Patents
Literature
187 results about "Linker peptide" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
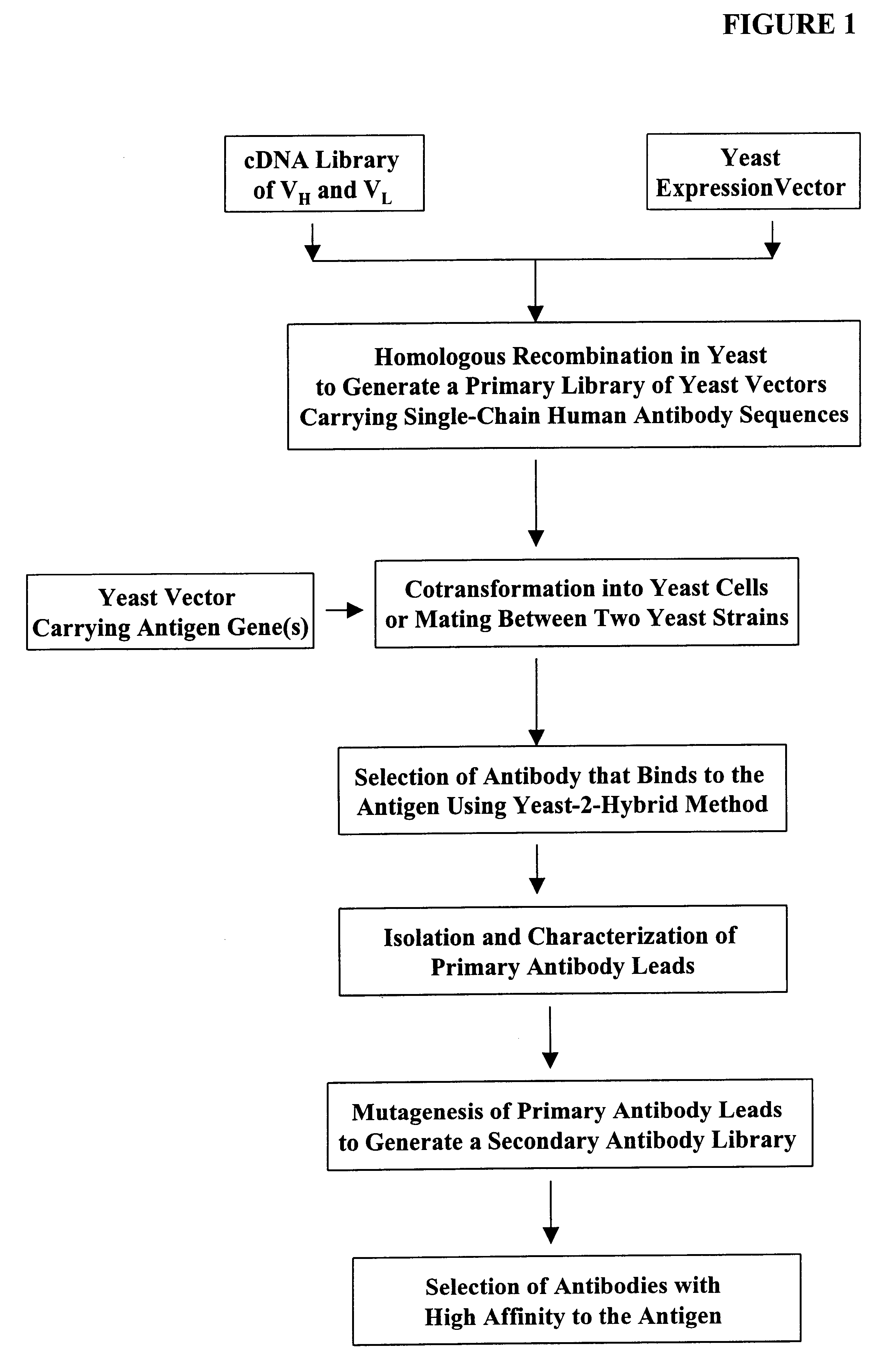
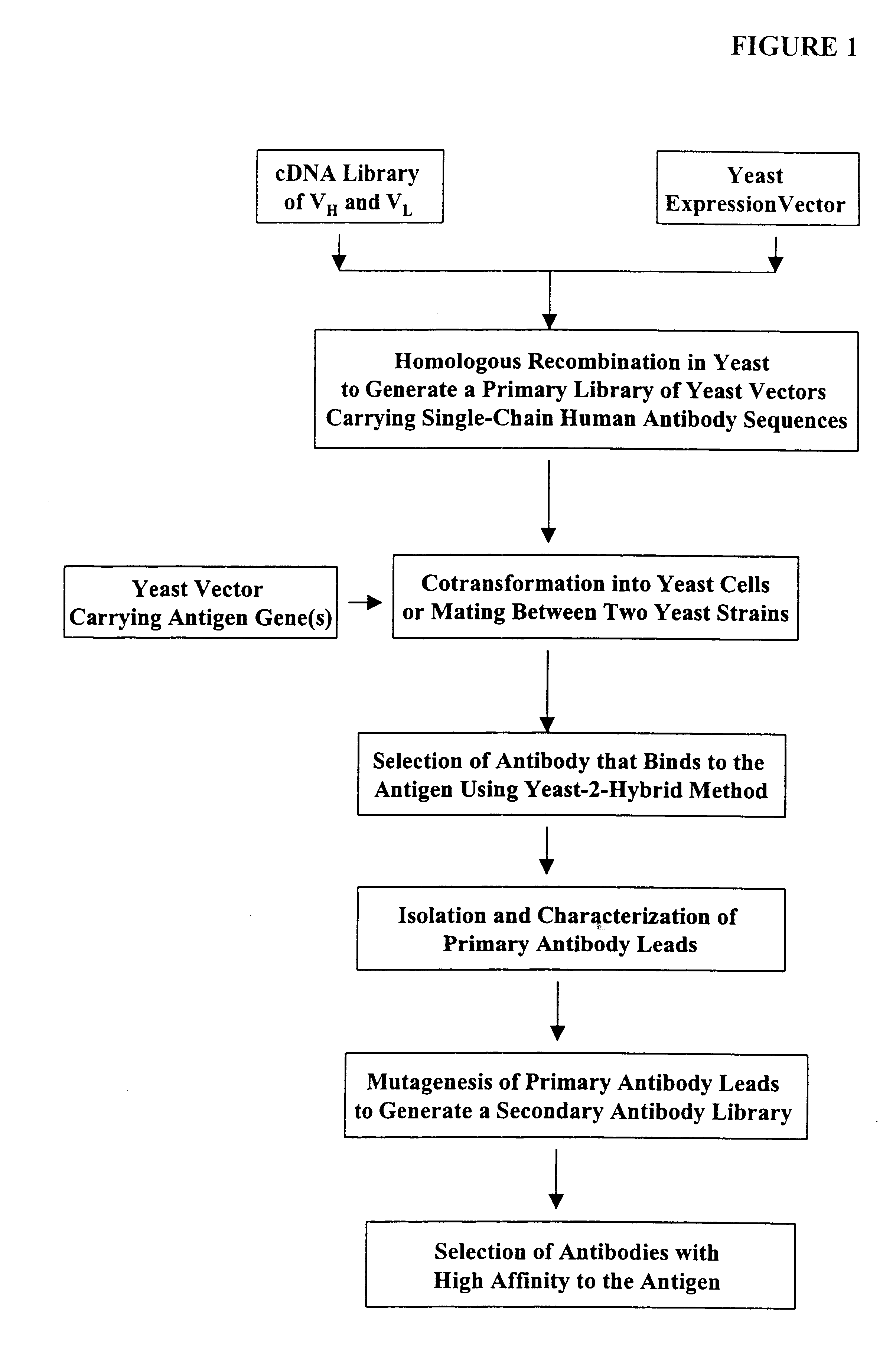
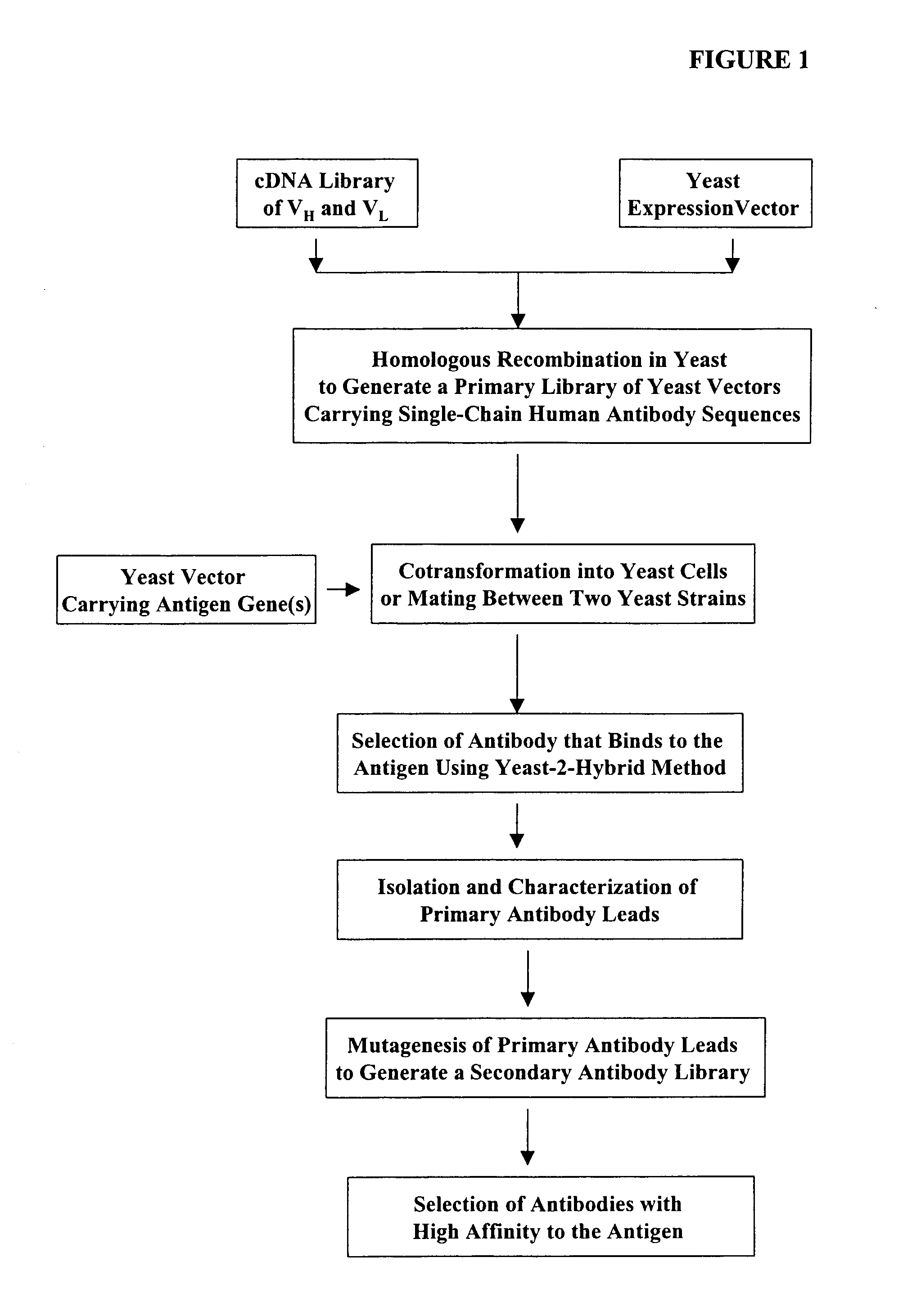
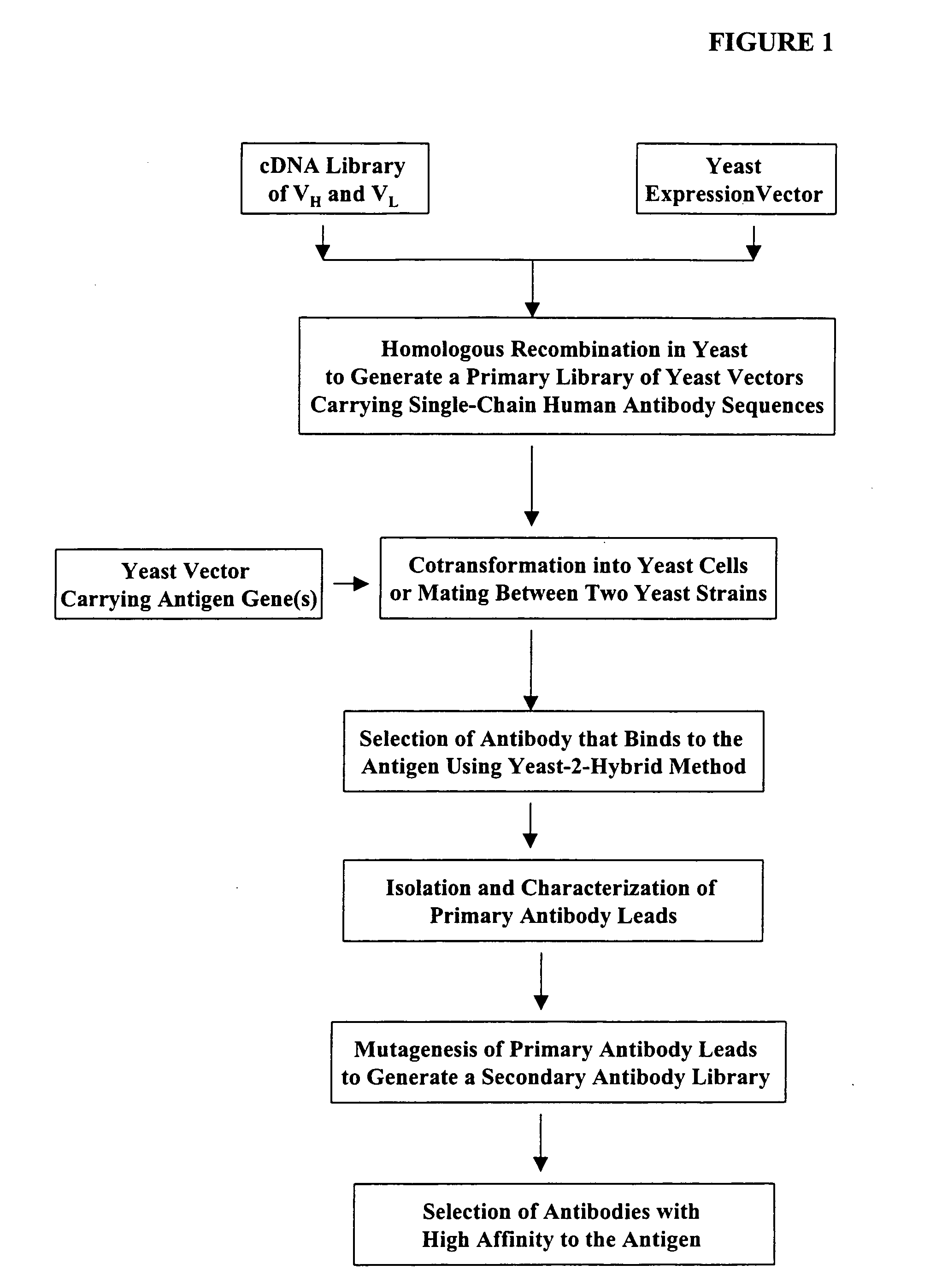
High throughput generation and screening of fully human antibody repertoire in yeast
InactiveUS6406863B1High affinityEasy to assembleMicrobiological testing/measurementImmunoglobulinsTarget peptideIn vivo
Compostions, kits and methods are provided for generating highly diverse libraries of proteins such as antibodies via homologous recombination in vivo, and screening these libraries against protein, peptide and nucleic acid targets using a two-hybrid method in yeast. The method for screening a library of tester proteins against a target protein or peptide comprises: expressing a library of tester proteins in yeast cells, each tester protein being a fusion protein comprised of a first polypeptide subunit whose sequence varies within the library, a second polypeptide subunit whose sequence varies within the library independently of the first polypeptide, and a linker peptide which links the first and second polypeptide subunits; expressing one or more target fusion proteins in the yeast cells expressing the tester proteins, each of the target fusion proteins comprising a target peptide or protein; and selecting those yeast cells in which a reporter gene is expressed, the expression of the reporter gene being activated by binding of the tester fusion protein to the target fusion protein.
Owner:GENETASTIX CORP
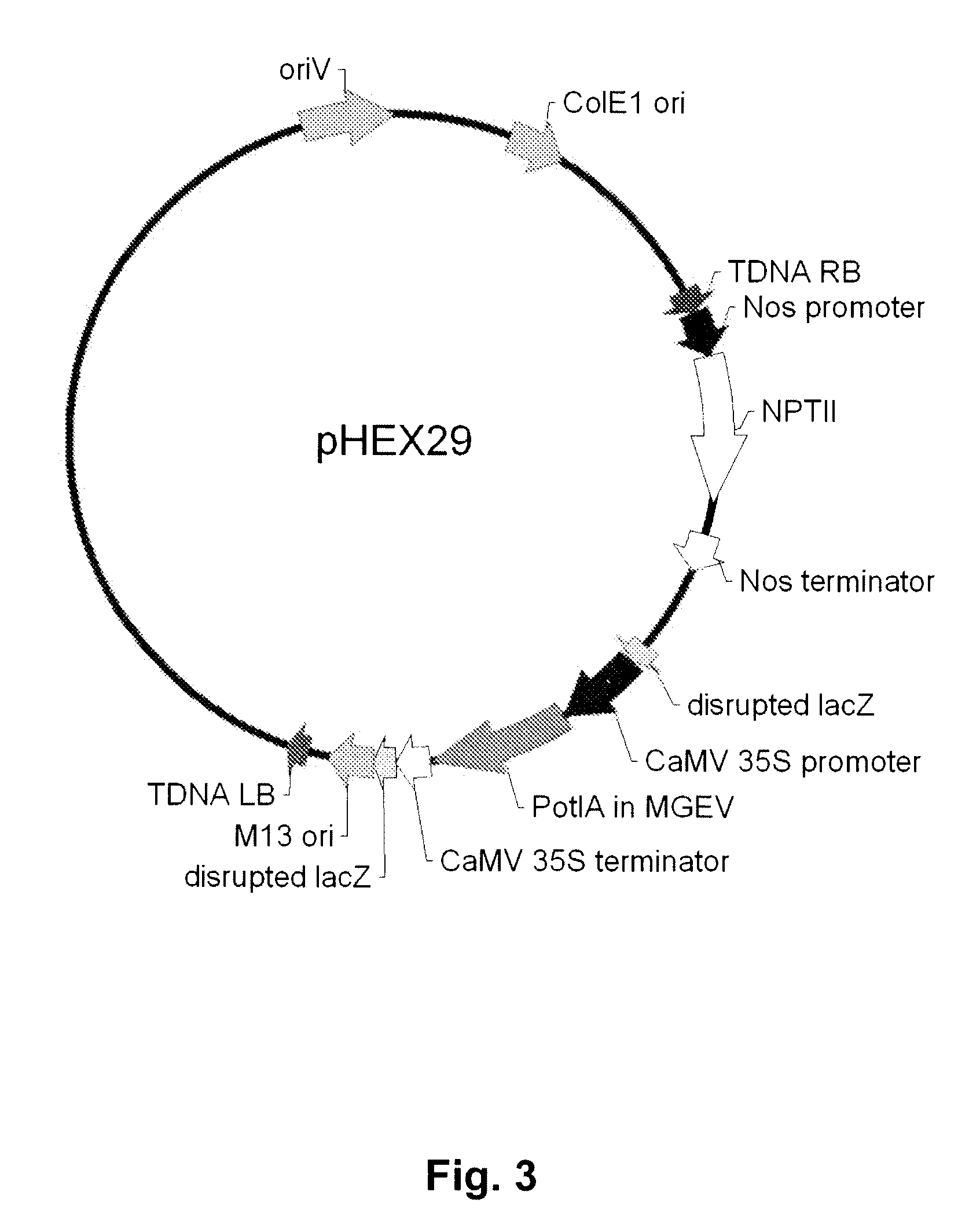
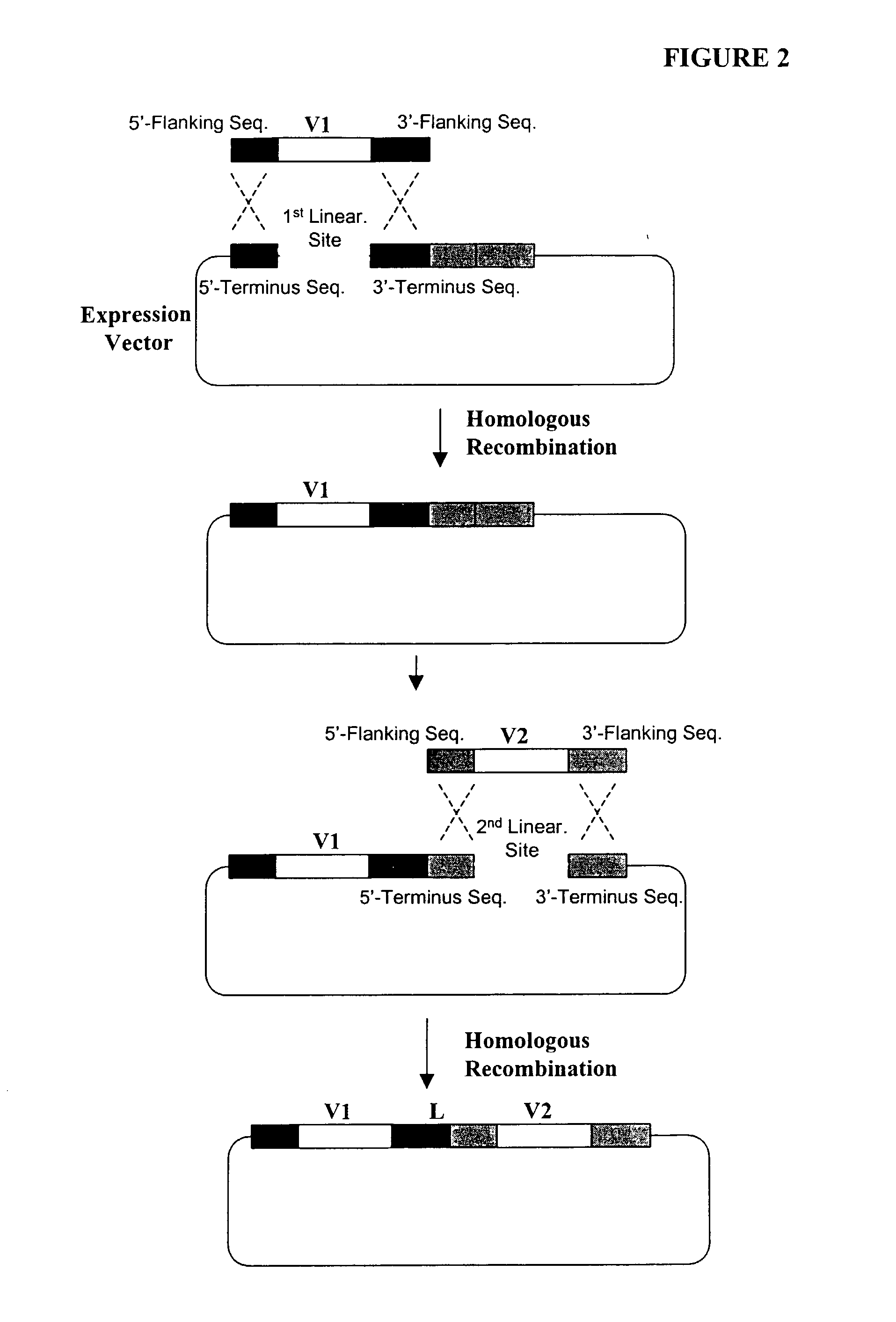
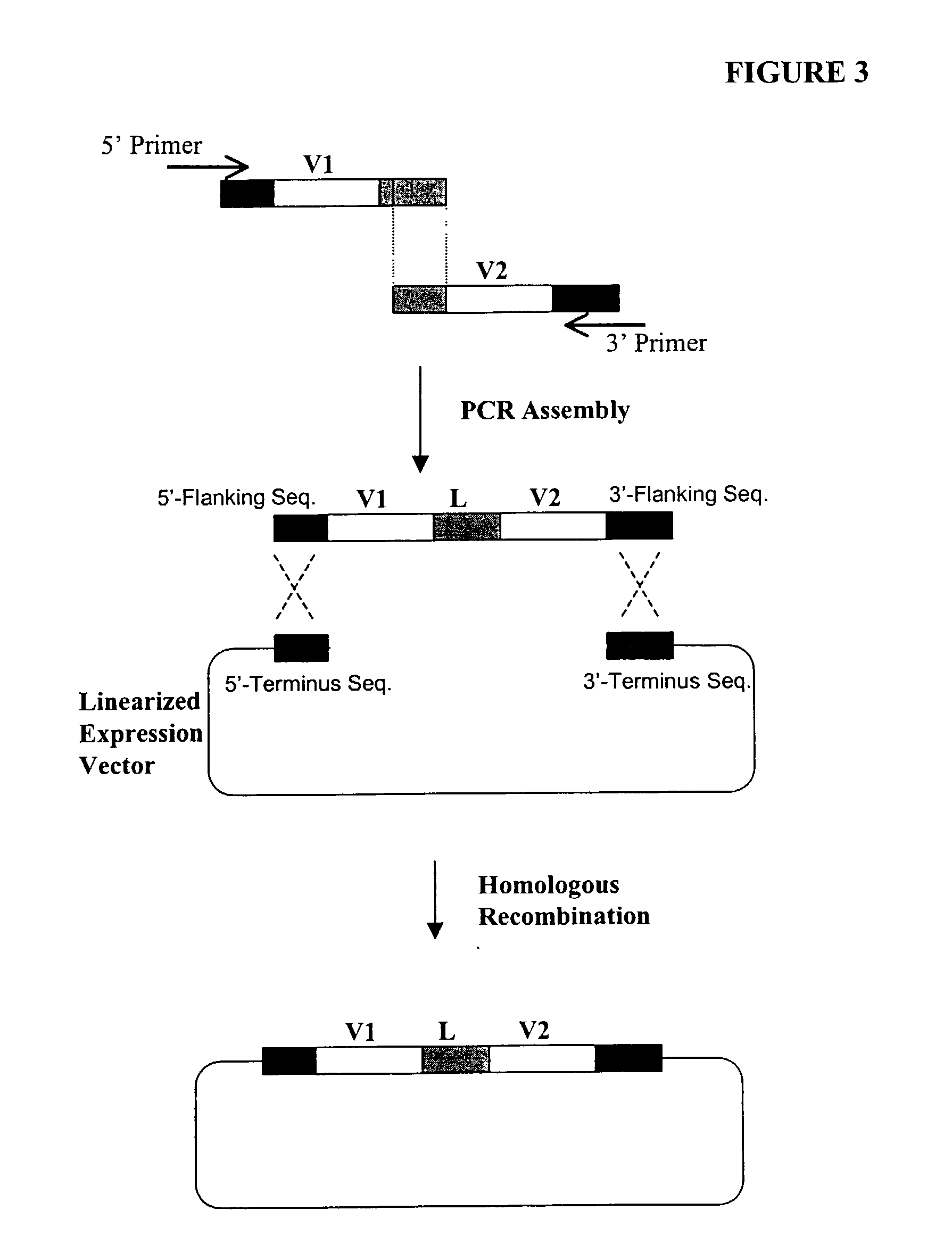
Multi-gene expression vehicle
InactiveUS20070277263A1Lack featureClimate change adaptationOther foreign material introduction processesMultigene expressionNucleotide
A multigene expression vehicle (MGEV) consisting essentially of a polynucleotide comprising 2 to 8 domain segments, D, each domain encoding a functional protein, each domain being joined to the next in a linear sequence by a Linker (L) segment encoding a Linker peptide, the D and L segments all being in the same reading frame, and at least one of the domains is not a type two protease inhibitor.
Owner:HEXIMA LTD
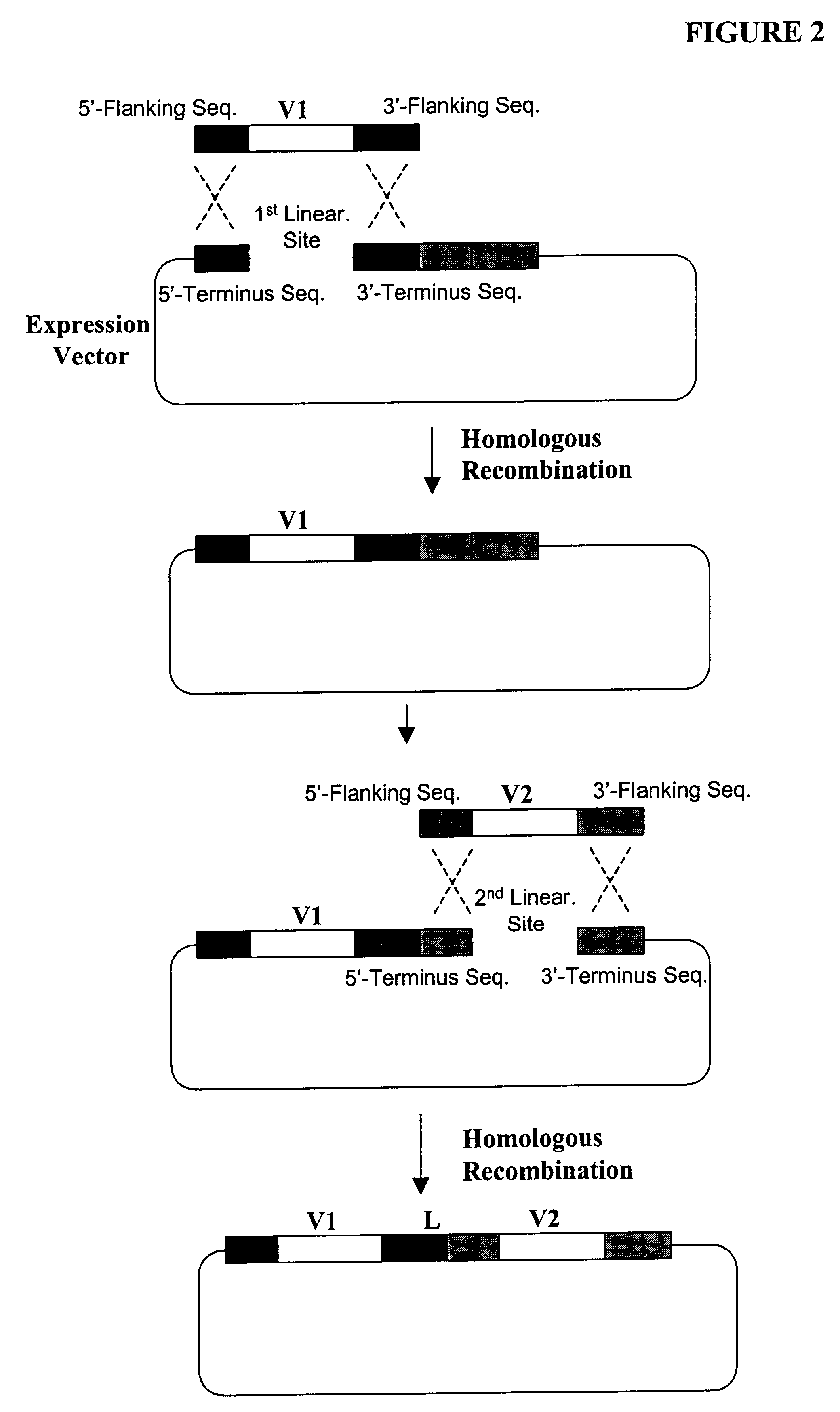
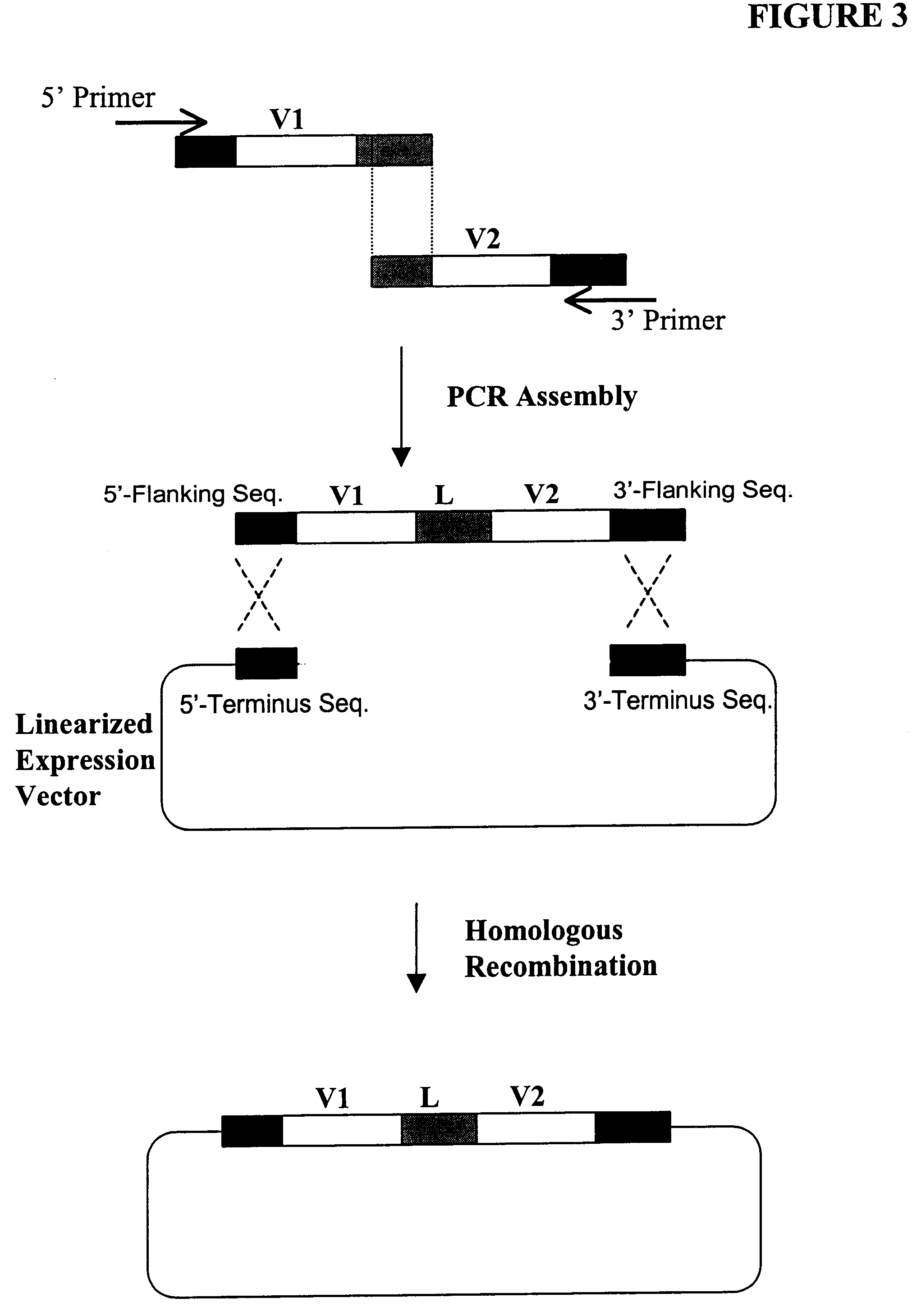
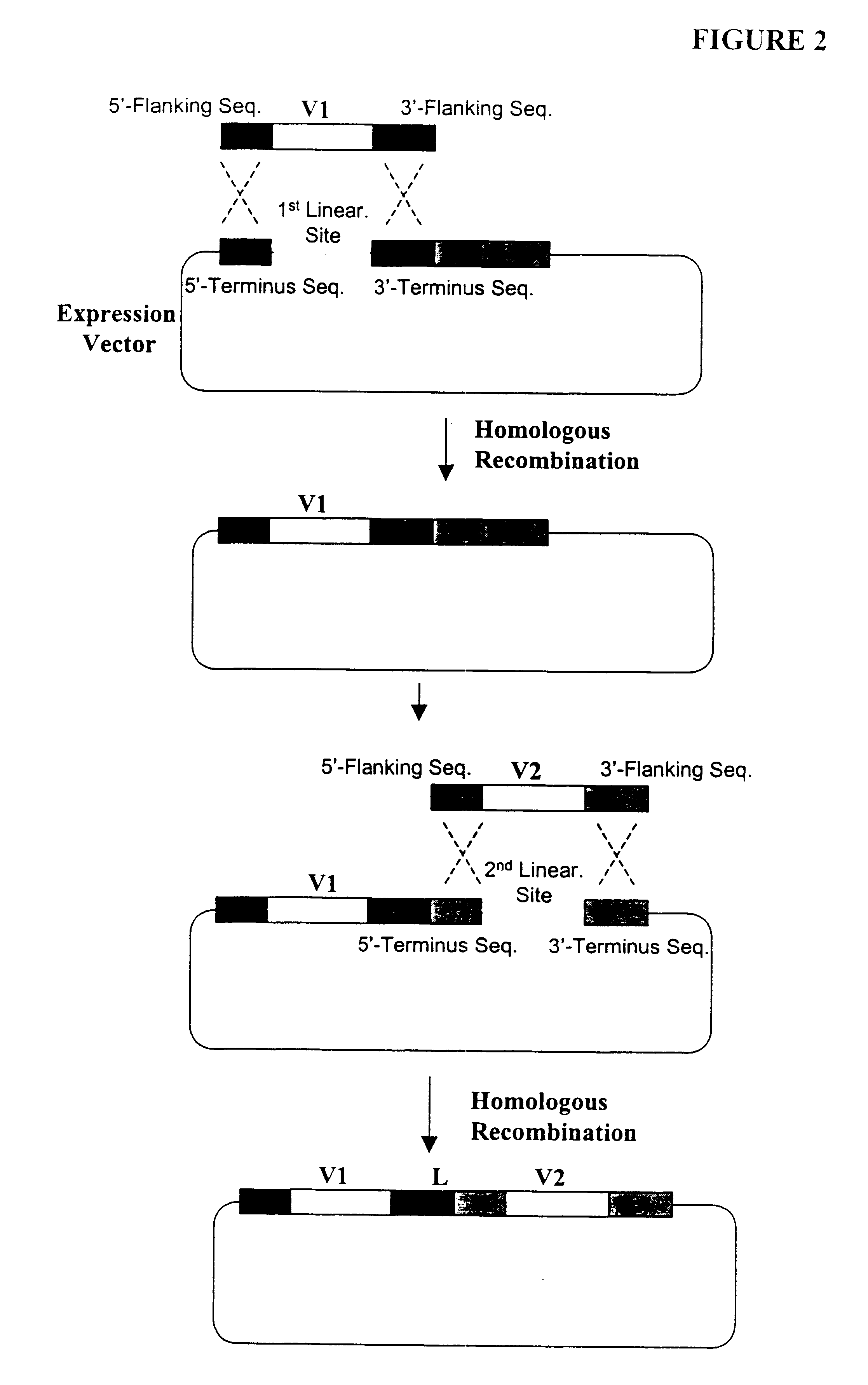
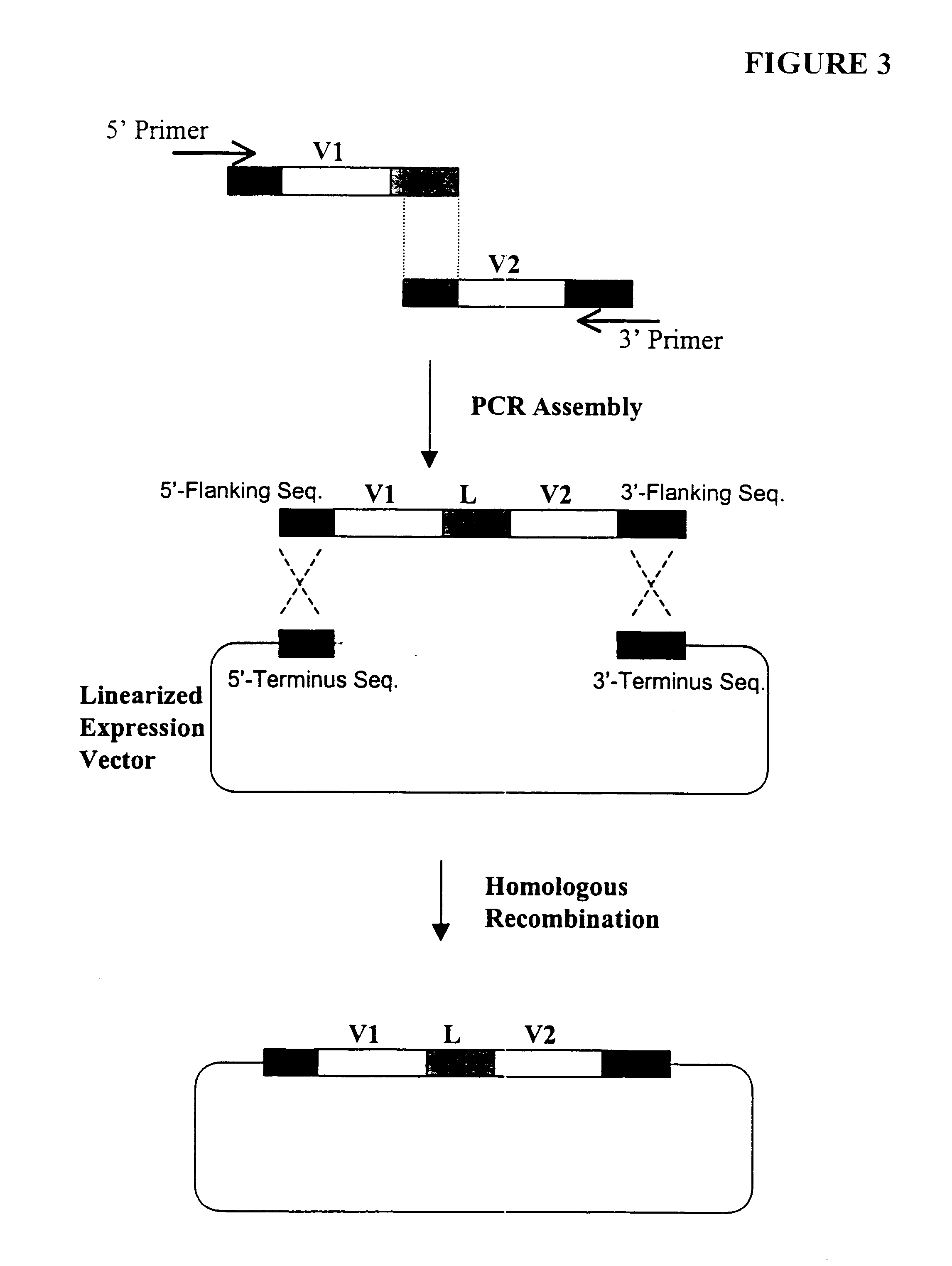
Highly diverse library of yeast expression vectors
A highly diverse library of yeast expression vectors encoding a library of fusion proteins such as antibodies is provided. The yeast expression vector formed in the library comprises: a first nucleotide sequence encoding a first polypeptide subunit; a second nucleotide sequence encoding a second polypeptide subunit; and a linker sequence encoding a linker peptide that links the first nucleotide sequence and the second nucleotide sequence. The first polypeptide subunit, the second polypeptide subunit, and the linker polypeptide are expressed as a single fusion protein within the library of fusion proteins. The first and second nucleotide sequences each independently varies within the library of expression vectors. The library of fusion proteins expressed by the library expression vectors can be used for screening against target molecules such as proteins, peptides, DNAs and small molecules in vitro and in vivo.
Owner:GENETASTIX CORP
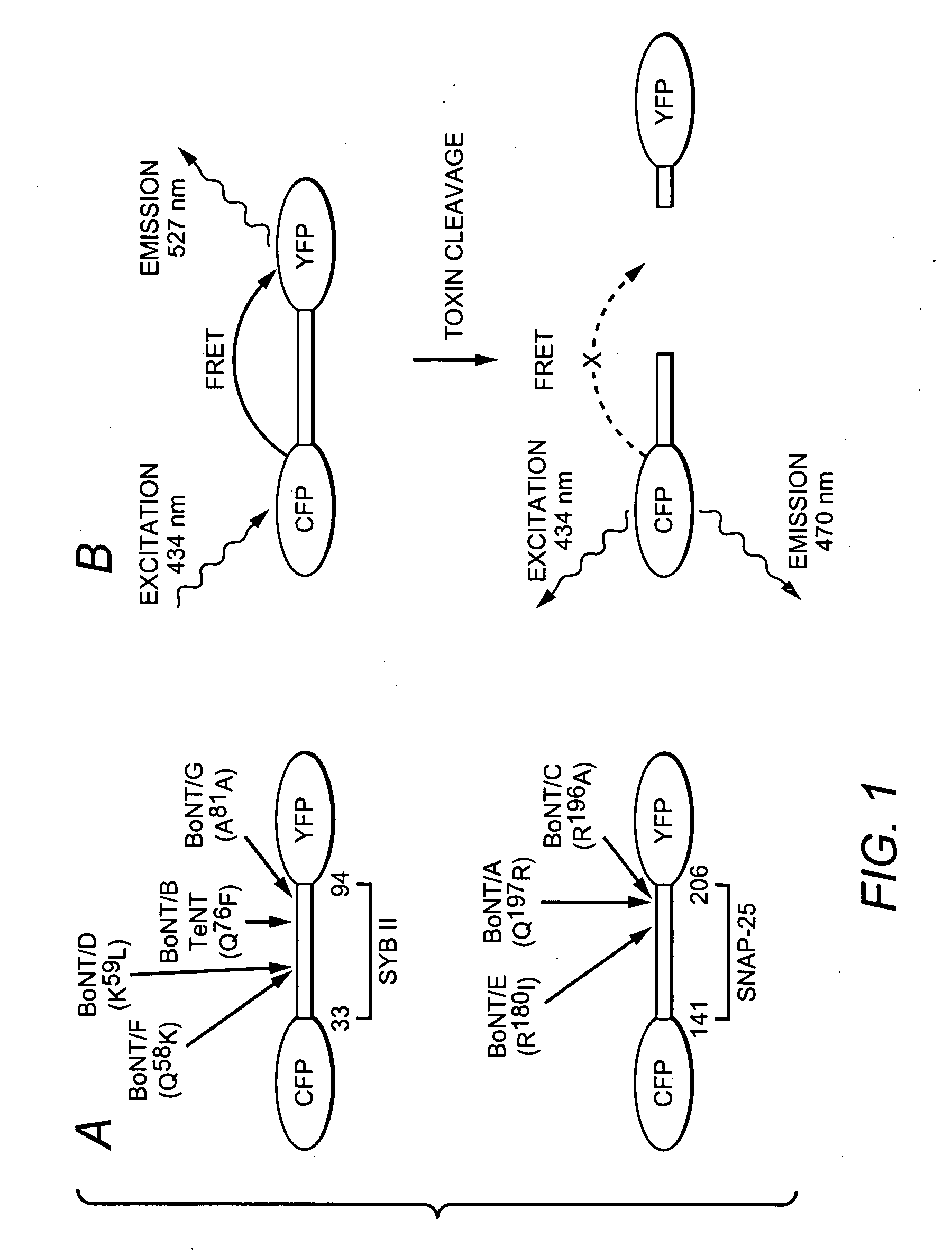
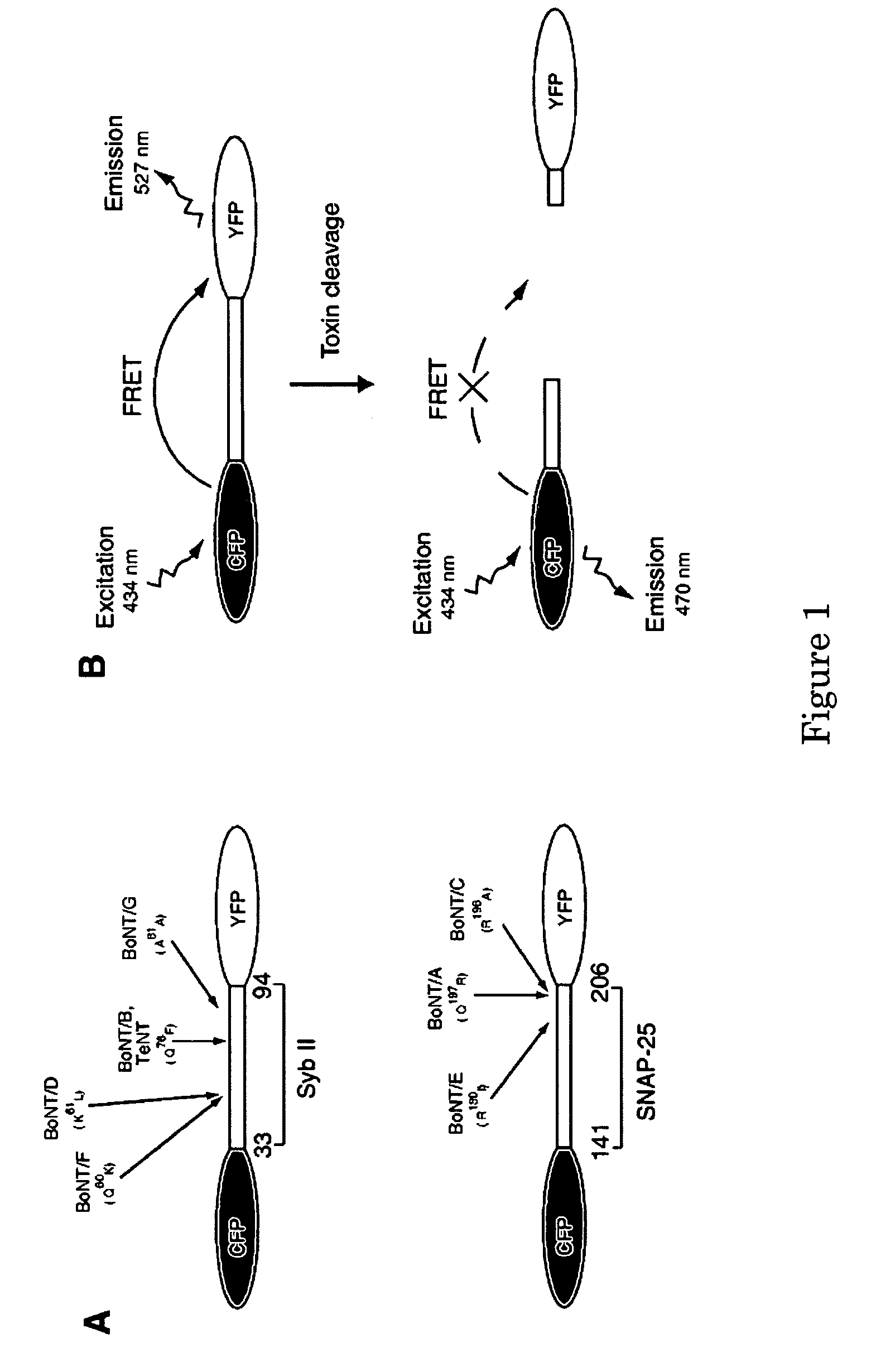
Method and compositions for detecting botulinum neurotoxin
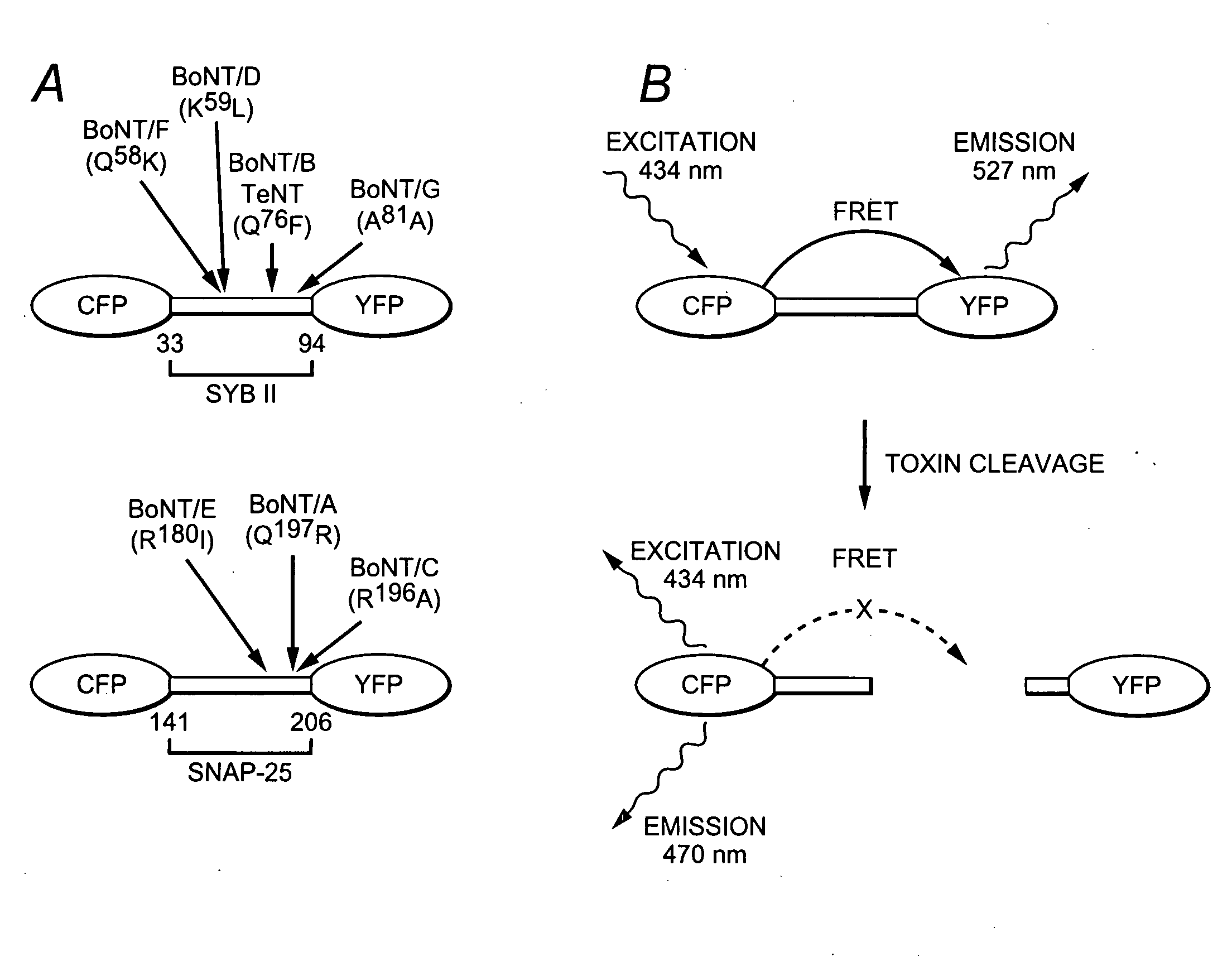
ActiveUS20060134722A1Antibacterial agentsNervous disorderSurface plasmon resonance imagingFluorophore
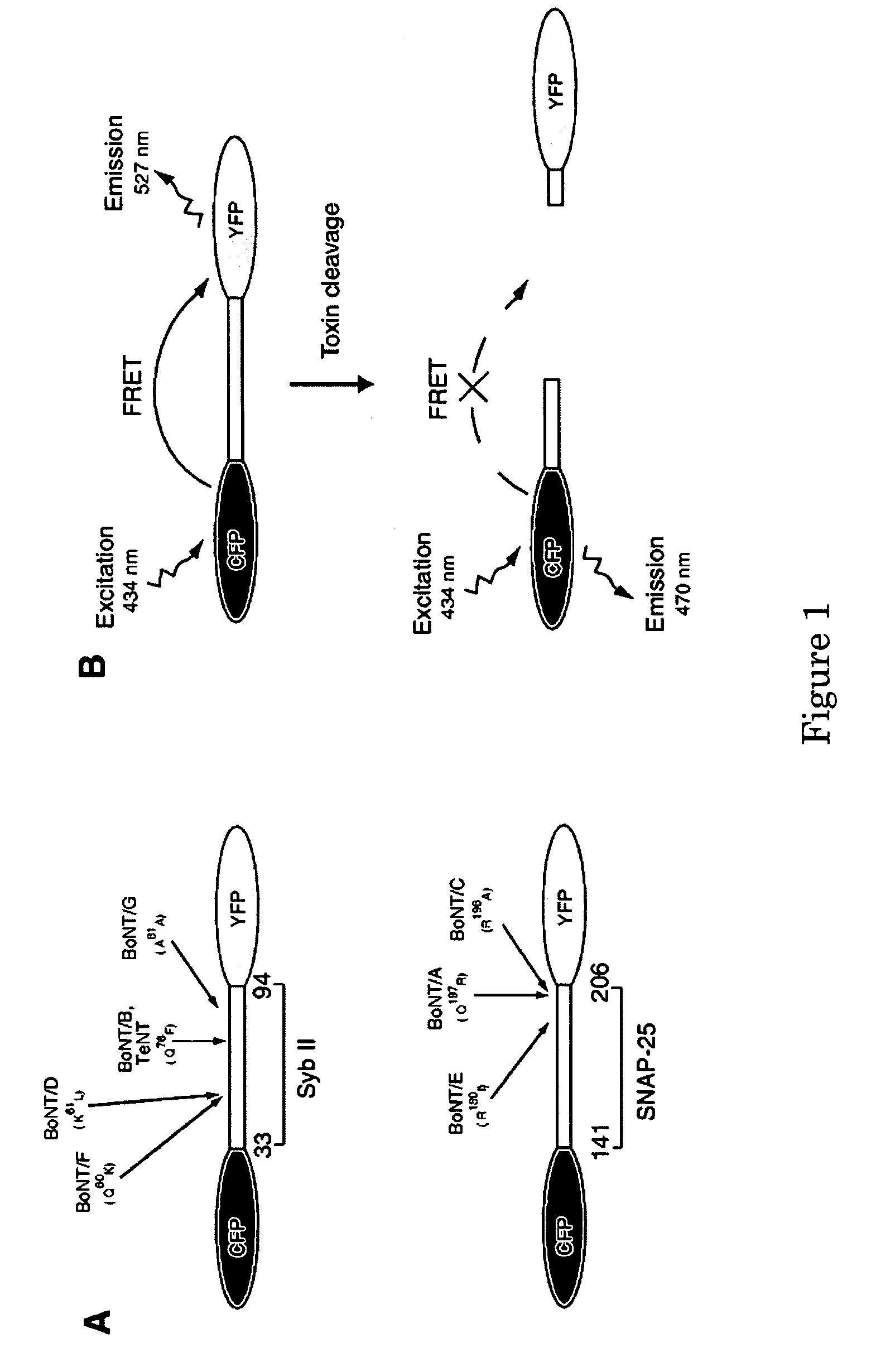
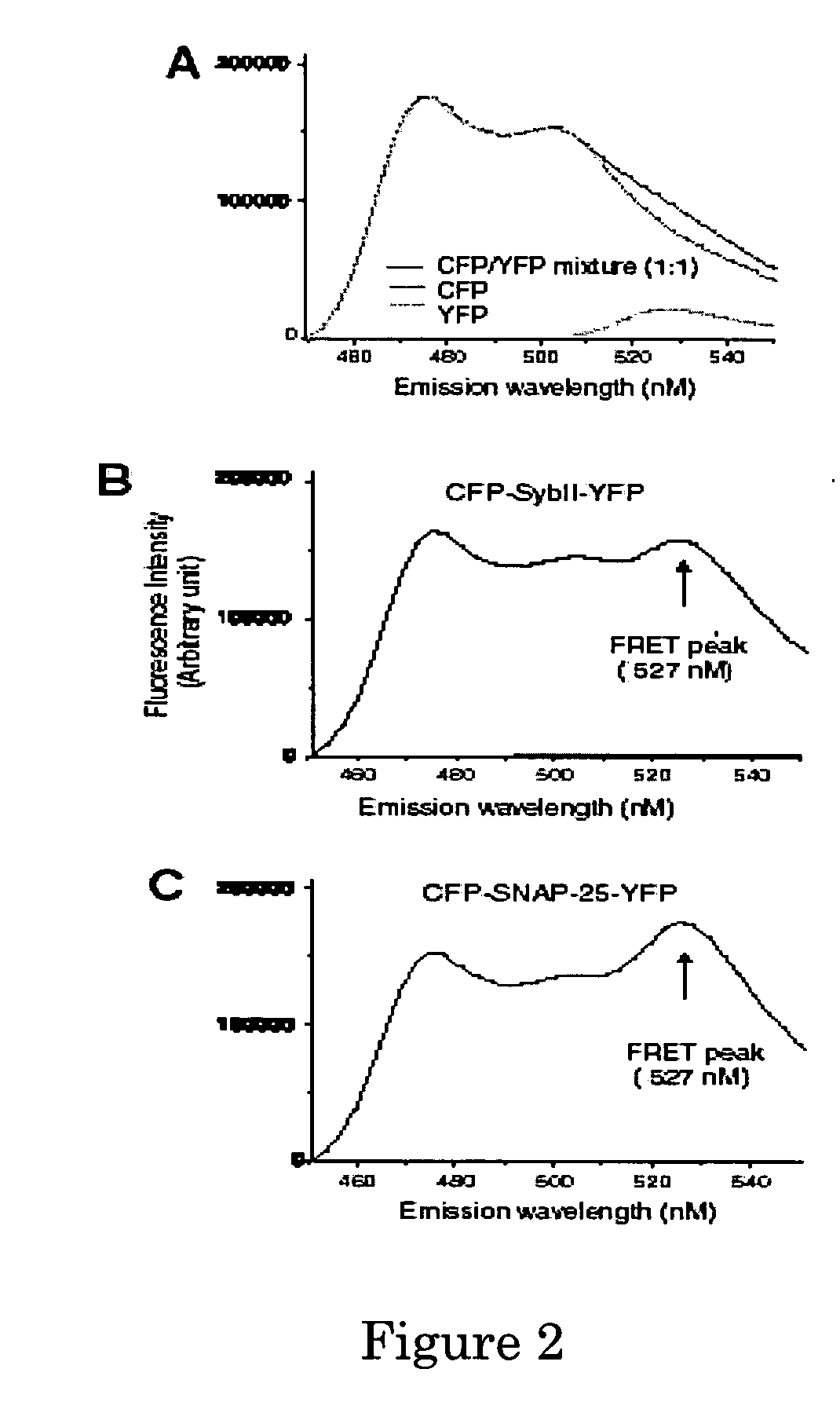
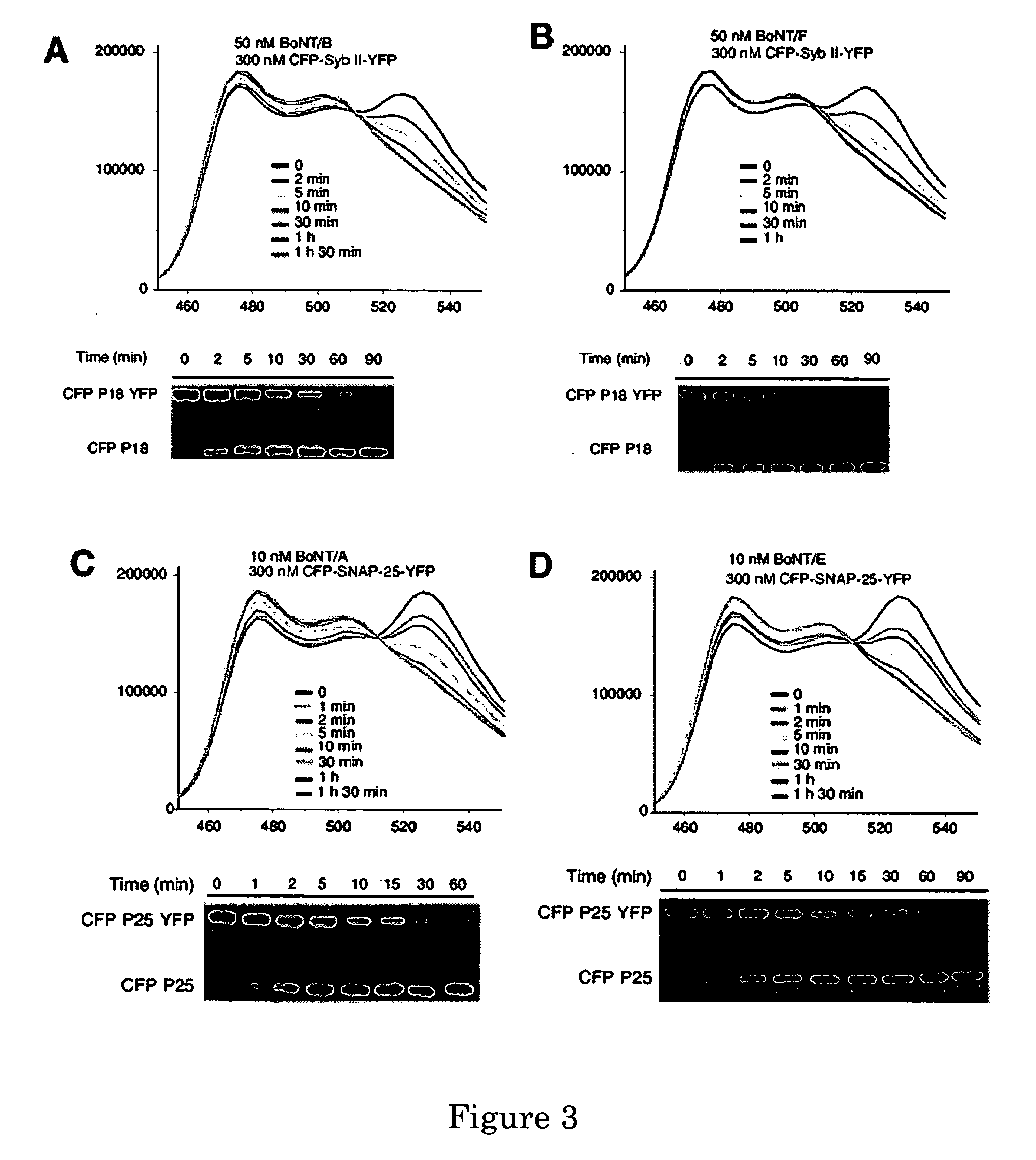
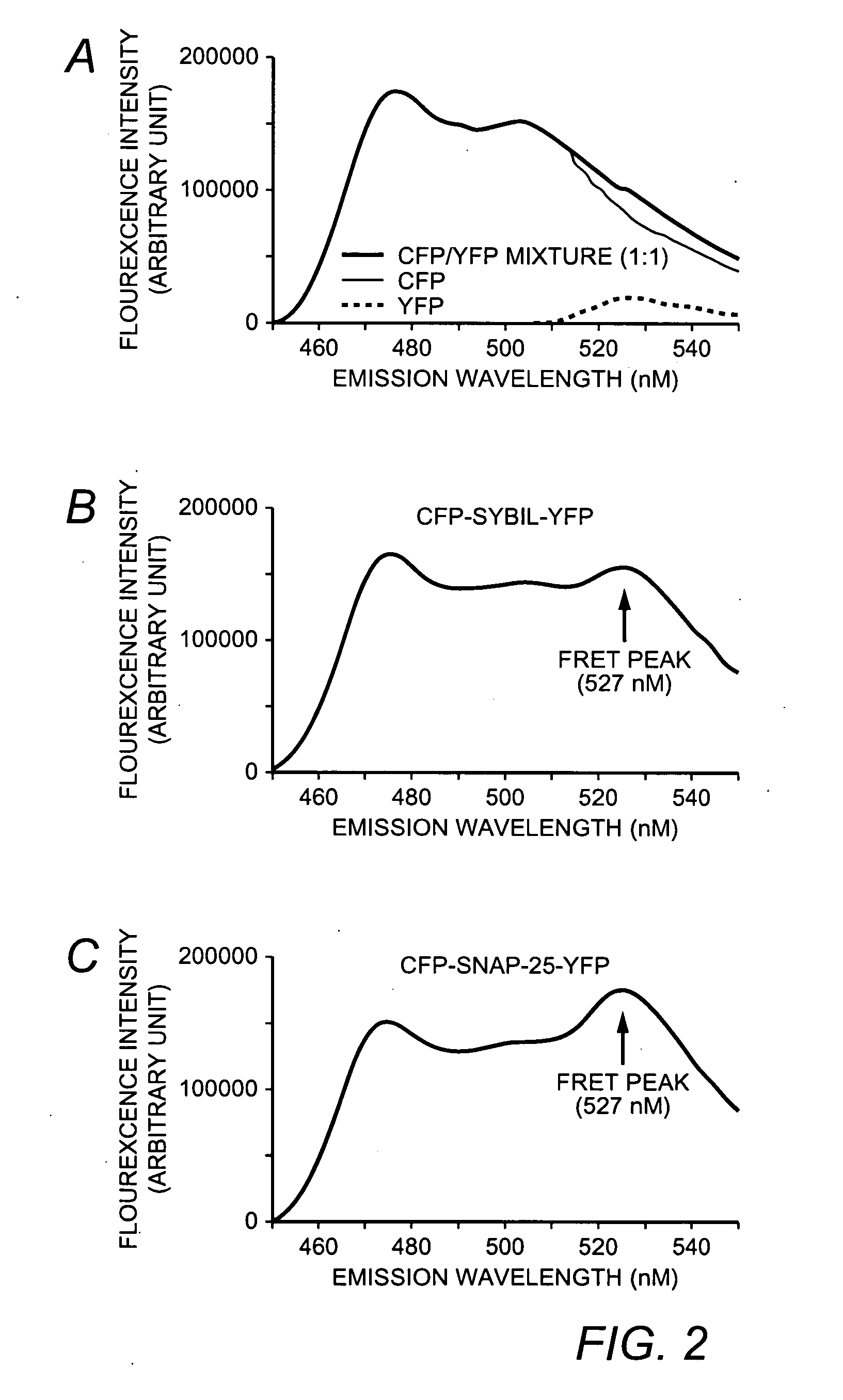
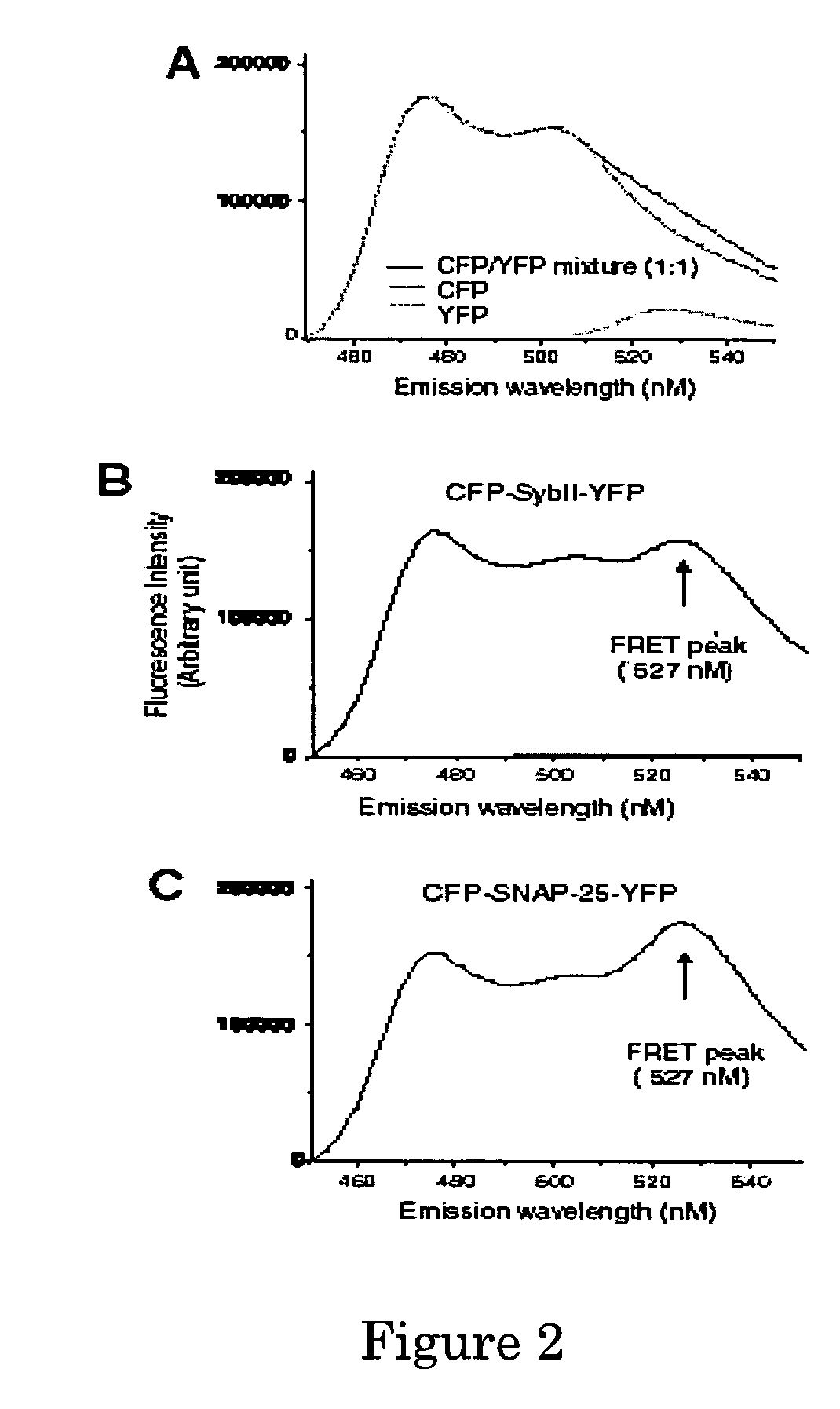
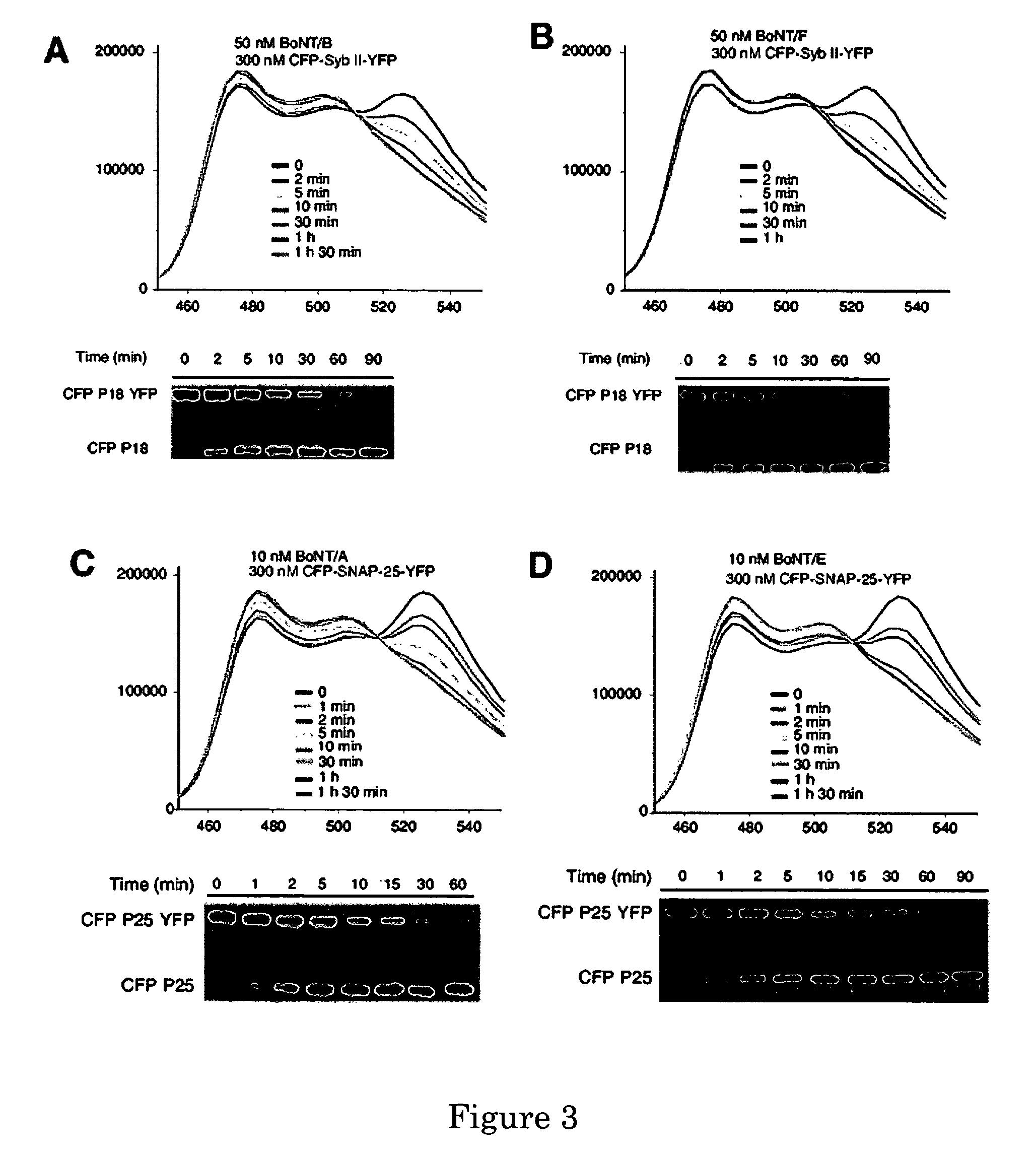
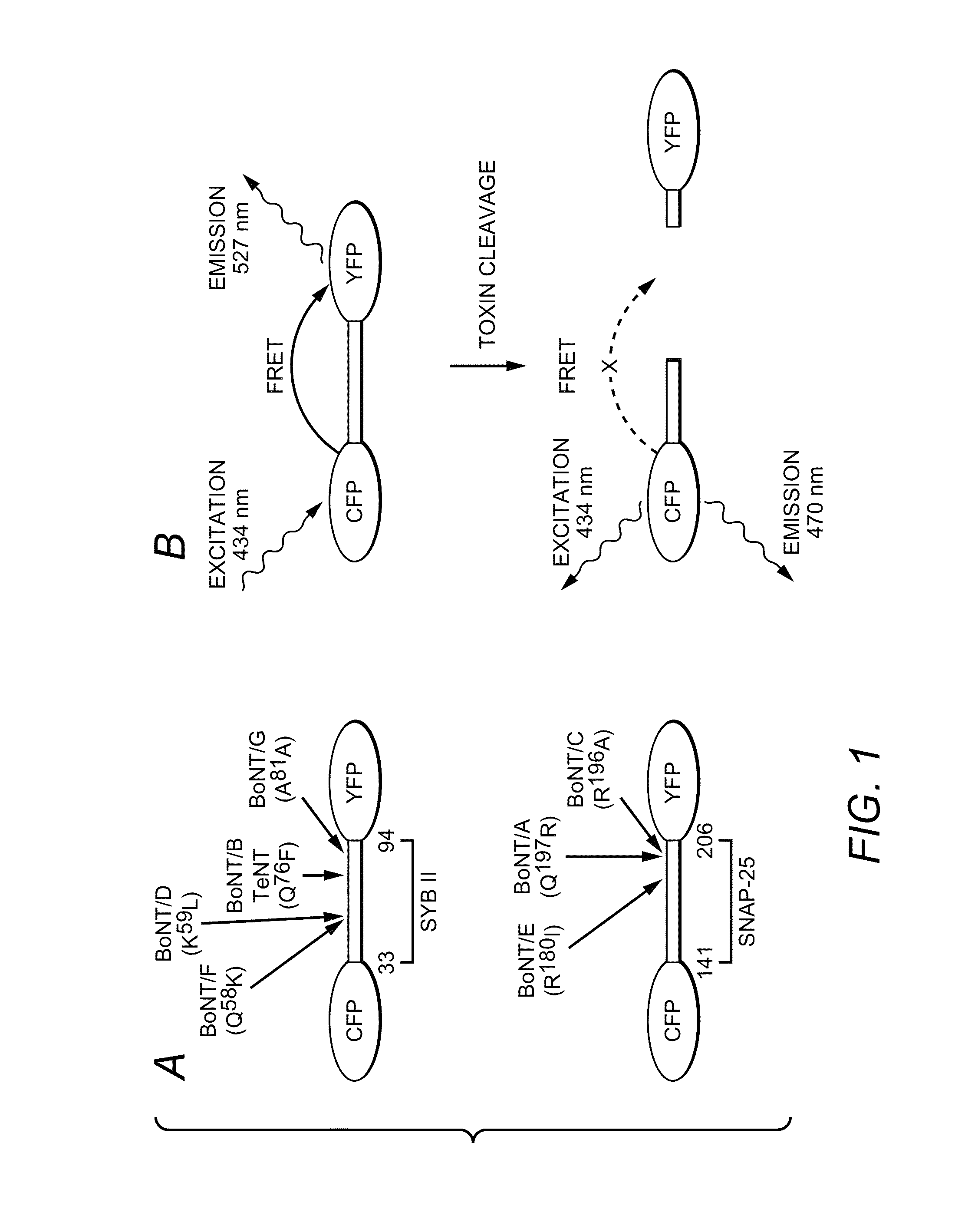
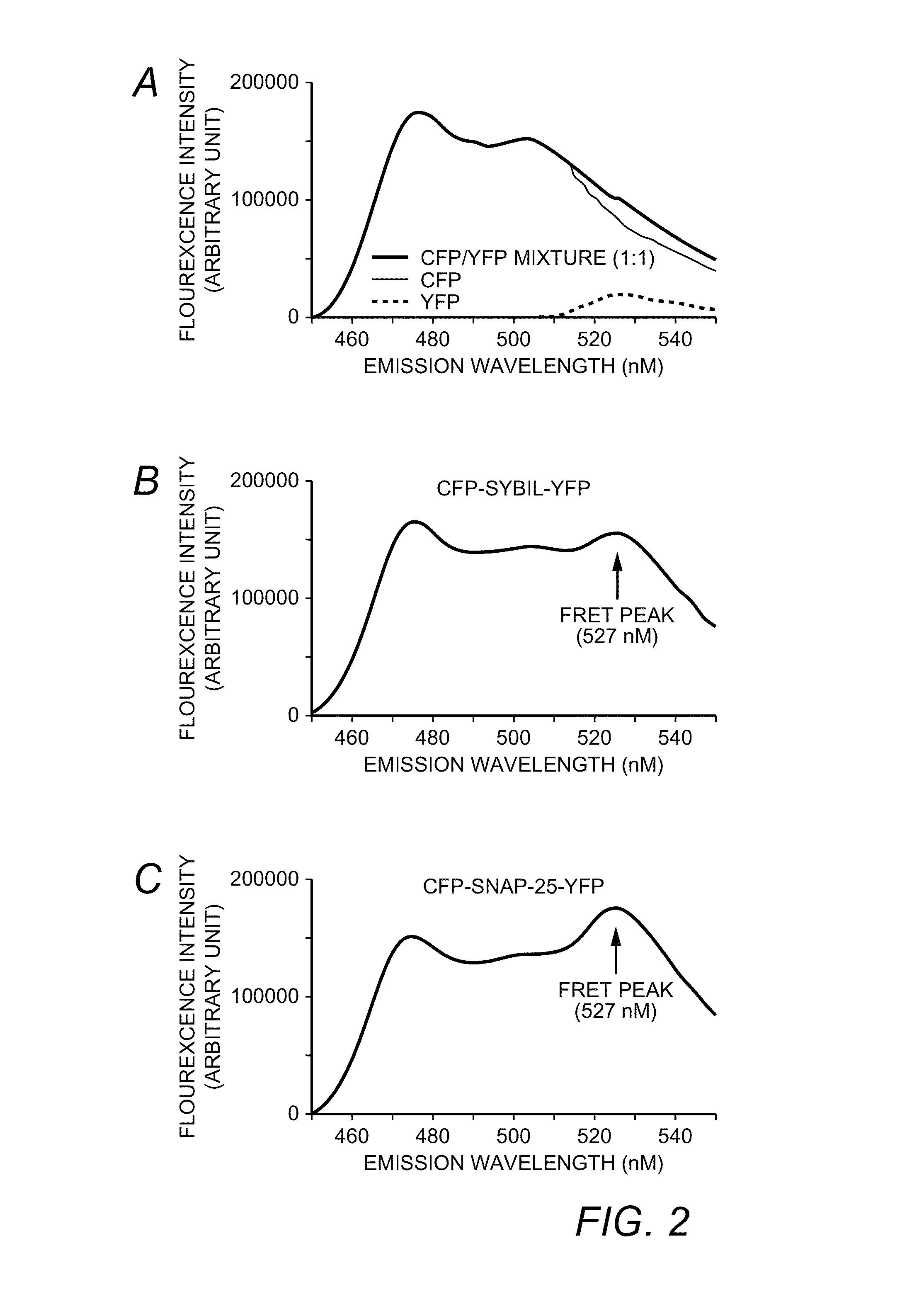
A molecular construct capable of fluorescent resonance energy transfer (FRET), comprising a linker peptide, a donor fluorophore moiety and an acceptor fluorophore moiety, wherein the linker peptide is a substrate of a botulinum neurotoxin selected from the group consisting of synaptobrevin, syntaxin and SNAP-25, or a fragment thereof capable being cleaved by the botulinum neurotoxin, and separates the donor and acceptor fluorophores by a distance of not more than 10 nm, and wherein emission spectrum of the donor fluorophore moiety overlaps with the excitation spectrum of the acceptor fluorophore moiety; or wherein the emission spectra of the fluorophores are detectably different. Also provided are isolated nucleic acid expressing the construct, kits comprising said construct and cell lines comprising said nucleic acid. Further provided are methods of detecting a BoNT using the above described construct via FRET, and methods for detecting a BoNT using surface plasmon resonance imaging.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
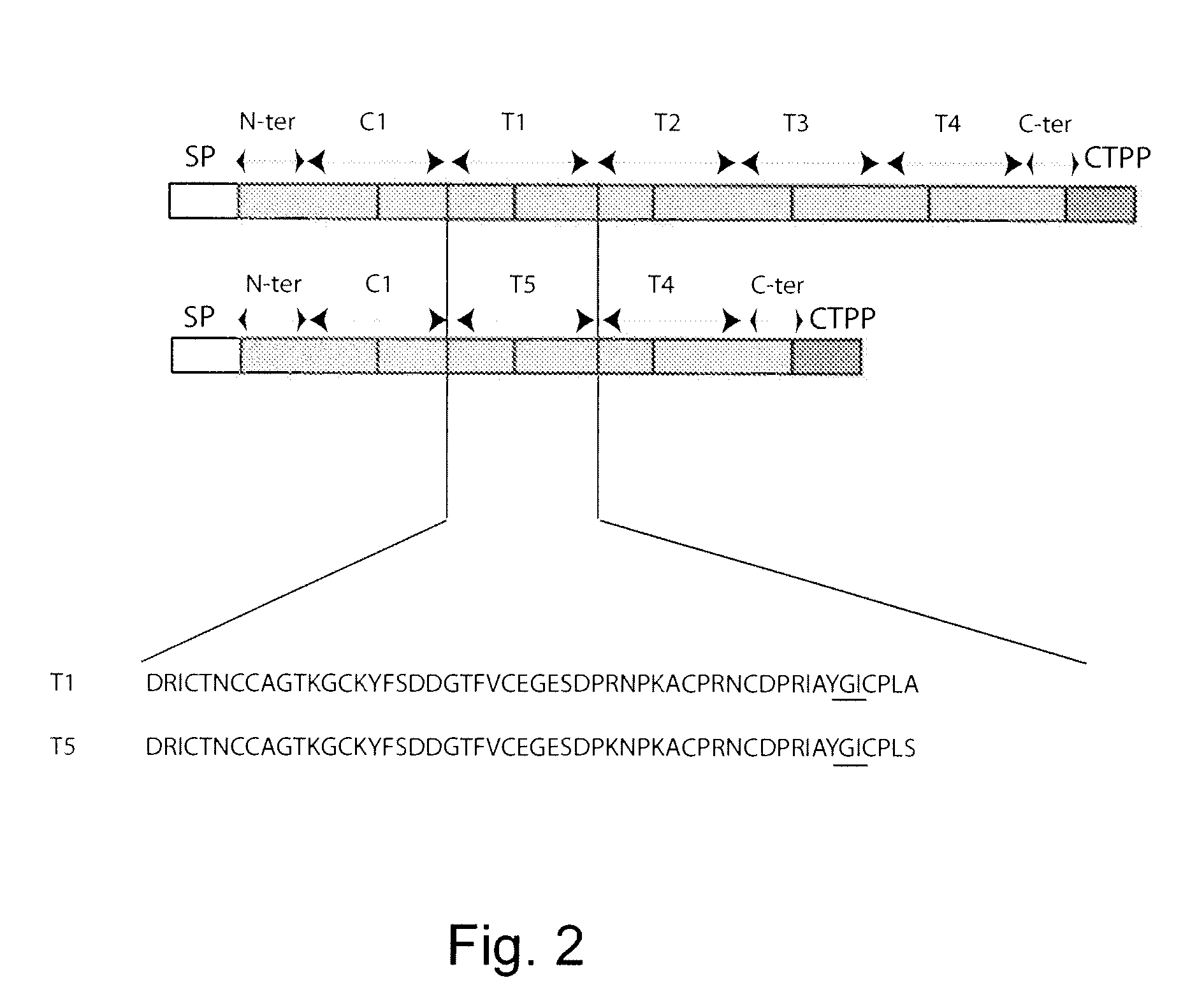
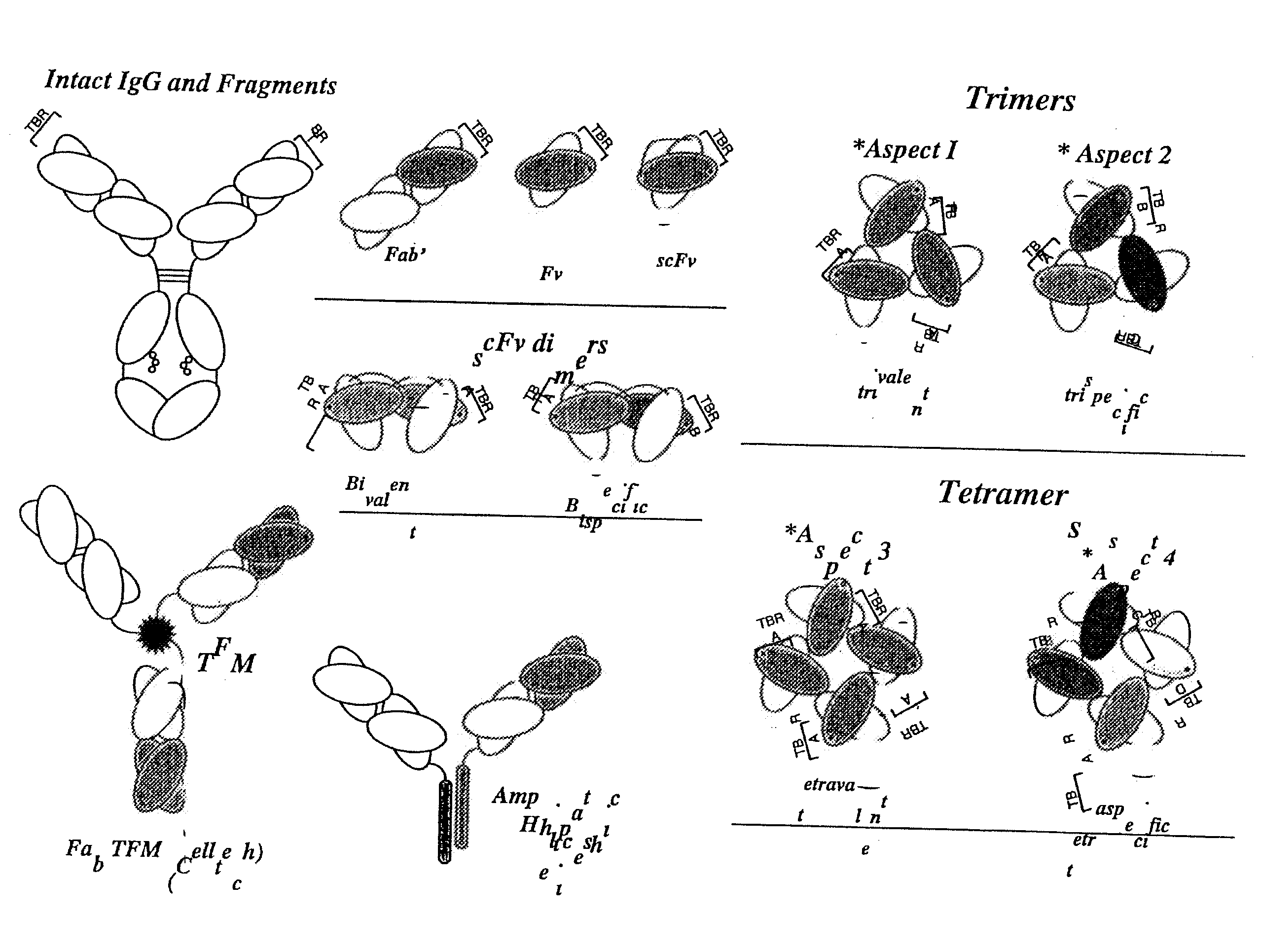
High avidity polyvalent and polyspecific reagents
InactiveUS20080152586A1In-vivo radioactive preparationsImmunoglobulins against animals/humansEGF-like domainImaging agent
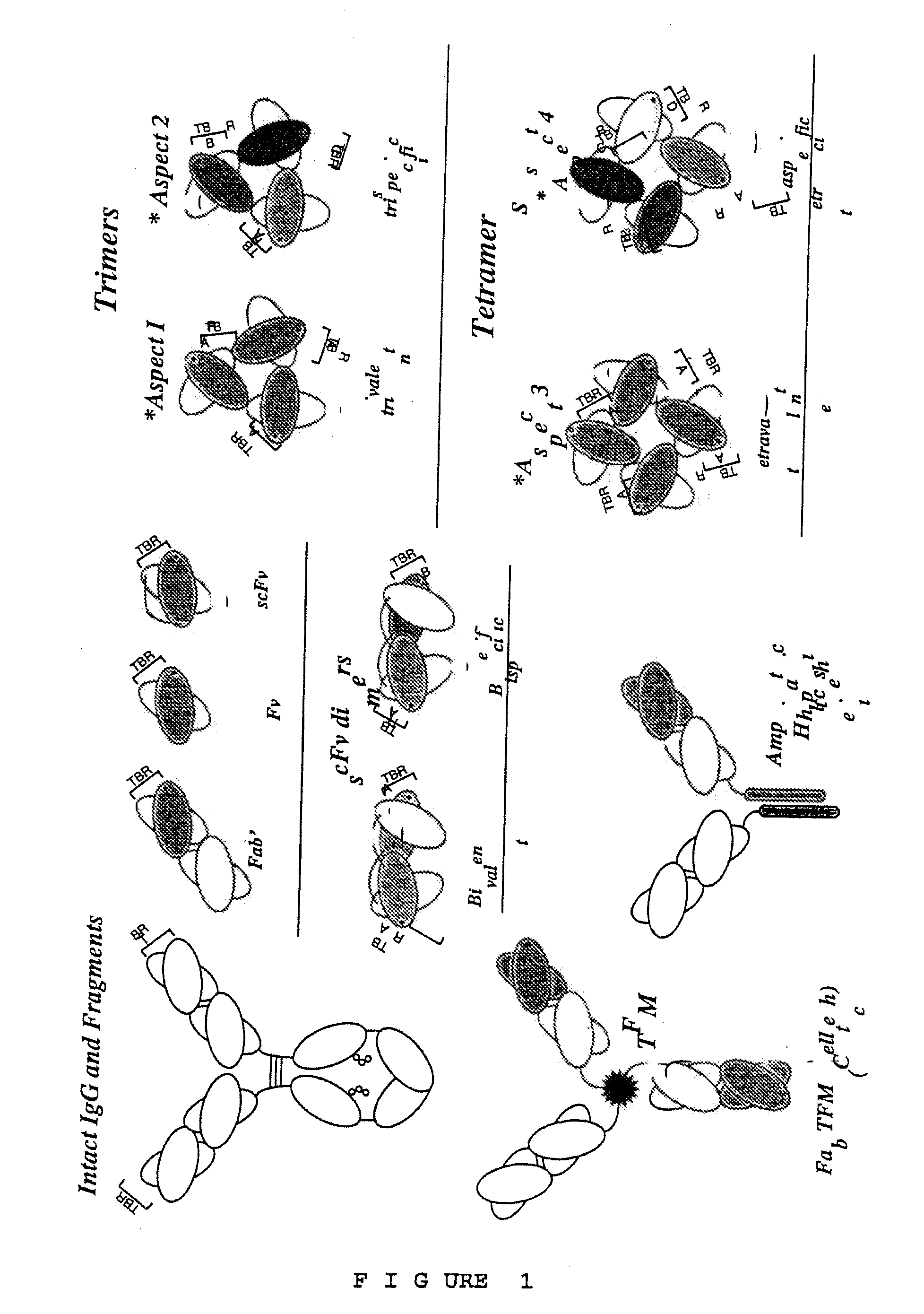
This invention provides polyvalent or polyspecific protein complexes, comprising three or more polypeptides which associate to form three or more functional target-binding regions (TBRs), and in which each individual polypeptide comprises two or more immunoglobulin-like domains which are covalently joined together, such that two Ig-like domains in a single polypeptide do not associate with each other to form a TBR. By using a linker peptide of fewer than three amino acid residues the immunoglobulin-like domains of the individual polypeptides are prevented from associating, so that complex formation between polypeptides is favoured. Preferably the polyvalent or polyspecific protein is a trimer or tetramer. The proteins of the invention have specificities which may be the same or different, and are suitable for use as therapeutic, diagnostic or imaging agents.
Owner:AVIPEP
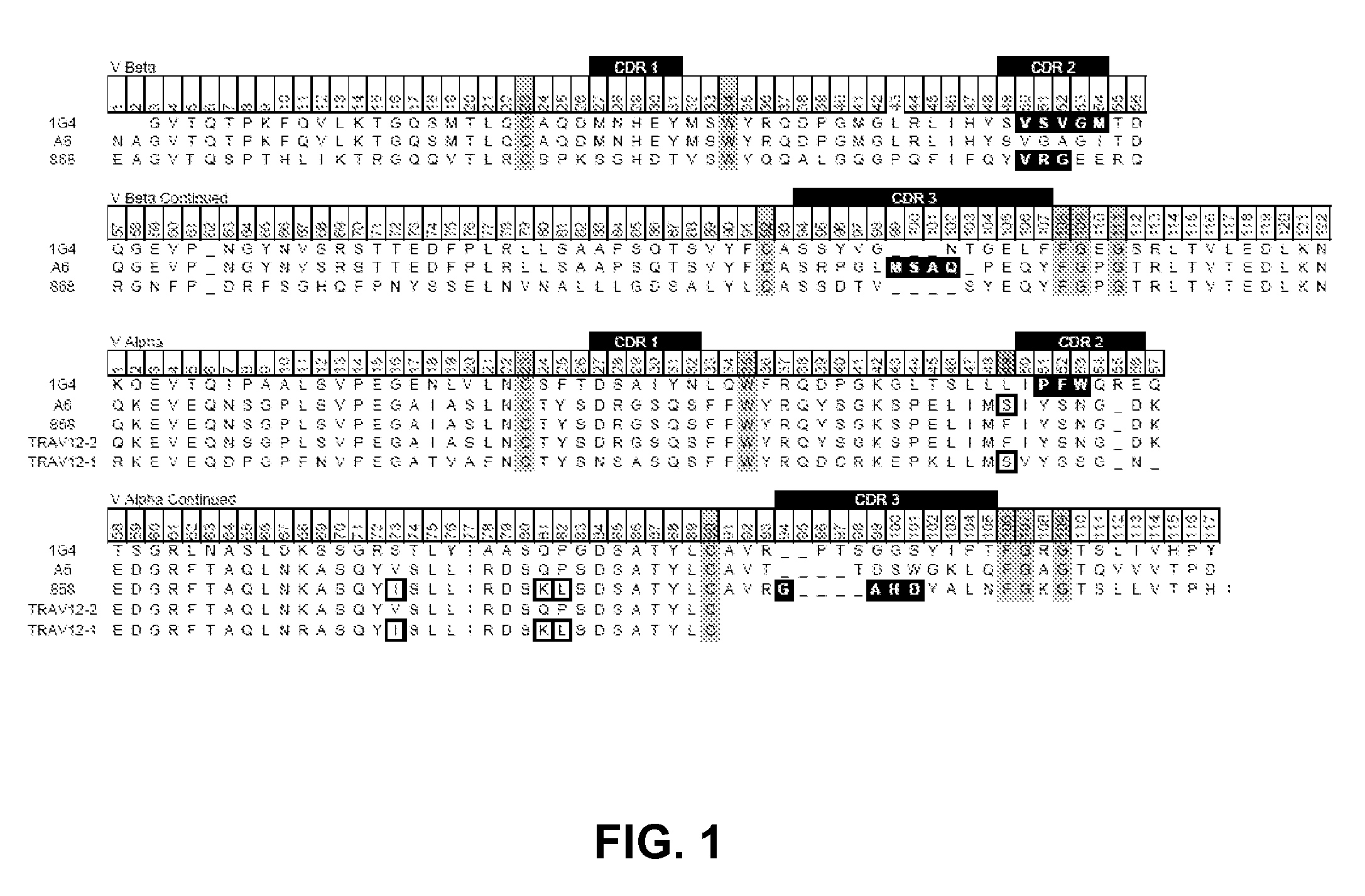
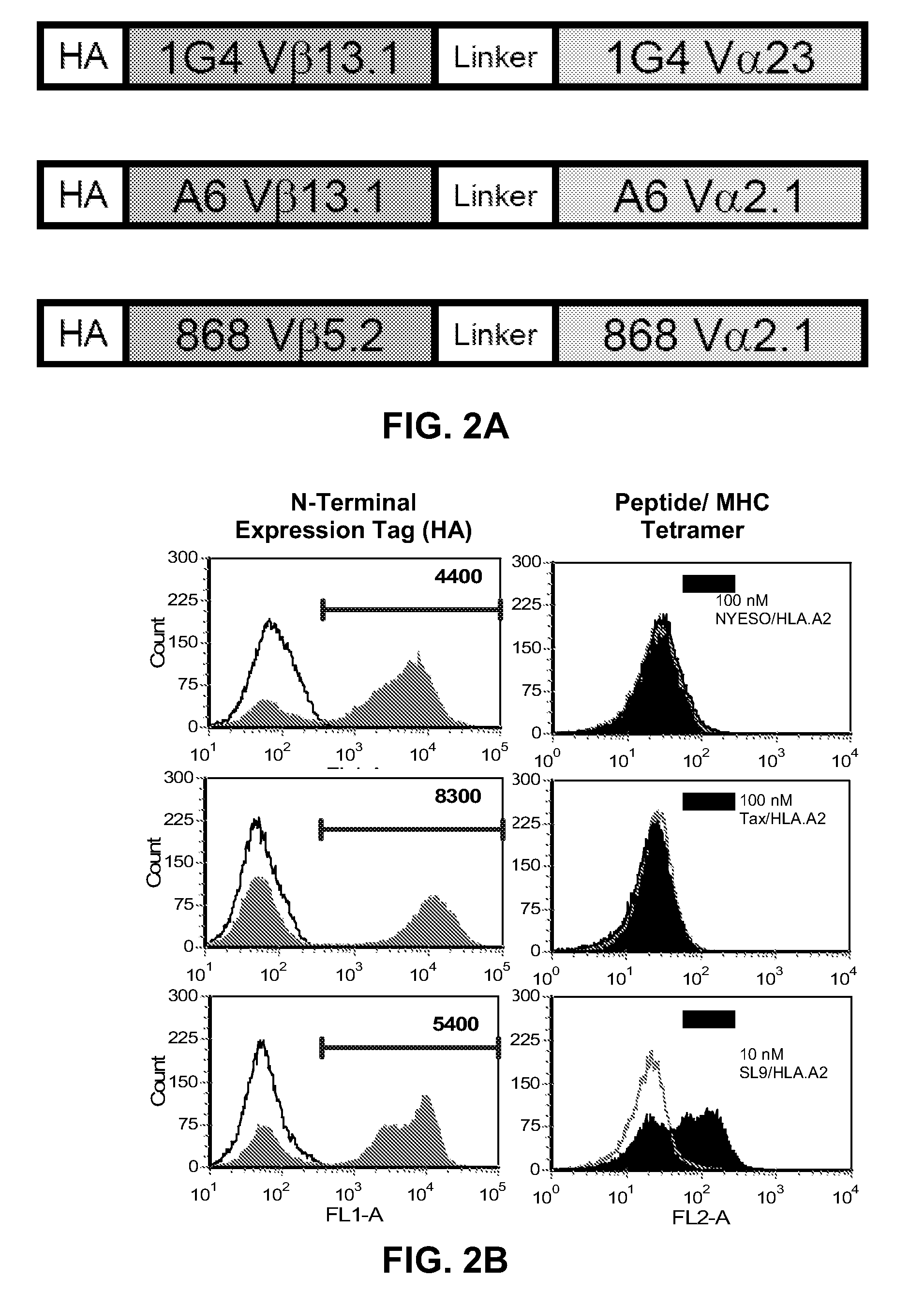
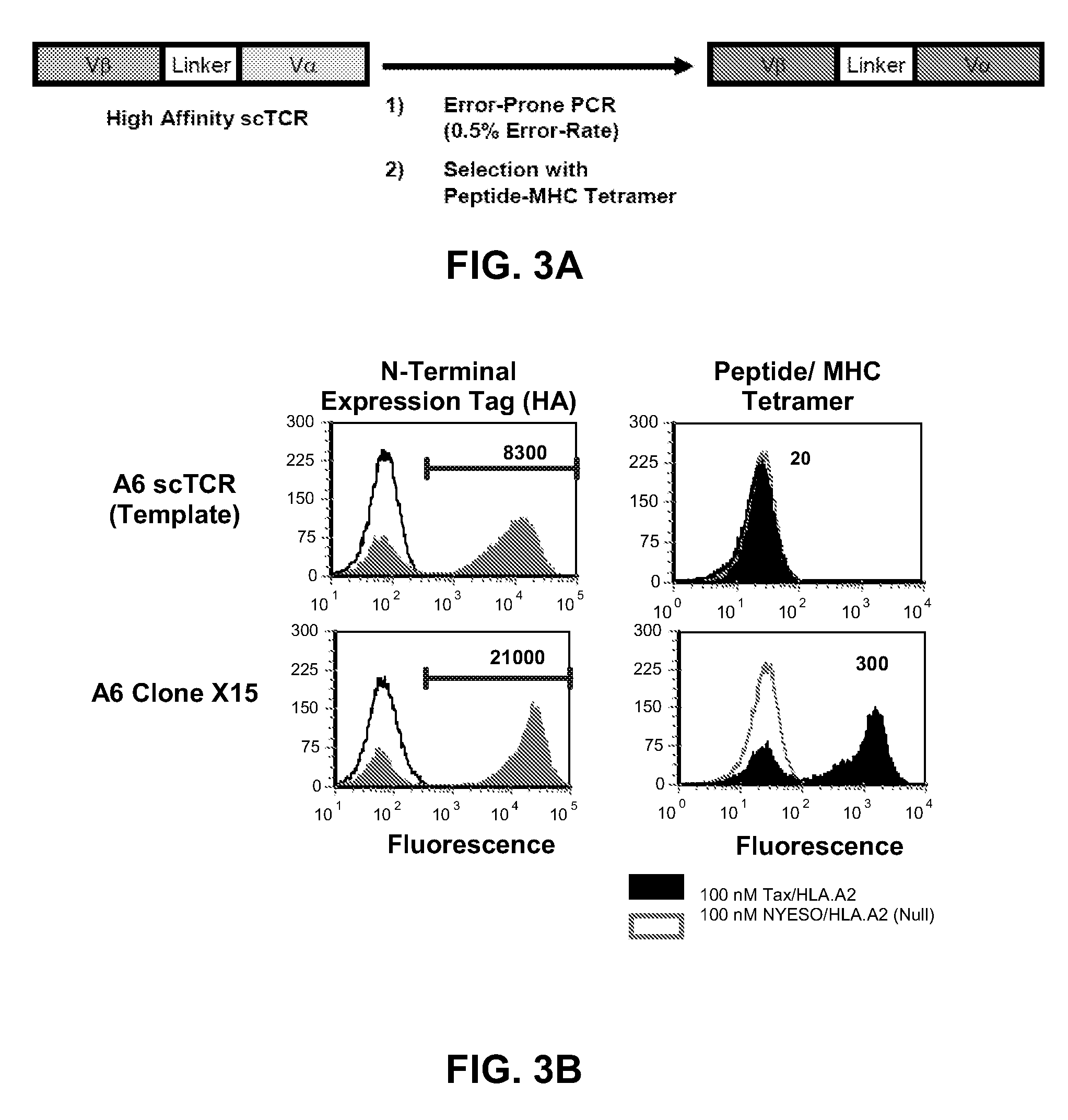
Human Single-Chain T Cell Receptors
ActiveUS20120252742A1High affinityEnhanced stability toward thermal denaturationAntibacterial agentsImmunoglobulin superfamilyDiseaseViral disease
A soluble human single-chain T cell receptor (TCR) having the structure: Vα2-L-Vβ or Vβ-L-Vα2, wherein L is a linker peptide that links Vβ with Vα, Vβ is a TCR variable β region, and Vα2 is a TCR variable α region of the family 2 is provided. The provided scTCR is useful for many purposes, including the treatment of cancer, viral diseases and autoimmune diseases.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
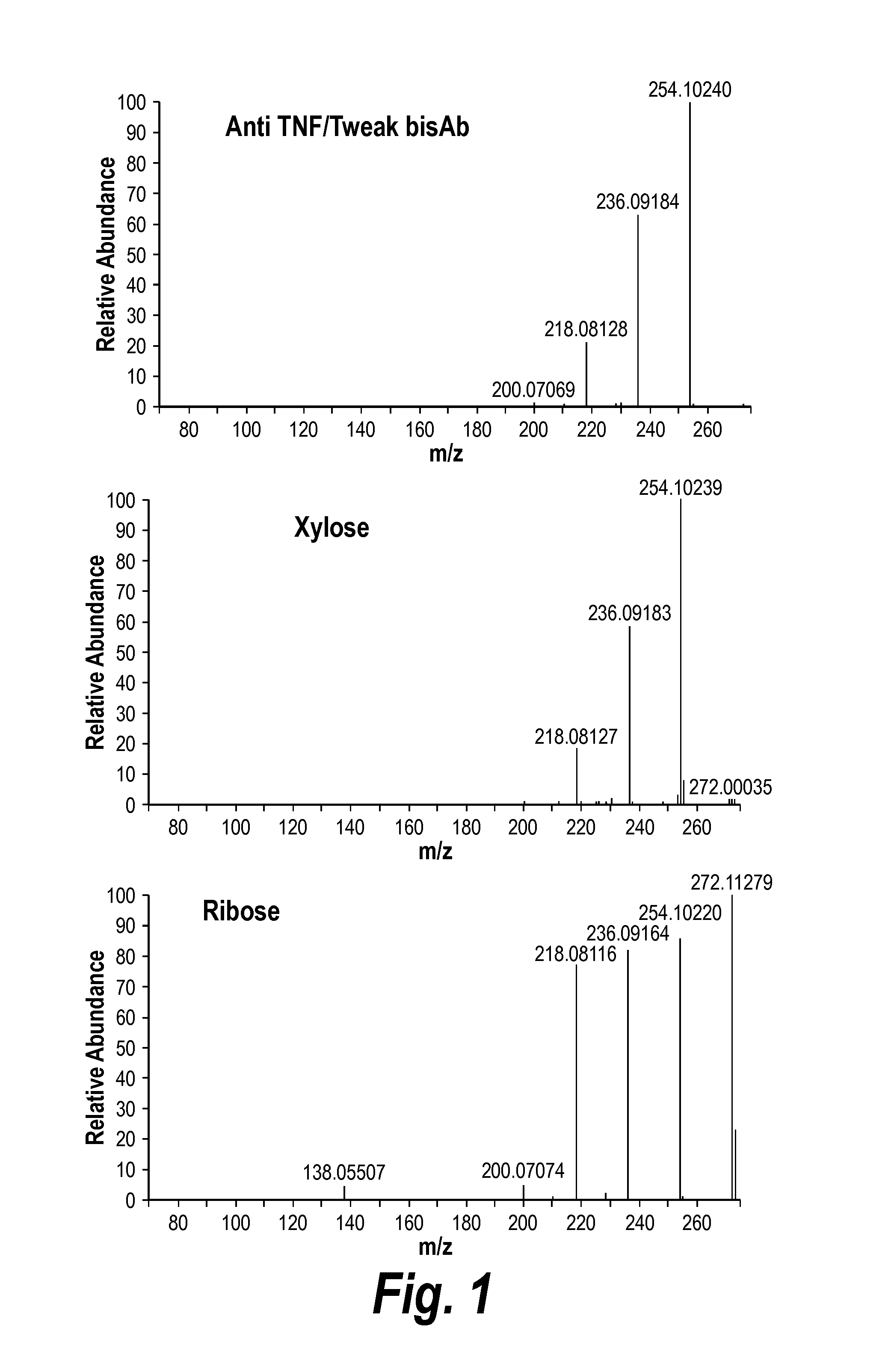
Linker peptides and polypeptides comprising same
ActiveUS20140079701A1Reduce aggregationImproves pH stabilityBacteriaAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsXylosyltransferaseLinker peptide
The invention is based, at least in part, on the finding that linker peptides which lack the amino acid sequence GSG reduce or eliminate the addition of posttranslational modifications to the polypeptides which comprise them. More specifically, the novel linker peptides disclosed herein reduce the ability of enzymes to link carbohydrate adducts to polypeptides comprising these linker peptides, e.g., reduce the ability of xylosyltransferase to link xylose to polypeptides. These novel linker peptides, molecules comprising same, and methods of their use are described.
Owner:BIOGEN MA INC
Resonance Energy Transfer Assay with Cleavage Sequence and Spacer
ActiveUS20110033866A1Improving sensitivity of energyHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisEnergy transferCoupling
A molecular construct comprises a donor label, an acceptor label, a linker peptide disposed between the donor and the acceptor, the linker having a cleavage site sequence, and a spacer between at least one of (a) the donor and the cleavage site sequence and (b) the acceptor and the cleavage site sequence. Preferably, the construct is selected from the group consisting of CFP-(SGLRSRA)-SNAP-25-(SNS)-YFP, and CFP-(SGLRSRA)-synaptobrevin-(SNS)-YFP. In preferred embodiments, the linker peptide is a substrate of a botulinum neurotoxin selected from the group consisting of synaptobrevin (VAMP), syntaxin and SNAP-25, or a fragment thereof that can be recognized and cleaved by the botulinum neurotoxin. Advantageously, the spacer increases the electronic coupling between the donor label and the acceptor label relative to a corresponding construct without the spacer.
Owner:BIOMADISON
Haploid yeast cells transformed with a library of expression vectors encoding a fully human antibody repertoire
InactiveUS20030027213A1High affinityEasy to assembleFungiMicrobiological testing/measurementProtein targetTarget peptide
Compostions, kits and methods are provided for generating highly diverse libraries of proteins such as antibodies via homologous recombination in vivo, and screening these libraries against protein, peptide and nucleic acid targets using a two-hybrid method in yeast. The method for screening a library of tester proteins against a target protein or peptide comprises: expressing a library of tester proteins in yeast cells, each tester protein being a fusion protein comprised of a first polypeptide subunit whose sequence varies within the library, a second polypeptide subunit whose sequence varies within the library independently of the first polypeptide, and a linker peptide which links the first and second polypeptide subunits; expressing one or more target fusion proteins in the yeast cells expressing the tester proteins, each of the target fusion proteins comprising a target peptide or protein; and selecting those yeast cells in which a reporter gene is expressed, the expression of the reporter gene being activated by binding of the tester fusion protein to the target fusion protein.
Owner:GENETASTIX CORP
Method of Increasing the In Vivo Recovery of Therapeutic Polypeptides
InactiveUS20100222554A1Improved in vivo recoveryIncreased in vivo recoveryAntibacterial agentsHydrolasesIn vivoLinker peptide
Owner:CSL BEHRING GMBH
Method and compositions for detecting botulinum neurotoxin
A molecular construct capable of fluorescent resonance energy transfer (FRET), comprising a linker peptide, a donor fluorophore moiety and an acceptor fluorophore moiety, wherein the linker peptide is a substrate of a botulinum neurotoxin selected from the group consisting of synaptobrevin, syntaxin and SNAP-25, or a fragment thereof capable being cleaved by the botulinum neurotoxin, and separates the donor and acceptor fluorophores by a distance of not more than 10 nm, and wherein emission spectrum of the donor fluorophore moiety overlaps with the excitation spectrum of the acceptor fluorophore moiety; or wherein the emission spectra of the fluorophores are detectably different. Also provided are isolated nucleic acid expressing the construct, kits comprising said construct and cell lines comprising said nucleic acid. Further provided are methods of detecting a BoNT using the above described construct via FRET, and methods for detecting a BoNT using surface plasmon resonance imaging.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
High throughput generation and screening of fully human antibody repertoire in yeast
InactiveUS20050142562A1High affinityHighly efficient homologous recombinationFungiMicrobiological testing/measurementTarget peptideIn vivo
Owner:GENETASTIX CORP
Dimeric flourescent polypeptides
InactiveUS6936428B2Peptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsLinker peptideFluorescent protein
The invention relates to proteins or polypeptides that comprise intramolecular dimers of fluorescent protein monomers. More specifically, the invention relates to recombinant polypeptides comprising a monomer of a fluorescent polypeptide, a linker peptide, and a second monomer of that fluorescent polypeptide, where the monomers form an intramolecular dimer. The invention also relates to nucleic acids encoding Intramolecular Dimer Fluorescent Proteins (IDFPs) and vectors comprising such nucleic acids. The invention further relates to methods of making IDFPs and methods of using them. IDFPs are, useful in any application suited for fluorescent proteins and are particularly useful in applications in which more than one fluorescent protein sharing complementary dimerization interfaces is present in the same mixture or is expressed in the same cell, because IDFPs do not form heterodimers.
Owner:STRATAGENE INC US
Fushion protein of melittin with gene mutant interleukin -2
The invention discloses a fusion protein of melittin and human mutant interleukin-2, which is characterized in that, a linker peptide gene is used to link the encoding genes of human mutant IL-2 and melittin. The invention can be used to screen cloning capable of improving CD8+T cell mediated CTL reactivity of the body after the tumor formation, the fusion protein can be used fine genetic medicament for the treatment of tumors.
Owner:QINGDAO UNIV
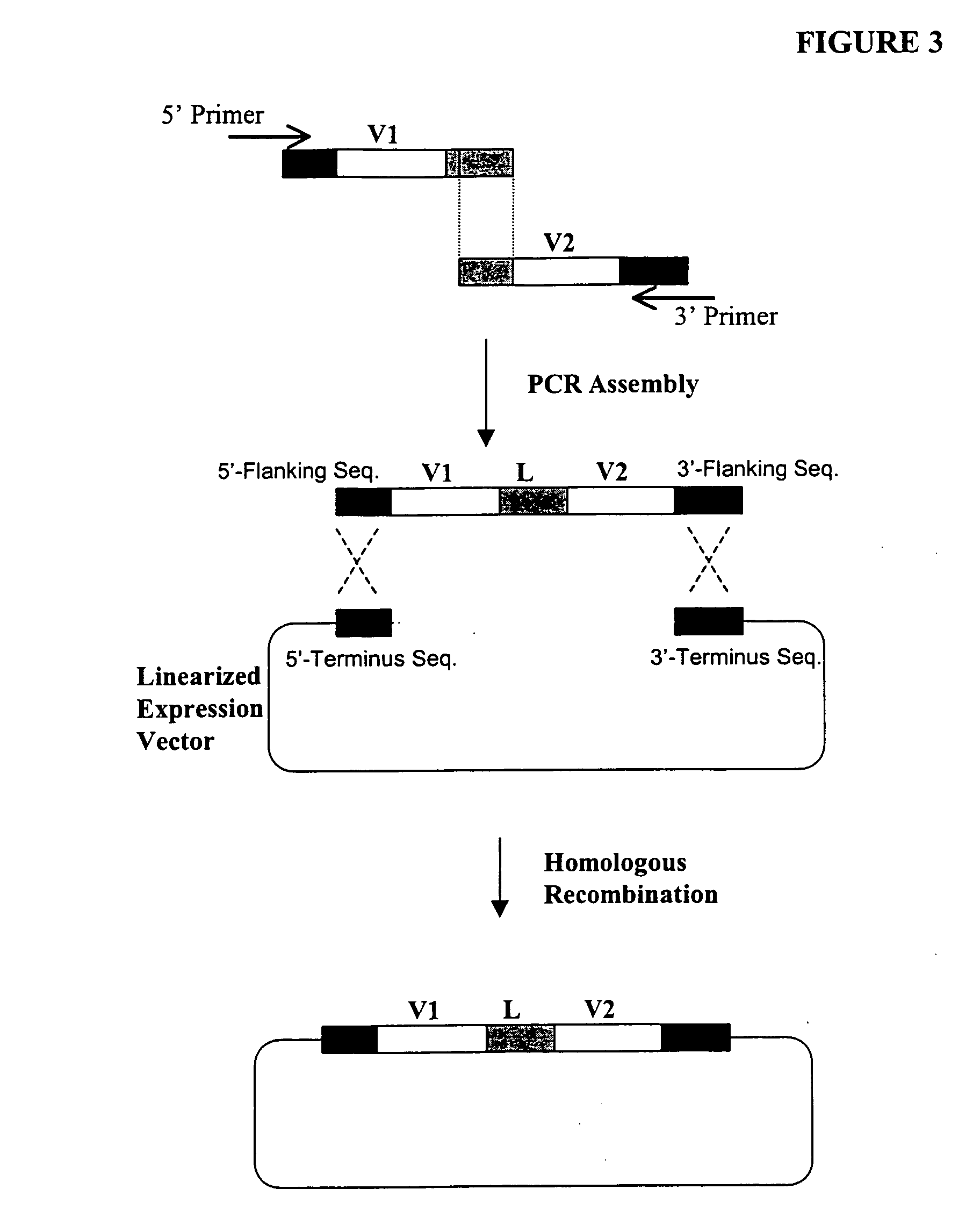
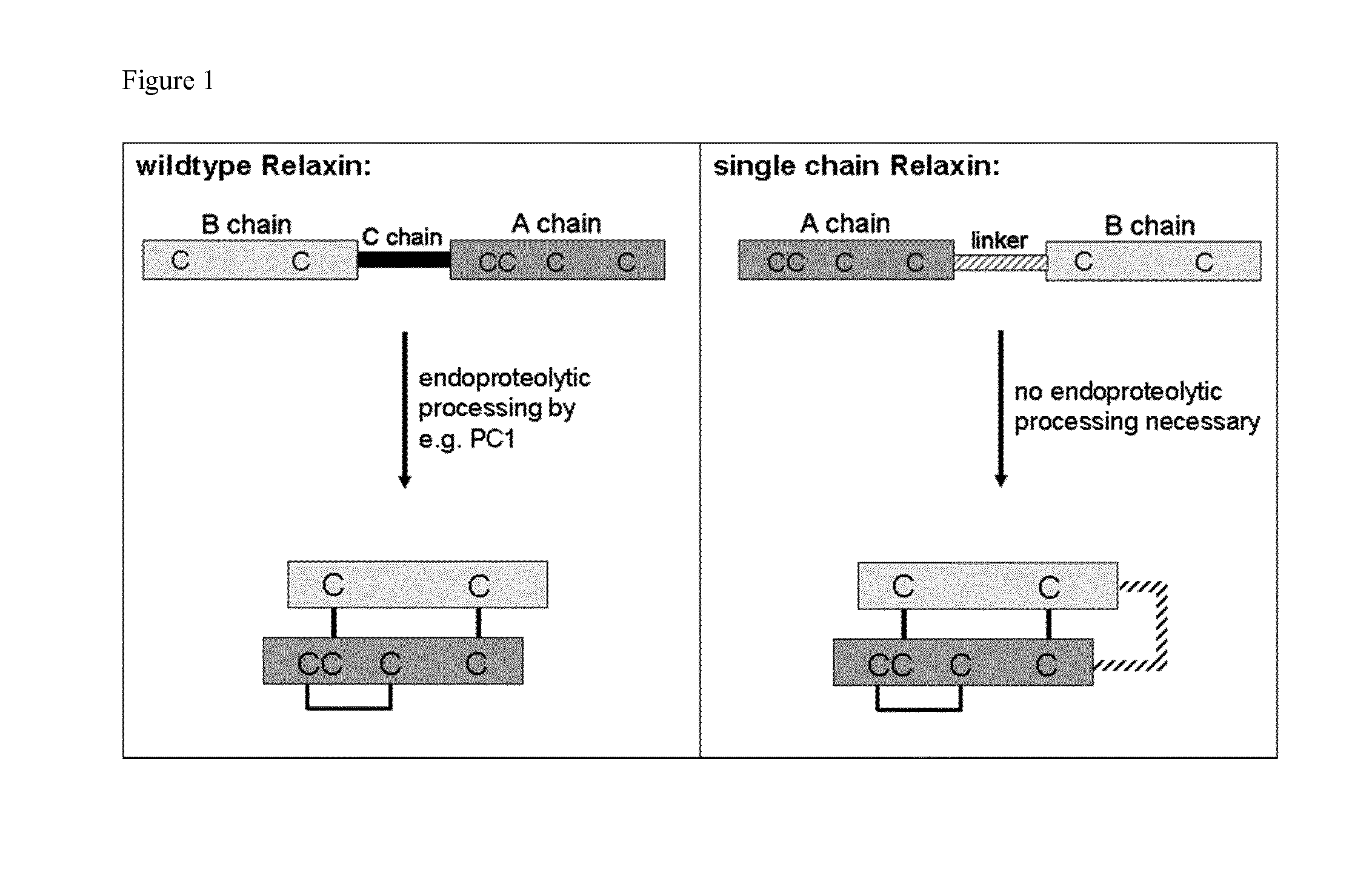
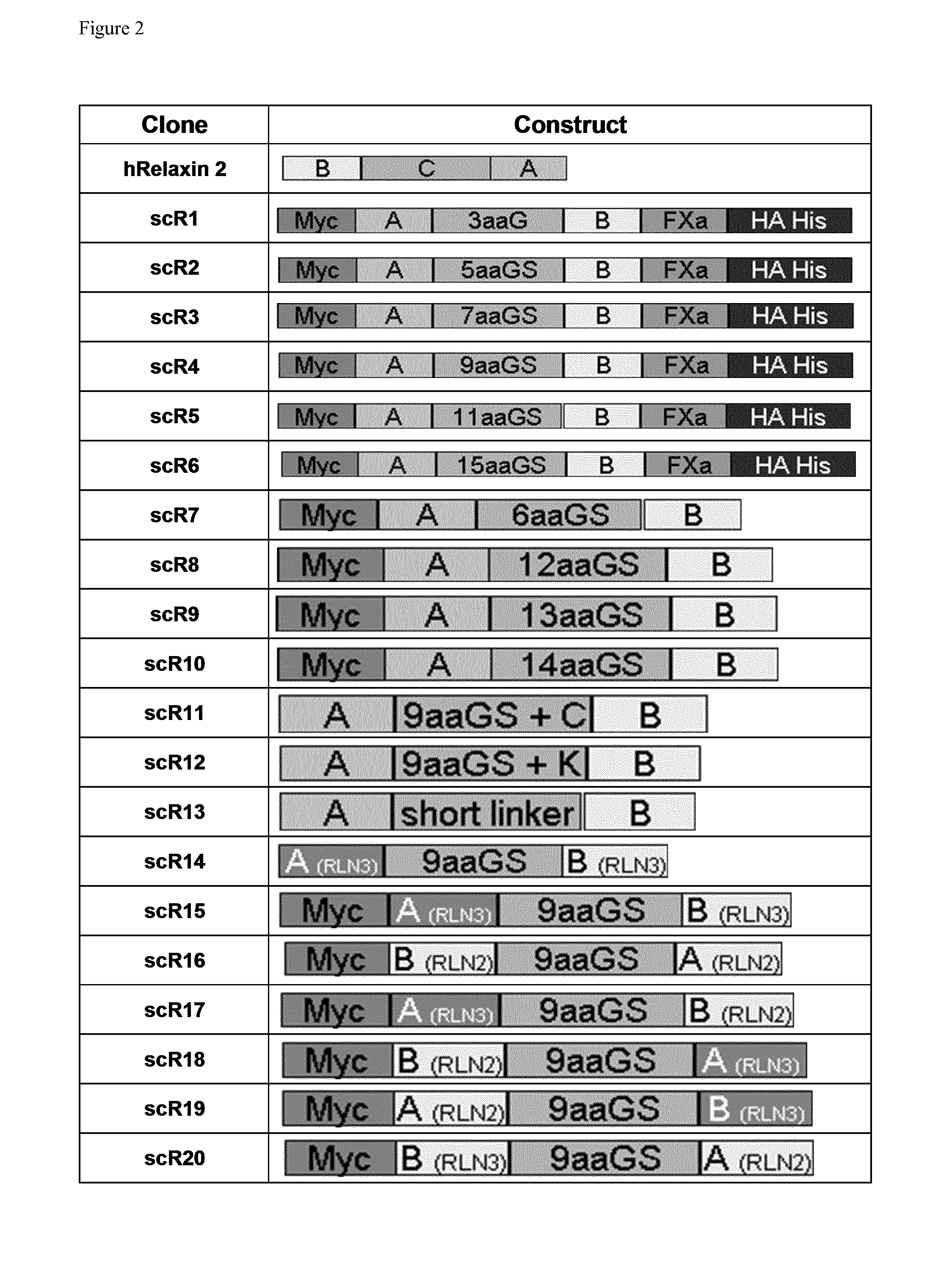
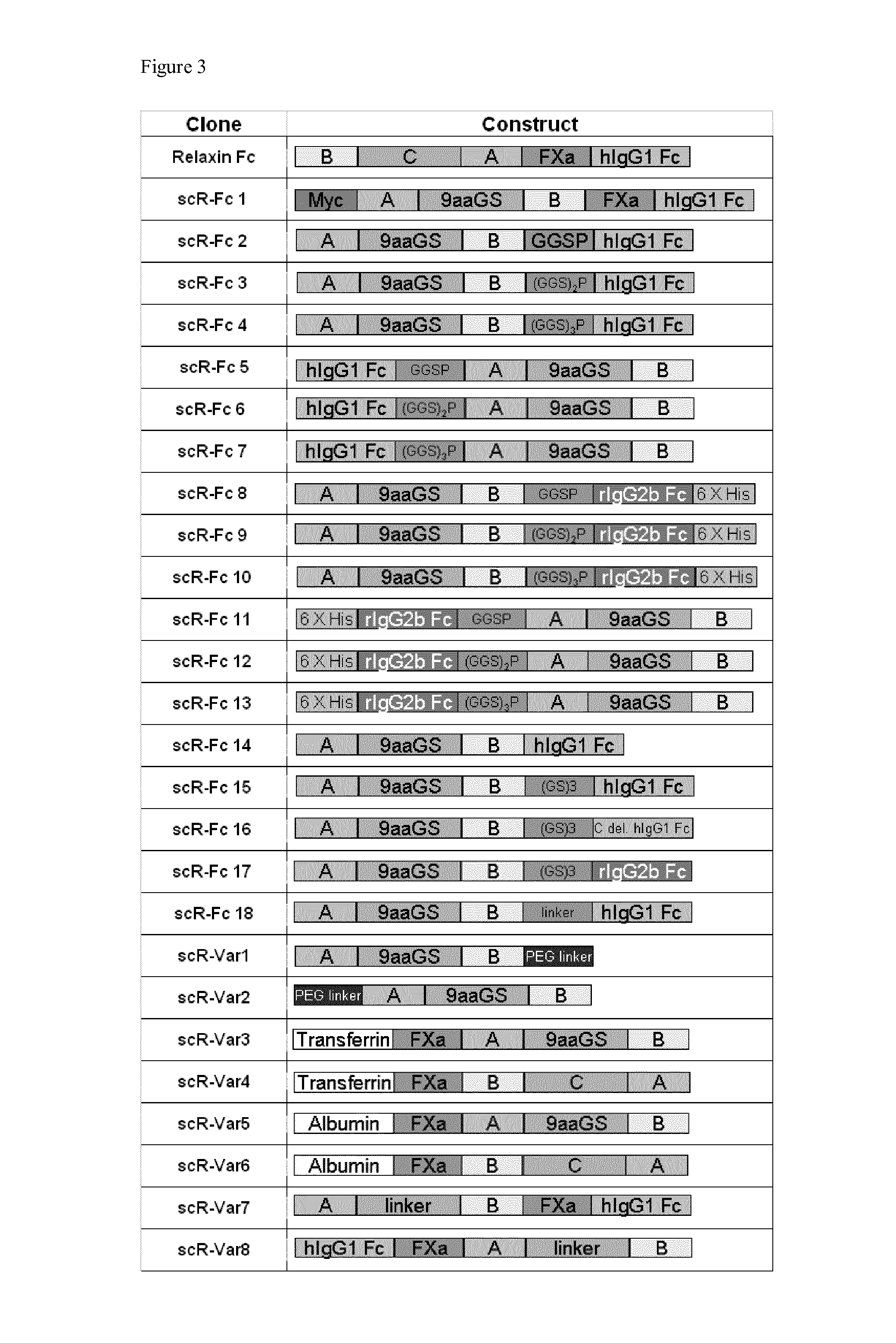
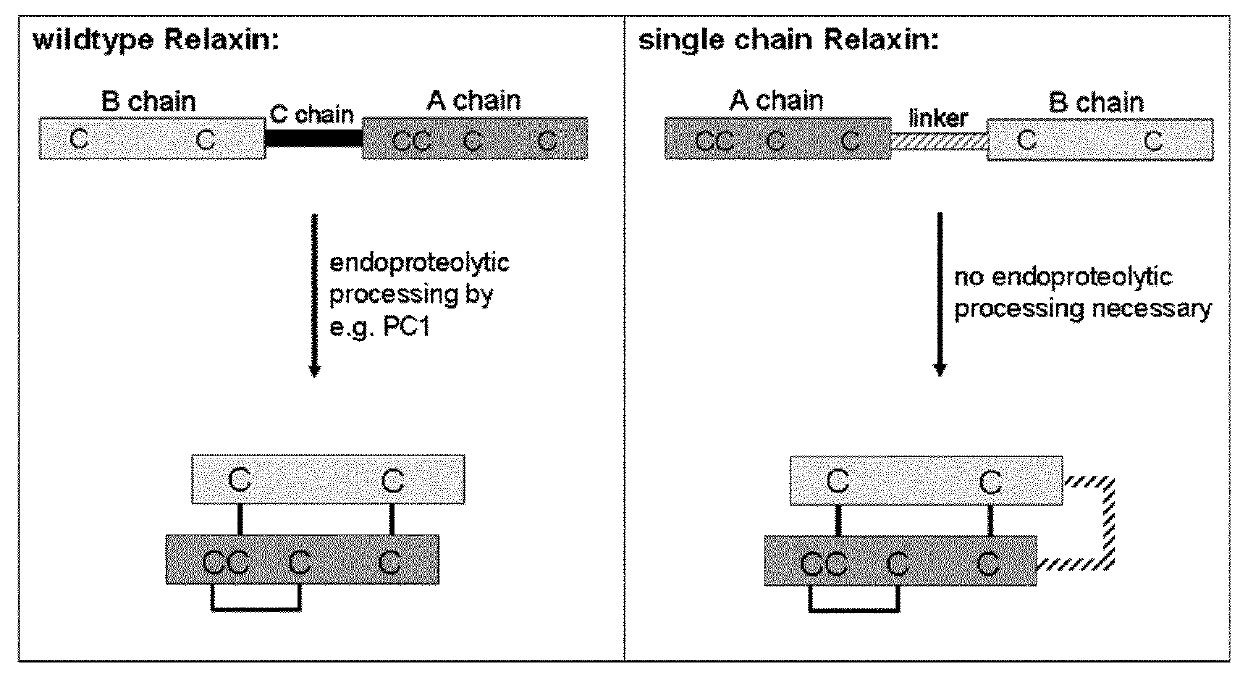
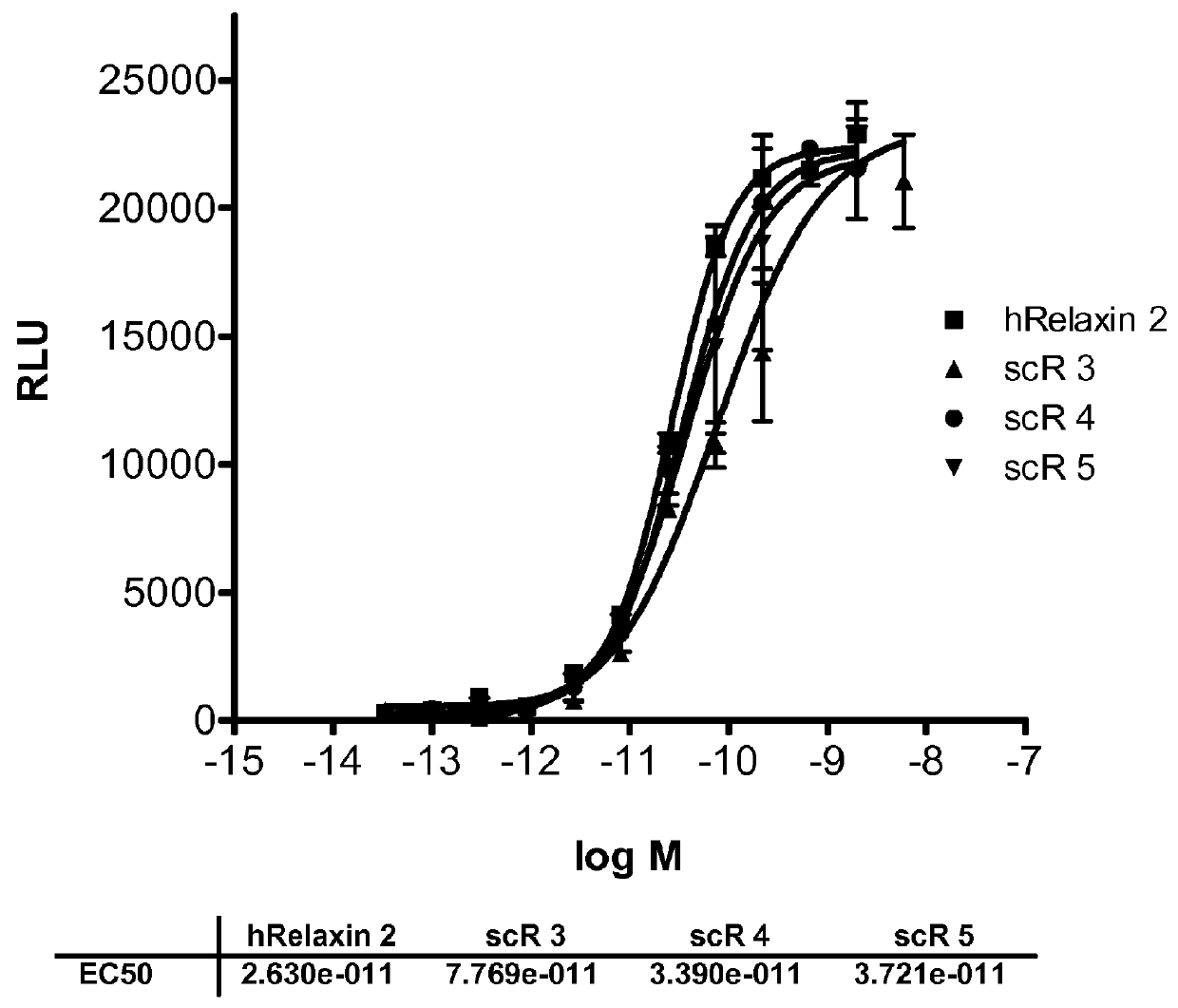
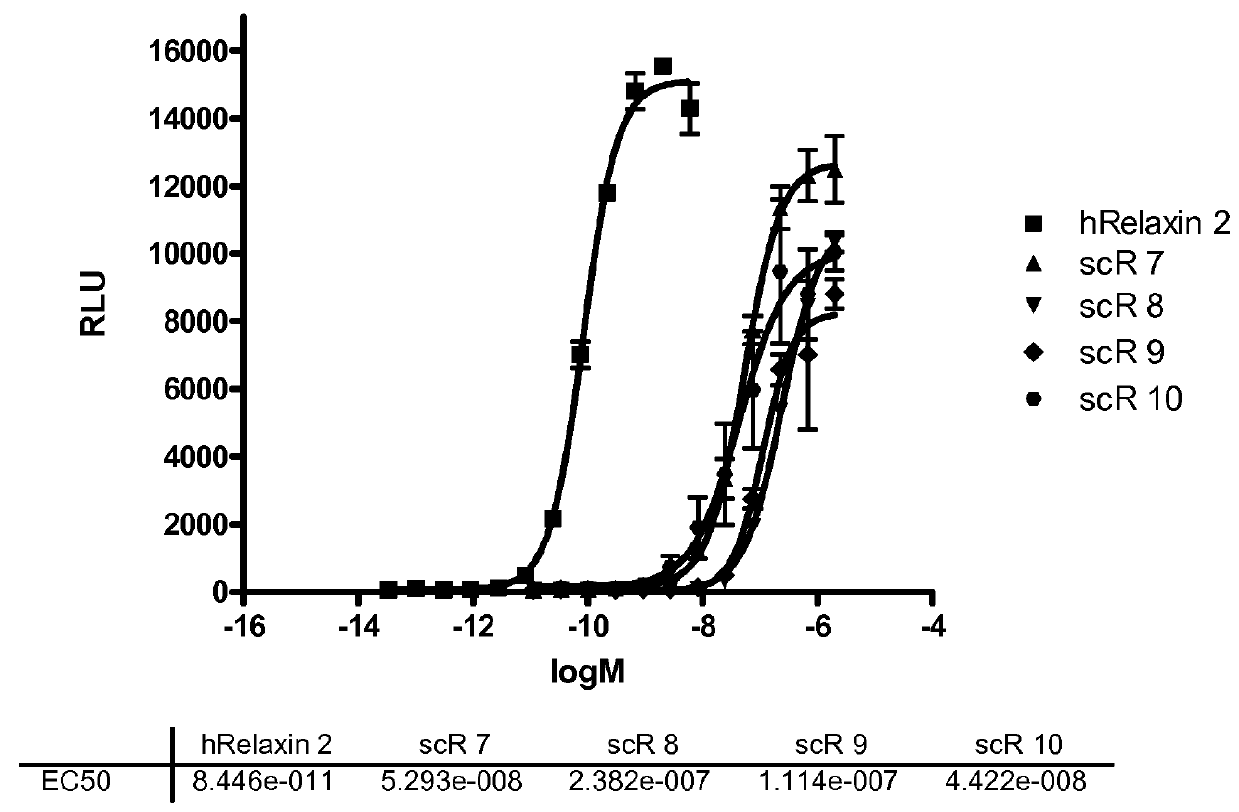
Relaxin fusion polypeptides and uses thereof
The present invention provides Relaxin fusion polypeptides A-L-B with a non-wild type array of the Relaxin A-chain and Relaxin B-chain, wherein the A- and B-chains are connected by a linker peptide. The invention further provides Relaxin fusion polypeptides with extended half-life. Furthermore, the invention provides nucleic acid sequences encoding the foregoing fusion polypeptides, vectors containing the same, pharmaceutical compositions and medical use of such fusion polypeptides.
Owner:BAYER INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY GMBH
Relaxin fusion polypeptides and uses thereof
Owner:BAYER INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY GMBH
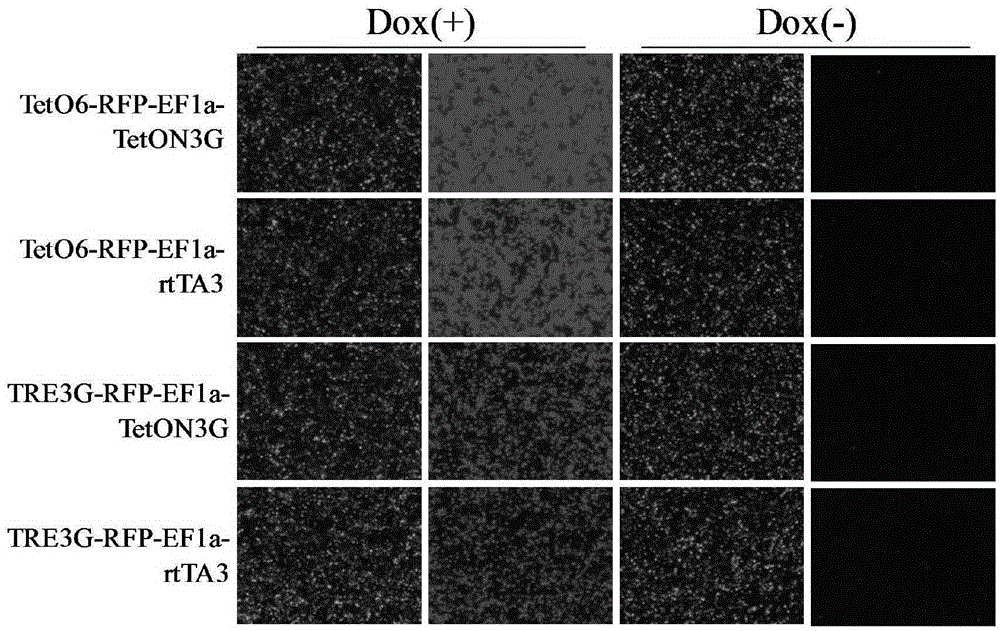
Induced slow virus expression system and construction method and application thereof
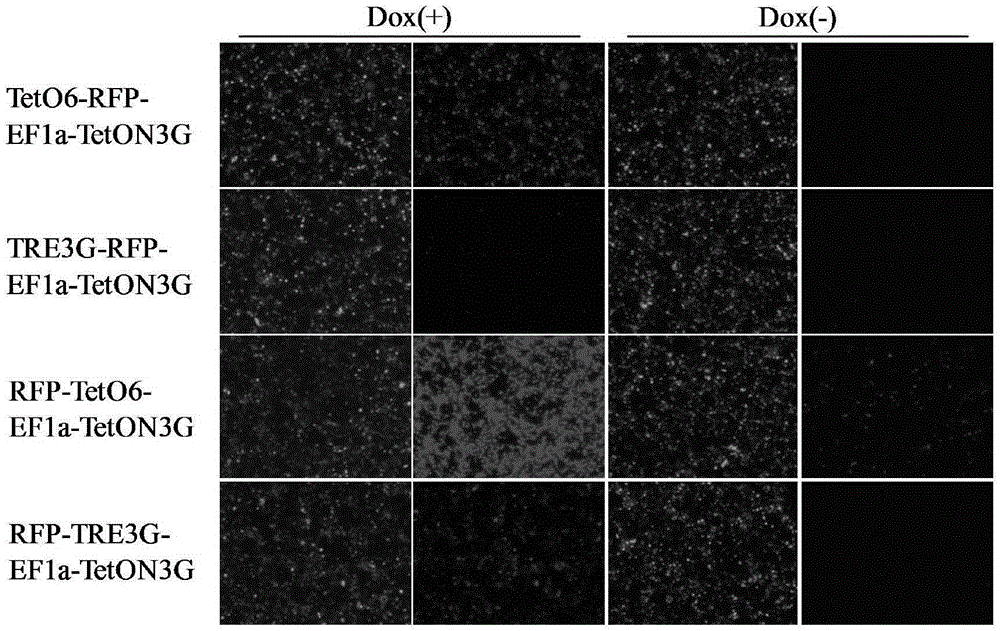
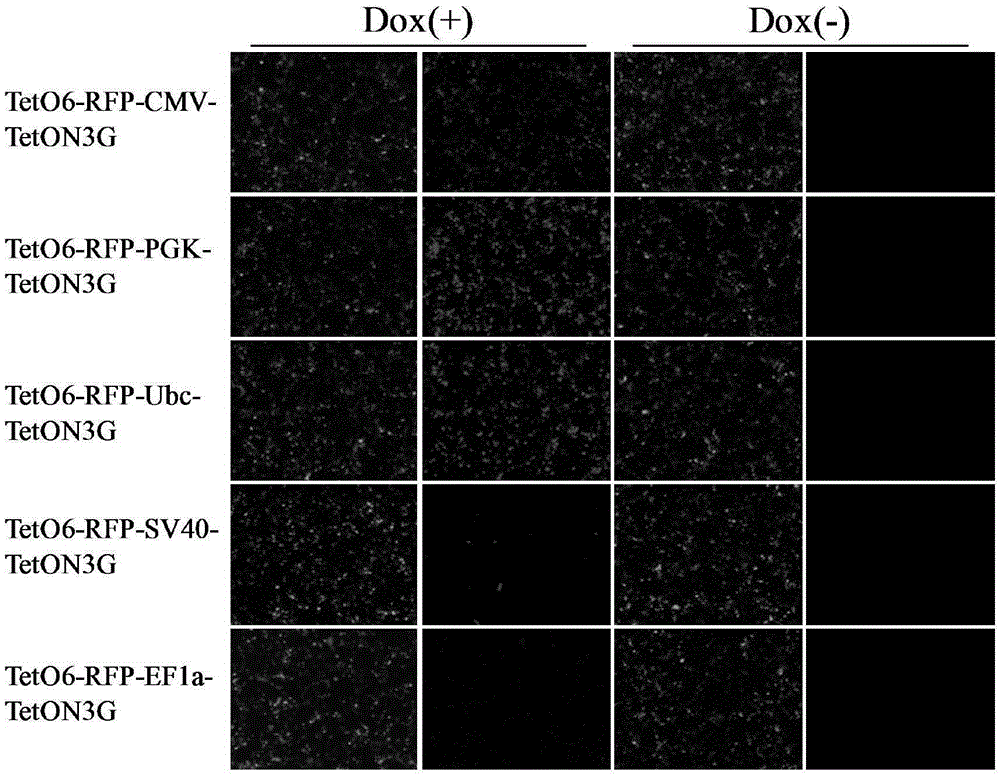
ActiveCN105331635ARapid responseImprove efficiencyFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionLinker peptideCancer research
The invention discloses an induced slow virus expression system which comprises a target gene expression cassette and an rtTA expression cassette. The target gene expression cassette comprises an induced promoter containing a tetracycline cis-acting response element and a target gene, and the rtTA expression cassette comprises a promoter, an rtTA, a linker peptide and a screening gene, wherein a P2A linker peptide is adopted as the linker peptide, the screening gene is Puro, and the induced promoter is TetO6 or TRE3G. The invention further discloses a construction method of the induced slow virus expression system. The construction method comprises the steps of pLVX-Puro carrier reconstructing; TetON3G gene synthesizing and cloning; pLVX-rtTA3 constructing; EF1a promoter subcloning; red fluorescence protein (RFP) subcloning; subcloning of the induced promoter TRE3G or TETO6 containing the tetracycline cis-acting response element. The induced slow virus expression system can carry out inducible expression of the target gene to the greatest level while keeping low background expression after cells are introduced into the system, is sensitive in response for an inducer, high in efficiency and low in molecular weight and can be widely applied to gene function research.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
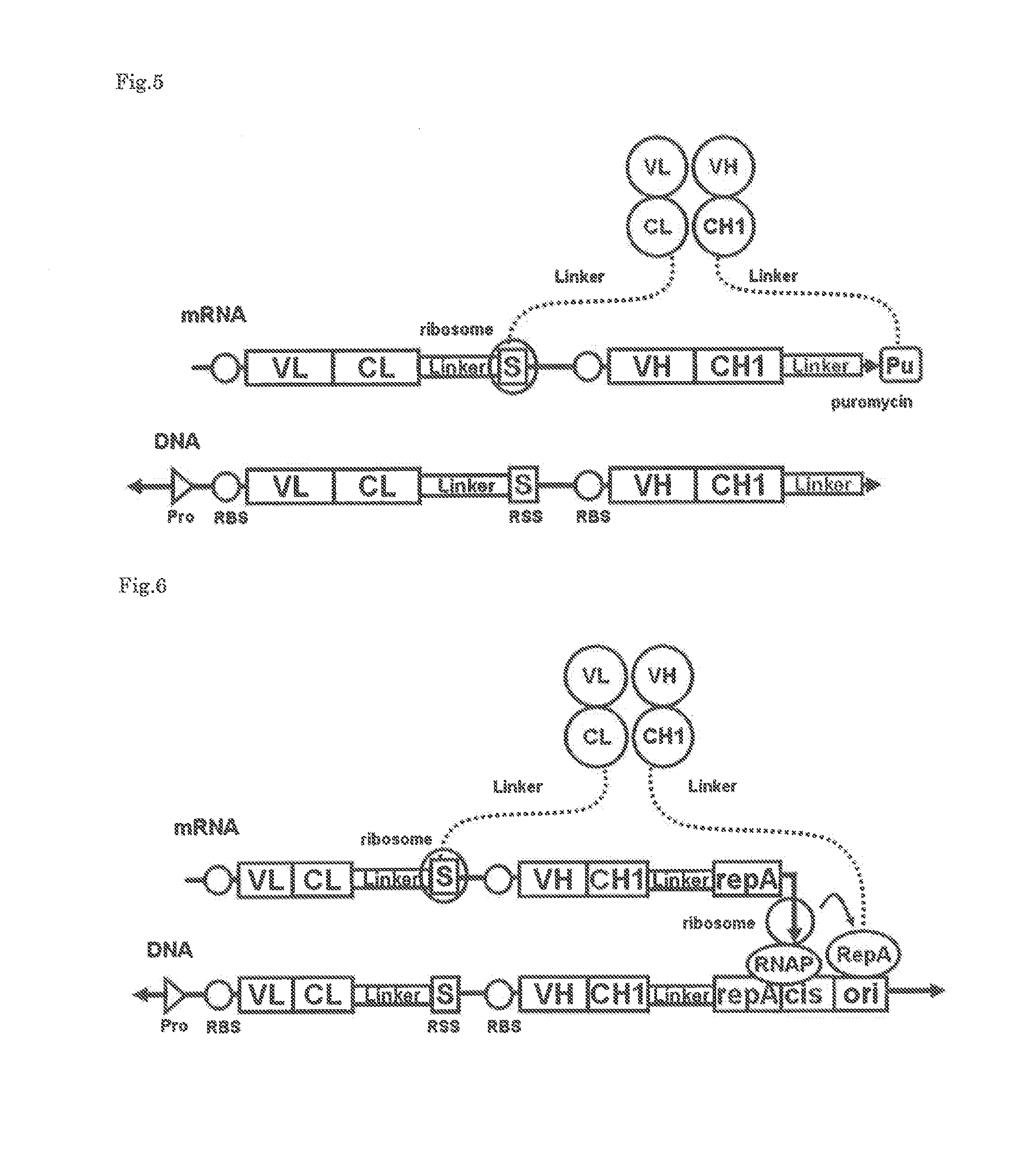
Polynucleotide construct capable of displaying fab in a cell-free translation system, and method for manufacturing and screening fab using same
InactiveUS20130288908A1Maximizing affinityHigh affinitySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementAntigenCell free
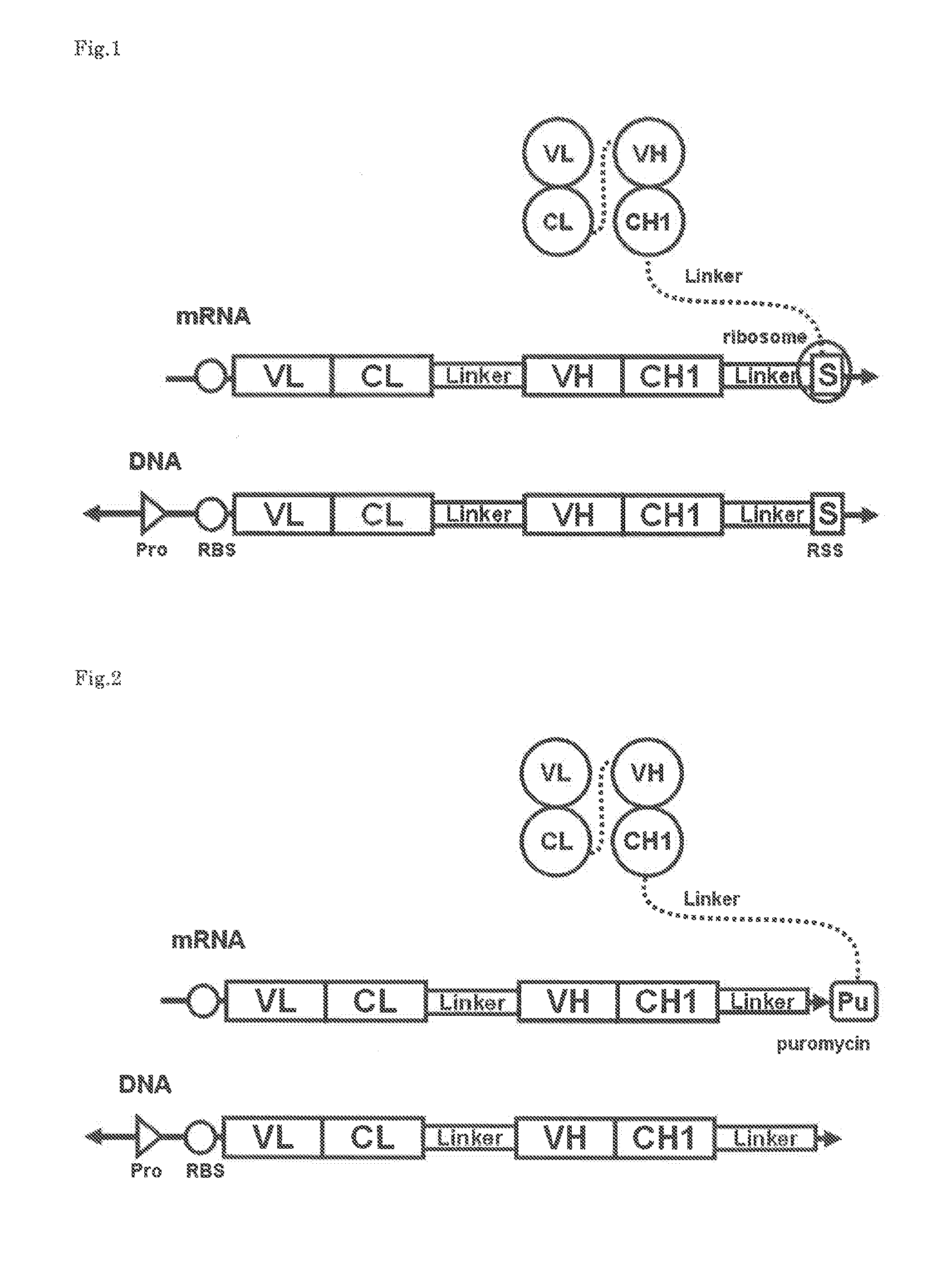
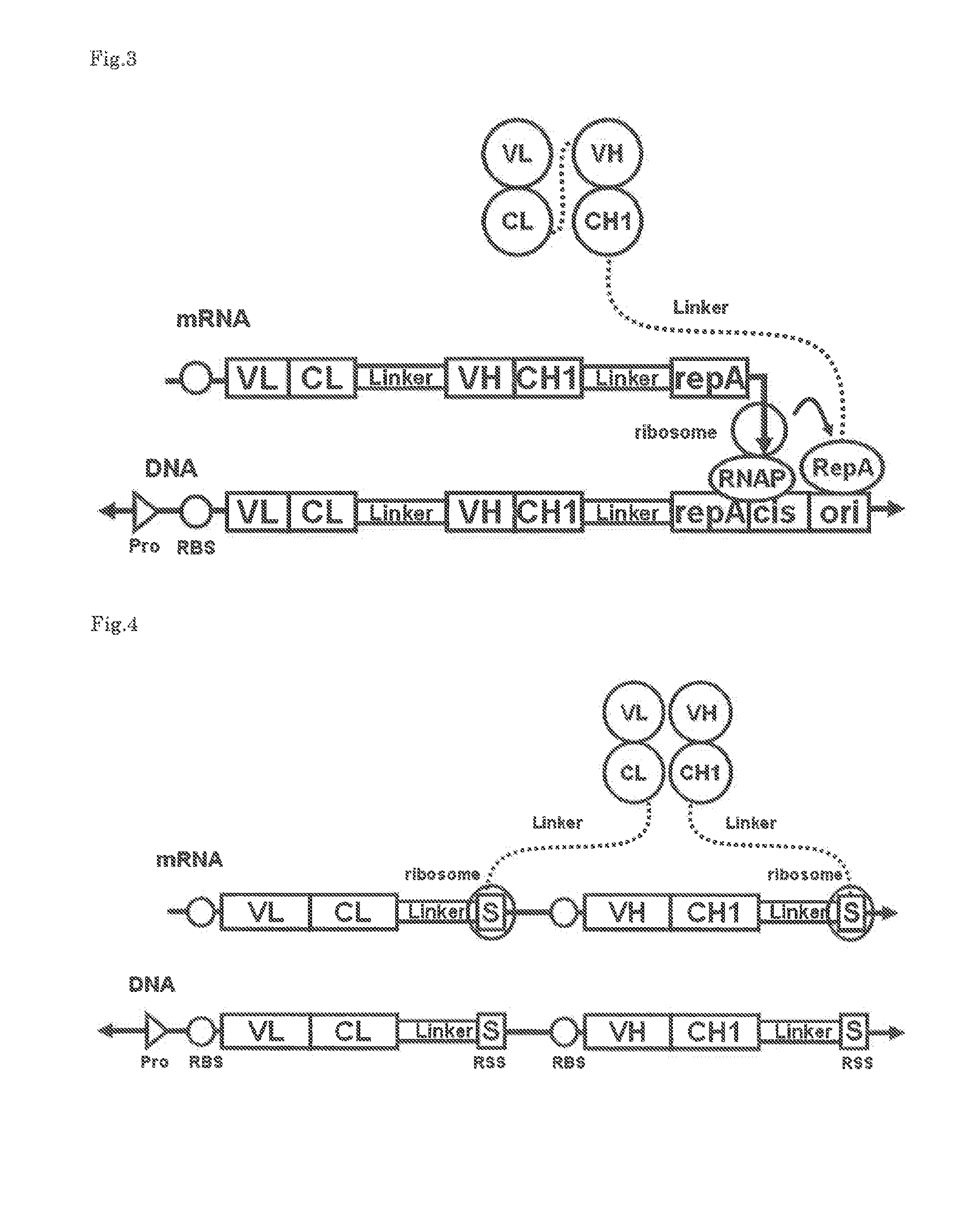
The polynucleotide construct of (1) or (2) below is used to perform ribosome display, CIS display and / or mRNA display in order to screen a Fab against an antigen of interest: (1) a polynucleotide construct which monocistronically comprises a ribosome-binding sequence, Fab first chain-coding sequence, linker peptide-coding sequence, Fab second chain-coding sequence and scaffold-coding sequence in this order, and further comprises at its 3′-end a structure necessary for maintaining a complex with the Fab encoded by itself, and (2) a polynucleotide construct which comprises a Fab first chain-expressing cistron and a Fab second chain-expressing cistron each containing a ribosome-binding sequence, a Fab first chain-coding sequence or Fab second chain-coding sequence, and a scaffold-coding sequence in this order, the first Fab-expressing cistron further comprising at its 3′-end a ribosome stall sequence, said Fab second chain-expressing cistron further comprising at its 3′-end a structure necessary for maintaining a complex with the Fab encoded by itself.
Owner:THE UNIV OF TOKYO +1
Preparation method of genetically engineered bacterium for synthesizing glutathione and product thereof
ActiveCN104059936AIncrease productionEnhanced synthetase activityFungiMicroorganism based processesTransformation efficiencyInositol-3-phosphate synthase
The invention discloses a preparation method of a genetically engineered bacterium for synthesizing glutathione. The preparation method comprises the following steps: (i) converting a gene for encoding gamma-glutamoyl cysteine synthetase-linker peptide-glutathione synthetase fusion protein into a host bacterium cell, and highly expressing the gene; (ii) converting a gene for encoding gamma-glutamoyl cysteine synthetase-linker peptide-glutathione synthetase into the host bacterium cell, and highly expressing the gene; (iii) knocking off the gamma-glutamyltranspeptidase of the host bacterium cell; (iv) knocking off an inositol-3-phosphatep synthase gene of the host bacterium cell; and completing the steps (i), (ii), (iii) and (iv) in any sequence, thereby obtaining the genetically engineered bacterium for synthesizing glutathione. The invention further relates to the prepared genetically engineered bacterium. The genetically engineered bacterium for synthesizing glutathione, which is disclosed by the invention, is not only high in efficiency in synthesizing glutathione, but also can greatly improve the conversion efficiency of exogenous cysteine, and can be applied to glutathione production.
Owner:唐星
Resonance energy transfer assay with cleavage sequence and spacer
ActiveUS8969016B2Enhanced electronic couplingHigh sensitivityPeptide/protein ingredientsMaterial analysis by optical meansSynaptobrevinLinker peptide
Owner:BIOMADISON
Binding molecules
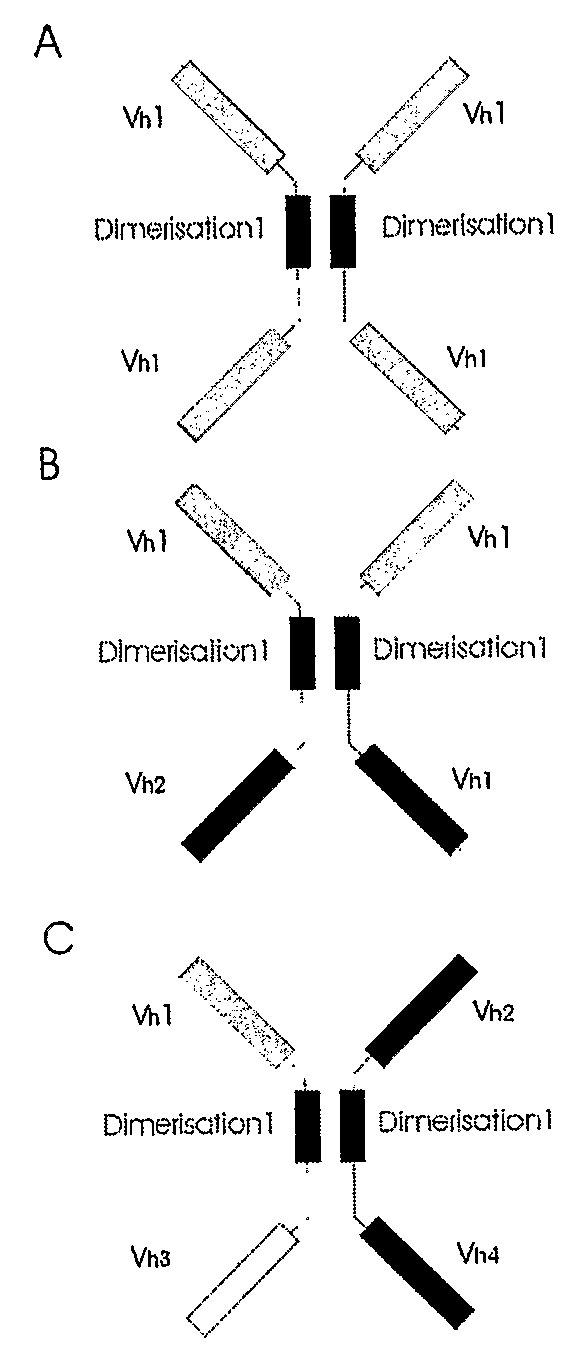
InactiveUS20090169548A1Improve in vivo stabilityReduce the possibilityOrganic active ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsNatural sourceHeterologous
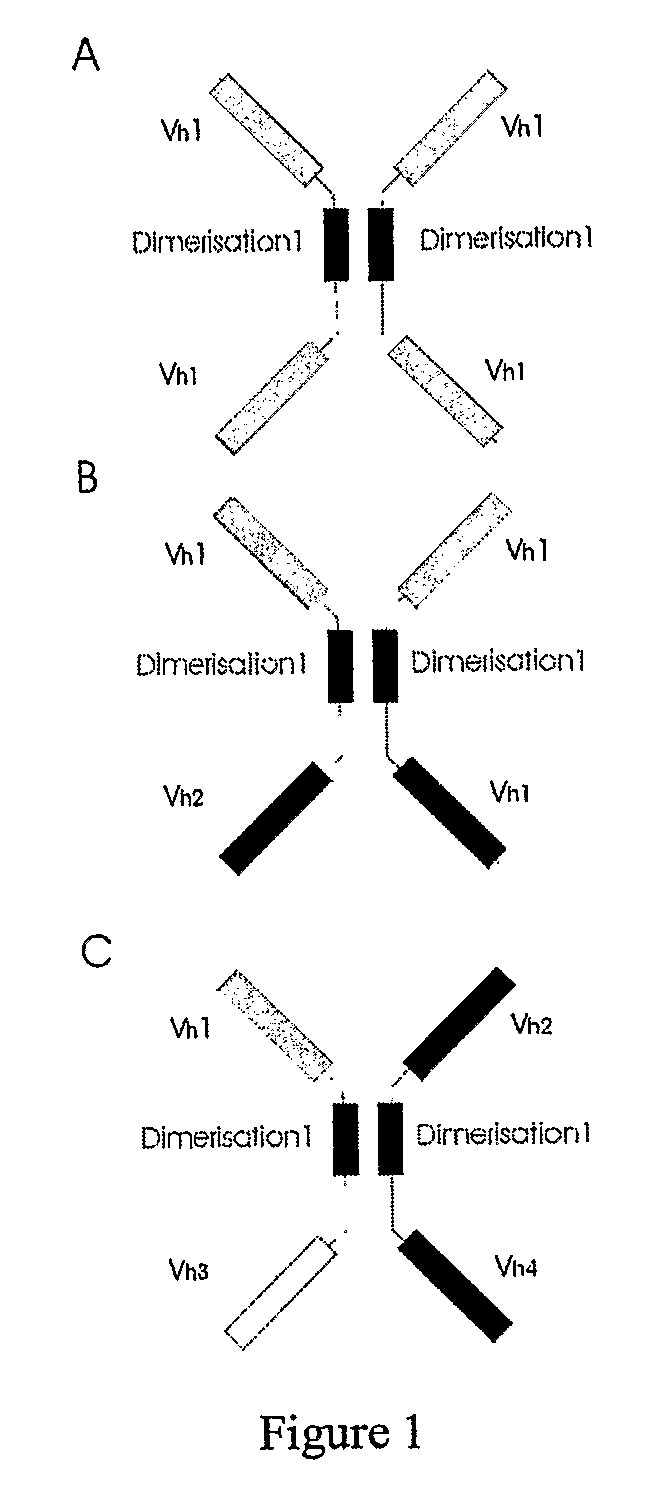
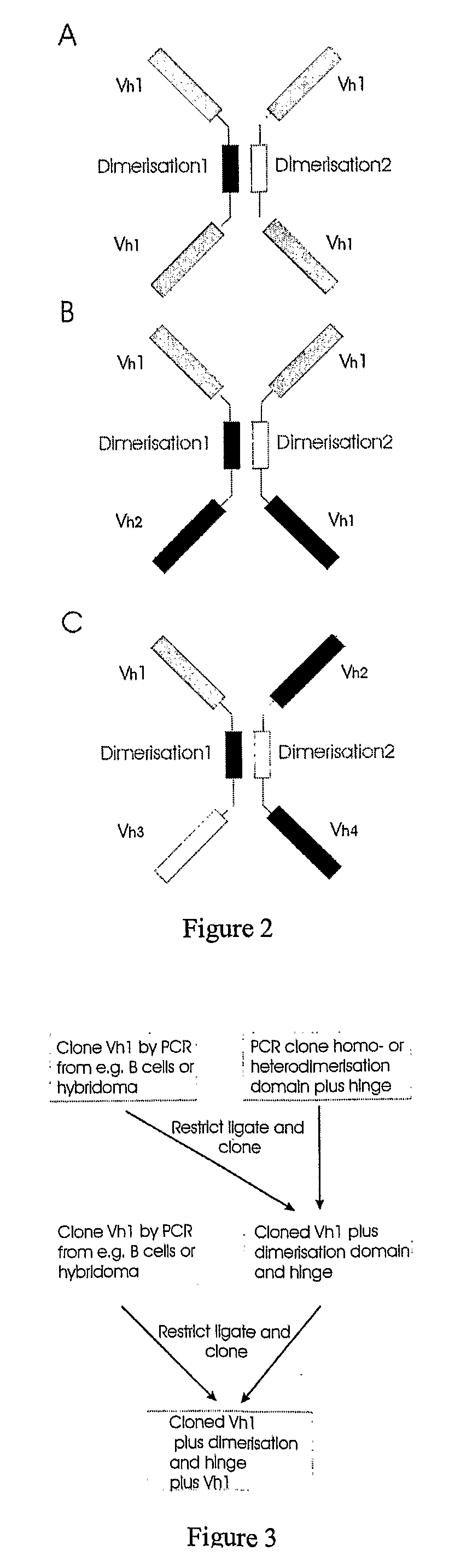
The present invention relates to the manufacture of mono, di and multivalent polypeptide binding complexes, also mono, di or multispecific polypeptide binding complexes and uses thereof. The invention also relates to the manufacture and use of a diverse repertoire of antigen specific VH binding domains derived from phage display libraries, transgenic animals or natural sources. Preferably the VH binding domains and the dimerisation domains comprise human sequences. The polypeptide binding complexes comprise homo or heterodimerisation domains with four antigen binding [VH] domains fused at the amino and carboxyl termini of the dimerisation domains preferably using natural hinge or linker peptides. Where the polypeptide binding complexes lack CH2-CH3 effector functions they are preferably less than 120 kDa in size. Routes of manufacture are described herein.
Owner:GROSVELD FRANKLIN GERARDUS +3
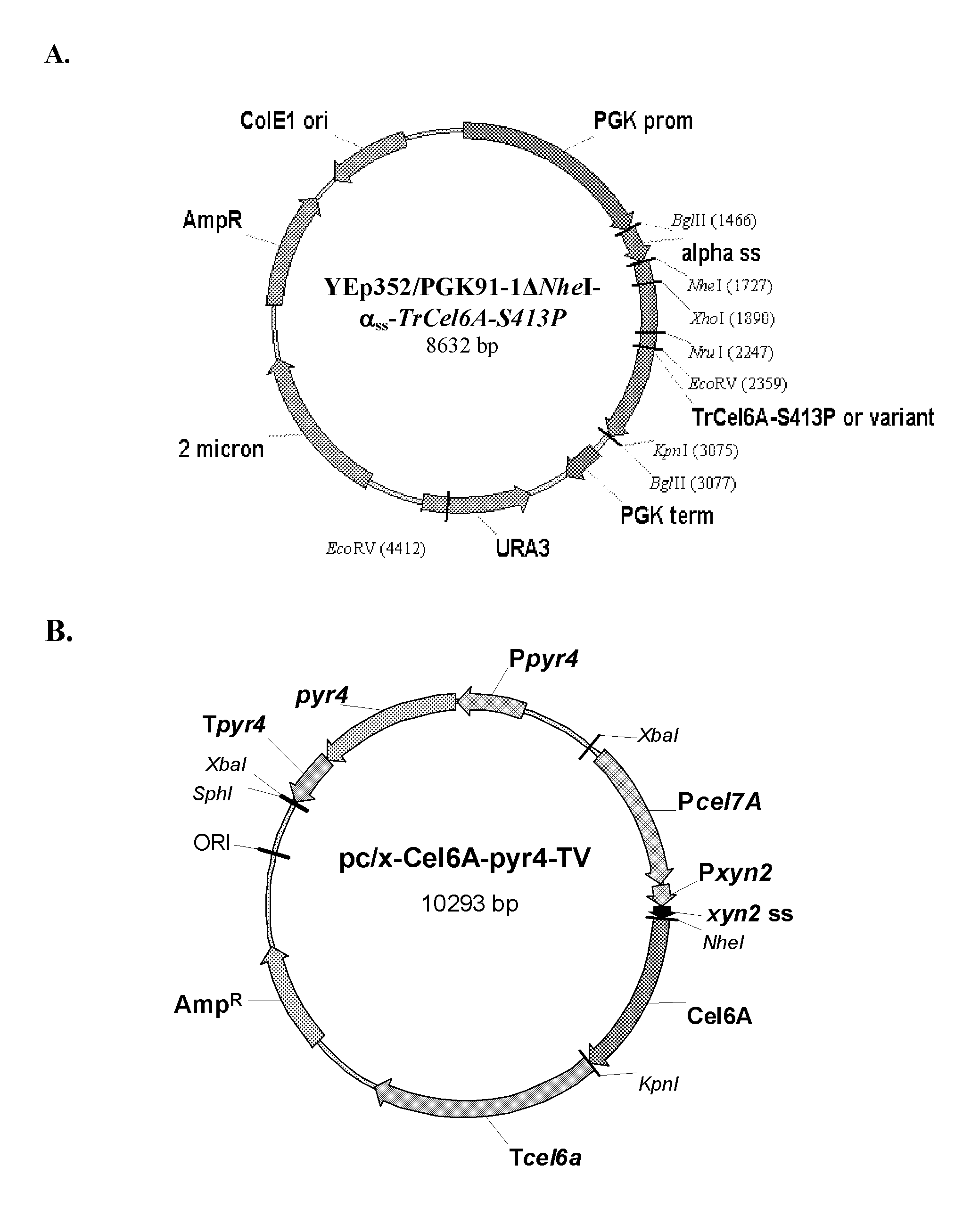
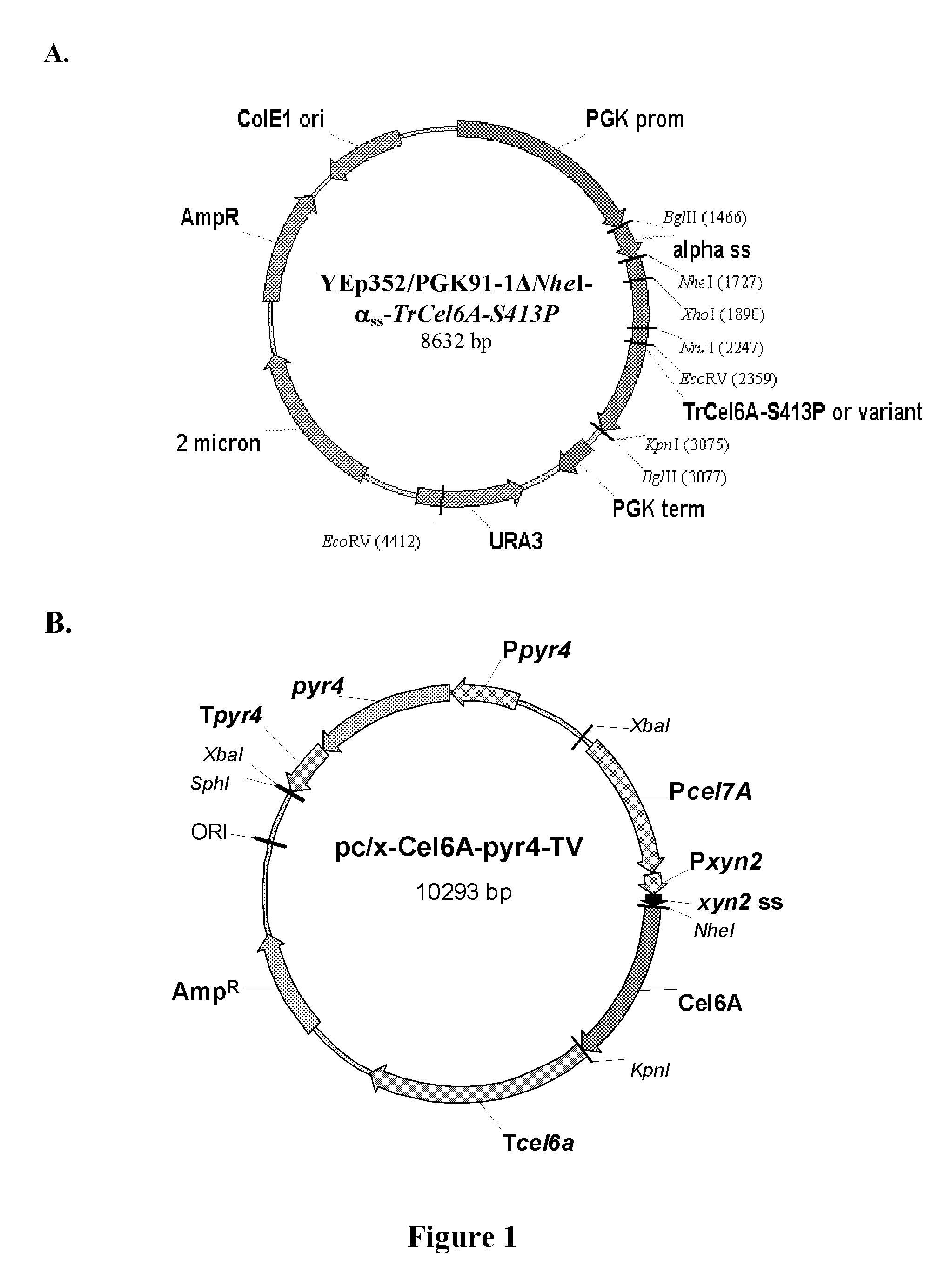
Novel lignin-resistant cellulase enzymes
ActiveUS20100221778A1Increase in cellulose-hydrolyzing activityDecrease in lignin bindingFungiEnzymesLignin degradationAmino acid substitution
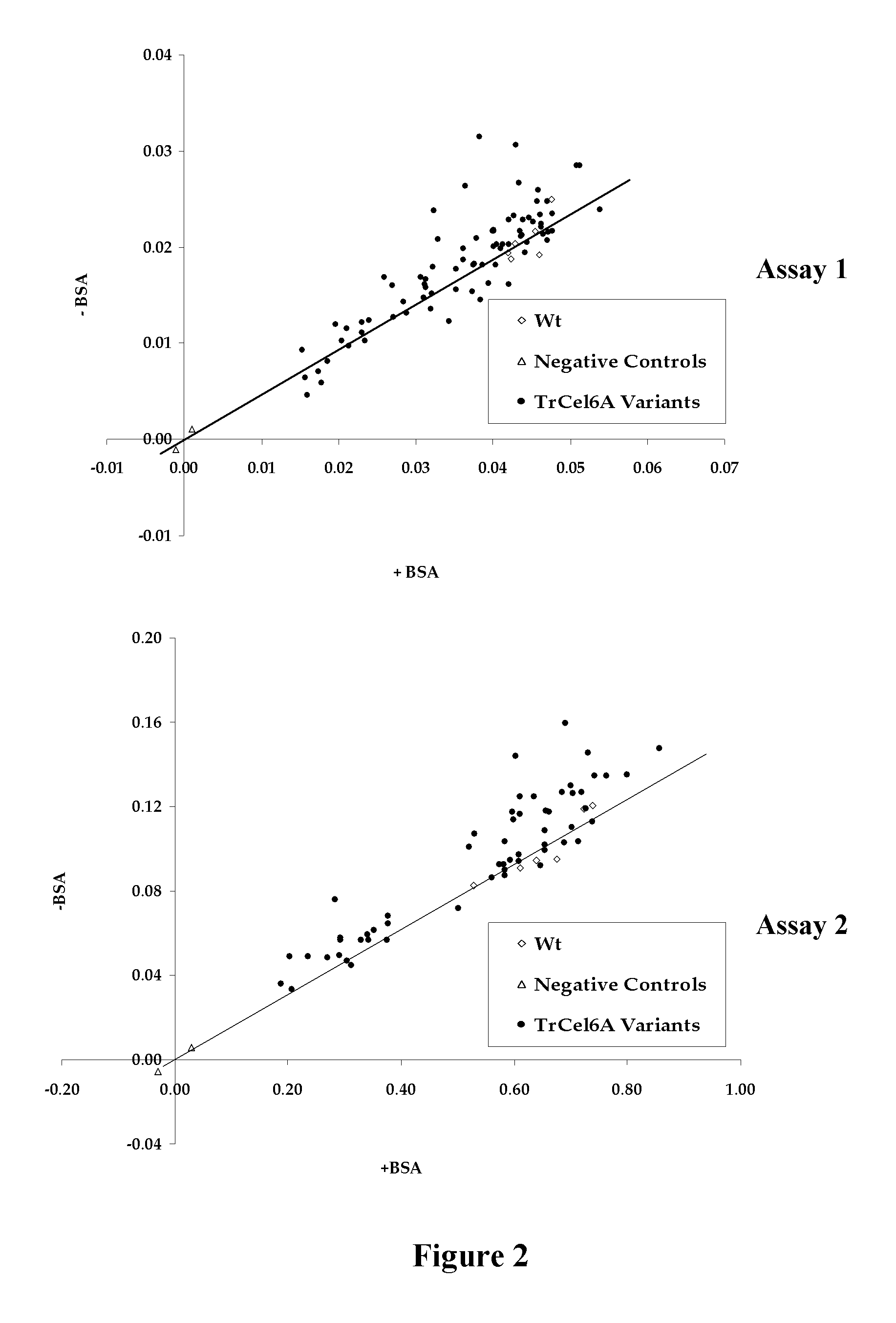
Provided are modified cellulase enzymes exhibiting increase cellulose-hydrolyzing activity in the presence of lignin and / or reduced binding to lignin comprising modified linker peptides comprising one or more amino acid substitutions, insertions, or deletions that result in (a) a decrease in the calculated isoelectric point of the linker peptide and / or (b) an increase in the ratio of threonine:serine in the linker peptide relative to a parental linker peptide from which said modified linker peptide is derived. Also provided are genetic constructs comprising nucleic acidsequences encoding for modified cellulase enzymes, methods for the production of the modified cellulase enzymes from host strains and a process for hydrolysing cellulose with the modified cellulases in the presence of lignin.
Owner:IOGEN ENERGY CORP
Recombinant human hepatitis B virus core protein fused protein
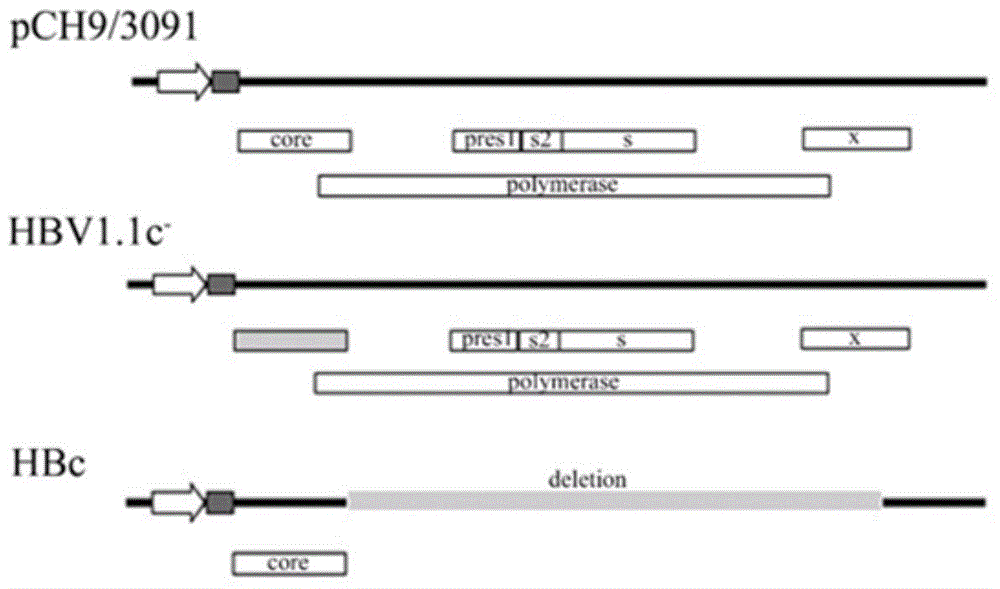
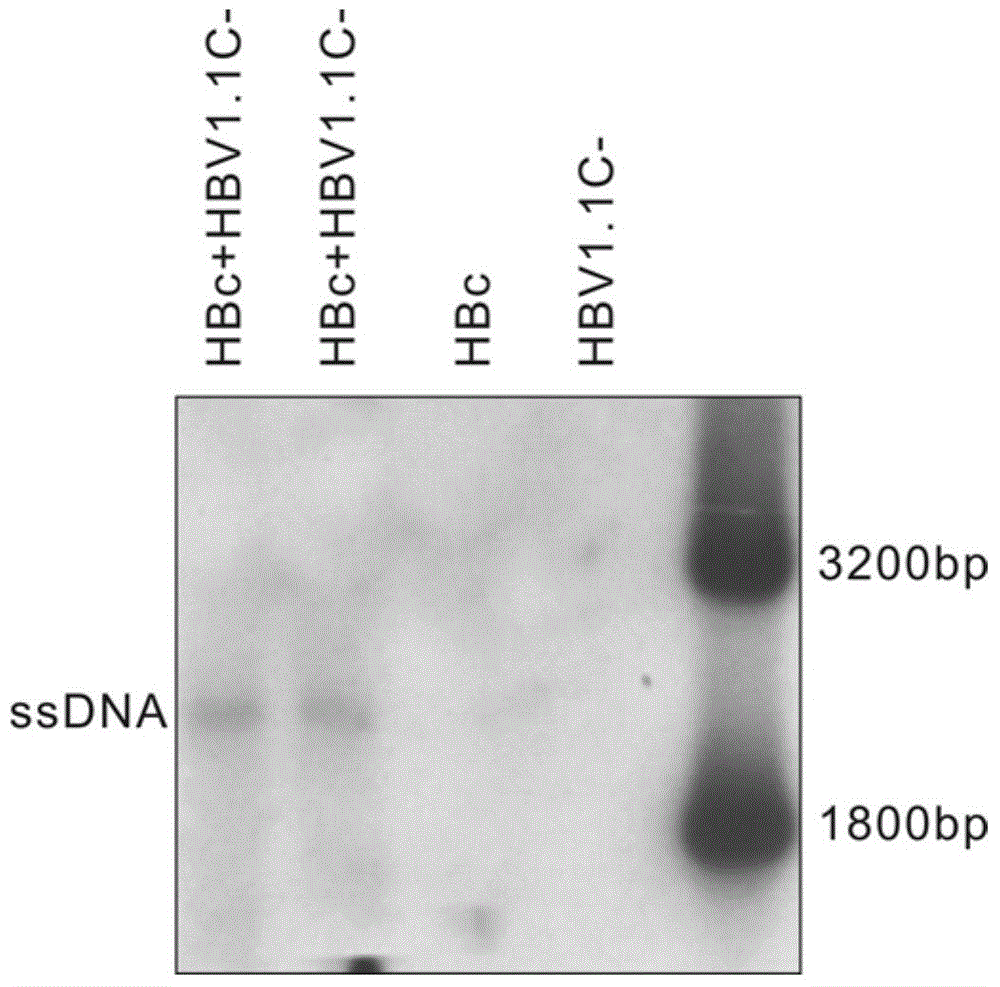
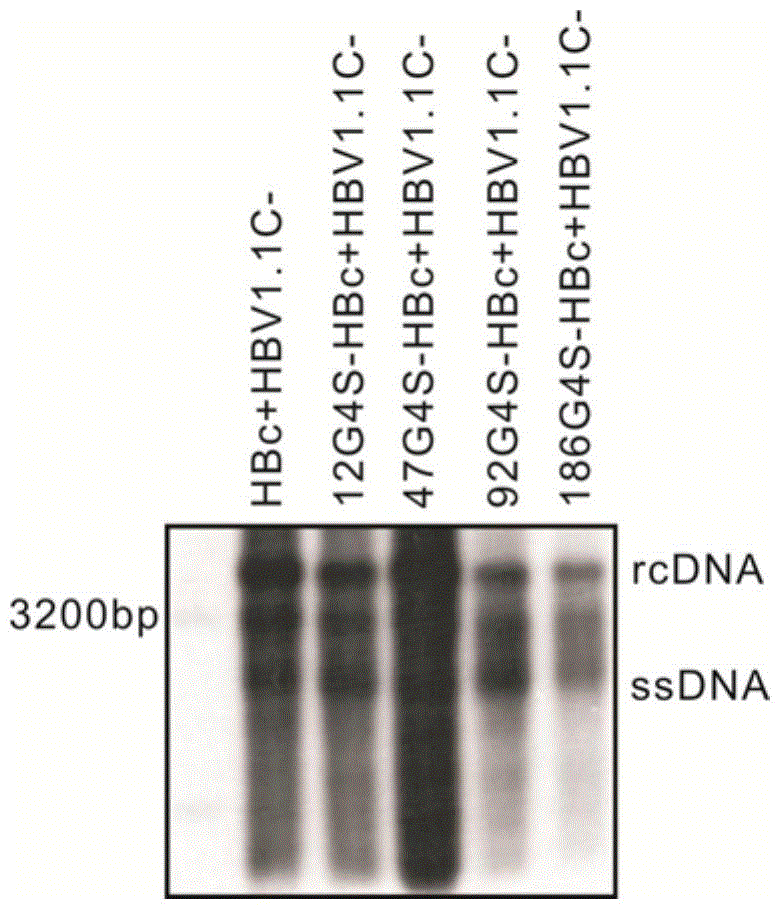
The invention discloses a recombinant human hepatitis B virus core protein fused protein. The fused protein comprises a protein (X), a linker peptide (L) and a hepatitis B virus core protein (HBc) from the end N to the end C in sequence; the linker peptide (L) has the amino acid sequence of Gly-Ser-(Gly-Gly-Gly-Gly-Ser)n, and n is an integer between 2 and 20 and is 9 or 18, particularly; the end C of the linker peptide (L) is connected with the end N of the hepatitis B virus core protein (HBc); the end C of the protein (X) is connected with the end N of the linker peptide (L); and the protein (X) is a red fluorescent protein or vesicular stomatitis virus G glycoprotein. The hepatitis B virus core protein (HBc) is connected with the functional protein, and the functions of the proteins on two ends of the linker peptide (L) can be both guranteed. The problem in the prior art that the functions of the hepatitis B virus core protein (HBc) and the functions of the functional protein can not be both guaranteed after the hepatitis B virus core protein (HBc) is fused with the functional protein is solved. The fused protein is of great importance to the research on the hepatitis B virus (HBV).
Owner:CHONGQING MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Single-chain antibody for resisting influenza viruses, preparation method for single-chain antibody, application of single-chain antibody
InactiveCN102558348ABlock bindingNeutralizing activityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesSerum igeSingle-Chain Antibodies
The invention discloses a single-chain antibody ScFv for resisting influenza viruses, a preparation method for the single-chain antibody ScFv, application of the single-chain antibody ScFv, a gene for encoding the single-chain antibody ScFv, a carrier containing the gene, a host cell and the like. The single-chain antibody ScFv for resisting the influenza viruses is one of the following proteins: 1) a single-chain antibody formed by connecting a heavy chain variable region and a light chain variable region of the antibody through a linker peptide, wherein an amino acid sequence of the light chain variable region and an amino acid sequence of the heavy chain variable region are shown as SEQ ID NO.1 and SEQ ID NO.2 in a sequence table respectively; and 2) a derived antibody obtained by improving the single-chain antibody in step 1), wherein the improvement comprises the deletion, substitution or insertion of amino acid, and the derived antibody has the antibody activity of resisting H1N1 influenza viruses. The molecular weight of the single-chain antibody is about 27kD; and the single-chain antibody can specifically identify the H1N1 influenza viruses and block the combination of the viruses and natural serum. The single-chain antibody can be used for diagnosing, preventing, controlling and treating the infection of the H1N1 influenza viruses, or is used for antiviral breeding of transgenic animals.
Owner:SHANGHAI VETERINARY RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
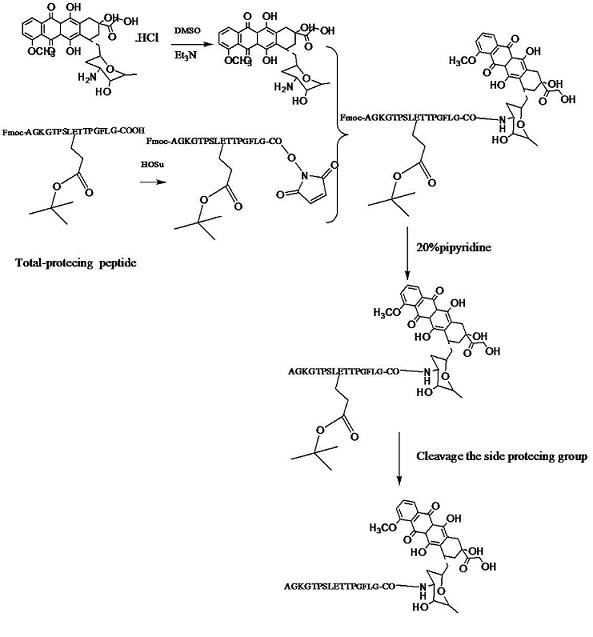
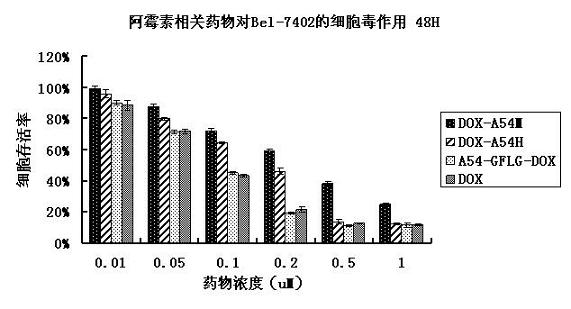
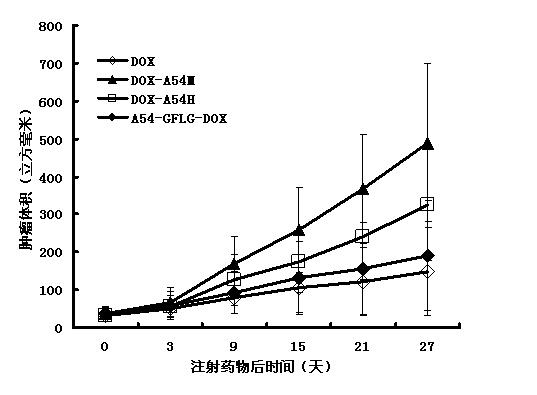
A54-GFLG-DOX conjugate as well as coupling method and application thereof
InactiveCN102127154AMaintain killing effectMitigation of lethalityPeptide/protein ingredientsPeptidesSide effectCoupling
The invention discloses an A54-GFLG-DOX conjugate which has the structure disclosed in a formula (1), wherein A54 is liver cancer specificity targeted peptide with the amino acid sequence of NH2-AGKGTPSLETTP-COOH, and the A54 is coupled with adriamycin by virtue of a linker peptide GFLG. The invention also discloses a preparation method of the A54-GFLG-DOX conjugate and an application of the A54-GFLG-DOX conjugate in preparing medicaments capable of treating liver cancer. The A54-GFLG-DOX conjugate has the beneficial effect of administrating the medicaments in a targeted mode, enhancing the medical effect, lightening the toxic and side effect and the like.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY
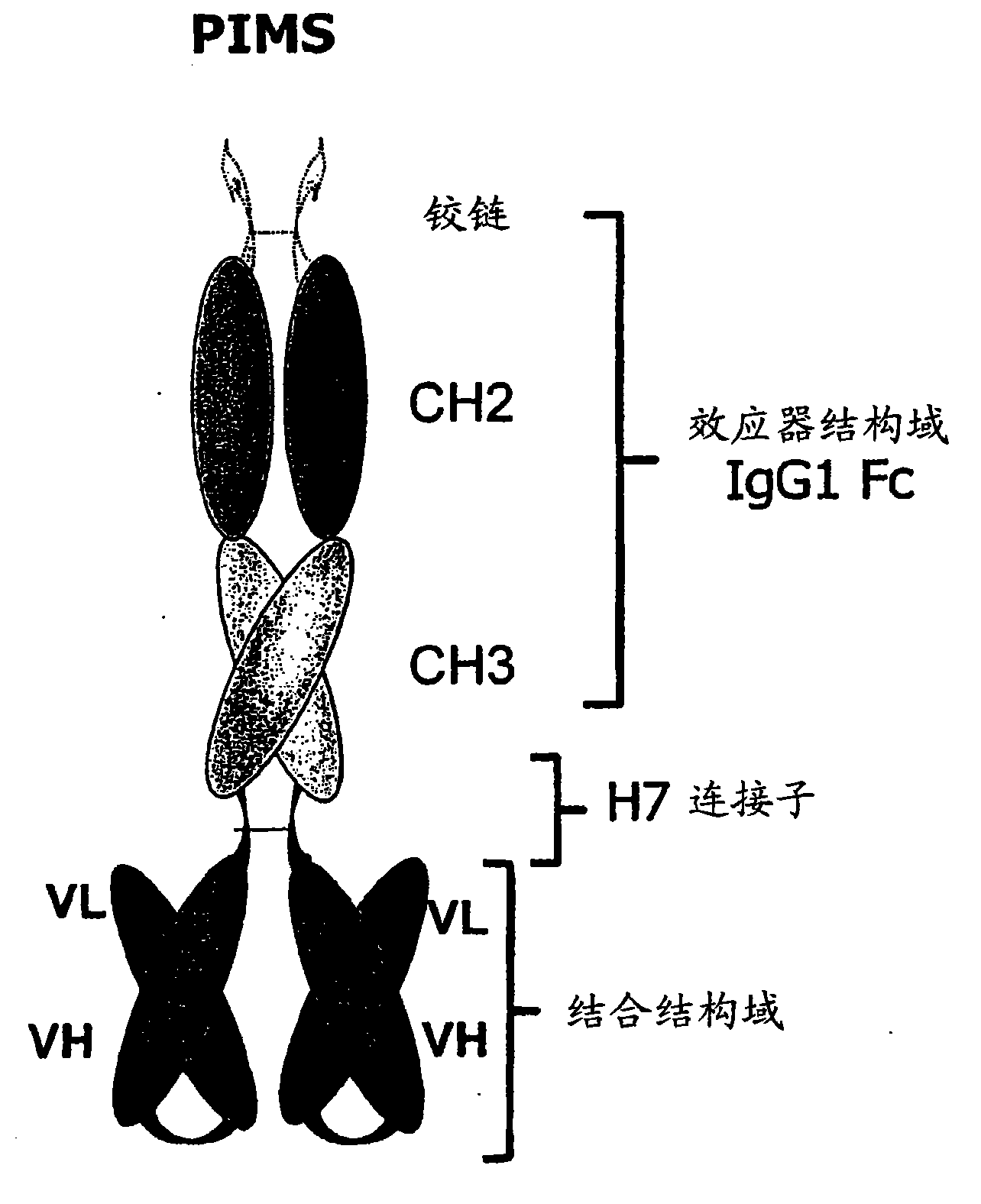
Binding peptides having a c-terminally disposed specific binding domain
Specific binding peptides having a general schematized structure of an optional N-terminal hinge region joined to an immunoglobulin-derived constant sub-region comprising a CH2 region and a CH3 region, followed by a PIMS linker peptide and at least one specific binding domain are provided, along with encoding nucleic acids, vectors and host cells. Also provided are methods for making such peptides and methods for using such peptides to treat or prevent a variety of diseases, disorders or conditions, as well as to ameliorate at least one symptom associated with such a disease, disorder or condition.
Owner:EMERGENT PRODUCTS DEVELOPMENT SEATTLE LLC
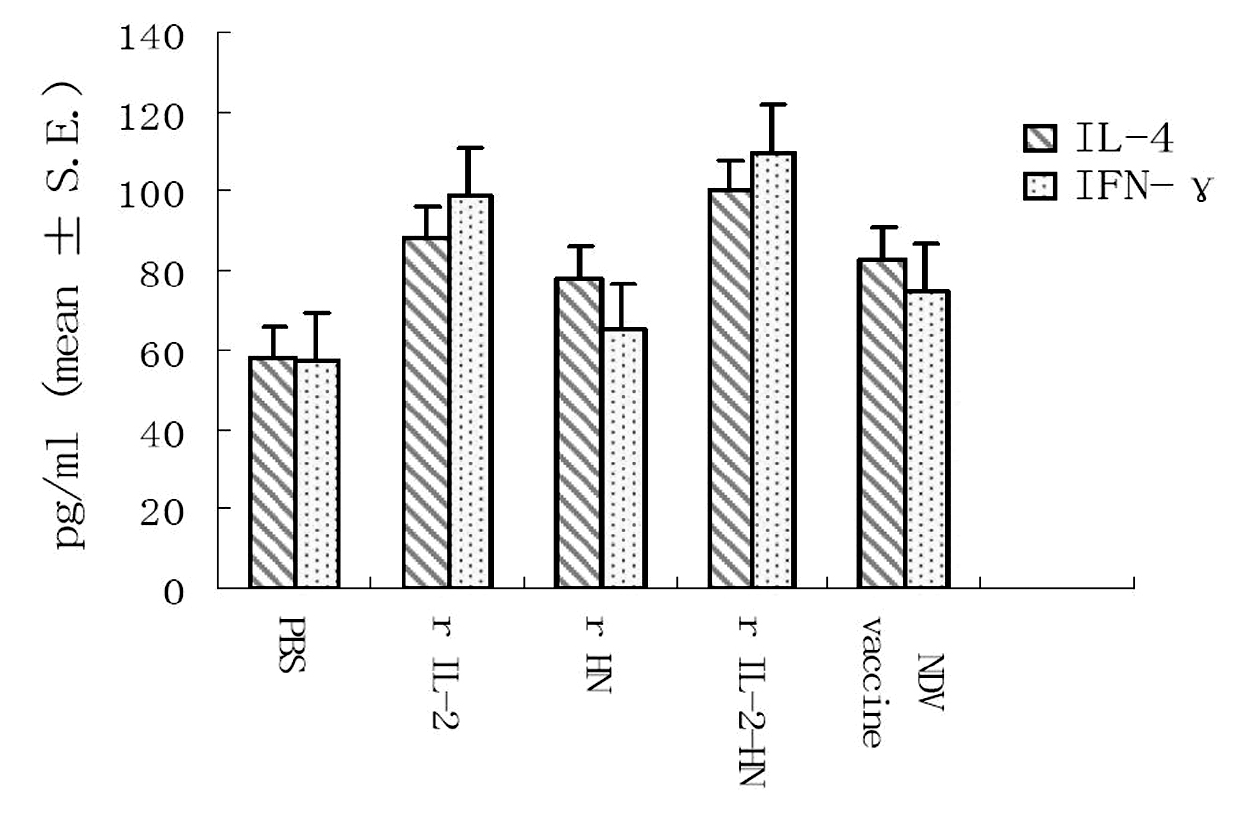
Poultry IL-2 and newcastle disease virus HN gene recombination fusion protein and application thereof
InactiveCN101870733AEnhance body fluidsEnhance cellular immune responseFungiViral antigen ingredientsSide effectHN Protein
The invention relates to a preparation method and application of fusion protein (chIL-2-HN fusion protein) of recombining poultry interleukin-2 (IL-2) and newcastle disease virus hemagglutinin-neuraminidase (HN), belonging to the technical field of biological engineering. The fusion protein is fused by poultry IL-2 protein and newcastle disease virus HN protein by flexible Linker peptide; a DNA sequence for coding the fusion protein is inserted into an expression vector pPICZ alpha A; saccharomycete X-33 is electrically converted to obtain a genetically engineered microorganism for efficiently expressing recombination chIL-2-HN fusion protein which is prepared by liquid culture and purification; the recombination fusion protein can serve as the novel genetic engineering vaccine and can serve as a novel immunologic adjuvant for newcastle disease common vaccine. The chIL-2-HN fusion protein of the invention has favourable safety and no toxic or side effect, which is verified by experiments of animal immunoassay. In addition, the chIL-2-HN fusion protein can effectively strengthen the level of organism cellular immunity and humoral immunity and has wide application prospect.
Owner:HENAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Functional polypeptide and application
ActiveCN109942714AEasy to removeReduce contentNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseAmyloid A Protein
The invention provides a functional polypeptide. The functional polypeptide includes a polypeptide fragment I identifying and blocking amyloid protein A beta aggregation and a polypeptide fragment IIwhich is a mimic peptide of an apoE receptor binding region, and the polypeptide fragment I and the polypeptide fragment II are linked through a linker peptide or directly linked. The polypeptide caninhibit amyloid protein A beta aggregation, inhibit the of A beta, accelerate removal of A beta through microglia, and the functional polypeptide can be used for preparing drugs for treating the Alzheimer disease.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV
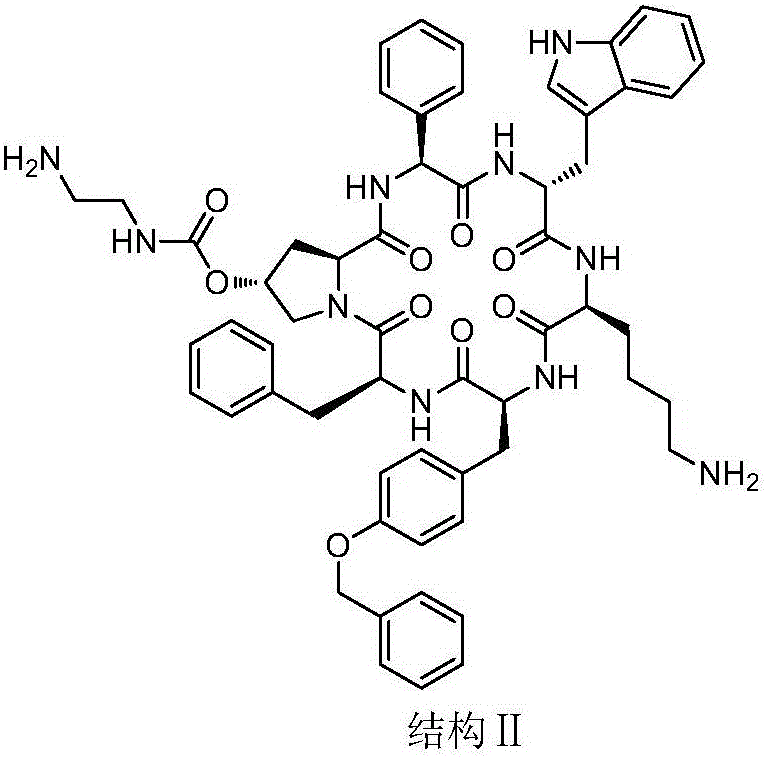
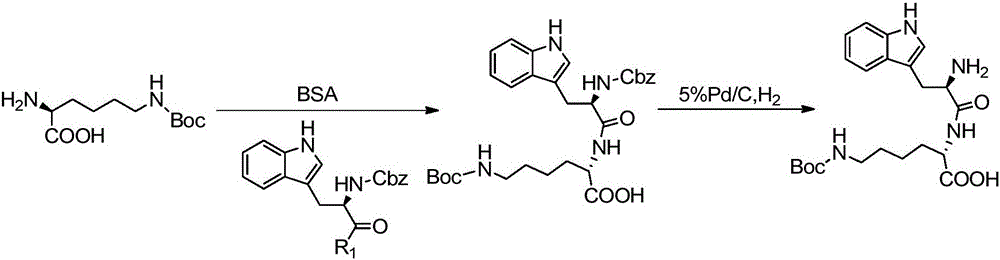
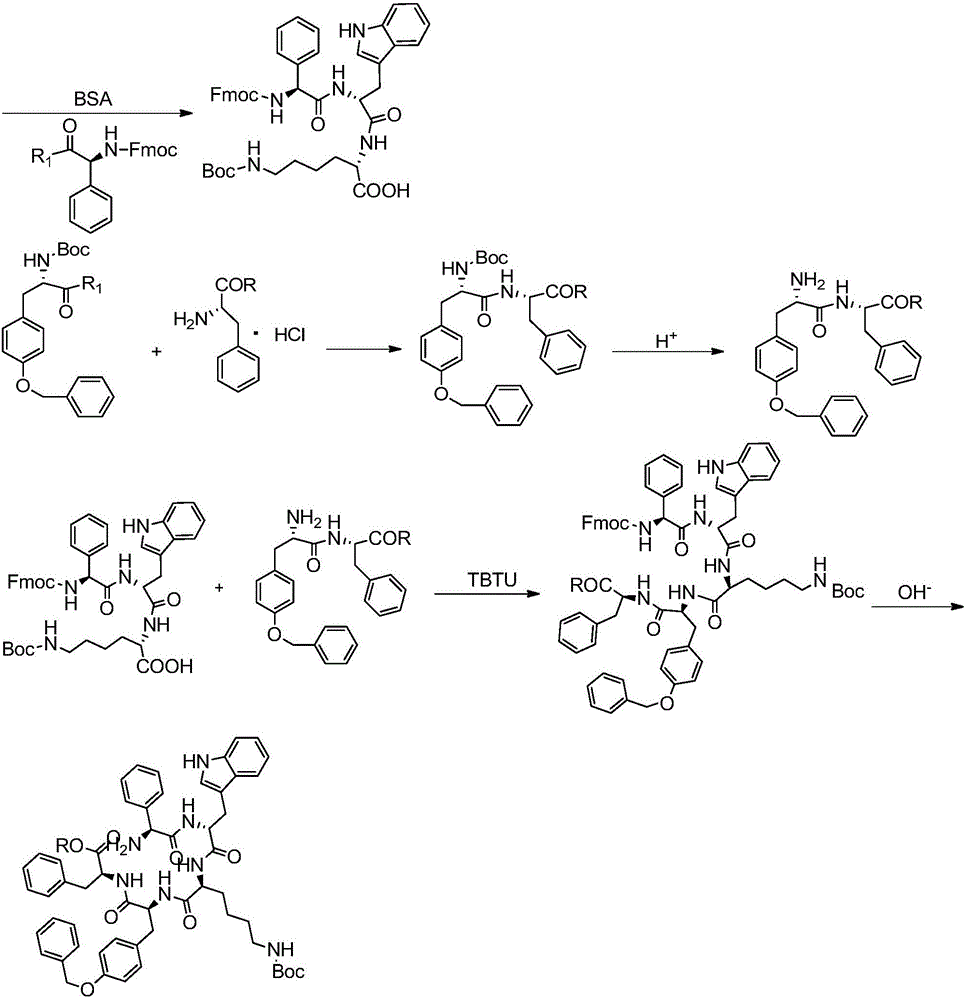
Synthesis and application of pasireotide pentapeptide intermediate
ActiveCN106188231AWide variety of sourcesLow pricePeptide preparation methodsBulk chemical productionDipeptideTert-Butyloxycarbonyl protecting group
The invention discloses a liquid synthetic method of pasireotide pentapeptide intermediate, i.e., a preparation method of H-Phg-D-Trp-Lys(Boc)-Tyr(Bzl)-Phe-OR. By using the liquid linker peptide synthetic method, reaction is easy to detect, the cost is lower than that of a solid synthetic method, and the method is more suitable for large-scale industrial production. The liquid synthetic method includes the main synthetic steps of linking carbobenzoxy-protected D-tryptophan and 9-fluorenylmethoxycarbonyl-protected phenylglycine one by one to Alpha-N terminals of lysine to obtain a tripeptide fragment in 3+2 mode through BSA protected lysine and N-hydroxysuccinimide ester method; condensing ester-protected phenylalanine and t-butyloxycarboryl-protected O-benzyl-tyrosine to obtain a dipeptide fragment through N-hydroxysuccinimide ester method; condensing the tripeptide and dipeptide through TBTU method to obtain the target product, pasireotide pentapeptide intermediate.
Owner:INST OF MATERIA MEDICA AN INST OF THE CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
FGF21 and IGF-1 fusion protein and applications thereof
PendingCN108440668ASignificant effectGood treatment effectNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsInsulin-like growth factorGlycolipid metabolism
The present invention provides a FGF21 and IGF-1 fusion protein, wherein fusion is performed through an appropriate linker peptide fragment in an optimal fusion manner, and the produced fusion proteinsuccessfully retains the respective biological activities. According to the present invention, specifically the fusion protein sequentially contains human fibroblast growth factor-21 (hFGF21), a flexible peptide linker (L), a human immunoglobulin Fc fragment, a flexible peptide linker (L) and an insulin-like growth factor (IGF-1) from the N terminal to the C terminal; and the fusion protein provides high regulation effect in glycolipid metabolism and the like compared to the single use of the proteins, enhances the treatment effects on metabolic disorders, cardiovascular diseases, liver fat lesions and other diseases, and overcomes the side effects (such as osteoporosis, cancer risk and the like).
Owner:REYOUNG SUZHOU BIOLOGY SCI & TECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com