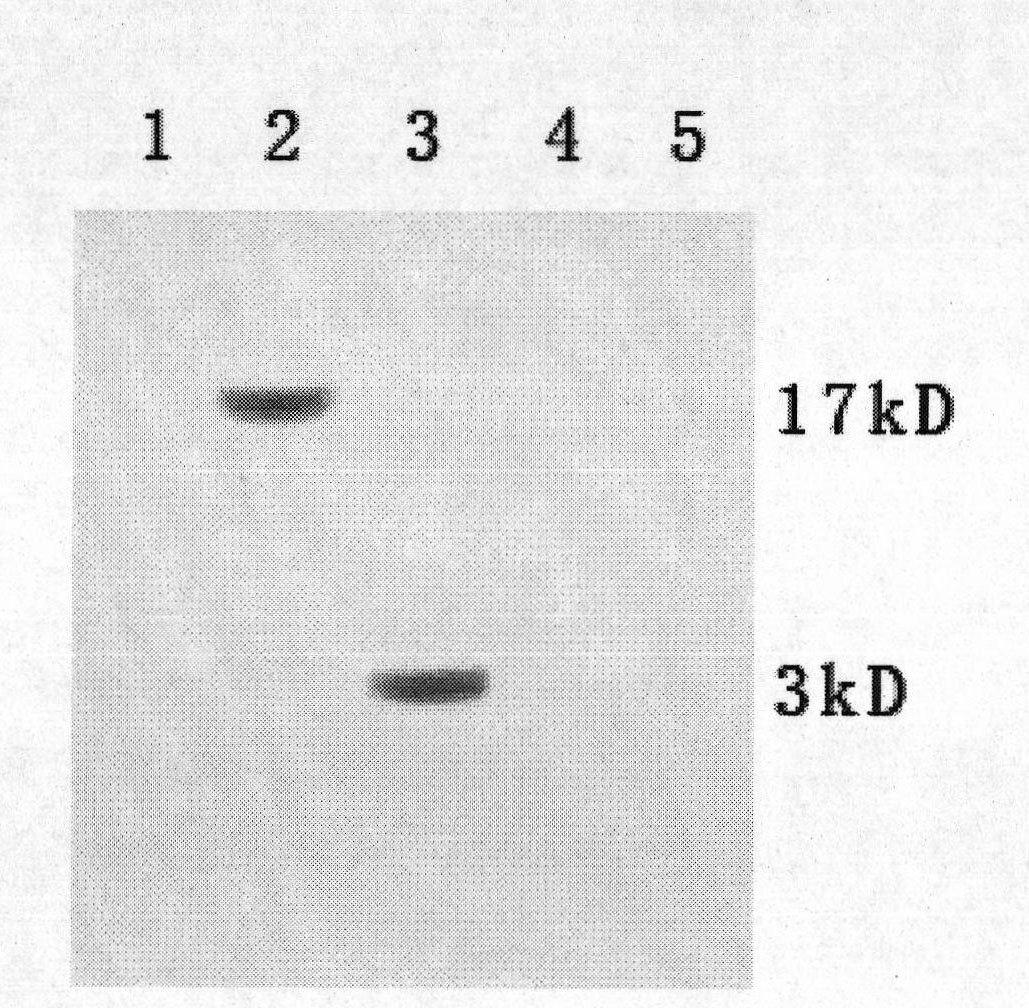
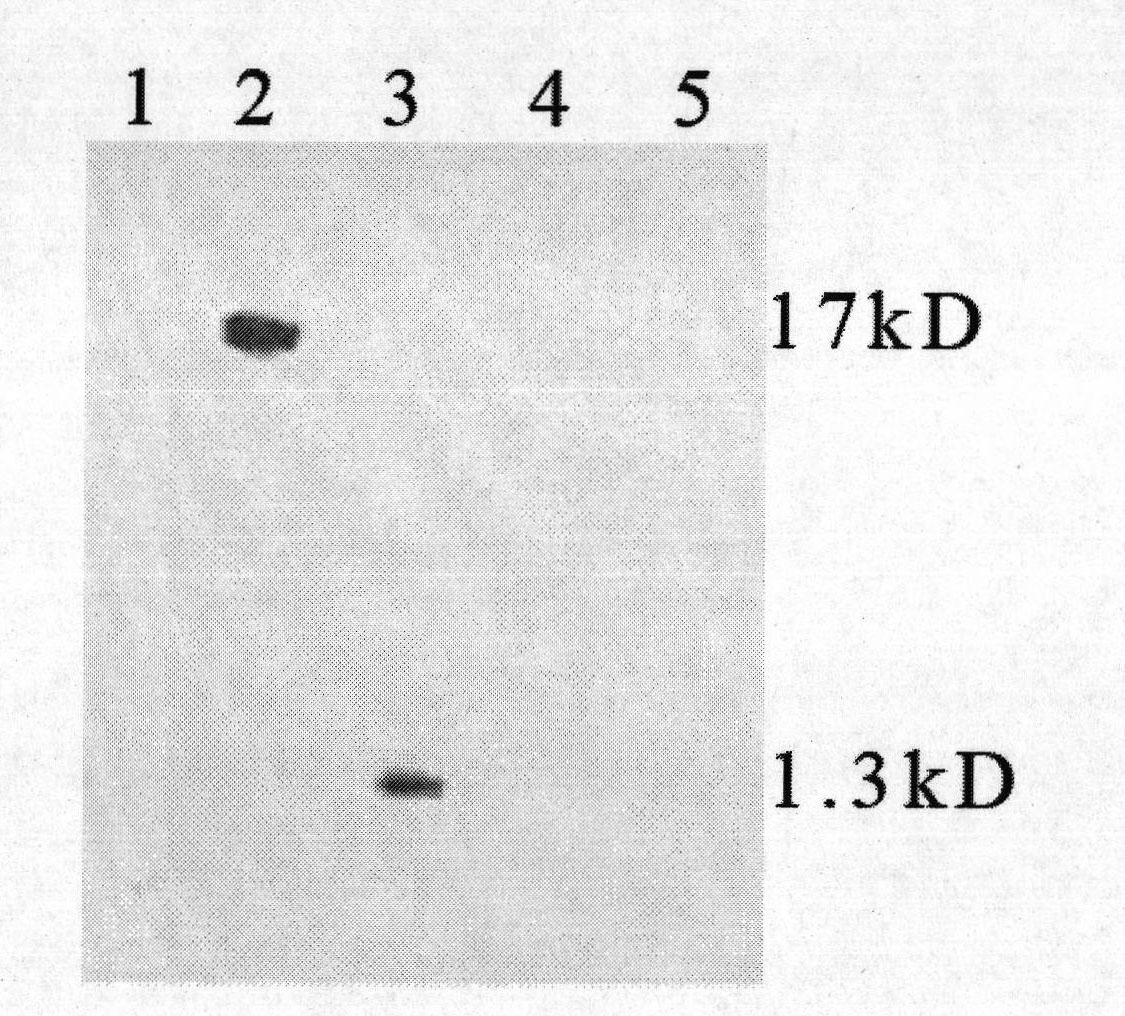
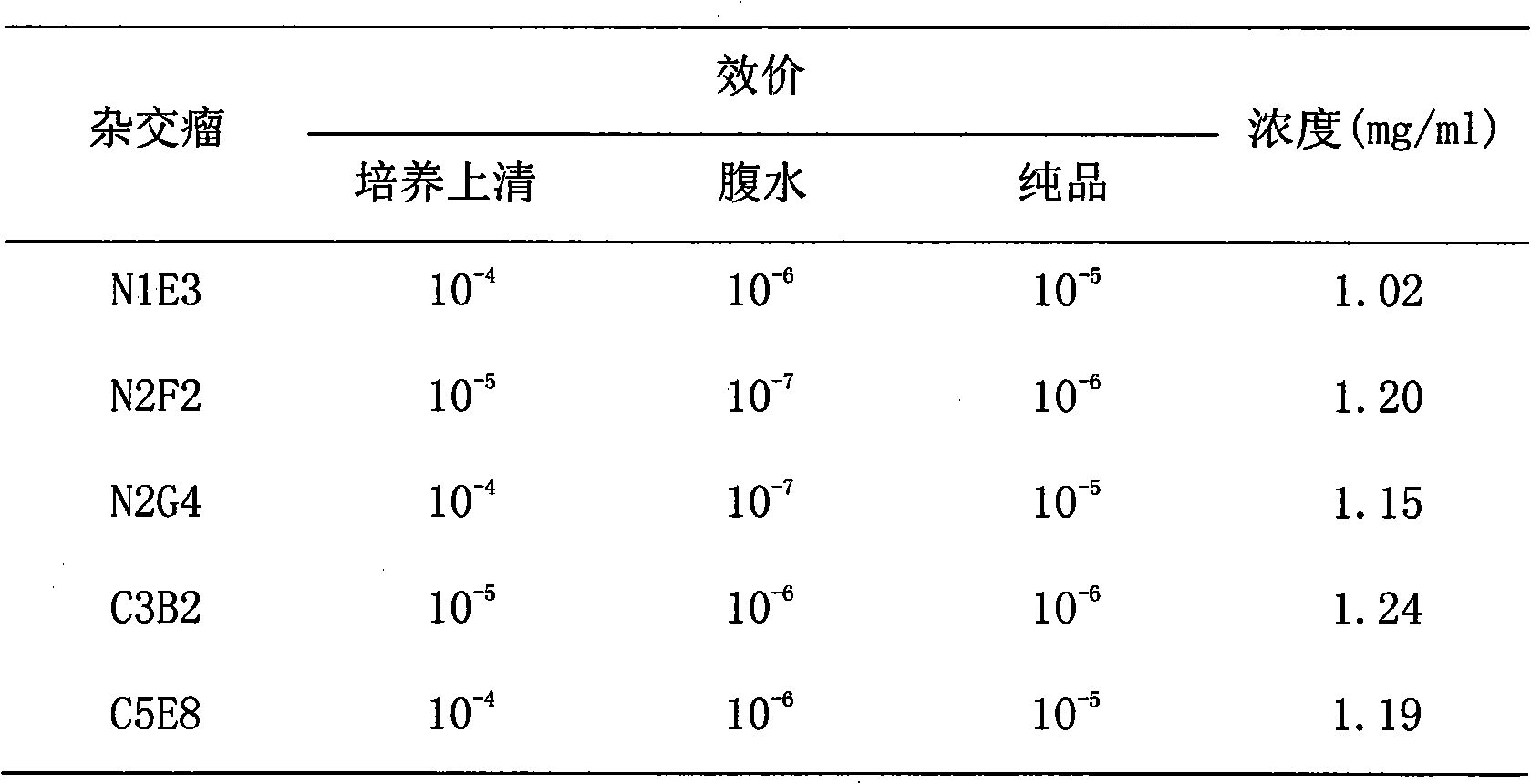
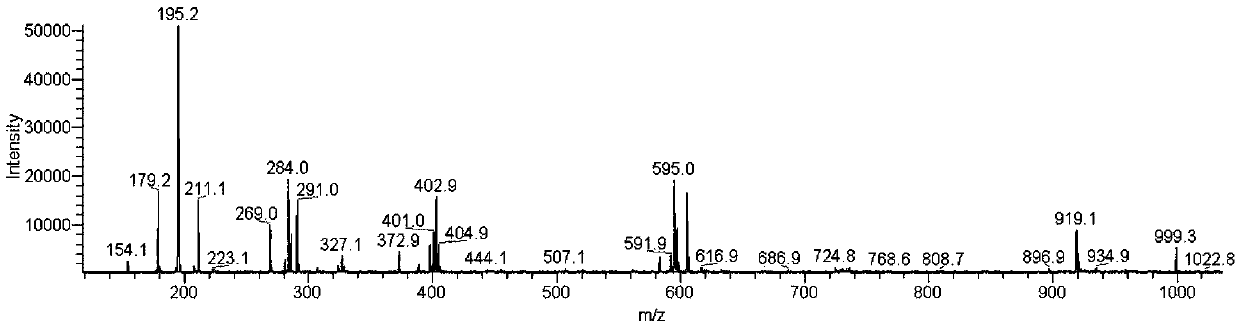
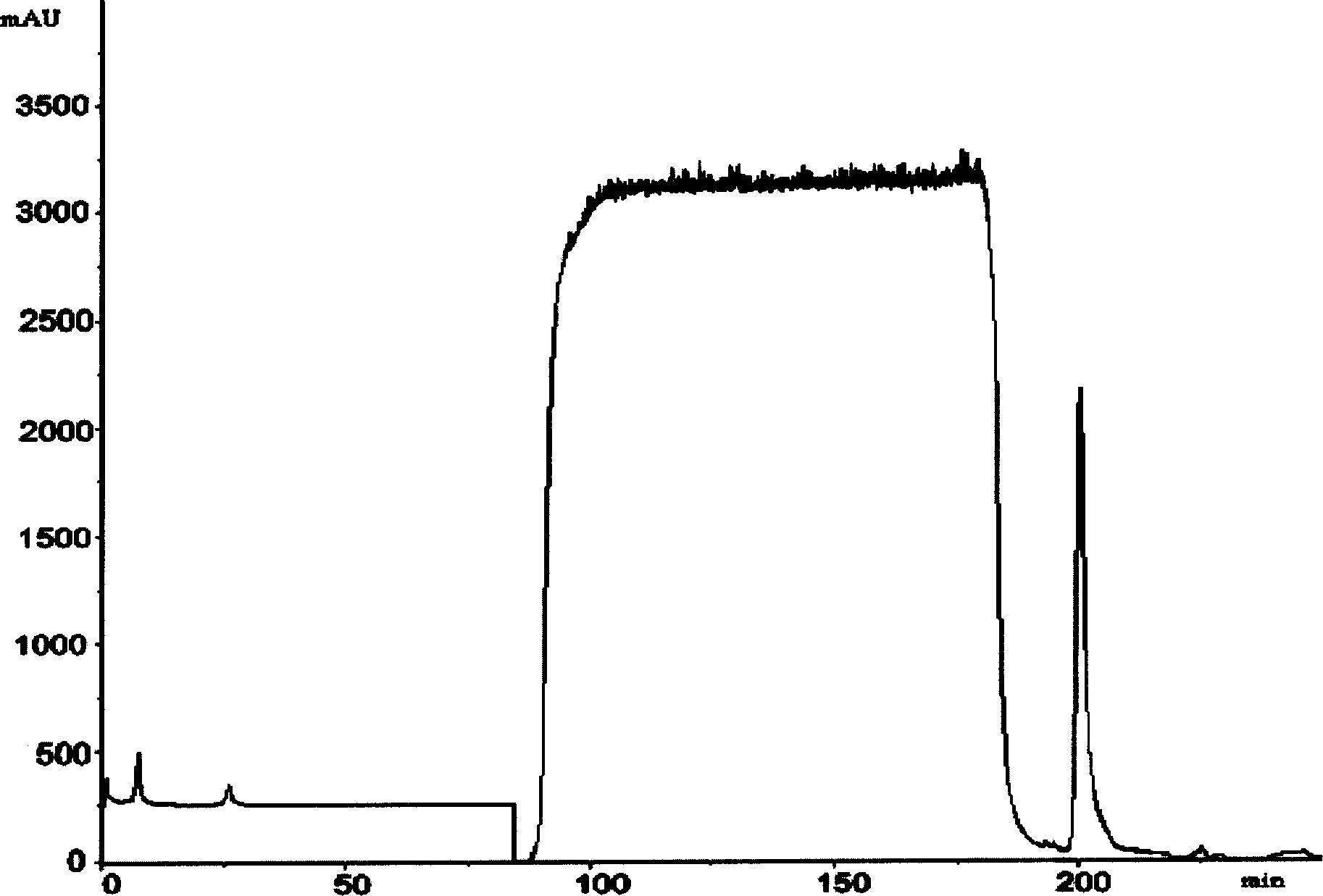
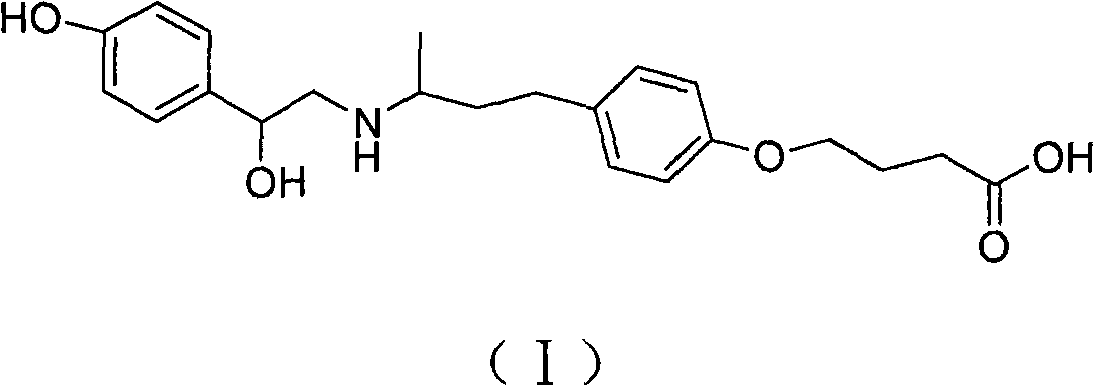
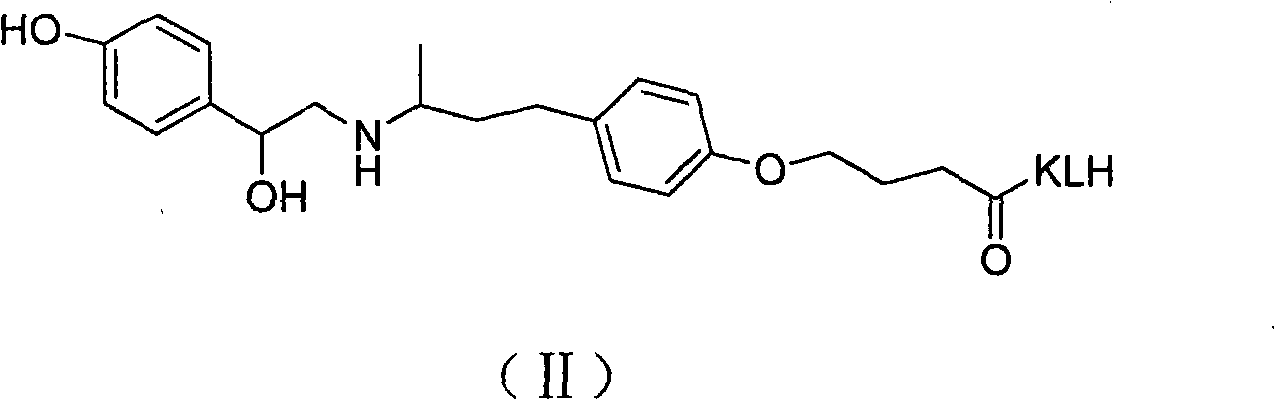
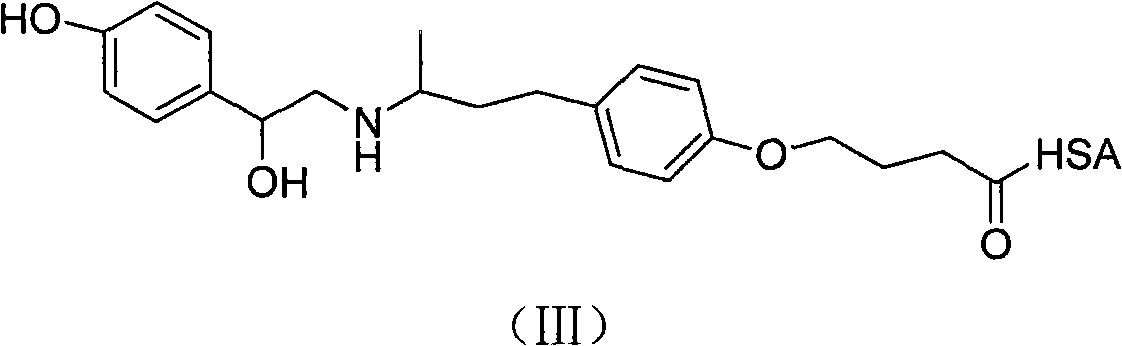
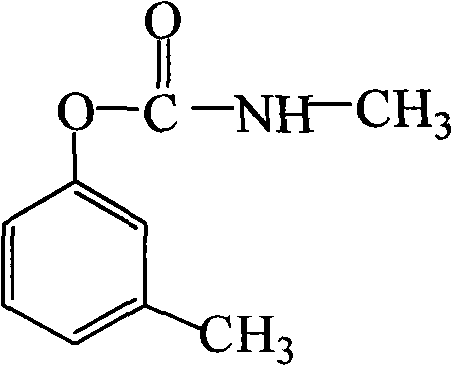
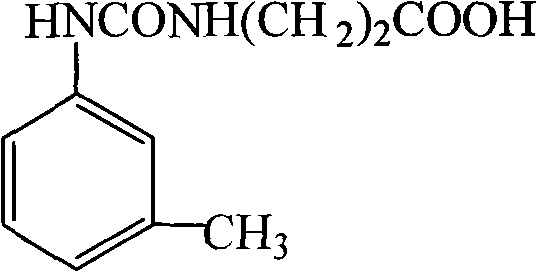
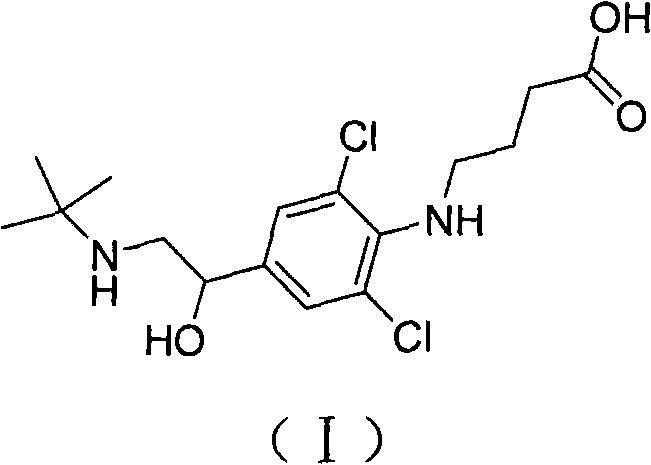
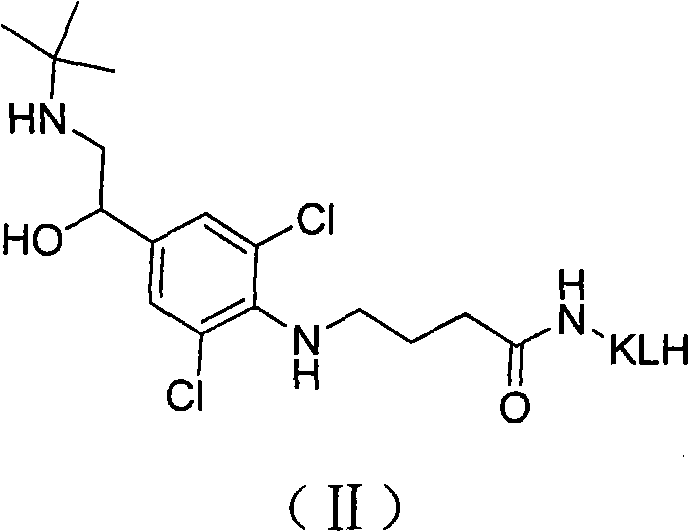
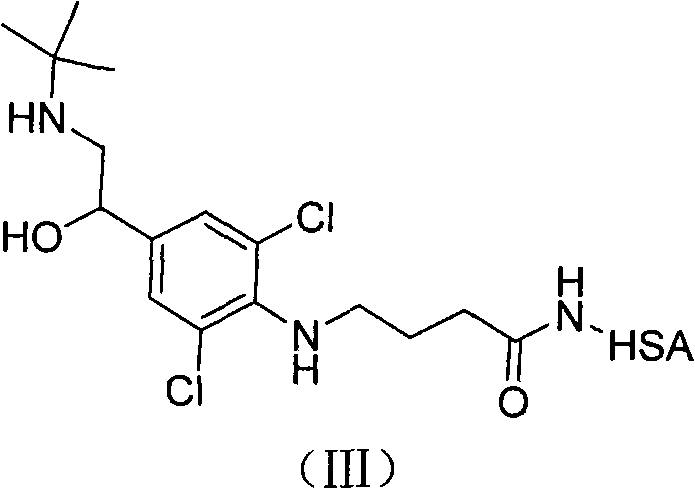
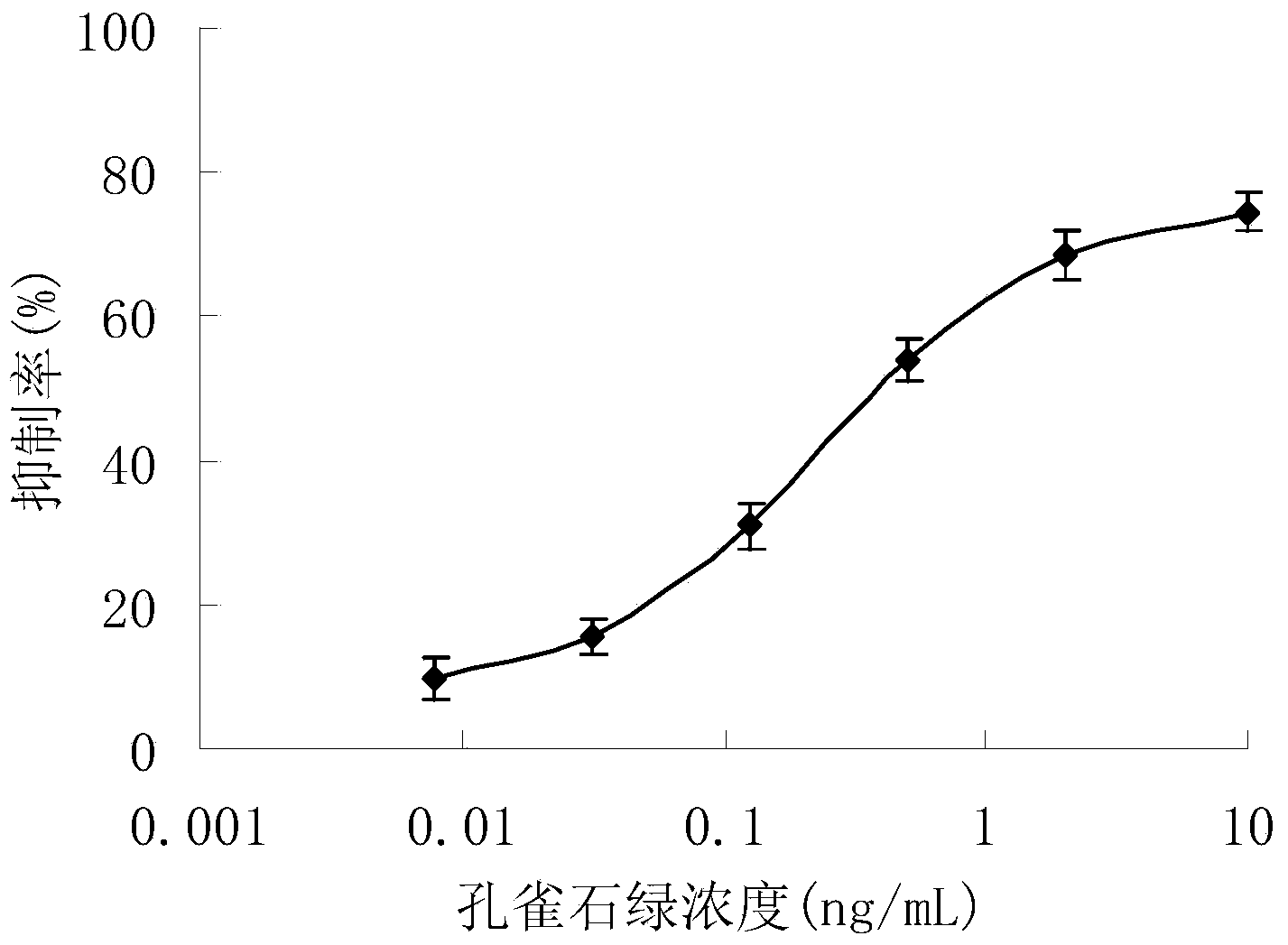
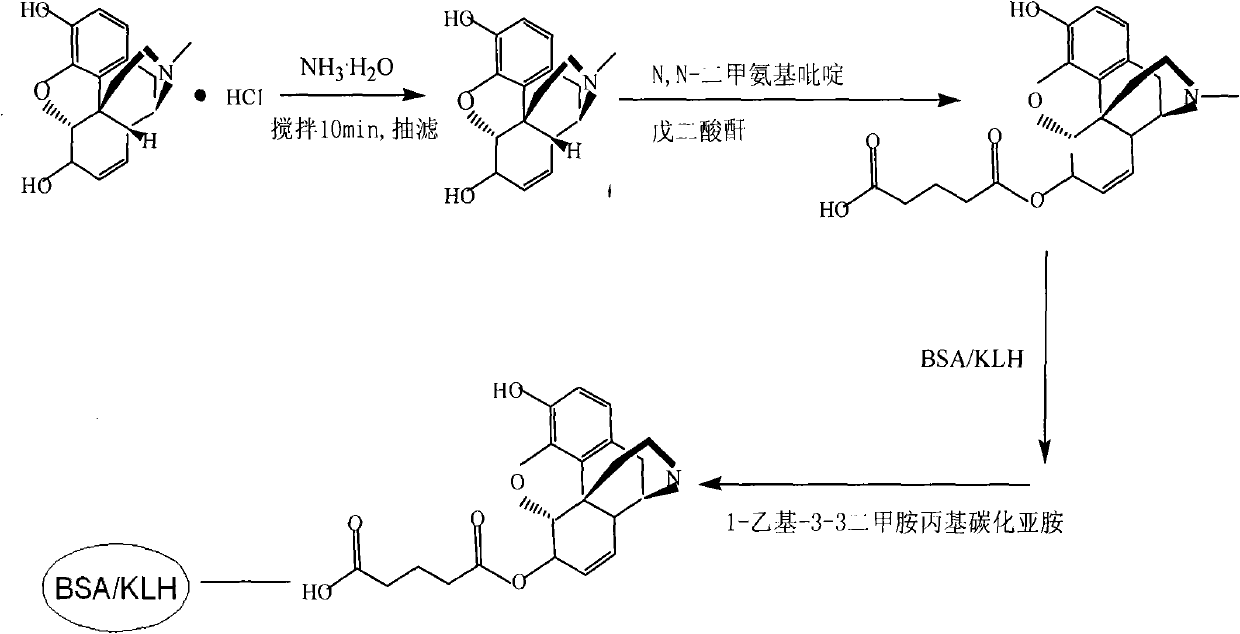
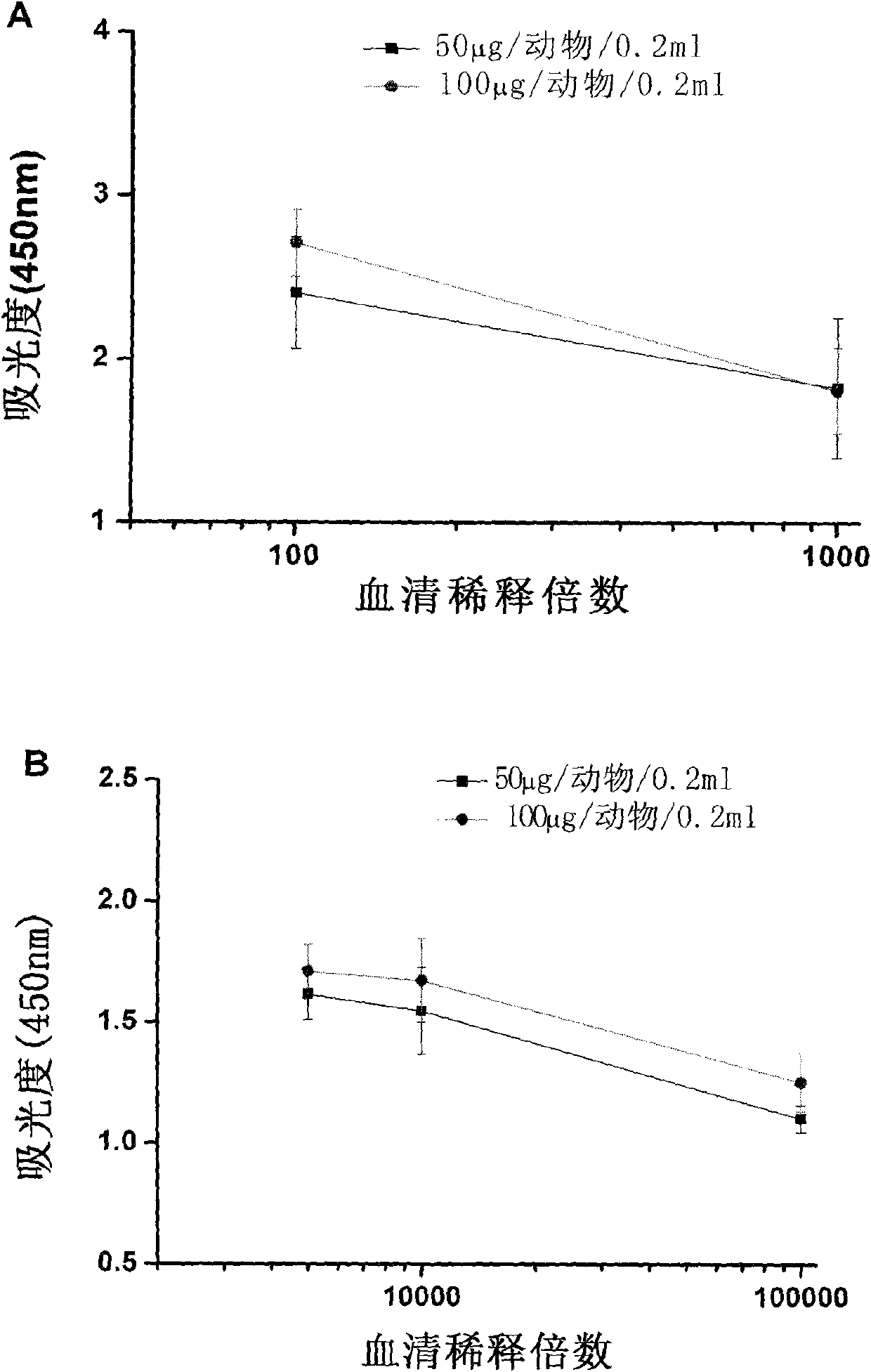
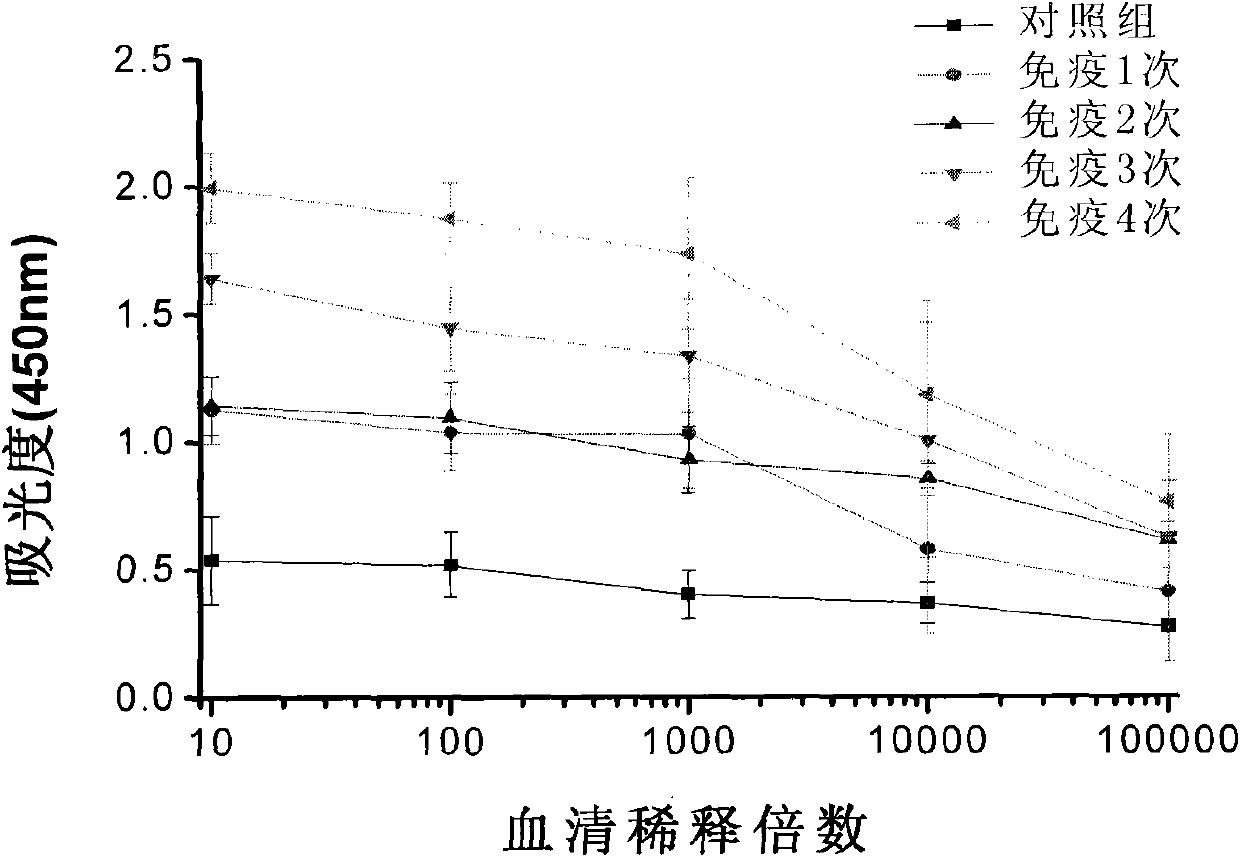
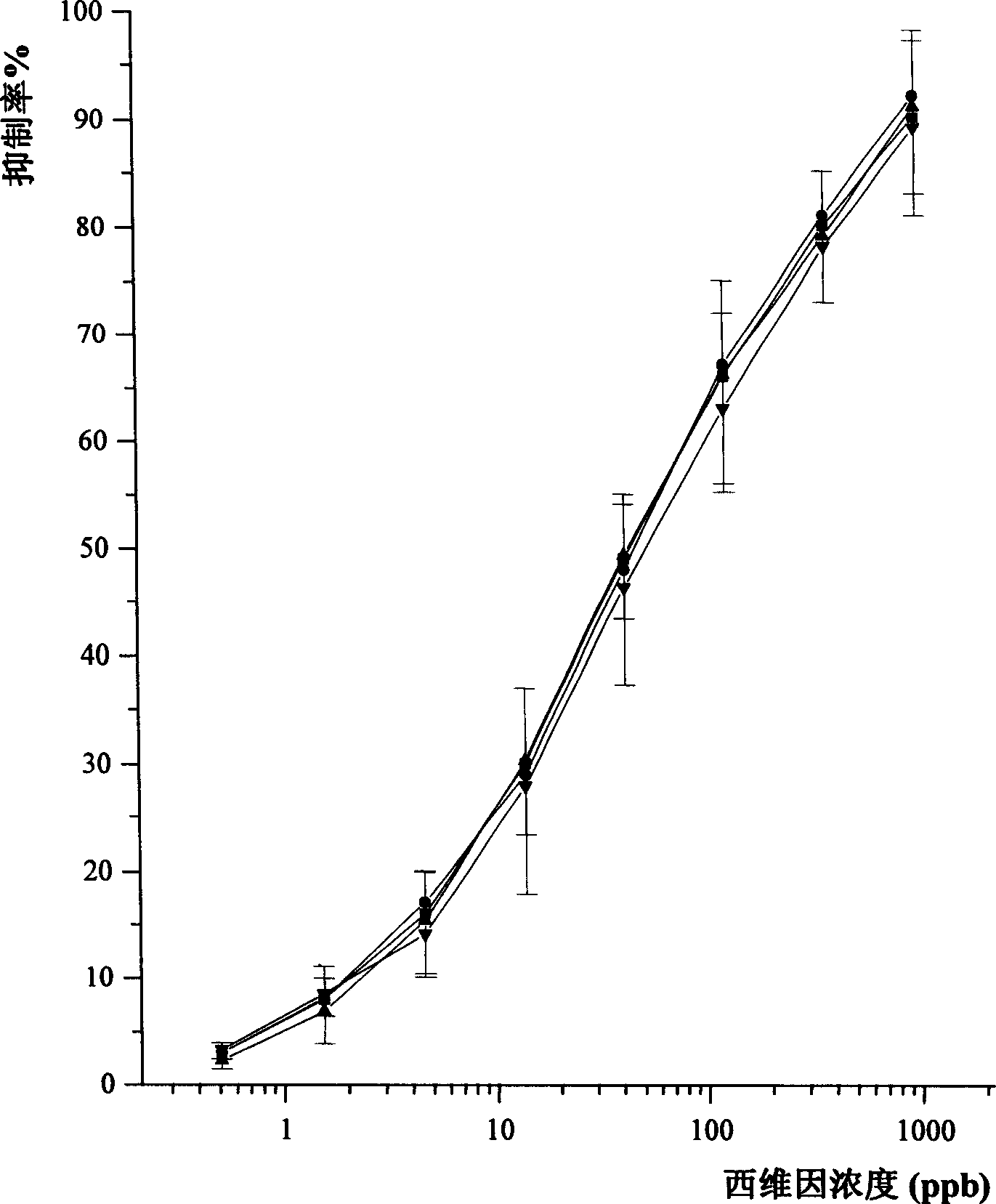
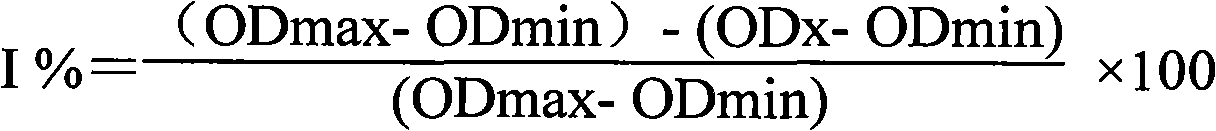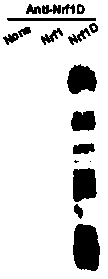Patents
Literature
156 results about "Hemocyanin" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
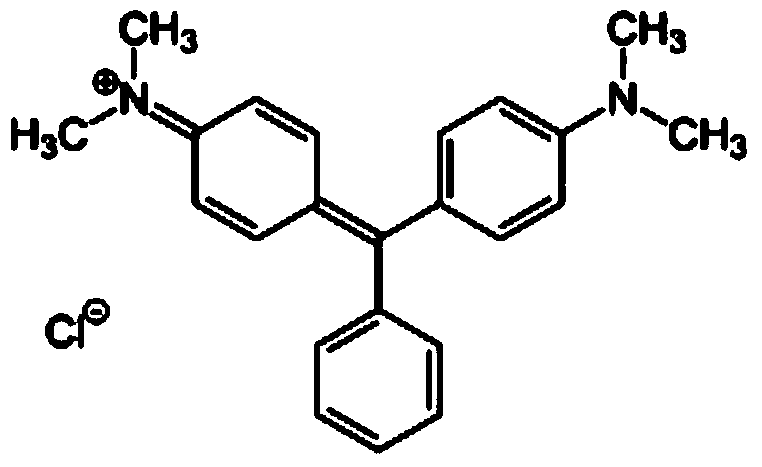
Hemocyanins (also spelled haemocyanins and abbreviated Hc) are proteins that transport oxygen throughout the bodies of some invertebrate animals. These metalloproteins contain two copper atoms that reversibly bind a single oxygen molecule (O₂). They are second only to hemoglobin in frequency of use as an oxygen transport molecule. Unlike the hemoglobin in red blood cells found in vertebrates, hemocyanins are not bound to blood cells but are instead suspended directly in the hemolymph. Oxygenation causes a color change between the colorless Cu(I) deoxygenated form and the blue Cu(II) oxygenated form.
Method of preparing bombyx mori silk fibroin specific antibody by utilizing characteristic polypeptide
InactiveCN103509107AStrong specificityStrong immune responseSerum immunoglobulinsImmunoglobulins against animals/humansPenicillinKeyhole-limpet haemocyanin
The invention discloses a method of preparing a bombyx mori silk fibroin specific antibody by utilizing a characteristic polypeptide. The method comprises the following steps: synthesizing a "CGAGAGSGAGAGS" polypeptide sequence by utilizing an Fmoc method, coupling the polypeptide with keyhole limpet hemocyanin (KLH) through the cysteine on the N terminus of the polypeptide so as to obtain a complete antigen; diluting the complete antigen with normal saline, mixing the diluted complete antigen with a complete Freund's adjuvant, adding streptomycin and penicillin to carry out an emulsion treatment so as to obtain a primary immunized antigen emulsion, subjecting a rabbit to a primary immunization by using the primary immunized antigen emulsion, then subjecting the rabbit to a strengthened immunization, wherein the strengthened immunization uses a strengthened immunized antigen emulsion, which is prepared by the following steps: mixing the diluted complete antigen with an incomplete Freund's adjuvant, and then adding streptomycin and penicillin to carry out an emulsion treatment so as to obtain the target product; collecting the blood of the immunized rabbit, when the antibody titer in the rabbit blood sample reaches 1 / 10000; making the blood blocks fully contract to completely separate out the antiserum, then collecting the antiserum, and subjecting the antiserum to a centrifugation treatment so as to obtain a supernate.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV +1
Polyclonal antibody of phosphorylating and corresponding non-phosphorylating protein in application for preparing reagent for disease diagnosis, and preparation method
A method for preparing multicloning antibody includes synthesizing polypeptide, connecting the coupling agent with keyhole limpet hemocyanin for forming hapten ¿C carrier protein system, immunizing rabbit then picking up its blood for separating out serum, purifying out multicloning antibody of anti ¿C specific site amino acid phosphorylation protein and anti ¿C corresponding non phosphorylation protein after two steps of antigen affinity chromatography .
Owner:南京川博生物技术有限公司
Method of preparing bombyx mori silk fibroin specific antibody by utilizing characteristic dodecapeptide
InactiveCN103509108AStrong specificityStrong immune responseSerum immunoglobulinsImmunoglobulins against animals/humansKeyhole-limpet haemocyaninPrimary immunization
The invention discloses a method of preparing a bombyx mori silk fibroin specific antibody by utilizing a characteristic dodecapeptide. The method comprises the following steps: synthesizing a polypeptide with a "CGYGAGAGAGYGA" sequence, coupling the polypeptide with keyhole limpet hemocyanin (KLH) so as to obtain a complete antigen; diluting the complete antigen with normal saline, mixing the diluted complete antigen with a complete Freund's adjuvant, carrying out an emulsion treatment so as to obtain primary immunized antigen emulsion, subjecting a rabbit to a primary immunization by using the primary immunized antigen emulsion, then subjecting the rabbit to a strengthened immunization, wherein the strengthened immunization uses a strengthened immunized antigen emulsion, which is prepared by the following steps: mixing the diluted complete antigen with an incomplete Freund's adjuvant, and then carrying out an emulsion treatment so as to obtain the target product; collecting the blood of the immunized rabbit, when the antiserum titer of rabbit arrives at 1 / 10000; making the blood blocks fully contract to completely separate out the antiserum, then collecting the antiserum, and subjecting the antiserum to a centrifugation treatment so as to obtain a supernate. The antibody prepared by the invention has a strong specificity, and can be used for detection and analysis of silk fibroin in textile, and the like.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV +1
Vitamin D synthetic antigen, and preparation method and preparation thereof
ActiveCN103588872AQuick checkAchieve batchOvalbuminSerum albuminVitamin D synthesisBovine serum albumin
The invention provides a vitamin D synthetic antigen and a preparation method thereof. The vitamin D synthetic antigen is a conjugate of vitamin D and a protein carrier. The vitamin D is 25-hydroxy vitamin D3 or 1,25-dihydroxy vitamin D3; and the protein carrier is one or more selected from bovine serum albumin, ovalbumin, hemocyanin and human serum albumin. The invention also provides application of the vitamin D synthetic antigen to vitamin D immunological detection. The invention further provides a vitamin D detection kit, which integrates the advantages of existing clinical vitamin D detection methods; and the kit can be applied to all enzyme mark instruments, chemiluminescence instruments and time-resolved analyzers, and has greatly shortened detection time, and sensitivity, accuracy and precision met the detection requirements. The immunosorbent assay kit with strong versatility provided by the invention can realize batch and rapid detection on vitamin D in serum (or plasma).
Owner:BEIJING BOHUI INNOVATION TECH
Monoclonal antibody of hepatitis B virus X protein and use thereof
The invention relates to a monoclonal antibody of hepatitis B virus X protein (HBx), which is characterized by having specificity reaction to N-end epitope or C-end epitope of HBx, but having no reaction to keyhole limpet hemocyanin (KLH) of carrier protein and other expressed proteins of hepatitis B virus (HBV). The preparation method of the monoclonal antibody comprises the steps of: fusing N-end and C-end antigen epitope polypeptides of HBx respectively with mice immunized with KLH in crosslinking way, and myeloma cells and screening to obtain the monoclonal antibody. The monoclonal antibody can be used for various immunodetection reagents and directed therapeutic drugs of HBx protein or HBx antibody and applied to diagnosis and treatment of diseases such as hepatitis b virus (HBV) infection, hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and the like.
Owner:王虹
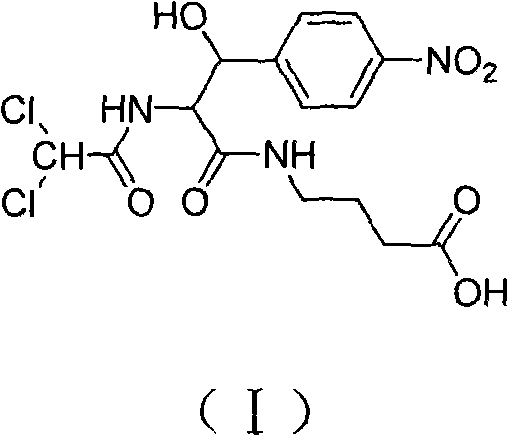
Alternarin tenuazonic acid artificial antigen, polyclonal antibody, preparation method and application
InactiveCN105503689AOptimal Coating Source ConcentrationBest dilutionSerum albuminDepsipeptidesPolyclonal antibodiesBovine serum albumin
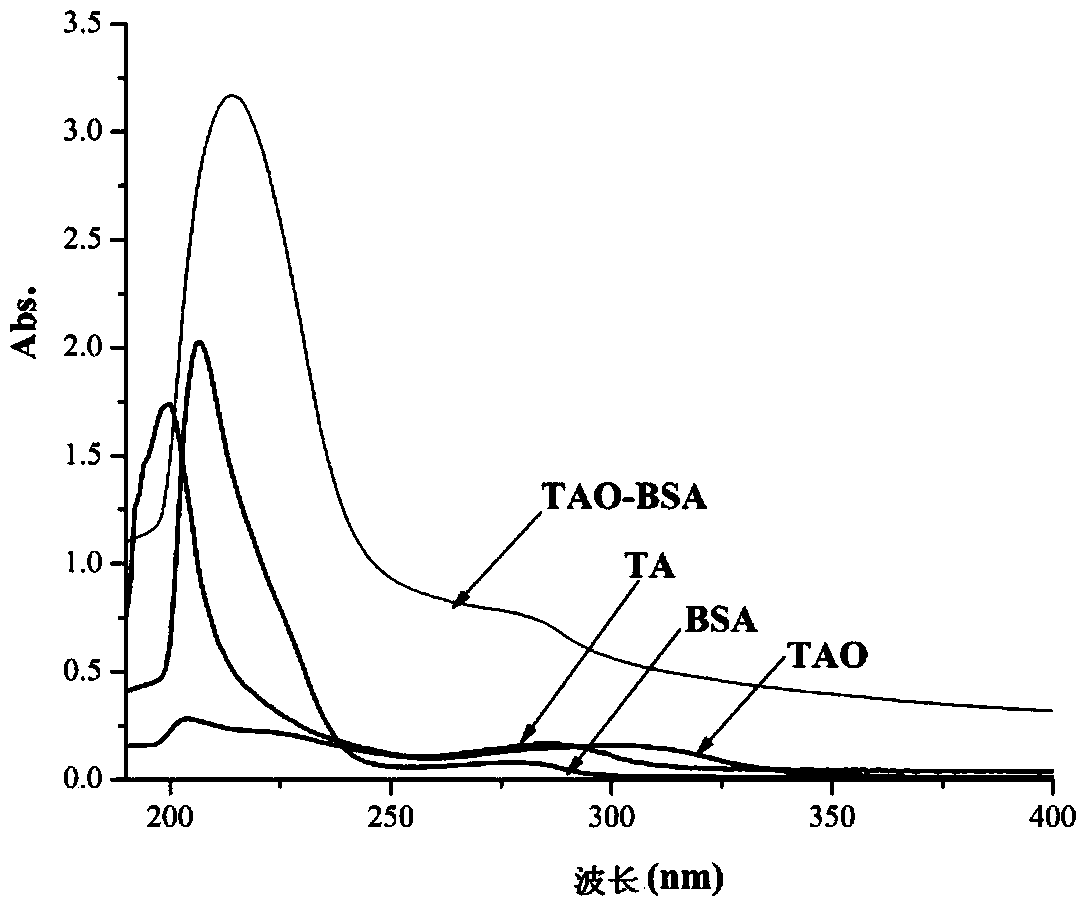
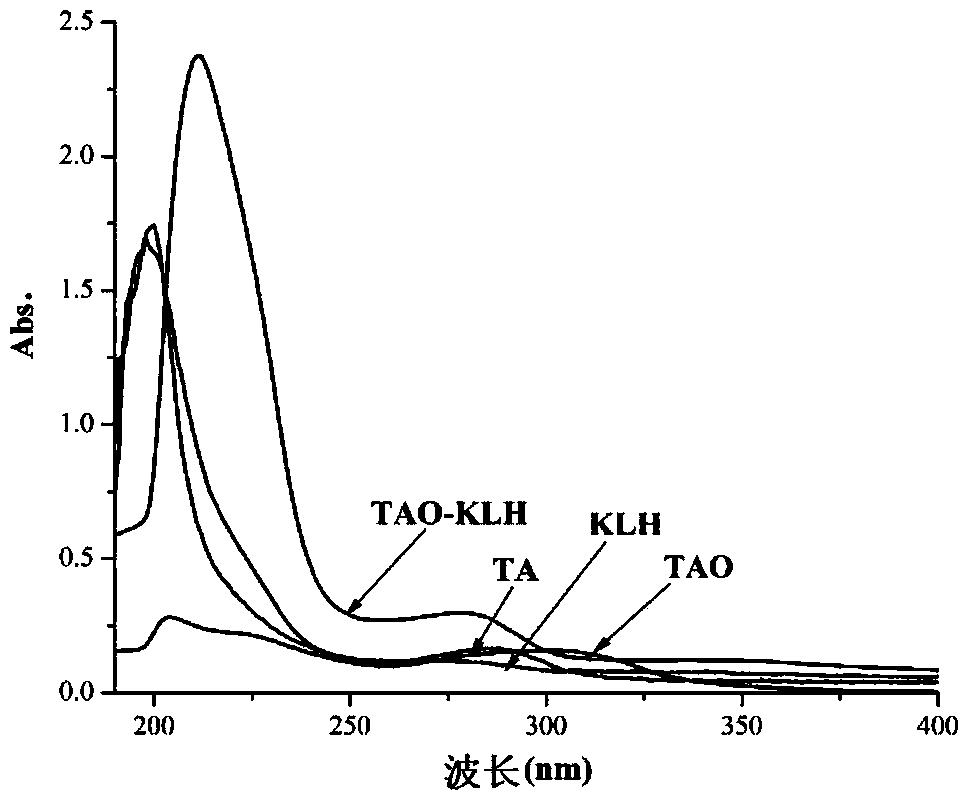
The invention discloses an alternarin tenuazonic acid artificial antigen, a polyclonal antibody, a preparation method and application, and particularly discloses an artificial antigen obtained by coupling a compound (formula I) serving as a tenuazonic acid hapten, a hapten TAO, bovine serum albumin, hemocyanin and other macromolecular protein, a polyclonal antibody prepared from the artificial antigen and application of the artificial antigen and the polyclonal antibody to tenuazonic acid detection. TA (tenuazonic acid) can be detected by setting up an indirect competitive ELISA method, a theoretical basis is provided for a TA immunological detection method, a foundation is laid for further developing and detecting TA immunology fast detection products, and a new path is provided for setting up the TA immunological detection method, developing the TA immunological series products, and fast and efficiently monitoring TA contamination conditions.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY
Test paper strip for rapidly detecting traces of chlorothalonil and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a test paper strip for rapidly detecting traces of chlorothalonil and a preparation method thereof. The test paper strip is characterized in that a supporting layer is used as the bottom layer, an adsorption layer is used as the intermediate layer, a protective layer is fixed on the adsorption layer, the adsorption layer comprises an adsorption fibrous layer, a gold-labeled antibody fibrous layer, a cellulose film and an absorbent material layer at the handle end in order from a test terminal, wherein the cellulose film is provided with detection blots printed by using a chlorothalonil coupling carrier protein solution and control blots printed by using a goat anti-mouse IgG or rabbit anti-mouse IgG (or goat anti-rabbit IgG) antibody solution; the gold-labeled antibody is a colloidal gold labeled chlorothalonil monoclonal antibody or polyclonal antibody; and the chlorothalonil coupling carrier protein is bovine serum albumin, chicken ovalbumin or haemocyanin. The test paper strip disclosed herein has the advantages of strong specificity, high sensitivity, simple, and accurate detection, low cost, wide application scope, and easiness in popularization and application.
Owner:HENAN ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Preparation and application of miniature high-efficiency clenbuterol immuno-affinity chromatography column
InactiveCN102553297ANo sheddingEfficient captureIon-exchange process apparatusOther chemical processesAntibody AffinitiesSpecific antibody
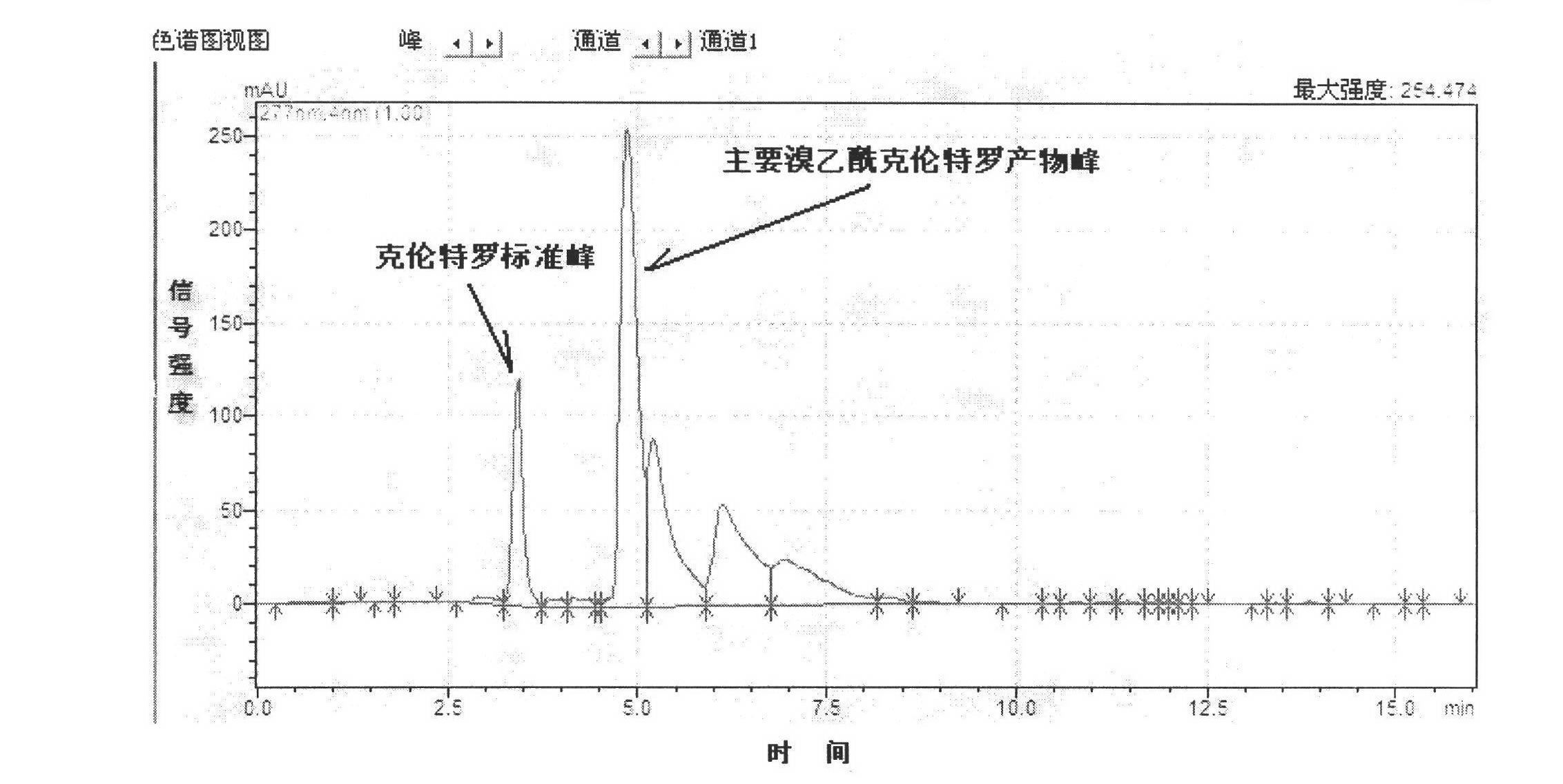
The invention relates to a preparation method and application of a miniature high-efficiency clenbuterol immuno-affinity chromatography column. The technical scheme is characterized by comprising the following steps of: preparing a high-quality antibody, synthesizing efficient prepared bromoacetyl chloride clenbuterol purified by a liquid chromatogram and thiolation hemocyanin into immunogen immune animals, and obtaining antiserum; reacting the purified bromoacetyl chloride clenbuterol with thiolation agarose to obtain clenbuterol-agarose padding, loading the padding into an antigen affinity chromatography column; and purifying a clenbuterol specific antibody in the antiserum by using the antigen affinity chromatography column. The preparation method of the clenbuterol immuno affinity chromatography column comprises the following steps of: coupling high-quality antibodies at high density to the agarose oxidized by periodic acid to prepare an antibody affinity padding, and placing 25 mul of padding in a small specially-made column to prepare the miniature immuno-affinity chromatography column. The immuno-affinity chromatography column provided by the invention can be used for specifically gathering clenbuterol in a sample to be tested at high efficiency and can increase the accuracy, reliability and sensitiveness of detection when being combined with an analytic instrument and colloidal gold test paper for use.
Owner:NANNING LANGUANG BLUE LIGHT BIOTECH
Preparation of human plasma protein fused long-effective interferon
A human hemocyanin fused long-acting interferon protein, DNA sequence of its coded fused protein and its production are disclosed. It has better interferon biological activity and longer interferon half-life.
Owner:NOVOPROTEIN SCI INC
Ractopamine immunogen, coating antigen and use thereof in colloid-gold test paper
ActiveCN101993488AImproving immunogenicityStrong specificitySerum albuminDepsipeptidesCelluloseCarrier protein
The invention relates to a ractopamine immunogen, a ractopamine coating antigen and use thereof in colloid-gold test paper and belongs to the technical field of immunology. The immunogen and coating antigen are products of the coupling of the hapten of the connecting arm of a hydroxyl terminal far away from a nitrogen atom of the ractopamine with a carrier protein. The hapten is similar to a ractopamine counterpart in terms of molecular structure, stereochemistry and electronic distribution. The molecule of the hapten has an active group for coupling with a protein carrier, and the existence of the active group exerts on influences on the electronic distribution of the molecules of a material to be tested. When coupled with hemocyanin, the hapten enables an organism to produce a high-potency and high-specificity antibody against ractopamine and be absorbed onto a glass cellulose membrane; and the coating antigen constructed by coupling with human haemocyanin can be absorbed onto a nitrocellulose membrane for constructing the colloid-gold test paper.
Owner:深圳市三方圆生物科技股份有限公司
Organic chlorine pesticide benzoepin artificial antigen and antibody, their preparation and use thereof
InactiveCN1700001AHigh similarityThe characteristic structure remains intactComponent separationBiological testingImmune profilingAntiendomysial antibodies
The invention relates to a pesticides benzoepin artificial antigen-antibody and it's preparing method and application, which specifically relates to preparing small molecular compound artificial hapten, antigen and antibody of cyclopentacliene pesticides benzoepin and application of establishing immunity analysis method. It uses benzoepin derivation as hapten to connect separately with carrier protein like hemocyanin and horse radish peroxidase so as to synthesis artificial antigen and enzyme antigen. Artificial antigen becomes antibody though animal immunity, taking-up blood, antiserum and purity.
Owner:黄永
Specific antibody against pesticide meta-tolyl-N-methylcarbamate
InactiveCN101747429AHigh similarityImprove featuresSerum immunoglobulinsDepsipeptidesBlood collectionCarrier protein
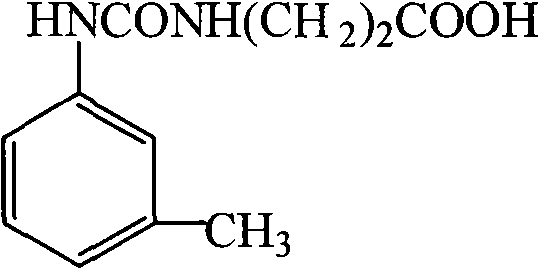
The invention relates to a specific antibody against a pesticide meta-tolyl-N-methylcarbamate and preparation of an artificial antigen and the antibody of the carbamate pesticide meta-tolyl-N-methylcarbamate, in particular to preparation of a hapten, the artificial antigen and the antibody of the carbamate pesticide meta-tolyl-N-methylcarbamate with the molecular structure of 3-methyl benzene. The invention solves the problem that the traditional physical and chemical analysis methods are complicated, high in cost and slow in analysis, and provides simple, convenient, sensitive and accurate immunoassay. In the method, 1-(3-carboxyethyl)-3-m-tolylurea is used as the hapten and is linked with such carrier proteins as hemocyanin and horseradish peroxidase respectively to synthesize the artificial antigen and an enzyme-labelled antigen. The artificial antigen is characterized by simple synthetic method and better stability. The antibody is prepared through animal immunization of the artificial antigen, blood collection and antiserum separation and purification. The antibody is stable, has good specificity and sensitivity, can be used for quick immunoassay of the carbamate pesticide meta-tolyl-N-methylcarbamate and has good application prospect.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Preparations and uses of streptomycin-carrier protein coupled product and streptomycin antibody
The invention discloses a coupling product of streptomycin and carrier protein, and a preparation method of a streptomycin antibody and an application thereof, which relate to a coupling method of the carrier protein such as keyhole limpet hemocyanin, human serum albumin, cow serum albumin, ovalbumin and the like with streptomycin, and immune BALB / C mouse spleen cells are fused with SP2 / 0 mouse myeloma cells by streptomycin immunogens coupled with the carrier protein, and the streptomycin coupled with the carrier protein is used as a coating antigen for screening positive hybridoma and hybridoma that can steady passage and excrete anti-specificity streptomycin monoclonal antibody can be obtained by the cell clone, and ascites monoclonal antibody is prepared. The prepared monoclonal antibody is used for building a direct competition ELISA method with high specificity, sensitivity and accuracy to the streptomycin and immunity colloidal gold test strips. The coupling of the streptomycin and the carrier protein and the preparation method of the streptomycin monoclonal antibody can provide services for detecting streptomycin residue in foods quickly.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Hapten, artificial antigen and antibody directly targeted to alternariol and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN105712970AStrong specificityImprove accuracyOvalbuminSerum albuminCarrier proteinKeyhole-limpet haemocyanin
The invention belongs to the technical field of food safety immunodetection and particularly discloses hapten, artificial antigen and antibody directly targeted to alternariol and a preparation method and application thereof. The alternariol hapten is of the structure as indicated in formula (I), wherein n=1, 2. The alternariol artificial antigen is of the structure as indicated in formula (III), wherein n=1, 2; carrier protein is keyhole limpet haemocyanin or bovine serum albumin or ovalbumin. The titer of antiserum obtained from an immune animal of the artificial antigen can reach 1: 128000, the minimum detection limit is 1.15 ng / mL, the half inhibiting concentration is 16.5 ng / mL, the antibody has the remarkable advantages of being high in specificity, good in sensitivity, high in accuracy and the like, therefore the antigen and the antibody can be used for establishing an alternariol enzyme linked immunosorbenption and analysis technology, and thereby the hapten, artificial antigen and antibody directly targeted to alternariol and the preparation method and application thereof can be used for rapidly detecting residual alternariol in food and have wide application prospect.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
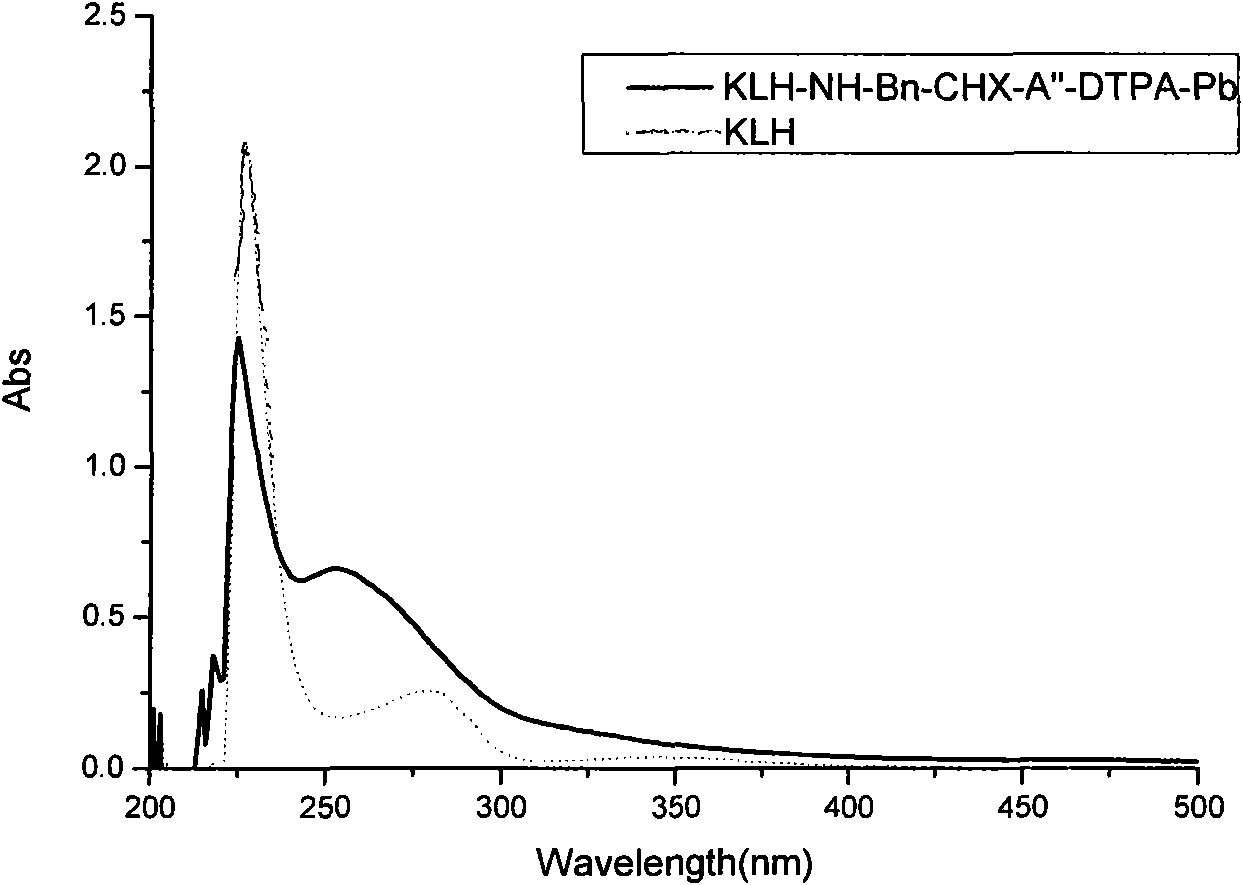
Pb<2+> antigen and corresponding monoclonal antibody and preparation method thereof
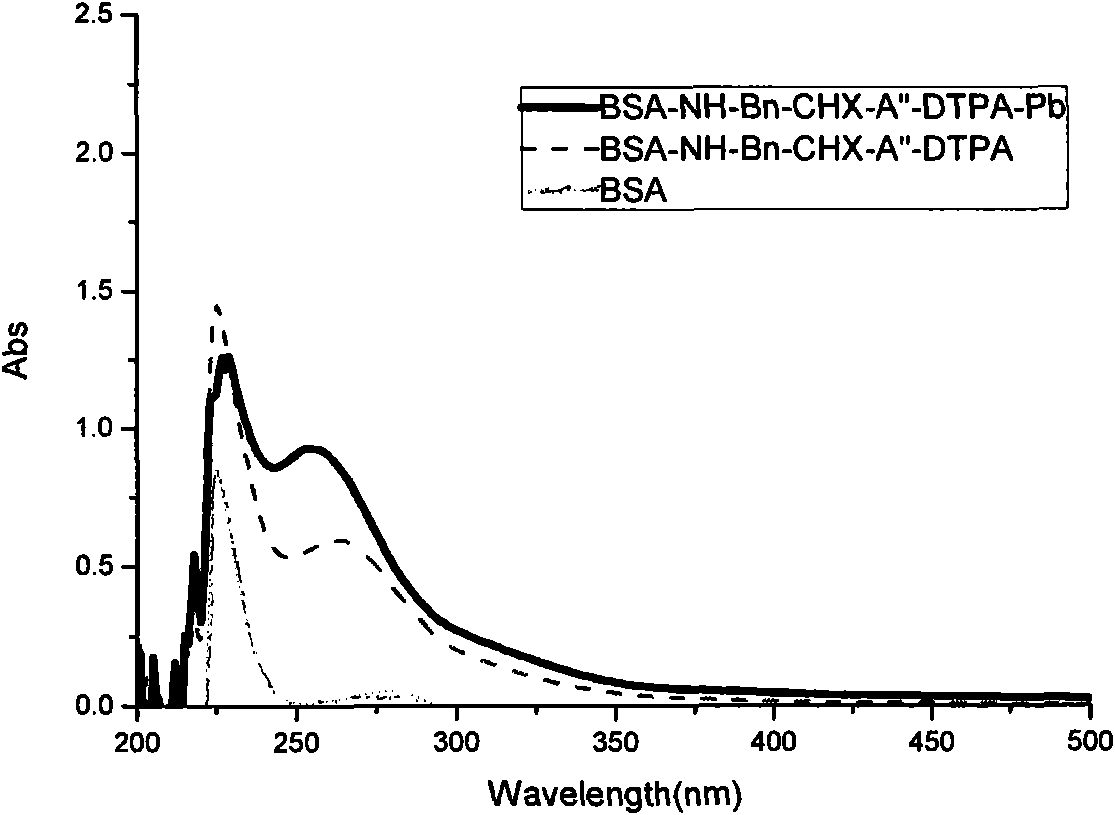
The invention discloses a Pb<2+> antigen and a corresponding monoclonal antibody, and also provides a method for preparing the same. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: chelating Pb<2+> with a chelating agent p-NH2-Bn-CHX-A''-DTPA; coupling glutaraldehyde with hemocyanin (KLH); performing ultra-filtration to obtain a full immunizing antigen (KLH-NH-Bn-CHX-A''-DTPA-Pb); merging splenic cells and myeloma cells of a mouse immunizing BALB / c; and screening a specific monoclonal antibody which has strong positive for BSA-NH-Bn-CHX-A''-DTPA-Pb and no cross reaction with BSA-NH-Bn-CHX-A''-DTPA and other various metal ions. The antibody can be used for developing ELISA kits and test paper for detecting the Pb<2+> and has great application prospect.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
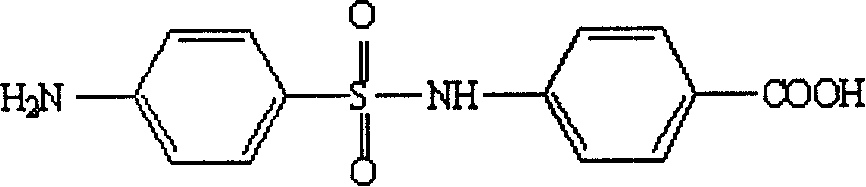
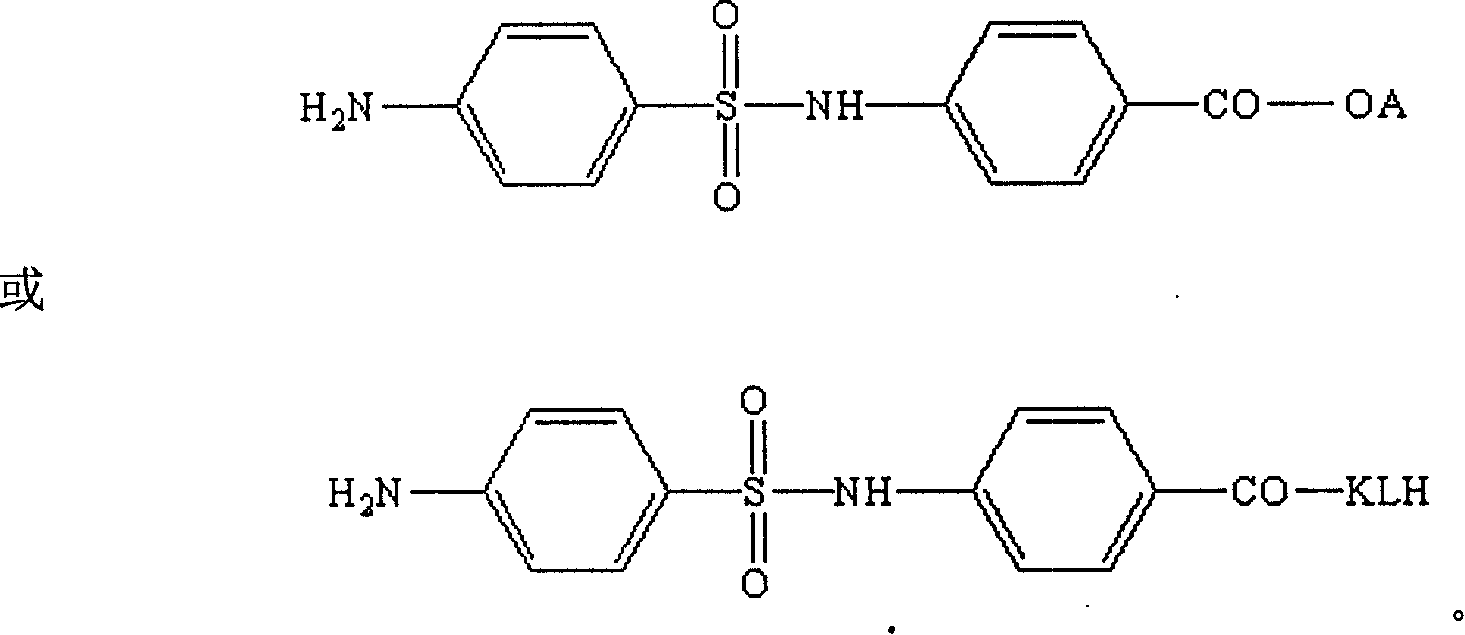
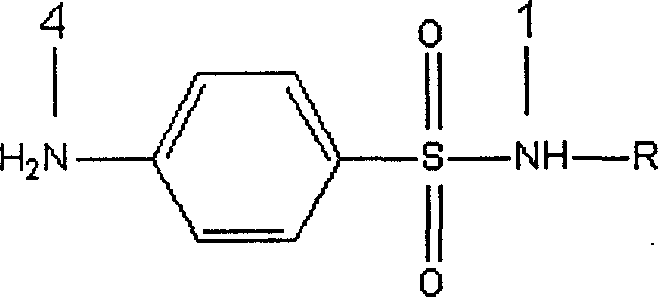
Artificial antigen used for immune analysis of sulfanilamide multi kind residue and antibody and its preparation
InactiveCN1904613AThe synthesis method is simpleAccelerated dilutionBiological testingBenzoic acidSulfanilamide
The invention relates to an artificial antigen and antibody that is used for analyzing sulfa plural residual immunity and the manufacturing method. It uses 4-(4- amino benzene sulfonyl) benzoic acid as hapten and compound artificial antigen with carrier protein and taking animal immunity to make antibody that could be used to rapidly test the residual to sulfa. It has good broad spectrum feather and has great application prospect.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Clenbuterol immunogen, coatingen and application thereof in colloidal gold test paper
ActiveCN101993486AImproving immunogenicityStrong specificitySerum albuminDepsipeptidesCelluloseHuman albumin
The invention relates to clenbuterol immunogen, coatingen and application thereof in colloidal gold test paper, and belongs to the technical field of immunology. The immunogen and the coatingen are products of hapten coupling carrier proteins obtained by reaction of clenbuterol and 4-bromobutyric acid. The hapten is similar to the clenbuterol corresponding body on molecular structure, stereo chemistry and electronic distribution. The hapten molecules have active groups convenient for coupling with protein carriers, and the presence of the active groups has no influence on the electronic distribution of molecules of an object to be detected. After the hapten is coupled with hemocyanin, the body can produce clenbuterol-orientated antigens with high titer and good specificity, wherein the antigens are adsorbed on a glass cellulose membrane; and the coatingen constructed after coupling the human albumin can be adsorbed on a nitrocellulose membrane to construct the clenbuterol colloidal gold test paper.
Owner:深圳市三方圆生物科技股份有限公司
Malachite green artificial antigen and antibody, and preparation method and application thereof
The invention provides preparation of malachite green artificial antigen and antibody, and relates to preparation of artificial hapten, artificial antigen and antibody of a triphenylmethane chemical substance malachite green. By adopting the preparation method, the problems of complex process, high cost and low analysis speed of the traditional physical and chemical analysis method are overcome. A simple, convenient, quick, sensitive and accurate enzyme immunoassay is provided. The method comprises the following steps: taking 4-[bi(4-dimethylamino)phenyl]methyl benzoic acid and 5-{4-[bi-(4-dimethylamino)phenyl]methyl} phenyl valeric acid as haptens to be respectively connected with carrier proteins such as hemocyanin, ovalbumin and the like to synthetize artificial antigen; carrying out animal immunization, taking blood, separating out antiserum, and purifying, so as to prepare the antibody. The antibody is stable, and has good specificity and sensitivity, and a good application prospect, and can be applied to fast immunodetection of the malachite green.
Owner:深圳市微宇藻业科技有限公司
Thomsen-friedenreich disaccharide modified immunogen (TFD), preparation procedure, compositions comprising it, uses, and treatment methods
InactiveUS20100297159A1Saccharide peptide ingredientsCancer antigen ingredientsKeyhole-limpet haemocyaninPreparation procedures
Modified Thomsen-Friedenreich disaccharide (TFD) immunogen, preparation procedure, compositions containing it, uses, and treatment methods. More specifically, the present invention refers to a immunogen obtained by modifying TFD, and comprising the general formula D-TFD-Lys(n)-C, wherein D is a hydrophobic terminal residue, TFD is disaccharide Galβ3GalNAcα; Lys(n) is a lysine connector, and n is an integer between 1 and 5, and C is a carrier. In a preferred embodiment, the modified invention immunogen comprises the general formula BzlαTFD-Lys5-KLHs, wherein Bzl is benzyl, TFD is disaccharide Galβ3GalNAcα; Lys5 is penta-lysine, and KLHs is succinilated Keyhole limpets hemocyanin.
Owner:CONSEJO NAT DE INVESTIGACIONES CIENTIFICAS Y TECH CONICET +2
Immunoassay kit for detecting ethopabate, and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN107422112AIncrease irritationHigh affinityBiological material analysisBiological testingFluorescenceBovine serum albumin
The invention relates to an immunoassay kit for detecting ethopabate, and a preparation method and application thereof, belonging to the field of immunological detection. The kit comprises an ELISA plate coated with an ethopabate antigen, an ethopabate monoclonal antibody solution, an enzyme-labeled or fluorescently-labeled goat anti-mouse secondary antibody, a standard ethopabate solution, a washing solution and a diluent, wherein the ethopabate antigen is a conjugate of ethopabate semiantigen and a vector, and the vector is one or two selected from a group consisting of ovalbumin, bovine serum albumin, thyroid protein, hemocyanin, human serum albumin and polylysine. When applied to detection of ethopabate residues in animal food, the kit has the advantages of high sensitivity, precision and accuracy, good specificity, low cross-reaction rate, good stability, long storage time, easy operation, quickness and suitability for on-site primary screening of large quantities of samples, and is beneficial for simplifying residue analysis of ethopabate.
Owner:HENAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Antigen and preparation method and application thereof
The invention discloses an antigen and a preparation method and application thereof. The antigen is a conjugate formed by connecting morphine-6-monoglutarate and a carrier protein through a covalent bond. The method for preparing the antigen comprises the following step of: conjugating the morphine-6-monoglutarate with the carrier protein so as to prepare the conjugate of the morphine-6-monoglutarate and the carrier protein, wherein the carrier protein is bovine serum albumin or hemocyanin. The antigen can stimulate an organism to generate a morphine antibody and specifically recognize the morphine and heroin. Mouse experiments prove that: a vaccine which takes the antibody as an active substance can prevent morphine relapse to a certain degree.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Edible oil
The invention discloses edible oil. The edible oil is characterized in that the formula of the edible oil comprises the following components in part by weight: 80-100 parts of olive oil, 46-60 parts of sunflower seed oil, 10-14 parts of arochidonic acid oil, 2-5 parts of taurine components, 3-4 parts of DHA components, 0.7-1.2 parts of EPA components, 0.2-0.4 part of zinc-enriched yeast, 0.1-0.2 part of selenium supplement ingredients, 2-2.3 parts of hemerythrin, 1.1-1.3 parts of hemocyanin, 3-4 parts of nutritious protein components, 3-6 parts of lipid-soluble vitamin, 2-4 parts of antioxidants and 2.2-4.1 parts of emulsifiers. The edible oil disclosed by the invention has the advantages that an iron supplement agent can be added to the oil environment because the hemerythrin is added as a carrier of iron; a human body can obtain the needed copper element on the one hand and the copper element can also promote the absorption of the iron on the other hand because the hemocyanin is added as a copper supplement agent; and the edible oil can also have multiple other health care effects.
Owner:HANGZHOU HONGSHENG GRAIN & OIL TRADE CO LTD
Pesticide sevin artificial antigen and antibody and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN1598582AAccurate detectionHigh similarityAntibody ingredientsCarrier-bound antigen/hapten ingredientsImmuno detectionBiology
The invention discloses pesticide carbaryl artificial antigen and antibody and its producing method and application, the invention has carbamate pesticide, which has 6-amino caproic acid structure, micromolecule compound artificial hapten, antigen and antibody producing and its application in immunity analysis field. The invention opercomes the problems, such as fussy, high cost, low analyzing speed, of traditional physics and chemistry analyzing method, it provides convenient, rapid, sensitive, exact immunity analysis system. It uses 1-(5-carboxyl)-3-(1-naphthyl) carbamide and N-(2-naphthoyl)-6-amino caproic acid as hapten, it is connected with carrier albumen and horseradish peroxide enzyme to become artificial antigen and enzyme antigen. The artificial antigen is made to antibody after animal immunity, taking blood, separating antiserum, puring. The antibody is stable, it has good specificity and sensitivity, and the synthesizing method is simple. The invention can be used to pesticide carbaryl rapid detection, and it has good application foreground.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Immunogen for obtaining Nrf1D protein antibody, Nrf1D protein antibody and Elisa detection kit
ActiveCN106699899AHas specific recognition abilityImprove featuresImmunoglobulins against animals/humansBiological material analysisNew Zealand white rabbitCentrifugation
The invention provides an immunogen for obtaining an Nrf1D protein antibody, the Nrf1D protein antibody and an Elisa detection kit. The immunogen is obtained as follows: polypeptide with the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO.1 is synthesized firstly, Sulfo-SMCC is used as a coupling agent, the polypeptide and KLH (keyhole limpet hemocyanin) are coupled; the antibody is obtained as follows: immunogen is taken as an antigen, the antigen is emulsified with FCA (freund's complete adjuvant) to immunize a New Zealand white rabbit, blood of the immunized New Zealand white rabbit is centrifuged, and a supernatant after centrifugation is collected; the Elisa detection kit comprises components including an ELISA plate, an enveloping solution, a blocking solution, an ELISA secondary antibody, a TMB color developing solution, a stop solution, a detection antigen and the Nrf1D protein antibody, the detection antigen is the polypeptide with the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO.1, glutaradehyde is used as a coupling agent, and the polypeptide and BSA bovine serum albumin are coupled.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Immunogen and coatinggen of chloramphenicol and application thereof in collaurum test paper
ActiveCN101993487AImproving immunogenicityStrong specificitySerum albuminDepsipeptidesCelluloseCarrier protein
The invention relates to immunogen and coatinggen of chloramphenicol and application thereof in collaurum test paper, and belongs to the technical field of immunology. The immunogen and the coatinggen are a product of hapten coupling carrier protein obtained by oxidizing the chloramphenicol through potassium permanganate. The hapten is similar to a chloramphenicol counterpart in the aspects of molecular structures, stereochemistry and electron distribution; and hapten molecules have active groups which are convenient to couple with a protein carrier, and the active groups do not influence the electron distribution of analyte molecules. After hemocyanin is coupled by the hapten, organisms can generate antibodies with high valence and good specificity aiming at the chloramphenicol, and the antibodies are adsorbed to glass cellulose membranes; and the coatinggen constructed by coupling human serum protein can be adsorbed to nitrocellulose membranes and is used for constructing the chloramphenicol collaurum test paper.
Owner:深圳市三方圆生物科技股份有限公司
Anti-viral nutraceutical
A method for the prophylaxis or treatment of a viral infection in a mammal is described. The method comprises administering to the mammal an effective amount of a mollusc hemocyanin and / or an active fragment thereof. The hemocyanin may be an abalone hemocyanin.
Owner:MARINE BIOTECH AUSTRALIA
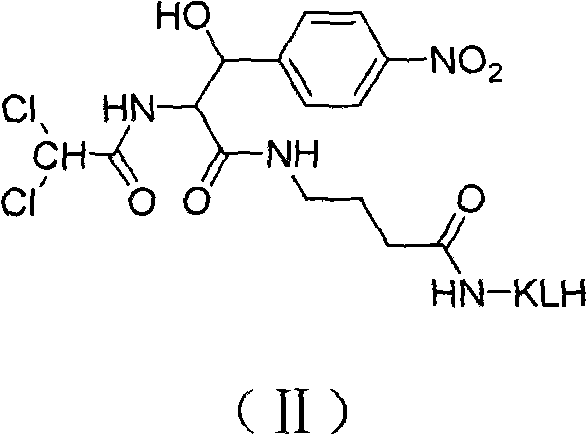
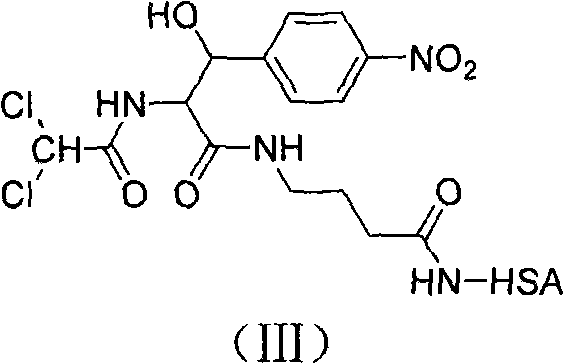
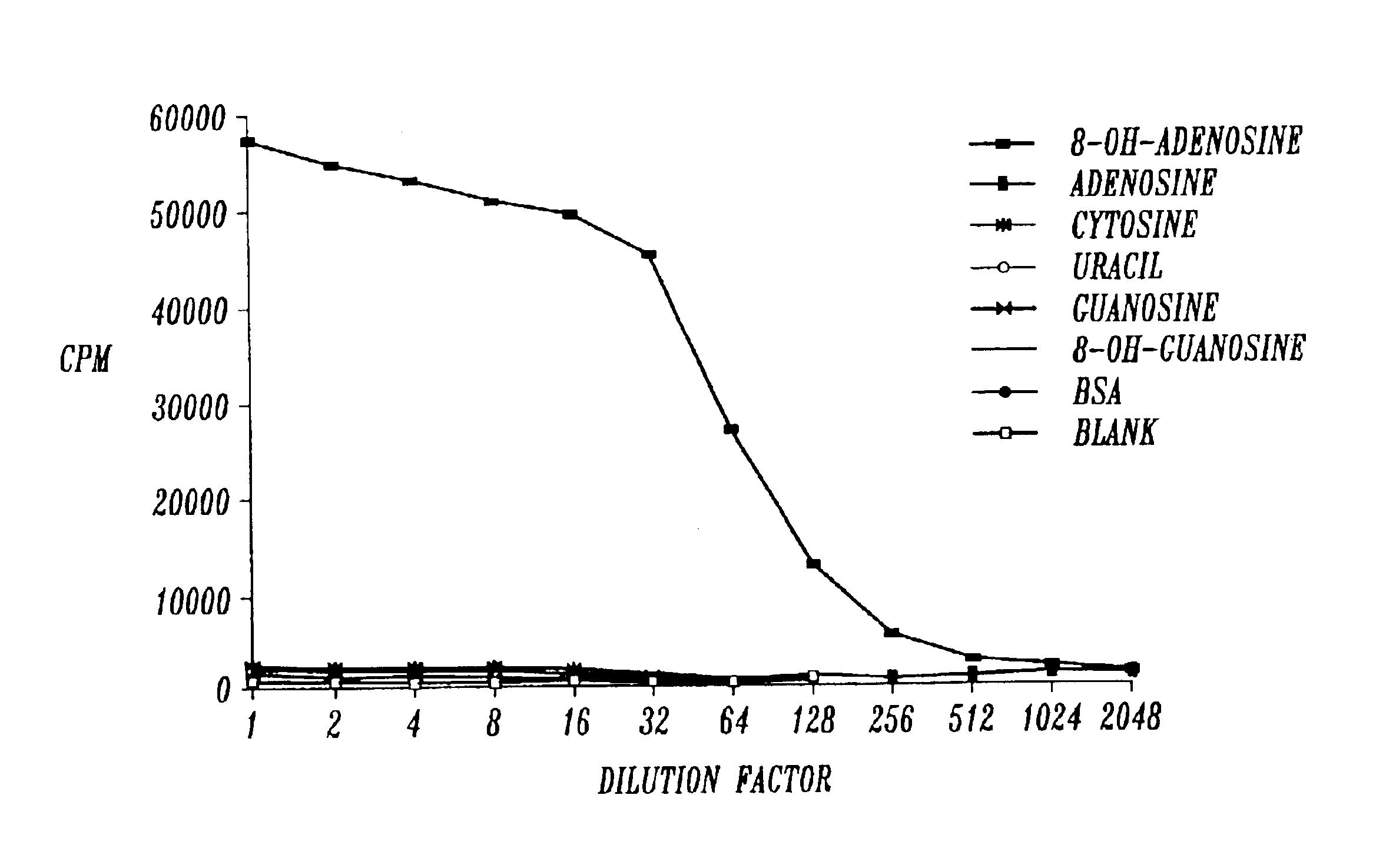
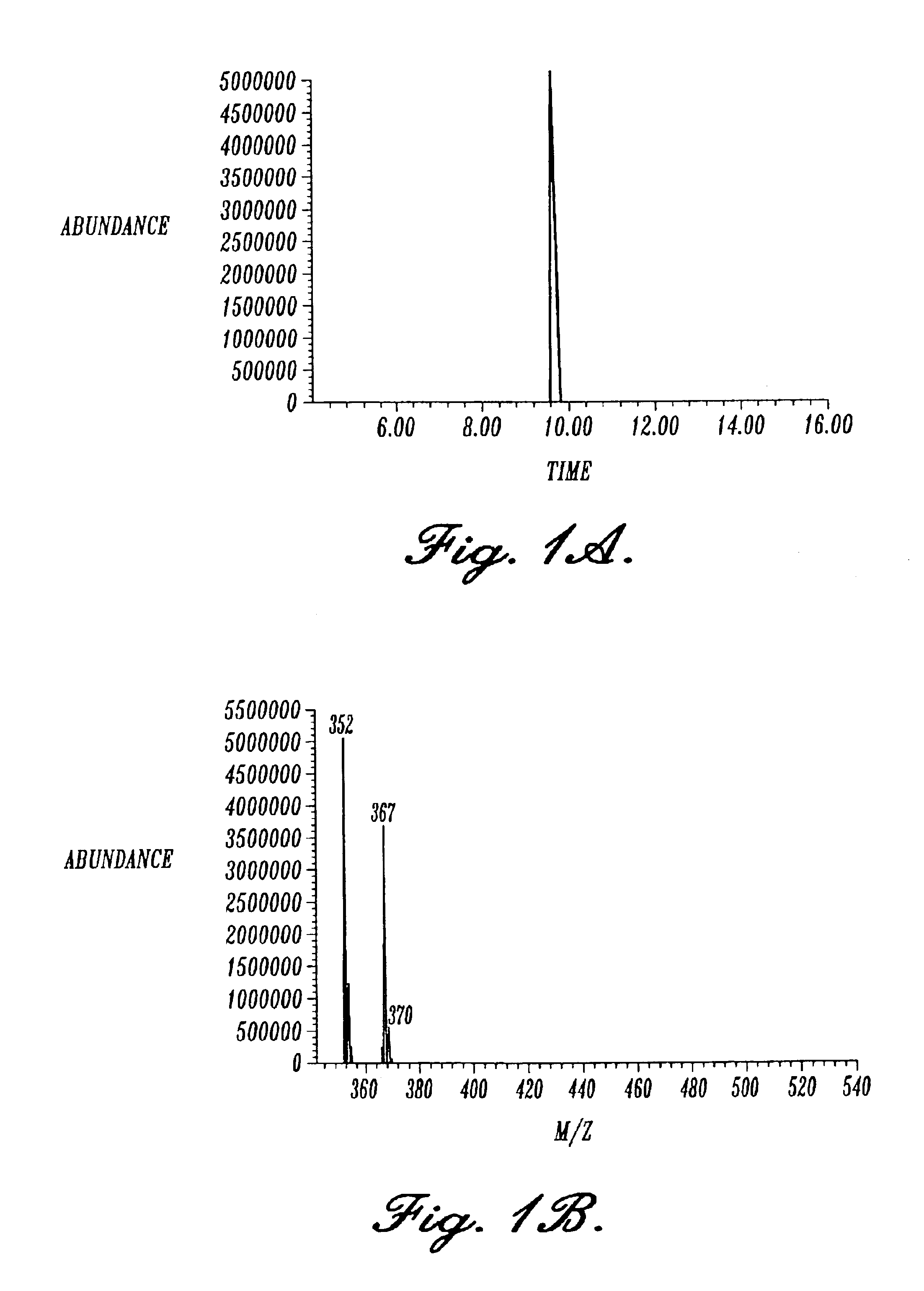
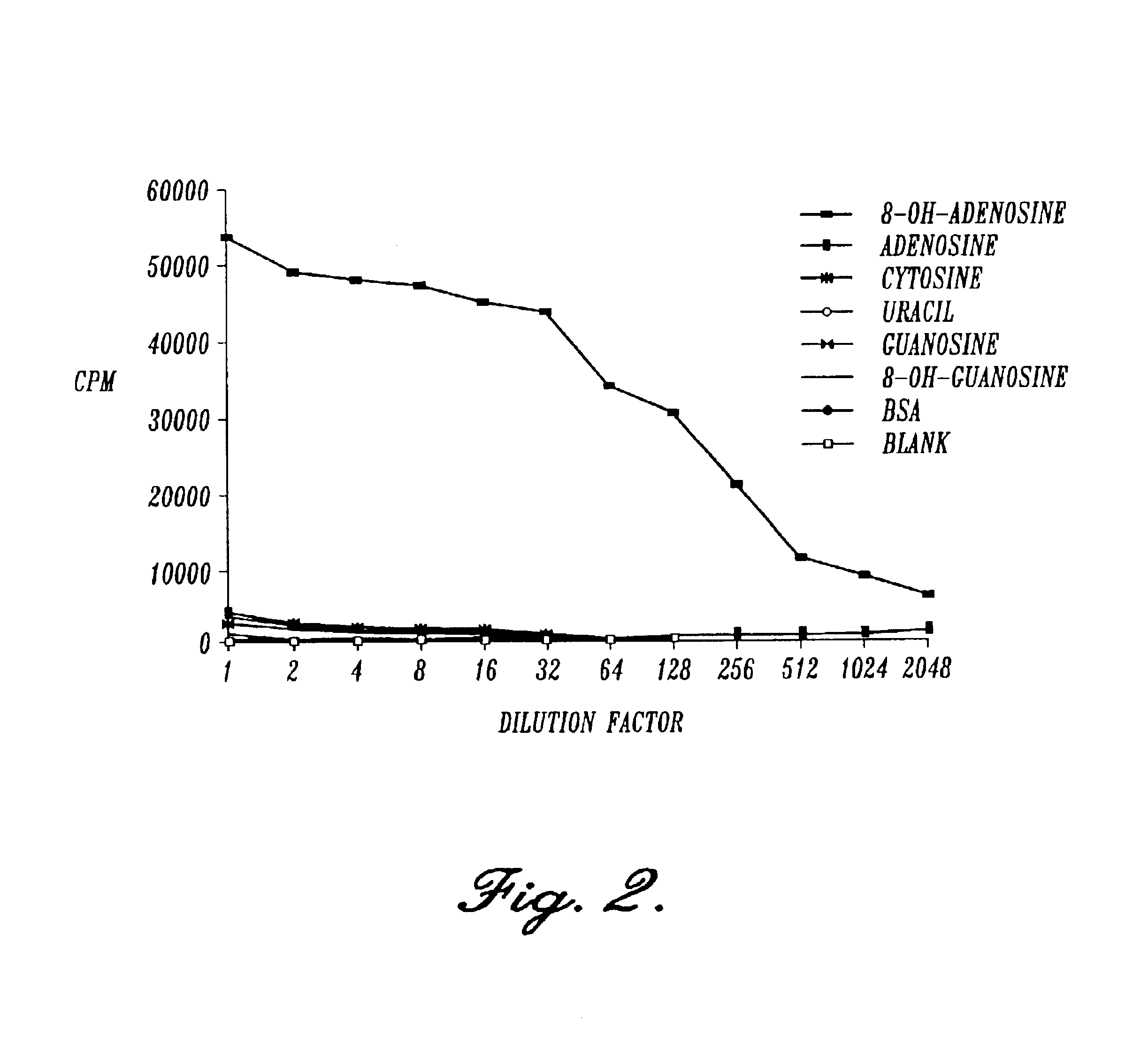
Detection and quantitation of 8-OH-adenine using monoclonal antibodies
The present invention relates to methods and materials for the detection and quantitation 8-OH-Ade in biological specimens. Specifically, the present invention is directed to a group of highly specific monoclonal antibodies reactive with the modified nucleoside structure 8-OH-Ade, and to various immunoassays for 8-OH-Ade utilizing these monoclonal antibodies. The monoclonal antibodies of the present invention may be used in assays for diagnosing or monitoring the progression of certain types of cancer, in addition to a variety of other diseases associated with mutagenesis resulting from oxidative damage of DNA. Assays utilizing the monoclonal antibodies of the present invention may also be used to analyze or monitor toxicant exposure, such as from environmental sources. The monoclonal antibodies of the present invention were prepared with the immunogen 8-OH-adenosine coupled to keyhole limpet hemocyanin (KLH), not to 8-OH-Ade directly. It is believed that the monoclonal antibodies bind with the base portion of the structure (8-OH-Ade) and not the carbohydrate (ribose) or protein linkage region of the conjugate, because, as demonstrated, conjugates bound to nucleosides other than 8-OH-adenosine were unreactive with these antibodies. Therefore, the antibodies of the present invention can be used to detect and quantitate (by the use of a standard curve) the presence of 8-OH-Ade in biological specimens of DNA. Procedures for such an assay include immobilizing the DNA, denaturing it to disrupt the base-pairing scheme exposing the free base structures, and quantitating the amount of 8-OH-Ade present per amount of DAN in a quantitative immunoassay.
Owner:CYTOCHEM
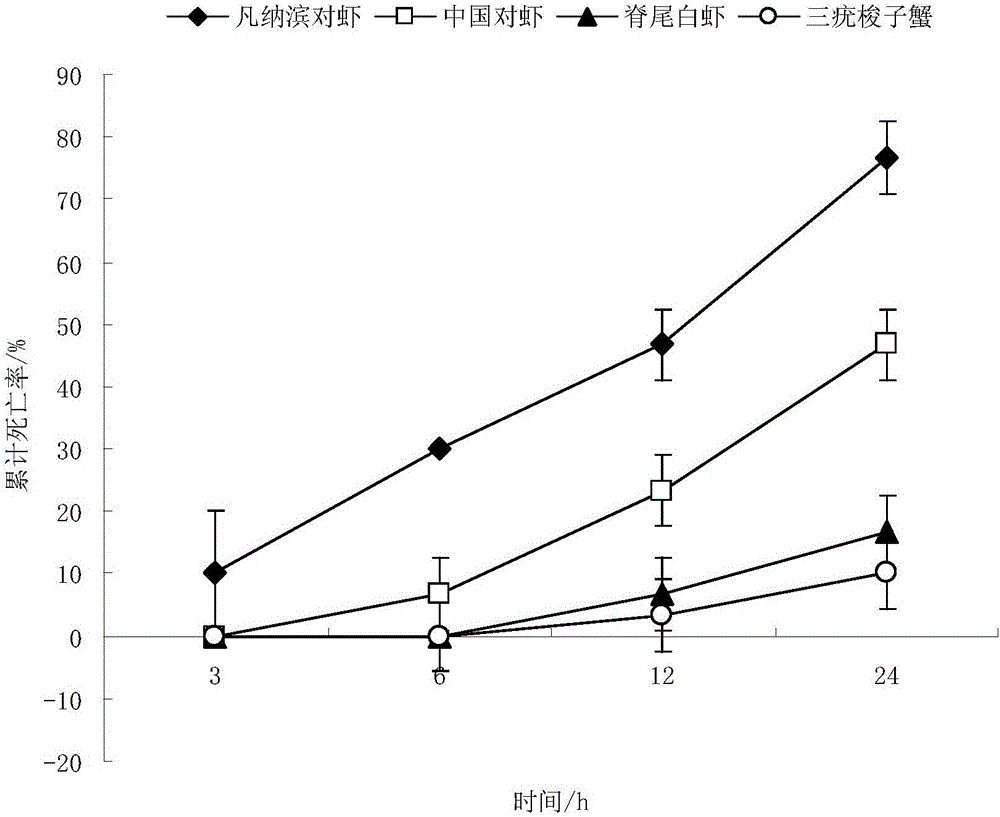
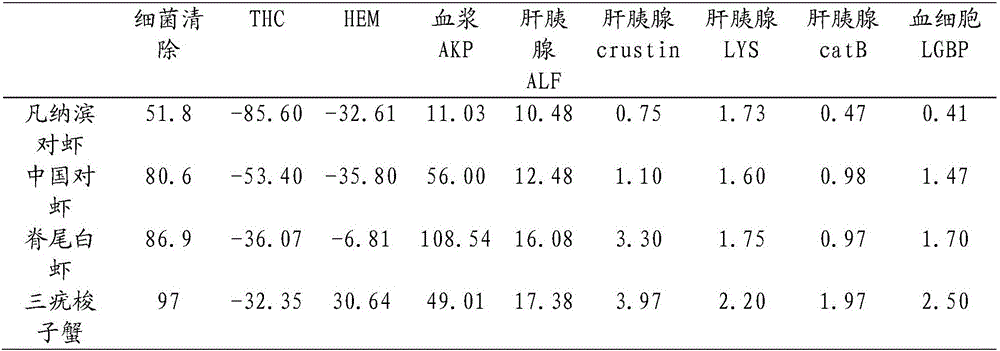
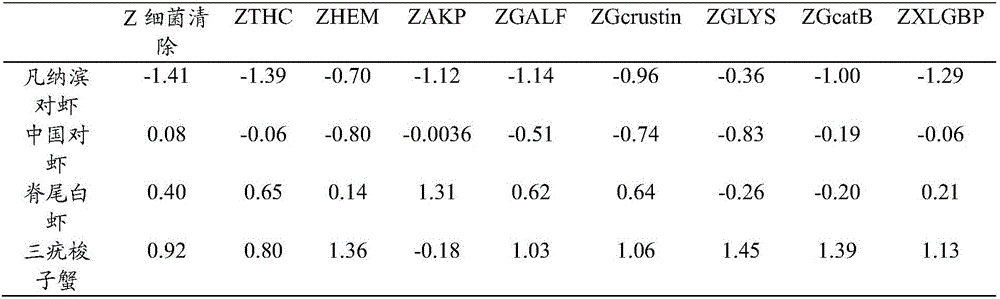
Disease resistance evaluation method of cultured shrimps and crabs
ActiveCN106035144AOvercome limitationsOvercome uncertaintyClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaDiseaseCathepsin B
The invention discloses a disease resistance evaluation method of cultured shrimps and crabs, and belongs to the technical field of aquatic products. Infection with equivalent pathogens is performed according to muscle weight proportions of the cultured shrimps and crabs, nine indexes of the cultured shrimps and crabs are measured including pathogen clearance power, blood cell quantities, haemocyanin contents, blood plasma AKP vitality, ALF, crustin, lysozyme, cathepsin B and LGBP, a disease resistance exponent f of an infected object is obtained by use of principal component analysis, it is indicated that the bigger the f value is, the stronger the disease resistance is, and the smaller the f value is, the weaker disease resistance is. A set of exponents adapted to integrate evaluation of the disease resistance of the cultured shrimps and crabs is constructed for solving the problem of lack of similar technologies in the field, the evaluation result is more accurate, and restrictions and uncertainties of the mode of evaluating the disease resistance through a single immunization index are overcome.
Owner:YELLOW SEA FISHERIES RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERIES SCI
Cell strain 16, monoclonal antibody produced by cell strain 16 and use of monoclonal antibody produced by cell strain 16
ActiveCN103911348AHigh sensitivityStrong specificityMicroorganism based processesTissue cultureBovine serum albuminAmmonium sulfate precipitation
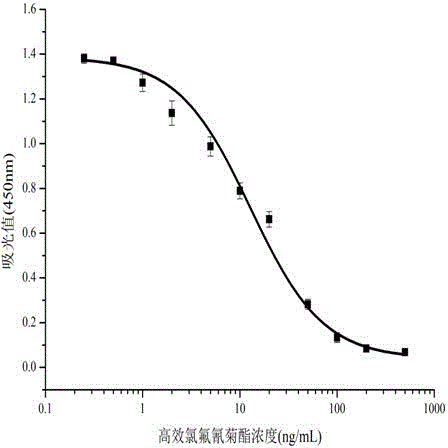
The invention relates to a cell strain 16, a monoclonal antibody produced by the cell strain 16 and a use of the monoclonal antibody produced by the cell strain 16. A preparation method of the cell strain 16 comprises the following steps of coupling hapten 1 (H1) 3-[cyano[cis-3-[2-chloro-3,3,3-trifluoroethyl-2, dimethyl]cyclopropane-phenoxy]phenylpropionic acid and hemocyanin KLH by an active ester method, coupling hapten 2 (H2) cyano-[3-(4-aminophenoxy)phenyl-cis-3-[2-chloro-3,3,3-trifluorovinyl-2,2-dimethyl]cyclopropionate and bovine serum albumin by a diazotization method to obtain a conjugate as a coating antigen, and carrying out animal immunization, serum determination, cell fusion, screening and subcloning to obtain the cell strain 16. Through a mouse internal ascites induced-production method, an ascitic fluid is produced, and then through a caprylic acid-ammonium sulfate precipitation method, the ascitic fluid is purified so that the corresponding monoclonal antibody is produced. The monoclonal antibody has high sensitivity, median inhibitory concentration (IC50) of 13.26+ / -1.23ng / mL and strong singularity, provides a technology for detection of high-efficiency cyhalothrin residue in domestic agricultural products and has a good market prospect.
Owner:HENAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Rapid detection method for phenytoin sodium
InactiveCN106153954AHigh potencyHigh sensitivityBiological testingPretreatment methodCarrier protein
The invention discloses a rapid detection method for phenytoin sodium. A phenytoin sodium antigen and an antibody which are prepared by virtue of the rapid detection method have relatively good specificity. A phenytoin sodium coupled carrier protein is selected from hemocyanin KLH or bovine serum albumin BAS. By virtue of immunization of a mouse by virtue of the antigen, the obtained phenytoin sodium antigen has relatively high valence and relatively good sensitivity. By utilizing a prepared phenytoin sodium detection card, the detection speed is high, a result is easily observed, and the rapid screening of batch samples can be realized, so that the detection cost can be greatly lowered, the workload is reduced, and the phenytoin sodium detection card has practical significance. According to the rapid detection method, aiming at solving the problem that a to-be-detected sample has complex components, a sample pretreatment method is optimized, the required sample amount is low, and the sample pretreatment can be finished only through two steps including extraction and dilution, so that the detection university and the detection efficiency are greatly improved.
Owner:广东省药品检验所
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com