Binding peptides having a c-terminally disposed specific binding domain
A combination of structural domains and specificity technology, applied in the direction of specific peptides, fusion polypeptides, peptides, etc., can solve problems such as high toxicity, hindering drug delivery, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0191] Antibody preparation
[0192] Through multiple subcutaneous or intraperitoneal injections of antigen polypeptides or fragments thereof and adjuvants, usually in animals (for example, rabbits, hamsters, goats, sheep, horses, pigs, rats, gerbils, guinea pigs, mice or any other suitable lactation Animals, and other non-mammalian species) produce polyclonal antibodies against antigen polypeptides in vivo. Adjuvants include, but are not limited to complete or incomplete Freund’s adjuvant, mineral gels such as aluminum hydroxide, surface active substances such as lysolecithin, pluronic polyols, polyanions, peptides, oil emulsions And dinitrophenol. BCG (Bacille Calmette-Guerin) and Corynebacterium parvum are also potentially useful adjuvants. It is useful to combine antigenic polypeptides with carrier proteins, which are immunogenic in the species to be immunized; typical carriers include keyholelimpet hemocyani, serum albumin, and bovine thyroglobulin Or soybean trypsin inh...
Embodiment 1
[0319] PIMS construction
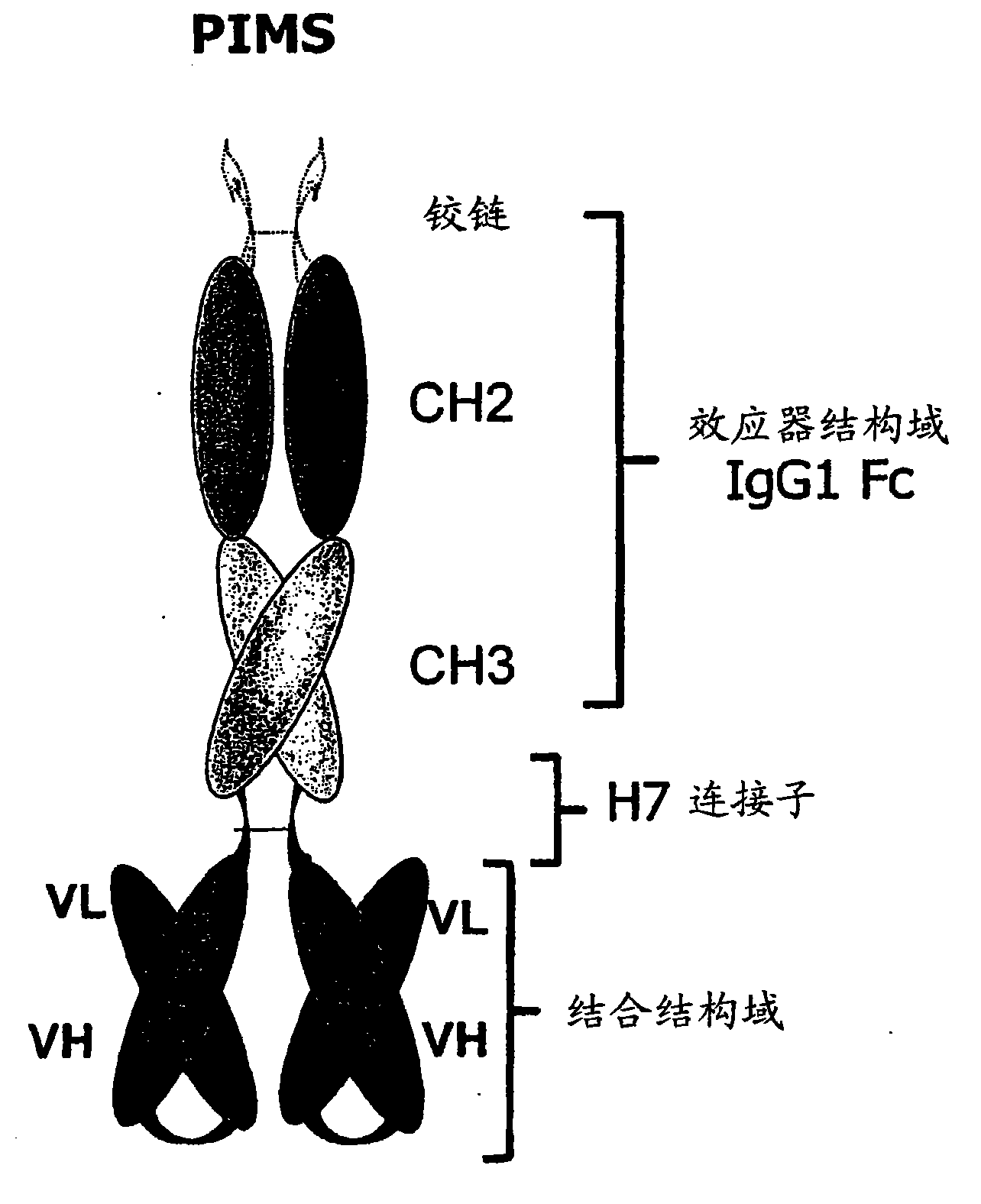
[0320] Such as figure 1 As shown, the PIMS peptide has the following domains: a constant subregion placed at the N-terminus and at least one specific binding site placed at the C-terminus. Each of these two domains can be derived from an immunoglobulin hinge. PIMS connection sub-connection. In some embodiments, the hinge region from the immunoglobulin is located at the N-terminus of the constant subregion, although the constant subregion is still located at the N-terminus of the specific binding site. In some embodiments, as known to those skilled in the art, the N-terminus of the nascently expressed PIMS molecule may be a leader peptide for the expression and secretion of the encoded peptide. Moreover, the leader peptide can be covalently linked to the region from the immunoglobulin hinge, or directly to the constant subregion (PIMS molecule lacking the N-terminal domain from the hinge region).
[0321] It is expected that the recombination engineering...
Embodiment 2
[0351] Transfection of PIMS-encoding polynucleotide into CHO-S cells
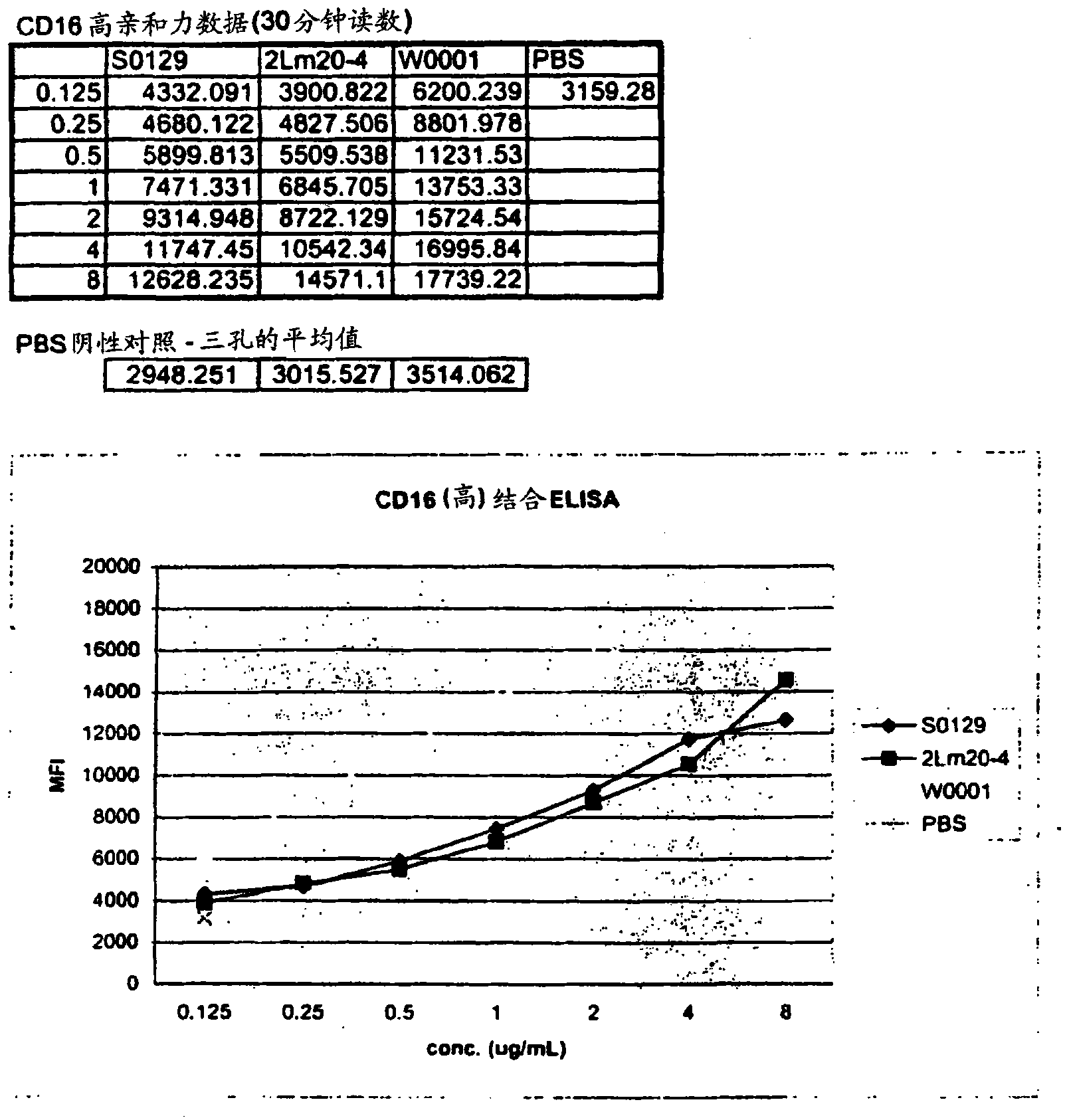
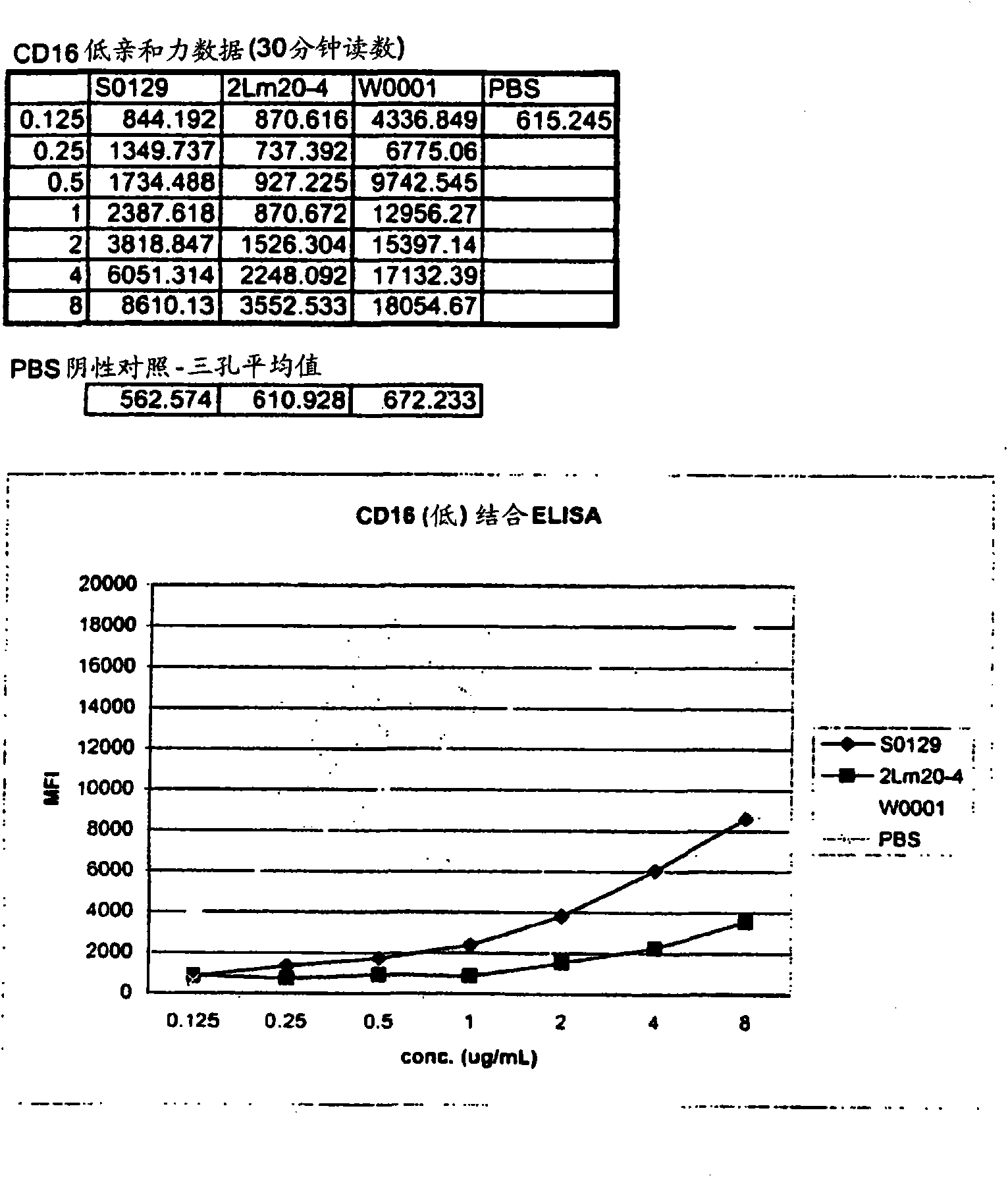
[0352] The day before the appropriate transfection experiment, each of the two sterile flasks was inoculated with 5x 10 5 Cells / ml, Freestyle with 8Mm L-glutamine added to 250ml TM CHO expression medium. Put the flask at 37°C with 8% CO 2 Incubate and rotate at 70 rpm. On the day of transfection, count the cells in each flask and add Freestyle TM Medium to provide 10 6 Cells / ml. In separate 15ml sterile tubes, put 313μg Freestyle TM Max transfection reagent (1.0μg / ml) added to 4,687μl OptiPro TM SFM, and add 313μg W0001DNA plasmid (1.0μg / ml) to 4,687μl OptiPro SFM TM in. Freestyle that will be diluted TM Max transfection reagent was added to the diluted W0001 plasmid and incubated for 10 minutes at room temperature. Then the DNA-Freestyle TM The Max reagent complex was slowly added to the flask containing the cells and the cells were heated at 37°C, 8% CO 2 Incubate at 70 rpm on an orbital shaker...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com