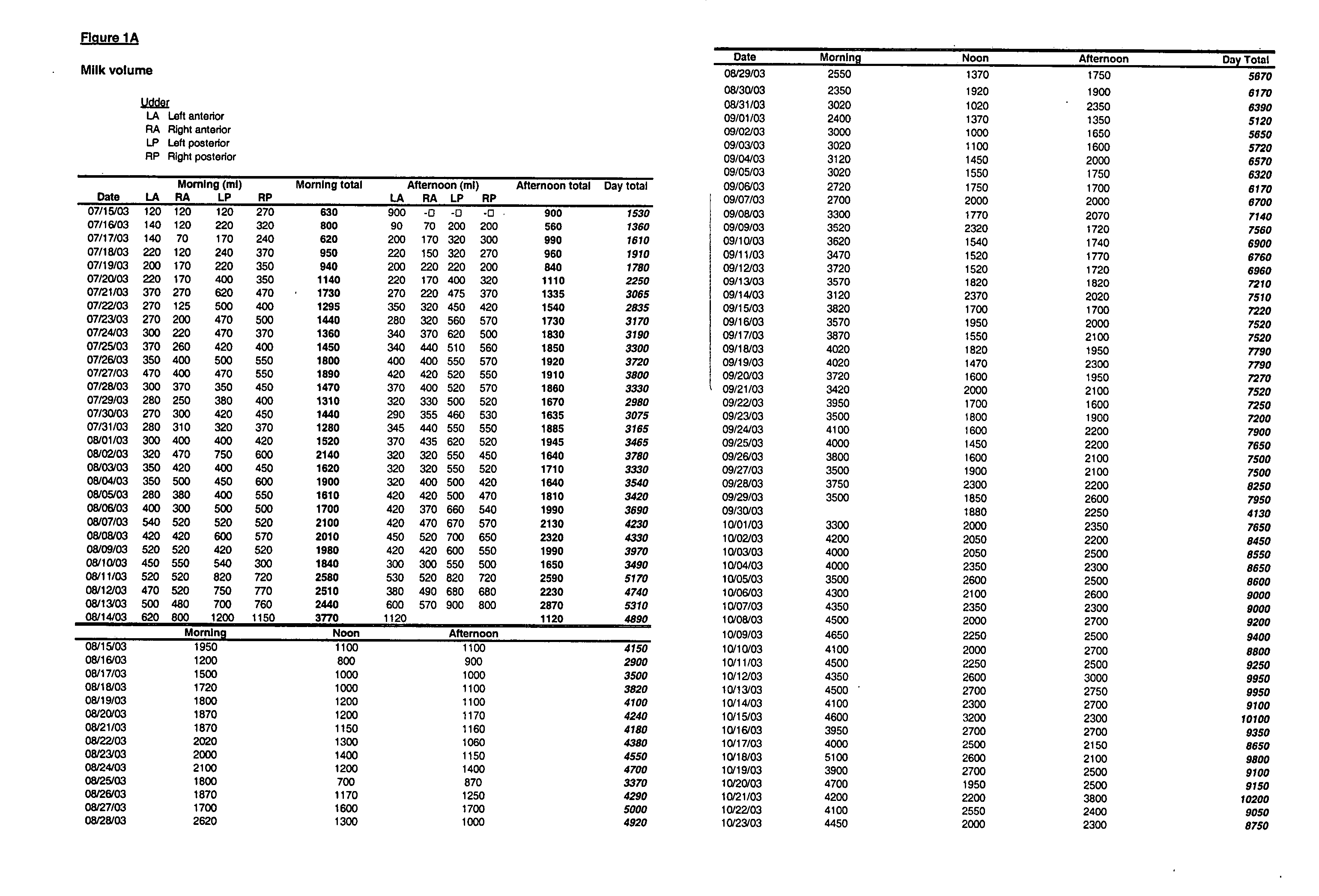
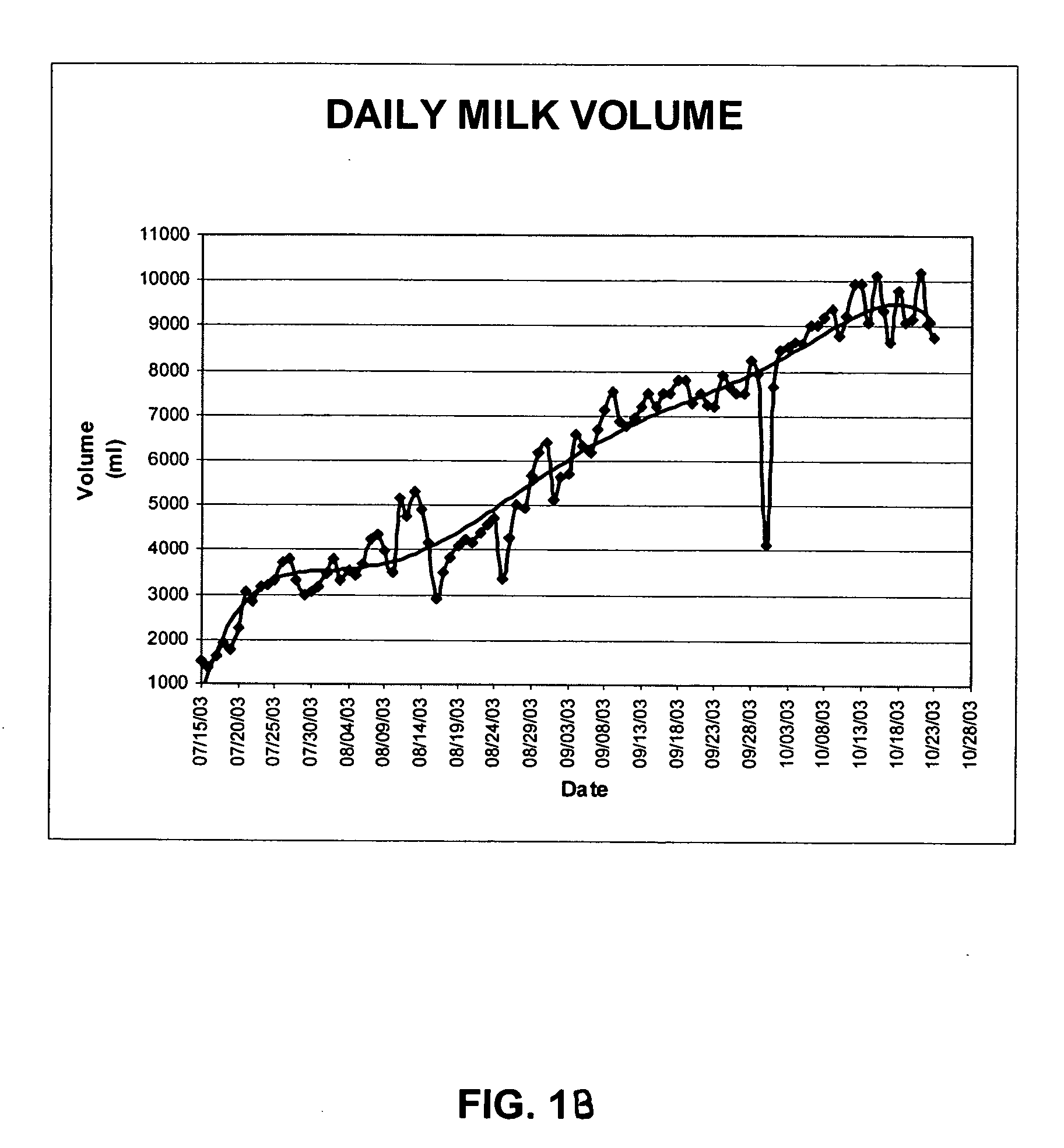
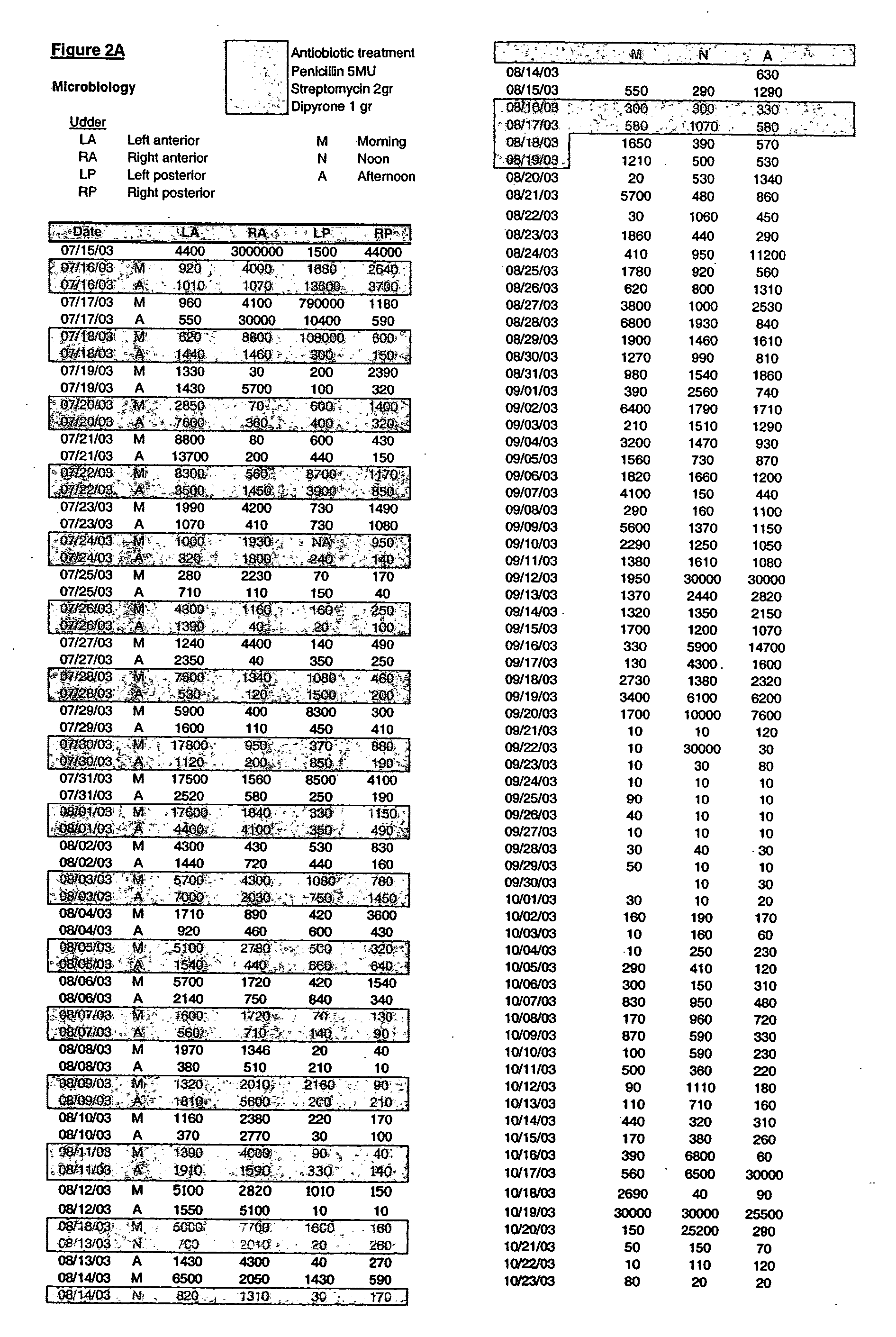
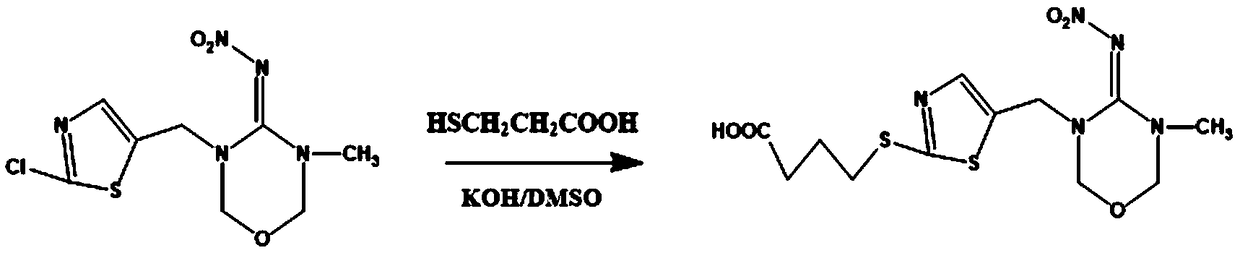
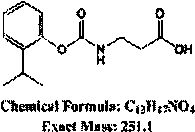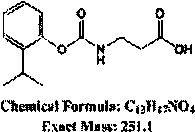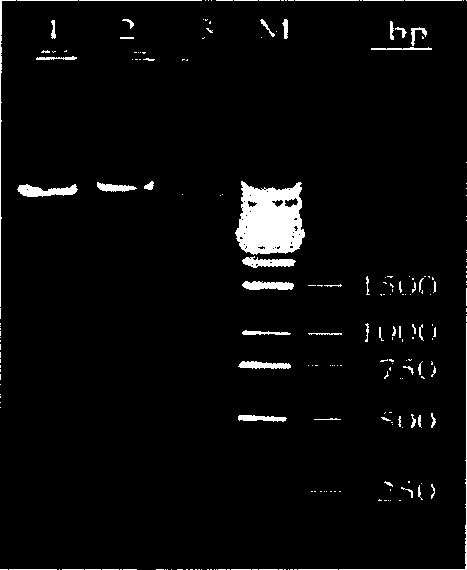Patents
Literature
213 results about "Subcloning" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
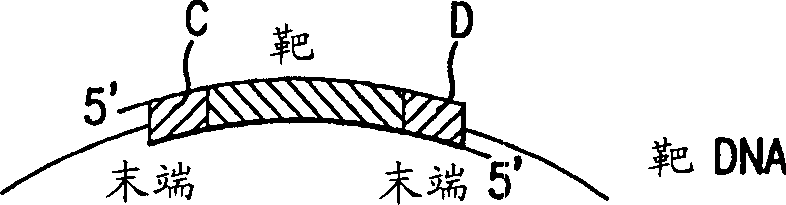
In molecular biology, subcloning is a technique used to move a particular DNA sequence from a parent vector to a destination vector. Subcloning is not to be confused with molecular cloning, a related technique.
Method of sequencing genomes by hybridization of oligonucleotide probes
InactiveUS6018041ASugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementMammalian genomeHomologous sequence
The conditions under which oligonucleotides hybridize only with entirely homologous sequences are recognized. The sequence of a given DNA fragment is read by the hybridization and assembly of positively hybridizing probes through overlapping portions. By simultaneous hybridization of DNA molecules applied as dots and bound onto a filter, representing single-stranded phage vector with the cloned insert, with about 50,000 to 100,000 groups of probes, the main type of which is (A,T,C,G)(A,T,C,G)N8(A,T,C,G), information for computer determination of a sequence of DNA having the complexity of a mammalian genome are obtained in one step. To obtain a maximally completed sequence, three libraries are cloned into the phage vector, M13, bacteriophage are used: with the 0.5 kb and 7 kbp insert consisting of two sequences, with the average distance in genomic DNA of 100 kbp. For a million bp of genomic DNA, 25,000 subclones of the 0.5 kbp are required as well as 700 subclones 7 kb long and 170 jumping subclones. Subclones of 0.5 kb are applied on a filter in groups of 20 each, so that the total number of samples is 2,120 per million bp. The process can be easily and entirely robotized for factory reading of complex genomic fragments or DNA molecules.
Owner:HYSEQ
Human SARS-CoV-2 monoclonal antibody and preparation method and application thereof
PendingCN111153991AHigh affinityStrong specificitySsRNA viruses positive-senseVirus peptidesBALB/cMonoclonal antibody agent
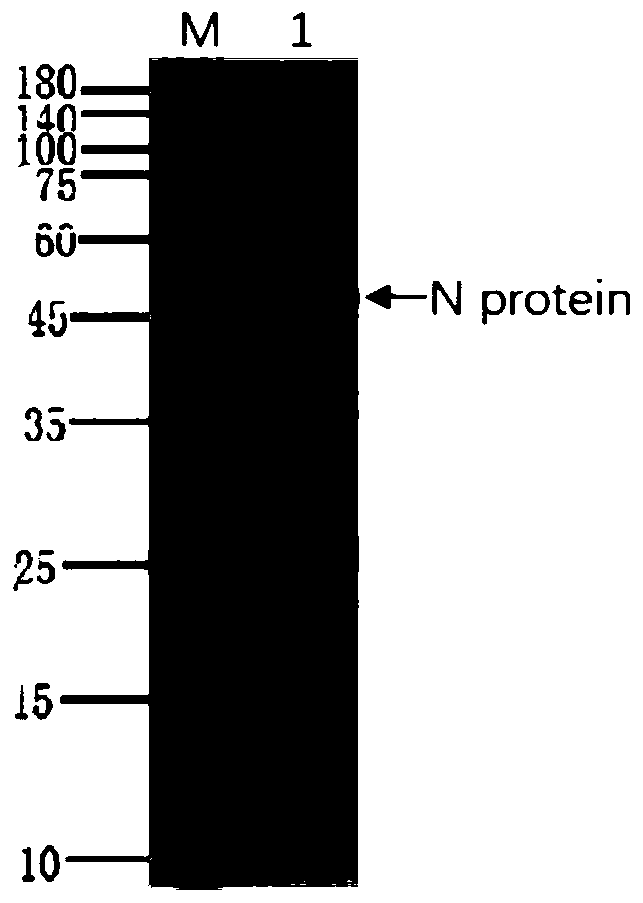
The invention discloses a human SARS-CoV-2 monoclonal antibody. The preparation method of the human SARS-CoV-2 monoclonal antibody comprises the steps: adopting SARS-CoV Nucleocapsid recombinant protein as immunogen, immunizing BALB / c mice, performing fusion and subcloning on spleen cells and myeloma cells of mice, then performing a large amount of repeated screening and domestication of cell lines through commercialized products SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid and MERS Nucleocapsid so as to obtain a hybridoma cell line capable of secreting the SARS-CoV-2-resistant N monoclonal antibody with high affinity and high specificity finally and successfully, and finally performing ascites preparation and purification so as to obtain the monoclonal antibody, wherein the amino acid sequence of the SARS-CoVNucleocapsid recombinant protein is shown in SEQ ID No. 1. The invention also discloses application of the monoclonal antibody in preparation of SARS-CoV-2 virus detection products and preparation ofdrugs for inhibiting the SARS-CoV-2 viruses. The monoclonal antibody can be used for detecting the SARS-CoV-2 in human throat swabs / pulmonary secretions and other samples by using a double-antibody sandwich method, and can be applied to diagnosis and prevention and control of SARS-CoV-2 virus infection and scientific researches of viruses and other study.
Owner:BEIJING BIOSYNTHESIS BIOTECH
System for the rapid manipulation of nuculeic acid sequences
InactiveUS20070128724A1Eliminate needFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionCell freeSite-specific recombination
Owner:INVITROGEN
Methods and compositions for efficient nucleic acid sequencing
InactiveUS7070927B2High discriminatory sequencingBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsNucleic acid sequencingSubcloning
Disclosed are novel methods and compositions for rapid and highly efficient nucleic acid sequencing based upon hybridization with two sets of small oligonucleotide probes of known sequences. Extremely large nucleic acid molecules, including chromosomes and non-amplified RNA, may be sequenced without prior cloning or subcloning steps. The methods of the invention also solve various current problems associated with sequencing technology such as, for example, high noise to signal ratios and difficult discrimination, attaching many nucleic acid fragments to a surface, preparing many, longer or more complex probes and labelling more species.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CHICAGO
Nucleic acids encoding glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF)
ActiveUS7226758B1Prevent nerve damageOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderGlial cell line-derived neurotrophic factorSerum free
A novel neurotrophic factor referred to as glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) has been identified and isolated from serum free growth conditioned medium of B49 glioblastoma cells. Rat and human genes encoding GDNF have been cloned and sequenced. A gene encoding GDNF has been subcloned into a vector, and the vector has been used to transform a host cell in order to produce biologically active GDNF in a recombinant DNA process.
Owner:AMGEN INC
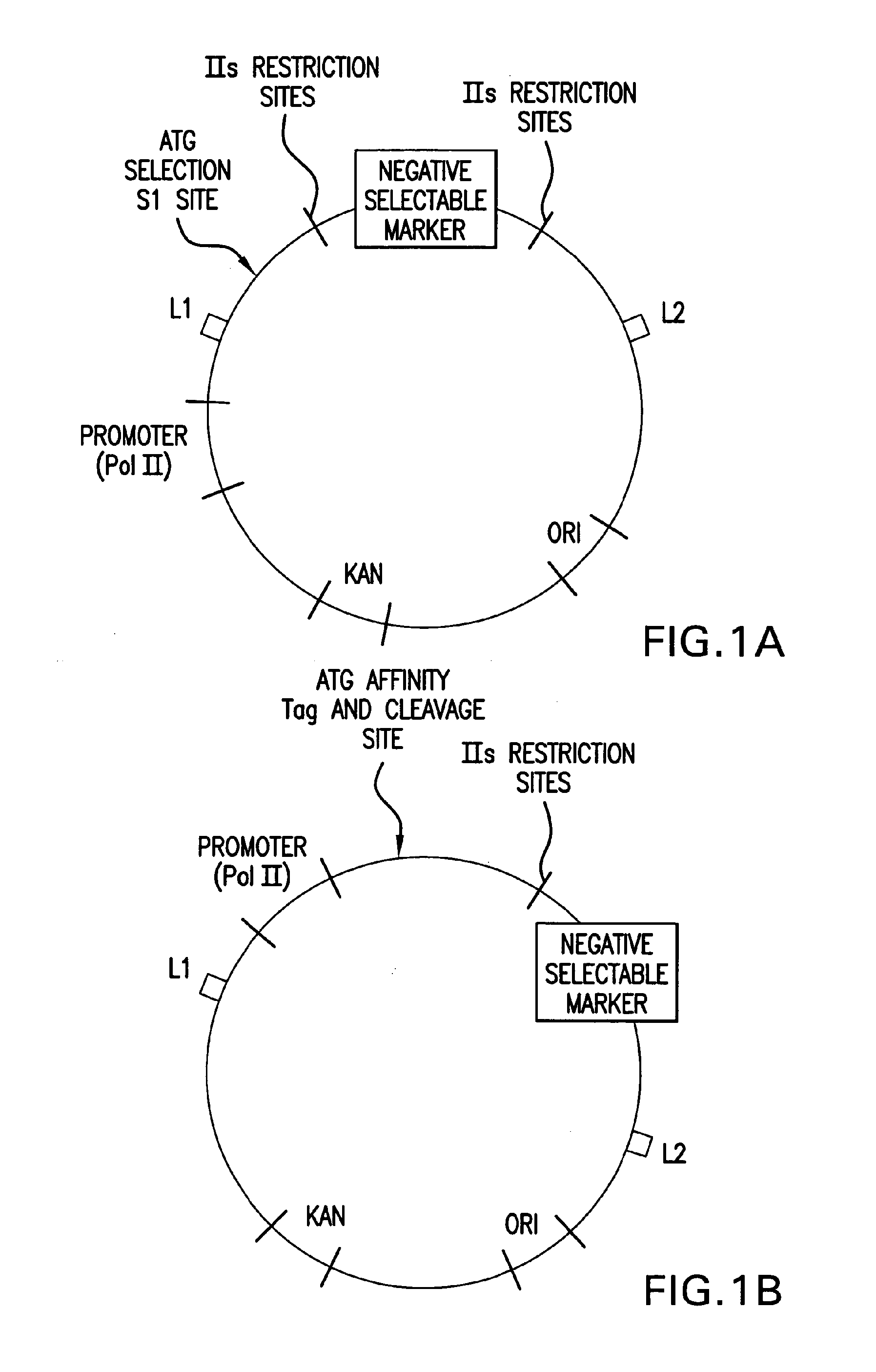
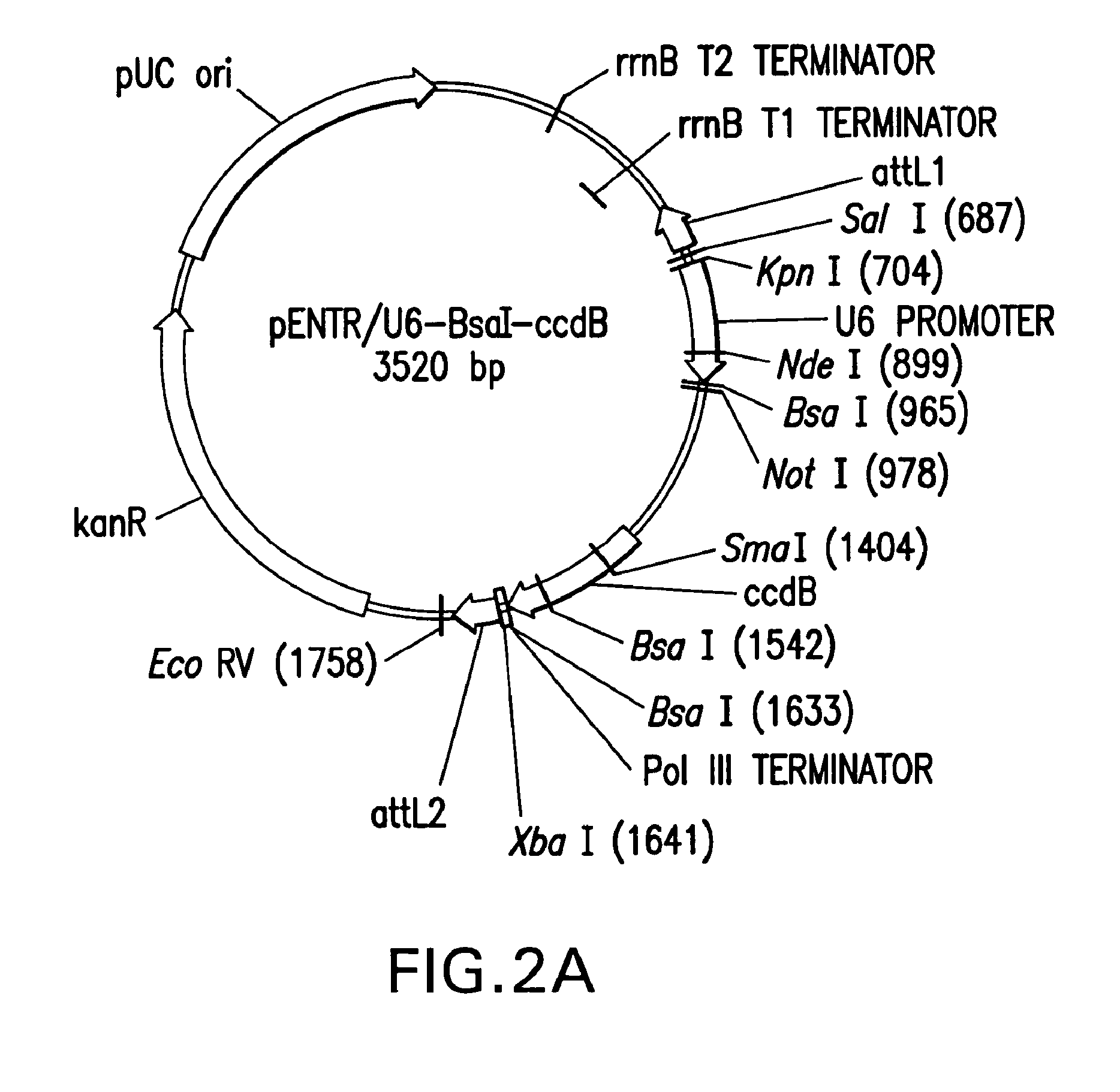
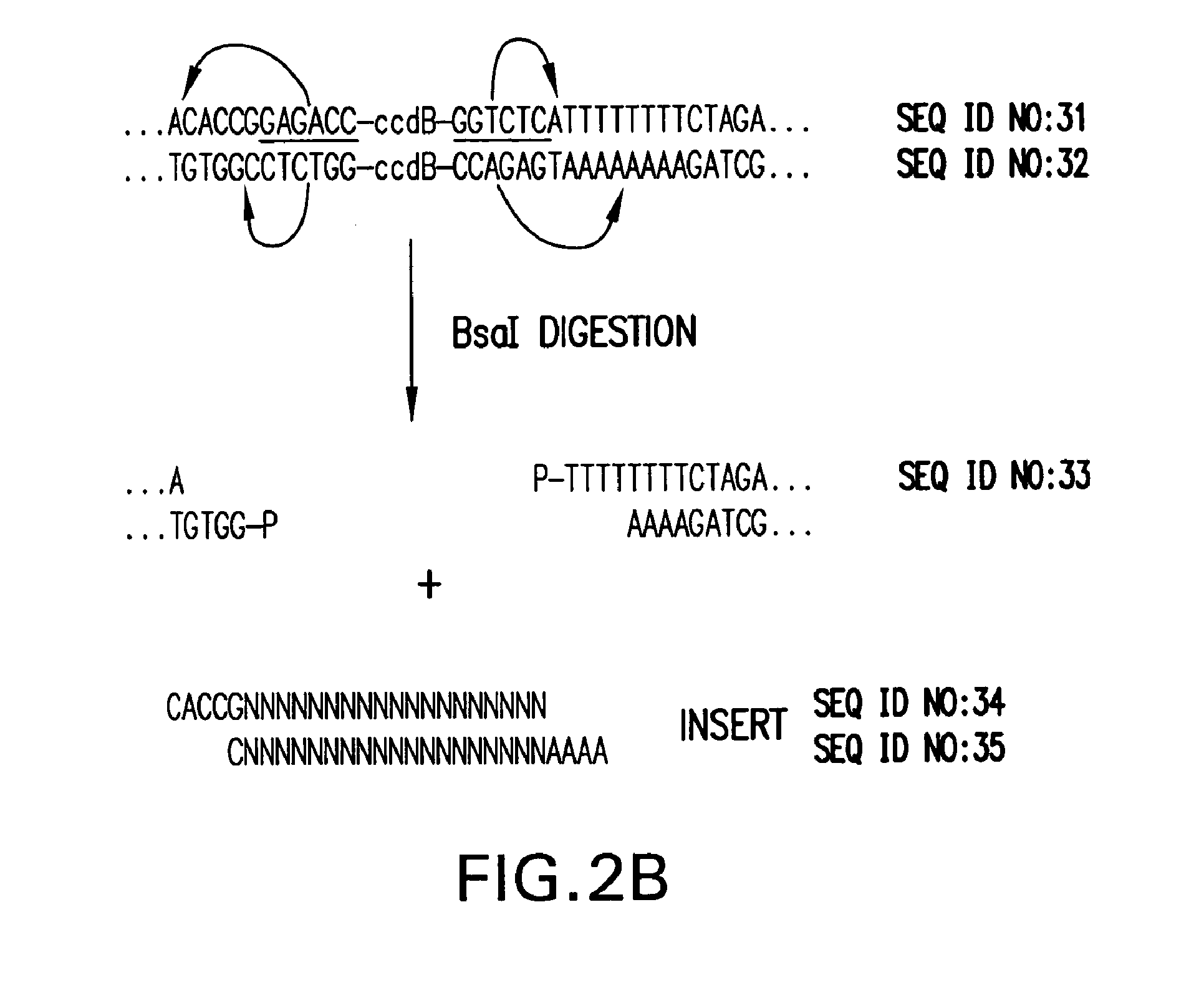
Method of cloning at least one nucleic acid molecule of interest using type iis restriction endonucleases, and corresponding cloning vectors, kits and system using type iis restriction endonucleases
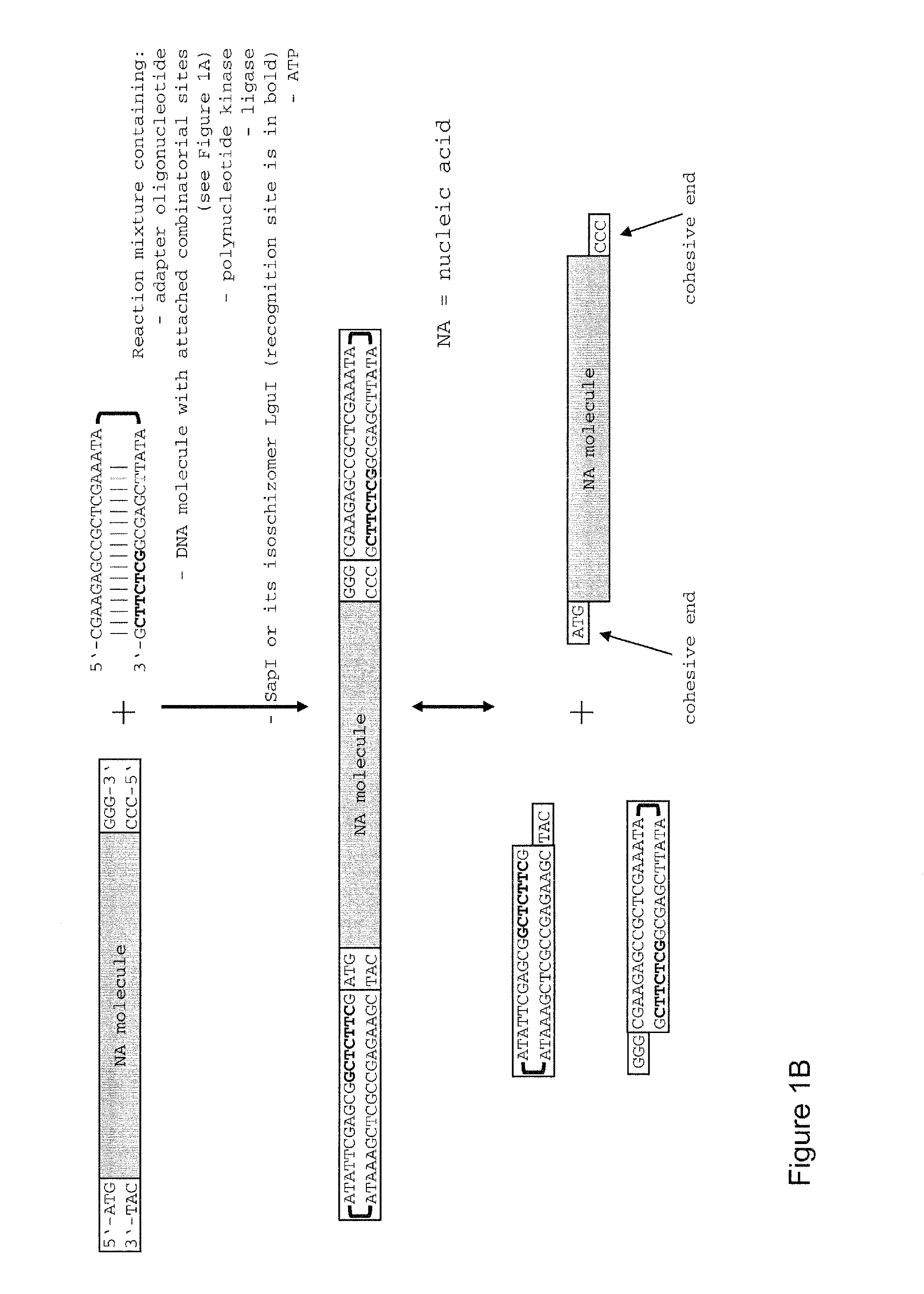
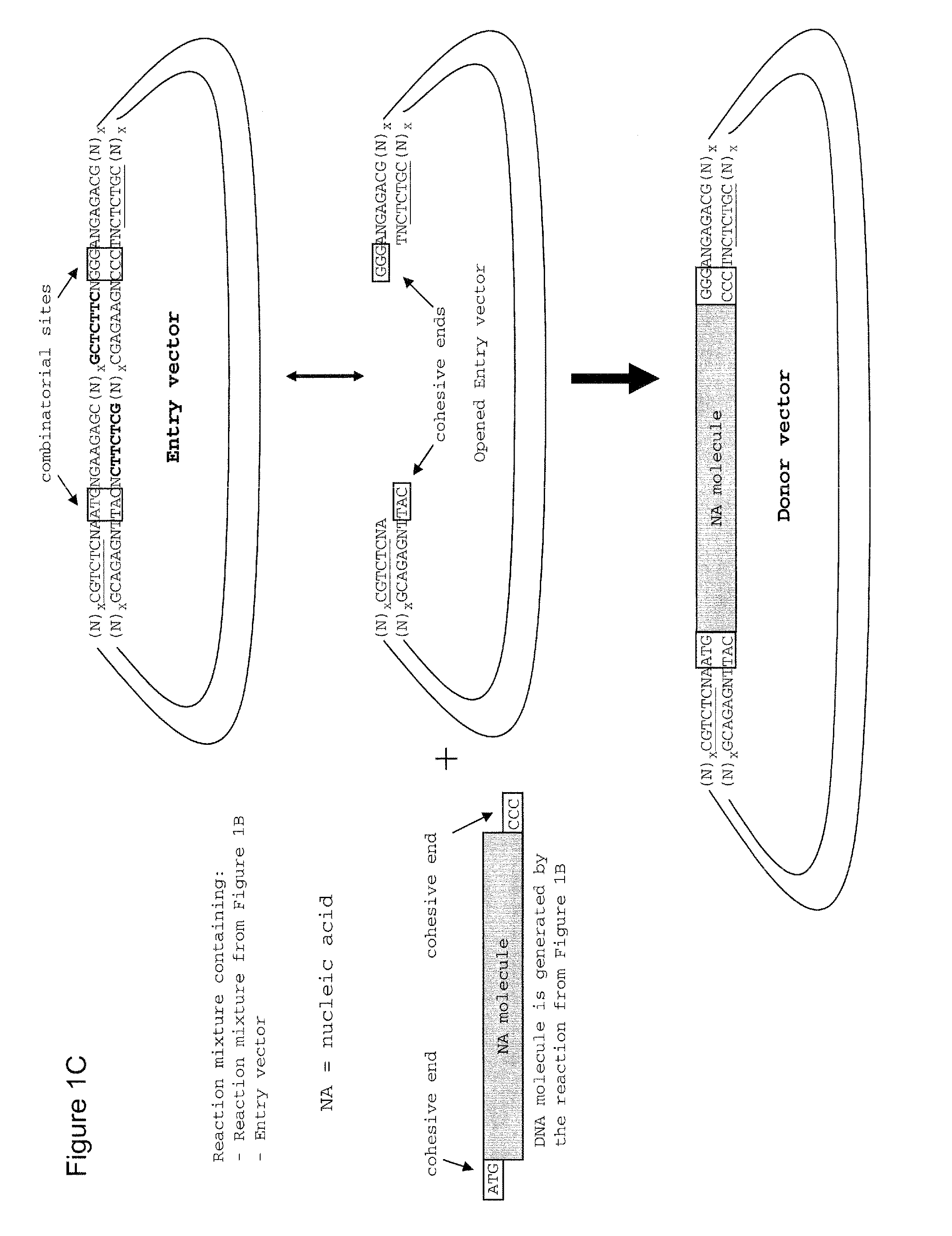
The present invention refers to methods of (sub)cloning at least one nucleic acid molecule of interest. One embodiment relates to a method of (sub)cloning at least one nucleic acid molecule of interest comprising a) providing at least one (replicable) Entry vector into which the at least one nucleic acid molecule of interest is to be inserted, wherein the at least one Entry vector carries two recognition sites for at least one first type IIS and / or type IIS like restriction endonuclease and wherein said at least one nucleic acid molecule of interest can be excised from the at least one Entry vector at two combinatorial sites with one (same) or more (different) cohesive ends that are formed by the at least one first type IIS or type IIS like restriction endonuclease, and b) providing an Acceptor vector, into which the at least one nucleic acid molecule of interest is transferred from the at least one Entry vector carrying the at least one nucleic acid molecule of interest, wherein said Acceptor vector comprises at least one recognition site for at least one second type IIS restriction endonuclease and / or at least one recognition sites for at least one type IIS like restriction endonuclease, and wherein said Acceptor vector provides two combinatorial sites identical to the two combinatorial sites present in the Entry vector. The inventions also relates respective cloning vector and kits.
Owner:PHILIPPS UNIV MARBURG
Method of sequencing of genomes by hybridization of oligonucleotide probes
InactiveUS6451996B1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementMammalian genomeHomologous sequence
The conditions under which oligonucleotides hybridize only with entirely homologous sequences are recognized. The sequence of a given DNA fragment is read by the hybridization and assembly of positively hybridizing probes through overlapping portions. By simultaneous hybridization of DNA molecules applied as dots and bound onto a filter, representing single-stranded phage vector with the cloned insert, with about 50,000 to 100,000 groups of probes, the main type of which is (A,T,C,G)(A,T,C,G)N8(A,T,C,G), information for computer determination of a sequence of DNA having the complexity of a mammalian genome are obtained in one step. To obtain a maximally completed sequence, three libraries are cloned into the phage vector, M13, bacteriophage are used: with the 0.5 kb and 7 kbp insert consisting of two sequences, with the average distance in genomic DNA of 100 kbp. For a million bp of genomic DNA, 25,000 subclones of the 0.5 kbp are required as well as 700 subclones 7 kb long and 170 jumping subclones. Subclones of 0.5 kb are applied on a filter in groups of 20 each, so that the total number of samples is 2,120 per million bp. The process can be easily and entirely robotized for factory reading of complex genomic fragments or DNA molecules.
Owner:COMPLETE GENOMICS INC
System for the rapid manipulation of nucleic acid sequences
InactiveUS20030153055A1Eliminate needLow backgroundFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionCell freeSite-specific recombination
The present invention is a cell-free subcloning system utilizing three elements: (1) a donor vector that contains a nucleic acid sequence to be transferred to another vector flanked by a site-specific recombination sequence and one or more optional additional nucleic acid sequences, (2) an acceptor vector that contains a site-specific recombination sequence and one or more optional additional nucleic acid sequences, and (3) a site-specific recombinase that recognizes the site-specific recombination sequences in the donor and acceptor vectors so as to transfer the transfer sequence from the donor to the acceptor vector upon contact of the three elements of the system. Also disclosed are rapid subcloning methods employing the vectors and enzymes disclosed herein and kits for use in such methods.
Owner:INVITROGEN
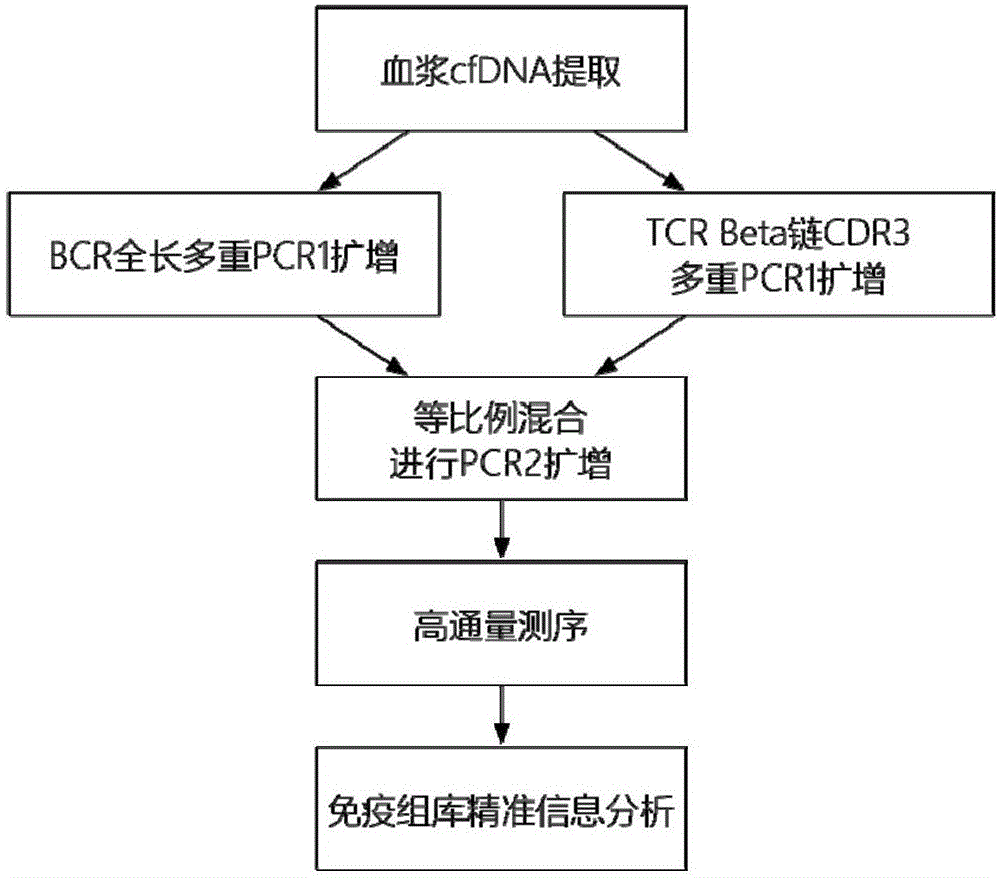
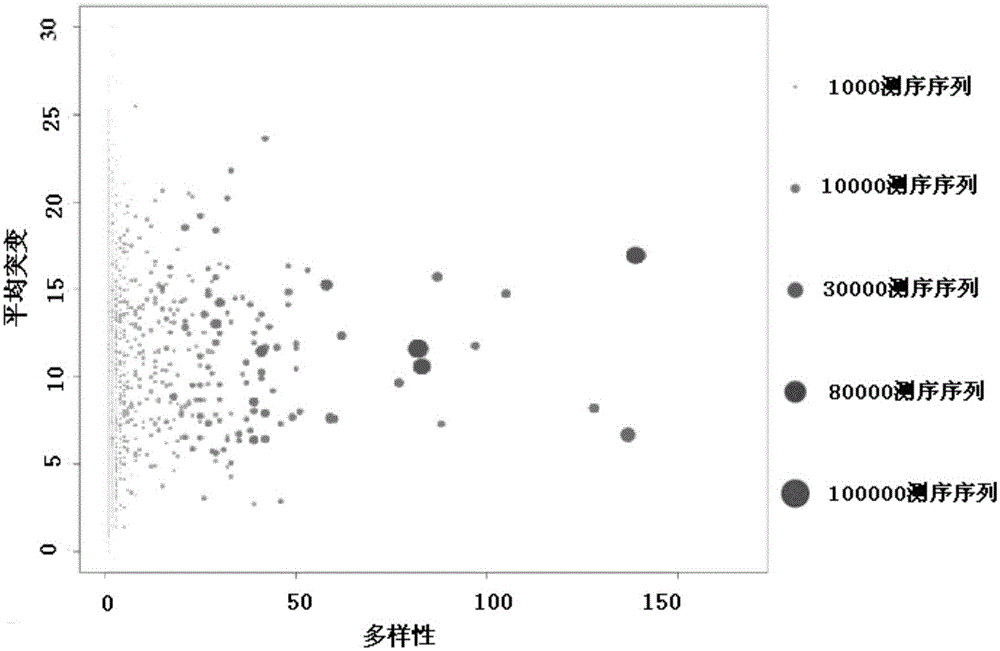
Method for detecting BCR and TCR immune repertoire in blood plasma cfDNA
ActiveCN105087789AEliminate errorsImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationInformation analysisSubcloning
The invention provides a method for detecting BCR and TCR immune repertoire in blood plasma cfDNA. The method includes: blood plasma cfDNA extraction, BCR H chain overall length multiple PCR amplification, TCR beta chain CDR3 multiple PCR amplification, PCR amplification after the products of the two previous amplifications are mixed in an equal-volume manner, high-throughput sequencing, and immune repertoire precise information analysis. The primers of the three amplifications are respectively shown in SEQ ID No. 1-28, SEQ ID No. 29-77 and SEQ ID No. 78-79. The invention further provides a kit, which contains the primers, for detecting the BCR and TCR in the blood plasma cfDNA. By the method and the kit which are promising in application prospect in the field of non-invasive detection, the BCR and TCR in the blood plasma cfDNA can be detected at the same time, precise information analysis and precise quantification of immune repertoire subcloning are achieved.
Owner:BEIJING GENEPLUS TECH +2
System for the rapid manipulation of nucleic acid sequenaces
InactiveUS20050181417A1Eliminate needMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationCell freeSite-specific recombination
The present invention is a cell-free subcloning system utilizing three elements: (1) a donor vector that contains a nucleic acid sequence to be transferred to another vector flanked by a site-specific recombination sequence and one or more optional additional nucleic acid sequences, (2) an acceptor vector that contains a site-specific recombination sequence and one or more optional additional nucleic acid sequences, and (3) a site-specific recombinase that recognizes the site-specific recombination sequences in the donor and acceptor vectors so as to transfer the transfer sequence from the donor to the acceptor vector upon contact of the three elements of the system. Also disclosed are rapid subcloning methods employing the vectors and enzymes disclosed herein and kits for use in such methods.
Owner:INVITROGEN
Cadmium chelate complex monoclonal antibody and preparation method and usage thereof
InactiveCN101139396AHigh potencyThe detection process is fastImmunoglobulins against animals/humansMaterial analysisAntiendomysial antibodiesBovine serum albumin
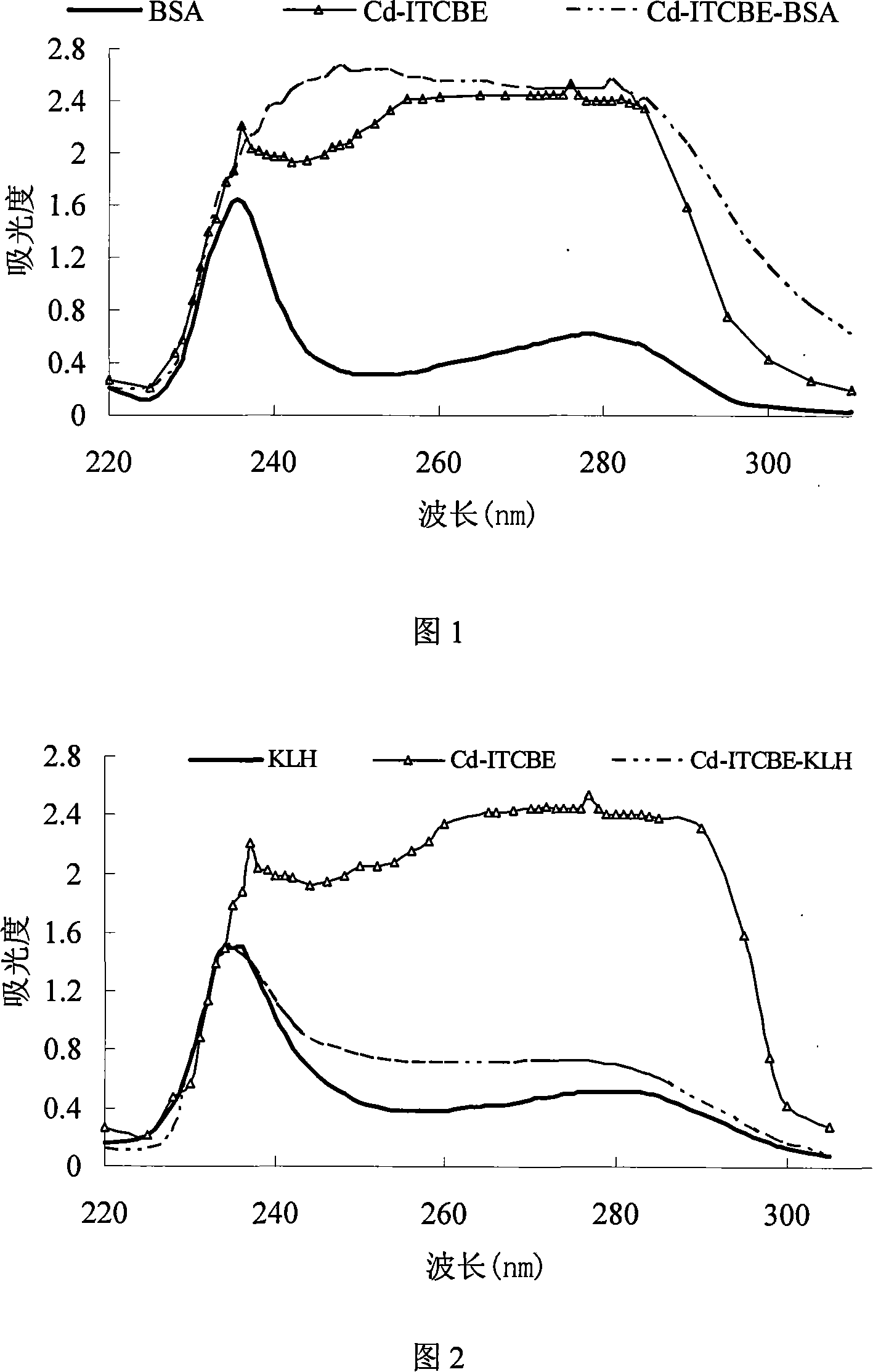
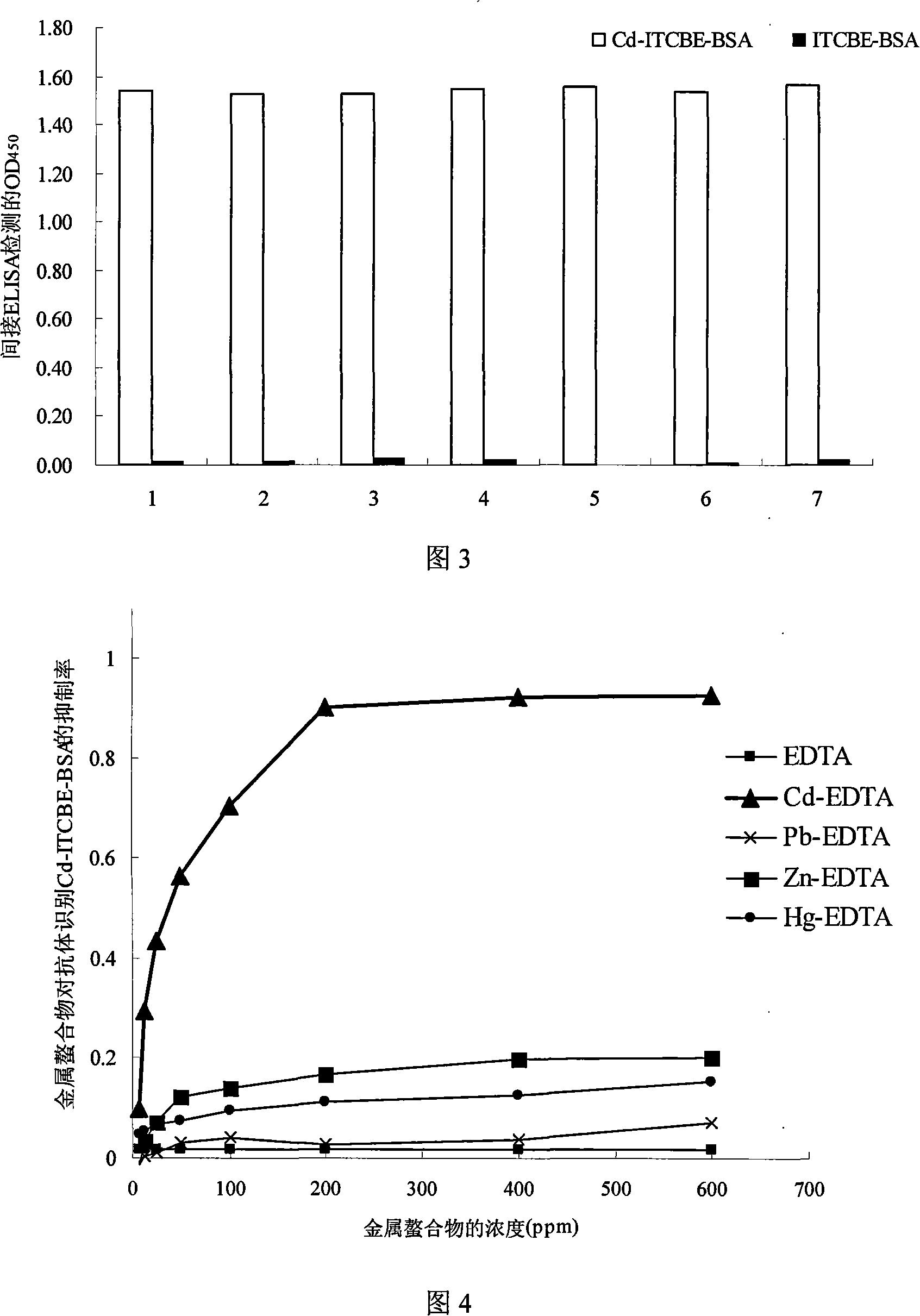
The present invention discloses a cadmium chelate monoclonal antibody and a preparation method as well as application of the monoclonal antibody. The monoclonal antibody is of specificity to cadmium -1 - (4 - isothiocyanate-benzyl) - EDTA - bovine serum albumin and the cadmium metal chelate. The preparation method of the cadmium chelate monoclonal antibody is as following: first of all, hapten is prepared and cadmium chelate complete antigen is formed; spleen cells of mouse which are Cd-ITCBE-KLH-immune are combined with SP2 / 0, and the positive clones are screened through a two-step method; after a plurality of times of subcloning, monoclonal antibody that can stably excrete anti-cadmium chelate is obtained. The cadmium chelate monoclonal antibody is used to measure the concentration of cadmium ion through the linear equation: Y = 0.0081X +0.1115, R 2 = 0.9922. The measurement is fast and the cost is low; the measurement result is accurate and is of high sensitivity and strong selectivity; the equipment is simple and can be easily carried for on-spot testing.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus receptor CD163 knock-out swine and cultivation method thereof
The invention provides a porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus receptor CD163 knock-out swine and a cultivation method thereof. A constructed CD163 gene knock-out carrier pSSC-Larm-Sarm-CD163 uses a genome of Chinese experimental miniature swines as a template, and adopts a PCR method to amplify a homologous left arm and a homologous right arm of the swine CD163 gene; the cloned homologous left arm and the homologous right arm of the CD163 gene are subcloned to a pSSC-9 carrier respectively; and the porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus receptor CD163 knock-out swine is cultivated, wherein the CD163 gene is not expressed, and the swine is not infected by the porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Glucosidase/xylosidase difunctional cellulose degradation enzyme RuGBGX2 as well as coding gene and application thereof
ActiveCN102041251AHigh activityReduce complexityMicroorganism based processesEnzymesChemical industryCellulose
The invention relates to a novel beta glucosidase / xylosidase difunctional cellulose degradation enzyme RuGBGX2 as well as a coding gene and application thereof. The coding sequence of amino acid of the RuGBGX2 contains 18-755th sites of an SEQ ID NO 2 sequence. The RuGBGX2 is sourced from the rumen microorganism of yak from China, a novel coding gene of the beta glucosidase / xylosidase difunctional cellulose degradation enzyme RuGBGX2 is obtained by function screening and sequencing analysis on a rumen metagenome cosmid library and a subclone library. The beta glucosidase / xylosidase difunctional cellulose degradation enzyme provided by the invention can be widely applied to the degradation of cellulose and the fields such as cellulose biotransformation, chemical industry, spinning, foods, bioenergy, feed additives, medical industry and the like. By utilizing the difunctional enzyme RuGBGX2 to degrade wood fiber, the varieties of added enzymes can be reduced, and an enzymolysis process can be simplified.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV +1
Process of making transgenic mammals that produce exogenous proteins in milk and transgenic mammals produced thereby
InactiveUS20050177878A1Improve the level ofVectorsPeptide preparation methodsBovine oocyteSomatotropic hormone
The invention relates to a method of producing a protein of interest, comprising making a non-human transgenic mammal that produces said protein in its milk, obtaining said milk from the non-human transgenic mammal and purifying said protein of interest from the milk. Transgenic bovine animals were generated, which are able to produce human growth hormone in mammary glands. The method involves cloning of a genetic construct encoding hGH gene and beta casein promoter conveniently in an expression vector. It also includes transfection procedures into fetal bovine somatic cells, generally fibroblasts, and the nuclear transfer into enucleated bovine oocytes, generating thus transgenic embryos. The method also includes other procedures to generate transgenic embryos for the further expansion of the transgenic herd, such as the subcloning of transgenic female bovines, the superovulation of transgenic cows and their insemination with semen from a non-transgenic or a transgenic male bovine, and the superovulation of non-transgenic cows and their insemination with semen from a transgenic male bovine. Afterwards, transgenic embryos give rise to transgenic cattle that produce human growth hormone in huge amounts in their milk, from which the hormone is completely purified and analysed to fulfill all the requirements for the manufacture of a pure biopharmaceutical product.
Owner:STERRENBELD BIOTECH NORTH AMERICA
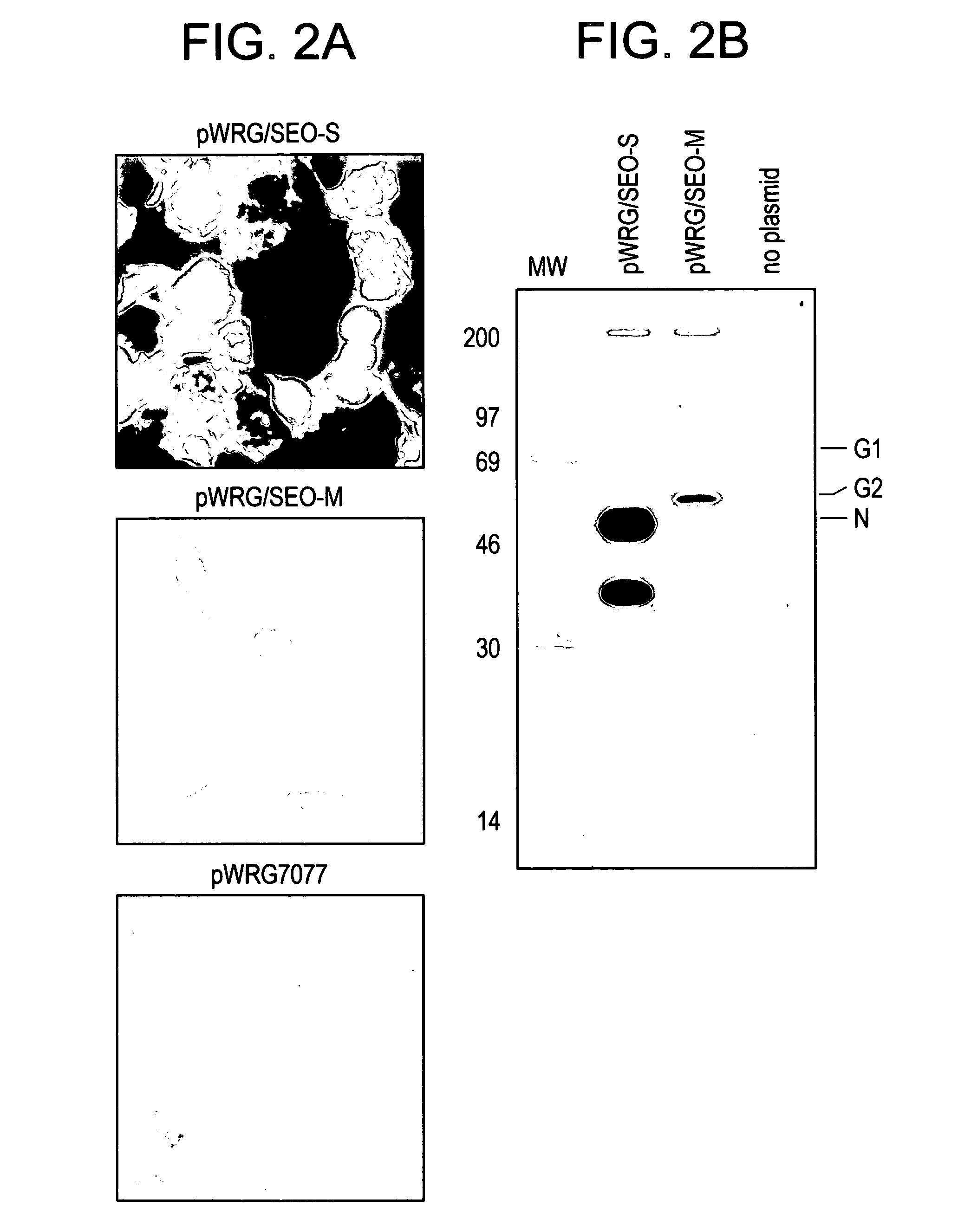
Extraneous DNA sequence that facilitates hantavirus gene expression
InactiveUS7217812B2Not painful to administerAvoid infectionSugar derivativesViral antigen ingredientsDiseaseSerum ige
In this application is described a protective DNA vaccines against infection with HFRS- and HPS-associated hantaviruses. The vaccines were constructed by subcloning cDNA representing the medium (M) (encoding the G1 and G2 glycoproteins) into the DNA expression vector pWRG7077. Animals vaccinated with the M construct developed a neutralizing antibody response. Passive transfer experiments show that serum from vaccinated animals, when injected on days 4 or 5 after challenge, protected animals from lethal disease.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA THE AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE ARMY
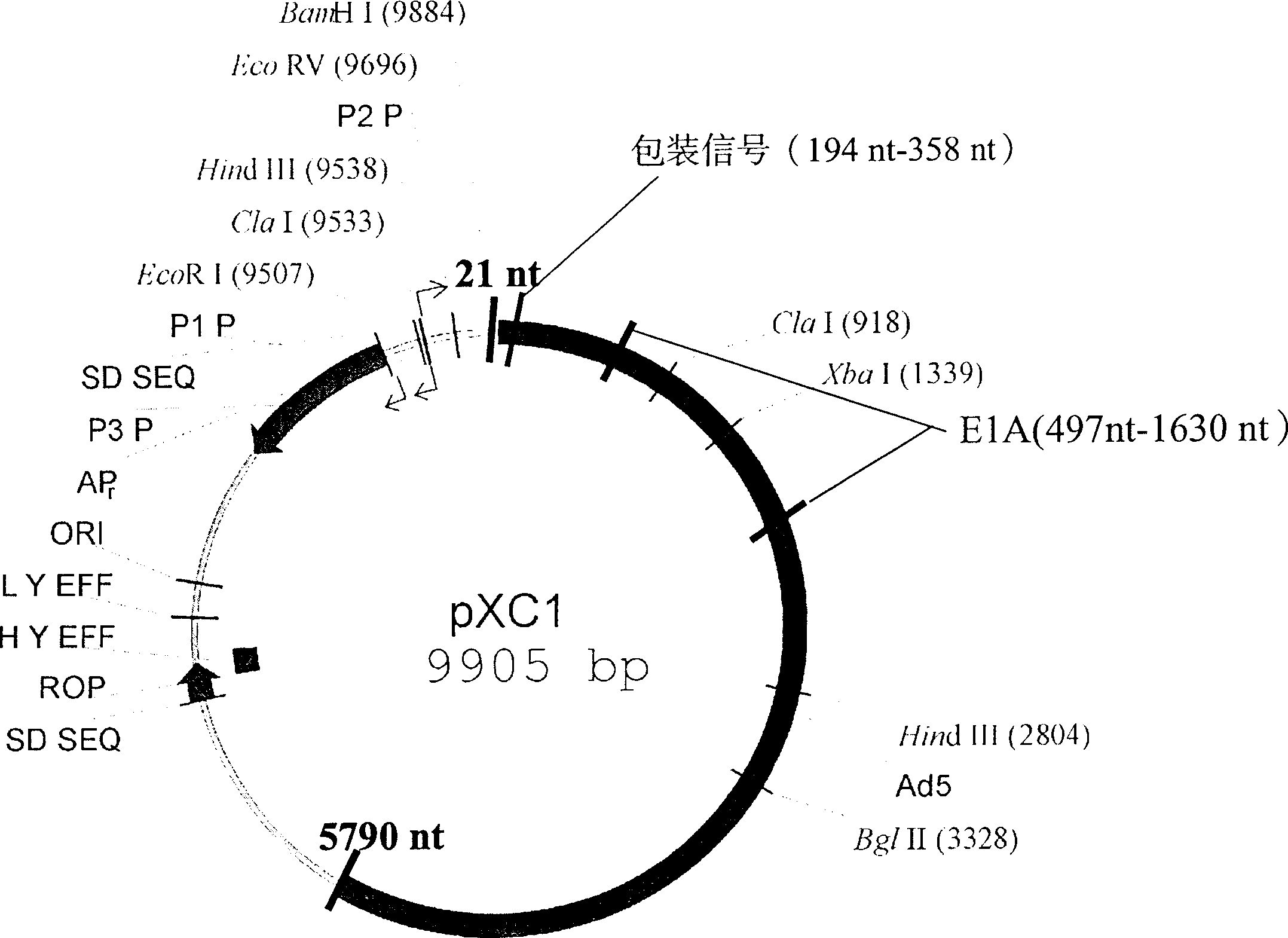
Recombination adenovirus construction body with deletion E1A code sequence and its use
InactiveCN1427075AReliable diagnosisNo significant effect on activityMicrobiological testing/measurementGenetic material ingredientsTumor cellsMutation
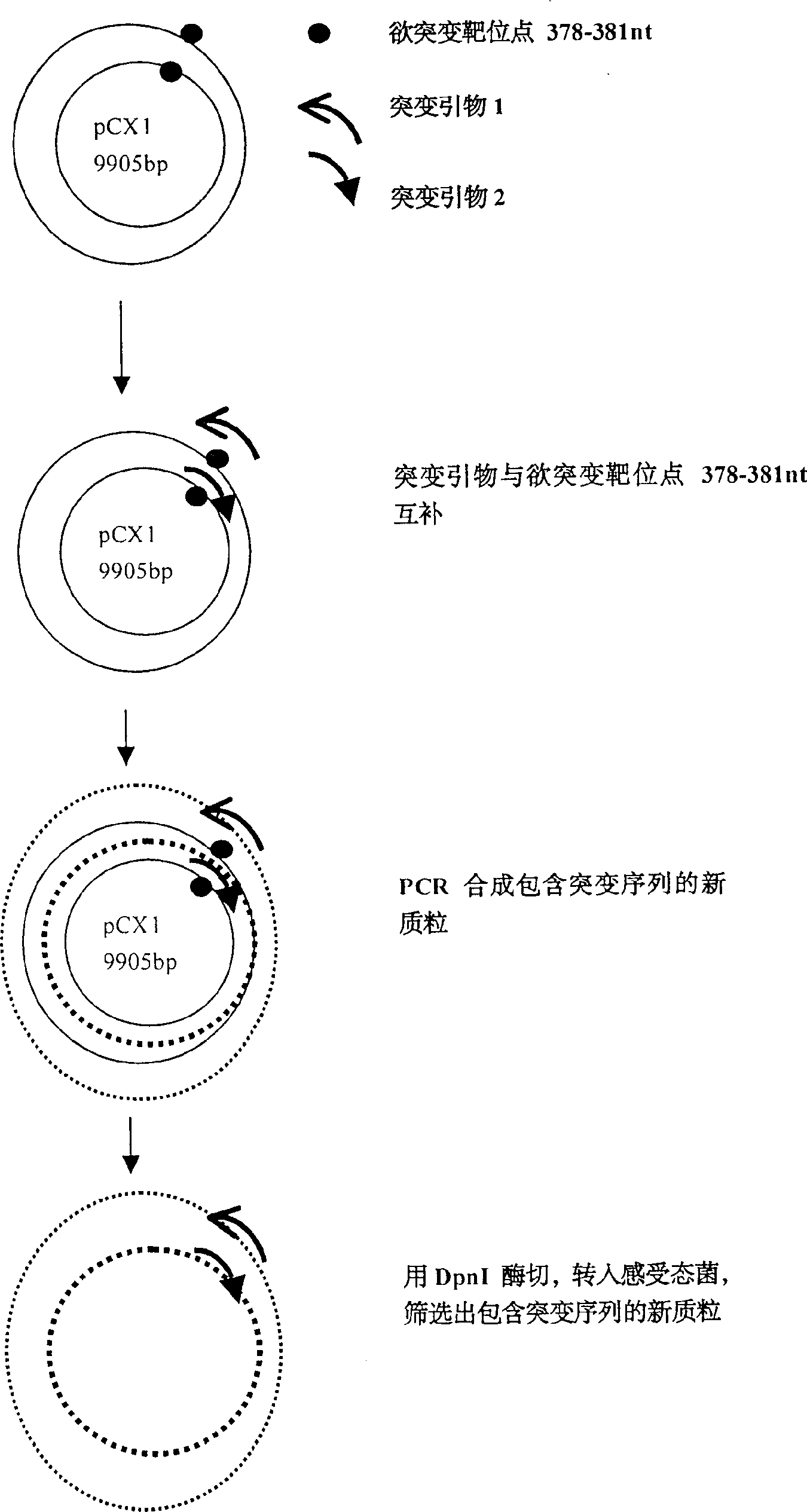
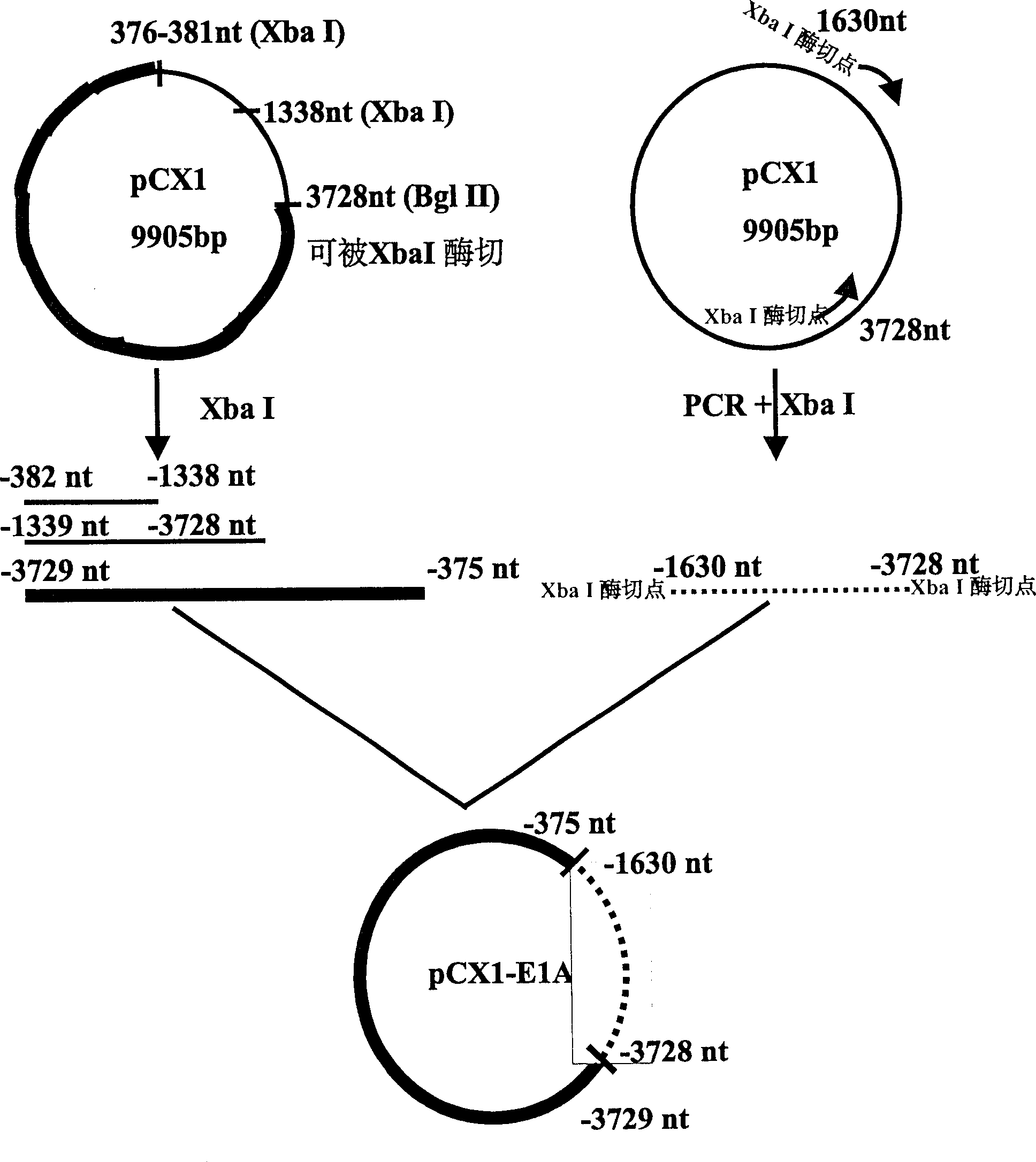
A recombinant adenovirus configurator deleted EIA coding sequence in human adenovirus type 5 genom and its application to diagnosing and treating tumor are disclosed. The site-directed mutation, PCR augmentation, enzyme severing, linking, subcloning, transfection, and single-cloning purification of recombinant adenovirus technologies, and the deleted EIA (382-1630 nt) sequence are used to screen the recombinant adenovirus configurator of being unable to express the EIA function protein. It can specifically kill tumor cells, but not normal cells, and has synergestic action to chemicotherapeutic medicines.
Owner:深圳市天达康基因工程有限公司
Induced slow virus expression system and construction method and application thereof
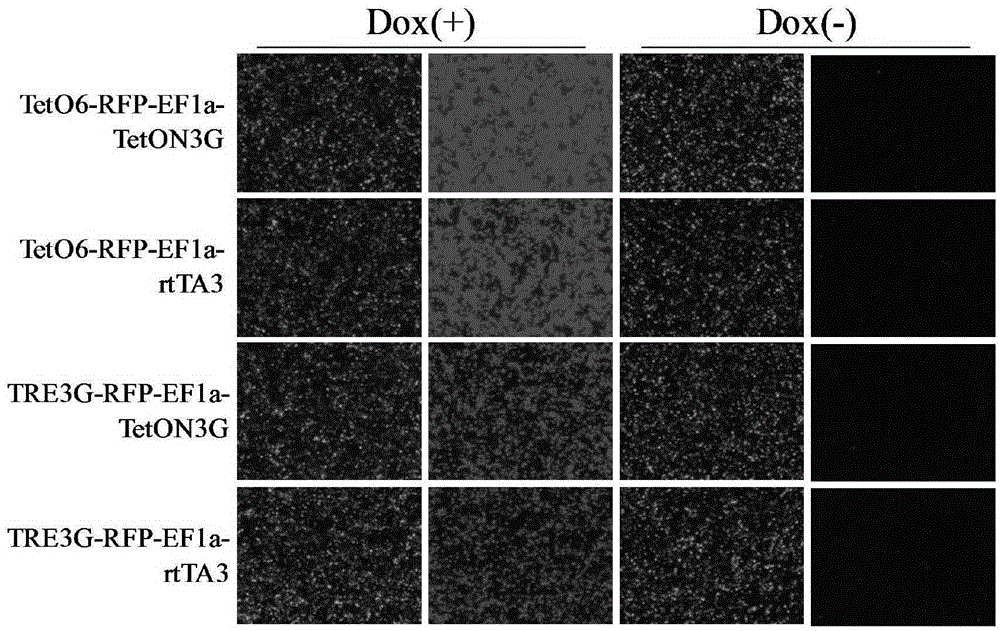
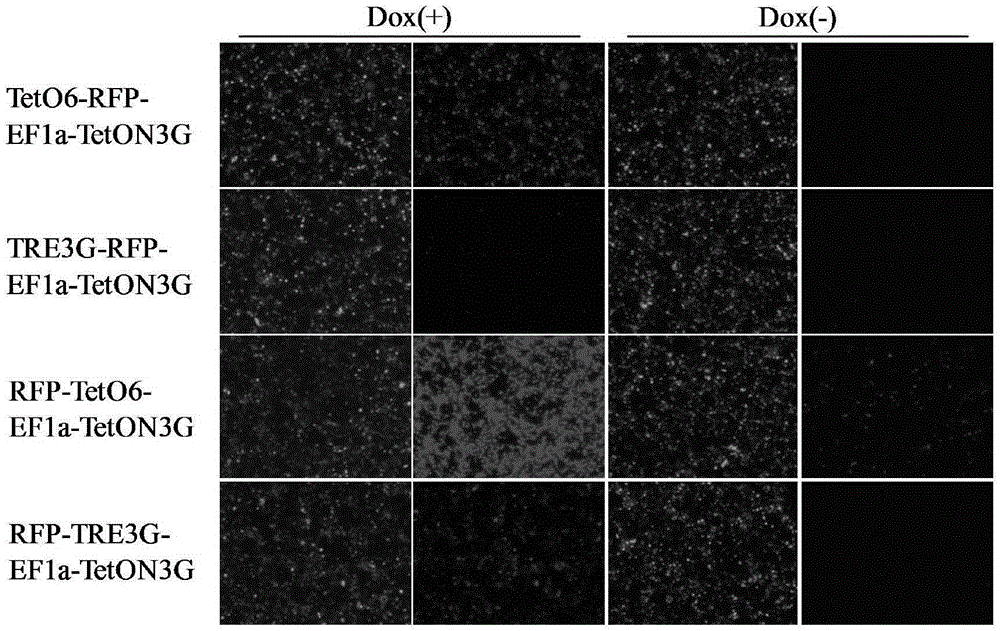
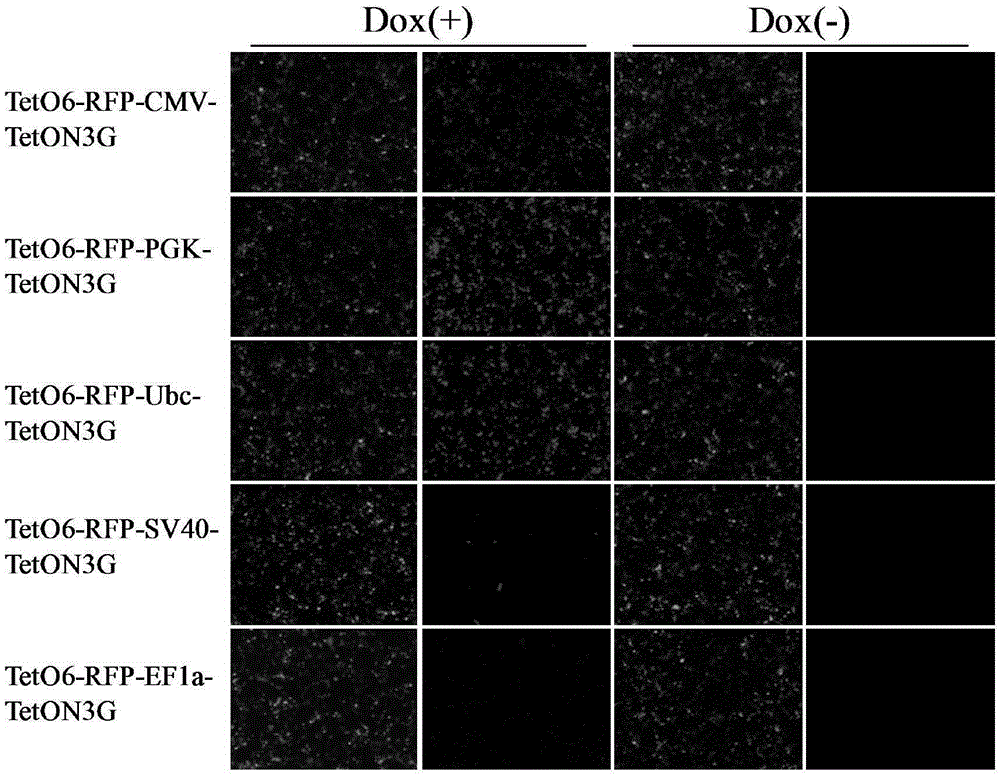
ActiveCN105331635ARapid responseImprove efficiencyFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionLinker peptideCancer research
The invention discloses an induced slow virus expression system which comprises a target gene expression cassette and an rtTA expression cassette. The target gene expression cassette comprises an induced promoter containing a tetracycline cis-acting response element and a target gene, and the rtTA expression cassette comprises a promoter, an rtTA, a linker peptide and a screening gene, wherein a P2A linker peptide is adopted as the linker peptide, the screening gene is Puro, and the induced promoter is TetO6 or TRE3G. The invention further discloses a construction method of the induced slow virus expression system. The construction method comprises the steps of pLVX-Puro carrier reconstructing; TetON3G gene synthesizing and cloning; pLVX-rtTA3 constructing; EF1a promoter subcloning; red fluorescence protein (RFP) subcloning; subcloning of the induced promoter TRE3G or TETO6 containing the tetracycline cis-acting response element. The induced slow virus expression system can carry out inducible expression of the target gene to the greatest level while keeping low background expression after cells are introduced into the system, is sensitive in response for an inducer, high in efficiency and low in molecular weight and can be widely applied to gene function research.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
Hybridoma cell strain secreting thiamethoxam monoclonal antibody and application thereof
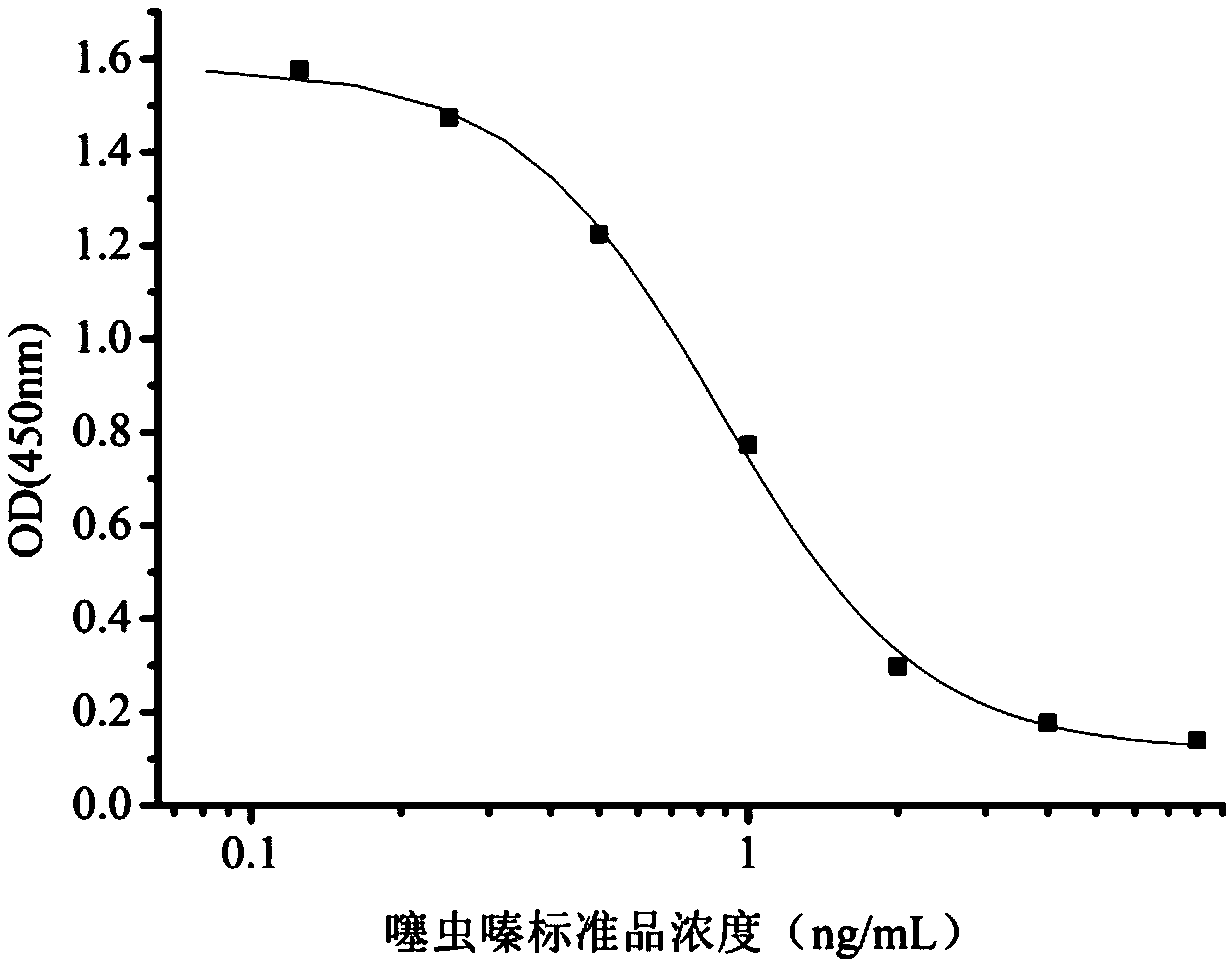
InactiveCN108998422AHigh detection sensitivityImprove featuresMicroorganism based processesDepsipeptidesBALB/cIc50 values
The invention relates to a hybridoma cell strain secreting thiamethoxacin monoclonal antibody and application thereof, belonging to the field of food safety immunodetection. The accession number of the hybridoma cell strain is CGMCC No. 14699. According to the invention, a complete Freund's adjuvant is used for primary immunization of a BALB / c mouse, then an incomplete Freund's adjuvant is used for booster immunization three times, and a thiamethoxam complete antigen containing no adjuvant is used for impact immunization once, so the BALB / c mouse is immunized; and then the high-titer low-IC50spleen cells of the immunized mouse are fused with mouse myeloma cells by using a PEG method, and then the cell strain is obtained through indirect competitive ELISA screening and subcloning three times. The monoclonal antibody secreted by the cell strain has good specificity and detection sensitivity (with an IC50 value of 0.81 ng / mL) to thiamethoxam and can be used for detection of thiamethoxamresidues in food.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV +1
Preparation method and application of enterovirus 71 type full-length infectious clone with tags
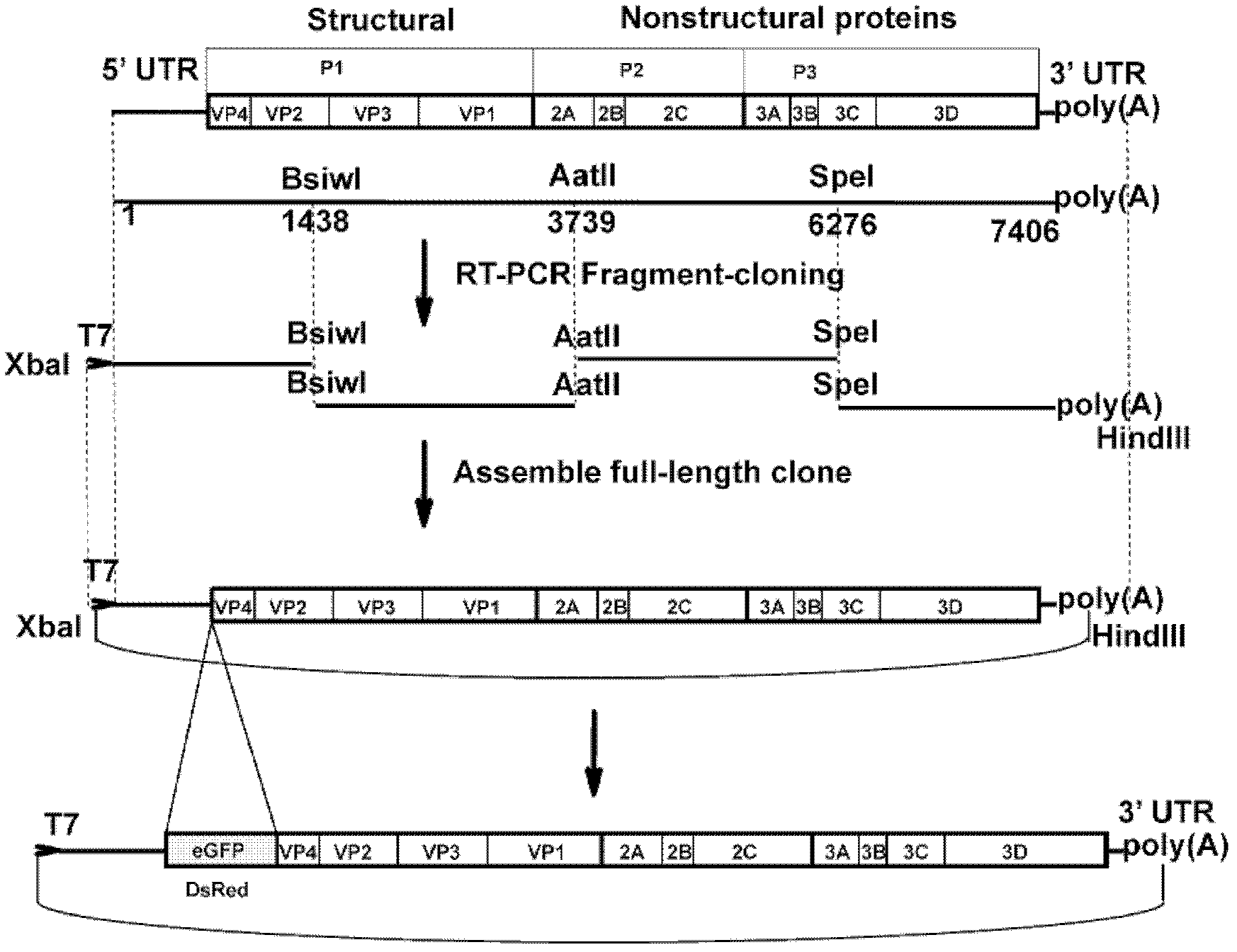
InactiveCN102517317AEffective generationEfficiently obtainedMicrobiological testing/measurementViruses/bacteriophagesCytopathic effectTotal rna
The invention discloses a preparation method and application of enterovirus (EV) 71 type full-length infectious clone with tags. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: (1) extracting total RNA; (2) performing reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) amplification on the EV71; (3) constructing EV71 subclone; (4) constructing recombinant clone containing EV71 genes; and (5) constructing the enterovirus 71 type full-length infectious clone with eGFP and DsRed. Tests, such as cytopathic effect, fluorescence detection, gene detection, virus plaque, medicine inhibition and the like, prove that the EV71 full-length infectious clone with the tags is obtained successfully. The invention has high application value in the aspects of research and development of animal models, virus replication and pathogenesis, medicine screening and medicine action mechanism, vaccine and diagnostic reagents and the like.
Owner:WUHAN INST OF VIROLOGY CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Method and compositions for directed clonning and subclonning using homologous recombination
The present invention relates to methods and compositions for DNA subcloning using bacterial recombinase-mediated homologous recombination technology. The present invention relates to methods of cloning, compositions containing polynucleotides used as cloning vectors, cells containing the polynucleotide compositions, and cloning kits mediated by bacterial recombinases such as RecE / T and Redα / β.
Owner:EURO LAB FUER MOLEKULARBIOLOGIE EMBL
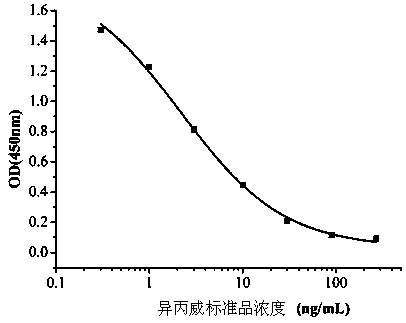
Hybridoma cell strain GTY for secreting anti-isoprocarb monoclonal antibody and application thereof
InactiveCN110423729AImprove featuresHigh detection sensitivityMicroorganism based processesDepsipeptidesLaboratory cultureCell strain
The invention relates to a hybridoma cell strain GTY for secreting an anti-isoprocarb monoclonal antibody and an application thereof, and belongs to the field of food safety immune detection. The hybridoma cell strain GTY has been preserved in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center with a preservation number CGMCC No.17393. The complete antigen of isoprocarb and the same amount of Freund's adjuvant are mixed and emulsified to immunize BALB / c mice. The first immunization uses complete Freund's adjuvant, the multiple reinforcement immunization uses incomplete Freund's adjuvant, and the last sprint immunization is carried out. The hybridoma cell strain GTY is prepared by the following steps of: fusing high-potency low-IC50 mouse spleen cells with mouse myeloma cells by aPEG method, and performing culturing and screening; and screening cells by indirect competitive enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, and performing subcloning three times. The monoclonal antibody secreted by the cell strain has good specificity and detection sensitivity on the isoprocarb, can realize the detection of the isoprocarb residue in fruits and vegetables, provides raw materials for the immunodetection of the isoprocarb residue in foods, and has practical application value.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
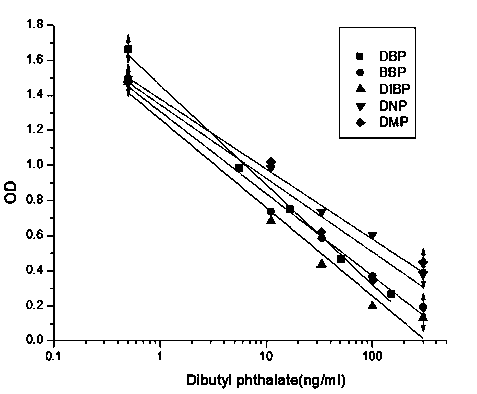
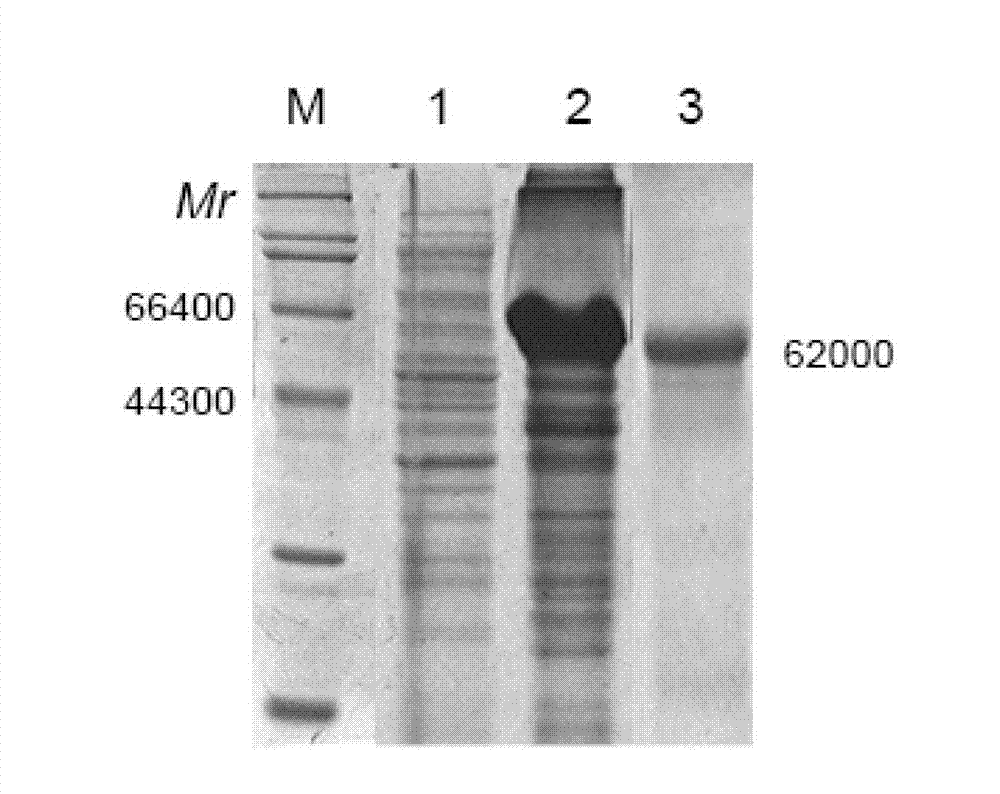
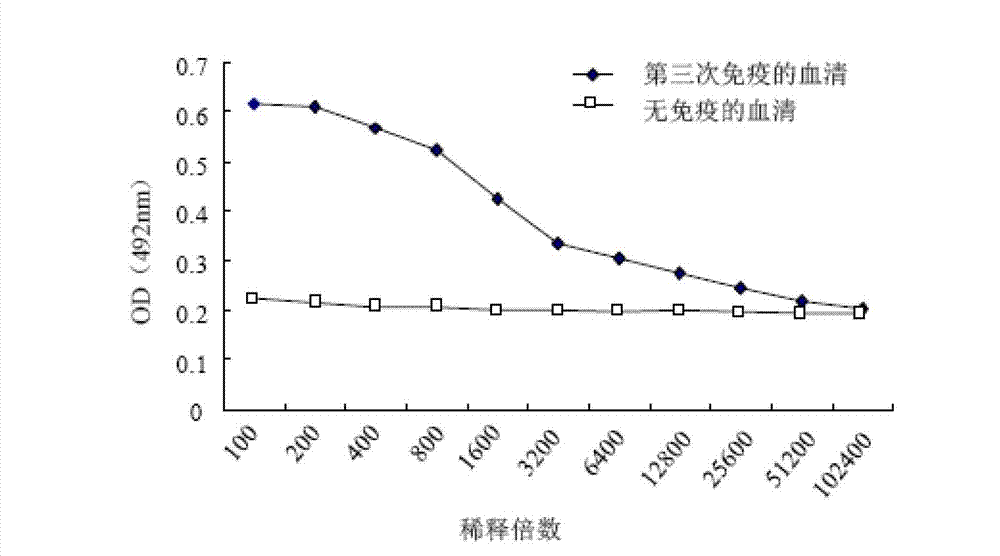
Universal phthalic acid esters monoclonal antibody hybridoma cell strain and application thereof
ActiveCN104004719AHigh affinityHigh detection sensitivityImmunoglobulins against animals/humansMicroorganism based processesBALB/cIndirect elisa
The invention discloses a universal phthalic acid esters monoclonal antibody hybridoma cell strain and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of food safety immunological detection. Hapten is prepared and is coupled with albumen based on the glutaraldehyde method to obtain phthalic acid dibutyl ester complete antigen, and the phthalic acid dibutyl ester complete antigen and freund's adjuvant are evenly mixed to be injected to immune BALB / c mice in a subcutaneous injection mode; envelope antigen is formed in a synthesis mode based on the diazotization method and is used for screening mouse serum and cell supernatant. The splenocyte of the immune mice is fused with myeloma cells of the mice based on a PEG method, and indirect ELISA, indirect competition ELISA screening and three times of subcloning are carried out to obtain selective group hybridoma cell strain monoclonal cell strain C. The monoclonal cell strain C has certain recognition capability on DEHP and DINP, and the requirement for phthalic acid ester plasticizer immunodetection products in current market can be met.
Owner:无锡迪腾敏生物科技有限公司
ELISA (enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay) method for quickly testing C-Myc by using monoclonal antibody
The invention relates to an ELISA (enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay) method for quickly testing C-Myc by using a monoclonal antibody. According to the method, prokaryotic expression C-Myc protein is purified through protein purification technology; immune mouse spleen cells are performed cell fusion with SP2 / 0 myeloma cell, and a clone capable of stably secreting an antibody against C-myc IgG1 and a Cmyc IgM antibody clone are obtained based on ELISA screening and the subtype identification of subclone and monoclonal antibody Ig. A sandwich ELISA method and the two direct ELISA methods for quickly testing c-Myc are built by using an antibody against c-Myc IgG1 and an antibody against c-Myc Ig. With the method, a C-myc protein sample is accurately detected, the detected C-myc protein concentration range is 0.01-1000 pmol / L, and the detection limit is 0.01-0.05 pmol / L; the specificity and the sensitivity of C-Myc detection are greatly improved, the operation is simple, and the repeatability is high; and the method detects the expression level of C-Myc in tumor tissues, and provides experimental data for screening of malignant tumor.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV
Toxophasma gondii detecting kit based on recombined antigen
InactiveCN1861633AImprove immune activityExcellent repeatabilityBiological testingAnimals/human peptidesSephadexEscherichia coli
A reagent kit based on recombinant antigen for detecting Toxoplasma is prepared through taking 542-1218 fragment (t SAG1) from the primary surface antigen gene SAG1 of Toxoplasma, subcloning it to soluble expression carrier pET32a(+), transferring it to colibacillus, configuring engineering bacterium pET32a-tSAG1 / BL21, IPTG induced efficient expression, ultrasonic splitting to obtain supernatant, purifying by Ni-NTA and Sephadex-G75, and coating the microholes on ELISA plate. Its test paper can also be prepared by same way.
Owner:深圳市绿诗源生物技术有限公司
Preparation method and application of aspergillus flavus specific single-chain antibody
InactiveCN103555732AHigh affinityEasy to operateMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliSingle-Chain Antibodies
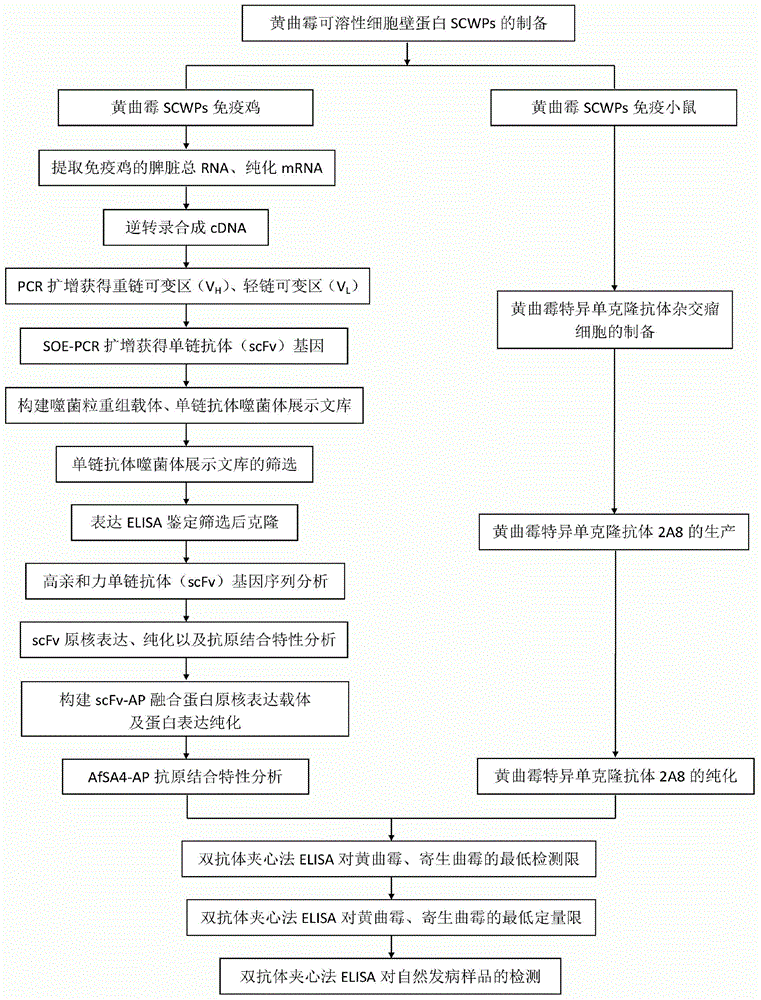
The invention belongs to the field of detection of harmful biological molecules in food, and relates to a preparation method and application of an Aspergillus flavus specific single-chain antibody. The cell wall proteins of the Aspergillus flavus hypha are used for immunizing chickens and mice respectively; messenger RNA of chicken splenic lymphocytes after immunization are extracted; a chicken source single-chain antibody library is constructed; a phage display technology is employed to screen the library to obtain an Aspergillus specific single-chain antibody gene with high affinity to Aspergillus flavus. The antibody gene is subcloned into an expression vector of an alkaline phosphatase protein, and expressed and purified in Escherichia coli, so as to obtain a fusion protein and a hybridoma cell 2A8 secreting Aspergillus flavus specific monoclonal antibody. The monoclonal antibody as a capture antibody and AfSA4-AP fusion protein as a detection antibody are employed to establish a SandWich ELISA immunological detection system for detecting Aspergillus flavus contamination in crops and stored plant-derived products.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Monoclonal antibody against CK8 protein and cell strain, preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN112940118AStrong specificityIncreased sensitivityImmunoglobulins against animals/humansBiological material analysisAntigenWhite blood cell
The invention relates to a monoclonal antibody capable of recognizing a human leukocyte differentiation antigen CK8, a secretory cell strain, a preparation method thereof and application in immunodetection. According to the technical scheme, 340-365 amino acid sequences at the C tail end of CK8 protein are selected as antigen peptides, and the antigen peptides are coupled with KLH carrier protein to obtain the immunogen; the amino acid sequence of the antigen peptide is shown as SEQID1, a mouse is immunized, and the mouse hybridoma cell strain 14C2 capable of efficiently secreting the anti-CK8 protein monoclonal antibody and the anti-CK8 protein monoclonal antibody secreted by the cell strain are obtained through cell fusion, screening and subcloning. The antibody obtained by the scheme has high specificity and sensitivity, can specifically recognize cells expressing the CK8 protein, and is suitable for immunological detection, especially immunohistochemical detection.
Owner:FUZHOU MAIXIN BIOTECH CO LTD
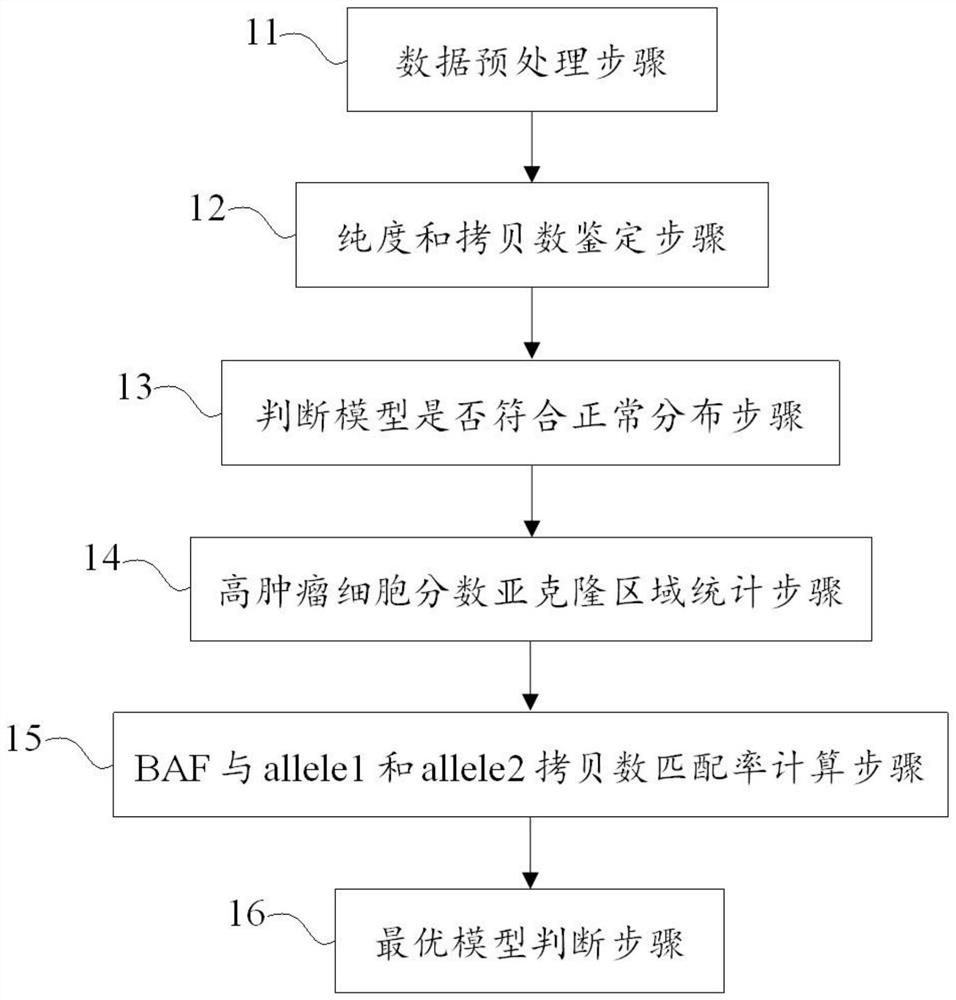
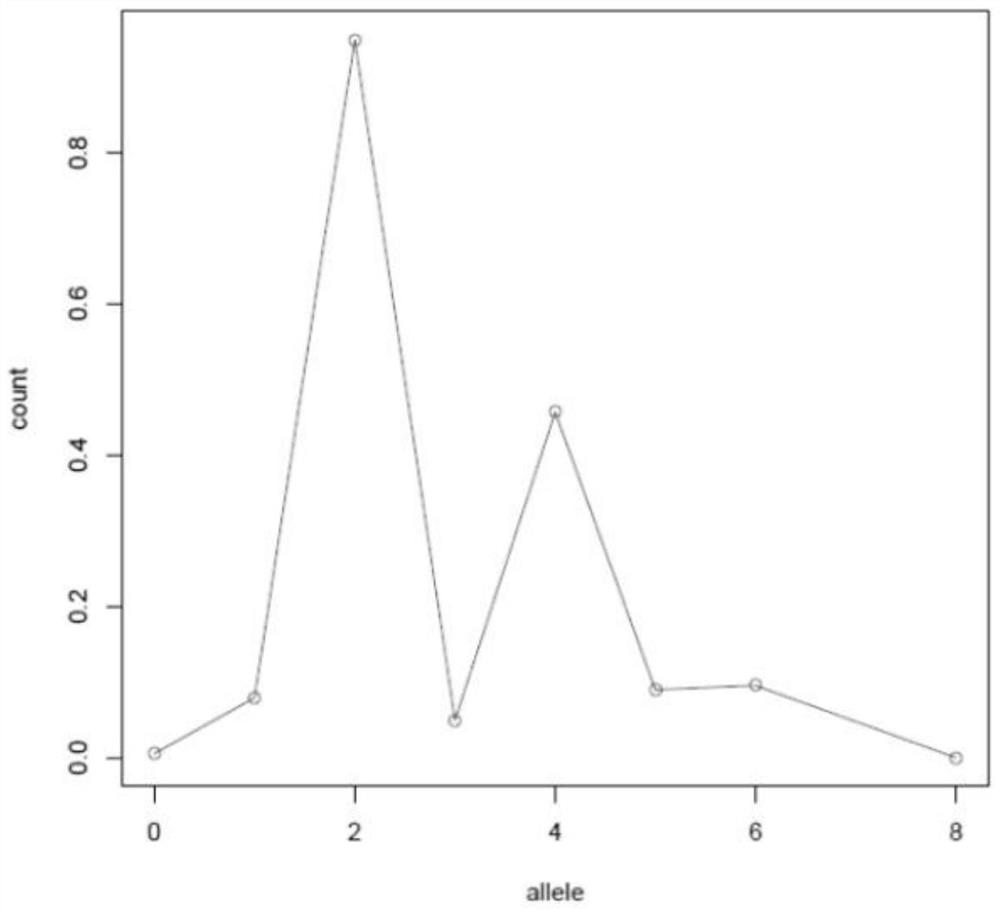
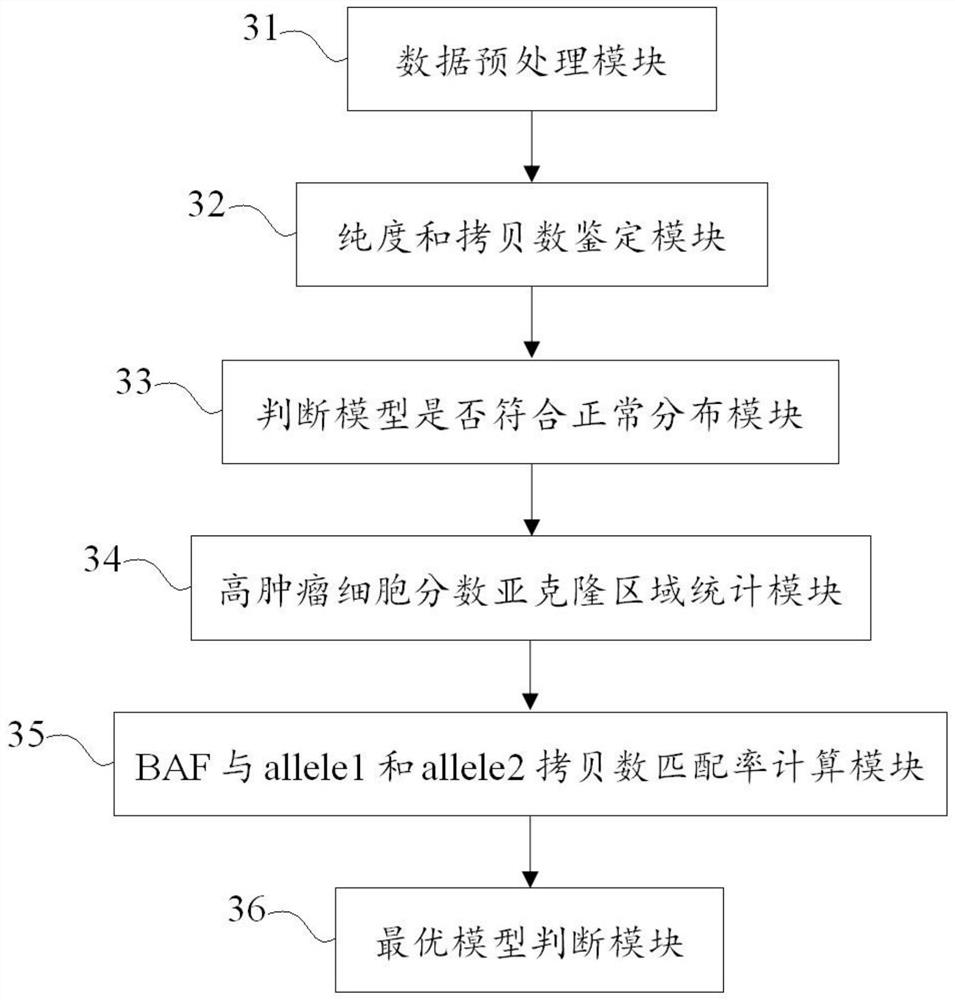
Method and device for identifying tumor purity and absolute copy number based on sequencing data
ActiveCN111755068AEfficient correctionAccurate purityProteomicsGenomicsGenome evolutionOptimality model
The invention discloses a method and a device for identifying tumor purity and absolute copy number based on sequencing data. The method comprises the following steps: comparing offline data after quality control to a reference genome, and carrying out variation detection and population database annotation; testing the preprocessed data of the tumor and the normal sample by using purity predictionsoftware to obtain a purity and copy number information model; and for the model conforming to normal distribution, further screening out the model with the maximum probe support number in the high tumor cell fraction subcloning region, and defining an optimal model in combination with the matching rate of BAF and alle1 and alle2 copy numbers. According to the method, the model of purity detection software is rapidly and efficiently corrected, and the purity and absolute copy number information of tumors can be obtained more accurately; the accuracy is guaranteed, the tedious process of manual verification is avoided, the labor cost is saved, and a foundation is laid for follow-up tumor genome evolution and tumor heterogeneity research.
Owner:深圳吉因加医学检验实验室
Methods and compositions for seamless cloning of nucleic acid molecules
ActiveUS8338091B2Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementSubcloningRestriction Enzyme Recognition Site
The present invention is in the fields of biotechnology and molecular biology. More particularly, the present invention relates to cloning or subcloning one or more nucleic acid molecules comprising one or more type IIs restriction enzyme recognition sites. The present invention also embodies cloning such nucleic acid molecules using recombinational cloning methods such as those employing recombination sites and recombination proteins. The present invention also relates to nucleic acid molecules (including RNA and iRNA), as well as proteins, expressed from host cells produced using the methods of the present invention.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
Plamid vector, VP7 expresses antigen of blue tongue virus VP7 gene recombined expression, and preparation method
InactiveCN1563383AOvercome the cumbersome operationOvercome the cumbersome extractionViral antigen ingredientsBiological testingAntigenGroup-specific antigen
This invention relates to a biological agent testing blue tongue of animals and its preparation method. The agent includes blue tongue virus VP7 gene recombination expression plasmid vectors and a blue tongue virus VPT recombination antigen got from its expression. The preparation method includes: 1, cloning BTV coding group specific antigen VP7 gene fragment to pMD18-T plasmid vector to make up of VP7 gene clone recombination plasmid, 2, sub-cloning plug pBAD / Thio TOPO expression vector, 3, converting TOP10cells, 4, screening the positive clones obtaining BTV VP7 gene segment forward plug with correct read code frame to set up BTV group specific antigen VP7 recombination expression vector 5, cultivating the vector with LB culture media containing 100mug / ml Amp.
Owner:CHECKOUT & QUARANTINE TECH CENT YUNNAN ENTRY &EXIT CHECKOUT & QUARANTINE BUR
Anti-major-royal-jelly-protein 3 monoclonal antibody and enzyme-linked immunoassay kit for detecting major royal jelly protein 3
ActiveCN107892713AImmunoglobulins against animals/humansBiological material analysisElisa kitLinear relationship
The invention discloses an anti-major-royal-jelly-protein 3 monoclonal antibody and an enzyme-linked immunoassay kit for detecting major royal jelly protein 3. According to the present invention, 112positive cell lines are obtained by using a sequence represented by SEQ ID No.1 as antigen through cell fusion, 14 fusion cell lines are obtained through cross reaction detection, the 7 cell lines with high affinity are selected through three rounds of subcloning, and subjected to antibody epitope detection and pairing experiment, and the standard curve drawing and sample determination results show that the two cell lines such as 3G4 and 2D2 have good linear relationship and high sensitivity; the enzyme-linked immunoassay kit for detecting major royal jelly protein 3 through a double antibodysandwich ELISA method is further constructed through the two cell lines such as 3G4 and 2D2; and the enzyme-linked immunoassay kit can specifically detect the MRJP3 and other related proteins, does not have cross reaction, has the detection range of 0.78-50 ng / mL, has the detection sensitivity of 194 pg / mL, and further has advantages of high precision and low batch difference.
Owner:BEE RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com