Biomarkers for liver diseases and method for using the same
a liver disease and liver disease technology, applied in the field of liver diseases, can solve the problems of reducing the activity of immune cells, prone to developing immune diseases, and people with impaired immune functions to develop immune diseases, and achieve the effect of greater accuracy and sensitivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
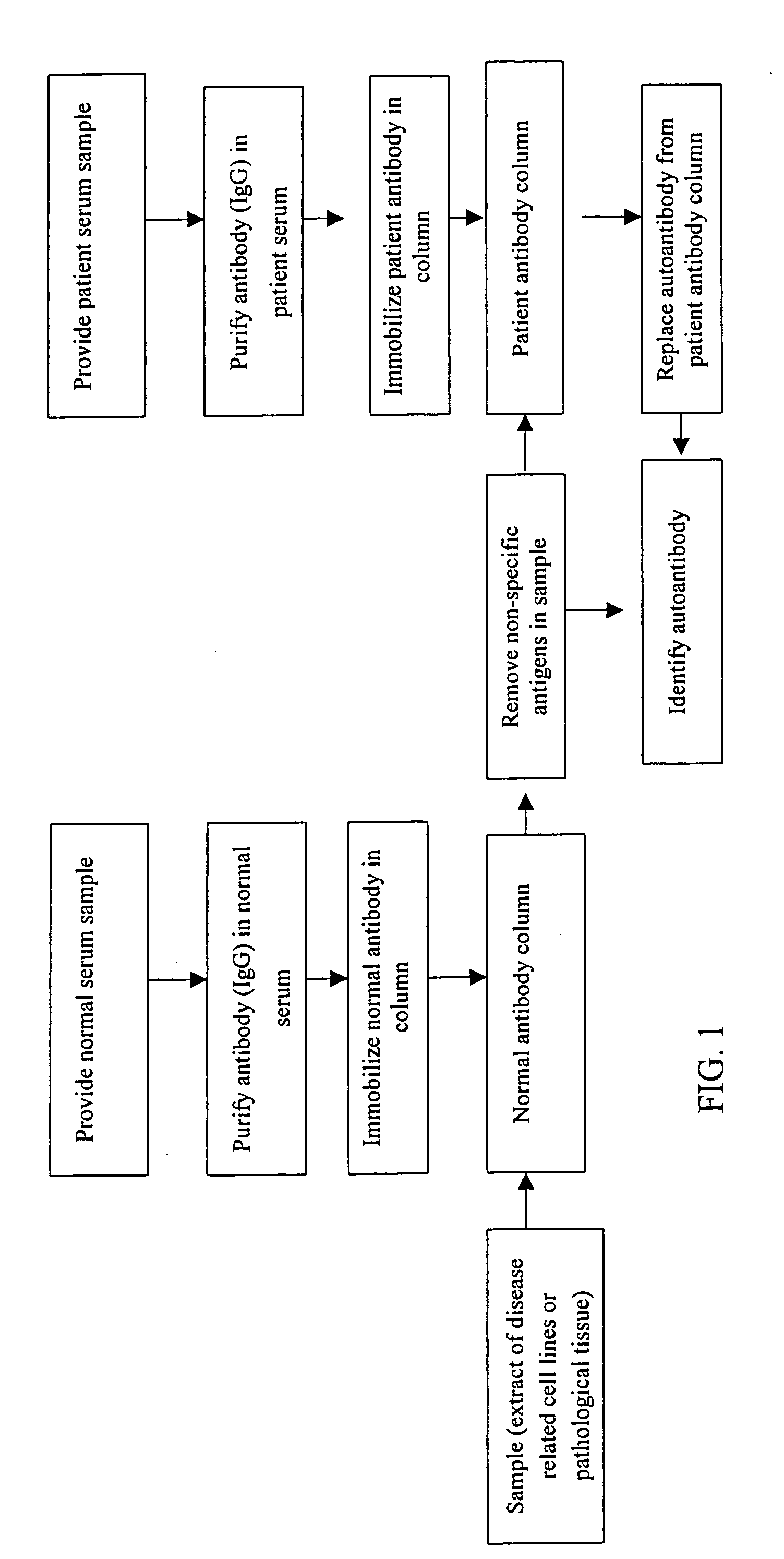
Screening of Autoantigens Using Autoantibodies in Sera of Patients with Liver Diseases Purification of Autoantibodies in the Serum Sample
[0031] Firstly obtaining a serum of a patient with liver cirrhosis or liver cancer, diluting the serum with a binding buffer (20 mM PBS, pH 7.0) at the ratio of 1:10, and then filtering the diluted serum using a 0.45 μm filter membrane to prevent the blockage of column in subsequent steps; next rinsing a Protein G affinity column with the binding buffer ten times the column volume at the rate of 1 ml / min, and then passing the filtered serum sample over the Protein G affinity column at the rate of 0.2 ml / min to retain the antibodies in the column through affinity; rinsing the Protein G affinity column again using the binding buffer 5-10 times the column volume at the rate of 1 ml / min to remove substances in the serum sample that do not form affinity bonding with the column. Eluting antibodies from the column using an elution buffer (0.1 M Glycine-...
example 2
Determining the Availability of Autoantigens Identified by the Autoantigen Screening Method
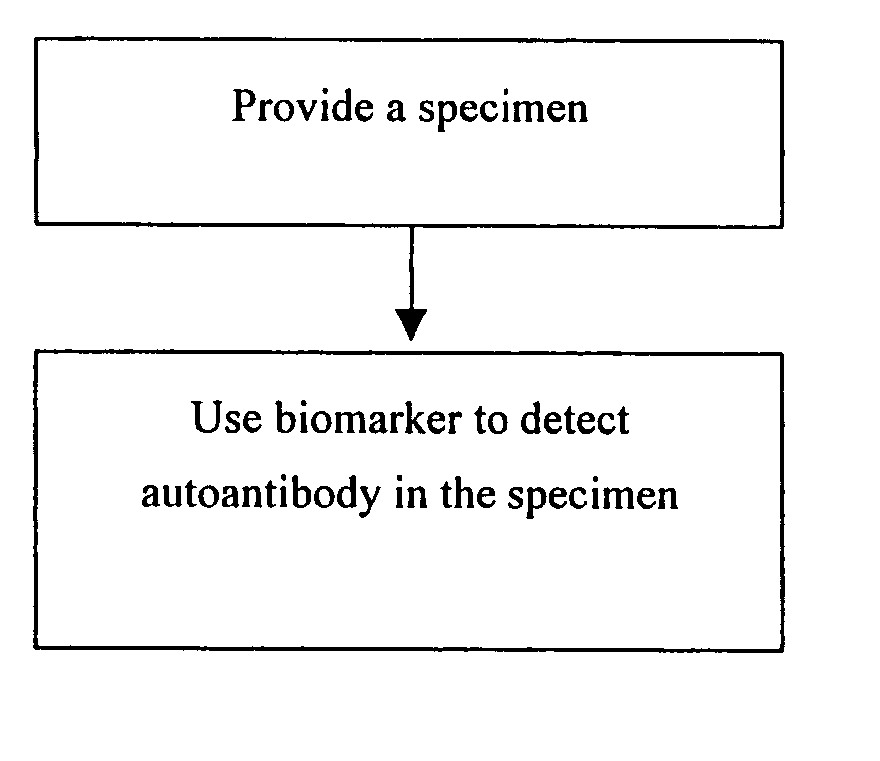
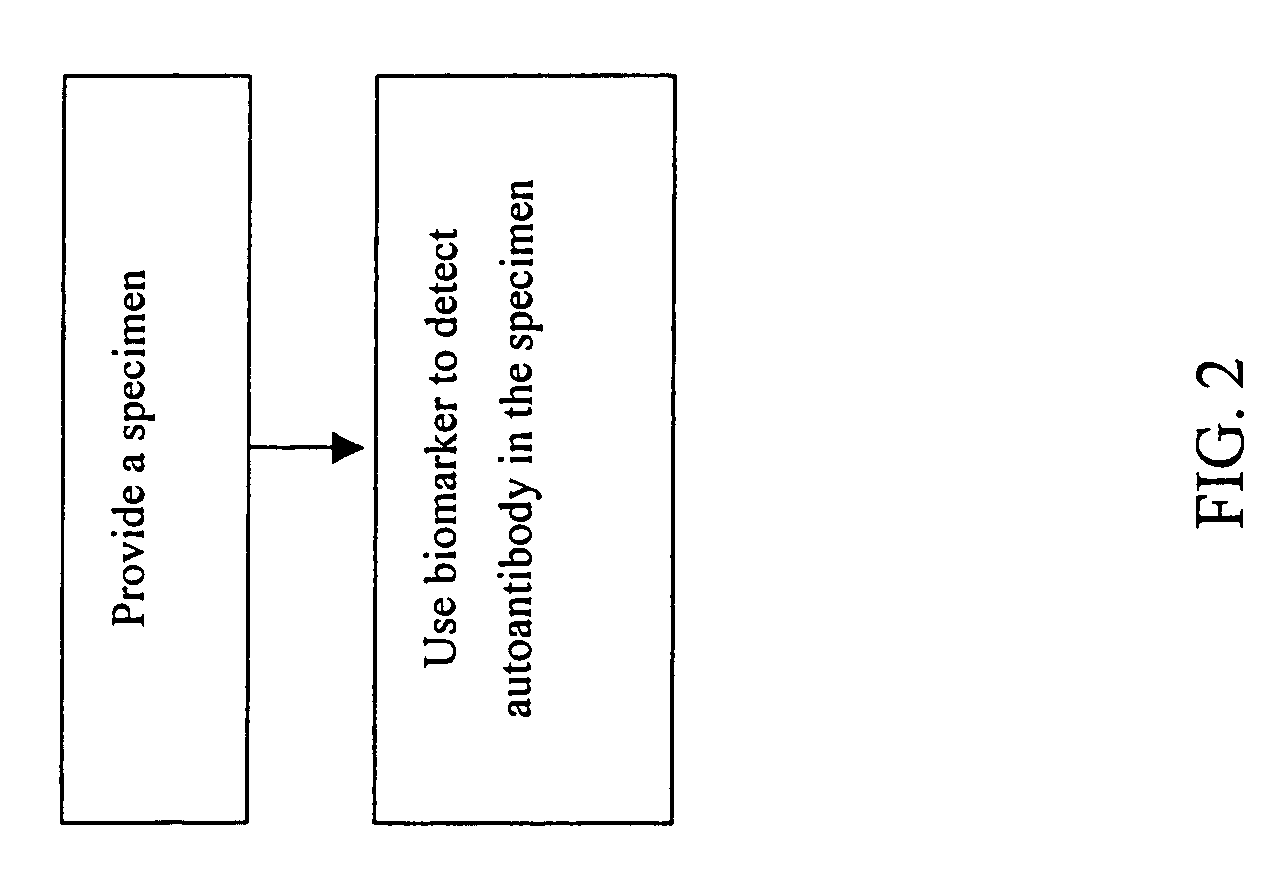
[0063] To demonstrate the availability of 24 autoantigens identified in Example 1, further assay of serum samples from normal persons, liver cirrhosis patients and liver cancer patients using immunoassay (ELISA, RIA or immunofluorescence) and the aforesaid 24 biomarkers is carried out. The assay method includes the following steps as shown in FIG. 2: providing a specimen; using the biomarker selected from any one of the amino acid sequences with SEQ ID NO:1 to SEQ ID NO:24 or derivatives or fragments or variants or the combination thereof to capture the autoantibody in the specimen; and detecting the auto antibody.
[0064] In the example of enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), the following steps are taken: firstly diluting the biomarker with a coating buffer (choice of a. 50 mM Na2HCO3, pH=9.6, or b. 20 mM Tris-HCl, pH=8.5, or c. 10 mM PBS, pH=7.4) to a concentration of 0.5˜10 μg / ml, w...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pH | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pH | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pH | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com