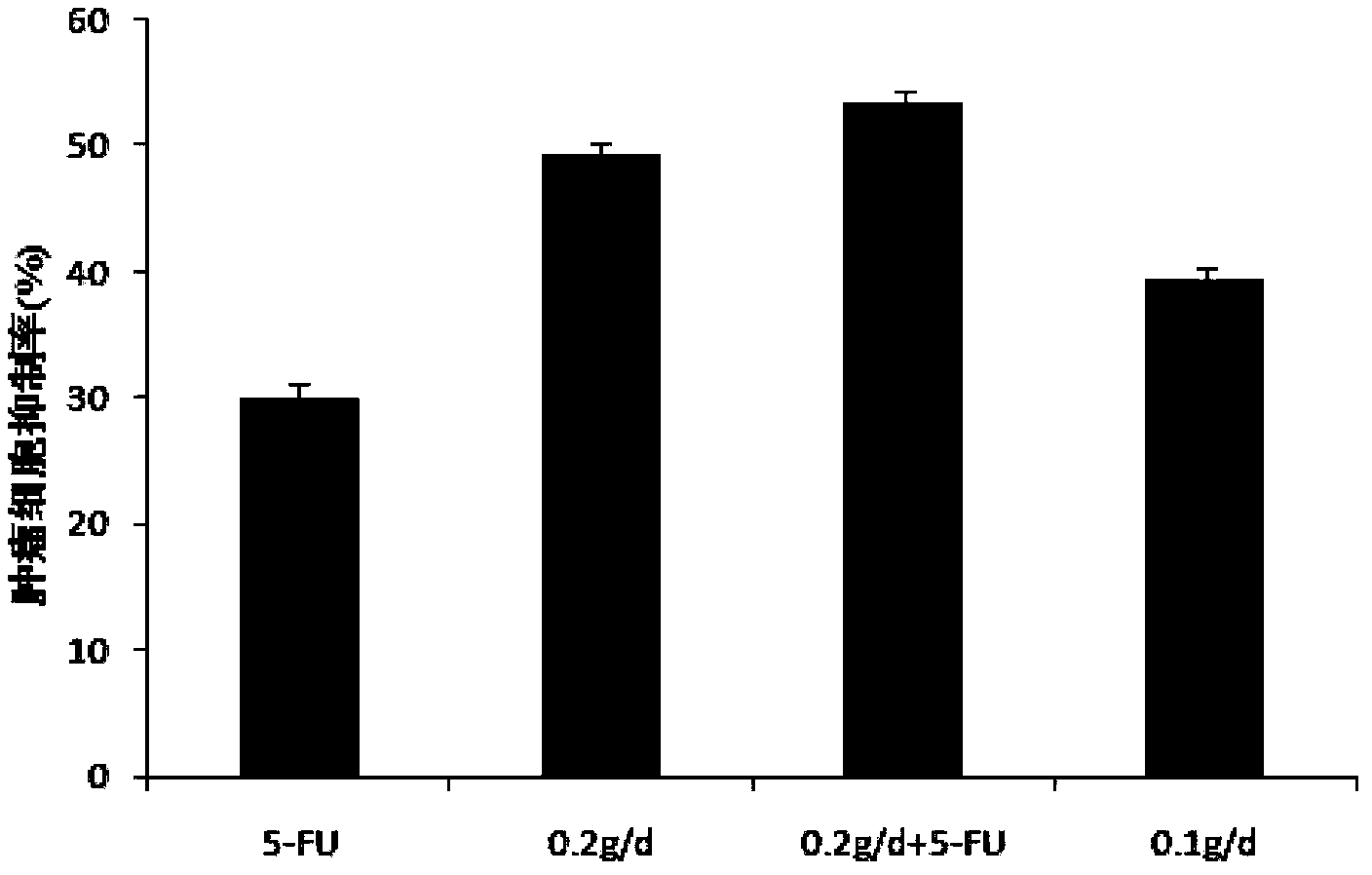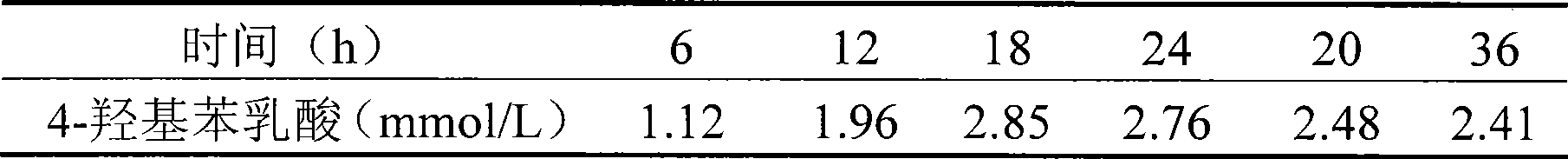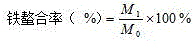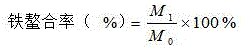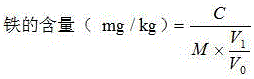Patents
Literature
323 results about "Food biotechnology" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Process for preparing food function factor gamma-amino-butyric acid
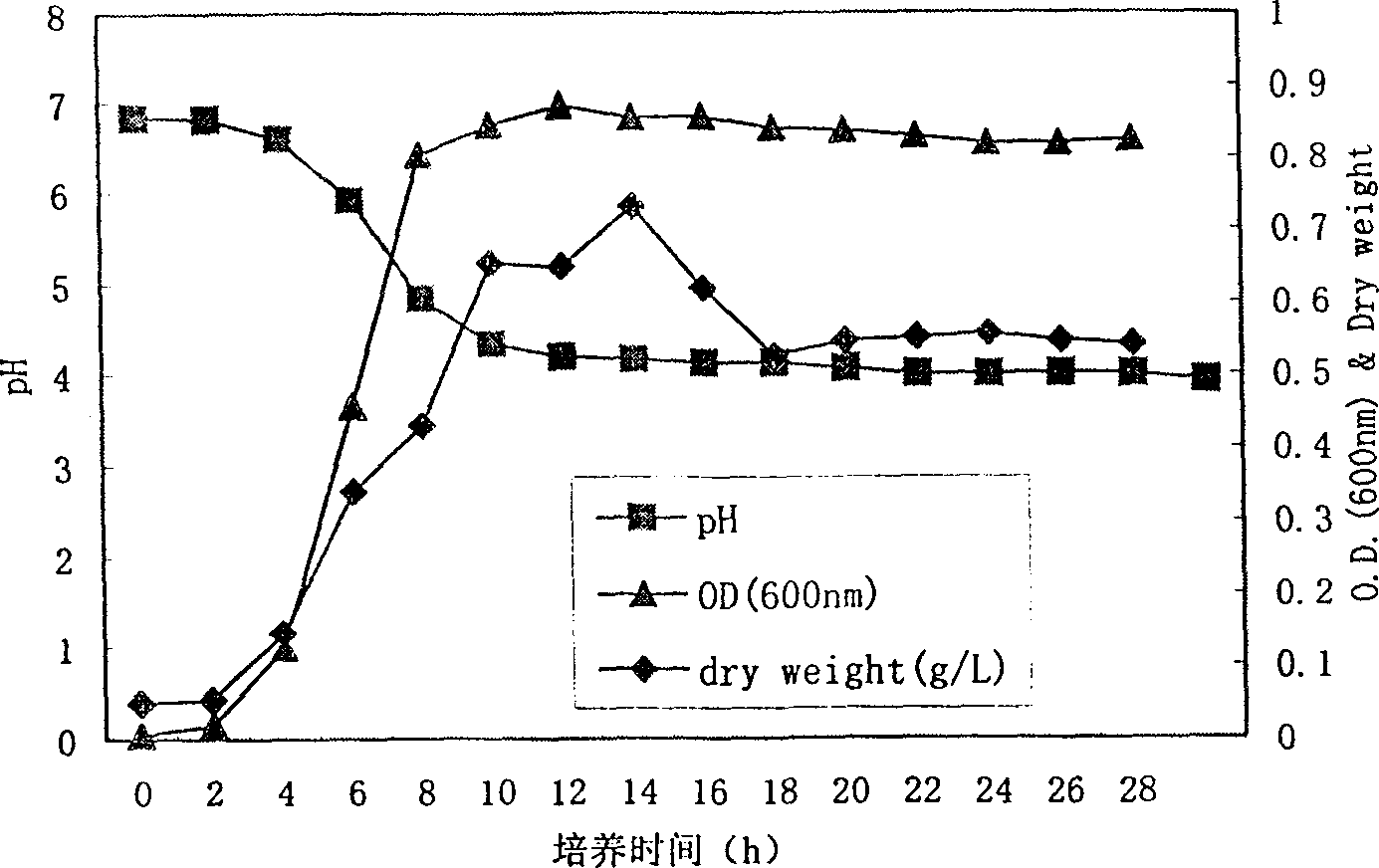
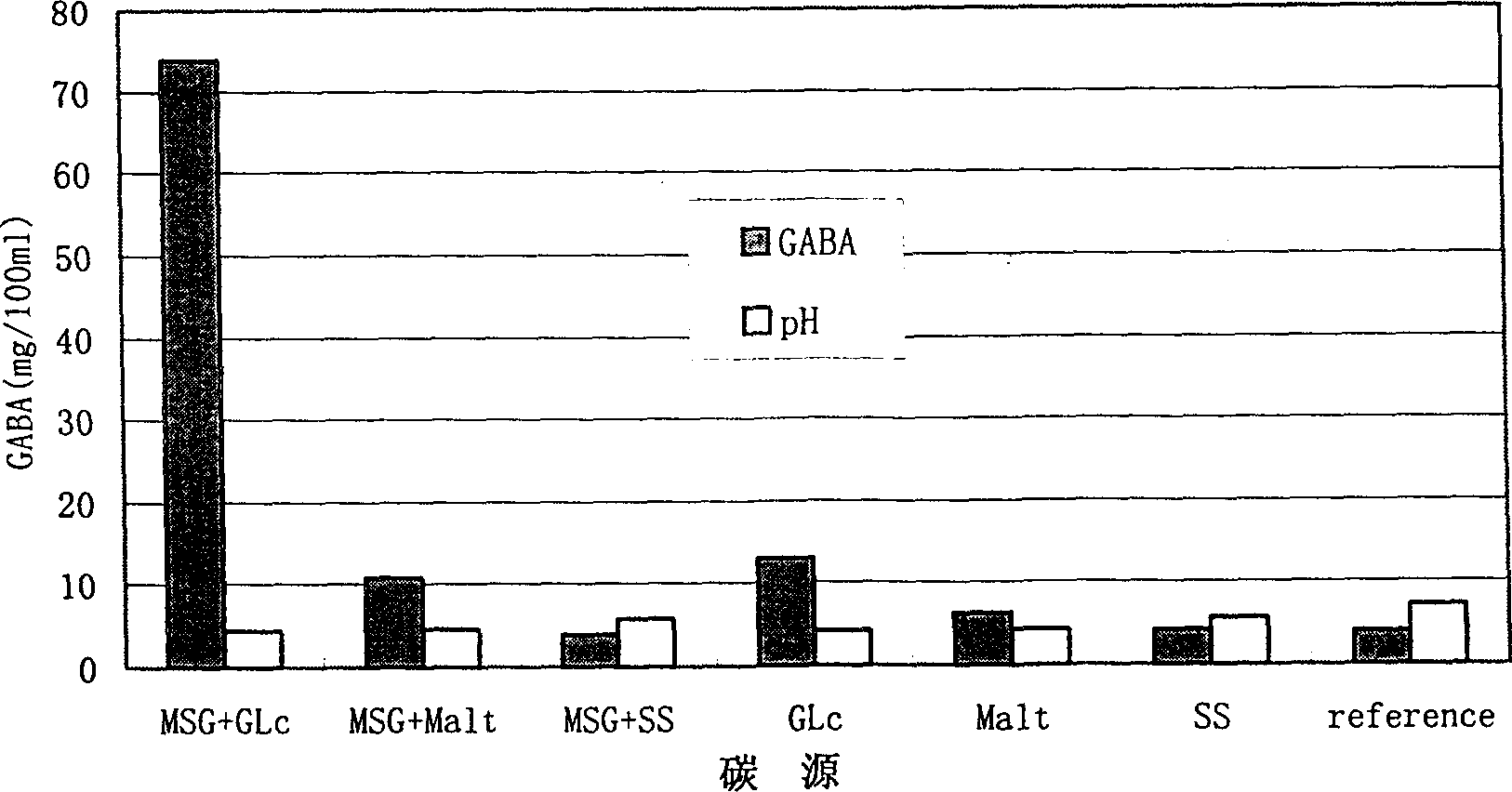
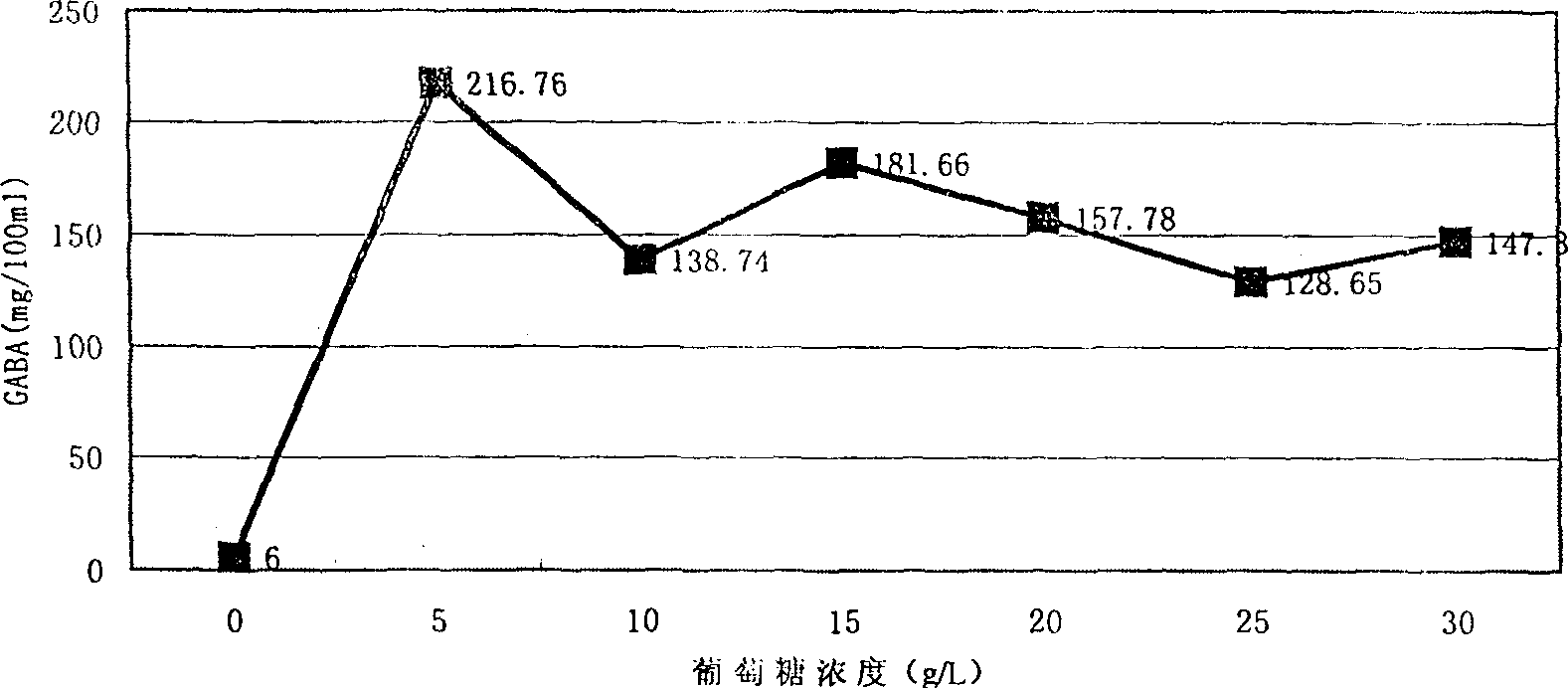
The present invention belongs to the field of food biotechnology and is especioally microbial conversion process of preparing gamma-amino butyric acid. Gamma-amino butyric acid is prepared with lactic acid bacteria or lactic acid bacteria and saccharomycete mixture as bacteria strain, sodium L-glutamate as converting substrate and through fermentating process with fermenting medium with carbon source, nitrogen source and inorganic salt. The selected lactic acid bacteria can growth well in MRS or PYG culture medium at 25-40 deg.c and may be used as culture seed liquid. Of the culture medium, the carbon source is glucose, and the nitrogen source may be one or several selected from corn paste, yeast paste, defatted peanut cake powder, etc. After fermentation, the concentration of gamma-aminoacid may reach as high as 300-500 ml / 100 ml.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Technique for continuously extracting sweet potate starch, sweet potato protein and dietary fiber from sweet potato
InactiveCN101411419ARealize full price utilizationHigh economic valueFood preparationHigh concentrationPotato starch
The invention provides a process for continuously extracting sweet potato starch, sweet potato protein and dietary fibre from sweet potato specially for processing the sweet potato and belongs to the filed of food biotechnology. The sweet potato is cleaned, is added with a color protective solution, and is pulverized, ground and squeezed in order to separate sweet potato residue and cell sap; a cleaning solution of the sweet potato residue and the cell sap are mixed and are filtered through a standard sieve with 200 meshes; a filtrate is subjected to centrifugal dehydration twice and is dried to obtain starch; after starch milk is separated out, the filtrate is degraded with starch; the filtrate with molecular weight of between 5,000 and 10,000 is intercepted, ultrafiltered, condensed and dried to obtain coarse protein of the sweet potato; and the sweet potato residue is added into a biological reactor, is added with water, protease and amylase for reaction, and is subjected to filter pressing, drying and pulverization to obtain insoluble the dietary fiber of the sweet potato. The method can fully utilize organic compositions in the sweet potato, minimize the generation and emission of organic wastewater and waste residue with high concentration, realize the full-value utilization of the sweet potato, and remarkably improve the economic value of the sweet potato.
Owner:JIANGSU ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
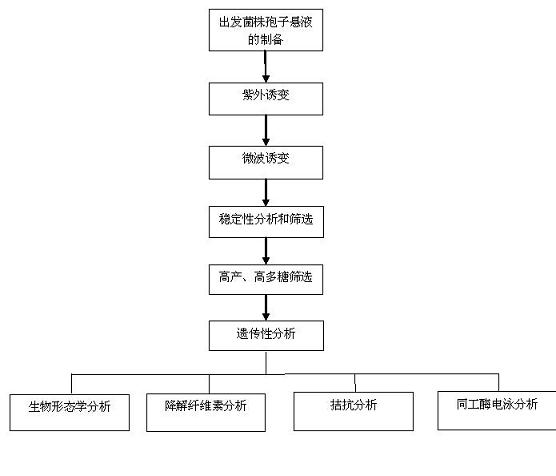
Grifola frondosa strain for producing polysaccharide with composite raw material of rice bran and wheat bran
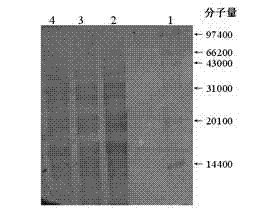
The invention discloses a Grifola frondosa strain for producing polysaccharide with a composite raw material of rice bran and wheat bran, which belongs to the technical field of microbial application technology and food biology. The Grifola frondosa strain JSU10 is preserved in China general microbiological culture collection center (CGMCC) in October 8th, 2010 with the CGMCC No. 4179 and is identified to be Grifolasp. The invention improves the positive mutation rate of the Grifola frondosa strain for rapidly growing and producing Grifola frondosa polysaccharide on a composite culture medium of rice bran and wheat bran by composite mutagenesis of ultraviolet rays and microwave to obtain a high-yield strain; the strain and the original strain are respectively a liquid fermentation rice bran and wheat bran composite culture medium; and hypha dry weight and polysaccharide of the mutated strain are respectively improved by 39.24 percent and 42.58 percent compared with the original strain.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Strain used for fermenting rice bran and wheat bran extracts for producing grifolan
InactiveCN102816701AReduce use costHigh polysaccharide yieldFungiMicroorganism based processesMyceliumMicrobiology
The invention belongs to the fields of microbe application technologies and food biotechnologies, and discloses a strain used for fermenting rice bran and wheat bran extracts for producing grifolan. The grifola frondosa strain is collected in China Center for Type Culture Collection (CCTCC) in Wuhan University in Wuhan, China on Aprial 7th, 2011, and has a strain collection number of CCTCC No: M2011113. The name of the strain is Grifolasp. JSU10-2. According to the invention, through protoplast laser mutation, the strain with high yield of mycelium polysaccharide produced from cheap raw materials is obtained. When the strain and an original strain are respectively used in liquid fermentation of a rice bran and wheat bran composite culture medium, the dry weight and polysaccharide of the mutant strain are respectively increased by 31.7% and 32.6% compared with those of the original strain.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Grifola frondosa strain produced through rice bran and wheat bran complete feed liquid fermentation
InactiveCN103416313AChange the disadvantages of low utilizationFast growthFungi productsLichen productsMutagenic ProcessFood biotechnology
The invention belongs to the technical field of microbe application and good bioscience and discloses a polysaccharide grifola strain produced through a rice bran and wheat bran complete feed liquid culture medium. grifola Grifola sp.JSU1301 is preserved in the China Typical Model Cultivation Center (CCTCC) in June 25th, 2013, and is numbered CCTCC NO: M 2013286 and named a grifola Grifola sp.CCTCC NO: M 2013286. According to the invention, a ultraviolet mutagenesis method is described with figures; a new strain capable of highly producing polysaccharide by starting with Grifola sp.CCTCC NO: M 2011113; the new strain quickly ferments and highly produces polysaccharide in the rice bran and wheat bran complete feed liquid culture medium; the mycelial dry weight and the mycelial polysaccharide productivity of a shake flask are increased by 16.8% and 8.57% compared with those of a starting strain, and those of fermentation in a tank are improved by 30.9% and 29.7%, which reach the highest level at present.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Bacterial strain used for producing ganoderma lucidum polysaccharides by complete feed liquid fermentation of rice bran and wheat bran
The invention belongs to the field of microbial application technology and food biotechnology, and discloses a ganoderma lucidum strain used for producing polysaccharides by complete feed liquid fermentation of rice bran and wheat bran. Ganoderma lucidum JSU6161314 is stored in China Center for Type Culture Collection (CCTCC) on 25th, June, 2013, preservation number is CCTCC M2013287, and the bacterial strain is named as Ganoderma lucidum CCTCC M2013287. According to a method disclosed in a drawing of the invention, the novel bacterial strain, which is capable of realizing high yield of ganoderma lucidum polysaccharides, is obtained by modifying ganoderma lucidum CFCC6043. The novel bacterial strain is used for rapid fermentation in a rice bran and wheat bran complete feed liquid culture medium and high yield of ganoderma lucidum polysaccharides. After fermentation, hypha dry weight and hypha polysaccharide yield increase 23.0% and 45% respectively compared with that of the original strain.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Strain and method for preparing D-allulose by microbial transformation of D-levulose
ActiveCN101177672AImprove conversion rateBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMicrobial transformationFreeze-drying
The invention discloses a strain for producing D-piscose by using microorganism to transform D-fructose and a preparation method thereof, pertaining to food biotechnology field. The invention relates to a strain of spherical Rhodobacter sphaeroides SK011 screened from bottom mud of a fish-pond with the preservation number, CCTCC NO: M 207185, and the preparation method that the spherical Rhodobacter sphaeroides SK011 is used for transforming the D-fructose and producing the D-piscose through culture and fermentation. The invention adopts the SK011 as the strain and a fermentation culture medium which consists of carbon and nitrogen sources, inducer and inorganic salt; the obtained strain is further treated, so as to obtain cell biocatalyst; then by using the D-fructose as a substrate to do bio-transformation, the D-piscose is prepared. Under optimum conditions during the fermentation culture, fermenting solution or free cells or permeability cells or frozen dry powder or solidified cells thereof are used for transforming the D-fructose for 0.5 to 4.8 hours, and the content of the D-piscose in the transformation solution is 2 to 50g / L.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
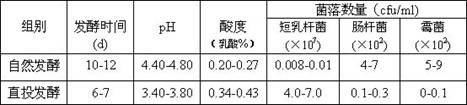
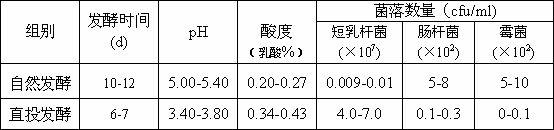
Jerusalem artichoke pickle produced by direct-vat-set lactobacillus brevis leavening agent, and process of same
ActiveCN102613518AIncrease productivityShort fermentation cycleFood preparationNutritionFermentation starter
The utility model relates to jerusalem artichoke pickle produced by direct-vat-set lactobacillus brevis leavening agent and a process of same, and belongs to the technical field of deep processing of vegetable and food bioscience. Lactobacillus brevis is adopted to be developed into high-density lactobacillus brevis leavening agent (the total number of bacterial colonies reaches 109 / ml); and the jerusalem artichoke pickle is produced by utilizing a direct-vat-set leavening process, so that a modern bioprocess technology of producing high-quality jerusalem artichoke pickle quickly is formed and achieved. The invention has a simple technological process and is easy to operate; compared with a conventional leavening process, the direct-vat-set leavening process has the advantages that the operation procedure is simplified, the production cost is reduced, and the nutritional ingredient and flavor substance of the jerusalem artichoke can be kept furthest at the same time; the jerusalem artichoke pickle is crispy, tasty, refreshing, and nourishing, and is a probiotic health product applicable to all ages. The invention is a green natural, safe and healthful production process and technology.
Owner:东台海滨科技创业园管理有限公司
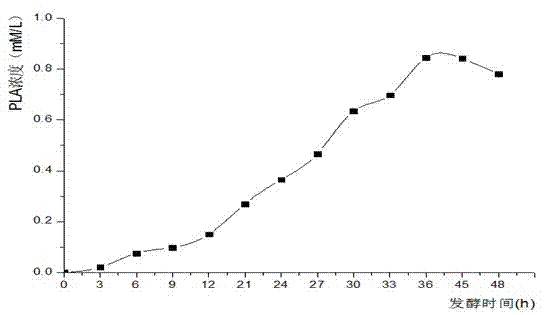
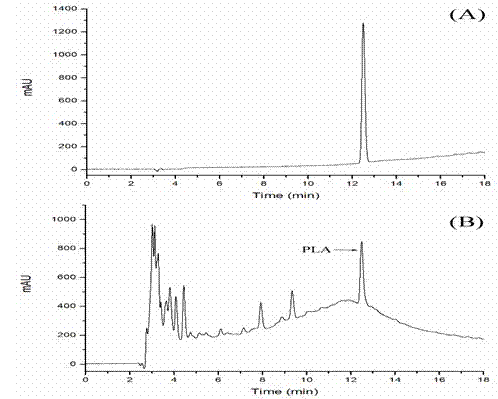
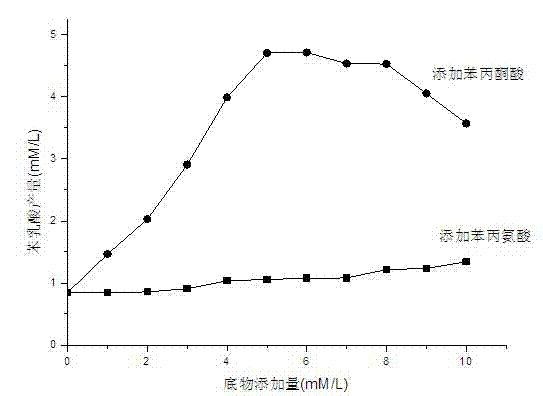
Bacterial strain for preparing phenyllactic acid and method for preparing phenyllactic acid through bacterial strain fermentation
InactiveCN102604858AIncrease productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesFood additiveBacterial strain
The invention provides a bacterial strain for preparing a phenyllactic acid and a method for preparing phenyllactic acid through bacterial strain fermentation, belonging to the food biotechnology. The invention discloses a pediococcus lactobacillus for preparing phenyllactic acid and particularly relates to Pediococcus pentosaceus SK25 capable of preparing phenyllactic acid, which is preserved inthe China center for type culture collection with a collection number of CCTCC NO: M2011360. According to the method provided by the invention, the pediococcus is used as a starting bacterial strain.In an MRS (Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus) culture medium fermentation liquor, the content of phenyllactic acid reaches 0.8 mmol / L. At present, the reported maximum yield of wild bacterial strains in the MRS culture medium fermentation liquor is only 0.57 mmol / L. When phenylalanine or phenylpyruvic acid is added to the MRS culture medium, the yield of phenyllactic acid is improved. If the phenylpyruvic acid is added in the MRS culture medium, the improvement of the yield of the phenyllactic acid is obvious, and the optimal addition quantity is determined to be 5-6 mmol / L. The product obtained by the invention is safe and reliable, can be used as a medicinal intermediate and a food additive, and has a very strong antibacterial and antiseptic function.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Lactobacillus plantarum and application thereof in rice wine brewing
ActiveCN103421723AWill not harmCompliance with safety regulationsBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMicroorganismReady to use
The invention discloses Lactobacillus plantarum and application of the Lactobacillus plantarum in rice wine brewing and belongs to the field of food biotechnology. The bacterial strain is named Lactobacillus plantarum. The bacterial strain is obtained from rice milk in a screened mode, the bacterial strain is preserved in the China general microbiological culture collection center in September 3, 2013, and the preservation number is CGMCC No.8097. The Lactobacillus plantarum and a ready-to-use starter of the Lactobacillus plantarum can be used for rice wine brewing, so that the production process is controllable and slightly affected by seasons, operation is simple and convenient, and the Lactobacillus plantarum has important significance in the innovation of the rice wine brewing technology.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV +1
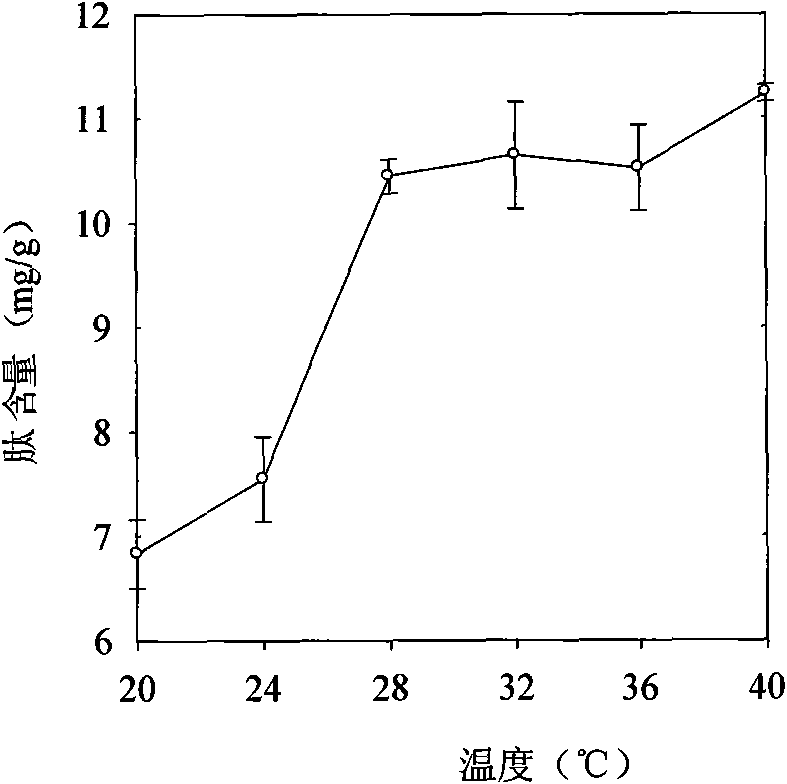
Germinated brown rice rich in bioactive peptide and production method thereof
InactiveCN101653216AIncrease protease activityProcess ScienceFood preparationBioactive peptideGibberellin
The invention discloses a germinated brown rice rich in bioactive peptide and a production method thereof, belonging to the food biotechnical filed, and also belonging to the technical field of healthfood production. The germinated brown rice is characterized in that paddy is placed in culture solution which contains 30-80mu mol / L of gibberellin, 2-10m mol / L of NaCl and 0.6-3.0 m mol / L of MnSO4 to be cultured for 36-96h after husking, selection, disinfection and soaking. In the duration of germination, vent processing is carried out in the case of ventilatory capacity being 0.1-3.0L.min<-1> and the temperature being 16-40 DEG C, finally the germinated brown rice is obtained after cleaning, enzyme destruction and drying. The method has simple process and strong maneuverability, and is suitable for industrialized production; in addition, the produced germinated brown rice is a health food safe to eat, with the peptide content being 10-13mg.g<-1>.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
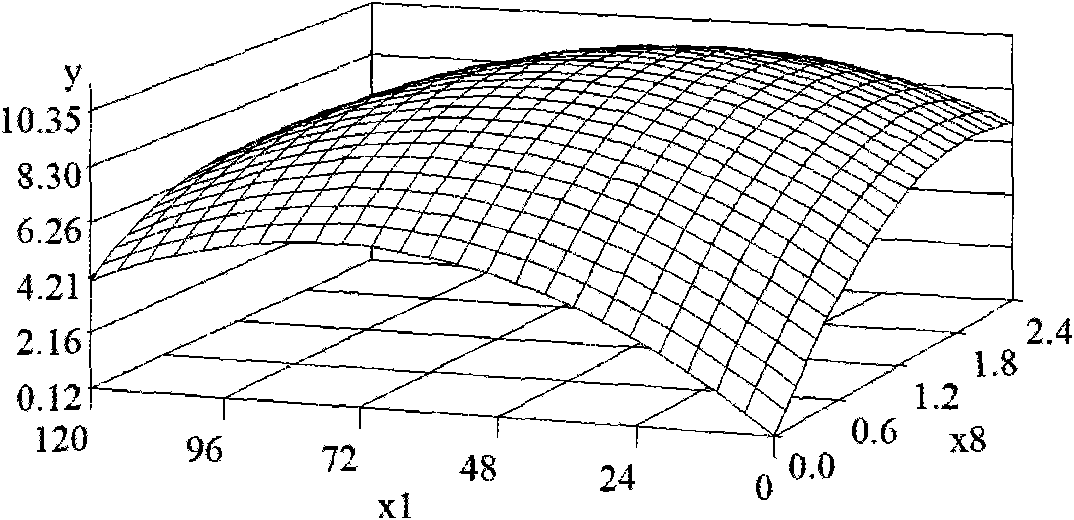
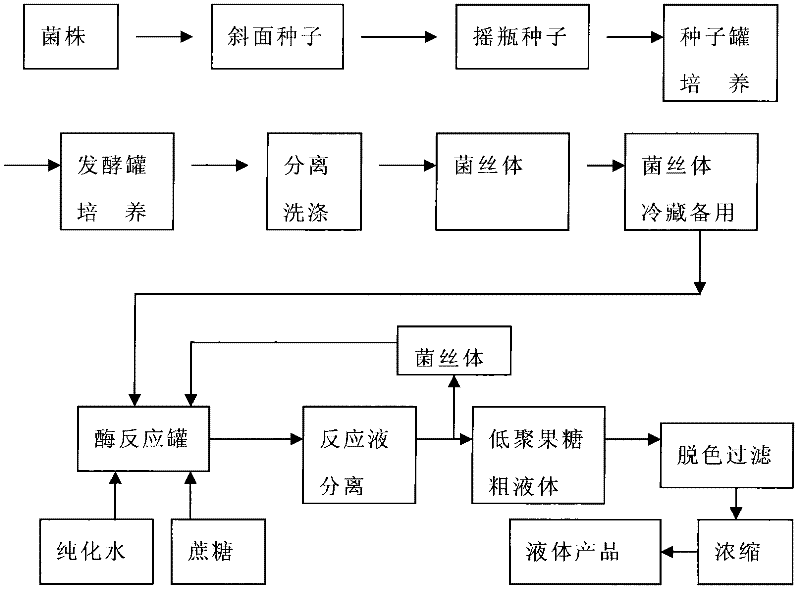
Method for producing fructooligosaccharide by using transfructosylase
InactiveCN102127574AImprove conversion rateHigh fructosyltransferase activityFermentationSucroseTrisaccharide
The invention relates to the technical field of food biotechnology, particularly a method for producing fructooligosaccharide by using transfructosylase, which comprises preparation of transfructosylase and industrial production of fructooligosaccharide by using the enzyme preparation. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: selecting a good strain containing high-activity transfructosylase, culturing the strain in an appropriate culture medium, separating to obtain large-scale cultured mycelia containing high-activity transfructosylase, and storing the mycelia for later use; and converting sucrose into fructooligosaccharide by a batch process by using the mycelia containing high-activity transfructosylase as a biocatalyst. The method provided by the invention has the advantages of short bioconversion time, and high conversion rate of fructooligosaccharide; the mycelia can be repeatedly used; and the content of fructooligosaccharide (trisaccharide) prepared by using the transfructosylase is up to 57-62%, which is 3-5% higher than that of the fructooligosaccharide prepared by using Aspergillus niger.
Owner:山东文远生物技术有限公司
Production of biological antiseptic agent phenyllactic acid
InactiveCN1940078AImprove conversion rateMicroorganism based processesFermentationAntiseptic AgentMaltose
Production of biological antiseptic benzyl lactic acid is carried out by taking lactic acid as bacteria, taking phenylalanine, phenyl-pyruvic acid or sodium phenyl-pyruvic acid as conversion substrate, adding into fermentation culture medium with carbon source, nitrogen source and inorganic salt, preparing benzyl lactic acid by biological conversion, culturing lactic acid in MRS culture medium at 25-40degree and inspecting. The fermentation culture medium carbon source is selected from glucose, maltose, lactose or cane sugar; nitrogen source is selected from corn liquor, yeast cream, protein peptone and soy mill cake. The concentration of benzyl lactic acid reaches to 50-150mg / 100ml. It's safe, reliable and has excellent sterilizing function.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method for producing alternan sucrase by fermenting Leuconostoccitreum and its application
InactiveCN102492673AImprove securityIncrease productionTransferasesMicroorganism based processesHigh densityThree stage
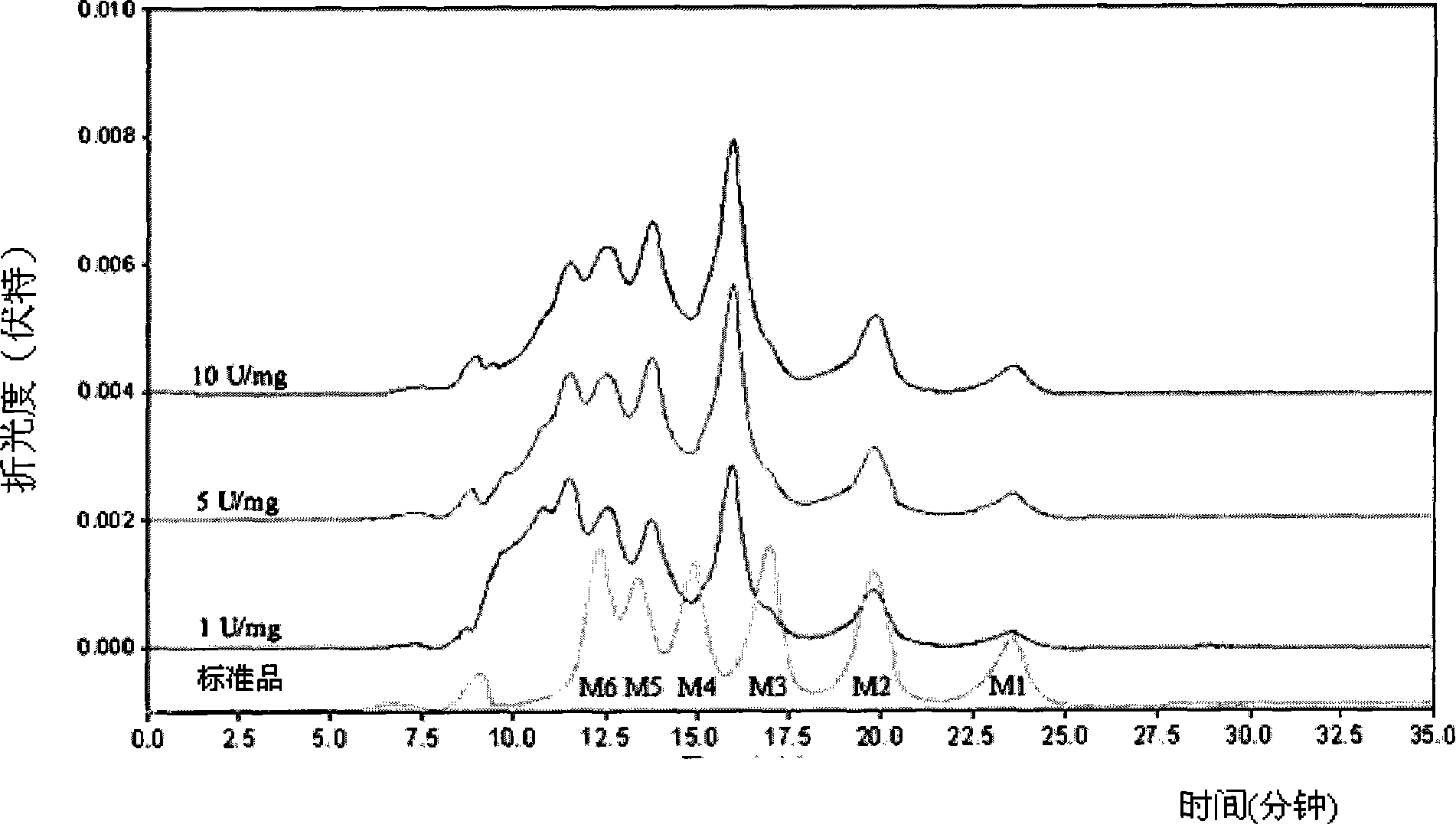
The invention relates to a method for producing alternan sucrase by fermenting Leuconostoccitreum and its application, which belongs to the food biology technical field. According to the invention, an alternan sucrase is used for producing Leuconostoccitreum SK24.002 for three-stage cultivation of slant cultivation, seed cultivation and fermentation cultivation, and the alternan sucrase is obtained by separating and purifying a broth and mycelium cells. The method for producing alternan sucrase by using the Leuconostoccitreum SK24.002 possesses the advantages of short fermentation time and low cost, the safety performance is reliable, and the deep fermentation of liquid and cell cultivation with high density can be carried out, thereby the method of the invention is suitable for large scale production. The activity of the produced alternan sucrase can reach more than 10U / mg. A fermented product is non-toxic, and can be directly used for producing a plurality of novel functional carbohydrates possessing prebiotics efficacy.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Process for preparing bioactive peptide-silk fibroin peptide
InactiveCN1392265AHigh desalination rateLarge amount of processingFermentationHigh concentrationBioactive peptide
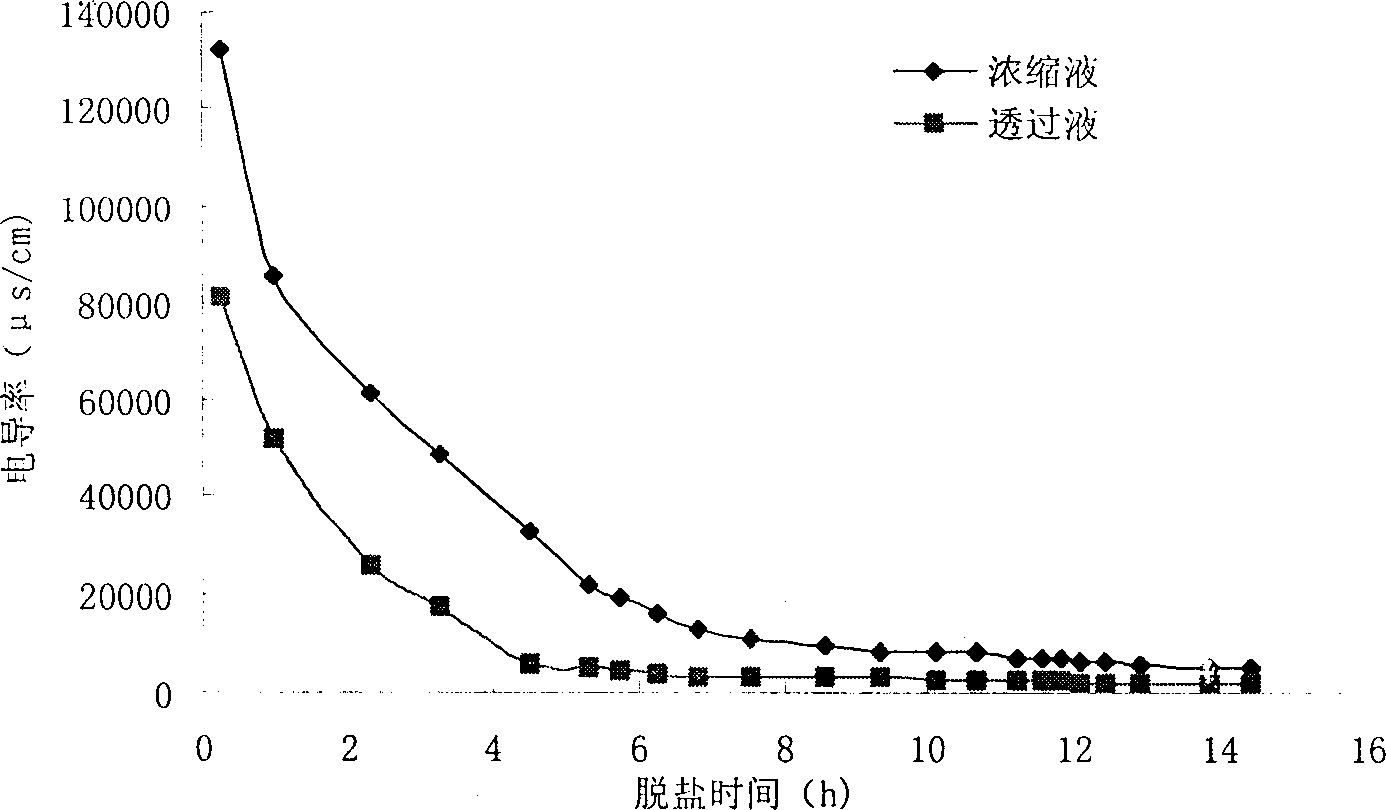
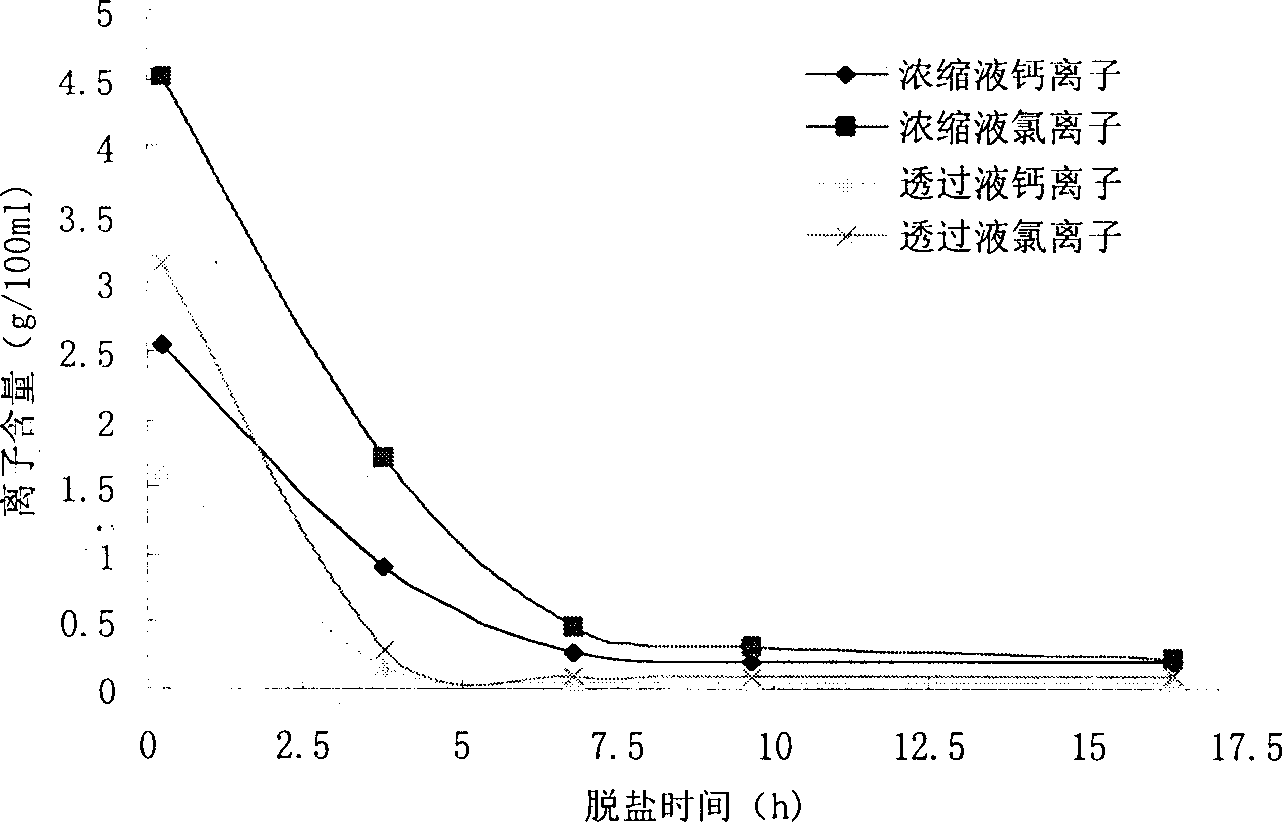
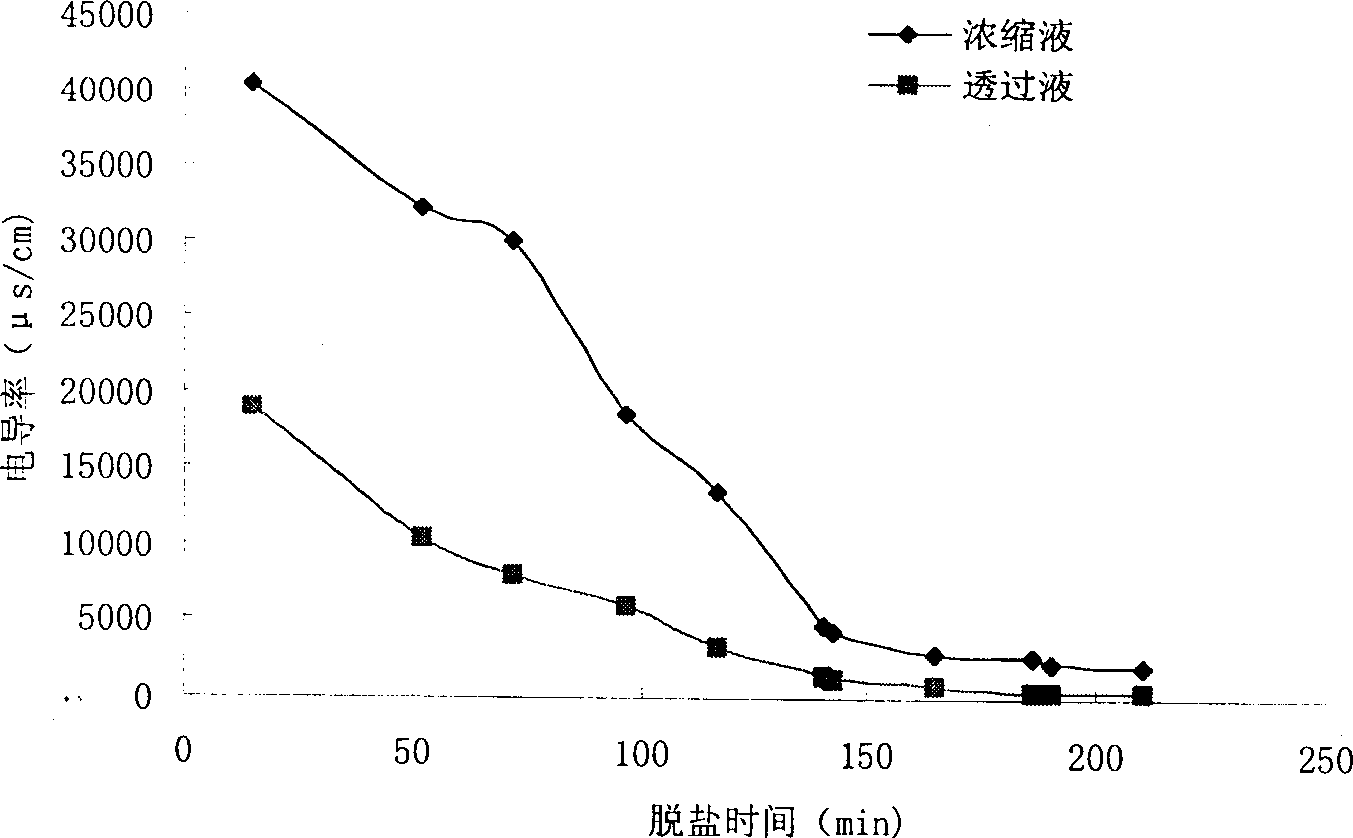
The present invention, the preparation process of silk fibroin peptide as one bioactive peptide, belongs to the field of food biotechnology. Silkworm cocoon leftover or waste cocoon as material is refined in Na2CO3 solution and dissolved in CaCl2 solution to obtain silk dissolving liquid; the silk dissolving liquid is enzyme hydrolyzed at pH 2.5-12.0 and 30-80 deg.c, nano filtered to elimiante high-concentration CaCl2 salt, concentrated and spray dried to obtain the product silk fibroin peptide powder. The present invention has the advantages of great treated amount, high desalting rate, mildseparation condition, simple process and low power consumption. The said process may be used in industry to prepare silk fibroin peptide for functional food.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Strain for producing glutamic acid decarboxylase and method for producing gamma-aminobutyric acid by utilizing strain
ActiveCN103320362AEfficient productionSuitable for mass productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesGlutamate decarboxylaseMarket potential
The invention relates to a strain for producing glutamic acid decarboxylase and a method for producing gamma-aminobutyric acid by utilizing the strain, belonging to the field of food biotechnology. The invention discloses lactobacillus plantarum SK30.001. The lactobacillus plantarum SK30.001 is screened from pickled vegetables and is preserved in China Center for Type Culture Collection (CCTCC), and the preserve number is CCTCC NO: M2013250. The invention further provides a method for producing the gamma-aminobutyric acid through fermentation by utilizing the strain. The method comprises the following steps of: (a) culturing the strain in a fermentation culture medium, so as to obtain lactobacillus plantarum thallus; (b) converting sodium glutamate by utilizing the lactobacillus plantarum thallus to generate the gamma-aminobutyric acid; and (c) carrying out separation and purification of the gamma-aminobutyric acid. The gamma-aminobutyric acid produced by utilizing method is safe and reliable, is a functional product with a good market potential and is widely applied to industries of foods, cosmetics, medicines and the like. According to the strain for producing the glutamic acid decarboxylase and the method for producing the gamma-aminobutyric acid by utilizing the strain, the gamma-aminobutyric acid can be efficiently produced, the mass production is realized easily, and a novel method for industrial preparation of the gamma-aminobutyric acid is provided.
Owner:健隆生物科技股份有限公司
Germinated brown rice low in cracking ratio and rich in gamma-aminobutyric acid and production method of germinated brown rice
The invention discloses germinated brown rice low in a cracking ratio and rich in gamma-aminobutyric acid and a production method of the germinated brown rice. The germinated brown rice belongs to biotechnology field of food. A production method for the germinated brown rice comprises the following steps of: screening and purifying a brown rice material; spraying ethanol to disinfect; humidifying and tempering by acid liquor; forcing the brown rice to germinate at a low-temperature low-oxygen environment; and drying in a moderate manner. The prepared germinated brown rice has a cracking ratio within 3%, and 15-30 mg / 100g of GABA (Gamma-amino Butyric Acid). The germinated brown rice prepared by the method provided by the invention has such characteristics of being low in cracking ratio, high in GABA and capable of whitening and the like, thereby solving a problem that the germinated brown rice produced by a traditional technology is high in cracking ratio, difficult to cook, poor in mouthfeel, and cannot be crushed.
Owner:广西月亮河长寿村生物科技有限公司
Preparation method of barley extract fermented by lactobacillus and anti-tumor effect of barley extract fermented by lactobacillus
ActiveCN103445068AFull of nutritionFunction increaseAntineoplastic agentsFood preparationCancer cellHordeum vulgare
The invention discloses a preparation method of a barley extract fermented by lactobacillus and an anti-tumor effect of the barley extract fermented by lactobacillus, belonging to the field of food biotechnology. Lactobacillus plantarum (lactobacillus plantarum Dy-1, CGMCC No.6016) is screened from pickled vegetables to serve as a fermentation strain for fermenting the barley, and fermentation conditions are controlled, so that the extract of fermented barley is obtained. Cell tests indicate that the extract has obvious effects on promoting apoptosis and suppressing multiplication of human colon cancer HT-29 cells and gastric cancer SGC-7901 cells, and a model test of the nude mouse bearing the tumor with the human colon cancer HT-29 indicates that the extract has obvious effects on suppressing tumor growth and improving the immune activity of the nude mouse bearing the tumor. According to the preparation method of the barley extract fermented by lactobacillus, the barley is pretreated simply and the production cost is low; and direct vat set fermentation is employed, so that the preparation method of the barley extract fermented by lactobacillus is convenient and rapid, safe and stable, and convenient to control the quality.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Preparation of biological preservative 4-hydroxyphenyl lactic acid
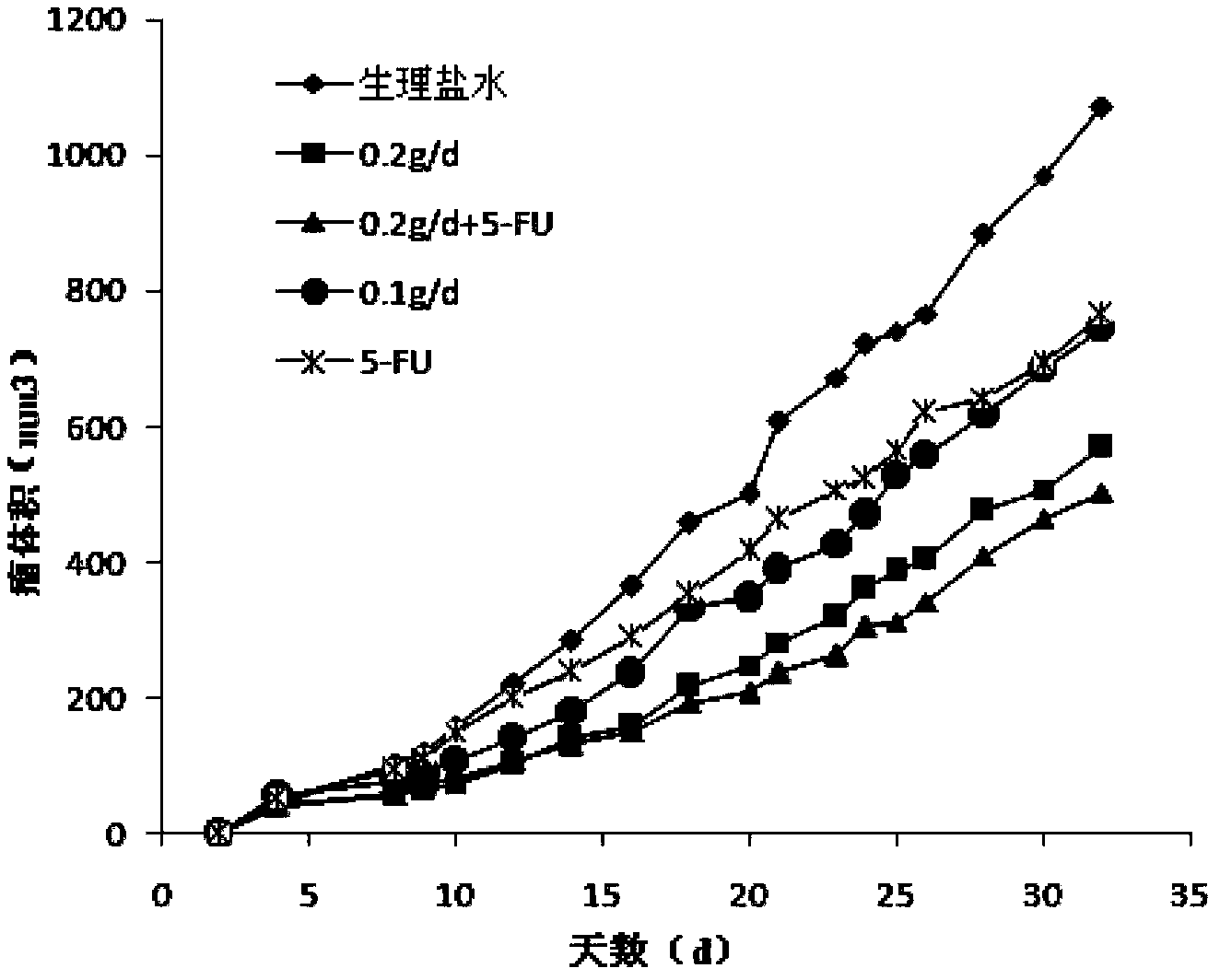
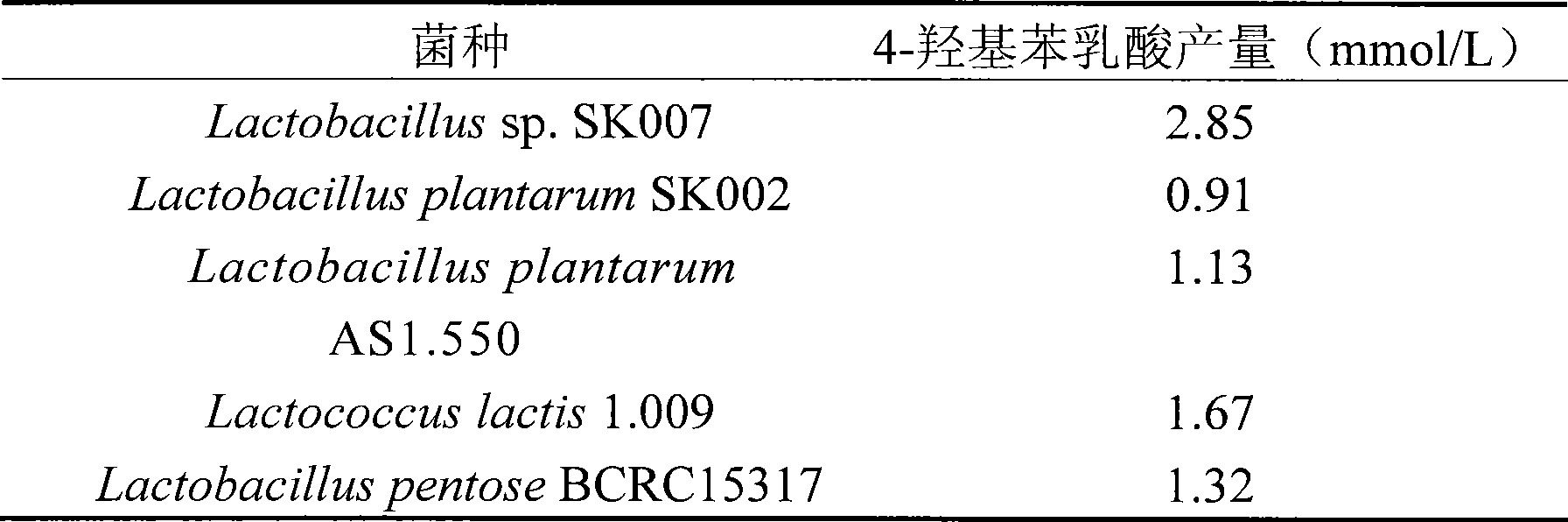
The invention provides a method for a biological antiseptic 4-hydroxyl phenyllactic acid, which relates to a method for preparing 4-hydroxyl phenyllactic acid by fermentation bioconversion of microbe, and belongs to the field of food biotechnology. The preparation method comprises that lactic acid bacteria are used as fungi, 4-hydroxyl phenylypruvic acid or 4-hydroxyl phenylypruvic acid salt is used as a conversion substrate; and by adding a fermentation medium formed by carbon sources, nitrogen sources and inorganic slat, the 4-hydroxyl phenyllactic acid is prepared by fermentation bioconversion. The lactic acid bacteria are cultured at a temperature of between 25 and 40 DEG C in an MRS culture medium, grow in good conditions and are used as a seed culture solution; the fermentation medium carbon source is glucose, maltose, lactose or sucrose, and the nitrogen source is a mixture of one or more than one of corn steep liquor, yeast extract, peptone and soy bean pulp; and after fermentation, detections show that the concentration of the 4-hydroxyl phenyllactic acid in the fermentation liquid is between 1.0 and 20.0mmol / L. The product prepared by the method has the advantages of safety, reliability and strong bacteria inhibiting function.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Fermented medlar and red date rice wine and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103789136AHigh nutritional valueMeet the needs of different tastesMetabolism disorderDigestive systemRed yeast riceNutritive values
The invention belongs to the food biotechnology field and in particular relates to fermented medlar and red date rice wine and a preparation method thereof. The rice wine and the preparation method have the beneficial effects that by adding peony ovary extracts fertilized before 2-3 weeks and lactobacillus to distiller yeast, not only is the nutritional value of the rice wine greatly increased, but also the fermented rice wine has peony taste and meets the requirement of people on different tastes; red yeast rice, the lactobacillus, saccharomycetes and the peony ovary extracts are mixed, and then the rice wine can be drunk after being fermented for 7-8 days, thus greatly improving the production efficiency; the rice wine is put into production and the sales indicate that the rice wine is popular with most people; by adding an xylose mixture to the sweet distiller yeast, the rice wine is suitable for different groups of people, thus greatly widening the application range of the rice wine and promoting the development of the rice wine industry.
Owner:HENAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for producing gamma-aminobutyric acid enriched high milled rice, and product thereof
InactiveCN1751599AAvoid problems such as difficult to controlHigh activityFood preparationGlutamate decarboxylaseGamma-Aminobutyric acid
A process for preparing the refined rice rich in gamma-aminobutanoic acid (GABA) includes such steps as preparing the culture liquid from CaCl2, sodium glutamate or glutamine, ascorbic acid or lactic acid, and B6 proportionally, immersing the long-grained non-glutinous rice grains in it, culturing while filling gas until they are germinated and rich in GABA, drying and milling.
Owner:建昊(南京)健康科技有限公司
Oyster-vegetable active lactobacillus beverage
ActiveCN101683175ASuitable for technical transformation needsRaw materials are easy to getFood preparationVegetable processingOyster
The invention discloses a preparation method of an oyster-vegetable active lactobacillus beverage, belonging to the field of food biotechnology. Oyster has the reputation of submarine milk and is richof physiological active substances, such as protein, hepatin, taurine, zinc, selenium and the like which are beneficial to the human body. Since many people are hard to accept the fishy smell of theoyster due to different dietary favors, such people are limited to eating the oyster. The fishy smell of the oyster can be obviously eliminated by a fermentation liquid which is prepared by mixing anoyster enzyme solution or a water extracting solution with vegetable juice and then inoculating substances containing active lactobacillus to ferment. Meanwhile, the fermentation liquid of a beverageor a solid beverage is obtained, and 1 mL of the fermentation liquid contains 5*10<8> active lactobacillus. In the method, seafood and vegetables are mixed and fermented, and nutrients are in mutual complementation, thereby the method is an innovative and high technology for developing seafood production. The invention has the advantages of easily obtained raw materials, simple process, small investment and easy implementation; and the oyster-vegetable active lactobacillus beverage is very suitable for the technical reform requirement for beverage, oyster and vegetable processing enterprises.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Eurotium cristatum strain and breeding method and application thereof
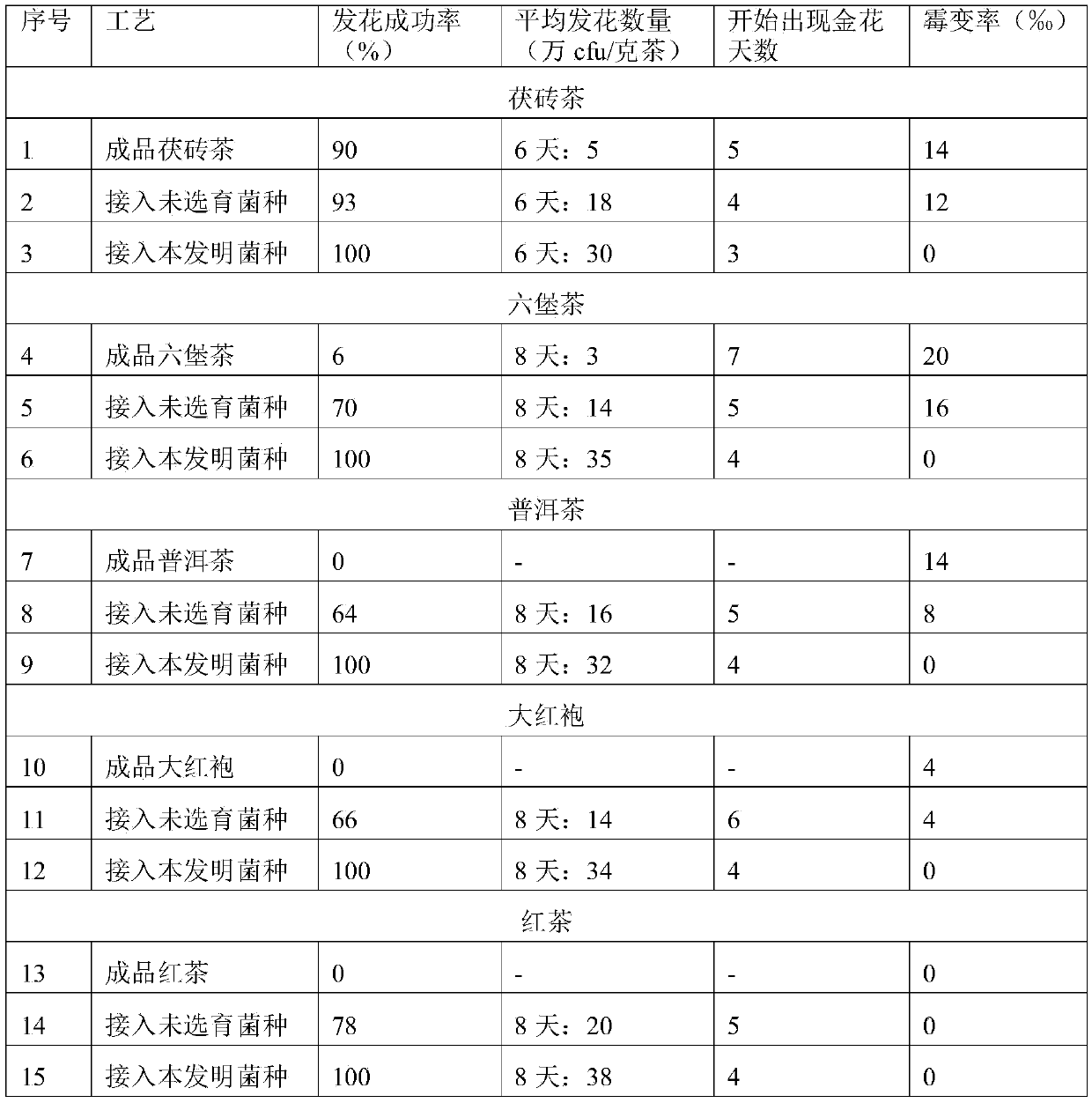
ActiveCN105368716AImprove qualityStable flowering processFungiPre-extraction tea treatmentMicroorganismFermentation
The invention belongs to the technical field of microorganisms and food biology, and particularly relates to a eurotium cristatum strain which has been preserved in the common microorganism center of the China Committee for Culture Collection of Microorganisms, and the preservation number of the eurotium cristatum strain is CGMCC NO.11304. Strict breeding authentication shows that the eurotium cristatum strain has a series of characteristics suitable for tea leaf production and fermentation and can be used for producing various golden flower tea leaves such as golden flower dark tea, golden flower Liupu tea, golden flower Pu'er tea and golden flower clovershrub tea, and produced tea leaves are clear in characteristic and good in quality.
Owner:中国土产畜产进出口有限责任公司
Lactic acid bacterium used for fermenting cereal and applications thereof
ActiveCN103468600AHas anti-tumor functionWith independent intellectual property rightsBacteriaMicroorganism based processesHordeum vulgareApoptosis
The invention discloses a lactic acid bacterium used for fermenting cereal and applications thereof, and belongs to the field of food biotechnology. Lactic acid bacterium Dy-1, suggested classification name is Lactobacillus plantarum, is delivered to China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center, Institute of Microbiology, China Academy of Science, in No.1 yard, No.3 building, Beichenxi road, Chaoyang district, Beijing, China, at April, 18th, 2012 for preservation, and the preservation number is CGMCC No.6016. Applications of the lactic acid bacterium comprise following steps: wheat germ or barley is fermented by freeze-dried powder of the lactic acid bacterium; a fermentation broth is subjected to centrifugation so as to obtain a supernatant; and the supernatant is subjected to freeze drying so as to obtain a fermentation extract. The fermentation extract possesses significant apoptosis promoting and propagation inhibiting effects on HT-29 colon cancer cells and SGC-7901 stomach cancer cells, and significant inhibiting effect on tumor growth of HT-29 colon cancer induced tumor-bearing nude mice models, and is capable of improving immunity of the HT-29 colon cancer induced tumor-bearing nude mice models.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Preparation method of edible and medicinal fungus protein peptide-ferrous chelate
InactiveCN105852135AHigh extraction rateHigh ferrous chelating activityProtein foodstuffs working-upNeutral proteaseHydrolysate
The invention belongs to the field of food biotechnology, and specifically relates to a preparation method of edible and medicinal fungus protein peptide-ferrous chelate, comprising: extracting protein from edible and medicinal fungi by alkali-dissolving acid precipitation method or ammonium sulfate precipitation method; Proteases, neutral proteases or complex proteases restrict the enzymolysis of edible and medicinal fungal proteins, and then inactivate the enzymes to prepare edible and medicinal fungal protein enzymatic hydrolysates; use inorganic ferrous chloride or ferrous sulfate in ferrous and Edible and medicinal mycoprotein peptide chelation to obtain edible and medicinal mycoprotein-ferrous chelate. The invention can significantly improve the extraction rate of edible and medicinal mycoprotein by alkali-soluble acid precipitation method or ammonium sulfate precipitation method; the degradation degree of protein can be effectively controlled by controlling the enzymatic hydrolysis time; the preparation process of the whole polypeptide-ferrous chelate is simple. The ferrous-peptide chelate prepared by the present invention has a unique chelation system and transport mechanism, is easily absorbed, safe and non-toxic, low in price, can supplement amino acids and ferrous at the same time, and will definitely become the first choice for ferrous supplements; The invention provides a new idea for the application of edible and medicinal fungi.
Owner:FUJIAN AGRI & FORESTRY UNIV
Method for producing polysaccharide by rice husk bran composite raw material and grifola frondosa mutant strain
InactiveCN102080113AIncrease productionImproving the value of adjuvant antineoplastic therapyFungiFermentationEthanol precipitationBran
The invention belongs to the fields of microorganism application and food biotechnology and discloses a method for producing polysaccharide by rice husk bran composite raw material and grifola frondosa mutant strain. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) treating rice husk and bran by adopting plant hydrolytic enzyme; (2) fermenting a grifola frondosa strain obtained by mutagenizing with the obtained treating fluid as a culture medium, wherein the preservation number of the strain is CGMCC (China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center) No.4179; (3) carrying out centrifugal separation on mycelia obtained by liquid culture, washing the mycelia with distilled water, and drying to be constant weight to obtain the mycelia; (4) carrying out the conventional water extraction, deproteinization and ethanol precipitation on the mycelia to obtain intracellular polysaccharide; and (5) sequentially carrying out deproteinization and ethanol precipitation on the supernate obtained after fermentation liquor is centrifuged to obtain intracellular polysaccharide. By adopting the method disclosed by the invention, the production cost can be reduced, the material cost can be saved, less land can be used, the production cycle can be shortened, and grifola frondosa polysaccharide with high value and auxiliary anti-tumor curative effect can be produced.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Antihypertensive peptide derived from sardine as well as preparation method and application of antihypertensive peptide
ActiveCN104031967AIncrease productionNo security issuesHydrolysed protein ingredientsPeptide preparation methodsSide effectFreeze-drying
The invention belongs to the fields of food biotechnologies and function healthcare and discloses an antihypertensive peptide derived from a sardine as well as a preparation method and application of the antihypertensive peptide. The method comprises the following main technical steps of after pretreating the sardine to obtain homogenate, adding papain to carry out enzymolysis firstly, and then, adding an alkaline protease to carry out enzymolysis; deactivating the enzyme after enzymolysis is finished, and centrifuging the enzyme-deactivated enzymatic hydrolysate; taking the centrifuged supernatant, and separating and purifying a crude product by using an ultrafiltration and gel chromatography method; carrying out freeze-drying on the separated and purified efficient component to obtain the antihypertensive peptide derived from the sardine. The sardine is high in yield and low in price, so that the comprehensive utilization value of the sardine can be sufficiently increased when the sardine is used as the raw material to prepare the antihypertensive peptide; in addition, the antihypertensive peptide derived from the sardine and obtained through enzymolysis is free of safety problems and side effects of chemical antihypertensive drugs and ideal in antihypertensive effect.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
Method for preparing manna oligosacchride with zymohydrolysis of konjaku flour
InactiveCN101508966AMeet needsBacteriaMicroorganism based processesManno-oligosaccharideOligosaccharide
The invention relates to a method for preparing mannan oligosaccharide by zymolytic konjaku flour, which belongs to the biological technical field of food. In the invention, beta-mannase is prepared after fermentation by using strain Bacillus sp. MSJ-5 producing beta-mannase and having the preservation number of CCTCC No: M208258, and then mannan oligosaccharide is prepared by using the prepared beta-zymolytic konjaku flour of mannase; and the zymolysis conditions are 50 to 55 DEG C, 50 to 70r / min for stirring and 20 to 30 hours for zymolysis. The method can conveniently and cheaply realize industrial production of mannan oligosaccharide, thereby meeting the requirements of the market on mannan oligosaccharide.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Green alga poly-saccharification nano-selenium and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN106539092AEasy to useUse, but these drugs are easy to use in large quantities over a long period of timeOrganic active ingredientsAntipyreticDiseaseNanometer size
The invention discloses green alga poly-saccharification nano-selenium and a preparation method and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of the food biotechnology. The natural green alga poly-saccharification nano-selenium (PSSNP) prepared by the preparation method easily and conveniently is a necessary micronutrient for a human body, and polysaccharide has an immune regulation effect on an organism. The novel safe effective poly-saccharification nano-selenium is developed, and homogeneity of the nanometer size, stability of liquid-phase conservation and high efficiency of poly-saccharification are achieved. Green alga poly-saccharification nano-selenium (PSSNP) products are mainly suitable for auxiliary treating of enteritis and inflammatory bowel diseases and can also be applied to auxiliary preventing and treating of hyperlipidaemia, atherosclerosis, diabetes and other inflammation-related diseases; and the green alga poly-saccharification nano-selenium is convenient to use, green, safe and low in price and can alleviate patient pains and greatly reduce economical burden.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
Germinant fagopyrum tararicum medicated-food composite powder rich in gamma-aminobutyric acid and preparation process of composite powder
ActiveCN103960595AGive full play to nutritional valueGood for healthFood thermal treatmentCultivating equipmentsLTM - Long-term memoryGamma-Aminobutyric acid
The invention relates to the field of food biotechnology, and in particular to a germinant fagopyrum tararicum medicated-food composite powder rich in gamma-aminobutyric acid and a preparation process of the composite powder. The germinant fagopyrum tararicum medicated-food composite powder is prepared from the following components in parts by weight: 40-60 parts of germinant fagopyrum tararicum powder, 20-35 parts of radix puerariae powder, 10-20 parts of medicated-food composite powder, 10-15 parts of dextrin and 0.04-0.06 part of a sweetening agent. The preparation process comprises the steps that the germinant fagopyrum tararicum powder, the radix puerariae powder, the medicated-food composite powder, the dextrin and the sweetening agent are uniformly mixed in a ratio by weight, the mixture is roasted until an obvious fragrance is sent out, and finally, the product is packaged in vacuum or by charging nitrogen. The content of GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid) in the germinant fagopyrum tararicum medicated-food composite powder prepared by the preparation process disclosed by the invention can reach 20-40 mg / 100 g, the total flavonoid content is up to10-15 mg / 100 g, and the nutritional ingredients in the medicated-food composite powder are greatly supplemented; the germinant fagopyrum tararicum medicated-food composite powder has the functions of reducing blood pressure, blood fat and blood sugar, improving brain functions, stabilizing nerves, promoting long-term memory and enhancing body immunity.
Owner:武汉特医中医药研究中心
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com