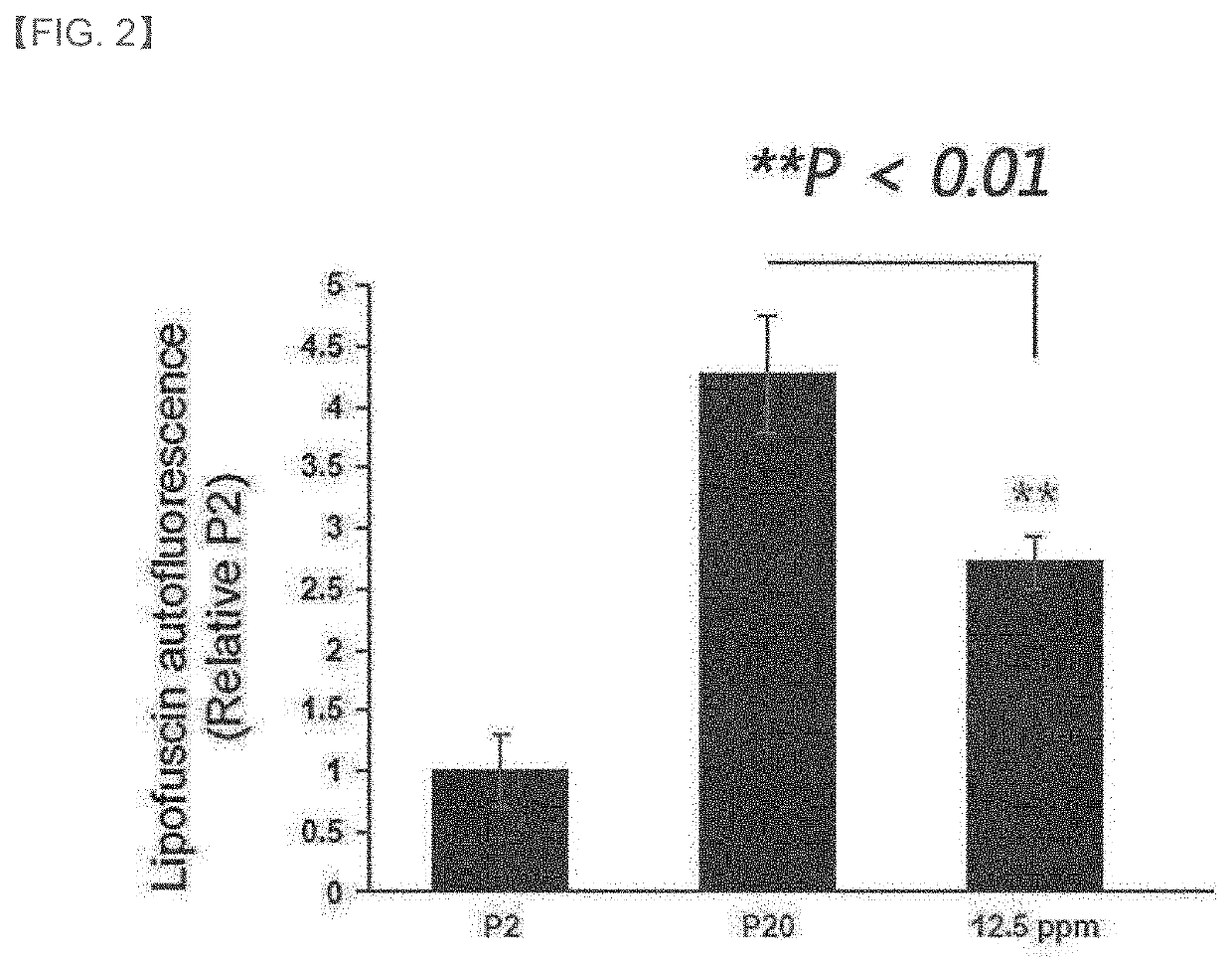
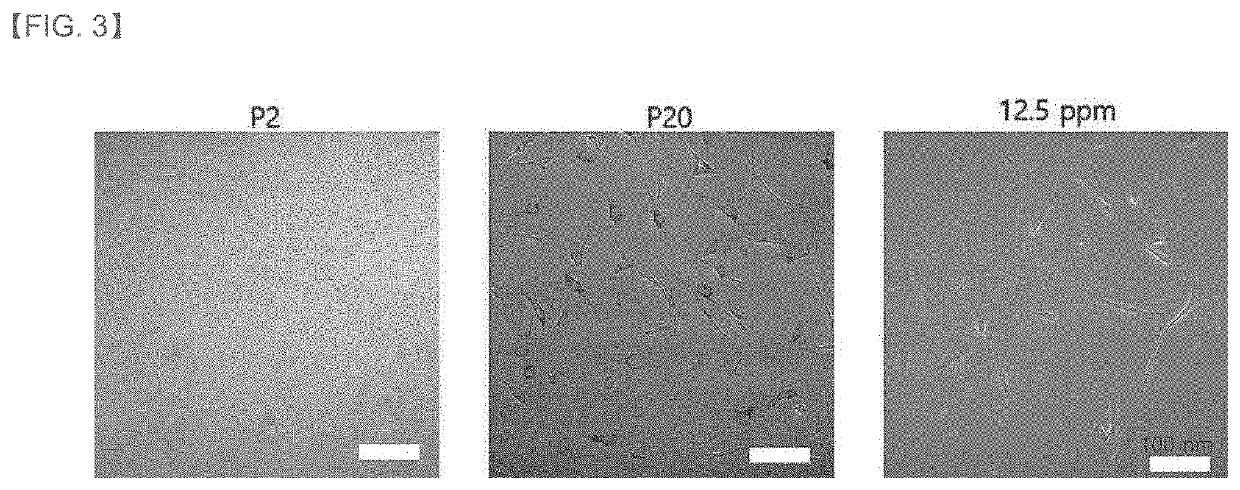
Composition for inhibiting lipofuscin accumulation or removing lipofuscin
PendingUS20220339210A1Remove lipofuscinCosmetic preparationsSenses disorderLipofuscin accumulationAmyotrophic lateral sclerosis
A composition for inhibiting lipofuscin accumulation or removing lipofuscin is disclosed. A Chryseobacterium sp. strain, a lysate of the Chryseobacterium sp. strain, a culture of the Chryseobacterium sp. strain, or an extract of the lysate or culture is included in the composition. The composition provides an anti-aging effect by inhibiting lipofuscin accumulation or removing lipofuscin. The composition also provides an effect of preventing, ameliorating or treating the diseases caused by the lipofuscin accumulation, such as skin hyperpigmentation, Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, myocardial infarction and age-related macular degeneration.
Owner:AMOREPACIFIC CORP
A kind of strain producing surfactant-resistant lipase and preparation method of surfactant-resistant lipase
The invention discloses a strain WBRD1.11121501 producing surfactant-resistant lipase and a preparation method of the surfactant-resistant lipase using the strain. The lipase prepared by utilizing the bacterial strain provided by the present invention and the preparation method has extremely strong stability in anionic surfactant SDS, nonionic surfactant AEO‑9, Triton X‑100 and cationic surfactant CTAB, and wherein Most surfactants enhance the reactivity of the enzyme. In addition, the oxidant hydrogen peroxide also enhances the reactivity of the Chrysobacterium aureus lipase provided by the present invention to a certain extent.
Owner:WILMAR SHANGHAI BIOTECH RES & DEV CENT
Anti-parasitic agents
PendingUS20210000123A1Reduce loadReduce infectionBiocideBacteria material medical ingredientsBiotechnologyAntiparasite agent
The invention relates to anti-parasitic agents, and particularly, although not exclusively, to the use of Chryseobacterium nematophagum for the control of nematode parasites.
Owner:THE UNIV COURT OF THE UNIV OF GLASGOW
Preparation method and application of microbial immobilized composite particles
PendingCN114540337APromote growthLarge specific surface areaWater contaminantsMicroorganism based processesPolyvinyl alcoholBioremediation
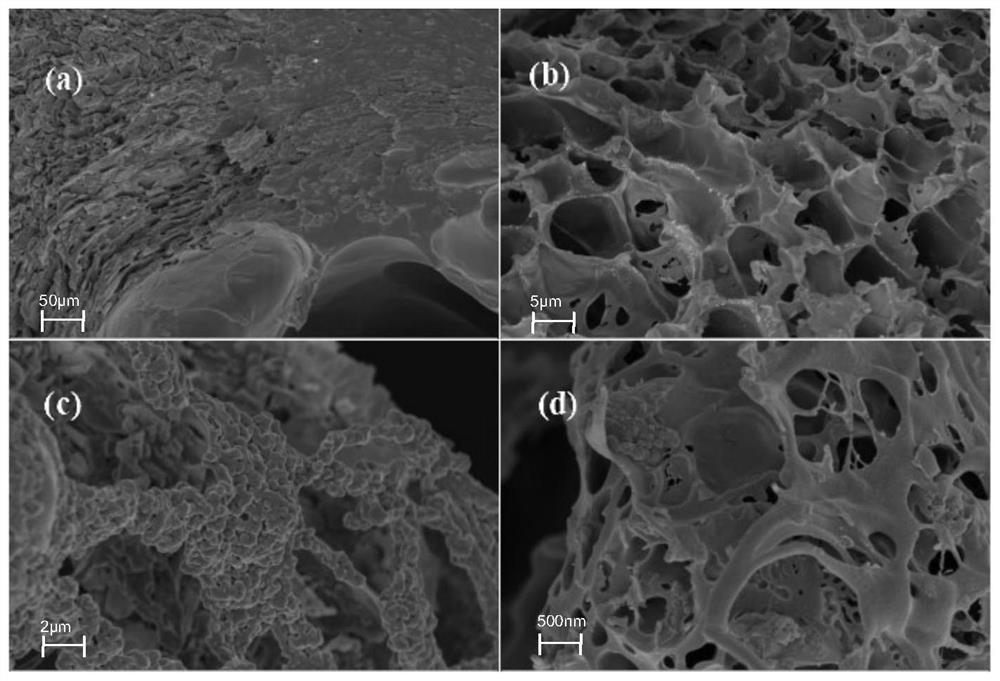
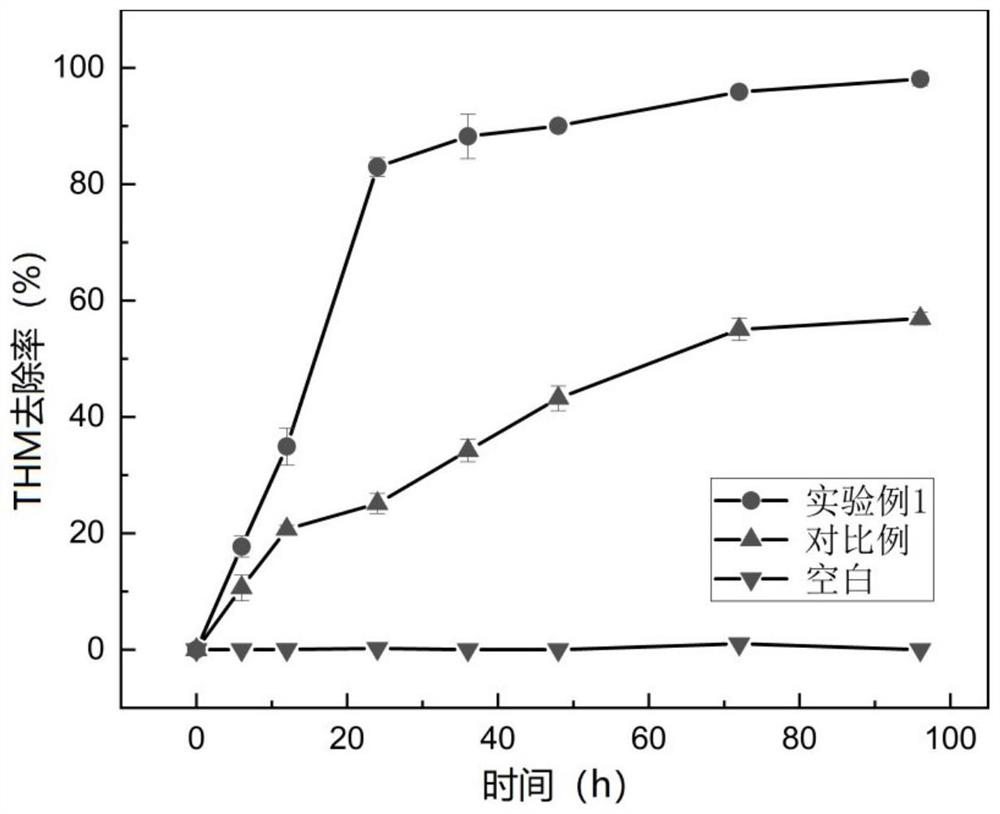
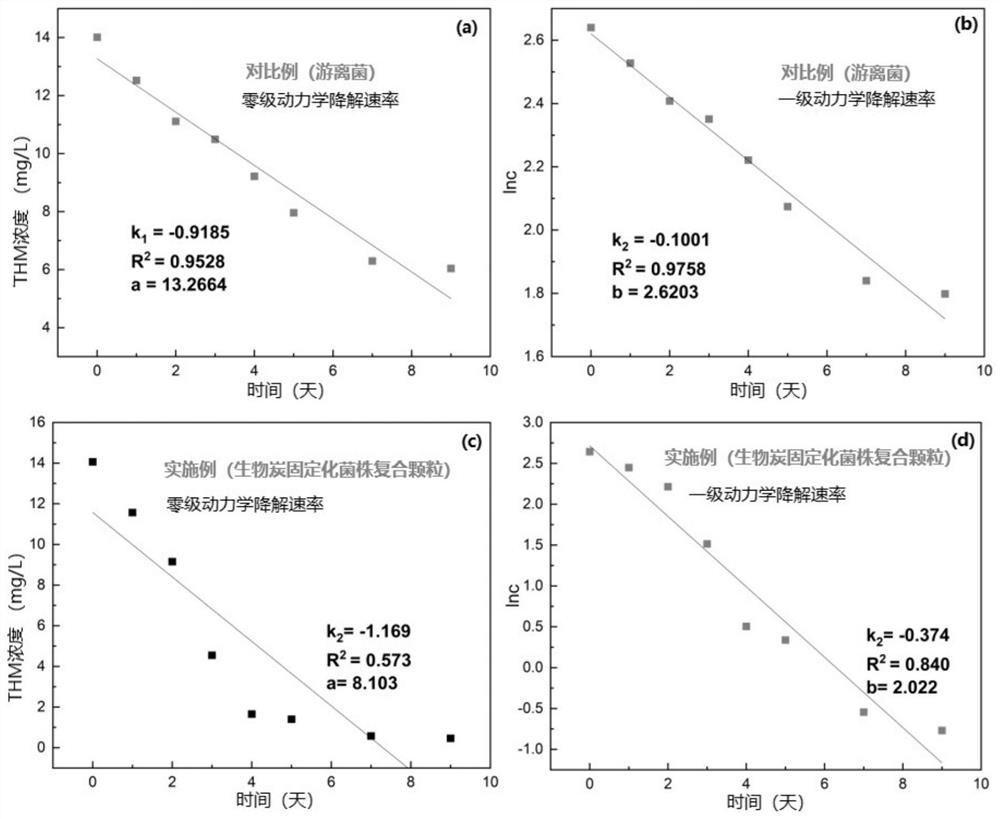
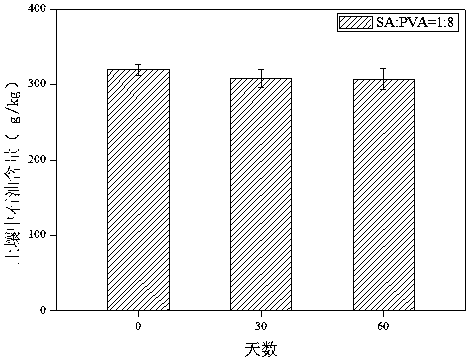
The invention relates to the field of environmental bioremediation, in particular to a preparation method and application of microbial immobilized composite particles. The preparation method comprises the following steps: S1, washing, drying and heating a biomass material for reaction, washing the biomass material with inorganic strong acid, and then drying, grinding and sieving the biomass material to obtain biochar; s2, culturing a Chryseobacterium strain, centrifuging, washing, resuspending to obtain a bacterial suspension, and adding the charcoal to obtain a mixed solution; heating and dissolving polyvinyl alcohol and sodium alginate, sterilizing, and adding the mixed solution to obtain an embedding solution; dissolving calcium chloride and boric acid in water to obtain a crosslinking solution; s3, dropwise adding the embedding liquid into the cross-linking liquid, and washing after reaction to obtain the microbial immobilized composite particles. The prepared microbial immobilized composite particles have the advantages of good mass transfer performance, good mechanical performance, large specific surface area and the like, and have a good degradation effect on neonicotinoid pesticides in water.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Feather degrading bacterium immobilization method
InactiveCN114657168AReduce manufacturing costPrevent leakageBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMicrobial agentBacterial strain
Owner:常州百鑫特生物科技有限公司
Chryseobacterium and application thereof in preparation of halophyte epiphytic repair and maintenance microbial inoculum
PendingCN113957004APromote growthPromote colonizationPlant growth regulatorsBiocideBiotechnologyHalophyte
The invention relates to a halophyte epiphytic repair and maintenance microbial inoculum, which is prepared by the following steps: respectively pre-culturing and propagating Chryseobacterium YTLJ-E-II12 and Acinetobacter YTLJ-N-L43, carrying out vacuum freeze drying to obtain corresponding single-bacterium powder, mixing the single-bacterium powder, and mixing with halophyte extract and the like to obtain the halophyte epiphytic repair and maintenance microbial inoculum. The Chryseobacterium YTLJ-E-II12 and the Acinetobacter YTLJ-N-L43 are preserved in the Guangdong Microbial Culture Collection Center, and the preservation numbers are respectively GDMCC 61770 and GDMCC 61691. The microbial inoculum can strengthen the combined removal of various toxic pollutants in the high-salt environment, has the effect of promoting the growth of halophyte, and is used for treating the organic-inorganic combined pollution of the high-salt environment such as ocean and coastal zones.
Owner:YANTAI INST OF COASTAL ZONE RES CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Metalloprotease from Chryseobacterium
ActiveUS20170114301A1HydrolasesDetergent mixture composition preparationMetalloproteinaseChryseobacterium
The present invention relates to a new metalloprotease and the use thereof in cleaning processes, such as laundry and dish wash. The invention also relates to detergent compositions and cleaning compositions comprising a metalloprotease.
Owner:NOVOZYMES AS
A kind of petroleum degrading bacterial agent and its preparation method and application
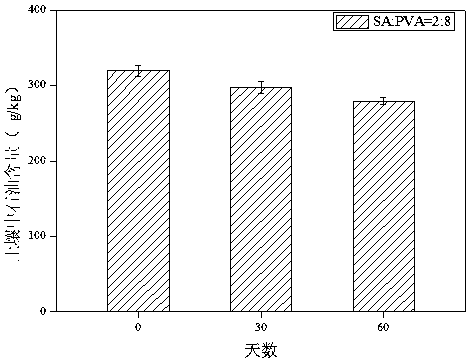
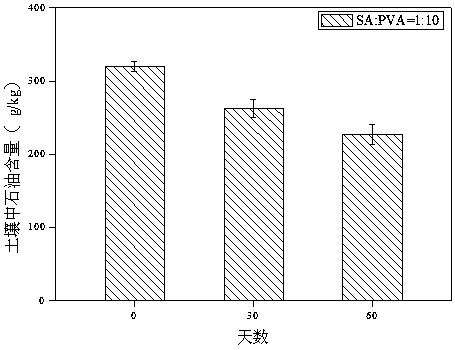
ActiveCN105087538BSolve environmental factorsImproved immobilization techniqueContaminated soil reclamationOn/in organic carrierPolyvinyl alcoholMicrosphere
The invention discloses a petroleum-degrading bacterial agent and its preparation method and application. The preparation method is as follows: mix polyvinyl alcohol and sodium alginate solution uniformly in proportion, then add activated carbon to mix evenly, and add 10:1 alginate after cooling. The ratio is mixed with the oil-degrading bacterial solution containing Chryseobacterium: Caulobacter: Achromobacter: Burkholderia (the mass ratio of each strain is 36:22:18:5); then use a syringe to drop the resulting mixed solution into chlorine Calcium chloride is saturated with boric acid solution to form balls; after standing still, the microspheres in the solution are taken out and washed with sterilized 0.9% NaCl solution to obtain a solid microsphere-shaped petroleum-degrading bacterial agent. The petroleum-degrading bacterial agent of the invention can be used to restore petroleum-contaminated soil; the form of the solid bacterial agent is also convenient for transportation and storage, and provides technical support for the practical application of microbial restoration of petroleum-contaminated soil.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Morchella nutrition bag made from edible fungus slag and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN106187515BIncrease productionLow costCalcareous fertilisersBioloigcal waste fertilisersMushroomPollution
The invention belongs to the field of toadstool cultivation, and in particular relates to a toadstool nutrition bag prepared by utilizing edible mushroom dregs and a preparation method thereof. The invention has the main improvement that the edible mushroom dregs are adopted as main raw materials, and are soaked by utilizing a liquid cultural substance of chryseobacterium HT2. The preparation method comprises the following steps of (1) collecting the mushroom dregs; (2) mixing the mushroom dregs and the liquid cultural substance of the chryseobacterium HT2, and soaking in an open vessel; (3) filtering to obtain the mushroom dregs, adding 1 to 6 percent of unslaked lime and 2 to 10 percent of husk or wheat bran, mixing to obtain a mixture, bagging, and sterilizing to obtain the nutrition bag. According to the method provided by the invention, the preparation raw materials of the nutrition bag are changed, the mushroom dregs remained after cultivating the edible mushrooms are adopted to replace traditional wheat berries and husks, and the chryseobacterium HT2 is utilized to ferment and decompose the mushroom dregs, so that cellulose and hemicellulose in the mushroom dregs are partially turned into saccharides easily utilized by the toadstool; agricultural wastes are utilized, so that the cost is reduced, the pollution is reduced, and the yield of the toadstool is improved.
Owner:四川省食用菌研究所
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com