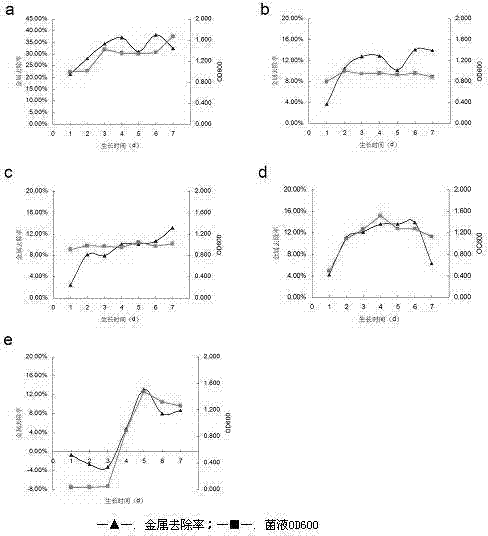
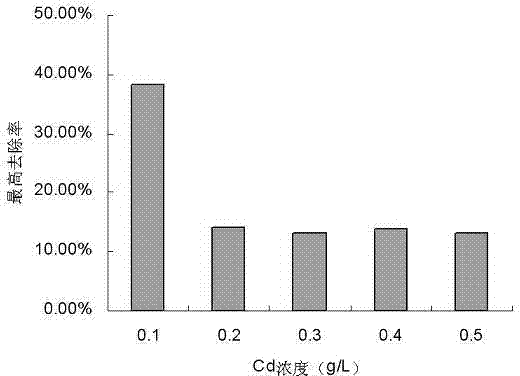
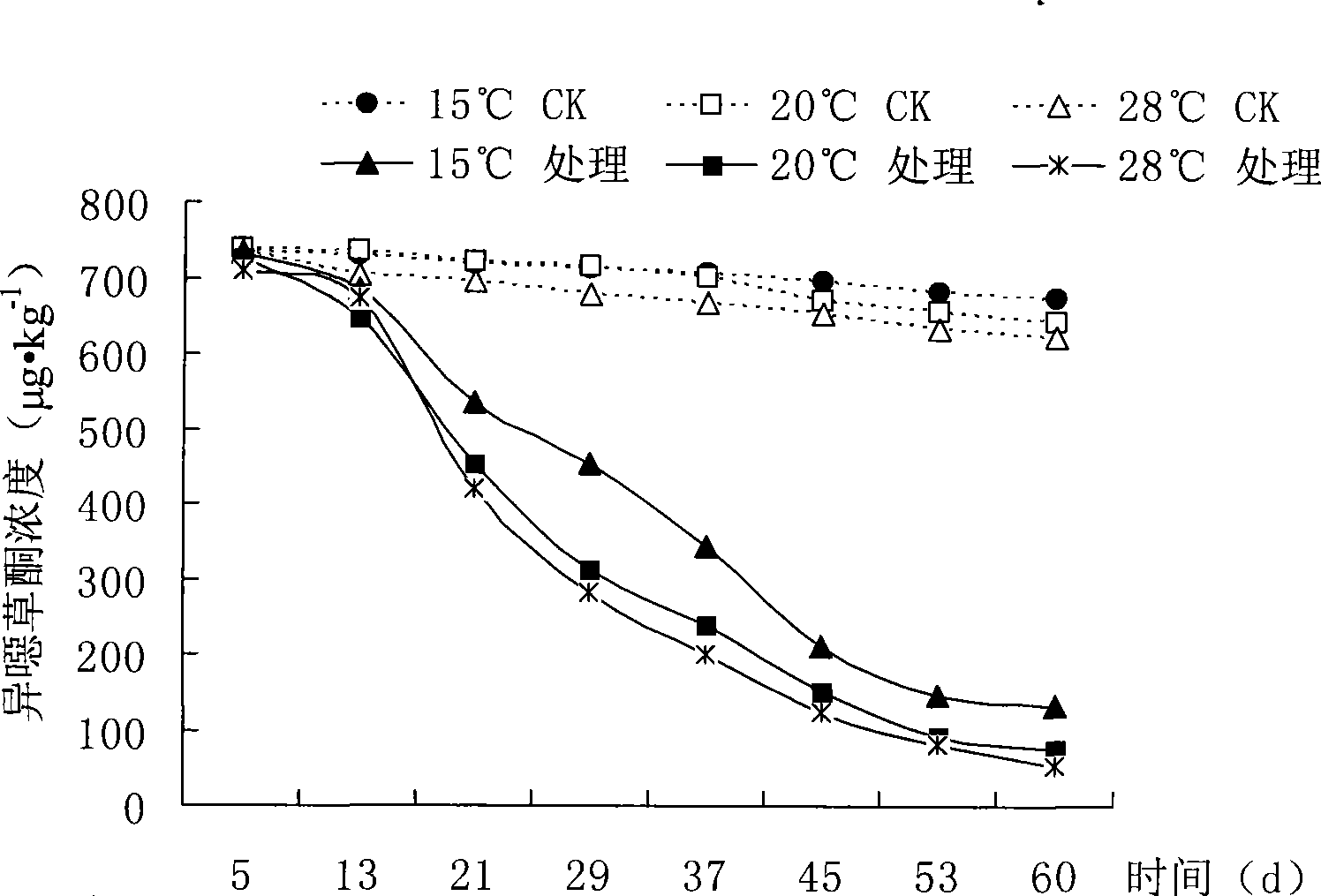
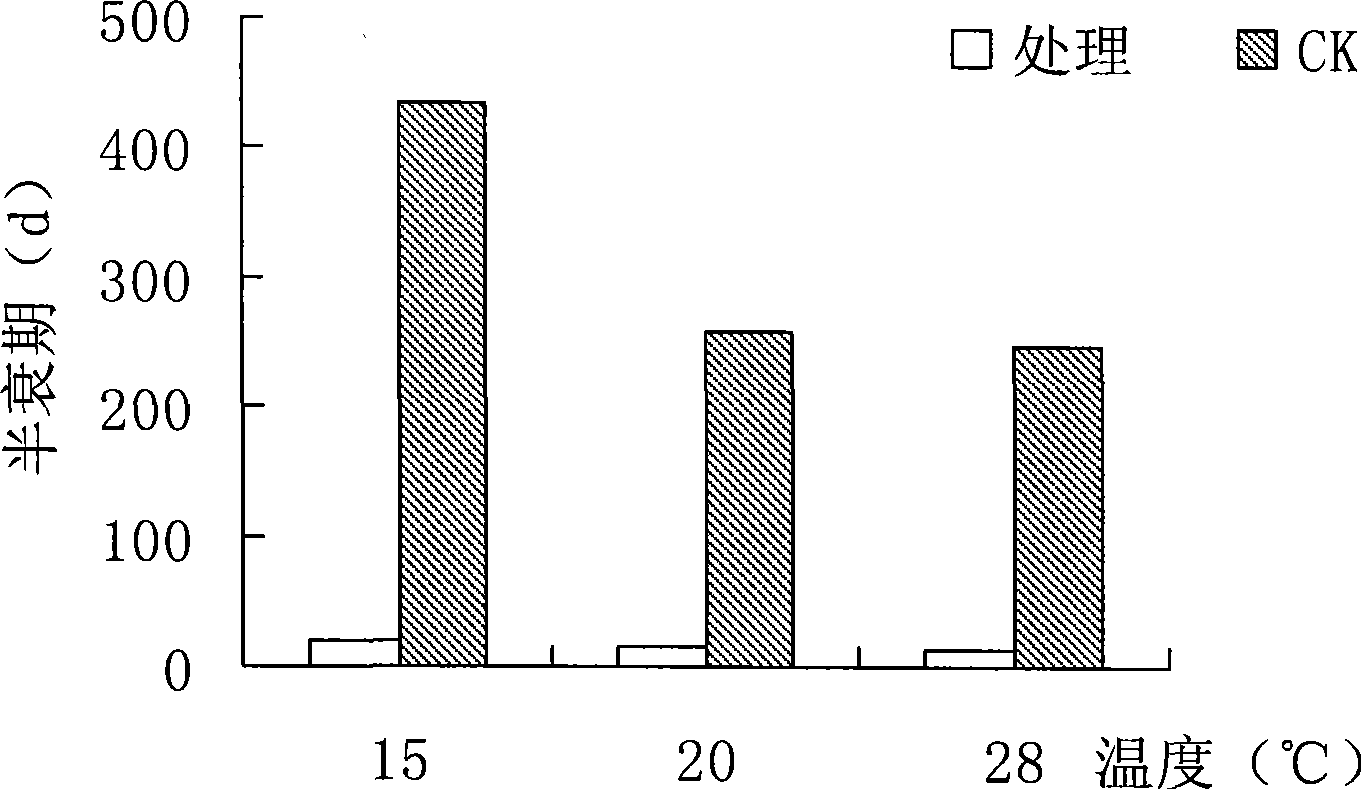
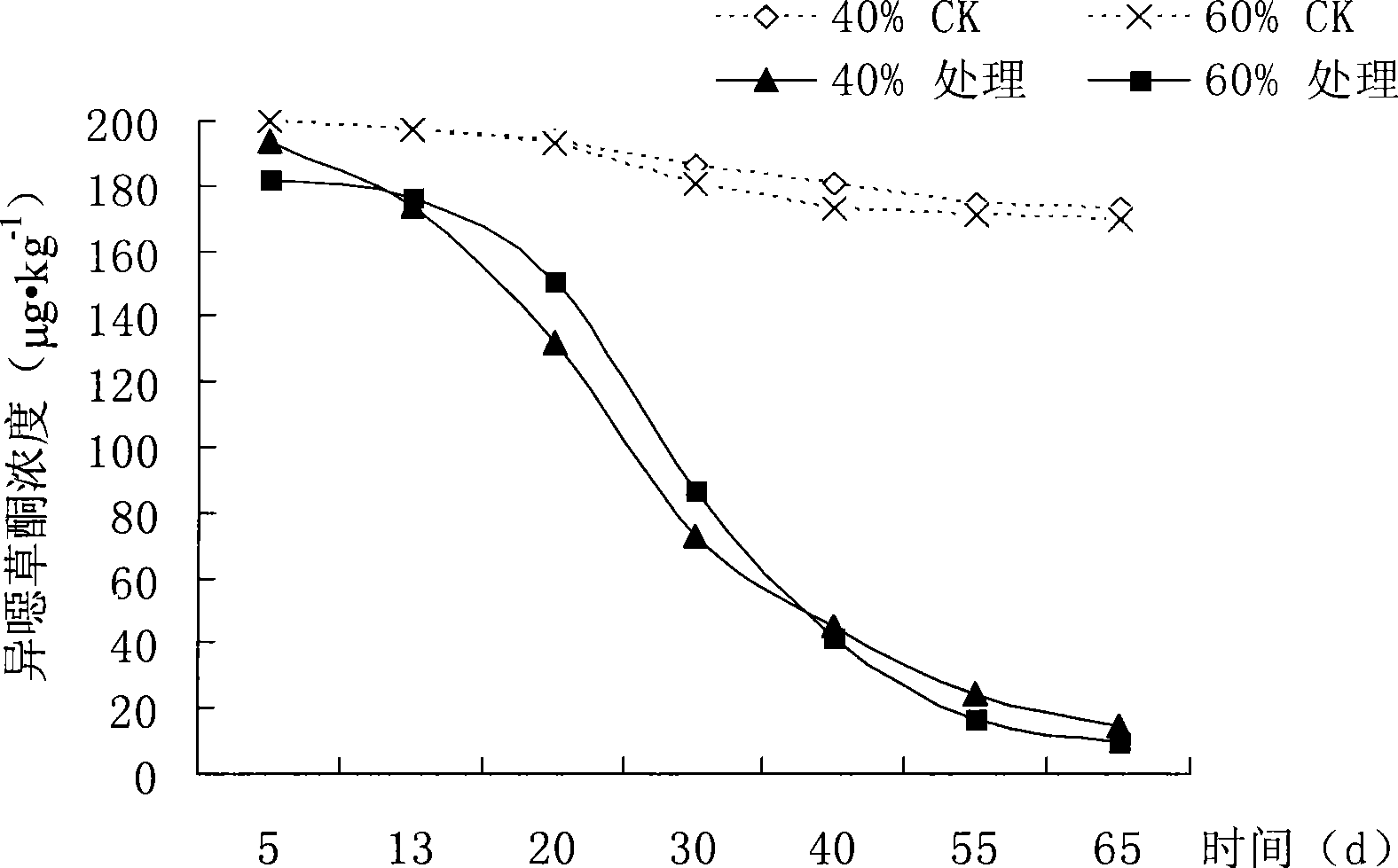
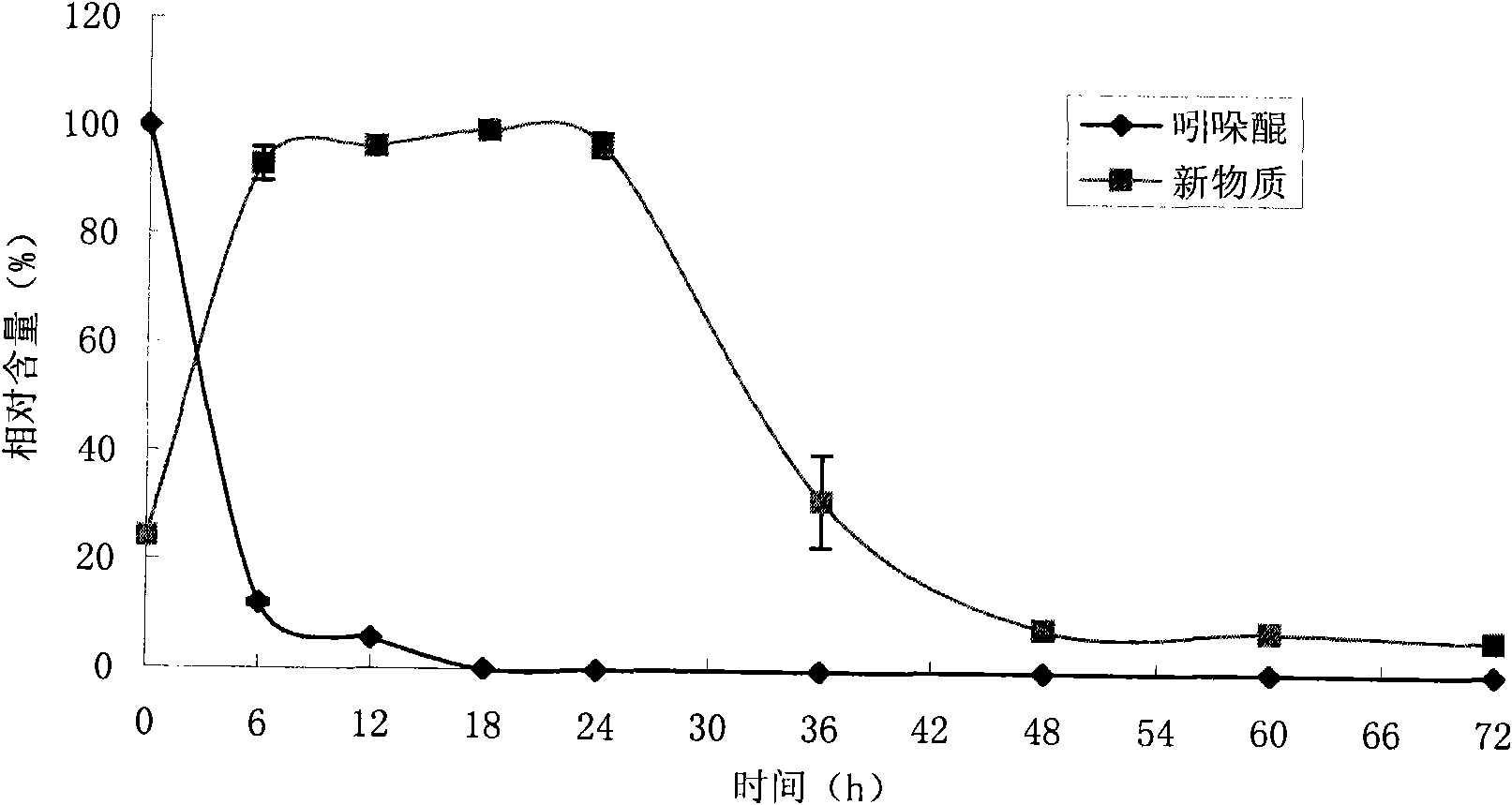
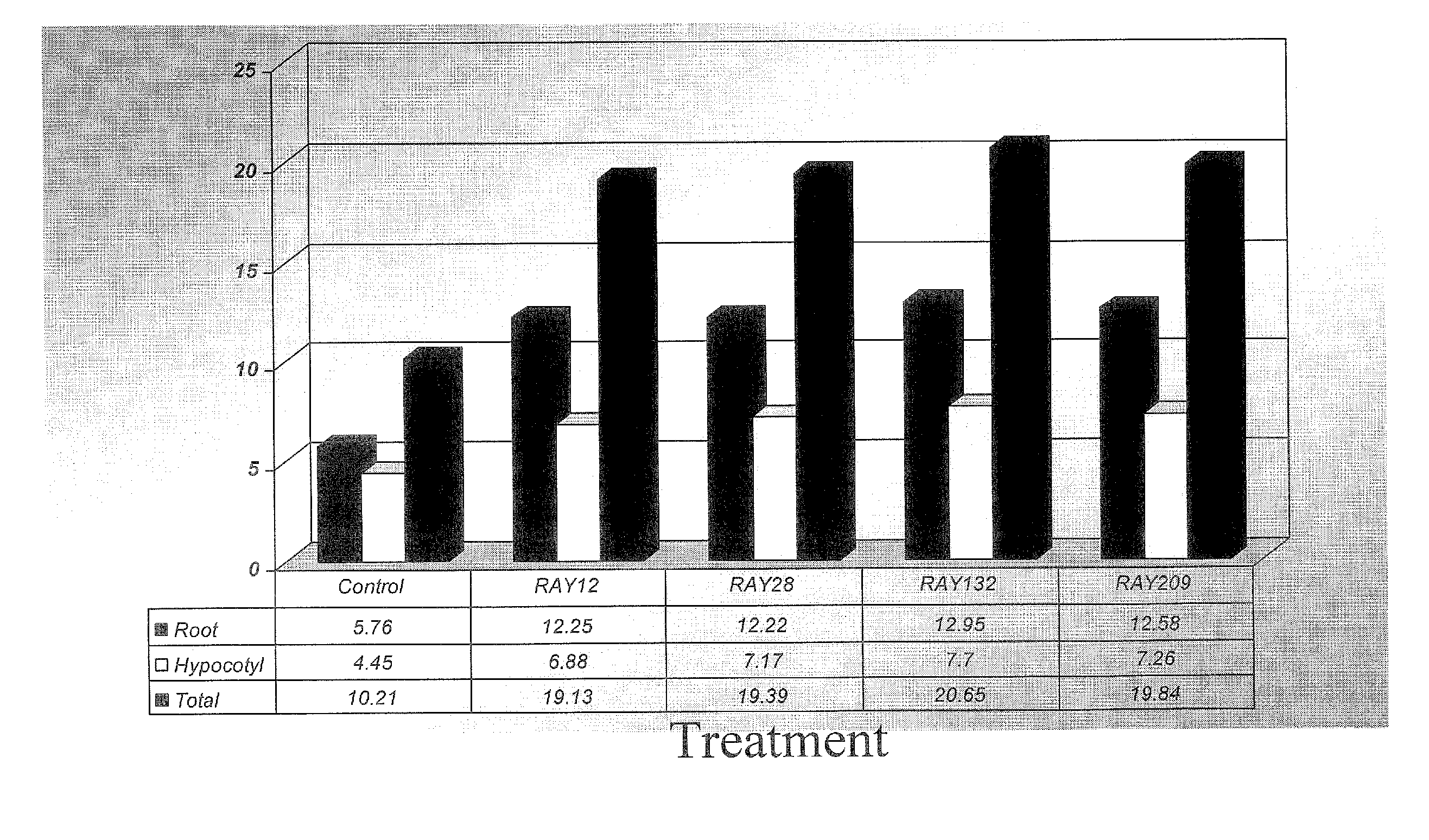Patents
Literature
102 results about "Achromobacter" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Achromobacter is a genus of bacteria, included in the family Alcaligenaceae in the order Burkholderiales. The cells are Gram-negative straight rods and are motile by using one to 20 peritrichous flagella. They are strictly aerobic and are found in water (fresh and marine) and soils. They have also been identified as a contaminant in laboratory cell cultures. They have been identified as opportunistic human pathogens in people with certain immunosuppressive conditions such as cystic fibrosis, cancer and kidney failure.
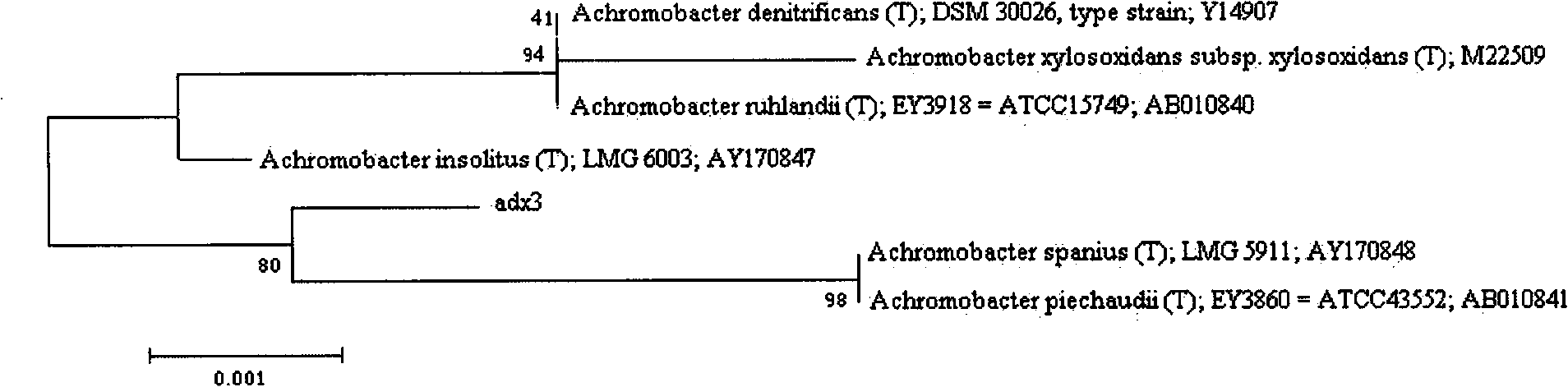
Achromobacter xylosoxidans strain for biological denitrificaion and application thereof
InactiveCN101560486ASimple processLow costBacteriaWater contaminantsAchromobacterMicrobiological culture
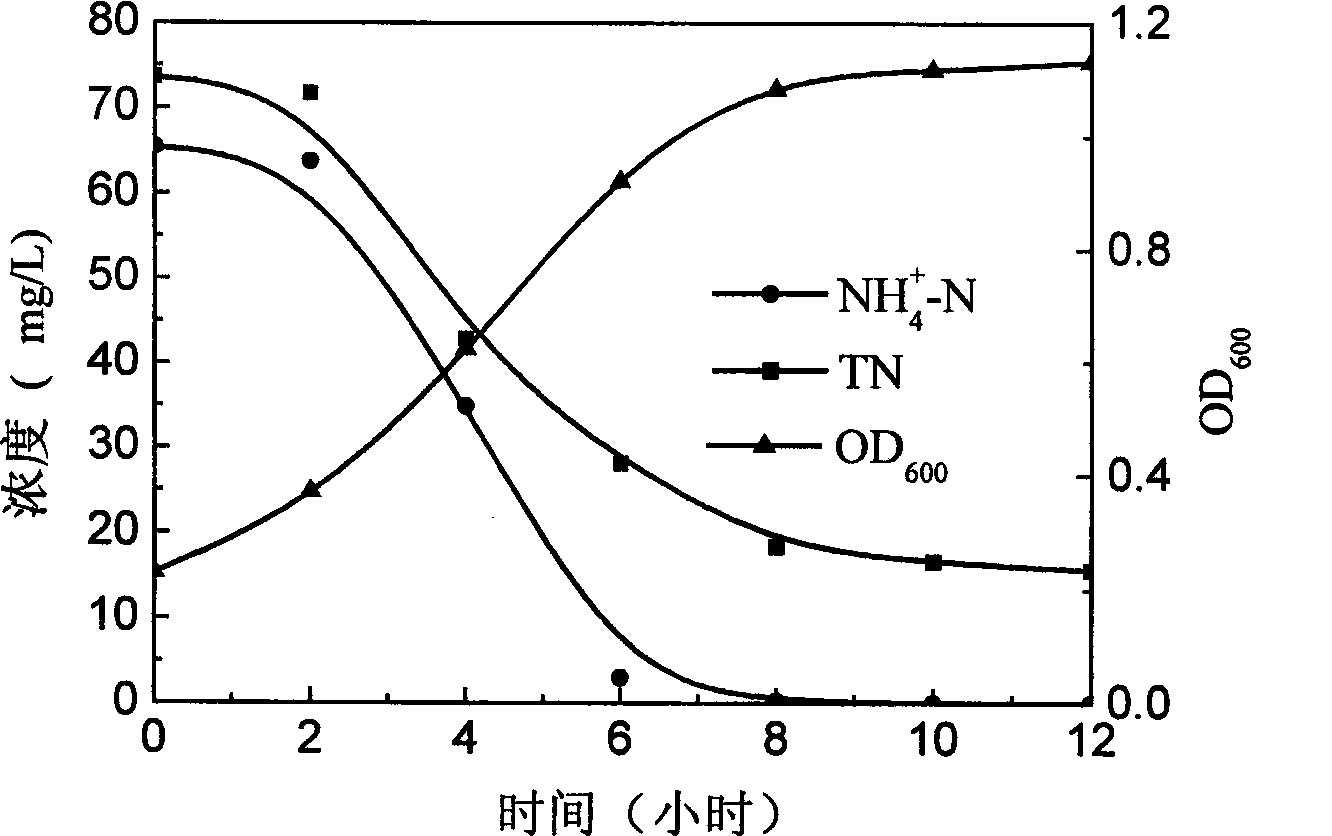
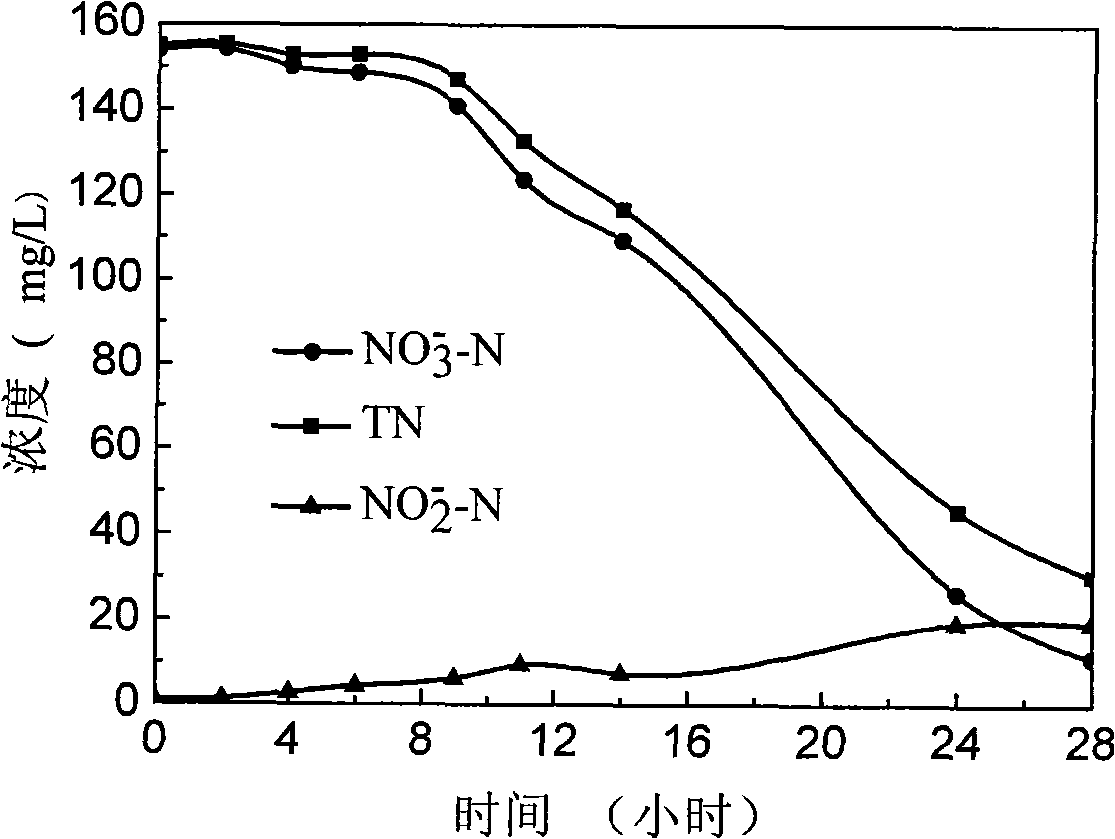
The invention discloses an achromobacter xylosoxidans strain for biological denitrificaion and application thereof. The achromobacter xylosoxidans strain GAD3 is preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC for short) with preservation number CGMCC No. 2964 in March 19th, 2009. The strain is added to nitrogenous effluent with 2 to 6mg / L of dissolved oxygen to realize biological denitrificaion. The strain not only has the capability of heterotrophic nitrification, but also has the capability of aerobic denitrification. In the process of treating the nitrogenous effluent, only one aerobic stage is needed, the denitrification efficiency is high, and the operation is convenient and quick; and compared with the conventional biological denitrification process, the application has huge economic benefits.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Autotrophic and allotrophic symbiosis ammonia oxidation bacterial agent as well as culture method and application thereof
ActiveCN101831392AConversion efficiency is not affectedPromote growthBacteriaMicroorganism based processesAchromobacter xylosoxidansAmmonia
The invention belongs to the technical field of environmental organisms and particularly relates to an autotrophic and allotrophic symbiosis ammonia oxidation bacterial agent for treating ammonia-nitrogen wastewater as well as a culture method and application thereof. The autotrophic and allotrophic symbiosis ammonia oxidation bacterial agent is prepared by mixing culturing nitrosomonas Nitrosomonas sp.N-1, pseudomonas Pseudomonas sp.He-X, thermomonas Thermomonas haemolytica D-2 and achromobacter Achromobacter xylosoxidans C-1 and is used for treating ammonia-nitrogen wastewater. The invention has the advantages of wide adaptation range, strong stability, environmental and toxic impact resistance and the like.
Owner:CHENGDU INST OF BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF S
Achromobacter capable of degrading aniline and application thereof
InactiveCN101514330AGood self-flocculation propertiesImprove degradation efficiencyBacteriaWater contaminantsGram stain negativeWastewater
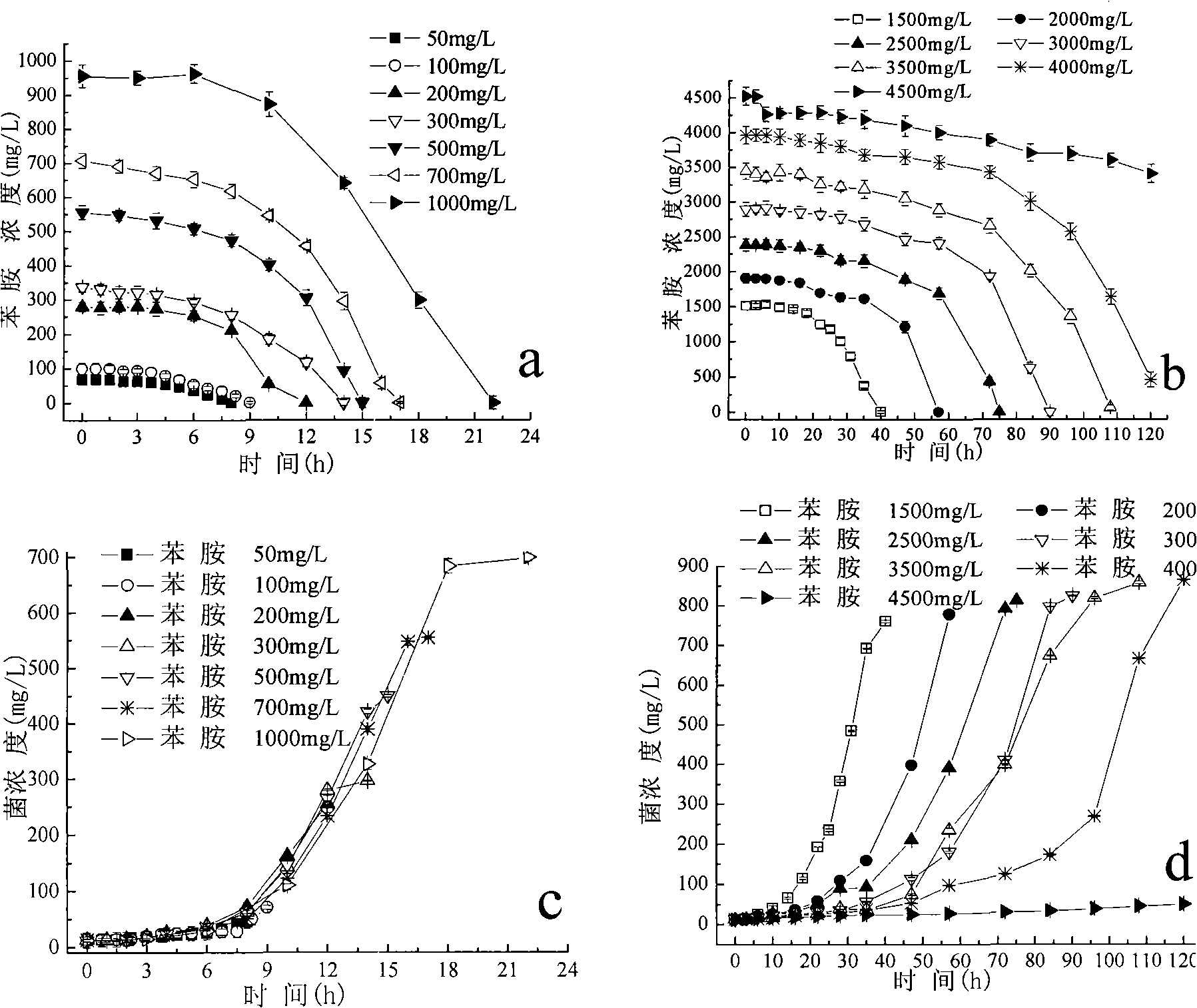
The invention discloses an achromobacter capable of degrading aniline, wherein the 16S rDNA of the achromobacter has a sequence of SEQ ID No.1. Colonies are yellow, round, smooth and humid with neat edges and convex bulges. Through electron microscope observation, the achromobacter does not have flagellum and spore bacteria; and under the observation of the electron microscope, the form of the achromobacter is a thicker bacillus which is gram staining negative and oxidase and catalase negative, and is reduced by nitrate to generate gas. The achromobacter can achieve the efficient degradation of aniline pollutants under an aerobic condition, the maximum tolerance concentration to the aniline is up to 4,500 milligrams per liter, the aniline of which the concentration is less than or equal to 4,000 milligrams per liter can be completely removed, thus the achromobacter plays an important role in the controlling practice of aniline industrial wastewater.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Culture method of biological cleaning strains in low-concentration volatile mixed organic waste gas
The invention relates to a culture method of biological cleaning strains in low-concentration volatile mixed organic waste gas. The method comprises the following steps: a), culturing a first strain; b), carrying out the combined inoculation of the first strain and a second strain and using tap water to prepare the sludge concentration of the mixed strains; and c), using mixed organic matter in the waste gas as a substrate to be cast into an insition culture medium so as to culture and train insitions. The first strain is prepared by culturing and training from activated mud taken from a printing and dyeing sewage treatment plant and is a mixed strain of flavobacterium and Bacillus cereus, and the second strain is prepared by collecting activated mud collected from a secondary sedimentation tank of a petrochemical sewage treatment plant and is a mixed strain comprising the flavobacterium, the Bacillus cereus, xylose oxidase Achromobacter and Pseudomonas stutzeri. The method facilitates the balanced growth of various cultured microorganisms and can simultaneously decompound various target configuration compounds at high efficiency.
Owner:GUANGZHOU HUANFA ENVIRONMENTAL ENG CO LTD
Petroleum degrading bacterium as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN105087538ASolve environmental factorsImproved immobilization techniqueContaminated soil reclamationOn/in organic carrierMicrosphereEngineering
The invention discloses a petroleum degrading bacterium as well as a preparation method and an application thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: uniformly mixing polyving akohol and sodium alginate solution at a certain ratio, adding with activated carbon, uniformly mixing, cooling, and adding petroleum degrading bacterium solution into the cooled mixture according to the ratio of the cooled mixture to petroleum degrading bacterium solution being 10 to 1, wherein the petroleum degrading bacterium solution contains flavobacterium indologenes, caulobacter, achromobacter and burkholderia cenocepacia at the weight ratio of 36 to 22, to 18 to 5; dropwise adding the mixed solution into calcium chloride saturated boric acid solution through an injection syringe for balling; and standing, taking out microspheres in the solution, washing by adopting sterilized 0.9% NaCl solution, and thus obtaining the solid microspherical petroleum degrading bacterium. The petroleum degrading bacterium can be used for restoring petroleum polluted soil, the solid petroleum degrading bacterium is convenient to transport and store; and technical support is provided for the practical application of restoring the petroleum polluted soil by microorganisms.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
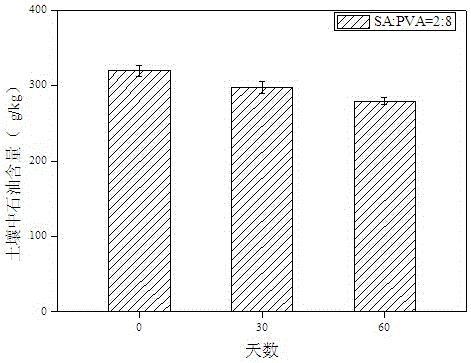
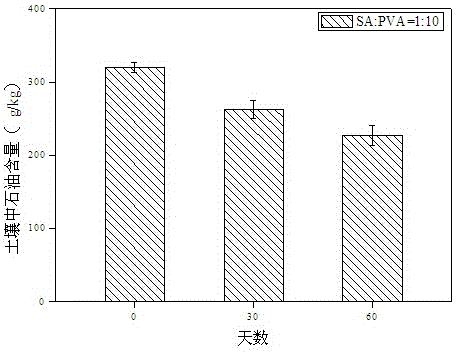
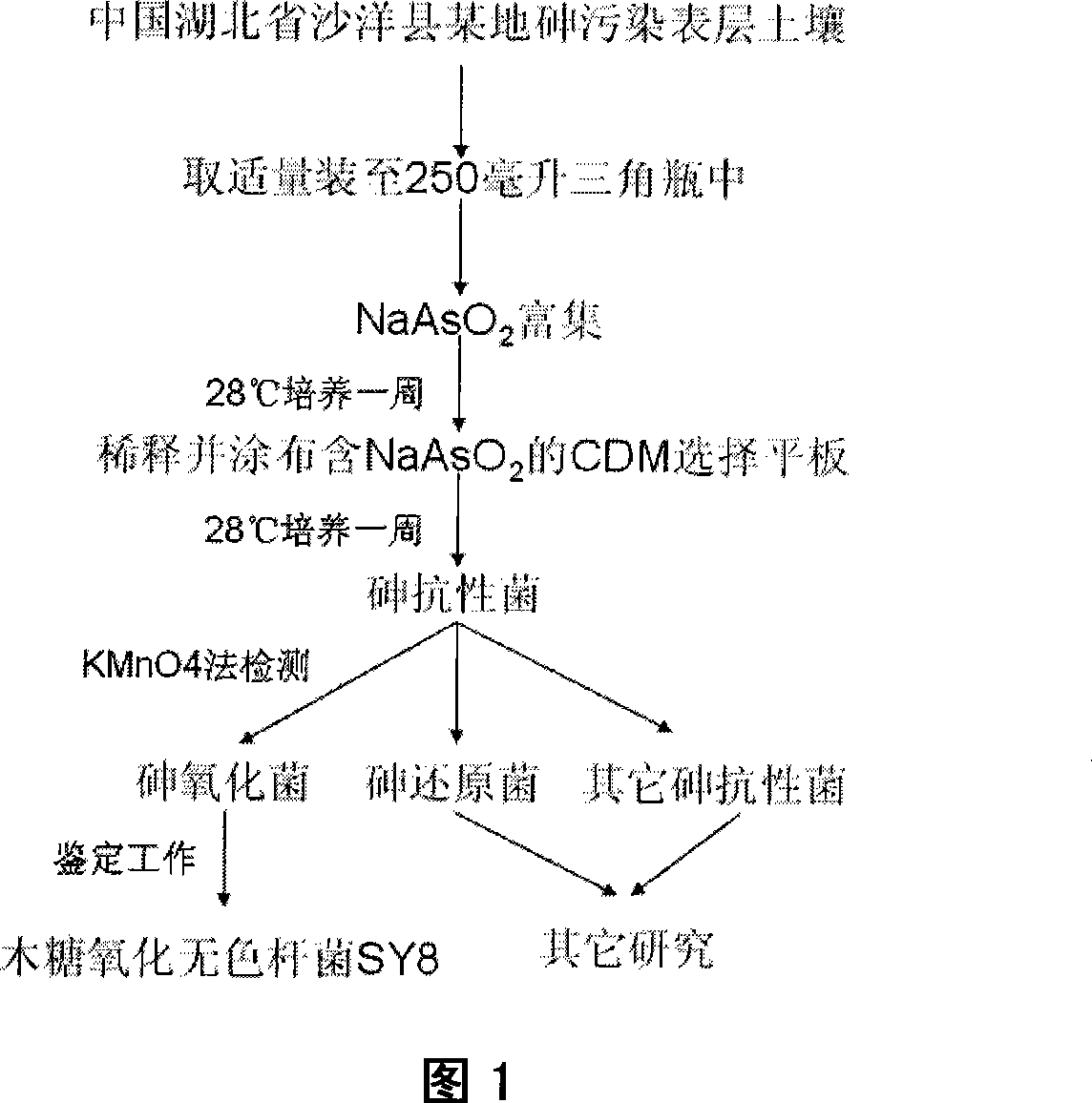
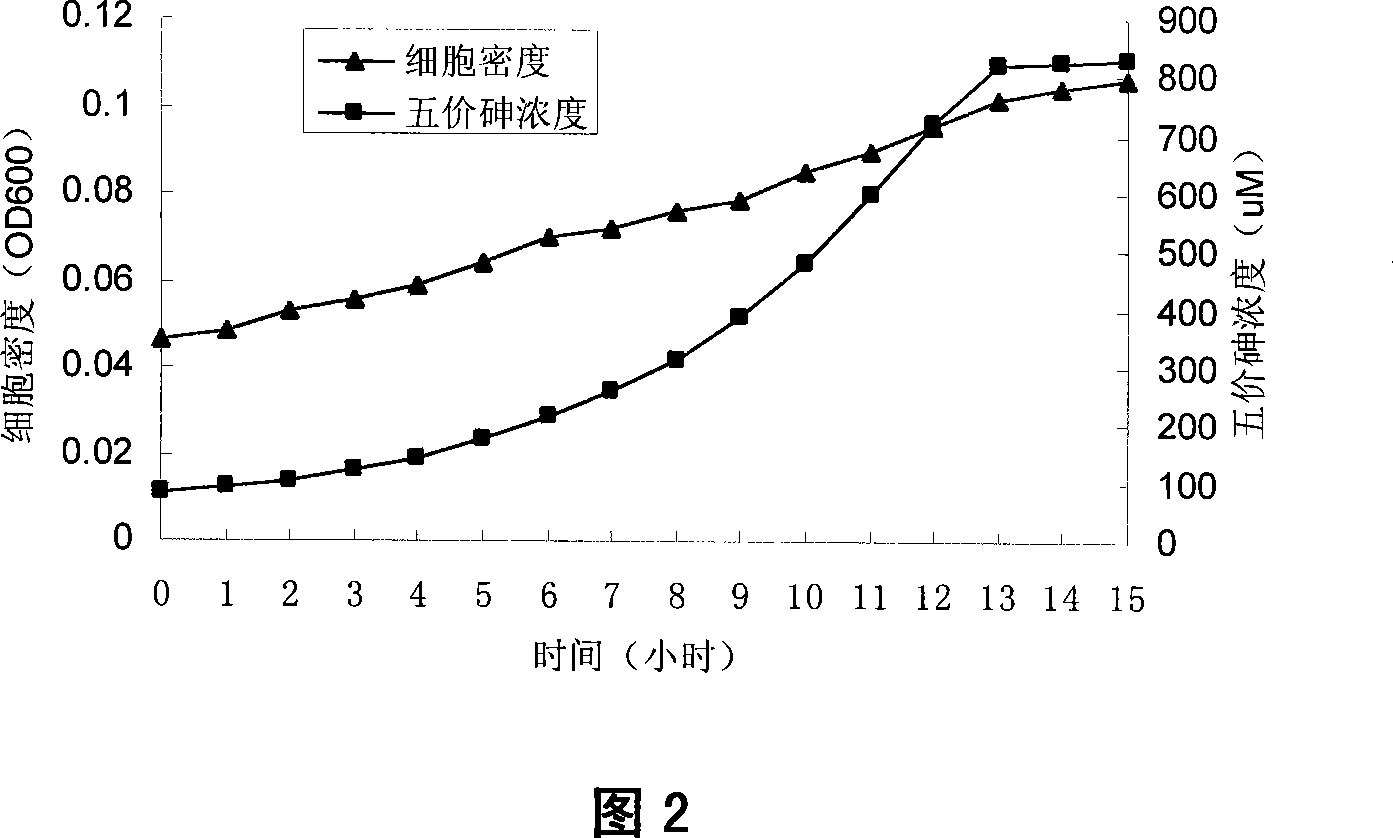
Xylose oxidation achromatous bacillus SY8 for purifying arsenic contamination and usage thereof
InactiveCN101063097AHarm reductionHighly toxicBacteriaContaminated soil reclamationBacteroidesMicroorganism
The invention discloses a wood sugar oxidation achromobacter SY8 and appliance in purifying arsenic contamination aspect in environmental microbiology technical domain, which is characterized by the following: separating a wood sugar oxidation achromobacter SY8 from arsenic contamination soil; possessing oxidation for inorganic tervalence arsenic; oxidizing inorganic tervalence arsenic to inorganic pentavalent arsenic in arsenic environmental pollution; decreasing toxicity of arsenic in environment; decreasing adsorbing removing property of arsenic; setting the preserved number as CCTCC NO: M207048. This strain possesses better applying prospect in arsenic pollution aspect.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Pyrene degrading bacterium and application thereof
InactiveCN101974442APromote degradationTreatment using aerobic processesBacteriaMicrobiologyAchromobacter
The invention discloses a pyrene degrading bacterium and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of biological degradation treatment. The pyrene degrading bacterium is authenticated as an achromobacter (Achromobacter sp.), and the strain collection number is CGMCC3637. The Genbank accession number of a 16S rDNA of the strain is EU220009.1. The strain is prepared into a bacterial suspension of which the bacterium content is 1.25*10<8>CFU / ml, and the degradation removal rates to the pyrenes of which the initial concentrations are 0.11mg / L, 0.26mg / L, 0.52mg / L and 1.14mg / L respectively after 7 days are 92.65%, 91.46%, 29% and 89.67% respectively.
Owner:BEIJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Composition of bacterial strains, bioremediation mixture and use of this composition for the removal of contaminants from the soil and the method for purifying the soil contaminants
InactiveUS20140141494A1Low costFacilitates quick acquisition of appropriate amountBacteriaBiochemical fibre treatmentBacteroidesFood contaminant
The object of the present invention is a composition of bacterial strains which may comprise Stenotrophomonas sp. strain 2L, Stenotrophomonas sp. strain 5L, Stenotrophomonas sp. strain 6L, Stenotrophomonas sp. strain 3N, Achromobacter sp. strain 4P, Arthrobacter sp. strain 1N, Brevundimonas sp. strain 2N, Brevundimonas sp. strain 5N, Brevundimonas sp. strain 6N, Pseudomonas sp. strain 3G, and Pseudomonas sp. strain 4, deposited under the number KKP 2041p (IAFB Collection of Industrial Microorganisms—Institute of Agricultural and Food Biotechnology in Warsaw), a bioremediation vaccine (bioremediation mixture) which may comprise the composition of these strains, the use of the vaccine in the removal of contaminants from the soil, and the method for the treatment of contaminated soil.
Owner:UNIWERSYTET WARSZAWSKI
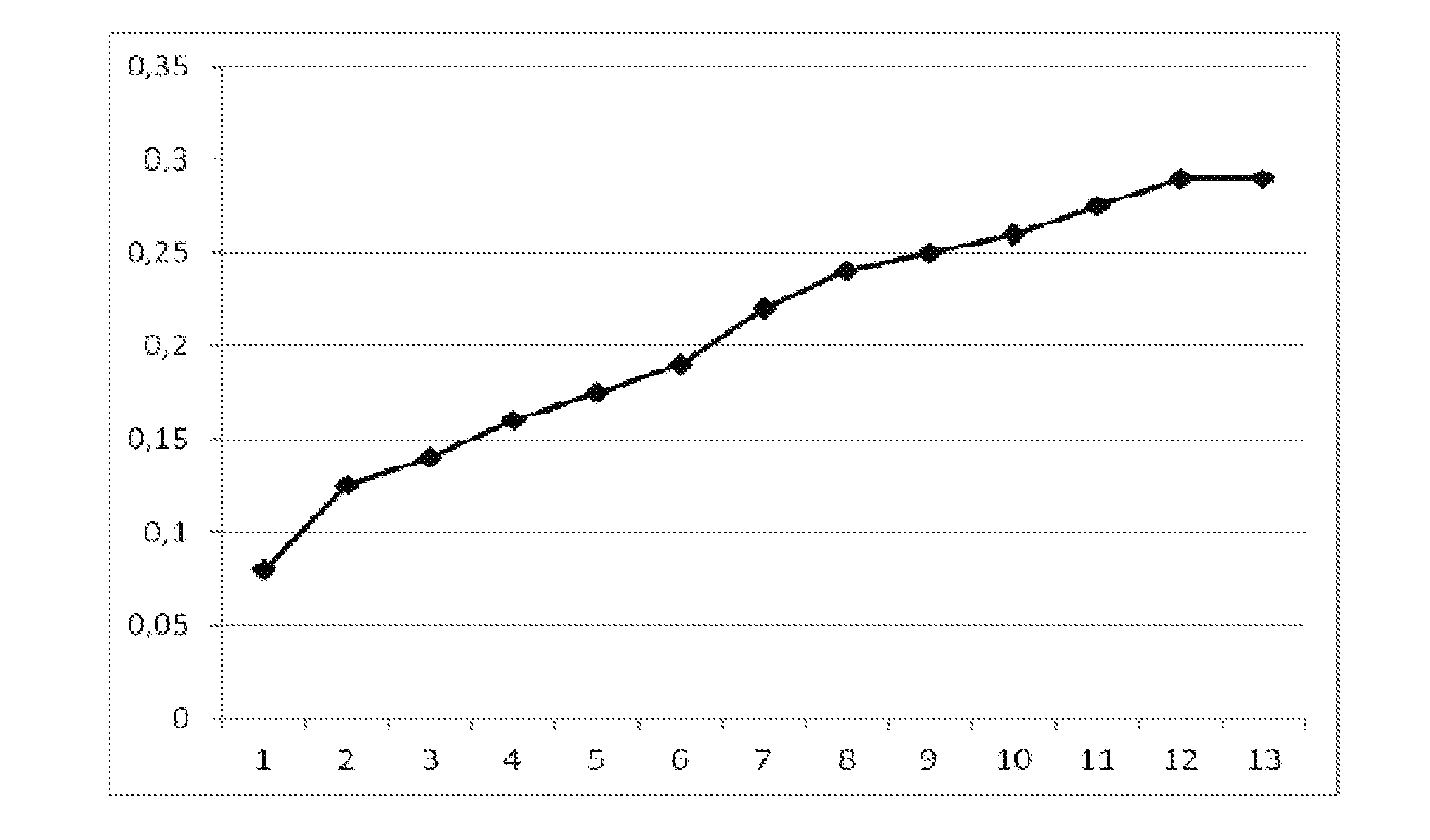
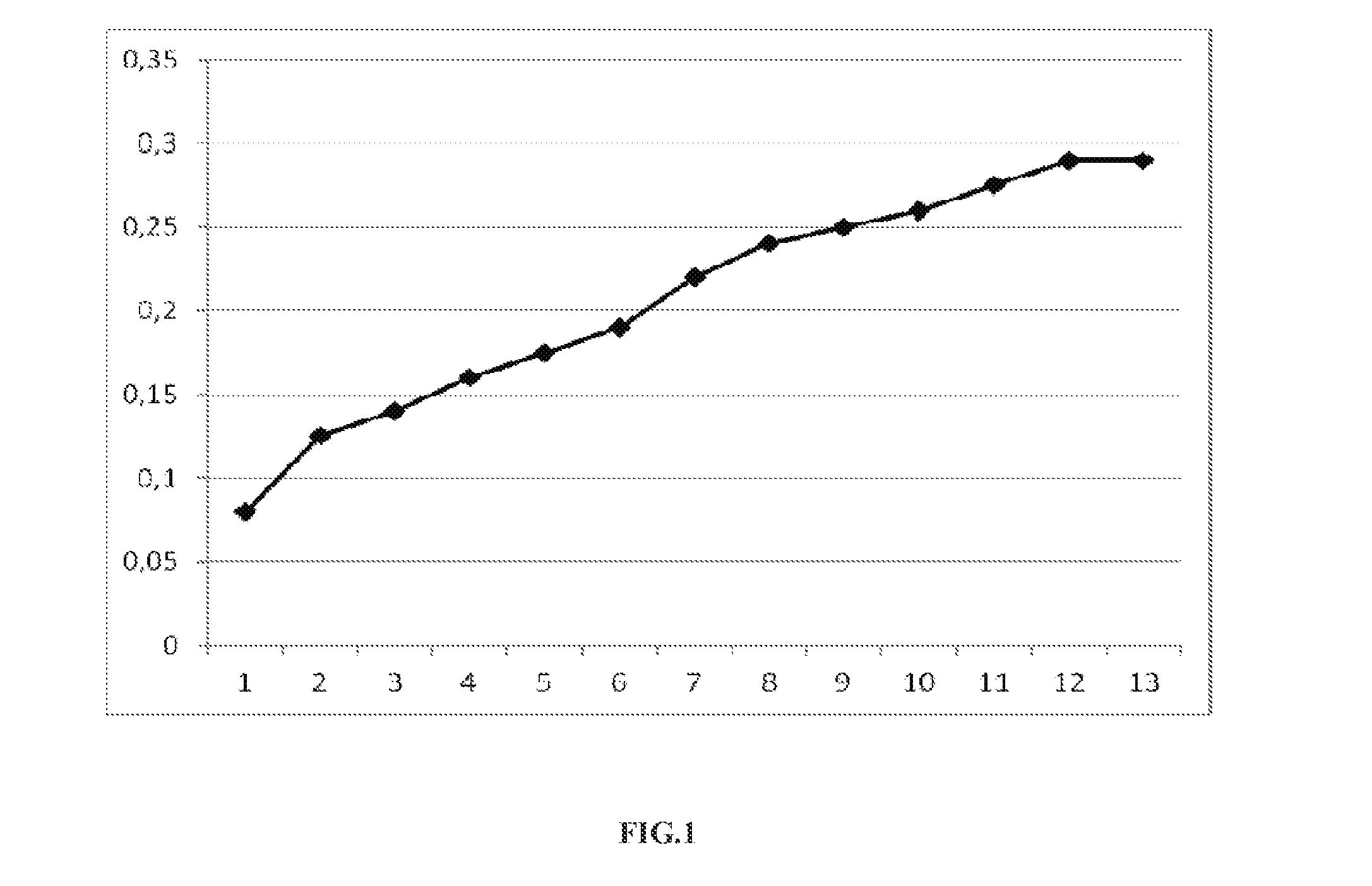
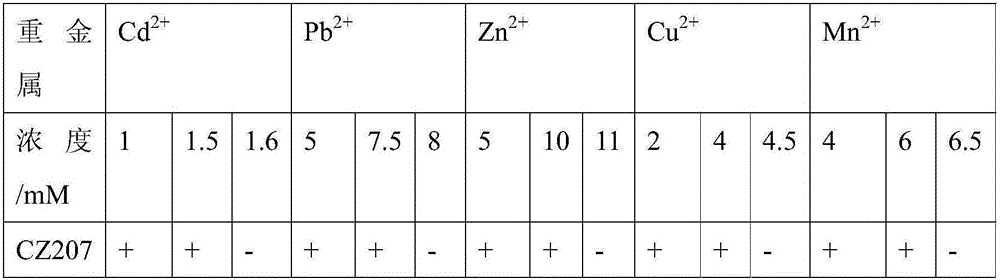
Achromobacter CZ207 strain capable of resisting heavy metal and promoting plant growth and application thereof
The invention provides an achromobacter sp CZ207 strain capable of resisting heavy metal such as cadmium, copper, lead, nickel and manganese and promoting the plant growth. The achromobacter sp CZ207 strain is preserved in CCTCC (China Center for Type Culture Collection) on March 7, 2016, the address is Wuhan University, Wuchang District, Wuhan City, Hubei Province, and the preservation number is CCTCC NO: M2016091; a 16S rDNA (Ribosomal Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid) sequence of the achromobacter sp CZ207 strain is as shown in an SEQ ID NO.1. Through observation on an LB solid culture medium, bacterial colonies are light yellow, tidy and moist, and the center parts of the bacterial colonies bulge; through microscopy observation, the bacterial colonies are in gram-negative, are rod-shaped and have no spores. The achromobacter sp CZ207 strain provided by the invention can tolerate multiple heavy metals, can secrete nutrient elements such as plant growth hormone, dissolved inorganic phosphorus and solid nitrogen and has the function of promoting the plant growth.
Owner:SOUTH CENTRAL UNIVERSITY FOR NATIONALITIES
Achromobacter insolitus and application of Achromobacter insolitus in heavy metal ion removing
InactiveCN103937705AEfficient removalNo secondary pollutionBacteriaWater contaminantsScreening methodPhysical chemistry
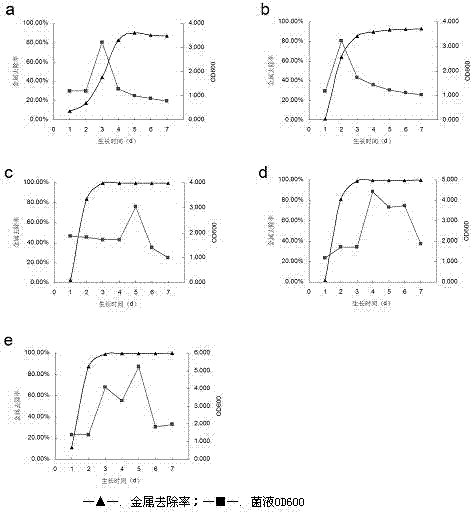
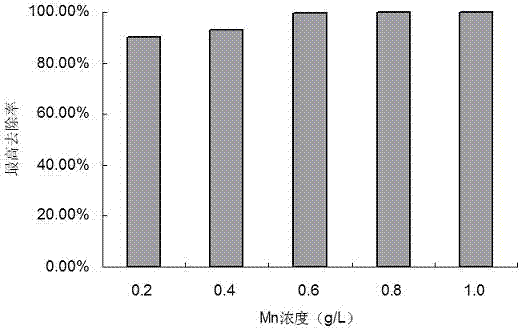
The present invention discloses a strain of Achromobacter insolitus CC6, and an application of the Achromobacter insolitus CC6 in heavy metal ion removing, wherein the Achromobacter insolitus CC6 provides a heavy metal ion Cd<2+> removing effect. The method for screening Achromobacter insolitus providing a heavy metal ion Cd<2+> removing effect from soil and water comprises: a, preparing a metal selective culture medium; b, carrying out enrichment acclimatization on a heavy metal resistance strain; c, screening and re-screening the heavy metal resistance strain; and d, detecting the heavy metal removing capability of the strain. According to the present invention, with the detection test on the heavy metal removing capability of the strain obtained by carrying out enrichment acclimatization on the heavy metal resistance strain with the metal ion-containing culture medium and purification, the reasonable and effective screening method for the heavy metal removing strain is established so as to obtain the strain suitable for requirements; and with application of the Achromobacter insolitus CC6 in the heavy metal pollution treatment, advantages of no secondary pollution, high treatment efficiency, wide application range, low cost and the like are provided.
Owner:江苏原元生物工程有限公司
A strain of Achromobacter xylosoxidans and use thereof for depredating clomazone
InactiveCN101463337AEfficient degradationBacteriaWater contaminantsAchromobacter xylosoxidansHigh concentration
The invention discloses an achromobacter xylosoxidans and the application thereof in the degradation of clomazone. The achromobacter xylosoxidans is achromobacter xylosoxidans CGMCC No. 2773. The bacterial strain can grow in the environment of high concentration clomazone, and can degrade the clomazone with high efficiency, so as to provide important foundation for the study of micro-biological degradation of residual weedicide clomazone, thus being applied to biological purification of the water body and soil which are polluted by the clomazone.
Owner:NORTHEAST AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Method of removing recalcitrant organic pollutants
InactiveUS20130334135A1Efficient biodegradationReducing the recalcitrant chemical oxygen demand (COD)Treatment using aerobic processesBacteriaChemical oxygen demandComamonas
Recalcitrant chemical oxygen demand (COD) of a liquid is reduced in a water treatment system. The method includes pretreating the liquid in a pretreatment unit to remove indigenous bacteria or microbes to a population level below which the indigenous organisms can interfere with the screened and externally introduced microorganisms. The liquid is then provided to a reactor that has a filter bed formed with a carrier material. Special microbes are screened and used to colonize the carrier material to remove recalcitrant COD. A biofilm is cultured on the surface of the carrier material to immobilize the screened microbes in the reactor. The method further includes percolating the liquid from the pretreatment unit through the filter bed colonized with the screened microbes to degrade at least part of the recalcitrant COD under aerobic conditions. In one embodiment, the filter is formed with biological granular activated carbon (GAC) as the carrier material and the screened microbes comprise at least one microbial species selected from the group consisting of Bacillus, Comamonas, Arthrobacter, Micrococcus, Pseudomonas, Pediococcus, Achromobacter, Flavobacterium, Mycobacterium, Rhodanobacter, Stenotrophomonas and Yeast.
Owner:BL TECH INC
Microbial herbicide
InactiveCN105053024AHigh selectivityGood environmental compatibilityBiocideAnimal repellantsBacteroidesChemical structure
The invention discloses a microbial herbicide and relates to the technical field of pesticides. The microbial herbicide comprises components in parts by weight as follows: 10-30 parts of cup fungi, 10-20 parts of pseudomonas pseudoacaligenes, 5-10 parts of citrobacter, 3-7 parts of fusarium, 1-5 parts of entyloma, 15-25 parts of sclerotinia sclerotiorum, 3-10 parts of achromobacter and 15-25 parts of halobacterium. The microbial herbicide is prepared from microorganisms such as cup fungi, pseudomonas pseudoacaligenes, citrobacter, fusarium, entyloma, sclerotinia sclerotiorum and the like and has the advantages of high selectivity, safety for non-target organisms and mammal animals, good environment compatibility, few development cost, novel chemical structure and unique action mode by optimizing the proportion of the components.
Owner:丁德凤
Complex bactericide for efficiently purifying sewage anaerobic outlet water of pig farm and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN105176868ACompatibility is reasonableEasy synergismBacteriaWaste water treatment from animal husbandryAchromobacter xylosoxidansPig farms
The invention discloses complex bactericide for efficiently purifying sewage anaerobic outlet water of a pig farm and a preparation method and an application thereof. The complex bactericide is formed by mixing rhodopseudomonas palustris, bacillus subtillis, nevskia, microbacterium esteraromaticum, paracoccus and xylose oxidized achromobacter. The complex bactericide has unique purifying effect on the sewage anaerobic outlet water of the pig farm, also has a good purifying effect for artificial synthetic sewage and has a popularization application value.
Owner:FUJIAN INST OF MICROBIOLOGY
Achromobacter xylosoxidans strain and application thereof
InactiveCN101914467AEfficient degradationBacteriaWater contaminantsAchromobacter xylosoxidansWastewater
The invention discloses an Achromobacter xylosoxidans strain and application thereof. The strain is Achromobacter xylosoxidans N4 with the collection number of CGMCC No.3632. The Achromobacter xylosoxidans N4 GCMCC No.3632 can quickly and efficiently degrade isatin and o-aminobenzoic acid, and can be used for biologically treating calico printing wastewater.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIV
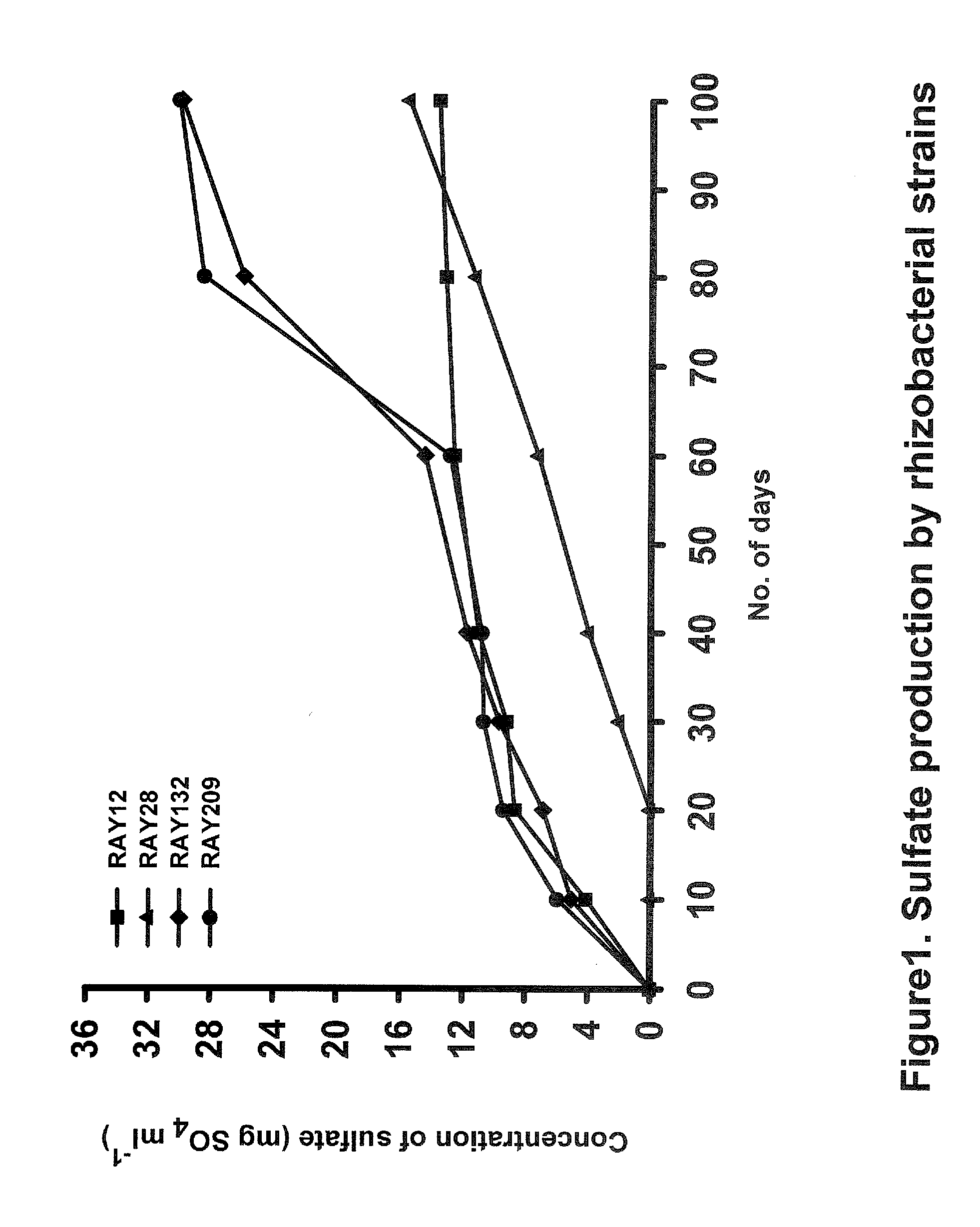
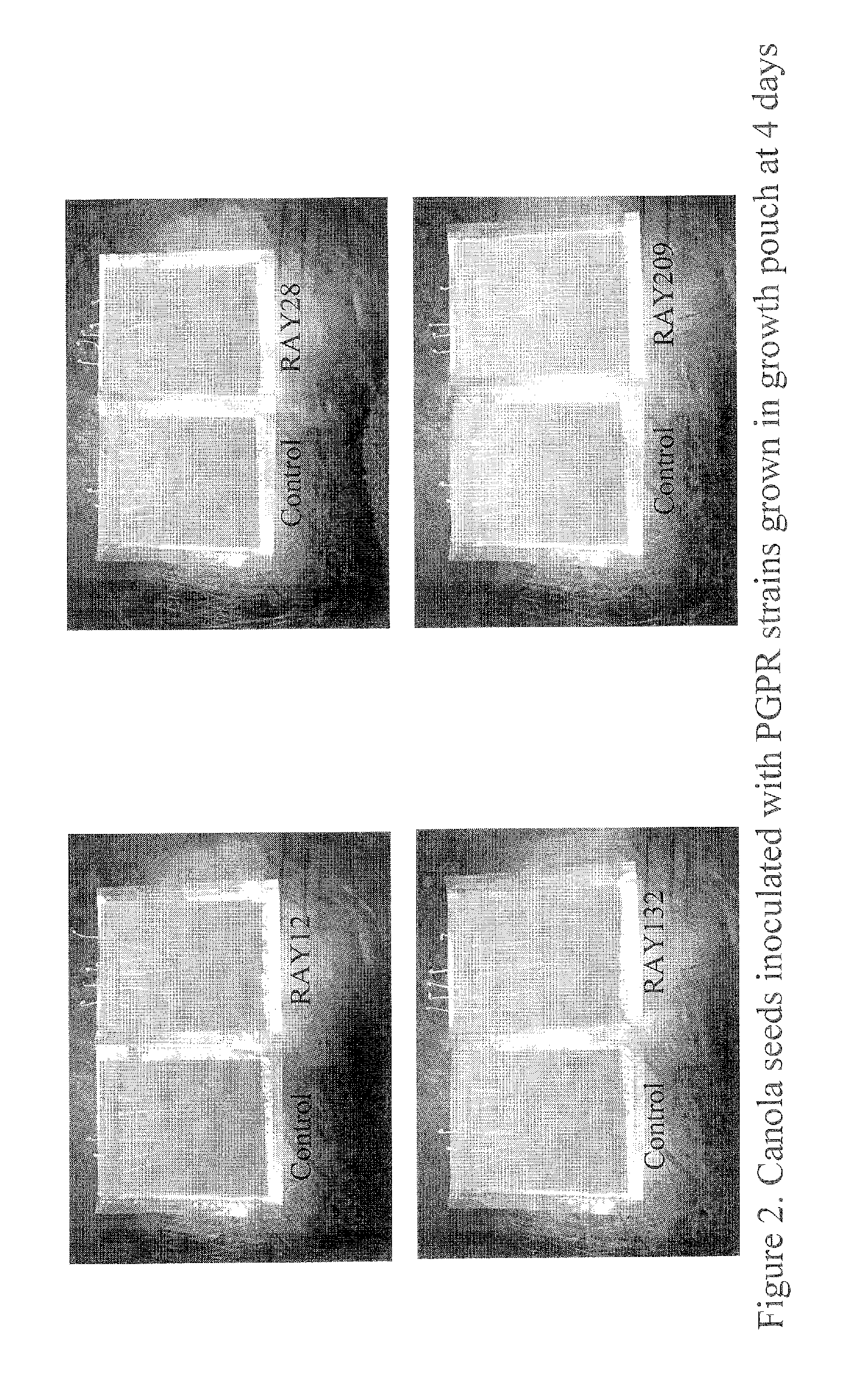
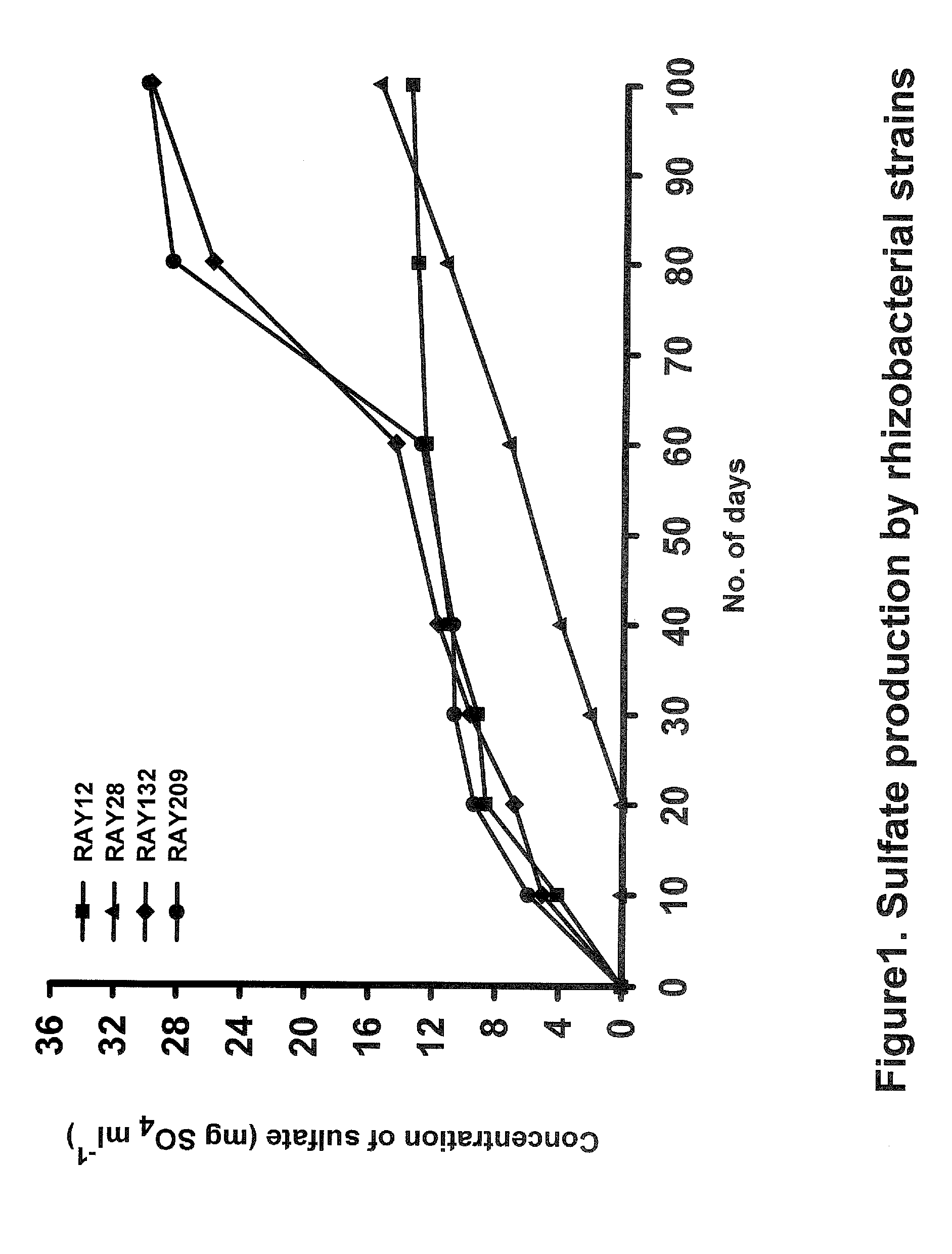
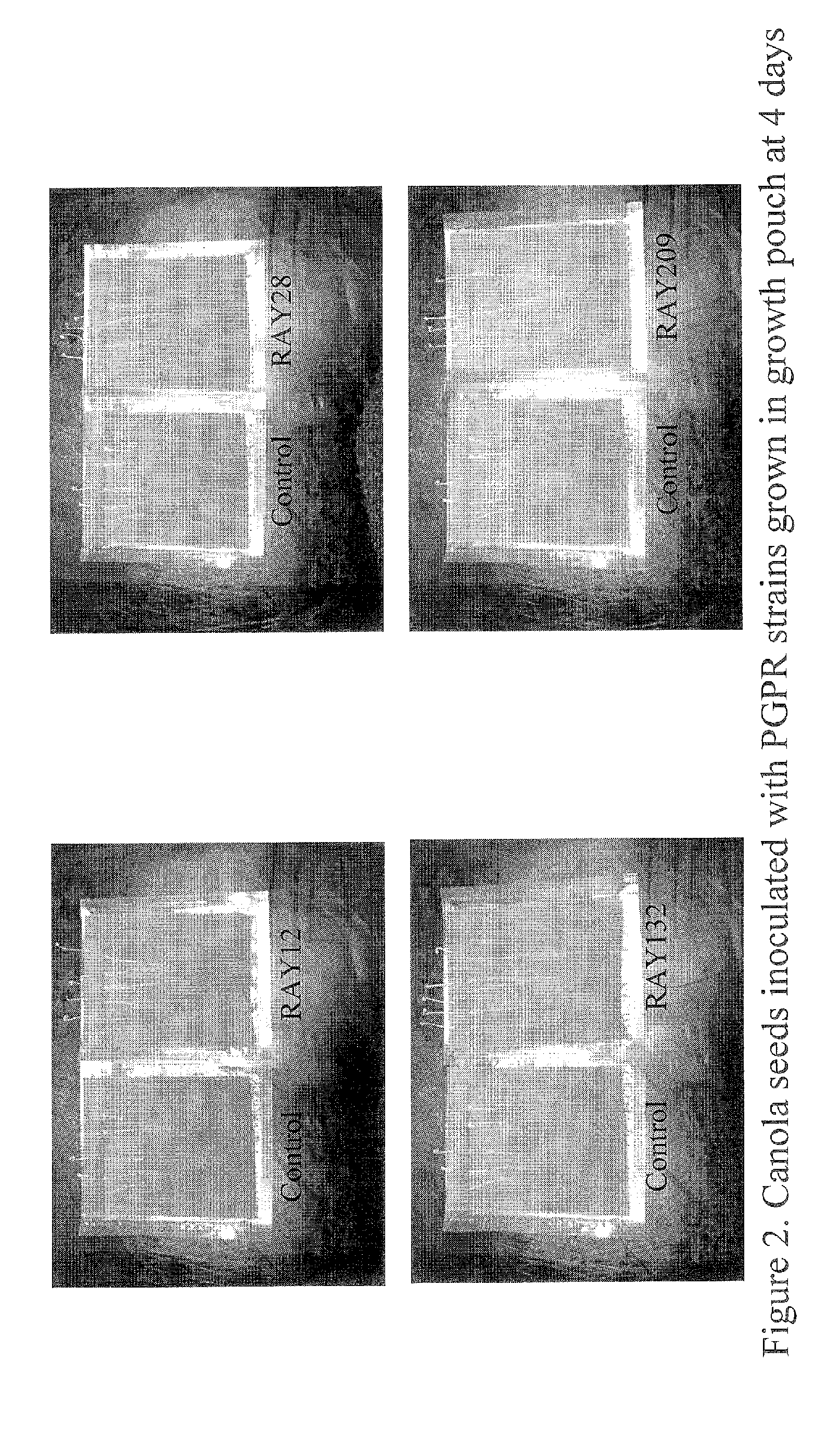
Sulfur-oxidizing plant growth promoting rhizobacteria for enhanced canola performance
Described herein is the isolation and identification of a number of sulfur oxidizing plant growth promoting rhizobacteria: RAY12, identified as Achromobacter piechaudii; RAY28, identified as Agrobacterium tumefaciens, RAY132, identified as Stenotrophomonas maltophilia; and RAY209, identified as Delftia acidovorans. The PGPR act to oxidize elemental sulfur which in turn provides sulfate for the plants. As a result of this arrangement, plants are able to grow more efficiently and effectively and have enhanced growth characteristics, for example, but by no means limited to, increased vigor, early emergence, increased emergence rate, increased biomass, increased plant leaf area, higher crop yield, increased pod number, increased pod weight, increased root biomass, increased seed weight, increased macro- and micro-nutrient uptake and the like. The sulfur-oxidizing PGPR may be applied to seeds, seed pieces, carrier materials, roots and planting soil.
Owner:LALLEMAND USA INC
Achromobacter strain with monomethylamine degradation ability and application thereof
ActiveCN107904188AHas the ability to degrade monomethylamineBacteriaWater contaminantsColony morphologyAchromobacter xylosoxidans
The invention discloses an achromobacter strain with monomethylamine degradation ability and application thereof. The name of the strain is Achromobacter xylosoxidans GDUTAN5 which is preserved in theChina Center for Type Culture Collection at Wuhan University, No. 299, Bayi Road, Wuchang District, Wuhan, Hubei Province, China. The preservation number is CCTCC NO:M 2017285. The preservation dateis May 24, 2017. The Achromobacter xylosoxidans GDUTAN5 is Gram-negative and rod-shaped, has a round colony morphology, is light yellow and opaque, and has a smooth surface and a colony diameter of 1-2 mm. The Achromobacter xylosoxidans GDUTAN5 can be applied to environmental remediation for degradation of monomethylamine in the environment and has a high degradation rate. When the substrate concentration is 5 mg / L, the degradation rate can reach 92.3% after 96 h of degradation.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
Serratia marcescens M7a and application of Serratia marcescens M7a in heavy metal ion removing
ActiveCN103937703AEfficient removalNo secondary pollutionBacteriaWater contaminantsScreening methodAchromobacter
The present invention discloses a strain of Serratia marcescens M7a, and an application of the Serratia marcescens M7a in heavy metal ion removing, wherein the Serratia marcescens M7a provides a heavy metal ion Mn<2+> removing effect. The method for screening Achromobacter xylosoxidans providing a heavy metal ion Mn<2+> removing effect from soil and water comprises: a, preparing a metal selective culture medium; b, carrying out enrichment acclimatization on a heavy metal resistance strain; c, screening and re-screening the heavy metal resistance strain; and d, detecting the heavy metal removing capability of the strain. According to the present invention, with the detection test on the heavy metal removing capability of the strain obtained by carrying out enrichment acclimatization on the heavy metal resistance strain with the metal ion-containing culture medium and purification, the reasonable and effective screening method for the heavy metal removing strain is established so as to obtain the strain suitable for requirements; and with application of the Serratia marcescens M7a in the heavy metal pollution treatment, advantages of no secondary pollution, high treatment efficiency, wide application range, low cost and the like are provided.
Owner:润桐(苏州)技术服务有限公司
Volatile compound methyl thiobutyrate and application thereof
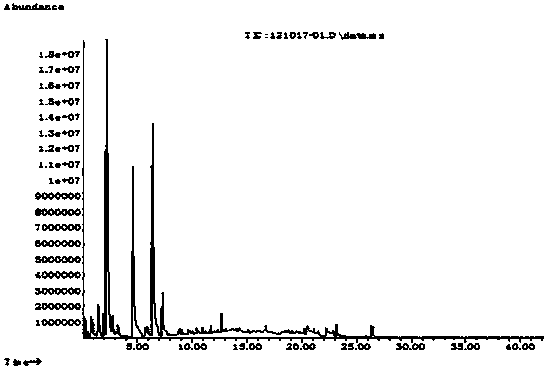
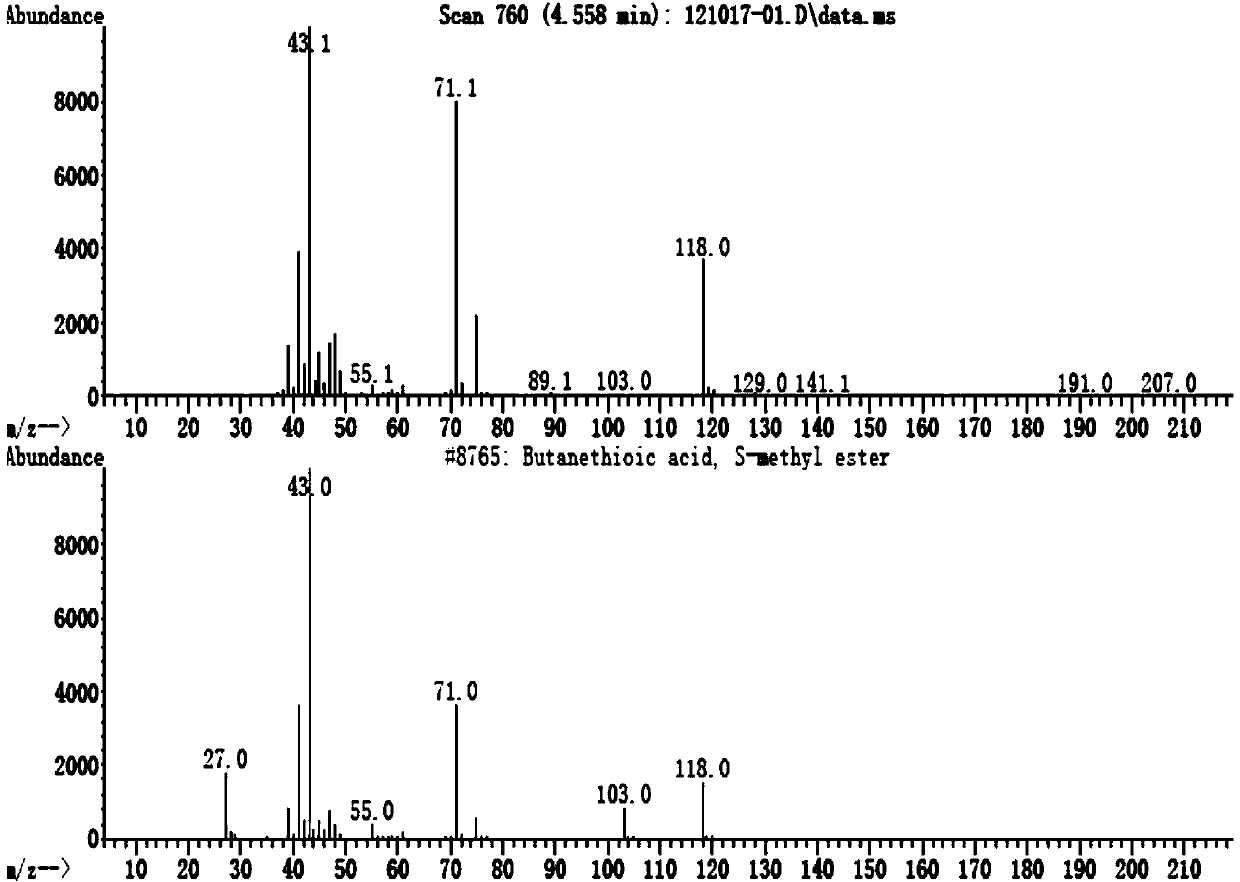
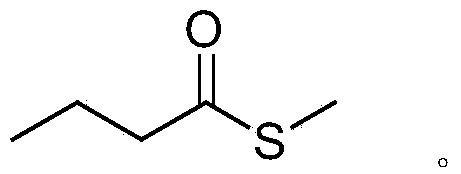
InactiveCN103439426ANo pollution in the processLow costBiocideOrganic chemistryNist databaseSolid-phase microextraction
The invention relates to volatile compound methyl thiobutyrate and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of a microbial biological pesticide. The volatile compound methyl thiobutyrate is detected by the following steps that a, the used bacterial strain is achromobacter (Achoromobacter sp.) CD-253, and the preservation number is CGMCC No6358; b, cultivating a CD-253 bacterial strain in an LB culture medium by using a conventional fermentation method, and carrying out headspace extraction on a fermentation liquor by using a solid-phase microextraction technology; c, carrying out gas chromatography-mass spectrometer (GC-MS) analysis on an extracting matter; and d, carrying out comparison of a national Institute of standards and Technology (NIST) database to obtain volatile metabolite methyl thiobutyrate. The volatile compound methyl thiobutyrate has inhibiting effects on caenorhabditis elegans (Caenorhabditis elegans) and meloidogyne incognita (Meloidogyne incognita), and can be applied to preparation of a vermifuge preparation and a precusor substance. Compared with the traditional nematicides pesticide, the volatile compound methyl thiobutyrate has the advantages of no environment pollution, low cost and excellent nematode killing effect.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
Method for processing and preserving salted sausage casing
ActiveCN102626130ANo oxidationNo feverSausage casingsMeat/fish preservation using chemicalsPseudomonas putidaDecomposition
The invention relates to a method for processing and preserving a salted sausage casing, which comprises the steps of cleaning, peeling, scraping, flushing, filling water to inspect, salting and storing. The method is characterized in that the sausage casing is placed in an airtight container in storage, and mixed gas is filled into the container and formed by mixing 20-30% of carbon dioxide, 10-30% of nitrogen and 40-70% of oxygen by concentration. Bacterium pseudomonas putida, achromobacter, proteus and the like which arouse putrefaction of the sausage casing are subjected to obvious inhibition in 20-30% of carbon dioxide, simultaneously excessive carbon dioxide is prevented from promoting growth of Clostridium botulinum, lactobacillus and other anaerobes, and the nitrogen and the oxygen of corresponding concentration are matched to enable the salt sausage casing to be located in the reasonable environment and inhibit deterioration and decomposition, thereby achieving storage, retaining freshness and prolonging the preserving time. The longest preserving period is up to 17 months, the sausage casing is not oxidized, free of heat and redness within the preserving period, and the bacterium content meets the standard.
Owner:RUGAO YONGXING CASING
Degradative bacteria capable of degrading allelochemicals in plant root exudates and application of degradative bacteria
The invention relates to the field of microorganisms and provides degradative bacteria capable of degrading allelochemicals in plant root exudates and an application of the degradative bacteria. The degradative bacteria are classified and named Achromobacter xylosoxidans and Pseudomonas nitroreducens, and strain preservation numbers are CGMCC NO.14517 and CGMCC NO.14518 respectively. The degradative bacteria for the allelochemicals can degrade the allelochemicals in multiple degraded plant root exudates.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
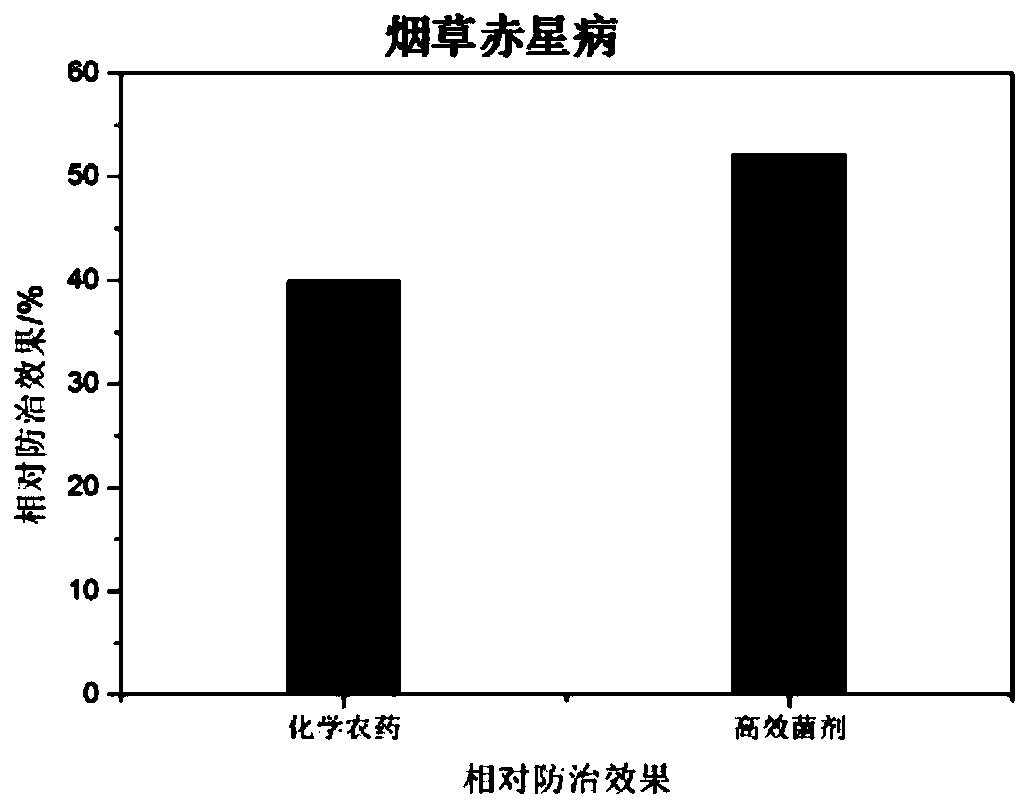
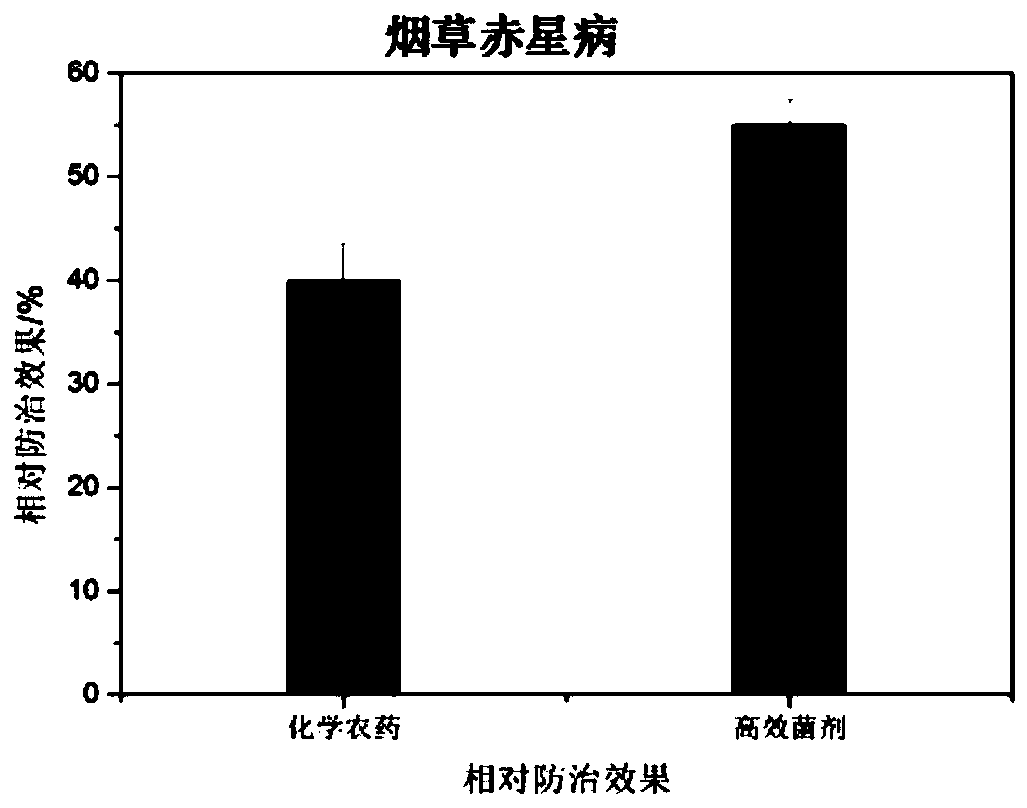
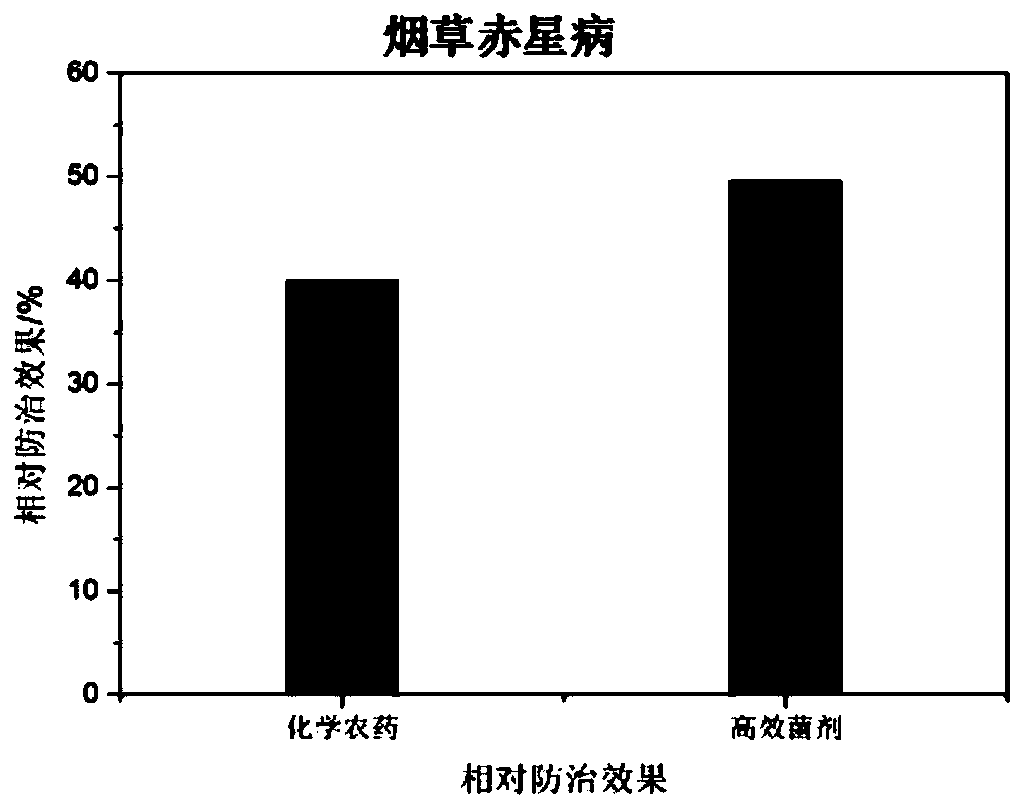
Microbial agent for preventing and controlling brown spot of tobaccos and preparation method of microbial agent
The invention discloses a mixed microbial agent for preventing and controlling brown spot of tobaccos and a preparation method of the mixed microbial agent, and belongs to the technical field of biological pesticide. The mixed microbial agent comprises 15-25% of Achromobacter, 5-15% of Enterobacter sp., 5-15% of Ochrobactrum sp., 40-60% of Stenotrophomonas sp. and 5-15% of Bacillus subtilis. The preparation method of the mixed microbial agent comprises the step of preparing the composite microbial agent from the Achromobacter, Enterobacter sp., Ochrobactrum sp., Stenotrophomonas sp. and Bacillus subtilis at a volume ratio, and the application mode of the microbial agent comprises the steps: adopting spray application, and spraying the microbial agent to both sides of leaves. It is proved through experiments that the prepared microbial agent has a high inhibitory effect on pathogenic bacteria of tobacco brown spot, and a good disease prevention effect on tobacco brown spot is achieved;and the microbial agent has low cost, a good effect and environmental protection, and therefore good prospects for biopesticide development are achieved.
Owner:CHINA TOBACCO CENTRAL SOUTH AGRICULTURAL EXPERIMENTAL STATION +1
Adjusting foliar fertilizer
InactiveCN106431629AIncrease productionImprove qualitySuperphosphatesAmmonium salt fertilisersPhosphoric acidAlternaria helianthi
The invention discloses an adjusting foliar fertilizer. The foliar fertilizer is prepared from, by weight, 30-40 parts of bacteria-containing yeast organic raw material, 25-35 parts of ammonium bicarbonate, 20-30 parts of calcium superphosphate, 10-15 parts of potassium chloride, 3-5 parts of amino acid, 3-5 parts of gibberellic acid, 1-3 parts of 2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic acid and 1-2 parts of brassinolide. The bacteria-containing yeast organic raw material includes bacterial liquor and a yeast organic raw material, the adsorption ratio of the bacterial liquor to the yeast organic raw material is 1:20-1:40, and the bacterial liquid is prepared by mixing klebsiella pneumoniae liquid, streptomyces microflavus liquid, achromobacter liquid and alternaria tenuissima plant activator protein according to the proportion of 3:2:2:1. The adjusting foliar fertilizer is provided for foliar fertilizer, can efficiently supplement elements necessary to plant growth, well guarantees growth and development of crops, and is quick to absorb and high in nutrient utilization rate.
Owner:广德明凯蔬果种植家庭农场
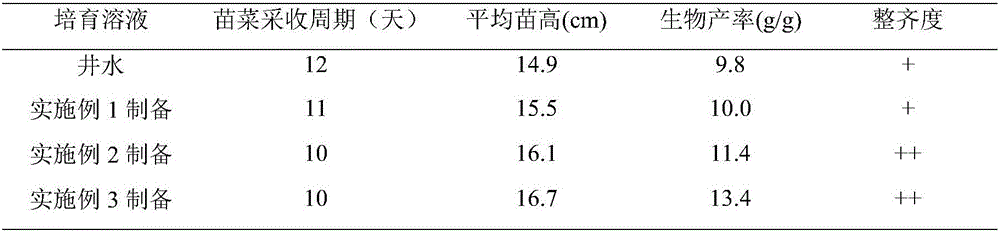
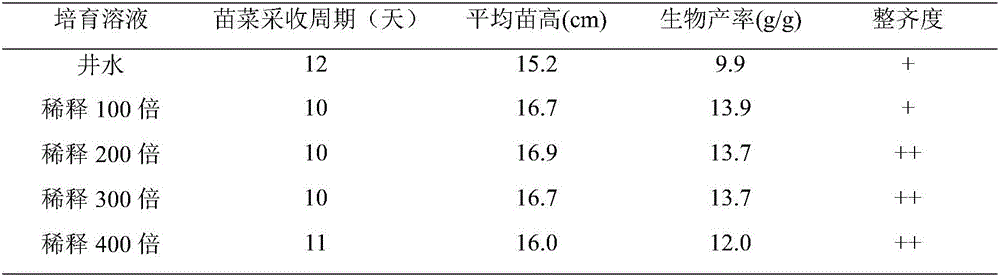
Sprouting vegetable cultivating bacteria agent and application thereof
InactiveCN105754910AIncrease productionGood colorPlant growth regulatorsBiocideBiotechnologySodium acetate
The invention discloses a sprouting vegetable cultivating bacteria agent and application thereof, and belongs to the field of agriculture microbes. The bacterial agent consists of five microorganisms, namely, rhodop seudanonas palustris, stenotrophomonas, paracoccus marcusii, nodule bacteria and achromobacter; a fermentation culture medium for preparing the bacteria agent consists of the following components in percentage by mass: 0.05 percent of KH2PO4, 0.05 percent of K2HPO4.3H2O, 0.05 percent of MgSO4.7H2O, 0.1 percent of NaCl, 1 to 4 percent of urea, 0.2 to 0.5 percent of sodium acetate and 0.01 to 0.06 percent of yeast extract. The components of the culture medium are low in cost and simple, and are rich in nutrients. The bacteria agent which is fermented and maturated is diluted by 200 to 300 times and is used for cultivating a sprouting vegetable, and the yield and the commodity of the sprouting vegetable can be remarkably improved. The bacteria agent disclosed by the invention is safe, pollution-free, simple in production process and remarkable in effect, and is applied to large-scale production in agricultural application.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV +1
Achromobacter xylosoxidans MG1 strain and application thereof
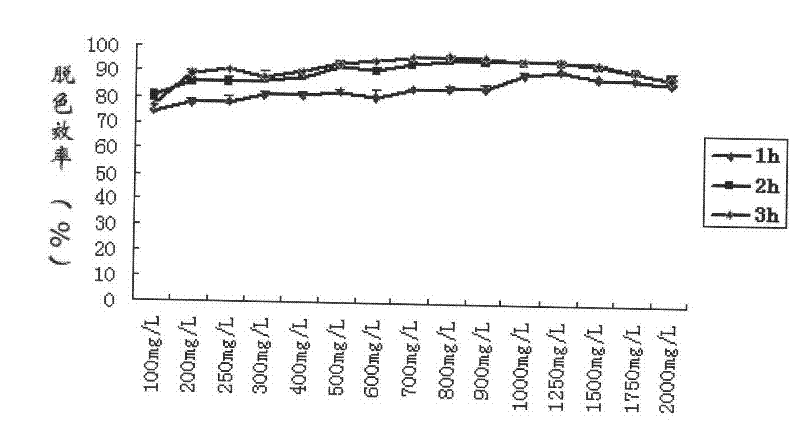
InactiveCN102181379AStrong decolorization efficiencyHigh decolorization rateBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBacteroidesMalachite green stain
The invention relates to an achromobacter xylosoxidans MG1 strain and application thereof, and belongs to the field of environmental application of microorganisms. The achromobacter xylosoxidans MG1 strain is prepared by screening bacteria obtained by separating printing and dyeing wastewater by the conventional method, and was collected in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center on December 15, 2010; and the collection number is CGMCC NO.4476. The achromobacter xylosoxidans MG1 strain has ultrastrong efficiency of decoloration on malachite green in triphenylmethane dyes, and the decolorization rate at 1 hour is up to 86+ / -1 percent when the concentration of the malachite green is up to 2,000mg / L. In addition, the MG1 strain also has a better effect of decolorizing crystalviolet, and can be applied to the preparation of biological decoloring agents. The achromobacter xylosoxidans MG1 strain has the advantages that: the range of strains which can degrade dyes can be broadened, so that an additional artificial degradation way is provided for the malachite green and the crystal violet in the environment, and the treatment cost for environmental pollution is reduced.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
Tylosin degrading bacterium and application thereof
The invention discloses a tylosin degrading bacterium and application thereof and belongs to the technical field of microbial degradation of antibiotic residues. The tylosin degrading bacterium LZ1 isachromobacter SP. and is preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC), the preservation date is April 25, 2017, the preservation number is CGMCC No. 14071, and the preservation address is Institute of Microbiology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, No. 3, No. 1 courtyard, Beichen west road, Chaoyang District, Beijing. According to the tylosin degrading bacterium disclosed by the invention, soil is utilized as a screened initial raw material; an obtained bacterial strain and a prepared microbial inoculum can be directly applied to treating of waste of tylosin enterprises and possibly can be applied to renovating of peripheral soil and water environment which is polluted by tylosin.
Owner:INST OF AGRI RESOURCES & REGIONAL PLANNING CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI +1
Sulfur-oxidizing plant growth promoting rhizobacteria for enhanced canola performance
Described herein is the isolation and identification of a number of sulfur oxidizing plant growth promoting rhizobacteria: RAY12, identified as Achromobacter piechaudii; RAY28, identified as Agrobacterium turnefaciens, RAY132, identified as Stenotrophomonas maltophilia; and RAY209, identified as Delftia acidovorans. The PGPR act to oxidize elemental sulfur which in turn provides sulfate for the plants. As a result of this arrangement, plants are able to grow more efficiently and effectively and have enhanced growth characteristics, for example, but by no means limited to, increased vigor, early emergence, increased emergence rate, increased biomass, increased plant leaf area, higher crop yield, increased pod number, increased pod weight, increased root biomass, increased seed weight, increased macro- and micro-nutrient uptake and the like. The sulfur-oxidizing PGPR may be applied to seeds, seed pieces, carrier materials, roots and planting soil.
Owner:LALLEMAND USA INC
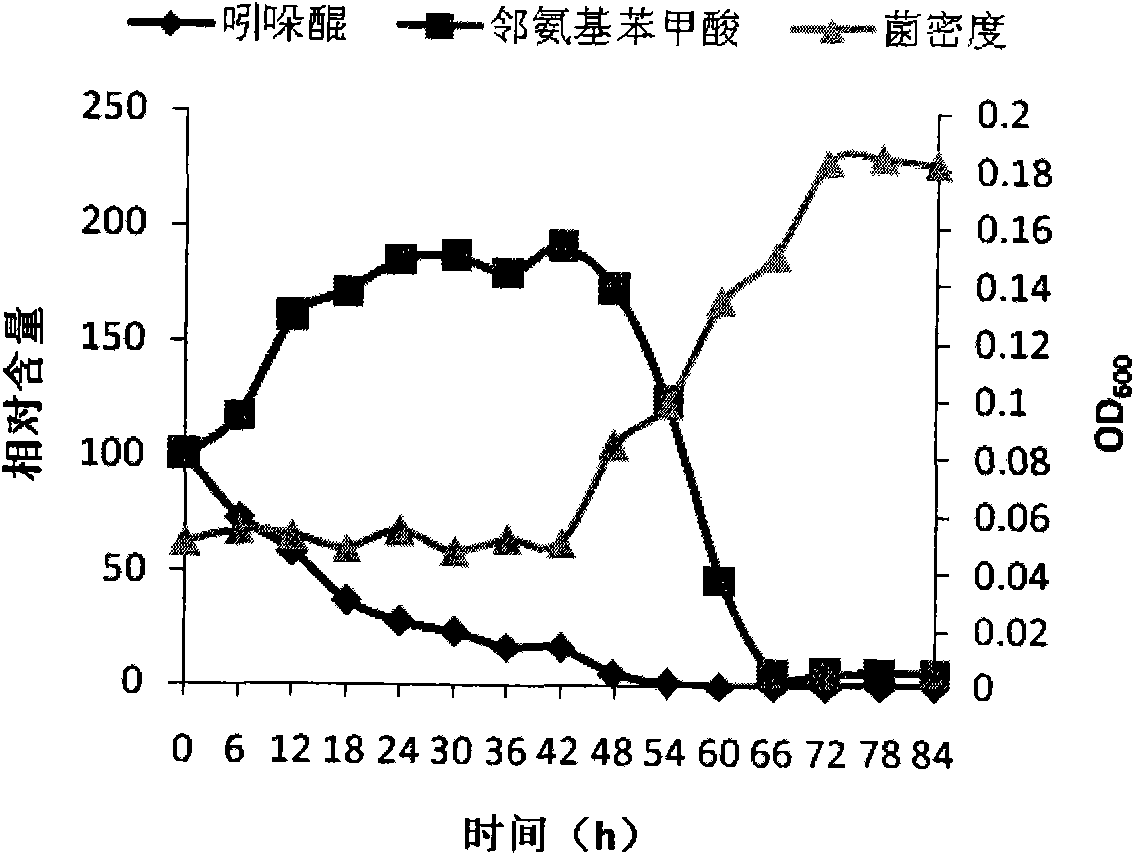
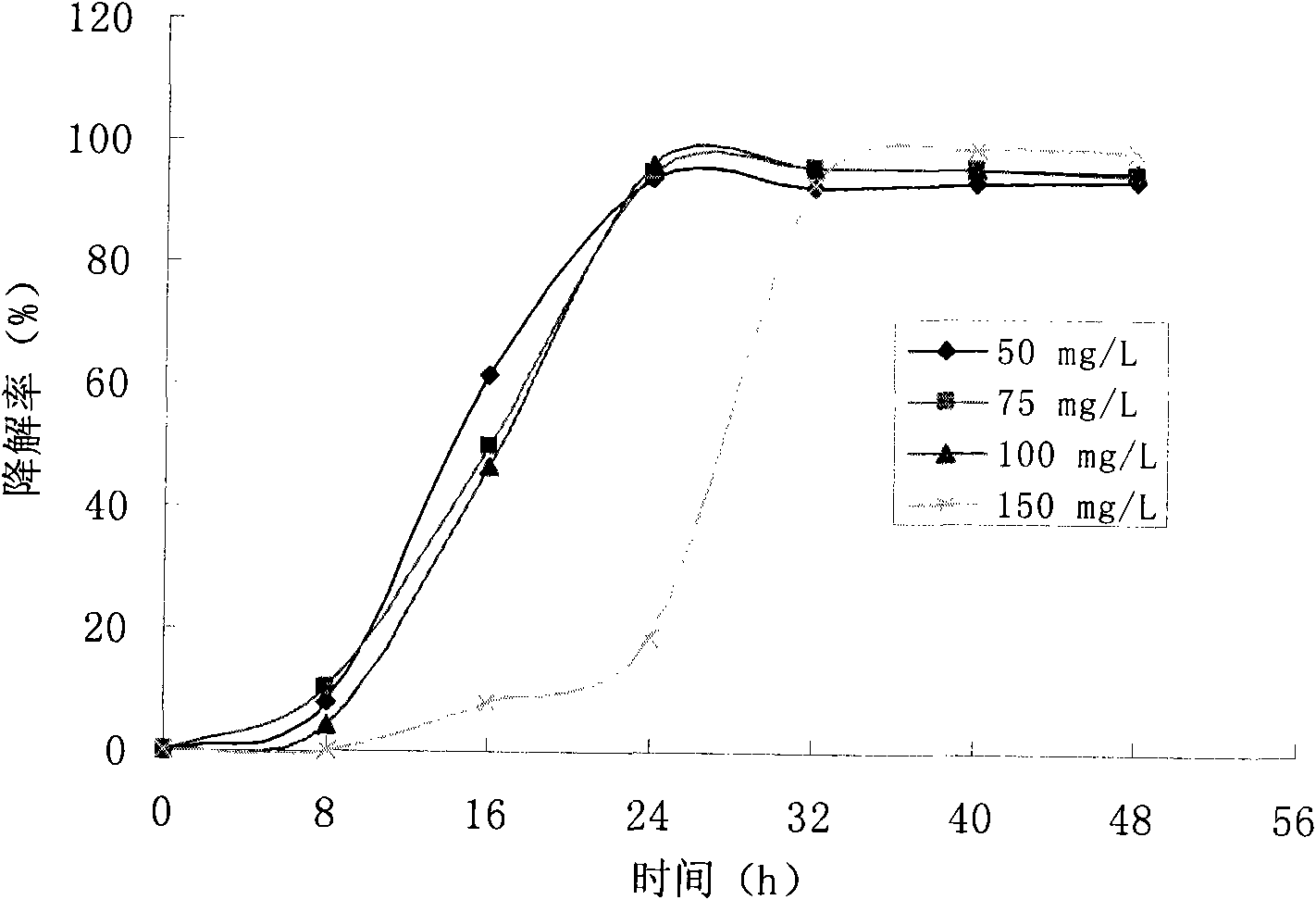
Achromobacter xylosoxidans and application thereof to degradation of isoquinoline
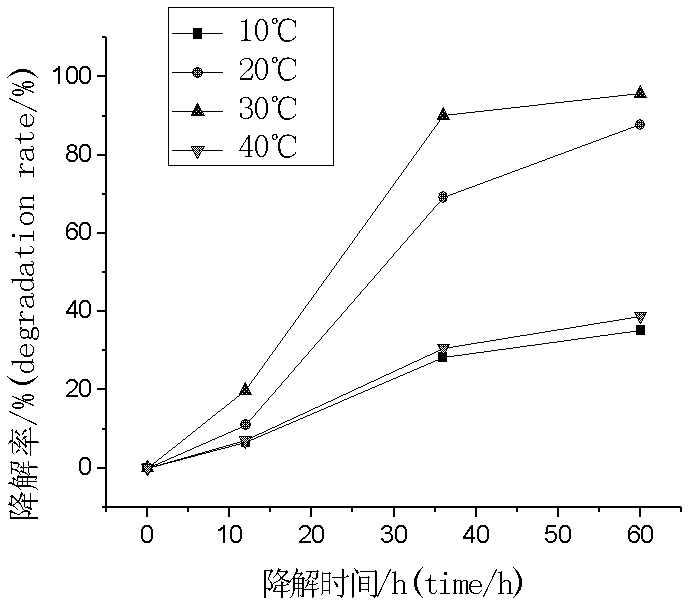
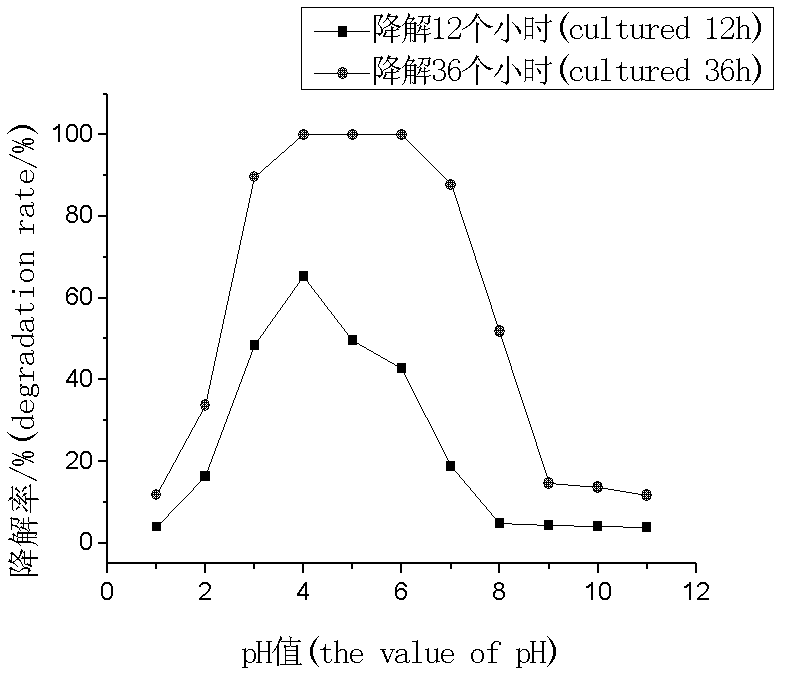
The invention discloses Achromobacter xylosoxidans and application thereof to degradation of isoquinoline. The conservation registration number of the Achromobacter xylosoxidans strain which is named Y-4 is CCTCC No. M2011308, and the Genbank accession number of the strain 16SrDNA is JN381516. The Achromobacter xylosoxidans Y-4 has unique degradationeffect on the isoquinoline, the maximum tolerance concentration (MTC) for the isoquinoline can reach 1000mg / L, and the isoquinoline with the concentration of not more than 500mg / L can be fully degraded in 36 hours, the optimal degradation temperature is 25-35 DEG C, the pH value is 4-8; meanwhile the Achromobacter xylosoxidans Y-4 also has better degradation effect on naphthalene, pyridine and quinoline, and has obvious effect particularly for the isoquinoline in biological purified coking wastewater. According to the Achromobacter xylosoxidans and application thereof disclosed by the invention, an important basis is provided for research on micro-biological degradation of the isoquinoline in the coking wastewater, and an important role can be played in practice of quinoline industrial wastewater treatment.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Casing processing preservation method
InactiveCN103931739ANo oxidationNo feverMeat/fish preservation using chemicalsBiotechnologyCARBON DIOXIDE/OXYGEN
The invention discloses a casing processing preservation method. The method comprises the processes of washing, immersing, scraping, flushing, water filling examination, salting and storage; and in the storage process, casings are placed in a sealed container, an alkaline solution with the pH value of 11-13 is added into the container, a mixed gas is finally introduced, and the mixed gas comprises carbon dioxide, oxygen and nitrogen. The casings obviously inhibit bacteria causing casing corruption, comprising Pseudomonas pseudoacaligenes, Achromobacter sp, proteusbacillus vulgaris and the like in a carbon dioxide gas with the concentration of 20-25%, can also avoid the promotion of the growth of anaerobic bacteria comprising Clostridium botulinum, Bacillus acidi lactic and the like due to too much carbon dioxide, and cooperate with corresponding concentrations of nitrogen and oxygen to make the casings in suitable environment in order to inhibit deterioration and corruption, so storage freshness keeping is realized, thereby the preservation time is prolonged. The longest freshness keeping time is 20 months, and the casings have the characteristics of no oxidation, no heating or red phenomenon, and realization of the bacterial content reaching standards within the freshness keeping time.
Owner:JIANGSU LIANZHONG CASING
Novel microbial agent and soybean planting method
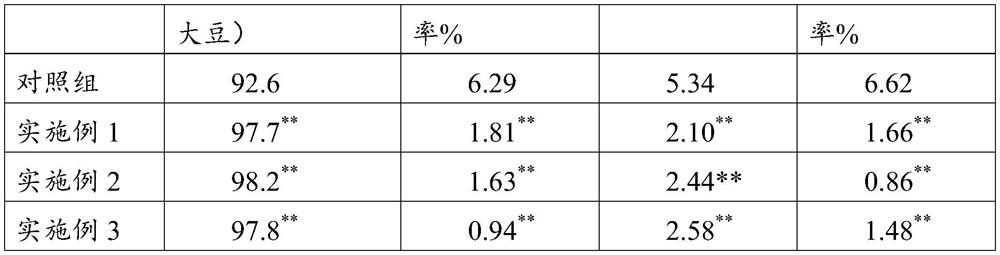
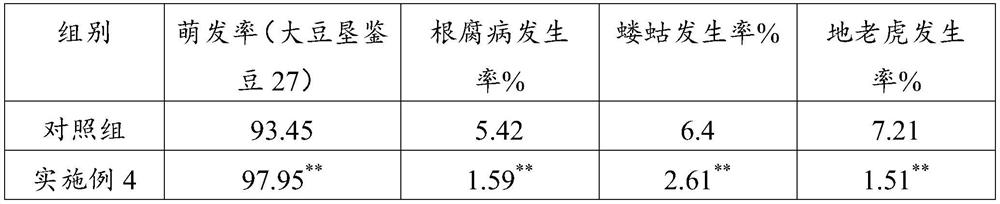
PendingCN112940969AImprove germination rateImprove seedling survival rateBacteriaSeed and root treatmentBiotechnologyMicrobial agent
The invention relates to the technical field of agricultural microorganisms, and particularly discloses a novel microbial agent and a soybean planting method. The novel microbial agent disclosed by the invention comprises the following strains: 1) one or more of corynebacterium, paracoccus, chromobacterium, achromobacter, acidithiobacillus, acidovorax, alcaligenes, arthrobacter, bacillus, cupriavidus, derxia, Herbaspirillum, hydrogenobacter, hydrogenophaga, pseudomonas, pseudonocardia, rhizobium, rhodococcus, rhodopseudomonas, rhodospirillum, thiocapsa, xanthomonas, flavobacterium and wautersia; and 2) azospirillum and azotobacter. The novel microbial agent can improve the emergence rate and the survival rate of soybeans, improve the growth of soybean seedlings, promote the accumulation of organic matter, improve the disease resistance of the soybeans to harmful bacteria and improve the nitrogen fertilizer utilization rate of the soybeans.
Owner:兴安盟莱绅生物农业有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com