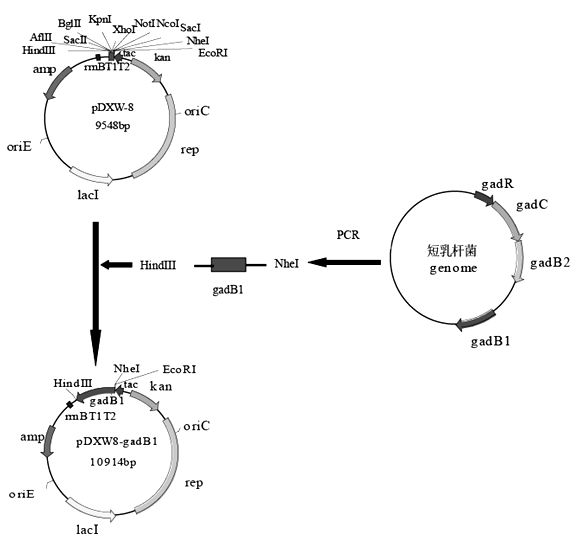
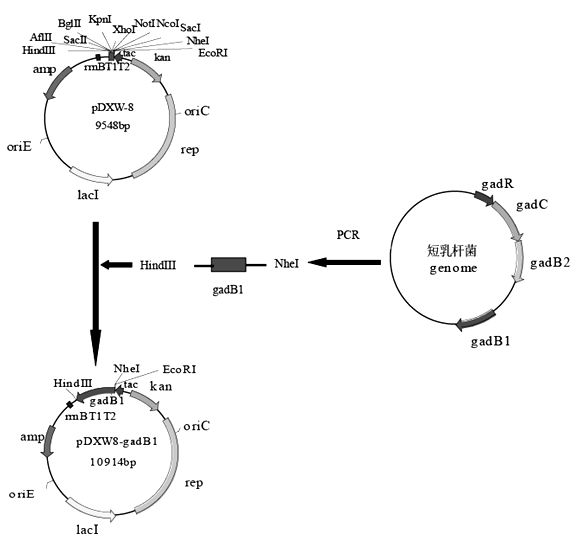
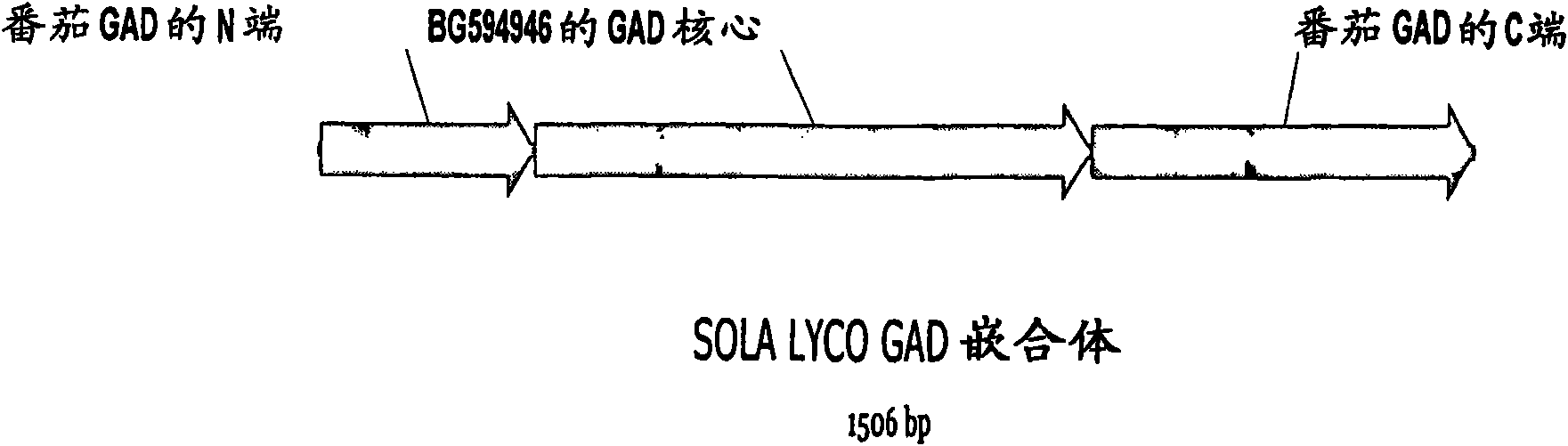
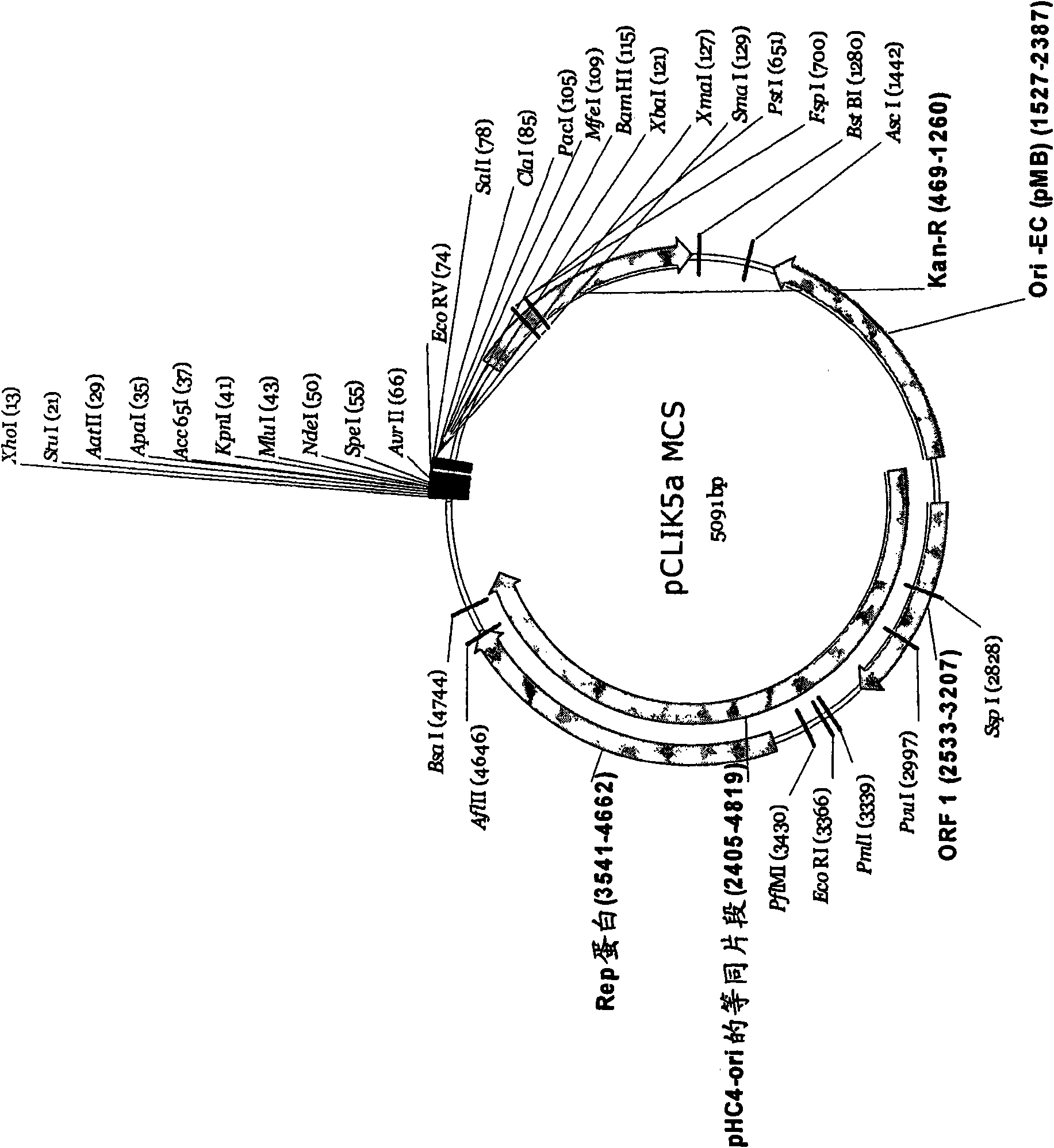
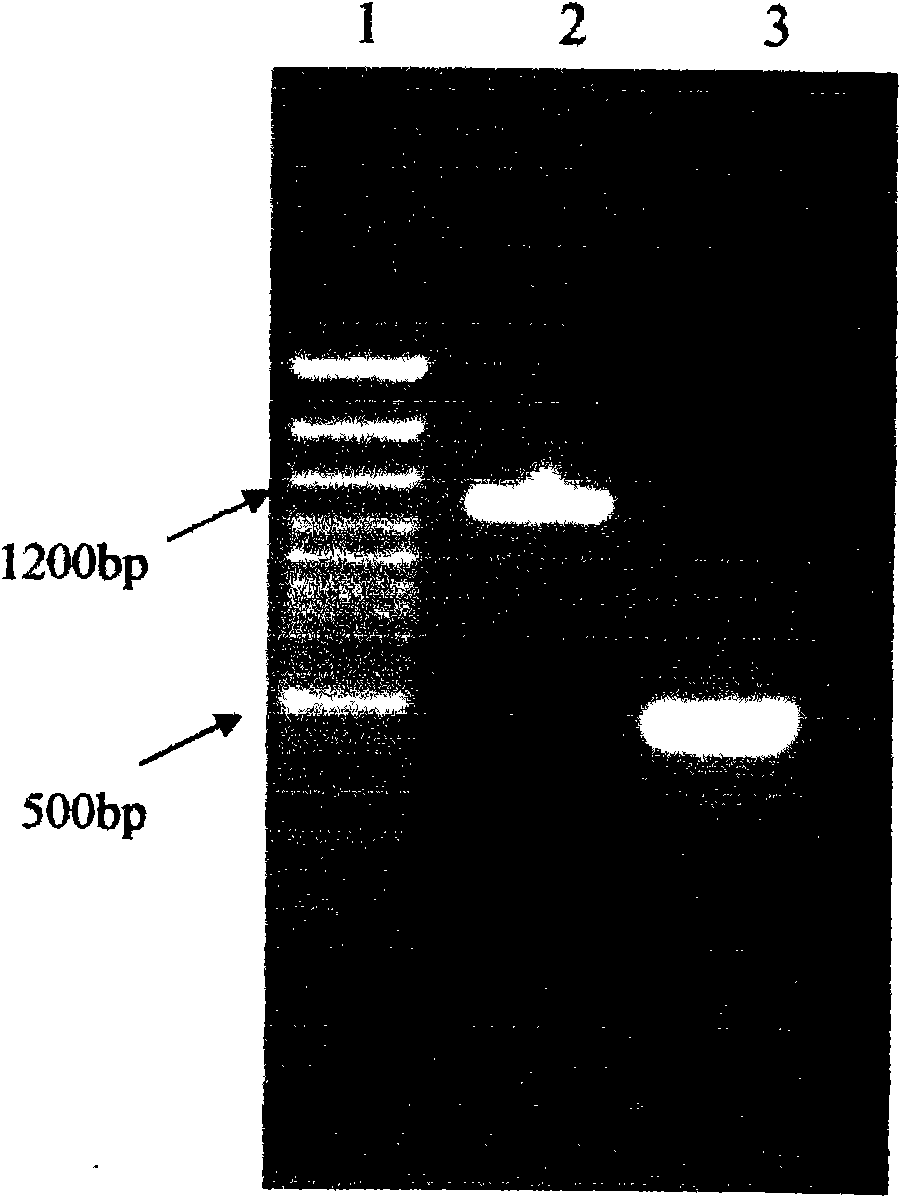
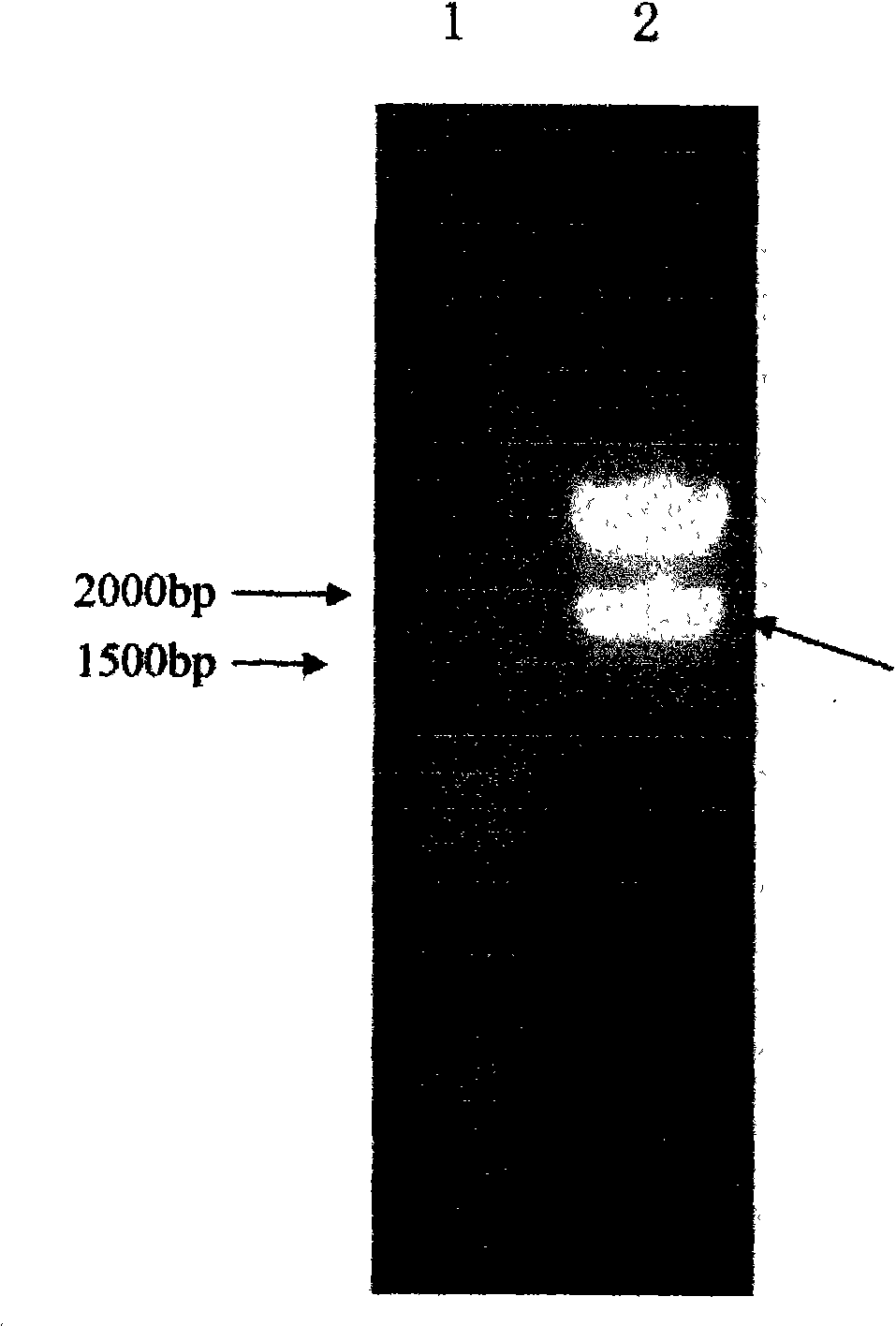
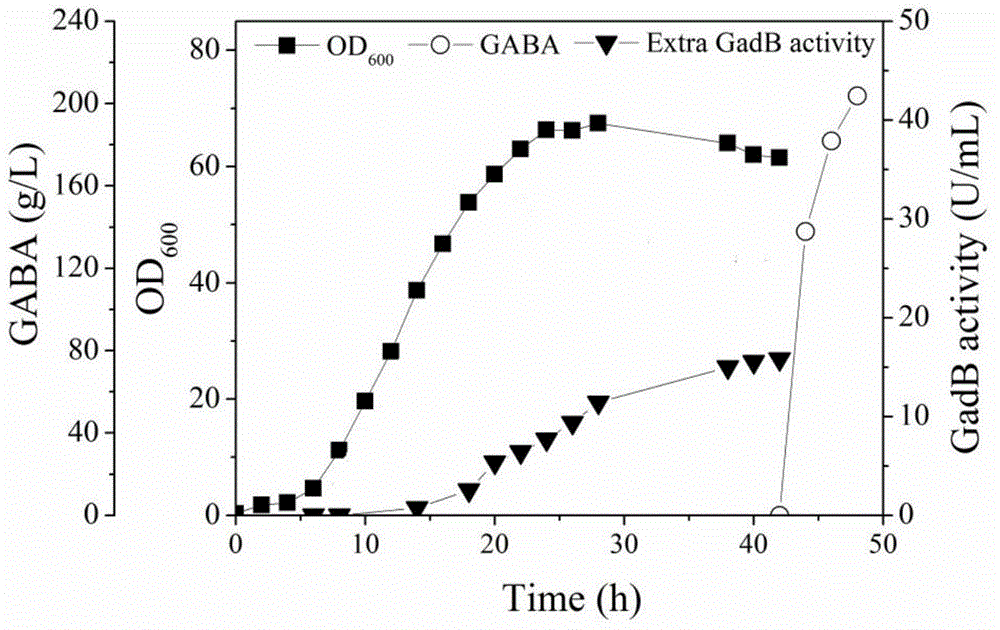
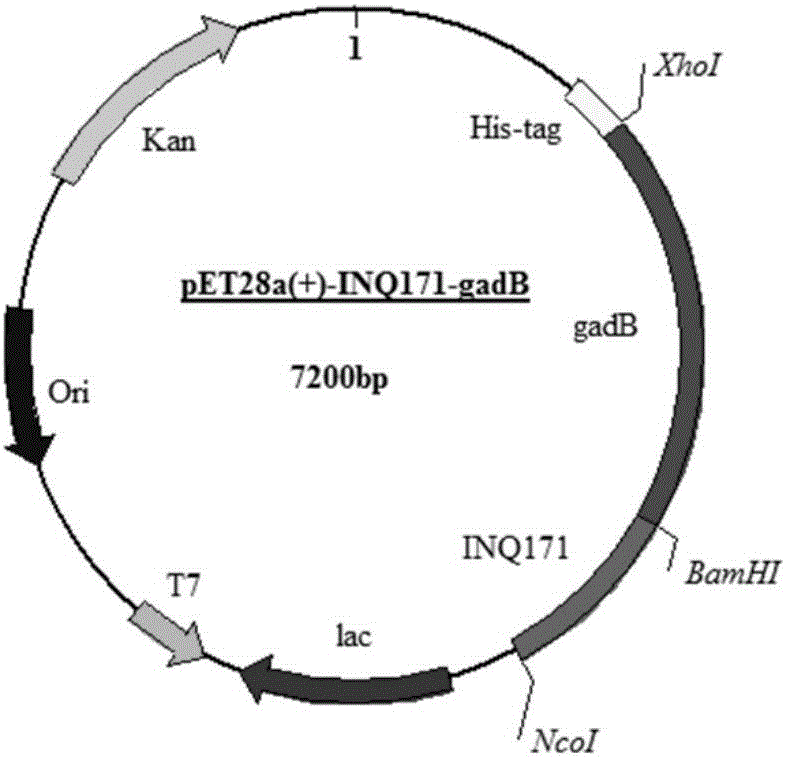
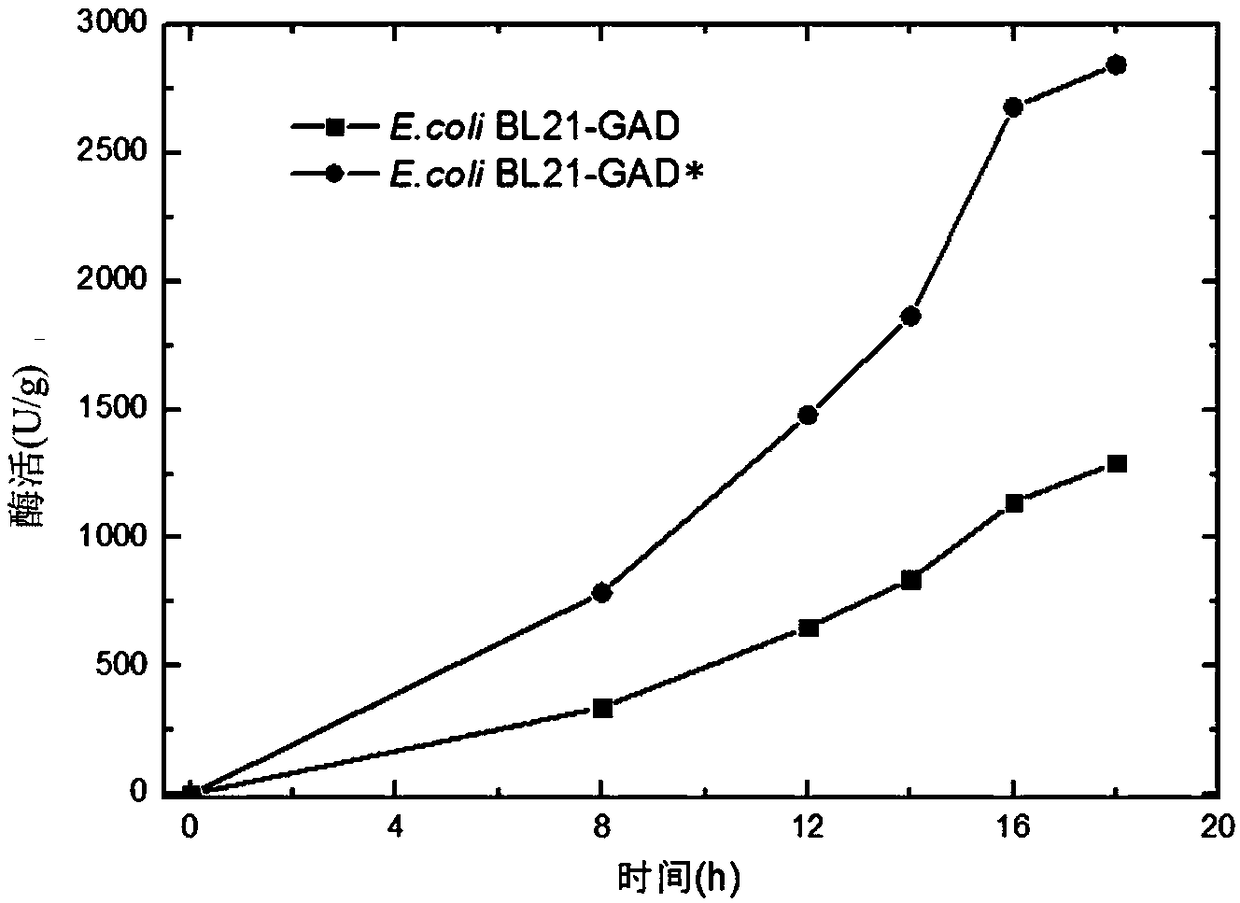
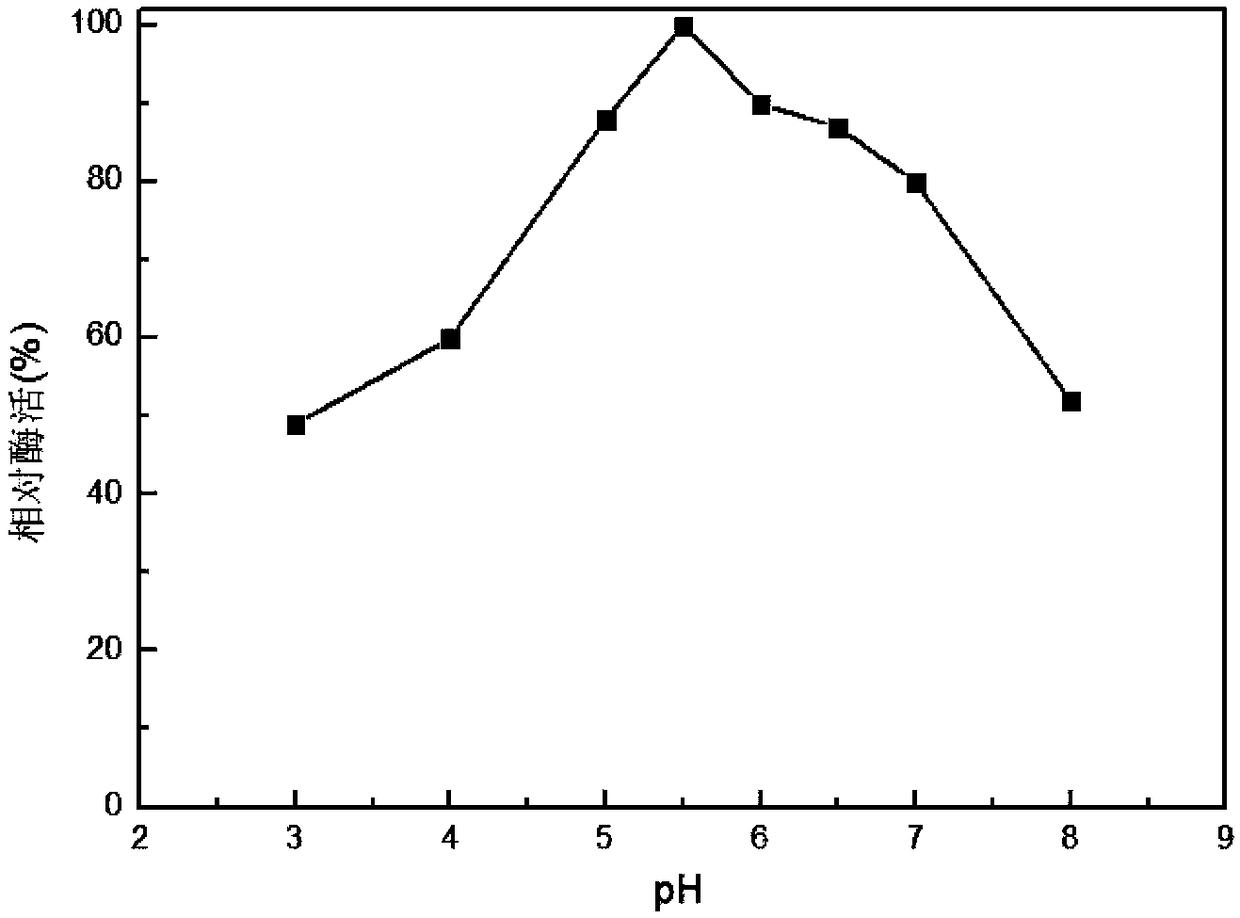
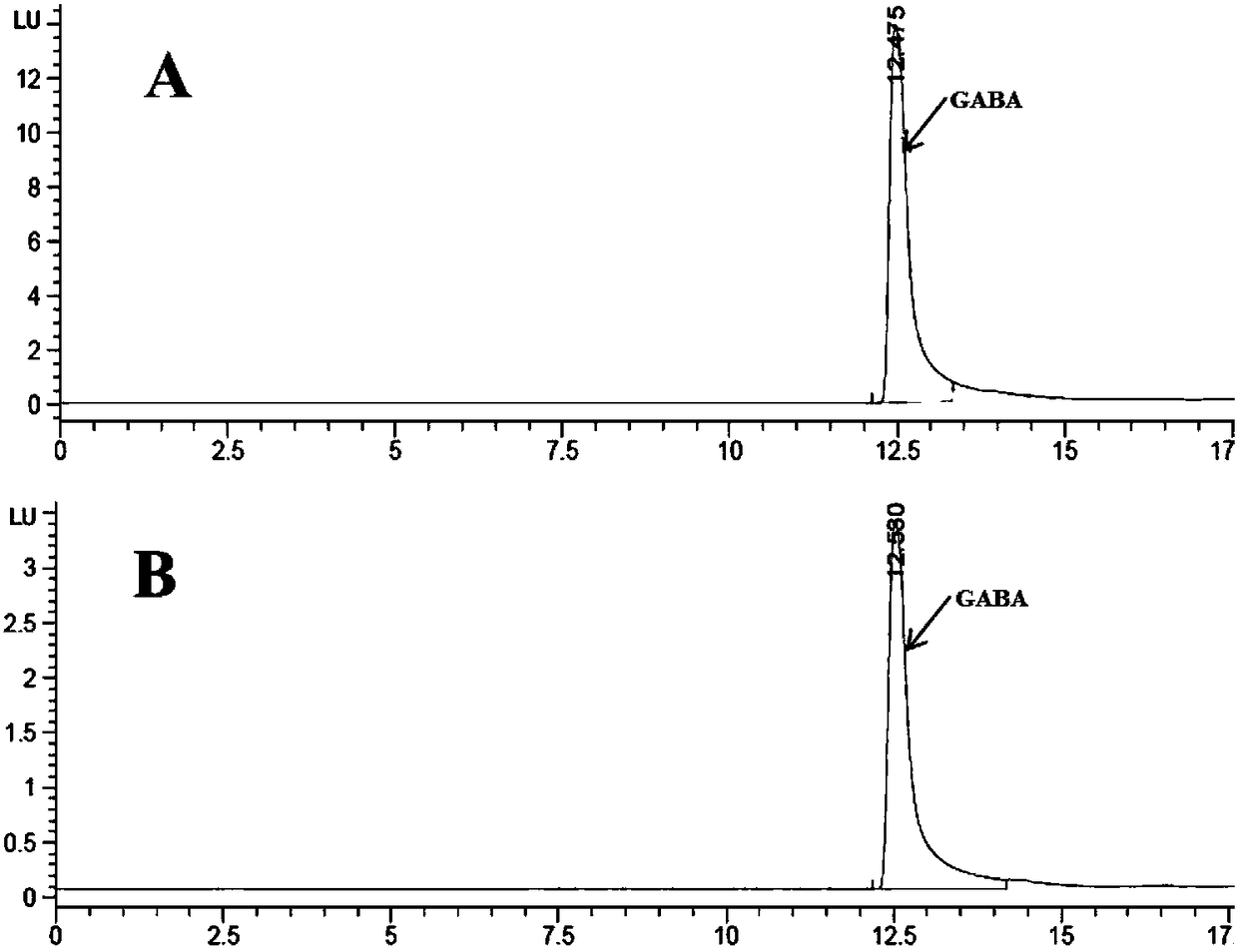
Patents
Literature
278 results about "Glutamate decarboxylase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
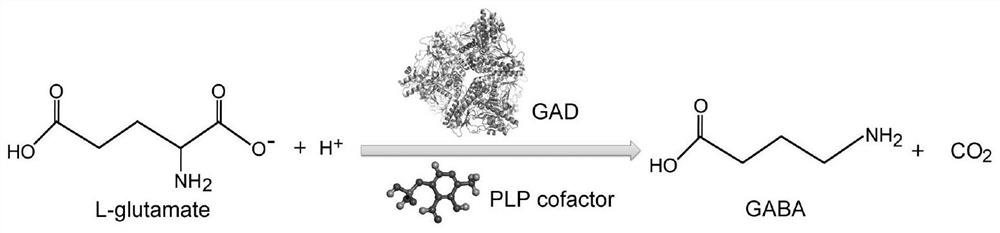
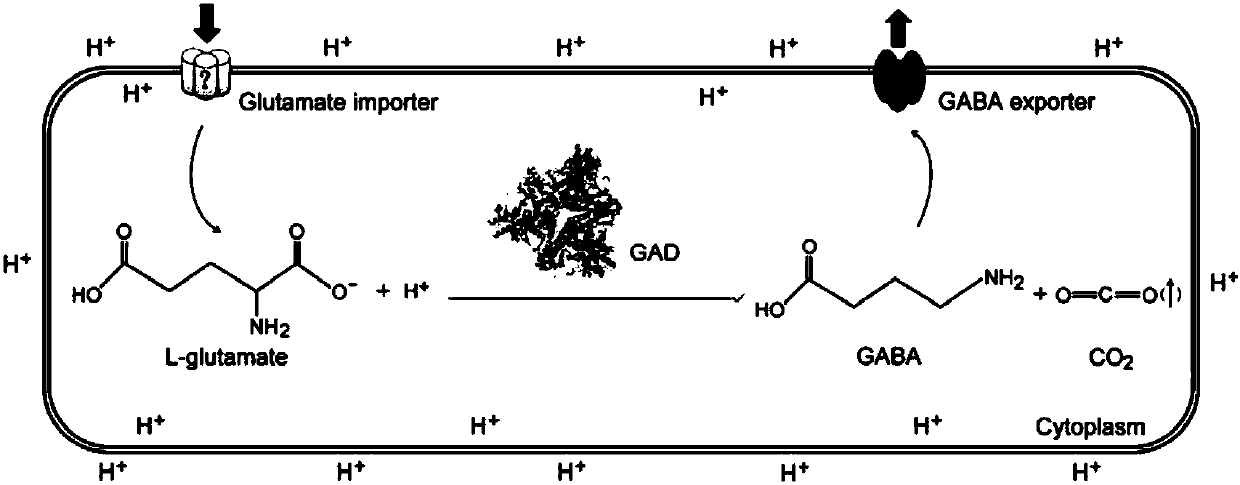
Glutamate decarboxylase or glutamic acid decarboxylase (GAD) is an enzyme that catalyzes the decarboxylation of glutamate to GABA and CO₂. GAD uses PLP as a cofactor. In mammals, GAD exists in two isoforms with molecular weights of 67 and 65 kDa (GAD₆₇ and GAD₆₅), which are encoded by two different genes on different chromosomes (GAD1 and GAD2 genes, chromosomes 4 and 10 respectively). GAD₆₇ and GAD₆₅ are expressed in the brain where GABA is used as a neurotransmitter, and they are also expressed in the insulin-producing β-cells of the pancreas, in varying ratios depending upon the species. Together, these two enzymes maintain the major physiological supply of GABA in mammals, though it may also be synthesized from putrescine in the enteric nervous system, brain, and elsewhere by the actions of diamine oxidase and aldehyde dehydrogenase 1a1.
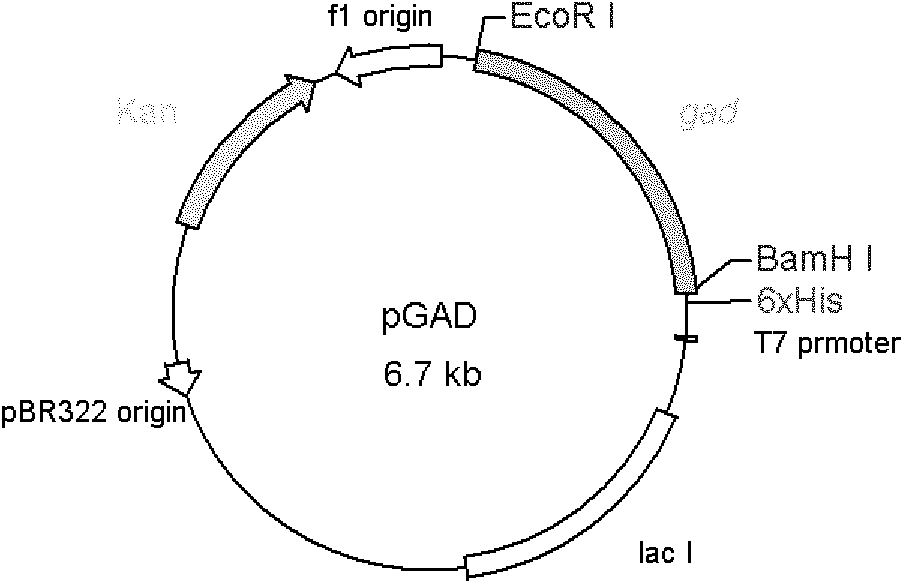
Cloned glutamic acid decarboxylase
InactiveUS20050164342A1Avoid small quantitiesAccurate classificationImmobilised enzymesBacteriaEpitopeGlutamate decarboxylase
cDNA molecules coding for GAD65 polypeptide. The invention provides cDNA molecules comprising a part of the cDNA sequence of GAD65 which encode at least one epitope for autoantibodies to GAD65. The invention also provides cloning vehicles capable of replication and expression comprising cDNA molecules coding for GAD65. The invention further provides for hosts transformed with a vehicle having a cDNA molecule coding for GAD65. In another embodiment, the invention provides for the detection of autoantibodies to GAD65 using the GAD65 polypeptides coded for by the cDNA molecules of the invention.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Process for preparing gamma-amino butyric acid through enzymatic conversion
InactiveCN1635128ASimultaneous productionStrong specificityFermentationGlutamate decarboxylaseCombined method
The invention discloses an enzyme conversion method for preparing gamma-butyric acid. The preparation method comprises employing two mixed acidic amino acids of L-glutamic acid and L-aspartic acid as raw material, mixing the cells of Escherichia.coli AS1.505 with highly active L-glutamic acid decarboxylases and the conversion liquid containing the mixture of L-glutamic acid and L-aspartic acid, implementing enzymatic reaction under the temperature of 28~45íµ, then separating the conversion products by isoelectric point crystallization process or isoelectric point crystallization and ion exchange resin combined method to obtain high purity gamma-butyric acid and L-aspartic acid. The invention solves the problem of the highly effective separation of two acidic mixed amino acids, and obtains gamma-butyric acid with higher additional value, and has advantages of low price, simple operation, short conversion time, and low production cost.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
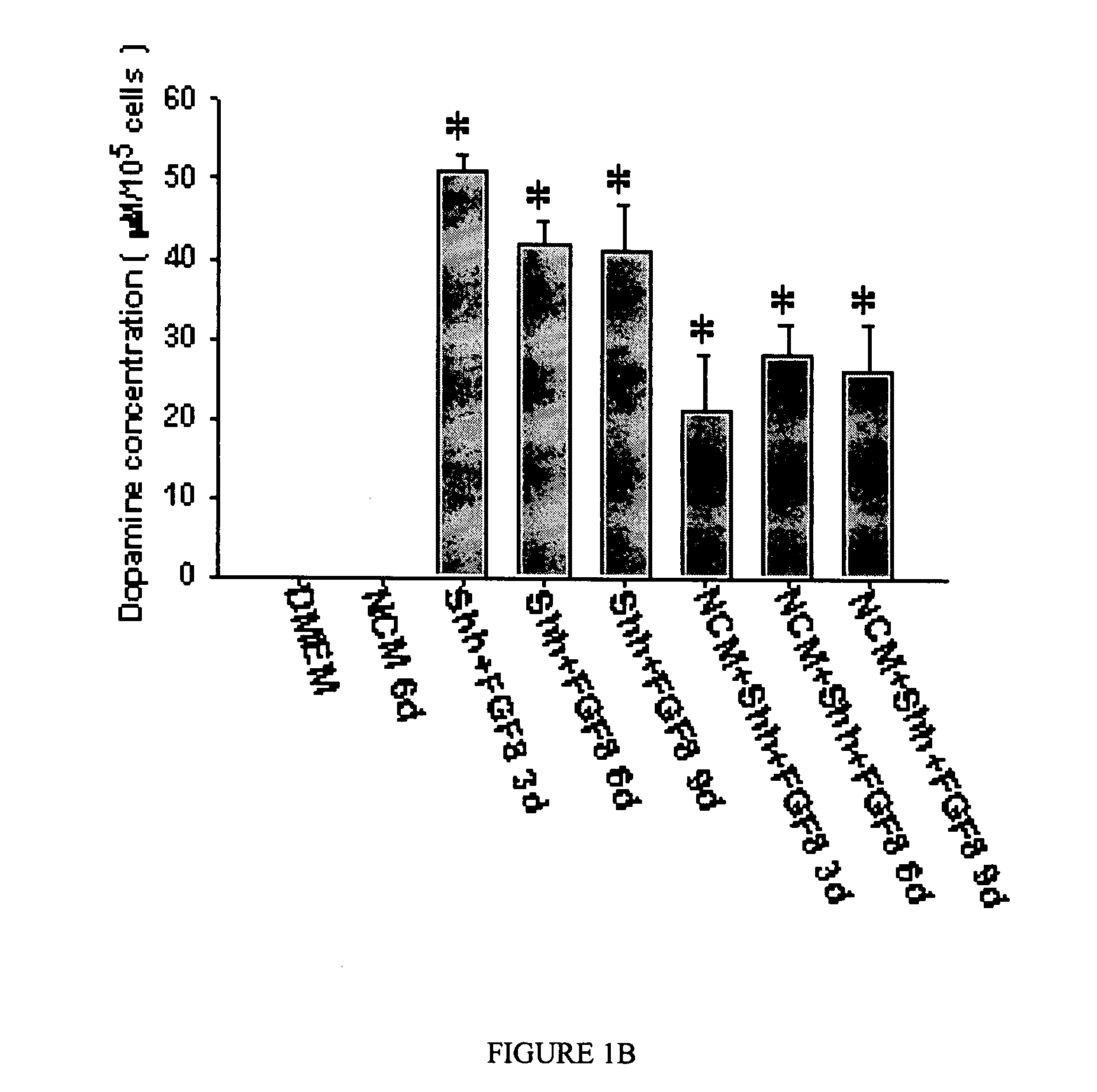
Cell system for alleviating syndromes of Parkinson's disease in a mammal
A cell system for treating neurodegenerative disorders in a mammal is provided. The cell system includes a population of neurons differentiated from umbilical mesenchymal stem cells for expressing at least one of tyrosine hydroxylase (TH), dopamine-β-hydroxylase (DBH), glutamate decarboxylase (GAD), aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase (AADC) and dopaminergic transporter (DAT) in a cell culture. A method for treating neurodegenerative disorders in a mammal is also provided. The method comprises the steps of differentiating umbilical mesenchymal stem cells into a population of neurons that express at least one of TH, DBH, GAD, AADC and DAT in a cell culture, and transplanting the population of neurons into the brain of the mammal.
Owner:FU YU SHOW +1
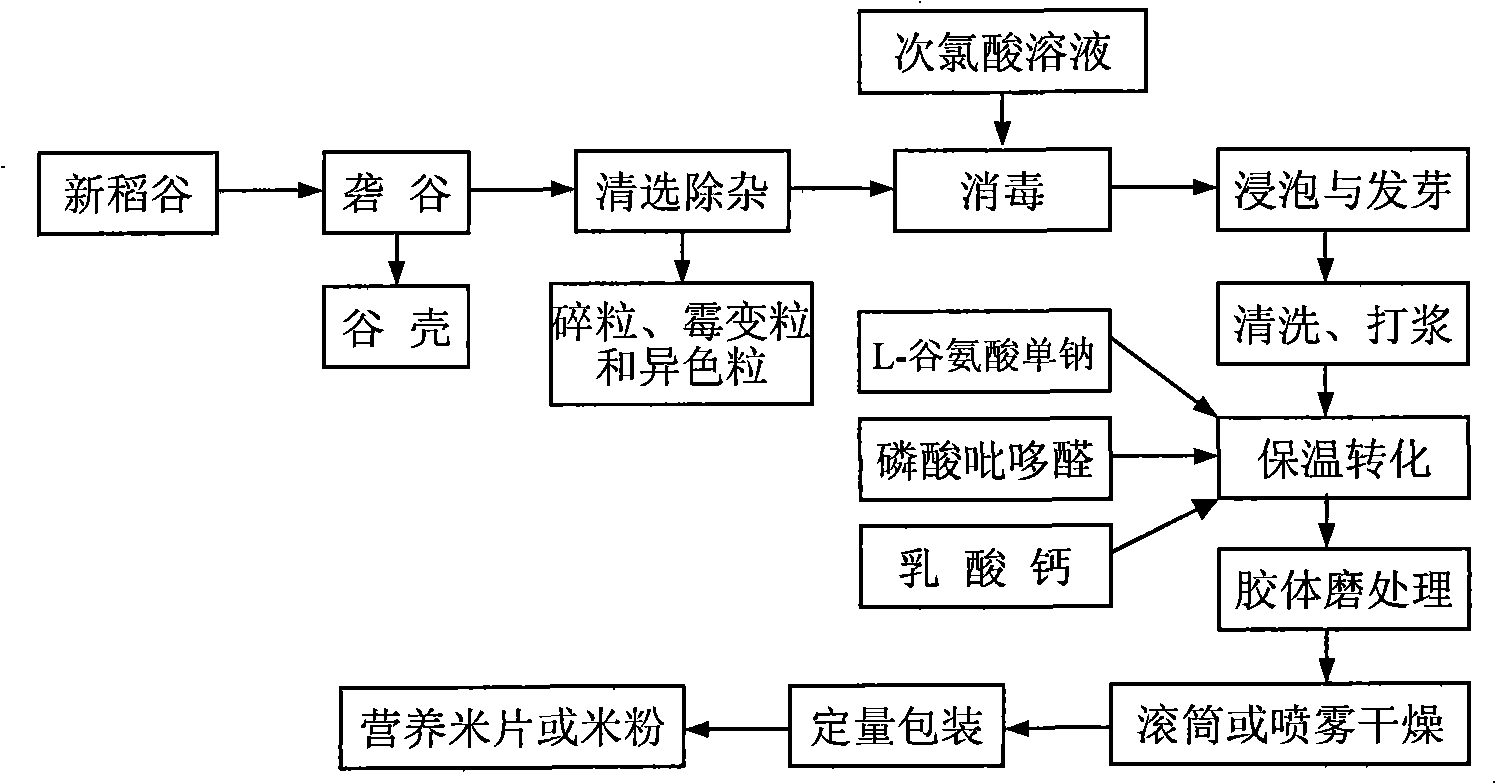
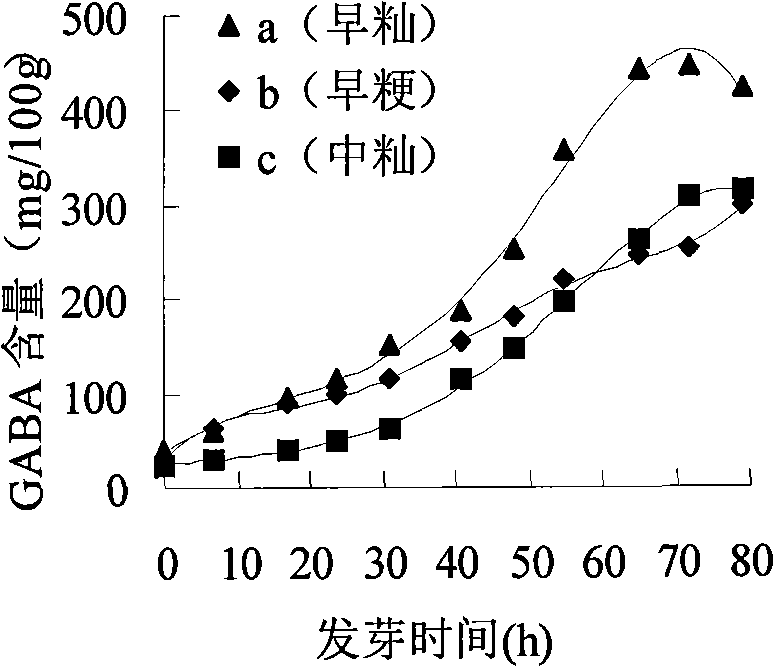
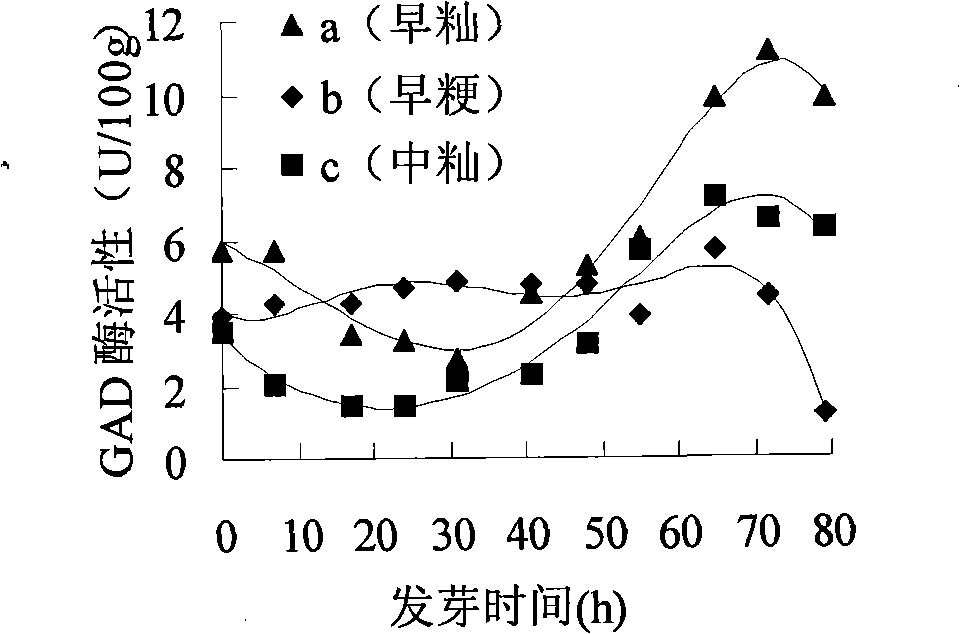
Rice product rich in gamma-aminobutyric acid and method for producing the same
The invention belongs to the technical field of rice deep processing, in particular to a production method of a functional rice product which has a special sweet flavor and is rich in Gamma-aminobutyric acid and a product thereof, the rice product is produced by virtue of the activities of high glutamate decarboxylase, amylase and protease in germinated brown rice of an indica type rice or a non glutinous rice. The invention takes the indica type rice or the non glutinous brown rice as a raw material which carries out the steps of cleaning, disinfection, soaking, germination, cleaning, beating into rice milk, heat insulation, transformation, drum drying or spray drying, and the like, to be produced into functional nutrition rice flake or rice powder which is rich in Gamma-aminobutyric acid. Compared with the prior art, the rice product makes full use of the activities of the glutamate decarboxylase, the amylase and the protease in the germinated brown rice; the produced rice product has the special sweet flavor; by calculating based on dry basis, the content of Gamma-aminobutyric acid is high (1,000-1,400mg / 100g), and the nutritional value and the digestibility are high. The rice product of the invention can be taken as the functional food for resisting fatigue and reducing blood lipid.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Production method and strain of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA)
InactiveCN102154393ASimplify production stepsReduce manufacturing costBacteriaMicroorganism based processesGlutamate decarboxylaseDrug biotransformation
The invention discloses a production method and strain of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), belonging to the technical field of gene engineering. The method comprises the following steps of: introducing a glutamate decarboxylase gene into a glutamic acid production bacterium to construct a gene engineering bacterium; and removing a carboxyl from a self-accumulated glutamic acid by using glutamate decarboxylase secreted by the gene engineering bacterium to synthesize the GABA. In the invention, fermentation of glutamic acid is combined with transformation of the GABA, so that the production steps of the GABA are simplified; moreover, glucose, urea and the like are taken as culturing raw materials, so that the production cost of the method disclosed by the invention is remarkably lowered compared with a biological transformation method in which L-glutamic acid or L-sodium glutamate serving as a precursor needs to be exogenously added.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Glutamate decarboxylase mutant with improved thermal stability and application thereof
ActiveCN106754850AImprove the stability of enzyme activitySuitable for industrial production needsFermentationGenetic engineeringEscherichia coliGlutamate decarboxylase
The invention relates to a glutamate decarboxylase mutant with improved thermal stability and an application thereof, belonging to the field of bioengineering. The mutant is prepared primarily by the following steps: performing saturated mutation of glutamine Q, valine V and threonine T on the sites 5-7 of the amino acid sequence of glutamate decarboxylase, and screening to obtain high-stability mutants Q5E / V6S / T7V, Q5Y / V6R / T7K and Q5N / V6Y / T7V. In the glutamate decarboxylase mutant prepared in the invention, the half-inactivation temperature is 45-50.5 DEG C which is 4.9-10.2 DEG C higher than that of wild type mutant; and the half-life period at 45 DEG C is 76-129min, which is 3.2-4.3 times higher than 24min of wild type mutant. By transforming glutamic acid for 12h with the whole cell of glutamate decarboxylase mutant synthesized from recombinant escherichia coli, 260-350g / L gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) can be obtained, and the molar yield is 76.6-97.8%. In the glutamate decarboxylase mutant prepared in the invention, the thermal stability is obviously improved, the production of gamma-aminobutyric acid is facilitated, and a foundation is laid for efficient synthesis of gamma-aminobutyric acid.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Strain for producing glutamic acid decarboxylase and method for producing gamma-aminobutyric acid by utilizing strain
ActiveCN103320362AEfficient productionSuitable for mass productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesGlutamate decarboxylaseMarket potential
The invention relates to a strain for producing glutamic acid decarboxylase and a method for producing gamma-aminobutyric acid by utilizing the strain, belonging to the field of food biotechnology. The invention discloses lactobacillus plantarum SK30.001. The lactobacillus plantarum SK30.001 is screened from pickled vegetables and is preserved in China Center for Type Culture Collection (CCTCC), and the preserve number is CCTCC NO: M2013250. The invention further provides a method for producing the gamma-aminobutyric acid through fermentation by utilizing the strain. The method comprises the following steps of: (a) culturing the strain in a fermentation culture medium, so as to obtain lactobacillus plantarum thallus; (b) converting sodium glutamate by utilizing the lactobacillus plantarum thallus to generate the gamma-aminobutyric acid; and (c) carrying out separation and purification of the gamma-aminobutyric acid. The gamma-aminobutyric acid produced by utilizing method is safe and reliable, is a functional product with a good market potential and is widely applied to industries of foods, cosmetics, medicines and the like. According to the strain for producing the glutamic acid decarboxylase and the method for producing the gamma-aminobutyric acid by utilizing the strain, the gamma-aminobutyric acid can be efficiently produced, the mass production is realized easily, and a novel method for industrial preparation of the gamma-aminobutyric acid is provided.
Owner:健隆生物科技股份有限公司
Food material including much gamma-aminobutyric acid and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20050202122A1Contribute to human healthEasy to carryTea extractionAnimal feeding stuffLactobacillusGamma-Aminobutyric acid
The method of the present invention is capable of manufacturing a food material, which is made from soybeans including much γ-aminobutyric acid and which can be widely used. The method of manufacturing a food material including much γ-aminobutyric acid comprises a step of incubating lactic acid bacteria having glutamic acid decarboxylase in a medium, which is made from steamed soybeans including glutamic acid or salt of glutamic acid.
Owner:MARUKOME
Method for extracting glutamic acid decarboxylase from banana peel and method for producing r-reanal
The invention relates to a method for extracting glutamic acid decarboxylase from a banana peel, which comprises the steps of smashing the banana peel to paste to separate fiber and protein, wherein the length of fiber does not exceed 2mm; adding a phosphate buffer which is 5.0-7.0 in pH and contains 0.01-0.2g / L vitamin B6, shaking uniformly and standing and extracting for 1-5h, wherein each kilogram of banana peel corresponds to 2-7 liters of phosphate buffer; centrifugalizing at 6000-10000rpm for 10-50min to obtain a GAD (Glutamic Acid Decarboxylase) enzyme solution. The invention further provides a method for producing r-reanal by extracting glutamic acid decarboxylase from the banana peel. According to the invention, the waste in banana processing industry can be effectively used, the GAD and GABA (r-reanal) production costs are reduced, and the method can be used to produce GABA in a large scale.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH +1
Construction method and application of high-yield gamma-aminobutyric acid recombinant escherichia coli/pET-28a-1pgad
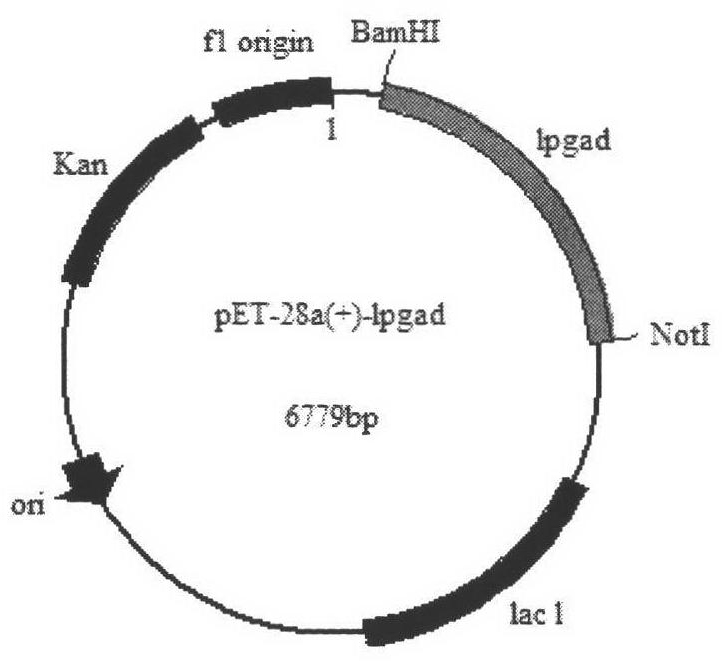
ActiveCN102367432AHigh expressionThe high expression level is controlled by the metabolic state of the bacteria, the expression levelBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliGlutamate decarboxylase
The invention relates to a construction method and an application of high-yield gamma-aminobutyric acid recombinant escherichia coli / pET-28a-1pgad, in particular to a genetic engineering bacterium construction method, recombinant enzyme enzymology property study and an application to the conversion of L-glutamic acid for producing gamma amino butyric acid (GABA), which belongs to the technical field of biology in the fermentation engineering. Firstly, lactobacillus plantarum GB 01-21 glutamic acid decarboxylase (GAD) genes are obtained through polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification, recombinant plasmids pET-28a-1pgad are constructed, in addition, the successful expression is realized in E.coli BL21(ED3), secondly, Ni column affiliation chromatography purification is adopted on crude enzyme liquid for obtaining recombinant GAD, in addition, the enzymology property of the recombinant GAD is primarily studied for guiding the optimization of conversion conditions, finally, conversion experiments are carried out on a 5L fermentation tank, the GABA accumulation concentration can reach 204.5g / L, the mol conversion rate is 97.92 percent, and good foundation is made on the further industrial application.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
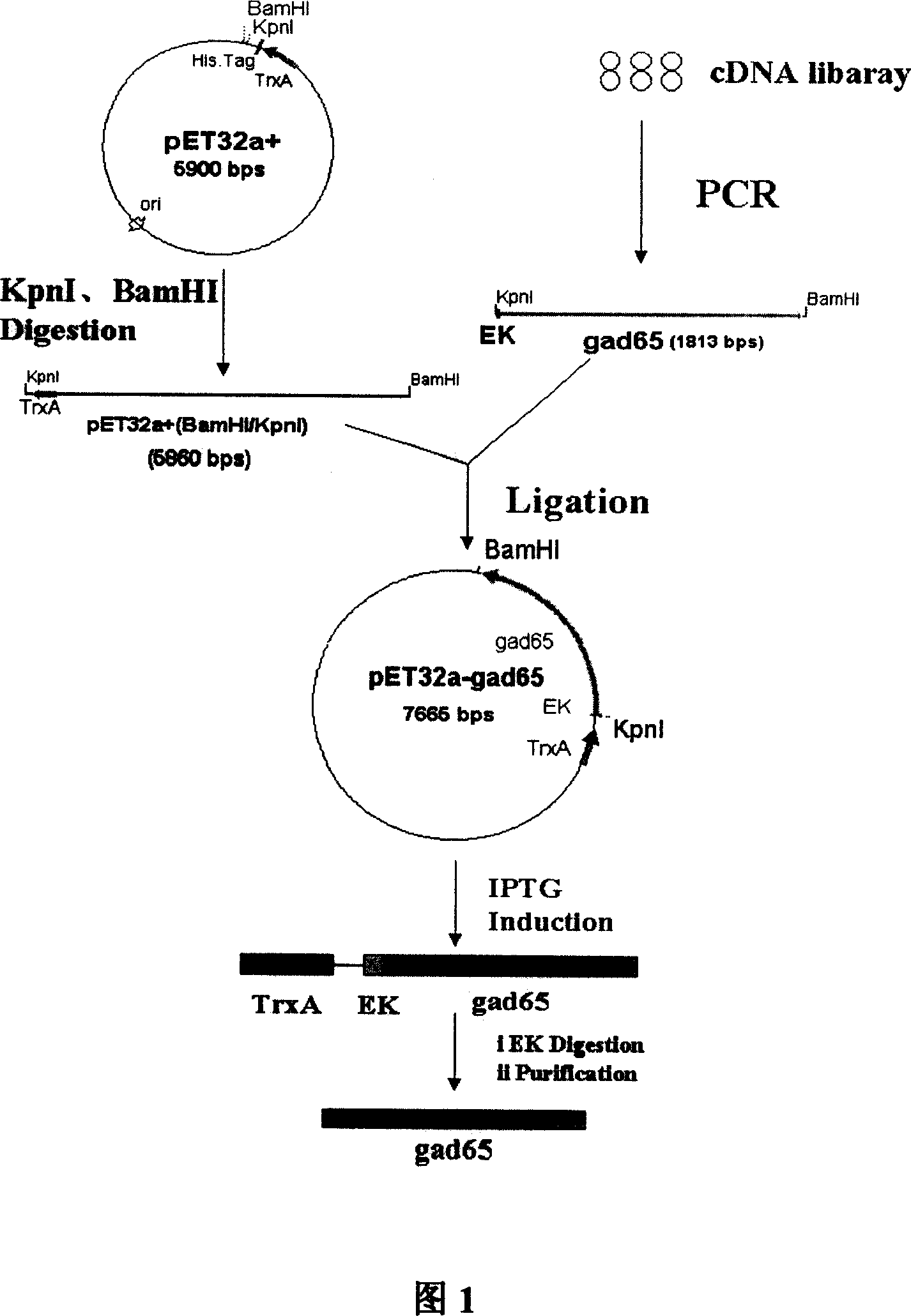
Gene engineering bacterium, preparation and use thereof
InactiveCN101054569AHigh expressionOptimize purification stepsBacteriaEnzymesEscherichia coliBiotechnology
The present invention relates to a gene engineered bacteria, and its preparation method and uses, belongs to biological engineering field. The gene engineered bacteria is composed of plasmid and host bacteria in which host bacteria is any one of Ecoli DH5alpha,BL21(DE3) or Rosetta-gami(DE3), the recombinant plasmid is pET32a(+) containing gene GAD65. The construction method of engineered bacteria comprise: designing Nest-PCR upper-stream primer and down-stream primer, amplifying human GAD65 gene fragment using PCR from human pancreas cDNA library, transforming Ecoli via vector and obtaining highly effective expression recombinant human GAD65 gene engineered bacteria. The inventive engineered bacteria can be used to produce soluble active thioredoxin- human Glutamic Decarboxylase 65 fusion protein and active recombinant human GAD65 which has enzymatic activity and immunological activity and are easy to purify. The expression volume is high and cost is low .
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV
Glutamate decarboxylase mutant and application thereof in preparation of gamma-aminobutyric acid
ActiveCN111635898AImprove catalytic performanceIncrease profitBacteriaMicroorganism based processesGlutamate decarboxylaseWild type
The invention discloses a glutamate decarboxylase mutant with improved enzyme activity and application thereof. The glutamate decarboxylase coding gene from bacillus megatherium is subjected to site-specific mutagenesis, and the catalytic performance of the obtained mutant is obviously improved compared with that of a wild type mutant. A recombinant engineering strain is constructed on the basis of the mutant, gamma-aminobutyric acid is prepared by taking a large amount of fermentation product L-glutamic acid as a substrate through a whole-cell catalysis method, the maximum yield of gamma-aminobutyric acid reaches 625.6 g / L, the molar conversion rate in a catalytic system is close to 100%, and no by-product is produced. The glutamate decarboxylase mutant disclosed by the invention has a very wide application prospect in efficient production and preparation of gamma-aminobutyric acid.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Cloning, expression and application of Lactobacillus brevis glutamate decarboxylase gene
InactiveCN102080090AOvercoming rateOvercome the cycleFermentationLyasesEscherichia coliRestriction enzyme digestion
The invention discloses cloning, expression and application of a Lactobacillus brevis glutamate decarboxylase gene. The gene is derived from Lactobacillus brevis CGMCC No.1306, and is obtained by amplifying a Lactobacillus brevis genome DNA through PCR (polymerase chain reaction); and the full length of the gene is 1407bp. BamH I and EcoRI restriction enzyme recognition sequences are respectively added to both ends of the gene; and the gene is connected with pET-28a(+) which is digested by the same restriction enzymes, and is converted into colibacillus expression host bacteria BL21 (DE3), thereby realizing the recombinant expression in the colibacillus; and the molecular weight of the expression product glutamate decarboxylase is 53538.6Da. The recombinant glutamate decarboxylase, or the engineering bacteria for expressing the recombinant glutamate decarboxylase can convert L-glutamic acid or salt thereof into gamma-aminobutyric acid by decarboxylation, and has the advantages of high conversion efficiency, high product purity and high production efficiency.
Owner:NINGBO INST OF TECH ZHEJIANG UNIV ZHEJIANG
High-r-aminobutyric-acid-content highland-barley red yeast and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102885303AIncrease contentIncreased r-aminobutyric acid contentFood preparationBiotechnologyGlutamate decarboxylase
The invention discloses a high-r-aminobutyric-acid-content highland-barley red yeast and a preparation method thereof, which belong to the field of biotechnical foods, and particularly relate to a highland-barley red yeast and a preparation method thereof. The highland-barley red yeast is prepared through the following steps of: preparing a slant medium, preparing a seed medium, preparing highland barley embryo buds, preparing a highland barley embryo bud medium, preparing a monascus fermentation seed liquid, inoculating, fermenting and drying. The high-r-aminobutyric-acid-content highland-barley red yeast and preparation method thereof disclosed by the invention have the beneficial effect that the natural r-aminobutyric acid content is improved through using a two-step method: the first step is implemented through catalyzing a glutamic acid or sodium glutamate to be converted into an r-aminobutyric-acid under the action of glutamic acid decarboxylase in the processes of highland barley sprouting and cultivating; and the second step is implemented through combing monascus with highland barley embryo buds, generating a metabolic product r-aminobutyric acid by using a characteristic that a starchiness part in highland barleys is taken as the nutrition metabolism energy of the monascus in the growth and metabolism processes of the monascus, and carrying out biological transformation on excess sodium glutamate, thereby improving the r-aminobutyric acid content.
Owner:西藏月王药诊生态藏药科技有限公司
Method for producing gamma-aminobutyric acid enriched high milled rice, and product thereof
InactiveCN1751599AAvoid problems such as difficult to controlHigh activityFood preparationGlutamate decarboxylaseGamma-Aminobutyric acid
A process for preparing the refined rice rich in gamma-aminobutanoic acid (GABA) includes such steps as preparing the culture liquid from CaCl2, sodium glutamate or glutamine, ascorbic acid or lactic acid, and B6 proportionally, immersing the long-grained non-glutinous rice grains in it, culturing while filling gas until they are germinated and rich in GABA, drying and milling.
Owner:建昊(南京)健康科技有限公司
Process for the production of gamma-aminobutyric acid
The present invention relates to a novel method for the fermentative production of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) by cultivating a recombinant micro-organism expressing an enzyme having a glutamate decarboxylase activity. The present invention also relates to corresponding recombinant hosts, recombinant vectors, expression cassettes and nucleic acids suitable for preparing such hosts as well as to a method for preparing polyamides making use of GABA as obtained fermentative production.
Owner:BASF AG
Recombinant virus with coexpression of anthropogenic glutamate decarboxylase and cell factor
InactiveCN101586096ANervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsGlutamate decarboxylaseAdeno associate virus
The invention relates to a recombinant virus containing a gene expression box expressing an anthropogenic GAD gene and a cell factor, in particular to a method for constructing a recombinant adeno-associated virus with the coexpression of an anthropogenic GAD 65 gene and a GDNF gene, an application and a meaning thereof. Anthropogenic GAD 65 gene and the GDNF gene protein products generated by the expression of the recombinant virus have favorable synergistic effect on the treatment of diseases relative to Parkinson's disease and the central nervous system and have important values for treatment of relative diseases.
Owner:王尚武 +2
Method for producing gamma-aminobutyric acid by whole cell transformation method
InactiveCN109722402AEasy to operateLow costBacteriaMicroorganism based processesHeterologousBacillus megaterium
The invention discloses a method for producing gamma-aminobutyric acid by a whole cell transformation method. Corynebacterium glutamicum is used as a production bacterial strain, glutamate decarboxylase of bacillus megaterium is in heterologous expression, and through high-density fermentation culture, protein over-expressed corynebacterium glutamicum thalli cells are obtained. L-glutamic acid orL-glutamate is used as a substrate, and the gamma-aminobutyric acid is produced through corynebacterium glutamicum whole cell catalyzing. According to the method disclosed by the invention, glutamatedecarboxylase high in catalytic activity and a production bacterial strain namely the corynebacterium glutamicum in food safety grade are used for producing the gamma-aminobutyric acid, and the methodhas the advantages that the yield of the gamma-aminobutyric acid is high, transformation liquid is single in ingredients, the production cycle is short, the operation is simple, the production cost is low, and potential safety hazard does not exist.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Short lactobacillus producing gamma-aminobutyric acid and use thereof
InactiveCN1673351AThere are no security risksBacteriaFermentationGlutamate decarboxylaseMicroscopic observation
The present invention discloses one kind of gamma-aminobutyric acid producing lactobacillus brevis and its use. The lactobacillus brevis has preservatioin number of CGMCC No. 1306; exhibits pairs or chains; and has no motion, no spore, small colony and smooth surface. It belongs to Gram positive bacteria and facultative anaerobe, and may be used in producing gamma-aminobutyric acid. By means of biological synthesis process, the high activity glutamate decarboxylase connected in the lactobacillus brevis and sodium L-glutamate as substrate, the sodium L-glutamate is decarboxylated to produce gamma-aminobutyric acid and CO2. Thus produced gamma-aminobutyric acid is safe in food level.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Preparation method for enriching gamma-aminobutyric acid by using fixed rice bran glutamic acid decarboxylase
InactiveCN101265487ARealize comprehensive utilizationScientific and reasonable designOn/in organic carrierFermentationFood additiveGlutamate decarboxylase
The invention relates to a preparation method of enriching GABA by immobilized rice bran glutamate decarboxylase, and belongs to the technology field of the deep processing of the rice bran. In the method, the rice bran which is byproducts obtained after paddies are processed is used as raw material; the rice bran is mixed with sodium alginate solution with certain concentration and evenly stirred after being crushed and screened, and then is put in a balling device; CaCl2 solution is dropwise dropped into the mixed solution to act spherulization; ball bodies are sclerotized; the redundant CaCl2 and the rice bran which is not immobilized are washed, so that the immobilized rice bran glutamate decarboxylase is obtained; the immobilized rice bran glutamate decarboxylase is mixed with PBS buffer solution, sodium glutamate is added in and used as zymolyte, the concentration of the sodium glutamate is 0.01 to 0.05mol / l, the mixed solution reacts in a table concentrator under the temperature of 45 DEG C to obtain GABA enriched solution, and products are obtained after being dried. The protein content and the sugar content thereof are only a tenth part of the products which are obtained by adopting a traditional method of enriching the GABA by directly utilizing the rice bran; the products obtained by the method can be used as functional food additives; the efficacies of lowering blood pressure, calming, aiding sleeping, protecting liver, etc. can be realized; the preparation method has scientific and reasonable design, and has great significance to realize the comprehensive utilization of rice bran resources and increase the added value thereof.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method for manufacturing tartary buckwheat tea
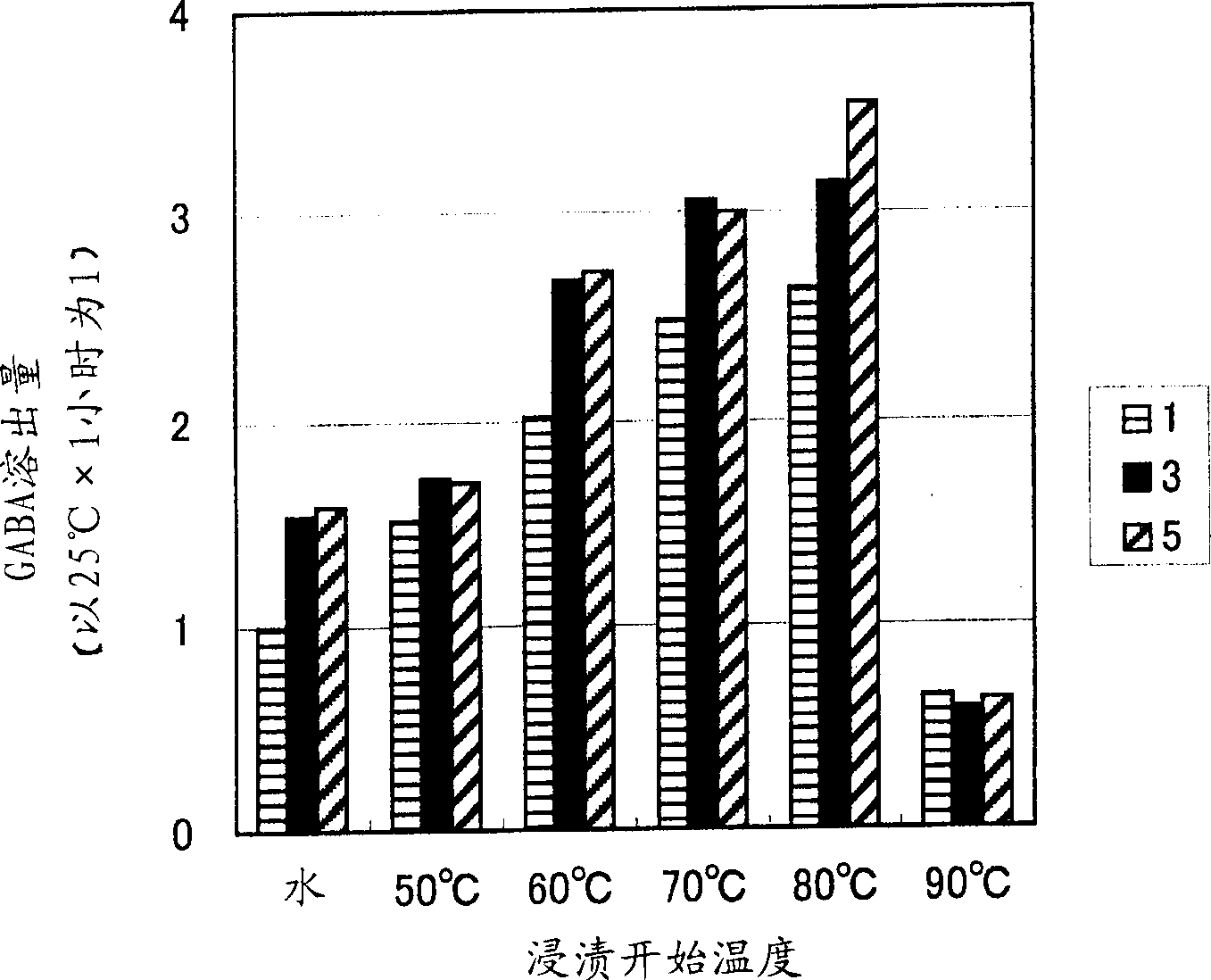
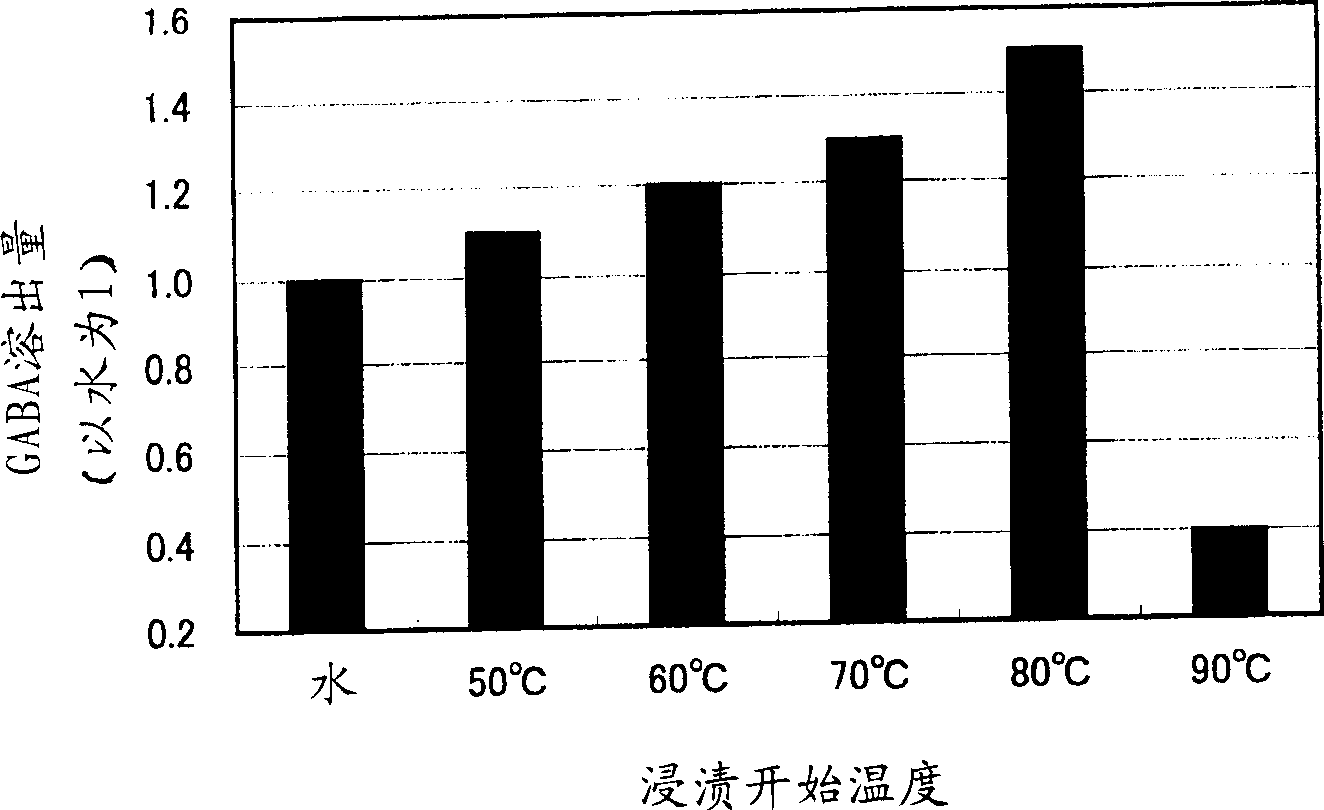
The invention provides a method for producing Tartary buchwheat tea enriching such a pharmaceutical component as [gamma]-amino butyric acid (GABA). The method for producing Tartary buchwheat tea comprises the following process: soaking Tartary buchwheat grains in hot water having initial temperature of 50-80 DEG C followed by steaming the Tartary buchwheat grains; drying the steamed Tartary buchwheat grains followed by separating seeds from husks of the grain to make the seed Tartary buchwheat tea. The Tartary buchwheat grains are soaked in the hot water having the initial temperature of 50-80 DEG C so that glutamic acid decarboxylase contained in the Tartary buchwheat is activated and thereby glutamic acid is changed into [gamma]-aminobutyric acid in the Tartary buchwheat, and thereby an elution amount of the [gamma]-aminobutyric acid is increased by 3 times as that when soaked in water having initial temperature of 25 DEG C.
Owner:SHOKUHIN SANGYO HIGH SEP
Glutamic acid decarboxylase mutant with enhanced pH stability and application thereof
ActiveCN105296456AImprove the stability of enzyme activitySuitable for industrial production needsFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionGlutamate decarboxylaseRecombinant escherichia coli
The invention discloses an acid-stable glutamic acid decarboxylase (GAD) mutant with pH stability migrating to neutral range, and belongs to the field of biological engineering. The encoding gene of glutamic acid decarboxylase derived from actobacillus plantarum GB01-21 glutamic acid decarboxylase is subjected to site-specific mutagenesis, and the glutamate E on the 89th site is mutated to arginine R or alanine A. The glutamic acid decarboxylase mutant has relative enzyme in pH value of 6.5 increased from the original 38% up to 72% or 84%, and the enzyme activity stability in the neutral pH range is increased significantly. For the transformation with a glutamic acid decarboxylase mutant synthesized by recombinant escherichia coli, the GABA yield reaches 260 g / L, and the yield is 99.6%; and for the transformation with a glutamic acid decarboxylase mutant synthesized by recombinant Corynebacterium glutamicum, the GABA yield reaches 116 g / L, and the yield is 99.5%. The invention reduces the fermentation equipment loss under acidic conditions, and lays foundation for the efficient synthesis of gamma-aminobutyric acid.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
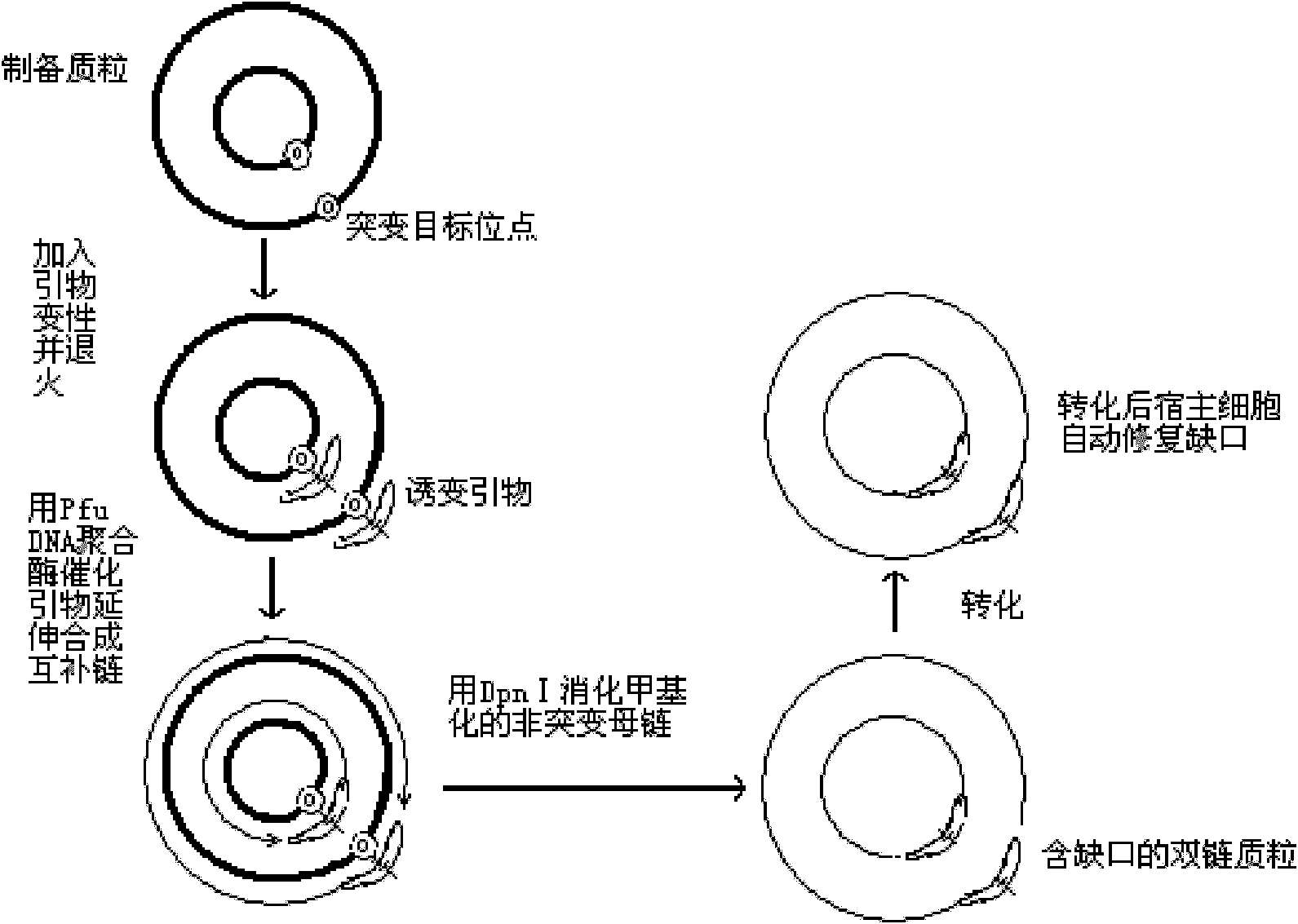
Variant gene of glutamate decarboxylase and purpose thereof
InactiveCN101914560ASolve the problem of low catalytic activityBroaden the optimum pH rangeFungiBacteriaSolubilityEnzyme Gene
The invention discloses a variant gene of glutamate decarboxylase. DNA sequence of the gene is SEQ ID: No.1. By site-directed mutagenesis on the basis of coded wild GAD enzyme gene, the variant gene according to the invention enhances catalytic activity of the corresponding variant enzyme thereof in neutral pH value and widens the most proper scope of pH value of enzyme, so that the GABA generation ability of the corresponding variant enzyme through the catalysis of glutamic acid on condition of pH=6.0 is twice as much as that of wild-type enzyme. As the most proper scope of pH value of enzyme is widened, catalysis reaction can be conducted on condition that pH is higher than 5.0, thus the problem that the solubility of substrate, i.e. glutamic acid, is low on condition of pH from 4.0 to 5.0 is solved, and conditions are created for GABA production by biotransformation of enzyme.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
High-yield gamma-aminobutyric acid lactobacillus and screening method thereof
InactiveCN104480187ASolve the problem of adding gamma-aminobutyric acidSolve the problem of low gamma-aminobutyric acid contentBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementGlutamate decarboxylaseGamma-Aminobutyric acid
The invention discloses a high-yield gamma-aminobutyric acid lactobacillus and a screening method thereof, belonging to the field of biotechnology. The high-yield gamma-aminobutyric acid lactobacillus is prepared by the following steps: 1) fermentation culture of lactobacillus for test; 2) preliminary screening of gamma-aminobutyric acid producing bacteria according to whether the lactobacillus has glutamate decarboxylase activity; and 3) secondary screening of high-yield gamma-aminobutyric acid lactobacillus. After screening with the method, the content of gamma-aminobutyric acid in the fermentation liquid after the fermentation culture reaches 5.025g / L, and the conversion rate of L-sodium glutamate reaches 90.05% of lactobacillus plantarum. The method disclosed by the invention can be used for solving the problem of exogenously adding gamma-aminobutyric acid or extremely low content of gamma-aminobutyric acid in traditional food, and reducing the production cost of the products.
Owner:LINYI GERUI FOOD
Glutamate decarboxylase mutant establishment improving enzyme activity and application thereof
ActiveCN105255849AIncreased potential for industrial applicationsBacteriaFermentationGlutamate decarboxylaseTyrosine
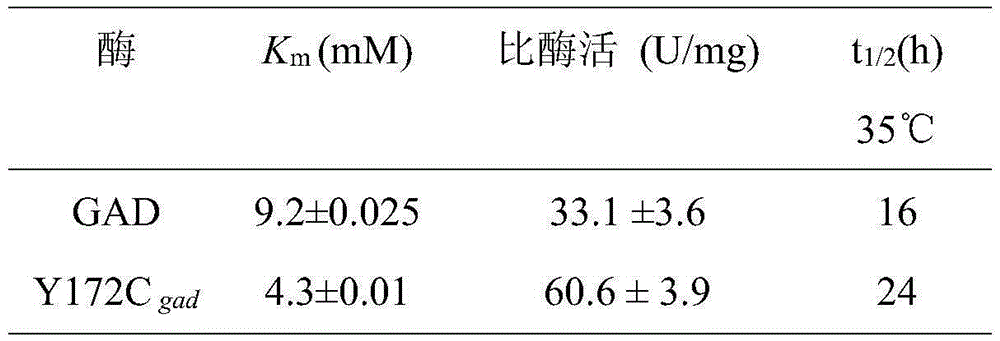
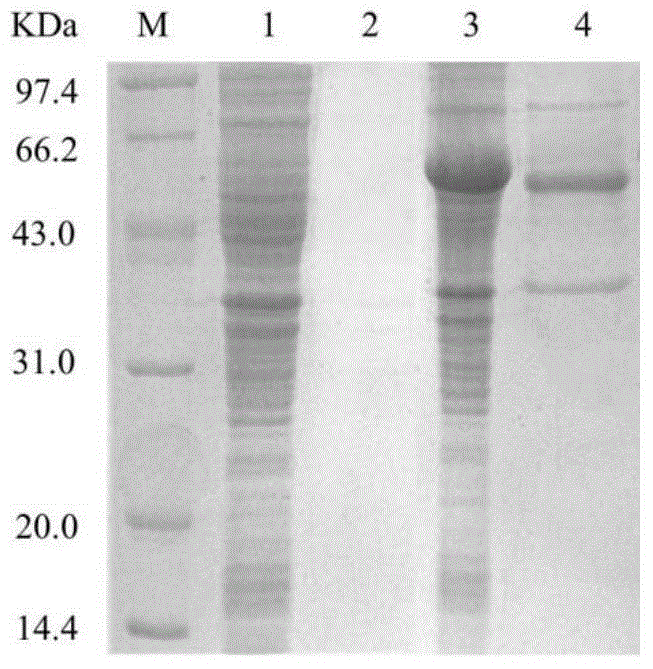
The invention discloses a glutamate decarboxylase mutant improving enzyme activity and an establishment method thereof, and belongs to the field of gene engineering. On the basis of an amino acid shown as SEQ ID NO.1, a 172 tyrosine is mutated to form cysteine. The obtained mutant is expressed in colibacillus, after being fermented for 24h in a shake flask, the enzyme activity is 28.6U / mL, the mutant enzyme activity is improved by 81 percent, compared with the original enzyme, the substrate affinity is reduced by 53 percent, the enzyme activity is improved by 83 percent, and the half-time period of the enzyme at 35 DEG C is increased from 16h to 24h. The recombinase is expressed in the colibacillus, and the glutamic acid is converted in a total cell manner for 18h to obtain 283.8g / L gamma-aminobutyric acid; the recombinase is expressed in glutamic acid coryneform bacteria, the glutamic acid is converted for 18h in a total cell manner to obtain 126.7g / L gamma-aminobutyric acid. The result shows that the 172 amino acid residue can severely influence the catalytic effect and stability of the enzyme, a foundation is set for researching the catalytic mechanism of the enzyme, and the industrial application potential of the enzyme is improved.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Clone, expression and application for lactic acid bacteria glutamic acid decarboxylase gene
InactiveCN101063144AOvercome the disadvantage of low yieldNot easy to polluteGenetic engineeringFermentationBiotechnologyRestriction enzyme digestion
The invention discloses a colony, expression and appliance of lactic acid bacteria aminoglutaric acid decarboxylase gene in food industry biotechnics domain, which is characterized by the following: coming from spittle streptococcus thermophilic subspecies (Streptococcus thermophilus) with length at 1380bp; augmenting from gene group DNA through PCR; adding NcoI and EcoRI on the two ends of the gene; limiting enzyme identification sequence; connecting to pET-DsbA of same limited enzyme alimentary; transforming expressing host bacteria BL21(DE3)pLysS of bacillus coli; realizing retooling expression in bacillus coli; getting glutamic acid decarboxylase molecule with molecular weight at 52. 4kDa; transforming L- glutamic acid decarboxylase to gamma-aminobutyric acid with retooling enzyme; providing a great amount of and high active rough enzyme for enzymatical synthesis of gamma-aminobutyric acid; decreasing cost of enzymatical synthesis of gamma-aminobutyric acid. This method possesses warm condition, which belongs to biological synthesis method.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Method for biotransformation production of gamma-aminobutyric acid with aquatic products and processing leftovers thereof as raw materials
ActiveCN103966274ALow costSuitable for industrial productionMicroorganism based processesFermentationFreeze-dryingGlutamate decarboxylase
The invention specifically relates to a method for biotransformation production of gamma-aminobutyric acid by using aquatic products and processing leftovers thereof, which belongs to the technical field of bio-processing of aquatic products. The method comprises the following steps: inoculating 0.5 to 5% (V / V) of lactic acid bacteria with glutamic acid decarboxylase activity into a medium, carrying out fermentation culture at a fermentation temperature of 30 to 35 DEG C at a rotating speed of 100 to 500 r / min for 20 to 50 h so as to allow a viable count in fermentation broth to be as high as 10<6> to 10<7> cfu / ml and standing the fermented lactic acid bacteria for subsequent usage; carrying out centrifugation or filtering on transformation liquid, taking supernatant and subjecting the supernatant to reduced pressure concentration so as to prepare a GABA crude extract; and removing impurities in the crude extract with absolute ethyl alcohol by using a precipitation method, then carrying out separation and purification by successively using a macroporous resin, Sephadex gel and a cation exchange resin and subjecting a GABA product obtained after separation and purification to rotary evaporation and freeze drying so as to obtain a crystal. With the method, a novel application direction for aquatic products and processing leftovers thereof is opened up, and theoretical bases are provided for comprehensive and high-value utilization of aquatic products.
Owner:中科海洋生物研究院盘锦有限公司
Efficient production method of gamma-aminobutyric acid
ActiveCN104830745ASimplify separation and purification proceduresEfficient synthesisBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliGlutamate decarboxylase
The invention discloses an efficient production method of gamma-aminobutyric acid, and belongs to the field of fermentation engineering. In the provided method, a twin-arginine signal peptide gene (torA) and a glutamic acid decarboxylase gene (gadB) are fused and transferred to a escherichia coil BL21(DE3) host so as to obtain a recombinant bacterium pET20b(+)-torA-gadB / E.coli BL21(DE3) that can secret and express glutamic acid decarboxylase. The extracellular glutamic acid decarboxylase activity level of the recombinant bacterium in a shaking bottle can reach 5.11 U / mL, and 15.82 U / mL in a fermentation tank. By using the system and a substrate (sodium glutamate monohydrate), the output of gamma-aminobutyric acid can reach 203.7 g / L.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Recombinant engineering bacterium with surface exhibiting and expressing glutamic acid decarboxylase as well as construction method and application of recombinant engineering bacterium
ActiveCN106754610AAvoid barrier effectImprove apparent vitalityFungiBacteriaGlutamate decarboxylaseGamma-Aminobutyric acid
The invention relates to a recombinant engineering bacterium with the surface exhibiting and expressing glutamic acid decarboxylase as well as a construction method and application of the recombinant engineering bacterium. The preparation method mainly comprises the steps of constructing ice nucleaiton protein-based recombinant engineering bacterium with the surface exhibiting glutamic acid decarboxylase, inoculating a glutamic acid decarboxylase recombinant engineering bacterium into a culture medium, carrying out shaking culture, adding IPTG or lactose to induce the expression of glutamic acid decarboxylase, and collecting recombinant bacteria with the surface exhibiting glutamic acid decarboxylase, wherein the recombinant bacteria with the surface exhibiting glutamic acid decarboxylase is used for preparation of gamma-aminobutyric acid from the substrate glutamic acid decarboxylation. According to the preparation method, a permeabilization treatment process required in whole-strain expression of conventionally expressed endoenzyme is avoided, recombinase is exhibited and expressed on the surface of the recombinant bacteria, and a substrate can be in contact with the recombinase to finish conversion without entering bacteria cells, so that the purpose of improving the expression activity of the recombinant bacteria is achieved. The preparation method is simple, convenient and low in cost, the operation is simple, and the expression activity of the recombinant bacteria can be efficiently improved.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for producing gamma-aminobutyric acid with high yield
ActiveCN108467860AIncreased enzyme activityImprove stabilityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBacillus megateriumGlutamate decarboxylase
The invention discloses a method for producing gamma-aminobutyric acid with a high yield, and belongs to the technical field of bioengineering. Glutamic acid decarboxylase derived from Bacillus megaterium is modified by protein engineering, and a modified glutamic acid decarboxylase gene is linked to a pET24a vector, and is epressed in E. coli BL21 (DE3). A recombinant strain is cultured in a fermenter for transforming glutamic acid to produce the gamma-aminobutyric acid, the wet cell addition amount is 7.0g / L, the transformation period is 8h, the yield can reach 425.0g / L, and the glutamic acid molar conversion rate is up to 99%, the space time yield of the gamma-aminobutyric acid is 53.1 g / L / h.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com