Patents
Literature
542 results about "Autoantibody production" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The causes of autoantibody production are varied and not well understood. It is thought that some autoantibody production is due to a genetic predisposition combined with an environmental trigger, such as a viral illness or a prolonged exposure to certain toxic chemicals.
Therapeutic using a bispecific antibody
Multivalent, multispecific molecules having at least one specificity for a pathogen and at least one specificity for the HLA class II invariant chain (Ii) are administered to induce clearance of the pathogen. In addition to pathogens, clearance of therapeutic or diagnostic agents, autoantibodies, anti-graft antibodies, and other undesirable compounds may be induced using the multivalent, multispecific molecules.
Owner:IMMUNOMEDICS INC
Antibody profiling for determination of patient responsiveness
InactiveUS20080026485A1Increase probabilityConvenient careDisease diagnosisDiseaseAutoimmune disease
Compositions and methods are provided for prognostic classification of autoimmune disease patients into subtypes, which subtypes are informative of the patient's need for therapy and responsiveness to a therapy of interest. The patterns of circulating blood levels of serum autoantibodies and / or cytokines provides for a signature pattern that can identify patients likely to benefit from therapeutic intervention as well as discriminate patients that have a high probability of responsiveness to a therapy from those that have a low probability of responsiveness. Additionally, serum autoantibody and / or cytokine signature patterns can be utilized to monitor responses to therapy. Assessment of this signature pattern of autoantibodies and / or cytokines in a patient thus allows improved methods of care. In one embodiment of the invention, the autoimmune disease is rheumatoid arthritis.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Methods and compositions for use in treatment of patients with autoantibody positive disease
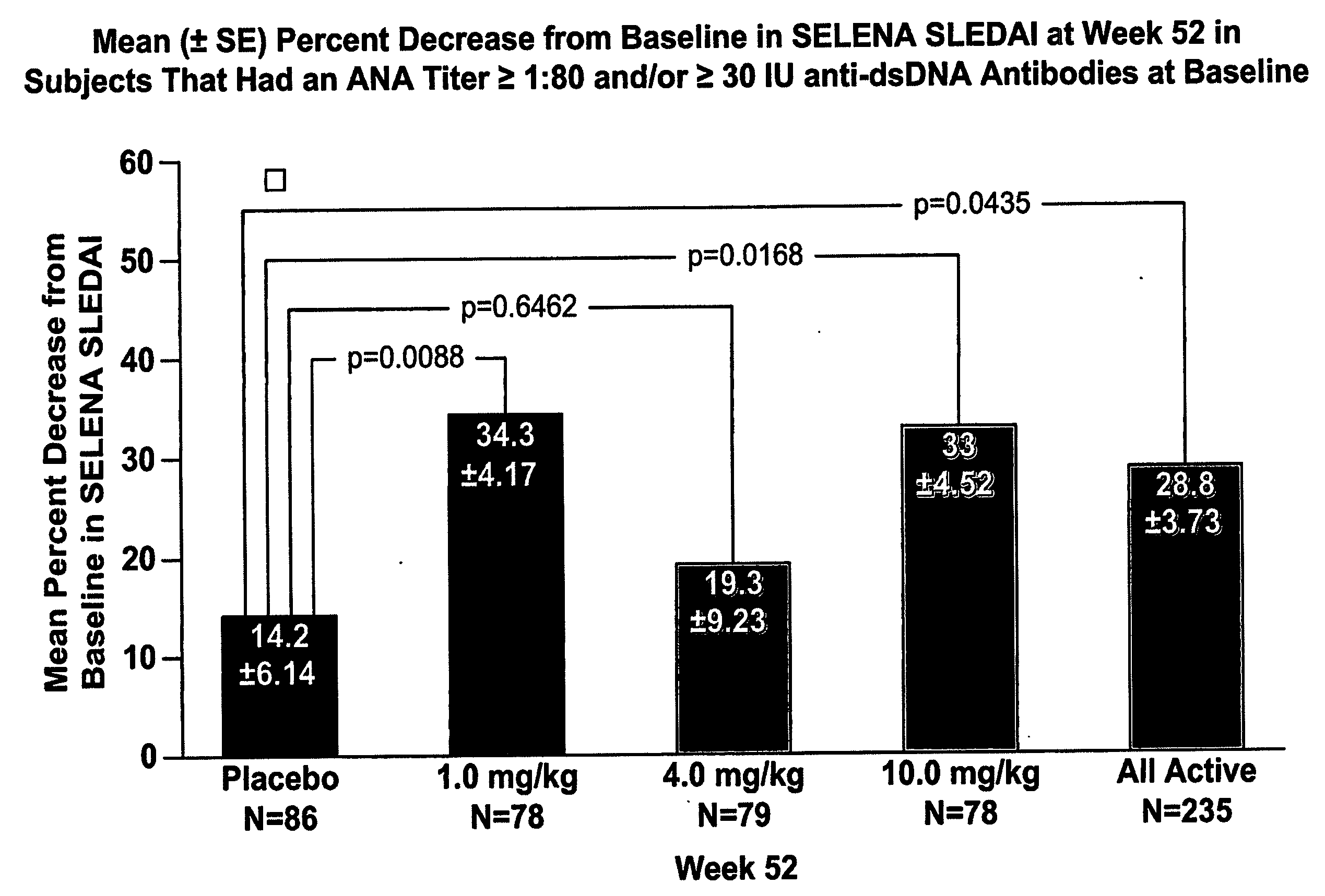
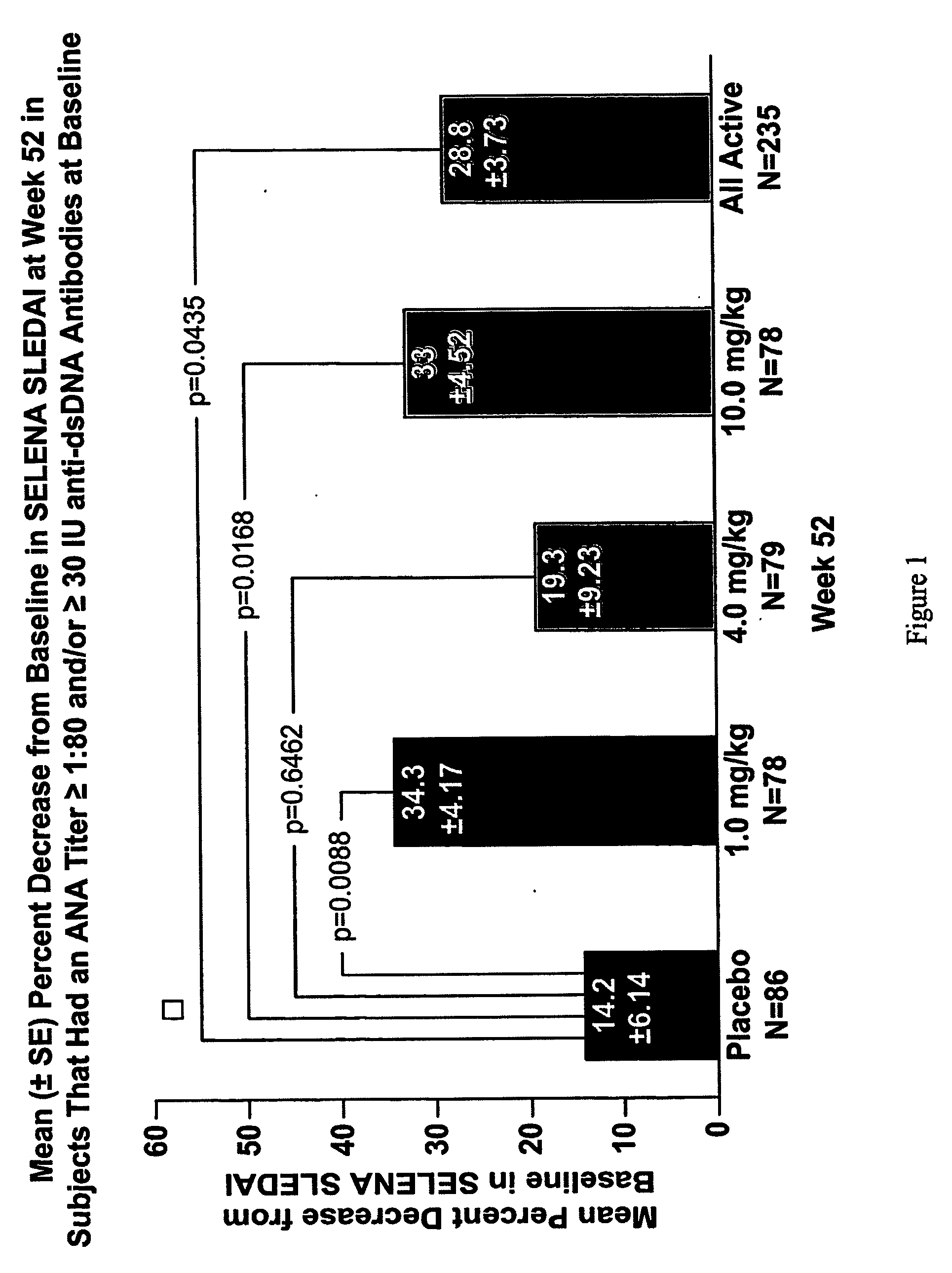
InactiveUS20070086979A1Reduce frequencyReduce in quantityPeptide/protein ingredientsAntipyreticAnti-dsDNA antibodiesSystemic lupus erythematosus
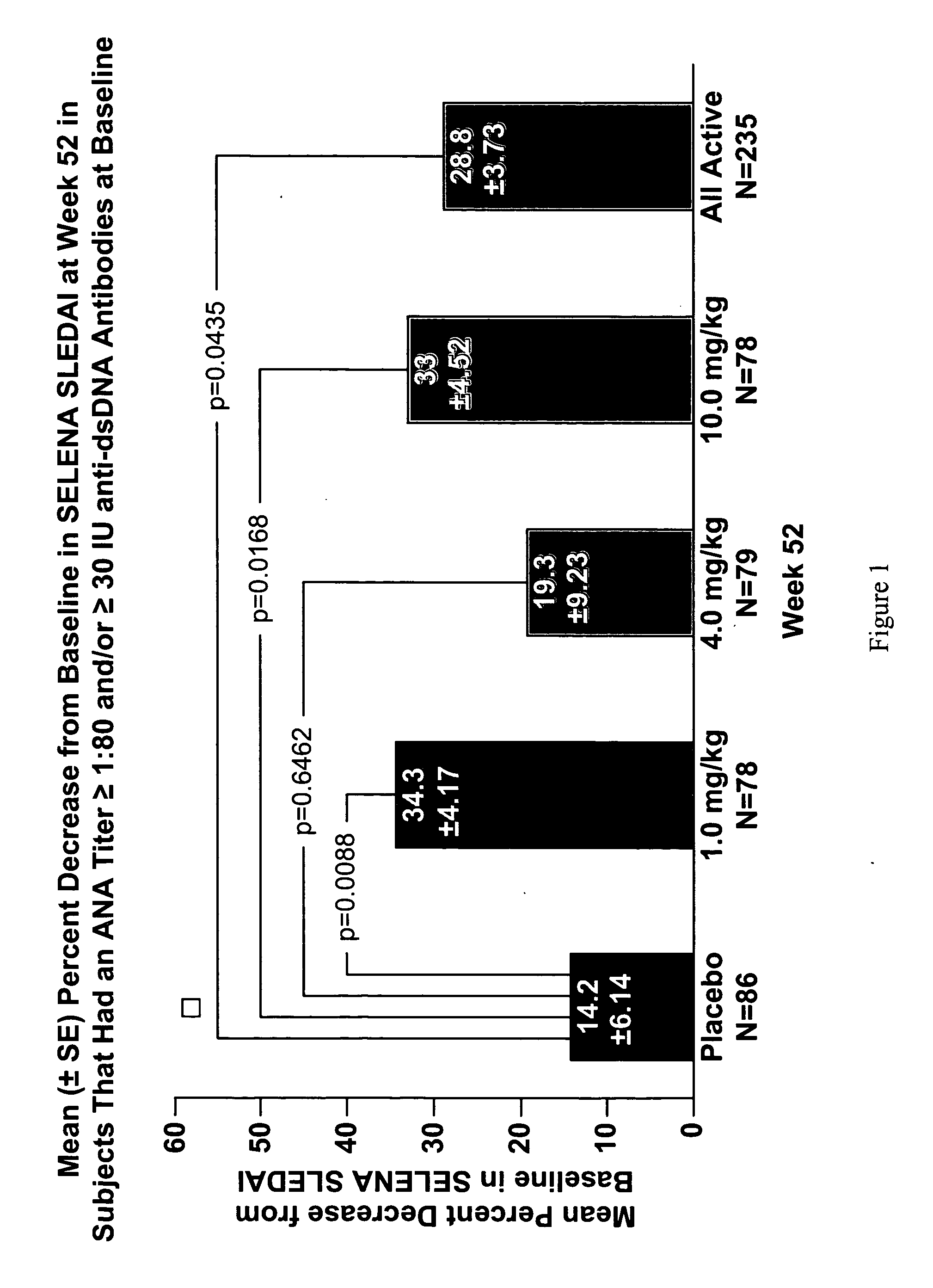
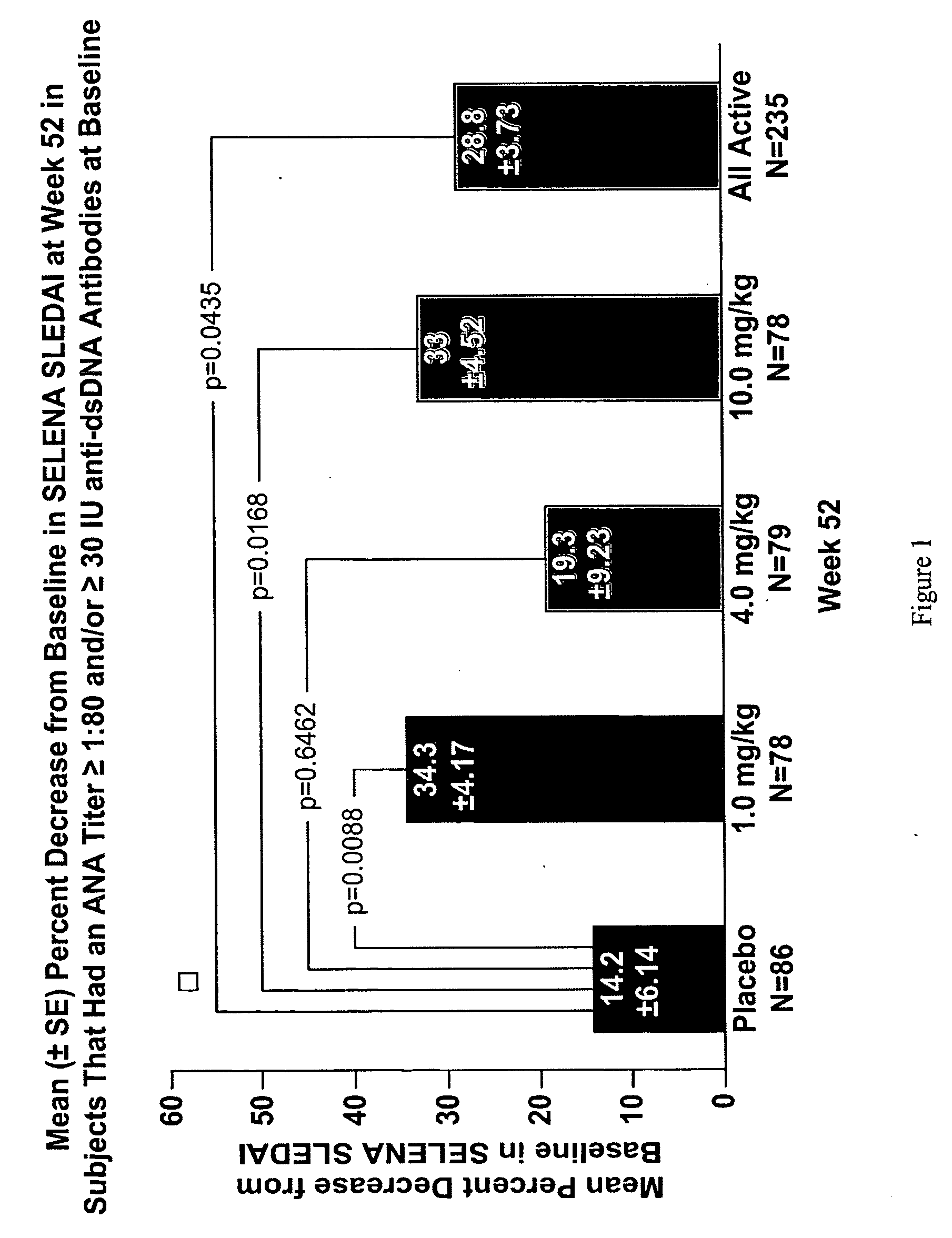
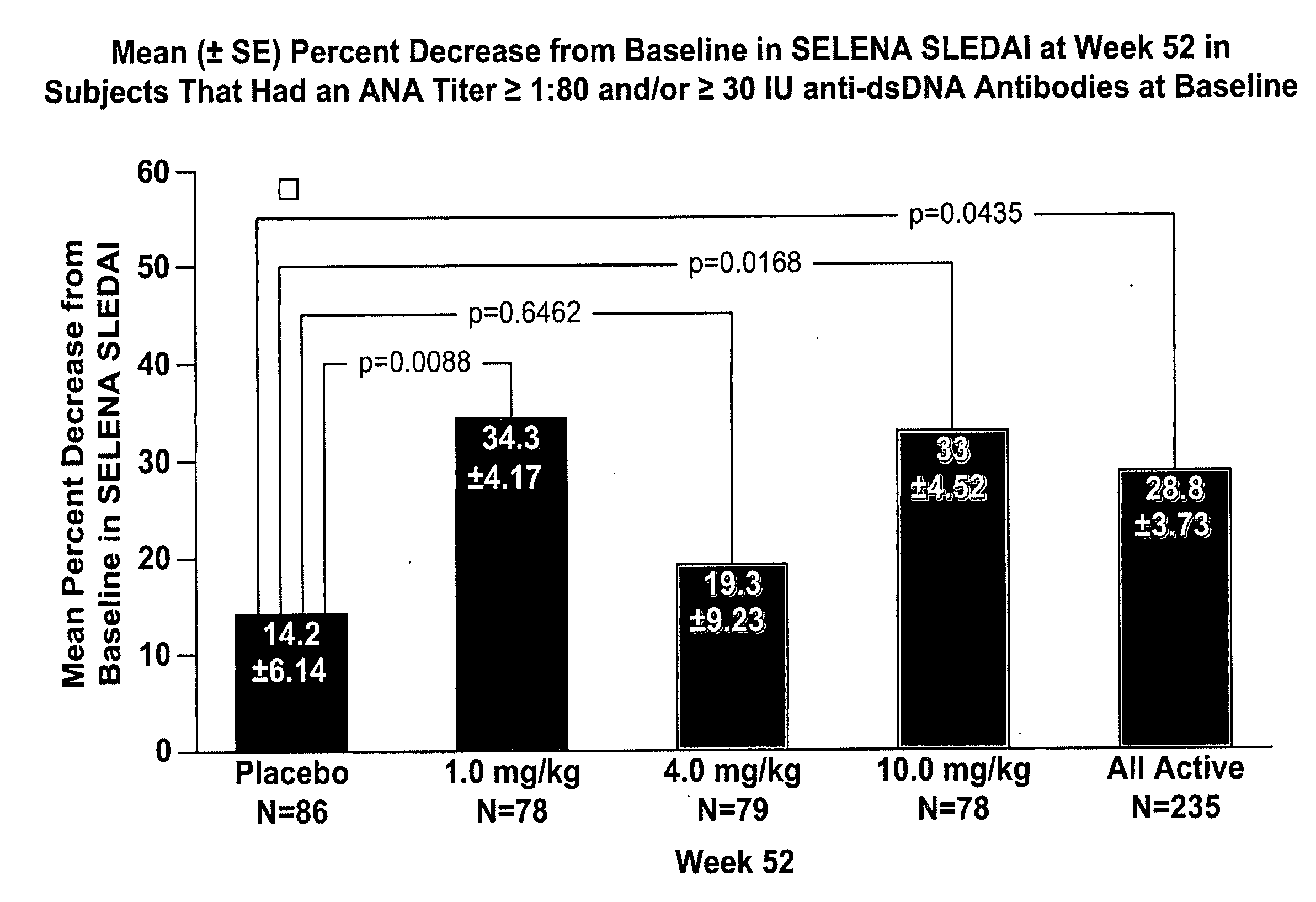
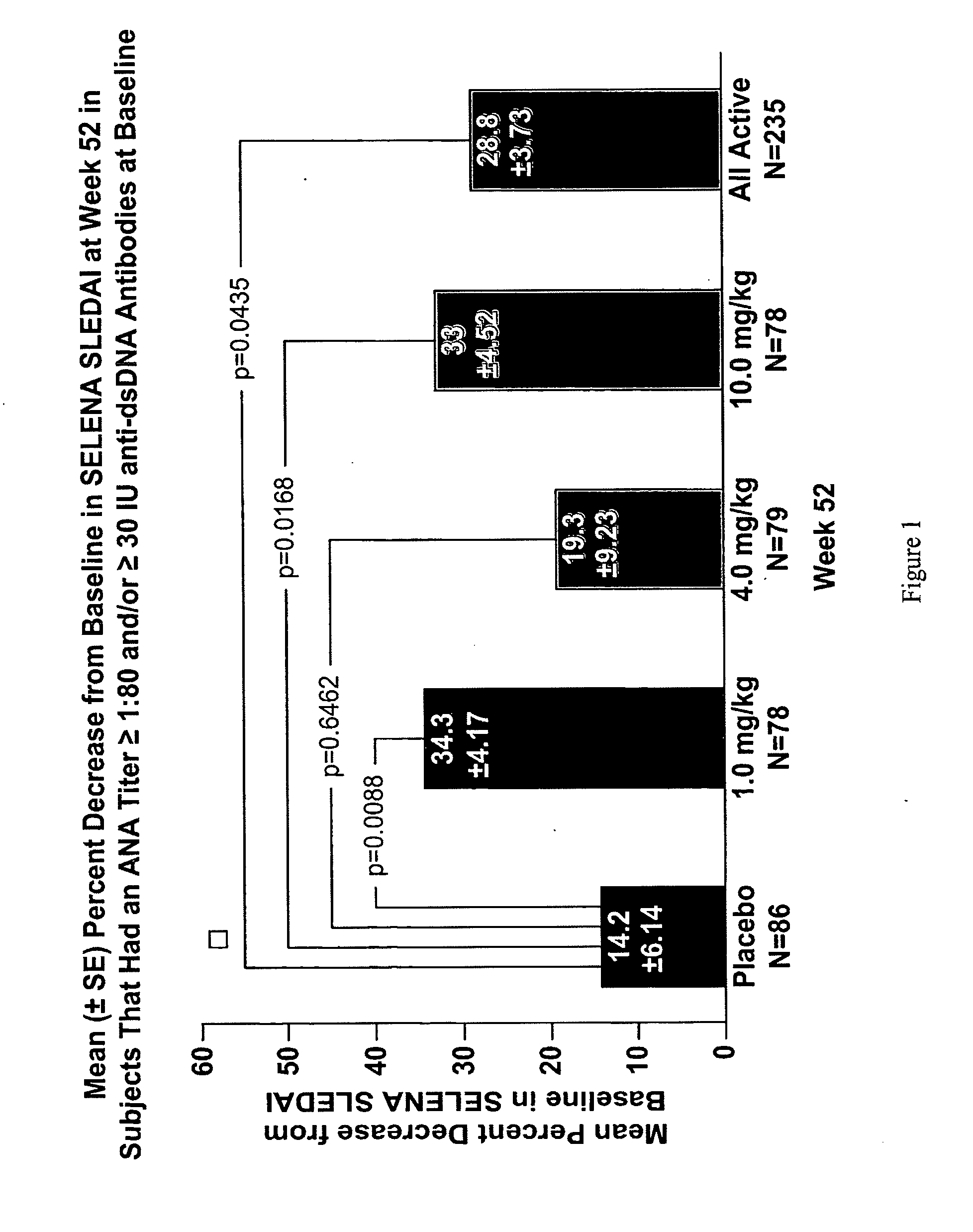
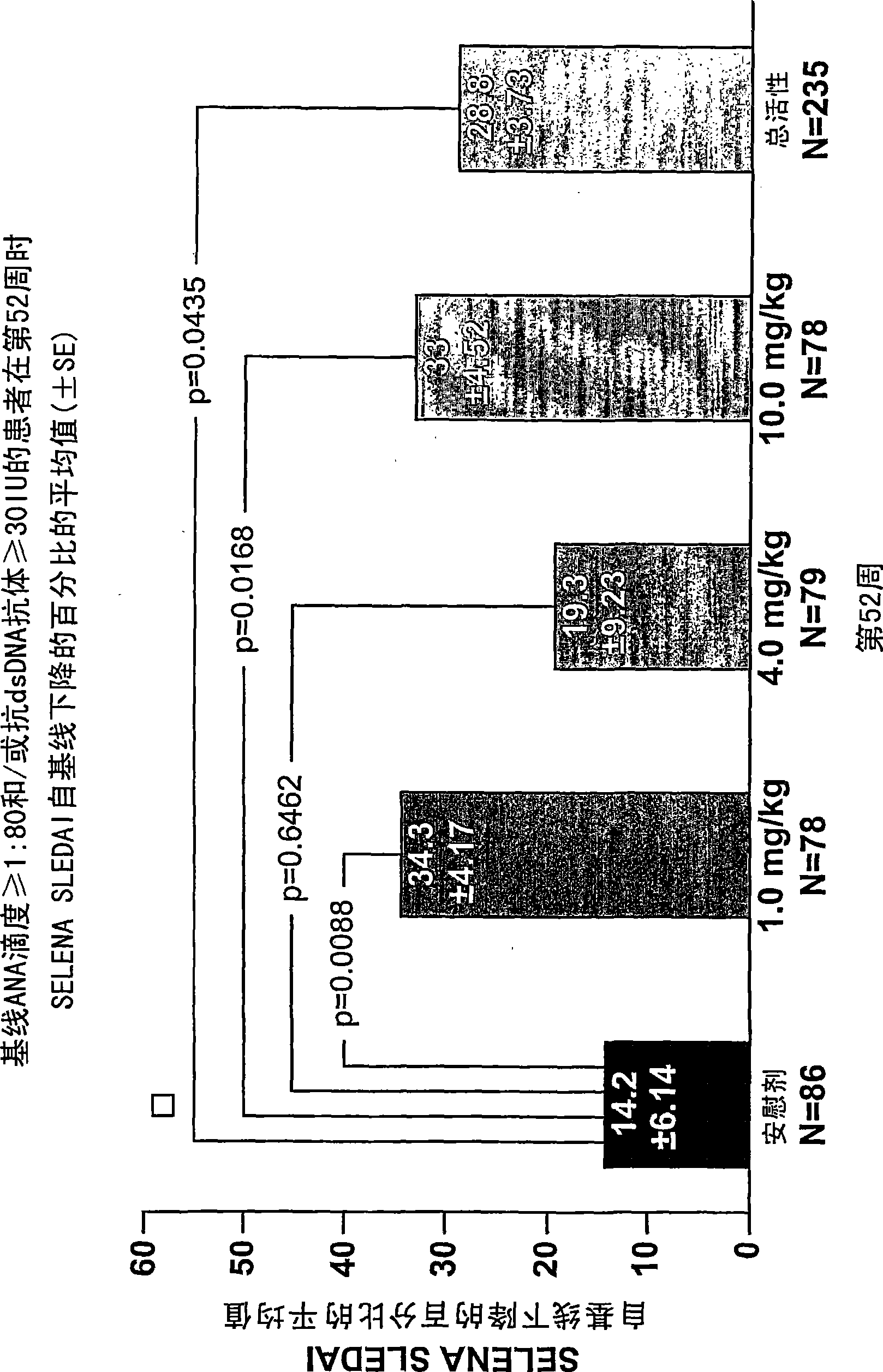
The present invention relates to methods and compositions for use in treatment of patients with autoantibody positive disease. In a specific embodiment, the present invention relates to a method of treating a patient that has an ANA titer of 1:80 or greater and / or greater than or equal to 30 IU / ml of anti-dsDNA antibodies in his / her blood plasma or serum comprising administering a therapeutically effective amount of an immunomodulatory agent, such as an antagonist of Neutrokine-alpha. Additionally provided is a method of reducing the frequency and / or quantity of corticosteroid administration to patients. In preferred embodiments, the patient has systemic lupus erythematosus. Methods for determining if a lupus patient is responding to medical treatment are also provided.
Owner:HUMAN GENOME SCI INC
Purified antigen for Alzheimer's disease and methods of obtaining and using same
The invention relates, among other things, a preparation comprising Alzheimer's disease antigen (A68), as well as methods of obtaining this purified antigen, and methods of using this purified antigen, for instance, for diagnosing Alzheimer's disease and for detecting human autoantibodies to the Alzheimer disease antigen. The antigen preparation according to the invention is purified in that it is substantially free of immunoglobulin G. The invention further relates to methods of making Alzheimer disease antigens that can be used instead of or along with the A68 antigen preparation (e.g., for diagnosing AD), such as recombinant human tau, tau isolated from various species including human, and phosphorylated recombinant human tau or isolated tau, as well as A68 anti-idiotypic antibodies.
Owner:MOLECULAR GERIATRICS
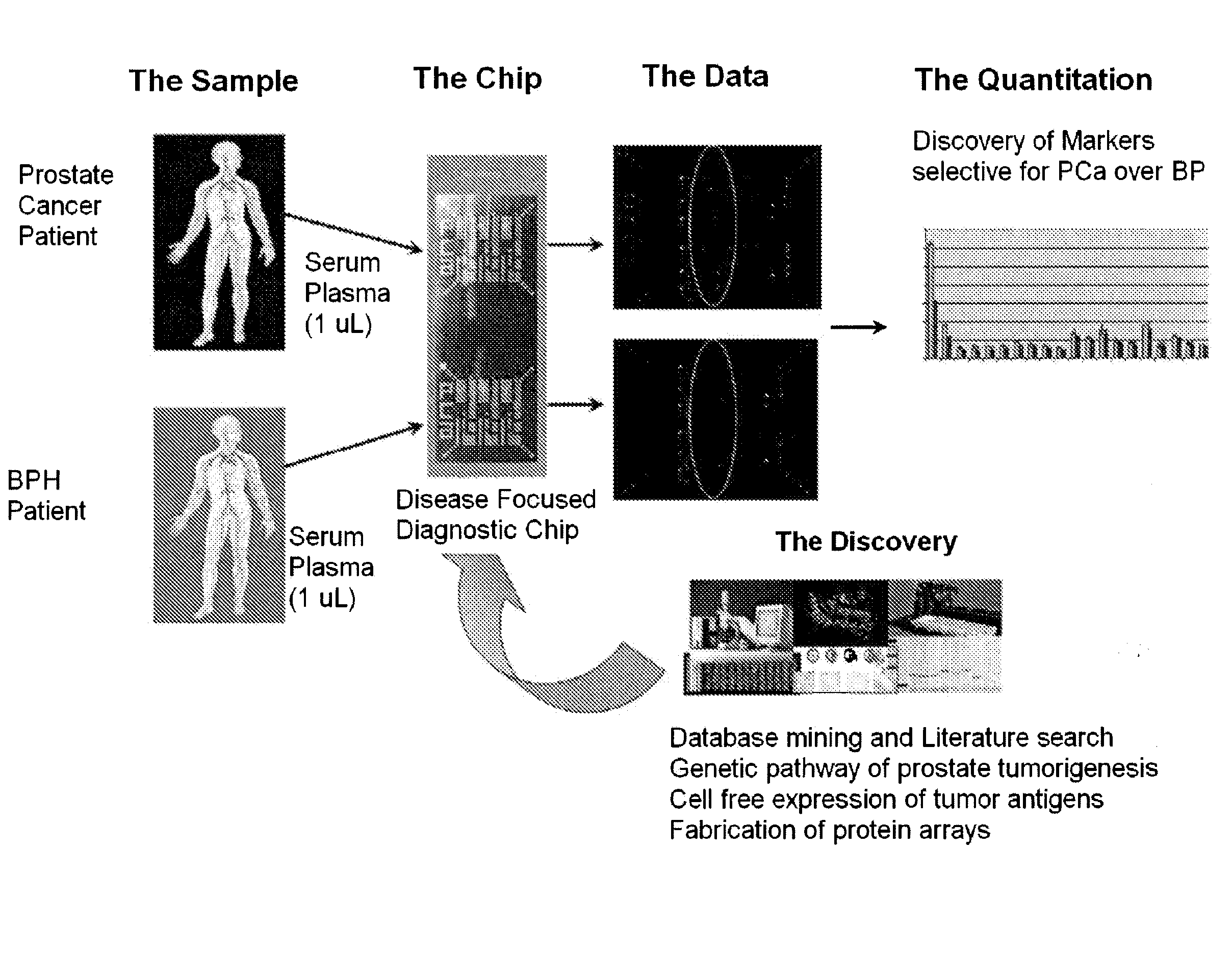
Methods and kits for detecting prostate cancer biomarkers
Provided herein are novel autoantibody biomarkers, and panels for detecting autoantibody biomarkers for prostate cancer, and methods and kits for detecting these biomarkers in the serum of individuals suspected of having prostate cancer.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
Methods and compositions for use in treatment of patients with autoantibody positive disease
ActiveUS20090148462A1Reduce frequencyReduce in quantityNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsAnti-dsDNA antibodiesSystemic lupus erythematosus
The present invention relates to methods and compositions for use in treatment of patients with autoantibody positive disease. In a specific embodiment, the present invention relates to a method of treating a patient that has an ANA titer of 1:80 or greater and / or greater than or equal to 30 IU / ml of anti-dsDNA antibodies in his / her blood plasma or serum comprising administering a therapeutically effective amount of an immunomodulatory agent, such as an antagonist of Neutrokine-alpha. Additionally provided is a method of reducing the frequency and / or quantity of corticosteroid administration to patients. In preferred embodiments, the patient has systemic lupus erythematosus. Methods for determining if a lupus patient is responding to medical treatment are also provided.
Owner:HUMAN GENOME SCI INC
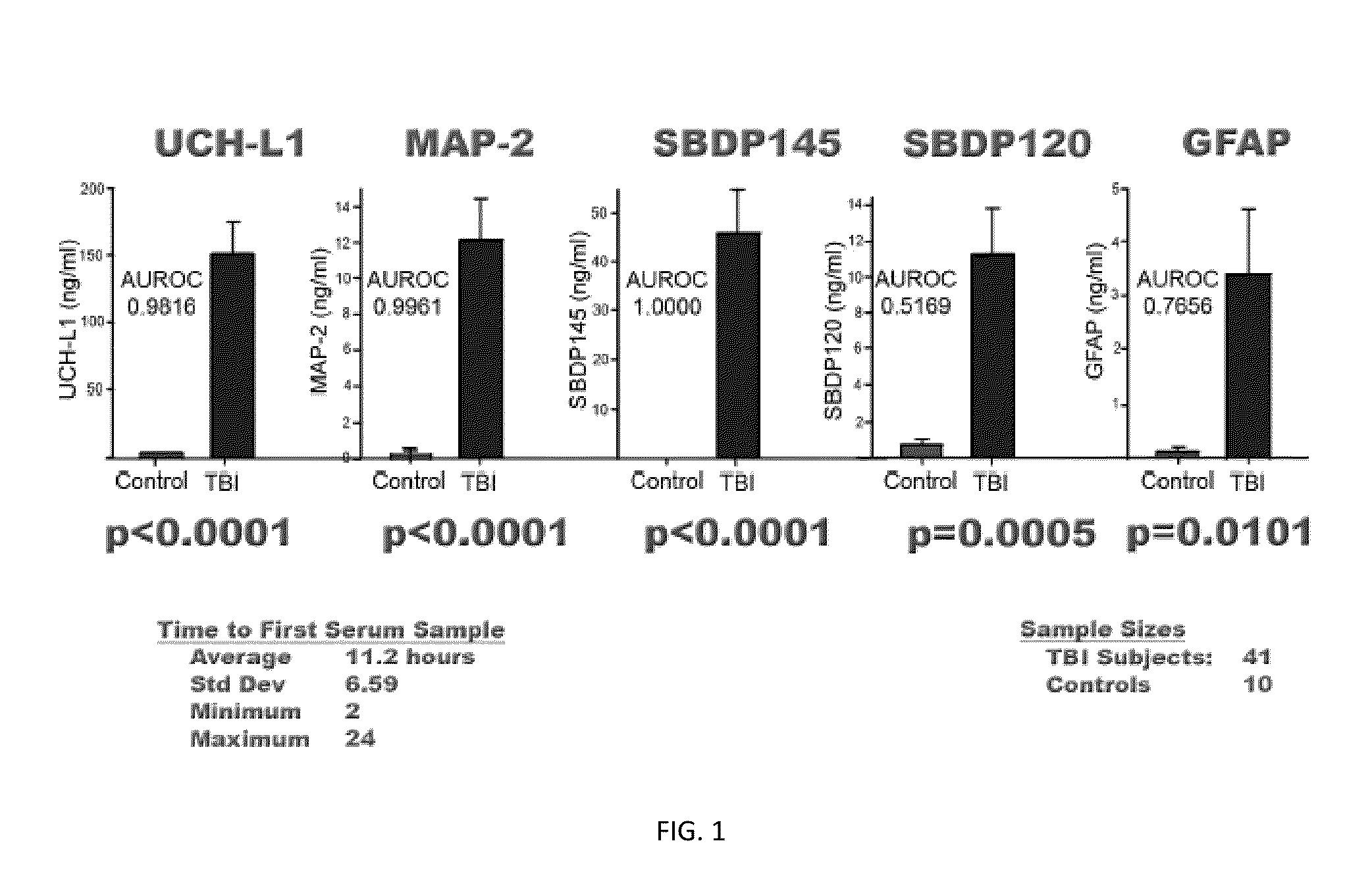
Micro-RNA, autoantibody and protein markers for diagnosis of neuronal injury
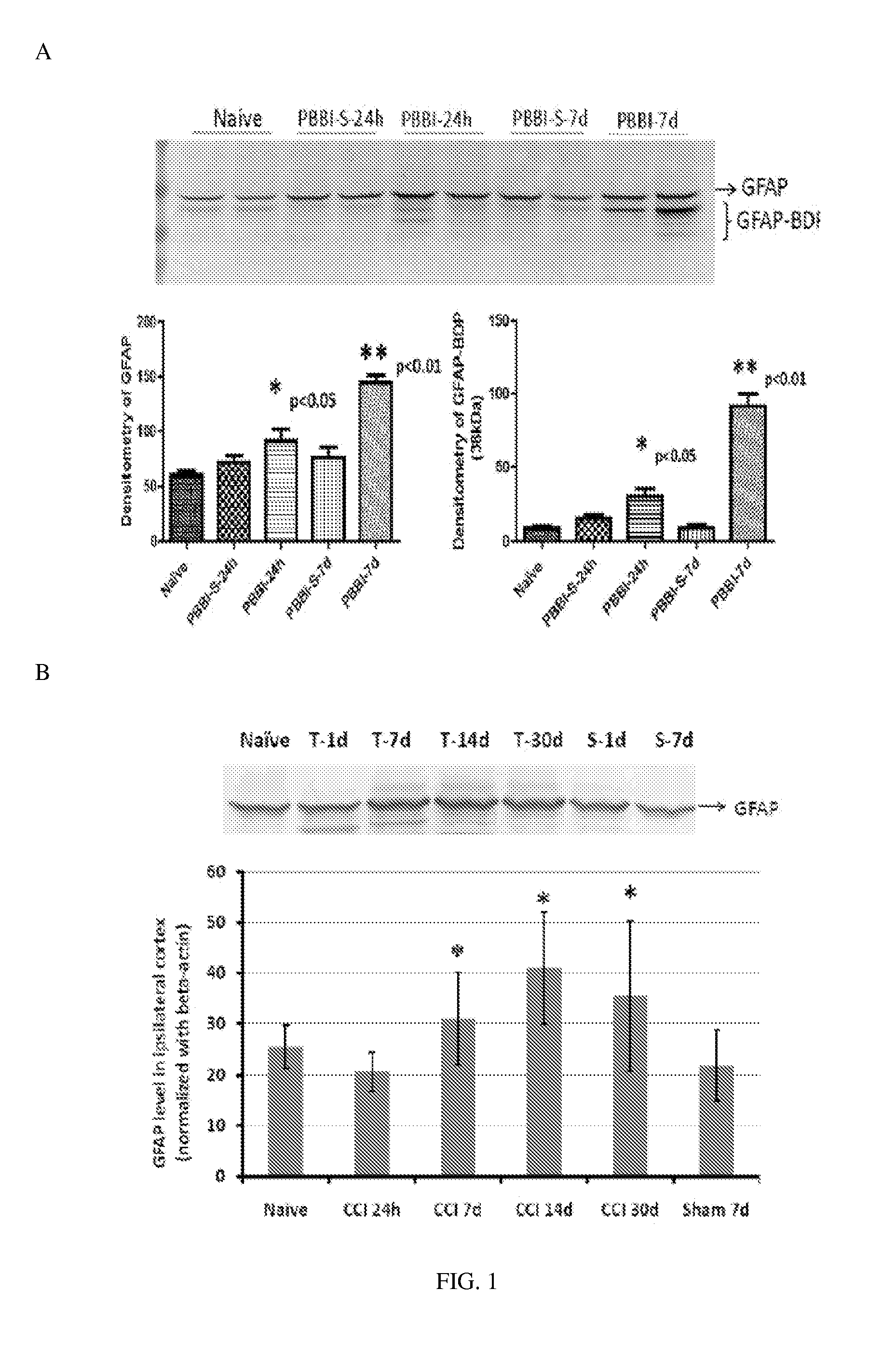
InactiveUS20130022982A1Microbiological testing/measurementImmunoglobulins against animals/humansProtein markersInjury brain
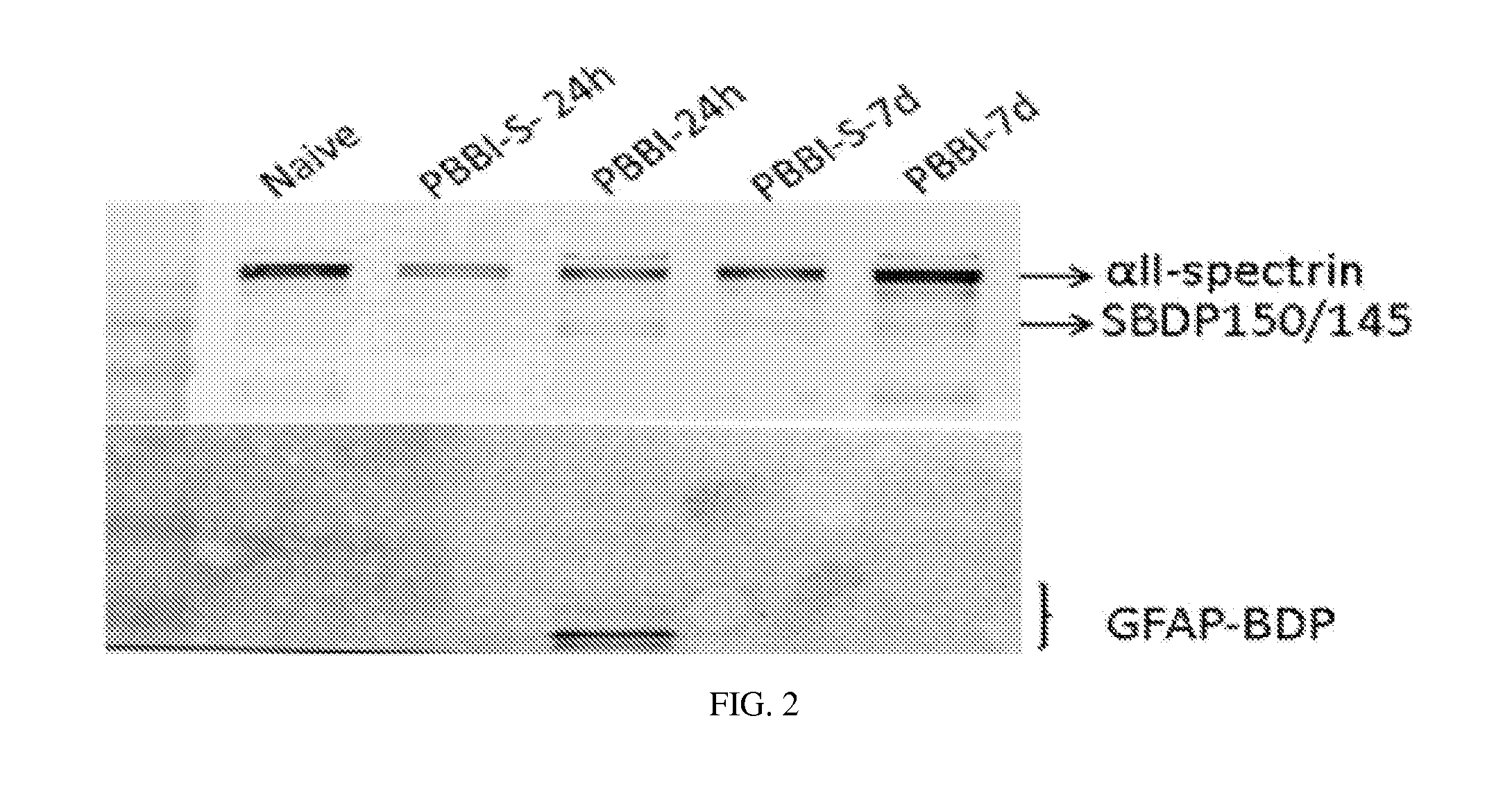
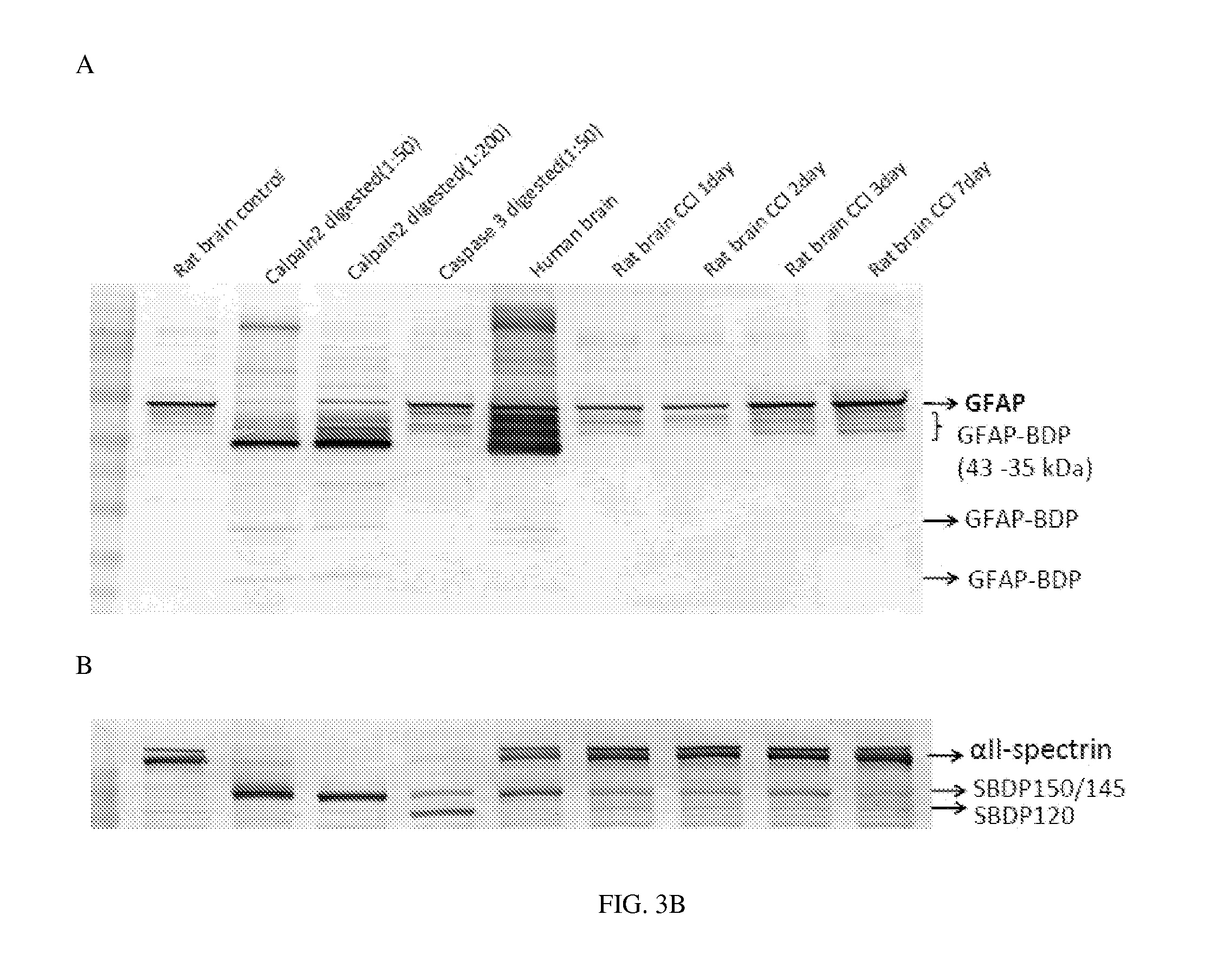
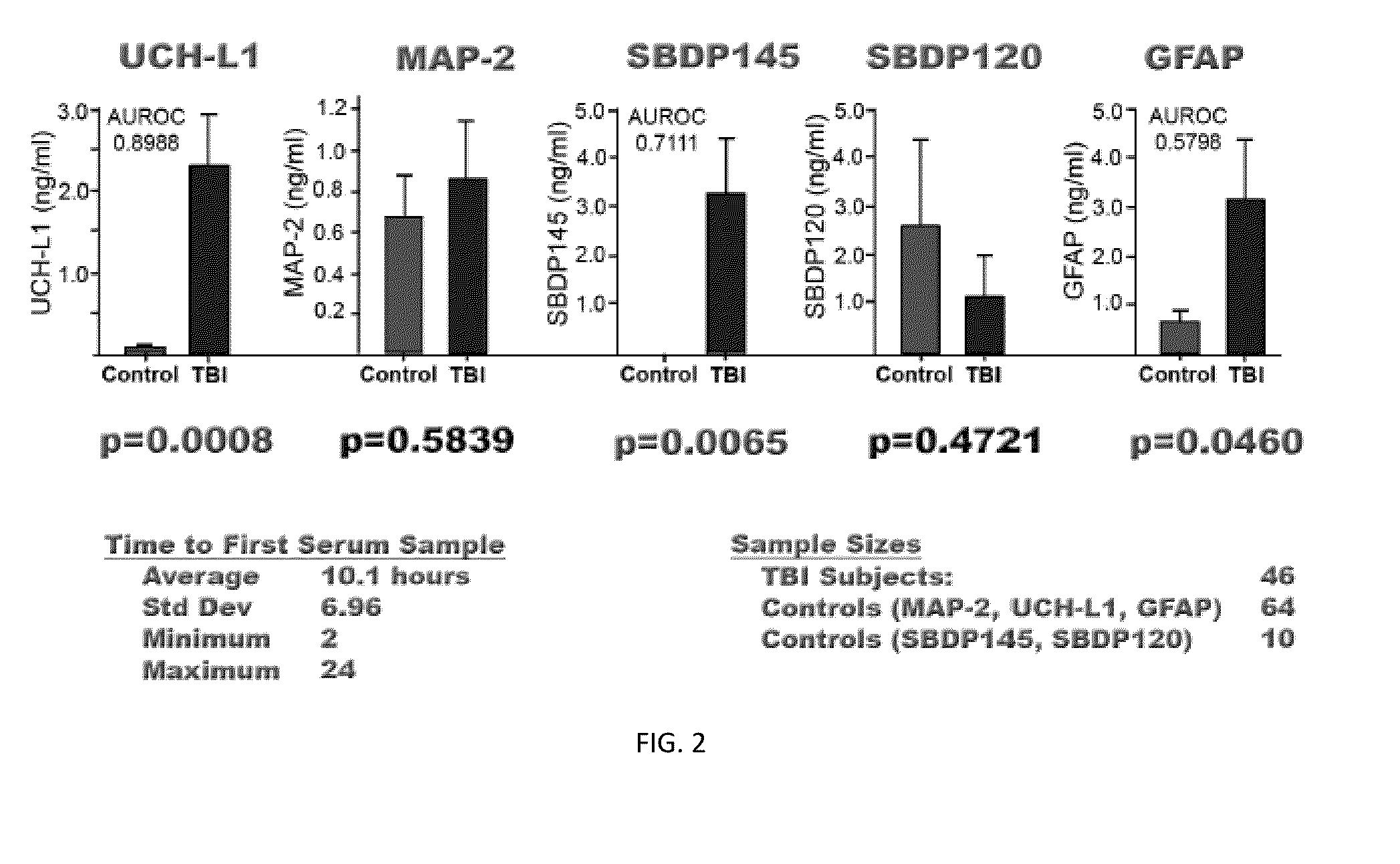
Processes and materials are provided for the detection, diagnosis, or determination of the severity of a neurological injury or condition, including traumatic brain injury, multiple-organ injury, stroke, Alzeimer's disease, Pakinson disease and Chronic Traumatic Encephalopathy (CTE). The processes and materials include biomarkers detected or measured in a biological sample such as whole blood, serum, plasma, or CSF. Such biomarkers include Tau and GFAP proteins, their proteolytic breakdown products, brain specific or enriched micro-RNA, and brain specific or enriched protein directed autoantibodies. The processes and materials are operable to detect the presence of absence of acute, subacute or chronic brain injuries and predict outcome for the brain injury.
Owner:BANYAN BIOMARKERS INC
Biomarkers for liver diseases and method for using the same
InactiveUS20050136489A1Improve accuracyHigh sensitivityMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorImmunoglobulins against animals/humansDiseaseAntigen
Biomarkers for liver diseases and method for using the same are provided. For detecting liver cirrhosis and liver cancer, the biomarkers are selected from any one of the amino acid sequences with SEQ ID NO:1 to SEQ ID NO:24 or derivatives or fragments or variants or the combination thereof or the antibodies against the amino acid sequences. Then the biomarkers are further developed into detection kits, such that by detecting the existence of autoantibodies or autoantigens in screened specimens, liver diseases are detected with higher accuracy and sensitivity.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Cloned glutamic acid decarboxylase
InactiveUS20050164342A1Avoid small quantitiesAccurate classificationImmobilised enzymesBacteriaEpitopeGlutamate decarboxylase
cDNA molecules coding for GAD65 polypeptide. The invention provides cDNA molecules comprising a part of the cDNA sequence of GAD65 which encode at least one epitope for autoantibodies to GAD65. The invention also provides cloning vehicles capable of replication and expression comprising cDNA molecules coding for GAD65. The invention further provides for hosts transformed with a vehicle having a cDNA molecule coding for GAD65. In another embodiment, the invention provides for the detection of autoantibodies to GAD65 using the GAD65 polypeptides coded for by the cDNA molecules of the invention.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Serum autoantibody detection kit
ActiveCN103869086AEfficient identificationIncreased sensitivityDisease diagnosisBiological testingCancers diagnosisSOX2
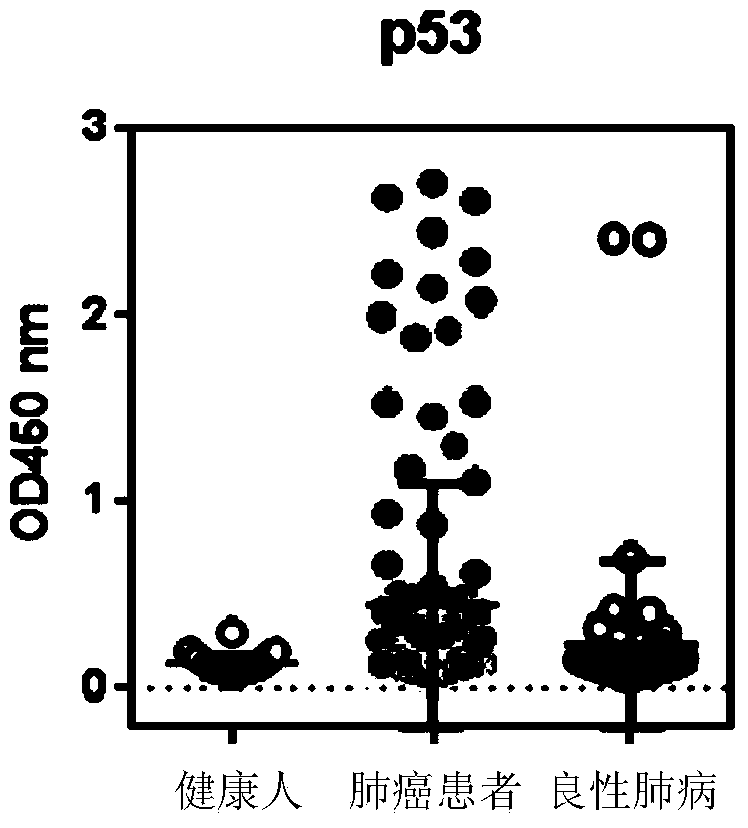
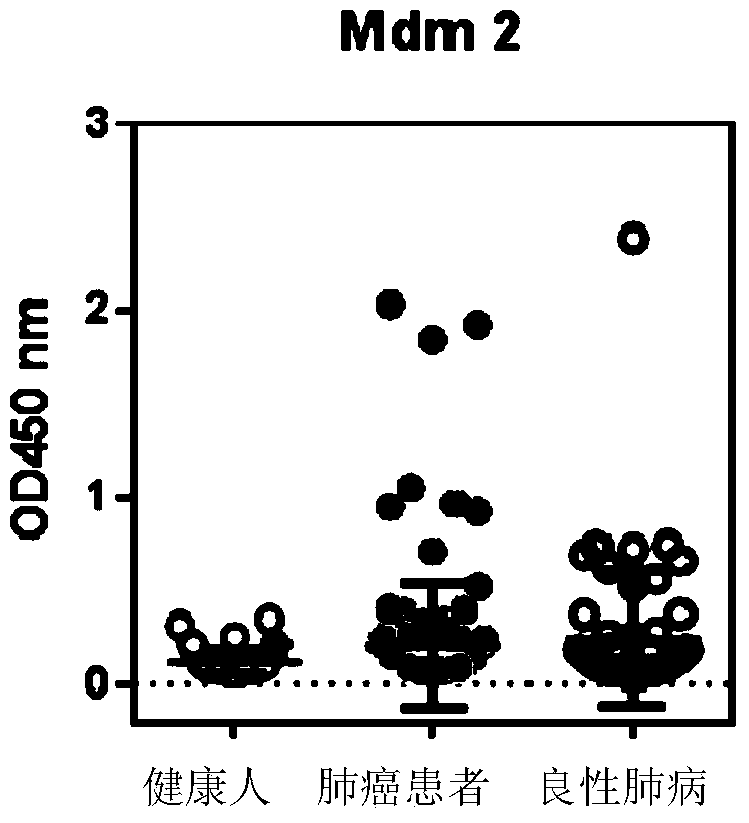
The invention discloses a detection kit used for detecting the serum autoantibody of mammals. The detection kit comprises an antigen protein, wherein the antigen protein is a combination of five or more out of p53, Annexin1, CAGE, NY-ESO-1, HuD, Cyclin D, PGP9.5, GBU4-5, MDM2, GAGE7, XAGE1b, SOX2, MAGE A1 and MAGE A4. The detection kit adopts a group of novel antigen combination corresponding to the autoantibody of a biomarker related to cancers, utilizes biotins to form characteristics of a polymer to envelope the antigen protein, and uses an anti-human label peptide as a standard of quantitative detection, thus increasing the detection sensibility and accuracy of the serum autoantibody, and providing an optimized detection method for using the autoantibody to carry out cancer diagnosis.
Owner:HANGZHOU KAIBAOLUO BIOLOGICAL SCI & TECH
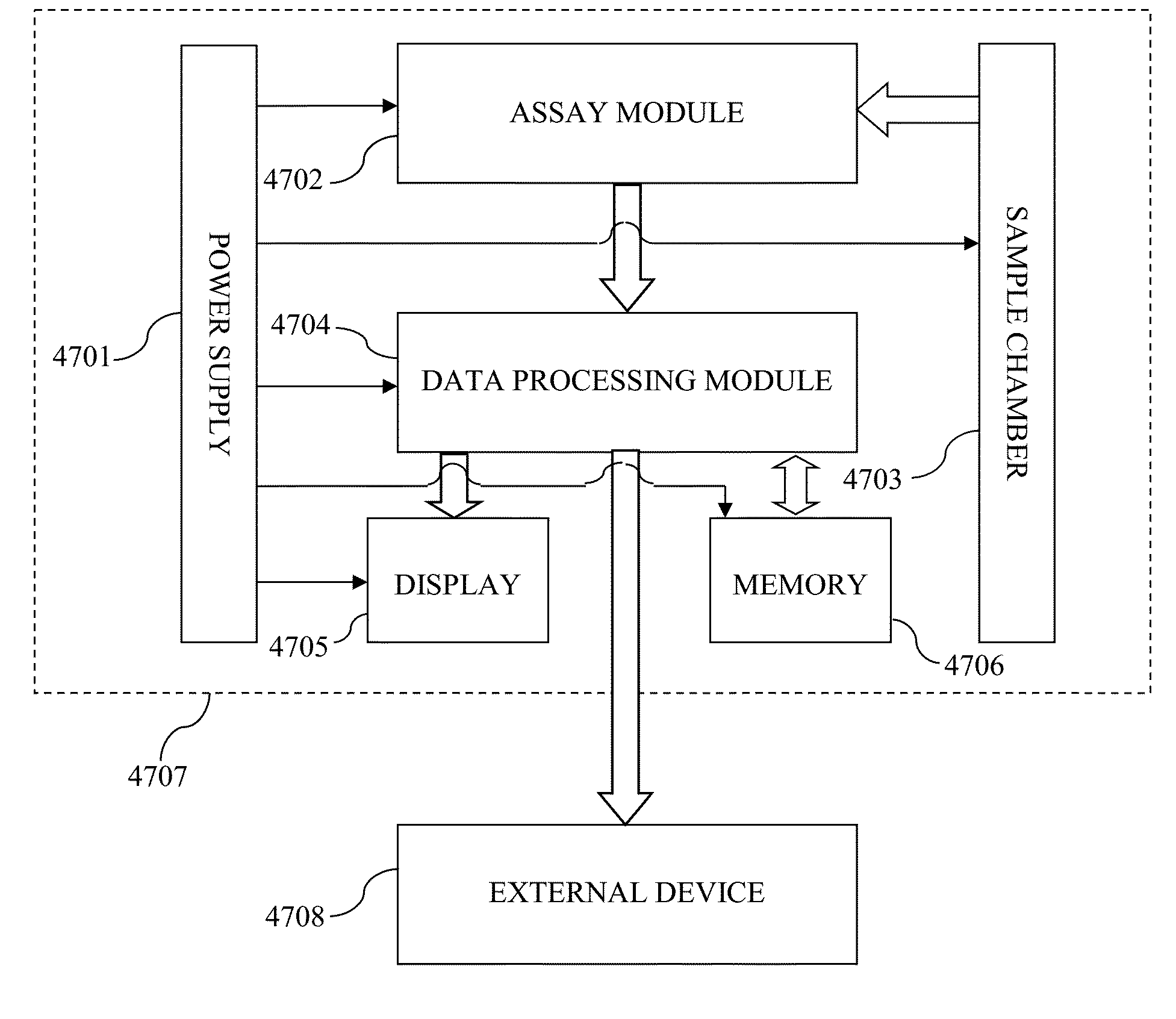
Biomarker assay of neurological condition
A robust, quantitative, and reproducible process and assay for diagnosis of a neurological condition in a subject is provided. With measurement of one or more autoantibodies to biomarkers in a biological fluid such as CSF or serum, the extent of neurological damage in a subject with an abnormal neurological condition is determined and subtypes thereof or tissue types subjected to damage are discerned.
Owner:BANYAN BIOMARKERS INC
Methods and compositions for use in treatment of patients with autoantibody positive disease
InactiveUS20090081213A1Reduce quantity and frequencyReduce frequencyPeptide/protein ingredientsAntipyreticAnti-dsDNA antibodiesSystemic lupus erythematosus
The present invention relates to methods and compositions for use in treatment of patients with autoantibody positive disease. In a specific embodiment, the present invention relates to a method of treating a patient that has an ANA titer of 1:80 or greater and / or greater than or equal to 30 IU / ml of anti-dsDNA antibodies in his / her blood plasma or serum comprising administering a therapeutically effective amount of an immunomodulatory agent, such as an antagonist of Neutrokine-alpha. Additionally provided is a method of reducing the frequency and / or quantity of corticosteroid administration to patients. In preferred embodiments, the patient has systemic lupus erythematosus. Methods for determining if a lupus patient is responding to medical treatment are also provided.
Owner:HUMAN GENOME SCI INC
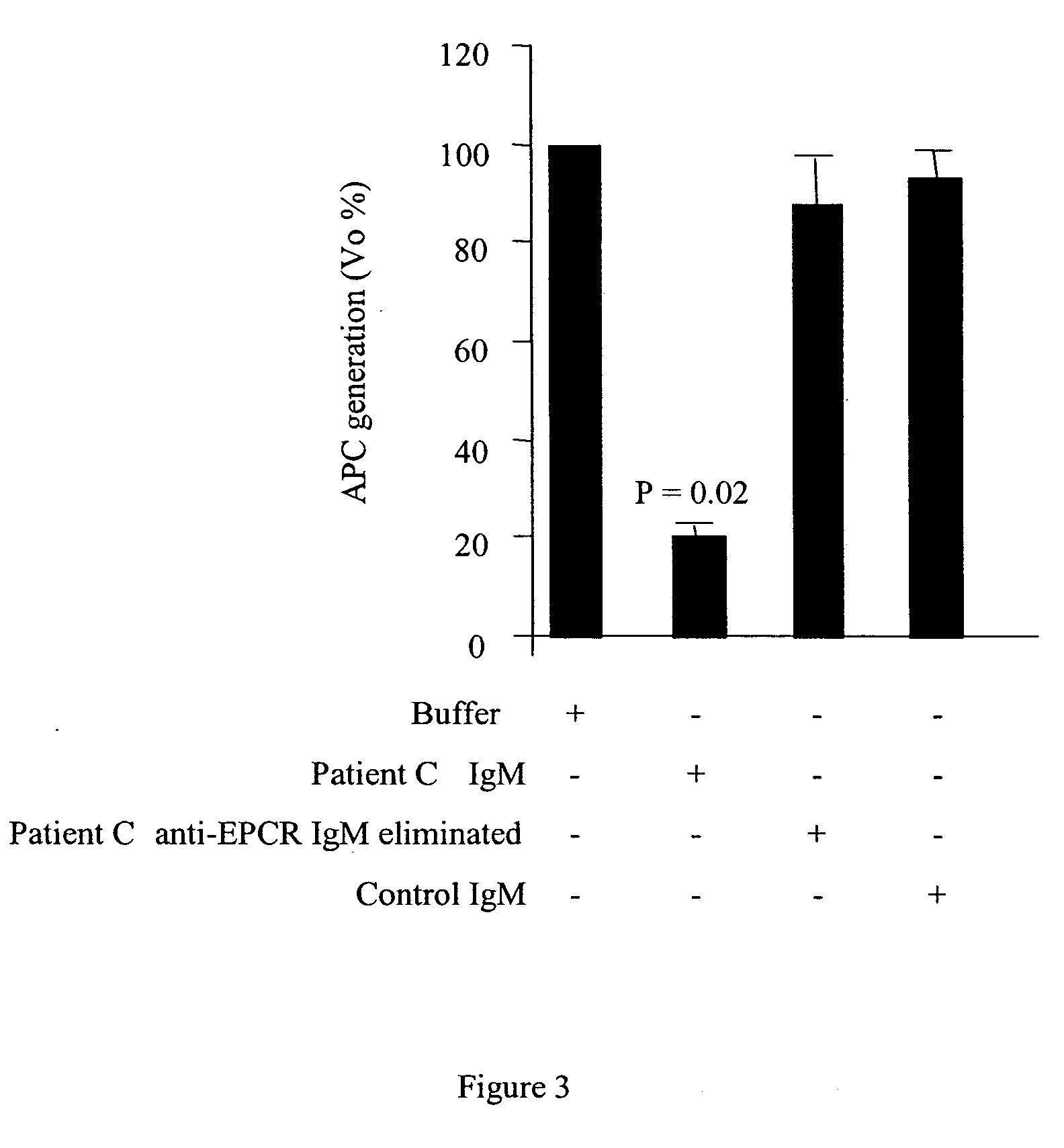
Method for assessing risk of and predisposition to development of a pathology related to the presence of anti-epcr autoantibodies
The present invention relates to a method for detecting the presence of high levels of autoantibodies against protein C / activated protein C endothelial receptor (EPCR). The invention is characterised in that it comprises in vitro detection and quantification of anti-EPCR autoantibodies in a sample.
Owner:PROYECTO DE BIOMEDICINA CIMA
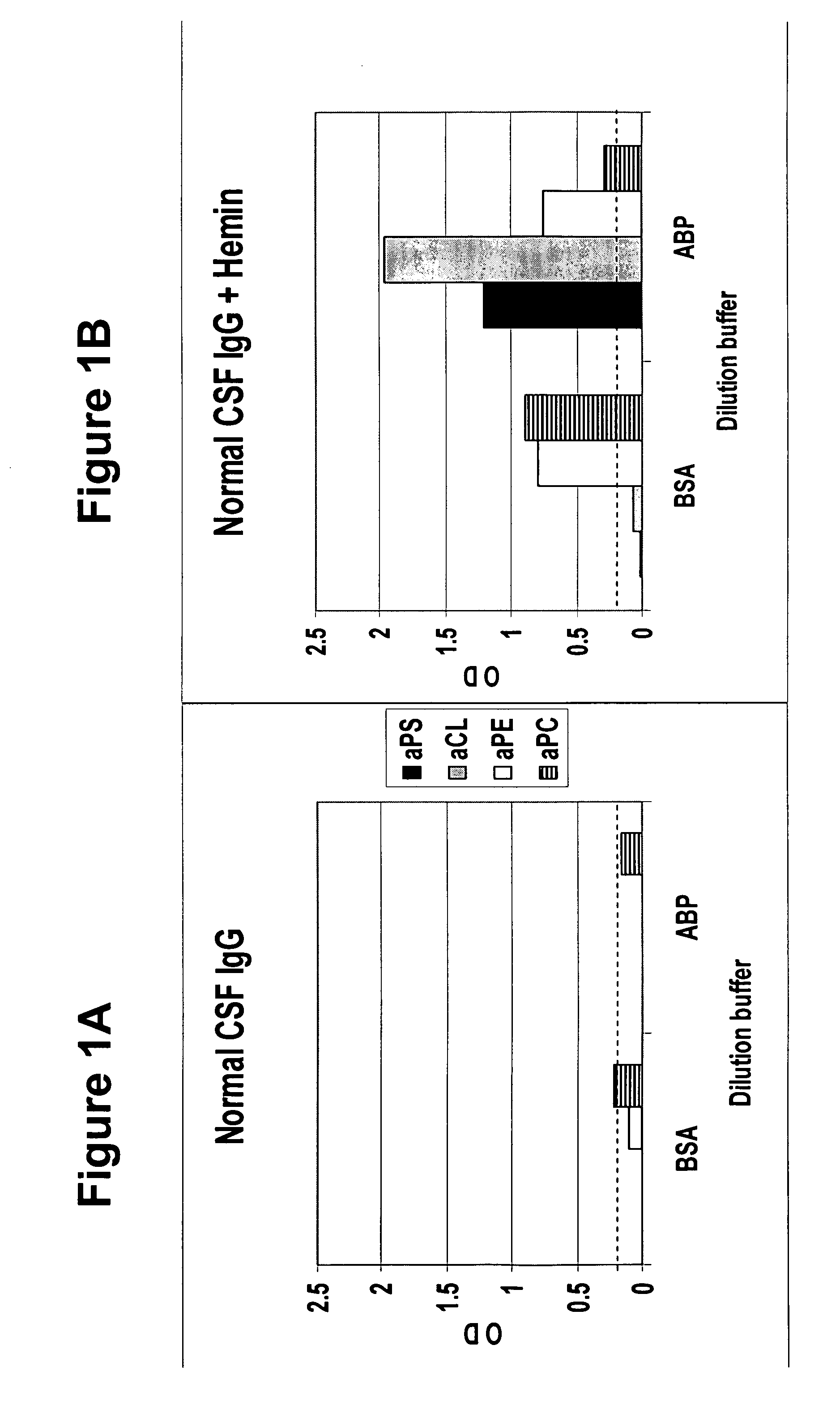
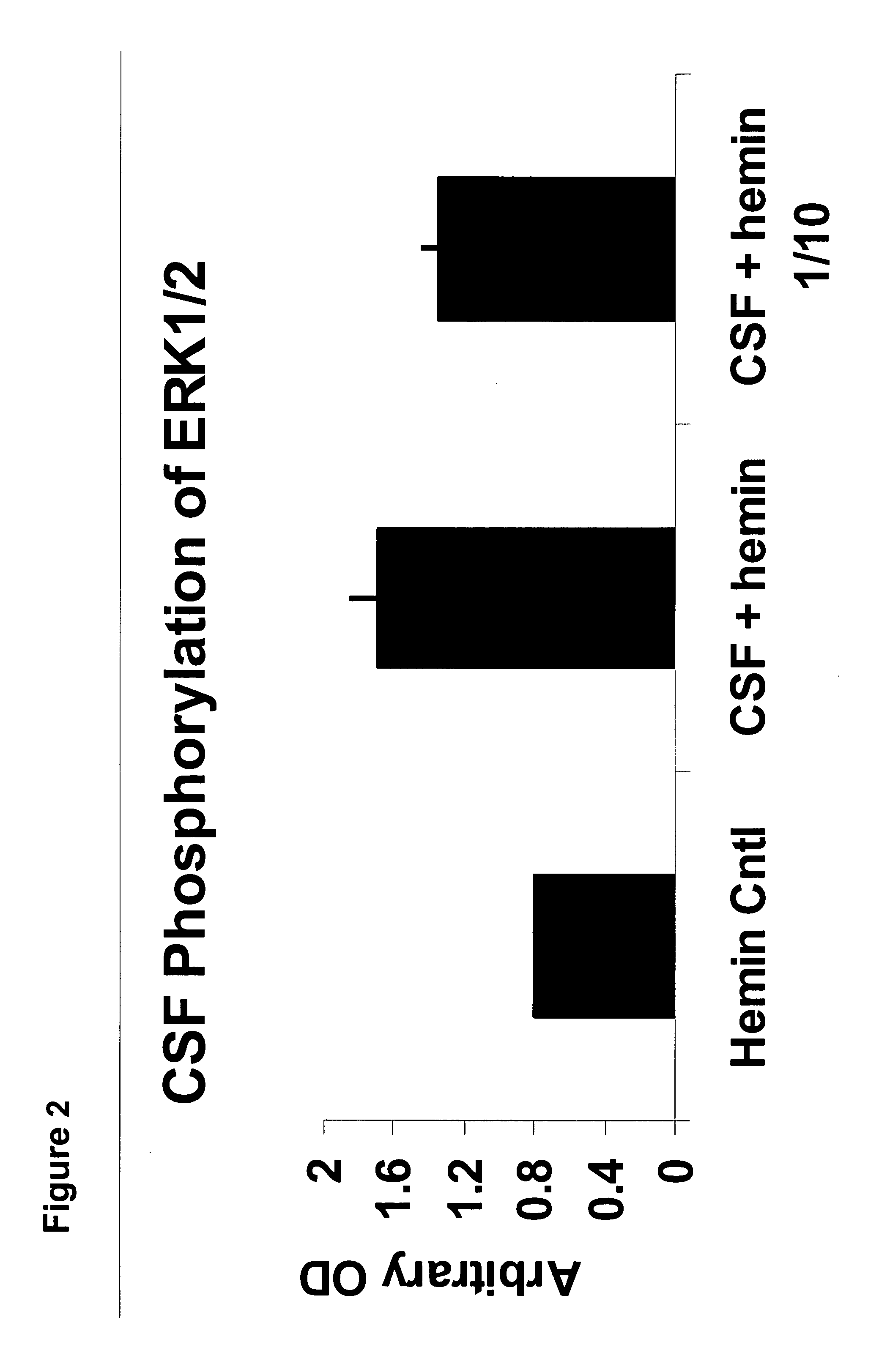
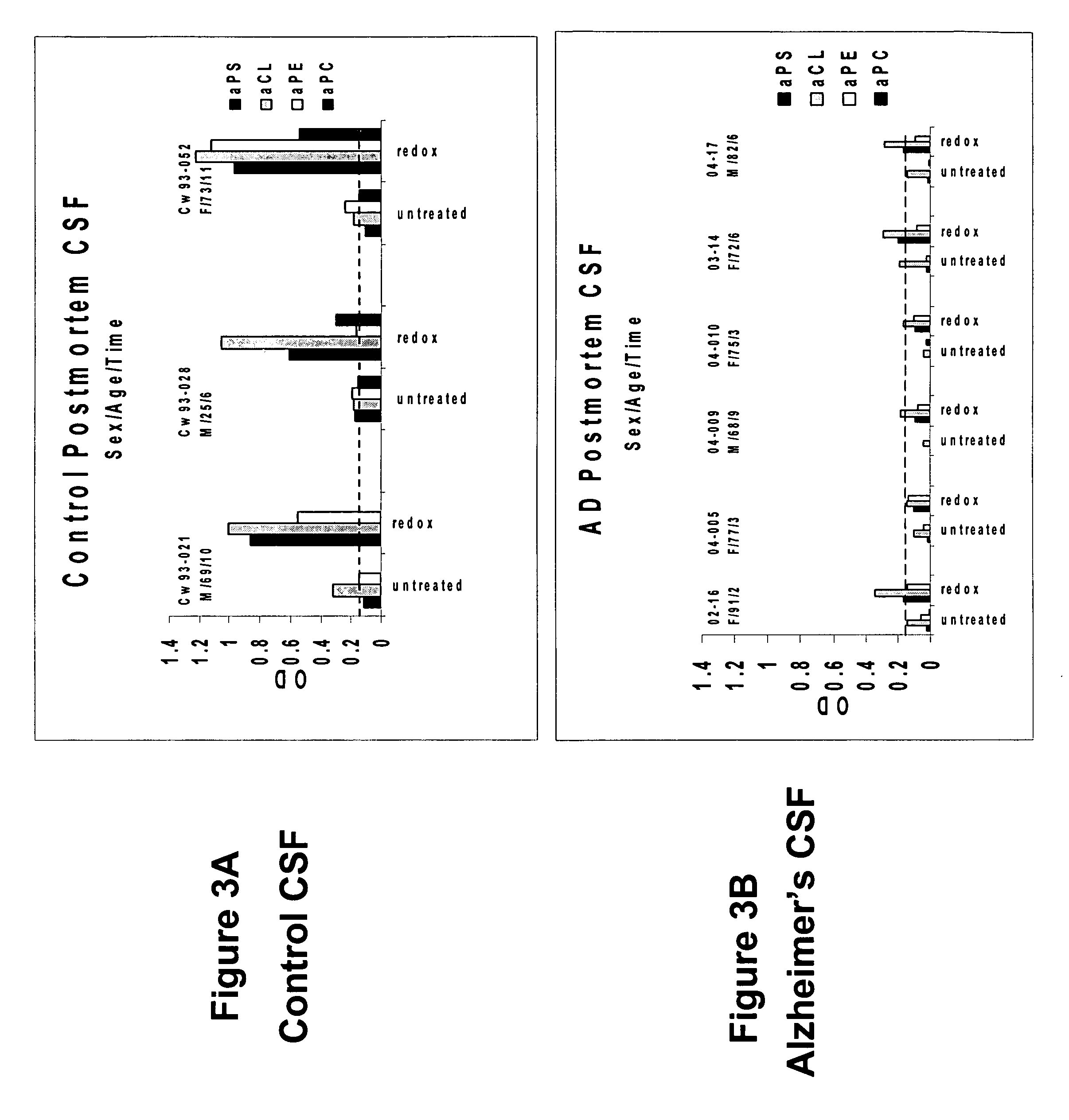
Method of detecting or diagnosing of a neurodegenerative disease or condition
InactiveUS20060141541A1Unknown materialsDisease diagnosisNeuro-degenerative diseaseAutoantibody production
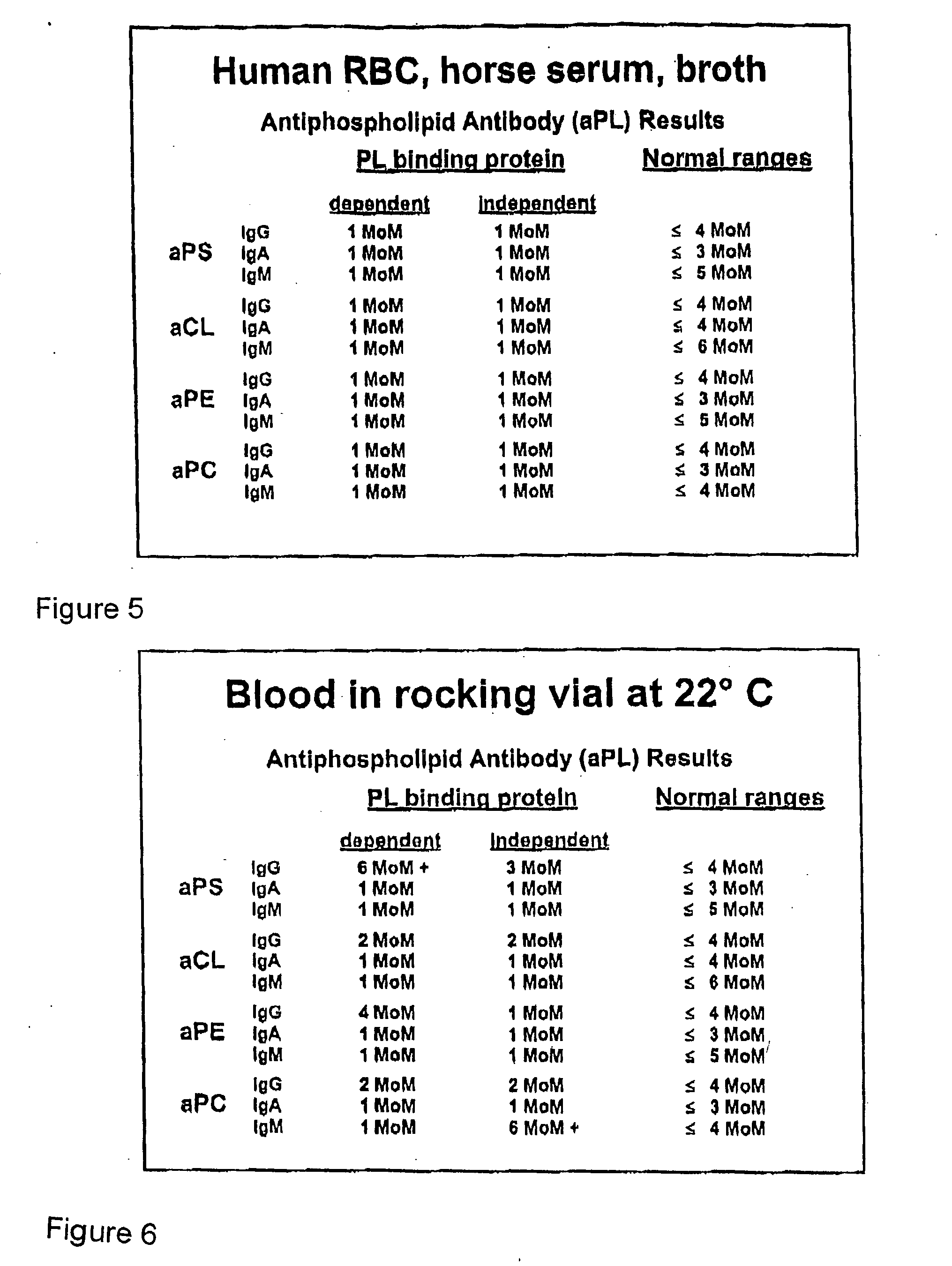
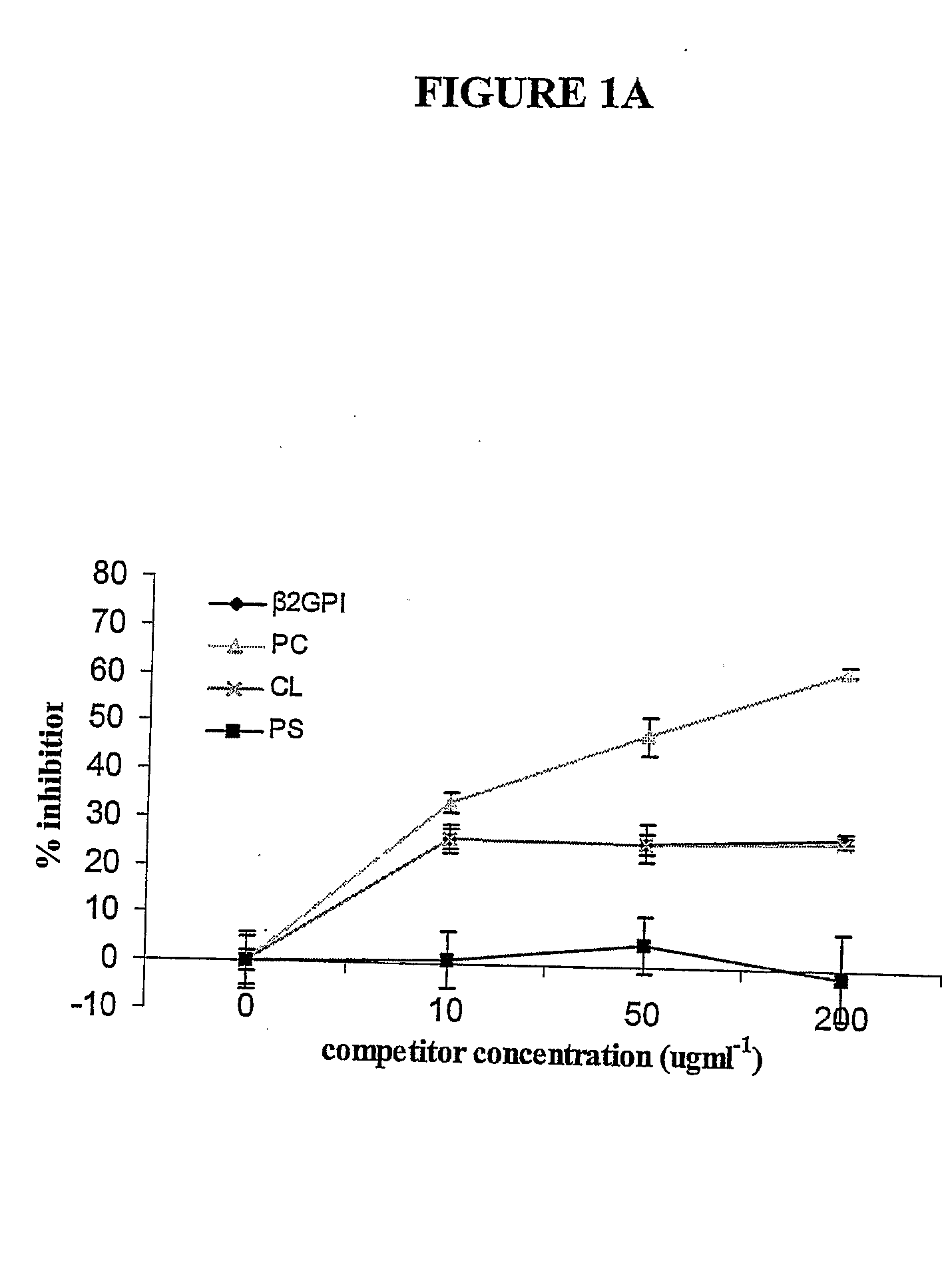
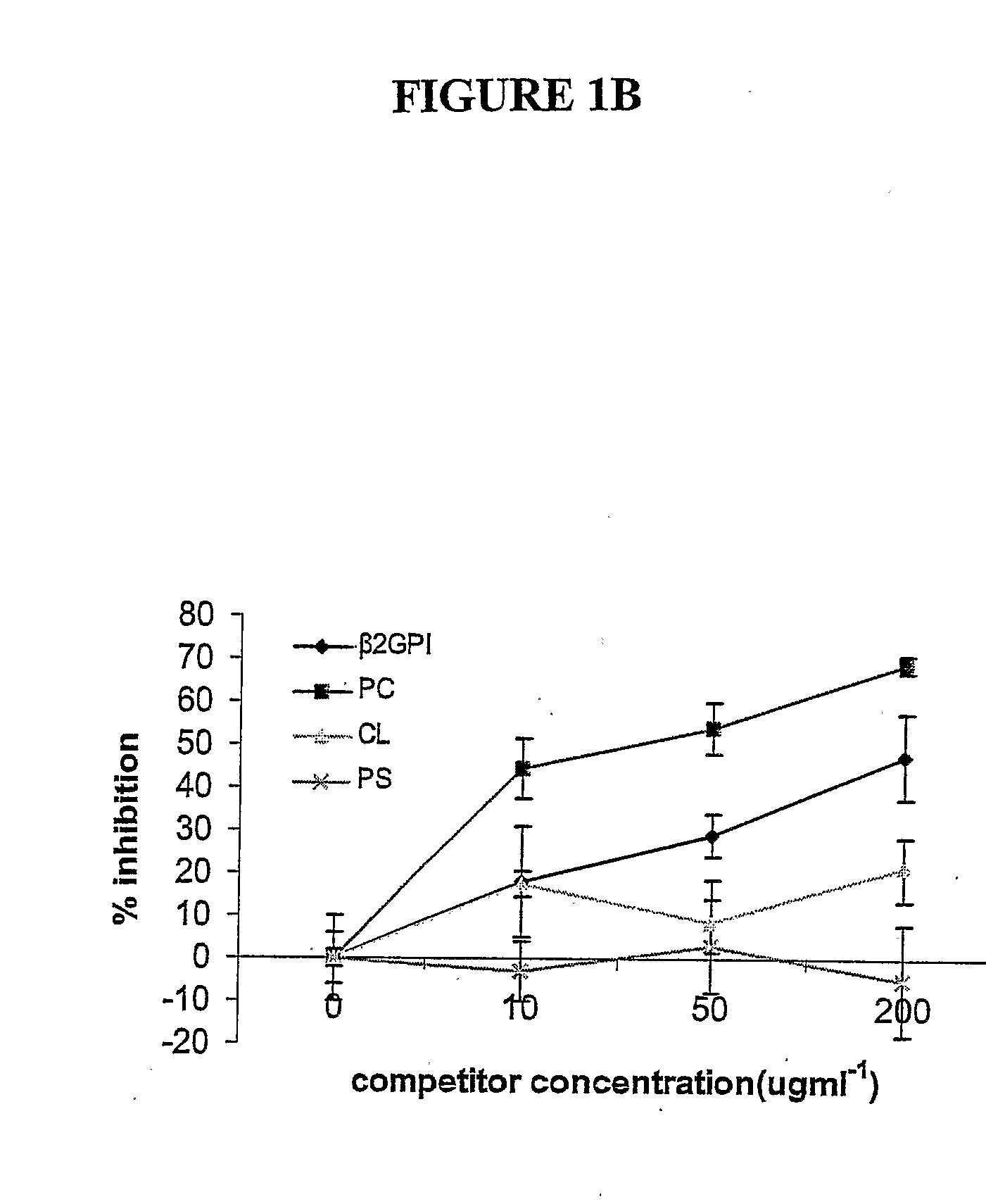
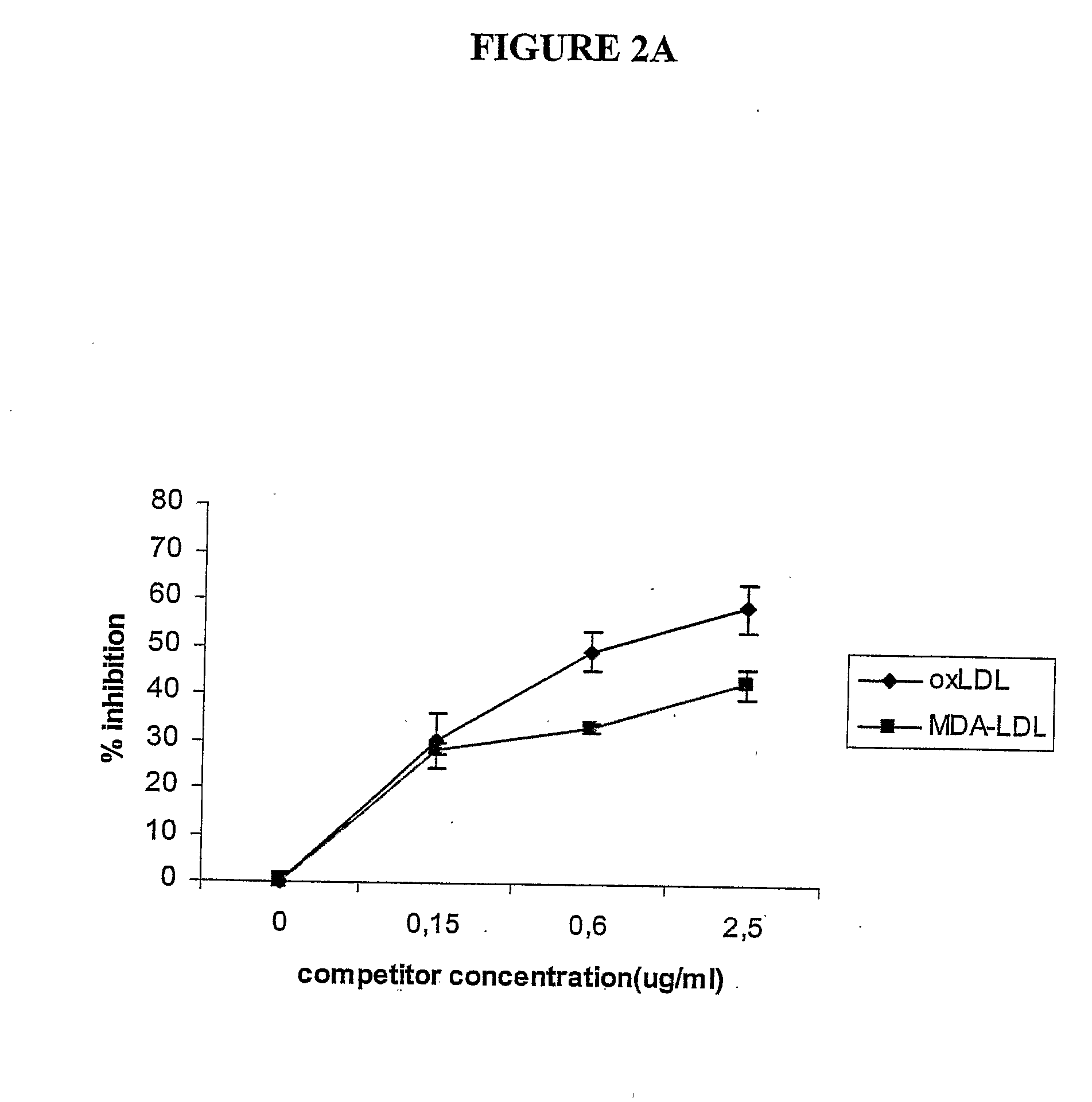
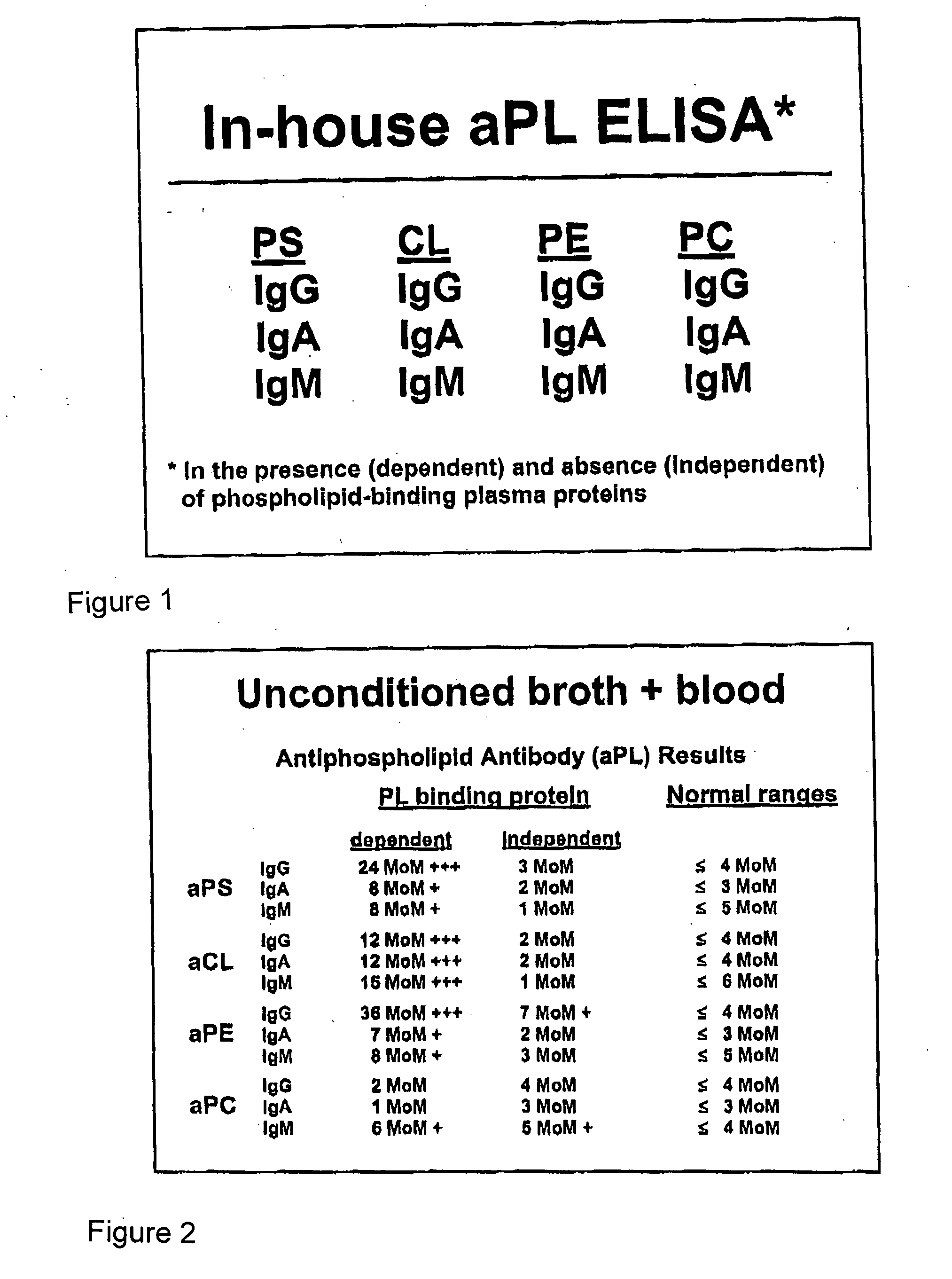
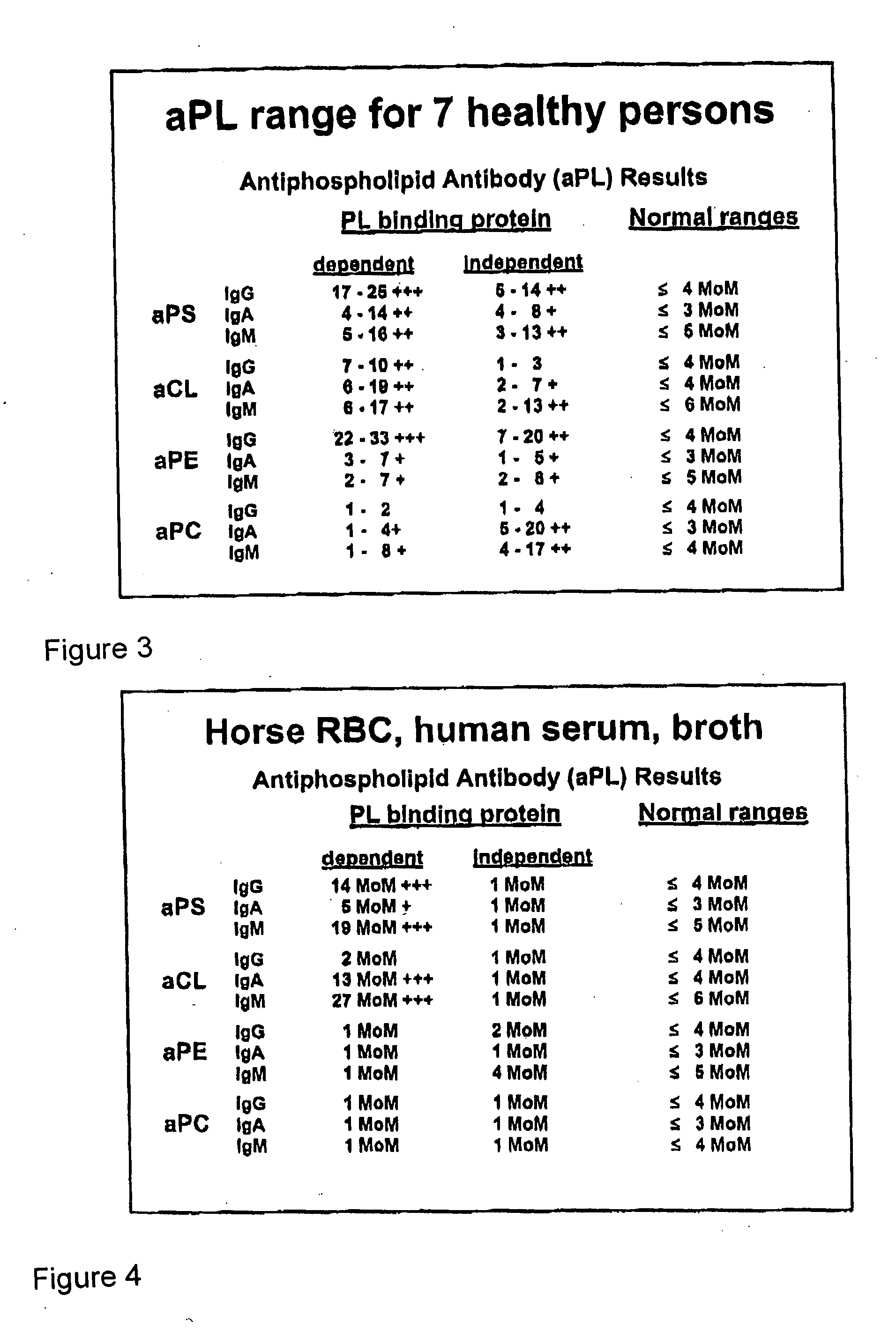
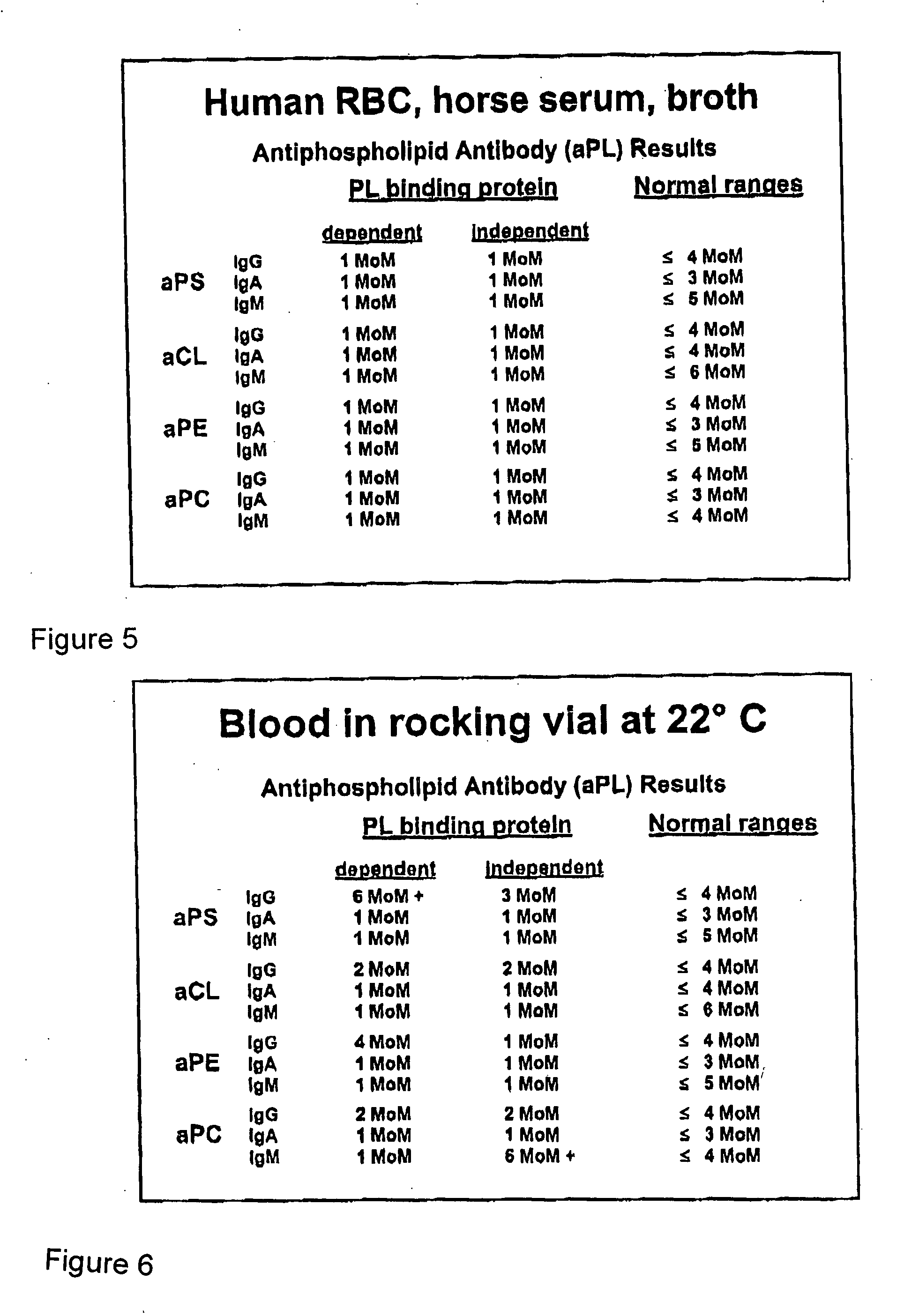
A neurodegenerative disease or condition is diagnosed in a subject by obtaining a sample of cerebral spinal fluid from the subject and assaying the sample by an assay method that detects the presence of at least one antiphospholipid autoantibody in the sample, wherein an elevated level of at least one antiphospholipid autoantibody in the sample of cerebral spinal fluid correlates with a neurodegenerative disease or condition in the subject. The neurodegenerative disease or condition may also be diagnosed by assaying a sample of cerebral spinal fluid to detect nitrosylated antibodies, wherein an elevated level of nitrosylated antibodies correlates with a neurodegenerative disease or condition in said subject. A neurodegenerative disease or condition is also detected or diagnosed by assaying a first sample of cerebral spinal fluid from the subject to determine a level of at least one autoantibody having a selected specificity, treating a second sample of cerebral spinal fluid with an oxidizing agent and assaying the oxidized second sample to determine a level the at least autoantibody having the selected specificity, and comparing the level of the at least one autoantibody in the first sample with the level of the at least one autoantibody in the oxidized second sample, wherein a lack of increase in the level of the at least one autoantibody in the oxidized second sample as compared to the level of the at least one autoantibody in the first sample correlates with a neurodegenerative disease or condition in said subject.
Owner:REDOX REACTIVE REAGENTS LLC
Methods and compositions for use in treatment of patients with autoantibody positive disease
InactiveUS20090081231A1Reduce quantity and frequencyReduce frequencyPeptide/protein ingredientsAntipyreticDiseaseAnti-dsDNA antibodies
The present invention relates to methods and compositions for use in treatment of patients with autoantibody positive disease. In a specific embodiment, the present invention relates to a method of treating a patient that has an ANA titer of 1:80 or greater and / or greater than or equal to 30 IU / ml of anti-dsDNA antibodies in his / her blood plasma or serum comprising administering a therapeutically effective amount of an immunomodulatory agent, such as an antagonist of Neutrokine-alpha. Additionally provided is a method of reducing the frequency and / or quantity of corticosteroid administration to patients. In preferred embodiments, the patient has systemic lupus erythematosus. Methods for determining if a lupus patient is responding to medical treatment are also provided.
Owner:HUMAN GENOME SCI INC
Method of altering the binding specificity of proteins by oxidation-reduction reactions
The binding specificity of at least one protein suspended or dissolved in a liquid medium is reversibly altered by exposing the protein to an oxidizing agent or an electric current. A masked protein such as an autoantibody can be detected, isolated and recovered from a biological fluid by subjecting the biological fluid to an oxidizing agent or an electric current to change the binding specificity of masked proteins contained therein.
Owner:REDOX REACTIVE REAGENTS LLC
Phosphorylcholine Conjugates and Corresponding Antibodies
ActiveUS20070286868A1Increased and decreased riskSignificant positive effectImmunoglobulins against animals/humansAntibody ingredientsPhosphorylcholineIgm antibody
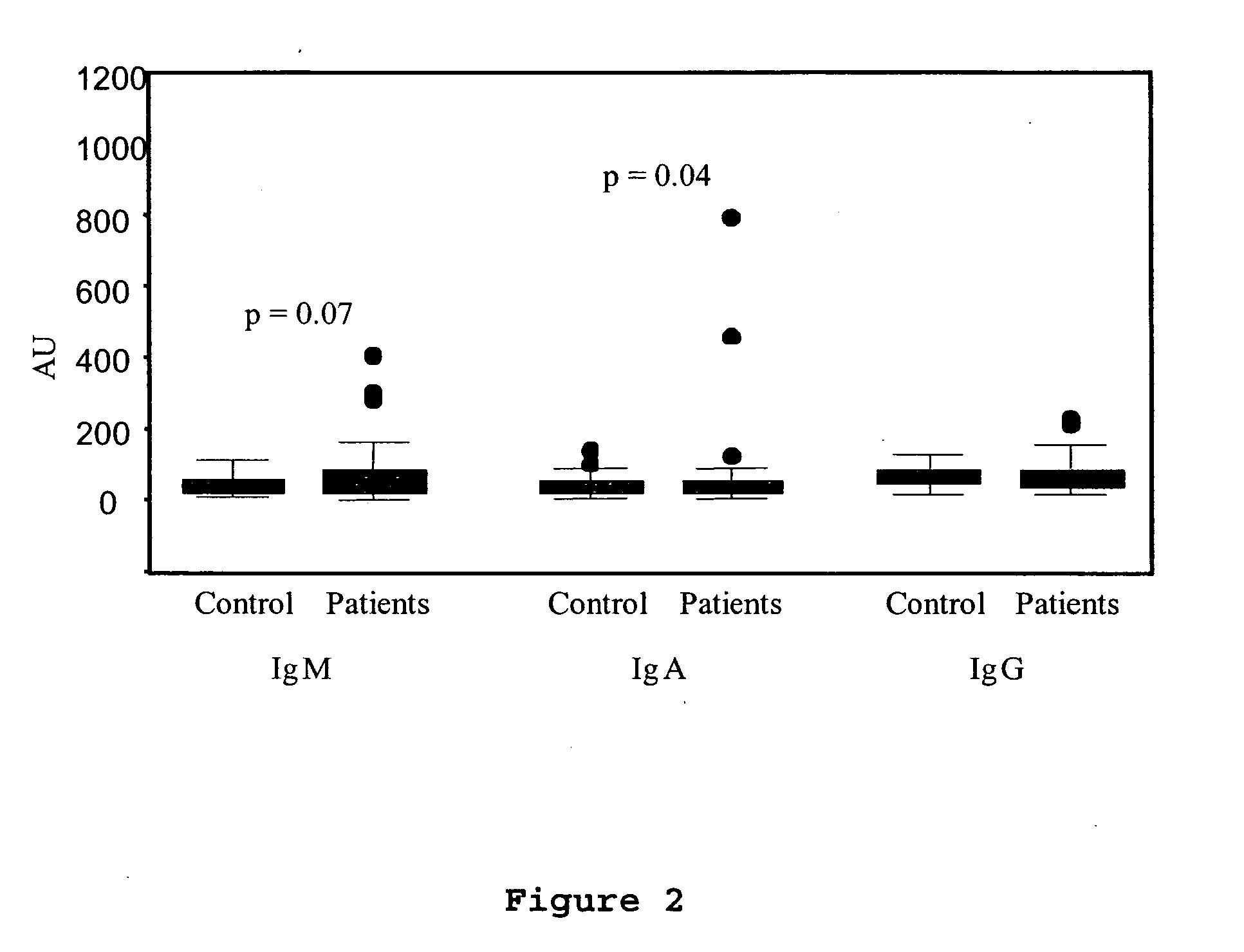
IgG and IgM autoantibody levels against phosphorylcholine in subjects with hypertension (diastolic pressure>95 mmHg) were determined at baseline in order to determine the importance of antibodies for the development of atherosclerosis. The results show that increases in intima-media thickness (IMT) at a follow-up four years after baseline were significantly less prevalent in subjects having high IgM autoantibodies to phosphorylcholine. The presence or absence of IgM autoantibodies against phosphorylcholine is thus related to an increased or decreased risk of developing ischemic cardiovascular diseases. A method to determine IgM antibodies toward phosphorylcholine is proposed in this invention to identify subjects at risk of developing ischemic cardiovascular diseases. Animal experiments show that medium to high levels of IgM antibodies can be detected in plasma after active immunization with a keyhole limpet hemocyanin (KLH)-phosphorylcholine conjugate. A pharmaceutical composition comprising a phosphorylcholine conjugate (active immunization) or a monoclonal antibody with specificity to a phosphorylcholine conjugate (passive immunization) is proposed and the use of these compositions as active or passive immunogens in the treatment or prevention of atherosclerosis.
Owner:ATHERA BIOTECH
Magnetic separation enzymatic chemical luminous immune detection method of human thyroglobulin antibody
InactiveCN1719256AEasy to separateAdequate and prompt responseChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceImmune complex depositionMagnetic bead
The present invention provides a human thyroglobulin antibody magnetic separation enzymatic chemiluminescent immunoassay method, belonging to the field of immunodetection and analysis technology. Said method includes the following steps: making antigen human thyroglobulin be connected with Fe3O4 mincrosphere surface as solid phase reagent, the diameter of Fe3O4 microsphere is 0.1-5.0 microns, after the self-body antibody human thyroglobulin antibody being in the sample is trapped and two antibodies are labeled by enzyme reagent, the solid phase-antigen-antibody-enzyme-labeled two-antibody sandwiched immune complex can be formed.
Owner:北京倍爱康生物技术有限公司
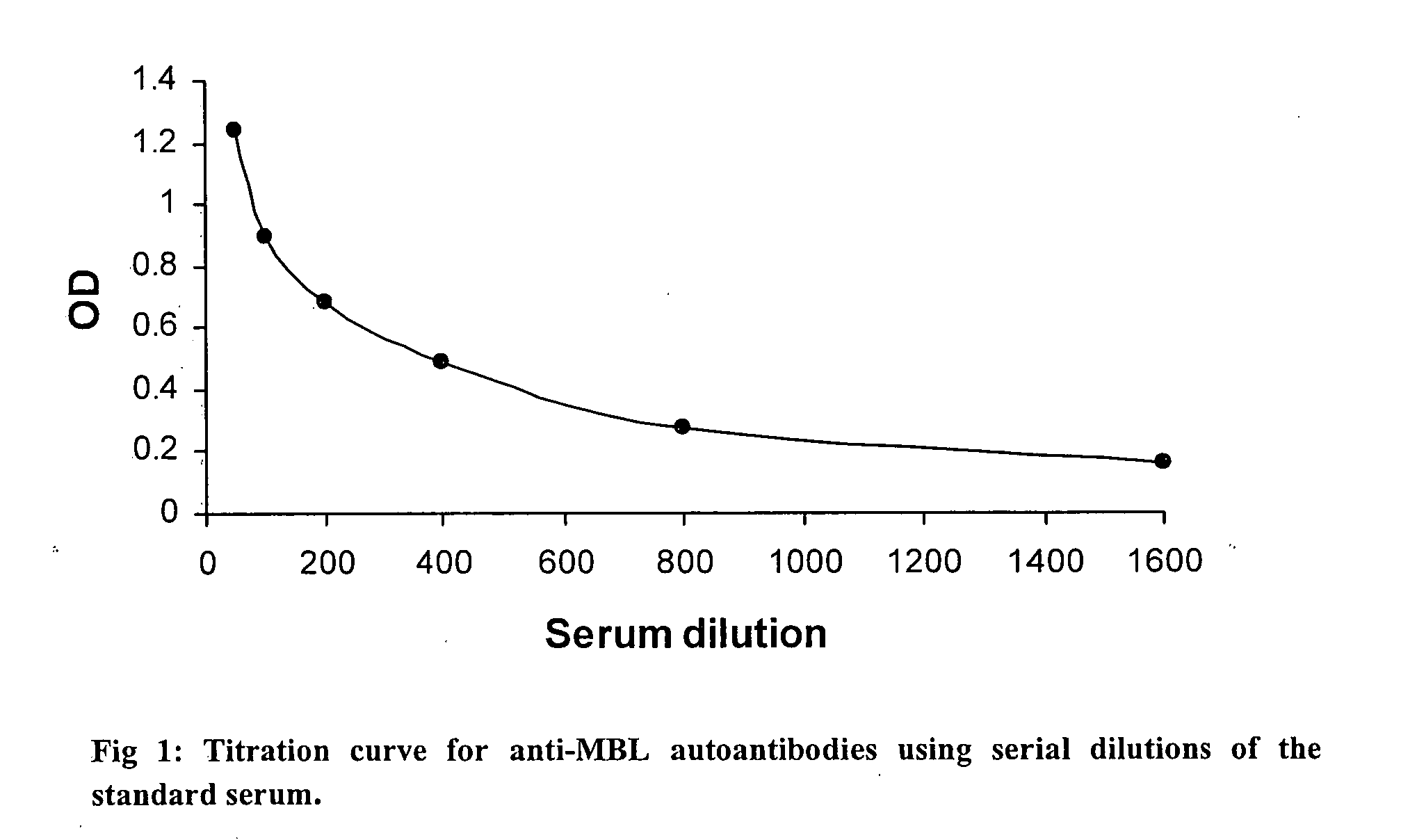
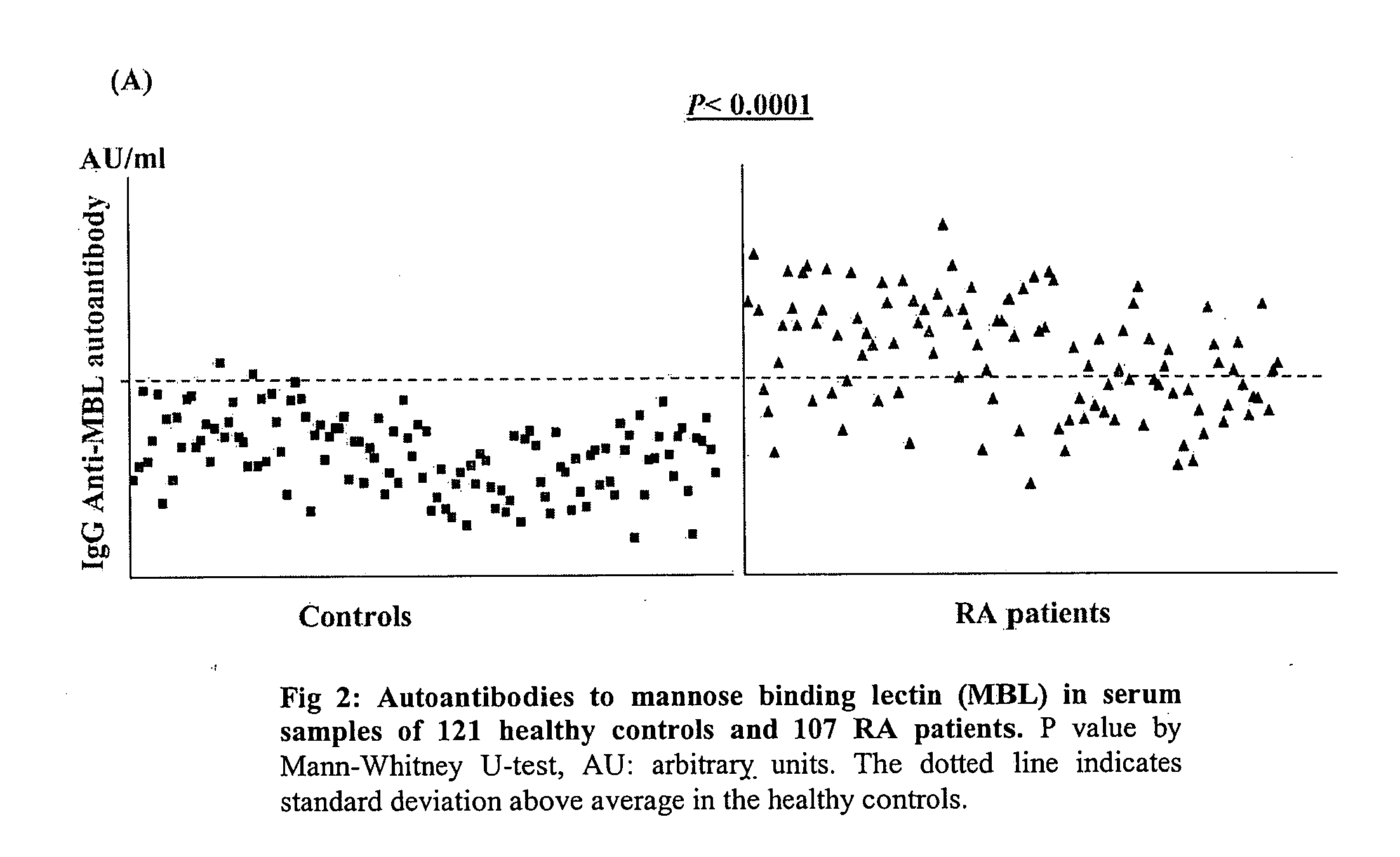
Novel diagnostic marker, a diagnostic kit and a method for diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis
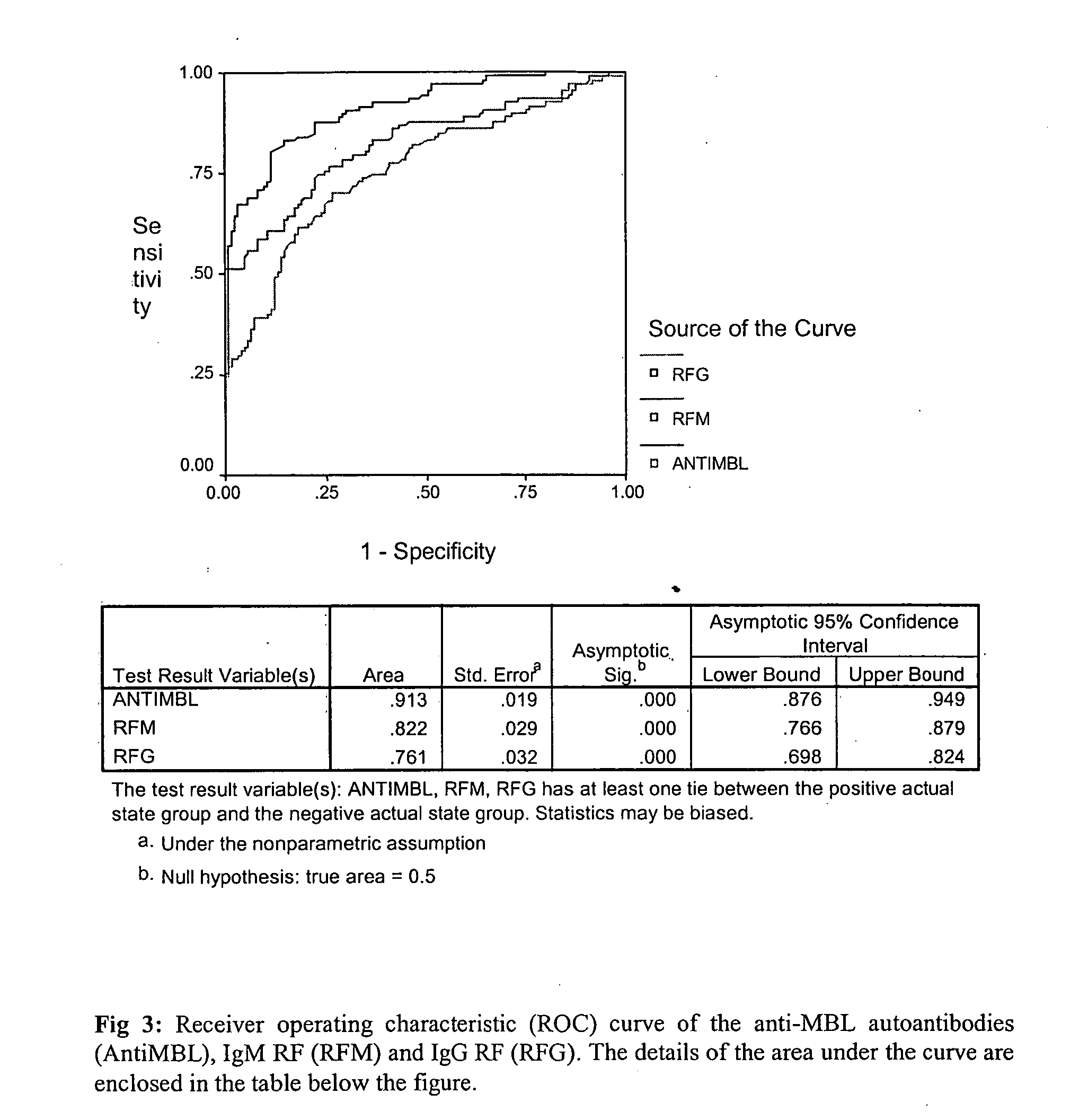
The present invention relates to a novel diagnostic marker useful for the diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis comprising the autoantibodies of mannose binding lectin protein and a process thereof.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
Method of altering the binding specificity of plasma proteins by oxidation-reduction reactions
ActiveUS20050101016A1Liquid separation by electricityElectrostatic separationLiquid mediumWhole blood product
The binding specificity of at least one plasma protein suspended or dissolved in a liquid medium is altered by exposing the protein to an oxidizing agent or an electric current sufficient to alter its binding specificity. A masked protein such as an autoantibody can be recovered from blood or blood products or extracts by oxidizing the protein to change its binding specificity.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL +1
Naturally occuring IgM antibodies that bind to lymphocytes
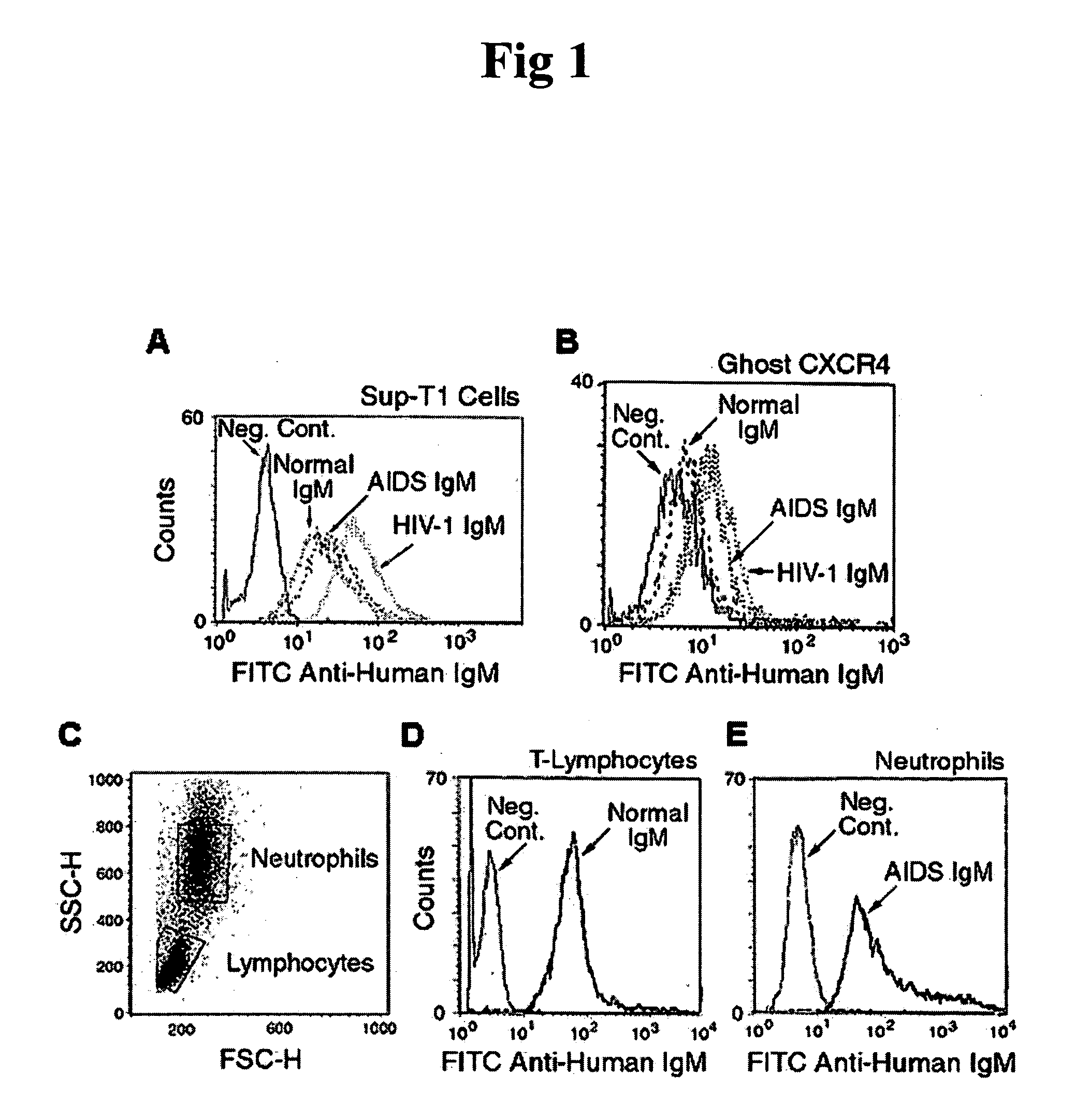
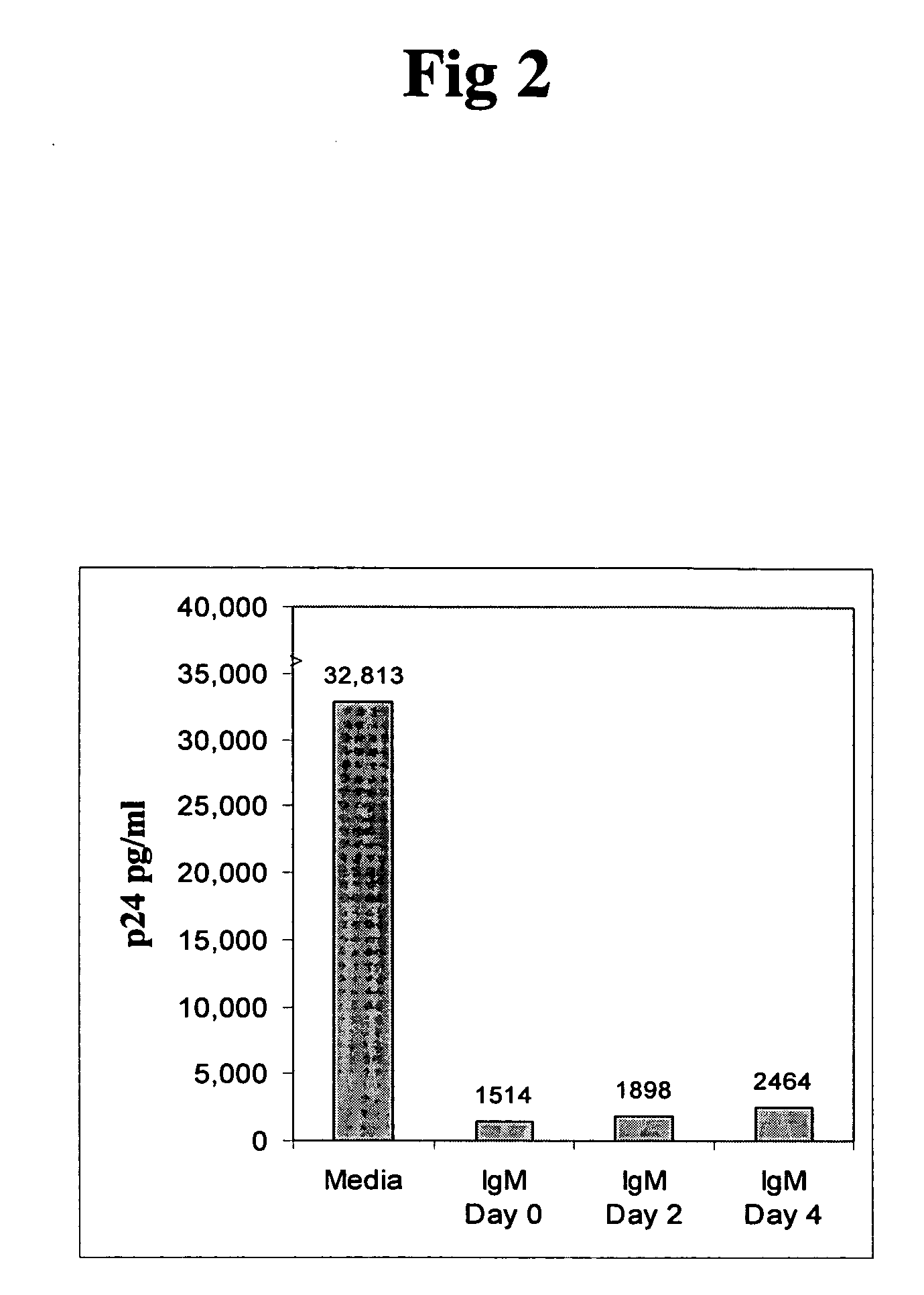
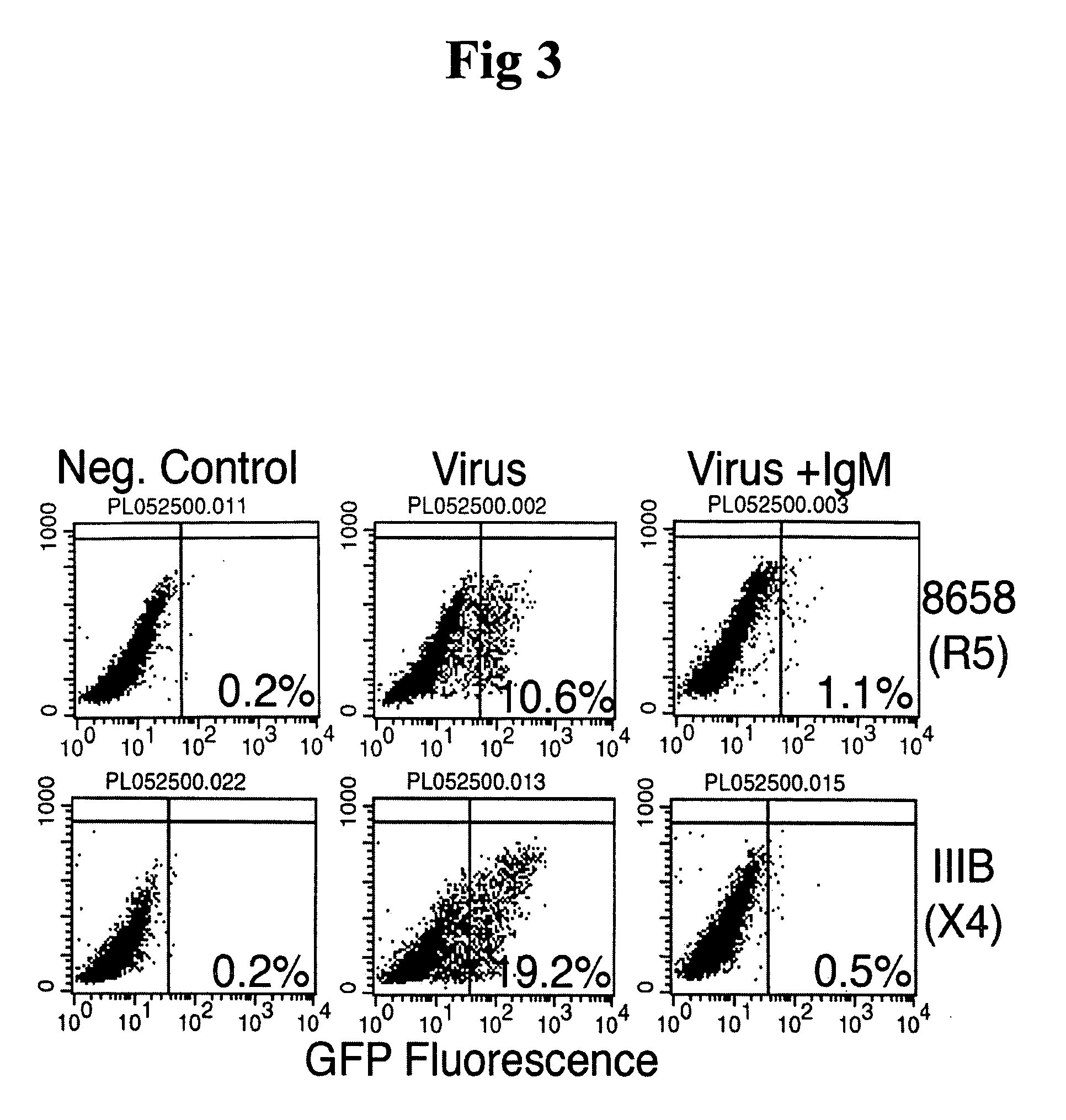
InactiveUS20050220787A1Inhibits HIV- infectivityImprove the level ofImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntibody ingredientsLymphocyte AntibodyDisease
In this invention, the inventor discloses that naturally occurring IgM anti-lymphocyte antibodies bind to chemokine and non-chemokine receptors on lymphocytes and other cells, and downmodulate certain receptors including CD4 and CD2 on T cells and CD80 and CD86 on macrophages. The inventor also discloses that such antibodies (i) inhibit HIV-1 and other viruses from infecting cells (ii) inhibits activation and proliferation of T lymphocytes (iii) inhibits cytokine and chemokine production (iv) inhibits inflammatory processes, and (v) enhances death of malignant cells. This art or invention is novel in that the antibodies described herein are “naturally occurring” i.e. develop in absence of deliberate immunization and secondly these antibodies are distinct from disease causing autoantibodies in that these naturally occurring antibodies are polyreactive with low binding affinity.
Owner:LOBO PETER ISAAC
Diagnostic autoantibody profiles for the detection and diagnosis of neurodegenerative diseases
The present invention provides methods, compositions, and kits for the detection of neurodegenerative disease specific autoantibodies for the diagnosis of neurodegenerative diseases and risk for developing neurodegenerative diseases, and for the generation of patient-specific neurodegenerative disease diagnostic autoantibody profiles.
Owner:ROWAN UNIVERSITY
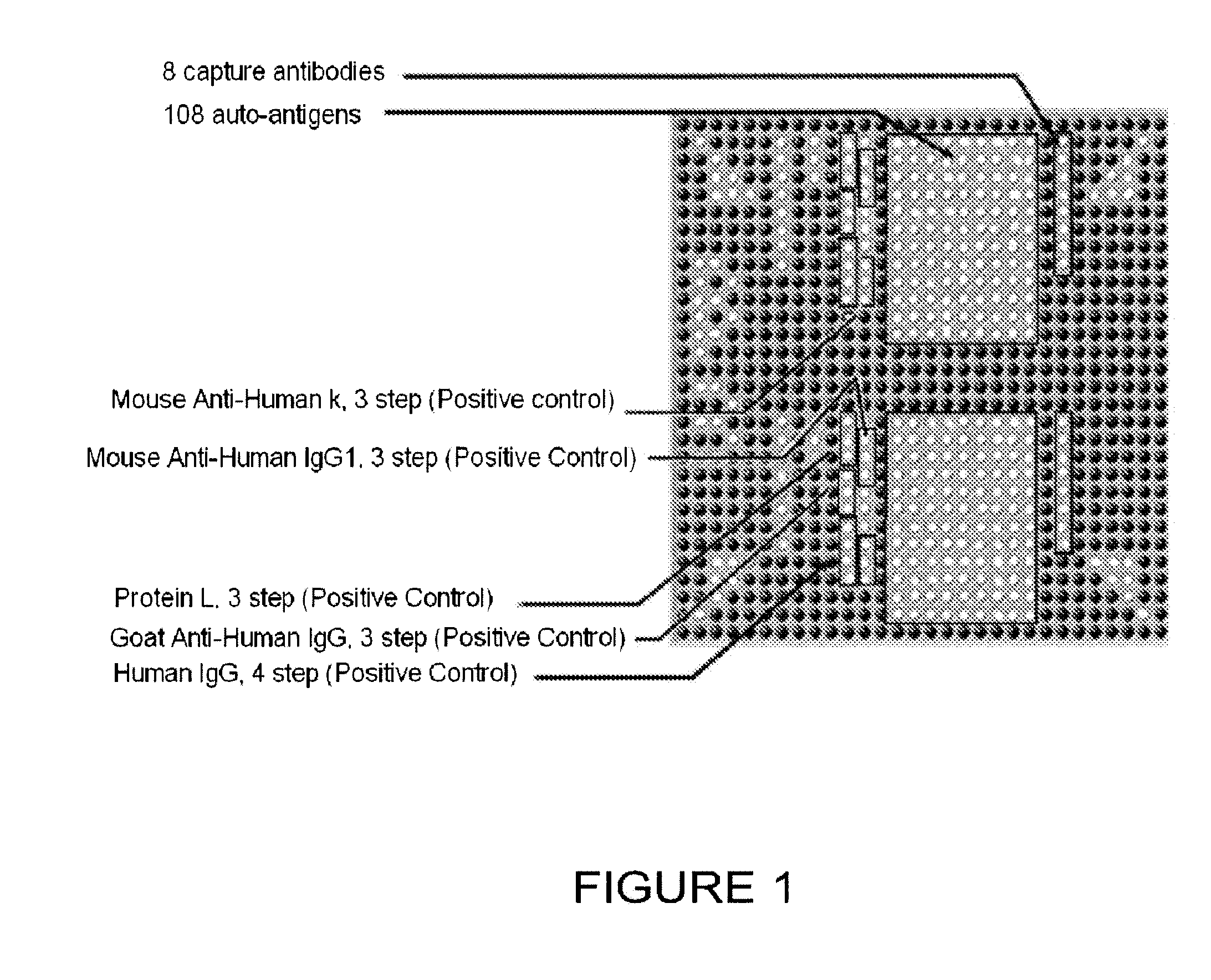
Addressable antibody arrays and methods of use
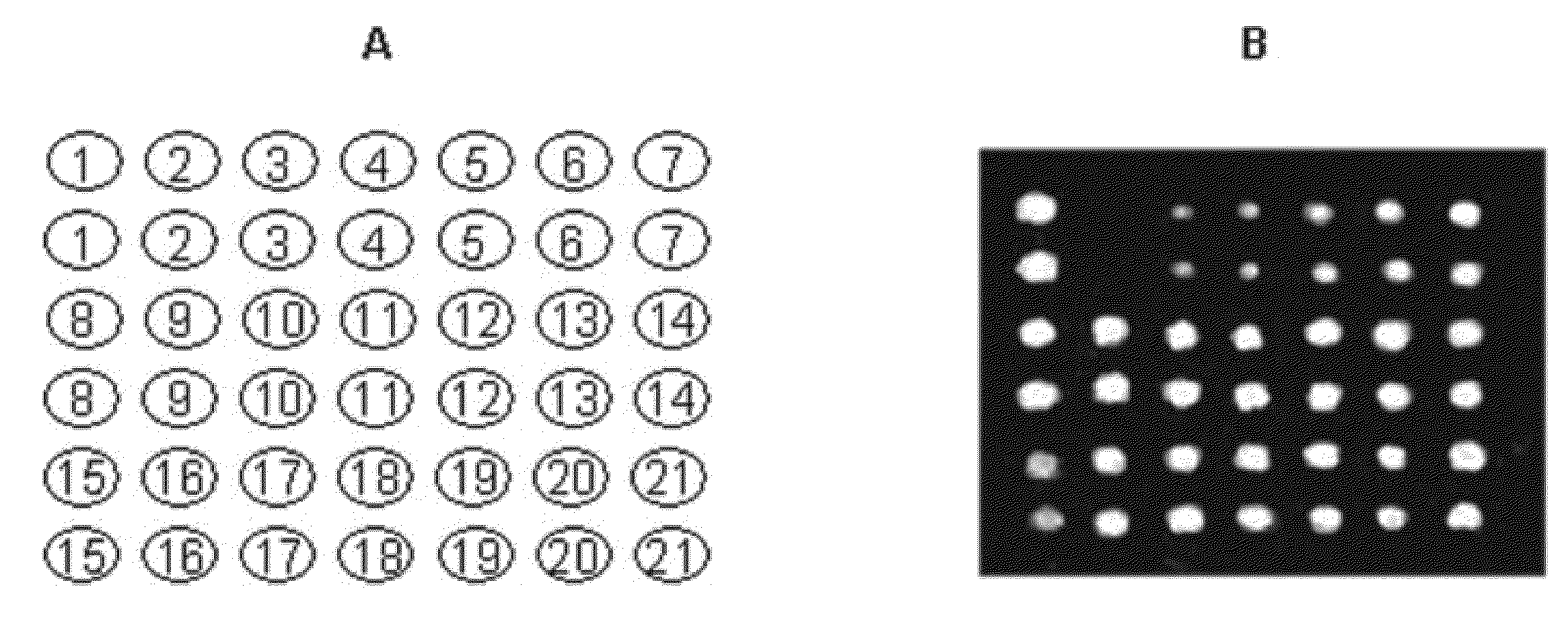
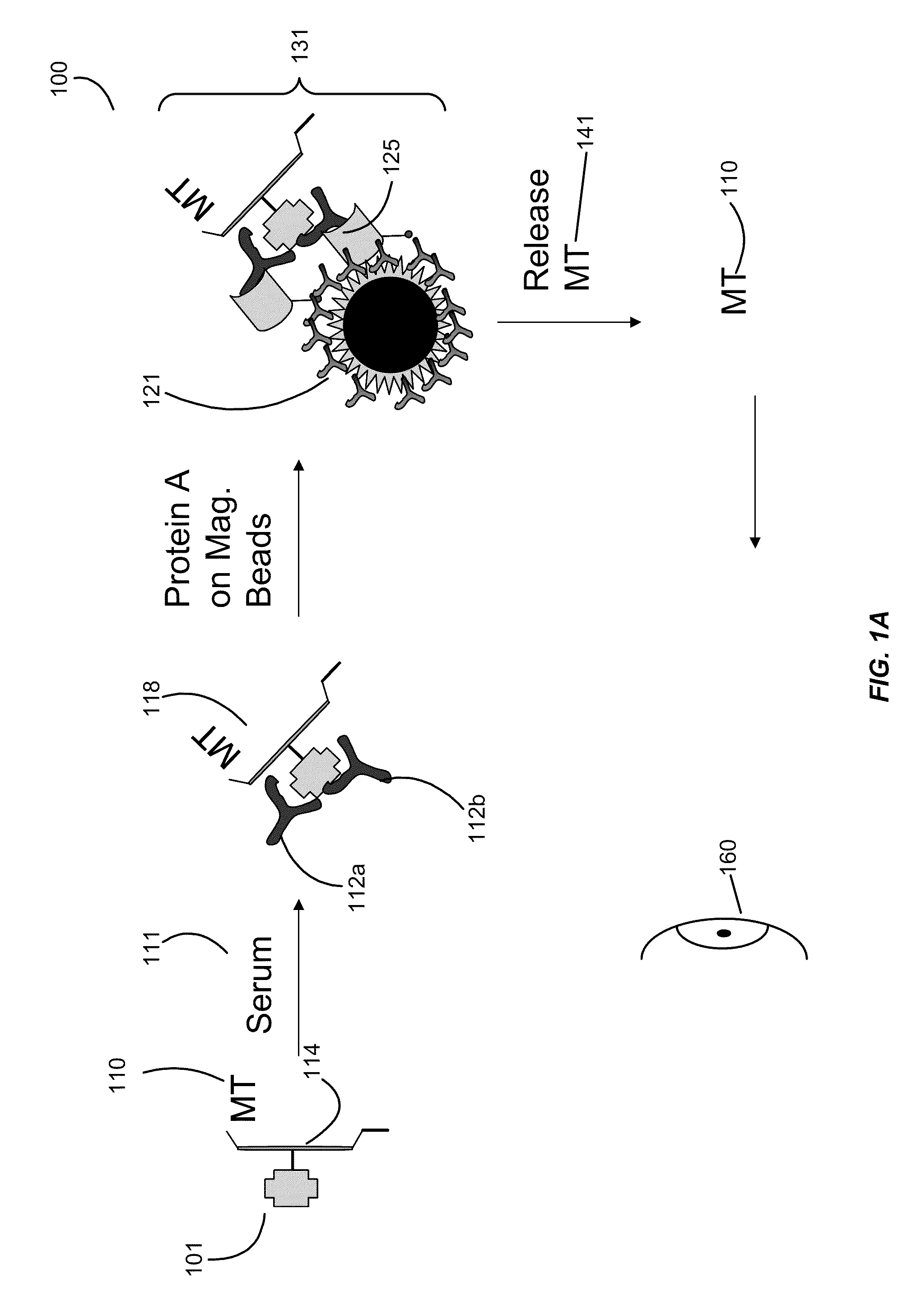
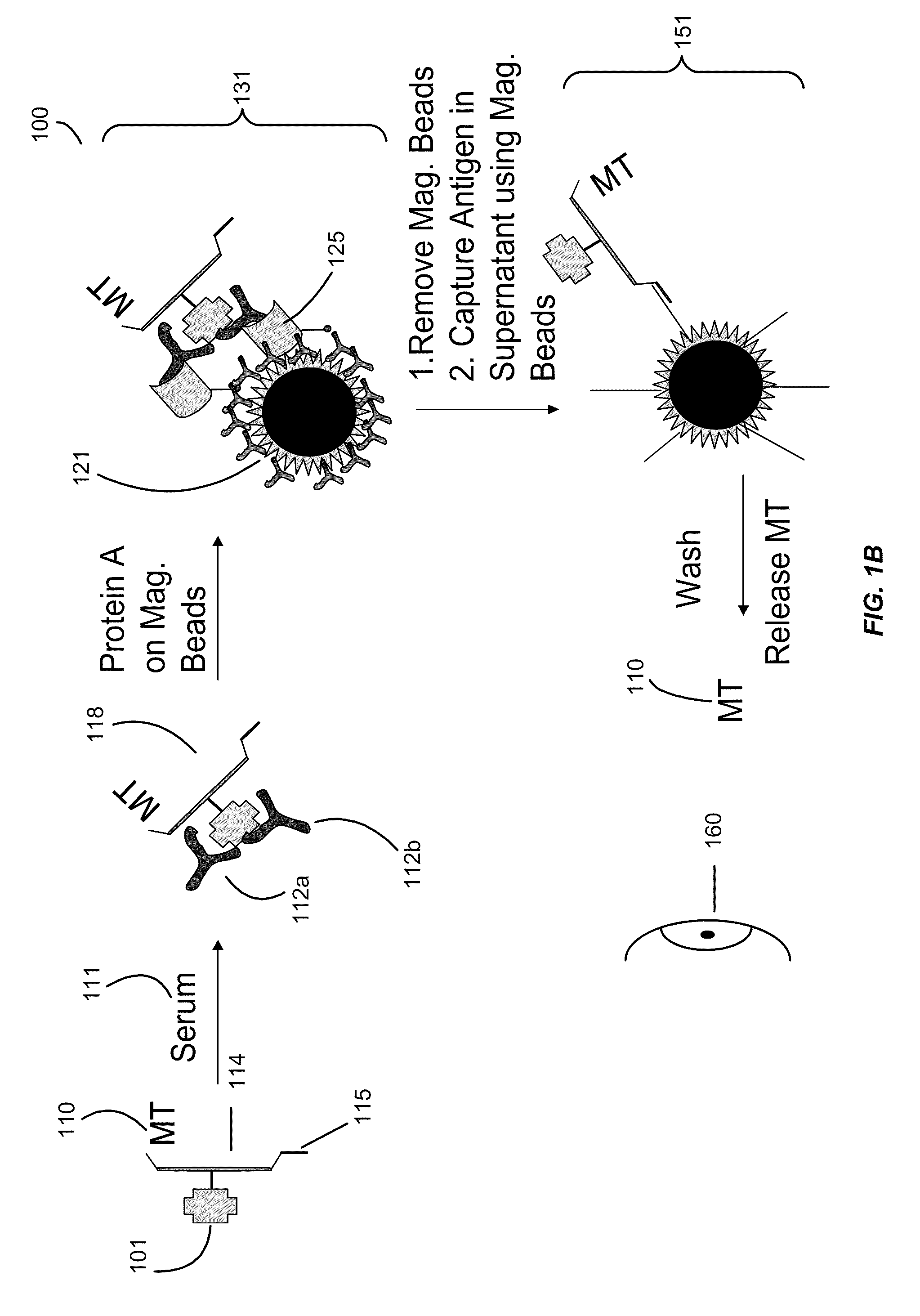
ActiveUS20100022408A1High sensitivityStrong specificityLibrary screeningDisease diagnosisAntigenFluorescence
Systems and assay methods are disclosed for detecting an autoantibody in a sample. In certain instances, the systems and methods employ a mass tag releasably connected to an antigen. The tag is thereafter released for detection. A tag can be detected by mass spectrometry or in certain instances the tag is fluorescent. Methods for diagnosing a disease or disorder in a subject are also disclosed.
Owner:PROMETHEUS LAB
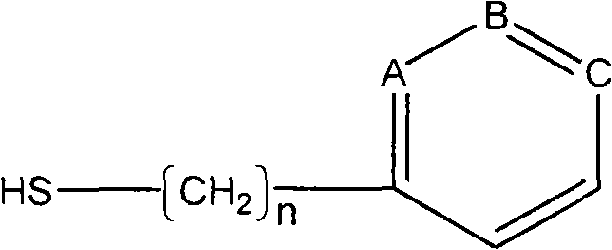
Blood-purifying adsorbing agent for cleaning antibody
InactiveCN101279242AHigh adsorption selectivityImprove stabilityOther blood circulation devicesOther chemical processesImmune complex depositionSorbent
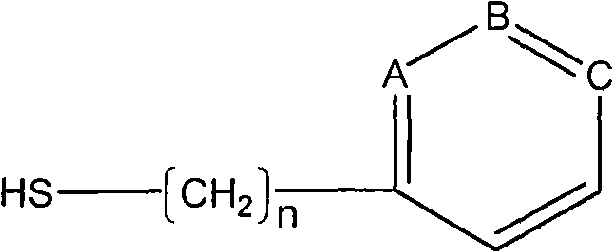
A blood purification sorbent for antibody removal belongs to the technical field of biomedicine, which consists of the two parts of solid-phase carrier material and a petunidin fixed on the carrier by chemical coupling. The molecular structure of the petunidin is shown as above, wherein, one atom among A, B and C is N, the others are C; n is 0-2. The blood purification sorbent can adsorb the antibody component in plasma and autoantibodies such as rheumatoid factor, antinuclear antibody, etc. in heavy load, has limited nonspecific adsorption to other plasma components such as seralbumin, etc., and also has low preparation cost and stable physicochemical property. The material can be used as adsorption filler of a blood purification device for removing the autoantibody and immune complex in the plasma.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
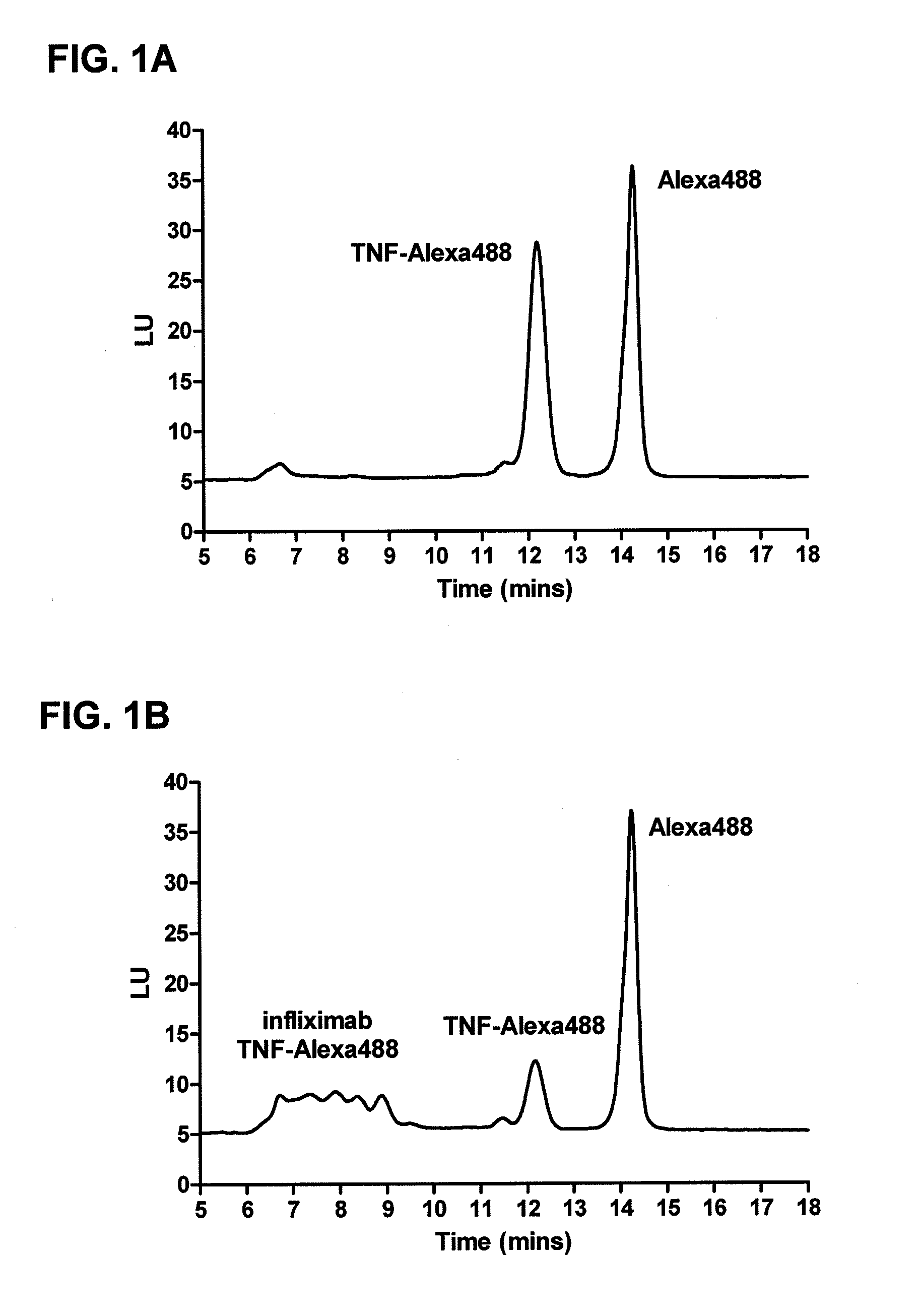
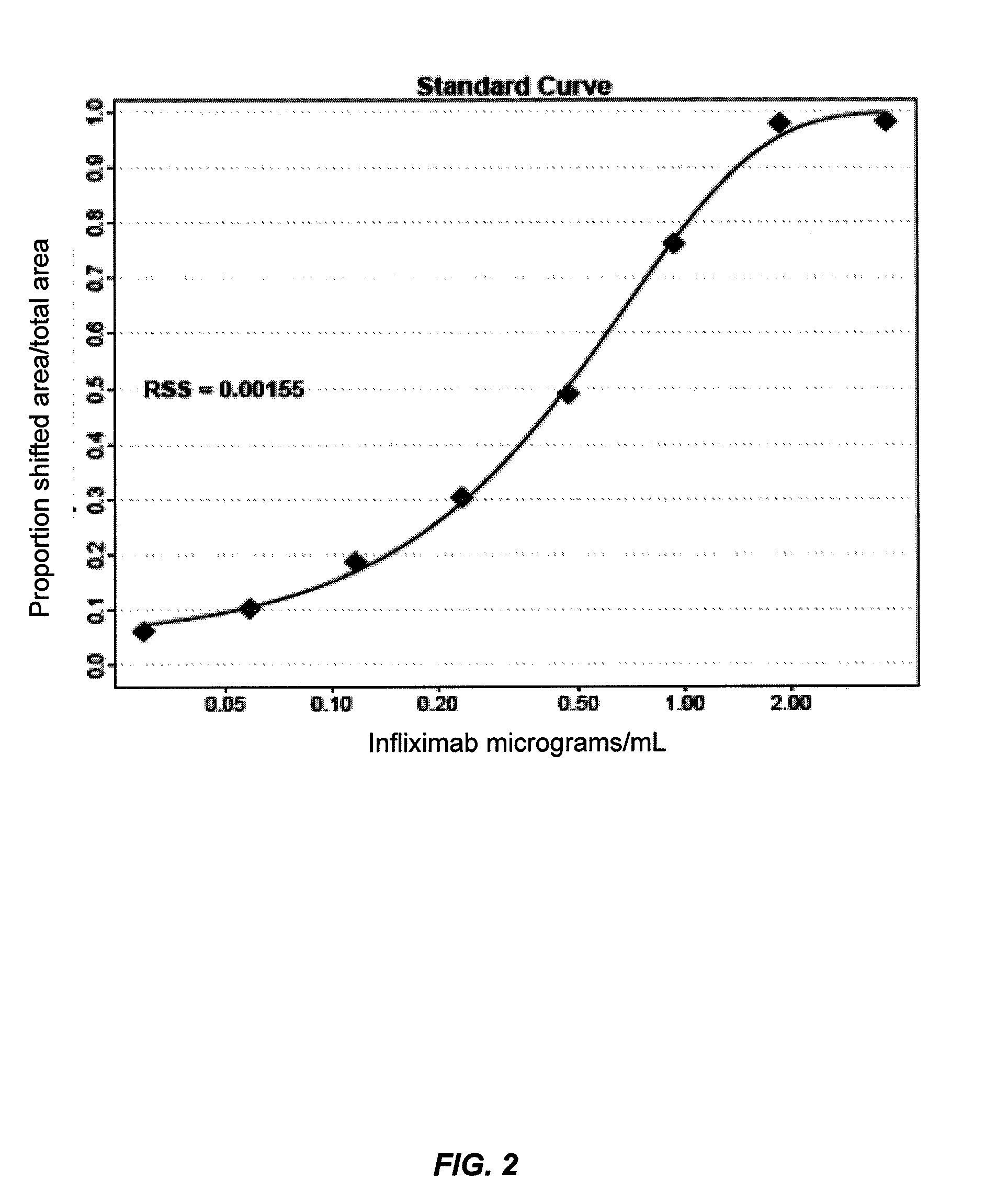
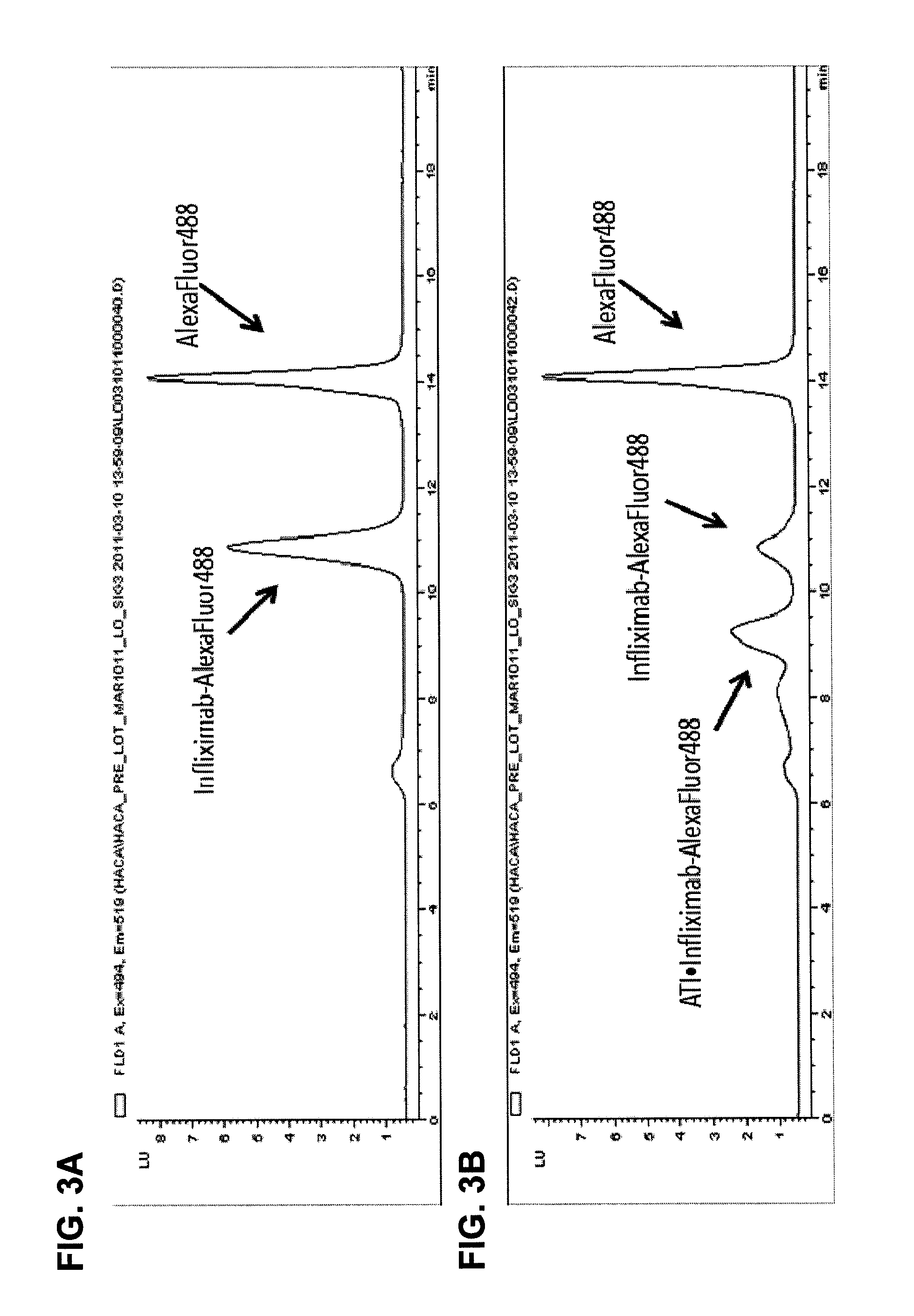
Mobility shift assays for detecting Anti-tnf alpha drugs and autoantibodies thereto
InactiveUS20140051184A1Low toxicityBiological material analysisBiological testingAutoantibody productionDrug treatment
The present invention provides assays for detecting and measuring the presence or level anti-TNFα drugs and / or the autoantibodies to anti-TNFα drugs in a sample. The present invention is useful for optimizing therapy and monitoring patients receiving anti-TNFα drug therapeutics to detect the presence or level of autoantibodies against the drug. The present invention also provides methods for selecting therapy, optimizing therapy, and / or reducing toxicity in subjects receiving anti-TNFα drugs for the treatment of TNFα-mediated disease or disorders.
Owner:NESTEC SA
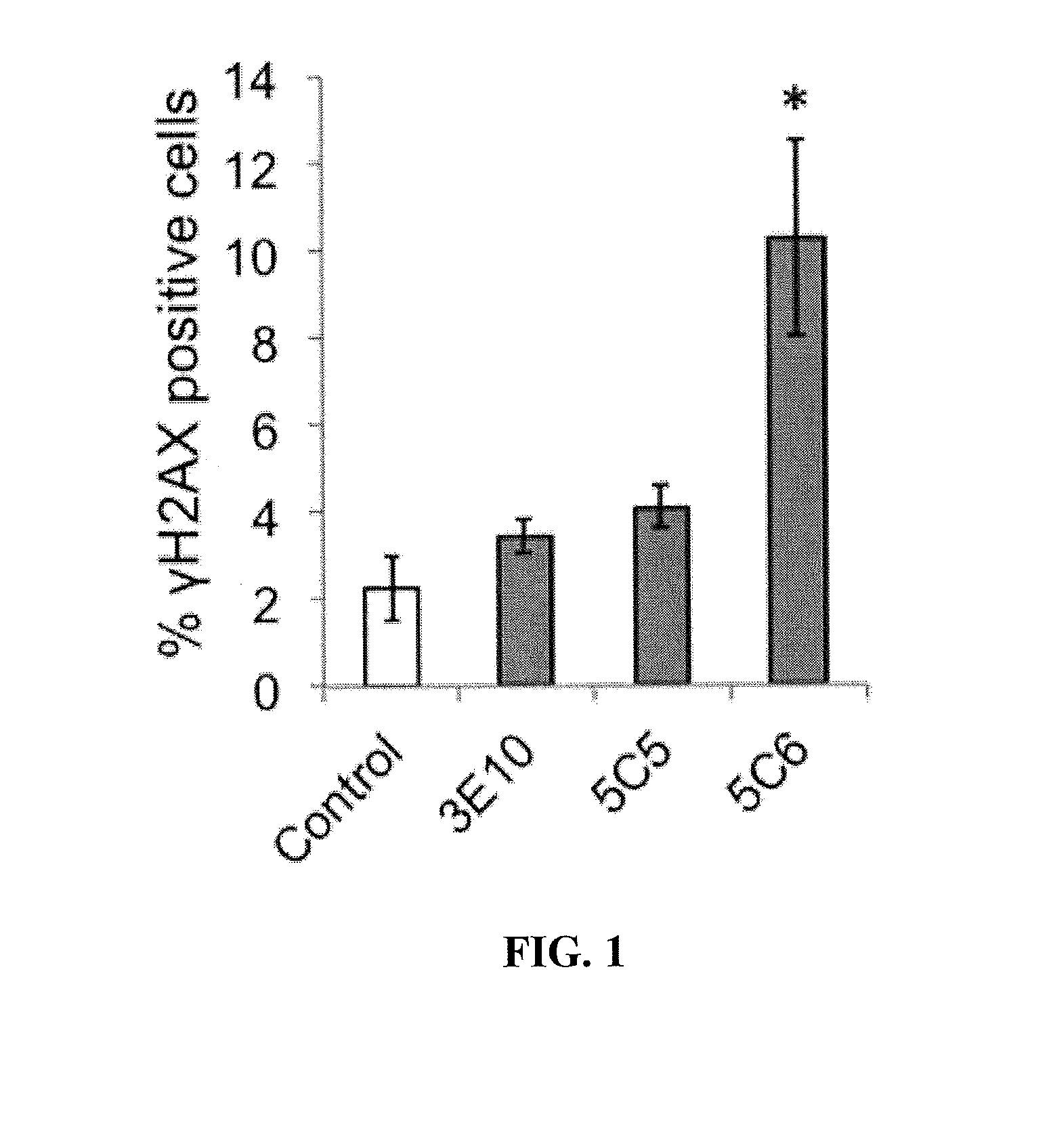
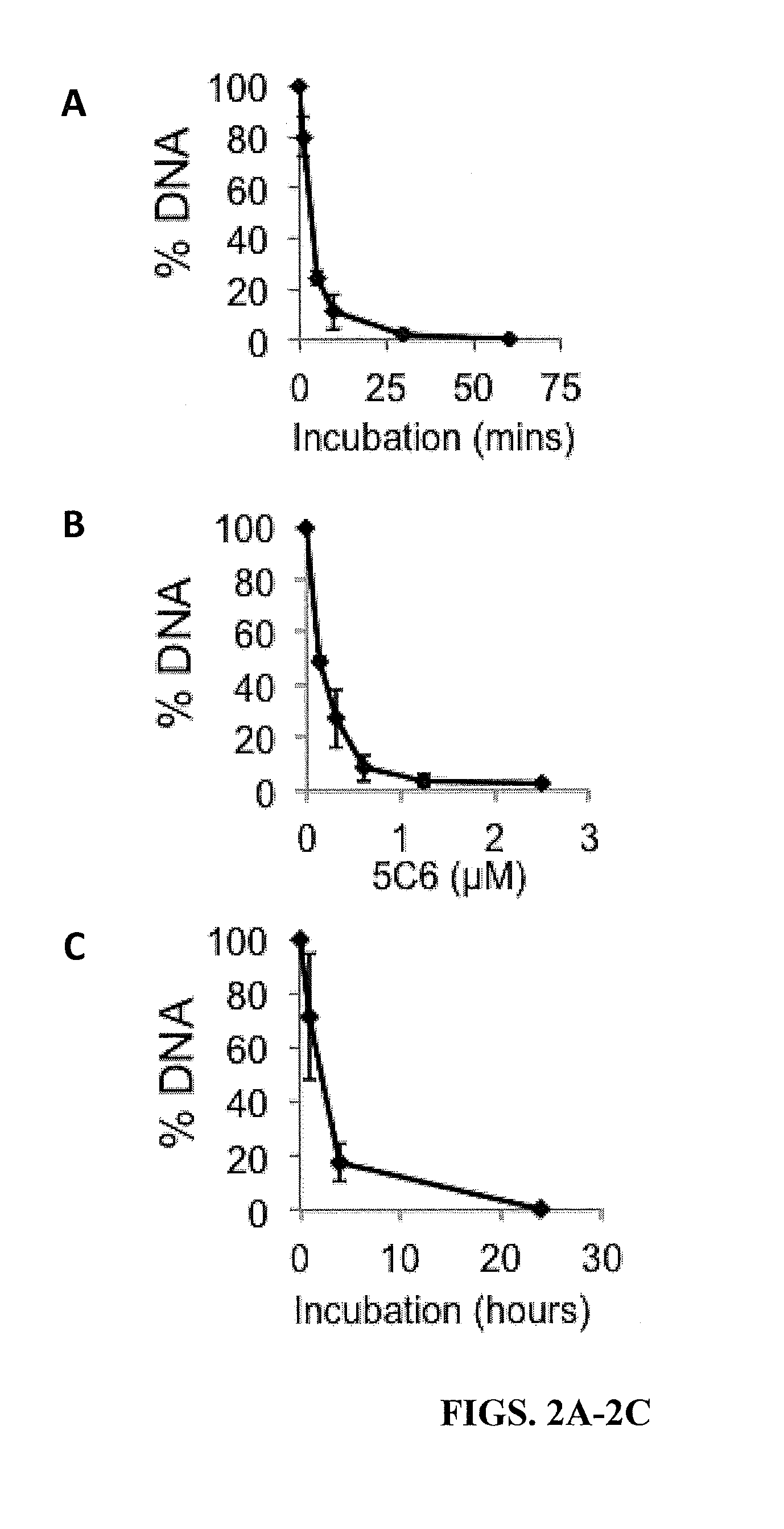
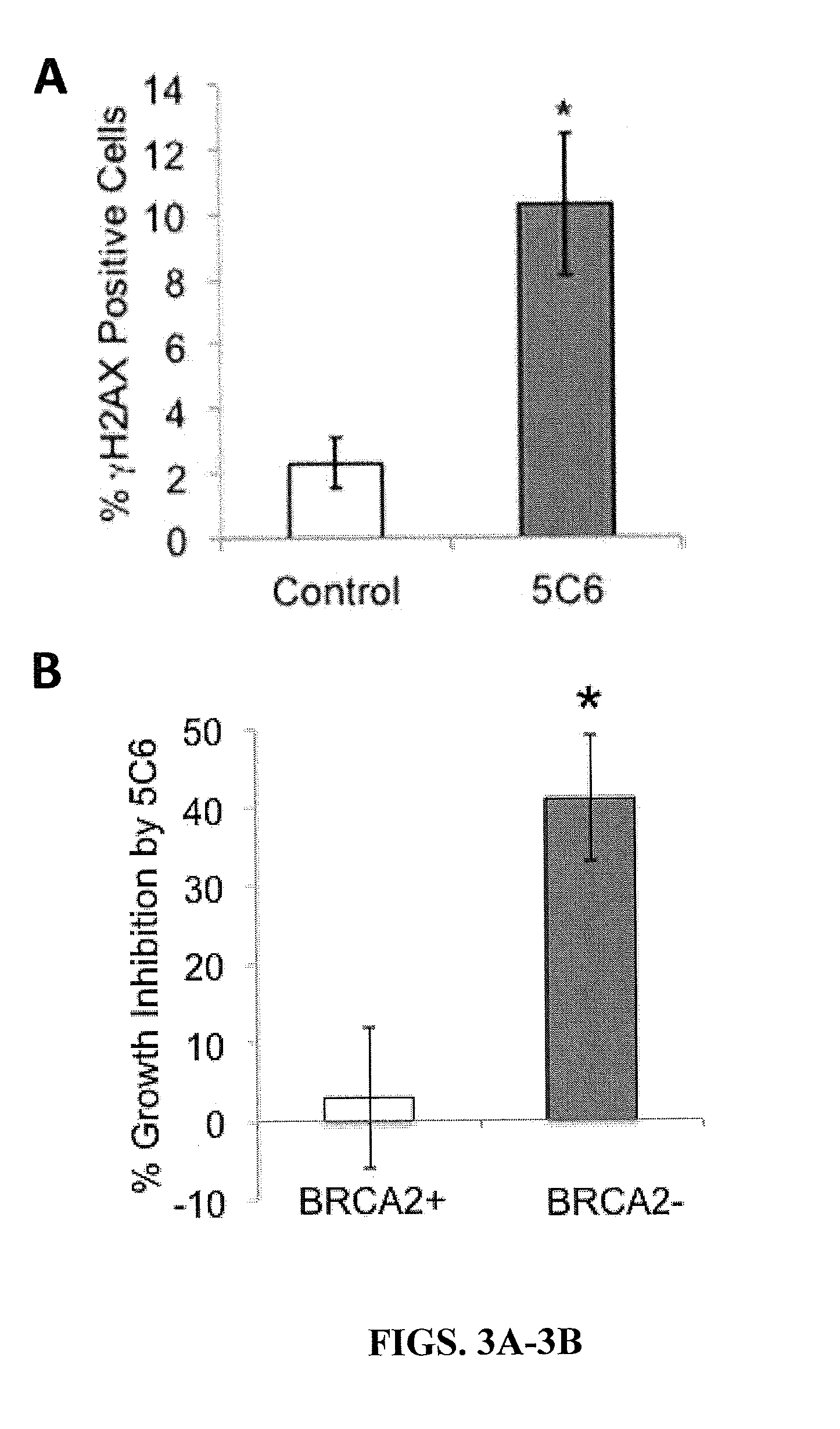
Cell penetrating nucleolytic antibody based cancer therapy
ActiveUS20150376279A1Enhance and augment efficacyImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntibody ingredientsCancer cellAutoantibody production
Cancer cells with defects in DNA repair are highly susceptible to DNA-damaging agents, but delivery of therapeutic agents into cell nuclei can be challenging. A sub-set of autoantibodies having nucleolytic activity are capable of nuclear penetration. These antibodies can be used as therapeutic agents targeted towards DNA repair-deficient malignancies.
Owner:THE GOVERNMENT OF THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE DEPT OF VETERANS AFFAIRS +1
Human anti-alpha-synuclein antibodies
Provided are human alpha-synuclein-specific autoantibodies as well as fragments, derivatives and variants thereof as well as methods related thereto. Assays, kits, and solid supports related to antibodies specific for α-synuclein are also disclosed. The antibody, immunoglobulin chain(s), as well as binding fragments, derivatives and variants thereof can be used in pharmaceutical and diagnostic compositions for α-synuclein targeted immunotherapy and diagnosis, respectively.
Owner:BIOGEN INT NEUROSCI +1
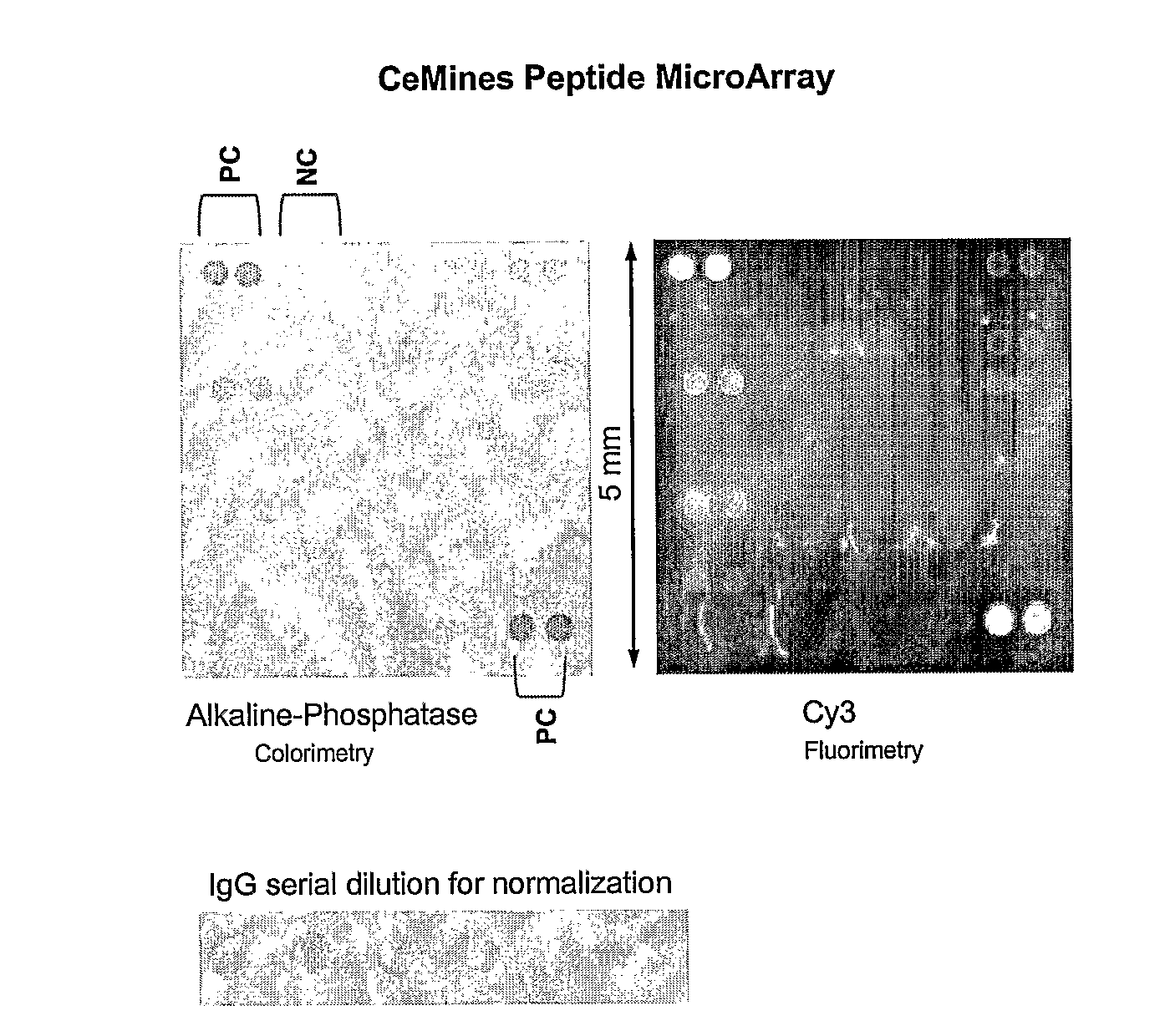
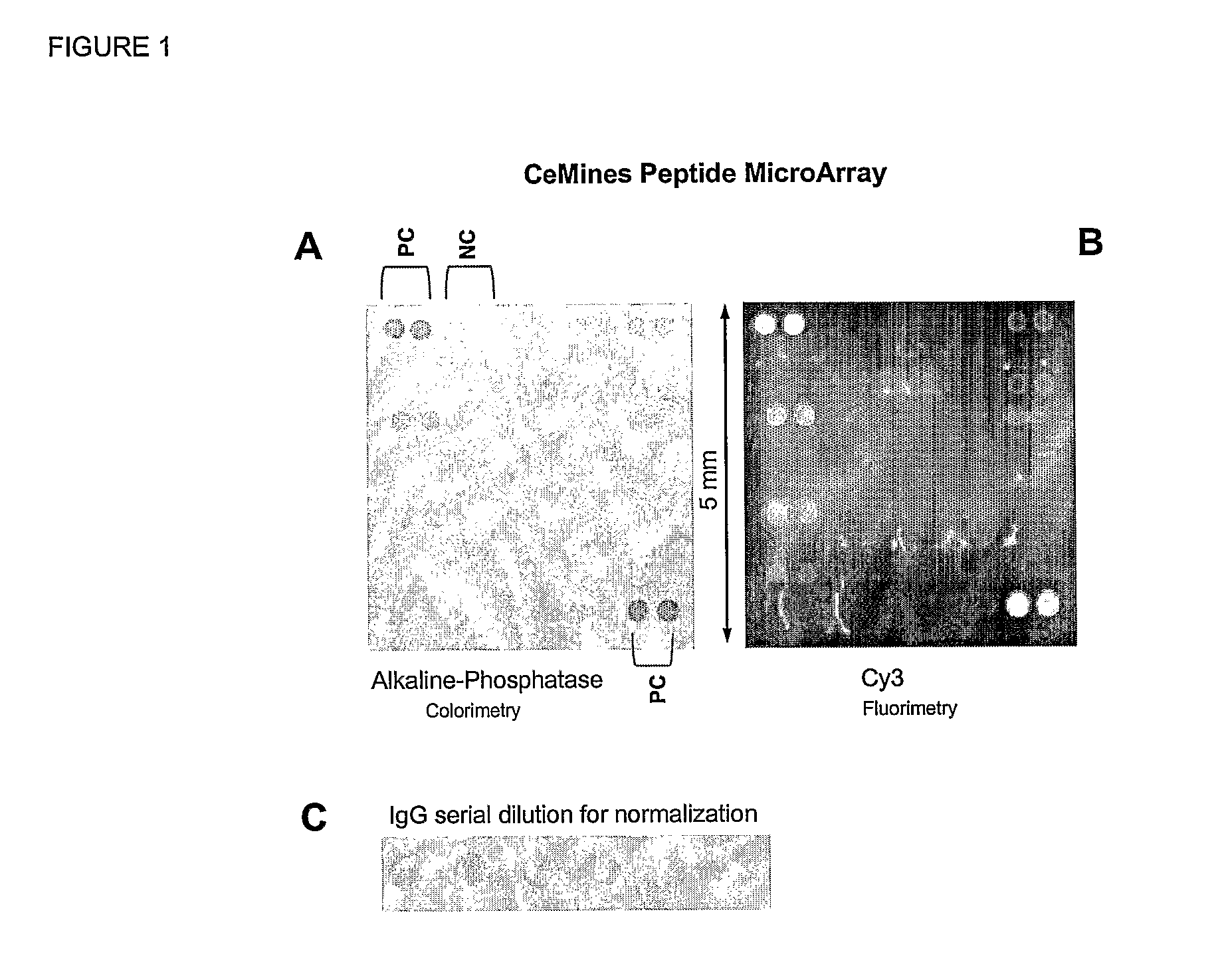
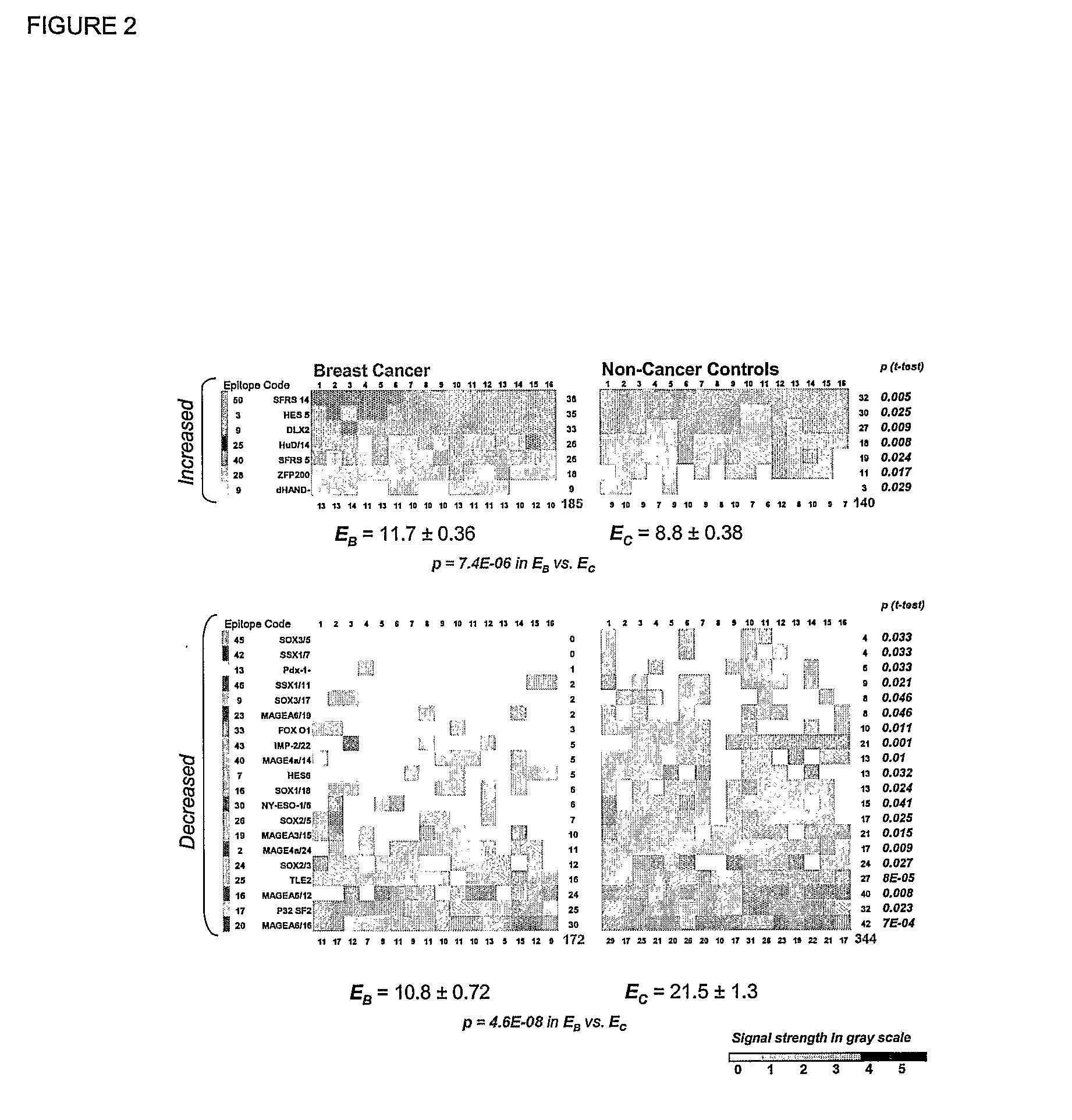
Compositions and Methods for Classifying Biological Samples
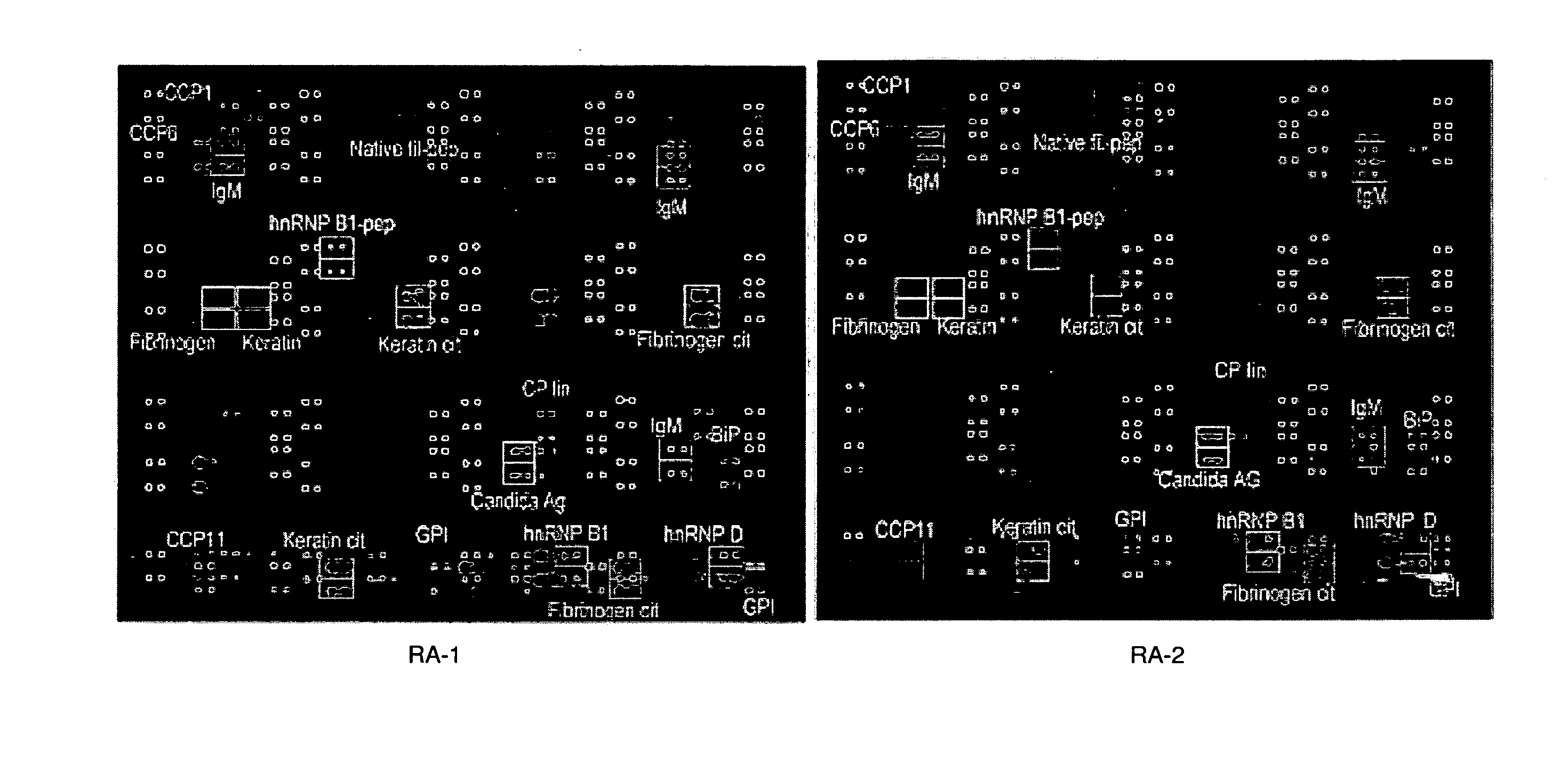
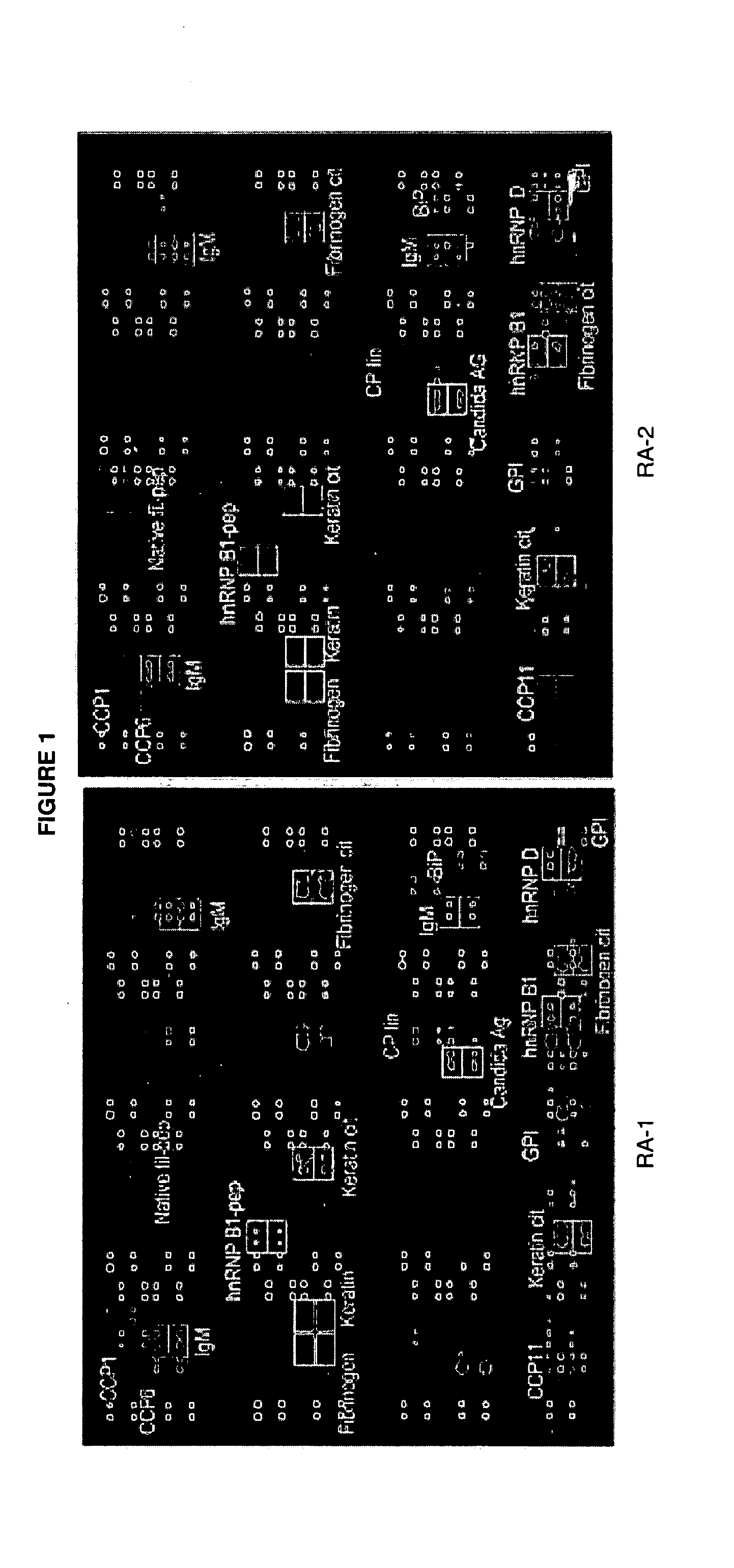
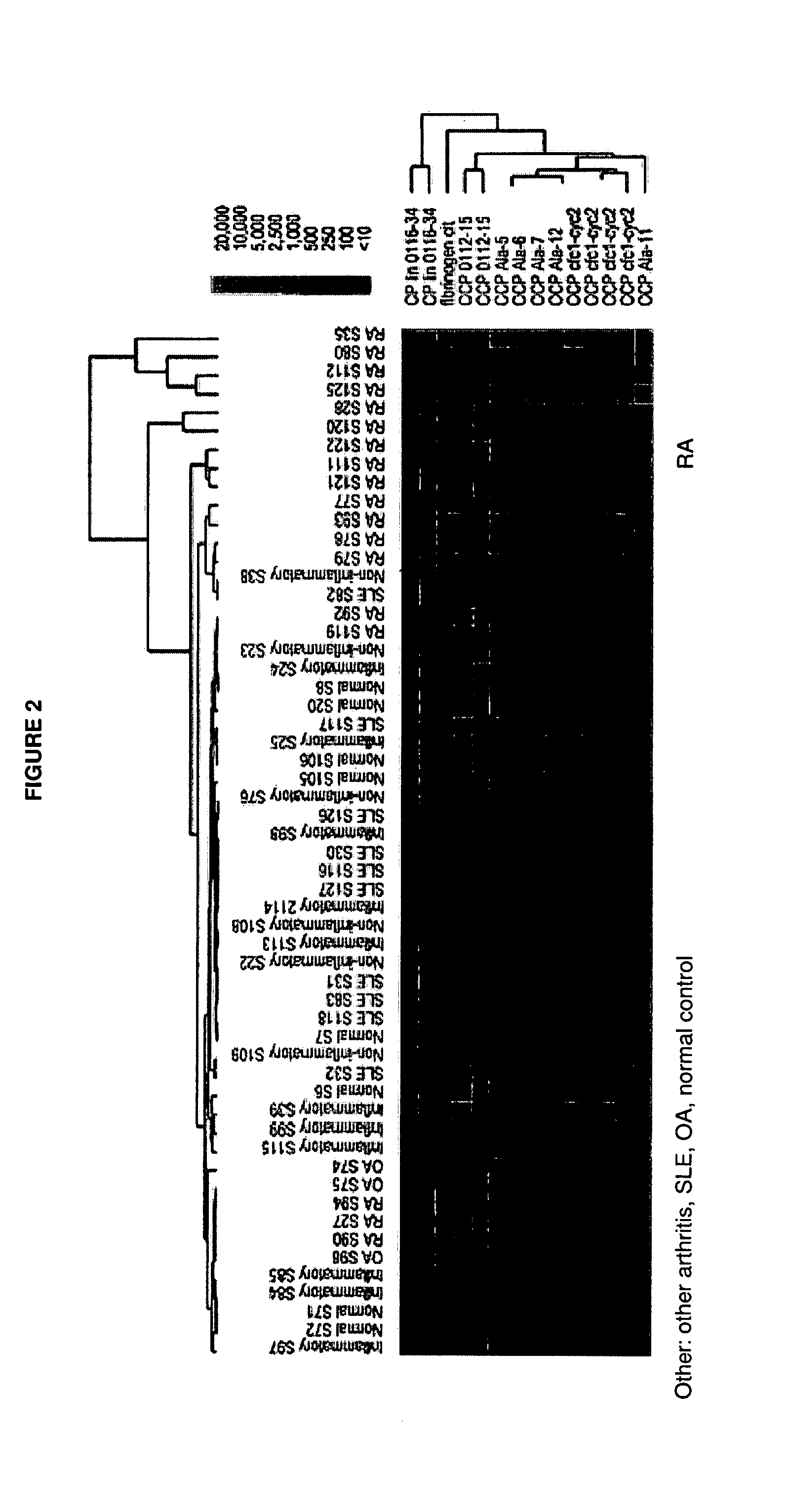
The present invention relates to autoantibodies and the detection thereof with peptide epitopes. The invention also relates to autoantibody patterns and their correlation with biological class distinctions.
Owner:CEMINES INC
Methods and compositions for use in treatment of patients with autoantibody positive diseases
InactiveCN101512007ASugar derivativesAntibody ingredientsAnti-dsDNA antibodiesSystemic lupus erythematosus
The present invention relates to methods and compositions for use in treatment of patients with autoantibody positive disease. In a specific embodiment, the present invention relates to a method of treating a patient that has an ANA titer of 1:80 or greater and / or greater than or equal to 30 IU / ml of anti-dsDNA antibodies in his / her blood plasma or serum comprising administering a therapeutically effective amount of an immunomodulatory agent, such as an antagonist of Neutrokine-alpha. Additionally provided is a method of reducing the frequency and / or quantity of corticosteroid administration to patients. In preferred embodiments, the patient has systemic lupus erythematosus. Methods for determining if a lupus patient is responding to medical treatment are also provided.
Owner:HUMAN GENOME SCI INC
Autoantibodies and their targets in the diagnosis of peripheral neuropathies
The present invention relates to methods of diagnosing peripheral neuropathies that comprise determining the titer of autoantibodies directed toward particular nervous system antigens. It also provides for substantially purified preparations of specific antigens, namely neuroprotein-1, histone H3 (NP-2), beta -tubulin (NP-3), neuroprotein-4, neuroprotein-5, NP-9 antigen, and SP neural antigen, which may be used in such diagnostic methods.
Owner:WASHINGTON UNIV IN SAINT LOUIS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com